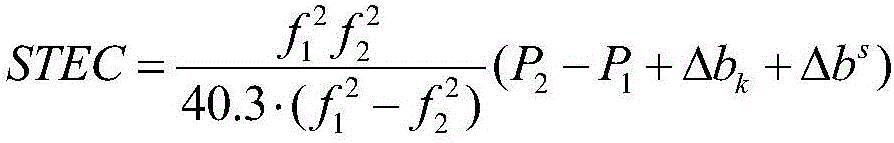Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
174 results about "Spherical harmonics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
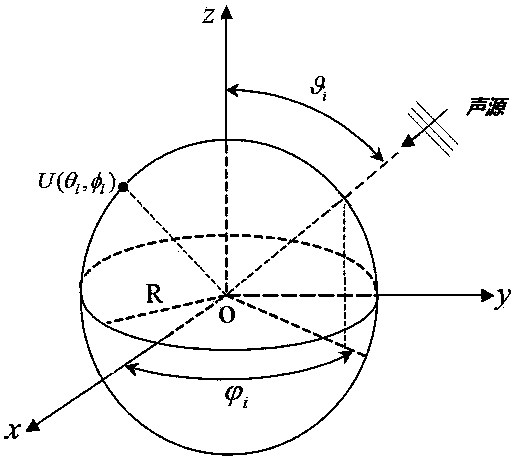
In mathematics and physical science, spherical harmonics are special functions defined on the surface of a sphere. They are often employed in solving partial differential equations in many scientific fields. The spherical harmonics are a complete set of orthogonal functions on the sphere, and thus may be used to represent functions defined on the surface of a sphere, just as circular functions (sines and cosines) are used to represent functions on a circle via Fourier series.
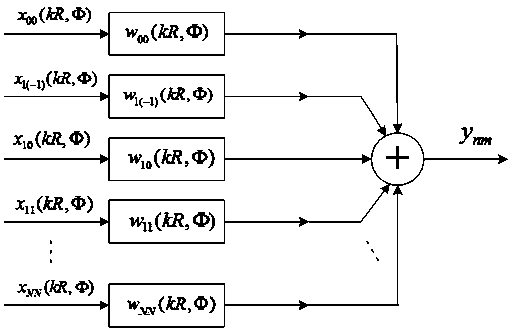
Systems and methods for all-frequency relighting using spherical harmonics and point light distributions
InactiveUS20050080602A1Efficient lighting sourceEffective lightingComputation using non-denominational number representationComplex mathematical operationsPoint lightDecomposition
The present invention is directed to systems and methods for all-frequency relighting by representing low frequencies of lighting with spherical harmonics and approximate the residual high-frequency energy with point lights. One such embodiment renders low-frequencies with a precomputed radiance transfer (PRT) technique (which requires only a moderate amount of precomputation and storage), while the higher-frequencies are rendered with on-the-fly techniques such as shadow maps and shadow volumes. In addition, various embodiments are directed to a systems and methods for decomposing the lighting into harmonics and sets of point lights. Various alternative embodiments are directed to systems and methods for characterizing the types of environments for which the described decomposition is a viable technique in terms of speed (efficiency) versus quality (realism).
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
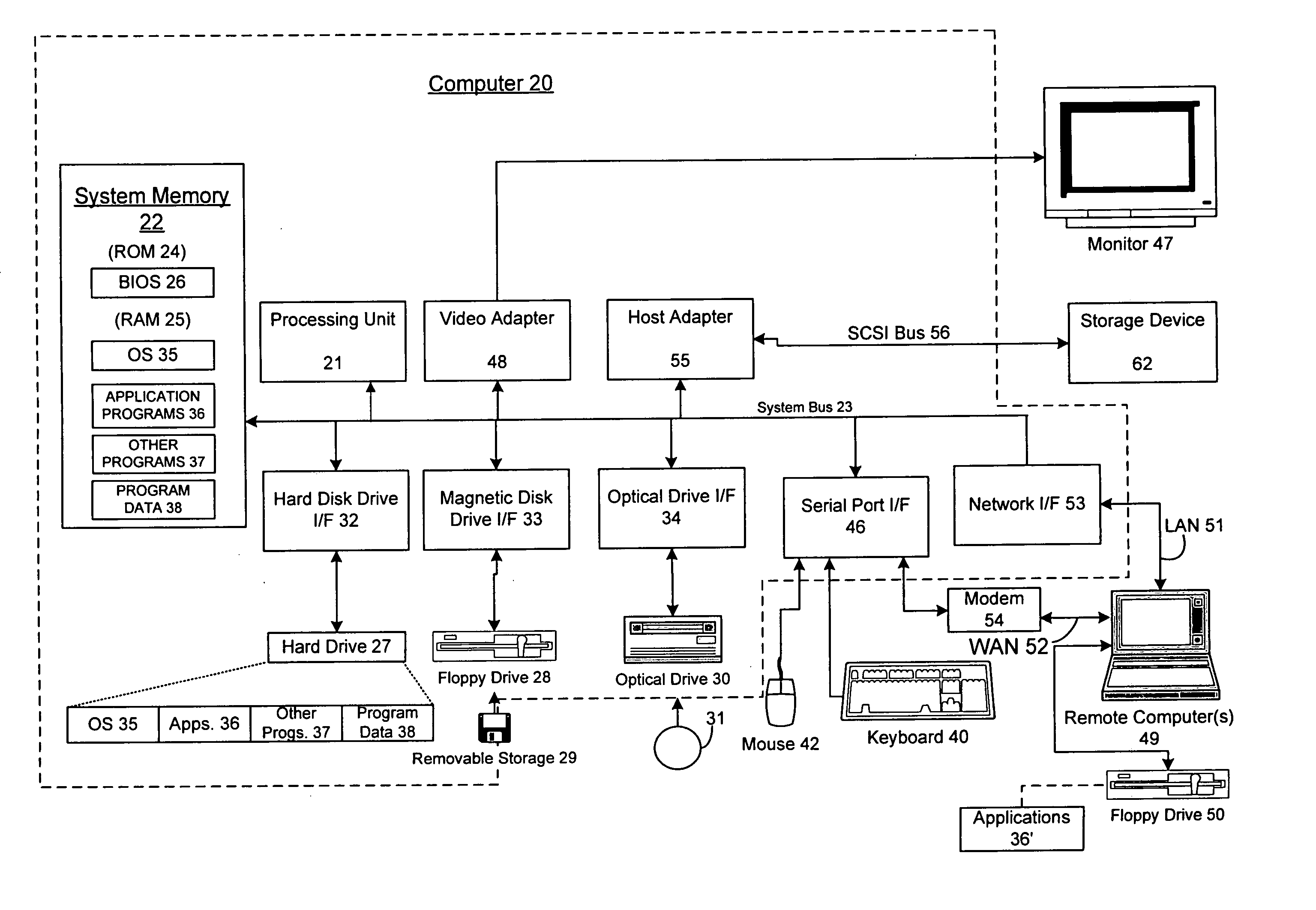
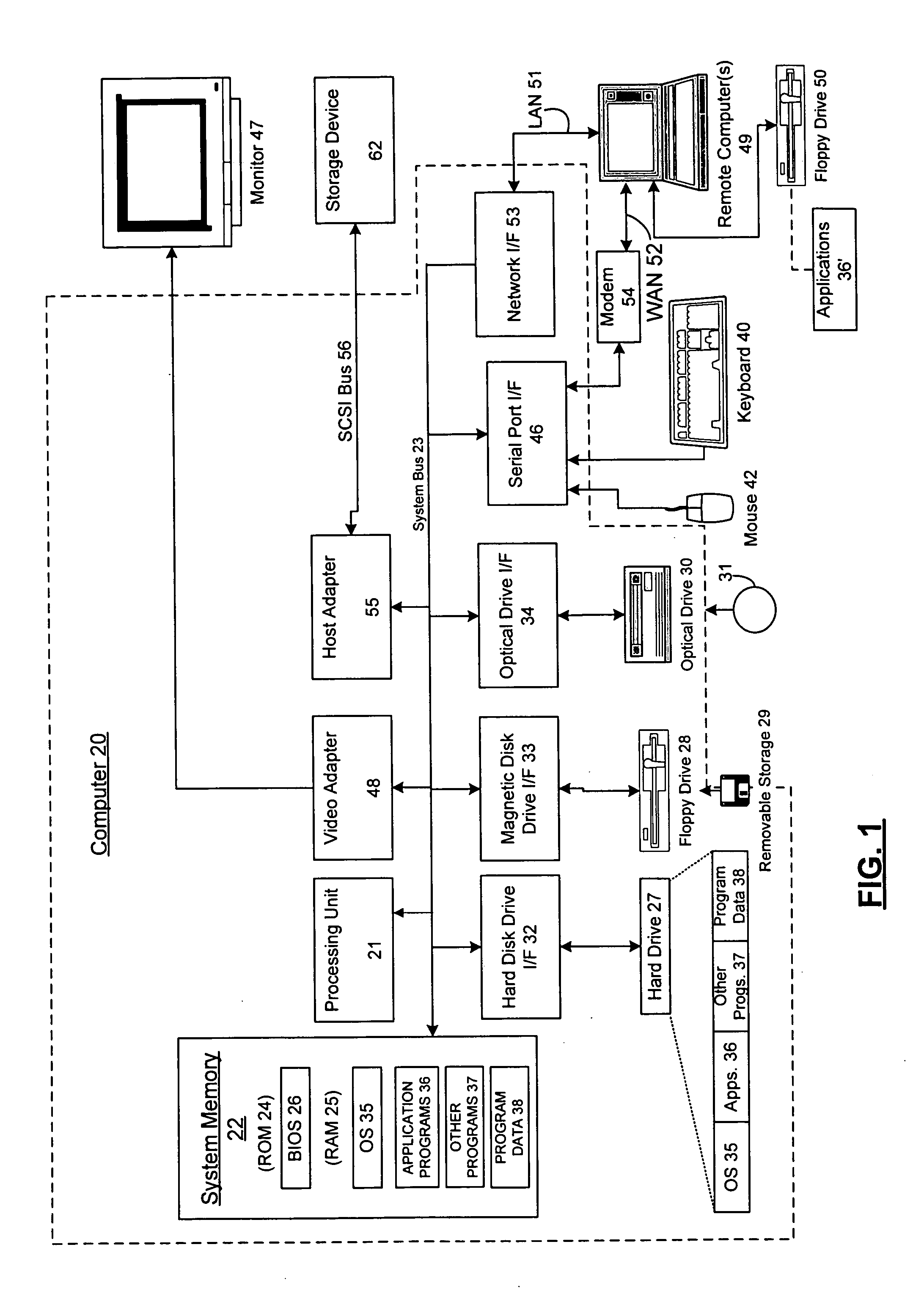
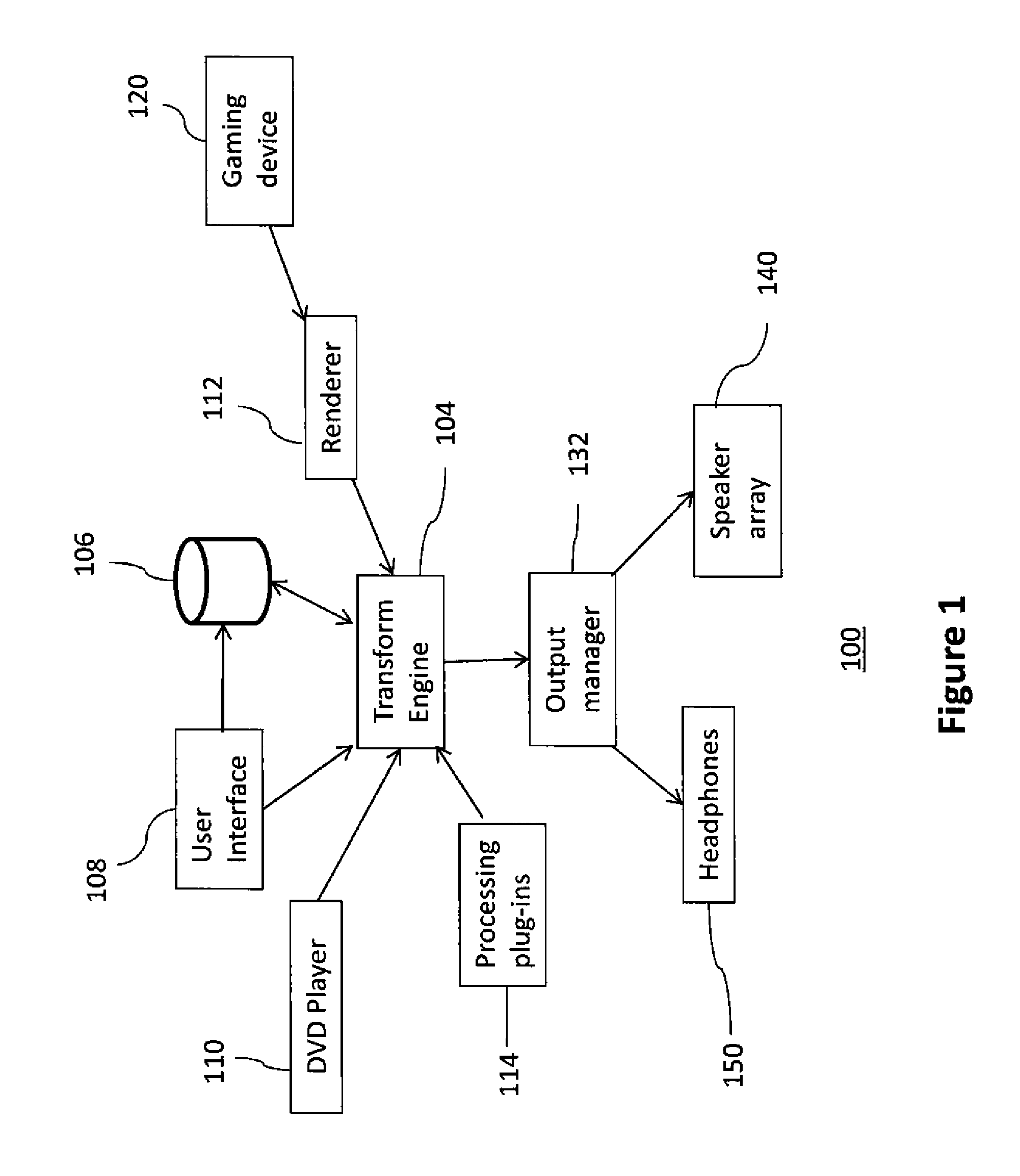
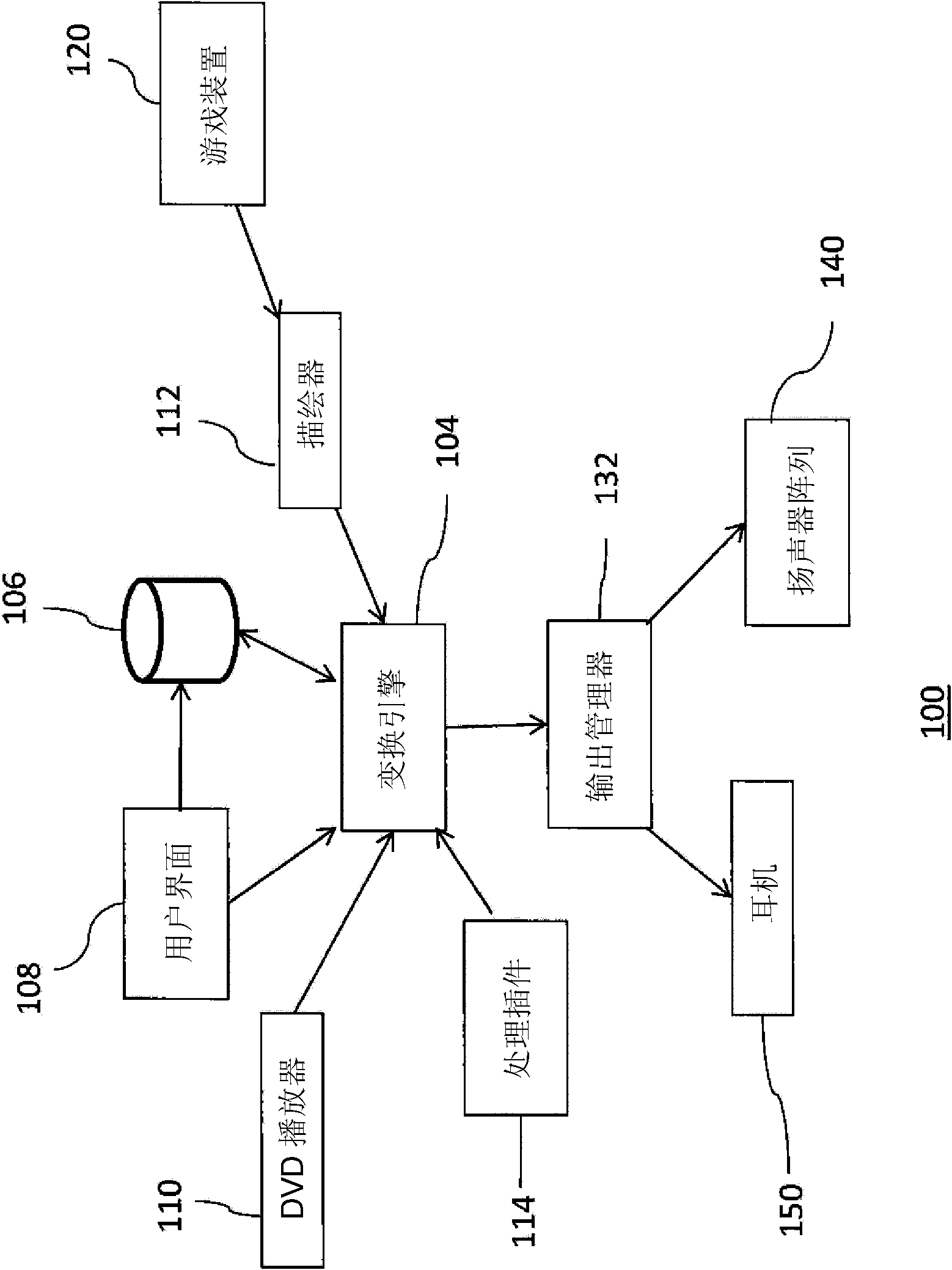
Sound system
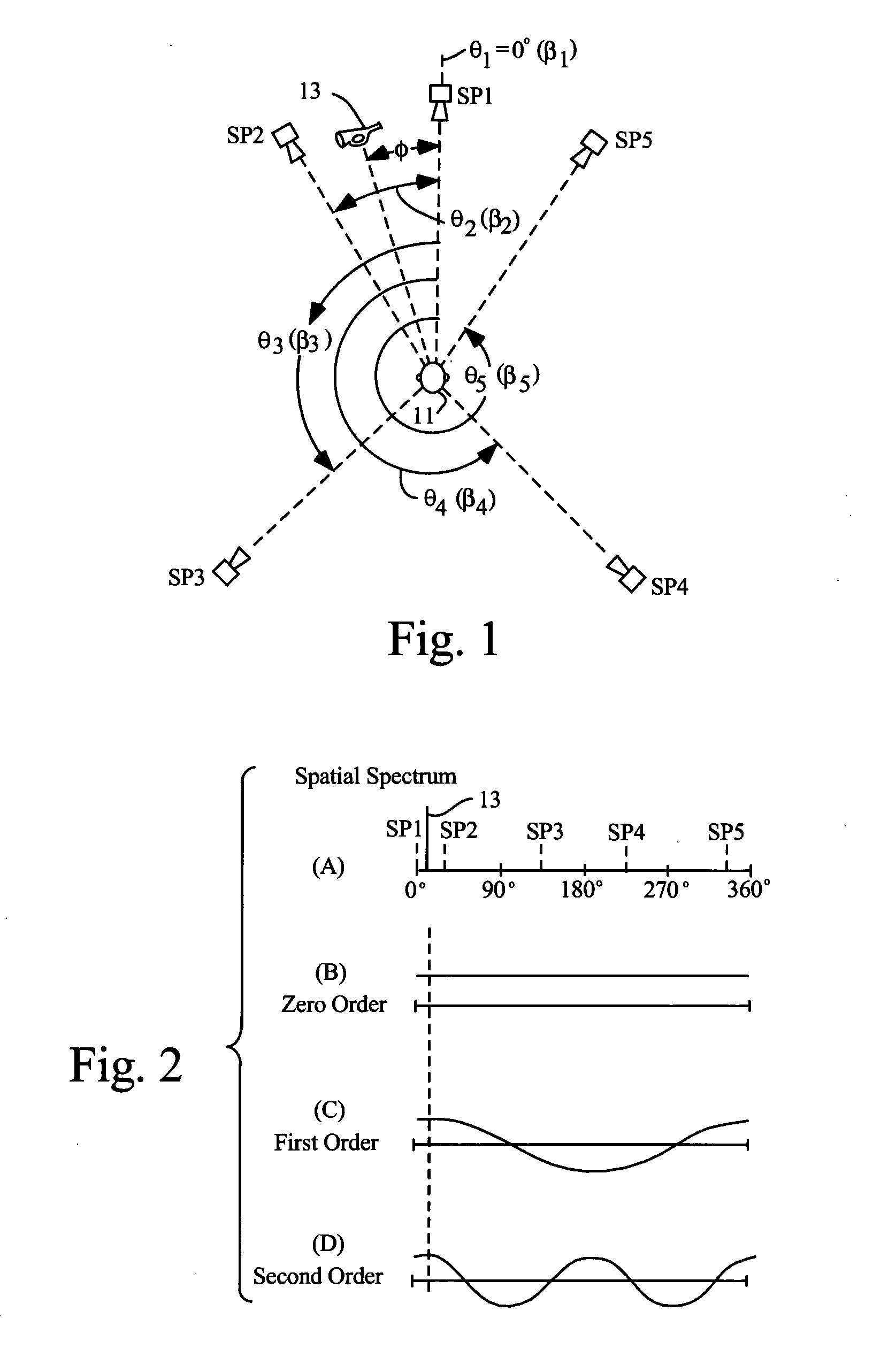
ActiveUS20120014527A1Easy to handleSpeech analysisTwo-channel systemsSpherical harmonicsTable of spherical harmonics
Methods and systems for processing audio data, such as spatial audio data, in which one or more sound characteristics of a given component of a spatial audio signal are modified in dependence on a relationship between a direction characteristic of the given component and a defined range of direction characteristics; this enhances the listening experience of the listener. A spatial audio in a format using a spherical harmonic representation of sound components is decoded by performing a transform on the spherical harmonic representation, in which the transform is based on a predefined speaker layout and a predefined rule, the predefined rule indicating a speaker gain of each speaker arranged according to the predefined layout, when reproducing sound incident form a given direction; this provides an alternative to existing method of decoding spatial audio streams, which focus on soundfield reconstruction. A plurality of matrix transforms is combined into a combined transform, and the combined transform is performed on an audio signal; this saves processing resources of the audio system being used.
Owner:FURSE RICHARD
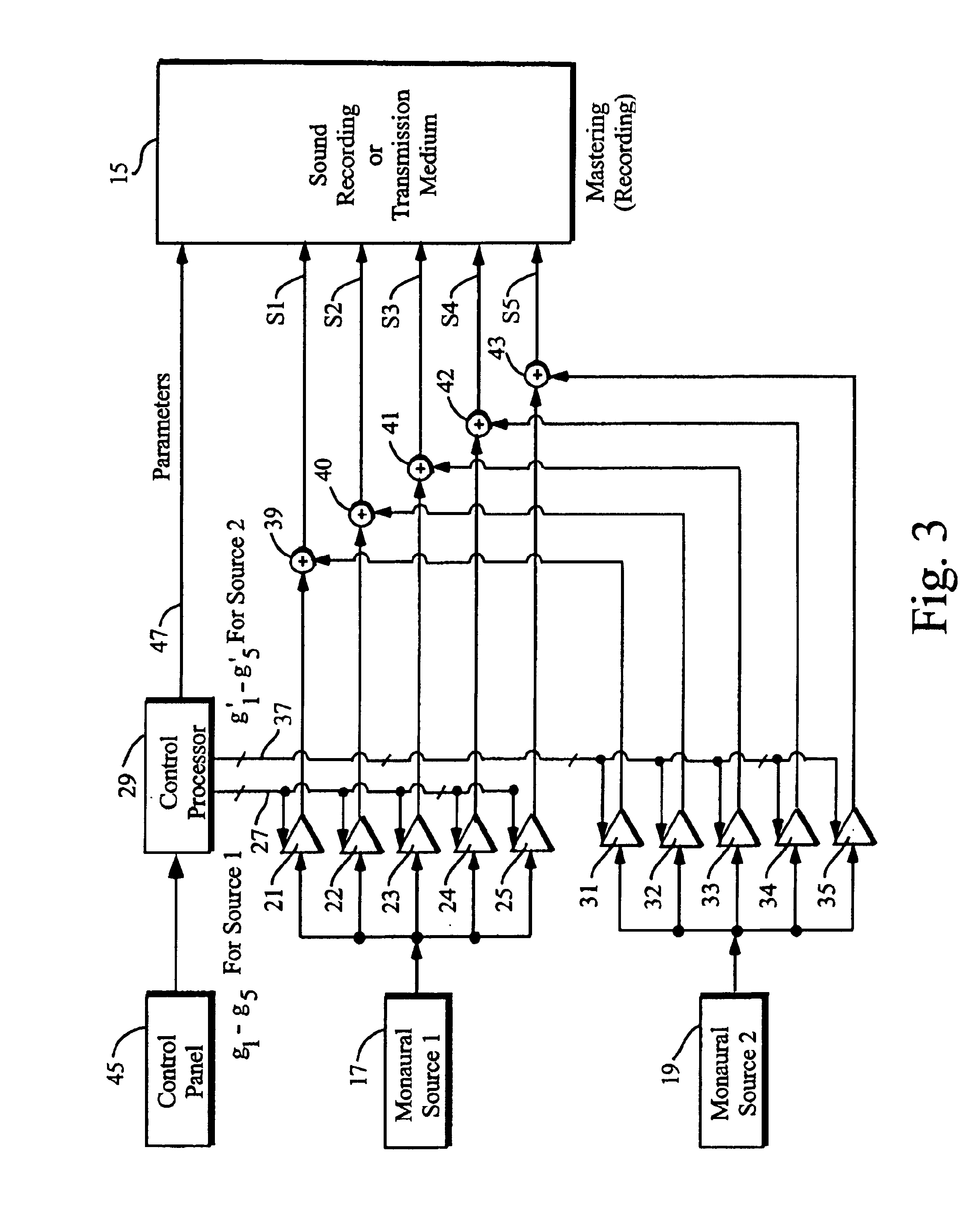
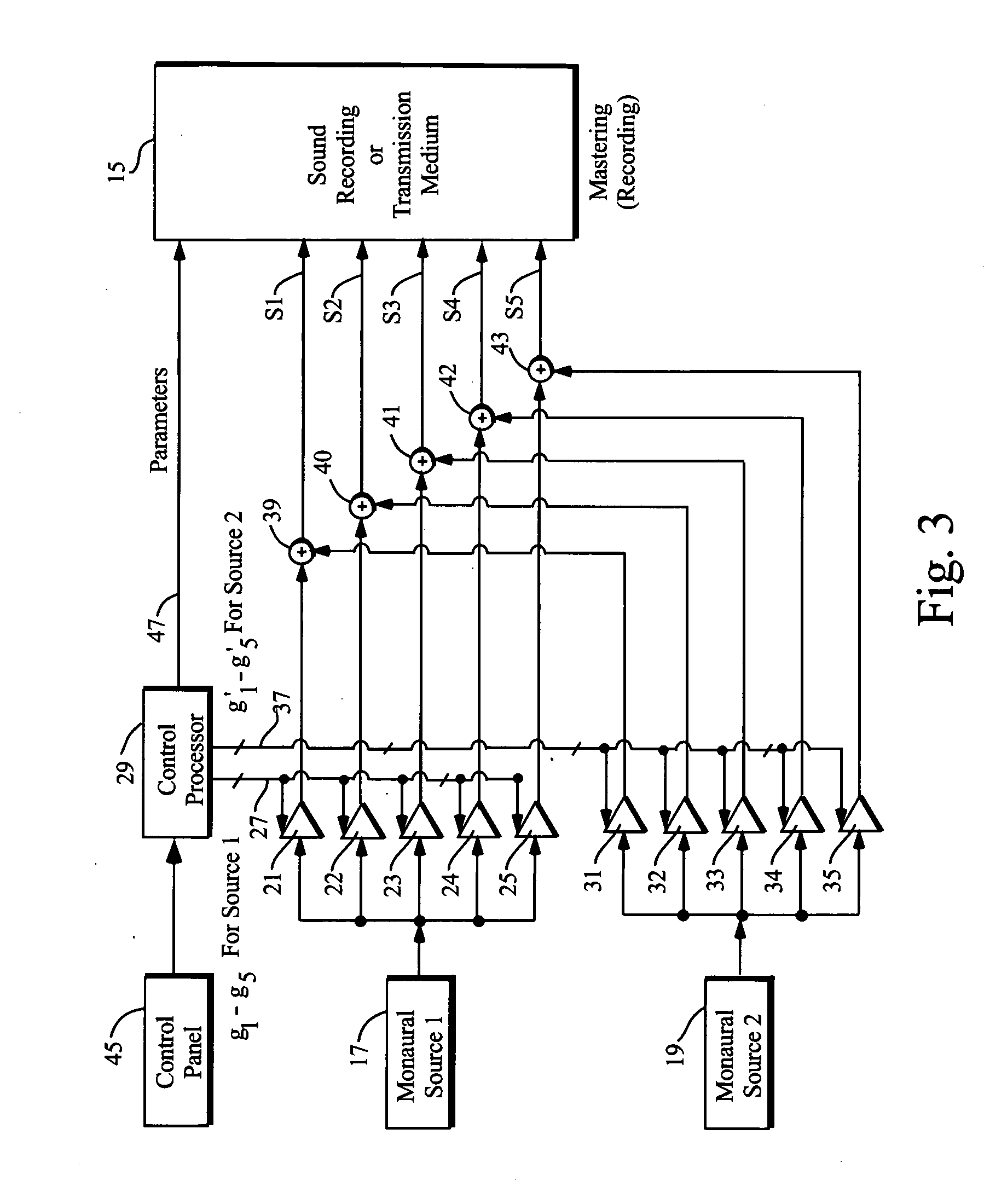
Multi-channel surround sound mastering and reproduction techniques that preserve spatial harmonics in three dimensions
InactiveUS6904152B1Improve realismExact reproductionGain controlPseudo-stereo systemsSound sourcesHarmonic
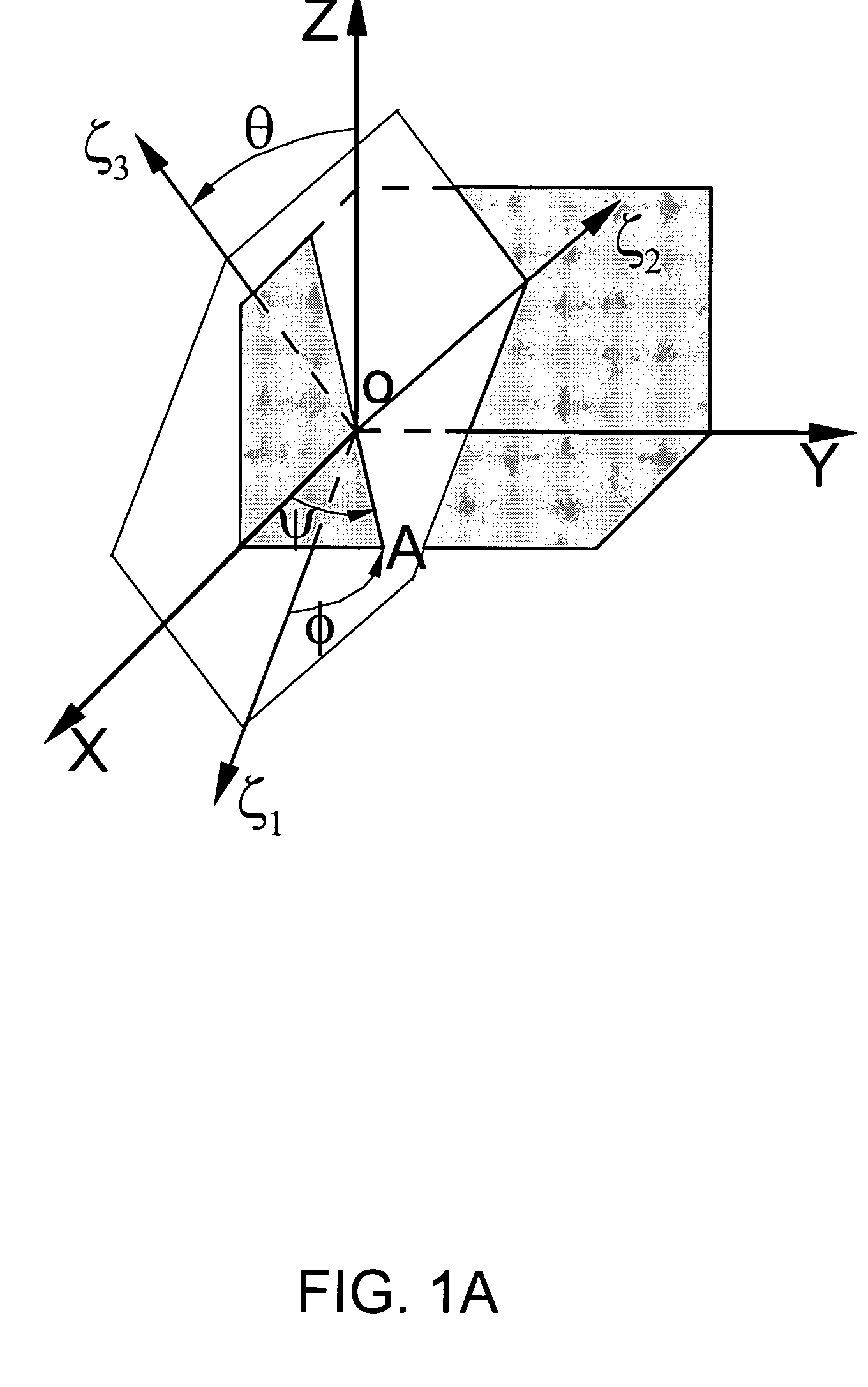
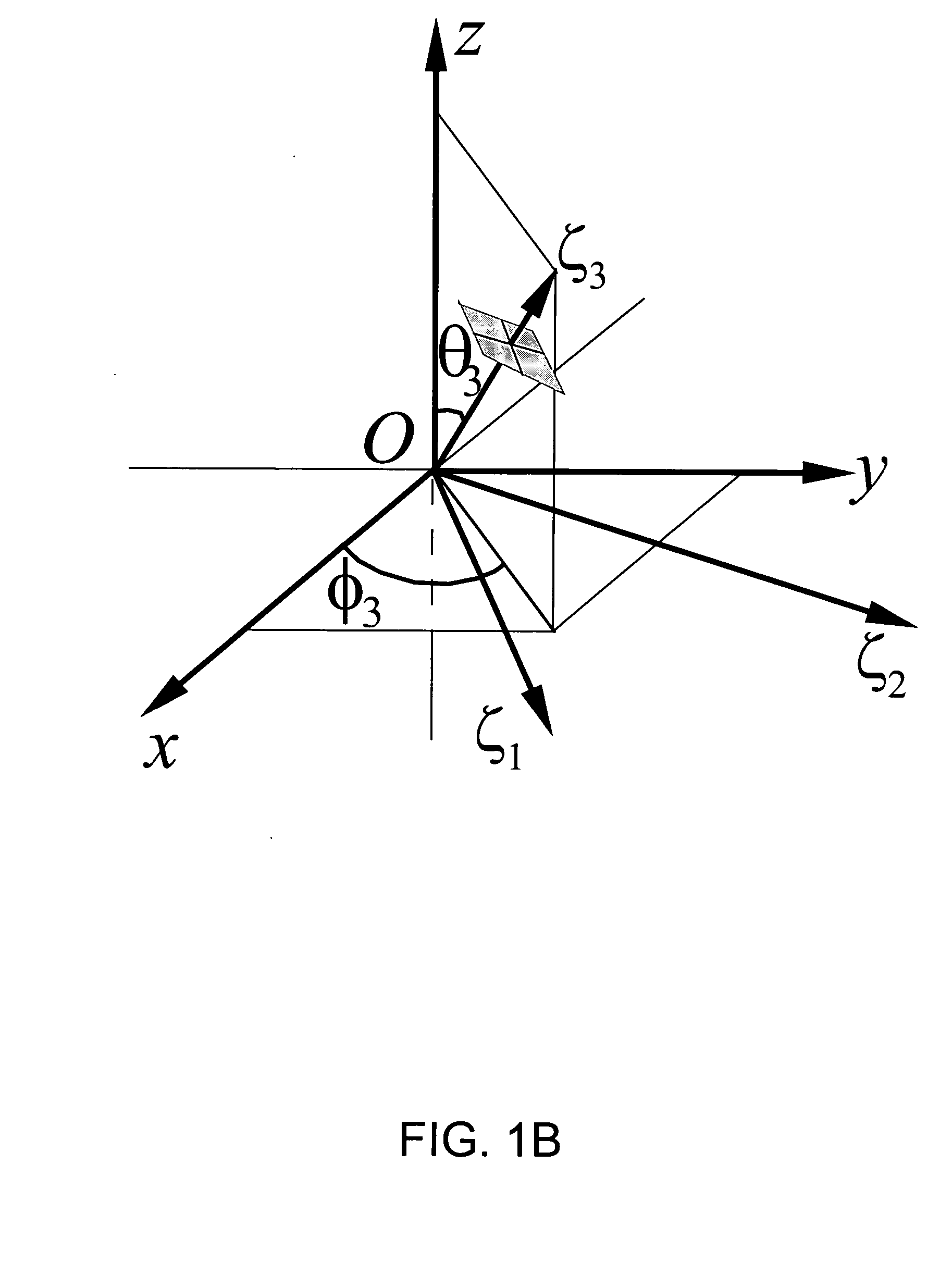
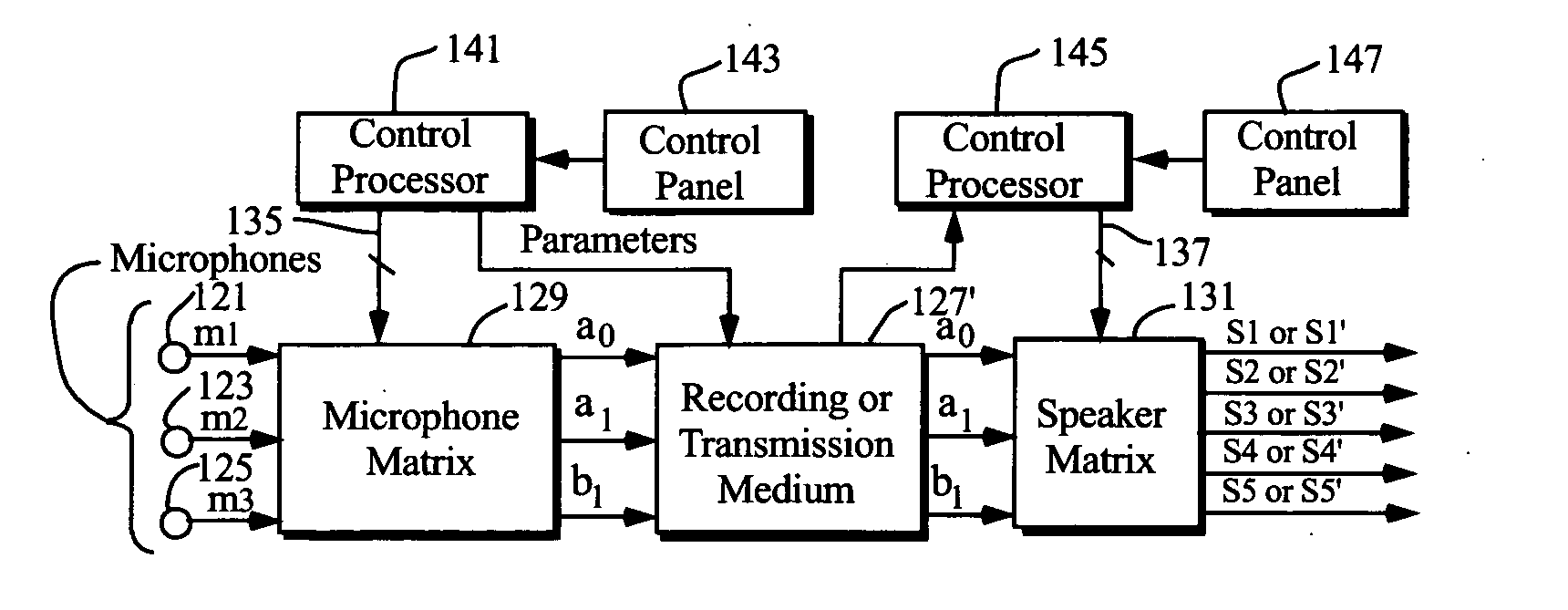
Techniques of making a recording of or transmitting a sound field from either multiple monaural or directional sound signals that reproduce through multiple discrete loud speakers a sound field with spatial harmonics that substantially exactly match those of the original sound field. Monaural sound sources are positioned during mastering to use contributions of all speaker channels in order to preserve the spatial harmonics. If a particular arrangement of speakers is different than what is assumed during mastering, the speaker signals are rematrixed at the home, theater or other sound reproduction location so that the spatial harmonics of the sound field reproduced by the different speaker arrangement match those of the original sound field. An alternative includes recording or transmitting directional microphone signals, or their spatial harmonic components, and then matrixing these signals at the sound reproduction location in a manner that takes into account the specific speaker arrangement. The techniques are described for both a two dimensional sound field and the more general three dimensional case, the latter based upon using spherical harmonics.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES FUND 83 LLC +1
Correction of magnetic resonance images
InactiveUS20050024051A1Avoid artifactsAccurate imagingMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetic field gradientFourier transform on finite groups
Spatial encoding in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques is achieved by sampling the signal as a function of time in the presence of magnetic field gradients, e.g., X, Y, and Z gradients. The gradient magnets have in the past been assumed to generate a linear gradient, and typical image reconstruction techniques have relied upon this assumption. However, to achieve high speed performance, gradient magnets often sacrifice linearity for speed. This non-linearity, in turn, results in distorted images, the distortion often being sufficiently large to compromise the usefulness of MRI images for stereotaxy or longitudinal studies, where precise volumetric information is required. The disclosure provides practical methods for correcting distorted images resulting from such non-linearity in the gradient fields, as well as distortions resulting from translational, rotational, and / or winding / design errors in the field generating devices. The methods employ spherical harmonic expansions of the gradient fields and fast Fourier transform techniques to provide well-corrected images without undue computational burdens.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
Multi-channel surround sound mastering and reproduction techniques that preserve spatial harmonics in three dimensions
InactiveUS20050141728A1Improve realismExact reproductionGain controlPseudo-stereo systemsSound sourcesHarmonic
Techniques of making a recording of or transmitting a sound field from either multiple monaural or directional sound signals that reproduce through multiple discrete loud speakers a sound field with spatial harmonics that substantially exactly match those of the original sound field. Monaural sound sources are positioned during mastering to use contributions of all speaker channels in order to preserve the spatial harmonics. If a particular arrangement of speakers is different than what is assumed during mastering, the speaker signals are rematrixed at the home, theater or other sound reproduction location so that the spatial harmonics of the sound field reproduced by the different speaker arrangement match those of the original sound field. An alternative includes recording or transmitting directional microphone signals, or their spatial harmonic components, and then matrixing these signals at the sound reproduction location in a manner that takes into account the specific speaker arrangement. The techniques are described for both a two dimensional sound field and the more general three dimensional case, the latter based upon using spherical harmonics.
Owner:THINKLOGIX LLC
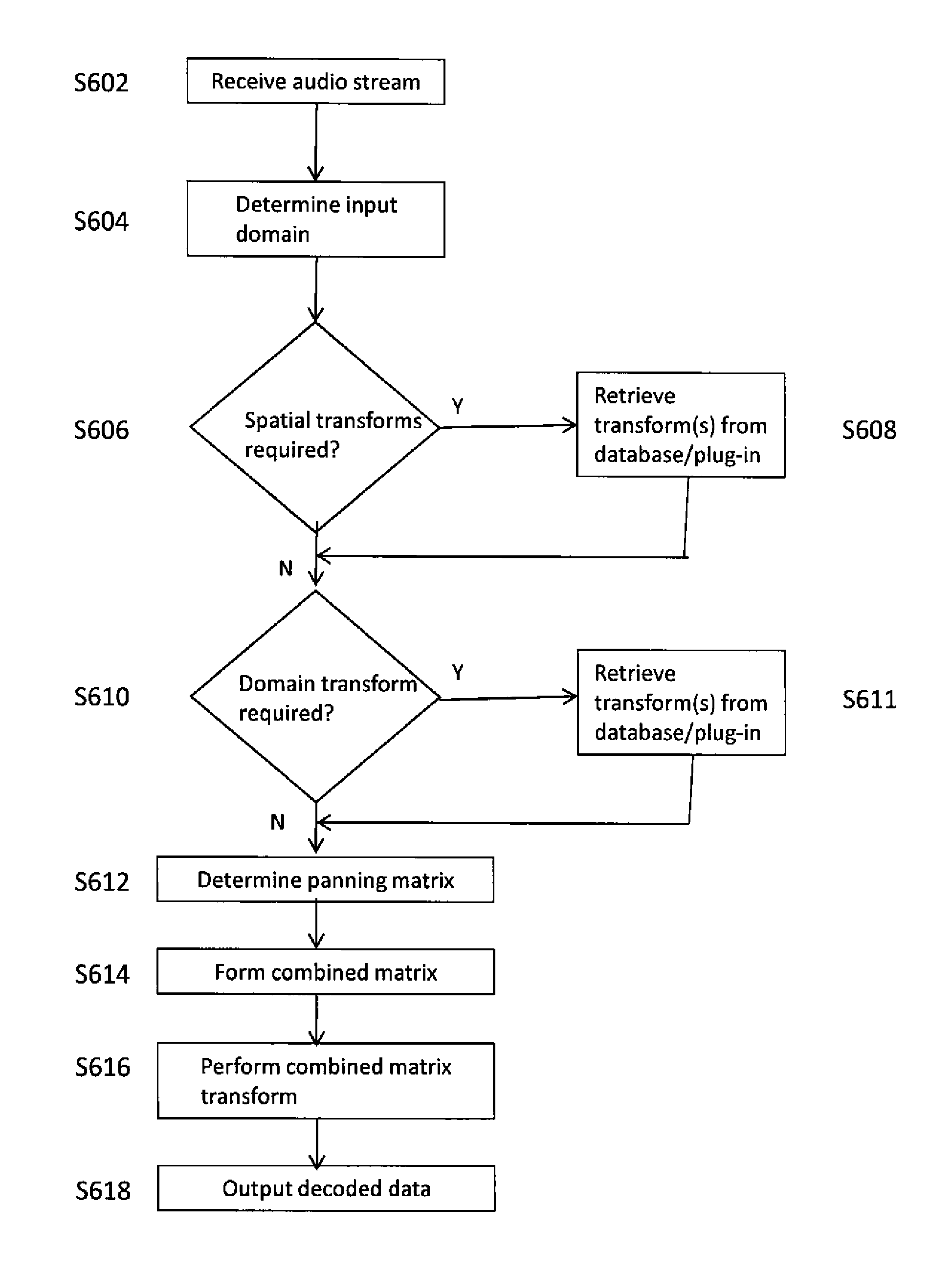
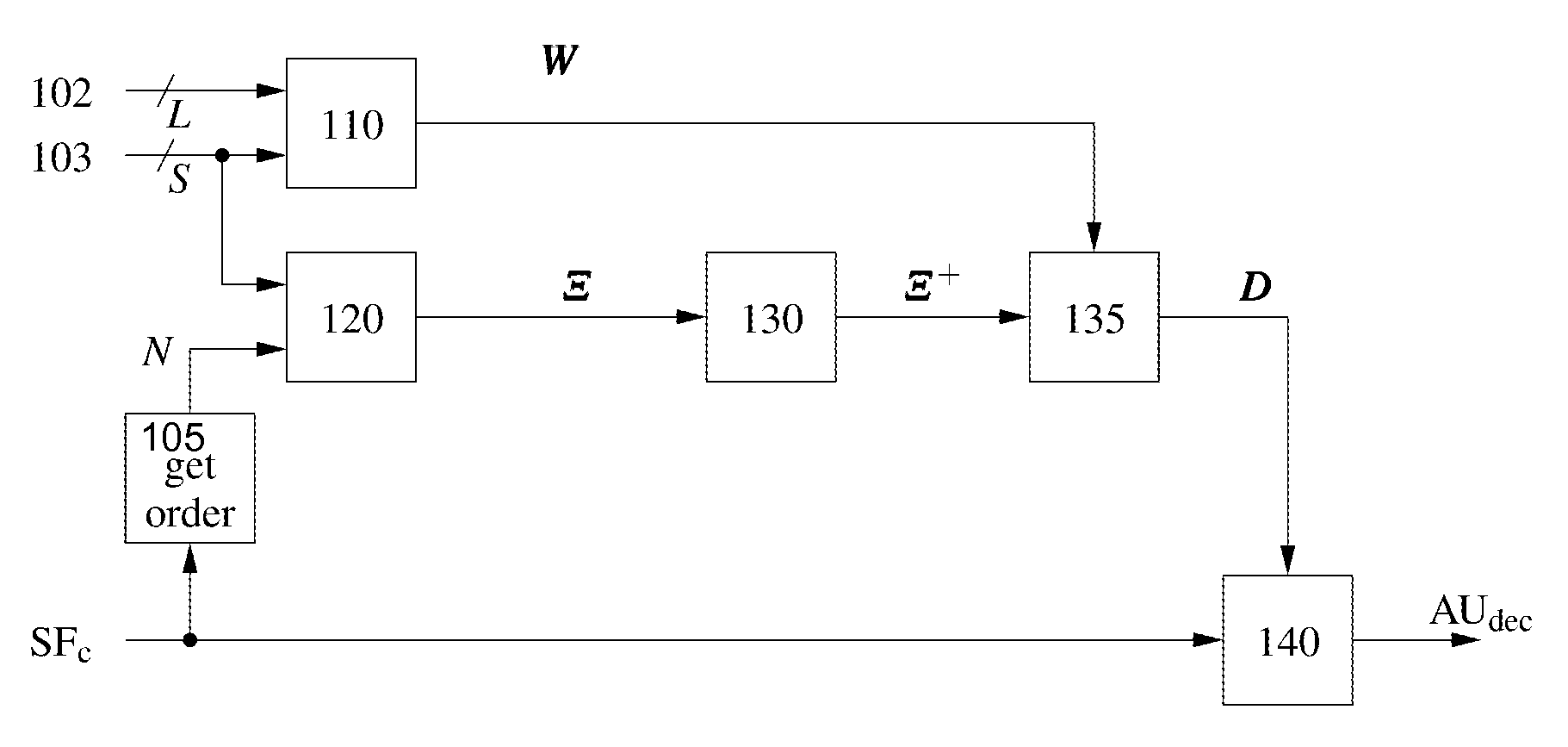
Method and device for decoding an audio soundfield representation for audio playback
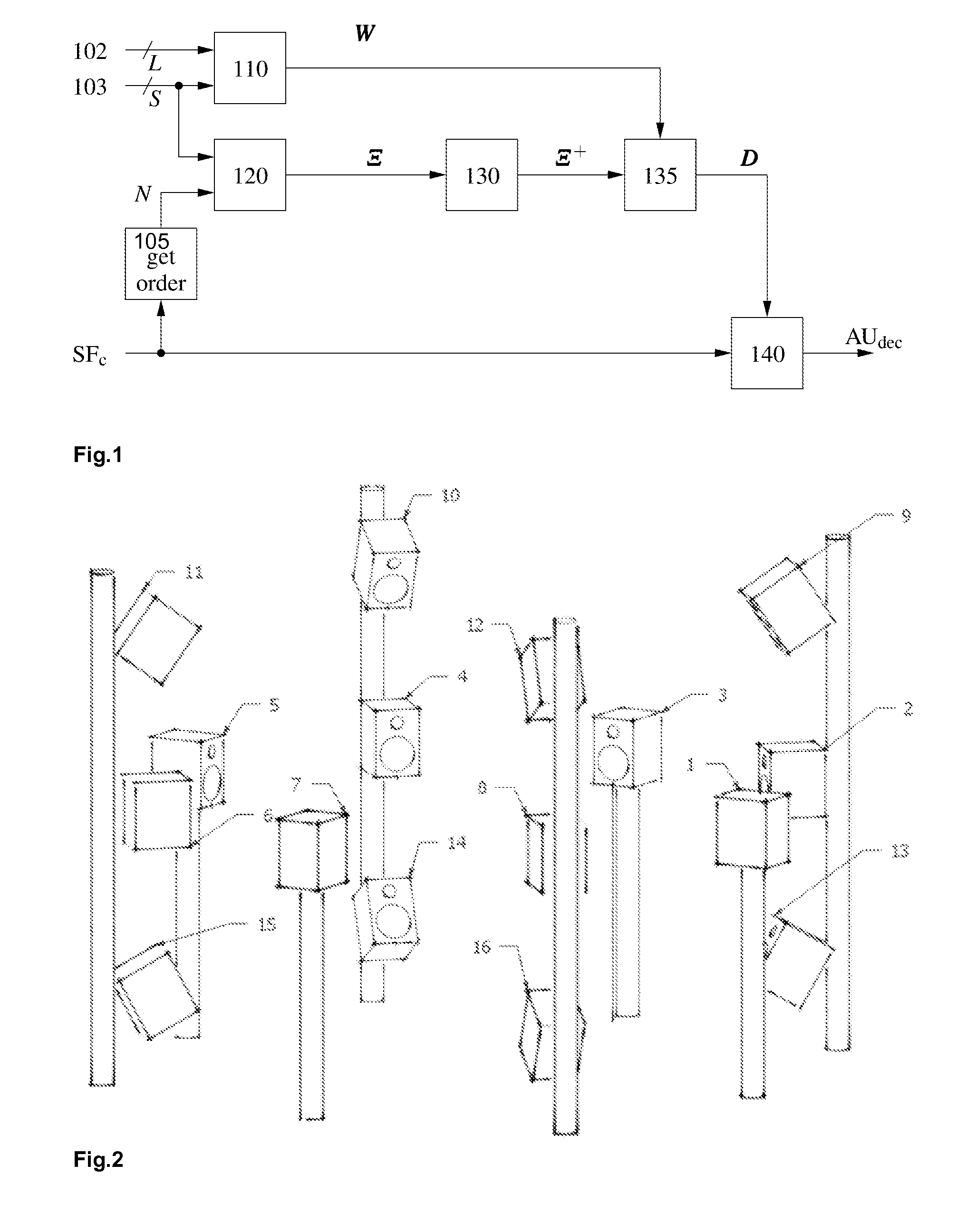
Soundfield signals as such e.g. Ambisonics carry a representation of a desired sound field. The Ambisonics format is based on spherical harmonic decomposition of the soundfield, and Higher Order Ambisonics uses spherical harmonics of at least 2nd order. However, commonly used loudspeaker setups are irregular and lead to problems in decoder design. A method for improved decoding an audio soundfield representation for audio playback comprises calculating a panning function using a geometrical method based on the positions of a plurality of loudspeakers and a plurality of source directions, calculating a mode matrix Ξ from the loudspeaker positions, calculating a pseudo-inverse mode matrix μ+ and decoding the audio soundfield representation. The decoding is based on a decode matrix that is obtained from the panning function and the pseudo-inverse mode matrix Ξ+.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Rendering apparatus and method for real-time global illumination in real light environment
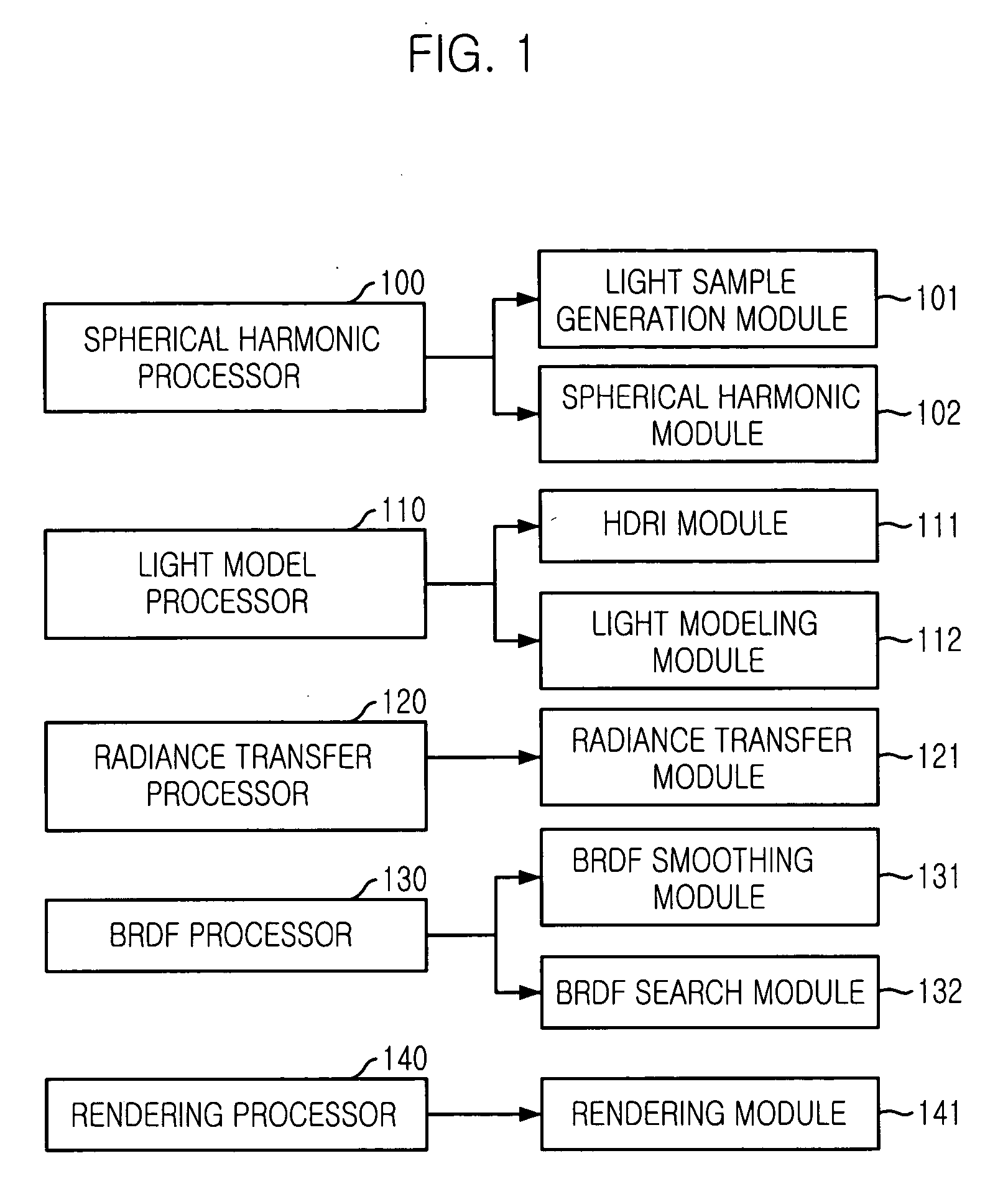
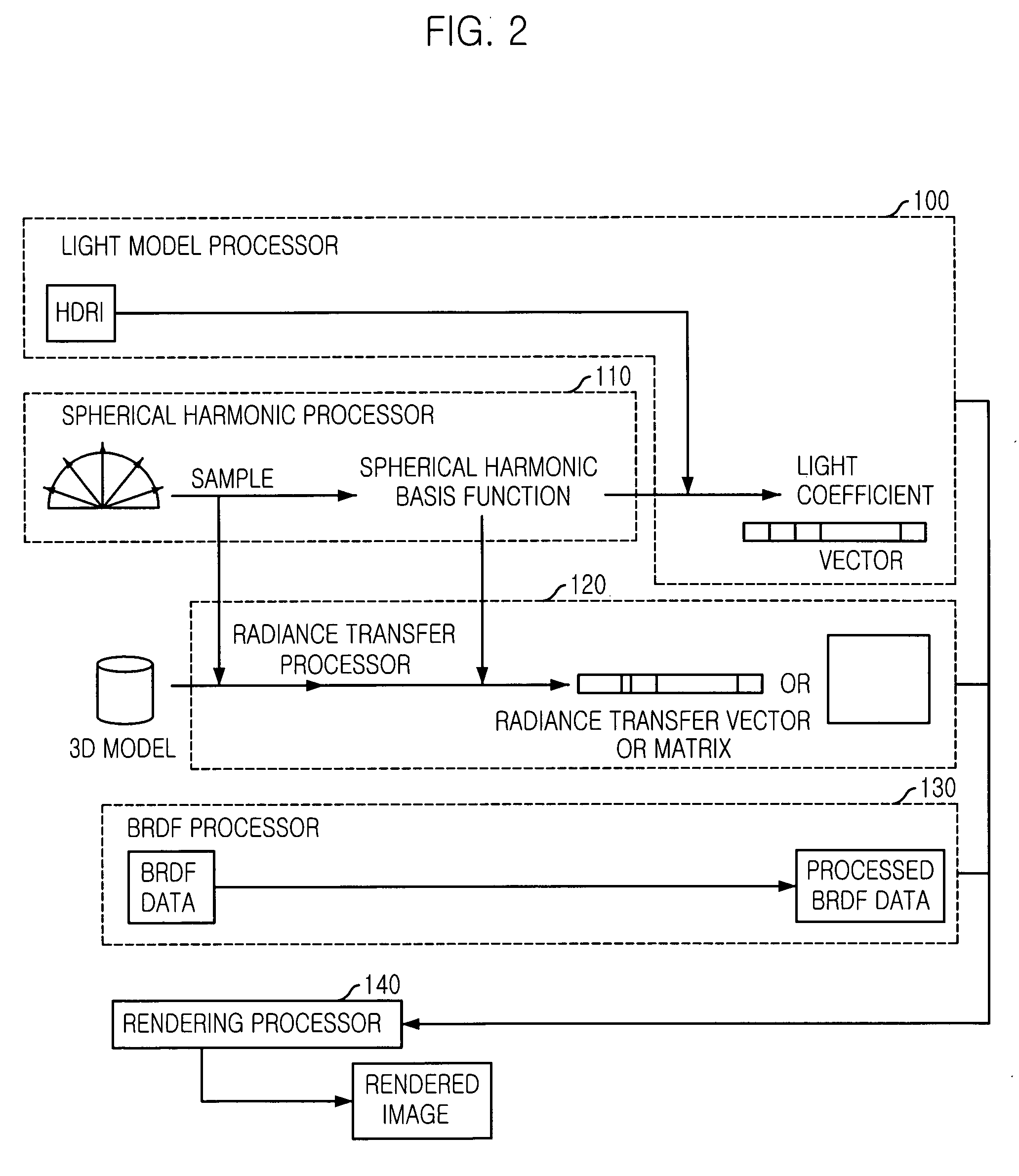
A rendering apparatus for real-time global illumination and a method thereof are disclosed. The rendering apparatus includes: a spherical harmonic processor for creating light samples and creating spherical harmonics basis functions; a light model processor for transforming radiance of a HDRI image to spherical harmonics light coefficients using the spherical harmonic basis functions; a radiance transfer processor for previously calculating coefficients of a visibility and a geometric term for a global illumination model using the spherical harmonic basis function; a BRDF processor for generating a database of BRDF data and calculating coefficients of the BRDF data through smoothing; and a render unit for rendering the spherical harmonic light coefficients, the coefficients for the visibility and the geometric term, and the BRDF data coefficient using a rendering equation expressed as a dot product of a vector.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method and device for decoding an audio soundfield representation for audio playback
Soundfield signals such as e.g. Ambisonics carry a representation of a desired sound field. The Ambisonics format is based on spherical harmonic decomposition of the soundfield, and Higher Order Ambisonics uses spherical harmonics of at least 2nd order. However, commonly used loudspeaker setups are irregular and lead to problems in decoder design, A method for improved decoding an audio soundfield representation for audio playback comprises calculating a panning function using a geometrical method based on the positions of a plurality of loudspeakers and a plurality of source directions, calculating a mode matrix from the loudspeaker positions, calculating a pseudo-inverse mode matrix and decoding the audio soundfield representation. The decoding is based on a decode matrix that is obtained from the panning function and the pseudo-inverse mode matrix.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
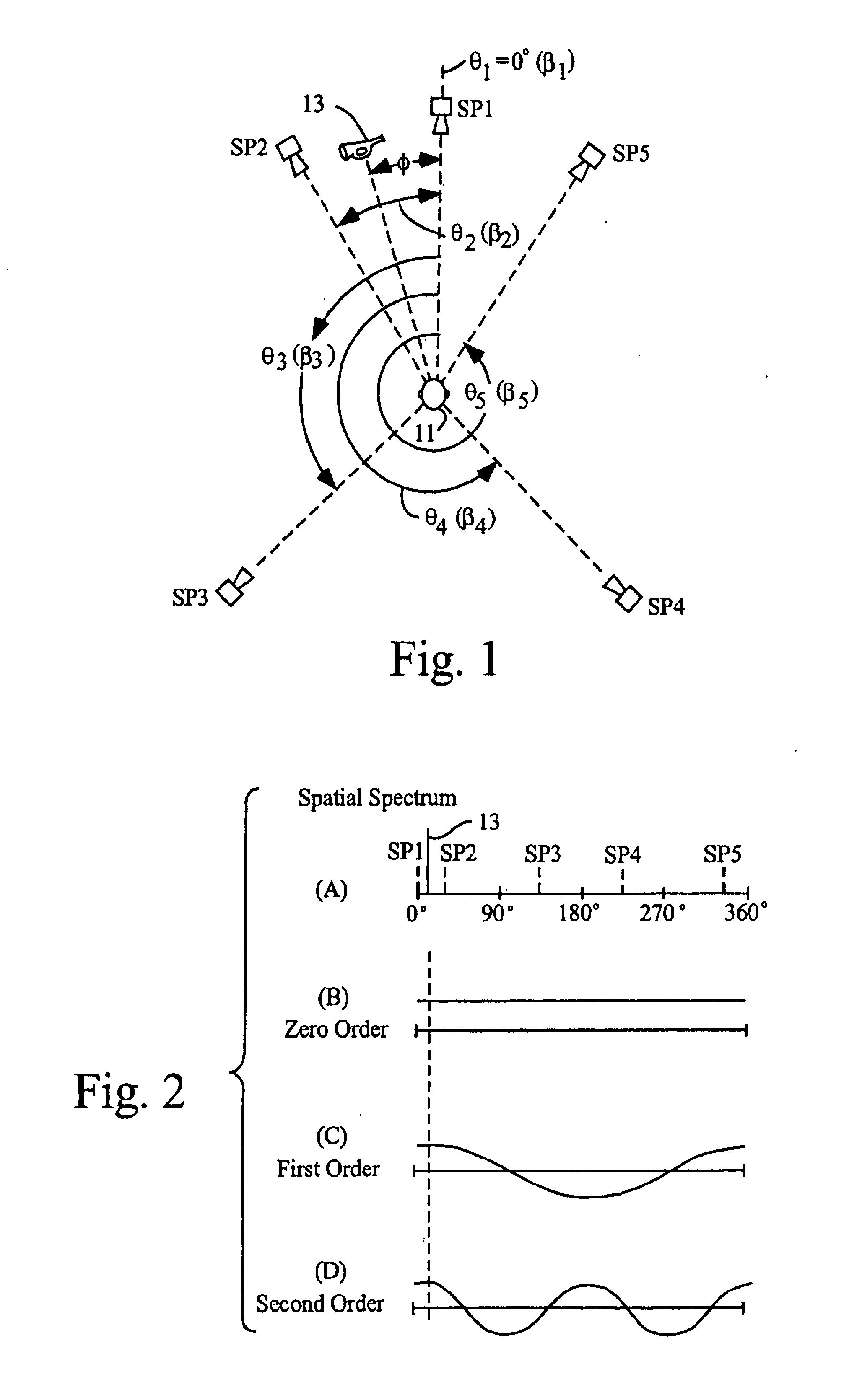
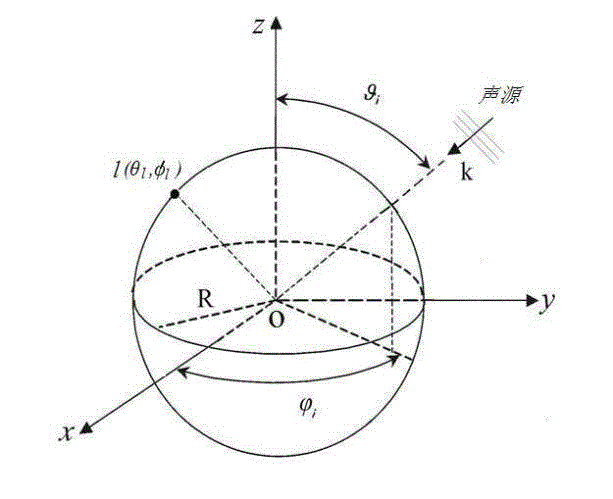
Multi-sound-source locating method based on spherical microphone array
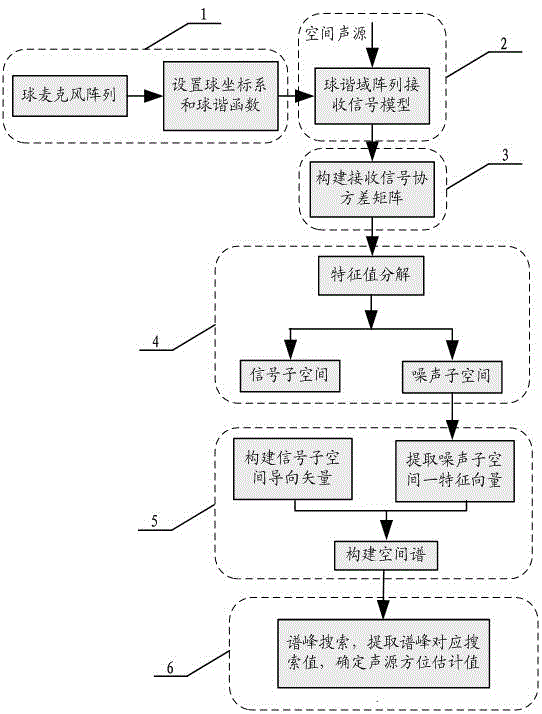
The invention discloses a multi-sound-source locating method based on a spherical microphone array, and the method comprises the following steps of firstly conducting spherical harmonics decomposition for high-order sound fields collected by a spherical microphone array, and building a noise-contained sound source signal model received by a spherical harmonics domain array; then expressing a covariance matrix of data received by the array; classifying the covariance matrix according to a subspace decomposition method to obtain two mutually-orthogonal signal subspace and noise subspace; utilizing the orthogonality of the signal subspace and the noise subspace to define a guide vector of the signal subspace, and extracting one characteristic vector of the noise subspace to build a space azimuth spectrum; and finally searching a spectrum peak position of an azimuth spectrum function, and determining a space azimuth of a sound source. The method utilizes a three-dimensional space rotary symmetric structure of the spherical microphone array to adequately sample the sound field, so that the operation quantity is remarkably reduced through the high-resolution spectrum estimation and dimensional-reduced noise subspace, the sound source azimuth is accurately estimated, and the method can be widely applied to the fields such as a voice signal processing field.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
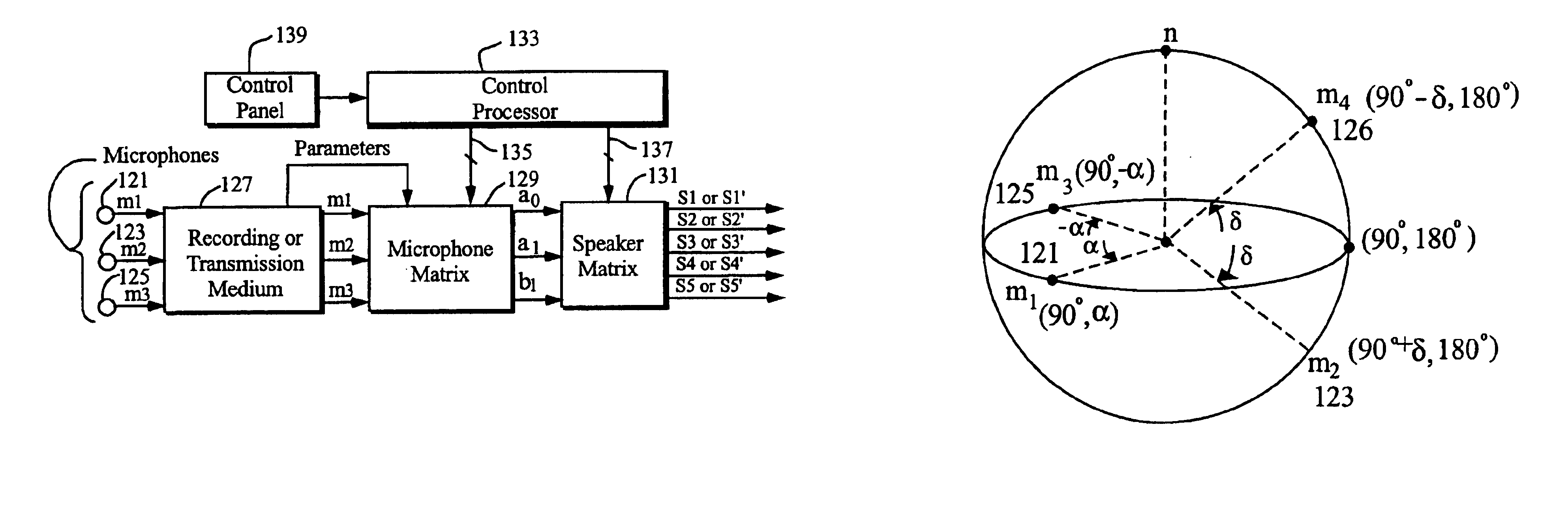
Microphone array
ActiveUS8406436B2Trend downReduce asymmetryMicrophonesTransducer detailsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Spherical harmonics
A sound capture device comprises a symmetric microphone array that includes non-radially-oriented directional sensors (101). The device typically derives a spherical harmonic representation of the incident sound field, and affords higher signal-to-noise ratios and better directional fidelity than prior arrays, across a wide range of audio frequencies.
Owner:CRAVEN PETER G +2
Sound system
InactiveCN102318372ASpeech analysisTwo-channel systemsSpherical harmonicsTable of spherical harmonics
In some embodiments of the invention one or more sound characteristics, such as gain or frequency, of a given component of a spatial audio signal are modified in dependence on a relationship between a direction characteristic of the given component and a defined range of direction characteristics. A plurality of transforms. each relating to a different frequency range, is preferably used to modify the sound characteristics. In some embodiments, spatial audio in a format using a spherical harmonic representation of sound components is decoded by performing a transform on the spherical harmonic representation, in which the transform is based on a predefined speaker layout and a predefined rule. The predefined rule indicates a gain of each speaker, when reproducing sound incident from a given direction. In some embodiments, a plurality of matrix transforms is combined into a combined transform, and the combined transform is performed on an audio signal.
Owner:理查德·福塞
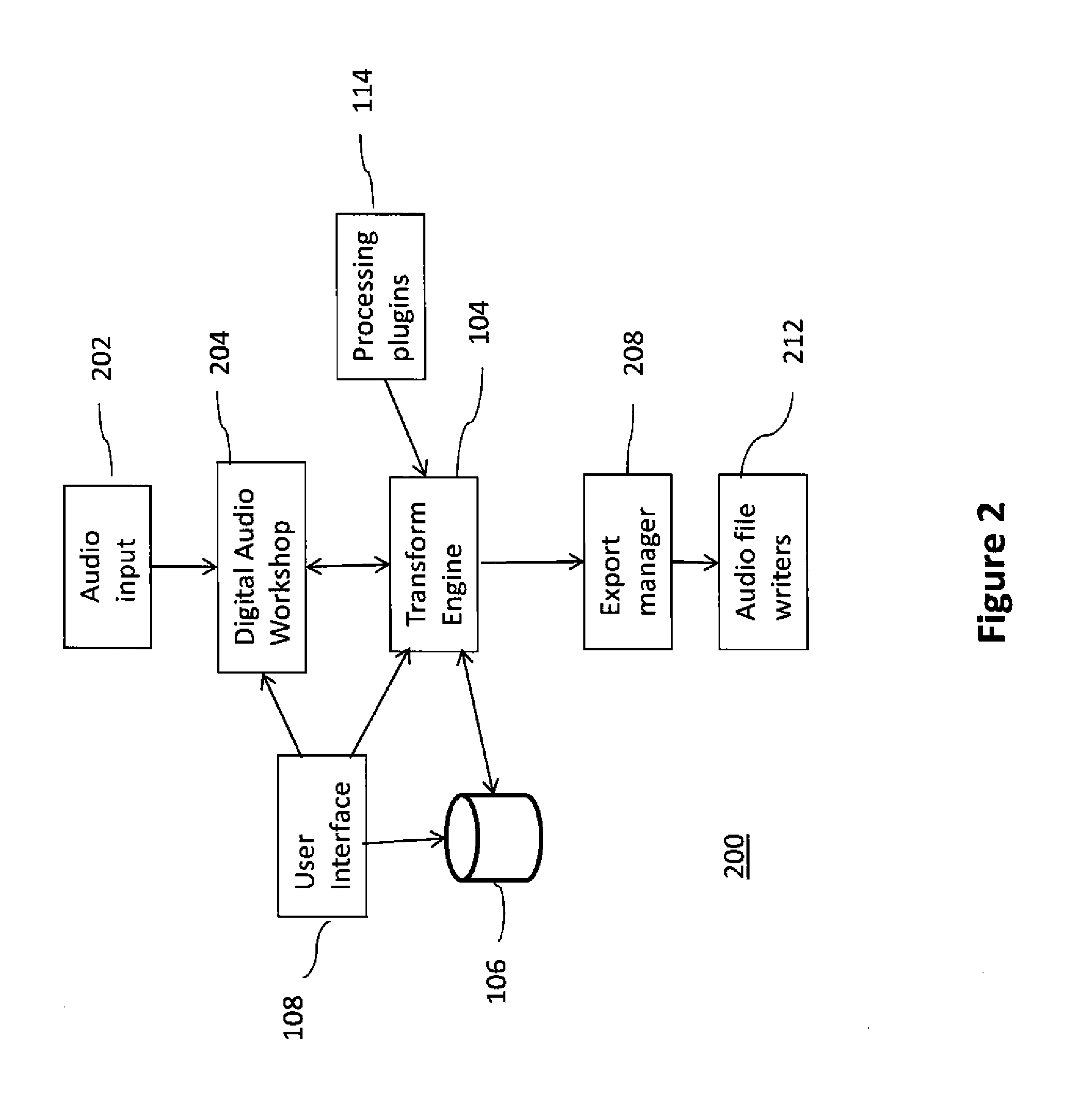
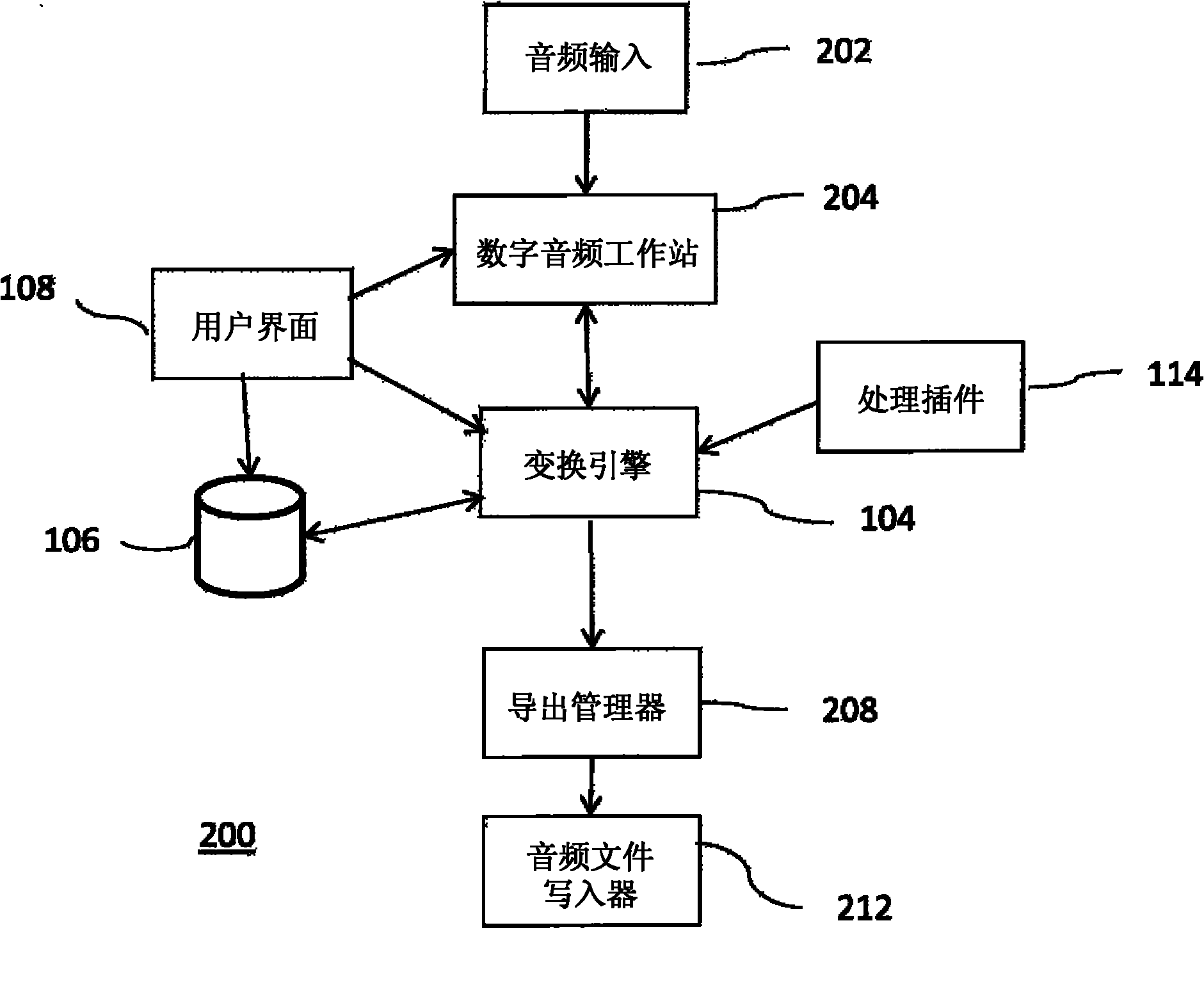
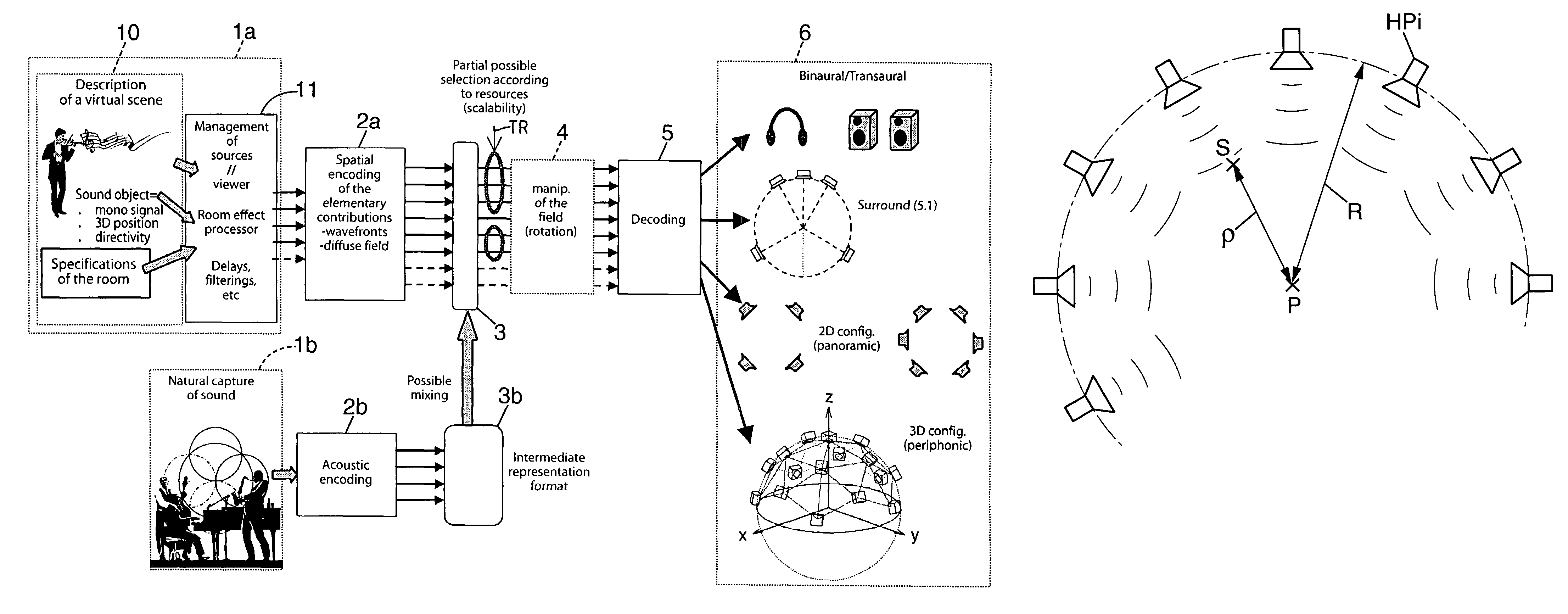
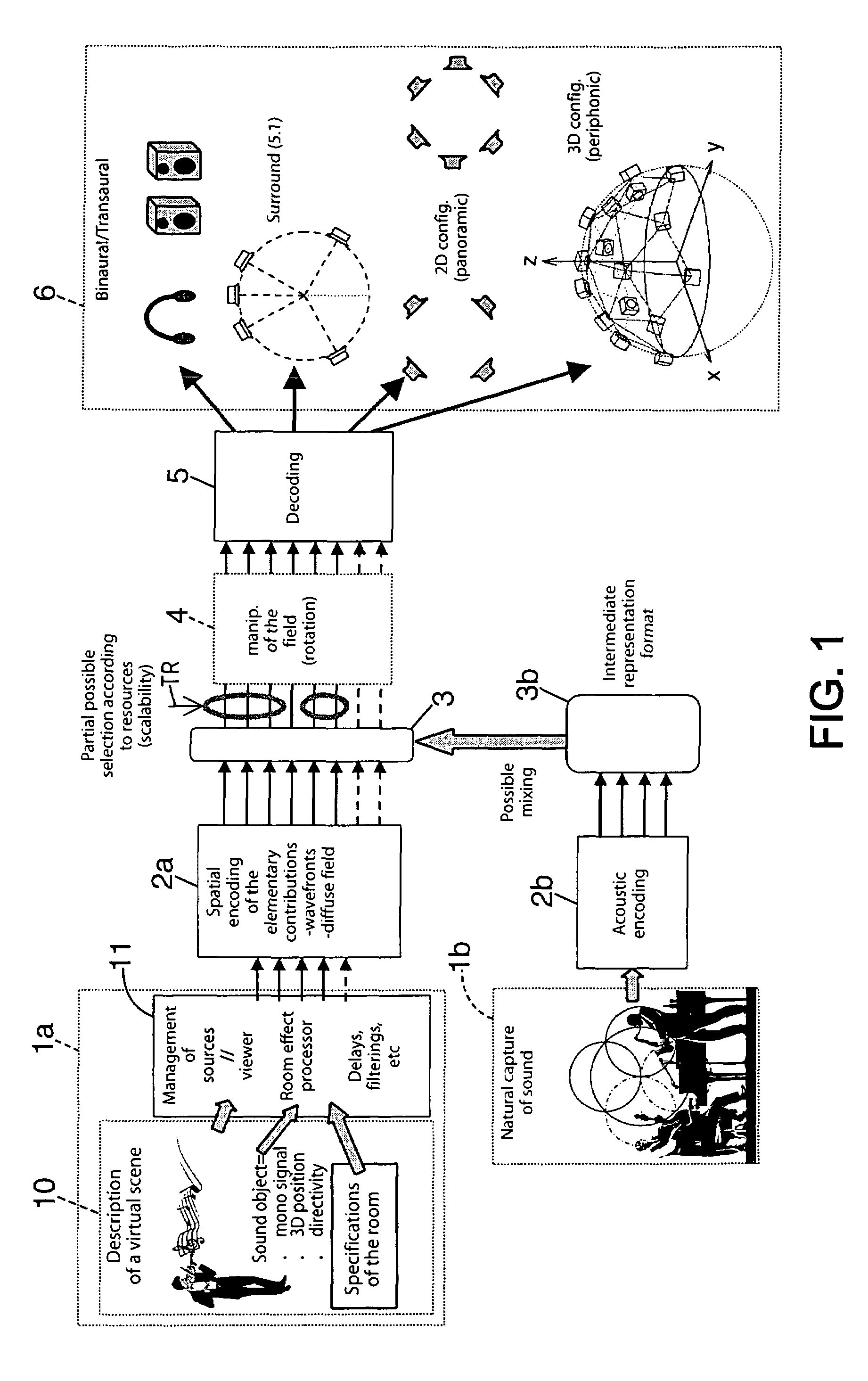
Method for processing audio data and sound acquisition device implementing this method
ActiveUS7706543B2Electrophonic musical instrumentsLoudspeaker spatial/constructional arrangementsThree-dimensional spaceHarmonic
The invention concerns the processing of audio data. The invention is characterized in that it consists in: (a) encoding signals representing a sound propagated in three-dimensional space and derived from a source located at a first distance (P) from a reference point, to obtain a representation of the sound through components expressed in a spherical harmonic base, of origin corresponding to said reference point, (b) and applying to said components compensation of a near-field effect through filtering based on a second distance (R) defining, for sound reproduction, a distance between a reproduction point (HPi), and a point (P) of auditory perception where a listener is usually located.
Owner:FRANCE TELECOM SA
Specular object scanner for measuring reflectance properties of objects
An apparatus to measure surface orientation maps of an object may include a light source that is configured to illuminate the object with a controllable field of illumination. One or more cameras may be configured to capture at least one image of the object. A processor may be configured to process the image(s) to extract the reflectance properties of the object including an albedo, a reflection vector, a roughness, and / or anisotropy parameters of a specular reflectance lobe associated with the object. The controllable field of illumination may include limited-order Spherical Harmonics (SH) and Fourier Series (FS) illumination patterns with substantially similar polarization. The SH and FS illumination patterns are used with different light sources.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
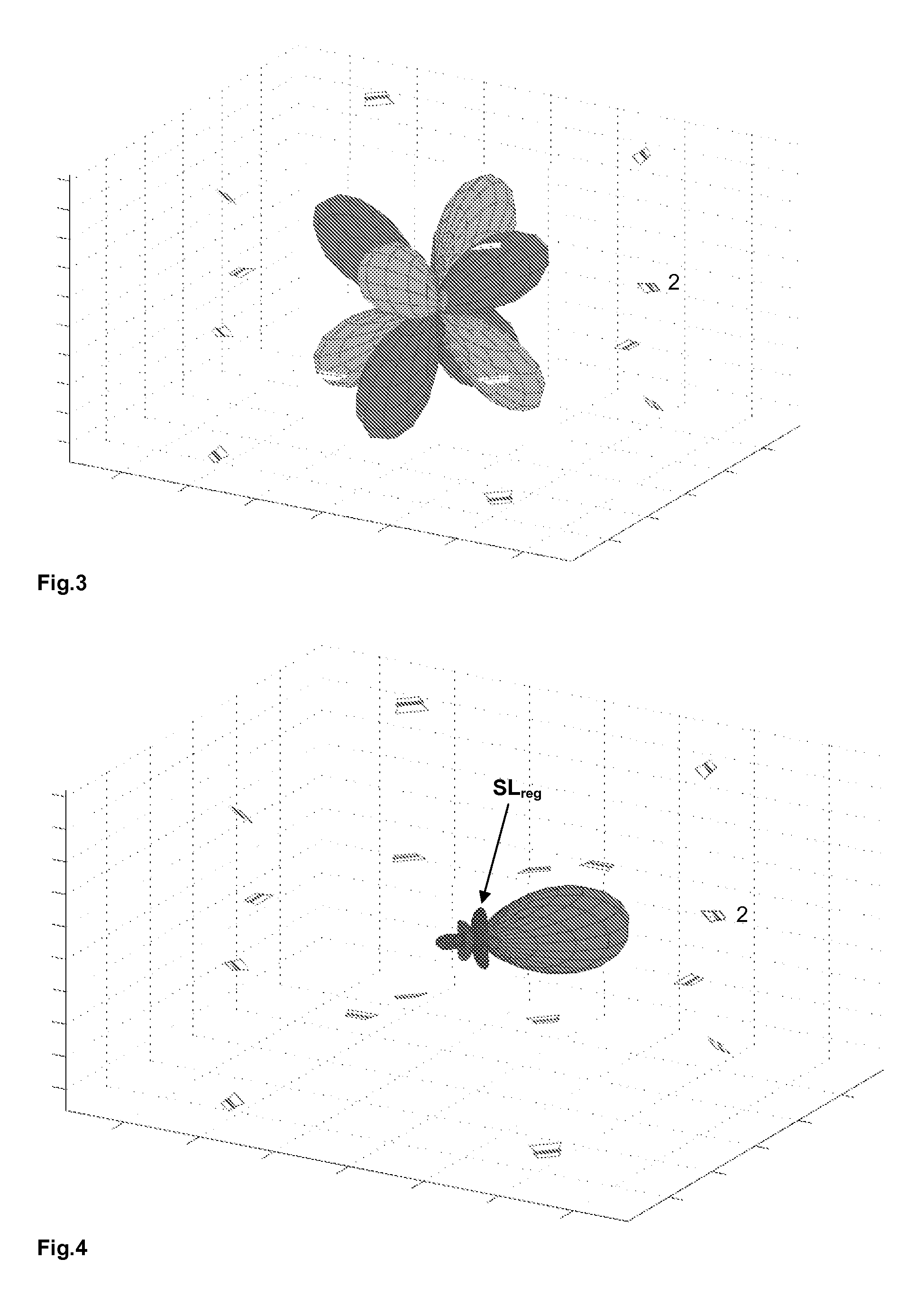
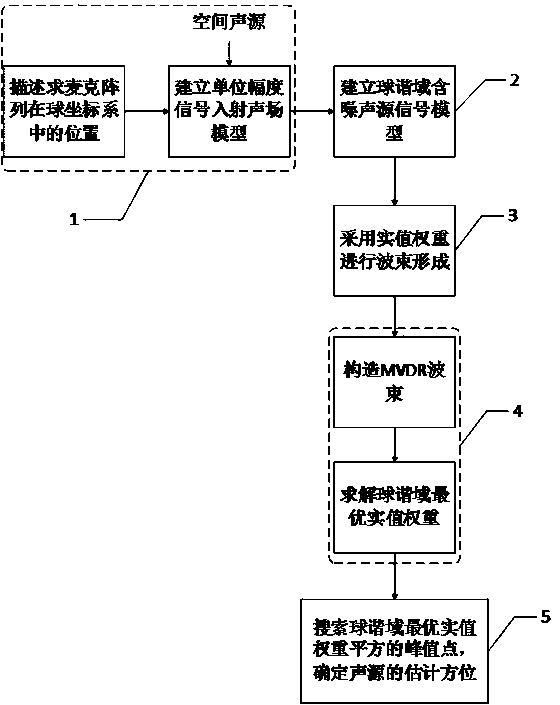
Multi-sound-source positioning method based on formation of real value weight beam in spherical harmonic domain
The invention discloses a multi-sound-source positioning method based on formation of a real value weight beam in a spherical harmonic domain. The multi-sound-source positioning method comprises the steps that a sound field model that unit amplitude plane waves enter a spherical microphone array is firstly established; then a spherical harmonic domain noise source signal model is constructed; spherical harmonic domain real value beam forming is carried out on noise source signals received by the spherical microphone array to obtain the beam in the spherical harmonic domain; an MVDR beam when the gain of the spherical microphone array is the maximum is constructed, and the optimal real value weight at the time is obtained; finally, the peak point of the square of the real value weight in the spherical harmonic domain is calculated, and the dimensional orientation maximum estimated value point of sound sources is extracted. According to the multi-sound-source positioning method based on formation of the real value weight beam in the spherical harmonic domain, the optimum real value weight in the spherical harmonic domain is obtained by utilizing the formation of the MVDR beam, the defects of large calculation amount and high calculation complexity of a traditional method are overcome, the calculation amount is obviously lowered, all-dimensional estimation of a free space is met, and the sound field is sampled more sufficiently.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
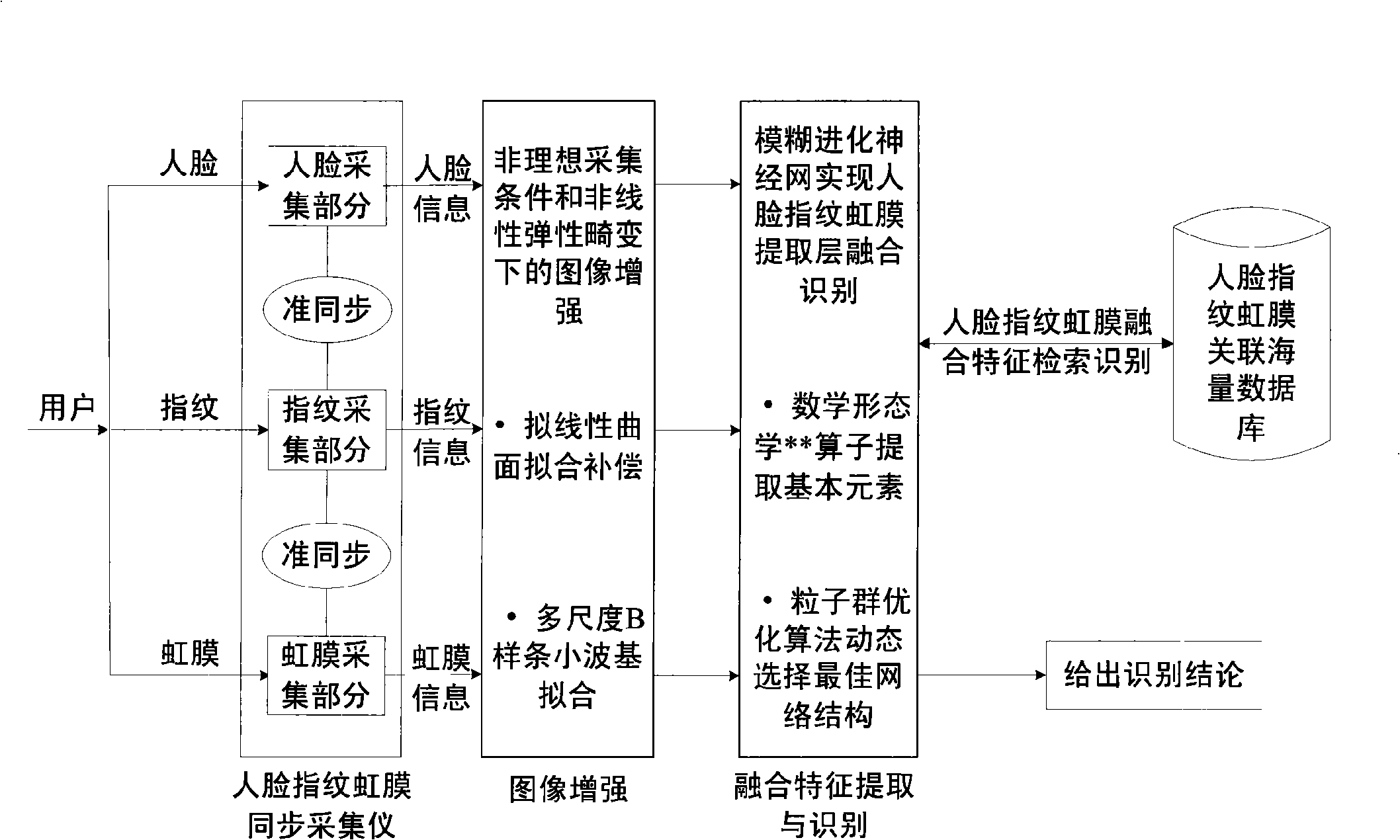
New method-feature extraction layer amalgamation for face and iris
The invention relates to a new face-iris combination identifying method-characteristic layer extraction and combination. A face-iris characteristic extraction layer combining system is established according to nerve network, evolution calculation and fuzzy theory. For structure design, full and local geometry topological structure is adopted. A particle-group optimizing arithmetic is utilized to optimize network control parameters. When the characteristics of the face and the iris image are extracted, techniques of a super-resolution image reinforcing arithmetic, an illumination compensating arithmetic based on improved spherical harmonic function, gesture estimation based on linear relevant filters, Candide model based on a three-dimensional face and expression analysis based on an ASM arithmetic, etc., are adopted to robustly extract the eigenvectors of the face and the iris, and a self-developed double face-iris collecting device is also adopted to collect images of the face and the iris image. The method not only can establish a new system which is provided with learning capability and can automatically choose optimal network topological structure and automatically regulate net control parameters, but also can overcome and reduce the bad impacts of factors of environment and physiology, etc., during the extraction process to the independent characteristics of the face and the iris, thus effectively enhancing the identifying rate of the face-iris combination identification and promoting the system performance based on the face-iris combination identification to develop towards practical, reliable and acceptable directions.
Owner:周春光
Method and device for sensing touch inputs
ActiveUS20160085333A1Minutely discriminatedDigital data processing detailsInput/output processes for data processingSpectral bandsFrequency spectrum
A method for sensing touch inputs to a digital equipment is provided, comprising the steps of sensing a sound / vibration signal generated by a touch, digitally processing the sensed sound / vibration signal, and determining the type of touch means that has generated the touch and the intensity of the touch based on the properties of the processed sound / vibration signal, wherein the properties include at least one of the following properties of the sound / vibration signal in time domain: maximum amplitude, average amplitude, average frequency, mean, standard deviation, standard deviation normalized by overall amplitude, variance, skewness, kurtosis, sum, absolute sum, root mean square (RMS), crest factor, dispersion, entropy, power sum, center of mass, coefficients of variation, cross correlation, zero-crossings, seasonality, DC bias, or the above properties computed for the first, second, third or higher order of derivatives of the sound / vibration signal; and the following properties of the sound / vibration signal in frequency domain: spectral centroid, spectral density, spherical harmonics, total average spectral energy, band energy ratios for every octave, log spectral band ratios, linear prediction-based cepstral coefficients (LPCCs), perceptual linear prediction (PLP) cepstral coefficients, mel-frequency cepstral coefficients, frequency topology, or the above properties computed for the first, second, third or higher order of derivatives of a frequency domain representation of the sound / vibration signal. There is also provided a device for sensing touch inputs.
Owner:QEEXO
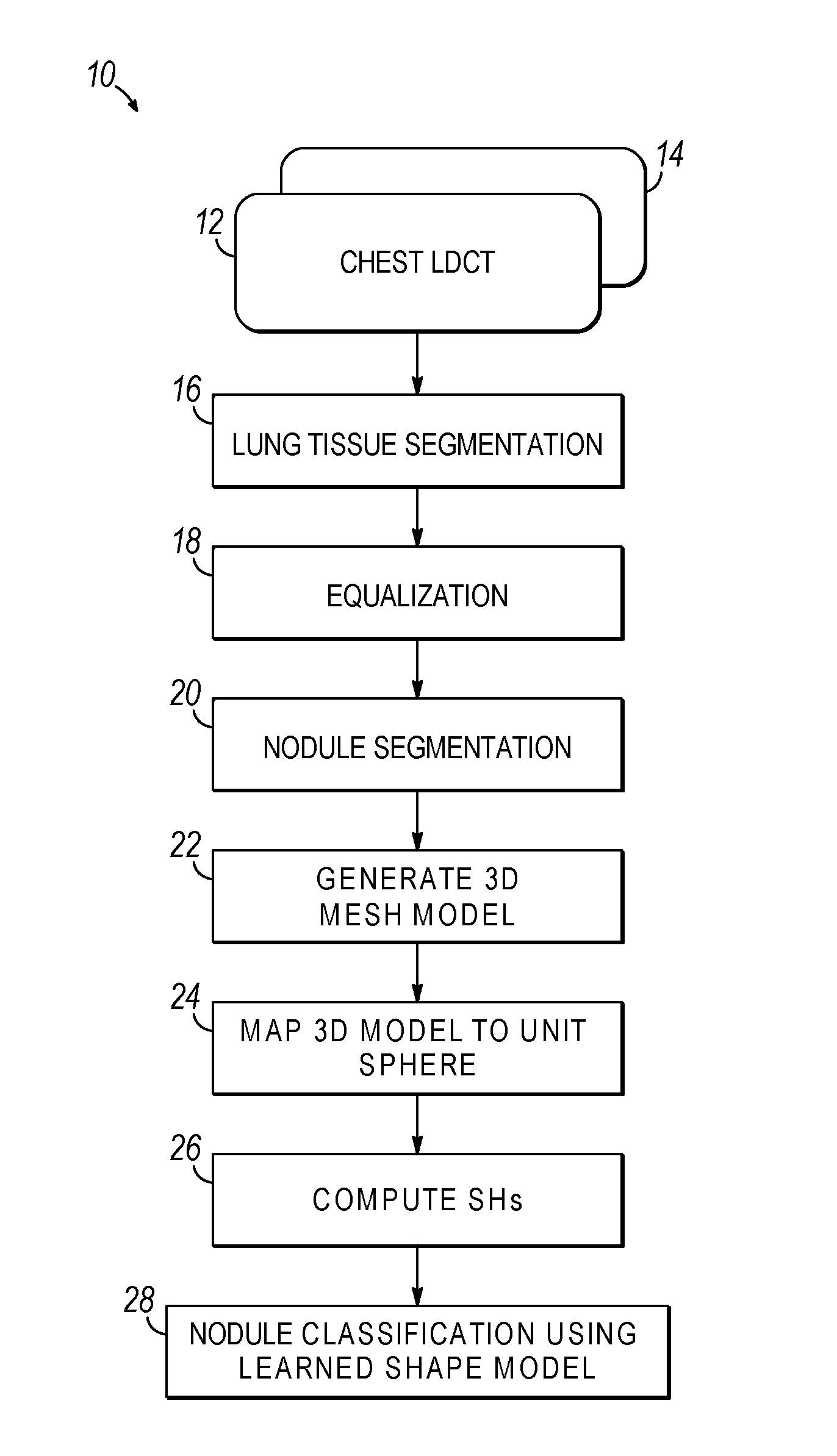
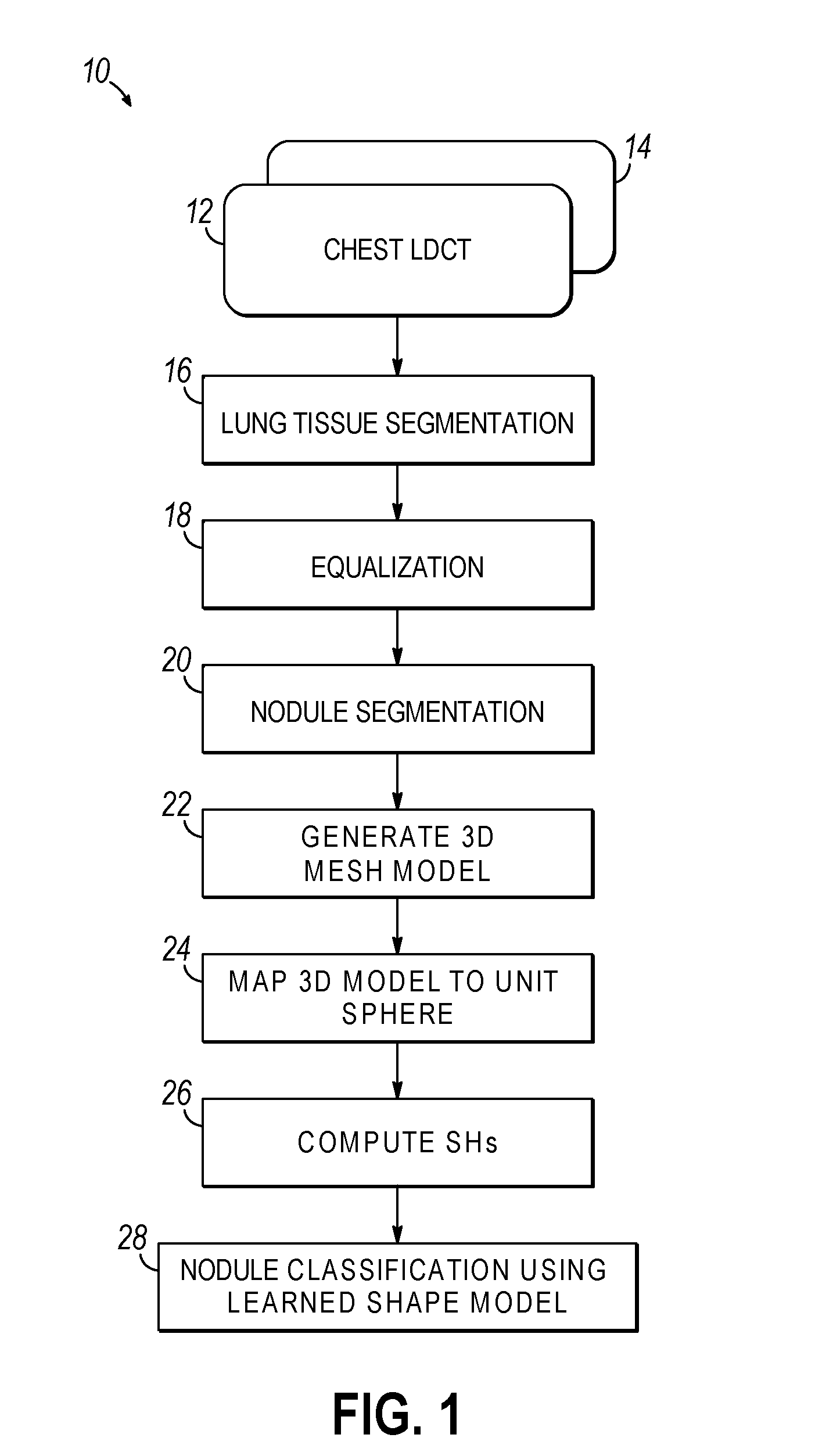
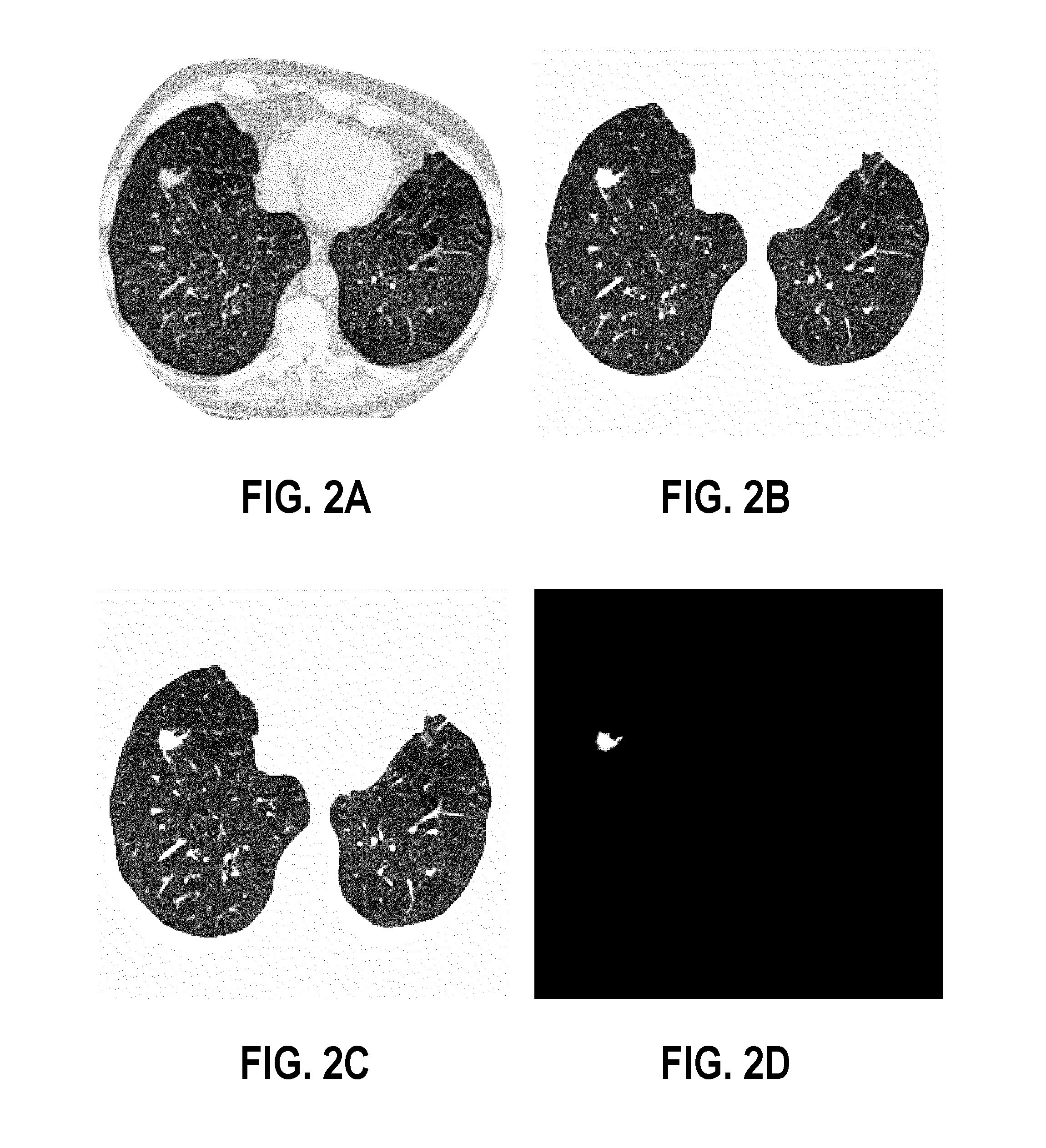
Computer aided diagnostic system incorporating shape analysis for diagnosing malignant lung nodules
A computer aided diagnostic system and automated method diagnose lung cancer through modeling and analyzing the shape of pulmonary nodules. A model used in such analysis describes the shape of pulmonary nodules in terms of spherical harmonics required to delineate a unit sphere corresponding to the pulmonary nodule to a model of the pulmonary nodule.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
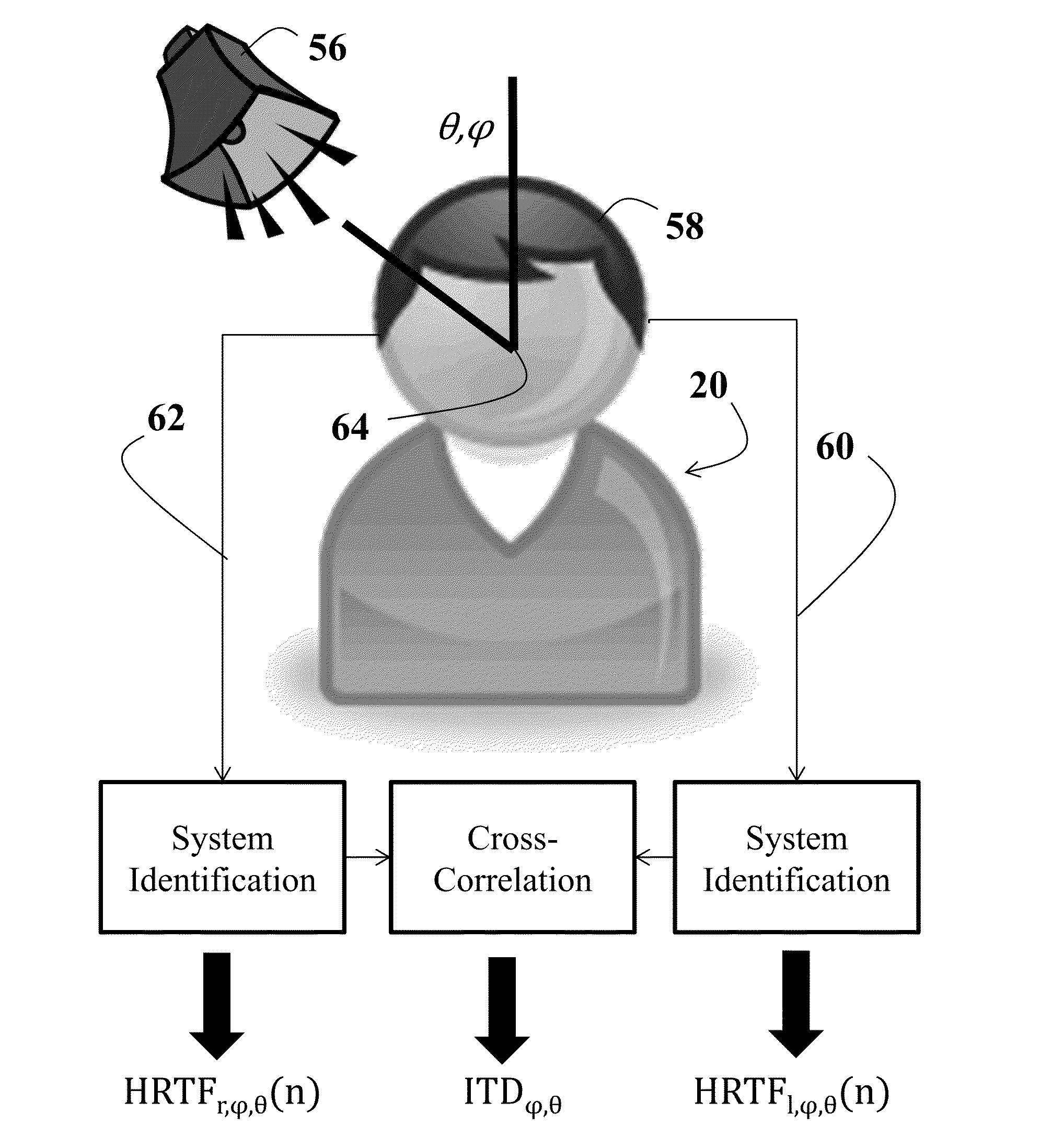
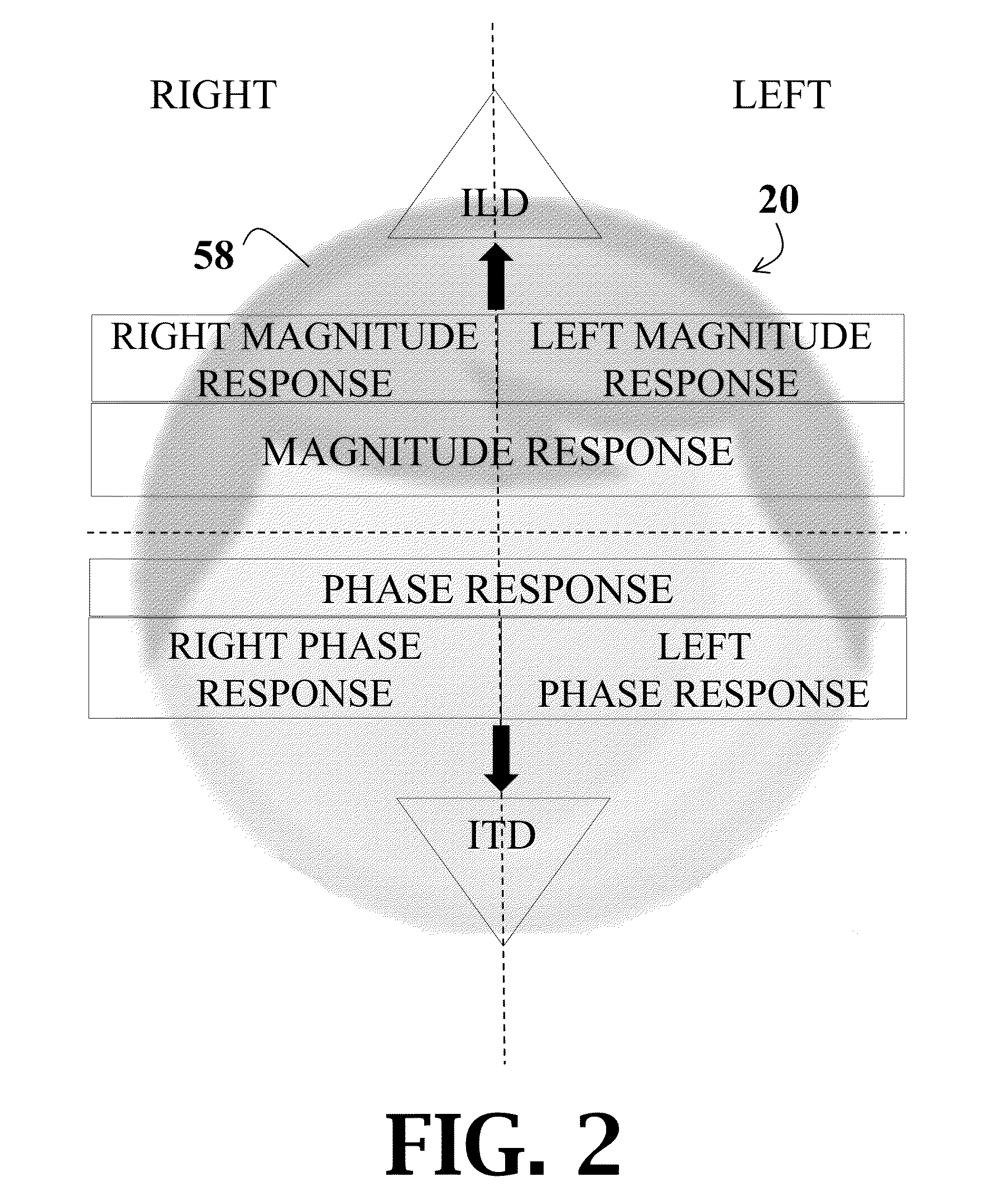
Efficient personalization of head-related transfer functions for improved virtual spatial audio
A method generating a virtual audio signal for a listener. The method includes estimating spherical harmonic coefficients based on an individual character of the listener. The estimated spherical harmonic coefficients are compared to a distribution of known spherical harmonic coefficients. The estimated spherical harmonic coefficients are iteratively updated and compared to the distribution of known spherical harmonic coefficients until convergence. The individual character and the converged spherical harmonic coefficients are then applied to a mono-channel sound.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
Correction of magnetic resonance images
InactiveUS7088099B2Reduce computing timeExtension of timeMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetic field gradientSpatial encoding
Spatial encoding in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques is achieved by sampling the signal as a function of time in the presence of magnetic field gradients, e.g., X, Y, and Z gradients. The gradient magnets have in the past been assumed to generate a linear gradient, and typical image reconstruction techniques have relied upon this assumption. However, to achieve high speed performance, gradient magnets often sacrifice linearity for speed. This non-linearity, in turn, results in distorted images, the distortion often being sufficiently large to compromise the usefulness of MRI images for stereotaxy or longitudinal studies, where precise volumetric information is required. The disclosure provides practical methods for correcting distorted images resulting from such non-linearity in the gradient fields, as well as distortions resulting from translational, rotational, and / or winding / design errors in the field generating devices. The methods employ spherical harmonic expansions of the gradient fields and fast Fourier transform techniques to provide well-corrected images without undue computational burdens.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
Software for mapping potential distribution of a heart chamber
A computer software program is described that maps the electrical activity of a patient's heart. The software program utilizes inputs from electrodes contained within a heart chamber. Inputs from the electrodes cause the program to calculate the heart chamber volume, and then to determine the position of the electrodes within the heart chamber. The program then utilizes inputs from the electrodes to calculate the three-dimensional volumetric electrical field distribution of said heart chamber. This calculation is accomplished using a spherical harmonic series expression. Finally, the computer program displays the electrical field distribution of the heart chamber.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Microphone array
ActiveUS20100142732A1Simple processUniform responseMicrophonesTransducer detailsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Spherical harmonics
A sound capture device comprises a symmetric microphone array that includes non-radially-oriented directional sensors (101). The device typically derives a spherical harmonic representation of the incident sound field, and affords higher signal-to-noise ratios and better directional fidelity than prior arrays, across a wide range of audio frequencies.
Owner:CRAVEN PETER G +2
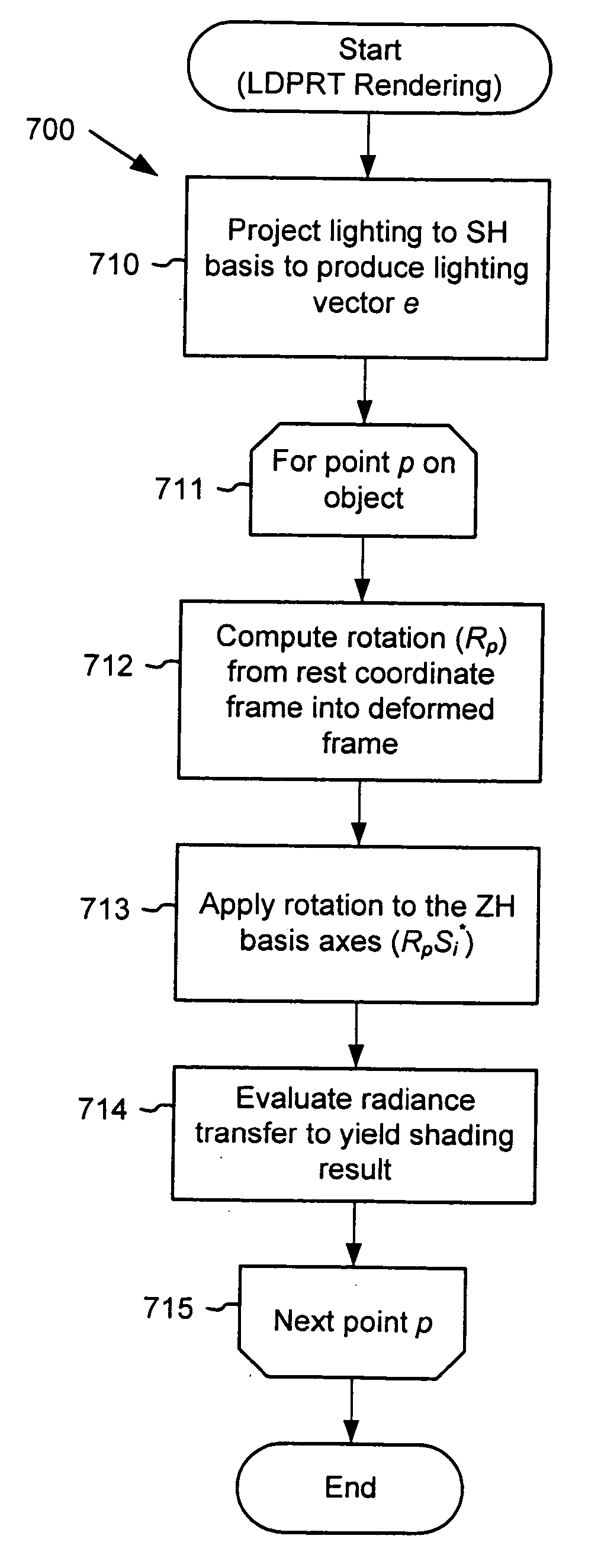
Local, deformable precomputed radiance transfer
ActiveUS20060214931A1Easily evaluated per-pixelFast transfer rotationCharacter and pattern recognition3D-image renderingGraphicsHarmonic
Computer graphics image rendering techniques render images using a precomputed radiance transfer (PRT) to model local effects such as bumps, wrinkles, or other detailed features on an arbitrarily deformable model's surface. The techniques apply zonal harmonics (ZH) which approximate spherical functions as sums of circularly symmetric functions around different axes. By spatially varying both the axes and coefficients of these basis functions, approximations can fit to spatially varying transfer signals. Compared to the spherical harmonic (SH) basis, the ZH basis yields a more compact approximation, and can be rotated at a low computational expense suitable for dense per-vertex or per-pixel evaluation. This allows PRT to be mapped onto deforming models which re-orient the local coordinate frame.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD +1
Small celestial body attachment detection descending trajectory optimization method
ActiveCN106778012AAvoid complicating the derivationAvoid questions that have no physical meaning and are not easy to guessInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsAviationState variable
The invention relates to a small celestial body attachment detection descending trajectory optimization method, and belongs to the field of aviation and aerospace. According to the method, an internal spherical harmonic gravitational field model is adopted for estimating gravitational acceleration near a target small celestial body, and a convex optimization algorithm is adopted for solving the optimal control problem. By adopting the internal spherical harmonic gravitational field model for estimating the gravitational acceleration near the target small celestial body, the advantage of being high in computational efficiency is achieved. By adopting the convex optimization algorithm for solving the optimal fuel control problem, the problems that derivation of a indirection method is complicated, and co-state variables are free of physical meaning and not likely to guess are avoided, the derivation step is simple, the computing time is saved, the estimation optimization method is rapid and high in precision, and the obtained result conforms to initial and end state constraint, dynamic constraint and control constraint.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
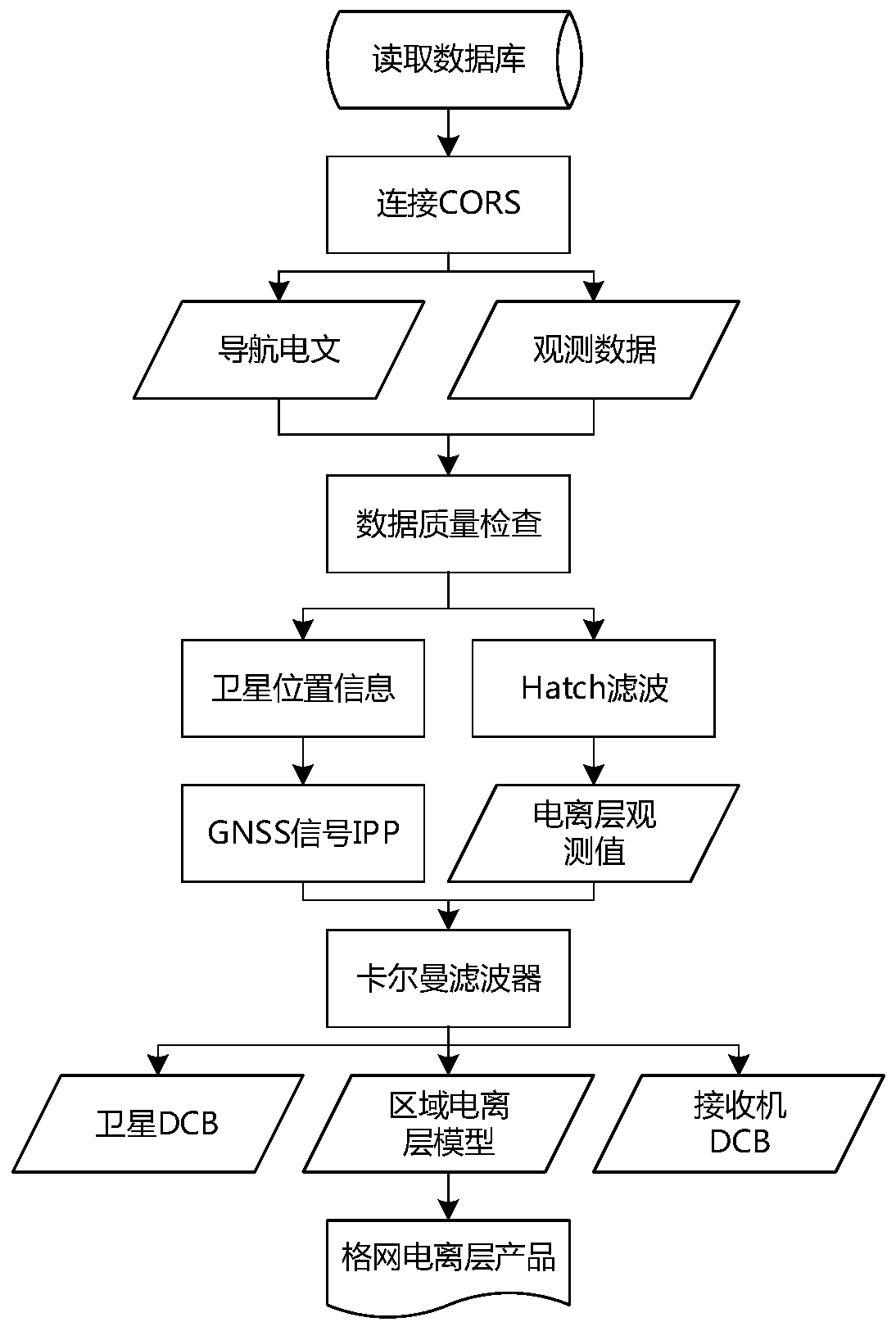
Real-time ionosphere modeling and monitoring method based on regional CORS
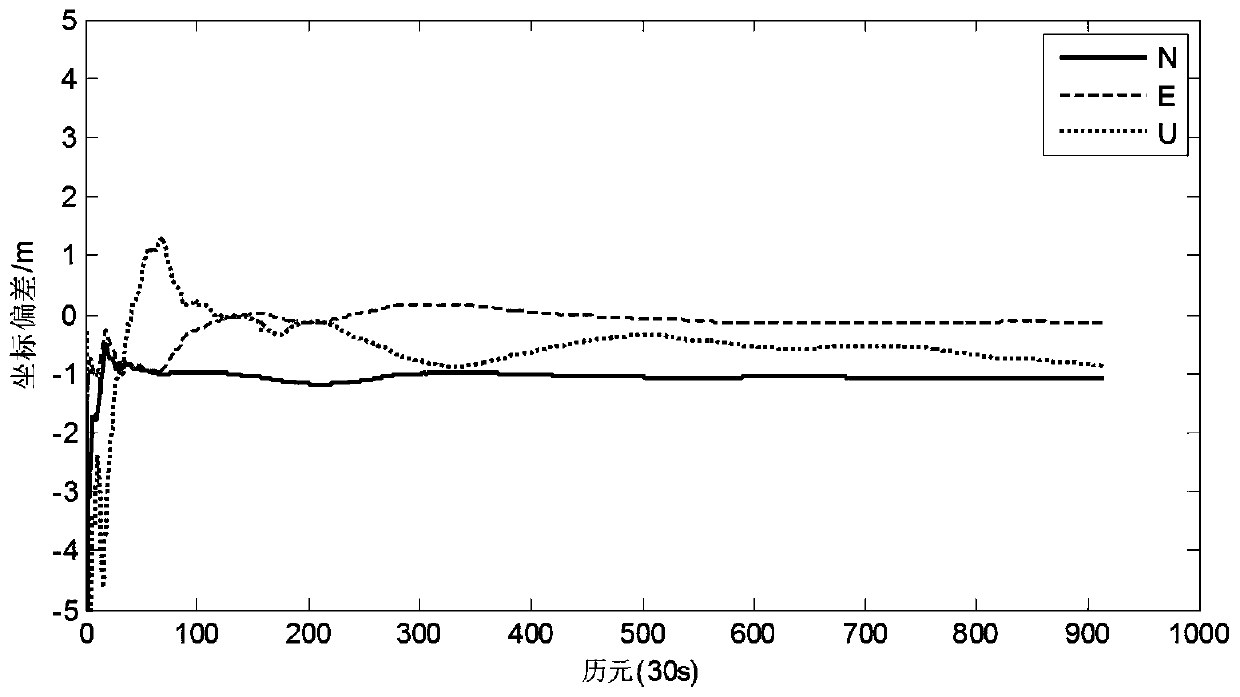
InactiveCN109828288AHigh positioning accuracyFaster convergence timeSatellite radio beaconingSimulationCarrier signal
The invention discloses a real-time ionosphere modeling and monitoring method based on a regional CORS (Continuous Operational Reference System). The method comprises the steps of: receiving originaldual-frequency observation data and a navigation message of a regional CORS station, rejecting a gross error, and then calculating a satellite position, an elevation angle and latitudes and longitudesof a puncture point; employing the Hatch filtering method and employing a carrier smooth pseudo-range observation value for differencing to obtain a TEC (Total Electron Contents) observation value without a geometric ionosphere; employing a spherical ion function to simulate the TEC distribution of the regional ionosphere, taking the model parameters and the satellite and the receiver differential code deviation as parameters to be estimated, constructing observation vectors by employing the observation data of all CORS stations of the single epoch to construct an observation equation; establishing a Kalman filter to perform real-time filtering processing for the parameters to be estimated, and separating from hardware delay to obtain an ionosphere TEC model; and finally, employing a model to calculate the grid point ionosphere delay, and storing and broadcasting the grid point ionosphere delay to regional users in a grid form. After an ionosphere product is obtained, a regional single-frequency PPP user location precision is obviously improved, and the dual-frequency PPP user convergence time is significantly improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method and device for determining global ionized layer grid model
InactiveCN106405589ASolve the problem that simple fusion cannot be performedSatellite radio beaconingSpace environmentSpherical harmonics
The invention provides a method and device for determining a global ionized layer grid model, belongs to the field of global navigation systems and space environment monitoring, and is used for solving the problems that systematic bias exists among various ionized layer data, and the various ionized layer data cannot be fused in a simple manner. The method includes determining an ionized layer VTEC1 in a zenith direction through formulae (1) and (2) according to GNSS observed data; adopting a formula (3) and combined with a smooth and resampling method to obtain an ionized layer VTEC2 in the zenith direction according to data of ocean height-measuring satellites; according to a double-frequency phase observed value of a DORIS, determining STEC<bias> through a formula (4), through a GIM interpolation principle, the double-frequency phase observed value of the DORIS and the STEC<bias>, determining corrected STEC, and determining an ionized layer VTEC3 in the zenith direction according to the corrected STEC and a calibration method; and performing fitting on the ionized layers VTEC1, VTEC2 and VTEC3 according to a spherical harmonics model, and determining the global ionized layer grid model based on multi-source data fusion.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Automatic implementation method for high-uniformity magnet shim coil design
ActiveCN102879753ACalculation takes less timeReduce memory usageMagnetic measurementsCode moduleNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention discloses an automatic implementation method for a high-uniformity magnet shim coil design. The method comprises the following steps of: measuring the magnetic field intensity distribution within a region range by utilizing a nuclear magnetic resonance probe, and fitting the first 10-order components of the magnetic field expanded according to spherical harmonics by utilizing a least square method so as to obtain the intensity value of the shimming quantity of each order; inputting a shimming intensity numerical value, selecting an algorithm, and then storing the shimming intensity numerical value and the algorithm; assigning the stored numerical value and algorithm to a shimming code module; loading a Radia three-dimensional electromagnetic field calculation packet into the shimming code module and carrying out optimal computation on the optimization model; optimizing the calculation result, calculating shim coil shape parameters, a coil three-dimensional structural drawing and an error iteration path by virtue of a linear programming method or a particle swarm optimization based on an analytical method; and manufacturing a shim coil according to the calculated specific coil shape parameters and coil three-dimensional topological structure. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for achieving the purposes of simplicity in operation and high precision.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
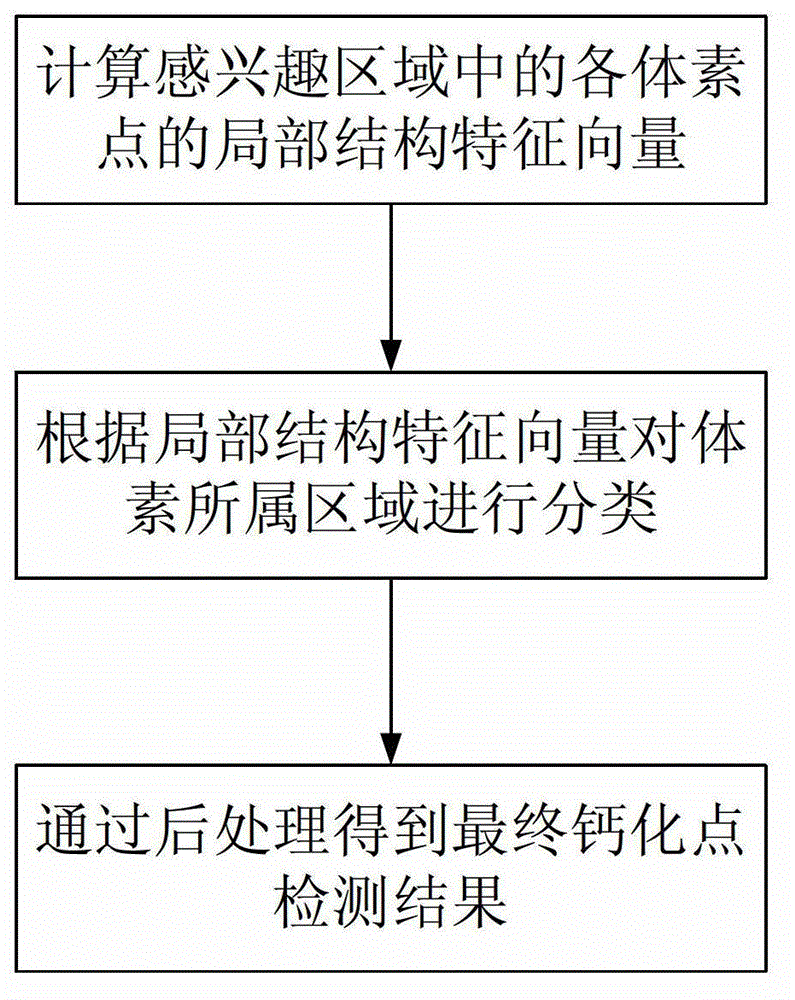
Coronary artery CT (computed tomography) contrastographic image calcification point detecting method
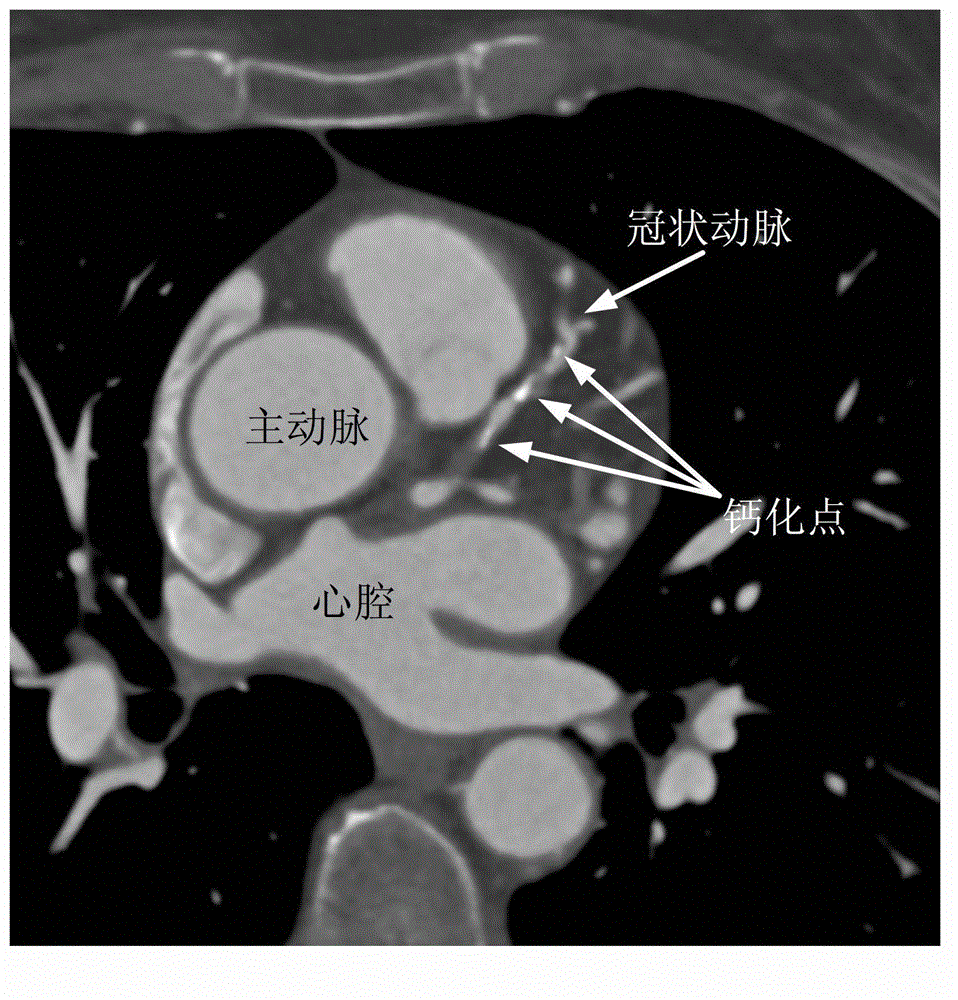
InactiveCN103337096APrecise positioningPrevent oversegmentationComputerised tomographsTomographyAcquired characteristicVoxel
The invention discloses a coronary artery CT (computed tomography) contrastographic image calcification point detecting method. According to the method, the existing coronary artery central axis is utilized, firstly, the local structural features of each voxel point in an interested region of a blood vessel are extracted, then, the spherical harmonic conversion is utilized for quantizing the local structural features, feature vectors are obtained, finally, a classification algorithm is adopted for classifying the obtained feature vectors, the local structural feature approximation degree of the voxel points to the calcification points, blood vessel lomens and image backgrounds in a training dataset is determined, and calcification point detecting results are finally obtained. The method has the advantages that calcification points positioned on the coronary artery blood vessel walls in the coronary artery CT contrastographic image can be precisely positioned, and the efficiency and the accurate rate of the computer auxiliary diagnosis are improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Clustered principal components for precomputed radiance transfer
ActiveUS20050035965A1Reduce computational overheadImprove accuracy3D-image renderingGraphicsRadiance
Real-time processing includes per-point transfer matrices forming a high-dimensional surface signal that is compressed using clustered principal component analysis (CPCA). CPCA partitions multiple samples into fewer clusters, each cluster approximating the signal as an affine subspace. Further, source radiance is input to a processor, which approximates source radiance using spherical harmonic basis to produce a set of source radiance coefficients. A graphics processing unit (GPU) processes the source radiance coefficients through the transfer matrix model for each cluster. The result of such processing is the exit radiance, which parameterizes the radiance leaving the surface of the object at each point, thus producing the shading for each point of the virtual object in real time.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
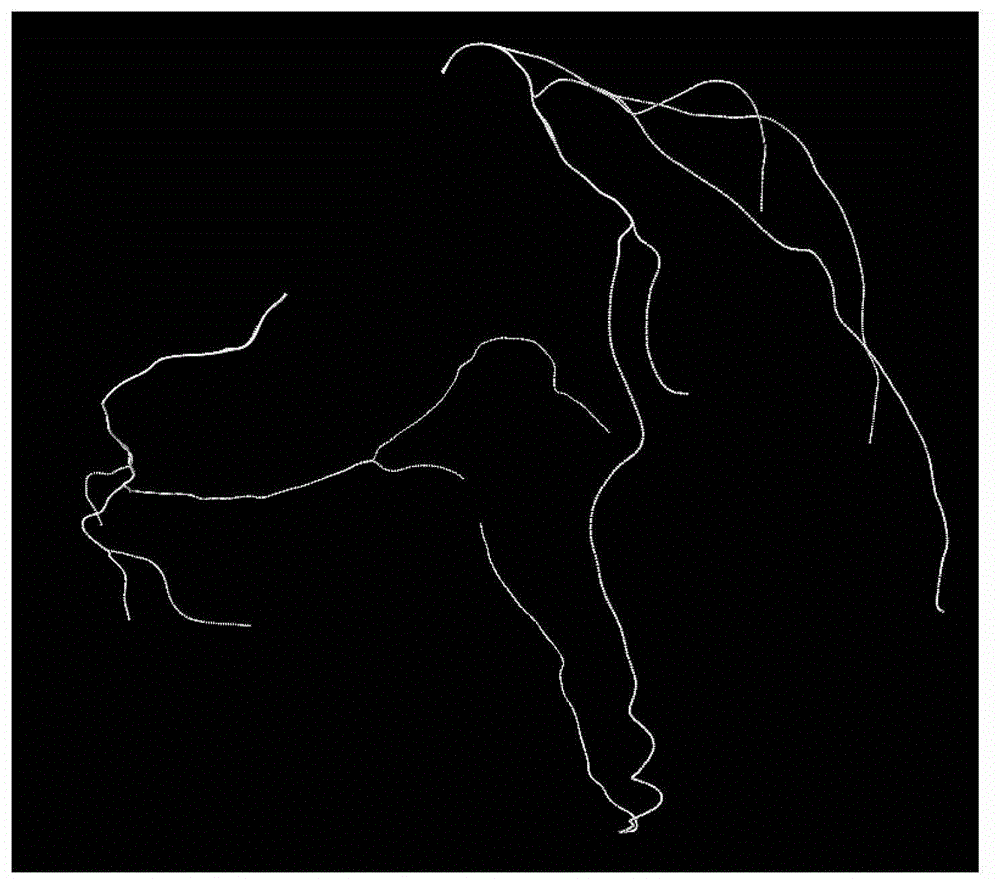
System and process for generating representations of objects using a directional histogram model and matrix descriptor
InactiveUS7343039B2Improve discriminationNoise robust3D-image renderingThree-dimensional object recognitionSpherical harmonicsHistogram
A system and process for determining the similarity in the shape of objects is presented that generates a novel shape representation called a directional histogram model. This shape representative captures the shape variations of an object with viewing direction, using thickness histograms. The resulting directional histogram model is substantially invariant to scaling and translation. A matrix descriptor can also be derived by applying the spherical harmonic transform to the directional histogram model. The resulting matrix descriptor is substantially invariant to not only scaling and translation, but rotation as well. The matrix descriptor is also robust with respect to local modification or noise, and able to readily distinguish objects with different global shapes. The typical applications of the directional histogram model and matrix descriptor include recognizing 3D solid shapes, measuring the similarity between different objects and shape similarity based object retrieval.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method of correcting gradient deformation of magnetic resonant image based on spherical harmonic function
ActiveCN101046506AFast convergenceOvercoming the disadvantages of differencesMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnetic field gradientSurgical treatment
The method of correcting gradient deformation of magnetic resonant image based on spherical harmonic function includes three steps of calculating spatial offset, compensating correction of image offset and searching correction of parameters. The 3D offset of each pixel in the 3D image is calculated based on the spherical harmonic function of magnetic induction intensity, and compensated to the image coordinate of the pixel. The present invention has high algorithm converging speed and high correction precision, and may be used widely magnetic resonant image led surgical treatment.
Owner:SYMBOW MEDICAL TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com