Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
75 results about "Gain compression" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
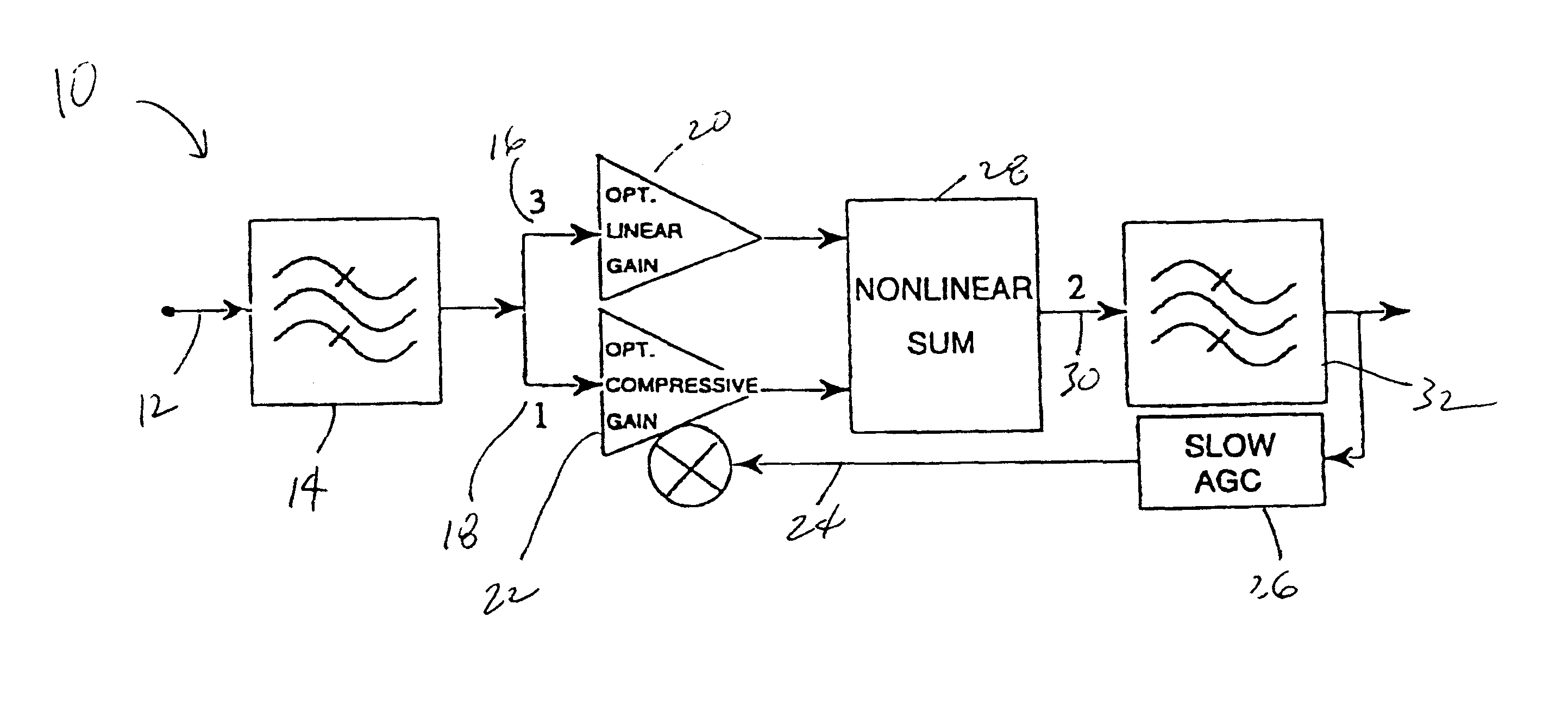
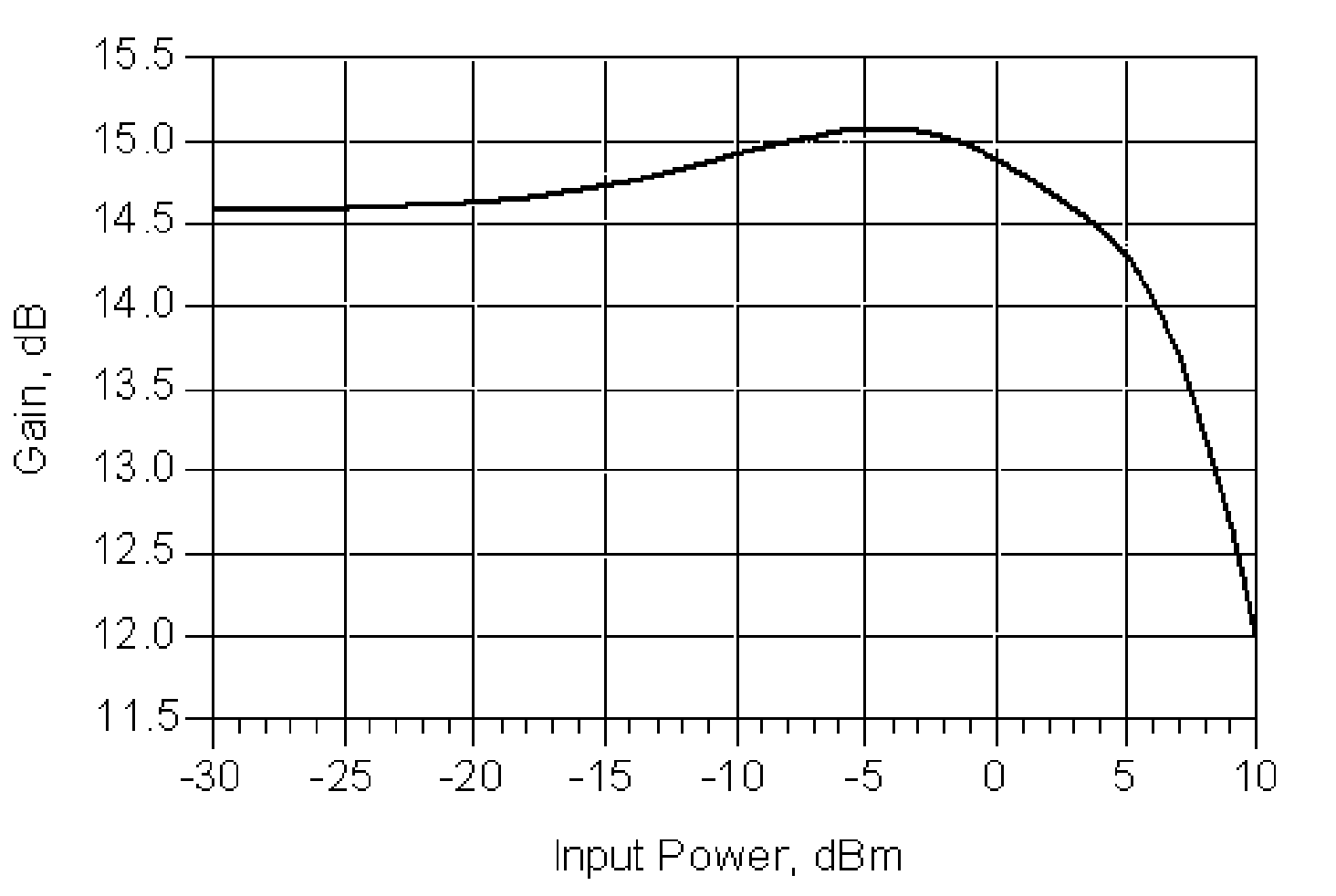
Gain compression is a reduction in "differential" or "slope" gain caused by nonlinearity of the transfer function of the amplifying device. This nonlinearity may be caused by heat due to power dissipation or by overdriving the active device beyond its linear region. It is a large-signal phenomenon of circuits.
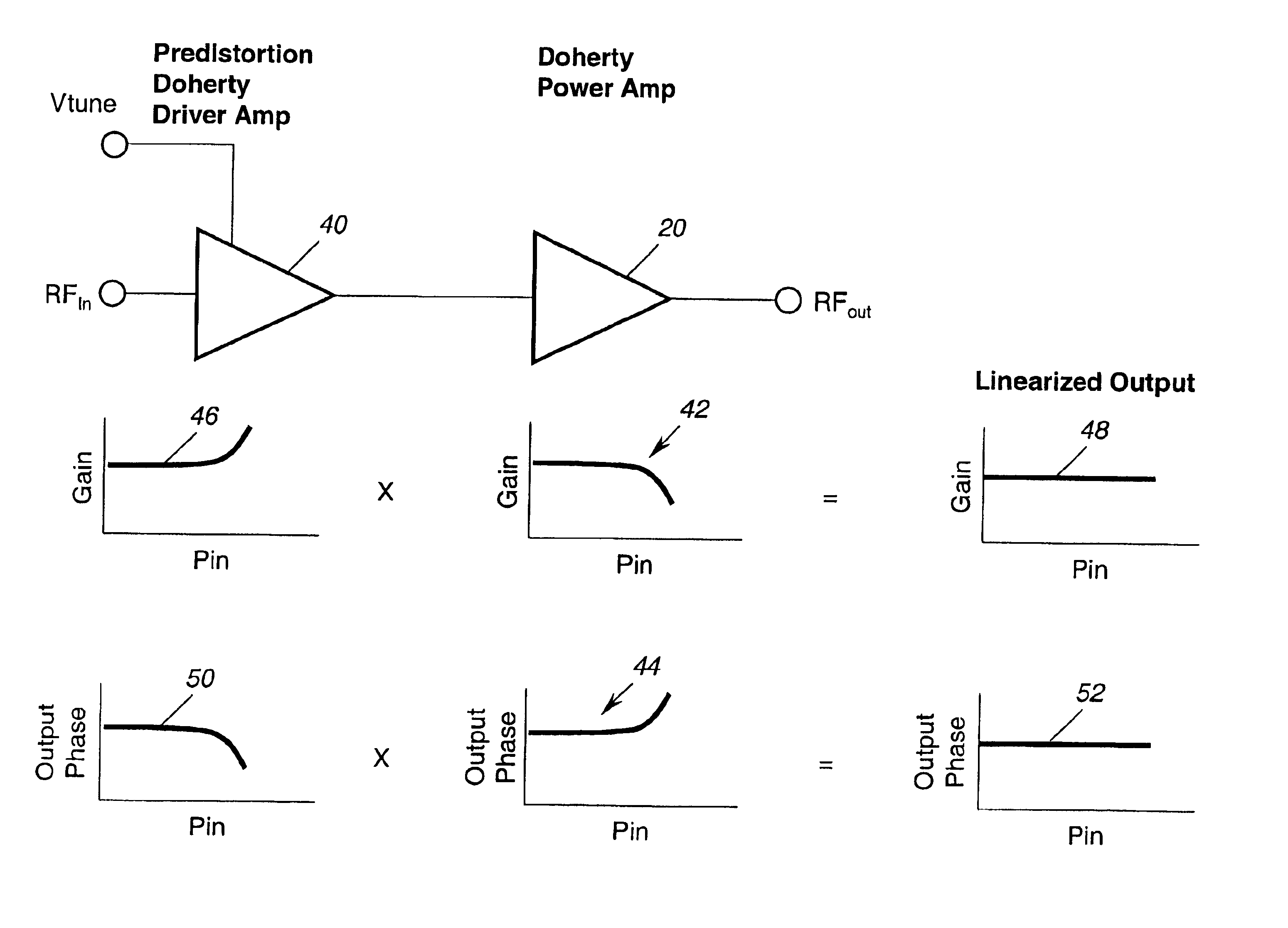
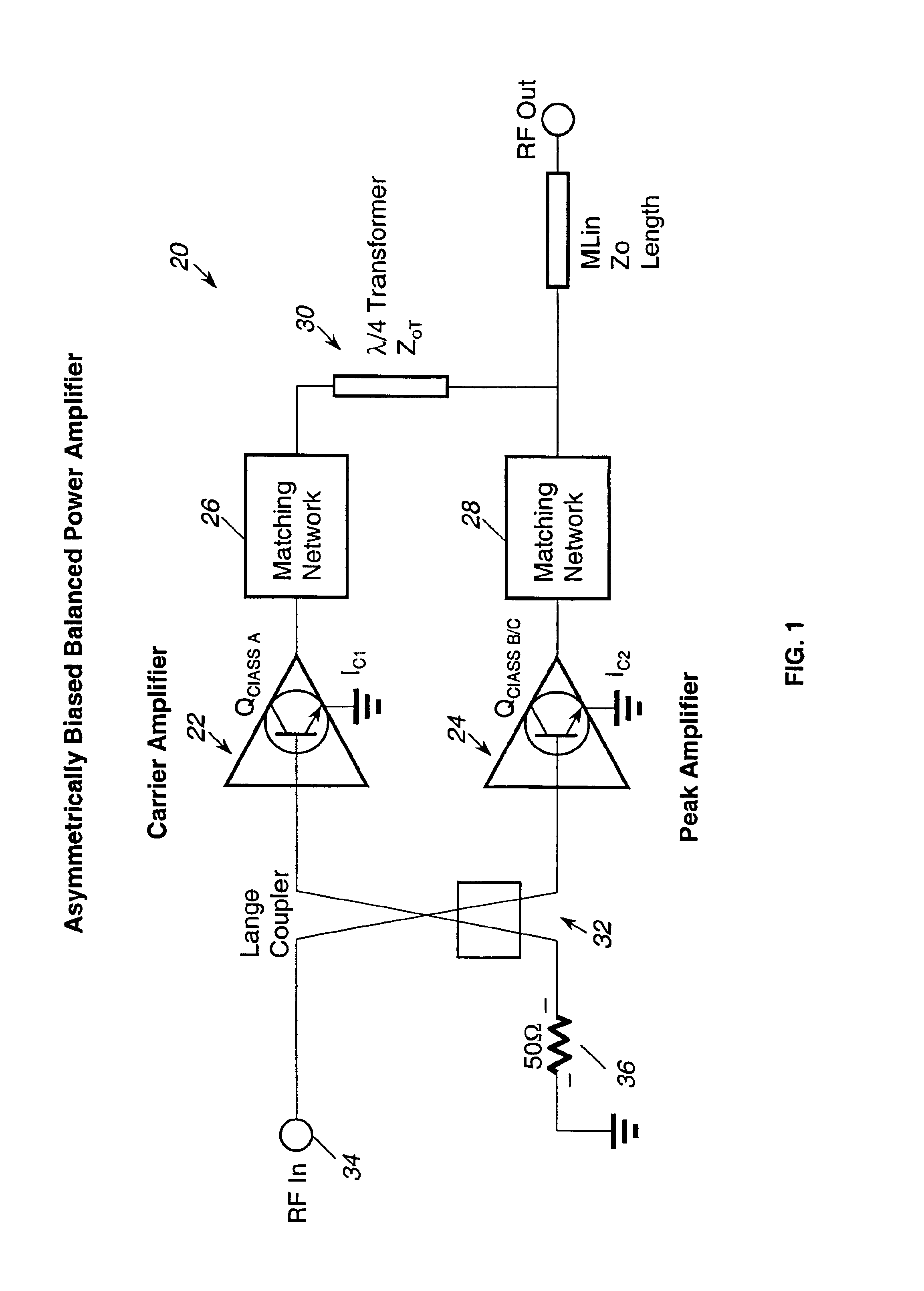
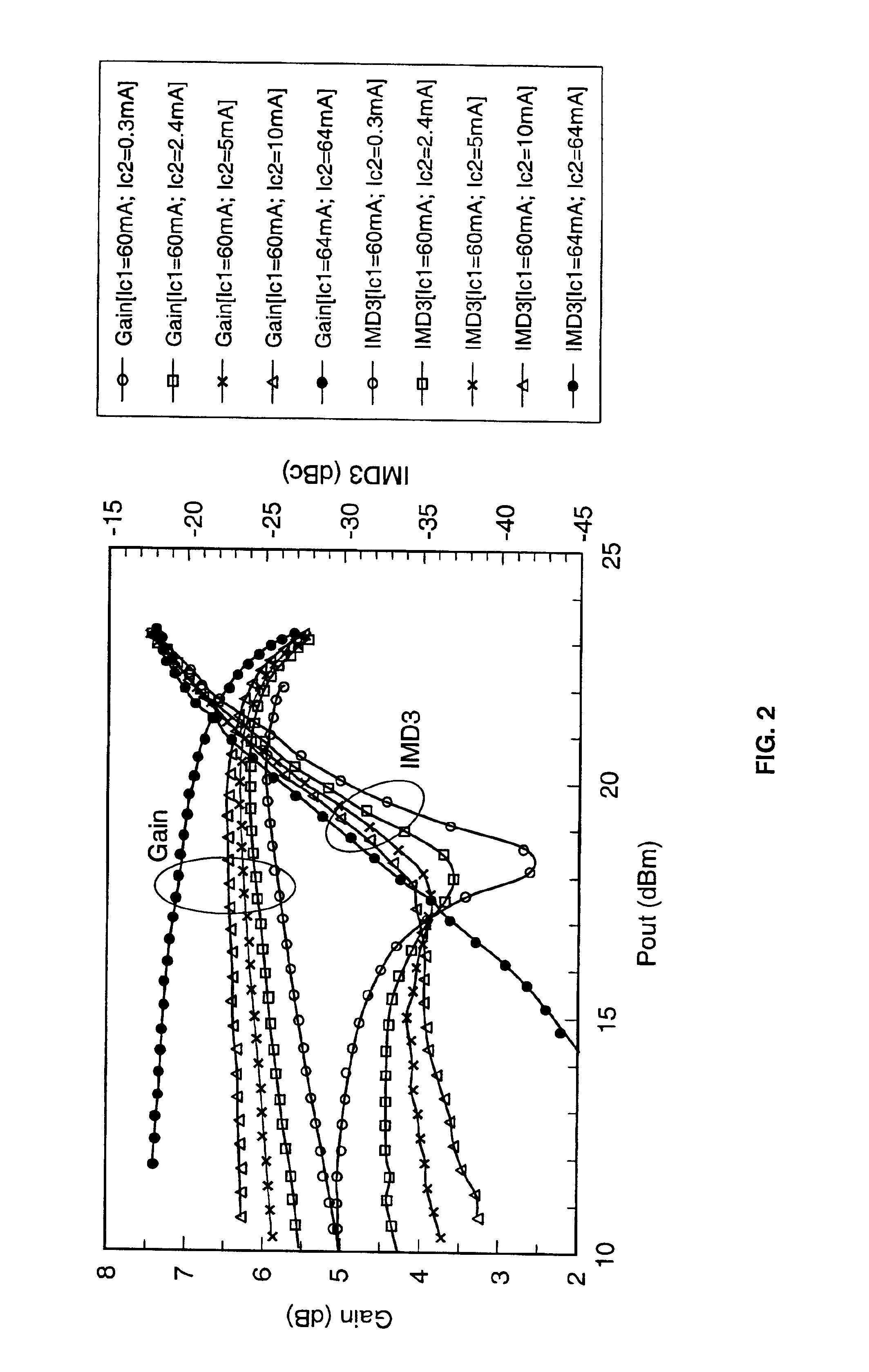
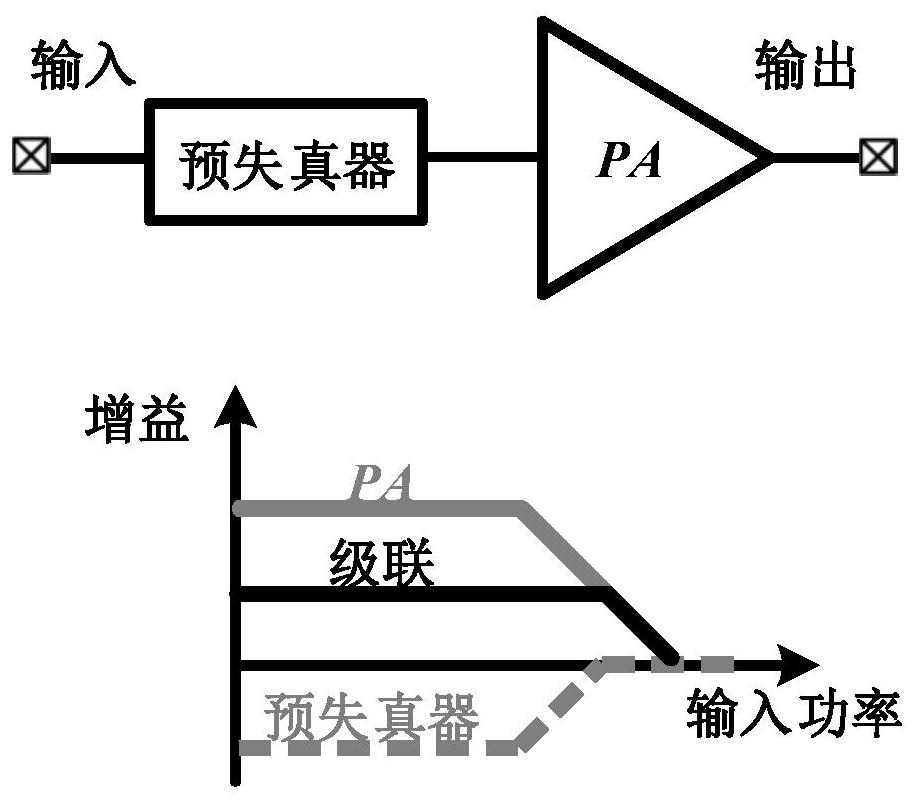
Application of the doherty amplifier as a predistortion circuit for linearizing microwave amplifiers
InactiveUS6864742B2Reducing intermodulation (IM) distortionImprove power added efficiencyAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influencePower-added efficiencyAudio power amplifier
A predistortion circuit for a microwave amplifier and more particularly to predistortion circuit configured as a Doherty amplifier. The predistortion circuit is adapted to be coupled to a downstream Doherty amplifier to precompensate for the gain compression and phase expansion of the downstream Doherty amplifier as the input power level is increased while simultaneously reducing the intermodulation (IM) distortion. In order to provide precompensation, the precompensation circuit is operated at bias level to provide gain expansion and phase compression to cancel out the gain compression and phase expansion of the downstream Doherty amplifier to provide a higher overall linear power added efficiency (PAE).
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Rf Power Amplifiers
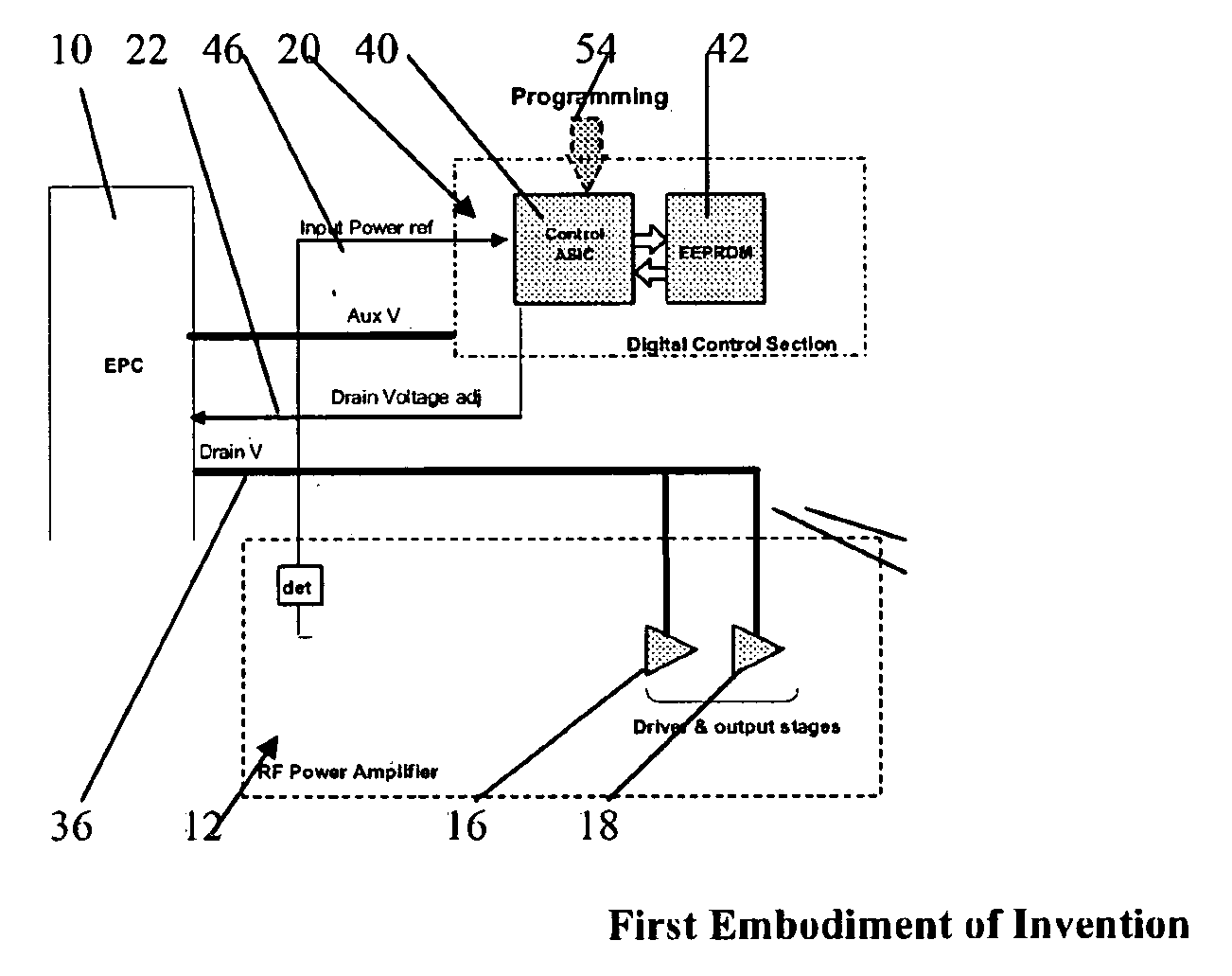
ActiveUS20080278236A1Improve featuresEliminating lossy and expensiveAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasControl signalGain compression
A Solid State Power Amplifier (SSPA) for powering a single element of a multi-element antenna, the SSPA comprising:an RF amplifier, having a signal amplifying path that includes preamplifier, driver amplifier and a power output stage;an Electronic Power Conditioner (EPC) for providing a variable value of DC voltage for powering the power output stage of the RF amplifier;a control ASIC for receiving an input power signal of the RF amplifier for providing a voltage control signal to the EPC to determine the value of the DC voltage, the control ASIC addressing an EEPROM holding a collection of control words that define output values of a control output signal for varying values of said input power, such that the value of the DC voltage to the power output stage is varied so as to control the gain compression of the RF amplifier for varying values of input power in order to maintain constant amplifier linearity.
Owner:ASTRIUM GMBH
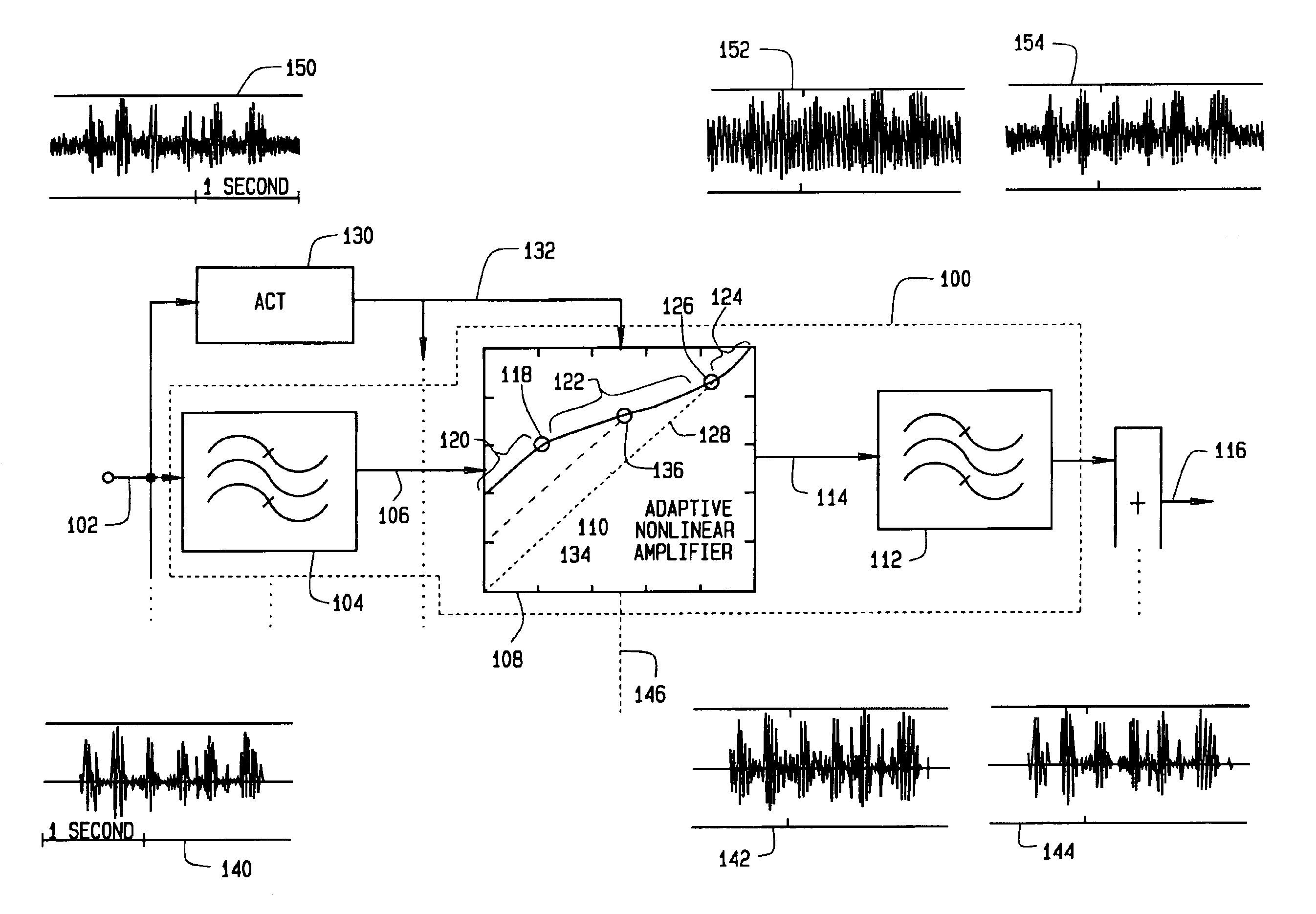
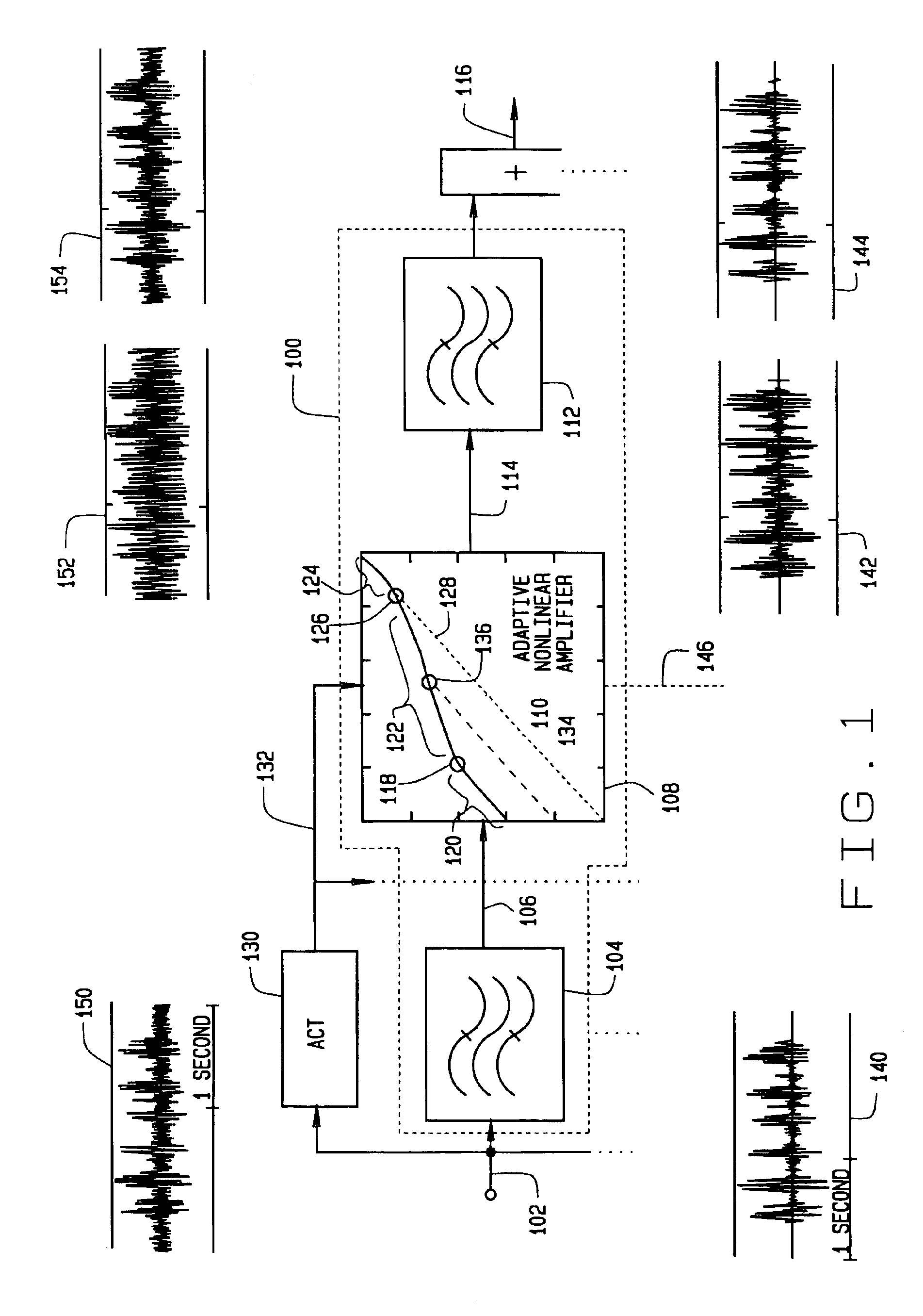
Hearing aids based on models of cochlear compression using adaptive compression thresholds
InactiveUS6970570B2Improve performanceHigh magnificationImplantable hearing aidsVolume compression/expansionBandpass filteringAdaptive compression
A hearing aid device providing instantaneous gain compression for sound signals and adaptive control of nonlinear waveform distortion, the device comprising: (a) at least one bandpass nonlinearity (BPNL) amplifier comprising a first bandpass filter, a second bandpass filter, and a memoryless nonlinear (MNL) compressive audio amplifier configured to receive a sound signal from the first bandpass filter and provide an MNL compressive audio amplifier output to the second bandpass filter, wherein the MNL compressive audio amplifier is configured to produce the MNL compressive audio amplifier output by providing memoryless gain compression directly on a sound signal that is (1) received from the first bandpass filter and (2) exhibits instantaneous amplitudes greater than a compression threshold, the BPNL amplifier thereby producing a desired gain compression on the received sound signal at an output of the second bandpass filter, and (b) a controller in communication with the BPNL amplifier, the controller being configured to adjust the compression threshold of the MNL compressive audio amplifier. Adjustment of the compression threshold in each BPNL amplifier may be achieved at least partially in response to a user input and / or to sound signal changes. By adaptively controlling the compression threshold, performance of the device can by optimized to match its environment.
Owner:HEARING EMULATIONS
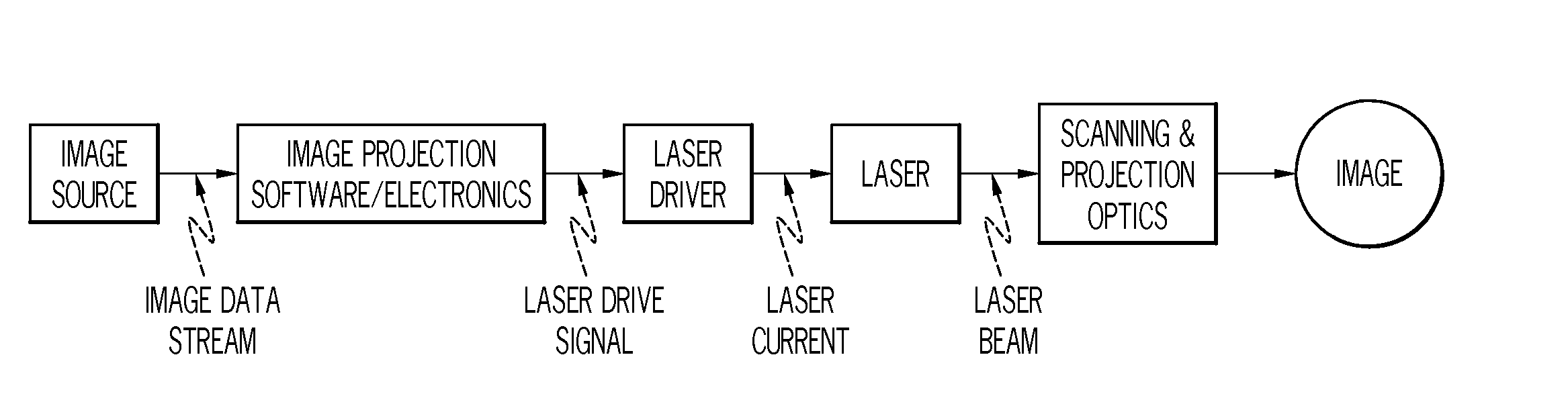
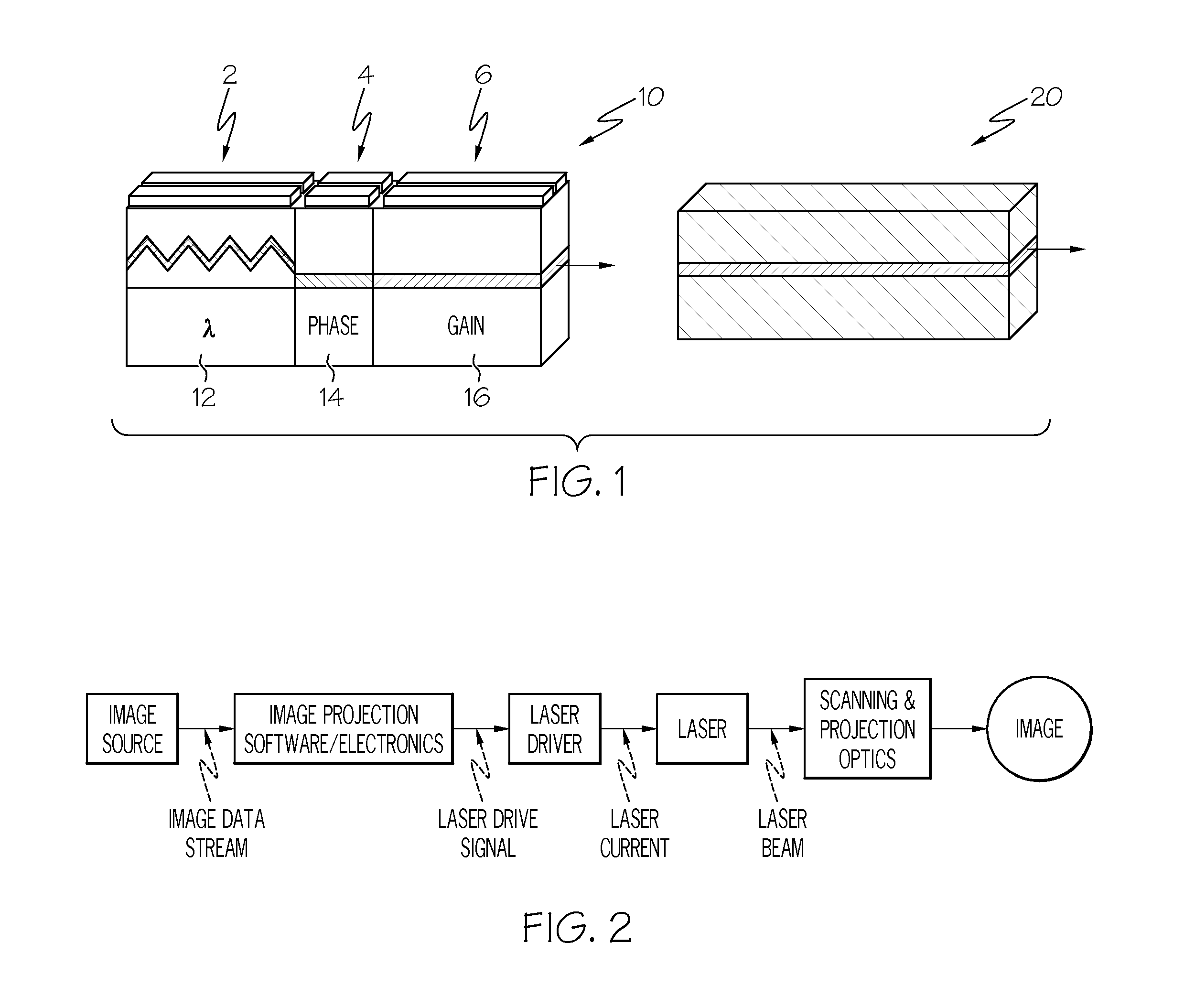
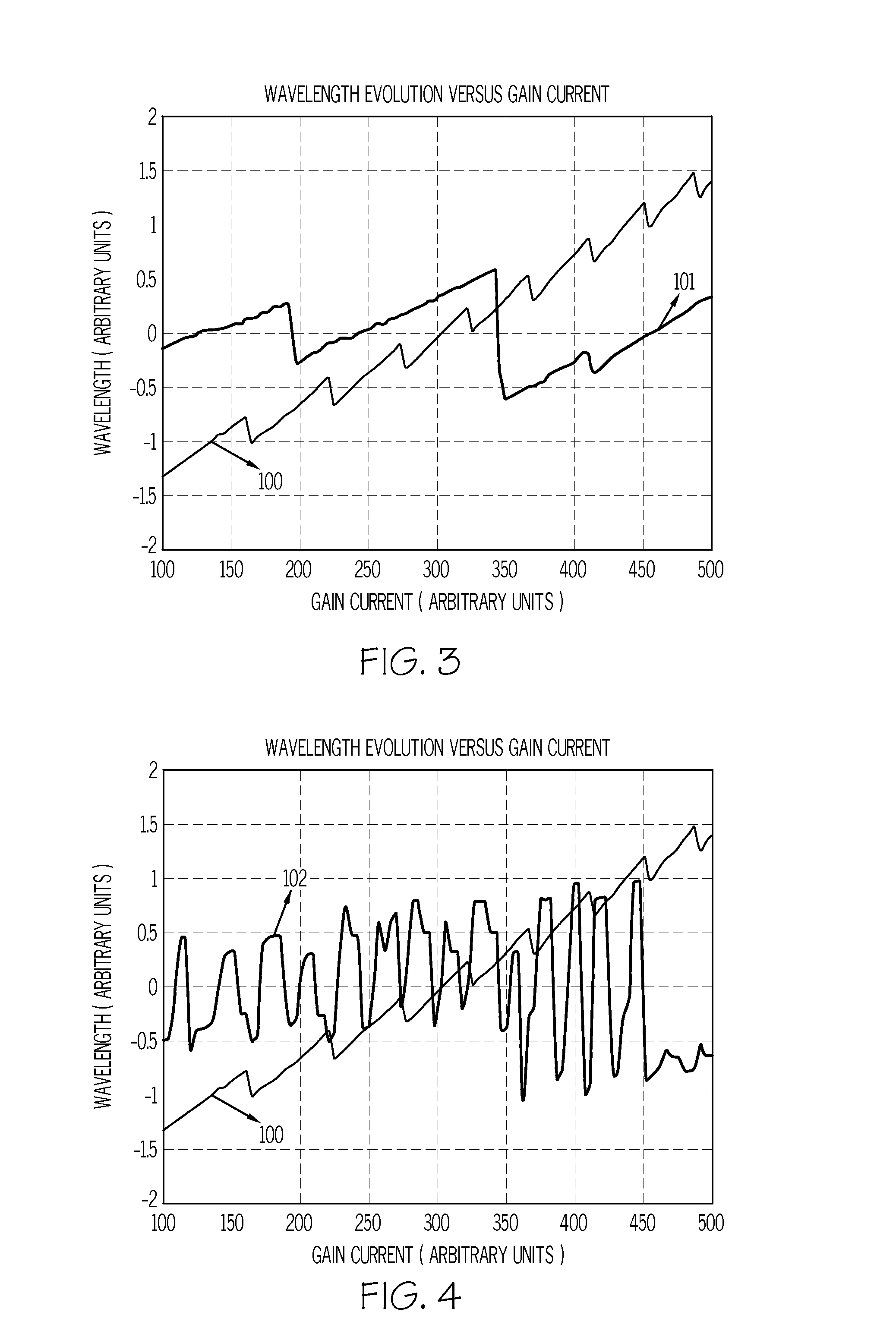
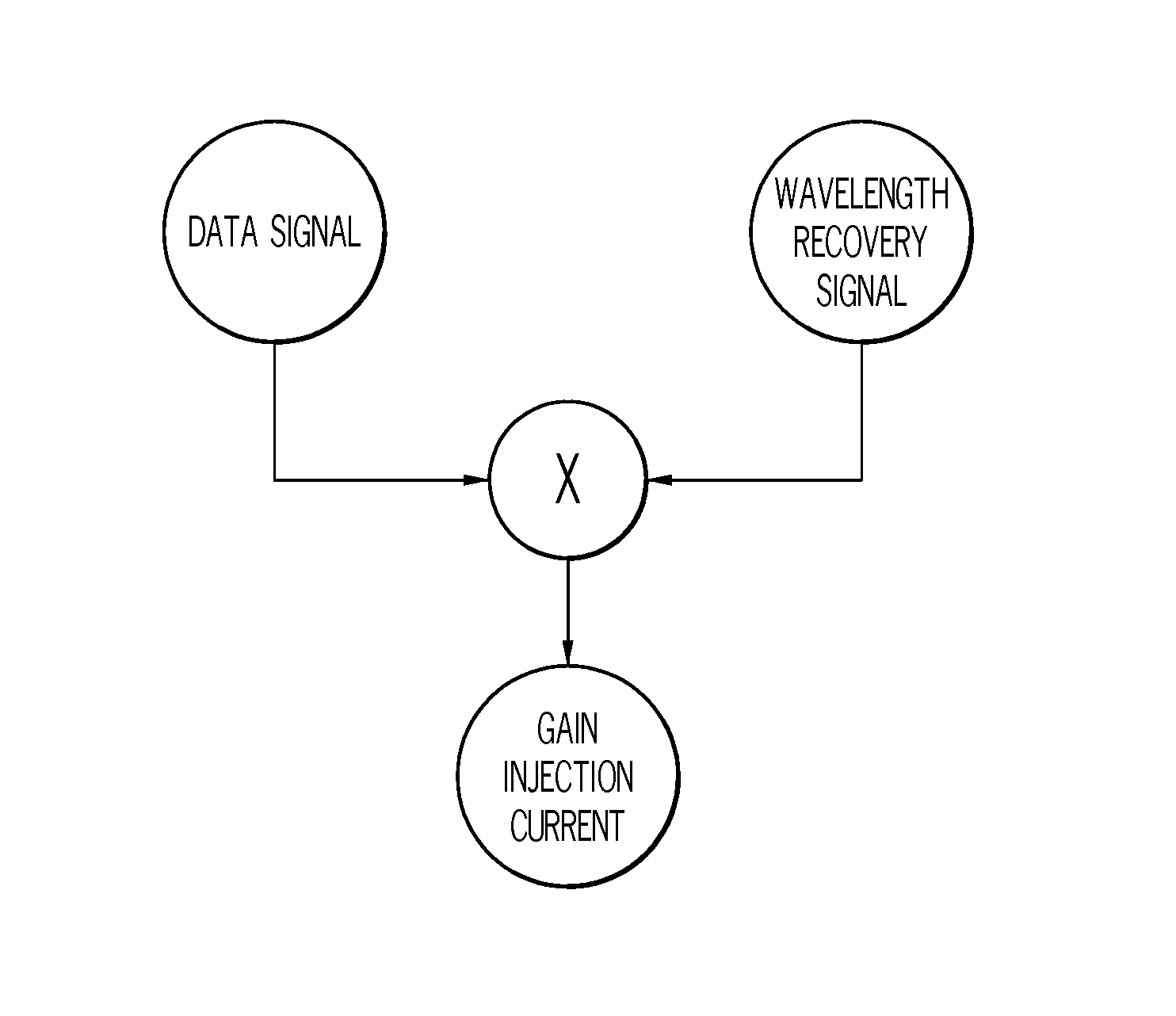
Wavelength control in semiconductor lasers
InactiveUS20080089373A1Minimizing wavelength variationFull recoveryLaser detailsColor television detailsDriving currentGain compression
The present invention relates generally to semiconductor lasers and laser scanning systems and, more particularly, to schemes for controlling wavelength in semiconductor lasers. According to one embodiment of the present invention, a method of minimizing laser wavelength variations in a semiconductor laser is provided. According to the method, one or more of the laser drive currents is configured to comprise a drive portion and a wavelength recovery portion. The wavelength recovery portion of the drive current comprises a recovery amplitude IR that is distinct from the drive amplitude ID and a recovery duration tR that is less than the drive duration tD. The recovery amplitude IR and duration tR are sufficient to recover carrier density distribution distorted by gain compression effects prior to recovery. Additional embodiments are disclosed and claimed.
Owner:CORNING INC
Adaptive biasing radio frequency power amplifier
ActiveCN106571780ALower on-resistanceReduce conduction voltage dropAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationPower amplifiersCapacitanceGain compression
The application discloses an adaptive biasing radio frequency power amplifier comprising a biasing circuit and a power level amplifying circuit. The biasing circuit is used for providing dynamic bias voltage for a transistor II in the power level amplifying circuit; the work voltage I is connected to one end of a resistor I; the other end of the resistor I is used as an output end of the biasing circuit; the work voltage II is connected to the anode of a diode I; the cathode of the diode I is connected to the output end of the biasing circuit; the value of the work voltage II makes the diode I in a default critical conduction status. the power level amplifying circuit comprises a transistor I and the transistor II, which adopt common source and common gate structures; the transistor I adopts common source connection and the grid of the transistor I receives radio frequency input signals; the transistor II adopts common grade connection and the drain electrode of the transistor II outputs drain voltage II. The application provides adaptive biasing voltage postponing gain compression and reducing phase distortion caused by non-linear capacity.
Owner:RDA MICROELECTRONICS SHANGHAICO LTD
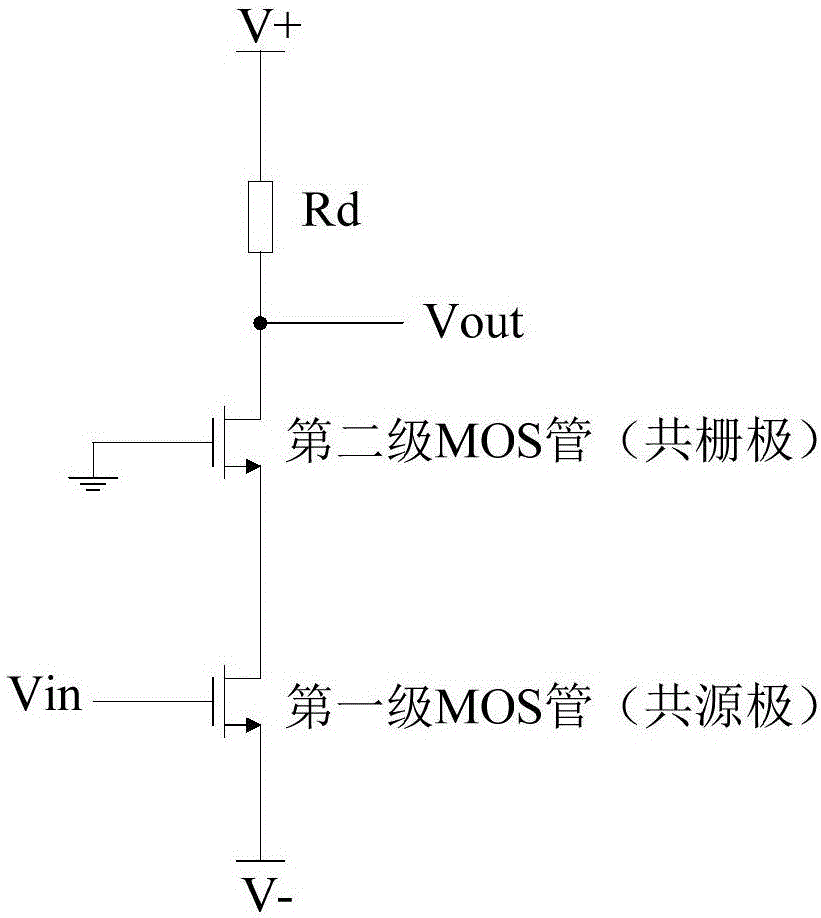
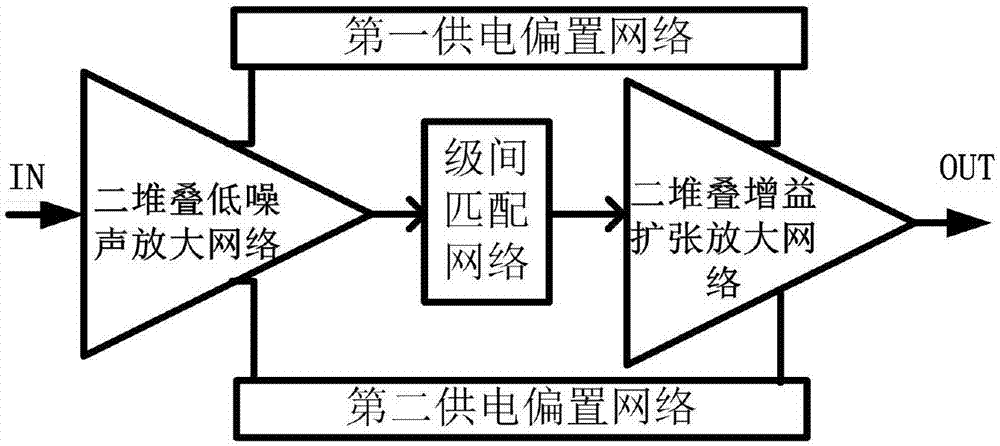
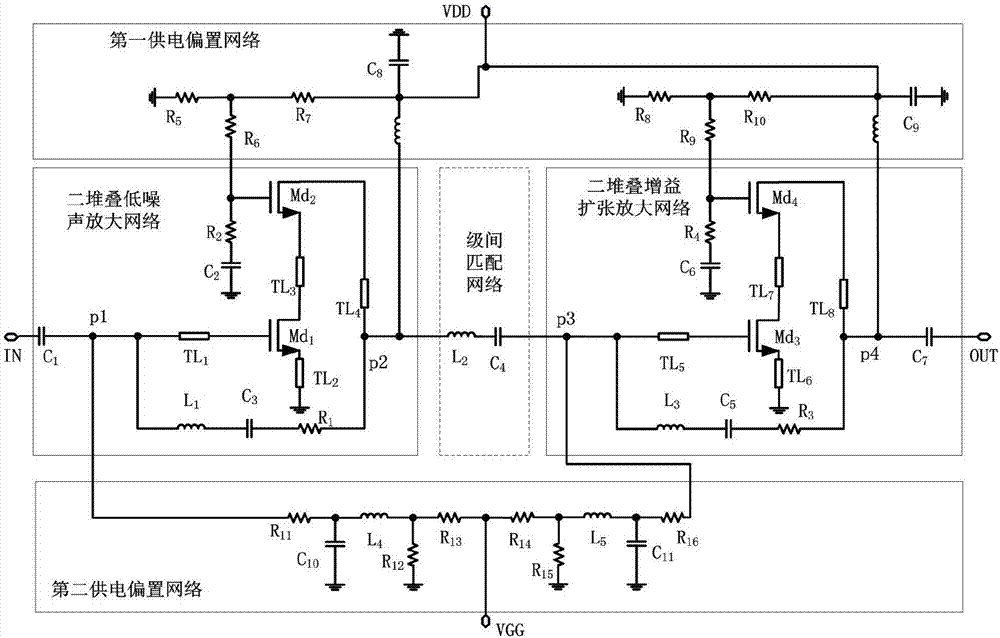
High-linearity broadband stacking low noise amplifier based on gain compensation technology
ActiveCN107332517AImprove linearity metrics1dB higher compression pointAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceUltra-widebandLow noise
The invention discloses a high-linearity broadband stacking low noise amplifier based on a gain compensation technology. The high-linearity broadband stacking low noise amplifier comprises a two-stacking low noise amplification network, an interstage matching network and a two-stacking gain expansion amplification network which are connected in sequence; and a first power supply bias network and a second power supply bias network which are connected with the two-stacking low noise amplification network and the two-stacking gain expansion amplification network. According to the high-linearity broadband stacking low noise amplifier, a serial stacking structure is realized through adoption of two transistors with different sizes and ultra wide band noise and impedance matching are realized through combination of an RLC feedback network; through utilization of the gain compression compensation technology, the gain compression property of the two-stacking low noise amplification network is cancelled within a certain bias range through the two-stacking gain expansion amplification network and a linearity index of the amplifier is improved, so the whole low noise amplifier has good broadband, linearity, low power consumption and low noise amplification capability; and moreover, the low breakdown voltage property of an integrated circuit technology is avoided and the stability and reliability of a circuit are improved.
Owner:CHENGDU GANIDE TECH
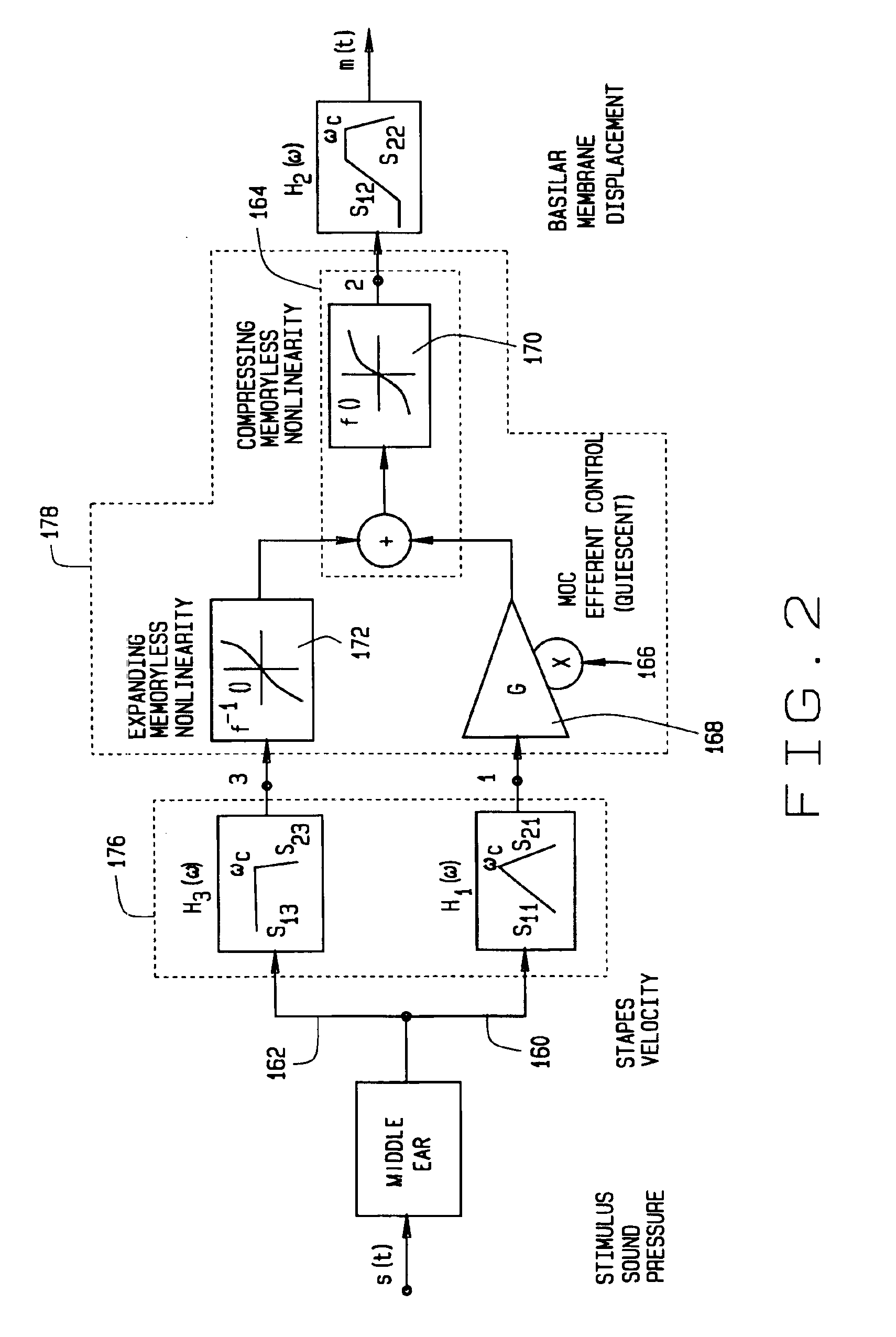
Hearing aids based on models of cochlear compression
InactiveUS6868163B1Improve intelligibilityAvoid annoying amplification of weak soundsImplantable hearing aidsDeaf aid adaptationGain compressionNonlinear element
Methods and devices for audio amplification suitable for hearing aid, hearing aid fitting, and diagnostic purposes include audio amplification having at least one variable gain channel configured to provide relatively higher gain at low levels, rapid gain compression at intermediate levels converging to linear gain at high signal levels, and slow feedback control of the compressive gain. Several such audio channels may be provided in a hearing aid or diagnostic device, and instantaneous gain compression is preferred. An analog implementation provides nonlinear elements in a feedback path to simulate a multiple feedback band-pass non-linearity cochlear filterbank hearing model (MFBPNL), while a digital implementation uses logarithmic representations of signals to minimize functional components in a multiple band-pass non-linearity cochlear filterbank hearing model (MBPNL). When used as a hearing aid, annoying amplification of weak sounds during brief interruptions of sustained intense sounds is prevented. Moreover, the quality of processing of intense sounds is improved, while still protecting the ear from uncomfortable, sudden intense sounds that occur too rapidly for effective correction by conventional automatic gain control.
Owner:HEARING EMULATIONS
Reflect forward adaptive linearizer amplifier
InactiveUS6573793B1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierGain compression
The Reflect Forward Adaptive Linearizer Amplifier (RFAL Amplifier) assembly (15) in FIG. 1 provides a linerizing method that uses the input reflected signal of the Main 1 Amplifier (23) to develop an intermodulation-correcting signal. The invention incorporates a directional coupler at the input of the Main 1 amplifier that samples and sums the input reflected signal from the Main 1 Amplifier and the forward fundamental input signal to form a distortion-correcting signal that contains both the fundamental and the distortion products of the output. By proper delay and amplification of this correcting signal, it can then be used to drive another Main amplifier (35) to both cancel the output distortion products and double the output power of the Main 1 Amplifier with significant improvement of the overall linearity and efficiency of the final amplifier assembly. The technique allows the use of lower cost transistor up to the Pout at the 1-dB Gain Compression Point with significant distortion cancellation.
Owner:GUTIERREZ ROMULO
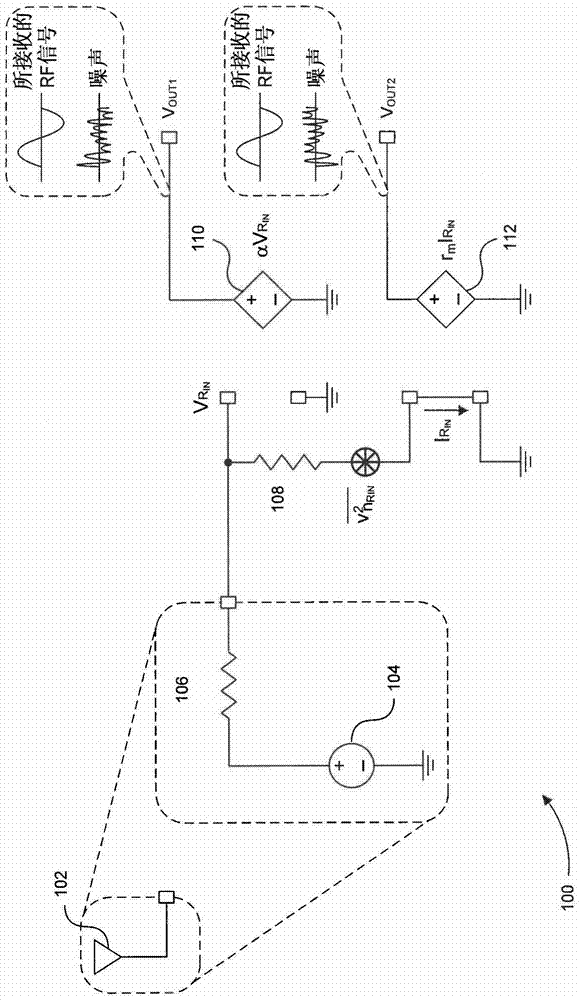
Low noise amplifier and receiver
ActiveUS20150280672A1High linearity low noise amplifierHigh P1dBHigh frequency amplifiersGain controlPower flowAudio power amplifier
A low noise amplifier is disclosed. The low noise amplifier comprises a current mirror circuit, a bias circuit, a cascode amplifying circuit and a power gain compensating circuit. The current mirror circuit is used for providing a first current and third current. The bias circuit is used for receiving a first current and third current and outputting a first bias voltage and a second bias voltage according to the first current and third current. The cascode amplifying circuit respectively receives the first bias voltage and the second bias voltage, and accordingly to work at an operation bias point. The power gain compensating circuit is used for receiving a RF output signal and accordingly outputs a gain compensating signal to the current mirror circuit so as to dynamically adjust current value of the first current and third current and further to compensates power gain of the low noise amplifier in order to increase 1 dB gain compression point (P1dB).
Owner:ADVANCED SEMICON ENG INC
METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MEASURING CROSS-POLARIZATION ISOLATION VALUE AND 1 dB GAIN COMPRESSION POINT
InactiveUS20090088082A1Receivers monitoringPolarisation/directional diversityGain compressionCross polarization
Exemplary embodiments include methods and systems for receiving a signal at a monitoring station, determining a transmit cross-polarization isolation value and / or 1 dB gain compression point based at least in part on the signal having one or more polarities; and outputting at about real-time the determination of the transmit cross-polarization isolation value and / or the 1 dB gain compression point to a user.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
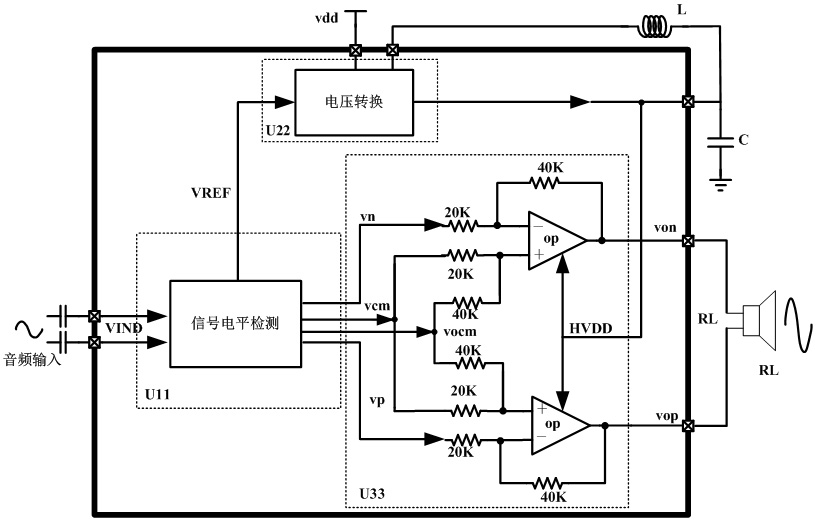
Bridge output power supply voltage adaptive variable audio power amplifier
The invention belongs to the technical field of power amplifiers, in particular to a bridge output power supply voltage adaptive variable audio power amplifier. The amplifier consists of a signal level detection circuit, a bridge output drive circuit and a power supply voltage conversion circuit. The gain compression and development technology is used, when the input signal amplitude is small, signals on two sides of the bridge output are amplified differentially; and when the input signal amplitude is large and the amplitude exceeds a set threshold, output signals on one side of the bridge structure are clamped to fixed level and the output signals on the other side are amplified by double gain. The gain control method can ensure extremely small distortion of signals, can obviously improve the efficiency of the audio power amplifier by combining adaptive power supply voltage technology, and can expand the dynamic range of the output signals. The circuit can be applied to portable equipment powered by batteries, such as mobile phones, MP3 and laptops.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Digital predistortion for power amplifier
InactiveUS6882221B2Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierGain compression
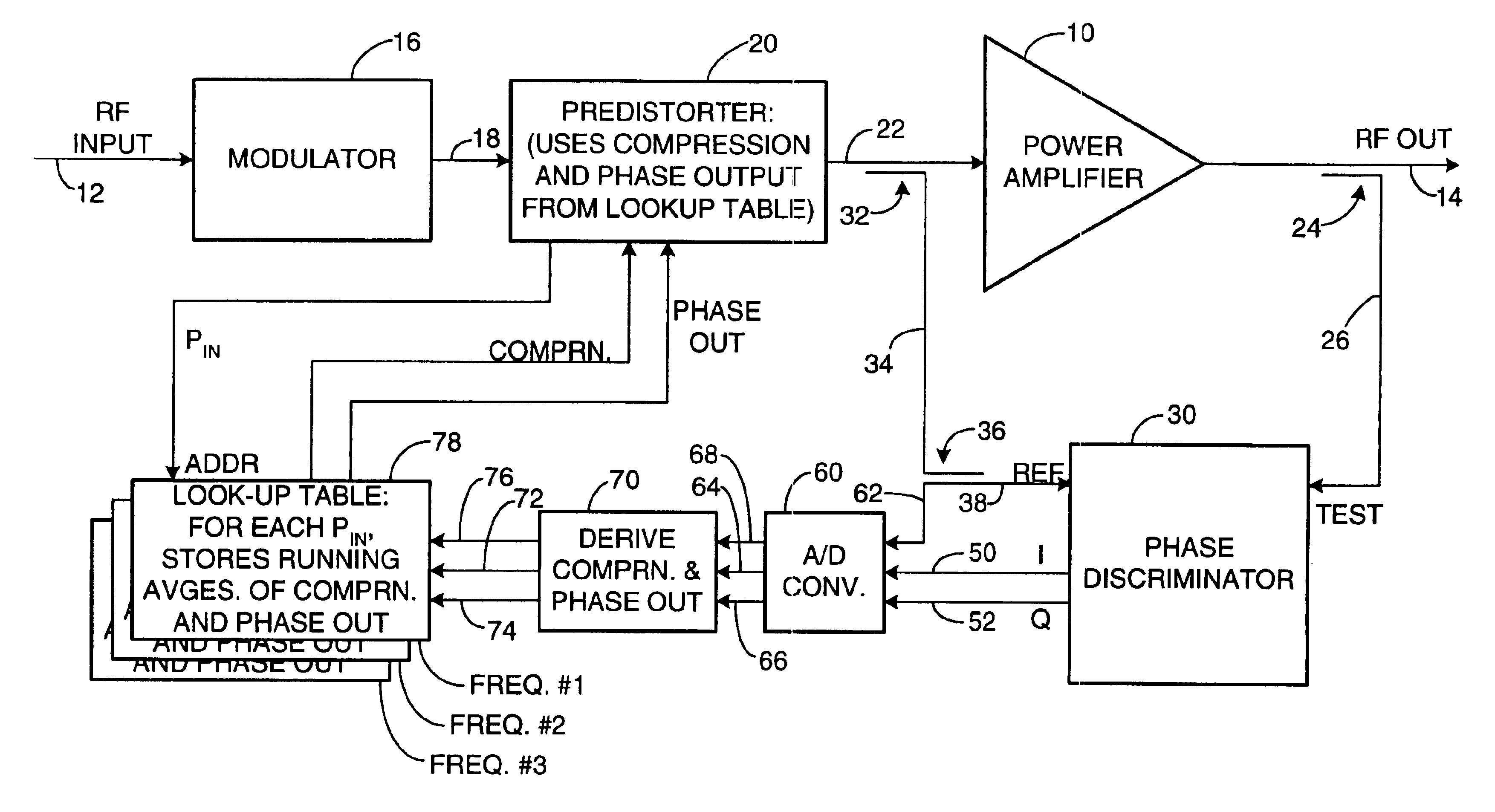
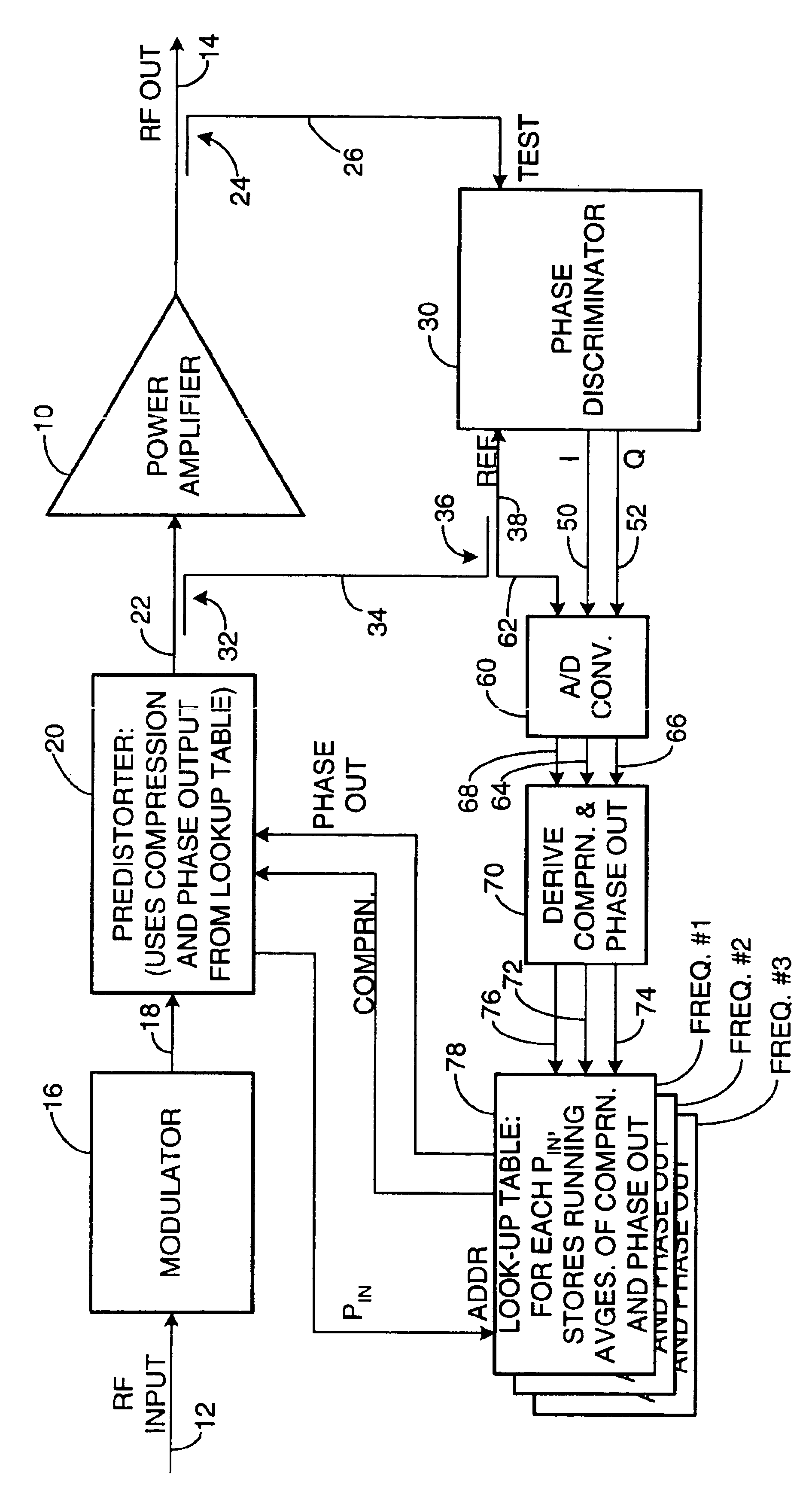
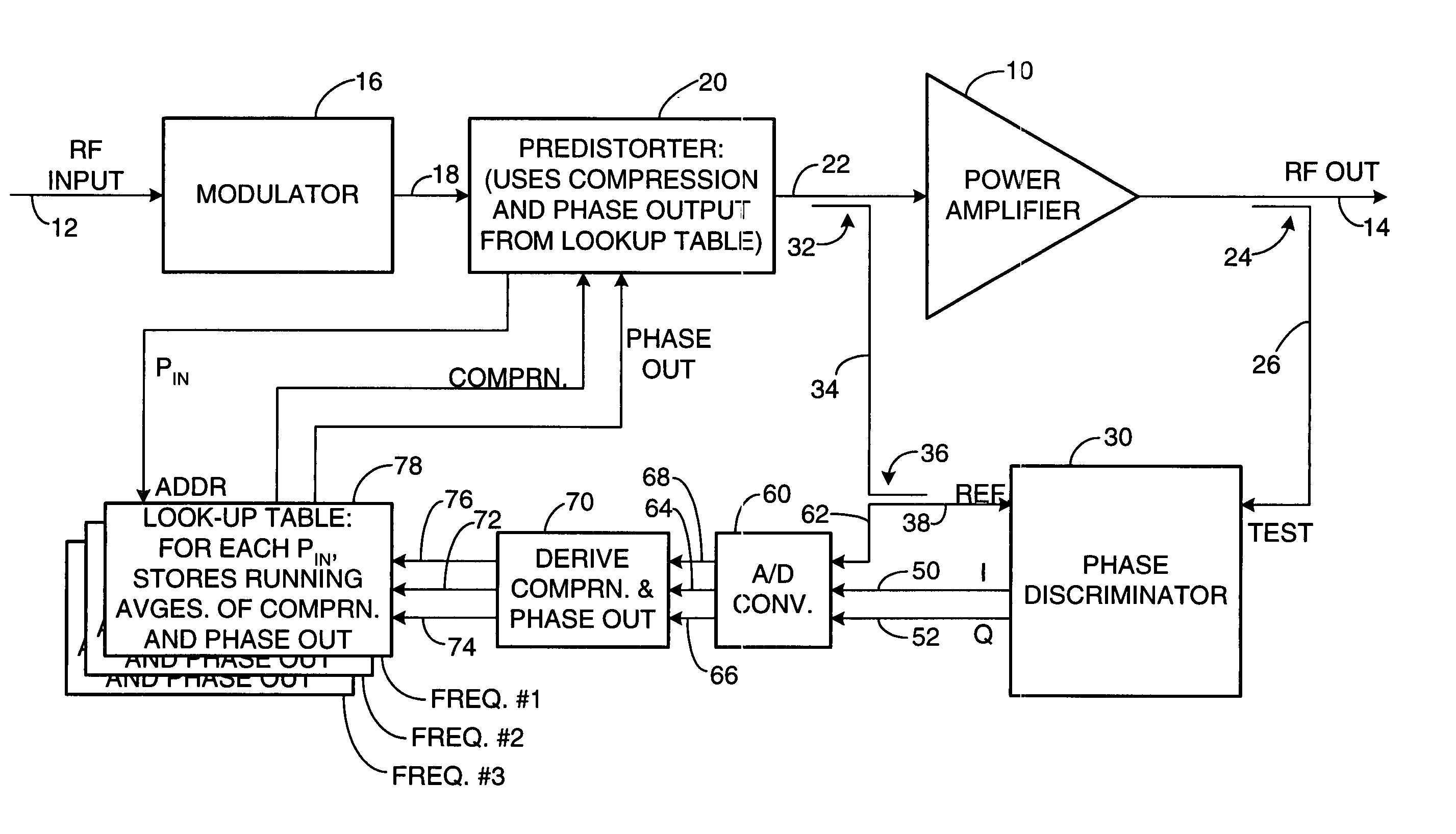
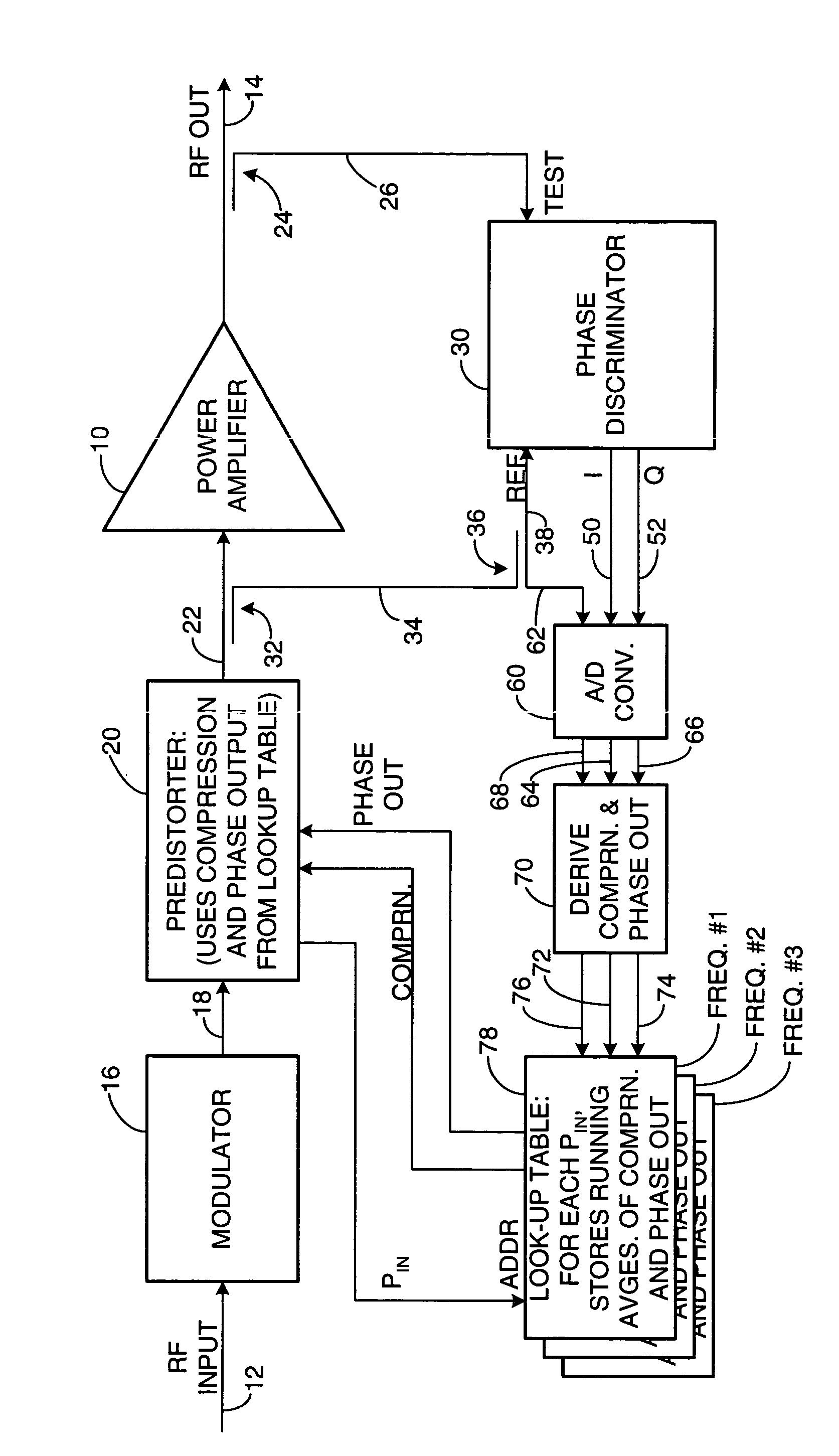
Apparatus and a corresponding method for predistorting an input signal applied to a radio frequency (RF) power amplifier, to compensate for amplifier distortion at high powers. The RF amplifier input and output signals are continuously monitored and difference signals are generated in an RF phase discriminator. The difference signals are converted to digital form and stored in a lookup table in the form of running averages of an RF amplifier gain compression value and an RF amplifier output phase value for each observed RF input power value. A predistorter module retrieves these values and predistorts the RF amplifier input by way of compensation.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Predistortion circuit for Doherty linear microwave amplifier
InactiveCN1391358AReduces Internal Modulation (IM) DistortionImprove linearityAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyPower-added efficiencyAudio power amplifier
The patent relates a predistortion circuit for application of the doherty amplifier as linearizing microwave amplifiers, and more particularly to predistortion circuit configured as a Doherty amplifier. The predistortion circuit is adapted to be coupled to a downstream Doherty amplifier to precompensate for the gain compression and phase expansion of the downstream Doherty amplifier as the input power level is increased while simultaneously reducing the intermodulation (IM) distortion. In order to provide precompensation, the precompensation circuit is operated at bias level to provide gain expansion and phase compression to cancel out the gain compression and phase expansion of the downstream Doherty amplifier to provide a higher overall linear power added efficiency (PAE).
Owner:TRW INC
Circuits and methods for controlling power amplifiers
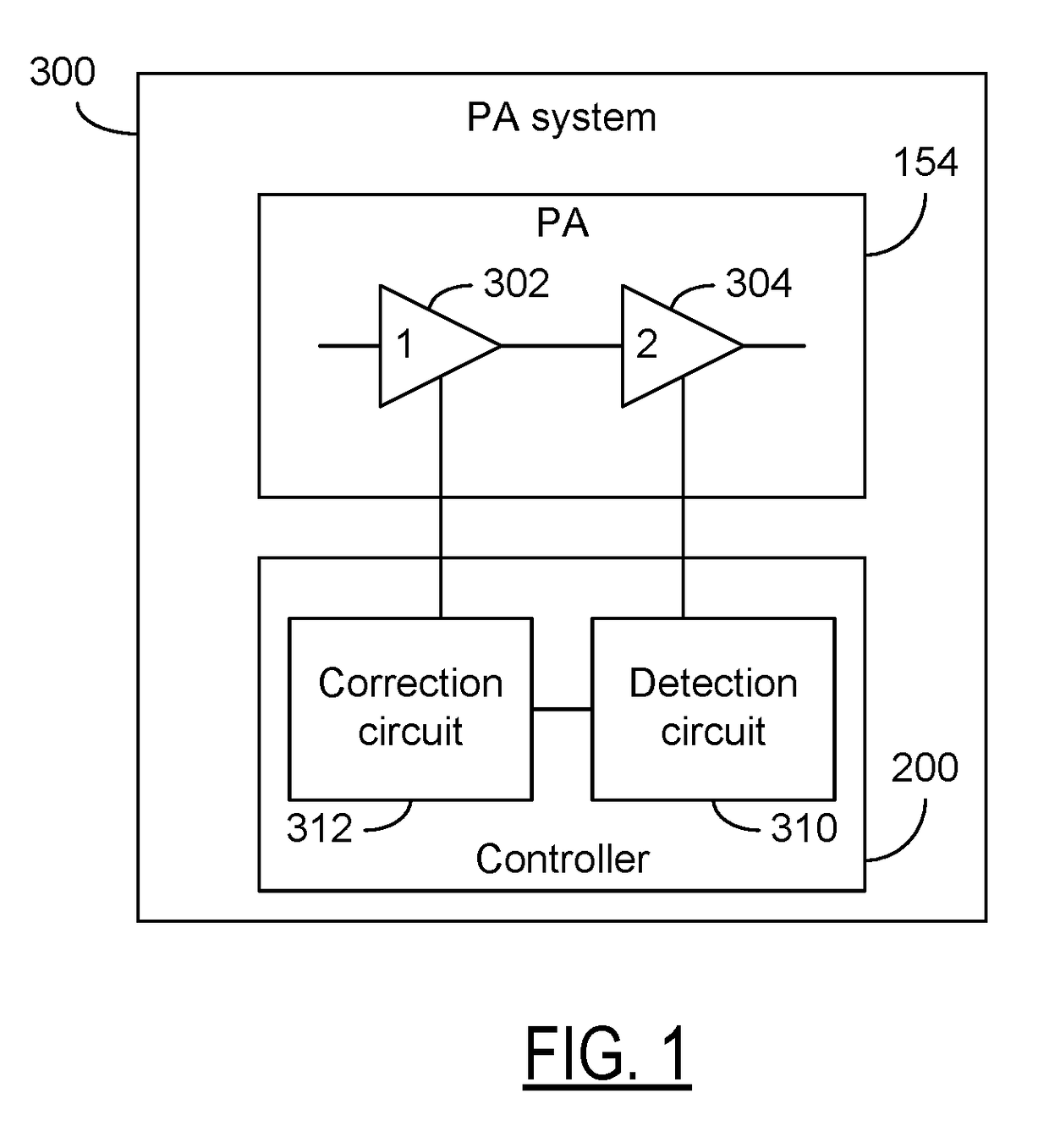
InactiveUS20170141734A1Facilitate linearity of gainImproved linearity of gainHigh frequency amplifiersGain controlControl powerGain compression
Circuits and methods for controlling power amplifiers. In some embodiments, a power amplification system can include a first amplification stage configured to operate with a first bias signal, and a second amplification stage configured operate with a second bias signal. The power amplification system can further include a control circuit coupled to the first amplification stage and the second amplification stage. The control circuit can be configured to generate the first bias signal based on the second bias signal. Such a first bias signal can result in the first stage having a gain profile that compensates for either or both of a gain expansion and gain compression of the second amplification stage.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
Serially concatenated multi-level radio-frequency power amplifier and front-end transmitter
ActiveCN102111113AHigh gainImprove linearityHigh frequency amplifiersPower amplifiersAudio power amplifierGain compression
The invention relates to the technical field of communications, in particular relates to a serially concatenated multi-level radio-frequency power amplifier which comprises a linearity compensation circuit and a power amplifier, wherein the linearity compensation circuit and the power amplifier are serially concatenated; the linearity compensation circuit comprises a primary radio-frequency amplifier and a bias circuit enabling the amplifier transistor to generate gain compression; and the power amplifier is biased at a class AB state. According to the invention, the circuit generating linearized compensation enables the bias current of the radio-frequency amplifier transistor of the level to increase along with the increment of input power through the adaptive adjustment of the bias circuit; the gain of the radio-frequency amplifier transistor is increased in the case of relatively higher power input so as to generate gain expansion; and by serially concatenated the primary radio-frequency amplifier transistor with the next level of amplifier, the generated gain expansion can be used for compensating the gain compression of the next level of amplifier so as to improve the linearity of the power amplifier.
Owner:北京中科微投资管理有限责任公司
High-linearity envelope tracking power amplifier with self-adaptive biased node
InactiveCN106230392AOffset Gain Compression FeatureOffset trueAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionPower amplifiersAudio power amplifierLinear power amplifier
The invention provides a high-linearity envelope tracking power amplifier with a self-adaptive biased node, comprising a drive common-source common gate and a common-gate self-biased circuit thereof, an output common-source common gate and a common-gate self-biased circuit thereof, and a two-stage common-source self-adaptive biased circuit. Compared to the traditional fixed-gate biased envelope tracking power amplifier and linear power amplifier, the invention can offset the gain variation which is generated by the variable power voltage of an envelope tracking power amplifier, increase the gain compression features of A and B type power amplifiers, eliminate some AM-AM distortion and greatly improve the linearity and stability of the whole envelope tracking power amplifier.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Digital predistortion for power amplifier
ActiveUS20050062531A1Compensation for amplifier distortionEasy to implementAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierGain compression
Apparatus and a corresponding method for predistorting an input signal applied to a radio frequency (RF) power amplifier, to compensate for amplifier distortion at high powers. The RF amplifier input and output signals are continuously monitored and difference signals are generated in an RF phase discriminator. The difference signals are converted to digital form and stored in a lookup table in the form of running averages of an RF amplifier gain compression value and an RF amplifier output phase value for each observed RF input power value. A predistorter module retrieves these values and predistorts the RF amplifier input by way of compensation.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Radio-frequency power amplifier and a front-end transmitter
ActiveCN102111112AImprove linearityHigh gainHigh frequency amplifiersPower amplifiersAudio power amplifierGain compression
The invention relates to the technical field of communications, in particular relates to a radio-frequency power amplifier which comprises a linearity compensation circuit and an amplifier, wherein the linearity compensation circuit and the amplifier are connected in parallel; the linearity compensation circuit comprises a primary radio-frequency amplifier transistor and a bias circuit enabling the amplifier transistor to generate gain compression; and the radio-frequency power amplifier is biased at a class AB state. According to the invention, the circuit generating linearized compensation enables the bias current of the primary radio-frequency amplifier transistor to increase along with the increment of input power through the adaptive adjustment of the bias circuit; the gain of the radio-frequency amplifier transistor is increased in the case of relatively higher power input so as to generate gain expansion; and by connecting the primary radio-frequency amplifier transistor with the other level of amplifier in parallel, the generated gain expansion can be used for compensating the gain compression of the level of amplifier so as to improve the linearity of the power amplifier.
Owner:北京中科微投资管理有限责任公司
A self-adaptive bias radio frequency power amplifier
PendingCN109818587AImprove AM-PM imbalanceDelay gain compressionHigh frequency amplifiersGain controlAudio power amplifierGain compression
The invention discloses a self-adaptive bias radio frequency power amplifier which comprises an amplifying circuit and a bias circuit. Wherein the amplifying circuit is provided with a power transistor, the biasing circuit is provided with a biasing transistor, and an emitting electrode of the biasing transistor is connected with a base electrode of the power transistor through a resistor to provide biasing current and / or biasing voltage for the base electrode. A capacitor series branch is also arranged in the biasing circuit and is formed by connecting at least two capacitors in series. One end of the capacitor series branch is connected with the base of the power transistor, and the other end is grounded. Base-to-base of power transistor is reduced. The adverse effect of the parasitic capacitance of the collector on the linearity is improved, and the AM-of the radio frequency power amplifier is improved. PM imbalance; The gain compression phenomenon of the radio frequency power amplifier is delayed, and the AM-AM imbalance of the radio frequency power amplifier is improved.
Owner:RDA MICROELECTRONICS TECH SHANGHAI CO LTD
Radio-frequency power amplifier circuit with adjustable predistortion function
ActiveCN101888215AReduce positive phase offsetModulation Feedback StrengthAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionPower amplifiersNegative feedbackAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses a radio-frequency power amplifier circuit with adjustable predistortion function, comprising a transistor in emitter follower structure; wherein the base electrode of the transistor is connected with the input terminal of the amplifier circuit, the emitter of the transistor is connected with the output terminal of the amplifier circuit by virtue of an output matching network, an RC parallel negative feedback network is connected between the base electrode of the transistor and the collector electrode of the transistor, a first RL series negative feedback network is connected between the collector electrode and an external adjustable bias voltage, and a second RL series negative feedback network is connected between the emitter of the transistor and the ground. Predistortion circuit can be caused to have better accuracy, gain compression and positive phase deviation produced by power amplifier post-stage circuit can be compensated, and linearity thereof can be improved.
Owner:SUZHOU INNOTION TECH
Blocker-tolerant wideband noise-canceling receiver
Because of associated disadvantages of narrow-band off-chip radio-frequency (RF) filtering, a mixer-first receiver front-end designed to tolerate blockers with minimal gain compression and noise factor degradation is disclosed. The mixer-first receiver front-end includes two separate downconversion paths that help to minimize added noise and voltage gain prior to baseband filtering, which are critical factors in eliminating narrow-band off-chip RF filtering.
Owner:BROADCOM CORP
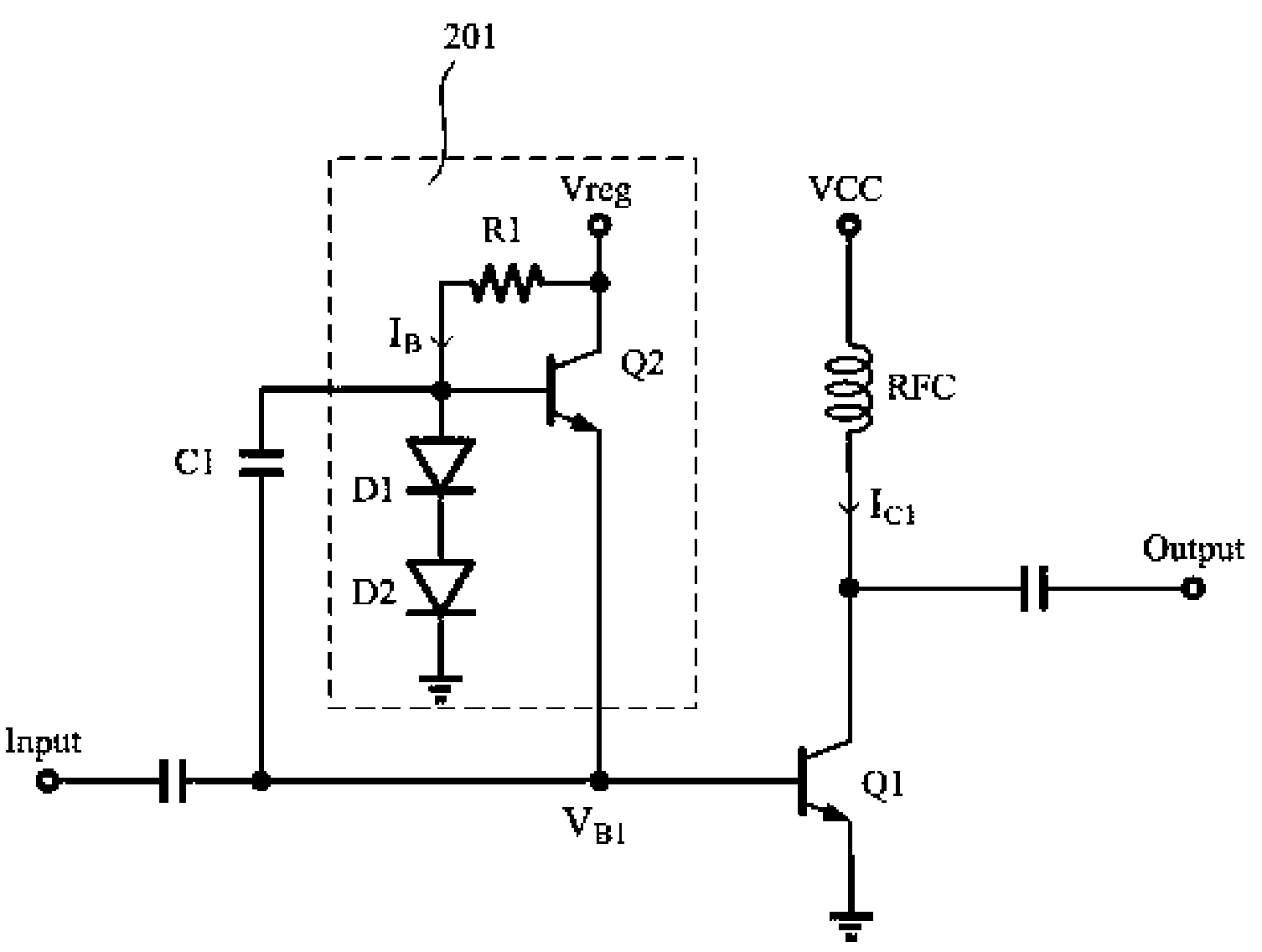
Amplifier bias enhancement technique
ActiveUS7049891B2Good effectAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierGain compression
A bias boost circuit is disclosed for use with an amplifier circuit for biasing thereof. The amplifier circuit includes at least a first transistor and a filter circuit for filtering of current pulses received from the bias boost circuit, where filtered current pulses form a variable bias current that is provided to the at least a first transistor. With this type of biasing circuit, large input signals that would normally compress the gain of the amplifier circuit are therefore amplified with less gain compression by virtue of the boost in bias current that is supplied to the at least a first transistor.
Owner:SIGE SEMICON
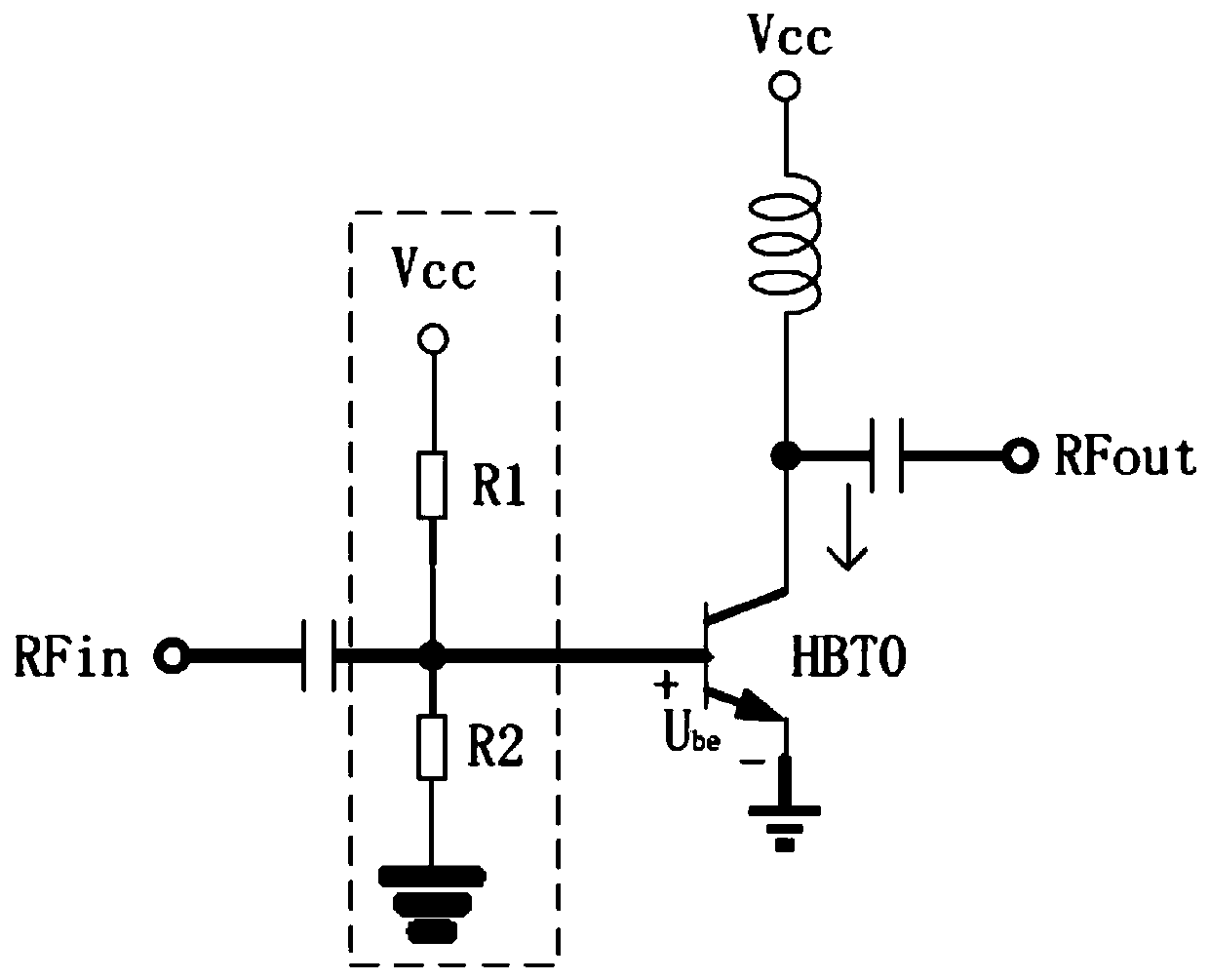
Self-adaptive linearization radio frequency bias circuit
ActiveCN110098806ASatisfy the linear requirementImproved Gain CompressionAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionHigh frequency amplifiersGain compressionEngineering
The invention discloses a self-adaptive linearization radio frequency biasing circuit which comprises a linearization biasing circuit and a radio frequency amplifier unit circuit. The linearization biasing circuit is connected with the radio frequency amplifier unit circuit through a self-adaptive linear compensation circuit; the linearization biasing circuit comprises a heterojunction bipolar transistor HBT2, a heterojunction bipolar transistor HBT3, a heterojunction bipolar transistor HBT4, a resistor R3, a resistor R4, a resistor R5 and a capacitor C2. The collector electrode of the heterojunction bipolar transistor HBT4 is connected with the port of the linearized bias circuit; self-adaptive linear compensation is achieved through feedback of the heterojunction bipolar transistor HBT4of the self-adaptive linear compensation circuit, the heterojunction bipolar transistor HBT0 can select a bias state according to the magnitude of output power, and the linearity is improved while theefficiency is considered by the power amplifier; the gain compression and phase distortion characteristics of the HBT can be effectively improved; the MMIC power amplifier is simple in structure, small in size, low in cost and suitable for design of the MMIC power amplifier.
Owner:SYNERGY INNOVATION INST OF GDUT HEYUAN
Wavelength control in semiconductor lasers
InactiveUS7483458B2Minimizing wavelength variationFull recoveryLaser detailsColor television detailsDriving currentGain compression
The present invention relates generally to semiconductor lasers and laser scanning systems and, more particularly, to schemes for controlling wavelength in semiconductor lasers. According to one embodiment of the present invention, a method of minimizing laser wavelength variations in a semiconductor laser is provided. According to the method, one or more of the laser drive currents is configured to comprise a drive portion and a wavelength recovery portion. The wavelength recovery portion of the drive current comprises a recovery amplitude IR that is distinct from the drive amplitude ID and a recovery duration tR that is less than the drive duration tD. The recovery amplitude IR and duration tR are sufficient to recover carrier density distribution distorted by gain compression effects prior to recovery. Additional embodiments are disclosed and claimed.
Owner:CORNING INC
Biasing circuit for radio frequency power amplifier
ActiveCN113114121AGood temperature compensation effectImproved Gain FlatnessHigh frequency amplifiersAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationGain compressionHemt circuits
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Variable gain linear power amplifier and chip
ActiveCN113328712AAvoid loss1dB compression point increaseGain controlPower amplifiersVariable-gain amplifierLinear power amplifier
The invention discloses a variable gain linear power amplifier and a chip. The variable gain linear power amplifier comprises a variable gain amplifier, and a post-distortion power amplifier, wherein the post-distortion power amplifier comprises a driving stage amplifier and a cascade power stage amplifier, the output end of the variable gain amplifier is connected with the input end of the driving stage amplifier, and the output end of the driving stage amplifier is connected with the input end of the cascade power stage amplifier; and the gain compression distortion characteristics of the driving stage amplifier are compensated according to the gain expansion distortion characteristics of the cascaded power stage amplifier, so that a gain curve of the post-distortion power amplifier obtains a higher 1dB compression point. According to the variable gain linear power amplifier, the gain expansion distortion characteristics generated by the post-stage low-bias class-C amplifier is utilized to compensate the gain compression distortion generated by the pre-stage high-bias class-A amplifier, the improvement of a 1dB compression point is realized under the condition of not introducing an additional predistorter, the additional loss caused by the predistorter is avoided, and the variable gain linear power amplifier can be widely applied to amplifier circuits.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Variable sensitivity control for a cochlear implant
ActiveUS7522960B2Improve understandingImprove responseElectrotherapySpeech recognitionCurrent noiseAuditory sense
The invention provides an amplifier for providing adaptive operation of an auditory prosthesis. The amplifier receives an input signal and produces an output signal, and comprises a gain control. Estimates of the current noise floor value of the input signal are obtained, and in response to a change in the current estimated noise floor value, the gain control alters the amount of gain applied to the input signal. Further, in response to the change in the current estimated noise floor value, the gain control alters a gain compression ratio of the amplifier across the dynamic range of the amplifier. The present invention allows for adaptive operation of the amplifier responsive to varying noise floor levels, while maintaining desired gain characteristics of the amplifier across a range of input signal levels.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
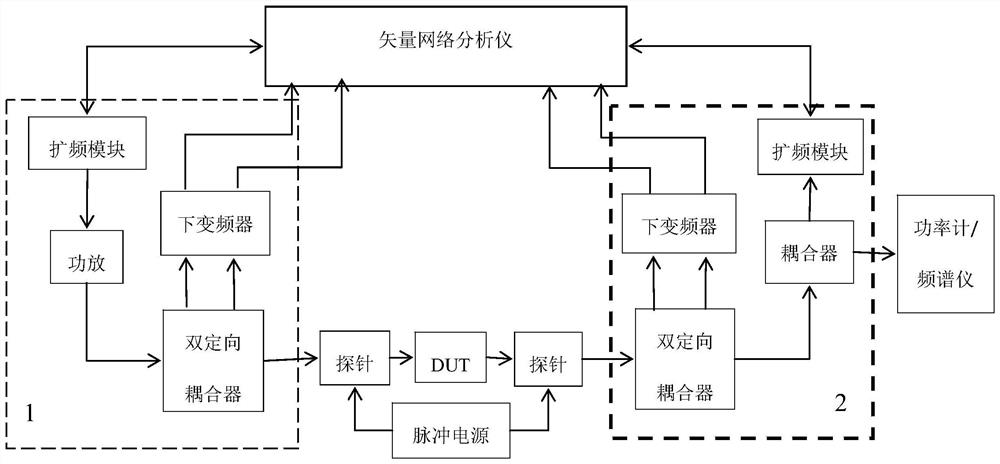
5G power amplifier testing device and method
ActiveCN111707874AHave self-production capacityLow costResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical testingTelecommunicationsGain compression
The invention relates to a 5G power amplifier testing device and method. The device comprises a vector network, a device under test (DUT), and a testing accessory, and is characterized in that the device also comprises a power amplifier integrated spread spectrum module at the output end and a power amplifier integrated spread spectrum module at the receiving end of the vector network; the power amplifier integrated spread spectrum module at the output end comprises a vector network output end spread spectrum module, a power amplifier and a double-shaped coupler which are electrically connected in sequence; the power amplifier integrated spread spectrum module at the receiving end comprises a vector network receiving end double-shaped coupler and a spread spectrum module which are electrically connected in sequence; and each double-shaped coupler is also electrically connected with the vector network through a respective down converter. The method adopts the spread spectrum module to perform index measurement after vector network spread spectrum, including power gain, power gain flatness, linear power gain, linear power flatness, 1dB gain compression output power, clutter suppression degree, input voltage standing-wave ratio, output voltage standing-wave ratio and power additional efficiency. According to the device and the method thereof, the test investment cost of the 5G power amplifier is greatly reduced, and meanwhile, the risks of prohibition and technology blocking are effectively avoided.
Owner:SHENZHEN CESI INFORMATION TECH CO LTD +1
Transient Short Optical Pulse Gain Compression Intercepting Waveform Sampling Method
The invention provides a gain compression and interception waveform sampling method for a transient short optical pulse semiconductor optical amplifier. , the sequence pulse amplitudes are arranged according to a fixed attenuation ratio. Then, according to the pulse sequence timing determined by the length of the passive optical fiber loop, the pulse is intercepted by the semiconductor optical amplifier. The intercepted pulse waveform is sent to a PIN photocell with a bandwidth of 100 megabytes, and then the data acquisition card is used to measure the output pulse amplitude of the PIN photocell to obtain the energy envelope of the intercepted pulse, and then combine the passive fiber ring pulse to copy. The original transient short optical pulse waveform is reversed by the replica amplitude variation law of the generator. The method provided by the invention adopts a simple system structure, low equipment requirements, easy debugging and integration, and can be used as an effective means for measuring transient short light pulses.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
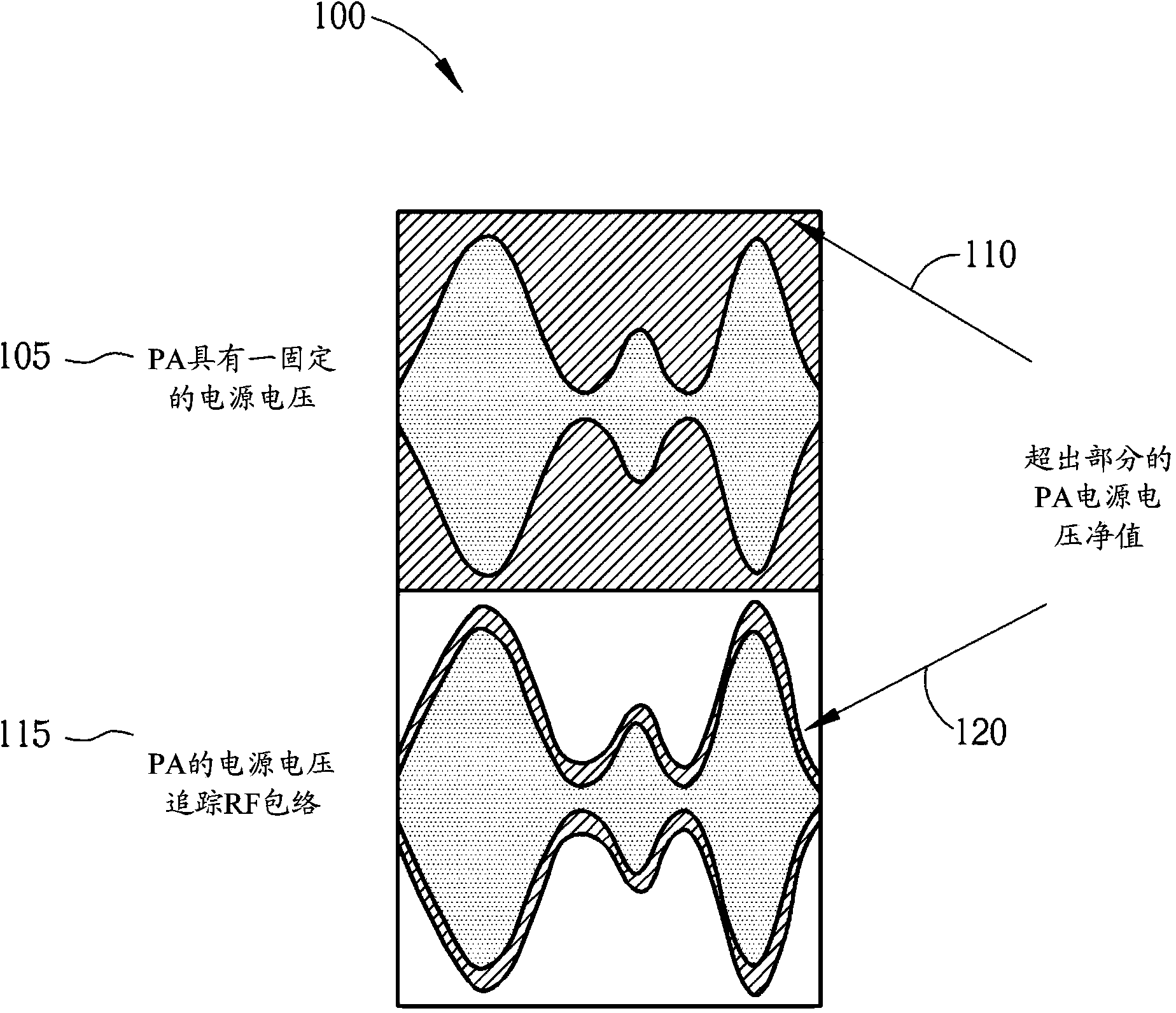
Method of calibrating an envelope tracking system, power voltage modulation method and apparatus thereof
InactiveCN104079243ALow costExcellent current consumptionTransmitters monitoringAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionCommunication unitGain compression
A method of calibrating an envelope tracking system for a supply voltage for a power amplifier module within a radio frequency (RF) transmitter module of a wireless communication unit. The method includes, within at least one signal processing module of the wireless communication unit, determining combinations of the power amplifier supply voltage and power amplifier input power that provide a power amplifier output power equal to a target output power, obtaining battery current indications for the determined combinations of the power amplifier supply voltage and power amplifier input power, selecting a combination of the power amplifier supply voltage and power amplifier input power that provide a power amplifier output power equal to a target output power based at least partly on the obtained battery current indications therefore, and calibrating the envelope tracking system using the selected combination of the power amplifier supply voltage and power amplifier input power.
Owner:MEDIATEK SINGAPORE PTE LTD SINGAPORE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com