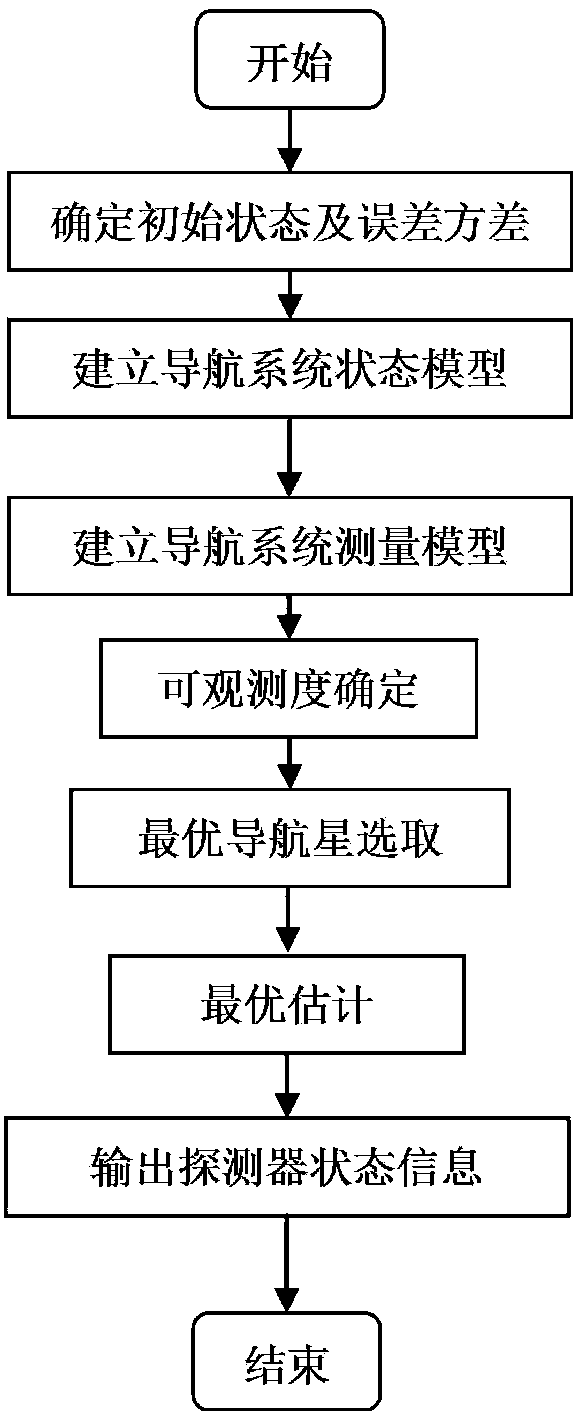
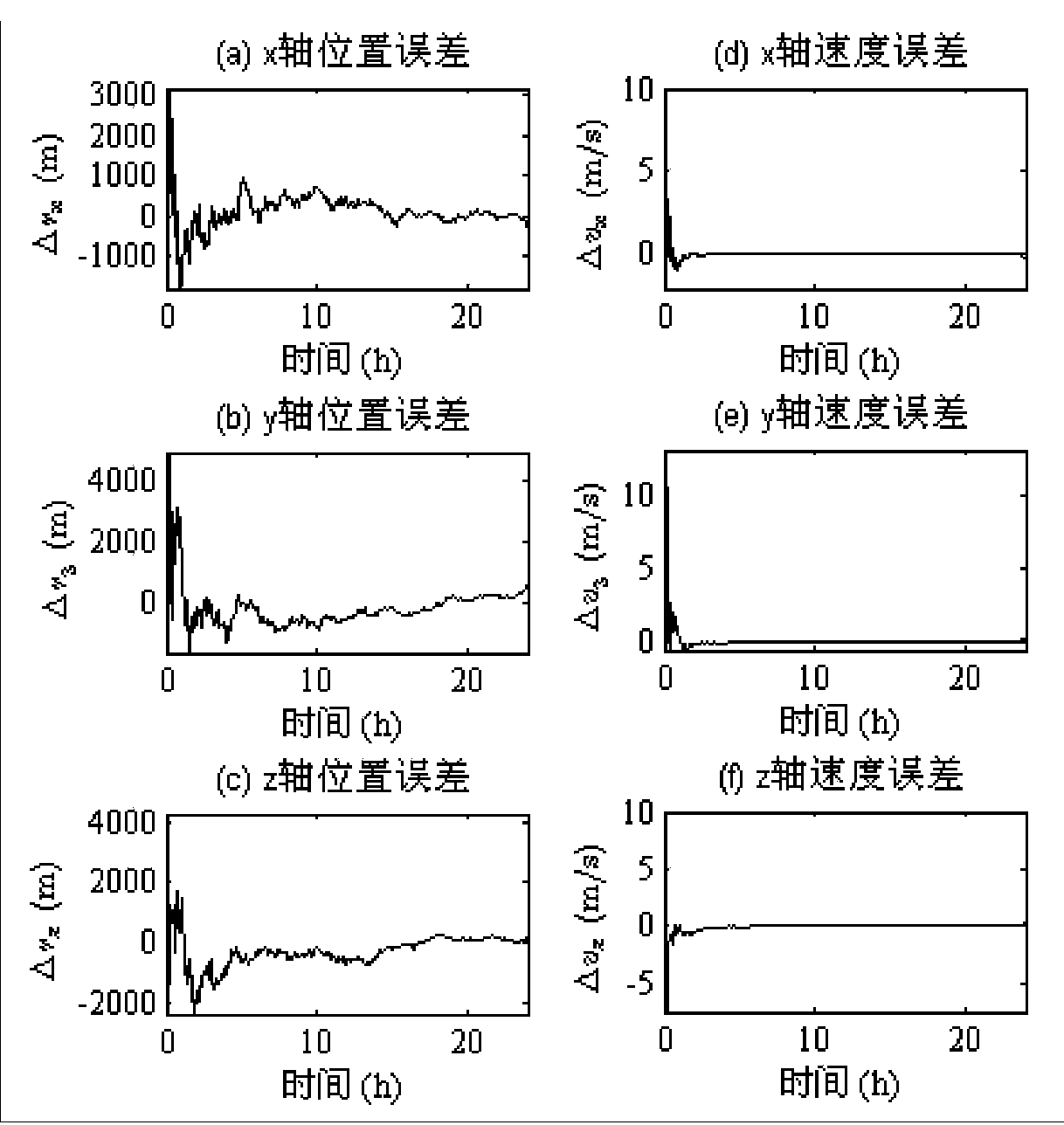
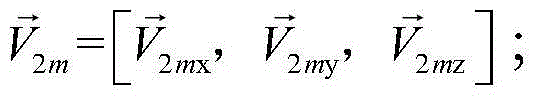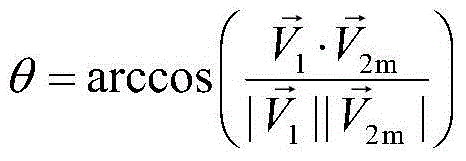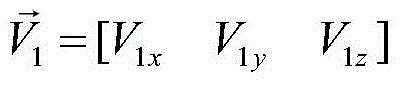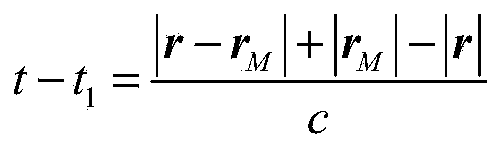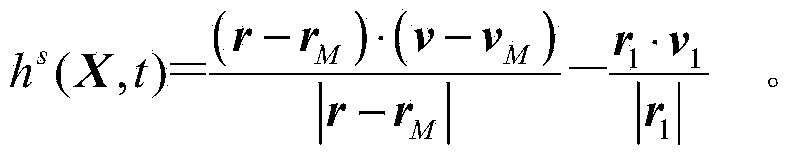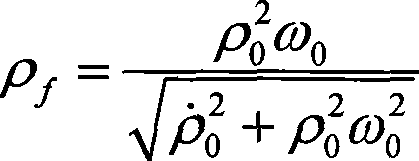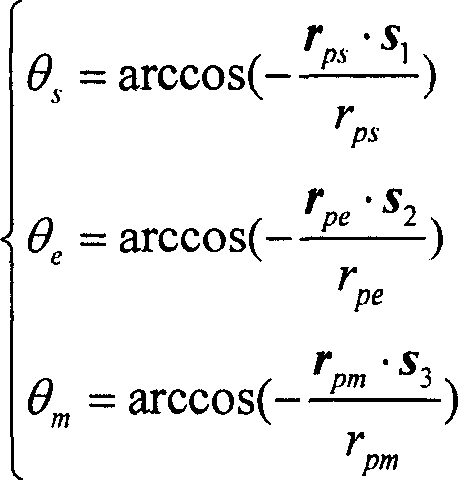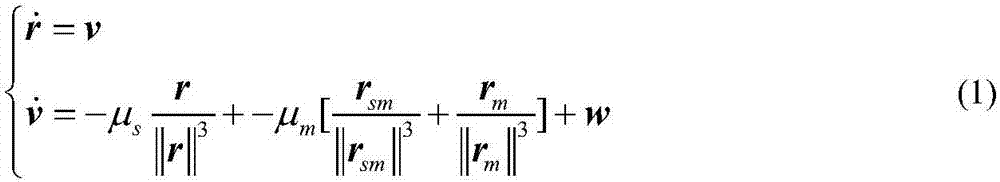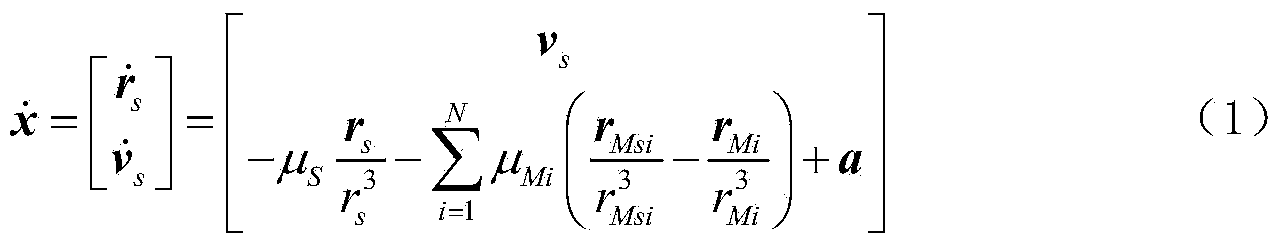Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
158 results about "Space probe" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A space probe is a robotic spacecraft that does not orbit Earth, but instead, explores further into outer space. A space probe may approach the Moon; travel through interplanetary space; flyby, orbit, or land on other planetary bodies; or enter interstellar space.. The space agencies of the USSR (now Russia and Ukraine), the United States, the European Union, Japan, China, India, and Israel ...
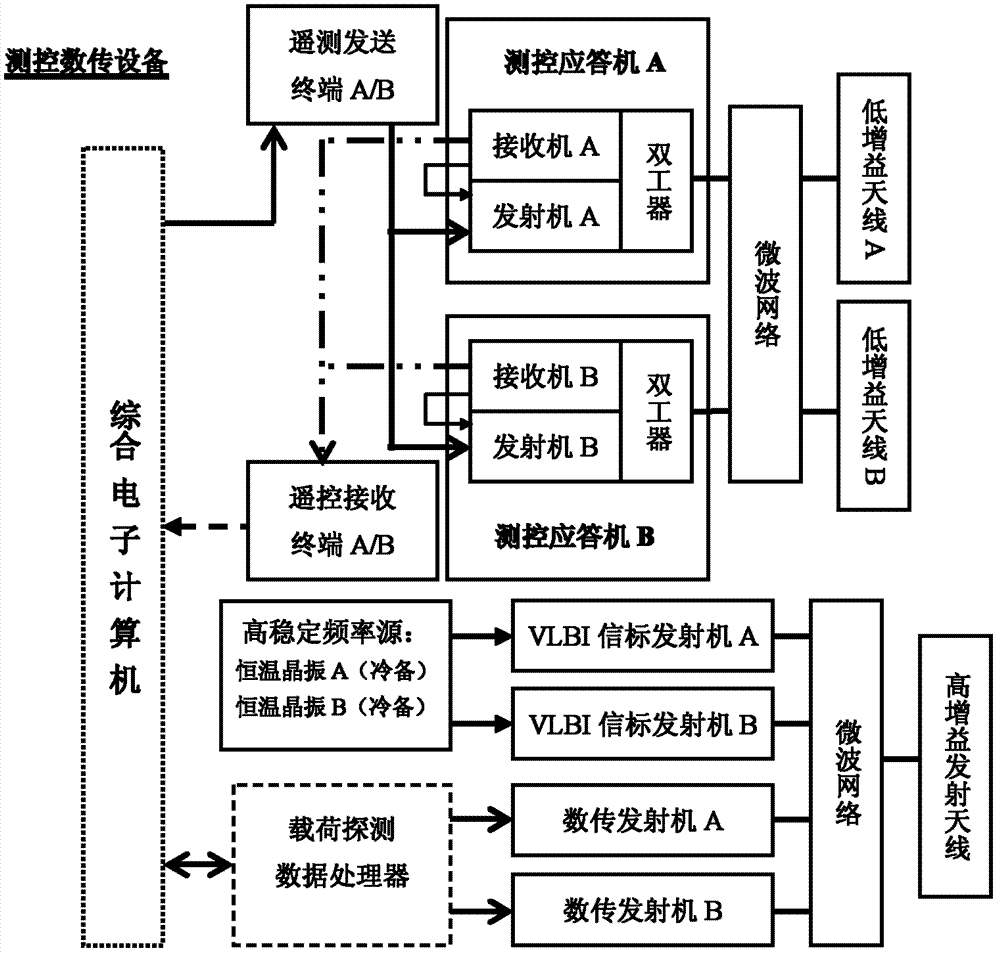
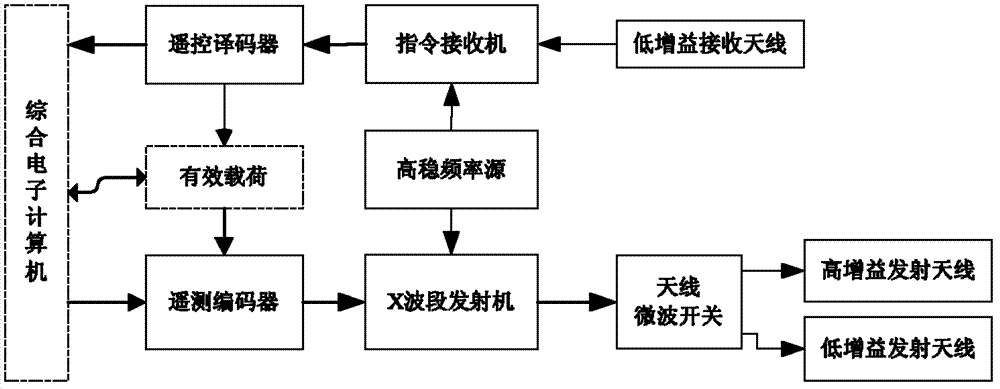
A measurement and control communication method for a deep space probe and a measurement and control communication system for a deep space probe
InactiveCN103368638AReduce weightReduce development difficultyRadio transmissionFrequency standardTransmitter
The invention provides a measurement and control communication method for a deep space probe and a measurement and control communication system for a deep space probe. The method is used for achieving information interaction between an earth station and a deep space probe and measurement of a probe track. The method comprises following steps. Four microwave radio signal channels are disposed between the deep space probe and the earth station by using an uplink carrier frequency and a downlink carrier frequency and comprise a telecontrol instruction channel, a telemetry data channel, a scientific data channel, and a VLBI track measurement beacon channel. Three channel signals including engineering telemetry data, scientific probing data, and VLBI track measurement beacon are combined into a downlink transmission signal. Finally, a transmitter is used to complete a transmitting function of all downlink transmission signals. A track measurement beacon is generated by using a frequency standard signal of a high-stability frequency source and is transmitted to an earth VLBI measuring network. Using a Doppler frequency speed measurement and signal interference angle measurement manner, the earth VLBI measuring network completes the track measurement tack of the deep space probe.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
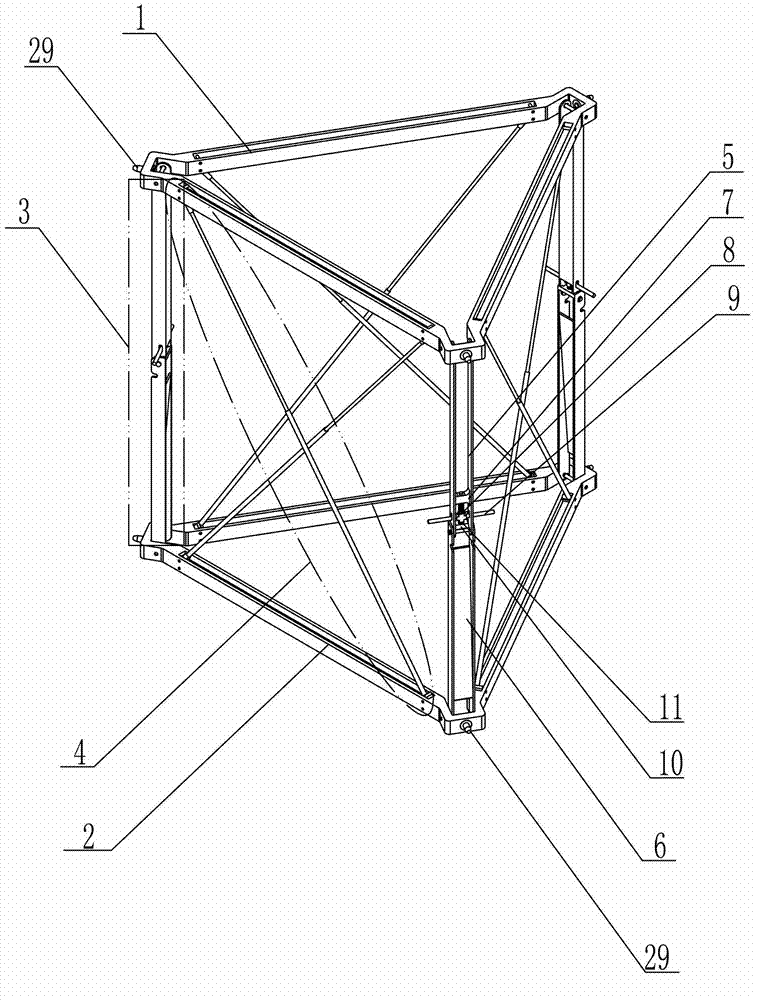
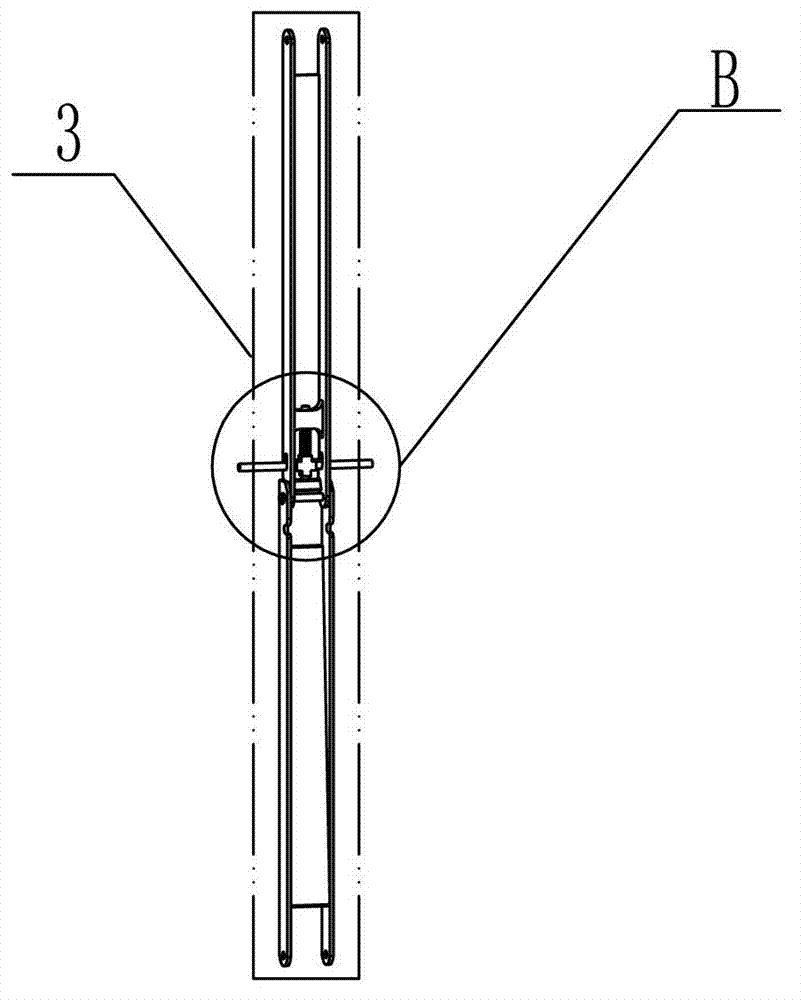
Unfoldable unit of triangular prism and unfoldable support arm consisting of unfoldable units
InactiveCN102923316AReduce volumeReduce weightPhotovoltaic supportsCosmonautic vehiclesSatelliteTriangular prism
The invention discloses an unfoldable unit of a triangular prism and an unfoldable support arm consisting of the unfoldable units, solving the problems that the existing hinged type support arm is large in folded size and low in repeated unfolding precision. According to the unfoldable unit, an upper triangular frame and a lower triangular frame are arranged from top to bottom in parallel; each corresponding top angle between the upper triangular frame and the lower triangular frame is respectively supported by a triangular prism folding arm and is rotatably connected with the triangular prism folding arm; a group of triangular prism inhaul cable assembly is arranged at the inner opposite angle of a rectangular plane formed by the upper triangular frame, the lower triangular frame and two adjacent triangular prism folding arms; and each two adjacent triangular prism unfoldable units are rotatably connected through a transit unfolding component. With the adoption of the inhaul cable component provided by the invention, the problem that inhaul cables at opposite corners are wound and move irregularly; and meanwhile the overall rigid and the repeated unfolding precision of the support arm are enhanced. The unfoldable unit is used in a satellite, a space station and a space probe.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Autonomous optical navigation method for soft landing for deep space probe
InactiveCN101762273AHigh precision determinationImprove reliabilityInstruments for comonautical navigationPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryAviationLaser ranging
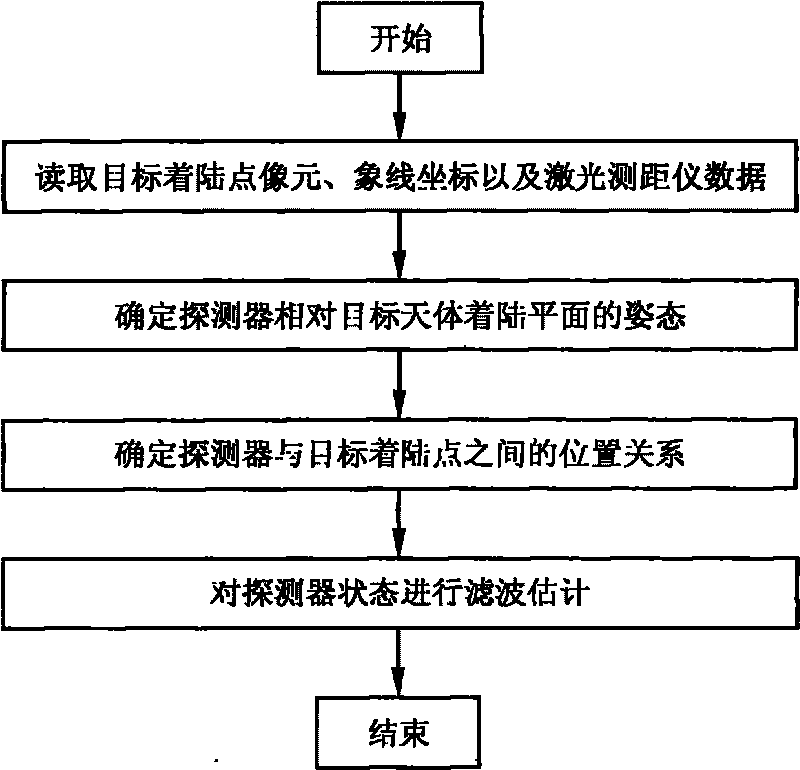
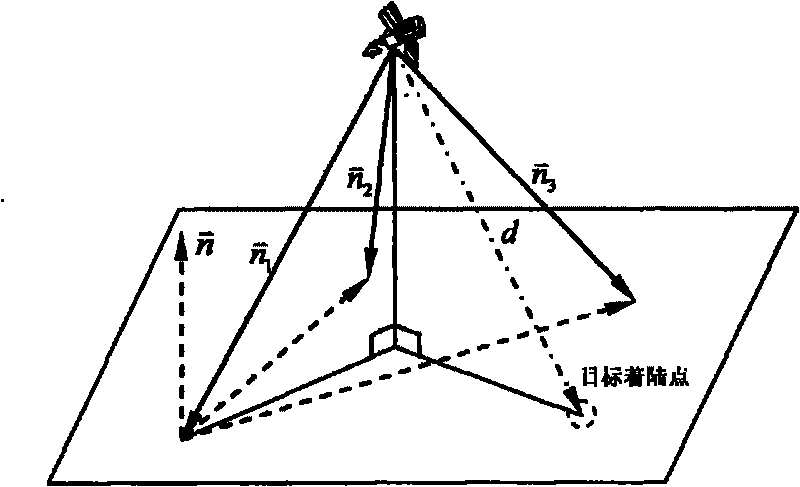
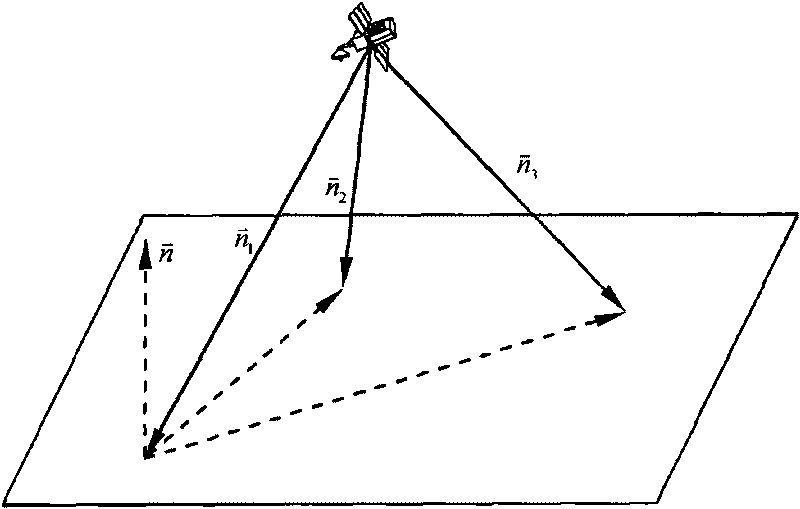
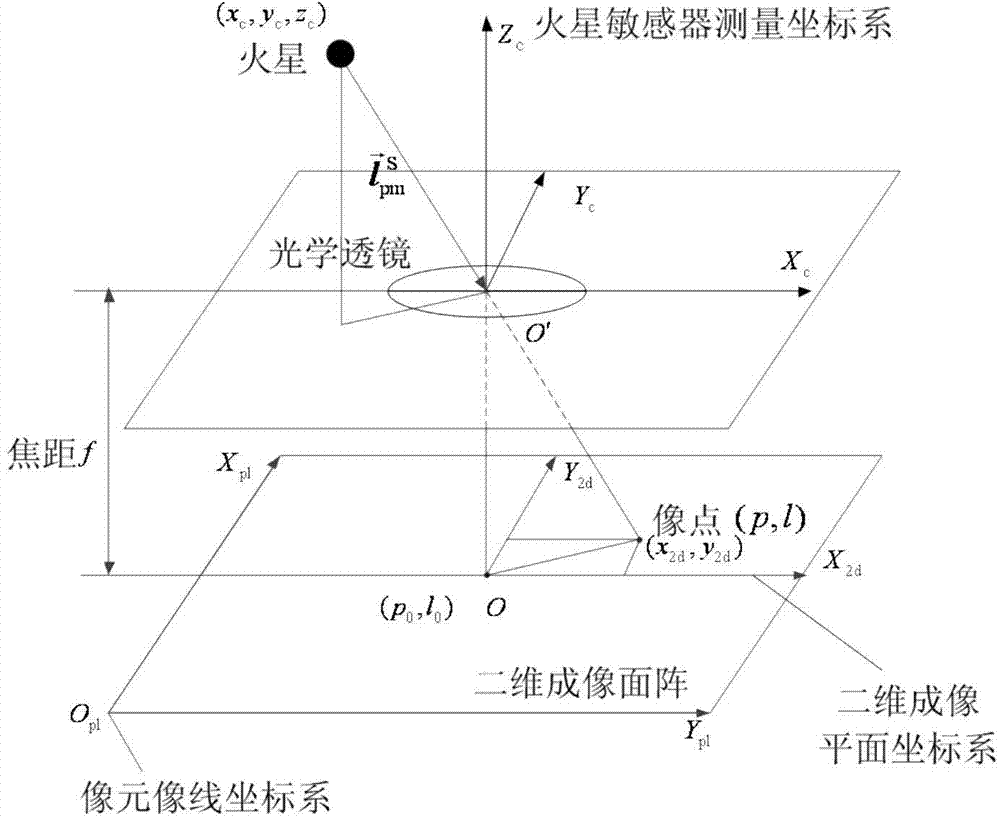
The invention relates to an autonomous optical navigation method for soft landing of a deep space probe, and belongs to the field of space flight and aviation. The autonomous optical navigation method comprises the following steps: firstly, reading a corresponding pixel and a pixel line coordinate of a target landing point on an image plane photographed by an optical navigation camera, and the distance of the probe from a landing plane in three laser ranging device mounting directions; secondly, determining the posture of the probe relative to a landing plane of a target astronomical body by using the obtained distance measured by the three laser ranging devices and the mounting azimuth angle and pitch angle of the known ranging device; thirdly, determining the position relationship between the probe and the target landing point by using the obtained distance di measured by the three laser ranging devices and the pixel and the pixel line coordinate of the target landing point; and finally, performing filter estimation on the position, speed, posture and angular speed information of the probe relative to the landing area. The autonomous optical navigation method for the soft landing of the deep space probe has the characteristics of high reliability, low cost and strong real-time, and can highly precisely determine the position and posture of the probe relative to the target landing point.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
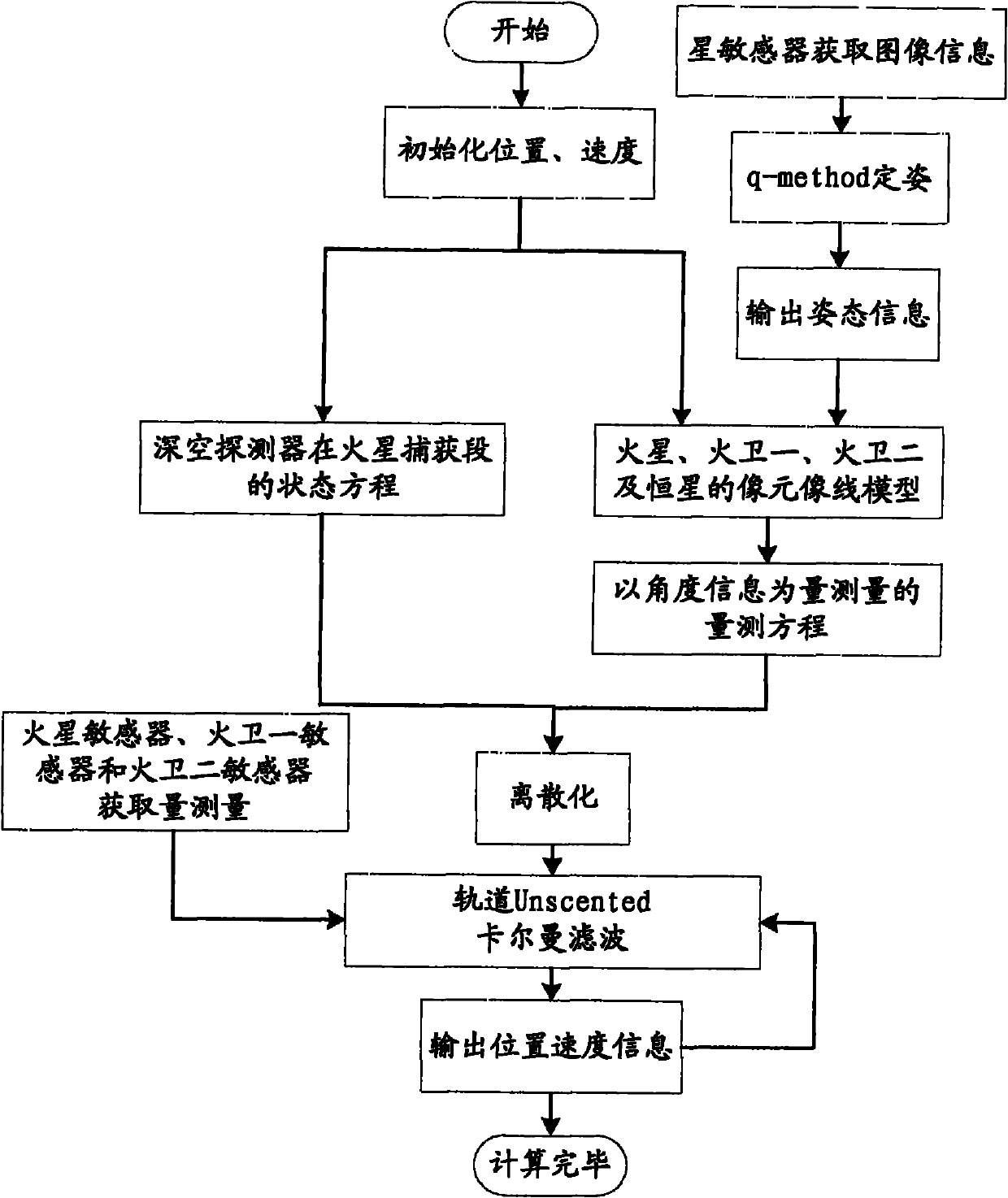
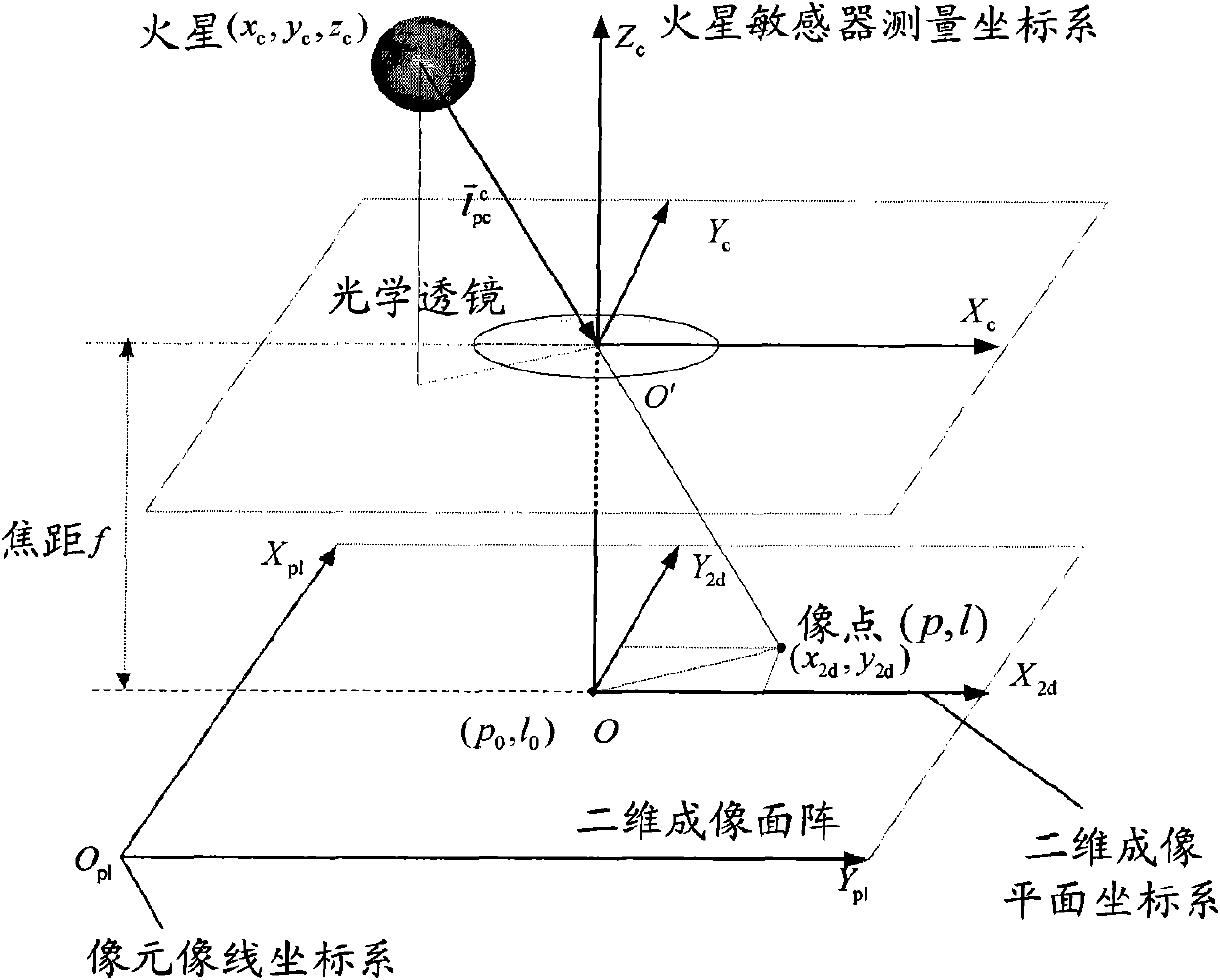
Independent celestial navigation method for Mars capturing section of deep space probe
ActiveCN102168981AAvoid Accuracy ImpactImprove navigation accuracyInstruments for comonautical navigationFixed starsDynamic models
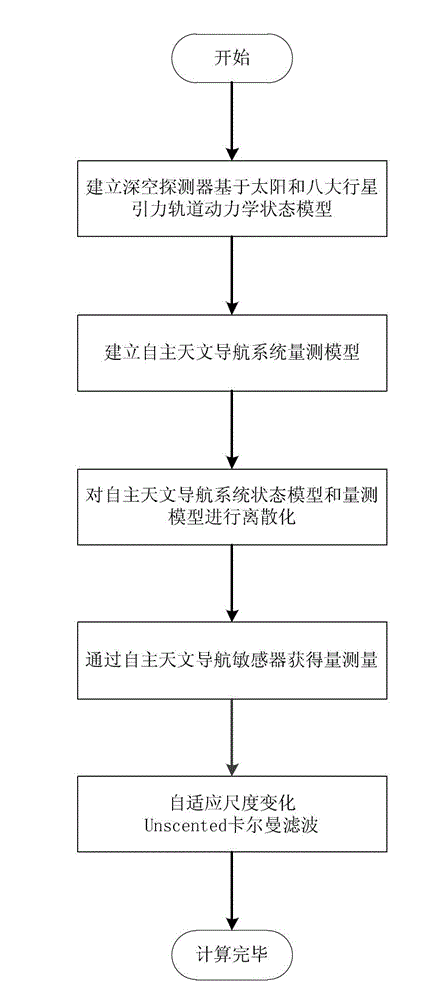
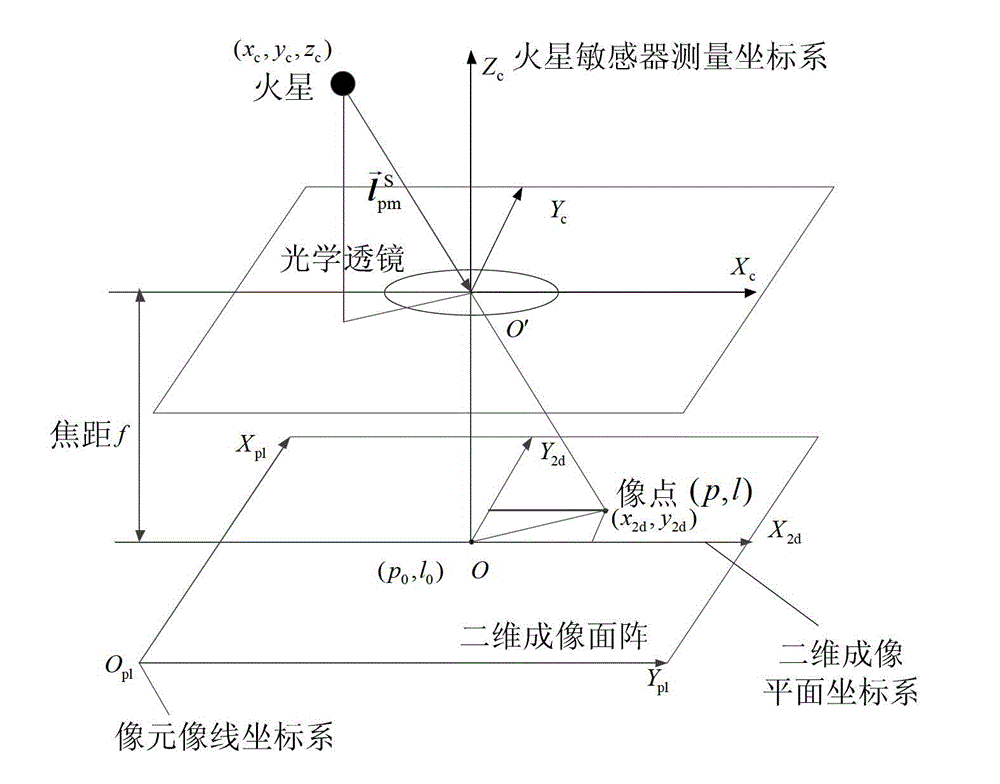
The invention relates to an independent celestial navigation method for a Mars capturing section of a deep space probe. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a state model of the deep space probe according to a circular restrictive four-body track dynamics model; acquiring picture element and picture line information of Mars, Martian satellites and a background fixed star, converting the acquired picture element and picture line information into angle information of the Mars, the Martian satellites and the background fixed star and establishing an angle measuring model of the Mars, a Martian satellite I and a Martian satellite II; and estimating the attitude information of the probe by adopting a q-method and estimating the position and speed of the deep space probe in combination with Unscented Kallman filtering. The method has high estimation accuracy, and is very suitable for independent navigation of Mars capturing. The method belongs to the technical field of aerospace navigation. By adopting the method, high-accuracy navigation parameters can be provided for Mars capturing of the deep space probe, and references can be provided for the design of an independent navigation system of the deep space probe.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Independent celestial navigation method of deep space probe based on minor planet intersection
ActiveCN102168980AHigh precisionRealize high-precision navigationInstruments for comonautical navigationFixed starsAutonomous Navigation System
The invention relates to an independent celestial navigation method of a deep space probe based on minor planet intersection. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a state model of the deep space probe according to a circular restrictive track dynamics model; acquiring picture element and picture line information of minor planets and a background fixed star by using a sensor, converting the acquired picture element and picture line information into angle information of the minor planets and the background fixed star and establishing an angle measuring model of the minor planets; and estimating the position and speed of the deep space probe in combination with self-adaptive Unscented Kallman filtering. The method has high estimation accuracy, and is very suitable for independent navigation during minor planet intersection. The method belongs to the technical field of aerospace navigation. By adopting the method, high-accuracy navigation parameters can be provided for the deep space probe, and references can be provided for the design of an independent navigation system of the deep space probe.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for designing pointing of antenna of deep space probe
ActiveCN104369877AReduce stepsReduce operational complexityCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsOmnidirectional antennaSpace probe
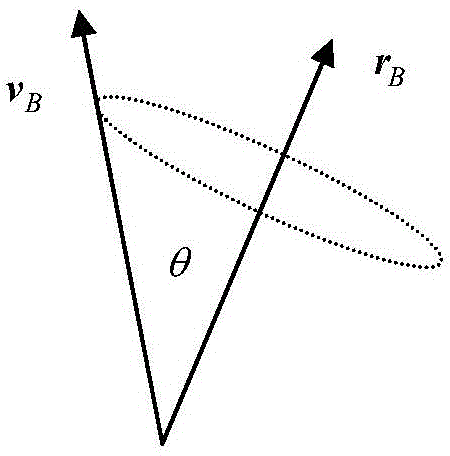
The invention provides a method for designing pointing of an antenna of a deep space probe. The method particularly comprises the steps that firstly, the expression (please see the formula in the specification) of the probe-geocentre position vector on a mechanical coordinate system is calculated; secondly, according to the V2m, the included angle theta between the full-direction antenna direction vector and a probe-control station is calculated; thirdly, when the included angle theta is larger than the maximum allowable angle gamma, the probe rotates around the +x axis of a mechanical coordinate system, and gains of the rotated full-direction antenna meet the requirements of an upper link and a down link. According to the method, the antenna rotates around the counterglow directional axis by a certain angle, and therefore continuity of the measuring and control process is ensured; the antenna using operation caused by ground switching is reduced; the ground operation complexity is reduced; and meanwhile, the antenna is located in the section with the large gains, and the link channel allowance is improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
Doppler differential velocity model and method for combined navigation by using doppler differential velocity model and X-ray pulsar
InactiveCN103954279AStable jobHigh precisionNavigation by astronomical meansKaiman filterSpace probe
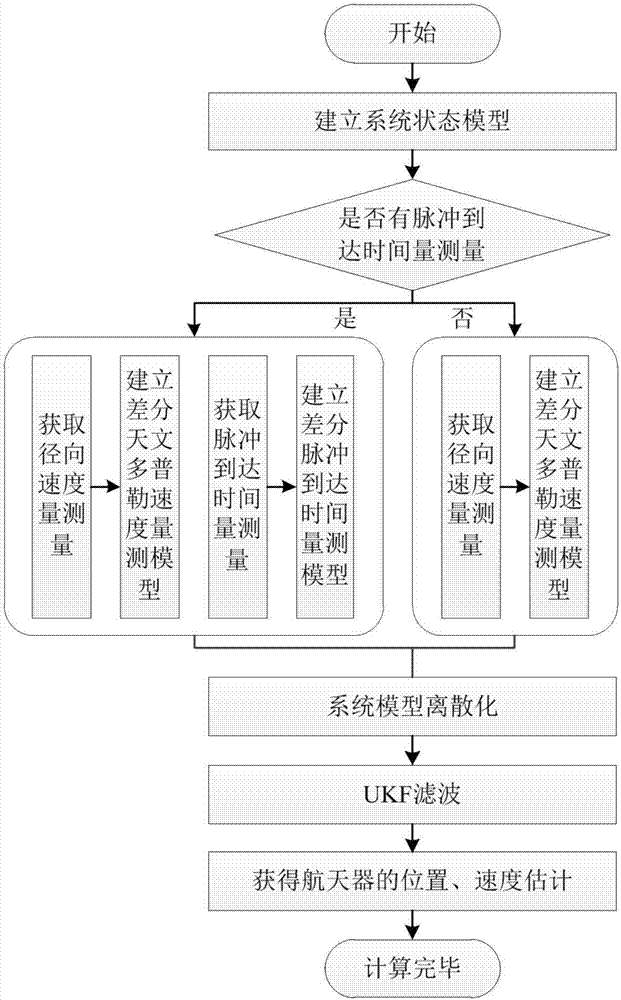
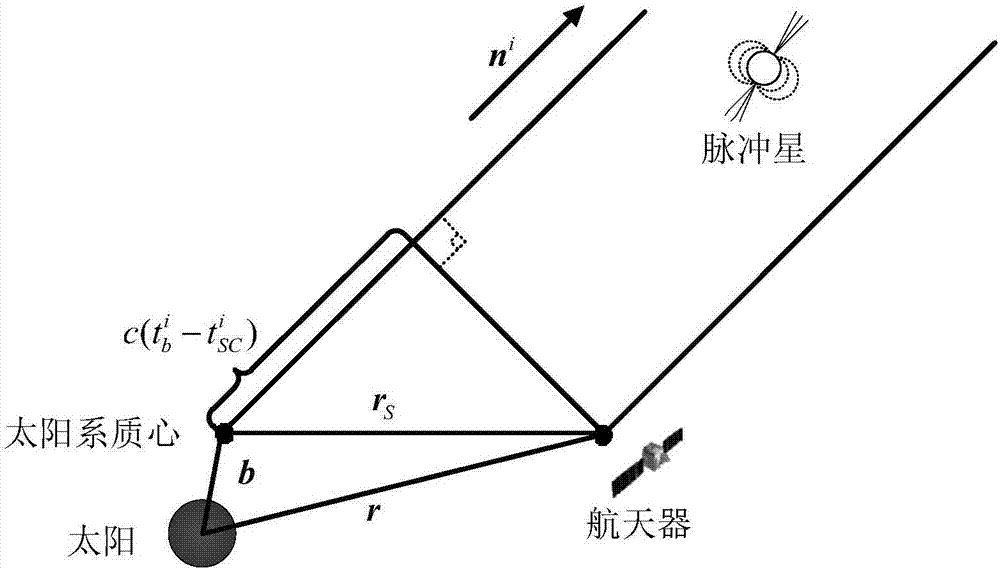
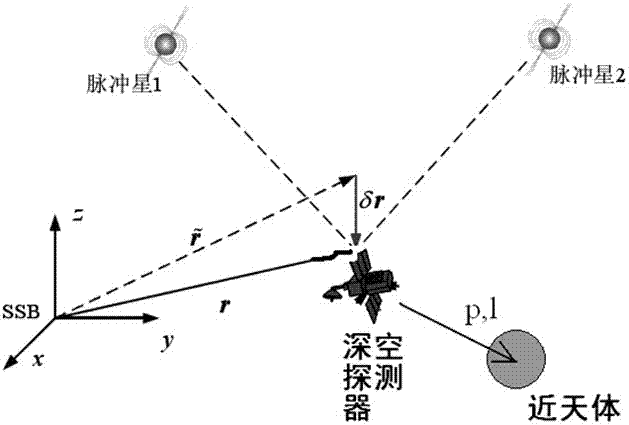
The invention discloses a doppler differential velocity model and a method for combined navigation by using a doppler differential velocity model and an X-ray pulsar. The doppler differential velocity model is Y<s>(t)=h<s>(X, t)+omegav, wherein omegav is doppler measurement noise; Y<s> and h<s> respectively represent a measurement value and a measurement equation; Y<s>=vD2-vD1; the equation is as shown in the specification. The method for combined navigation by using the doppler differential velocity model and the X-ray pulsar comprises the following steps: 1, building an orbital dynamics model of a deep space probe; 2, building an X-ray pulsar navigation ranging model; 3, building the doppler differential velocity model; 4, filtering by using an extended kalman filter. Compared with the prior art, the doppler differential velocity model has the advantages that (1) compared with the existing pulsar / doppler combined navigation methods, the doppler differential velocity model still can normally and stably work under an unstable solar spectrum; (2) compared with the pulsar navigation method and the doppler navigation method, a plurality of navigation messages are fully utilized by the method, the method has complete observability, and the locating information with higher precision can be provided.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Autonomous celestial navigation method for deep space explorer on swing-by trajectory
ActiveCN101692001AOvercome inaccuraciesAchieve precise positioningInstruments for comonautical navigationNavigation by astronomical meansNavigation systemCelestial navigation
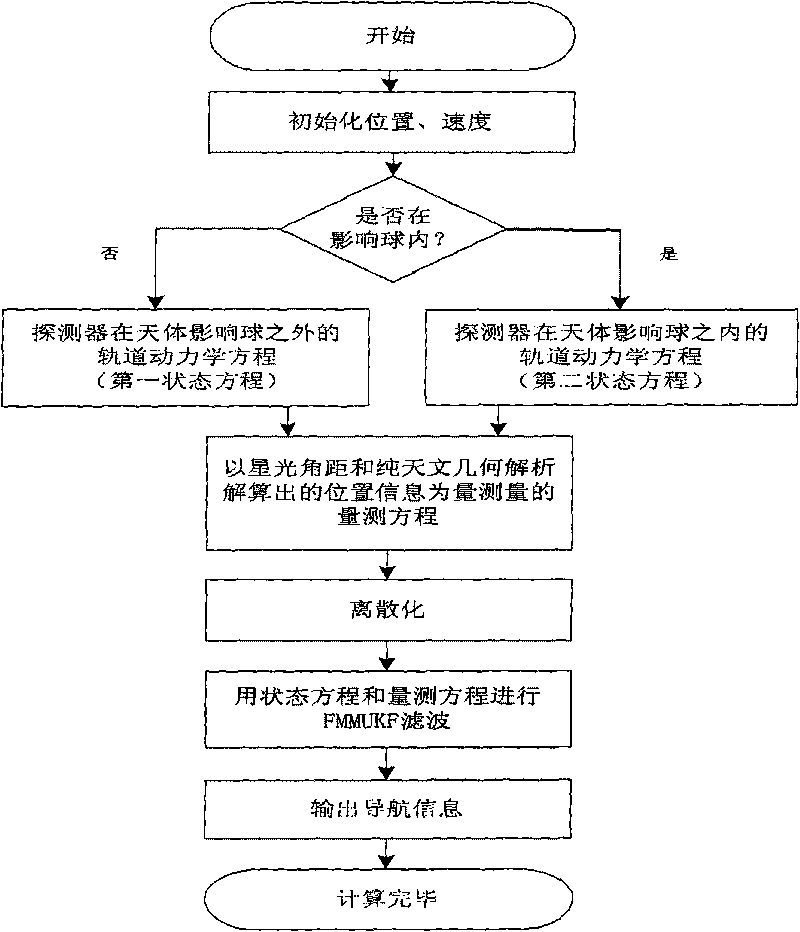
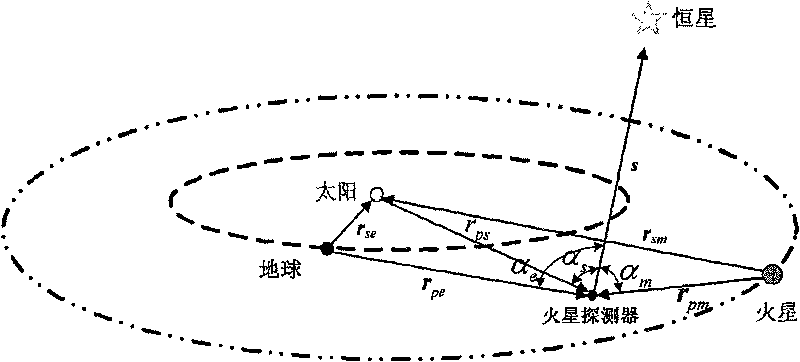
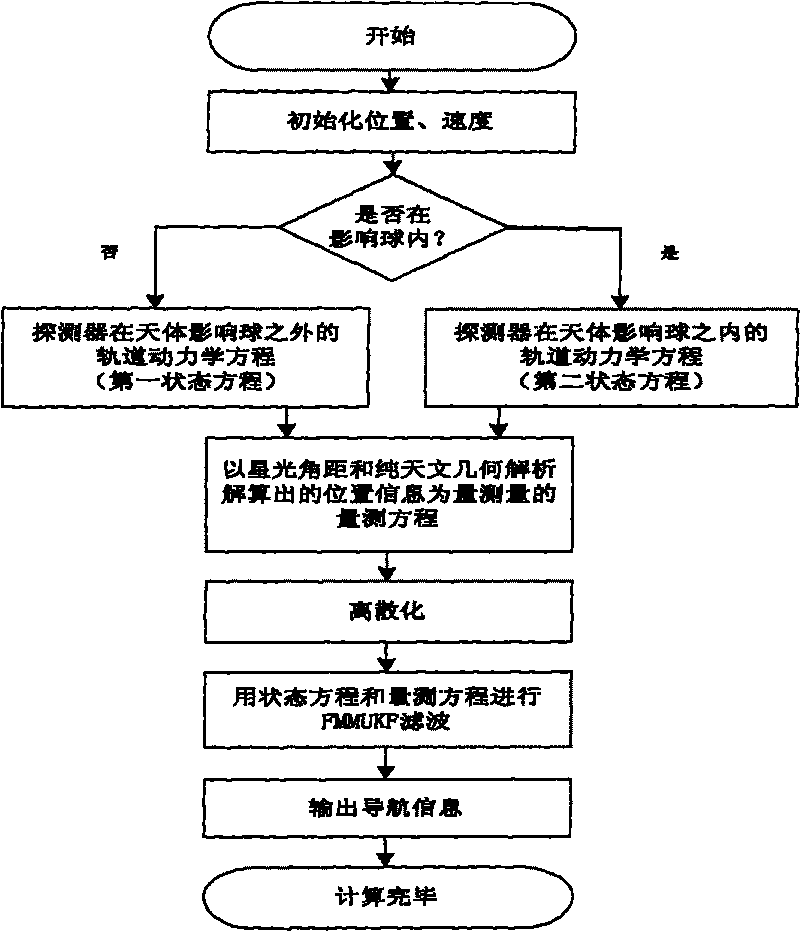
The invention relates to an autonomous celestial navigation method for a deep space explorer on a swing-by trajectory. The autonomous celestial navigation method comprises the following steps: establishing the corresponding equation of state according to the distance to a planet; calculating the location information of the planet by using the sensitive starlight angle distance detected by a star sensor and calculated by pure astronomic and geometry analytic method; and estimating the parameters of the navigation system by using a fuzzy multiple-model adaptive unscented Kalman filtering (FMMUKF) method. The invention is suitable for the navigation location of a deep space probe on a swing-by trajectory and applicable to the determination of navigation parameters of the deep space probe on a multi-celestial-body intersection swing-by trajectory, belonging to the technical field of aerospace navigation.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
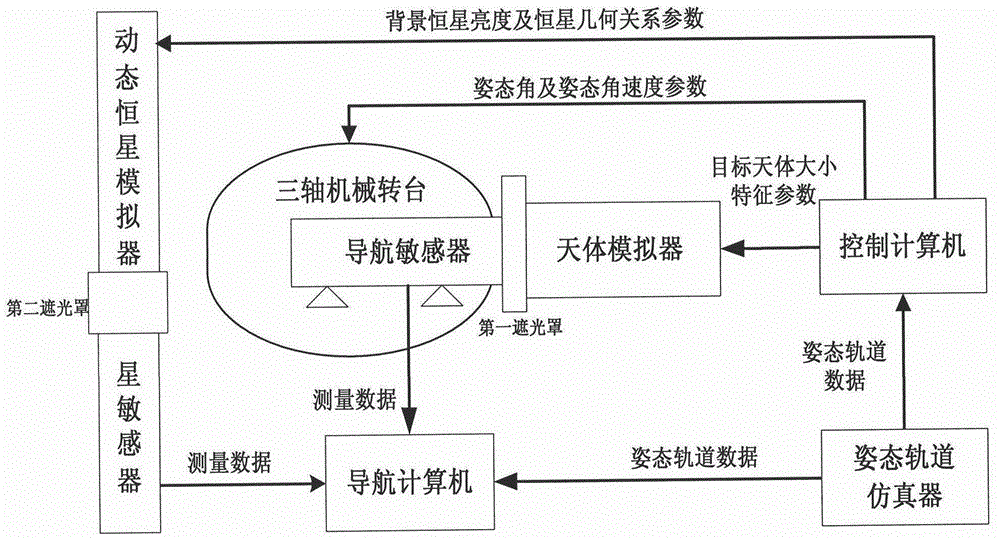
Optical imaging autonomous navigation semi-physical simulation testing system for deep space exploration proximity process
An optical imaging autonomous navigation semi-physical simulation testing system for a deep space exploration proximity process is characterized in that a navigation sensor is mounted on a rotary table to be docked with a celestial simulator, a star sensor is docked with a dynamic fixed star simulator, an attitude and orbit simulator generates deep space probe reference attitude and orbit data and transmits the data to a control computer and a navigation computer, the control computer drives the celestial simulator, the dynamic fixed star simulator and the rotary table to move, the celestial simulator simulates position changes of a deep space probe and a target celestial body, the dynamic fixed star simulator simulates inertial attitude changes of the deep space probe, the rotary table simulates attitude disturbance of the deep space probe, and the navigation computer acquires measurement data of the navigation sensor and the star sensor, performs navigation filtering computation and compares a computed result with the reference data so that autonomous navigation precision is obtained. The optical imaging autonomous navigation semi-physical simulation testing system for the deep space exploration proximity process achieves hardware-in-the-loop semi-physical simulation testing on the basis of real measurement data of the sensors and can effectively test and verify the performances of an optical imaging autonomous navigation system for the deep space exploration proximity process on the ground.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Deep space autonomous navigation method based on observability degree analysis
InactiveCN101762272AImprove adaptabilityImprove reliabilityInstruments for comonautical navigationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsDynamic modelsFilter algorithm
The invention discloses a deep space autonomous navigation method based on observability degree analysis, which relates to the field of aerospace. The invention solves the problems that when the current autonomous navigation systems comprehensively use different observing models to provide measuring information, different types of measuring information of different sensors need to be processed, thereby reducing the utilization ratio of the observed information and simultaneously reducing the adaptive ability and reliability of the autonomous navigation systems. The method of the invention is established on the basis of a dynamic model of an earth-moon transfer orbit deep space probe, obtains the observability degree of the deep space autonomous navigation system under two observing models of a geocentric sight line vector and a selenocentric sight line vector by a nonlinear system observability degree analyzing method, and acquires the orbit parameters of the deep space probe by a UKF based federal filtering algorithm. The invention is suitable for determining the orbit parameters of deep space separated section and transfer section probes. The invention can be used for improving the accuracy and reliability of the deep space autonomous navigation system, and is especially suitable for the information fusion autonomous navigation technologies under various observing models.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
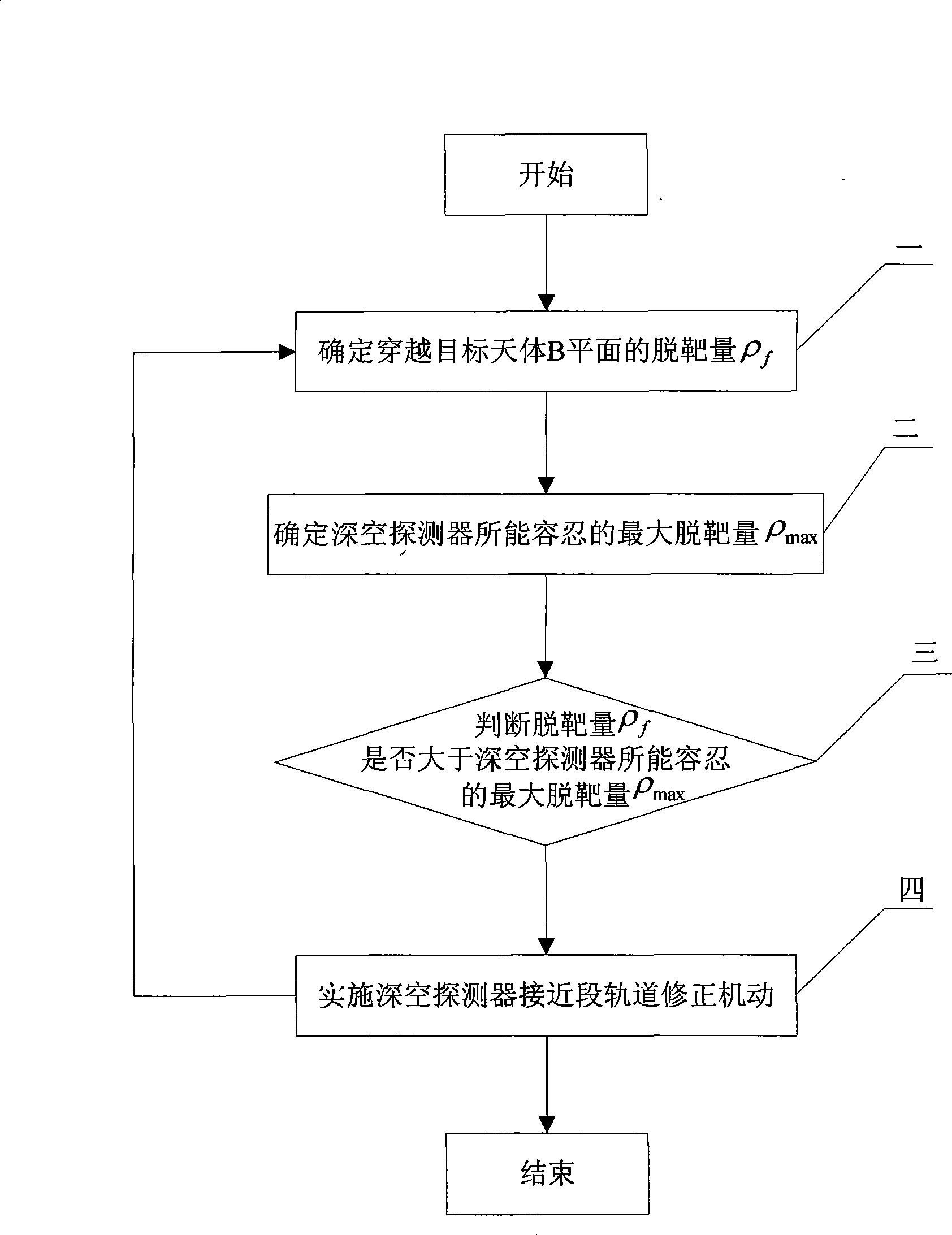
Medication maneuvering time selecting method for deep space detector approaching orbit
InactiveCN101462597AMeet the requirements of brake implementationReduce consumptionArtificial satellitesNavigation by astronomical meansAviationCelestial body
The invention relates to a method for selecting time of deep space probe approach orbit correction maneuver, which belongs to the field of spaceflight and aviation and solves the problems of deep space probe approach orbit correction maneuvering time including low control precision, great calculation amount and poor independency in the prior method for selecting time of deep space probe approach section orbit correction maneuver. The method comprises: 1, determining miss distance rhof passing through the B plane of an object celestial body; 2, determining the acceptable maximum miss distance rhomax of a deep space probe; 3, judging whether the miss distance rhof is more than the acceptable maximum miss distance rhomax, if yes, executing step 4; otherwise, returning to step 1; and 4, executing deep space probe approach section orbit correction maneuver. The method not only can save fuel at a rate of 6m / s, but also can ensure that final passing-through precision is increased by more than 100m as compared with ground station designated maneuver time precision under the same condition and reaches within 250m.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
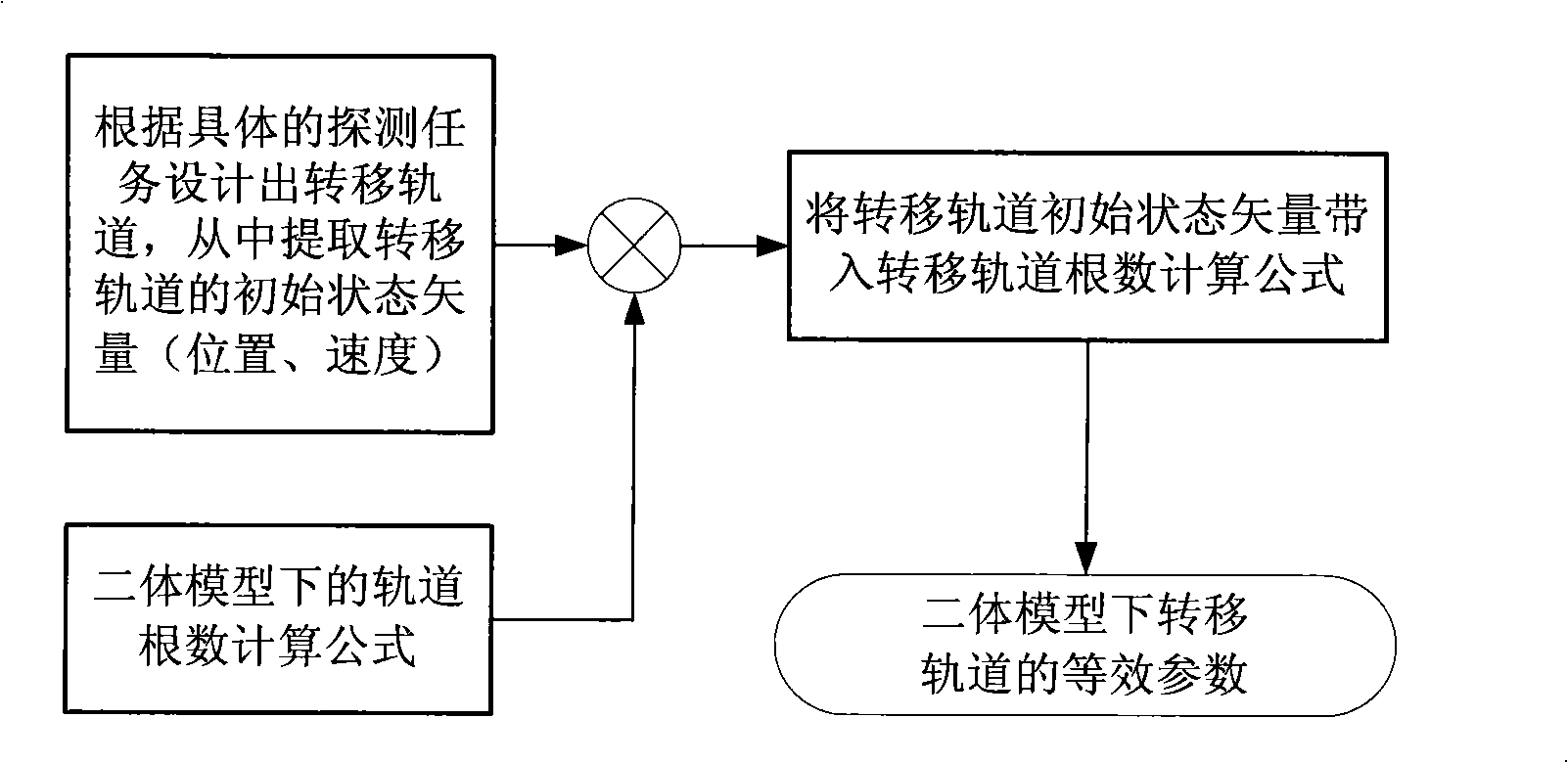
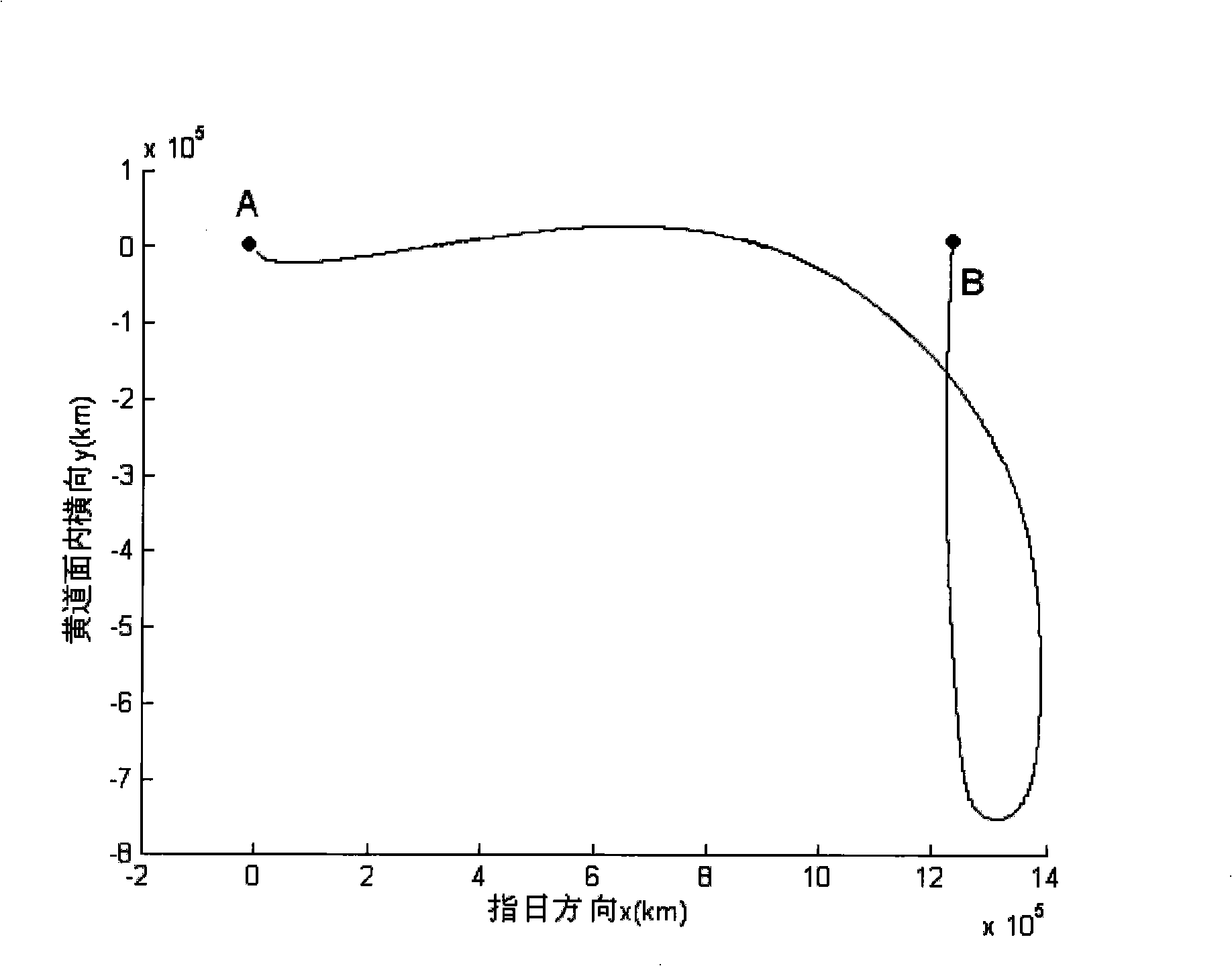
Method for determining deep space detector equivalent transfer orbit
The invention discloses a method for determining an equivalent transfer orbit of a deep space probe, which comprises the steps: (1) the equivalent transfer orbit of the deep space probe is designed according to an orbit dynamic model, and the orbit parameter of the designed transfer orbit is extracted; (2) the near-earth equivalent parameter of the transfer orbit of the deep space probe is solved according to the orbit parameter extracted in the step (1) and the spatial geometric relationship. By the method of the invention, when a carrier rocket directly sends a probe into the transfer orbit, the carrying party does not need to establish a complex dynamic model for the deep space probe, and the existing model used for estimating the launching precision can estimate the transmission precision more correctly, thereby solving the problem that the current carrier rocket in China does not have an upper stage and can not send the probe into the transfer orbit by using the upper stage for firing. The method of the invention adopts the concept of equivalence to solve the problem and is simple and reliable.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG SATELLITE
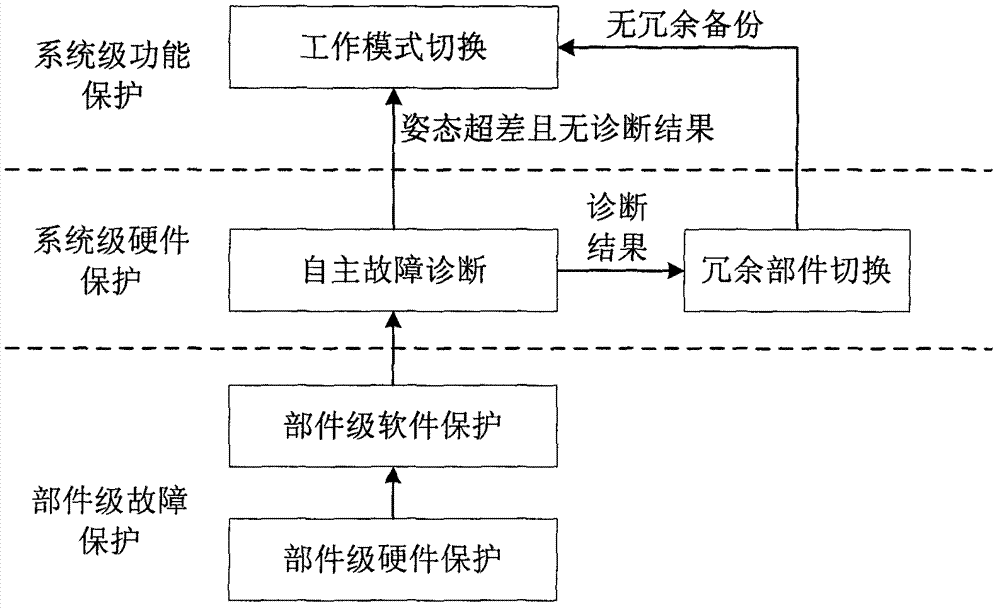
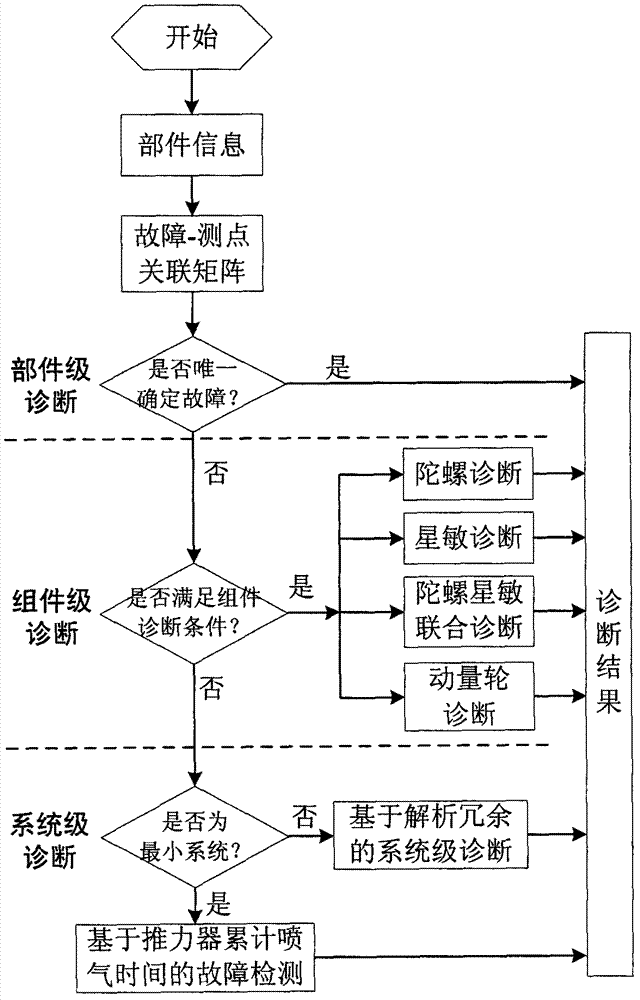
Automatic failure handling and protection method of deep space probe global navigation chart (GNC) system base on layered structure
ActiveCN103034232ACause harmReduce misdiagnosis rateElectric testing/monitoringSpace probeSelf locking
Disclosed is an automatic failure handling and protection method of a deep space probe global navigation chart (GNC) system base on a layered structure. The automatic failure handling and protection method of the deep space probe GNC system base on the layered structure comprises the steps of carrying out hardware protection to avoid a failure which can result in permanent damage or invalidation of other parts or other parts inside a part according to a result of failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA), judging whether the data of measuring points are normal with an infrared ray method for other failures, marking the states of parts and handling the data and state information to a controller for analyzing of system-level failures; carrying out failure analyzing according to the state information and the data of the measuring points handed to the controller: if hardware redundancy or analysis redundancy exists, a failure part is switched to a normal redundancy part; if the hardware redundancy or the analysis redundancy dose not exist, the next step is carried out; switching to a counter-glow orientation mode when the prior step can not position a failure source or no redundant backup can replace the failure source and gesture is pretty poor and directing is out of control, switching off equipments not necessary for flying of a deep space probe to reduce power consumption, and switching off a self-locking valve and switching to a control-stop mode to reduce propellant consumption of the probe when the probe is out of control, a pushing system spray gas at random and star bodies roll.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
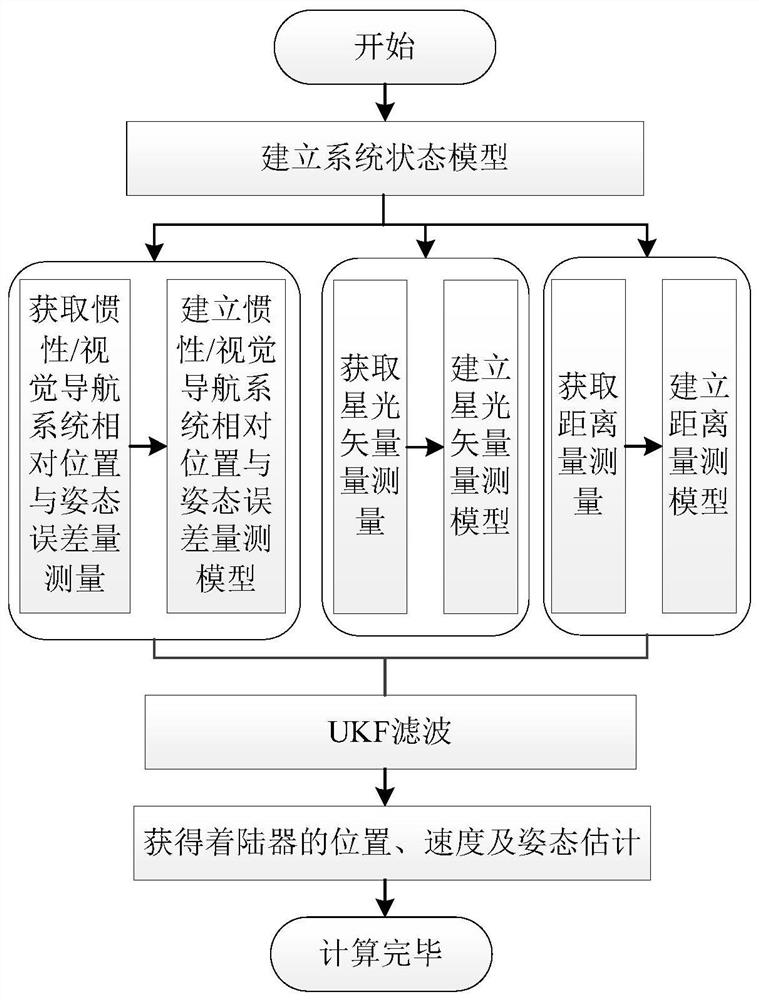
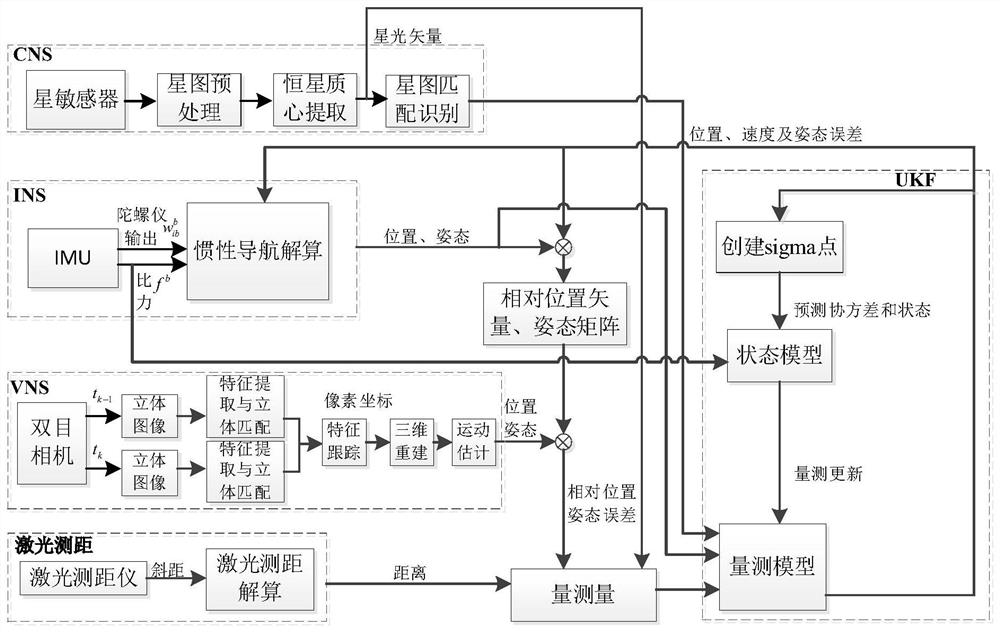
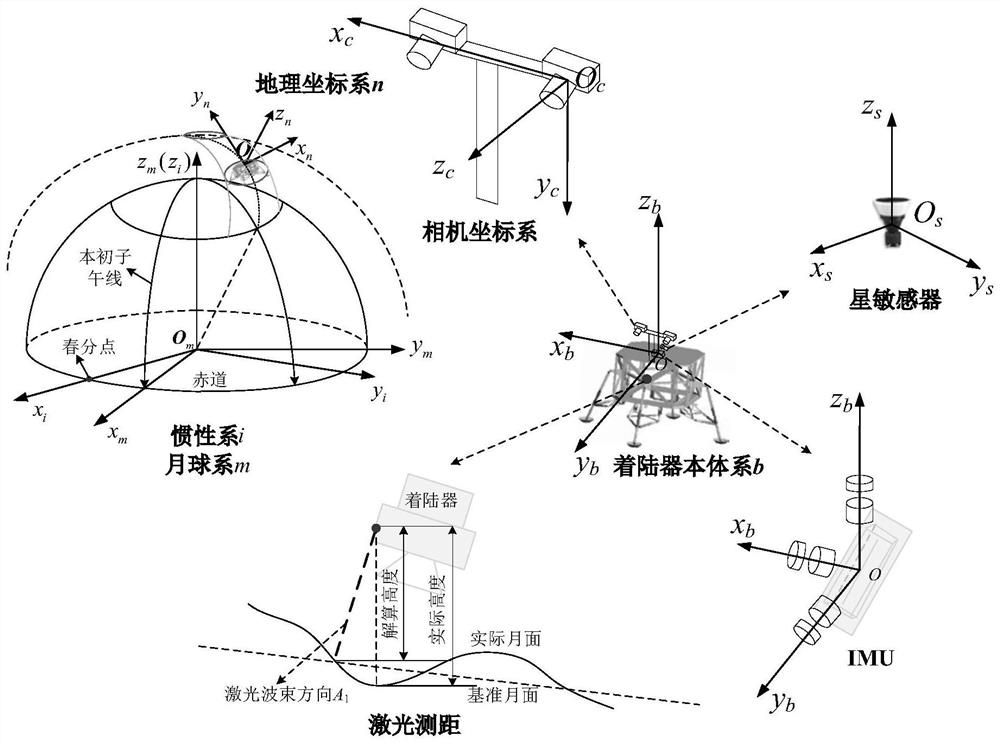
Inertia/vision/astronomy/laser ranging integrated navigation method suitable for lunar lander
ActiveCN111947652AHigh precisionImprove reliabilityNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsNavigation by astronomical meansLaser rangingSpace probe
The invention relates to an inertia / vision / astronomy / laser ranging combined navigation method suitable for a lunar lander. The method includes: firstly, according to mechanical arrangement of inertialnavigation under a lunar fixed connection coordinate system, taking an inertial navigation error equation as a state model, and then taking the relative position and attitude error obtained by an inertial / visual navigation system, the starlight vector obtained by an astronomical navigation system and the distance obtained by a laser range finder as measurement quantities; then respectively establishing measurement models of relative position and attitude errors, starlight vectors and laser ranging of the inertial / visual navigation system according to the measurements; and finally, estimatingthe position, the speed and the attitude of the lander by using UKF filtering, and correcting the attitude error and the inertial device error of the lunar lander. The invention belongs to the field of deep space probe autonomous navigation, can provide high-precision position, speed and attitude information for a lunar lander, and has important practical significance for deep space detection.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
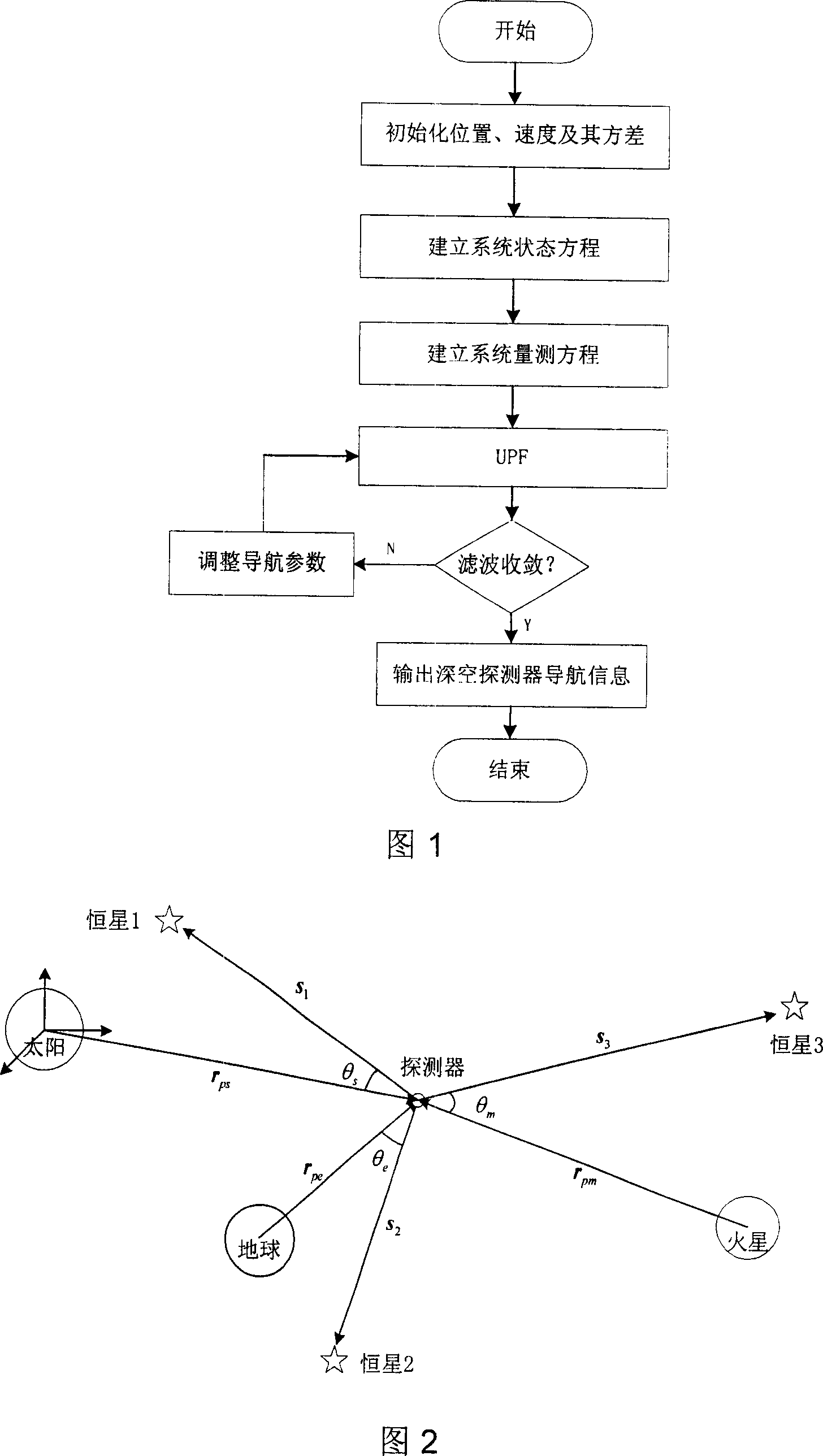
Deep space probe UPF celestial self-navigation method based on starlight angle
InactiveCN1995915AImprove navigation accuracyImprove utilization efficiencyNavigational calculation instrumentsInstruments for comonautical navigationSelf navigationAngular distance
The invention relates to an UPF automatic astrogation based on the star angular distance. It starts with precise modeling of the UPF track dynamics, using the star angular distance as the measuring unit, and optimizing the estimation based on the UPF (unscented particle filter) for the guide parameter. It applies to UPF guide location on the track transfer for the guide parameter determination.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Initial orbit determination method for deep space target celestial body based on space-based autonomous optical observation
InactiveCN104457705ASimple measurement schemeEasy to implementInstruments for comonautical navigationPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryMeasurement deviceTrack algorithm
The invention discloses an initial orbit determination method for a deep space target celestial body based on space-based autonomous optical observation, relates to an optical autonomous initial orbit determination method for a deep space celestial body, and belongs to the technical field of deep space detection. The method comprises the following implementation steps: 1, acquiring angle measurement information (right ascension beta and declination epsilon) of the target celestial body from a detector; 2, establishing an orbital kinetic equation of the target celestial body under a heliocentric inertia coordinate system; 3, establishing an observation condition equation set of the autonomous initial orbit determination of the detector by utilizing the angular position information of the target celestial body solved in the step 1 and known detector orbit parameter information; and 4, solving the orbital element information of the target celestial body by utilizing a Newton homotopy path following algorithm, thereby realizing initial orbit determination. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the position and speed information of the target celestial body can be accurately acquired in real time in the field of deep space probe navigation, the initial value sensitivity is reduced, the convergence rate, solving success rate and calculation efficiency are improved, and the positioning efficiency is further improved. Moreover, the method is simple in measurement device and easy to implement.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Swing-by probe autonomous celestial navigation method based on adaptive scale change
ActiveCN103148856AInstruments for comonautical navigationInertial coordinate systemNavigation system
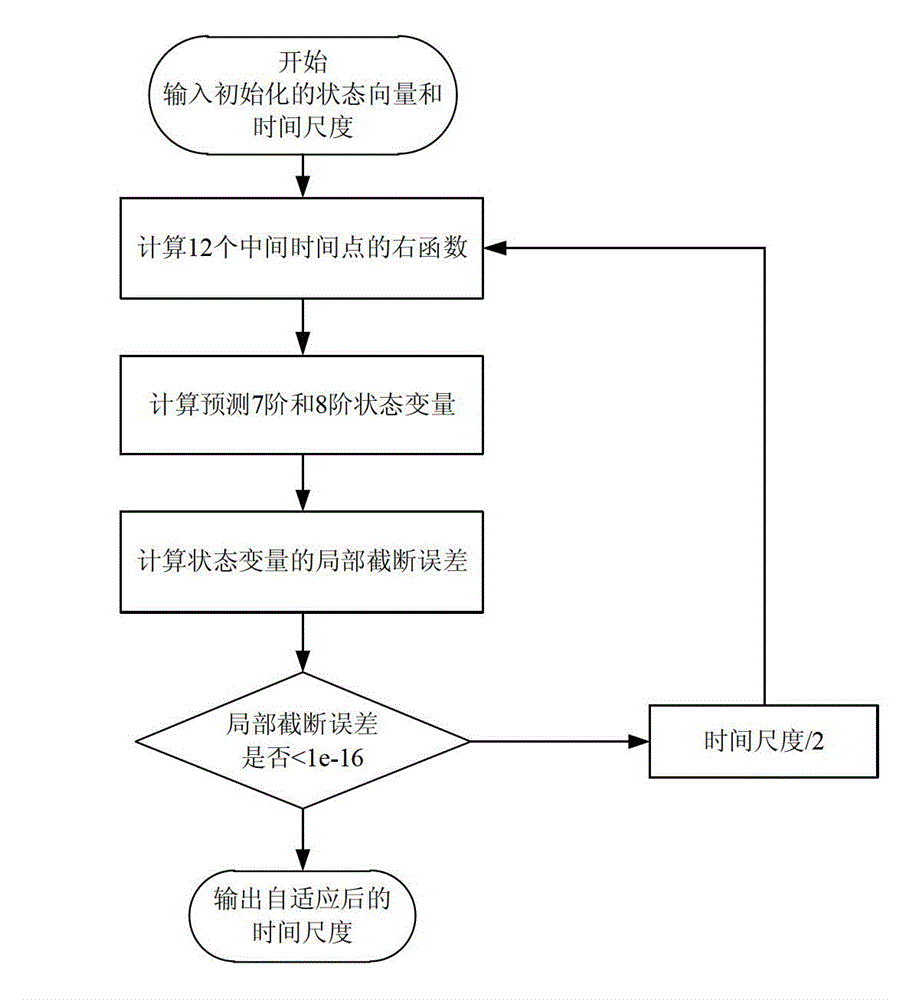
The invention relates to a swing-by probe autonomous celestial navigation method based on adaptive scale change. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a deep space probe state model and an autonomous celestial navigation system measurement model; acquiring measurement quantity of the autonomous celestial navigation system, and employing an adaptive scale change Unscented Kalman filtering method, so that the time scale suitable for the current model is obtained, and the position and speed of the detector in an inertial coordinate system which takes a target object as the center are obtained; applying the obtained time scale, position and speed to navigation at the next moment. The method belongs to the technical field of aerospace navigation, the time scale can be adaptively changed along with the time change according to the gravity acceleration stressed by the probe, the navigation system model error caused by the fixed time scale time update is reduced, and the method is suitable for a swing-by deep space probe.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
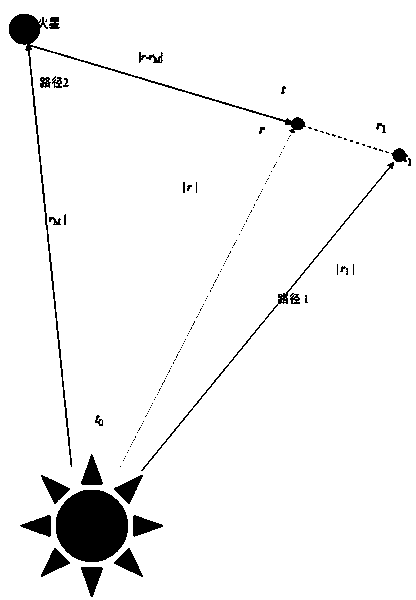
X-ray pulsar/time difference astronomical Doppler combined navigation method of deep space probe
ActiveCN107024212ARealize autonomous navigationHigh precisionInstruments for comonautical navigationDoppler velocitySpace probe
The invention discloses an X-ray pulsar / time difference astronomical Doppler combined navigation method of a deep space probe. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a state model of a spacecraft according to orbital dynamics, adopting an X-ray pulsar probe to obtain a pulse arrival time measured value, adopting a spectrograph to obtain an astronomical Doppler velocity measured value, and then respectively establishing a pulse arrival time measured model and a time differential astronomical Doppler velocity measured model according to the measured values. The position and the velocity of the spacecraft are estimated through UKF filter after discretization. The method belongs to the field of autonomous navigation of the spacecraft, can provide high-accuracy position and speed information for the deep space probe, and has important practical significance for the autonomous navigation of the spacecraft.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
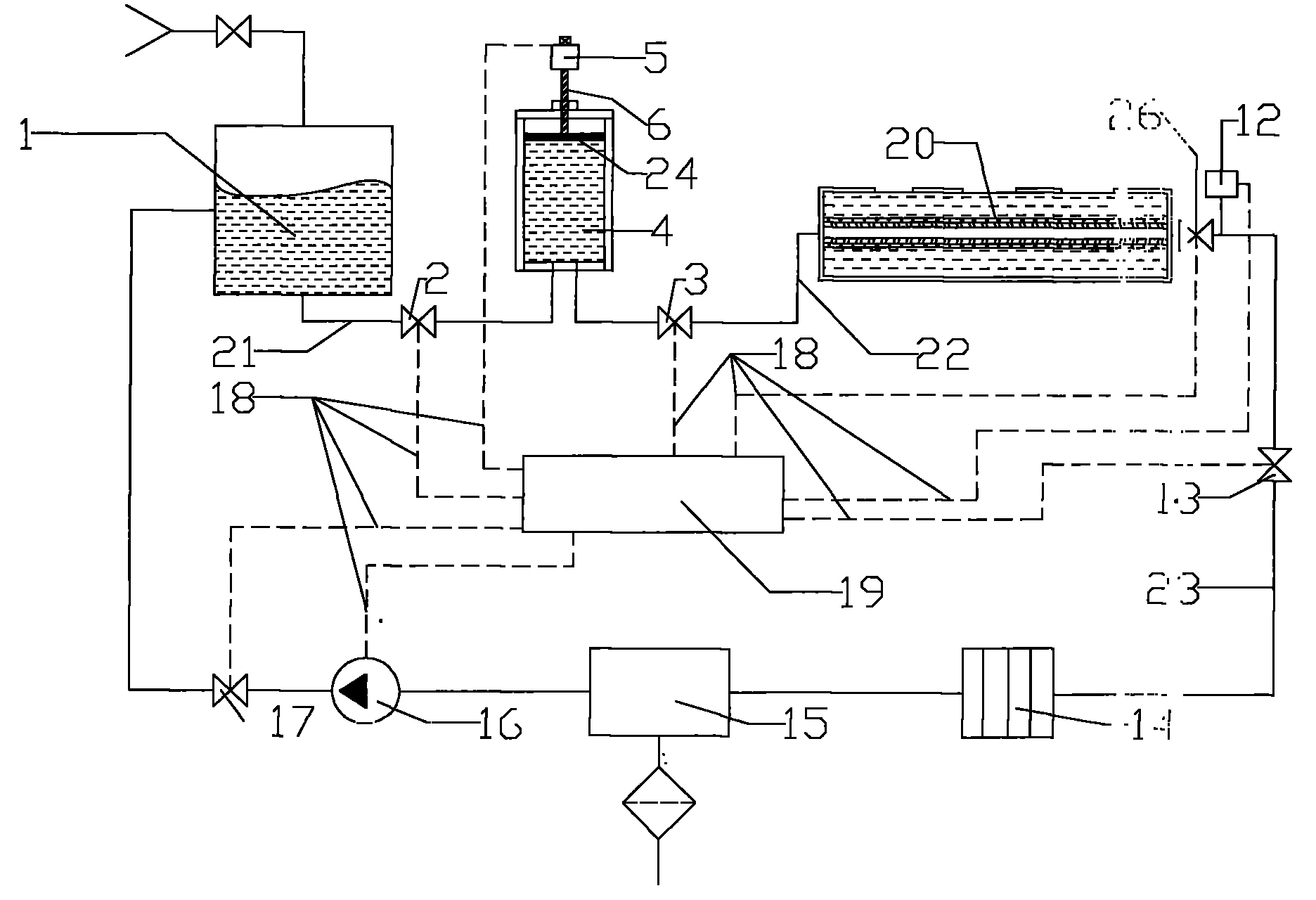
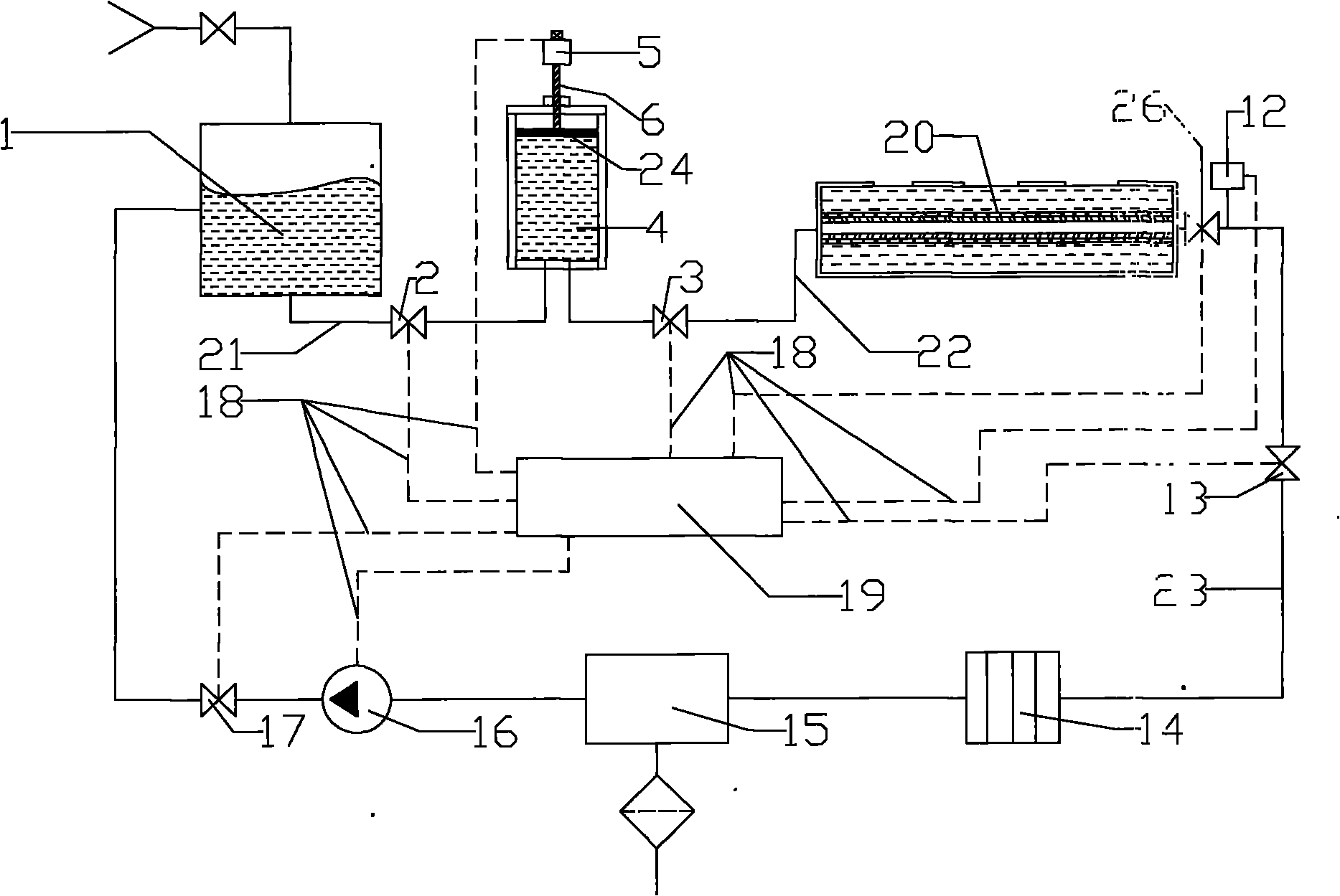
Water content supply device for vegetable culture under spacial microgravity
InactiveCN101810127APromote growthEfficient use ofSelf-acting watering devicesAgriculture gas emission reductionPeristaltic pumpWater saving
The invention discloses a water content supply device for vegetable culture under spacial microgravity, which is mainly used for providing high-efficiency water content supply for the vegetable culture in a long-time and remote-distance deep space manned space probe and in a space station where personnel stays for a long term. The device consists of a water tank, an enclosed cylinder, a culture module, a pressure sensor, a filter, a gas-liquid separator, a peristaltic pump and a programmable logic controller. The device can ensure to provide stable water content supply for vegetable culture under the spacial microgravity, and also has the advantages of degassing, purification, water saving, labor saving, simple and convenient operation and the like.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
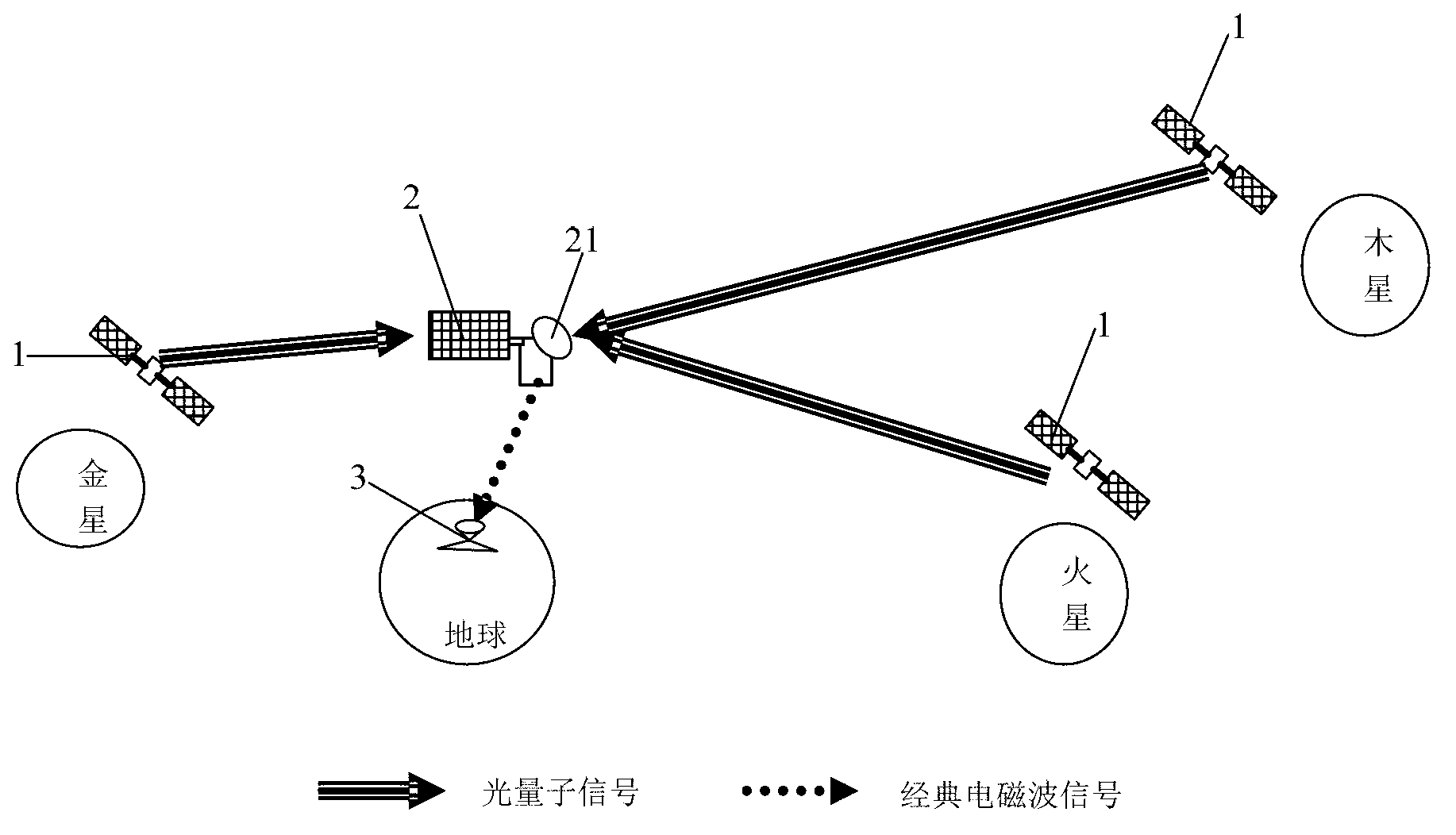
Deep space exploration communication system based on light quantum communication technology
ActiveCN103023578ASolve lossSolve the speed problemPhotonic quantum communicationTelecommunications linkGround station
The invention provides a deep space exploration communication system based on light quantum communication technology. The deep space exploration communication system comprises a plurality of deep space probes, an earth track satellite and a ground station. The deep space probes are provided with quantum information sending sub-systems, the earth track satellite is provided with a quantum communication receiving station, and the quantum communication receiving station is respectively in communication connection with the quantum information sending sub-systems and the ground station. Quantum communication is conducted among the quantum information sending sub-systems and the quantum communication receiving station, and scientific probing data explored by the deep space probes is converted into light quantum signals to be sent to the quantum communication receiving station. The quantum communication receiving station receives the light quantum signals, conducts information decoding on the light quantum signals, and restores the light quantum signals into digital signals, and the digital signals are sent to the ground station through a radio frequency communication method. By means of the deep space exploration communication system, an energy consumption problem of a traditional classic communication scheme is solved fundamentally, and an effective method for building a high-speed broadband communication link for deep space exploration tasks is provided.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
Autonomous celestial navigation method for deep space probe on near-earth parking orbit
ActiveCN103968834AHigh precisionEliminate the effects ofNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by astronomical meansSpace probeStratosphere
The invention relates to an autonomous celestial navigation method for a deep space probe on a near-earth parking orbit. The method comprises the following steps: performing continuous height (20-50km) modeling and fitting in the stratosphere on density scale height H according to data given by United States atmosphere standard in 1976, establishing a stellar atmospheric refraction model, establishing a novel measurement model by taking height difference at adjacent moments as observed quantity, and estimating the navigation parameters by adopting a method for correspondingly improving extended Kalman filter parameters. The autonomous celestial navigation method is applied to navigational positioning of the deep space probe on the near-earth parking orbit, errors caused by the environment can be eliminated on the basis that extra observed quantity is not increased, and the navigation accuracy is guaranteed.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
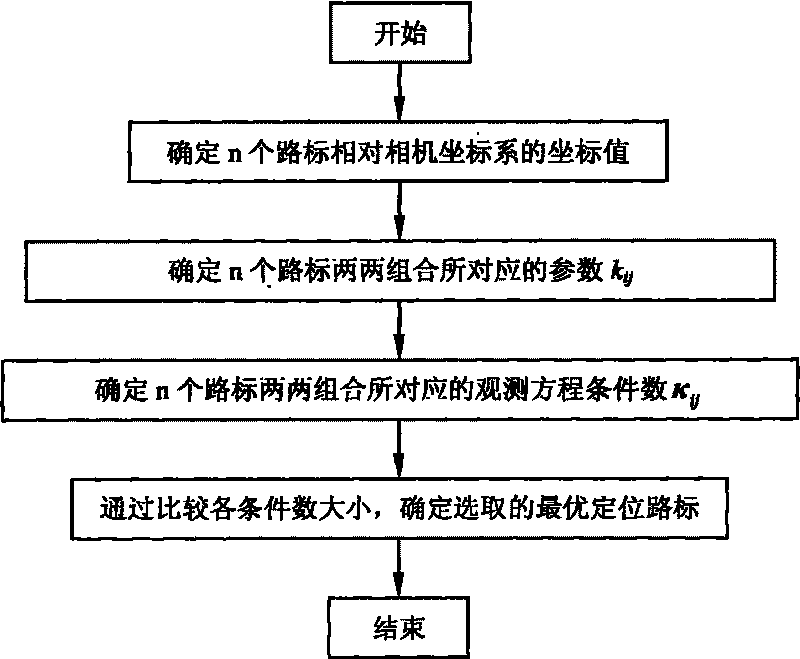
Observation condition number-based method for selecting autonomously located road sign of deep space probe
InactiveCN101762274AAnalysis is possibleSmall amount of calculationInstruments for comonautical navigationCelestial bodySpace probe
The invention relates to an observation condition number-based method for selecting an autonomously located road sign of a deep space probe, which is particularly applicable to an autonomously location determining system for a dual-road-sign detector, belonging to the field of autonomous navigation. By calculating and comparing the number of observation matrix conditions, the method can construct the position of the detector in a target celestial fixedly connected coordinate system by selecting two road signs, ensures the precision of determining the detector position can be greatly improved, and provides an accurate and practical located road sign autonomously selecting method for the deep space probe in low-earth orbit flight. The method not only considers the impact of the road sign position to navigation precision, but also has the characteristics of small calculation, practical analysis and the like.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
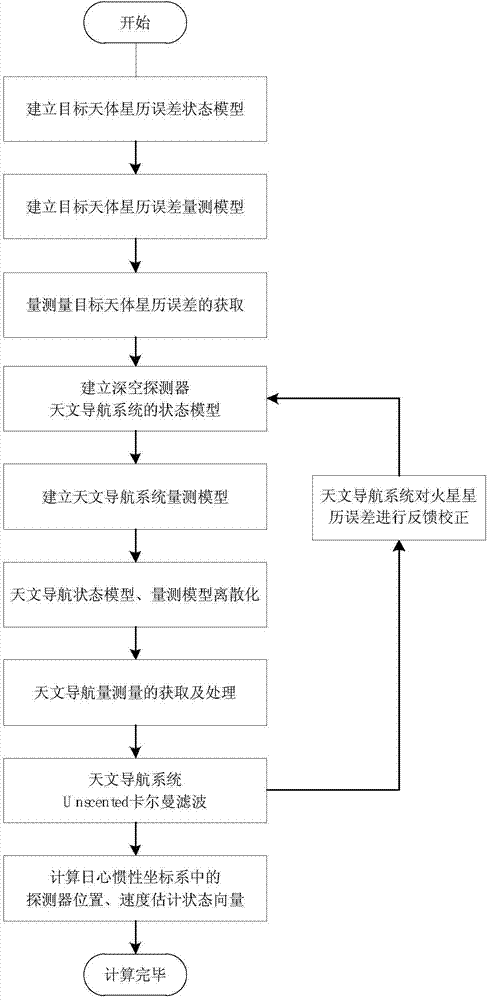
Ephemeris correction-based autonomous celestial navigation method for deep space probe in capturing stage
ActiveCN104764449ALittle impact on accuracyAchieving High-Precision EstimationNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by astronomical meansAngular distanceDynamic models
The invention discloses an ephemeris correction-based autonomous celestial navigation method for a deep space probe in a capturing stage. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing an ephemeris error state model and an ephemeris error measurement model of a target celestial body, and measuring ephemeris error according to a position difference between a predicted celestial body image and an actual celestial body image; secondly, simultaneously taking the ephemeris error state model and an orbital dynamic model as a celestial navigation system state model, taking the ephemeris error measurement model and a starlight angular distance measurement model as measurement models of a celestial navigation system, estimating the position and speed of the probe and the ephemeris error of the target celestial body by a Unscented Kalman filtering method, feeding back the estimated ephemeris error to the state model, and correcting the ephemeris data of the target celestial body, thereby obtaining the position and speed of the probe, relative to the target celestial body and the heliocenter, after autonomously correcting the ephemeris error. The method provided by the invention belongs to the technical field of aerospace navigation, can perform on-line estimation on ephemeris error of celestial bodies and correct model error of the navigation system, and is suitable for the probe capturing stage.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Autonomous attitude maneuver control method of deep space probe
InactiveCN104635740AImprove search efficiencyReduce planning timeAttitude controlSpacecraft attitude controlSpace probe
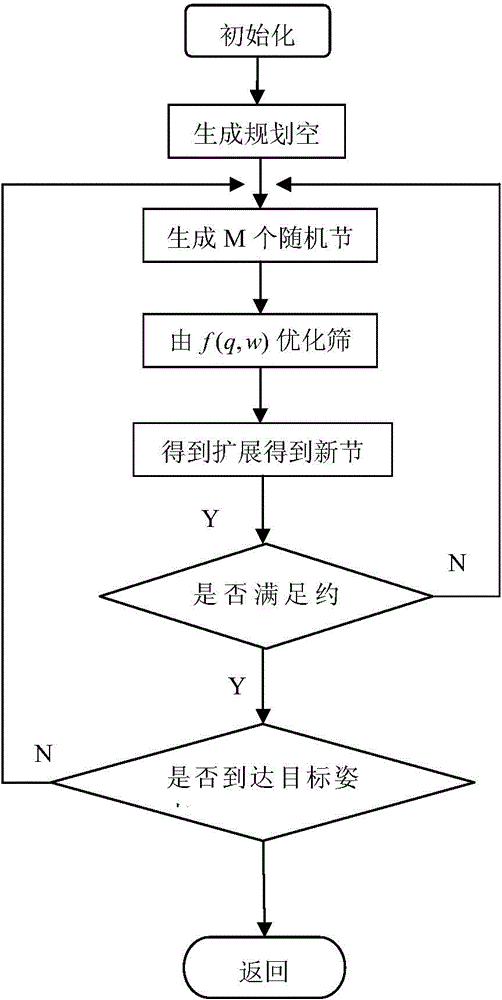
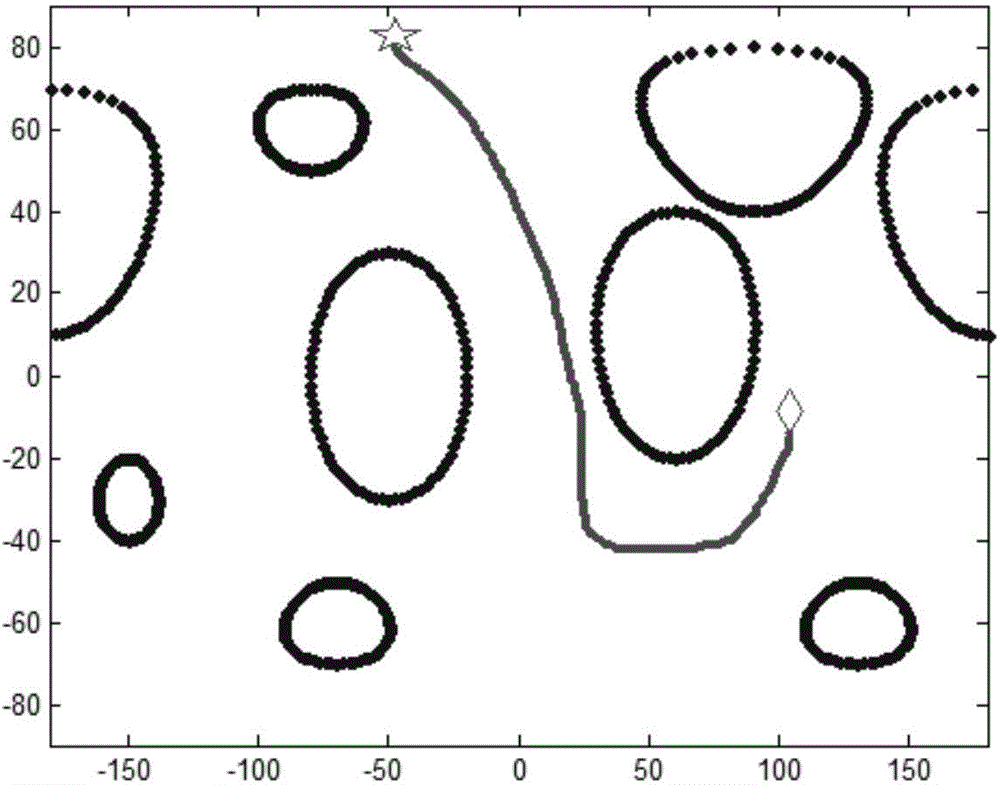
The invention discloses an autonomous attitude maneuver control method of a deep space probe, which relates to the autonomous attitude maneuver control method and belongs to the technical field of spacecraft attitude control. The autonomous attitude maneuver control method comprises the following steps of carrying out random sampling on uniformly-distributed nodes of an attitude space with an ORRT (Optimized Rapidly Exploring Random Tree) algorithm as a path planning method, making a balance and choosing the optimum path to expand, carrying out incremental expansion in a safety space in a greedy expansion manner, respectively establishing a probe attitude maneuver dynamic constraint model, an actual engineering constraint model and a probe geometric constraint model under a probe body coordinate system to obtain path nodes which meet the constraint and generate a control moment for the nodes, thereby generating a probe attitude maneuver path and a required control moment, and implementing the purpose that probe maneuvers to a target attitude according to the generated probe attitude maneuver path and the required control moment. According to the autonomous attitude maneuver control method, the path planning time is shortened and the efficiency that the probe maneuvers to the target attitude from the initial attitude is improved under the condition that all kinds of complicated constraint conditions faced by the probe are met.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Observable analysis based deep space probe autonomous-navigation method
ActiveCN103591956AReduce power consumptionHigh precisionNavigational calculation instrumentsInstruments for comonautical navigationNonlinear filterSpace probe
The invention relates to an observable analysis based deep space probe autonomous-navigation method, and belongs to the technical field of deep space detection. The method combines the observable analysis with an optical measurement based autonomous navigation scheme, the autonomous navigation scheme is constructed by utilizing the optical measurement, and an optimal navigational star is selected through the observable analysis to make the observability of a navigation system strongest in order to realize the optimal navigation performance. The method provides navigation information through an optical measurement means, and has the advantages of low power consumption, high precision and strong autonomy; the combination of the observable analysis to select the navigational star makes the observability of the navigation system strongest, and guarantees the navigation performance; and a nonlinear filter is utilized to carry out navigation filtering solution, so the accuracy and the convergence of the navigation filtering are improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Construction method and device for deep space probe autonomous navigation system
ActiveCN109612472AHigh precisionInstruments for comonautical navigationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAutonomous Navigation SystemSpace environment
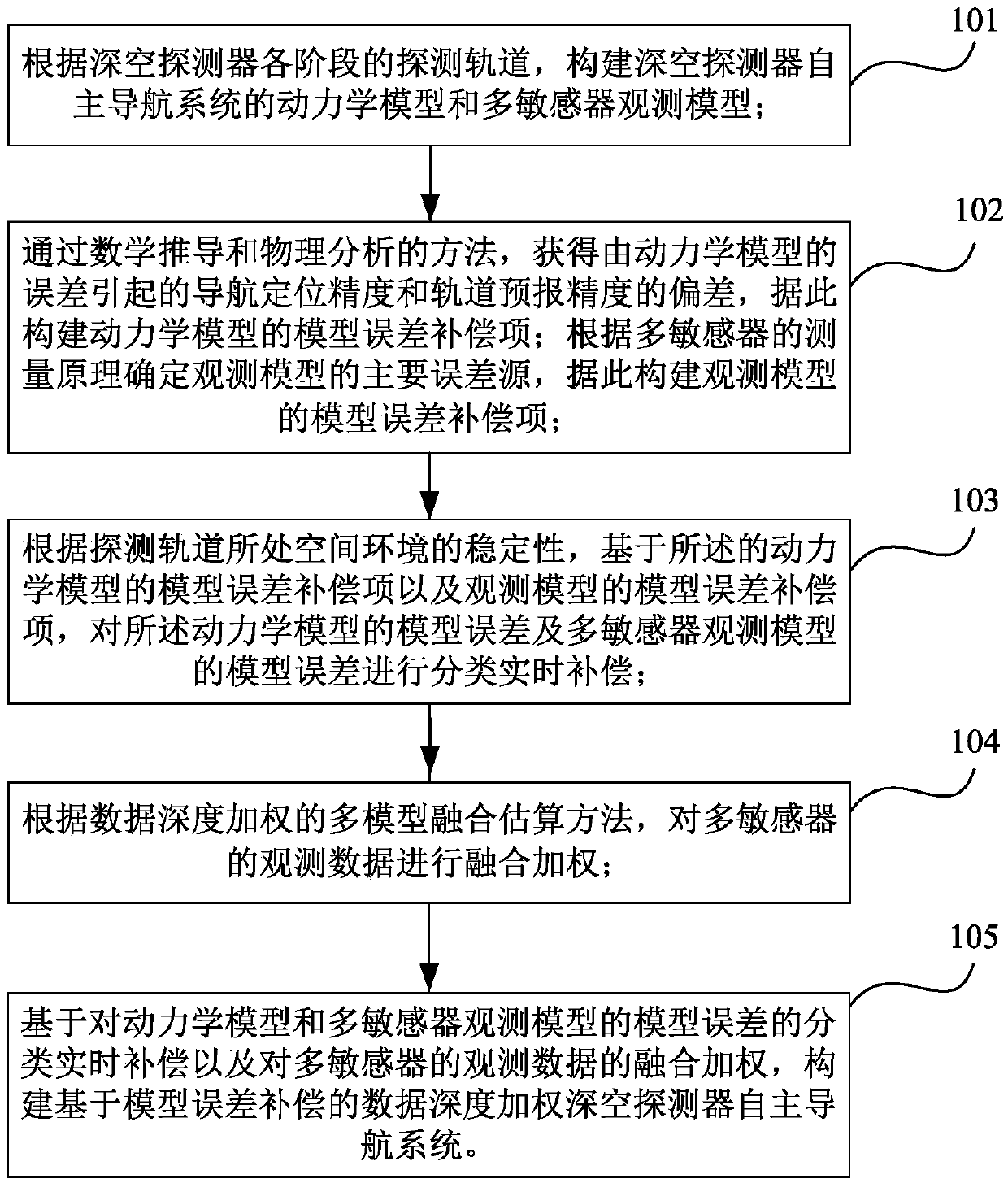
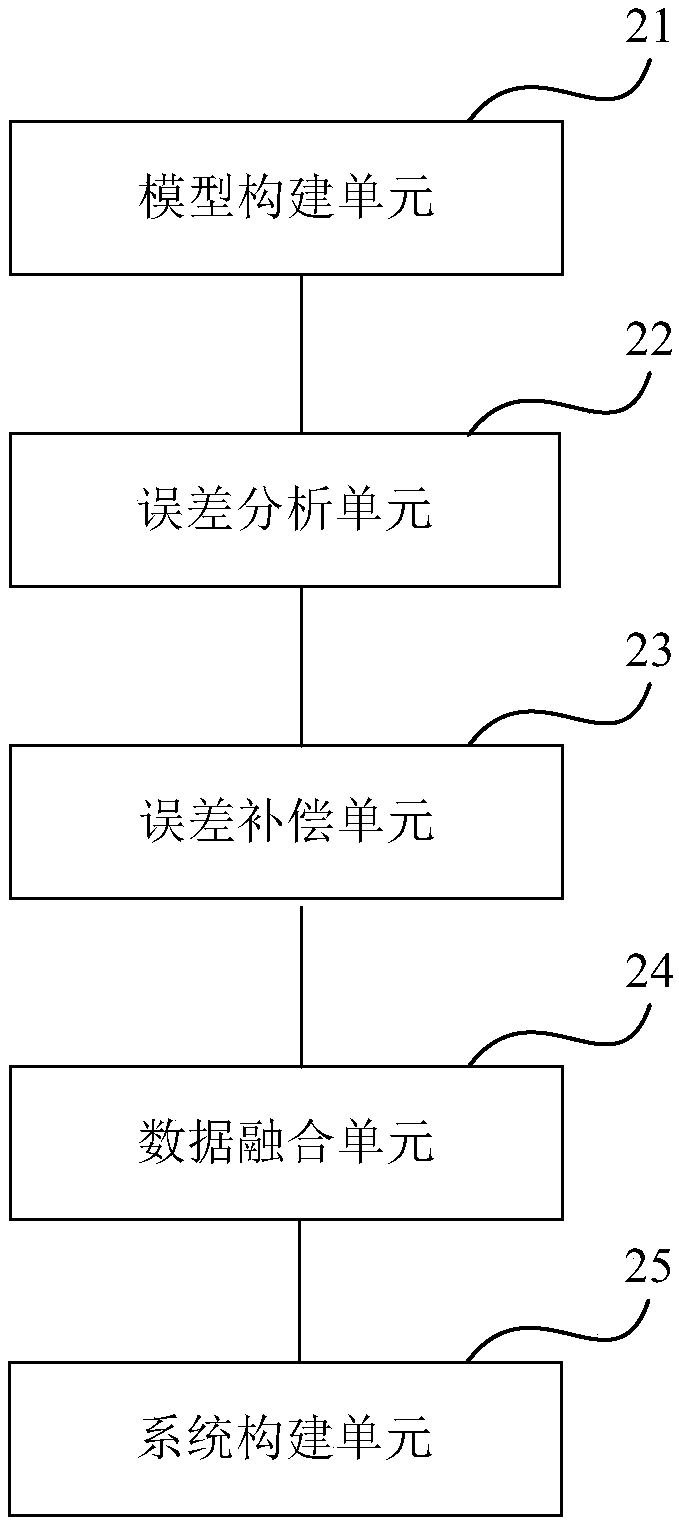
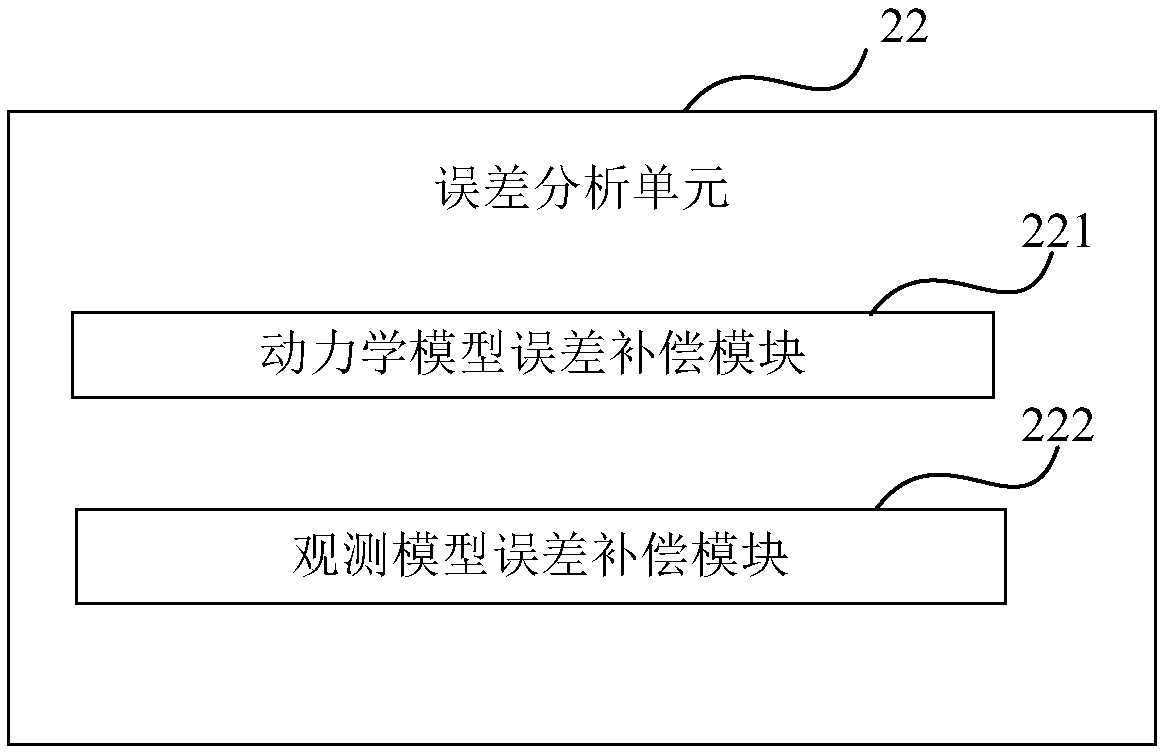
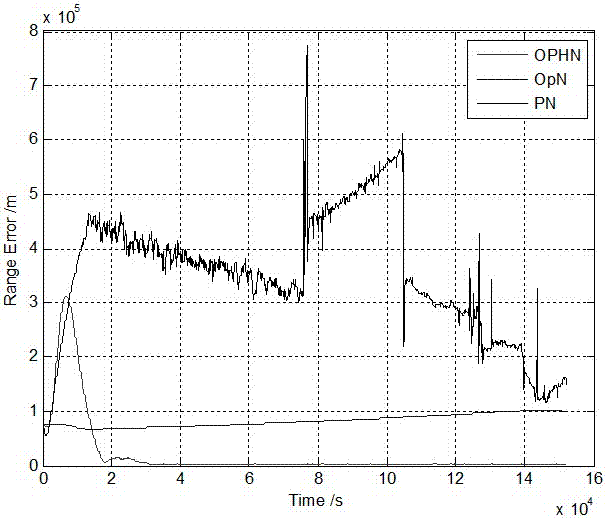
The invention relates to the field of deep space detection, in particular to a construction method and device for a deep space probe autonomous navigation system. The method comprises the following steps that: according to the probing orbit of each stage of the deep space probe, and constructing the kinetic model and the multi-sensor observation model of the autonomous navigation system; further constructing the model error compensation items of two categories of models; according to the stability of space environment where the probing orbit is positioned, on the basis of the model error compensation items, carrying out classified real-time compensation on two categories of model errors; according to a data depth weighing multi-model fusion estimation method, carrying out fusion weighing on the observation data of multiple sensors; and on the basis of the classified real-time compensation of the model errors and the fusion weighing of the observation data, constructing the autonomous navigation system. By use of the method, two categories of model errors, including the kinetic model, the observation model and the like of the deep space probe, are subjected to classified real-time compensation processing, and data is deeply applied to the fusion rule of the multi-sensor observation data so as to improve the accuracy of the deep space probe autonomous navigation system.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
High-observability optical pulsar hybrid navigation method for deep space probe
InactiveCN107144283AOvercoming the problem of large cumulative errorsSolve the problem of weak observabilityInstruments for comonautical navigationNavigation systemEquation of state
The invention discloses a high-observability optical pulsar hybrid navigation method for a deep space probe. The high-observability optical pulsar hybrid navigation method comprises the following steps: 1: mixing a pulsar observation equation with an optical observation equation to build a hybrid observation equation; 2: building a probe state equation by using a deep space probe multibody gravity model and taking an inertia position and the speed of the probe as state quantities; 3: constructing extended Kalman filter to perform optimal estimation calculation on the state of the probe in order to obtain a position and a speed under an accurate probe inertial system. By adopting the high-observability optical pulsar hybrid navigation method disclosed by the invention, the problem of large inertial navigation accumulative error is solved, the problem of poor observability in pulsar navigation is solved, the observability of a navigation system is enhanced greatly, the convergence time of the navigation system is shortened greatly, and the navigation accuracy is increased effectively; the high-observability optical pulsar hybrid navigation method can be directly applied to autonomous control of the deep space probe.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
Deep space exploration autonomous mission planning method based on constraint satisfiable technology
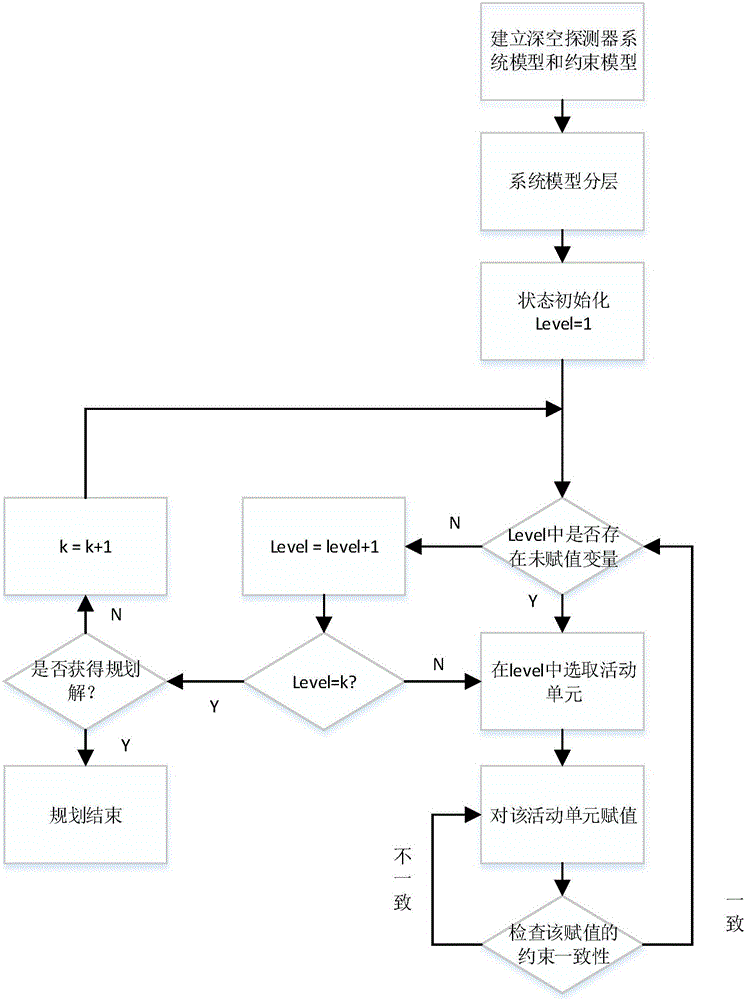
ActiveCN105760652AReduce complexityOvercoming complexitySpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsAviationMission plan
The invention discloses a deep space exploration autonomous mission planning method based on the constraint satisfiable technology, relates to deep space exploration autonomous mission planning methods and belongs to the technical field of aerospace engineering.The deep space exploration autonomous mission planning method comprises the following steps that a deep space probe system model is established; a deep space probe constraint model is established; the deep space probe system model is layered according to the deep space probe constraint model; planning missions are initialized; a movable unit (the symbol is shown in the description) is selected from a level layer, a state is selected from a state collection Di corresponding to the movable unit (the symbol is shown in the description), and a value is assigned to the movable unit (the symbol is shown in the description); consistency inspection is carried out on constraints of the movable unit; value assigning and circulating are carried out until all constraints in a constraint collection C of the deep space probe constraint model are met, a value assigning result serves as a deep space exploration autonomous mission planning result, and autonomous mission planning is completed.By means of the deep space exploration autonomous mission planning method based on the constraint satisfiable technology, the problems that in existing deep space missions, constraints are complex, and the coupling relations between the constraints are strong are solved, the autonomous mission planning efficiency of a deep space probe is improved, and the requirement for the real-time performance of the probe is met.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Deep space probe autonomous mission planning time constraint geometric processing method
ActiveCN105487546AHigh real-time requirementsMake up for the shortcoming of long calculation timeCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsSpace probeDeep space exploration
The invention relates to a deep space probe autonomous mission planning time constraint geometric processing method and belongs to the technical field of deep space exploration. The invention discloses a method for verifying time constraint consistency (active variable value domain can meet all constraints) and geometrically processing the constraints, so that the time constraint consistency in the planning process of a deep space probe can be verified and time constraint is processed quickly, the final active variable value domain can be obtained, and the defect of long calculation time caused by adopting a time constraint network to process a large number of active variables is solved. Compared with the time processing method based on the time constraint network, the method in the invention solves the same time constraint problem, the computation time is short and efficiency is high; and the method is more suitable for the deep space probe having high real-time performance requirement.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Autonomous optical navigation target imaging analog system for landing of deep space probe
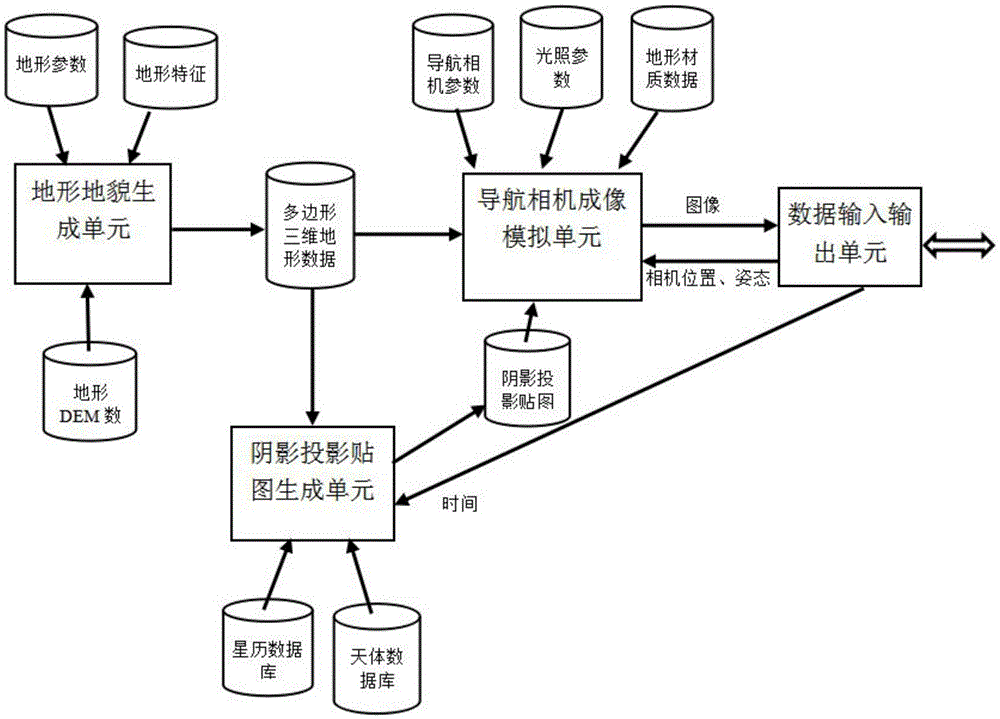
The invention discloses a kinetics analog system for the landing of an asteroid probe. A target celestial body topography generation unit is in charge of reading topographical gross DEM (Dynamic Effect Model) data, surface physical parameter profiles, and surface feature profiles, and polygon three dimensional topographical data conforming with the target celestial body topographical features are generated by an algorithm; a shadow projection generation unit is in charge of calculating the position of the target celestial body relative to the sun and the incident angle of solar ray at the current analog time according to an ephemeris, and rendering to generate a shadow projection map; a navigation camera imaging analog unit is in charge of rendering to generate an image in accordance with the requirements of a camera according to the information of current camera parameters, positions, illumination parameters, and topographical texture; a data input and output unit is in charge of receiving and resolving the data of the camera position, attitude parameters and current analog time sent over by a client side according to a protocol, meanwhile packaging and sending the image data generated by rendering to the client side according to the protocol so as to be used in the resolution of an autonomous optical navigation system, thus realizing the imaging analog of the navigated target.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com