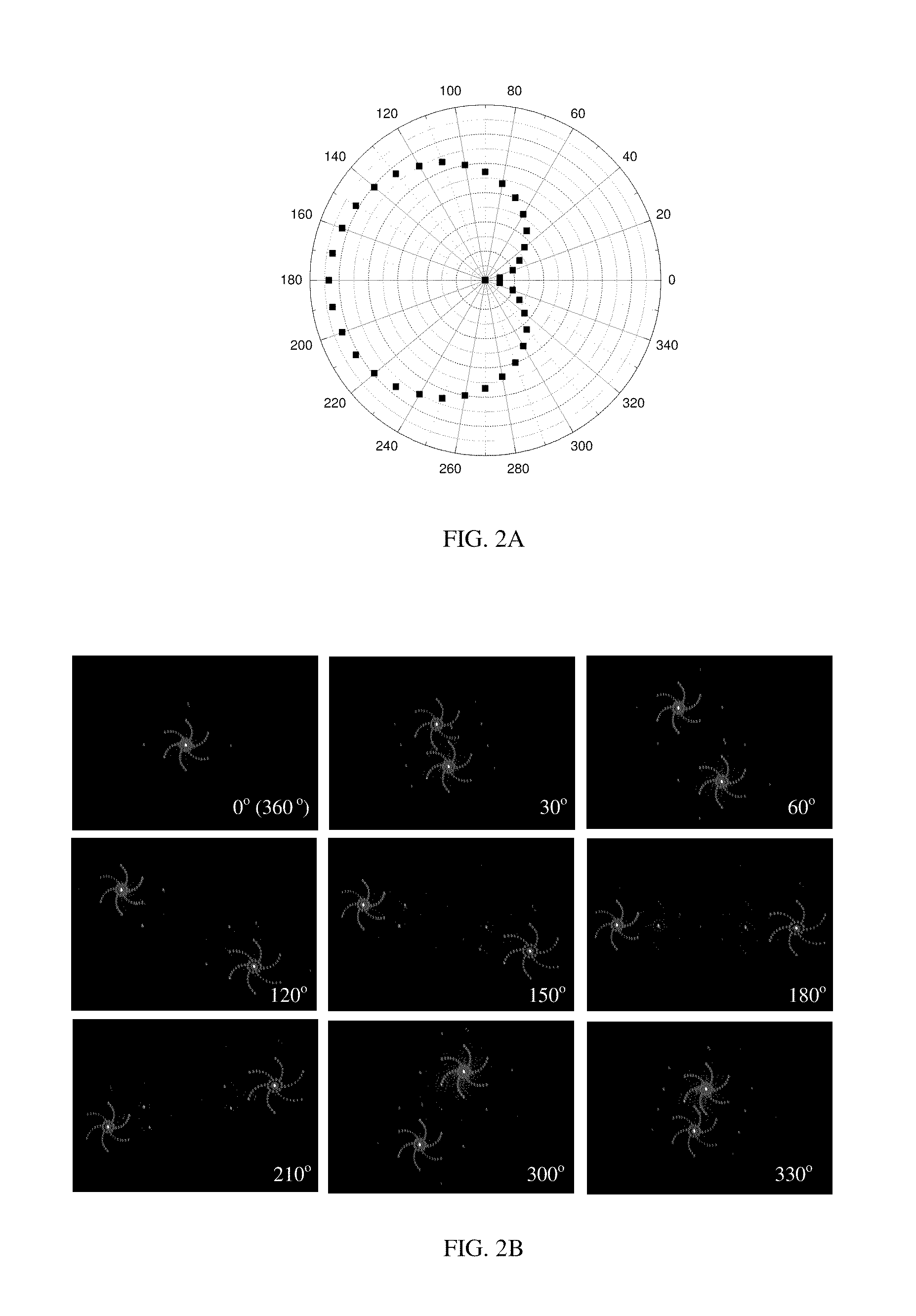
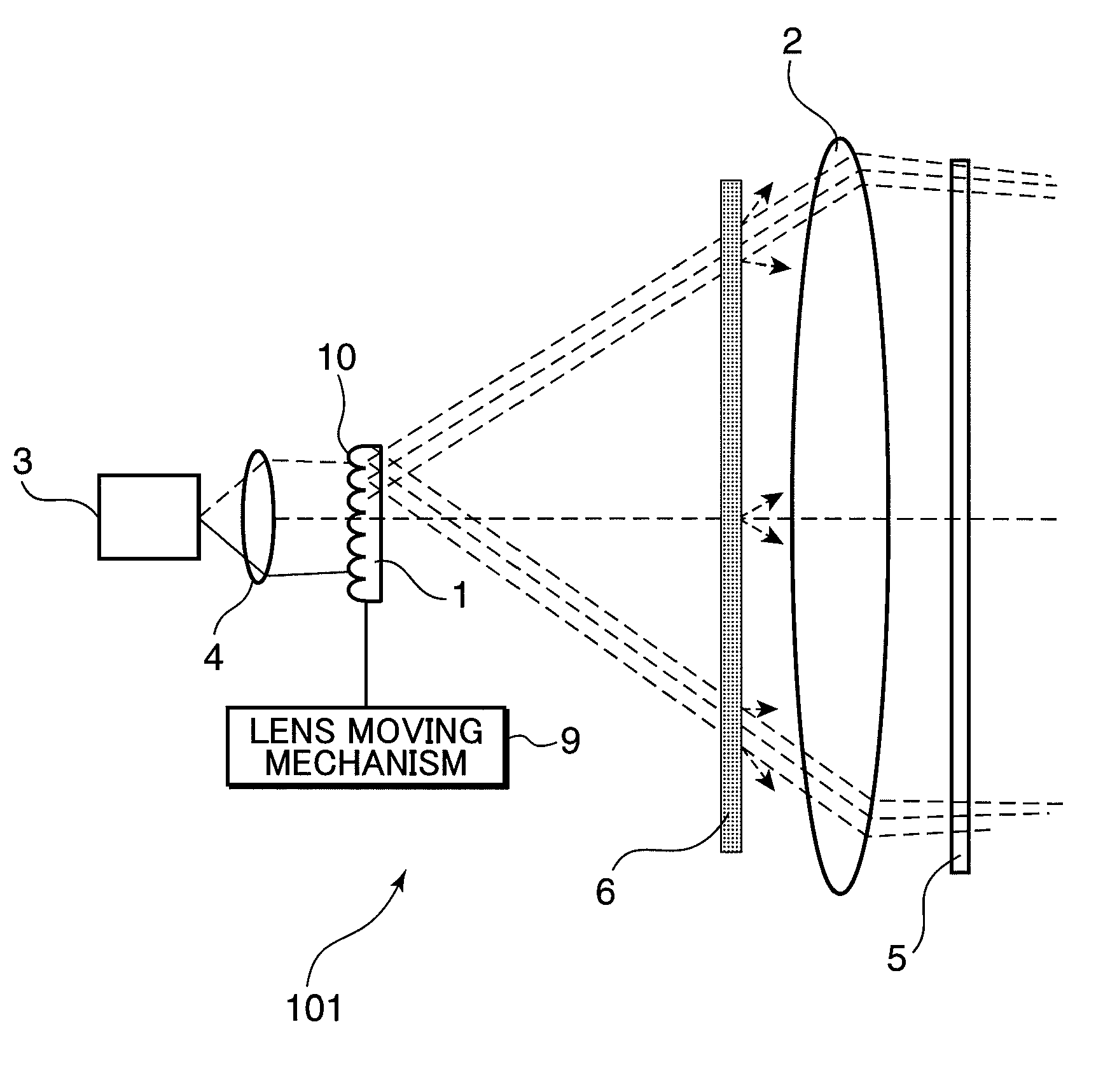
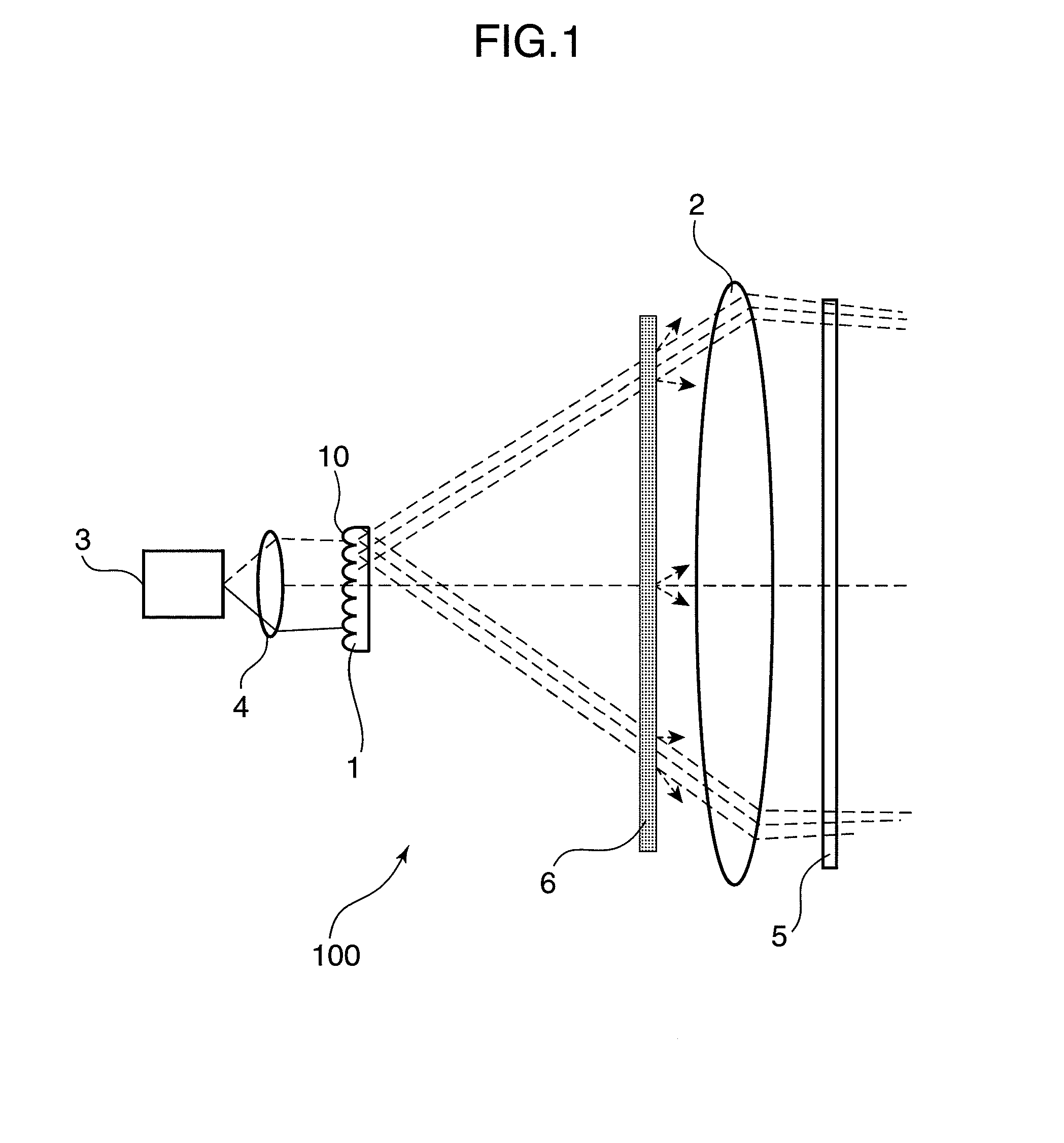
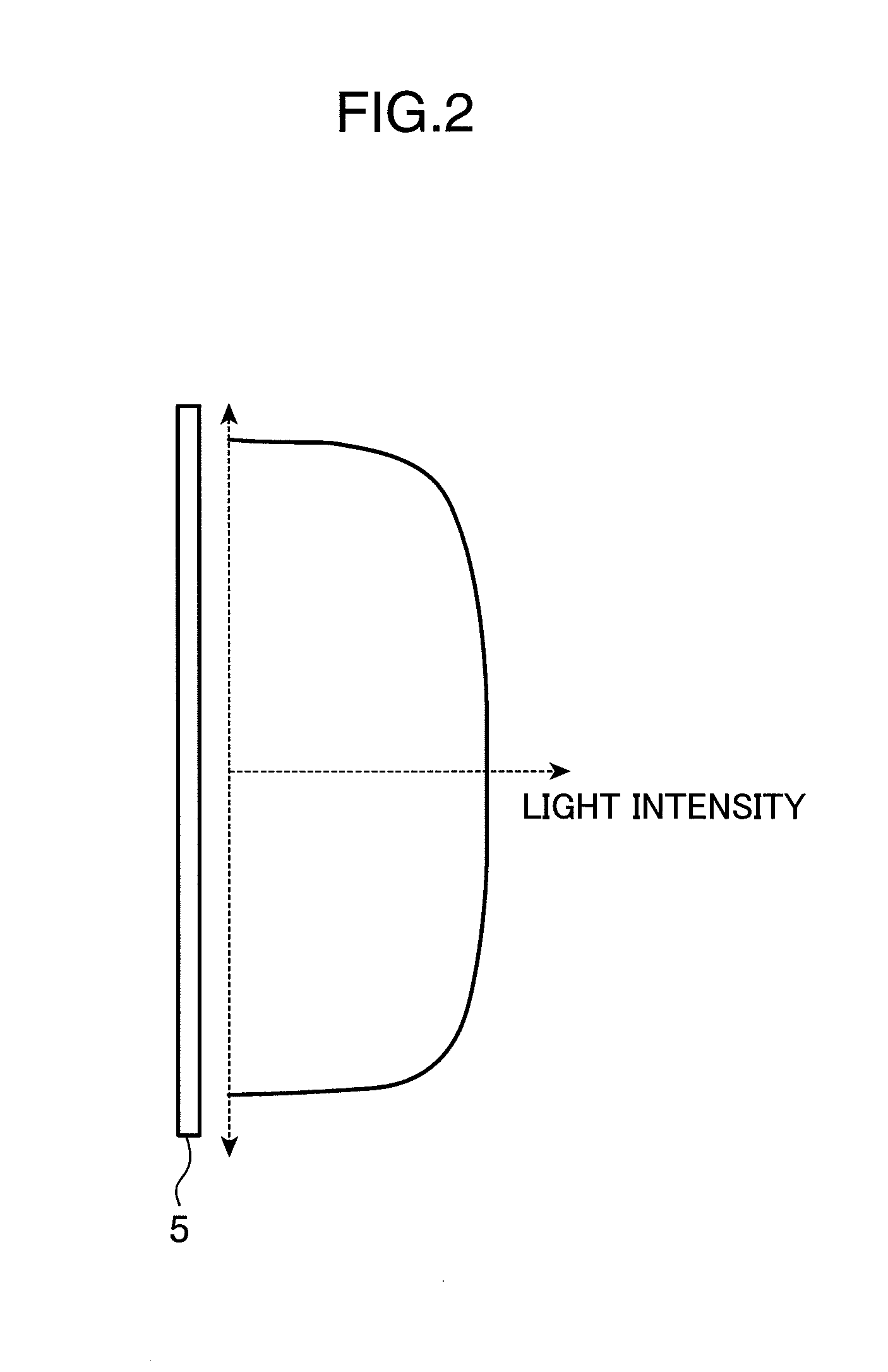
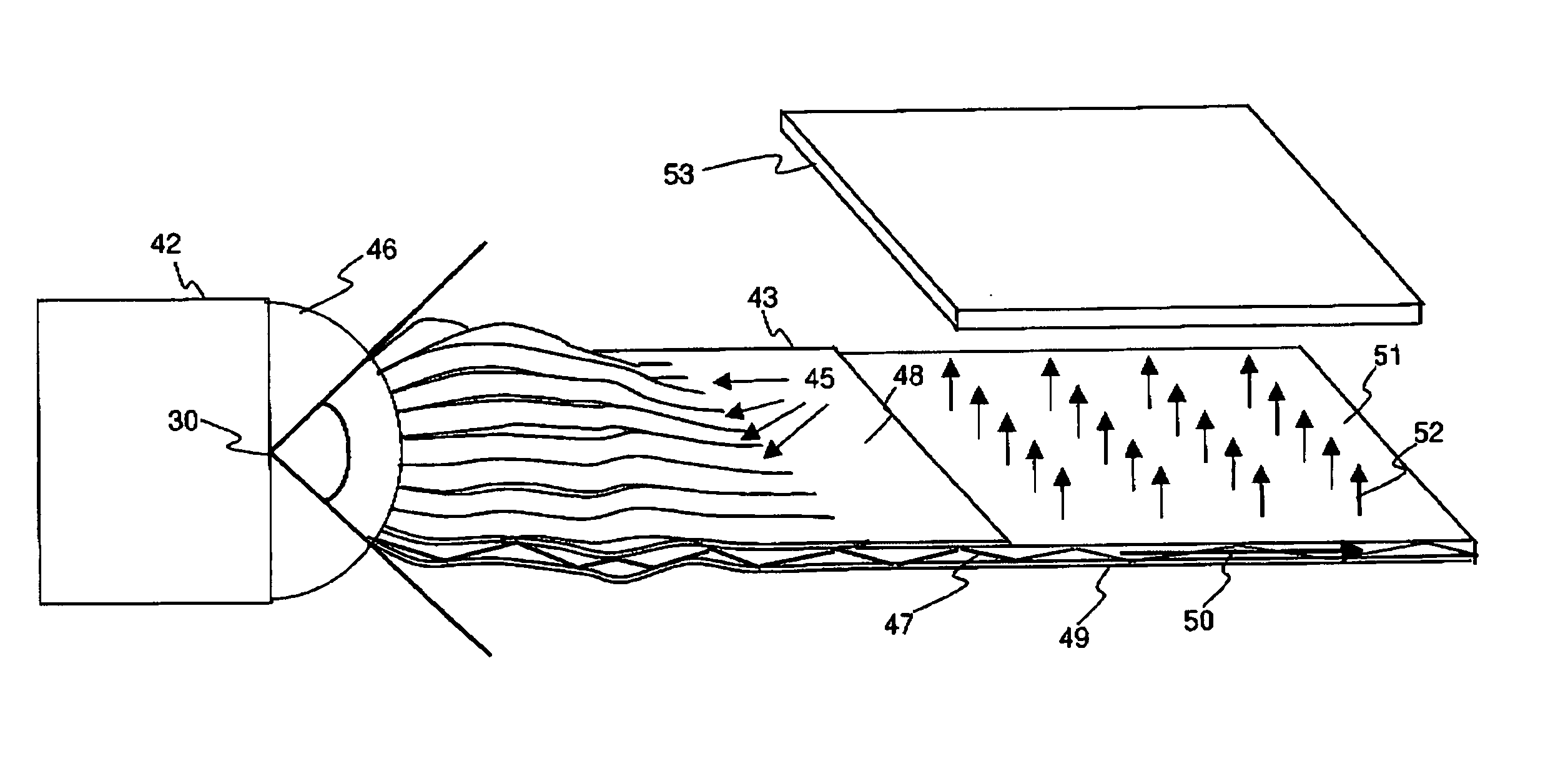
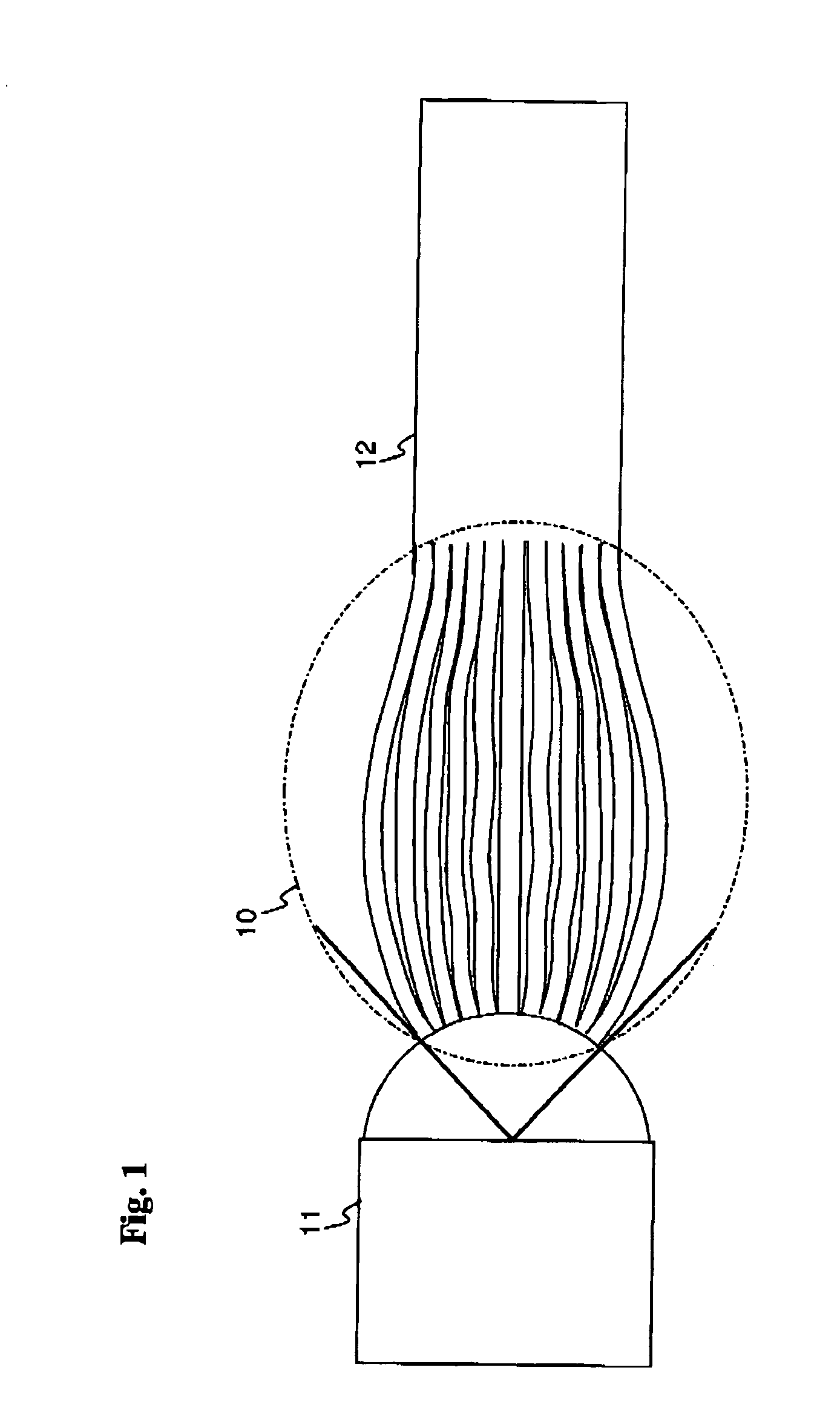
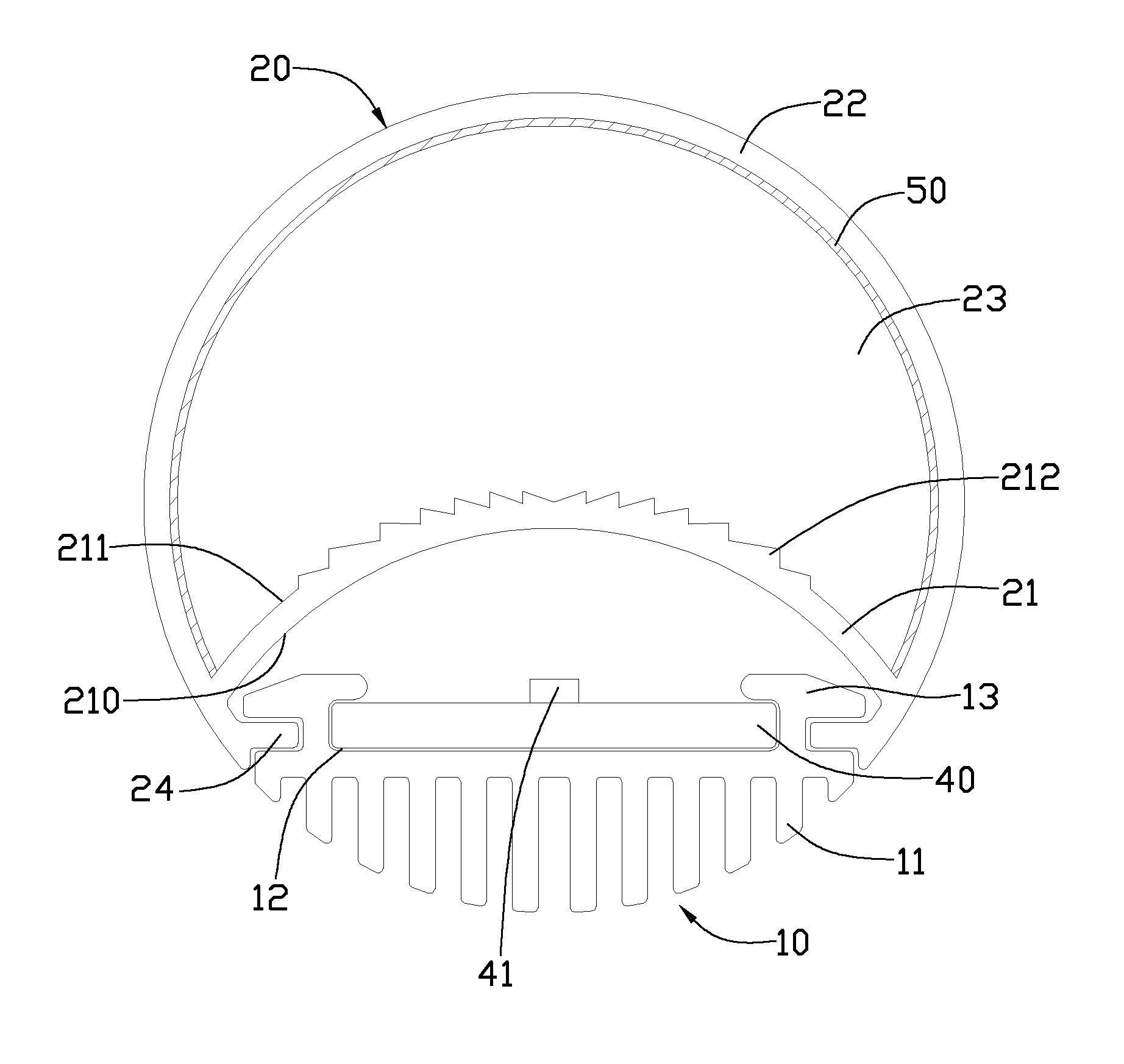
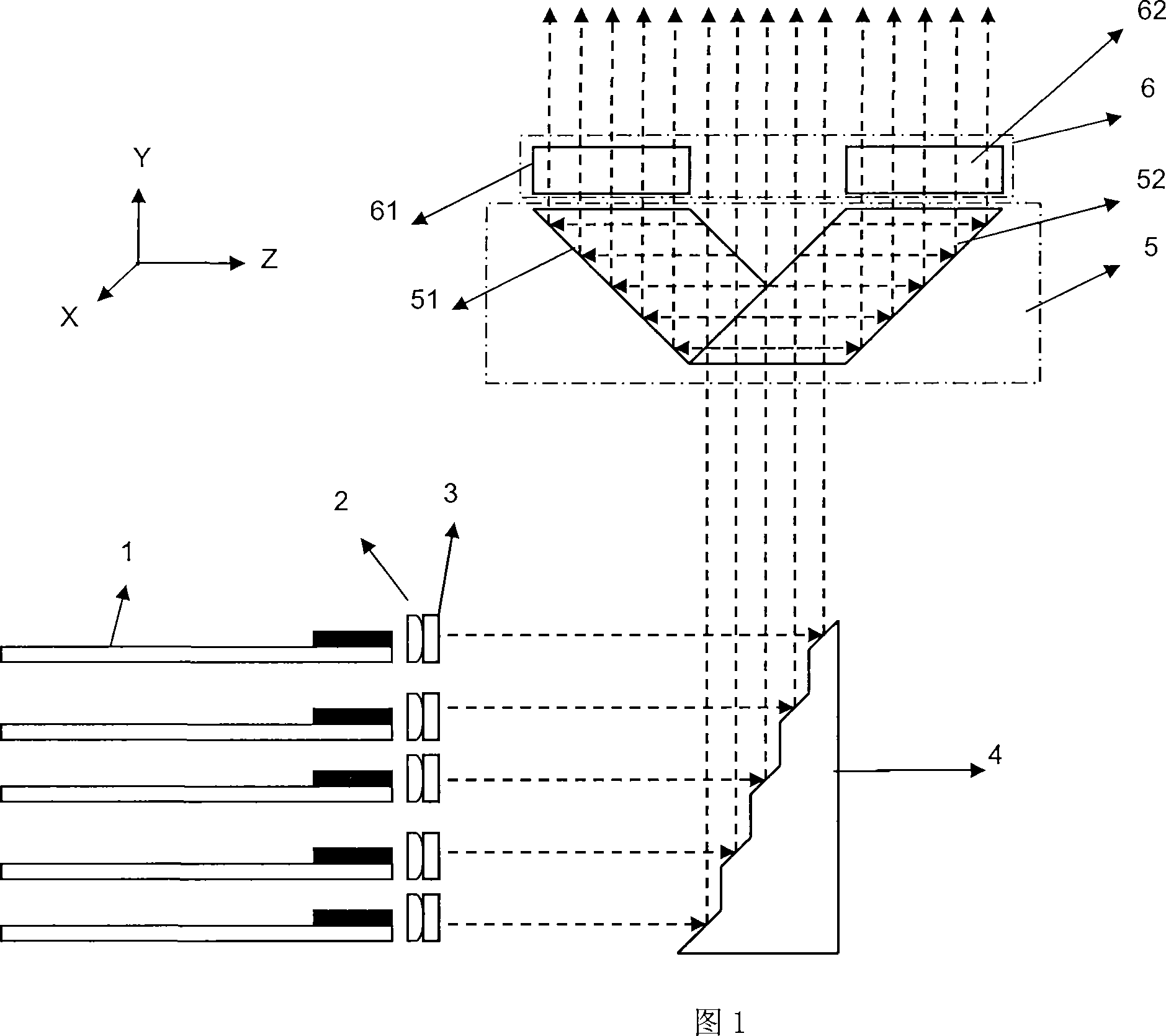
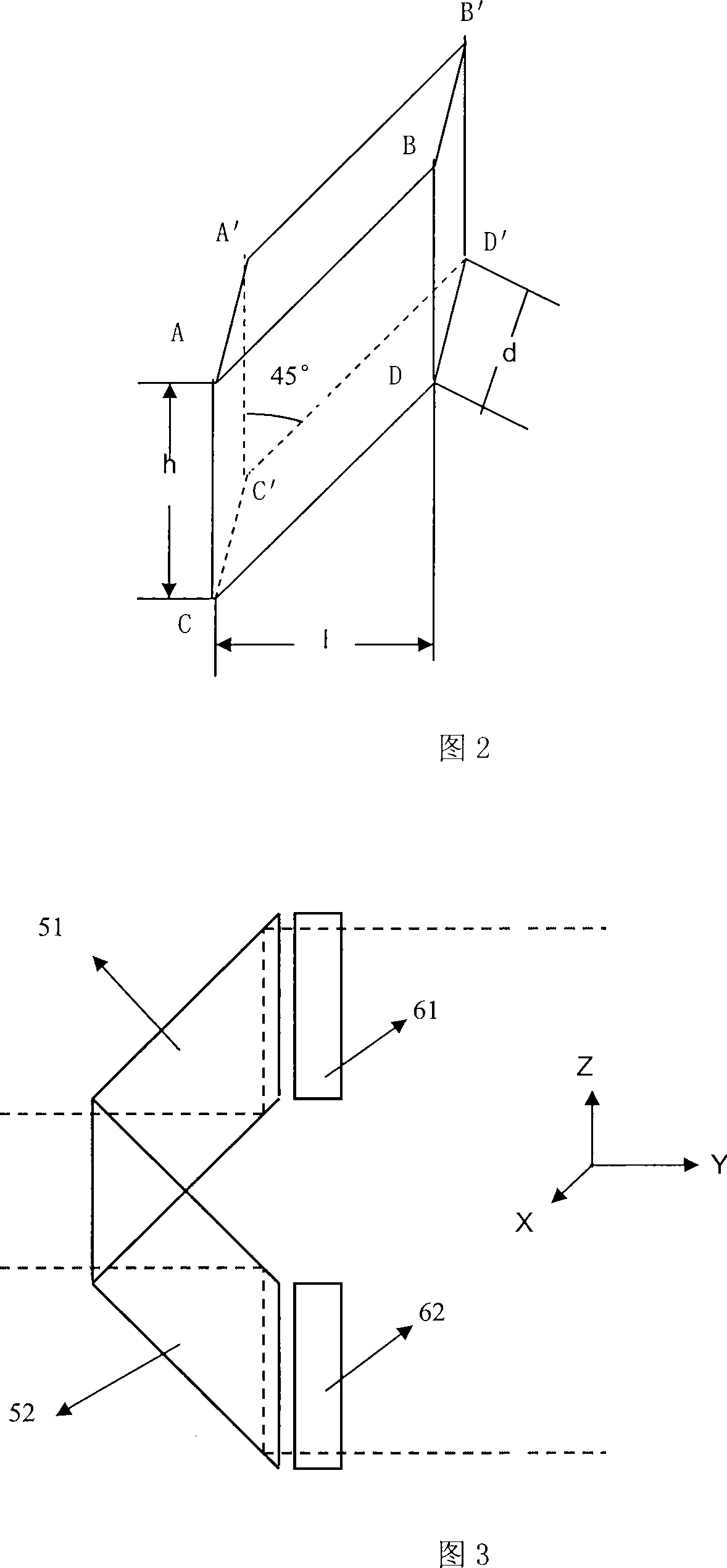
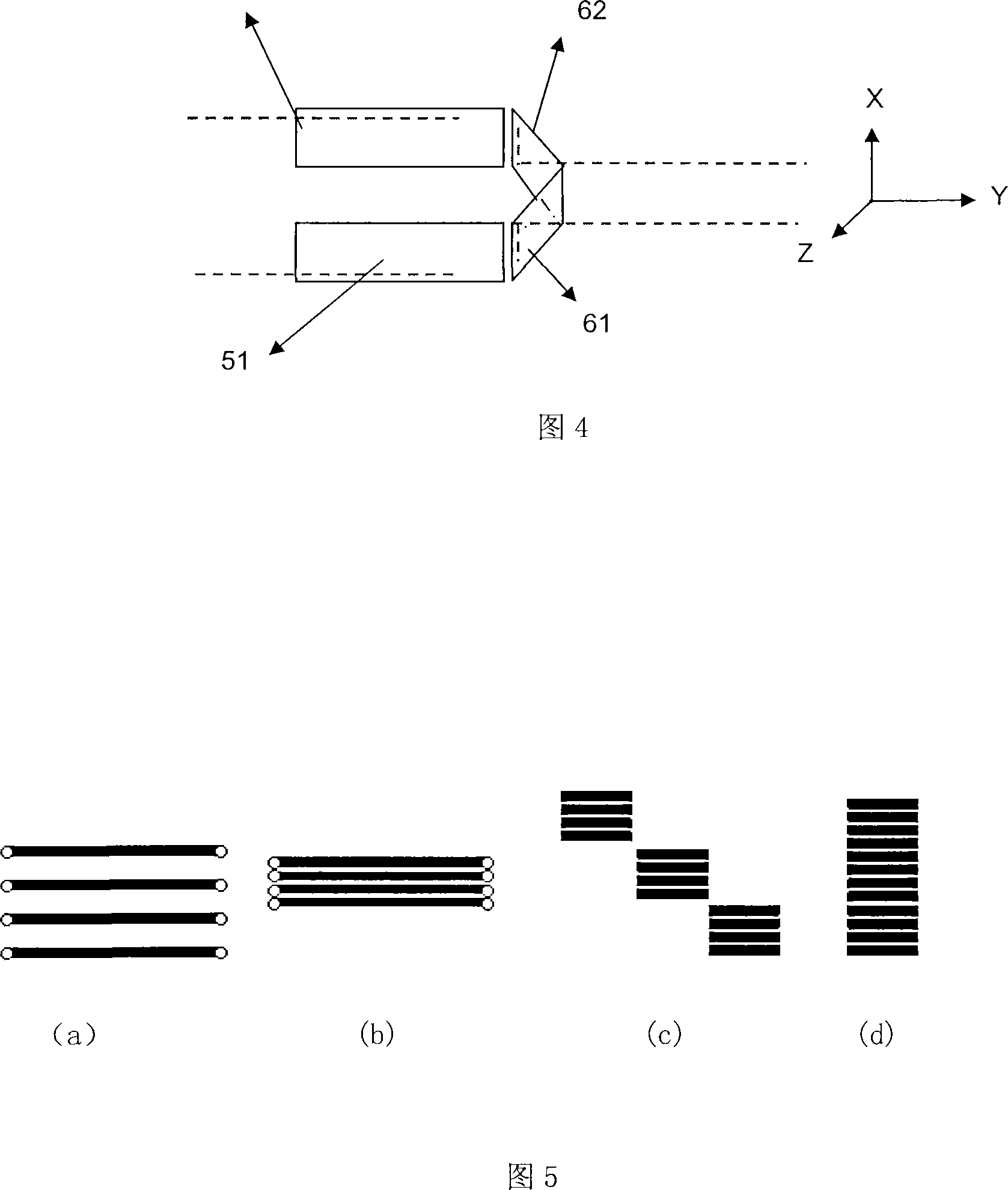
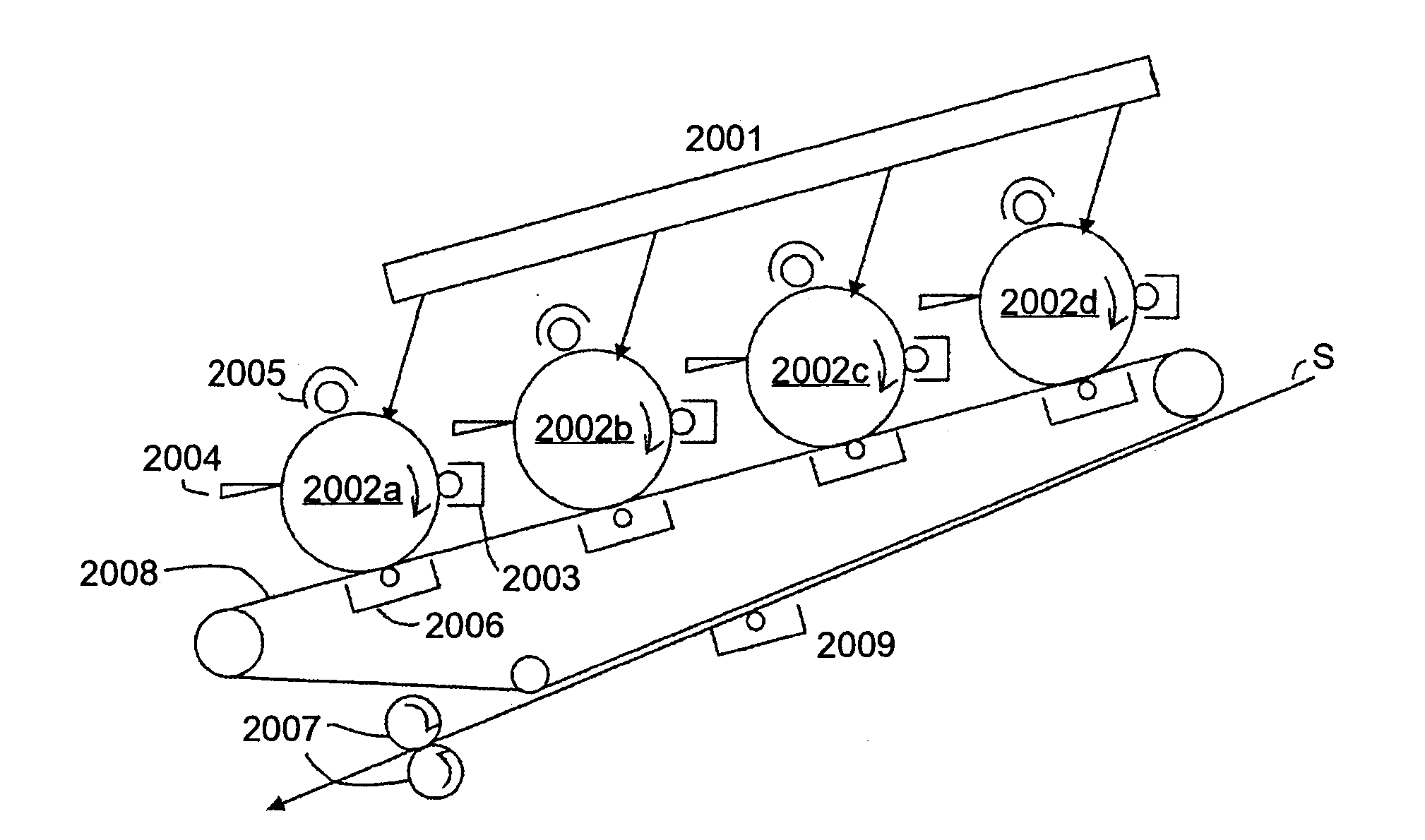
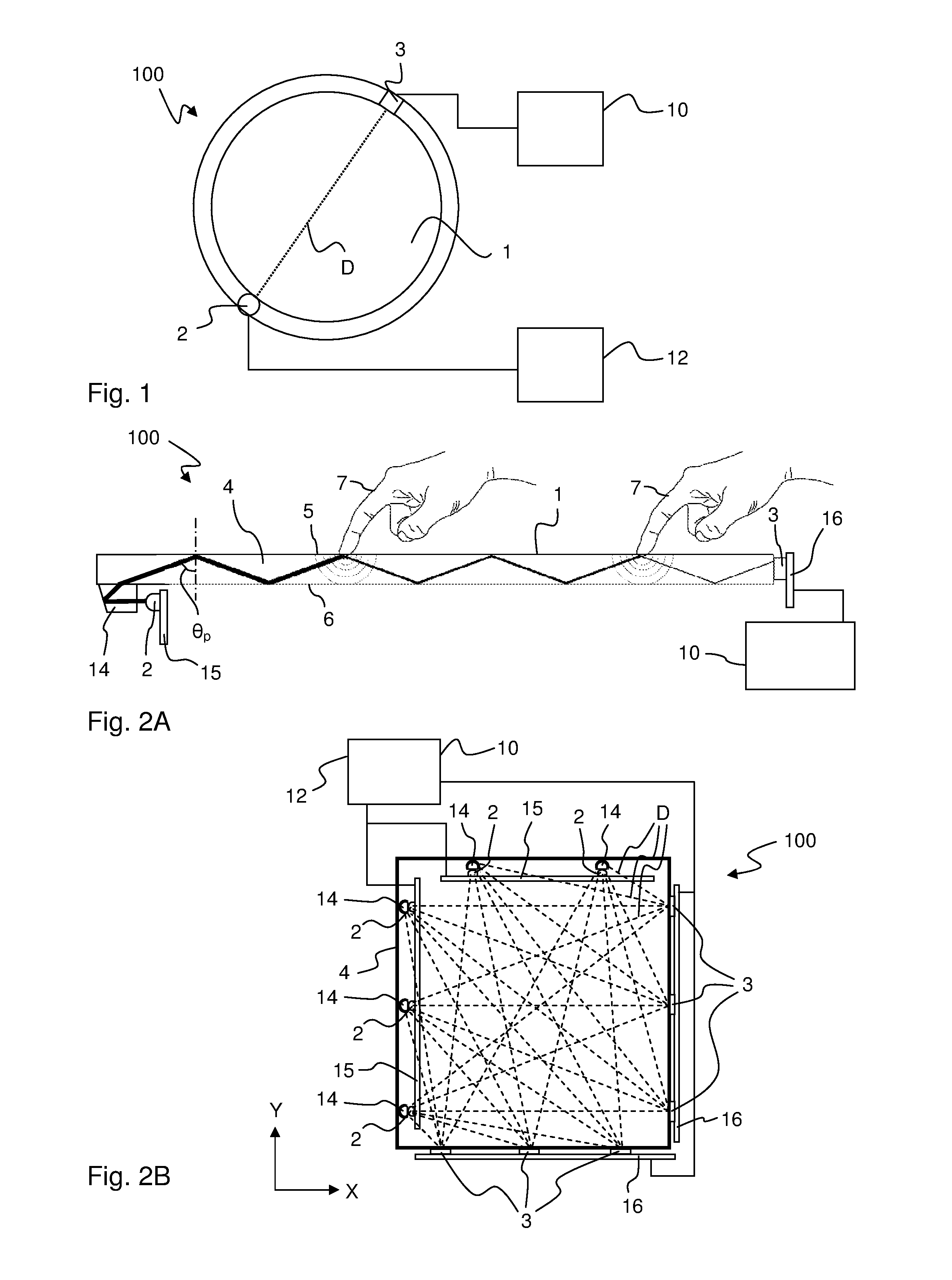
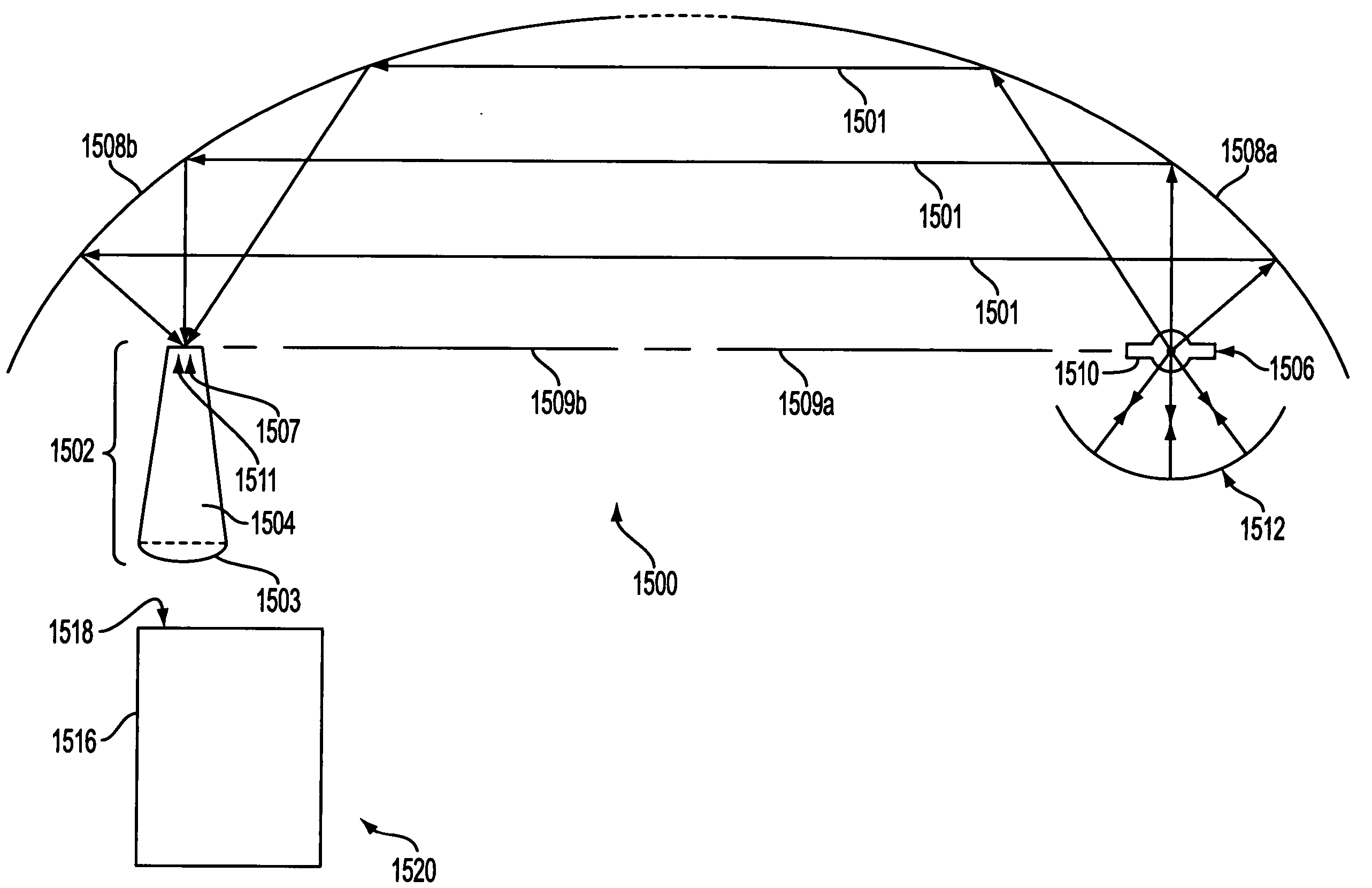
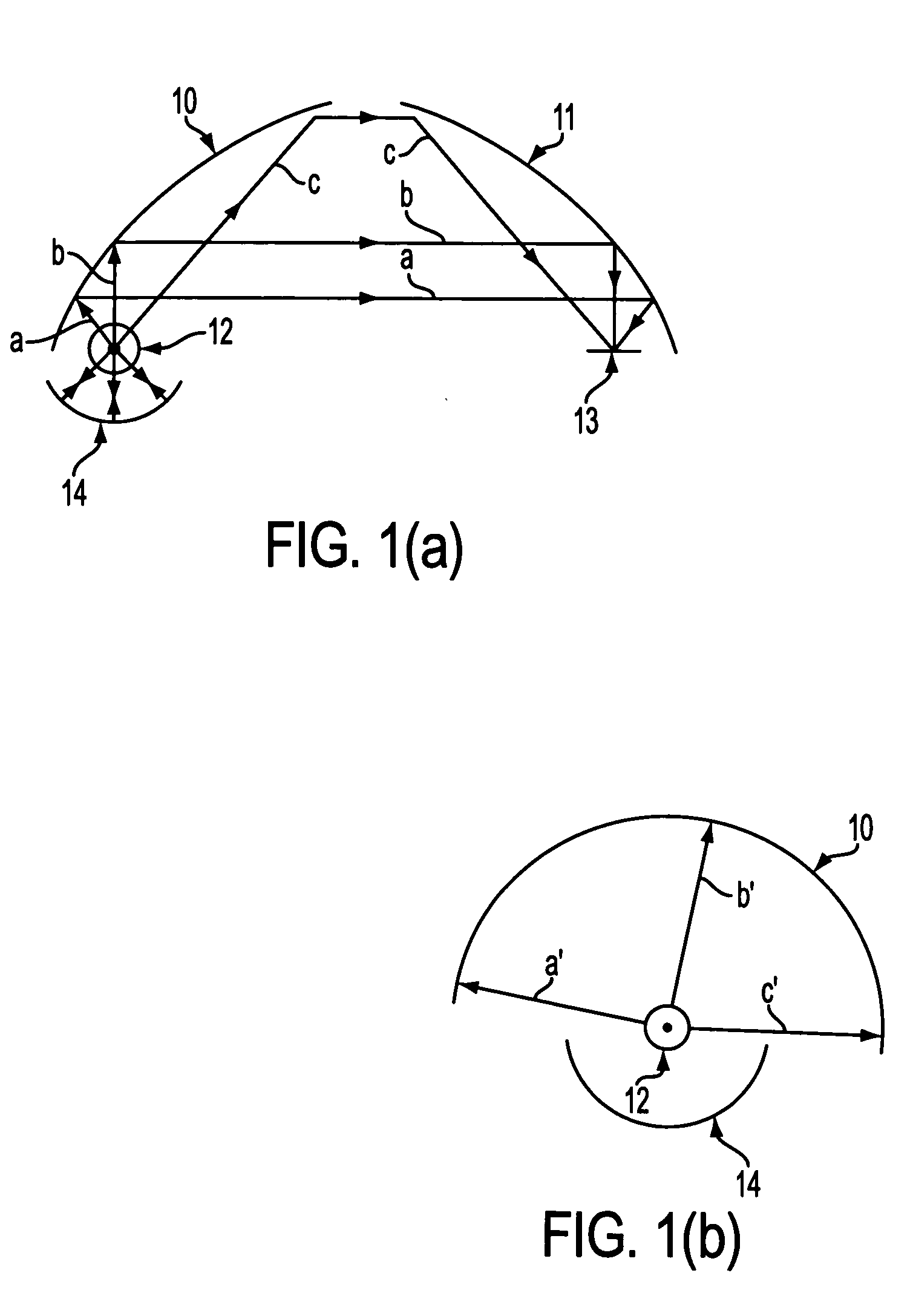
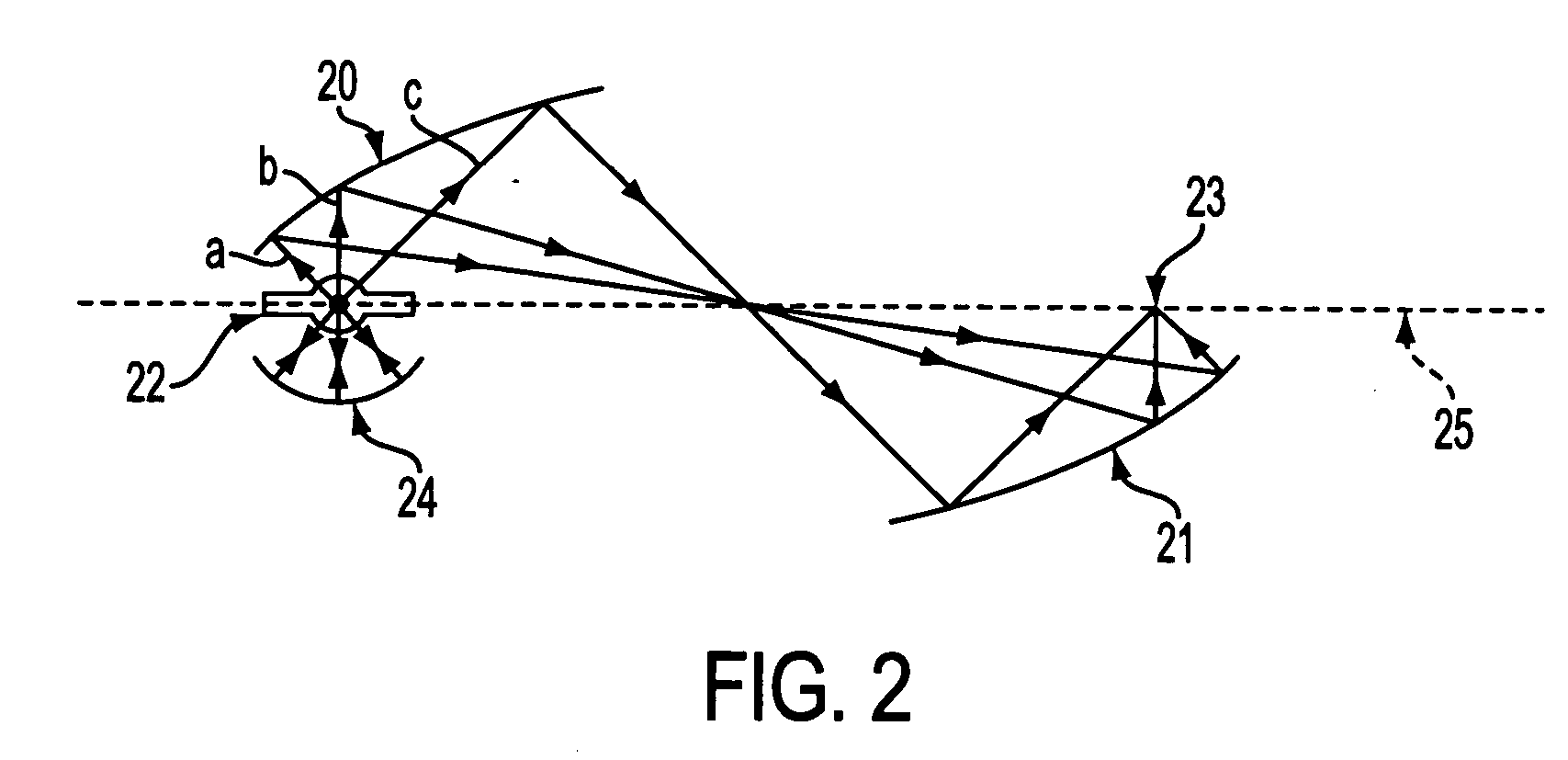
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1523 results about "Divergence angle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
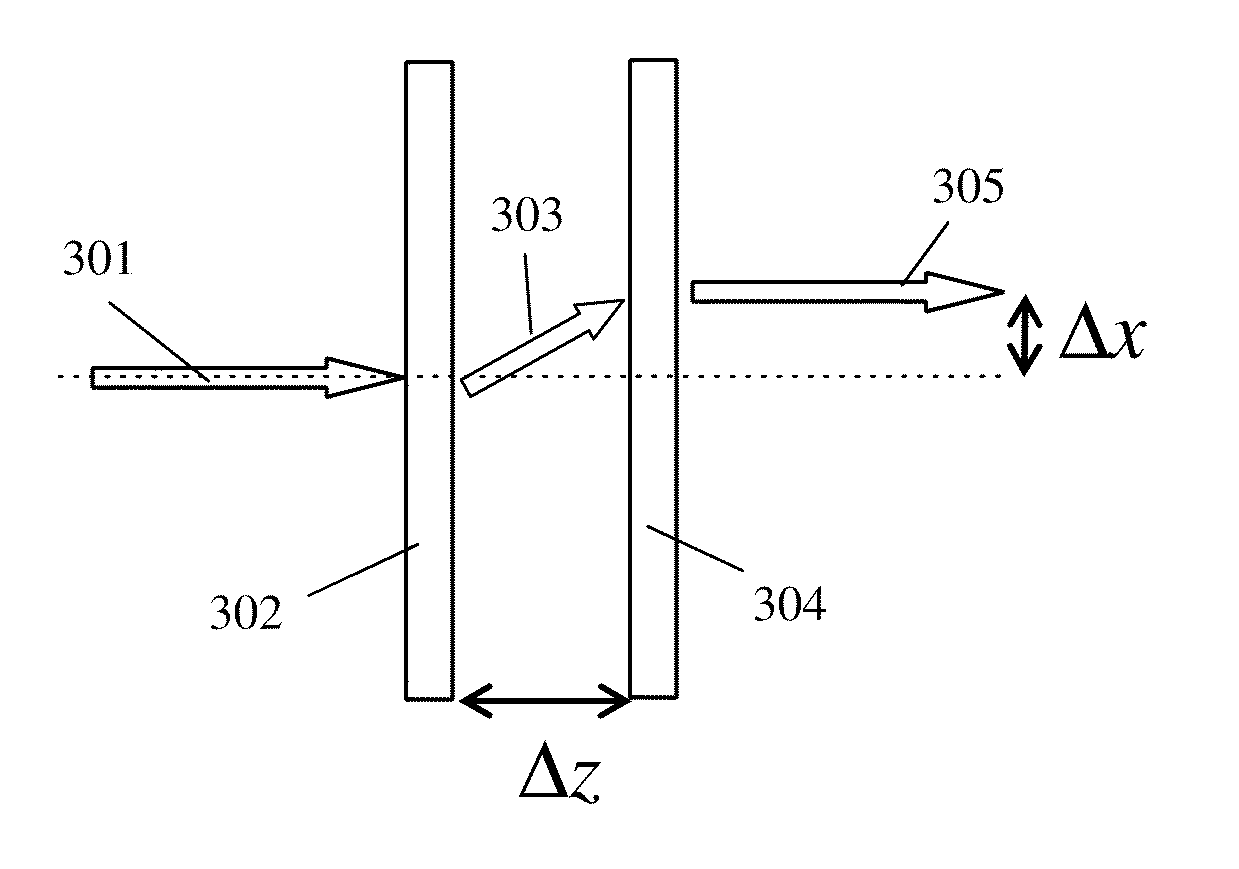
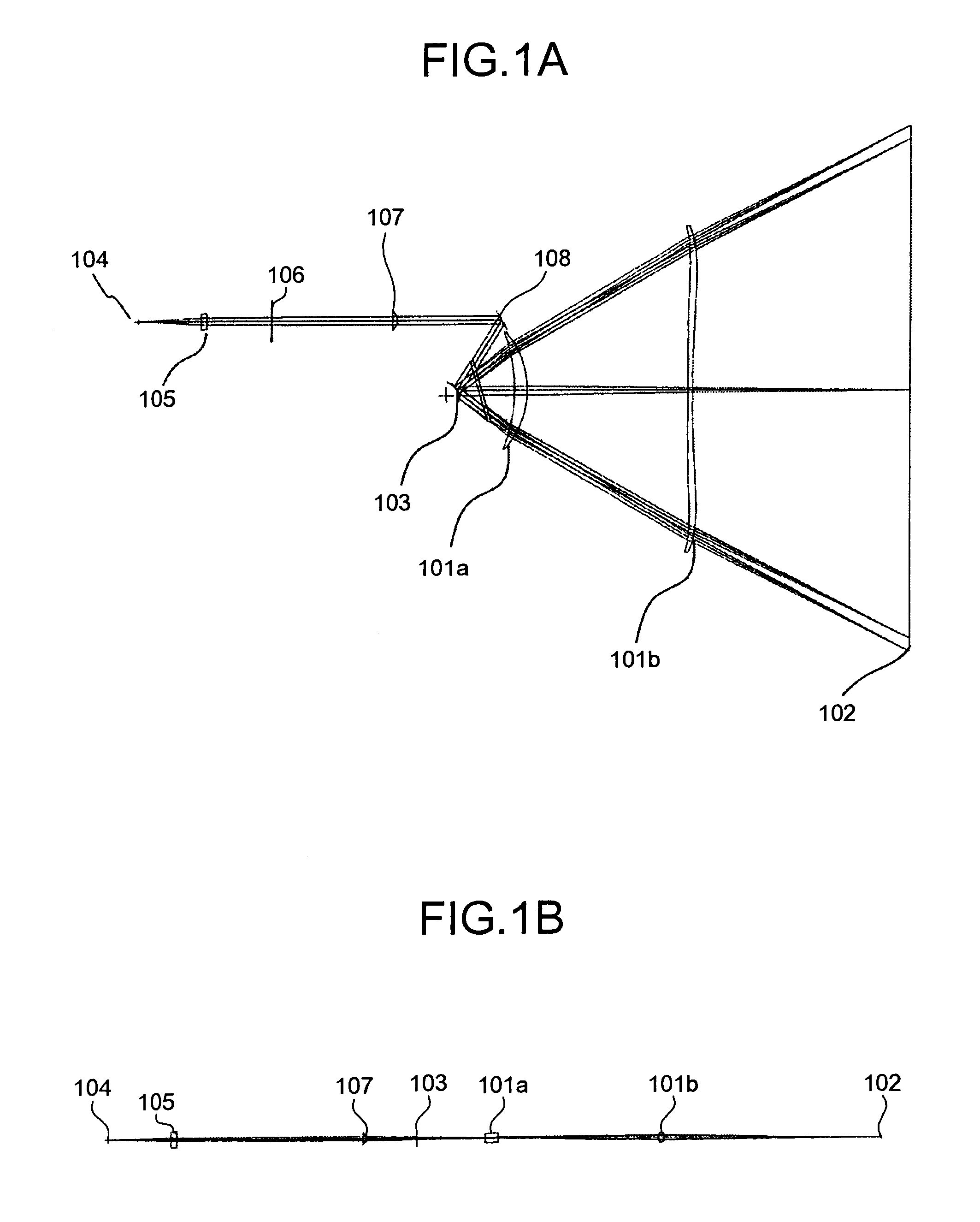
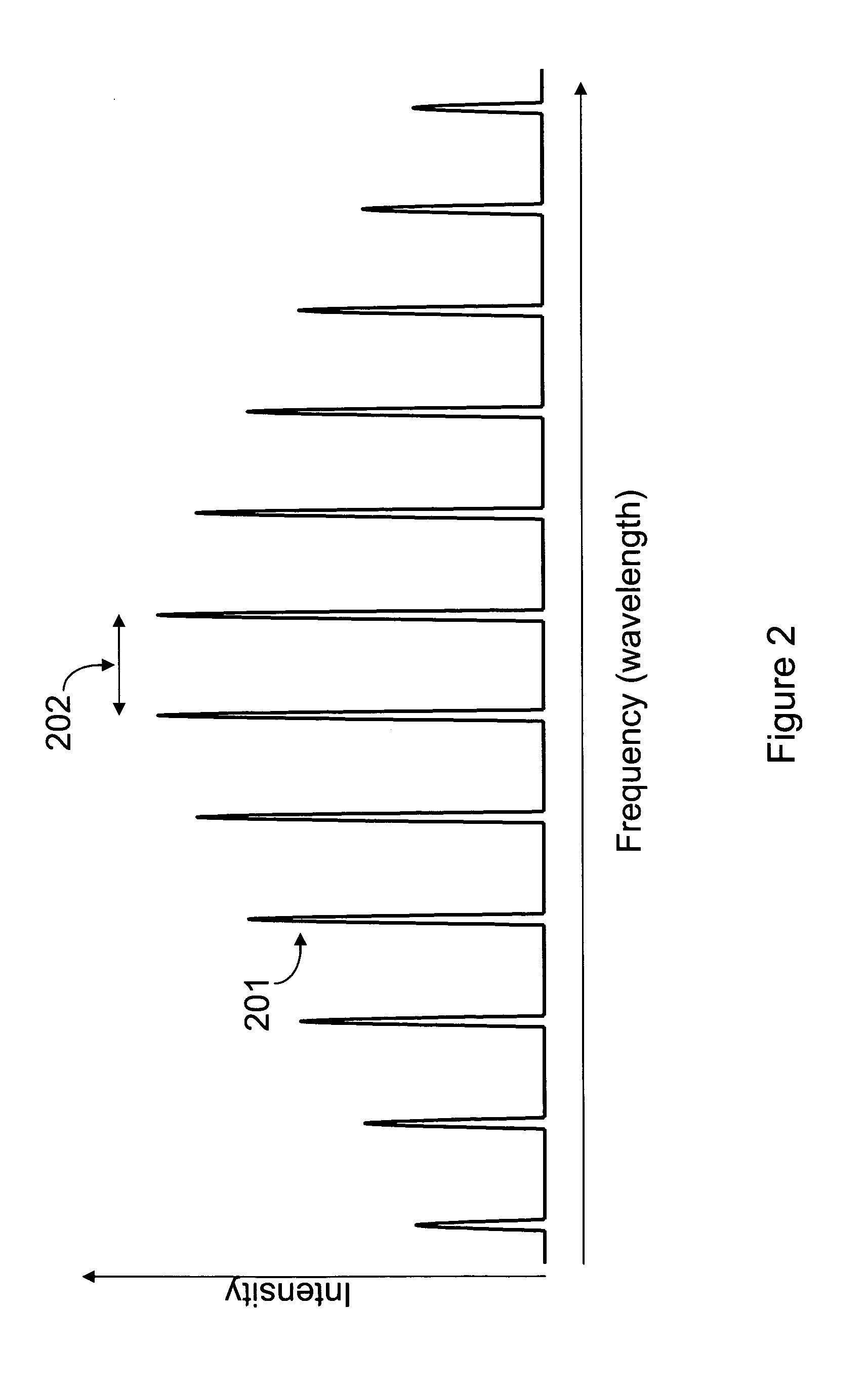
Usually, divergence angle is taken as the full angle of opening of the beam. Then, Half of the divergence angle can be calculated as where w 1 and w 2 are the radii of the beam at z 1 and z 2.
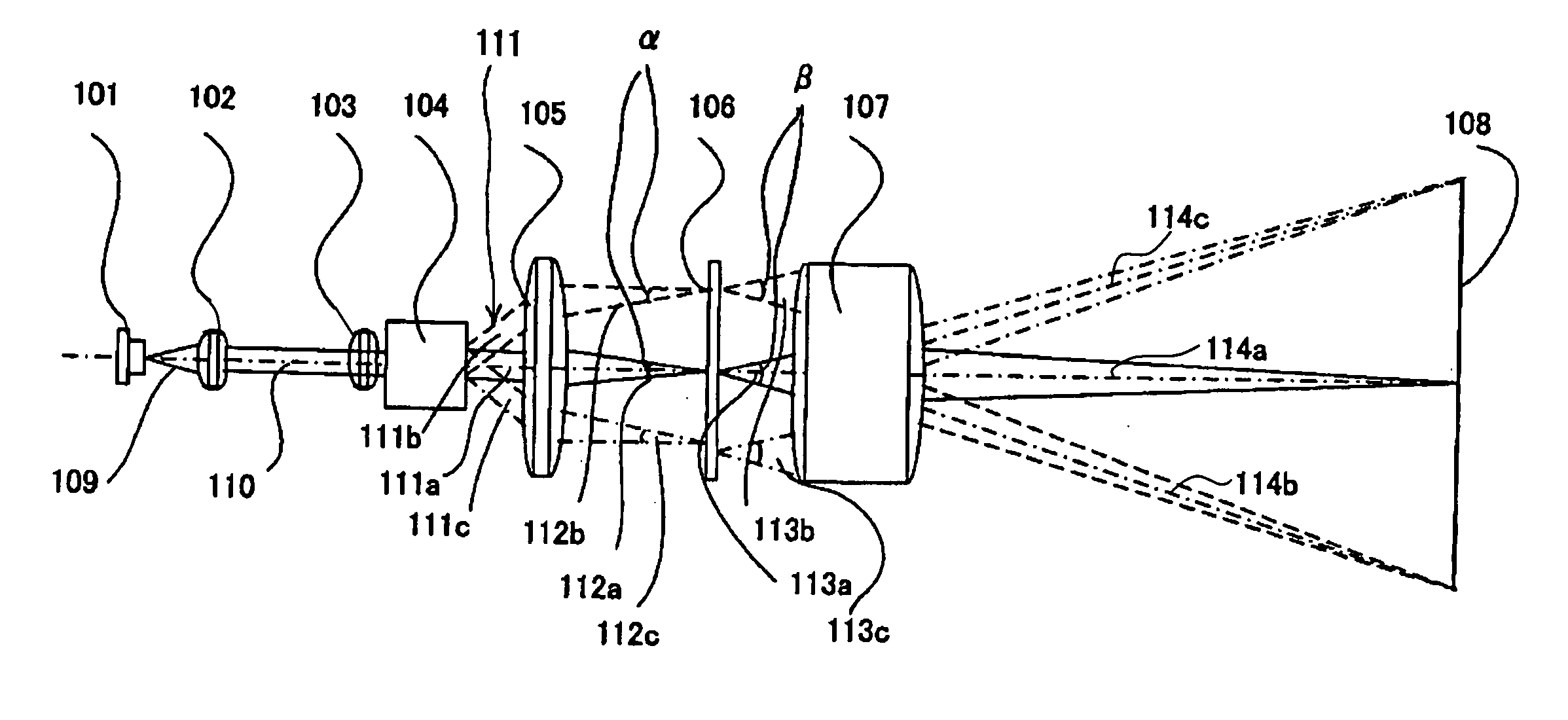
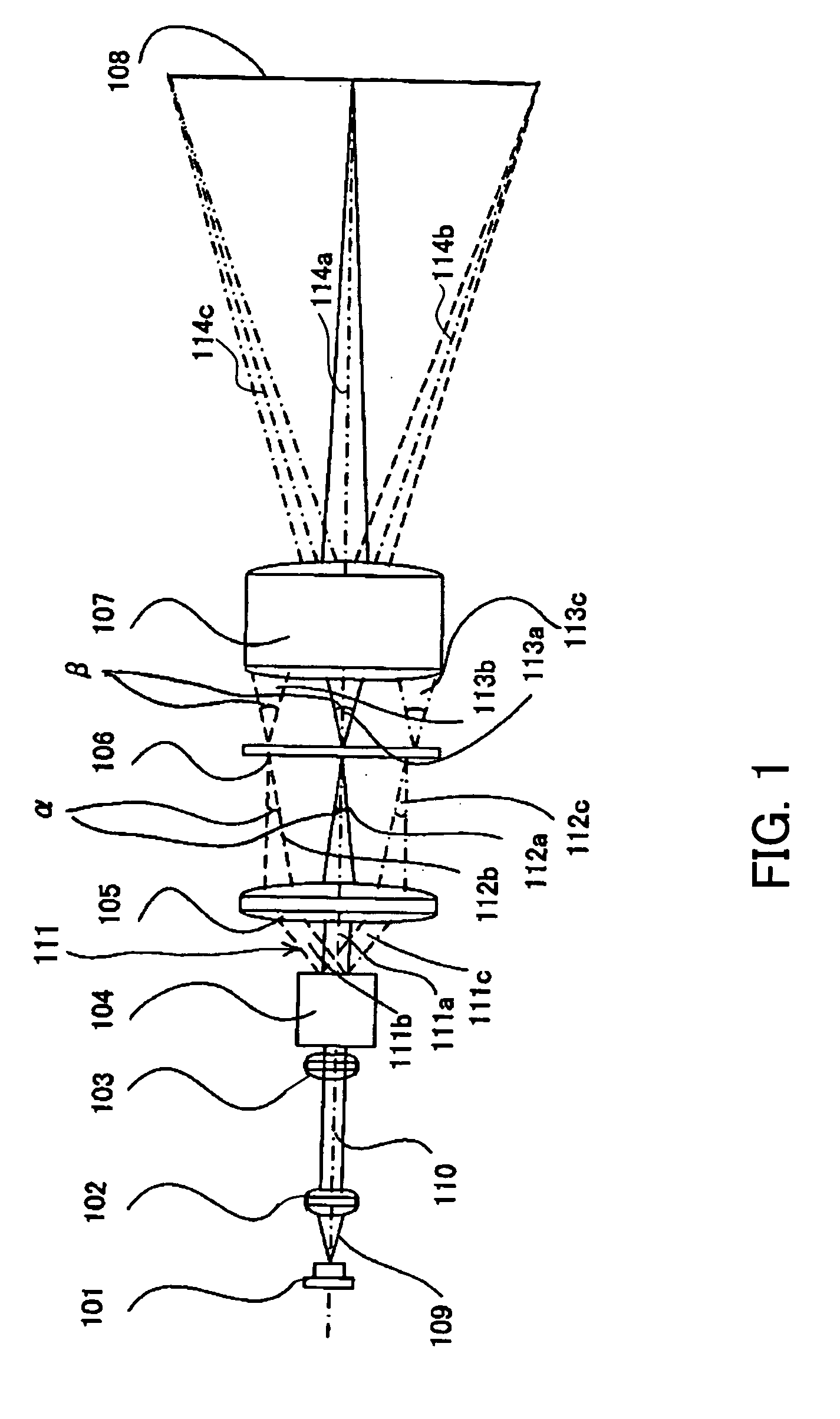
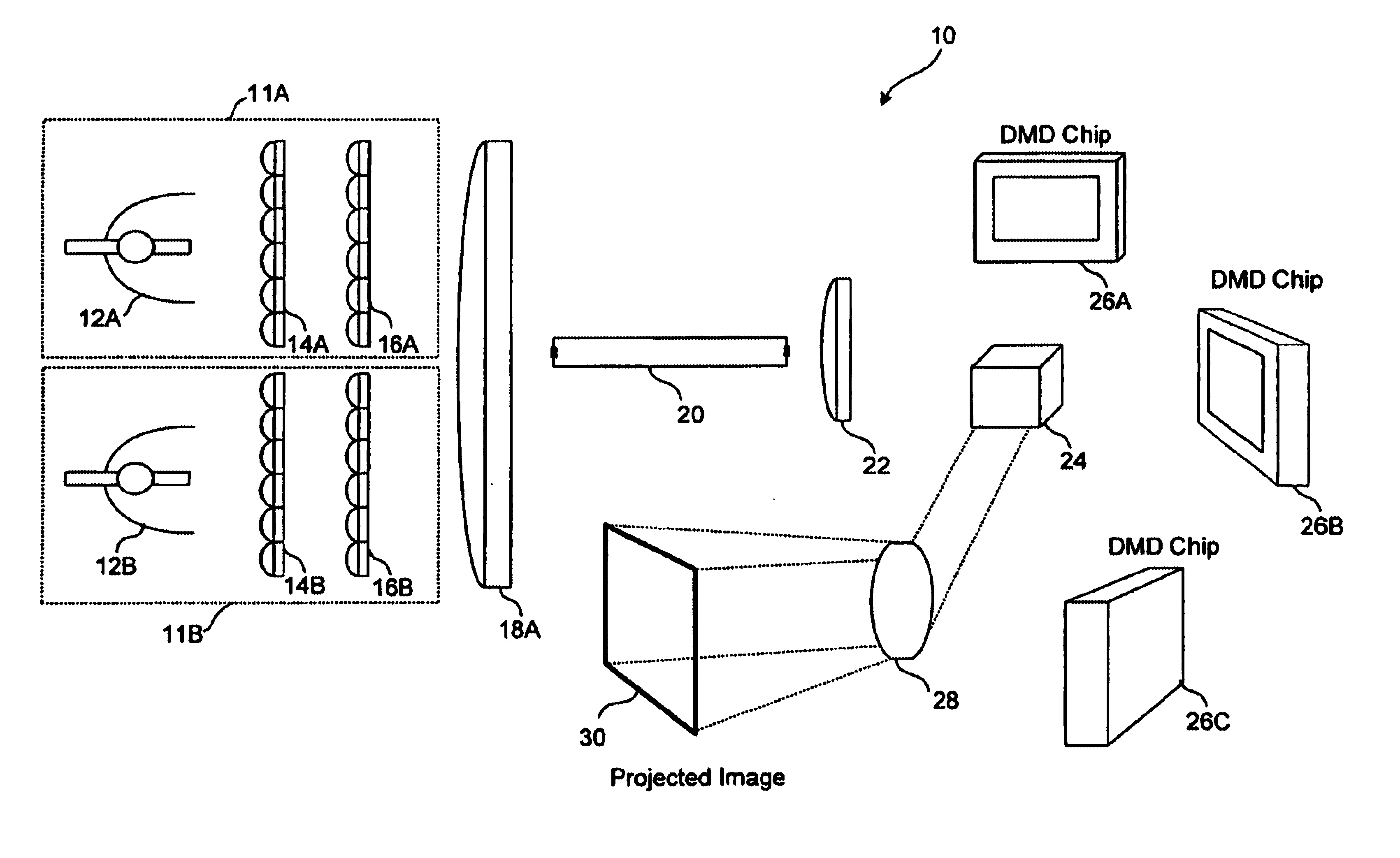
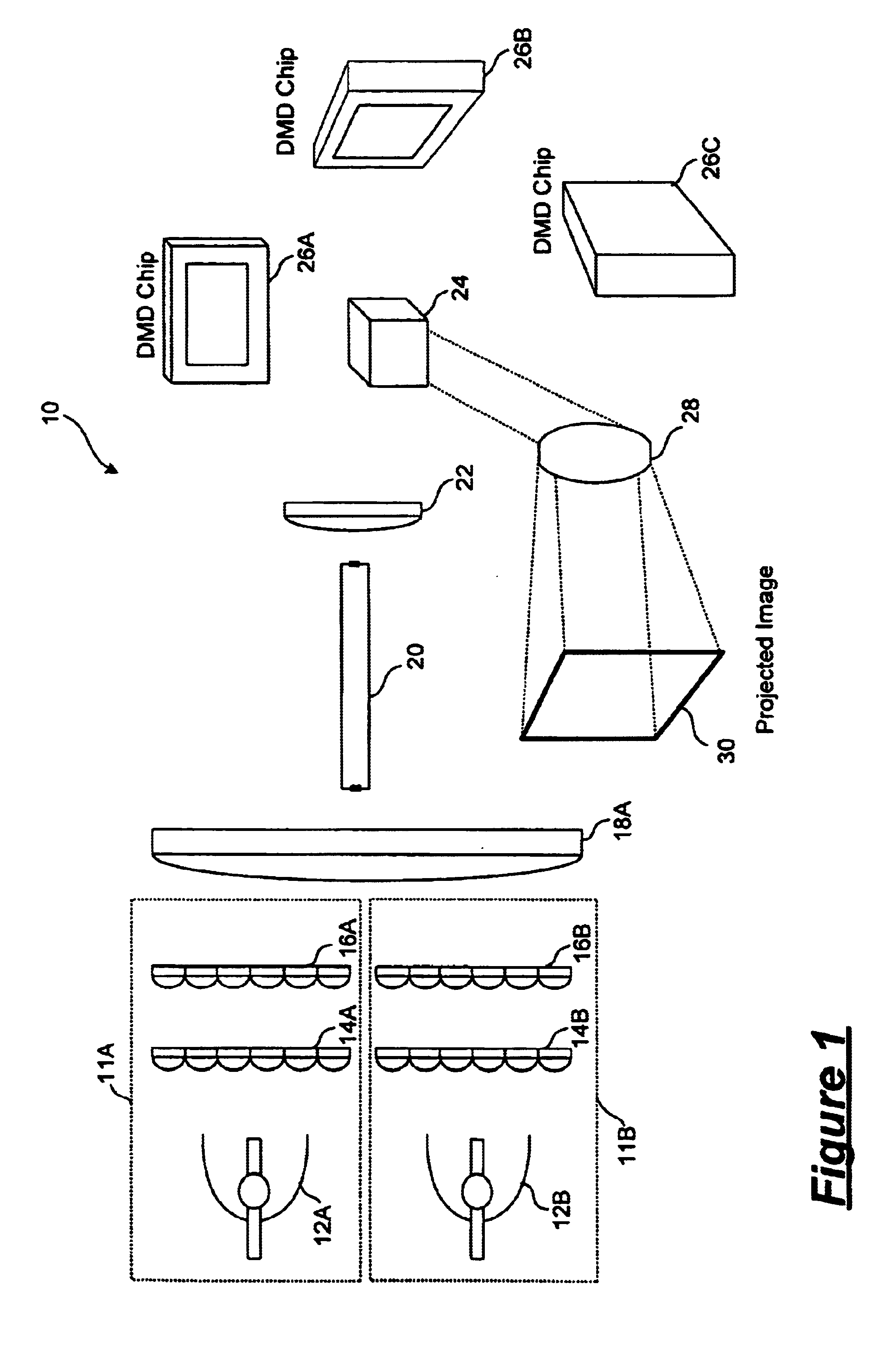
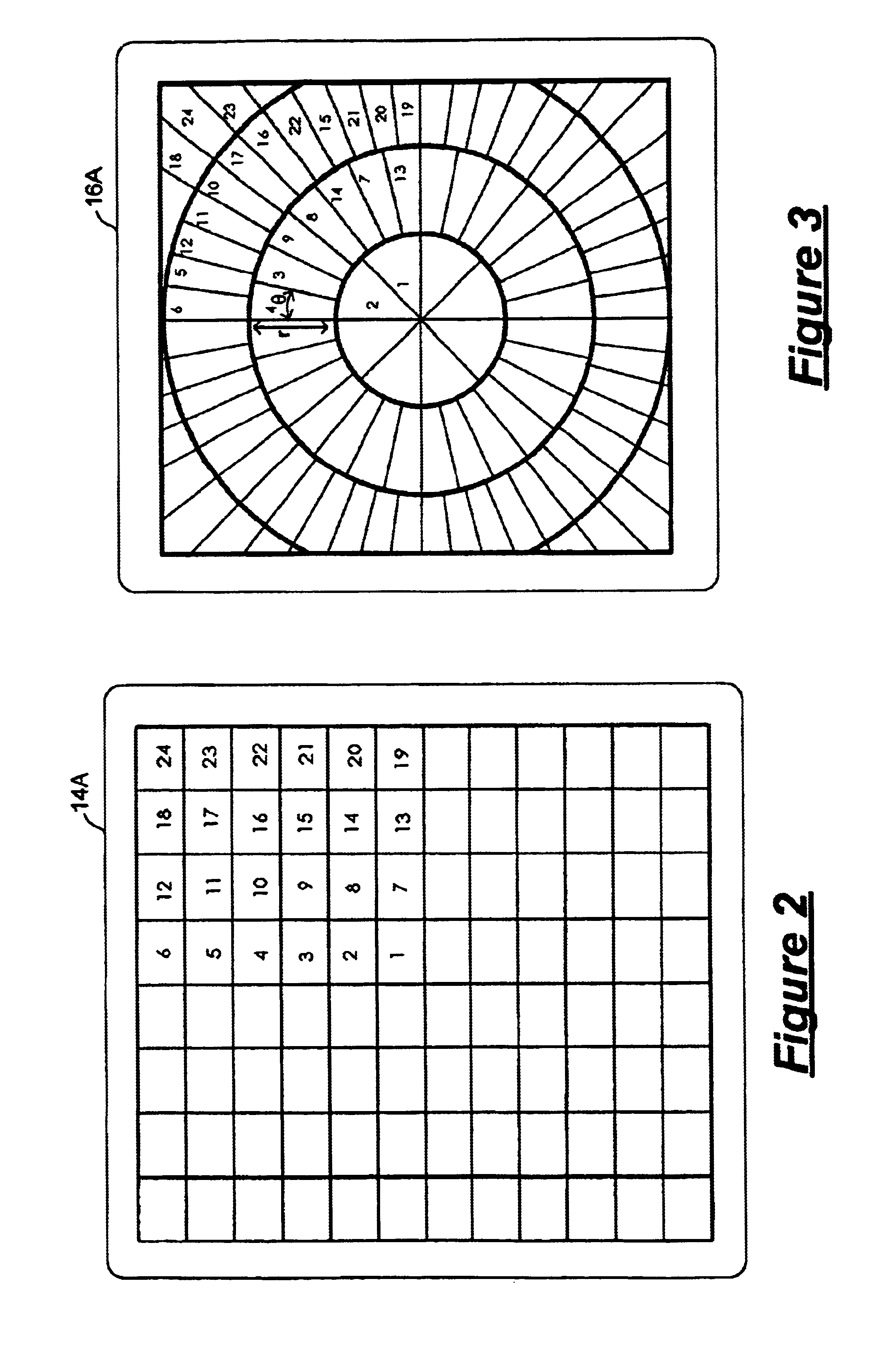
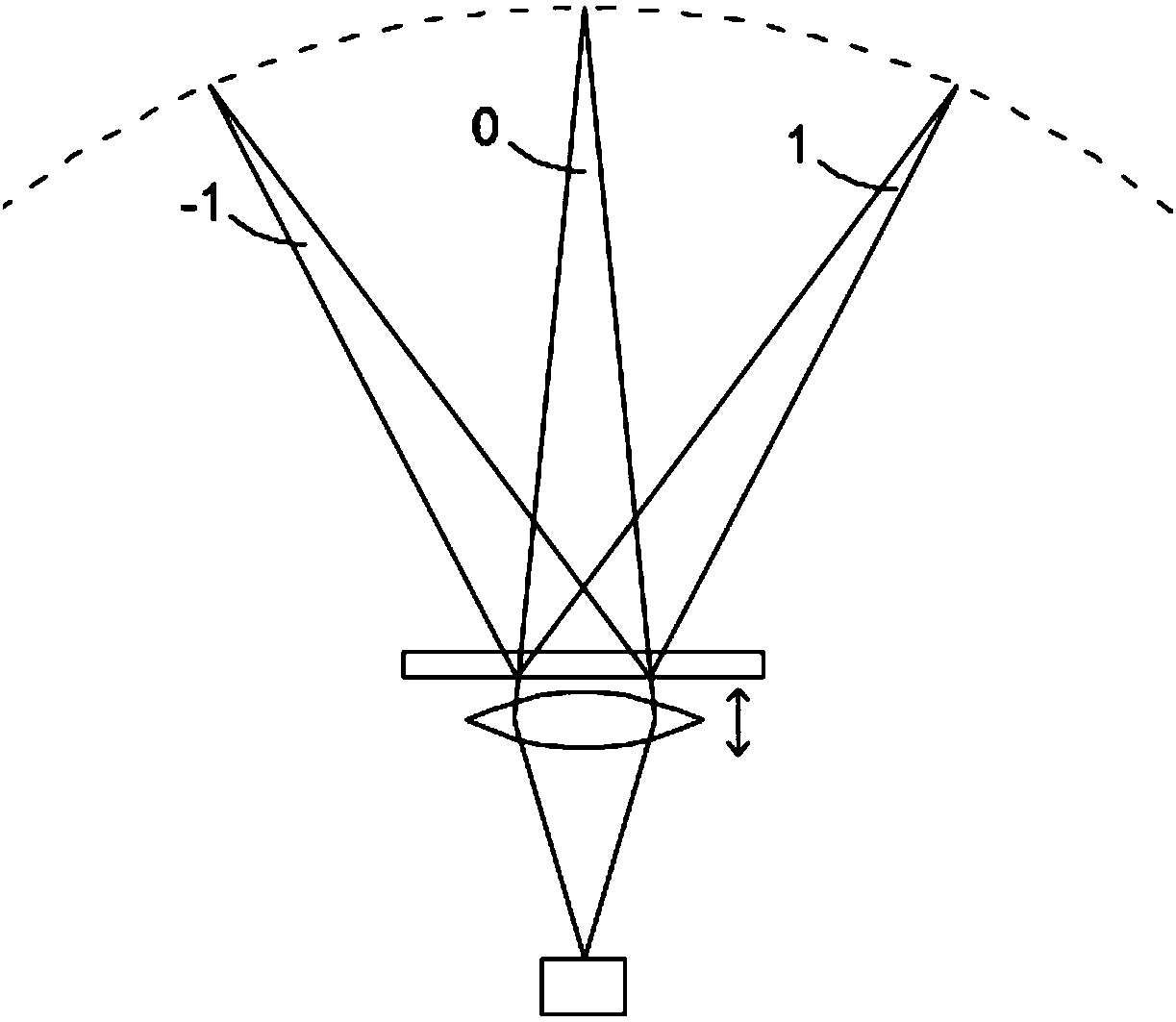
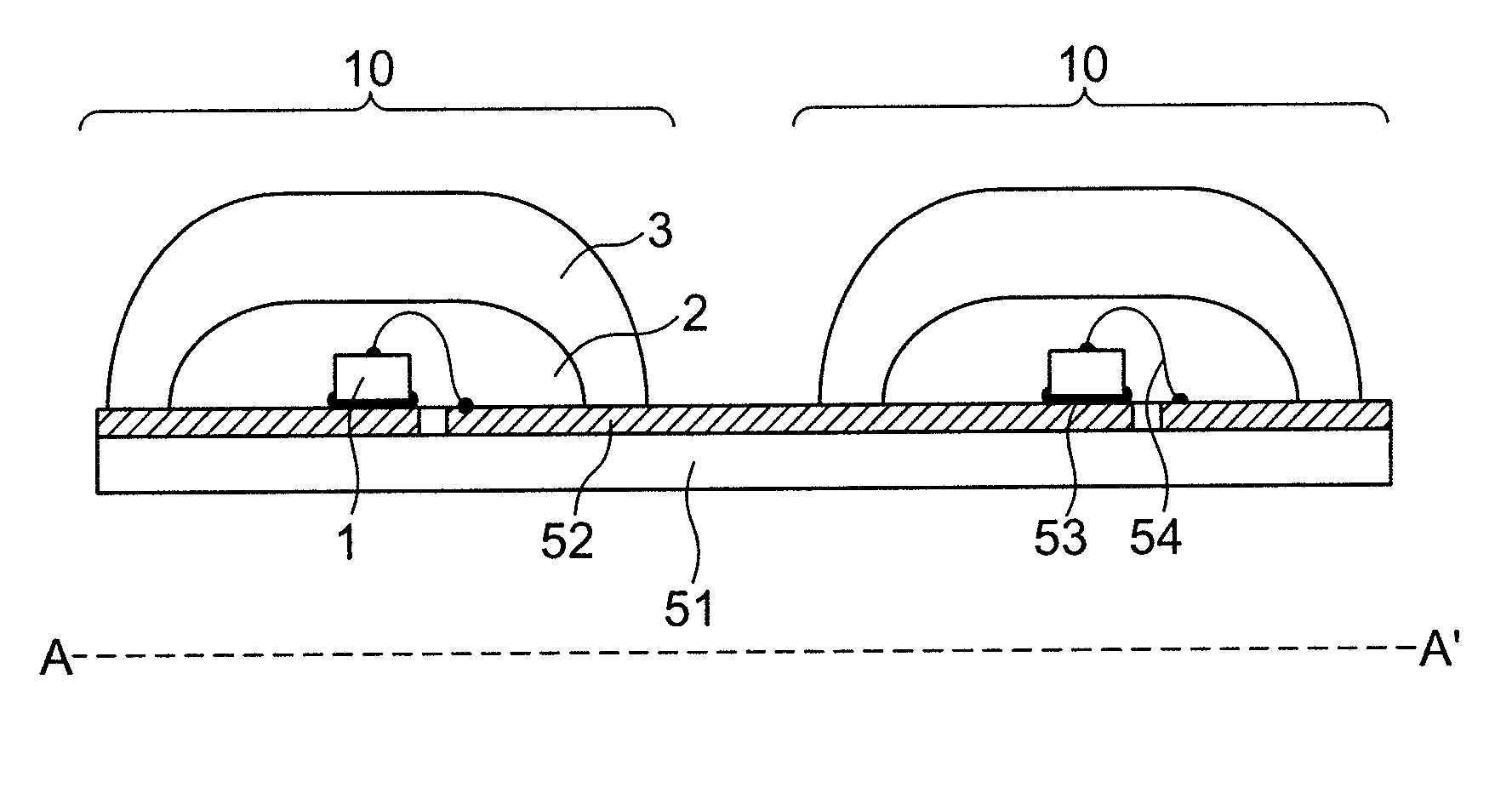
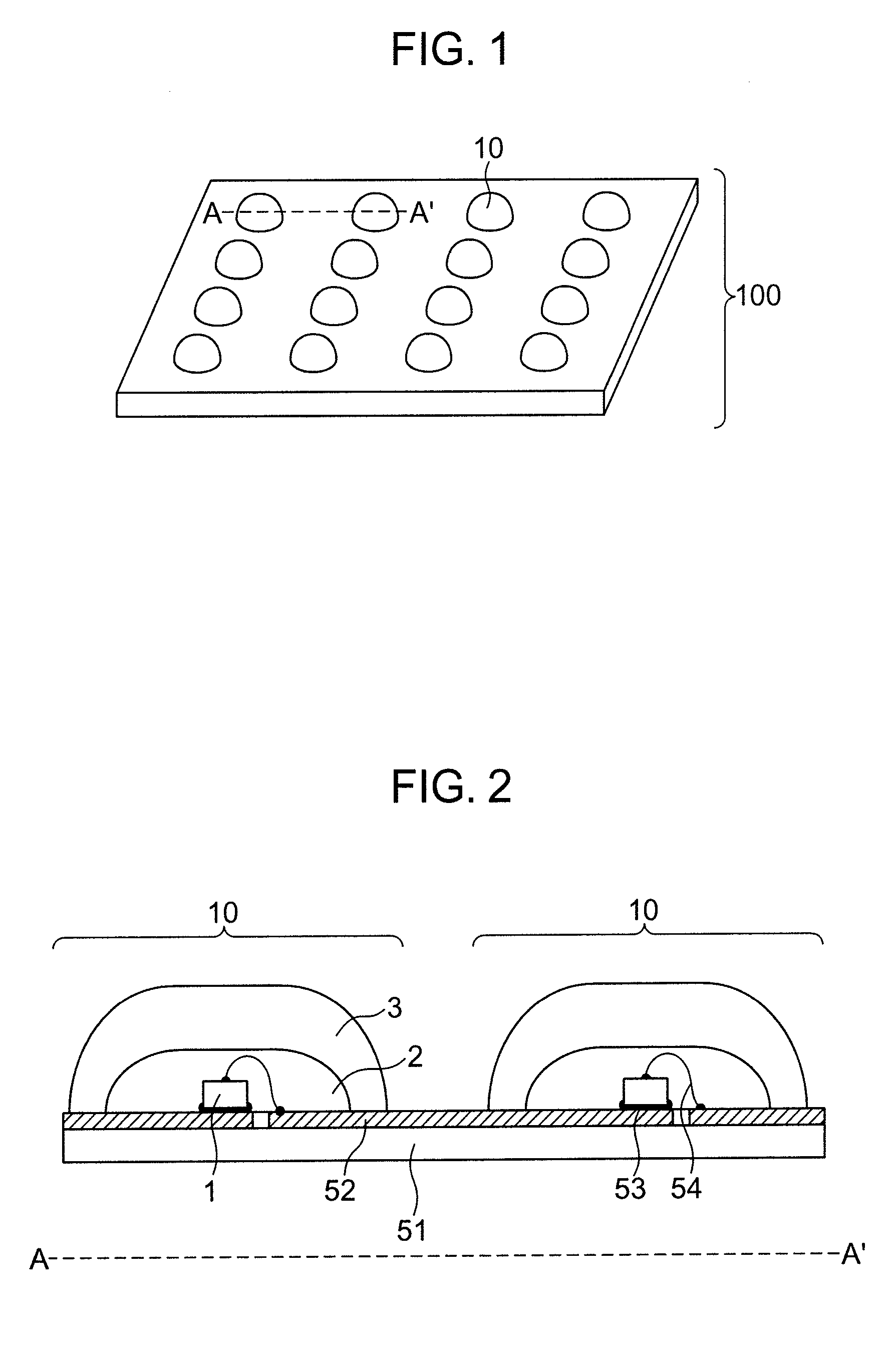
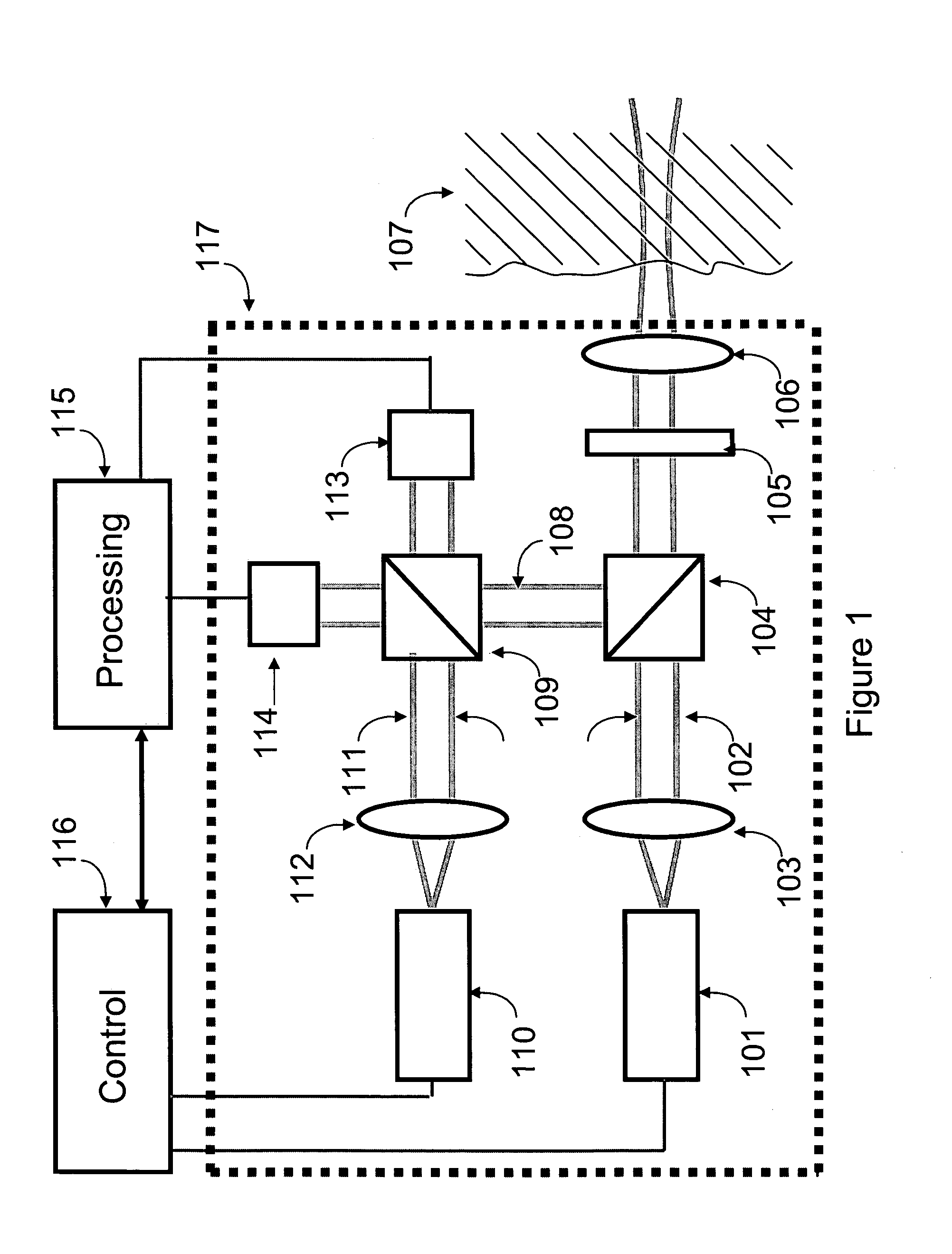
Displaying optical system and image projection apparatus
InactiveUS20060033009A1Reduce light lossReduce speckle noiseTelevision system scanning detailsProjectorsIntermediate imageDivergence angle
A displaying optical system is disclosed, which is capable of reducing a speckle noise. The displaying optical system comprises a light source emitting coherent light, a scanning device scanning the light, a first optical system causing the light from the scanning device to form an intermediate image, a second optical system causing the light from the intermediate image to form an image on a real display surface, and an optical element arranged between the first and second optical systems. The optical element widens the divergence angle of the light emerged from the optical element toward the second optical system more than the incident angle of the light on the optical element from the first optical system.
Owner:CANON KK
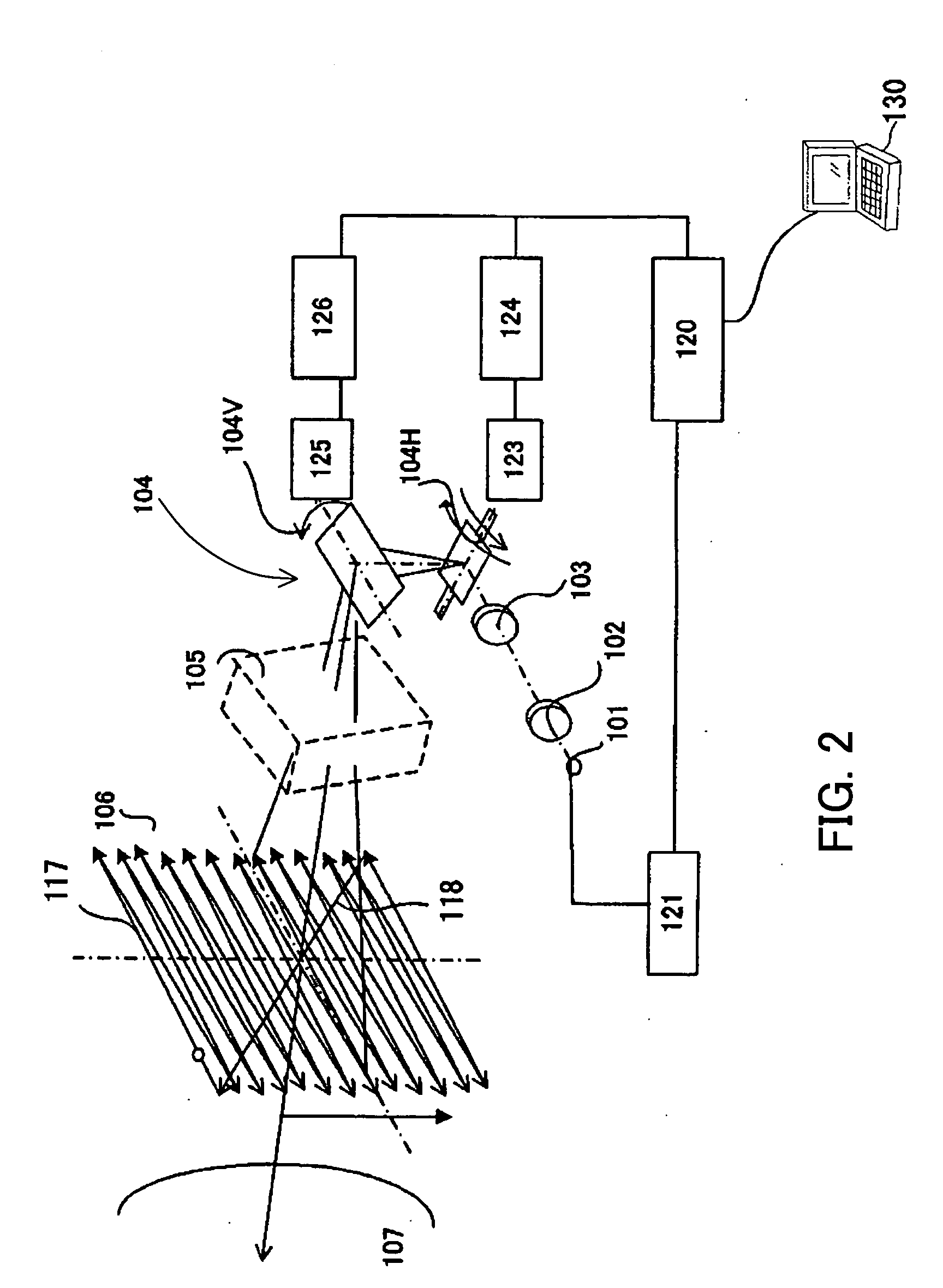
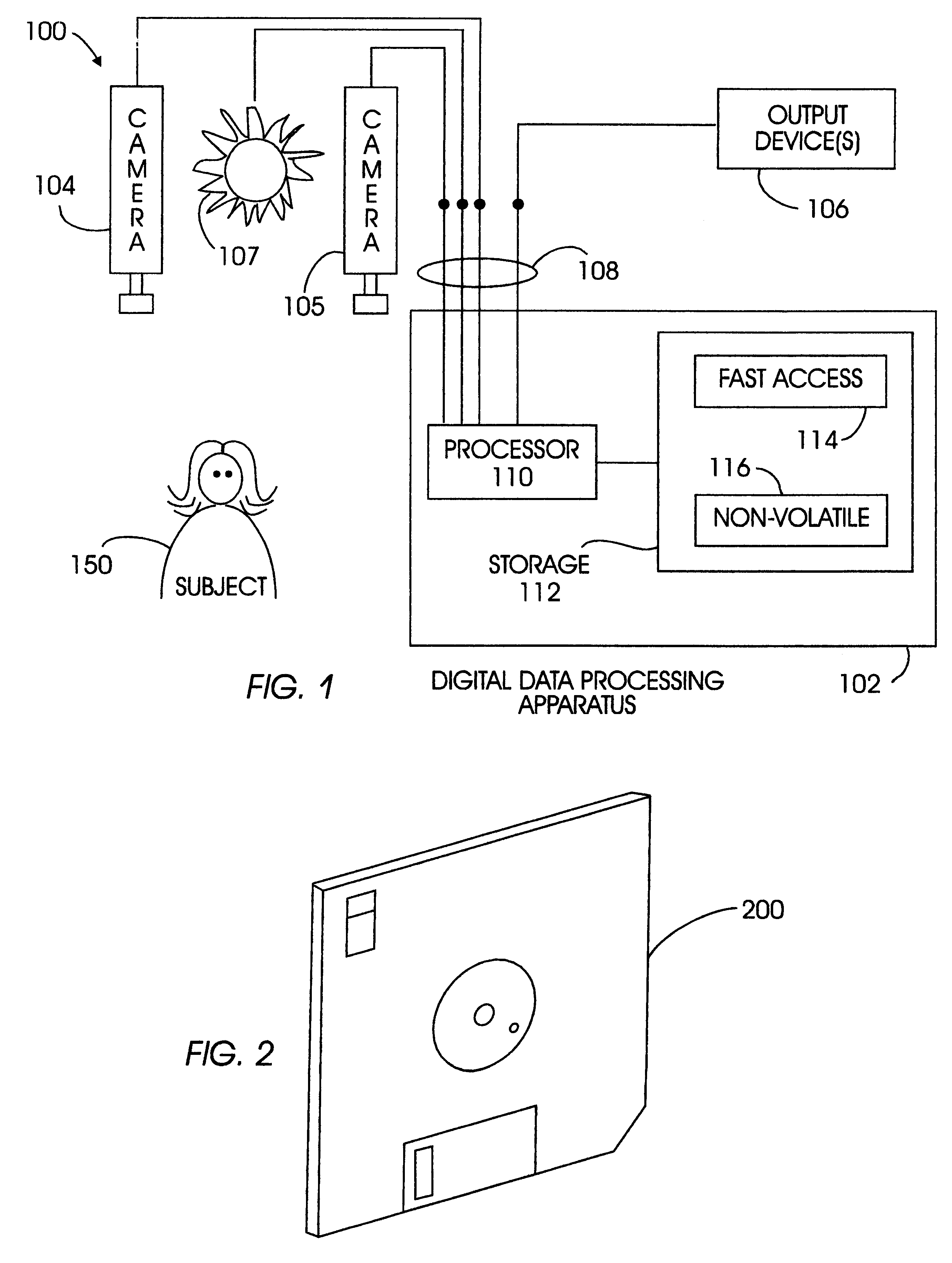
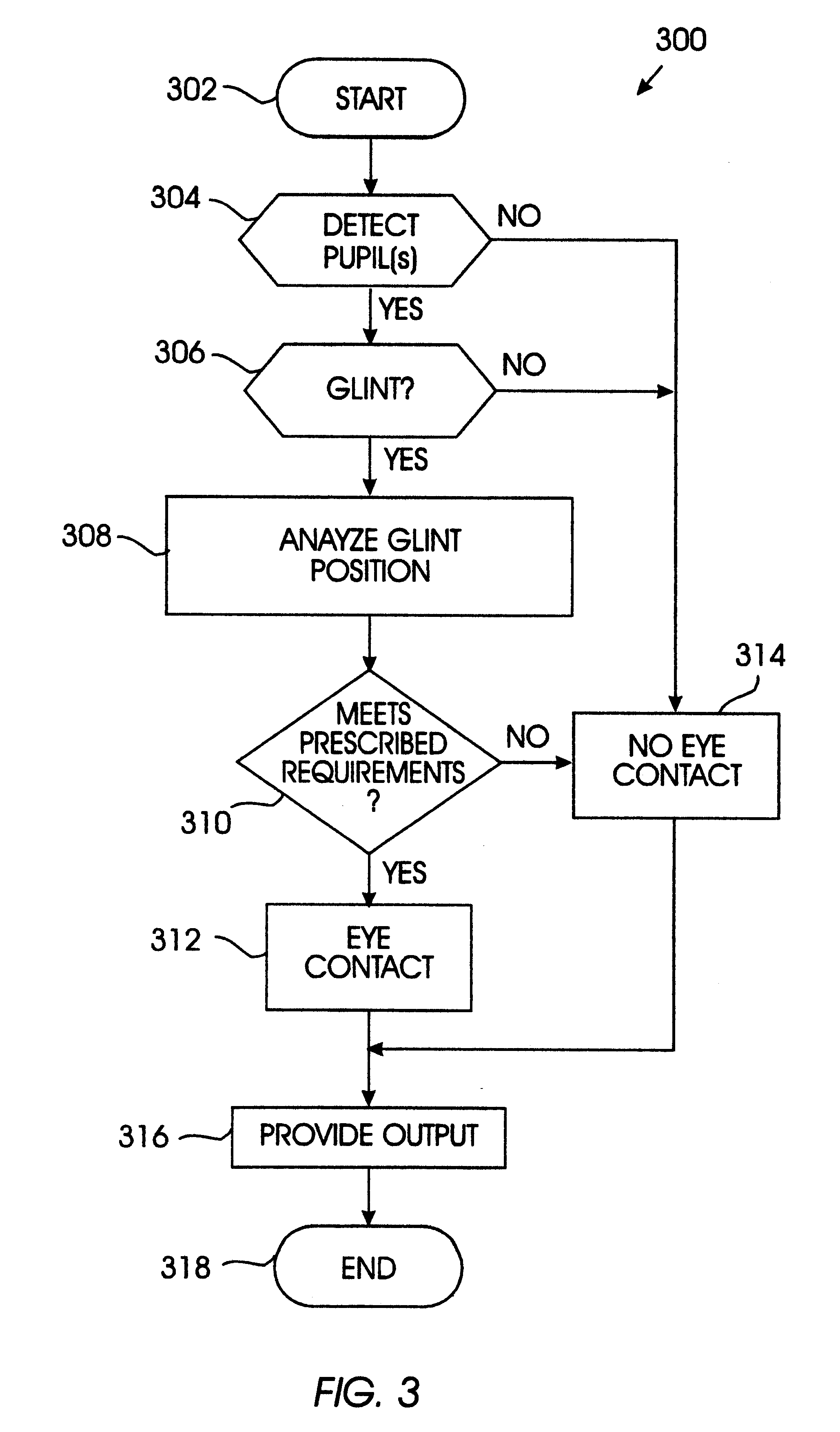
Method and apparatus for determining eye contact
InactiveUS6393136B1Input/output for user-computer interactionTelevision system detailsOphthalmologyDivergence angle
A method and apparatus determine when a subject is looking at a specific target area by estimating a divergence angle between (1) the direction in which the subject is looking and (2) the direction from the subject directly to the target area. This technique accesses whether the subject is looking at a particular area. The invention may further condition this determination according to the subject's distance from the target area, because there is less tolerance for divergent angles when the subject is farther away. In one embodiment, the divergence angle is estimated using the position of a glint of light in the subject's pupil. The glint is created by a light source located in the target area. If the glint is sufficiently central to the pupil, with the camera and light source being near the target area, the subject is looking at the target area. At long distances, when the glint is not sufficiently discernable from the pupil, another technique may be employed to estimate divergence angle. Namely, the plane of the subject's face is computed, and analyzed with respect to a vector between the subject's face and the target area. If the plane is substantially normal to the vector, the subject is looking at the target area.
Owner:TOBII TECH AB
Broadband optics for manipulating light beams and images
InactiveUS20110188120A1Enhancing optical manipulation capabilityDiffraction gratingsLight beamDivergence angle
The objective of the present invention is providing optical systems for controlling with propagation of light beams in lateral and angular space, and through optical apertures. Said light beams include laser beams as well as beams with wide spectrum of wavelengths and large divergence angles. Said optical systems are based on combination of diffractive waveplates with diffractive properties that can be controlled with the aid of external stimuli such as electrical fields, temperature, optical beams and mechanical means.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Laser illuminating device and image display device
InactiveUS20100053565A1Remove speckle noiseUniform lightDiffusing elementsProjectorsDivergence angleLaser light
An object of the invention is to provide a laser illuminating device and an image display device that enable to remove speckle noises in a diffraction field and an image field, uniformly illuminate an illumination plane, and realize miniaturization. A laser illuminating device 100 includes a laser light source 3, a first lens 1 including a plurality of microlenses 10 each having a predetermined numerical aperture in an in-plane direction, each of the microlenses 10 being adapted to expand laser light emitted from the laser light source 3 to thereby superimpose the laser light transmitted through each of the microlenses 10; and a second lens 2 having an effective diameter larger than an effective diameter of the first lens 1, and for compensating for a divergence angle of the laser light expanded by each of the plurality of the microlenses 10.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
High efficacy waveguide coupler
An optical coupling apparatus for coupling a waveguide to a light source, when the light source emits light at a divergence angle that is larger than the critical angle of the waveguide. The optical coupler comprises a plurality of light-guides, preferably cut from the edge of the waveguide. The light-guides are arranged to connect the waveguide to the light source via a plurality of orientations so that the entire divergence angle is covered within the critical angle of the light-guides.
Owner:OREE ADVANCED ILLUMINATION SOLUTIONS LTD +1
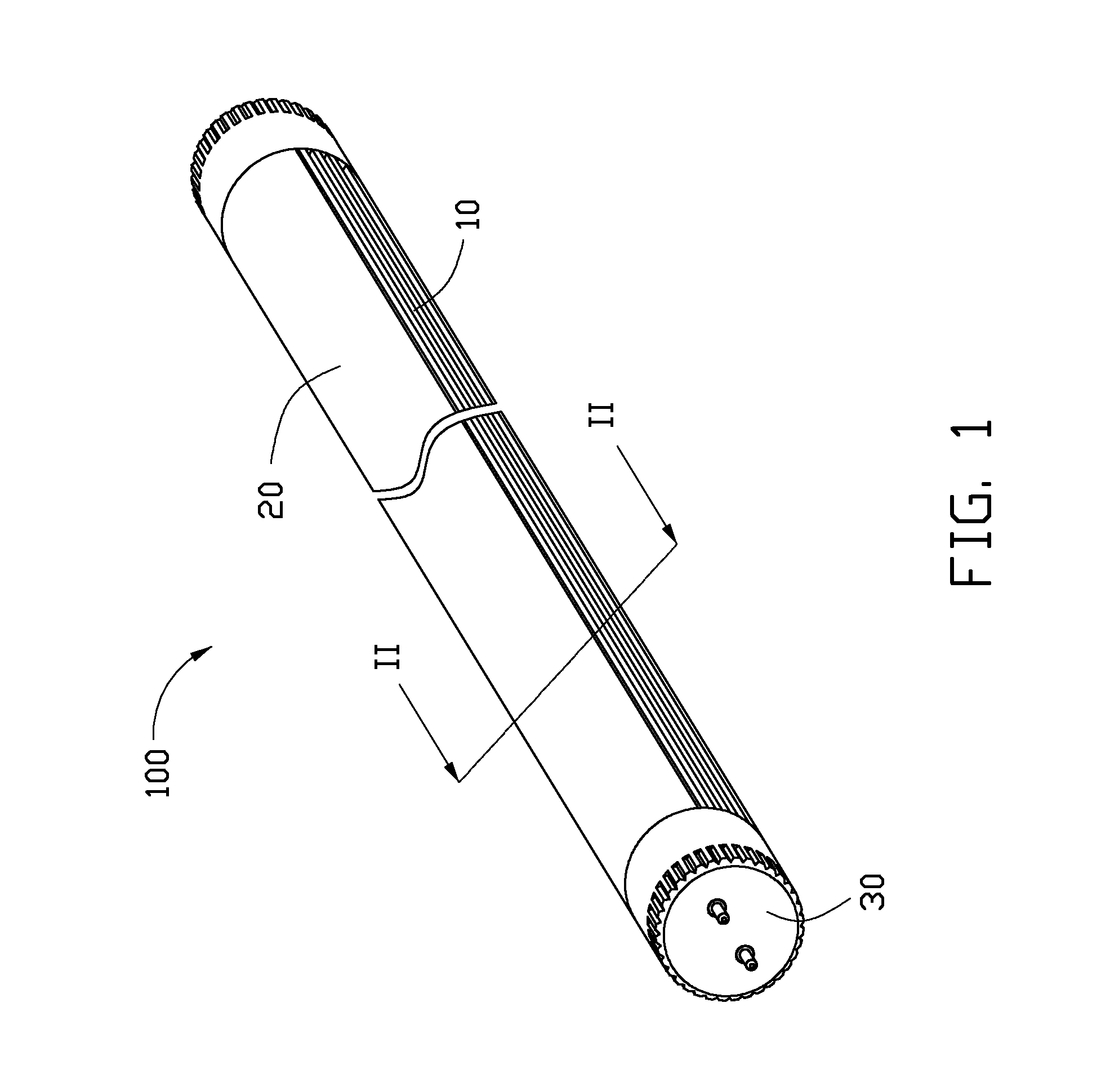
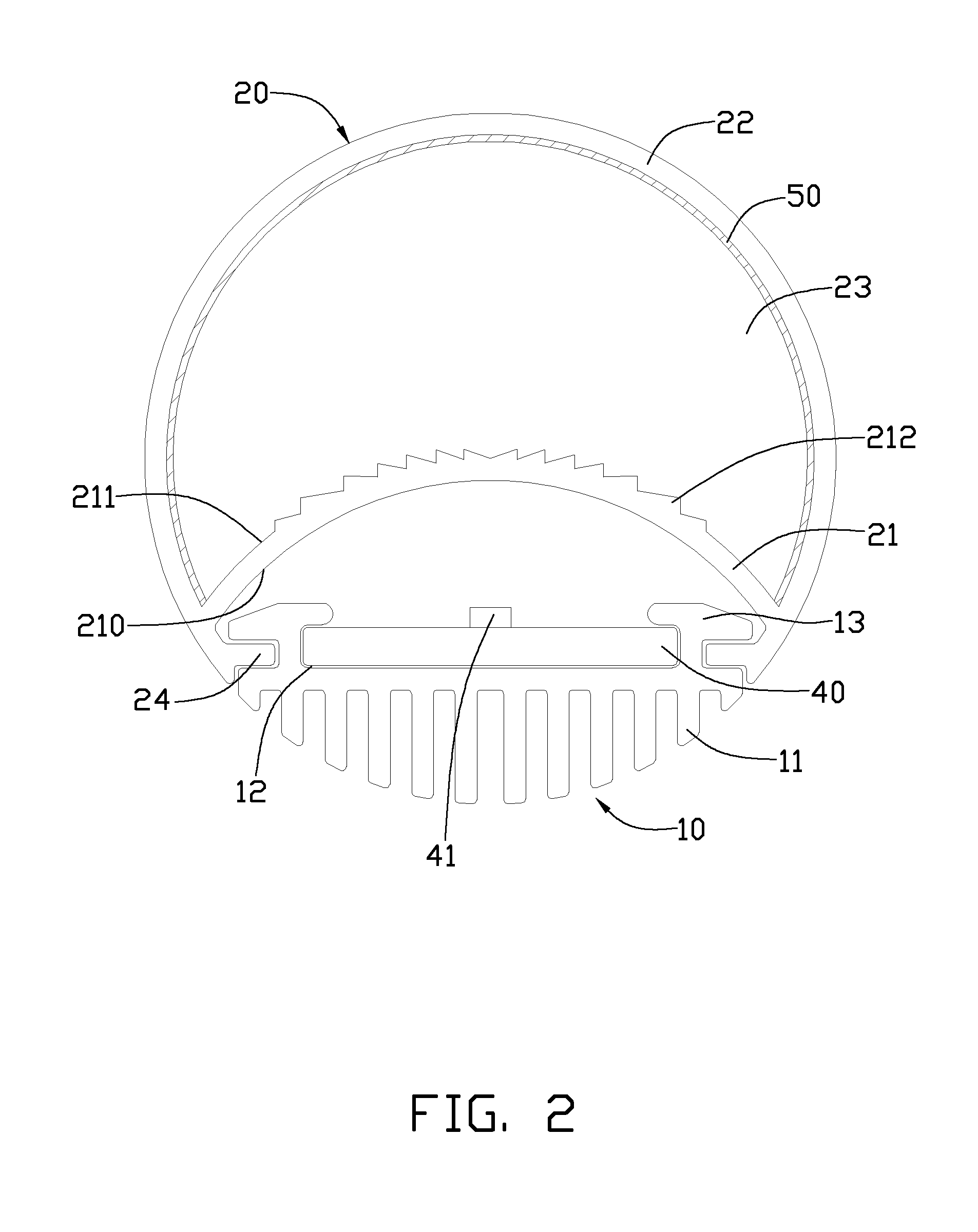
LED tube lamp
An LED tube lamp includes a heat sink, an LED substrate, a cover fixed to the heat sink. The cover includes a first cover and a second cover, the first cover is closer to the LED substrate than the second cover, and a plurality of lenses are arranged on the surface of the first cover to refract the light beams entering into the first cover. The light beams are scattered by the lenses to enlarge the light divergence angle of the LED tube lamp.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
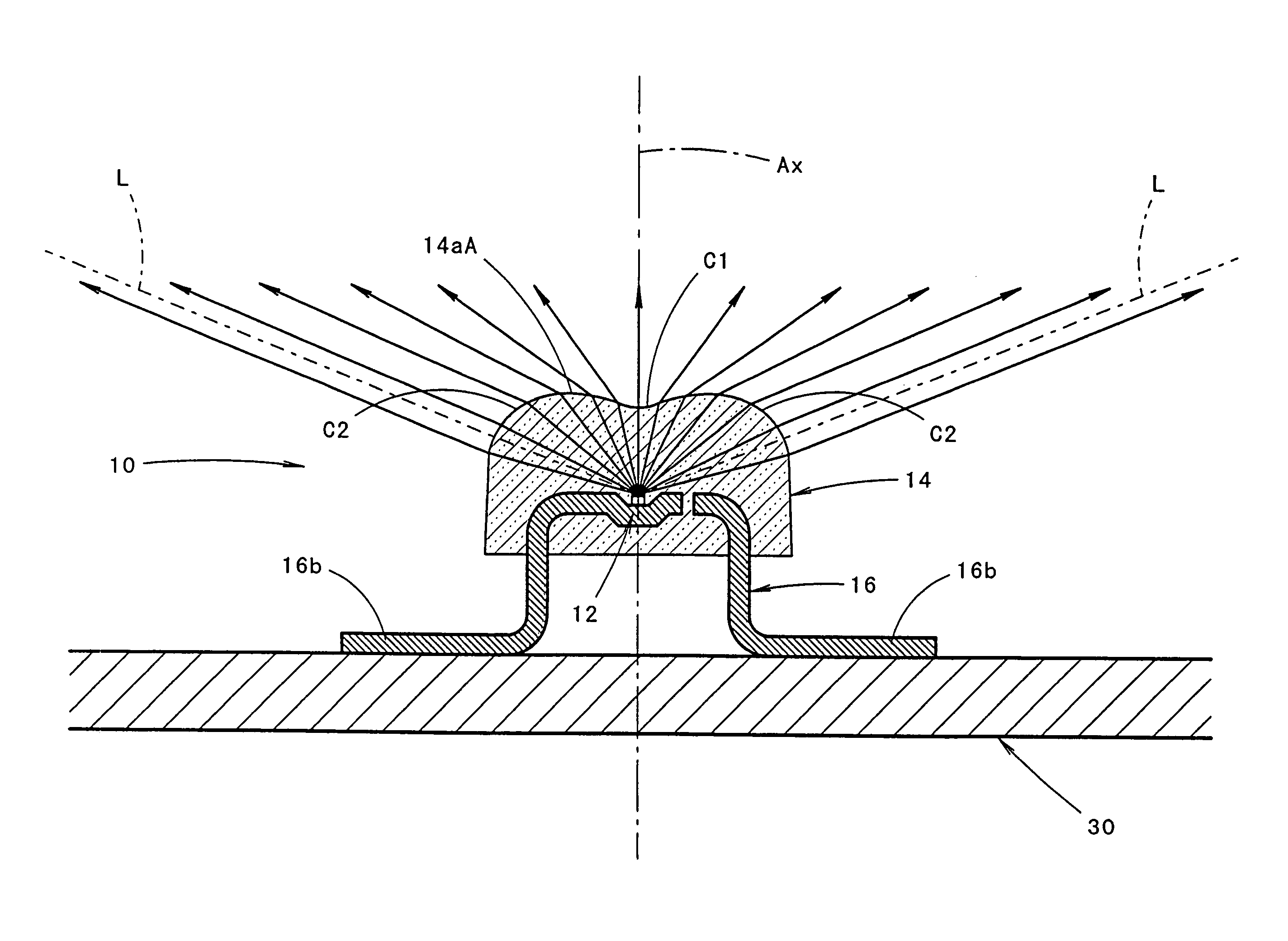
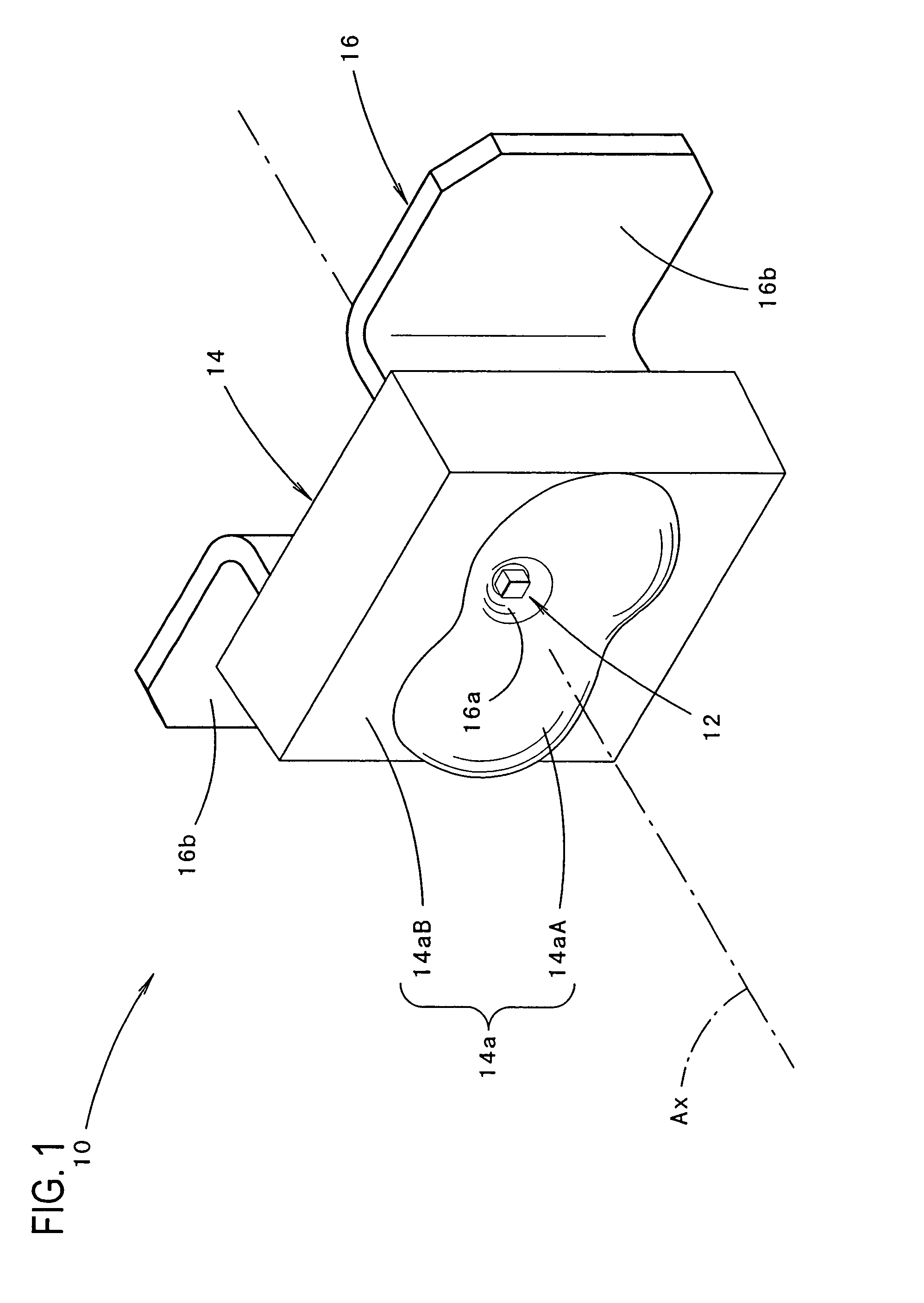
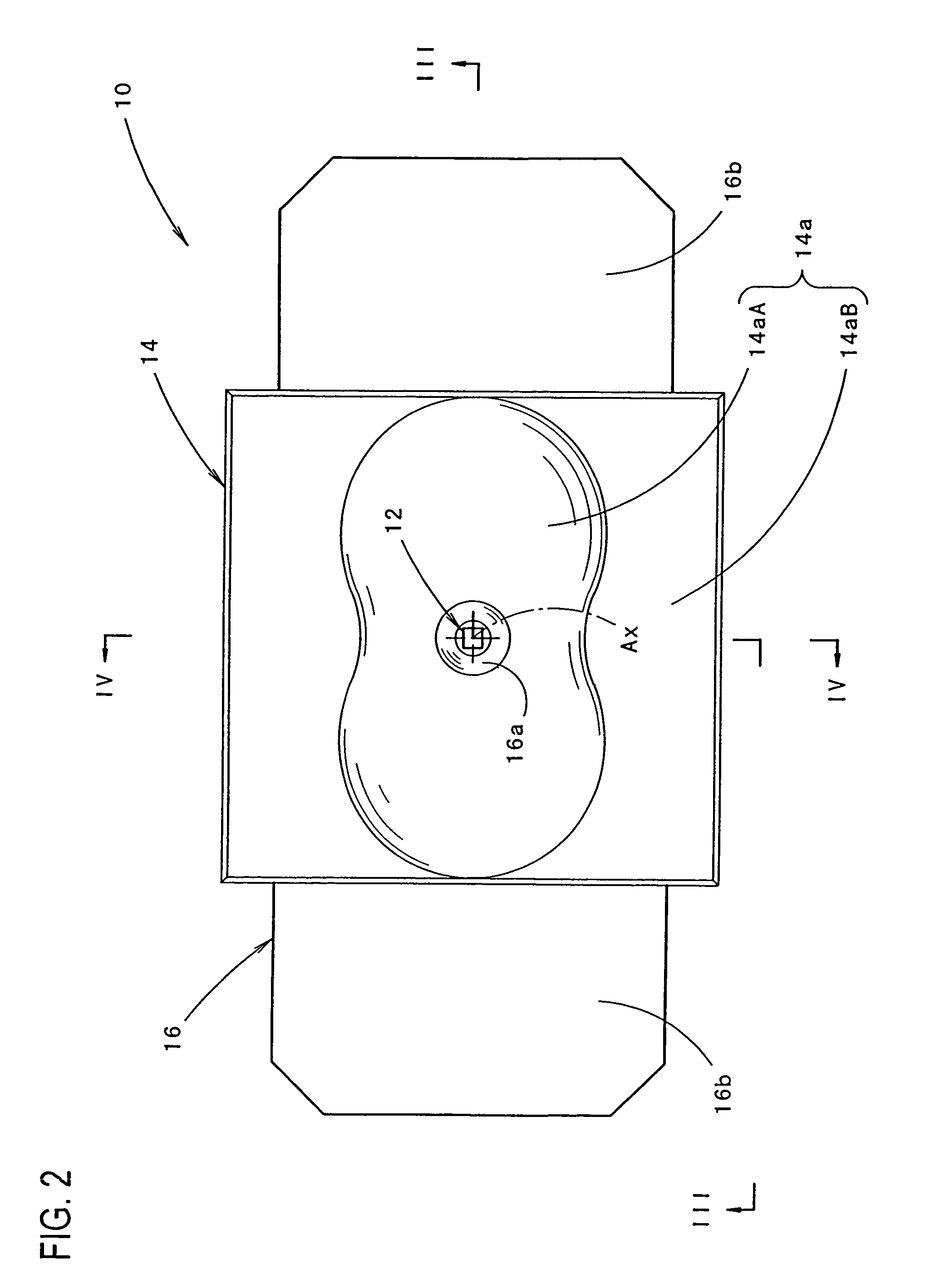
Light-emitting diode and vehicular lamp
ActiveUS7339200B2Decrease in luminanceIncrease brightnessVehicle headlampsPoint-like light sourceOptical axisDivergence angle
A light-emitting diode including a curved surface portion 14aA formed in the front face of a sealing member 14 with the cross-sectional shape of the curved surface portion being in the shape of an undulating curve that has a concave curve C1 near the optical axis and convex curves C2 on both sides of concave curve C1, thus allowing the light emitted from a light-emitting chip 12 at a small divergence angle centered on the optical axis Ax to reach the concave curve C1 and to be directed forward as diffused light deflected from the optical axis and further allowing the light emitted at a large divergence angle centered on the optical axis Ax to reach the convex curves C2 and to be directed forward as light deflected toward line L positioned at the divergence angle θ.
Owner:KOITO MFG CO LTD
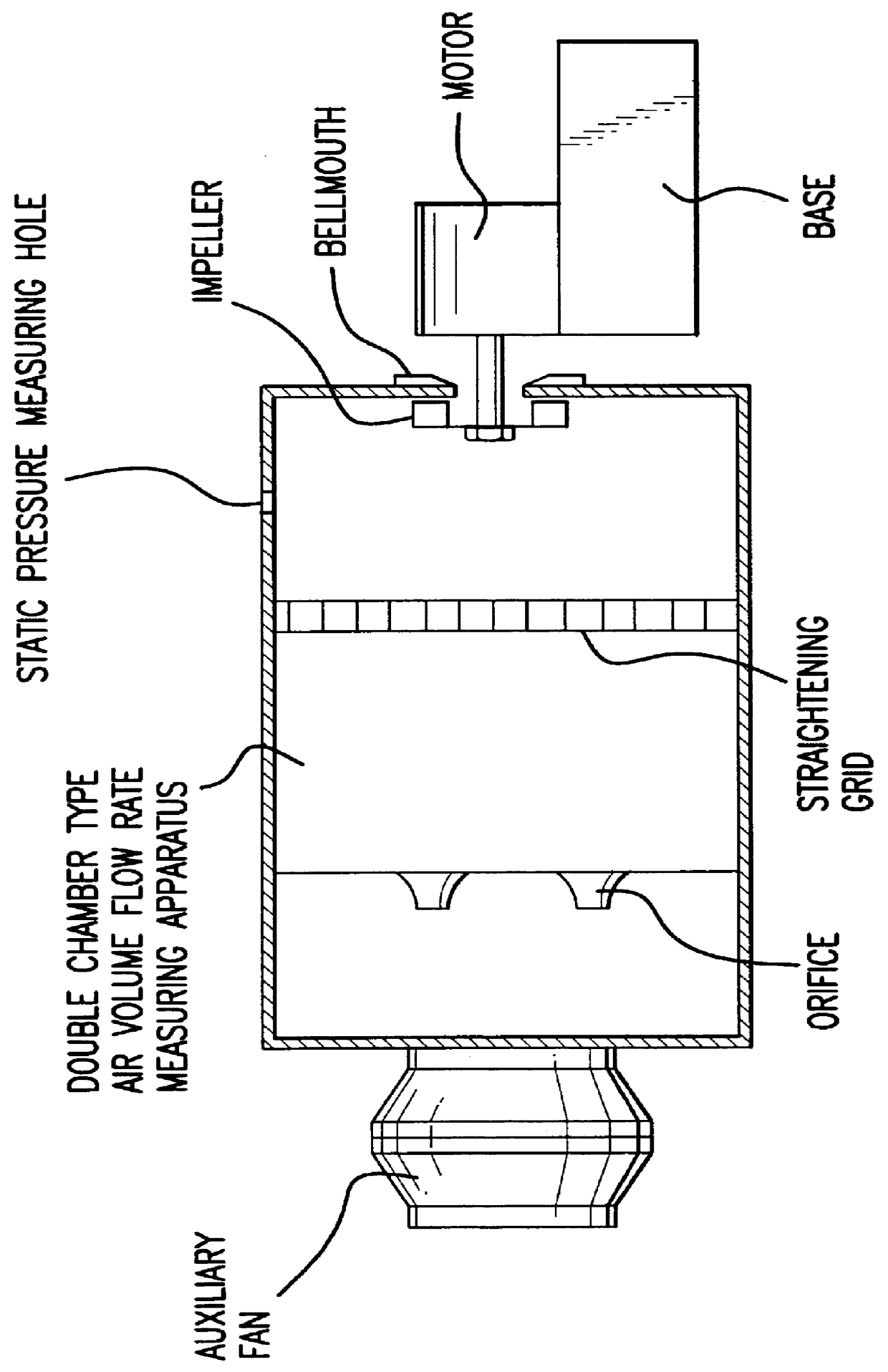
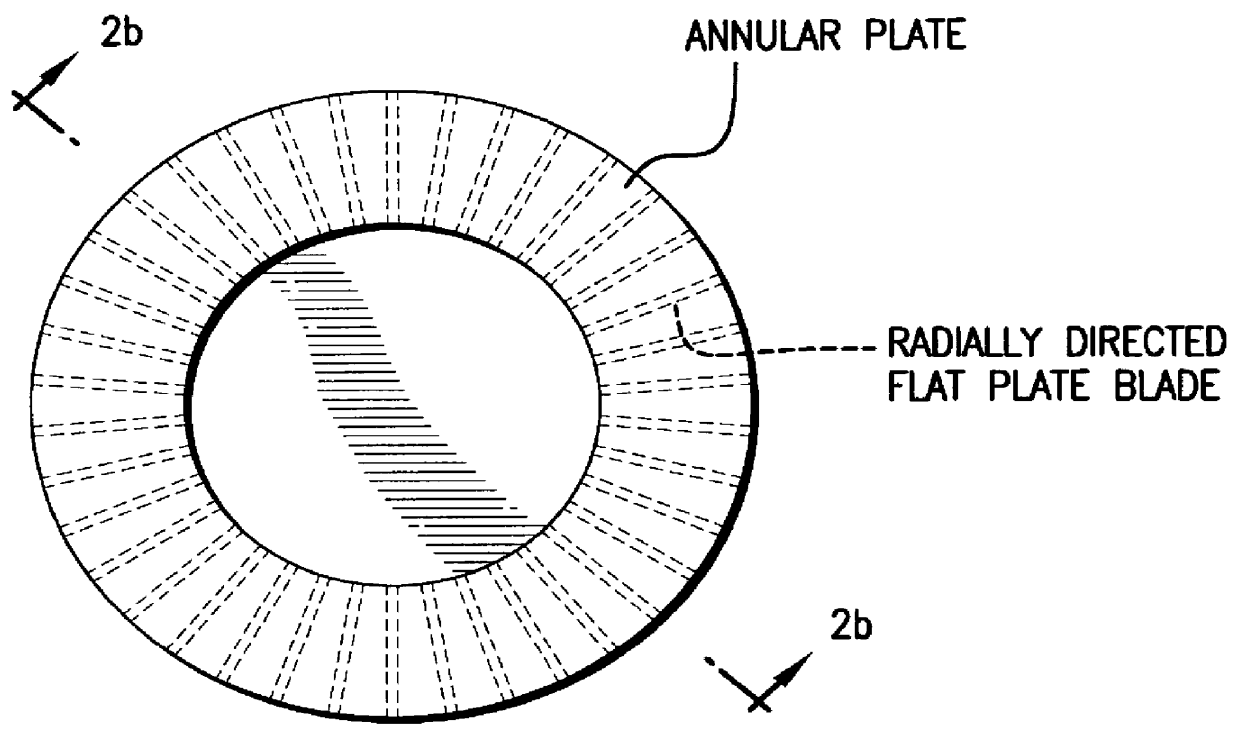
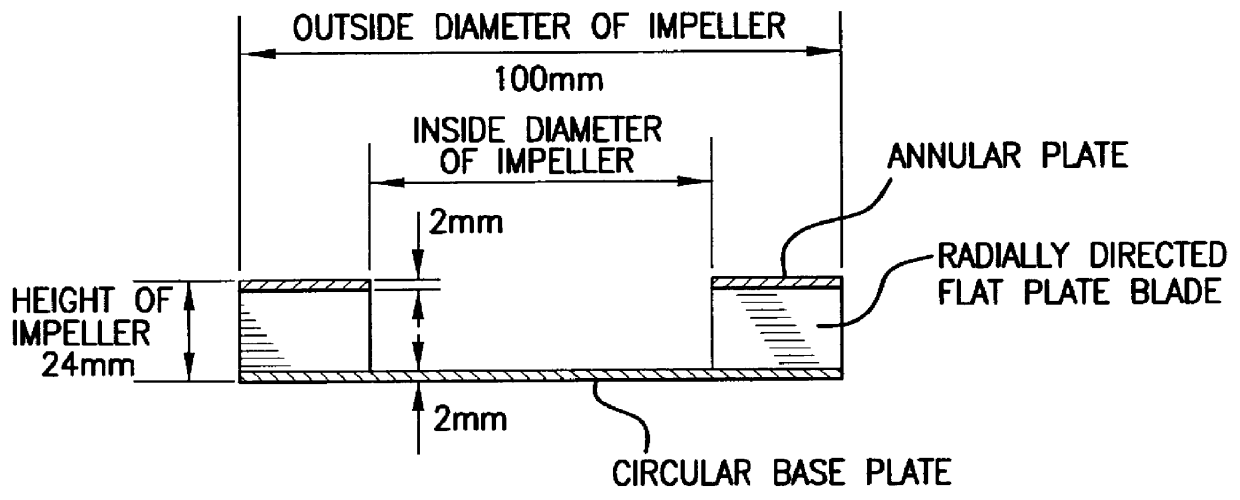
Method for designing a multiblade radial fan and a multiblade radial fan
InactiveUS6050772AImprove quietnessMost efficientPump componentsReaction enginesImpellerDivergence angle
PCT No. PCT / JP96 / 02391 Sec. 371 Date Apr. 18, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Apr. 18, 1997 PCT Filed Aug. 27, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 08463 PCT Pub. Date Mar. 6, 1997Specifications of the impeller and the scroll type casing of a multiblade radial fan comprising an impeller having numerous radially directed blades circumferentially spaced from each other and a scroll type casing accommodating the impeller are determined so as to make divergence angle of the scroll type casing substantially coincide with divergence angle of the free vortex formed by the air discharged from the impeller.
Owner:NIPPON DENSAN CORP
Semiconductor laser apparatus capable of routing laser beams emitted from stacked-array laser diode to optical fiber with little loss
ActiveUS20060126690A1Small lossSemiconductor laser optical deviceOptical resonator shape and constructionLaser beamsSemiconductor
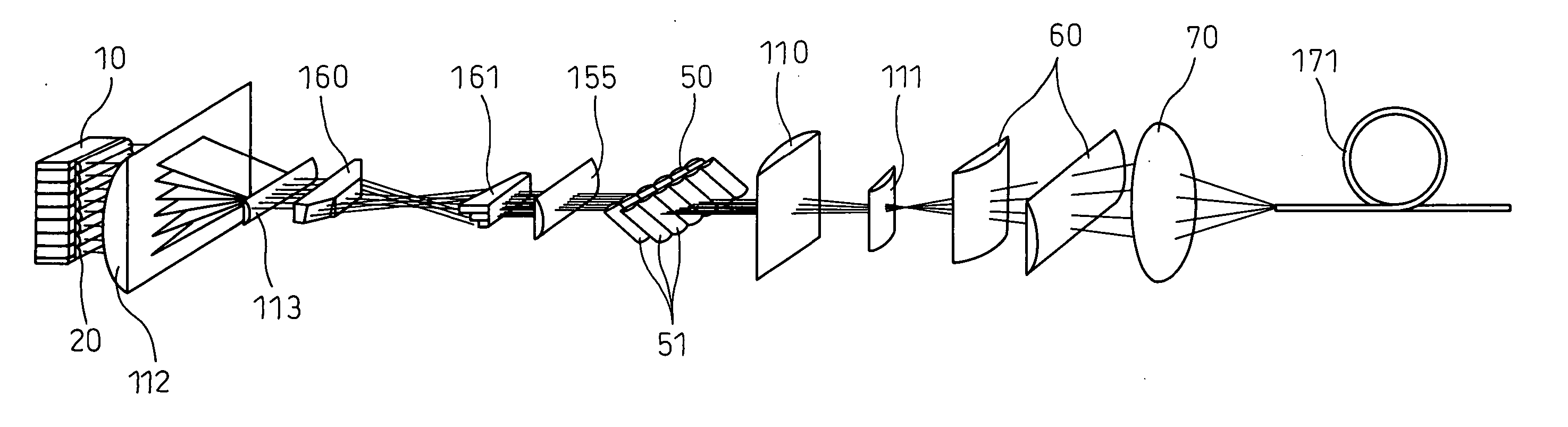
A semiconductor laser apparatus according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention is provided. For example, the apparatus may include a single or a plurality of stacked-array laser diodes, first beam compressors, and a separating optical device separating the group of laser beams into subgroups of laser beams in a first direction, and deflecting the subgroups of laser beams so that the subgroups of laser beams approach in the first direction and recede from one another in a second direction. In addition, a collimating optical device may be provided which is adapted to deflect the subgroups of laser beams in the first and second directions by the same angles. Further, a beam converter may be included which divides each subgroup of laser beams and turning the axis thereof, and second beam compressors and a group of cylindrical lenses can be provided that can make the angle of divergence in the first direction close to the angle of divergence in the second direction.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
LED lighting fixture
InactiveUS6905228B1Uniform light distributionWider divergence anglePoint-like light sourceLighting support devicesDivergence angleEngineering
In the centers of each of unit-type lenses that constitute a lens, a plurality of elliptically light distributing LEDs being arranged circularly in a horizontal direction in such a way that a wider divergence angle of each LED is set to be oriented horizontally. The unit-type lenses are stacked and fastened by a screw that runs through the bosses of the unit-type lenses.
Owner:ZENI LITE BUOY
Differential Interference Phase Contrast X-ray Imaging System
InactiveUS20100091947A1Photon energy is highWide emission angleImaging devicesX-ray tube electrodesPhotoconductive detectorHigh energy
A differential phase-contrast X-ray imaging system is provided. Along the direction of X-ray propagation, the basic components are X-ray tube, filter, object platform, X-ray phase grating, and X-ray detector. The system provides: 1) X-ray beam from parallel-arranged source array with good coherence, high energy, and wider angles of divergence with 30-50 degree. 2) The novel X-ray detector adopted in present invention plays dual roles of conventional analyzer grating and conventional detector. The basic structure of the detector includes a set of parallel-arranged linear array X-ray scintillator screens, optical coupling system, an area array detector or parallel-arranged linear array X-ray photoconductive detector. In this case, relative parameters for scintillator screens or photoconductive detector correspond to phase grating and parallel-arranged line source array, which can provide the coherent X-rays with high energy.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Surface array semiconductor laser light beam shaping device
InactiveCN101144909AEasy to manufactureSimple structureLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersDivergence angleLight beam
The present invention relates to a beam reshaping device for a plane array semiconductor laser. The device includes a fast axis collimating lens, a slow axis collimating lens, a ladder lens, a first parallelepiped prism unit, and a second parallelepiped prism unit. The beam emitted by the plane array semiconductor laser passes through the fast axis collimating lens and the slow axis collimating lens, and lowers the divergence angle of the fast axis and the divergence angle of the slow axis. The irradiance interspace between bars can be eliminated by the ladder lens and can be compressed in the direction of the fast axis. Finally, part of beam can be moved parallel along the fast axis direction by the first parallelepiped prism unit and the second parallelepiped prism unit, and then be moved along the slow axis direction. Through the above process, the beam is realigned, and the purpose that the quality of the fast axis beam and the quality of the slow axis beam tend to be coincident is reached. The realigned beam can get high-power high-brightness facula after being focused. The optical apparatus used in the present invention is easy to be produced and convenient to be adjusted with simple structure.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical scanning device and image forming apparatus
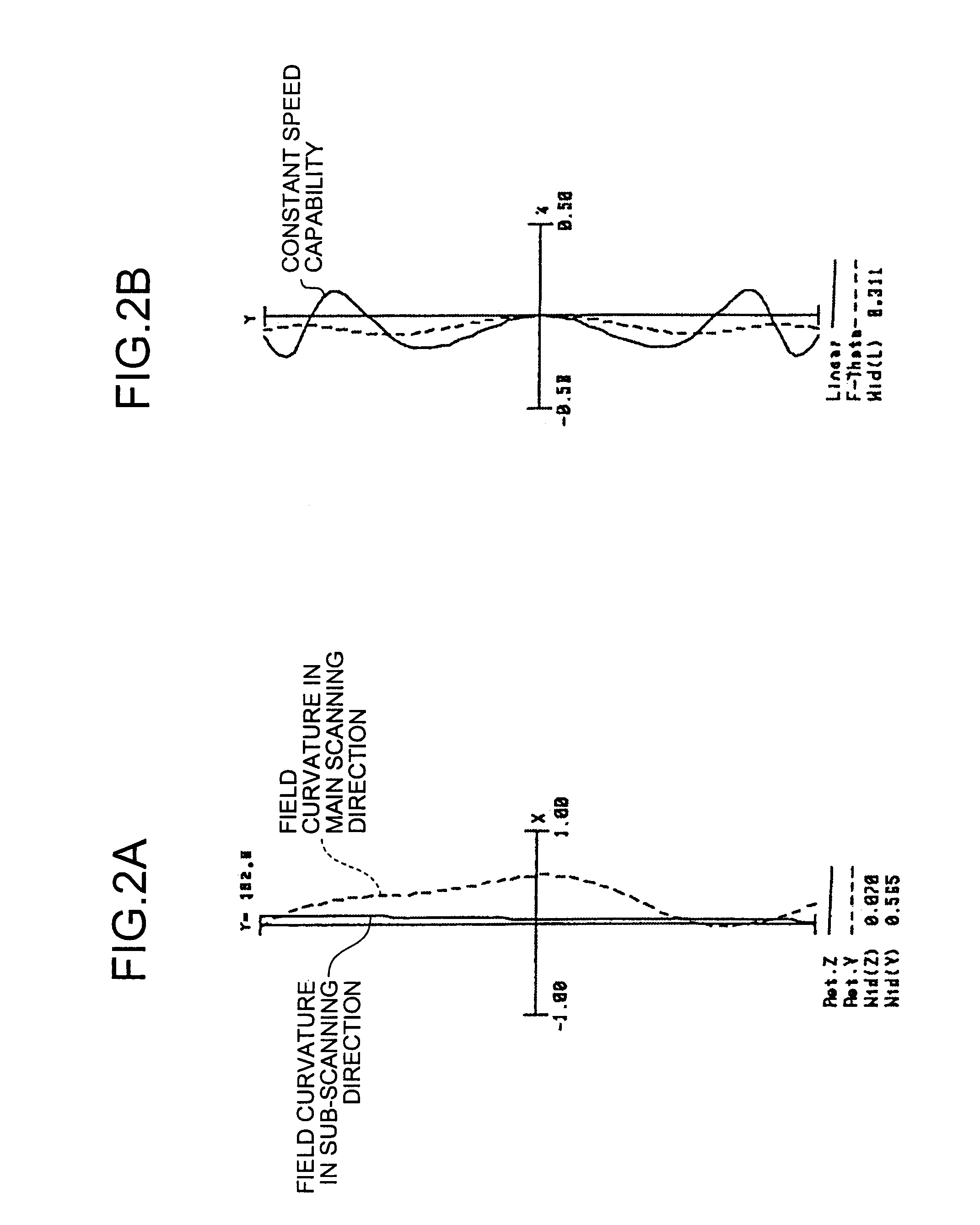
An optical scanning device includes a light source having light emitting points for emitting light beams, a coupling optical element that couples the light beams, a deflecting unit that deflects and scans the light beams, and a scanning optical system that focus the light beams to form an image. The optical scanning device satisfies the following condition:F tan(θ / 2)+A<D / 0.7 where A is the maximum distance between the light emitting points and an optical axis of the coupling optical element, θ is a divergence angle (full-width half-maximum) of the light beams, F is a focal length of the coupling optical element, and D is an effective radius of the coupling optical element.
Owner:RICOH KK
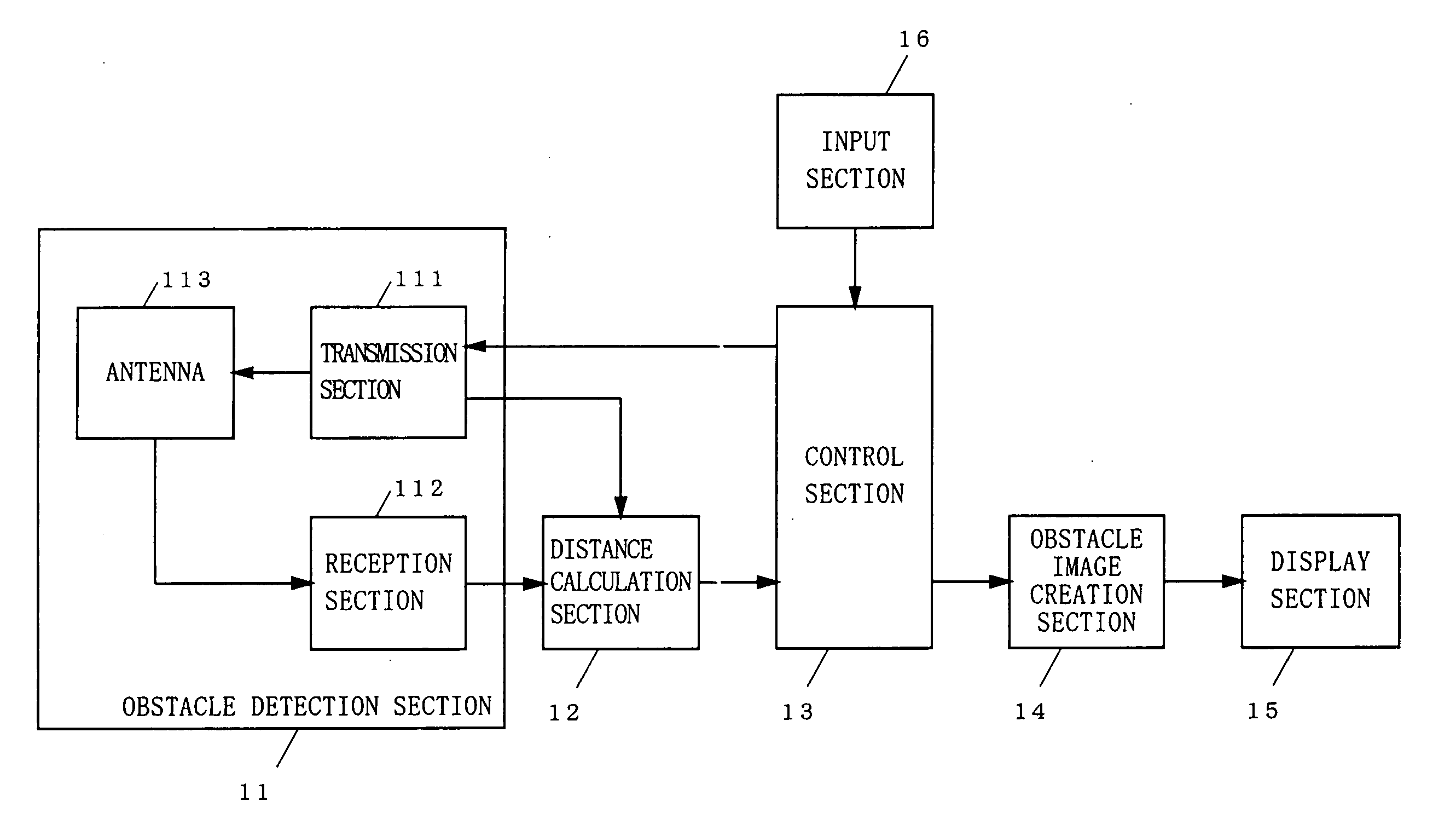
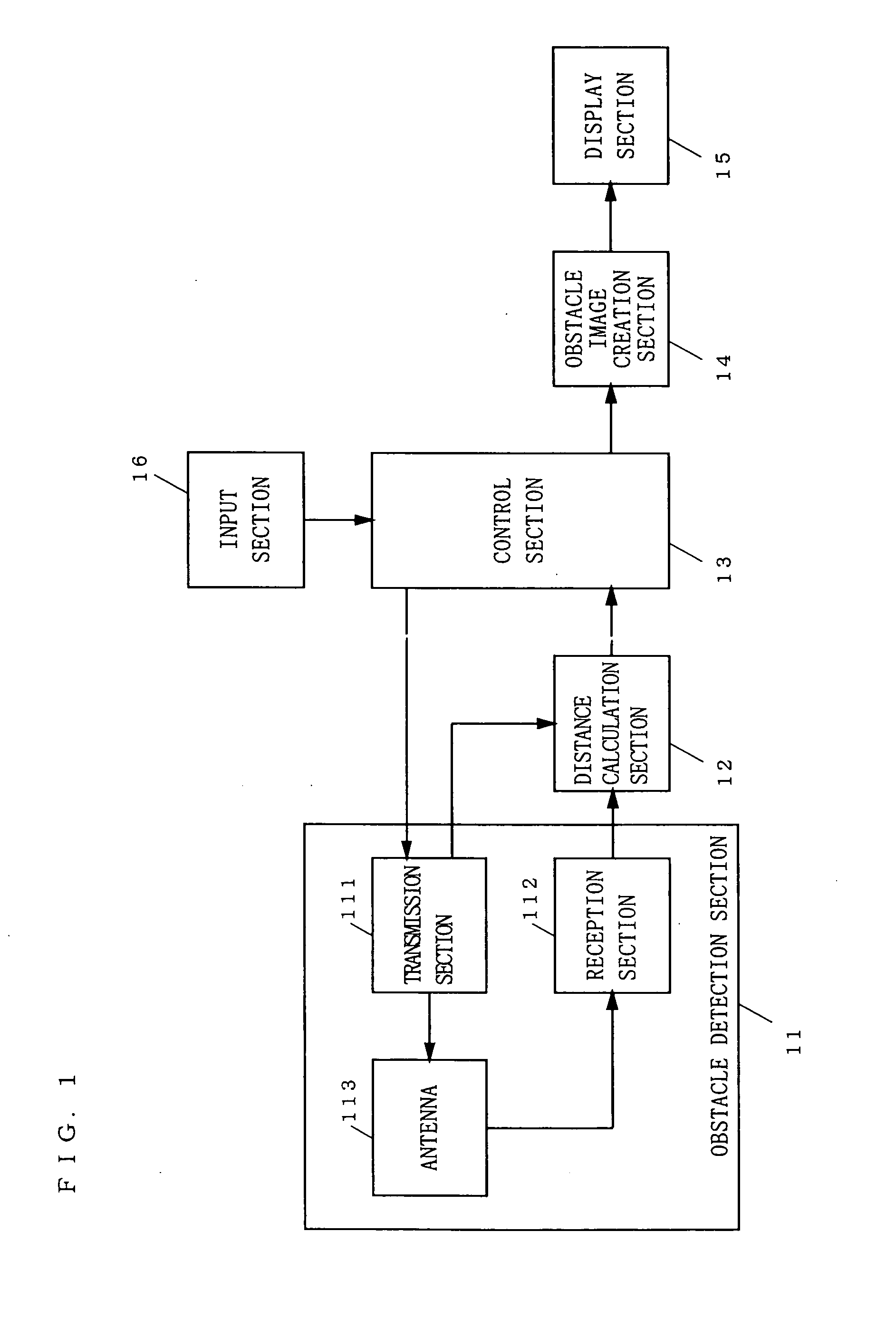
Obstacle detection device
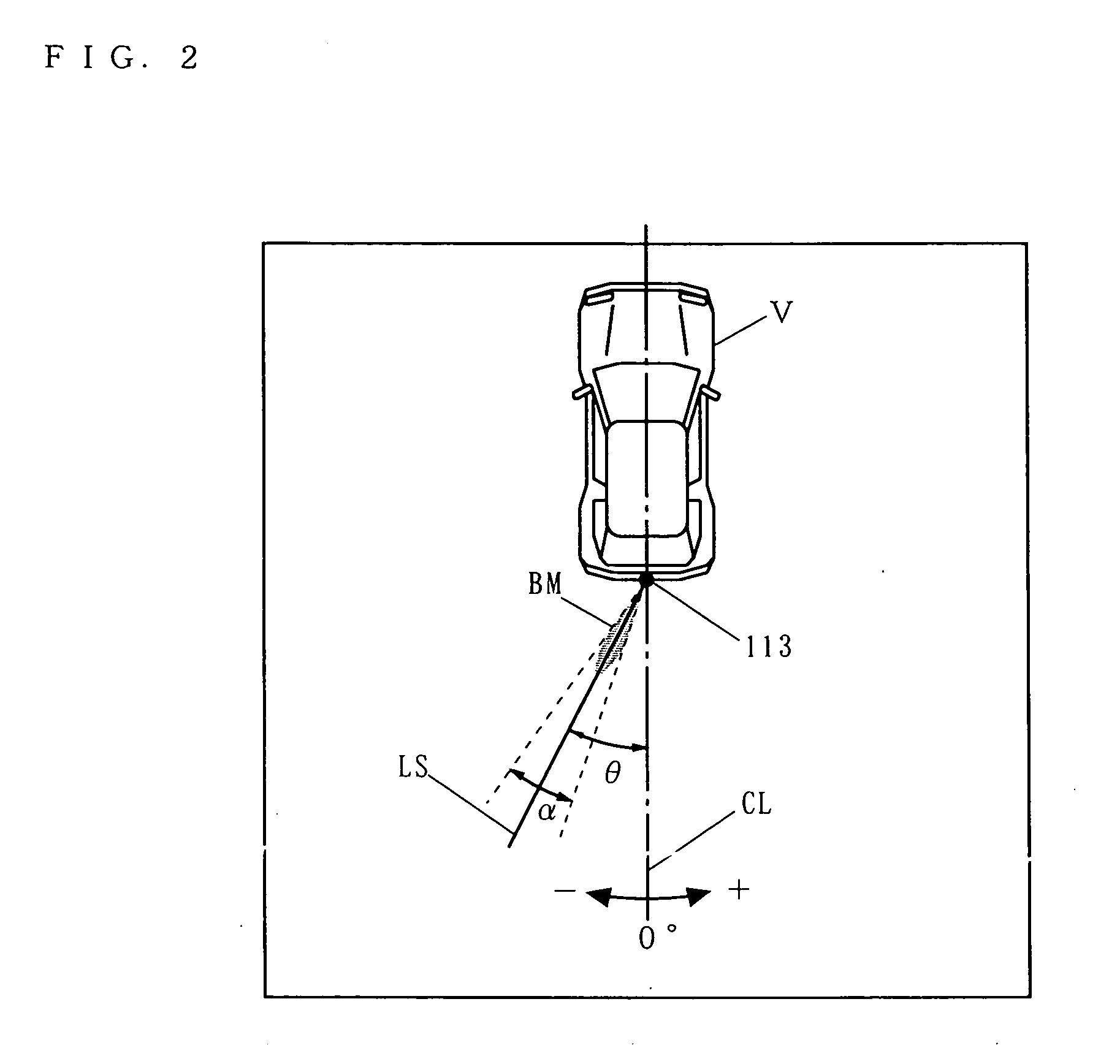
InactiveUS20050225439A1Easy to masterPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementAnti-collision systemsGraphicsDivergence angle
An obstacle detection device includes: an obstacle detection section (11) for emitting beams having a predetermined divergence angle consecutively in a plurality of different directions, receiving a reflected wave from an obstacle for each direction, and detecting the obstacle existing within an emission angle range of the beam for the direction; a distance calculation section (12) for calculating a distance representative of an interspace between the obstacle and the vehicle for each direction based on a received signal of the reflected wave for the direction outputted from the obstacle detection section; an obstacle image creation section (14) for creating, as an obstacle image, a figure two-dimensionally developed in the emission angle range of the beam emitted in each direction while treating, as a basis for image creation, the distance calculated by the distance calculation section for the direction, and for creating and outputting image data for displaying the obstacle image; and a display section (15) for receiving the image data created by the obstacle image creation section and displaying an image showing a positional relationship between the obstacle and the vehicle.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Optical navigation chip, optical navigation module and optical encoder
ActiveUS20160306446A1Small sizeInput/output for user-computer interactionDigital data processing detailsRelative displacementLight beam
The present disclosure illustrates an optical navigation chip. The optical navigation chip is disposed on an optical navigation module. The optical navigation module includes a light-emitting unit. The light-emitting unit provides a light beam to irradiate a surface of a displacement generating unit. The light beam has a low divergence angle to reduce scattering. The optical navigation chip includes a sensing array and a displacement calculating unit. The sensing array is disposed corresponding to the surface. The sensing array receives a reflected light beam which the surface reflects, and captures an image once every capturing interval based upon the reflected light beam. The displacement calculating unit calculates a relative displacement between the optical navigation chip and the surface according to the images.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
Illumination system for a projection system
An illumination system for illuminating an object includes a light source and a lens array system. The light source includes an illumination element emitting light rays and surrounded by a parabolic reflector. The lens array system includes a first lens array plate and a second lens array plate. The first lens array plate includes a matrix of lenslets where, in one embodiment, each lenslet has a shape matching the aspect ratio of the object to be illuminated. The second lens array plate includes a radial pattern of wedge shaped lenslets each corresponding to a lenslet in the first lens array plate. Each wedge shaped lenslet in the second lens array plate has dimensions that are selected to provide a radial and theta collection angles matching the maximum divergence angle of the light source and the maximum divergence angles of the corresponding lenslet in the first lens array plate.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
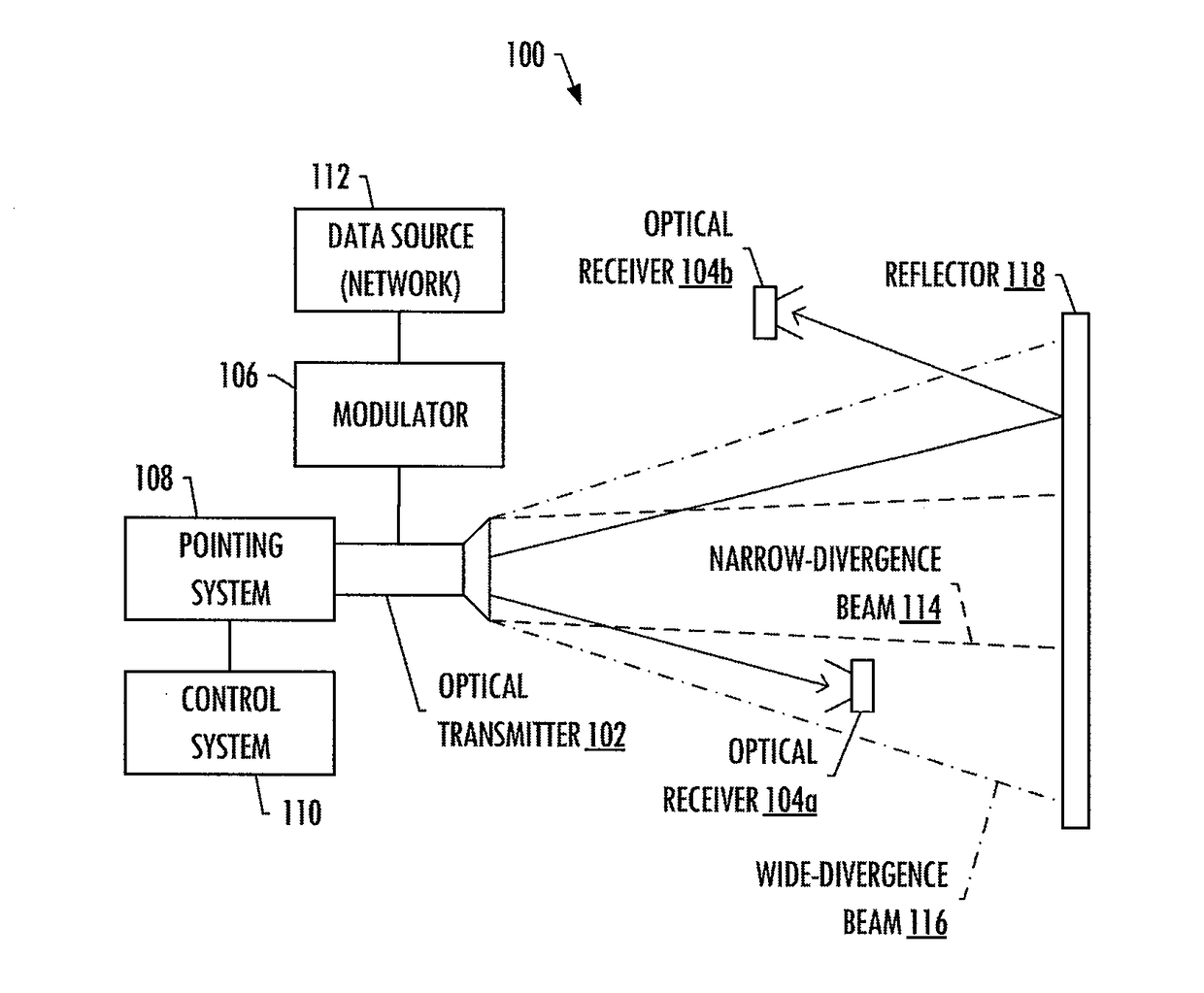
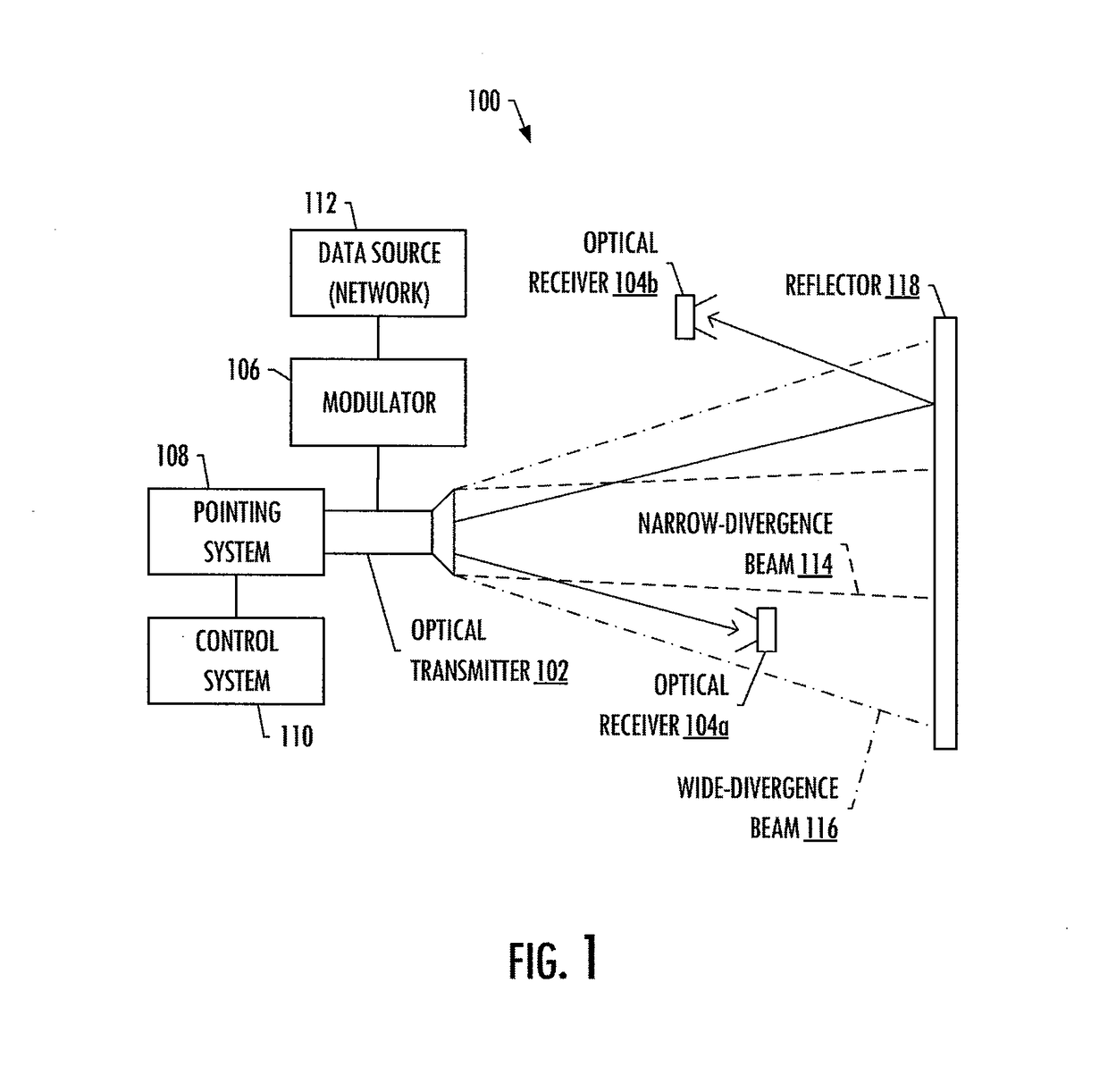
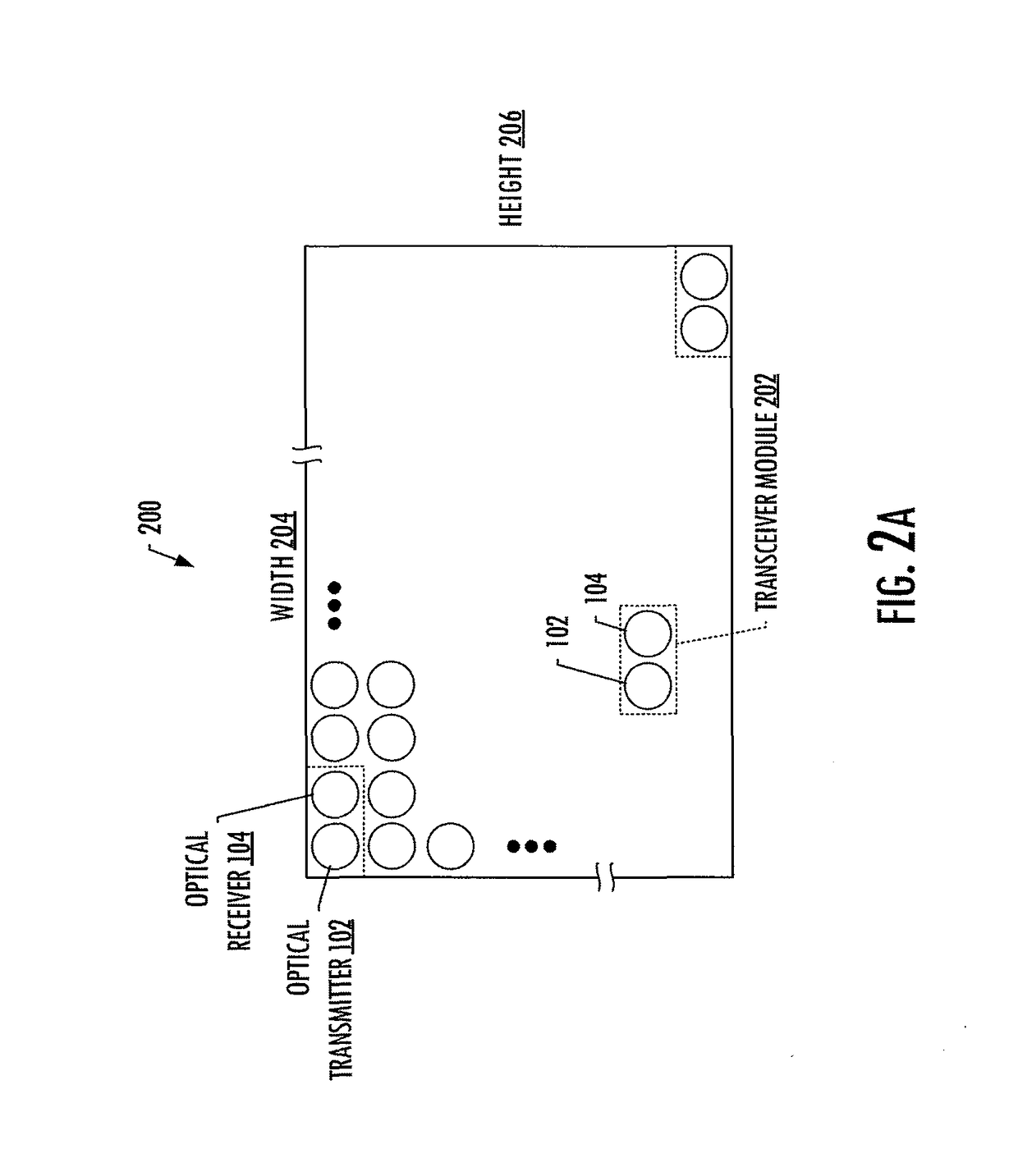
Diverged-beam communications system
InactiveUS20180048390A1Increased angular toleranceReduce impactSpatial transmit diversityLine-of-sight transmissionCommunications systemDivergence angle
Owner:8 RIVERS CAPTTAL LLC
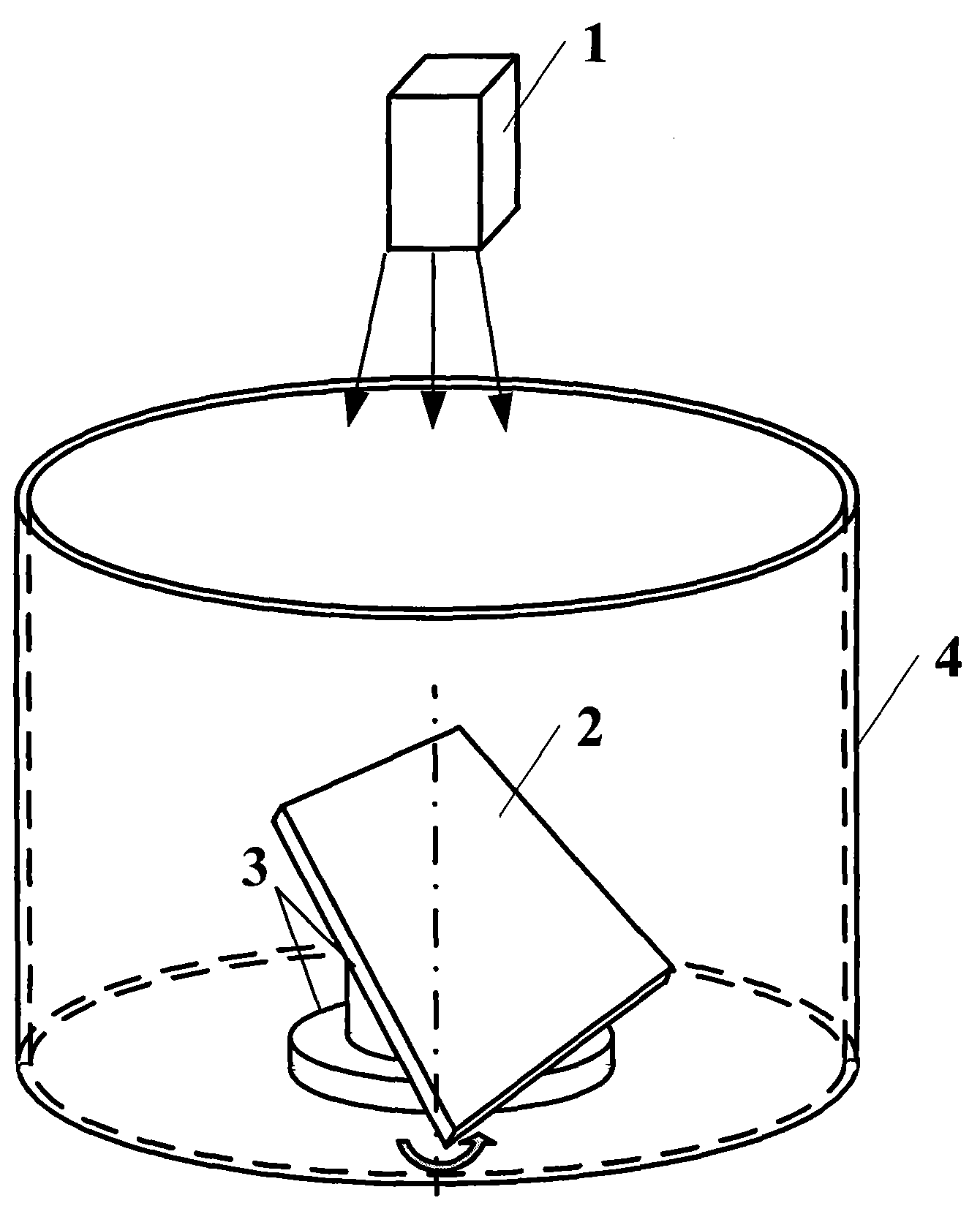
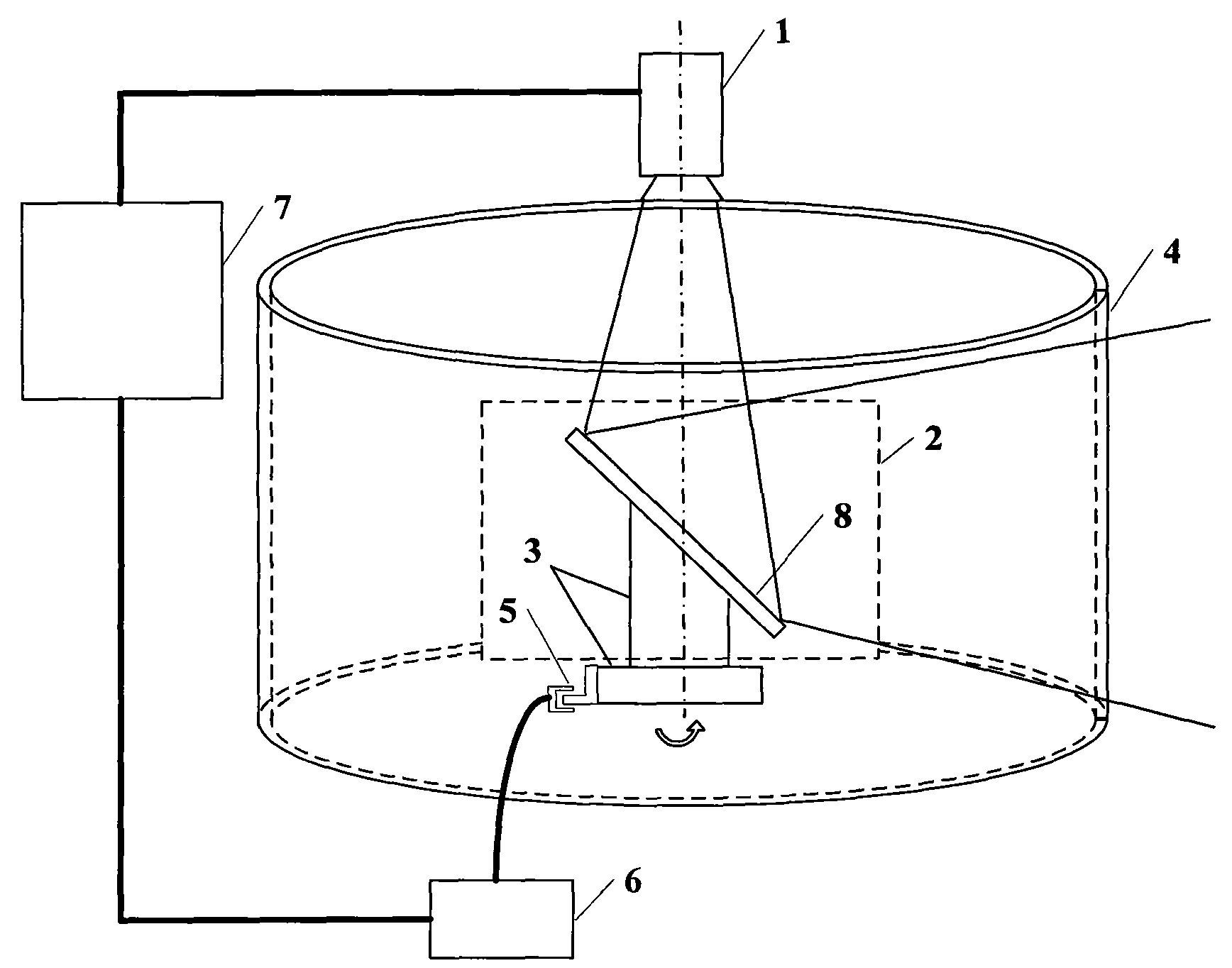
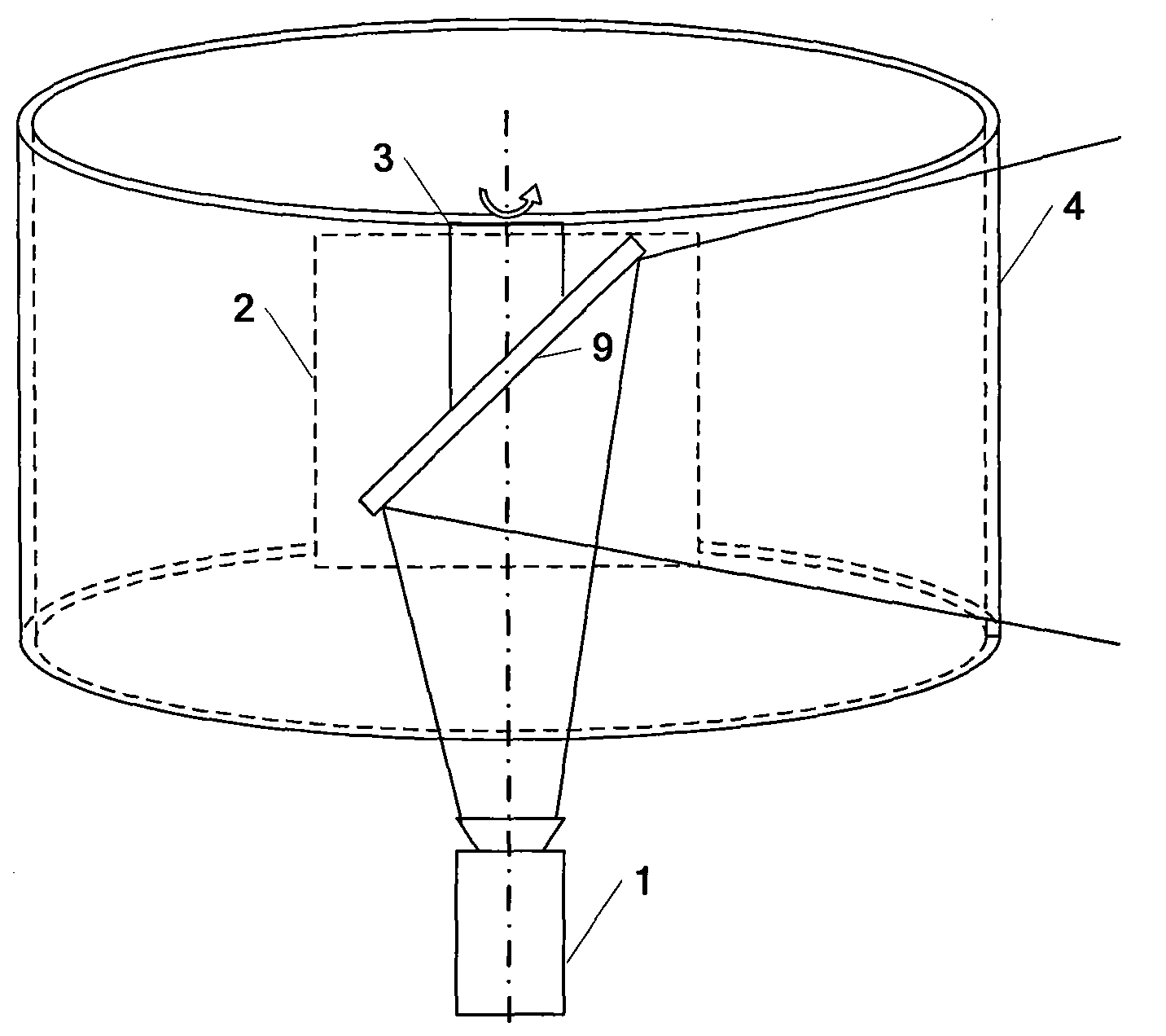
Three-dimensional display device of full-view visual field based on high-speed projector
InactiveCN101630066AEasy to operateReduce image distortionStereoscopic photographySteroscopic systemsDivergence angleAngular degrees
The invention discloses a three-dimensional display device of a full-view visual field based on a high-speed projector. The device comprises a high-speed projector, a transmission type directional diffusing screen, a reflector system, a rotation device, a sensor, a rotation synchronous detection module and an upper computer. The high-speed projector projects combined images of the horizontal 360-degree full-view visual fields of three-dimensional objects on the reflector system rotating at high speed, and the images are projected on the fixed cylindrical transmission type directional diffusing screen after the images realize the turning of light paths by the reflector system. The transmission type directional diffusing screen can control the divergence angle of outgoing light, the left eye and the right eye of an observer see images with different visual angles, and the three-dimensional display of the three-dimensional objects on the full-view visual field is realized. The rotation synchronous detection module detects a rotation signal, is communicated with the upper computer and ensures that the positions of the combined images and the position of the rotating reflector system are synchronous. The invention can realize that both eyes of the observer see images with binocular parallaxes in different positions, thereby realizing the three-dimensional display.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Backlight device and liquid crystal display apparatus
InactiveUS20130033901A1Suppress power consumptionExtended range of color reproductionMechanical apparatusPlanar/plate-like light guidesLiquid-crystal displayDivergence angle
A planar light source device includes a first light source for emitting a first light ray having a punctate spatial luminance distribution; a second light source for emitting a second light ray; a first spatial luminance distribution conversion portion for changing the first light ray to a linear spatial luminance distribution; a second spatial luminance distribution conversion portion for changing a spatial luminance distribution of the first and second light rays to a planar spatial luminance distribution; wherein the first light ray is a laser light; the second light ray has a divergence angle larger than the divergence angle of the first light ray when the first light ray is emitted from the first light source; and a slow-axis direction of the first light ray entering the second spatial luminance distribution conversion portion is parallel to an outgoing direction of the planar light.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Target object processing method and target object processing apparatus
ActiveUS20120111310A1Suppress generationPreventing of sectionFine working devicesGlass severing apparatusDivergence angleLight beam
There is provided a target object processing method capable of self-breaking a target object with a laser beam. The target object processing method includes: generating a laser beam from a laser beam source; correcting a divergence angle of the generated laser beam; and forming a spot by condensing the corrected laser beam to the inside of the target object. A shape or a size of the spot is adjusted by correcting the divergence angle of the laser beam, a phase transformation area is formed within the target object by the spot, and the target object is subject to self-breaking with the phase transformation area as the starting point.
Owner:QMC +1
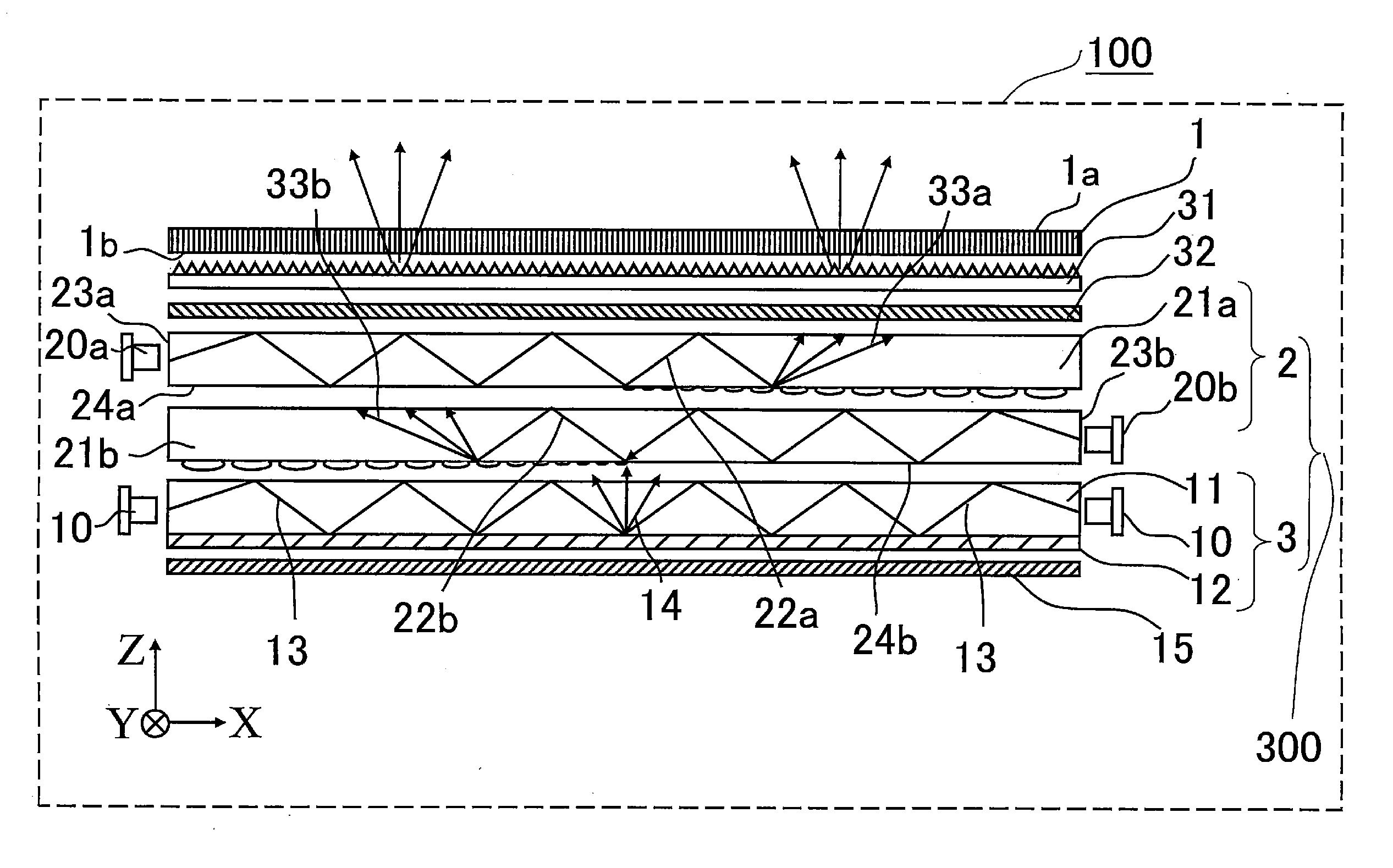
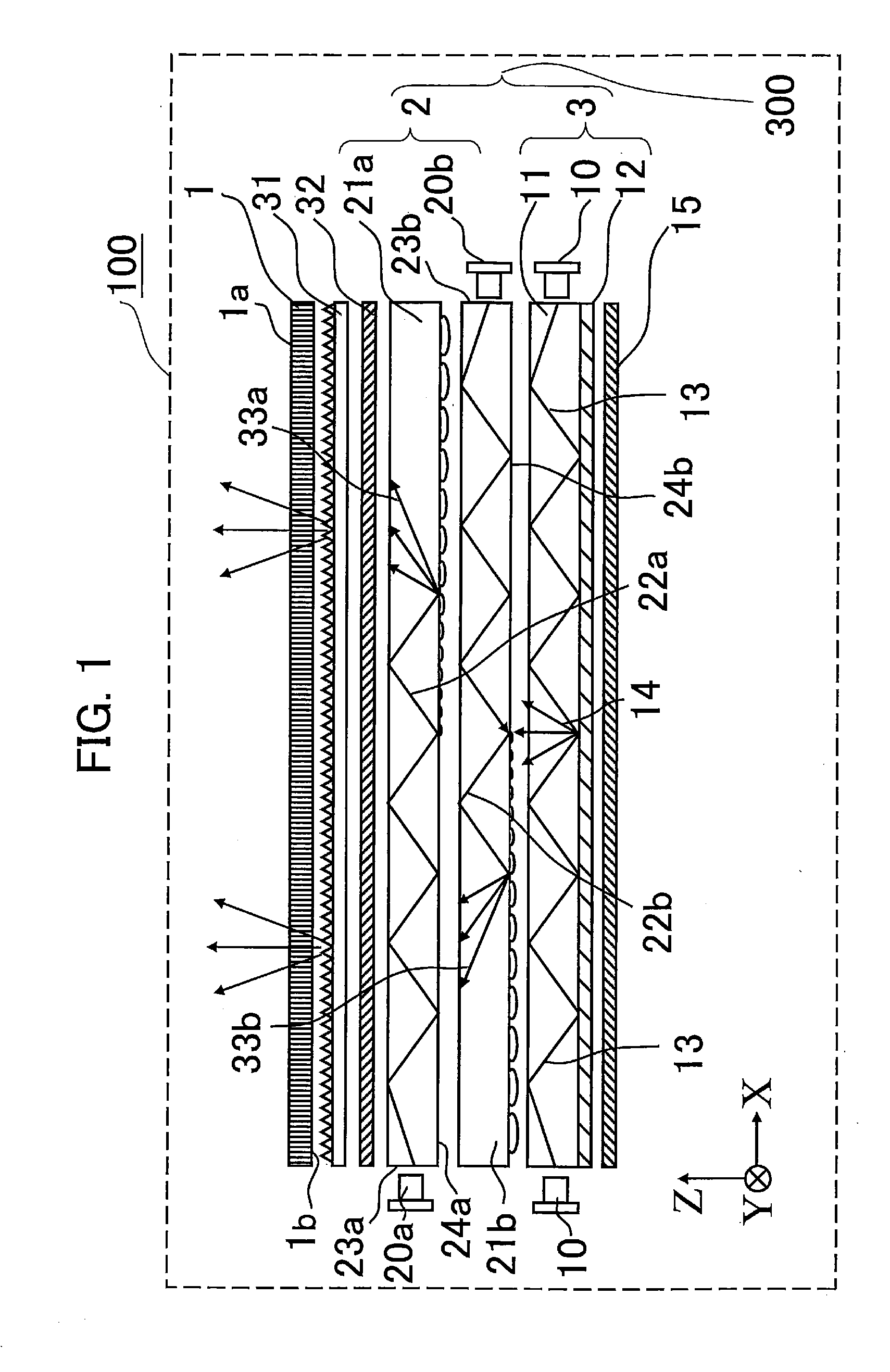
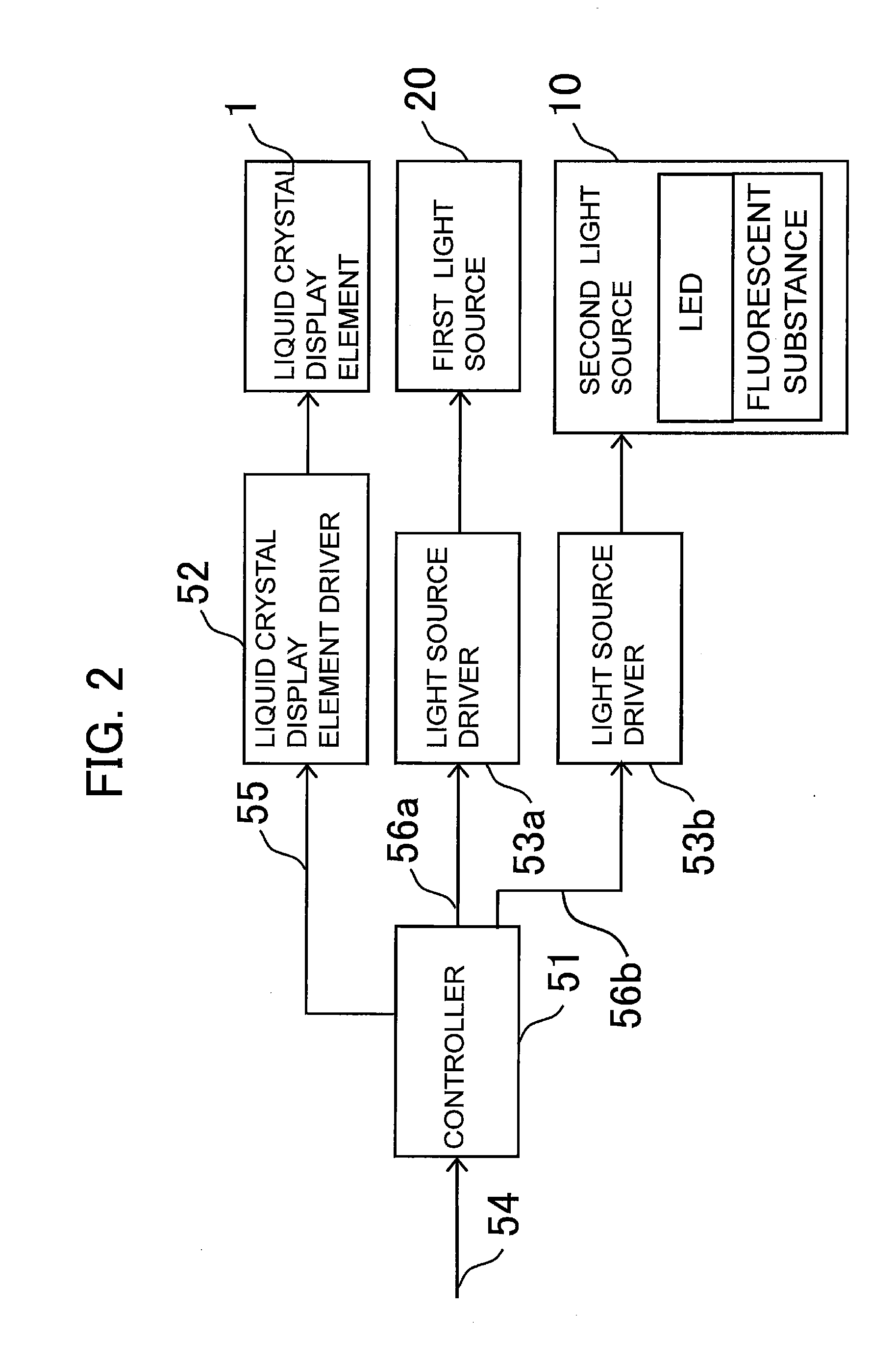
Display apparatus and illumination unit
ActiveUS20150293402A1Increase volumeIncrease brightnessStatic indicating devicesSteroscopic systemsDivergence angleOptoelectronics
An illumination unit of an embodiment of the present technology includes: an illumination optical system configured to generate illumination light; and a plurality of lenses configured to reduce a divergence angle of the illumination light. The illumination optical system includes: a light source (20) configured to apply light onto an end surface of one of a first substrate and a second substrate; and a light modulation layer (30) provided in a gap between the first substrate and the second substrate. The illumination optical system includes an electrode configured to generate an electric filed that generates, in the light modulation layer (30), a plurality of linear scattering regions (30B) in a three-dimensional mode, and to generate an electric field that generates, in the light modulation layer, a planar scattering region in a two-dimensional display mode. The lenses are arranged side by side in a direction in which the linear scattering regions extend, and are also arranged side by side in a direction intersecting with the direction in which the linear scattering regions extend.
Owner:SONY CORP
Multifunctional lighting module
PendingCN108169981AAchieving Synchronized LightingReduce volumeCharacter and pattern recognitionEnergy saving control techniquesEffect lightDivergence angle
The invention provides a multifunctional lighting module, which comprises a first light source for emitting a first light beam, a second light source for emitting a second light beam, and a diffractive optical element, wherein the wavelength of the first light beam is different from that of the second light beam; the diffractive optical element copies and extends the first light beam and the second light beam; a divergence angle of a first incident beam formed by the first light beam is not smaller than an included angle between adjacent diffraction beams formed after the first light beam passes through the diffractive optical element to achieve floodlighting; the divergence angle of a second incident beam formed by the second light beam is not smaller than an included angle between adjacent diffraction beams formed after the second light beam passes through the diffractive optical element to achieve structured lighting. According to the lighting module, two functions of floodlightingand structured light projection are integrated into one module, so that synchronous lighting of floodlighting and structured lighting is achieved; and meanwhile, the multifunctional lighting module has the characteristics of being small in volume and low in power consumption, and is beneficial to integration into intelligent equipment.
Owner:SHENZHEN ORBBEC CO LTD
Dodging special-shaped lens used for shaping semiconductor laser leams, dodging laser source and optical system
The invention provides a dodging special-shaped lens used for shaping semiconductor laser leams. The lens comprises an entrance face receiving laser injection and an exit face allowing laser ejection, the entrance face which is a half-cylindrical curved surface and the exit face which is an aspheric surface are arranged oppositely, and the distance between two ends of a generatrix of the aspheric surface is larger than that of the half-cylindrical surface, so that lasers injected through the entrance face are enabled to be wholly injected onto the exit face. The dodging special-shaped lens is simple in structure, easy for batch processing, low in cost and especially capable of well realizing adjusting of divergence angles of laser beams output by semiconductor lasers of various wavelengths and homogenized adjusting of Gaussian curve distribution of light energy output by lasers, and utilization rate of laser energy is improved while good dodging and aberration-eliminating performances are provided.
Owner:XIAN HUANIC OPTOELECTRONICS CORP
Laser processing device and method thereof
ActiveCN104162741AShort duration of actionImprove work efficiencyLaser beam welding apparatusLaser processingOptical axis
The invention provides a laser processing device and a method of the laser processing device. The laser processing device comprises a laser, a lens set, a Dove prism, a plane mirror, a focus lens and a workpiece to be processed which are all sequentially arranged in the direction of an optical axis, wherein the lens set is composed of two lenses, and the distance between the two lenses can be adjusted so that the spot sizes and the divergence angles of outgoing beams of the laser can be adjusted; the Dove lens is installed in a rotary motor and rotates with the optical axis as the center, and the beams going out from the Dove lens also rotate with the optical axis as the center; the plane mirror is used for deflecting the transmission direction of the beams; the position of the focus lens in the beam transmission direction can be adjusted, and the beams are focused on the surface of the workpiece to be processed after passing through the focus lens; the workpiece to be processed is placed on an electric displacement platform and can make two-dimensional movement in the plane perpendicular to the transmission direction of the beams.
Owner:北京中科镭特电子有限公司
Light coupling structures for optical touch panels
InactiveUS20140253831A1Large divergence angleUniform touch sensitivityMechanical apparatusPlanar/plate-like light guidesDivergence angleFirst light
A coupling element (14) for use in a touch-sensitive apparatus is arranged to transfer light between an electro-optical device (2) and a panel (4) for light transmission. The electro-optical device (2) is an emitter or a detector and has an operative solid angle given by orthogonal device divergence angles. The coupling element (14) is an optical component with a first light transmission surface (21) for facing the electro-optical device (2), and a second light transmission surface (22) for mounting on the panel (4). The coupling element (14) has an optical structure (23) that directs the light between the first and second light transmission surfaces (21, 22) by one or more reflections while expanding one device divergence angle (αx) into a component divergence angle at the second light transmission surface (22). Thereby, the component divergence angle defines a divergence (φp) in the plane of the panel (4) with respect to light propagating by internal reflections inside the light transmissive panel (4).
Owner:FLATFROG LAB
Lensed tapered optical waveguide
An optical coupling element for use in large numerical aperture collecting and condensing systems. The optical coupling element includes a curved surface such as a lens at the output of a tapered light pipe (TLP). The TLP in combination with the curved surface alters the divergence angle and the area of the light exiting the curved surface. Electromagnetic radiation emitted by a source is collected and focused onto a target by positioning the source of electromagnetic radiation substantially at a first focal point of a primary reflector so that the primary reflector produces rays of radiation reflected from the primary reflector that converge at a second focal point of the secondary reflector. The optical coupling element is positioned so that its input end is substantially proximate with the second focal point of the secondary reflector. The converging rays of radiation reflected from the secondary reflector pass through input end and are transmitted towards the curved surface, where their divergence angle and area are adjusted.
Owner:MEADOWSTAR ENTERPRISES
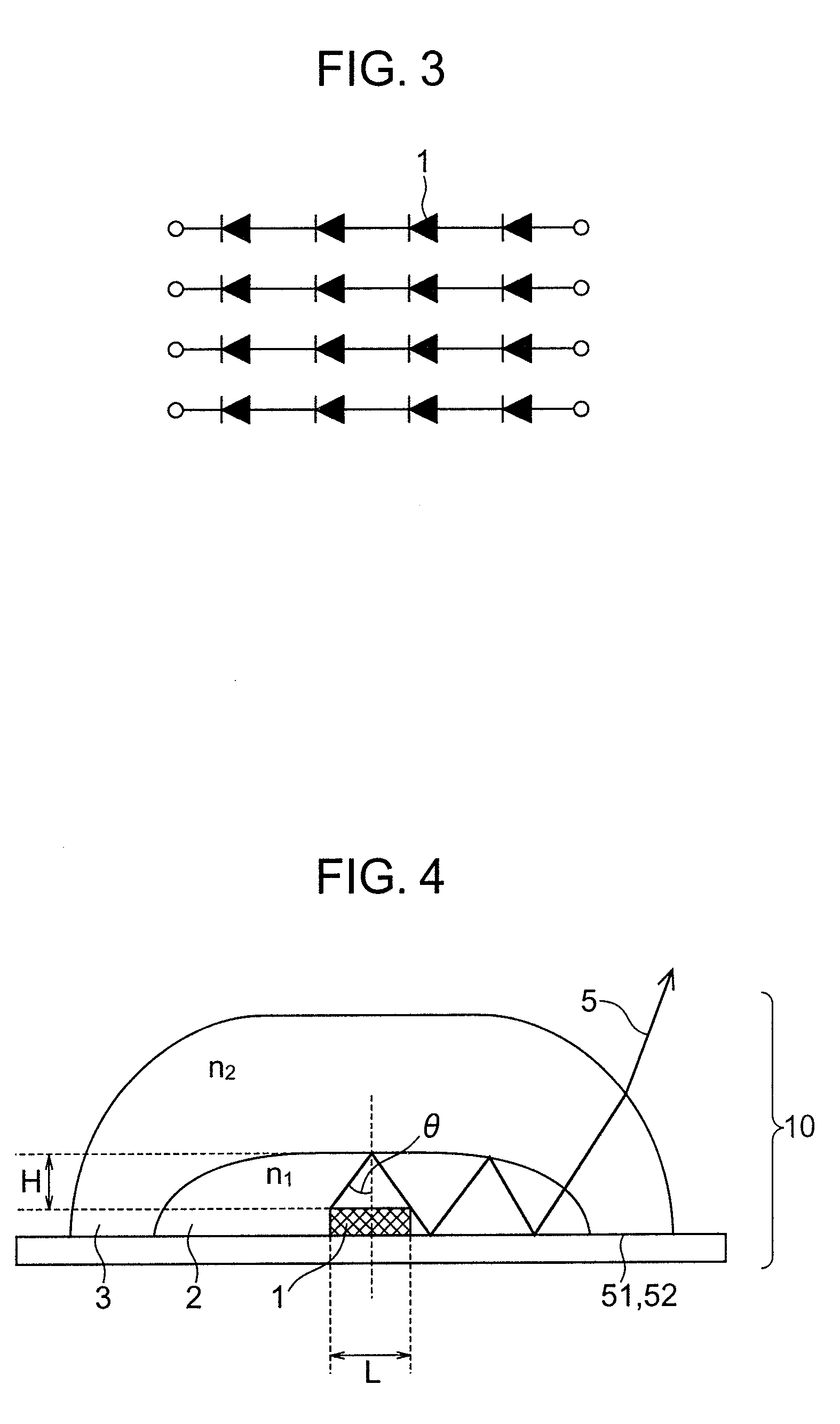
Illumination device and display device incorporating the same
ActiveUS20080137331A1Improve lighting efficiencyImprove light uniformitySolid-state devicesCondensersDivergence angleDisplay device
An illumination device has a plurality of sealing structures each including a light-emitting diode, sealed by a high refractive index transparent material member which is further sealed by a low refractive index transparent material member. To increase a divergence angle of light radiation, the portion of the high refractive index transparent material member which covers an upper surface of the light-emitting diode is structured so as to satisfy a relation H>(L / 2) / tan { sin−1(n1 / n2)}, where H represents a thickness of the high refractive index transparent material member measured at the central portion of the upper surface of the light-emitting diode, L represents the length of one side of the upper surface of the light-emitting diode, n1 represents the refractive index of the high refractive index transparent material member and n2 represents the refractive index of the low refractive index transparent material member.
Owner:PANASONIC LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY CO LTD +1
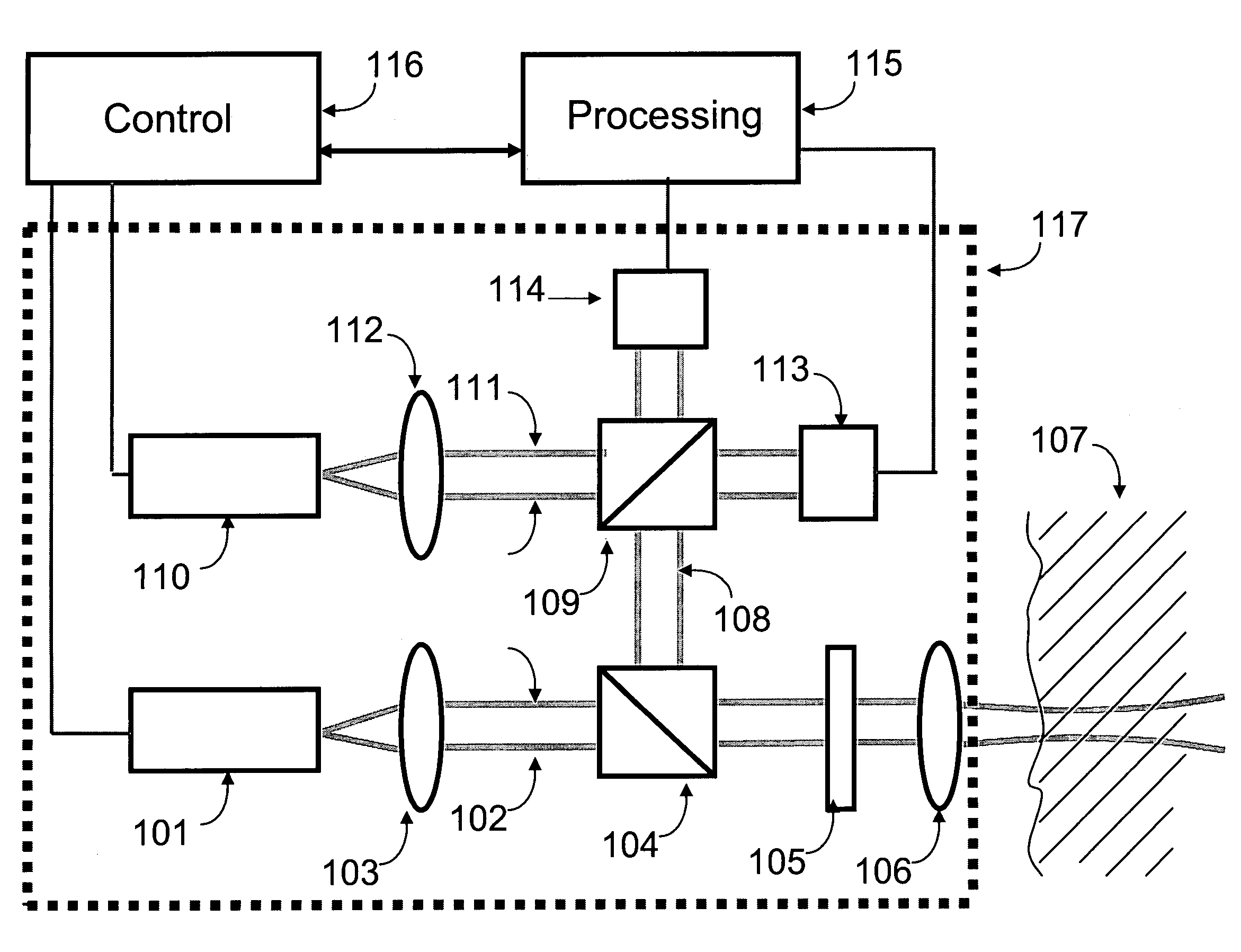
Non-invasive analysis system
A non-invasive analysis system suitable for measuring blood glucose concentration includes a broadband set of coherent beams, with relatively low divergence angle, optical source. It further includes an optical processing system which provides a probe and a reference beam, applies the probe beam to the target to be analyzed, recombines the beams interferometrically and varies the relative phase relationships of the two beams. It further includes control and processing systems.
Owner:COMPACT IMAGING
LED optical lens and illumination device thereof
A LED optical lens and an illumination device thereof are revealed. The optical lens includes a light-source side surface and an image side surface of the LED optical lens that both are designed respectively according to mathematical expressions of freeform surfaces such as Anamorphic formula and Toric formula Thus the optical lens has different curvatures along different axes. After light from LED emitting into the optical lens at a fixed incident angle, emergent light with different divergence angles along different axes is generated. For example, the divergence angle along the long axis is larger than that along the short axis. Therefore a uniform and near rectangular distribution pattern is formed on the target area Moreover, a plurality of optical lenses aligned along the same axes is arranged at a holder to form a lens array. The lens array is used together with a LED array so as to form a LED illumination device.
Owner:CREATE ELECTRONICS OPTICAL
Display apparatus and illumination unit
ActiveUS20140300528A1Decrease in display luminanceIncrease volumeStatic indicating devicesOptical light guidesDivergence angleOptoelectronics
An illumination unit capable of obtaining high luminance and a display apparatus including it are provided. The illumination unit includes an illumination optical system generating the illumination light, and a lens sheet narrowing a divergence angle of the illumination light. The illumination optical system includes a first transparent substrate and a second transparent substrate that are separated from each other and are arranged to face each other, and a light source applying light to an end face of the first transparent substrate or of the second transparent substrate. The illumination optical system is provided in a gap between the first transparent substrate and the second transparent substrate, and includes a light modulation layer exhibiting scattering characteristics or transparent characteristics with respect to the light from the light source in accordance with a magnitude of an electric field. The illumination optical system includes an electrode generating an electric field that generates a plurality of linear scattering regions in the light modulation layer in a three-dimensional display mode, and generating an electric filed that generates a planar scattering region in the light modulation layer in a two-dimensional display mode.
Owner:SONY CORP
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com