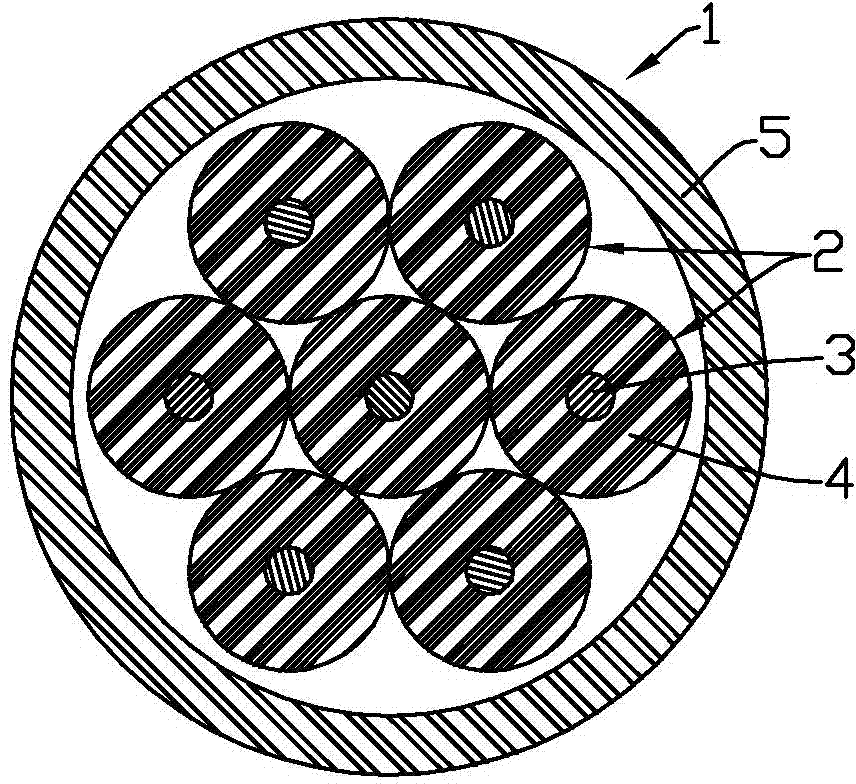
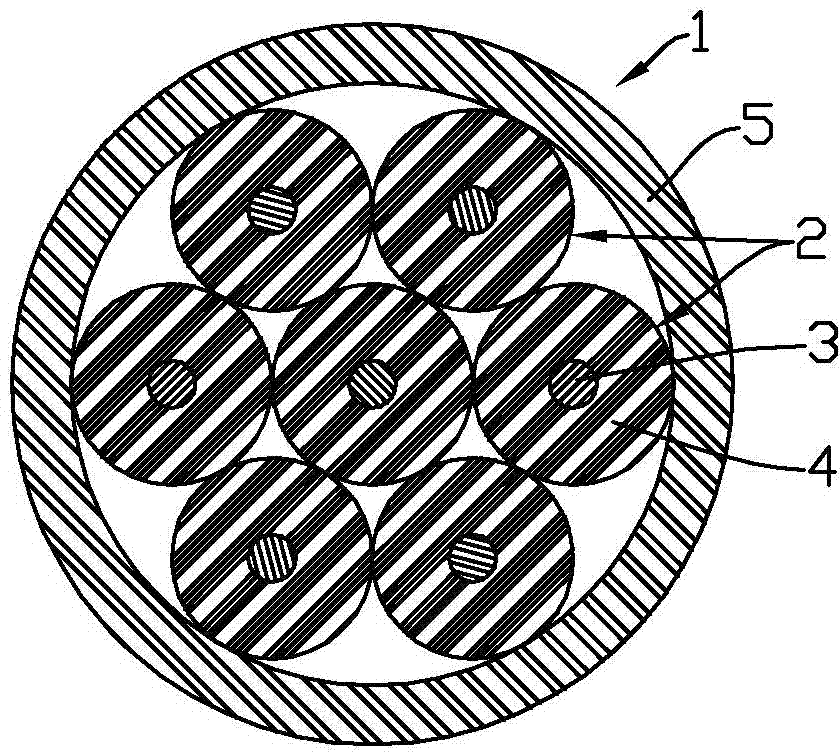
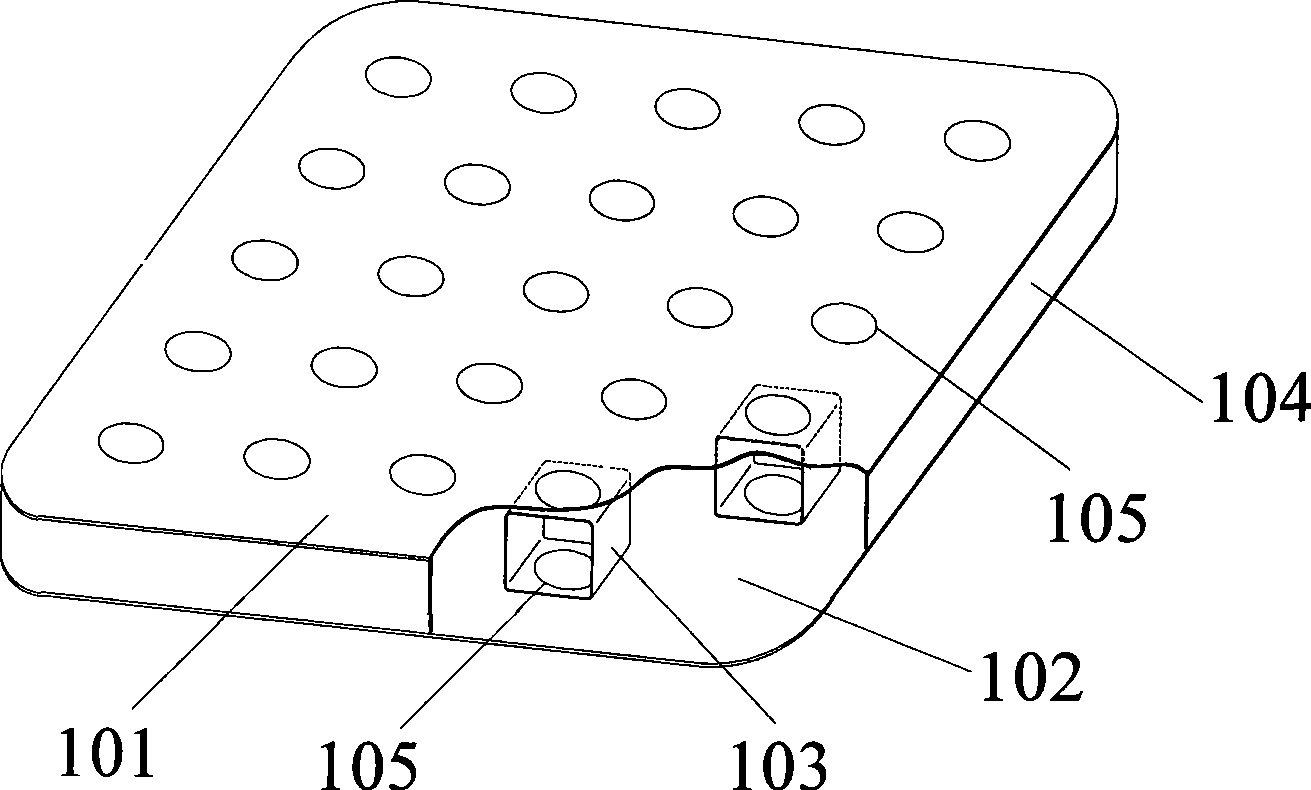
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
399 results about "Fusion splicing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
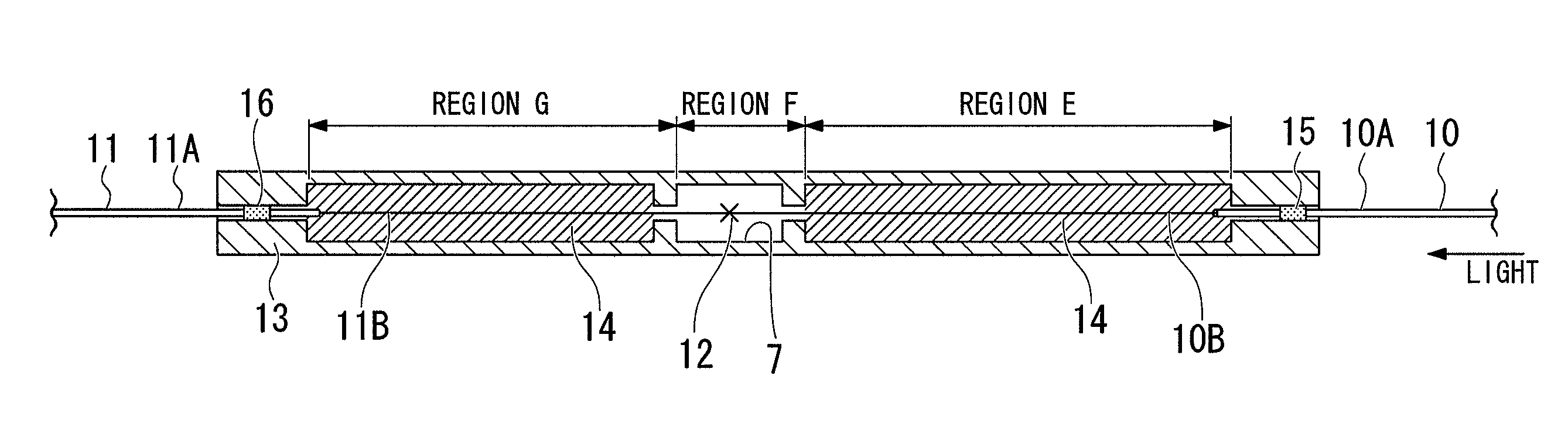
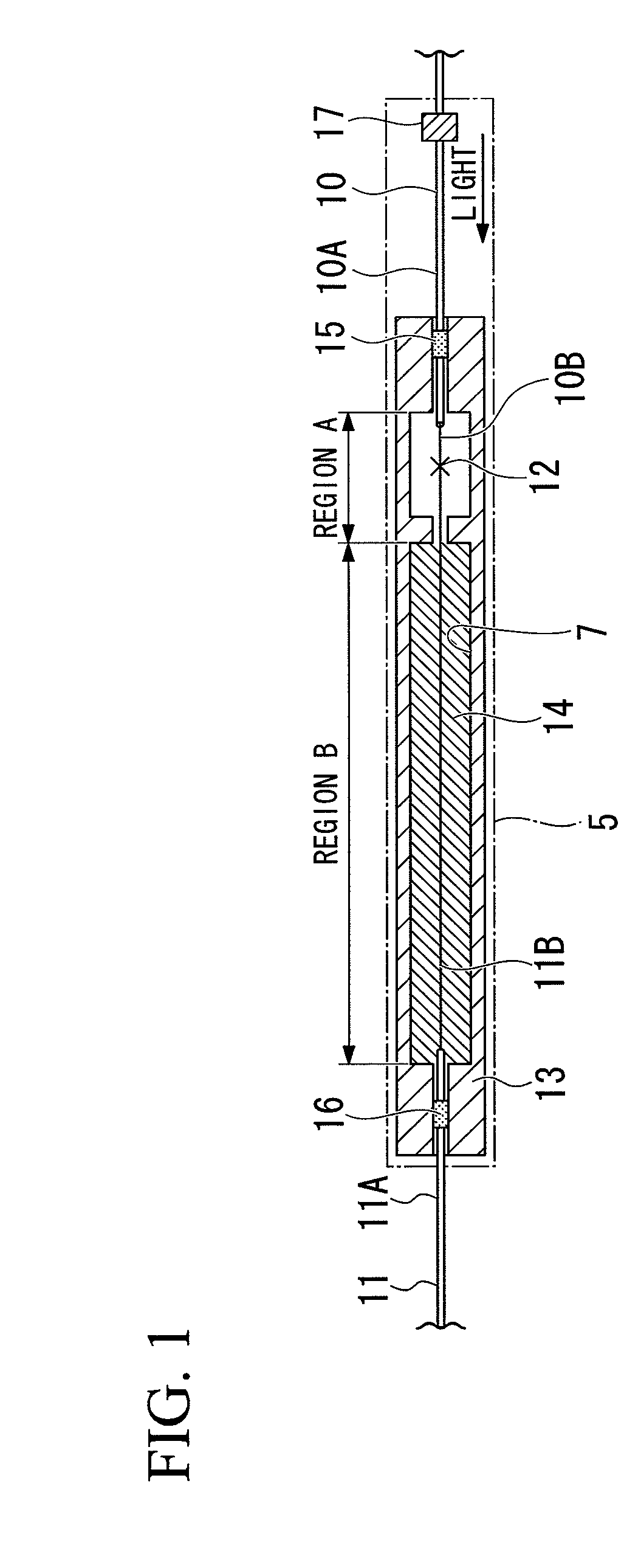
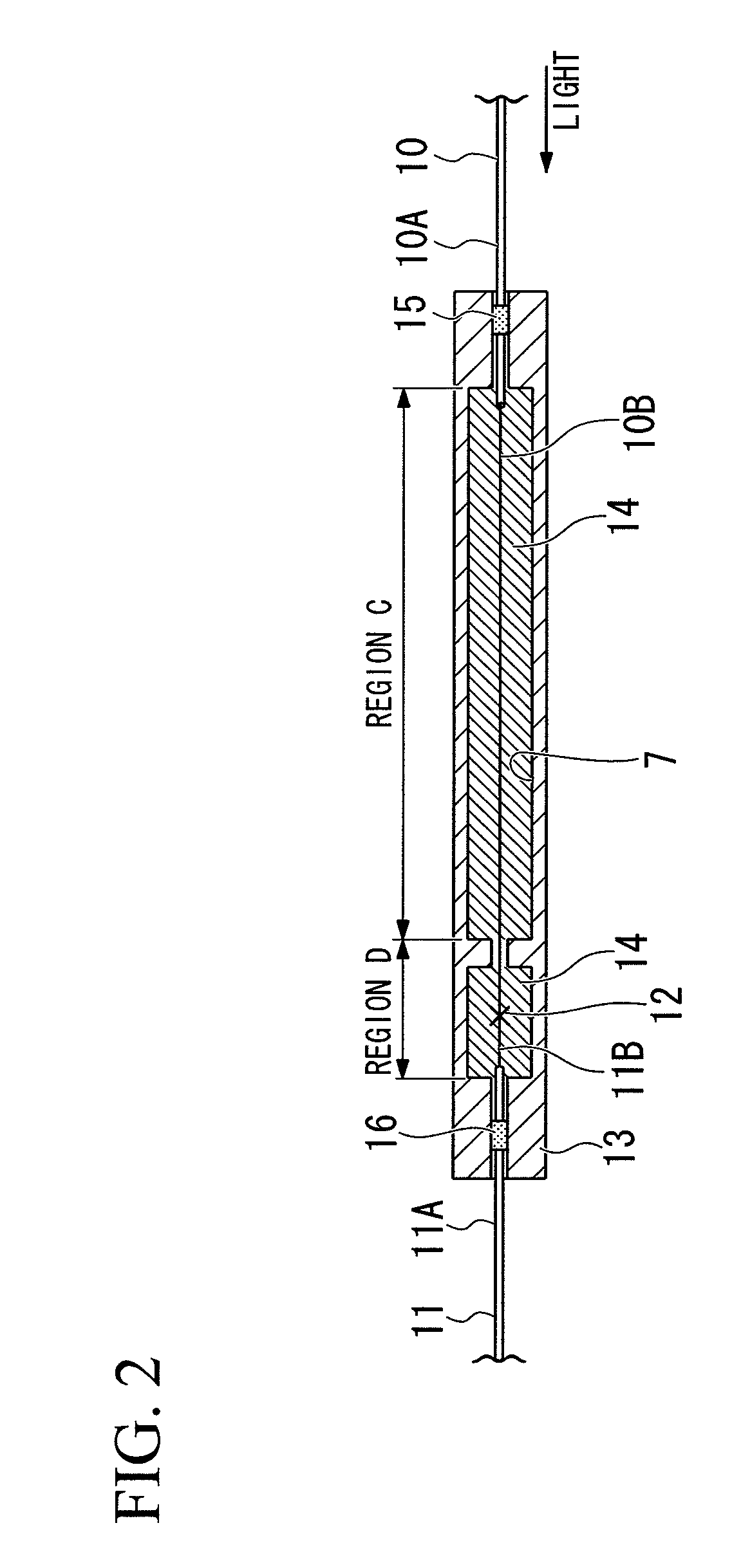
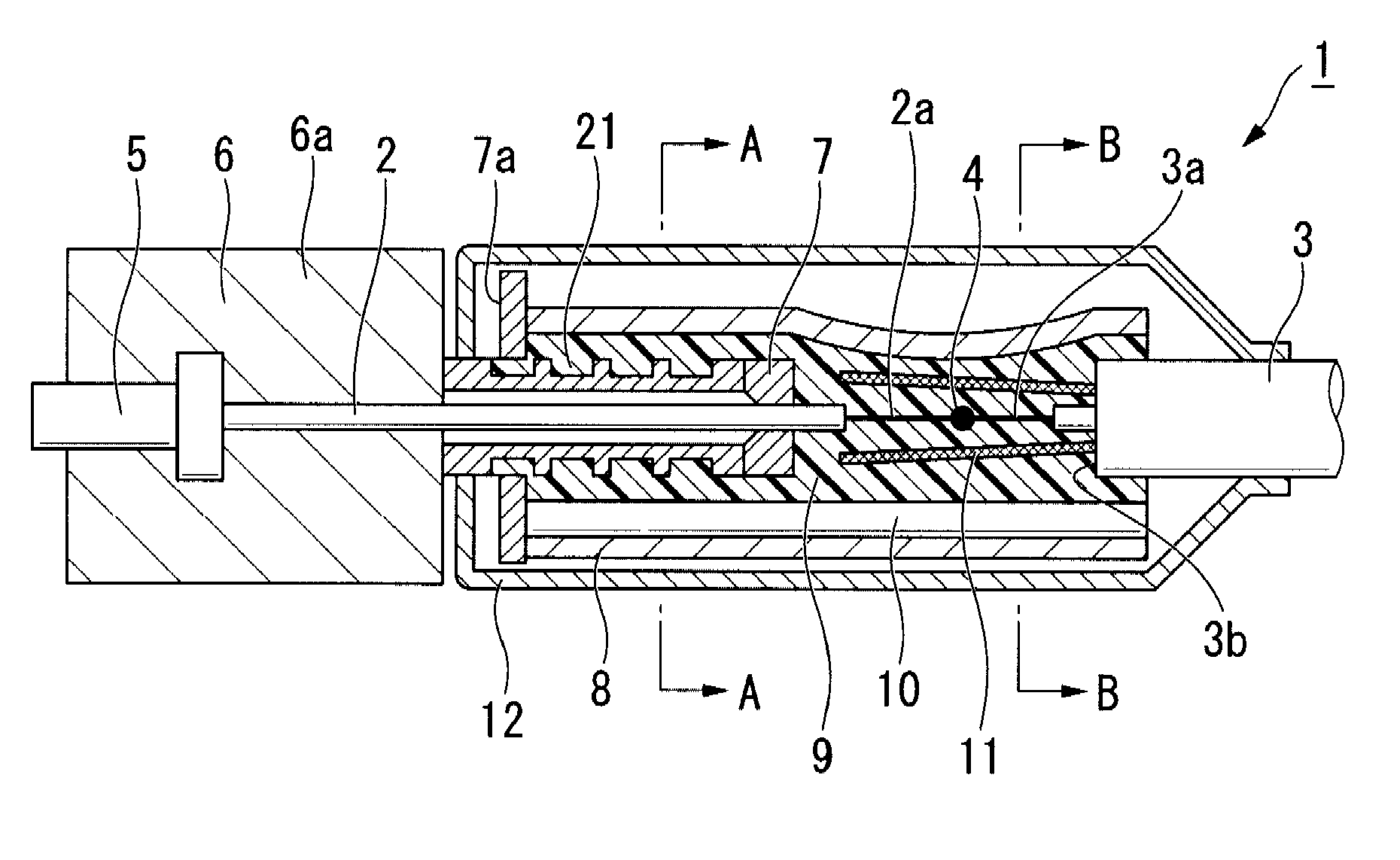
Fusion splicing is the act of joining two optical fibers end-to-end.The goal is to fuse the two fibers together in such a way that light passing through the fibers is not scattered or reflected back by the splice, and so that the splice and the region surrounding it are almost as strong as the intact fiber. The source of heat is usually an electric arc, but can also be a laser, or a gas flame, or a tungsten filament through which current is passed.
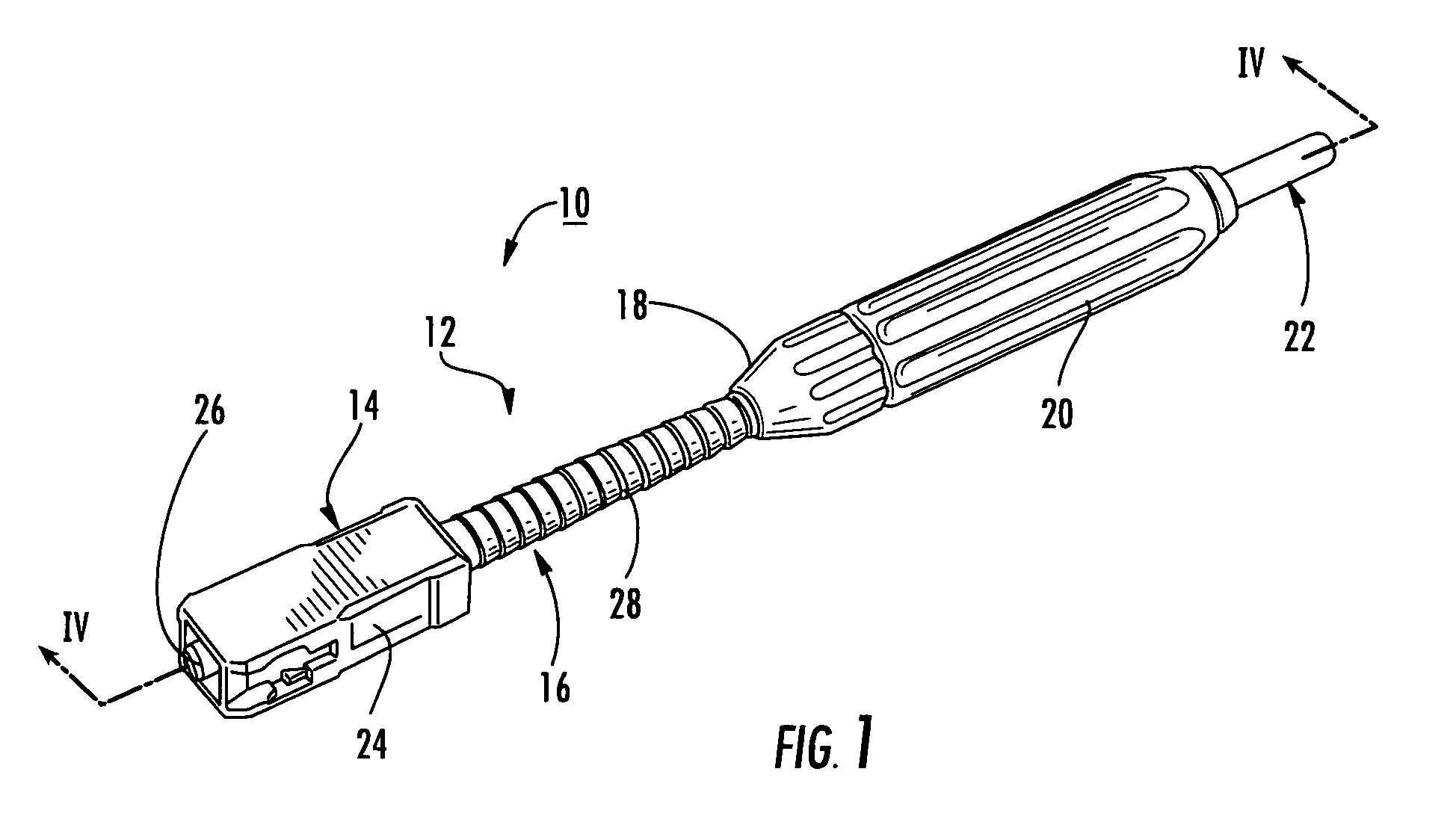
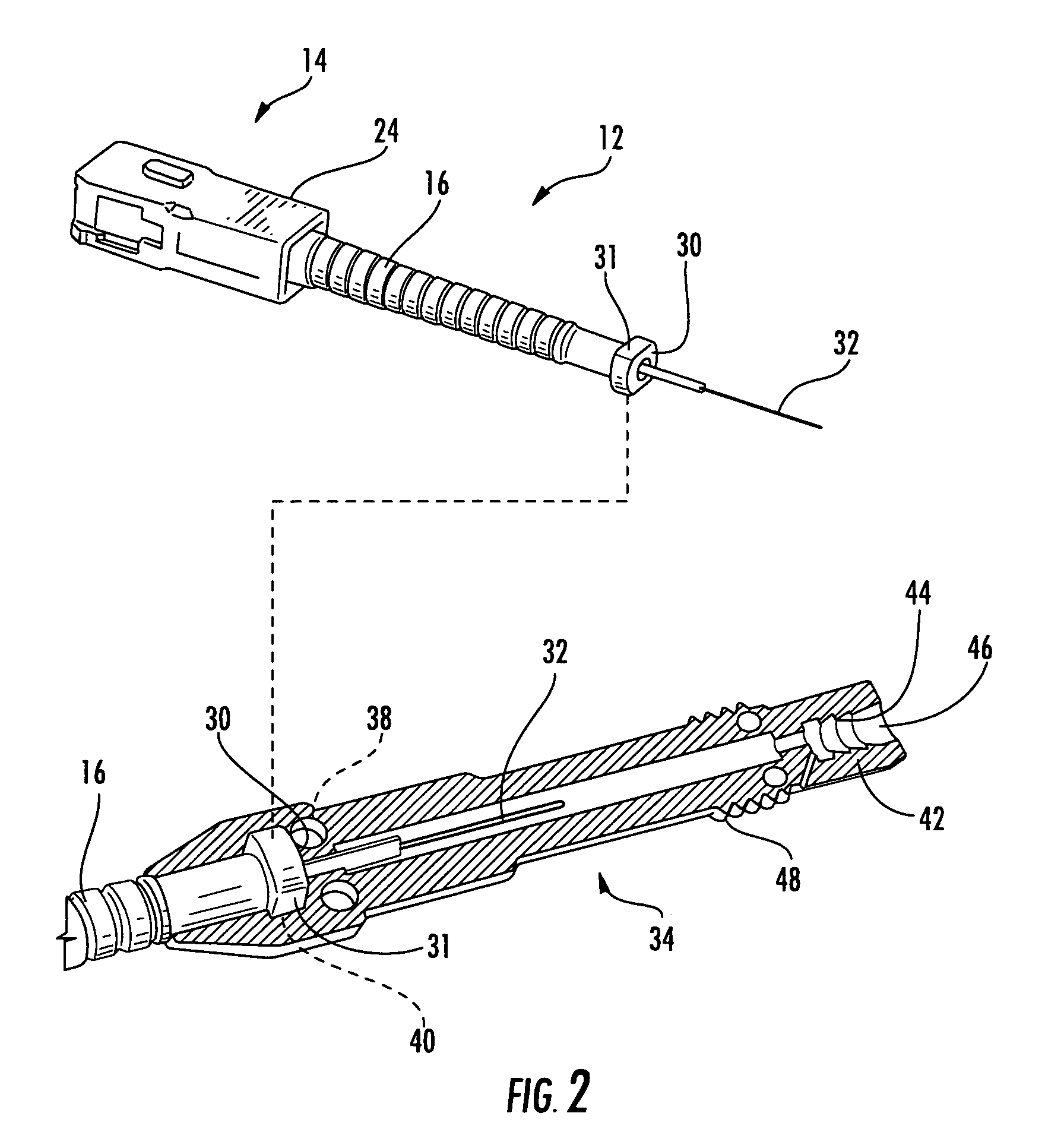
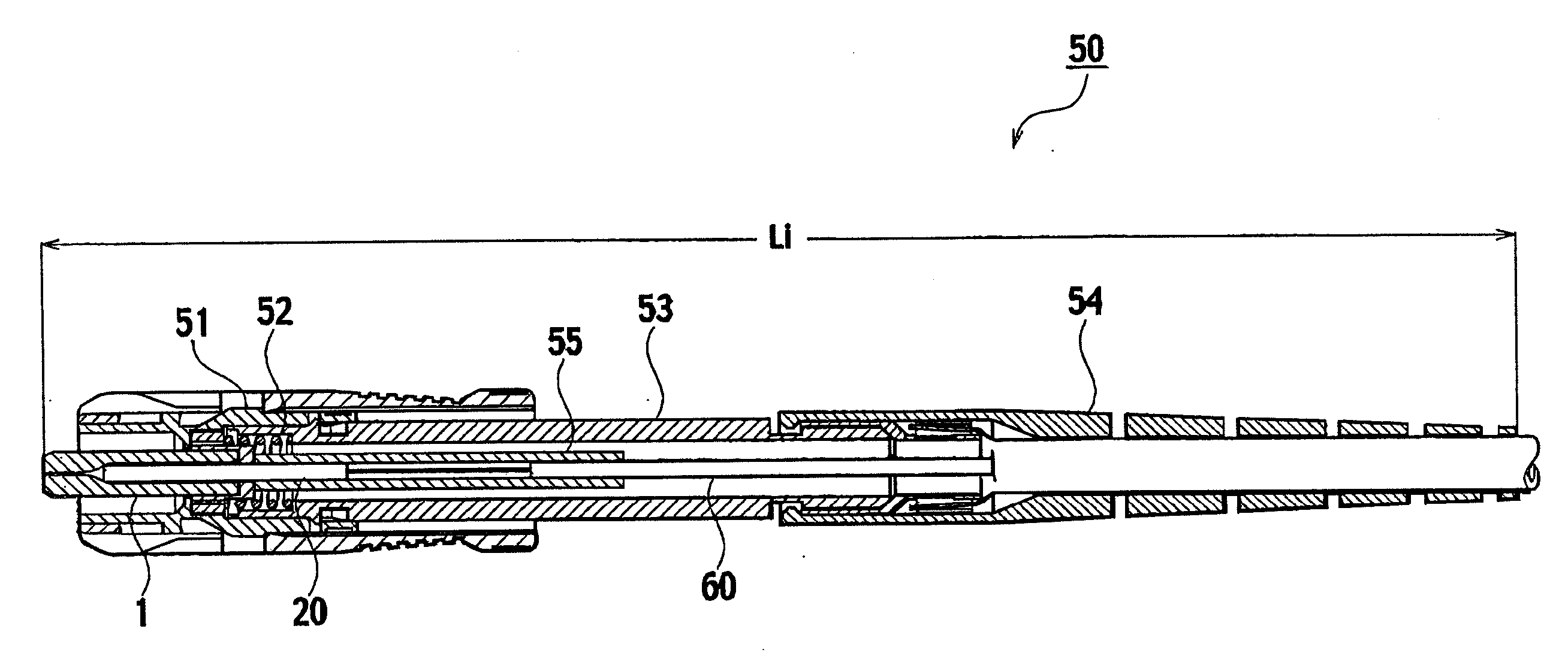
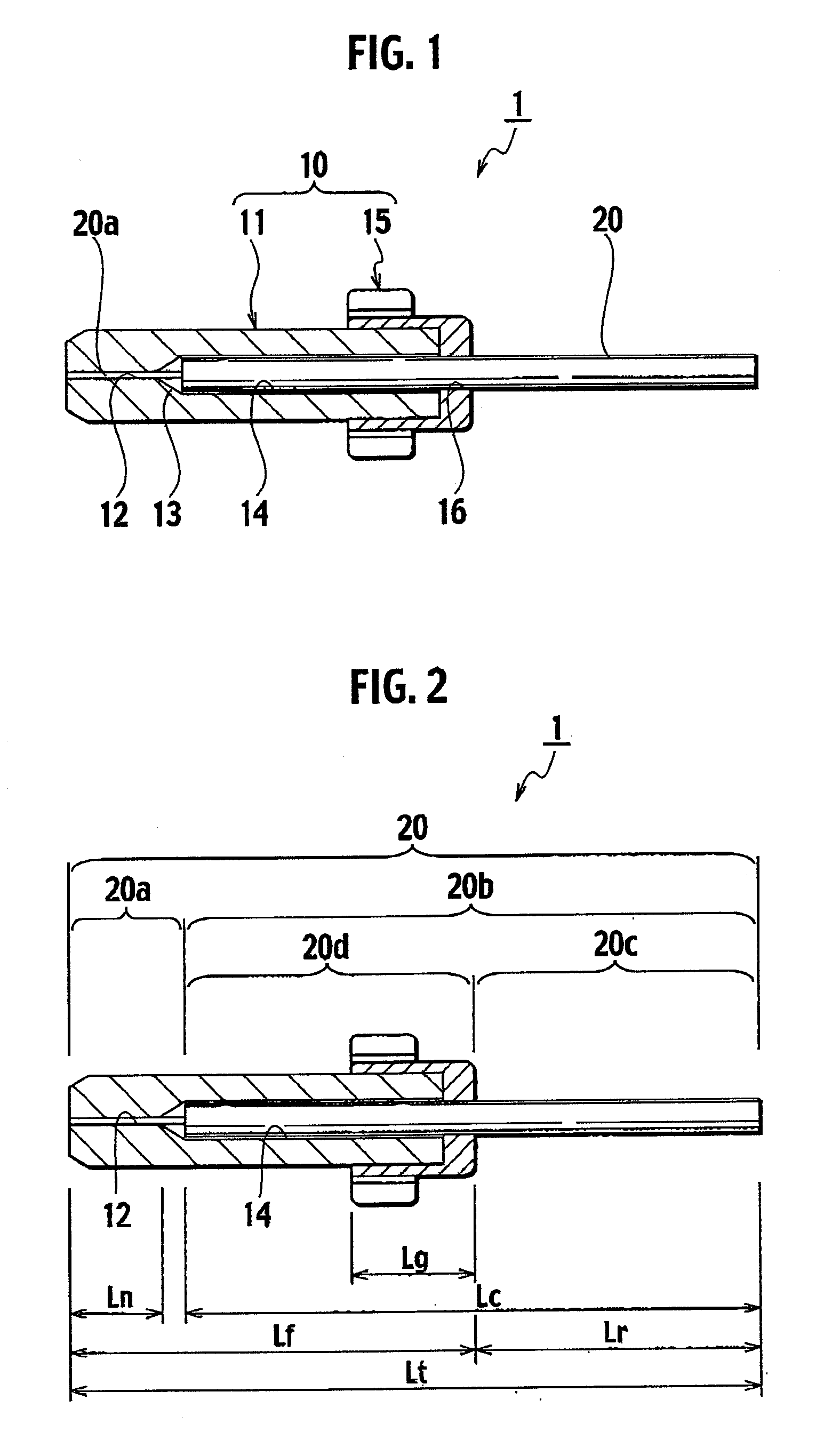
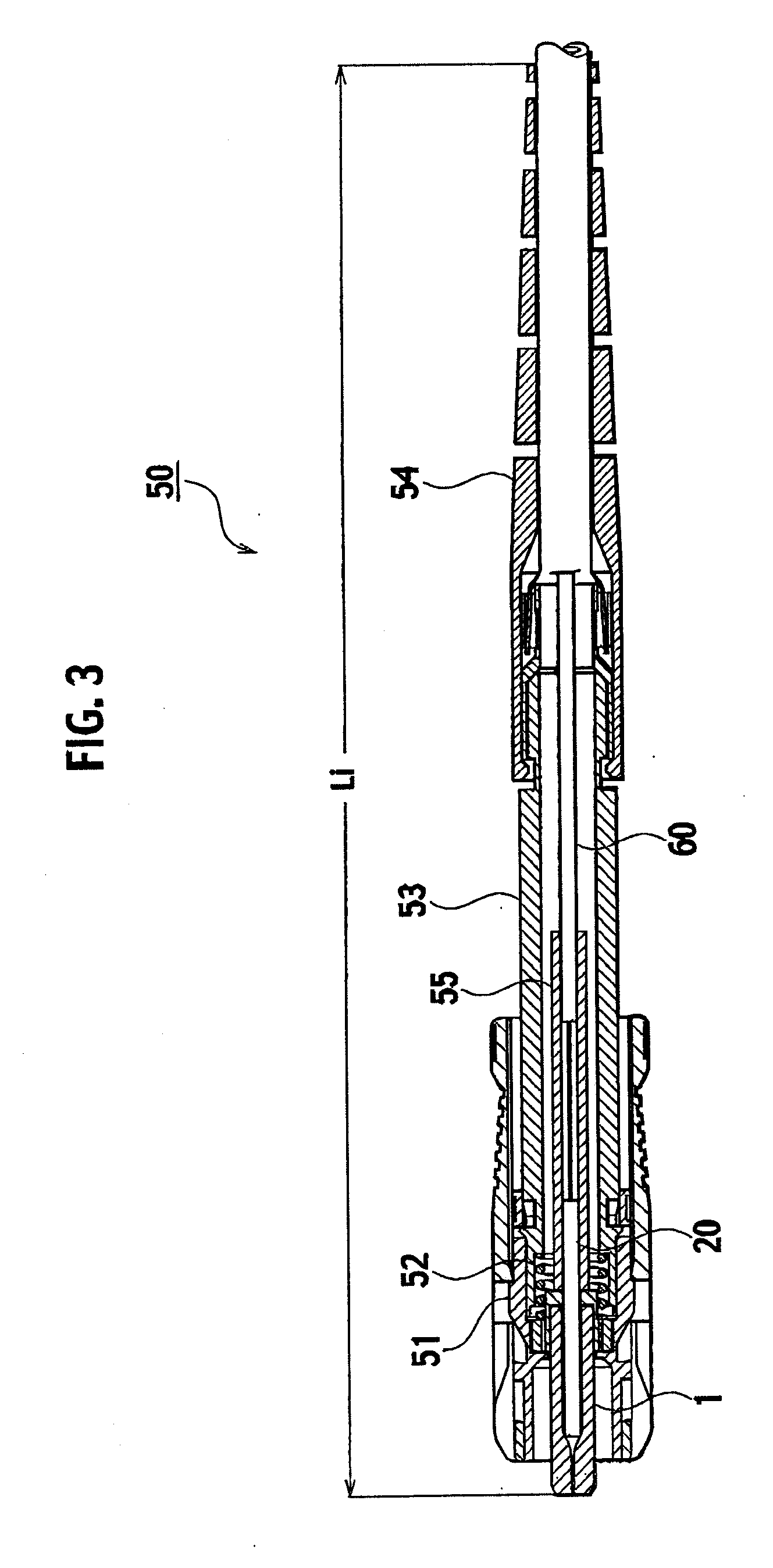
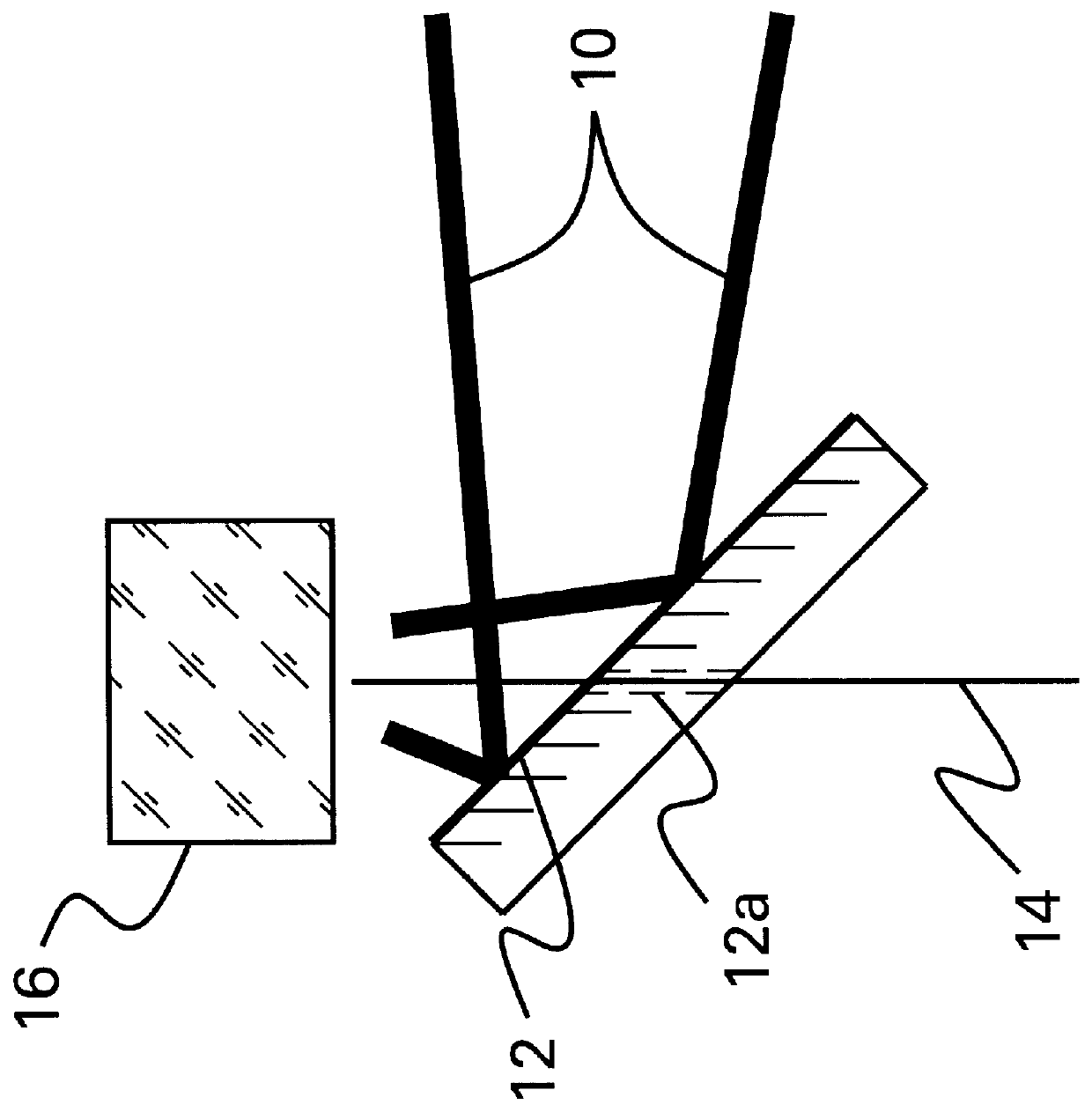
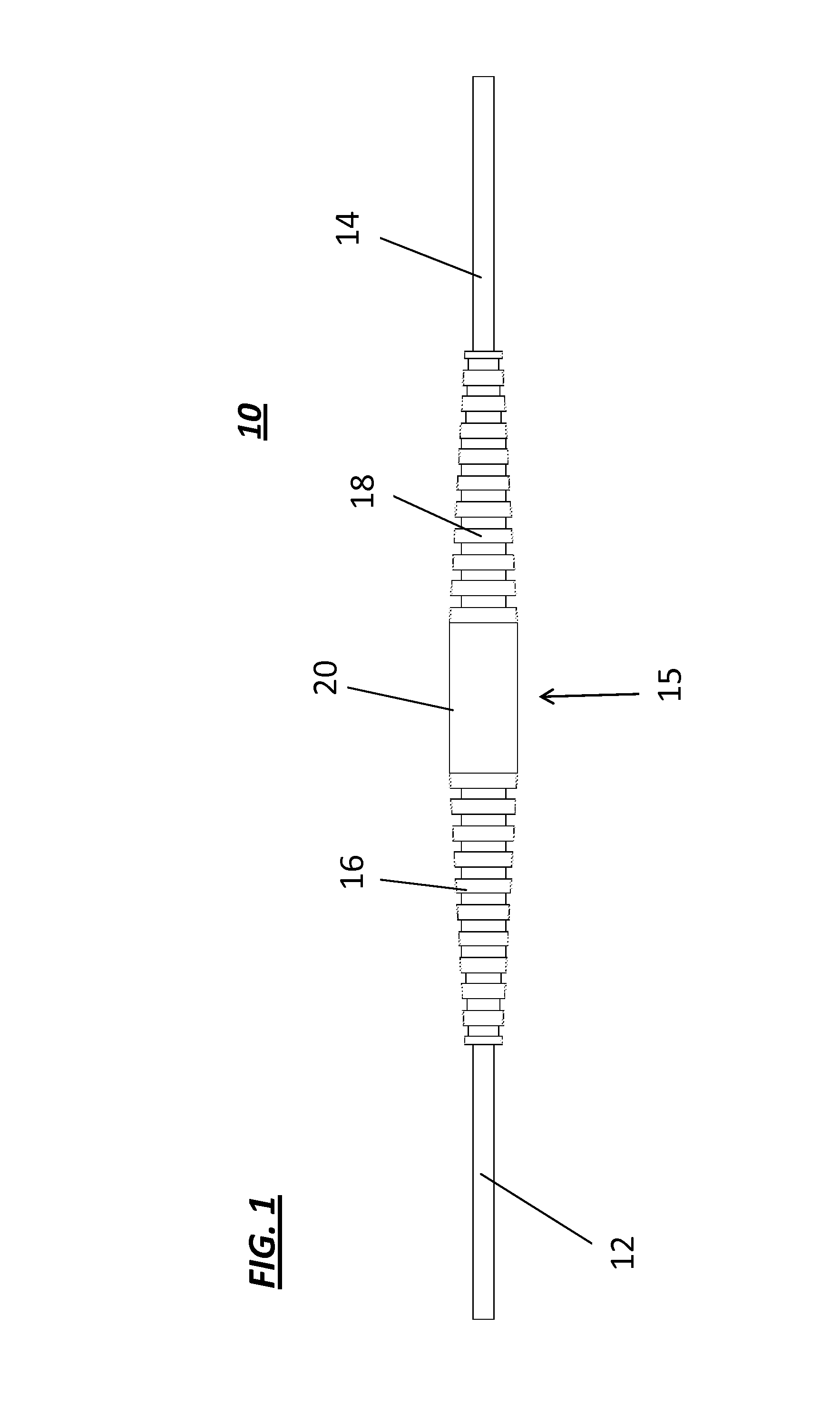
Fusion-splice fiber optic connectors and related tools
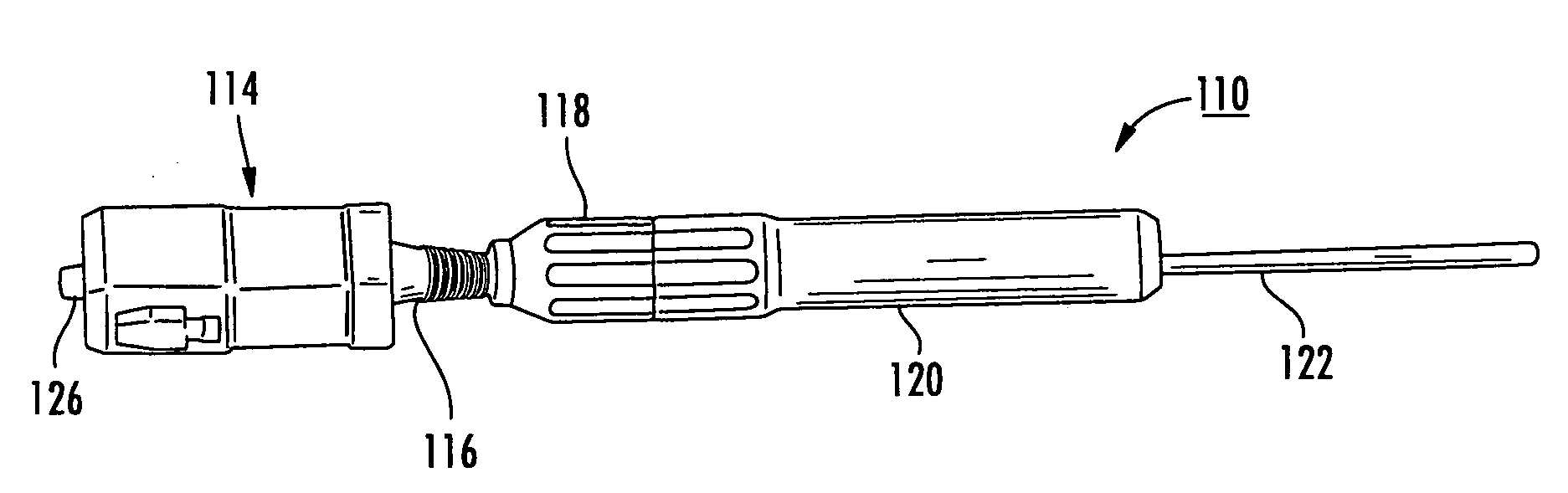
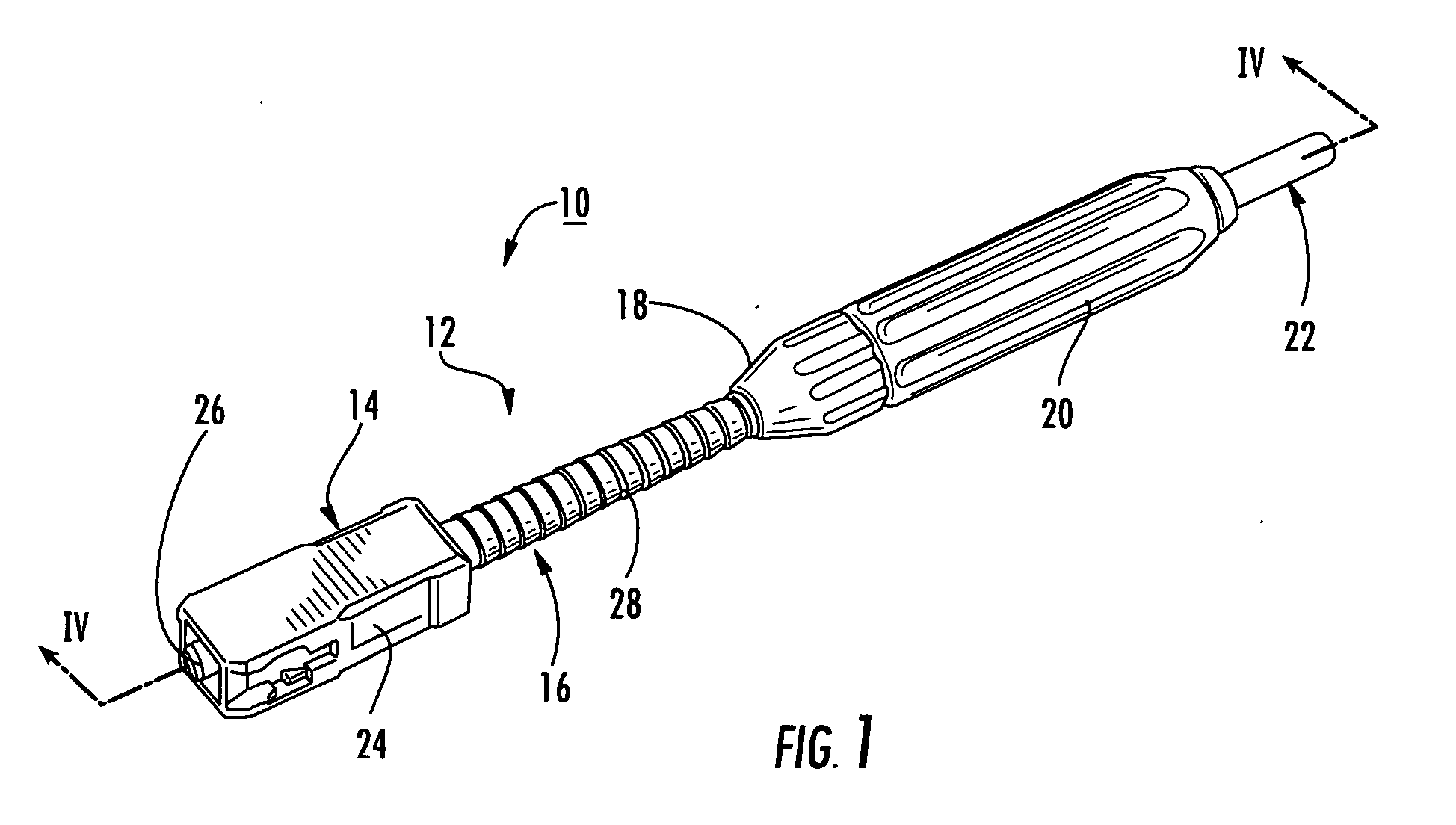
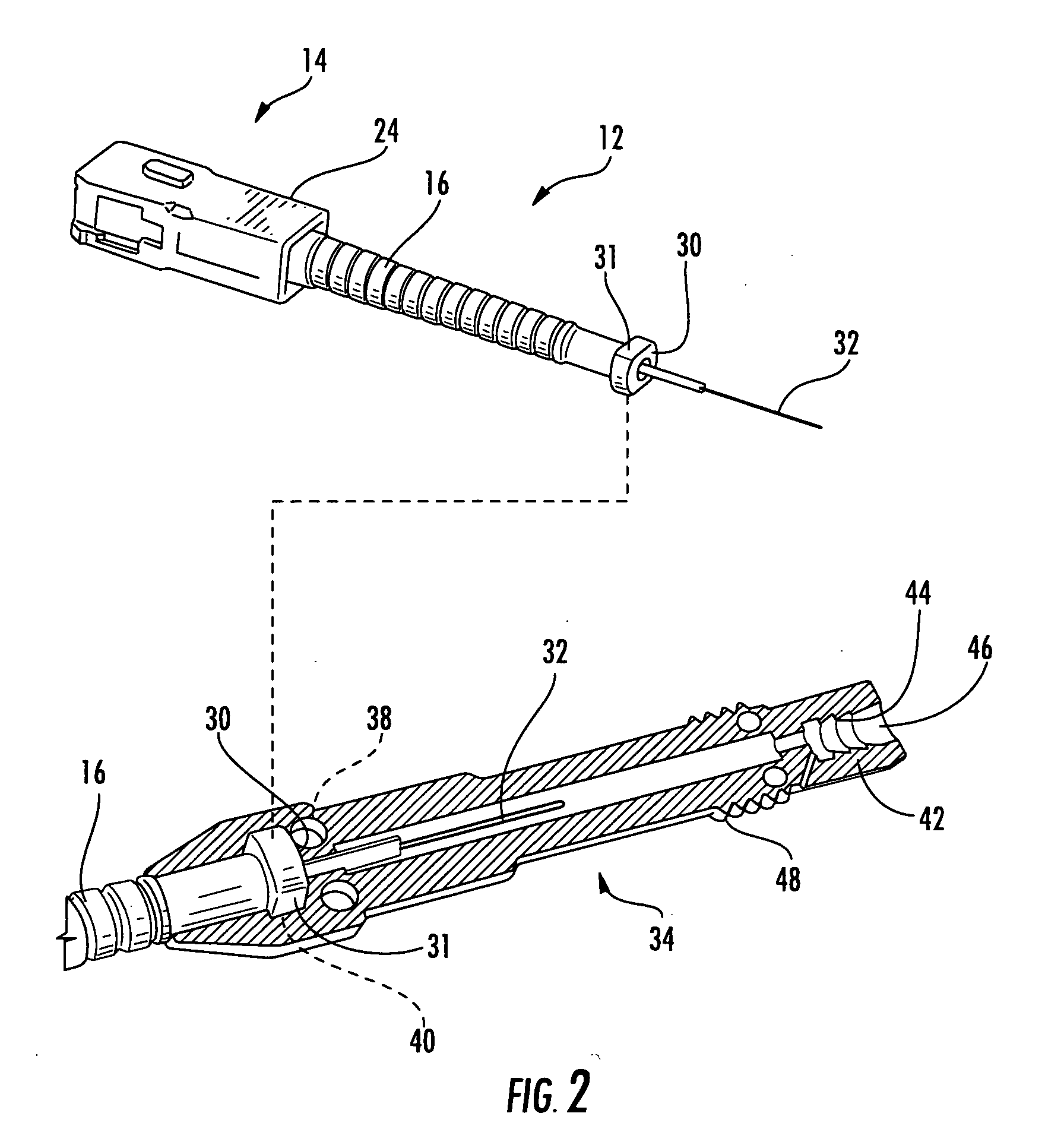
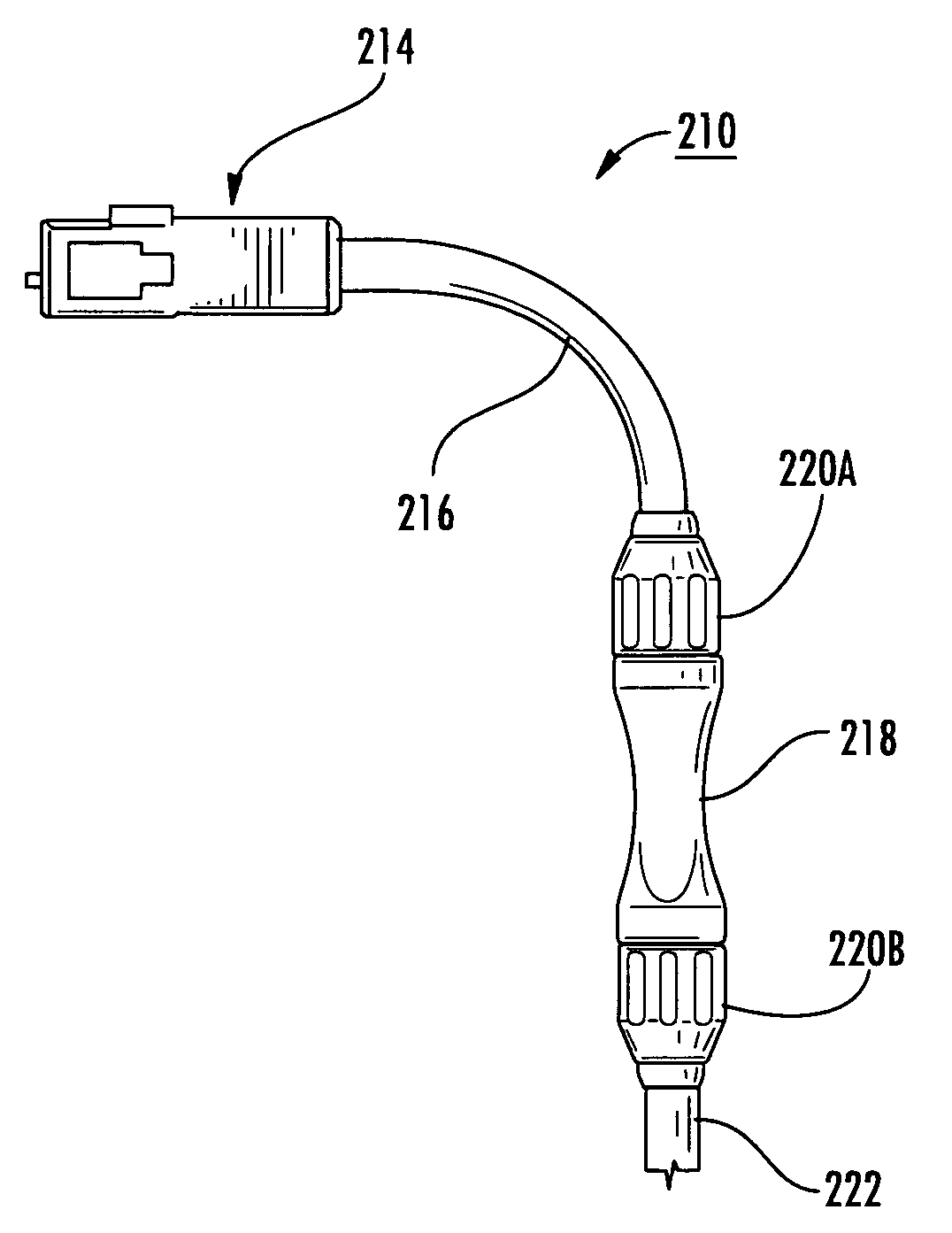
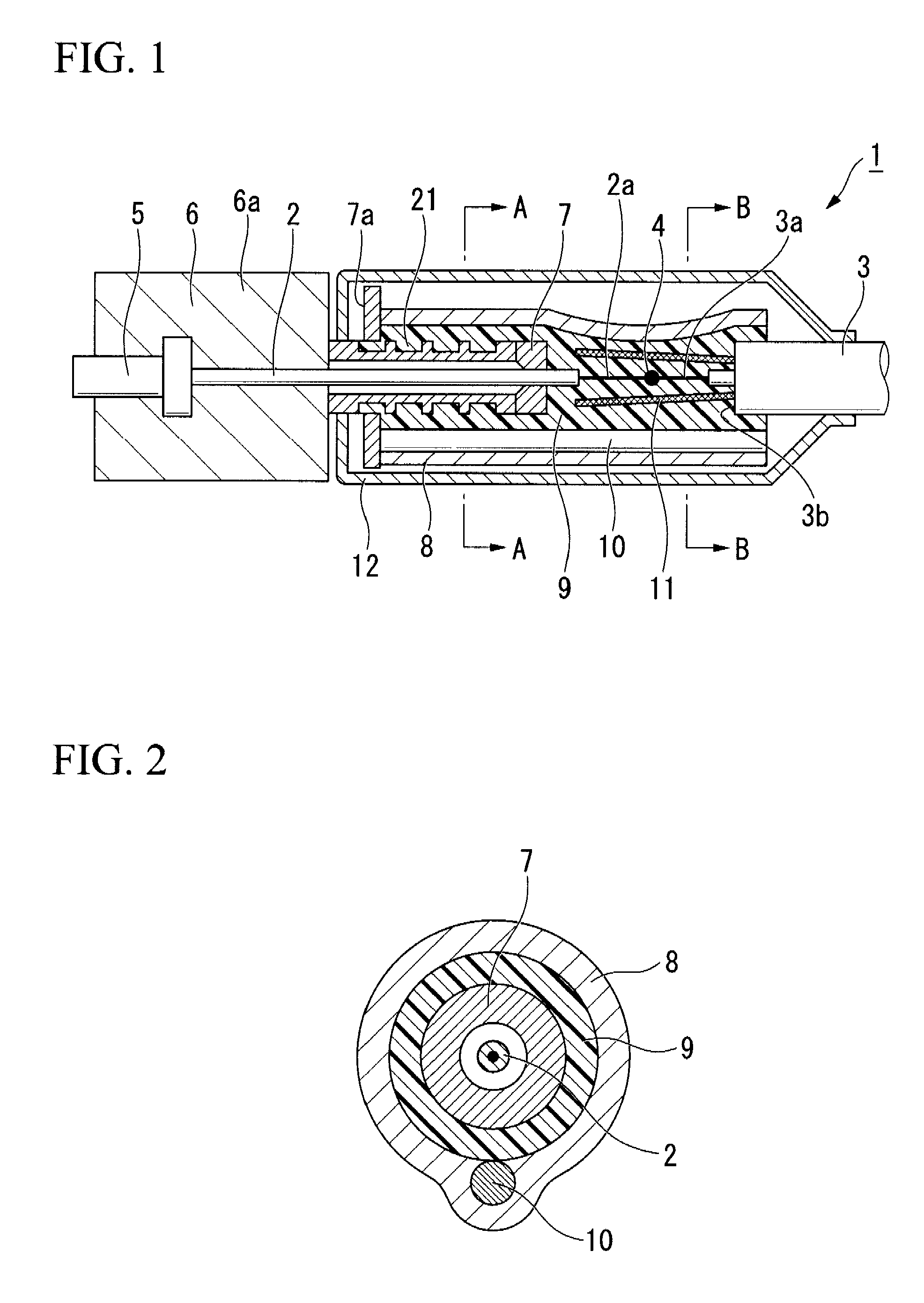
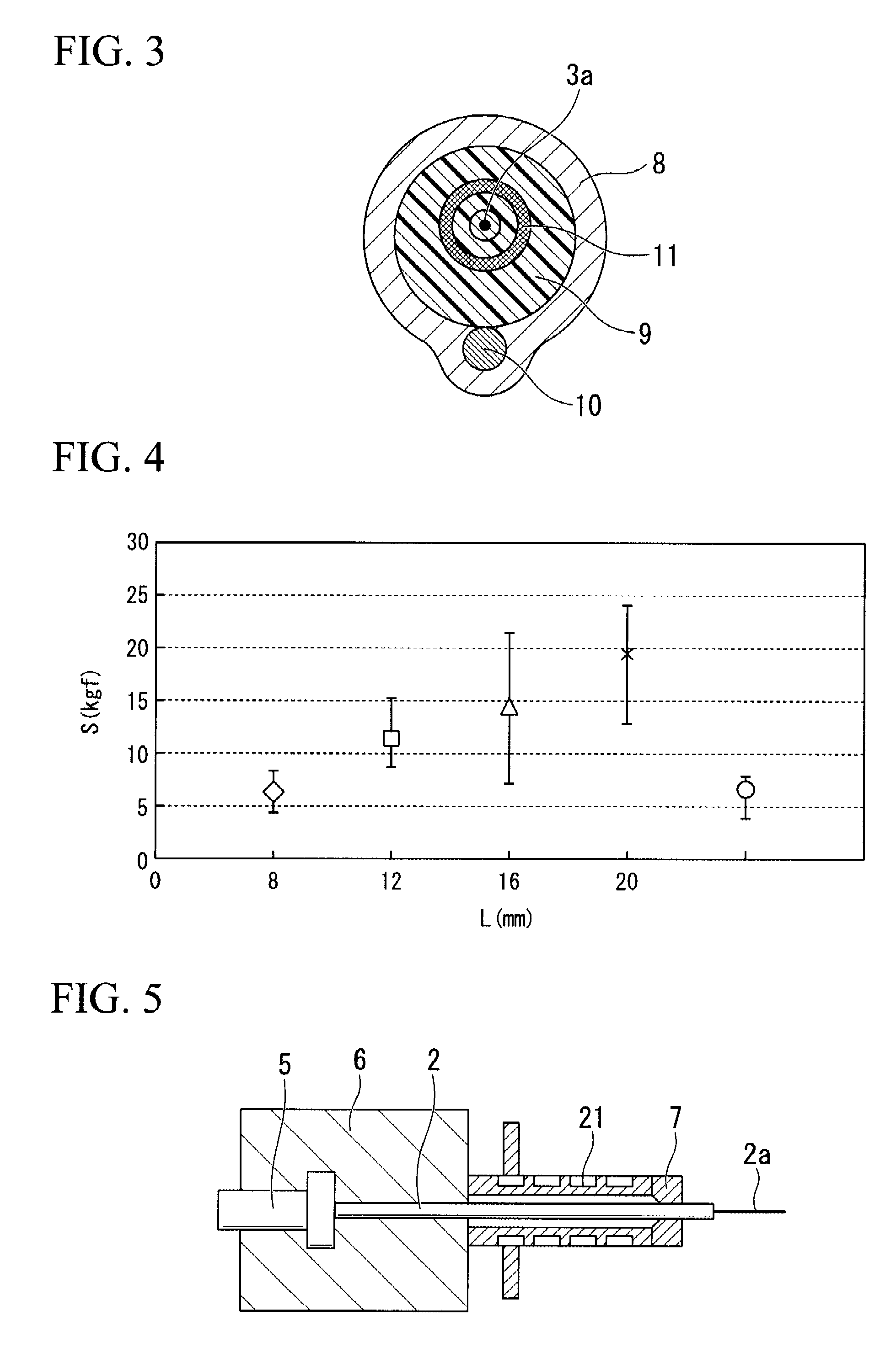
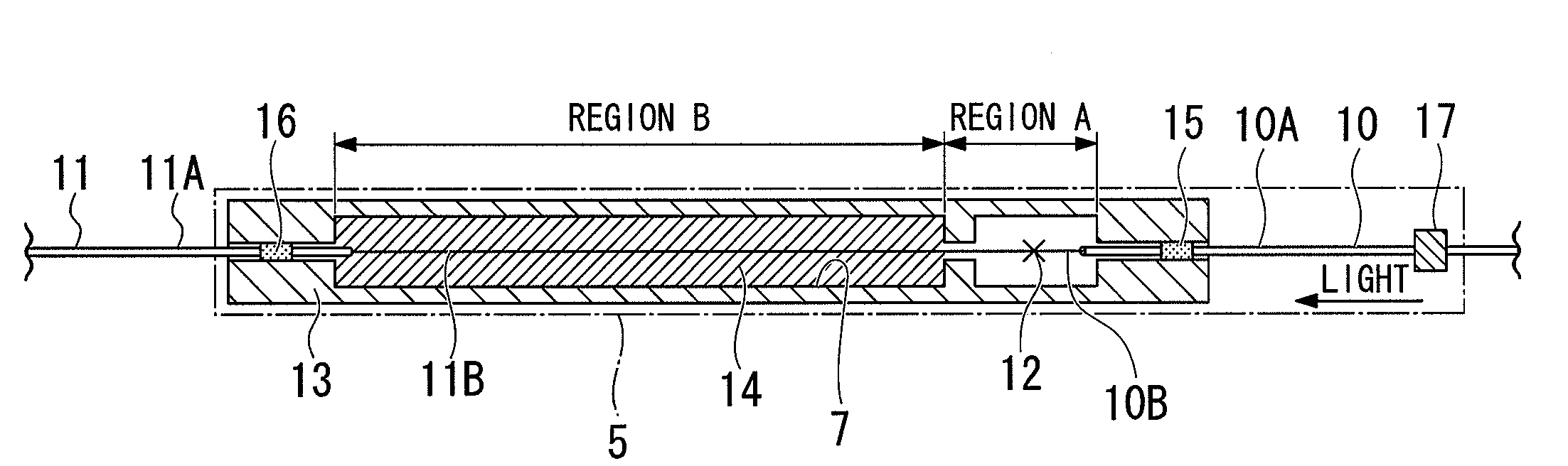
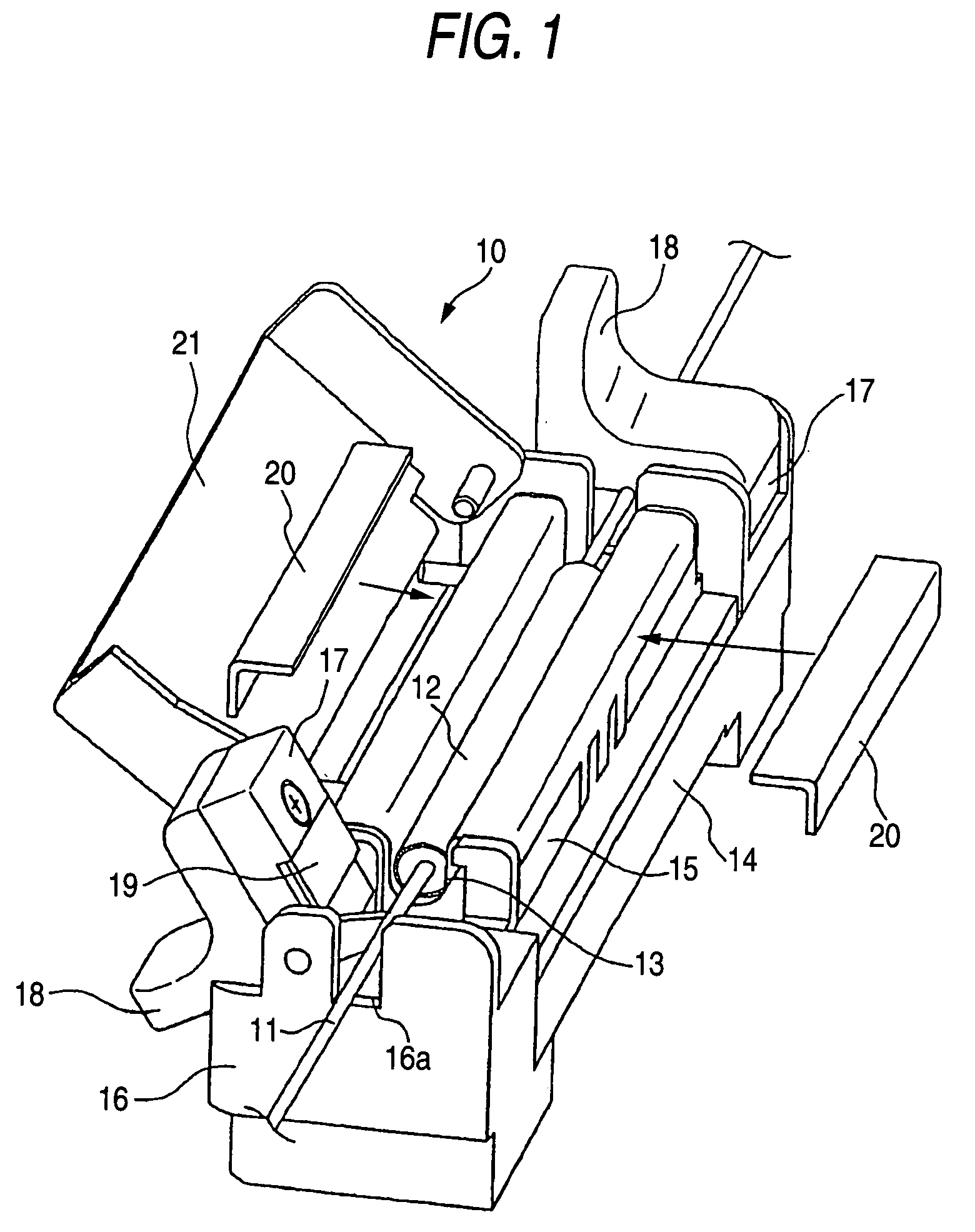
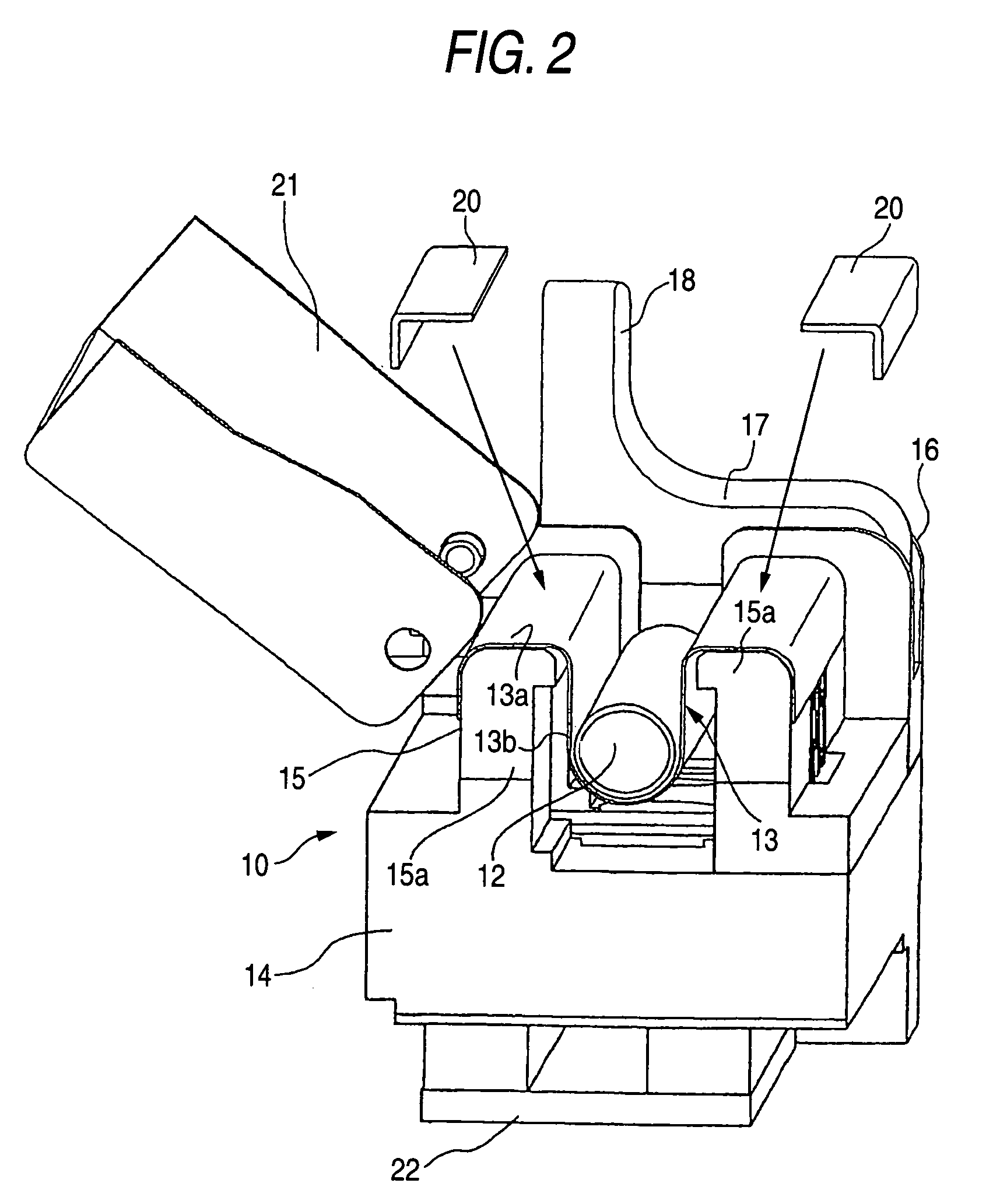
Fiber optic connectors having an optical fiber stub that is fusion-spliced for optical connection and related tools for the fiber optic connectors are disclosed. Specifically, the connector assembly for fusion-splicing includes a fiber optic connector having an optic fiber stub and a boot attachable to the fiber optic connector. The boot is configured to transfer the majority of the axial force from the fiber optic cable to the fiber optic connector. Specifically, a splice housing for housing the fusion splice is configured for attachment to an end of the boot for transferring forces from the fiber optic cable to the boot. Consequently, the boot preferably has an extensibility of less than about 2 millimeters under an axial load of about fifteen pounds to inhibit excess forces from acting on the optical fiber stub.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
Fusion-splice fiber optic connectors and related tools
Fiber optic connectors having an optical fiber stub that is fusion-spliced for optical connection and related tools for the fiber optic connectors are disclosed. Specifically, the connector assembly for fusion-splicing includes a fiber optic connector having an optic fiber stub and a boot attachable to the fiber optic connector. The boot is configured to transfer the majority of the axial force from the fiber optic cable to the fiber optic connector. Specifically, a splice housing for housing the fusion splice is configured for attachment to an end of the boot for transferring forces from the fiber optic cable to the boot. Consequently, the boot preferably has an extensibility of less than about 2 millimeters under an axial load of about fifteen pounds to inhibit excess forces from acting on the optical fiber stub.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
Splice protection heater, fusion splicer including the splice protection heater, and fusion splicing method
ActiveUS20060280417A1Efficient executionPerformed quickly and efficientlyCoupling light guidesHeating timeEngineering
A splice protection heater capable of quickly and efficiently performing a fusion process without an excessive heating time, a fusion splicer including the splice protection heater, and a fusion splicing method are provided. The apparatus has a heating part for heat shrinking a protection sleeve that covers a fusion spliced portion of an optical fiber, a plurality of heating elements that can individually heat a plurality of protection sleeves with different timings by being individually turned ON / OFF by switches, or a heating element turned ON / OFF by a switch. This apparatus may also be provided with detecting section that detects whether or not the protection sleeve is set on the heating element, and turns the switch ON / OFF.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Optical Connector Component and Optical Connector Using the Same
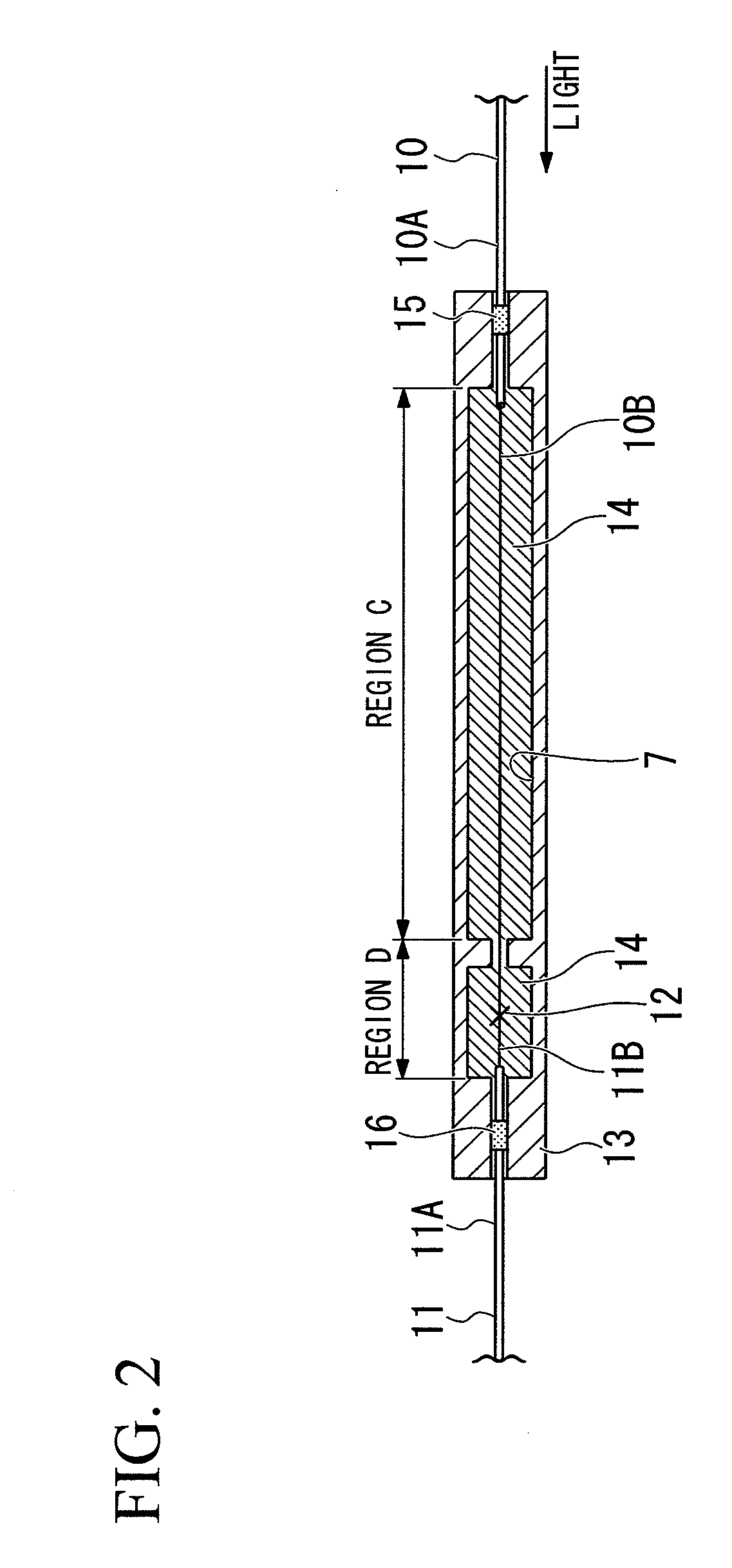
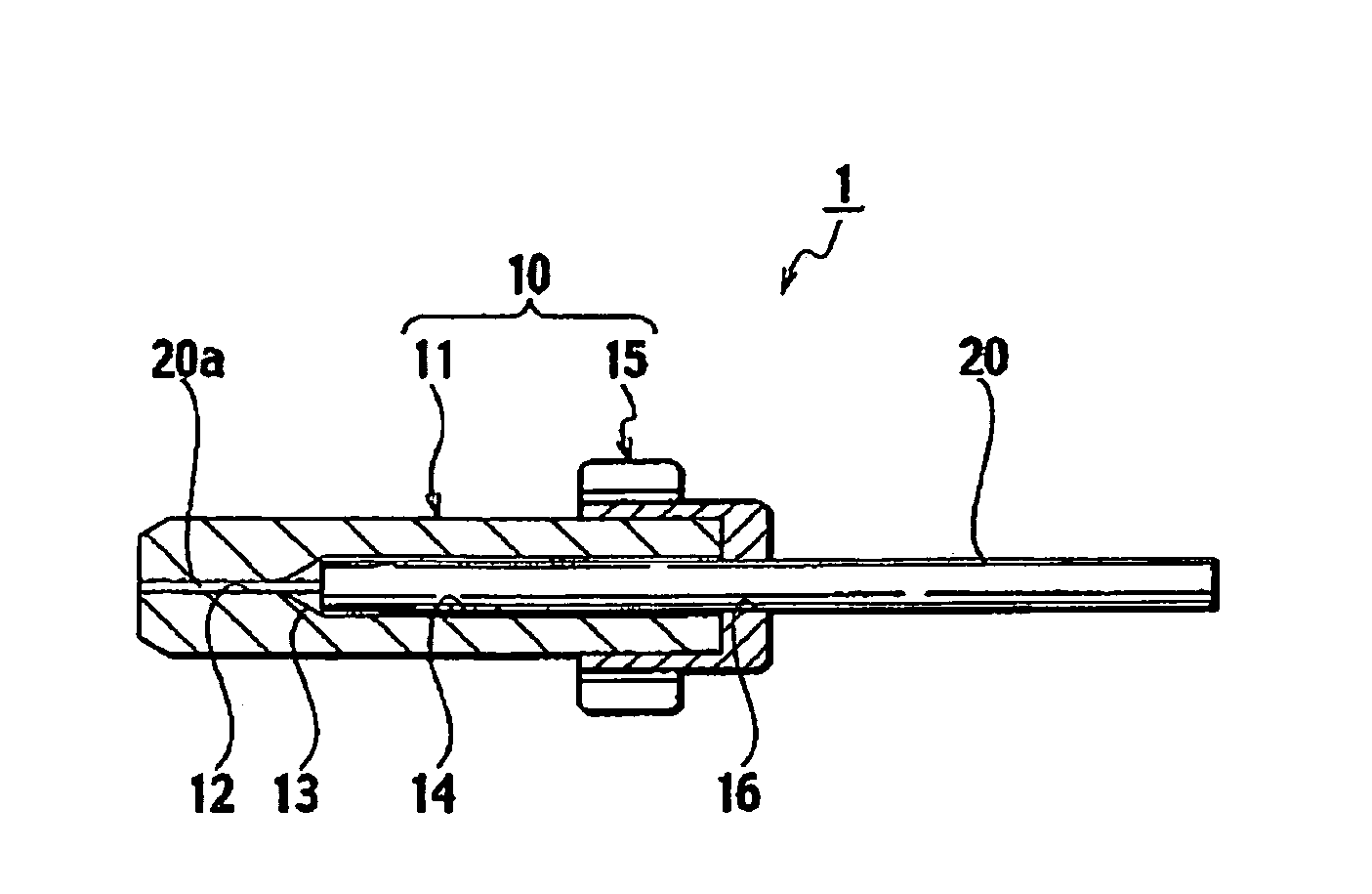
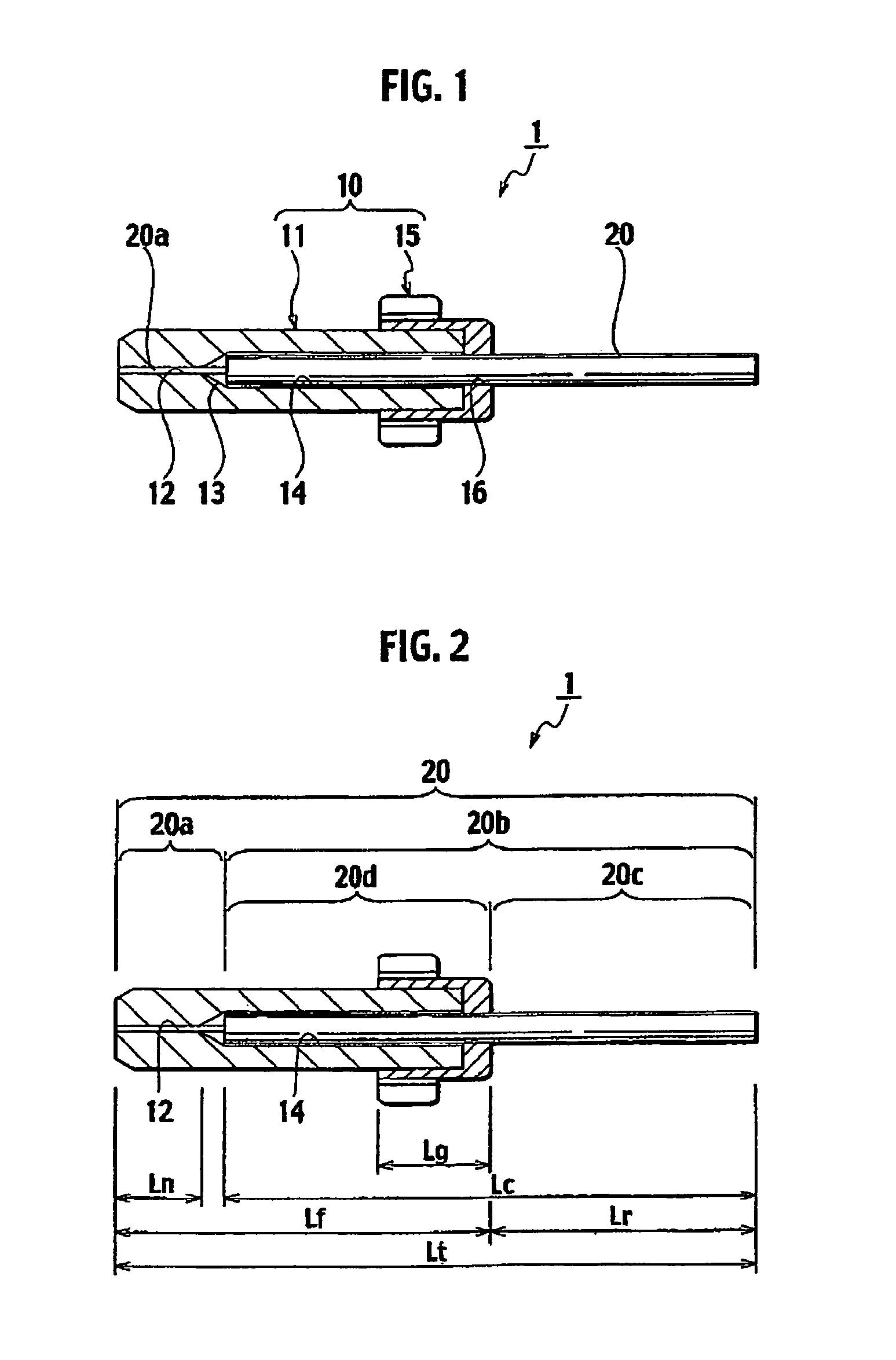
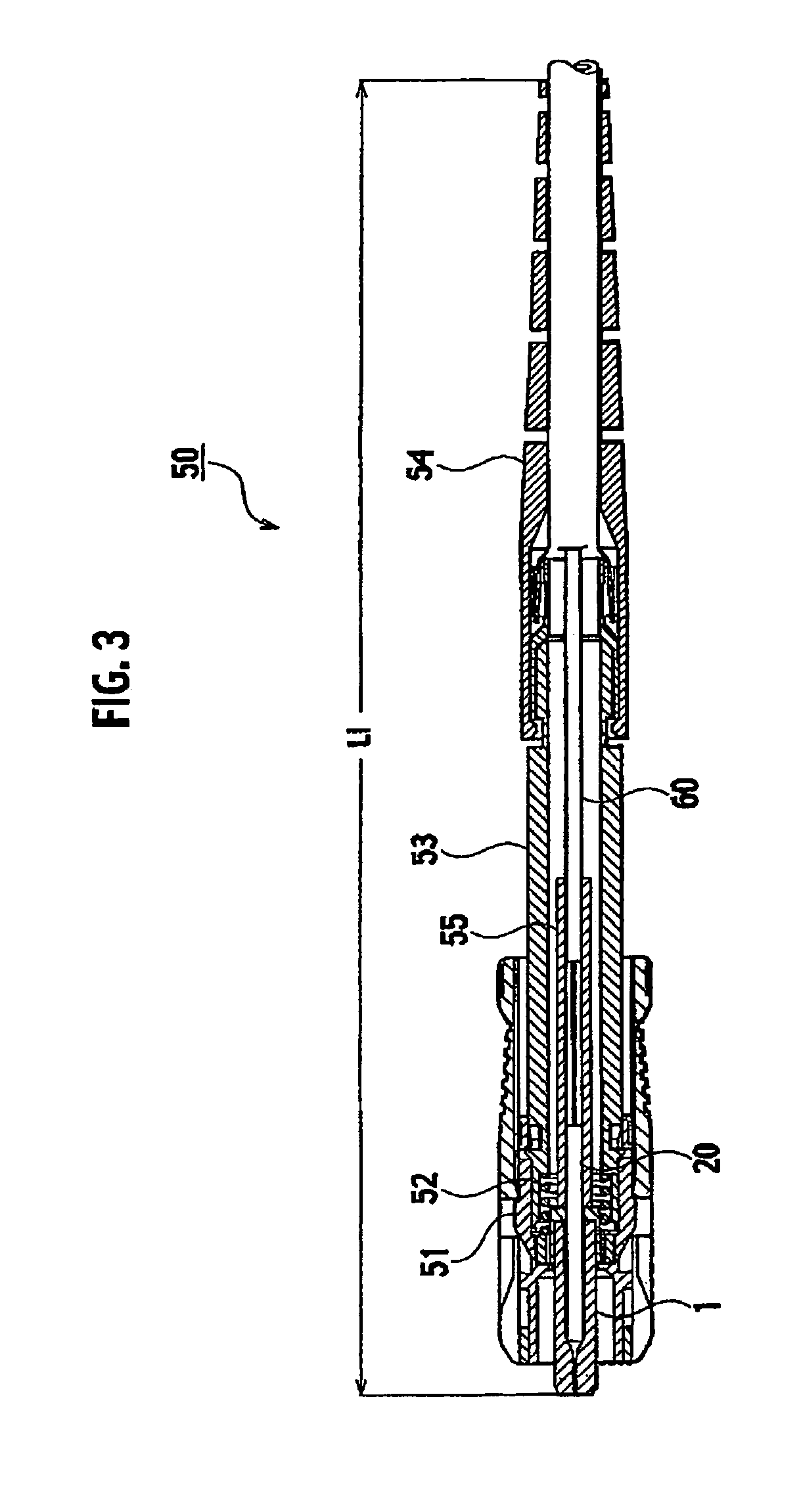
To provide a fusion-spliced optical connector capable of easily performing a fusion-splicing operation at an actual site in a short time, without need to perform additional special operations. An optical connector component is configured to attach a short-length optical fiber to a ferrule including a capillary and a flange. The capillary comprises a minute through hole and a coated-portion storage hole formed in the capillary, the minute through hole to be stored therein the bare optical fiber portion of the short-length optical fiber and the coated-portion storage hole to be stored therein a part of a coated optical fiber portion of the short-length optical fiber continuous to the bare optical fiber portion. The flange includes a coated-portion penetrating hole formed in the flange to be penetrated therein a very short portion continuous to the part of the coated optical fiber portion stored in the coated-portion storage hole. The short-length optical fiber extends rearward from the coated-portion penetrating hole of the flange by a length of a required extra-length splice portion when the bare optical fiber portion is fixedly stored in the minute through hole of the capillary and the part of the coated optical fiber portion continuous to the bare optical fiber portion is fixedly stored in the coated-portion storage hole of the capillary.
Owner:SEIKOH GIKEN
Use of a laser to fusion-splice optical components of substantially different cross-sectional areas
InactiveUS6033515ALow costNegates needGlass making apparatusLamination ancillary operationsFusion splicingLaser beams
A method is provided for fusion-splicing with a laser beam two optical components, one of the optical components (e.g., an optical element such as a lens) having a surface that has a comparatively larger cross-sectional area than a surface of the other optical component (e.g., an optical fiber). The method comprises: (a) aligning the two optical components along one axis; (b) turning on a directional laser heat source to form the laser beam; (c) directing the laser beam to be collinear with that optical component having a smaller cross-sectional area; (d) ensuring that the laser beam strikes the surface of the optical component having the larger cross-sectional area at normal or near normal incidence so that absorption of the laser beam is much more efficient on the surface; (e) adjusting the power level of the laser beam to reach a temperature equal to or higher than the softening temperature of the surface of the optical component having the larger cross-sectional area to form a softening region thereon, thereby achieving the fusion-splicing; and (f) turning off the laser.
Owner:LIGHTPATH TECH INC
Optical module
InactiveUS20100188735A1Improve efficiencyHigh refractive indexCoupling light guidesFibre transmissionOptical ModuleComputer module
The present invention relates to an optical module having a structure for reducing adverse contingencies such as increased number of fusion splicing points, drops in output, and higher costs associated with a greater number of optical components. The optical module comprises an amplification optical fiber, a transmission optical fiber, and a fusion splicing structure that fusion-splices the amplification optical fiber to the transmission optical fiber, in a state where a cover layer is removed at the tip portions, including the end faces, of these optical fibers. The fusion splicing structure includes a pumping light removing resin that covers directly the tip portions of the amplification optical fiber and the transmission optical fiber from which the cover layer is removed. The pumping light removing resin has a higher refractive index than a first cladding of the amplification optical fiber. The above configuration allows transmitted pumping light, for which the confinement effect by the first cladding of the amplification optical fiber is cancelled, to escape more efficiently out of the fusion splicing portion.
Owner:MEGAOPTO
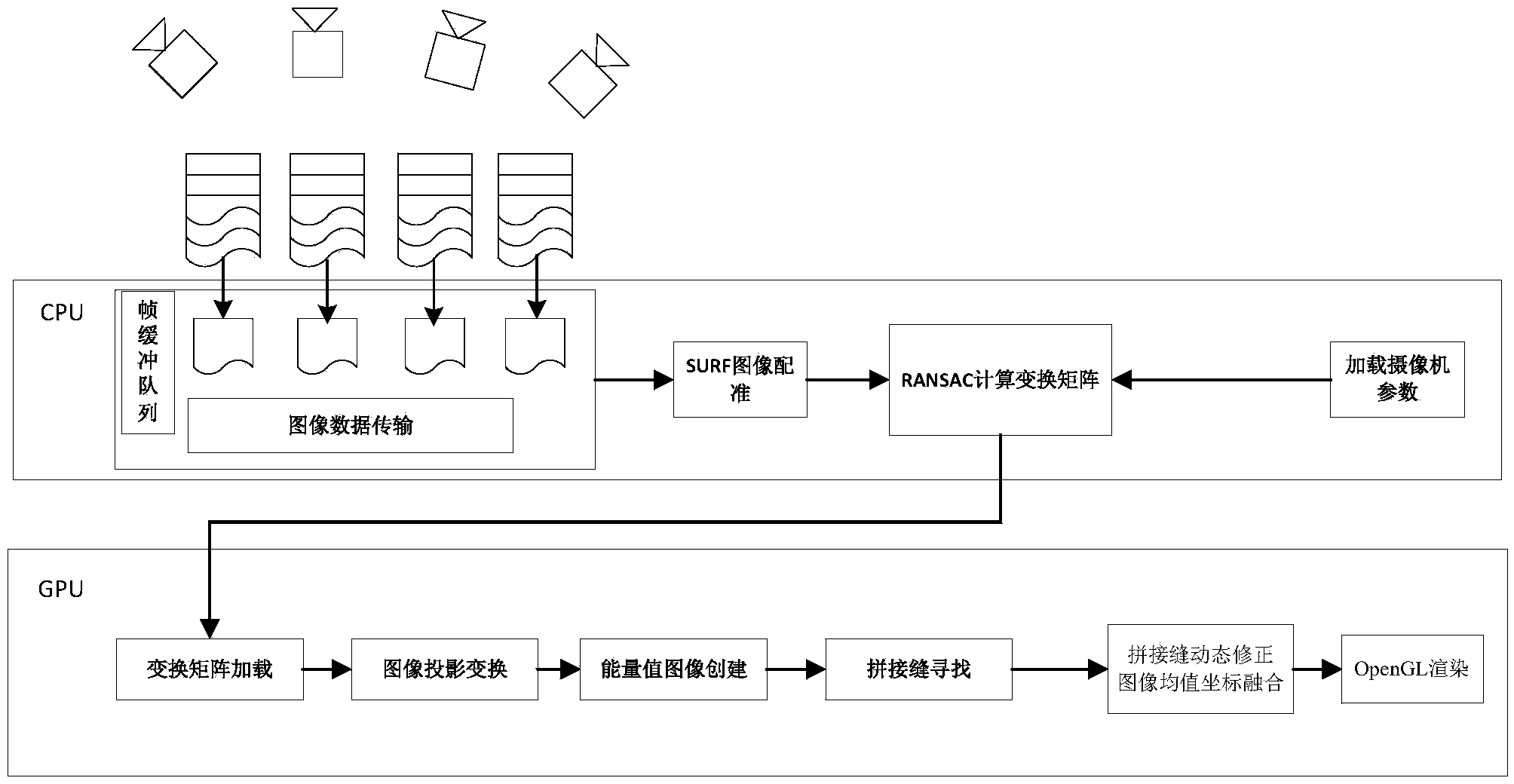
Multi-video real-time panoramic fusion splicing method based on CUDA
InactiveCN103997609AImprove monitoring effectImage enhancementTelevision system detailsUltrahigh resolutionImage resolution
The invention discloses a multi-video real-time panoramic fusion splicing method based on a CUDA. The splicing method includes the step of system initialization and the step of real-time video frame fusion, wherein the step of system initialization is executed at the CPU end of the CUDA, and the step of real-time video frame fusion is executed at the GPU end; according to CUDA-based stream processing modes S21, S22, S23 and S24, four concurrent processed execution streams are set up at the GPU end, and S21, S22, S23 and S24 are deployed to corresponding stream processing sequences. Compared with the prior art, the multi-video and real-time panoramic fusion splicing method has the following advantages that multi-video real-time panoramic videos without ghost images or color brightness difference are achieved, the ultrahigh-resolution overall monitoring effect on large-scale scenes such as an airport, a garden and a square is remarkable, and the application prospect is wide.
Owner:WISESOFT CO LTD +1
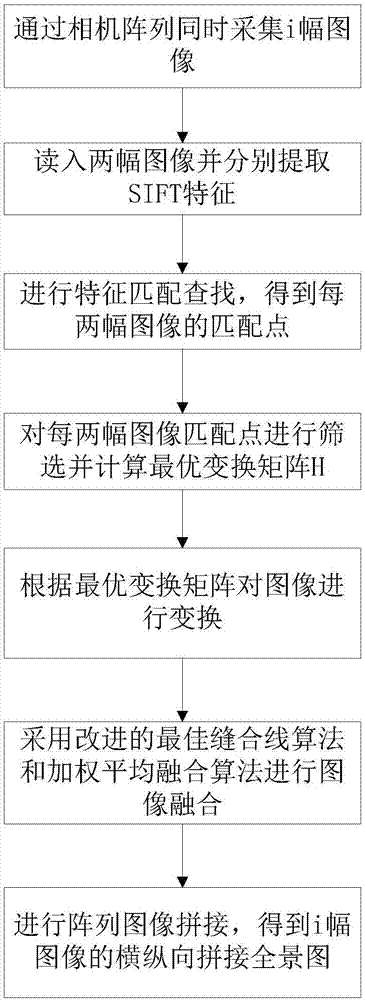
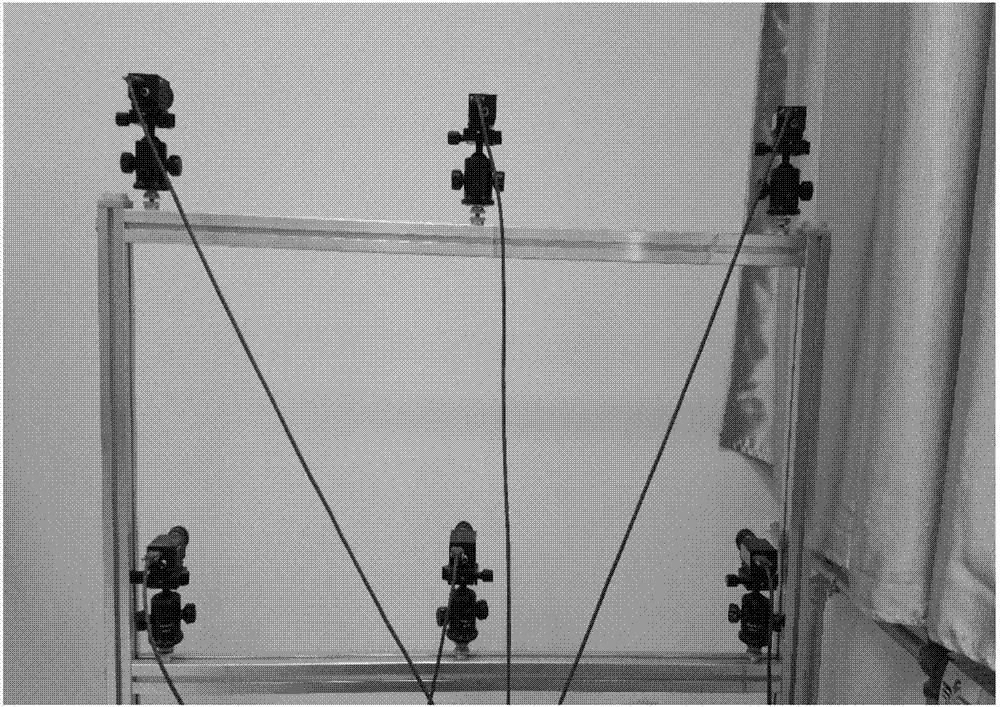
Panoramic imaging method based on camera array
ActiveCN107301620ASave stitching timeRealize the combinationImage enhancementImage analysisImage resolutionFusion splicing
The invention discloses a panoramic imaging method based on a camera array and mainly aims to solve the problems that in the prior art, a splicing scene is small, and a "ghost shadow" exists. According to the scheme, (1) array cameras are used to acquire multiple images, two images are read, SIFT features of the two images are extracted respectively, feature matching search is performed, matching points of the two images are obtained and screened, an optimal transformation matrix is calculated, the images are transformed according to the optimal transformation matrix, and an improved optimal stitching line algorithm and a weighted average fusion algorithm are adopted to perform fusion splicing on the images; and (2) the step (1) is repeated till splicing of the upper image and the lower image is completed, the splicing image is used as a to-be-spliced image, splicing is continued after the to-be-spliced image is rotated counterclockwise by 90 degrees, and the result is rotated clockwise by 90 degrees to obtain a final splicing panoramic image. Through the method, the "ghost shadow" phenomenon is remarkably eliminated, and the obtained panoramic image is large in view field, high in resolution, more approximate to a real panorama and capable of being used for splicing of larger scene images in the horizontal direction and the vertical direction.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Apparatus and method for heat-treatment of optical fiber reinforcing member and optical fiber fusion splicing apparatus
ActiveUS20050123253A1Temperature differenceInhibit temperature riseHeater elementsHeating element shapesEngineeringFusion splicing
A heat-treatment apparatus according to the present invention comprises a sheet-like heating body, which is bent like a letter “U”, and a heat equalizing plate constituted by a metal plate bonded to a heat generating part of the sheet-like heating body. The heat equalizing plate is bonded to the inner surface of the sheet-like heating body bent like a letter “U”. Alternatively, a fluorocarbon resin is coated on the surface of the heat equalizing plate.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
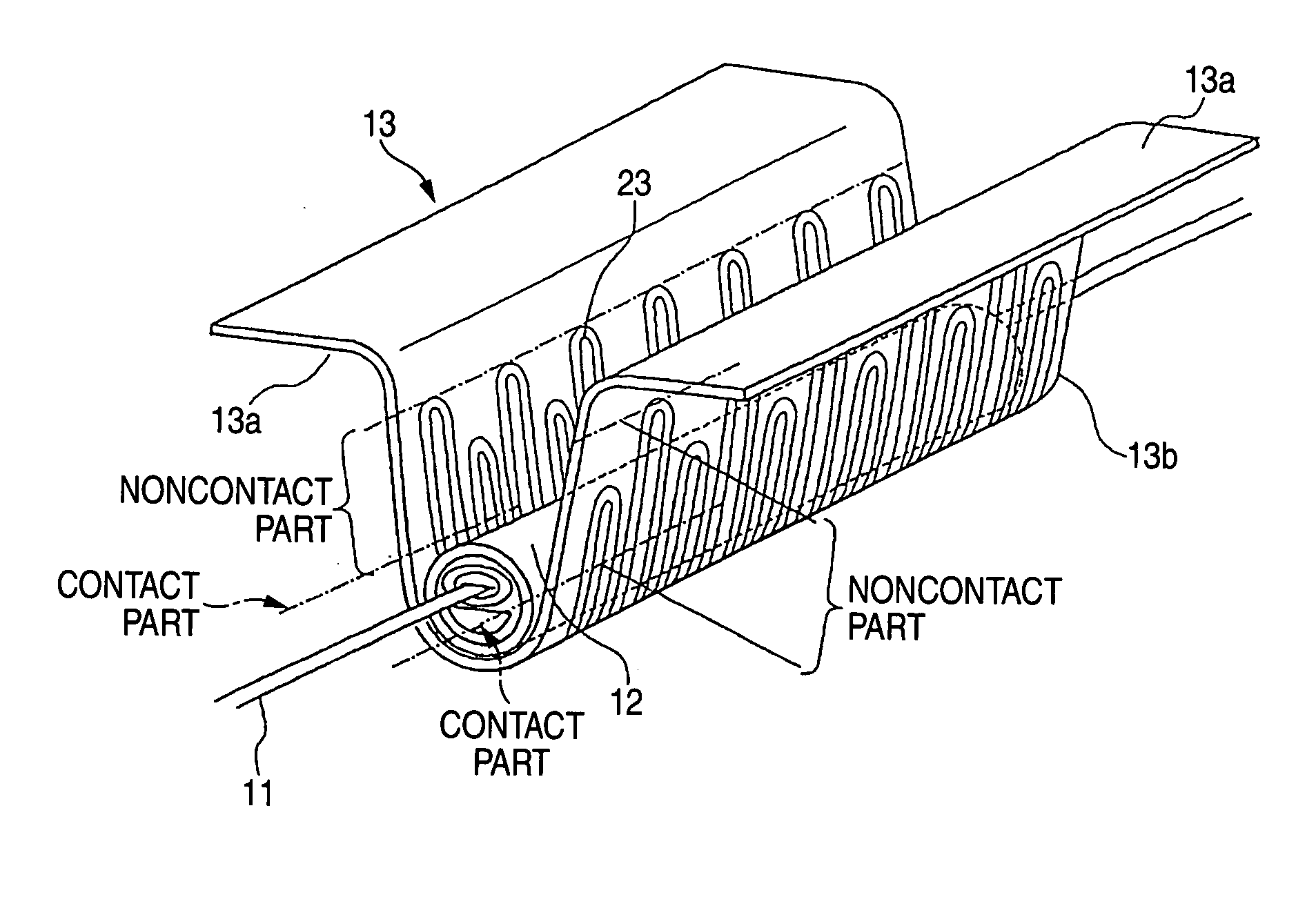
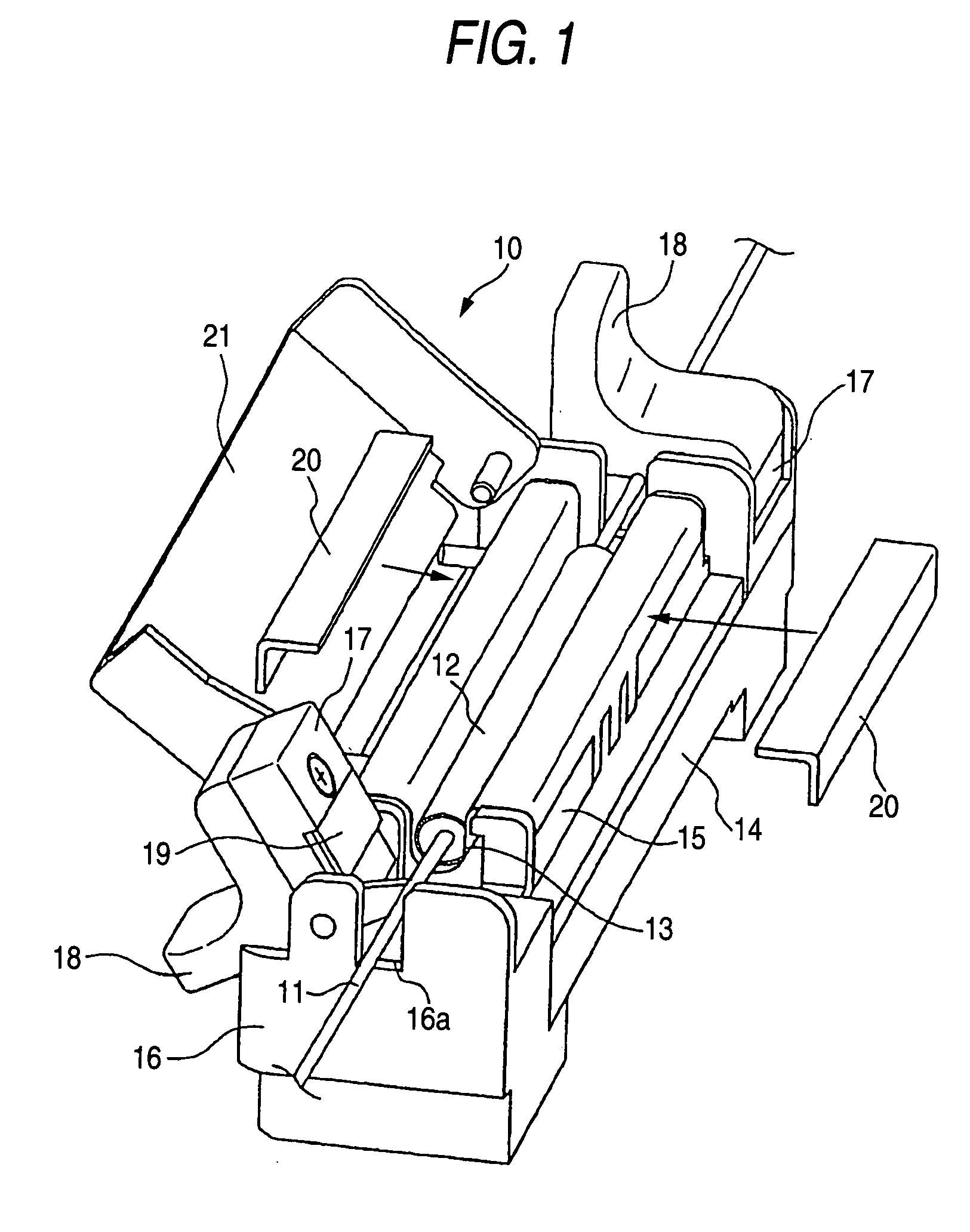
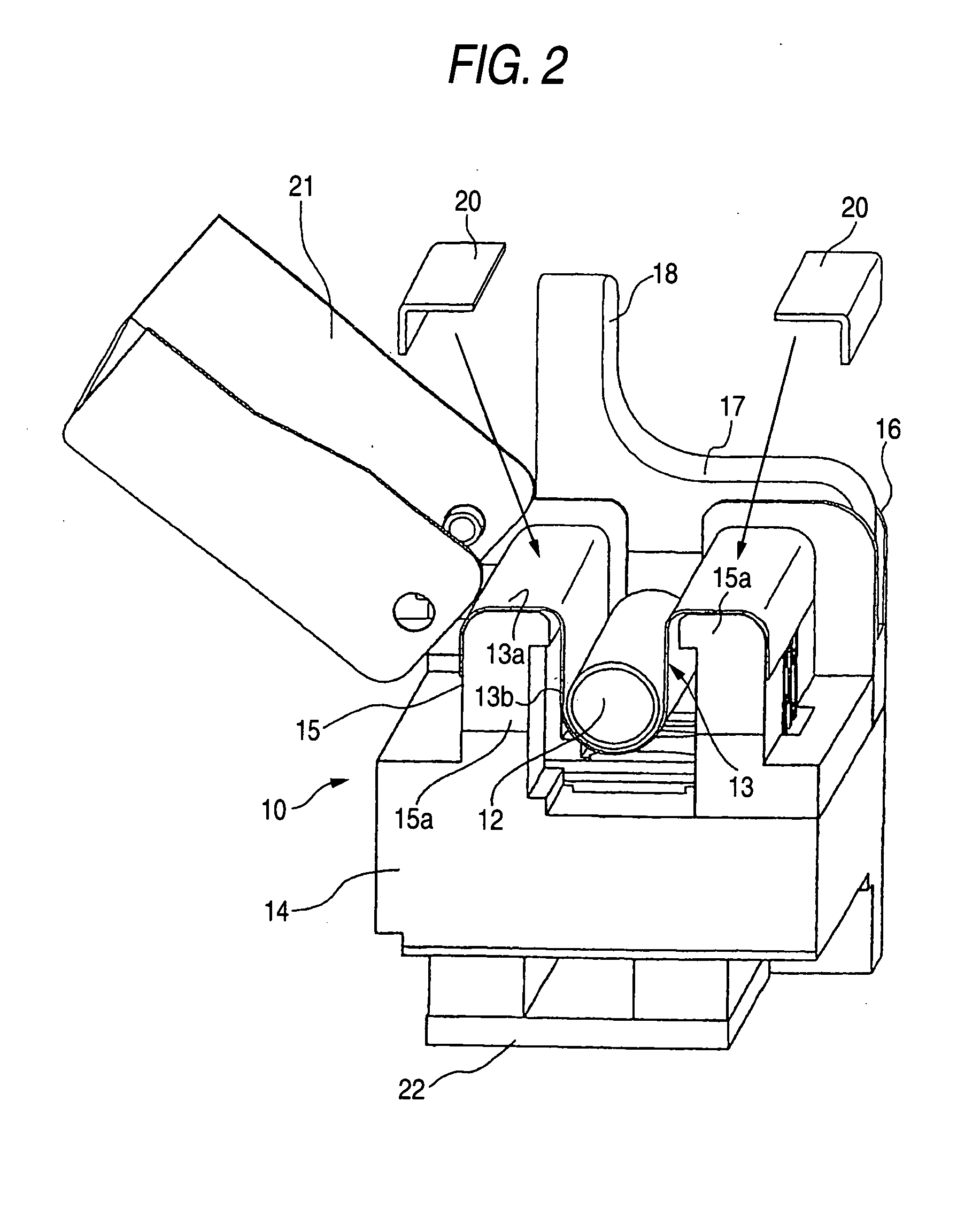
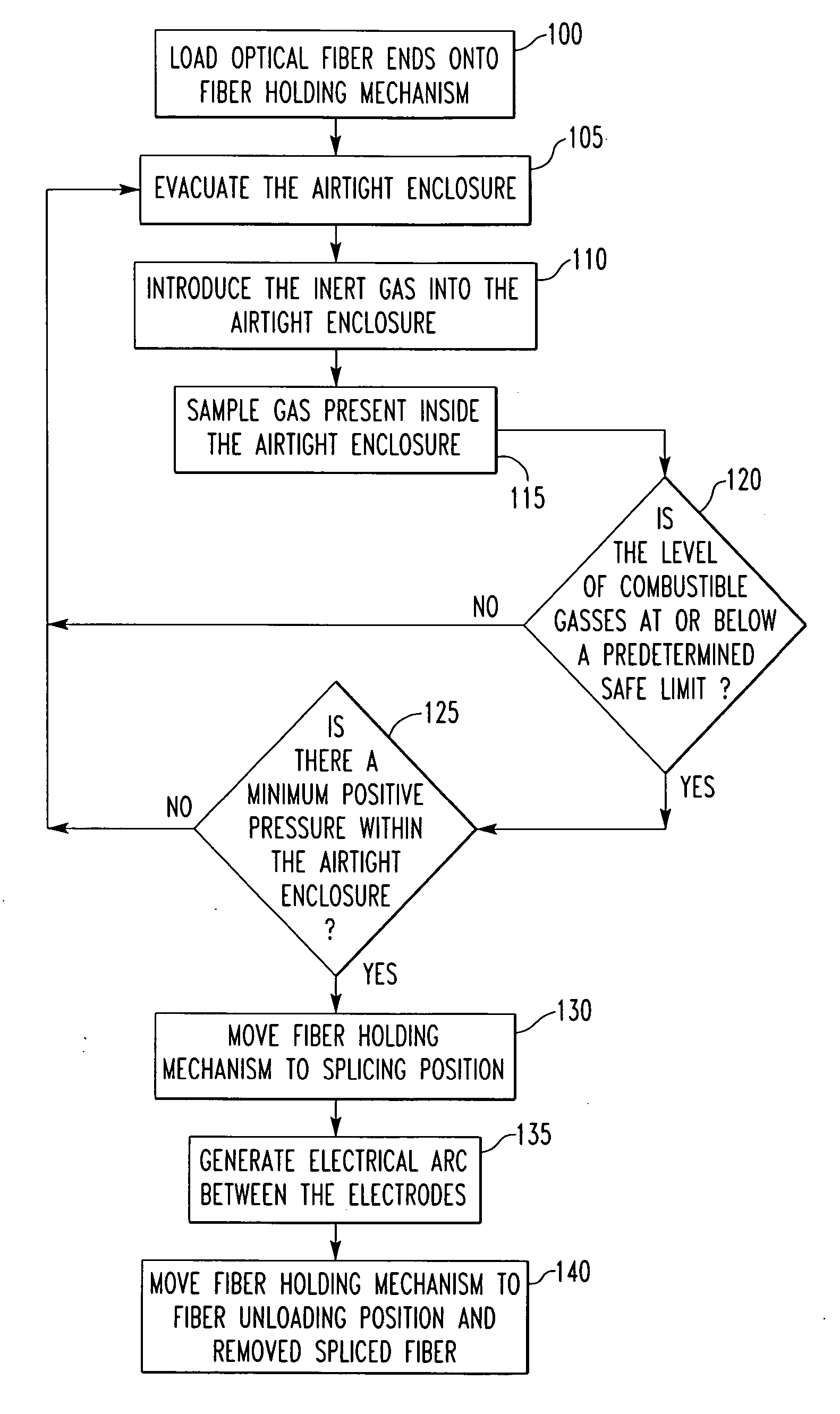
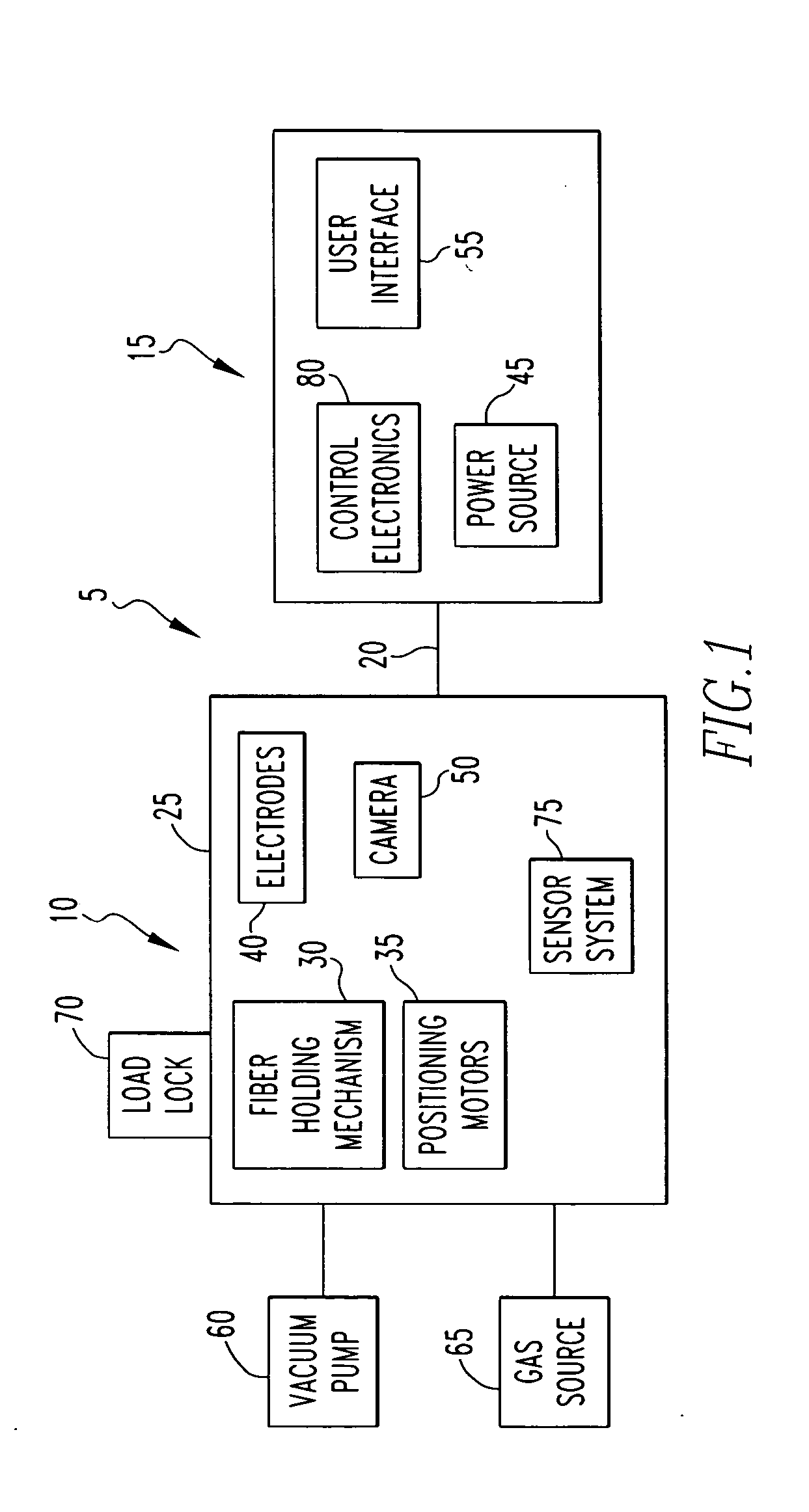
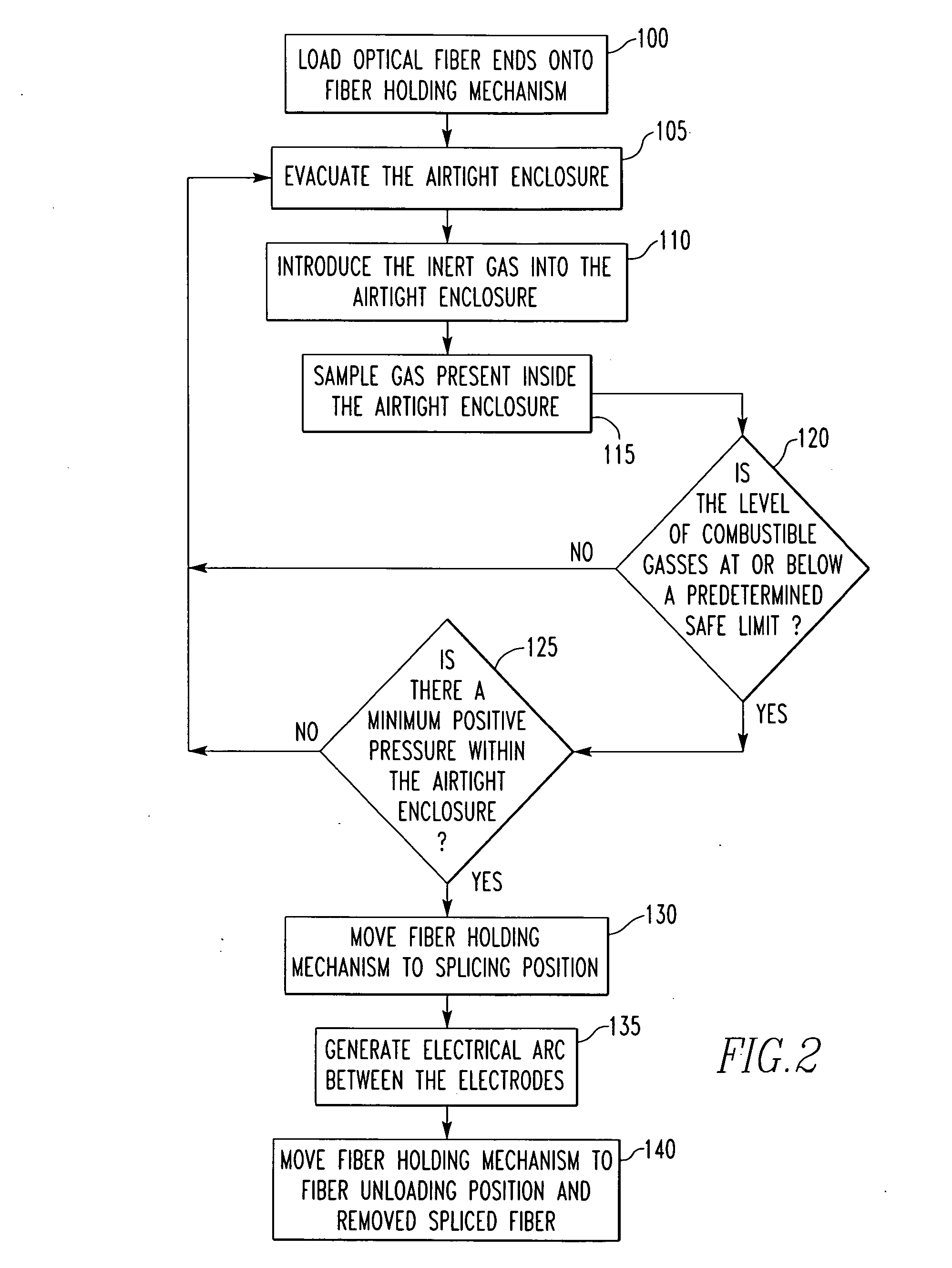
Method and apparatus for fusion splicing optical fibers
An apparatus for fusion splicing optical fibers includes an airtight enclosure, a vacuum pump for evacuating the enclosure, first and second electrodes positioned within the enclosure, and a power source separate from an external to the enclosure for applying a voltage to the first electrode for generating an arc between the electrodes that is used to splice the first and second optical fiber portions together. Also, a method of fusion splicing optical fibers includes receiving first and second fiber portions within an airtight enclosure, evacuating the airtight enclosure, and applying a voltage to a first electrode within the enclosure from a source located separate from and external to the enclosure to cause the generation of an arc between the first electrode and a second electrode within the enclosure that is used to splice the first and second optical fiber portions together.
Owner:3SAE TECH
Fabrication of collimators employing optical fibers fusion-spliced to optical elements of substantially larger cross-sectional areas
InactiveUS6360039B1Reduce back reflectionImprove pointing accuracyLamination ancillary operationsLaminationRefractive indexFusion splicing
A fiber collimator is provided, comprising at least two optical components, one of the optical components (e.g., an optical element such as a collimating lens or a plano-plano pellet) having a surface that has a comparatively larger cross-sectional area than the surface of the other optical component(s) (e.g., at least one optical fiber). The optical components are joined together by fusion-splicing, using a laser. A gradient in the index of refraction is provided in at least that portion of the surface of the optical element to which the optical fiber(s) is fusion-spliced or at the tip of the optical fiber. The gradient is either formed prior to or during the fusion-splicing. Back-reflection is minimized, pointing accuracy is improved, and power handling ability is increased.
Owner:LIGHTPATH TECH INC
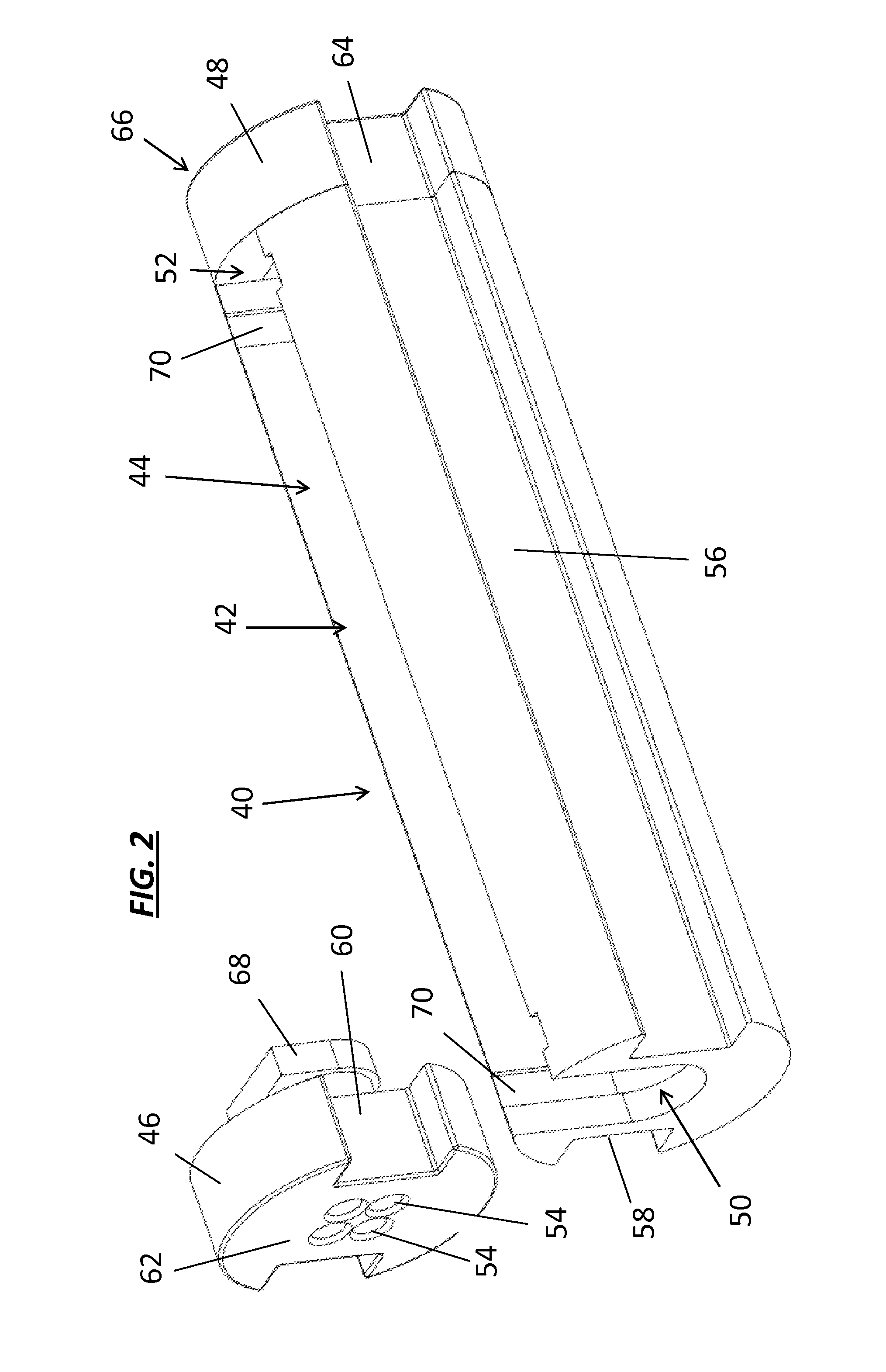
Fusion splicing structure of optical fibers
InactiveUS7748913B2Inhibit deteriorationEasy to useOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCoupling light guidesDouble-clad fiberSingle fiber
The present invention is a splicing structure of optical fibers for fusing a double clad fiber and a single clad fiber, the splicing structure is provided with a block covering a fusion splicing point of the double clad fiber and the single clad fiber, and which is made of a highly thermal conductive material.
Owner:FUJIKURA LTD
Optical connector connecting method and structure
A method and apparatus of connecting an optical connector and an optical fiber cord are provided. The method includes providing the optical connector, a connector housing, a stop-ring structure, and an optical fiber; fusion-splicing a fiber end of the optical fiber of the optical connector and a fiber end of an optical fiber protruding from a cord end of an optical fiber cord; enclosing the cord end of the optical fiber cord and at least the stop-ring structure end. The sleeve includes an annular sleeve body, a hot melt resin layer applied to an inner surface of the sleeve body, a tensile-strength body embedded in the sleeve body or the hot melt resin layer. The sleeve is heated such that the hot melt resin layer is melted into molten resin which in turn fills the inner space of the sleeve and solidifies therein.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
Fusion splicing structure of optical fibers
InactiveUS20090074362A1Inhibit deteriorationEasy to useOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCoupling light guidesDouble-clad fiberSingle fiber
The present invention is a splicing structure of optical fibers for fusing a double clad fiber and a single clad fiber, the splicing structure is provided with a block covering a fusion splicing point of the double clad fiber and the single clad fiber, and which is made of a highly thermal conductive material.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
Optical connector component and optical connector using the same
To provide a fusion-spliced optical connector capable of easily performing a fusion-splicing operation at an actual site in a short time, without need to perform additional special operations. An optical connector component is configured to attach a short-length optical fiber to a ferrule including a capillary and a flange. The capillary comprises a minute through hole and a coated-portion storage hole formed in the capillary, the minute through hole to be stored therein the bare optical fiber portion of the short-length optical fiber and the coated-portion storage hole to be stored therein a part of a coated optical fiber portion of the short-length optical fiber continuous to the bare optical fiber portion. The flange includes a coated-portion penetrating hole formed in the flange to be penetrated therein a very short portion continuous to the part of the coated optical fiber portion stored in the coated-portion storage hole. The short-length optical fiber extends rearward from the coated-portion penetrating hole of the flange by a length of a required extra-length splice portion when the bare optical fiber portion is fixedly stored in the minute through hole of the capillary and the part of the coated optical fiber portion continuous to the bare optical fiber portion is fixedly stored in the coated-portion storage hole of the capillary.
Owner:SEIKOH GIKEN
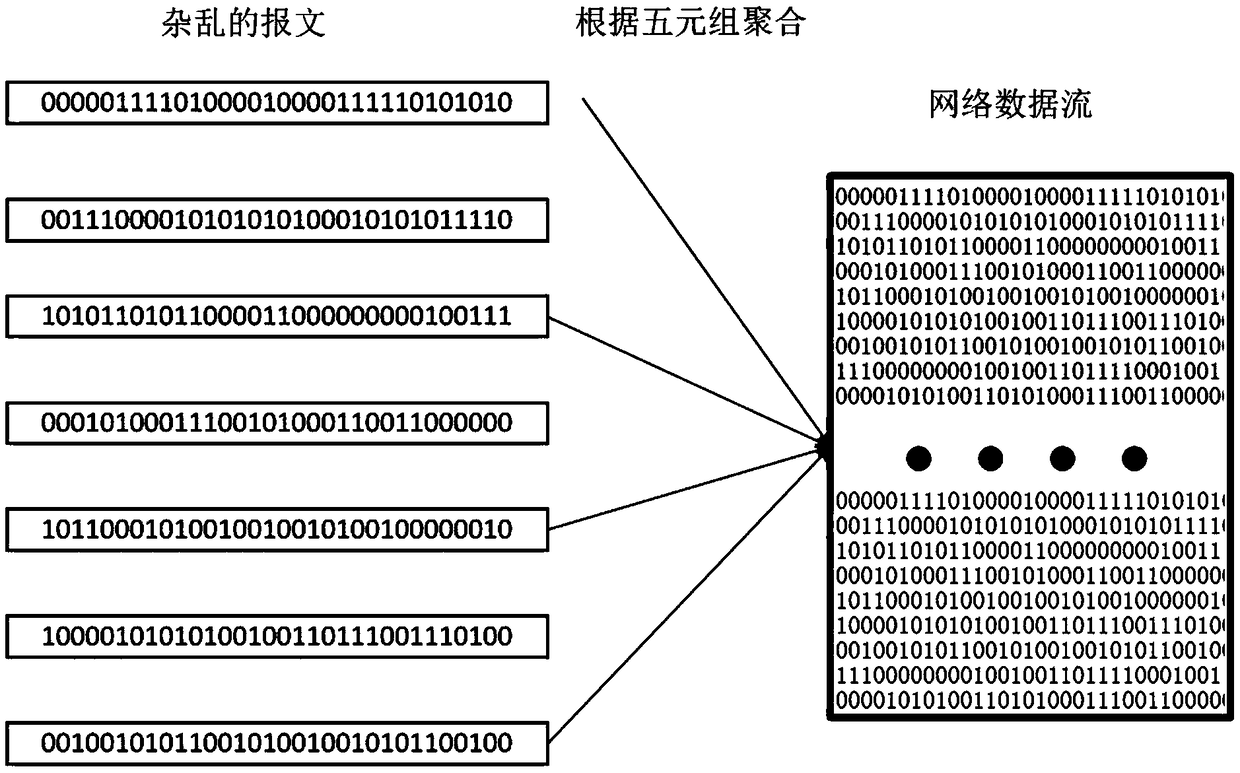
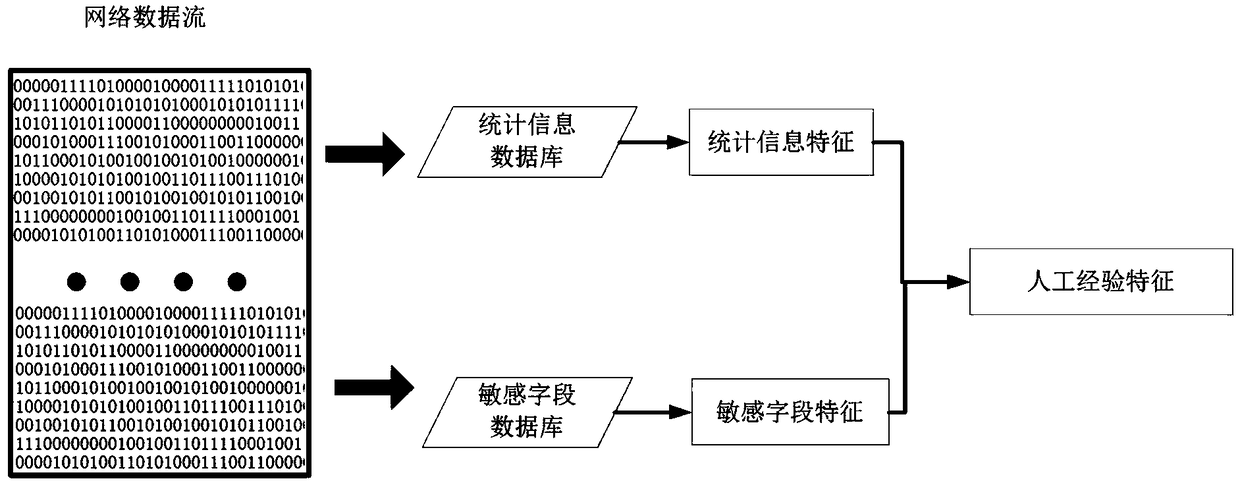
Data stream anomaly detection system based on empirical features and convolution neural network
ActiveCN109284606AEasy to detectMeet real-time requirementsCharacter and pattern recognitionPlatform integrity maintainanceDistillationComplex network
The invention discloses a data stream anomaly detection system based on empirical characteristics and convolution neural network. The system includes an empirical feature extraction module, which is used to identify statistical features and header features as features based on artificial experience, which play a more important role in data packet anomaly recognition; a bit stream conversion picture module used to convert the data stream into the form of two-dimensional gray-scale picture, and then through the convolutional neural network perception, the global high-level perception features are extracted; a fusion splicing module used for fusing the above modules as the data stream characteristics and identifying abnormal data streams by using the full connection layer of the neural network; a distillation model module that replaces complex networks in actual deployment; a concept drift fine-tuning module updates the detection model of concept drift; an update experience database module adding new network attacks or hidden attack instructions to the artificial experience database. The invention accurately and efficiently detects abnormal behaviors such as network failure, user misoperation, network attack and the like.
Owner:ARMY ENG UNIV OF PLA
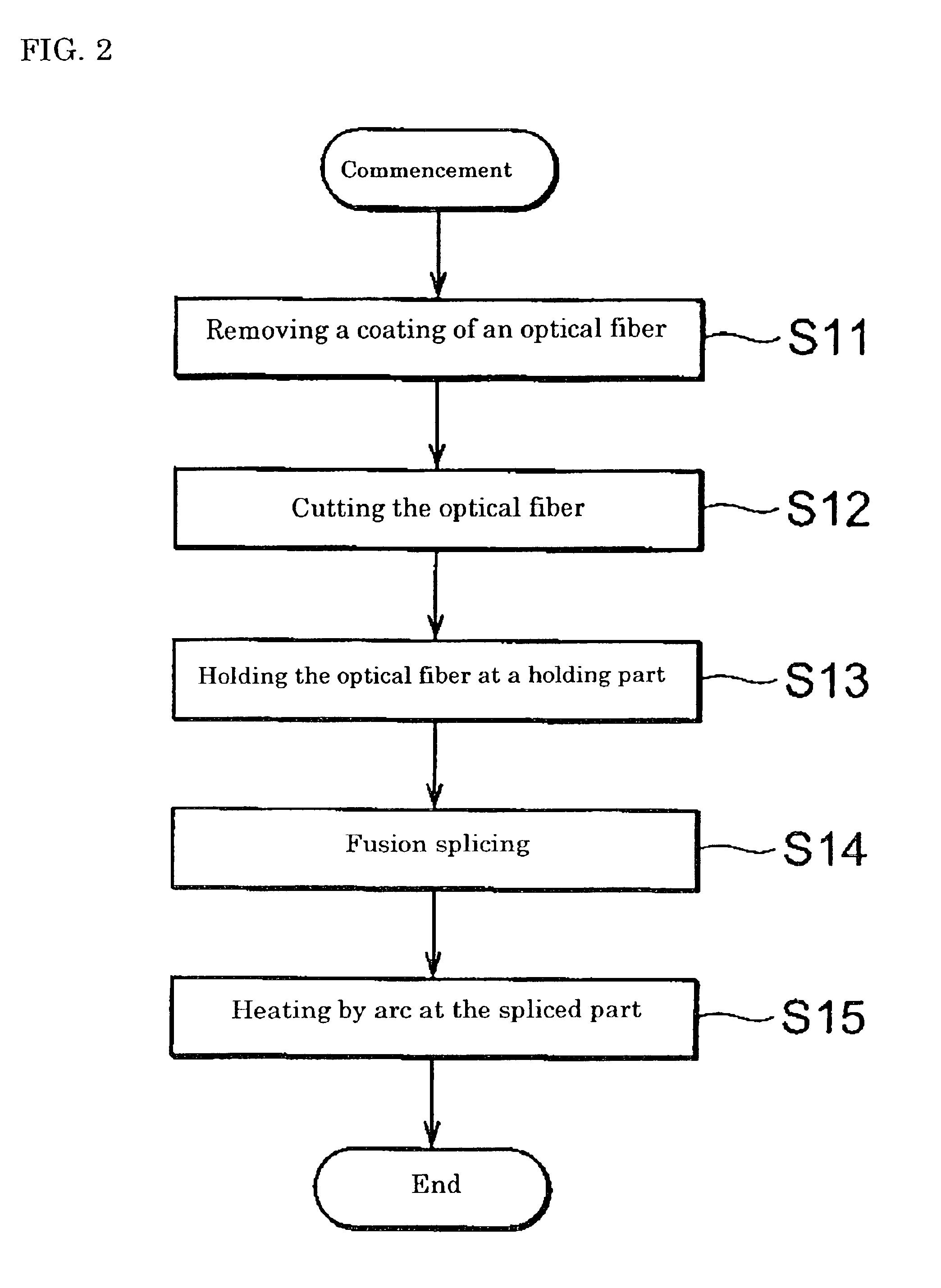
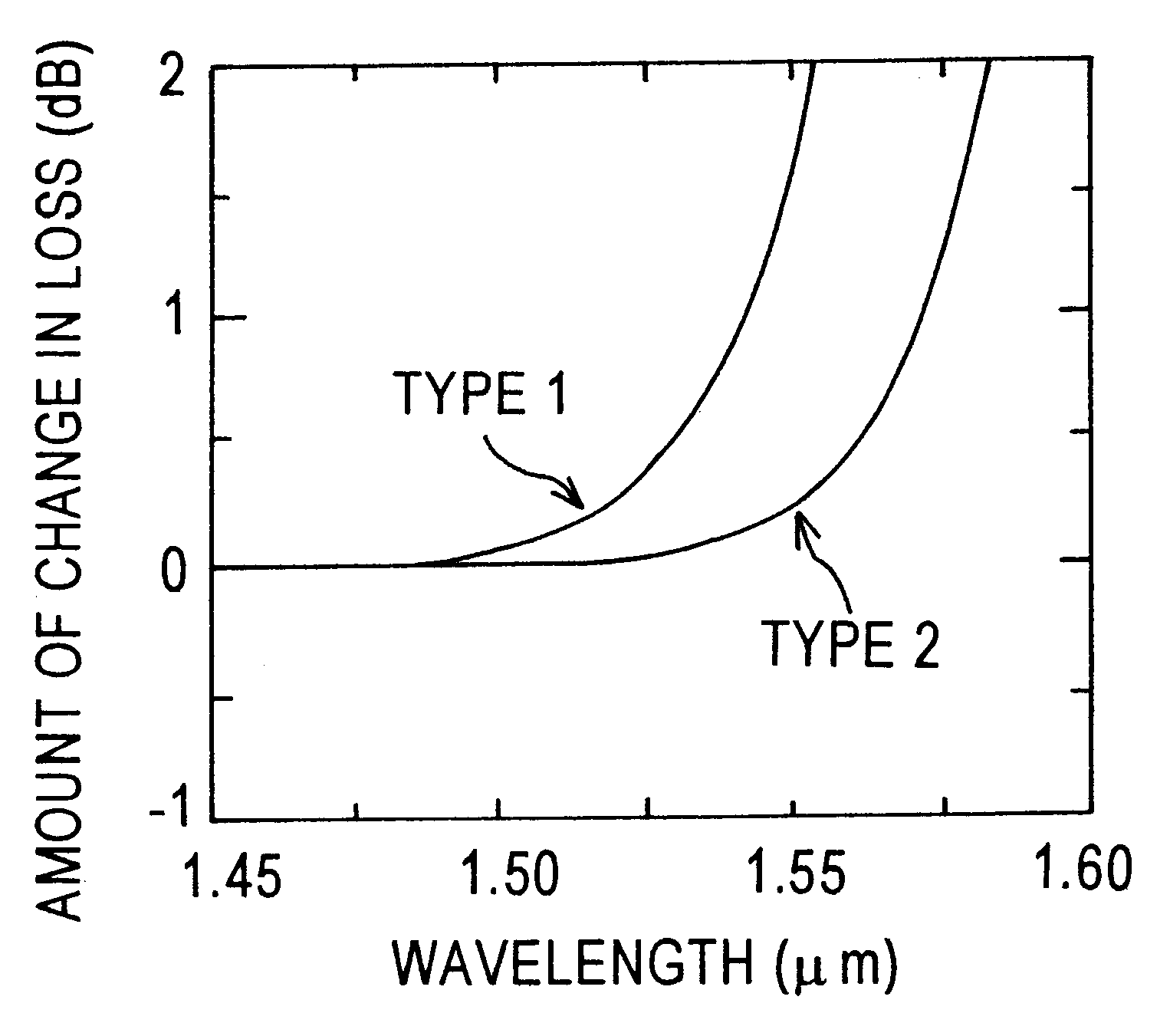
Method for fusion splicing optical fibers and apparatus for heating spliced part by arc
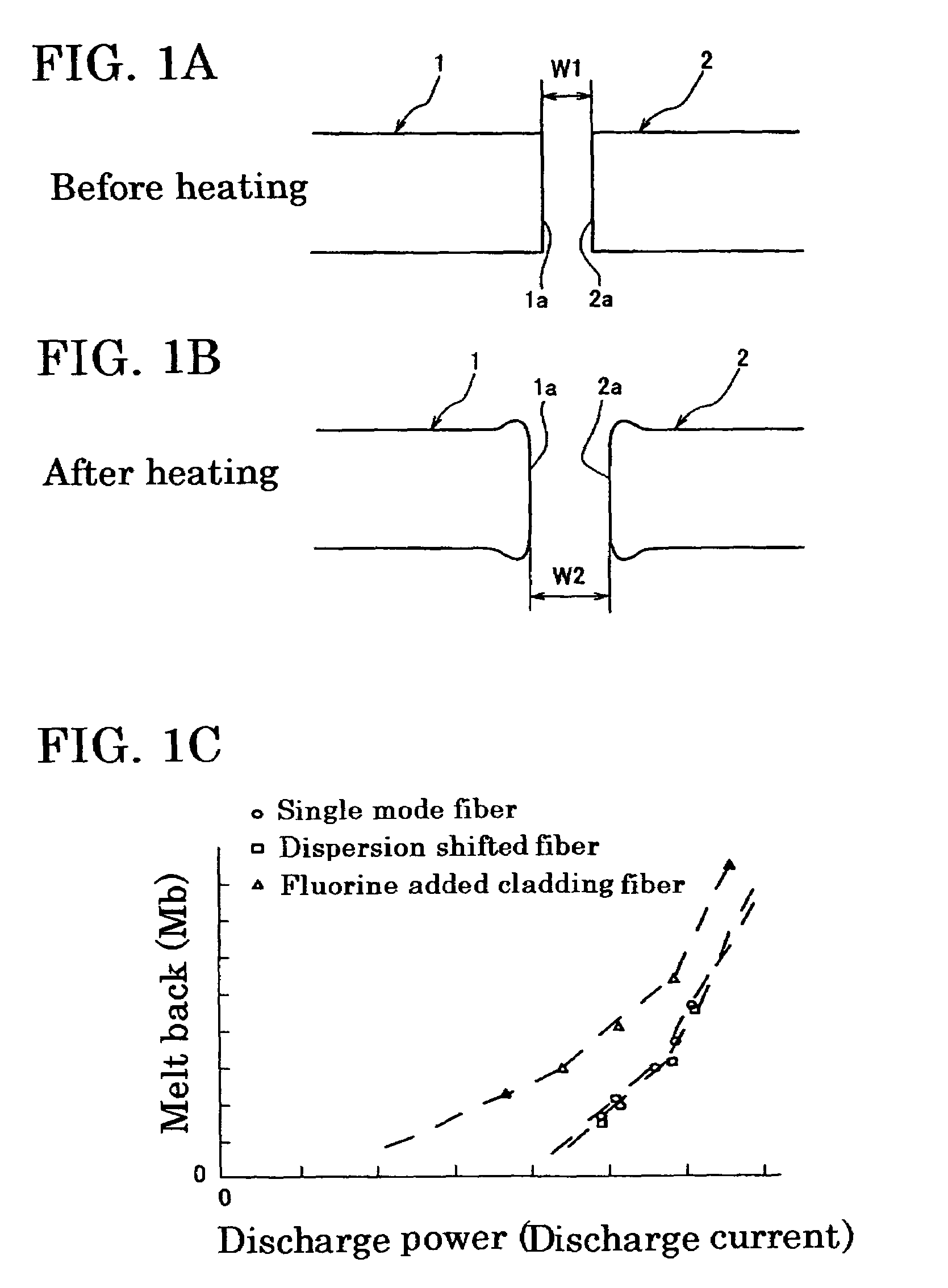
InactiveUS6886998B2Splice loss can be reducedArc welding apparatusCoupling light guidesElectric arcFusion splicing
An object is to provide an optical fiber fusion splicing method in which splice loss can be reduced, and also to provide an arc-heating unit used for heating the fusion spliced part of an optical fiber. The method comprises a process of fusion-splicing together the end faces of two optical fibers and a process of continuously heating the fusion spliced part by arc while moving one pair of electrodes provided opposite to each other across the fusion spliced part. The arc heating process is performed with the operation for decreasing arc temperature. The operation for decreasing arc temperature may be achieved by flowing a gas having a molecular weight greater than the average molecular weight of air into a gas atmosphere in which arc heating is performed, or by adding a modulation to an electric discharge current such that the maximum value becomes equal to or more than an electric current for starting arc discharge and the minimum value becomes more than zero and less than the electric current for starting arc discharge.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
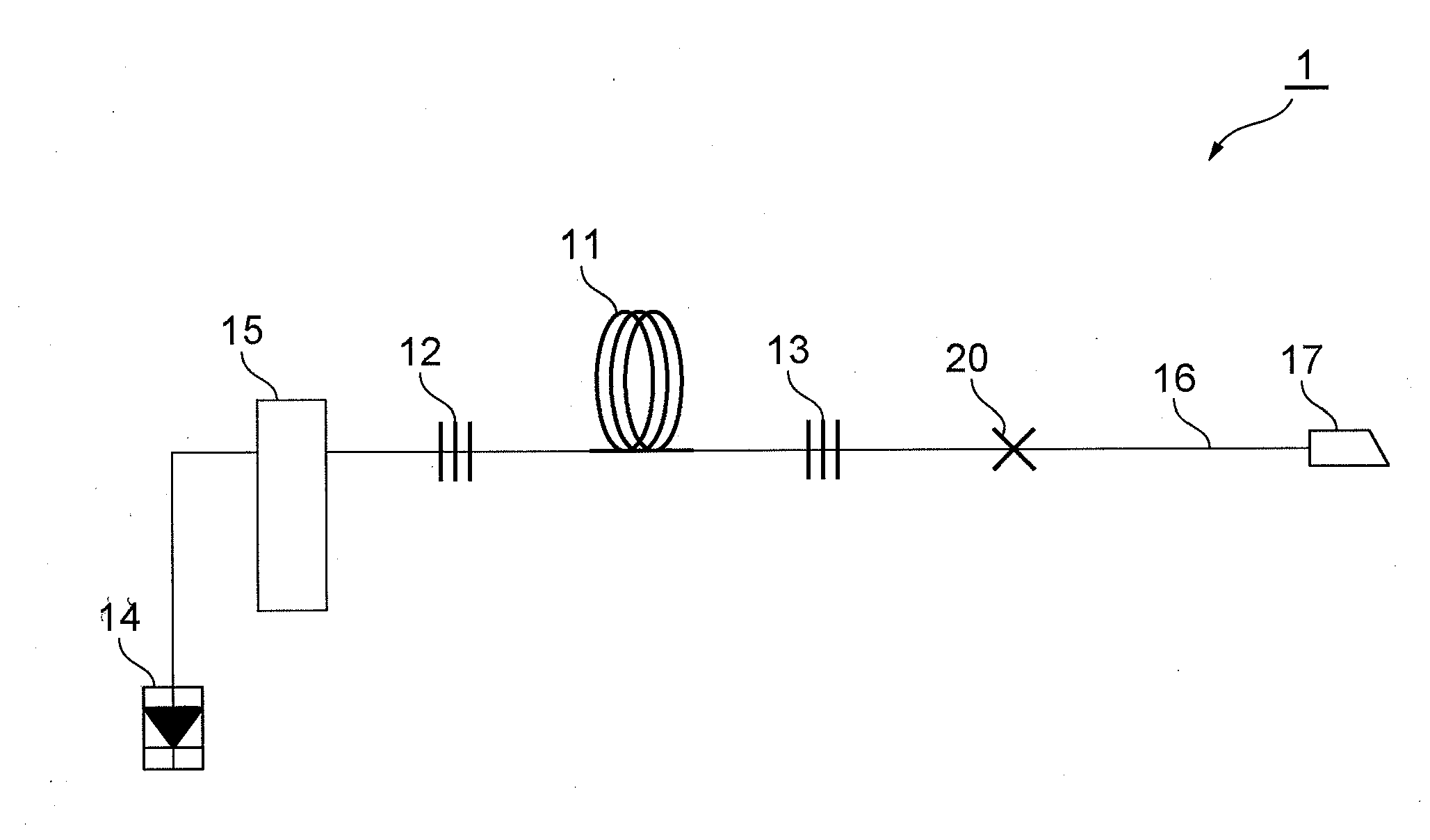
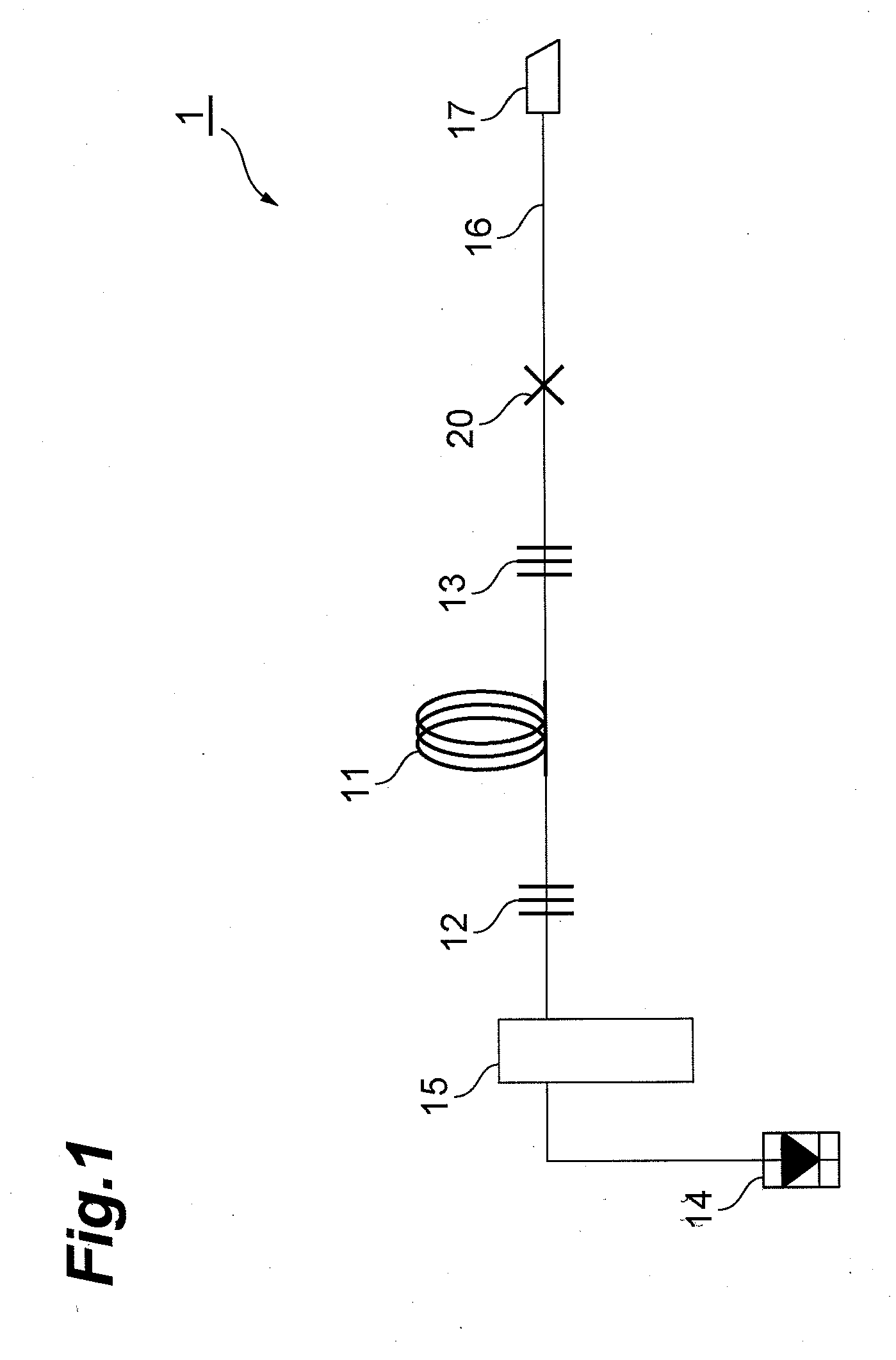
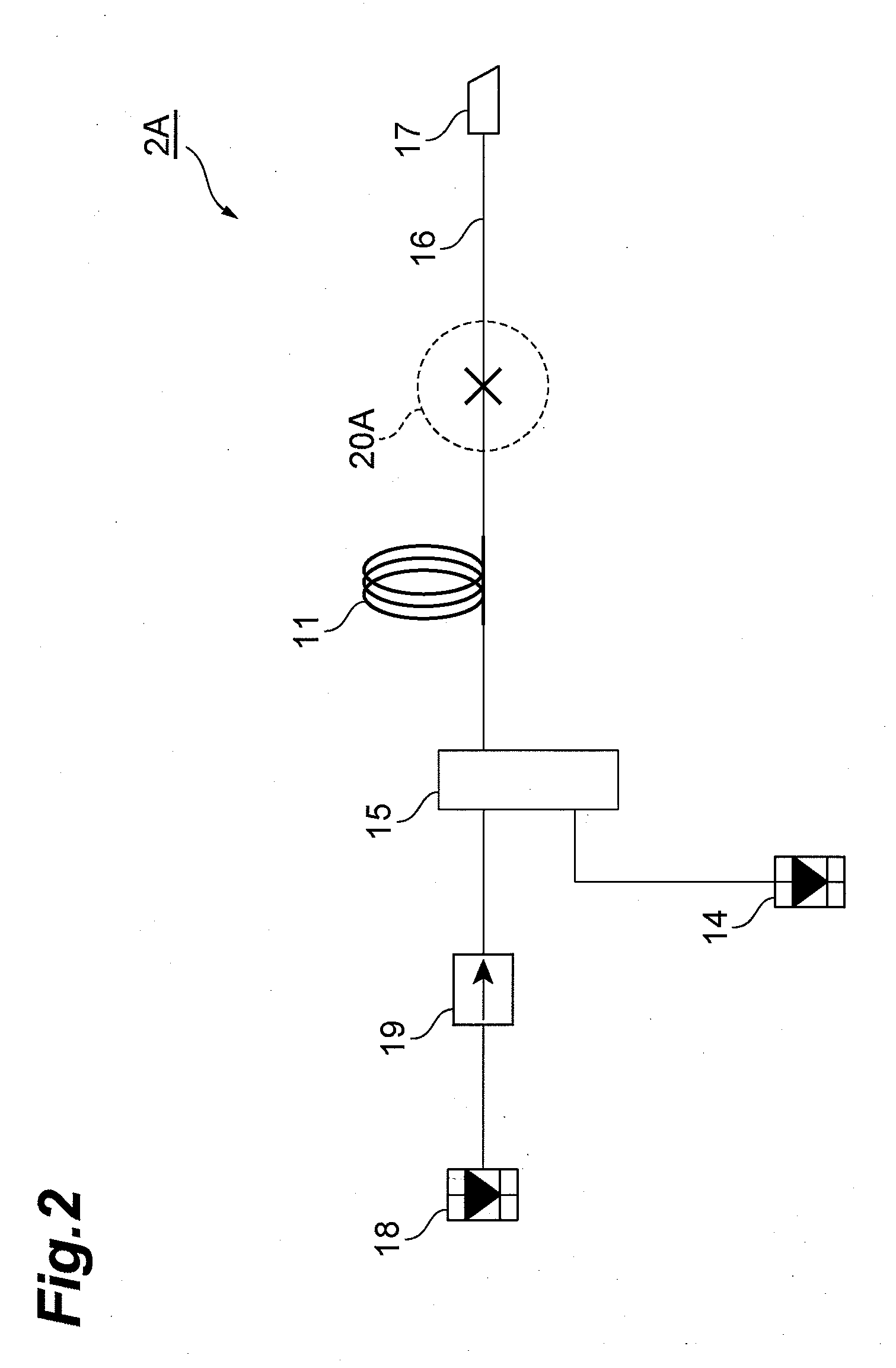
Coiled optical assembly and fabricating method for the same
After a wide-band DCF is wound around a bobbin to form an optical fiber coil 32, the latter is removed from the bobbin and placed into a bundle state (the state where the increase in transmission loss in the wavelength band of 1.55 mum caused by distortions in winding is reduced by 0.1 dB / km or more) released from distortions in winding. A resin 42 is used as a coil-tidying member so as to secure the optical fiber coil 32 to a storage case 40 at four positions. Both ends of the optical fiber coil 32 are connected to pigtail fibers at fusion-splicing parts 44; respectively. Even when the storage case 40 is closed with a lid after the optical fiber coil 32 is secured to the storage case 40 with the resin 42, there remain interstices within the bundle of the optical fiber coil 32 and a space between the optical fiber coil 32 and the storage case 40. As a result, even when the optical fiber coil 32 in a bundle state is accommodated in the storage case 40, transmission loss and the like would not increase.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Light input/output terminal module of the optical components and beam converting apparatus
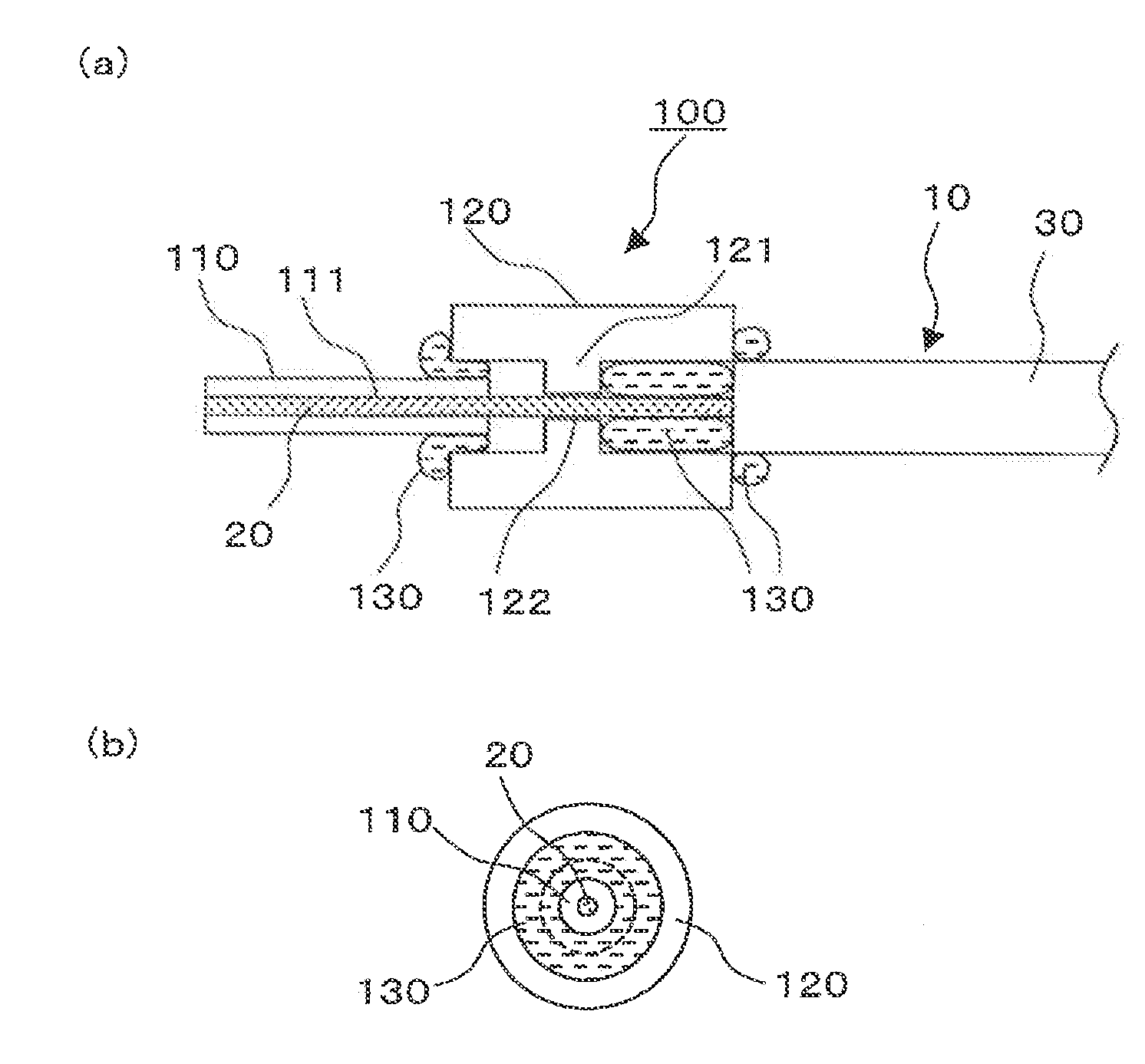
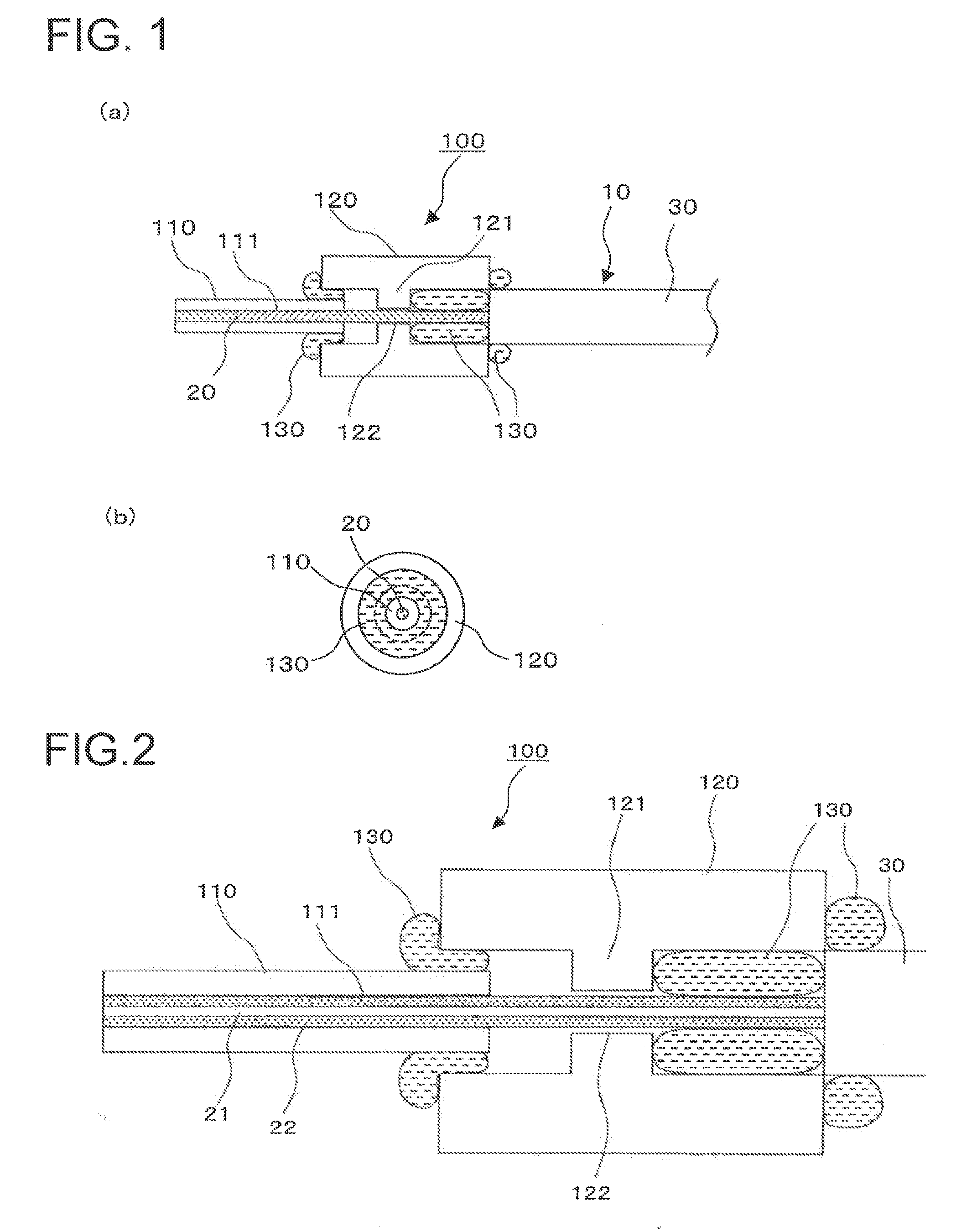
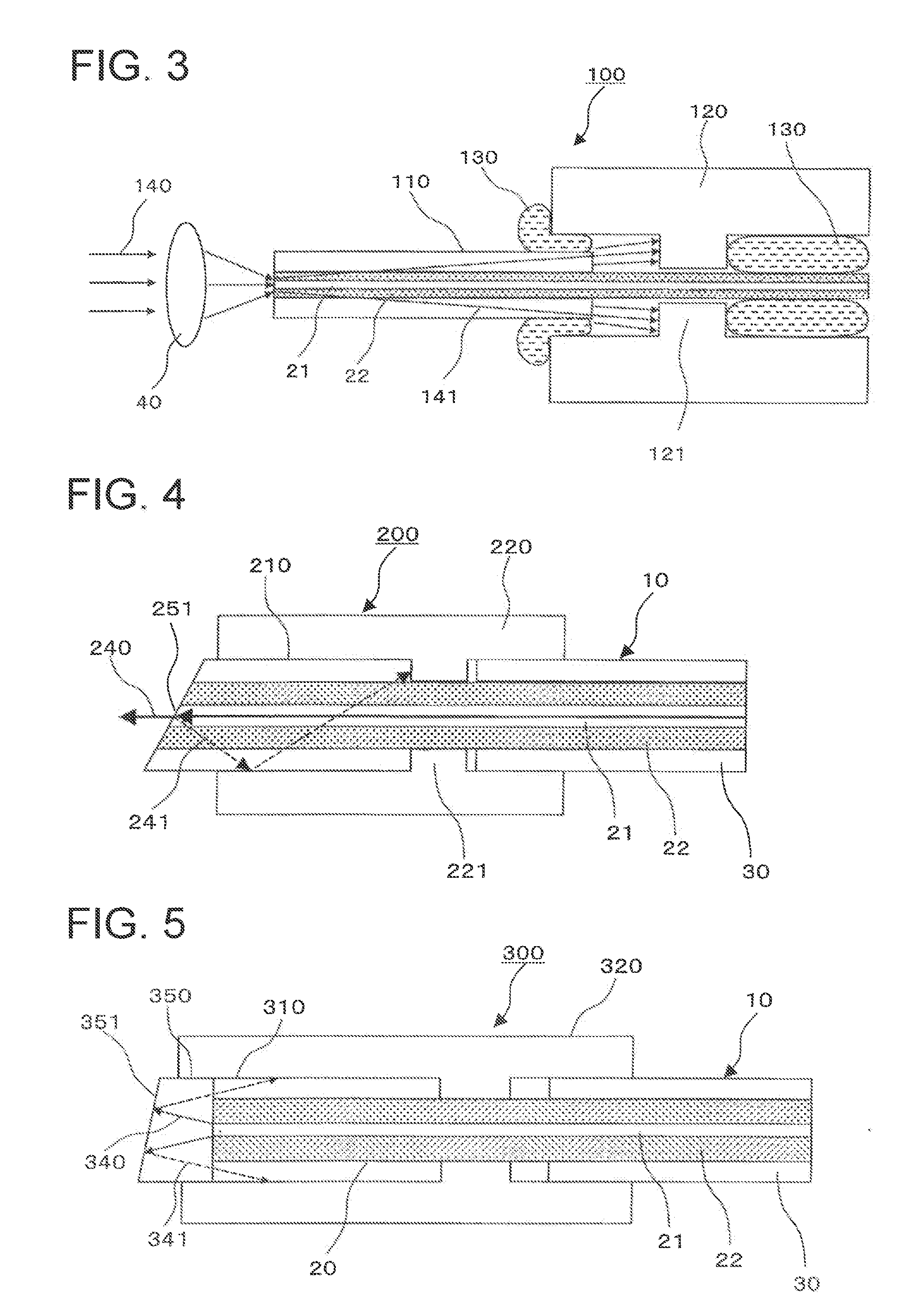
ActiveUS20090092358A1Increase light rateAvoid damageOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCoupling light guidesBeam diameterLight beam
A light input / output terminal module 100 comprises a jacket tube 110 and a flange 120. A glass portion 20 of the optical fiber is inserted in the center portion thereof. To efficiently remove the leaked light in a cladding 22 to the jacket tube 110, the jacket tube 110 is made of silica glass or the same material as that of the cladding 22. The jacket tube 110 is fixed by fusion splicing or adhesion to the cladding so as to integrally unify the jacket tube 110 and the cladding 22. The beam diameter at the fiber end portion is enlarged by an optical component which fusion bonds the tip end of the optical fiber to the coreless fiber so that the optical power density at the light input / output terminal module is reduced.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Multi-core optical fiber manufacturing method
ActiveCN103936277AStable positionGeometrically accurateGlass making apparatusStructural engineeringFusion splicing
The invention discloses a multi-core optical fiber manufacturing method, and belongs to an optical fiber manufacturing method. In the prior art, the relative position of a core rod in a casing pipe cannot be accurately fixed, the fusion splicing loss is increased for the reason of the fiber core position deviation after a multi-core optical fiber is prepared by drawing. According to the method, at least two core rods are fixed to a fixture, the fixture is installed onto a chuck of a lathe; a transition casing pipe with a sleeve is arranged on the other chuck of the same lathe; a core rod is inserted into the sleeve; the chucks are rotated for synchronization, an end part near to a clamping end of the core rod is heated, so that the end part is collapsed onto the core rod; then an interface position of the sleeve and the transition sleeve is heated, and tapering treatment of the sleeve and the core rod is performed, so that one end of the sleeve is sealed; the assembled core rod and the sleeve are respectively welded with an auxiliary quartz rod and a transition quartz sleeve after, then are installed onto a wire-drawer-tower for online vacuum wire drawing to obtain the multi-core optical fiber. In the assembly process of the core rods and the sleeve, a fixture is used for fixing the core rods, so that the relative position of the core rods is more accurate to ensure that the prepared multi-core optical fiber has accurate geometric dimension.
Owner:TIANJIN XINMAO SCI & TECH
Fusion splicing technological process and equipment for hollow drawstring of air bed body
InactiveCN101439583AEasy to operateShort processing timeFluid mattressesDomestic articlesEngineeringFusion splicing
The invention discloses a heat-sealing technique for an airbed hole drawstring, comprising the following steps: (A) a plurality of hole drawstrings are positioned between the upper piece and the lower piece of a bed body in a certain position and in a certain arrangement mode; (B) lower heat transmission moulds are positioned at the bottom surface of the lower piece of the bed body and corresponding to hole drawstrings; upper heat transmission moulds are positioned at the superface of the upper piece of the bed body and corresponding to the hole drawstrings; the upper heat transmission moulds and the lower transmission moulds are clamped so that the upper piece and the lower piece of the bed body are tightly against each other; (C) a power supply is started to heat the upper heat transmission moulds and the lower heat transmission moulds; the upper heat transmission moulds heat-seal the upper piece and the hole drawstrings on the superface and the lower heat transmission moulds heat-seal the lower piece and the hole drawstring from the bottom surface; (D) the upper heat transmission moulds and the lower heat transmission moulds are separated and the bed body is taken out. The invention heat-seals the bed body and the hole drawstrings outside the bed body, thereby having the advantages of clear weld mark decorative patterns on the finished products, steady heat-sealing quality and fixed hole drawstring intervals. Meanwhile, the invention discloses heat-sealing equipment for the airbed hole drawstrings with high production efficiency.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN ZHANXIN PLASTIC PROD
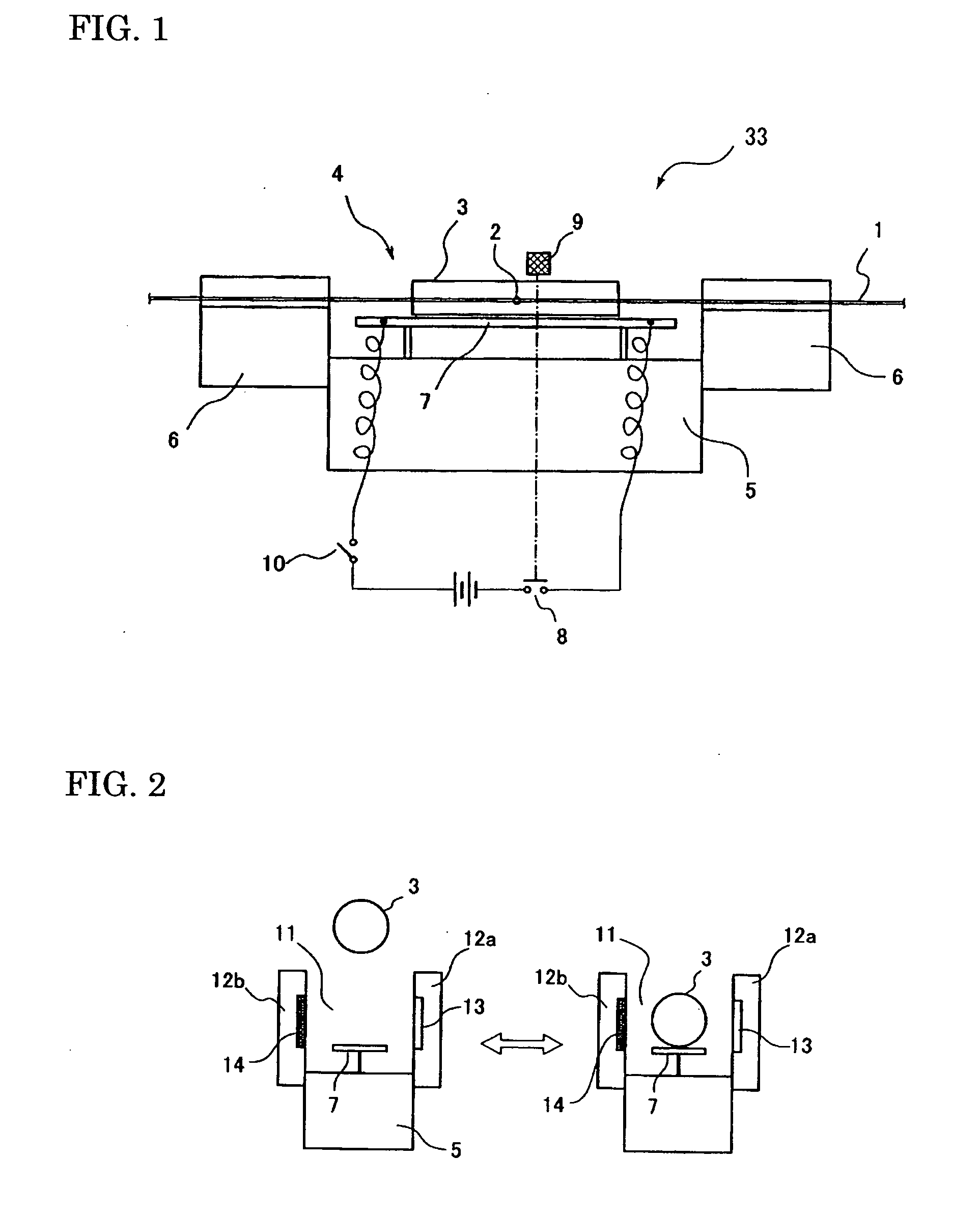
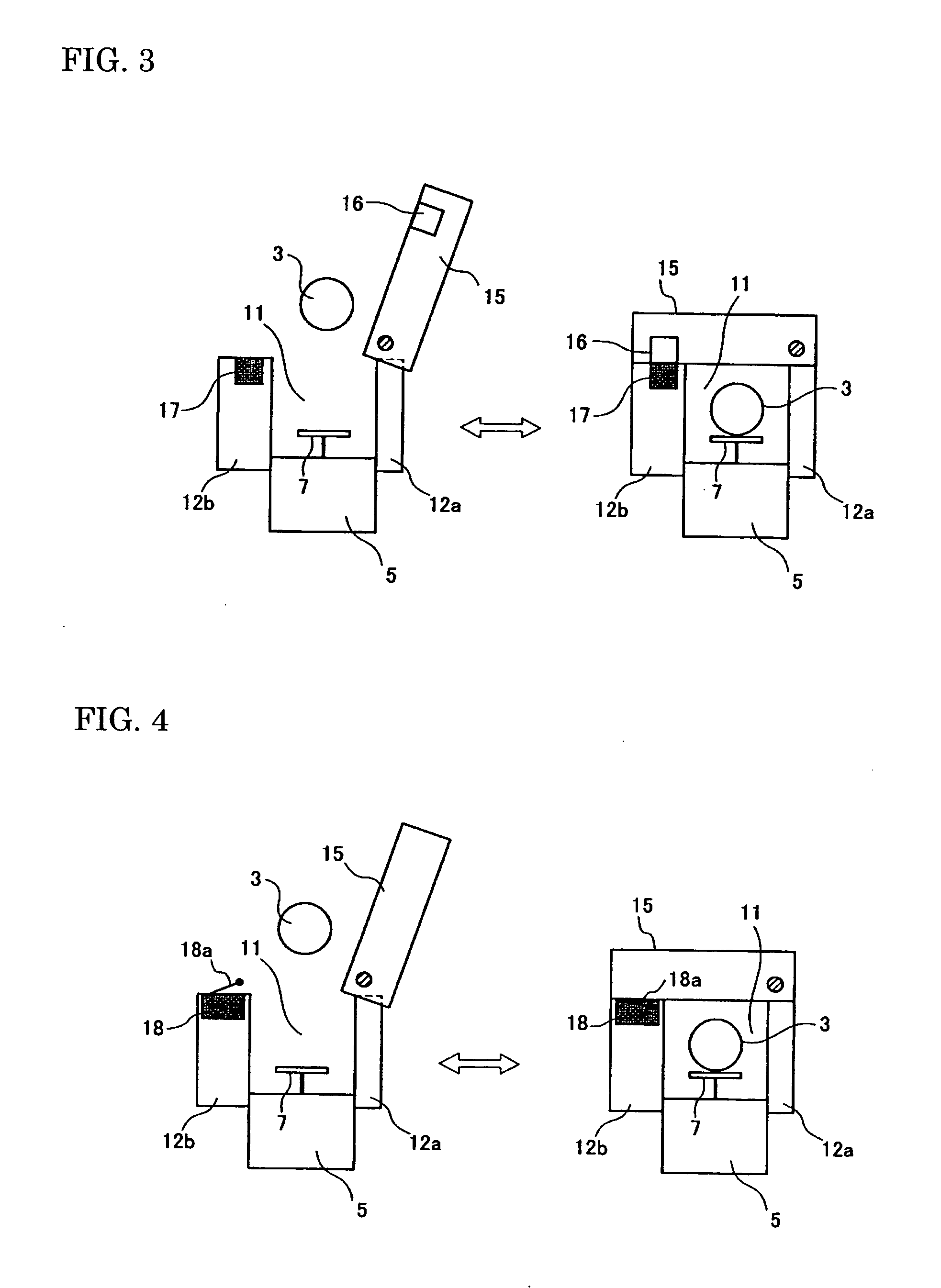
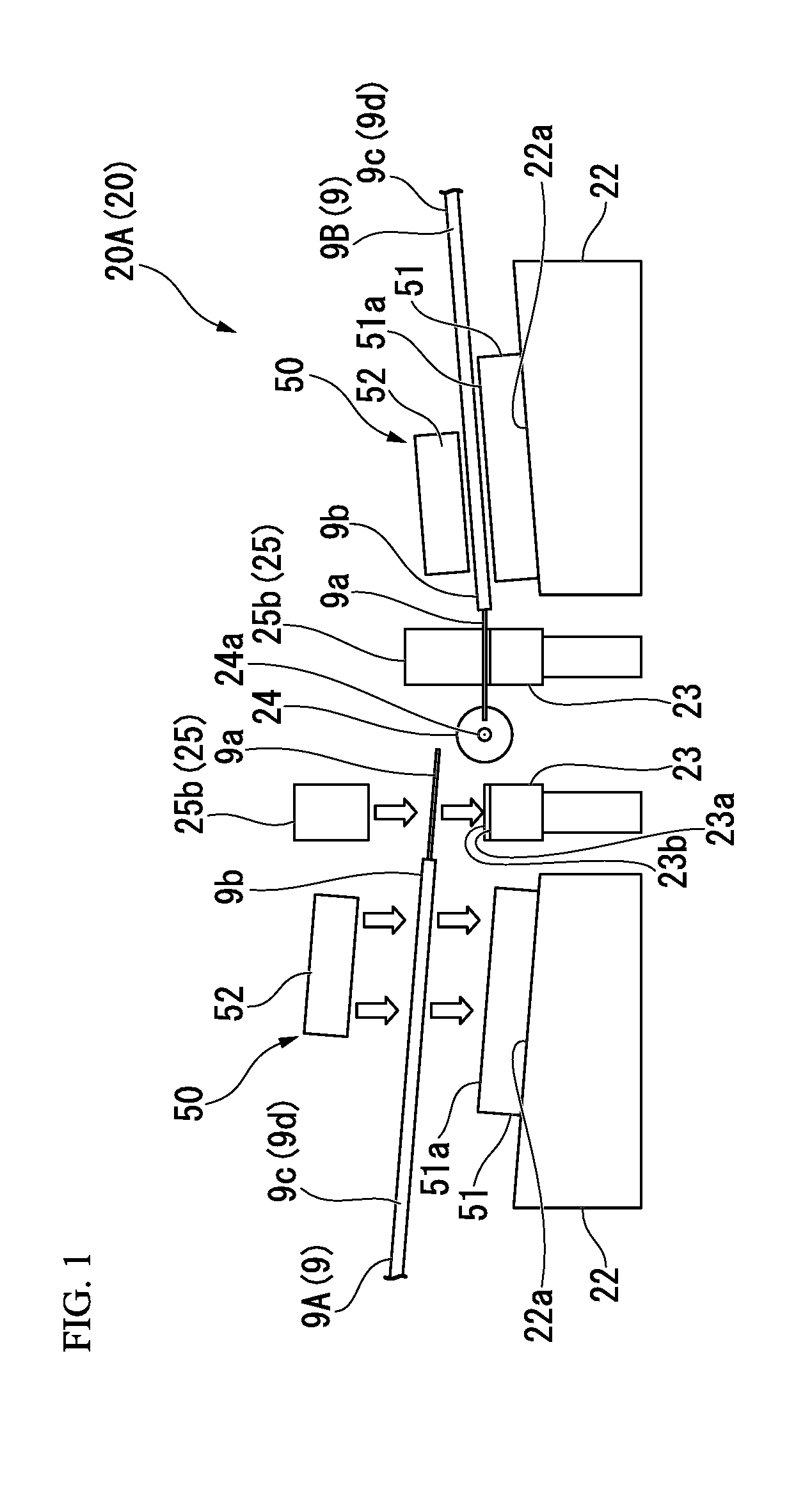
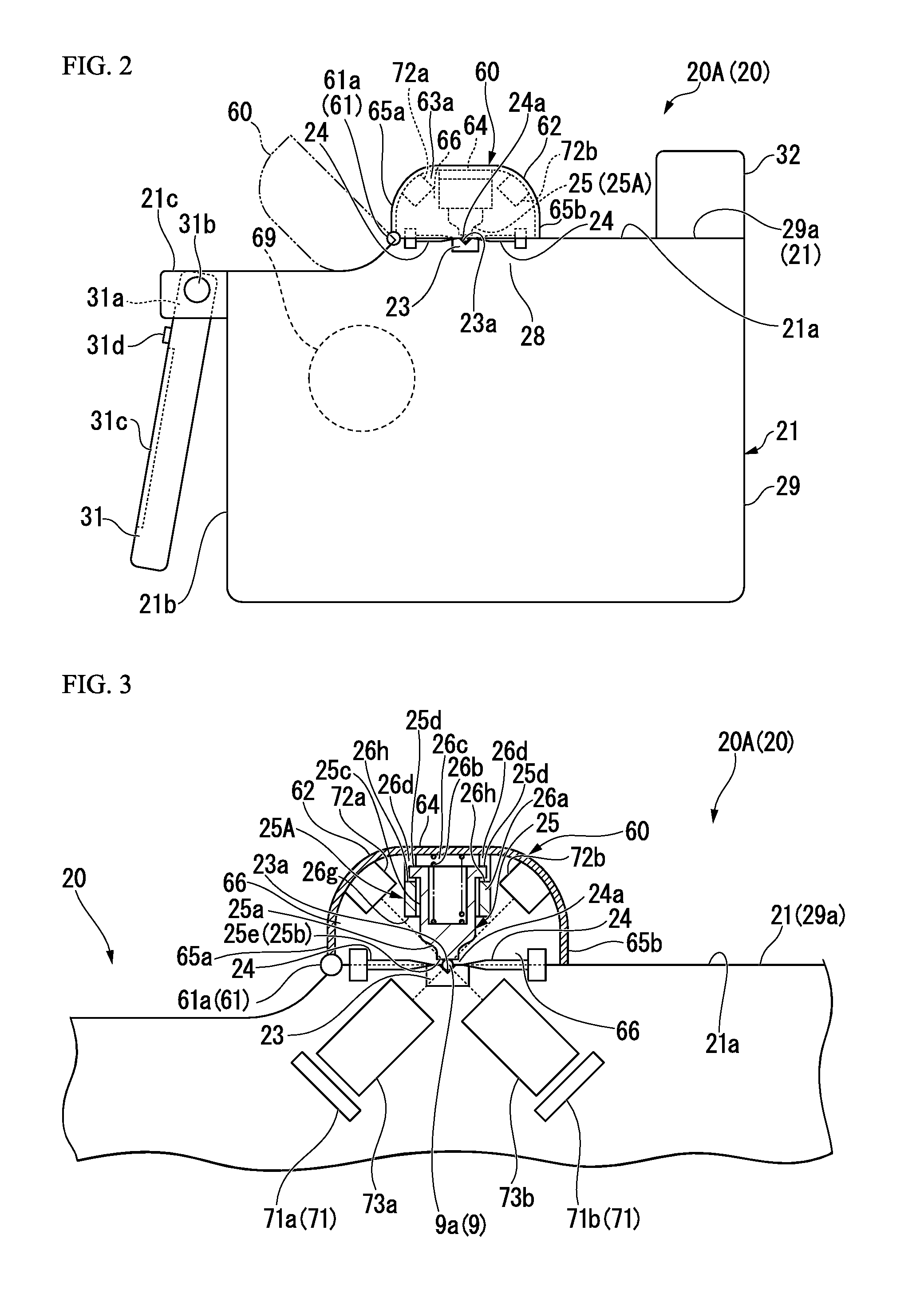
Fusion splicing device and fusion splicing method
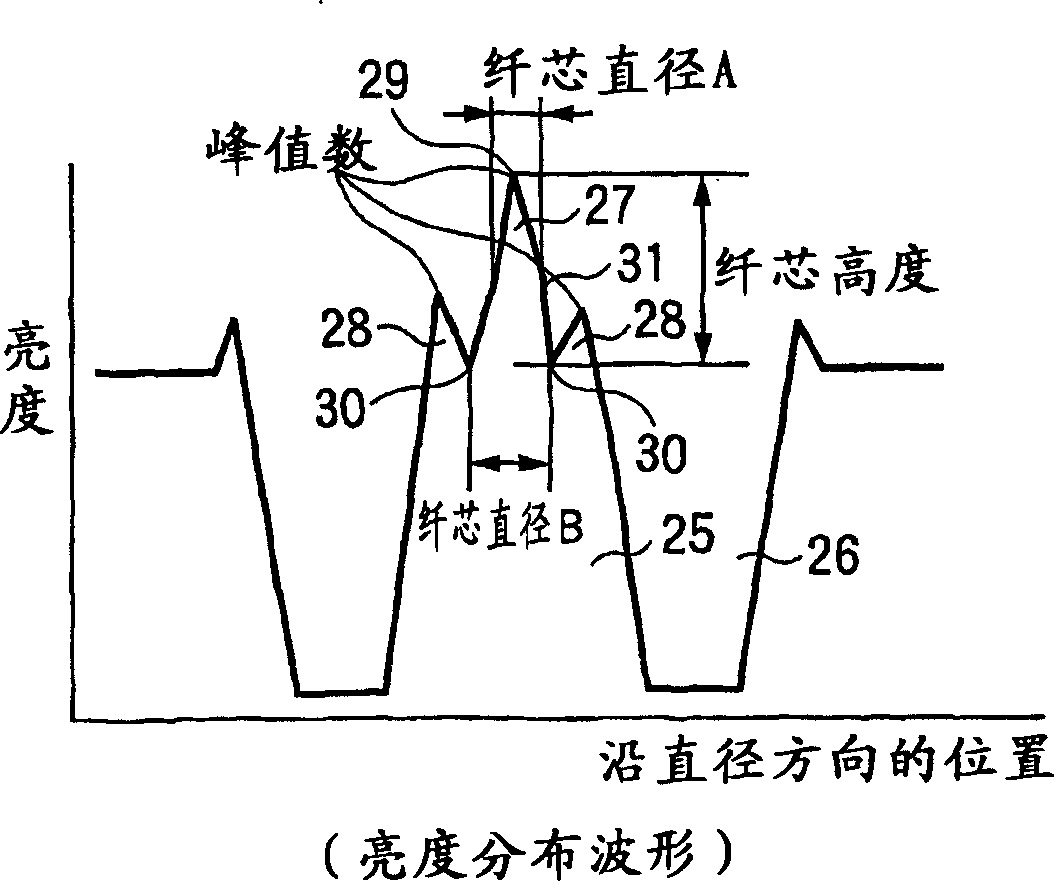
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a method and device which can discriminate all kinds of the optical fibers and carry out the melting-connection using the connection conditions suitable to the various optical fibers. The present invention is the melting-connection device which melt-connects through the discharge by pressing near the end portion of the optical fiber, and it is provided with: the image observation mechanism (1) which observes the end portion of the optical fiber; the image treatment department (2), which measures the parameter data of the illumination distribution waveform of the optical fiber cross section based on the image taken; the fuzzy-calculation-department (4) which identifies the optical fiber categories through the correlations obtained by fuzzy-calculating the fuzzy-calculation data by registering the measured parameter data in the registration department (3) in advance; the cross-reference department (6) which cross-references the identified optical fiber category to the optical fiber category melting-conditions registered in the melting-connection-condition-registration-department (5) prepared in advance; the display device (7) which displays the results of the cross-references; the melting-connection mechanism (9); and the control department (8).
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Apparatus and method for heat-treatment of optical fiber reinforcing member and optical fiber fusion splicing apparatus
ActiveUS7212718B2Curb riseEasily be wiped awayHeater elementsHeating element shapesEngineeringFusion splicing
A heat-treatment apparatus according to the present invention comprises a sheet-like heating body, which is bent like a letter “U”, and a heat equalizing plate constituted by a metal plate bonded to a heat generating part of the sheet-like heating body. The heat equalizing plate is bonded to the inner surface of the sheet-like heating body bent like a letter “U”. Alternatively, a fluorocarbon resin is coated on the surface of the heat equalizing plate.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
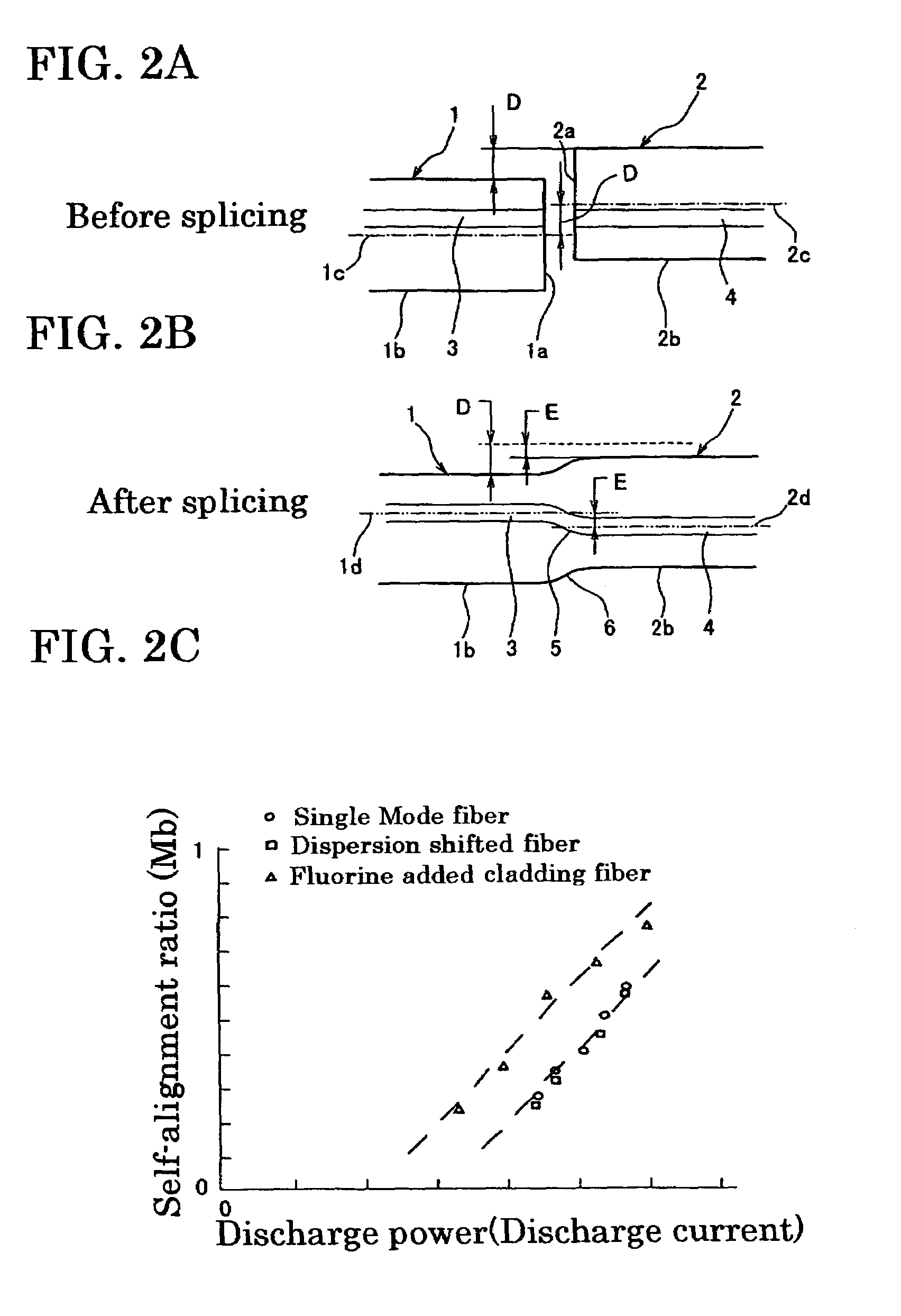
Method for fusion splicing optical fibers and fusion splicer
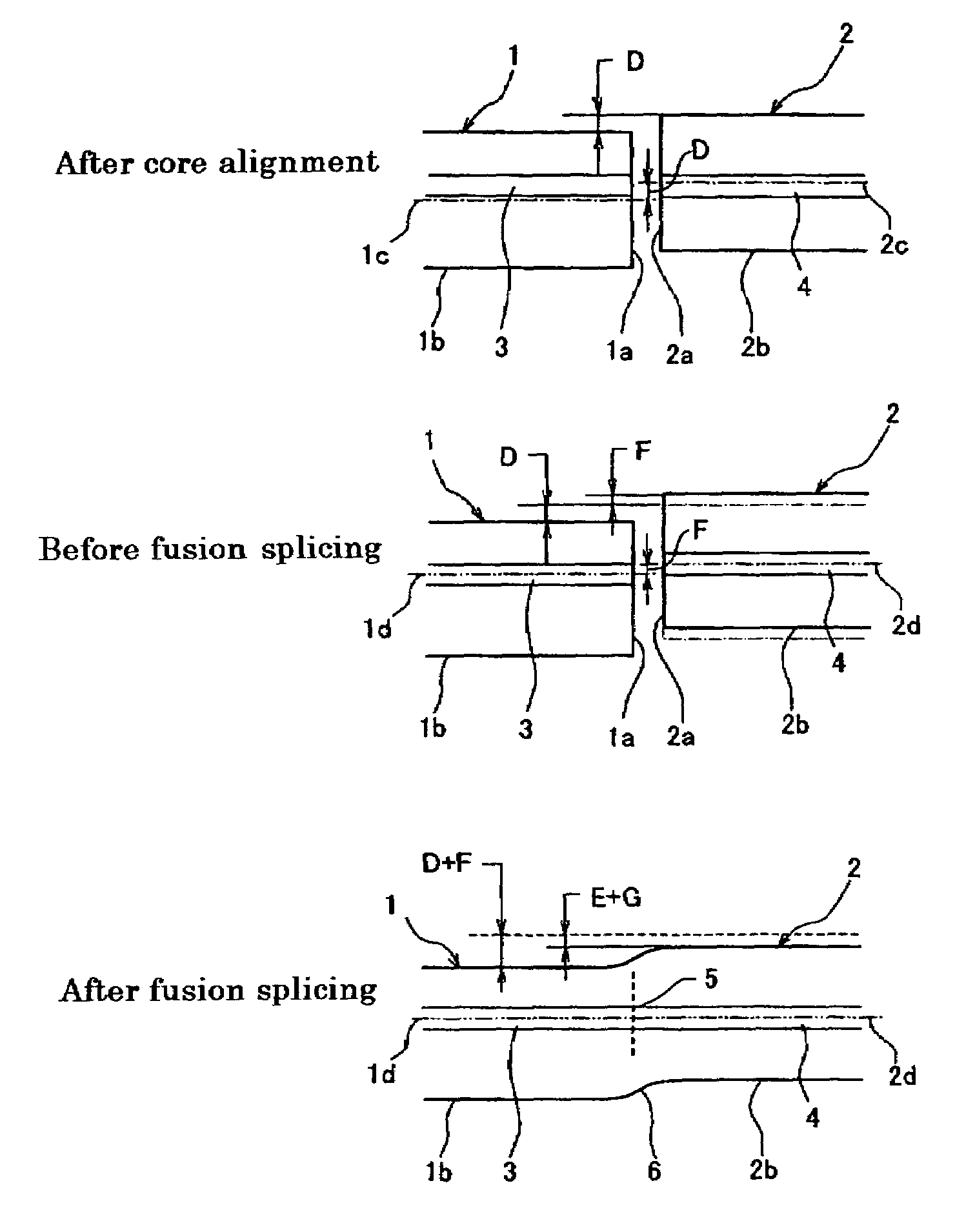
A method and apparatus capable of fusion splicing optical fibers to have a low loss or a prescribed loss. The method includes (a) detecting fiber positions and core positions of optical fibers to be spliced at an abutting position and a fiber offset that is caused when said optical fibers are in core alignment (b) determining the self-alignment ratio corresponding to the preferred melted condition value based on a predetermined expression for a relationship between melted condition value and self-alignment ratio, (c1) determining an intentional offset that achieves a prescribed splicing loss based on the fiber offset and the self-alignment ratio, (d1) aligning the core positions by offsetting the intentional offset value, and (e1) heating and fusing the optical fibers.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
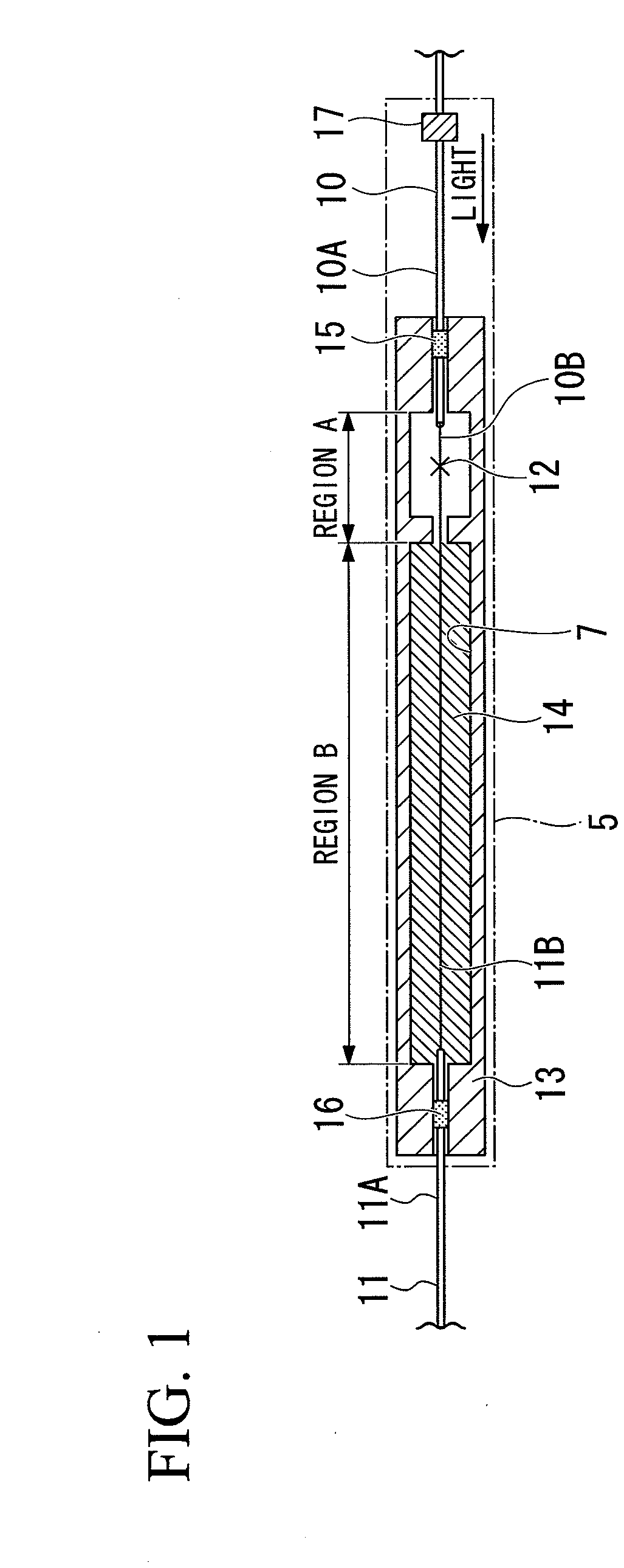
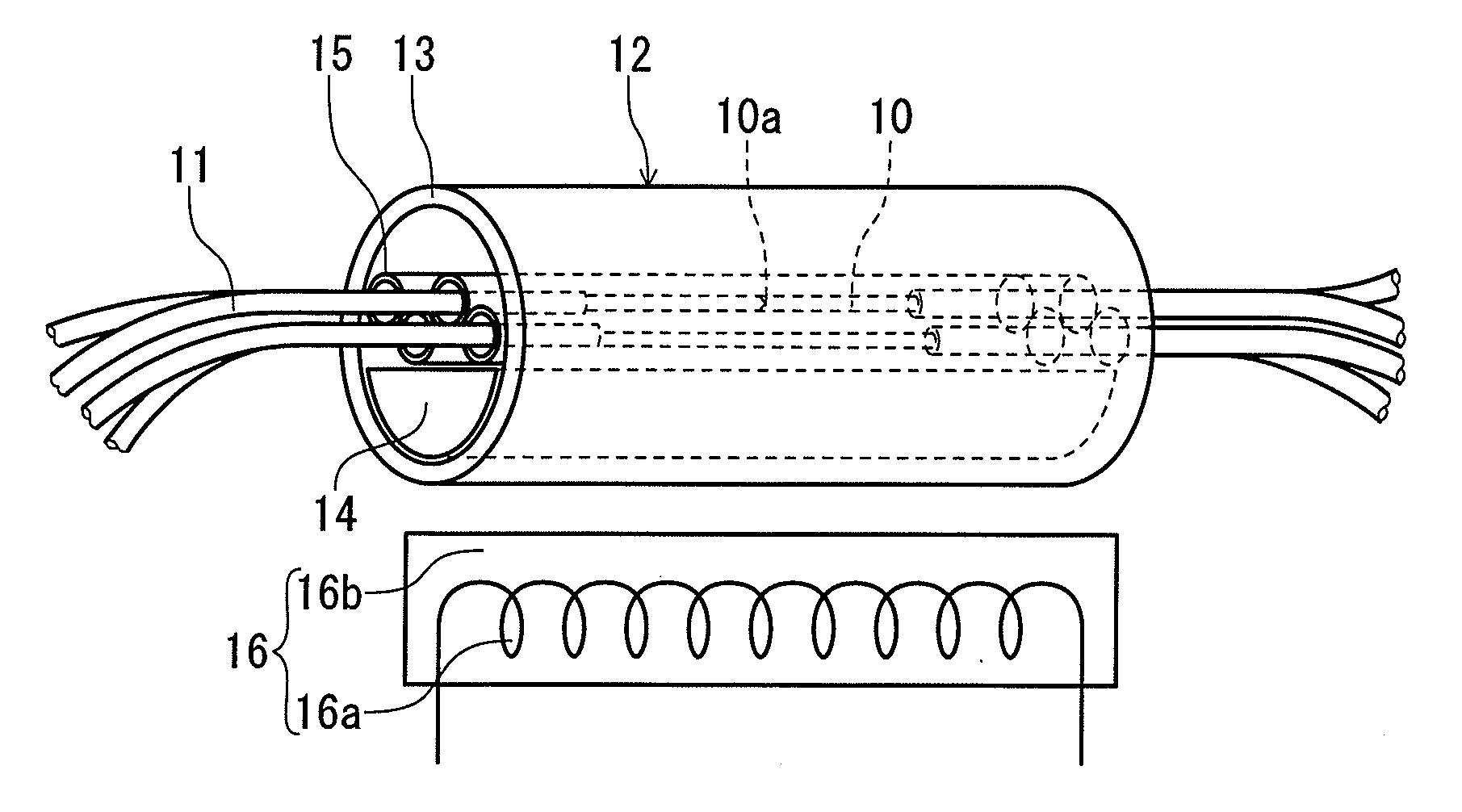
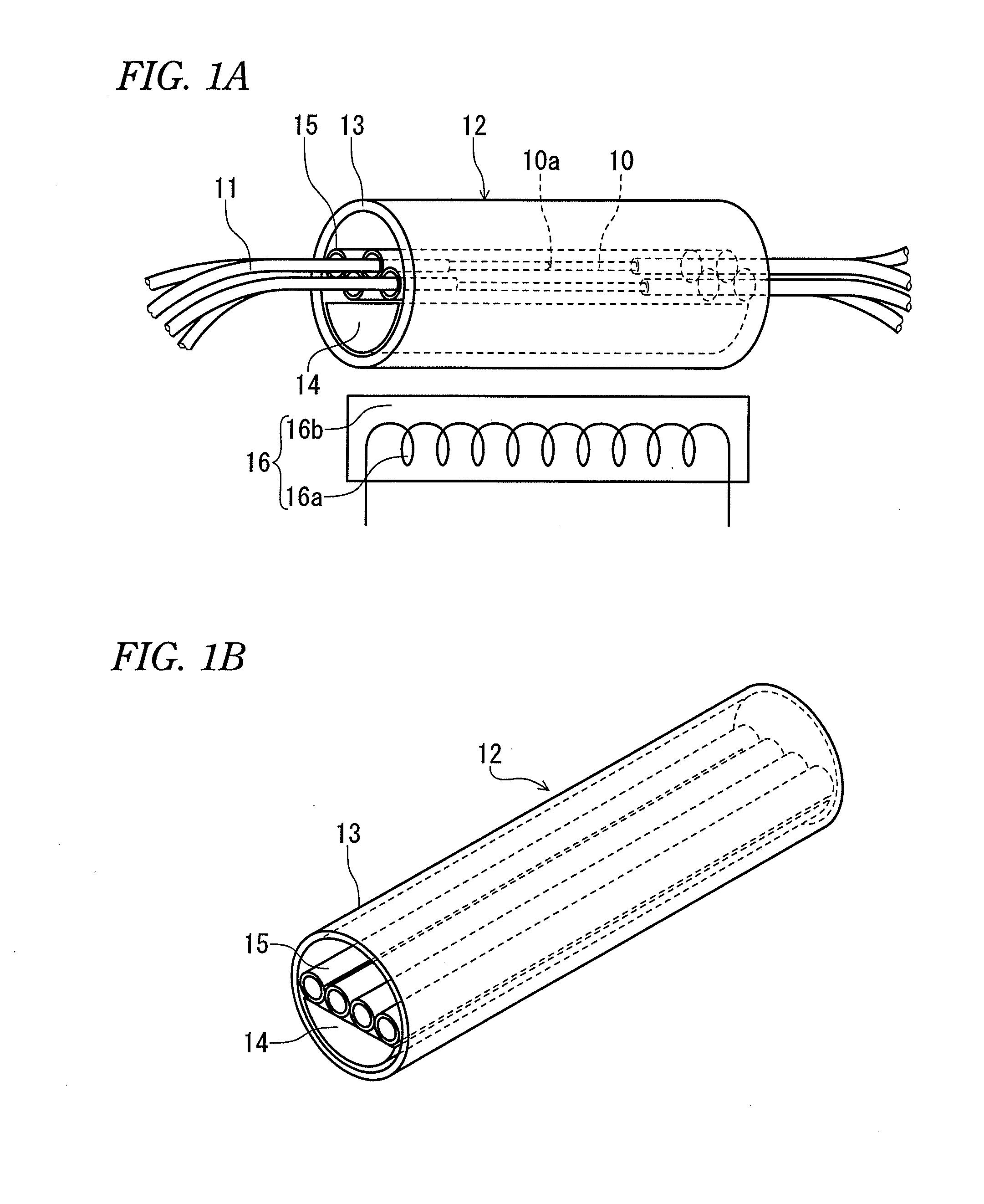
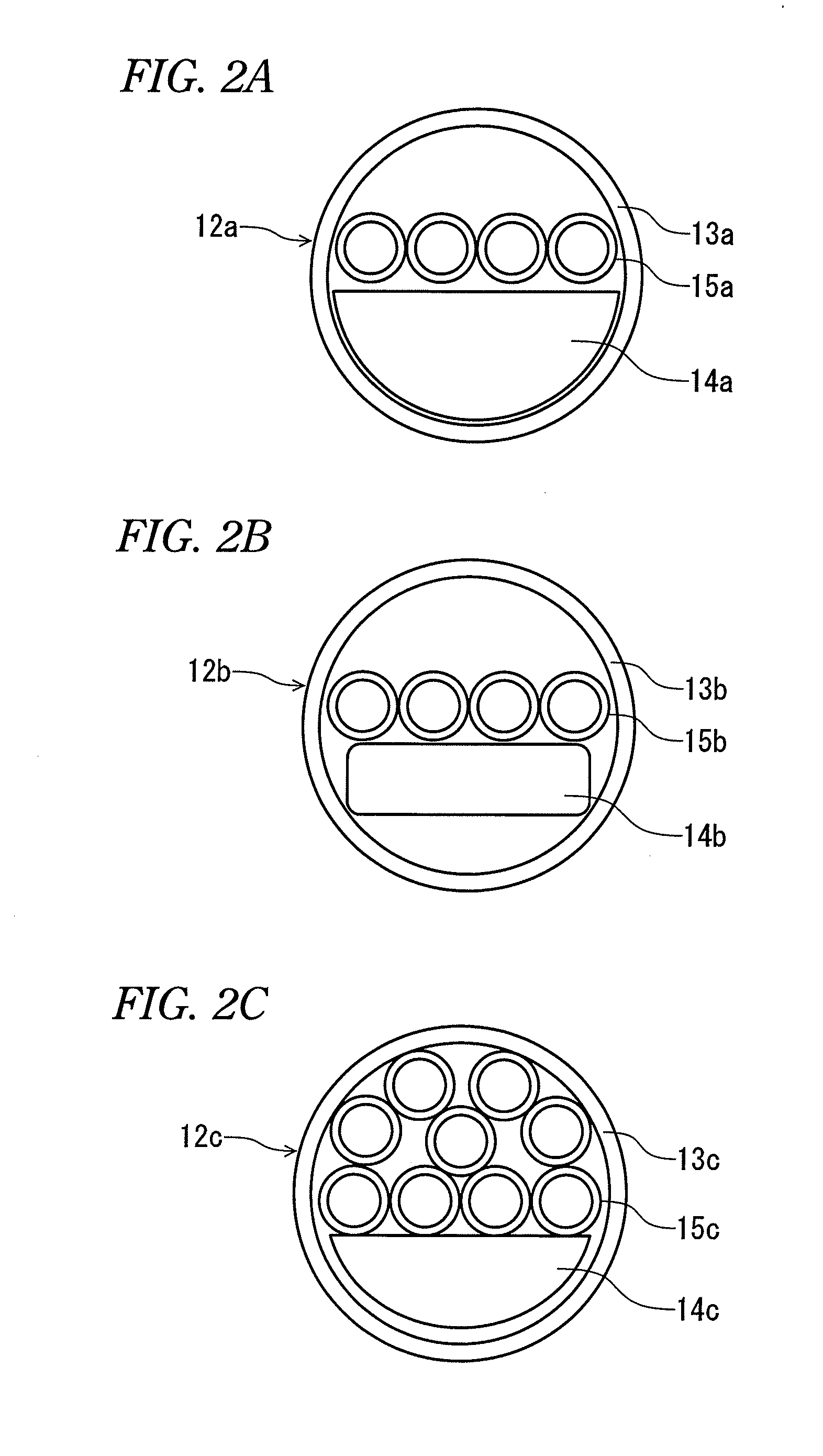
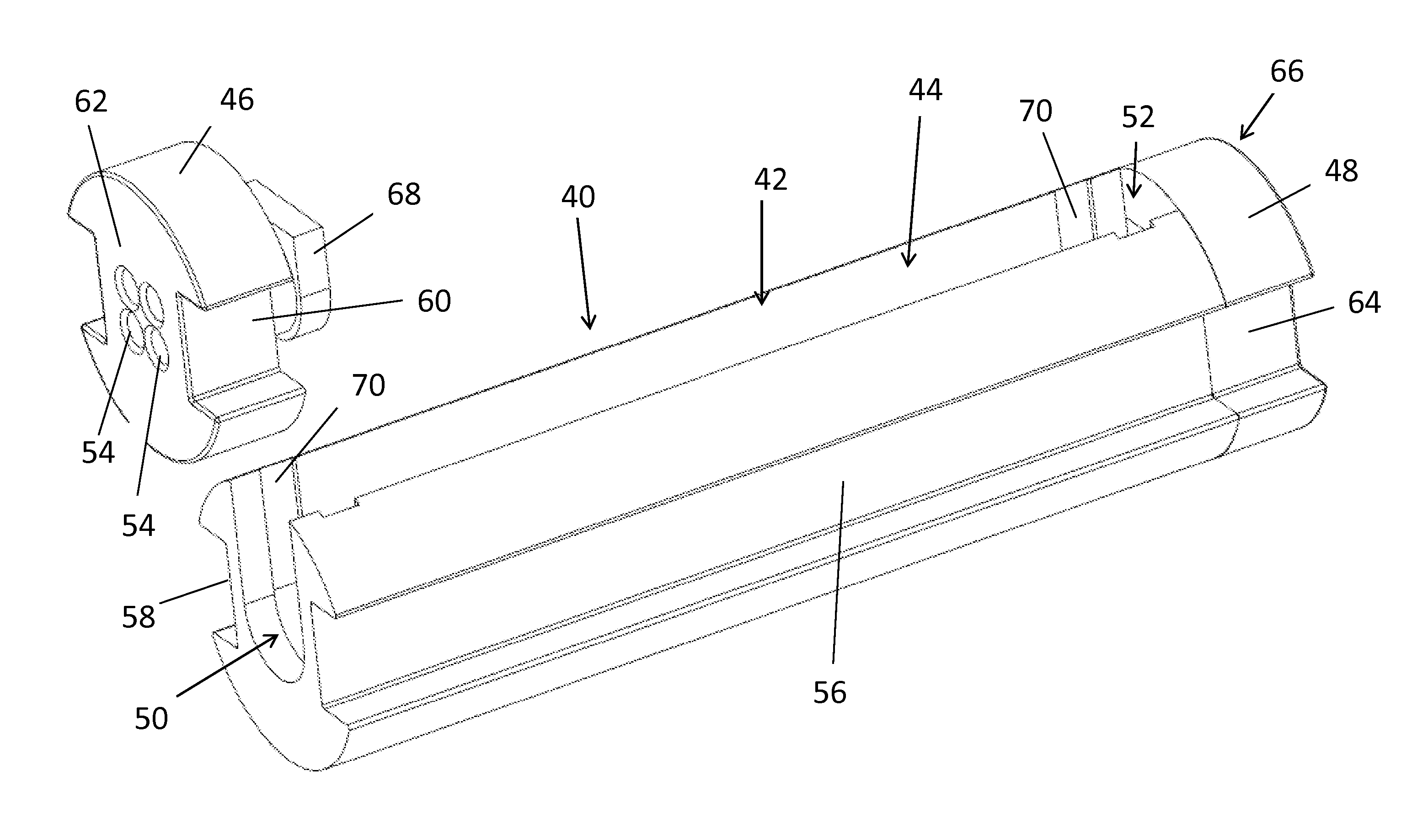
Reinforcing member for optical fiber fusion-splicing portion and reinforcing method therefor
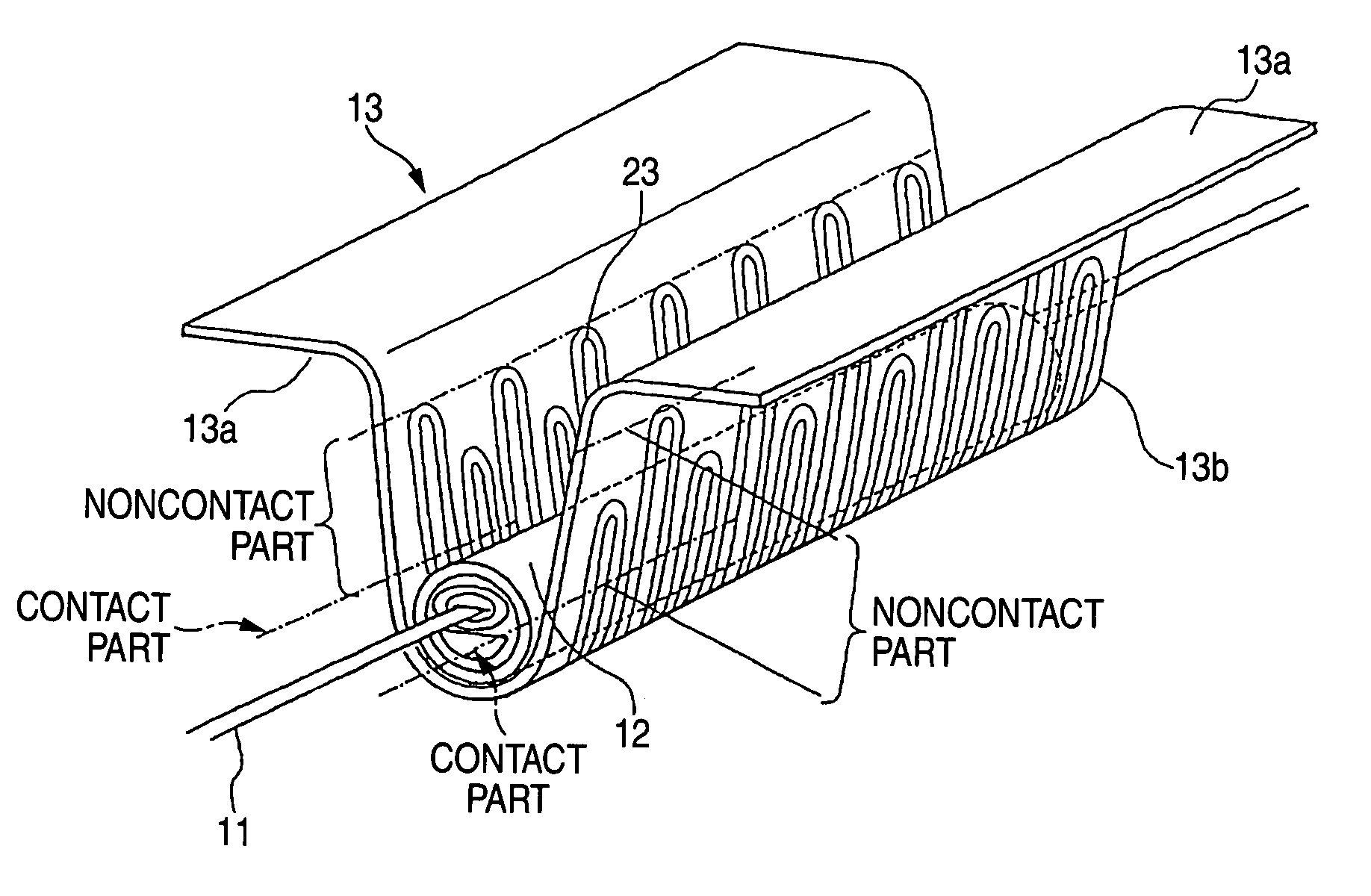
A reinforcing member of optical fiber fusion-splicing portion and a reinforcing method thereof are provided, in which plural coated optical fibers can be collectively reinforced in the high density, and a heating mechanism for collective reinforcement can be configured at a low cost.A reinforcing member 12 which reinforces collectively fusion-splicing portions 12a of plural coated optical fibers 11 includes a heat-shrinkable tube 13, a rod-shaped tensile strength member 14 arranged so that a part of its surface comes into contact with an inner surface of the heat-shrinkable tube, and plural tube-shaped heat-fusible adhesive members 15 arranged in the heat-shrinkable tube and into which the fusion-splicing portions of the single-core coated optical fibers are individually inserted. All of the plural tube-shaped heat-fusible adhesive members 15 are arranged in one of space portions formed between the tensile strength body 14 and the heat-shrinkable tube.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Optical fiber welding machine and welding method
InactiveCN1399150AGood spreadReduce the discharge current valueCoupling light guidesElectric dischargeImaging processing
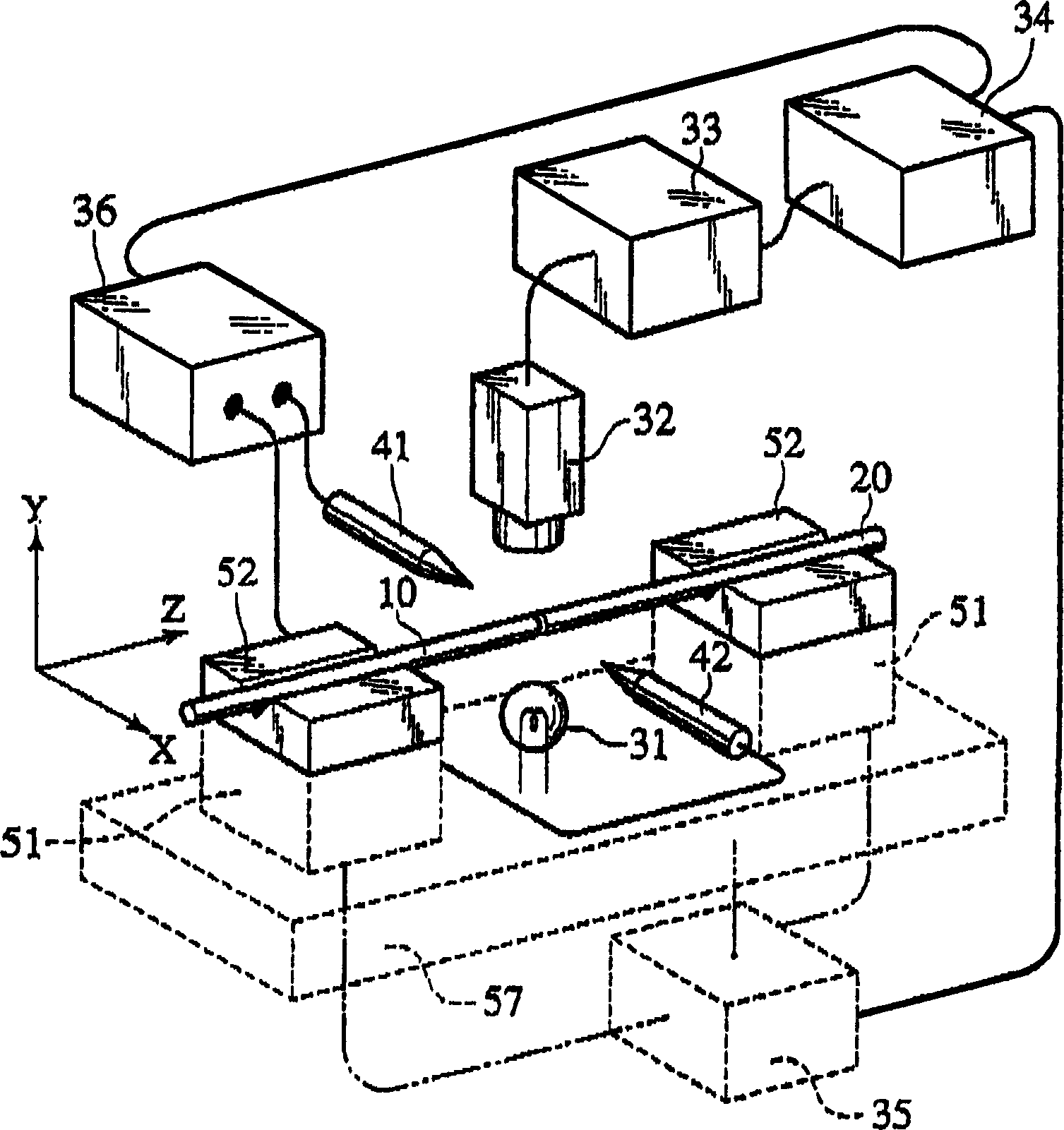
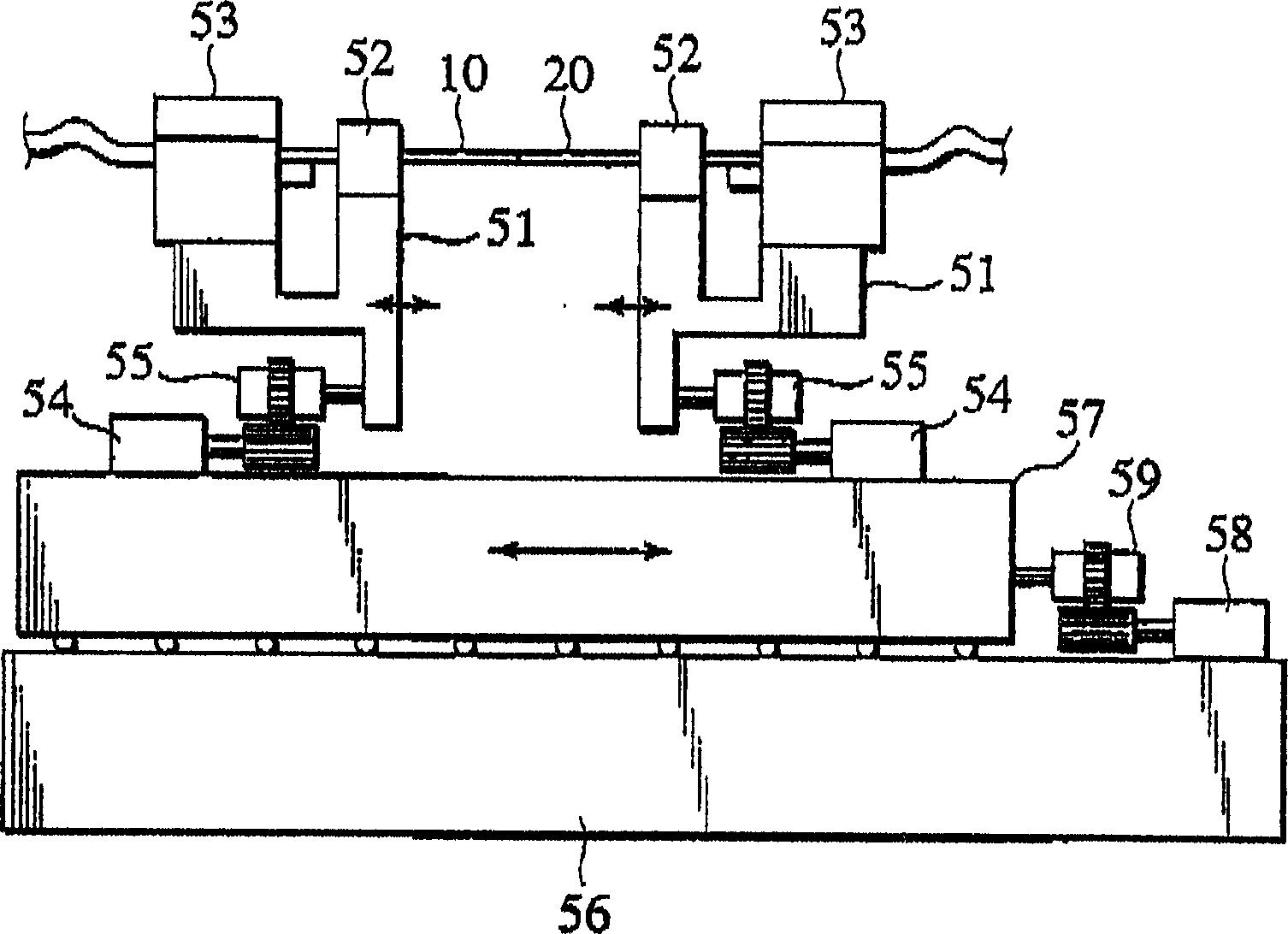
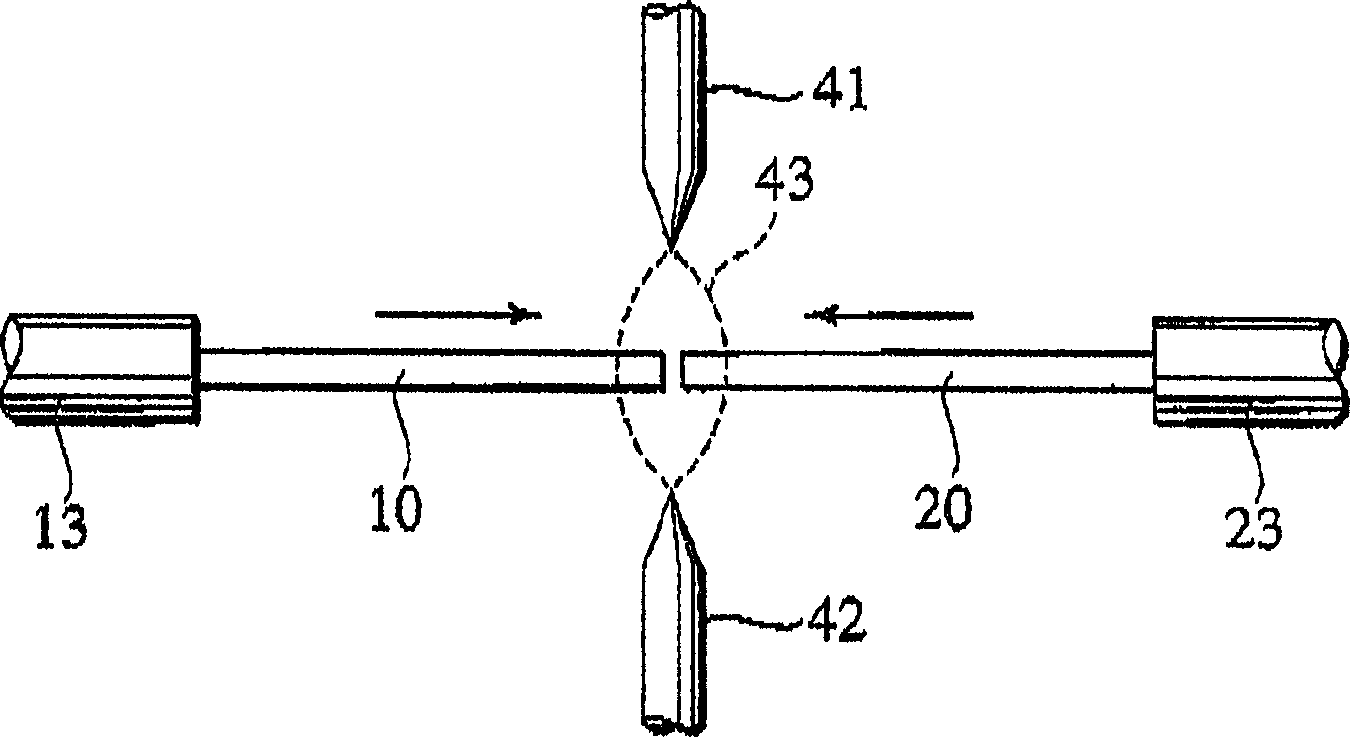
A fusion splicer and fusion splicing method for optical fibers is disclosed including a TV camera 32 which obtains transmitted light images passing through side areas of respective optical fibers 10, 20, an image processing unit 33 which calculates mode field diameters of the respective optical fibers from brightness distributions of the images in terms of directions traverse to the optical fibers to calculate a diametric difference between the mode field diameters, a movable base 57 to move abutted portions between the optical fibers relative to an electric discharge beam position, a drive unit 35 which implements additional electric discharge heating after applying electric discharge fusion splicing heating to the abutted portions while moving the electric discharge beam position toward one of the optical fibers, of which mode field diameter is regarded to be small, and a control unit 34 which controls an electric discharge power supply 36.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
Method for controlling optical fiber fusion splicer through mobile phone and optical fiber fusion splicer for realizing method
ActiveCN103926652ALow costEasy to updateSubstation equipmentCoupling light guidesComputational physicsFusion splicing
The invention relates to the field of optical fiber fusion splicing, in particular to a method for controlling an optical fiber fusion splicer through a mobile phone and the optical fiber fusion splicer for realizing the method. According to the method, the process that the mobile phone is used for controlling the optical fiber fusion splicer to achieve welding is disclosed, convenience is achieved, adaptability is high, and meanwhile the cost of the entire device is lowered. The invention further discloses the optical fiber fusion splicer for realizing the method. By means of the method for controlling the optical fiber fusion splicer through the mobile phone and the optical fiber fusion splicer for realizing the method, the equipment cost can be lowered, and updating is convenient.
Owner:SIGNAL FIRE TECH CO LTD
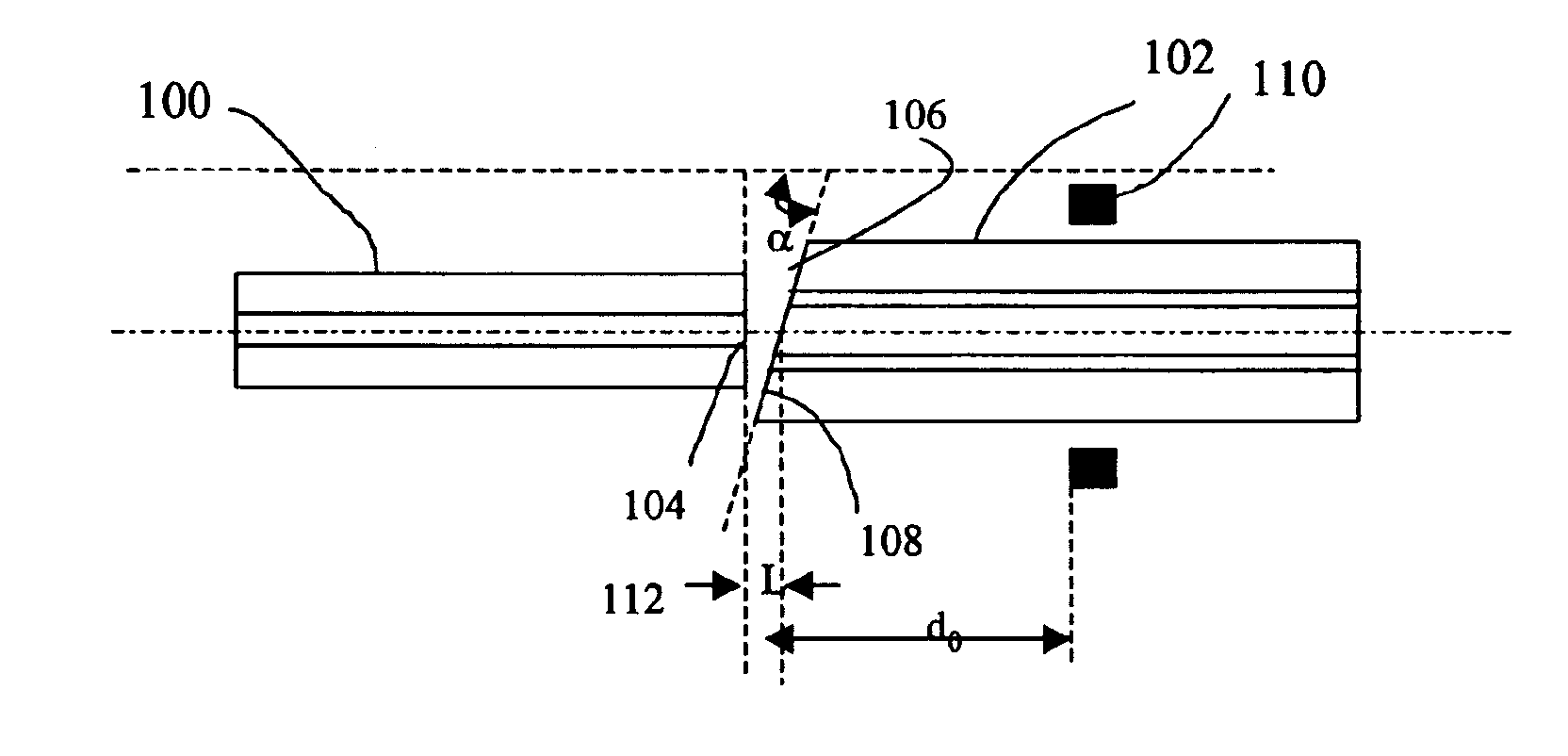
Method of fusion splicing thermally dissimilar glass fibers
InactiveUS6921216B1Speed up heat dissipationReduce direct heatingGlass making apparatusCoupling light guidesGlass fiberFusion joints
Thermally dissimilar glass fibers are fusion spliced by pretreating the cleaved end surface of the high-temperature fiber to provide a smooth surface for making good contact with the low-temperature fiber. The fibers are heated to a temperature that is high enough to soften the low-temperature fiber but not the high-temperature fiber and brought in contact to form the fusion joint.
Owner:NP PHOTONICS A CORP OF DELAWARE
Flex tactical cable splice
InactiveUS9063286B2Coupling light guidesFibre mechanical structuresFusion splicingBiomedical engineering
Owner:ADVANCED FIBER PROD LTD
Optical fiber fusion splicer
ActiveUS20140083141A1Reduce in quantityShorten operation timeGlass furnace apparatusMaterial analysis by optical meansBiochemical engineeringPlastic optical fiber
An optical fiber fusion splicer that heats and fusion-splices optical fibers to each other, the optical fiber fusion splicer includes: a coating clamp installation base; a coating clamp that is attached to the coating clamp installation base and has a coating clamp lid that is openable and closable; and a first power source for advancing the coating clamp installation base and opening the coating clamp lid. An operation of opening the coating clamp lid is performed using the first power source after the fusion splicing is completed.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com