Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
482 results about "Optical navigation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
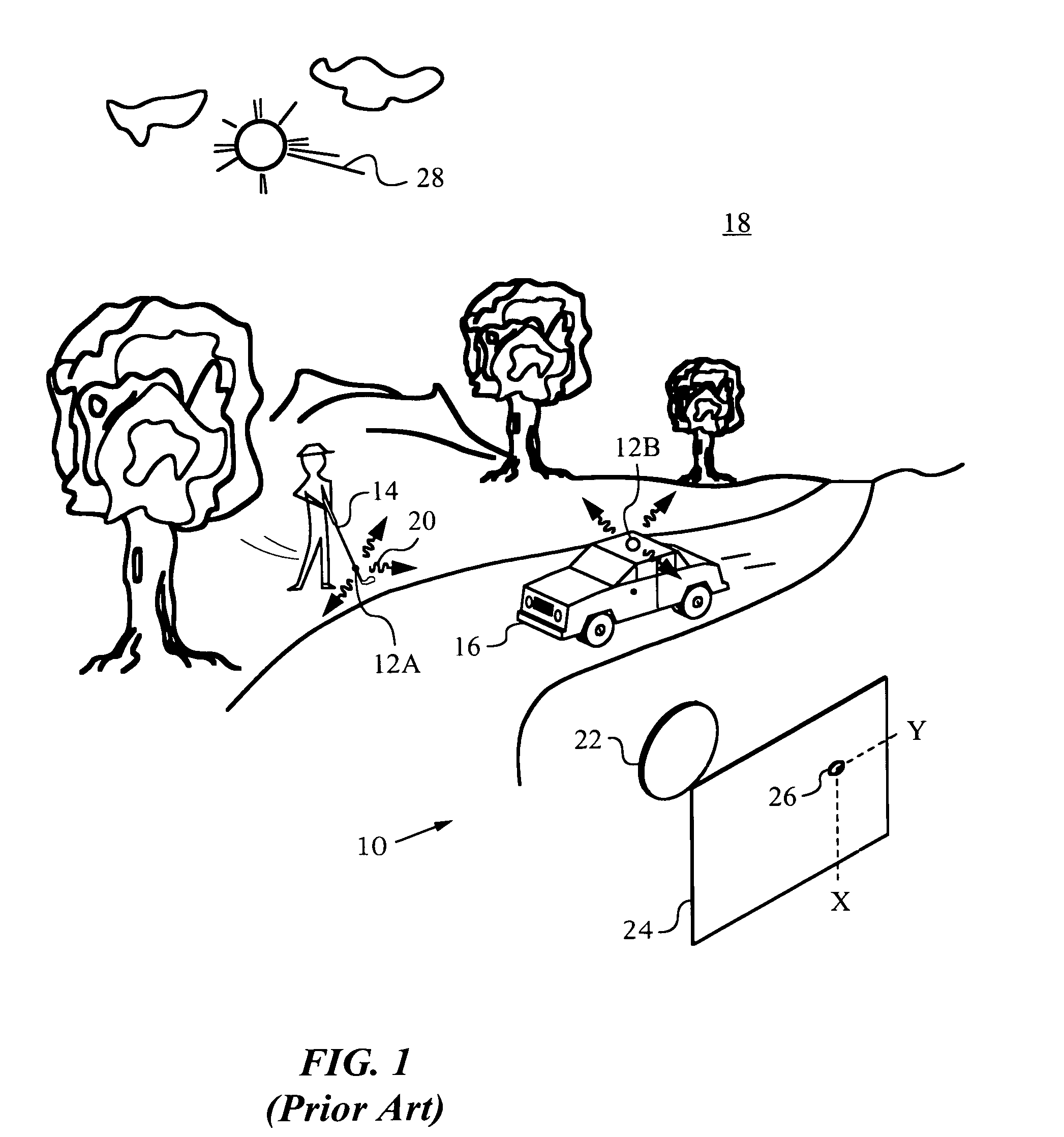
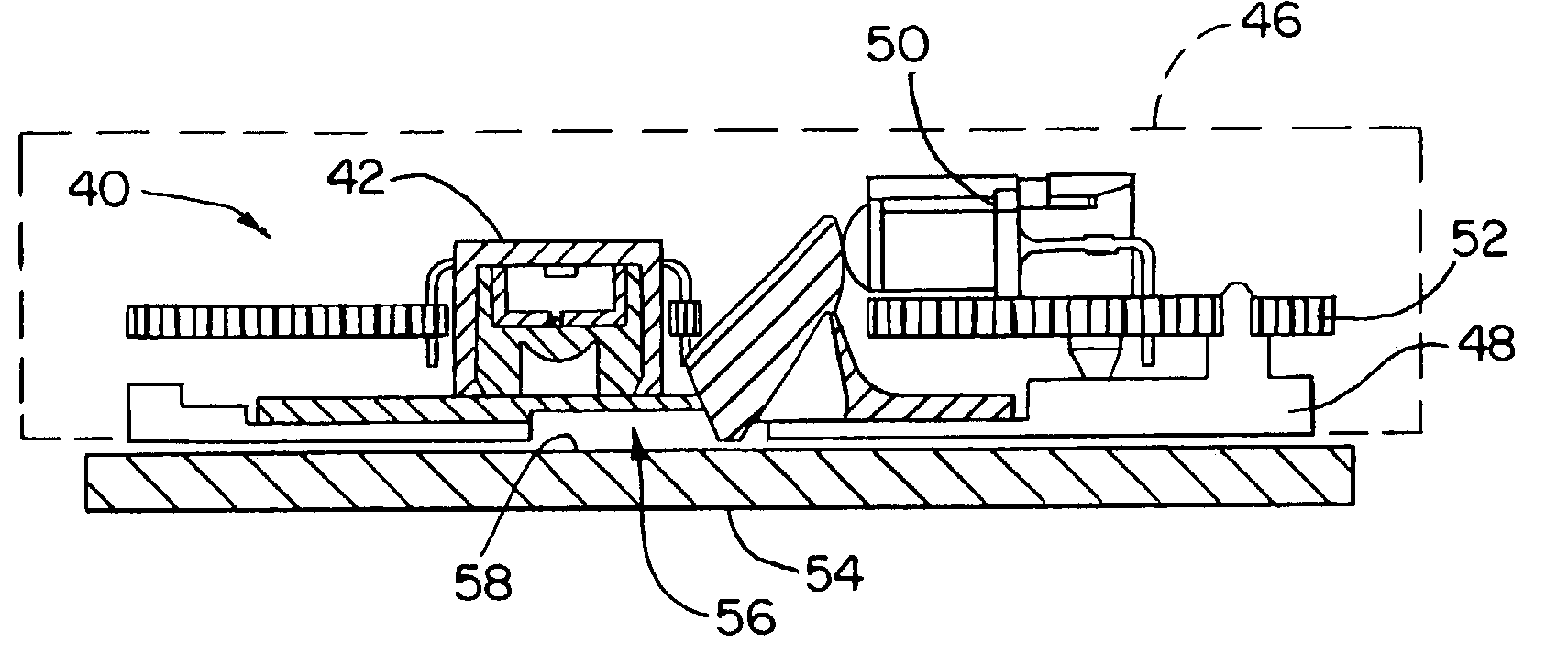
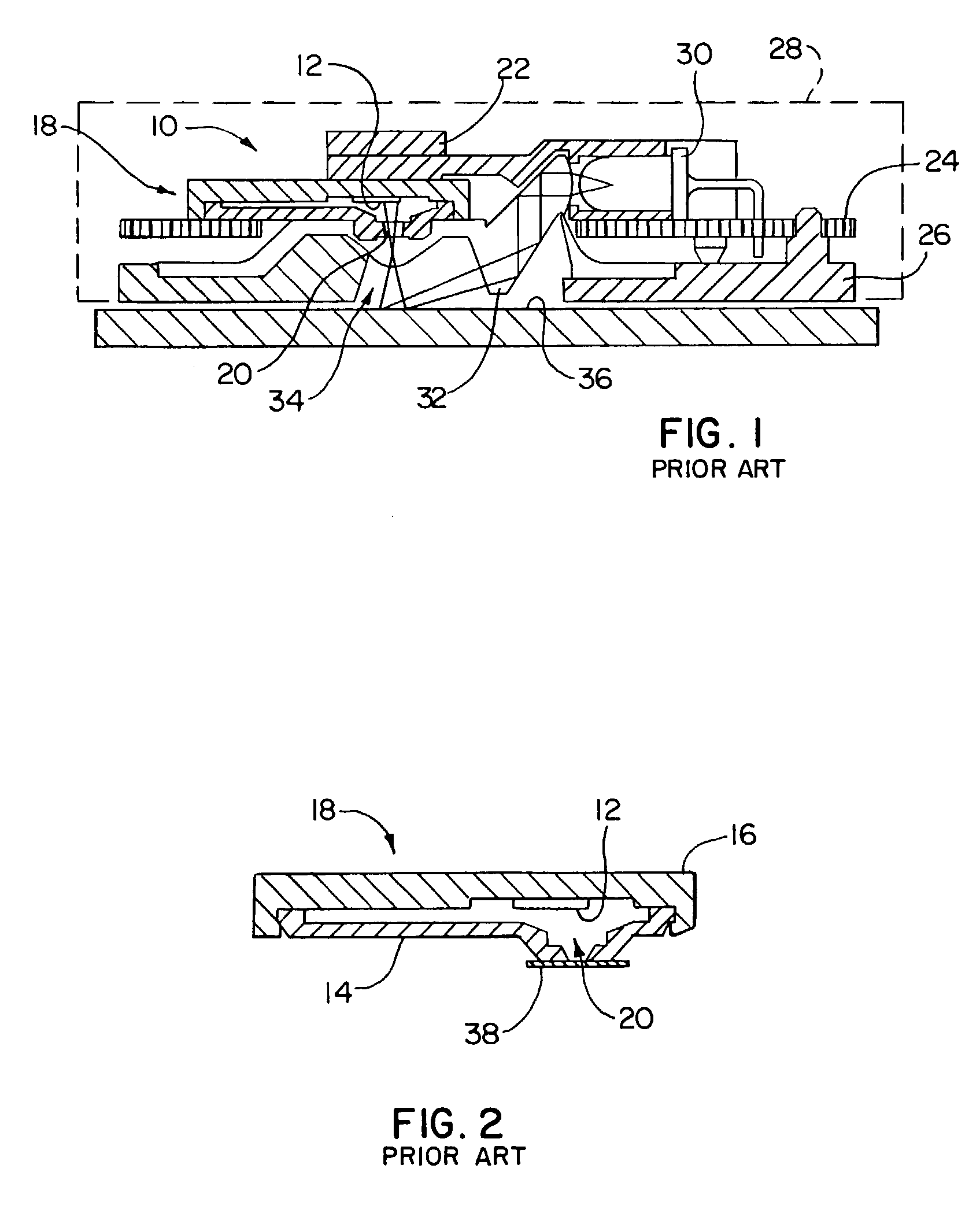
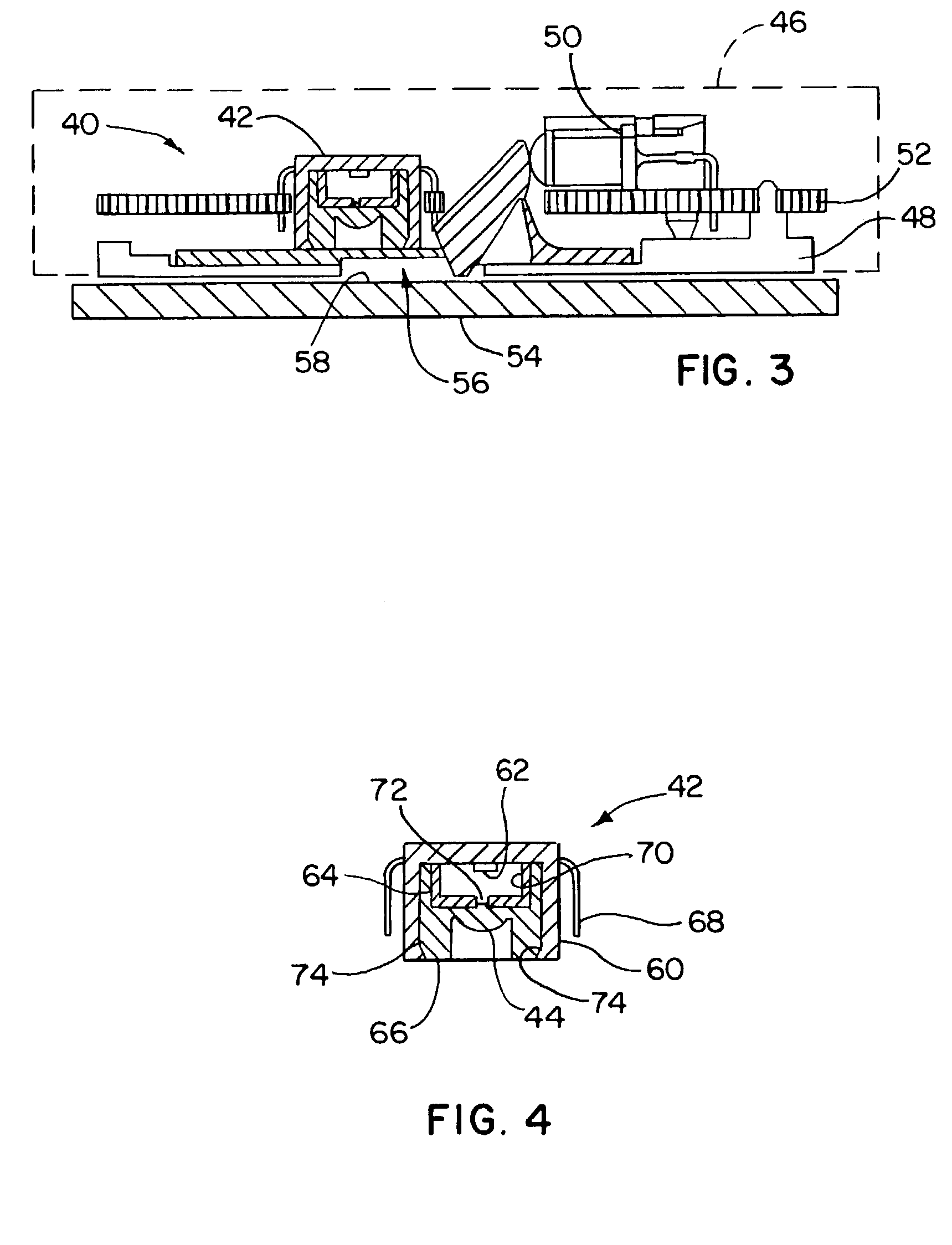
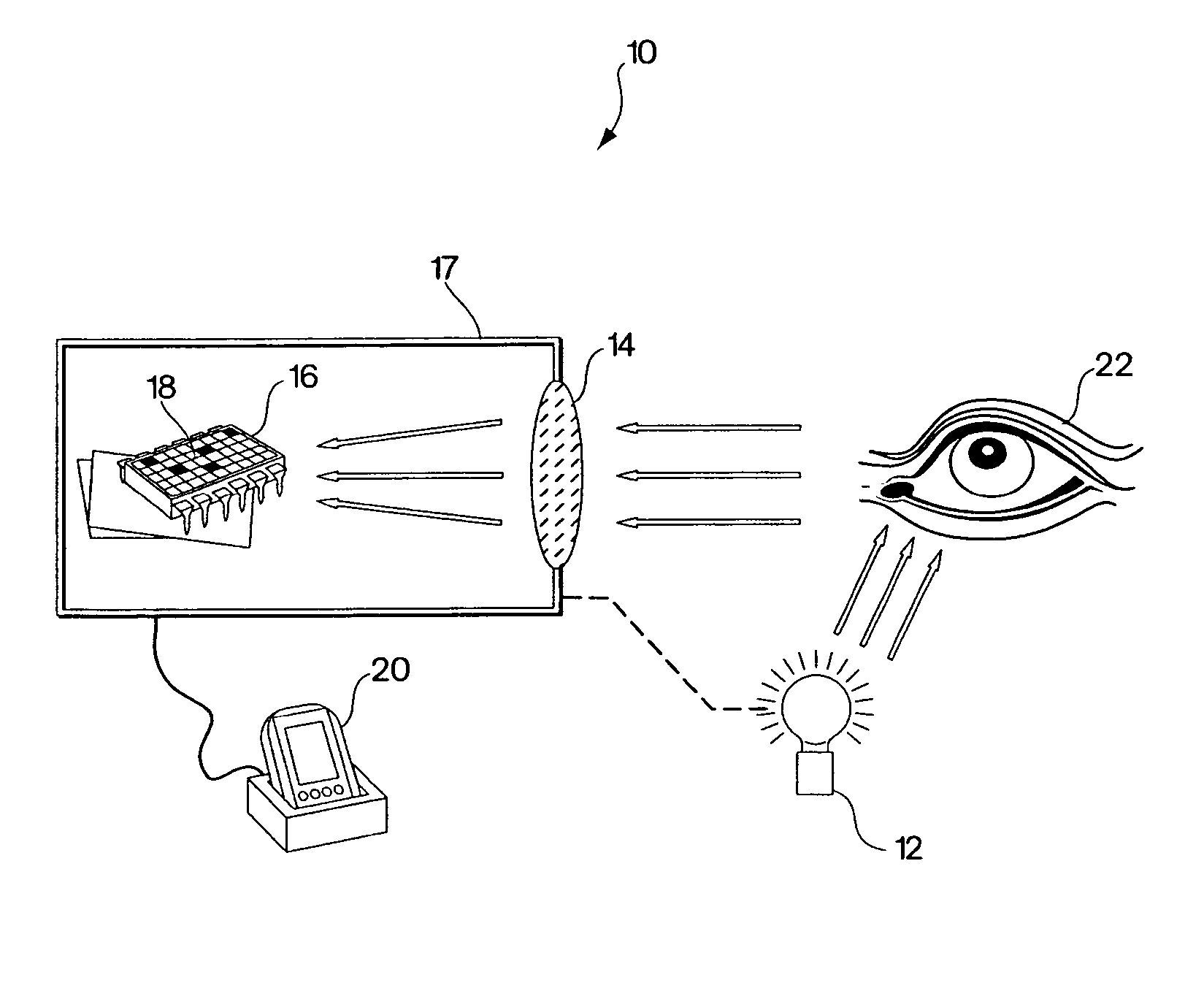
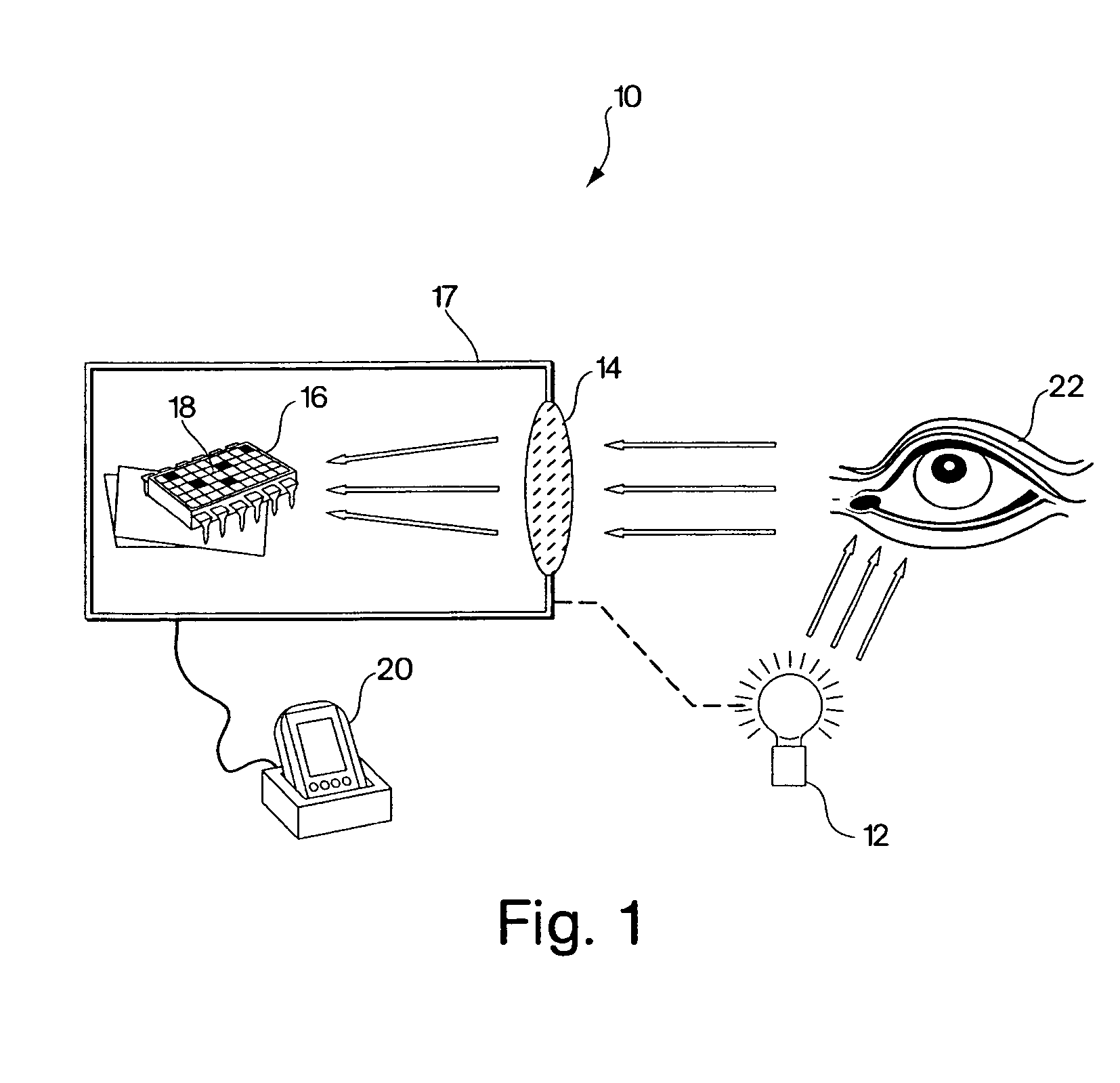
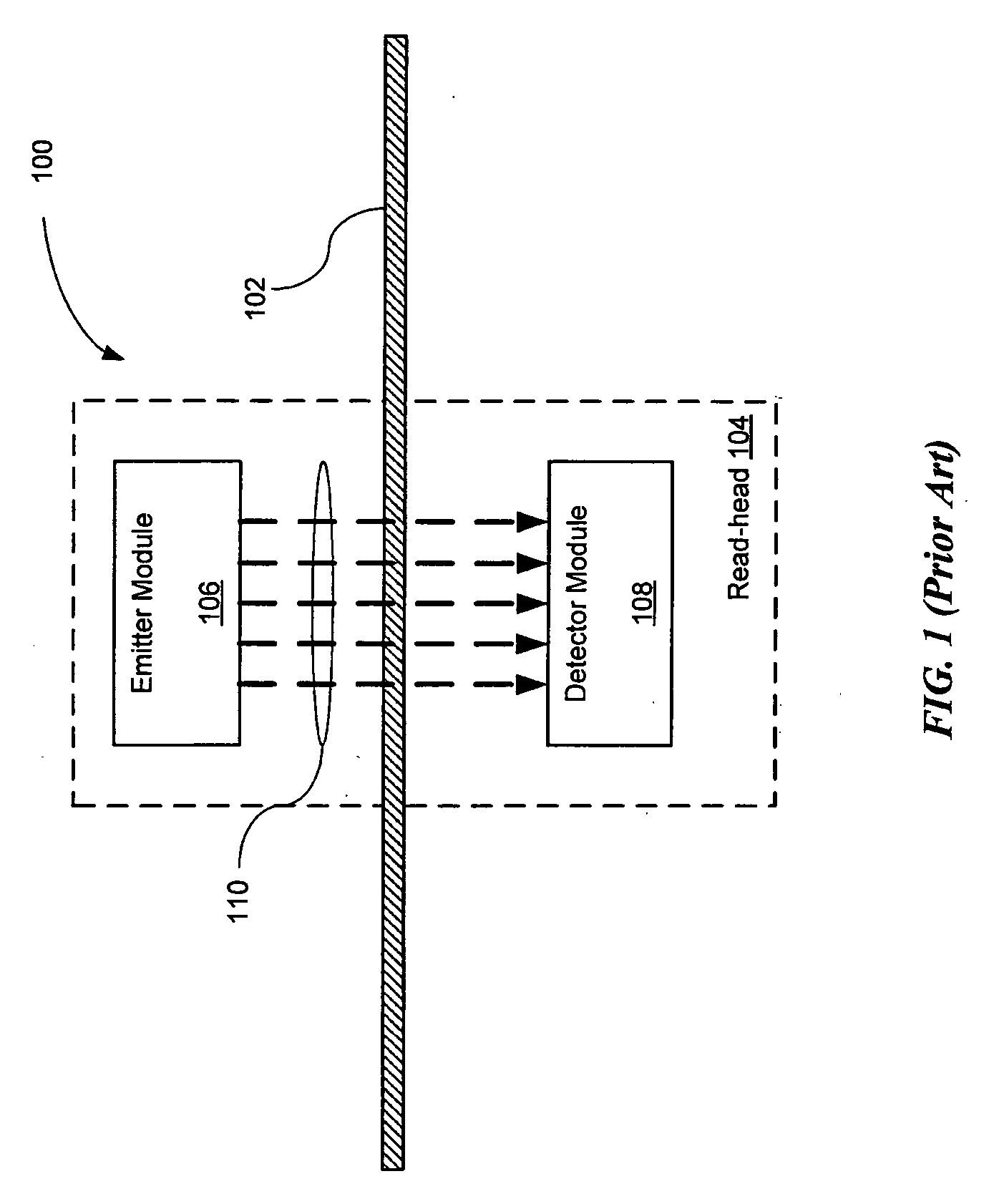
Optical navigation apparatus using fixed beacons and a centroid sensing device
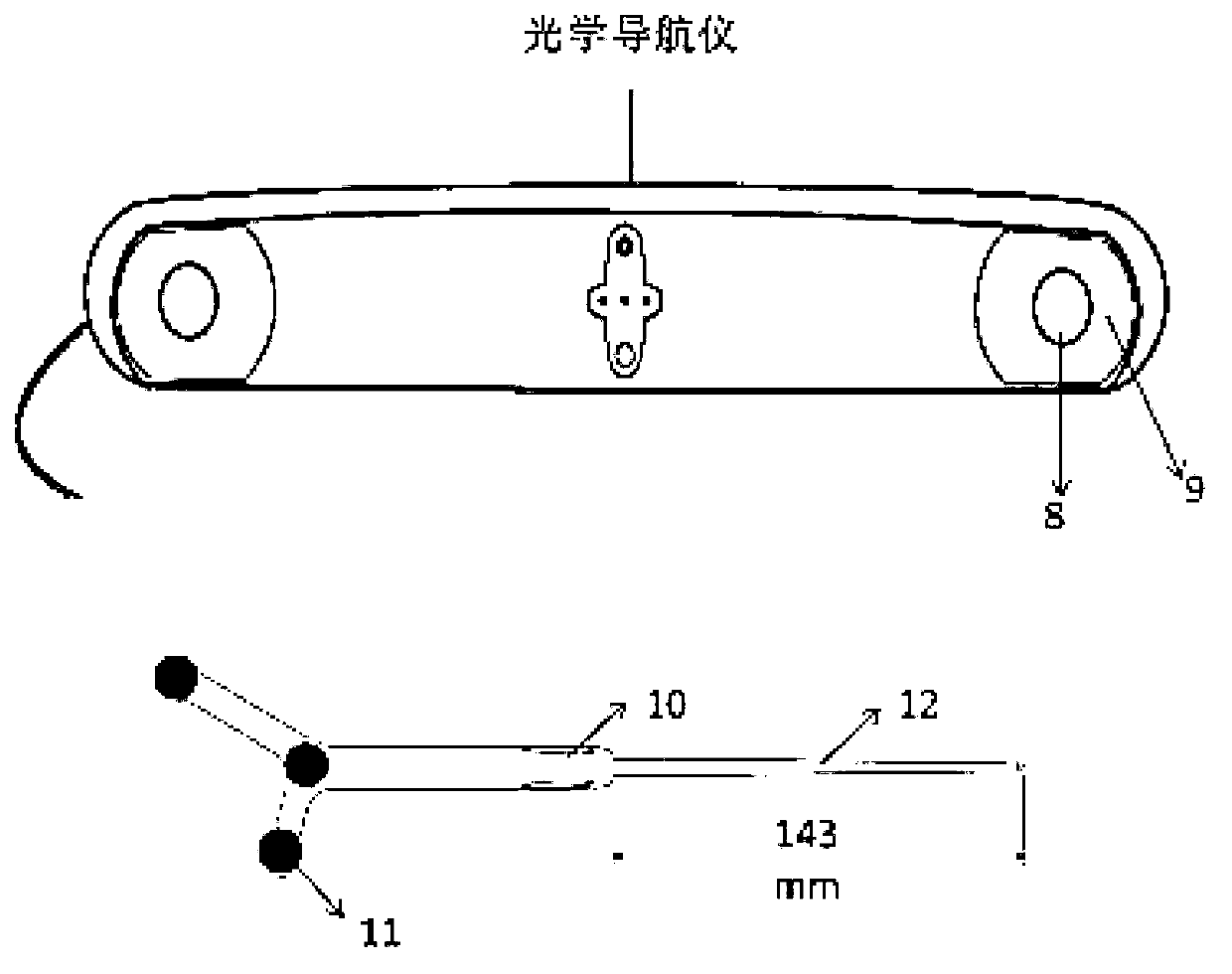
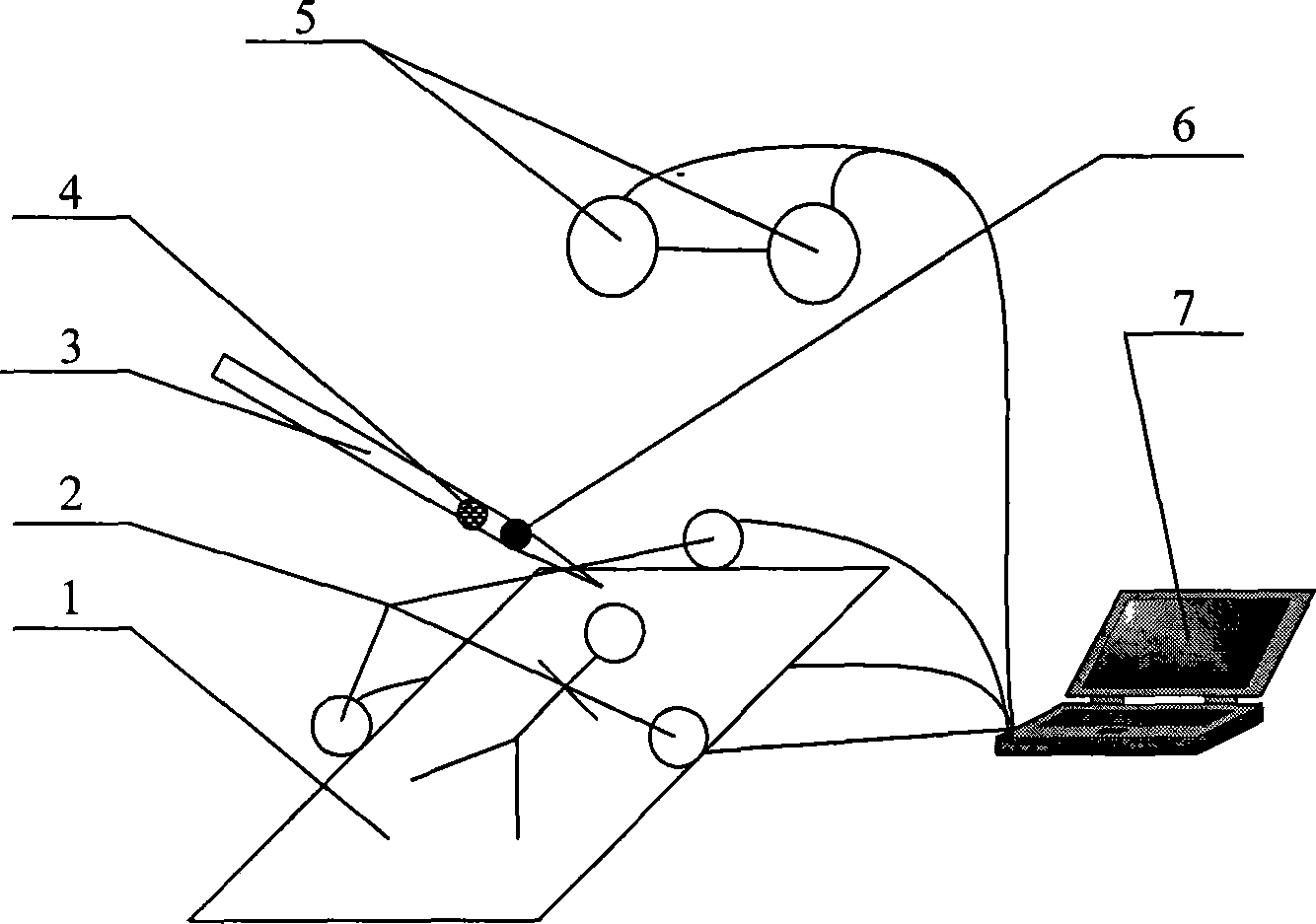
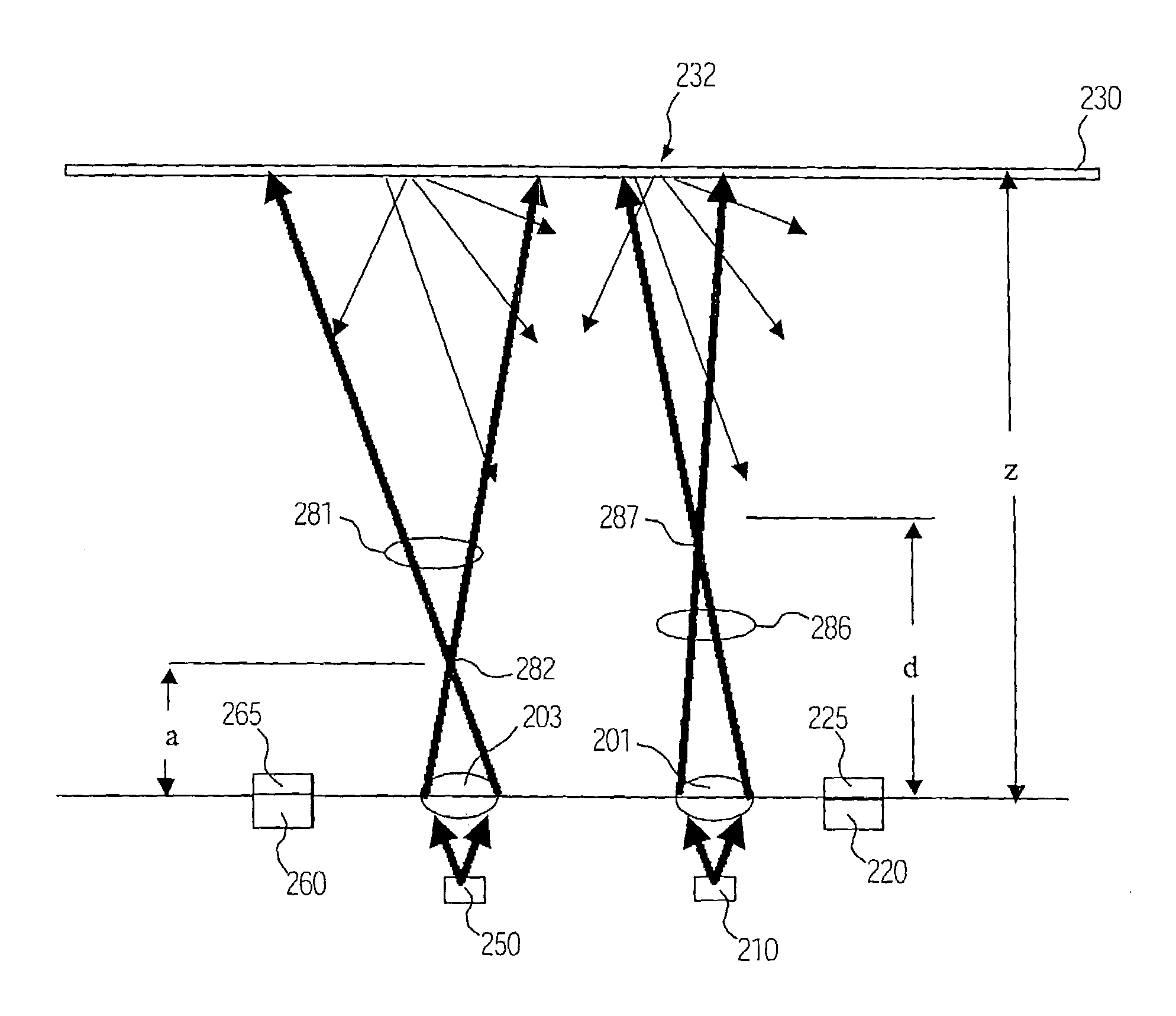
The present invention relates to an optical navigation system for determining a pose, which includes the position and orientation of an object in an environment. The optical navigation system uses a number of beacons affixed at known locations in the environment to provide electromagnetic radiation in a sequenced pattern. An on-board optic images the radiation from the beacons onto an on-board centroid sensing device to obtain an imaged distribution of the radiation on the on-board centroid sensing device. The centroid sensing device determines the centroid of the imaged distribution and provides centroid information to a navigation unit for determining the pose of the object from the centroid. The navigation system is particularly well-suited for navigating hand-held objects.
Owner:ELECTRONICS SCRIPTING PRODS
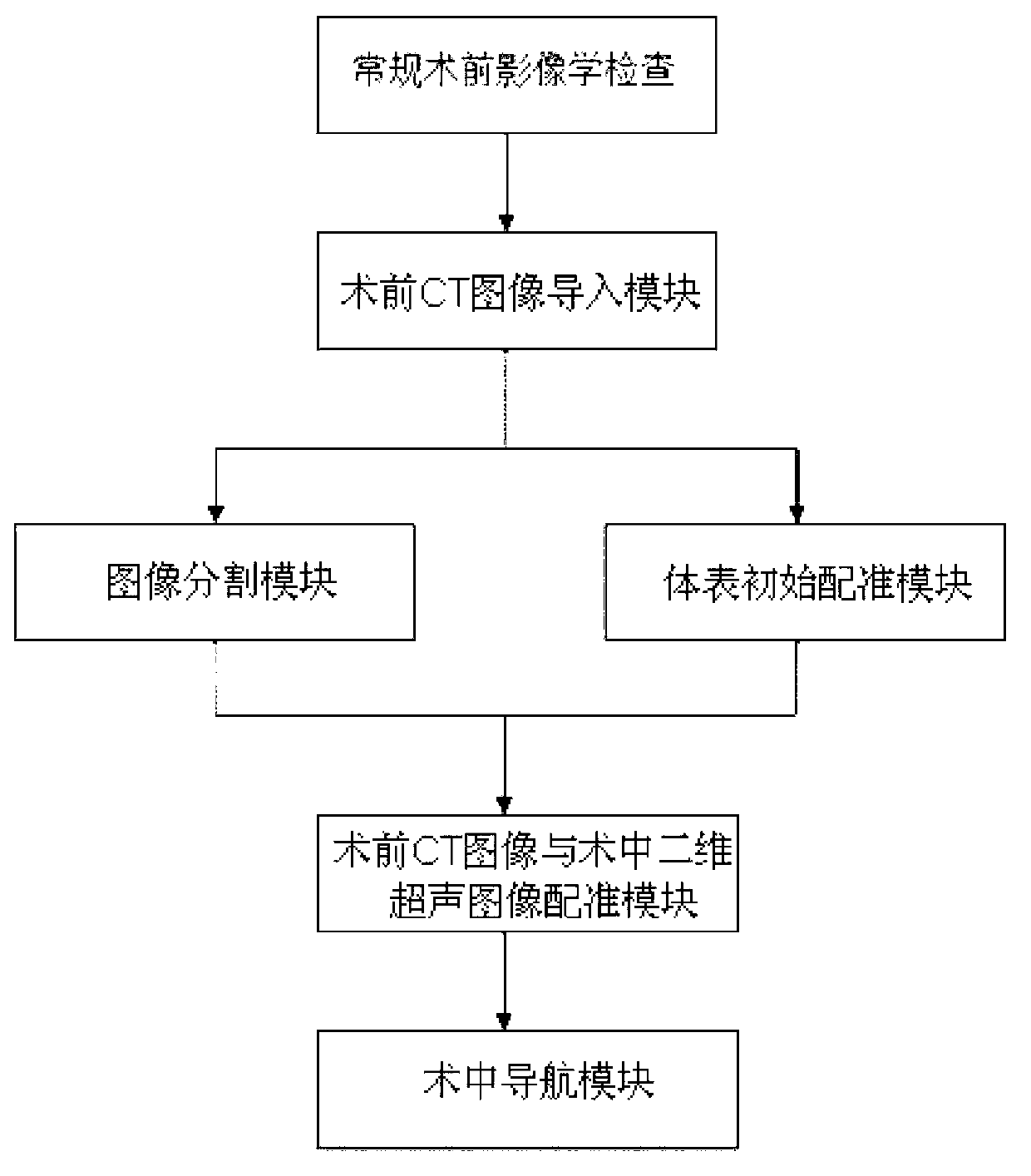
Optical navigation positioning system based on CT (computed tomography) registration results and navigation method thereby
ActiveCN102999902AResolve uncertaintyImage analysisDiagnosticsImage segmentationIntraoperative ultrasound
Disclosed are an optical navigation positioning system based on CT (computed tomography) registration results and a navigation method thereby. The system comprises a preoperative CT image guide input module, an image segmentation module, a body surface initial-registration module, a preoperative CT image and intraoperative two-dimensional ultrasound image module and an intraoperative navigation module. By combining virtual reality and intraoperative ultrasound, intraoperative positioning errors caused by factors such as breathing are compensated, and accordingly a target point for coronary artery bypass grafting is accurately positioned and navigated. Cardiac and coronary vessel tree in preoperative cardiac CT image data is manually segmented and reconstructed, an augmented virtual reality environment integrating endoscope and virtual endoscope is built by the aid of optical navigation apparatus and CT-ultrasound-based intraoperative registration error correction, and accordingly the target point of coronary artery bypass grafting is accurately positioned and navigated.
Owner:RUIJIN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
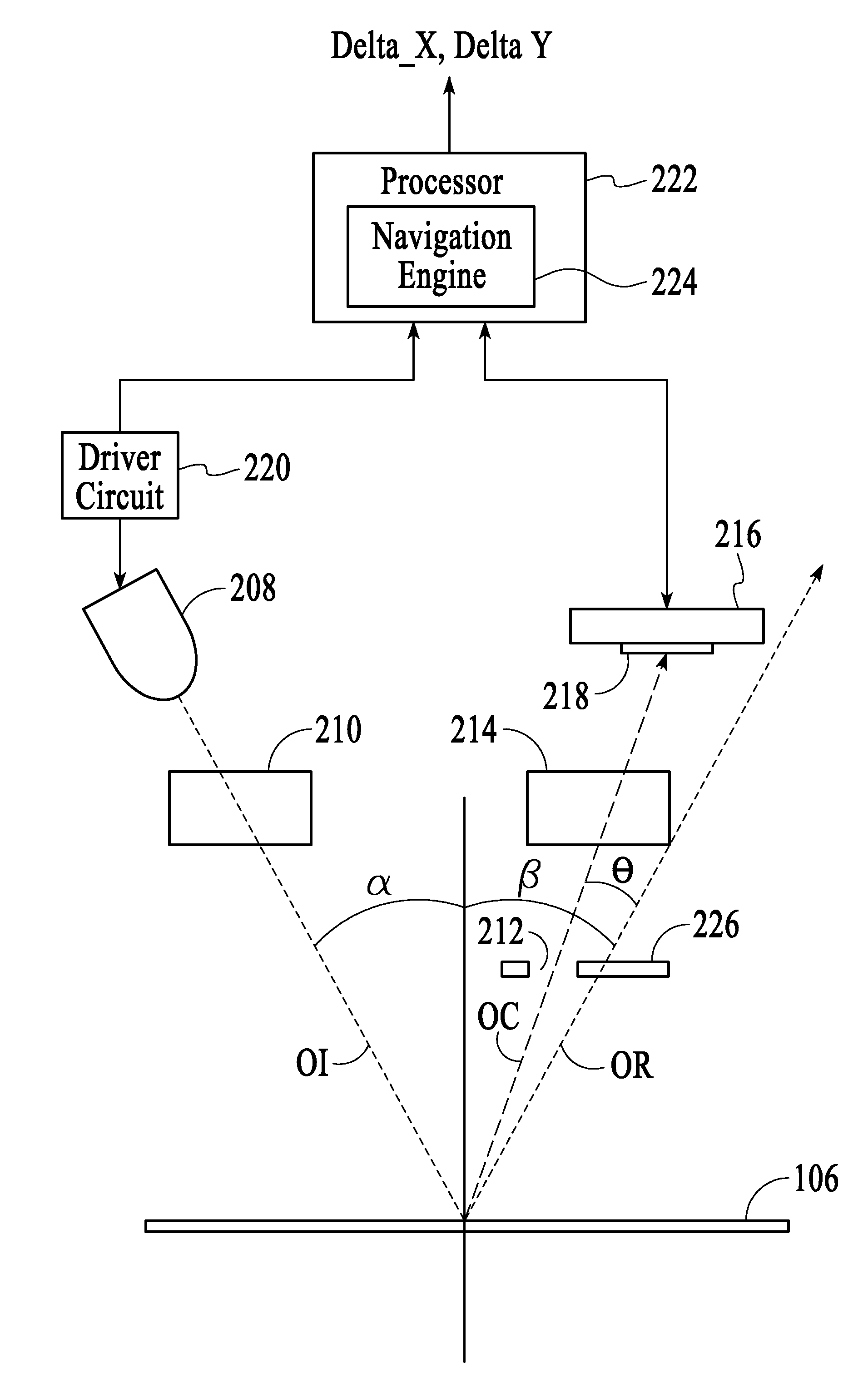
Method and device for optical navigation
InactiveUS20050024336A1Good signalHigh contrast imageInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsRelative motionSpecular reflection
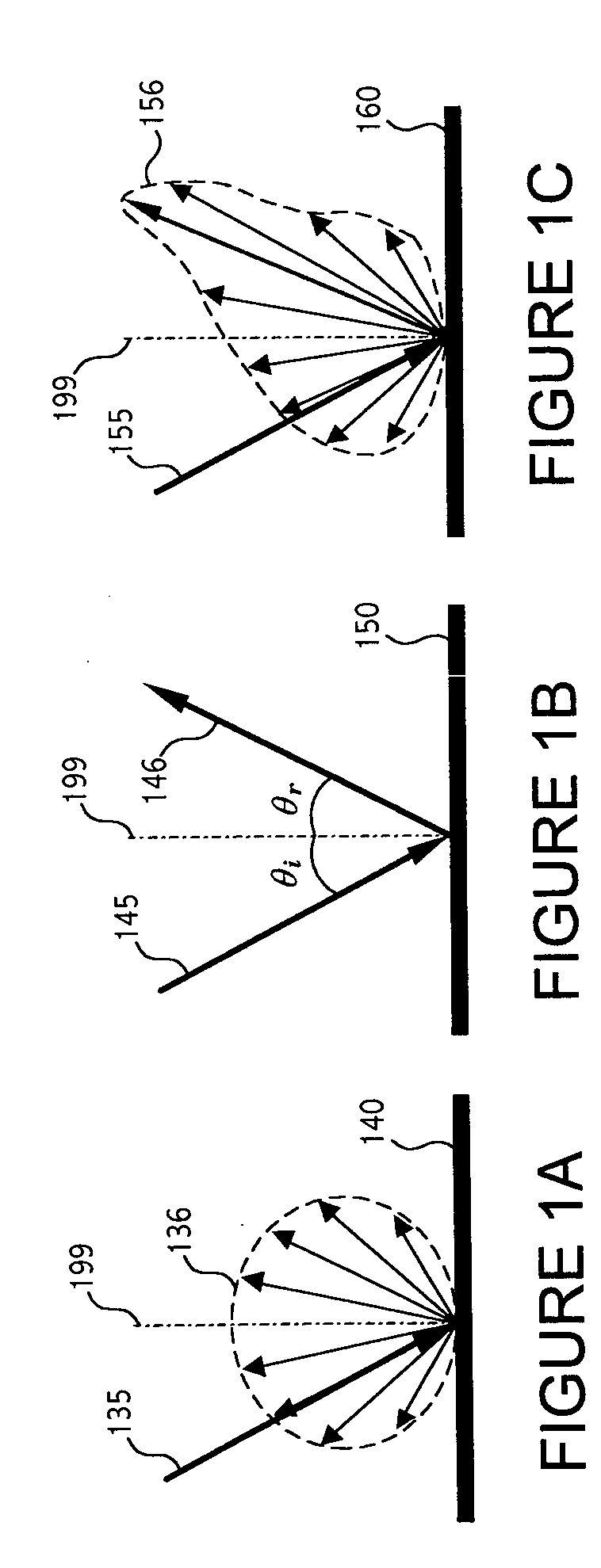
An method and device suitable for navigation on a wide variety of surfaces is introduced. Specular reflection is used to determine relative motion over typical surfaces. A specific application is a computer mouse.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
Method and device for optical navigation
ActiveUS20050024623A1Good signalHigh contrast imageInput/output for user-computer interactionOptical rangefindersRelative motionSpecular reflection
An method and device suitable for navigation on a wide variety of surfaces is introduced. Specular reflection is used to determine relative motion over typical surfaces. A specific application is a computer mouse.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
Device for determining the longitudinal and angular position of a rotationally symmetrical apparatus
InactiveUS20050075558A1Accurately determineEasy to trackDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMeasuring instrumentImage conversion
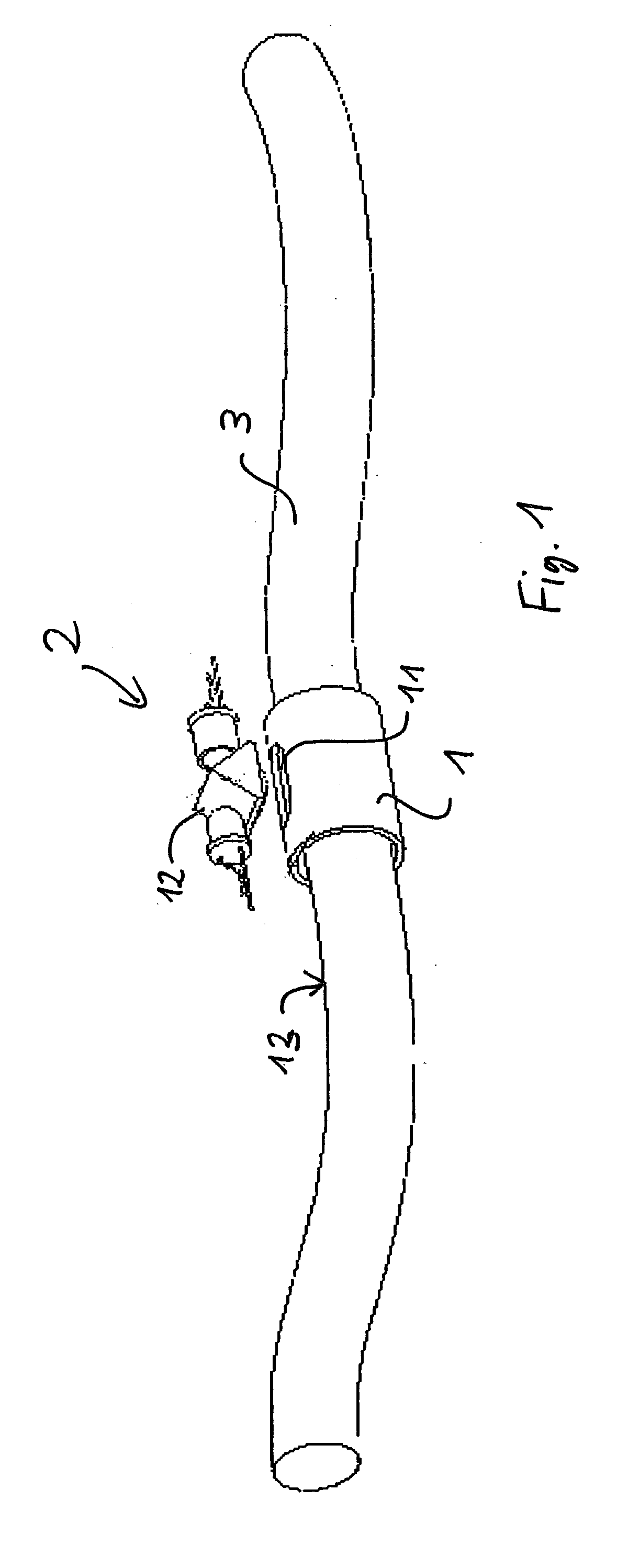
A device for determining the longitudinal and angular position of a rotationally symmetrical apparatus when guided inside a longitudinal element surrounding the same, including an imaging optical navigation sensor that measures the motion of the underlying surface by comparing successive images, and translates this image translation into a measurement of the longitudinal and rotational motion of the instrument. Features of the captured image are used to identify the insertion or withdrawal of the instrument, and to identify specific areas of the moving surface passing underneath the sensor, therefore allowing to establish the absolute position of the instrument, or to identify which instrument was inserted or in what cavity a tracking instrument was inserted. The device comprises a light source and a light detector. Light emitted by said light source is directed onto a surface of the rotationally symmetrical apparatus. Reflected light from said surface is detected by said light detector to produce a position signal showing a locally varying distribution in the longitudinal direction and in the peripheral direction to enable said precise position and angular measurement.
Owner:XITACT
Signal processing circuit and method using analog voltage signal to pulse width modulation conversion
InactiveUS7247832B2Television system detailsPhotometry using reference valueSignal processing circuitsAudio power amplifier
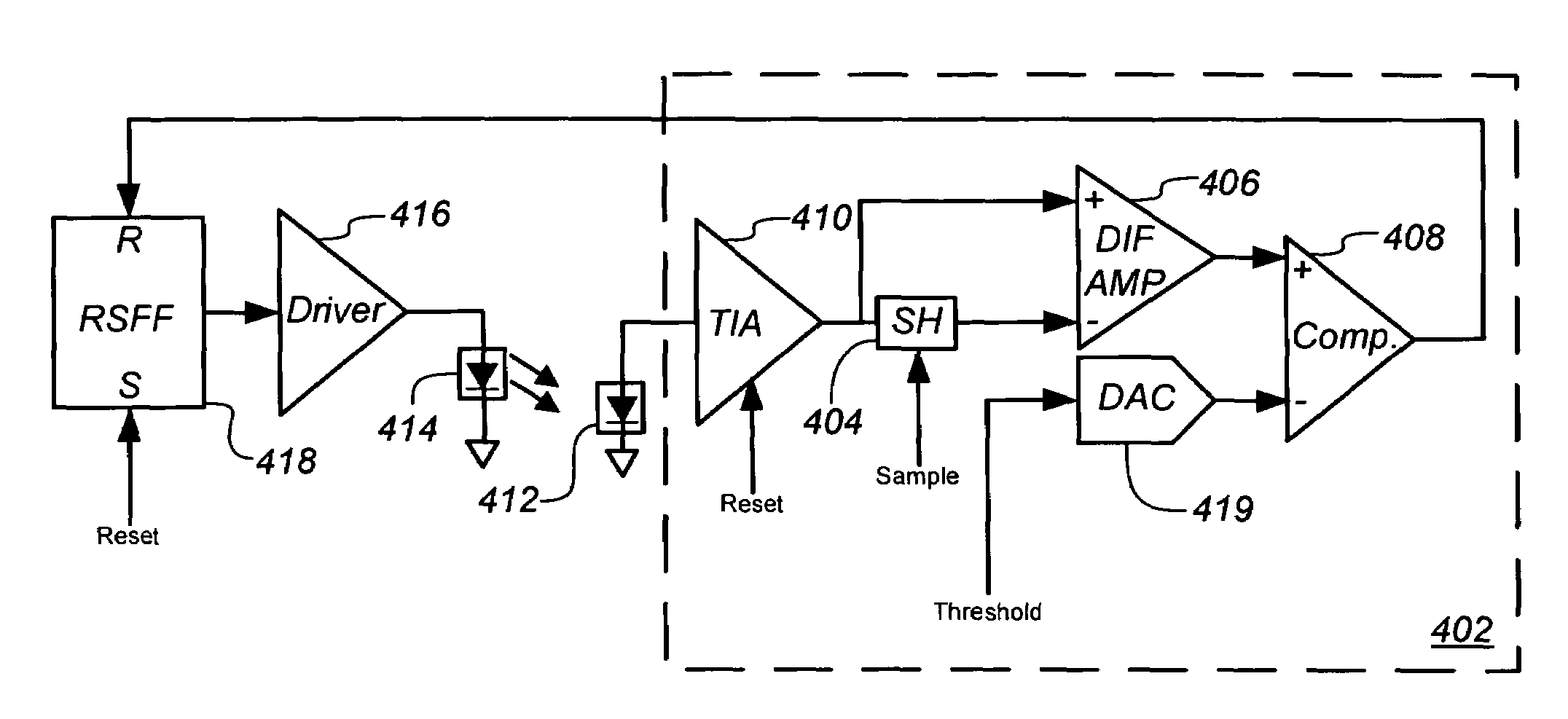
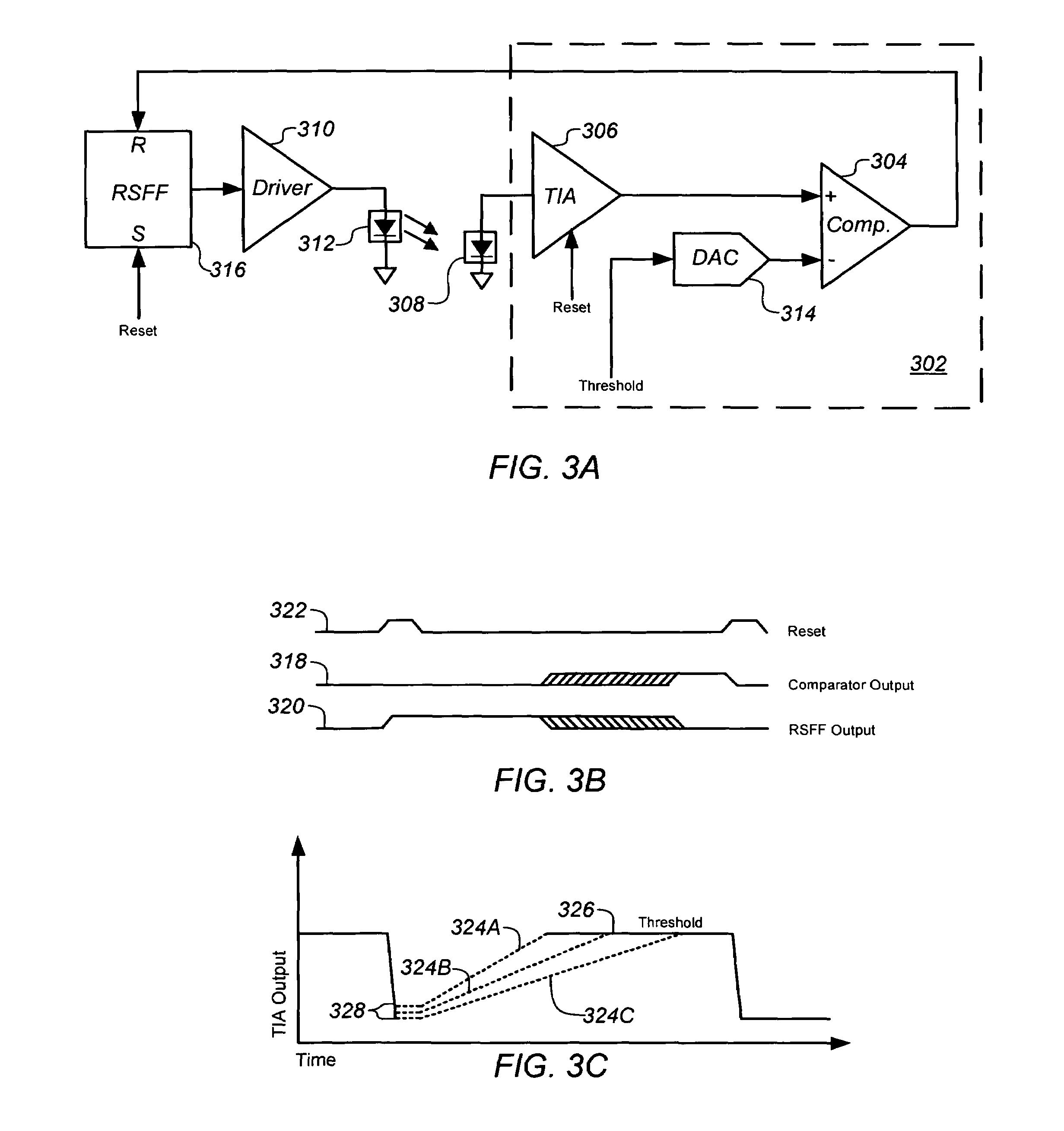
A signal processor and processing method are provided for measuring current received from a photo-detector. Generally, the processor includes a transimpedance amplifier (TIA) to integrate a current received from a photo-detector in the optical navigation system to generate a voltage signal having a slope that is proportional to the received current, and a comparator having a first input coupled to an output of the TIA to receive the voltage signal, and a second, inverting, input coupled to a threshold voltage. The comparator is configured to compare the voltage signal to the threshold voltage and to generate an output pulse having a predetermined voltage and a duration or width that is a function of the received current.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
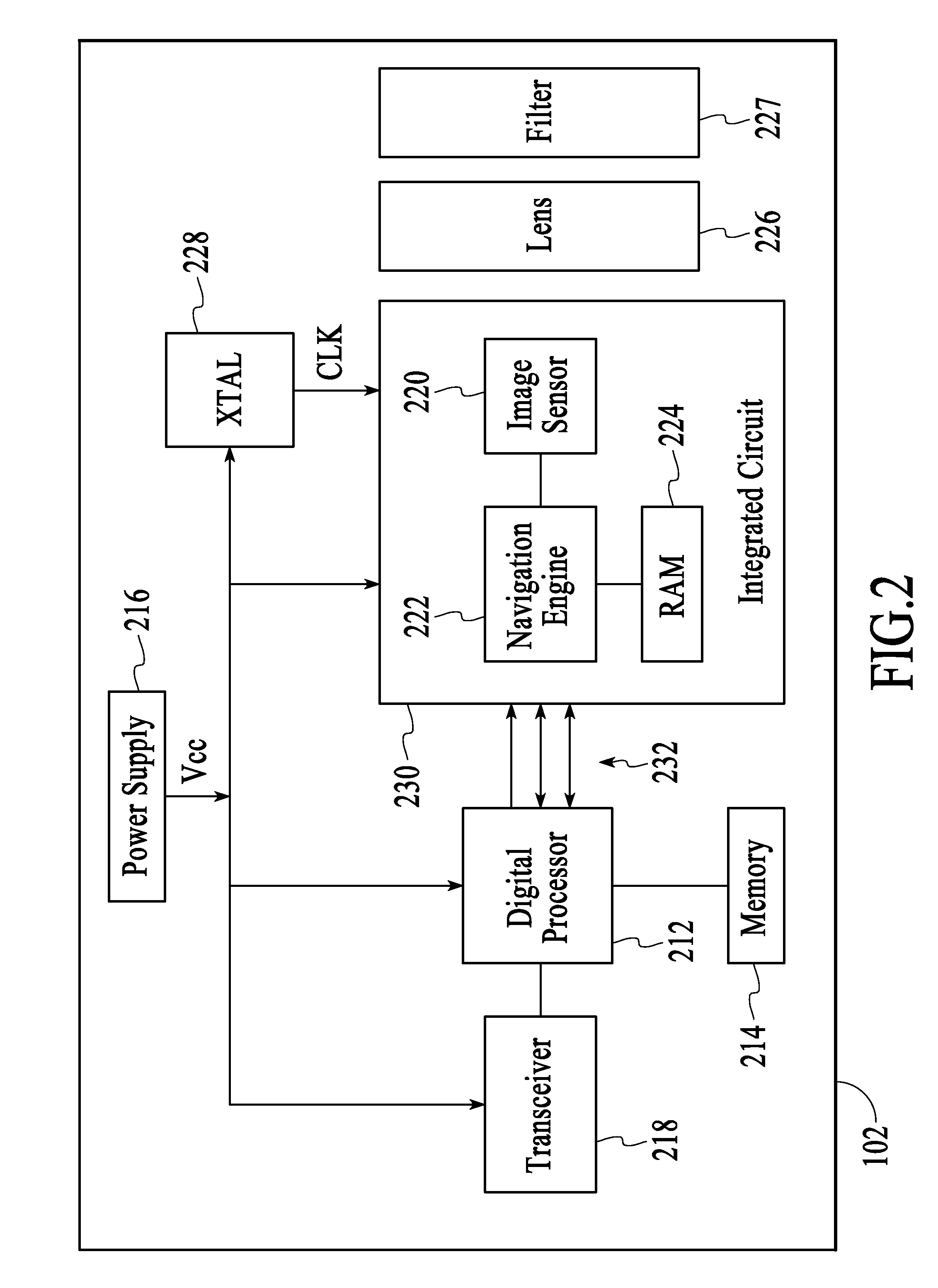
Optical navigation sensor with integrated lens
InactiveUS6967321B2Reduce in quantityOptimize generation and captureInput/output for user-computer interactionBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsForeign matterImaging lens
An optical navigation sensor apparatus for an optical mouse includes an optical navigation sensor having an electronic chip, an aperture plate and an imaging lens integrated into a single package. The imaging lens includes a lens housing surrounding the aperture and providing a barrier to the entry of foreign matter into the aperture. In one form, the optical navigation sensor also includes a light emitting diode (LED) for illuminating a small area of a surface under the sensor and generating a reflected image that is detected by the electronic chip. In a sensor having an integral LED, an integral collimating lens is included for receiving light from the LED and focusing the light from the LED on the surface to be illuminated. The collimating lens is incorporated into a lens housing surrounding the LED and protecting the LED from exposure to foreign material.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and method for performing optical navigation using scattered light
ActiveUS8138488B2High contrast frameMinimizing volume of systemSolid-state devicesInvestigating moving sheetsTarget surfaceOptical axis
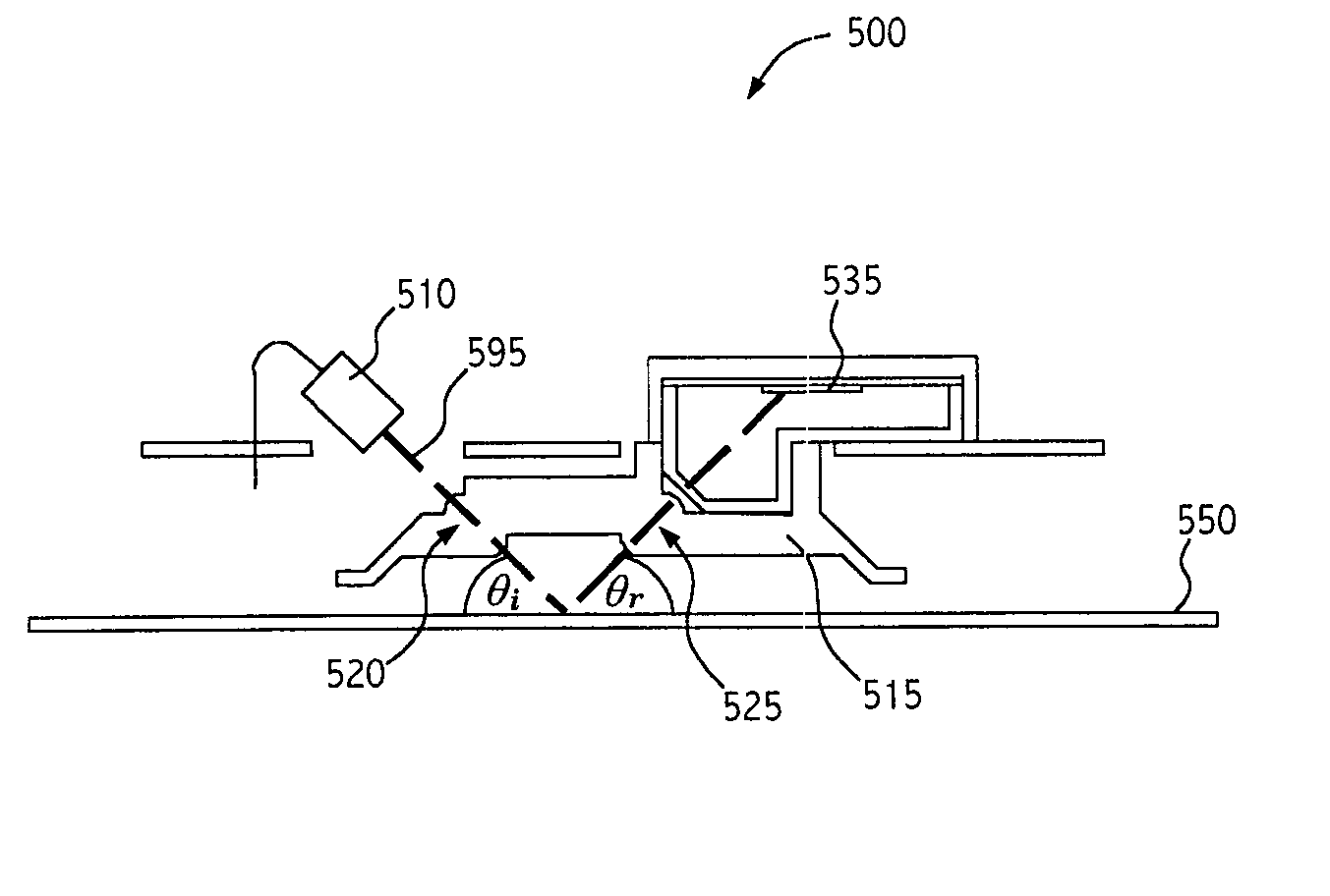
A system and method for performing optical navigation uses scattered light to produce frames of image data to estimate displacement with respect to a target surface. The scattered light is produced from an illumination beam of light emitted along a first optical axis onto the target surface. The illumination beam of light also produces a specularly reflected beam of light along a second optical axis. The scattered light about a third optical axis, which is offset by a predefined angle with respect to the second optical axis, is received at an image sensor array to produce the frames of image.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
Low power consumption, broad navigability optical mouse
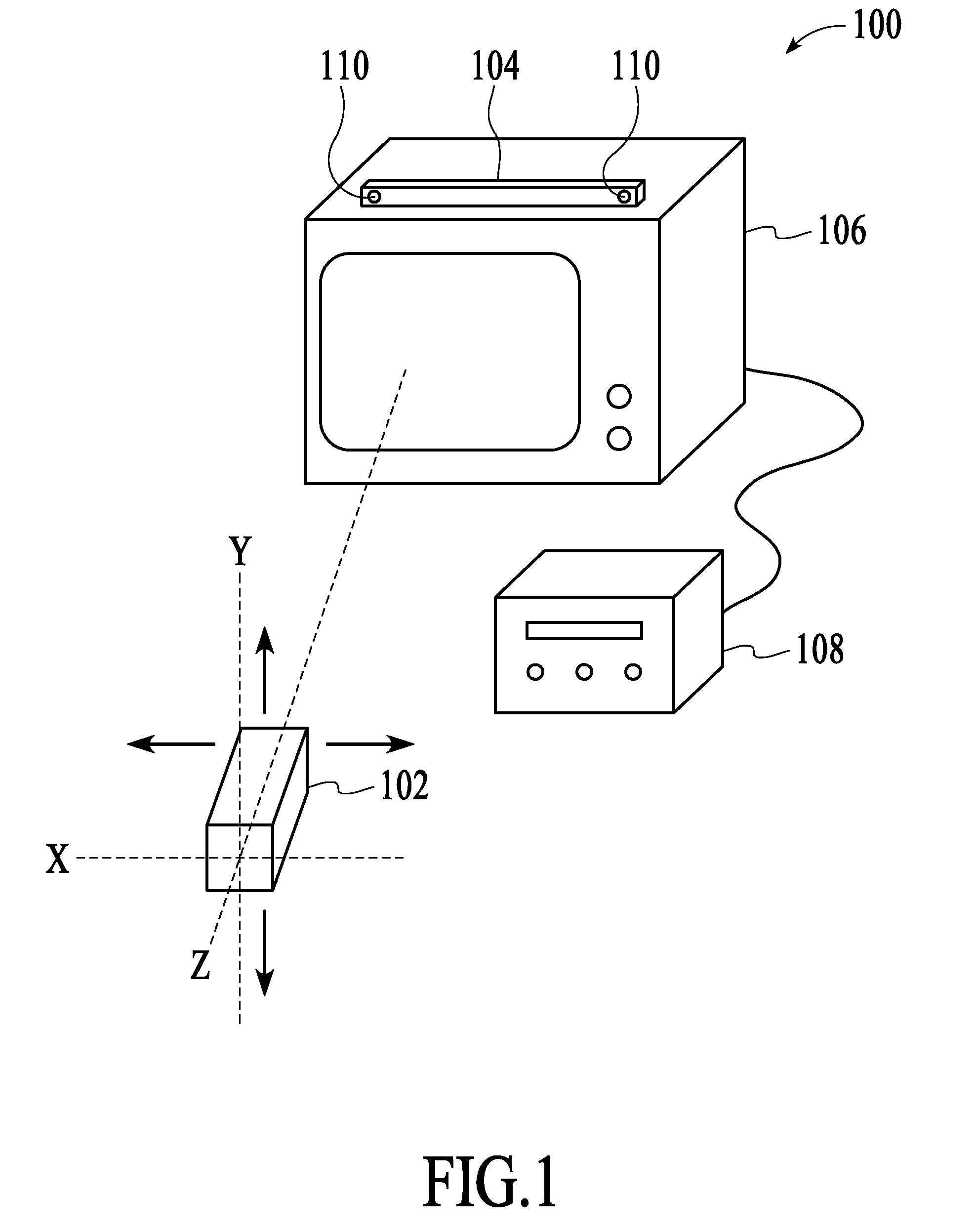
An optical navigation system for determining movement relative to a navigation terrain includes a first source and a second source of optical radiation for illuminating the navigation terrain, the first source differing from the second source in at least one operating parameter. The system further includes means to select the first source and the second source independently based on decision criteria. The system further includes a detector for capturing patterns in the optical radiation subsequent to illuminating of the navigation terrain.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
Low power consumption, broad navigability optical mouse
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
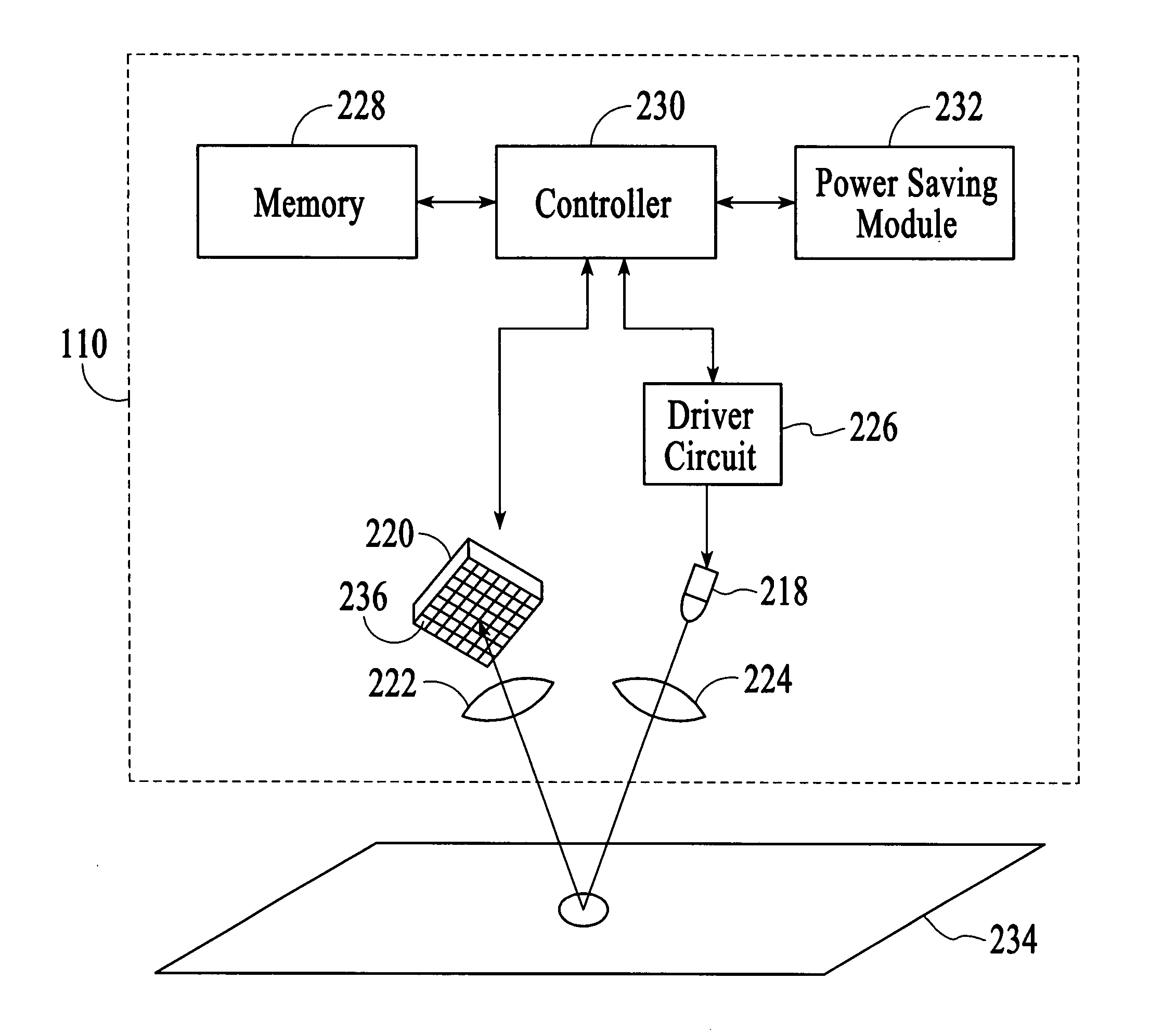
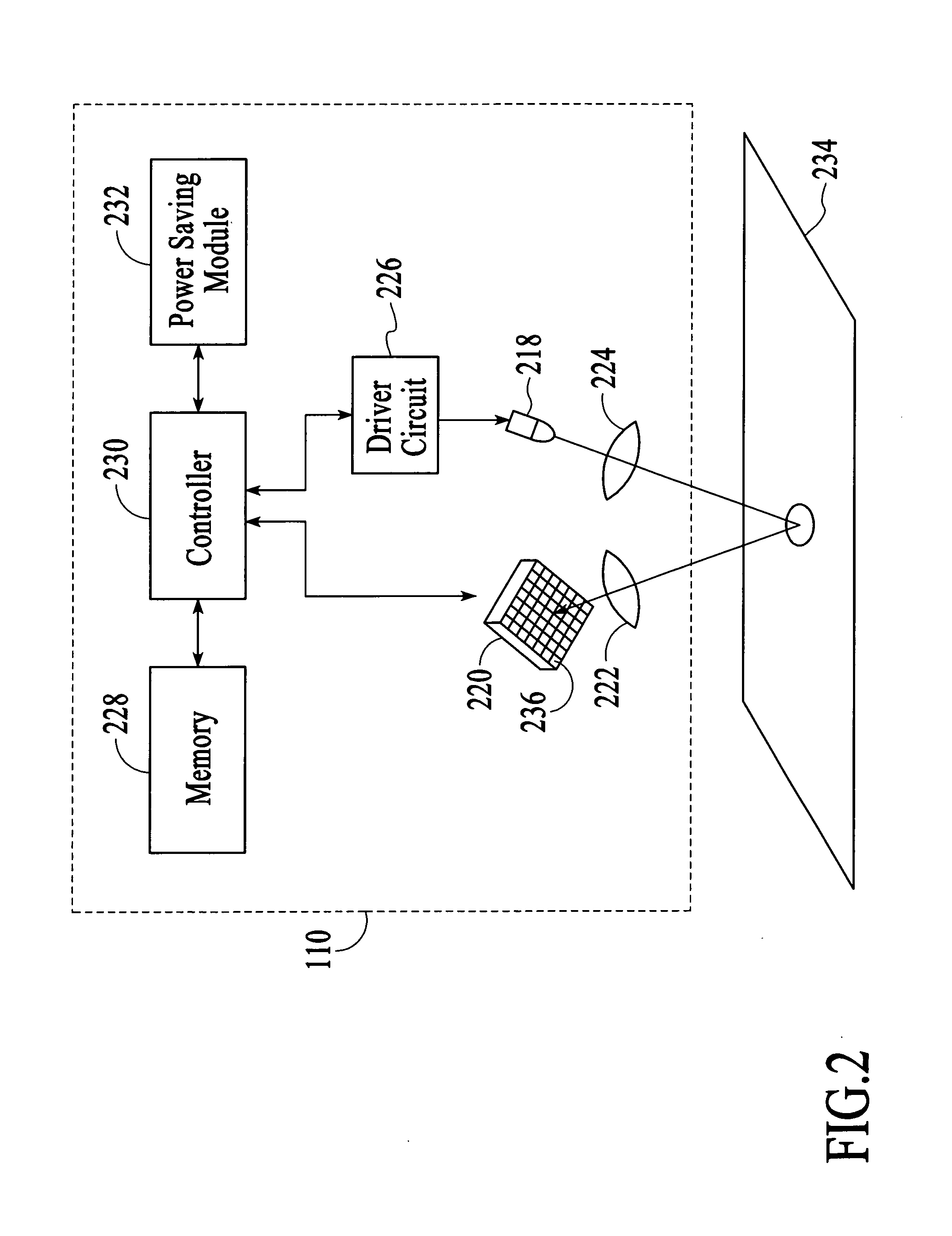
Power-saving method for an optical navigation device
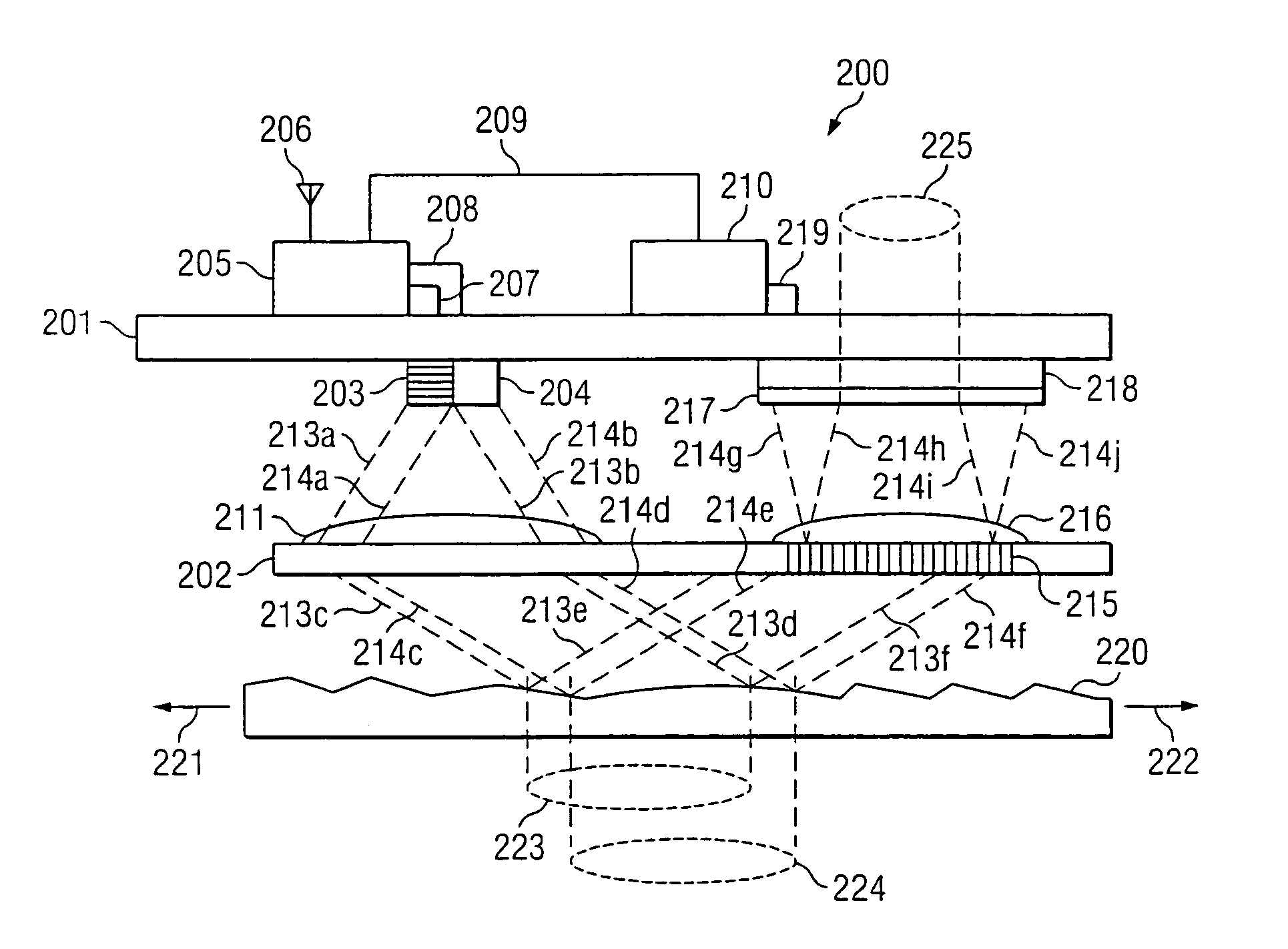
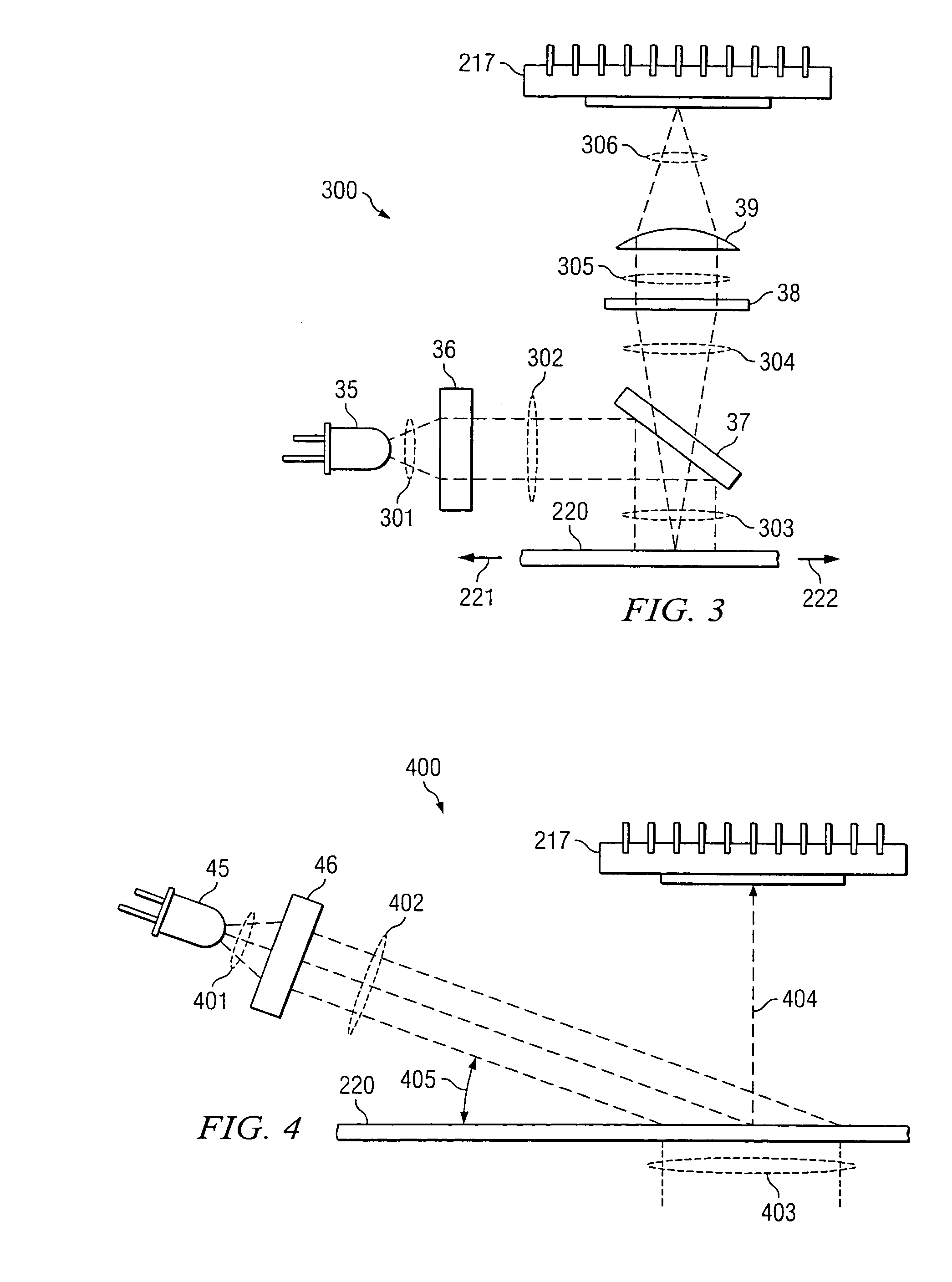
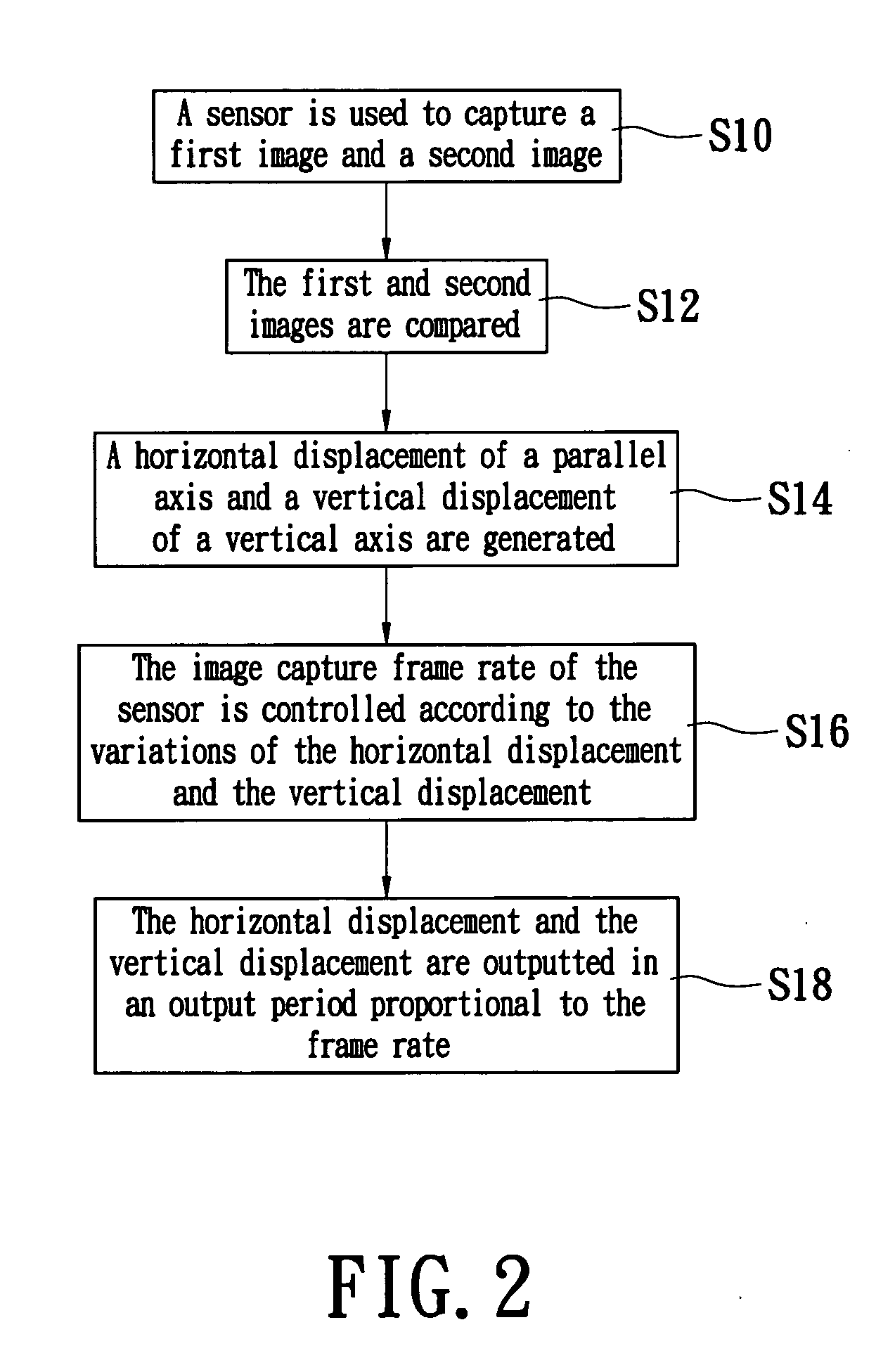
InactiveUS20050110746A1Reduced image captureImprove image captureEnergy efficient ICTDigital data processing detailsVertical displacementComputer science
A power-saving method for an optical navigation device is proposed, wherein the image capture frame rate of a sensor is controlled according to the moving speed of the optical navigation device. The image capture frame rate is determined based on the variations of a horizontal displacement and a vertical displacement of the optical navigation device for saving power. Moreover, when the optical navigation device is in the sleeping mode, it is not necessary to generate a current to drive the sensor to monitor whether the optical navigation device moves or not. A displacement detector (e.g., a mechanical displacement trigger) is used instead to generate a current for breaking off the sleeping mode to accomplish the power-saving object.
Owner:HOU ALPHA
Method and device for optical navigation
InactiveUS7161682B2Good signalHigh contrast imageInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsRelative motionSpecular reflection
An method and device suitable for navigation on a wide variety of surfaces is introduced. Specular reflection is used to determine relative motion over typical surfaces. A specific application is a computer mouse.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
Optical navigation chip, optical navigation module and optical encoder
ActiveUS20160306446A1Small sizeInput/output for user-computer interactionDigital data processing detailsRelative displacementLight beam
The present disclosure illustrates an optical navigation chip. The optical navigation chip is disposed on an optical navigation module. The optical navigation module includes a light-emitting unit. The light-emitting unit provides a light beam to irradiate a surface of a displacement generating unit. The light beam has a low divergence angle to reduce scattering. The optical navigation chip includes a sensing array and a displacement calculating unit. The sensing array is disposed corresponding to the surface. The sensing array receives a reflected light beam which the surface reflects, and captures an image once every capturing interval based upon the reflected light beam. The displacement calculating unit calculates a relative displacement between the optical navigation chip and the surface according to the images.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
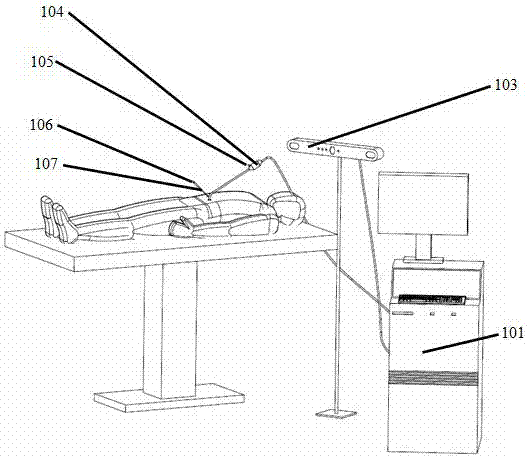
Optical, magnetic, electric composite navigational surgery positioning device and method
InactiveCN101049248AAchieve consistencyImprove calibration accuracySurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetic sourceMachine vision
An electric, magnetic and optical navigations combined locating system for medical operation features that the magnetic source and marking point are arranged on operation tool, at least three magnetic receivers and a group of two CCD cameras, which are electrically connected to a computer, are respectively fixed to and above the operation table for taking the information about the position of operation tool in optical, magnetic and electric coordinate systems and its posture.
Owner:XIAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIV
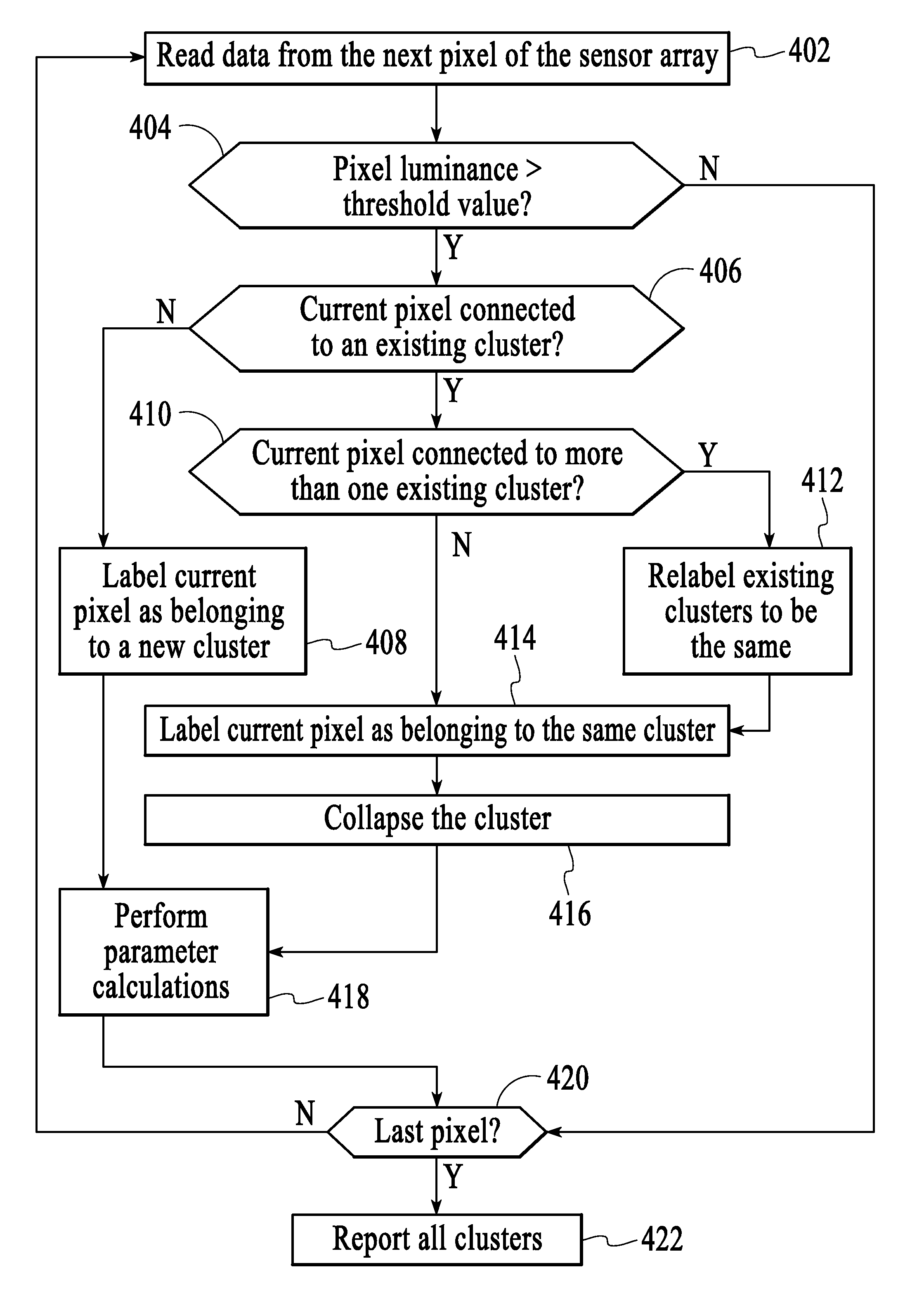
System and method for labeling feature clusters in frames of image data for optical navigation
A system and method for labeling feature clusters in frames of image data for optical navigation uses distances between feature clusters in a current frame of image data and feature clusters in a previous frame of image data to label the feature clusters in the current frame of image data using identifiers associated with the feature cluster in the previous frame of image data that have been correlated with the feature clusters in the current frame of image data.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
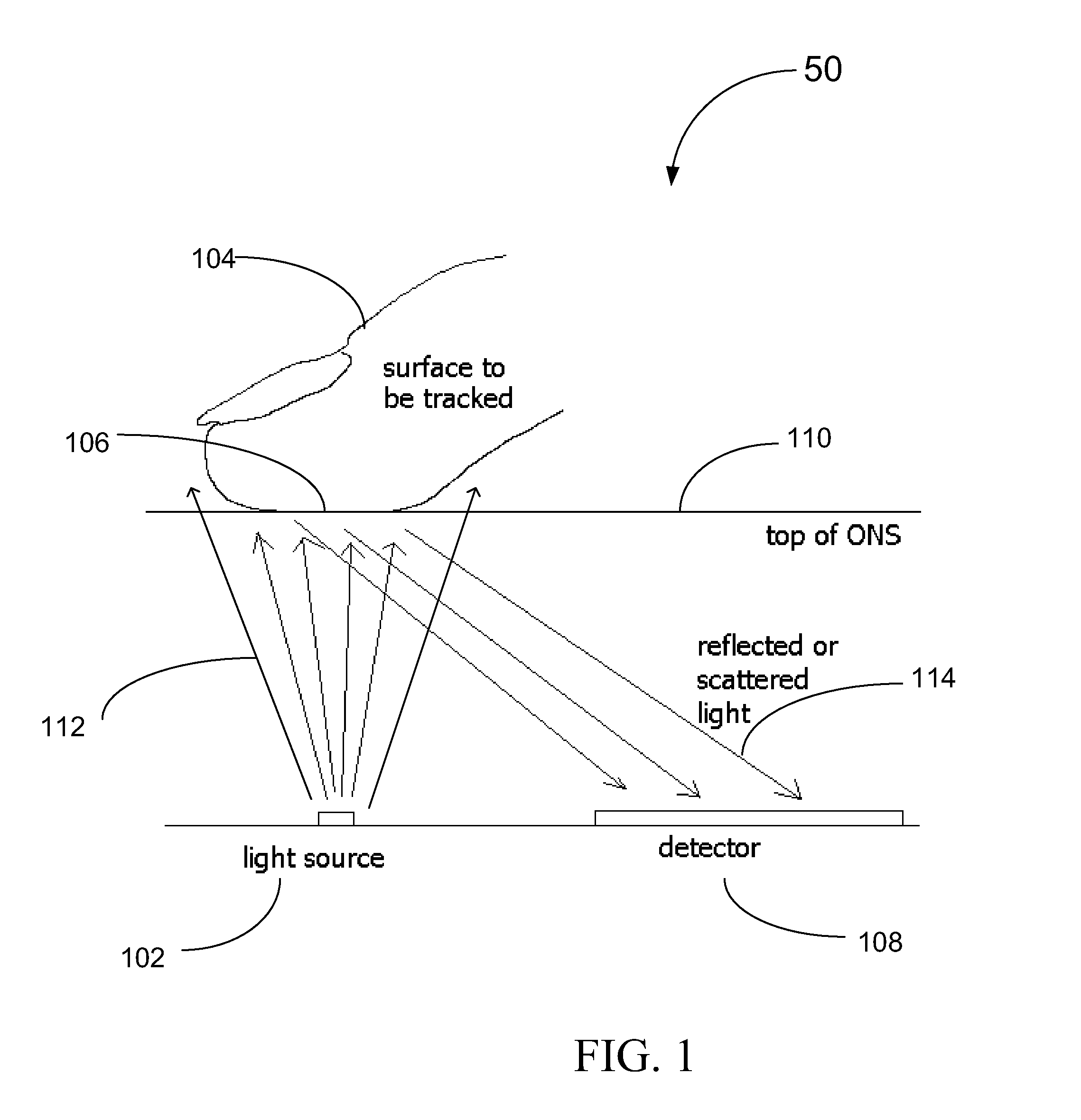
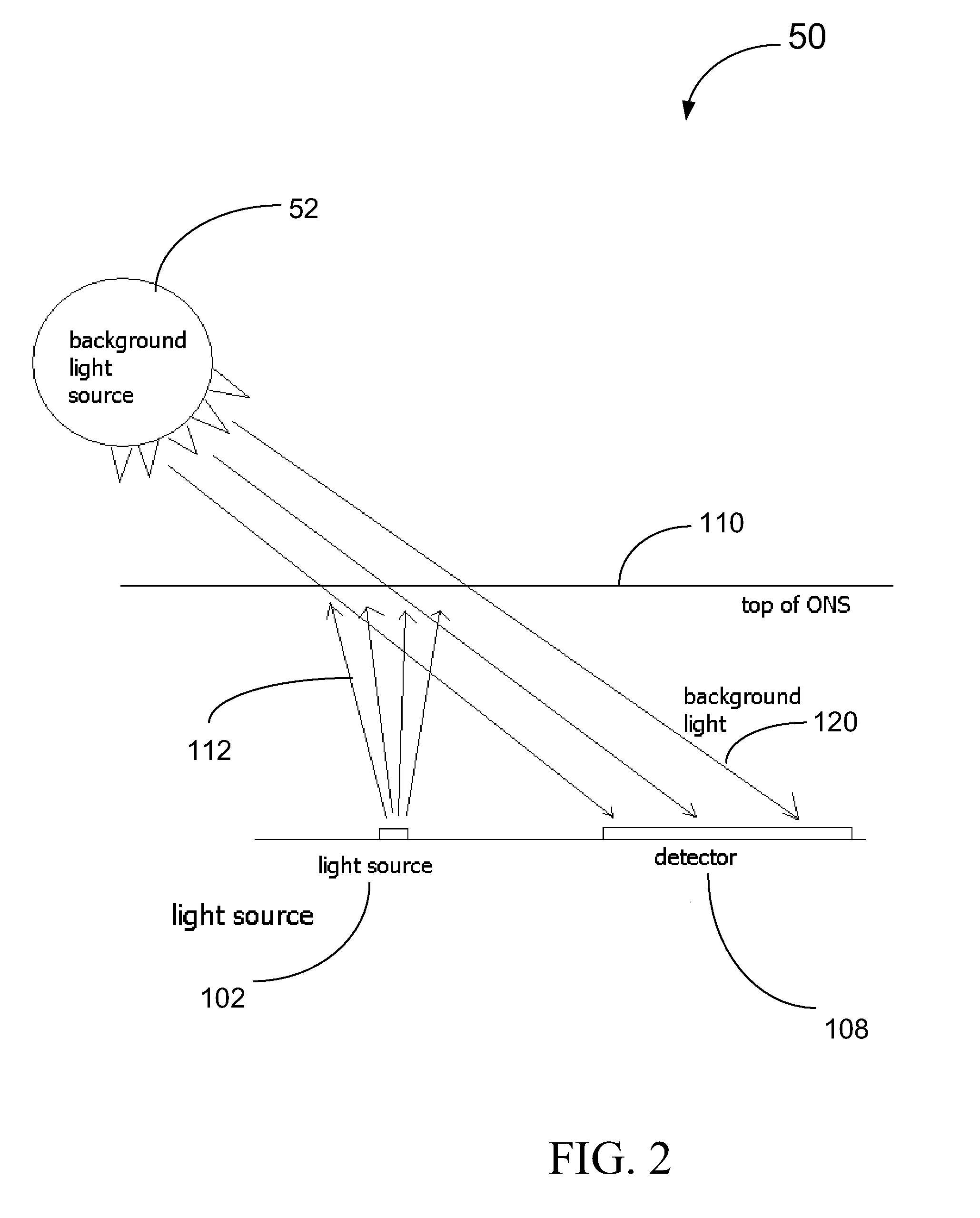
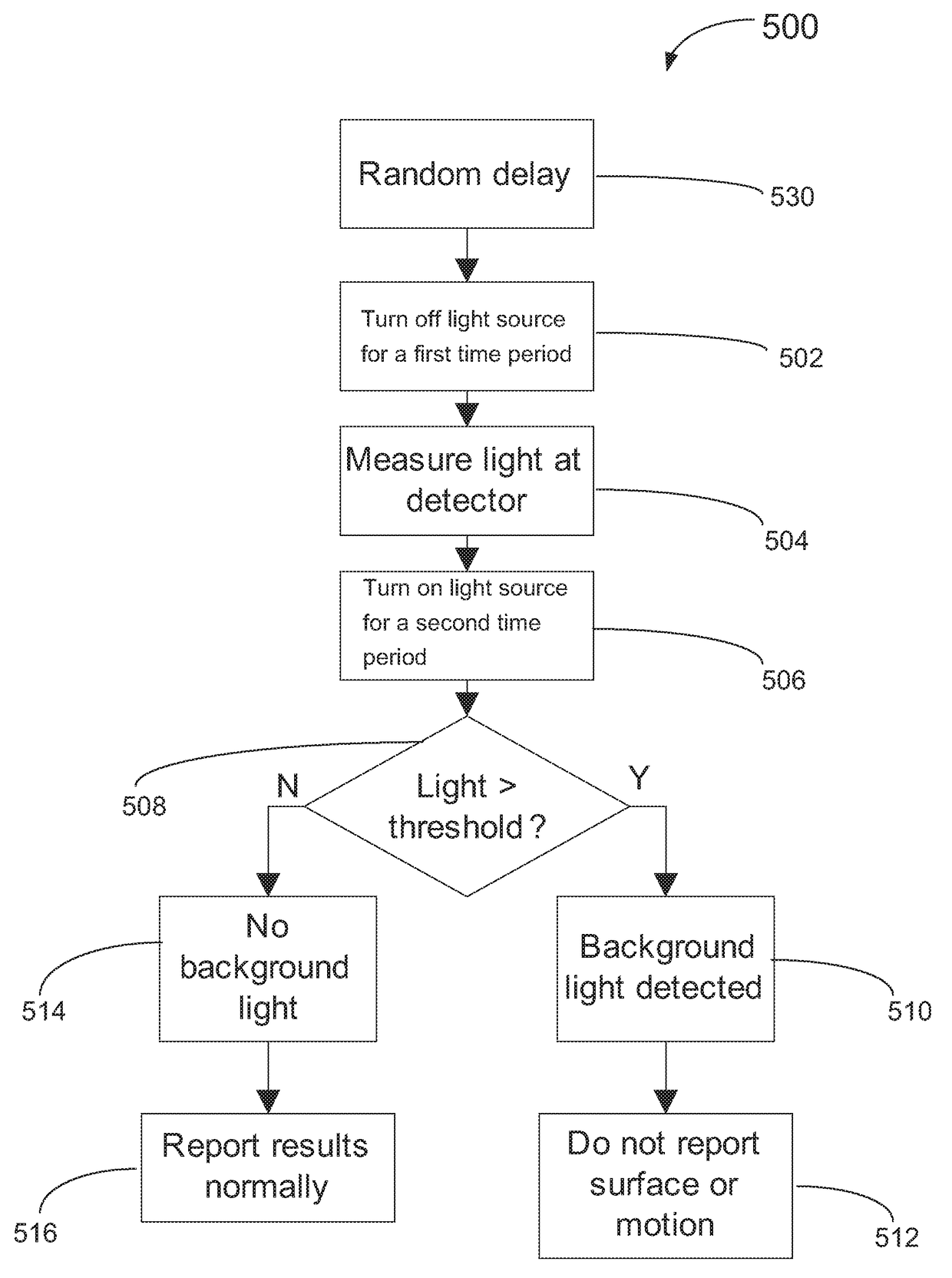
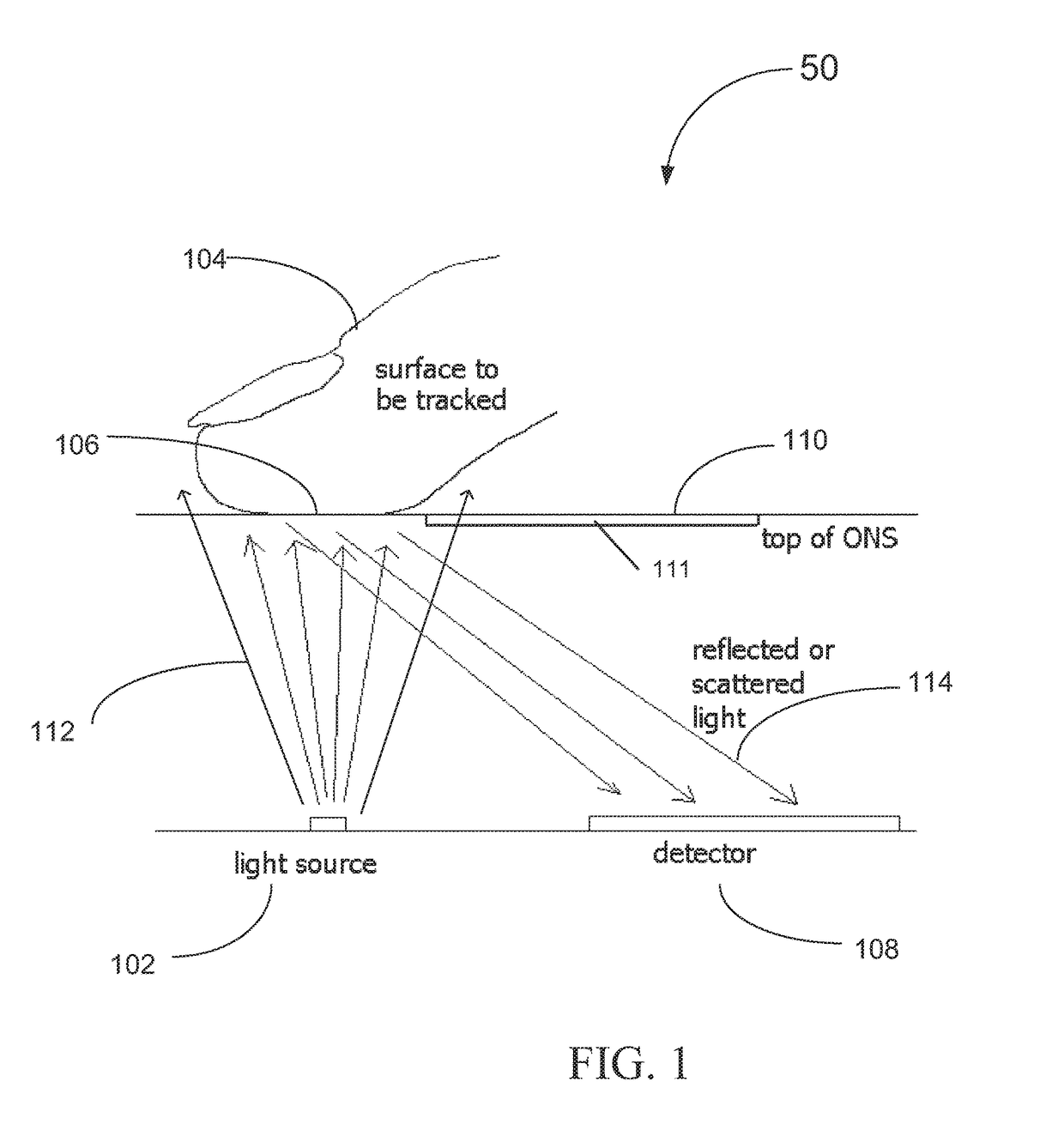
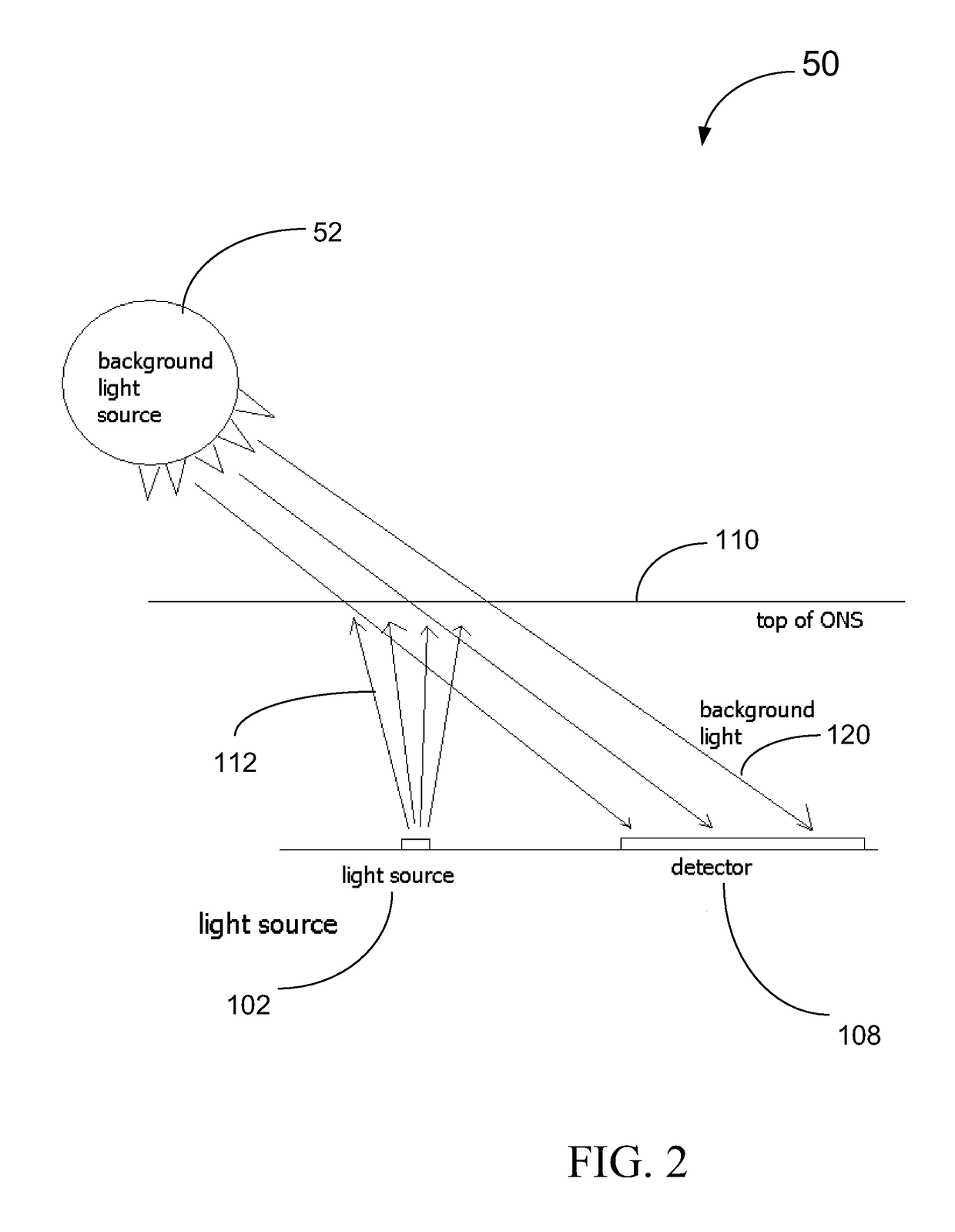
Background Light Detection for Optical Navigation Systems
ActiveUS20160117048A1Complicates industrial designImprove performanceDigital data processing detailsEnergy efficient computingFalse detectionLight induced
A method of operating an optical navigation system which includes disabling a light source to measure the ambient or external light level, comparing the measurement to a threshold level to determine whether the ambient light would cause false detection and light induced motion, and adjusting sensing parameter(s) to mitigate the effect of the ambient light.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
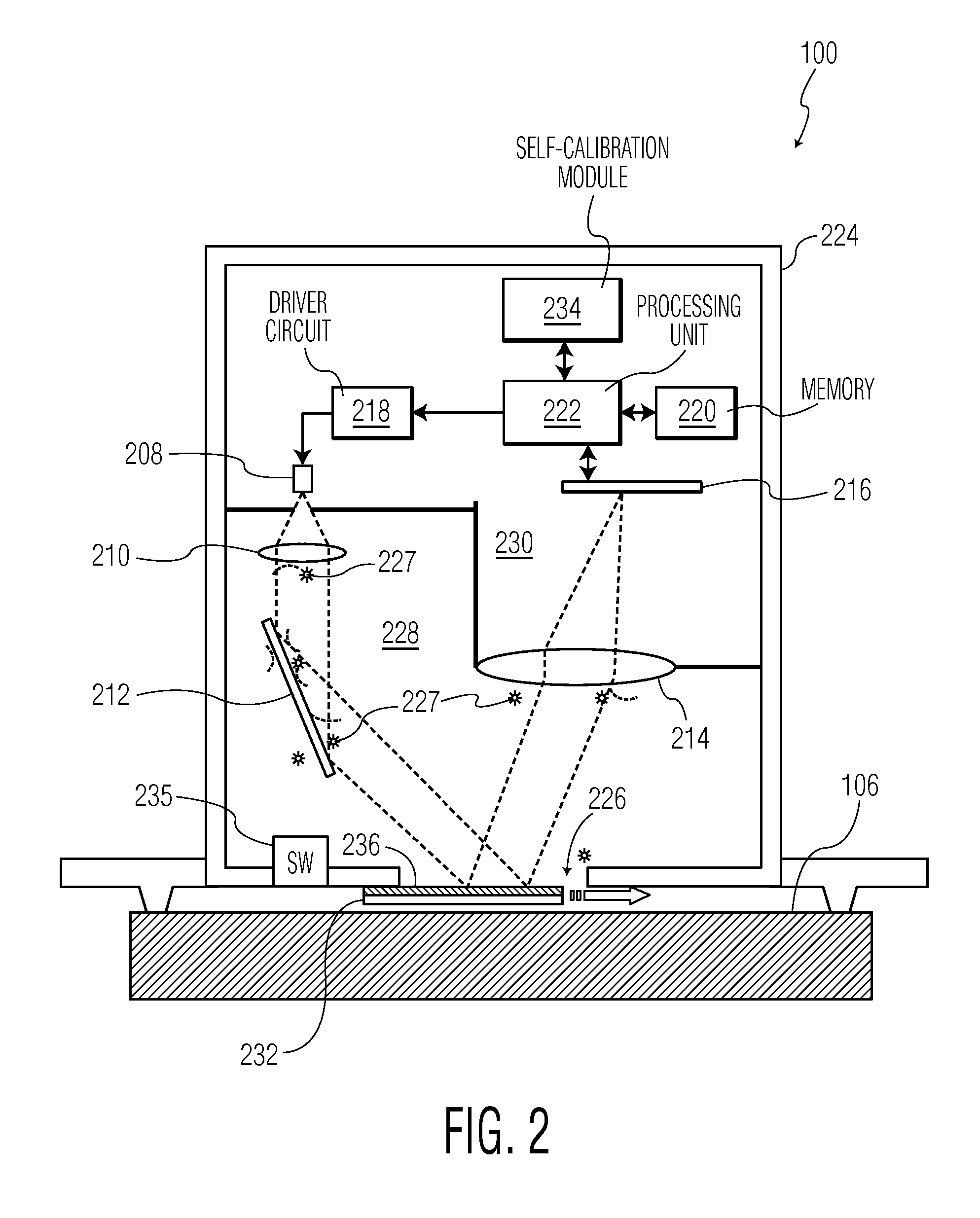
Optical navigation system and method for performing self-calibration on the system using a calibration cover
An optical navigation system and method for performing self-calibration on the system uses captured frames of image data of an interior surface of a calibration cover of the system to detect a performance-related change of the system. In response to the detected performance-related change, a predefined procedure is then initiated.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
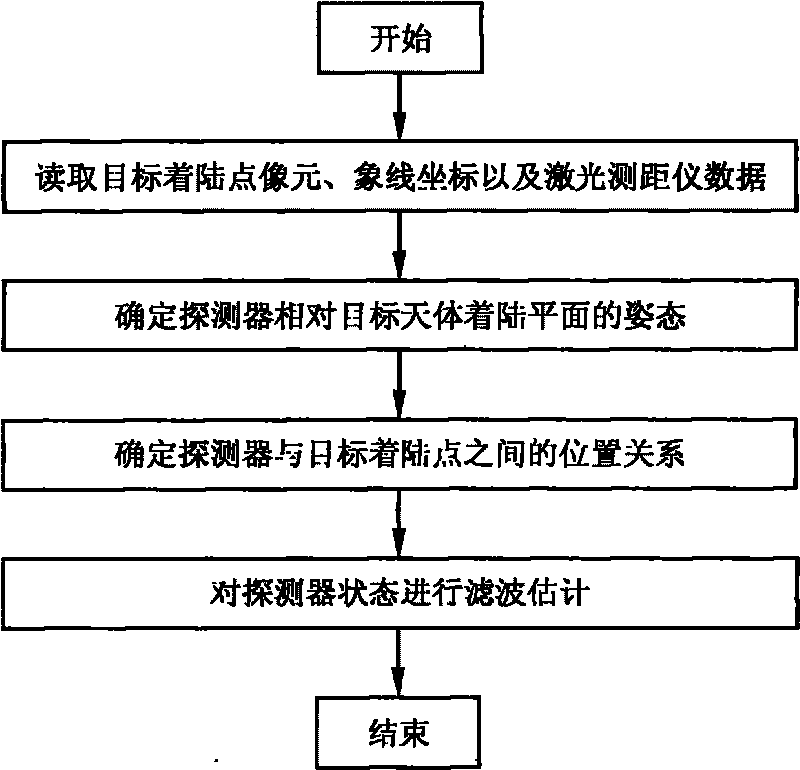
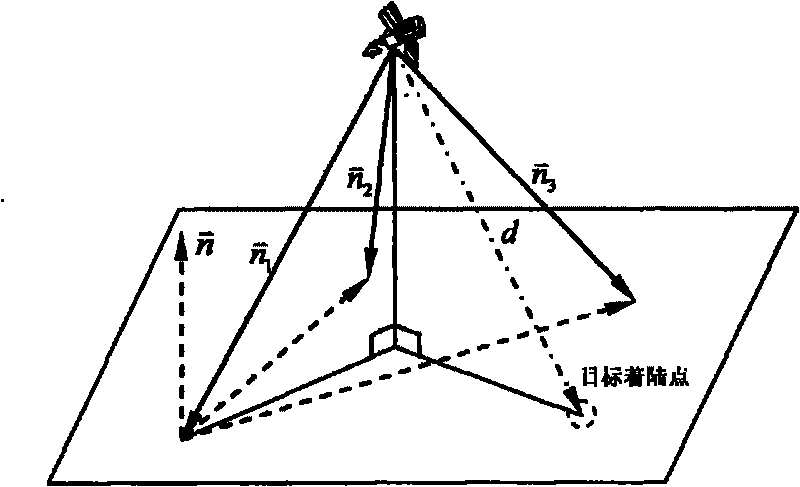
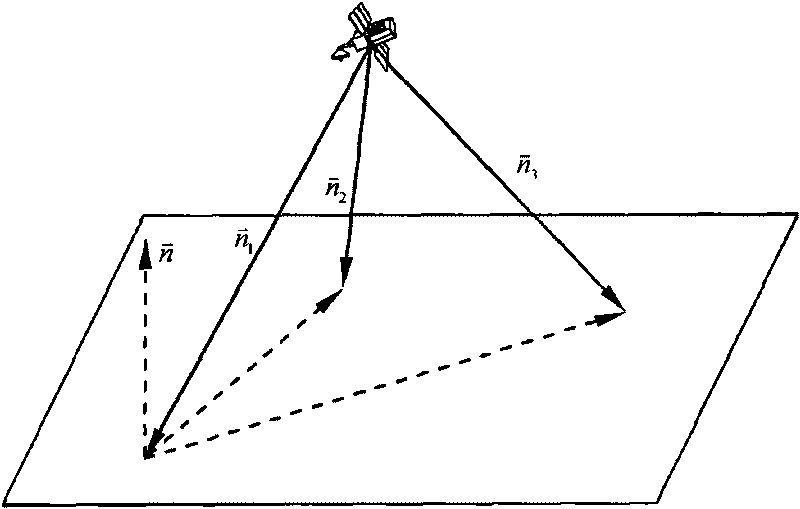
Autonomous optical navigation method for soft landing for deep space probe
InactiveCN101762273AHigh precision determinationImprove reliabilityInstruments for comonautical navigationPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryAviationLaser ranging
The invention relates to an autonomous optical navigation method for soft landing of a deep space probe, and belongs to the field of space flight and aviation. The autonomous optical navigation method comprises the following steps: firstly, reading a corresponding pixel and a pixel line coordinate of a target landing point on an image plane photographed by an optical navigation camera, and the distance of the probe from a landing plane in three laser ranging device mounting directions; secondly, determining the posture of the probe relative to a landing plane of a target astronomical body by using the obtained distance measured by the three laser ranging devices and the mounting azimuth angle and pitch angle of the known ranging device; thirdly, determining the position relationship between the probe and the target landing point by using the obtained distance di measured by the three laser ranging devices and the pixel and the pixel line coordinate of the target landing point; and finally, performing filter estimation on the position, speed, posture and angular speed information of the probe relative to the landing area. The autonomous optical navigation method for the soft landing of the deep space probe has the characteristics of high reliability, low cost and strong real-time, and can highly precisely determine the position and posture of the probe relative to the target landing point.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Optical navigation systems and methods for background light detection and avoiding false detection and auto-movement
ActiveUS9927915B2Complicates industrial designImprove performancePower supply for data processingSingle machine energy consumption reductionNavigation systemFalse detection
A method of operating an optical navigation system which includes disabling a light source to measure the ambient or external light level, comparing the measurement to a threshold level to determine whether the ambient light would cause false detection and light induced motion, and adjusting sensing parameter(s) to mitigate the effect of the ambient light.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
Navigation system and method of minimally invasive surgery
ActiveCN106890025AReduce surgical riskSurgical navigation systemsComputer-aided planning/modellingEntry pointNavigation system
The invention discloses a navigation system and method of a minimally invasive surgery. The navigation system comprises a composite endoscope body, a spatial positioning device and a surgery navigation server. The method comprises the steps that preoperative diagnostic images are subjected to three-dimensional model reconstruction and preoperative planning before navigation is performed; during the navigation, three-dimensional optical image signals and two-dimensional ultrasonic image signals of intraoperative organs and tissue are simultaneously acquired and three-dimensional reconstruction is performed, a three-dimensional model of the preoperative diagnostic images with preoperative planning information is subjected to organ and tissue deformation correction, and a three-dimensional optical model and a dynamic preoperative registration model are subjected to registration and fusion, so that the functions of optical navigation and ultrasonic navigation are simultaneously achieved, the intraoperative optical navigation can be switched to the intraoperative ultrasonic navigation continuously in real time, and a key position point, an optimum surgical entry point and an internal travel path of the intraoperative organs and tissue are continuously achieved in all dimensions from surfaces of organs and tissue to inner structure of organs and tissue. The navigation system and method of the minimally invasive surgery overcomes the defect of relatively single and discontinuous functions existing in the prior art, and is capable of lowering surgical risks.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Saccadic motion sensing
Owner:THORPE WILLIAM P +1
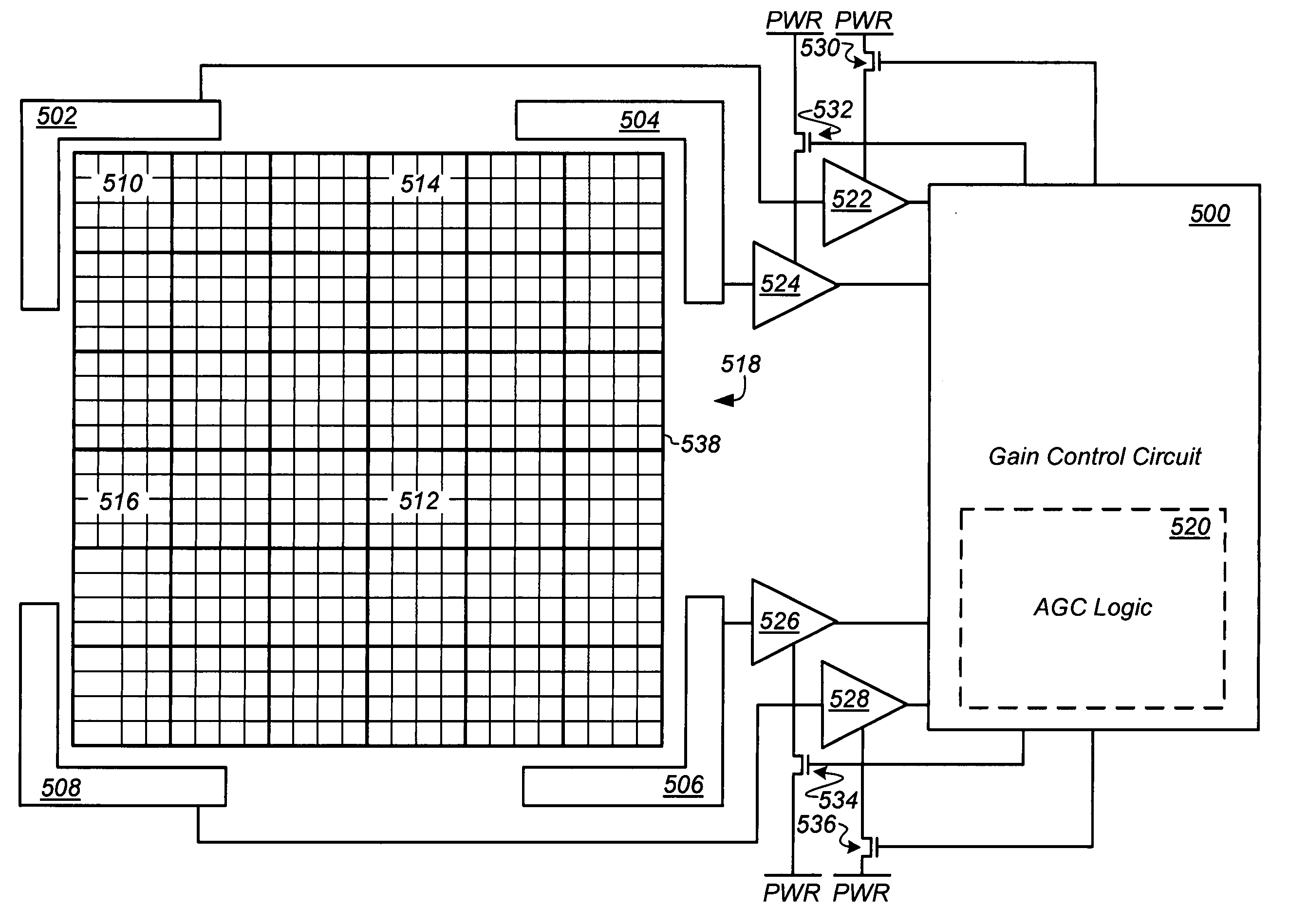
Circuit and method for reducing power consumption in an optical navigation system having redundant arrays
ActiveUS7297912B1Reduce power consumptionPhotometry using reference valueSolid-state devicesUltimate tensile strengthControl circuit
A circuit and method are provided for reducing power consumption in an optical navigation system for use in an input device to sense displacement of the device relative to a surface. Generally, the system includes: (i) an optical sensor having at least first and second arrays of photosensitive elements; (ii) imaging optics to map an illuminated portion of the surface to the optical sensor; (iii) a signal processor including a first and second sensor circuits coupled to the respective first and second arrays to generate from each array a set of signals in response to motion of light received thereon; and (iv) a control circuit capable of independently switching power to the sensor circuits. In one embodiment, the control circuit powers down one sensor circuit when the strength of the set of signals from the other is greater than a predetermined minimum thereby maintaining device performance. Other embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
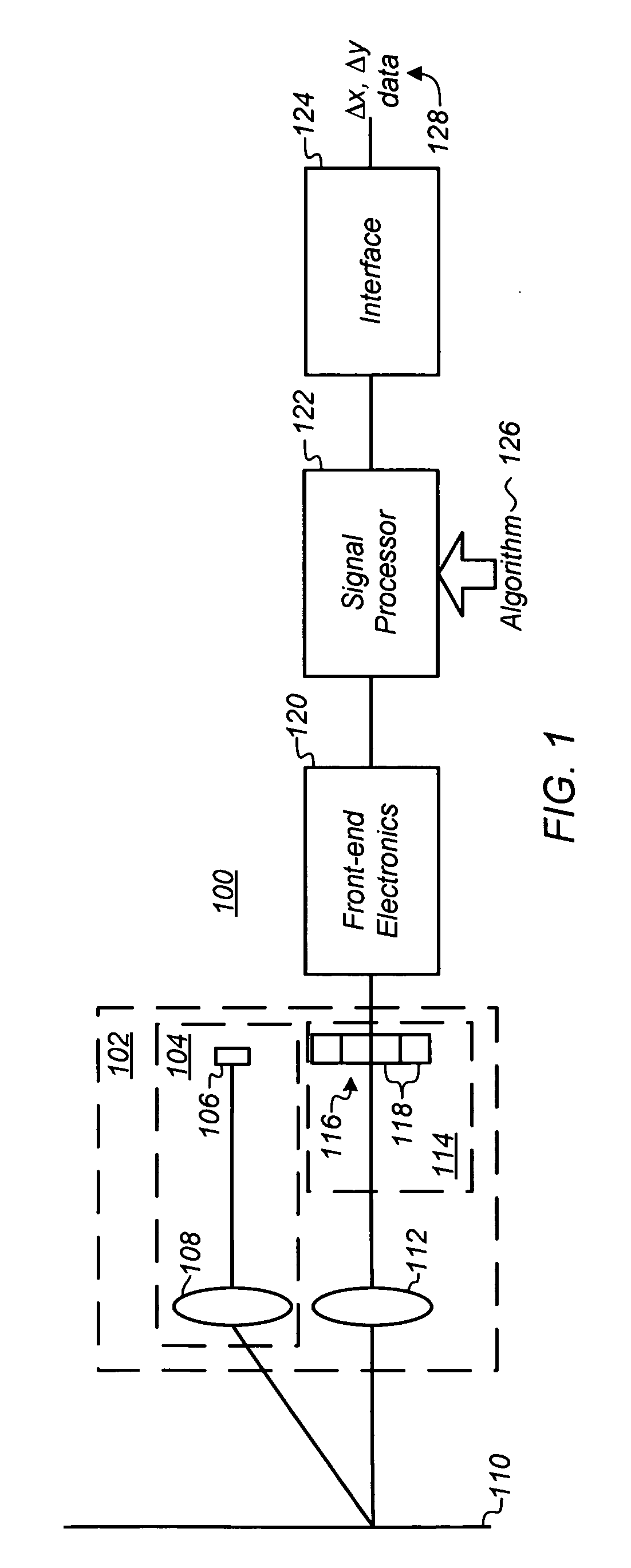
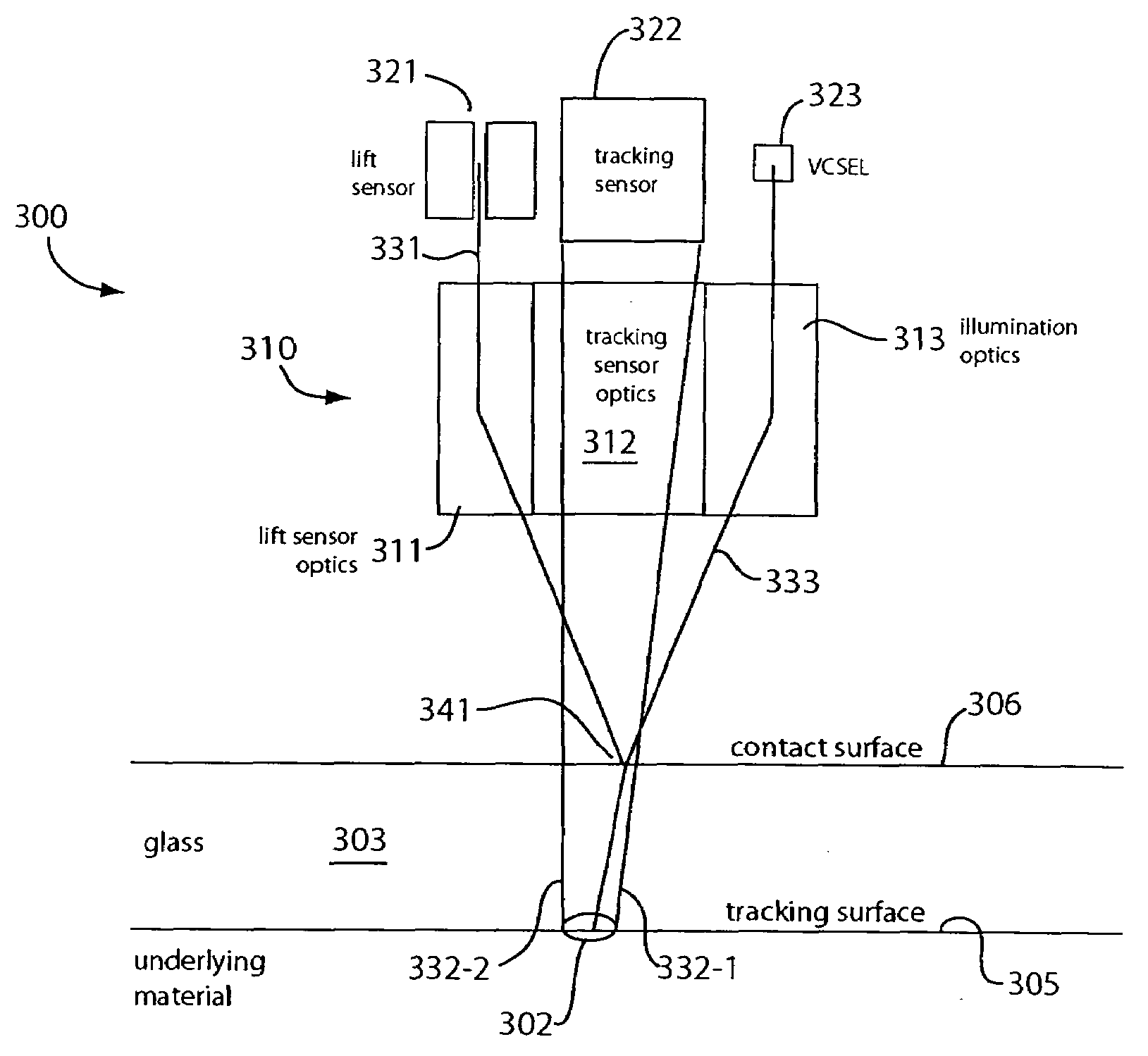
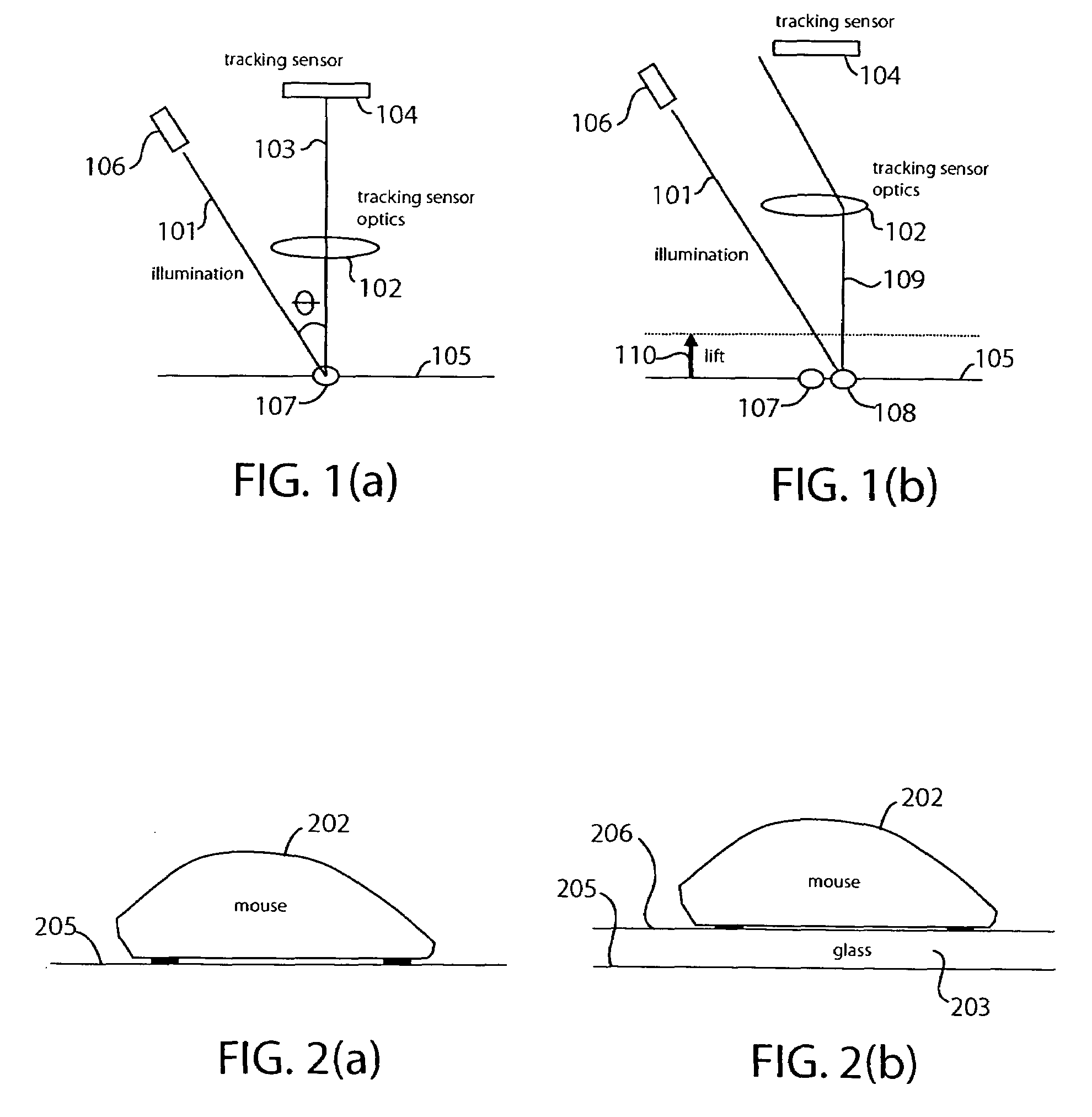
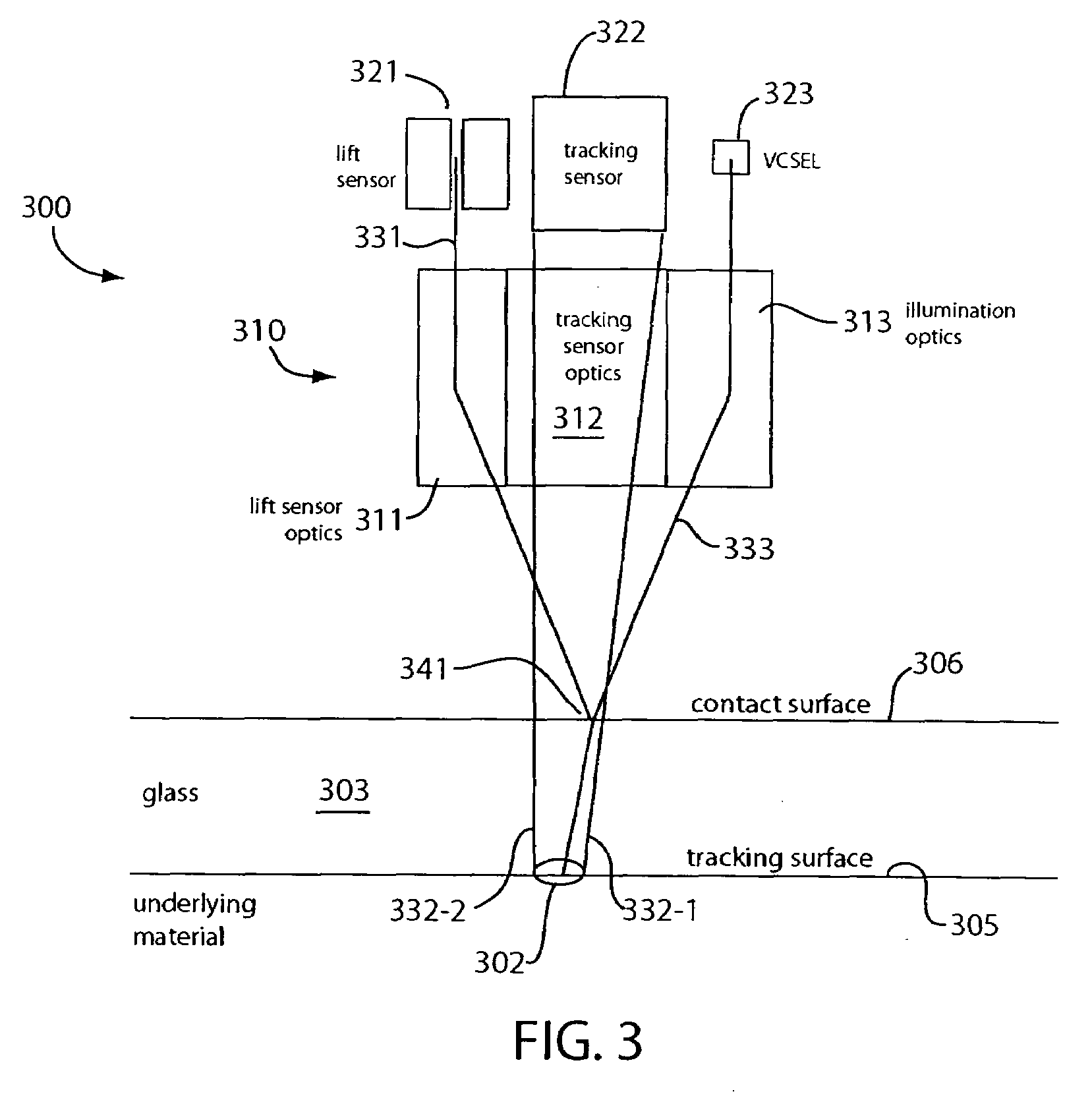
Optical navigation sensor with tracking and lift detection for optically transparent contact surfaces
InactiveUS20070291001A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingEngineeringSpecular reflection
In one embodiment, an optical navigation sensor for a computer mouse is designed to be operable on an optically transparent material. The optically transparent material may include a contact surface on which the mouse sits during normal operation. An optically rough tracking surface is provided below the contact surface. The mouse includes a light source that illuminates an area on the contact surface and an area on the tracking surface. The mouse may include a tracking sensor onto which the illuminated area on the tracking surface is imaged to detect mouse displacement. The mouse may also include a lift sensor that picks up specular light reflected from the illuminated area on the contact surface to generate lift information indicative of whether the mouse has been lifted off the contact surface. Tracking of the mouse displacement may be qualified with the lift information.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Optical navigation system and method for reducing the power consumption of the system
ActiveUS20070262243A1Reduce power consumptionReduce in quantityDigital data processing detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansTarget surfaceComputer science
An optical navigation system and method for reducing the power consumption of the system uses a surface quality value of a captured image frame of a target surface to selectively reduce the number of photosensitive pixel elements to be used to capture a subsequent image frame.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
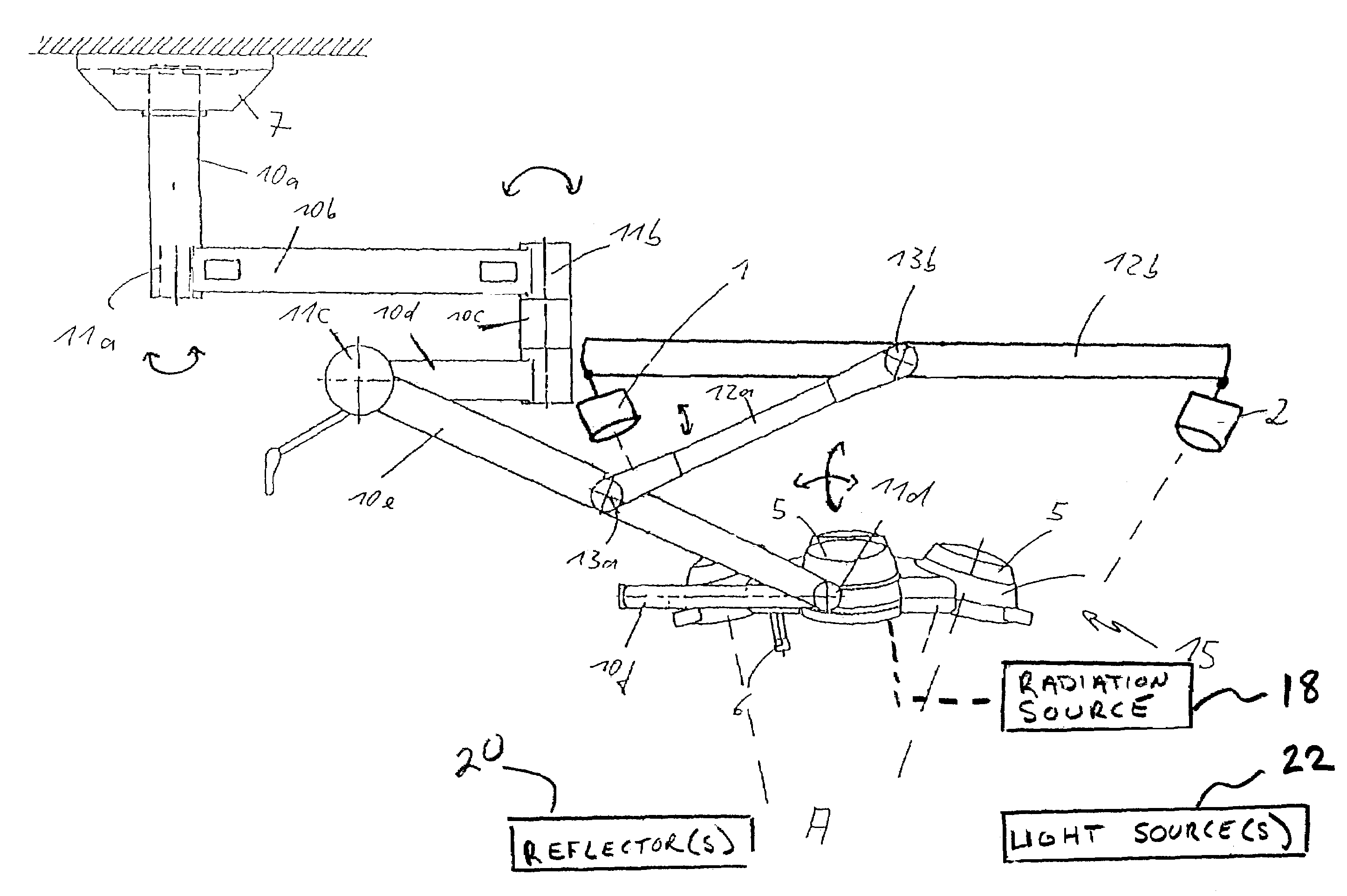
Operation lamp with camera system for 3D referencing
ActiveUS7224472B2Easy to adjustEasy to operateMechanical apparatusTreatment roomsThree-dimensional spaceCo ordinate
The invention relates to a system for the combined shadow-free illumination of a pre-definable area and for referencing three-dimensional spatial co-ordinates, and to an active or passive referencing system, each in particular for referencing surgical or medical instruments. The system is characterized in that at least two cameras and the light source (operation lamp) are held together such that the optical signals detected by the cameras, for referencing three-dimensional spatial co-ordinates in the area illuminated by the light source, can be evaluated. Since the field of view of the light source, in its conventional use, is not obscured or only negligibly obscured, this field of view can simultaneously be used for optical navigation by the cameras held together with the light source. In accordance with the invention, the cameras are automatically aligned optimally for optical navigation.The cameras can be rigidly or flexibly connected to the light source. The position and / or orientation of the cameras can be adjustable.
Owner:BRAINLAB
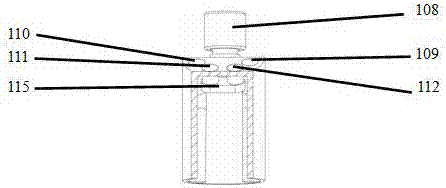
Optical projection encoder
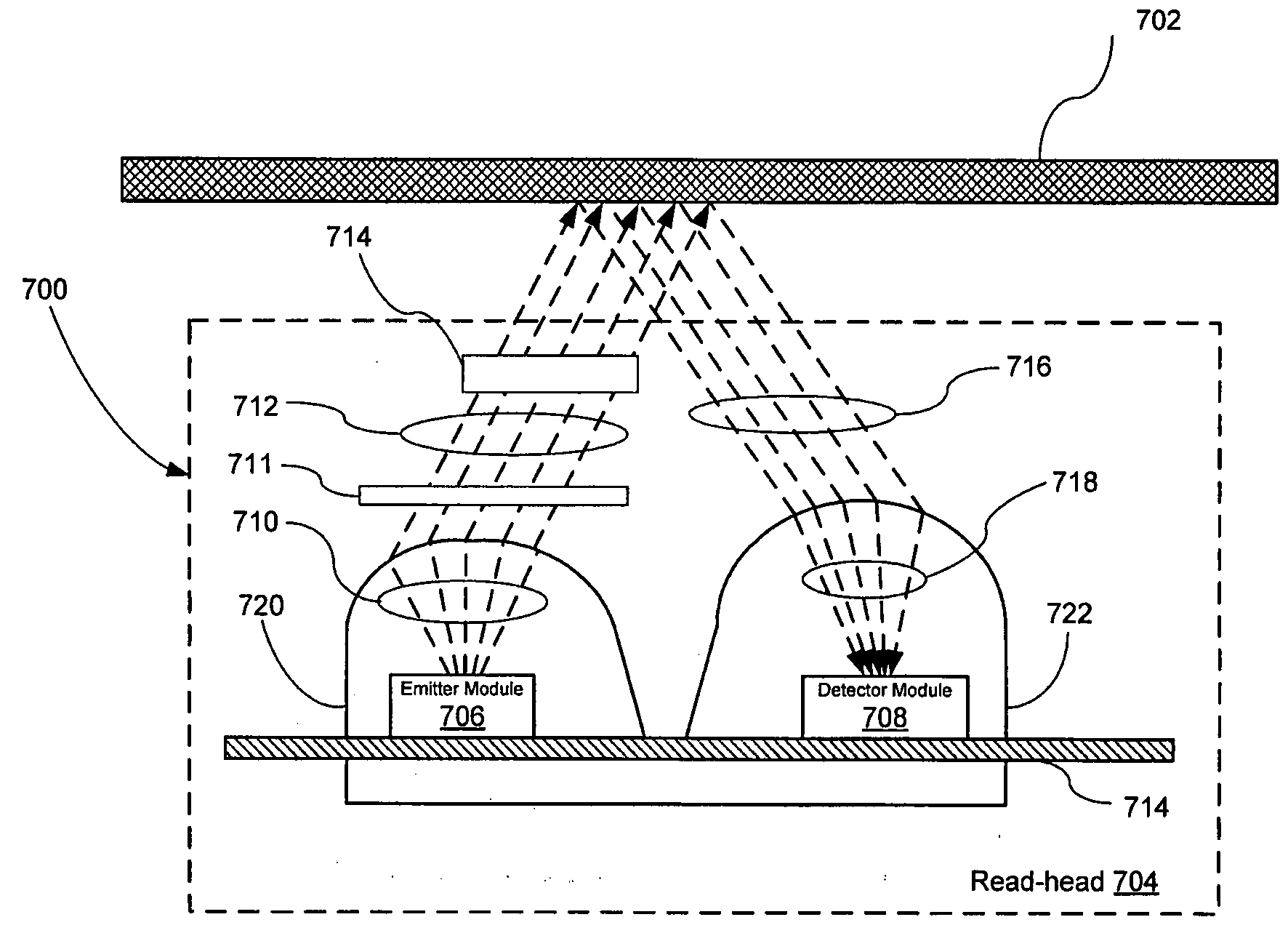
InactiveUS20070246646A1Material analysis by optical meansCounting objects on conveyorsOptical radiationEncoder
An Optical Projecting Encoder (“OPE”) having an emitter module for transmitting emitted optical radiation through a mask to a moving object, and a detector module for receiving reflected optical radiation from the moving object. The reflected optical radiation from the moving object may include a predetermined image cast by the mask and a surface texture image from the moving object. The OPE may include a transmissive layer covering both the emitter module and the detector module, where the transmissive layer covering the emitter module collimates the optical radiation from the emitter module, and the transmissive layer covering the detector module concentrates the optical radiation reflected from the moving object to the detector module. The detector module may include an optical navigation sensor that continuously acquires and compares predetermined images cast by the mask and surface texture images from the moving object.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
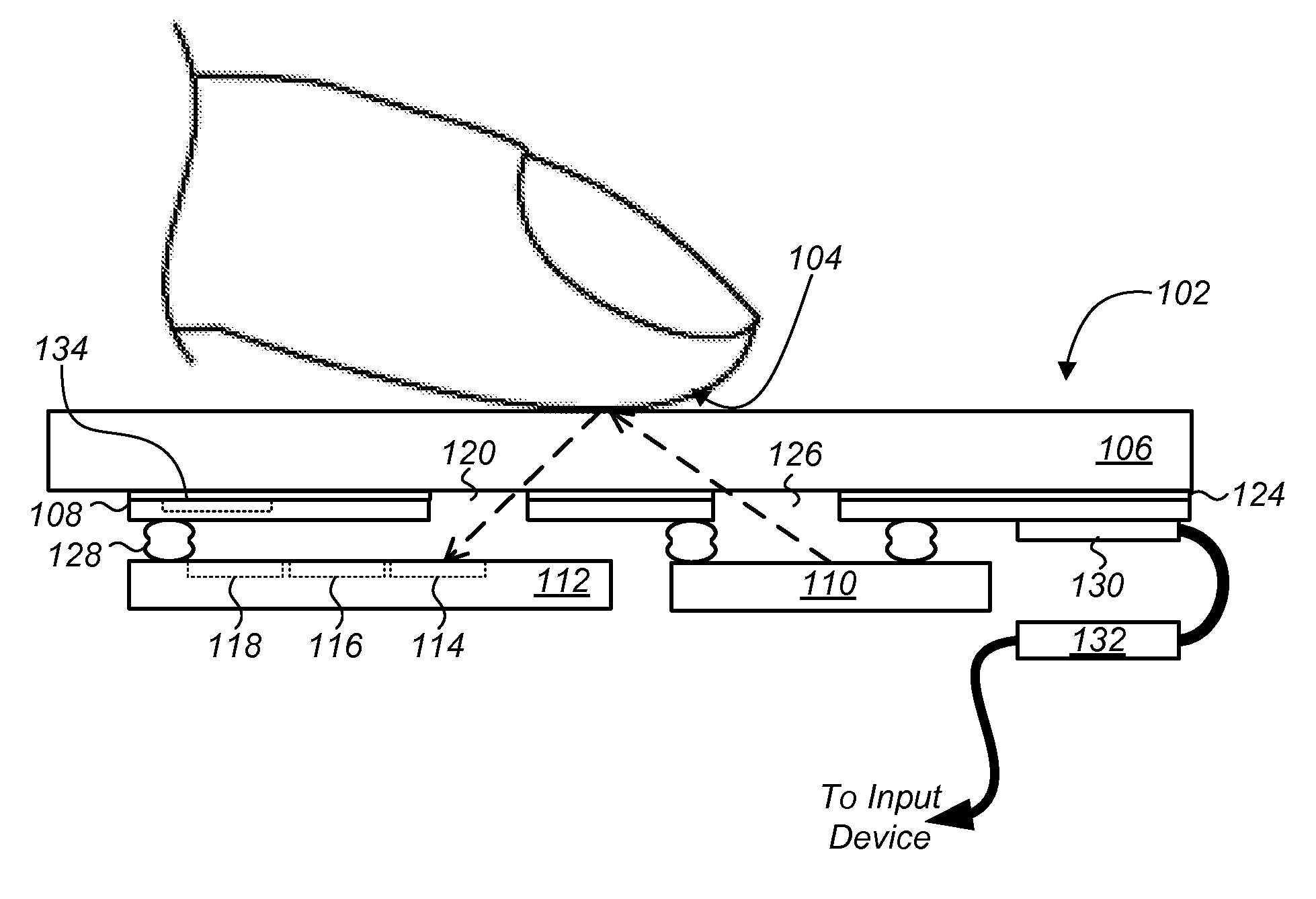
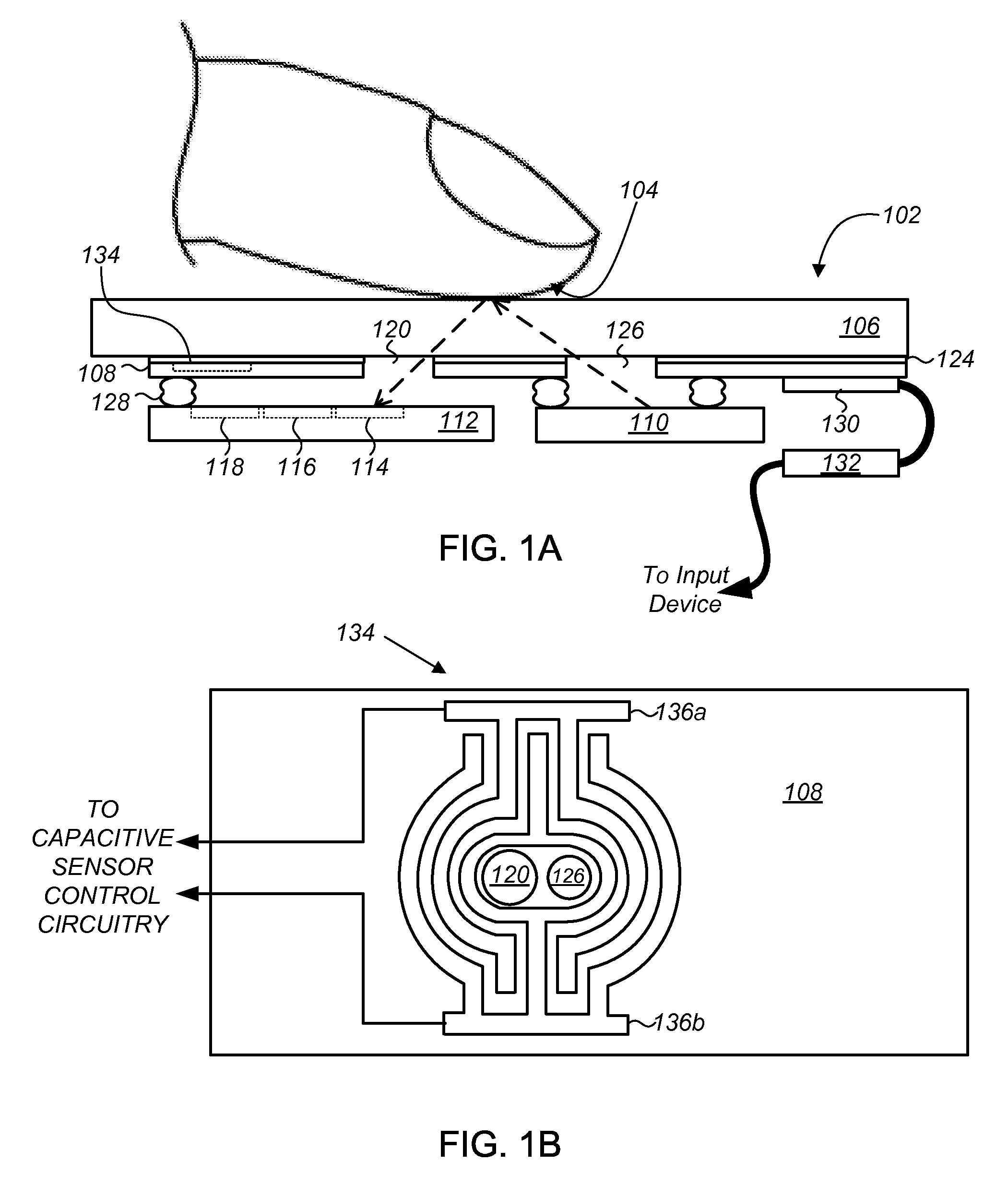
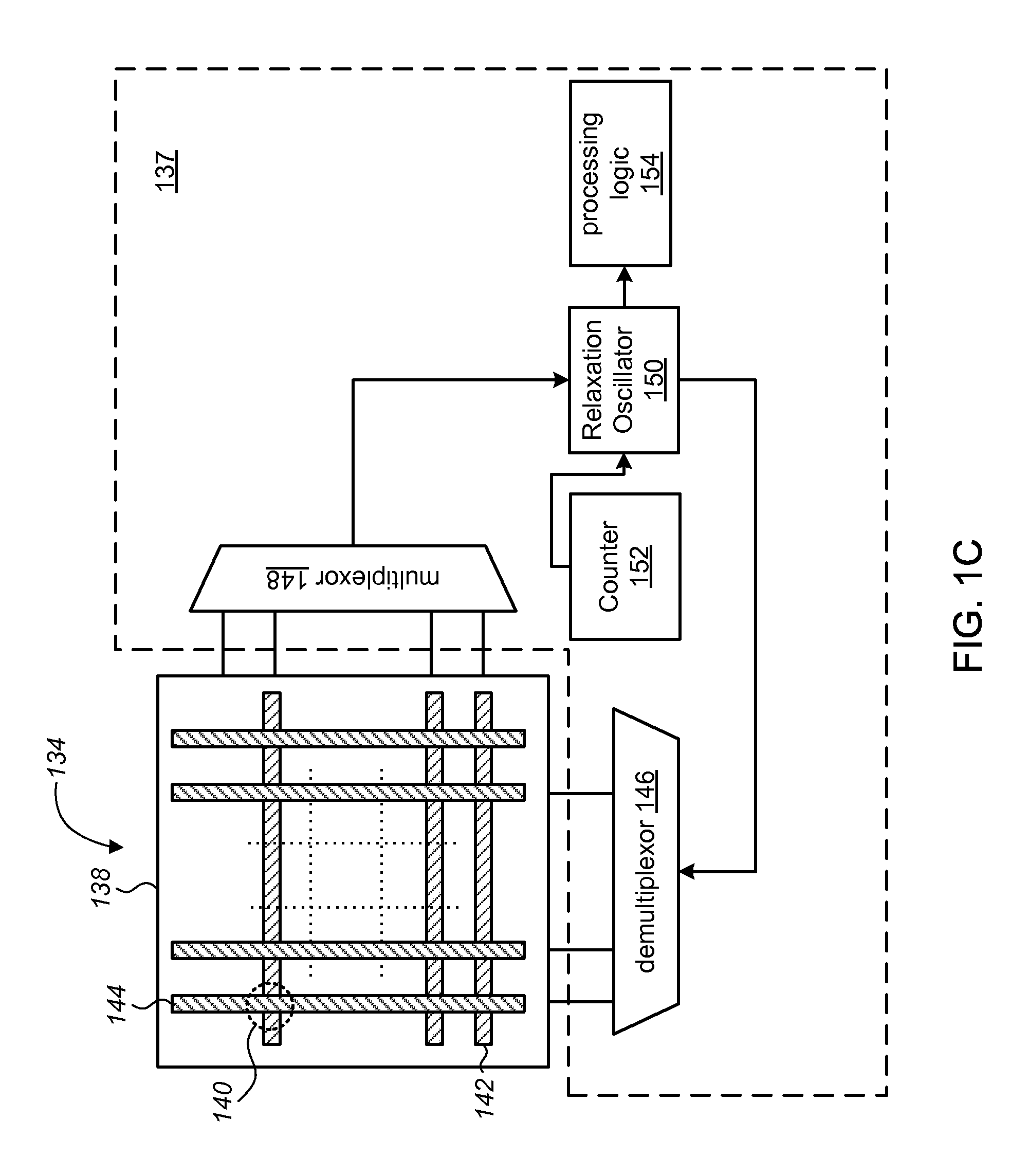
Optical navigation module with capacitive sensor
ActiveUS20120320385A1Using optical meansInput/output processes for data processingPhotovoltaic detectorsDetector array
Optical navigation modules and methods of operating the same to sense relative movement between the optical navigation module and a tracking surface are provided. In one embodiment, the optical navigation module comprises: (i) a light source to illuminate at least a portion of a surface relative to which the optical navigation module is moved; (ii) an integrated circuit (IC) including a photo-detector array (PDA) to detect a light pattern propagated onto the PDA from the surface, and a signal processor to translate changes in the light pattern propagated onto the PDA into data representing motion of the optical navigation module relative to the surface; and (iii) a substrate to which the light source and IC are mounted, the substrate including an aperture in a light path between the surface and the PDA. Other embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
Speckle based sensor for three dimensional navigation
Motion of a speckle pattern is employed to provide for navigation in three dimensions. Non-speckle optical navigation methods may also be used to provide for two dimensional surface navigation with speckle being used to provide for navigation in the third dimension.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
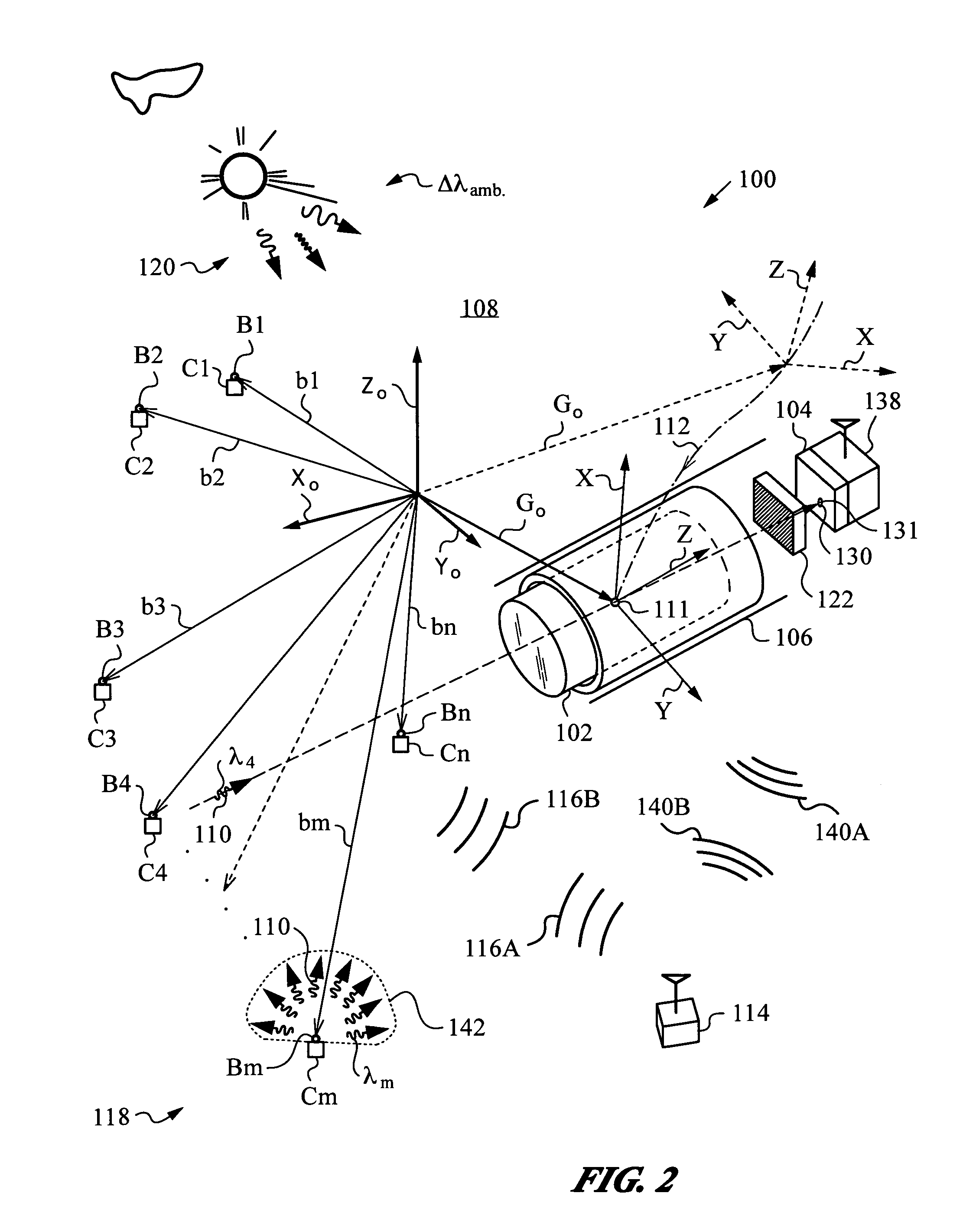
Optical navigation apparatus using fixed beacons and a centroid sensing device
The present invention relates to an optical navigation system for determining at least one parameter of a pose, which includes the position and orientation of an object in an environment. The optical navigation system uses a number of beacons affixed at known locations in the environment to provide electromagnetic radiation in a sequenced pattern. An on-board optic images the radiation from the beacons onto an on-board centroid sensing device to obtain an imaged distribution of the radiation on the on-board centroid sensing device. The centroid sensing device determines the centroid of the imaged distribution and provides centroid information to a navigation unit for determining at least one parameter of the pose of the object from the centroid. The navigation system is particularly well-suited for navigating hand-held objects.
Owner:ELECTRONICS SCRIPTING PRODS
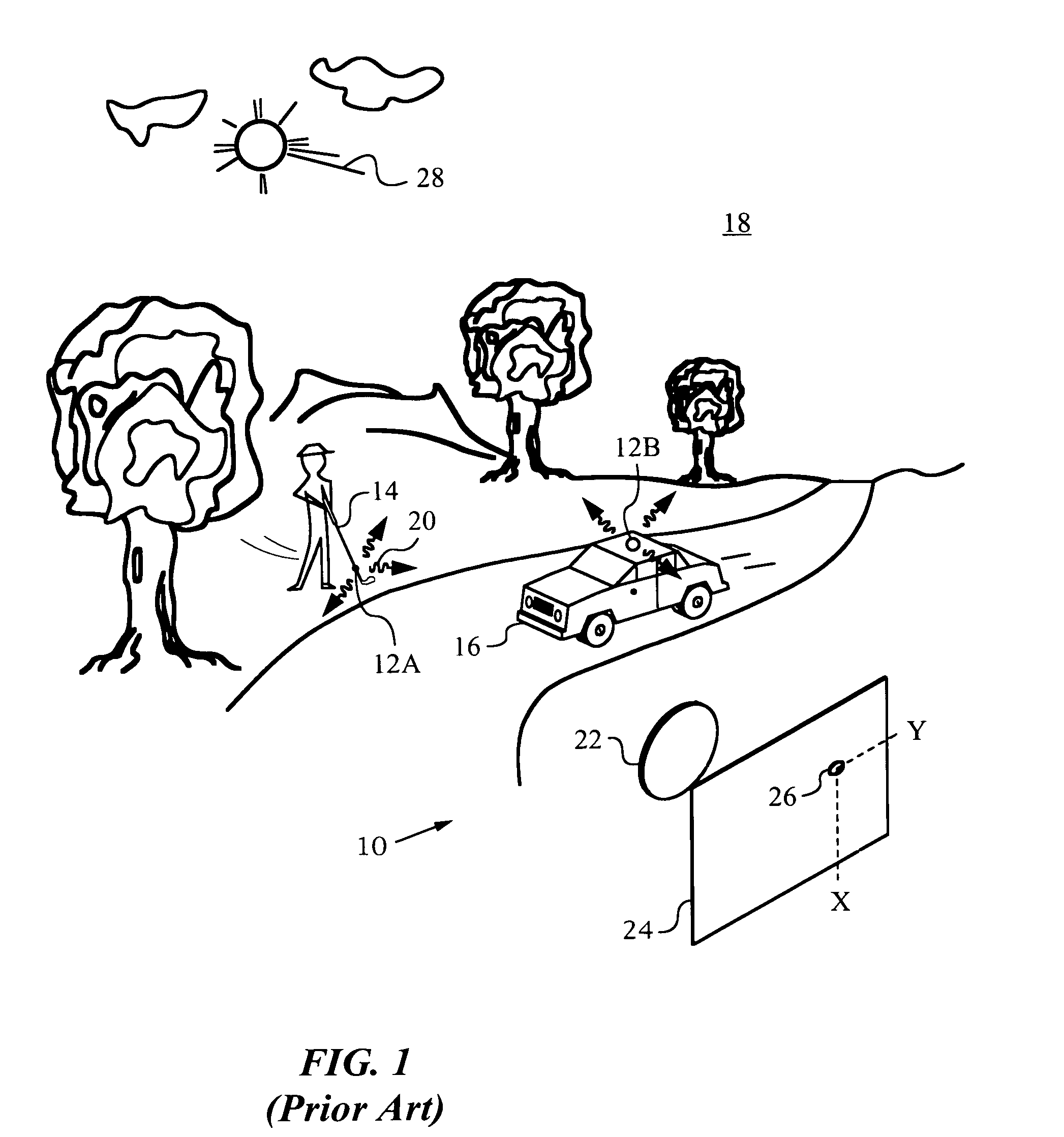
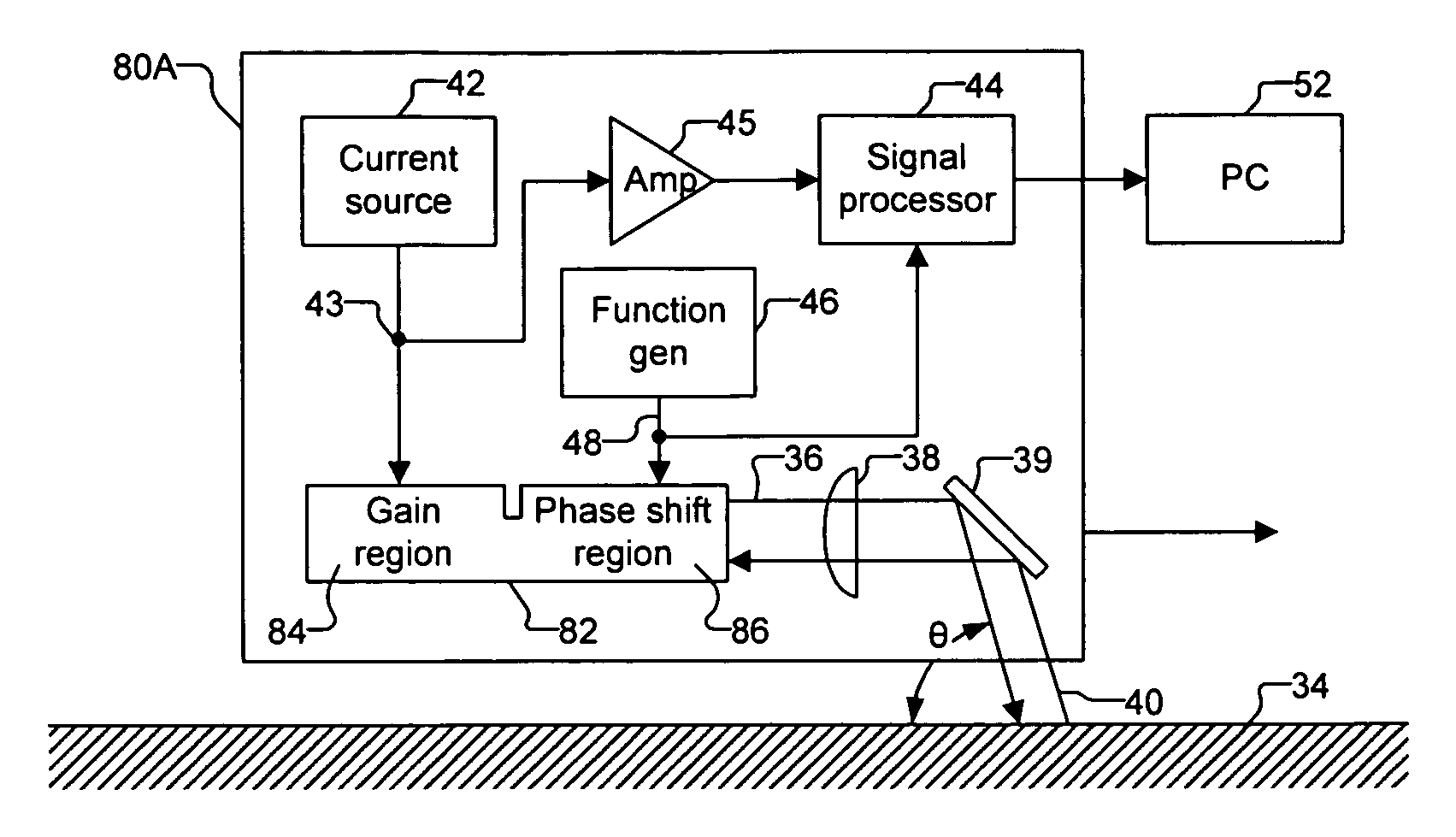
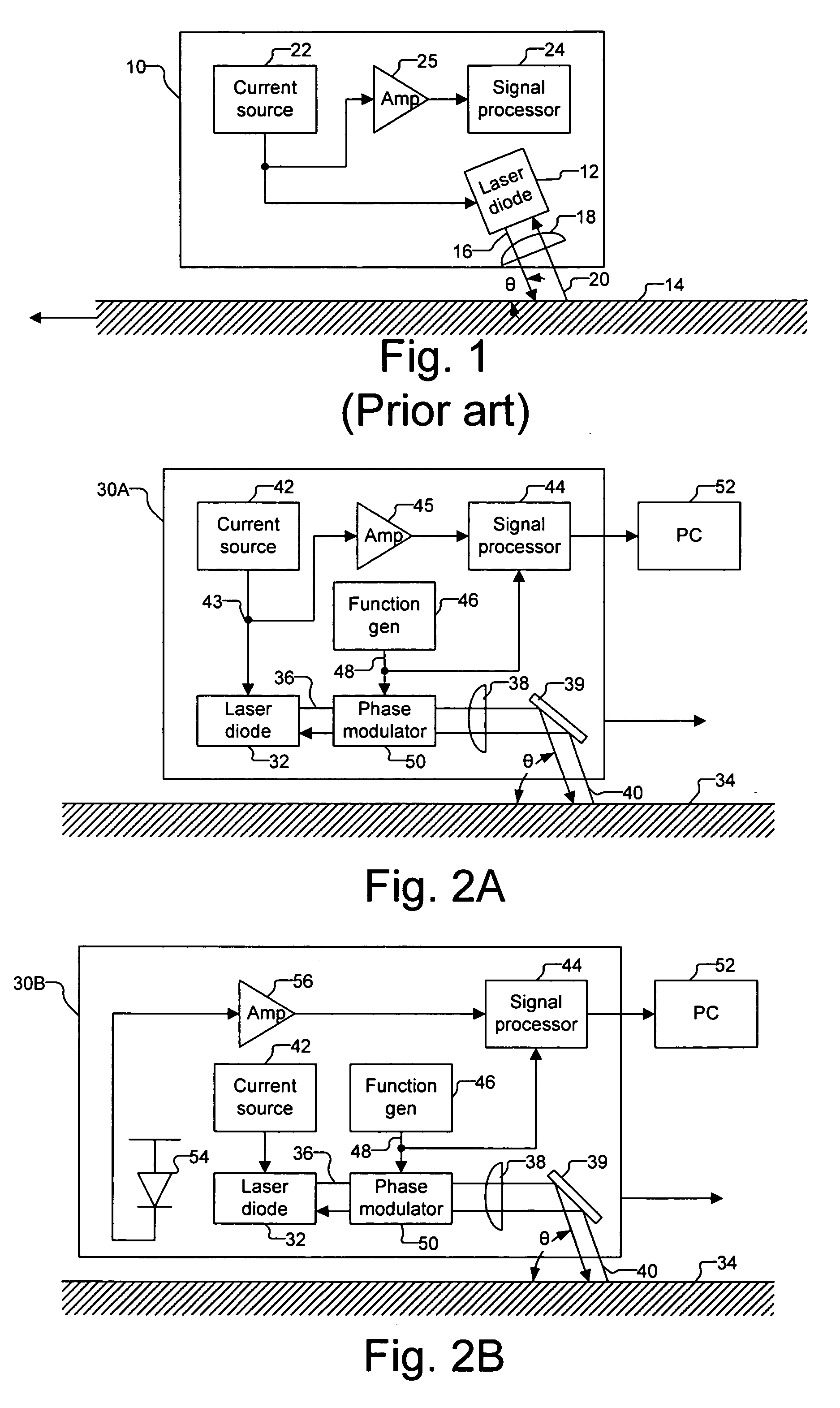
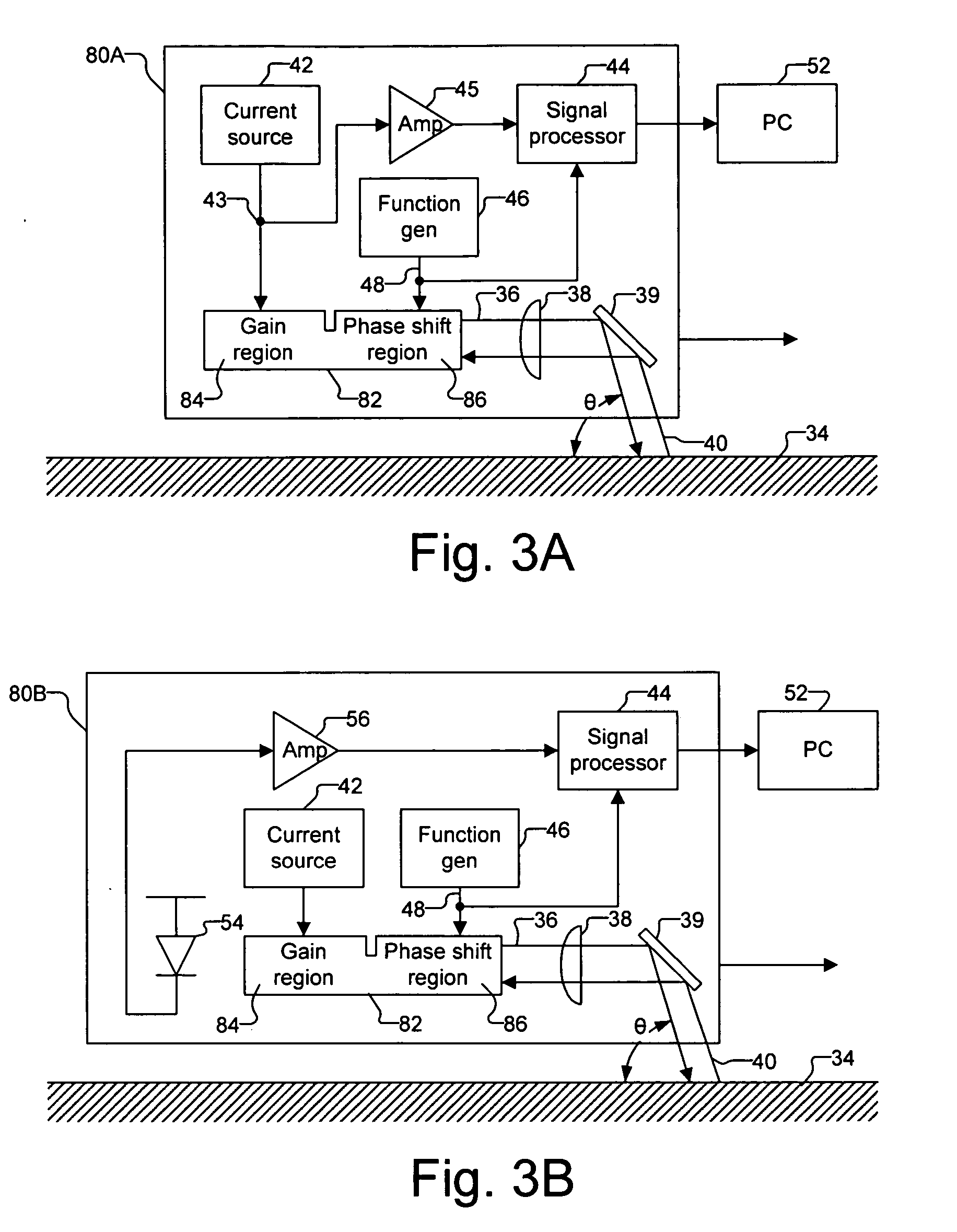
Optical navigation based on laser feedback or laser interferometry
A computer cursor control device includes (1) a light source generating light directed toward a stationary surface, (2) an optional phase modulator, (3) an optional function generator causing the phase modulator to periodically phase shift the light, and (4) a signal processor determining a direction in which the device is moving from a beat frequency or an asymmetry in the light intensity. Another computer cursor control device includes (1) an optical element combining reference and measurement beams to form a heterodyned beam, (2) a phase modulator located in an optical path of the reference beam or the measurement beam, (3) a function generator causing the phase modulator to phase shift the reference beam, and (4) a signal processor determining a direction in which the device is moving from a beat frequency of the heterodyned beam.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com