Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1110results about How to "Improve directivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method and system for wireless communication networks using relaying
InactiveUS20050014464A1Easy to adjustCharacterization is accurate and reliableSite diversityTransmission path divisionRadio channelTransmitter
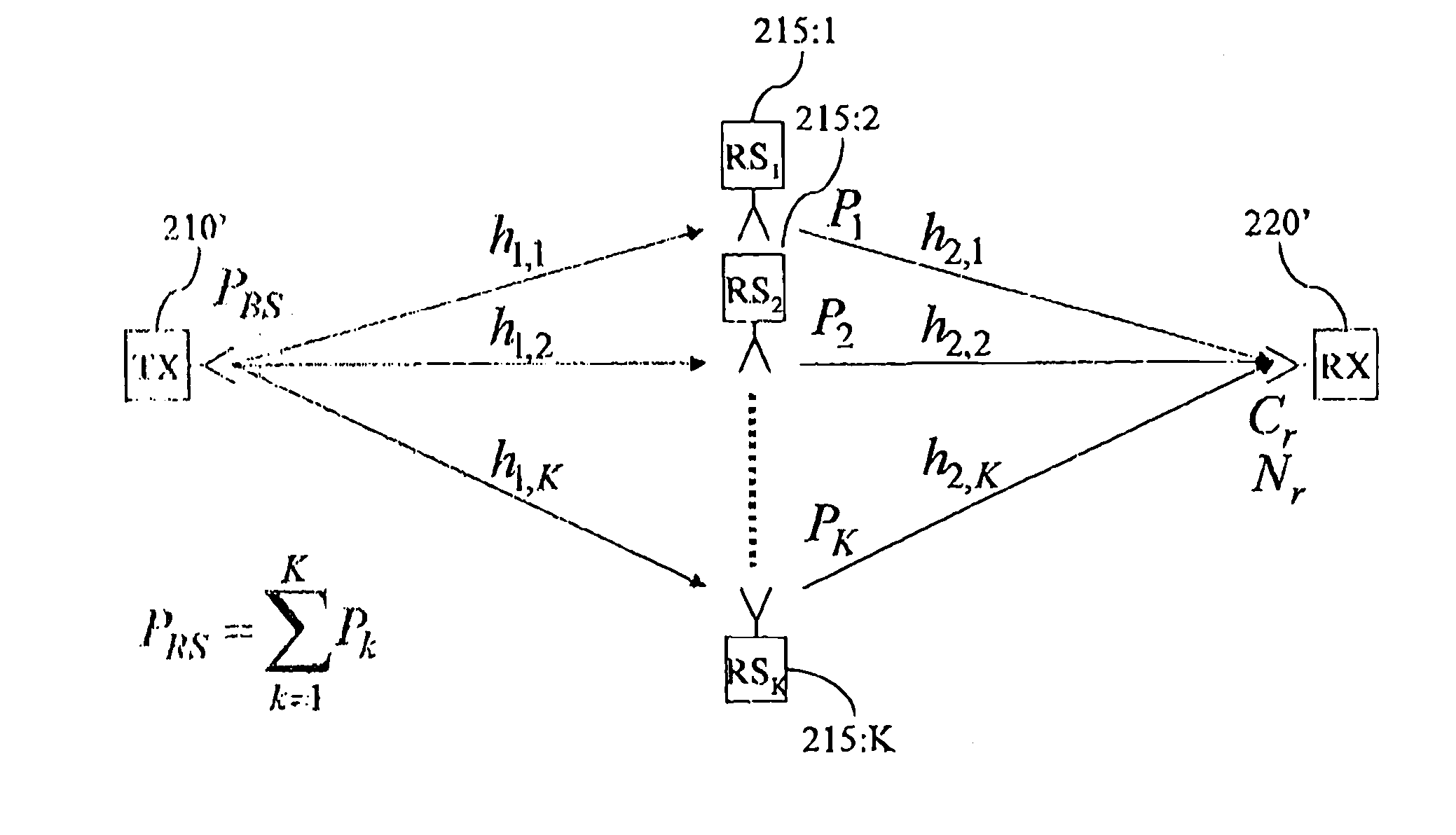
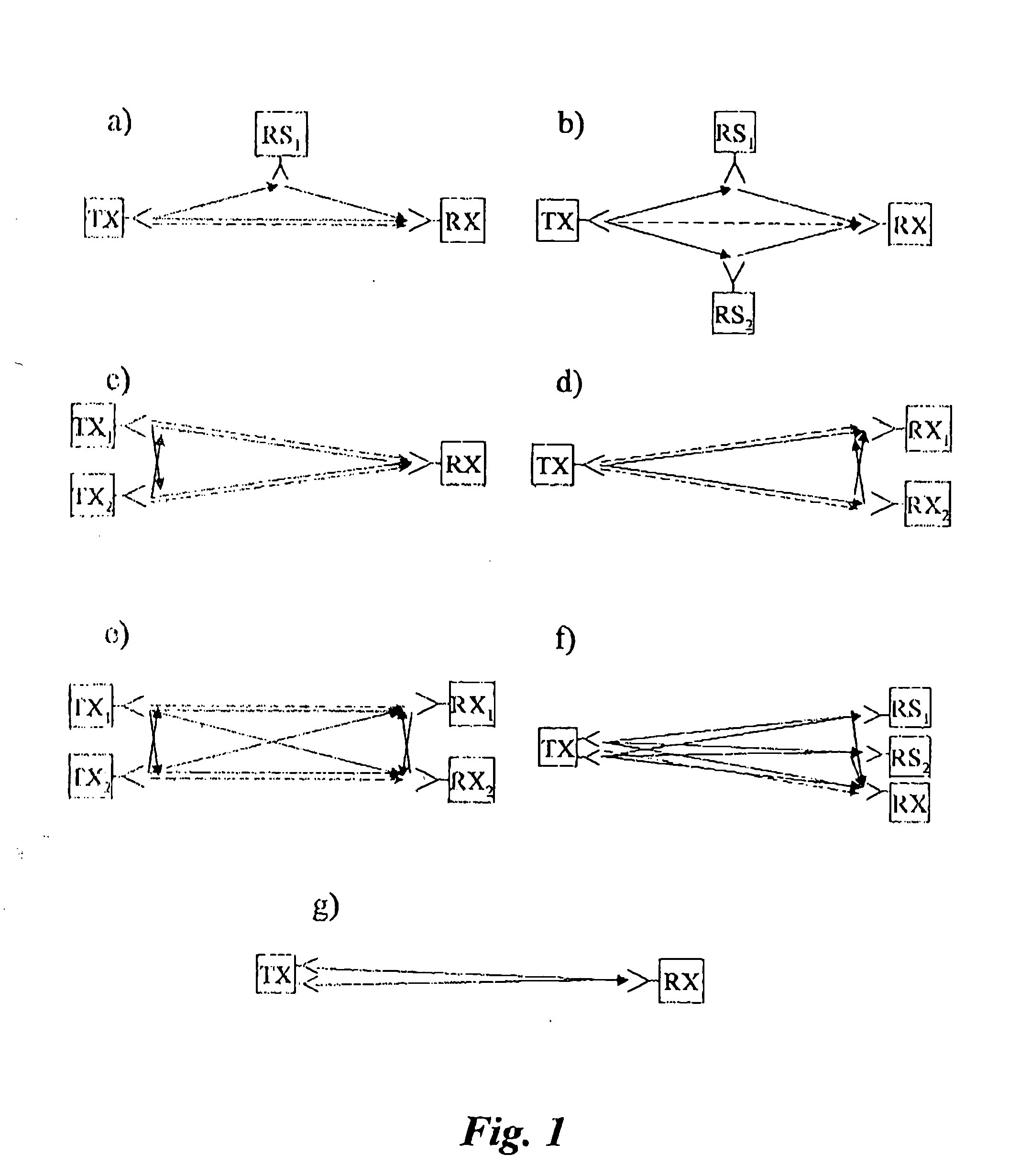
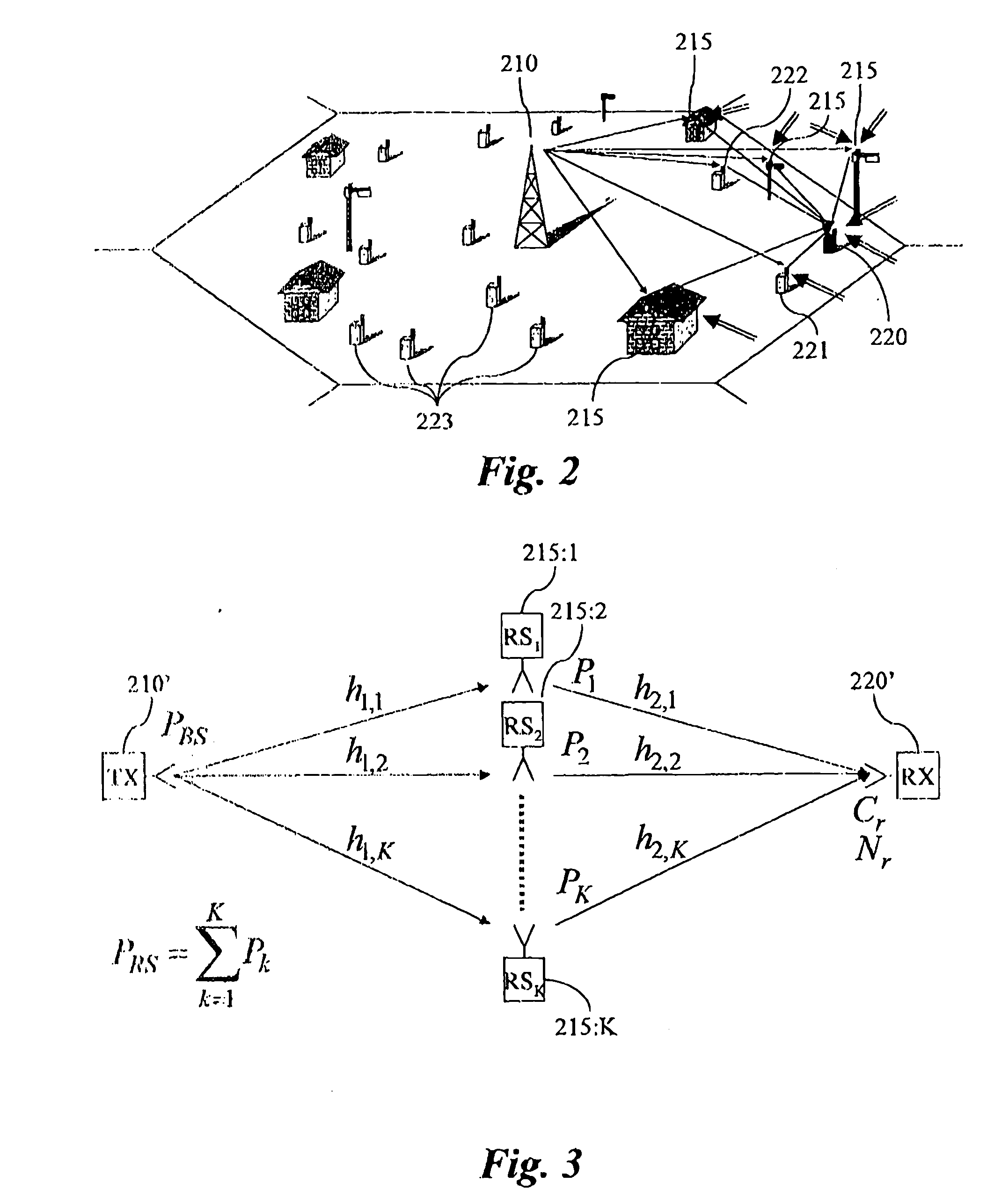
The present invention relates to wireless networks using relaying. In the method according to the present invention of performing communication in a two-hop wireless communication network, a transmitter 210, a receiver 220 and at least one relay station 215 are engaged in a communication session. The relay station 215 forwards signals from a first link between the transmitter 210 and the relay station 215 to a second link between the relay stations 215 and the receiver 220. The forwarding performed by the at least one relay station 215 is adapted as a response to estimated radio channel characteristics of at least the first link. Preferably the forwarding is adapted as a response to estimated radio channel characteristics of both the first and second link.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
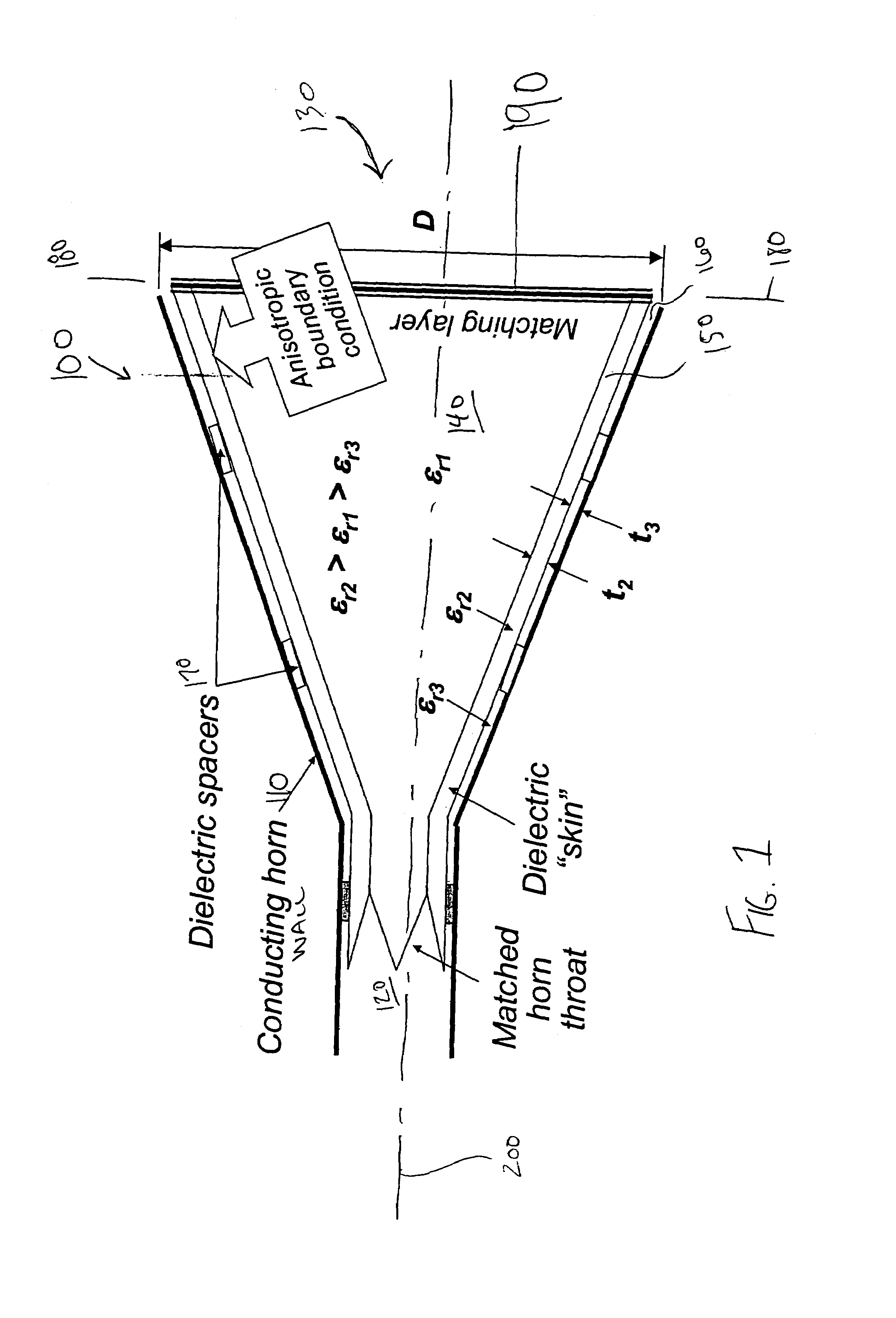
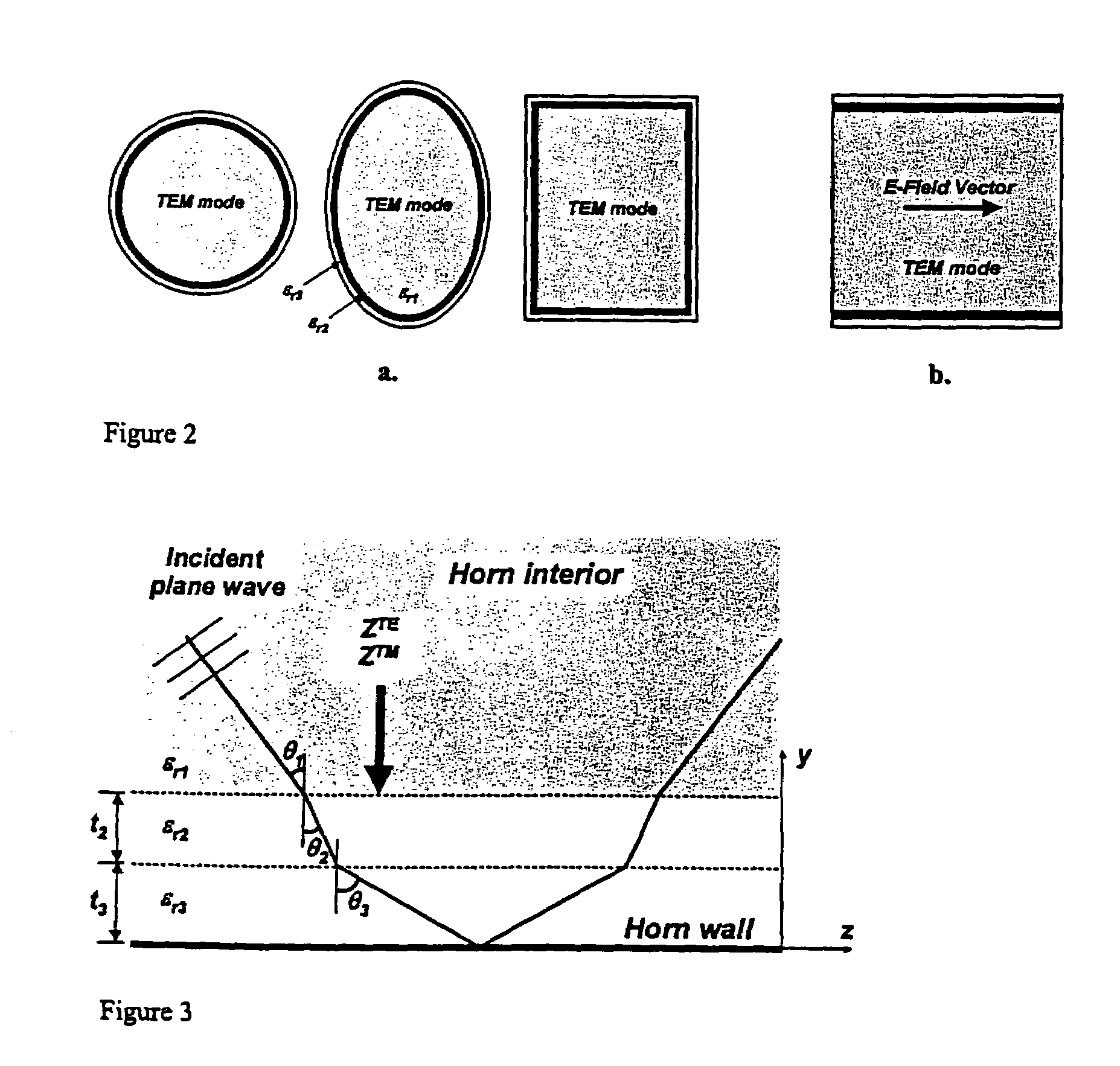
Hybrid-mode horn antenna with selective gain
ActiveUS6992639B1Designing can be facilitatedMechanically simpleWaveguide hornsHorn antennaMixed mode
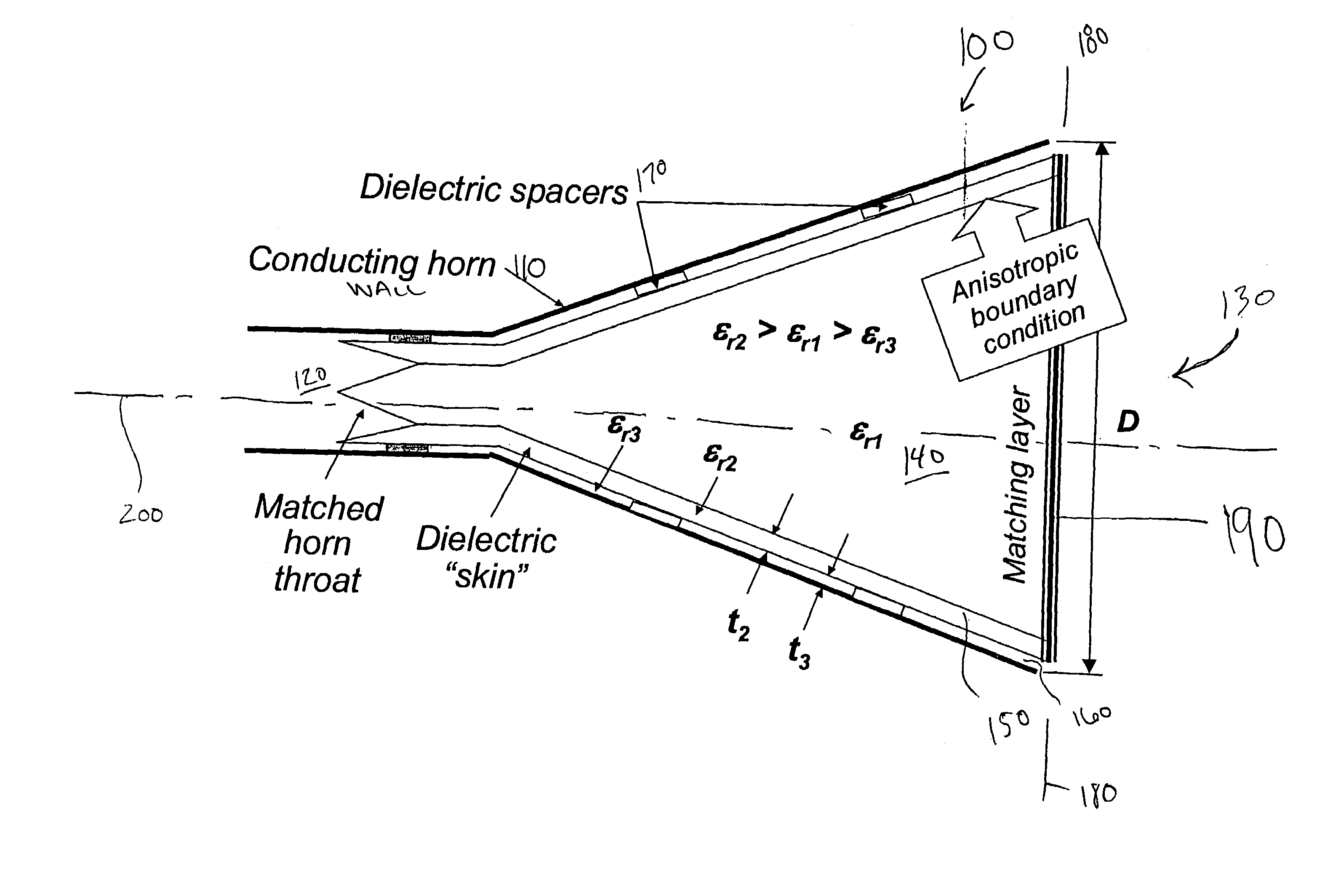
The present invention provides a new class of hybrid-mode horn antennas. The present invention facilitates the design of boundary conditions between soft and hard, supporting modes under balanced hybrid condition with uniform as well as tapered aperture distribution. In one embodiment, the horn antenna (100) is relatively simple mechanically, has a reasonably large bandwidth, supports linear as well as circular polarization, and is designed for a wide range of aperture sizes.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
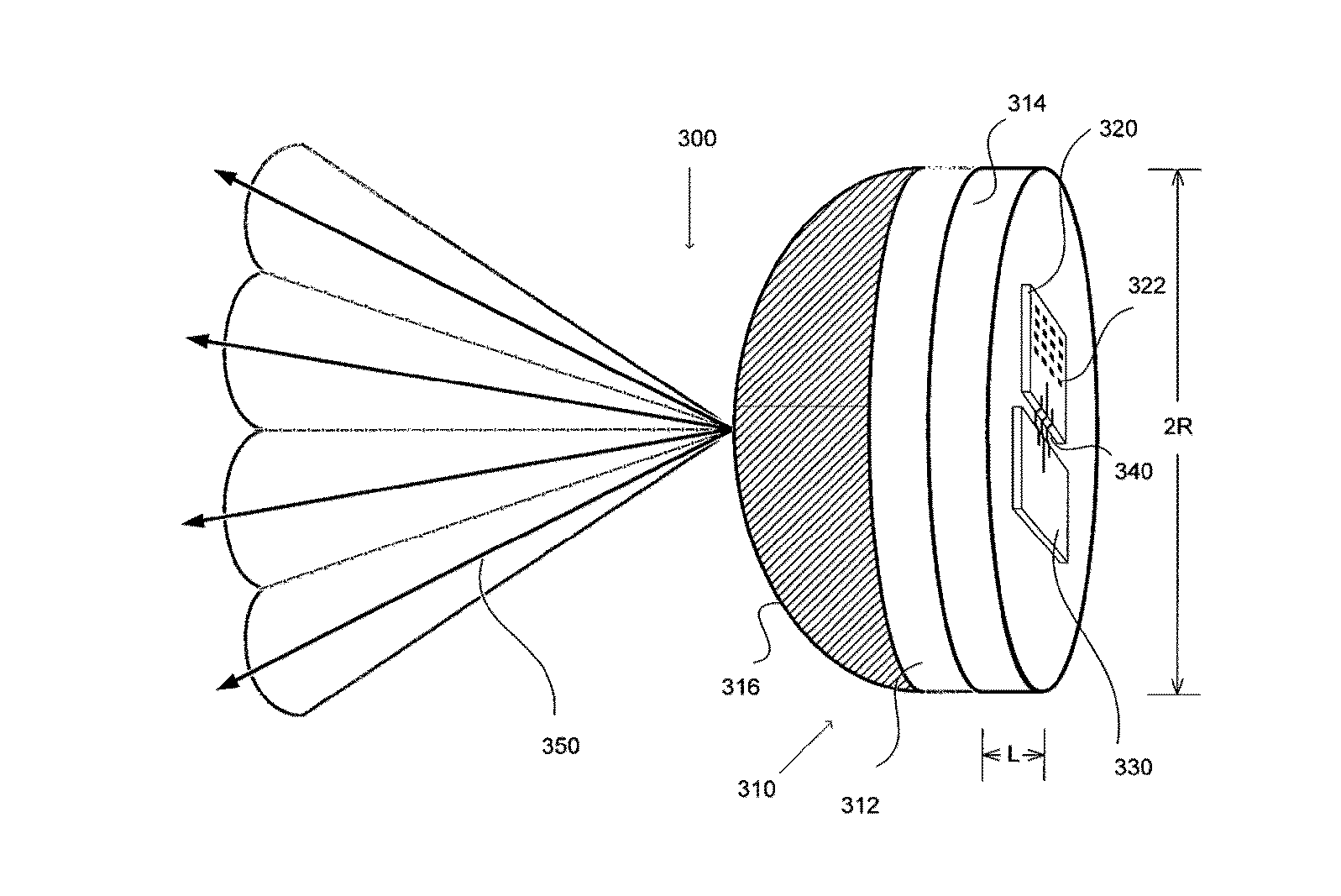
Lens antenna with electronic beam steering capabilities
InactiveUS20150116154A1Improve directivityImprove radiation efficiencyWaveguide hornsAntenna gainRadio relay
The invention discloses a lens antenna with high directivity intended for use in radio-relay communication systems, said antenna providing the capability of electronic steering of the main radiation pattern beam by switching between horn antenna elements placed on a plane focal surface of the lens. Electronic beam steering allows antenna to automatically adjust the beam direction during initial alignment of transmitting and receiving antennas and in case of small antenna orientation changes observed due to the influence of different reasons (wind, vibrations, compression and / or extension of portions of the supporting structures with the temperature changes, etc.). The technical result of the invention is the increase of the antenna directivity with simultaneously provided capability of scanning the beam in a continuous angle range and also the increase of the antenna radiation efficiency and, consequently, the increase of the lens antenna gain. This result is achieved by the implementation of horn antenna elements with optimized geometry.
Owner:OBSHCHESTVO S OGRANICHENNOJ OTVETSTVENNOSTYU RADIO GIGABIT
Method and apparatus for high-performance compact volumetric antenna with pattern control
InactiveUS20150102972A1Increase intrinsic inductive reactanceOptimize the magnetic fieldAntenna feed intermediatesElectronPhysics
A wide-bandwidth antenna with antenna pattern control includes a radiator and a feed. The radiator includes two or more volumetric radiating elements. The feed includes two or more feed units, the feed units configured to provide wave signals to the volumetric radiating elements. The feed units provide an independent signal for each radiating element. The wave signals can be fed out of phase to each other. Depending on the dielectric filler inside the volume of the antenna and the phase shift between feeds, the pattern can be modified electronically leading to pattern control. The radiating elements are spaced at a distance at least one order of magnitude smaller than half of an operational wavelength of the antenna. At least one electrically conductive element of the antenna is capable of conducting a current that generates a magnetic field. The magnetic field lowers the total reactance of the antenna, thereby resulting in enhanced performance of the antenna in terms of bandwidth, gain, and pattern control. The volumetric design allows miniaturization of the antenna.
Owner:SCIRE SCAPPUZZO FRANCESCA
Small wave-guide radiators for closely spaced feeds on multi-beam antennas
Owner:PRO BRAND INT
Antenna module and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20140225129A1Easy to assembleReduce manufacturing costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSemiconductor
An electrode is formed on at least one surface of first and second surfaces of a dielectric film formed of resin to be capable of receiving or transmitting an electromagnetic wave in a terahertz band. A semiconductor device operable in the terahertz band is mounted on at least one surface of the first and second surfaces of the dielectric film to be electrically connected to the electrode. A portion of a support layer is formed on the first or second surface of the dielectric film, and a dielectric lens is supported by another portion of the support layer. Another portion of the support layer is bent with respect to the portion such that the electromagnetic wave in the terahertz band transmitted or received by the electrode permeates through the dielectric lens.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Horn antenna device and step-shaped signal feed-in apparatus thereof
ActiveUS20150029065A1Sure easyAssembly precisionWaveguide hornsAntennas earthing switches associationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Noise rate
The present invention relates to a horn antenna device. The horn antenna device has a step-shaped signal feed-in apparatus and a conical horn antenna. The step-shaped signal feed-in apparatus has a stepped body having multiple stairs and a connecting pin. The stepped body is adapted to radiate electromagnetic waves and receive a reflection of the electromagnetic waves. According to the structure of the step-shaped signal feed-in apparatus of the invention, the resonating modes are easy to be determined. The directivity and the signal-to-noise rate are improved. In addition, the connecting pin is directly connected to the stairs for improving the signal stability of the horn antenna device.
Owner:FINETEK CO LTD
Light emitting apparatus and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20100320479A1Inhibition lossIncrease brightnessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical controlInorganic materials
A light emitting apparatus and a production method of the apparatus are provided that can emit light with less color unevenness at high luminance. The apparatus includes a light emitting device, a transparent member receiving incident light emitted from the device, and a covering member. The transparent member is formed of an inorganic material light conversion member including an externally exposed emission surface, and a side surface contiguous to the emission surface. The covering member contains a reflective material, and covers at least the side surfaces of the transparent member. Substantially only the emission surface serves as the emission area of the apparatus. It is possible to provide emitted light having excellent directivity and luminance. Emitted light can be easily optically controlled. In the case where each light emitting apparatus is used as a unit light source, the apparatus has high secondary usability.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
Apparatus and method for constructing and packaging printed antenna devices
ActiveUS7119745B2Improve bandwidth efficiencySimple designSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsTransceiverHigh bandwidth
Printed antenna devices are provided, which can operate at RF and microwave frequencies, for example, while simultaneously providing antenna performance characteristics such as high gain / directivity / radiation efficiency, high bandwidth, hemispherical radiation patterns, impedance, etc., that render the antennas suitable for voice communication, data communication or radar applications, for example. Further, apparatus are provided for integrally packaging such printed antenna devices with IC (integrated circuit) chips (e.g., transceiver) to construct IC packages for, e.g., wireless communications applications.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Vapor deposition method and apparatus
ActiveUS20090017192A1Improve cooling effectAvoid misalignmentVacuum evaporation coatingSolid-state devicesGas phaseEvaporation
Provided is a method for moving, in a vacuum chamber carrying therein a fixedly-provided evaporation source, a substrate toward the evaporation source together with a mask closely attached to the substrate surface, and onto the surface substrate, evaporating a material vaporized in the evaporation source through an aperture formed to the mask. In this method of the invention, means for moving the substrate toward the evaporation source is provided with cooling means not to come in contact with but to be in proximity to a surface of the mask on the evaporation source side, and a cooling plate formed with an aperture proximal to the evaporation source is disposed. With such a configuration, the steam of the material coming from the evaporation source is directed to the mask and the substrate through the aperture of the cooling plate. As such, the material film evaporated on the substrate surface shows a satisfactory distribution of film thickness, and any possible misalignment from desired positions of evaporation can be accordingly suppressed.
Owner:HITACHI DISPLAYS +1
Touch panel-including illuminator and reflective liquid-crystal display device
InactiveUS6891530B2Good perpendicular directivityDisplay brightMechanical apparatusElongate light sourcesLiquid-crystal displayLight pipe
A touch panel-including illuminator having: a light pipe made of a transparent plate-like material having an upper surface, a lower surface and at least one incidence side surface, the upper surface being provided with light output means through which light incident on the incidence side surface is made to emerge from the lower surface; a light source disposed on the incidence side surface of the light pipe; an adhesive layer; and a touch panel bonded to the upper surface of the light pipe through the adhesive layer; wherein the light output means are constituted by fine grooves which are disposed discontinuously, each of which is made of a concave portion, and each of which is shaped like an approximate triangle in section; and wherein each of the fine grooves has an optical path changing slope and a steep slope.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Lens antenna system
ActiveUS20180269576A1Increase signal strengthFacilitate communicationAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesIndividually energised antenna arraysEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:ALL SPACE NETWORKS LTD
Apparatus and method for constructing and packaging printed antenna devices
ActiveUS20060001572A1Reduce radiationImproved radiation patternSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsHigh bandwidthTransceiver
Printed antenna devices are provided, which can operate at RF and microwave frequencies, for example, while simultaneously providing antenna performance characteristics such as high gain / directivity / radiation efficiency, high bandwidth, hemispherical radiation patterns, impedance, etc., that render the antennas suitable for voice communication, data communication or radar applications, for example. Further, apparatus are provided for integrally packaging such printed antenna devices with IC (integrated circuit) chips (e.g., transceiver) to construct IC packages for, e.g., wireless communications applications.
Owner:IBM CORP
Microphone system for vehicle
InactiveUS7657052B2Minimize adverse affect of turbulent air flowImprove directivityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesElectrostatic transducer microphonesEngineeringDirectivity
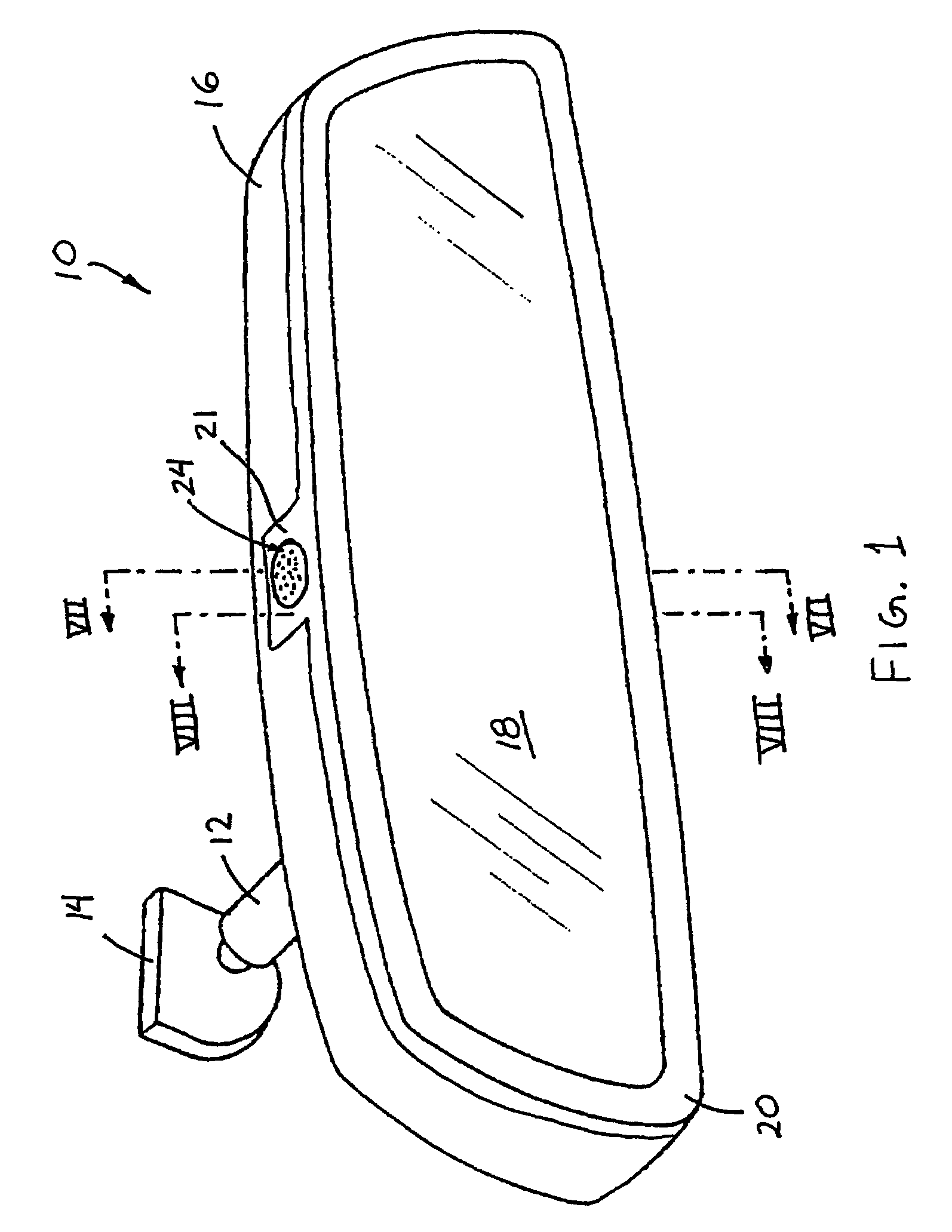
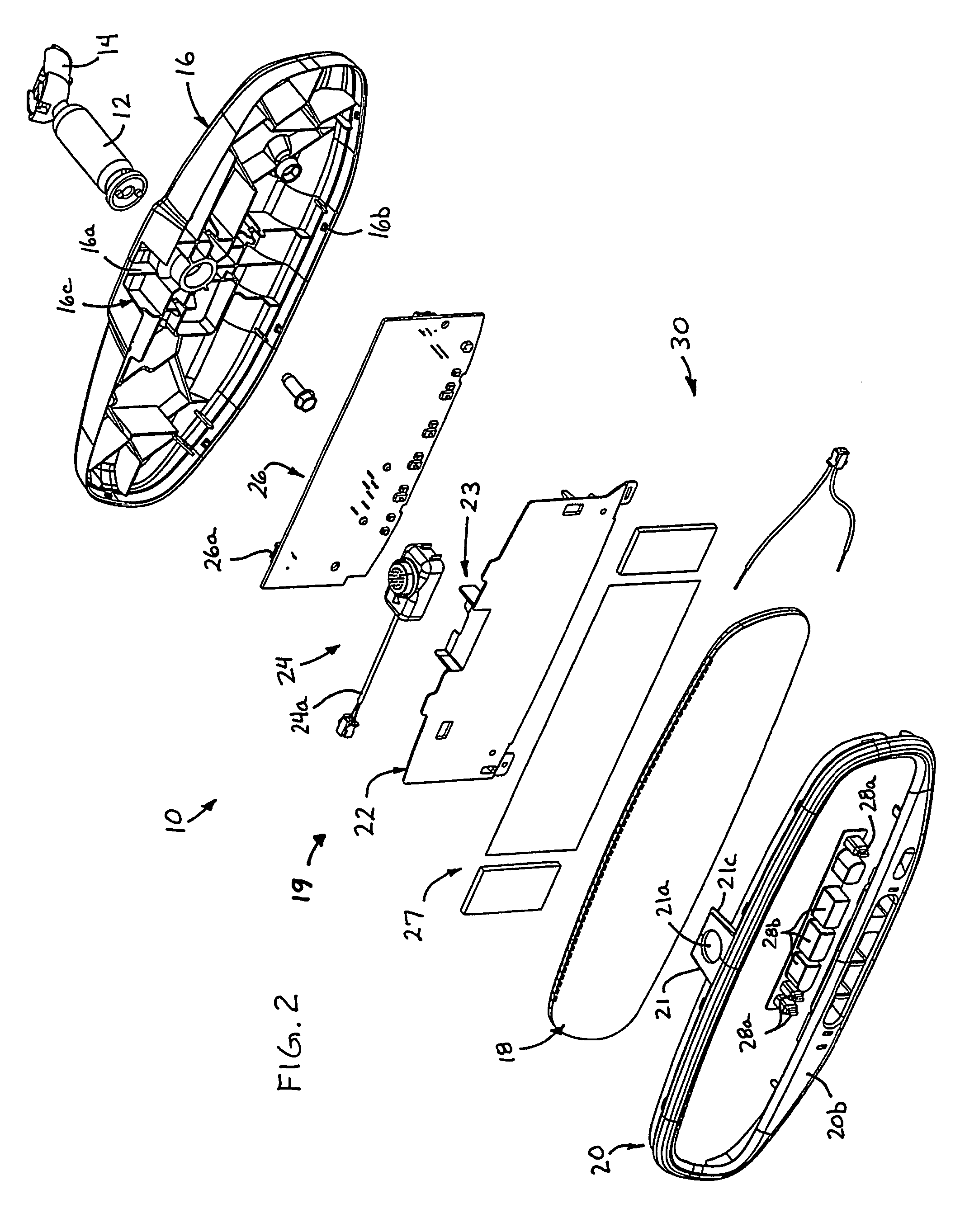
A vehicle interior rearview mirror assembly (10) comprises an accessory (24), a reflective element (18) and a bezel (20). The mirror assembly may define portions of a pocket (23) that at least partially receives and secures the accessory therebetween when the reflective element is at least partially received in the bezel. The mirror assembly (11) may include a microphone (124) and an acoustic cover (126) positioned at least partially over one or more inlet ports (124j, 124k) of the microphone. The acoustic cover may include an outer air flow limiting layer (130b) that substantially limit air flow therethrough and a diffusing material (130a) that may space and support the outer layer from the inlet ports to substantially diffuse air flow that penetrates the outer layer. An acoustic barrier (132) may be positioned between a pair of inlet port of the microphone to enhance the directivity of the microphone.
Owner:DONNELLY CORP
Film formation source, vacuum film formation apparatus, organic EL panel and method of manufacturing the same
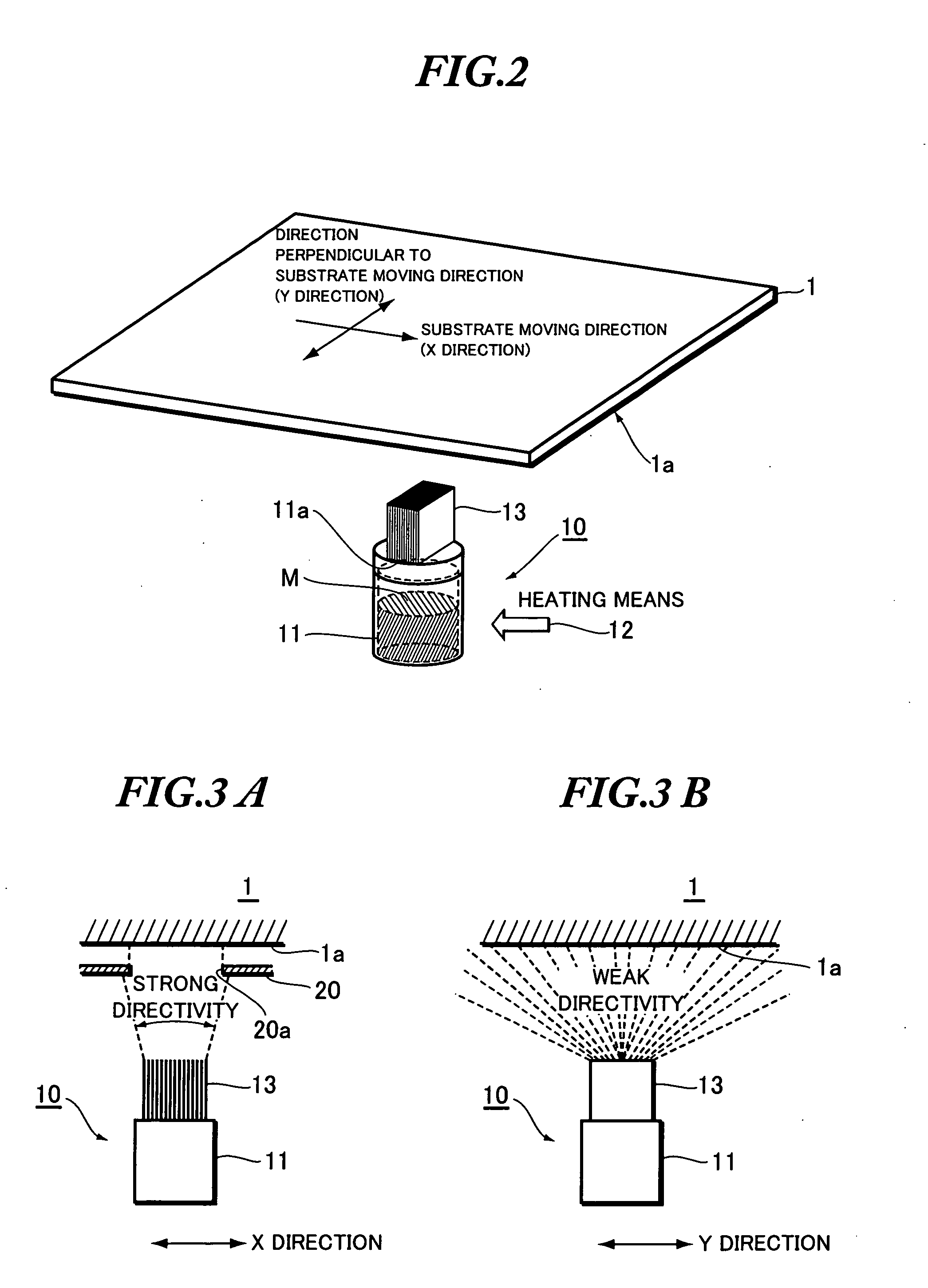
InactiveUS20050263074A1Acceptable precisionImprove utilization efficiencyLiquid crystal compositionsElectroluminescent light sourcesEngineeringFree space
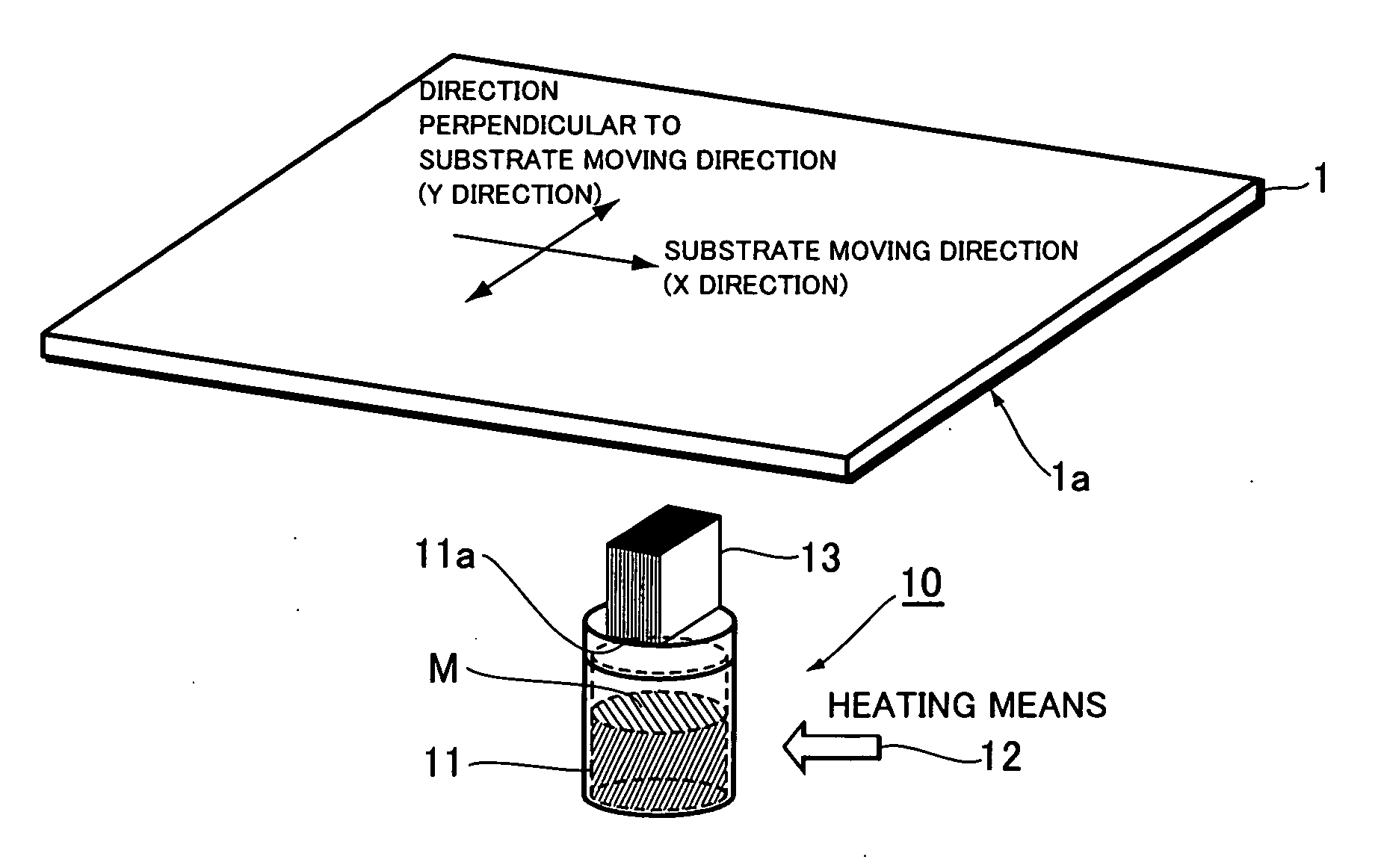
A film formation source of a vacuum film formation apparatus for forming thin film on the film formation surface of a substrate comprises: a material accommodating unit containing a film formation material; heating means for heating the film formation material contained within the material accommodating unit; a film formation flow control unit provided at an emission outlet of the material accommodating unit for controlling the direction of the film formation flow. The film formation flow control unit provides a strong directivity to the film formation flow with respect to the moving direction of the film formation surface relative to the film formation source.
Owner:TOHOKU PIONEER CORP
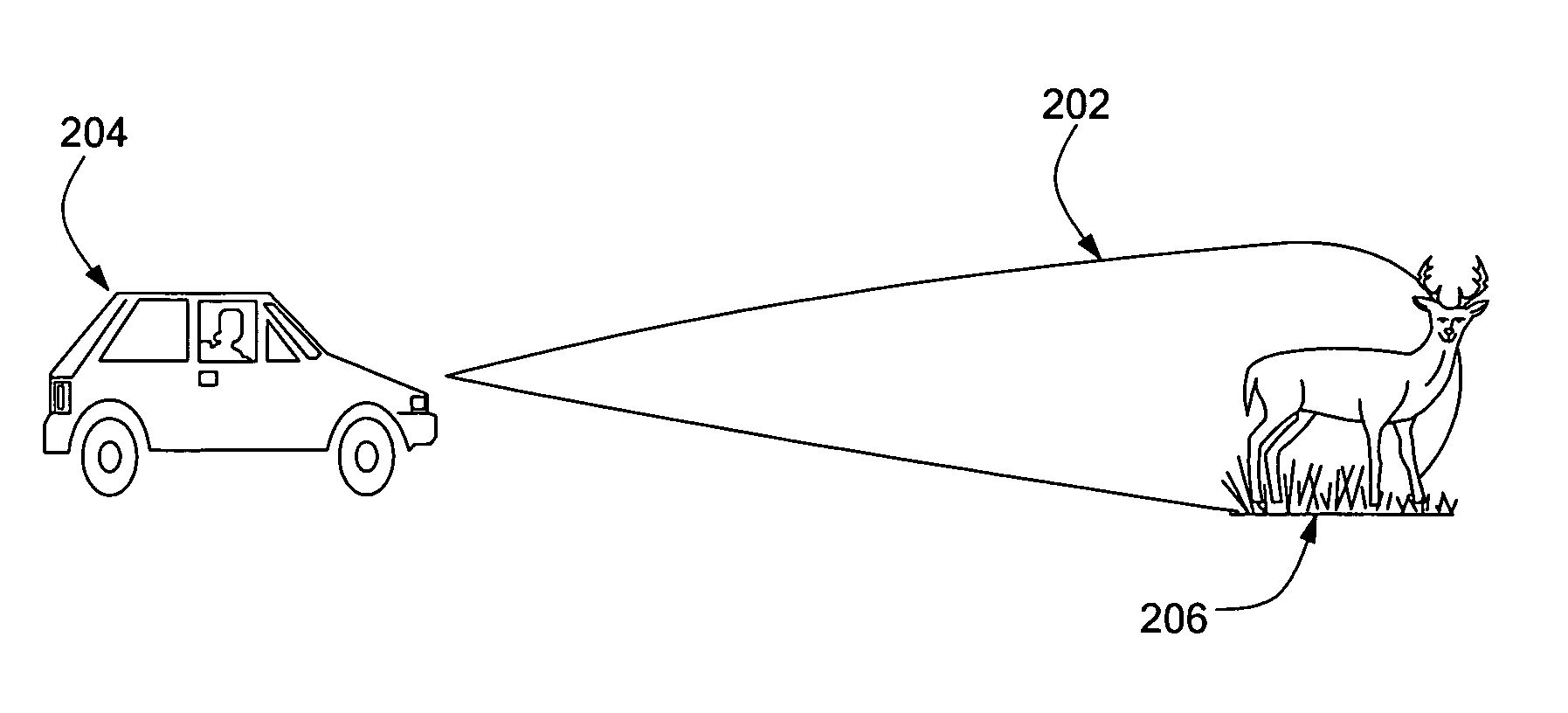
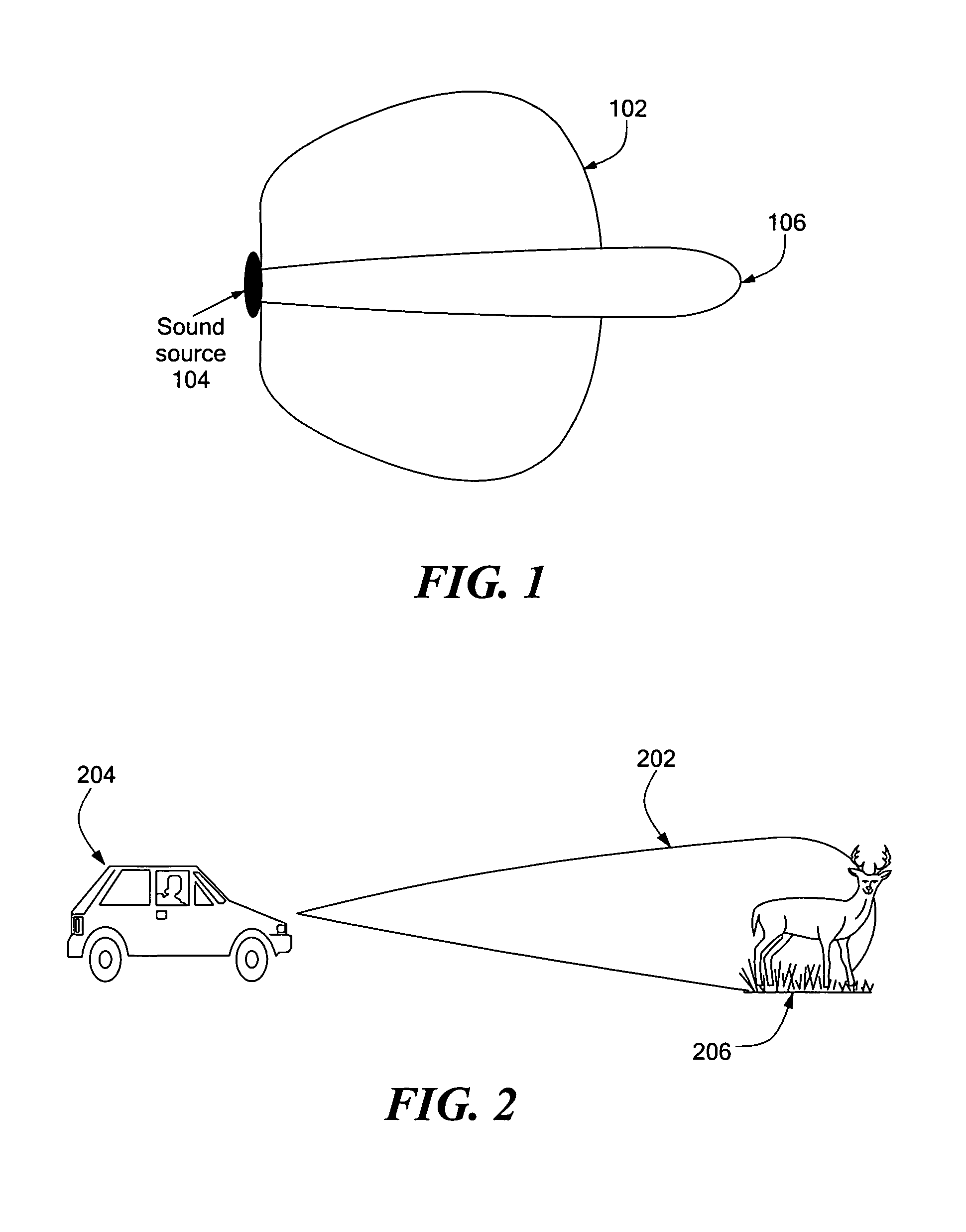
Directional acoustic alerting system
InactiveUS7106180B1Improve directivityReduce chanceContact mechanismsHigh-tension/heavy-dress switchesParametric arrayCarrier signal
An acoustic warning or alerting system for directing an audible warning signal to at least one intended recipient, while reducing the chance that the warning signal will be heard by others within the proximity of the system. The system includes a modulator for modulating an ultrasonic carrier signal with a processed audio signal, a driver amplifier for amplifying the modulated carrier signal, and a parametric array of acoustic transducers for projecting the modulated and amplified carrier signal through a propagation medium for subsequent regeneration of the audio signal along a pre-selected projection path. The parametric array of audio transducers operates by employing the nonlinear interaction between high frequency sound components and the propagation medium to generate at least one highly directional beam of lower frequency sounds within the propagation medium. The directional acoustic alerting system may be employed as a replacement for conventional alerting systems such as horns, whistles, and bells to assure that primarily only those people and / or animals intended to hear the warning signal actually hear the sound.
Owner:POMPEI FRANK JOSEPH
Collimating plate, lighting apparatus and liquid crystal display apparatus
InactiveUS6876408B2Excellent capabilityHigh luminanceMechanical apparatusLight guides for lighting systemsMicrolensLiquid-crystal display
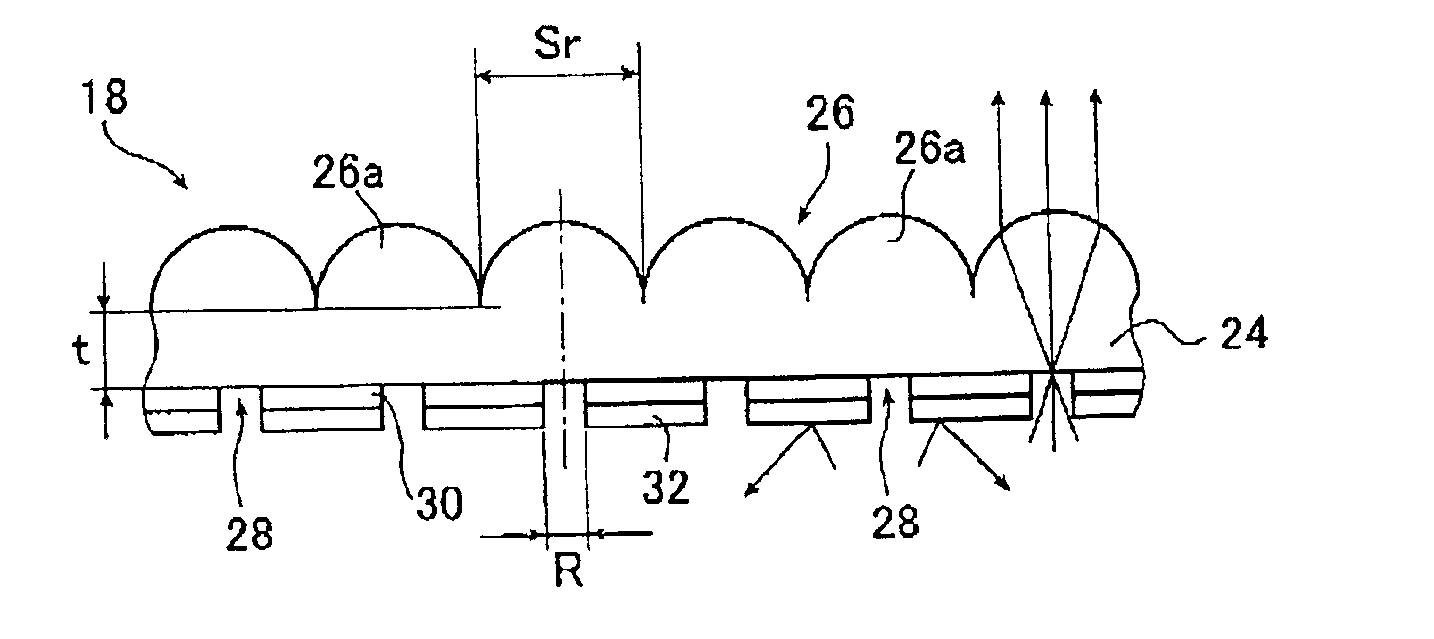
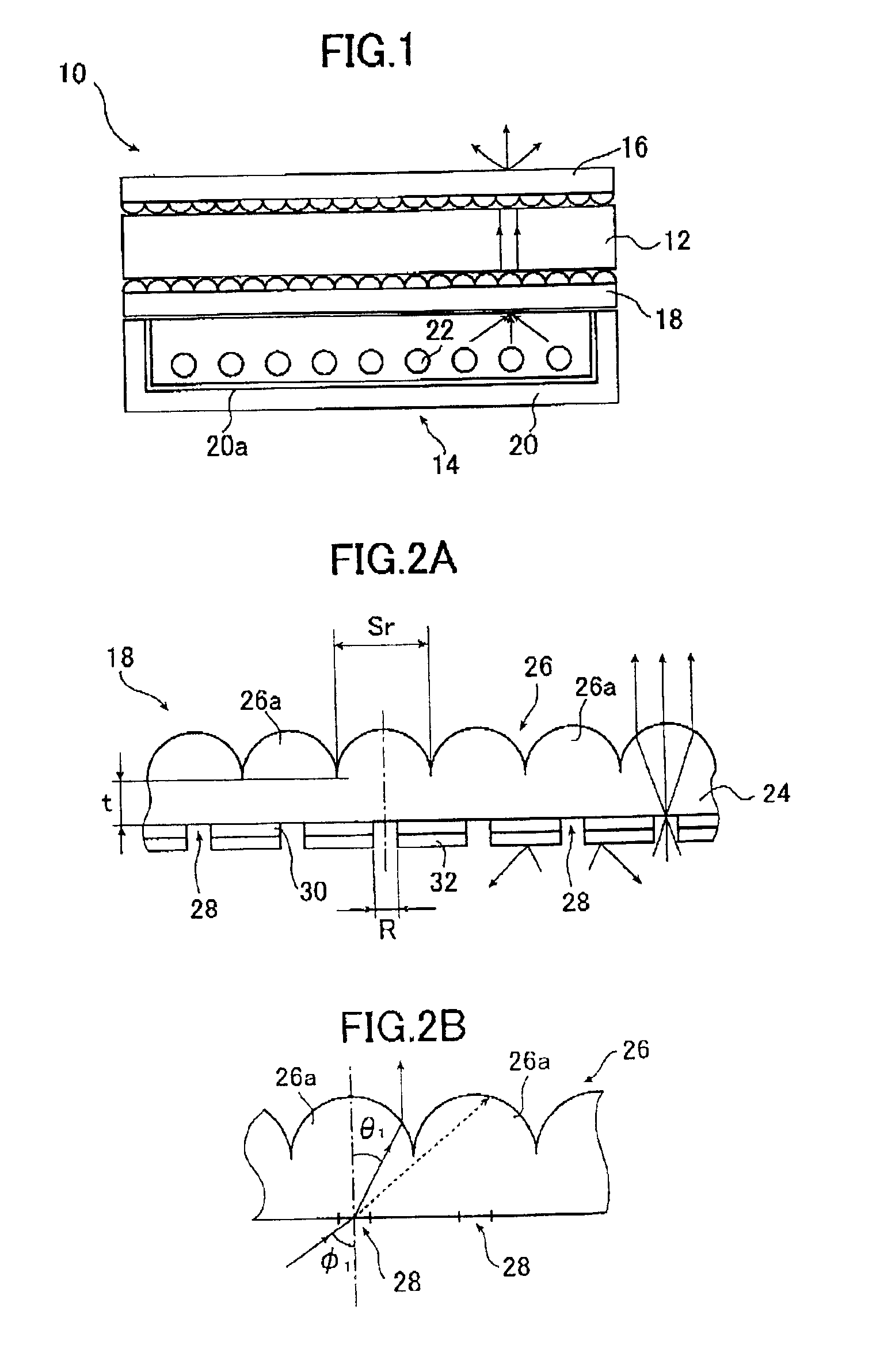
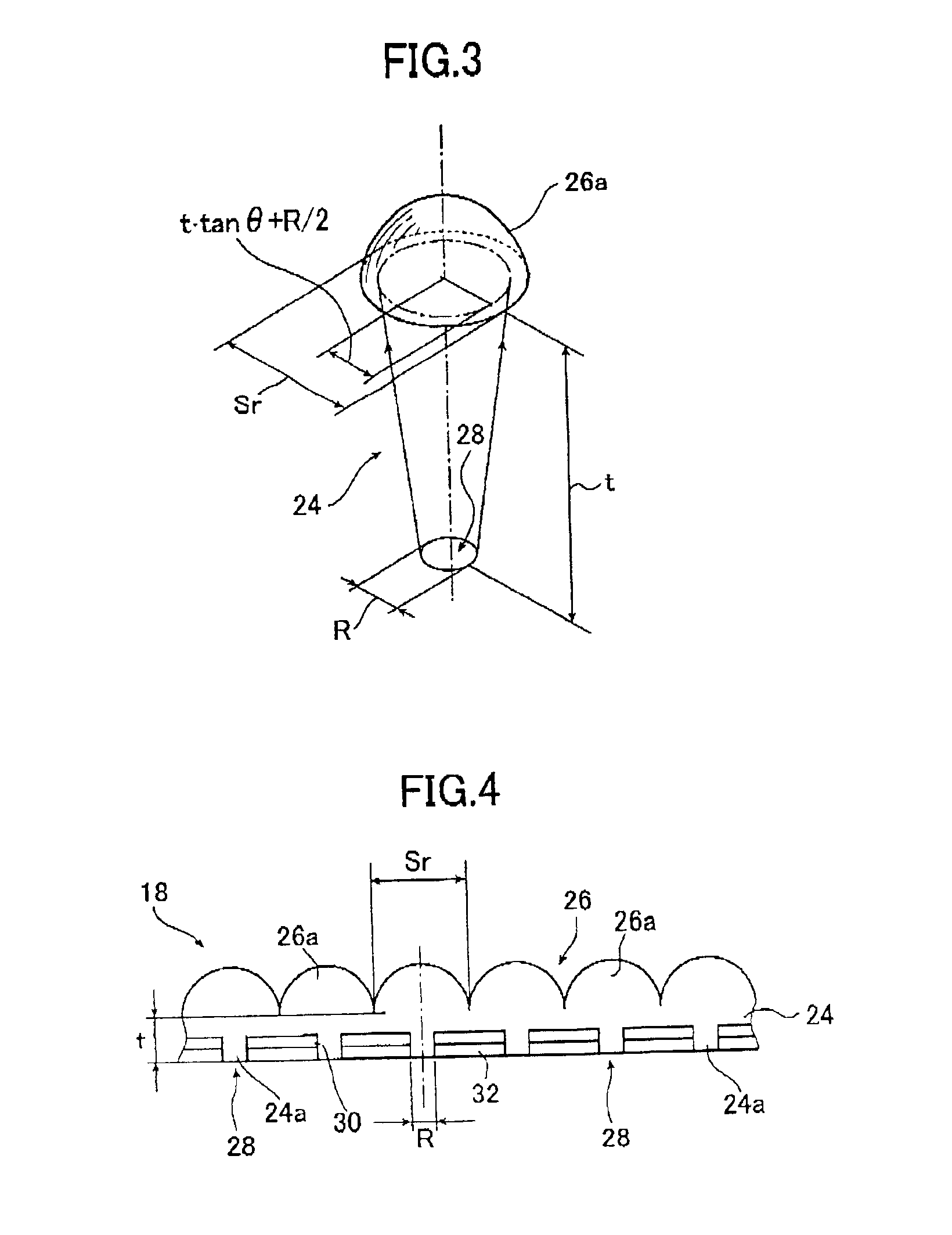
The light collimating plate includes a lens substrate, a plurality of microlenses disposed on a surface of the lens substrate, a plurality of light entrance areas, each having a circular or rectangular form a center of which is on an optical axis of the microlens, and a light shield layer formed on another surface of the lens substrate, and covering other area than the light entrance areas. When n and t are a refractive index and a thickness of the lens substrate, respectively, and C (R; diameter, A, B; sides of rectangle) is a size of light entrance area, a size of the microlens Sr satisfies the following formula in the light collimating plate: Sr≧2t×tan θ+C (with the proviso that θ=sin−1 (1 / n)). Or, a form of the microlens in the light collimating plate is a part of an ellipsoid shown in the following formula X2 / a2+y2 / a2+z2 / c2=1 (x and y represent axis on the surface of the lens substrate, z represents the optical axis), it's accentricity ε is shown in the following formula ε=(c2−a2)1 / 2 / c=1 / n and it's far focal point is on a position of the light entrance area. The lighting apparatus and the liquid crystal display apparatus use the light collimating plate.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Light source device, display device, and terminal device
ActiveUS20070076434A1Less power consumptionReduce power consumptionShow cabinetsImpedence networksPhysicsAngular range
In a display device equipped with a light source device, a second light-guide member is provided to the back surface of a first light-guide member that has an emitted light control sheet provided to the front surface thereof. The emitted light control sheet is composed of a flat plate portion and protrusions. A first light source mounted to a side surface of the first light-guide member, and a second light source mounted to a side surface of a second light-guide member are switched and turned on. The emitted light control sheet has light-condensing effects when the first light source is on, and has diffusing effects when the second light source is turned on. The angle range of illuminating light can thereby be switched.
Owner:VISTA PEAK VENTURES LLC
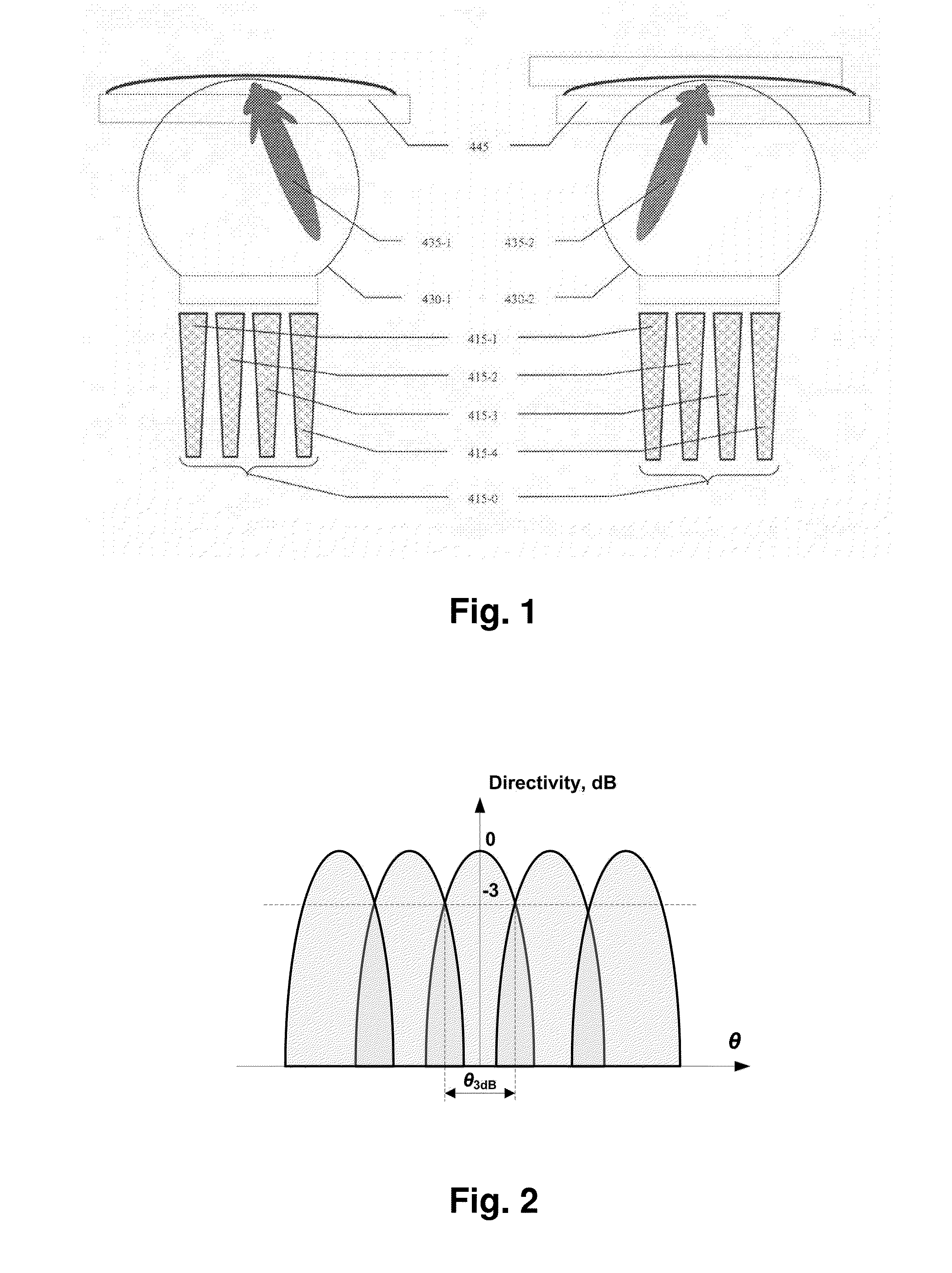
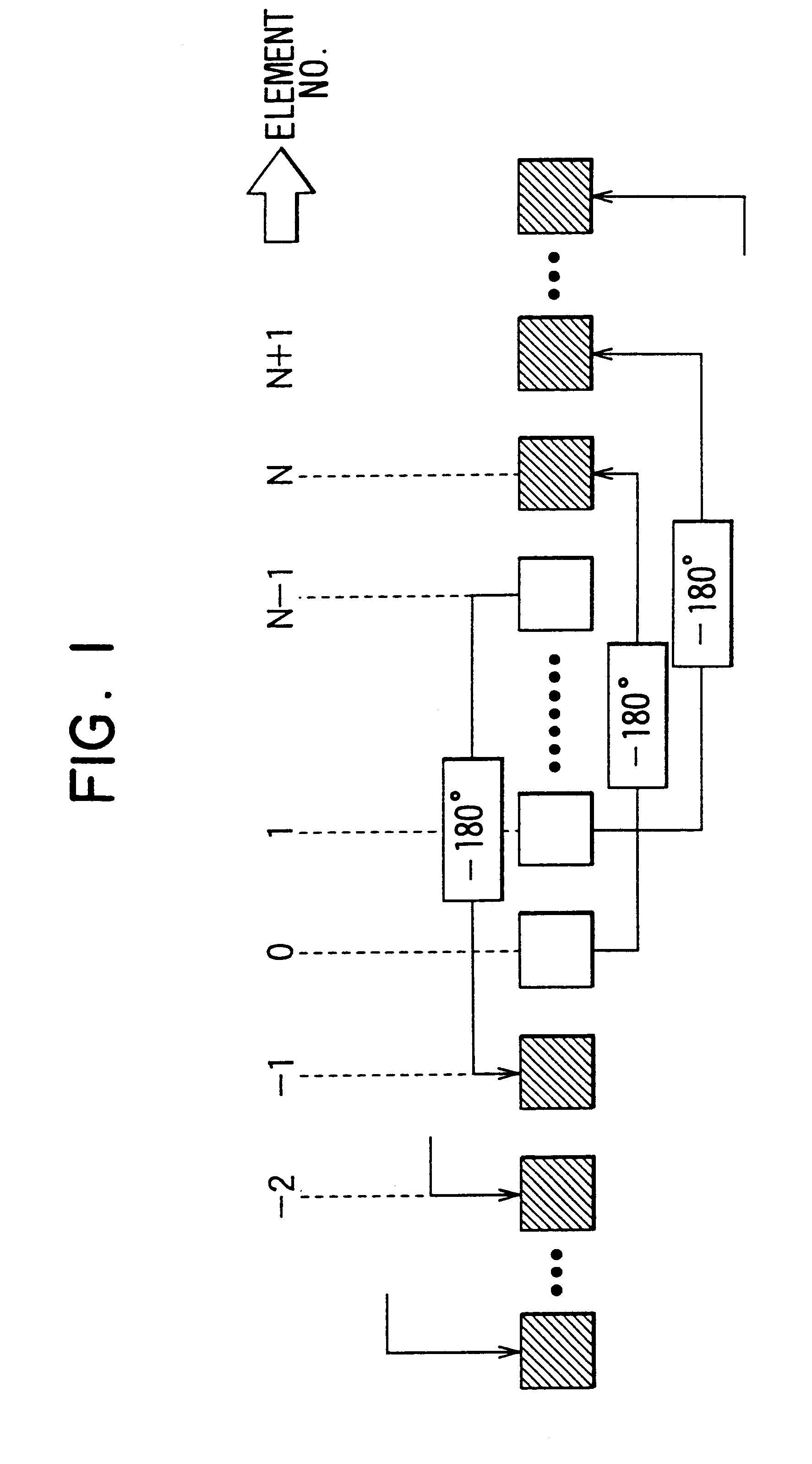
Multibeam antenna having auxiliary antenna elements
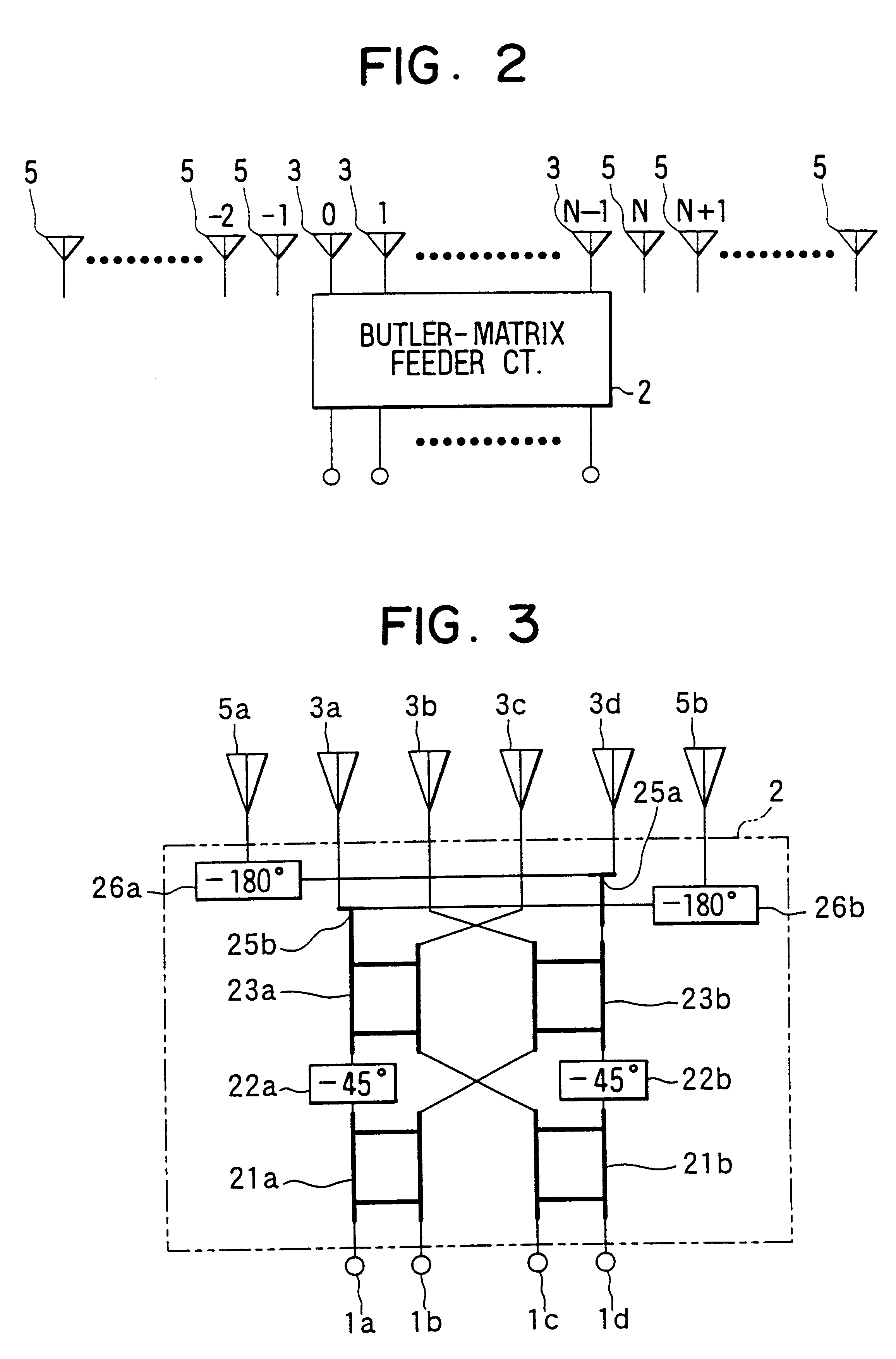
InactiveUS6252560B1Improve directivityReduce sidelobeAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesIndividually energised antenna arraysPhase shiftedEngineering
A multibeam antenna for forming multiple beams includes an antenna array and a Butler-matrix feeder circuit. The antenna array is composed of 2.sup.n main antenna elements and a group of 2.sup.n or less auxiliary antenna elements placed at either one or both sides of the main antenna elements. Antenna power is supplied to the antenna array from the Butler-matrix feeder circuit and is distributed to all the antenna elements with higher power to the elements located in the middle of the array and lower power to the elements located at sides of the array. Phase of the power supplied to the main antenna elements is shifted by 180-degree, and the phase-shifted power is distributed to predetermined auxiliary antenna elements. Thus, sidelobes associated with antenna beams are reduced and the beam directivity is improved.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Light transmission tubes
InactiveUS6278827B1Increase brightnessImprove directivityMechanical apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingBand shapeRefractive index
A light transmission tube includes a tubular clad and a core section having a higher refractive index than that of the tubular clad. A belt-like reflecting layer is formed between the tubular clad and the core section, extending in the longitudinal direction of the tubular clad, in a manner such that a light passing through the core section is reflected and scatterred by the reflecting layer and then emitted from an outer surface area of the tubular clad, which outer surface area is located opposite to one side of the tubular clad where the reflecting layer has been formed. Further, the reflecting layer may be so formed that a light is allowed to be emitted in a plurality of directions. Moreover, the belt-like reflecting layer may be formed into a spiral configuration. The width of the belt-like reflecting layer may be changed in the longitudinal direction of the light transmission tube. The tubular clad is allowed to have a non-circular cross section. The clad formation material may contain an ultraviolet light shielding material or an ultraviolet light absorbing material.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
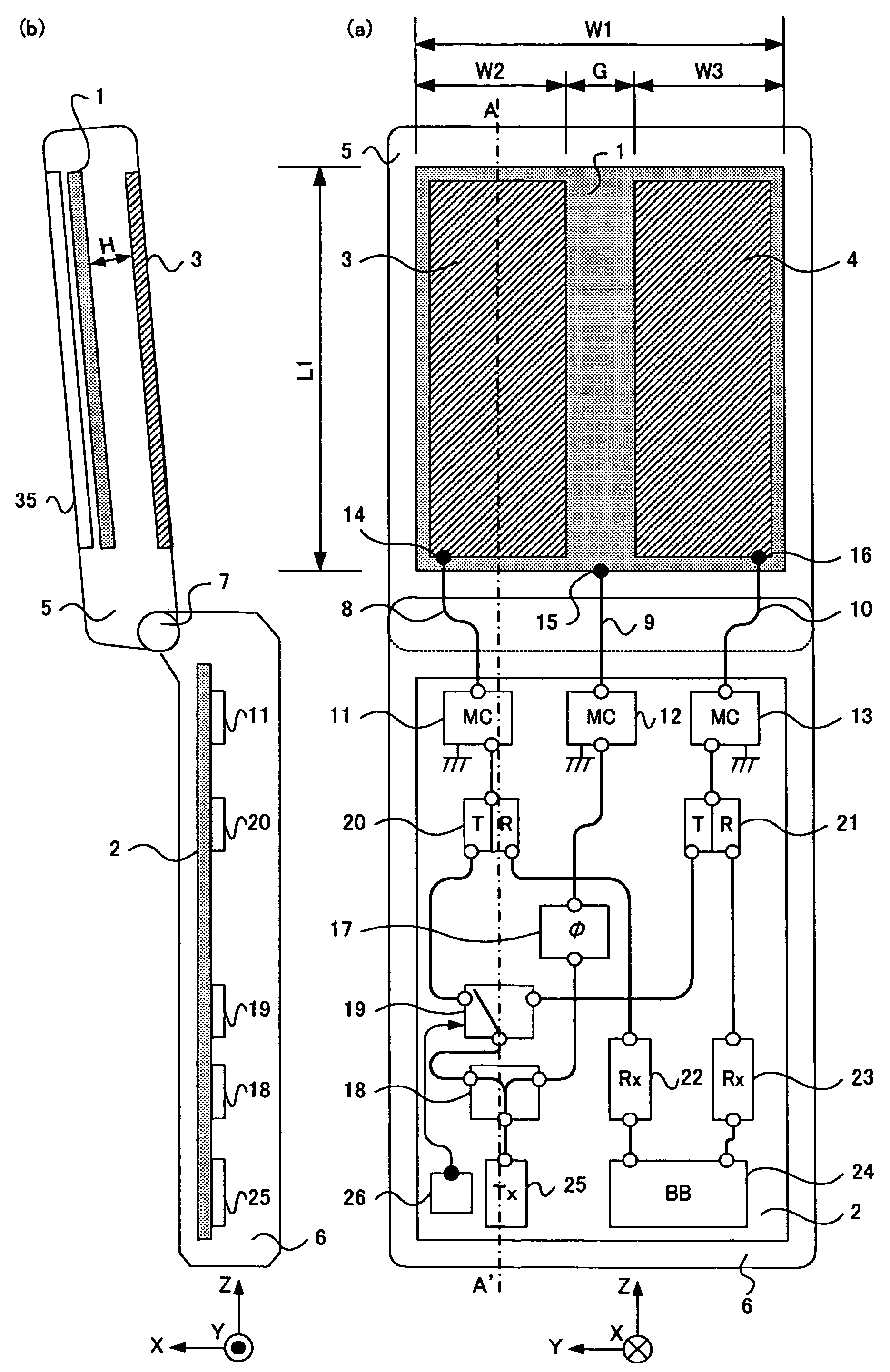
Portable wireless device
InactiveUS7453405B2Easy to controlImprove efficiencySpatial transmit diversityAntenna arraysElectrical conductorWeight coefficient
A portable wireless device realizing high-speed transmission in downlink communication in a used state that a foldable portable wireless device is held in a hand of the user and ensuring a high antenna radiation efficiency. In the portable wireless device, platy conductors (1, 3, 4) are arranged in the longitudinal direction on the back of a display section (35) of an upper case (5). The signal of a transmission circuit (25) is distributed by a power distributor (18). One signal is fed to a platy conductor (1) through a phase shifter (17) and the other is fed to the platy conductor (3) or the platy conductor (4) from a high-frequency switch (19) through a transmission / reception duplexer (20) or a transmission / reception duplexer (21). The high-frequency switch (19) selectively feeds power to either the platy conductor (3) or the platy conductor (4) according to the signal from a gravity sensor (26). The received signal is extracted by the transmission / reception duplexers (20, 21), amplified by a receiving circuit (22) and a receiving circuit (23), and multiplied by a predetermined weight coefficient by a demodulating section (24) and combined.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Projection type image display apparatus and image display system
InactiveUS6951393B2Efficient captureIncrease costStatic indicating devicesProjectorsProjection opticsOptical axis
A projection type image display apparatus includes a projection optical system the projects light emitted from an organic EL element onto a target object. The projection optical system has a characteristic non-telecentric toward the EL element with principal rays which pass through the median point of the aperture pupil that captures light diffusively emitted from the EL element converging when seen from the EL element at a pixel position where the object height on the EL element from the optical axis of the projection optical system reaches a maximum.
Owner:CANON KK
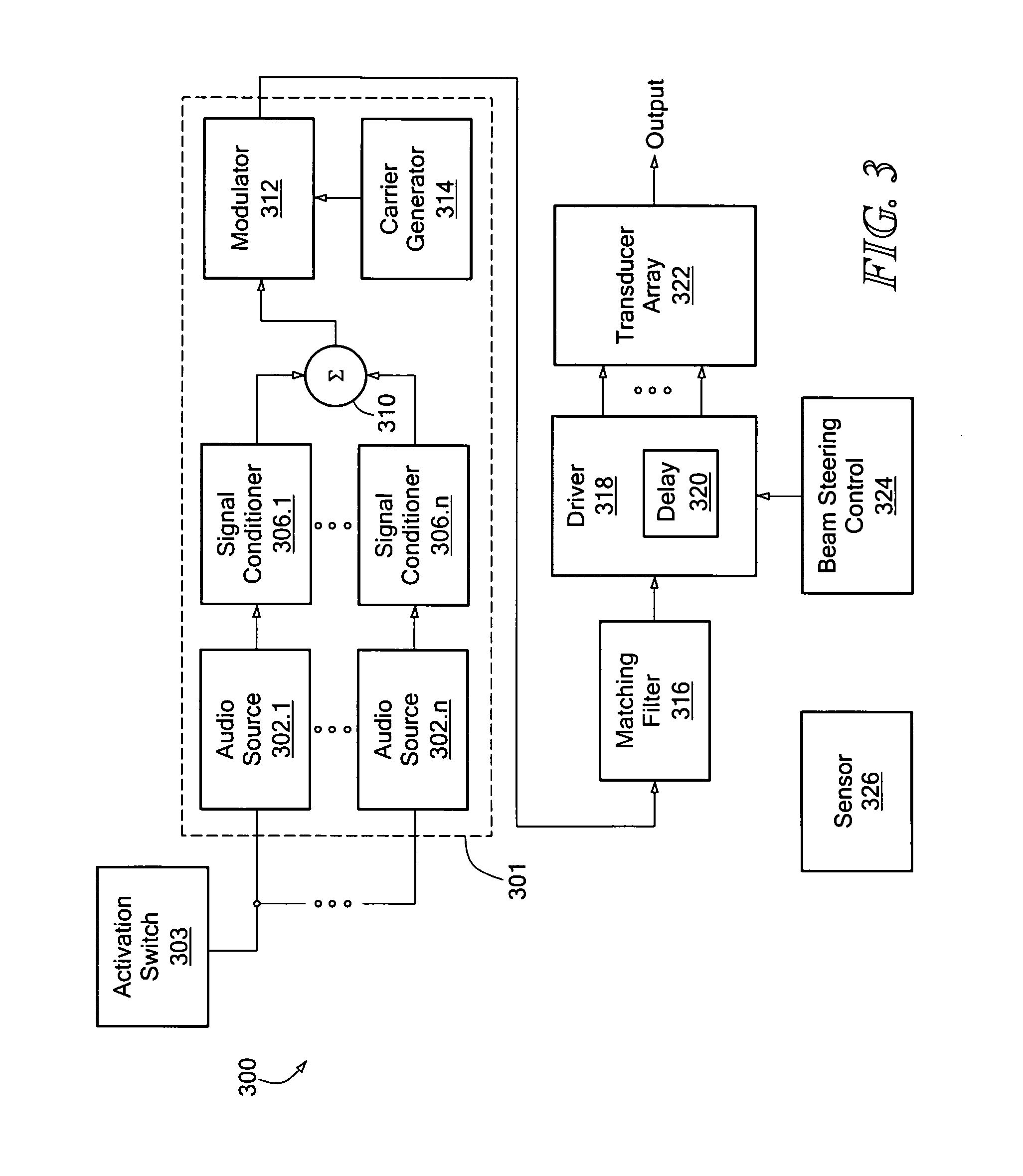
Hybrid audio delivery system and method therefor
ActiveUS20110103614A1Improve directivityReduce chanceMicrophonesLoudspeakersSonificationCarrier signal
Methods and systems to produce audio output signals from audio input signals. In one embodiment, a first portion of the audio input signals can be pre-processed, with the output used to modulate ultrasonic carrier signals, thereby producing modulated ultrasonic signals. The modulated ultrasonic signals can be transformed into a first portion of the audio output signals, which is directional. Based on a second portion of the audio input signals, a standard audio speaker can output a second portion of the audio output signals. Another embodiment further produces distortion compensated signals based on the pre-processed signals. The distortion compensated signals can be subtracted from the second portion of the audio input signals to generate inputs for the standard audio speaker to output the second portion of the audio output signals. In yet another embodiment, noise can be added during pre-processing of the first portion of the audio input signals.
Owner:IPVENTURE
Antenna coil
InactiveUS20150137612A1Reduced strengthTransmission limitLoop antennas with ferromagnetic coreCharging stationsMagnetic fluxPhysics
Provided is an antenna coil capable of forming a magnetic field in a desired direction in an efficient manner, while suppressing leakage of magnetic flux into a space other than the space in which the magnetic field is formed. The antenna coil includes a main coil portion formed by winding a length of conductor wire around a first reference axis and an auxiliary coil portion formed by winding the conductor wire around a second reference axis. The second reference axis is set to intersect the magnetic flux of the main coil portion at an axial end of the auxiliary coil portion. The main coil portion and the auxiliary coil portion are connected to together form a closed circuit.
Owner:EQUOS RES
Planar Light Emitting Element, Image Display Element, and Image Display Device Using the Same
ActiveUS20090086466A1High directivityEffectively focusIlluminated signsNon-linear opticsDirectivityLight guide
A planar light emitting element is capable of outputting light having high directivity in at least one direction. The planar light emitting element has a light guide plate and first and second low refractive index layers. Light incident on the light guide plate is totally reflected on the interface between the light guide plate and the second low refractive index layer, propagates in the light guide plate, and is output from the light guide plate to the first low refractive index layer through a light output opening section. When a refractive index of the first low refractive index layer is sufficiently smaller than a refractive index of the light guide plate, the light propagates in the light guide plate at a large angle with respect to a light output surface of the light guide plate. When the difference between the refractive indexes of the first and second low refractive index layers is small, a spreading angle of light output to the first low refractive index layer is small. The light having high directivity is reflected on a reflective mirror and output from the planar light emitting element.
Owner:PANASONIC LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY CO LTD +1
Illuminator
InactiveUS20050213320A1More LEDUneven illuminationMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceVector distributionLight-emitting diode
The present invention of illuminator pertains to converting spot light source, especially light-emitting-diode, into planar light source with some kind of intensity distribution mode, including a spot light source and a reflector, characterized in that spot light source is located at lateral and nook position, and the reflector can be designed elastically according to requirement of mode of reflected light vector distribution in space and mode of reflected light intensity distribution on illuminated surface. Spot light sources of the present invention include light-emitting-diode LCD. The modes of reflected light include space distribution mode in which light vectors are more orientated or nearly parallel and intensity distribution mode, of reflected light on illuminated surface, in which intensity is nearly even on illuminated surface; Both types of modes can co-exist in a illuminator. The illuminator of the present invention can be applied to display of mobile phone, personal digital assistant PDA, and notebook computer, backlight module, and general illuminating usage.
Owner:ACE T
Directional coupler and dual-band transmitter using the same
InactiveUS7187910B2Improve directivityMinimized in process errorResonant long antennasSubstation equipmentCapacitanceCoupling
Disclosed herein are a directional coupler which is implemented with strip lines for signal coupling and inter-digital capacitors for phase compensation, and a dual-band transmitter using the same. The directional coupler includes a first transmission device, a first directional coupling device for coupling a part of a signal from the first transmission device, a first inter-digital capacitor connected between the first transmission device and the first directional coupling device, a second transmission device, a second directional coupling device for coupling a part of a signal from the second transmission device, and a second inter-digital capacitor connected between the second transmission device and the second directional coupling device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Multilayer Broadband Microstrip Antenna
InactiveCN102299418ADirectionalHigh bandwidthRadiating elements structural formsBroadband microstrip antennaAntenna gain
The invention discloses a multilayer broadband microstrip antenna, comprising an upper dielectric baseplate, a middle dielectric baseplate, a lower dielectric baseplate, an upper low dielectric constant insulating dielectric layer, a lower low dielectric constant insulating dielectric layer, a reflection plate and a feed probe, wherein rectangle radiators of metallic copper pasters are arranged on the lower surface of the upper dielectric baseplate and the upper surface of the middle dielectric baseplate and provided with U-shaped slot structures with different sizes respectively. Due to a special double-layer inverted U-shaped slot coupling feed way, the symmetry of directional diagrams on an E surface or H surface of the antenna is good, thus ensuring that the antenna has more consistent performances in more directions, and having more actual meanings as an exploration antenna and a communication antenna. The reflection plate with an EBG (electromagnetic band gap) structure can preferably restrain backward radiation in the specified frequency relative to a traditional metal reflection plate, thus improving the directivity of the antenna, thereby further improving the gain of theantenna.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Light source module and optical member
InactiveUS20120218752A1Good shading effectSufficiently blockNon-electric lightingMirrorsEffect lightReflective layer
A light source module includes: a light source; a lighting curtain that partially blocks light from the light source; and a reflective layer that is provided on the lighting curtain and that has a planar shape smaller than the lighting curtain.
Owner:SHARP KK
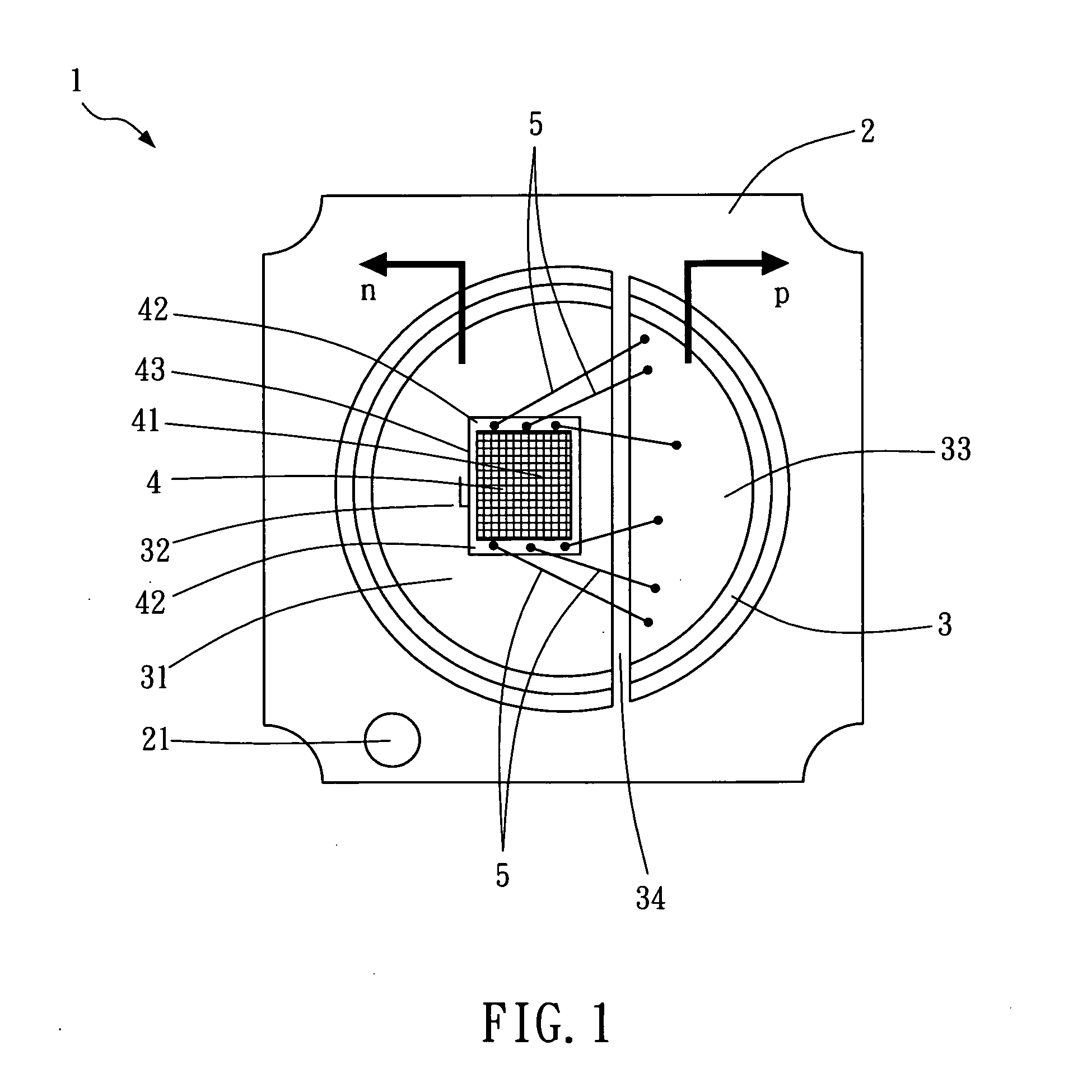
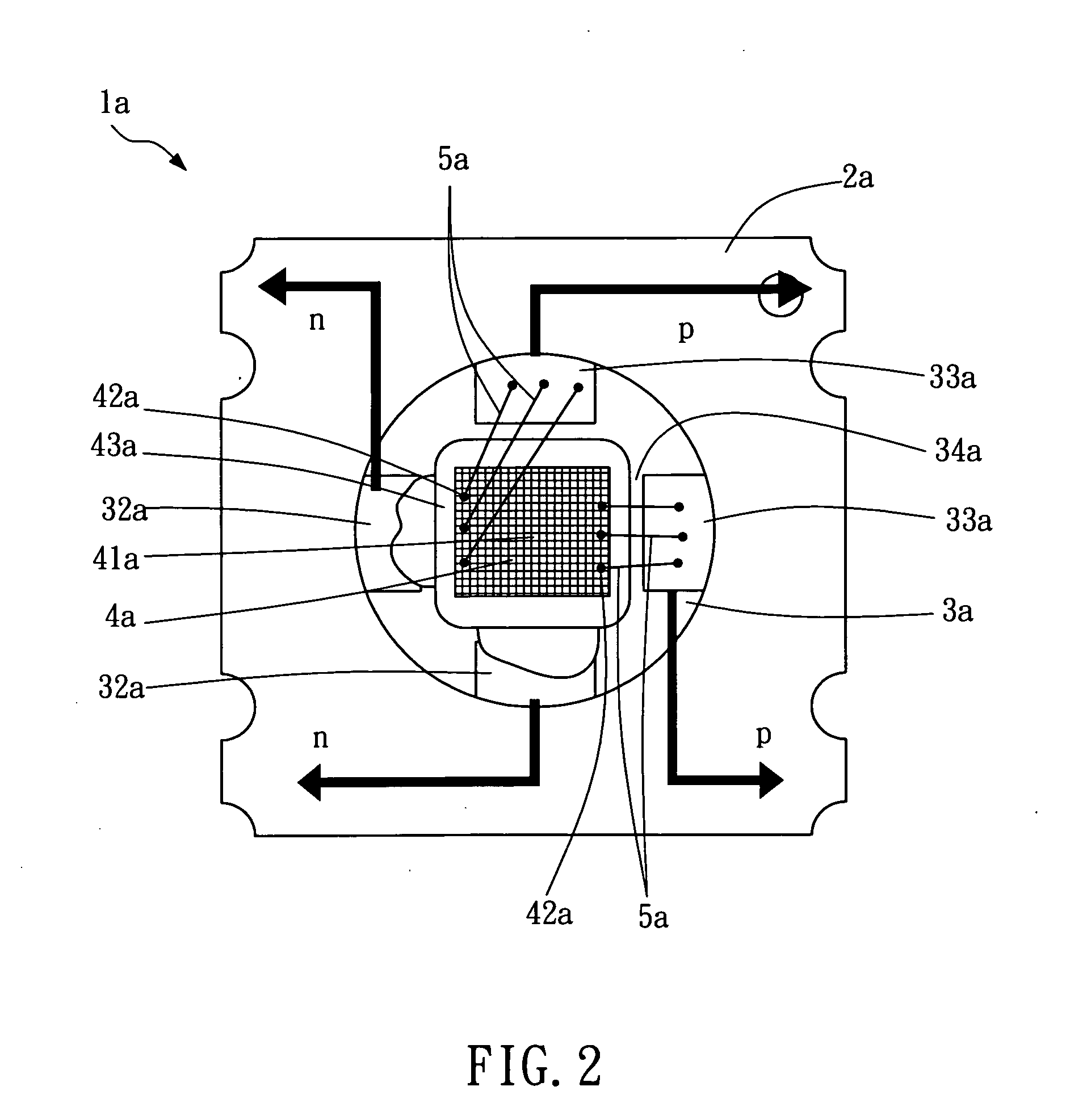
Packaging device for matrix-arrayed semiconductor light-emitting elements of high power and high directivity
ActiveUS20110121323A1High powerHigh directivitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDirectivityHigher Power
A packaging device for matrix-arrayed semiconductor light-emitting elements of high power and high directivity comprises a metal base, an array chip and a plurality of metal wires. The metal base is of highly heat conductive copper or aluminum, and a first electrode area and at least one second electrode area which are electrically isolated are disposed on the metal base. The array chip is disposed on the first electrode area, on which multiple matrix-arranged semiconductor light-emitting elements and at least one wire bond pad adjacent to the light-emitting elements are disposed. The light-emitting element is a VCSEL element, an HCSEL element or an RCLED element. The metal wires are connected between the wire bond pad and the second electrode area to transmit power signals. Between the bottom surface and the first electrode area is disposed a conductive adhesive to bond and facilitate electrical connection between the two.
Owner:TRUE LIGHT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com