Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
116results about How to "Improved radiation pattern" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
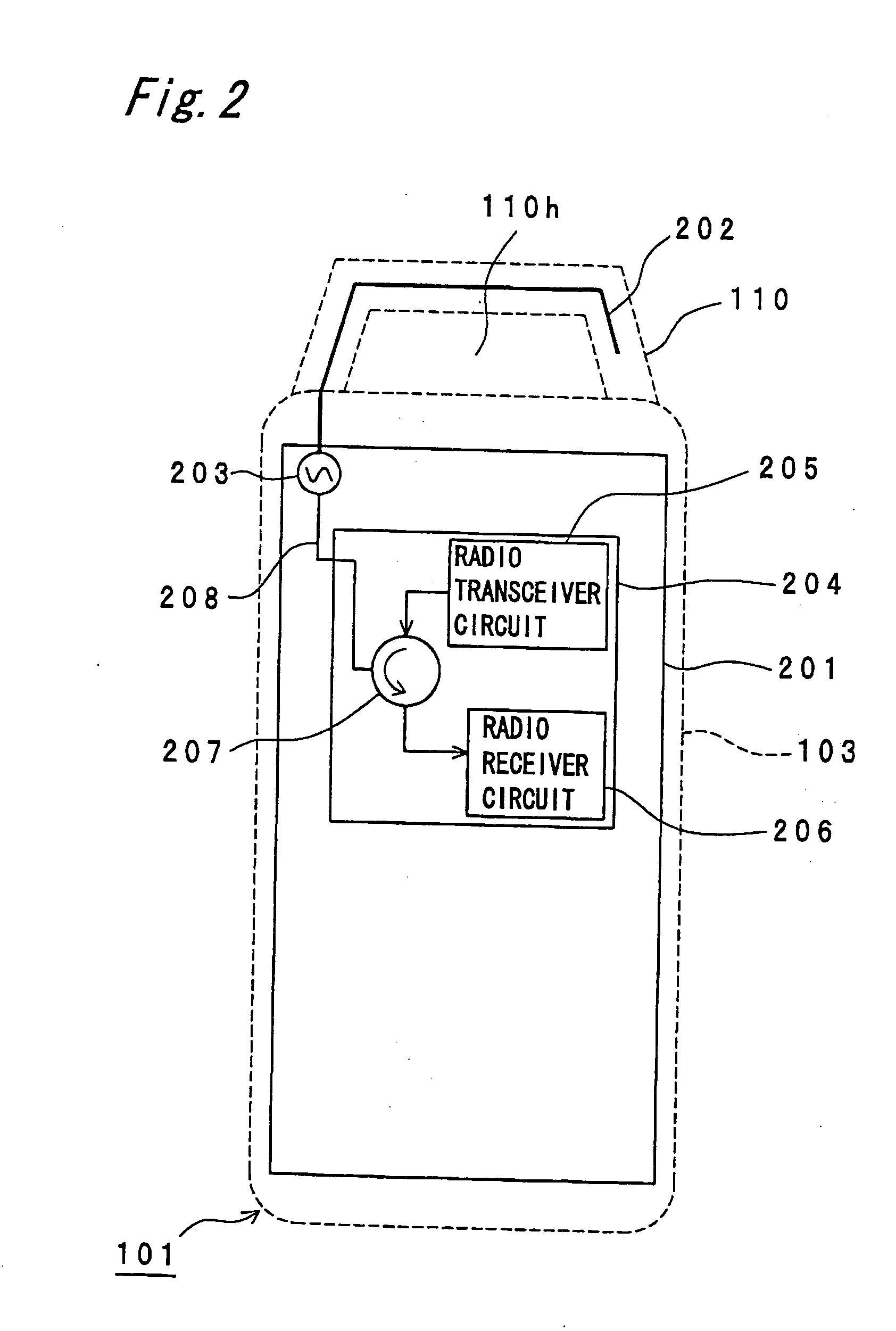
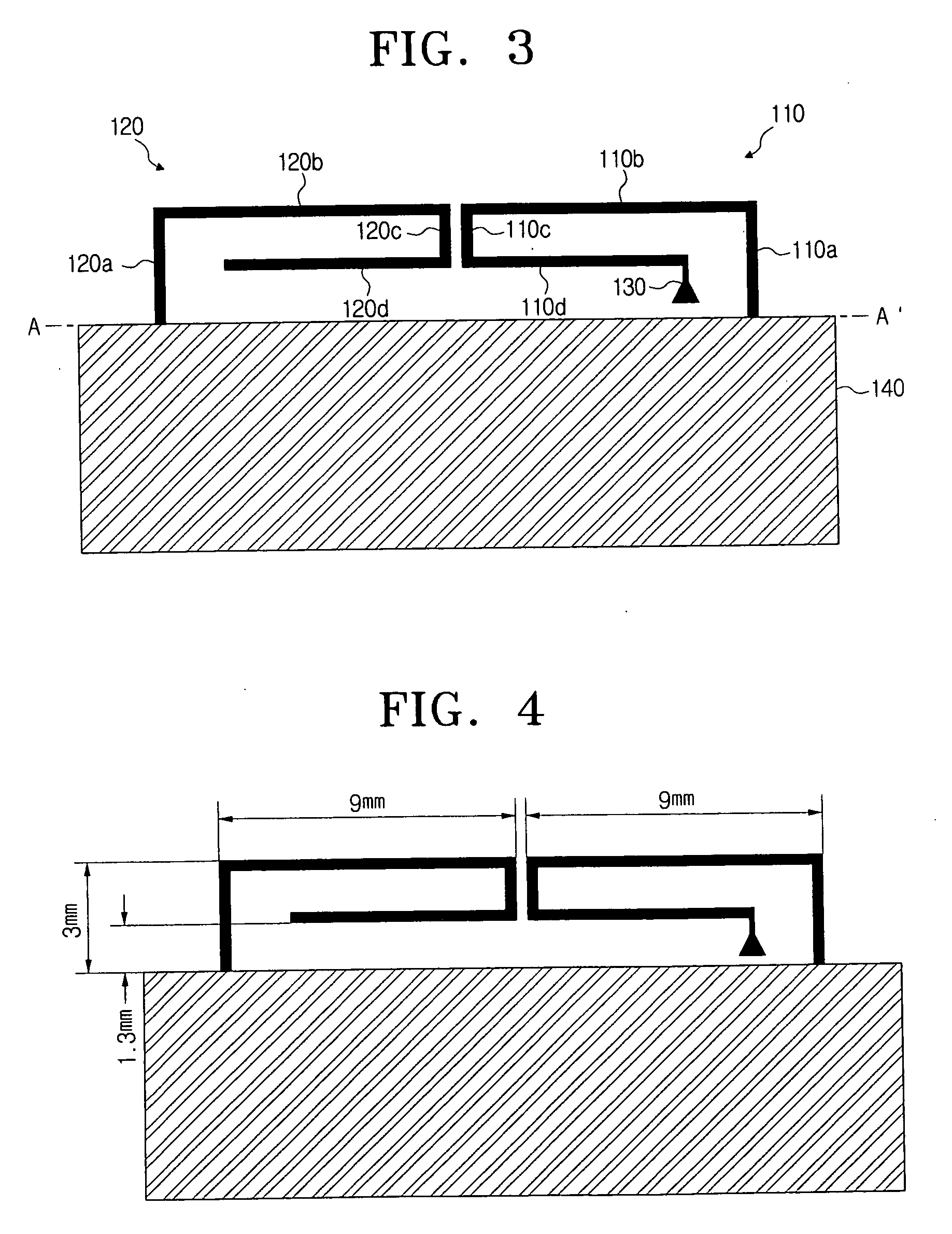
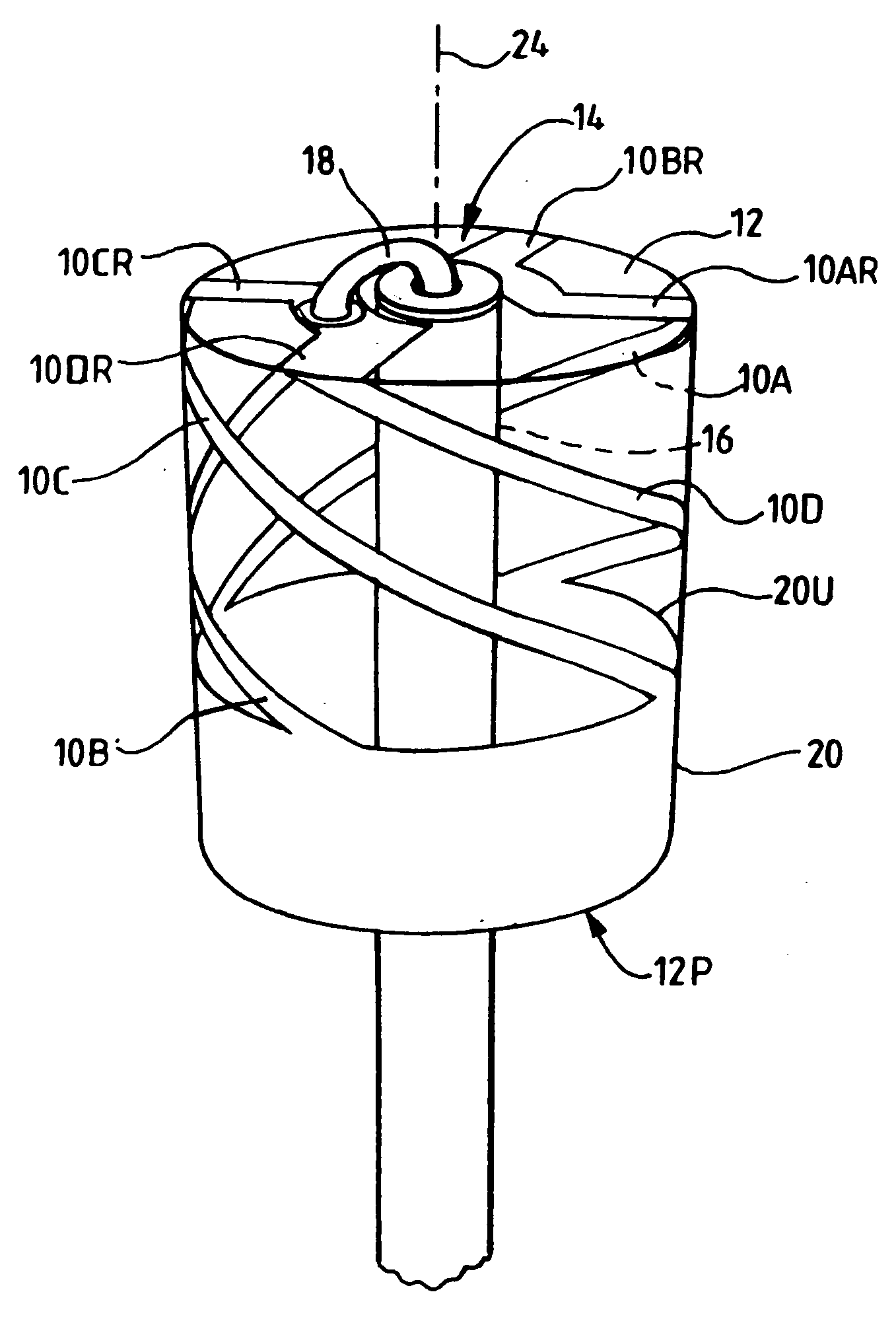
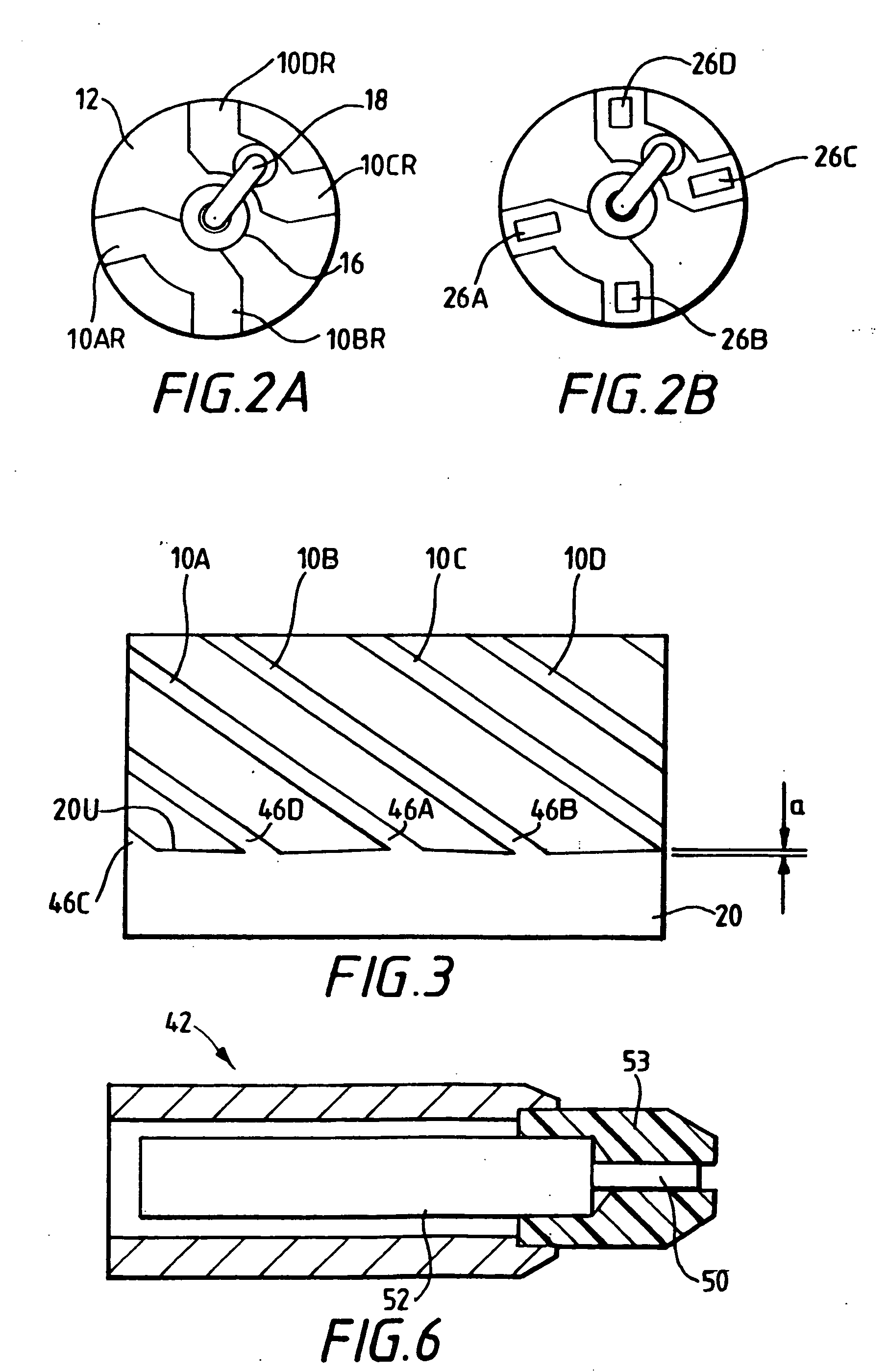
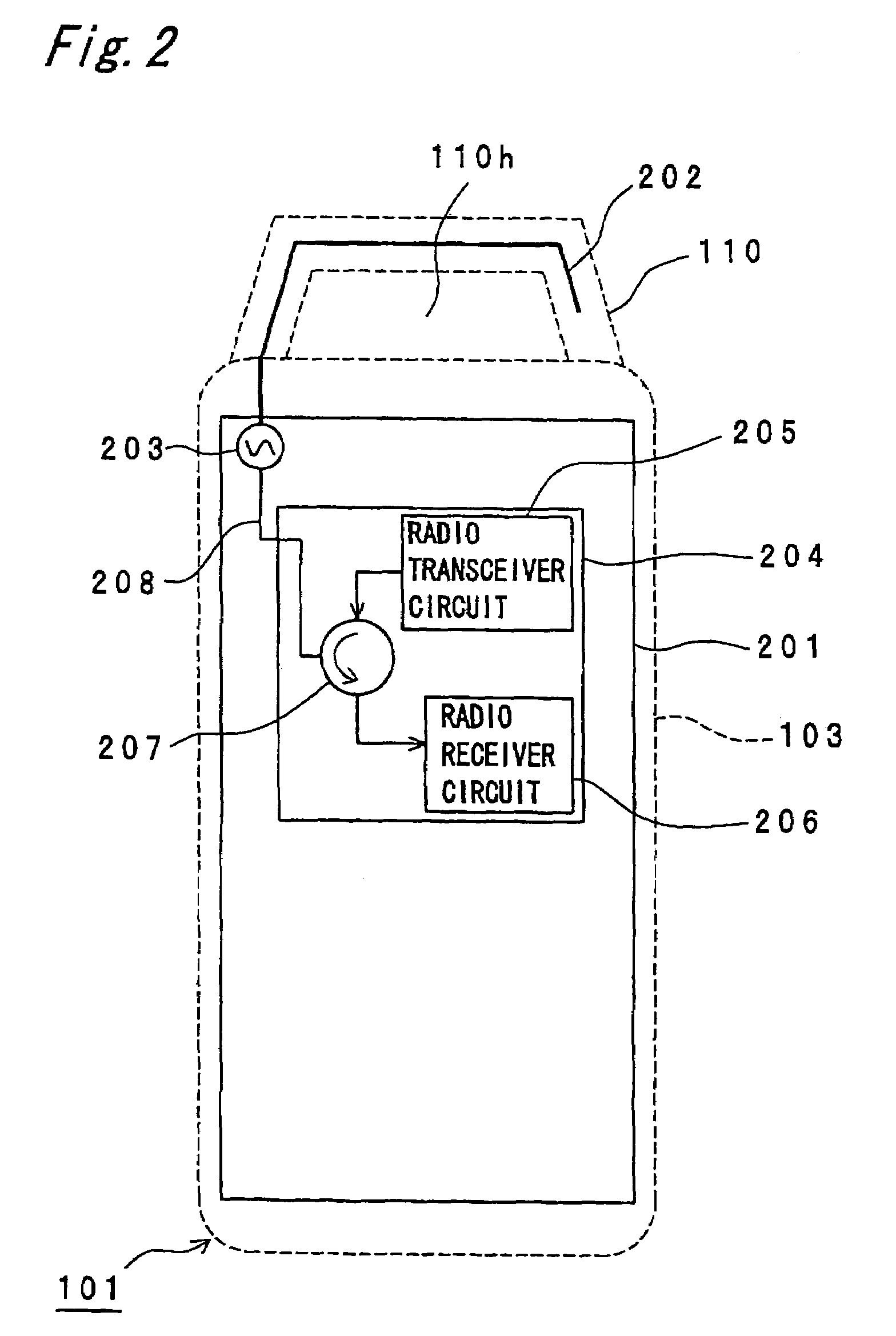
Smart Active Antenna Radiation Pattern Optimising System For Mobile Devices Achieved By Sensing Device Proximity Environment With Property, Position, Orientation, Signal Quality And Operating Modes
ActiveUS20140128032A1Save battery powerImprove signal qualityPower managementUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionDistortionActive antenna
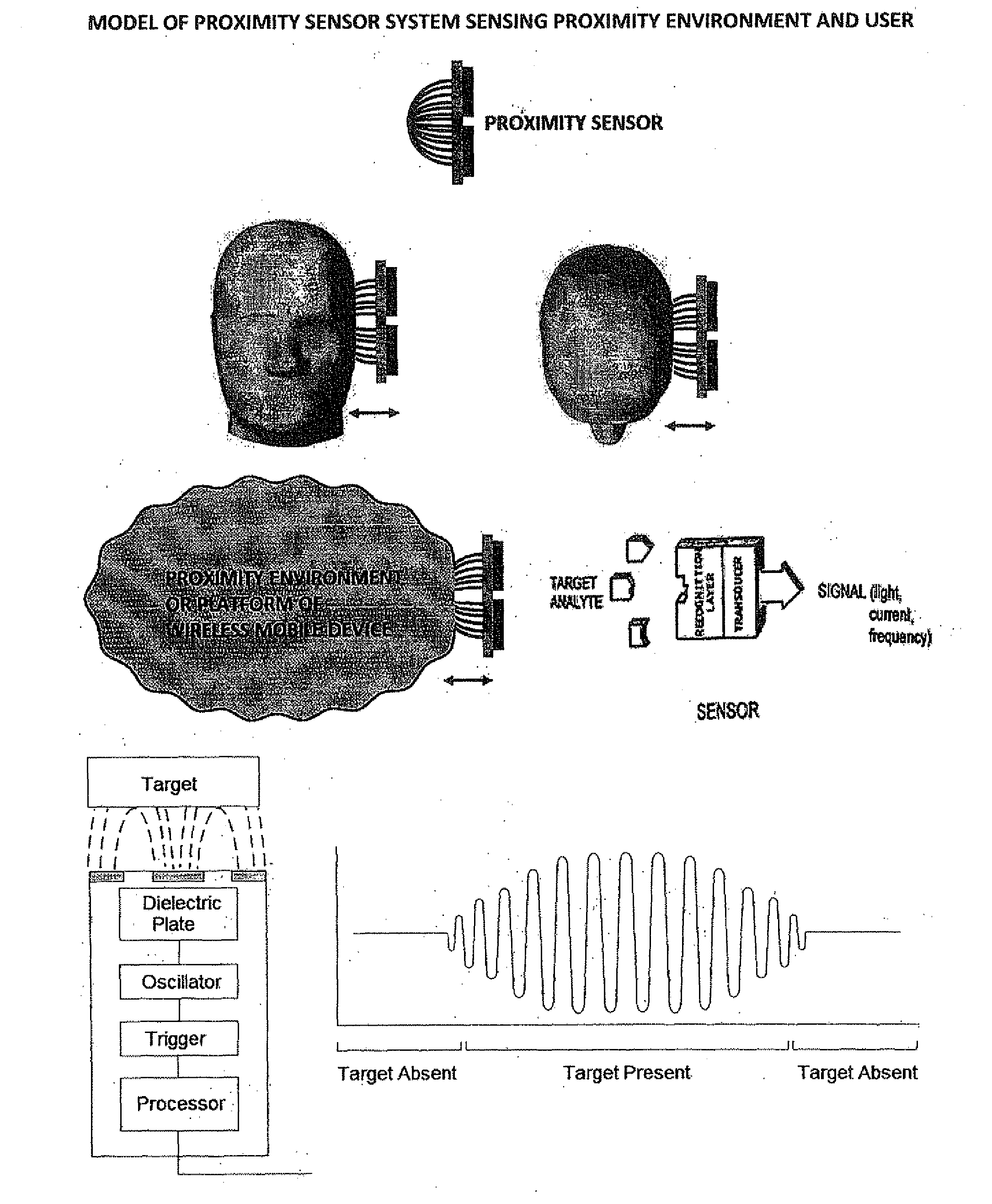
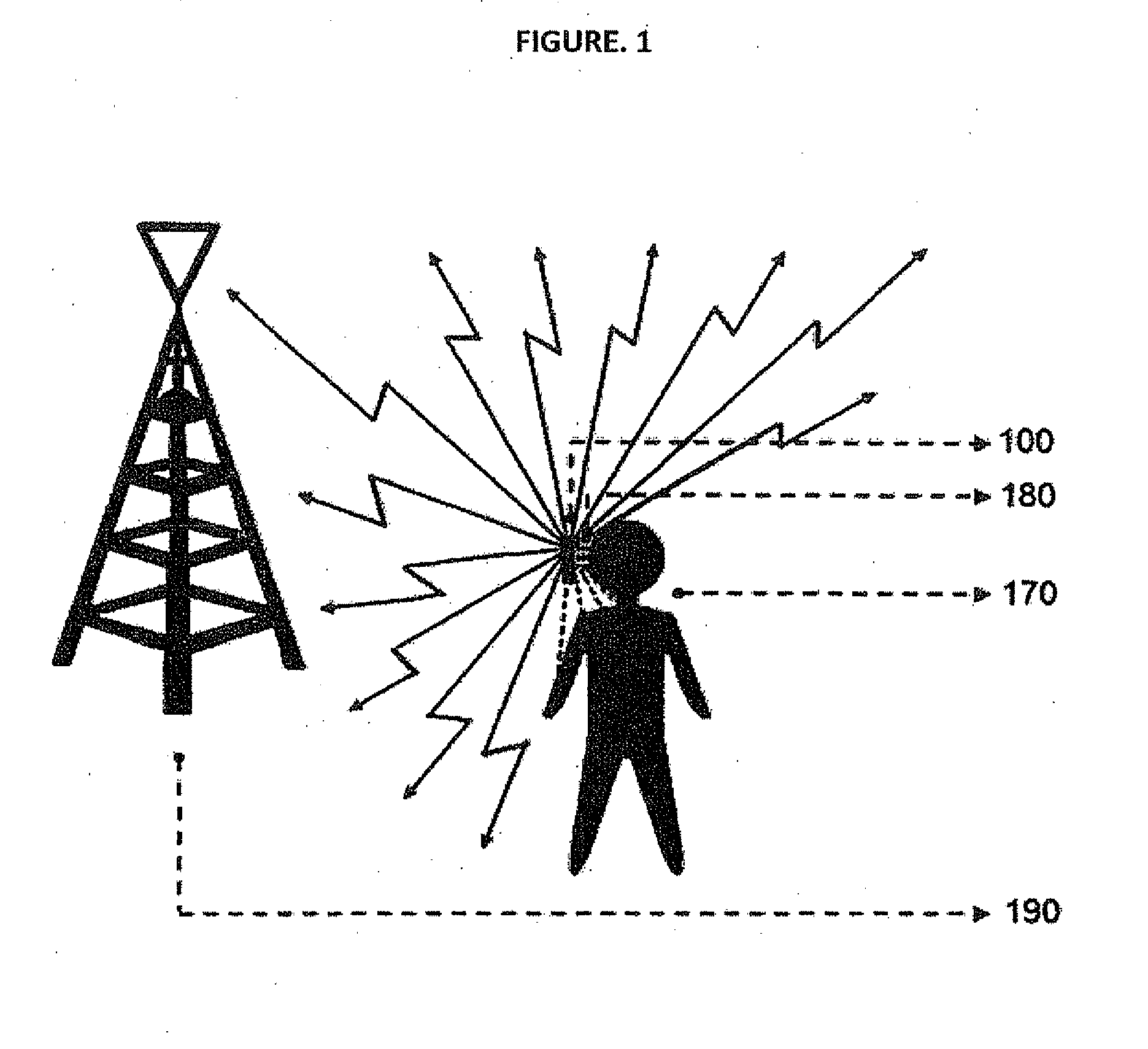
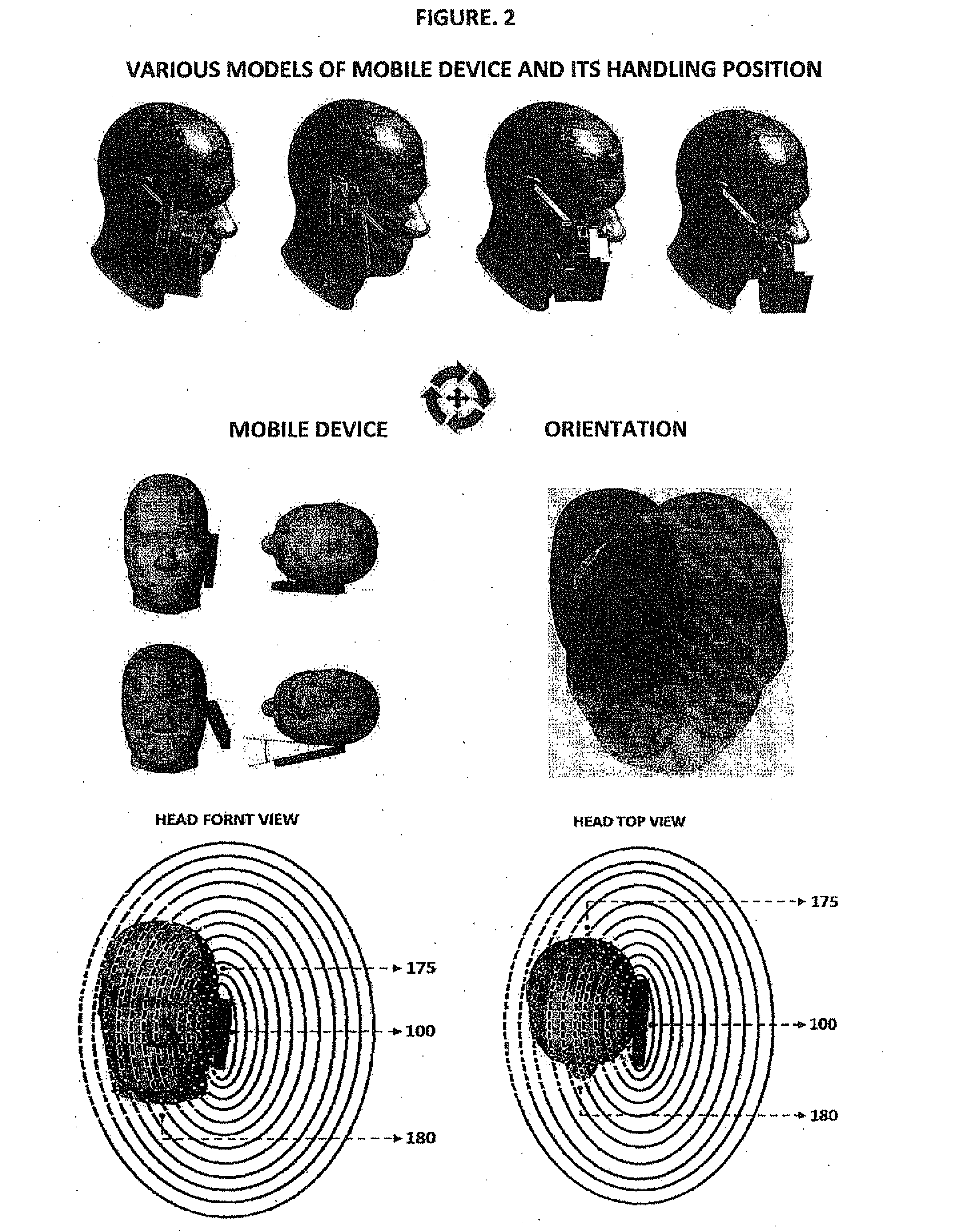
The smart dynamic radiation pattern optimising system is a design and technique to actively shape & optimise the radiation pattern of mobile device controlled by smart RF / Antenna system with signal processing algorithm that works by sensing the change in device proximity environment with nature or property, range, orientation, position, location, signal quality parameters and ambient intelligence to protect the user by controlling radiation exposure, enhance RF signal quality and to save battery power. Mobile devices are handled in different proximity environment which influence the antenna performance due to electromagnetic interaction based on environments properties that leads to detuning, radiation pattern distortion, impedance mismatch etc which in turn degrades the signal quality. Also change in device orientation according to usage leads to power loss due to polarization mismatch. So when the signal quality degrades the system will sense & compute in an adaptive closed loop manner to actively optimise the radiation pattern according to scenarios. The design consist of (a) a sensor system 220 to determine the change in proximity environment [close vicinity] with sensing its property, sensing multi-direction, dimension, layer, position & range of proximity environment with respect to device, sensing device (antenna) orientation, visual sensing, infrared or thermal vision, user recognition, user head & hand hold effect, location, usage scenarios & operating modes and accordingly generate the trigger signal 230; (b) a processing unit 150 for computing the interrupt control signal 140 according to the nature of trigger signal & existing signal quality parameters; (c) Smart active radiation pattern optimiser 120 that works based on control signal; (d) Antenna system 110 capable of achieving dynamic radiation pattern coupled with radiation pattern optimiser that actively shapes and controls the radiation pattern accordingly to protect the user and also restores radiation according to scenarios to optimise communication. Other aspects of the present invention are the same sensor system 220 is utilised to develop an application that guides the user locate & position the mobile device in living space to achieve optimised performance, protect the mobile device from theft and ambient intelligence to alert & interact with the user.
Owner:MUTHUKUMAR PRASAD
Wideband dual polarized base station antenna offering optimized horizontal beam radiation patterns and variable vertical beam tilt
ActiveUS6924776B2Improved radiation patternImprove front-to-back ratioLogperiodic antennasAntenna supports/mountingsRadiation patternPhysics
A dual polarized variable beam tilt antenna (10) having a plurality of offset element trays (12) each supporting pairs of dipole elements (14) to orient the dipole element pattern boresight at a downtilt. The maximum squint level of the antenna is a consistent downtilt off of boresight and which is at the midpoint of the antenna tilt range. The antenna provides a high roll-off radiation pattern through the use of Yagi dipole elements configured in this arrangement, having a beam front-to-side ratio exceeding 20 dB, a horizontal beam front-to-back ratio exceeding 40 dB, and is operable over an expanded frequency range.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Apparatus and method for constructing and packaging printed antenna devices
ActiveUS20060001572A1Reduce radiationImproved radiation patternSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsHigh bandwidthTransceiver
Printed antenna devices are provided, which can operate at RF and microwave frequencies, for example, while simultaneously providing antenna performance characteristics such as high gain / directivity / radiation efficiency, high bandwidth, hemispherical radiation patterns, impedance, etc., that render the antennas suitable for voice communication, data communication or radar applications, for example. Further, apparatus are provided for integrally packaging such printed antenna devices with IC (integrated circuit) chips (e.g., transceiver) to construct IC packages for, e.g., wireless communications applications.
Owner:IBM CORP
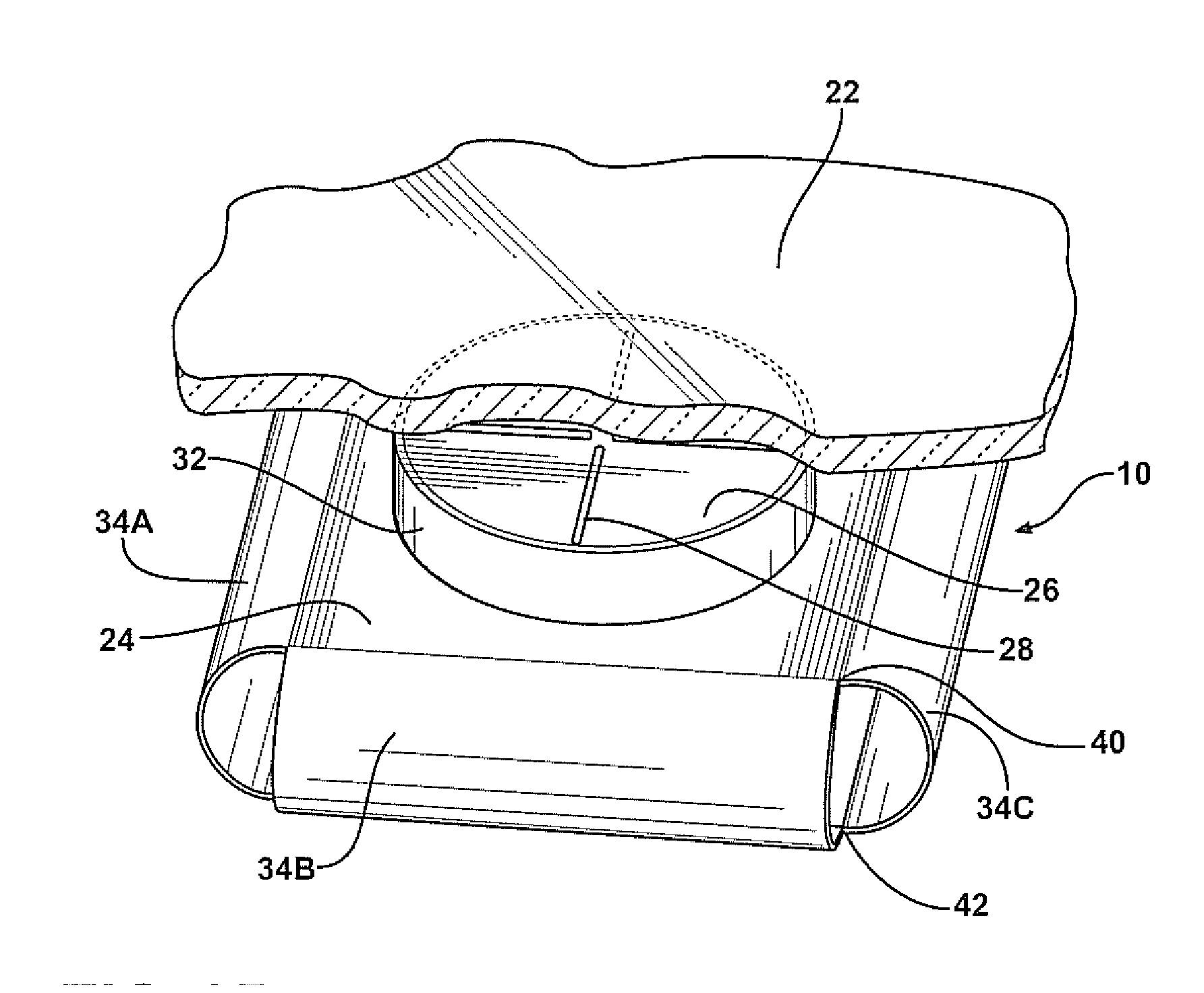
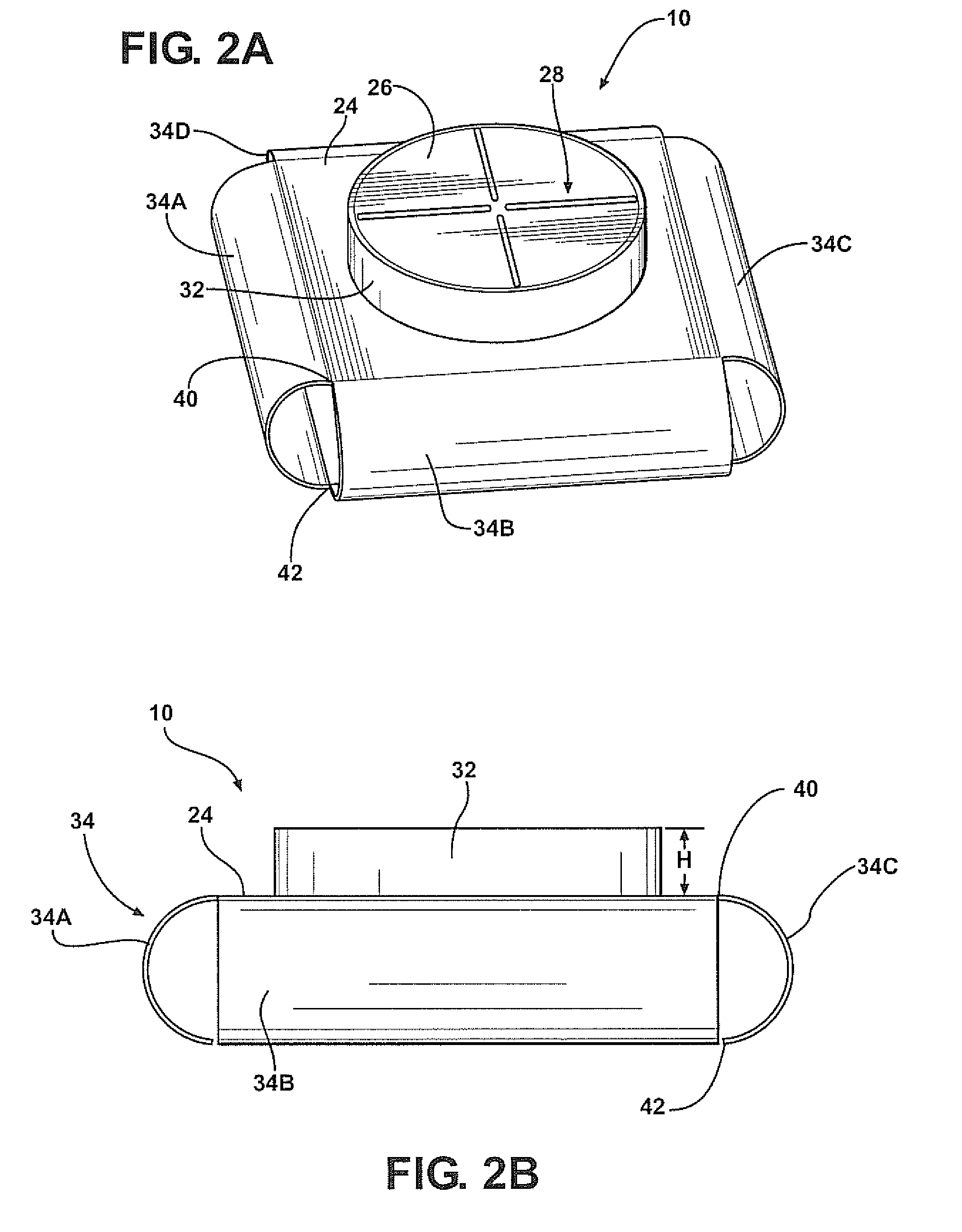
Trim panel comprising an integral acoustic system
InactiveUS6377695B1Large gainImprove uniformityVehicle componentsPlane diaphragmsTrim tabEngineering
A trim panel, e.g., a roof lining for a vehicle passenger compartment, characterized in that the trim panel comprises an integral acoustic radiator and a vibration exciter mounted on the radiator to launch bending waves into the radiator to cause it to resonate to produce an acoustic output. The acoustic radiator has a periphery which is integral with the radiator and the trim panel.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Microwave antenna apparatus, packing and manufacturing method
ActiveUS20170324135A1Relatively large bandwidthImproved radiation patternWaveguide hornsSolid-state devicesRedistribution layerMicrowave
A microwave antenna apparatus includes: a redistribution layer including a carrier layer, a ground plane arranged on a first or second surface of the carrier layer, and a microstrip line arranged on the other one of the first or second surface of the carrier layer; a semiconductor element mounted on the first surface of the carrier layer and coupled to the ground plane and the microstrip line; a mold layer that covers the semiconductor element and the first surface of the carrier layer; and a waveguide arranged within the mold layer and on the first surface of the carrier layer and coupled to the semiconductor element by the microstrip line, wherein a solid state filling material is arranged within the waveguide. Further, integrated antennas and transitions are presented within eWLB packages.
Owner:SONY CORP
Wideband dual polarized base station antenna offering optimized horizontal beam radiation patterns and variable vertical beam tilt
ActiveUS20050001778A1Improves horizontal plane radiation patternIncreased horizontal pattern front-to-back ratioLogperiodic antennasAntenna supports/mountingsRadiation modeRoll-off
A dual polarized variable beam tilt antenna (10) having a plurality of offset element trays (12) each supporting pairs of dipole elements (14) to orient the dipole element pattern boresight at a downtilt. The maximum squint level of the antenna is a consistent downtilt off of boresight and which is at the midpoint of the antenna tilt range. The antenna provides a high roll-off radiation pattern through the use of Yagi dipole elements configured in this arrangement, having a beam front-to-side ratio exceeding 20 dB, a horizontal beam front-to-back ratio exceeding 40 dB, and is operable over an expanded frequency range.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Dielectric resonator antenna with bending metallic planes
InactiveUS20090102739A1Decrease effective aperture areaImproved radiation patternAntenna earthingsElectrically short antennasGround planeWiMAX
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Semiconductor light-emitting device and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20050161696A1Improve light extraction efficiencyImproved radiation patternSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDevice formSemiconductor package
In a semiconductor light-emitting device formed by stacking a plurality of semiconductor layers including an active layer, at least a portion of a semiconductor layer of the plurality of semiconductor layers is made porous. The semiconductor layer made porous has a surface serving as a light-extraction surface for extracting light emitted from the active layer.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method of producing an antenna
InactiveUS6886237B2Increase inductanceImprove circularly polarised radiation patternLogperiodic antennasElectronic circuit testingCapacitanceLaser etching
In a method of producing a quadrifilar antenna for circularly polarised radiation at frequencies above 200 MHz, the antenna is tuned by coupling it to a test source, measuring the relative phases and amplitudes of currents at predetermined positions in the individual elements of the antenna by means of probes capacitively coupled to the elements, and laser etching apertures in the elements to increase their inductance, the sizes of the apertures being computed according to the deviation of the measured relative phases from predetermined values.
Owner:SARANTEL LTD
Structure and method for index-guided buried heterostructure AlGaInN laser diodes
InactiveUS6875627B2Improve stabilityLower average currentOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsFar field radiation patternRefractive index
An index-guided buried heterostructure AlGalnN laser diode provides improved mode stability and low threshold current when compared to conventional ridge waveguide structures. A short period superlattice is used to allow adequate cladding layer thickness for confinement without cracking. The intensity of the light lost due to leakage is reduced by about 2 orders of magnitude with an accompanying improvement in the far-field radiation pattern when compared to conventional structures.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Portable radio communication apparatus provided with boom portion with through hole
ActiveUS20050075082A1Improve balanceUniform processAntenna supports/mountingsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesEngineeringCantilever
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Antenna system and method
ActiveUS8421704B2Improved radiation patternLow costWaveguide hornsRadiating elements structural formsEngineeringGround plane
A radiator coupled to an antenna patch disposed along a first end of the radiator, said patch disposed on an insulator. A ground plane is connected to the insulator and a radome is disposed opposite a second end of the radiator. The radome may have a region presenting a convex surface towards the radiator, and the radome has a second region presenting a concave surface towards the radiator. The first end of the conical radiator is the apex of the cone. A ground plane is included and a portion of the ground plane is a planar surface and another portion extends away from the planar portion towards the radome. Also disclosed is a method for forming a radiation pattern by shaping the radome to effectuate a predetermined radiation pattern using localized convex and concave surfaces positioned on the radome at different points in relation to the conical radiator.
Owner:UBIQUITI INC
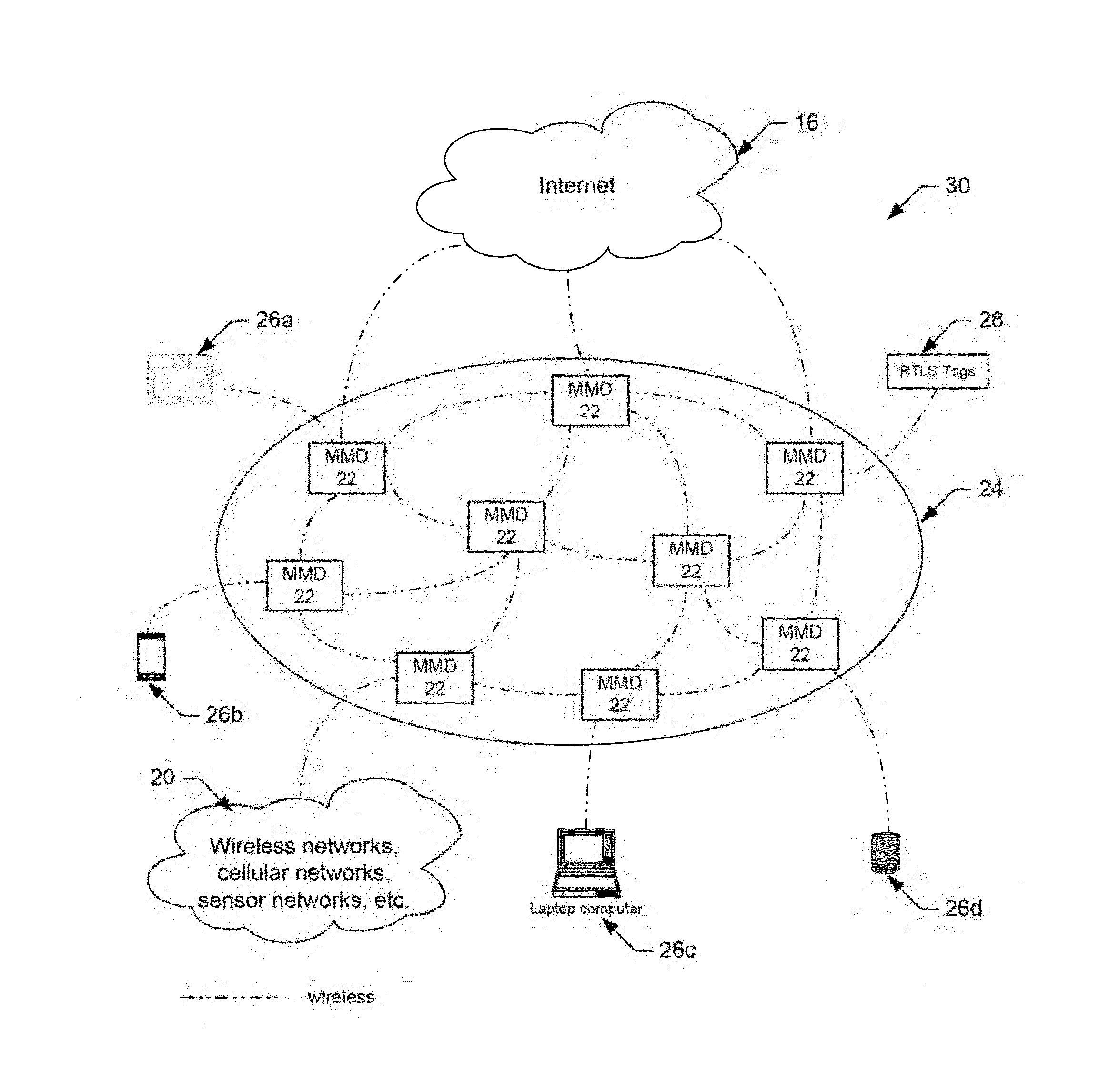
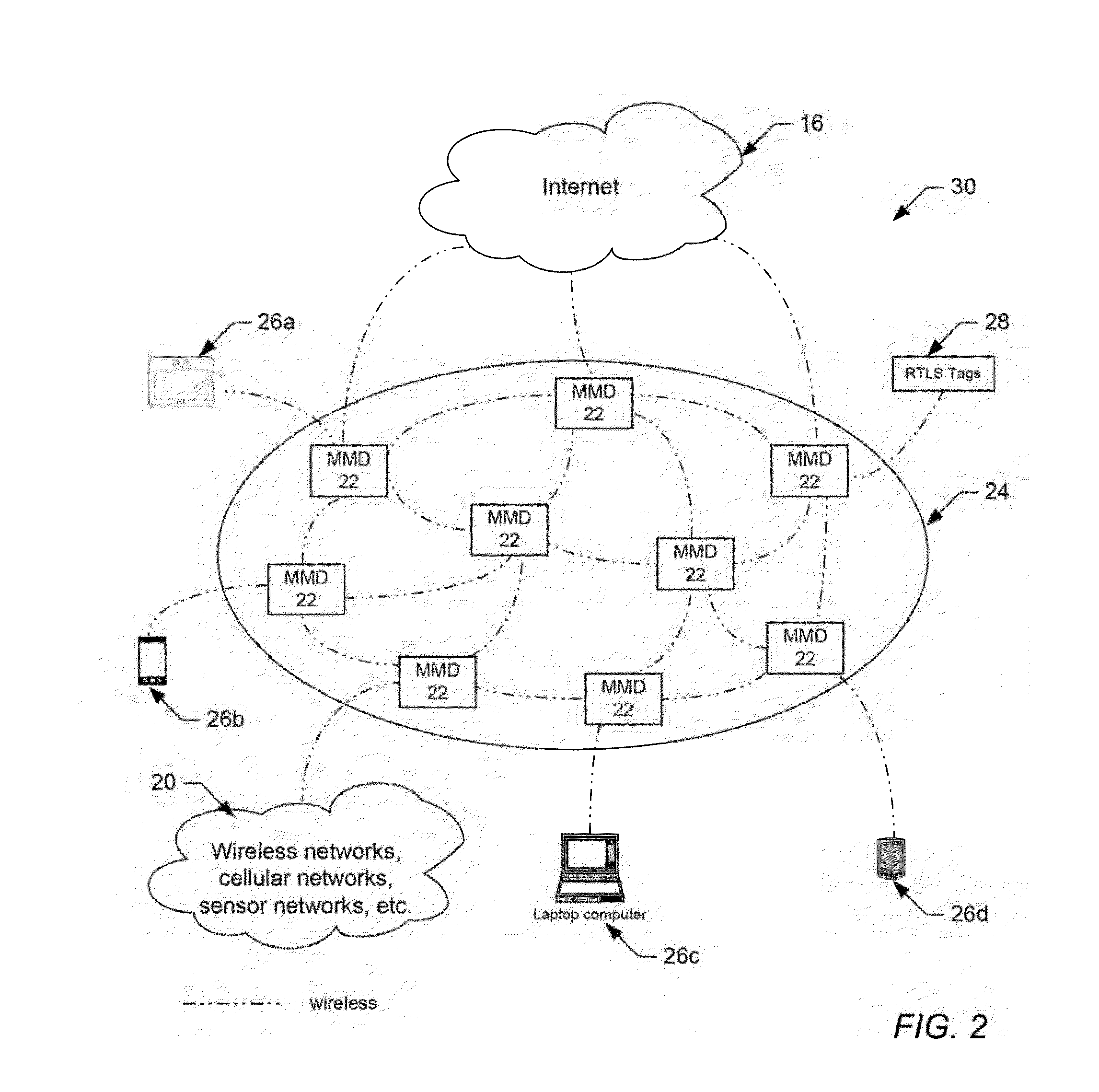
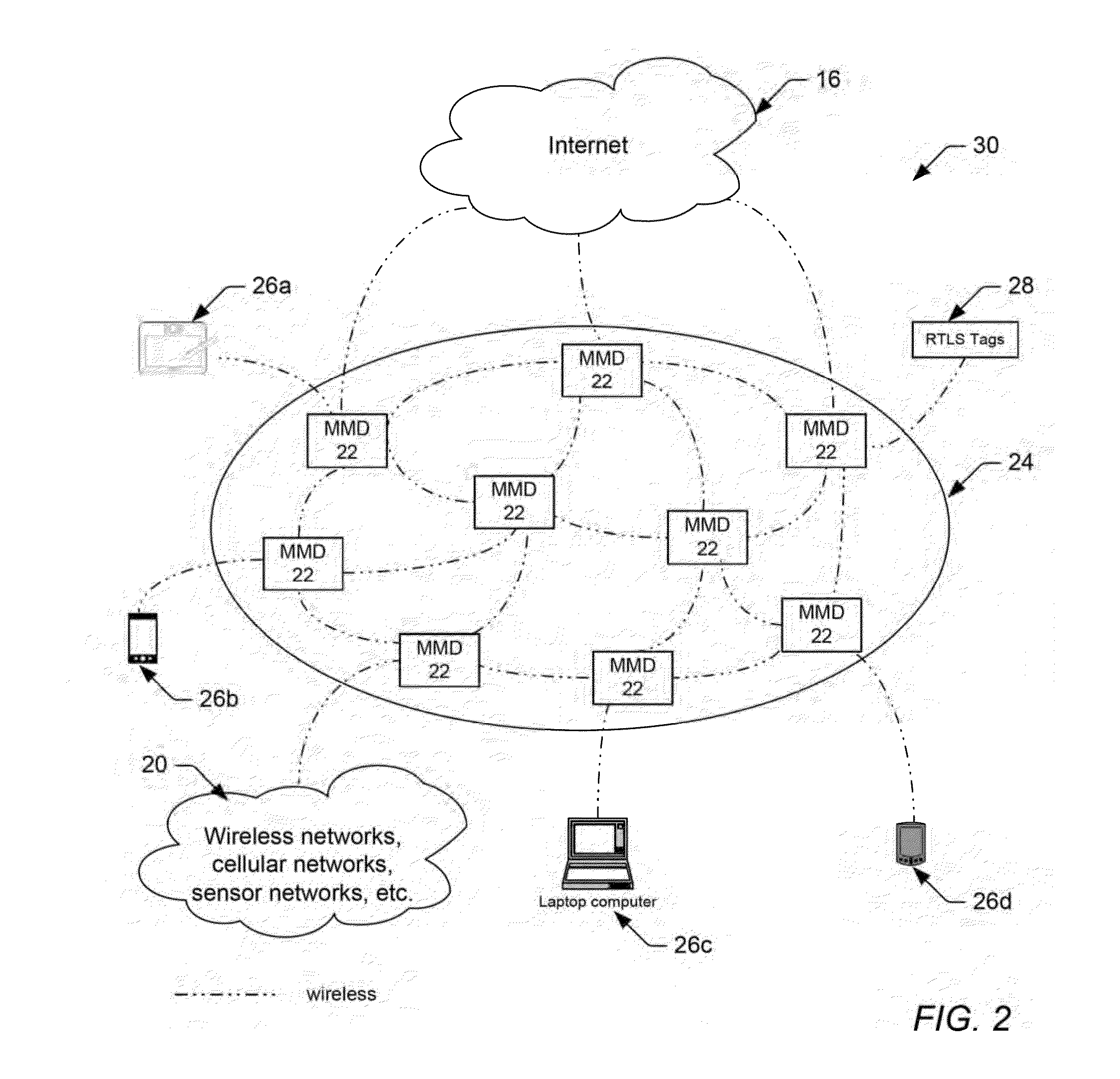
Portable Wireless Mesh Device
InactiveUS20150071163A1Significant cost and timeReduce in quantityAntenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsTraffic volumeMesh networking
A wireless mesh network comprising a plurality of mobile mesh devices coupled as nodes in a mesh network topology is provided herein. Generally speaking, each mobile mesh device may be a portable, self-contained unit, which does not require network or power wiring to communicate network traffic between the nodes. According to one embodiment, the mobile mesh device may include a small cell gateway for capturing, converting and re-routing cellular signals throughout and beyond the wireless mesh network. According to another embodiment, the mobile mesh device may include a real-time locating services (RTLS) hardware / software engine for capturing network traffic, identifying the identity and location of the device transmitting the network traffic, and triggering an action in response to either the identity and / or the location of the transmitting device. In some embodiments, the RTLS hardware / software engine may be combined with the small cell gateway to automatically re-route converted cellular signals throughout and beyond the wireless mesh network based on the identity of captured data packets.
Owner:OLEA NETWORKS
Antenna structures and their use in wireless communication devices
InactiveUS7233291B2Guaranteed uptimeImproved radiation patternSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsEngineeringCommunication device
An antenna structure for use in a wireless communication device, the structure comprising (i) a plurality of antenna portions each having a substantially planar radiating surface and (ii) a conducting ground portion; wherein the radiating surfaces of the antenna portions are substantially parallel to one another in a side-by-side relationship and are substantially parallel to part of the conducting ground portion located behind the antenna portions with respect to a direction of transmission of radiation from the antenna portions, the conducting ground portion comprising a first part galvanically connected to each of the antenna portions and, electrically coupled to the first part, a second conducting part forming at least part of a cover for a wireless communication device.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
Antenna for dual band operation
InactiveUS20070057849A1Long distanceImproved radiation patternSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsDual band antennaDouble frequency
Provided is a dual band antenna including: a ground surface; a feeder feeding a predetermined current; an induction radiator including one end connected to the ground surface and the other end connected to the feeder; and a parasitic radiator including an end connected to the ground surface and the other end opened. An antenna having a smaller size than an existing IFA mainly used as an internal antenna in a portable terminal can be provided through the dual band antenna including the induction radiator and the parasitic radiator.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Omnidirectional ultra-wideband monopole antenna
ActiveUS20060071871A1Improving Impedance MatchingGood omnidirectional radiation patternAntenna arraysAntennas with plural divergent straight elementsUltra-widebandOmnidirectional antenna
An omnidirectional ultra-wideband monopole antenna, with the characteristics of simple structure, easy fabrication and low cost, mainly comprises a ground plane, a U-shaped radiating member above the ground plane and a feeding member for feeding signals to the radiating member. The radiating member further comprises a first sub-radiating member parallel to the ground plane, with a first side edge and a corresponding second side edge, a second sub-radiating member connected to the first side edge and perpendicular to the first sub-radiating member, forming a first angle therebetween, and a third sub-radiating member connected to the second side edge to form a second angle. The second sub-radiating member and the third sub-radiating member are extended in the same upright direction above the ground plane. The antenna can provide good omnidirectional radiation patterns for frequencies across a very wide operating bandwidth.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Antenna manufacture including inductance increasing removal of conductive material
InactiveUS20050115056A1Increase inductanceLarge scaleLogperiodic antennasRadiating elements structural formsCapacitanceLaser etching
In a method of producing a quadrifilar antenna for circularly polarised radiation at frequencies above 200 MHz, the antenna is tuned by coupling it to a test source, measuring the relative phases and amplitudes of currents at predetermined positions in the individual elements of the antenna by means of probes capacitively coupled to the elements, and laser etching apertures in the elements to increase their inductance, the sizes of the apertures being computed according to the deviation of the measured relative phases from predetermined values.
Owner:SARANTEL LTD
Portable radio communication apparatus provided with boom portion with through hole
ActiveUS7457650B2Uniform processImproved radiation patternAntenna supports/mountingsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesEngineeringCantilever
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Method and apparatus for improving antenna radiation patterns
InactiveUS7081865B2Improve antenna radiation patternImproved radiation patternAntenna supports/mountingsRadiating elements structural formsElectromagnetic diffractionAntenna radiation patterns
Several electromagnetic scattering structures are designed to improve antenna radiation patterns. The electromagnetic scattering structure has a conductive layer with certain patterns, and is applied on the radome of the base-station sector antenna. The electromagnetic waves radiating from the antenna therein induce scattering effects, which, together with the electromagnetic diffractions from the rear metal panel of the antenna, can substantially reduce the back lobe and the fields in regions not covered by the antenna. Thus, the antenna radiation patterns are improved so that a lower possibility of co-channel interferences between adjacent base stations can be achieved and therefore better efficiency of the base-station coverage also can be obtained.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Multiple meander strip monopole antenna with broadband characteristic
InactiveUS20050248499A1Improved radiation patternReduced change in impedanceSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsBand shapeMeander
Disclosed is a multiple meander strip monopole antenna, which can have a broad bandwidth and easily miniaturize the antenna by using a meander structure. A grounding conductor plate is coupled to the under face of a dielectric base plate. A radial cross-strip is disposed symmetrically at the center of the upper surface of the dielectric base plate. Each radiating member of a multiple radiator is connected to the end portion of each corresponding branch of the radial cross-strip and stands substantially perpendicular to the base plate. Each radiating member is composed of a vertical strip section having a tapered structure, in which its width is progressively widened upwardly for an impedance matching and at least one meander strip section connected integrally to the upper end of the vertical strip section. When a feeding is carried out at the center of the radial cross-strip, a signal radiated from the multiple radiator is cancelled out in the axial direction of θ=0° and a radiation gain is increased as θ increases, thereby providing a conical beam radiation pattern. A broad bandwidth from 2.9 GHz to 10.85 GHz can be achieved and an excellent monopole radiation pattern having the same gain in all directions can also be achieved.
Owner:AJOU UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
Shielding for radiotelephones with retractable antennas
InactiveUS6137998ALower performance requirementsImproved radiation patternAntenna supports/mountingsElongated active element feedInductorCapacitor
Shields for radiotelephones with a retractable antenna include a conductive tubular antenna guide operably associated with an electronic ground, and preferably configured to form an inductor or capacitor in a matching circuit operable when the antenna is in the retracted position. Associated methods include directing RF radiation produced by the antenna positioned internal to the radiotelephone along a longitudinal exit path out of the radiotelephone.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
Portable Wireless Mesh Device Having Improved Antenna System
ActiveUS20150072628A1Reduce in quantityReduce radiationAntenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsTelecommunicationsWireless mesh network
A wireless mesh network comprising a plurality of mobile mesh devices coupled as nodes in a mesh network topology is provided herein. Generally speaking, each mobile mesh device may be a portable, self-contained unit, which does not require network or power wiring to communicate network traffic between the nodes. According to one embodiment, the mobile mesh device may include a plurality of dipole antennas, which are enclosed within the mobile mesh device and configured to forward network traffic. At least one of the dipole antennas may be a frequency adjustable end-fed dipole antenna comprising a channel selection pin, which can be adjusted up or down along the dipole axis to change a resonant frequency of the dipole antenna. A method for setting or adjusting a resonant frequency of a frequency adjustable end-fed dipole antenna is also provided herein.
Owner:OLEA NETWORKS
Monopole antenna
InactiveUS20070052591A1Low costSmall sizeSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsElectrical conductorAntenna gain
A monopole antenna is disclosed. The monopole antenna comprises a base board, a first substantially L-shaped conductor, a first ground plane, a second substantially L-shaped conductor, a second ground plane and a feeding strip, and the monopole antenna further has a plurality of evenly-distributed through holes penetrating the base board from the first substantially L-shaped conductor to the second substantially L-shaped conductor. When the monopole antenna is operated at about 2.4-2.5 GHz, good radiation patterns and antenna gain are obtained for being applicable to IEEE802.11b / g specifications.
Owner:ARCADYAN
Printed antenna and a wireless network device having the antenna
InactiveUS7561110B2Improved radiation patternHigh gainAntenna supports/mountingsRadiating elements structural formsDipole antennaMonopole antenna
A printed antenna suitable for wireless networking device comprising a base plate, a grounding member, a first antenna, a second antenna and a third antenna is disclosed. The base plate is made of dielectric material where on a surface of which a first direction and a second direction perpendicular to each other are defined. The grounding member is electrically grounded and covers at least a partial area of the base plate surface. The first antenna is a dipole antenna extending from the grounding member generally towards the first direction. The second antenna is a monopole antenna extending from the grounding member generally towards the second direction. The third antenna is a monopole antenna extending from the grounding member generally towards the second direction. The second antenna and the third antenna are substantially disposed on the two opposing sides of first antenna.
Owner:CAMEO COMM
Microwave broadband decoupled network based on signal interference concept
InactiveCN104134866AImproved radiation patternAntenna couplingsElectrical resistance and conductanceMicrowave
The invention provides a microwave broadband decoupled network based on a signal interference concept. According to the structure, removal of mutual coupling between coupled antennas serves as a design starting point, according to a signal interference method, two same broadband directional couplers are connected to serve as a guide-in path, mutual coupling energy of the antennas and energy of the guide-in path generate voltage zero points on a connecting line and then are offset, and therefore the broadband decoupled network is obtained. The decoupled network is of a plane micro-strip structure, and a dielectric slab is made of FR4. With the cooperation of thin film chip resistors, the structure is simple, machining is easy, cost and weight are low, and therefore large-scale production can be achieved. A novel technical scheme is provided for front end design of a broadband receiving and transmitting system, and the combination modes of microwave passive circuits are increased.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Difference coplanar waveguide UWB (Ultra Wide Band) wide slot trapped wave antenna with high attenuation band characteristic
InactiveCN103633425AImproved radiation patternEasy to integrateRadiating elements structural formsSlot antennasResonanceCoplanar waveguide
The invention discloses a difference coplanar waveguide UWB (Ultra Wide Band) wide slot trapped wave antenna with a high attenuation band characteristic. The difference coplanar waveguide UWB wide slot trapped wave antenna comprises a dielectric substrate, wherein a first feed circuit, a second feed circuit and a wide slot ground structure are arranged on the front face of the dielectric substrate; the first feed circuit and the second feed circuit are in bilateral symmetry to form a difference coplanar waveguide feed structure; the first feed circuit comprises a first feed port, a first micro-strip feed wire and a first radiating body; the second feed circuit comprises a second feed port, a second micro-strip feed wire and a second radiating body; the first radiating body is connected with the first feed port by the first micro-strip feed wire; the second radiating body is connected with the second feed port by the second micro-strip feed wire; a first resonance branch knot and a second resonance branch knot are respectively arranged on the upper part and the lower part of the inner side of a polygonal wide slot on the wide slot ground structure; the first and second resonance branch knots are vertically symmetrical. The antenna is simple in structure and is capable of realizing a trapped wave function.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Subreflector of a dual-reflector antenna
A subreflector of a dual-reflector antenna comprises a first extremity comprising a convex inner surface, a second extremity adapted for coupling to the extremity of a waveguide, and a body extending between the first extremity and the second extremity. The body comprises a first dielectric part having a portion penetrating into the waveguide and a portion outside the waveguide, and a second metallic part comprising a first cylindrical portion, contiguous with the first extremity of the subreflector, whose diameter is greater than the portion outside the waveguide of the first dielectric part, and a second cylindrical portion, adjacent to the first cylindrical portion, extended by a conical portion that penetrates into the first dielectric part. The first cylindrical portion features a flat ring-shaped surface that forms an angle less than 90° with the axis of the subreflector so as to face the primary reflector.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Antenna For Increasing Beamwidth Of An Antenna Radiation Pattern
InactiveUS20120019425A1Avoid sudden interruptionReducing undesired diffraction effectSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsDielectricAntenna radiation patterns
An antenna includes a ground plane, a dielectric, and an active radiating element. The dielectric is disposed on the ground plane, and the active radiating element is embedded in the dielectric for transmitting and / or receiving an RF signal. The antenna also includes a feeding element and a passive radiating element. The feeding element extends into the dielectric and is electrically coupled to the active radiating element. The passive radiating element is disposed on the ground plane and surrounds a periphery of the dielectric for perturbating the RF signal. The ground plane has a plurality of edges. At least one of the edges extends as a curvilinear lip. The curvilinear lip extends in a direction opposite the passive radiating element for directing the RF signal and for preventing abrupt discontinuity of the RF signal.
Owner:AGC AUTOMOTIVE AMERICAS
Printed Antenna
InactiveUS20110156969A1Wide range of applicationsEasily and precisely fabricatedSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsGlass sheetHard substrate
A printed antenna comprises an ink-printed layer, a hard substrate and a radiation conductor layer. The hard substrate has a surface, and the ink-printed layer is coated on the surface to form a non-transparent area. The uncoated region of the surface is a transparent area. The radiation conductor layer is formed on the ink-printed layer and does not exceed the non-transparent area of the hard substrate. In the present invention, a conductive ink is coated on the surface of a non-metallic plate, such as a glass plate, an acrylic plate or an LCD panel, to form the radiation conductor layer. Therefore, the printed antenna of the present invention is exempt from the complicated processes of fabricating the conventional metallic radiation conductors with the application field thereof expanded.
Owner:ADVANCED CONNECTEK INC
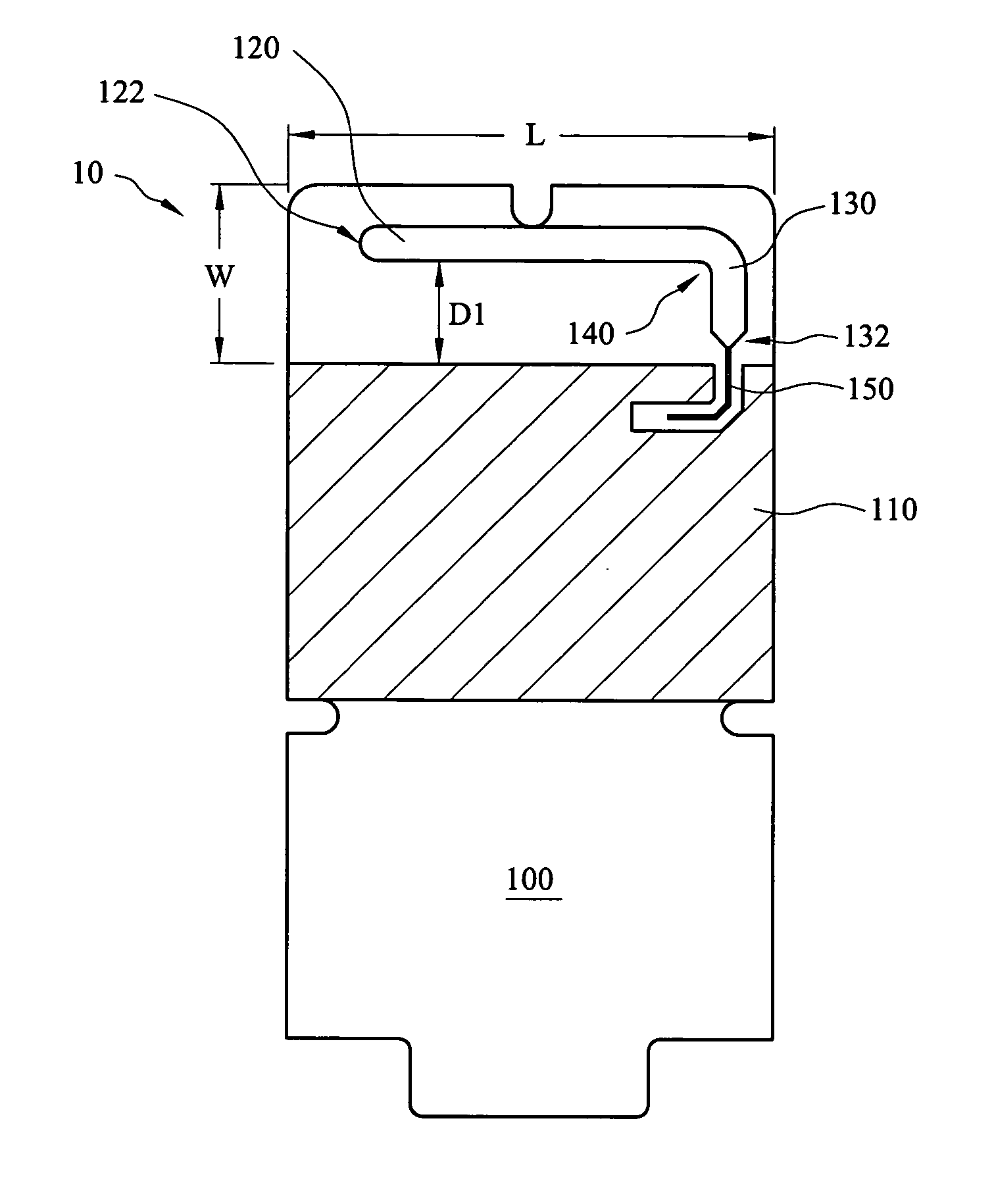
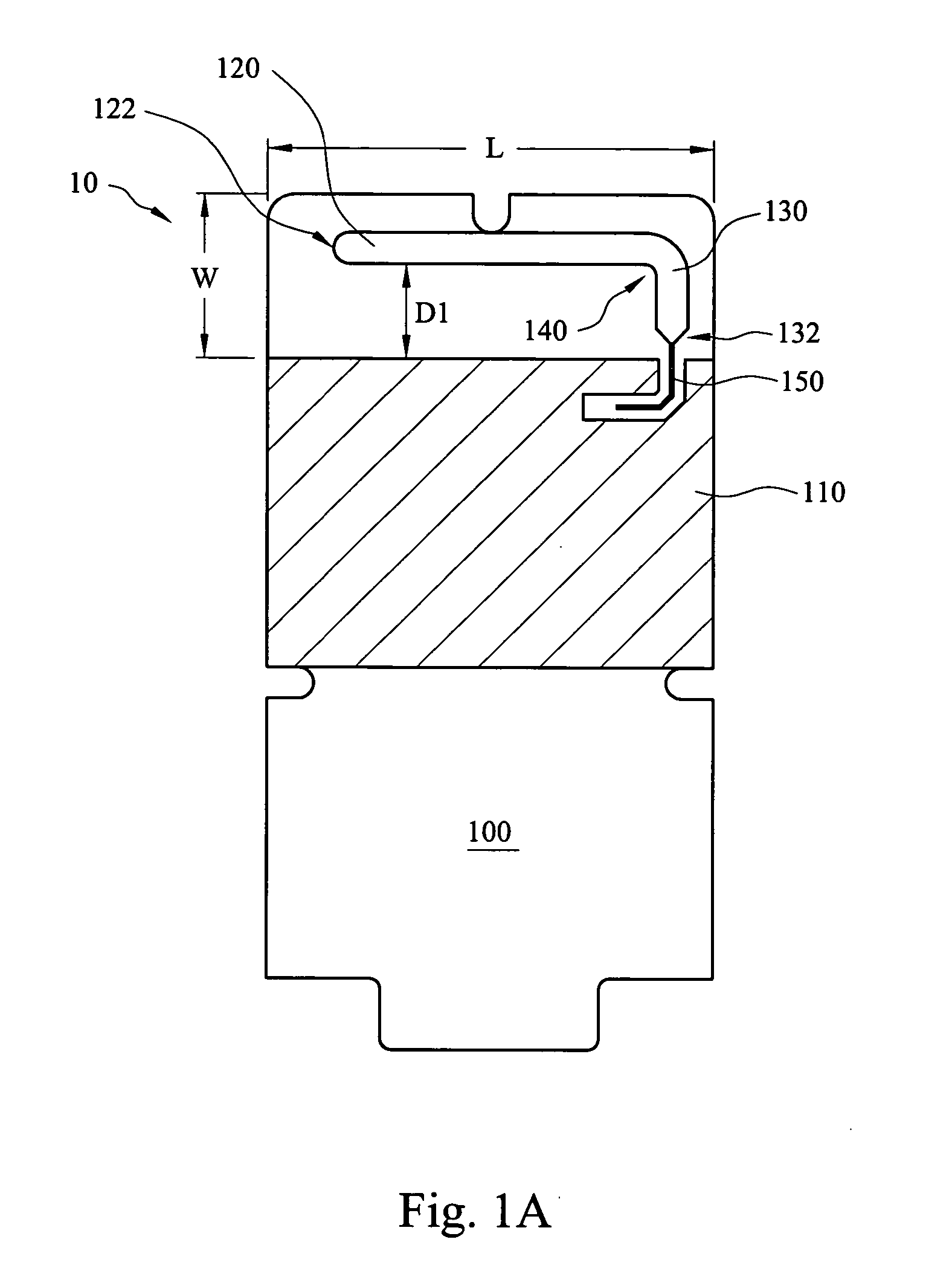
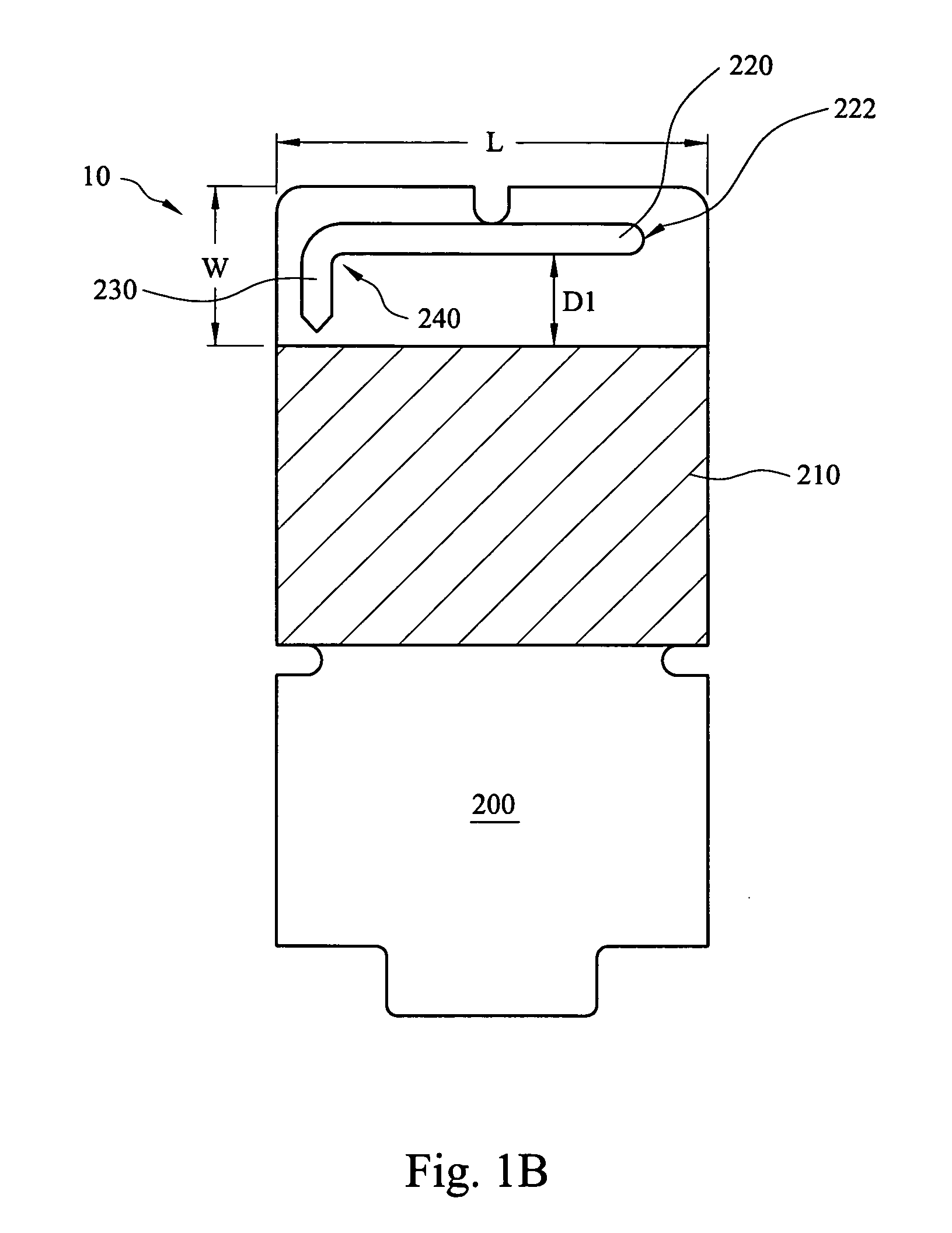
Radial-free collinear omni-directional triband half wavelength antenna with virtual ground, single coaxial cable feedpoint, and with minimal interaction of adjustment between bands
ActiveUS9608336B1Acceptable standing wave ratio (SWR) performanceGood omni-directional RF radiation performanceRadiating elements structural formsAntenna feed intermediatesCoaxial cableIntermediate frequency
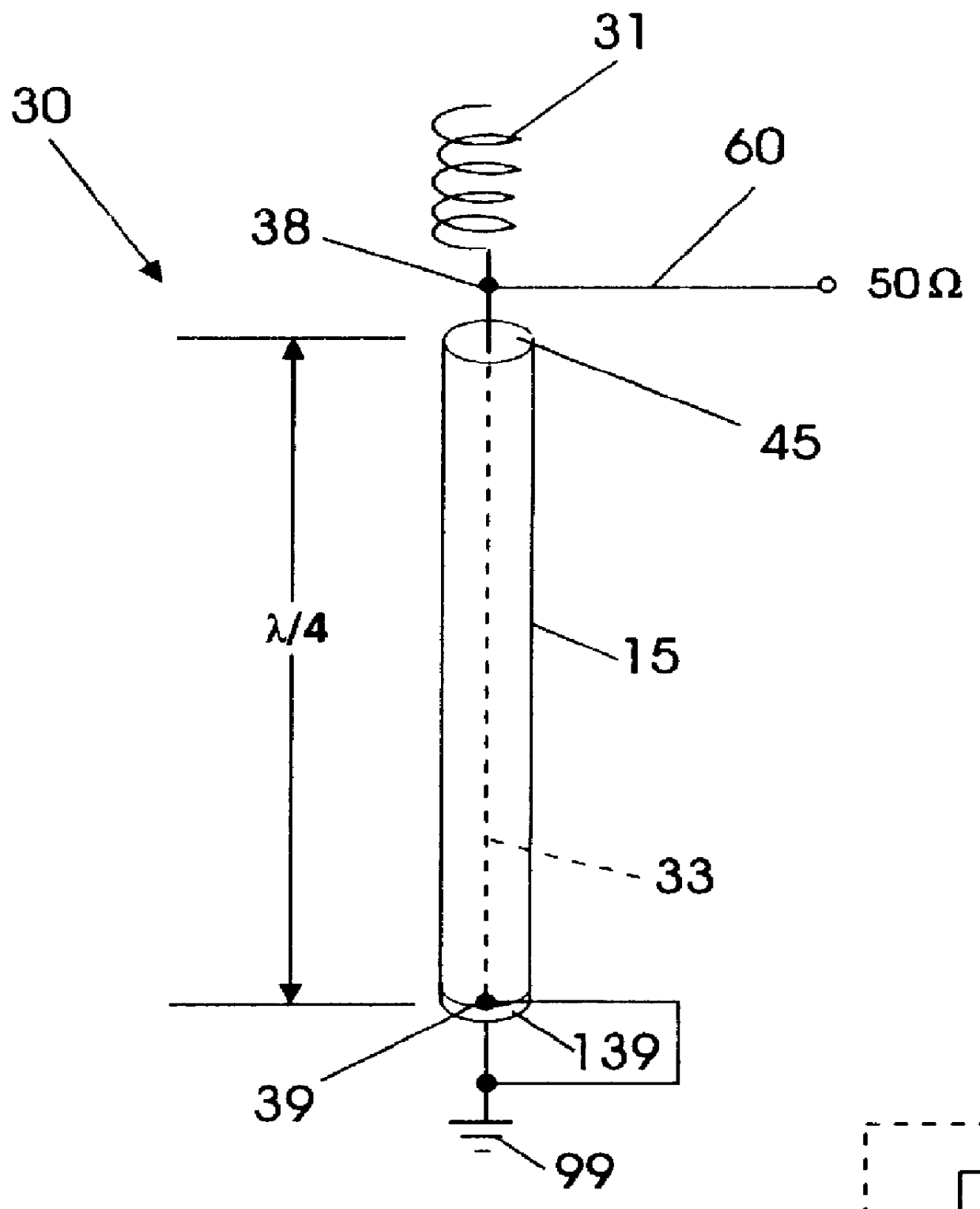
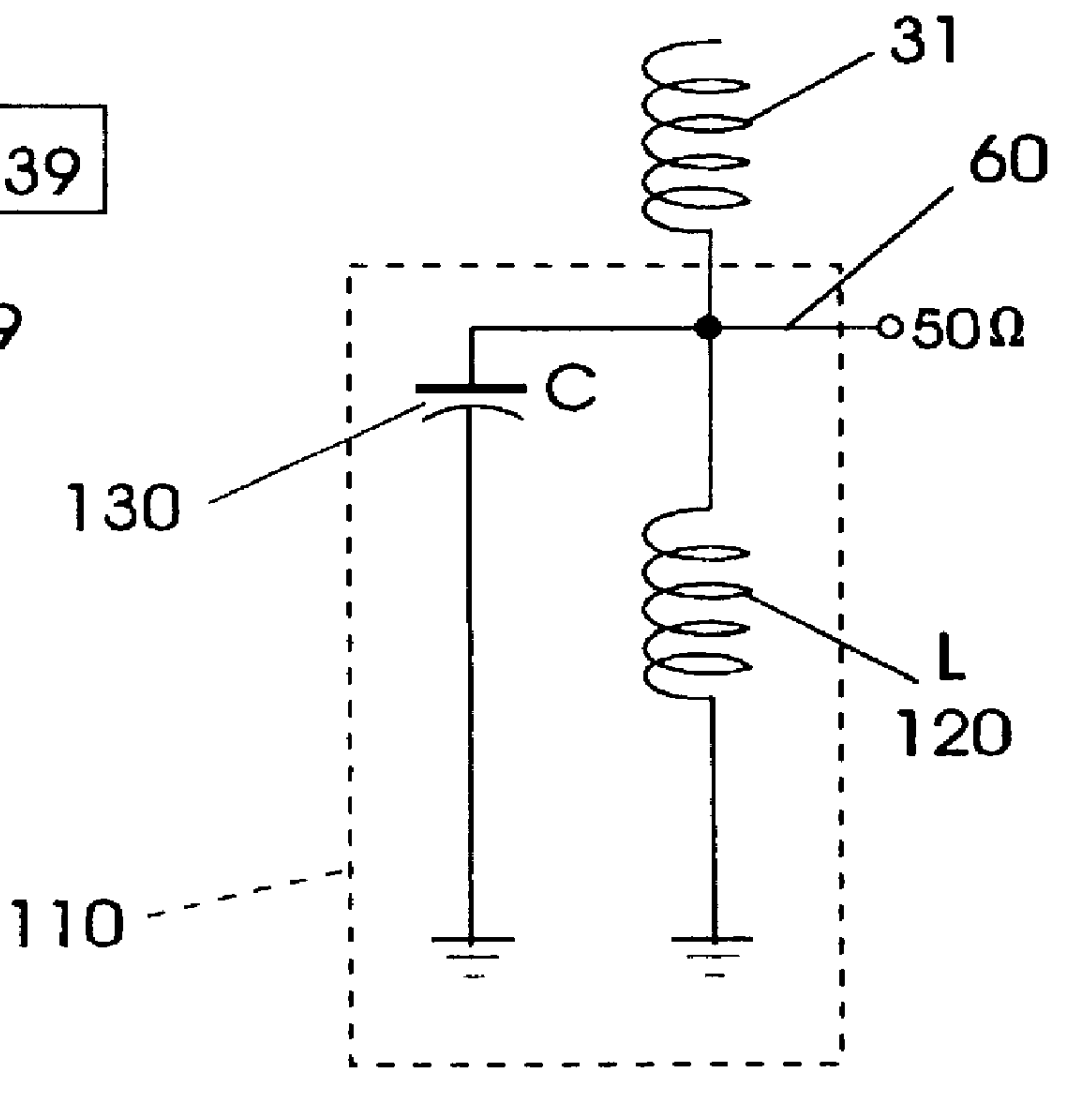
An omni-directional triband antenna operates without ground radials with gain commensurate with a half wavelength vertical on each band. The triband antenna includes a dual-band twinlead J-pole providing half wavelength radiators for UHF and VHF, and an impedance transformer defining feedpoints to which a length Lc of coaxial cable is attached. The Lc lower end is the triband antenna connector port. Intermediate band radiators are first and second wire elements that collectively are a half-wavelength at the intermediate band. The first element is wound helically about the impedance transformer, with upper end floating and lower end connected to a first feedpoint. The second element is wound helically about the Lc upper portion of coaxial cable, with upper end connected to the remaining feedpoint, and lower end of the element floating. The helical windings radiate vertically and there is no cross-interference between antenna radiation in any of the three bands.
Owner:FONG EDISON
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com