Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
48results about How to "Reduce optical power density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
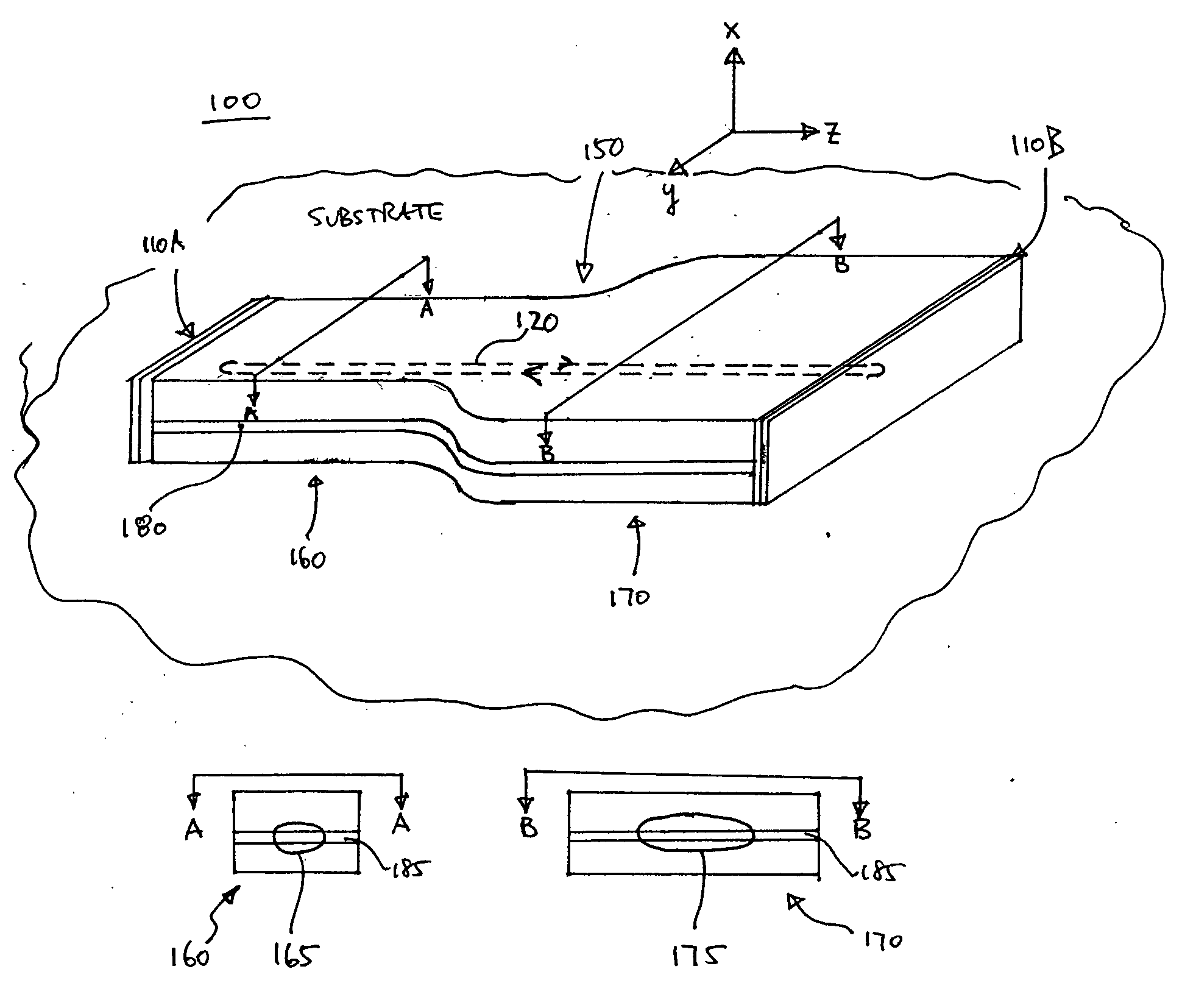
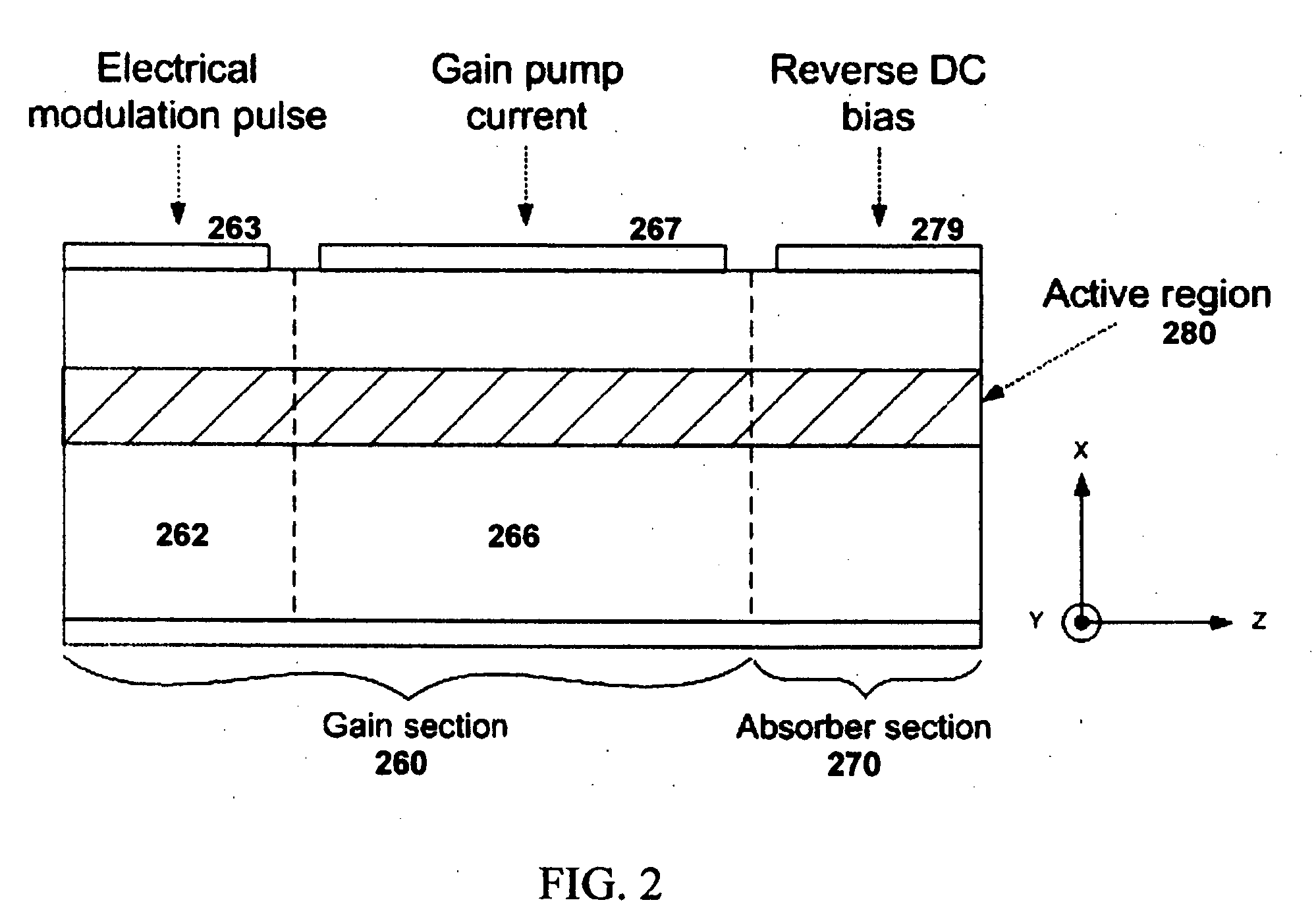
Mode-locked semiconductor lasers with quantum-confined active region
InactiveUS20060222024A1Reduce optical power densityHigh peak powerOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsOptical powerSemiconductor package
A mode-locked integrated semiconductor laser has a gain section and an absorption section that are based on quantum-confined active regions. The optical mode(s) in each section can be modeled as occupying a certain cross-sectional area, referred to as the mode cross-section. The mode cross-section in the absorber section is larger in area than the mode cross-section in the gain section, thus reducing the optical power density in the absorber section relative to the gain section. This, in turn, delays saturation of the absorber section until higher optical powers, thus increasing the peak power output of the laser.
Owner:INNOLUME ACQUISITION
TM-polarization GaAsP/GaInP active-region 808nm quantum-well laser
InactiveCN103457158AReduce oxidationReduce internal lossOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsLower limitOhmic contact
The invention provides a TM-polarization GaAsP / GaInP active-region 808nm quantum-well laser. The laser structurally comprises a substrate, a buffer layer, a type-N lower limit layer, a lower waveguide layer, a quantum well layer, an upper waveguide layer, a type-P upper limit layer, and an ohmic contact layer sequentially from bottom to top. The upper waveguide layer and the lower waveguide layer are made of aluminum-free material GaInP. The quantum well layer is made of GaAsP material. The waveguide layer and the quantum well layer form a wide-waveguide aluminum-free active region. The laser has the advantages that the influence of Al oxidization, growth interface roughness and accessory electric field at cavity surface upon the reliability in high power output, long service life and the like of the laser can be reduced effectively, the waveguide layer and the limit layers are optimally designed into wide-waveguide asymmetric structures, and internal loss can be reduced effectively, and maximum output power and reliability can be improved.
Owner:Shandong Huaguang Optoelectronics Co. Ltd.
Uncaging device
ActiveUS20050051706A1Reduce optical power densitySpectrum investigationGenetic material ingredientsAnalytical chemistryMultiwell plate
Uncaging devices that can be used to uncage photoactivatable caged components are provided. Consistent, uniform and / or high throughput processing of reactions and assays that include caged components is provided. Masked multiwell plates that can be used for uncaging photoactivatable caged components are provided. Methods and apparatus for initiating assays involving caged components are provided.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
High-power laser diffraction type spatial filter
InactiveCN101738739AImproved angular spectral selectivityIncreased bandwidthOptical elementsLaser burnGrating
The invention discloses a high-power laser diffraction type spatial filter. The left side of the high-power laser diffraction type spatial filter is provided with an interstage isolation filter of which the central axis is a vertical line BC, the middle of the high-power laser diffraction type spatial filter is provided with a group of gain medium of which the central axis is a transverse line CD, the right side of the high-power laser diffraction type spatial filter is provided with a multi-pass cavity filter of which the central axis is a vertical line DE, the central axis of the entire device forms a BCDEF broken line, one optical grating which enables light beams to be deflected at 90 degrees is respectively arranged at a point B, a point C, a point D and a point E, the optical gratings are separate type volume Bragg optical gratings or double-piece integrated type optical gratings, and one reflecting mirror is arranged at a point F. The invention uses an optical grating double-pass spatial filter component which does not have a lens and a pinhole and has compact appearance to replace a pinhole filter in a multi-pass amplifier, can realize the wider width of a diffraction frequency band and can meet the requirement of short-pulse and ultrashort-pulse spatial filtering; the borne laser power is higher, and the requirement of high-power laser spatial filtering can be met, thereby eliminating the probability that laser burns out the filter component because of no lens and no pinhole in the device.
Owner:谭吉春
Low-loss large-effective area single mode fiber and manufacturing method thereof
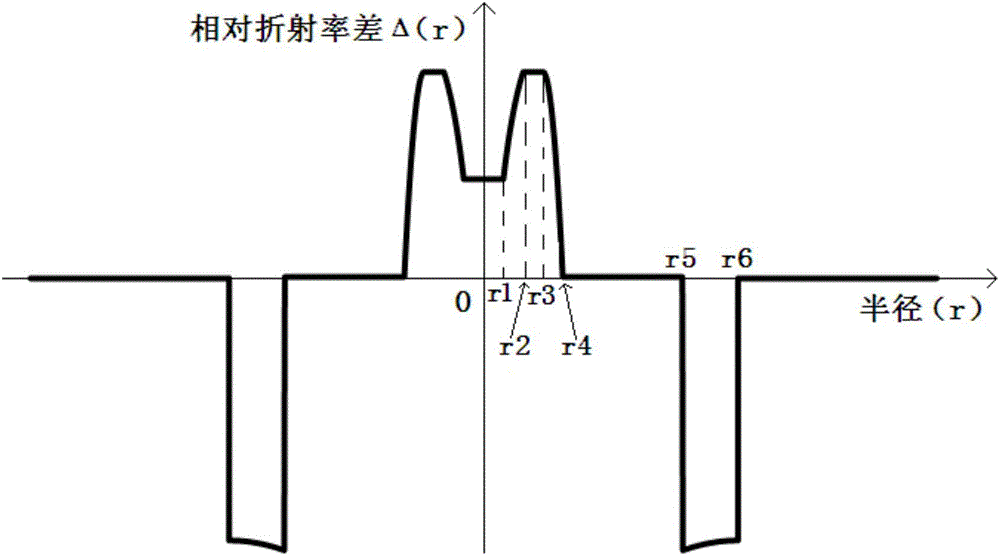
ActiveCN103472525AIncrease the effective areaReduce optical power densityGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingRefractive indexScattering loss
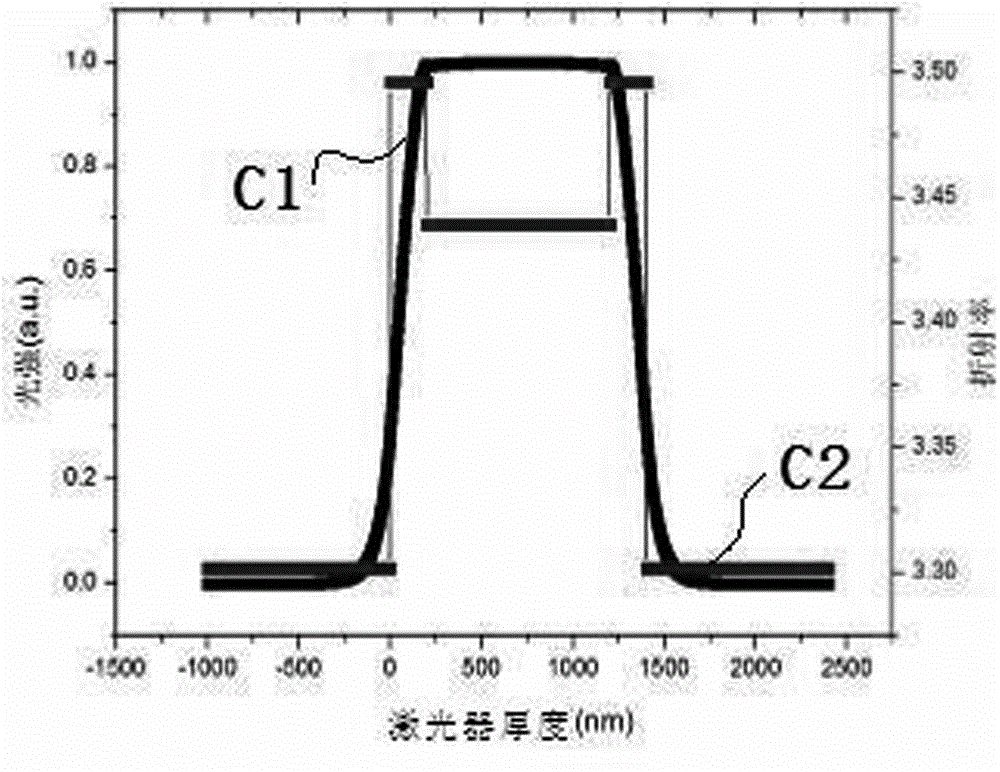
The invention discloses a low-loss large-effective area single mode fiber and a manufacturing method of the low-loss large-effective area single mode fiber, and relates to the field of optical fibers. The low-loss large-effective area single mode fiber comprises a quartz glass cladding, an internal coating and an external coating, wherein the quartz glass cladding, the internal coating and the external coating are arranged in sequence from inside to outside; the inside of the quartz glass cladding comprises a first fiber core area, a second fiber core area, a third fiber core area, a fourth fiber core area and a refractive index concave cladding, wherein the first fiber core area, the second fiber core area, the third fiber core area, the fourth fiber core area and the refractive index concave cladding are arranged in sequence from inside to outside; the refractive index concave cladding is subjected to deposition through a PCVD process; the quartz glass cladding is manufactured through an OVD process or a sleeving process. According to the low-loss large-effective area single mode fiber and the manufacturing method of the low-loss large-effective area single mode fiber, the scattering loss of the low-loss large-effective area single mode fiber and the additional loss of the low-loss large-effective area single mode fiber in a bent state can be reduced; due to the fact that the spire distribution of fiber core basic mode electromagnetic field power is adjusted into flattop distribution, optical power density is reduced, the effective area of the low-loss large-effective area single mode fiber is enlarged, the nonlinearity of the low-loss large-effective area single mode fiber is reduced, the incident power of an optical fiber communication system is increased by 0.4-2.6 dB, and the low-loss large-effective area single mode fiber is suitable for mass production.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD +1
High-power optical fiber end cap and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN109031527AReduce optical power densityAvoid energy lossCoupling light guidesActive medium shape and constructionOptical powerEngineering
The invention provides a high-power optical fiber end cap and a manufacturing method thereof. The optical fiber end cap comprises a double-clad optical fiber, a core-free optical fiber and a quartz rod which are coaxially arranged; the quartz rod comprises a first cylindrical section, a circular table section and a second cylindrical section which are coaxially connected in sequence, the diameterof the first cylindrical section is smaller than that of the second cylindrical section; the double-clad optical fiber is connected with one end of the core-free optical fiber in a welding mode, and the other end of the core-free optical fiber is connected with one end of the first cylindrical section in a welding mode; the diameter of the cladding layer of the core-free optical fiber is larger than or equal to the diameter of the double-clad optical fiber; and the diameter of the cladding layer of the core-free optical fiber is smaller than or equal to the diameter of the first cylindrical section. The laser firstly passes through the core-free optical fiber, so that energy is expanded, and the light power density in the connecting place of the output end plane and the quartz rod is lowered; by selecting the proper length of the core-free optical fiber, the output light spot can be large enough when the laser outputs from the core-free optical fiber, so that the optical power densityon the output surface can be effectively reduced; and meanwhile, energy is not output from the side surface of the core-free optical fiber, and loss of energy is avoided.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Semiconductor laser device having inGaAs compressive-strain active layer, GaAsP tensile-strain barrier layers, and InGaP optical waveguide layers
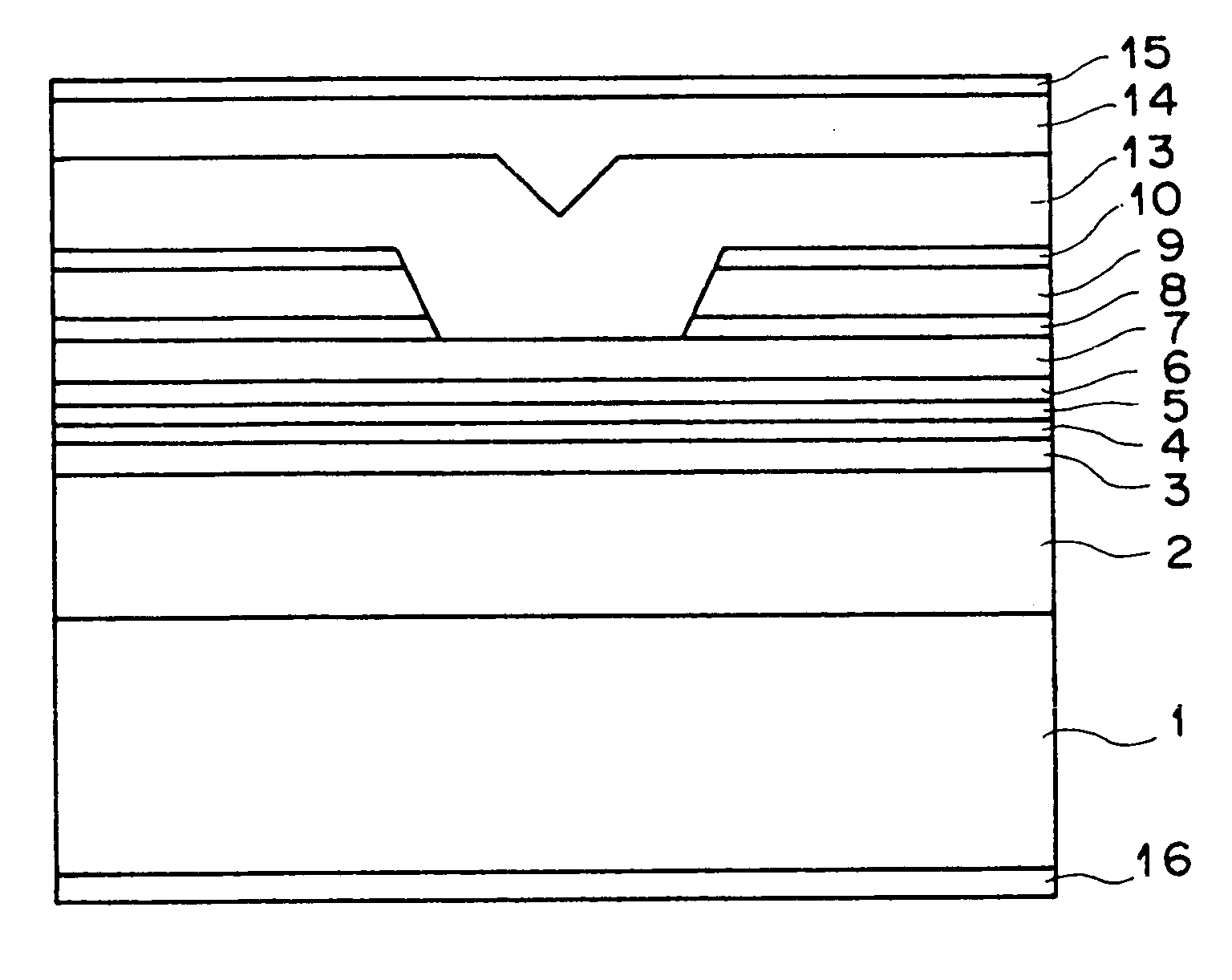
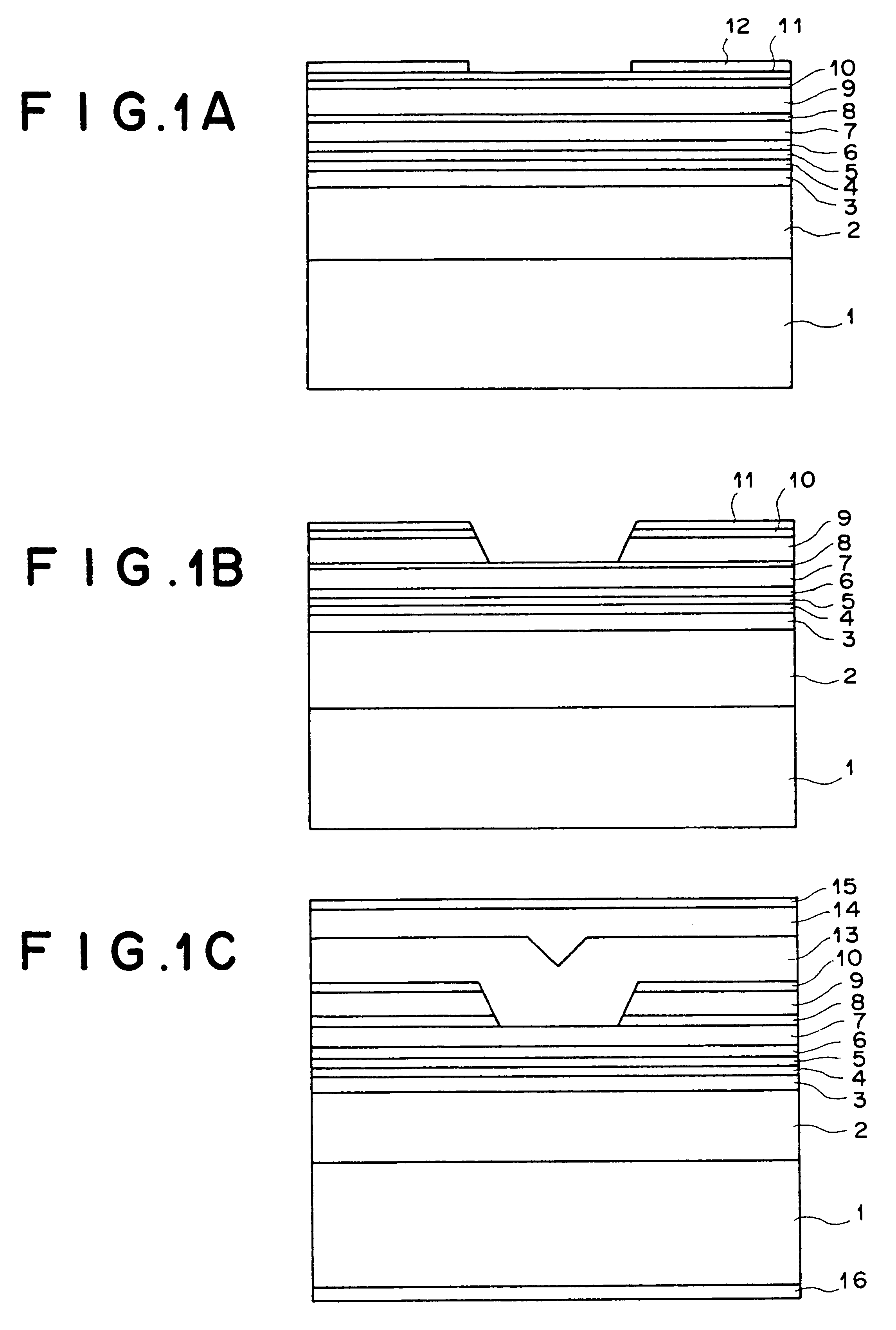
InactiveUS20020122447A1Reduce layeringQuality improvementOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsPhysicsTotal thickness
In a semiconductor-laser device: a compressive-strain quantum-well active layer is made of Inx3Ga1. x3As1-y3Py3 (0<x3<=0.4 and 0<=y3<=0.1); tensile-strain barrier layers made of Inx2Ga1-2AS1-y2P1-y2 (0<=x2<0.49y2 and 0<y2<=0.4)are formed above and under the compressive-strain quantum-well active layer; and optical waveguide layers being made of either p-type or i-type In0.49Ga0.51P are formed above the upper tensile-strain barrier layer and under the lower tensile-strain barrier layer. Preferably, the absolute value of a sum of a first product and a second product is less than or equal to 0.25 nm, where the first product is a product of a strain and a thickness of said compressive-strain active layer, and the second product is a product of a strain of said lower and upper tensile-strain barrier layers and a total thickness of the lower and upper tensile-strain barrier layers.
Owner:NICHIA CORP +1
Laser line width compressing module and narrow-line-width laser
The invention discloses a line width narrowing module of a laser resonant cavity. The module is an integrated optical element, wherein two side surfaces of a prism-like body respectively form an incident surface and a reflecting surface; the reflecting surface is a reflective blazed grating. The module can be used for solving the problem of difficult light emission caused by a complex optical system and surface abrasion of an optical element in a low-gain laser and is high in optical integrity and simple to regulate and use. The module is good in wavelength selection characteristic and relatively good in damage resistance threshold value. The laser resonant cavity built by using the module has few optical elements, is high in interference resistance and can be applied to places which are complex in environment.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
Triply coated fiber, pump combiner, fiber grating and fiber laser
ActiveCN110187437AHigh damage thresholdImprove stabilityLaser detailsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingGratingFiber gratings
The invention is suitable for the optical field, and provides a triply coated fiber, a pump combiner, a fiber grating and a fiber laser. A triply coated passive fiber comprises a fiber core, an innercladding layer covering outside the fiber core, an outer cladding layer covering outside the inner cladding layer, and a coating layer covering outside the outer cladding layer, the diameter of the fiber core is 10-50micrometer, the diameter of the inner cladding layer is 250-800micrometer, the diameter of the outer cladding layer is greater than the diameter of the inner cladding layer, the diameter of the outer cladding layer is 300-1000micrometer, or, the diameter of the inner cladding layer is 80-100micrometer, and the diameter of the outer cladding layer is 110-130micrometer. In the triply coated passive fiber, the outer cladding layer wrapping outside the inner cladding layer greatly reduces damage of pump light to the organic coating, the coating as a full reflection interface has ultrahigh damage threshold, so that the fiber laser is more reliable and stable.
Owner:MAXPHOTONICS CORP
High-power fundamental transverse mode flat plate coupling optical waveguide semiconductor laser structure
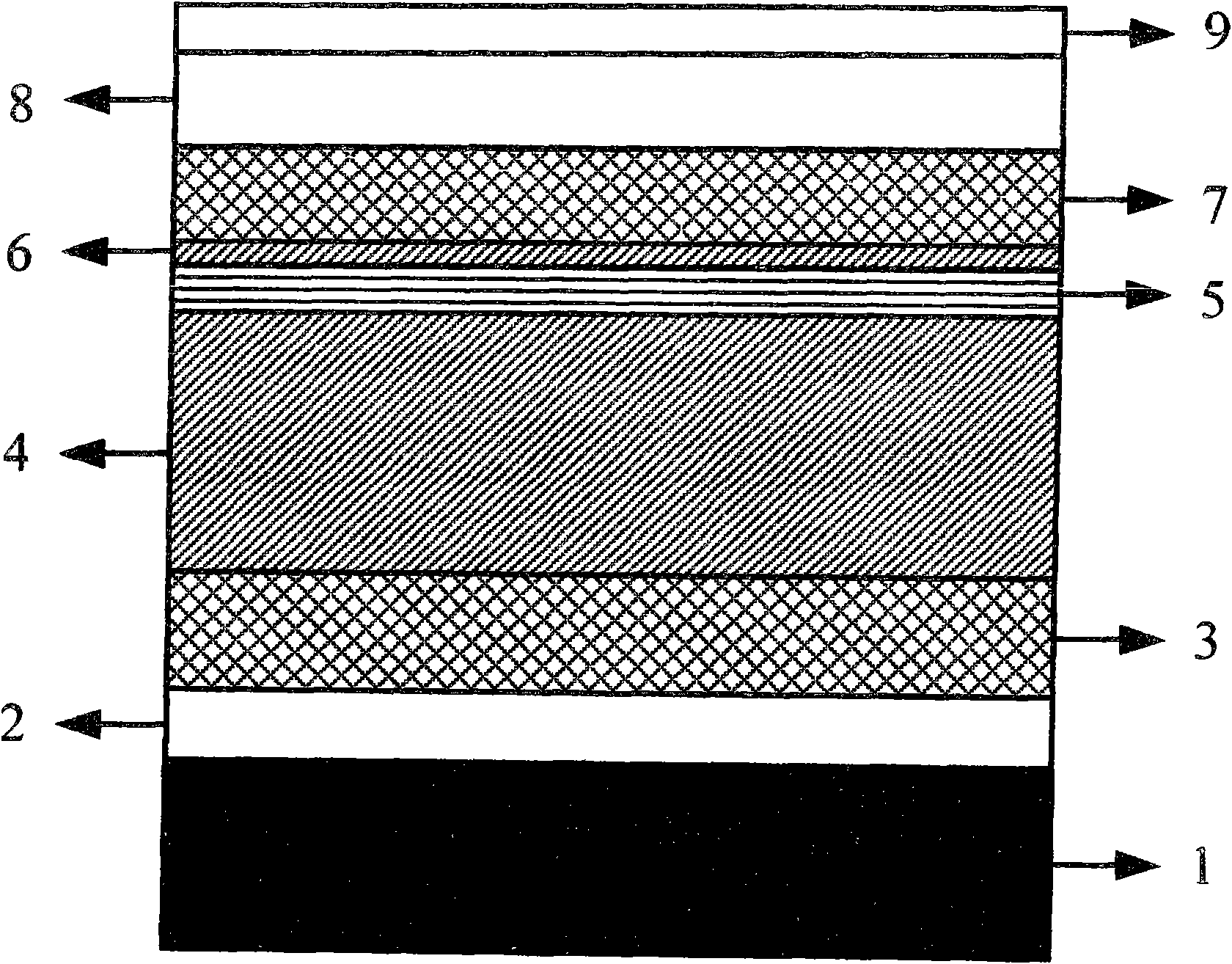
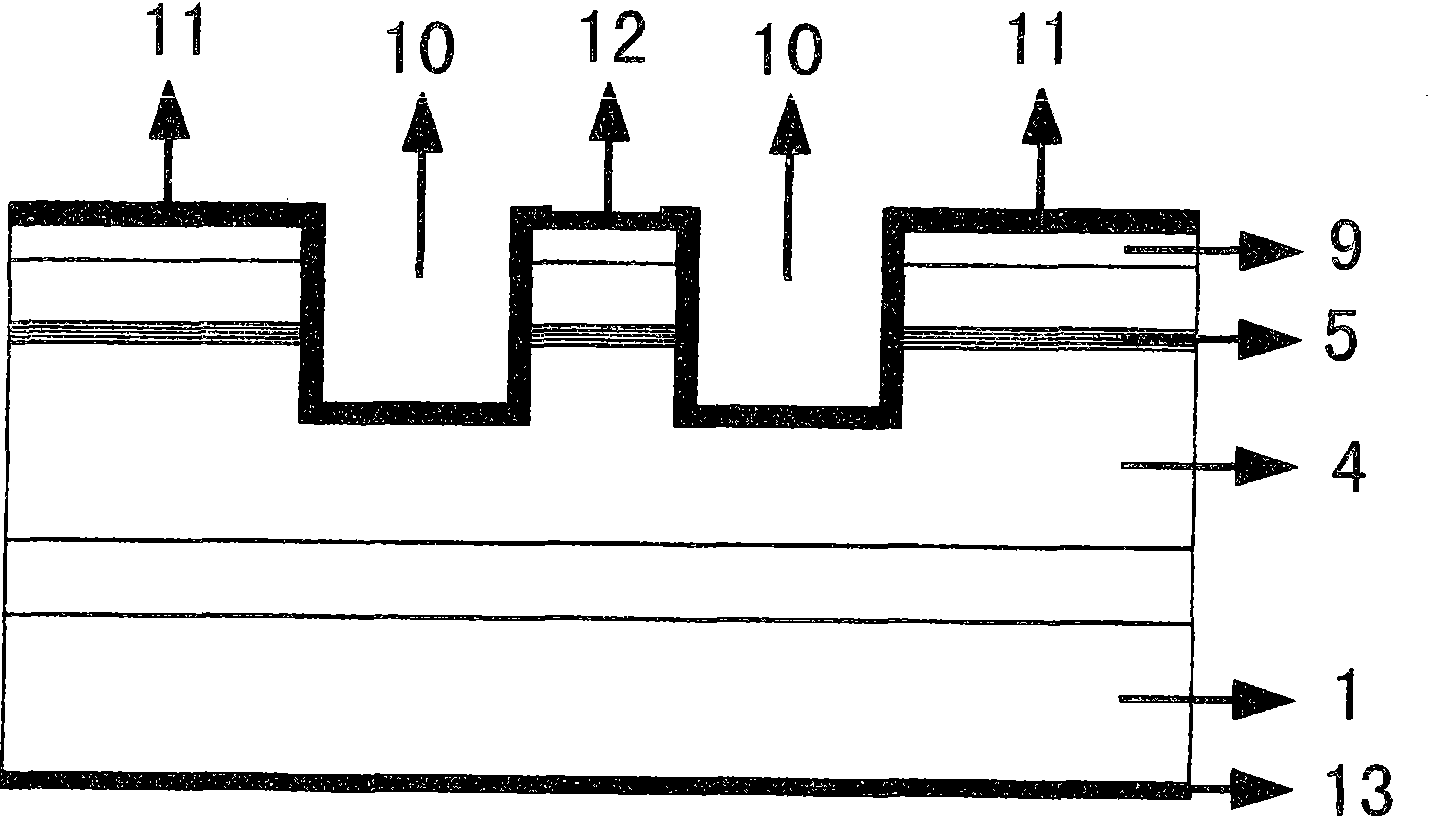
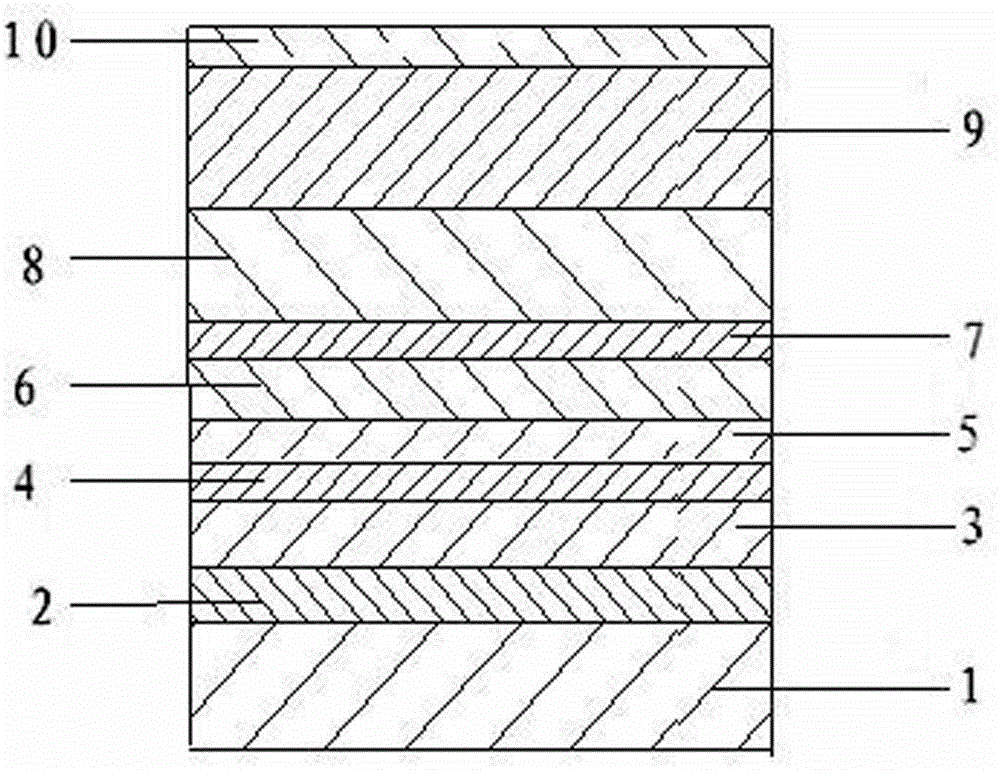
InactiveCN101841124AAchieve outputReduce optical power densityLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionInterface layerTransverse mode
The invention discloses a high-power fundamental transverse mode flat plate coupling optical waveguide semiconductor laser structure which comprises a substrate, a buffer layer, an N-type lower limiting layer, a lower waveguide layer, an active area, an interface layer, a P-type upper limiting layer, an intermediate layer, an electrode contract layer, a double channel, a passivating film layer, a P side electrode and an N side electrode. The substrate is used for the growth of all epitaxial layer materials of the laser on the substrate; the buffer layer is made on the substrate; the N-type lower limiting layer is made on the buffer layer; the lower waveguide layer is made on the N-type lower limiting layer; the active area is made on the lower waveguide layer; the interface layer is made on the active area; the P-type upper limiting layer is made on the interface area; the intermediate layer is made on the P-type limiting layer; the electrode contact layer is made on the intermediate layer; the double channel is etched on the electrode contact layer, the etching depth is kept within the lower waveguide layer, and a ridge-type table top is formed in the middle of the double channel; the passivating film layer is made on the upper surface of the electrode contact layer and the bottom and the two sides of the double channel and the passivating film layer on the ridge-type table top is disconnected; the P side electrode is made on the ridge-type table top and is in contact with the electrode contact layer; and the N side electrode is made under the substrate.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
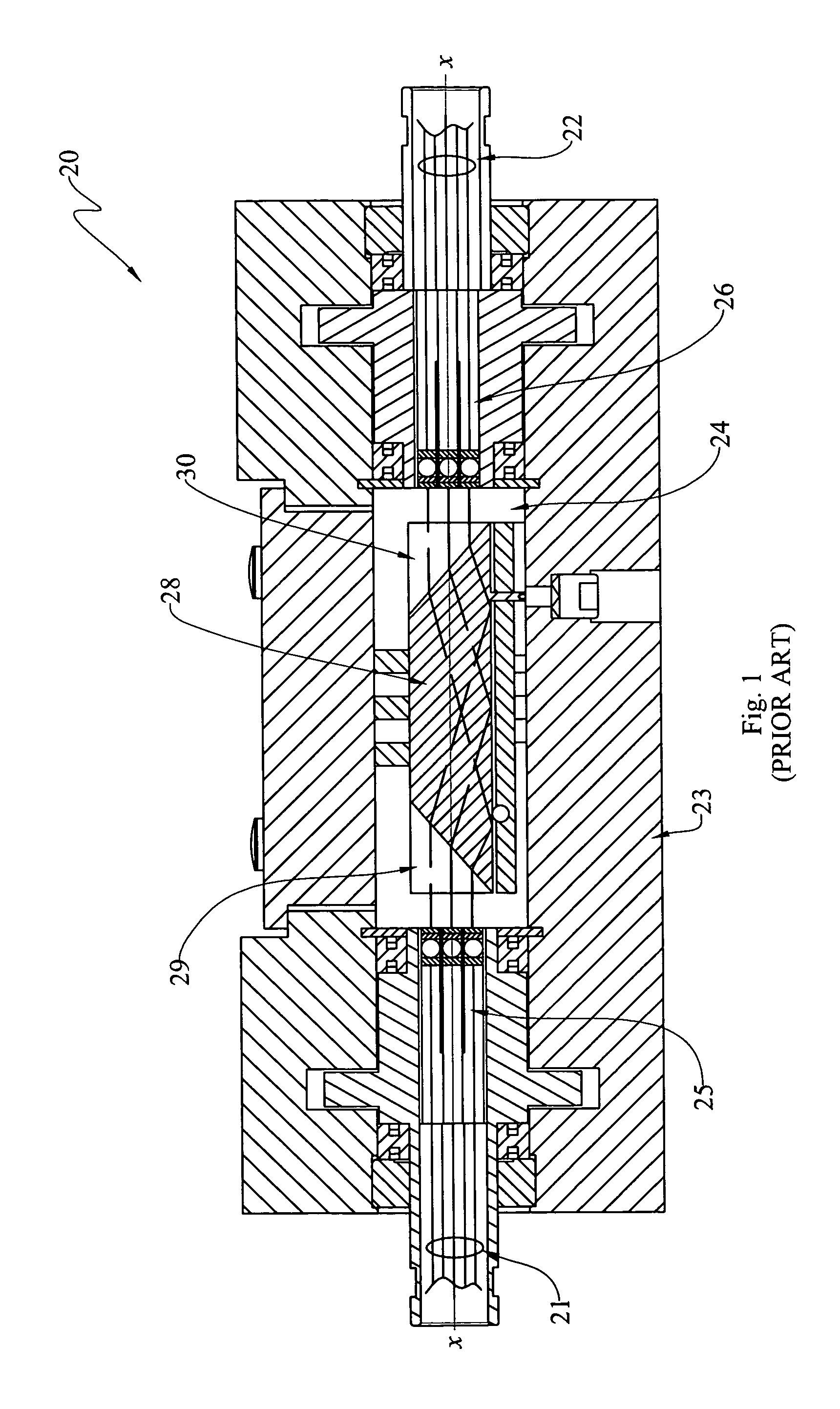
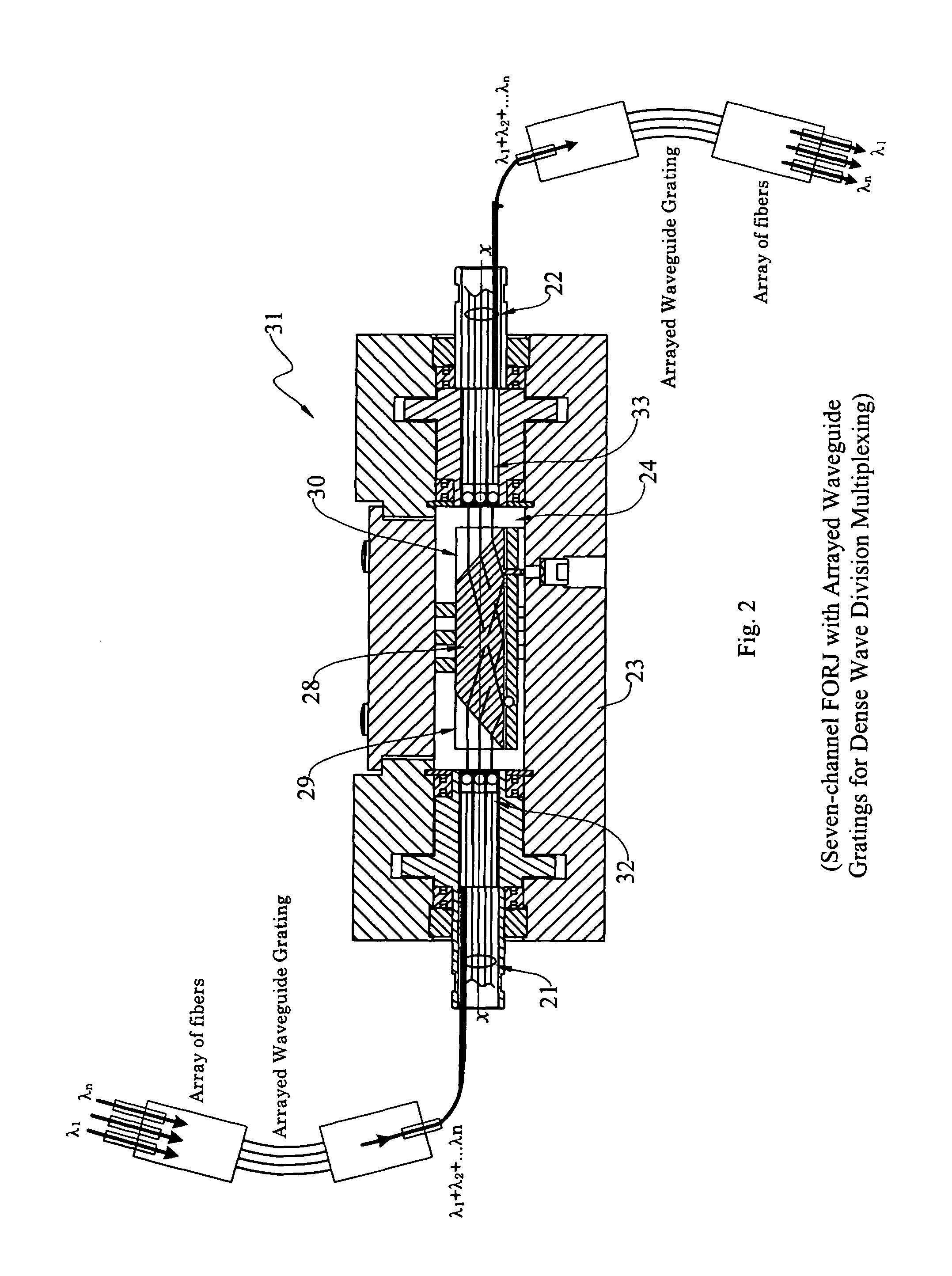
High-power collimating lens assemblies, and methods of reducing the optical power density in collimating lens assemblies
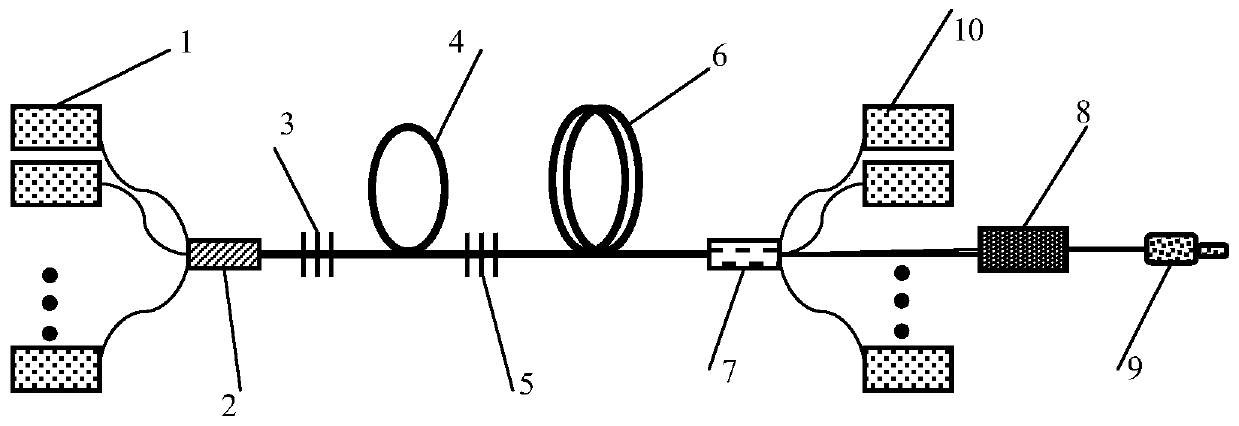
ActiveUS20110262072A1Reduce optical power densitySimple methodLine/current collector detailsCoupling light guidesEpoxyIndex-matching material
The present invention provides improved collimating lens assemblies (32), improved methods of reducing the optical power density in collimating lens assemblies, and to improved fiber optic rotary joints (31) incorporating such improved collimating lens assemblies. The improved collimating lens assembly broadly includes: a singlemode fiber (38) terminating in a distal end; a step-index multimode fiber (44) having a proximal end abutting to the singlemode fiber distal end, and having a distal end; a graded-index multimode fiber (45) having a proximal end abutting the step-index multimode fiber distal end, and having a distal end; and a collimating lens (34) longitudinally spaced from the graded-index multimode fiber distal end by an intermediate air gap (43), and operatively arranged to collimate light rays emanating from the graded-index multimode fiber distal end. The improved collimating lens assembly is characterized by the fact that there is no epoxy, silicone gel or index-matching material between the graded-index multimode fiber distal end and the collimating lens. Rather, these various elements are fusion-spliced together. The improved collimating lens assembly is capable of handling energy levels that are typically used in various wavelength division multiplexing techniques.
Owner:MOOG INC
High-power polarization-maintaining optical fiber and preparation method thereof
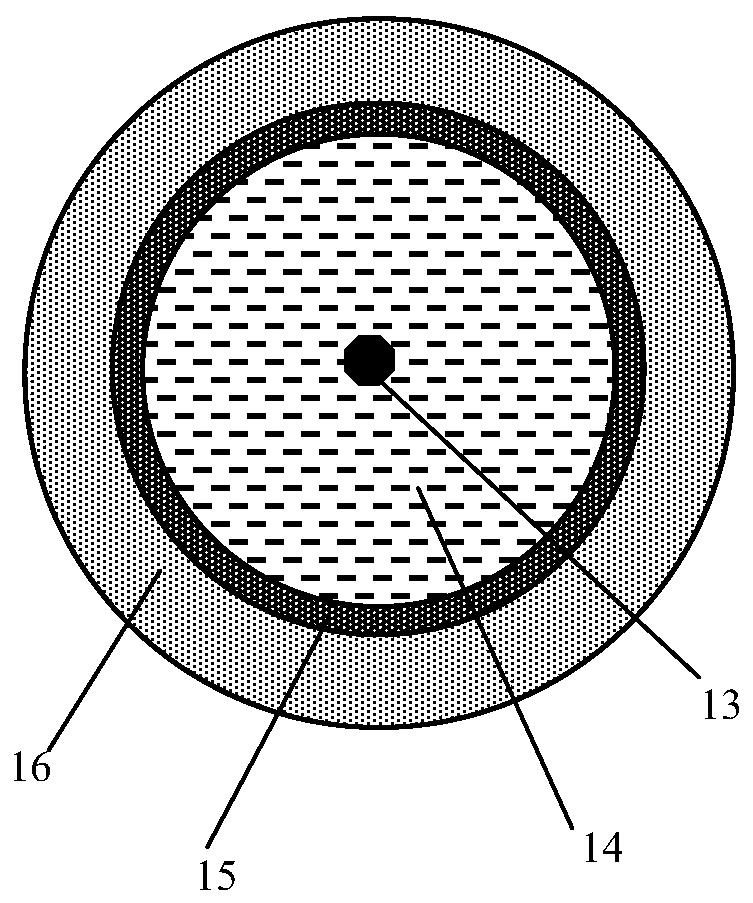
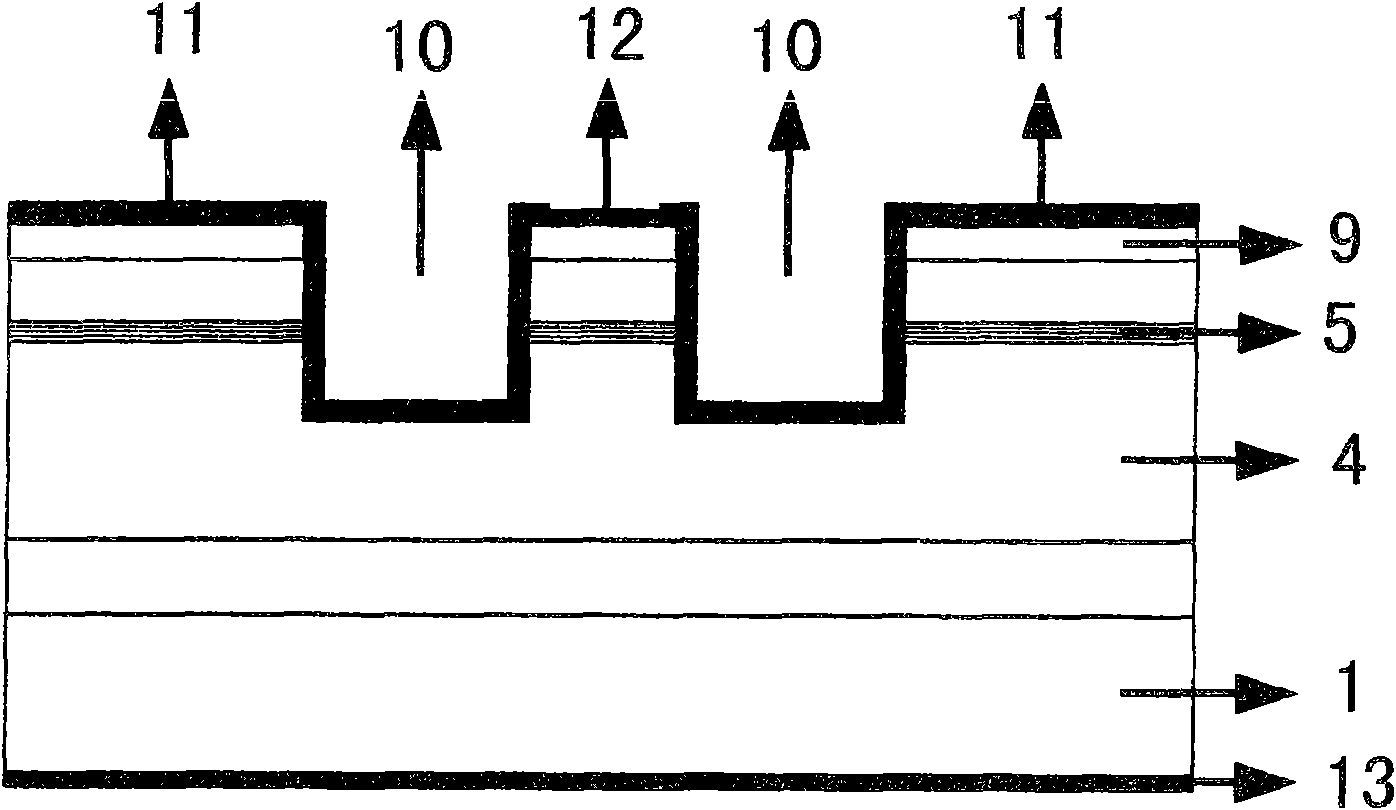
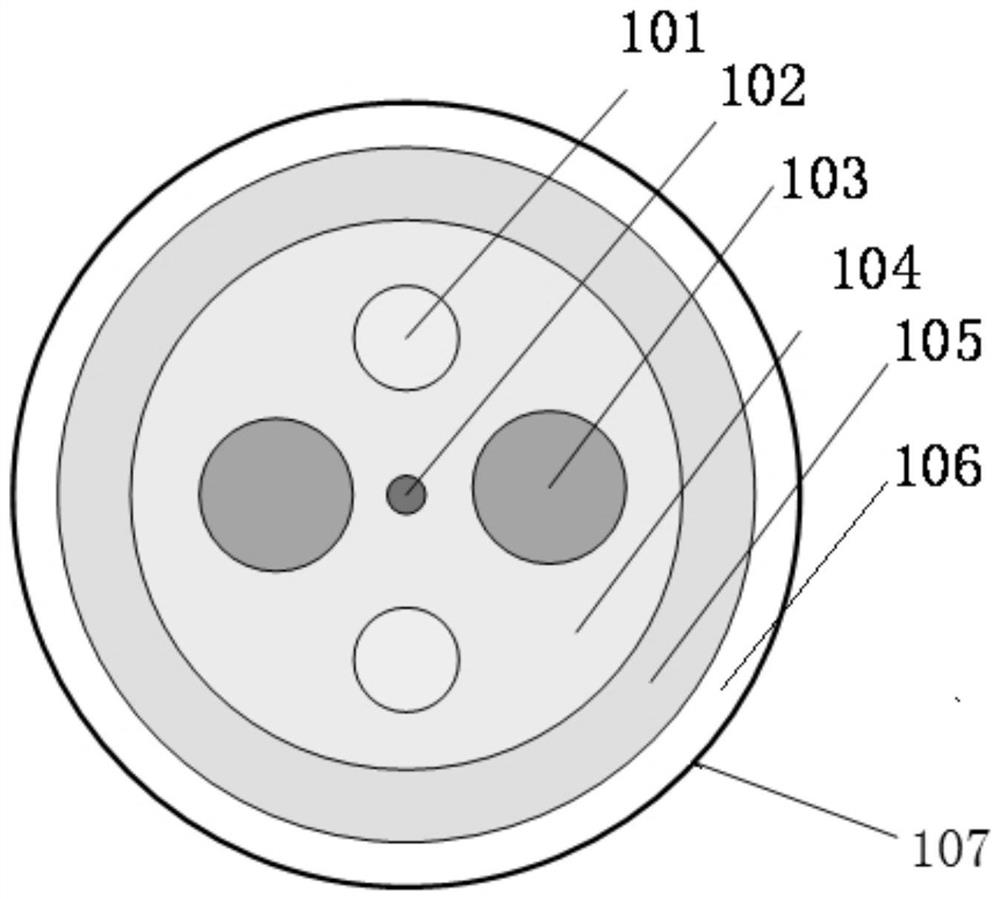
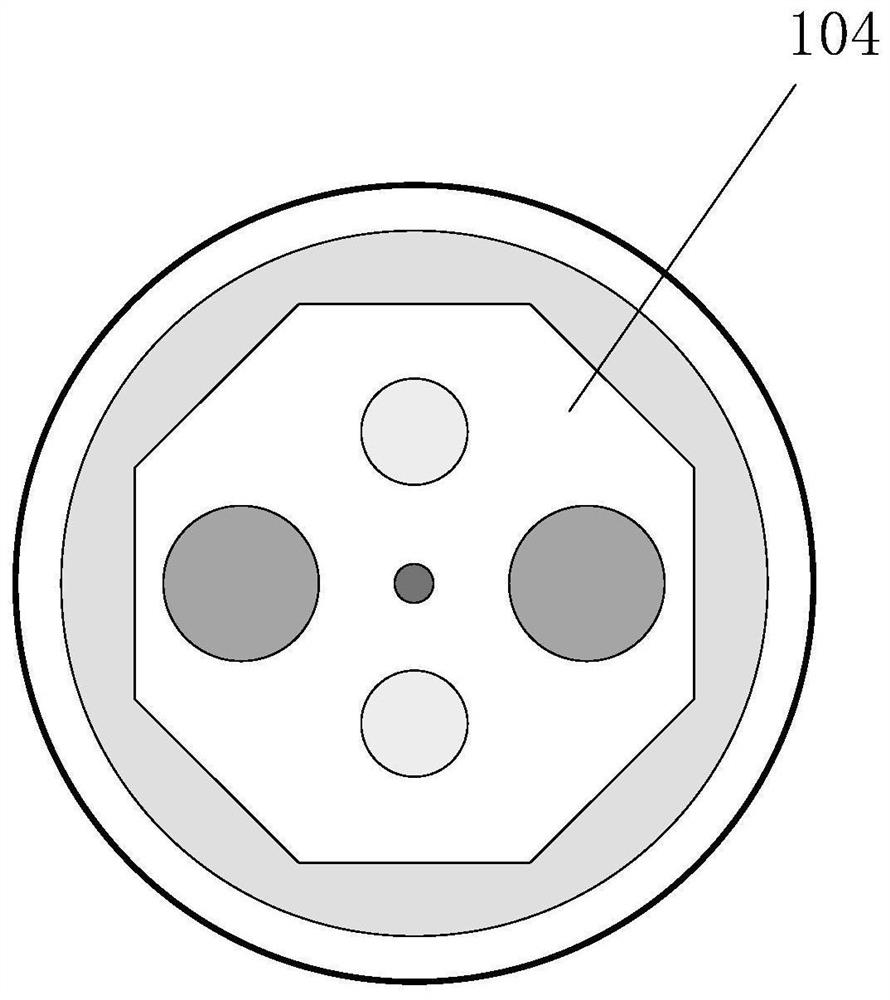
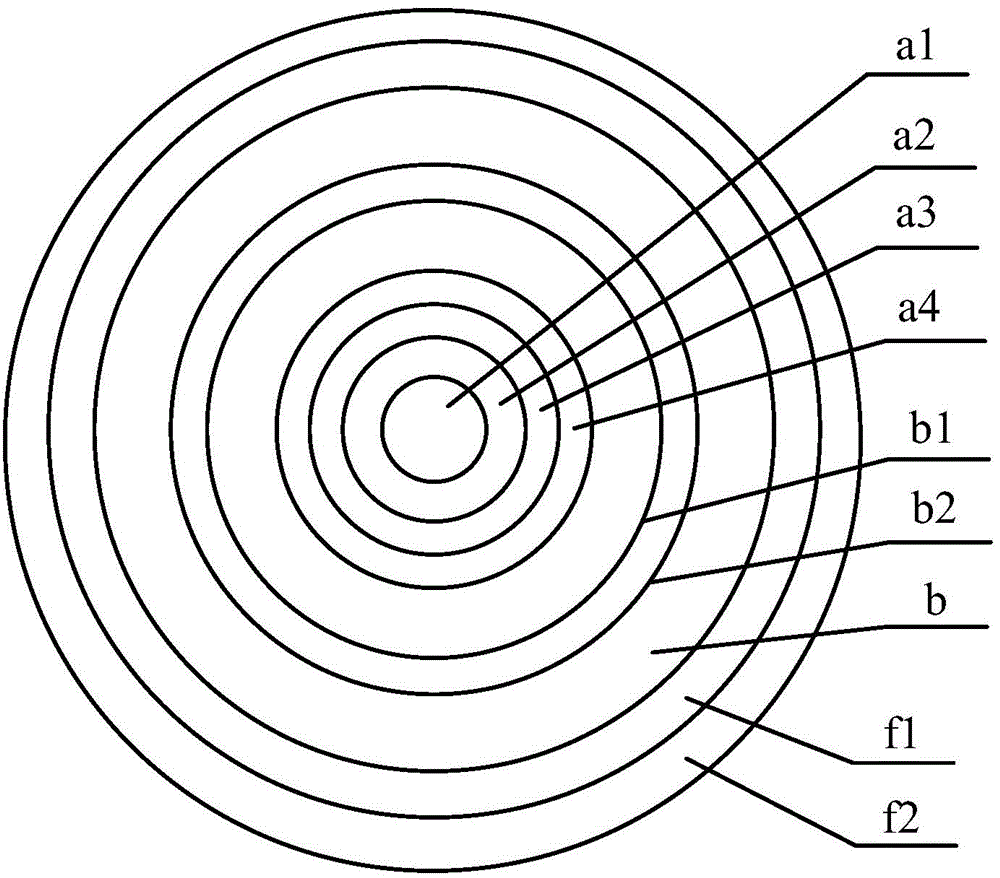
ActiveCN112456788AIncrease output powerReduce optical power densityGlass making apparatusFiberPhysical chemistry
The invention relates to a high-power polarization-maintaining optical fiber and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of polarization-maintaining optical fibers. The crosssection structure of the optical fiber sequentially comprises a fiber core (102), a first cladding (104), a second cladding (105), an outer cladding (106) and an external coating (107) from inside tooutside, the fiber core (102) is fluorine-doped quartz containing rare earth, alkali metal and a dispersing agent, and the first cladding (104) is filled with two shallow fluorine-doped quartz rods symmetrically distributed along the fiber core (102) to form a fluorine-doped area (101); the first cladding (104) is also filled with two stress rods which are symmetrically distributed along the fibercore (102) to form a stress area (103); and the symmetry axis of the fluorine-doped area (101) and the symmetry axis of the stress area (103) perpendicularly intersect at the center of the fiber core(102). According to the optical fiber, the existence of spiral light can be reduced to a greater extent, the input of pump light is increased, the reflection frequency of a cladding is improved, thereflection path is shortened, and the effects of reducing the optical power density and improving the laser output power are achieved.
Owner:JIANGSU FASTEN OPTOELECTRONICS TECH
Narrow lateral waveguide laser
InactiveUS6845116B2Promote growthReduce optical power densityOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsCurrent limitingWaveguide lasers
As edge-emitting semiconductor laser incorporating a narrow waveguide design is disclosed. The narrow waveguide expands the lateral mode size, creates a large modal spot size, and insures higher-order modes are beyond cutoff. Separate current confinement allows the current injection region to match the mode size. The resulting device exhibits single-mode operation with a large spot-size to high output powers.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
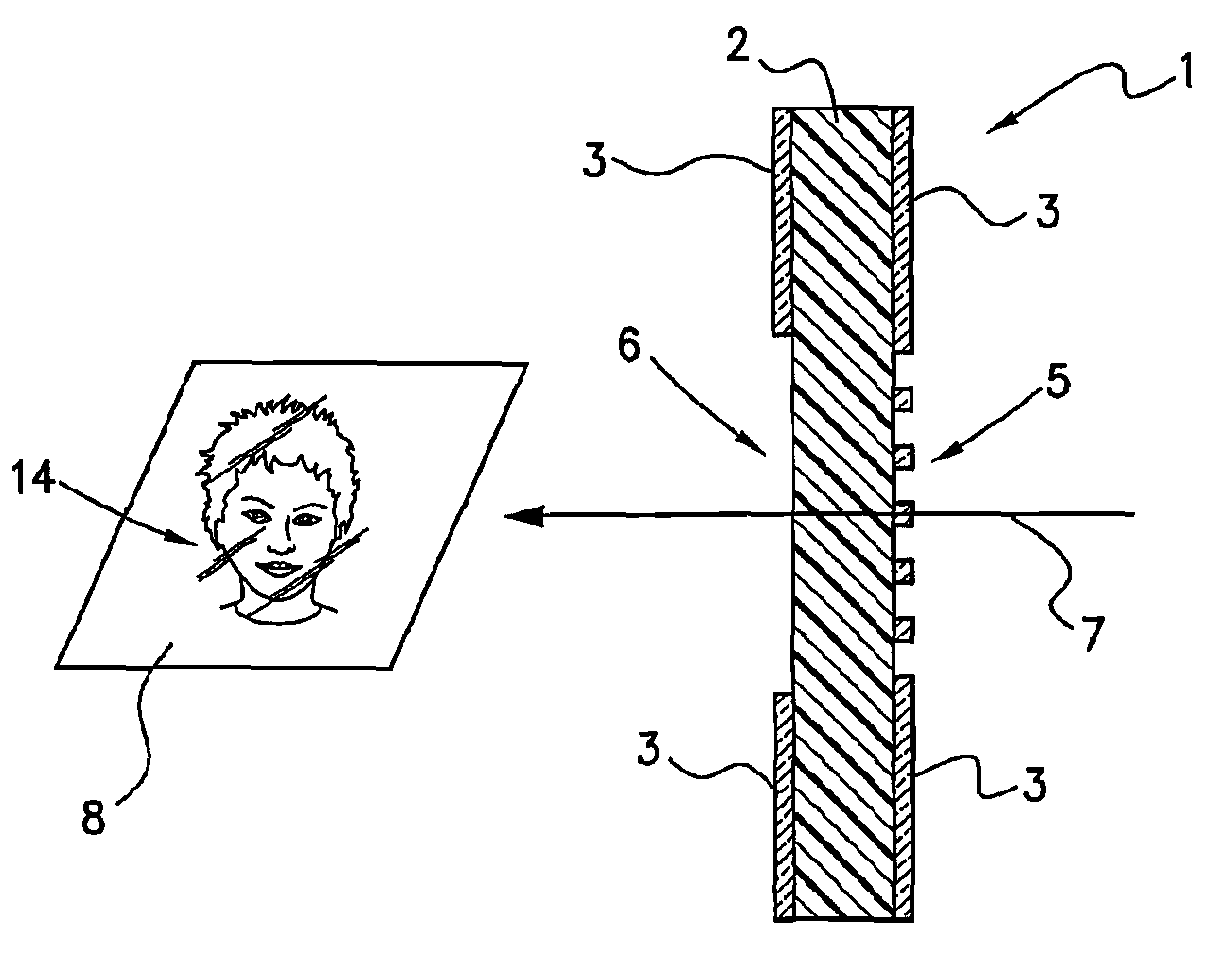
Security Documents with Personalised Images and Methods of Manufacture
InactiveUS20100182698A1Reduce restrictionsPrecise processElectrolysis componentsRadiation applicationsPersonalizationDocumentation
A method of producing a personalized security document or article includes providing a substrate which is transparent at least to visible light. A diffractive optical microstructure is formed in a substantially opaque layer disposed on a surface of the substrate. The diffractive structure comprises a plurality of apertures formed in the opaque layer, such that when the structure is suitably illuminated, for example by a beam of collimated light, a projected image is generated which is unique to a particular individual. Also, personalized security documents or articles made in accordance with the method.
Owner:CCL SECURE PTY LTD
Light source system, wavelength conversion device and related projection system
ActiveCN105867057AReduce optical power densityHigh light conversion efficiencyProjectorsSpectral modifiersLight spotProjection system
The embodiment of the invention discloses a light source system, a wavelength conversion device and a related projection system. The light source system comprises an excitation light source and a wavelength conversion device, wherein the excitation light source is used for generating an excitation light; the excitation light enters the wavelength conversion device; the wavelength conversion device comprises a microstructure array; the microstructure array comprises a plurality of microstructure bodies which are in a projection form; each microstructure body comprises a wavelength conversion material; the distance between any two adjacent microstructure bodies is greater than zero; scattering surfaces coat the microstructure bodies; the undulating surface of the microstructure array faces the incident excitation light; and a light spot, of the excitation light, formed on the wavelength conversion device covers at least one part of one microstructure body and also covers at least one part of the scattering surface between the microstructure body and one adjacent microstructure body, so that the excitation light is scattered through the scattering surface, mixed with excited light and emitted. The light source system which is efficient and emits hybrid light of the excitation light and the excited light can be provided.
Owner:APPOTRONICS CORP LTD
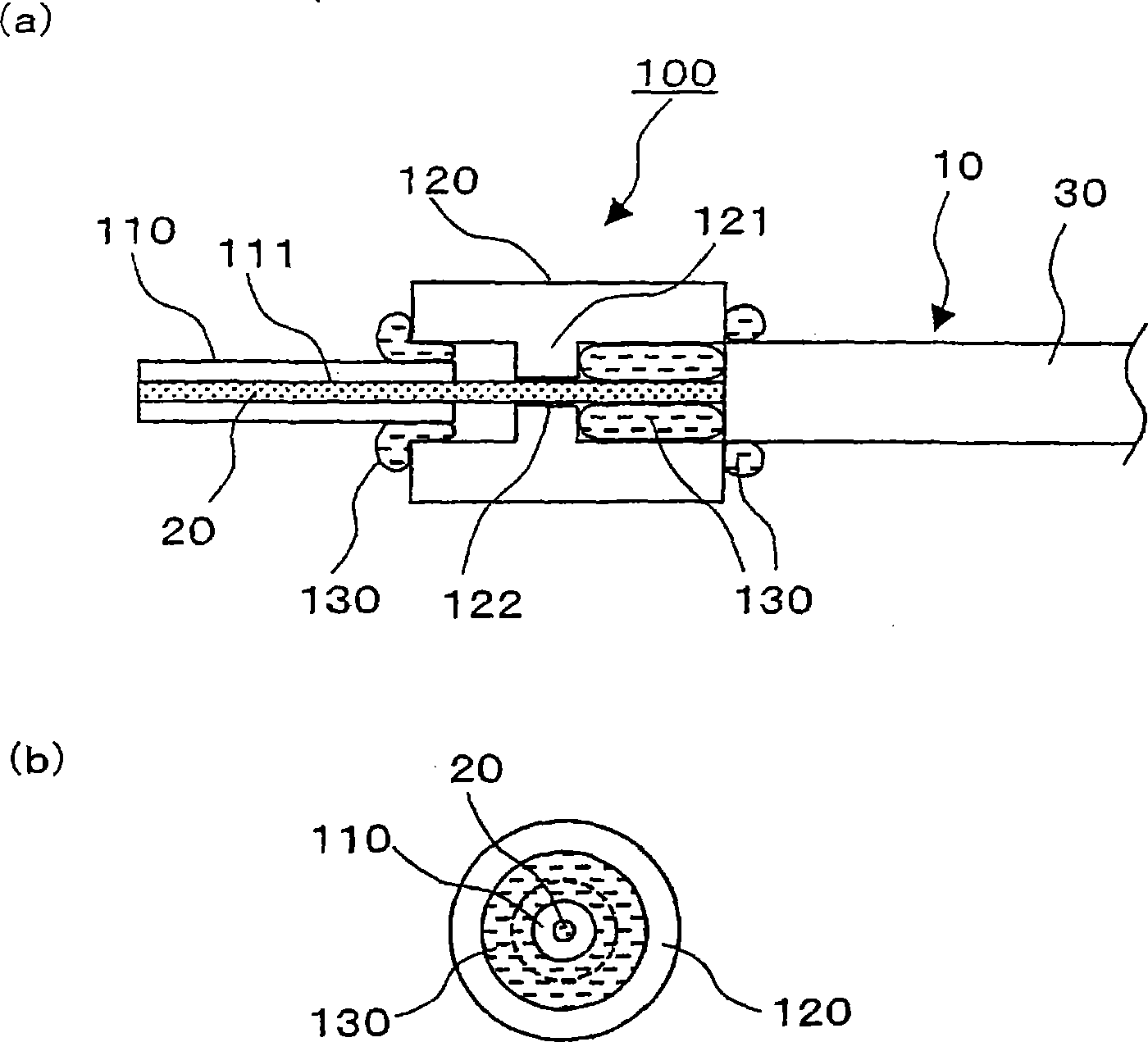
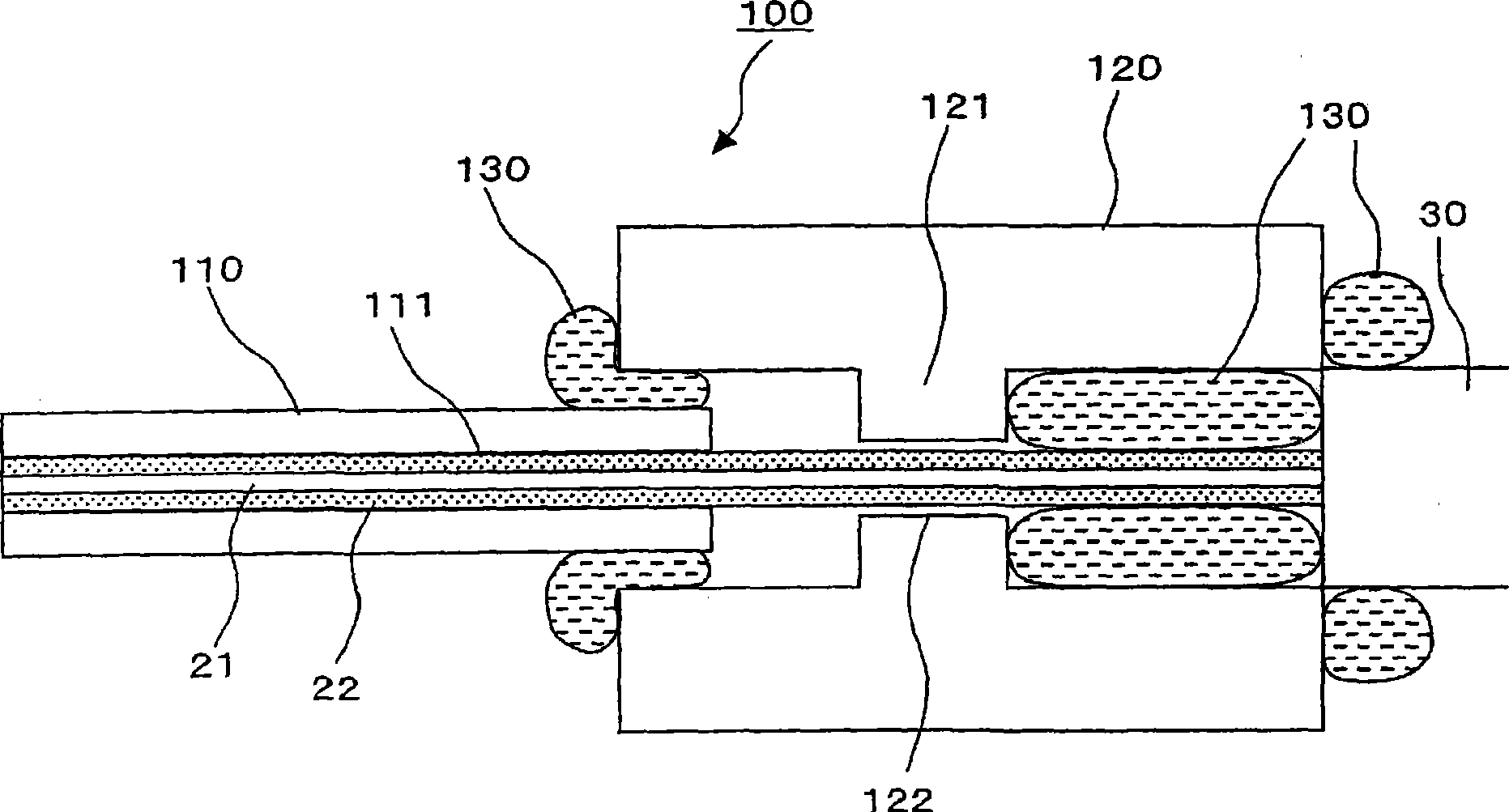
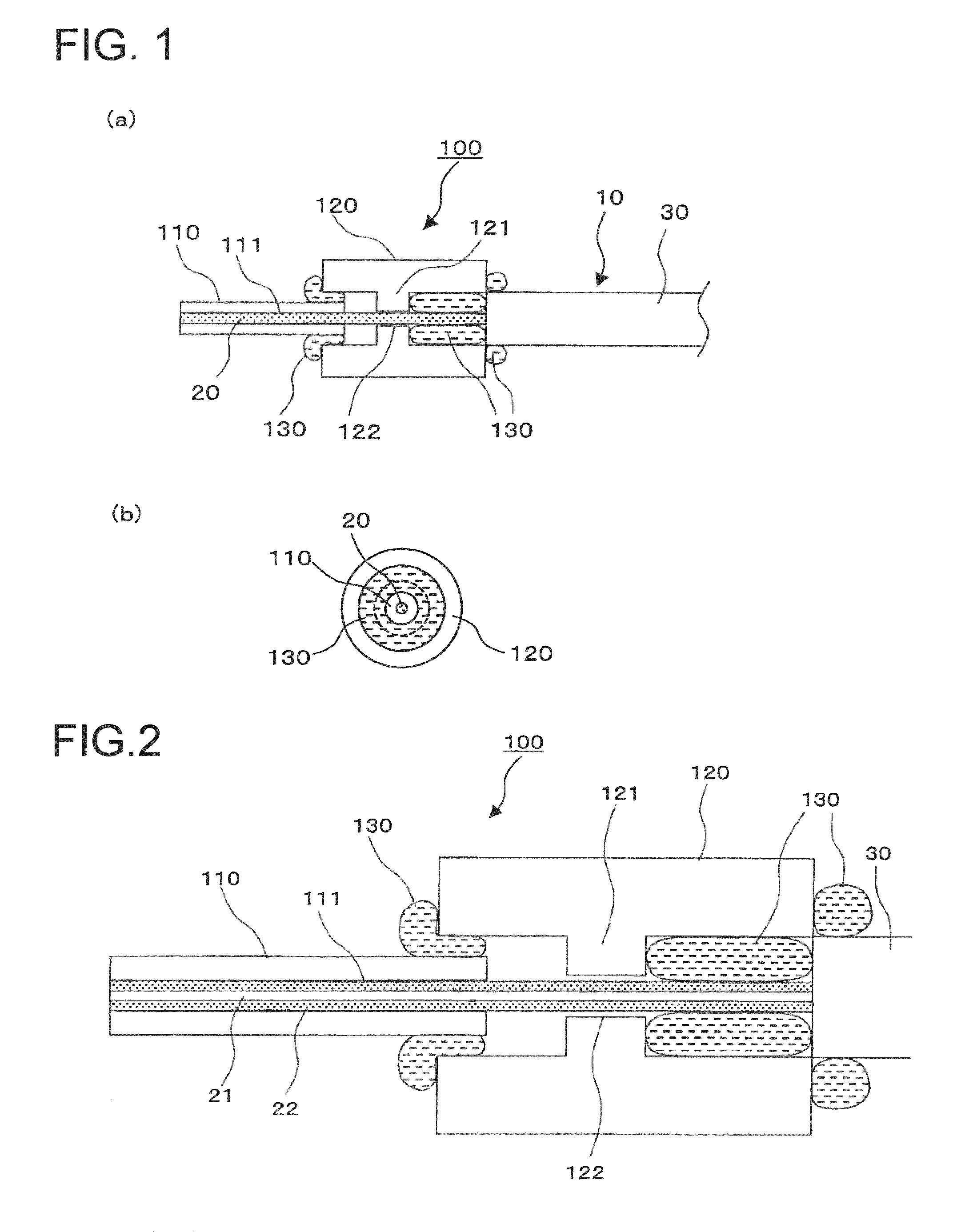
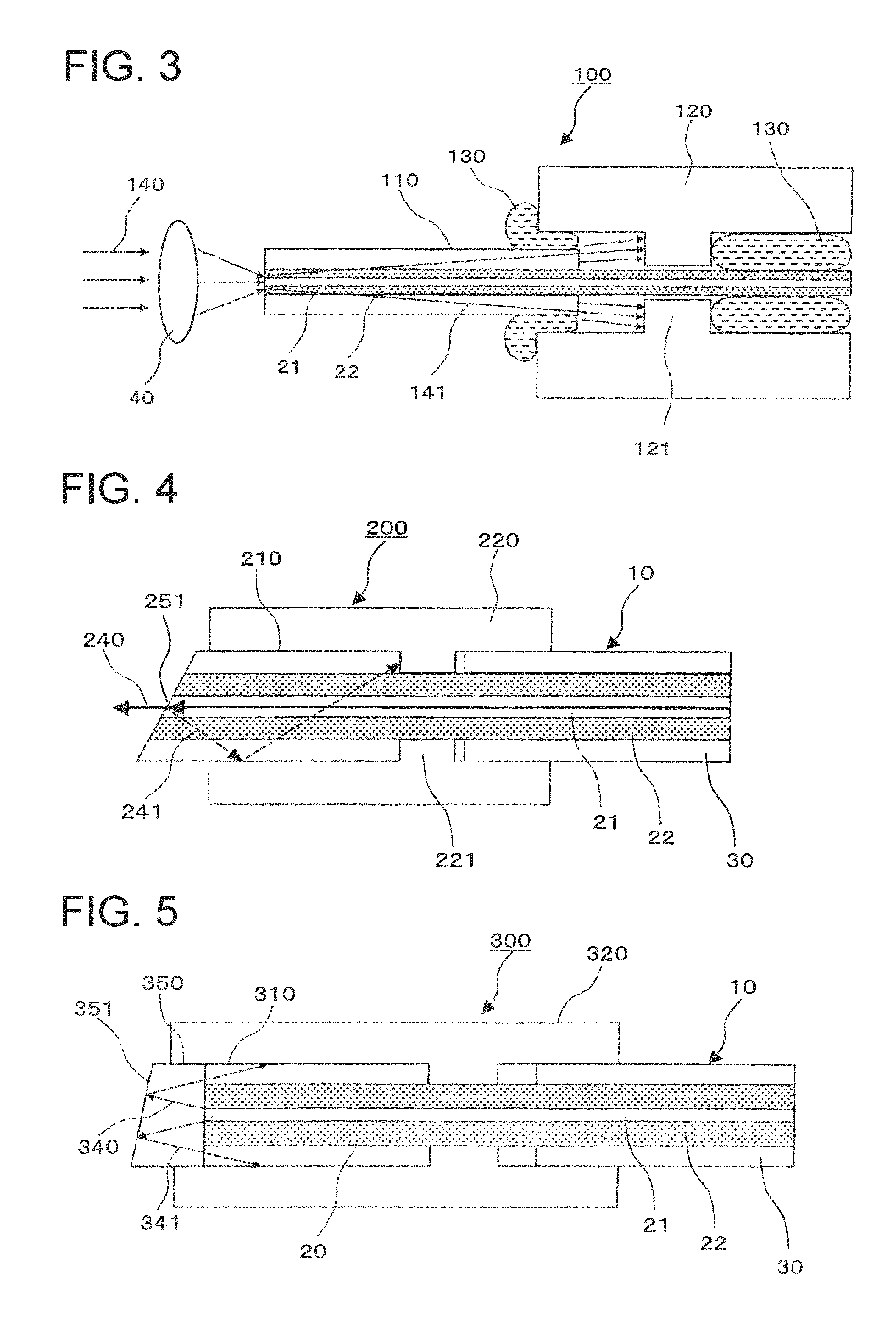
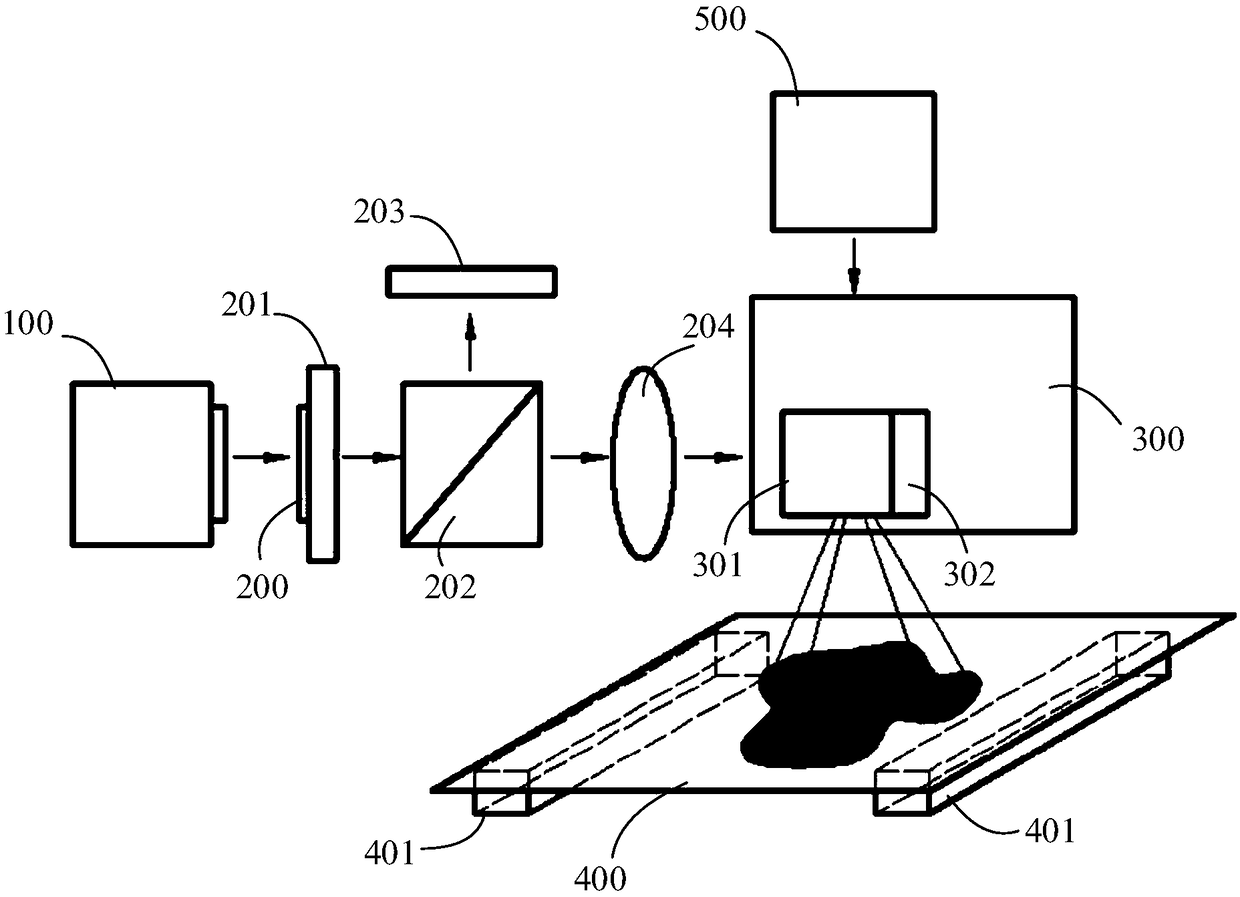
Light input/output port of optical component and beam converting apparatus
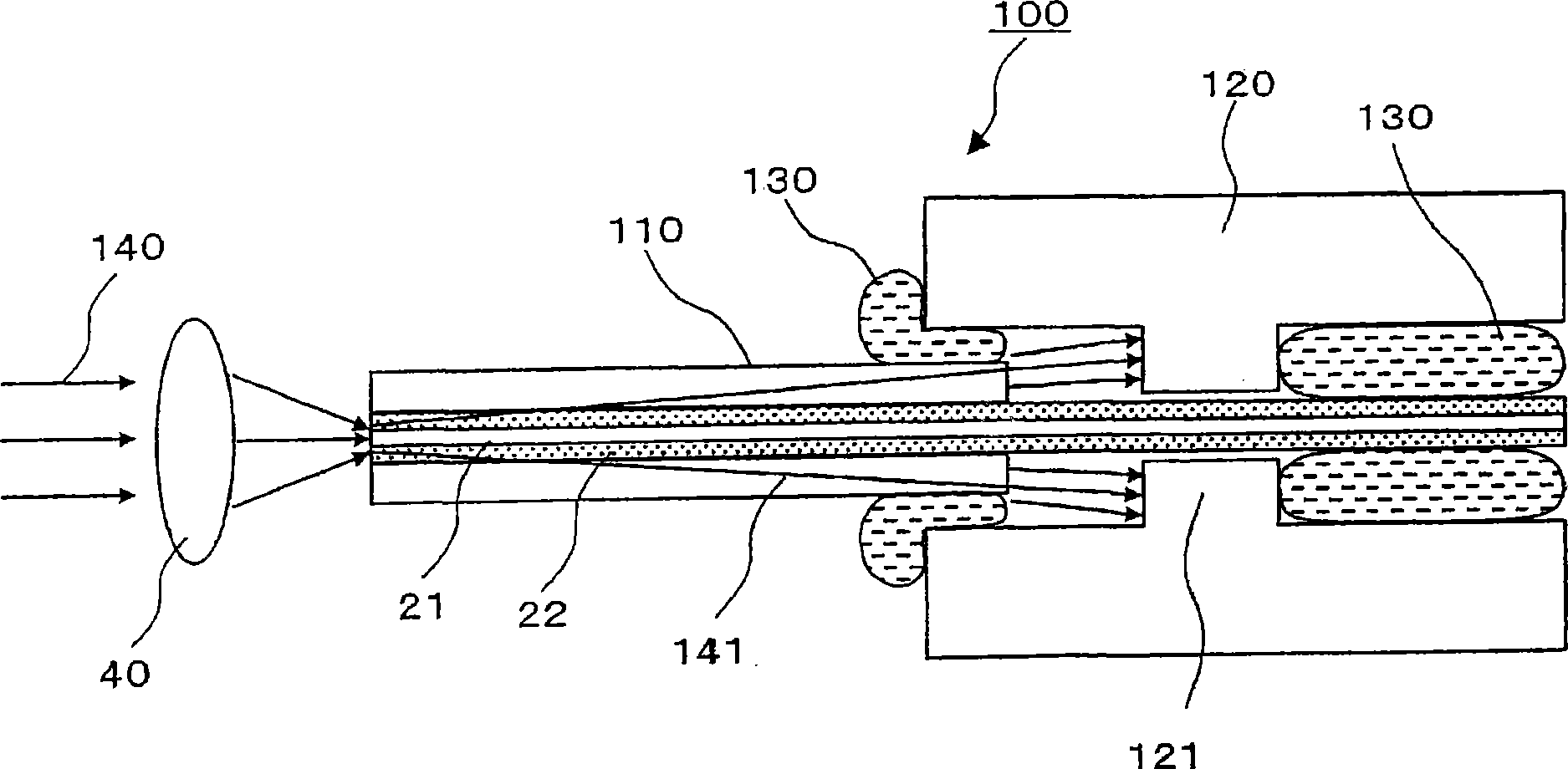
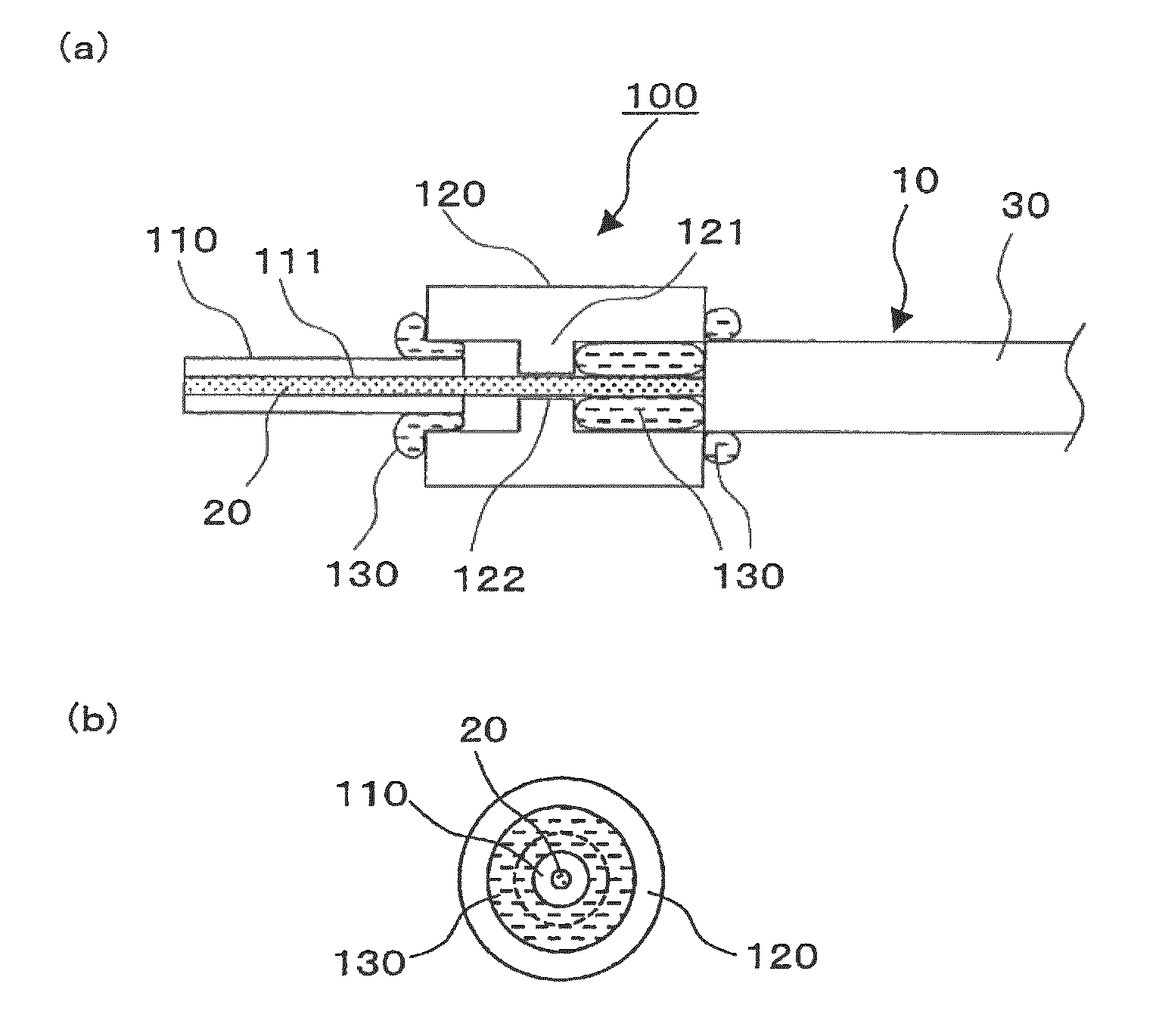
A light input / output terminal module 100 comprises a jacket tube 110 and a flange 120. A glass portion 20 of the optical fiber is inserted in the center portion thereof. To efficiently remove the leaked light in a cladding 22 to the jacket tube 110, the jacket tube 110 is made of silica glass or the same material as that of the cladding 22. The jacket tube 110 is fixed by fusion splicing or adhesion to the cladding so as to integrally unify the jacket tube 110 and the cladding 22. The beam diameter at the fiber end portion is enlarged by an optical component which fusion bonds the tip end of the optical fiber to the coreless fiber so that the optical power density at the light input / output terminal module is reduced.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Photoelectric detector
ActiveCN111129202ANo need to add lengthImprove responsivenessSemiconductor devicesLight signalWaveguide
The embodiment of the invention discloses a photoelectric detector, and the photoelectric detector comprises a silicon layer which comprises a doped region of a first doping type; a germanium layer incontact with the silicon layer, wherein the germanium layer comprises a doped region of a second doping type; a first layer of waveguide, wherein the first layer of waveguide comprises a first detection coupling region arranged above the germanium layer; a second layer of waveguide which comprises a second detection coupling region arranged on the side surface of the germanium layer, wherein thefirst layer of waveguide and the second layer of waveguide are used for transmitting optical signals, and the first layer of waveguide and the second layer of waveguide are used for coupling the optical signals to the germanium layer through the first detection coupling region and the second detection coupling region respectively, and the germanium layer is used for detecting the optical signal and converting the optical signal into an electric signal.
Owner:WUHAN OPTICAL VALLEY INFORMATION OPTOELECTRONICS INNOVATION CENT CO LTD
Semiconductor laser device having InGaAs compressive-strain active layer, GaAsP tensile-strain barrier layers, and InGaP optical waveguide layers
InactiveUS6560261B2Reduce layeringQuality improvementOptical wave guidanceLaser active region structureTensile strainQuantum well
In a semiconductor-laser device: a compressive-strain quantum-well active layer is made of Inx3Ga1-x3As1-y3Py3 (0<x3<=0.4 and 0<=y3<=0.1); tensile-strain barrier layers made of Inx2Ga1-2AS1-y2P1-y2 (0<=x2<0.49y2 and 0<y2<=0.4)are formed above and under the compressive-strain quantum-well active layer; and optical waveguide layers being made of either p-type or i-type In0.49Ga0.51P are formed above the upper tensile-strain barrier layer and under the lower tensile-strain barrier layer. Preferably, the absolute value of a sum of a first product and a second product is less than or equal to 0.25 nm, where the first product is a product of a strain and a thickness of said compressive-strain active layer, and the second product is a product of a strain of said lower and upper tensile-strain barrier layers and a total thickness of the lower and upper tensile-strain barrier layers.
Owner:NICHIA CORP +1
Light input/output terminal module of the optical components and beam converting apparatus
ActiveUS8064742B2Increase ratingsEfficient transferOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCoupling light guidesBeam diameterLight beam
A light input / output terminal module 100 comprises a jacket tube 110 and a flange 120. A glass portion 20 of the optical fiber is inserted in the center portion thereof. To efficiently remove the leaked light in a cladding 22 to the jacket tube 110, the jacket tube 110 is made of silica glass or the same material as that of the cladding 22. The jacket tube 110 is fixed by fusion splicing or adhesion to the cladding so as to integrally unify the jacket tube 110 and the cladding 22. The beam diameter at the fiber end portion is enlarged by an optical component which fusion bonds the tip end of the optical fiber to the coreless fiber so that the optical power density at the light input / output terminal module is reduced.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Super-continuum spectrum optical fiber laser output apparatus and laser system
InactiveCN105490158AHigh damage thresholdIncrease powerLaser detailsPhotovoltaic detectorsLight beam
The invention provides a super-continuum spectrum optical fiber laser output apparatus and a laser system. The output apparatus comprises a laser transmission module, a returned-light processor, an optical stripper, a thermal processor and a packaging module; the laser transmission module comprises transmission optical fibers, an output end cap and a light beam focusing collimation part that are connected in sequence, and a photoelectric detector arranged on one side, close to the transmission optical fibers, of the output end cap; the photoelectric detector is used for monitoring the returned-light power at the output end of the output end cap; the returned-light processor is arranged on one side, connected with the transmission optical fibers, of the output end cap; the optical stripper is arranged on the transmission optical fibers close to the output end cap; the thermal process is arranged below the laser transmission module; and the packaging module is used for packaging the laser transmission module, the returned-light processor, the optical stripper and the thermal processor. According to the super-continuum spectrum optical fiber laser output apparatus, high-power and broadband spectrum stable laser output can be realized by performing special treatment on the output end of the whole apparatus, and by performing prompt processing on the returned light and thermal accumulation.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
High-power collimating lens assemblies, and methods of reducing the optical power density in collimating lens assemblies
ActiveUS8520990B2Weaken energyReduce optical power densityLine/current collector detailsCoupling light guidesSilicone GelsEpoxy
The present invention provides improved collimating lens assemblies (32) which include: a singlemode fiber (38) terminating in a distal end; a step-index multimode fiber (44) having a proximal end abutting to the singlemode fiber distal end, and having a distal end; a graded-index multimode fiber (45) having a proximal end abutting the step-index multimode fiber distal end, and having a distal end; and a collimating lens (34) longitudinally spaced from the graded-index multimode fiber distal end by an intermediate air gap (43), and operatively arranged to collimate light rays emanating from the graded-index multimode fiber distal end. The improved collimating lens assembly is characterized by the fact that there is no epoxy, silicone gel or index-matching material between the graded-index multimode fiber distal end and the collimating lens.
Owner:MOOG INC
A high-power optical fiber end cap and its manufacturing method
ActiveCN109031527BAvoid lostReduce optical power densityCoupling light guidesActive medium shape and constructionFiberDouble-clad fiber
The invention provides a high-power optical fiber end cap and a manufacturing method thereof. The optical fiber end cap comprises a double-clad optical fiber, a core-free optical fiber and a quartz rod which are coaxially arranged; the quartz rod comprises a first cylindrical section, a circular table section and a second cylindrical section which are coaxially connected in sequence, the diameterof the first cylindrical section is smaller than that of the second cylindrical section; the double-clad optical fiber is connected with one end of the core-free optical fiber in a welding mode, and the other end of the core-free optical fiber is connected with one end of the first cylindrical section in a welding mode; the diameter of the cladding layer of the core-free optical fiber is larger than or equal to the diameter of the double-clad optical fiber; and the diameter of the cladding layer of the core-free optical fiber is smaller than or equal to the diameter of the first cylindrical section. The laser firstly passes through the core-free optical fiber, so that energy is expanded, and the light power density in the connecting place of the output end plane and the quartz rod is lowered; by selecting the proper length of the core-free optical fiber, the output light spot can be large enough when the laser outputs from the core-free optical fiber, so that the optical power densityon the output surface can be effectively reduced; and meanwhile, energy is not output from the side surface of the core-free optical fiber, and loss of energy is avoided.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Structure of high power edge emission laser diode
InactiveUS7577175B2Good confinement factorReduce divergenceOptical wave guidanceNanoopticsDivergence angleOptical power
A structure of high power edge emission laser diode that has plural mode extension sublayers with a chirp periodic distribution is provided. The Near Field Pattern (NFP) is an L shape, and the high intensity portion is nicely overlapped with the multi quantum wells. Furthermore, the low intensity portion will extend to the n-type cladding as it can as possible. Accordingly, the optical power density on the mirror surface of the high power edge emission laser diode is lower down and the vertical divergence angle is decreased, so as to prolong its lifetime.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Structure of high power edge emission laser diode
InactiveUS20090016396A1Good confinement factorExtended service lifeOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsDivergence angleOptical power
A structure of high power edge emission laser diode that has plural mode extension sublayers with a chirp periodic distribution is provided. The Near Field Pattern (NFP) is an L shape, and the high intensity portion is nicely overlapped with the multi quantum wells. Furthermore, the low intensity portion will extend to the n-type cladding as it can as possible. Accordingly, the optical power density on the mirror surface of the high power edge emission laser diode is lower down and the vertical divergence angle is decreased, so as to prolong its lifetime.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
High-power laser for 808nm ceiling light field
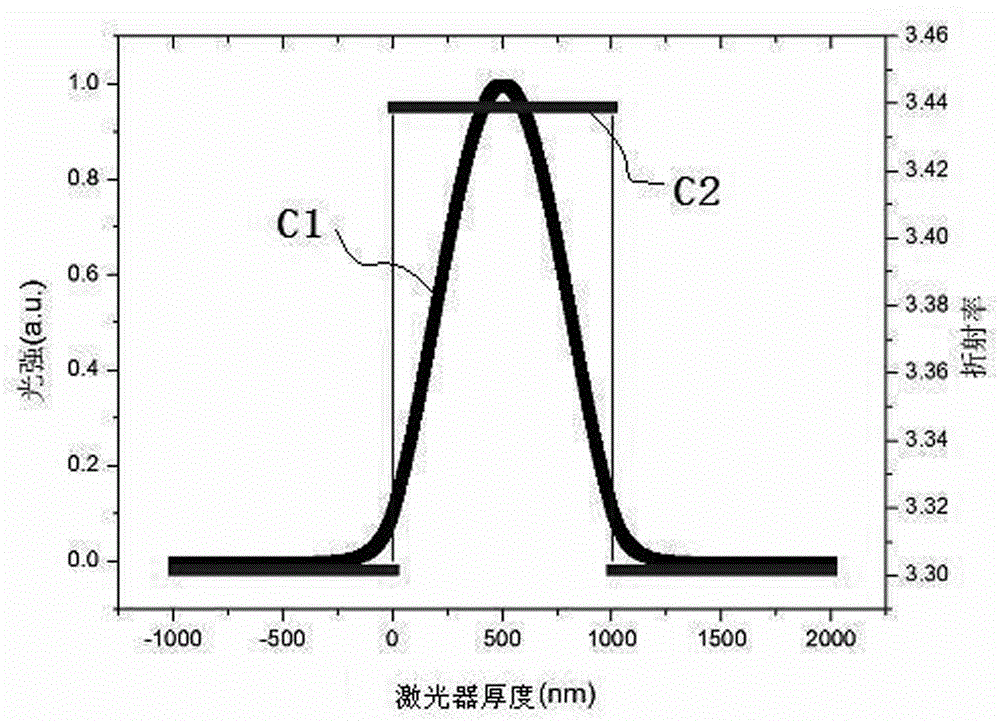
ActiveCN104600562AEven top distributionReduce optical power densityOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsOptical powerHigh power lasers
The invention discloses a high-power laser for a 808nm ceiling light field and relates to the technical field of a semiconductor laser; the high-power laser comprises a substrate, wherein a buffer layer, a lower limiting layer, a lower light-field active layer, a lower waveguide layer, a quantum well layer, an upper waveguide layer, an upper light-field active layer, an upper limiting layer and an electrode contact layer are sequentially grown on the substrate from top to bottom; the lower light-field active layer is made of a highly doped N-type AlGaAs material, and the upper light-field active layer is made of a highly doped P-type AlGaAs material. The light field top of the fast axis is uniformly distributed, so that the optical power density in the active region can be further reduced, and reliability and durability of the laser are improved.
Owner:THE 13TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP CORP
Low-loss large-effective area single mode fiber and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103472525BIncrease the effective areaReduce optical power densityGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingScattering lossRefractive index
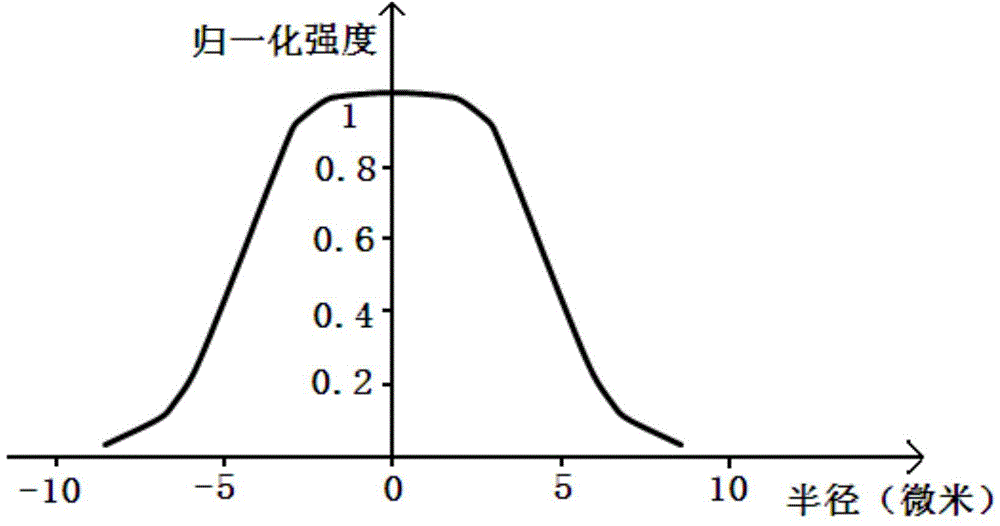
The invention discloses a low-loss large-effective area single mode fiber and a manufacturing method of the low-loss large-effective area single mode fiber, and relates to the field of optical fibers. The low-loss large-effective area single mode fiber comprises a quartz glass cladding, an internal coating and an external coating, wherein the quartz glass cladding, the internal coating and the external coating are arranged in sequence from inside to outside; the inside of the quartz glass cladding comprises a first fiber core area, a second fiber core area, a third fiber core area, a fourth fiber core area and a refractive index concave cladding, wherein the first fiber core area, the second fiber core area, the third fiber core area, the fourth fiber core area and the refractive index concave cladding are arranged in sequence from inside to outside; the refractive index concave cladding is subjected to deposition through a PCVD process; the quartz glass cladding is manufactured through an OVD process or a sleeving process. According to the low-loss large-effective area single mode fiber and the manufacturing method of the low-loss large-effective area single mode fiber, the scattering loss of the low-loss large-effective area single mode fiber and the additional loss of the low-loss large-effective area single mode fiber in a bent state can be reduced; due to the fact that the spire distribution of fiber core basic mode electromagnetic field power is adjusted into flattop distribution, optical power density is reduced, the effective area of the low-loss large-effective area single mode fiber is enlarged, the nonlinearity of the low-loss large-effective area single mode fiber is reduced, the incident power of an optical fiber communication system is increased by 0.4-2.6 dB, and the low-loss large-effective area single mode fiber is suitable for mass production.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD +1
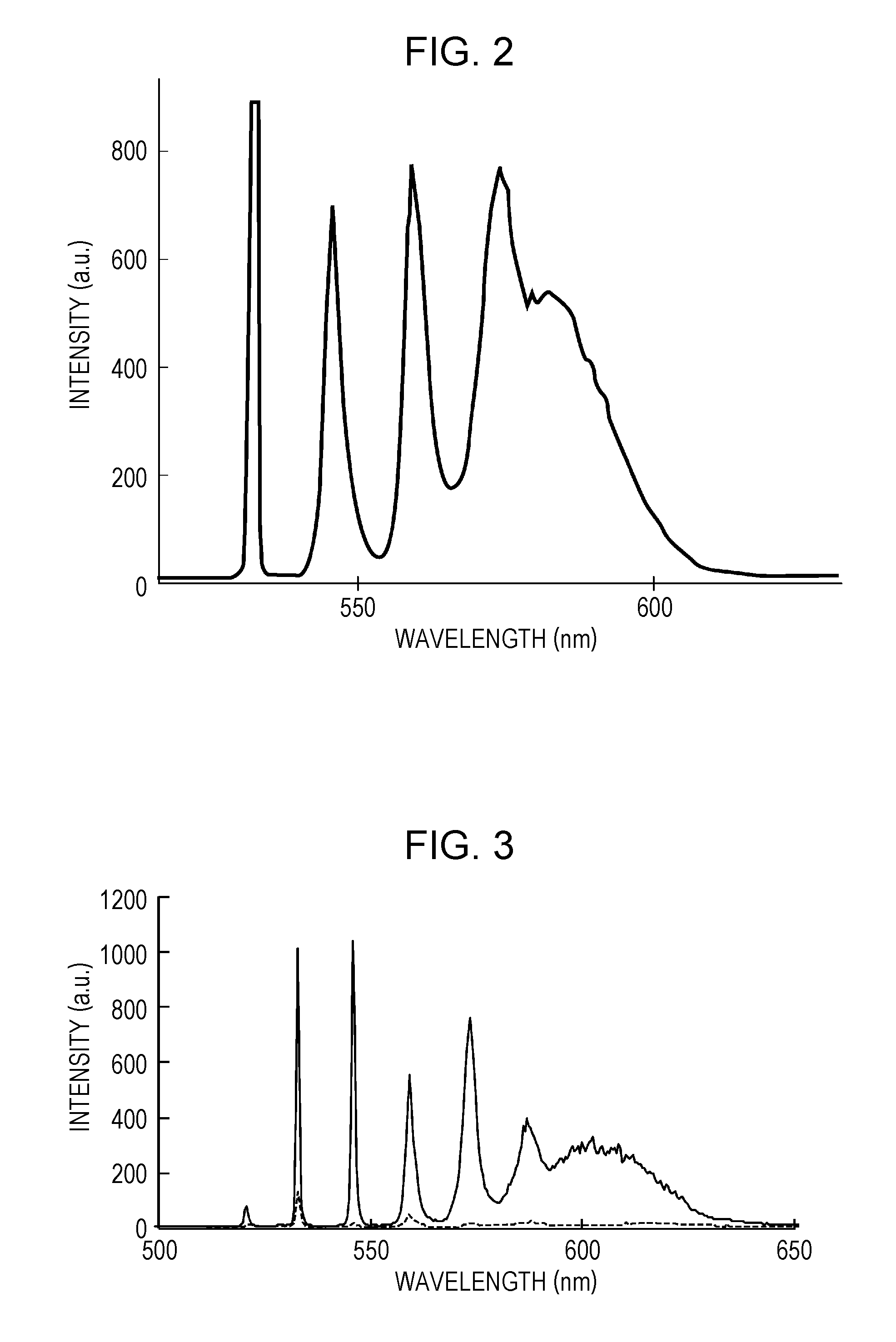
Non-linear Raman spectroscopy apparatus, non-linear system, and non-linear raman spectroscopy method
InactiveUS8873039B2Wideness of its spectrum can be ensuredReduce optical power densityRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringPulse beamPeak value
A non-linear Raman spectroscopy apparatus includes a light source unit emitting a pulse beam having a pulse width of 0.2 ns to 10 ns, a pulse peak power of 50 W to 5000 W, and a wavelength of 500 nm to 1200 nm, and a single-mode fiber through which continuous white light is generated from the pulse beam. A test sample to be measured is radiated with a pump-cum-probe beam formed of the pulse beam and a Stokes beam formed of the continuous white light to obtain a Raman spectrum.
Owner:SONY CORP
Projection type laser heating system and 3D printer
ActiveCN108248026ALow absorption rateReduce heat production rateAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyBeam splitterOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a projection type laser heating system and a 3D printer. The projection type laser heating system comprises an infrared laser, a laser power adjustment device, a beam splittergroup, not less than two projection assemblies and a workbench; the workbench is provided with a preheating device and is used for laying a powder material; the laser power adjustment device comprisesa first rotating clamping assembly, a power meter, a first half-wave plate, a polarization beam splitter mirror and a beam expander group; the first half-wave plate, the polarization beam splitter mirror and the beam expander group are sequentially distributed in the same direction; the first half-wave plate is arranged on the first rotating clamping assembly; the not less than two projection assemblies are arranged at the exit direction of the beam splitter group; and each projection assembly comprises a DMD chip. The projection type laser heating system further comprises a control system; and the control system controls the first rotating clamping assembly and the DMD chips, and independently controls the projection shape and direction of each DMD chip, so that the shapes of the DMD chips projected to the workbench are the same and are coincident. With the adoption of the technical scheme, projection type laser heating can be realized in 3D printing.
Owner:SHENZHEN UPRISE 3D TECH CO LTD
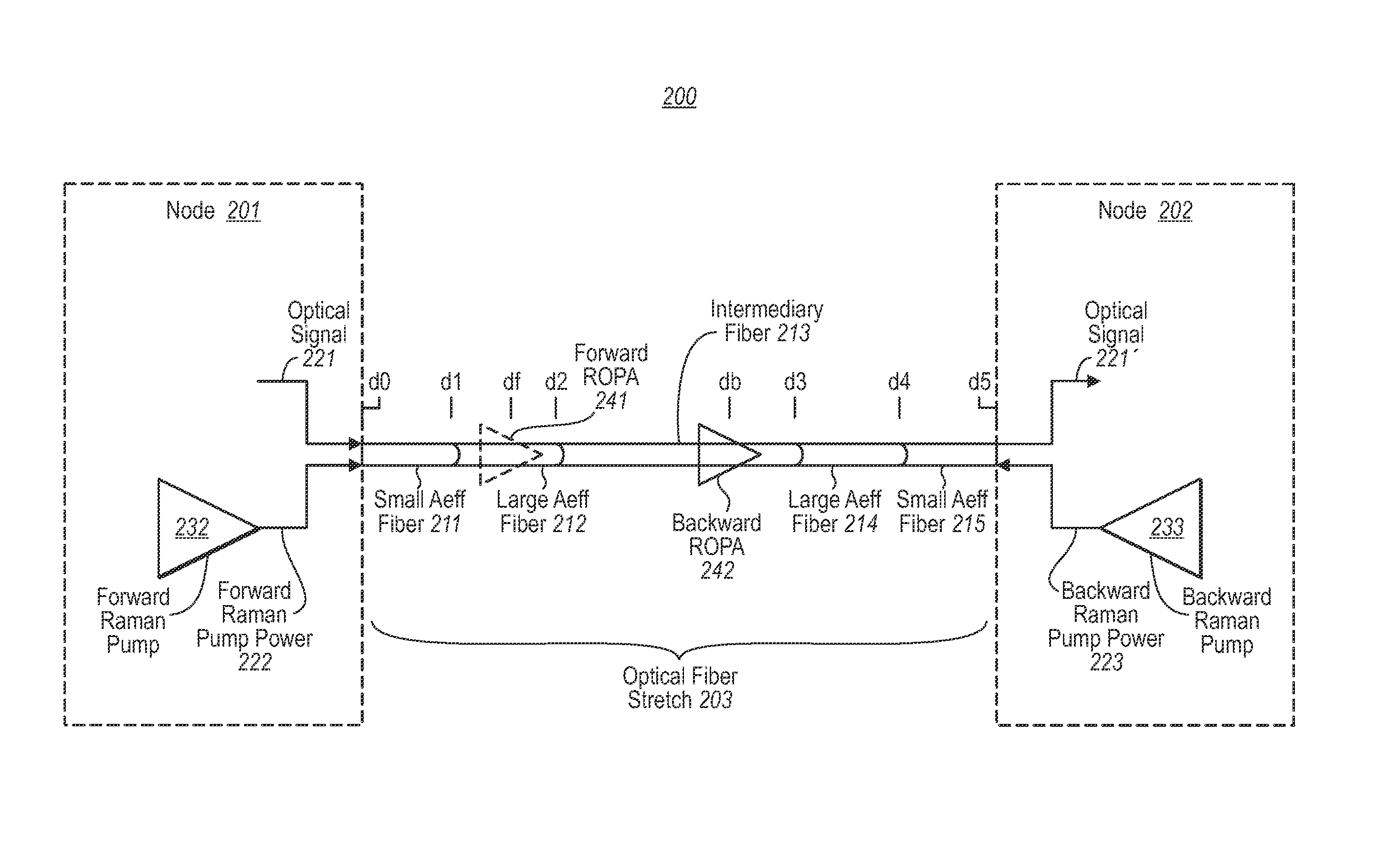
Remote larger effective area optical fiber
ActiveUS7869673B2Increase the areaReduction in optical signal power densityLaser detailsCoupling light guidesFiberSignal quality
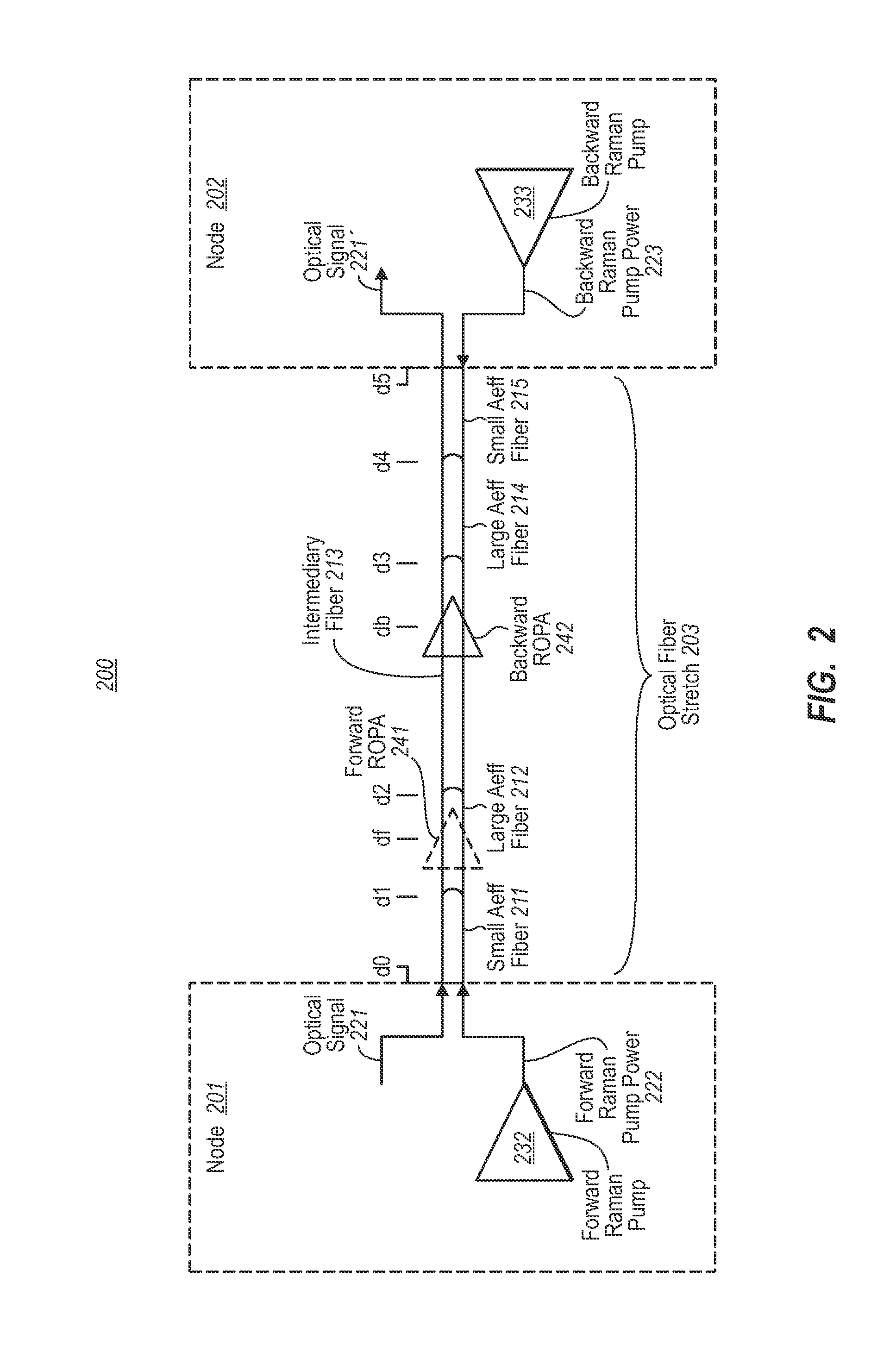
Embodiments described herein relate to an optical fiber stretch that may experience forward Raman amplification in which the peak optical signal power occurs at some distance from the transmitter. Smaller effective area optical fiber is used at a portion of the optical fiber stretch in which the optical signal power is increasing, while larger effective area optical fiber is used at a more remote stretch of the optical fiber stretch that experiences the peak optical signal power. Thus, the quality of the signal is better preserved since the larger effective area fiber reduces maximum optical signal density thereby reducing non-linear degradations on signal quality.
Owner:NEPTUNE SUBSEA IP LTD
A cone-rod laser amplifier
ActiveCN113036583BStable optical power densityImprove extraction efficiencyActive medium shape and constructionLaser cooling arrangementsLight energyGain
A cone-rod laser amplifier provided by the present invention belongs to the field of solid-state lasers, and includes a pump source, a seed source, a diverging lens, a cone-rod gain medium and a collimating lens arranged coaxially in sequence, the incident end face of the cone-rod gain medium and The exit end surface is coaxial and the spherical conical cap of the spherical cone is located at the focal point of the diverging lens, which satisfies:; The present invention also proposes a cone-rod gain medium group composed of multi-stage cone-rod gain media with a spherical conical profile , and the improved cone-rod laser amplifier with the cone-rod gain medium itself having the function of a diverging lens, so that the maximum efficiency of the seed light energy can be extracted from the energy storage of the reversed particle number in the cone-rod gain medium, so that the cone-rod laser amplifier can work close to saturation state; the cone-rod laser amplifier proposed by the present invention is small in size and simple in structure.
Owner:四川光天下激光科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com