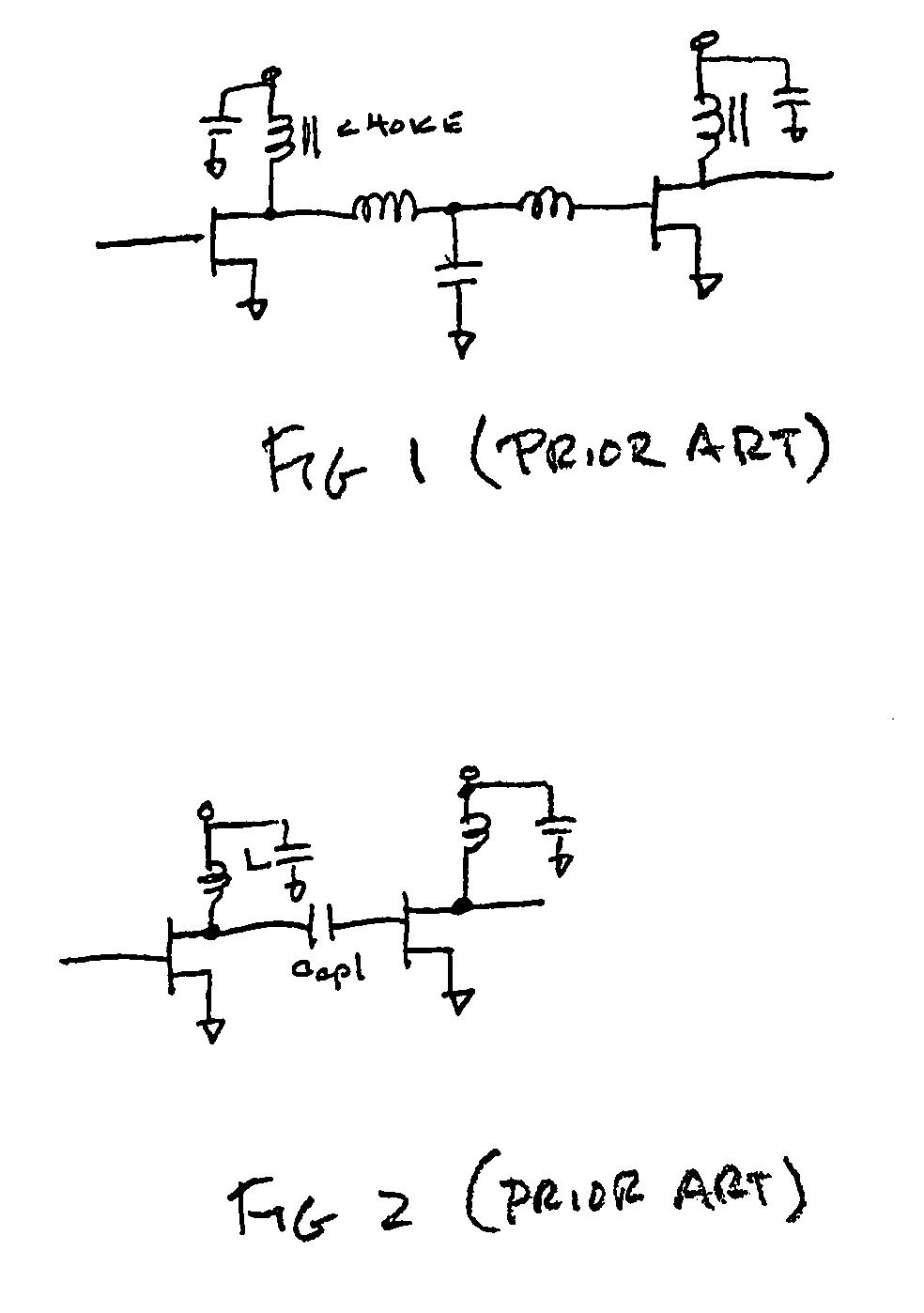
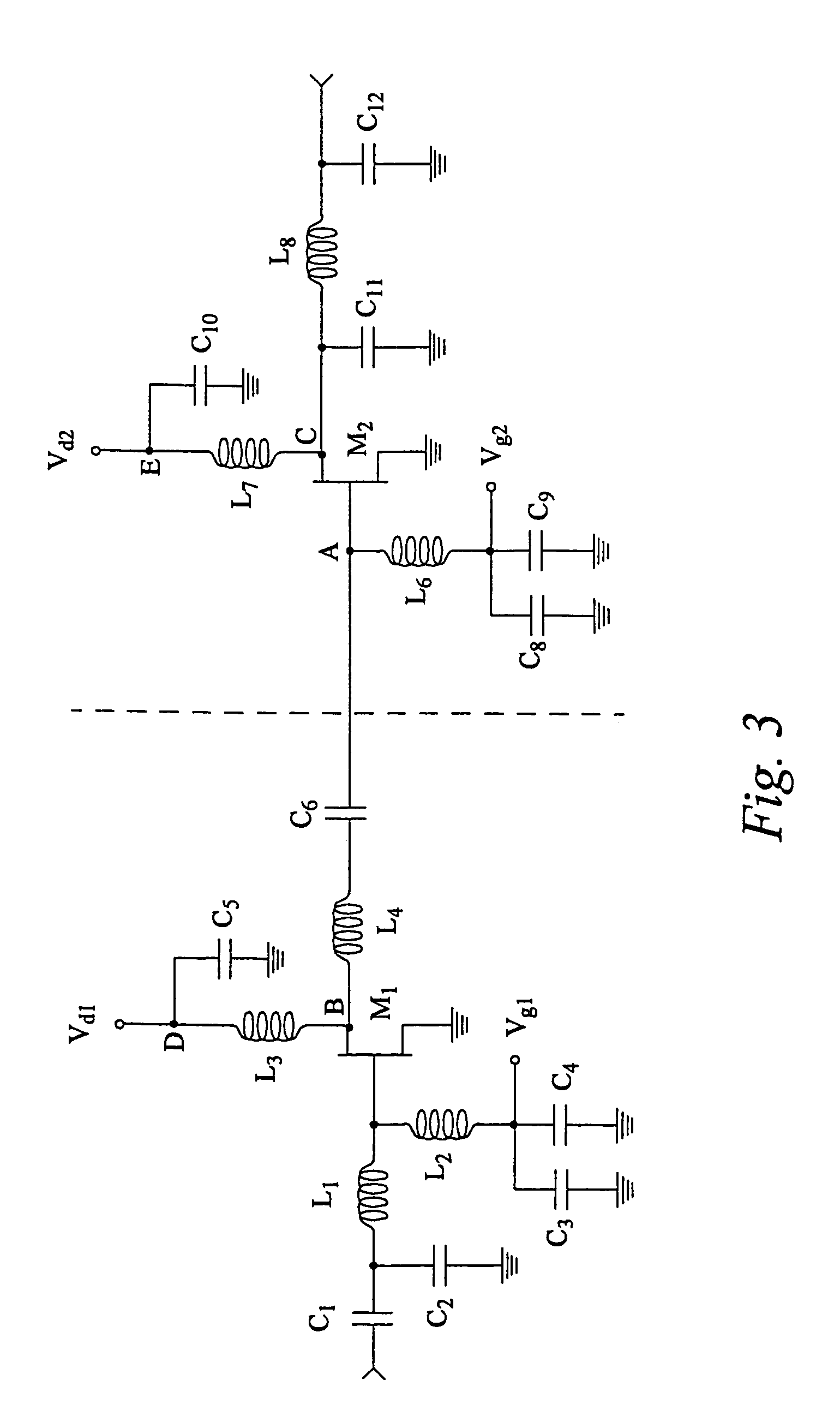Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
158 results about "Driver amplifier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
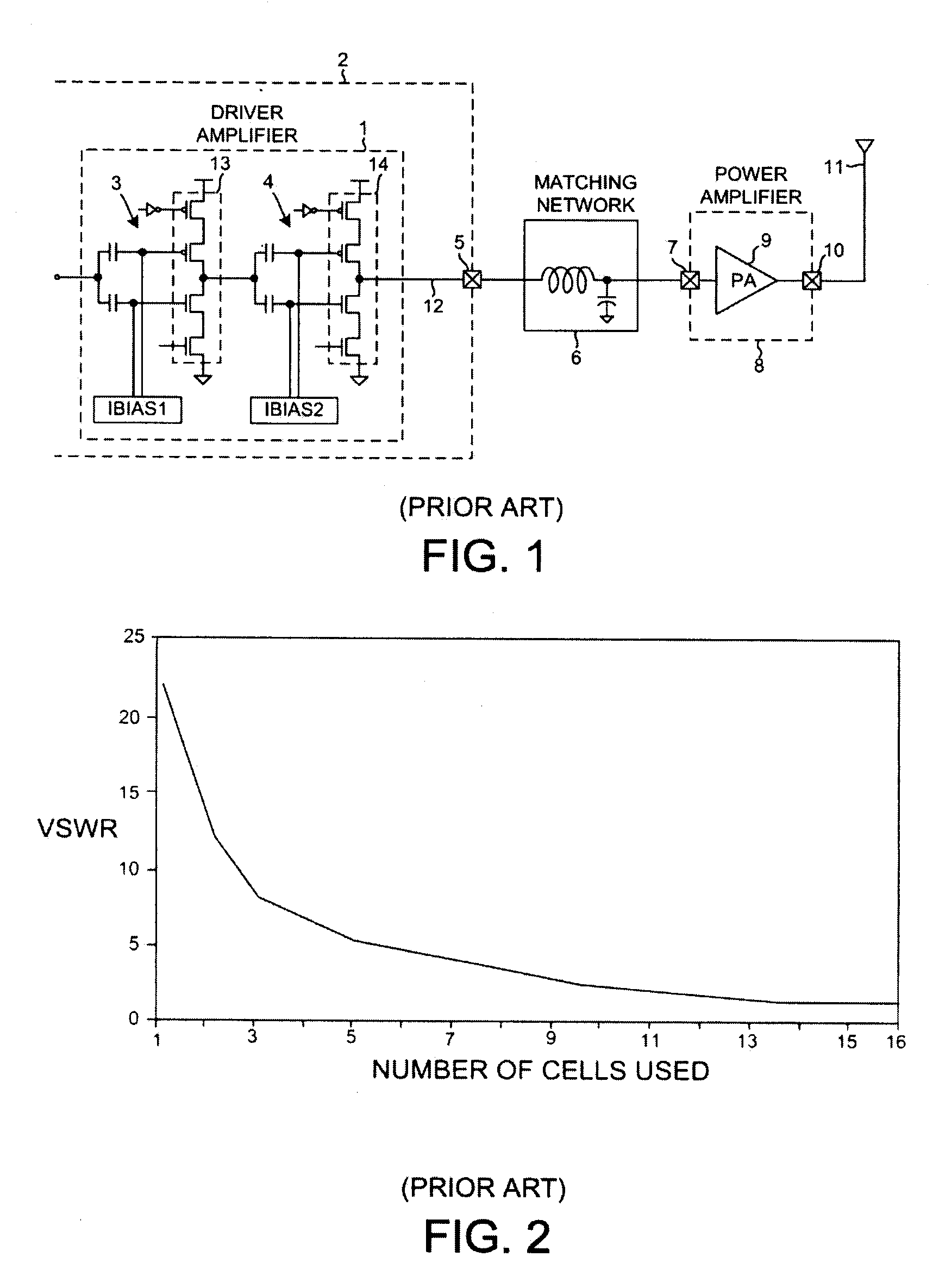
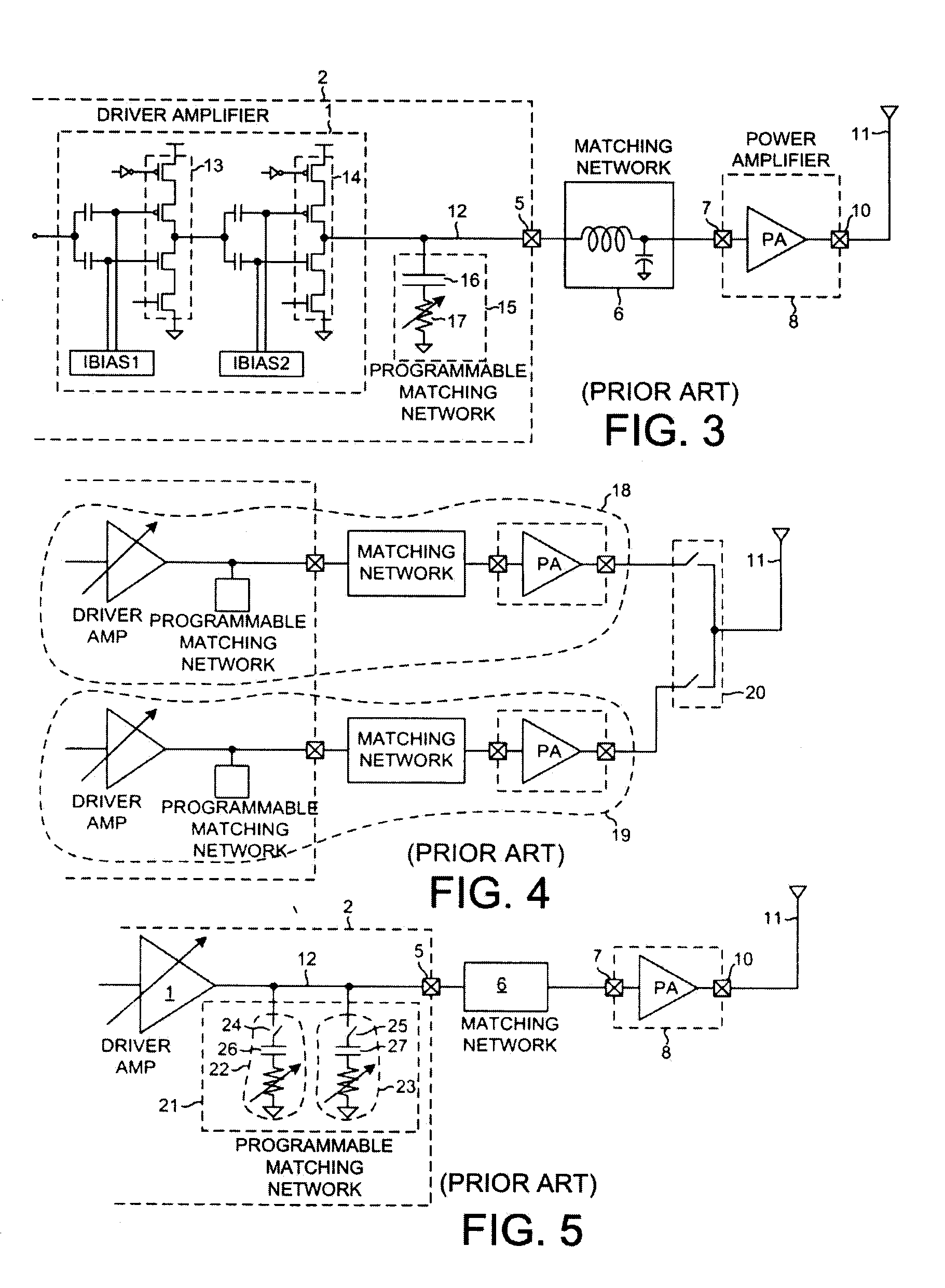
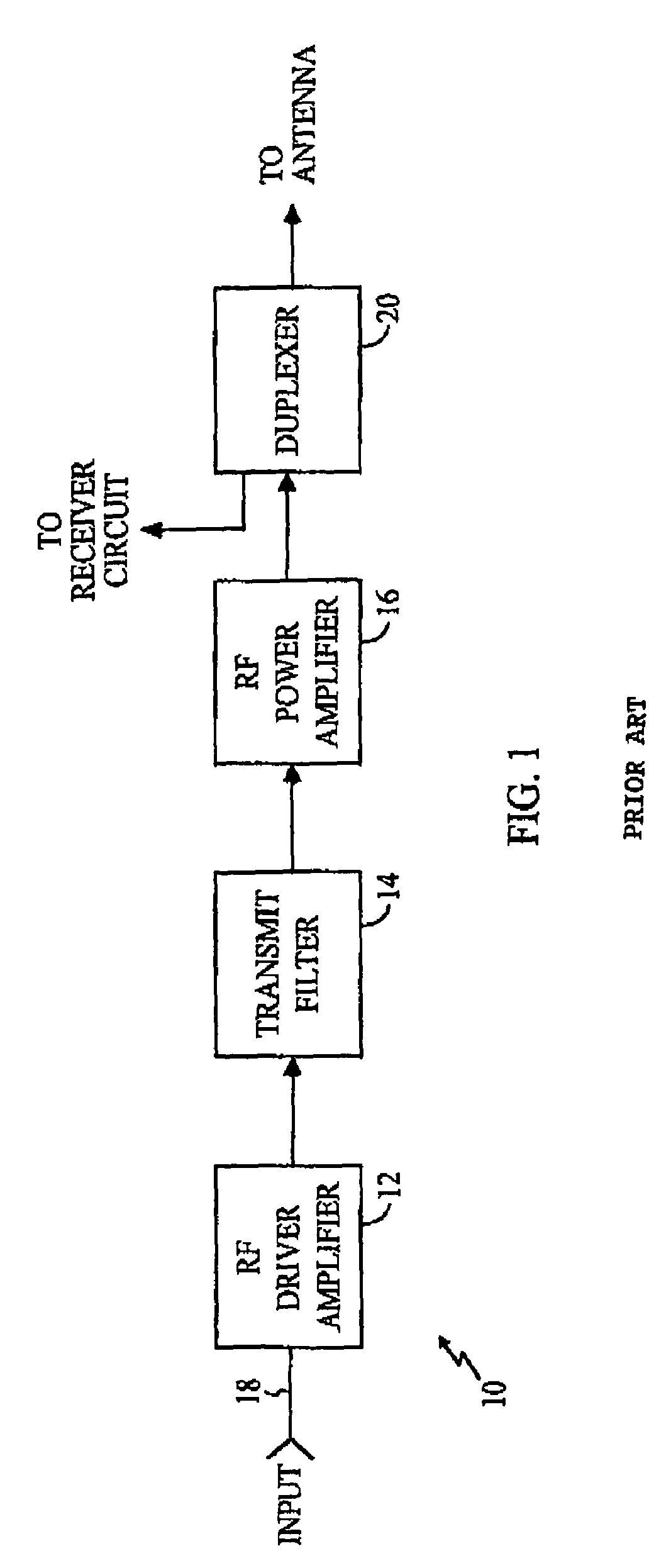
What is a driver amplifier In my opinion, a driver amplifier can be simply considered as a driver (to amplify power) that is capable of providing sufficient current (power) to drive the following stage of the circuit.
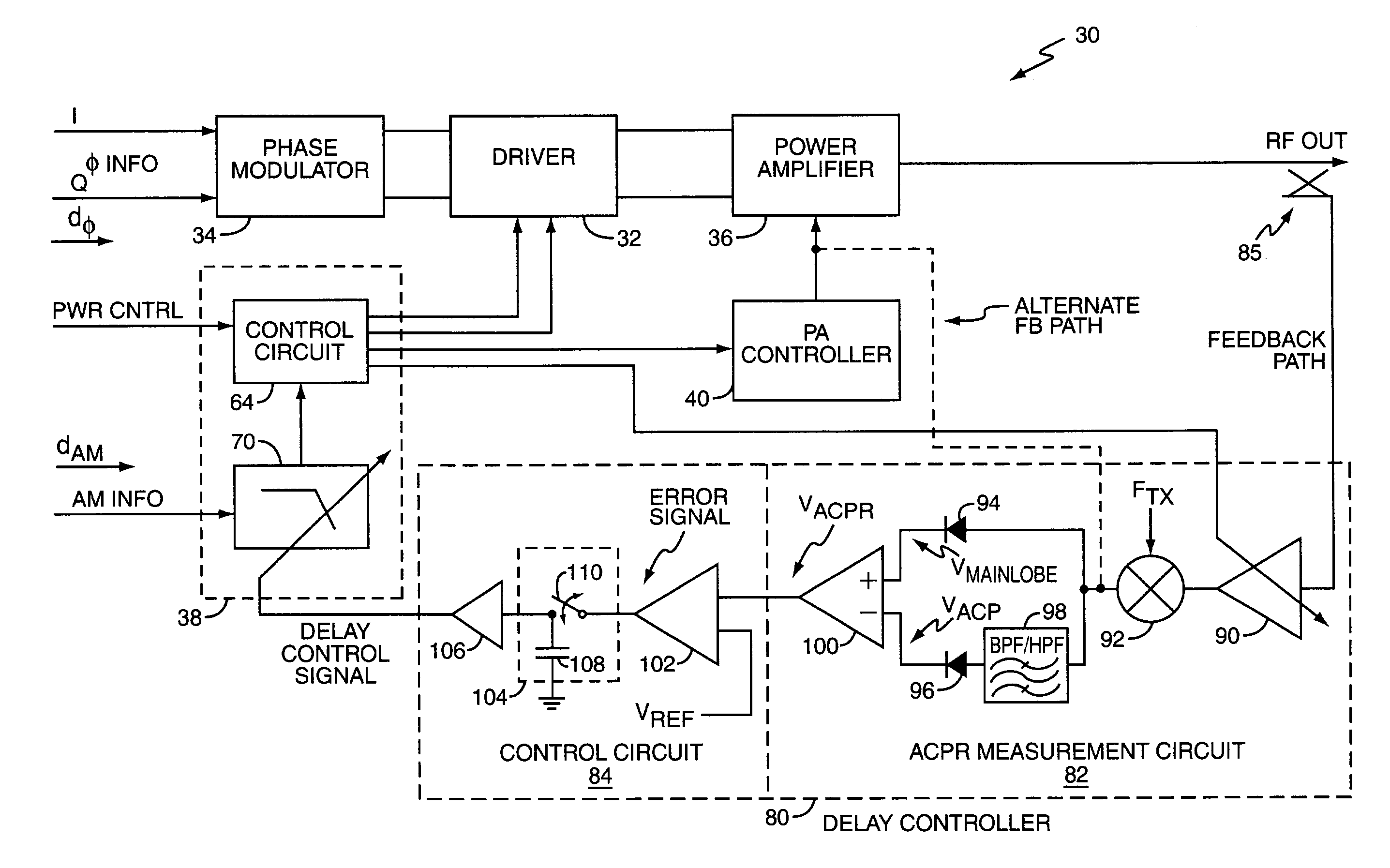
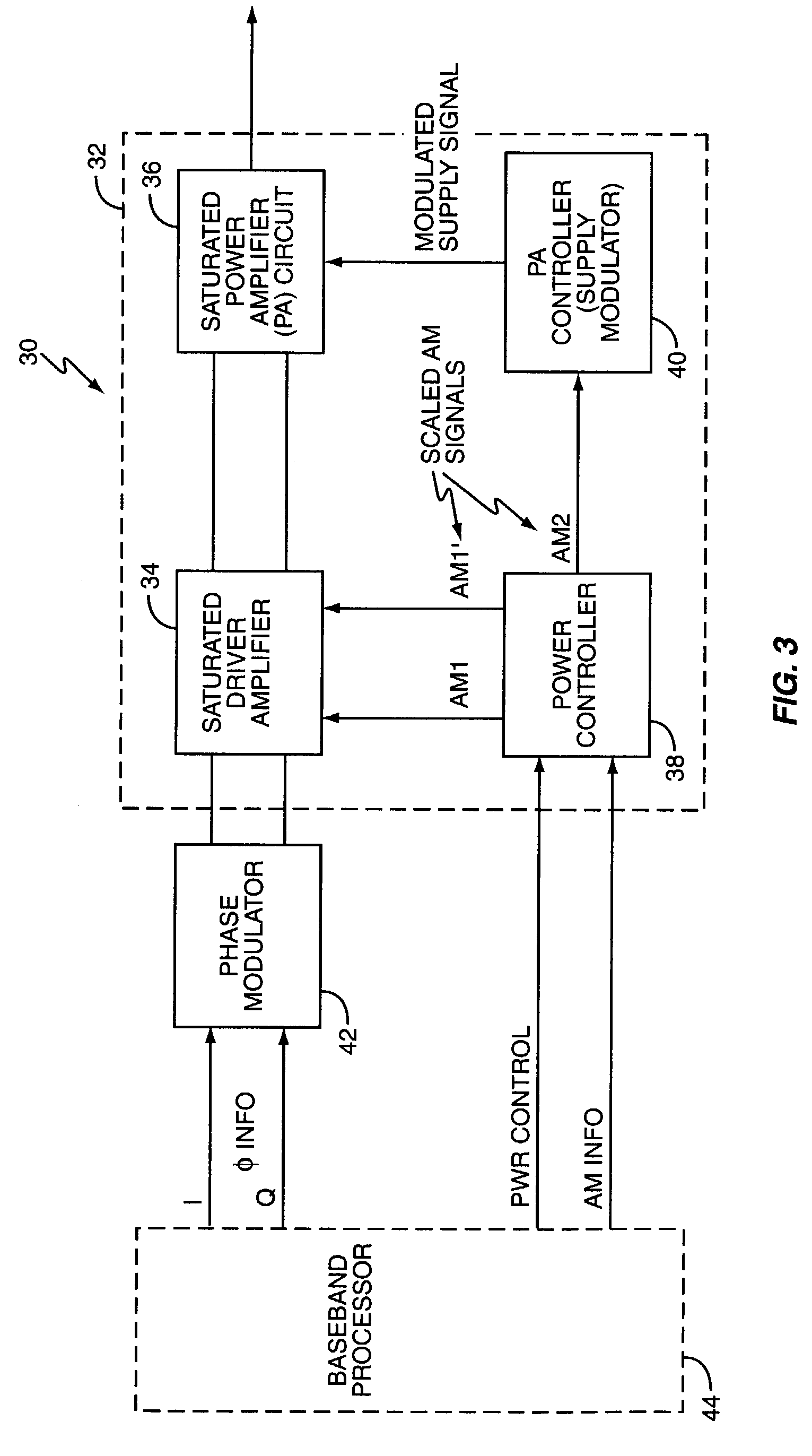
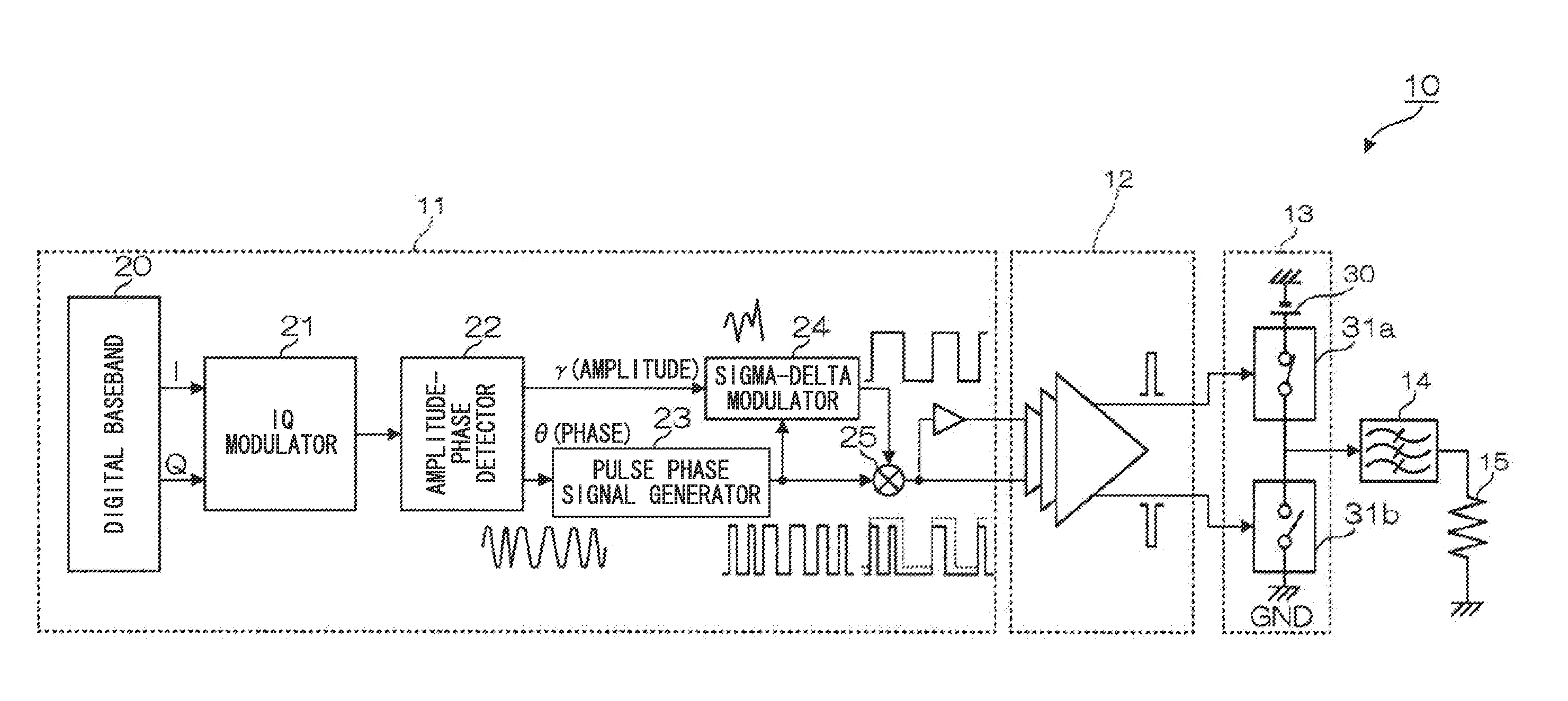
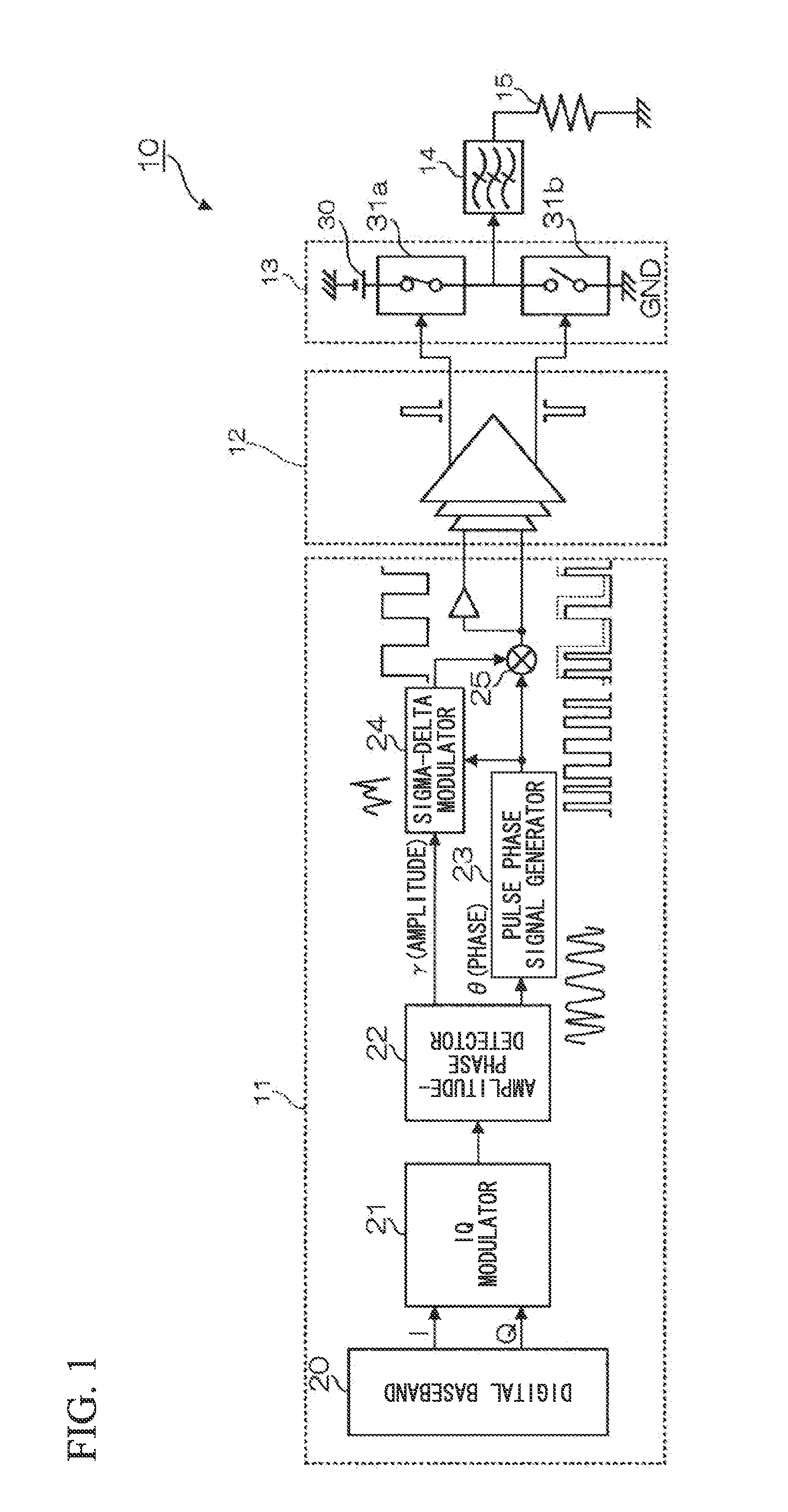
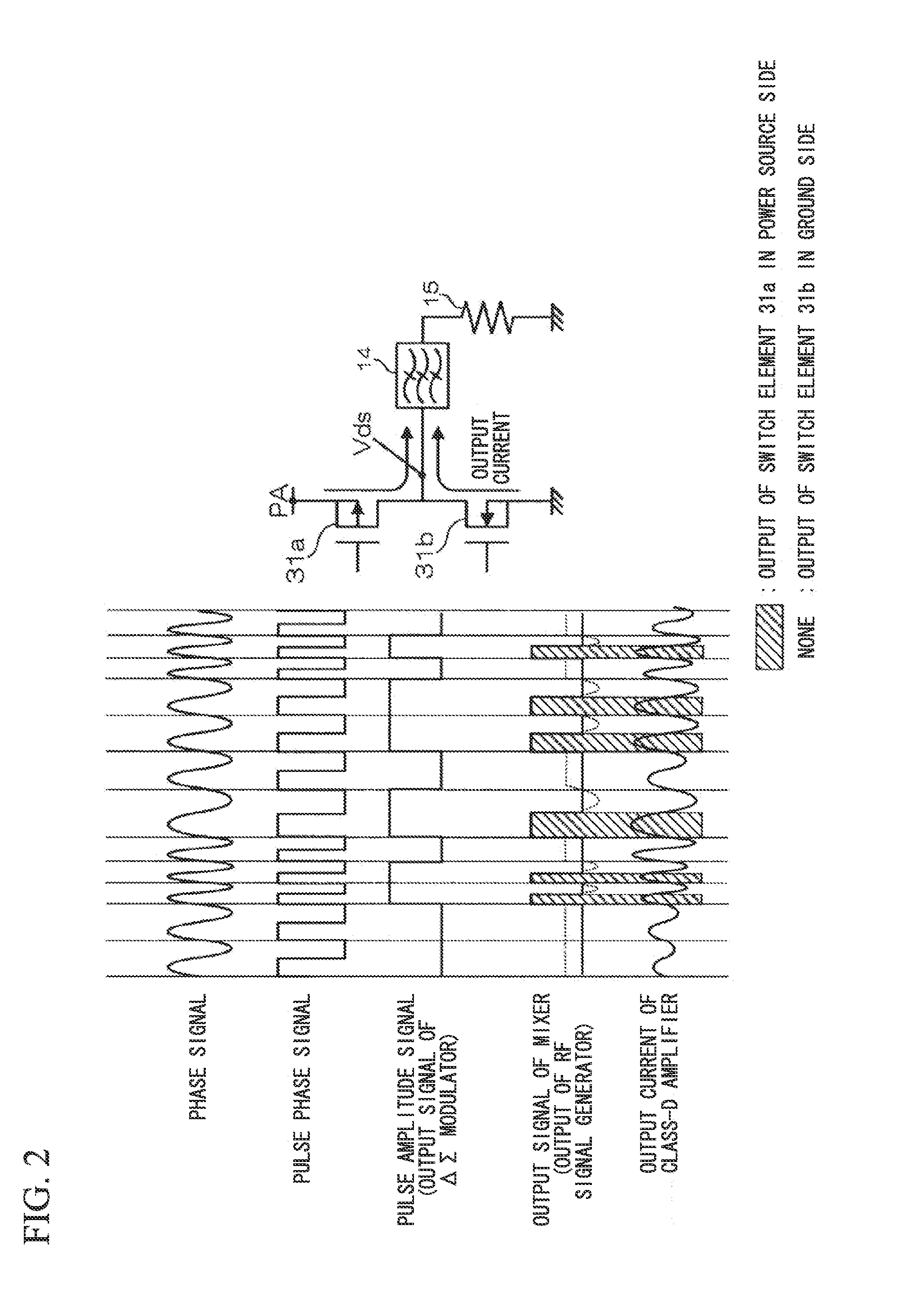
Polar modulation transmitter
ActiveUS7072626B2Improve performanceReduce ratio of average powerResonant long antennasPower amplifiersTransceiverAudio power amplifier
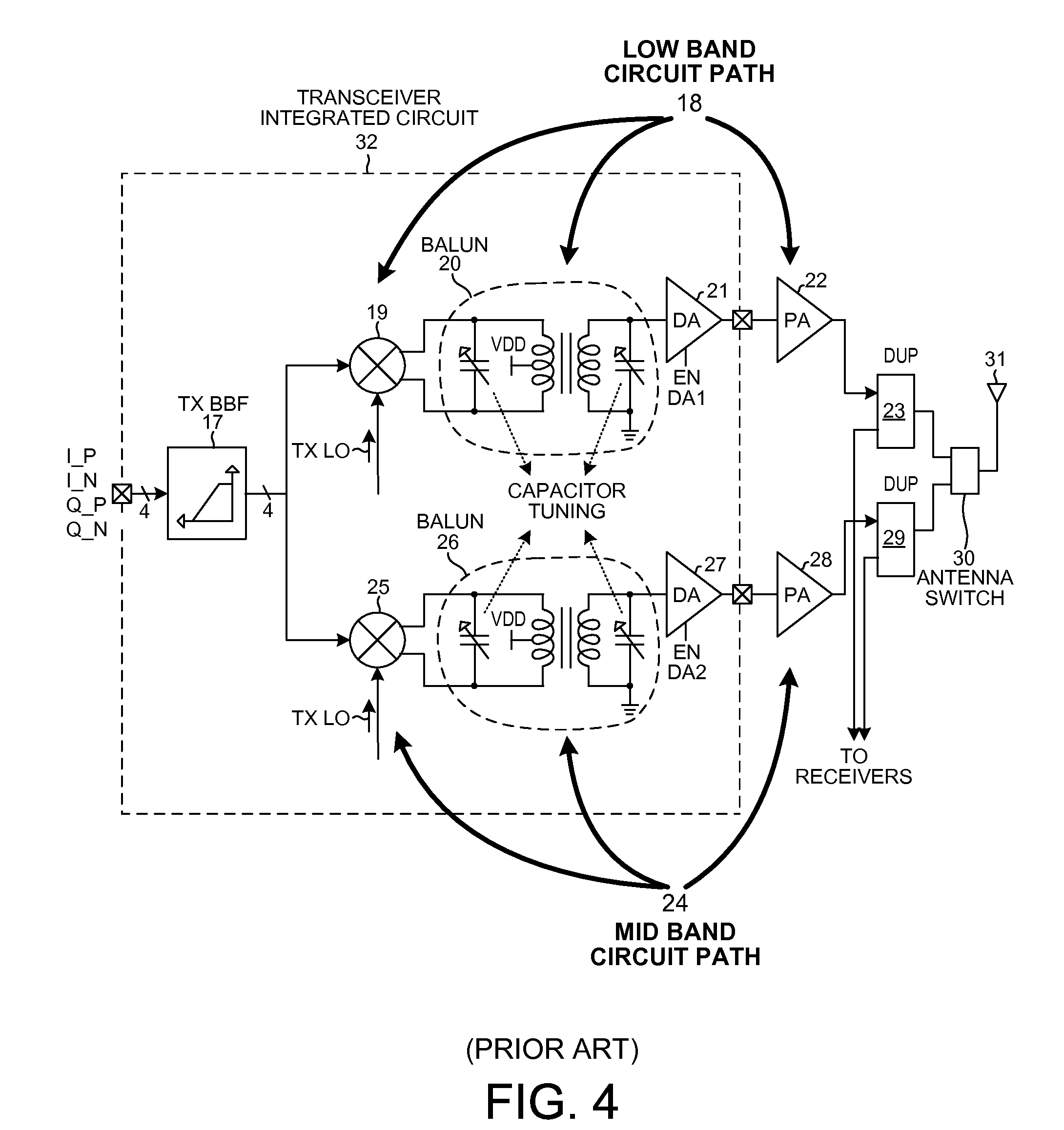
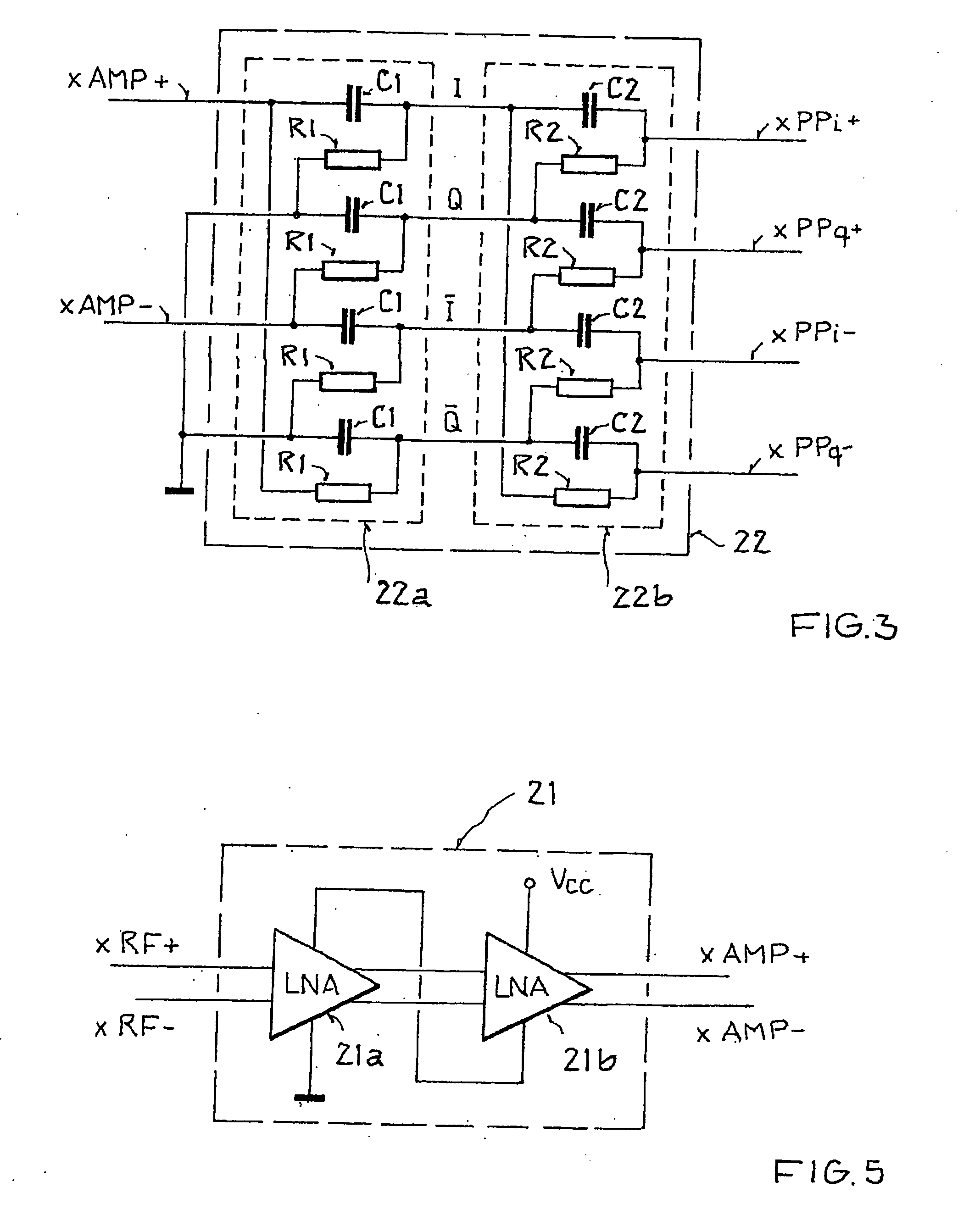
A polar modulation transmitter circuit provides reduced ACPR in its output signal by controlling the relative delay between its envelope and phase modulation operations based on direct or indirect feedback measurement the output signal's ACPR. Such measurement and associated control may be based on a delay controller that includes an ACPR measurement circuit and a delay control circuit. Additionally, or alternatively, the polar modulation transmitter circuit provides a greatly extended transmit power control range by using a staged amplifier circuit that includes a driver amplifier circuit operating in combination with a power amplifier circuit to impart desired envelope modulation. In an exemplary embodiment, the driver amplifier circuit is implemented as differential transistor pairs responsive to tail current modulation. As such, the driver amplifier circuit is suited in particular for economical and space saving integration within a transmitter or transceiver integrated circuit (IC).
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
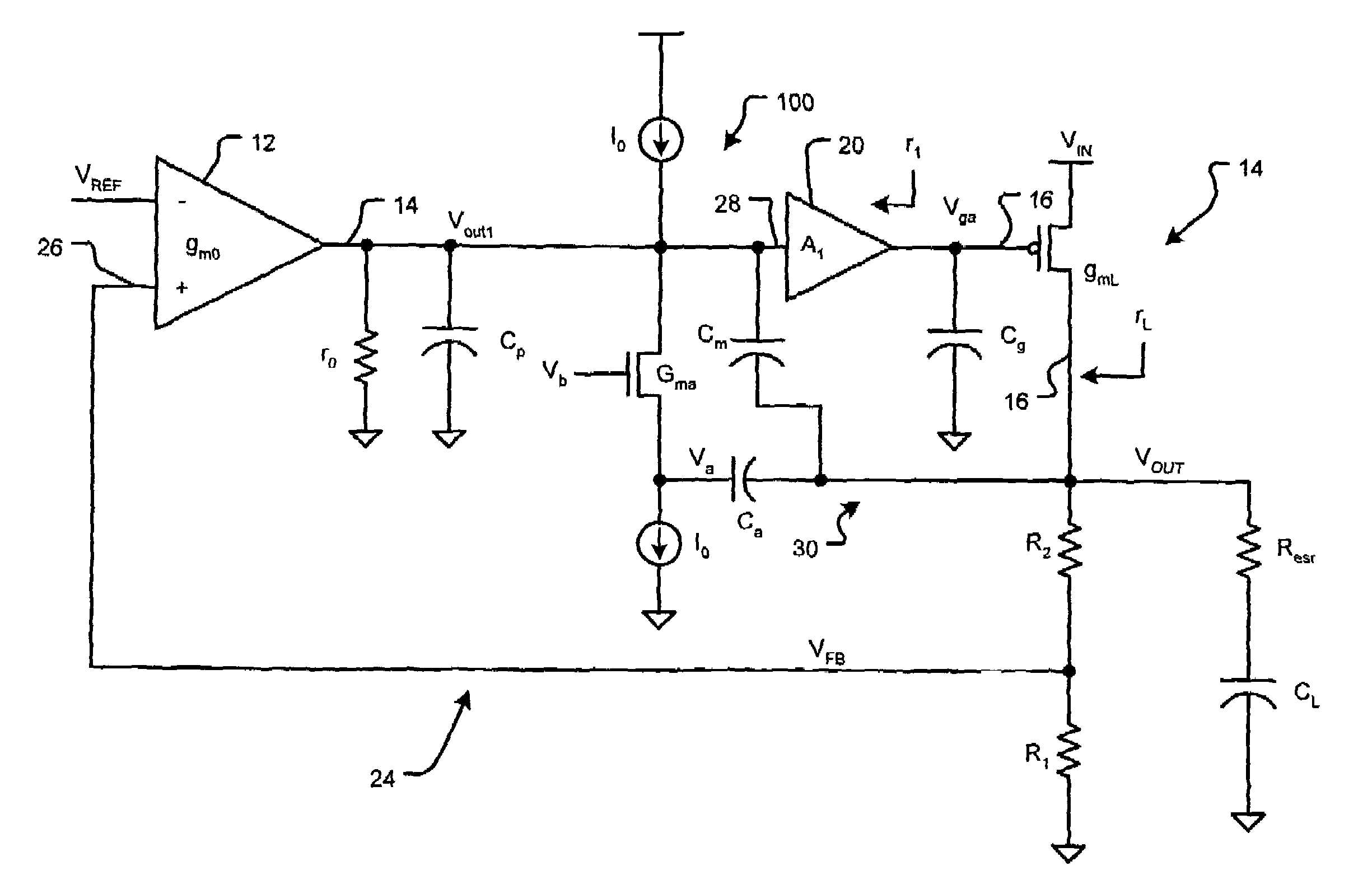
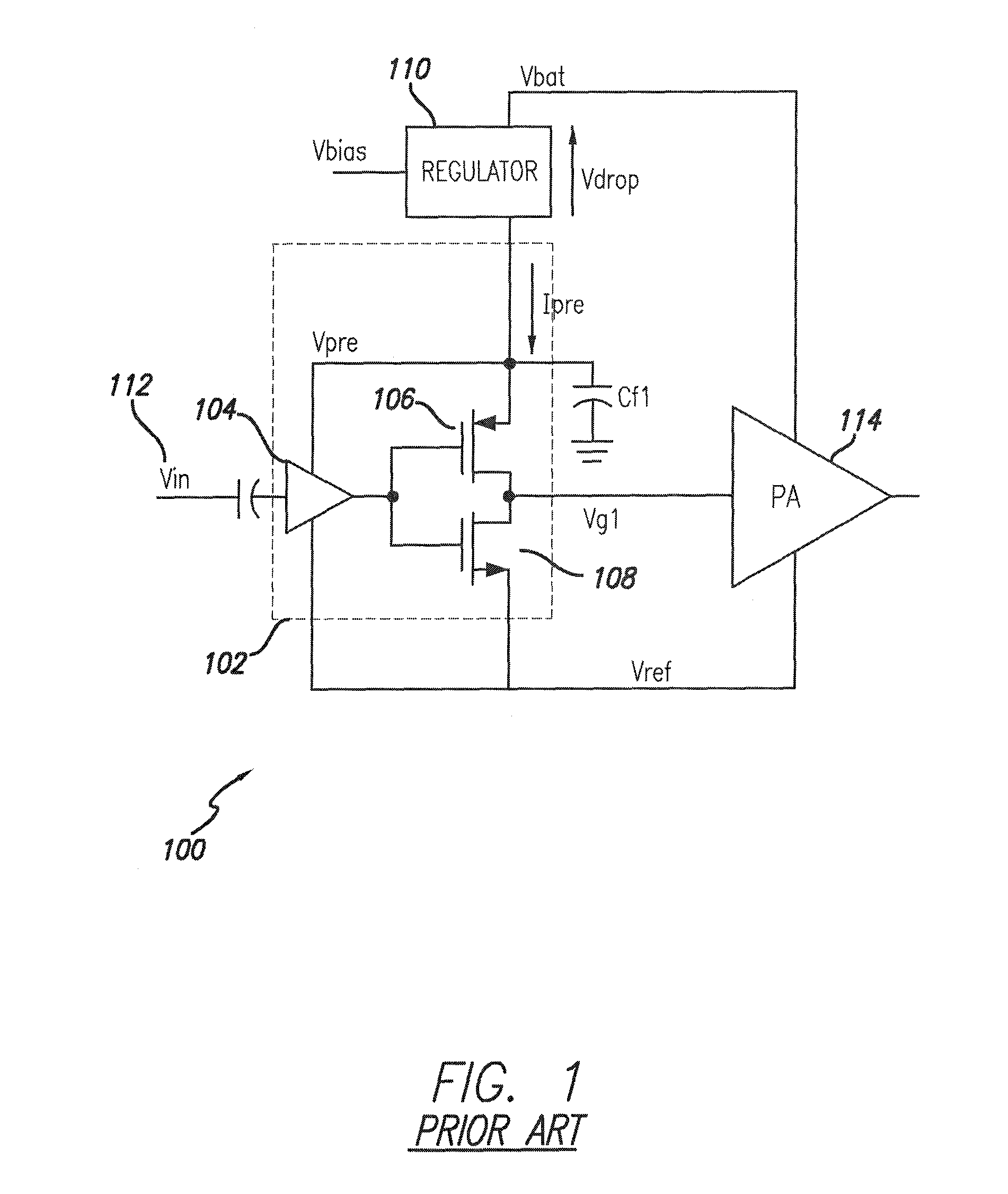
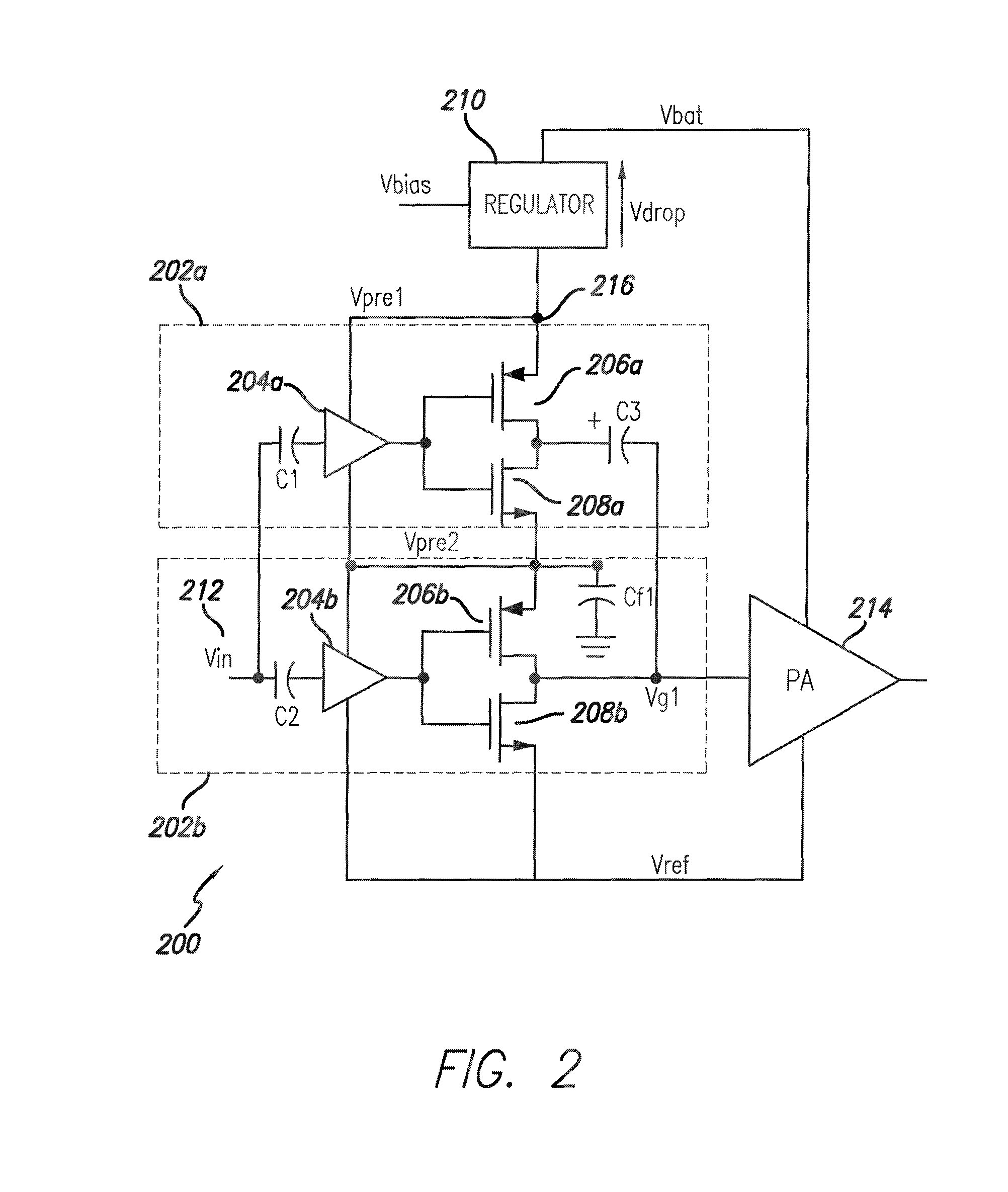
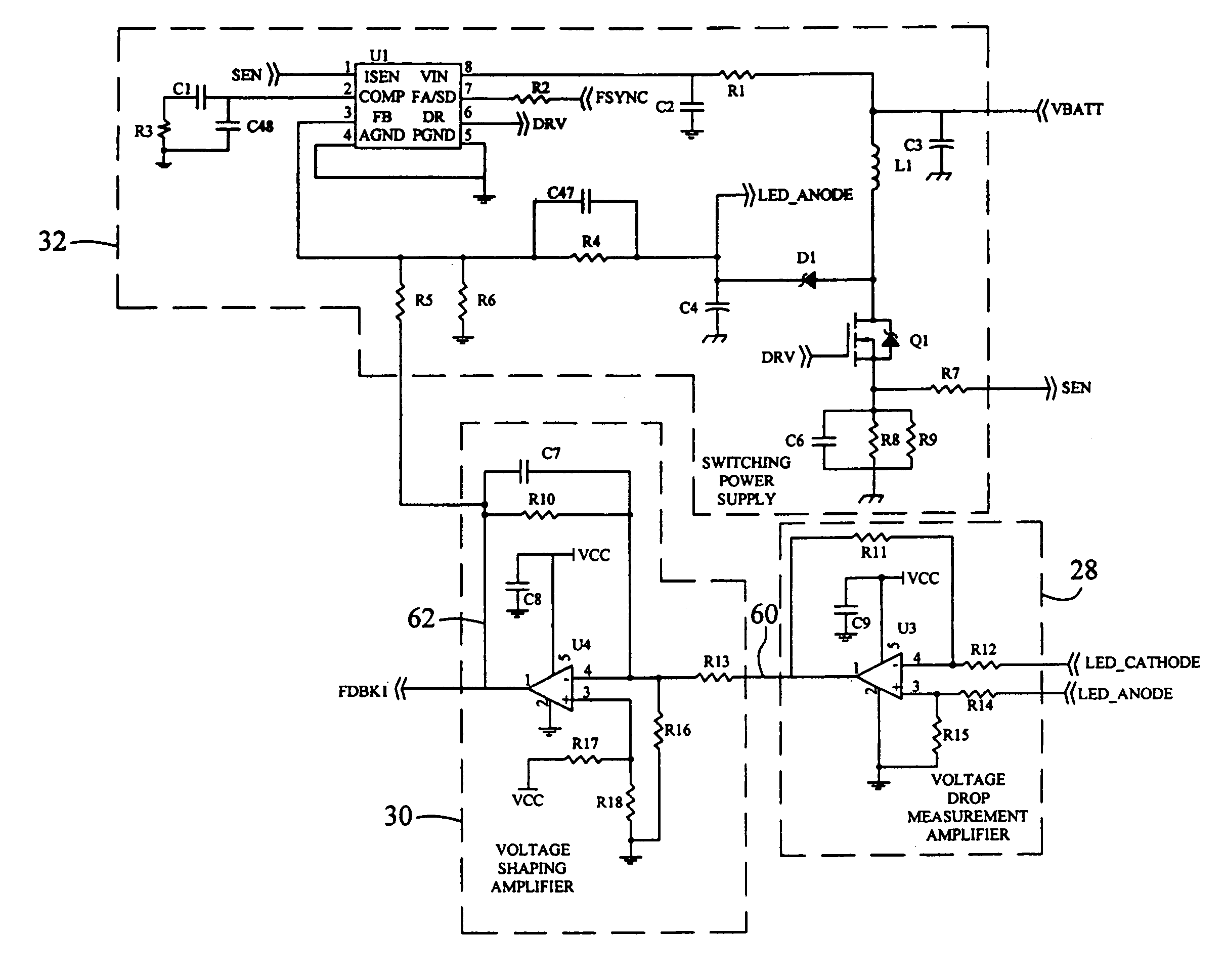
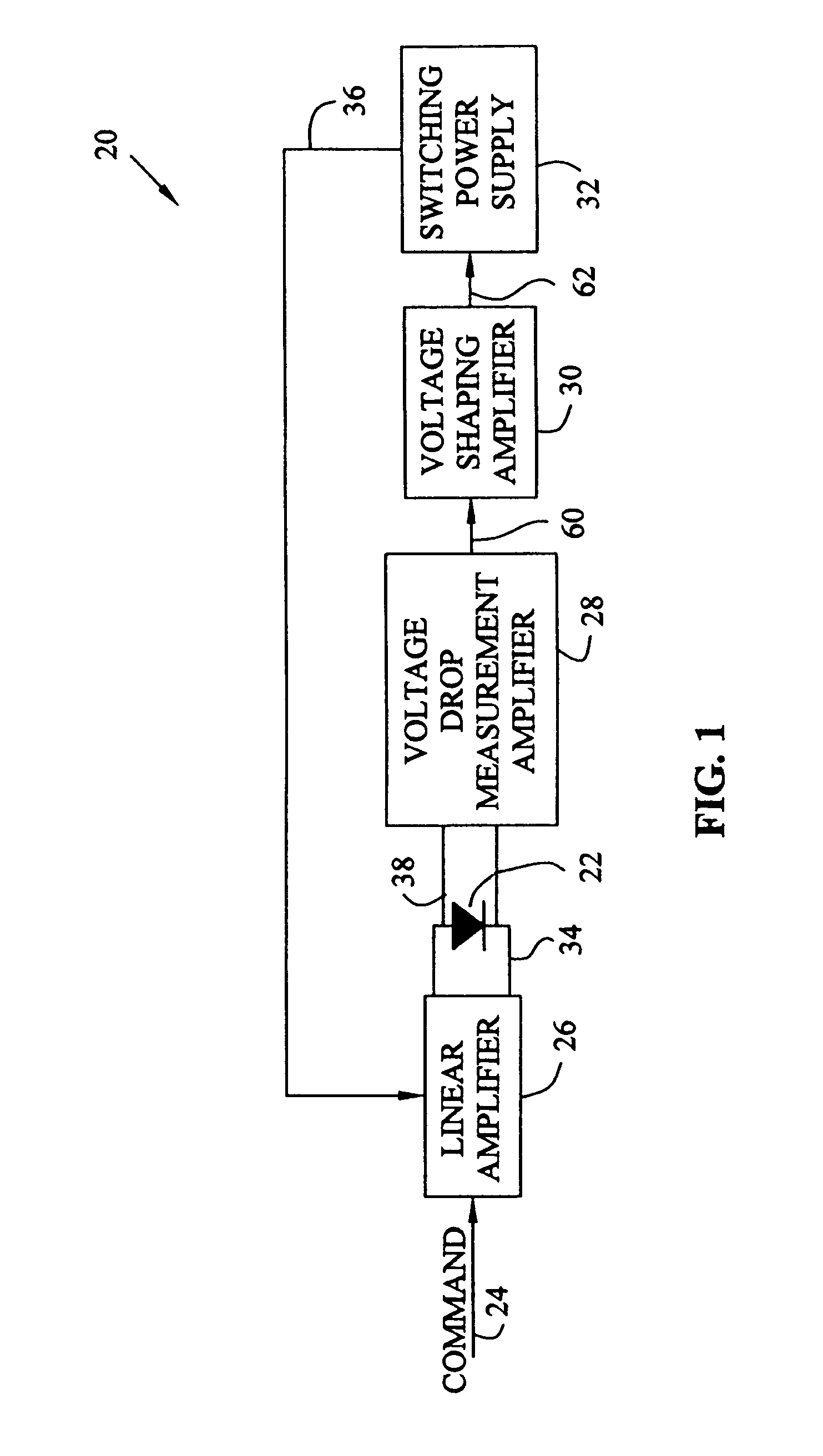
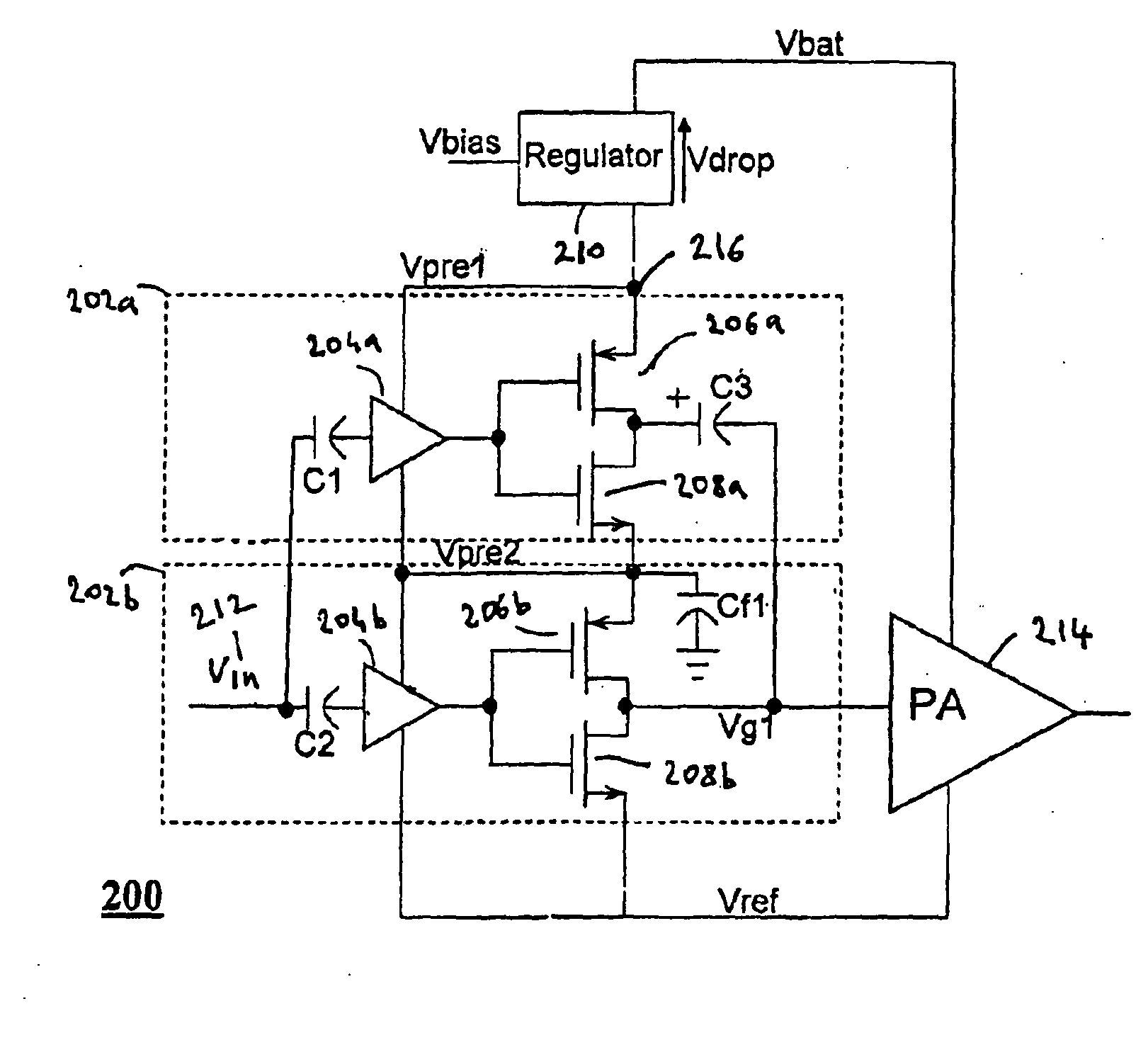
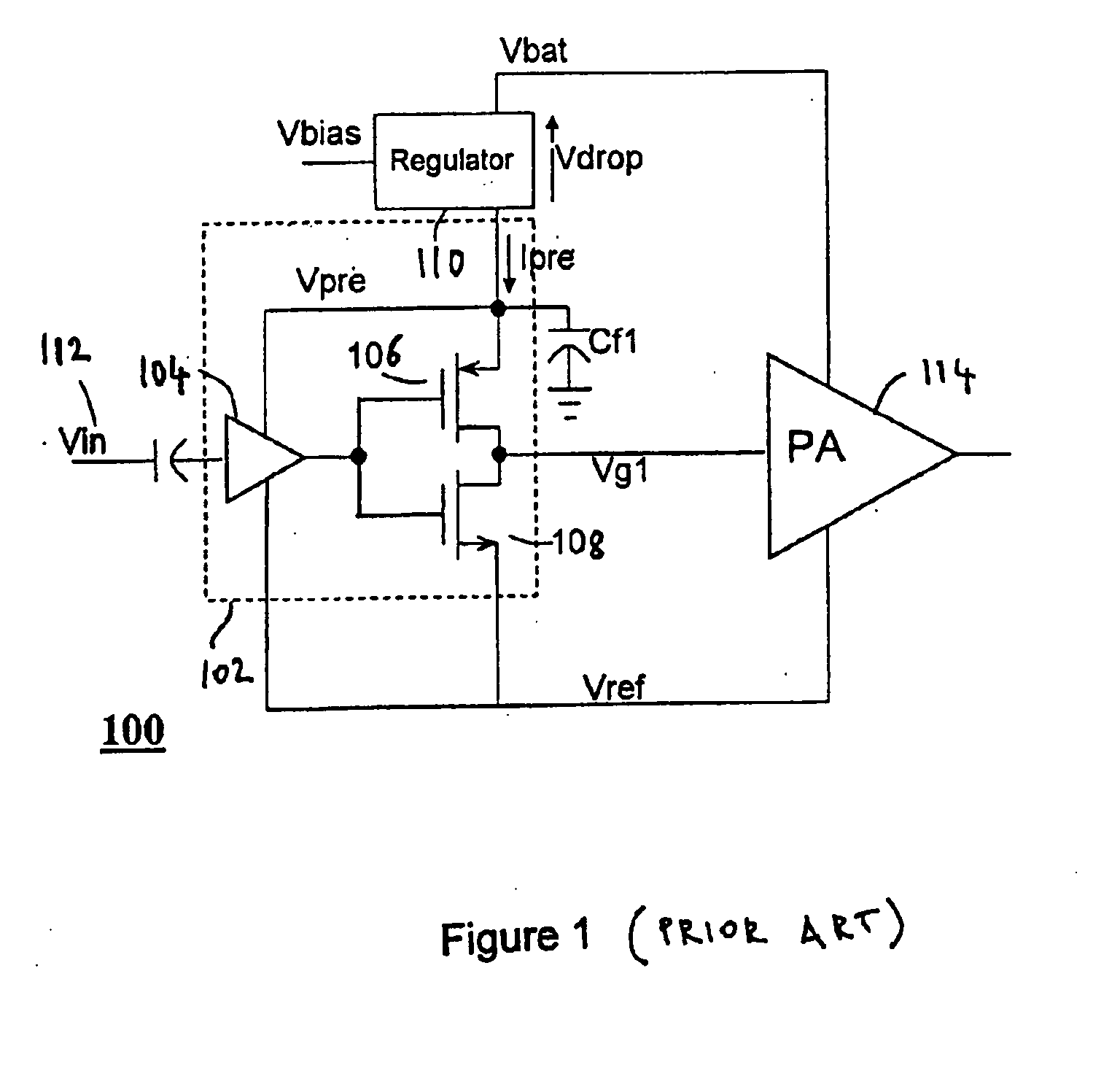
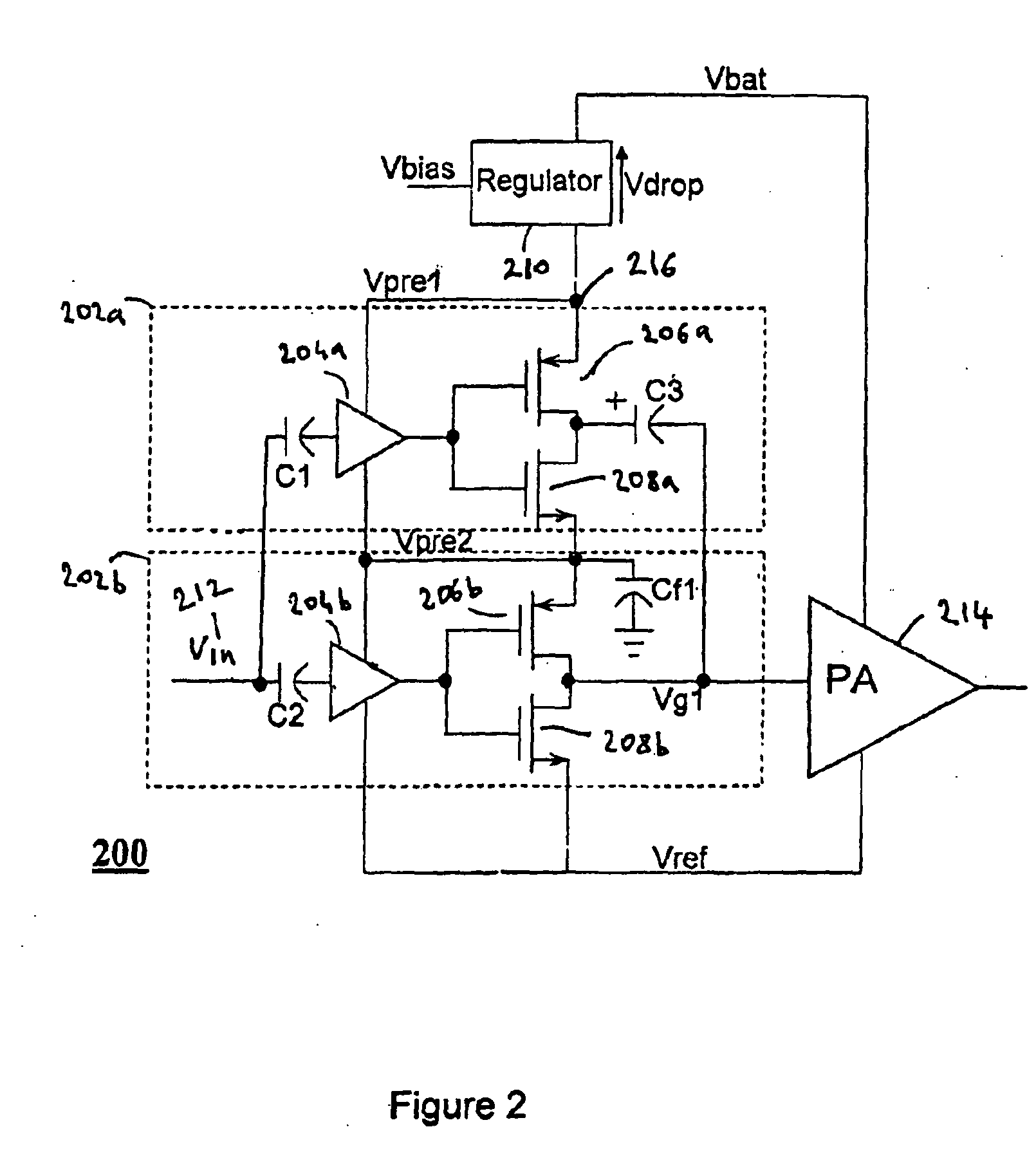
Compensation for low drop out voltage regulator
ActiveUS6977490B1High gainDesign moreElectric variable regulationAudio power amplifierVoltage regulation
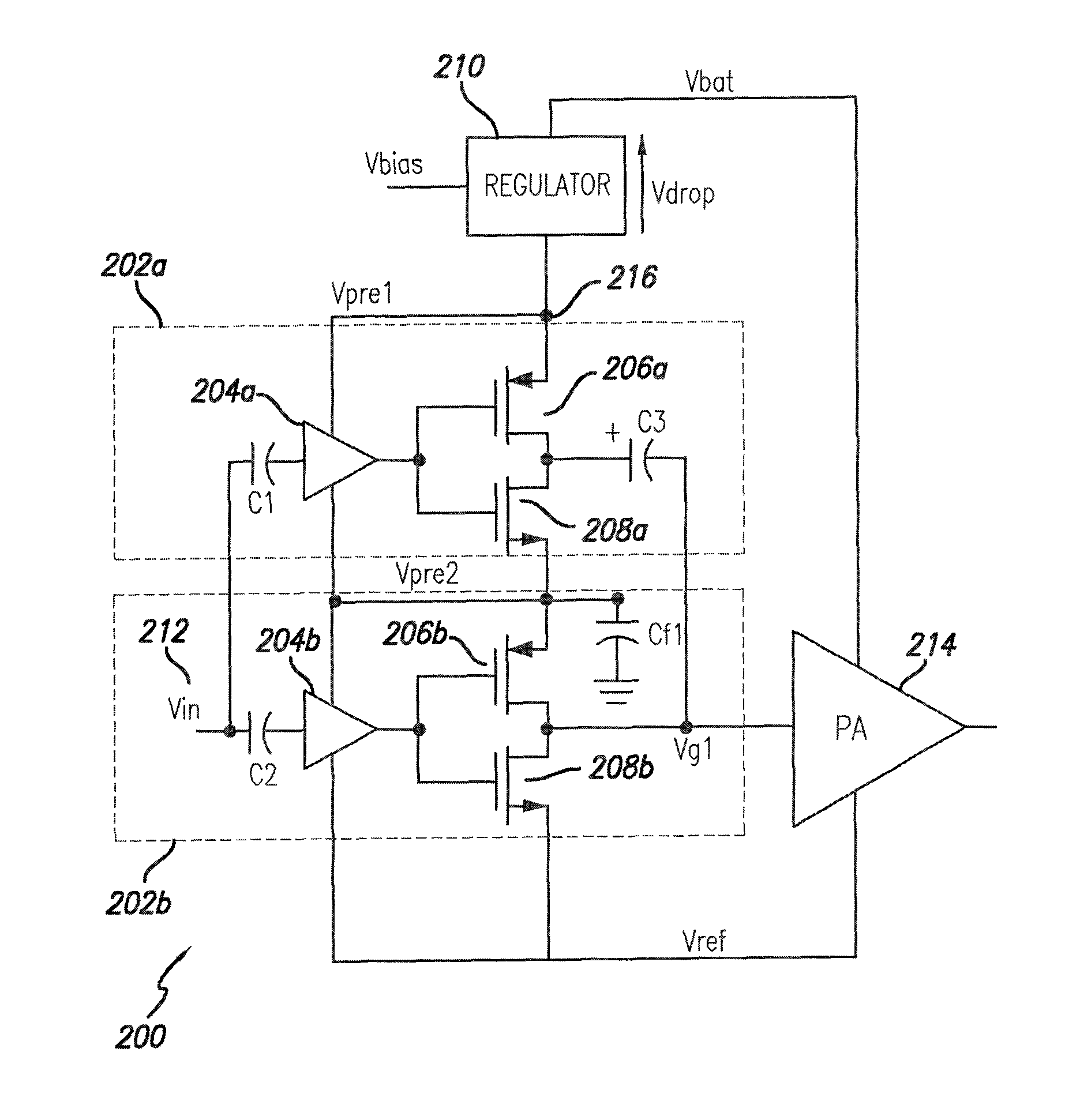
A voltage regulator apparatus includes an error amplifier that amplifies a voltage difference between a reference and a sampled output voltage of the voltage regulator apparatus. A driver amplifier has an input that is responsive to the amplified voltage difference to produce a gate driving voltage at its output. An output transistor having a drain, a gate, and a source is also included. The gate is responsive to the gate driving voltage to produce a regulated output voltage at the source. To stabilize the voltage regulator apparatus, a Miller compensation capacitor is provided to feed a sample of the regulated output voltage back to the input of the driver amplifier; and additionally, an Ahuja compensation circuit is provided to feed back a portion of the regulated output voltage back to the input of the driver amplifier.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Directional acoustic alerting system
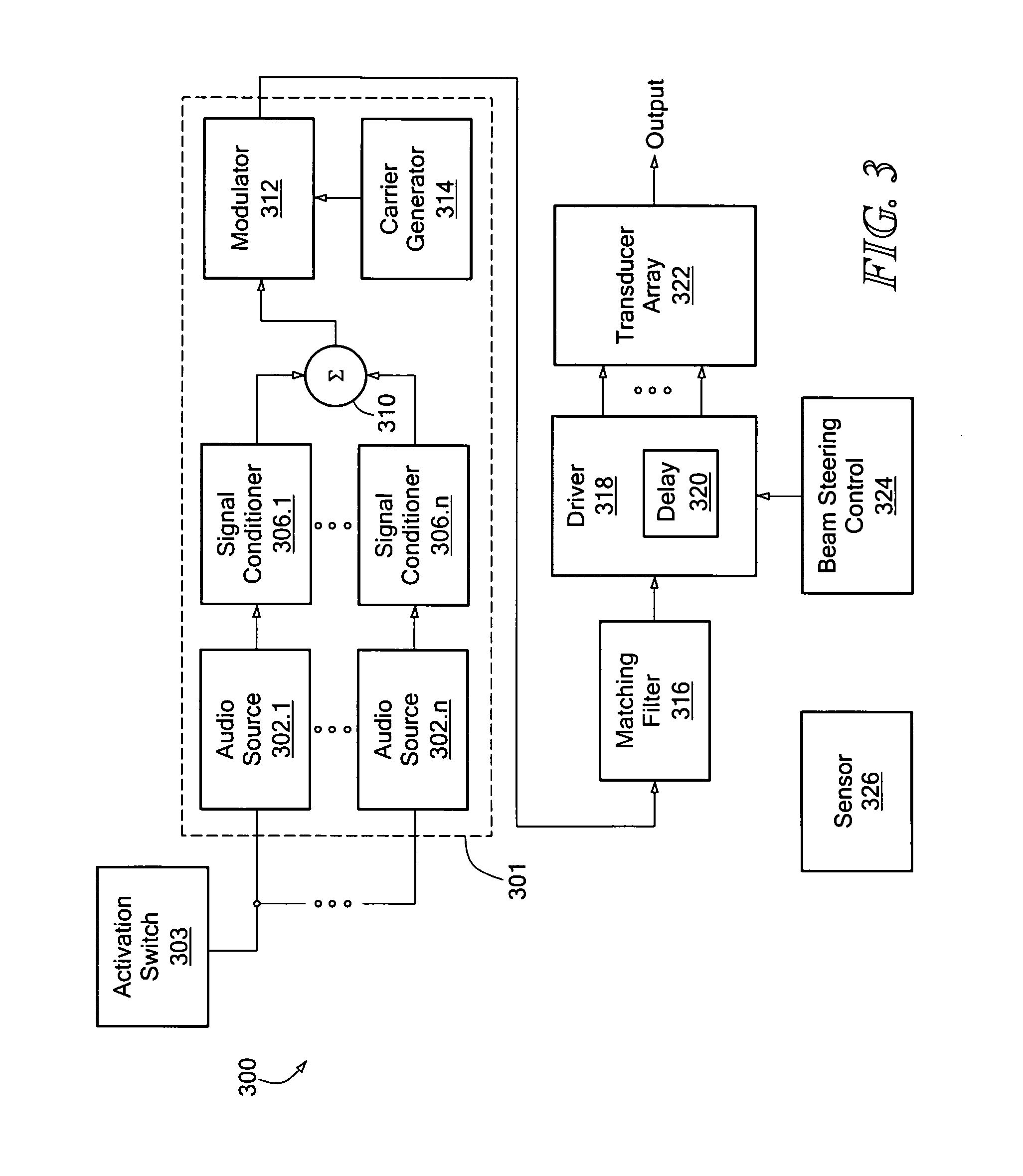
InactiveUS7106180B1Improve directivityReduce chanceContact mechanismsHigh-tension/heavy-dress switchesParametric arrayCarrier signal
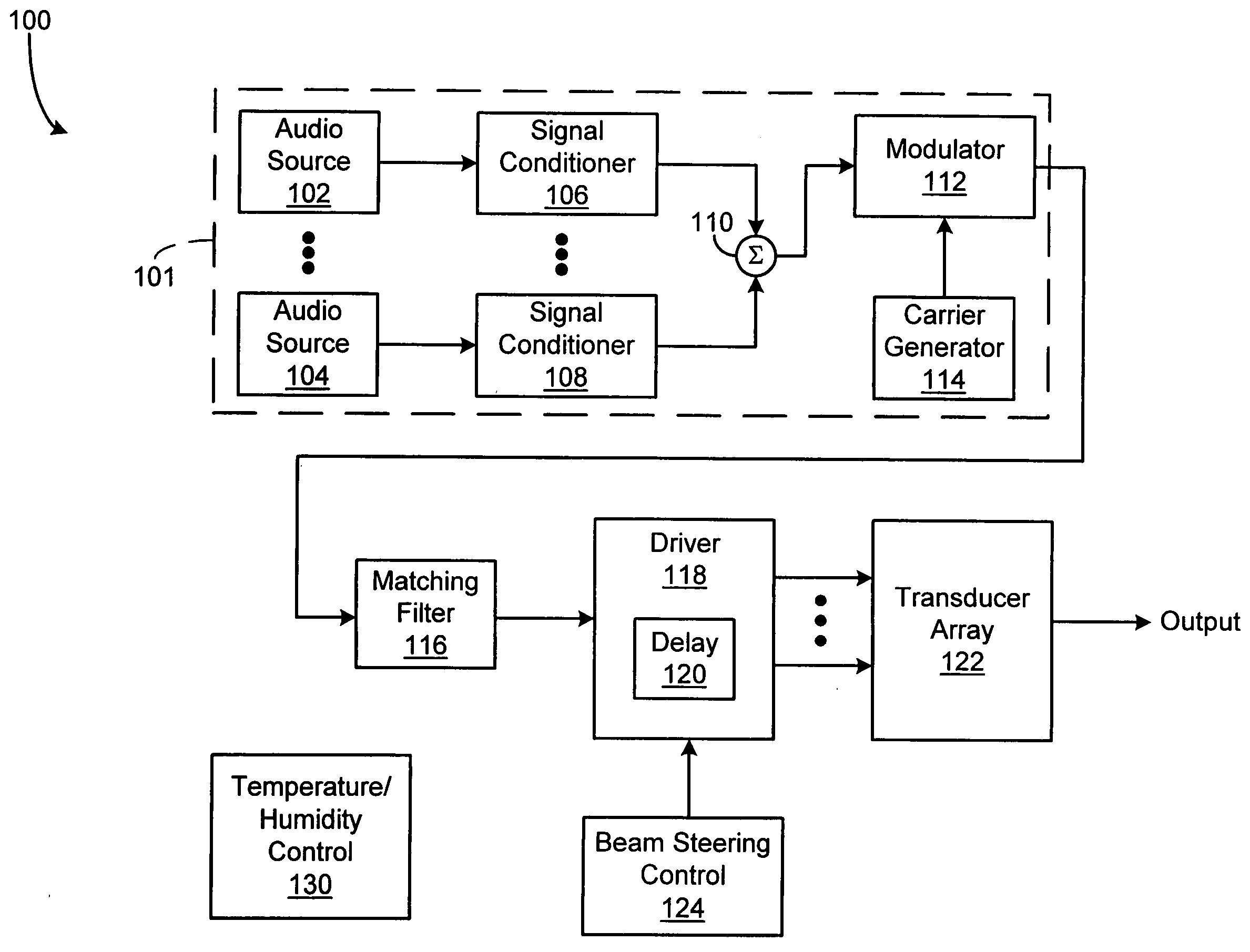
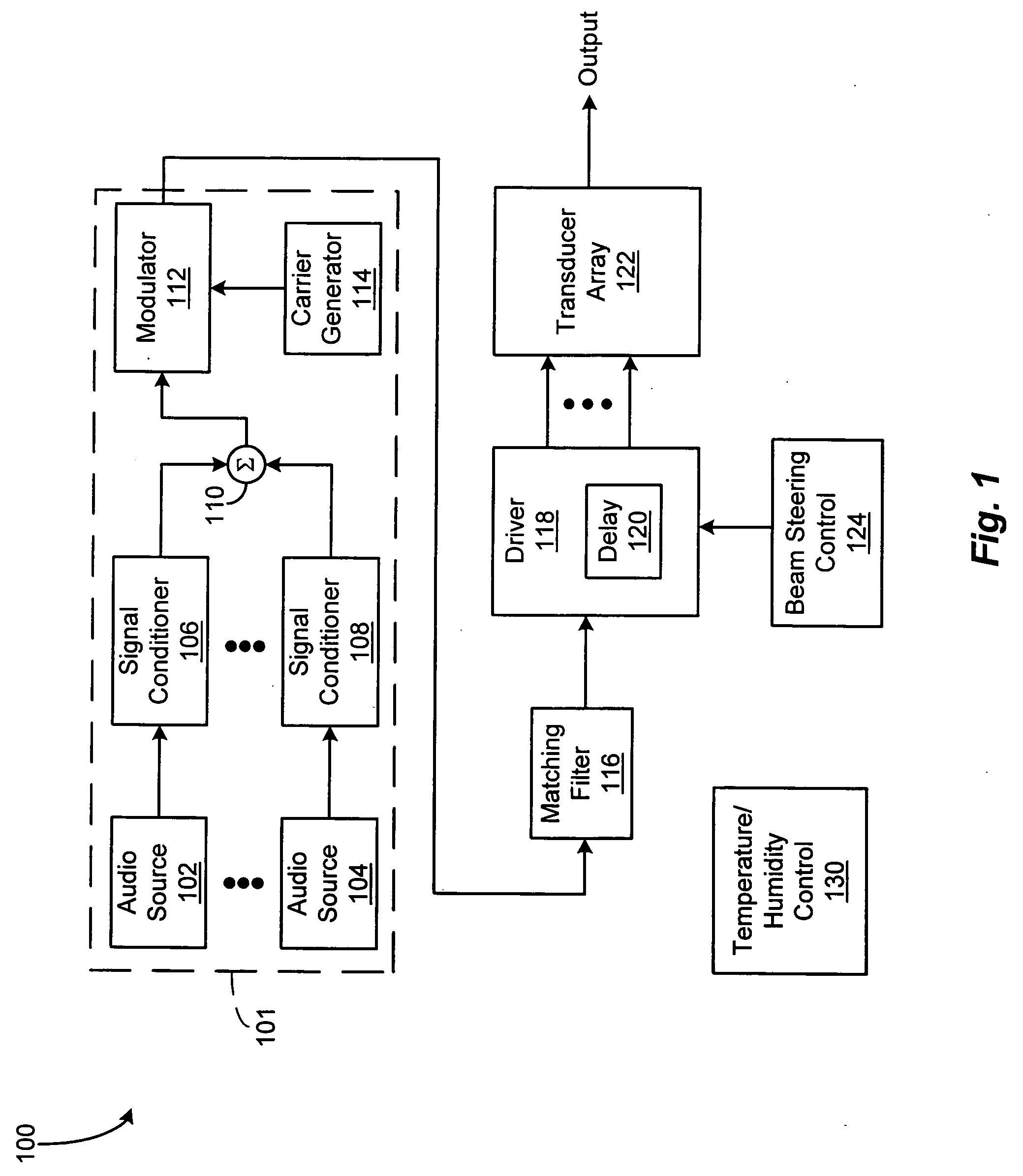
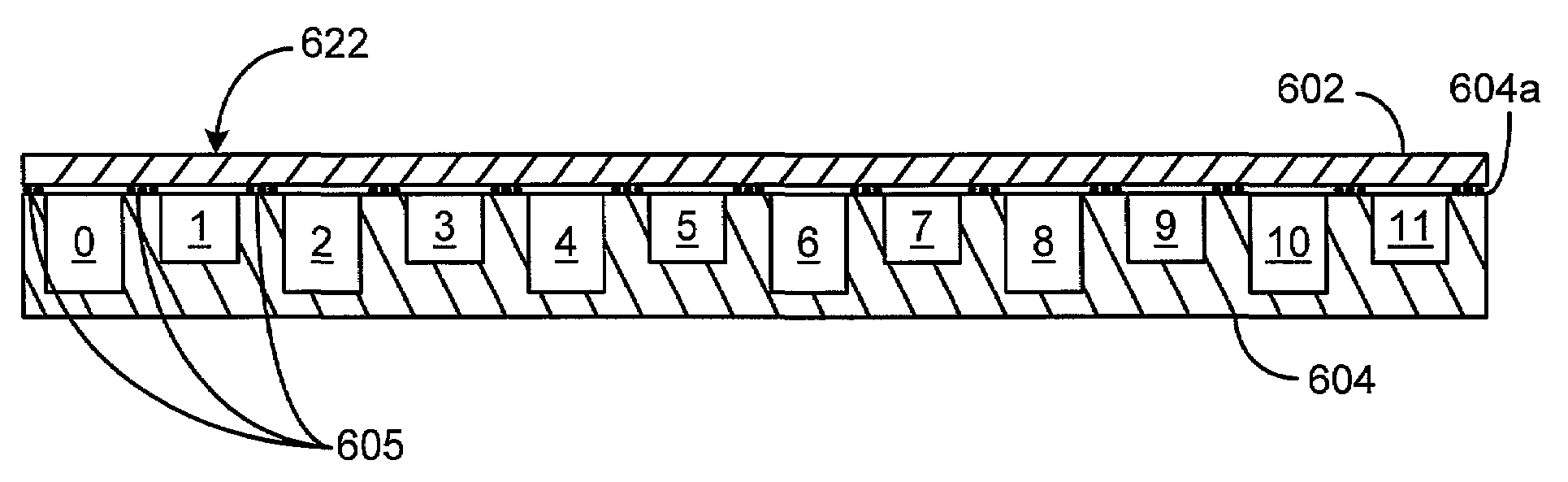
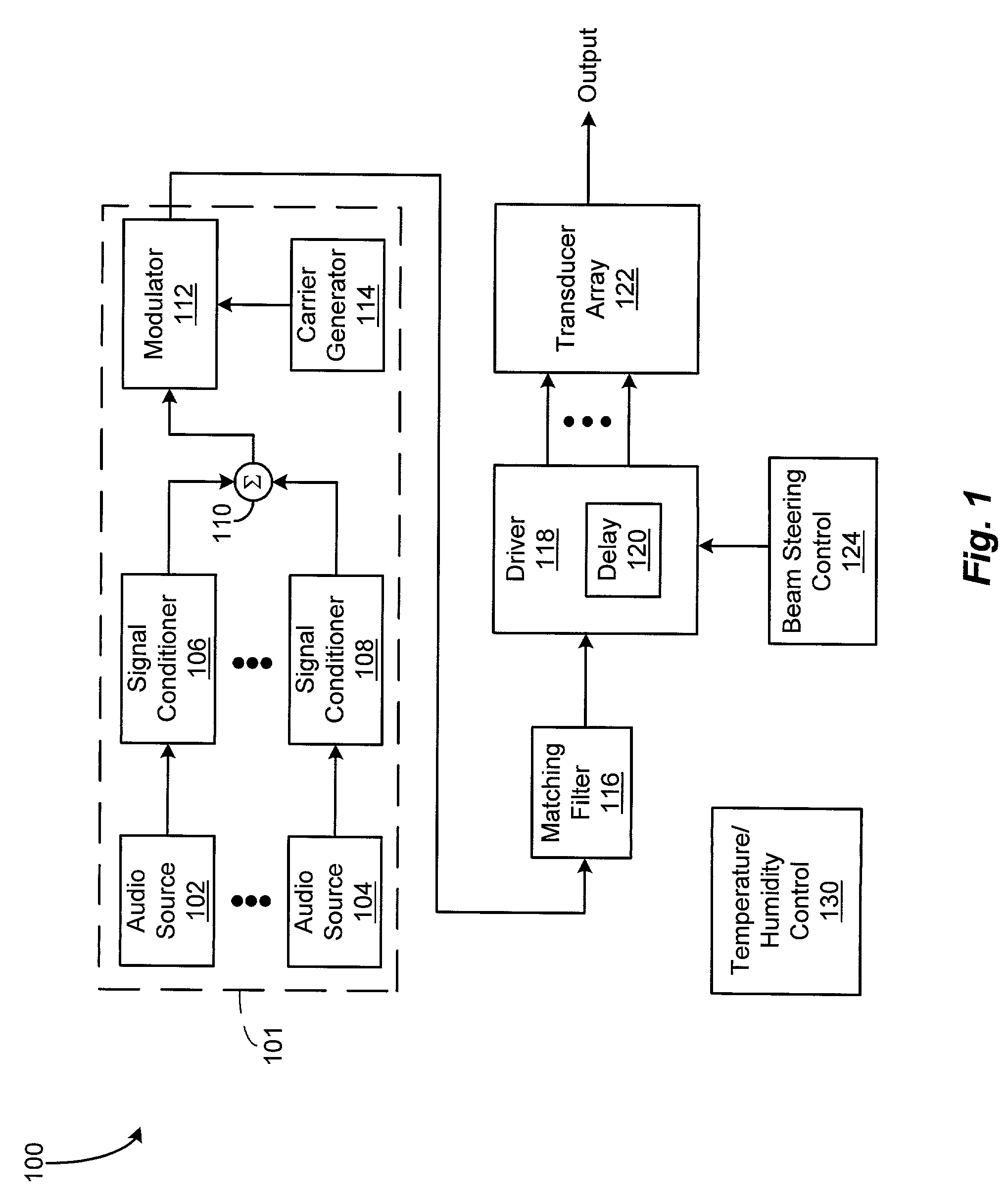
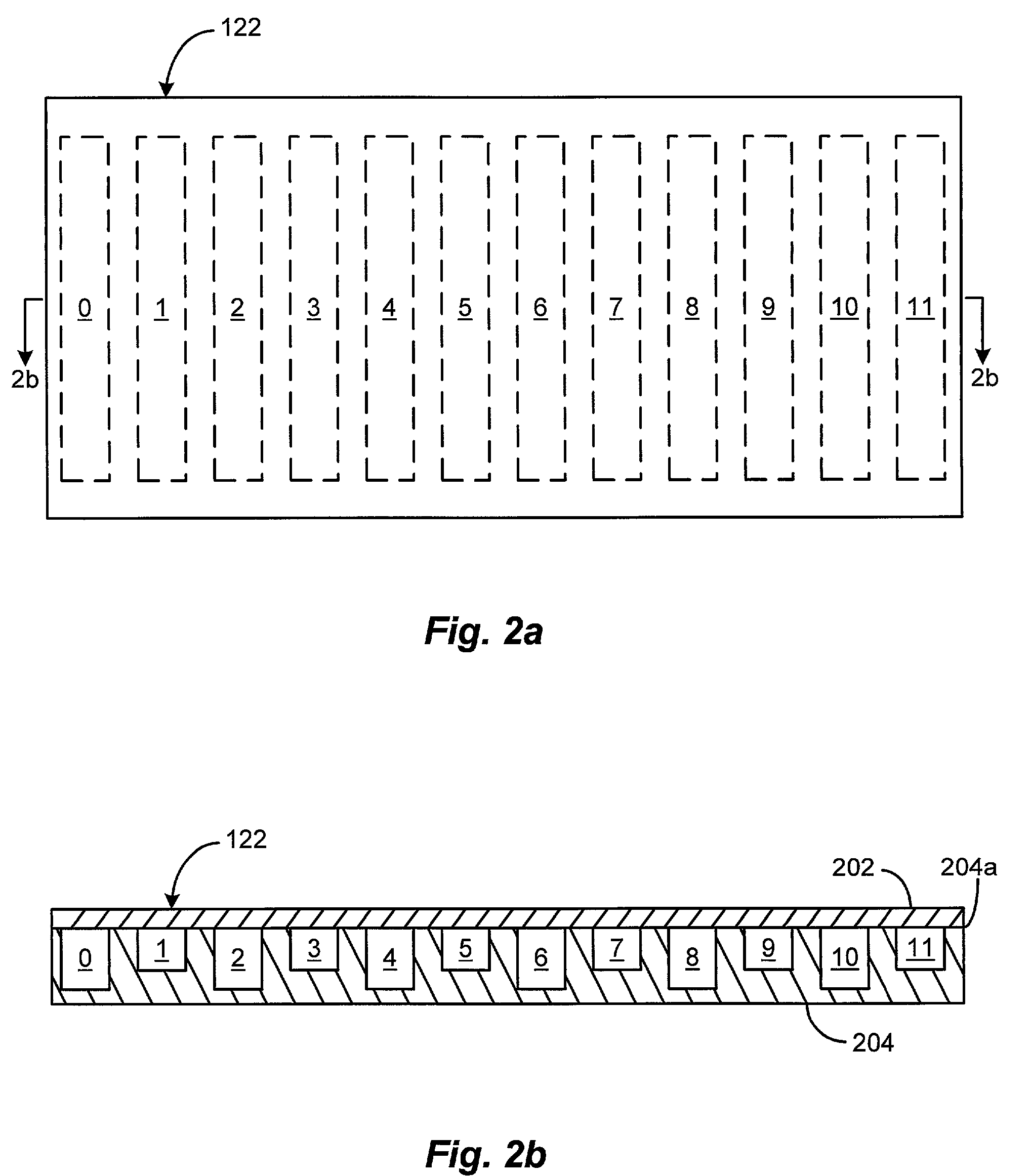
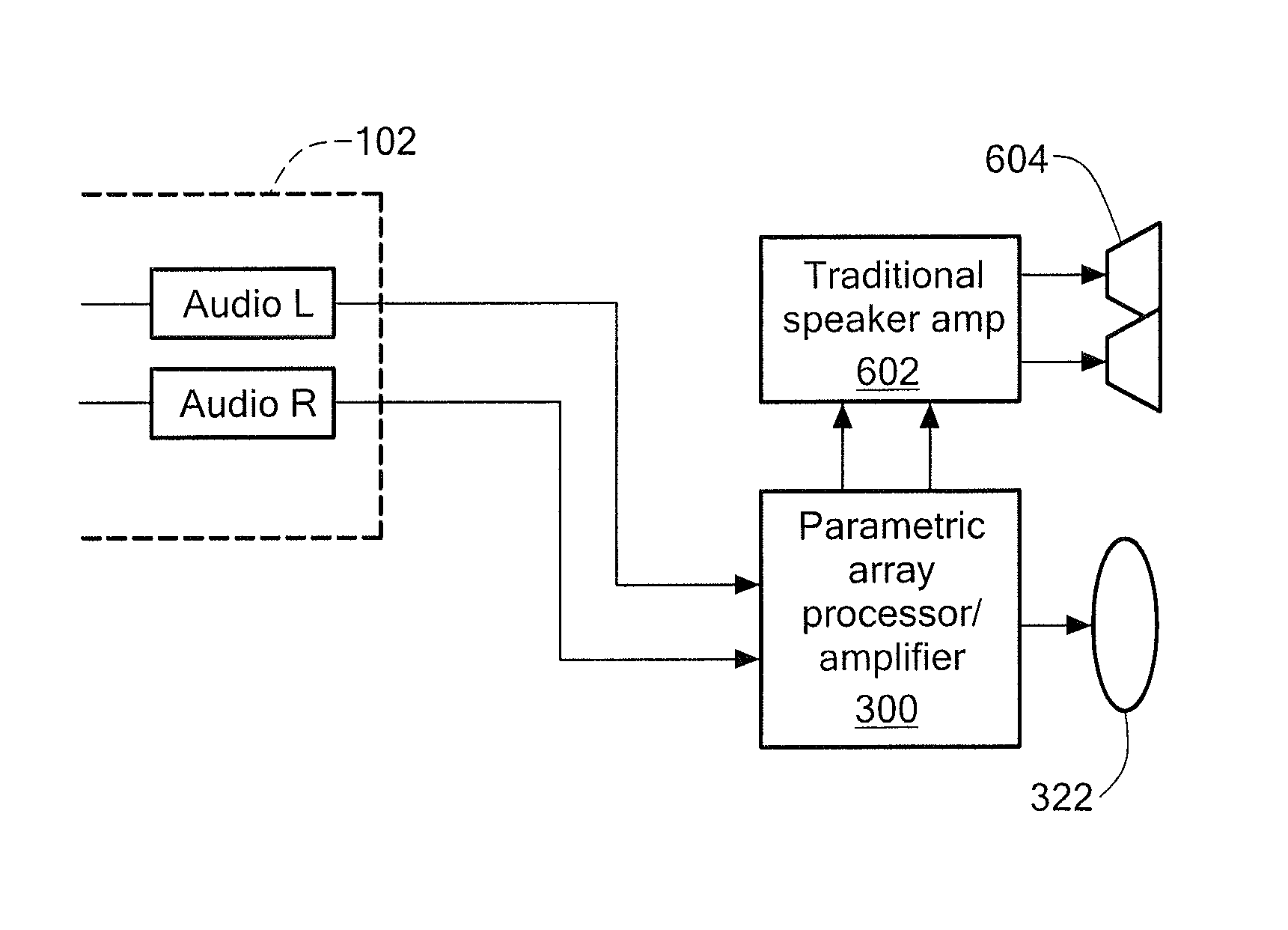
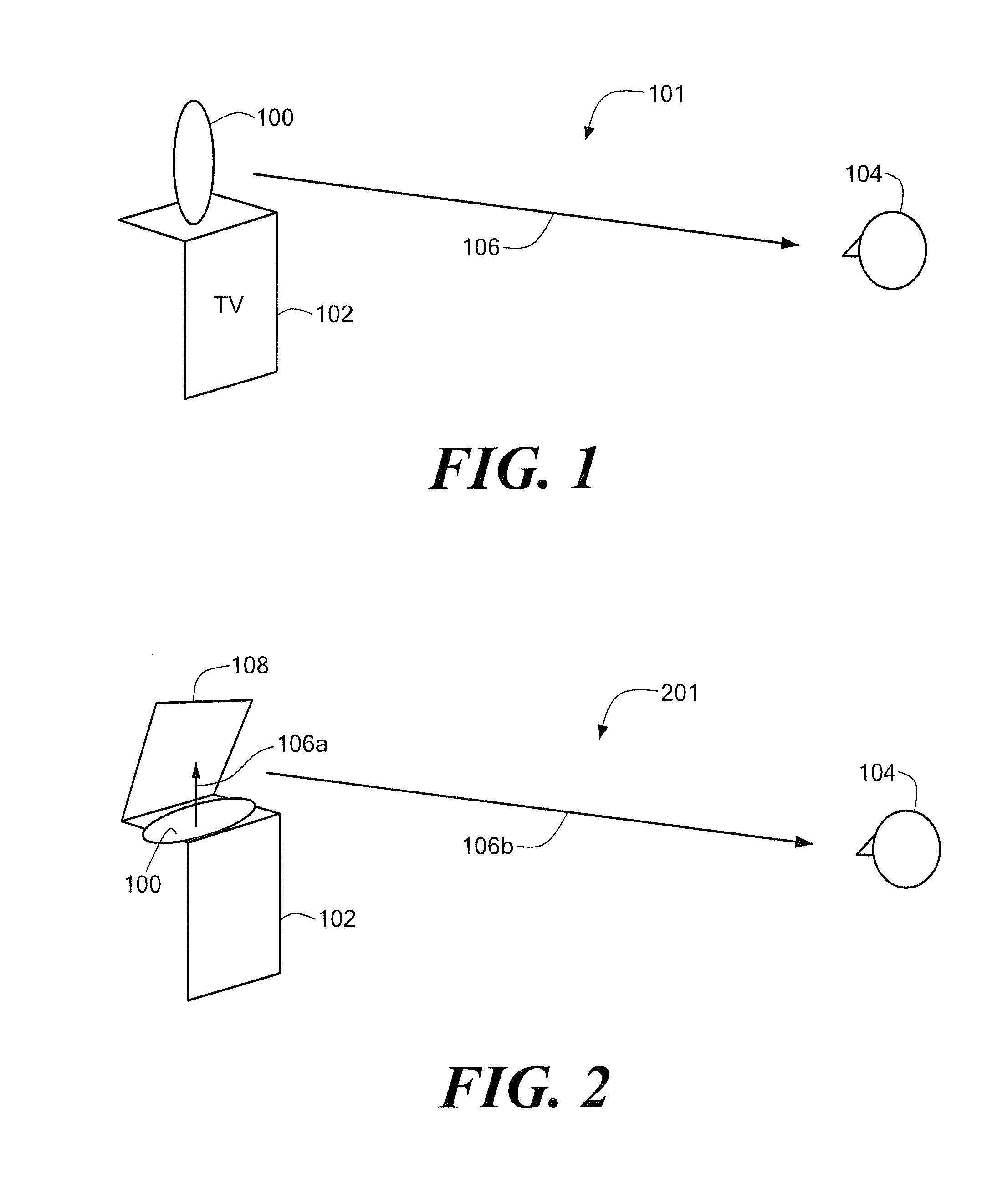
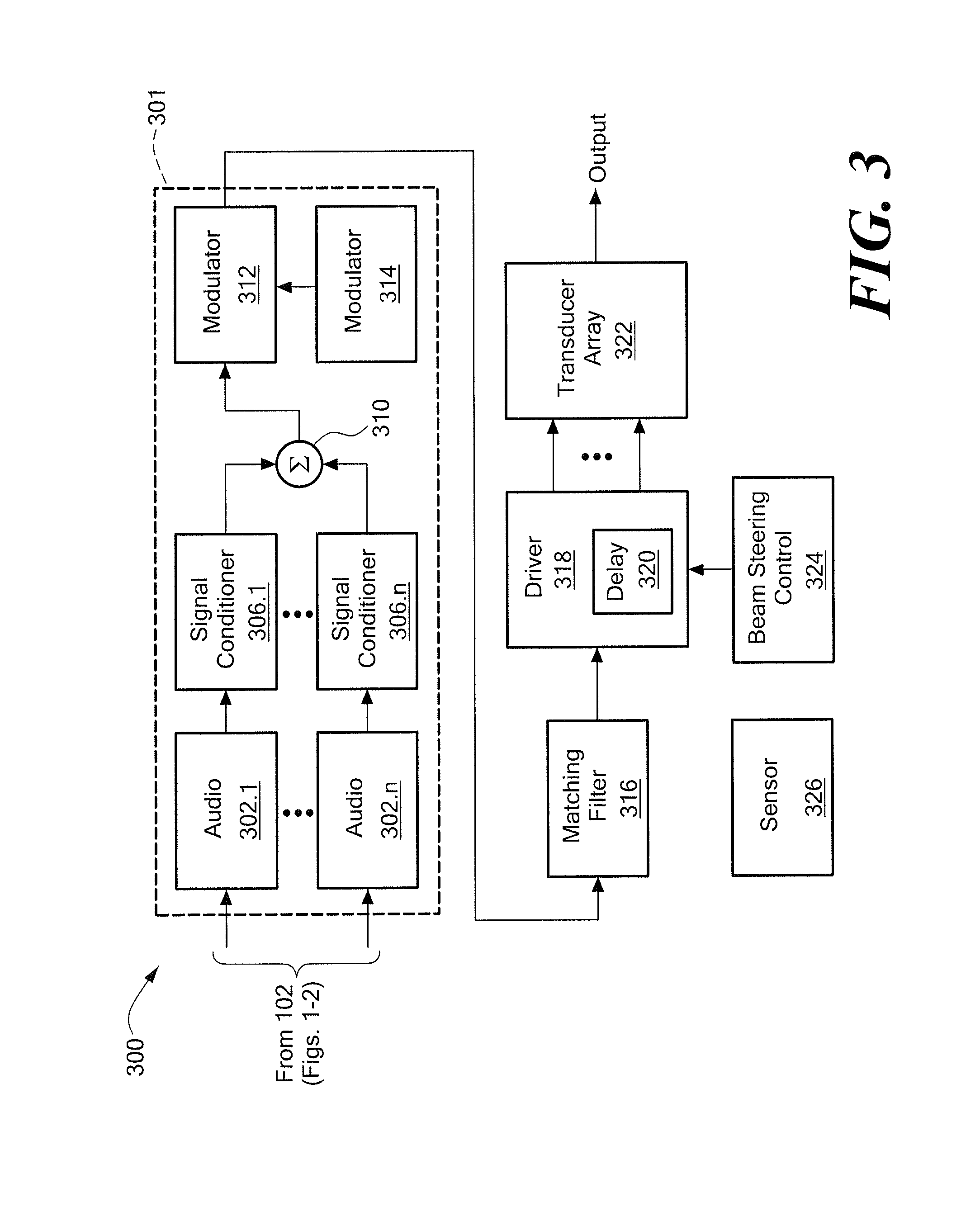
An acoustic warning or alerting system for directing an audible warning signal to at least one intended recipient, while reducing the chance that the warning signal will be heard by others within the proximity of the system. The system includes a modulator for modulating an ultrasonic carrier signal with a processed audio signal, a driver amplifier for amplifying the modulated carrier signal, and a parametric array of acoustic transducers for projecting the modulated and amplified carrier signal through a propagation medium for subsequent regeneration of the audio signal along a pre-selected projection path. The parametric array of audio transducers operates by employing the nonlinear interaction between high frequency sound components and the propagation medium to generate at least one highly directional beam of lower frequency sounds within the propagation medium. The directional acoustic alerting system may be employed as a replacement for conventional alerting systems such as horns, whistles, and bells to assure that primarily only those people and / or animals intended to hear the warning signal actually hear the sound.
Owner:POMPEI FRANK JOSEPH
Rf Power Amplifiers
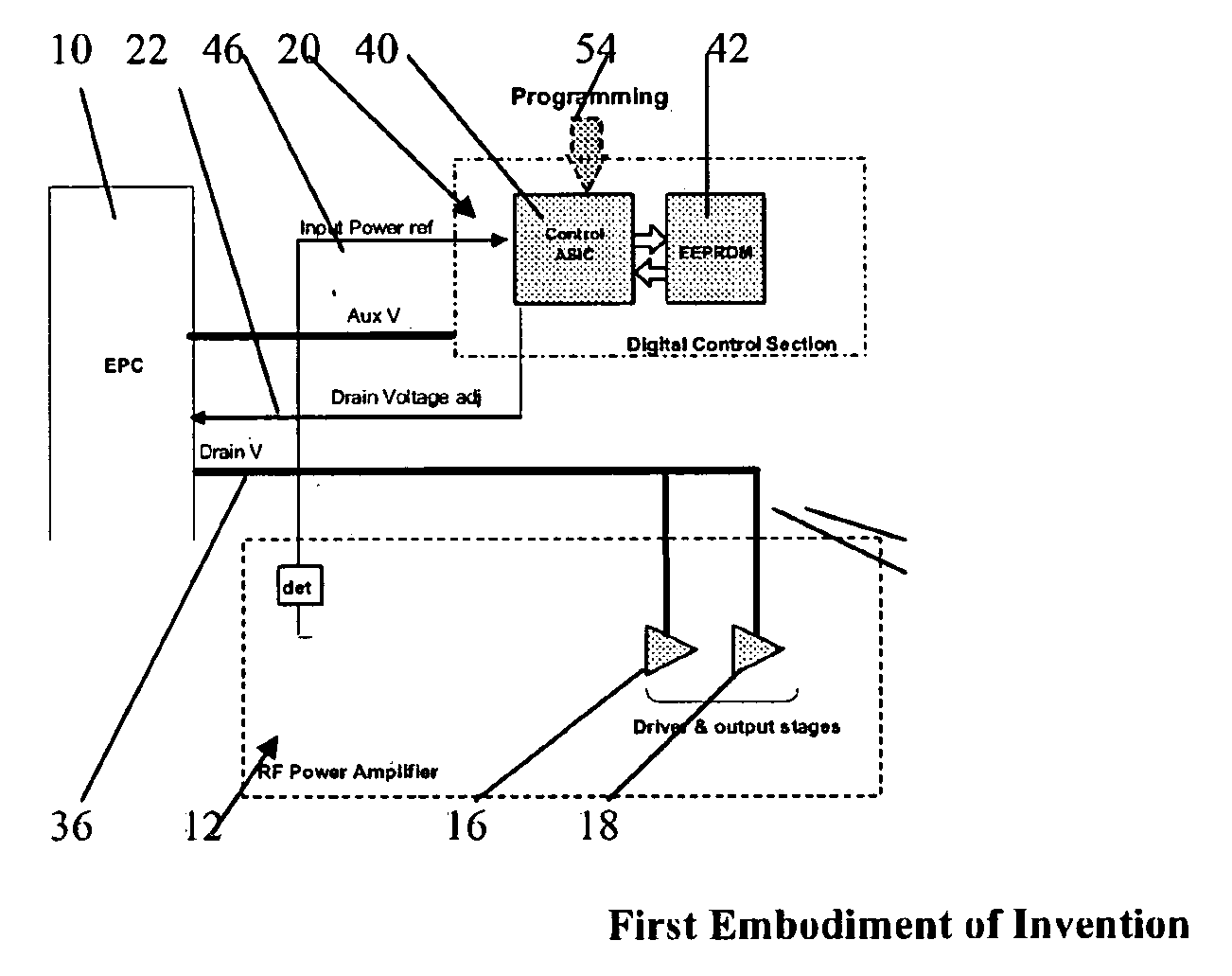
ActiveUS20080278236A1Improve featuresEliminating lossy and expensiveAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasControl signalGain compression
A Solid State Power Amplifier (SSPA) for powering a single element of a multi-element antenna, the SSPA comprising:an RF amplifier, having a signal amplifying path that includes preamplifier, driver amplifier and a power output stage;an Electronic Power Conditioner (EPC) for providing a variable value of DC voltage for powering the power output stage of the RF amplifier;a control ASIC for receiving an input power signal of the RF amplifier for providing a voltage control signal to the EPC to determine the value of the DC voltage, the control ASIC addressing an EEPROM holding a collection of control words that define output values of a control output signal for varying values of said input power, such that the value of the DC voltage to the power output stage is varied so as to control the gain compression of the RF amplifier for varying values of input power in order to maintain constant amplifier linearity.
Owner:ASTRIUM GMBH
Wideband balun having a single primary and multiple secondaries
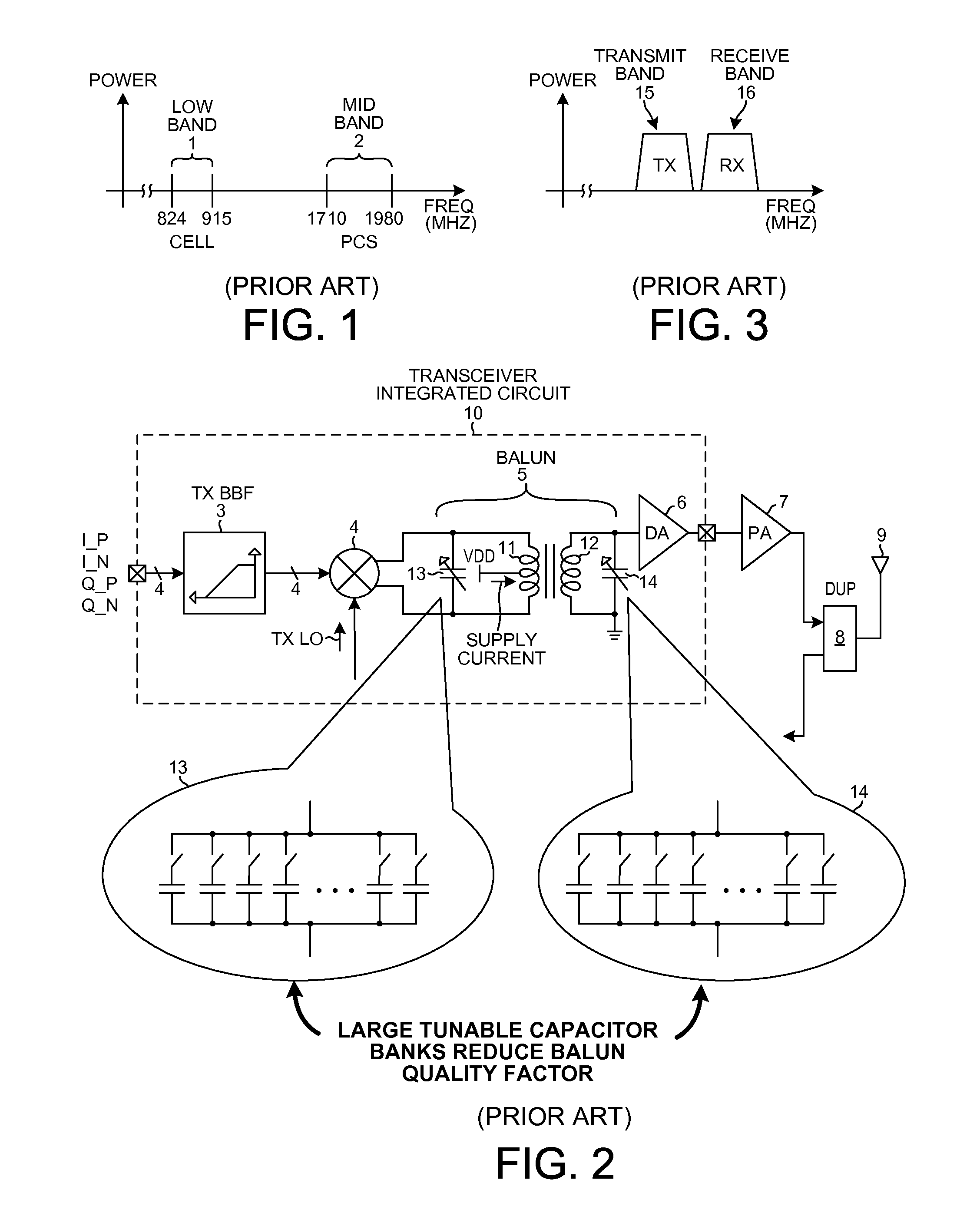
ActiveUS20120013387A1Reduce power consumptionPerformance requirementMultiple-port networksModulation transferenceWideband balunAudio power amplifier
An RF transmitter capable of transmitting over a wide range of frequencies includes a mixer, a wideband high-Q balun, a first driver amplifier and a second driver amplifier. The balun has a single primary winding and two secondary windings. A differential output of the mixer is coupled to the primary winding. A first of the two secondary windings is coupled to drive the first driver amplifier. A second of the two secondary windings is coupled to drive the second driver amplifier. One driver amplifier is used when transmitting at lower frequencies whereas the other driver amplifier is used when transmitting at higher frequencies. By appropriate sizing of the inductances of the secondary windings and by switching out one of the secondary windings at certain times, the balun is tunable to operate over the wide frequency range while having a high quality factor Q, thereby facilitating reduced power consumption while simultaneously meeting performance requirements.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
High q transformer disposed at least partly in a non-semiconductor substrate
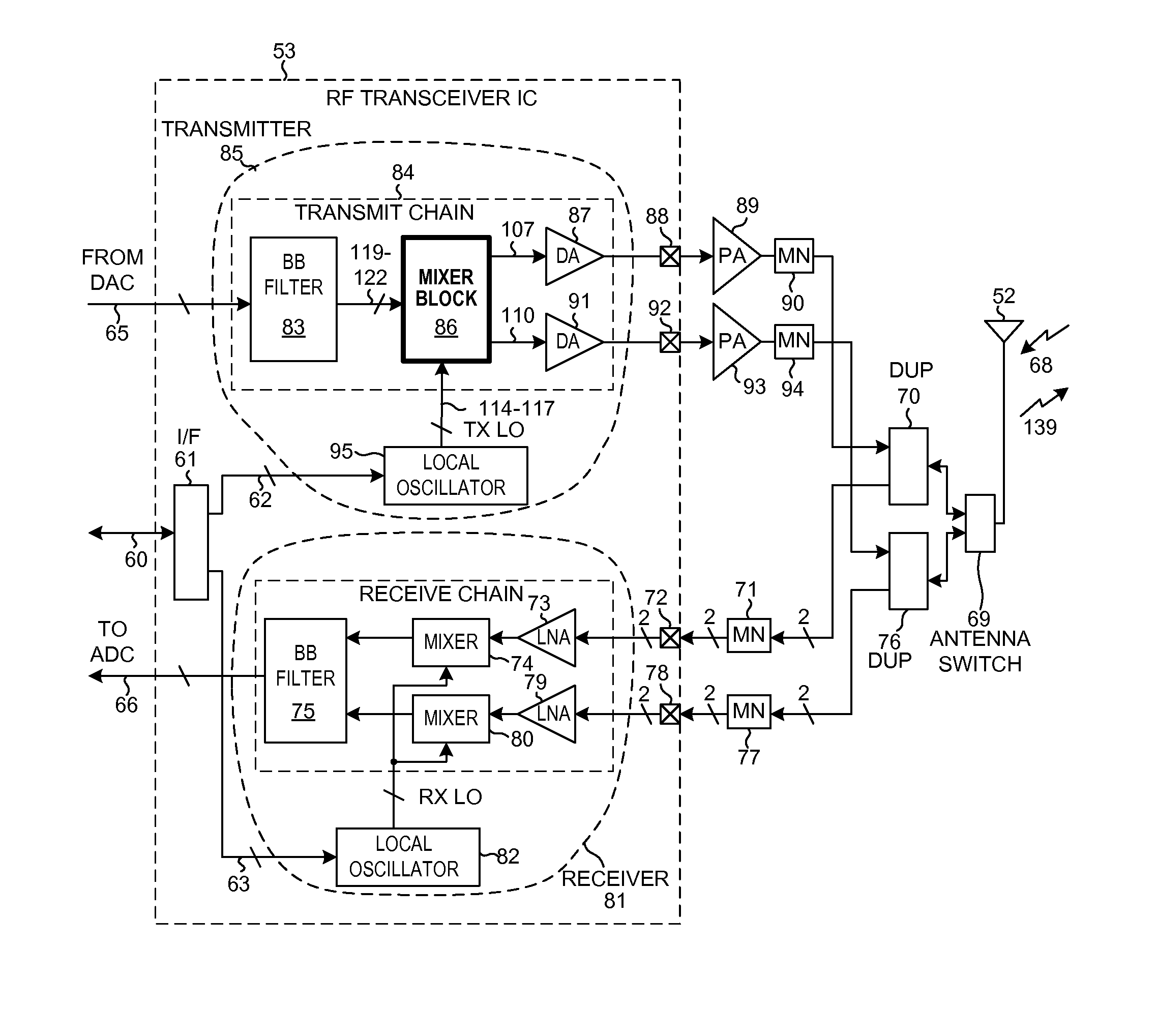
ActiveUS20100026368A1High degree of couplingReduce parasitic capacitanceComputations using contact-making devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsTransceiverTransformer
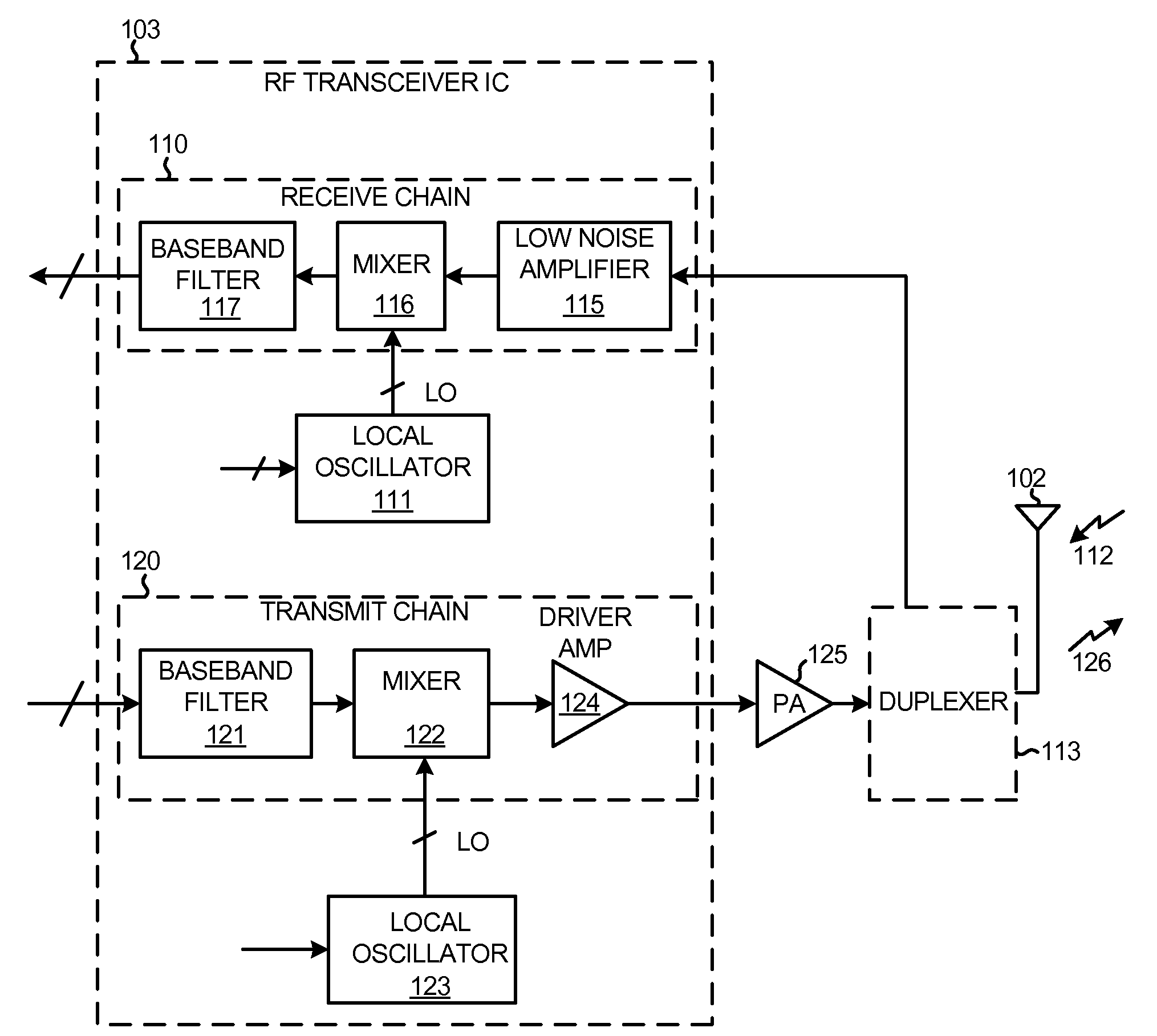
An assembly involves an integrated circuit die that is bonded, e.g., flip-chip bonded, to a non-semiconductor substrate by a plurality of low-resistance microbumps. In one novel aspect, at least a part of a novel high-frequency transformer is disposed in the non-semiconductor substrate where the non-semiconductor substrate is the substrate of a ball grid array (BGA) integrated circuit package. At least one of the low-resistance microbumps connects the part of the transformer in the substrate to a circuit in the integrated circuit die. At two gigahertz, the novel transformer has a coupling coefficient k of at least at least 0.4 and also has a transformer quality factor Q of at least ten. The novel transformer structure sees use in coupling differential outputs of a mixer to a single-ended input of a driver amplifier in a transmit chain of an RF transceiver within a cellular telephone.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Parametric audio system
InactiveUS20080285777A1High bandwidthReduce distortion problemsSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionPiezoelectric/electrostrictive transducersSonificationCarrier signal
A parametric audio system having increased bandwidth for generating airborne audio signals with reduced distortion. The parametric audio system includes a modulator for modulating an ultrasonic carrier signal with a processed audio signal, a driver amplifier for amplifying the modulated carrier signal, and an array of acoustic transducers for projecting the modulated and amplified carrier signal through the air along a selected projection path to regenerate the audio signal. The acoustic transducer array includes a backplate having a succession of depressions formed thereon with at least one varying feature and / or dimension, and a membrane disposed along the backplate. The feature and / or dimension of the respective depressions vary so that the center frequencies of the respective acoustic transducers span a desired frequency range, thereby broadening the frequency response of the acoustic transducer array.
Owner:POMPEI FRANK JOSEPH
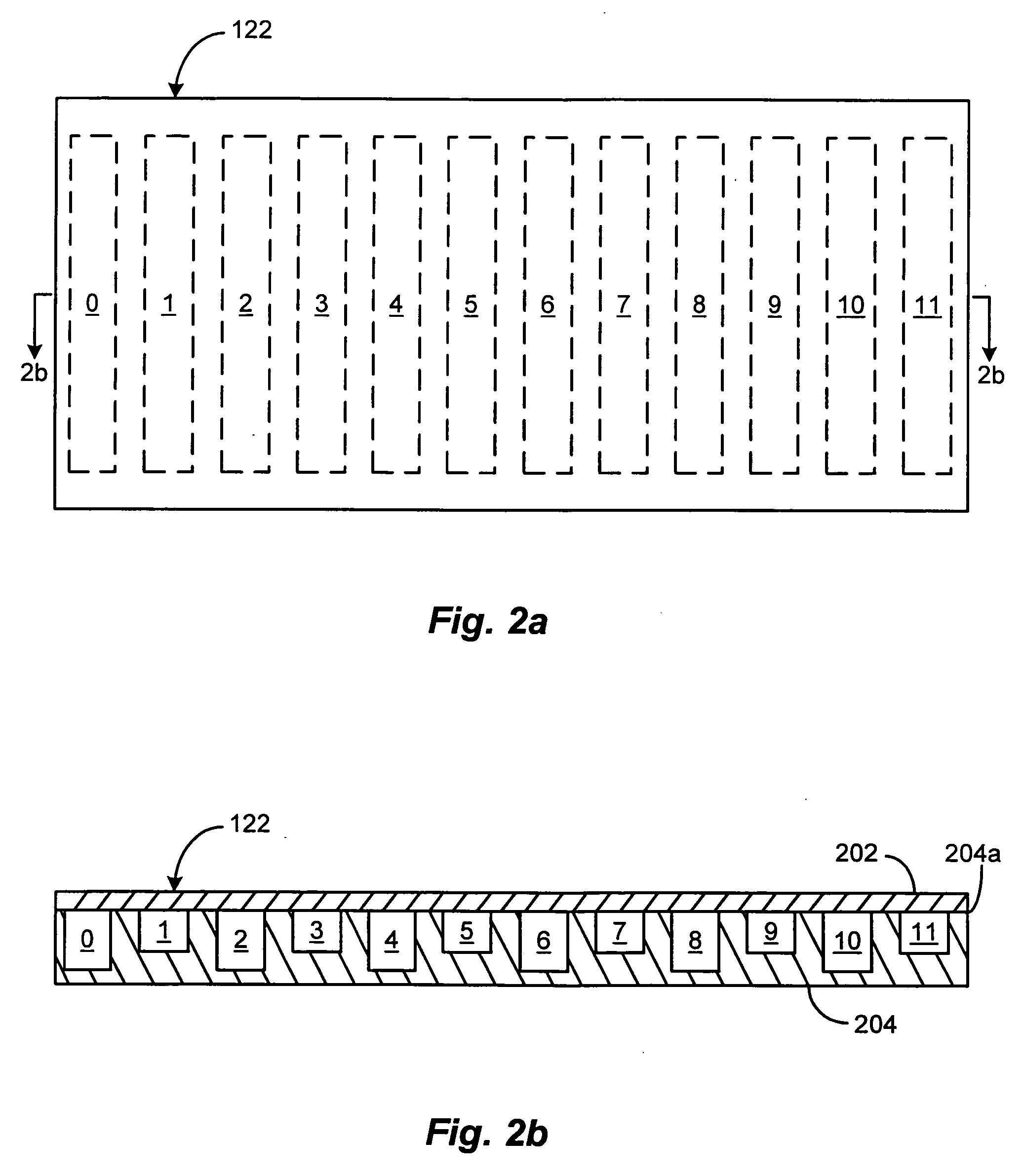
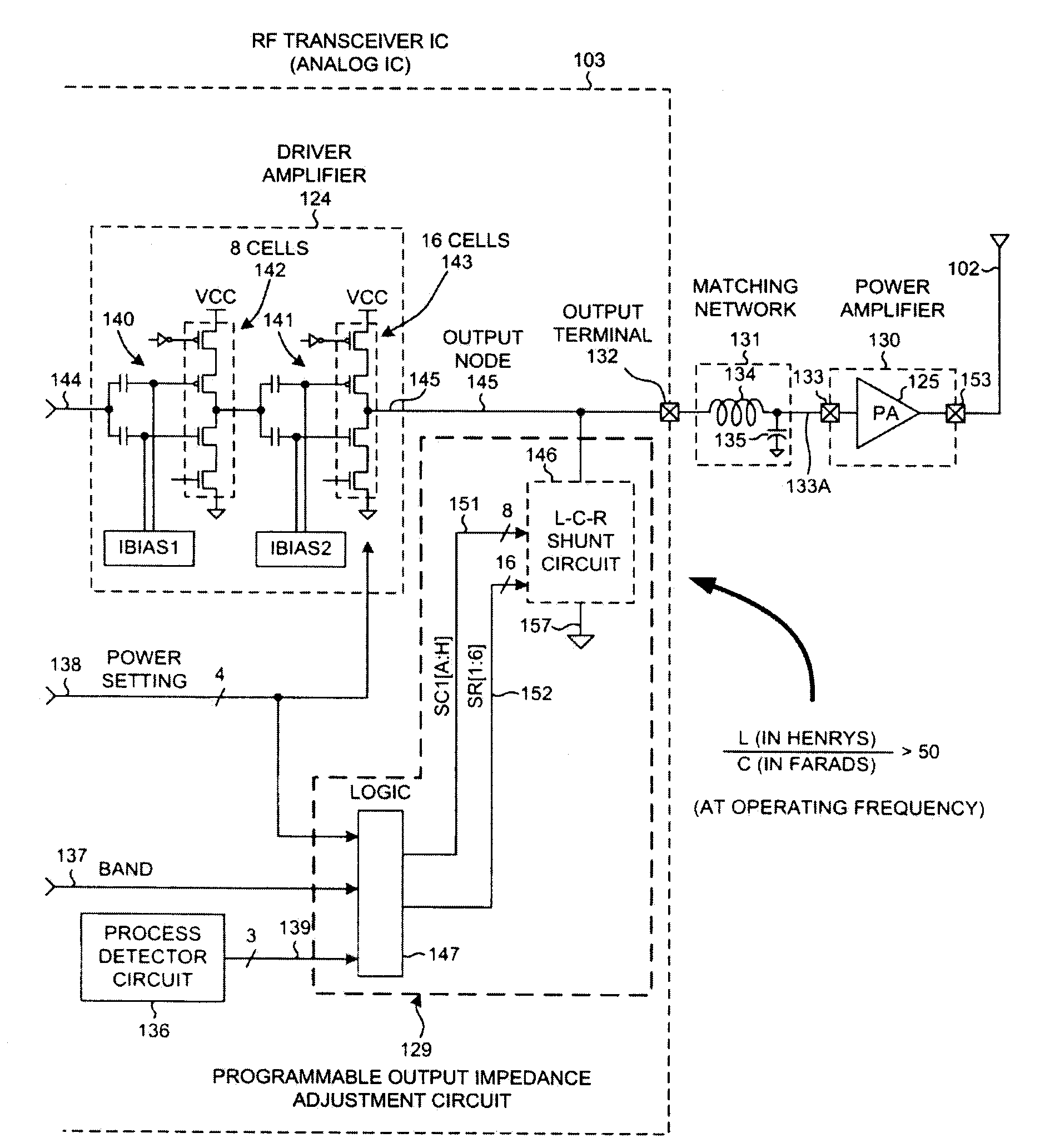
Driver amplifier having a programmable output impedance adjustment circuit
ActiveUS20100026393A1Improving Impedance MatchingReduce the amount requiredModulation with suppressed carrierTransmission monitoringCapacitanceMulti band
A driver amplifier in an integrated circuit is suitable for driving a signal onto an output node and through an output terminal, and through a matching network to a power amplifier. A novel Programmable Output Impedance Adjustment Circuit (POIAC) within the integrated circuit is coupled to the output node and affects an output impedance looking into the output terminal. When the output impedance would otherwise change (for example, due to a driver amplifier power gain change), the POIAC adjusts how it loads the output node such that the output impedance remains substantially constant. The POIAC uses a series-connected inductor and capacitor L-C-R circuit to load the output node, thereby reducing the amount of capacitance and die area required to perform multi-band impedance matching with a power amplifier. Multi-band operation is accomplished by changing an effective capacitance in the L-C-R circuit depending on communication band information received by the POIAC.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Parametric audio system
InactiveUS7391872B2High bandwidthReduce distortion problemsDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionAudio power amplifierSonification
A parametric audio system having increased bandwidth for generating airborne audio signals with reduced distortion. The parametric audio system includes a modulator for modulating an ultrasonic carrier signal with a processed audio signal, a driver amplifier for amplifying the modulated carrier signal, and an array of acoustic transducers for projecting the modulated and amplified carrier signal through the air along a selected projection path to regenerate the audio signal. Each of the acoustic transducers in the array is a membrane-type transducer. Further, the acoustic transducer array is a phased array capable of electronically steering, focusing, or shaping one or more audio beams.
Owner:POMPEI FRANK JOSEPH
Stacked pre-driver amplifier
ActiveUS8106711B2Reducing and eliminating powerReduce voltageAmplifier combinationsRF amplifierAudio power amplifierVoltage drop
A stacked pre-driver stage and a power amplifier including the stacked pre-driver stage are described. The stacked pre-driver stage comprises stacked pre-drivers arranged in series between a supply voltage and a reference voltage. Each pre-driver includes a pre-driving amplifier, together with MOS transistors. Each pre-driver is subject, in operation, to a voltage difference which is inferior to a maximum allowed use voltage of the MOS transistors with a largely reduced voltage drop across the regulator included in the power amplifier.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
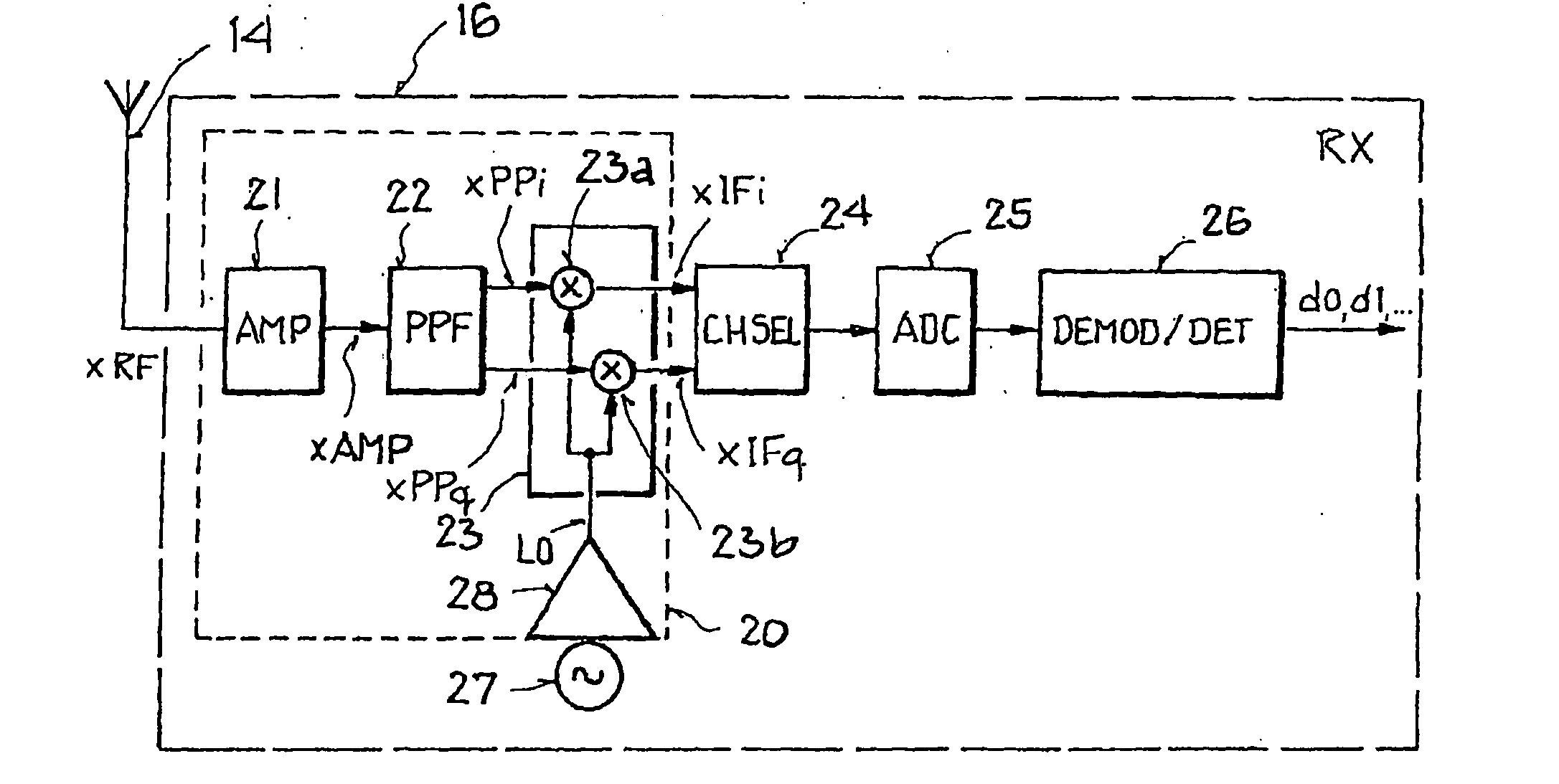
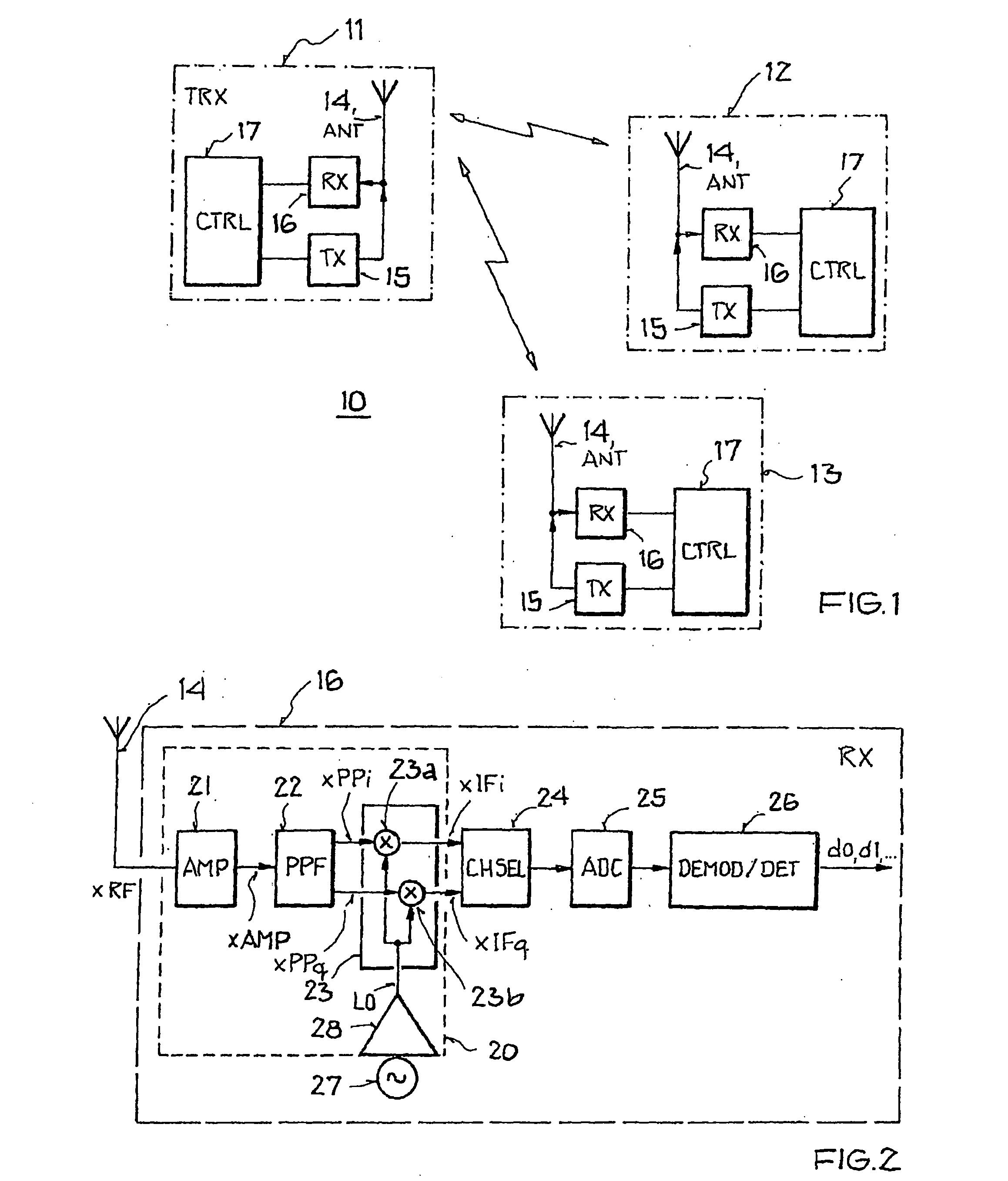
Integrated circuit arrangement for converting a high-frequency bandpass signal to a low-frequency quadrature signal
InactiveUS20070177693A1Energy-efficient and powerful transmitting/receivingRealized cost-effectivelyModulation transferencePhase-modulated carrier systemsLocal oscillator signalAudio power amplifier
An integrated circuit arrangement is provided for converting a high-frequency bandpass signal to a low-frequency quadrature signal with a first in-phase component and a first quadrature-phase component, which has: an amplifier arrangement, which is designed to generate an amplified signal and has a first amplifier stage for amplifying the high-frequency bandpass signal, a mixer unit with a first mixer to provide the first in-phase component and a second mixer to provide the first quadrature-phase component, and a driver amplifier, which is designed to generate a local oscillator signal. According to the invention, between the amplifier arrangement and the mixer unit a polyphase filter is disposed, which converts the amplified signal to a complex-valued polyphase signal with a second in-phase component and a second quadrature phase component. Furthermore, according to the invention each mixer is connected to the driver amplifier, and the first mixer is designed to multiply the second in-phase component by the local oscillator signal, and the second mixer is designed to multiply the second quadrature-phase component by the local oscillator signal.
Owner:ATMEL AUTOMOTIVE
Led driver current amplifier
InactiveUS7038594B2Avoid image distortionMinimize power consumptionElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesAudio power amplifierElectrical devices
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
Complementary metal oxide semiconductor power amplifier
An RF power amplifier circuit is disclosed. A driver amplifier stage includes a first set of a plurality of amplifier transistors in a cascode configuration, a driver amplifier stage input, and a driver amplifier stage output. A final amplifier stage includes a second set of a plurality of amplifier transistors in a cascode configuration, a final amplifier stage input connected to the driver amplifier stage output, a final amplifier stage output, and a power supply input. An envelope signal amplifier has an input connectible to an envelope signal source, and an output capacitively coupled to the power supply input. A power converter input is connected to the power supply input to provide supplemental power to the final amplifier stage based on an envelope signal from the envelope signal source that corresponds to an input RF signal.
Owner:MORFIS SEMICON
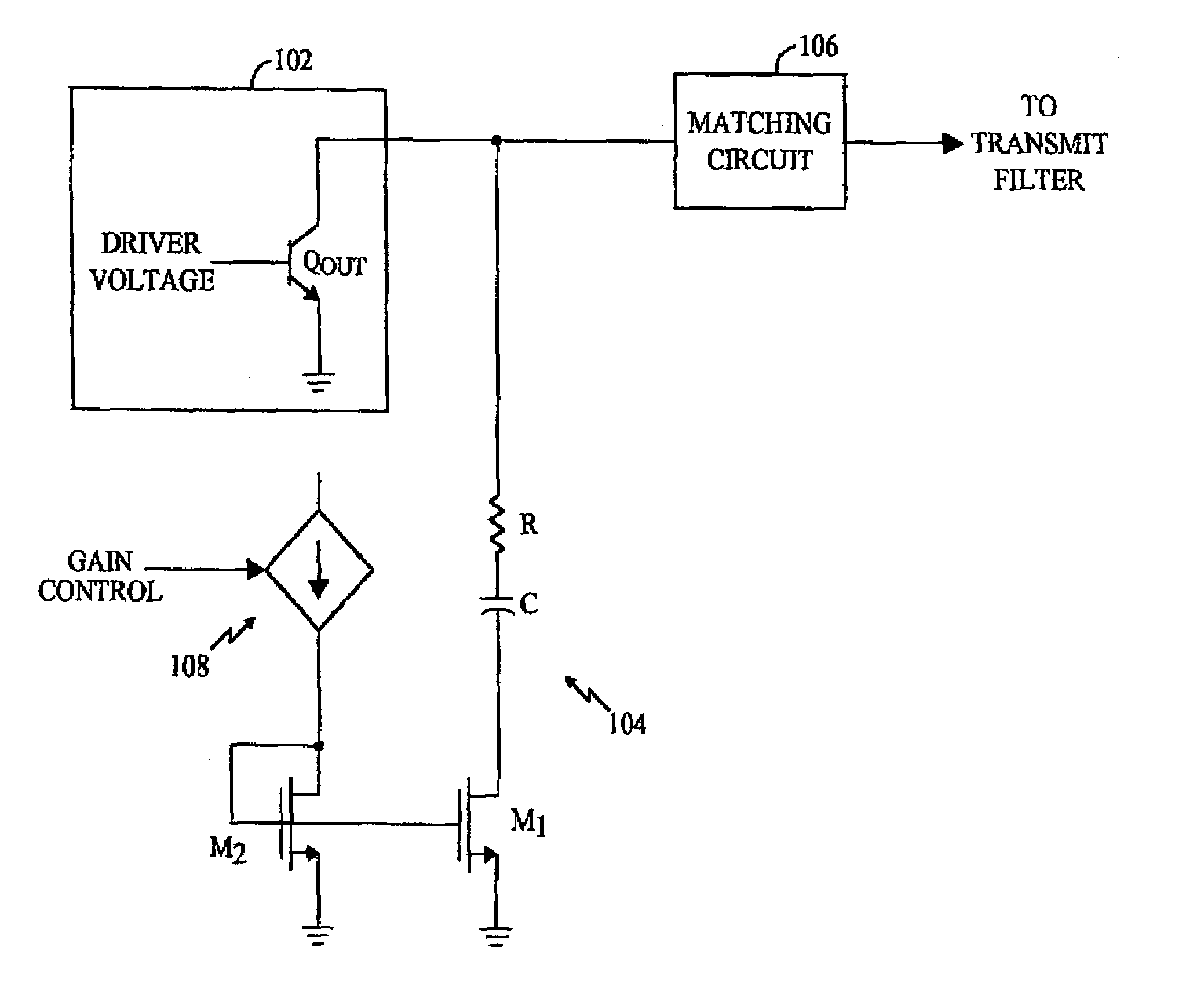
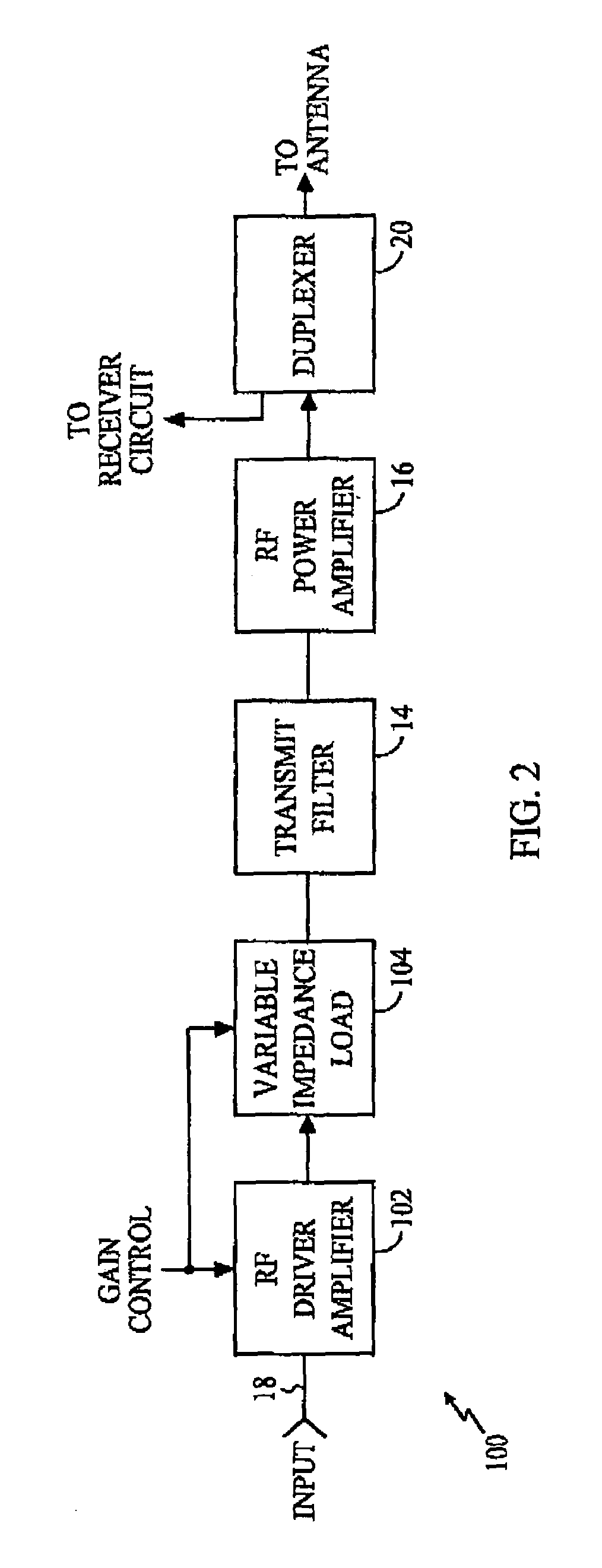
Variable impedance load for a variable gain radio frequency amplifier
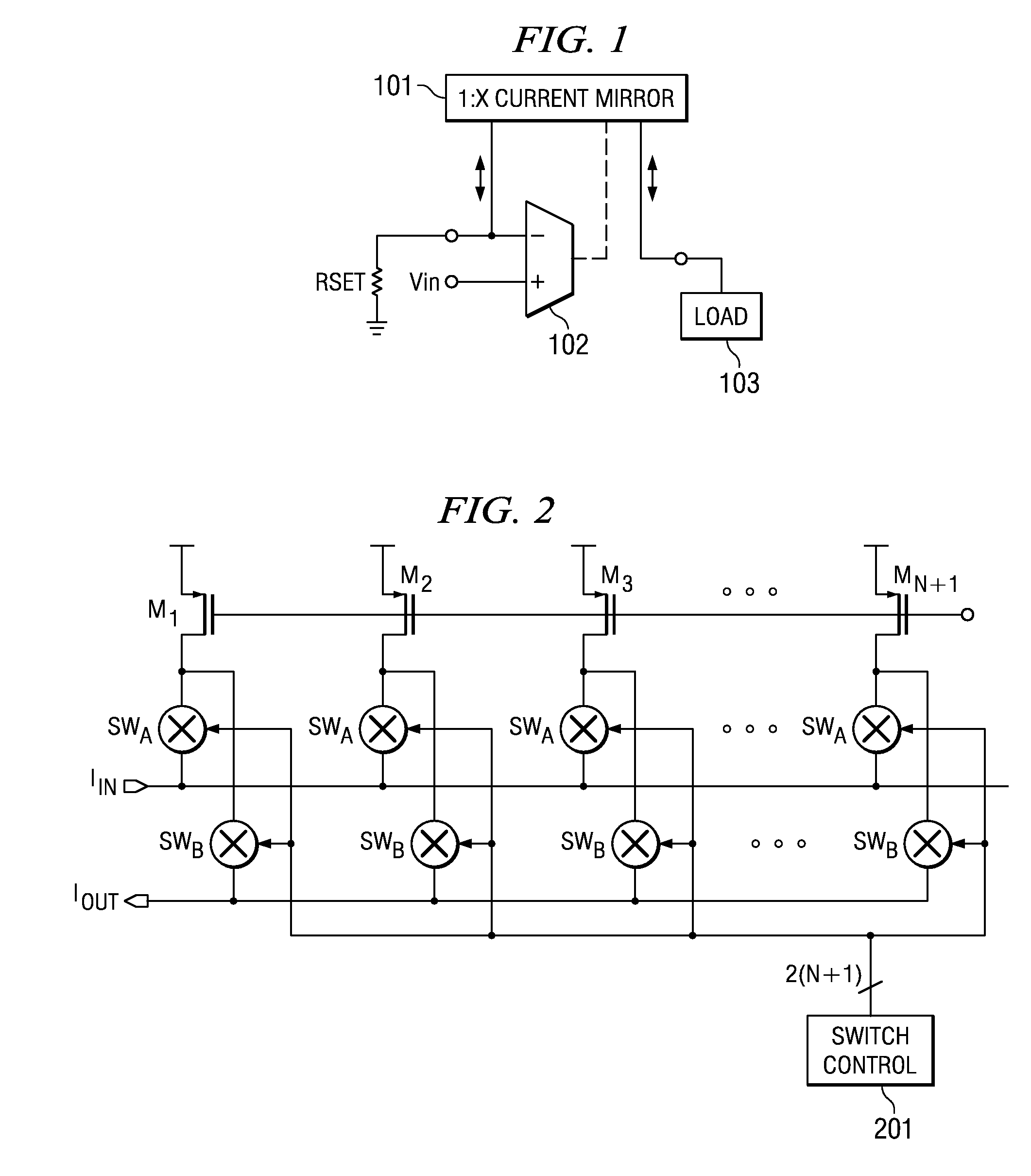
A variable impedance load (104) is provided at the output of a radio frequency (RF) driver amplifier (102) having a variable gain. In an exemplary embodiment, the variable load (104) comprises a resistor (R) in series with a semiconductor device (M1). The semiconductor device (M1) has an impedance level determined by a drive current. The value of the drive current is related to the gain of the RF driver amplifier (102).
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Circuit and method for driving a liquid crystal display device using low power
InactiveUS7317440B2Minimize power consumptionReduce power consumptionAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyCathode-ray tube indicatorsVoltage generatorAudio power amplifier
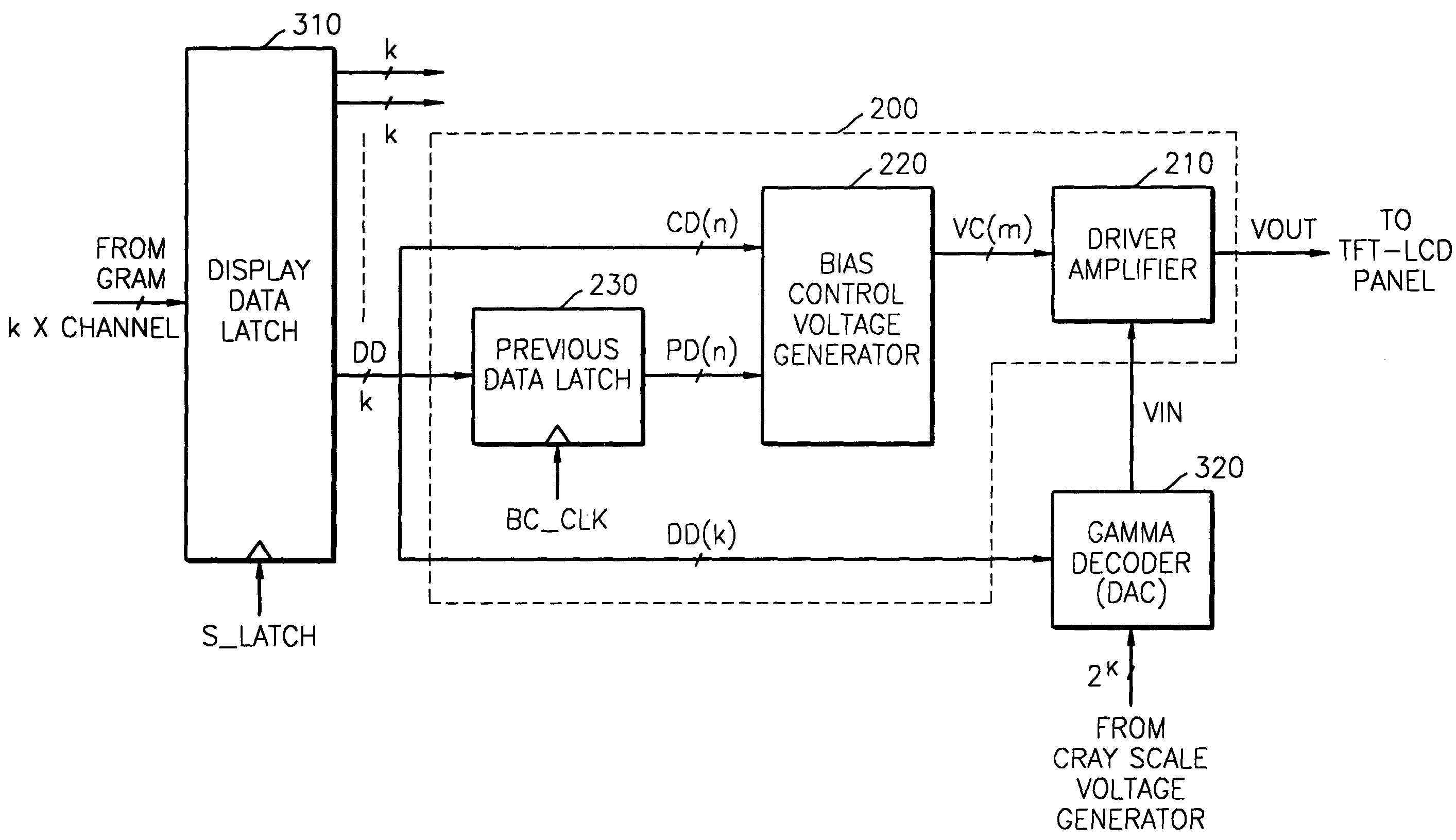
Provided are a circuit and method for driving a liquid crystal display device using low power. The circuit includes a display data latch, a gamma decoder, and a driver cell circuit. The display data latch latches display data from a memory. The gamma decoder receives a plurality of gray scale voltages, and selects and outputs one of the plurality of gray scale voltages in response to the display data. The driver cell circuit receives an output voltage of the gamma decoder and generates an output voltage applied to the liquid crystal display device. The driver cell circuit controls a slew rate in response to comparison result of current data and previous data of the display data. The driver cell circuit includes a previous data latch, a bias control voltage generator, and a driver amplifier. The previous data latch receives a portion or the whole of the display data and outputs the portion or the whole of the display data as the previous data. The bias control voltage generator compares the current data and the previous data of the display data and generates a control signal. The driver amplifier receives the output voltage of the gamma decoder, generates the output voltage applied to the liquid crystal display device, and controls the slew rate in response to the control signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
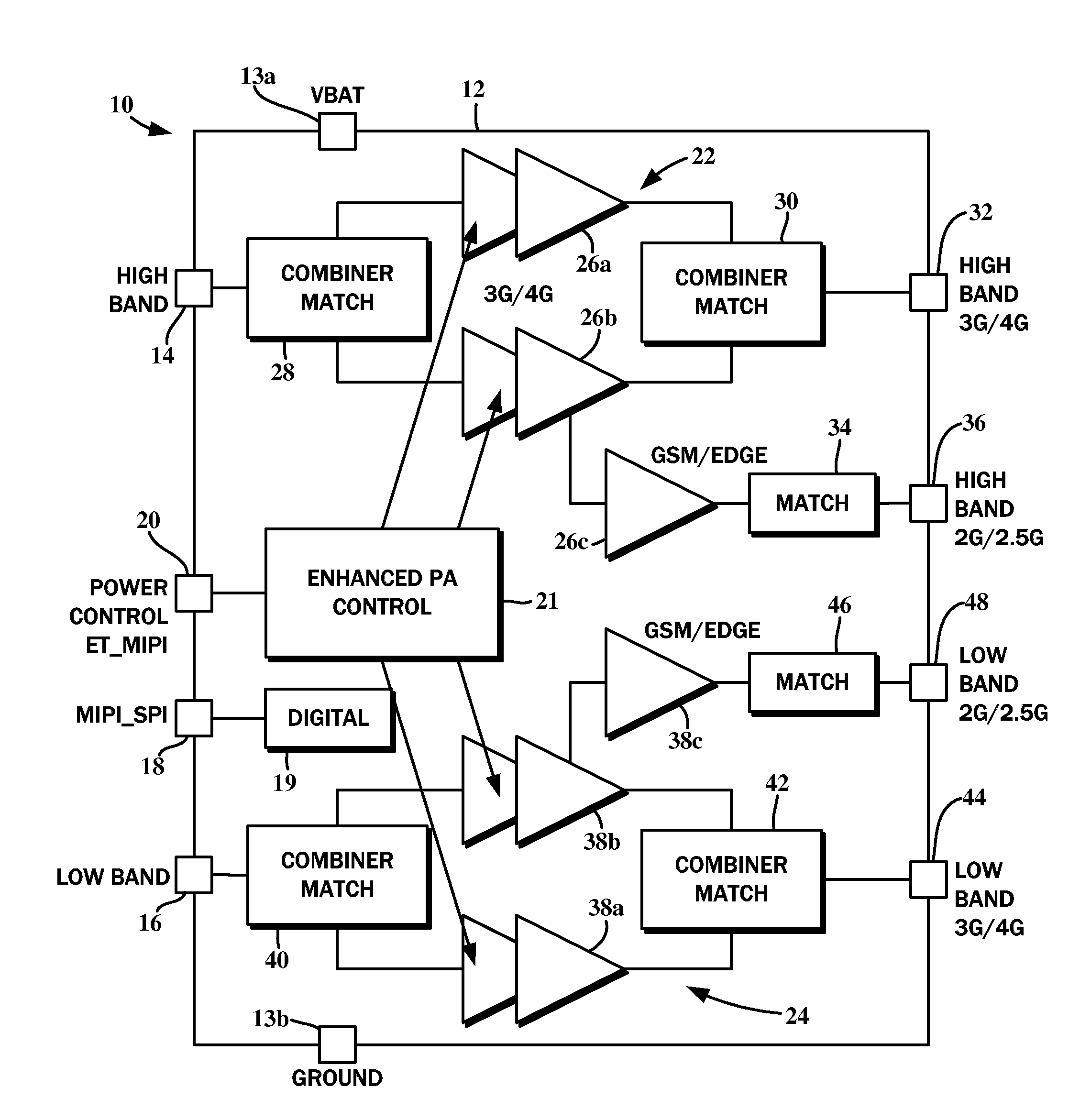
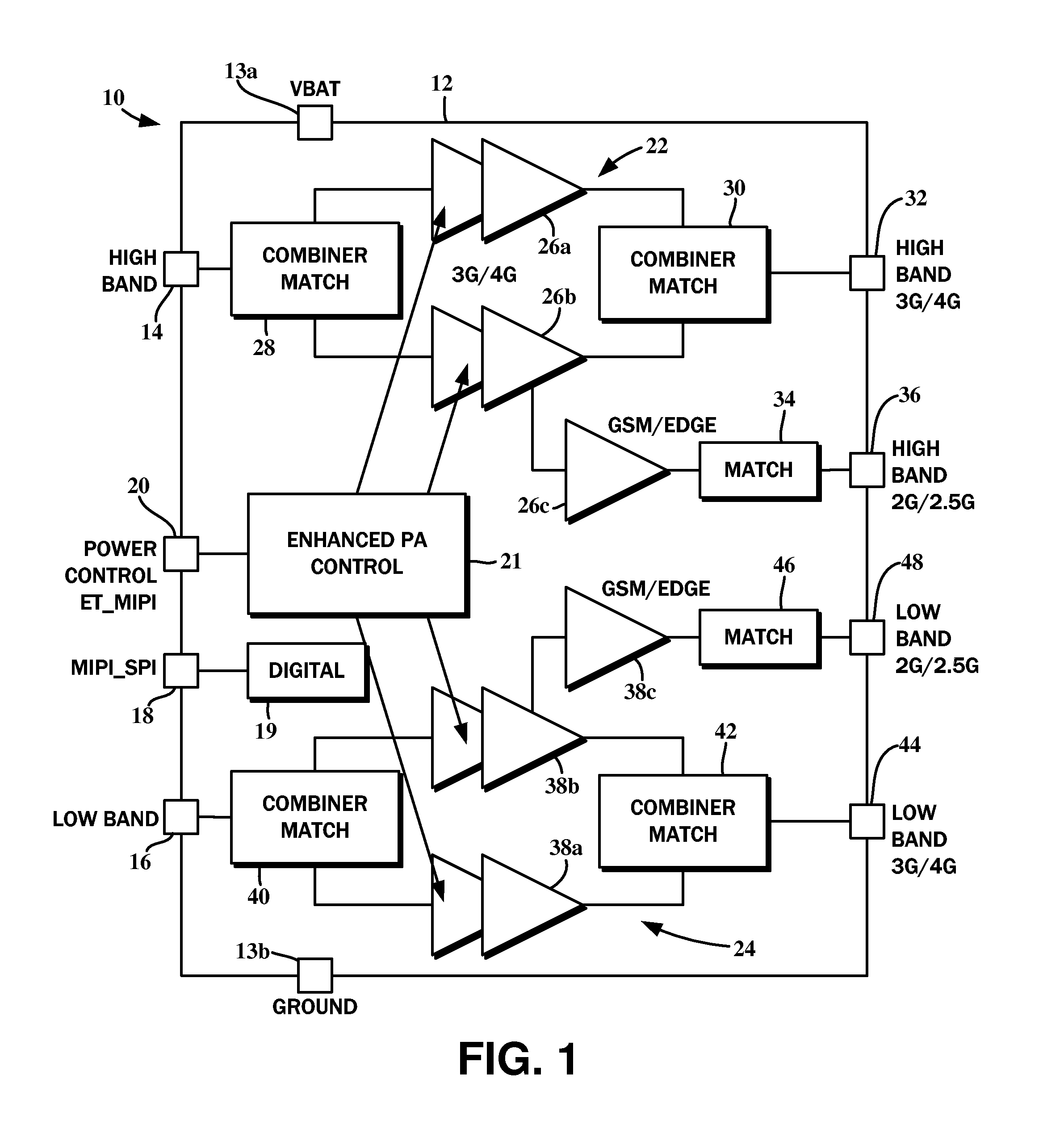
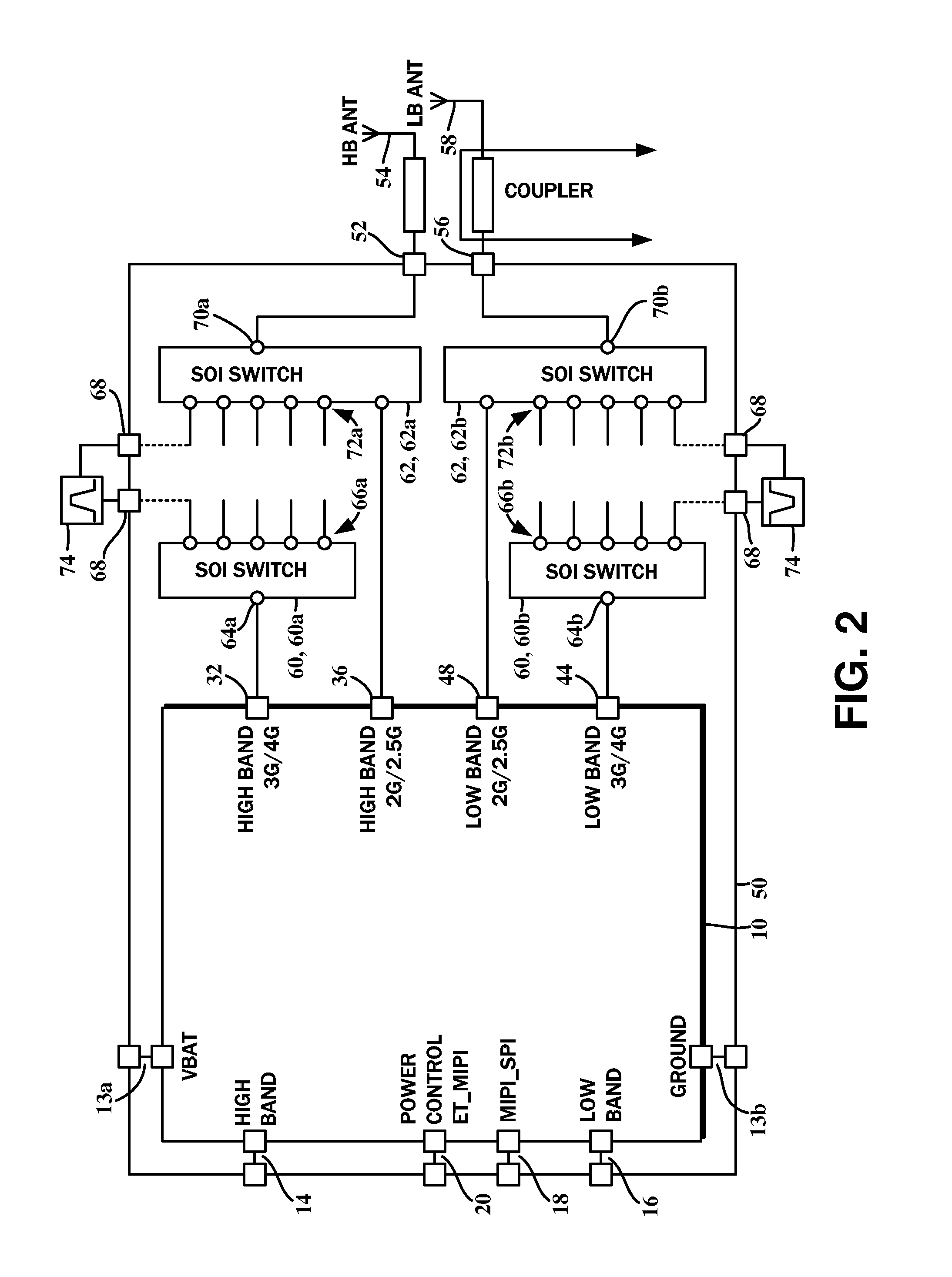
Multi-mode multi-band power amplifier module
A multi-mode multi-band power amplifier (PA) module is described. In an exemplary design, the PA module includes multiple power amplifiers, multiple matching circuits, and a set of switches. Each power amplifier provides power amplification for its input signal when selected. Each matching circuit provides impedance matching and filtering for its power amplifier and provides a respective output signal. The switches configure the power amplifiers to support multiple modes, with each mode being for a particular radio technology. Each power amplifier supports at least two modes. The PA module may further include a driver amplifier and an additional matching circuit. The driver amplifier amplifies an input signal and provides an amplified signal to the power amplifiers. The additional matching circuit combines the outputs of other matching circuits and provides an output signal with higher output power. The driver amplifier and the power amplifiers can support multiple output power levels.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
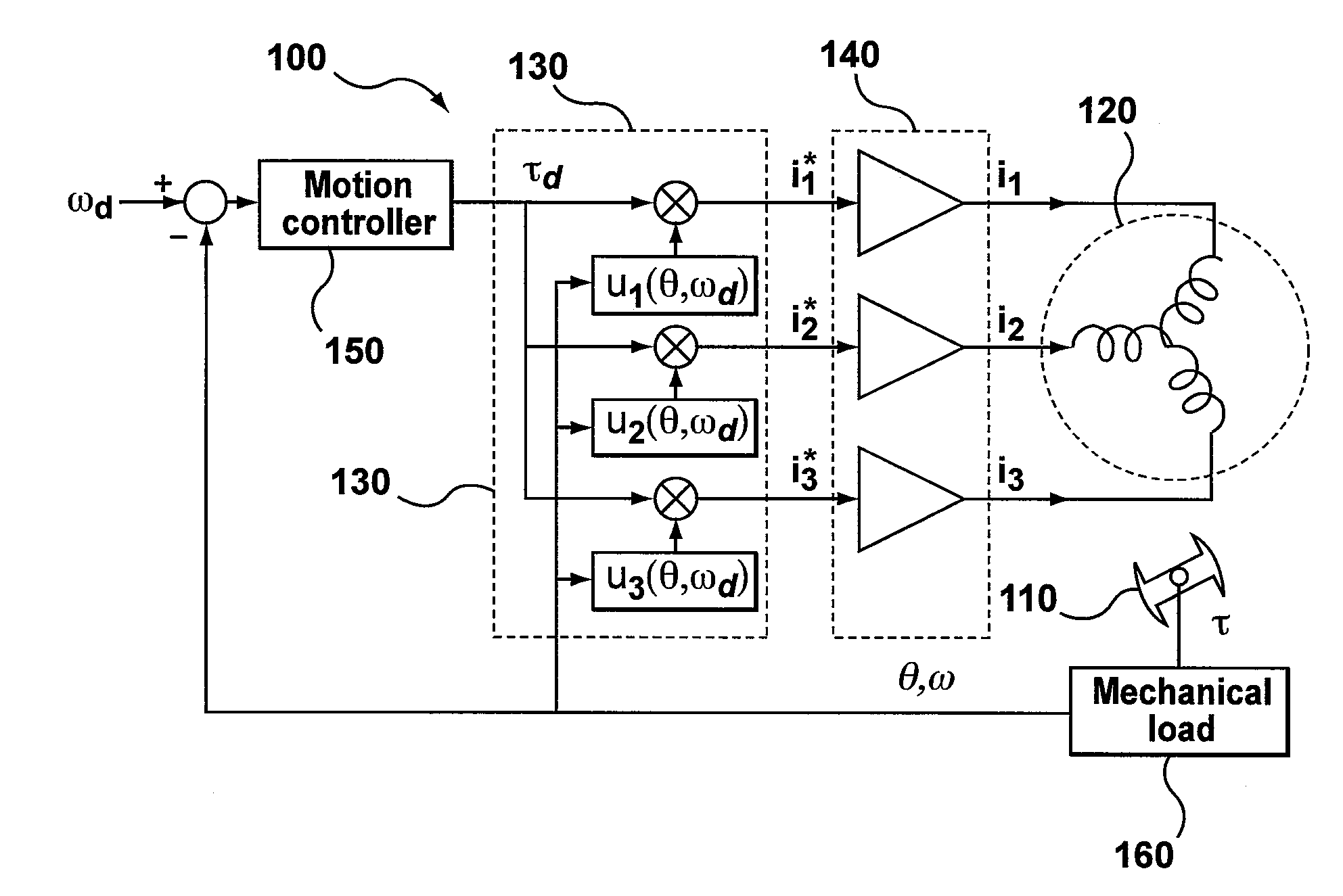
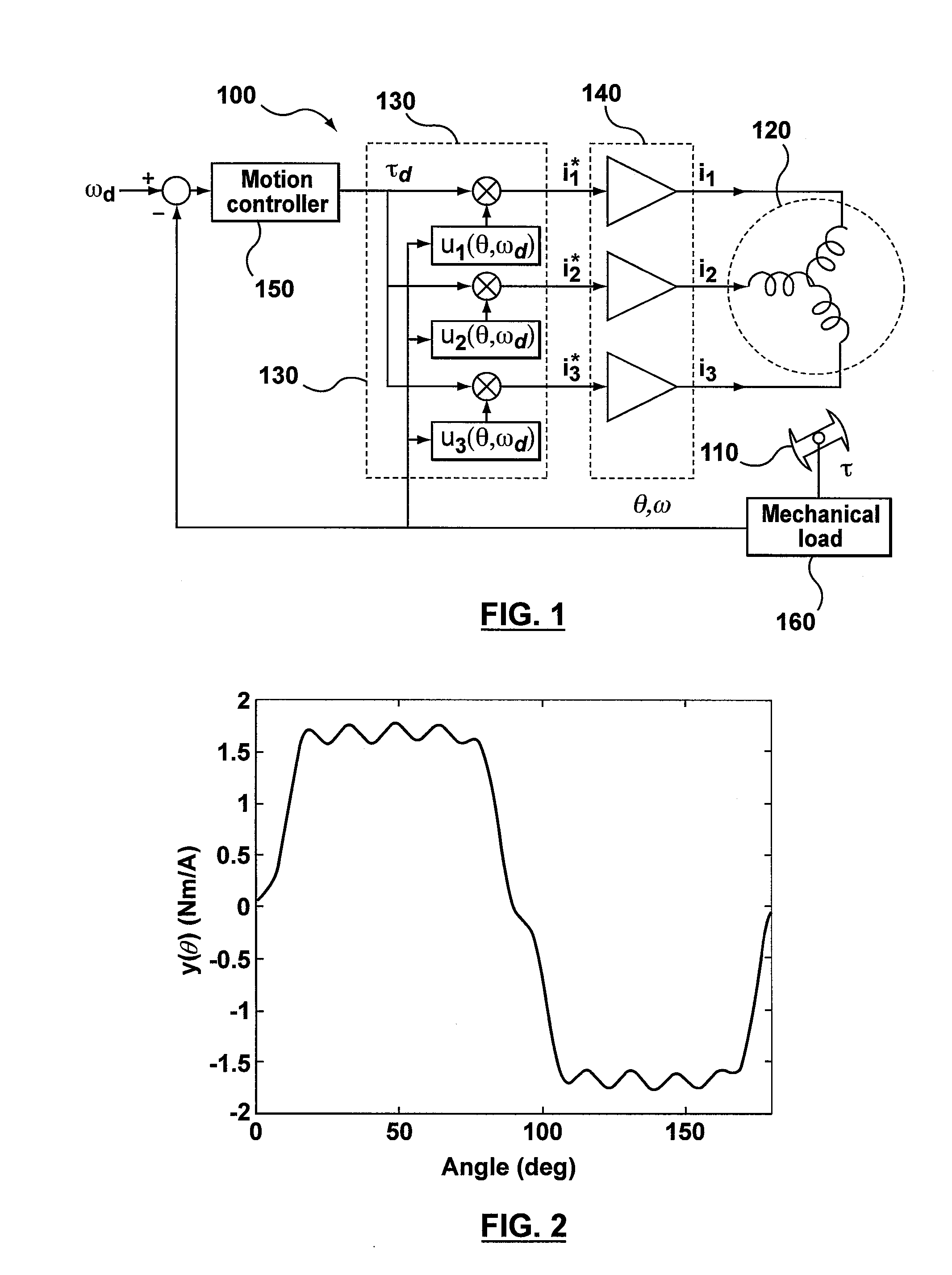
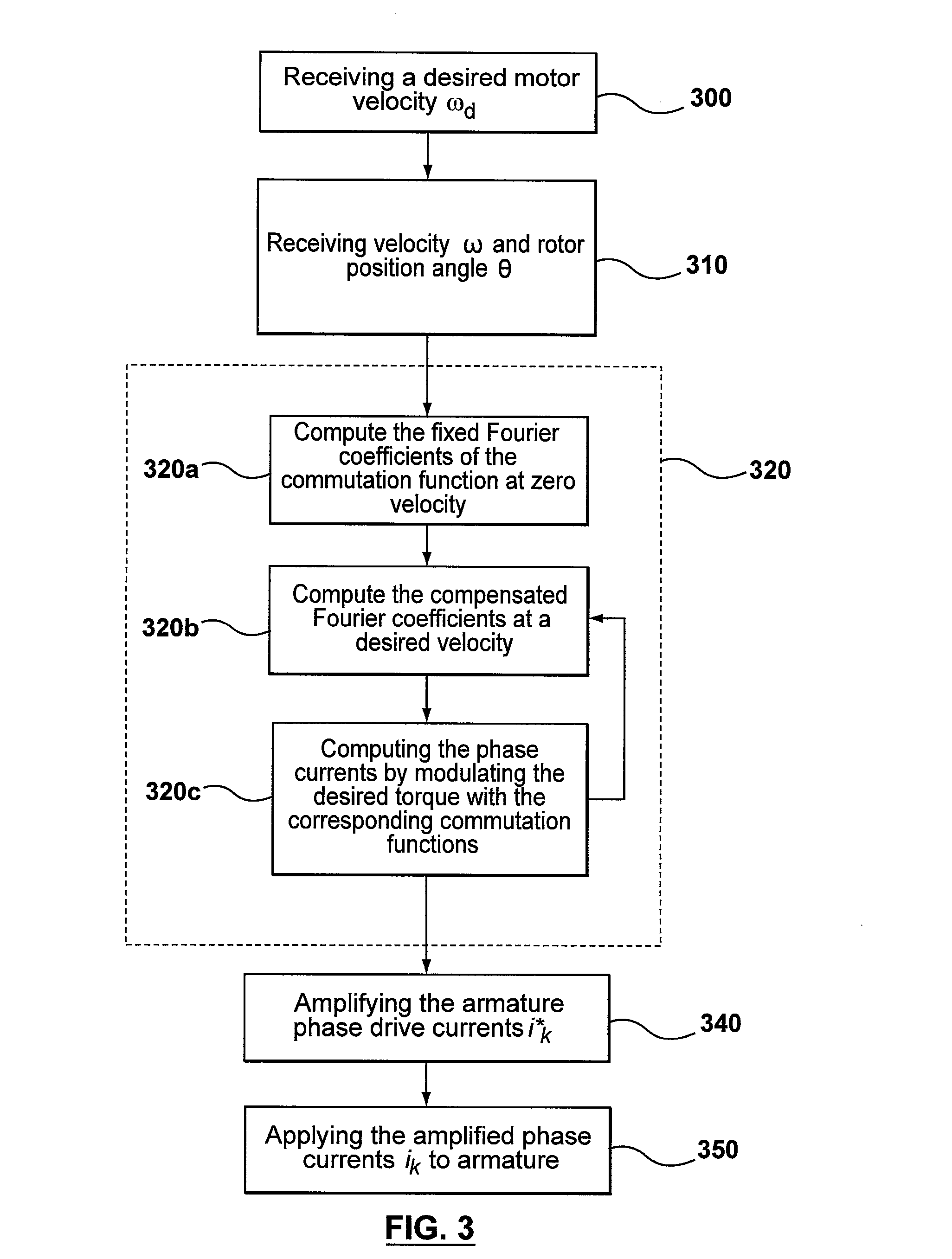
Method and apparatus for high velocity ripple suppression of brushless DC motors having limited drive/amplifier bandwidth
A method and apparatus are provided for ripple suppression of brushless DC motors at any given velocity irrespective of the limited bandwidth of the driver / amplifier supplying the excitation currents to the stator. In a preferred embodiment, Fourier coefficients of the current waveform are calculated as a function of rotor velocity by taking into account the driver / amplifier's finite bandwidth dynamics. For a given velocity, Fourier coefficients of the series approximating the waveform (control signal) are calculated as a function of the rotor velocity and the amplifier dynamics, to generate a waveform that results in no torque or velocity pulsations. When changing the motor speed, the coefficients are updated (recalculated) based on the new desired velocity (and amplifier dynamics), resulting in generation of an updated waveform that results in no torque or velocity pulsations at the new motor speed.
Owner:CANADIAN SPACE AGENCY
RF power amplifier having high power-added efficiency
InactiveUS7265618B1High PAEReduces DC supply powerSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationPower amplifiersPower-added efficiencyAudio power amplifier
The present invention, generally speaking, provides an RF power amplifier that exhibits high PAE at high output powers. The design of the power amplifier is based on the observation that the switching transistor is controlled by either voltage (for a FET) or current (for bipolar transistors), but not both. Thus, it is not necessary to develop power from the driver amplifier in order to operate the final stage as a switch. This recognition runs exactly counter to conventional wisdom, i.e., the concept of impedance matching for interstage design of high efficiency power amplifiers. It is impossible to develop solely a voltage waveform or a current waveform in a passband (resonant) network such as an RF power amplifier—both voltages and current must exist. In accordance with one aspect of the invention, however, instead of maximizing power transfer, power consumption is reduced while maintaining the magnitude of the voltage (or current) waveform. In accordance with another aspect of the invention, the driver is designed to, along with the final stage, operate in switch mode. In this instance, the design of the interstage network is similar to that of a Class E output stage. In the case of the interstage network, however, the objective is not to develop maximum power across the load (as in the case of the Class E output stage). Rather, the objective is to develop the maximum voltage across the driver's load (which is the switch input). In this arrangement, the input drive of the switch may be sufficiently high that the operating voltage of the driver stage may be reduced. This reduction further reduces the DC supply power to the driver, enhancing PAE.
Owner:APPLE INC
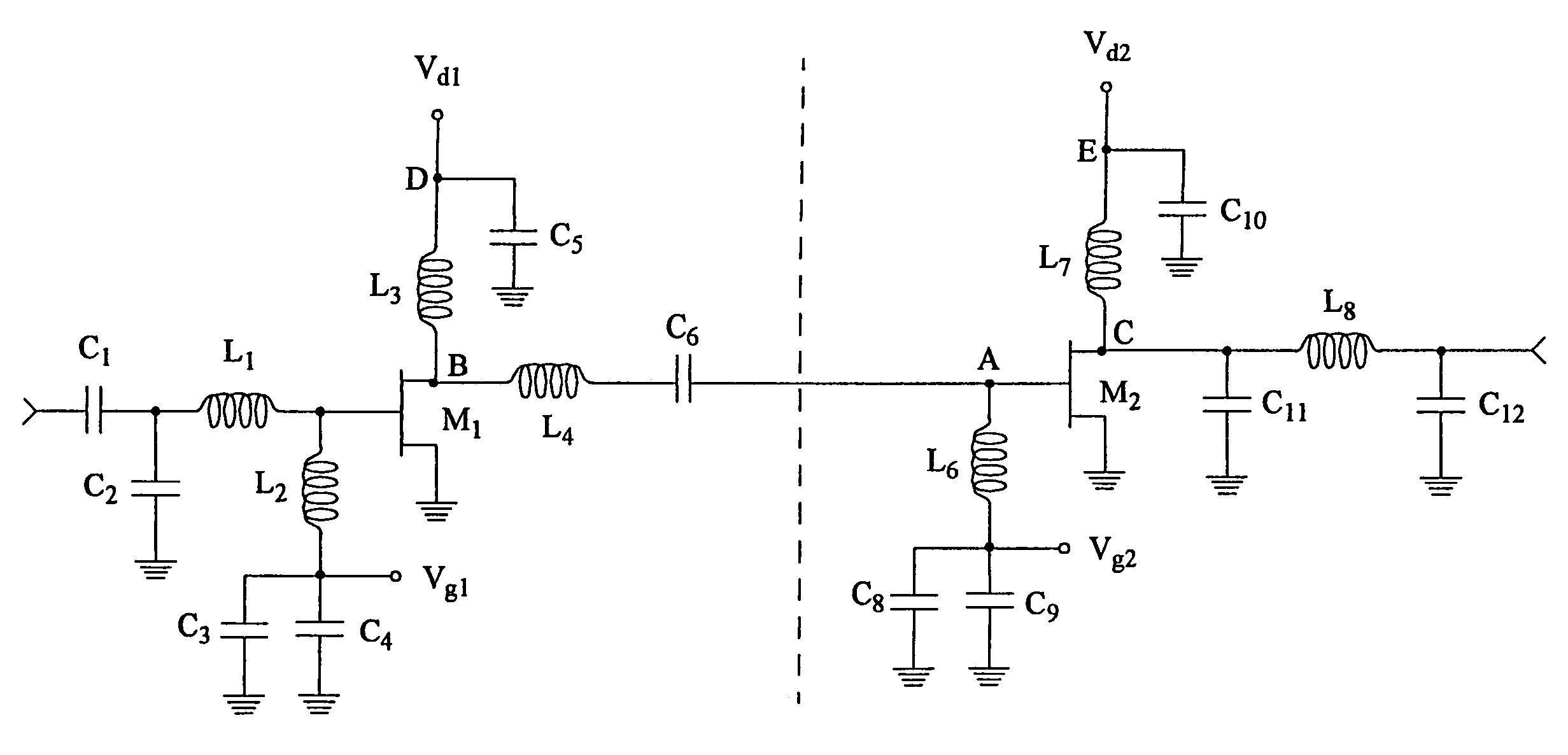
A broadband high-gain-flatness power amplifier
PendingCN109167575AIncrease output powerImprove reverse isolationAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyDifferential amplifiersCapacitanceBroadband power amplifier
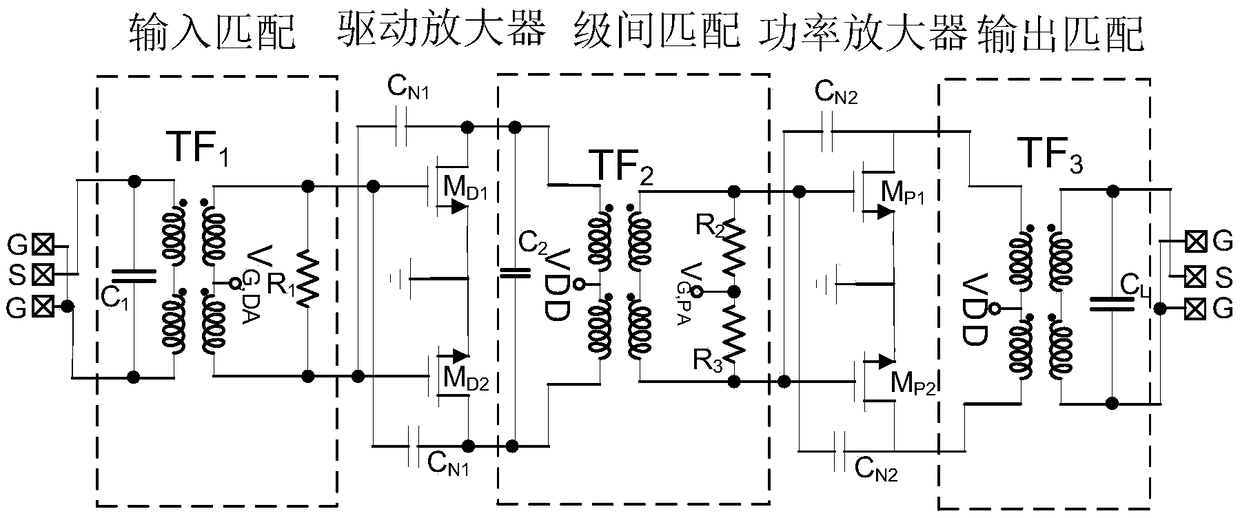
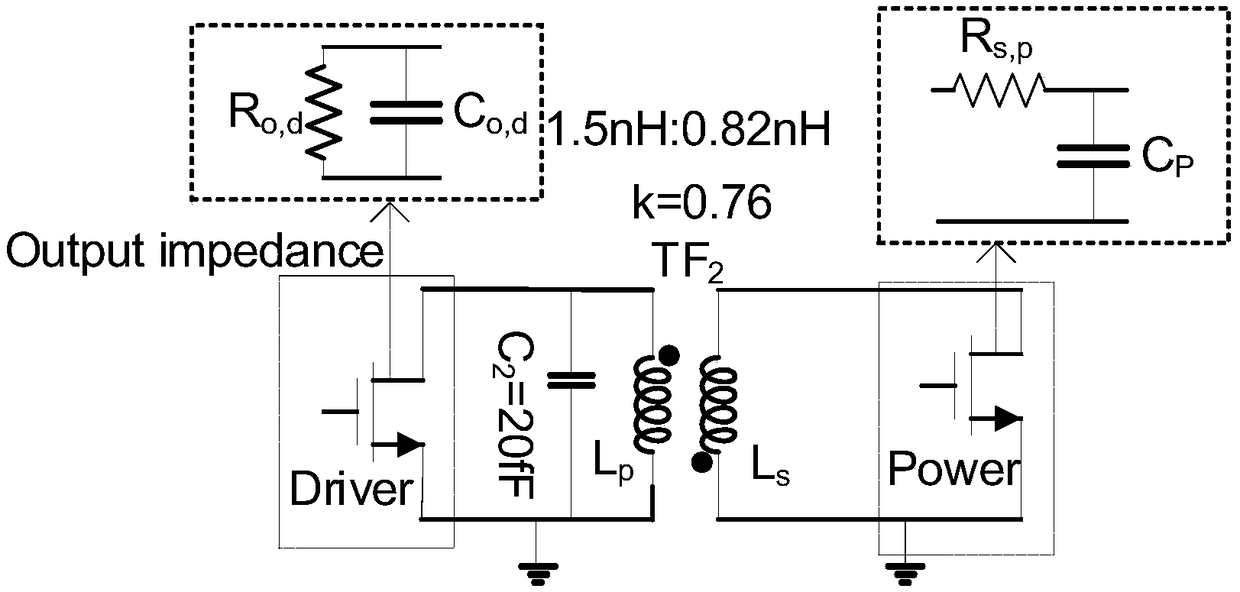
The invention belongs to the field of radio frequency microwave integrated circuit design, in particular to a broadband high-gain-flatness power amplifier. The power amplifier mainly includes: an input matching network composed of a high coupling factor transformer and a capacitor resistor; a differential common-source driver amplifier with neutralization capacitance; an inter-stage matching network composed of high coupling factor transformers; a differential common-source power amplifier with neutralizing capacitance for power amplification; and an output matching network which is composed of a high-coupling-factor transformer and a load capacitor. The power amplifier adopts high-coupling-factor transformers in three-stage matching network. The in-band gain fluctuation of broadband is reduced by compensating three-stage matched gain fluctuation, which effectively solves the problem of poor gain flatness caused by large inter-stage matched gain fluctuation of traditional broadband power amplifiers and improves the gain at the same time. Compared with the prior art, the invention can significantly improve the gain flatness of the wideband power amplifier while realizing high gain.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
High voltage, high current, and high accuracy amplifier
A method and system to use voltage isolated and floating differential output amplifiers wired in series and parallel to achieve arbitrary output drive voltage and current for the applications load. A second embodiment uses multiple matched voltage-isolated and floating differential output amplifiers in a single chassis to enable selection between a multi-channel amplifier and a high current and / or high voltage mono amplifier. A third embodiment uses a step-up transformer and paralleled unity-gain buffer amplifiers, on input and / or output stages, to produce a zero feedback, high performance, high drive amplifier. A fourth embodiment uses a high voltage unity-gain driver amplifier to bias a unity-gain buffer amplifier and its power supply to achieve an ultra low distortion high voltage buffer amplifier. A fifth embodiment uses multiple voltage-isolated and linearized devices to enable dynamically modifiable, Class A, Class B, and Class AB topologies of predetermined voltage and current performance. A sixth embodiment corrects an output by linearizing one or more devices in a circuit by utilizing a linearization module (e.g., including one or more digital lookup tables, an error simulation circuit, or an equivalent) to linearize at least one parameter of at least one device in the circuit.
Owner:HOOVER D ROBERT
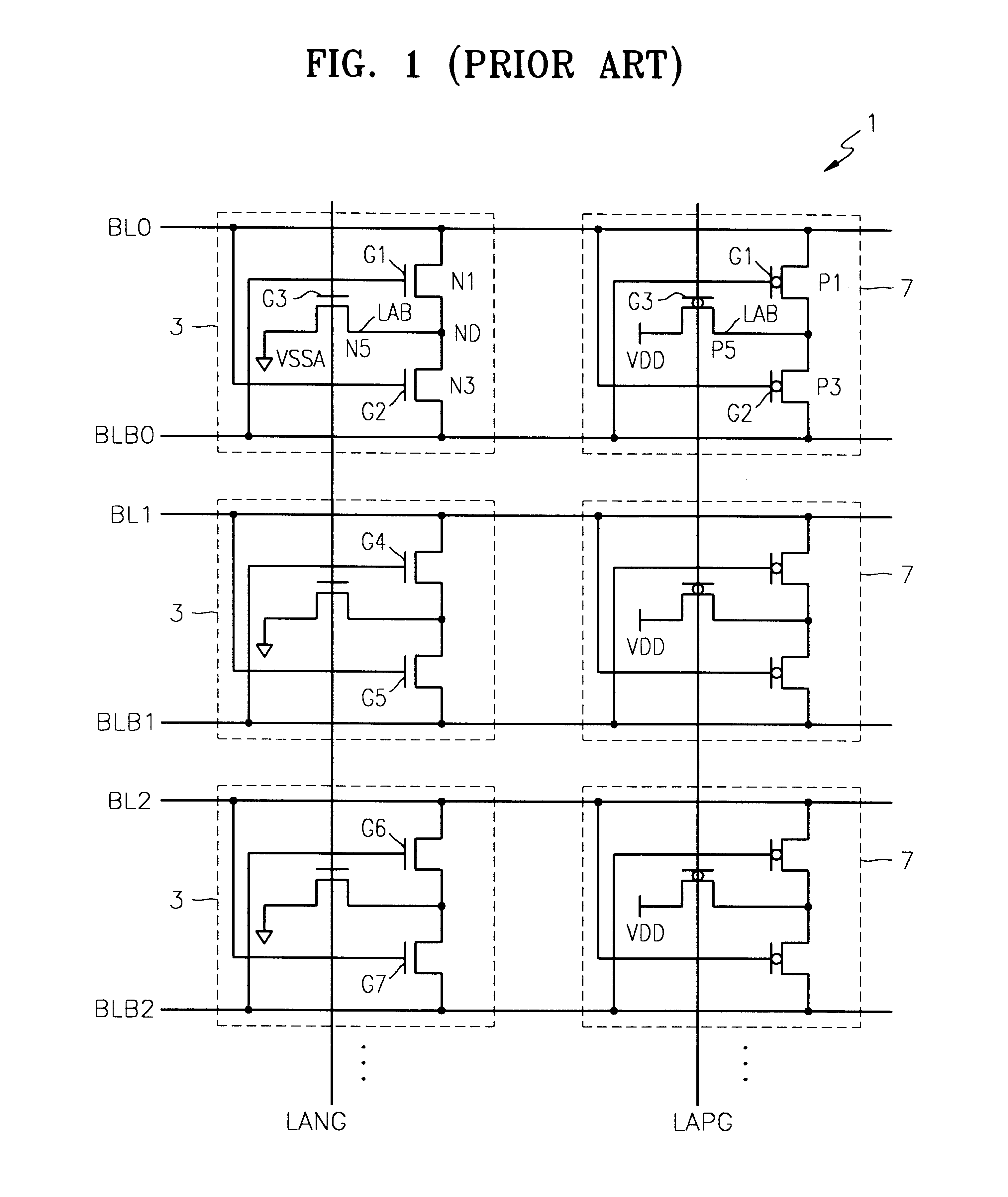
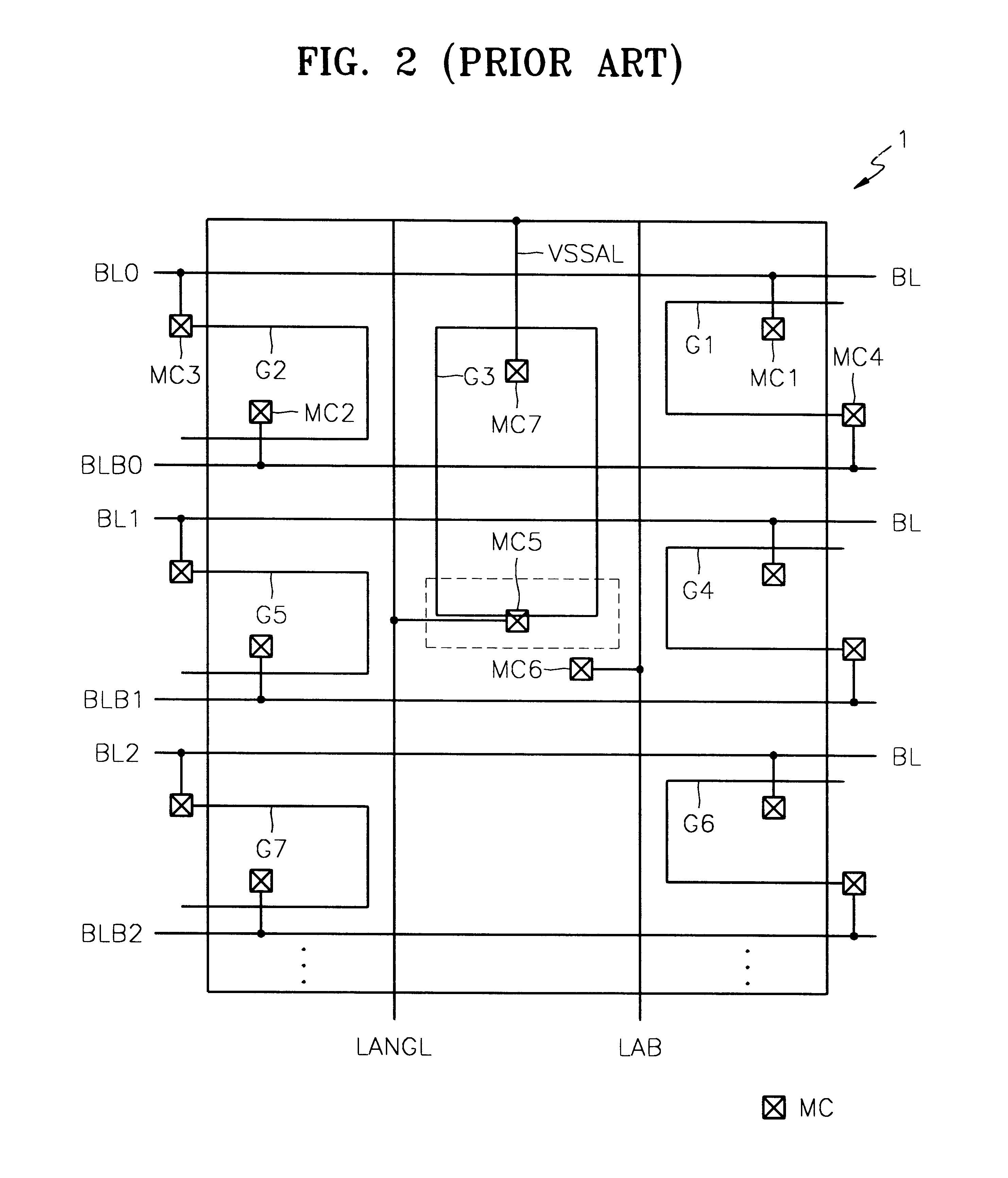
Layout method for bit line sense amplifier driver
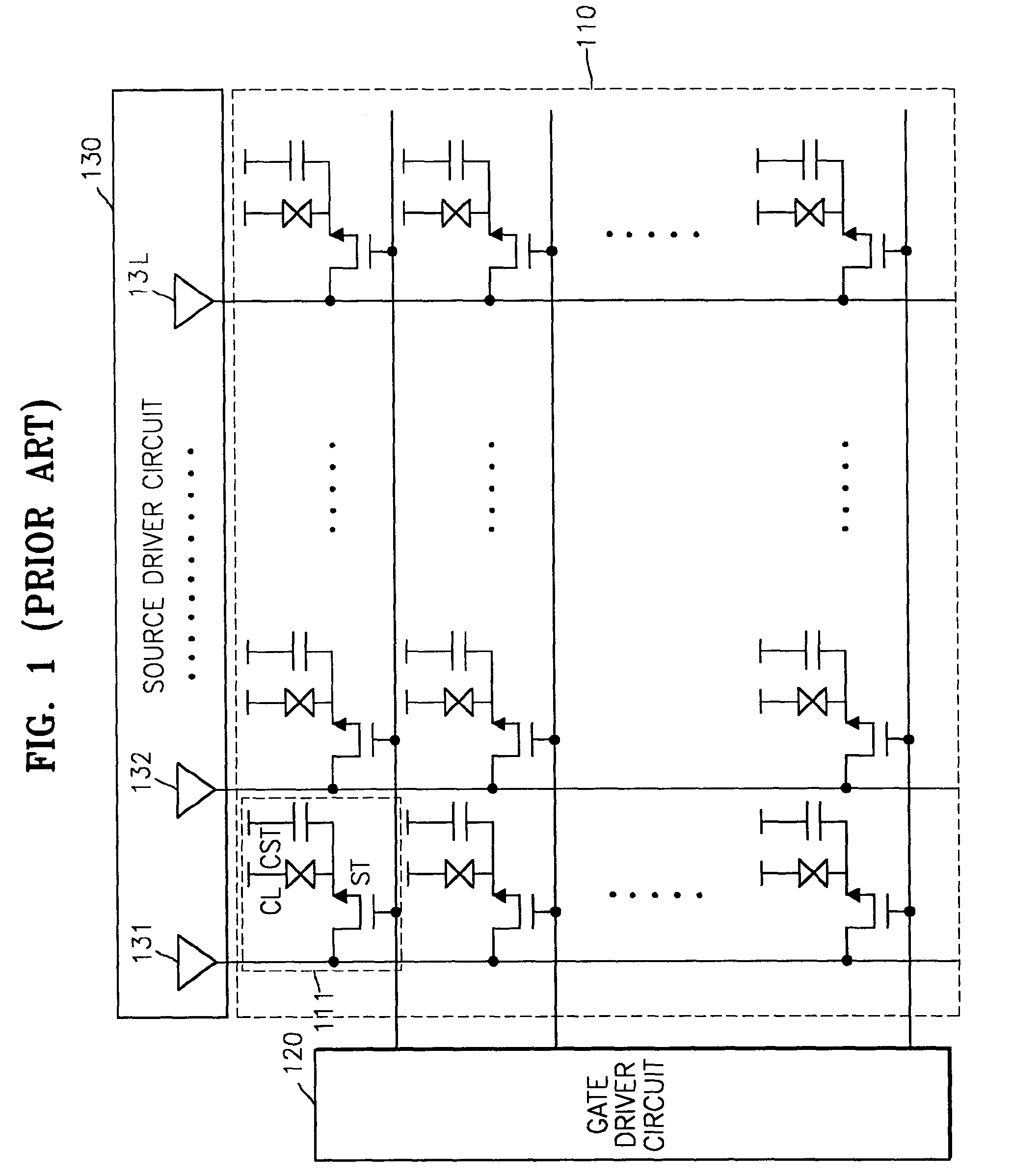
A bit line sense amplifier is provided. The bit line sense amplifier includes a first sense amplifier block in which a plurality of first sense amplifiers for sensing and amplifying data of a bit line or a complementary bit line are laid out, and first drivers, which are arranged outside the plurality of first sense amplifiers, for pulling down the bit line or the complementary bit line to a first voltage level. The bit line sense amplifier further includes a second sense amplifier block with a plurality of second sense amplifiers and second drivers for pulling up the bit line or the complementary bit line to a second voltage level. By arranging the drivers outside the bit sense amplifiers, effects caused by variation in critical dimensions (CDs) of gates are minimized and the entire area of the bit line sense amplifier is reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Stacked pre-driver amplifier
ActiveUS20110109393A1Reducing and eliminating powerReduce voltageAmplifier combinationsRF amplifierAudio power amplifierVoltage drop
A stacked pre-driver stage and a power amplifier including the stacked pre-driver stage are described. The stacked pre-driver stage comprises stacked pre-drivers arranged in series between a supply voltage and a reference voltage. Each pre-driver includes a pre-driving amplifier, together with MOS transistors. Each pre-driver is subject, in operation, to a voltage difference which is inferior to a maximum allowed use voltage of the MOS transistors with a largely reduced voltage drop across the regulator included in the power amplifier.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
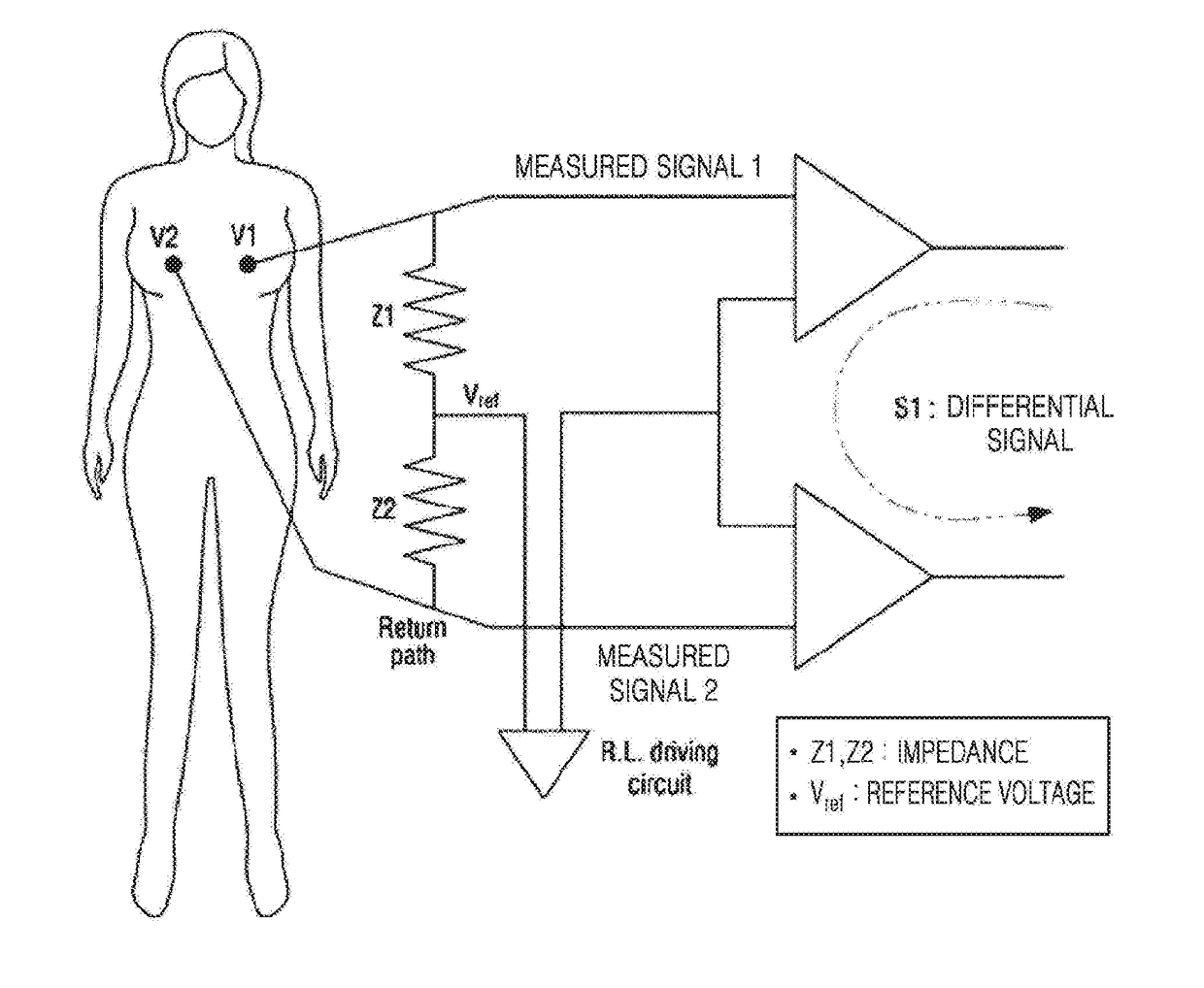
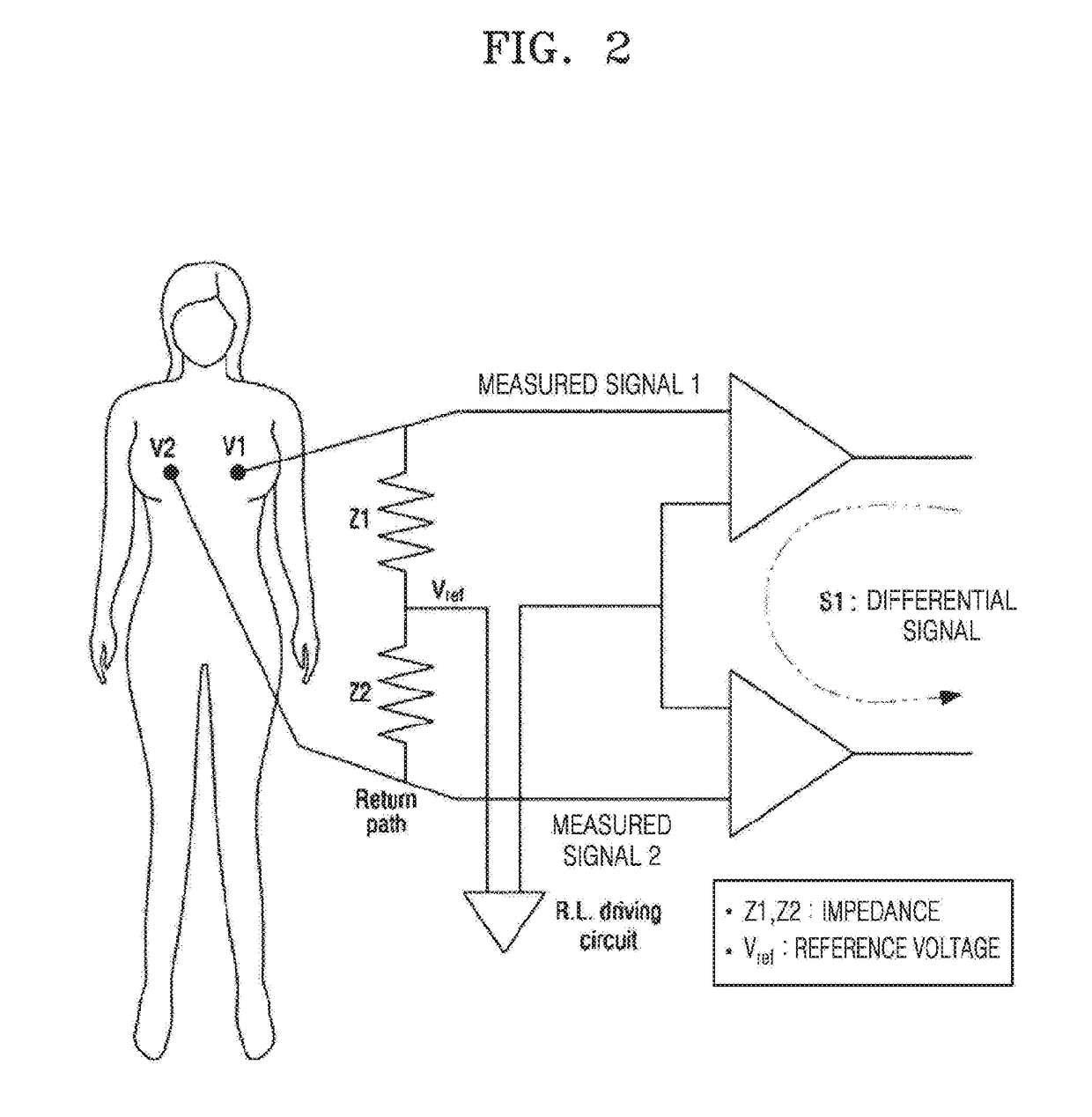
Portable apparatus for detecting breast cancer
InactiveUS20170188878A1Accurate diagnosisShort timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsAudio power amplifierLow-pass filter
An apparatus for detecting abnormal masses such as breast cancer includes a measurement sensor configured to obtain a voltage at a first area of a first breast of a subject; a reference sensor configured to obtain a voltage at a second area of a second breast of the subject, a position of the first area corresponding to a position of the second area; and a detector, wherein the detector includes a differential amplifier configured to amplify a voltage input from the at least one of the measurement sensor and the reference sensor; an active low pass filter configured to pass a signal frequency of a low frequency band among signals transmitted from the differential amplifier; a driver amplifier configured to amplify a signal passed through the active low pass filter; and an analog-to-digital (AD) converter configured to convert the signal amplified by the driver amplifier into a digital signal.
Owner:LEE KYONGHO
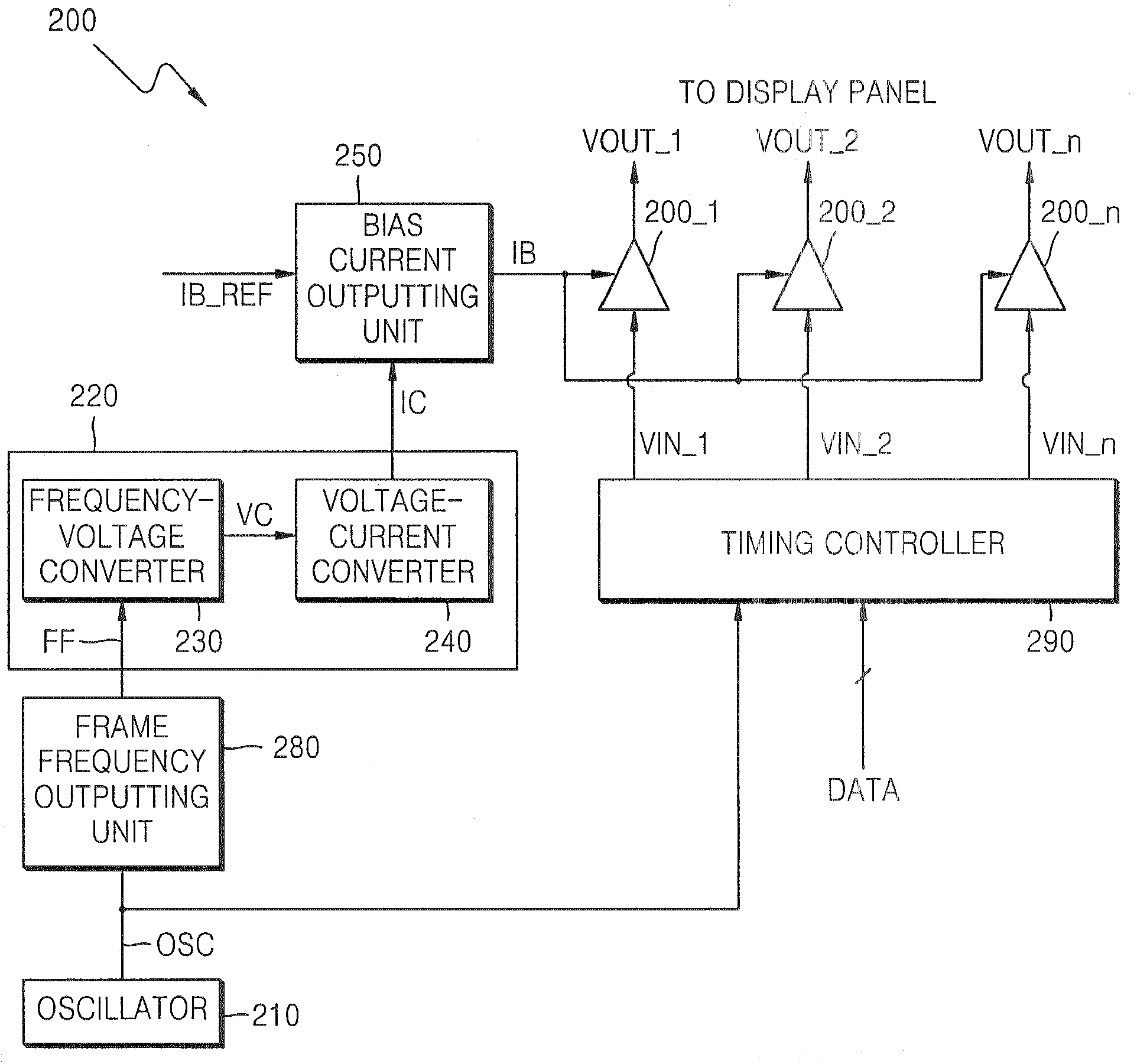
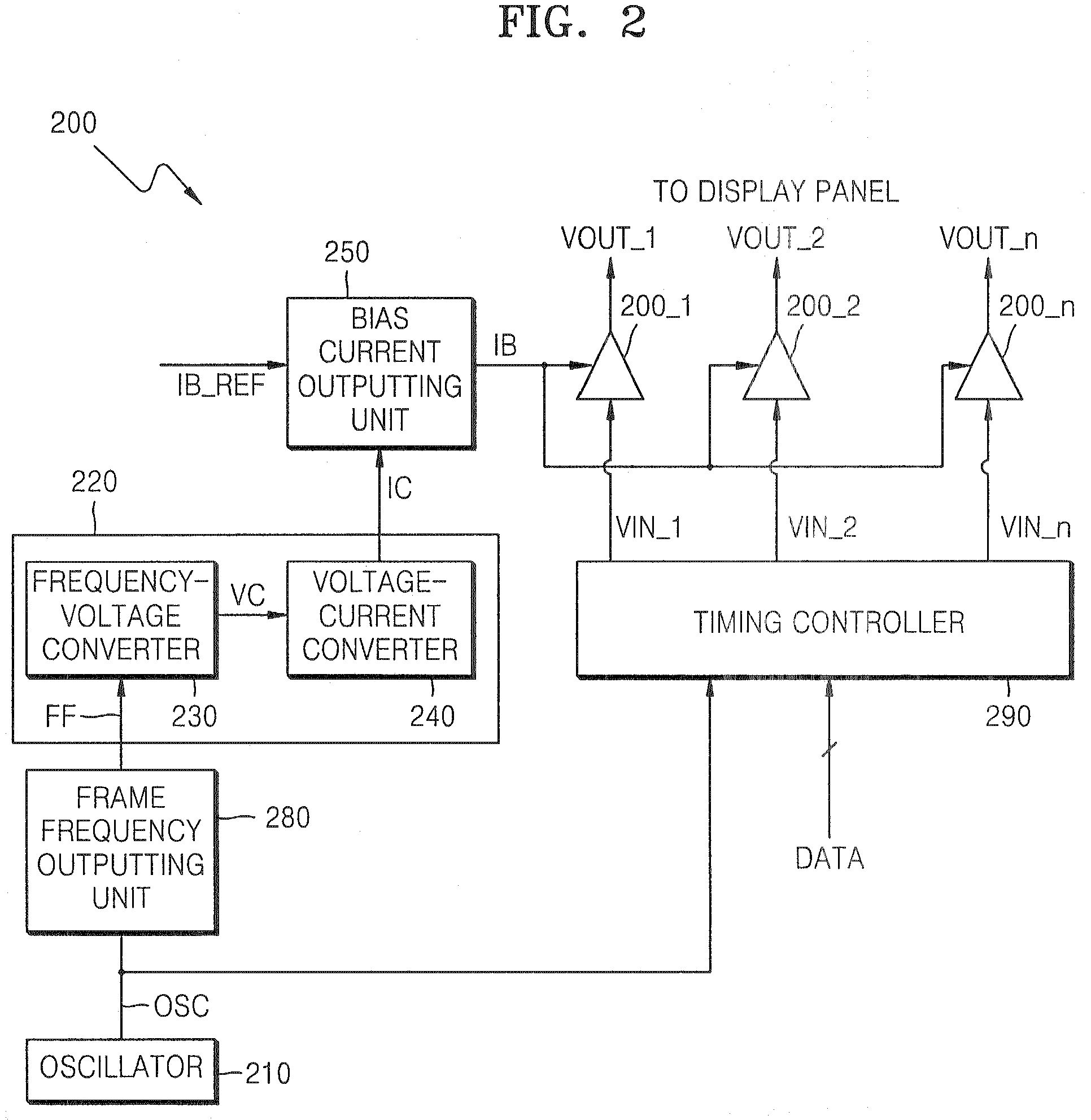
Source driver circuit for controlling slew rate according to frame frequency and method of controlling slew rate according to frame frequency in the source driver circuit
InactiveUS20070195054A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesLighting and heating apparatusDriver circuitAudio power amplifier
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Voltage controlled current source device
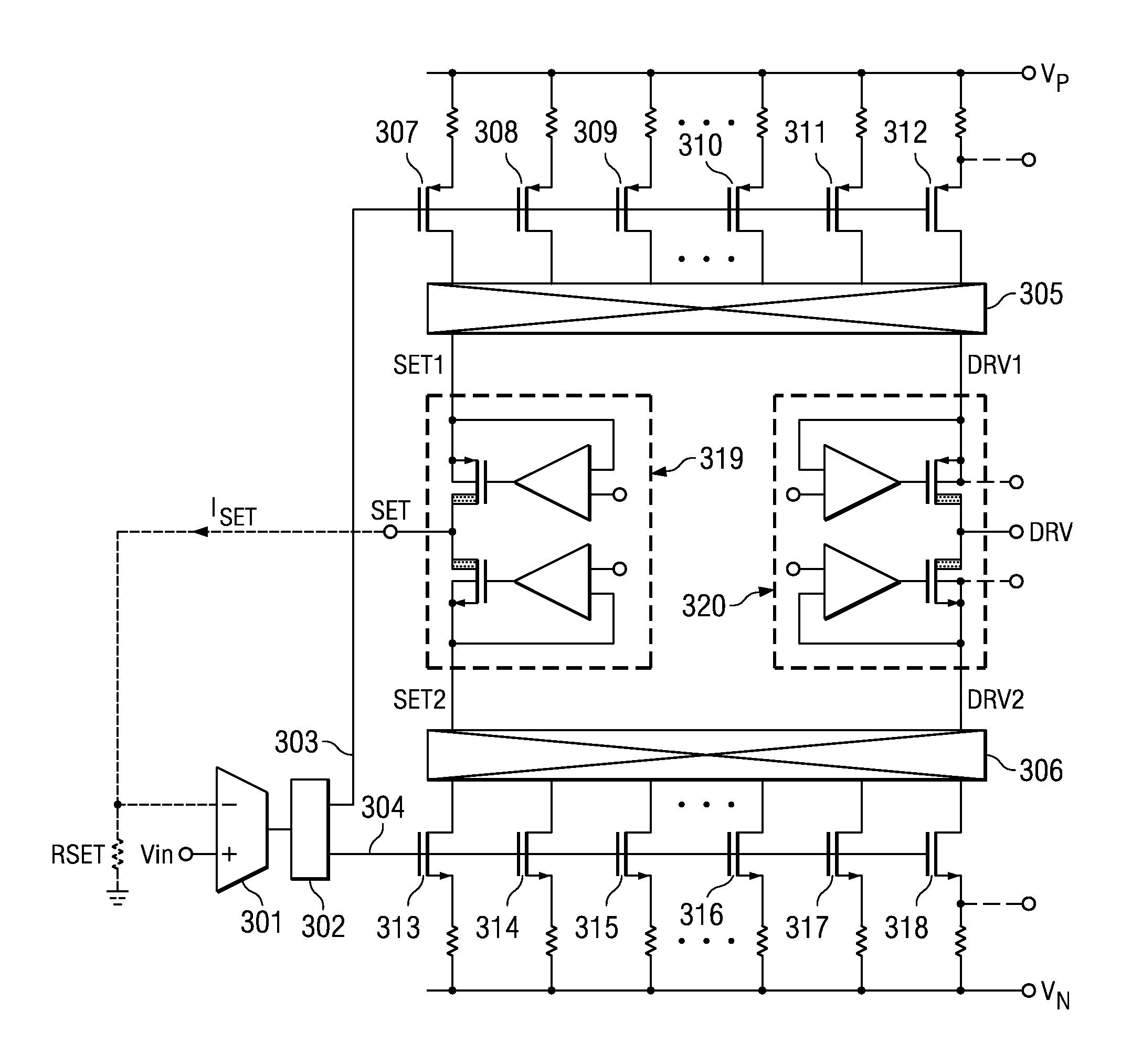
ActiveUS20060255787A1Improve accuracyQuick applicationElectric variable regulationElectrical resistance and conductanceInstrumentation amplifier
An integrated voltage controlled current source device is provided, that extends the high accuracy, low drift output current over a large current range, and provides more headroom and better power efficiency than the standard shunt resistor and INA (instrumentation amplifier) current source arrangement. The device has a control voltage input, a load current output and a current set terminal for a connection of a current set resistor. It contains a selected leg biasing set voltage, corresponding to a control voltage applied to the control voltage input of a regulating driver amplifier providing a regulated voltage to be applied across the current set resistor, thereby causing a reference current to flow through the current set resistor and selected leg(s) of a current mirror. Furthermore, the device contains a dynamically matched current mirror that mirrors the reference current to the load output current. The algorithm for selecting the current mirror legs may be a pseudo-random or a defined pattern.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
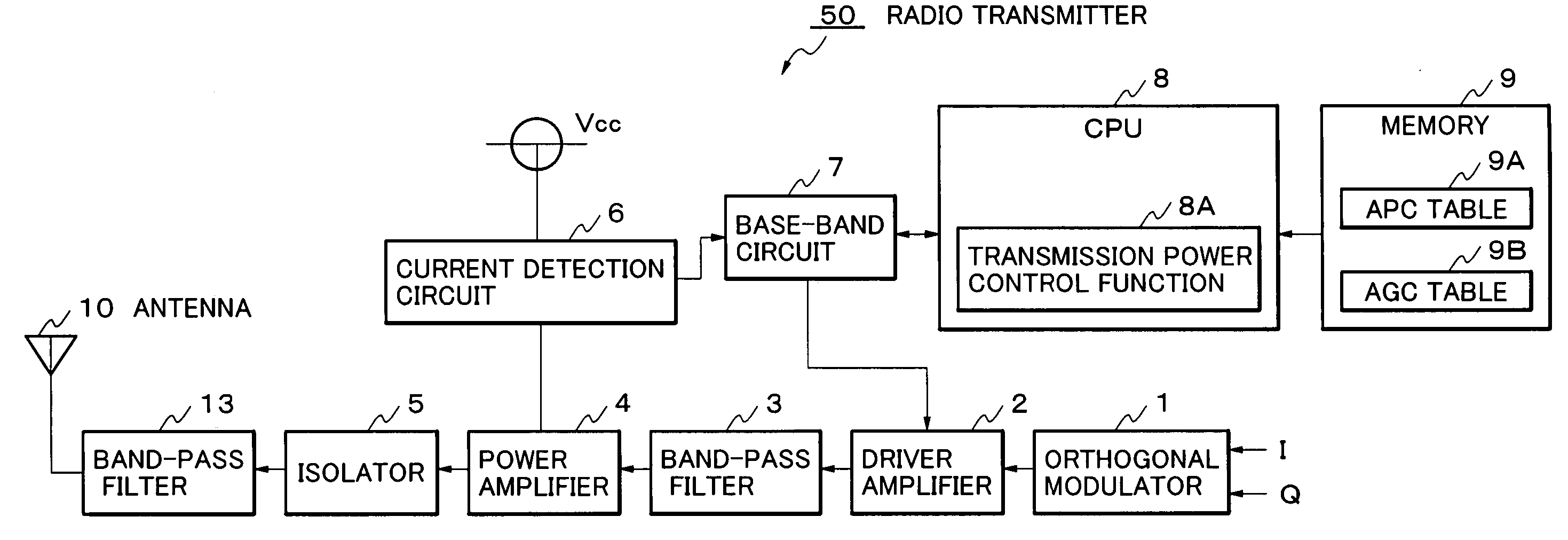
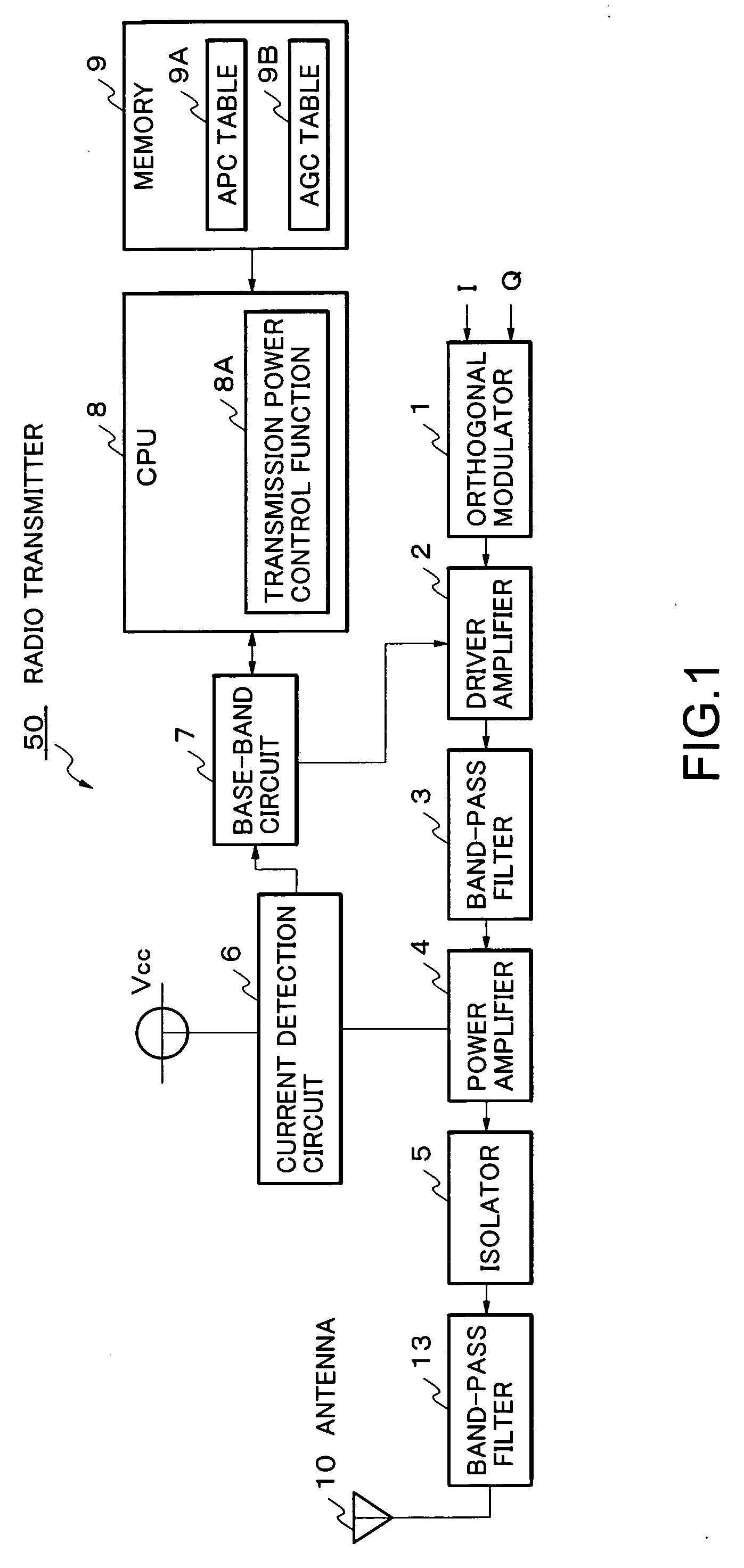
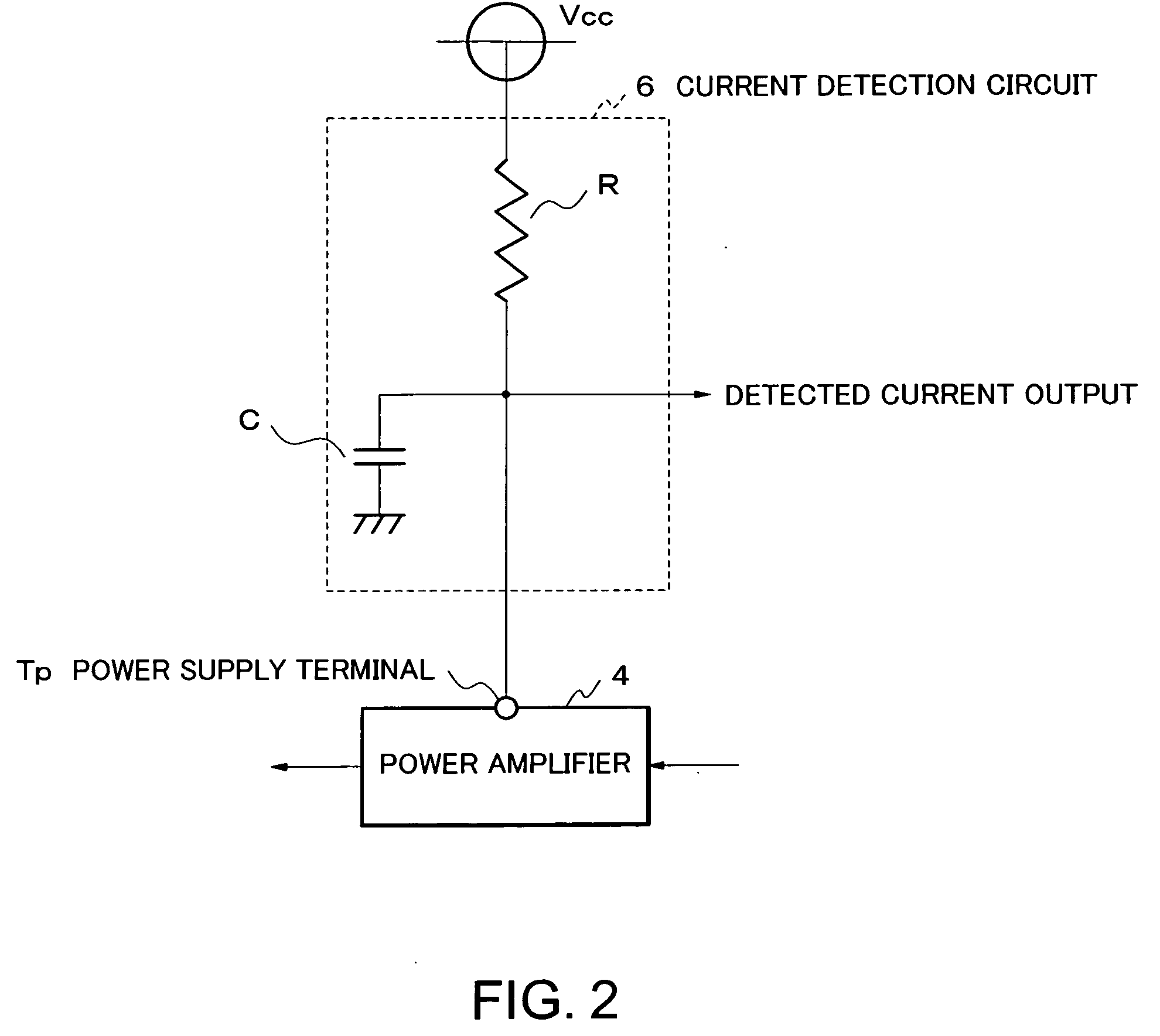
Transmission power control device and method thereof, computer program for transmission power control device, and radio transmitter
InactiveUS20050156669A1Reduce lossesResonant long antennasGain controlAudio power amplifierControl equipment
A transmission power control device which amplifies in a driver amplifier 2, and in a power amplifier 4 to which the output from the driver amplifier is inputted, so that the power of a signal to be transmitted may become predetermined target transmission power, detects an electric-current which flows to the power amplifier 4 from a power supply, and adjusts the gain of the driver amplifier 2 based on this detected electric-current.
Owner:LENOVO INNOVATIONS LTD HONG KONG
Directed acoustic sound system
ActiveUS8538036B2Improve directivityAvoid distracting coworkersPublic address systemsLine-transmissionAudio power amplifierCarrier signal
An acoustic sound system usable in electronic entertainment systems that generates highly directional sound. The directed acoustic sound system includes a parametric audio sound system having a modulator for modulating an ultrasonic carrier signal with a processed audio signal, a driver amplifier for amplifying the modulated signal, and a parametric loudspeaker for projecting the modulated and amplified signal through the air for subsequent regeneration of the audio signal along a pre-selected path. The acoustic sound system allows a user to select the parametric loudspeaker, a connectable non-directional loudspeaker, or both loudspeakers for producing audible sound. The acoustic sound system may be employed in the home, in the workplace, or in any other environment where audio leakage is undesirable.
Owner:POMPEI FRANK JOSEPH
Rotating transfer mechanism and zooming camera having the same
Provided are a circuit and method for driving a liquid crystal display device using low power. The circuit includes a display data latch, a gamma decoder, and a driver cell circuit. The display data latch latches display data from a memory. The gamma decoder receives a plurality of gray scale voltages, and selects and outputs one of the plurality of gray scale voltages in response to the display data. The driver cell circuit receives an output voltage of the gamma decoder and generates an output voltage applied to the liquid crystal display device. The driver cell circuit controls a slew rate in response to comparison result of current data and previous data of the display data. The driver cell circuit includes a previous data latch, a bias control voltage generator, and a driver amplifier.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
RF signal generation circuit and wireless transmitter
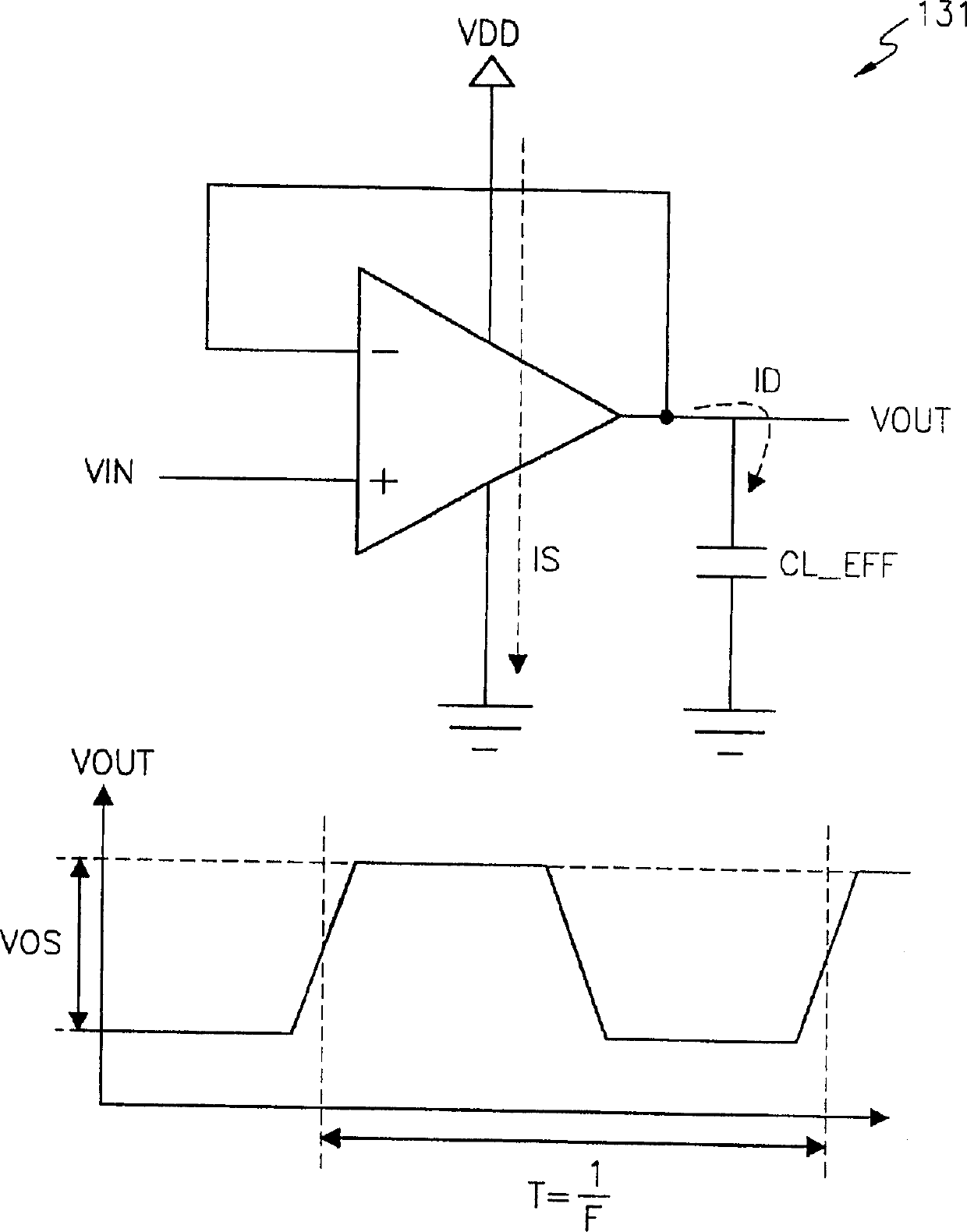
ActiveUS20120262214A1Total current dropImprove noise characteristicsPower amplifiersAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyClass-D amplifierVoltage reference
Owner:NEC CORP
Duobinary optical transmitter
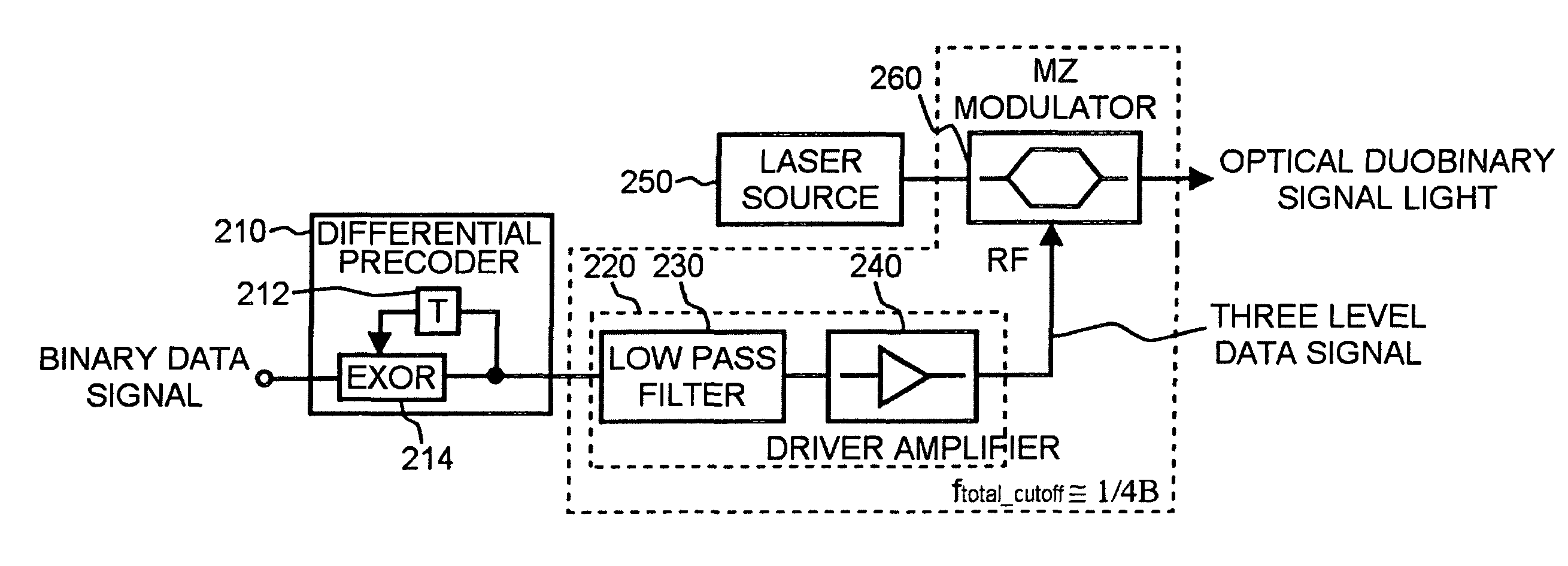
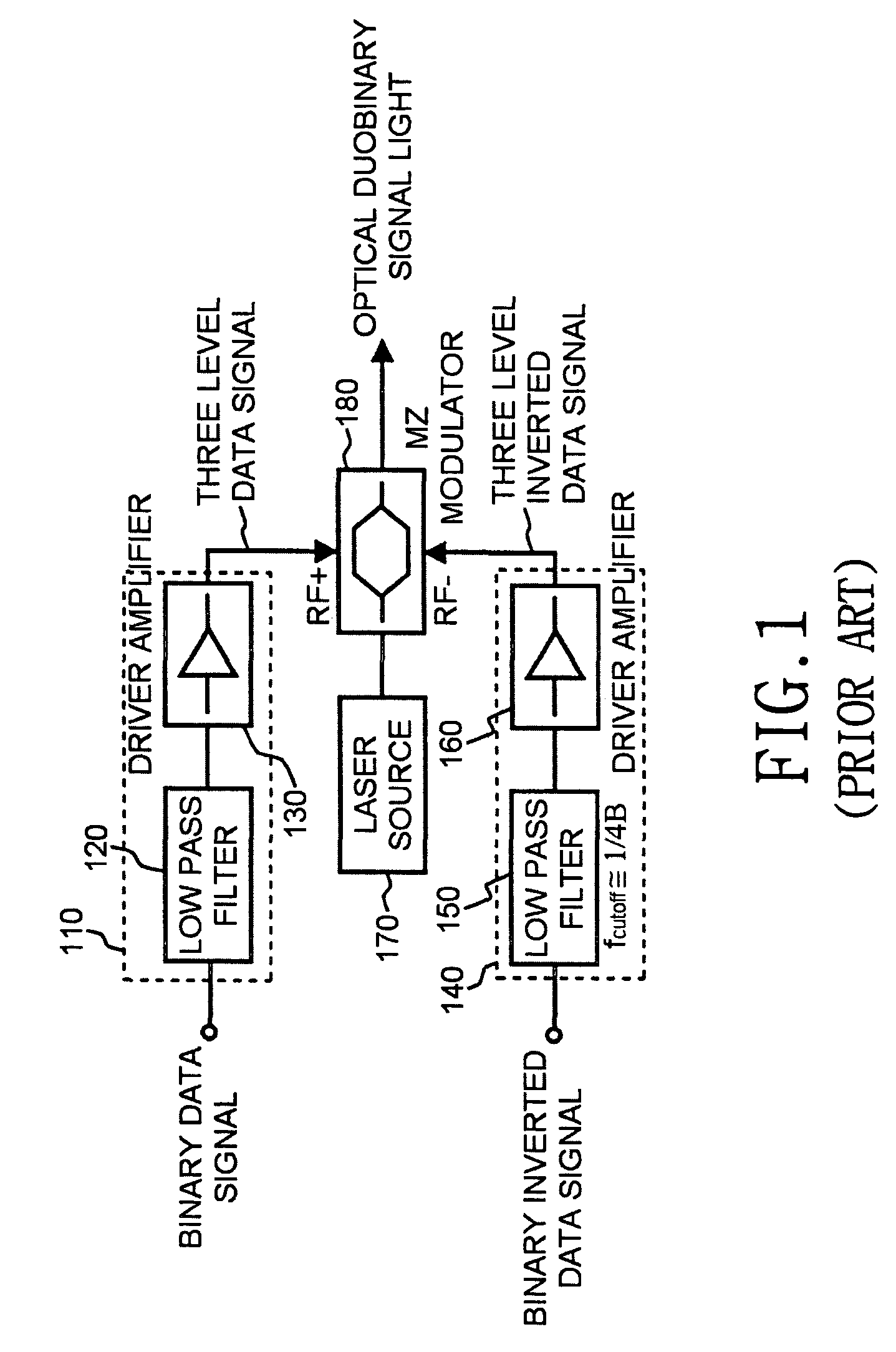
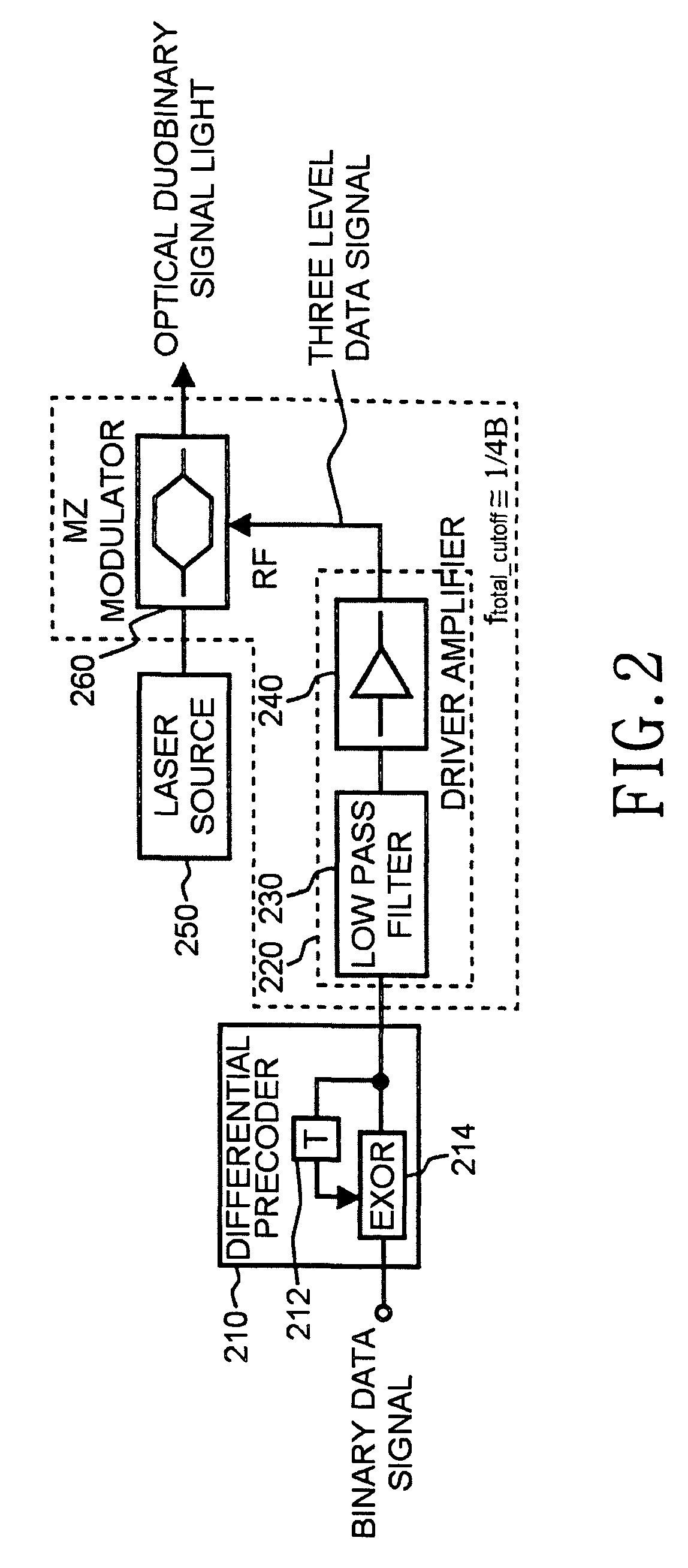
InactiveUS7215892B2Improve cost competitivenessLow bandwidthElectromagnetic transmittersElectromagnetic receiversThree levelLow-pass filter
Disclosed is a duobinary optical transmitter, which includes a laser source for outputting light with a predetermined wavelength; a Mach-Zehnder interferometer-type optical intensity modulator for modulating the intensity of the light according to a three-level data signal inputted through a modulation terminal; a low-pass filter for converting an inputted two-level binary data signal into a three-level data signal through an interference among codes; and, a modulator driver / amplifier for amplifying the three-level data signal and then outputting it to the modulation terminal, wherein the overall bandwidth of the low-pass filter, the modulator driver / amplifier, and the optical intensity modulator corresponds to approximately ¼ of the clock frequency of the two-level binary data signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com