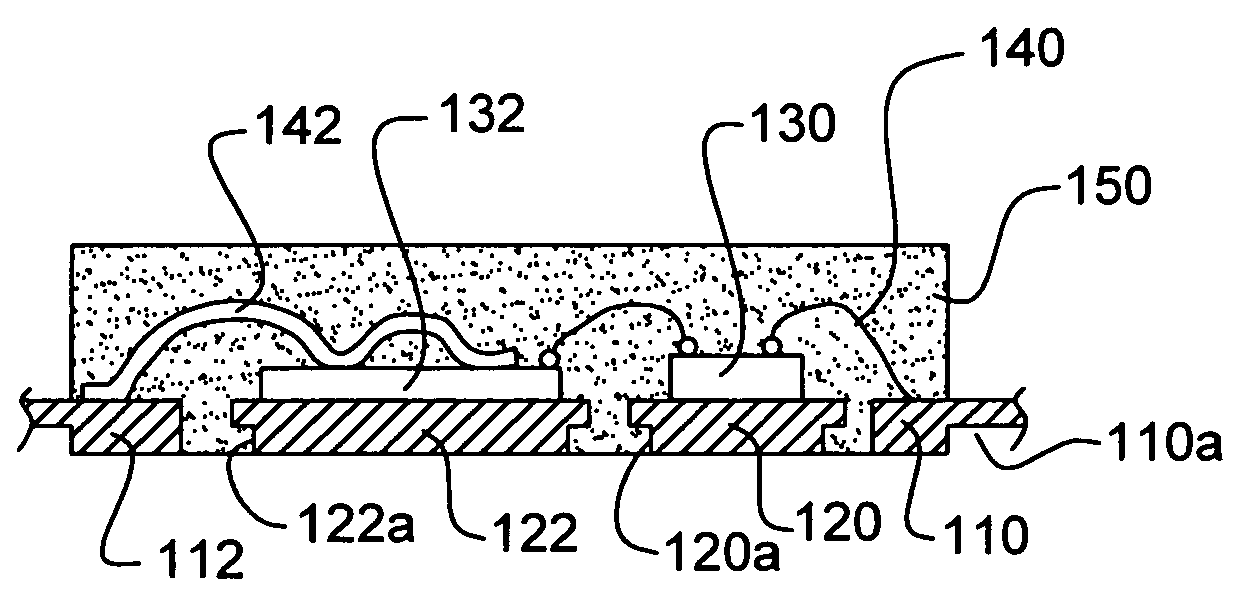
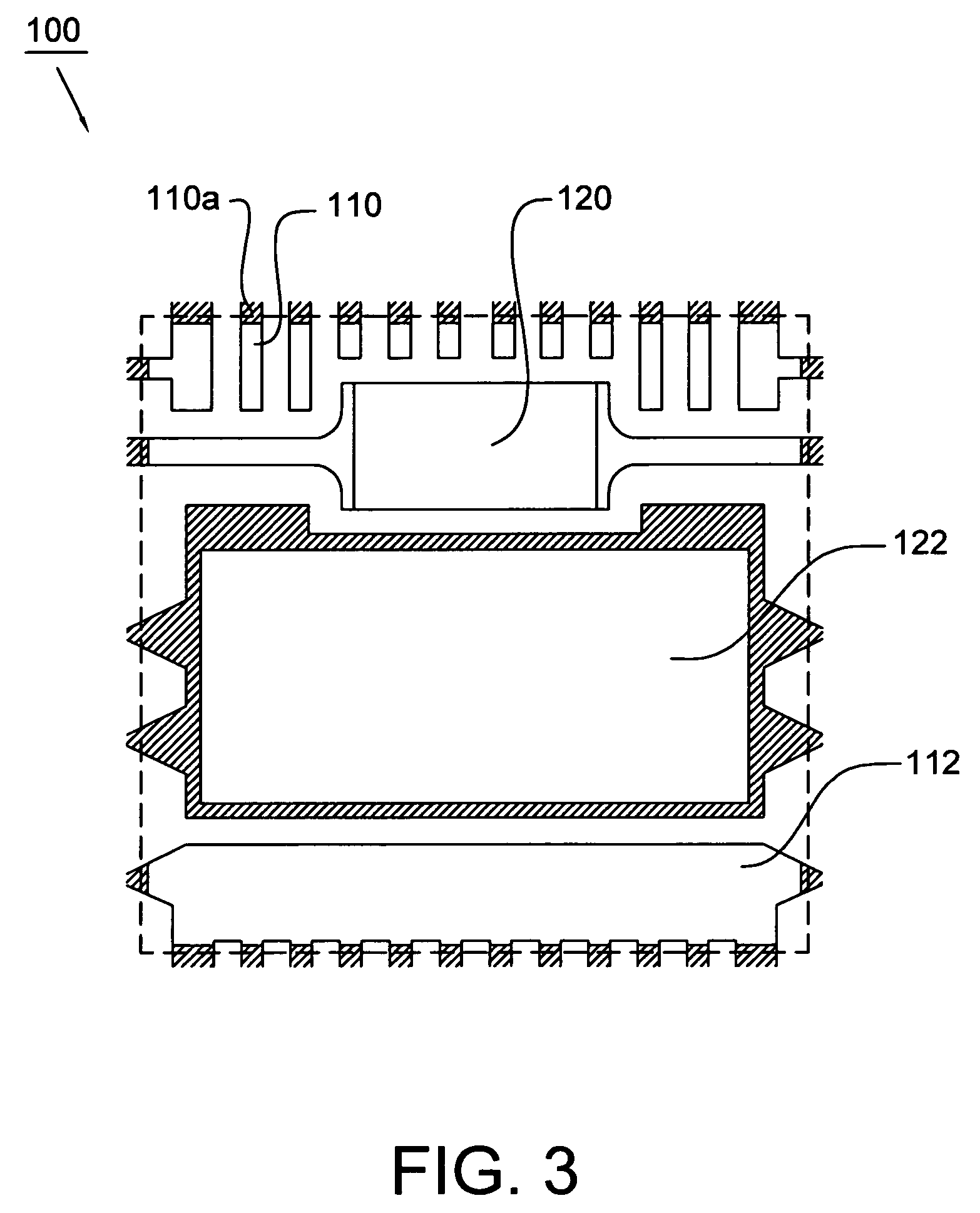
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2608results about How to "Lower on-resistance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
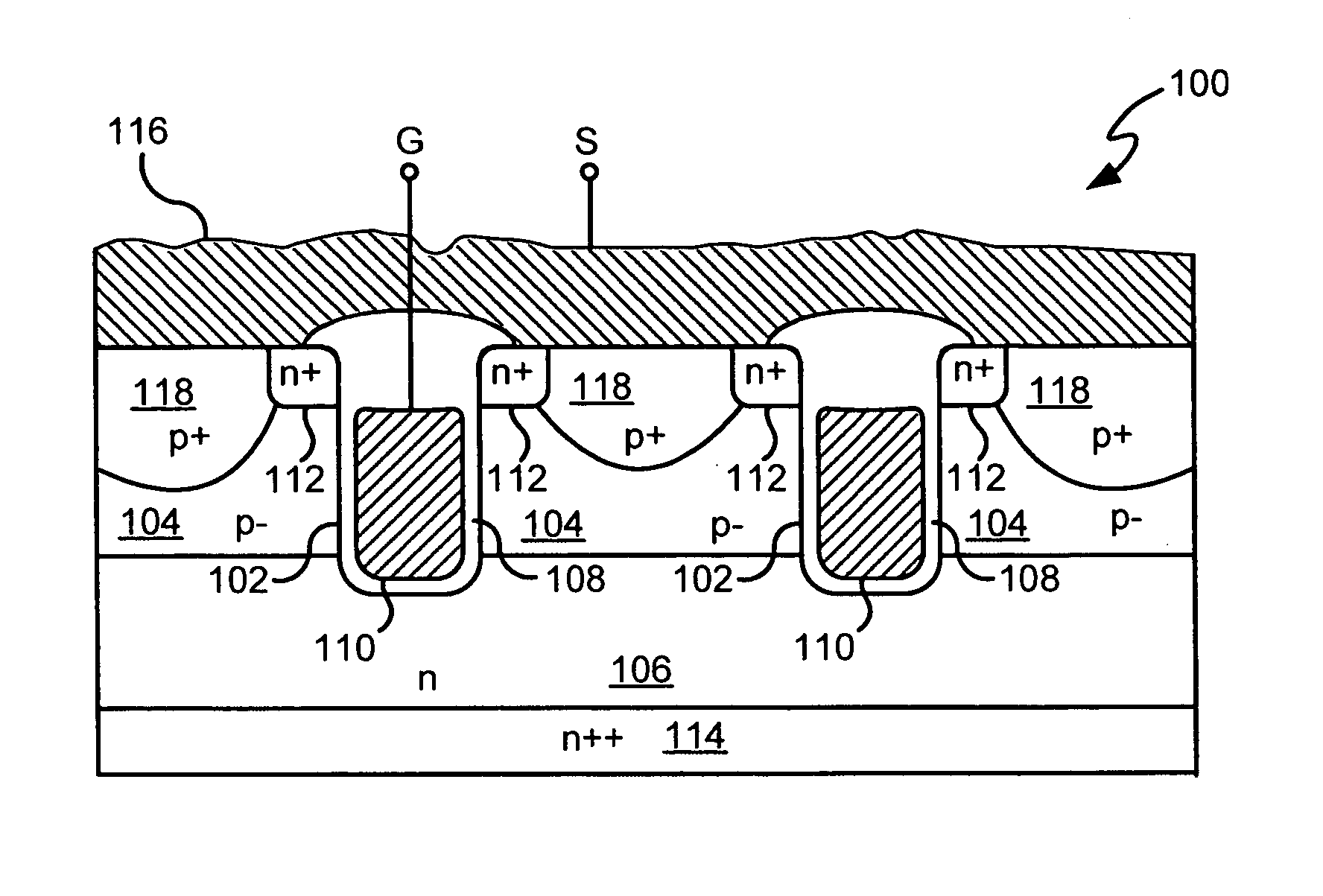
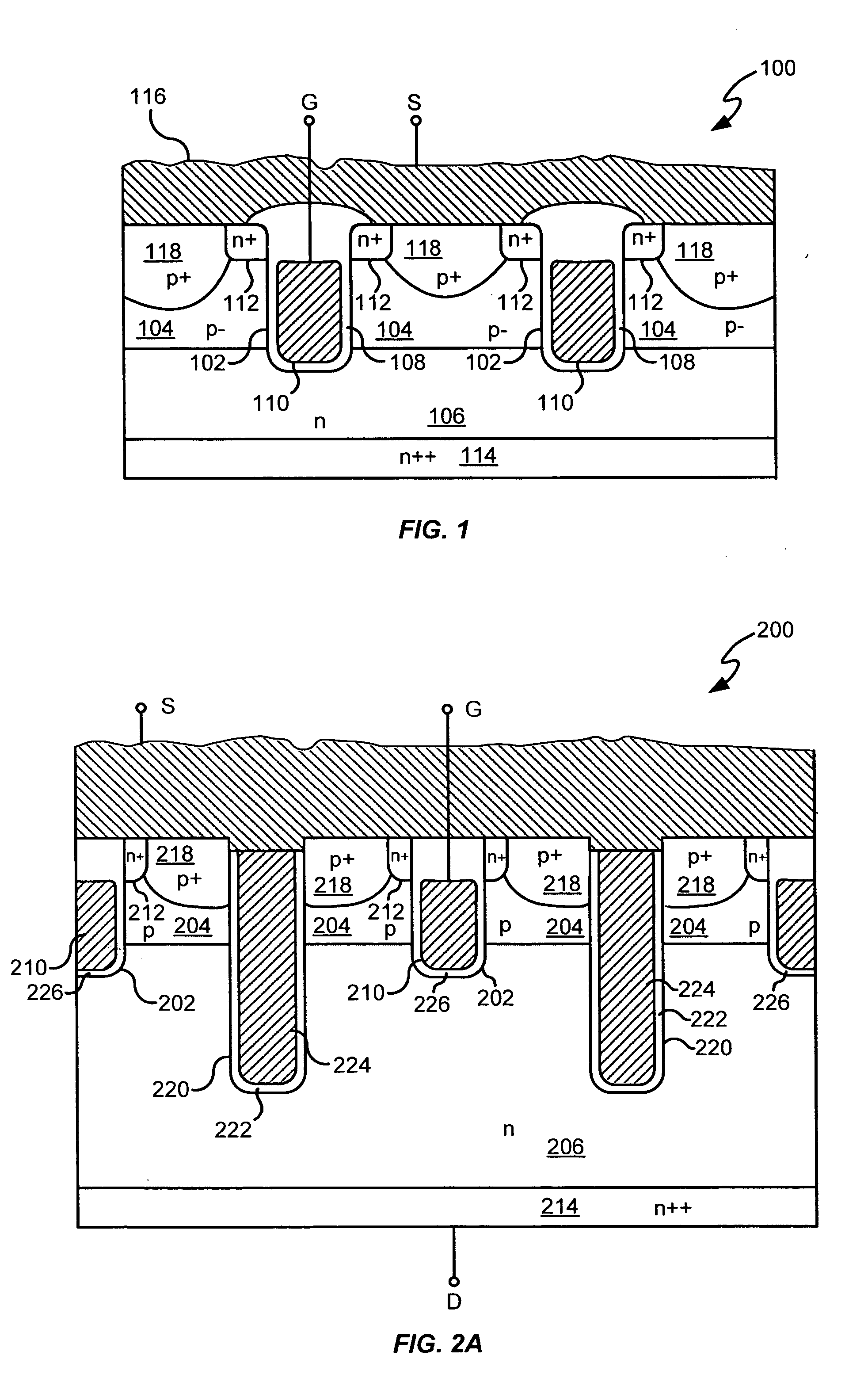
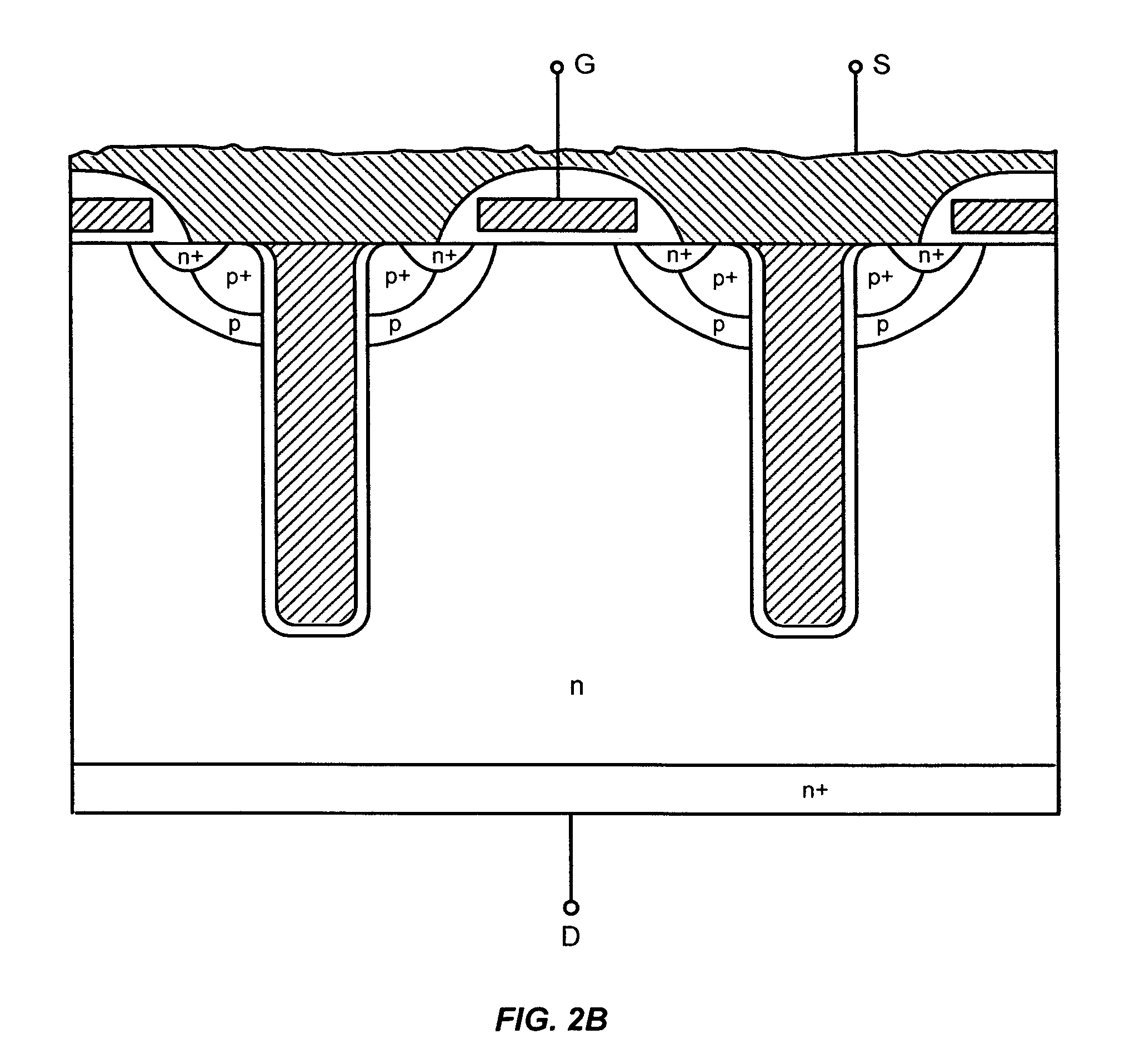
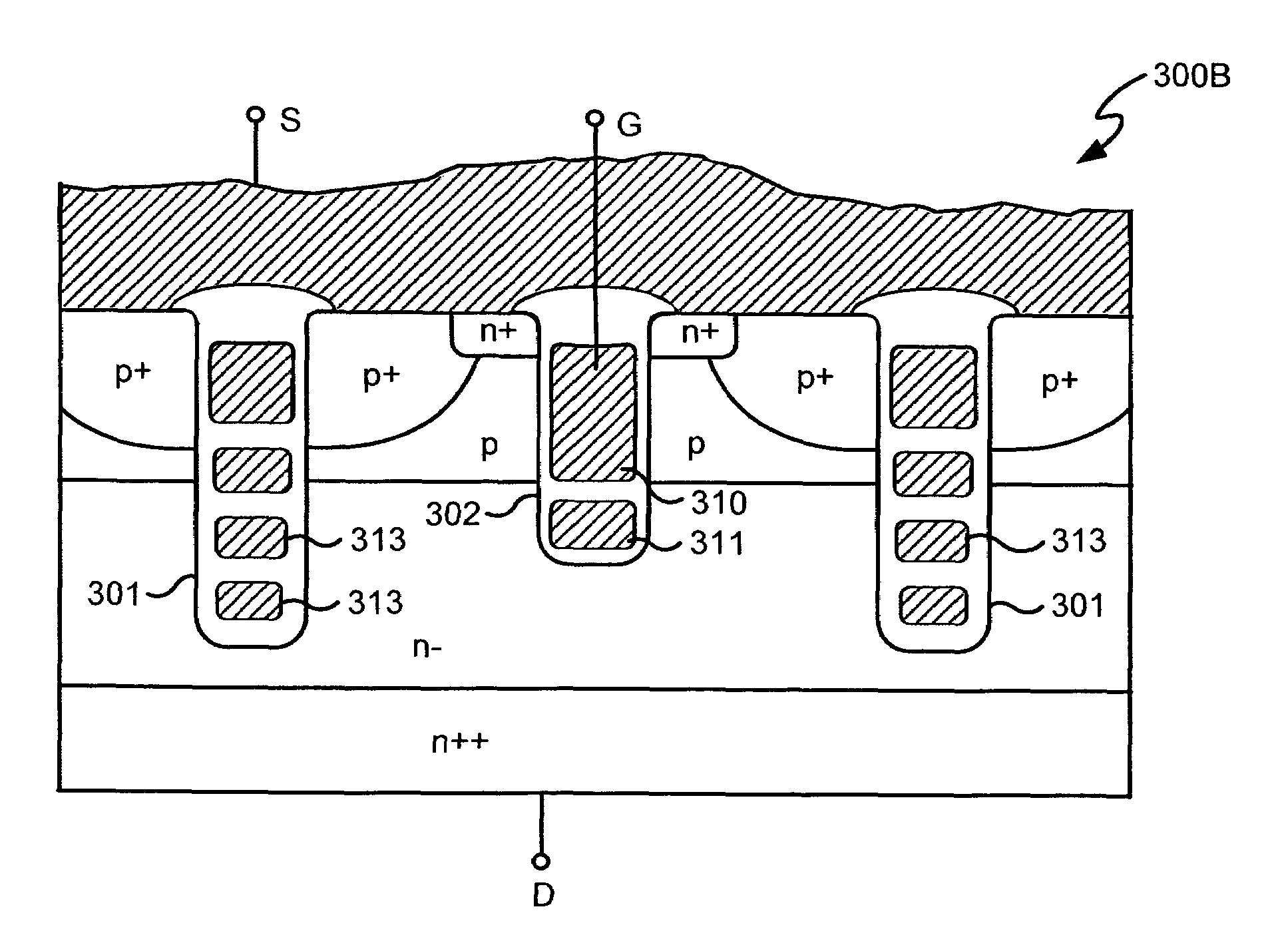
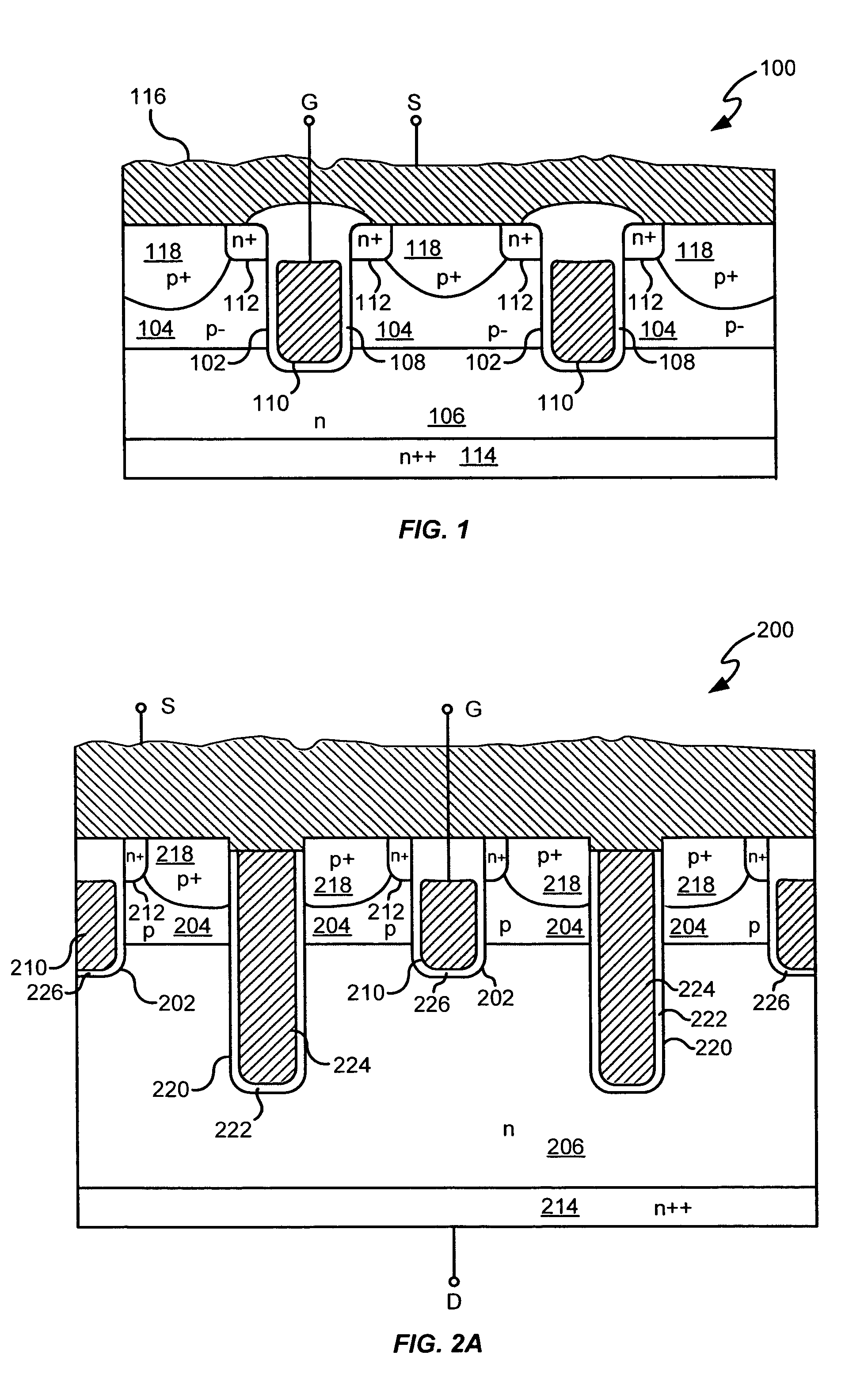
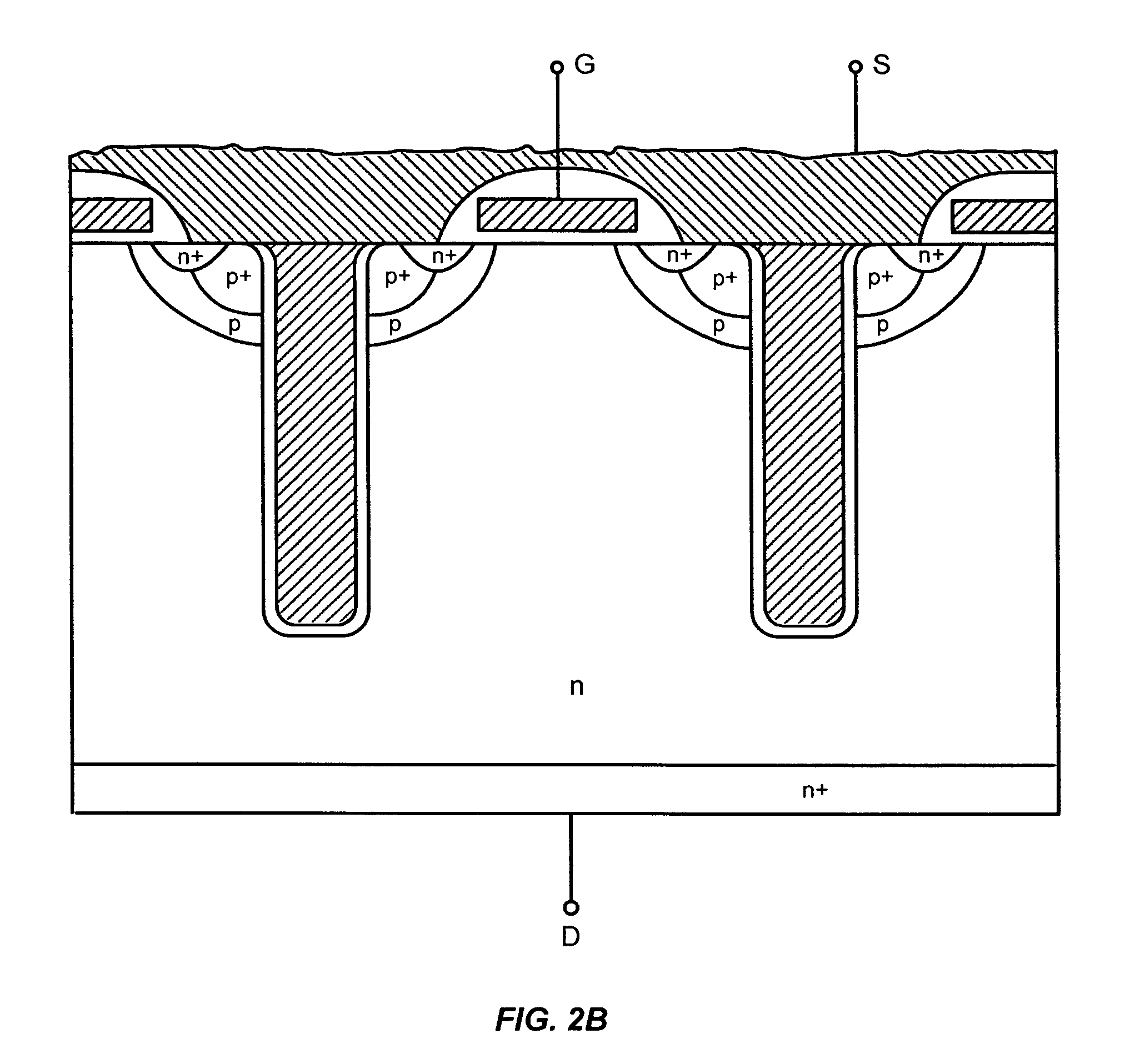
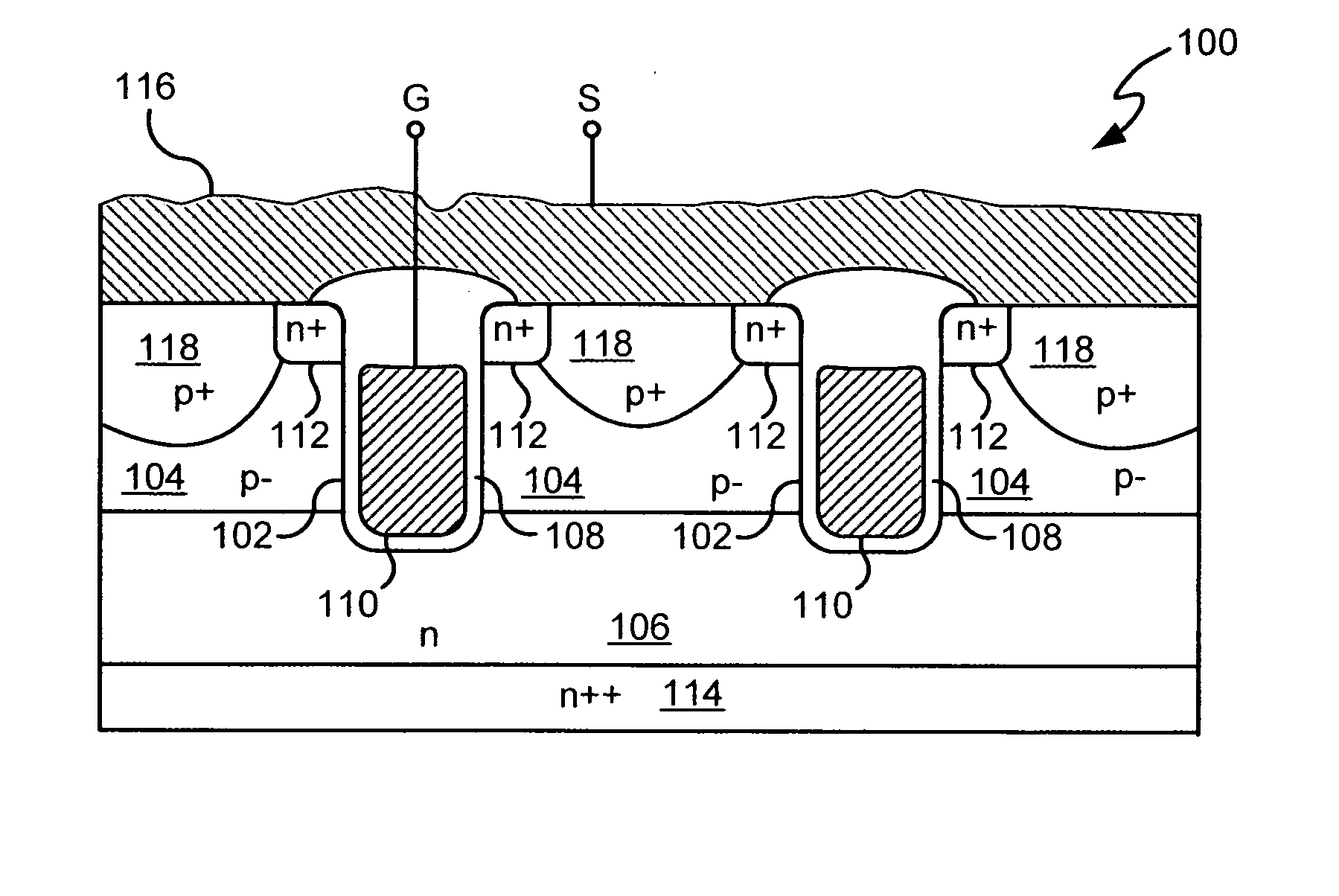
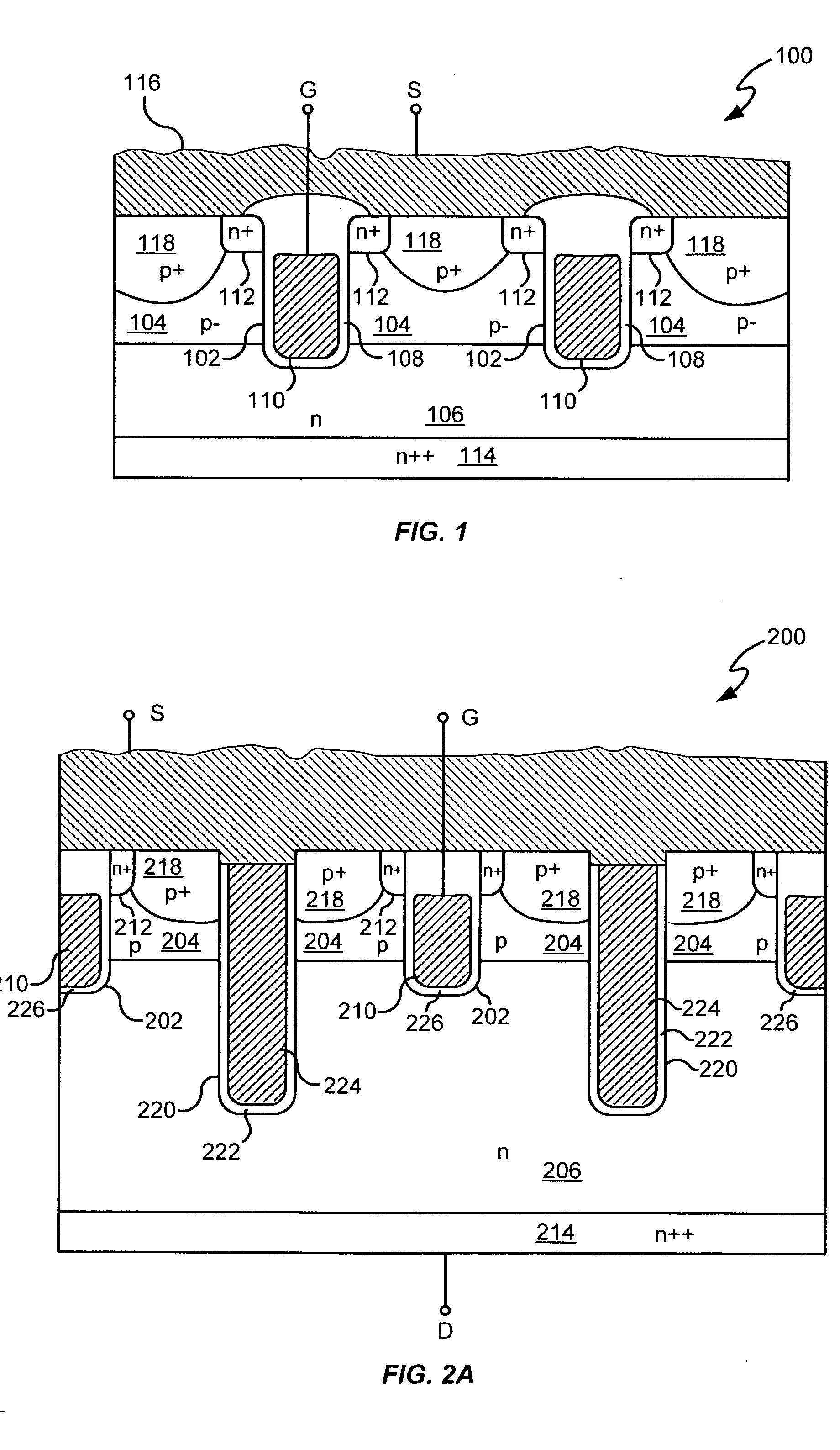
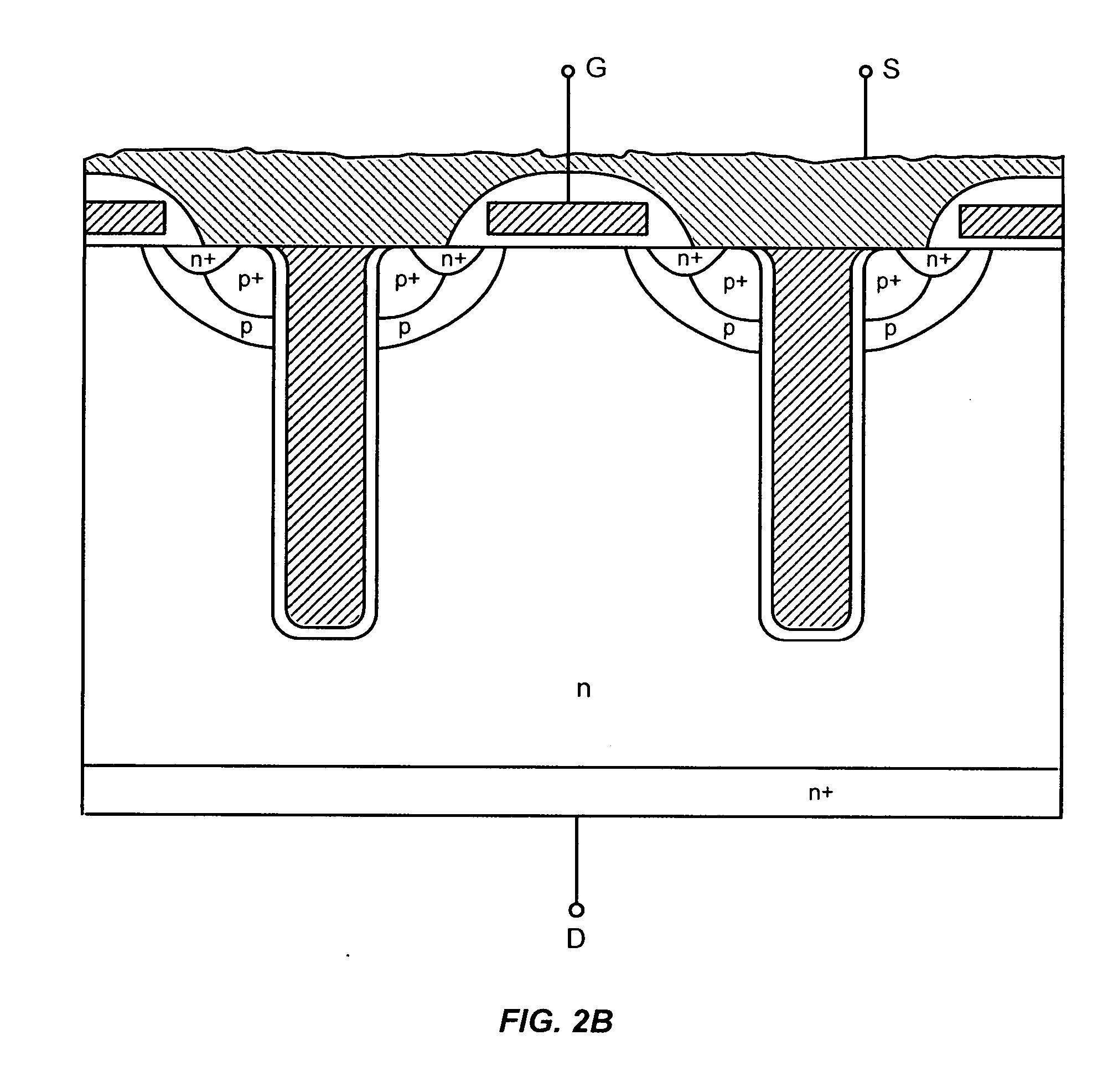
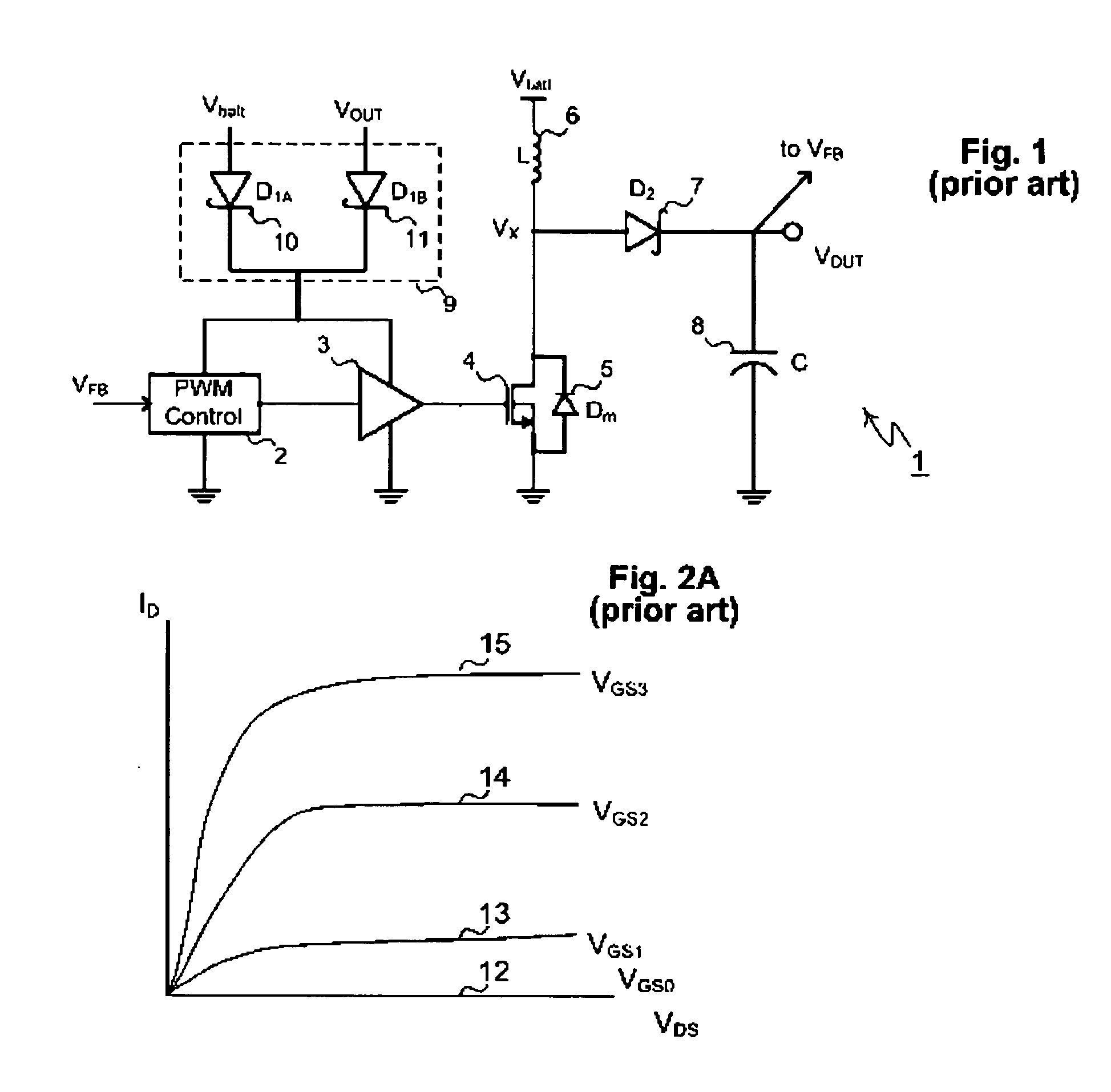
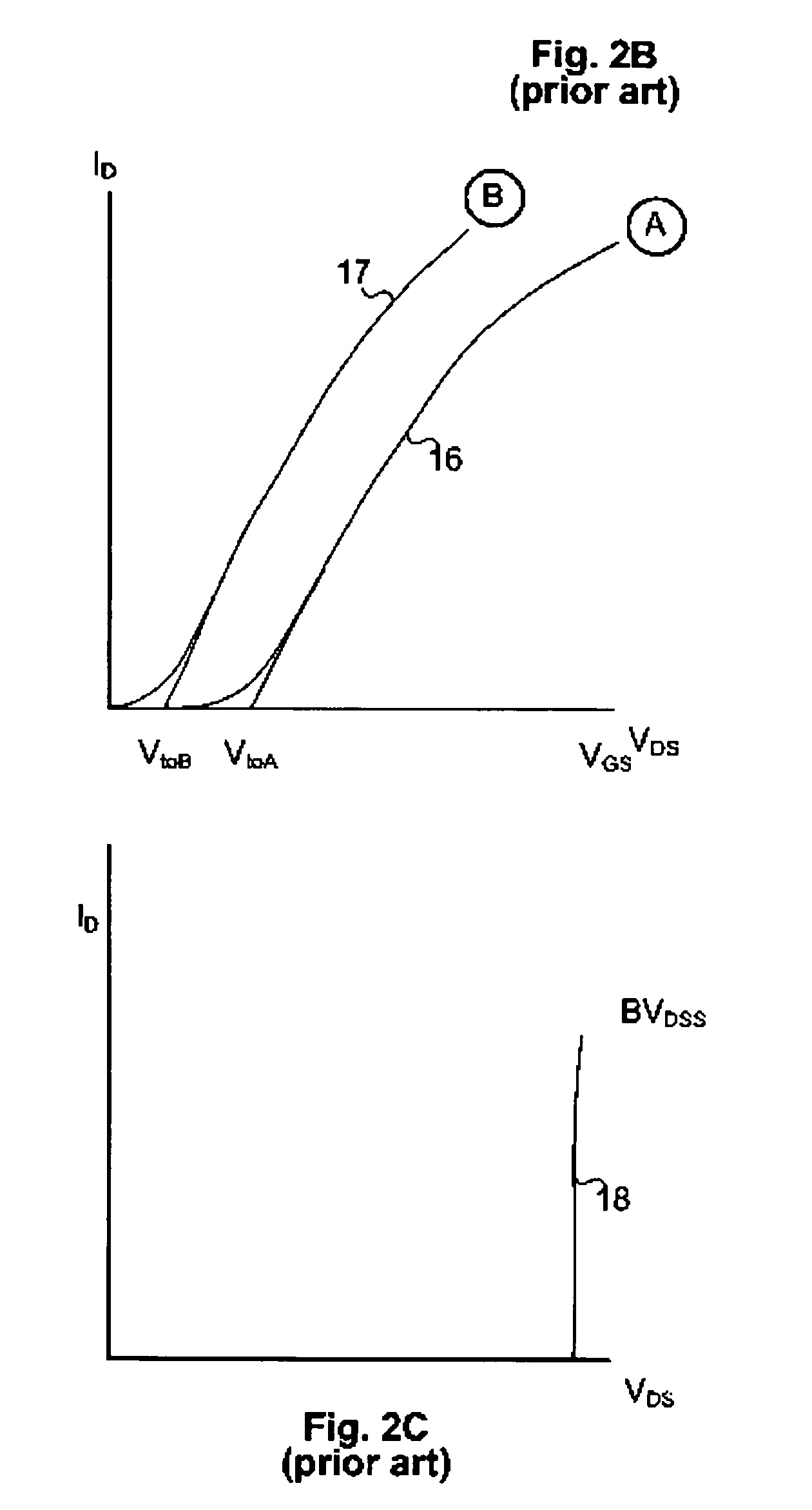
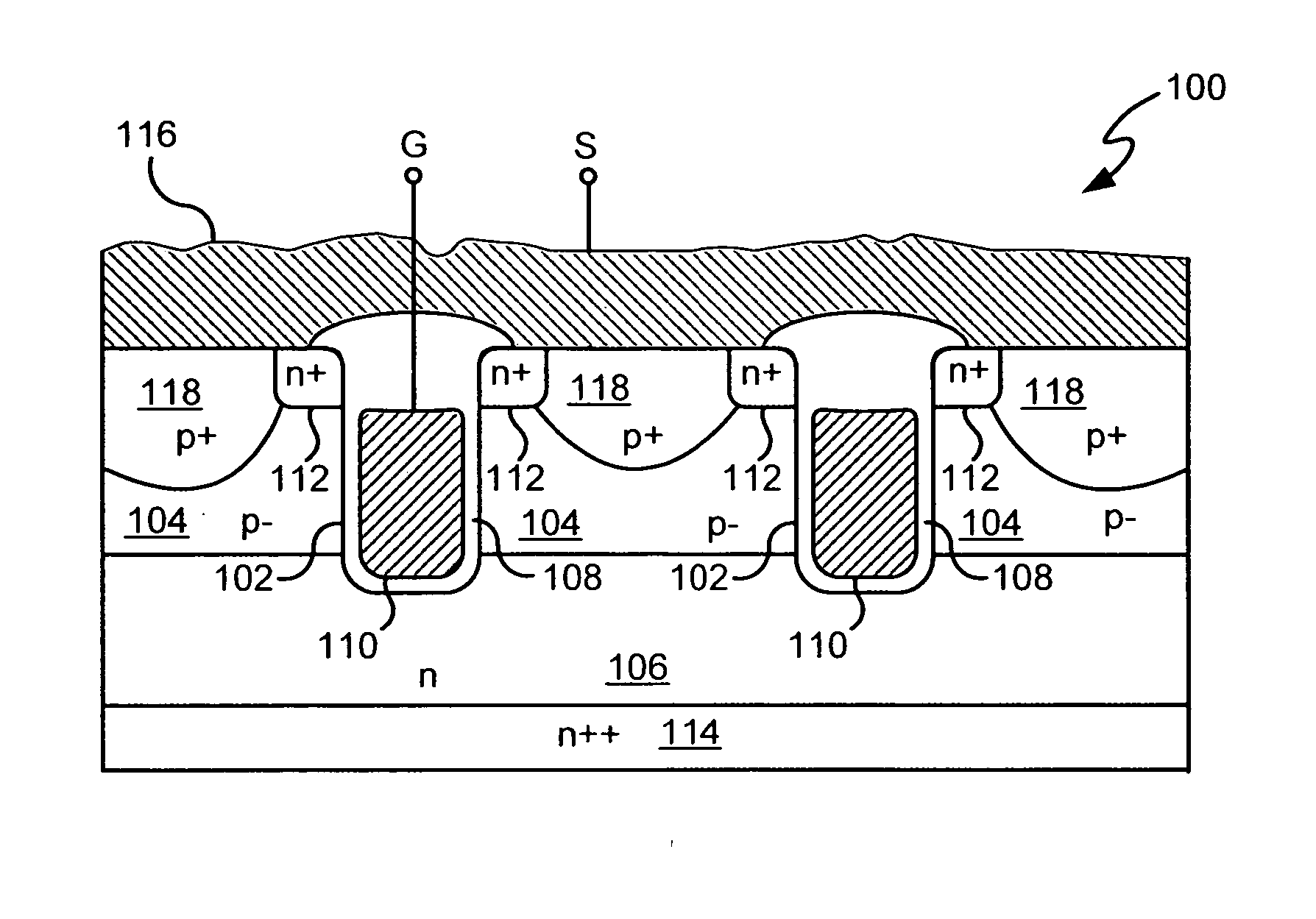
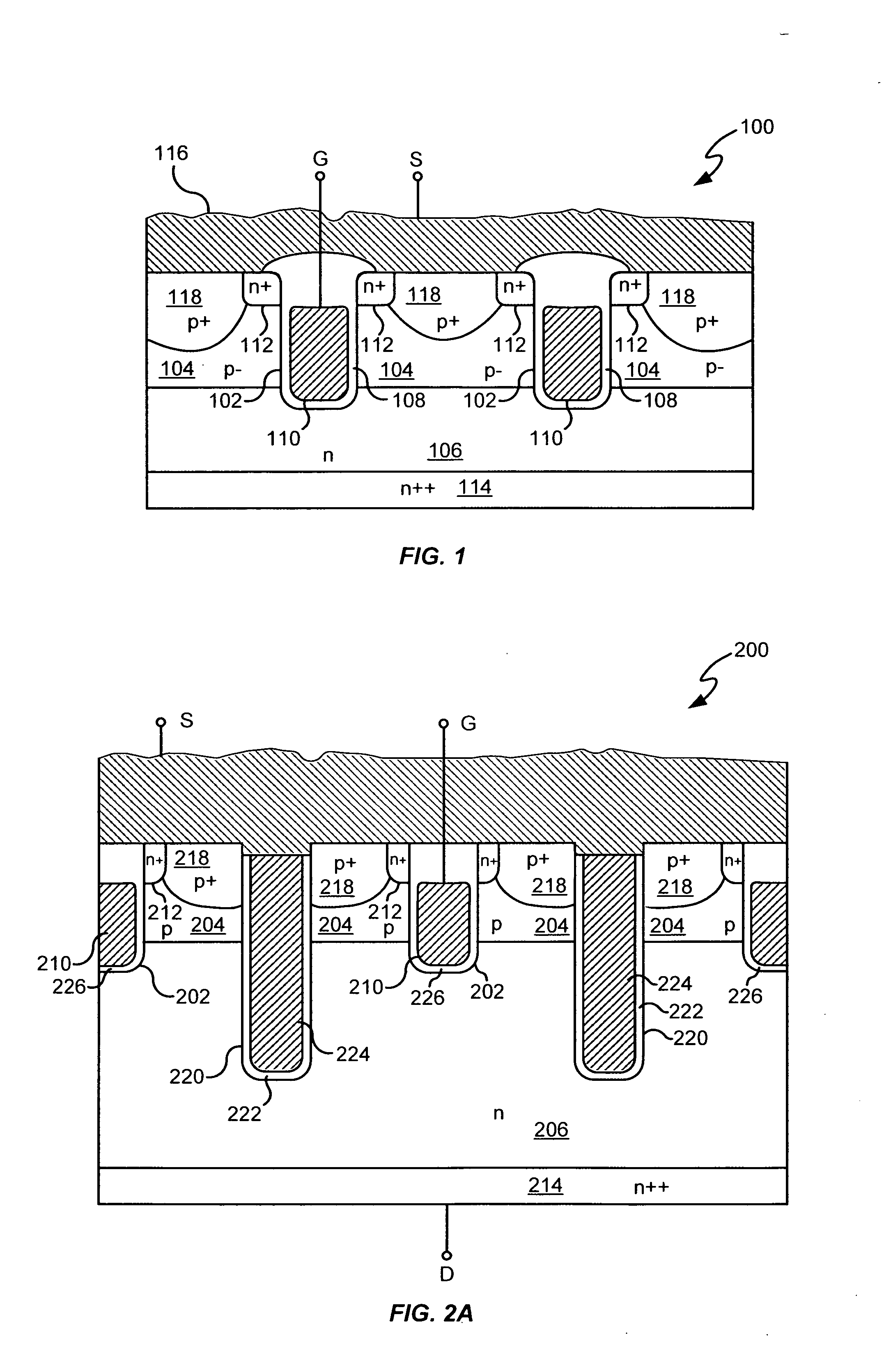
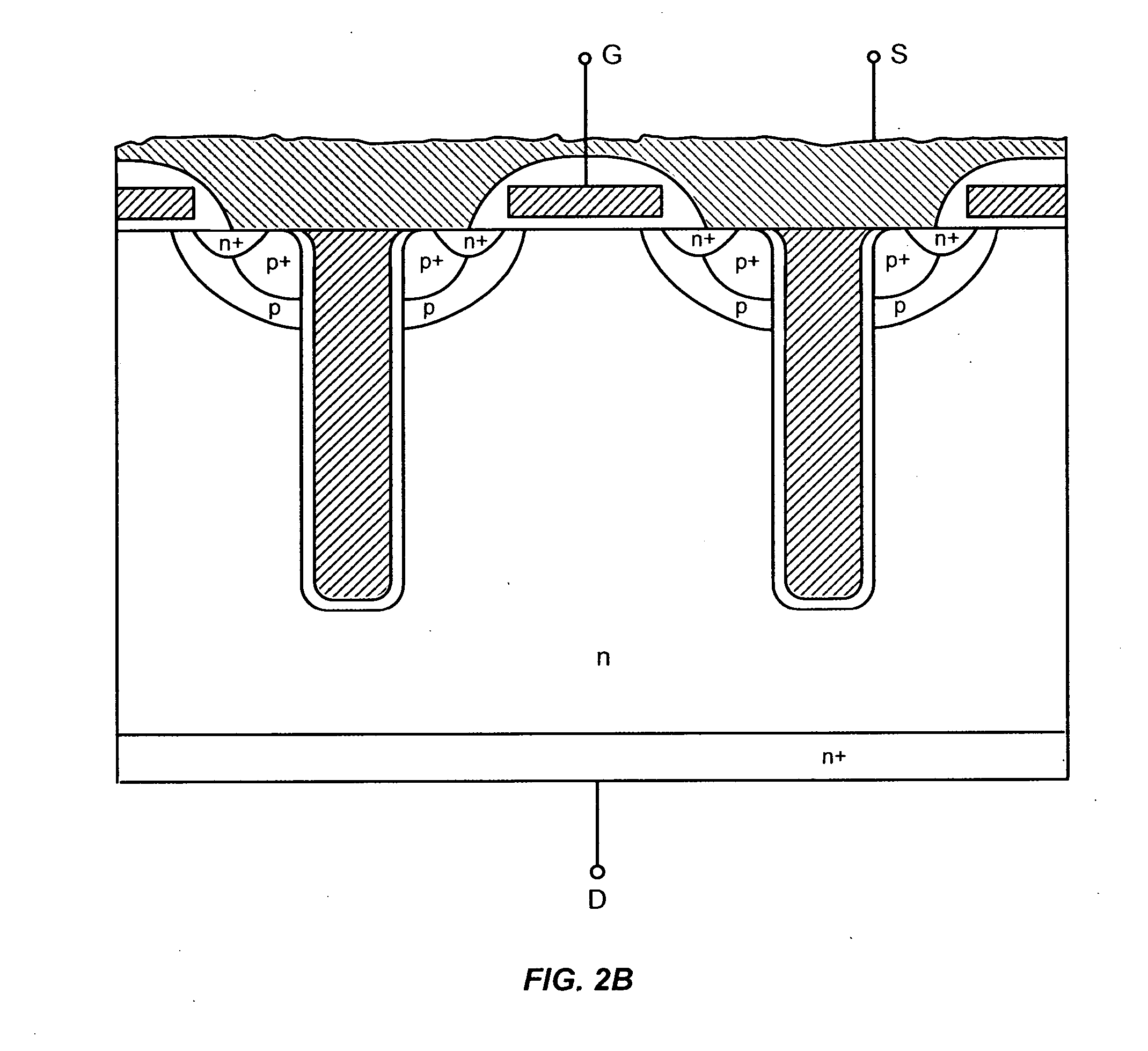
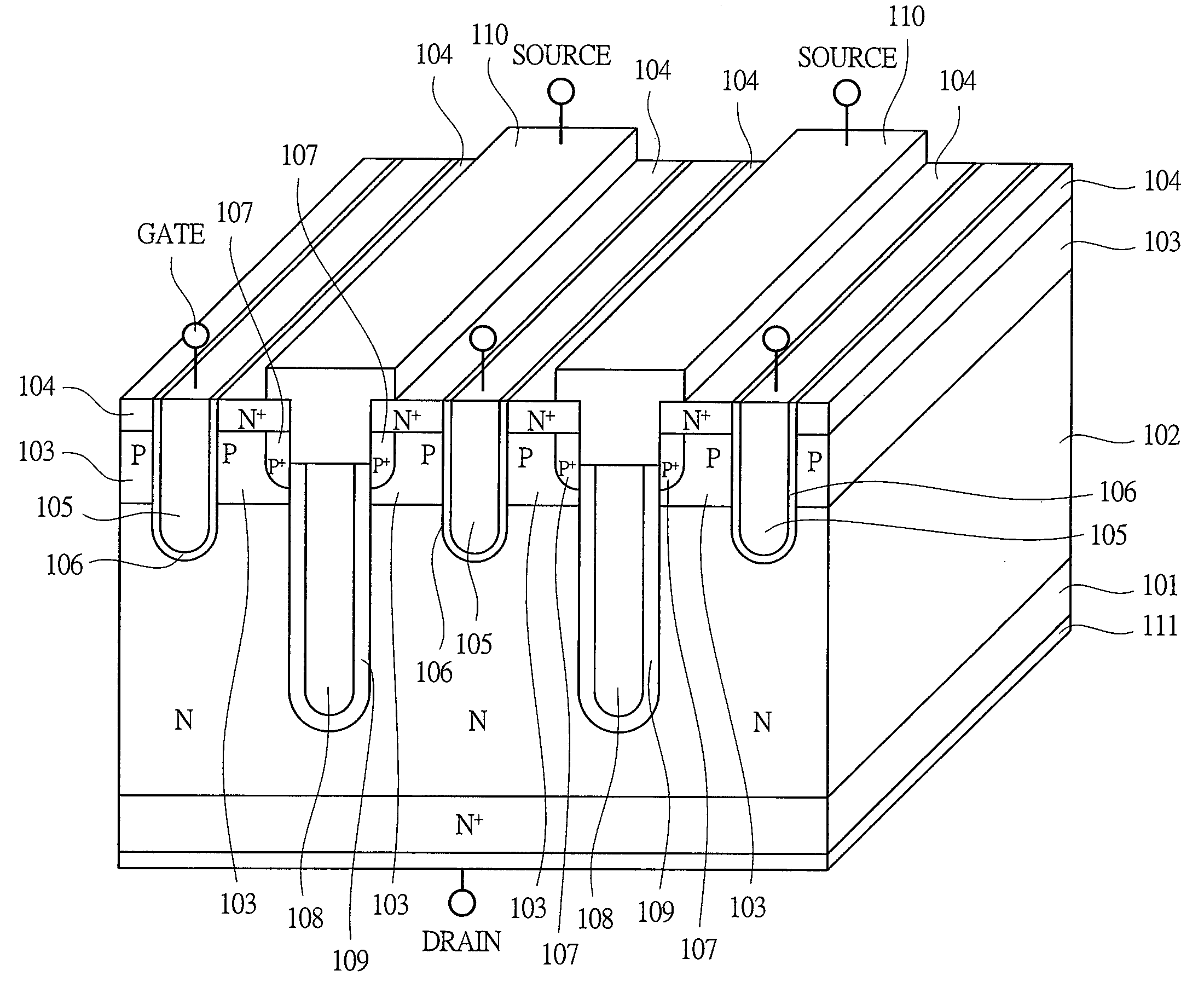
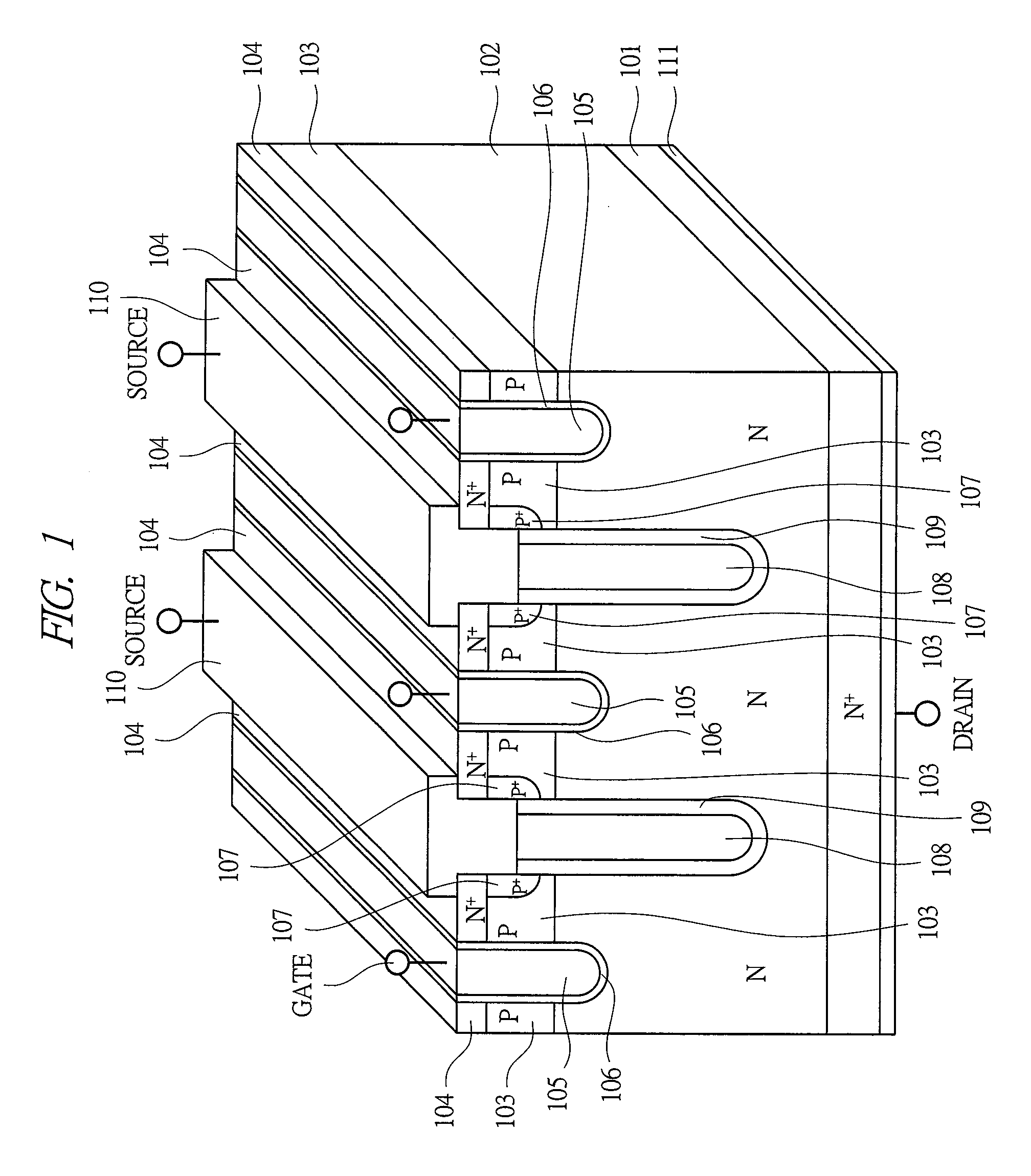
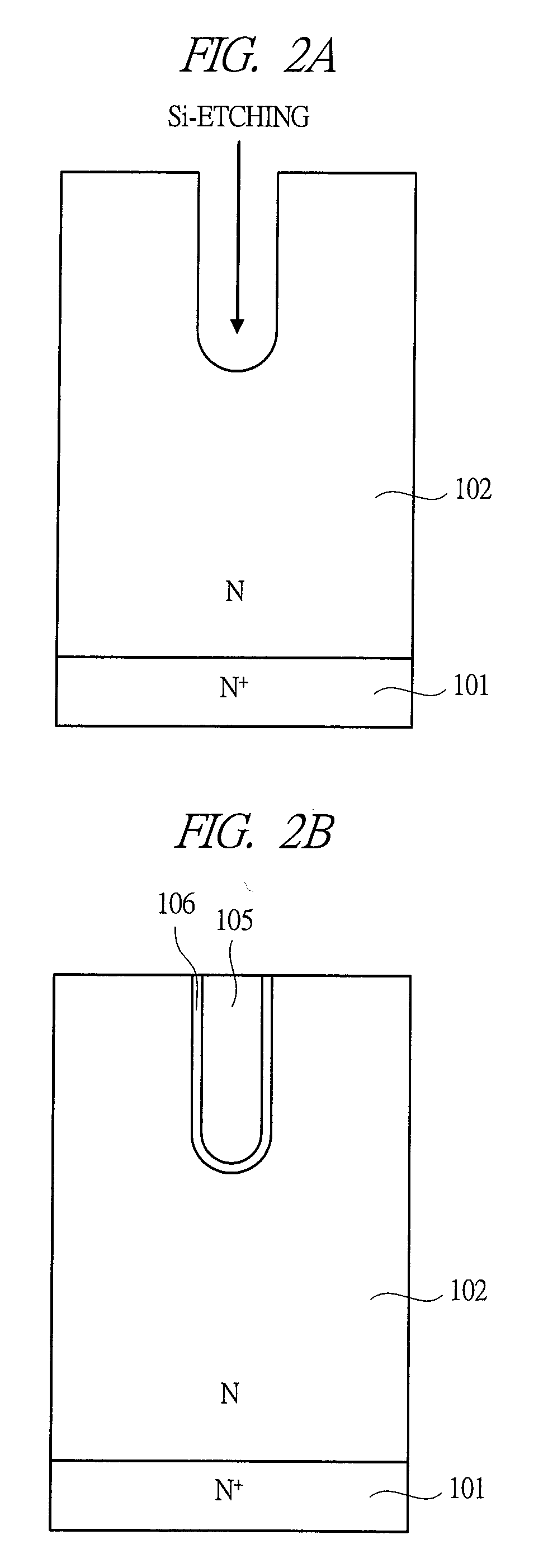
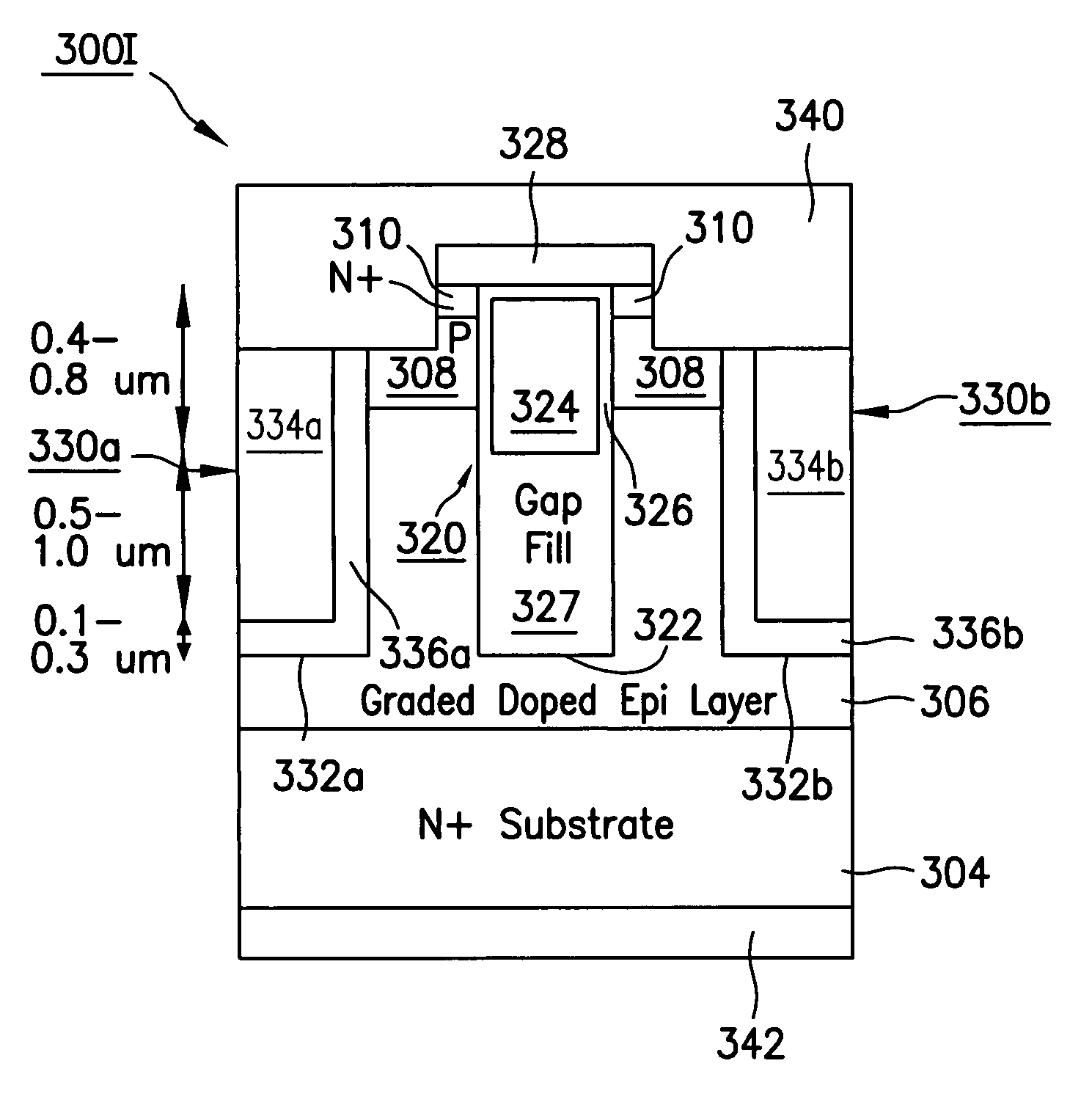
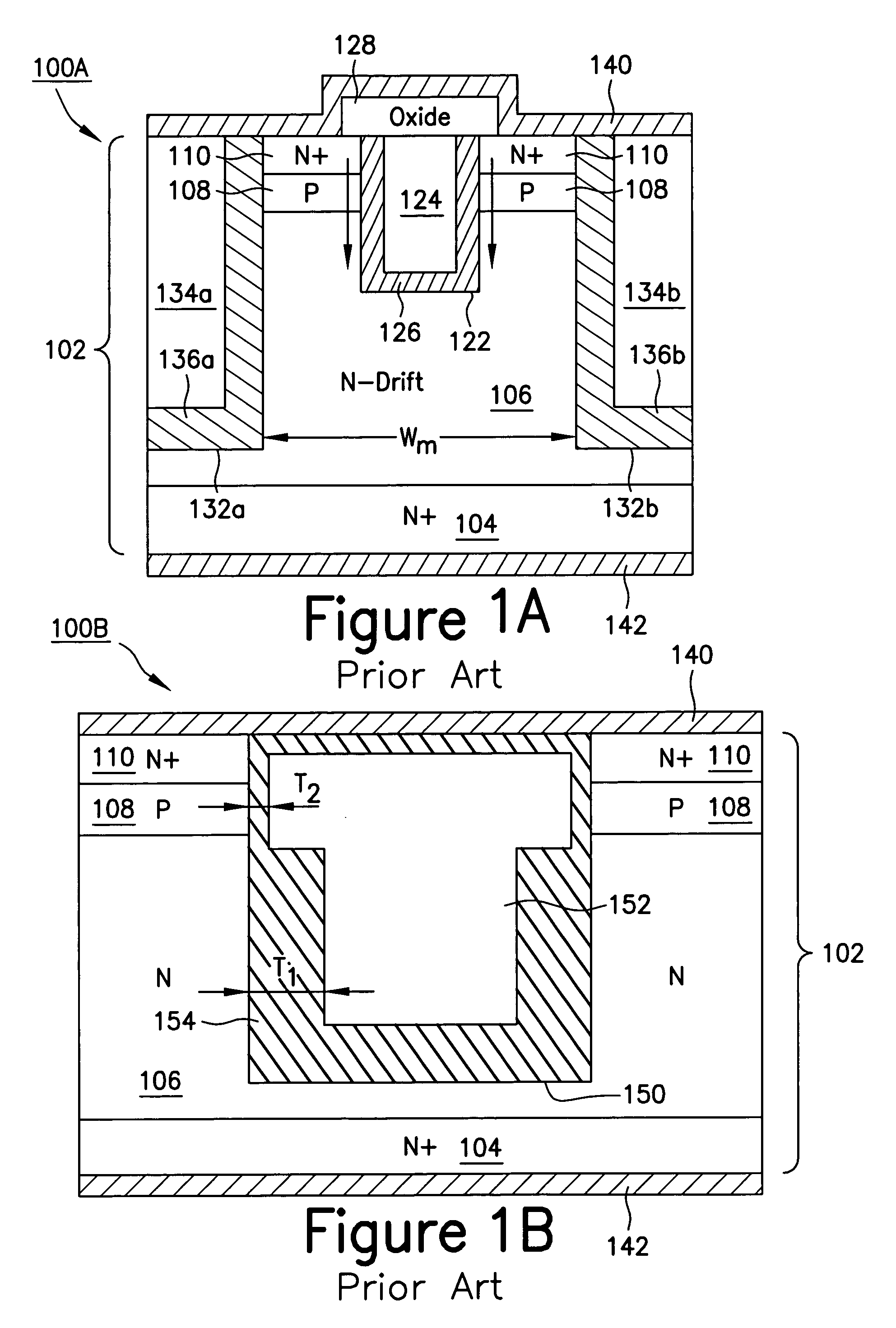
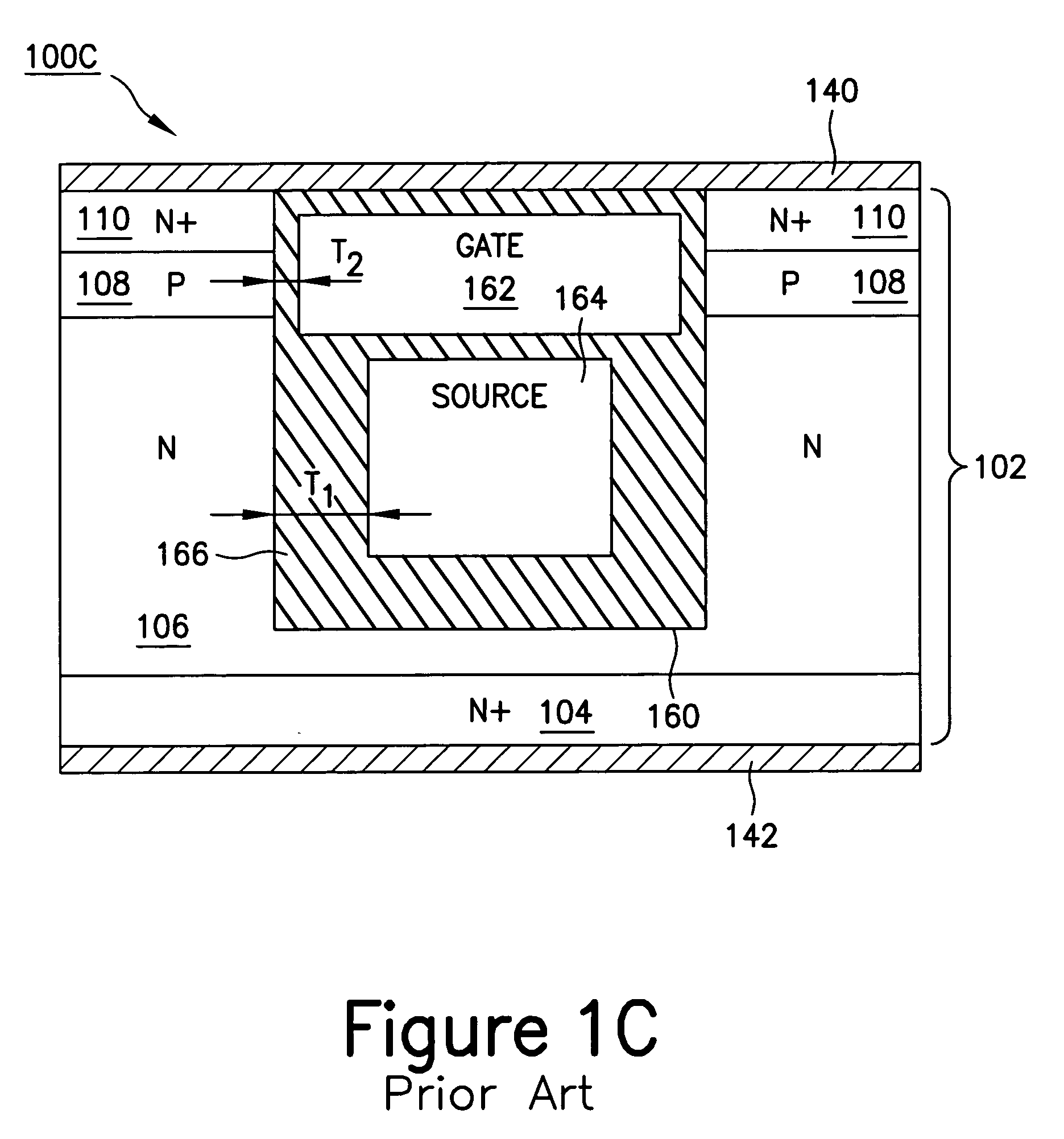
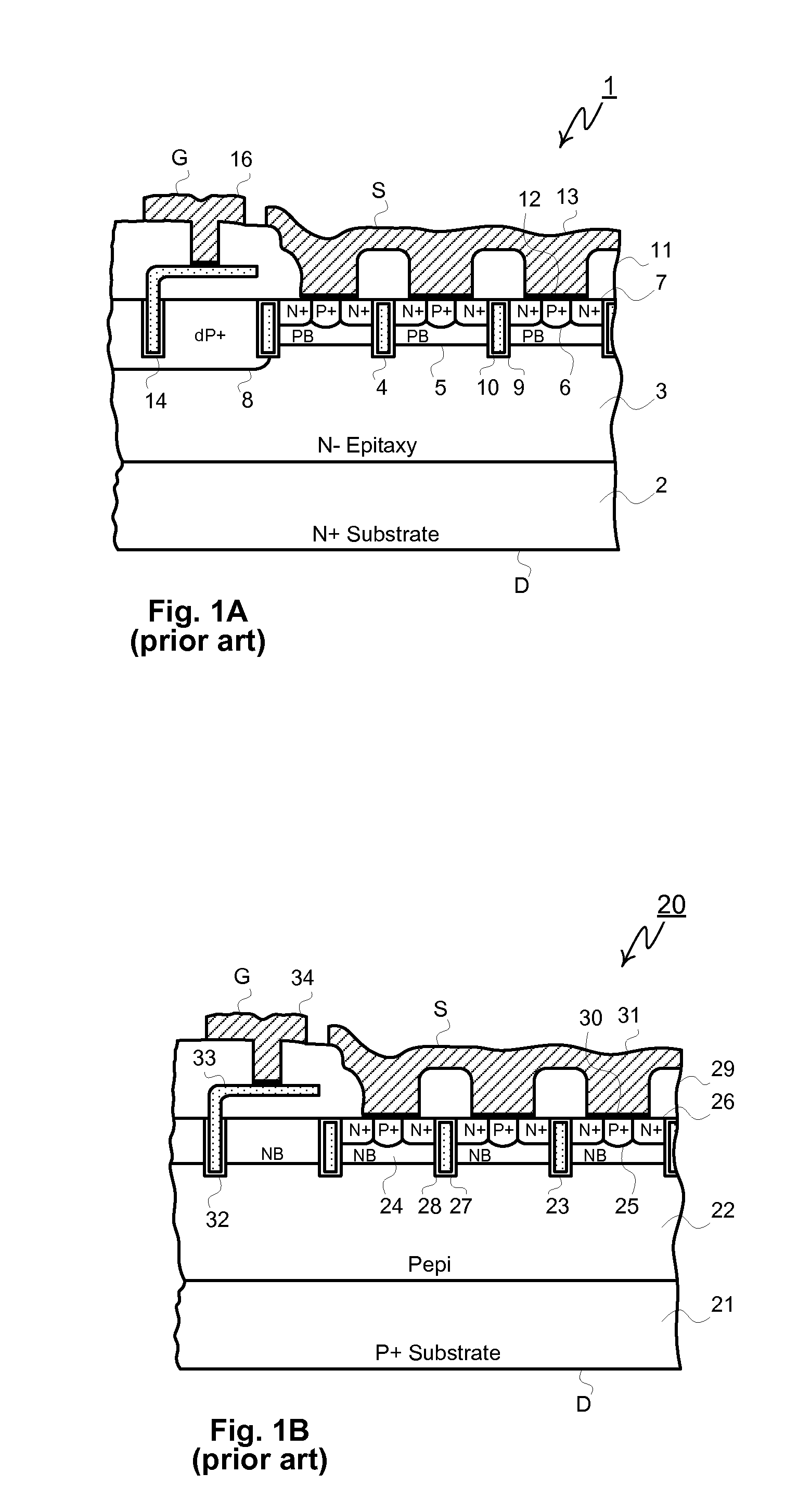
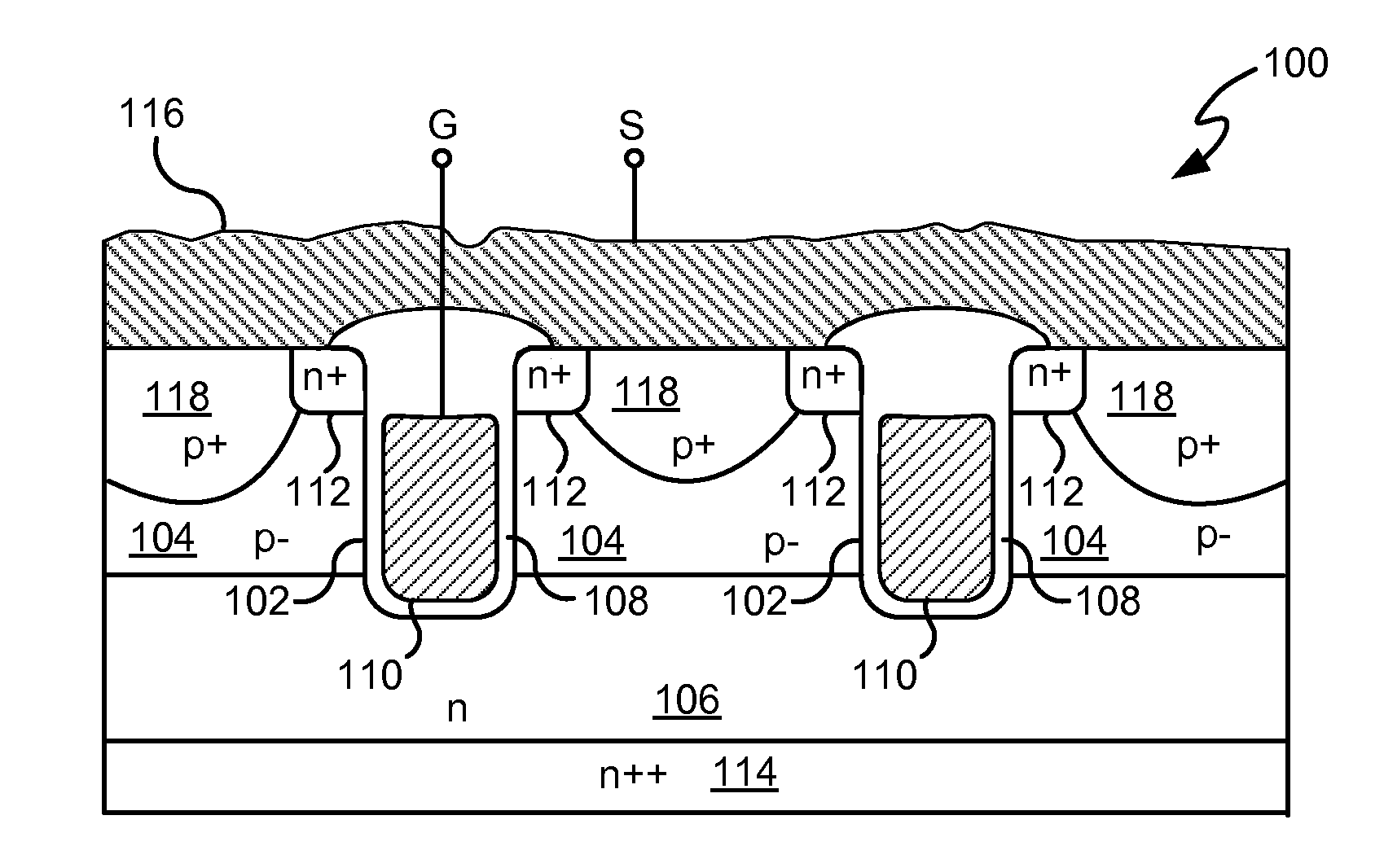
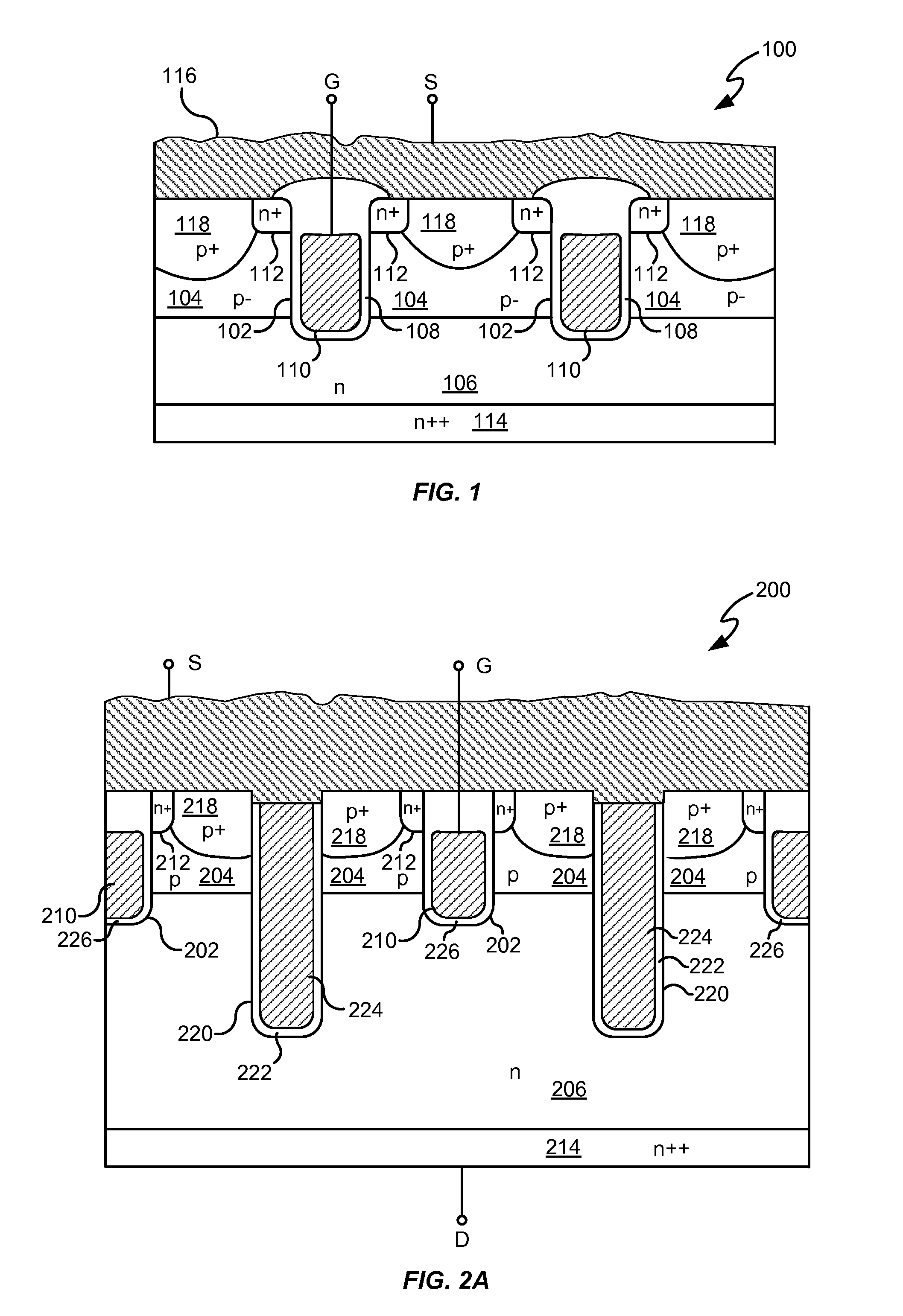
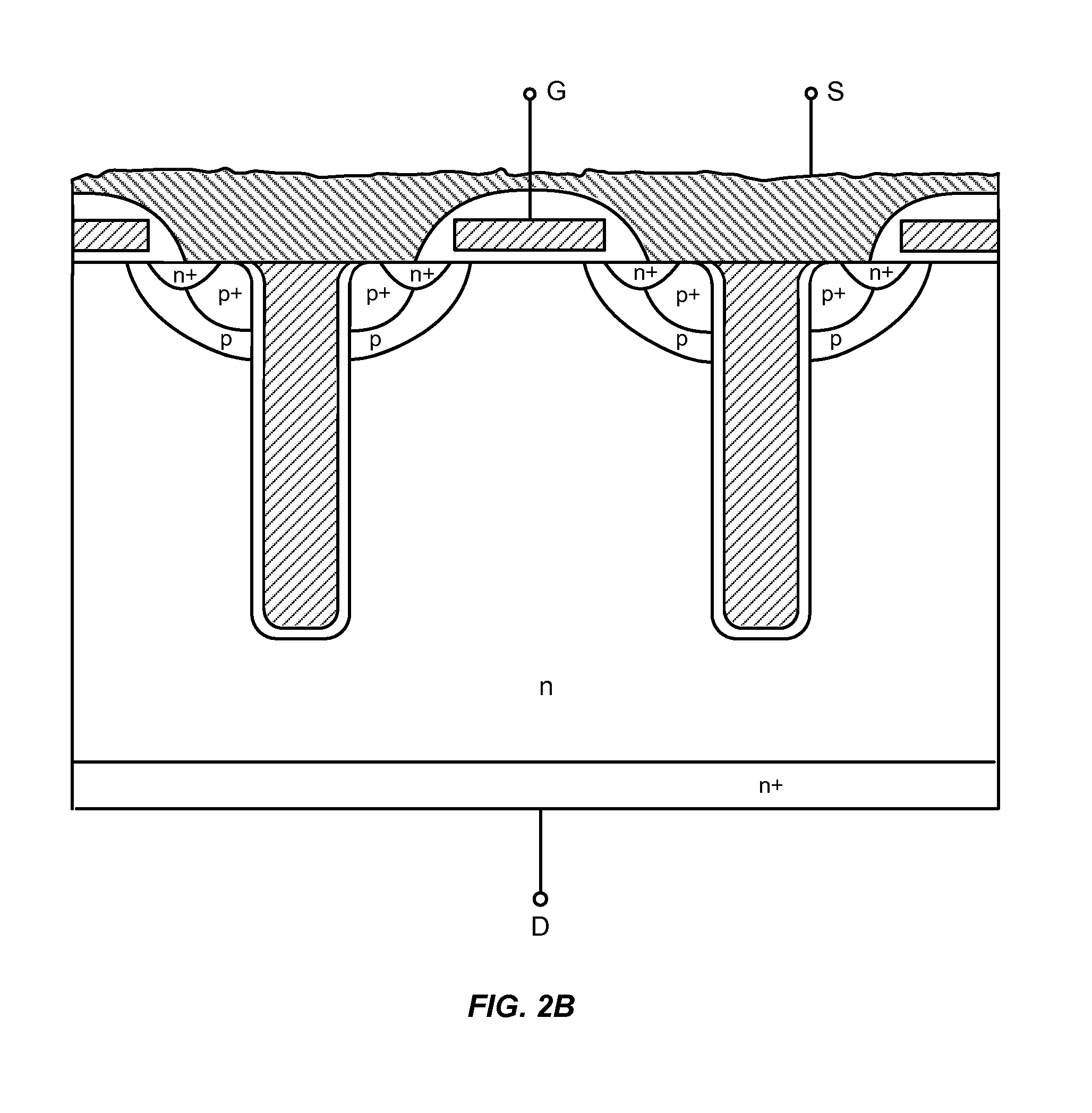
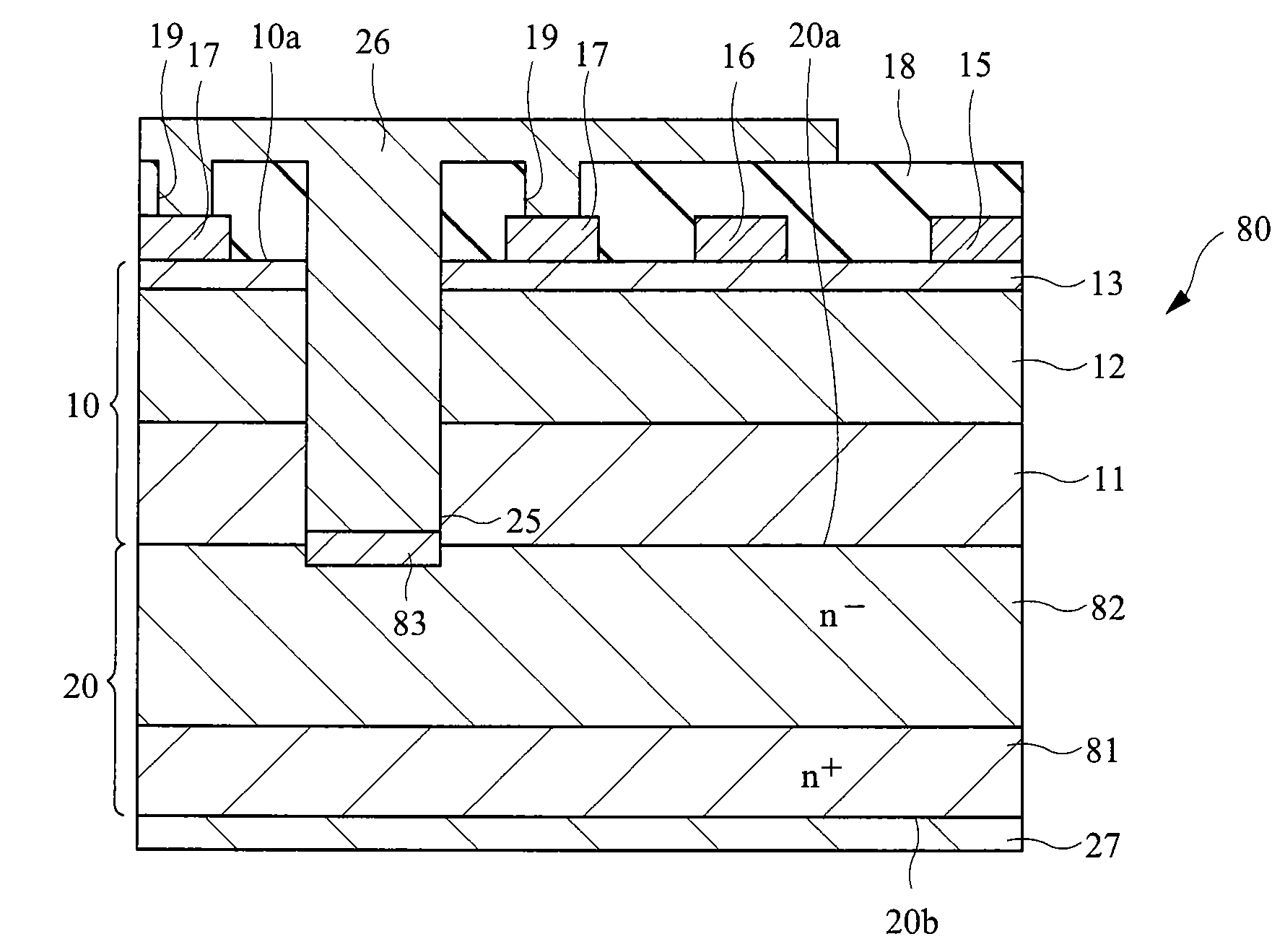
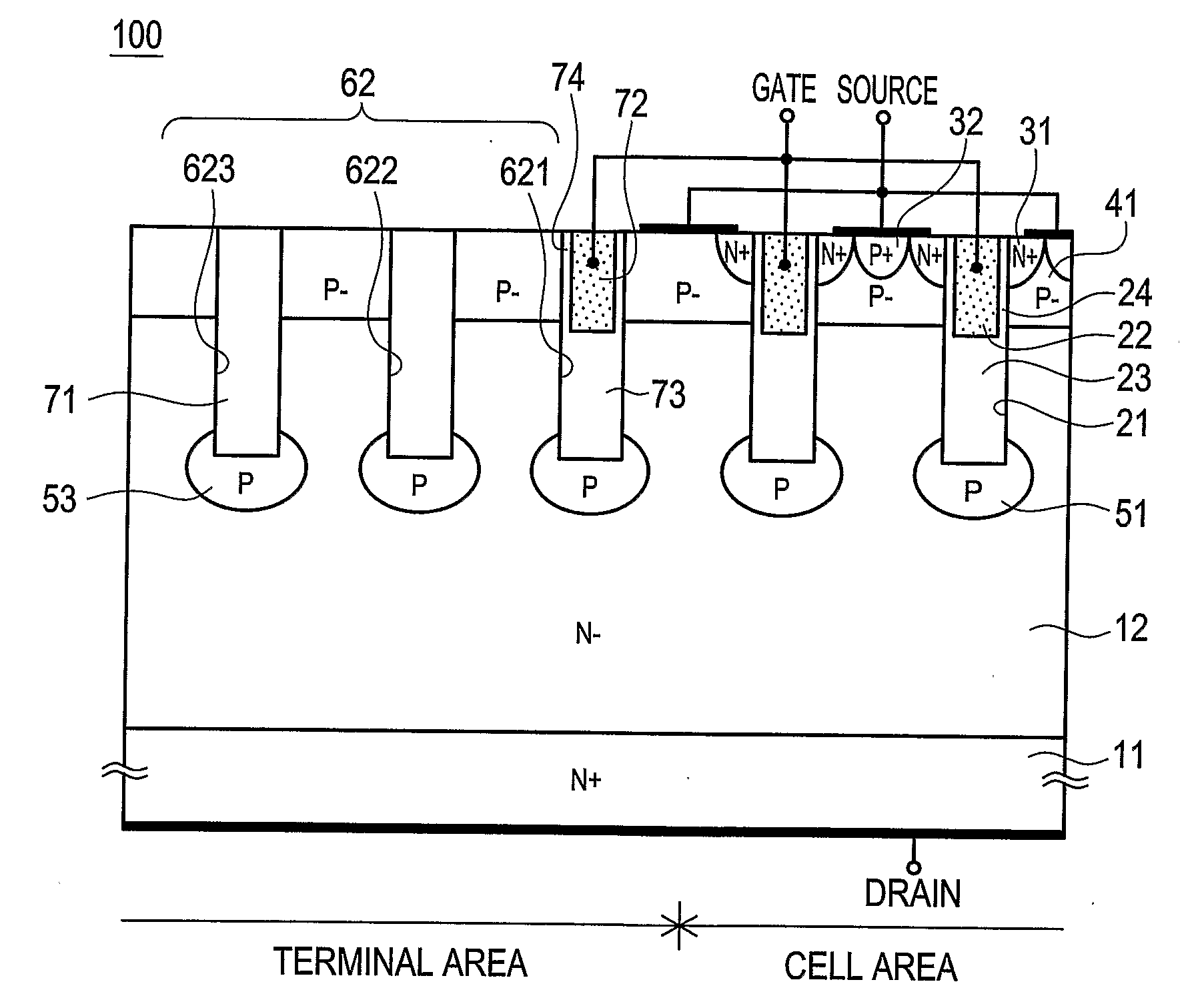
Power semiconductor devices and methods of manufacture
ActiveUS20050167742A1Improved voltage performanceFast switching speedEfficient power electronics conversionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringHigh voltage
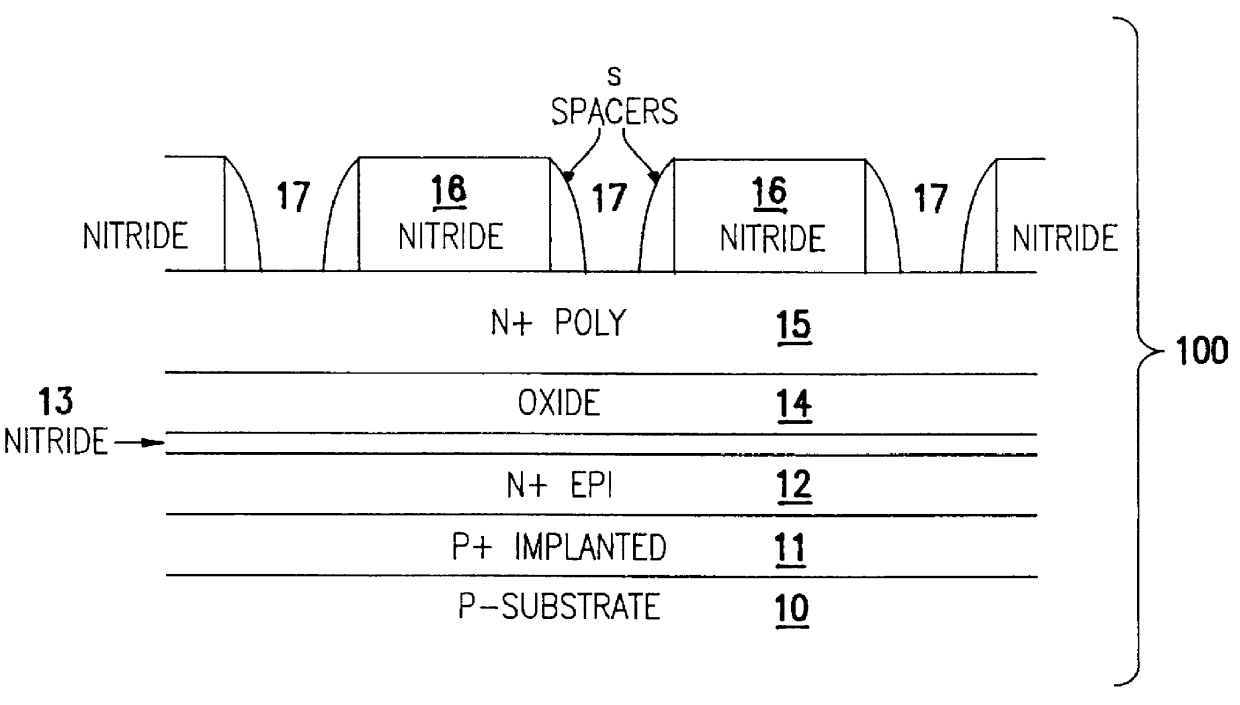
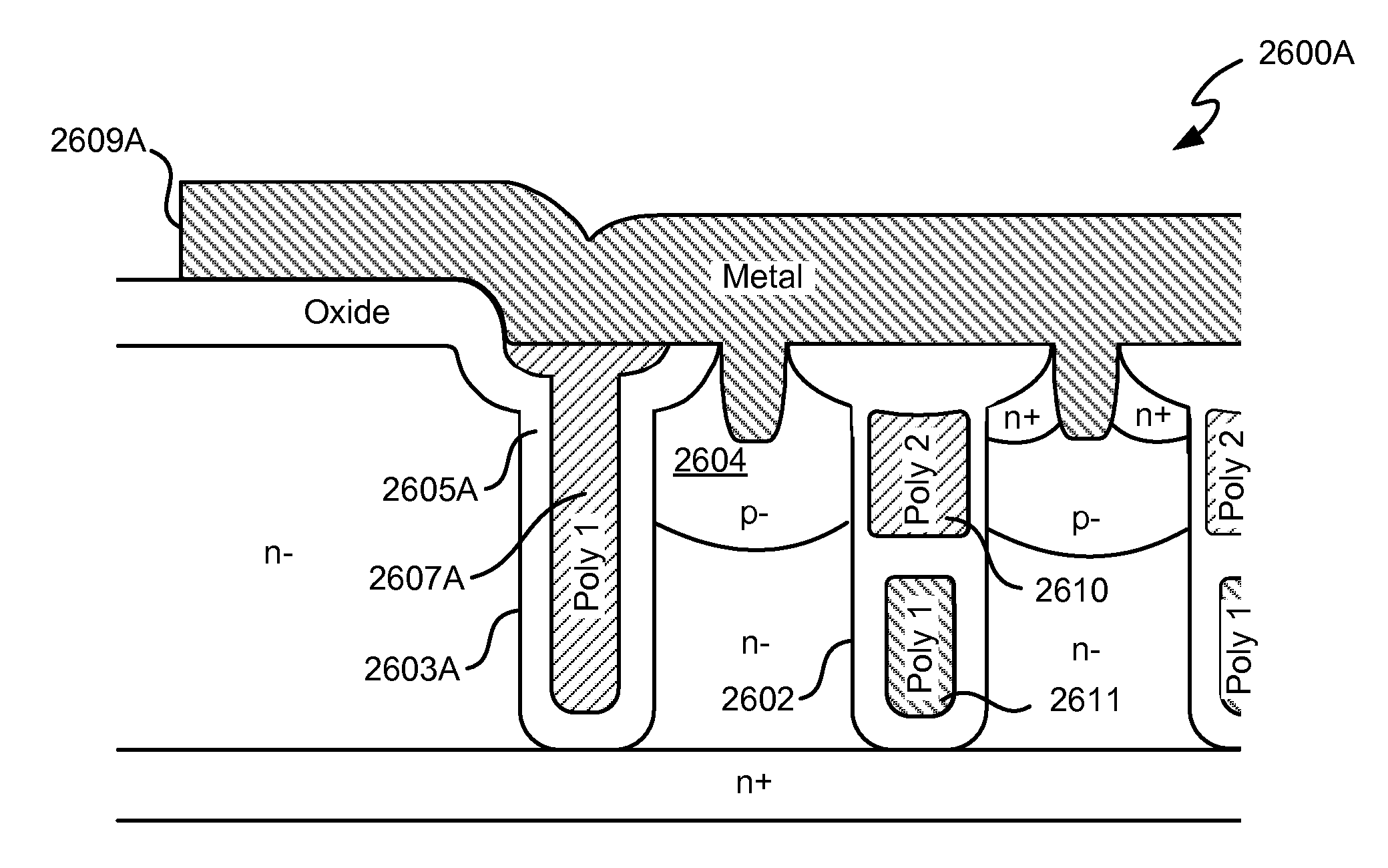
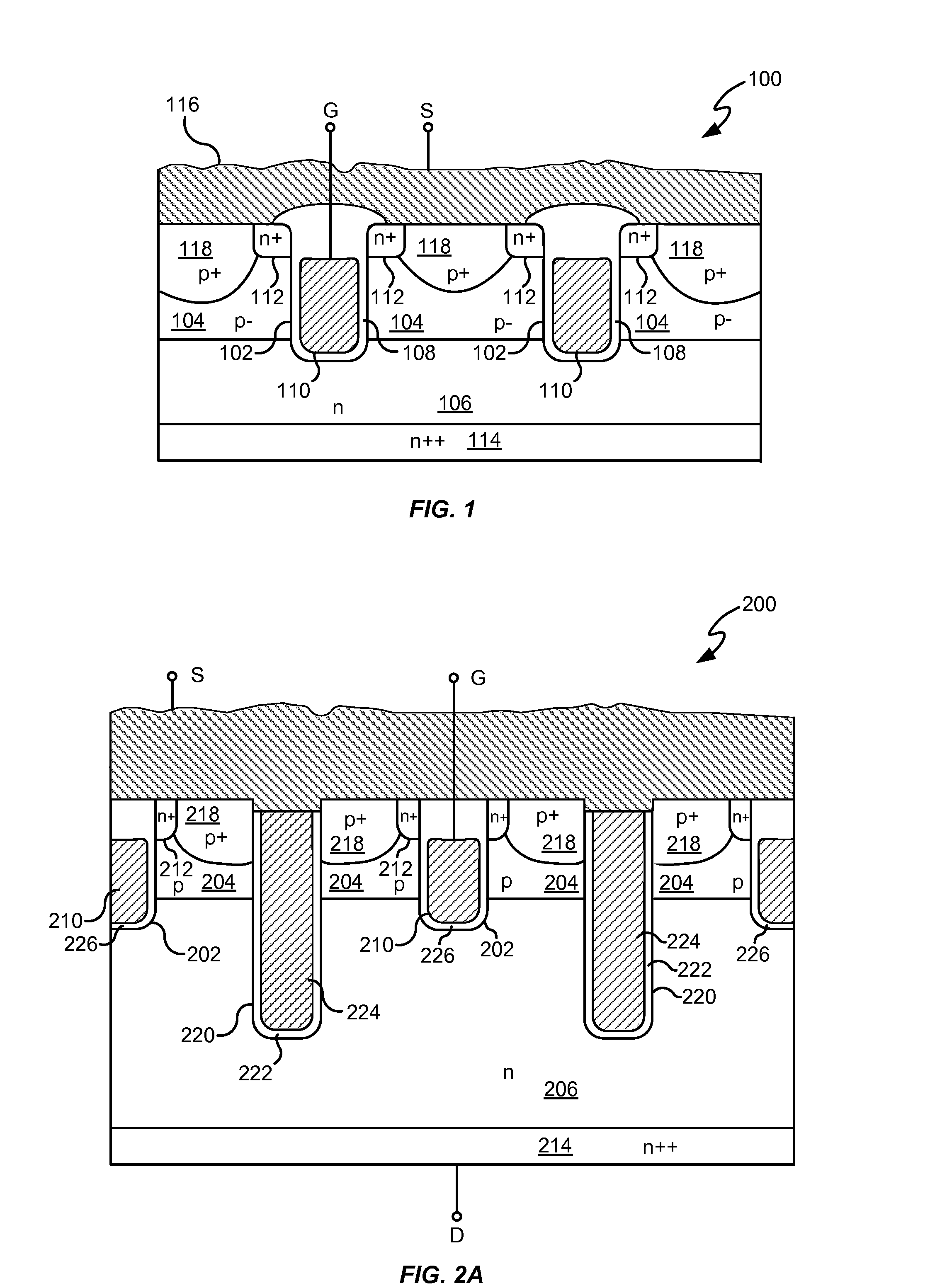
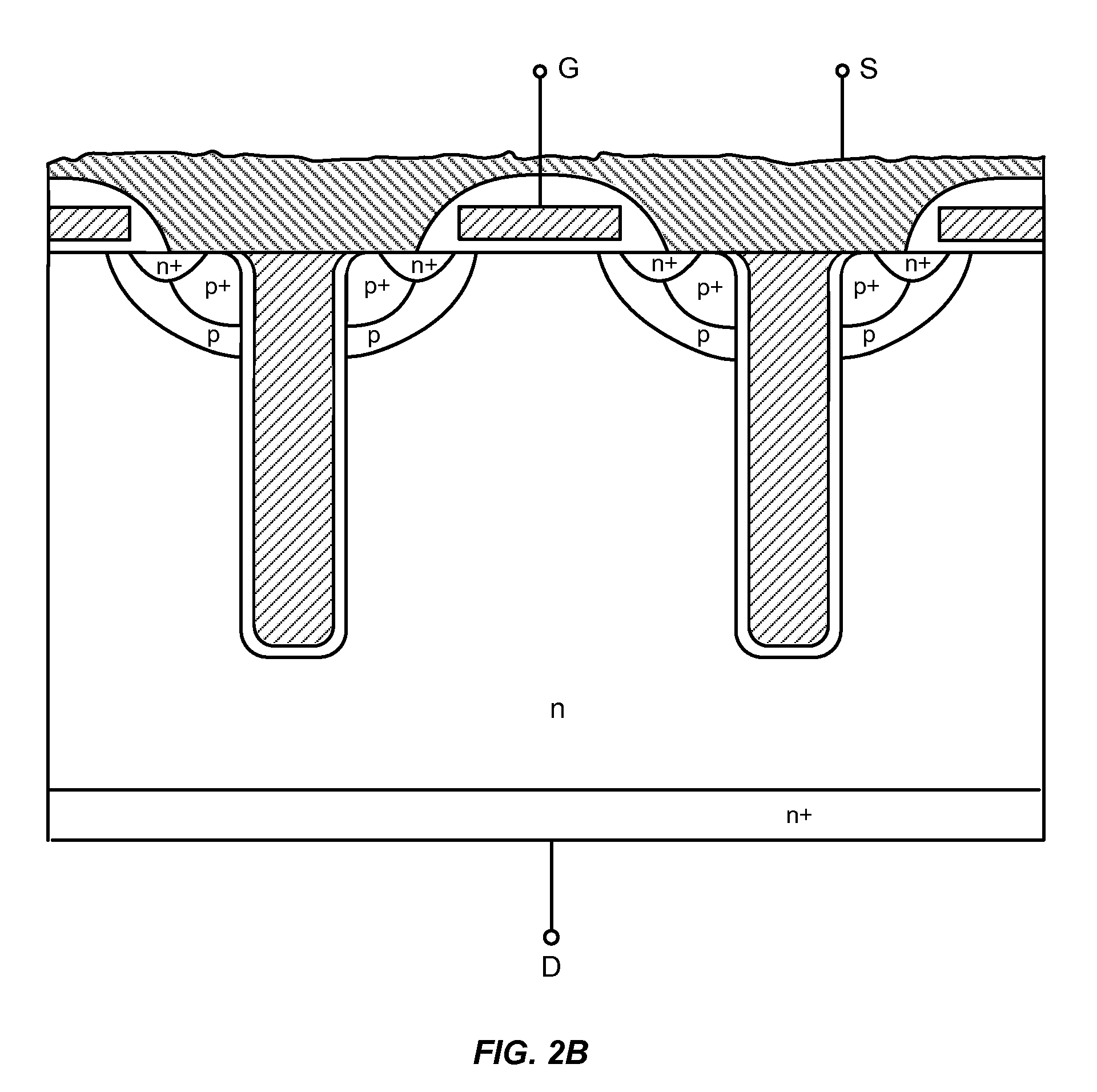
Various embodiments for improved power devices as well as their methods of manufacture, packaging and circuitry incorporating the same for use in a wide variety of power electronic applications are disclosed. One aspect of the invention combines a number of charge balancing techniques and other techniques for reducing parasitic capacitance to arrive at different embodiments for power devices with improved voltage performance, higher switching speed, and lower on-resistance. Another aspect of the invention provides improved termination structures for low, medium and high voltage devices. Improved methods of fabrication for power devices are provided according to other aspects of the invention. Improvements to specific processing steps, such as formation of trenches, formation of dielectric layers inside trenches, formation of mesa structures and processes for reducing substrate thickness, among others, are presented. According to another aspect of the invention, charge balanced power devices incorporate temperature and current sensing elements such as diodes on the same die. Other aspects of the invention improve equivalent series resistance (ESR) for power devices, incorporate additional circuitry on the same chip as the power device and provide improvements to the packaging of charge balanced power devices.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Power semiconductor devices and methods of manufacture
ActiveUS7345342B2Simple structureEasy to packEfficient power electronics conversionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringHigh pressure
Various embodiments for improved power devices as well as their methods of manufacture, packaging and circuitry incorporating the same for use in a wide variety of power electronic applications are disclosed. One aspect of the invention combines a number of charge balancing techniques and other techniques for reducing parasitic capacitance to arrive at different embodiments for power devices with improved voltage performance, higher switching speed, and lower on-resistance. Another aspect of the invention provides improved termination structures for low, medium and high voltage devices. Improved methods of fabrication for power devices are provided according to other aspects of the invention. Improvements to specific processing steps, such as formation of trenches, formation of dielectric layers inside trenches, formation of mesa structures and processes for reducing substrate thickness, among others, are presented. According to another aspect of the invention, charge balanced power devices incorporate temperature and current sensing elements such as diodes on the same die. Other aspects of the invention improve equivalent series resistance (ESR) for power devices, incorporate additional circuitry on the same chip as the power device and provide improvements to the packaging of charge balanced power devices.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
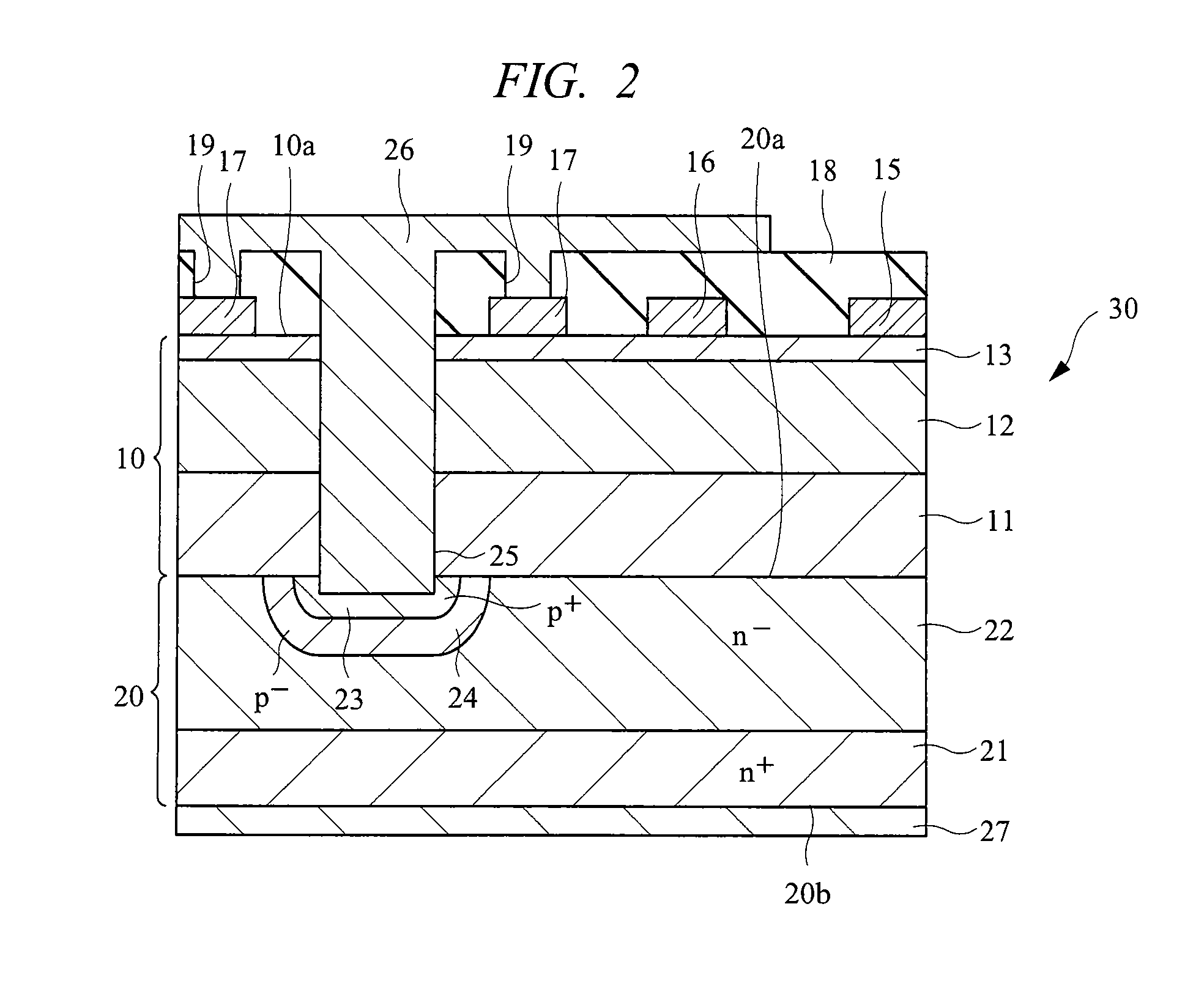
Silicon carbide semiconductor device and silicon carbide semiconductor device manufacturing method
ActiveUS20160336392A1Lower on-resistanceImprove breakdown voltageSemiconductor devicesDevice materialSemiconductor
A silicon carbide semiconductor device capable of achieving a decrease in ON resistance and an increase in breakdown voltage and a method for manufacturing a silicon carbide semiconductor device. A silicon carbide semiconductor device includes a silicon carbide substrate and a drift layer. The drift layer includes a breakdown voltage holding layer extending from a point where a doping concentration has a predetermined value to a surface of the drift layer. The doping concentration in the breakdown voltage holding layer continuously decreases from the point where the doping concentration has the predetermined value to a modulation point located further toward the surface of the drift layer than a midpoint in a film thickness direction of the breakdown voltage holding layer. The doping concentration in the breakdown voltage holding layer continuously increases from the modulation point to the surface of the drift layer.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Power semiconductor devices and methods of manufacture
InactiveUS20060214221A1Improved voltage performanceFast switching speedTransistorEfficient power electronics conversionEngineeringHigh pressure
Various embodiments for improved power devices as well as their methods of manufacture, packaging and circuitry incorporating the same for use in a wide variety of power electronic applications are disclosed. One aspect of the invention combines a number of charge balancing techniques and other techniques for reducing parasitic capacitance to arrive at different embodiments for power devices with improved voltage performance, higher switching speed, and lower on-resistance. Another aspect of the invention provides improved termination structures for low, medium and high voltage devices. Improved methods of fabrication for power devices are provided according to other aspects of the invention. Improvements to specific processing steps, such as formation of trenches, formation of dielectric layers inside trenches, formation of mesa structures and processes for reducing substrate thickness, among others, are presented. According to another aspect of the invention, charge balanced power devices incorporate temperature and current sensing elements such as diodes on the same die. Other aspects of the invention improve equivalent series resistance (ESR) for power devices, incorporate additional circuitry on the same chip as the power device and provide improvements to the packaging of charge balanced power devices.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
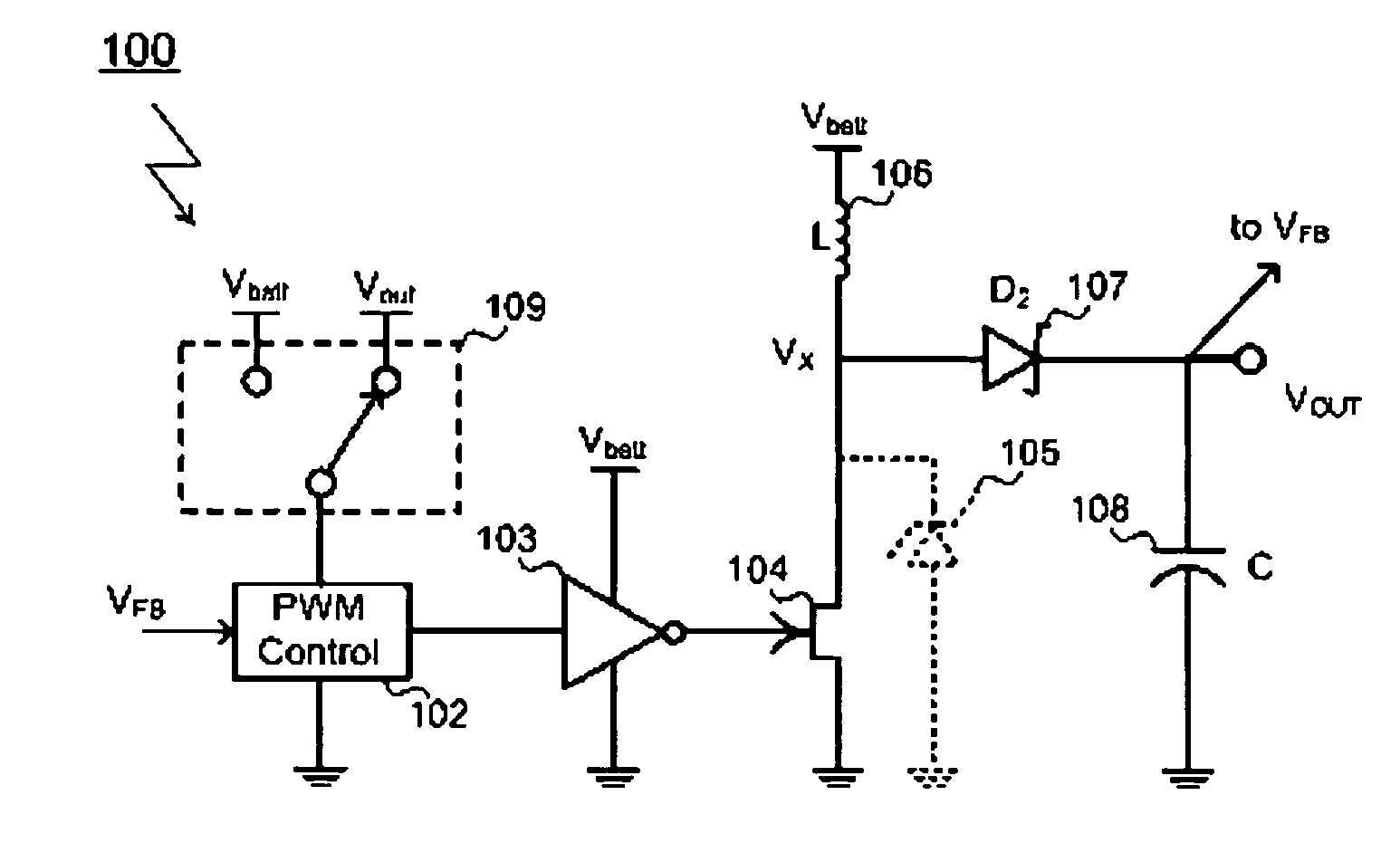
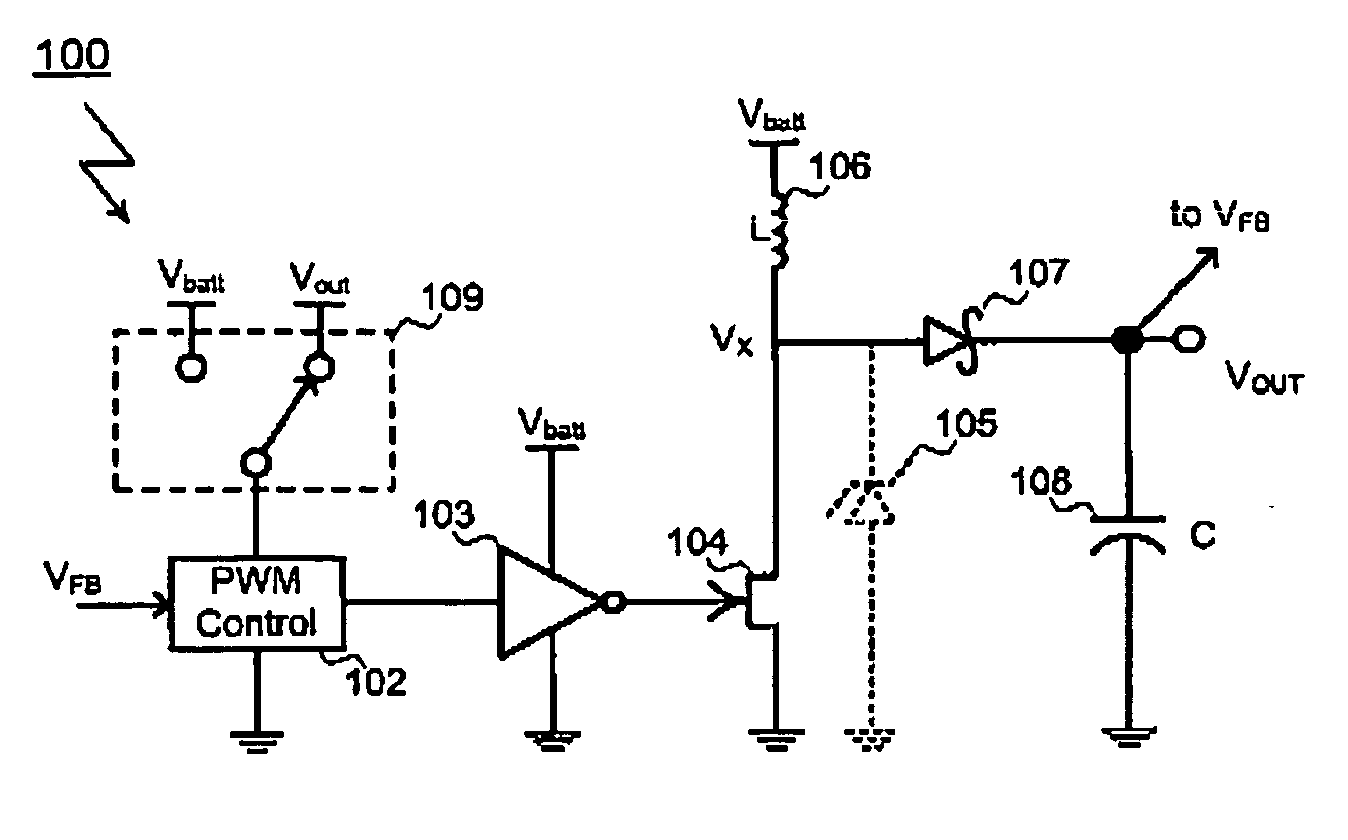
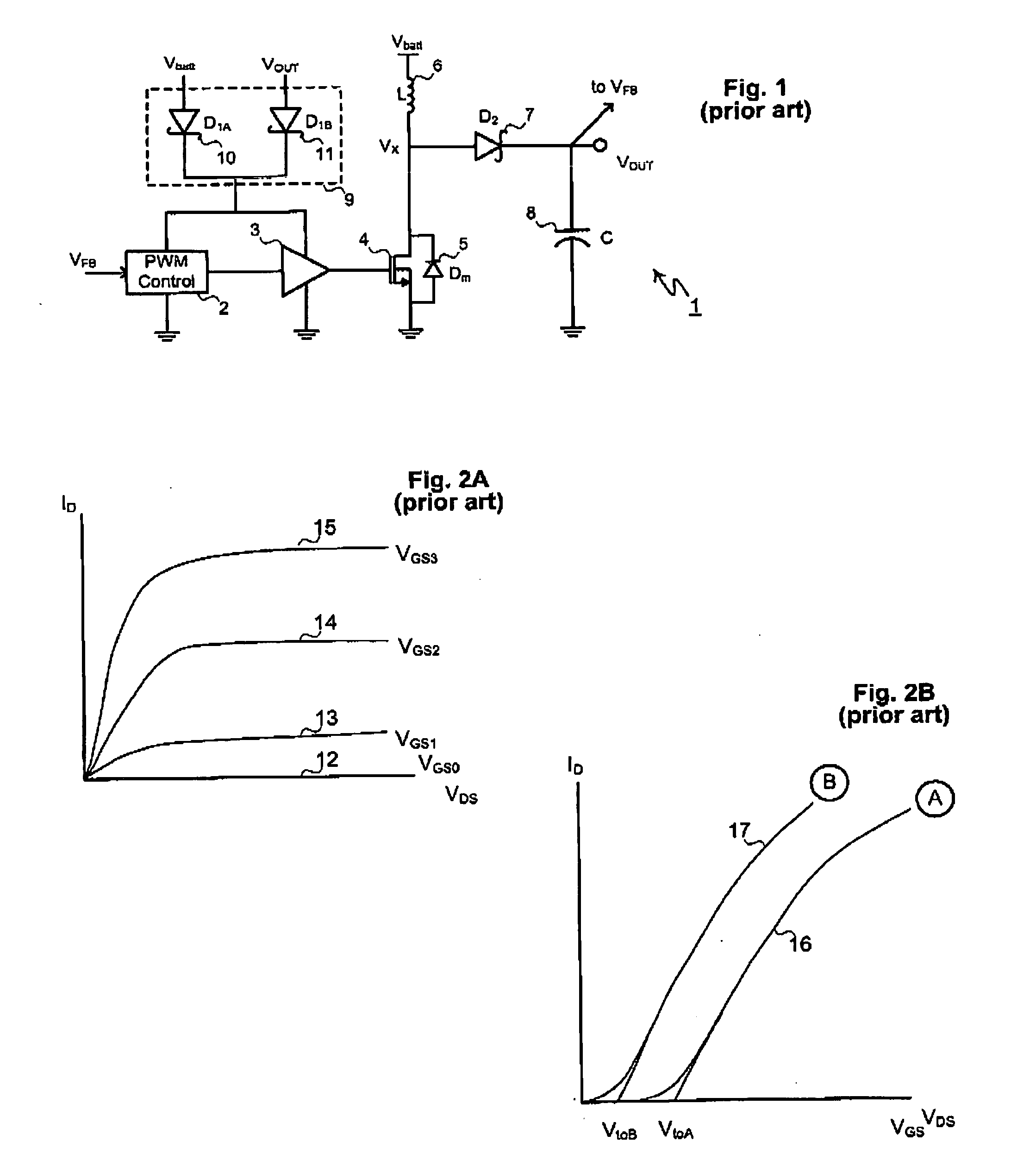
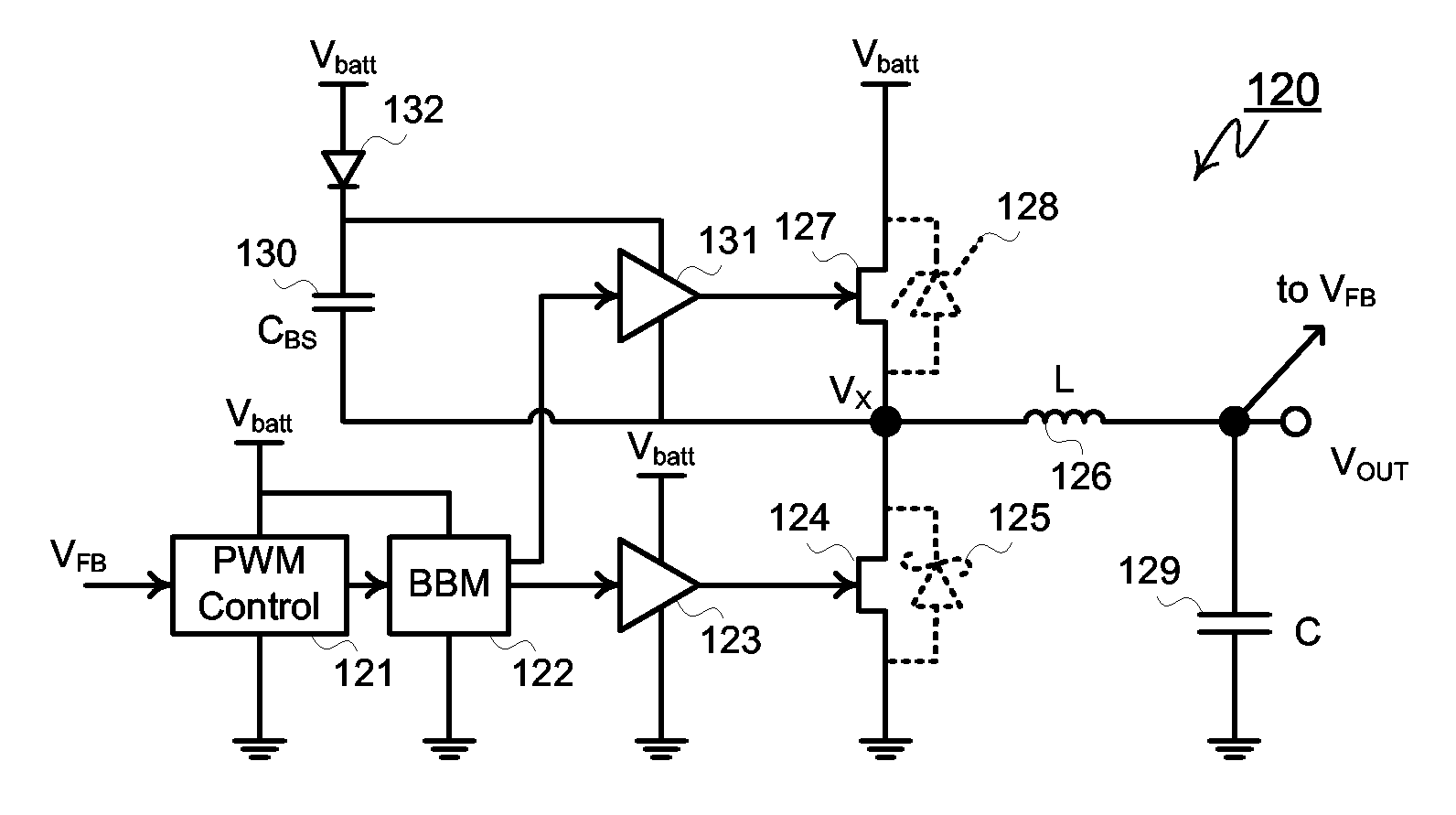
High-Frequency Power MESFET Boost Switching Power Supply
InactiveUS20080186004A1Lower on-resistanceLow off-state drain leakageTransistorDc-dc conversionMOSFETHigh frequency power
A MESFET based boost converter includes an N-channel MESFET connected to a node Vx. An inductor connects the node Vx to a battery or other power source. The node Vx is also connected to an output node via a Schottky diode or a second MESFET or both. A control circuit drives the MESFET (and the second MESFET) so that the inductor is alternately connected to ground and to the output node. The maximum voltage impressed across the low side MESFET is optionally clamped by a Zener diode. In some implementations, the MESFET is connected in series with a MOSFET. The MOSFET is switched off during sleep or standby modes to minimize leakage current through the MESFET. The MOSFET is therefore switched at a low frequency compared to the MESFET and does not contribute significantly to switching losses in the converter. In other implementations, more than one MESFET is connected in series with a MOSFET, the MOSFETs being switched off during periods of inactivity to suppress leakage currents.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
Power semiconductor devices and methods of manufacture
ActiveUS20060214222A1Improved voltage performanceFast switching speedTransistorEfficient power electronics conversionEngineeringHigh pressure
Various embodiments for improved power devices as well as their methods of manufacture, packaging and circuitry incorporating the same for use in a wide variety of power electronic applications are disclosed. One aspect of the invention combines a number of charge balancing techniques and other techniques for reducing parasitic capacitance to arrive at different embodiments for power devices with improved voltage performance, higher switching speed, and lower on-resistance. Another aspect of the invention provides improved termination structures for low, medium and high voltage devices. Improved methods of fabrication for power devices are provided according to other aspects of the invention. Improvements to specific processing steps, such as formation of trenches, formation of dielectric layers inside trenches, formation of mesa structures and processes for reducing substrate thickness, among others, are presented. According to another aspect of the invention, charge balanced power devices incorporate temperature and current sensing elements such as diodes on the same die. Other aspects of the invention improve equivalent series resistance (ESR) for power devices, incorporate additional circuitry on the same chip as the power device and provide improvements to the packaging of charge balanced power devices.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method of the same
InactiveUS20090140327A1Increase impurity concentrationLower on-resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesTrench mosfetElectrode Contact
The vertical trench MOSFET comprises: an N type epitaxial region formed on an upper surface of an N+ type substrate having a drain electrode on a lower surface thereof; a gate trench extending from a front surface into the N type epitaxial region; a gate electrode positioned in the gate trench so as to interpose an insulator; a channel region formed on the N type epitaxial region; a source region formed on the channel region; a source electrode formed on the source region; a source trench extending from the front surface into the N type epitaxial region; and a trench-buried source electrode positioned in the source trench so as to interpose an insulator, wherein the source electrode contacts with the trench-buried source electrode.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Power devices having trench-based source and gate electrodes
ActiveUS20060060916A1Improve breakdown voltageIncrease the on-resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiodePower semiconductor deviceDevice material
A power semiconductor device includes a plurality of trenches formed within a semiconductor body, each trench including one or more electrodes formed therein. In particular, according to embodiments of the invention, the plurality of trenches of a semiconductor device may include one or more gate electrodes, may include one or more gate electrodes or one or more source electrodes, or may include a combination of both gate and source electrodes formed therein. The trenches and electrodes may have varying depths within the semiconductor body.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
Nitride semiconductor device
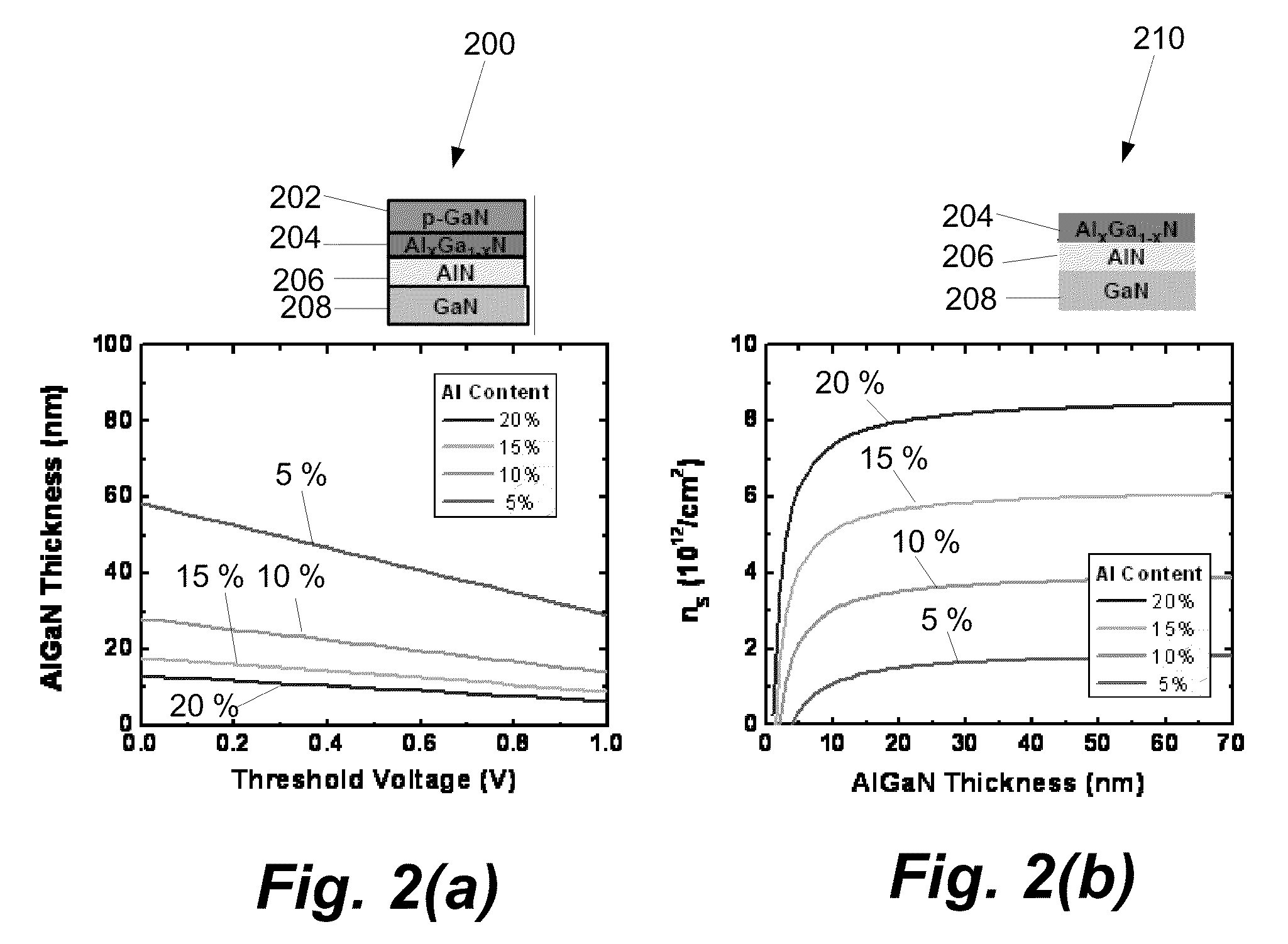
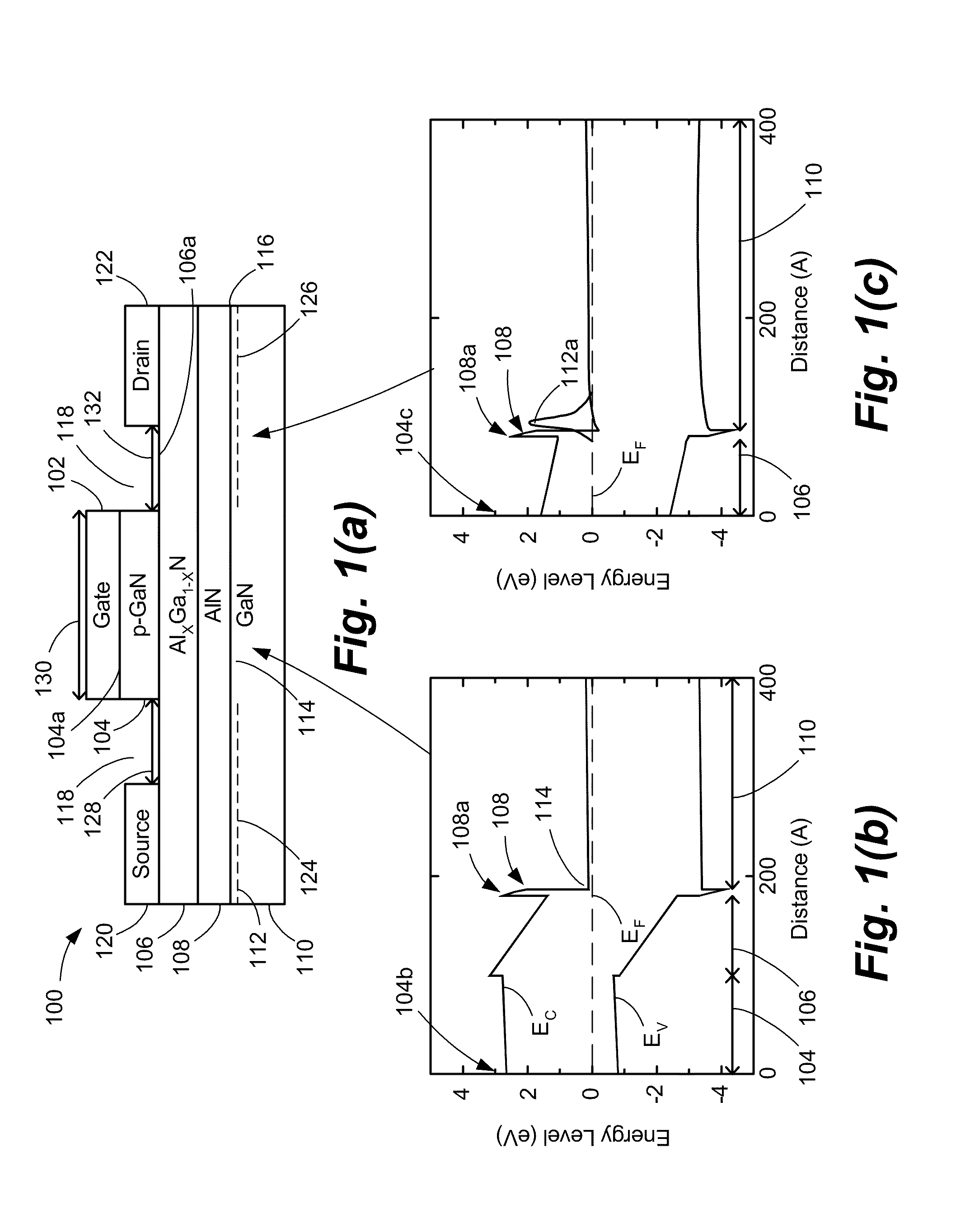
ActiveUS20080093626A1Threshold voltage be control easilyHigh yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGalliumAluminium
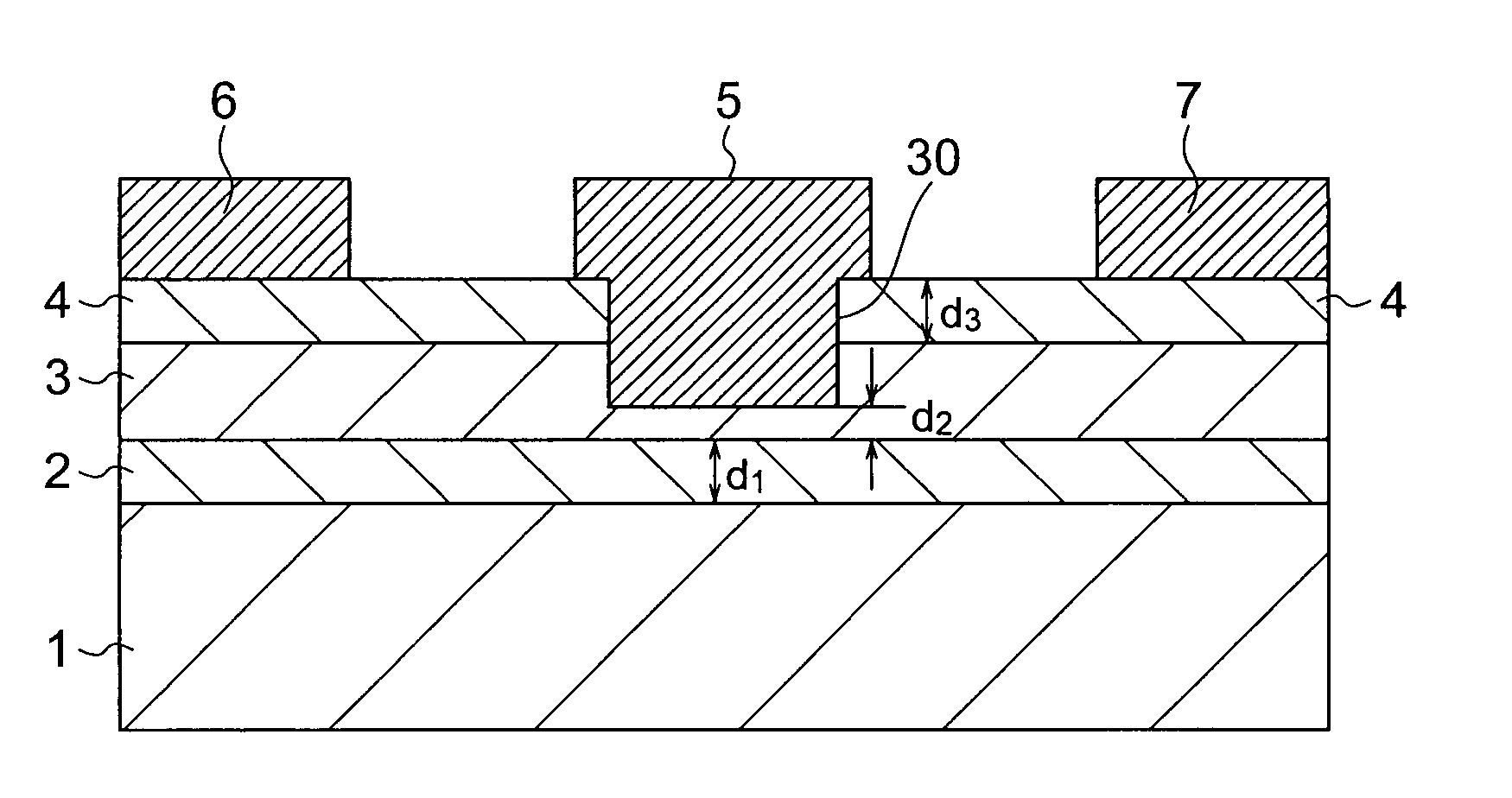
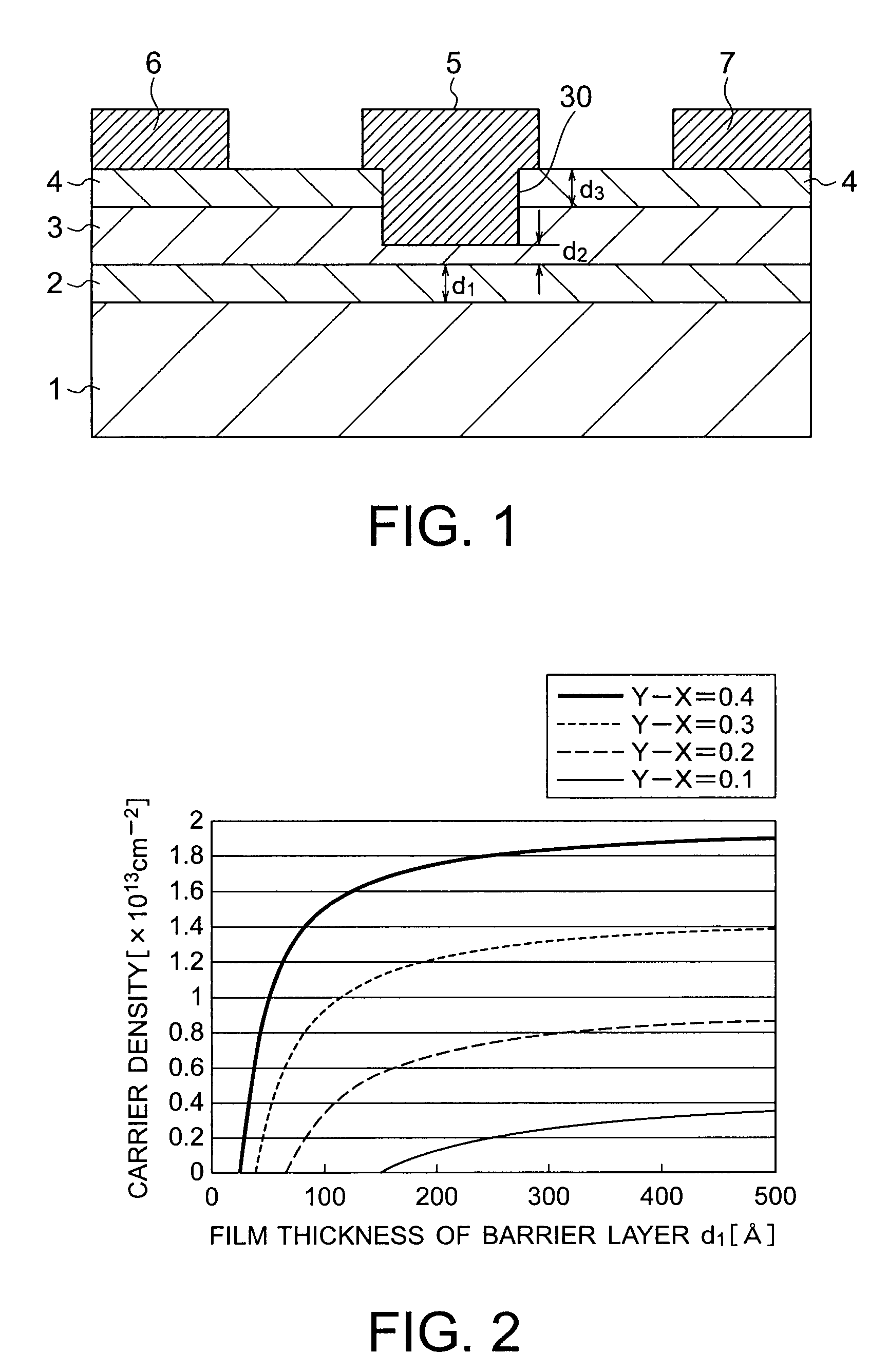
A nitride semiconductor device includes: a first nitride semiconductor layer formed of non-doped AlxGa1-XN (0≦X<1); a second nitride semiconductor layer formed on the first nitride semiconductor layer of non-doped or n-type AlYGa1-YN (0<Y≦1, X<Y), and having a smaller lattice constant than that of the first nitride semiconductor layer; a third nitride semiconductor layer formed on the second nitride semiconductor layer of a non-doped or n-type nitride semiconductor, and having a lattice constant equal to that of the first nitride semiconductor layer; a fourth nitride semiconductor layer formed on the third nitride semiconductor layer of InWAlZGa1-W-ZN (0<W≦1, 0<Z<1); a gate electrode formed in a recess structure having a bottom face which arrives at the third nitride semiconductor layer; and a source electrode and a drain electrode.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
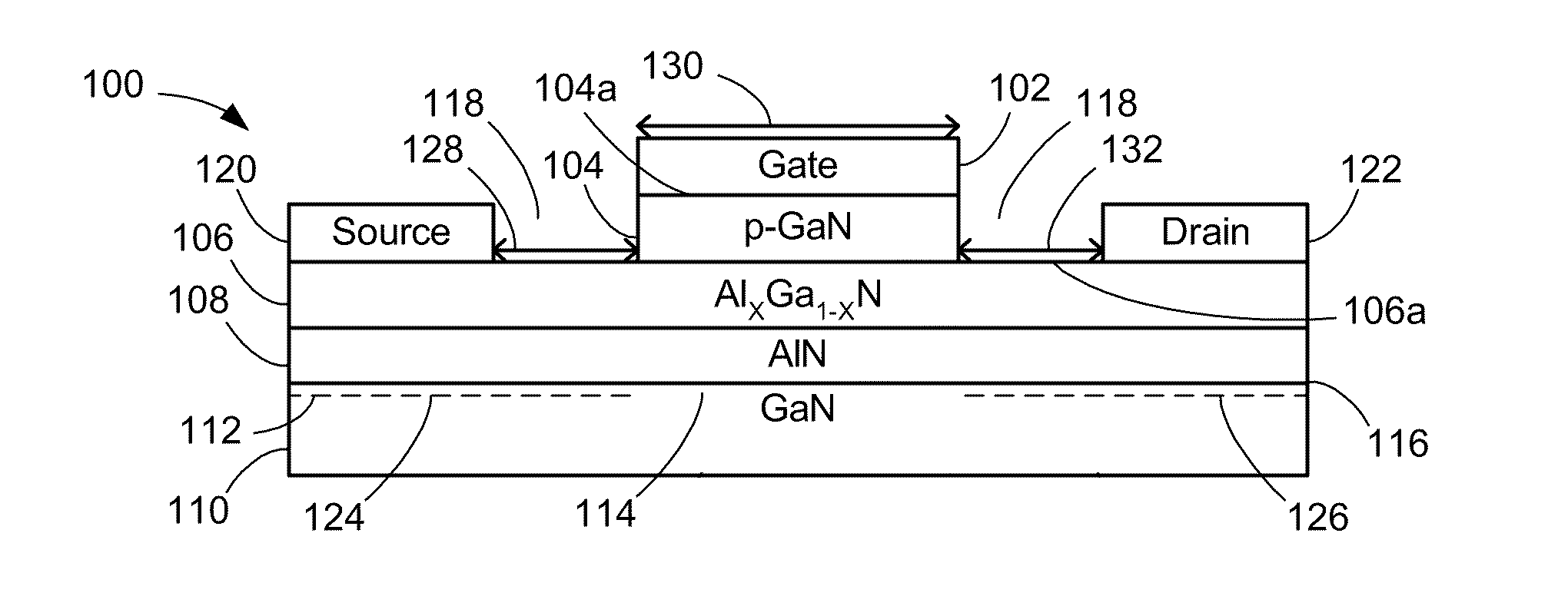
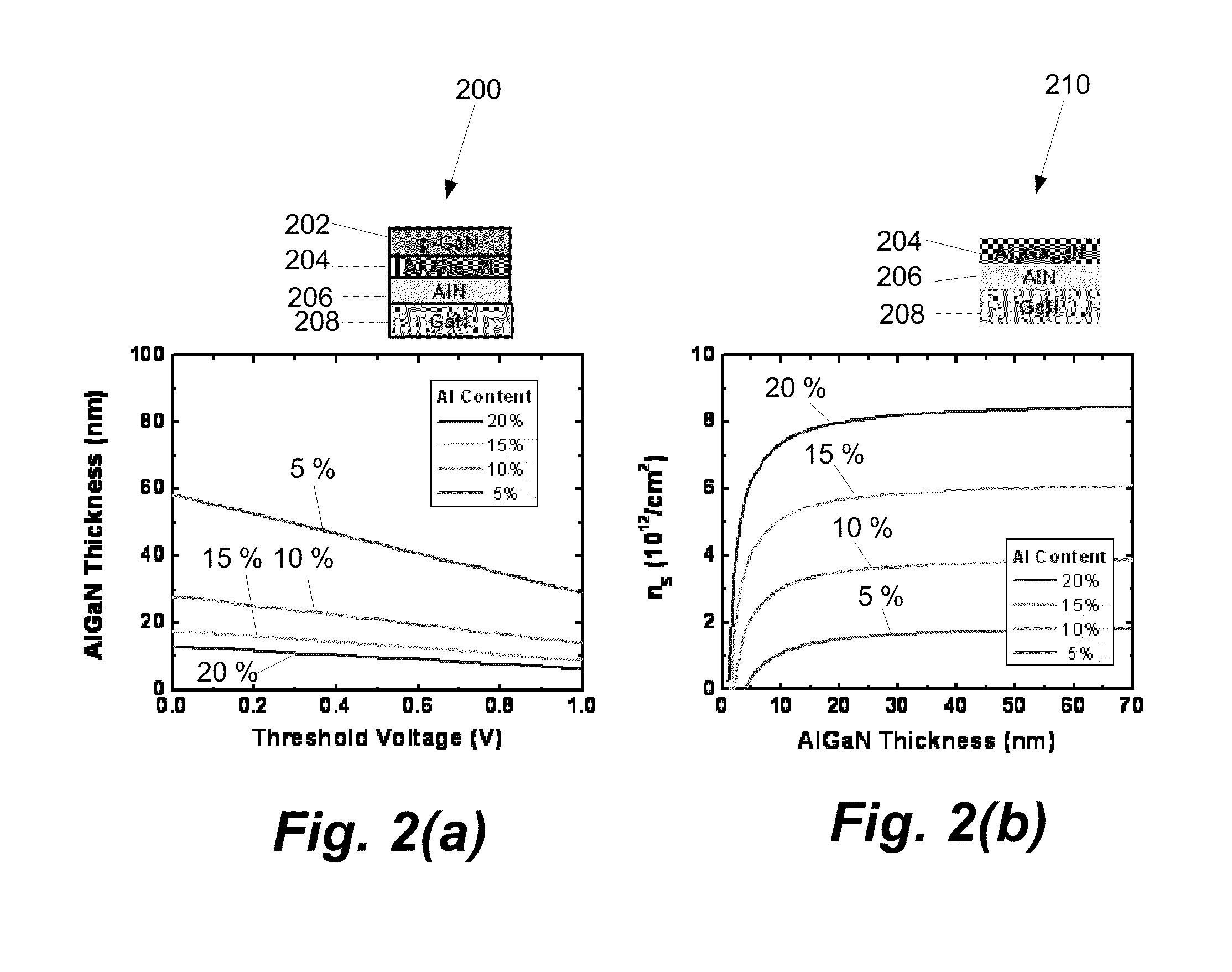
P-GaN/AlGaN/AlN/GaN ENHANCEMENT-MODE FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR
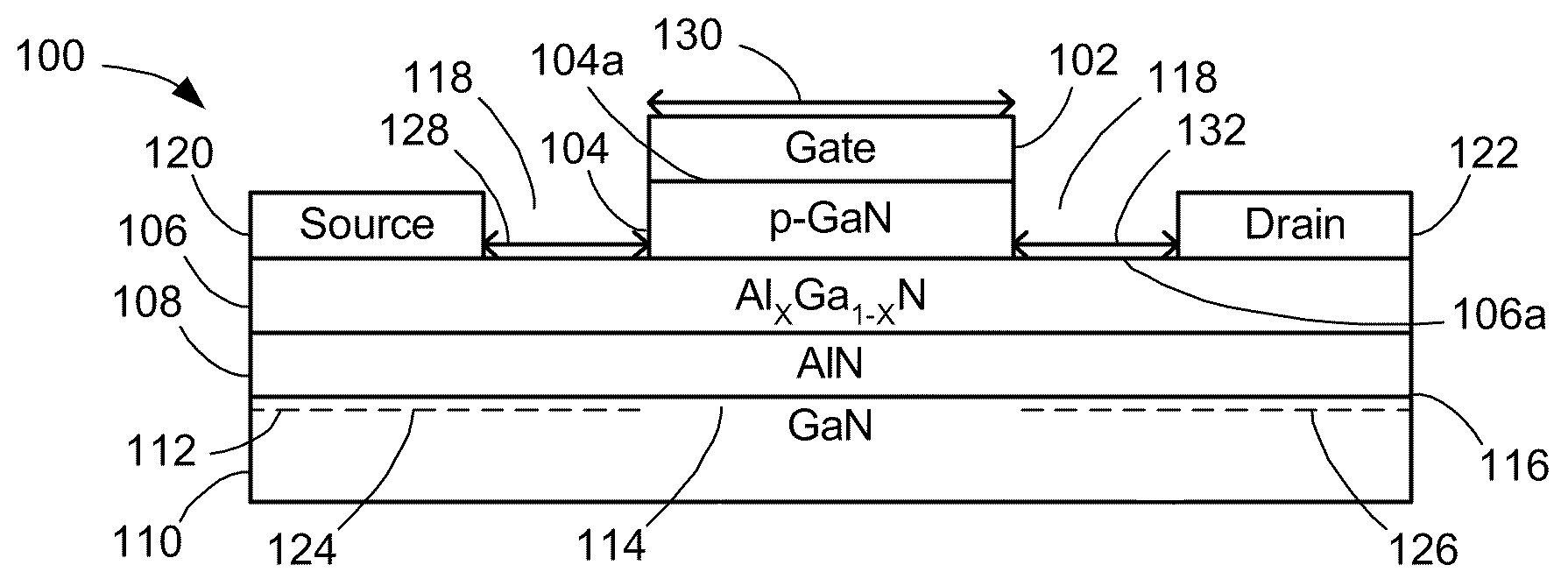
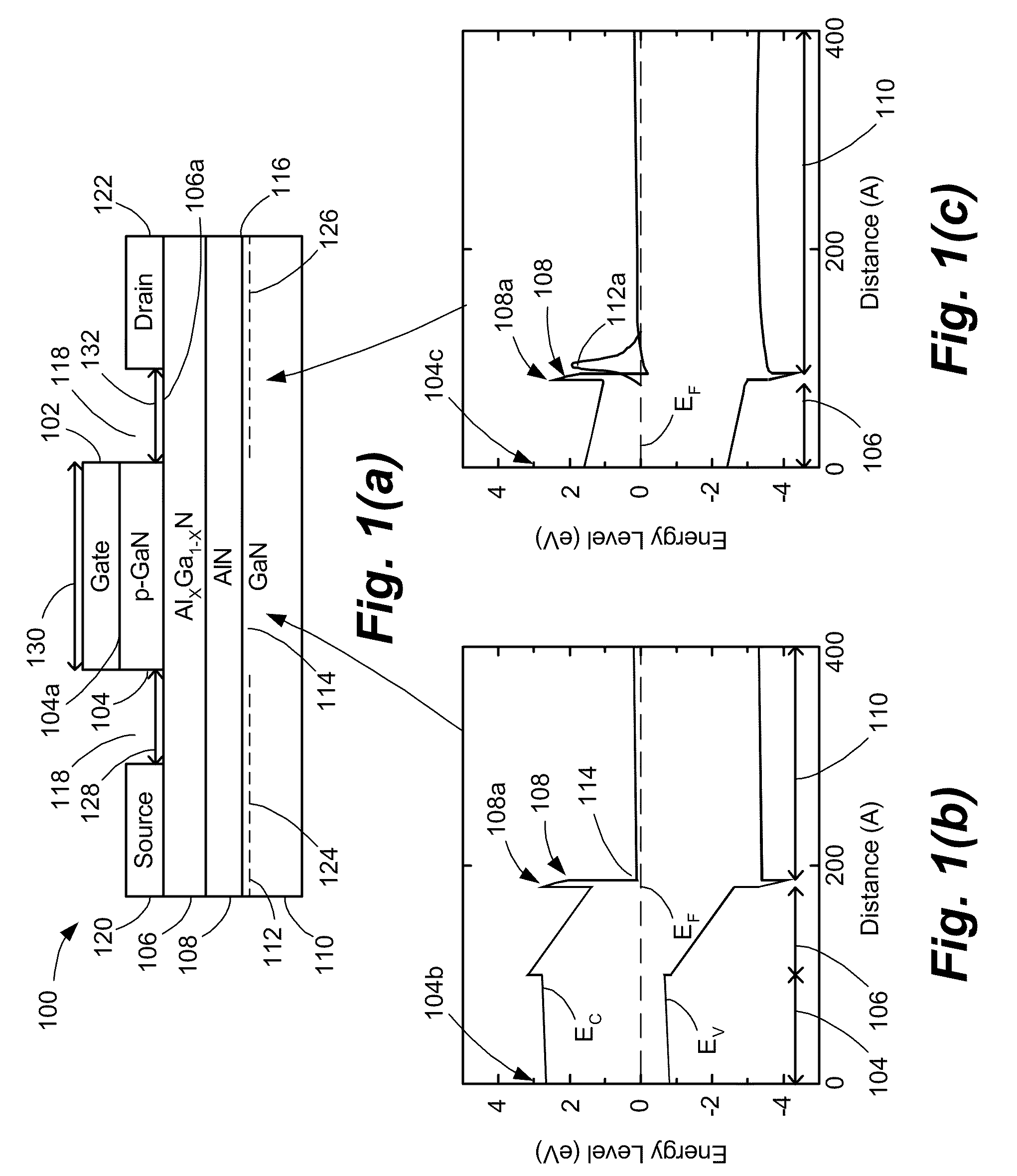
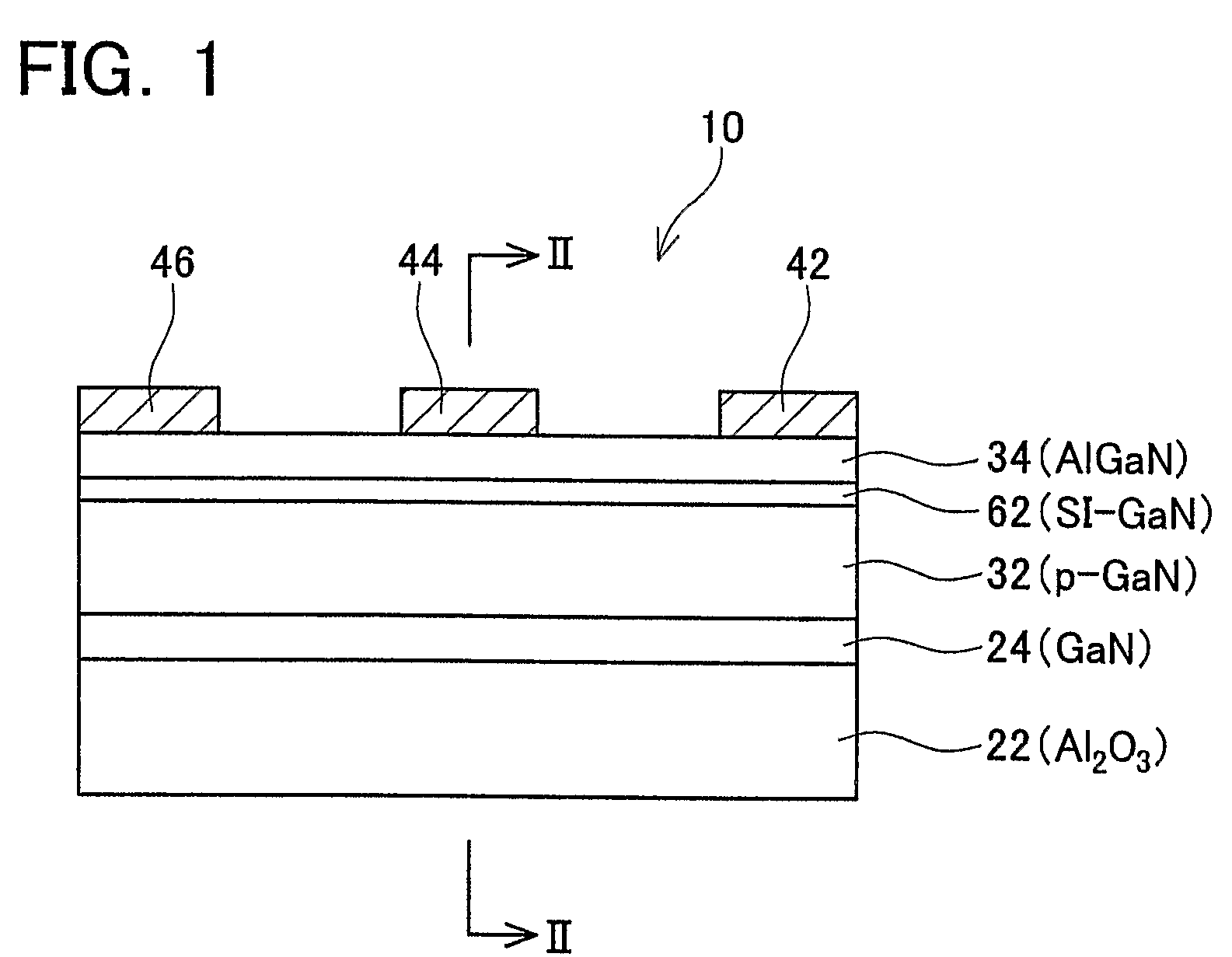
ActiveUS20080296618A1Lower on-resistanceHigh electron mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh-electron-mobility transistorField-effect transistor
An enhancement mode High Electron Mobility Transistor (HEMT) comprising a p-type nitride layer between the gate and a channel of the HEMT, for reducing an electron population under the gate. The HEMT may also comprise an Aluminum Nitride (AlN) layer between an AlGaN layer and buffer layer of the HEMT to reduce an on resistance of a channel.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Silicon carbide substrate, epitaxial layer provided substrate, semiconductor device, and method for manufacturing silicon carbide substrate
InactiveUS20120119225A1Lower on-resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSingle crystal substrateSingle crystal
The present invention provides a silicon carbide substrate, an epitaxial layer provided substrate, a semiconductor device, and a method for manufacturing the silicon carbide substrate, each of which achieves reduced on-resistance. The silicon carbide substrate is a silicon carbide substrate having a main surface, and includes: a SiC single-crystal substrate formed in at least a portion of the main surface; and a base member disposed to surround the SiC single-crystal substrate. The base member includes a boundary region and a base region. The boundary region is adjacent to the SiC single-crystal substrate in a direction along the main surface, and has a crystal grain boundary therein. The base region is adjacent to the SiC single-crystal substrate in a direction perpendicular to the main surface, and has an impurity concentration higher than that of the SiC single-crystal substrate.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
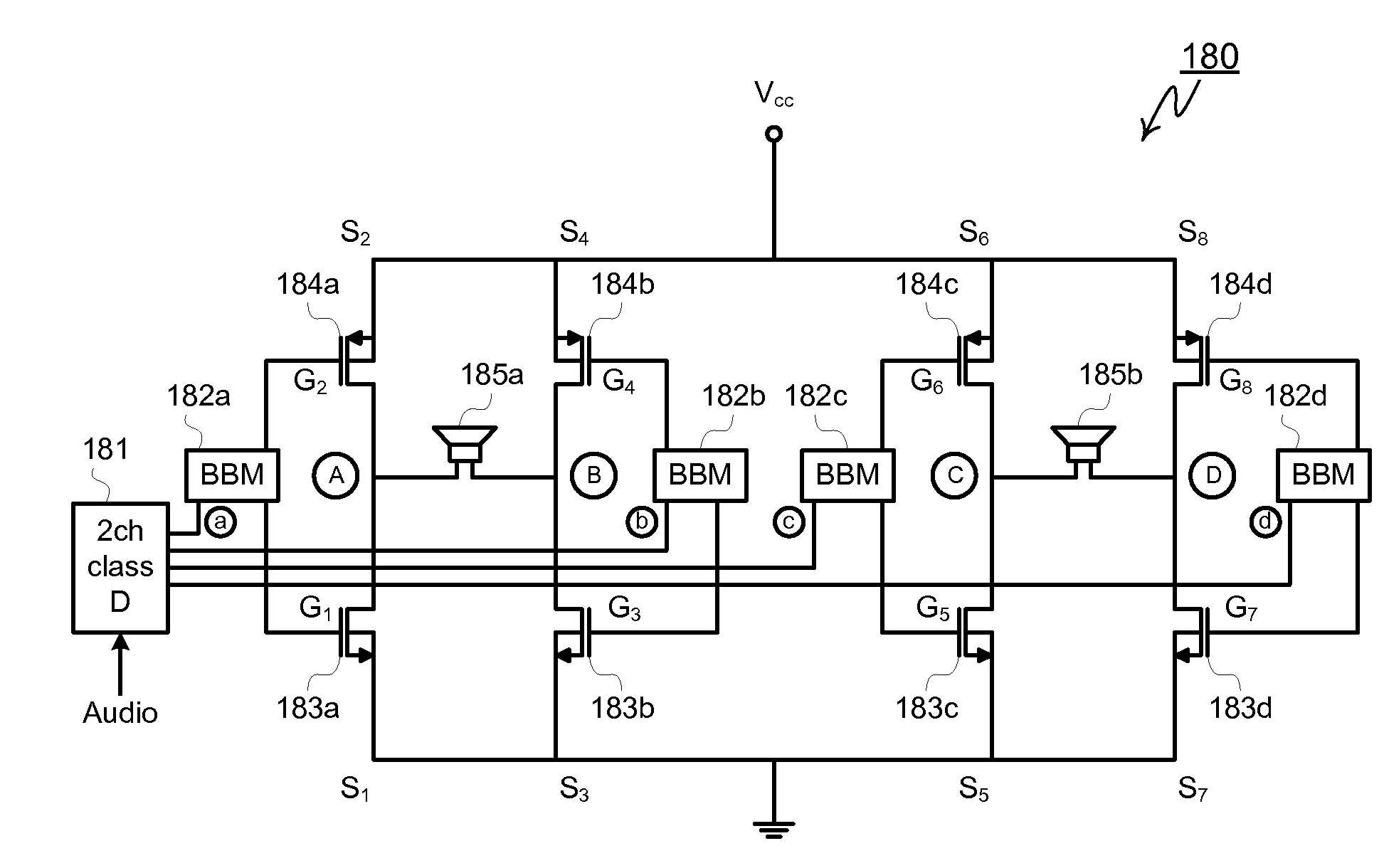
Power-MOSFETs with Improved Efficiency for Multi-channel Class-D Audio Amplifiers and Packaging Thereof
InactiveUS20080252372A1Lower on-resistanceSimple preparation techniqueTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsGround contactAudio power amplifier
A stereo class-D audio system includes a first die including four monolithically integrated NMOS high-side devices and a second a second die including four monolithically integrated PMOS low-side devices. The audio system also includes a set of electrical contacts for connecting the high and low-side devices to components within the a stereo class-D audio system, the set of electrical contacts including at least one supply contact for connecting the drains of the high-side devices to a supply voltage (Vcc) and at least one ground contact for connecting the drains of the low-side devices to ground, the electrical contacts also including respective contacts for each source of the high and low-side devices allowing the source of each high-side device to be connected to the source of a respective low-side device to form two H-bridge circuits.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
Conductive sheet and capacitive touch panel
ActiveUS20110290631A1Probability of complete disconnectionIncrease awarenessConductive layers on insulating-supportsElectronic switchingEngineeringTouch panel
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Trench MOSFET with Trench Termination and manufacture thereof
InactiveUS20090057756A1Easily triggerEvenly reduce on-resistanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOxide semiconductorBody region
A trench MOSFET (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor) with a trench termination, including a substrate including a drain region which is strongly doped and a doping epi layer region, which is weekly doped the same type as the drain region, on the drain region; a plurality of source and body regions formed in the epi layer; a metal layer including a plurality of metal layer regions which are connected to respective source and body, and gate regions forming metal connections of the MOSFET; a plurality of metal contact plugs connected to respective metal layer regions; a plurality of gate trenches filled with polysilicon to form a plurality of trenched gates on top of epi layer; an insulating layer deposited on the epi layer formed underneath the metal layer with a plurality of metal contact holes therein for contacting respective source and body regions; a margin terminating gate trench which is around the gate trenches; and a margin terminating active region which is formed underneath the margin terminating gate trench.
Owner:FORCE MOS TECH CO LTD
Methods of Making Power Semiconductor Devices with Thick Bottom Oxide Layer
ActiveUS20080138953A1Simple structureEasy to packTransistorEfficient power electronics conversionPower semiconductor deviceHigh density
A method for forming thick oxide at the bottom of a trench formed in a semiconductor substrate includes forming a conformal oxide film that fills the trench and covers a top surface of the substrate. and etching the oxide film off the top surface of the substrate and inside the trench to leave a substantially flat layer of oxide having a target thickness at the bottom of the trench. The oxide film can be deposited by sub-atmospheric chemical vapor deposition processes, directional Tetraethoxysilate (TEOS) processes, or high density plasma deposition processes that form a thicker oxide at the bottom of the trench than on the sidewalls of the trench.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method of the same
ActiveUS20060157779A1Lower on-resistanceSuppress and prevent operation of parasiticSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceDevice material
The on-resistance of a semiconductor device having a power transistor with a trench gate structure is reduced. A power MIS-FET with a trench gate structure is so formed that the relation expressed as 0≦b≦a holds, where a is the distance between an end of an interlayer insulating layer over the upper face of a semiconductor region for source and the end (position on the periphery of a trench) of the upper face of the semiconductor region for source farther from the gate electrode; and b is the length of the overlap between the interlayer insulating layer and the upper face of the semiconductor region for source. (b is the distance between the position of the end of the interlayer insulating layer over the upper face of the semiconductor region for source and position on the periphery of a trench). As a result, the area of contact between source pads and the semiconductor regions for source is increased, and further the distance between the source pads and a channel forming region can be shortened. Therefore, the on-resistance of the power MIS-FET with a trench gate structure can be reduced.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Power transistor having vertical FETs and method for making same
InactiveUS6060746ALower resistanceEasy to controlTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETElectrical and Electronics engineering
A power transistor having of a plurality of vertical MOSFET devices combined in parallel to achieve high-performance operation and methods of fabricating this device.
Owner:IBM CORP
Power Semiconductor Devices Having Termination Structures and Methods of Manufacture
InactiveUS20080135931A1Simple structureEasy to packTransistorEfficient power electronics conversionPower semiconductor deviceDielectric
A semiconductor power device includes a drift region of a first conductivity type, a well region extending above the drift region and having a second conductivity type opposite the first conductivity type, an active trench extending through the well region and into the drift region, source regions having the first conductivity type formed in the well region adjacent the active trench, and a first termination trench extending below the well region and disposed at an outer edge of an active region of the device. The sidewalls and bottom of the active trench are lined with dielectric material, and substantially filled with a first conductive layer forming an upper electrode and a second conductive layer forming a lower electrode, the upper electrode being disposed above the lower electrode and separated therefrom by inter-electrode dielectric material. The first termination trench can be lined with a layer of dielectric material that is thicker than the dielectric material lining the sidewalls of the active trench, and is substantially filled with conductive material.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
High Frequency Power MESFET Gate Drive Circuits
InactiveUS20070146020A1Lower on-resistanceRobust avalancheTransistorDc-dc conversionDriver circuitHigh frequency power
A series of gate drive circuits for MESFETs are provided. The gate drive circuits are intended to be used in switching regulators where at least one switching device is an N-channel MESFET. For regulators of this type, the gate drive circuits provide gate drive at the correct voltage to ensure that MESFETs are neither under driven (resulting in incorrect circuit operation) nor over driven (resulting in MESFET damage or excess current or power loss).
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
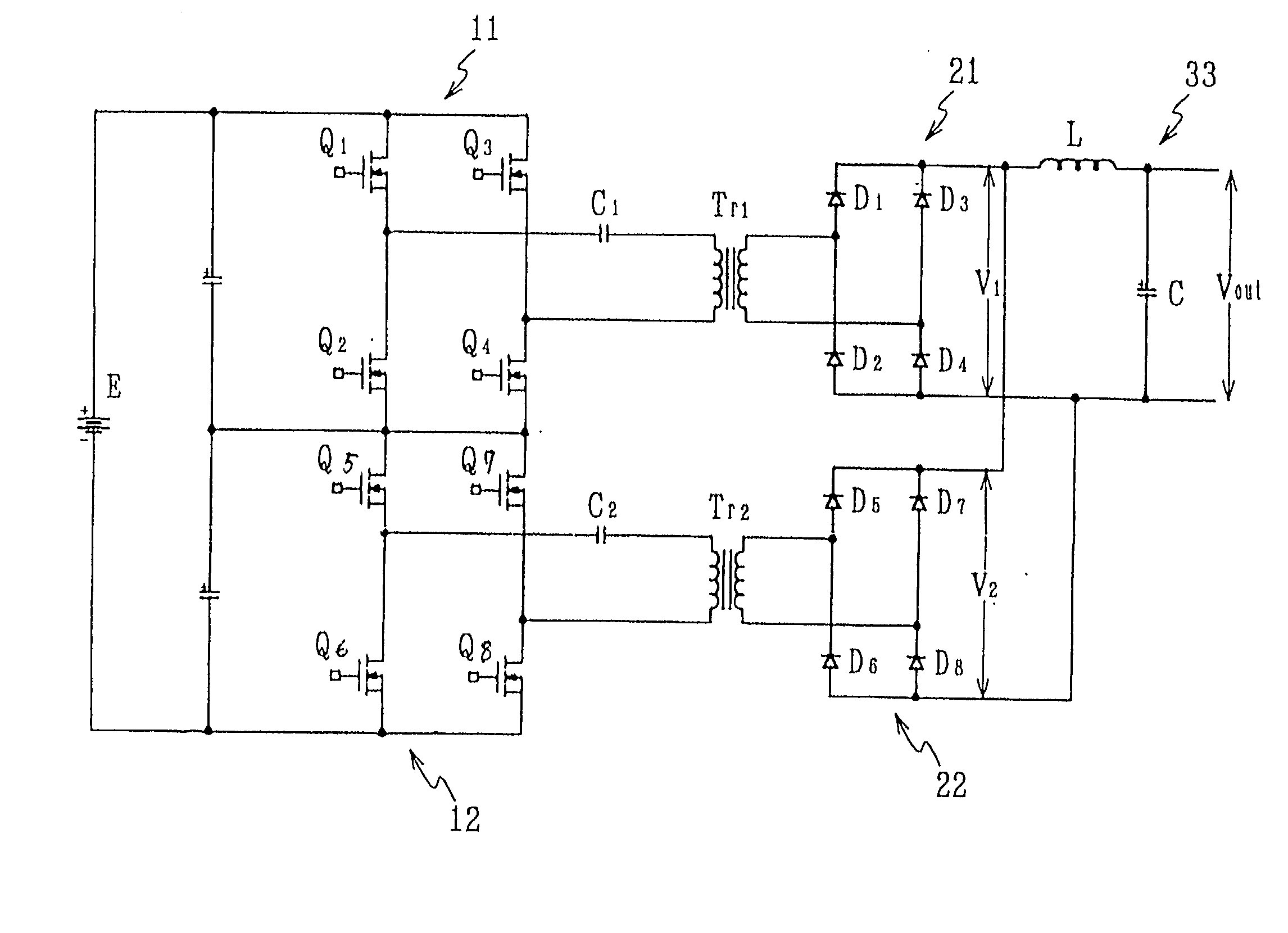
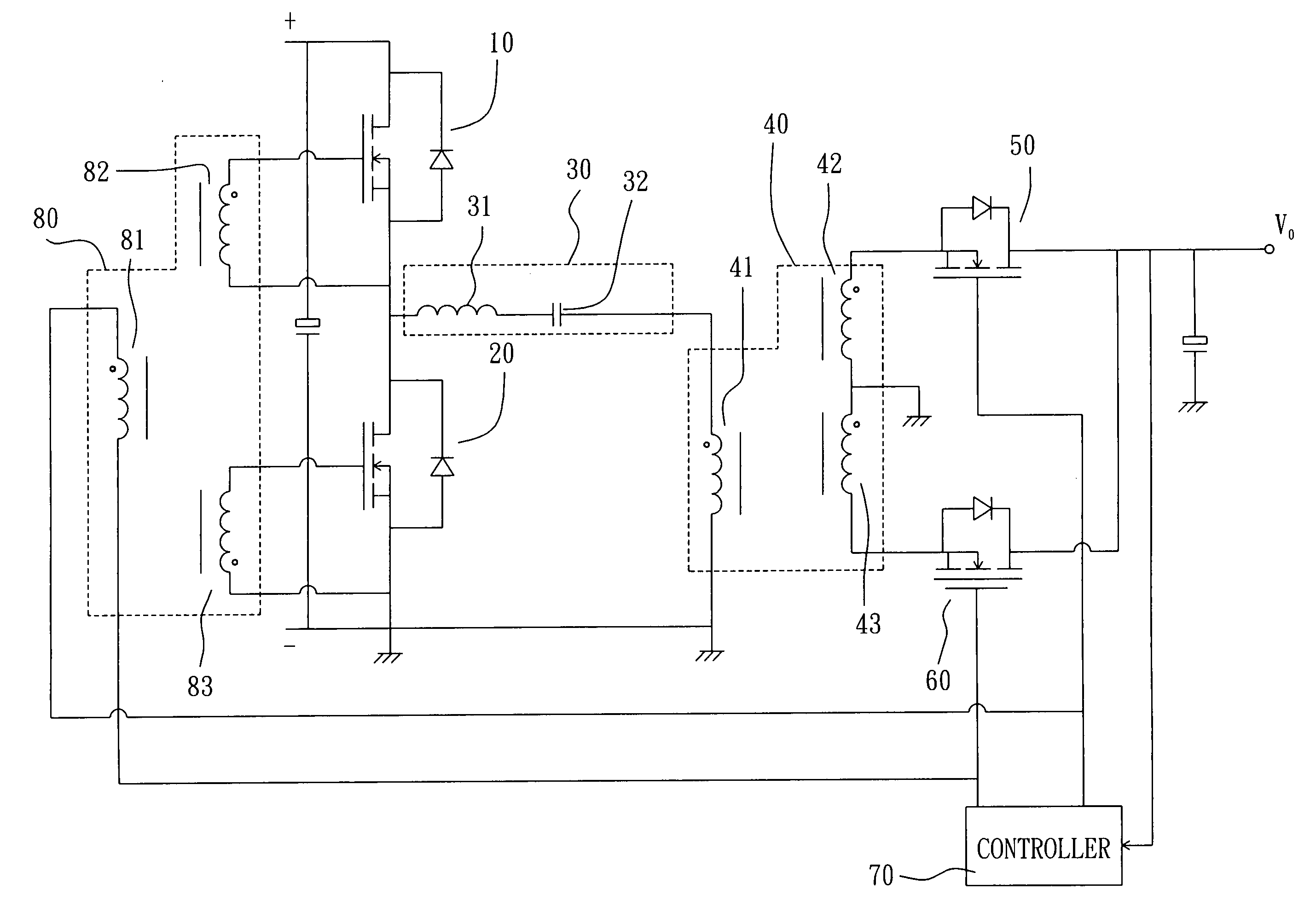
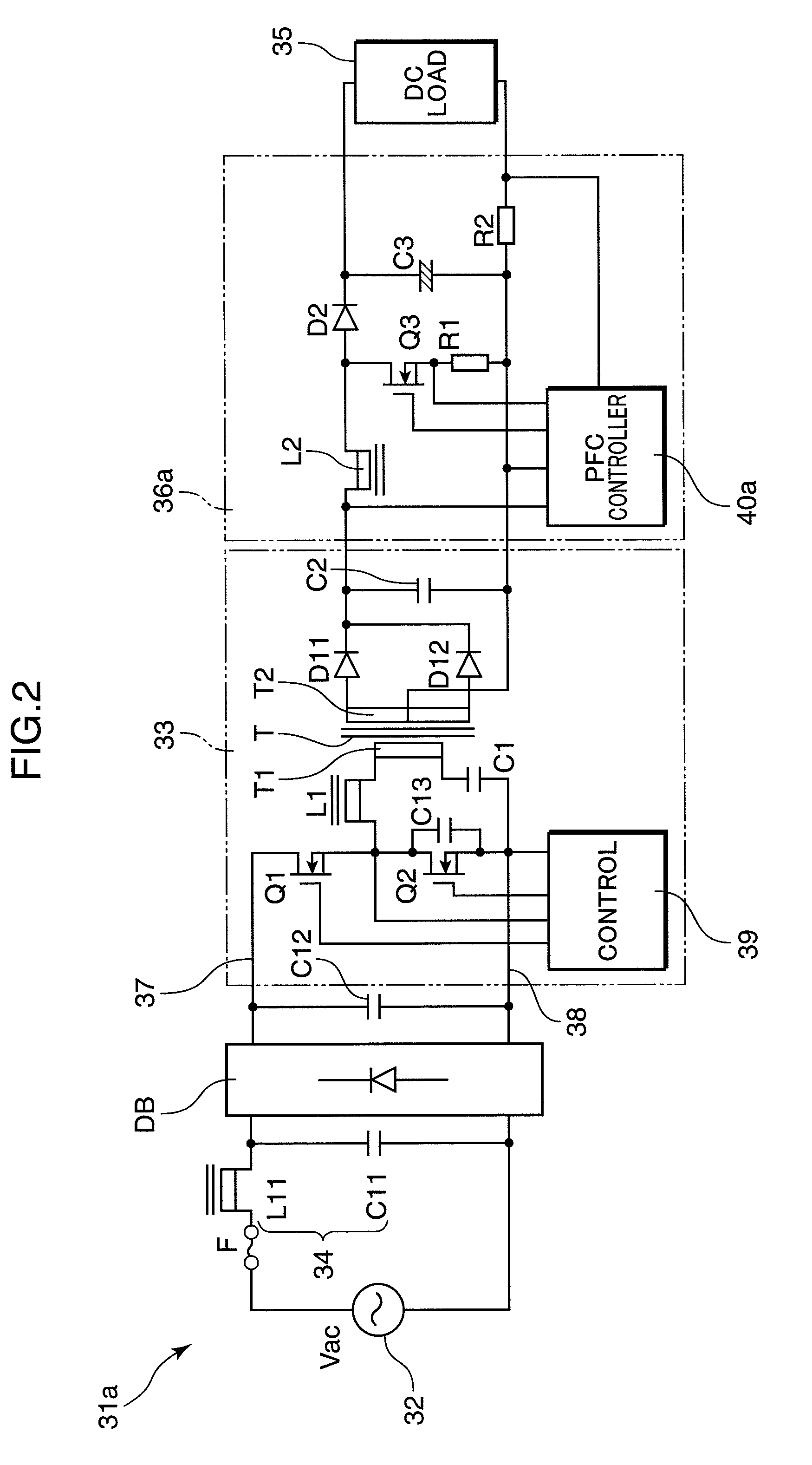
DC-DC converter and bi-directional DC-DC converter and method of controlling the same
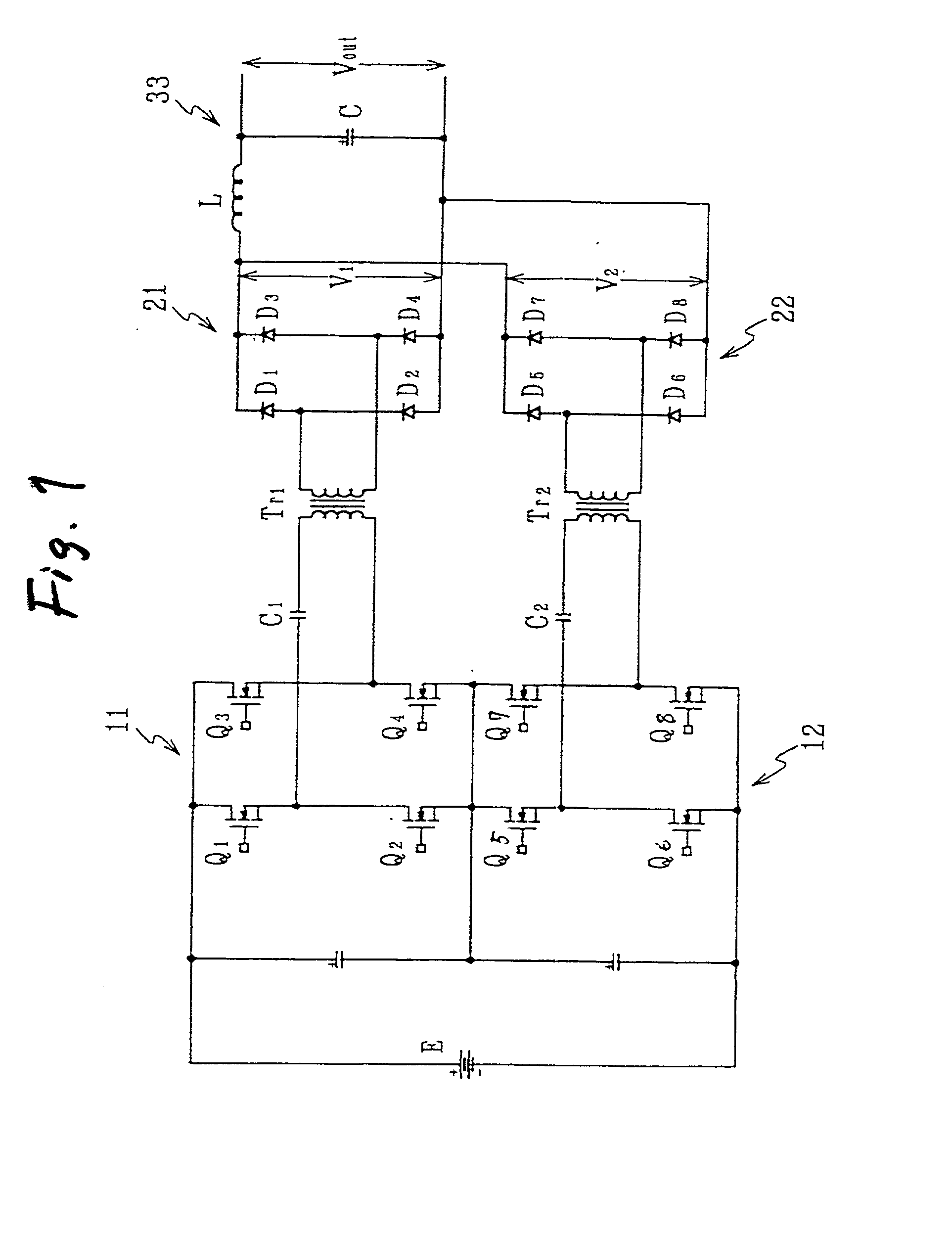
InactiveUS20020126517A1Lower on-resistanceReduce switching lossesAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc dc converterTransverter
A DC-DC converter has converter circuit portions 11 and 12, transformers Tr.sub.1 and T r.sub.2, and rectifier circuit portions 21 and 22. Two sets of converter circuit portions 11 and 12 respectively include two pairs of switching elements Q.sub.1 to Q.sub.4, and two pairs of switching elements Q.sub.5 to Q.sub.8 connected in full bridge configuration, series capacitors C.sub.1 and C.sub.2 are inserted and connected between the converter circuit portions 11 and 12 and the transformers Tr.sub.1 and Tr.sub.2 respectively. The switching phase of one switching element Q.sub.4 or Q.sub.8 is shifted by a 1 / 3n period from the switching phase of the other switching element Q.sub.1 or Q.sub.5 in the pair of switching elements. The switching phases of corresponding switching elements Q.sub.1 and Q.sub.5 in the converter circuit portions 11 and 12 are shifted by a 1 / 2n period from each other.
Owner:NISSIN ELECTRIC CO LTD
III-V hemt devices
ActiveUS7777252B2Guaranteed uptimeOn-resistance can be decreasedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductorImpurity
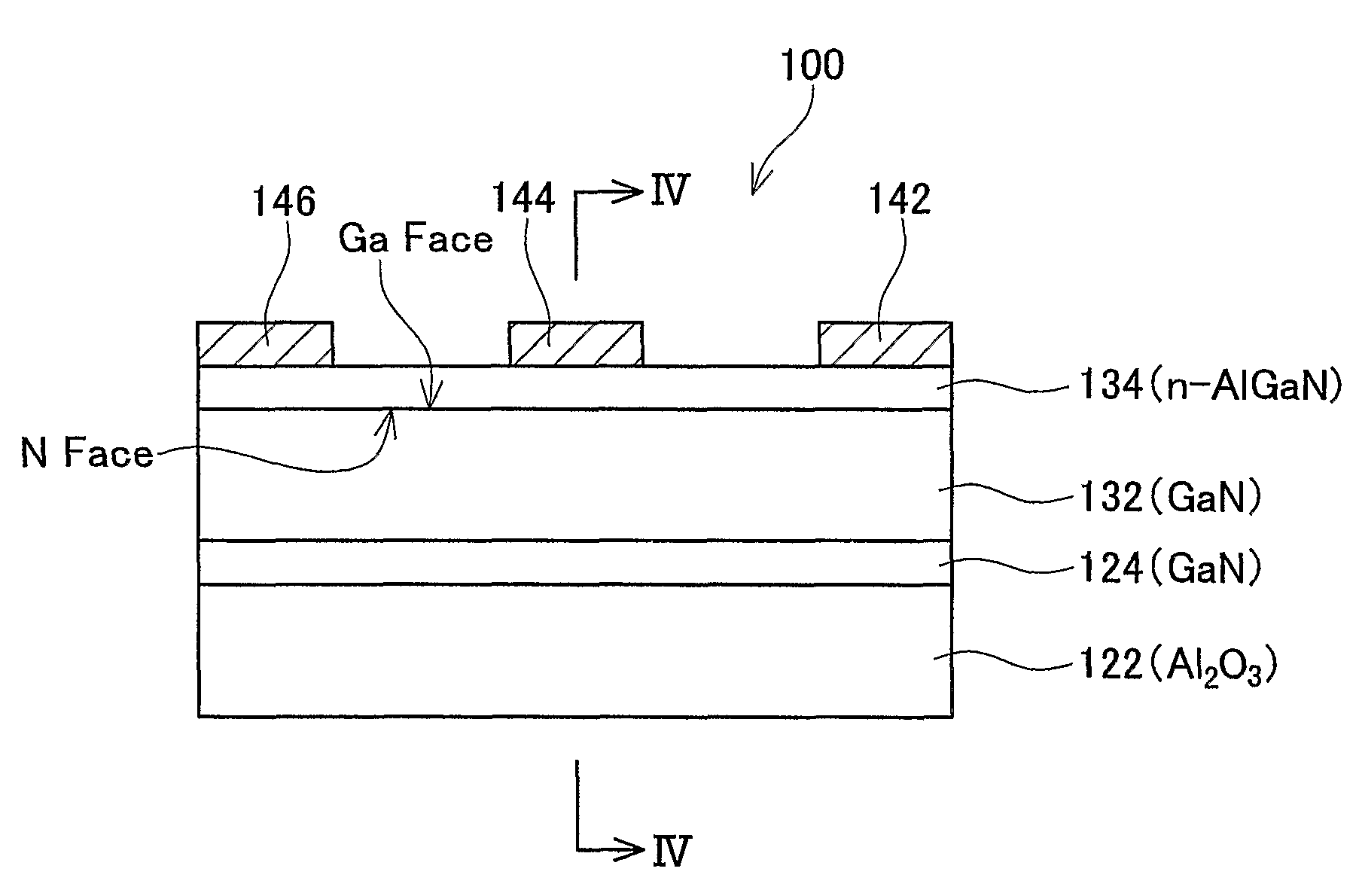
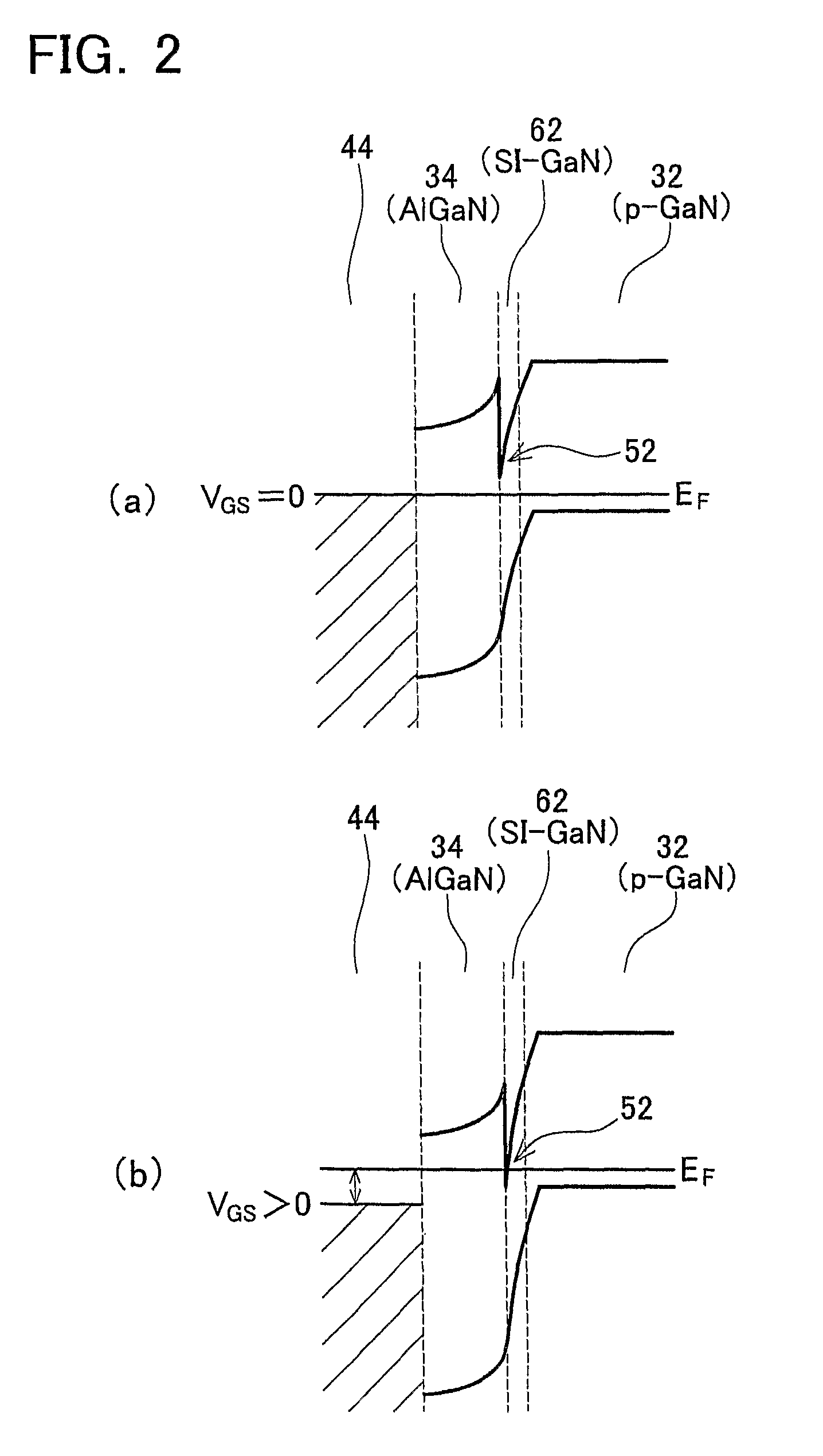
A semiconductor device has a stacked structure in which a p-GaN layer, an SI-GaN layer, and an AlGaN layer are stacked, and has a gate electrode that is formed at a top surface side of the AlGaN layer. A band gap of the AlGaN layer is wider than a band gap of the p-GaN layer and the SI-GaN layer. Moreover, impurity concentration of the SI-GaN layer is less than 1×1017 cm−3. Semiconductor devices including III-V semiconductors may have a stable normally-off operation.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Semiconductor device and power conversion device using the same
ActiveUS20080315257A1Large switching lossIncreased power lossTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice materialSemiconductor chip
In a semiconductor device in which a diode and a high electron mobility transistor are incorporated in the same semiconductor chip, a compound semiconductor layer of the high electron mobility transistor is formed on a main surface (first main surface) of a semiconductor substrate of the diode, and an anode electrode of the diode is electrically connected to an anode region via a conductive material embedded in a via hole (hole) reaching a p+ region which is the anode region of the main surface of the semiconductor substrate from a main surface of the compound semiconductor layer.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
P-GaN/AlGaN/AlN/GaN enhancement-mode field effect transistor
ActiveUS7728356B2High electron mobilityLower on-resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectron populationField-effect transistor
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Insulated Gate-Type Semiconductor Device and Manufacturing Method Thereof
ActiveUS20100224932A1Good on-resistance characteristicReliable suppressionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate voltageBody region
A semiconductor 100 has a P− body region and an N− drift region in the order from an upper surface side thereof. A gate trench and a terminal trench passing through the P− body region are formed. The respective trenches are surrounded with P diffusion regions at the bottom thereof. The gate trench builds a gate electrode therein. A P−− diffusion region, which is in contact with the end portion in a lengthwise direction of the gate trench and is lower in concentration than the P− body region and the P diffusion region, is formed. The P−− diffusion region is depleted prior to the P diffusion region when the gate voltage is off. The P−− diffusion region serves as a hole supply path to the P diffusion region when the gate voltage is on.
Owner:DENSO CORP
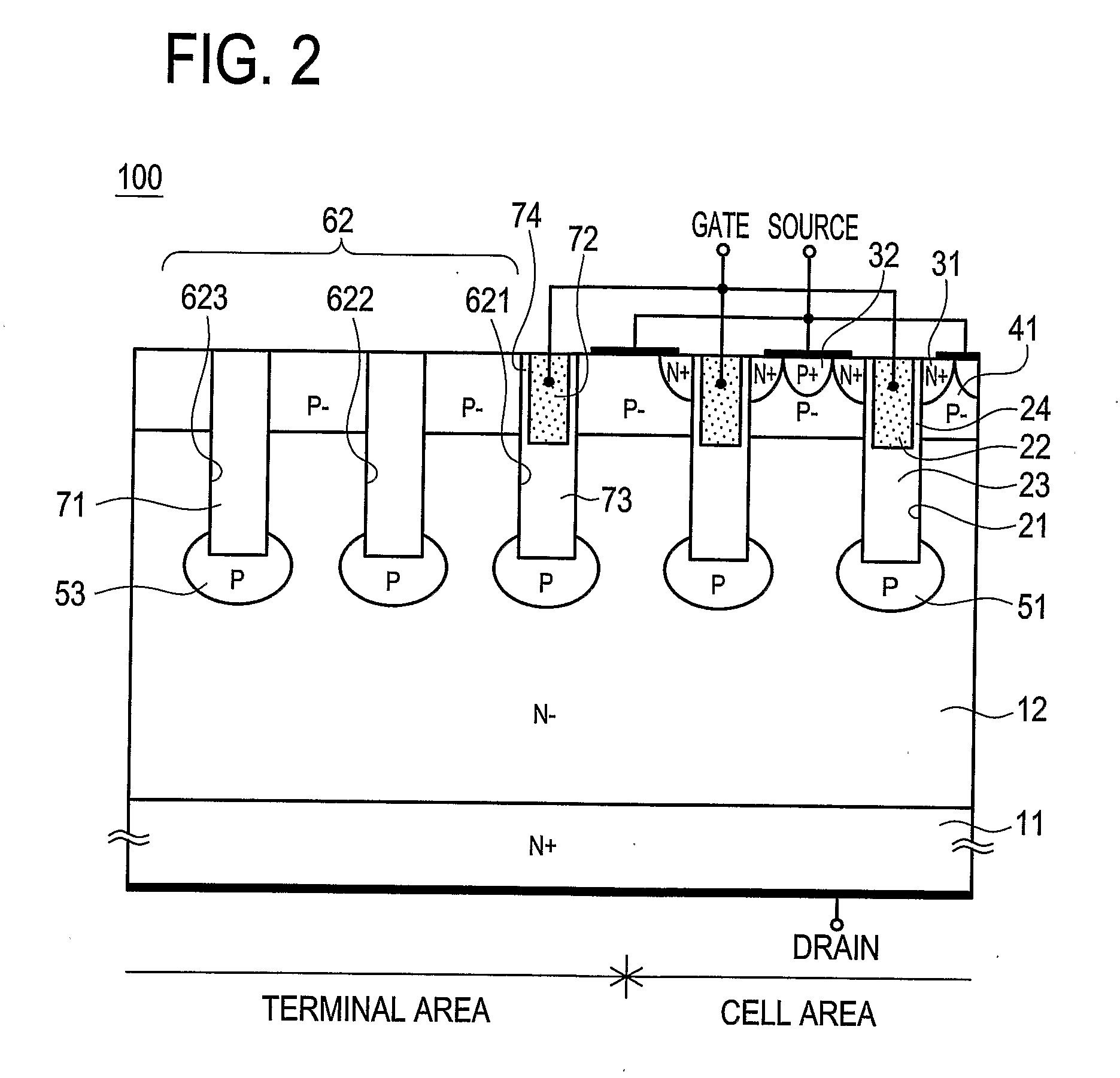
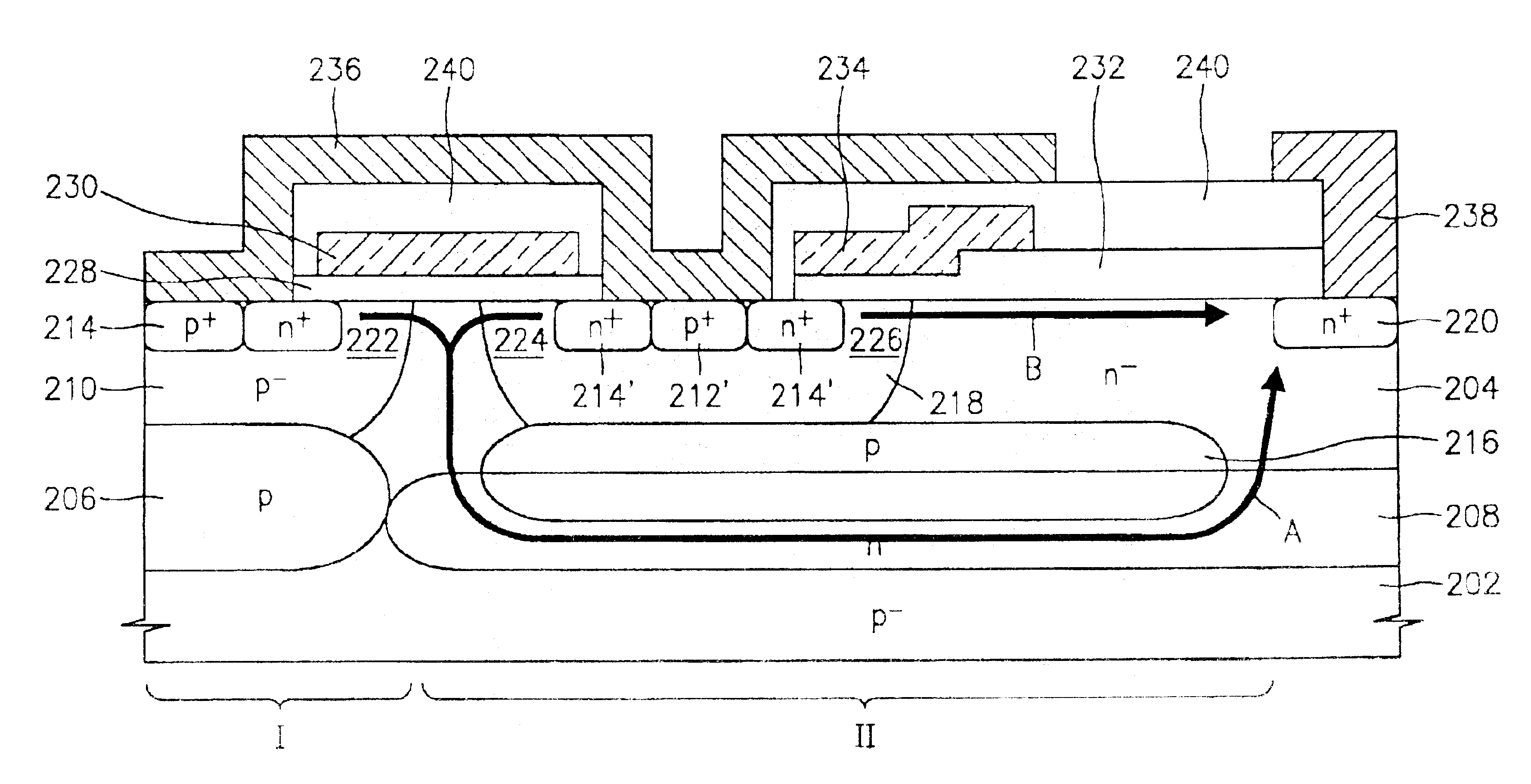
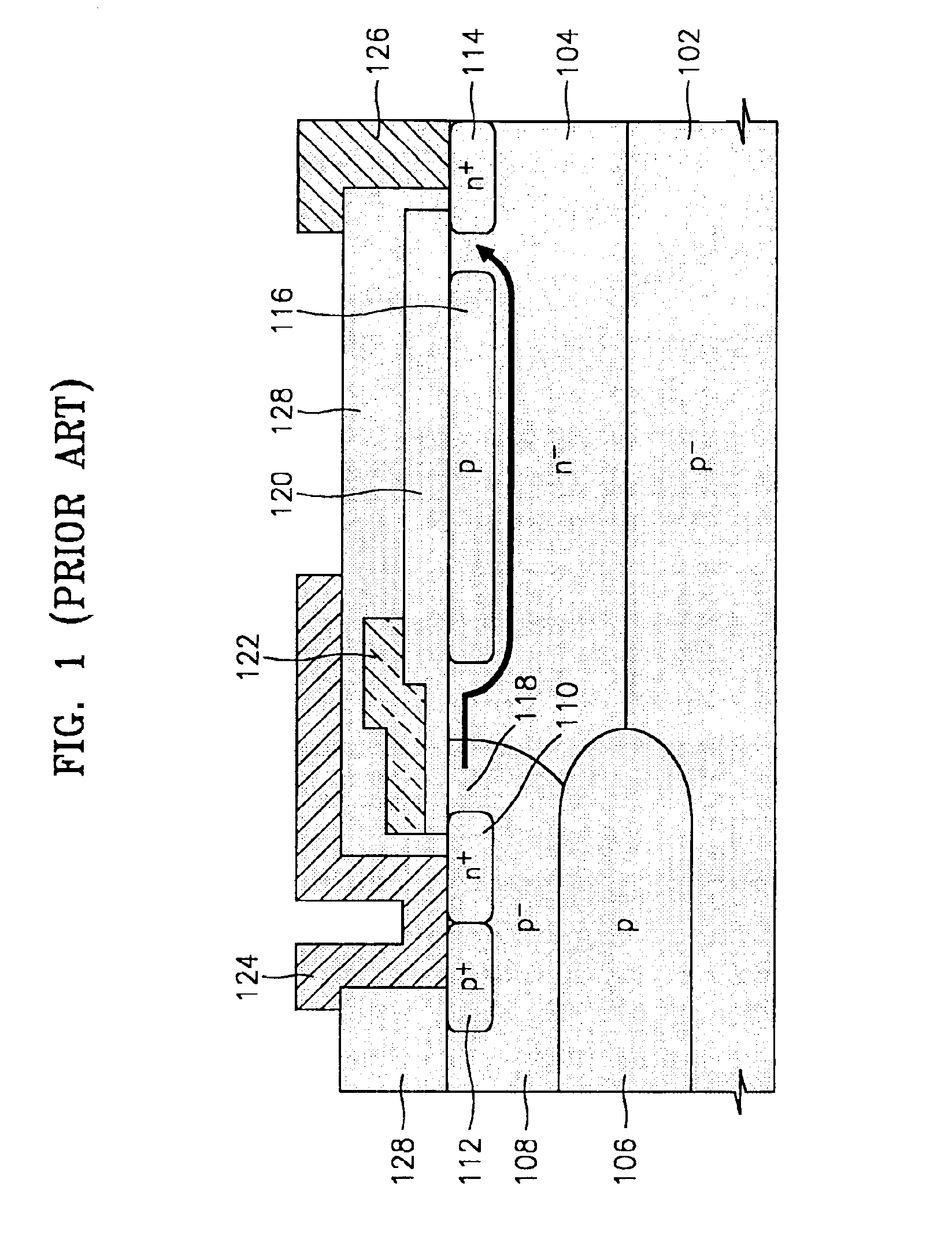
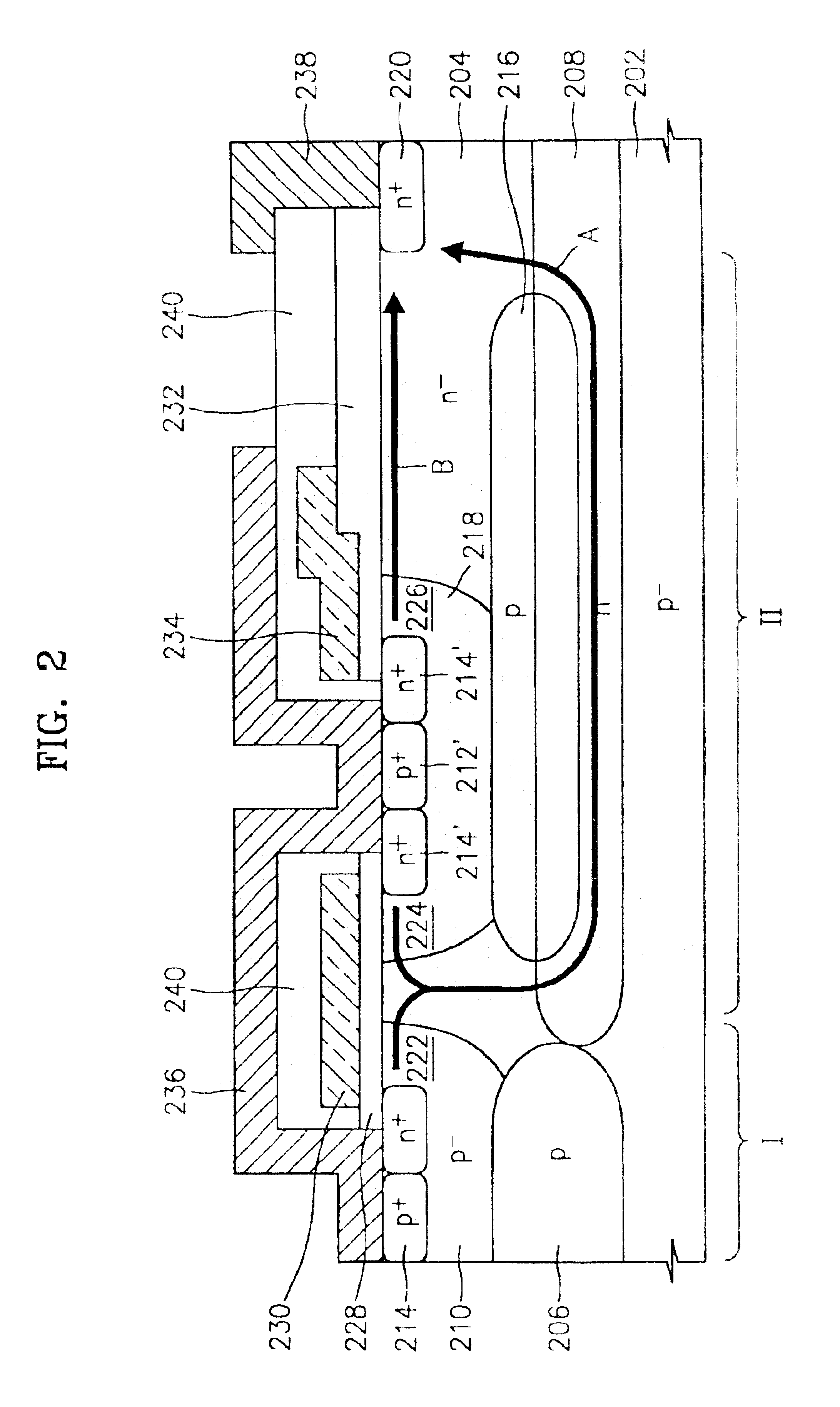
Lateral double-diffused MOS transistor having multiple current paths for high breakdown voltage and low on-resistance
ActiveUS6909143B2Evenly reduce on-resistanceLower on-resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLDMOSSemiconductor
A lateral double-diffused MOS (LDMOS) transistor is provided. The LDMOS transistor includes a semiconductor substrate 202 formed of a material having p-conductivity type impurities, a drift region formed of a material having n-conductivity type impurities on the semiconductor substrate, a first buried layer 206 of p-type material and a second buried layer 208 formed of n-type material. Layers 206 and 208 are arranged at the boundary between the semiconductor substrate and the drift region. A first well region 210 of p-type material contacts the first buried layer 206 n-type in a first portion 1 of the drift region. A first source region 214 conductivity in a predetermined upper region of the first well region, a drain region formed of a material having second conductivity type impurities in a predetermined region of the drift region, the drain region being spaced a predetermined gap apart from the first well region, a third buried layer formed of a material having first conductivity type impurities in a second region of the drift region, the third buried layer being overlapped with a part of an upper portion of the first buried layer, a second well region formed of a material having first conductivity type impurities in the second region of the drift region, the second well region being overlapped with the third buried layer, a second source region formed of a material having second conductivity type impurities in a predetermined upper region of the second well region, a gate insulating layer formed in a first channel region inside the first well region and in a second channel region inside the second well region, a gate electrode formed on the gate insulating layer, a source electrode formed to be electrically connected to the first source region and the second source region, and a drain electrode formed to be electrically connected to the drain region.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
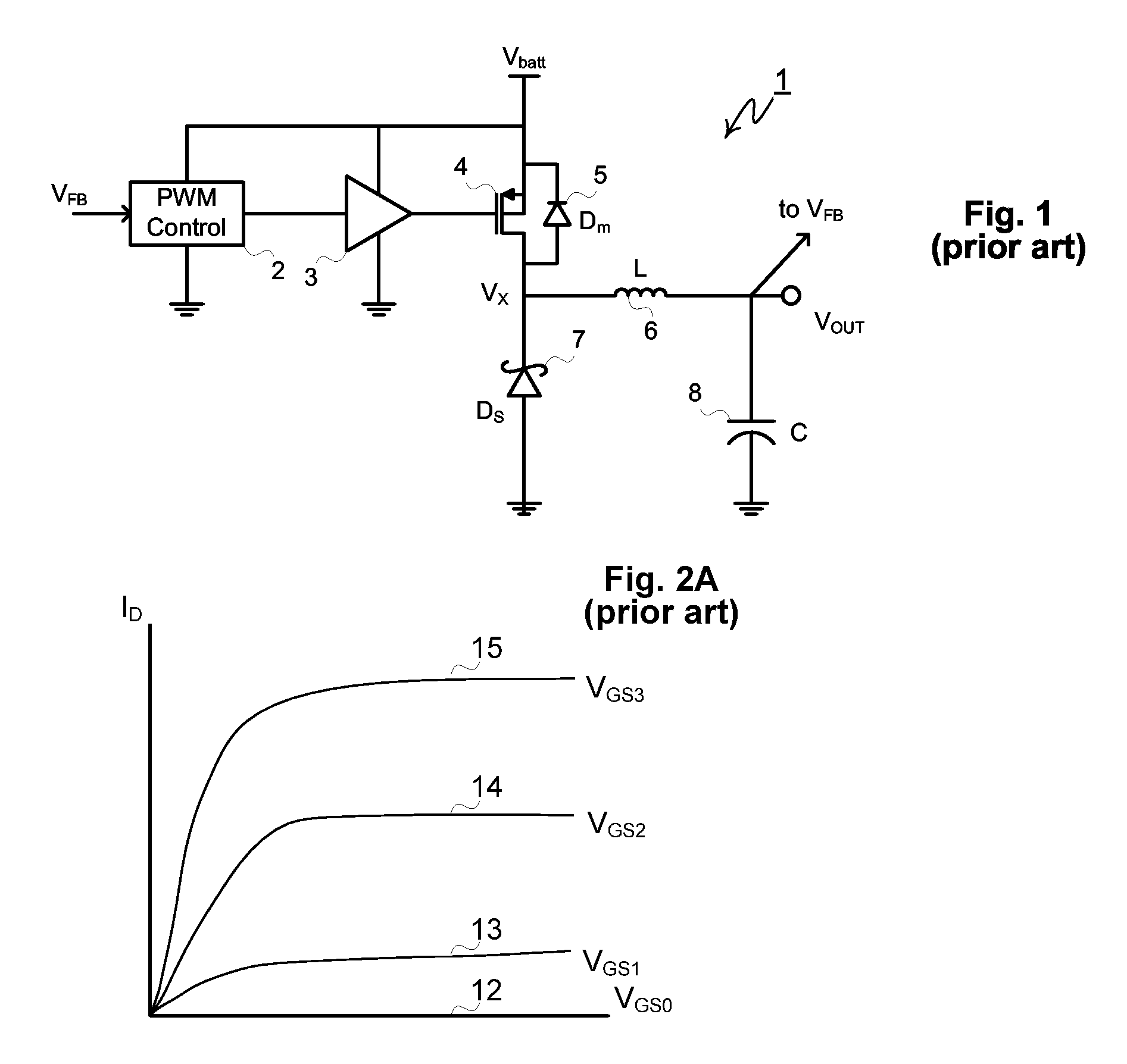
High-Frequency Power MESFET Buck Switching Power Supply
InactiveUS20070170897A1Lower on-resistanceLower turn-on voltageDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationMOSFETInductor
A MESFET based buck converter includes an N-channel MESFET between a battery or other power source and a node Vx. The node Vx is connected to an output node via an inductor and to ground via a Schottky diode or a second MESFET or both. A control circuit drives the MESFET (and the second MESFET) so that the inductor is alternately connected to the battery and to ground. The maximum voltage impressed across the high side MESFET is optionally clamped by a Zener diode. In some implementations, the MESFET is connected in series with a MOSFET. The MOSFET is switched off during sleep or standby modes to minimize leakage current through the MESFET. The MOSFET is therefore switched at a low frequency compared to the MESFET and does not contribute significantly to switching losses in the converter. In other implementations, more than one MESFET is connected in series with a MOSFET the MOSFETs being switched off during periods of inactivity to suppress leakage currents.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
Trench mosfet with resurf stepped oxide and diffused drift region
ActiveUS20130168760A1Super cost-effectiveEasy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesTrench mosfetEngineering
A trench MOSFET with split gates and diffused drift region for on-resistance reduction is disclosed. Each of the split gates is symmetrically disposed in the middle of the source electrode and adjacent trench sidewall of a deep trench. The inventive structure can save a mask for definition of the location of the split gate electrodes. Furthermore, the fabrication method can be implemented more reliably with lower cost.
Owner:FORCE MOS TECH CO LTD
Leadless semiconductor package and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS7053469B2Reduce thermal resistanceLower on-resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor packageEngineering
A leadless semiconductor package mainly includes a semiconductor device securely attached to an upper surface of a die pad by solder paste and a plurality of leads arranged about the periphery of the die pad. The thickness of the leads and the die pad are within a range of 10 to 20 mils. The semiconductor device is electrically coupled to one of the leads. A package body is formed over the semiconductor device and the leads in a manner that the lower surfaces of the die pad and the leads are exposed through the package body. Preferably, the first semiconductor device is electrically coupled to one of the leads by at least one heavy gauge aluminum wire. The present invention further provides a method of producing the semiconductor package described above.
Owner:ADVANCED SEMICON ENG INC
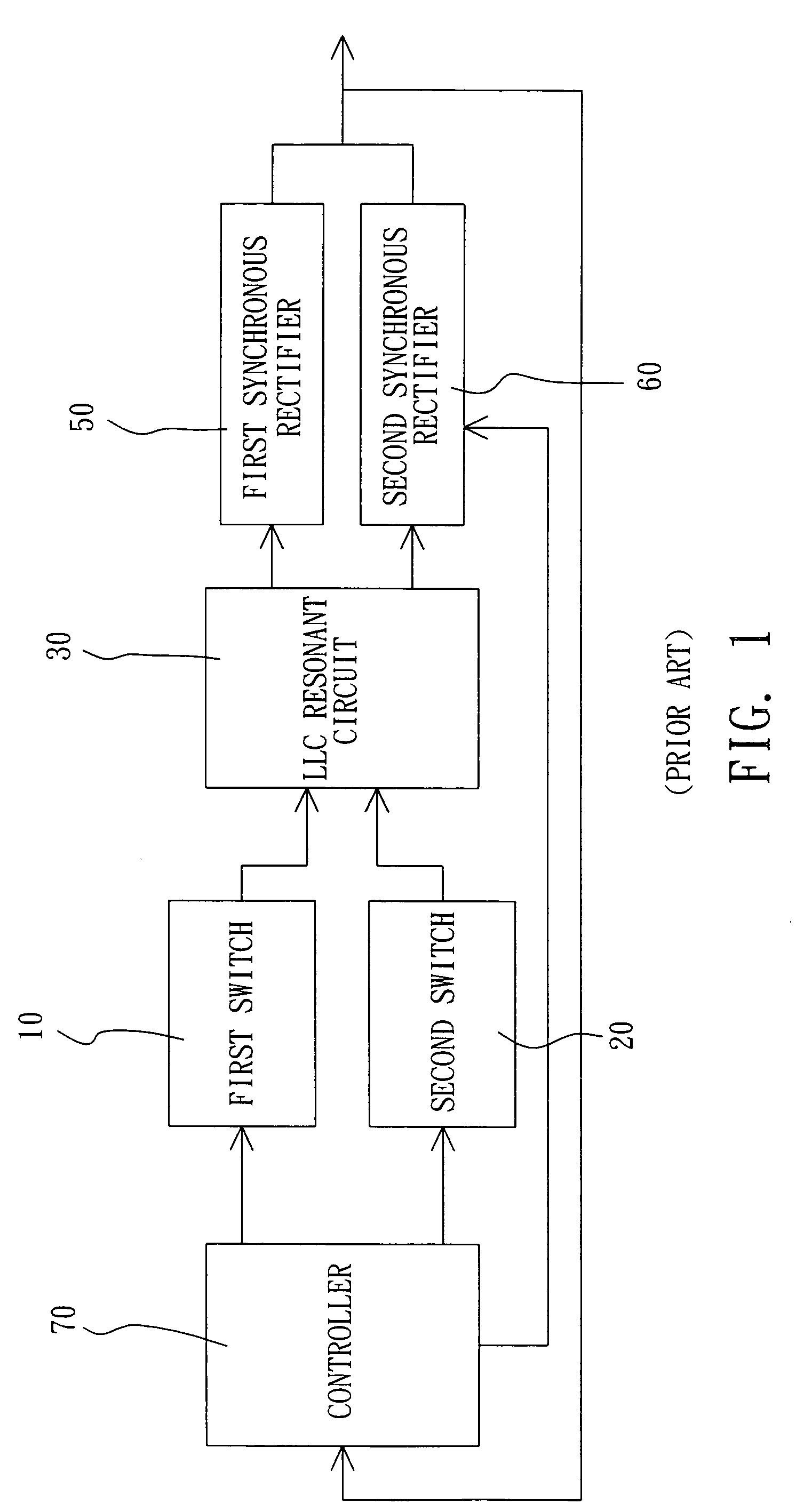
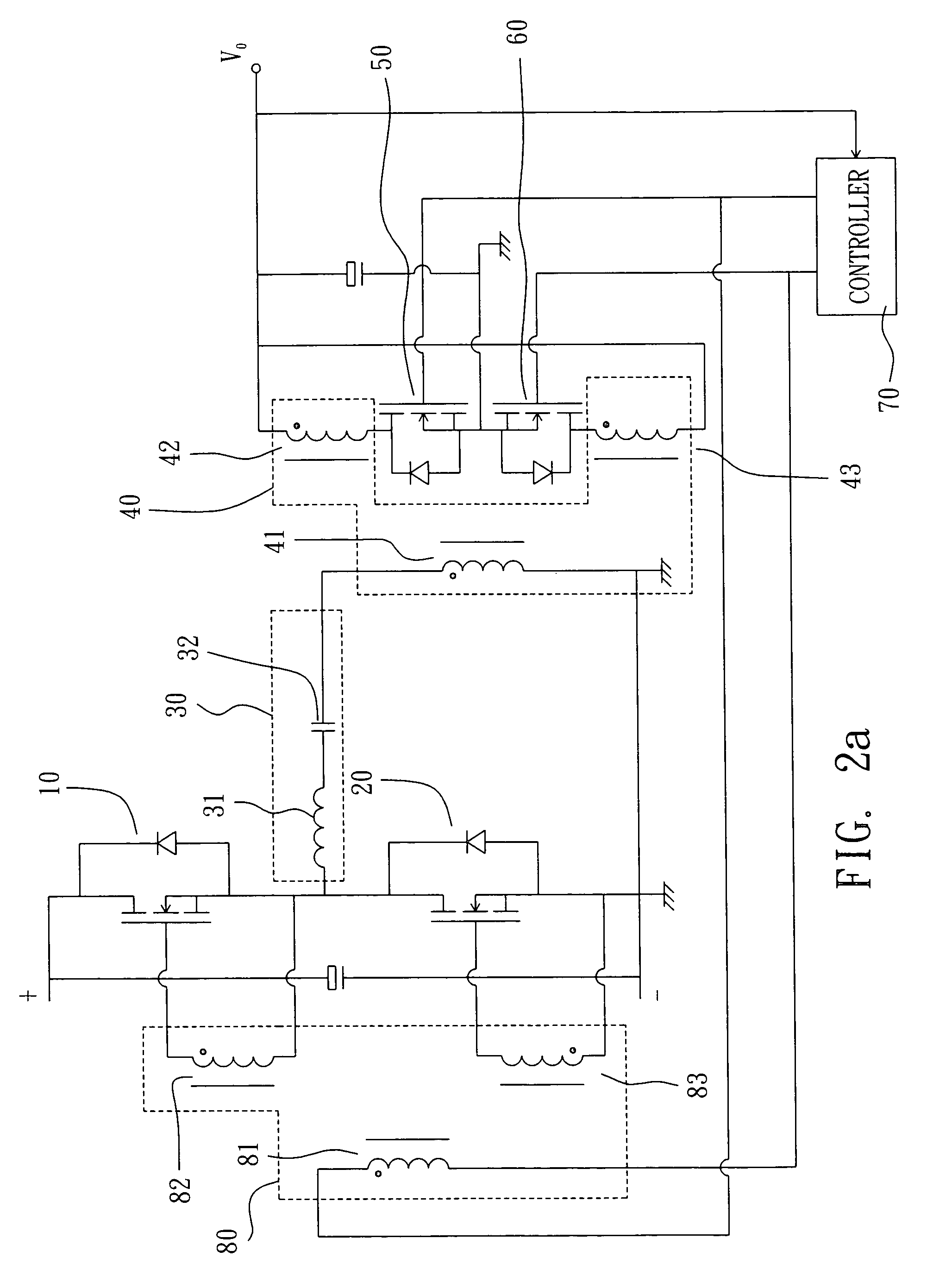
Half-bridge LLC resonant converter with a synchronous rectification function
InactiveUS7193866B1Reduce power consumptionLower on-resistanceEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionControl signalResonant converter
The invention discloses a half-bridge LLC resonant converter with a synchronous rectification function that includes a first switch; a second switch; a first transformer; a first synchronous rectifier; a second synchronous rectifier; a controller; and a second transformer. The controller of the half-bridge LLC resonant converter with a synchronous rectification function can control the first synchronous rectifier and the second synchronous rectifier directly and the connected second transformer also can control the first switch and the second switch directly. The first synchronous rectifier and second synchronous rectifier having a low conducting resistance substitute the rectifier and greatly lower the power consumption. The controller outputs a control signal to drive a transformer to output a signal to the primary winding, and its signal delay is formed by a delay of an electronic circuit and a power MOS switch of the first switch and second switch.
Owner:CHICONY POWER TECH CO LTD
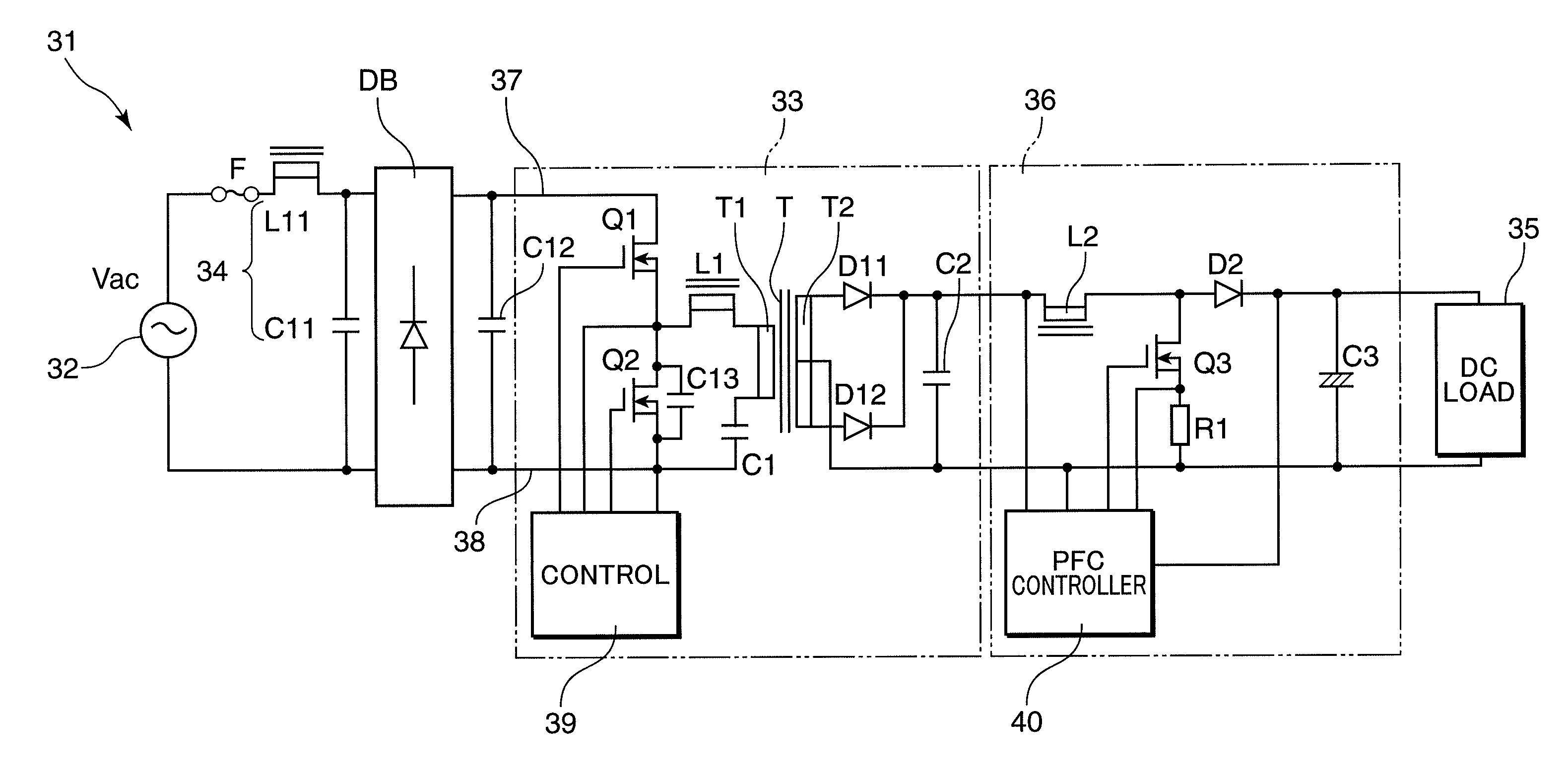
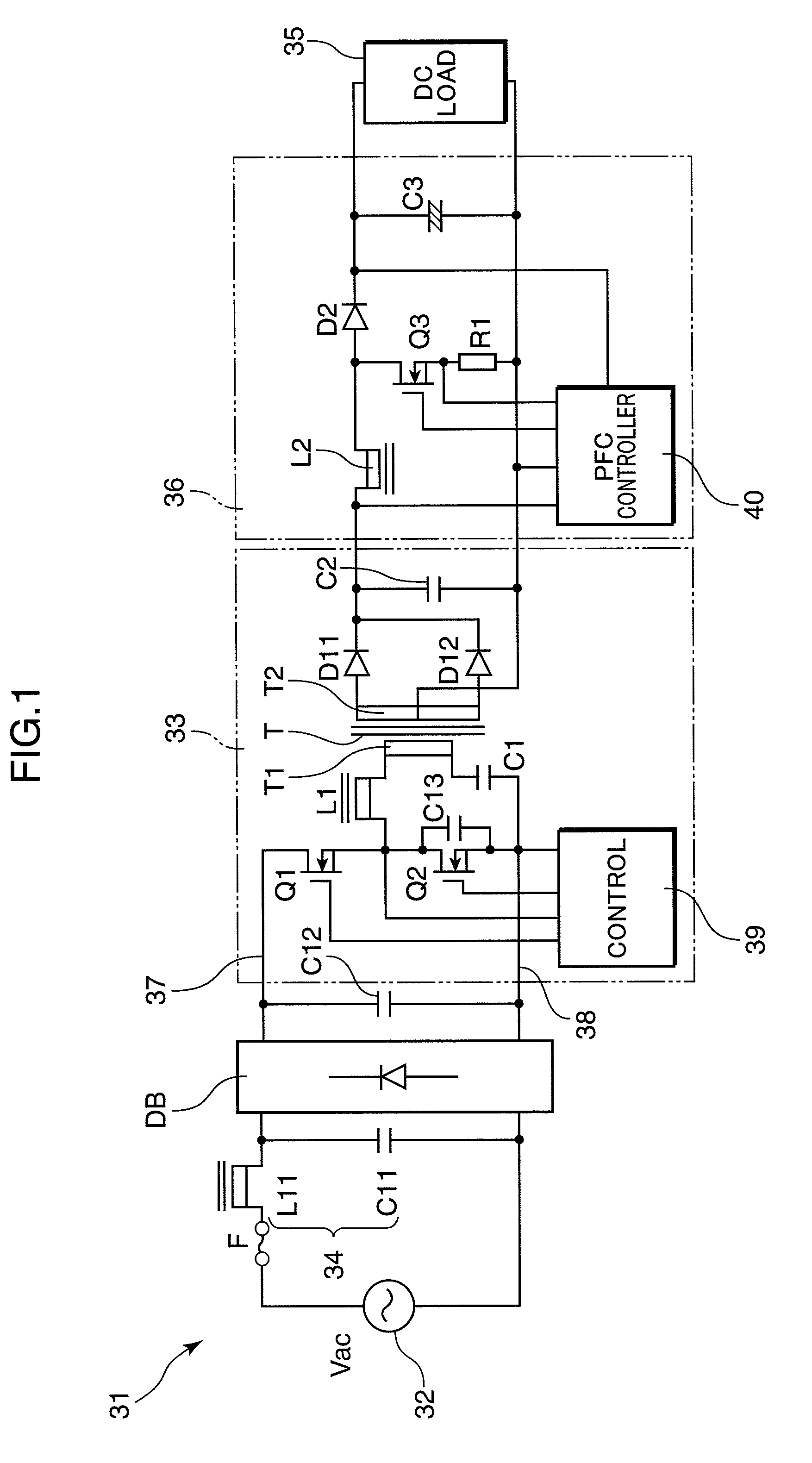
Insulation type ac-DC converter and LED DC power supply device using the same
ActiveUS20100109571A1Promote resultsImprove efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionElectroluminescent light sourcesTransformerPower factor
In an insulation type AC-dc converter in which input current from a commercial power supply is converted to obtain insulated direct current, the overall efficiency is raised and the structure is simplified. A multi-resonance type half-bridge DC-DC converter having an insulation transformer T is used as a first converter, and a boosting chopper circuit for power factor improvement is used as a second converter. Hence through multi-resonance operation, increases in losses can be suppressed even when the switching frequency is raised, and because a half-bridge circuit is used, switching elements and similar with lower voltage ratings can be employed, whereby overall efficiency can be increased. Moreover, a voltage substantially similar to the full-wave rectified waveform of the power supply voltage is obtained from the output capacitor at the boosting chopper circuit input, whereby there is no need for a feed-forward circuit across the insulation transformer, and moreover the electrolytic capacitor which had to be provided on the converter input side is unnecessary. This is advantageous for achieving miniaturization and a thin design.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com