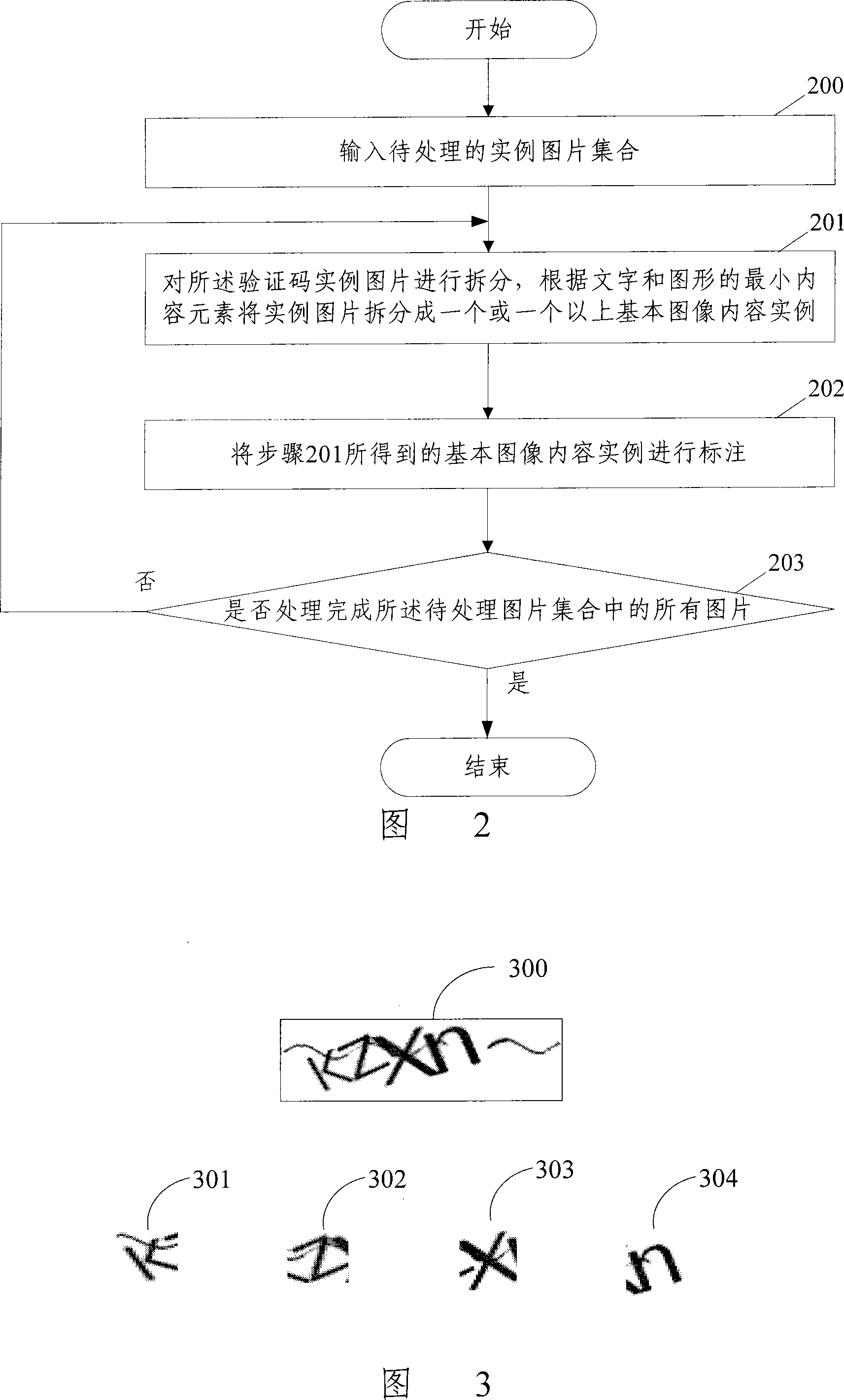
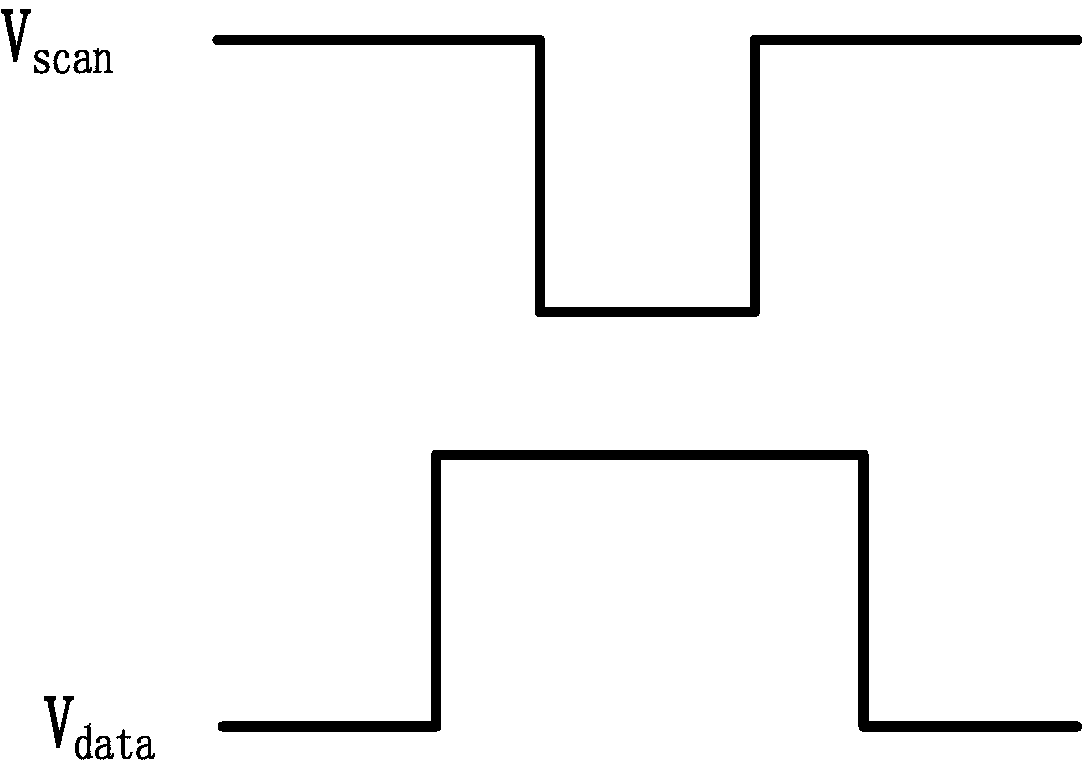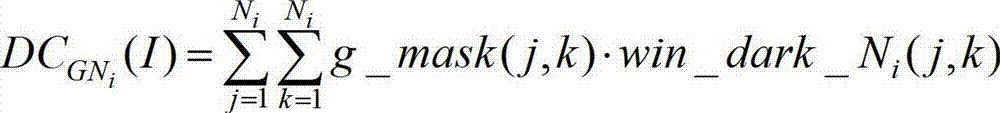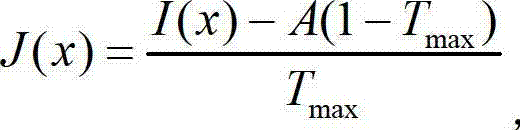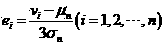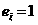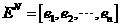Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3685results about How to "Reduce operational complexity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
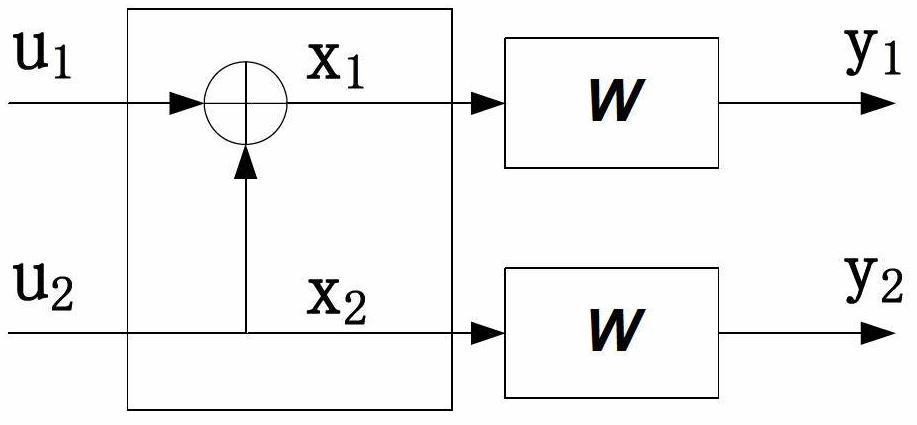
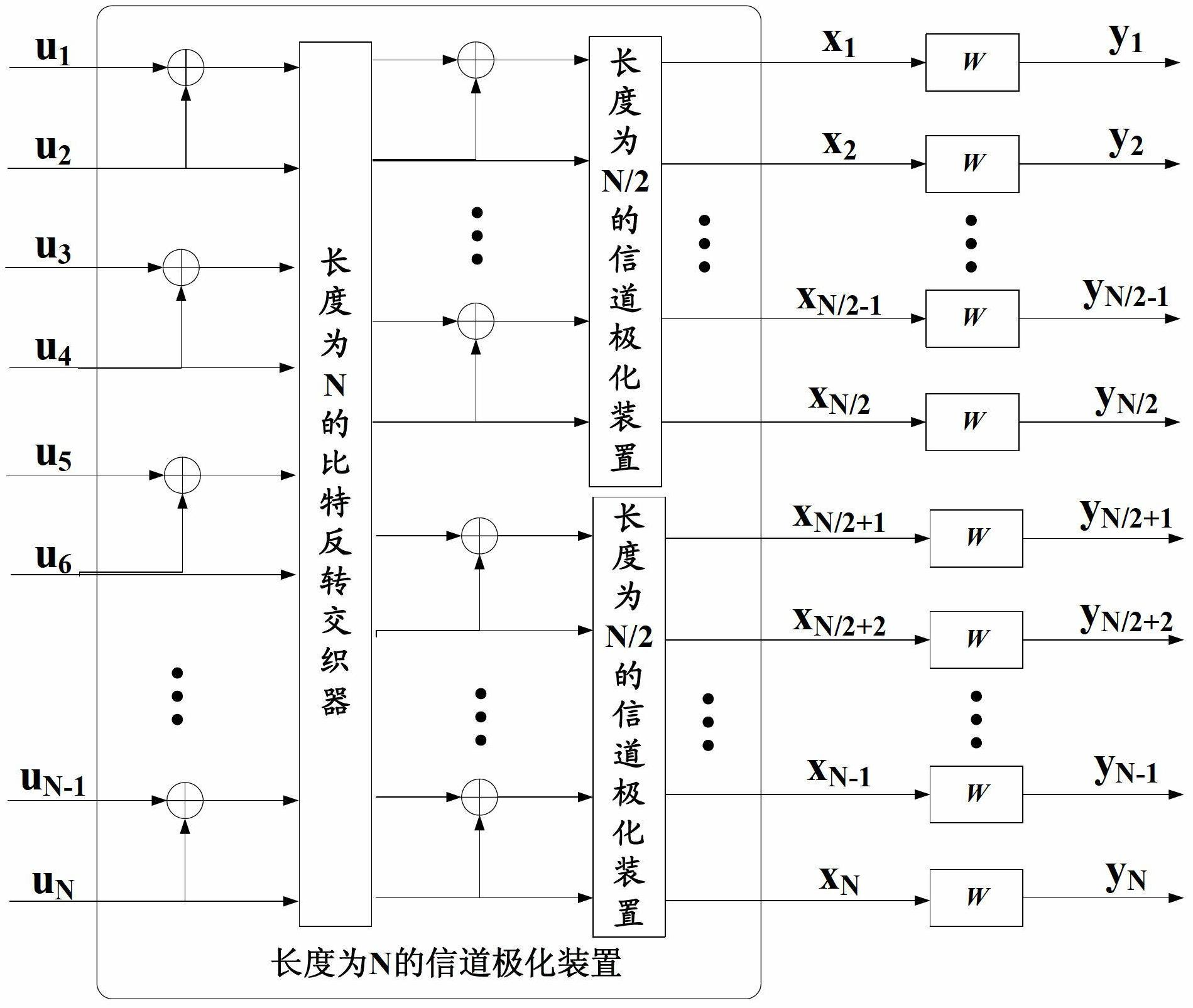
Polarization code decoding method for cyclic redundancy check assistance
InactiveCN102694625AStrong error correction abilityReduce operational complexityError preventionError correction/detection using linear codesCommunications systemCode division multiple access
The invention relates to a polarization code decoding method for cyclic redundancy check assistance. When a polarization code is decoded, in all the routes with cyclic redundancy check values of corresponding bit estimation sequences of being zero from a root node to leaf nodes on a code tree corresponding to the polarization code, one route with maximum reliability metric value is searched by taking a list or stack as assistance for route search, and the bit estimation sequence corresponding to the route is output as a decoding result. The method comprises the following operation steps of: determining parameters according to a search assistance method, constructing an auxiliary structure of the decoding method, searching a candidate bit estimation sequence and executing cyclic redundancy check. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, error correcting capability of a communication system which adopts the polarization code as channel coding is greatly improved, operation steps are simpler, and operation complexity is equivalent to or even lower than that of a Turbo code coding and decoding method used in a WCDMA (wideband code division multiple access) system, thus the method disclosed by the invention has a good practical prospect.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Vending machine and operation method thereof
ActiveCN106781014ALarge capacityLow costCoin-freed apparatus detailsApparatus for dispensing discrete articlesCost of goodsPurchasing process
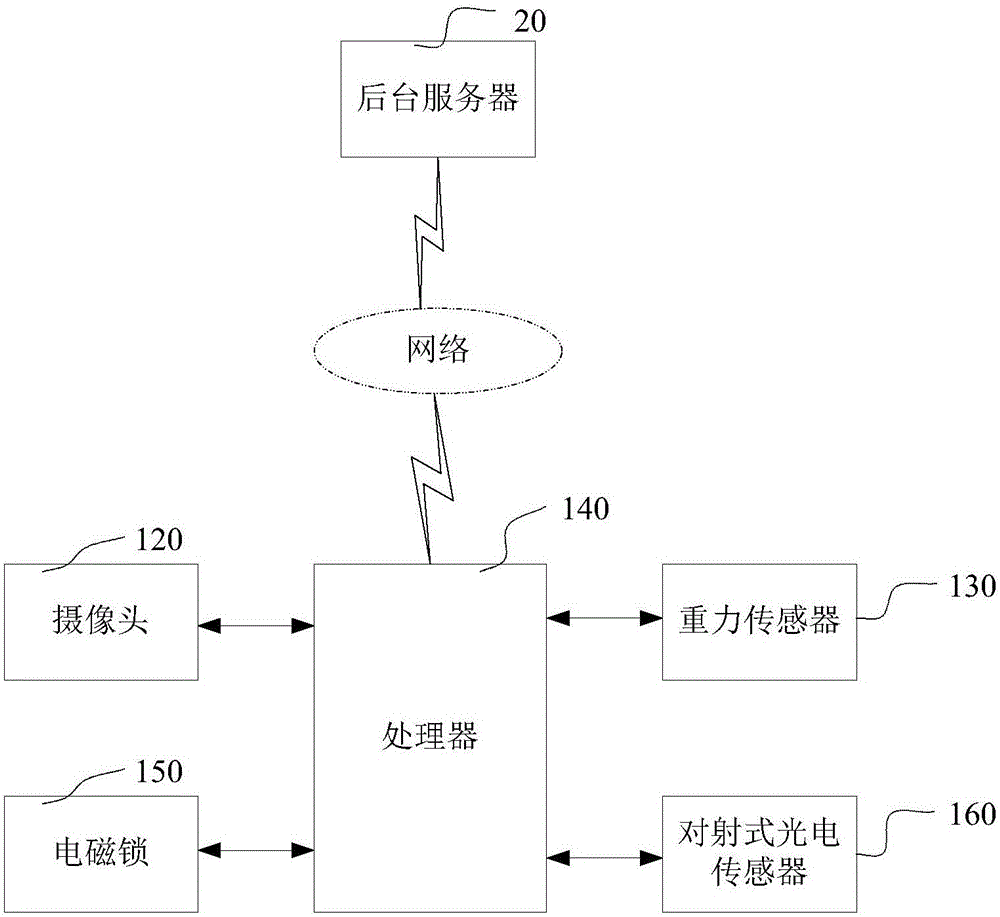
The invention relates to a vending machine and an operation method thereof. The vending machine comprises cameras which are connected to a processor, and the processor is connected to a background server through the network. The cameras shoot real-time image information of commodities for sale on goods racks, and send the real-time image information to the background server through the processor; the cameras shoot real-time image information of the commodities for sale on the goods racks, and identify first types and first quantity of the commodities for sale on the goods racks according to the real-time image information; the background server determines the types and quantity of the extracted commodities for sale according to the first types and the first quantity of the commodities for sale, and closes an account according to the types and quantity of the commodities for sale. By means of the technology, the cost of goods passages is reduced, the capacity of the goods racks is increased, the operation complexity of a user in the purchasing process can be further reduced, and the maintenance requirement is reduced.
Owner:GUANGZHOU YIDAO HULIANWANG CO LTD
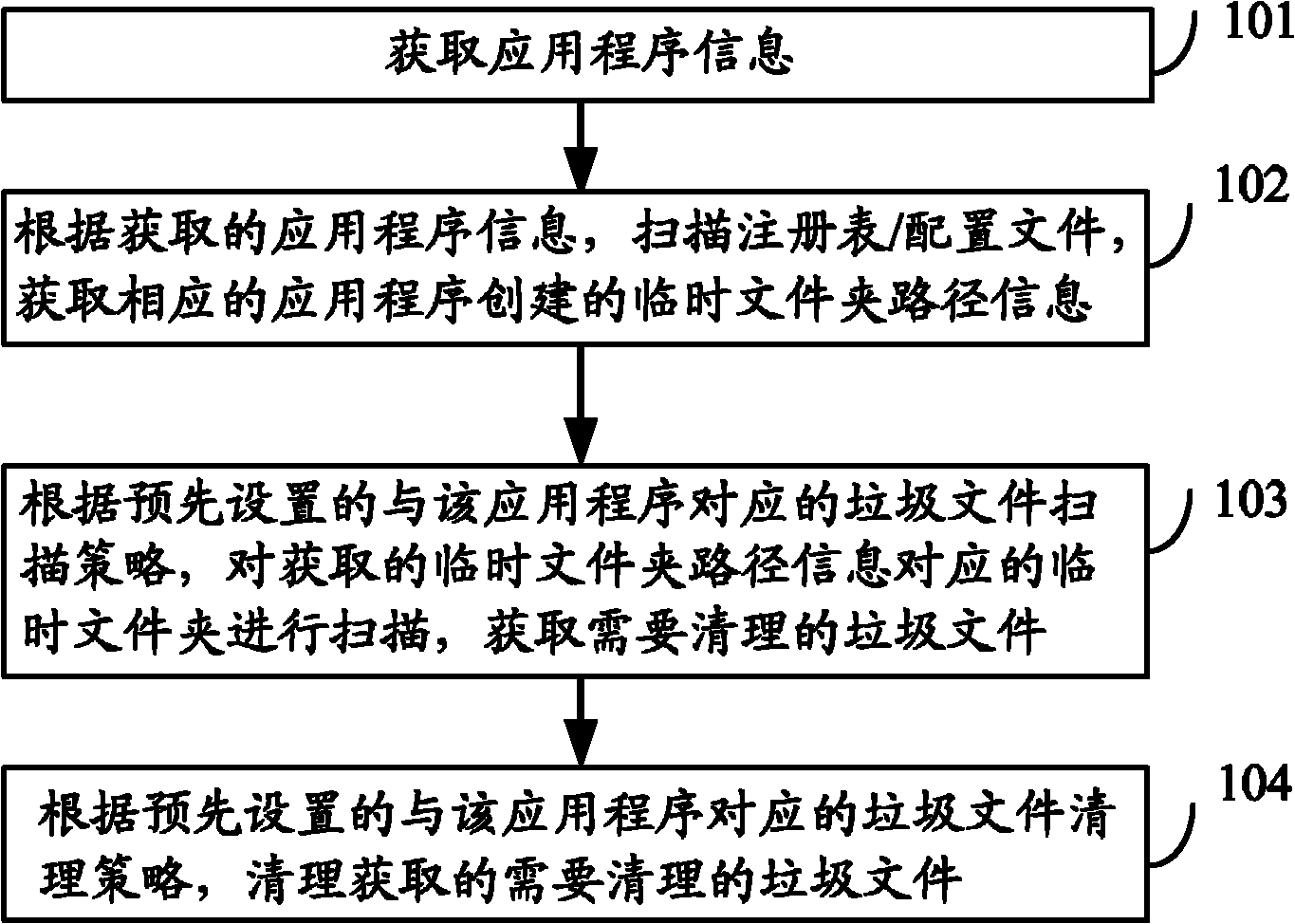
Method and device for cleaning junk files generated by application programs
InactiveCN102654872AEasy to cleanImprove utilization efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsApplication softwareTemporary folder
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Alarm association rule obtaining method of mobile internet
ActiveCN102098175AAccurate resultsImprove operational efficiencyData switching networksData conversionData cleansing
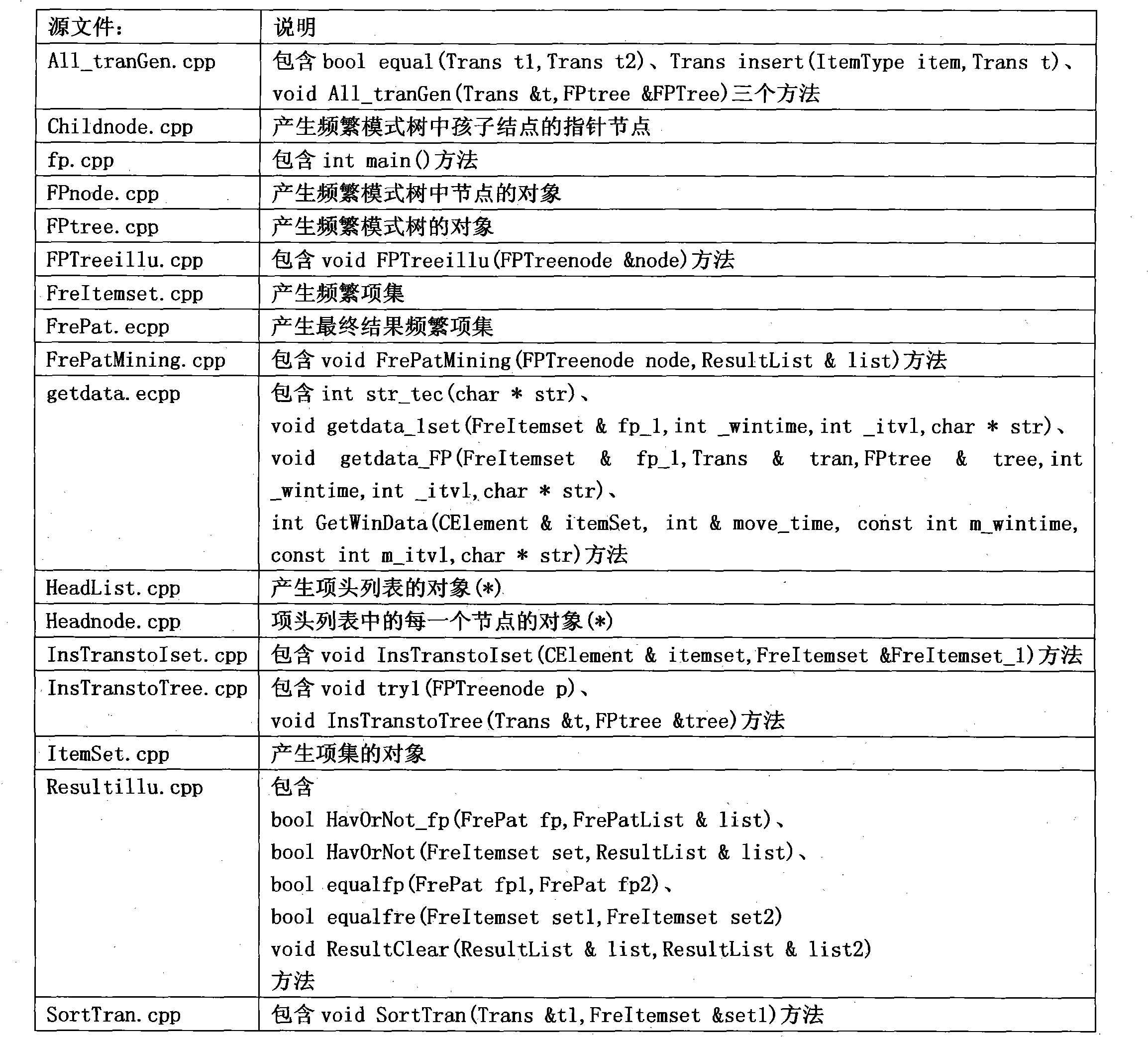
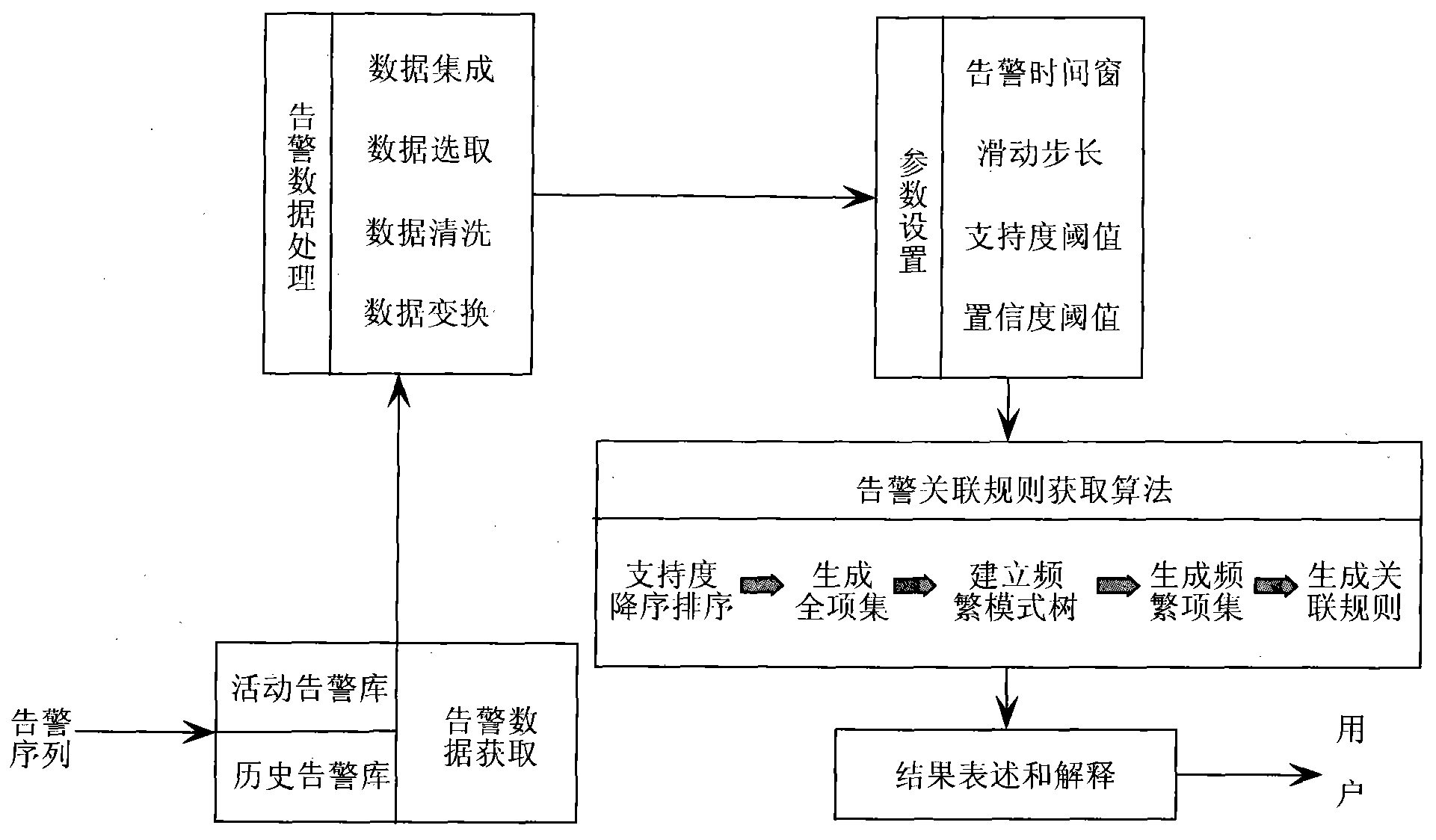
The invention provides an alarm association rule obtaining method of the mobile internet. A system comprises five parts of the obtaining of alarm data, the preprocessing of the data, the setting of parameters, the acquisition algorithm of the alarm association rule, and the expressing and the explaining of the association rule. The method comprises the steps: integrating, selecting, cleaning and changing communication alarm data; setting an alarm time window and an alarm sliding step length, and converting preprocessed relation type data into conventional type data to be convenient to obtain the alarm association rule; and setting support level and confidence level parameters, calling the acquisition algorithm of the alarm association rule based on a full itemset, obtaining the association rule from the alarm data according to the set parameters, and expressing and explaining the obtained alarm association rule. On the basis of the alarm association rule obtaining method, the alarm association analysis of the mobile internet can be realized without the participation of specialists, operation personnel and maintenance personnel, and the processing efficiency is doubled and redoubled under the condition that the operation cost is lower; and independent of a topological structure of a communication network, the method can be adapted to the complex, variable and isomerous communication network, can be used for automatically discovering the alarm association rule, is particularly suitable for the alarming and the monitoring of the mobile internet, and is wide in application prospect and good in practical value.
Owner:INSPUR TIANYUAN COMM INFORMATION SYST CO LTD
Safety identification method based on safe computer
ActiveCN101165696AReduce operational complexityImprove usabilityInternal/peripheral component protectionDigital data authenticationLog managementTrusted Platform Module
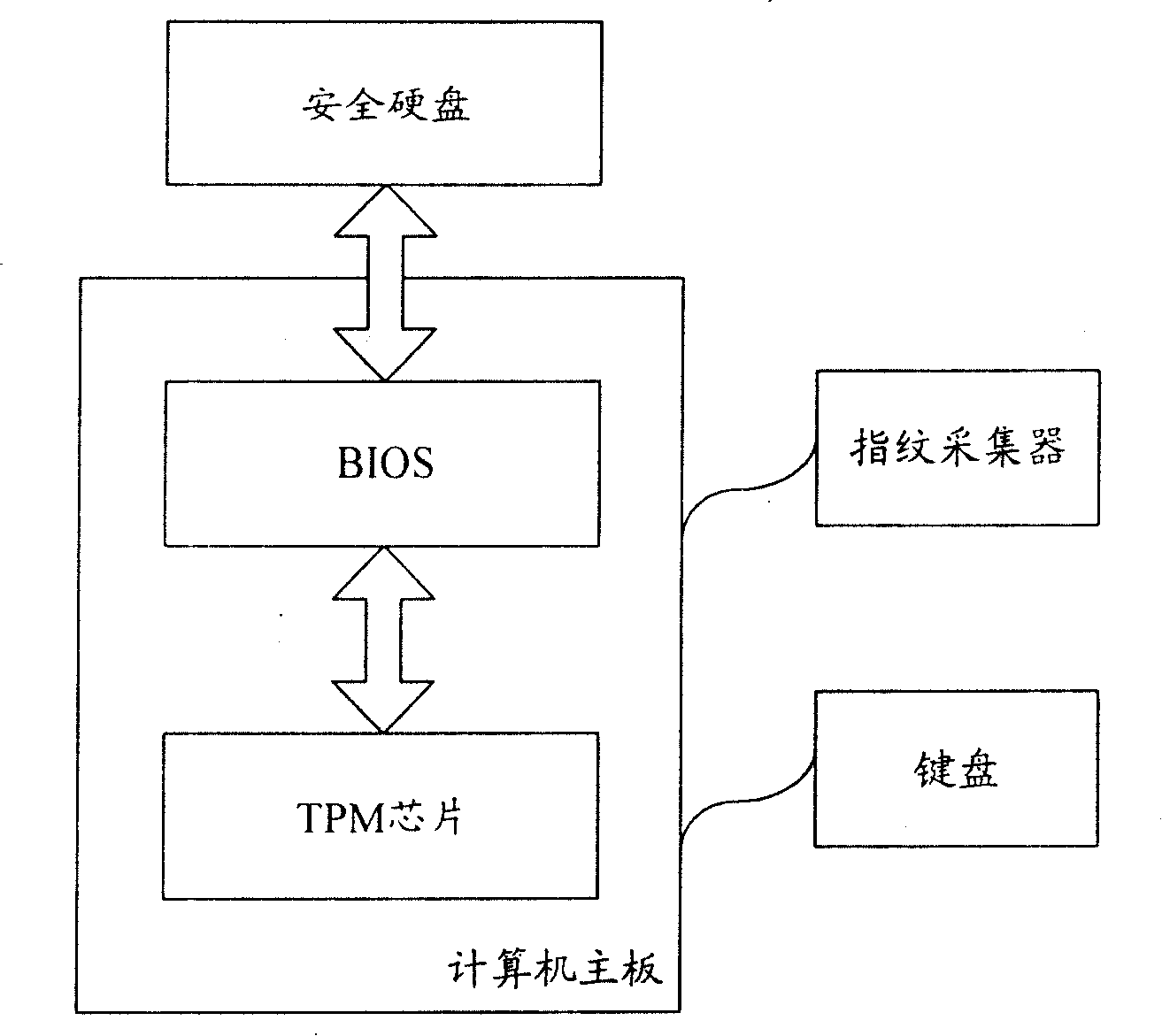
Said security computer comprises a computer mother board, a security hard drive, a basic input / output system (BIOS) located on said mother board and a trusted platform module (TPM) chip. Both Said TPM chip and the security hard drive are respectively connected to the BIOS. The method comprises: after said BIOS completes the system self-testing and initialization and before the mutual authentication is made between the BIOS and security hard drive, the BIOS make a forced ID authentication for user powering the computer; after passing through the ID authentication, the BIOS and the security hard drive make mutual authentication each other; if the authentication is passed, then the security authentication is successful.
Owner:CHINA GREATWALL TECH GRP CO LTD
Information processing method and electronic device
InactiveCN103533143AReduce operational complexityEasy to handleAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingRecord information storageInformation processingSpeech sound
The invention discloses an information processing method and an electronic device. The method comprises: when the electronic device is at a voice conversation state, detecting whether a voice recording instruction is received; when the received voice recording instruction is detected, executing voice recording operation; detecting whether a voice recording stopping instruction is received; when the received voice recording stopping instruction is detected, stopping voice recording; determining whether the voice data recorded through the voice recording operation comprises data in a predetermined form, and obtaining a first determination result; when the first determination result indicates that the voice data recorded through the voice recording operation comprises the data in the predetermined form, converting the data in the predetermined form into texts; and displaying the texts on the display unit of the electronic device. By adopting the method and the electronic device provided by the invention, the key information in the voice data can be automatically extracted, and voice information can be processed in a simple and convenient manner.
Owner:LENOVO (BEIJING) LTD
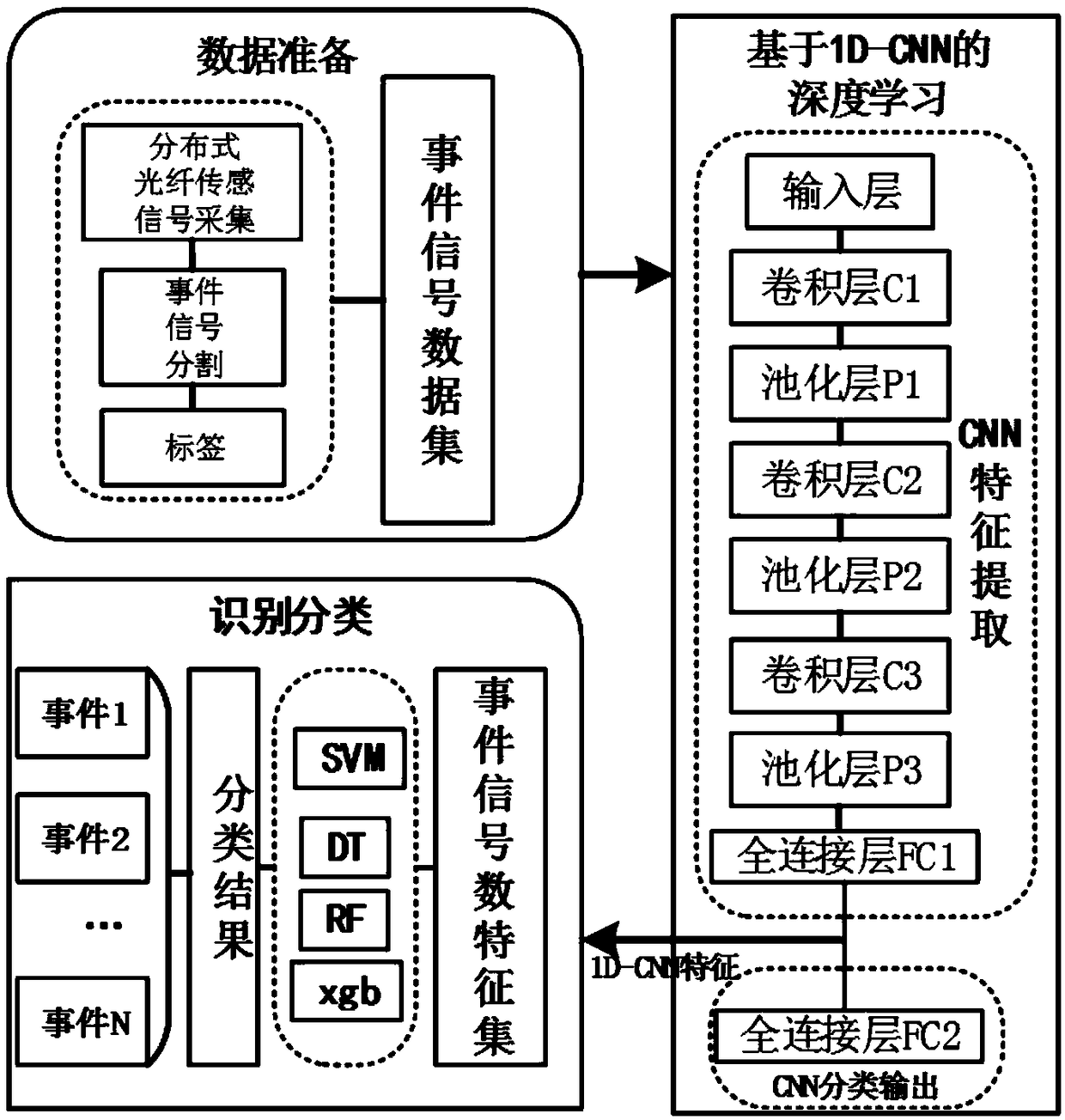
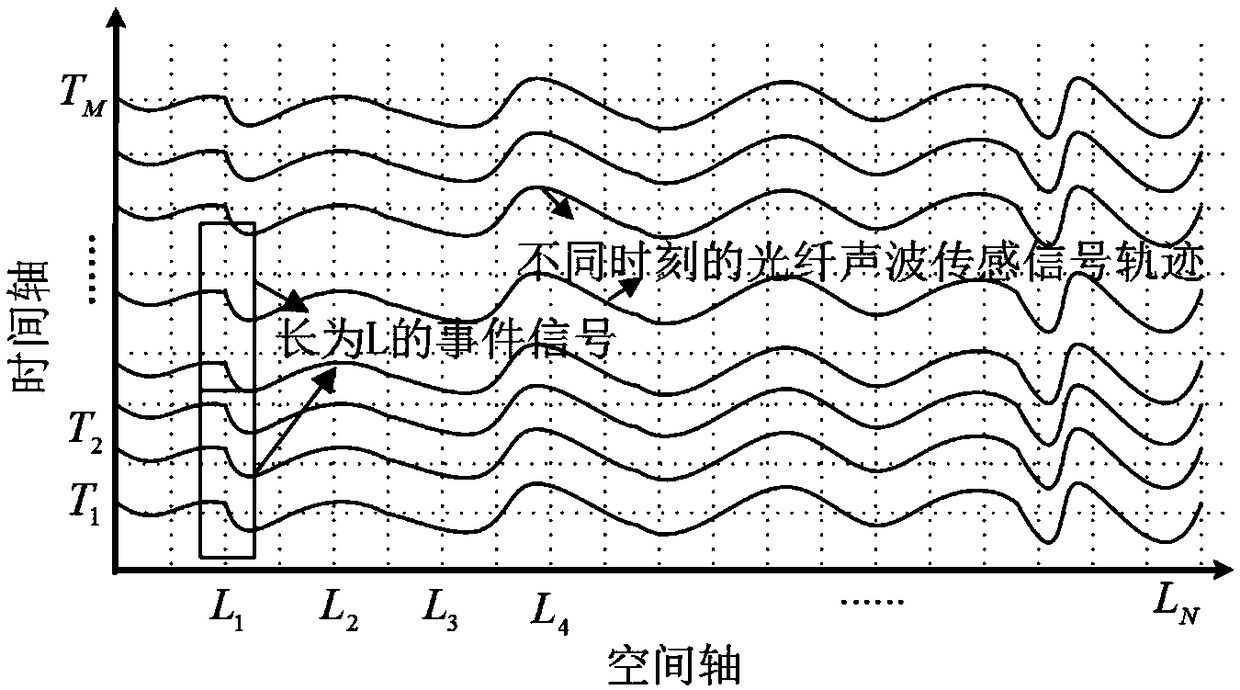
1D-CNN based distributed optical fiber sensing signal feature learning and classification method
ActiveCN108932480ARealize deep miningImprove recognition accuracyEnsemble learningKernel methodsData setFeature set
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
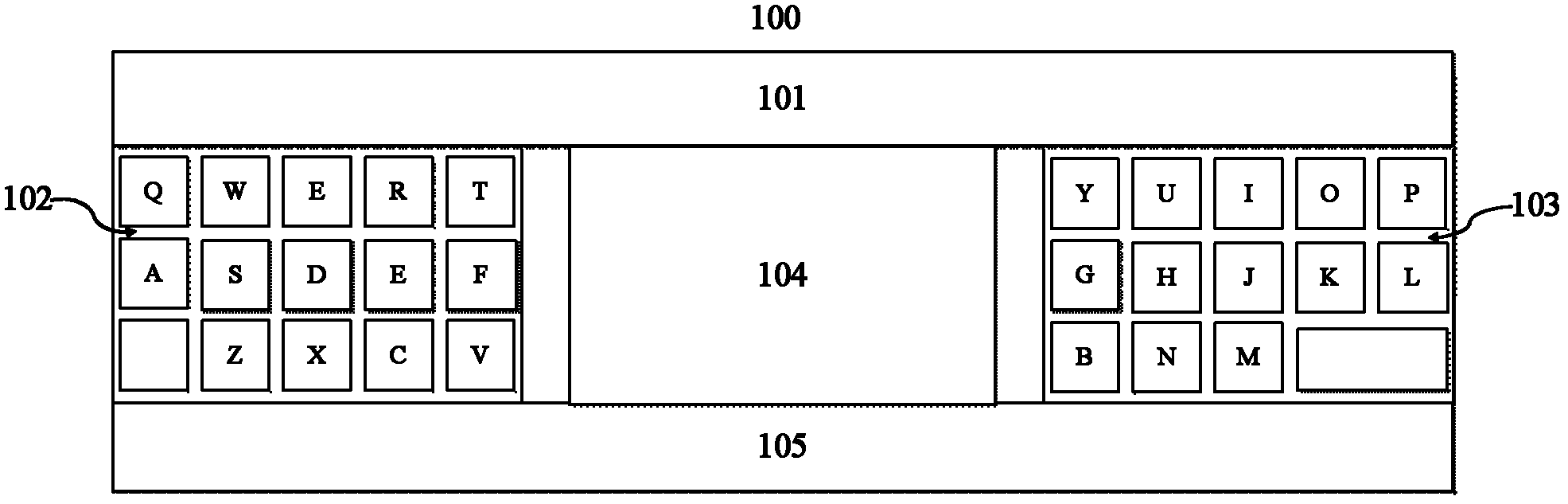
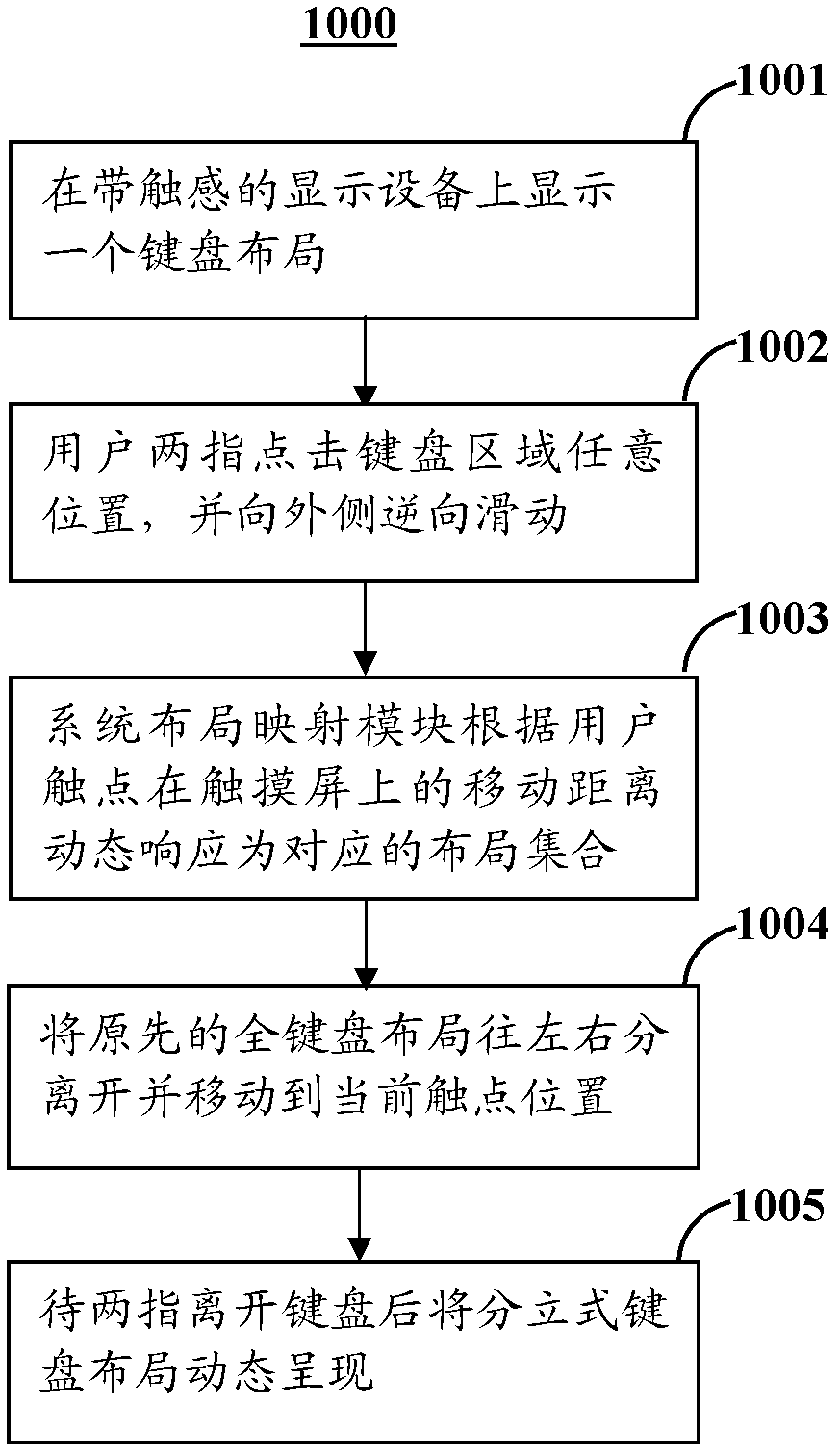
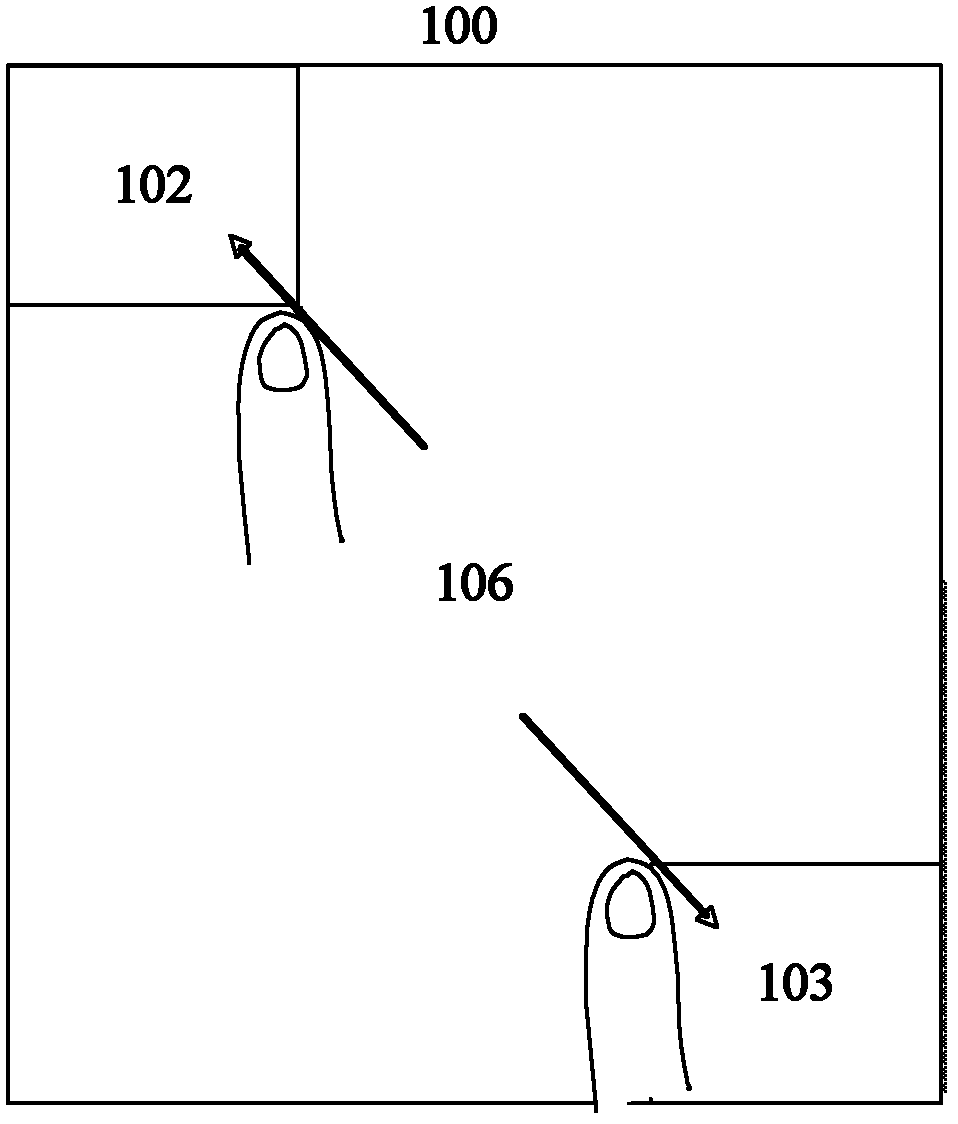
Discrete keyboard layout system and setting method, corresponding portable electronic device and control method
ActiveCN102360249AReduce operational complexityFriendly interfaceInput/output for user-computer interactionEmbedded systemHuman engineering
The invention relates to a discrete keyboard layout system used in a touch screen of a portable electronic device. The system comprises a left master keyboard area, a right master keyboard area and an additional function area, wherein the additional function area is arranged between the left master keyboard area and the right master keyboard area. The invention also relates to a method for carrying out keyboard layout switching setting and dynamic zooming on the discrete keyboard layout system, an electronic device system for implementing the discrete keyboard layout system, and a method for implementing the setting control of discrete keyboard layout switching based on the electronic device system. By using the discrete keyboard layout system and setting method, corresponding portable electronic device and control method disclosed by the invention, the keyboard position layout function can be changed flexibly so as to accord with the human engineering, thereby obviously reducing the operating complexity of a user and solving the continuity problem of overall error correction of an area of a keyboard; meanwhile, an interface is friendly, the implementation procedure is simple, the application is flexible and efficient, the performance is stable and reliable, and the application range is wide.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHULE (COOTEK) INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
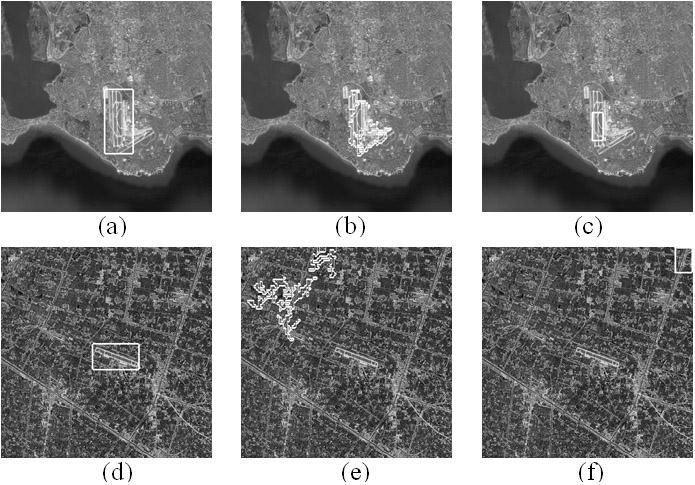
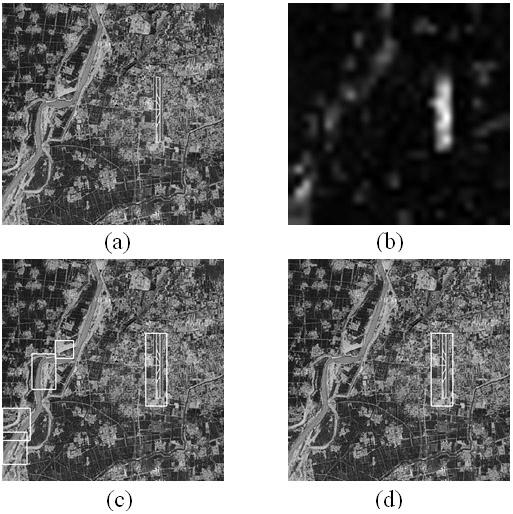
Method for detecting and identifying airport target by using remote sensing image based on selective visual attention mechanism
InactiveCN102214298AReduce operational complexityFix inaccurate positioningCharacter and pattern recognitionIdentification rateImage based
The invention belongs to the technical field of remote sensing image target detection and identification, and in particular relates to a method for quickly detecting and identifying an airport target by using a remote sensing image based on a selective visual attention mechanism. By the method, the saliency of the original remote sensing image is analyzed by an improved attention selection model,namely graph-based visual saliency (GBVS), to acquire a saliency area, and the aim of identifying the airport target is fulfilled according to a scale-invariant feature transform (SIFT) characteristic on the area by combining a hierachical discriminant regression (HDR) tree. The method can effectively overcome the defect that the image is analyzed pixel by pixel in the conventional airport detection method. Compared with the conventional other airport detection methods, the method is characterized by high speed, high identification rate and low false alarm rate, has high noise robustness, andgreat significance and high value in practical application, and is very suitable for real-time detection under complex backgrounds in the fields of military use and civilian use.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
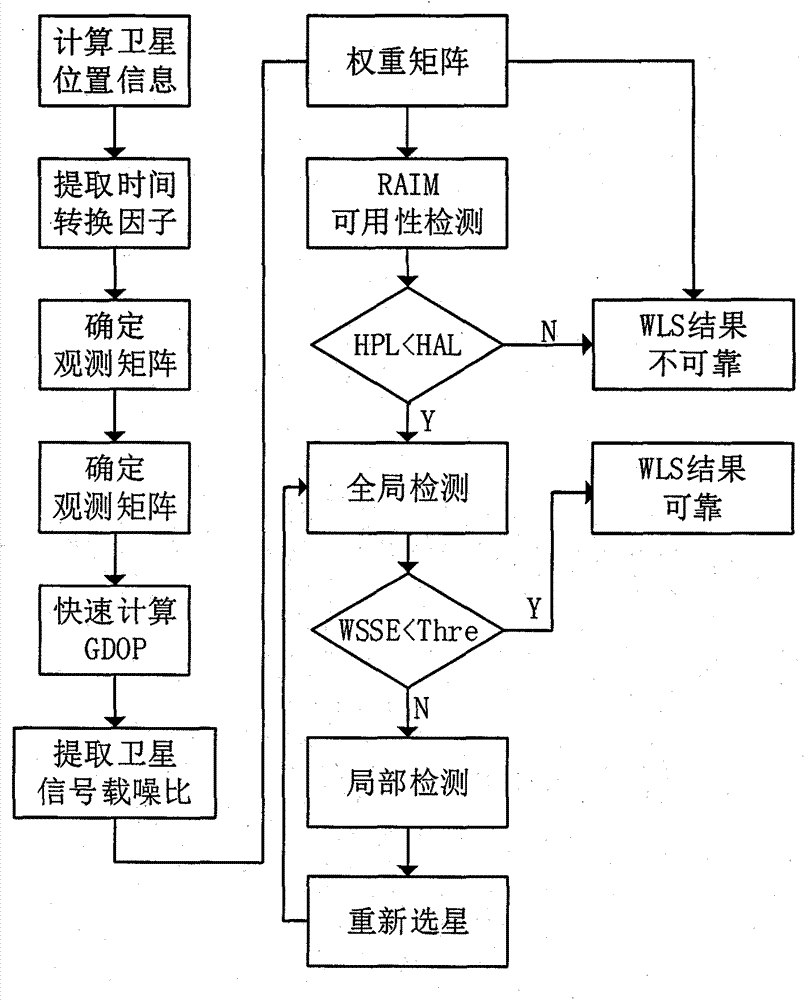
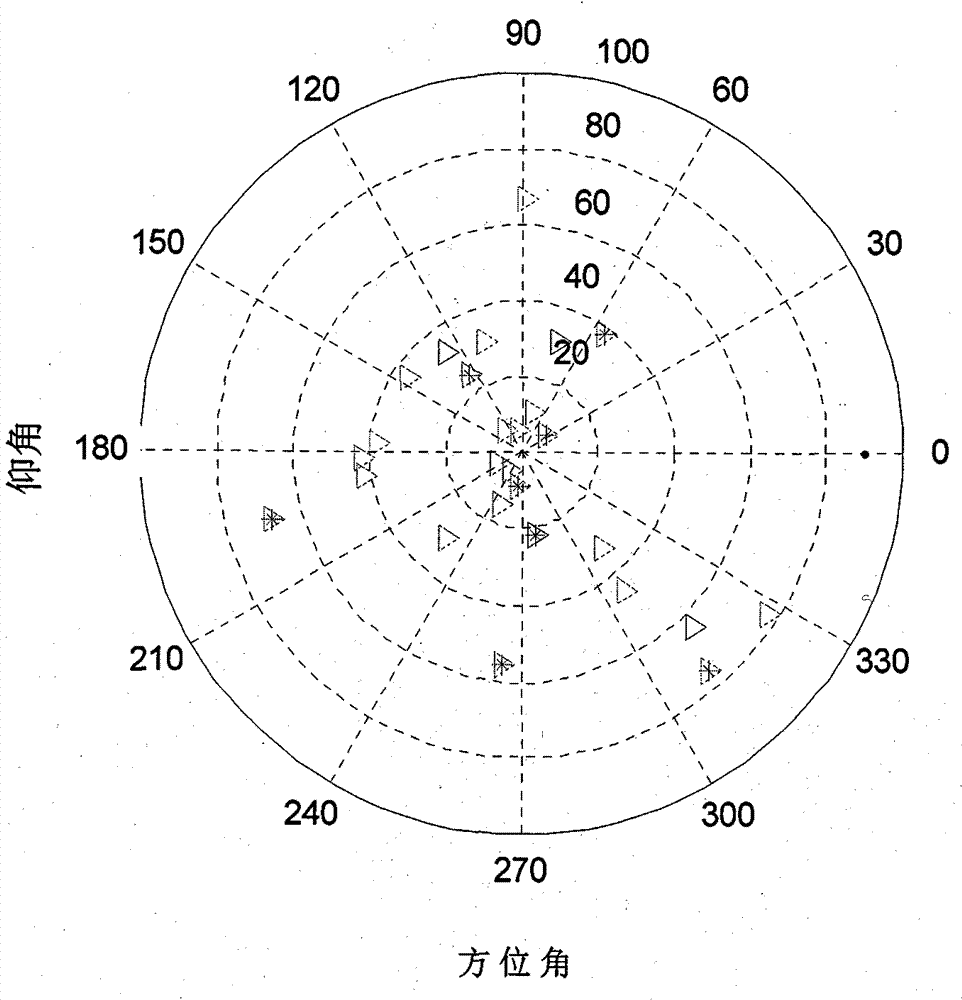
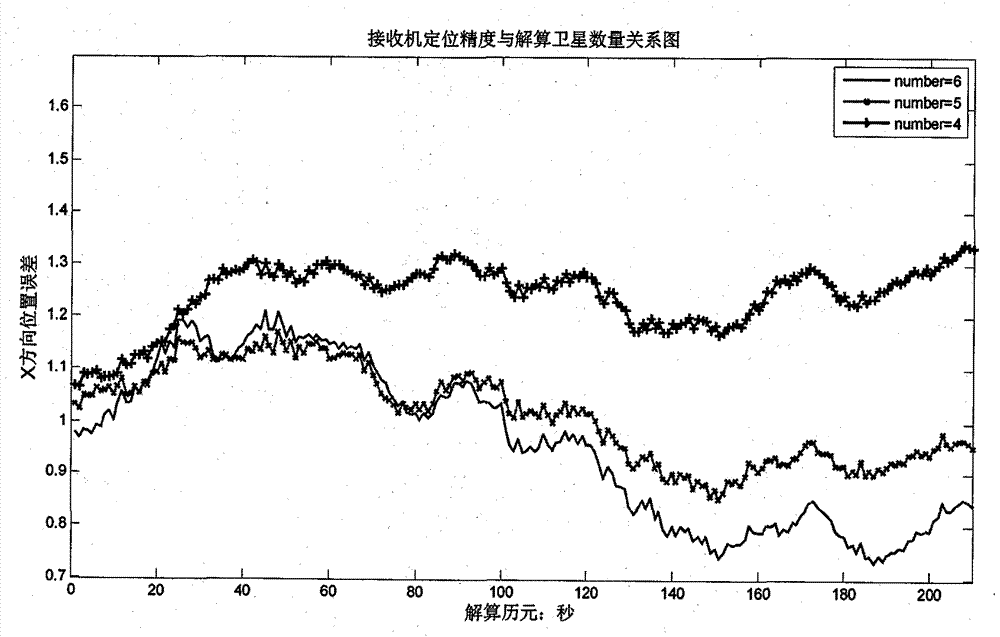
New method for RAIM (receiver autonomous integrity monitoring) based on satellite selecting algorithm in multimode satellite navigation system
InactiveCN103592658AReduce operational complexityHigh positioning accuracySatellite radio beaconingLoop bandwidthClock correction
The invention discloses a new method for RAIM (receiver autonomous integrity monitoring) based on a satellite selecting algorithm in a multimode satellite navigation system. The method comprises the steps of first determining space position information of satellites according to a navigation message and eliminating satellites with a small elevation angle according to a shielding angle; determining an observation matrix including only one clock correction item according to clock correction conversion factors in the navigation message; selecting p satellites from N visible satellites so as to be used for positioning calculation of a receiver, acquiring a satellite combination, which enables the GDOP (geometric dilution of precision) to be minimum, through the satellite selecting algorithm to act as calculating satellites, and determining a weight matrix in WLS (weighted least squares) according to parameters such as the carrier-to-noise ratio, the loop bandwidth, pre-check integral time and the like of satellite signals; carrying out RAIM availability detection according to a false alarm rate and a missed alarm rate which are preset by the receiver, and calculating a pseudo-range residual error threshold value after positioning according to the false alarm rate and a degree of freedom in Chi-squared distribution; carrying out global detection at first, then carrying out local monitoring in a circumstance that a fault satellite exists, determining calculation satellites again through satellite selection, and finally carrying out positioning calculation through selecting satellite combinations within the threshold value. The method disclosed by the invention is simple, high in fault recognition rate, not only applicable to multi-mode and multi-fault satellite navigation systems, but also applicable to single-mode and multi-fault satellite navigation systems, thereby providing new ideas for carrying out RAIM by a modern GNSS (global navigation satellite system).
Owner:PEKING UNIV
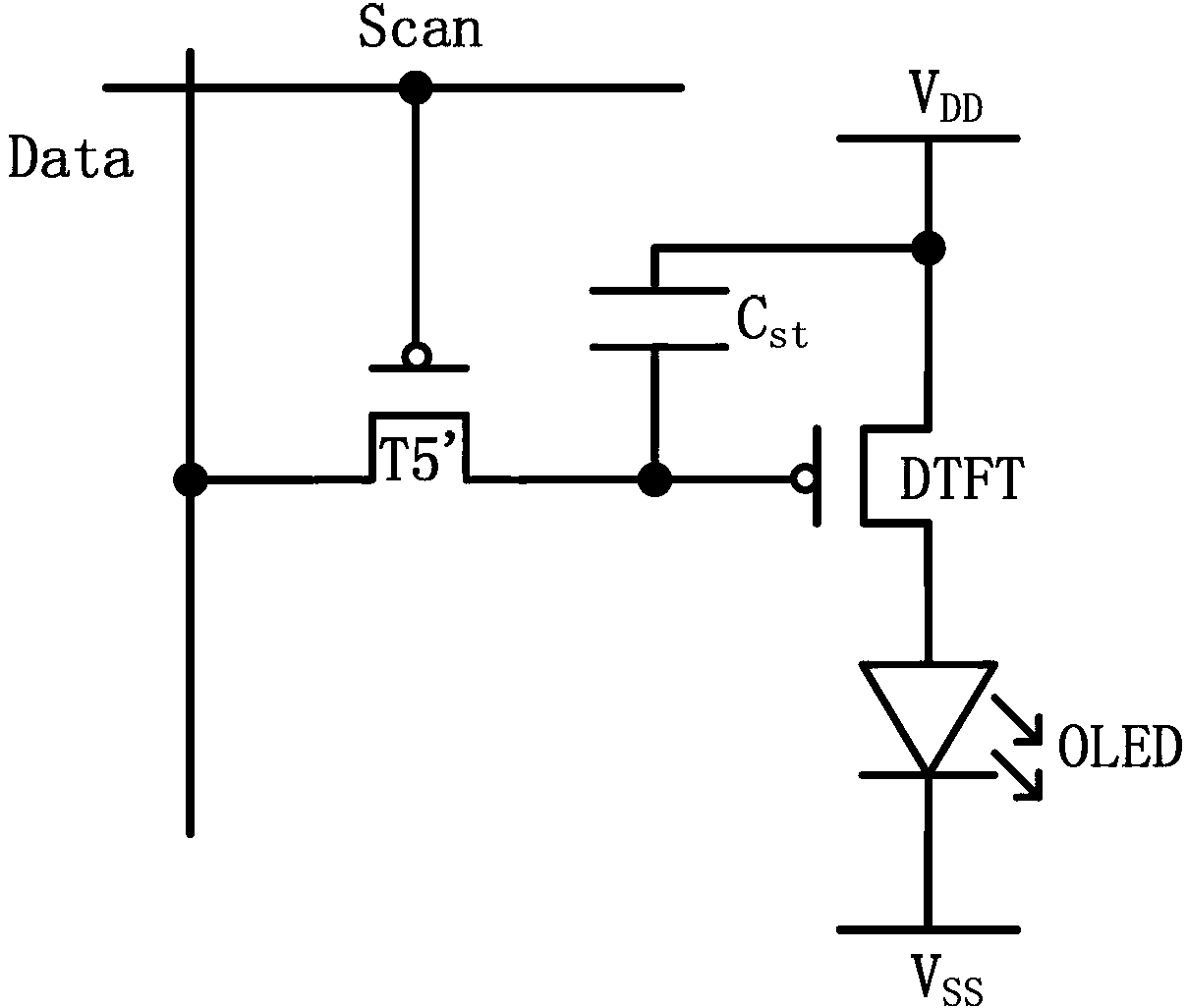
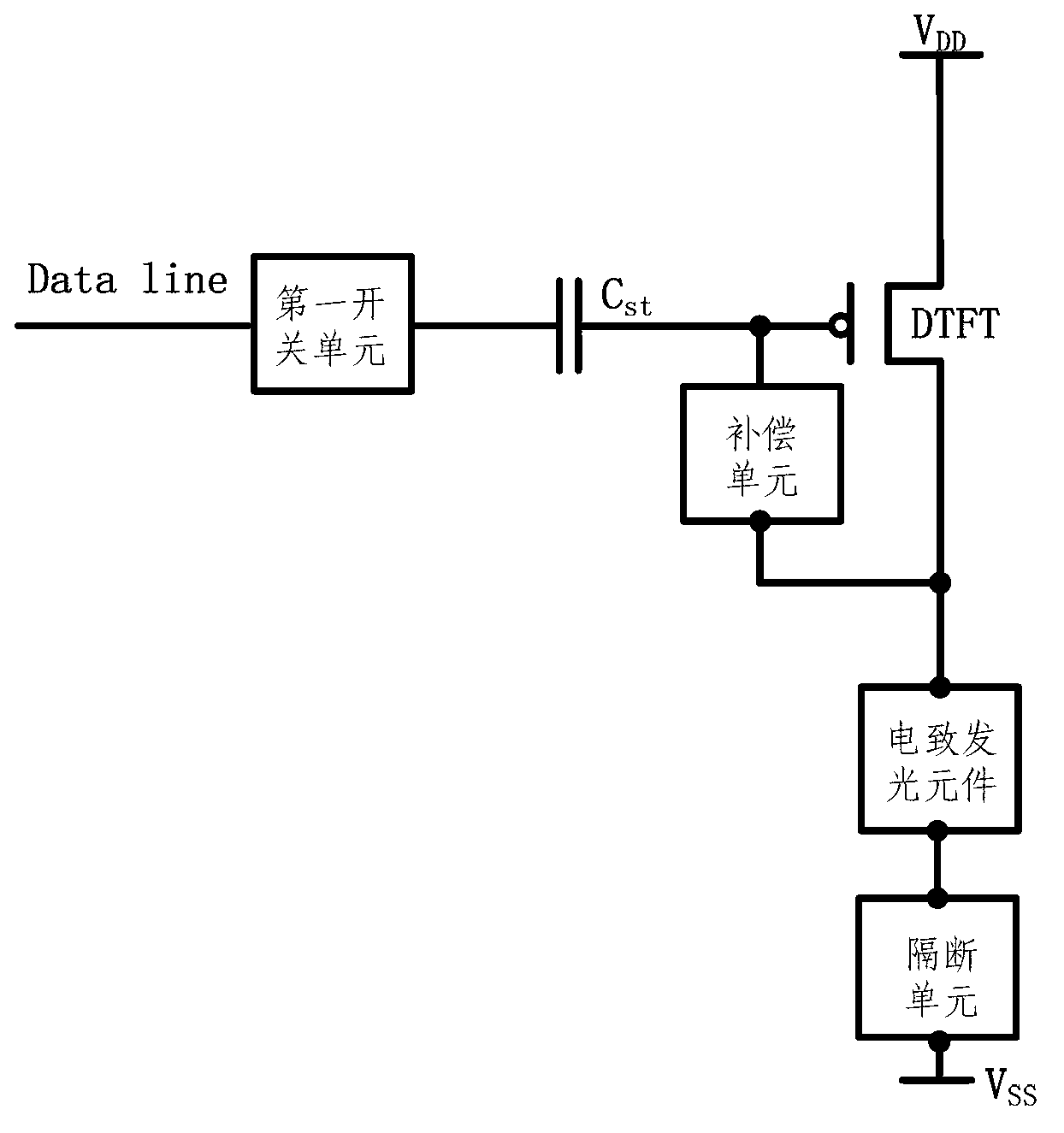
Pixel circuit, pixel circuit driving method and display device
ActiveCN103218972AReduce structural complexityReduce operational complexityStatic indicating devicesCapacitanceDriving current
The invention relates to the technical field of organic light emitting display, in particular to a pixel circuit, a driving method for driving the pixel circuit and a display device comprising the pixel circuit. The pixel circuit is connected by using a diode which is formed by a driving transistor when data are written into a storage capacitor, the storage capacitor is used for prestoring threshold voltages and data voltage signals of the driving transistor, effective compensation is achieved to threshold voltage drifts, and the evenness and the stability of drive currents are guaranteed. Further, multiplexing of control signals of the pixel circuit by a touch circuit is achieved, charging is conducted on the storage capacitor, and at the same time, charging is conducted on a coupling capacitor in the touch circuit through a charging transistor. Therefore, the circuit structure and operation complexity are not added, and meanwhile the integration of the touch circuit in the pixel circuit is perfectly achieved.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
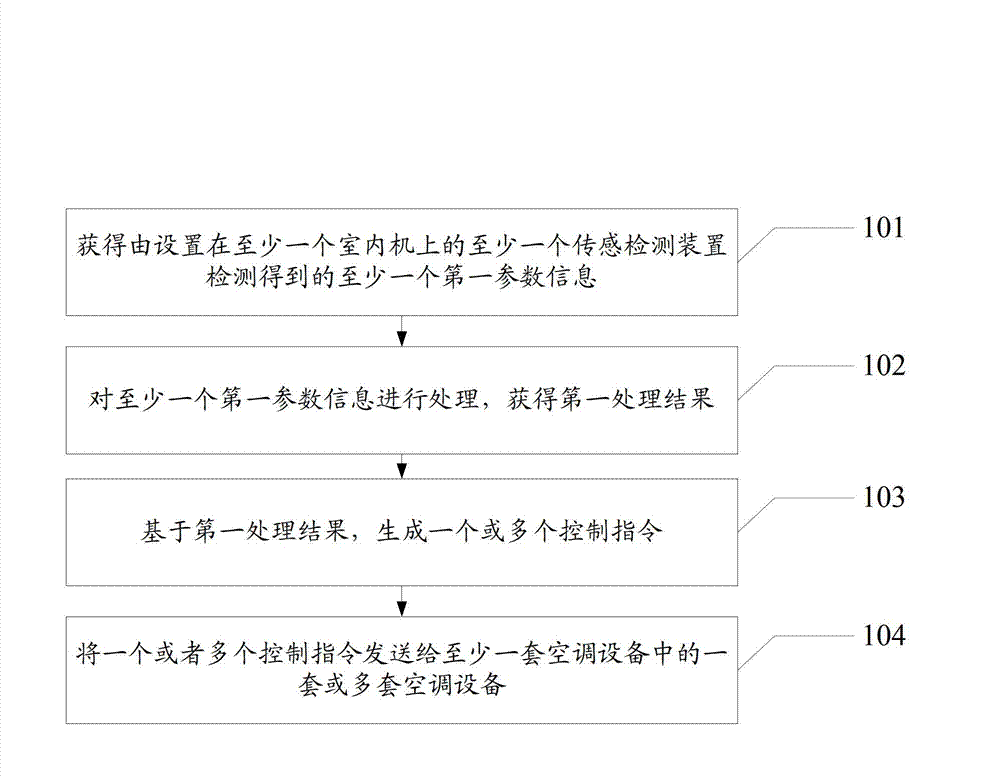
Method and system for controlling air conditioner
ActiveCN102901180ARealize automatic controlReduce the operation processMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsAutomatic controlEngineering
The invention provides a method and system for controlling an air conditioner. The method is applied to the control system which is connected with at least one set of air-conditioning equipment, and each set of air-conditioning equipment comprises at least one indoor unit and at least one outdoor unit, wherein at least one sensing detection device is arranged on each indoor unit. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring at least one piece of first parameter information which is detected by at least one sensing detection device on the at least one indoor unit; processing the first parameter information to acquire a first processing result; generating one or more control instructions according to the first processing result; and transmitting the one or more control instructions to one or more in the at least one set of air-conditioning equipment to be executed. By the method and the system, the automatic control of the air-conditioning equipment is realized, the operating procedures of an air conditioner are reduced, the intellectualization of the air-conditioning equipment is further improved, and the experience degree of a user is boosted.
Owner:SICHUAN CHANGHONG ELECTRIC CO LTD
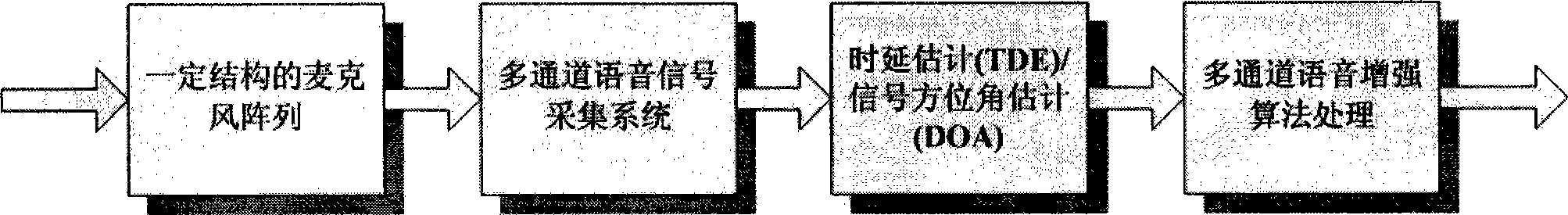
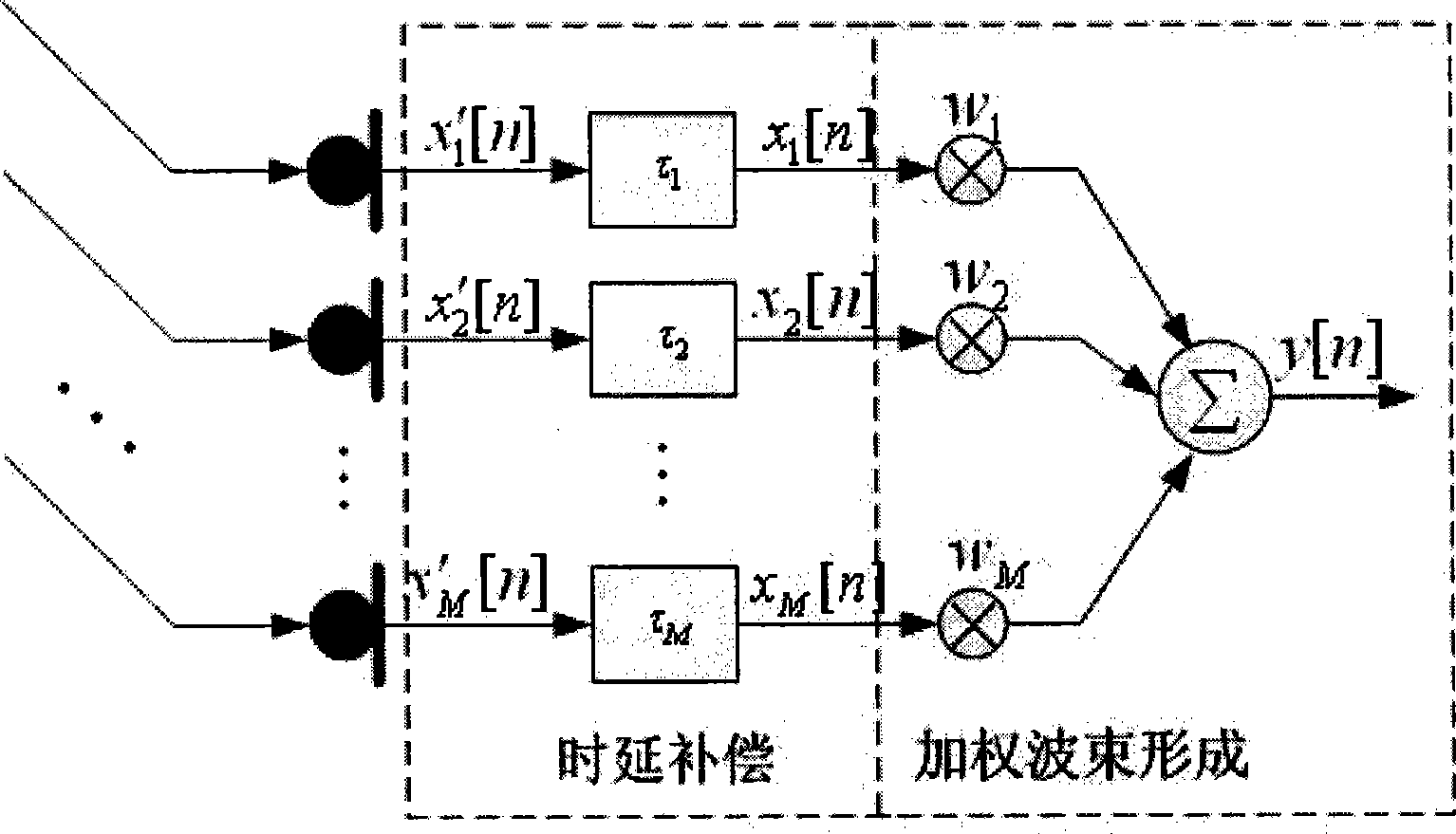
Voice enhancement method employing combination of nesting-subarray-based post filtering and spectrum-subtraction
InactiveCN101447190AImprove frequency responseSimple structureSpeech analysisPost filteringFrequency response
The invention discloses a voice enhancement method employing a combination of nesting-subarray-based post filtering and spectrum-subtraction and is suitable for indoor environment, comprising the enhancement of multi-channel voice signal in vehicle environment; as the problems of unstable the broadband of the voice signals, the inconsistent frequency response of the microphone-array-based multi-channel voice-enhancement method to the voice signal and the correlation among all-channel noise in actual noise-field environment are considered, by utilizing the microphone array nested by the subarrays with different spacing, the voice signals are collected; and the voice signals formed by subarray beams are divided into a high-frequency section and a low-frequency section, different voice-enhancement algorism are adopted for carrying out the treatment; all the advantages are complementary with each other, thus improving the effect of voice enhancement.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
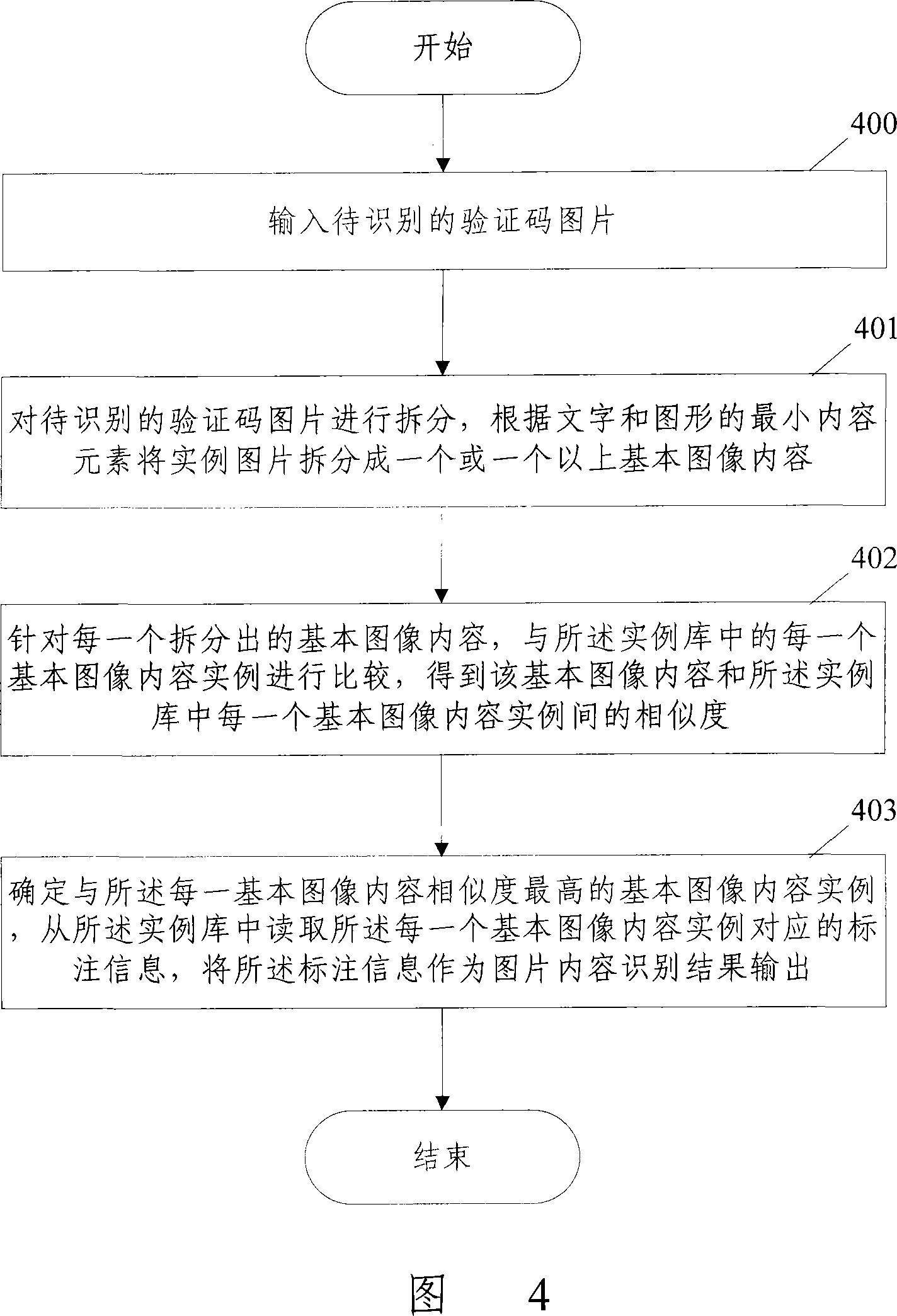
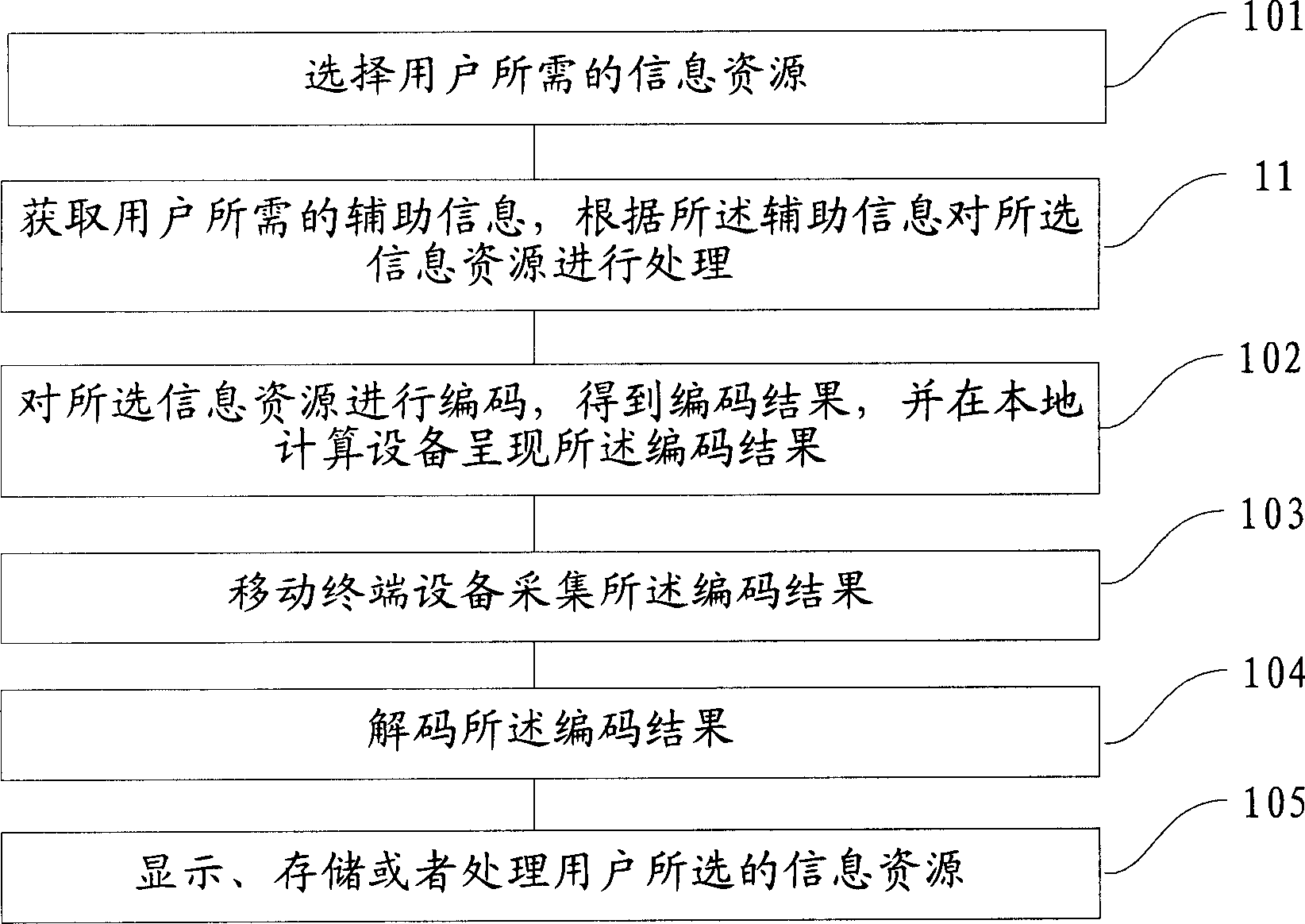
Image content recognizing method and recognition system
ActiveCN101196994AReduce computational overheadReduce occupancyUser identity/authority verificationCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer moduleComputer science
The present invention discloses a picture content identification method and system, wherein the method comprises the following steps that basic image content examples and corresponding marking information are stored in an example base beforehand. During identification, one or more than one item of basic image content is split from a to-be-identified picture by a split module; the split basic image content is compared with the basic image content examples in the example base by a similarity comparison module, obtaining corresponding similarity; a result output module determines the basic image content example having the highest similarity with each item of the basic image content, and outputs the marking information corresponding to the basic image content examples as a picture content identification result. The present invention can decrease the computation cost of computers and the occupancy to system resources, and can enlarge the species of recognizable content.
Owner:SHENZHEN TENCENT COMP SYST CO LTD
Method and system for mobile terminal device obtaining computer information
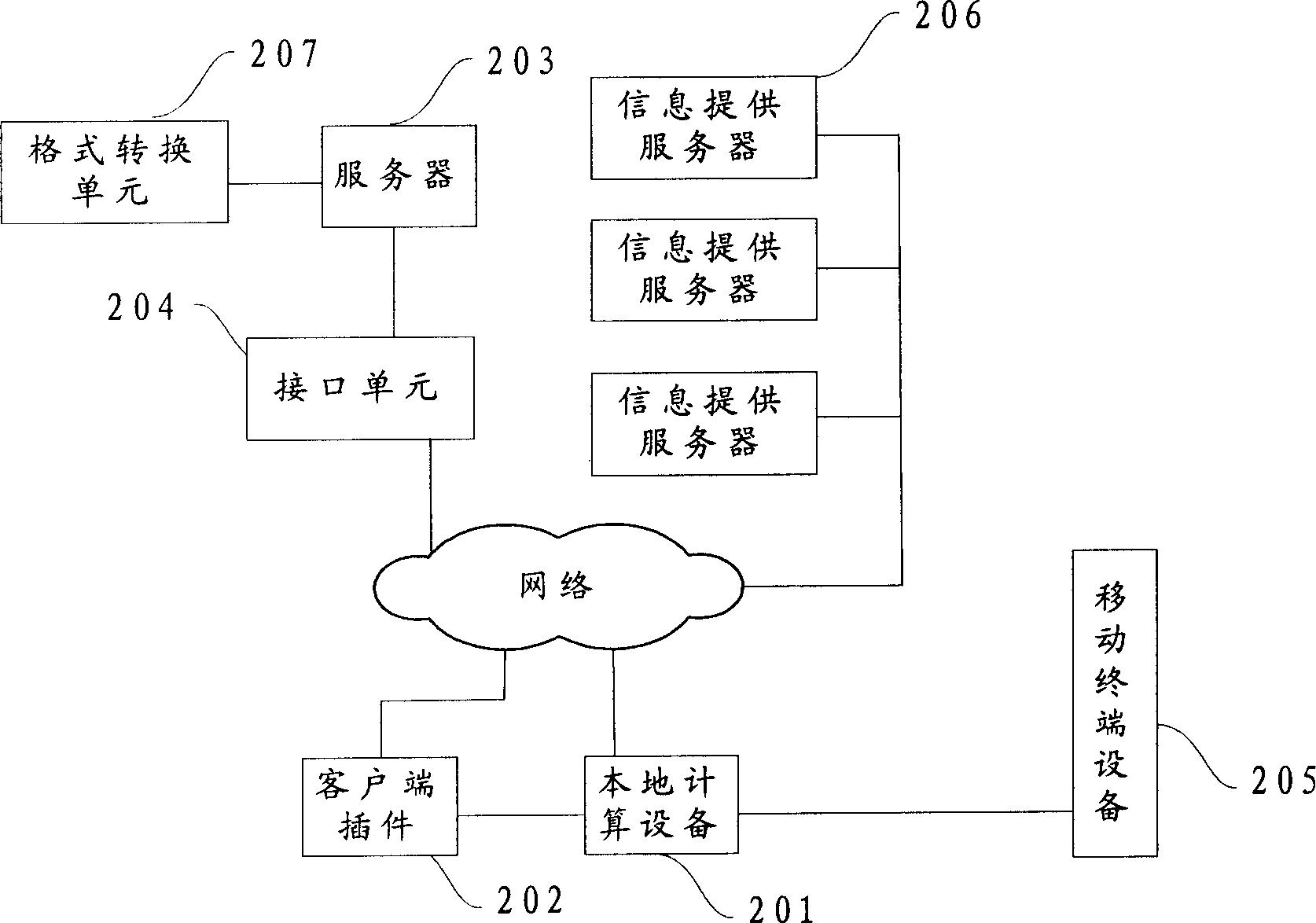
InactiveCN1867142AEasy to collectEasy accessInformation formatContent conversionInformation resourceTerminal equipment
The invention relates to a method for using mobile terminal to obtain information resource, which comprises: selecting needed information resource; coding said information resource, to obtain the coded result to be displayed on the local computer; the mobile terminal collects the coded result; decoding the coded result; the mobile terminal obtains needed information resource. The invention also provides relative client system and server. Compared with present technique, the invention can reduce the process, the complexity of each step, improve the safety of user information, reduce the demand for local computer, and accelerate the speed for obtaining information.
Owner:钟杨 +3
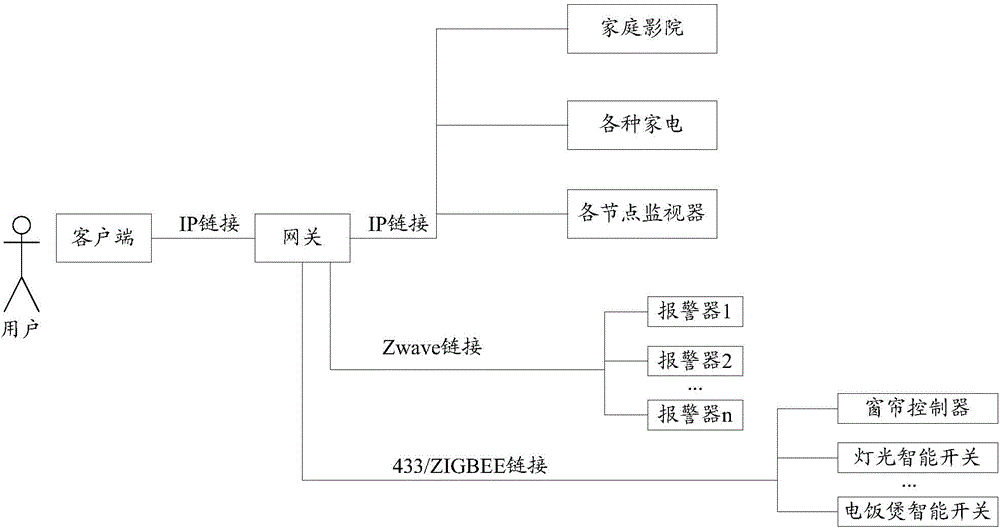
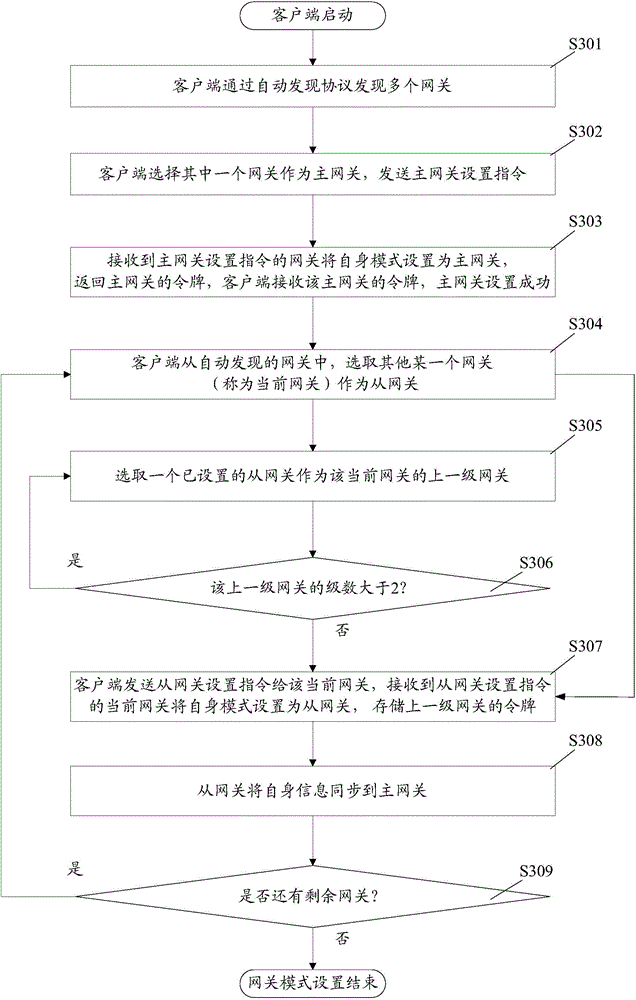
Smart home gateway and networking method thereof
InactiveCN104811375AIncrease the network scaleEasy to controlData switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsComputer hardwareClient-side
The invention discloses a smart home gateway and a networking method thereof. The networking method comprises the following steps: a master gateway setting instruction of a client side is received and an own mode of a gateway is set into a master gateway; or, a slave gateway setting instruction of the client side is received and an own mode of the gateway is set into a slave gateway; when the gateway is used as the slave gateway, the gateway configuration information of the slave gateway and the governed equipment information detected by the slave gateway are reported to the master gateway, and a control command from the master gateway to the governed equipment is received and forwarded to the governed equipment; when the gateway is used as the master gateway, the governed equipment information detected by the master gateway is recorded, the slave gateway configuration information and the governed equipment information of the slave gateway, which are reported by the salve gateway, are recorded; the recorded equipment information is displayed to the client side, a control command to the equipment from the client side is received, if the control command is a control command for the governed equipment of the master gateway, the control command is sent to the governed equipment; if the control command is a control command for the governed equipment of the slave gateway, the control command is sent to the governed equipment. According to the invention, the networking scale of a smart home network can be improved, and meanwhile the operation complexity can be reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CHINA R&D CENT +1
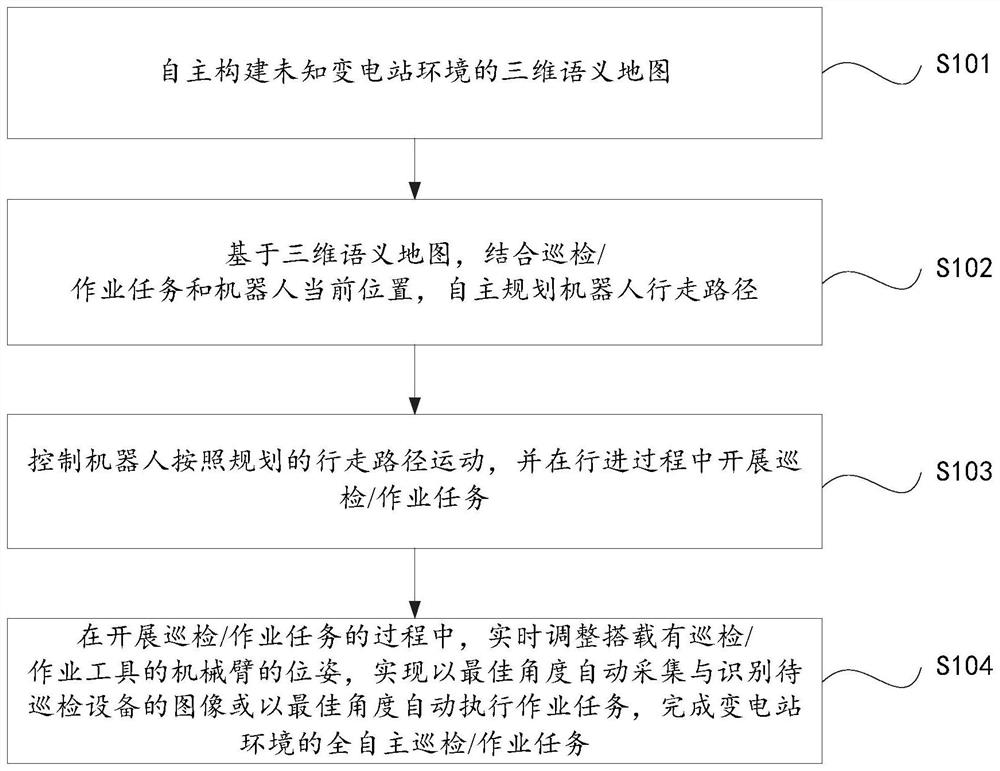
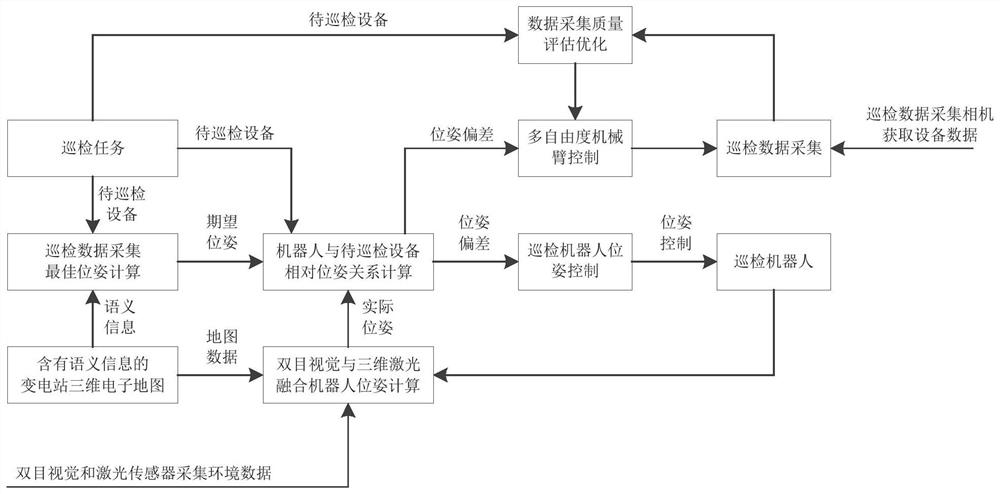
Humanoid patrol operation method and system for semantic intelligent substation robot
ActiveCN111897332AShoot accuratelyAchieving Active Self-AwarenessPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesReal-time computingSmart substation
The invention provides a humanoid patrol operation method and system for a semantic intelligent substation robot. The robot humanoid patrol operation method for the semantic intelligent substation comprises the following steps: autonomously constructing a three-dimensional semantic map of an unknown substation environment; based on the three-dimensional semantic map, combining the inspection / operation task and the current position of the robot to autonomously plan the walking path of the robot; controlling the robot to move according to the planned walking path, and carrying out an inspection / operation task in the advancing process; in the process of carrying out the inspection / operation task, adjusting the pose of the mechanical arm carrying the inspection / operation tool in real time, sothat the image of the equipment to be inspected is automatically collected and recognized at the optimal angle or the operation task is automatically executed at the optimal angle, and the full-autonomous inspection / operation task of the transformer substation environment is completed.
Owner:STATE GRID INTELLIGENCE TECH CO LTD
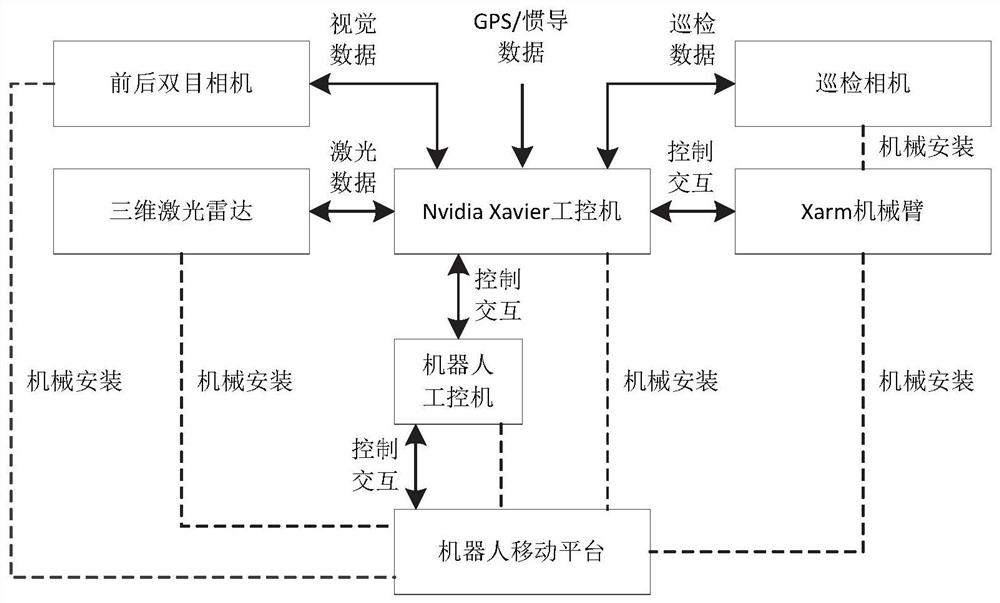
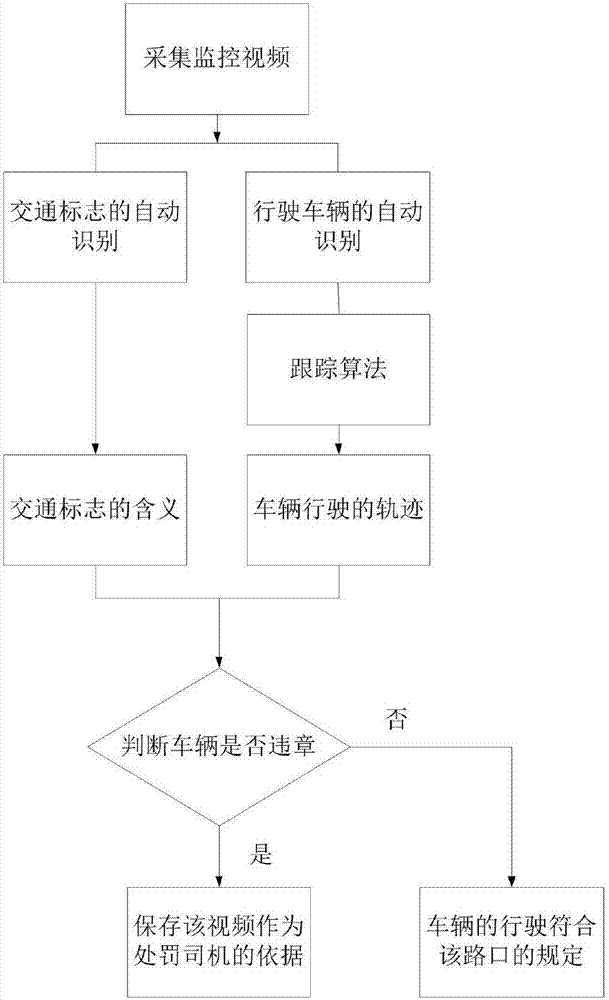
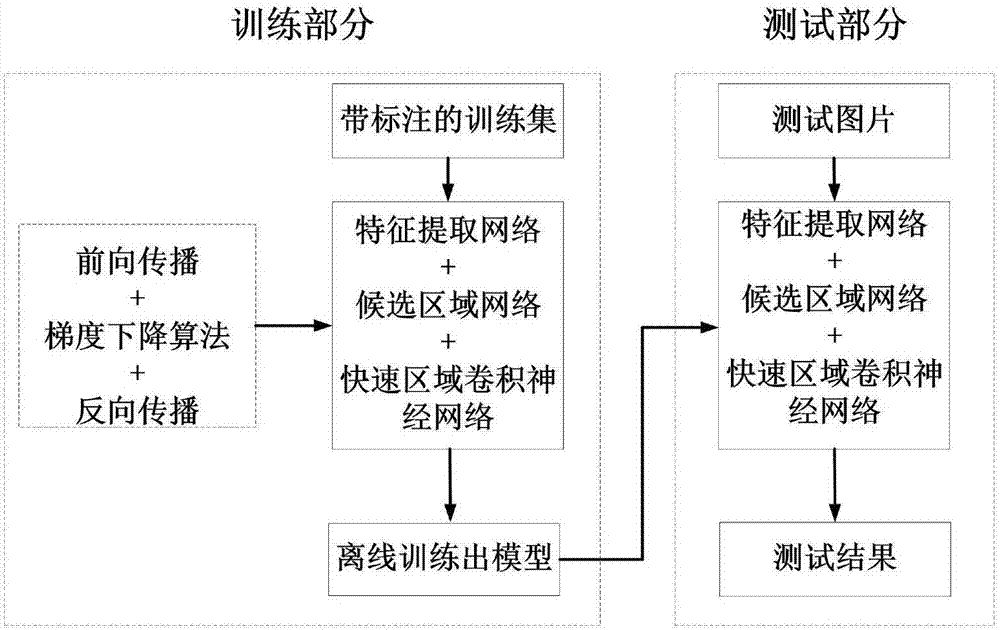
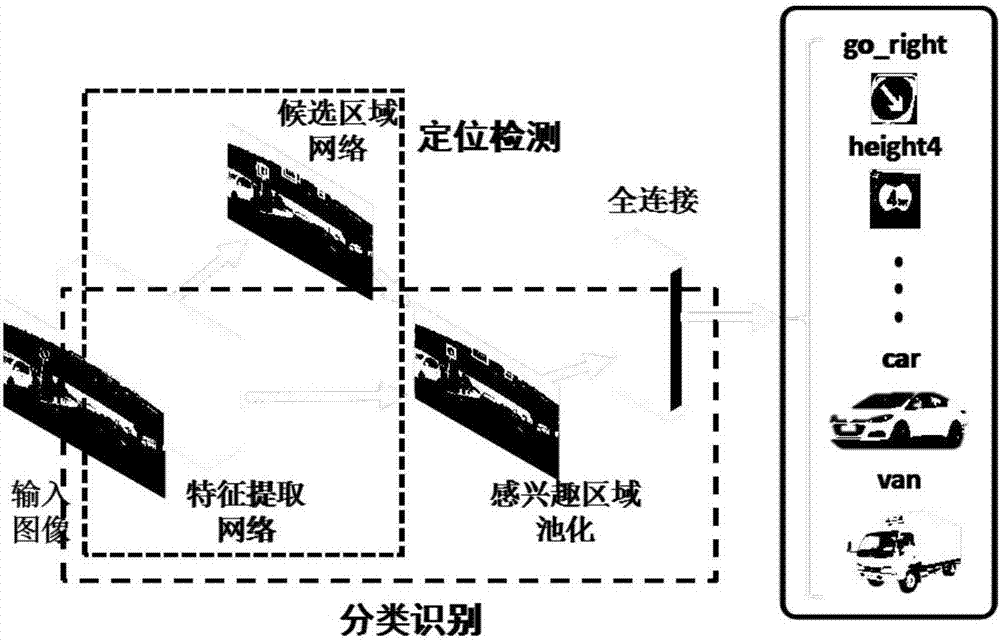
Intersection vehicle violation detection system based on traffic sign identification
InactiveCN106886755AReduce false positivesImprove efficiencyRoad vehicles traffic controlCharacter and pattern recognitionFalse detectionDeep learning
The patent discloses an intersection vehicle violation detection and identification method based on deep learning. The method comprises the following steps of 1, collecting intersection video detection images; 2, identifying traffic signs and vehicles; 3, tracking the vehicles; and 4, performing vehicle violation detection and identification. Based on automatic identification and tracking of the traffic signs and the vehicles in the intersection monitoring videos, the violation conditions of vehicles at the intersection can be automatically identified, and the system has few false detection and high efficiency.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
System and method for detecting quality of metal cap based on machine vision
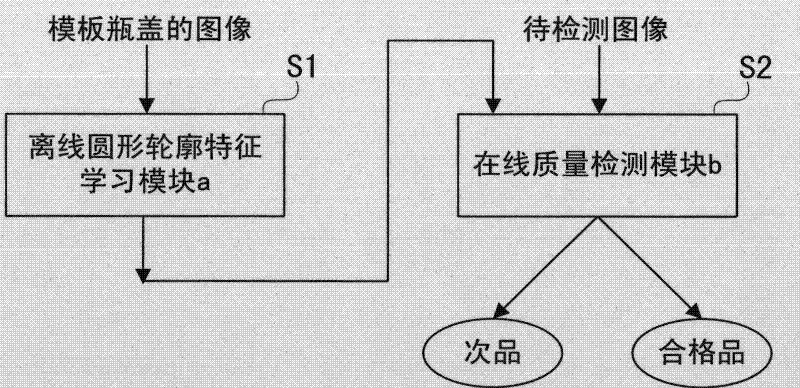
InactiveCN102192911AImprove function scalabilityEasy to operateOptically investigating flaws/contaminationUsing optical meansImaging processingMachine vision
The invention relates to a system and method for detecting the quality of a metal cap based on machine vision, used for detecting the quality defect of the metal cap and rejecting the inferior quality product. The detection system comprises an optical imaging device, an image processing device, a rejecting device and a conveying belt, wherein the optical imaging device comprises a planar array industrial camera, a first optical detection sensor and a light source; the image processing device is used for processing the image; and the rejecting device comprises a control circuit board, a second optical detection sensor, a solenoid valve and an injection tube. The method for detecting the quality of the metal cap based on machine vision comprises the following steps of: acquiring an interested maximum outline scale of a template cap image; establishing a rotational invariance characteristic template matrix for the template cap image; acquiring a round outline of the cap to be detected according to the interested maximum outline scale; calculating the rotational invariance characteristic matrix in the coverage of the round outline of the cap to be detected; and matching the rotational invariance characteristic matrix with the rotational invariance characteristic template matrix, so as to judge whether the cap to be detected is a qualified product or an inferior product.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Image defogging method based on dark channel information
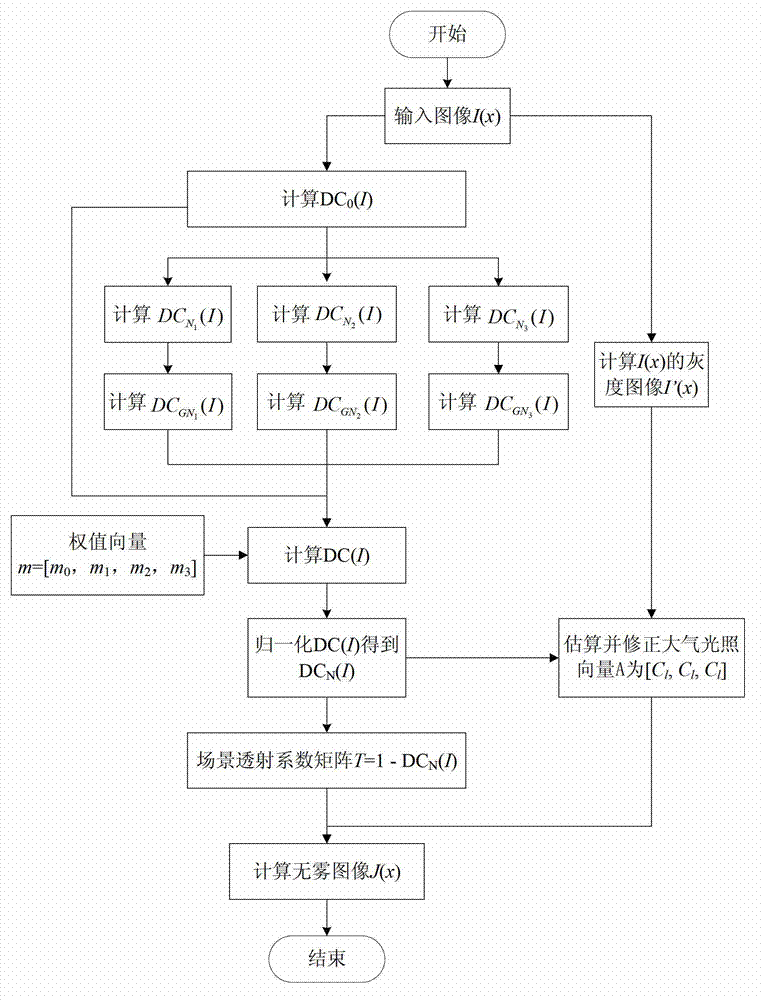
ActiveCN102968772AReduce computational complexityAvoid handlingImage enhancementPattern recognitionTransmission coefficient
The invention discloses an image defogging method based on dark channel information, belonging to the technical field of image treatment and computer vision. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of: calculating the minimum value of each pixel of each color channel of an input image via a minimum value filter; then calculating dark channel counting values of the image under different scale parameters and carrying out Gaussian smoothing filter on the dark channel counting value corresponding to each scale parameter; distributing different weight values to the filtered dark channel counting values according to different scale parameters; and carrying out weighted optimization on the dark channel counting values and calculating a transmission coefficient of the scene so that the defogging of the image is realized. The application of the invention can avoid complex soft matting optimization steps and computing complexity of the defogging; the image with high quality can be obtained after the defogging; and the requirement on real-time treatment application can be met.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
A method, a device and a system for realizing software online upgrade
InactiveCN101533356AImprove upgrade efficiencyReduce operational complexityProgram loading/initiatingData switching networksSoftware engineeringSoftware upgrade
Owner:崔剑 +1
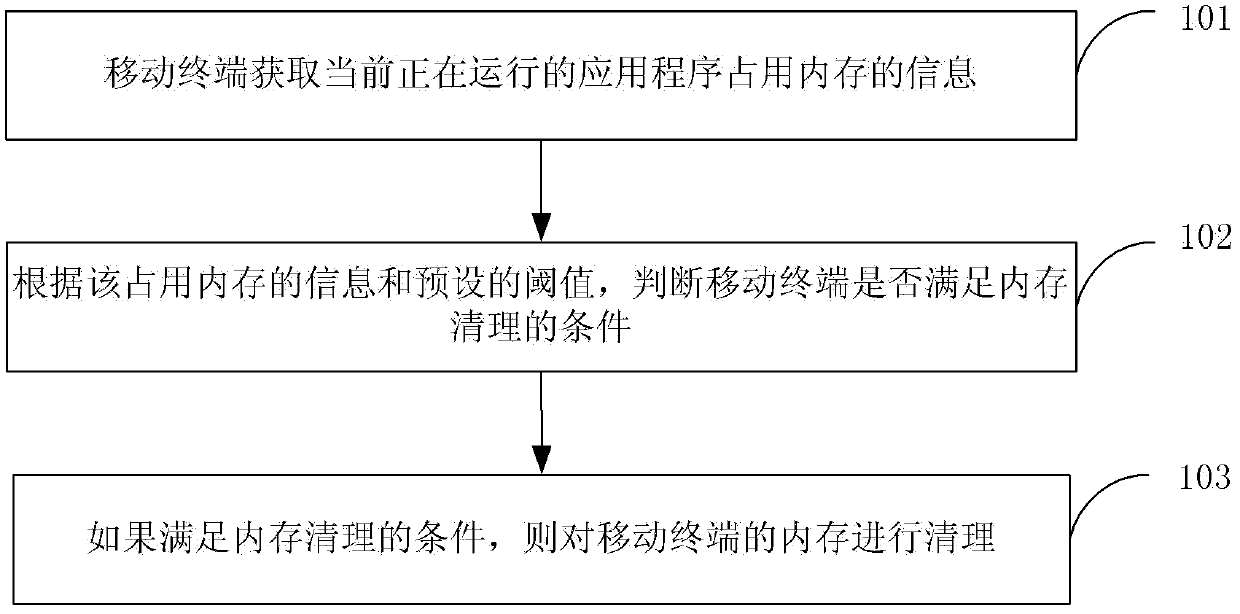
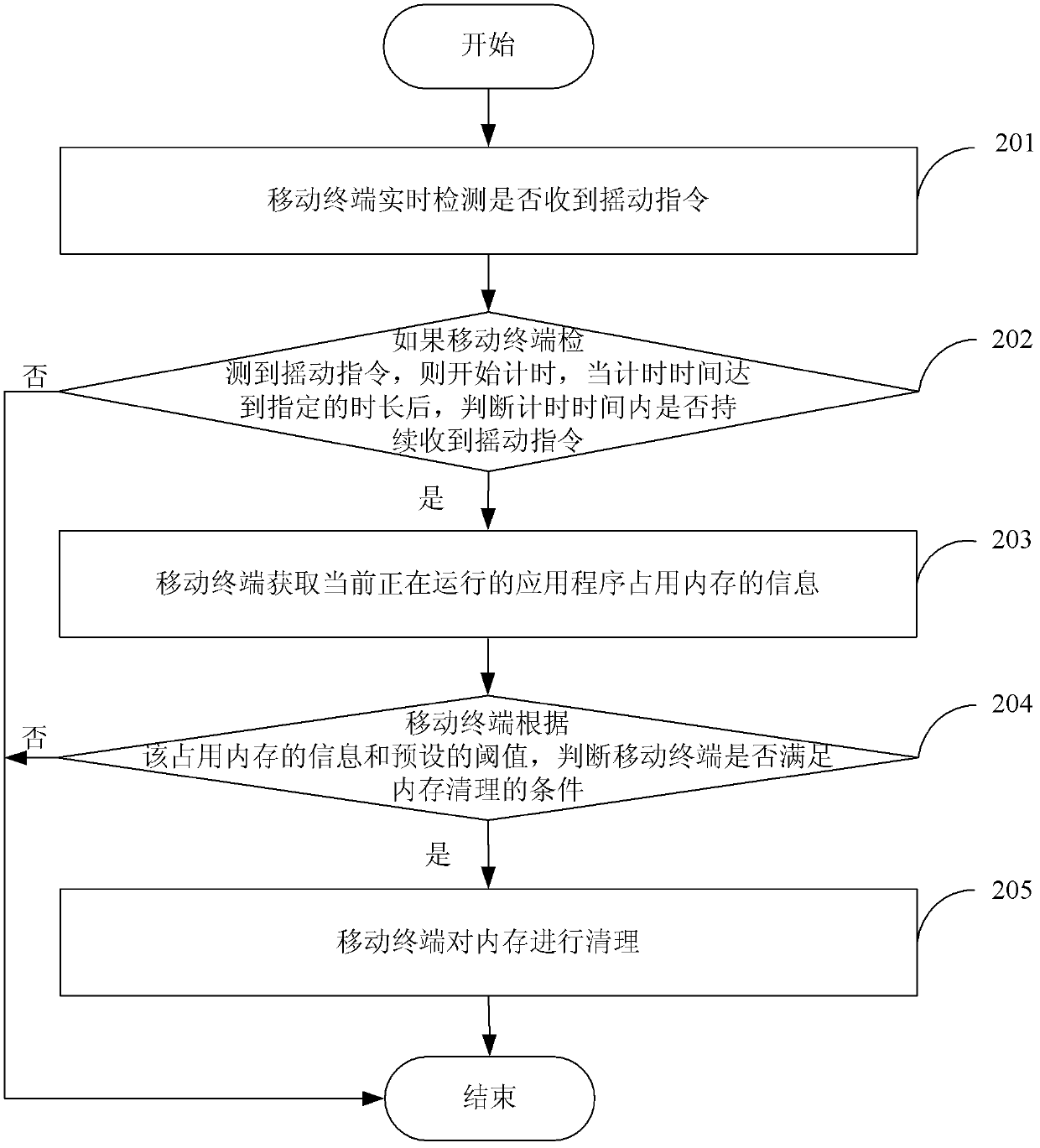
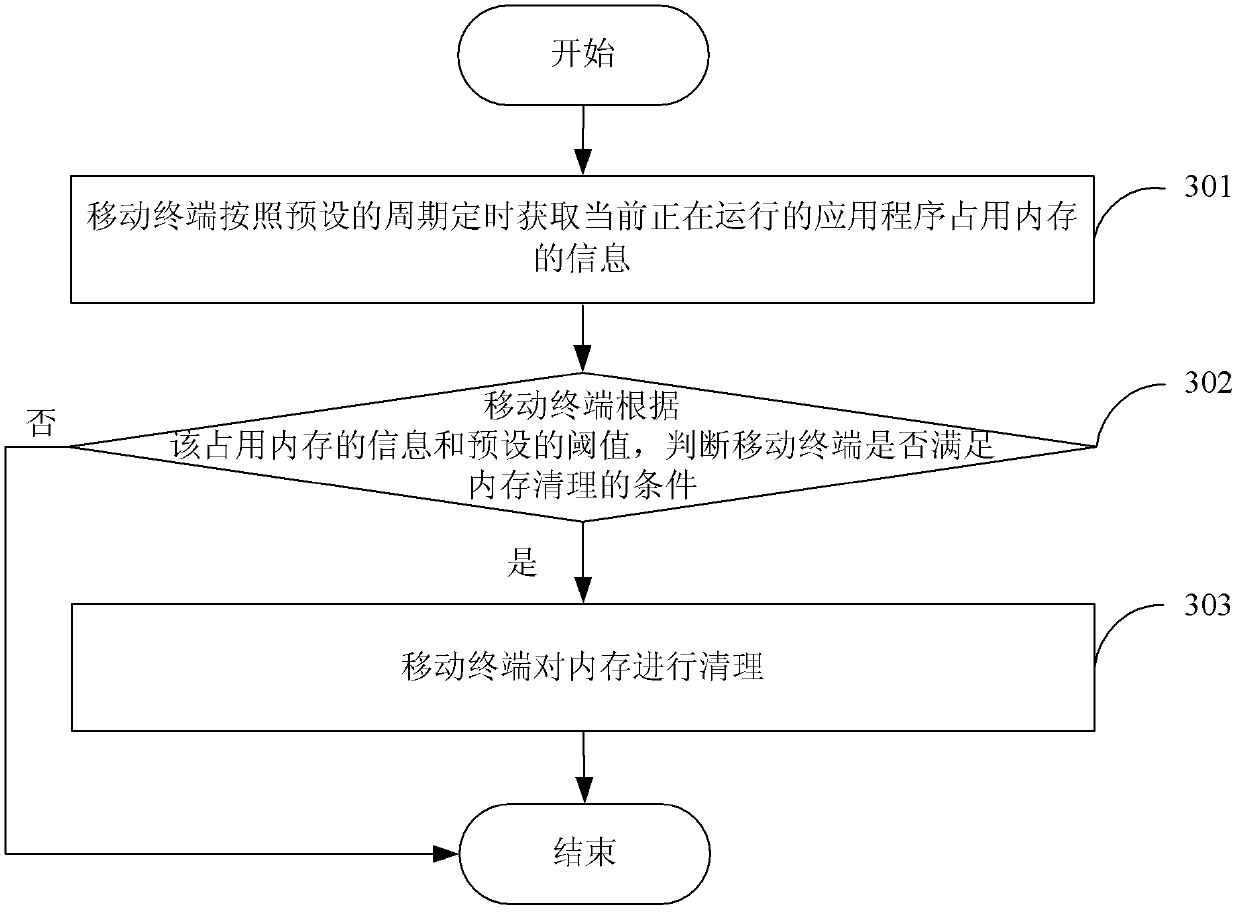
Memory clearing method and mobile terminal
ActiveCN103324575AProcessing speedPerformance impactMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer terminalComputer science
The invention discloses a memory clearing method and a mobile terminal, which belongs to the field of mobile communication. The method comprises the steps: the mobile terminal acquires information about memory occupied by application program in running; according to the information about the occupied memory and a preset threshold value, whether the mobile terminal meets the condition of clearing the memory is judged, if so, the memory of the mobile terminal is cleared. The invention further discloses the mobile terminal, comprising an acquisition module, a judgment module and a clearing module. According to the invention, the processing speed of the mobile terminal is improved, and the effect on the performance of the mobile terminal is lowered; in addition, when the mobile terminal meets the condition of clearing the preset memory clearing is judged, the memory clearing is automatically performed, the operation complexity of clearing the memory of the mobile terminal is lowered, and the operation steps are simplified for a user.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Real-time object three-dimensional reconstruction method based on depth camera
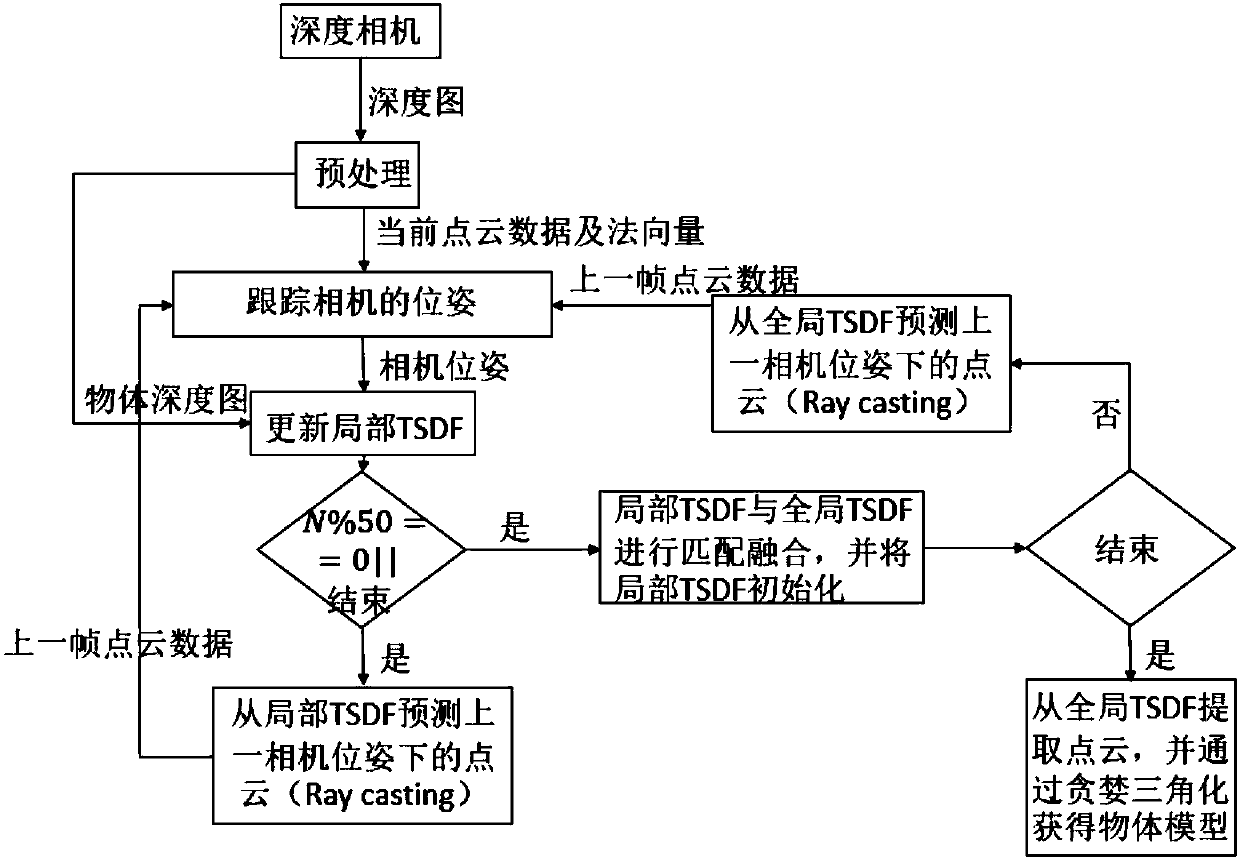
ActiveCN107833270AReduce operational complexityEasy to splitImage enhancementImage analysisPoint cloudReconstruction method
The invention provides a real-time object three-dimensional reconstruction method based on a depth camera. The method comprises the steps that a frame pf depth image is sequentially acquired from thedepth camera as a current frame and is preprocessed; the relative pose of the current frame and the previous frame is estimated through a centroid ICP algorithm, and the precise pose of the camera ofthe current frame is calculated by using the precise pose of the previous frame and the relative pose of the current frame and the previous frame; the current frame data are fused into the local TSDFby using the precise pose of the camera; and point cloud integrated into the local TSDF in the step 3 is acquired from the local TSDF, and the point cloud is used as the point cloud of the previous frame, or match fusion is carried out on the local TSDF and the global TSDF, and the local TSDF is initialized. According to the invention, the failure of the ICP matching algorithm is avoided; accumulated errors are reduced; the accuracy of a model is improved; and the method is suitable for reconstructing a specified object or person.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
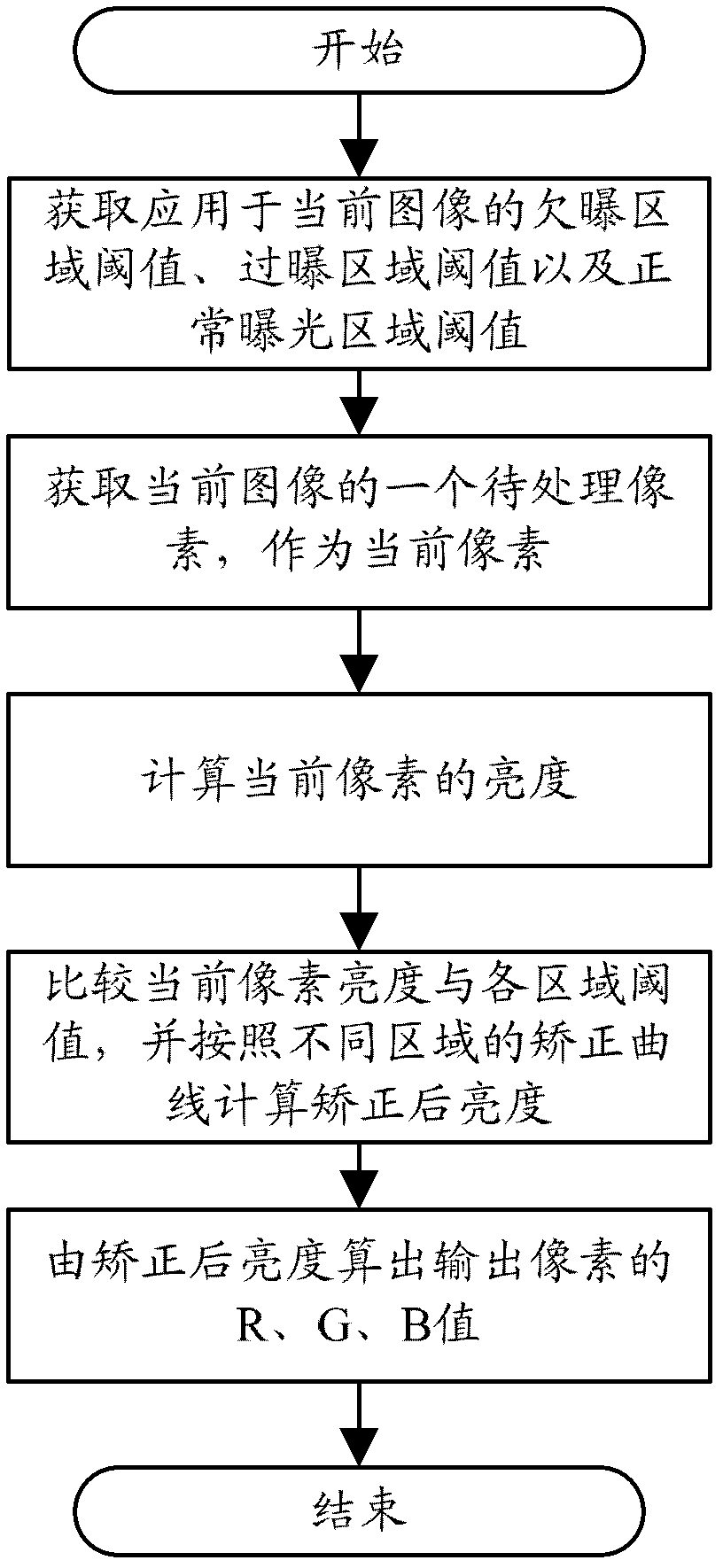
System and method for realizing image high dynamic range compression
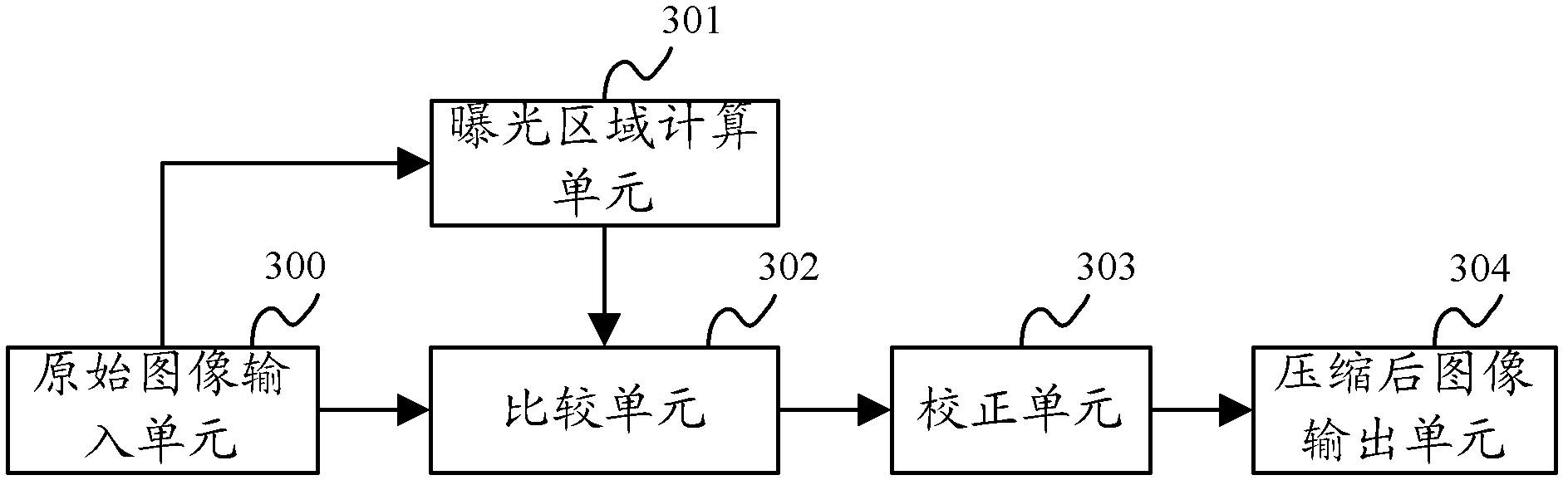
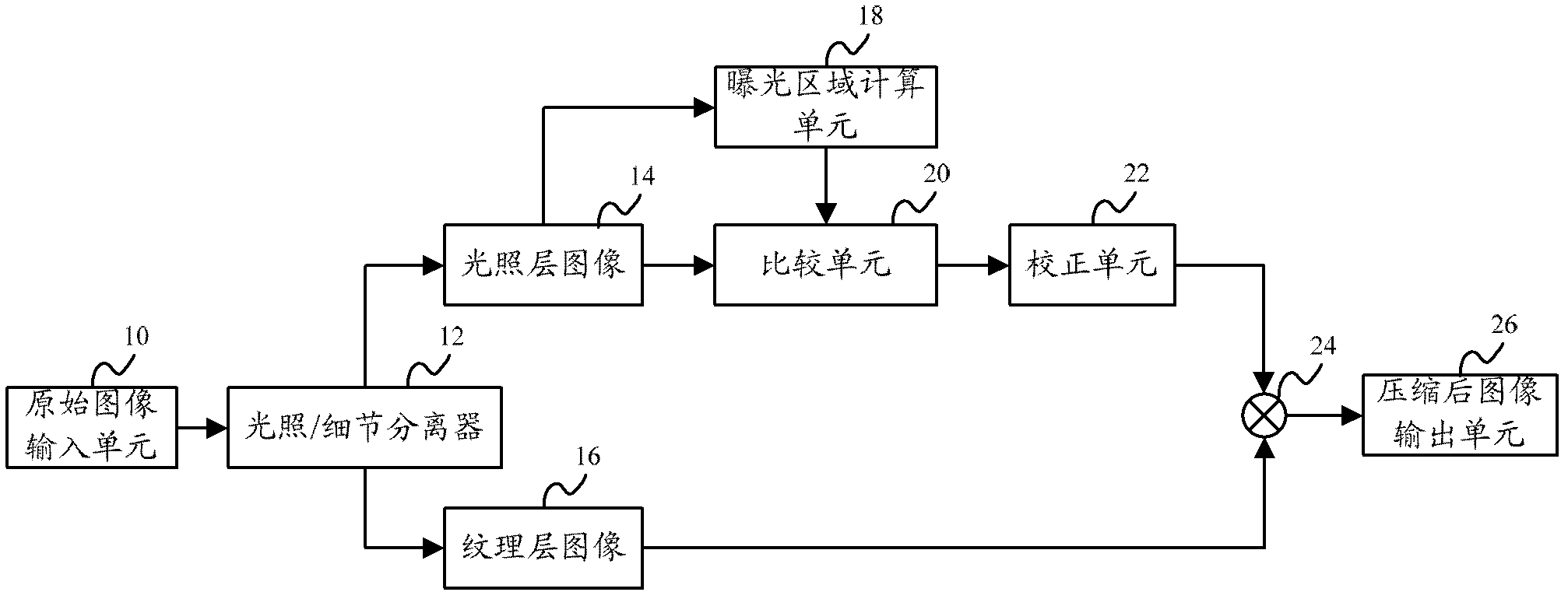
ActiveCN102497490AImprove visibilityIncrease brightnessColor television with bandwidth reductionImage codingVisibilityWork performance
The invention relates to a system for realizing image high dynamic range compression. The system comprises a primary image input unit, an exposure area calculation unit, a comparison unit, a correction unit, and a compressed image output unit. The invention also relates to a method for realizing the image high dynamic range compression. By adopting the system and the method for realizing the image high dynamic range compression, the problems of damage to a normal exposure area, Halo existing at the edge and over loss of image contrast in the method are effectively solved; the contrast of the normal exposure area is reserved, at the same time, the visibility of the under exposure area and the exposure area is improved; the system and method not only are directly applied in an overall high dynamic compression method, but also can be applied in the brightness (lighting layer) compression in a partial high dynamic compression manner; and besides, the complexity of the operation in the invention is extremely low, so that real time process is facilitated, the process is quick and efficient, the working performance is stable and reliable, and the scope of the application is broad.
Owner:SHANGHAI FULLHAN MICROELECTRONICS
OFDM (orthogonal frequency division multiplexing) system symbol timing synchronization realizing method suitable for low-signal-to-noise-ratio channel environments
ActiveCN104125190AReduce complexityReduce operational complexityMulti-frequency code systemsSynchronising arrangementComputation complexityRound complexity
The invention discloses an OFDM (orthogonal frequency division multiplexing) system symbol timing synchronization realizing method suitable for low-signal-to-noise-ratio channel environments. The OFDM system symbol timing synchronization realizing method includes: adopting two conjugated OFDM symbols based on frequency domain PN (pseudo-noise sequence) to serve as a training sequence; subjecting symbol positions of the training sequence and a receiving sequence to sliding conjugation correlation at a receiving end, obtaining a timing offset estimation function via summation and modulus computation; for every moment, taking an estimation function of one timing offset section at every moment to solve a weighted average so as to obtain a dynamic threshold for the corresponding moment; comparing the estimation function with the corresponding dynamic threshold to lock a timing position. Due to the facts that only data symbol position information is required, data are not involved in computation and normalization computation for computation results is not required, the OFDM system symbol timing synchronization realizing method has the advantages that complexity is low and performance cannot be affected by size of received signal power. In addition, the OFDM system symbol timing synchronization realizing method is accurate and stable in timing under a low-signal-to-noise-ratio environment, easy to implement and low in computation complexity.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Cell searching method in LTE (long term evolution) system
InactiveCN102223696AHigh-precision detectionReduce operational complexitySynchronisation arrangementAssess restrictionLow-pass filterCell search
The invention discloses a cell searching method in an LTE (long term evolution) system. The method comprises the following steps specifically; a user terminal obtains a receiving signal in a PSS (primary synchronization signal) signal frequency band through a low-pass filter; the PSS is detected according to the receiving signal to obtain 5ms time synchronization and identification (ID) in a physical layer cell group; the circular prefix (CP) length is detected by utilizing the receiving signal, so as to obtain the frequency synchronization and compensate the receiving signal; an SSS (secondary synchronization signal) is detected by utilizing the compensated signal, so as to obtain 10ms time synchronization and identification (ID) in the physical layer cell group. In the method of the invention, while the user terminal and the cell obtain time and frequency synchronization, a main synchronizing signal, an auxiliary synchronizing signal, the CP and the ID of the physical layer cell aredetected. By adopting the method, high correct detection probability to the PSS, the SSS and the CP is realized, and the operation complexity is low.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
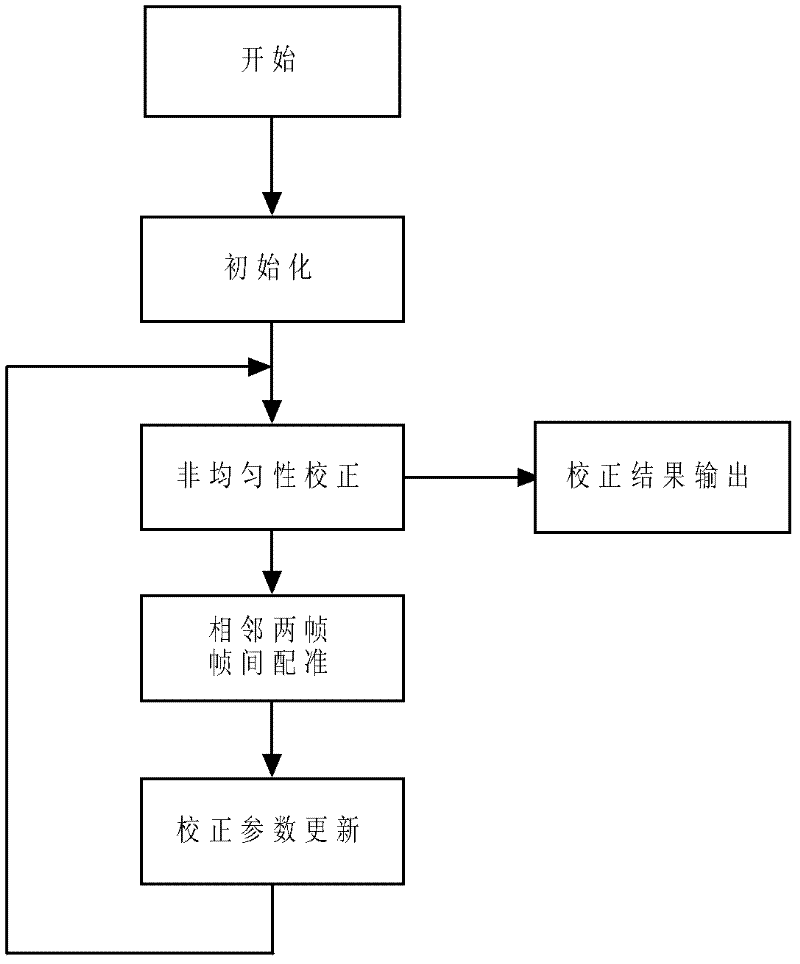
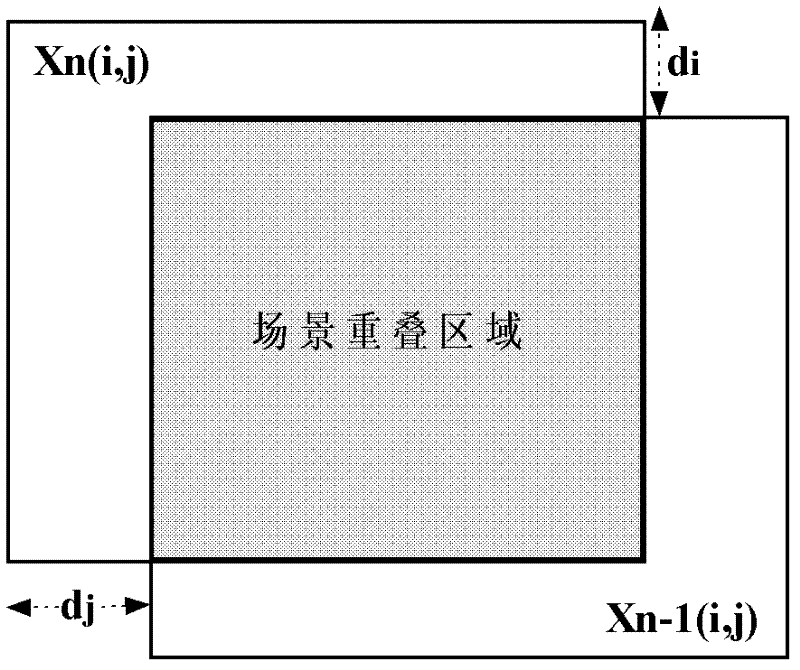
Rapidly converged scene-based non-uniformity correction method
InactiveCN102538973APrevent erroneous updatesBug update avoidanceRadiation pyrometryPhase correlationSteep descent
The invention discloses a rapidly converged scene-based non-uniformity correction method, wherein the aim of non-uniformity correction is achieved by minimizing interframe registration error of two adjacent images. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: initializing gain and offset correction parameters and acquiring an uncorrected original image; acquiring a new uncorrected original image, and carrying out non-uniformity correction on the new uncorrected original image and the previous uncorrected original image by utilizing the current non-uniformity correction parameters; obtaining relative displacement, scene correlation coefficient and interframe registration error of two corrected images by utilizing an original point masking phase correlation method; and updating correction parameters along the negative gradient direction by adopting a steepest descent method. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high correction accuracy, fast convergence speed, no ghost effect and low calculated amount and storage content and is especially applicable to being integrated into an infrared focal plane imaging system, and the effect of improving imaging quality, environmental suitability and time stability of an infrared focal plane array is achieved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
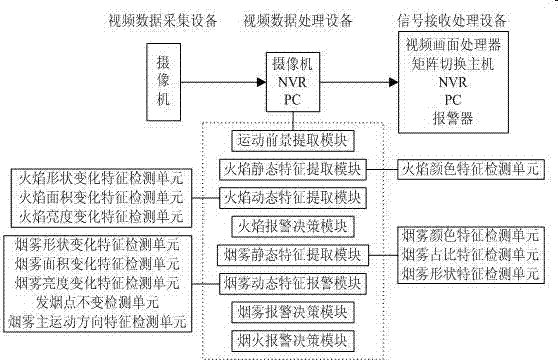
Smog detection method and device based on video analysis
InactiveCN106897720AHigh alarm accuracyReduce false positivesImage enhancementImage analysisData acquisitionVideo image
The invention discloses a smog detection method based on video analysis. The smog detection method based on video analysis comprises steps of video image data acquisition, video image preprocessing, forward target extraction, flame static characteristic detection, flame dynamic characteristic detection, flame alarm decision, smog static characteristic detection, smog dynamic characteristic detection and smog alarm decision. The method is advantaged in that smog and flame are simultaneously detected in a combined static and dynamic characteristic mode, smog detection accuracy and stability are improved, operation complexity is further reduced, hardware realization is convenient, and the method can be applied to relatively complex environments.
Owner:JINAN JOVISION TECH CO LTD
Trojan horse detection method based on communication behavior clustering
InactiveCN104168272AClear demarcationGet rid of dependenceData switching networksFeature vectorCluster algorithm
The invention discloses a Trojan horse detection method based on communication behavior clustering, and belongs to the field of information safety. The unknown Trojan horse detection method is excellent in feature extraction performance, proper in clustering algorithm and high in detection efficiency and accuracy in order to resolve the problems that the existing Trojan horse detection technology is low in feature extraction capacity, improper in clustering algorithm selection and the like. According to the technical scheme, the Trojan horse detection method comprises the steps of extracting a network flow data package, recombining a TCP conversation, extracting a Trojan horse reverse connecting feature, an entropy feature, a heart beat feature and the like, building a feature vector of the TCP conversation and carrying out real-time clustering on the feature vector based on a real-time increment clustering algorithm of LSH. According to the difference of communication behavior features of a Trojan horse conversation and normal network communication behaviors, the Trojan horse detection method marks the difference of the communication behavior features of the Trojan horse conversation and the normal network communication behaviors by combining the statistic analysis and the time series analysis technology, guarantees high detection accuracy and a zero false alarm rate, lowers the false alarm rate, and can effectively carry out real-time detection on the abnormal communication behaviors of a Trojan horse.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Method and device for updating local advertisement software development kit
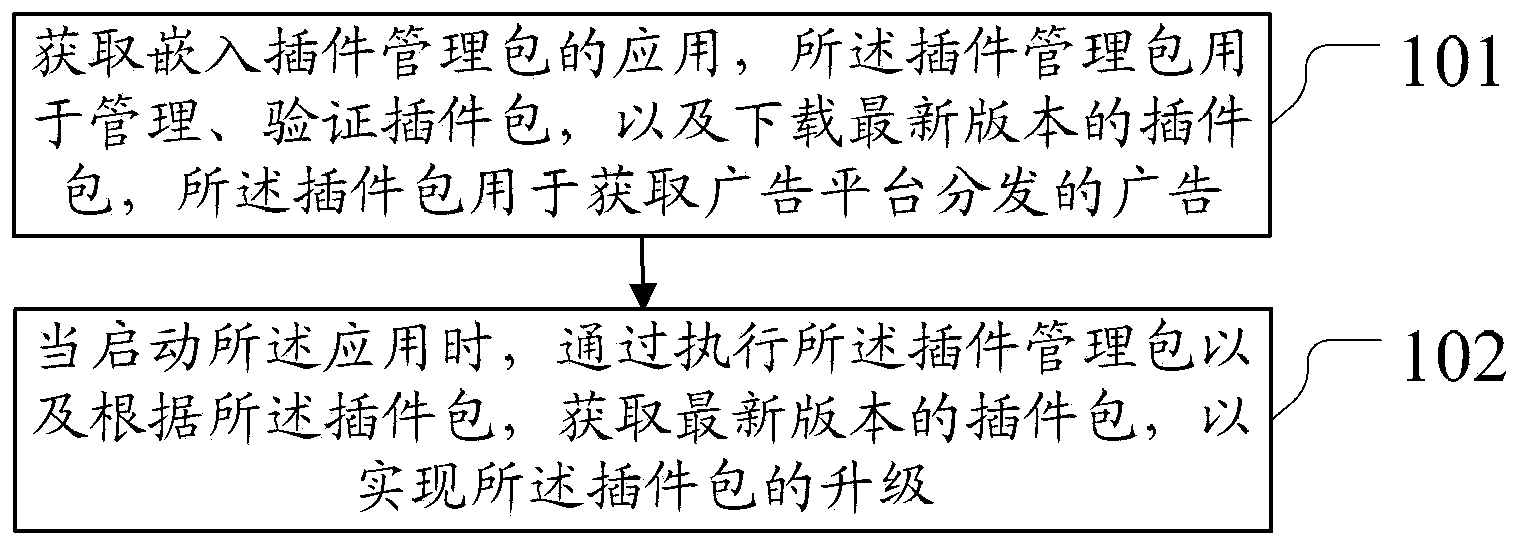
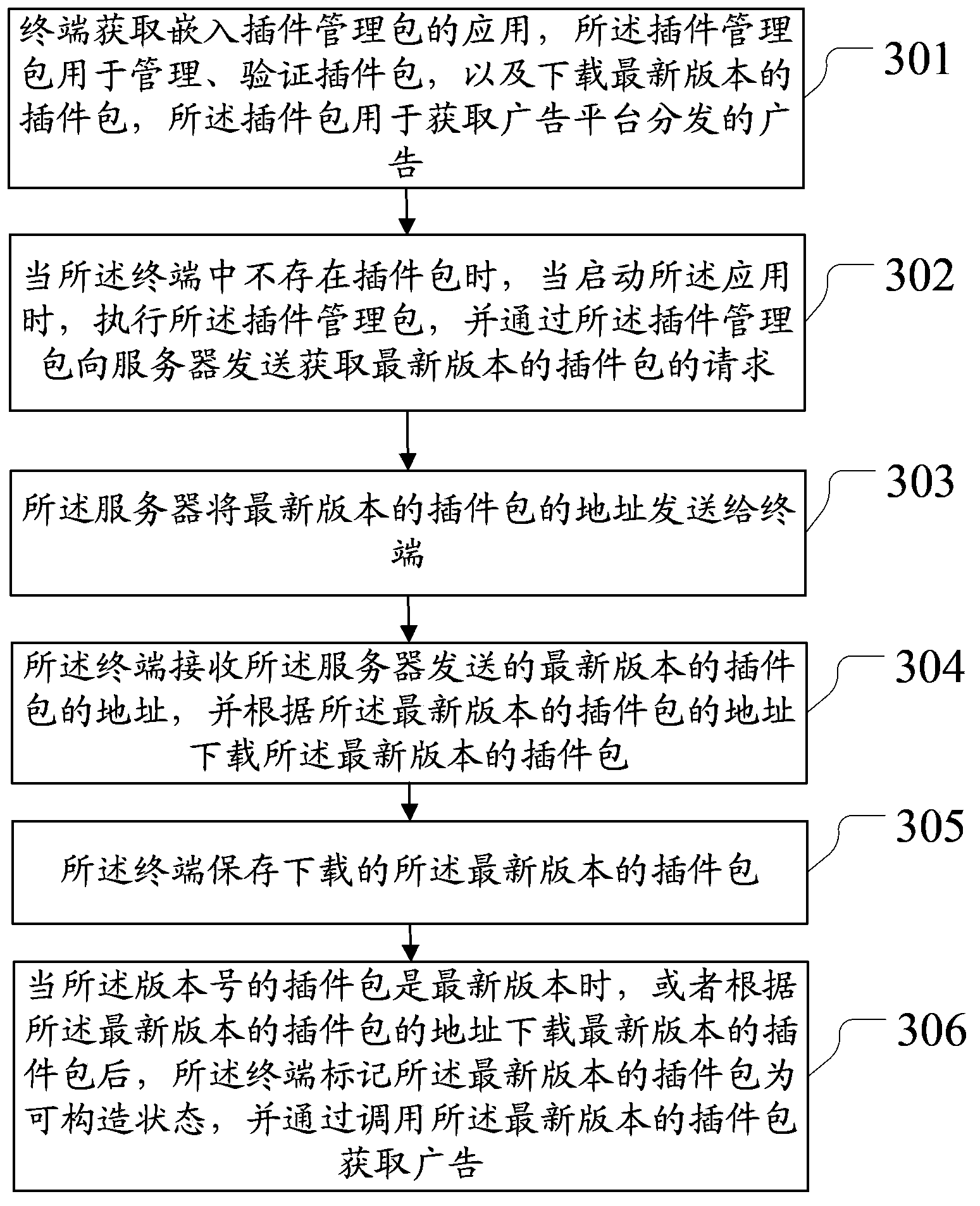
ActiveCN103677877ATimely repairReduce operational complexityProgram loading/initiatingOperational costsSoftware engineering
The invention discloses a method and device for updating a local advertisement software development kit, and belongs to the technical field of advertisements. According to the method and device, the SDK can be automatically updated, operation complexity and operation cost are lowered, and moreover, the SDK can be timely repaired when serious bugs occur after the SDK is issued. According to the technical scheme, an application embedded to a plug-in management pack is obtained, the plug-in management pack is used for managing and verifying plug-in packs and downloading the plug-in pack in the latest version, the plug-in packs are used for obtaining advertisements distributed by an advertisement platform, when the application is started, the plug-in management packs are executed and the plug-in packs in the latest version are obtained, so that updating of the plug-in pack is achieved. The method and device are suitable for updating the local advertisement software development kit.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com