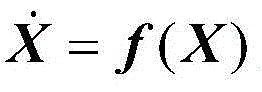Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
141 results about "Right ascension" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
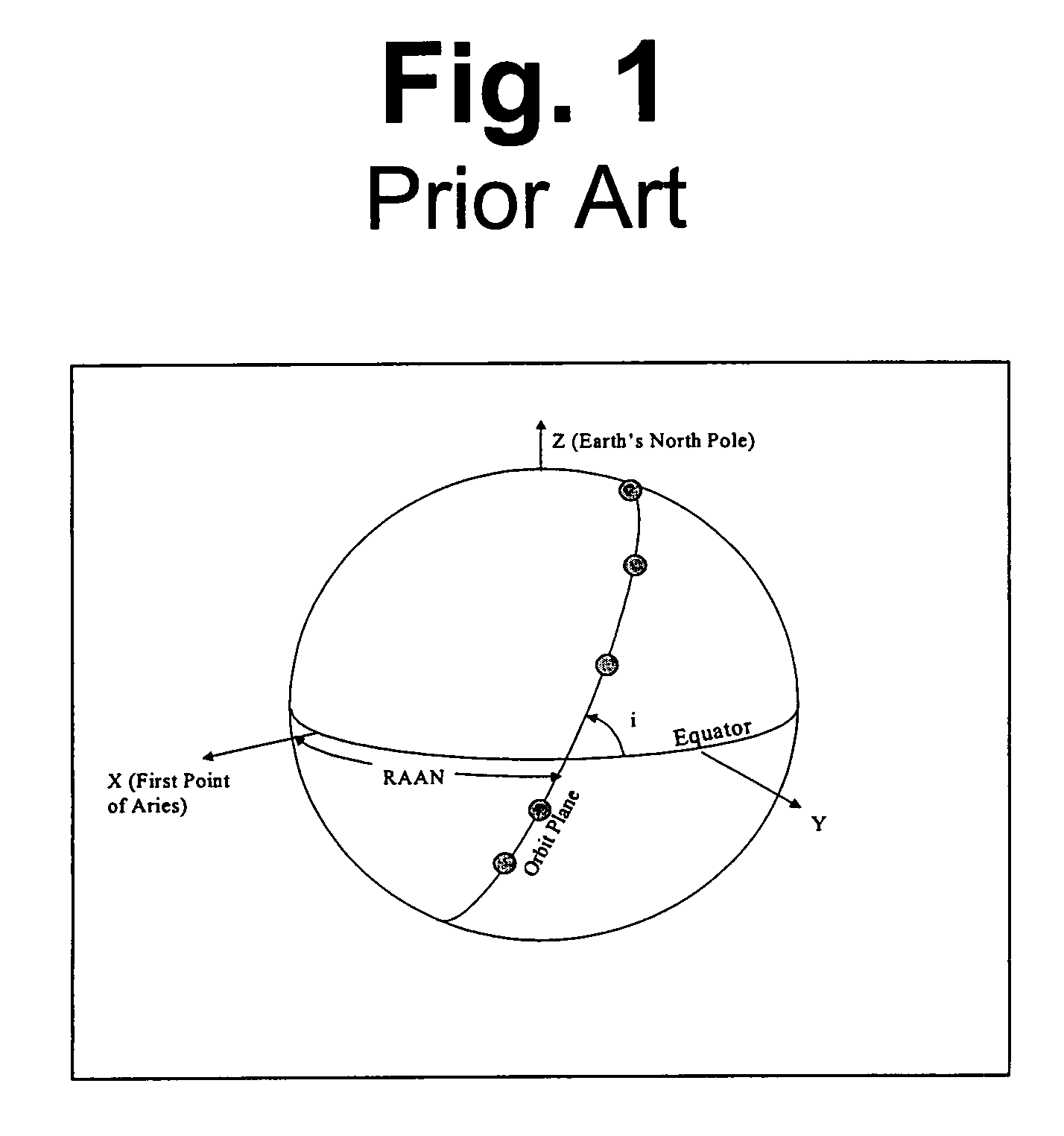
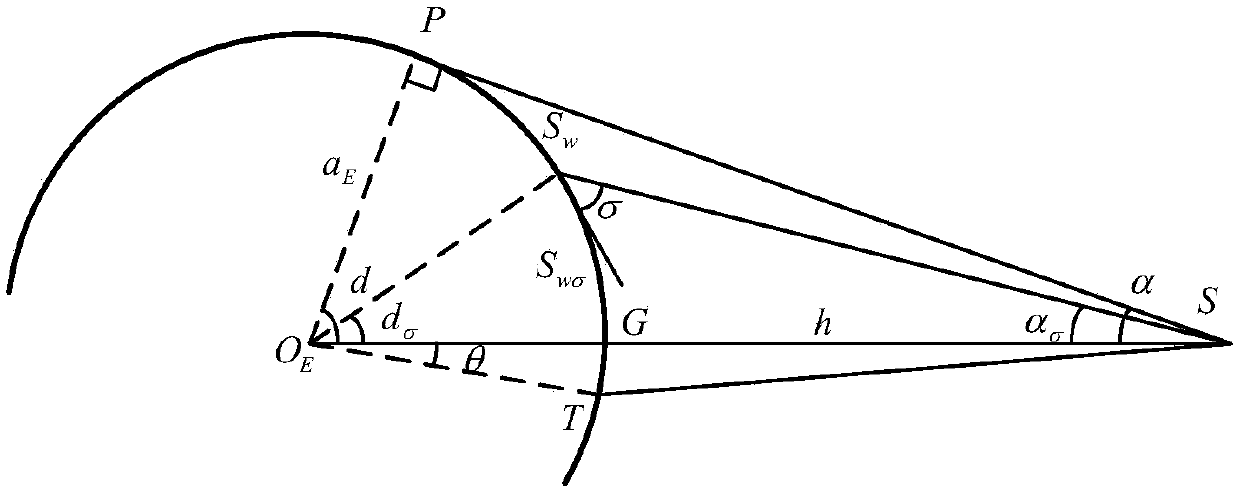
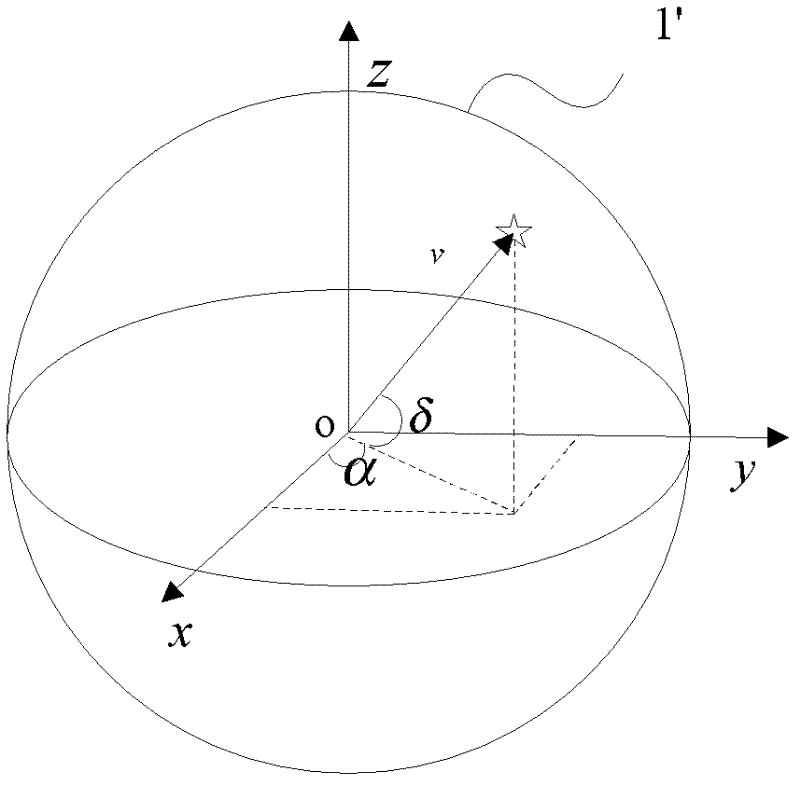
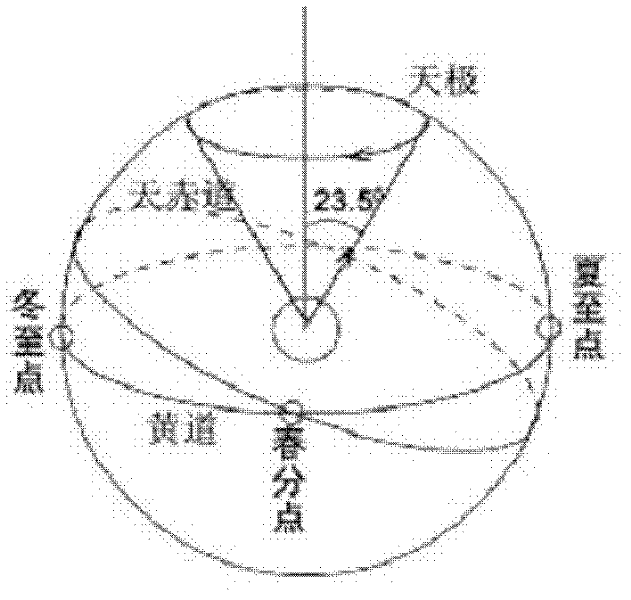
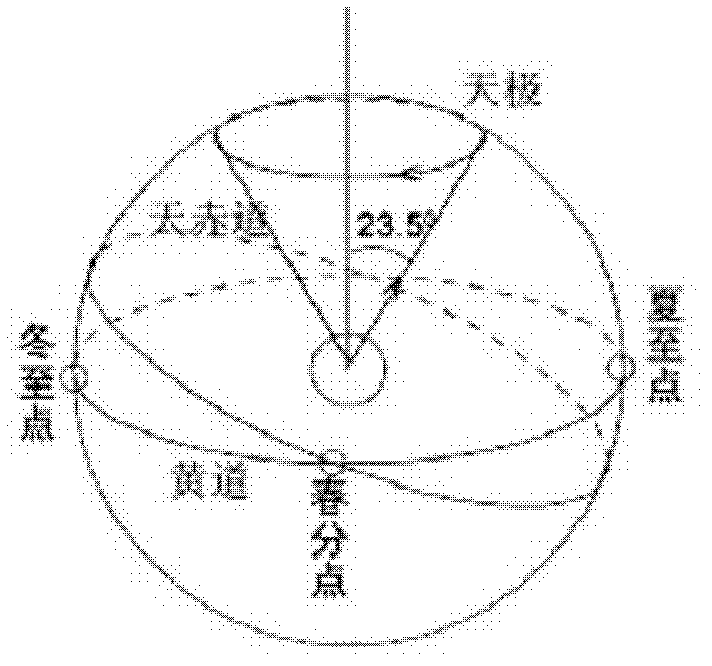
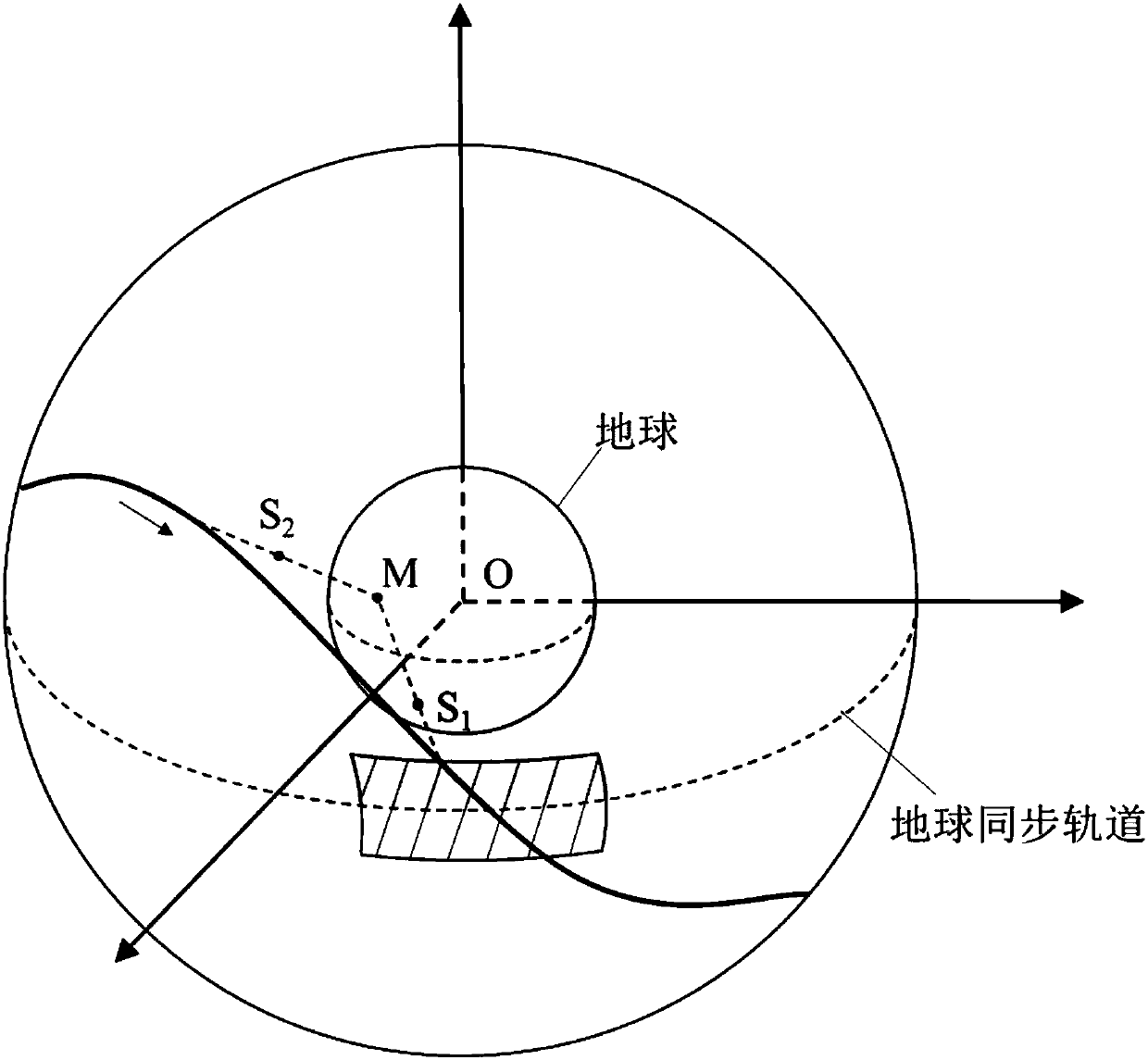
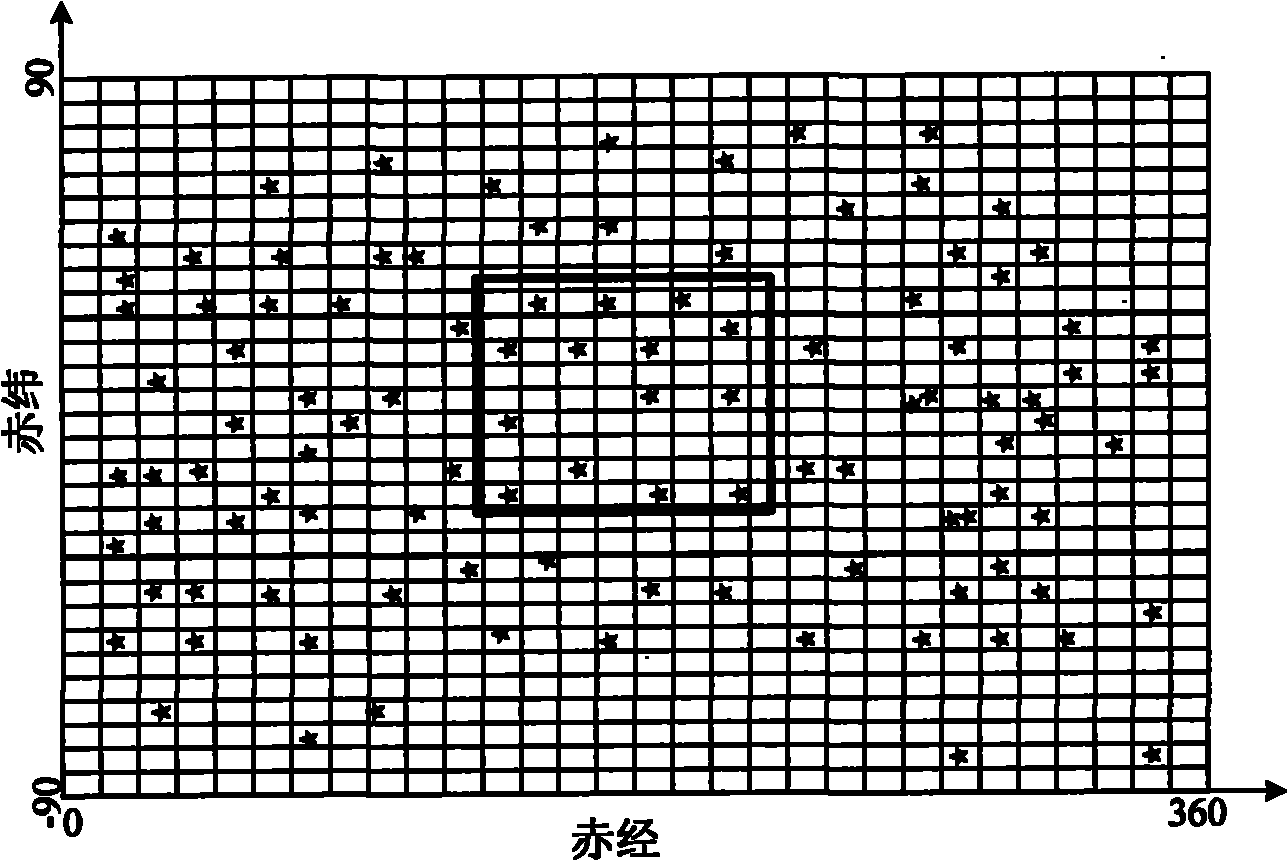
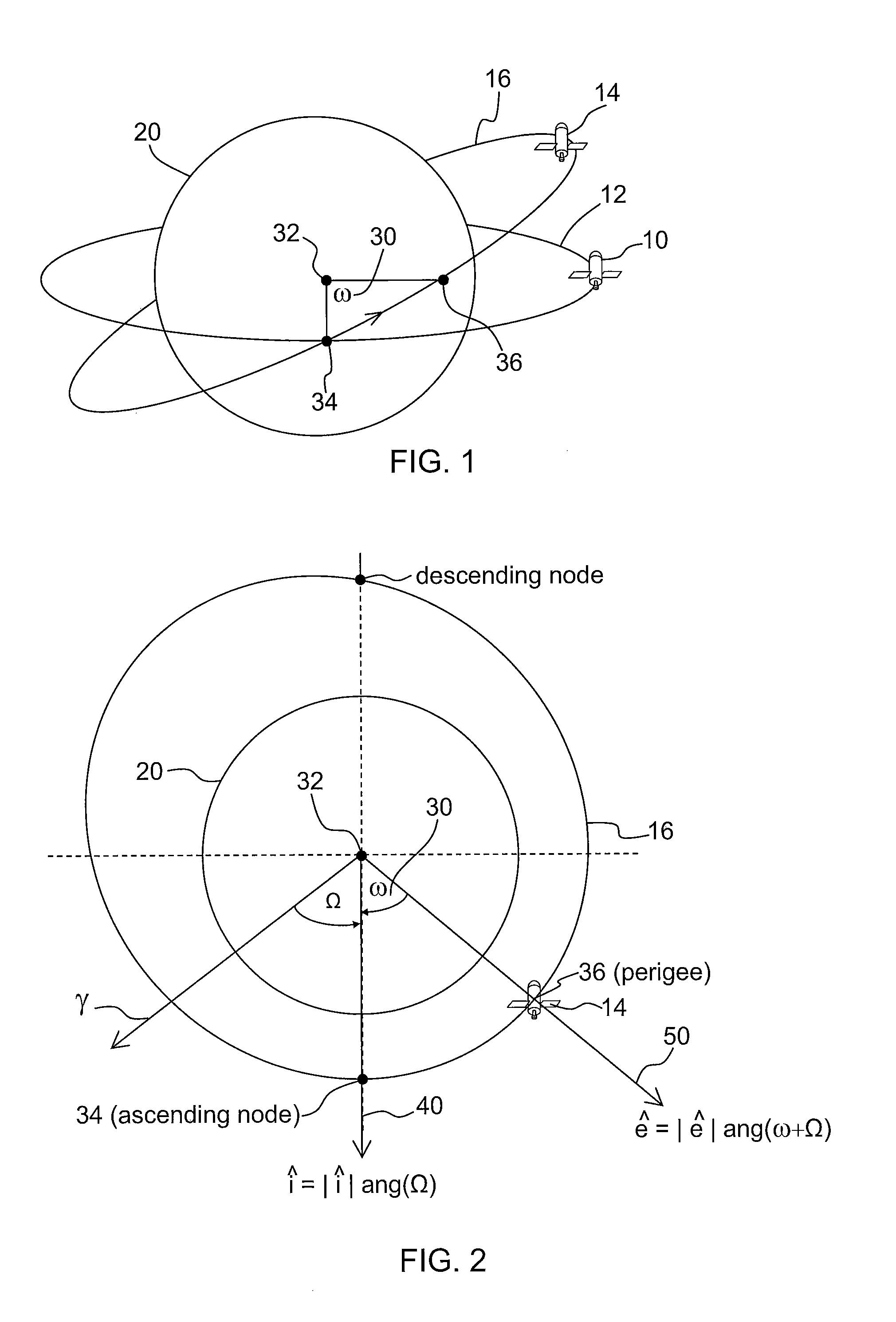
Right ascension (abbreviated RA; symbol α) is the angular distance of a particular point measured eastward along the celestial equator from the Sun at the March equinox to the (hour circle of the) point above the earth in question. When paired with declination, these astronomical coordinates specify the direction of a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system.
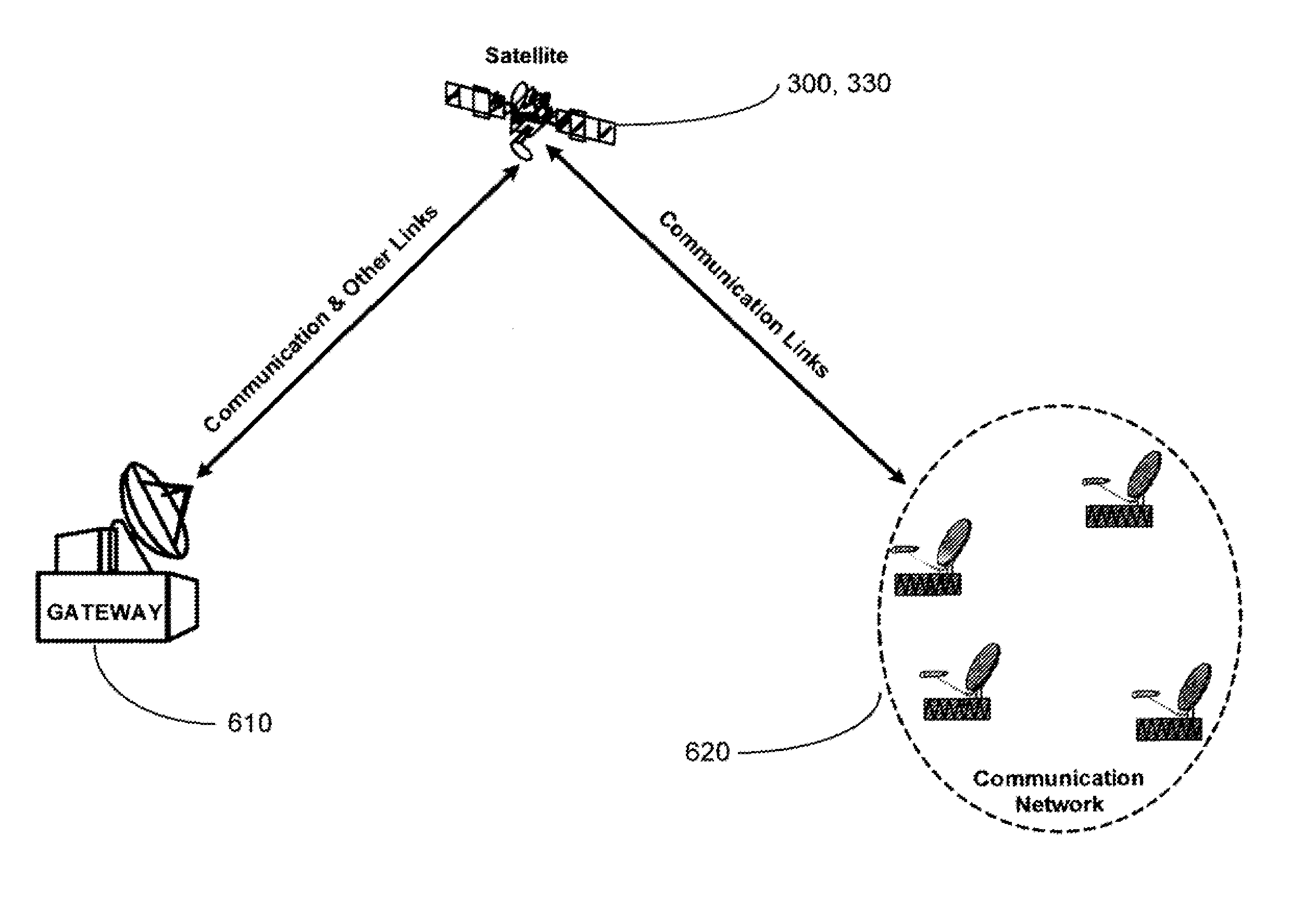
Space based change detection using common ground track constellations
InactiveUS7270299B1Minimal image blurring and distortionReduce in quantityCosmonautic partsArtificial satellitesEarth's rotationPhase angle difference
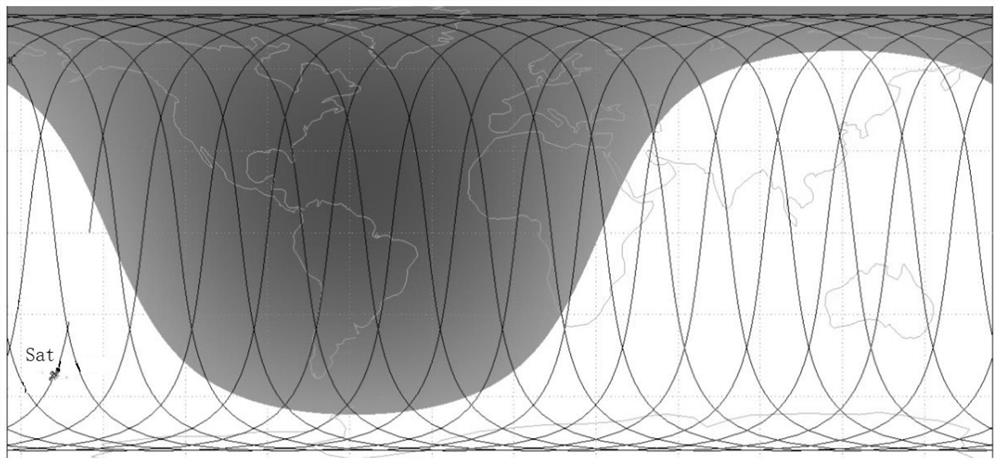
A new approach for designing satellite constellations whereby each satellite follows a common ground track is being proposed for performing high-precision change detection imagery for long periods of time. By precisely prescribing the orbital parameters, i.e., the relationship between the right ascension of the ascending nodes (RAAN) and the phase angle difference between successive satellites, for example, sharpened change detection images may be taken from successive satellites in the constellation without the need to process out blurring by any special image re-working software. The relationship between the orbital parameters of the satellites is precisely tuned to the earth's rotation rate for the altitude of the satellites. A reduction in the total satellite count is achievable due to tiling the satellite coverage in near optimal arrangements. Such high-precision change detection imaging by successive satellites in orbit around the earth is at least useful in the detection of underground facilities activities and the detection of slow moving objects.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
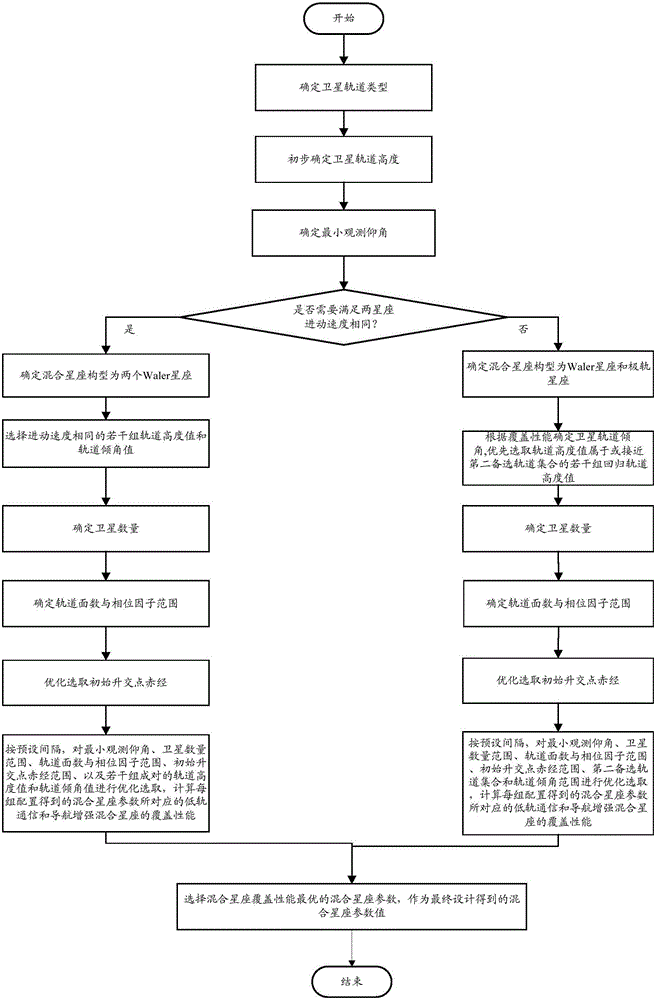
Optimization design method of low-orbit communication and navigation enhancement mixed constellation
ActiveCN106249253AImprove compatibilityFacilitate communicationRadio transmissionSatellite radio beaconingElevation angleIntersection of a polyhedron with a line
The invention provides an optimization design method of a low-orbit communication and navigation enhancement mixed constellation. The method comprises the following steps: determining a satellite orbit type; determining a satellite orbit height; determining a minimum observation elevation angle; selecting constellation configuration; determining an orbit inclination angle; determining a satellite quantity; determining an orbit surface quantity and a phase factor; selecting initial ascending node right ascension in an optimized mode; analyzing coverage performance of the low-orbit communication and navigation enhancement mixed constellation; and after traversing ends, comparing all mixed constellation parameters satisfying design requirements, and selecting an optimal solution. The method has the following advantages: through combination of factors needing to be considered for design of a communication and navigation enhancement constellation at each phase, the designed low-orbit communication and navigation enhancement mixed constellation can satisfy user demands, is excellent in constellation performance, is small in satellite quantity and quite good in compatible mutual operation capability between constellations.
Owner:PLA PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY OF CHINA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE AEROSPACE ENG UNIV
Stationkeeping optimization for inclined elliptical satellite orbit constellations
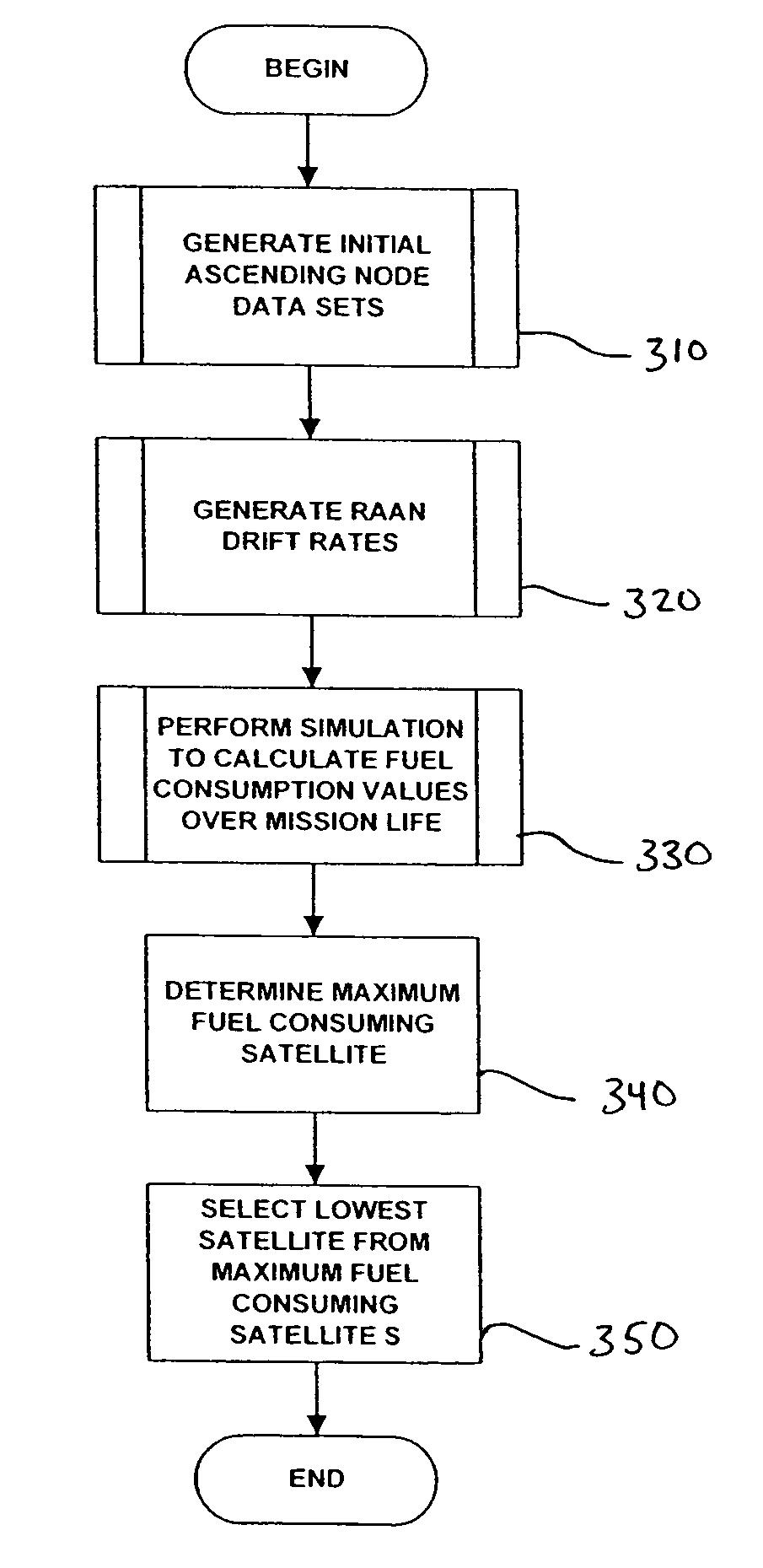
ActiveUS7720604B1Reduce fuel consumptionMinimum consumptionInstruments for comonautical navigationCosmonautic partsEllipseSatellite orbit
A satellite constellation optimized for stationkeeping fuel consumption is provided. The satellite constellation includes a plurality of satellites, each satellite having a corresponding inclined elliptical orbit, each orbit having an initial right ascension of ascending node (“RAAN”) value, a RAAN drift rate, a semi-major axis, an eccentricity, an argument of perigee and an inclination. Each satellite has a fuel consumption value required to maintain the RAAN drift rate, the semi-major axis, the eccentricity, the argument of perigee and the inclination of the corresponding orbit. The initial RAAN value and the RAAN drift rate for each orbit correspond to a minimized fuel consumption value for the satellite having the highest fuel consumption value. The initial RAAN value and RAAN drift rate may be determined by calculating, for each possible data combination of an initial RAAN value for each orbit and a RAAN drift rate for the constellation, a fuel consumption value for each satellite in the constellation, and selecting, from the fuel consumption values thus determined, the data combination corresponding to a lowest fuel consumption for a highest fuel-consuming satellite.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
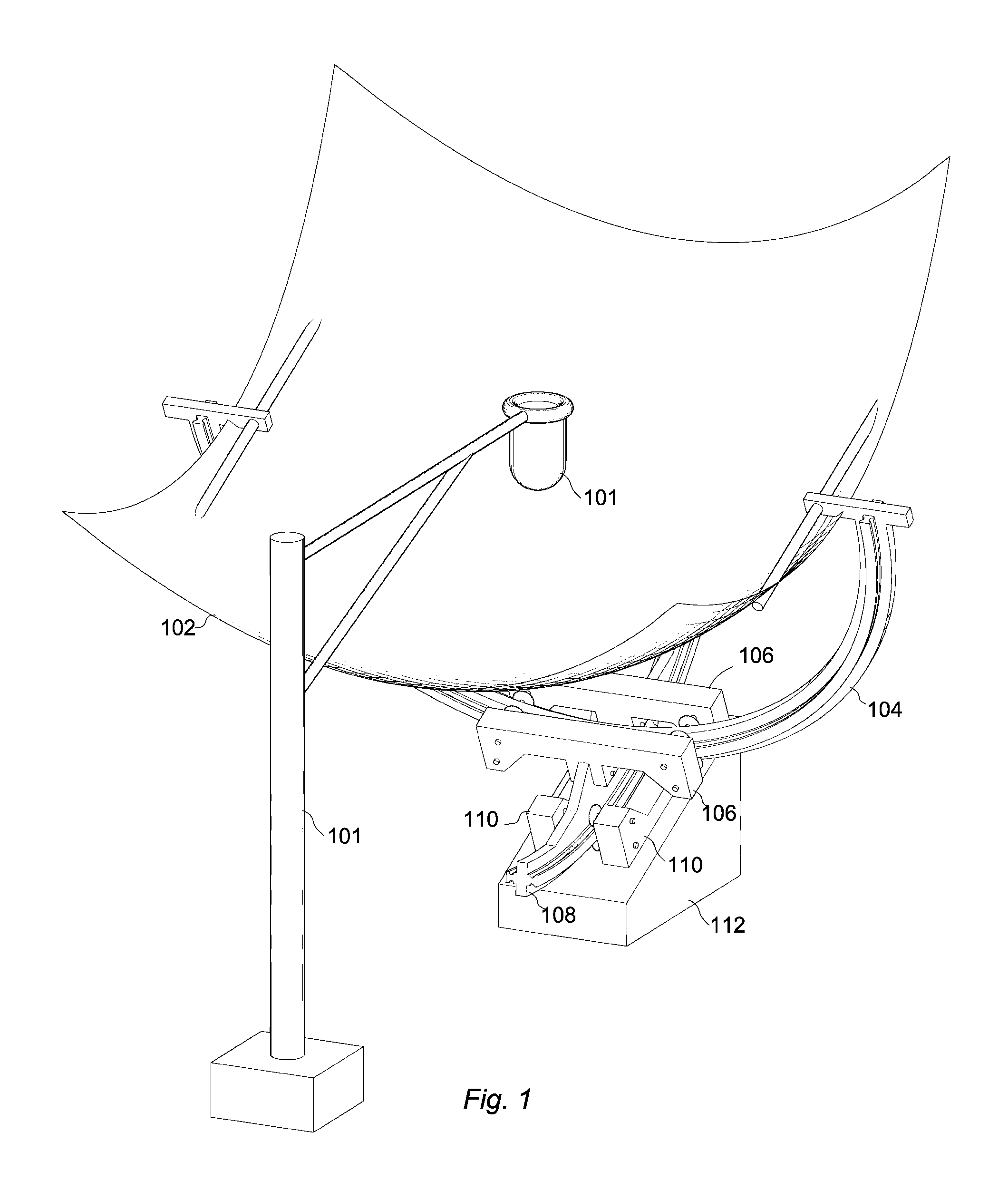
Apparatus and A Method for Solar Tracking and Concentration af Incident Solar Radiation for Power Generation
A method and an apparatus are presented for solar tracking and concentration of incident solar radiation for power generation. The apparatus includes a solar tracking system, an optical concentrator system and a radiation collection device. The solar tracking system includes a right ascension track and a declination track for dual axis solar tracking along equatorial coordinates of the sun, wherein the right ascension track and the declination track are driven at their respective rims. The optical concentrator system is moved by the solar tracking system to concentrate the incident solar radiation into a stationary focal point. The radiation collection device couples concentrated incident solar radiation to a power generation means. The radiation collection device is disposed proximate the stationary focal point to collect the incident solar radiation.
Owner:BANERJEE RAJARSHI
Efficient multi-objective optimization method for satellite constellation
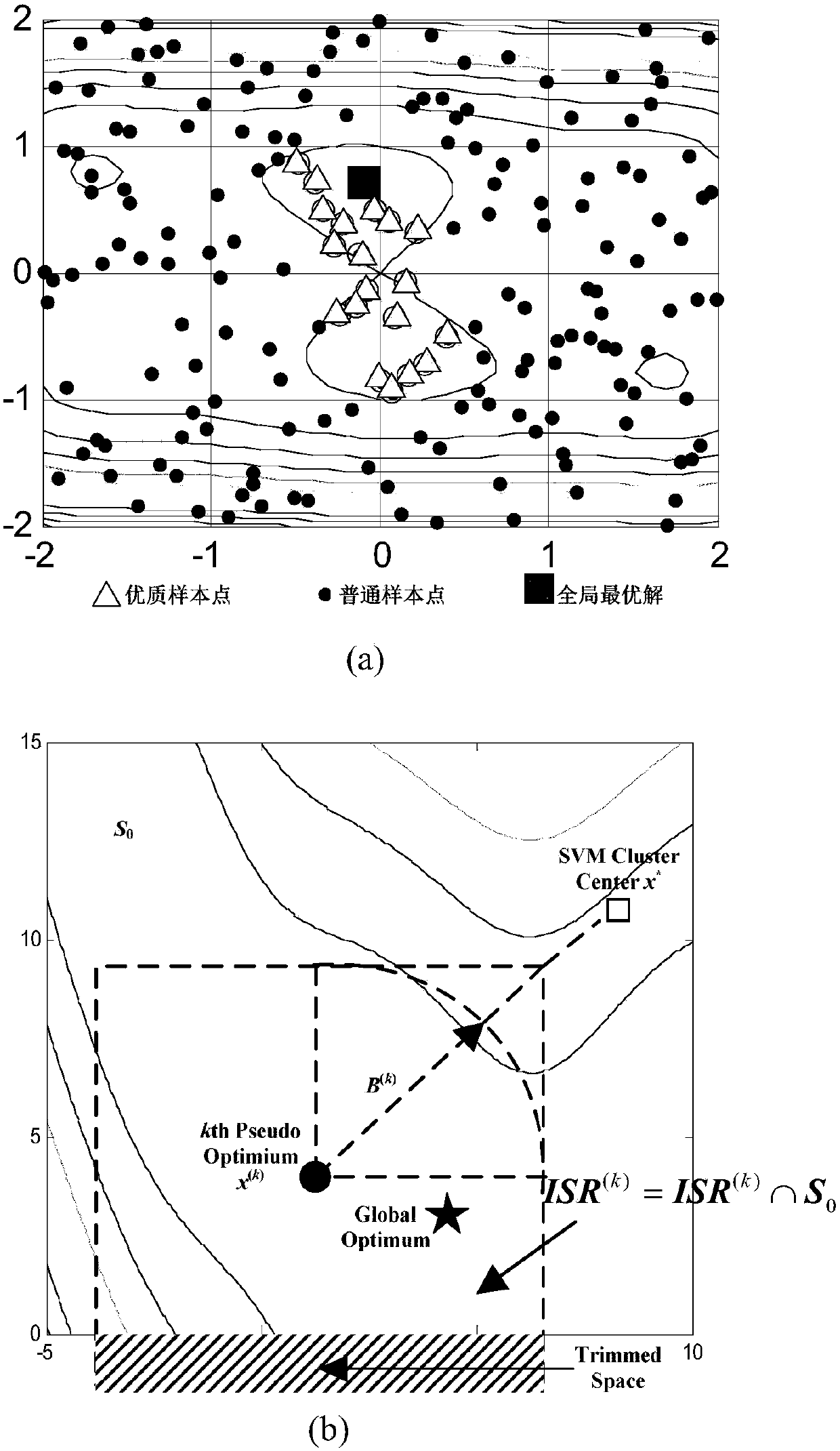
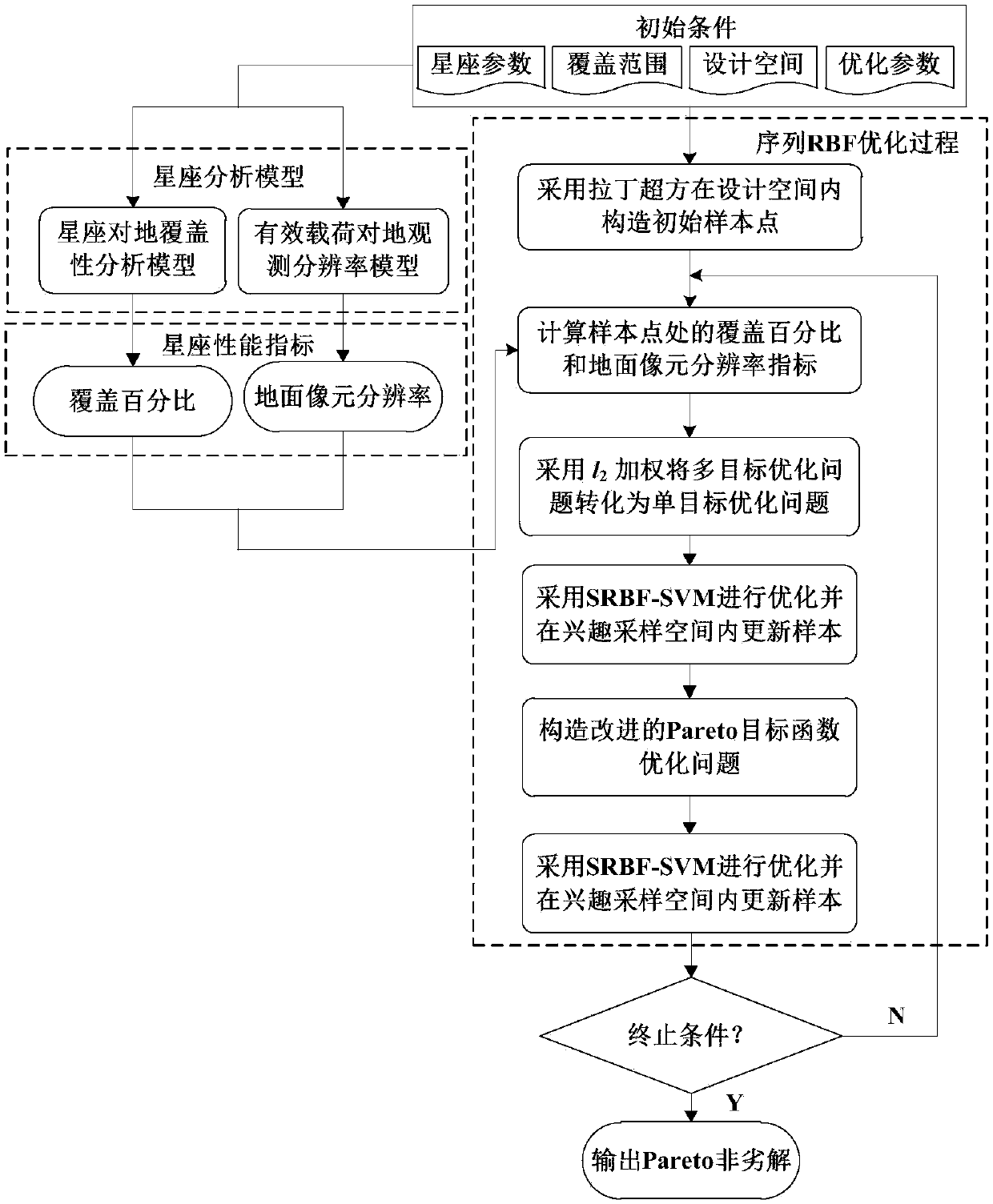
ActiveCN107798187AReduce computing costReduce design costGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationEarth observationIntersection of a polyhedron with a line
The invention discloses an efficient multi-objective optimization method for a satellite constellation and belongs to the field of constellation system of a spacecraft. The method comprises the stepsof determining an initial condition based on a Walker-delta constellation configuration, and establishing a constellation orbit kinetic equation, an earth coverage analysis module and an earth observation resolution model; optimizing an earth orbit height, an orbital inclination and an ascending node right ascension with a coverage percentage and a ground pixel resolution by use of a sequential radial basis function multi-objective optimization strategy; and constructing an objective function based on l2 weighting and an improved Pareto fitness function, replacing a high time-consuming constellation performance simulation model with an RBF (Radial Basis Function) agent model to optimize design, and updating and managing the RBF agent model through sequence sampling in an interest interval.Therefore, a Pareto non-inferior solution set satisfying engineering requirements is acquired as a satellite constellation design scheme, the coverage percentage of a constellation for a target observation region is realized as high as possible, the pixel resolution of an effective load is realized as low as possible, the calculation cost and the design cost of the satellite constellation are reduced, and the Pareto leading edge search capability is improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
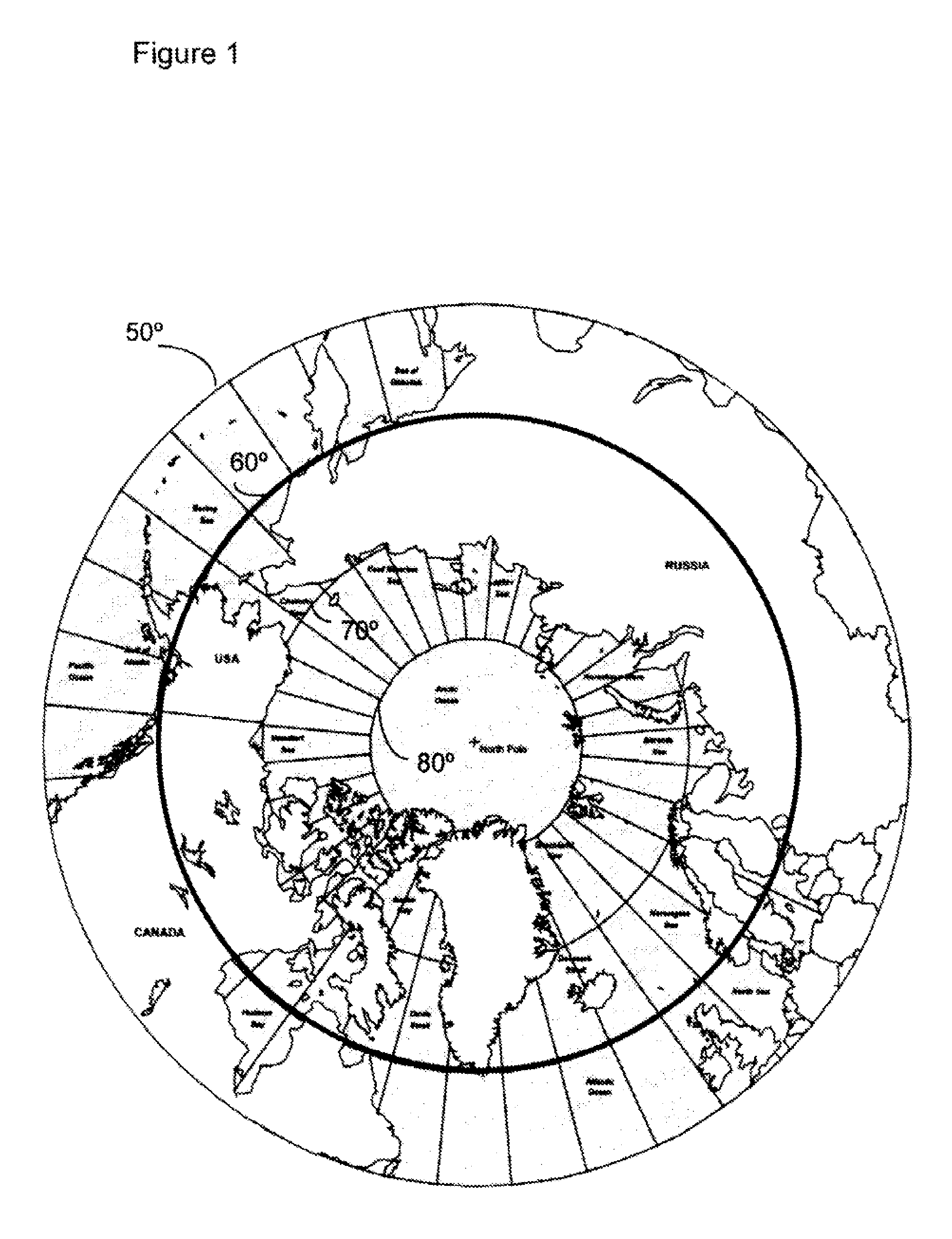
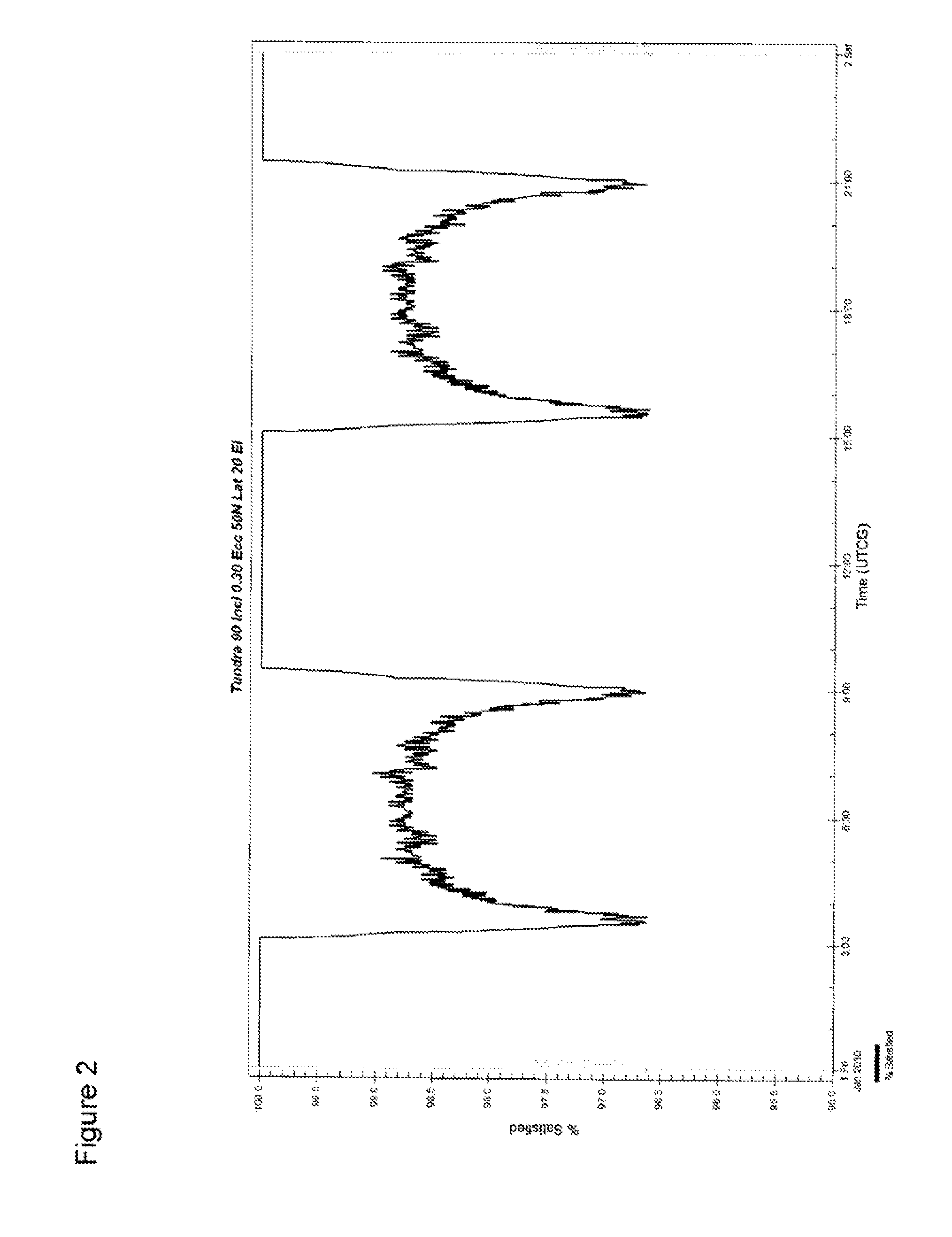
Satellite system and method for circumpolar latitudes
The present invention relates to satellite systems and more particularly, to the provision of a satellite system for weather and climate monitoring, communications applications, and scientific research at higher latitudes, referred to as the circumpolar region and defined here as the area with latitudes greater than 60°, in either the northern hemisphere or the southern hemisphere. Contrary to the teachings in the art it has been discovered that a satellite system and method may be provided using satellites in 24 sidereal hour orbits (geosynchronous) with inclinations (70° to 90°), orbital planes, right ascensions and eccentricities (0.275-0.45) chosen to optimize coverage of a particular service area located at high latitudes. A constellation of two satellites can provide continuous coverage of the circumpolar region. The satellites in this orbit avoid most of the Van Allen Belts.
Owner:TELESAT CANADA
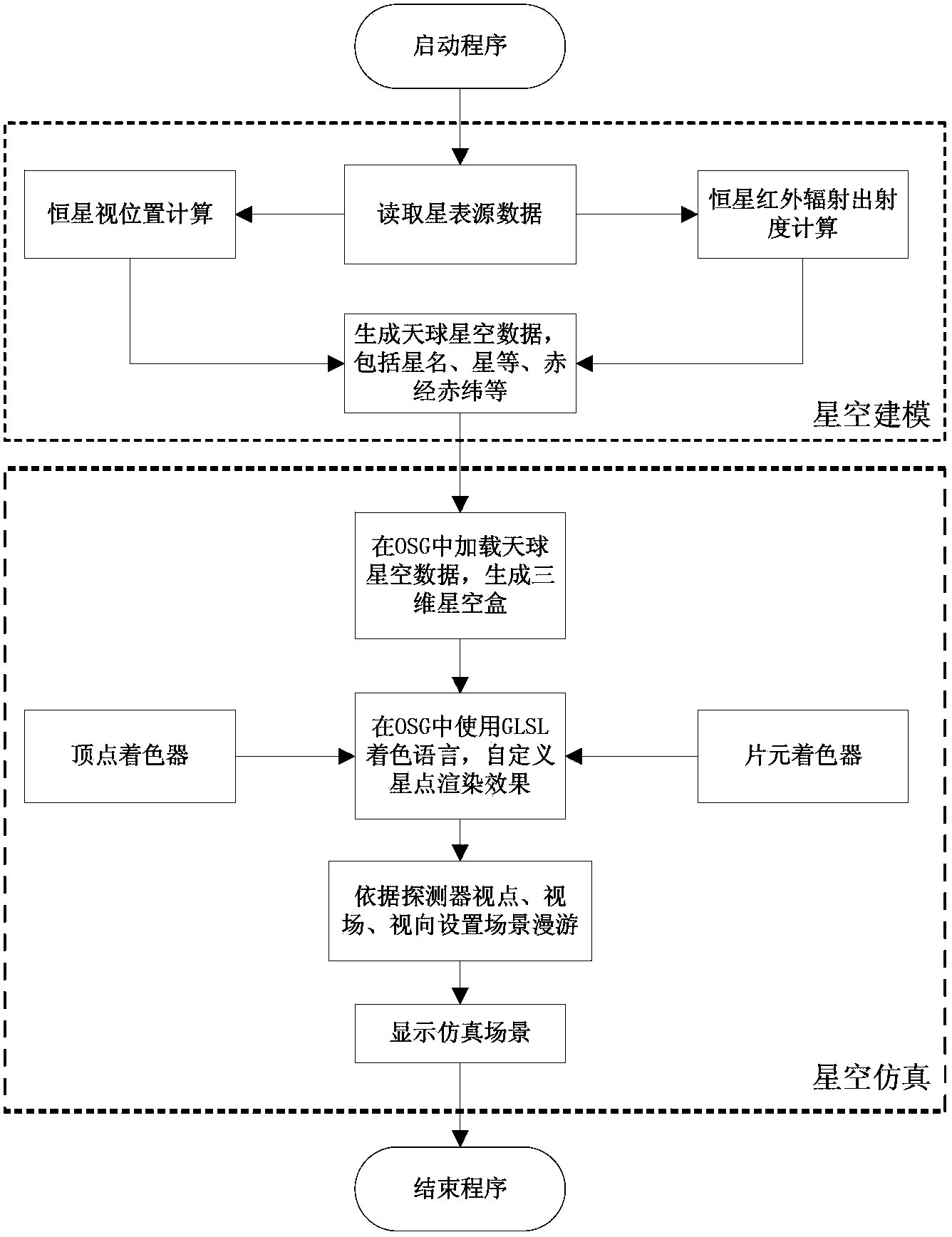
A method for fast generating an optical starry sky background
InactiveCN103679799APrevent size changeIncrease generation speedPlanetaria/globes3D modellingFixed starsNutation
The invention belongs to optical technical field and specifically relates to a method for fast generating an optical starry sky background. The method comprises following steps including: a step 1, modeling a sky background in which star catalogue data of fixed stars is used as a source, by means of transformation of time and a coordinate system and correction of the apparent positions of heavenly bodies, starry sky background models at any observation point any time are constructed and a calculating result is inputted into a base in order to be used for simulation, wherein the calculating result comprises star names, star magnitudes, right ascension, and declination; and a step 2, simulating the established starry sky background model. The step 1 uses Hipparcos Catalogue as a data source of a visible light band. According to the selected Hipparcos Catalogue, the apparent positions of the fixed stars are calculated. Considered factors comprise annual parallax and proper motion caused by revolution of the earth, aberration caused by the self motion of an observer, annual aberration, precession, and nutation caused by earth revolution about the sun. The speed for generating a starry sky background by using the method may reach 50Hz.
Owner:中国航天科工集团第二研究院二〇七所
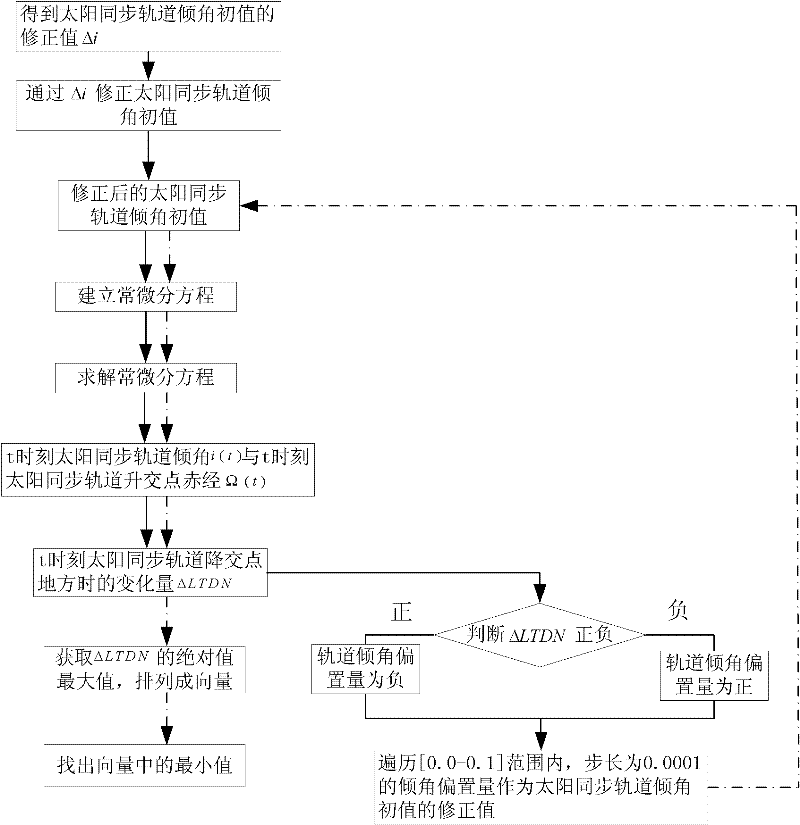
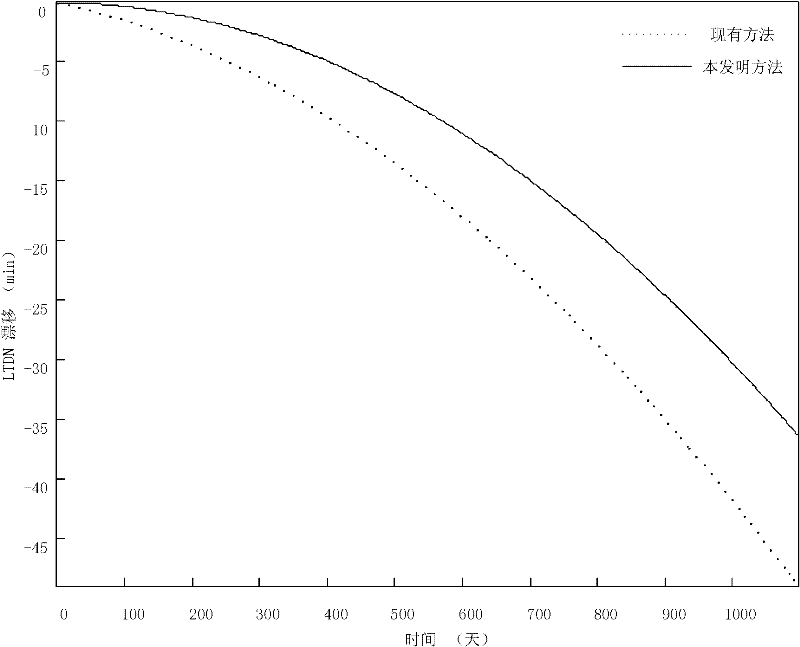
Acquisition method of inclination biased quantity for sun synchronous orbit
InactiveCN102495950AHigh precisionImprove controlSpecial data processing applicationsOrbitRight ascension
The invention discloses an acquisition method of inclination biased quantity for sun synchronous orbit. The method comprises the following steps: 1, correcting an initial value i0 of an orbit inclination by virtue of a correction value delta I of the initial value of the orbit inclination; 2, establishing an ordinary differential equation to acquire an orbit inclination at moment t and orbit right ascension of ascending node, and variation delta LTDN of local time of descending node at moment t; 3, judging the orbit drifting direction, wherein the biased quantity of the orbit inclination is negative if the direction is toward east, while the biased quantity of the orbit inclination is positive if the direction is toward west; and 4, traversing inclination biased quantities with step length of 0.0001 degree in a range from 0.0 to 0.1 degree, and respectively adding the corrected initial value of the sun synchronous orbit inclination in the step 1 to serve as an orbit initial value with inclination biased quantity, and carrying out the step 2 to obtain the variation of the local time of descending node at the moment t, arranging the maximum values of absolute values of variations into vectors according to a sequence, and the minimum value in the vectors is the inclination biased quantity. According to the method, the defect of low calculation accuracy of inclination biased quantity of the conventional sun synchronous orbit inclination biased quantity is overcome, and the orbit control capability is effectively improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Sub-satellite point circular geosynchronous orbit design method
InactiveCN103678787AMeet the needs of multi-angle earth observationSpecial data processing applicationsNatural satelliteGeosynchronous orbit
Disclosed is a sub-satellite point circular geosynchronous orbit design method. The method includes: (1) analyzing and determining sub-satellite point circular geosynchronous orbit generating conditions including that (1.1) an orbital semi-major axis is 42164km, (1.2) a satellite drifts back and forth in the north-south direction every day, (1.3) the satellite drifts back and forth in the east-west direction every day, (1.4) the distance of north-south direction drift is equal to that of east-west direction drift, and (1.5) the satellite passes the equator twice every day with relative distance of sub-satellite points when the satellite passes the equator twice equal to east-west direction drift distance of the satellite; (2) according to the conditions in the step (1), determining orbital parameters, satisfying the five conditions at the same time, namely the orbital semi-major axis a, eccentricity ratio e, inclination angle i, right ascension of ascending node Omega, argument of perigee omega and true anomaly theta. Design of a sub-satellite point circular geosynchronous orbit is completed by utilizing the determined orbital parameters.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
Accuracy measurement method for star sensor
The invention discloses a precision measurement method for a star sensor, which comprises the following steps of: 1) fixing the star sensor on the earth; 2) inputting time T of measurement starting time relative to J2000.0 into the star sensor; 3) determining the direction vector of J2000.0 right angle coordinate system according to the declination and right ascension as well as apparent motion parameter (alpha', delta') of a navigator star under the J2000.0 coordinate system; 4) converting the direction vector of the navigation star under the J2000.0 right angle coordinate system into the direction vector under an epoch ecliptic coordinate system; 5) converting the direction vector under the epoch ecliptic coordinate system into the direction vector (v CRFT) under a spherical coordinate system; and 6) changing the direction vector of the navigation star under the spherical coordinate system into the direction vector (v TRF) under a fixed ground coordinate system, on the basis of the direction vector (v TRF) under the fixed ground coordinate system, obtaining the precision of the star sensor. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the precision measurement of the starsensor can be easily realized.
Owner:北京天银星际科技有限责任公司
Method for automatically aligning telescope
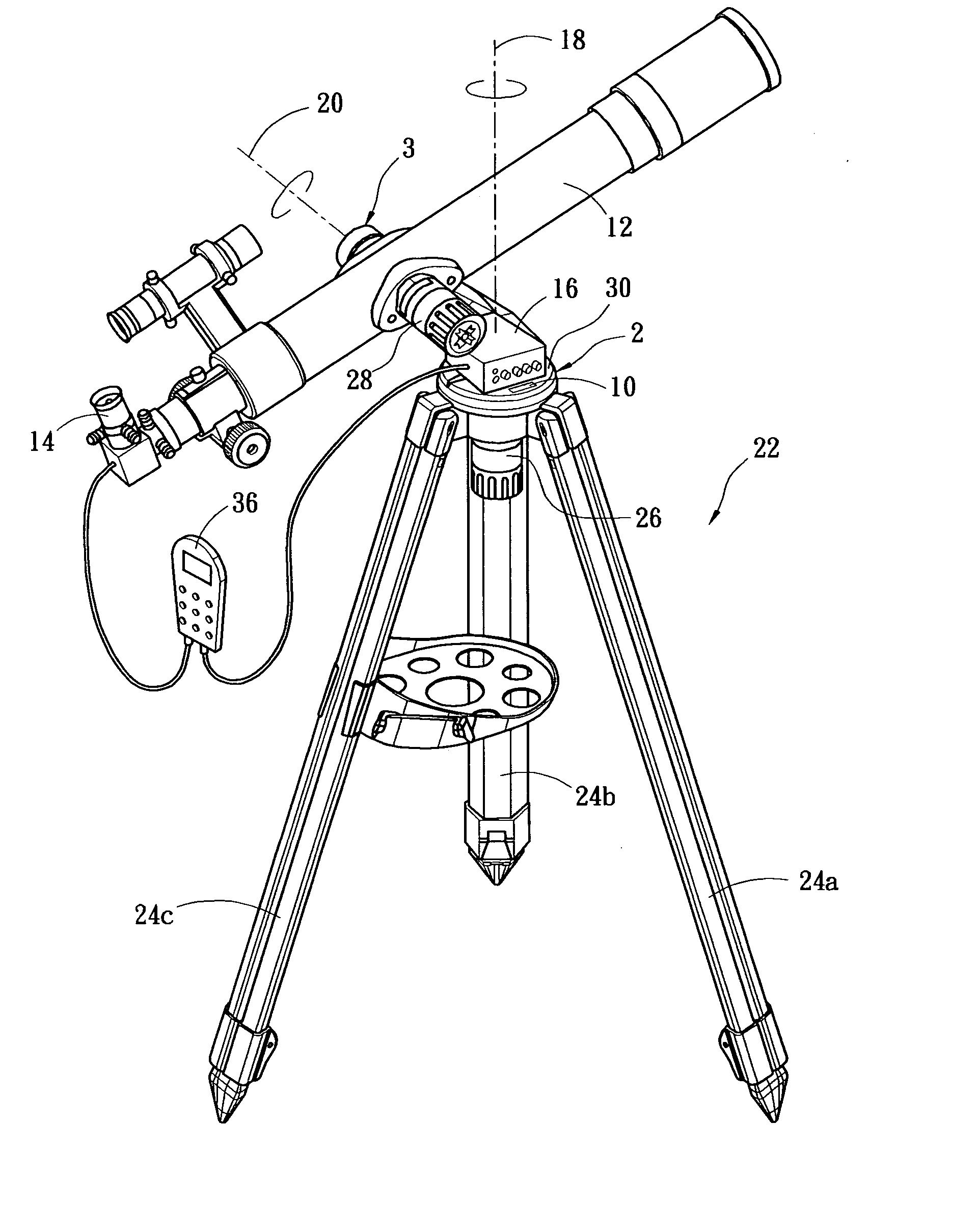
A manual controller commands a telescope mount to automatically track a specific bright star after the image of the star is located to center of an electronic eyepiece and a timer is started. The average moving speed of the bright star is calculated after a predetermined elapsed time to acquire the right ascension (RA) and the declination (DEC) coordinates of this bright star. Subsequently, the RA and DEC coordinates are compared with pre-stored data contained within a database used to identify the bright star. The celestial sphere coordinates of the telescope can be determined after a minimum of one bright star is identified. In the auto-tracking procedure, the manual controller controls movement of telescope by feedbacks of the drifting speed and direction of the specific bright star in an electronic eyepiece for the purpose of keeping the specific bright star in the center of the electronic eyepiece.
Owner:NANTONG SCHMIDT OPTO ELECTRICAL TECH CO LTD
Accurate Telescope Tracking System with a Calibrated Rotary Encoder
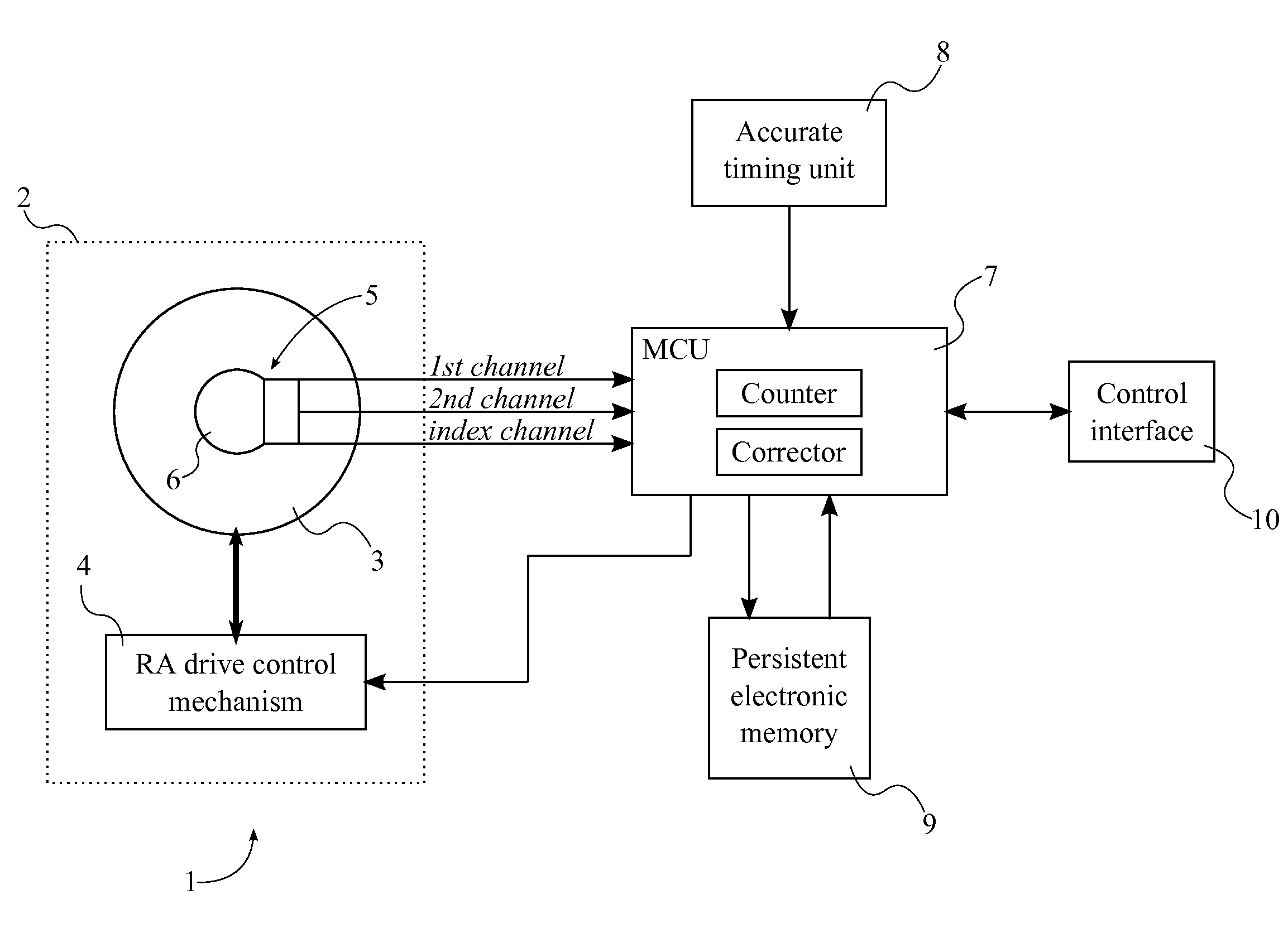
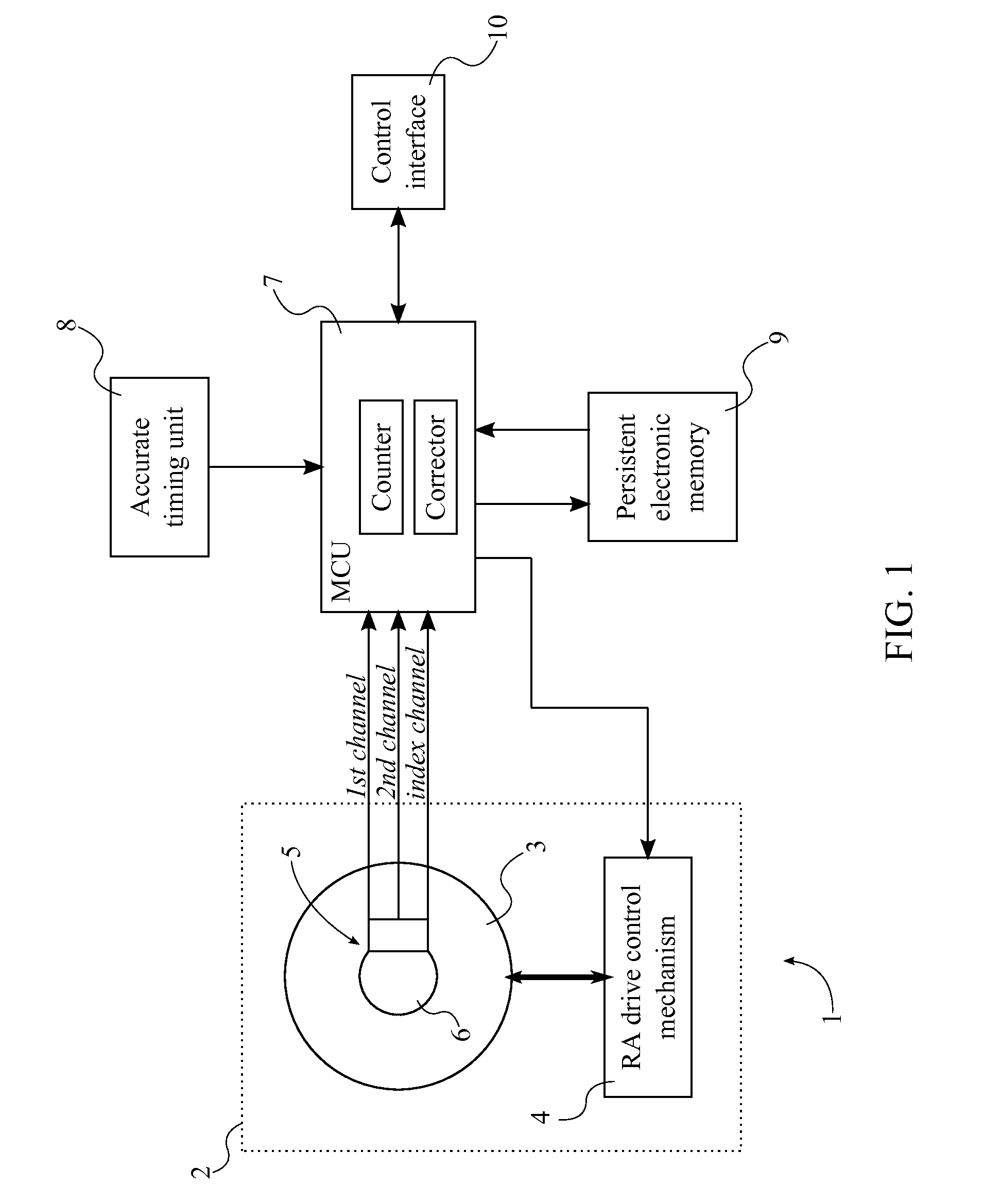
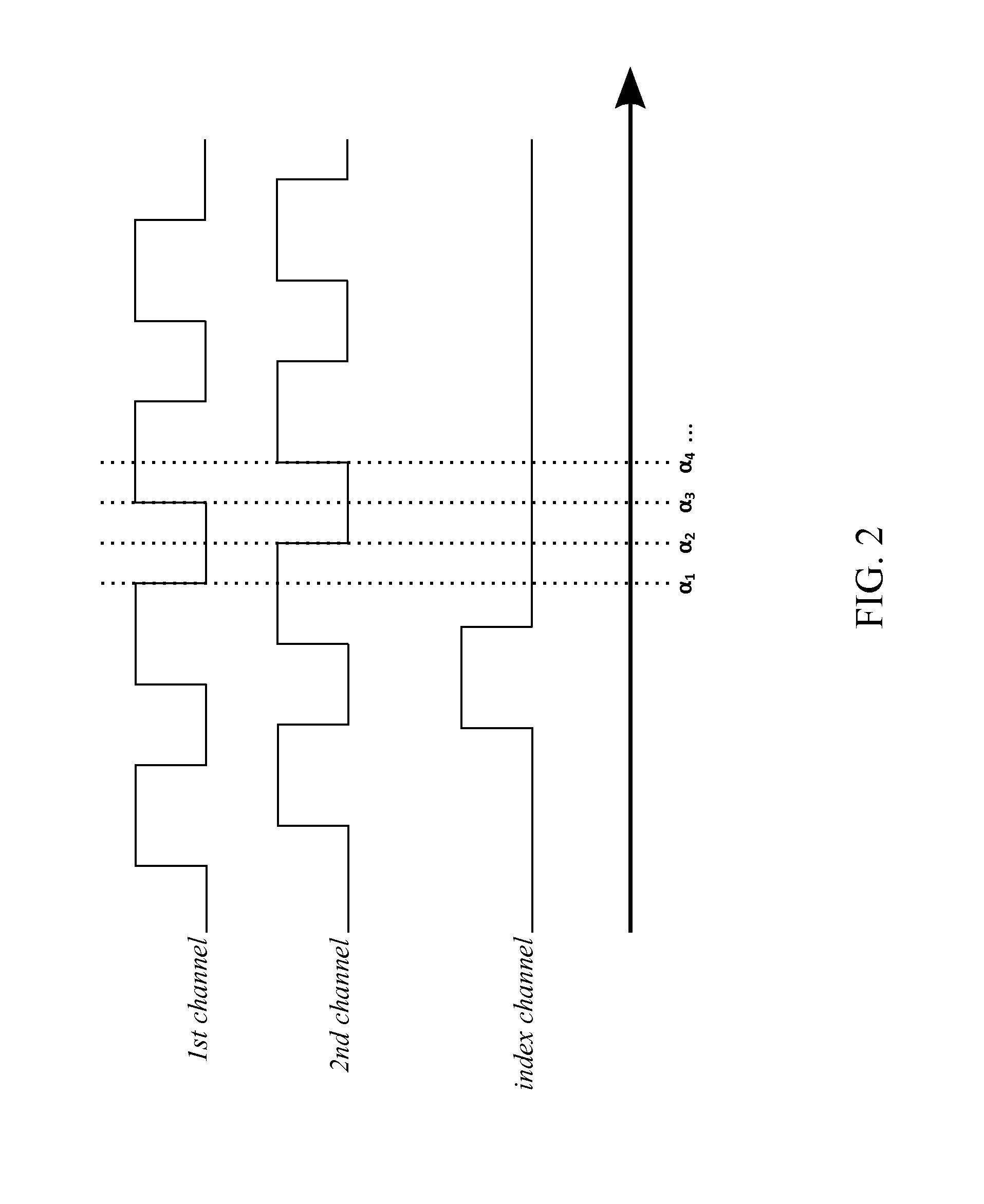
InactiveUS20130265639A1Improve accuracyExpensive encoderComputer controlTelescopesMicrocontrollerEarth's rotation
A system with a calibrated rotary encoder can be used for accurate telescope tracking along the Right Ascension (RA) rotation axis. The system includes an incremental quadrature optical encoder, a microcontroller unit (MCU), a timer, an electronic memory, and a control interface. The rotor of the encoder is coaxially attached to the RA drive shaft of the telescope mount in order to send angular position data for the RA drive shaft to the MCU. The MCU evaluates the angular position data for errors and send corrections to the control mechanism of the RA drive shaft. The electronic memory stores calibrated reference data, which is compared to the angular position data by the MCU. The calibrated reference data can be found by measuring the movement of a reference star across an image. The system can also calculate an accurate visible speed for the Earth's rotation in a desired direction.
Owner:BATCHVAROV ANDREY BORISSOV
Accuracy Measurement System for Star Sensor
ActiveCN102288200AImprove pointing accuracyGuaranteed accuracyMeasurement devicesStar trackerRectangular coordinates
The invention discloses an accuracy measurement system for a star sensor. The accuracy measurement system comprises a fixer and a star sensor accuracy measurement unit, wherein the fixer is used for fixing the star sensor to make a main shaft of the star sensor aligned with a zenith; the star sensor accuracy measurement unit is used for measuring the accuracy of a navigation star; a test startingmoment T is input into the star sensor; a direction vector under a J2000.0 rectangular coordinate system is determined according to declination, right ascension and apparent motion parameters of the navigation star under a J2000.0 coordinate system; the direction vector is converted into the direction vector under an epoch ecliptic coordinate system and then converted into a direction vector (VCRFT) under a celestial sphere coordinate system; the direction vector of the navigation star under the celestial sphere coordinate system is changed into a direction vector (VTRF) under an earth-fixed coordinate system; and based on the direction vector (VTRF) under the earth-fixed coordinate system, the accuracy of the star sensor is obtained. According to the accuracy measurement system provided by the invention, the star sensor is fixedly connected to the earth by using the accuracy of rotation of the earth, and the main shaft of the star sensor is aligned with the zenith for observation.
Owner:北京天银星际科技有限责任公司
Position maintaining method and system under fault mode of electric thruster of full-electric propulsion satellite
ActiveCN108490963AThe ignition parameters are clearSimple calculationAttitude controlElectricityDrift angle
The invention discloses a position maintaining method and system under a fault mode of an electric thruster of a full-electric propulsion satellite. The method comprises the following steps that whencertain electric thruster of the full-electric propulsion satellite has a fault, a branch including the electric thruster is not used any longer, and two electric thrusters in the other branch are used to carry out position maintenance control by that 1) controlled variables needed by essential track factors are calculated according to orbit measurement data; 2) a controlled variable of the totaleccentricity vector is calculated according to a controlled variable of an inclination angle and north-south and east-west position maintaining coupling relation; 3) a drift angle of an electric thruster ignition position is calculated; 4) the ignition speed increment and the middle-point right ascension of an ignition arc are calculated; and 5) ignition time and time length of the electric thruster are calculated. The method and system are suitable for autonomous calculation on the satellite, the problem in maintaining the position in the fault mode of the electric thruster is solved, and thepropellant utilization efficiency is higher.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
Satellite constellation implementation method for implementing communication by utilizing recursive orbit
ActiveCN107980210AReduce co-channel interferenceRealize coexistence at the same frequencyCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsGeostationary orbitIntersection of a polyhedron with a line
The invention relates to a satellite constellation implementation method for implementing communication by utilizing a recursive orbit, and the method comprises the steps: a regression period, an orbital semi-major axis, an inclination of an orbit, an eccentricity ratio and an argument of perigee of the orbit are determined; the number of satellites and orbital planes are determined as n; right ascension of ascending node and a mean anomaly of a first satellite are determined, and according to service needs of the satellite, right ascension of ascending node and mean anomaly of following satellites are determined in sequence; a geostationary orbiting satellite network set that needs to be coordinated and the width of a non-geostationary satellite to geostationary satellite interference protection band are determined; all set satellites successively passes the top in the air along a same fixed orbit are seen at any position of the ground, and when multi-coverage is formed, users on theground can see a plurality of satellites; and if satellite trails pass the interference protection band for the geostationary satellite, when present accessed satellite enters the protection band, theusers on the ground switch to another satellite that does not in the protection band to continuously implement communication.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Real-time correction method for pointing direction of radio telescope
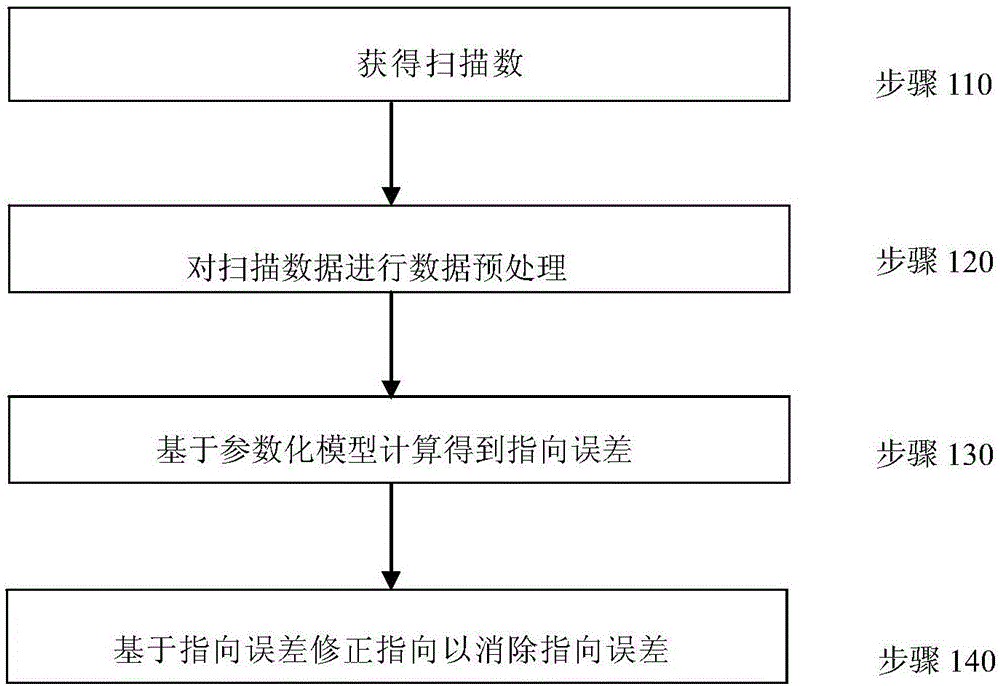
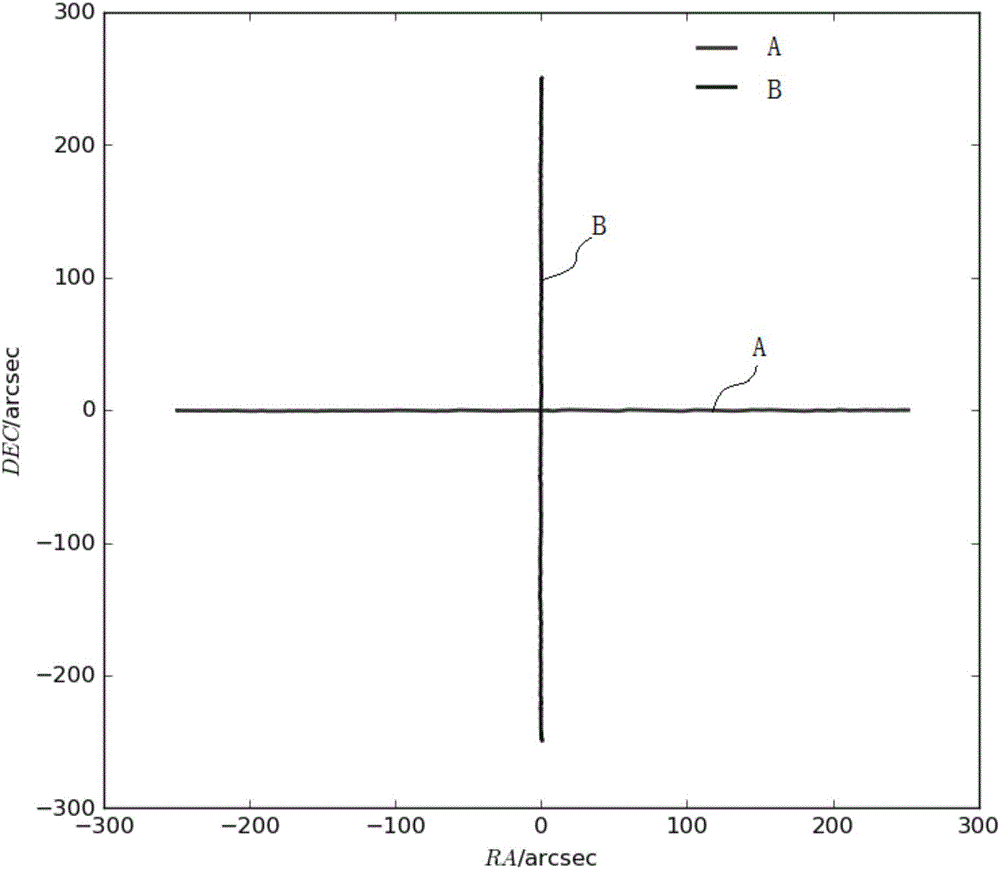
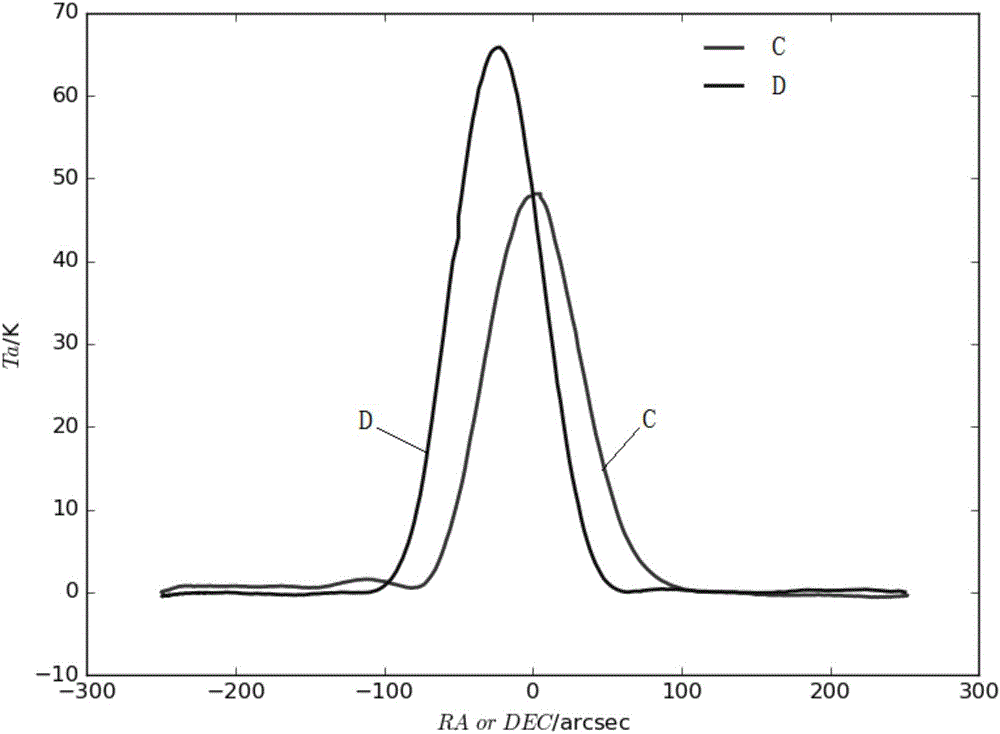
ActiveCN106200697AEliminate pointing errorsImprove pointing accuracyControl using feedbackAntennasHigh elevationRadio telescope
The invention discloses a real-time correction method for the pointing direction of a radio telescope. The method includes the following steps that the radio telescope is controlled to carry out at least one time of scanning on a radio source in the right ascensison direction and the declination direction respectively to obtain right ascensison scanning data and declination scanning data; based on a linear function and a Gaussian function, a parameterized model for describing the right ascensison scanning data and the declination scanning data is established, and parameters for describing pointing errors are contained in the parameterized model; the right ascensison scanning data and the declination scanning data are substituted into the parameterized model, pointing errors in the right ascensison direction and the declination direction are acquired through a fitting algorithm, and pointing errors of the orientation and the pitching direction are acquired through coordinate conversion; the pointing direction of the radio telescope is controlled to be corrected based on the pointing errors to eliminate the pointing errors. The real-time correction method for the pointing direction of the radio telescope can be used for real-time correction of the pointing direction of the radio telescope to eliminate the pointing errors in real time, and meanwhile can solve the problem that the orientation operating speed is too high in the high-elevation scanning process under the orientation and a pitching coordinate system.
Owner:SHANGHAI ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
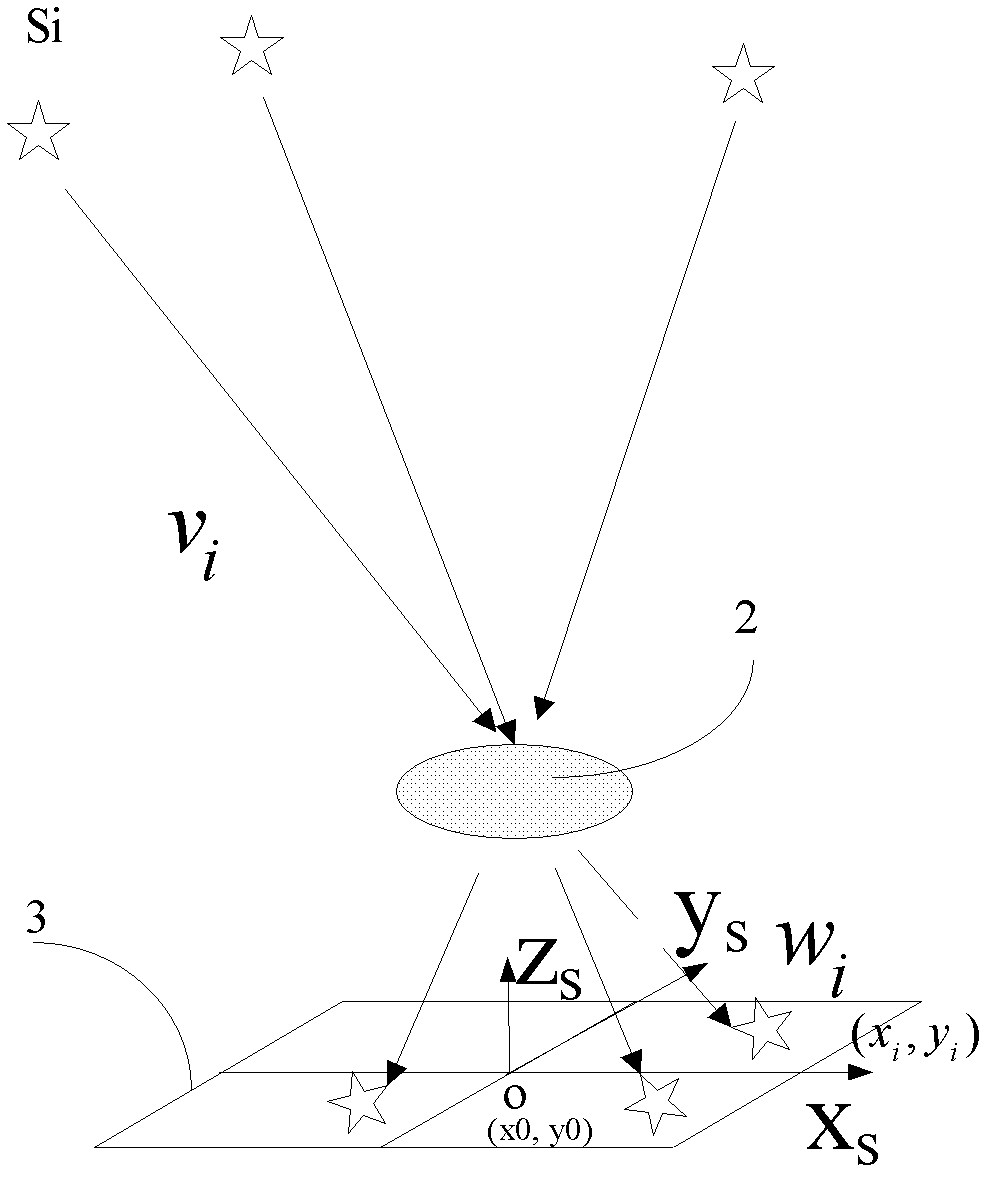
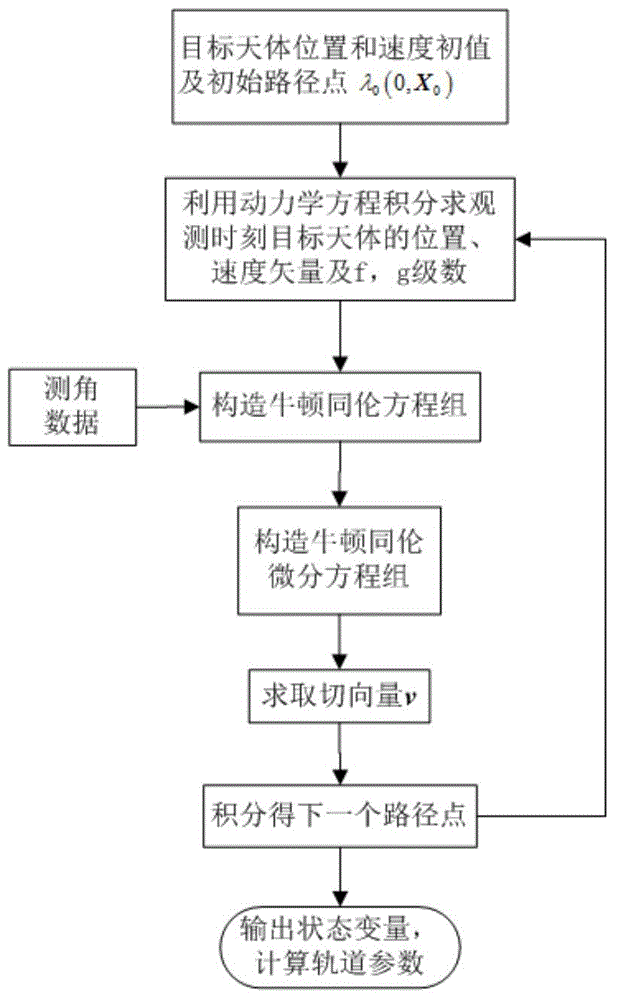
Initial orbit determination method for deep space target celestial body based on space-based autonomous optical observation
InactiveCN104457705ASimple measurement schemeEasy to implementInstruments for comonautical navigationPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryMeasurement deviceTrack algorithm
The invention discloses an initial orbit determination method for a deep space target celestial body based on space-based autonomous optical observation, relates to an optical autonomous initial orbit determination method for a deep space celestial body, and belongs to the technical field of deep space detection. The method comprises the following implementation steps: 1, acquiring angle measurement information (right ascension beta and declination epsilon) of the target celestial body from a detector; 2, establishing an orbital kinetic equation of the target celestial body under a heliocentric inertia coordinate system; 3, establishing an observation condition equation set of the autonomous initial orbit determination of the detector by utilizing the angular position information of the target celestial body solved in the step 1 and known detector orbit parameter information; and 4, solving the orbital element information of the target celestial body by utilizing a Newton homotopy path following algorithm, thereby realizing initial orbit determination. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the position and speed information of the target celestial body can be accurately acquired in real time in the field of deep space probe navigation, the initial value sensitivity is reduced, the convergence rate, solving success rate and calculation efficiency are improved, and the positioning efficiency is further improved. Moreover, the method is simple in measurement device and easy to implement.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
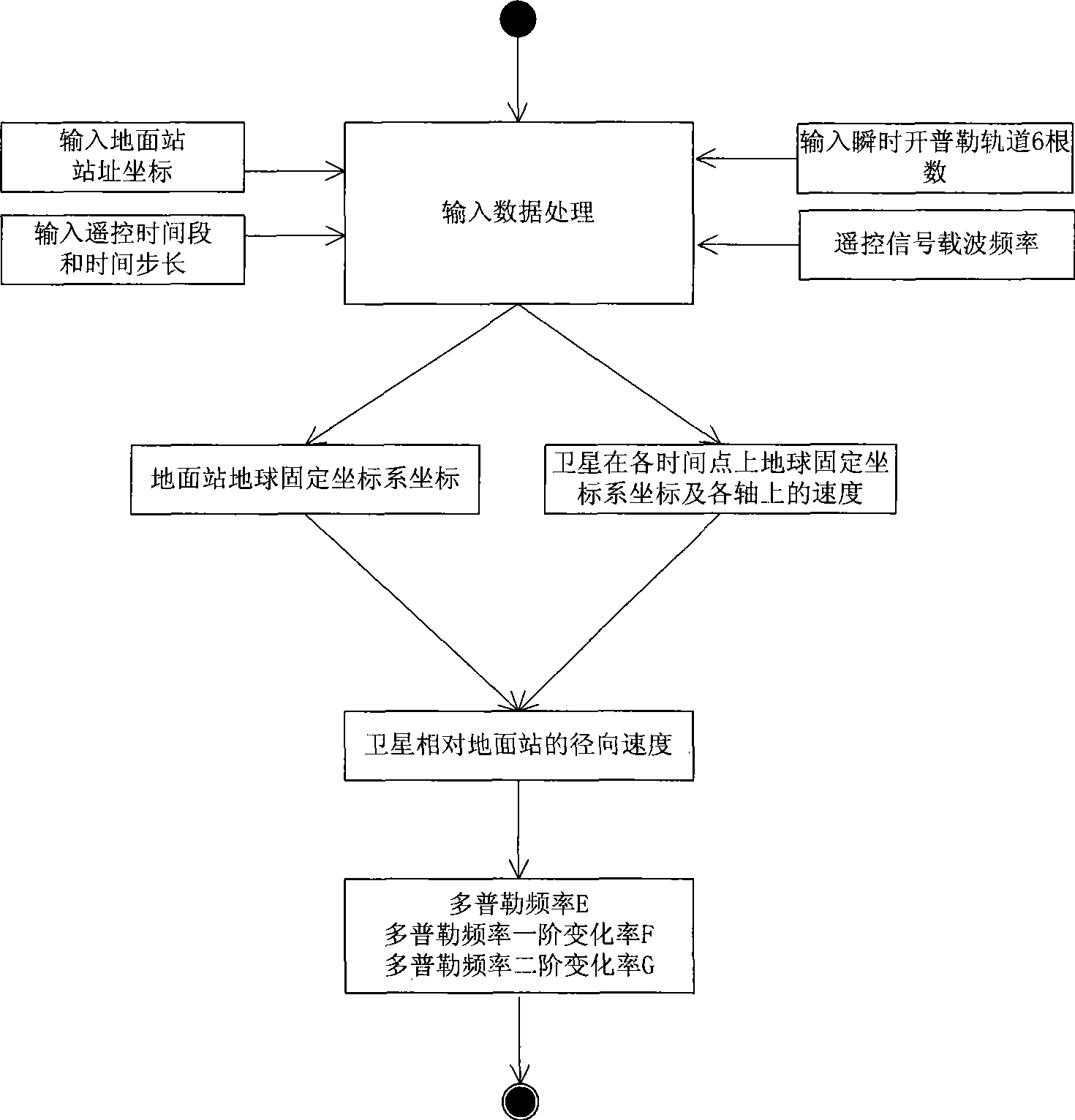
Doppler compensation method for full arch satellite remote control
InactiveCN101420253AImprove calculation accuracyHigh frequency accuracyRadio transmissionLongitudeCarrier signal
The present invention provides a whole arc section satellite remote-control Doppler compensation method by calculating satellite orbit and using DDS to realize the compensation, wherein, the satellite orbits calculation method comprises that input data of earth station location coordinates (latitude, longitude and height), satellite transient Keplerian orbit 6 root number including major semi-axis, eccentricity, obliquity, right ascension of the ascending node and mean anomaly, and time point, earth station remote-control time period and time step, and remote-control signal carrier frequency, are used for performing geometry calculation to obtain accurate orbit location of the satellite within the remote-control time period, furthermore, a Doppler frequency bias value, a Doppler frequency first-order change rate and a Doppler frequency second-order change rate are obtained. The calculated Doppler corresponding data are transmitted to the DDS module to generate a frequency with a sign opposite to that of the Doppler frequency bias value and a same absolute value for modulating remote-control signals and generating Doppler frequency bias compensation. According to the present invention, after receiving remote-control signals, the satellite can realize capture of remote-control signal carriers by using a smaller phase-lock loop bandwidth, therefore, carrier capture time is shortened, carrier capture capability is improved, and interference to useful signals from the noise in the loop bandwidth is reduced.
Owner:SPACE STAR TECH CO LTD
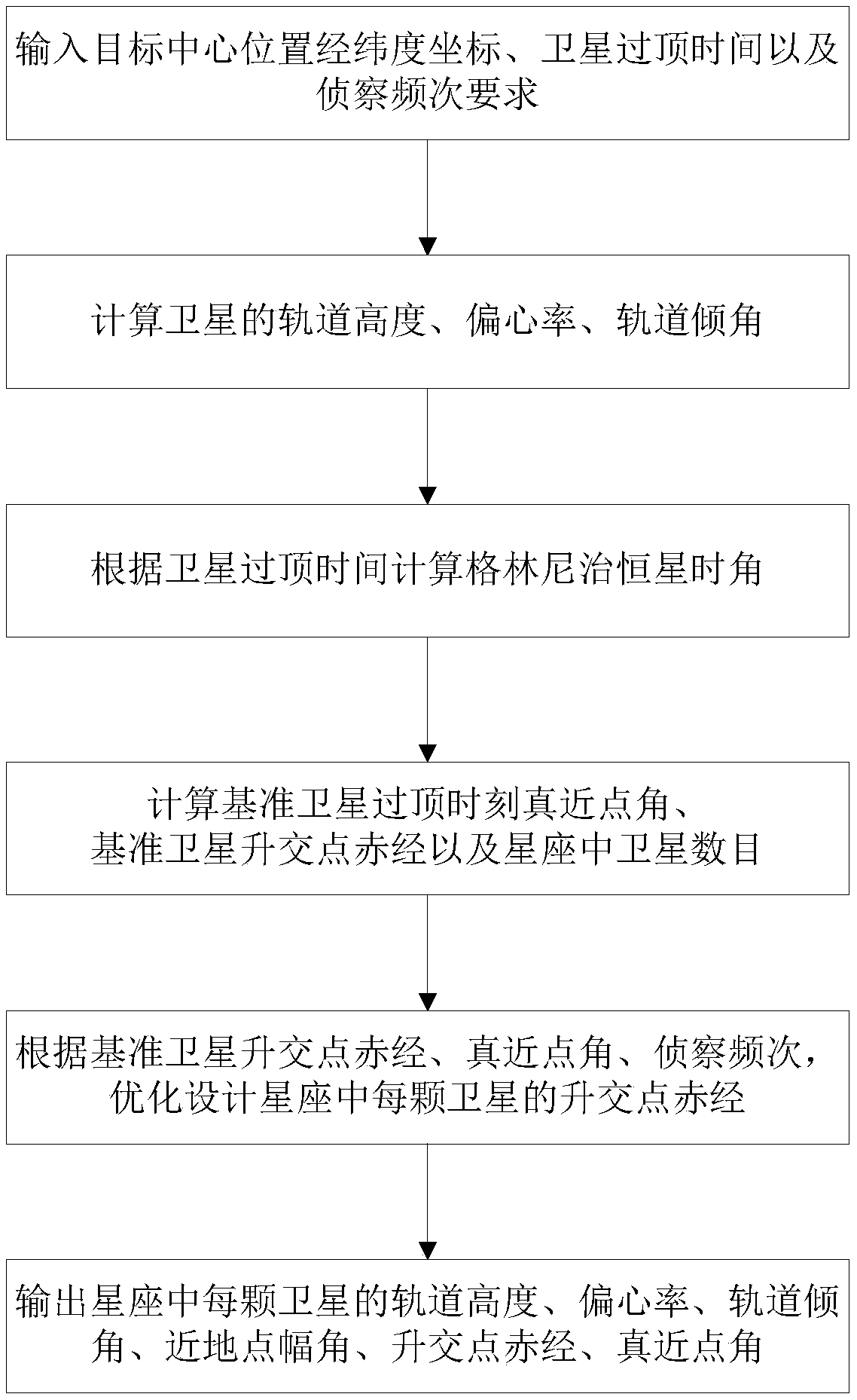
An optimal design method of common trajectory emergency reconnaissance constellation based on sun synchronous return orbit
ActiveCN109146157AAchieve multiple coverageStrong engineering practicabilityForecastingLongitudeOrbital inclination
The invention provides an optimization design method of a common track emergency reconnaissance constellation based on a sun synchronous return orbit. Firstly, the longitude and latitude coordinates of a target center position, the satellite overhead time and the reconnaissance frequency requirements are inputted. Secondly, the orbital altitude, eccentricity and orbital inclination of the satellite are calculated. Thirdly, the Greenwich star time angle is calculated according to the satellite overhead time. Then, the true nearest point angle, the right ascension of the reference satellite andthe number of satellites in the constellation are calculated. Then, the right ascension of each satellite in the constellation is optimized according to the right ascension of the ascending intersection point of the reference satellite, the true nearest point angle and the reconnaissance frequency. Finally, the orbital altitude, eccentricity, orbital inclination, perigee amplitude, right ascensionand true proximity of each satellite in the constellation are output. By using the method, the emergency reconnaissance constellation which meets the requirement of target area coverage can be designed quickly.
Owner:PLA PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY OF CHINA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE AEROSPACE ENG UNIV
Optimal selection method of navigational stars of star map simulator based on star density
The invention discloses an optimal selection method of navigational stars of a star map simulator based on star density. The optimal selection method comprises the following steps: firstly, processing a star catalogue, extracting effective data fields, carrying out related data processing to obtain six pieces of data corresponding to each fixed star, and then performing proper motion, precession and nutation correction on extracted right ascension and declination values respectively; secondly, according to given optical axis orientation and the size of a field range, extracting fixed stars in the field range and establishing an observational star database; thirdly, on the basis of the observational star database, performing image surface partition and star density calculation respectively by use of an ITSI (Information Technology System Infrastructure) optimal selection method of the navigational stars, and satisfying a set navigational star threshold, and finally realizing the optimal selection of the navigational stars and establishing a navigational star database. The method is relatively simple, but the navigational star database obtained by use of the method is relatively low in standard deviation and relatively even in distribution, and both efficiency and effect are achieved; the established navigational star database is reasonable and significant for smooth implementation of star map matching.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
GNSS Ephemeris with Graceful Degradation and Measurement Fusion
InactiveUS20110071808A1High precisionComputation using non-denominational number representationSatellite radio beaconingHarmonicEphemeris
A method for providing an extended propagation ephemeris model for a satellite in Earth orbit, the method includes obtaining a satellite's orbital position over a first period of time, applying a least square estimation filter to determine coefficients defining osculating Keplarian orbital elements and harmonic perturbation parameters associated with a coordinate system defining an extended propagation ephemeris model that can be used to estimate the satellite's position during the first period, wherein the osculating Keplarian orbital elements include semi-major axis of the satellite (a), eccentricity of the satellite (e), inclination of the satellite (i), right ascension of ascending node of the satellite (Ω), true anomaly (θ*), and argument of periapsis (ω), applying the least square estimation filter to determine a dominant frequency of the true anomaly, and applying a Fourier transform to determine dominant frequencies of the harmonic perturbation parameters.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Method for rapidly searching navigation star catalogue
ActiveCN101995248AEvenly Overlapped PartitionEasy retrievalInstruments for comonautical navigationVisual field lossStar catalogue
The invention relates to a method for rapidly searching a navigation start catalogue, which comprises the steps of: firstly, dividing a sky region by directly using an original right ascension and declination circle of a celestial sphere; secondly, calculating a right ascension and declination span range of a region covered by a star sensor according to the direction of a visual axis, and searching the navigation star catalogue in the right ascension and declination span range to obtain a navigation star in a visual filed; thirdly, spreading the celestial sphere into a two-dimensional plane with 180*360 to obtain a two-dimensional array of celestial sphere navigation star distribution; and fourthly, compressing the two-dimensional array into a one-dimensional array through two stages of compressions and then indexing the one-dimensional array by using a hash technology. The navigation star is subjected to no redundancy storage by adopting the two stages of compressions and a Hash mapping technology, therefore, the invention realizes that the index time of the navigation star catalogue is 0(1), can be used for rapidly indexing the navigation star in the visual field of the star sensor from the navigation star catalogue when the given visual axis points 8, and has the characteristics of high indexing speed and high efficiency.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Design method for layout optimization of spacecraft multi-star sensor
ActiveCN108681617AImprove design efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsOptical axisRight ascension
The invention discloses a design method for the layout optimization of a spacecraft multi-star sensor. The method comprises the steps of: (1) determining the change range of declination and right ascension of a direct shone point of sunlight, which is caused by the revolution and the rotation of earth, defining a star-sensitive optical axis vector and establishing a sunlight constraint expression;(2) analyzing the relative position relationship between an elliptical orbit of a satellite and the earth, determining the included angle between the optical axis direction of a star sensor and a satellite-ground connection line when the satellite moves to a perigee and establishing an earth atmosphere light constraint expression; (3) describing rays starting from the star sensor, which are inside a star sensor sunshade, by using a cone set, describing cube parts and cylinder parts in the satellite in the form of sets and describing that the rays within the cone range of the star sensor sunshade are not shielded through an analytic expression; and (4) constructing an index function for optimizing the layout of a multi-star sensor, obtaining the optimal orientation of the multi-star sensorand determining the optimal layout of the multi-star sensor.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
Method for designing eccentricity ratio prebias of critical inclination nearly-circular orbit
ActiveCN103678814ATo overcome the shortcomings of gradually increasing eccentricityReduce eccentricitySpecial data processing applicationsNatural satellitePulse rate
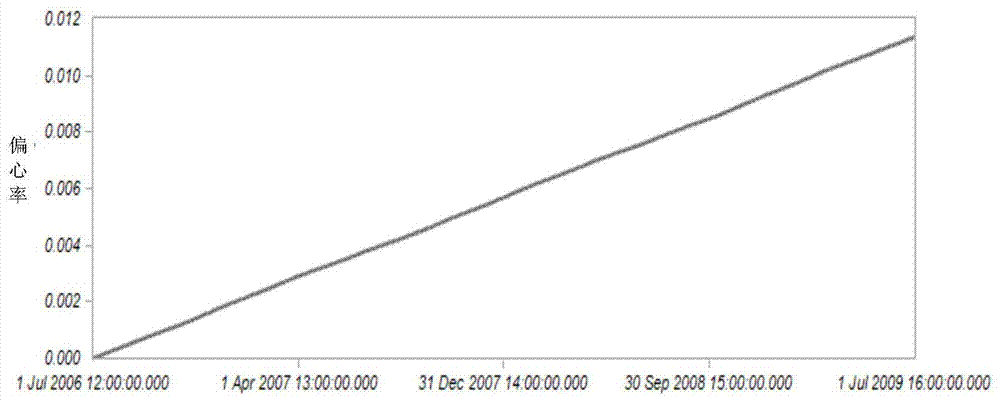
The invention provides a method for designing eccentricity ratio prebias of a critical inclination nearly-circular orbit, and belongs to the technical field of satellite orbits. The method comprises the steps that firstly, the mean elements of the six parameters of the eccentricity ratio, the argument of perigee, the mean anomaly, the ascending node right ascension, the orbit semi-major axis and the orbit inclination are transformed into instant elements; then, the instant elements are substituted into STK satellite simulation software for orbit calculation, and the instant elements of the six parameters in the tail period of the service life are obtained; the instant elements are transformed into the mean elements, the mean element prebias amount of the eccentricity ratio is designed to be half of the mean element of the eccentricity ratio in the tail period of the service life at last, and the mean element of the argument of perigee is designed to be 180 degrees. The eccentricity ratio of the tail period of the service life can be reduced by half to overcome the defect that the eccentricity ratio of the nearly-circular orbit of the critical inclination is gradually enlarged.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
Calculation method of subsatellite points and photographic point trajectory self-intersection points of near-earth regression orbit satellite
ActiveCN111680354AQuality improvementEnhance the imageGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsOrbital planeOrbit perturbation
The invention discloses a calculation method of subsatellite points and photographic point trajectory self-intersection points of a near-earth regression orbit satellite. Based on an orbital perturbation model of the earth oblateness (J2), the mean influence of the earth oblateness on the long-term perturbation of the right ascension of the ascending node, the perigee argument and the aplanatic angle is utilized, so that the mean drift period and the orbital intersection period of the satellite orbital plane relative to the earth resonate, and revisit regression of the orbital relative to thesubsatellite point and the photographic point trajectory of the earth surface is formed. After the orbit inclination angle, the eccentricity ratio, the regression days and the period number are given,the orbit semi-major axis can be solved, then the longitude of the sub-satellite point trajectory self-intersection point is analyzed and solved, the latitude of the self-intersection point under thecorresponding precision is screened out through numerical screening, and the distribution situation of the sub-satellite point trajectory self-intersection point in one regression period can be obtained. The invention provides a practical near-earth regression orbit sub-satellite point trajectory self-intersection point calculation method, and the method has important application value in near-earth surveying and mapping, remote sensing, reconnaissance, InSAR and other regression orbit satellite measurement tasks.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Methods and apparatus for node-synchronous eccentricity control
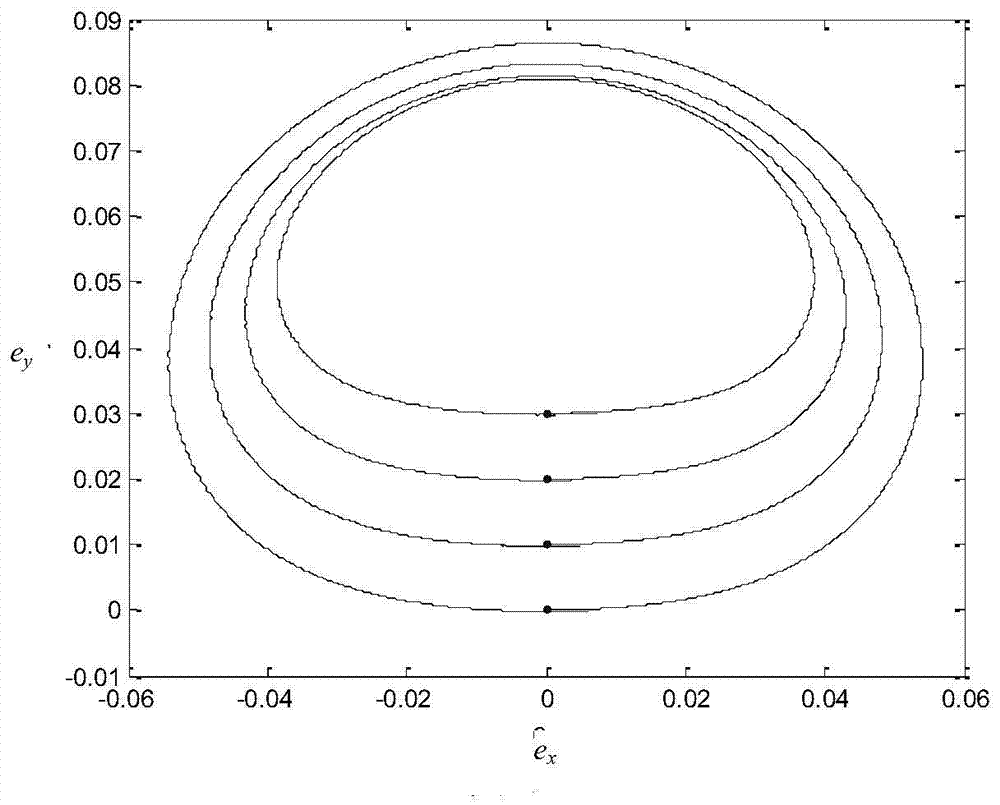
A method for performing east-west station keeping for a satellite in an inclined synchronous orbit is described. The method includes averaging a value of a right ascension of the ascending node for an inclination vector associated with the satellite over a period of the control cycle, and managing corrections for the satellite such that an eccentricity vector, directed at perigee, is substantially collinear with the inclination vector.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Classical orbit three-dimensional spatial relationship construction method based on OSG three-dimensional engine
ActiveCN105035371ASolve the display effectResolving orbital radicals requires a secondary transformationCosmonautic condition simulationsSpecial data processing applicationsAxis–angle representationAngular degrees
The invention discloses a classical orbit three-dimensional spatial relationship construction method based on an OSG three-dimensional engine. Spatial relationships are directly established based on six elements of an orbital system, and geometrical angle changing processes of the right ascension of an ascending node, the orbit inclination, the perigee argument and the true anomaly can be dynamically displayed. An orbital element parameter representation process is based on the space geometry relationships, and satellite visual angle tracking and position calculation are not subjected to secondary coordinate transformation. The orbital elements can be visually displayed, and an orbital system (VVLH) visual angle positioning problem under a traditional model is solved by the introduction of two layers of new coordinate systems. Four attitude input interfaces of matrixes, Euler angles, Euler axial angles and the quaternion of a relative orbital system are provided by a spacecraft, and the spacecraft body axis and the orbit axis are displayed and customized through the spacecraft, the analysis of the correctness of the in-orbit attitude of the spacecraft is facilitated, and problems that the orbital elements cannot be visually displayed, the orbital elements need the secondary transformation, the attitude adjustment and visual angle adjustment of the orbital system require additional data, and the position and orientation of the spacecraft cannot be accurately displayed are solved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Inexpensive high-precision two-dimensional sun tracking mechanism for concentrating to generate power
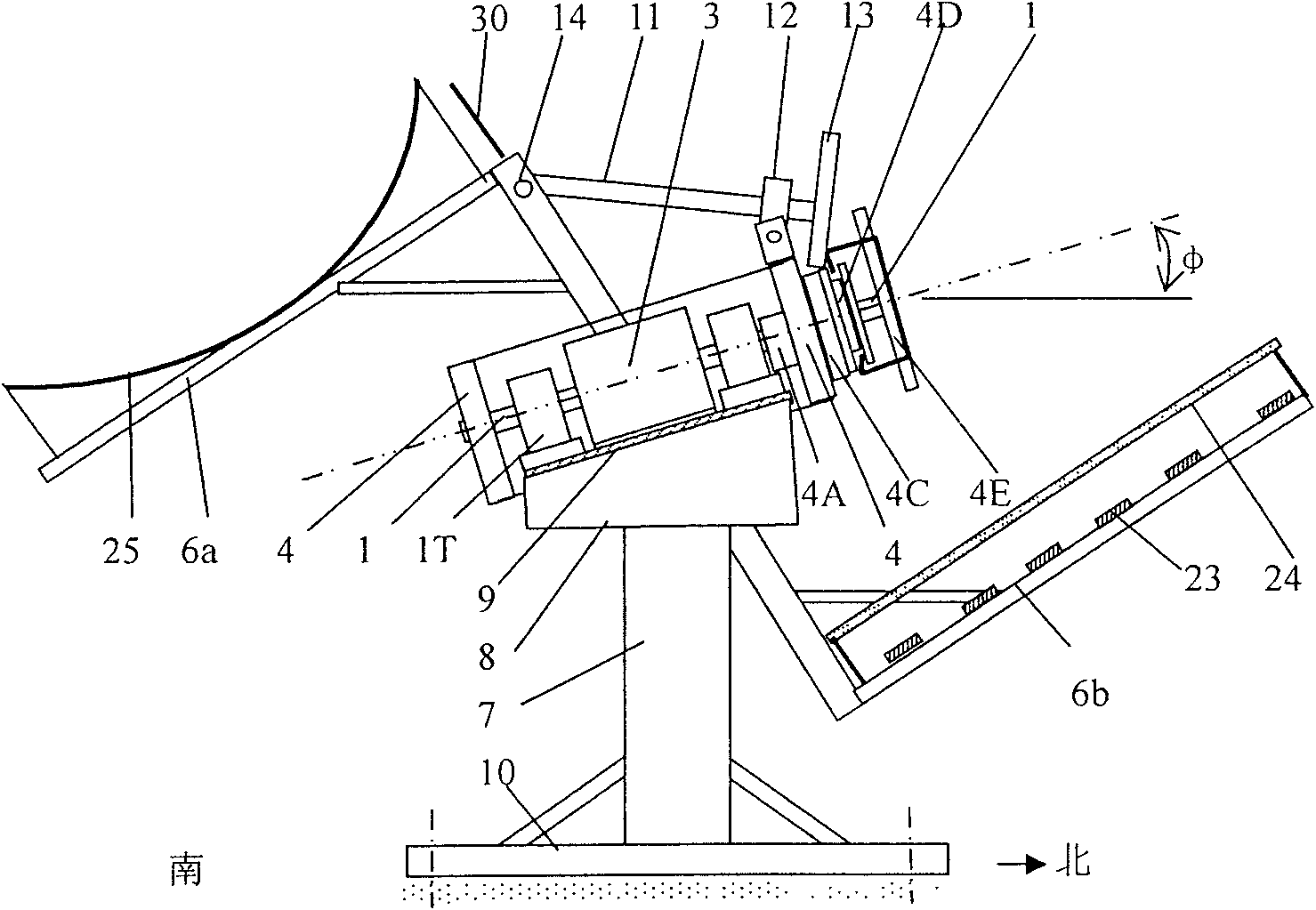
InactiveCN101610044AOvercome precisionOvercome costsPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyEngineeringRight ascension
The invention discloses an inexpensive high-precision two-dimensional sun tracking mechanism used for concentrating to generate power. The two-dimensional sun tracking mechanism is characterized in that a one-dimensional rotating frame, a two-dimensional rotational mesosome framework, a latitude adjuster, a declination angle adjuster and a tracking deviation indicator are designed; the one-dimensional rotating frame is connected with a right-ascension axle and the two-dimensional rotational mesosome framework sleeved on an outer ring of the right-ascension axle; a carrier platform framework is divided into a south block and a north block, the two blocks are respectively connected with an upper side frame and a lower side frame of the two-dimensional rotational mesosome framework, and condensing lenses, photovoltaic cells, and the like, are installed on the carrier platform framework; and the right-ascension axle parallel to the earth axle rotates at a fixed speed and drives a carrier platform with an included angle (equal to the declination angle on the same day) with the right-ascension axle to rotate along with the sun. The two-dimensional sun tracking mechanism has the advantages of simple tracking method, high tracking accuracy, balanced deadweight of the device from all directions due to the layered and symmetrical carrier platforms, saved material, small wind resistance and driving power, low fabricating cost of the complete machine, effectively reduced cost of concentrating solar photovoltaic power generation and medium-high heat utilization device and improved efficiency.
Owner:陈则韶
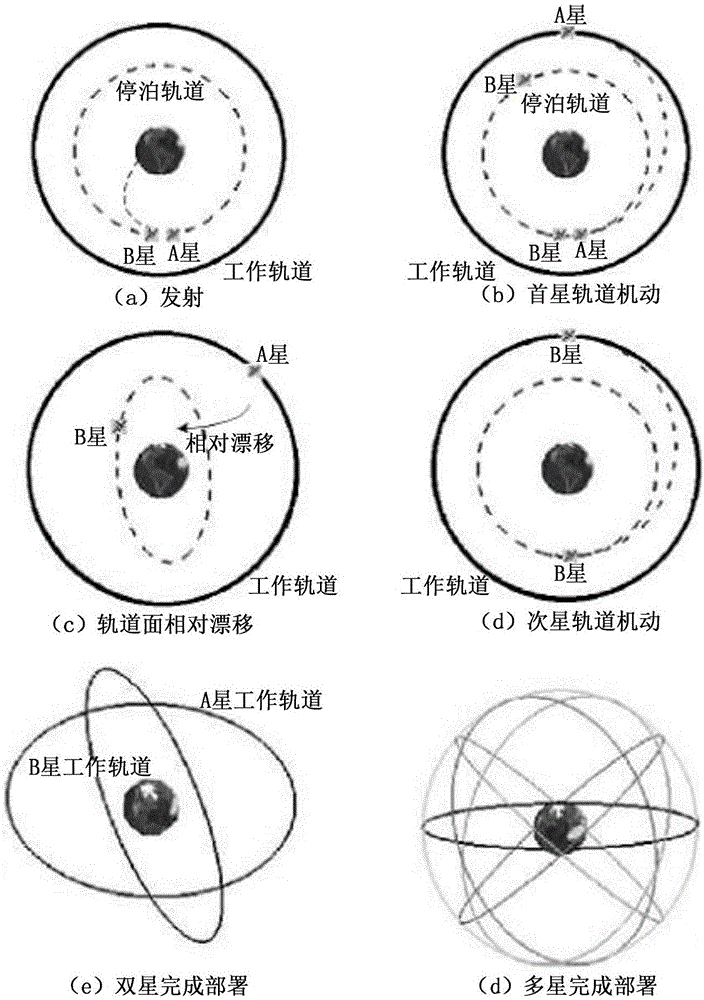
Walker constellation deployment method based on double berthing orbits
ActiveCN106802667ASolve the shortcomings of the long deployment cycle of different planesOptimizing Deployment Accuracy AnglePosition/course control in three dimensionsDeployment timeEngineering
The invention provides a Walker constellation deployment method based on double berthing orbits. The method comprises the following steps of: S1, delivering satellites for deploying a Walker constellation to a first berthing orbit and the second berthing orbit respectively; S2, enabling the first satellite to enter a working orbit through orbital maneuver and enabling the remaining satellites to remain in the first berthing orbit and the second berthing orbit; S3, waiting for the precessional motion of the orbital surface of the current berthing orbit relative to the orbital surface of a working orbit of an adjacent satellite until an ascending node of orbital surface and the right ascension have a preset angle, and then enabling the next satellite to enter the working orbit through orbital maneuver, and in the same way, enabling all the satellites for deploying the Walker constellation to enter the working orbits successively. The method can solve the limitation of a single-orbit plane deployment using one rocket with multi satellites, and solve the long single-berthing-orbit different-surface deployment period of the one rocket with multi satellites, and optimizes constellation deployment time and satellite deployment precision angle of the satellite relative position.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG DEV LTD
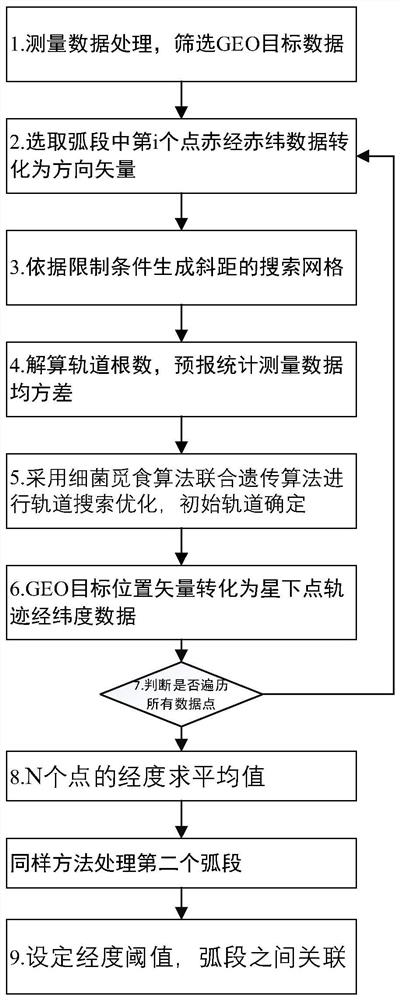
Space-based optical angle measurement segmental arc initial orbit determination and association method for GEO target
ActiveCN113204917AImprove global search performanceImprove the determination accuracyDesign optimisation/simulationGenetic algorithmsGenetics algorithmsLongitude
The invention discloses a space-based optical angle measurement segmental arc initial orbit determination and association method for a GEO target, and the method comprises the steps: screening a space-based platform measurement segmental arc, and carrying out the coordinate system conversion of the height and latitude and longitude data of a space-based platform, and obtaining a position vector and a velocity vector under a J2000 coordinate system; selecting two space-based platform measurement arc segments aiming at the GEO target from the screened measurement arc segments, and respectively sampling right ascension and declination data in the two arc segments; for each arc section, according to right ascension and declination data of a sampling point, determining a distance range from the space-based platform to the GEO target to generate a slope distance search grid point, in the search grid point, determining an initial orbit corresponding to each sampling point by adopting a bacterial foraging algorithm and a genetic algorithm, and obtaining a corresponding sub-satellite point trajectory; further obtaining a longitude average value of each arc section; and calculating a difference value of the longitude average values of the two arc segments, and when the difference value is smaller than a preset threshold value, determining that the two arc segments are associated.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com