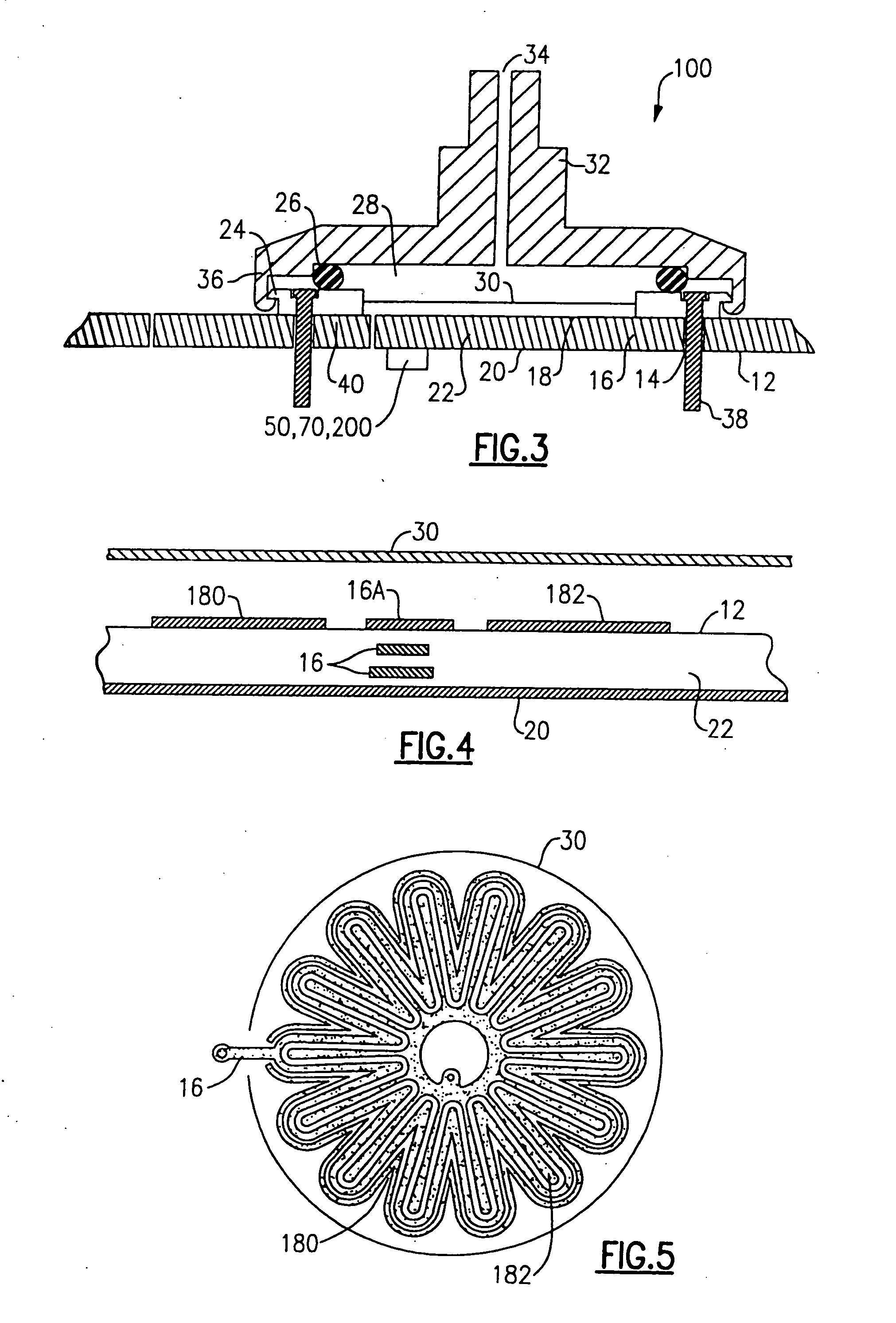
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
407 results about "Gravitational field" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
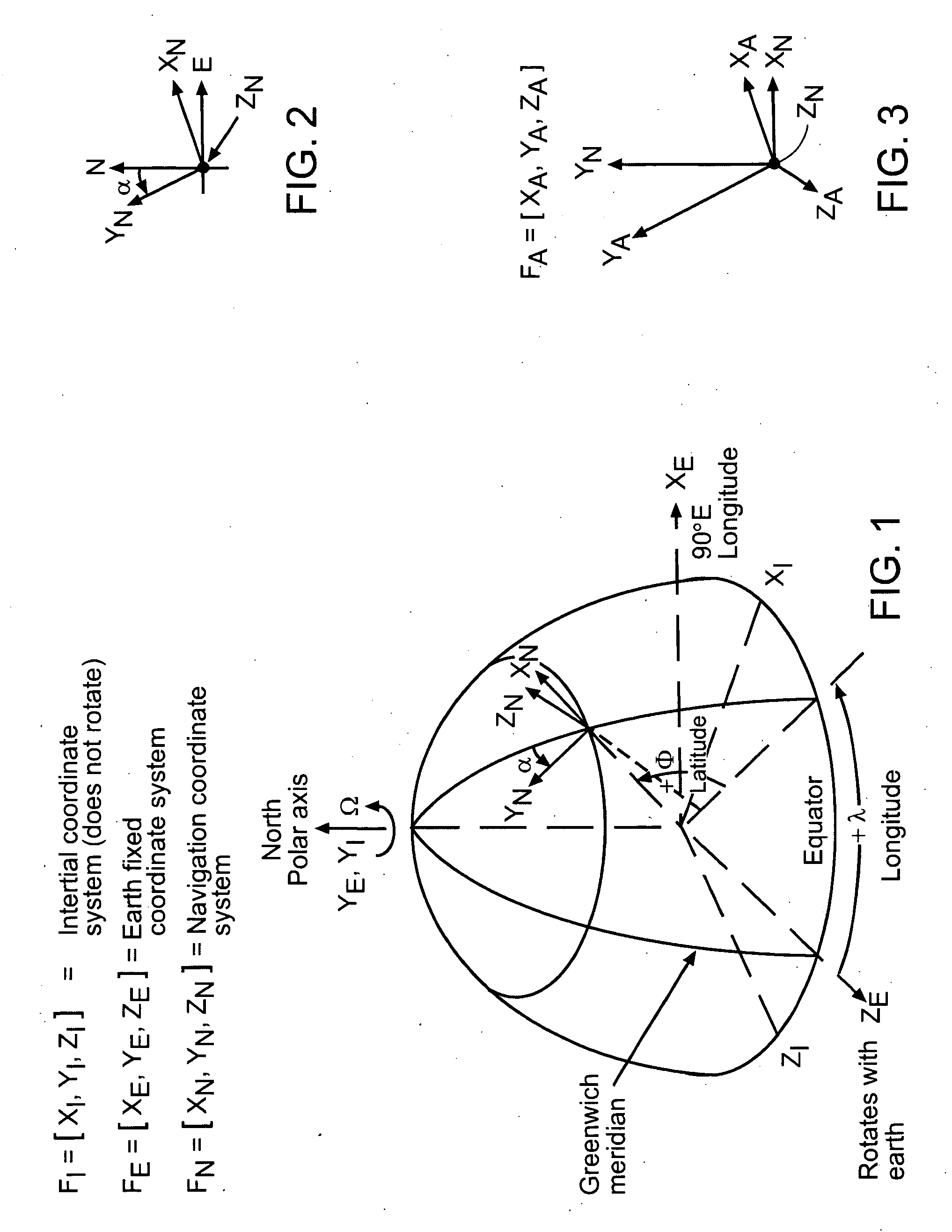
In physics, a gravitational field is a model used to explain the influence that a massive body extends into the space around itself, producing a force on another massive body. Thus, a gravitational field is used to explain gravitational phenomena, and is measured in newtons per kilogram (N/kg). In its original concept, gravity was a force between point masses. Following Isaac Newton, Pierre-Simon Laplace attempted to model gravity as some kind of radiation field or fluid, and since the 19th century explanations for gravity have usually been taught in terms of a field model, rather than a point attraction.
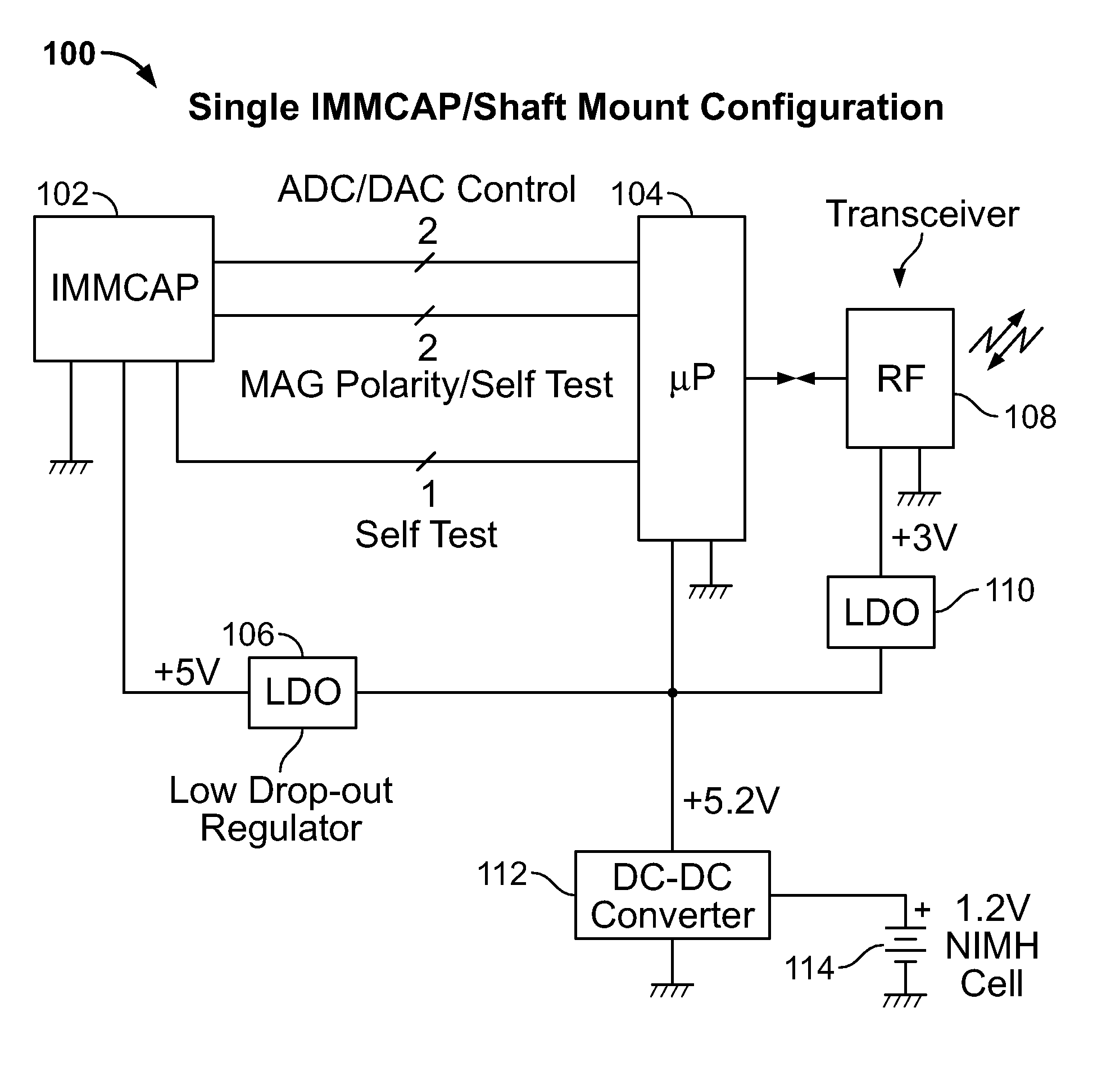
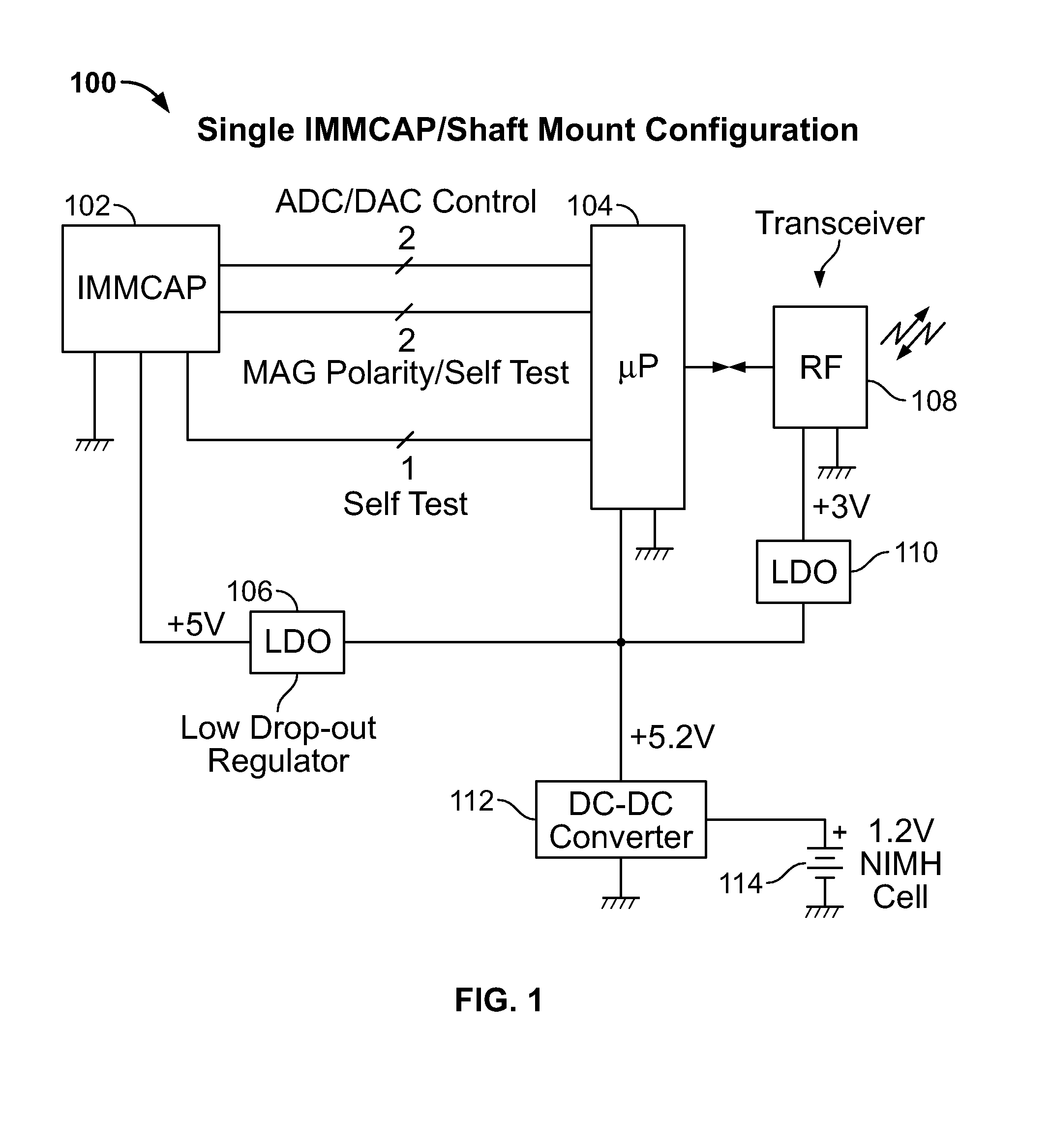
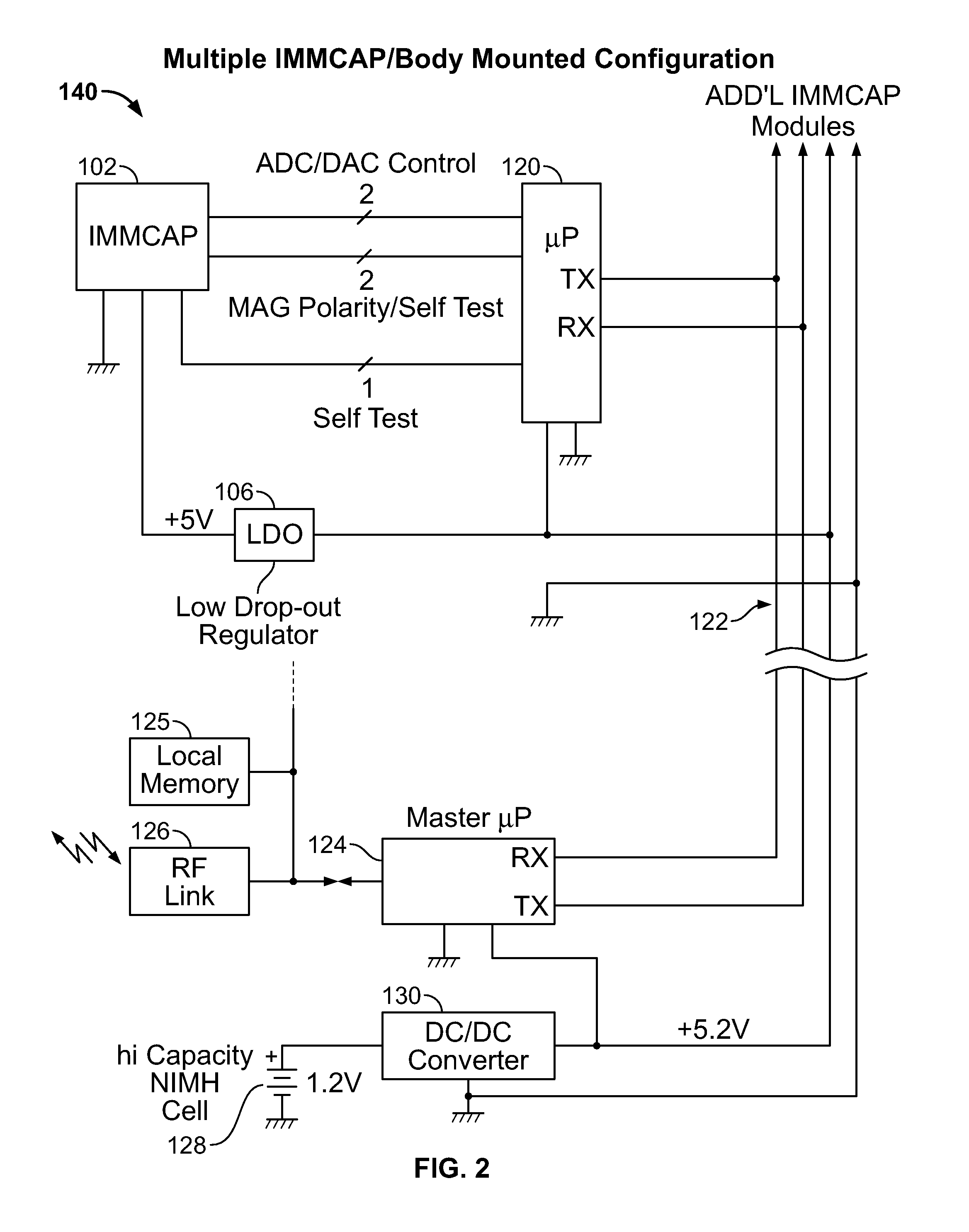
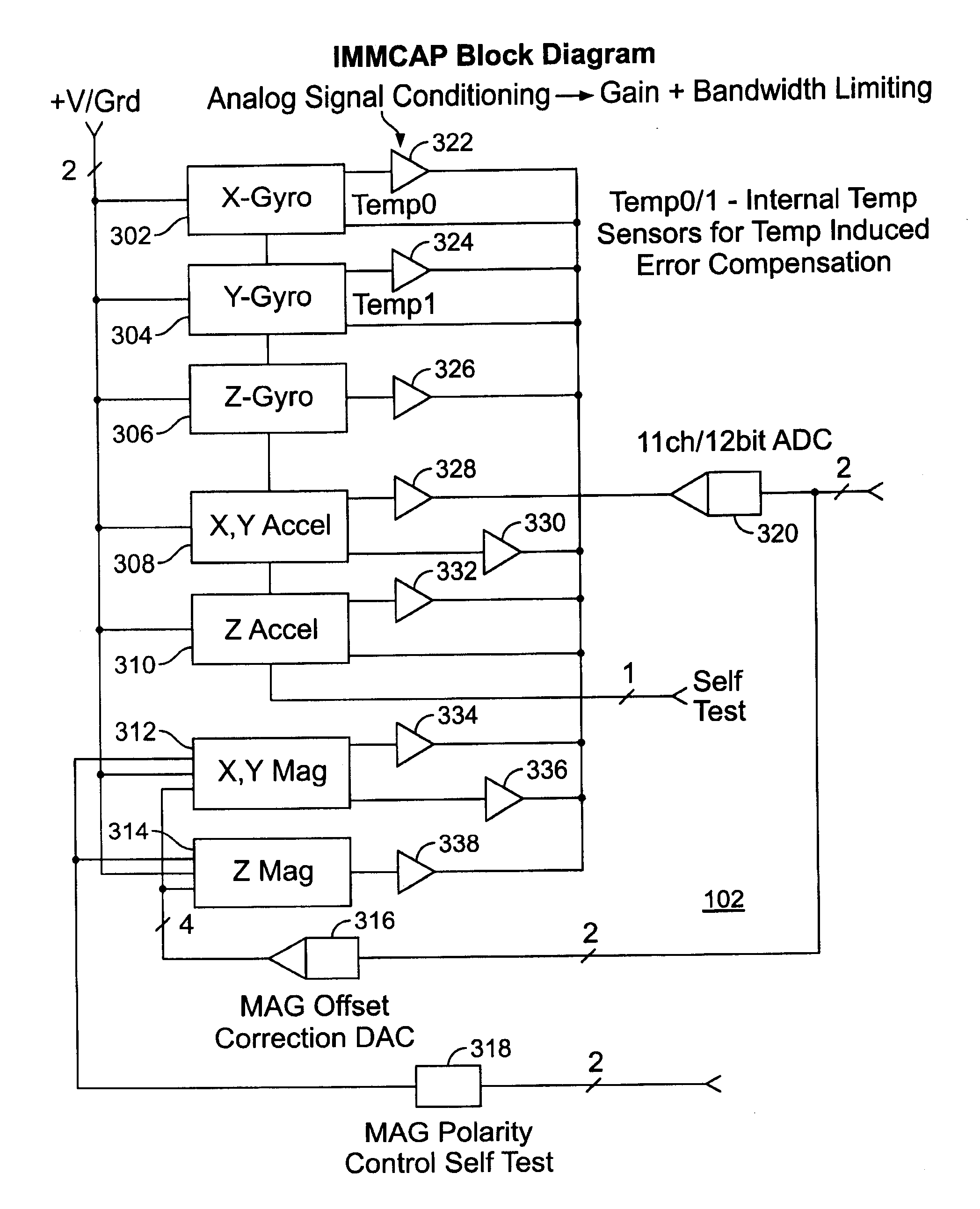
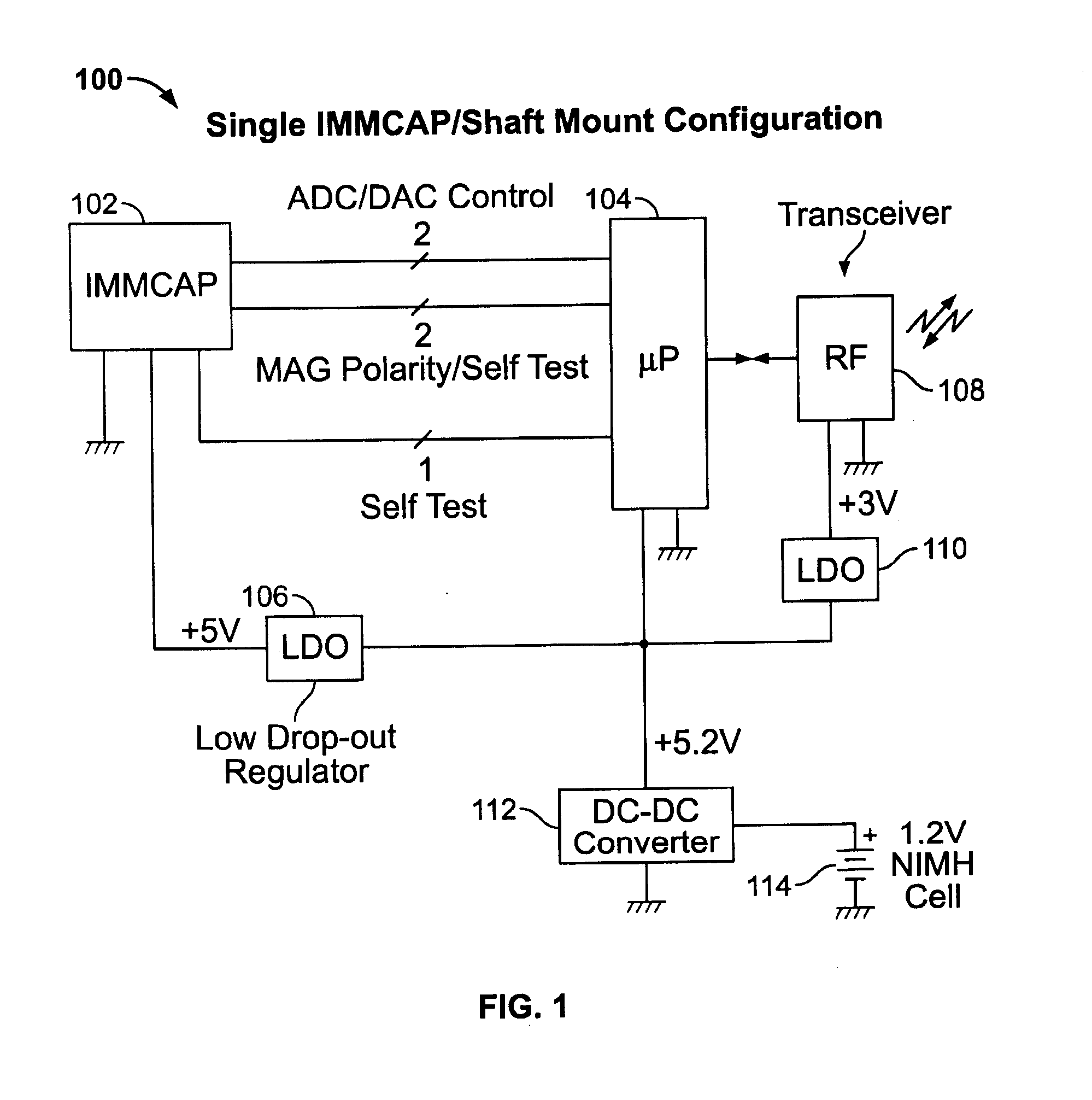
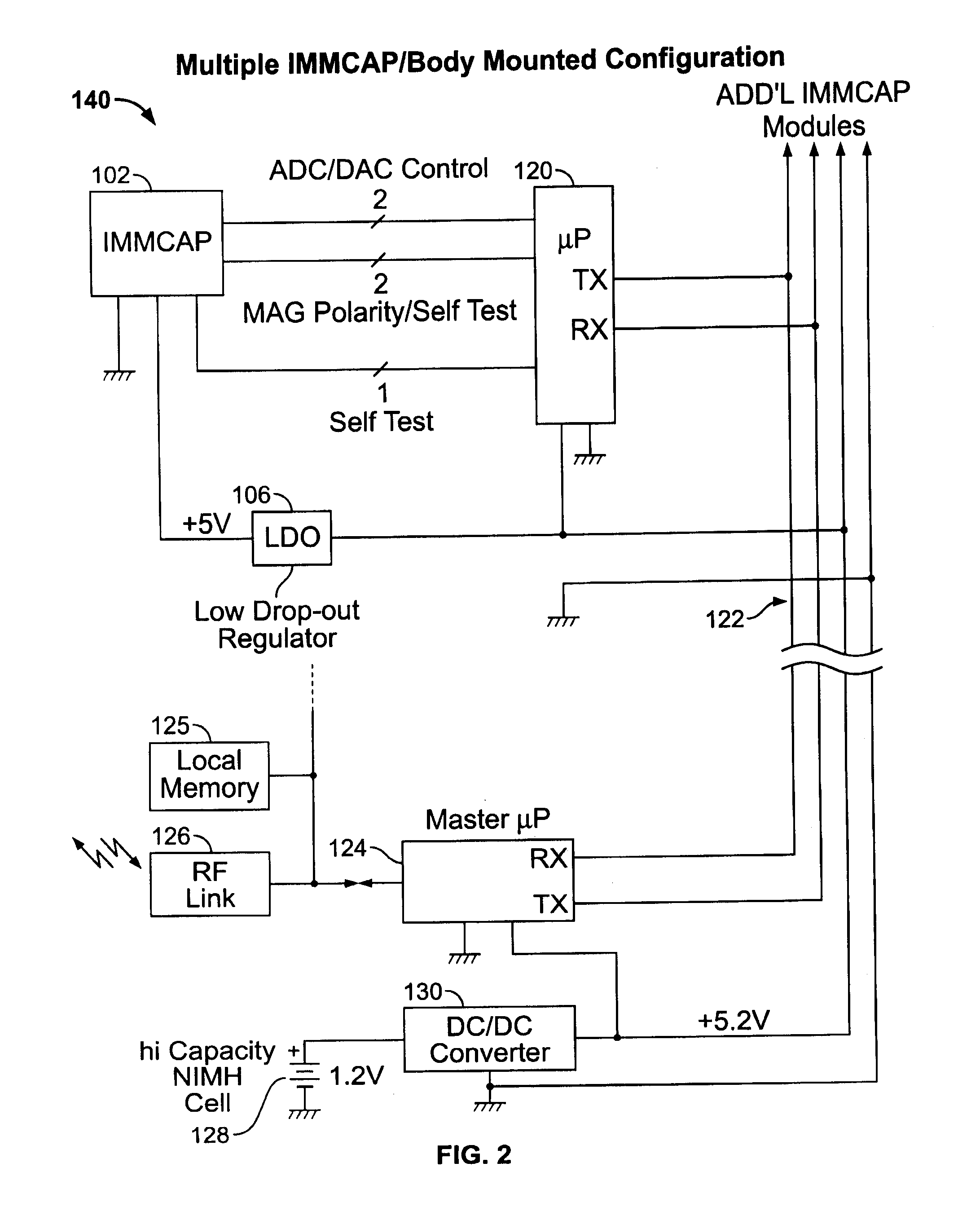
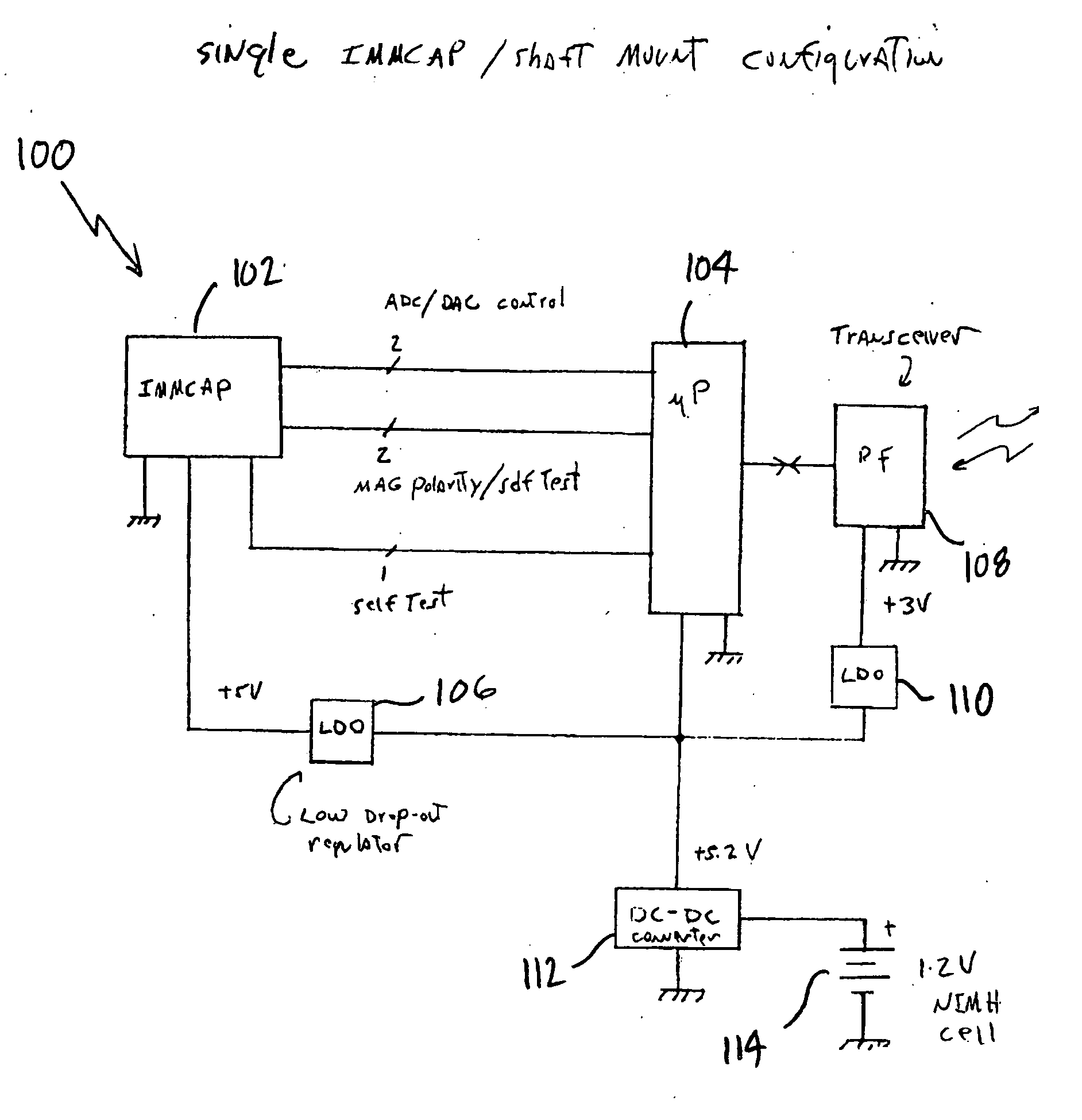
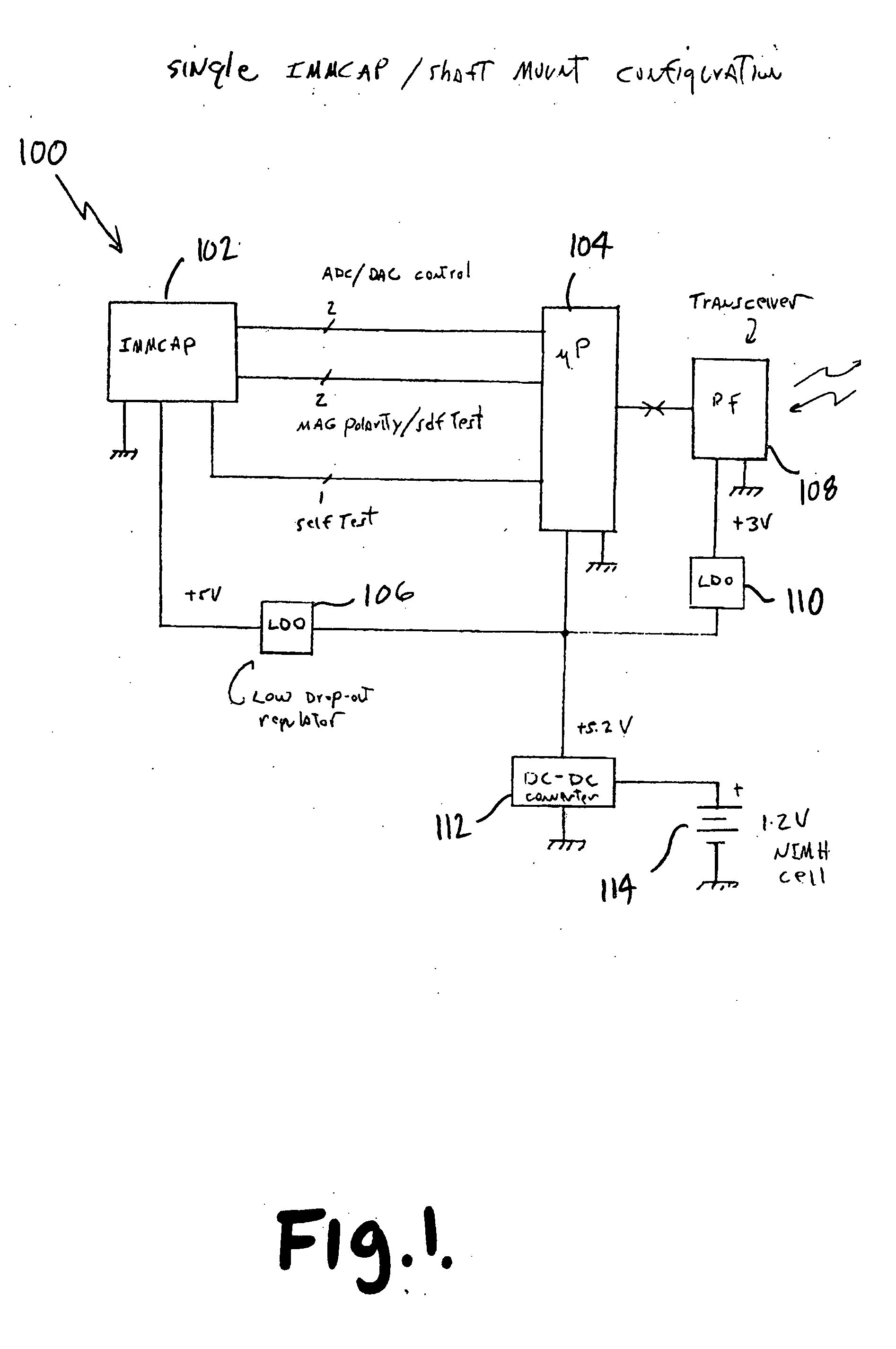
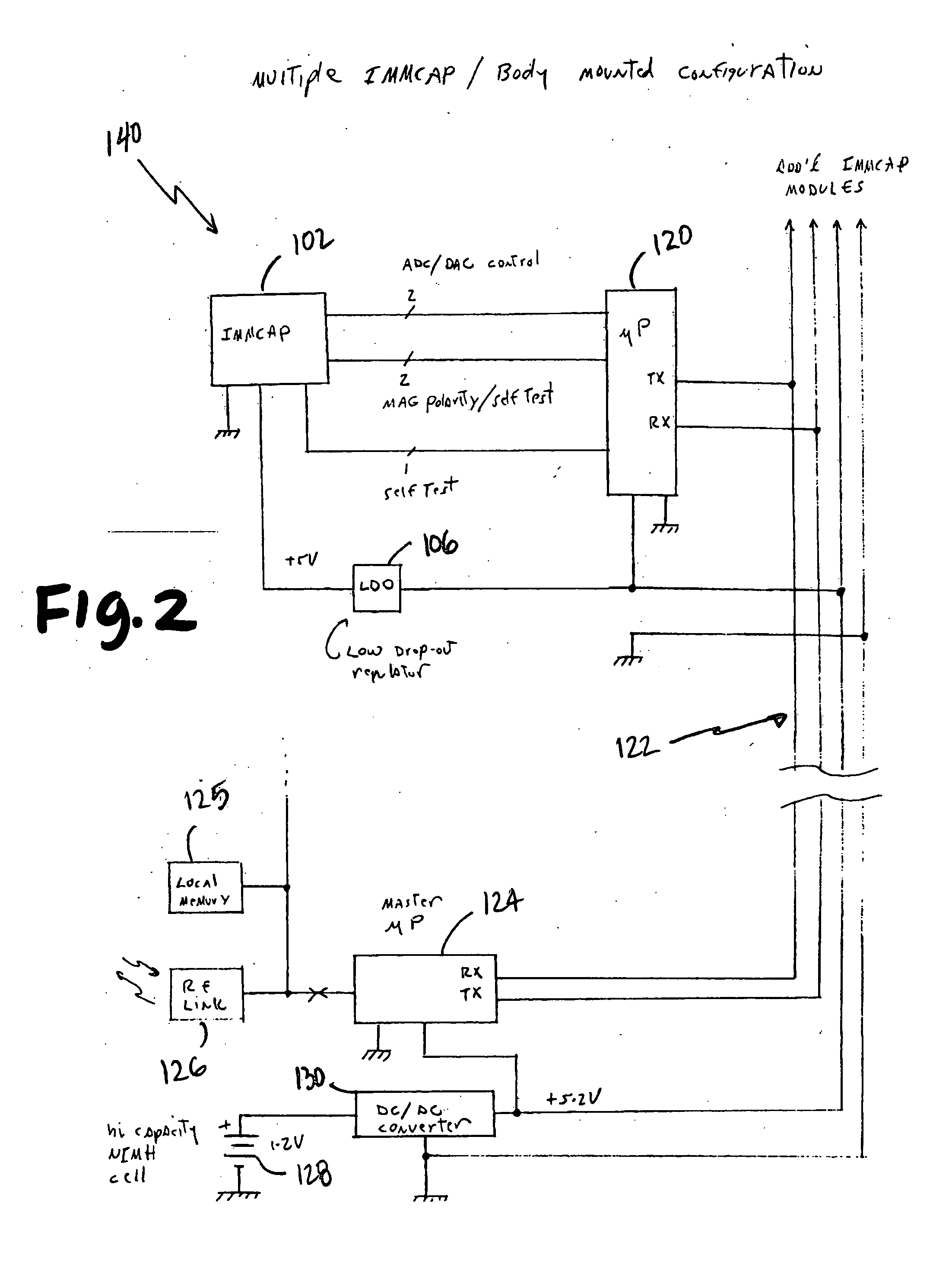
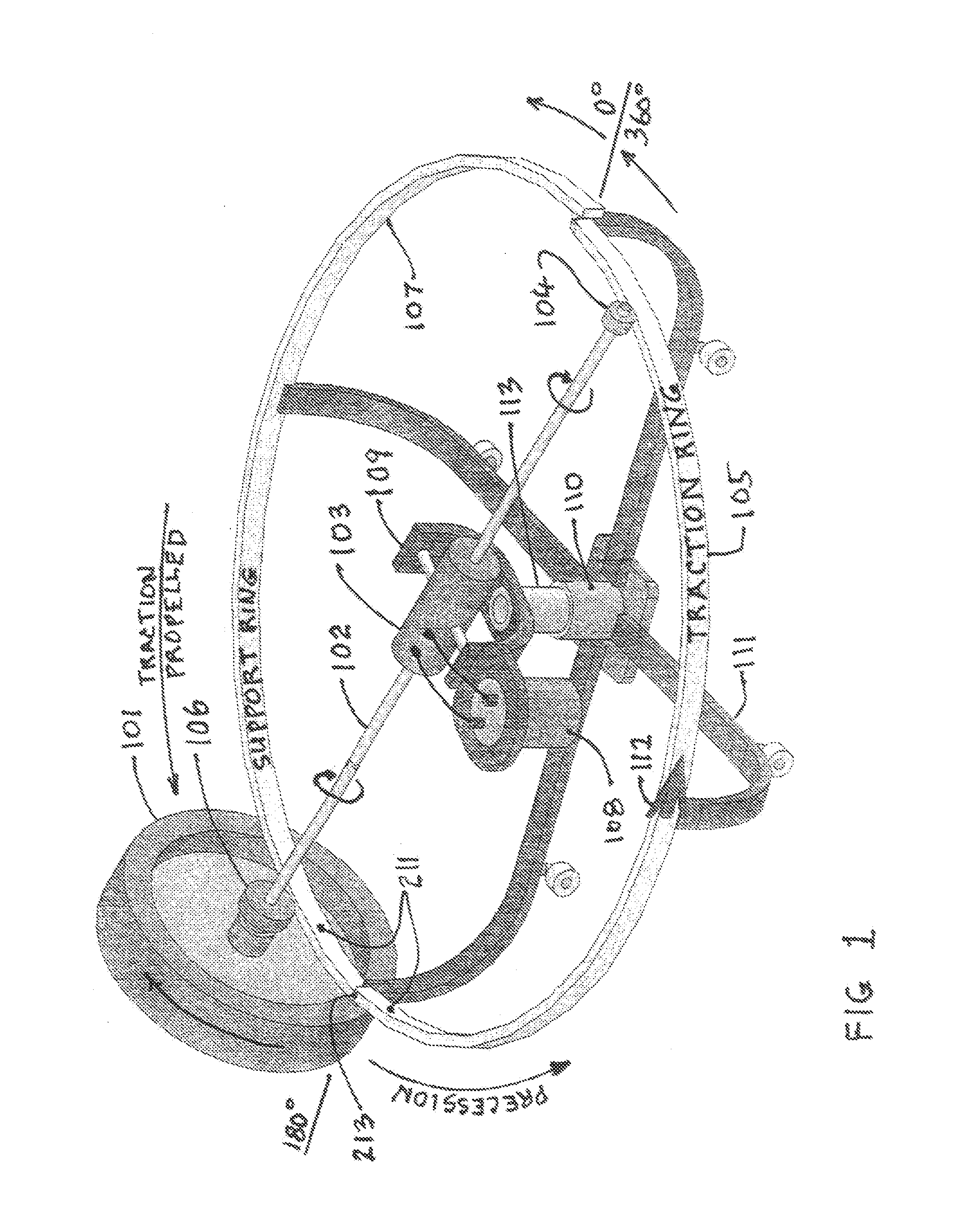
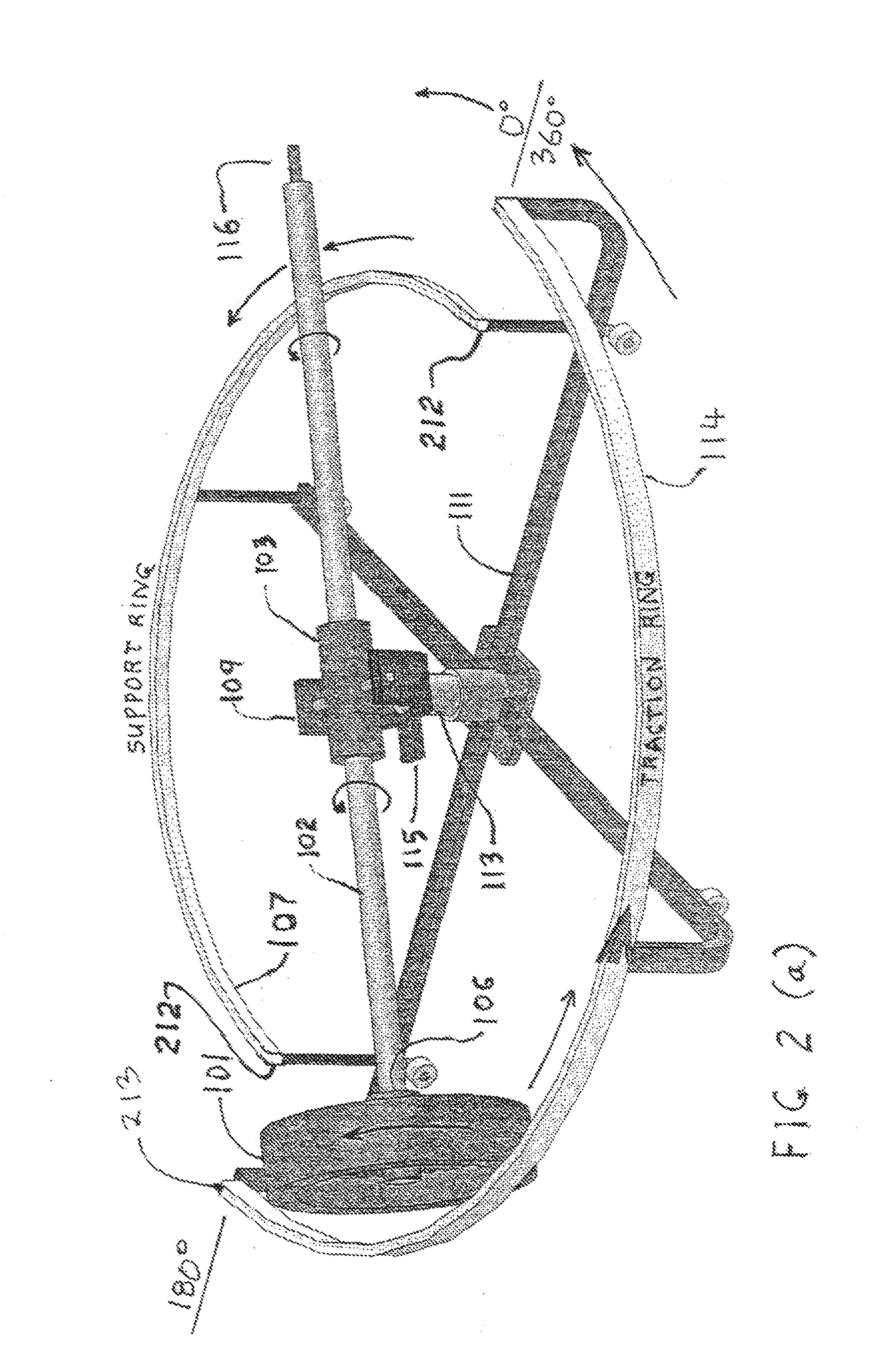
Single/multiple axes six degrees of freedom (6 DOF) inertial motion capture system with initial orientation determination capability
A highly miniaturized electronic data acquisition system includes MEMS sensors that can be embedded onto moving device without affecting the static / dynamic motion characteristics of the device. The basic inertial magnetic motion capture (IMMCAP) module consists of a 3D printed circuit board having MEMS sensors configured to provide a tri-axial accelerometer; a tri-axial gyroscope, and a tri-axial magnetometer all in communication with analog to digital converters to convert the analog motion data to digital data for determining classic inertial measurement and change in spatial orientation (rho, theta, phi) and linear translation (x, y, z) relative to a fixed external coordinate system as well as the initial spatial orientation relative to the know relationship of the earth magnetic and gravitational fields. The data stream from the IMMCAP modules will allow the reconstruction of the time series of the 6 degrees of freedom for each rigid axis associated with each independent IMMCAP module.
Owner:MAGNETO INERTIAL SENSING TECH
Motion sensing apparatus, systems and techniques
InactiveUS20070219744A1Gymnastic exercisingNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsDigital data3d print
A highly miniaturized electronic data acquisition system includes MEMS sensors that can be embedded onto moving device without affecting the static / dynamic motion characteristics of the device. The basic inertial magnetic motion capture (IMMCAP) module consists of a 3D printed circuit board having MEMS sensors configured to provide a tri-axial accelerometer; a tri-axial gyroscope, and a tri-axial magnetometer all in communication with analog to digital converters to convert the analog motion data to digital data for determining classic inertial measurement and change in spatial orientation (rho, theta, phi) and linear translation (x, y, z) relative to a fixed external coordinate system as well as the initial spatial orientation relative to the know relationship of the earth magnetic and gravitational fields. The data stream from the IMMCAP modules will allow the reconstruction of the time series of the 6 degrees of freedom for each rigid axis associated with each independent IMMCAP module.
Owner:C LAN WIRELESS
Single/multiple axes six degrees of freedom (6 DOF) inertial motion capture system with initial orientation determination capability
A highly miniaturized electronic data acquisition system includes MEMS sensors that can be embedded onto moving device without affecting the static / dynamic motion characteristics of the device. The basic inertial magnetic motion capture (IMMCAP) module consists of a 3D printed circuit board having MEMS sensors configured to provide a tri-axial accelerometer; a tri-axial gyroscope, and a tri-axial magnetometer all in communication with analog to digital converters to convert the analog motion data to digital data for determining classic inertial measurement and change in spatial orientation (rho, theta, phi) and linear translation (x, y, z) relative to a fixed external coordinate system as well as the initial spatial orientation relative to the know relationship of the earth magnetic and gravitational fields. The data stream from the IMMCAP modules will allow the reconstruction of the time series of the 6 degrees of freedom for each rigid axis associated with each independent IMMCAP module.
Owner:MAGNETO INERTIAL SENSING TECH
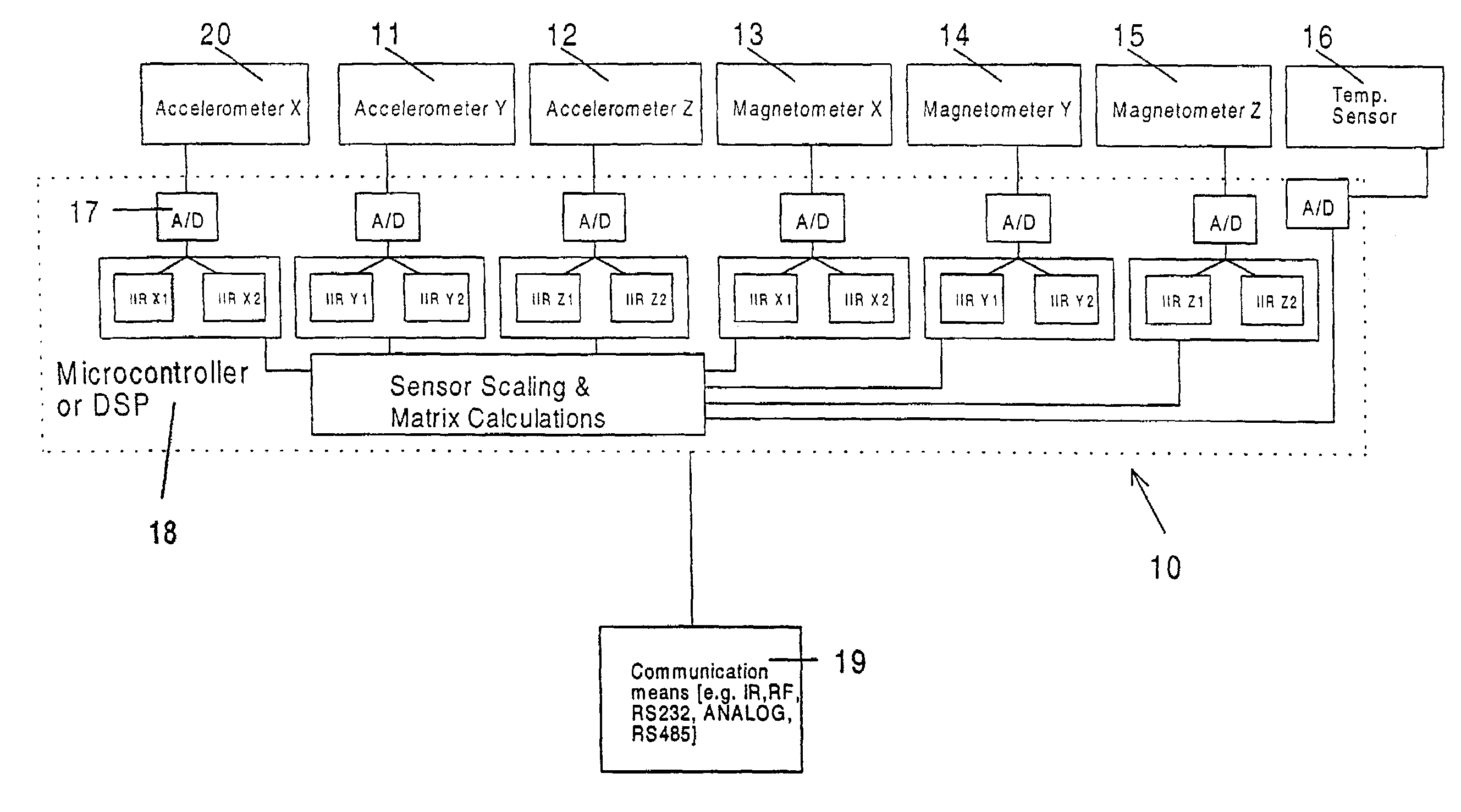
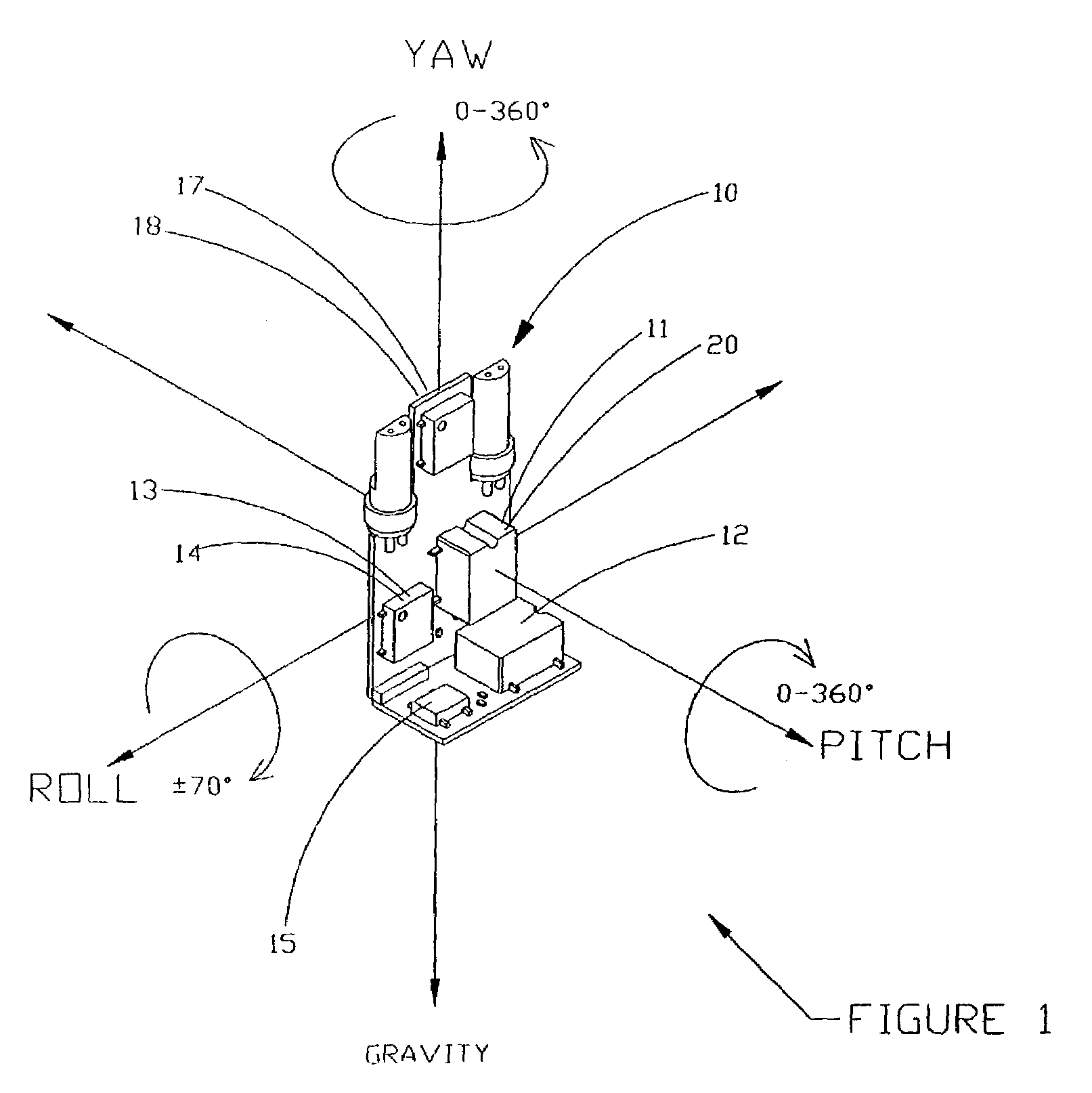
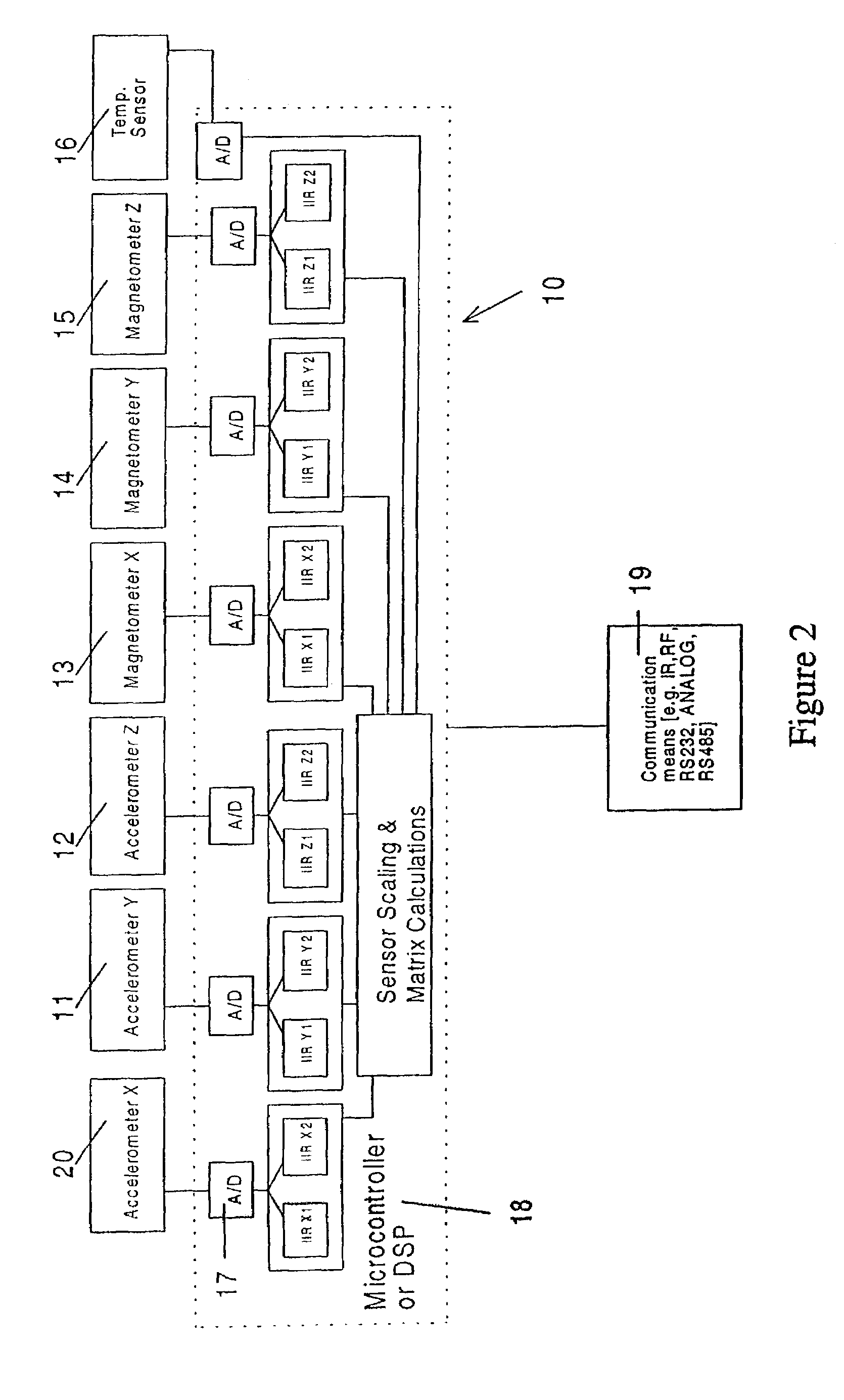
Solid state orientation sensor with 360 degree measurement capability
InactiveUS7143004B2Navigation by terrestrial meansDigital computer detailsRoboticsTriaxial accelerometer
The device is a miniature, self-contained solid state orientation sensor. The unit utilizes three magnetometers and three accelerometers to calculate pitch, roll, and yaw (compass heading) angles relative to the earth's magnetic and gravitational fields. The three orientation angles are output in digital RS232 or optional multi-drop RS485. The device can also be programmed to provide raw accelerometer and magnetometer data in true physical units. The device is capable of measuring angles from 0 to 360 degrees on the yaw axis, 0 to 360 degrees on the pitch axis, and −70 to +70 degrees on the roll axis. The yaw output is compensated for errors due to pitch and roll using embedded algorithms. Applications include fast solid state compassing, robotics, virtual reality, down-hole well drilling, and body position tracking for biomedical and multimedia applications.
Owner:LORD CORP
Processing signals to determine spatial positions
ActiveUS8436808B2Increase investmentCathode-ray tube indicatorsElectric switchesDisplay deviceComputer science
An apparatus is disclosed for supplying input signals to a computer. A sensor having the form of a sphere has a touch sensitive surface for generating position data for touch events. The sensor includes orientation sensors that determine rotation with respect to the earth's magnetic and gravitational fields. Orientation data may be combined with position data to interpret the orientation of touch events on the surface with respect to the computer's display. Cursor movement or text may be generated from touch events. Preferably the sphere has a roughened surface that generates sound when touched. Position data is generated by processing signals from microphones under the sphere's surface.
Owner:ELO TOUCH SOLUTIONS INC
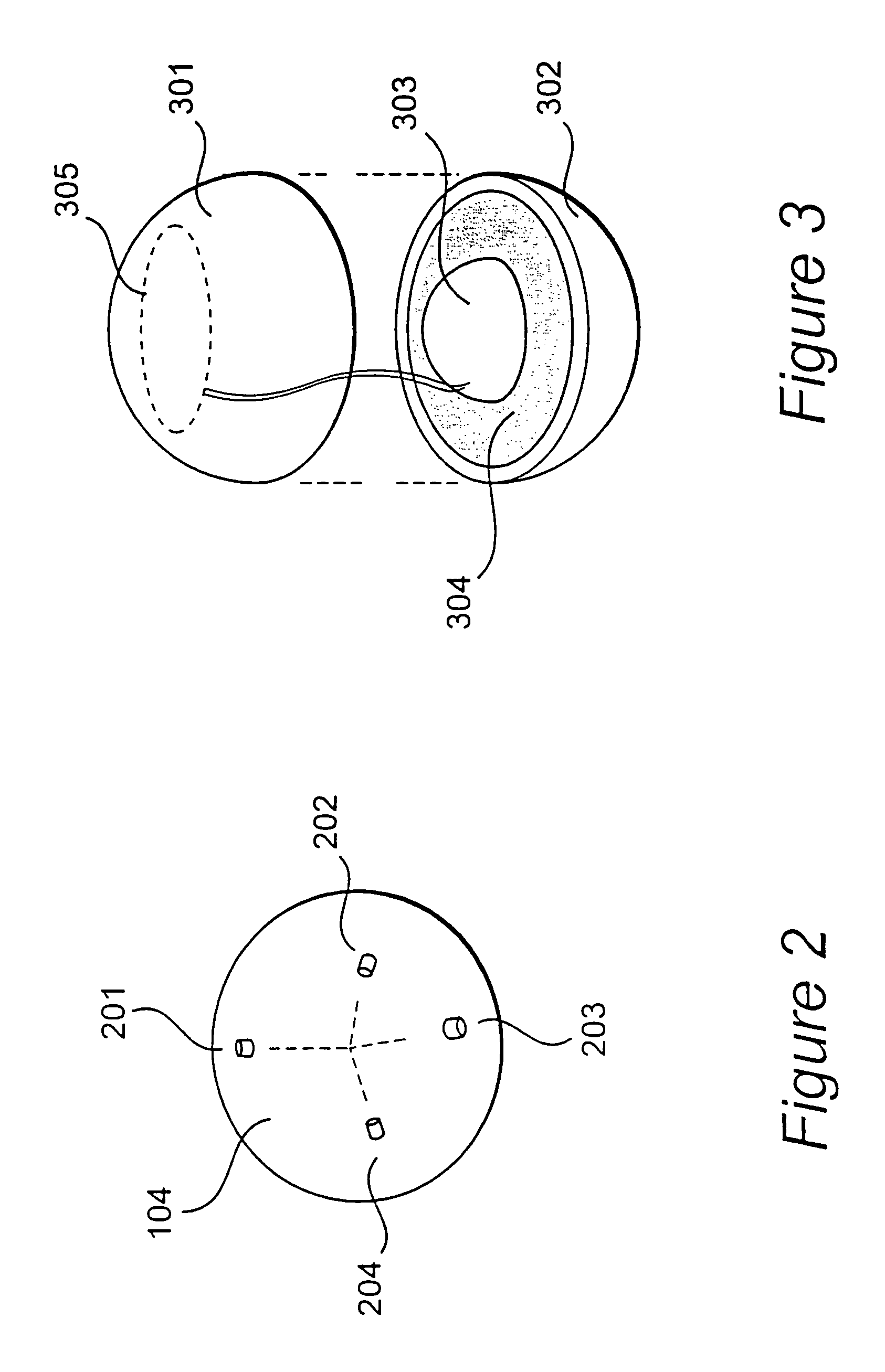
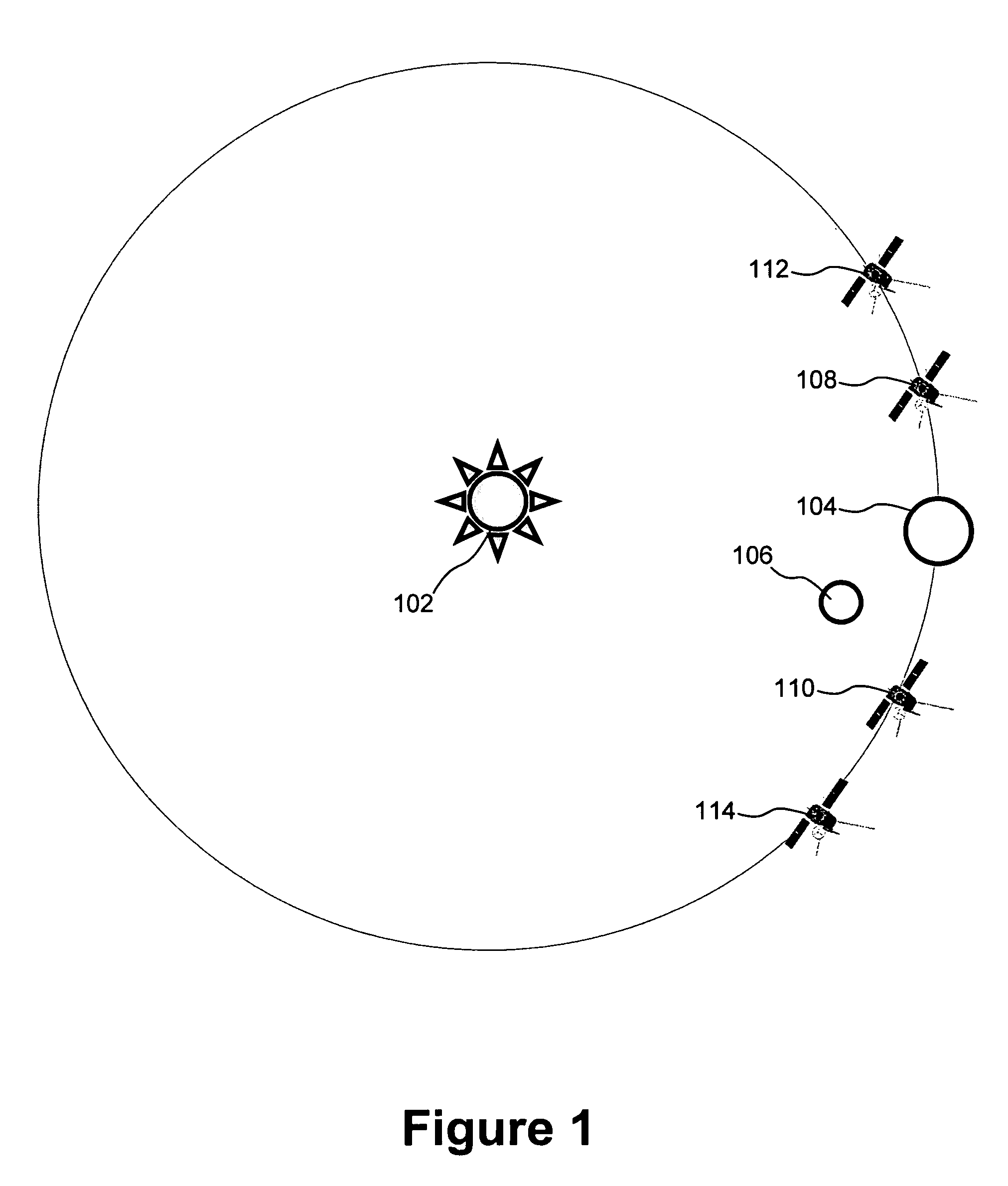
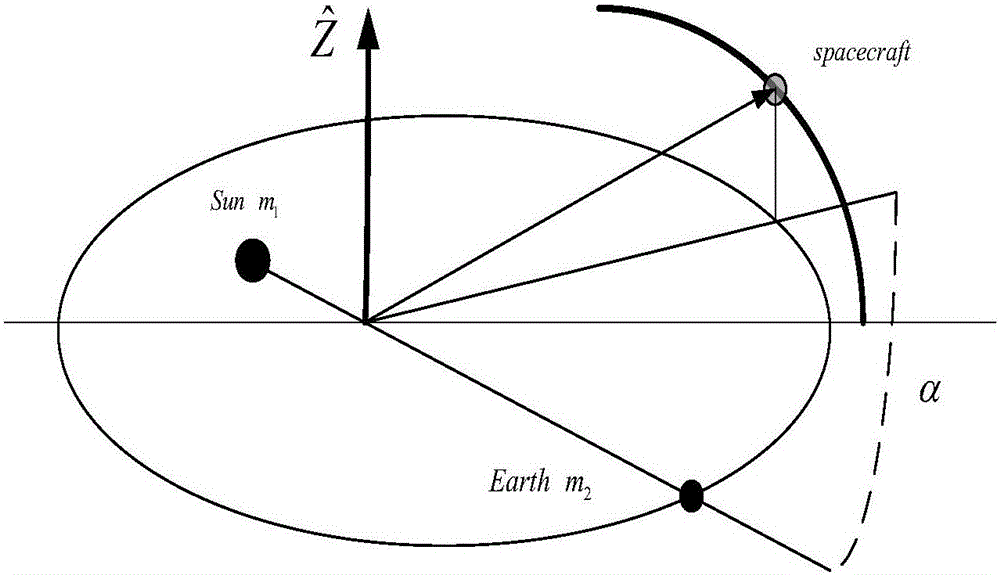
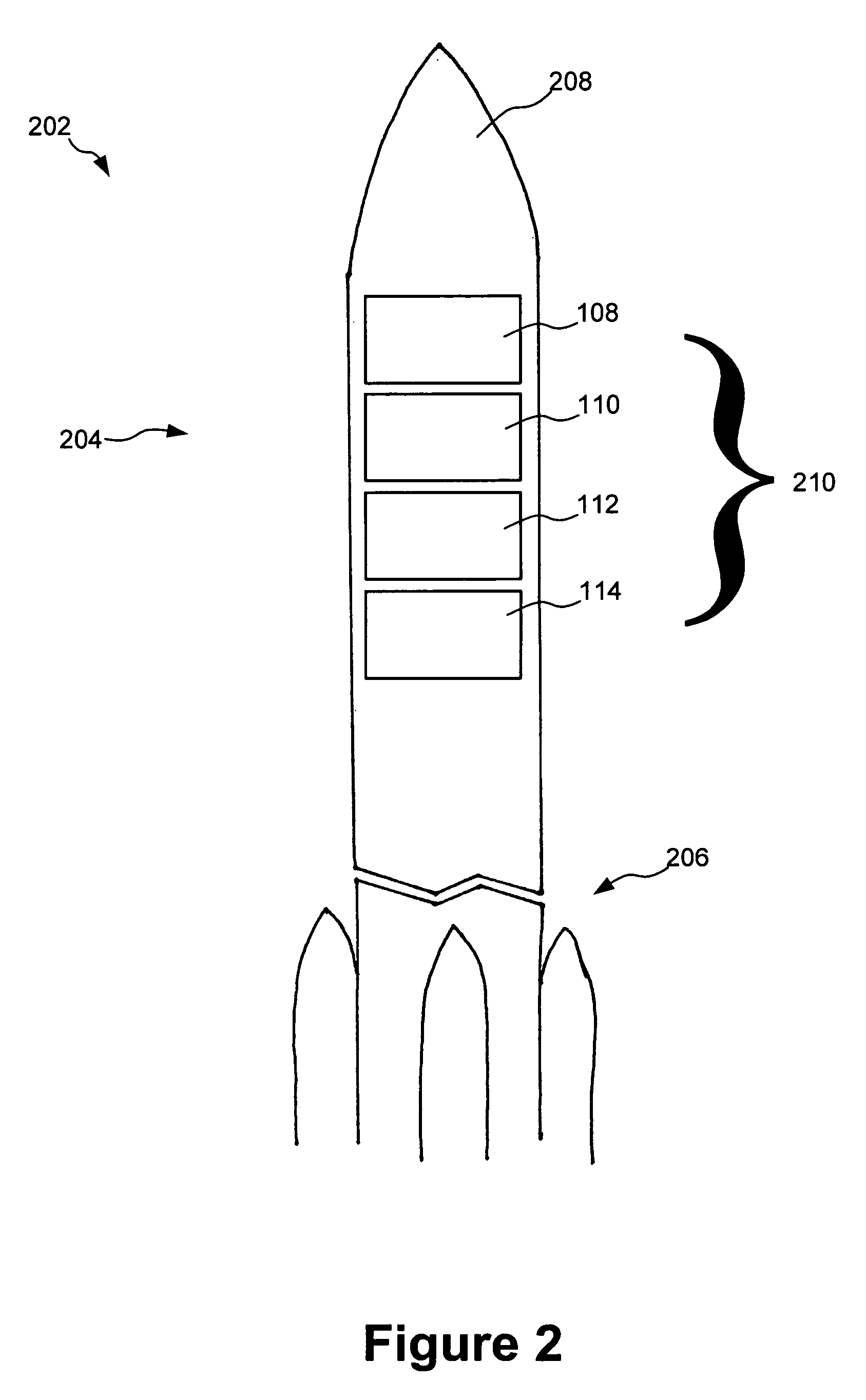
Method for deploying multiple spacecraft
A method for deploying multiple spacecraft is disclosed. The method can be used in a situation where a first celestial body is being orbited by a second celestial body. The spacecraft are loaded onto a single spaceship that contains the multiple spacecraft and the spacecraft is launched from the second celestial body towards a third celestial body. The spacecraft are separated from each other while in route to the third celestial body. Each of the spacecraft is then subjected to the gravitational field of the third celestial body and each of the spacecraft assumes a different, independent orbit about the first celestial body. In those situations where the spacecraft are launched from Earth, the Sun can act as the first celestial body, the Earth can act as the second celestial body and the Moon can act as the third celestial body.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
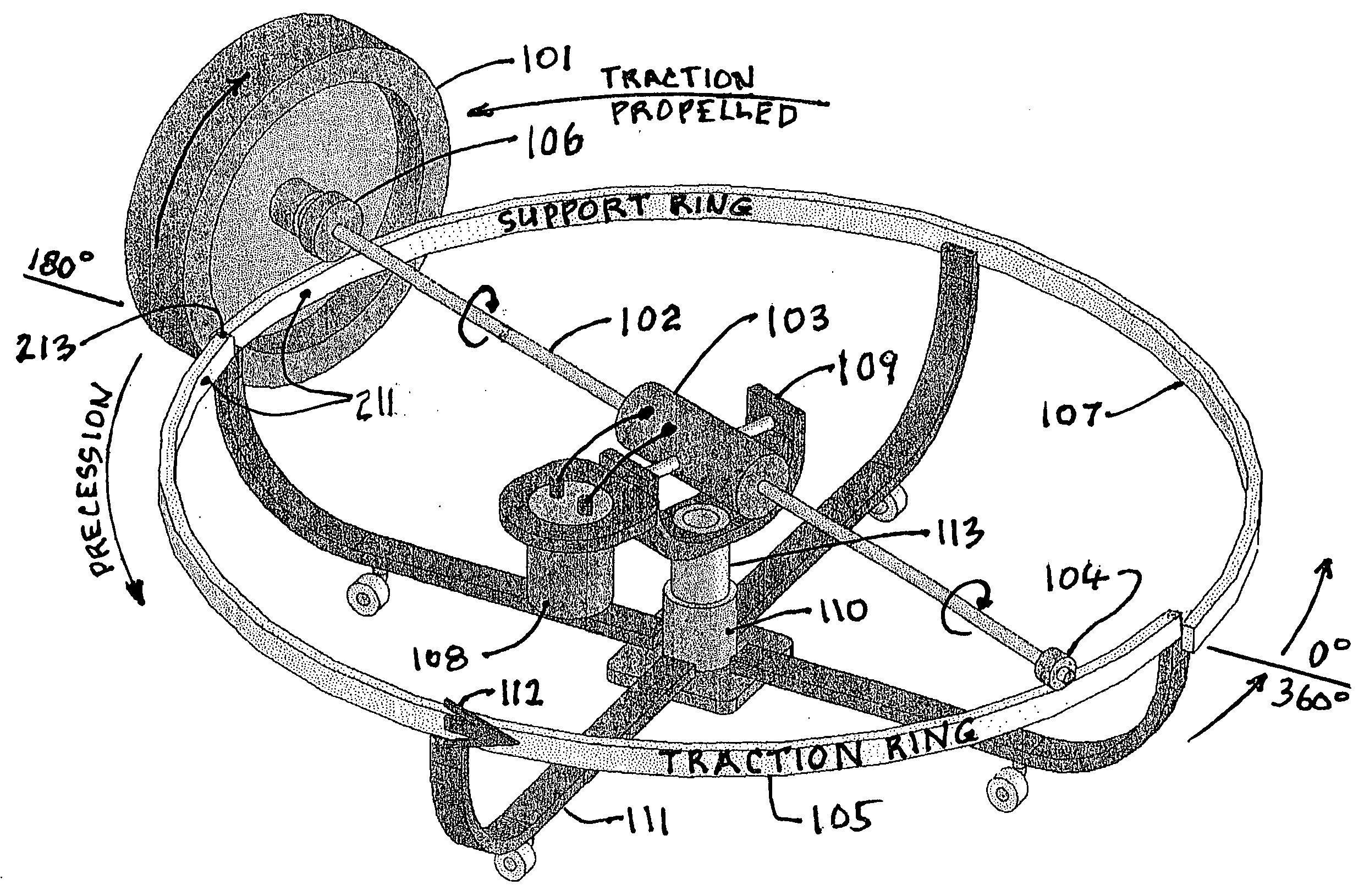
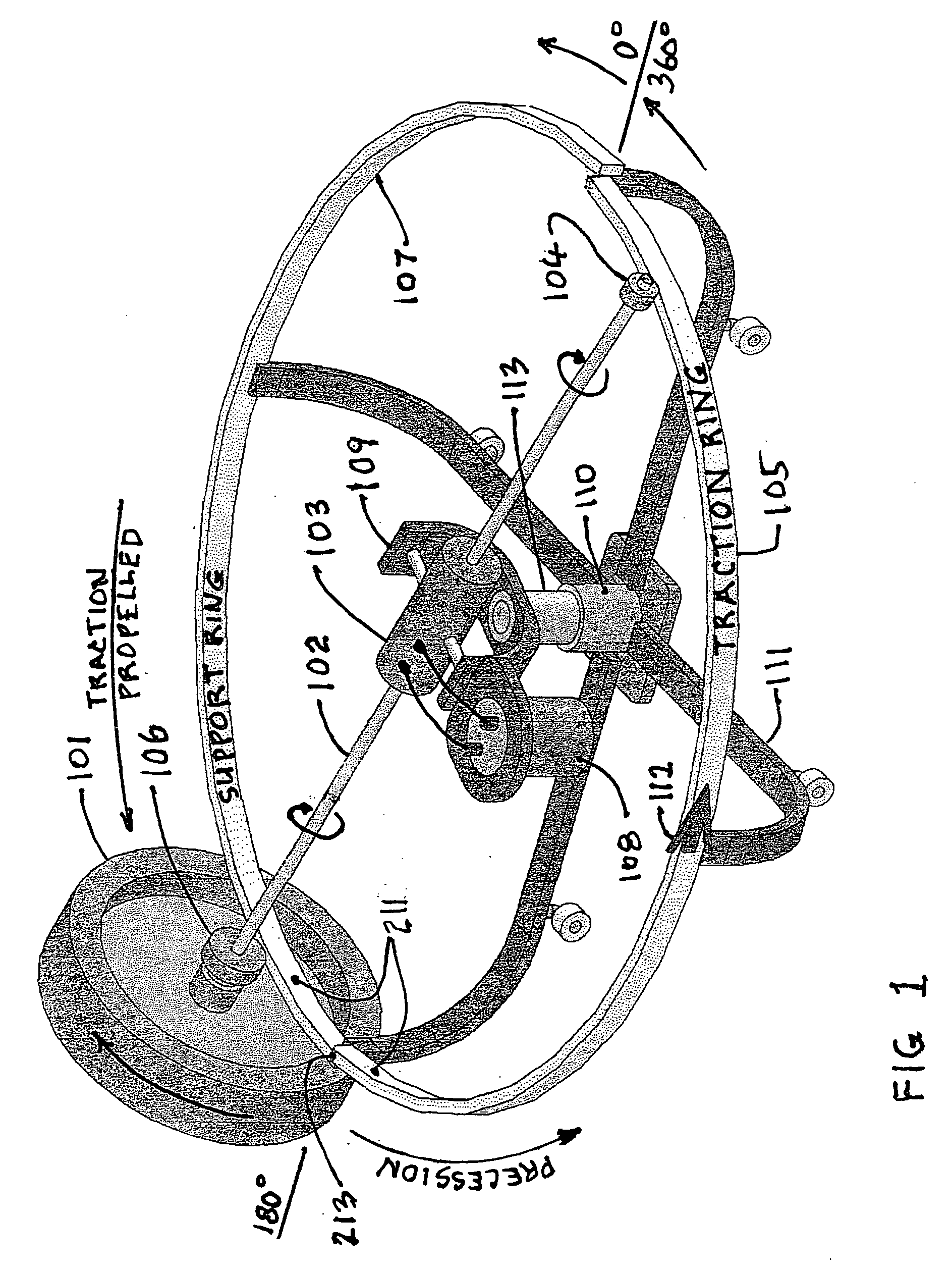
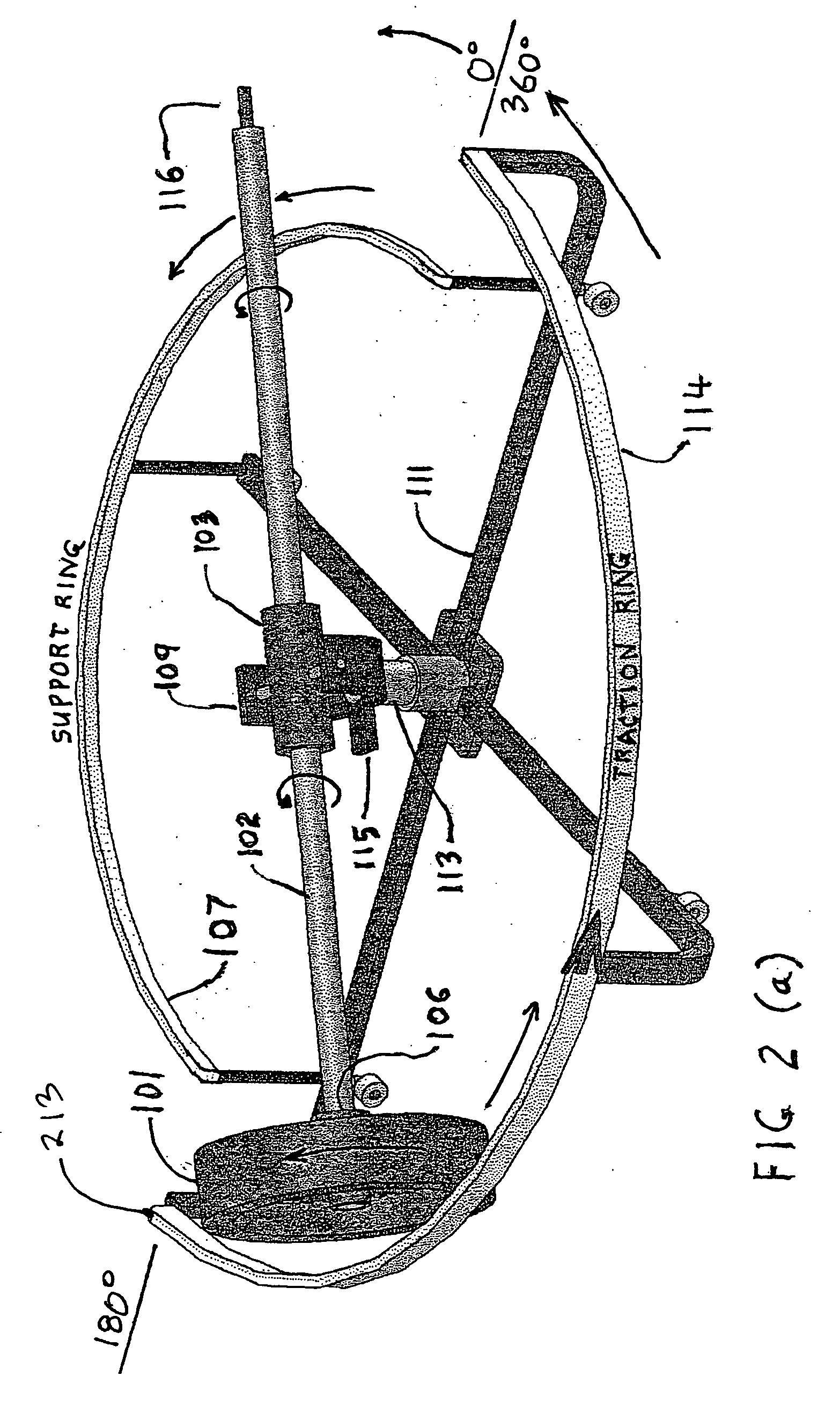
Inertial propulsion device to move an object up and down
ActiveUS20110219893A1Process controlImprove efficiencyCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsGyroscopePrecession
Disclosed herein are two separate processes that do not require a propellant and do not produce an equal and opposite reaction against any external form of matter in the Local Inertial Reference Frame and do not violate Newton's Laws in the Universal Reference Frame. The first process produces horizontal motion, relies on the earth's gravitational field as an external force, and has been successfully tested. The second process produces vertical motion and relies only on the aether. It has been successfully tested considering the effect of the earth's gravity. Due to the law of conservation of angular momentum, the first process is considered by some to not be possible, but with the proper use of an external field (for example, gravity) and the phenomenon of precession, it is clearly possible. A clear distinction is made between a simple rotor and a gyroscope which is a far more complex device.
Owner:FIALA HARVEY E +2
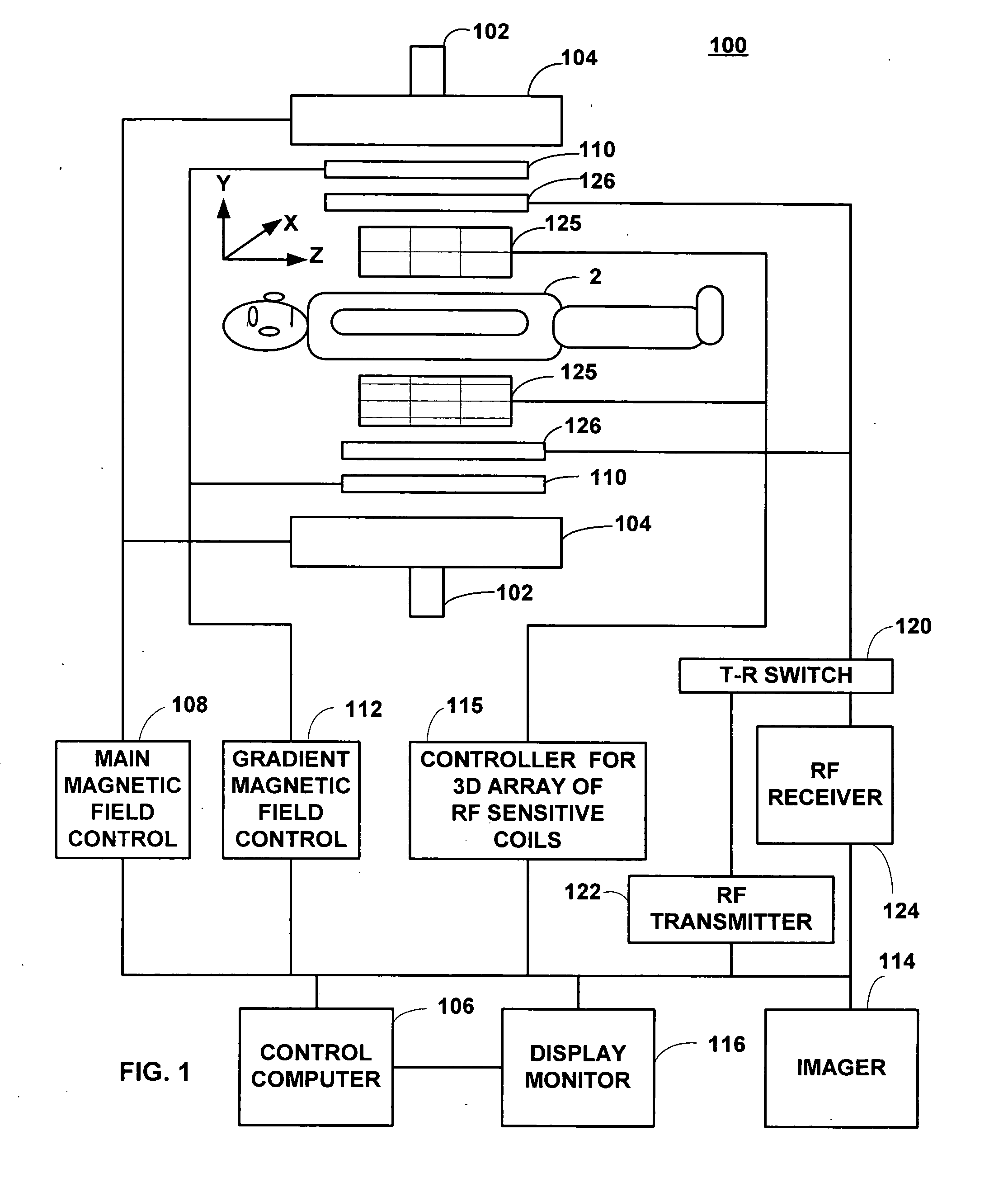
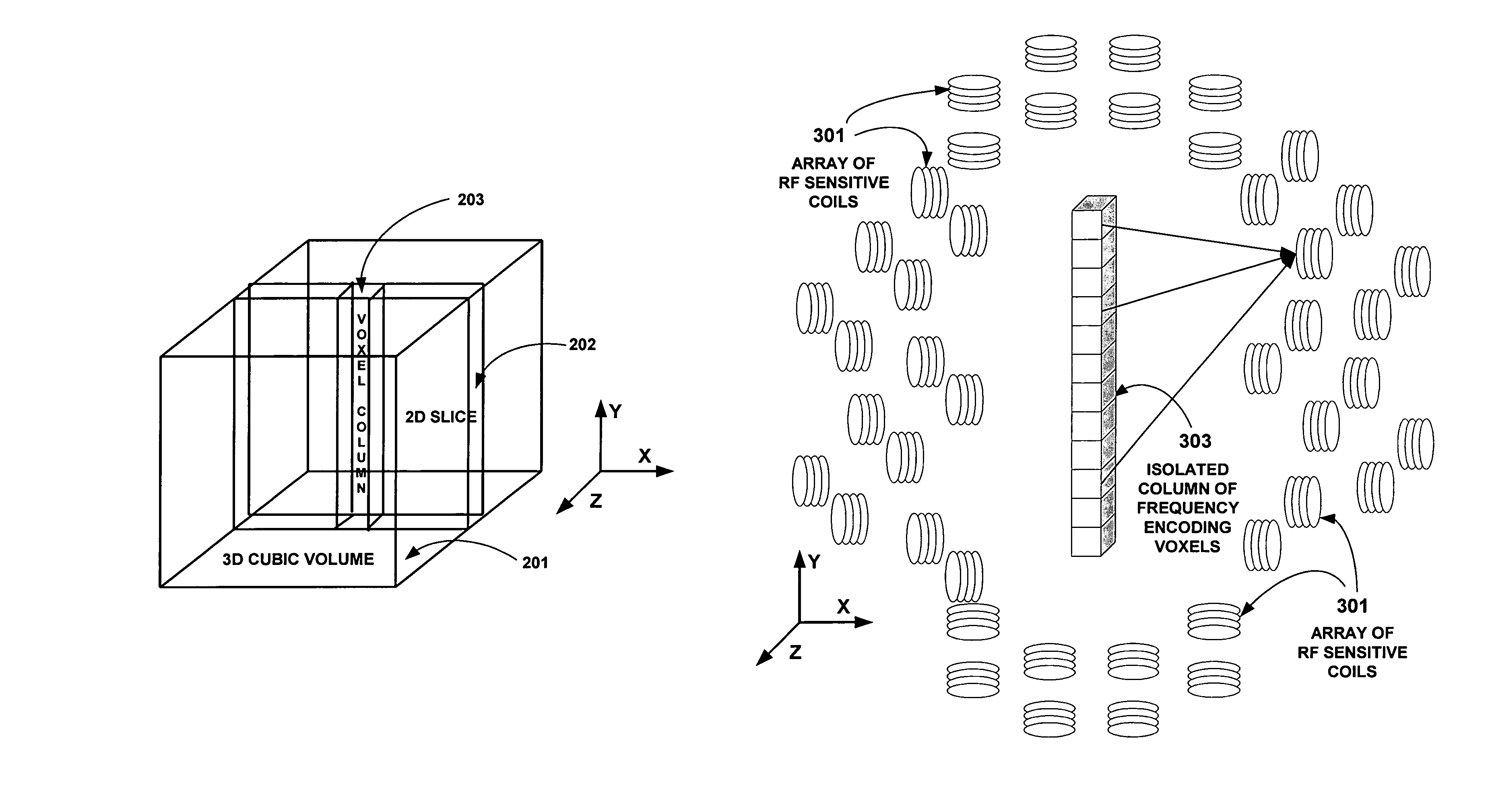
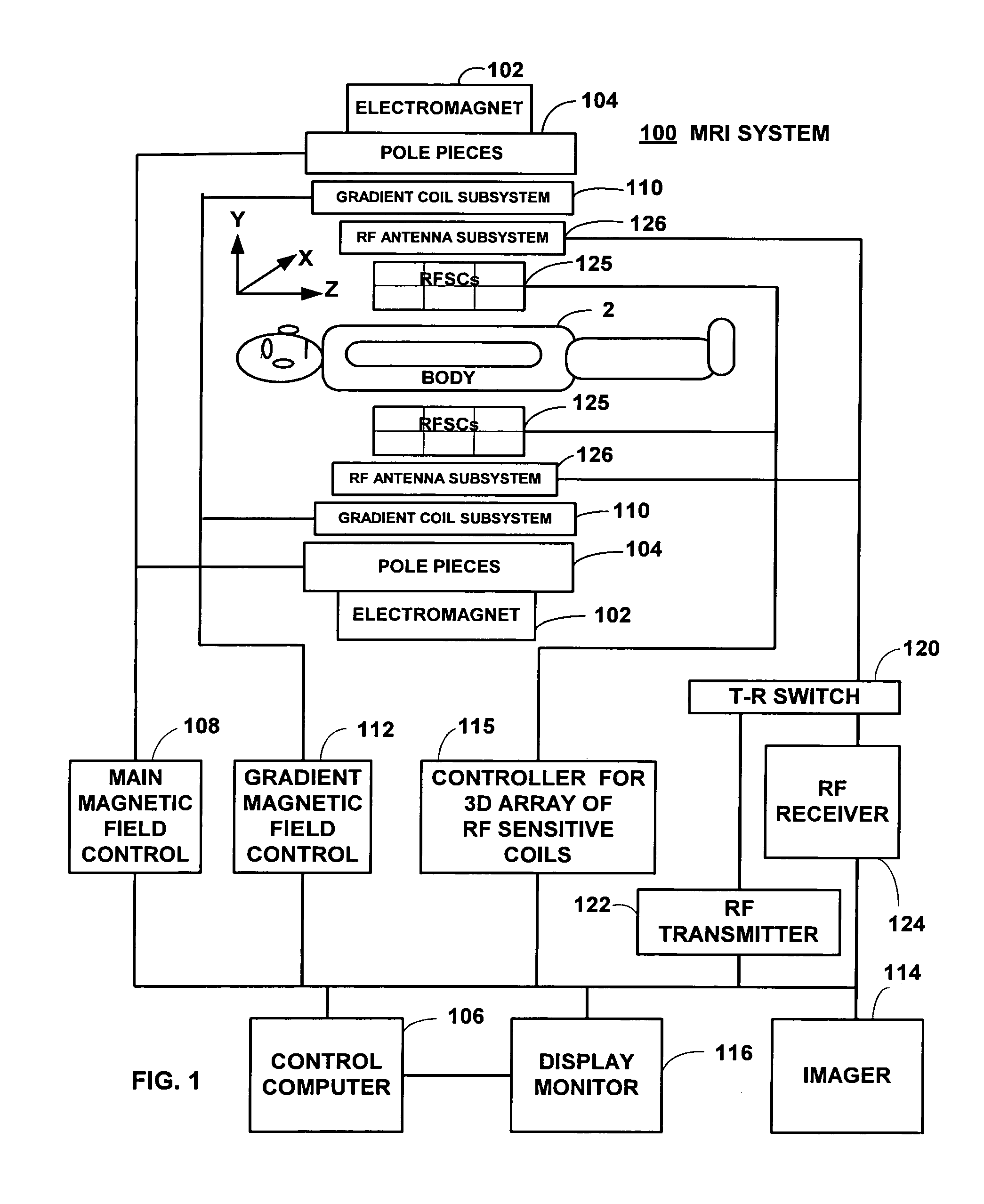
Field image tomography for magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20110115485A1Shorten the length of timeReduce usageMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionObject basedSystem matrix
Field Image Tomography (FIT) is a fundamental new theory for determining the three-dimensional (3D) spatial density distribution of field emitting sources. The field can be the intensity of any type of field including (i) Radio Frequency (RF) waves in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), (ii) Gamma radiation in SPECT / PET, and (iii) gravitational field of earth, moon, etc. FIT exploits the property that field intensity decreases with increasing radial distance from the field source and the field intensity distribution measured in an extended 3D volume space can be used to determine the 3D spatial density distribution of the emitting source elements. A method and apparatus are disclosed for MRI of target objects based on FIT. Spinning atomic nuclei of a target object in a magnetic field are excited by beaming a suitable Radio Frequency (RF) pulse. These excited nuclei emit RF radiation while returning to their normal state. The intensity or amplitude distribution of the RF emission field g is measured in a 3D volume space that may extend substantially along the radial direction around the emission source. g is related to the 3D tomography f through a system matrix H that depends on the MRI apparatus, and noise n through the vector equation g=Hf+n. This equation is solved to obtain the tomographic image f of the target object by a method that reduces the effect of noise.
Owner:SUBBARAO MURALIDHARA
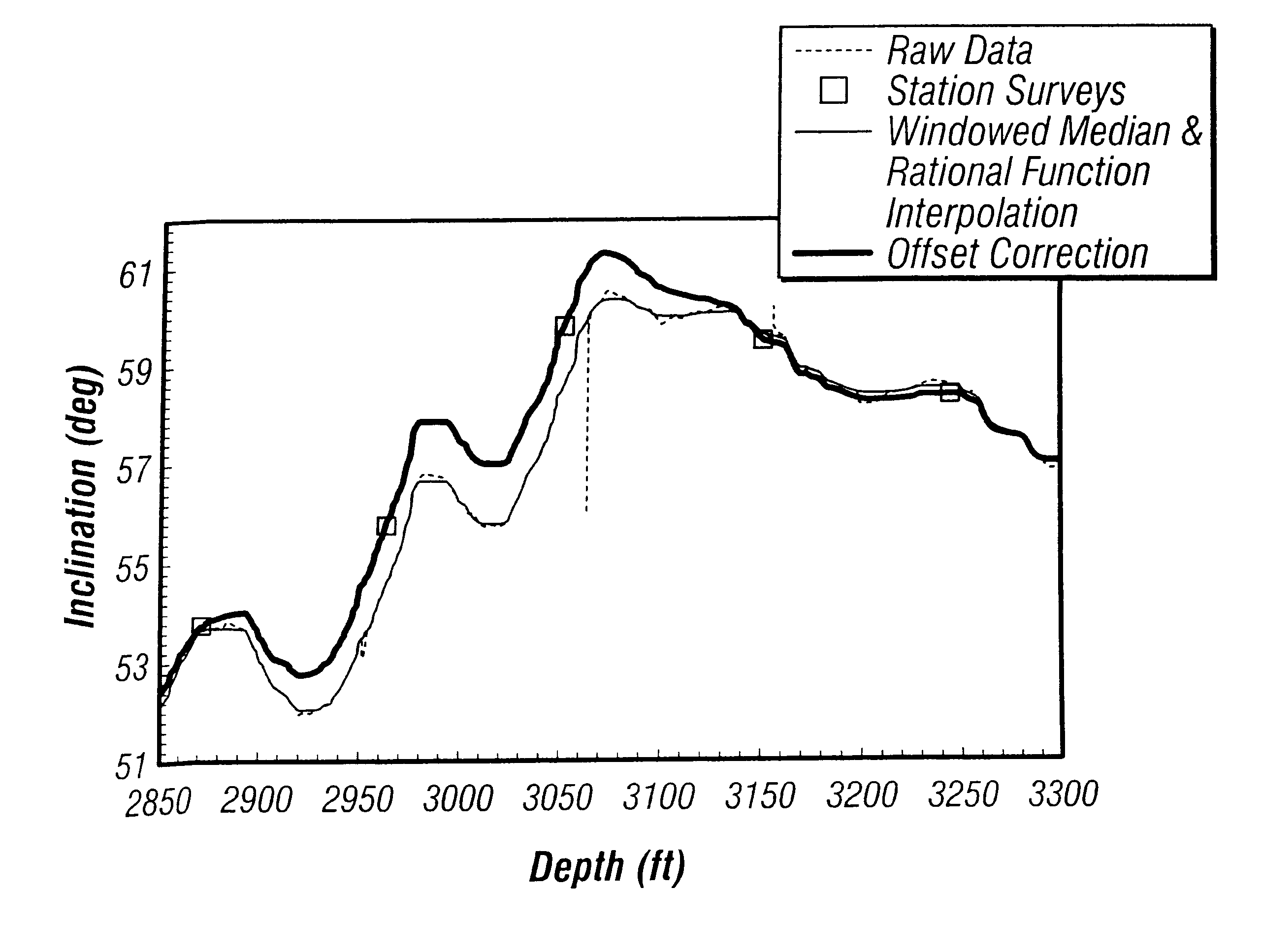
Borehole survey method utilizing continuous measurements
InactiveUS6633816B2Improve accuracyEliminate and reduce errorElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyContinuous measurementGeological survey
A borehole survey method is provided for processing continuous measurements of the earth's magnetic and gravitational fields obtained while drilling a borehole. The present invention improves borehole acquisition of targeted geological structures by substantially reducing continuous measurement errors attributable to noise, shock and vibrations from turning the drill bit against rock.< / PTEXT>
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
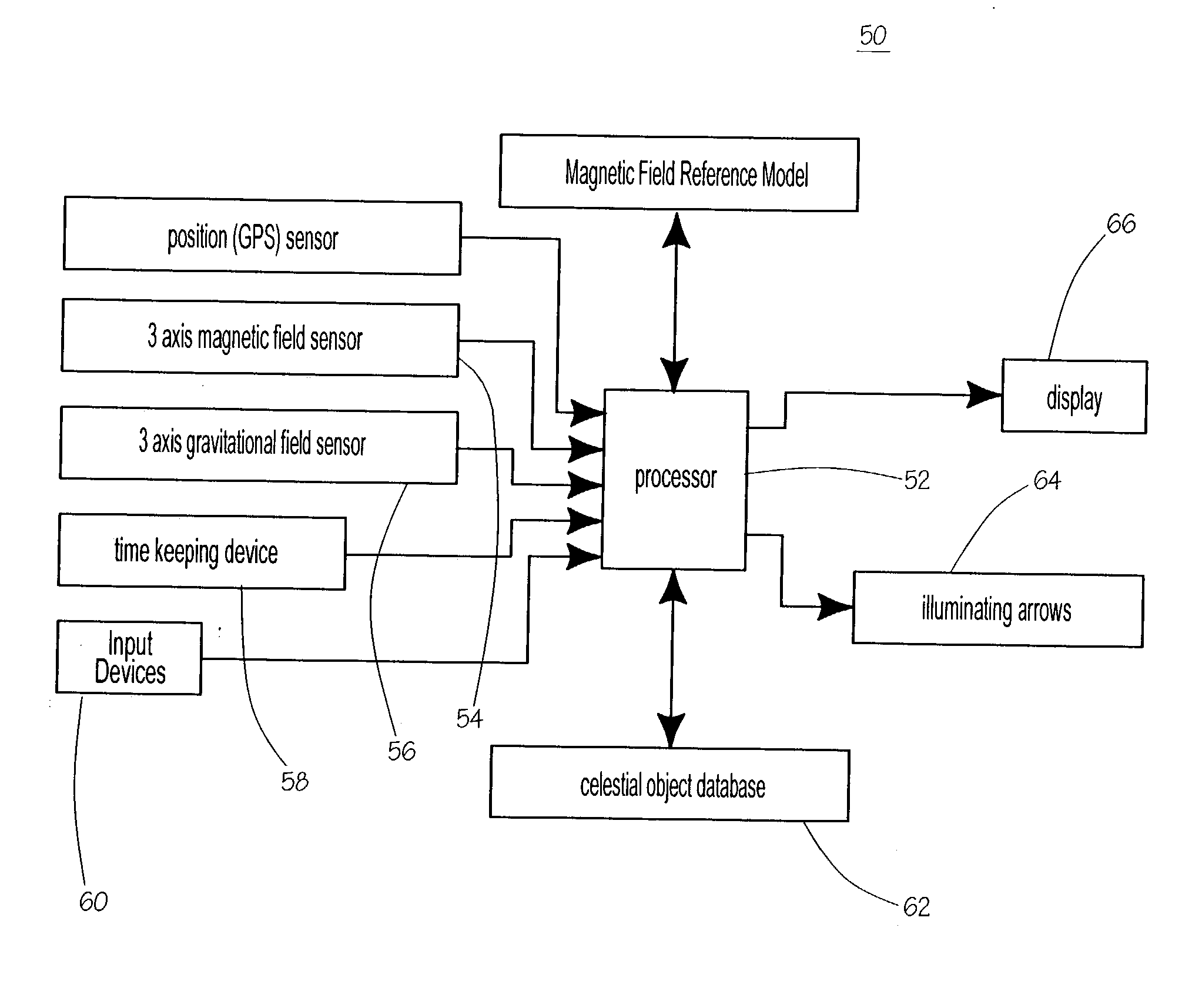
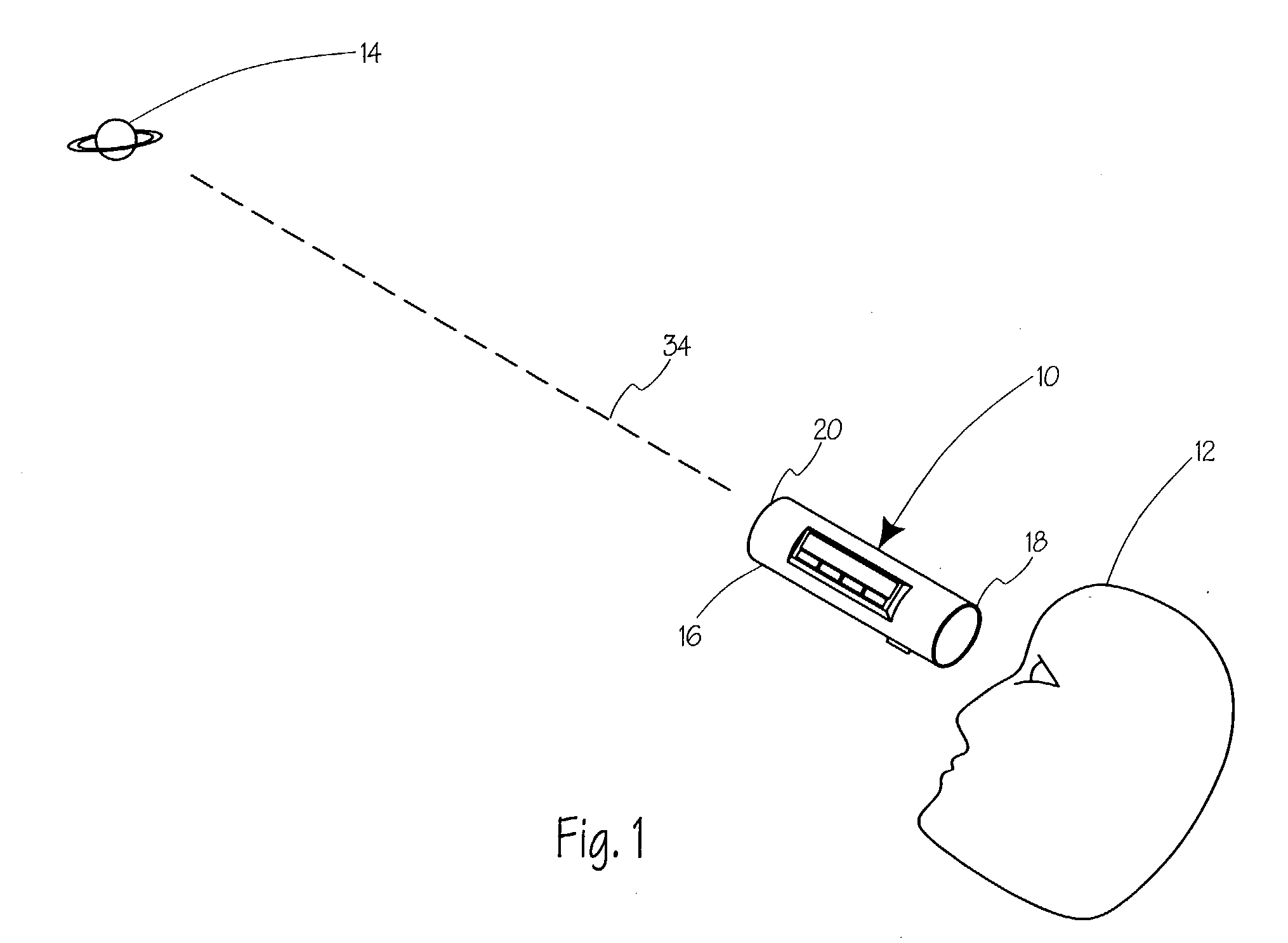
Celestial object location device
A hand-held electronic celestial object-locating device assists in identifying a celestial object or directing a user to a desired celestial object. The device is useful for locating or identifying any celestial object including stars, constellations, planets, comets, asteroids, artificial satellites, and deep sky objects to name a few. The device utilizes sensors for 3-axis magnetic field and 3-axis gravitational field detection. The device utilizes a processor and an electronic database to perform the required calculations. The device's database may be updated through access to the Internet through which the updates may be purchased.
Owner:YAMCON
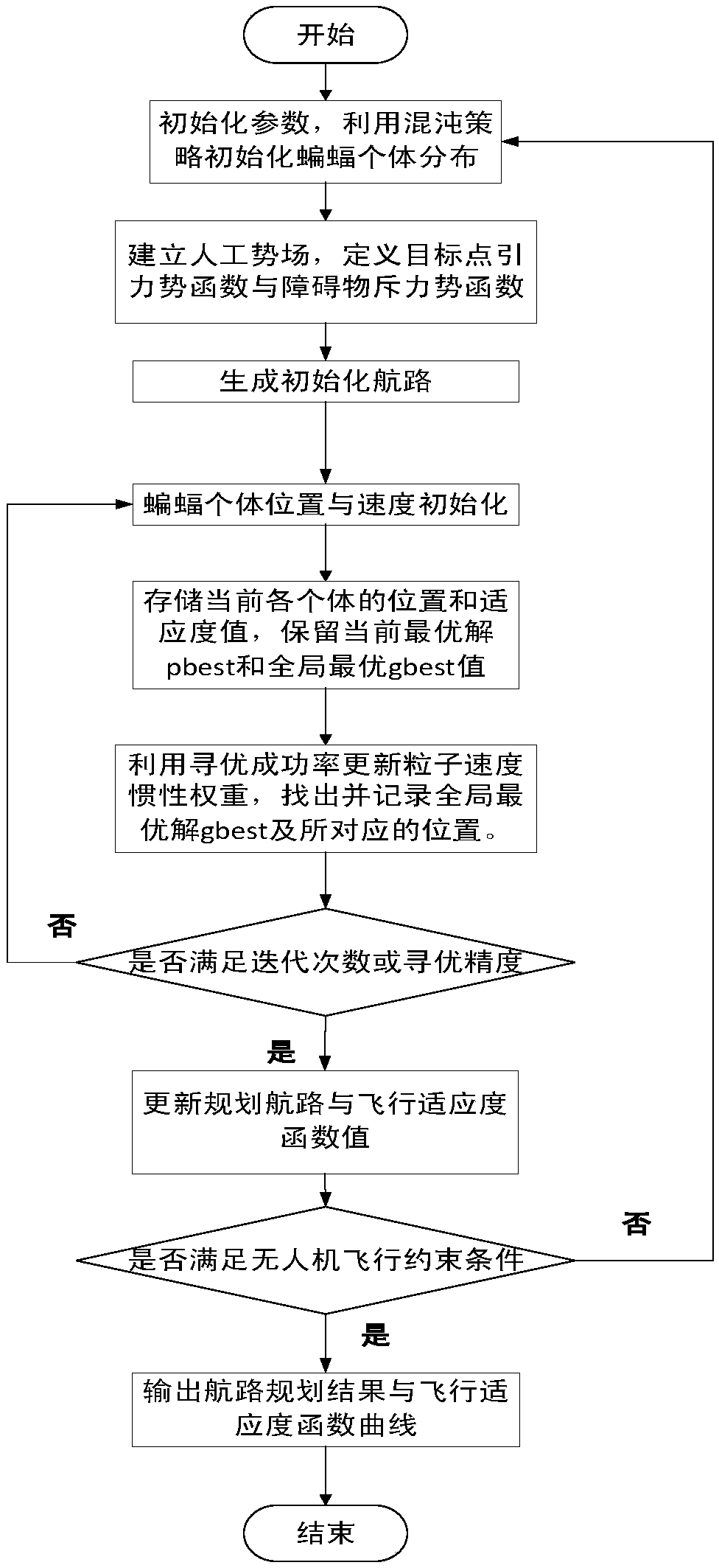
Unmanned aerial vehicle route planning method based on improved bat algorithm
Owner:SHENYANG AEROSPACE UNIVERSITY
Dual membrane single cavity Fabry Perot MEMS filter
InactiveUS20050134962A1Effective rangeSpectrum generation using multiple reflectionNon-linear opticsEngineeringMembrane configuration
Owner:AXSUN TECH
Celestial object location device
A hand-held electronic celestial object-locating device assists in identifying a celestial object or directing a user to a desired celestial object. The device is useful for locating or identifying any celestial object including stars, constellations, planets, comets, asteroids, artificial satellites, and deep sky objects to name a few. The device utilizes sensors for 3-axis magnetic field and 3-axis gravitational field detection. The device utilizes a processor and an electronic database to perform the required calculations. The device's database may be updated through access to the Internet through which the updates may be purchased.
Owner:YAMCON
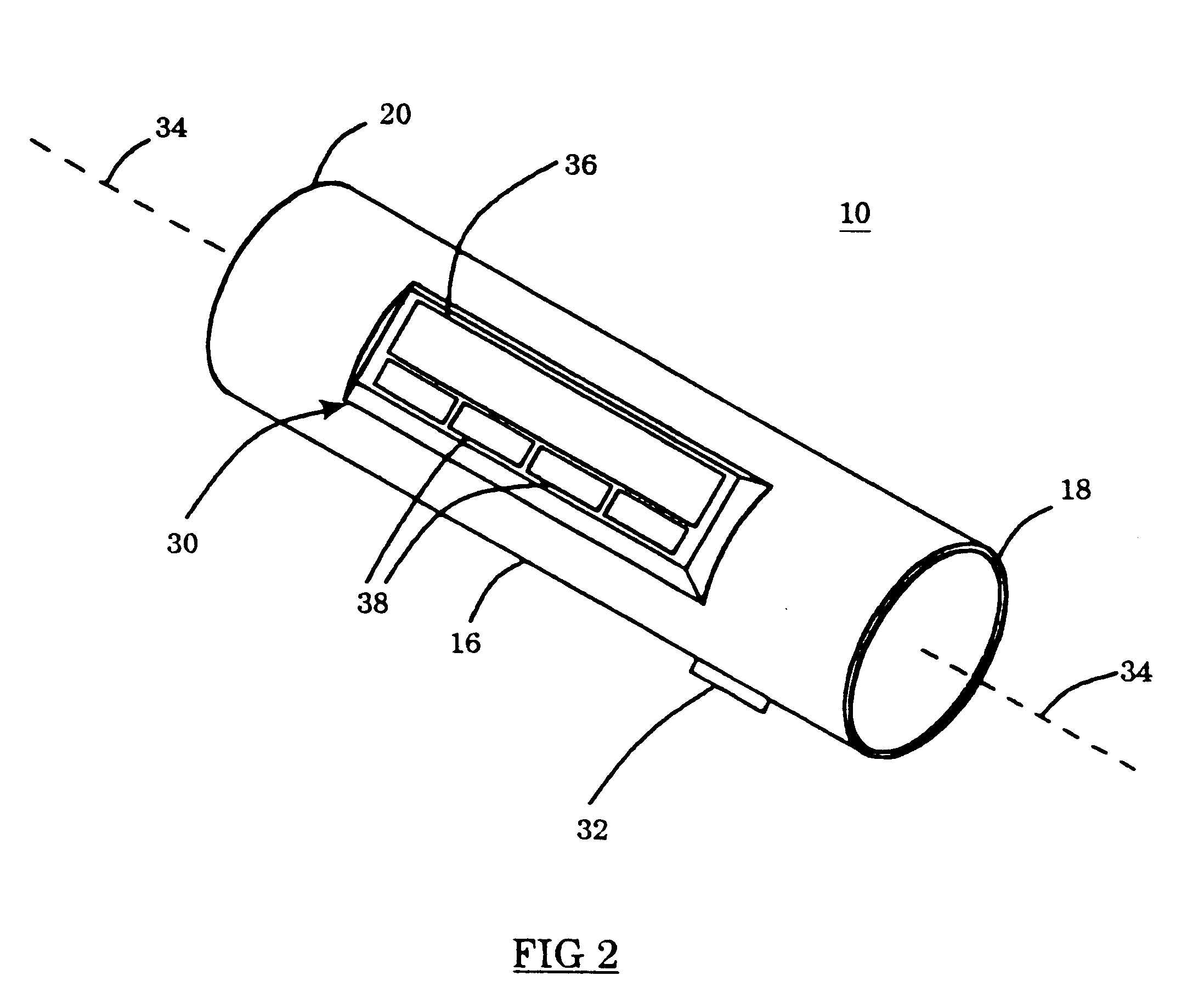
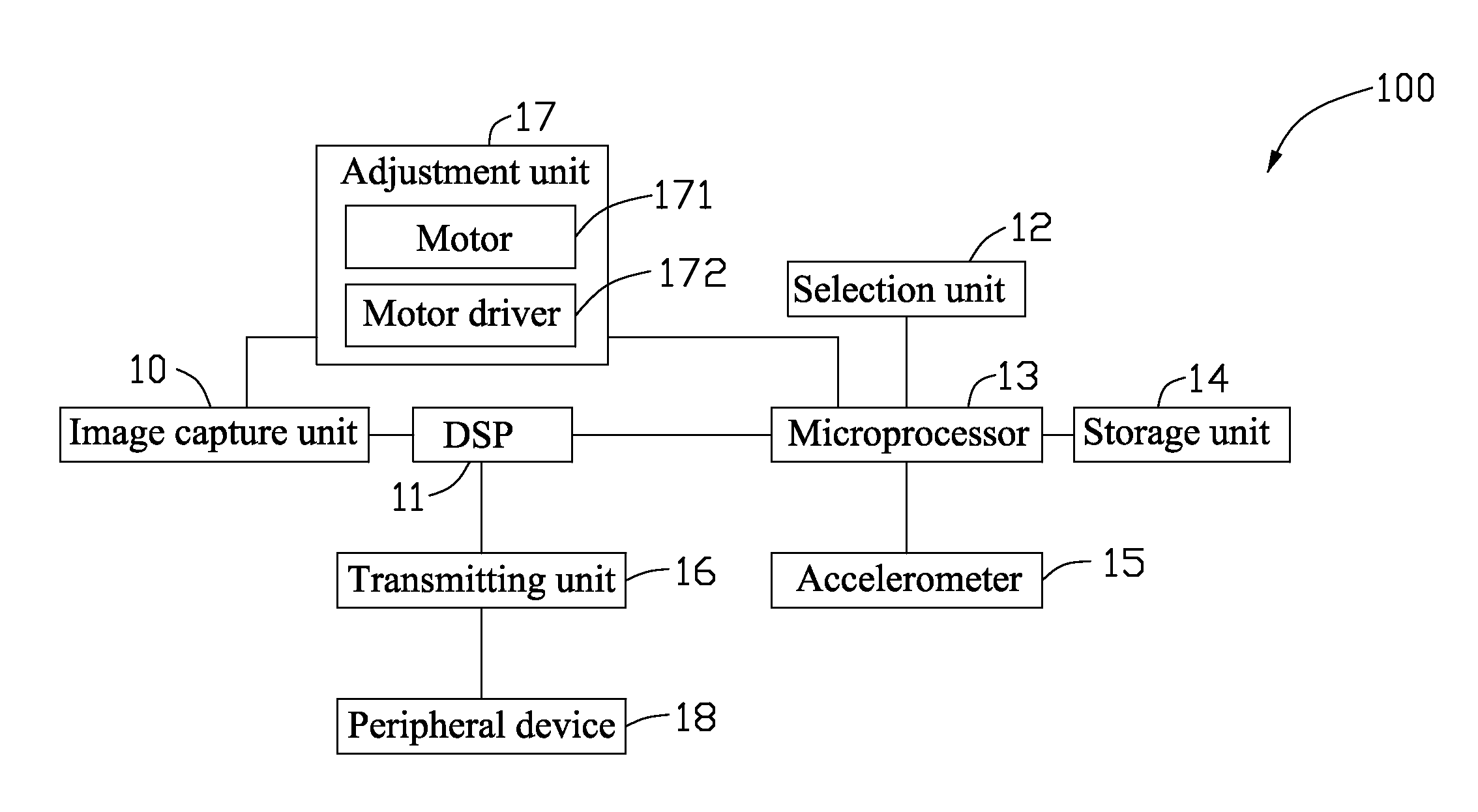
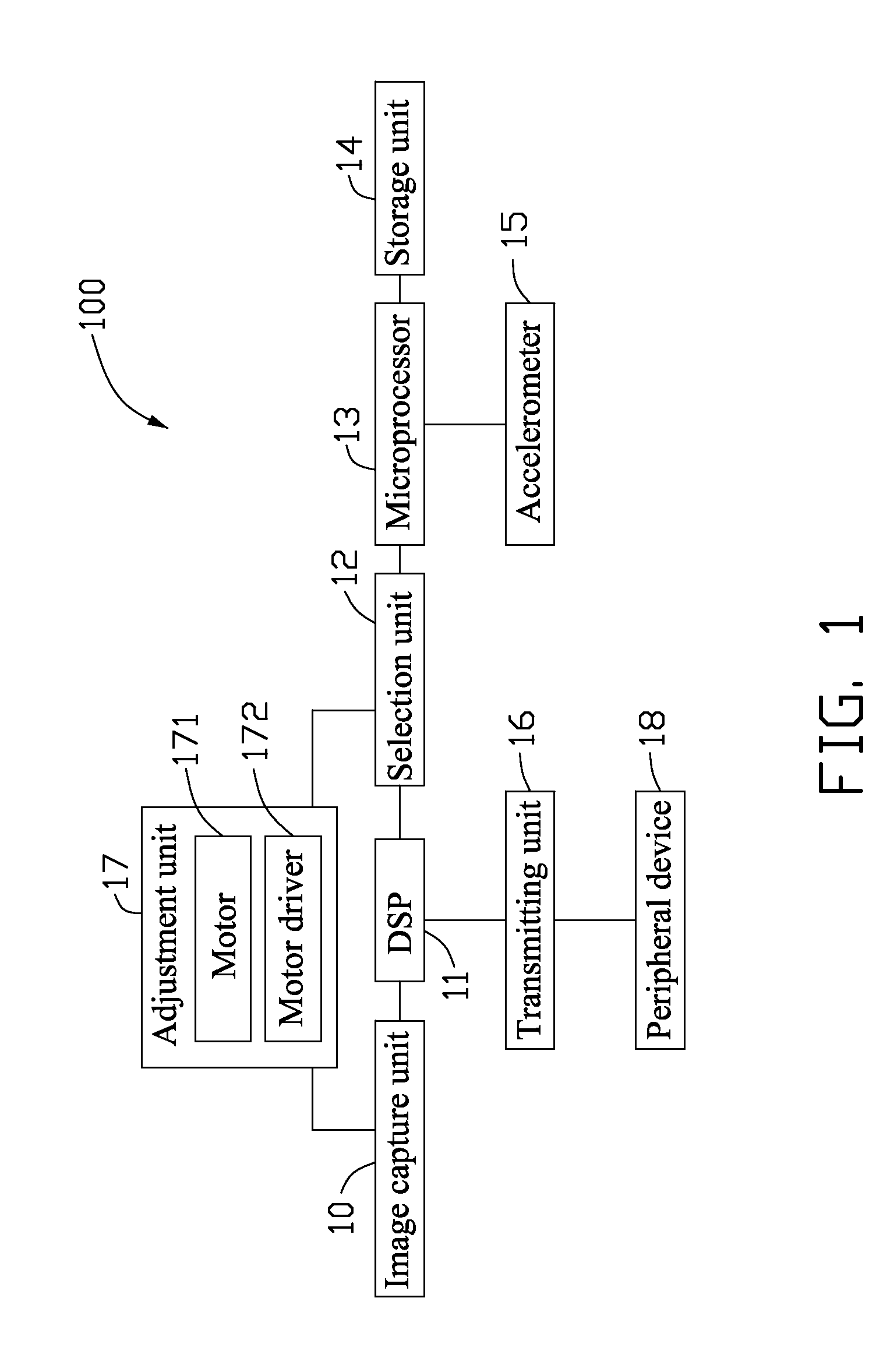
Image capturing device and method for adjusting photographing angle thereof
ActiveUS20100220205A1Television system detailsColor television detailsAccelerometerComputer graphics (images)
A image capturing device includes an image capture unit, a digital signal processor (DSP), a selection unit, an adjustment unit, a microprocessor, a storage unit, and a accelerometer. The image capture unit photographs a subject to output image data representing the subject to the DSP. The accelerometer detects an angle between a vertical axis of the image capture unit and the direction of the gravitational field to output an adjustment signal. The microprocessor outputs an adjustment value after comparing the adjustment signal with a reference adjustment value preset in the storage unit. When a first photograph angle adjustment manner is selected by the selection unit, the DSP adjusts the image data according to the adjustment value. When a second photograph angle adjustment manner is selected by the selection unit, the adjustment unit adjusts photographing angle of the image capture unit according to the adjustment value.
Owner:CLOUD NETWORK TECH SINGAPORE PTE LTD
Intertial propulsion device
ActiveUS20090183951A1Save on fuel costsIncrease flight speedCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsGyroscopeEngineering
Inertial propulsion is a largely undeveloped field. Inertial propulsion is defined as propelling a vehicle without the use of a propellant such as rocket fuel or ions, or by the application of an external force.Disclosed herein are two separate processes that do not require a propellant and do not produce an equal and opposite reaction against any external form of matter in the Local Inertial Reference Frame and do not violate Newton's Laws in the Universal Reference Frame. The first process produces horizontal motion, relies on the earth's gravitational field as an external force, and has been successfully tested. The second process produces vertical motion and relies only on the aether. It has been successfully tested considering the effect of the earth's gravity. The two processes referenced above are examples of converting the rotary motion of a spinning rotor into unidirectional linear motion. Due to the law of conservation of angular momentum, the first process is normally considered not possible, but with the proper use of an external field (for example, gravity) and the phenomenon of precession, it becomes possible. A clear distinction is made between a simple rotor and a gyroscope which is a far more complex device.
Owner:FIALA HARVEY EMANUEL +2
Satellite Gravity Retrieval Method Based on 3D Interpolation Principle of Double Star Space
InactiveCN102262248ALower performance requirementsSmall amount of calculationGravitational wave measurementNatural satelliteFixed stars
The invention relates to a method for precisely measuring an earth gravitational field, in particular to a satellite gravity inversion method based on a double-satellite spatial three-dimensional interpolation principle. An earth disturbing potential (obtained by computing an inter-satellite speed of a GRACE satellite K wave band measuring instrument, a satellite orbit position and a satellite orbit speed of a global positioning system (GPS) receiver, a satellite nonconservative force of an accelerometer and a satellite three-dimensional attitude data of a fixed star sensitive device) which is positioned on a gravity double-satellite orbit with a relatively irregular spatial position is interpolated three-dimensionally onto a reference spherical surface with a relatively regular spatial position and uniform grid division, so that the earth gravitational field is precisely and quickly inversed. By the method, satellite gravity inversion precision is high, physical meaning in the resolving process is clear, the computing speed is high, requirements on performance of a computer are low, and the method is sensitive to high-frequency signals in the gravitational field, so that the double-satellite spatial three-dimensional interpolation method is an effective method for resolving the earth gravitational field with high precision and high spatial resolution.
Owner:INST OF GEODESY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
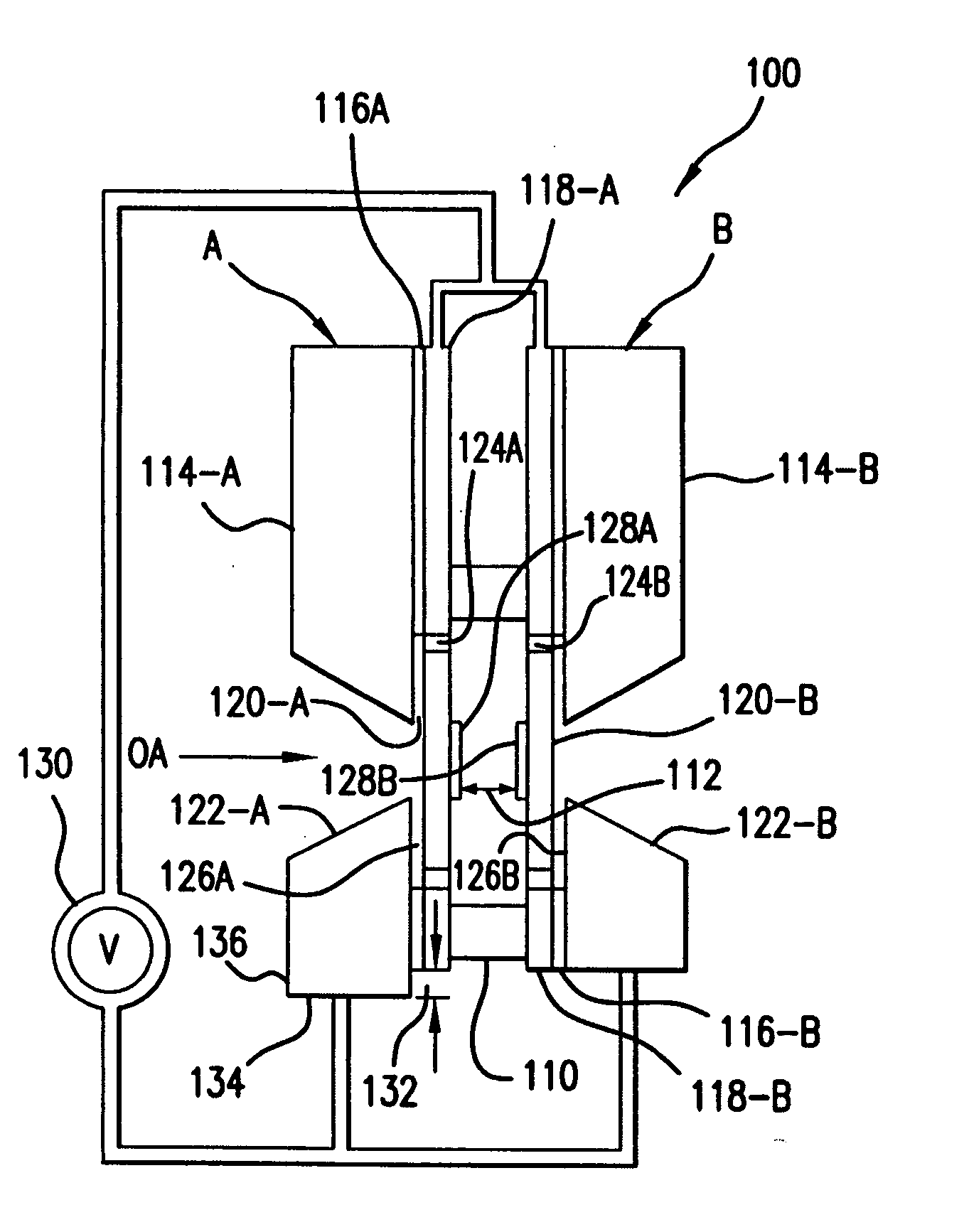
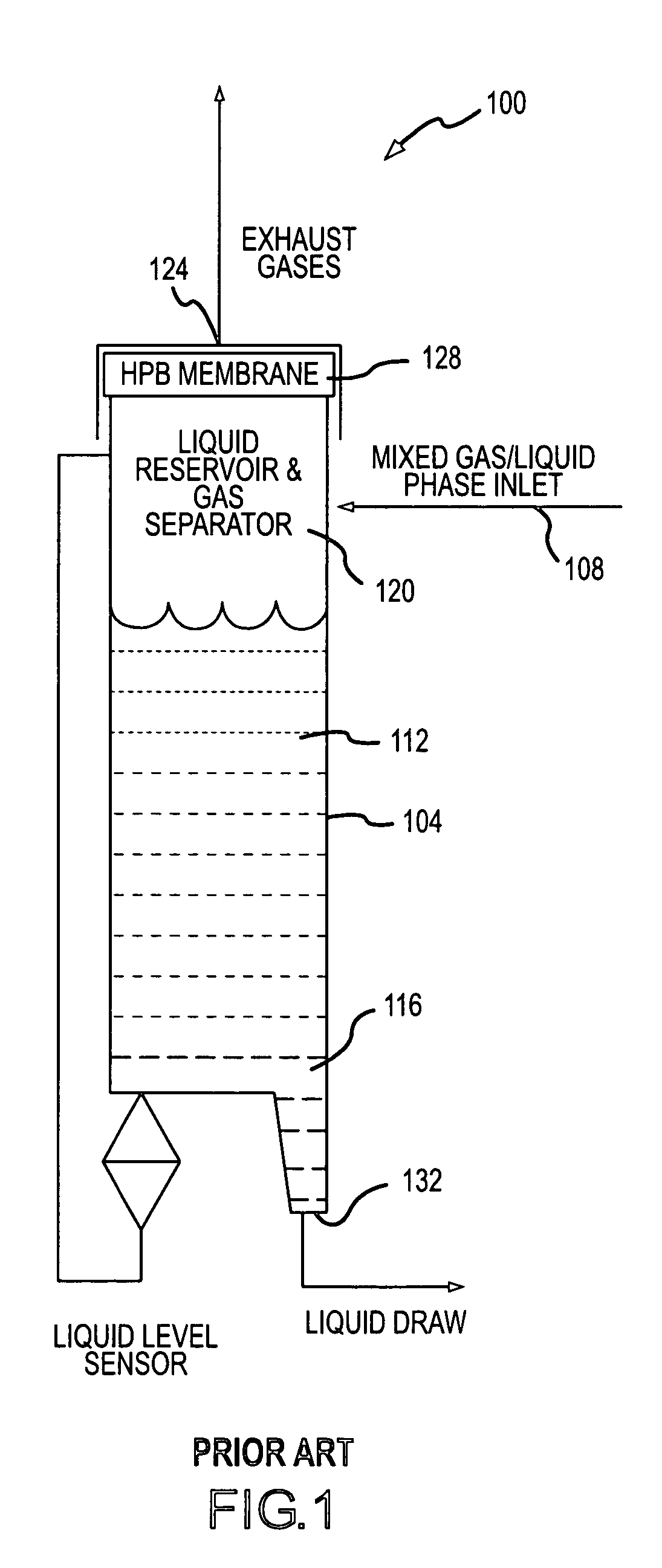
Orientation insensitive combined liquid reservoir and gas/liquid separator
InactiveUS6942718B1Reliable separation of liquidReliable separationIsotope separationLiquid degasification by filtrationGas phaseReservoir volume
In accordance with the present invention, a system for separating gas and liquid phases from a mixed phase system is provided. Furthermore, the present invention provides for the reliable separation of liquid and gas phases, regardless of the orientation of the system with respect to a gravitational field, and in low or zero gravity environments. The system of the present invention generally provides a reservoir having a variable volume that is formed from a gas permeable, hydrophobic, microporous, polymer material. Material confined within the reservoir is maintained under pressure, to expel any gases introduced to the interior of the reservoir as part of a mixed phase inlet stream. The liquid phase component of the mixed phase inlet stream may be removed from the reservoir through an outlet located within the reservoir volume.
Owner:BALL AEROSPACE & TECHNOLOGIES
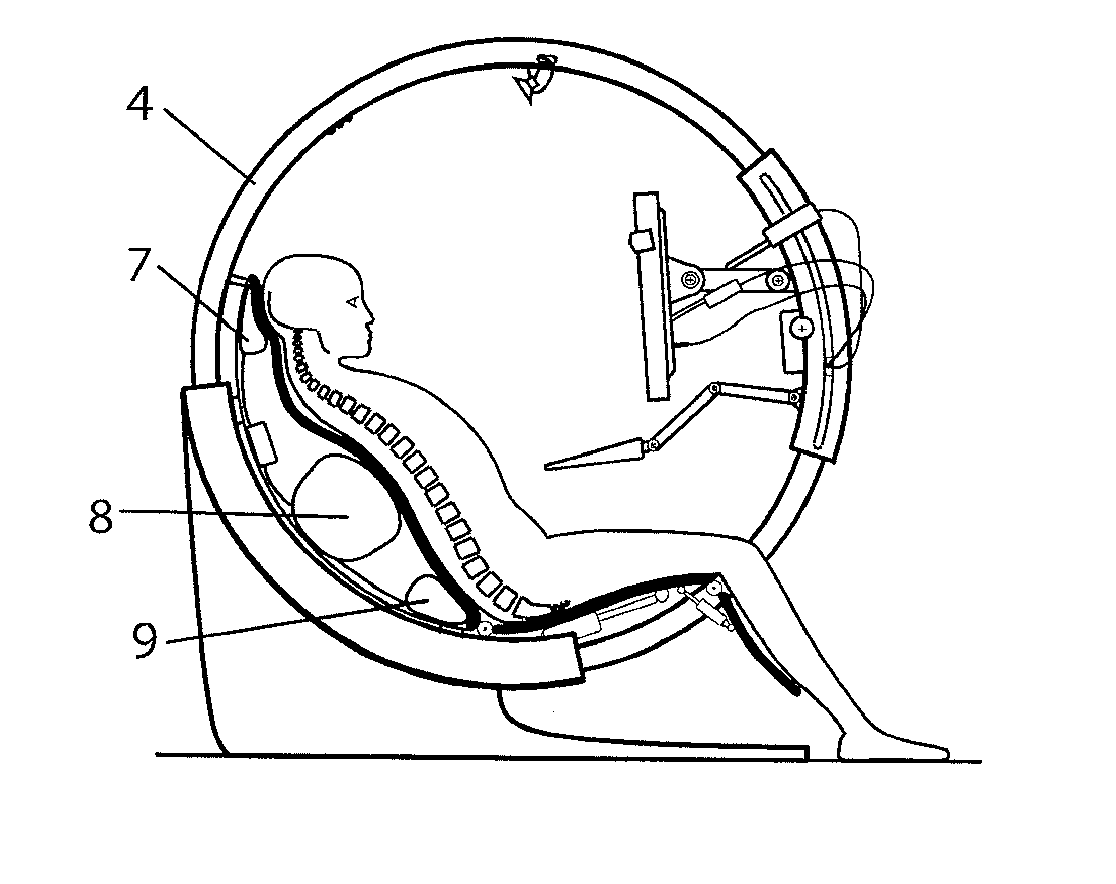
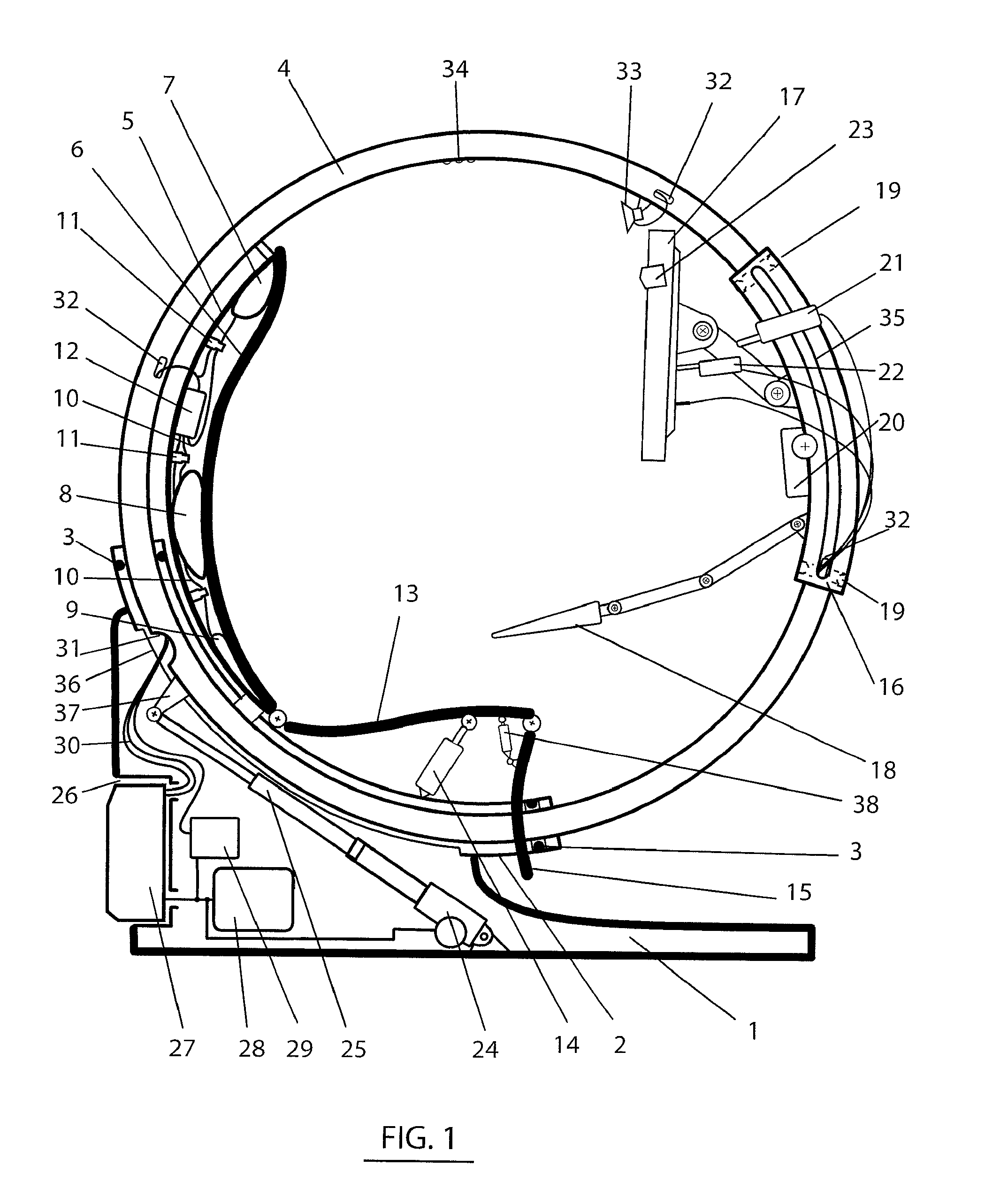
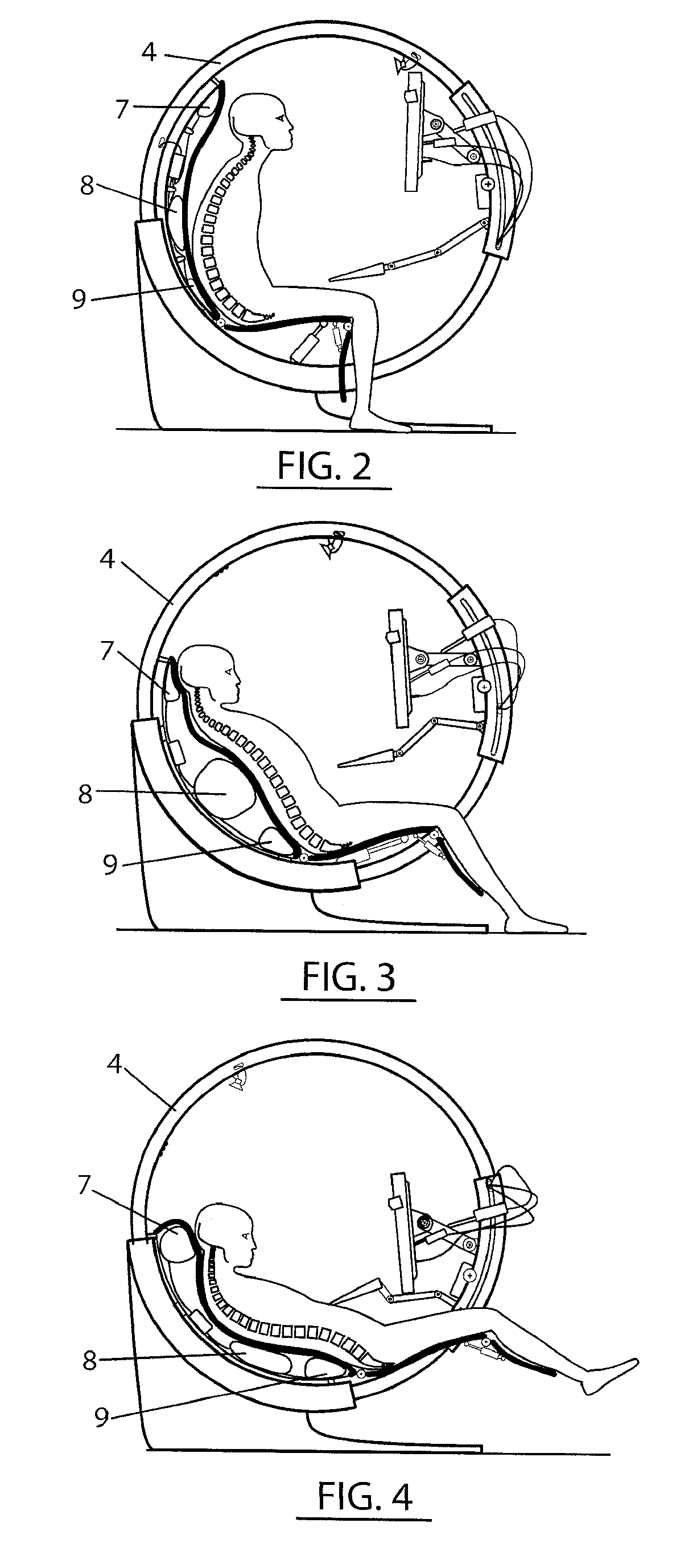
Ergonomic computer chair
ActiveUS20110031788A1Reduce probabilityReduce fatigueOperating chairsDental chairsComputer usersEngineering
The present ergonomic computer chair relates to chairs for special purposes, and more particularly, to computer operator's chair which is ergonomically designed to prevention of orthopedic and cardiovascular diseases and creation of psychophysical comfort, especially as regards reduction of fatigability during long-lasting work with computer. The ergonomic computer chair includes a seat with a backrest and a pedestal with a support frame made in the circular arc form, a support ring installed on the support frame wherein said support ring can rotate around its axis. The backrest is made of a rigid part and an elastic part separated from one other by at least three elastic bladders connected to a compressor by air tubes having electric valves. The rigid part of the backrest is hinged to the seat, and the seat is hinged to a seat inclination drive and to a footrest. A mounting of the computer monitor and keyboard is made by means of a movable sector which is made as a arched pipe with centering bearings. The chair has electric drives to move the support ring along the support frame of the pedestal, to move the movable sector along the support ring, to move the monitor longitudinally and to control monitor's inclination. This makes it possible to change the user's body position within the space against the Earth's gravitational field vector during the entire time of the work with computer. The use of the proposed device reduces the probability of orthopedic diseases occurrence, creates comfort and increases efficiency of the computer user.
Owner:GRAVITONUS
Field image tomography for magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS8378682B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionObject basedSystem matrix
Field Image Tomography (FIT) is a fundamental new theory for determining the three-dimensional (3D) spatial density distribution of field emitting sources. The field can be the intensity of any type of field including (i) Radio Frequency (RF) waves in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), (ii) Gamma radiation in SPECT / PET, and (iii) gravitational field of earth, moon, etc. FIT exploits the property that field intensity decreases with increasing radial distance from the field source and the field intensity distribution measured in an extended 3D volume space can be used to determine the 3D spatial density distribution of the emitting source elements. A method and apparatus are disclosed for MRI of target objects based on FIT. Spinning atomic nuclei of a target object in a magnetic field are excited by beaming a suitable Radio Frequency (RF) pulse. These excited nuclei emit RF radiation while returning to their normal state. The intensity or amplitude distribution of the RF emission field g is measured in a 3D volume space that may extend substantially along the radial direction around the emission source. g is related to the 3D tomography f through a system matrix H that depends on the MRI apparatus, and noise n through the vector equation g=Hf+n. This equation is solved to obtain the tomographic image f of the target object by a method that reduces the effect of noise.
Owner:SUBBARAO MURALIDHARA
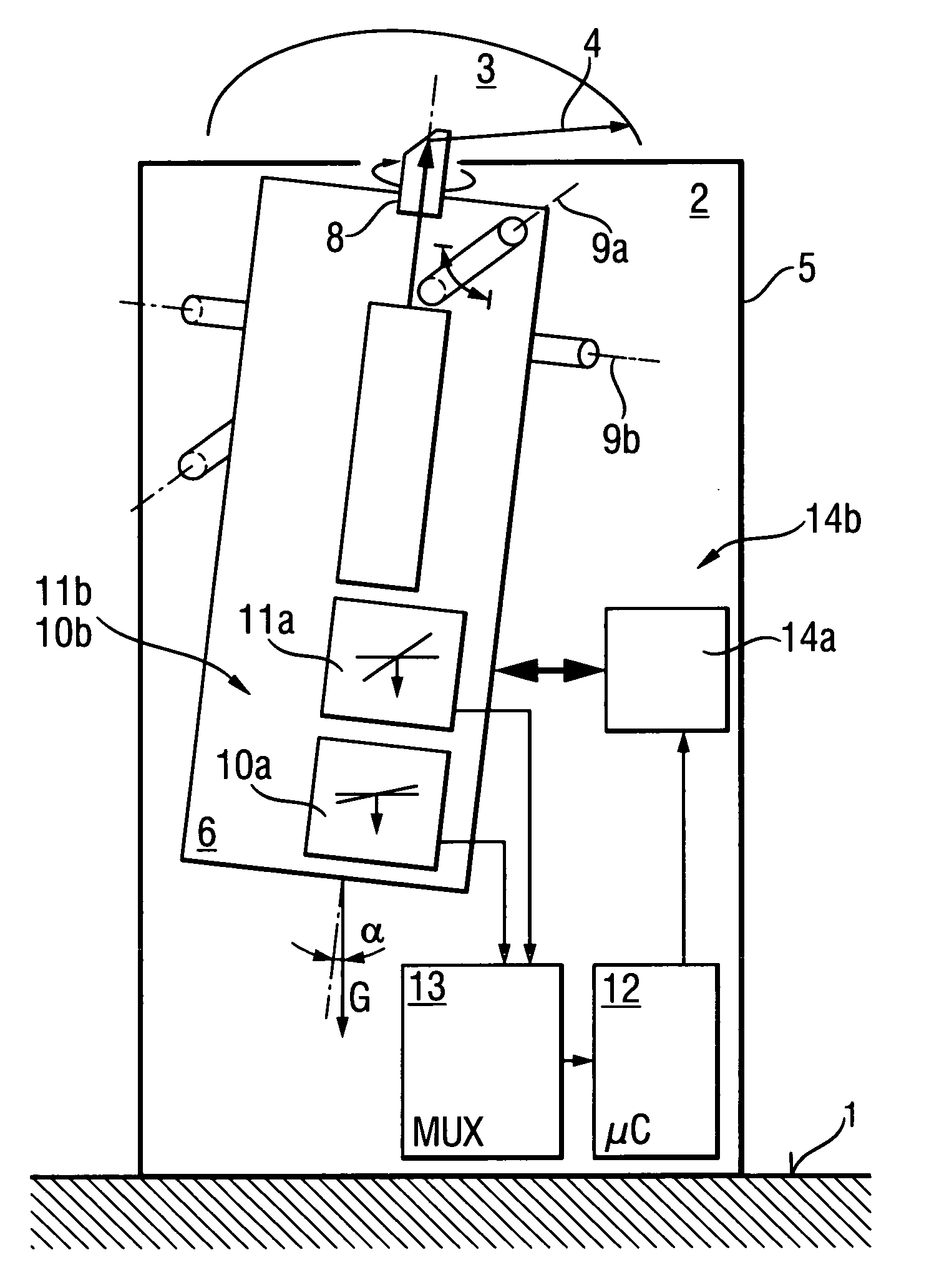
Tiltable construction laser
ActiveUS20060242850A1Simple technologyHigh resolutionHeight/levelling measurementReference line/planes/sectorsLevel sensorLaser beams
A construction laser with at least one laser beam (4) defining a plane (3) has a laser unit (6) which is tiltable with respect to a housing (5) around at least one swiveling axis (9a) and includes at least one leveling sensor (10a) which is sensitive to the swiveling axis (9a) for a highly precise orientation to the gravitational field (G), and at least one tilt sensor (11a) which is sensitive to the swiveling axis (9a) for direct measurement of an inclination angle [alpha] relative to the gravitational field (G).
Owner:HILTI AG
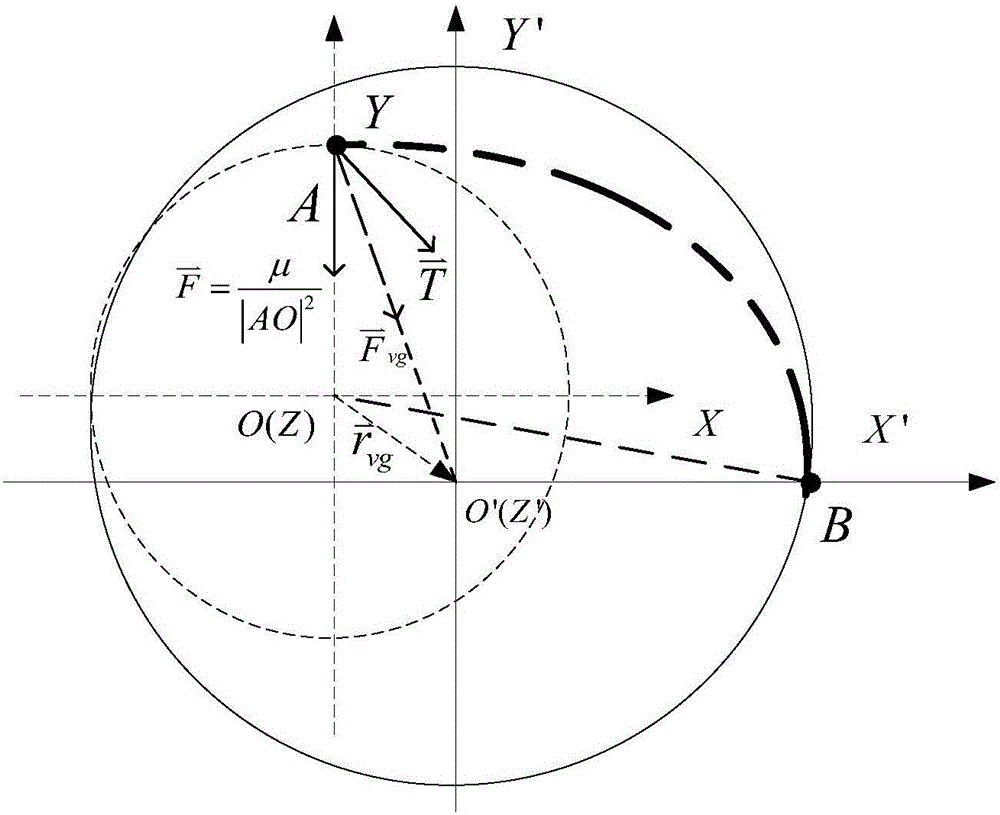
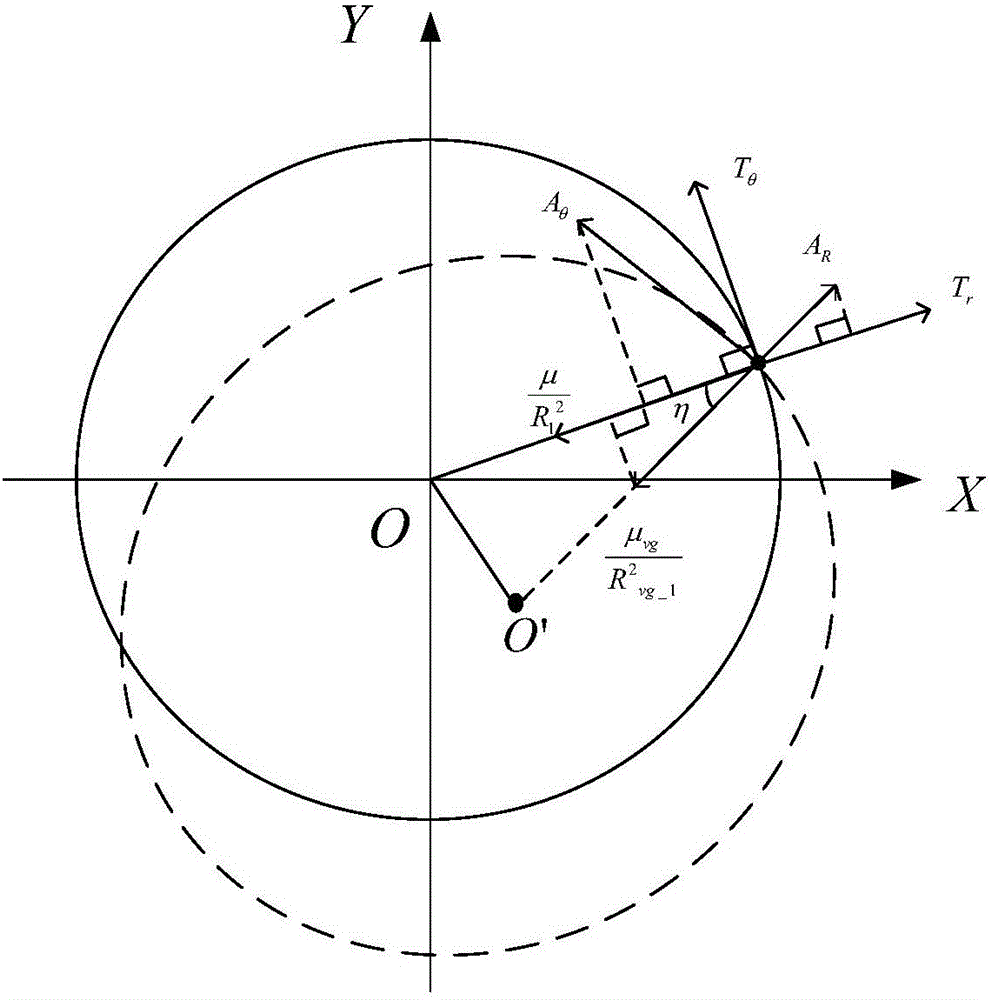
Method for designing bias orbit of spacecraft in halo orbit in sun-earth three-body gravitational field
ActiveCN106202640AGuaranteed accuracyReduce consumptionSpecial data processing applicationsElectricityMassive gravity
The invention discloses a method for designing a bias orbit of a spacecraft in a halo orbit in a sun-earth three-body gravitational field. The invention proposes a semi-analytic-solution-based orbit design method for a task demand of thrusting the spacecraft in the halo orbit to a heliocentric grave orbit by adopting a small thrust force in the sun-earth three-body gravitational field. According to the method, the calculation amount can be greatly reduced while the orbit precision is ensured. In addition, the invention proposes a method for realizing orbit maneuvering by adopting a minute continuous thrust system which mixes a variable reflectivity solar sail with electric propulsion. The method for realizing the orbit maneuvering by a mixed thrust force is capable of greatly reducing fuel consumption. The purpose of orbit maneuvering with minimum fuel consumption is achieved through optimization design of a posture angle of the solar sail. Compared with a conventional pulse bias orbit design method, the method proposed by the invention has the advantages that the calculation time can be shortened to a great extent on the premise of ensuring the solving precision.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Method for deploying multiple spacecraft
A method for deploying multiple spacecraft is disclosed. The method can be used in a situation where a first celestial body is being orbited by a second celestial body. The spacecraft are loaded onto a single spaceship that contains the multiple spacecraft and the spacecraft is launched from the second celestial body towards a third celestial body. The spacecraft are separated from each other while in route to the third celestial body. Each of the spacecraft is then subjected to the gravitational field of the third celestial body and each of the spacecraft assumes a different, independent orbit about the first celestial body. In those situations where the spacecraft are launched from Earth, the Sun can act as the first celestial body, the Earth can act as the second celestial body and the Moon can act as the third celestial body.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
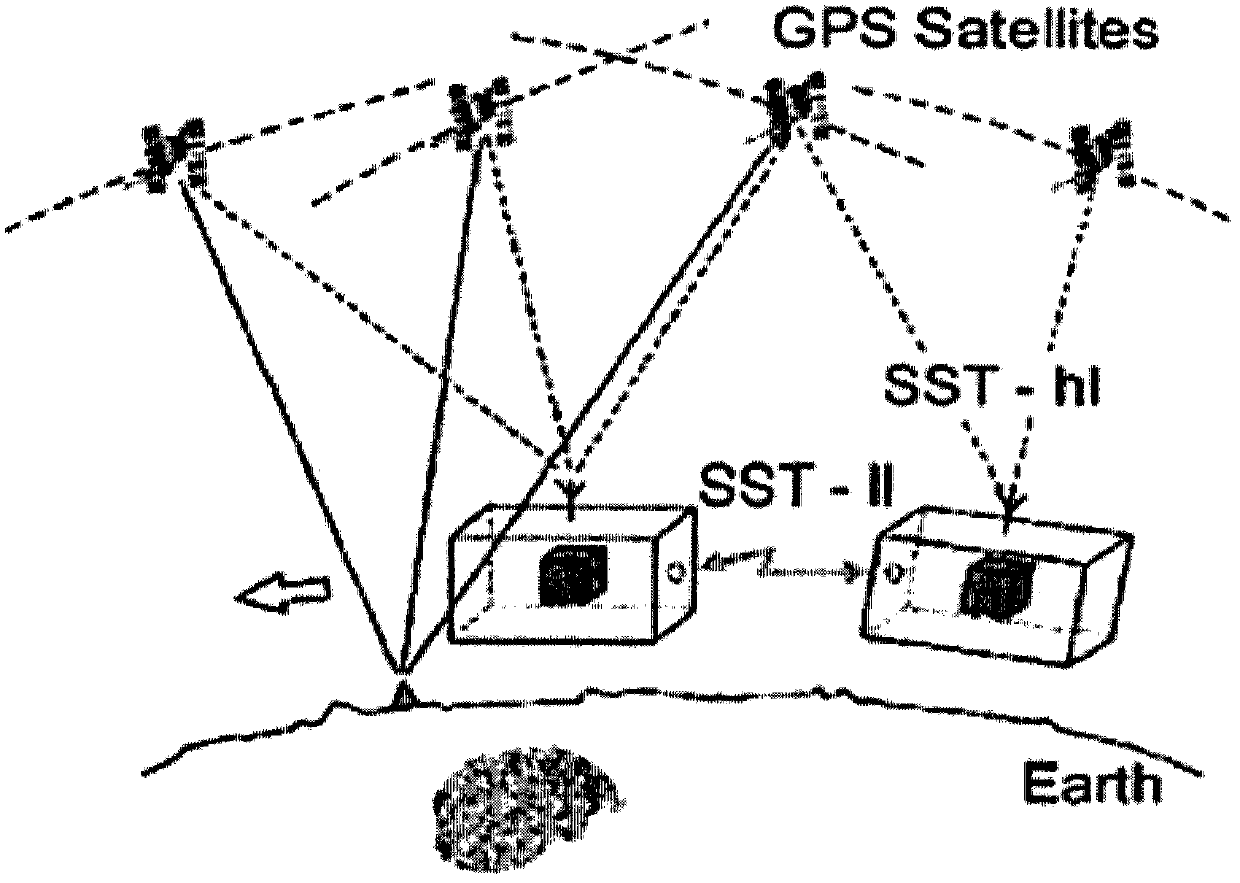
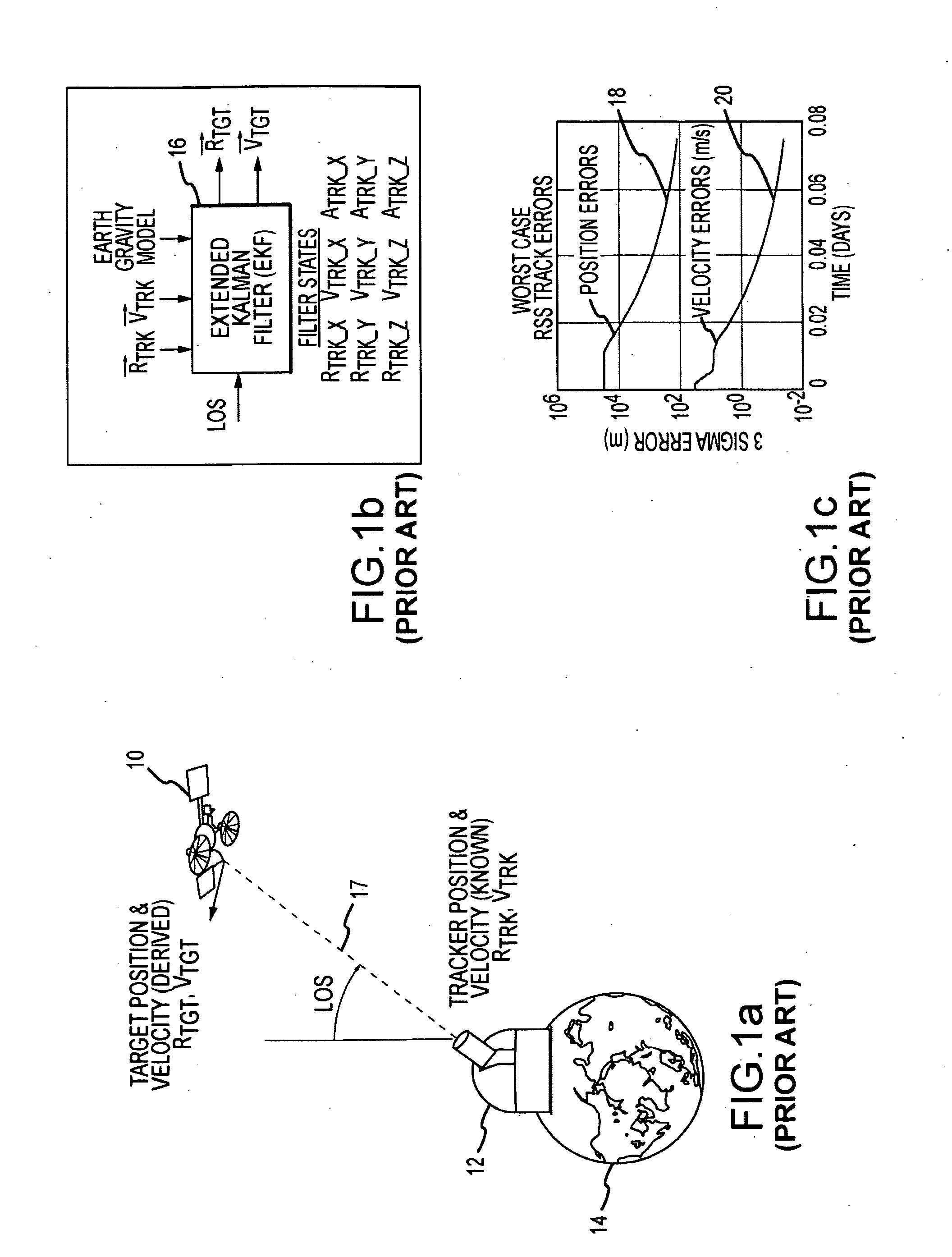
System and method of passive and autonomous navigation of space vehicles using an extended kalman filter
ActiveUS20100036612A1Cosmonautic vehiclesInstruments for comonautical navigationKaiman filterInvariant extended Kalman filter
It is presumed and commonly accepted by those skilled in the art of satellite navigation and Kalman filter design that the filter must be provided with the tracker position and velocity a priori in order to determine target position and velocity. Indeed, it is generally asserted that without a priori knowledge (known or measured values) of the tracker position and velocity, line of sight measurements between satellites do not contain adequate information to infer target states. Passive and autonomous navigation of space vehicles without a priori values for the position and velocity of either the target or tracker vehicle is achieved by reconfiguring the extended Kalman filter, or more generally any predictor / correction class filter, to include states for both the target and tracker vehicles. The target and tracker vehicles must both follow trajectories in an inertial frame of reference through the gravitational field of a gravitational body having a known gravitational model. The reconfigured filter simultaneously estimates the position and velocity of both tracking and target space-based vehicles from line-of-sight measurements.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
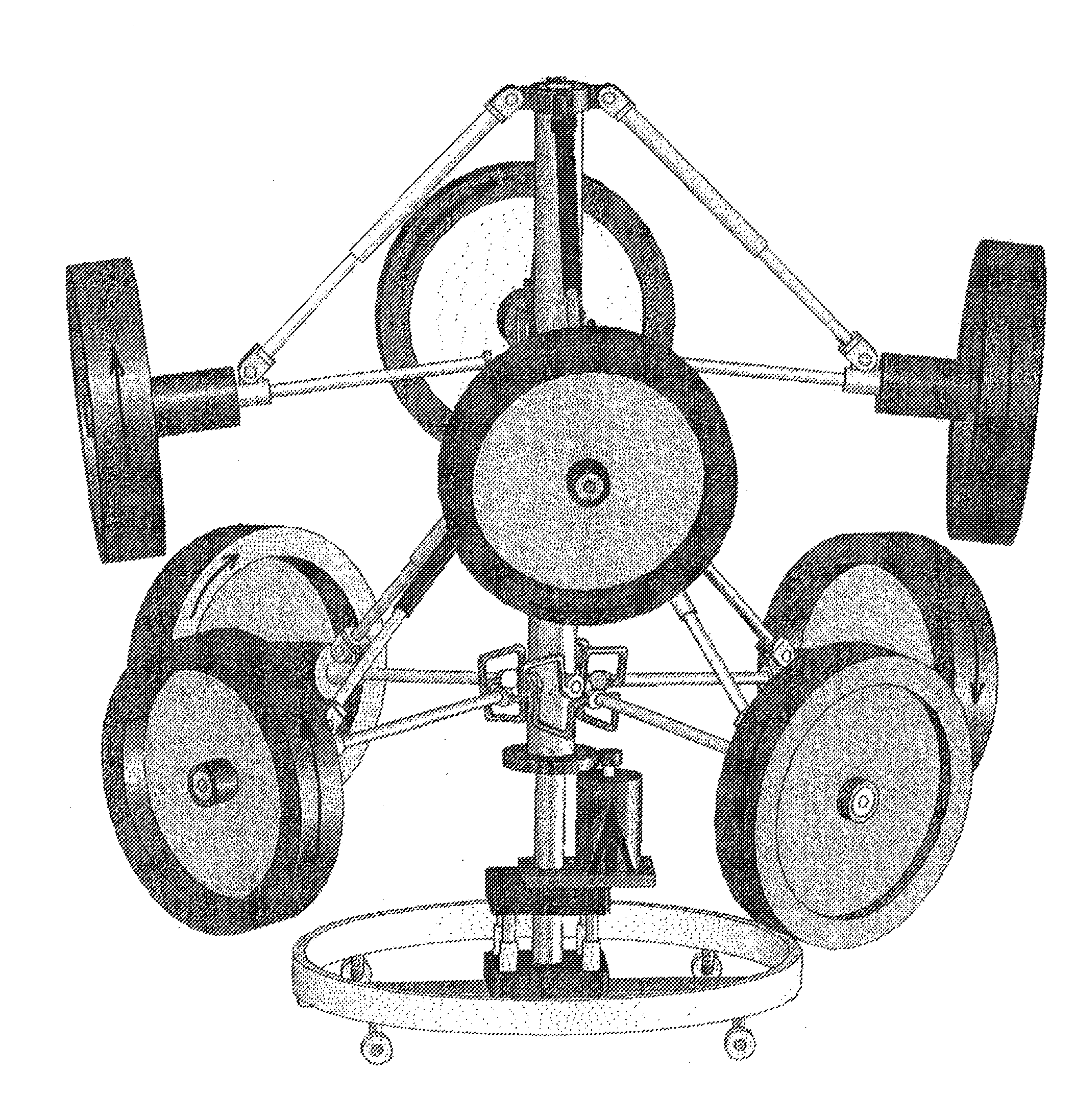
Apparatus and Method For Gripping and Releasing Objects
InactiveUS20120319416A1Counteracting forceReducing and eliminating flow of airGripping headsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPressure-gradient forceRobotic arm
Improved devices and methods for gripping, supporting and releasing objects, which may be used with robotic arms, manipulators or vehicles, to hold, move or rotate objects in automated manufacturing, packaging, assembling and construction applications. The device comprises a body, an adapter flange for mounting an object gripper with an intake, a vacuum supply port, an airflow passageway configured to couple the intake to the vacuum supply port to define a substantially contiguous vacuum path, and an actuating system to open and close a breach in the substantially contiguous vacuum path. Admitting suction via the vacuum supply port while the breach is closed and the intake is in contact with the object produces a pressure gradient force having sufficient magnitude to support the object's weight in a gravitational field. Operating the actuating system to open the breach releases the object and preferably propels it away from the device.
Owner:ELLIS JOSEPH D +1
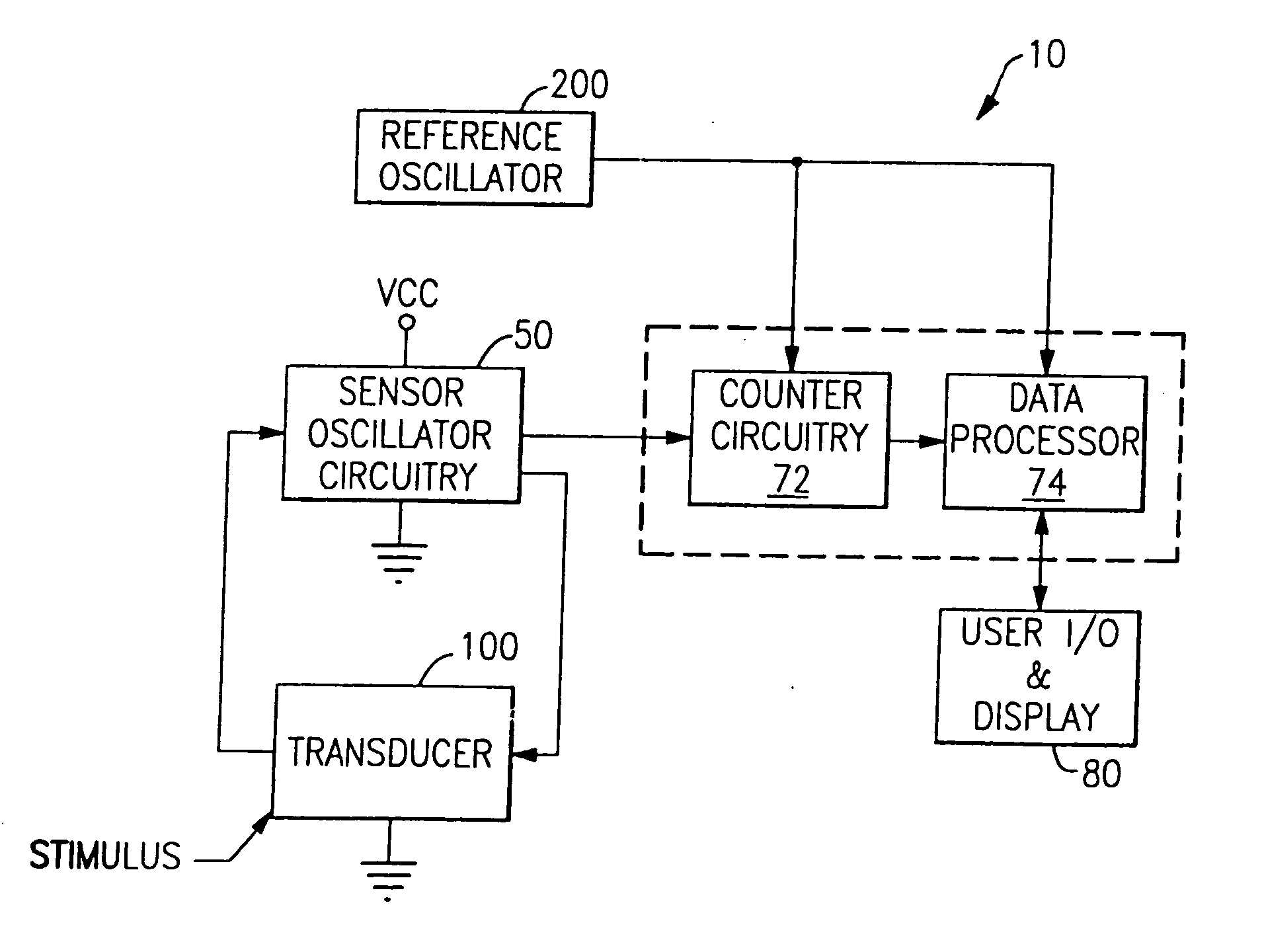
Capacitive sensor
InactiveUS20050088184A1Reduce the impactCompact and inexpensiveResistance/reactance/impedenceFluid pressure measurement using elastically-deformable gaugesVibration accelerationEngineering
A capacitive sensor is disclosed that includes a variable capacitor transducer that varies its capacitance with changes in an environmental parameter. The present invention is adapted to measure any linear parameter such as pressure, force, or distance. The sensor of the present invention is compact, inexpensive to make, and easily fabricated using commonly available components. Furthermore, it is not susceptible to errors caused by vibration, acceleration, and its orientation to the earth's gravitational field. The output of the capacitive sensor does not substantially drift with changes in temperature.
Owner:WELCH ALLYN INC
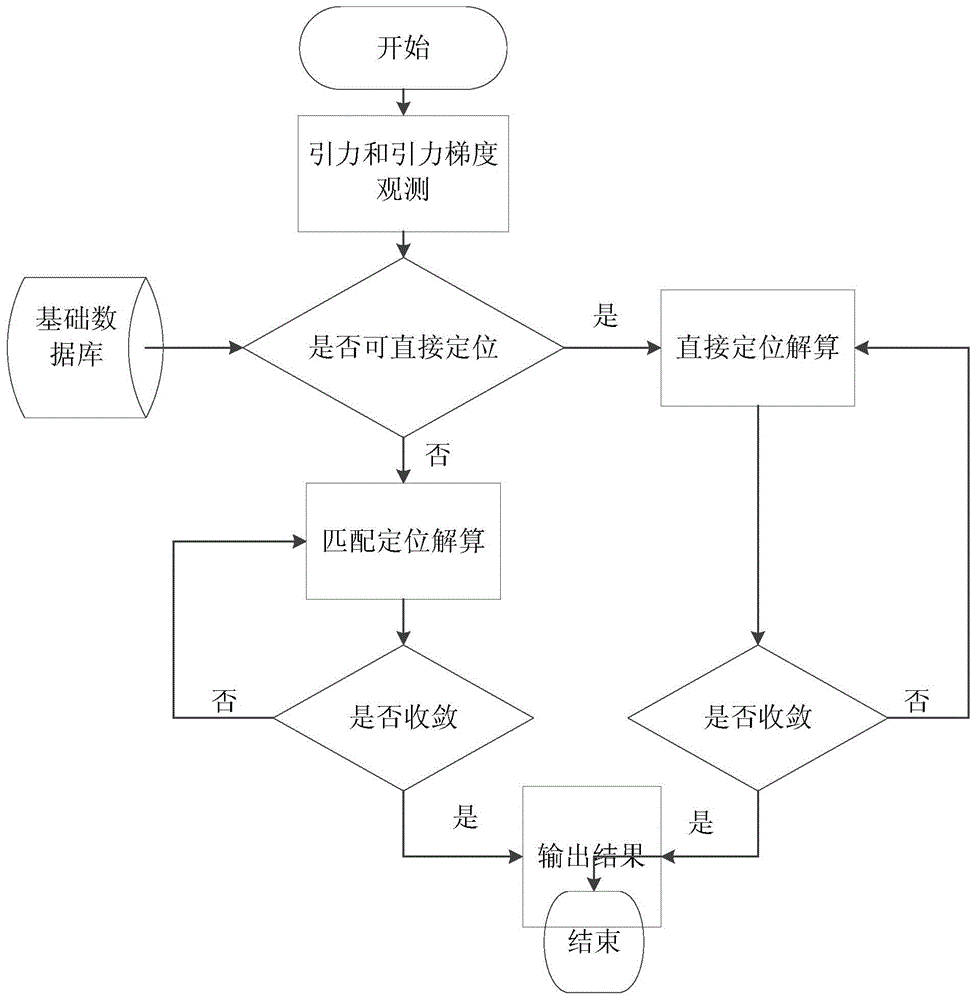
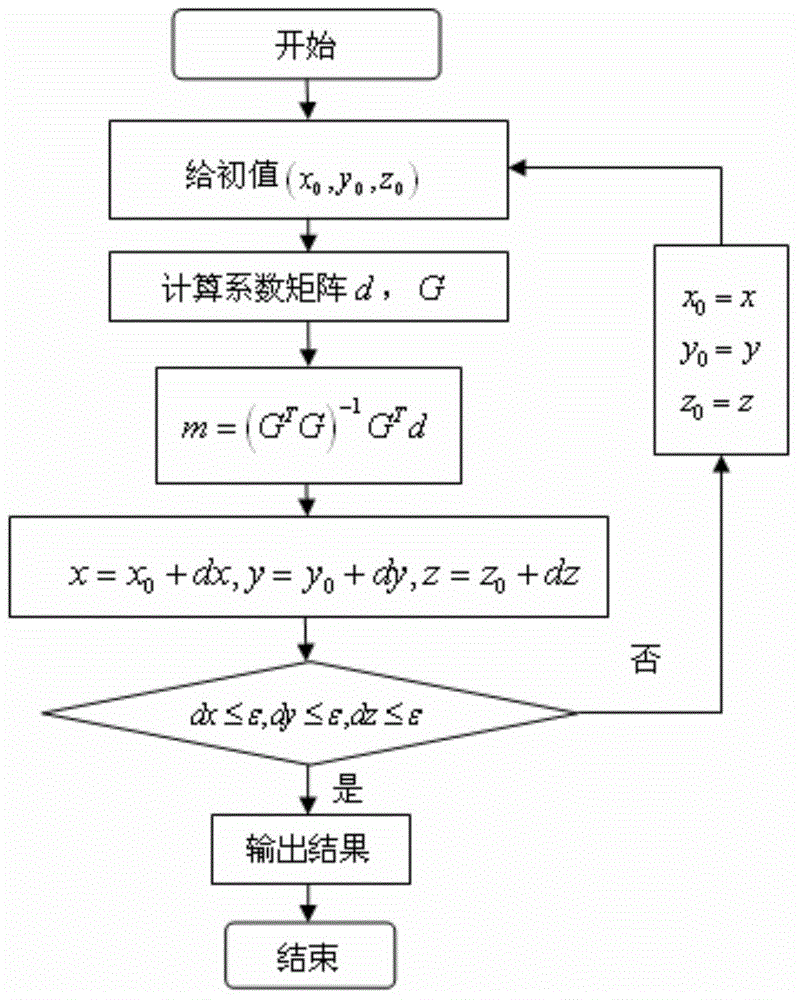
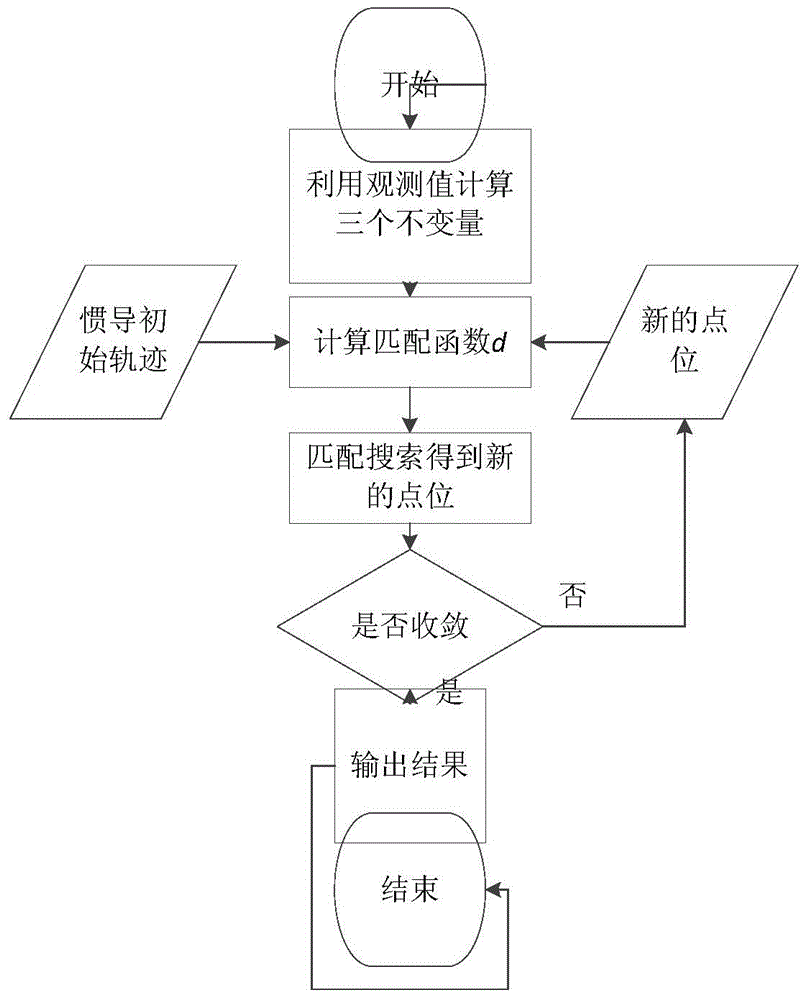
Method for navigation positioning by using gravitation vector and gradient tensor
ActiveCN104061932AGood autonomyGood navigationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsMassive gravityIterative search
The invention discloses a method for navigation positioning by using a gravitation vector and gradient tensor. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing a background field three-dimensional information databank of a target area according to beforehand observation, wherein basic elements comprise position coordinates of different points, gravitation vector invariants and gravitation gradient tensor invariants, subsequently observing and calculating according to the gravitation and the gravitation gradient in real time so as to obtain three invariants, judging whether navigation positioning can be performed directly or not by judging whether a resolving matrix is of full rank, if navigation positioning can be performed directly, performing iterative computation to obtain the position of a point to be positioned according to a least squares algorithm, if navigation positioning cannot be performed directly, performing matching search with the combination of an inertial navigation positioning technique, and performing iterative search for multiple times so as to obtain the position of the point to be positioned. The method has the outstanding characteristics that the gravitation vector invariants and gravitation gradient tensor invariants are adopted, and not only is contribution of all components of gravitation field information considered, but also the components are not related to the posture, so that compared with a conventional algorithm, the method can greatly reduce the influence of posture errors.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
High-precision double star laser interference dynamic distance measuring ground simulation device
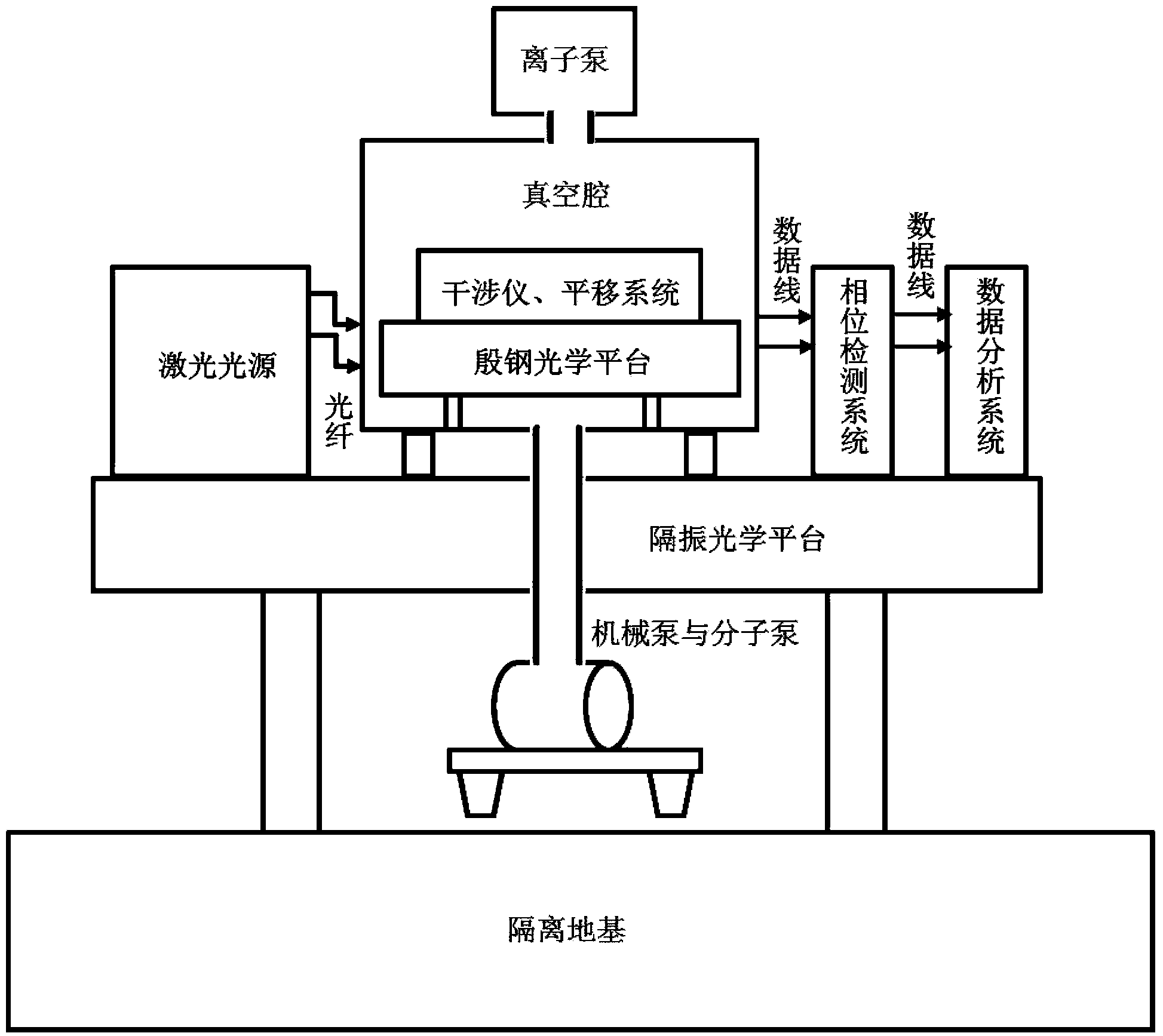
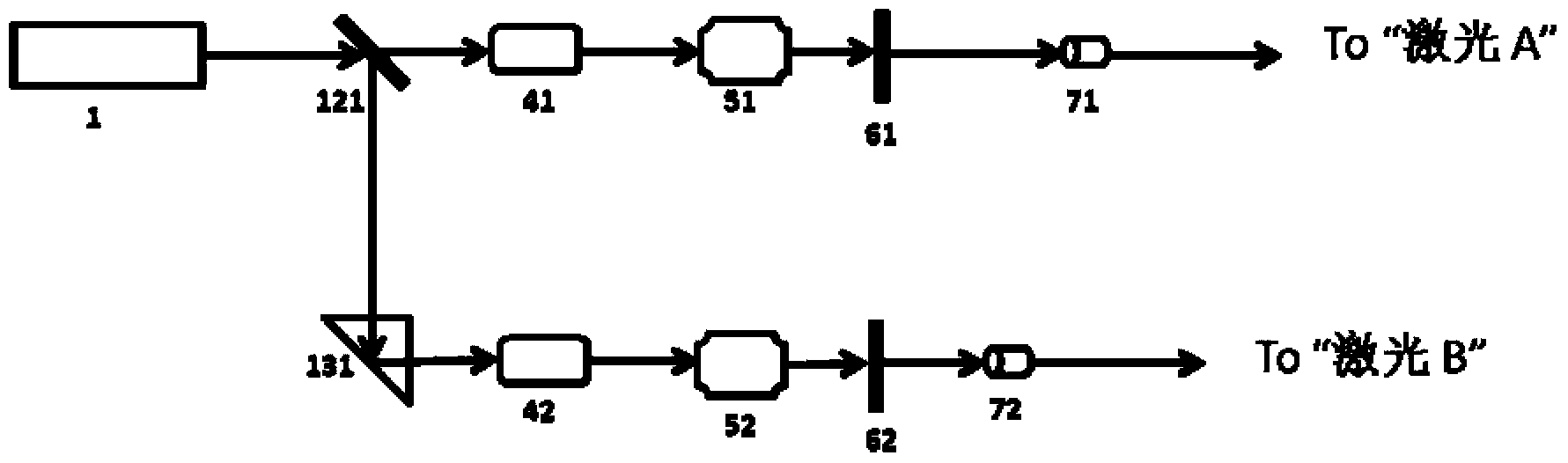
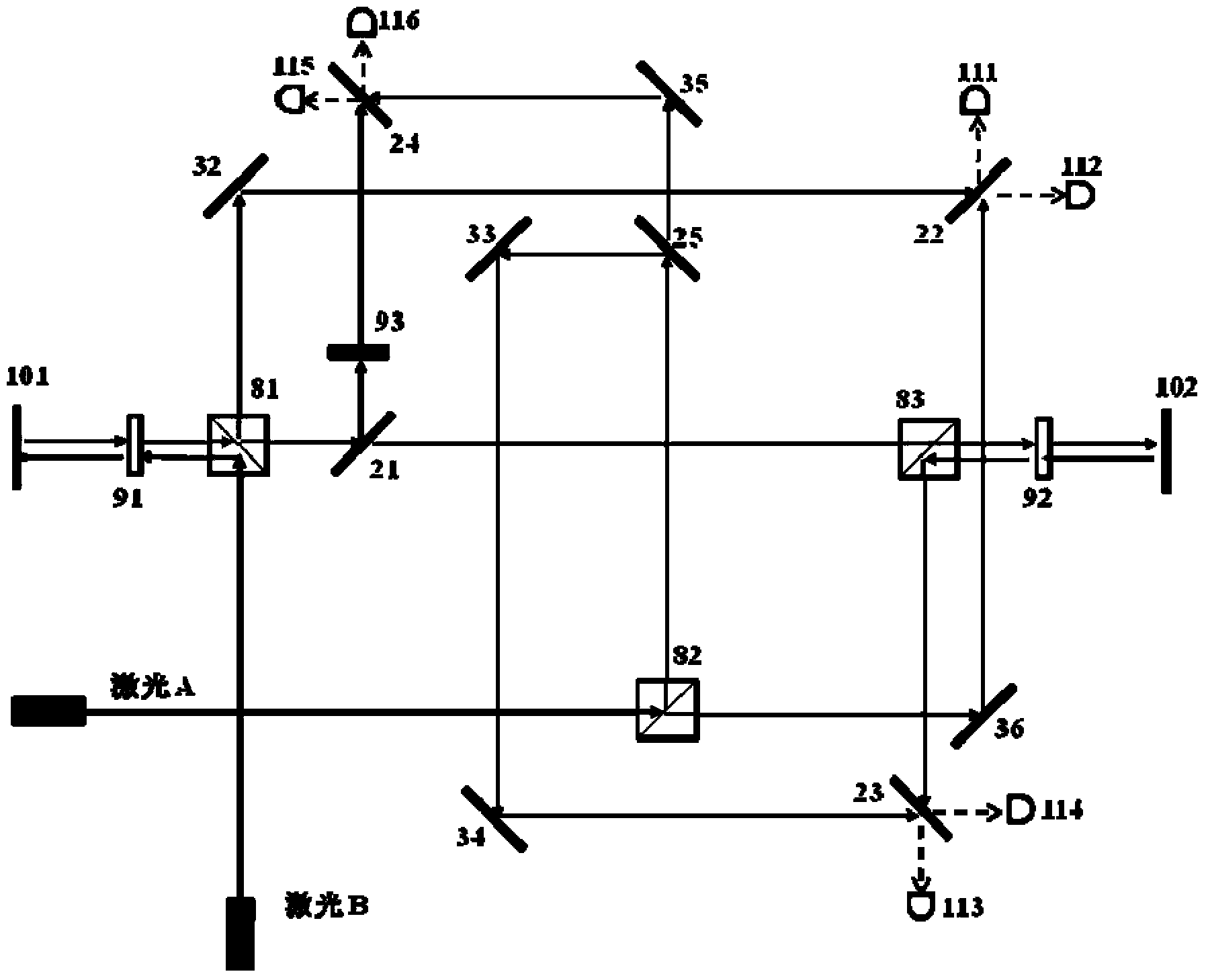
InactiveCN103513254AEliminate the effects ofIsolation impactElectromagnetic wave reradiationFrequency stabilizationDouble star
The invention provides a high-precision double star laser interference dynamic distance measuring ground simulation device which at least comprises a vibration-isolation system, a vacuum system, a light source system, an interferometer, a first horizontal moving system, a second horizontal moving system, a phase detection system and a data analyzing system. The vibration-isolation system is used for isolating and filtering outside vibration noise and reducing the vibration noise of a system. The vacuum system is used for reducing thermal noise brought by temperature fluctuation of the system. The light source system is used for providing two laser beams which are high in stability and high in frequency stabilization. The interferometer is used for generating three paths of heterodyning interference signals which have the identical arm length and simulating satellite orbit dissociating motion information and scientific signal information caused by gravitational waves or a gravitational field or the like. The first horizontal moving system is used for simulating scientific signals caused by gravitational waves or a gravitational field or the like. The second horizontal moving system is used for simulating satellite orbit dissociating signals. The phase detection system is used for carrying out phase detection on interference signals, collecting phase information and carrying out inversion displacement. The data analyzing system is used for estimating dynamic distance measuring precision of an interfering system and extracting scientific signals from mixed signals. The high-precision double star laser interference dynamic distance measuring ground simulation device can achieve ground simulation of high-precision double star laser interference dynamic distance measuring.
Owner:INST OF MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Capacitive sensor
InactiveUS6992492B2Reduce impactEasy to makeResistance/reactance/impedenceFluid pressure measurement using elastically-deformable gaugesEngineeringCapacitive sensing
A capacitive sensor is disclosed that includes a variable capacitor transducer that varies its capacitance with changes in an environmental parameter. The present invention is adapted to measure any linear parameter such as pressure, force, or distance. The sensor of the present invention is compact, inexpensive to make, and easily fabricated using commonly available components. Furthermore, it is not susceptible to errors caused by vibration, acceleration, and its orientation to the earth's gravitational field. The output of the capacitive sensor does not substantially drift with changes in temperature.
Owner:WELCH ALLYN INC
Apparatus for separation and processing of materials
ActiveUS20140225286A1Effectively frictionlessFineness is limitedLiquid degasificationReversed direction vortexCyclonic separationEngineering
This invention relates to a tubular cyclonic separation device the style of which was presented in PCT / ZA2003 / 000160 and which enables all of the inlet and outlet connections to be completely contained within a tubular profile, the diameter of which is that of the body of the cyclonic section. This disclosure adds further novel and inventive developments to the cyclonic device which enable it to be used as a separating device for systems involving all three phases (gas, liquid and solid) and where two, three or more different product streams may be separated, all within the same cylindrical profile. These further inventive developments also relate to the use of externally supplied gas and / or additional liquid phases which are injected through the walls of the cyclonic body using specifically located slots and / or holes in combination with specifically located stepped edges. These further novel and inventive developments enable the concepts of froth floatation (FF) and Dispersed Air Floatation (DAF) to be exploited within an enhanced gravitational field together with the options for washing the separated froth and / or the separated heavier fractions, all within the same cyclonic unit. As part of the novel and inventive introduction of the stepped edges, means are provided whereby gas bubbles smaller than 30 microns can be created on a large scale and with a reduced energy input relative to typical conventional equipment. Also the size of the gas bubbles may be controlled together with the intensity of any particle on particle interactions that may be created. This latter has many potential applications within FF and / or DAF processes, including applications within oil and tar separation from solid surfaces and within many ore preparation and ore leaching processes. The tubular profile enables processing and separation to be achieved “within the pipe line” or for very closely packed arrangements to be assembled within carrier vessels.
Owner:CYDAF TECH
Inertial navigation system error correction
ActiveUS20090037107A1Road vehicles traffic controlNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsGyroscopeAccelerometer
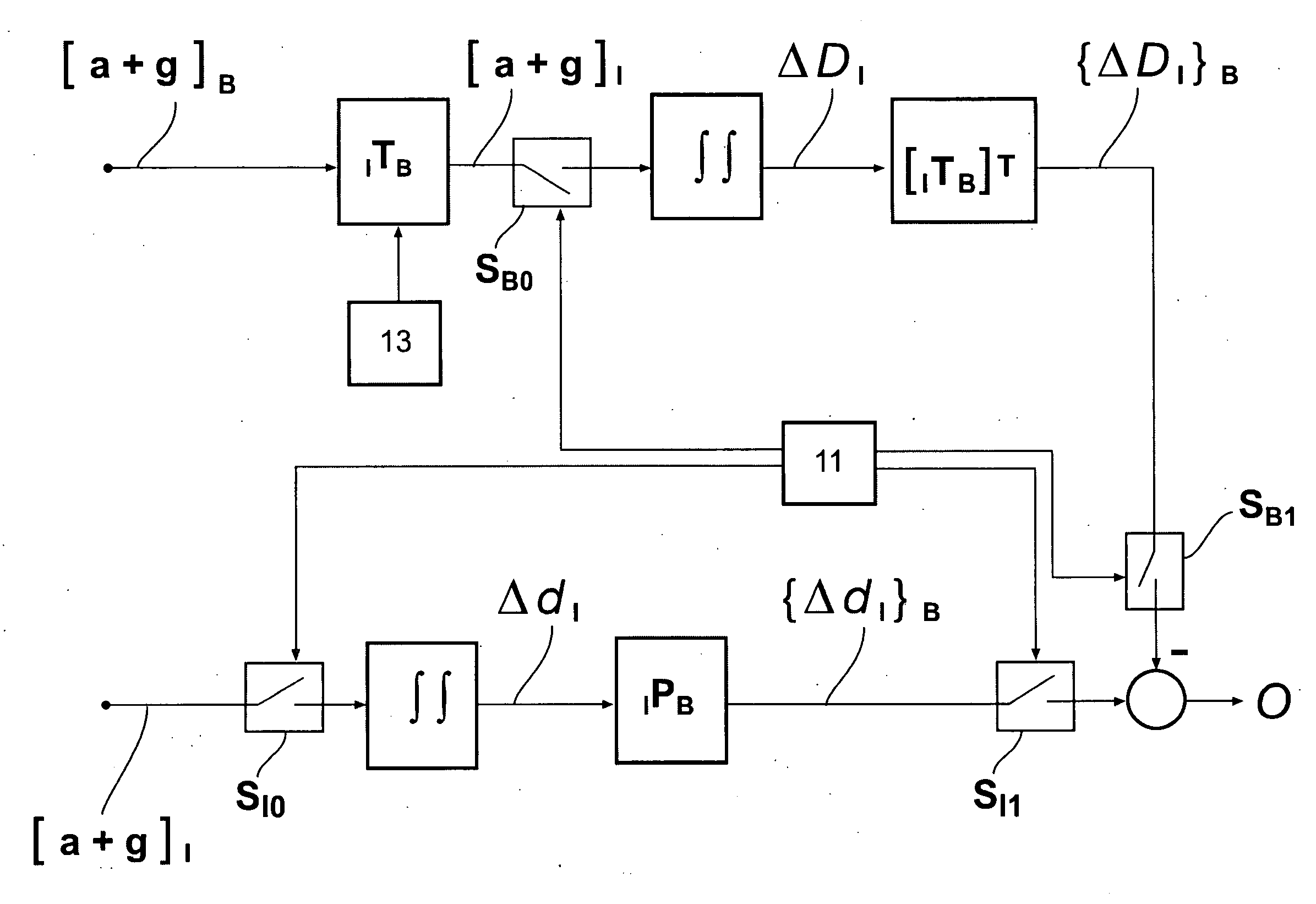
Methods and apparatus for: (a) the correction of one or more elements determined from a first set of continuous gyro and accelerometer measurements comprising using a second set of discontinuously measured higher accuracy accelerometer measurements doubly integrated in an inertial coordinate system, (b) determining relative movement of a vehicle using a first set of acceleration measurements that do not include components of acceleration caused by the Earth's gravitational field, and a second set of acceleration measurements that do include components of acceleration caused by the Earth's gravitational field; and (c) correcting errors in an inertial navigation system positioned in a vehicle comprising using independently measured changes in position of the vehicle relative to an inertial coordinate frame.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN GUIDANCE & ELECTRONICS +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com