Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
258 results about "Axis–angle representation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics, the axis–angle representation of a rotation parameterizes a rotation in a three-dimensional Euclidean space by two quantities: a unit vector e indicating the direction of an axis of rotation, and an angle θ describing the magnitude of the rotation about the axis. Only two numbers, not three, are needed to define the direction of a unit vector e rooted at the origin because the magnitude of e is constrained. For example, the elevation and azimuth angles of e suffice to locate it in any particular Cartesian coordinate frame.
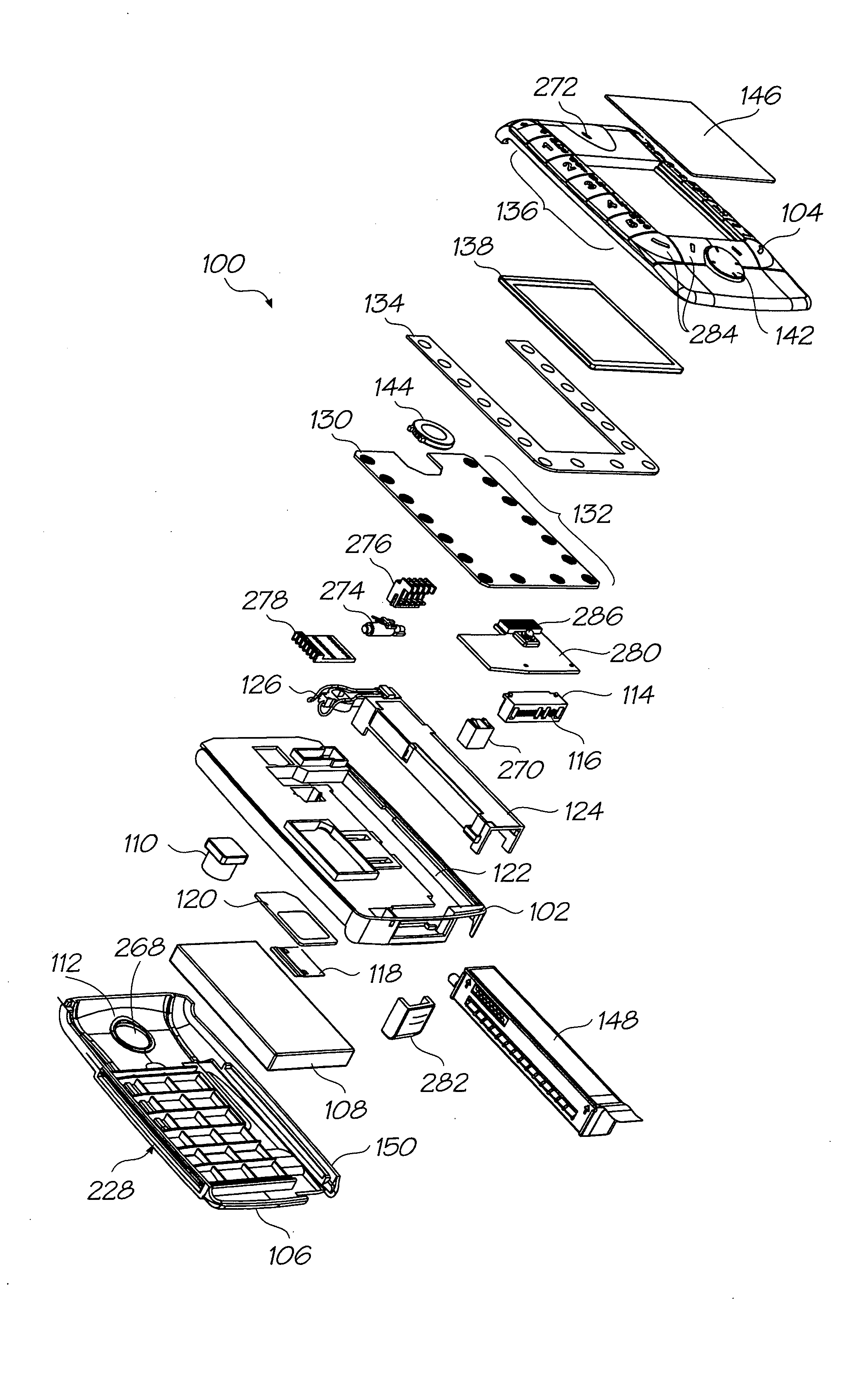
Mobile telecommunication device with a printhead and single media feed roller
InactiveUS20060250489A1Increase contact frictionReduce angular velocityTypewritersOther printing apparatusAxis–angle representationDrive shaft
A mobile telecommunications device comprising: an inkjet printhead for printing to a media substrate; a drive shaft for feeding the media past the printhead; and, a print engine controller for operatively controlling the printhead; wherein during use, the print engine controller senses the number of complete and partial rotations of the media feed roller and adjusts the operation of the printhead in response to variations in the angular velocity of the drive shaft.
Owner:ZAMTEC
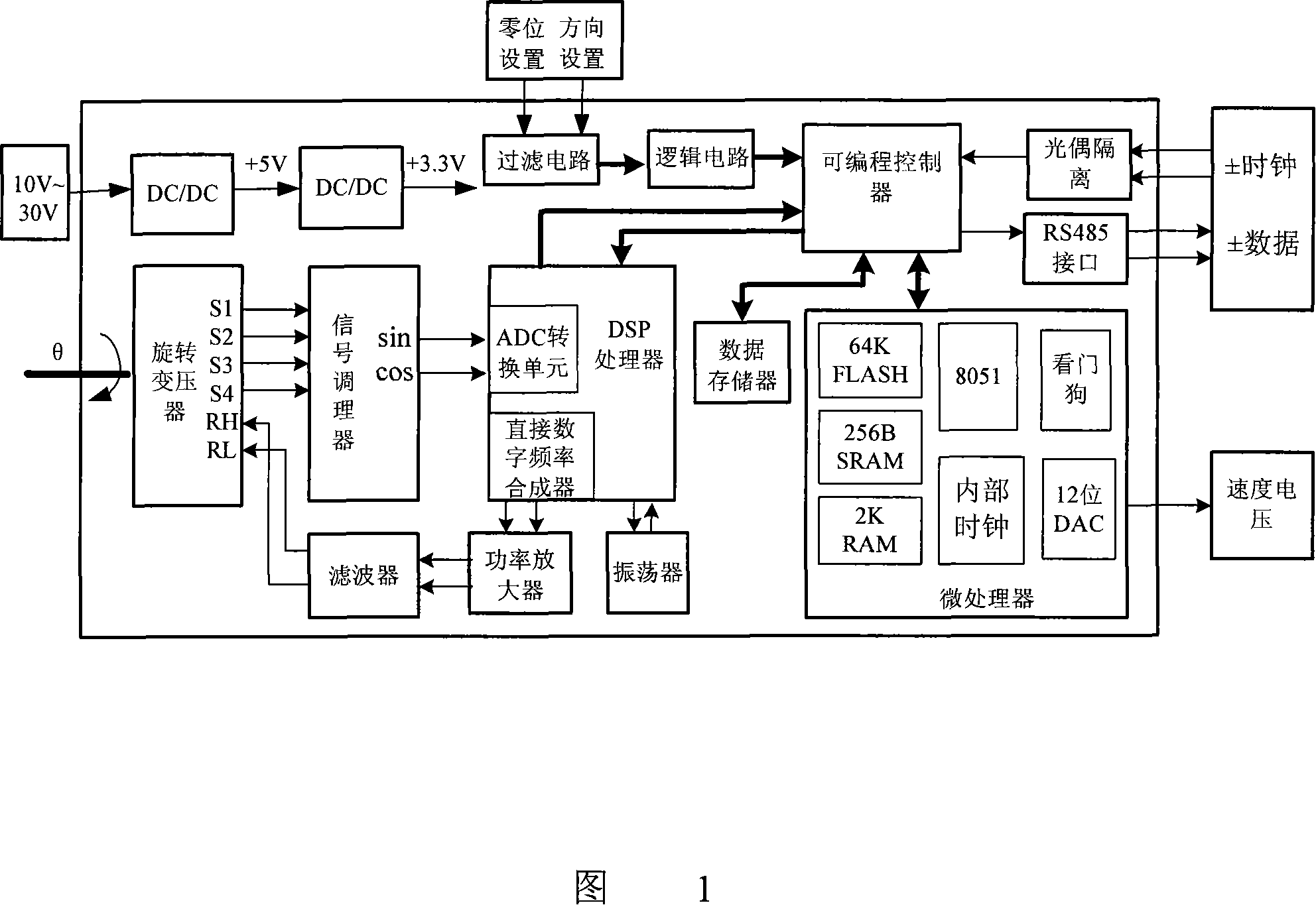
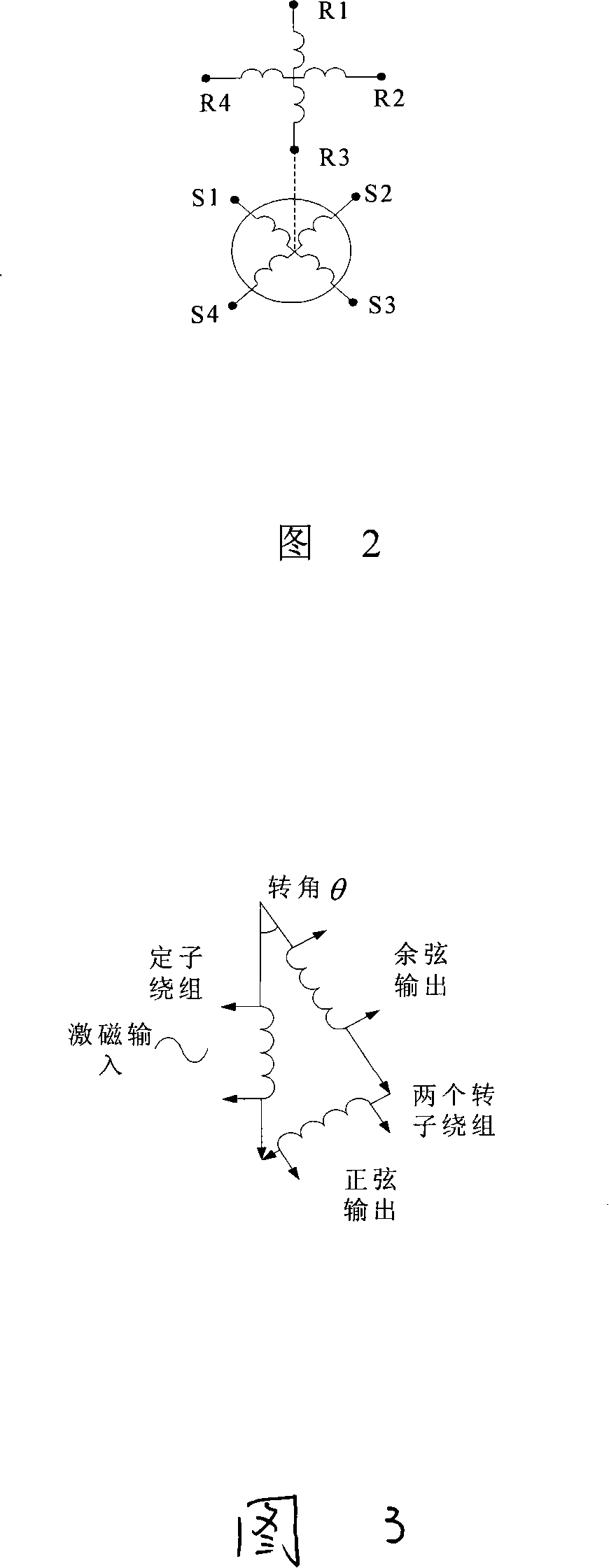
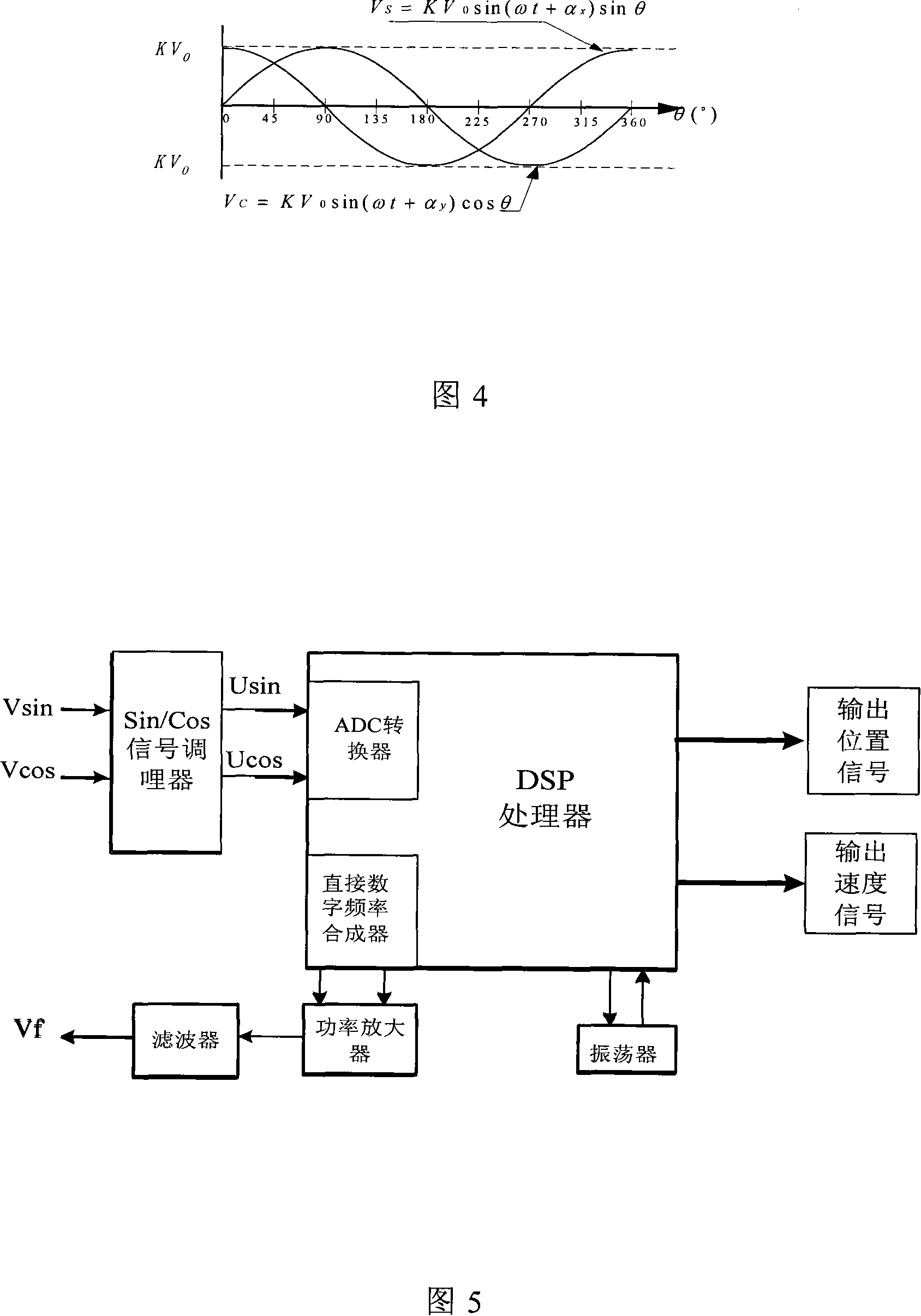
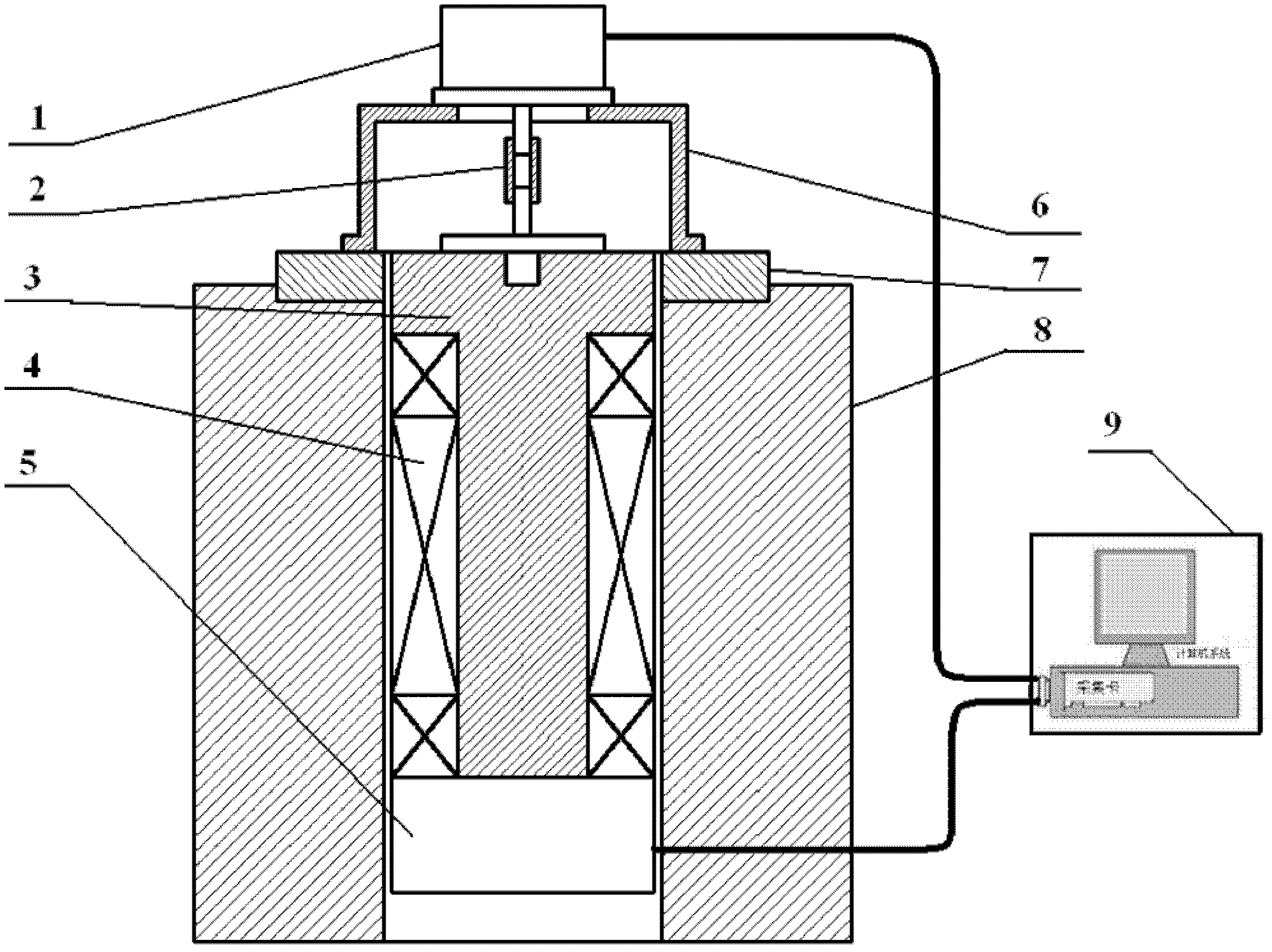
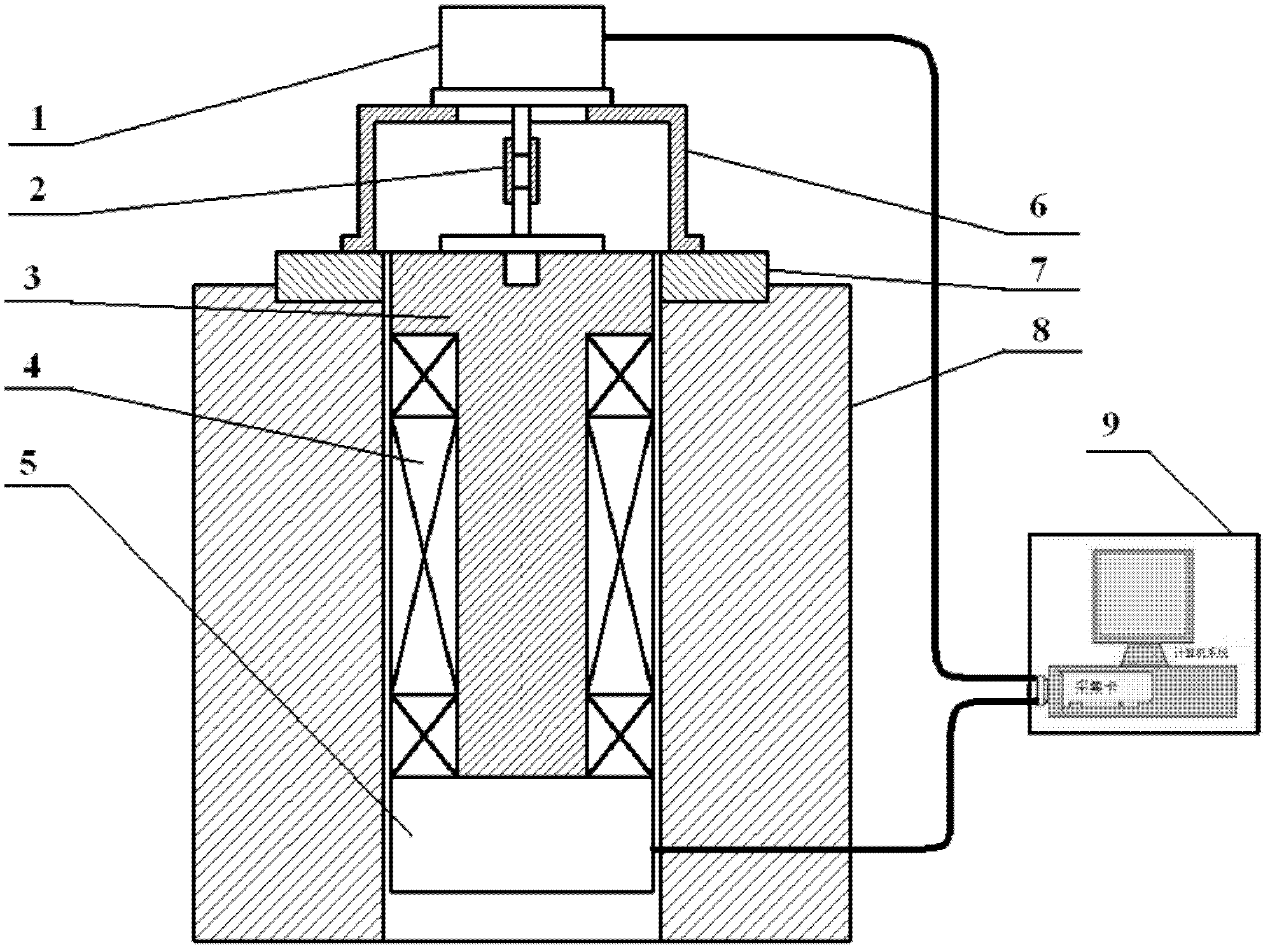
Multiple-loop absolute type rotary encoder based on rotating transformer
ActiveCN101226066AImprove anti-interference abilityImprove moisture resistanceConverting sensor outputDigital signal processingAxis–angle representation
The invention relates to a multiturn absolute rotary encoder based on a rotary transformer, which is characterized in that: a sensor is displaced by taking the rotary transformer as a shaft angle; a shaft angle decoding circuit can be formed by adopting DSP as a core processor; a sine wave which can be controlled by frequency and phase in the method that the circuit is synthesized by direct digital frequency for the numerical control of an oscillator; and the sine wave is directly taken as an excitation rotary transformer signal via a power amplifier and a filter circuit; the rotary transformer signal is transferred to A / D converter after being run through a matching circuit of electronic transformer; after sampling, digital filtering and digital signal processing, the sine and cosine value for the actual angle of two channels is generated; the angle error change is tracked dynamically by the PI algorithm; the mechanical displacement of the rotating object is converted into digital shaft angle position and speed. The multiturn absolute rotary encoder based on a rotary transformer has the advantages of high tracking speed, high conversion accuracy, high reliability, simple structure, sensitive movement, low environmental condition, strong anti-interference capability, high measuring accuracy and speed voltage output.
Owner:连云港杰瑞电子有限公司
Inertia sensor
InactiveUS20100077858A1Easy to processSmall sizePiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyAcceleration measurement using interia forcesAxis–angle representationAngular rate sensor
A multi-axis accelerometer or a multi-axis angular rate sensor which can be made by an easy process and the size of which can be greatly reduced is provided. An inertia sensor has a substrate, a flat proofmass formed on the substrate and a stacked structure including at least a lower electrode, a piezoelectric film, and an upper electrode, an anchor unit formed in a cutout inside of the proofmass and fixed on the substrate, and a plurality of flat piezoelectric beams each having one end connected to the proofmass, the other end connected to the anchor unit, and a stacked structure formed in a cutout inside of the proofmass and including at least a lower electrode, a piezoelectric film, and an upper electrode, wherein the inertia sensor enables to detect an acceleration applied on the proofmass based on charges generated to the electrodes of the piezoelectric beams.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
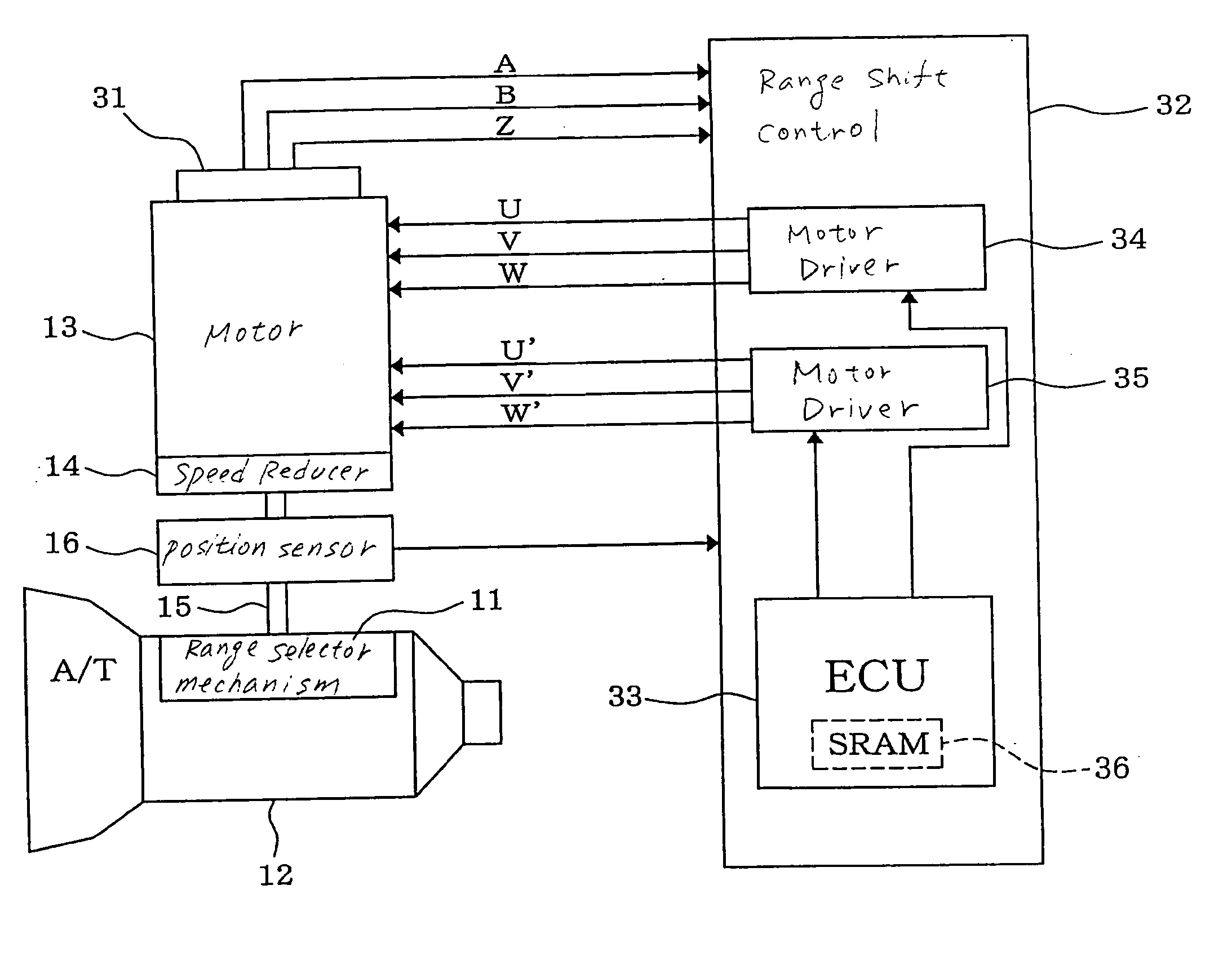
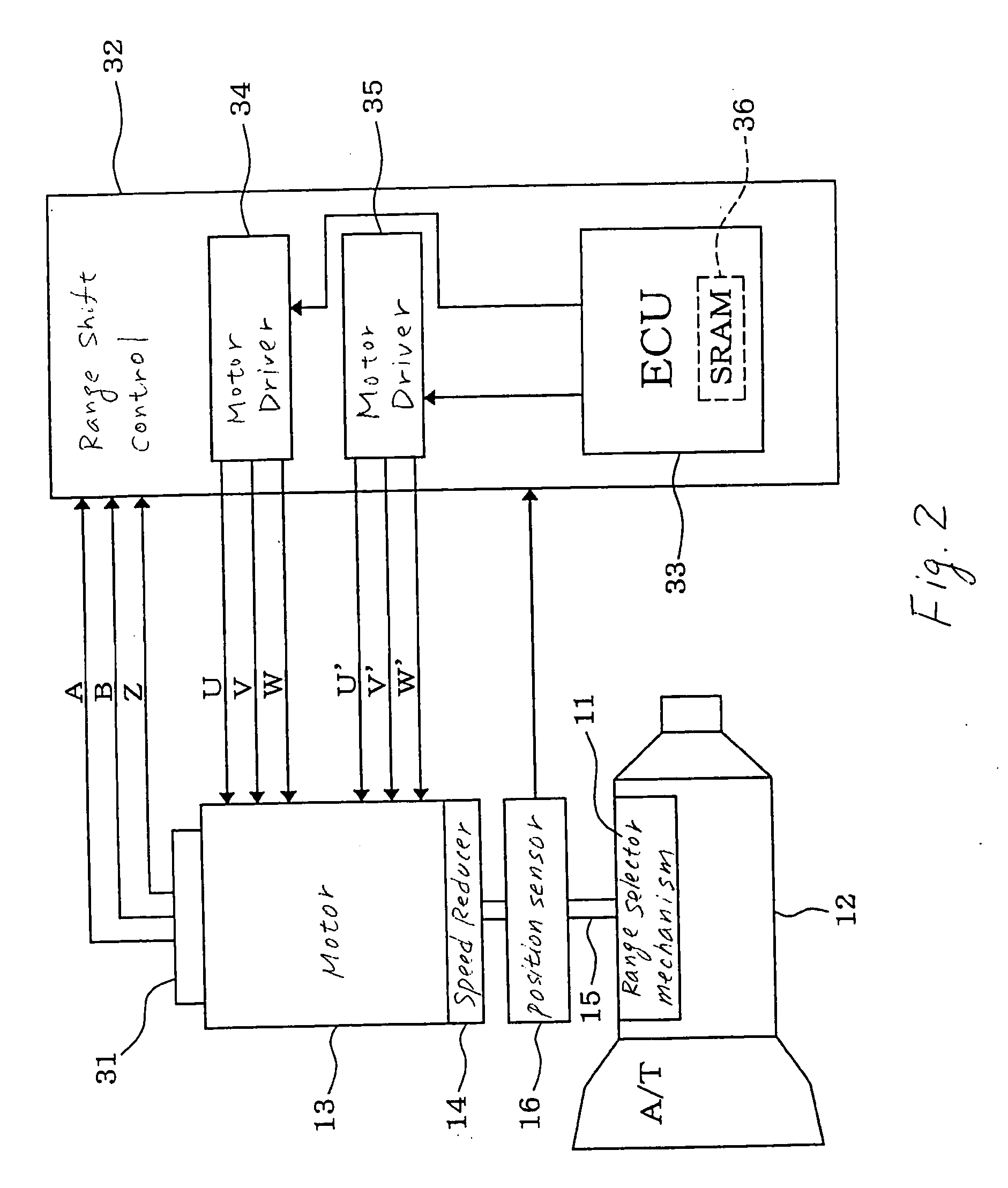
Failure monitor for motor drive control system
ActiveUS20050156550A1Avoid disadvantagesCommutation monitoringDigital data processing detailsAxis–angle representationMotor drive
A failure monitor designed to monitor a failure in operation of a motor drive control system. The system works to drive a motor-driven member through an output shaft and an electric motor and includes an output shaft angular position sensor for determining an angular position of the output shaft and an encoder for determining an angular position of the motor for use in controlling the motor. The system works to discriminate among failures in operation of the output shaft angular position sensor and the encoder and another type of a failure using outputs of the sensors.
Owner:DENSO CORP
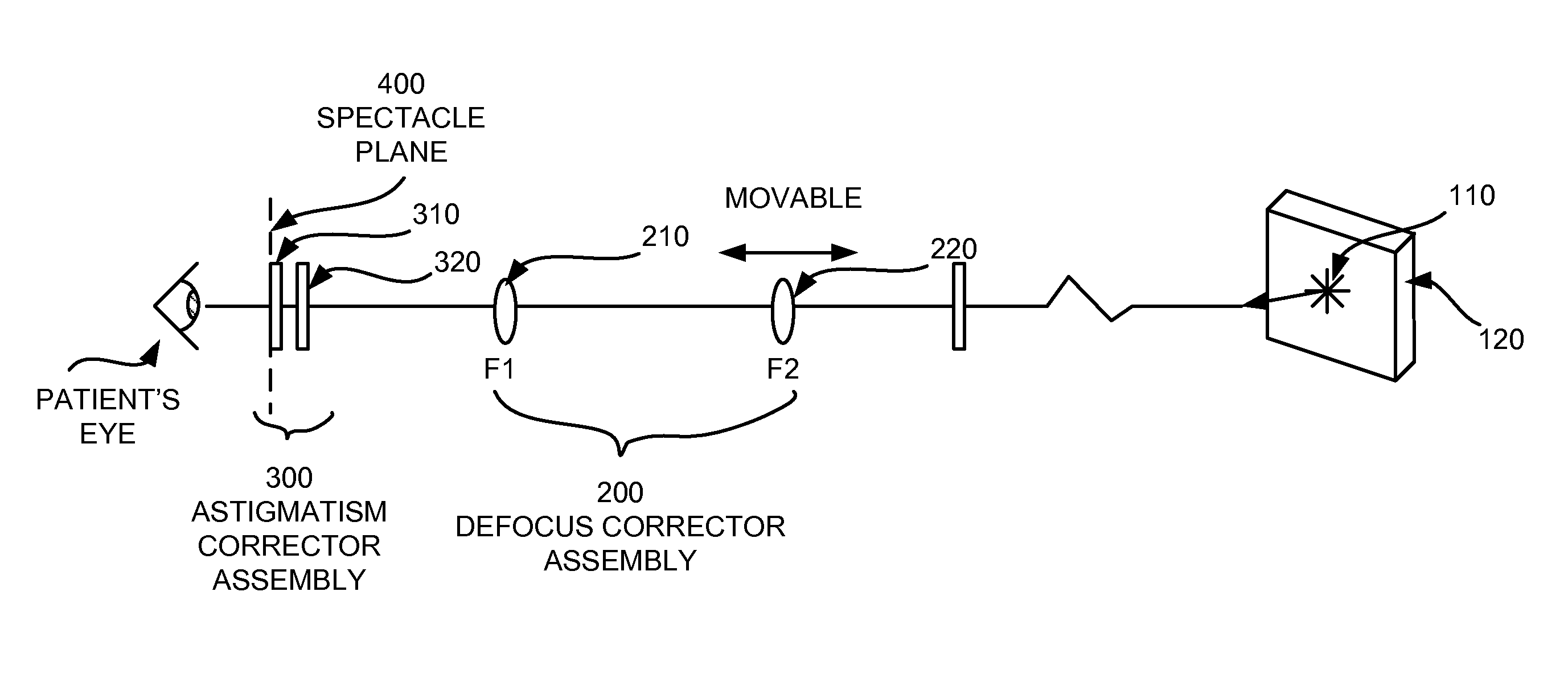
Subjective Refraction Method and Device for Correcting Low and Higher Order Aberrations
ActiveUS20070195264A1Drawback can be obviatedLong dimensionPhoroptersOptical partsAxis–angle representationOptical axis
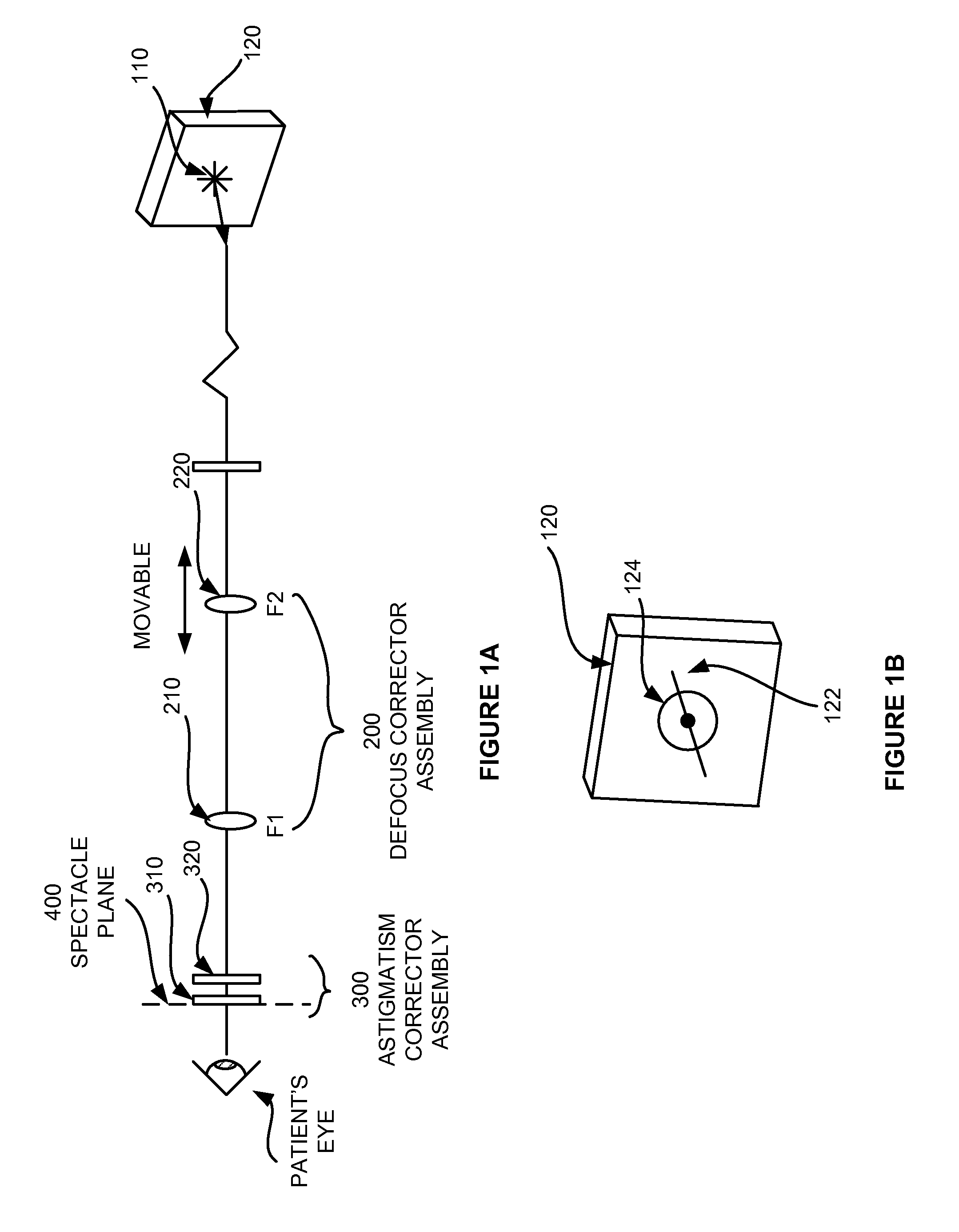
A subjective refraction technique uses a plane wave light source including substantially a point as a viewing target. The refraction method provide for a number of distinct identifiable end points. By finding such end points the process leads to an aberration-corrected vision. A defocus corrector assembly (DCA) includes a lens that is moveable along an optical axis between a patient's eye and the point light source for adjusting defocus power until the patient indicates that the blurry image has become a relatively focused line image. An astigmatism corrector assembly (ACA) which is capable of continuously variable in its amplitude is provided including a pair of astigmatism plates for adjusting astigmatism power and axis angle. The ACA is adjusted until the patient indicates that the line image has become a substantially round image. A reference marker provides displayed items including a sweep line overlapping at the point source and having an orientation which is adjustable. The patient may subjectively control the sweep angle of the sweep line and indicate that the sweep line is aligned with the sharp line image of the point source, thereby providing axis angle data of astigmatism errors of the patient's eye.
Owner:LAI SHUI T
Scanning irradiation device of charged particle beam
ActiveUS8222613B2Thermometer detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsAxis–angle representationOptical axis
An inexpensive scanning irradiation device of a particle beam is obtained without using a rotating gantry. A first scanning electromagnet and a second scanning electromagnet, whose deflection surfaces of the particle beam are the same, and which bend the particle beam having an incident beam axis angle of approximately 45 degrees relative to a horizontal direction in reverse directions to each other; an electromagnet rotation driving mechanism which integrates the first and the second scanning electromagnets and rotates these scanning electromagnets around the incident beam axis; and a treatment bed are provided. The particle beam deflected by the first and the second scanning electromagnets can be obtained at a range of −45 degrees to +45 degrees in deflection angle from an incident beam axis direction.
Owner:SHIZUOKA PREFECTURE
Off-Axis Angle Estimation Method and Apparatus Using the Same
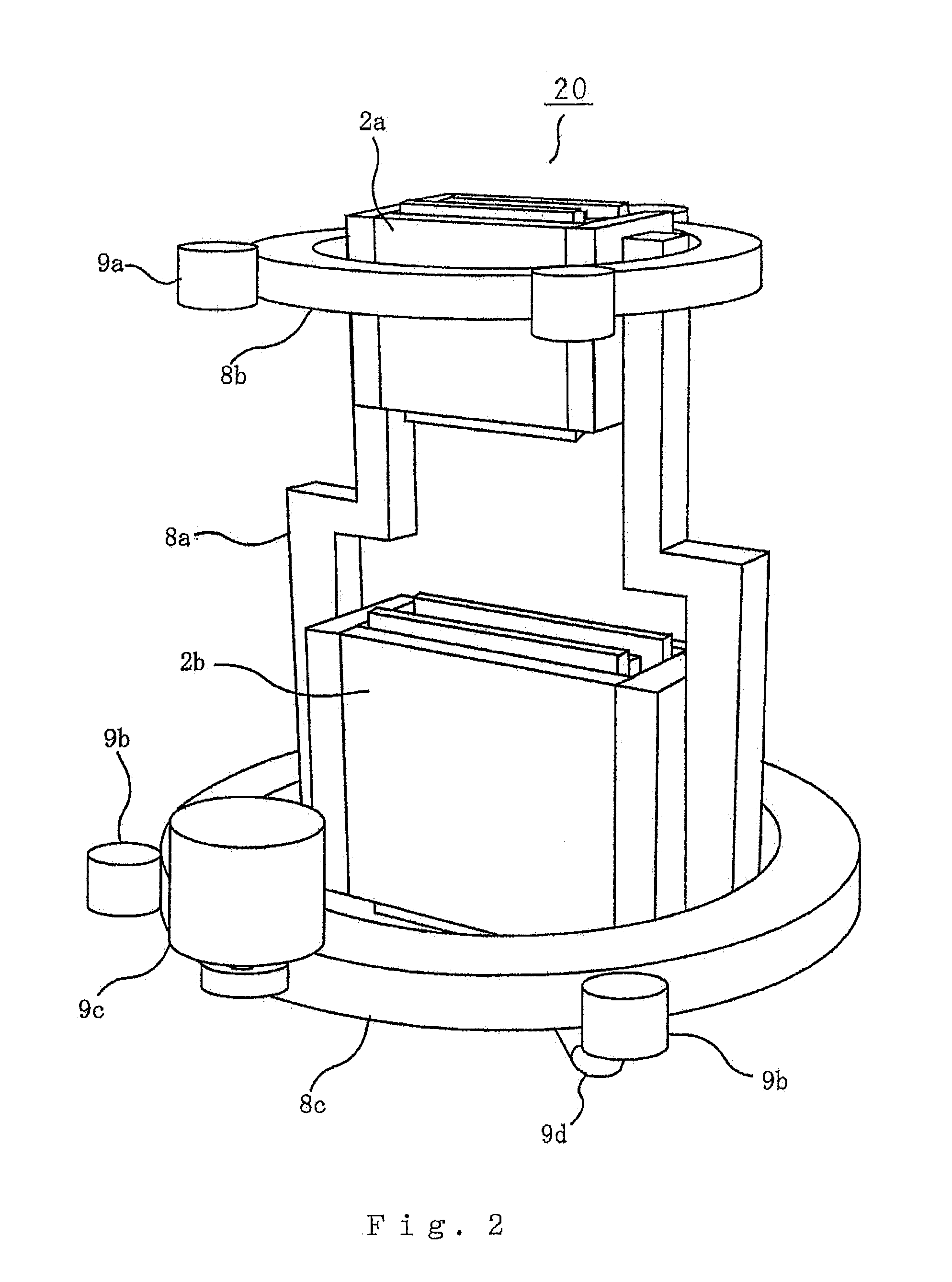
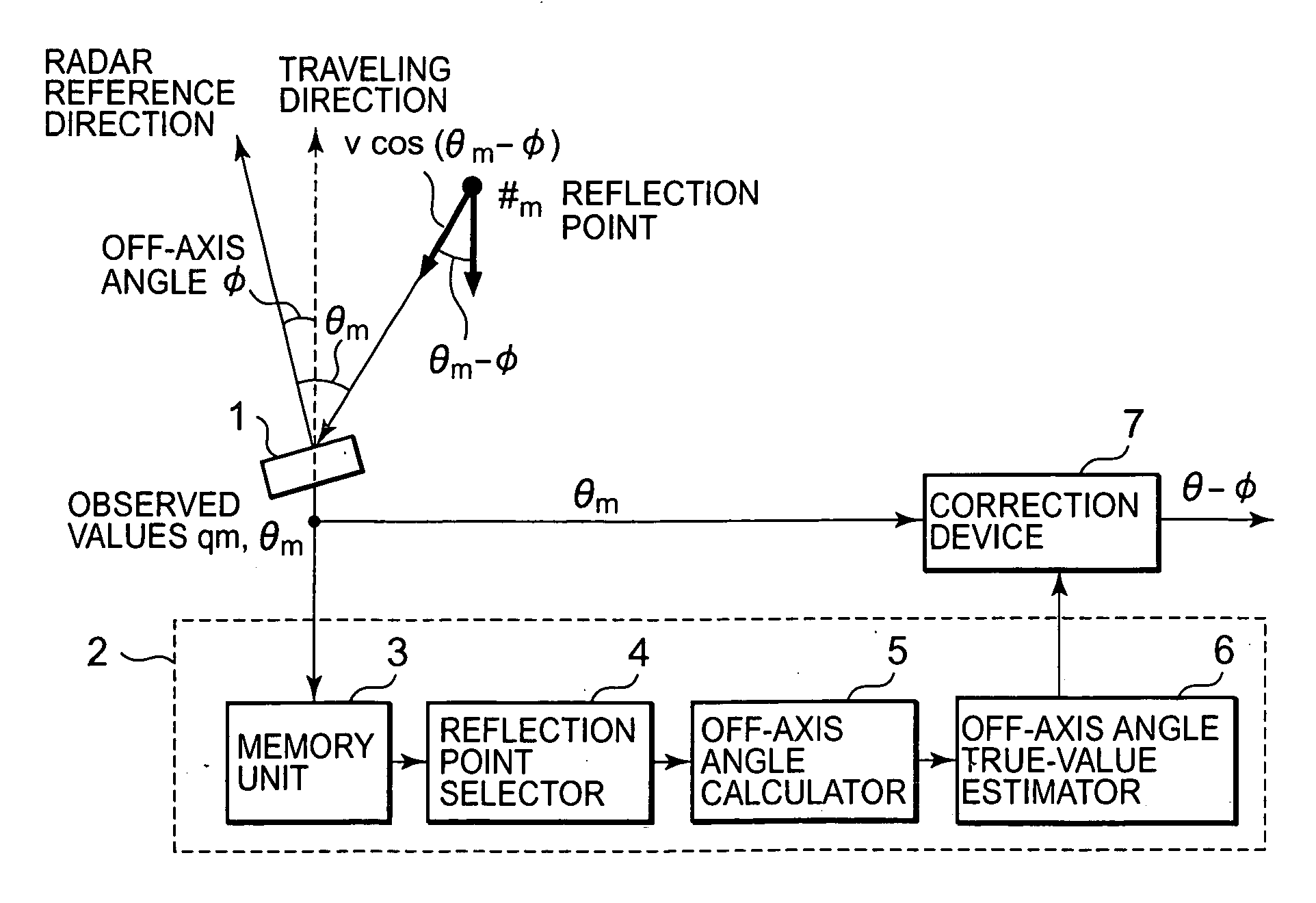
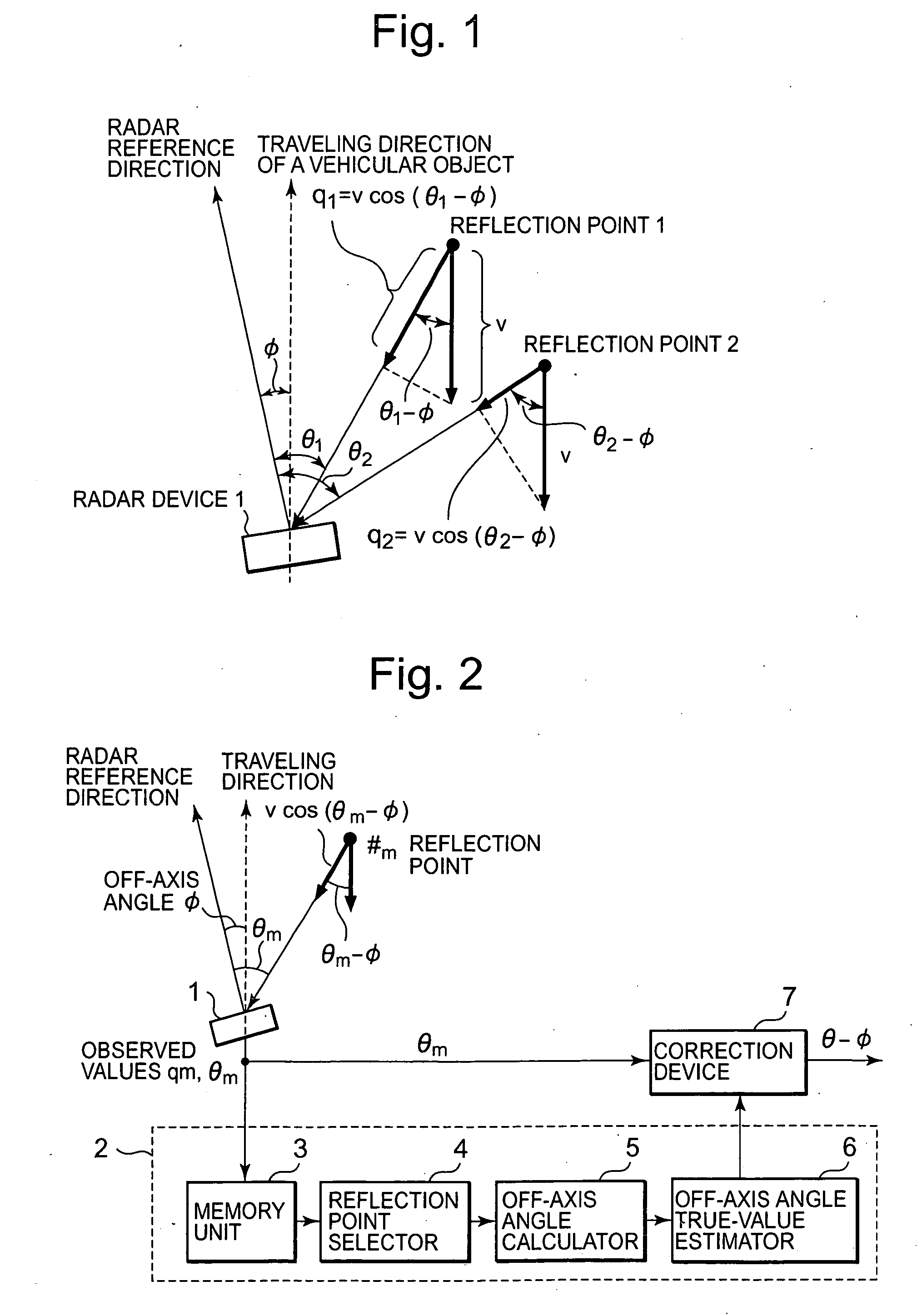
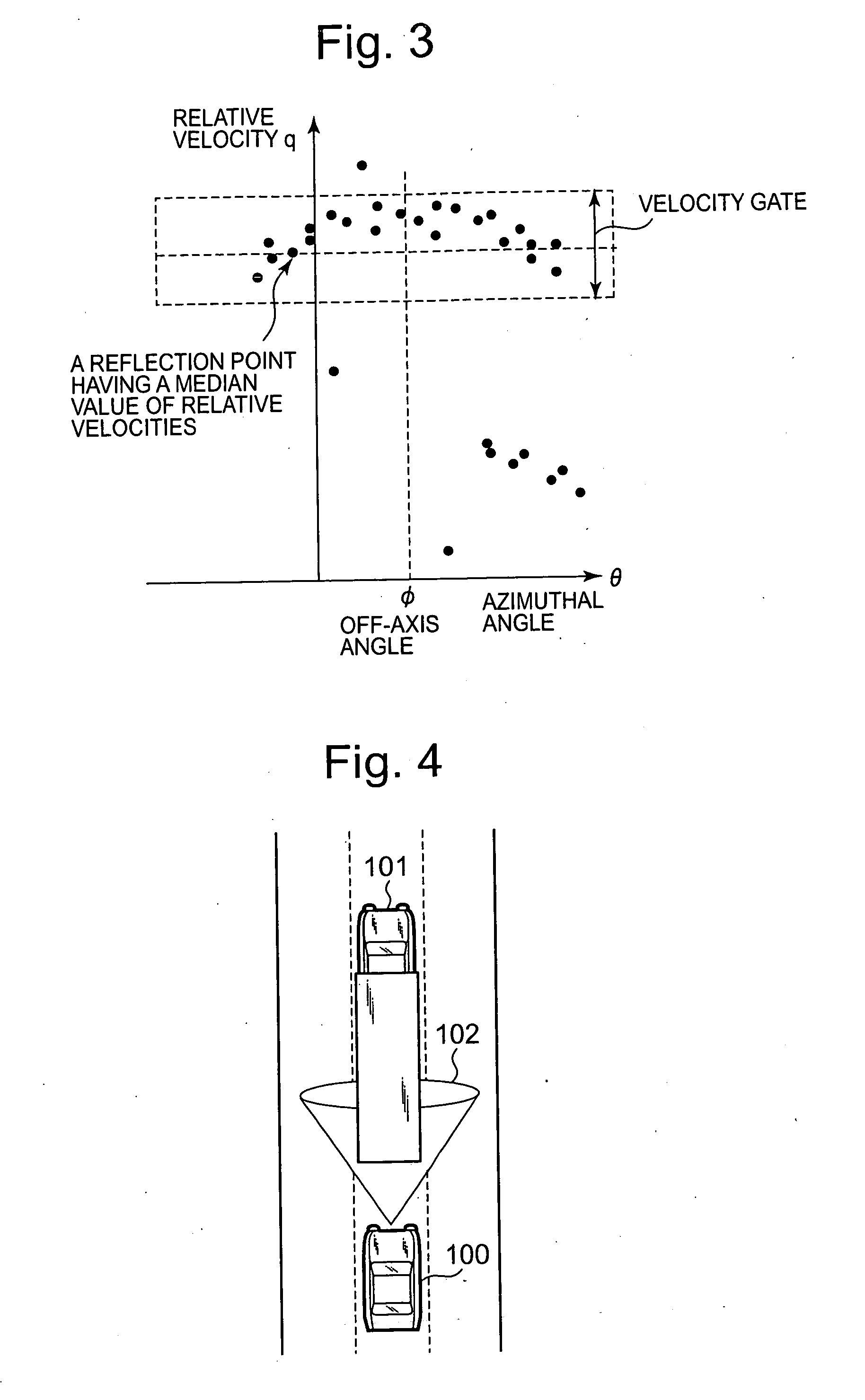
ActiveUS20080012752A1Stably achieve off-axis angle estimationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAxis–angle representationRadar
Without using a traveling velocity of a vehicular object mounted with a radar device, an off-axis angle which is an offset angle between a reference direction of the radar device and a traveling direction of the vehicular object is estimated. An off-axis angle estimation method for estimating an off-axis angle (φ) of a radar device (1) mounted on the vehicular object having a predetermined traveling direction includes that, from among reflection points of which a relative-velocity component (q) along the line of radar sight and an azimuthal angle (θ) are detected by the radar device (1), a plurality of reflection points of which the relative-velocity components in the traveling direction of the vehicular object being approximately equal to one another is selected without using the traveling velocity of the vehicular object; and based on the relative-velocity components along the line of radar sight, and on the azimuthal angles, of the plurality of reflection points having been selected, the off-axis angle (φ) is autonomously calculated solely from the observed values based on radar waves.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Projection display apparatus
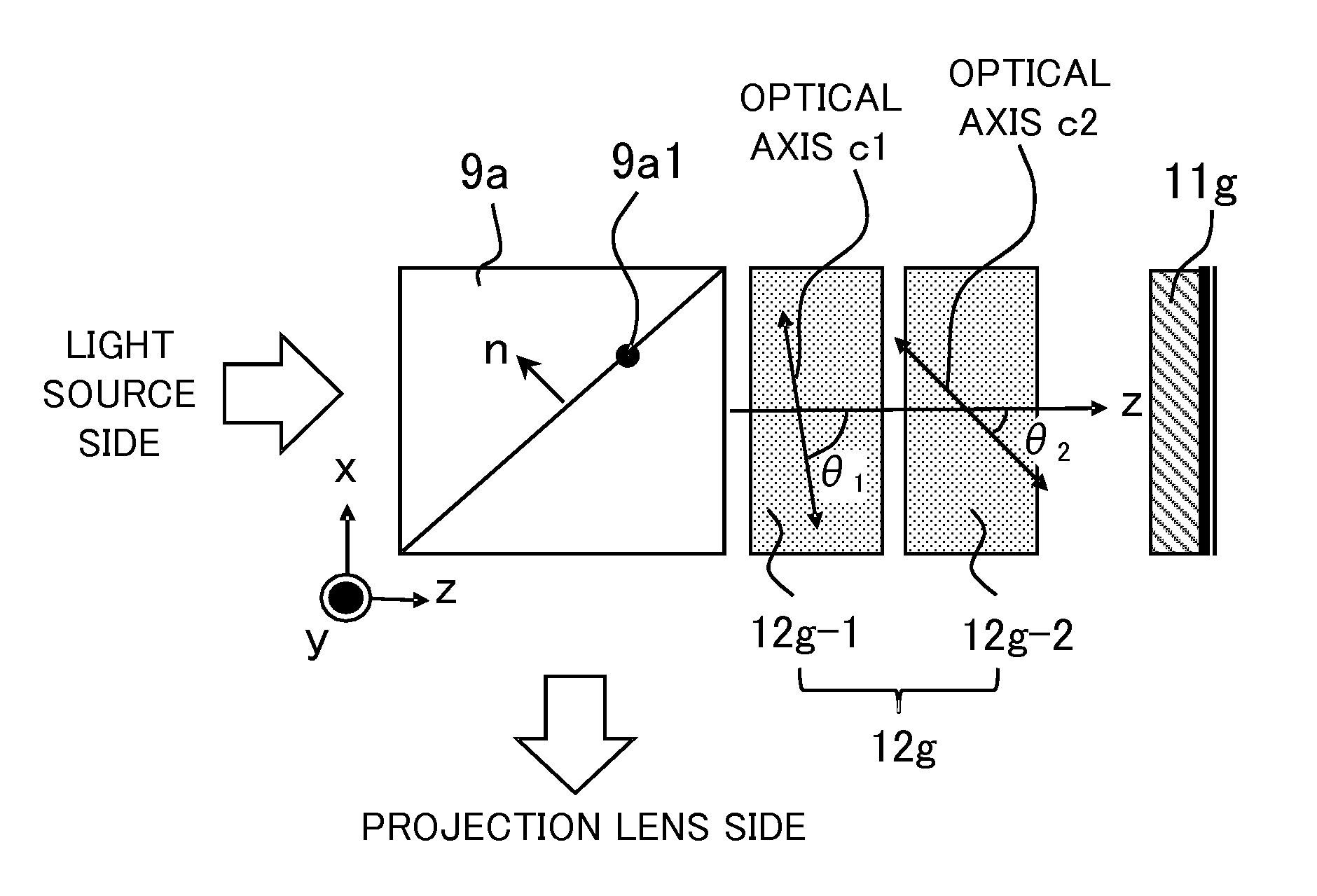
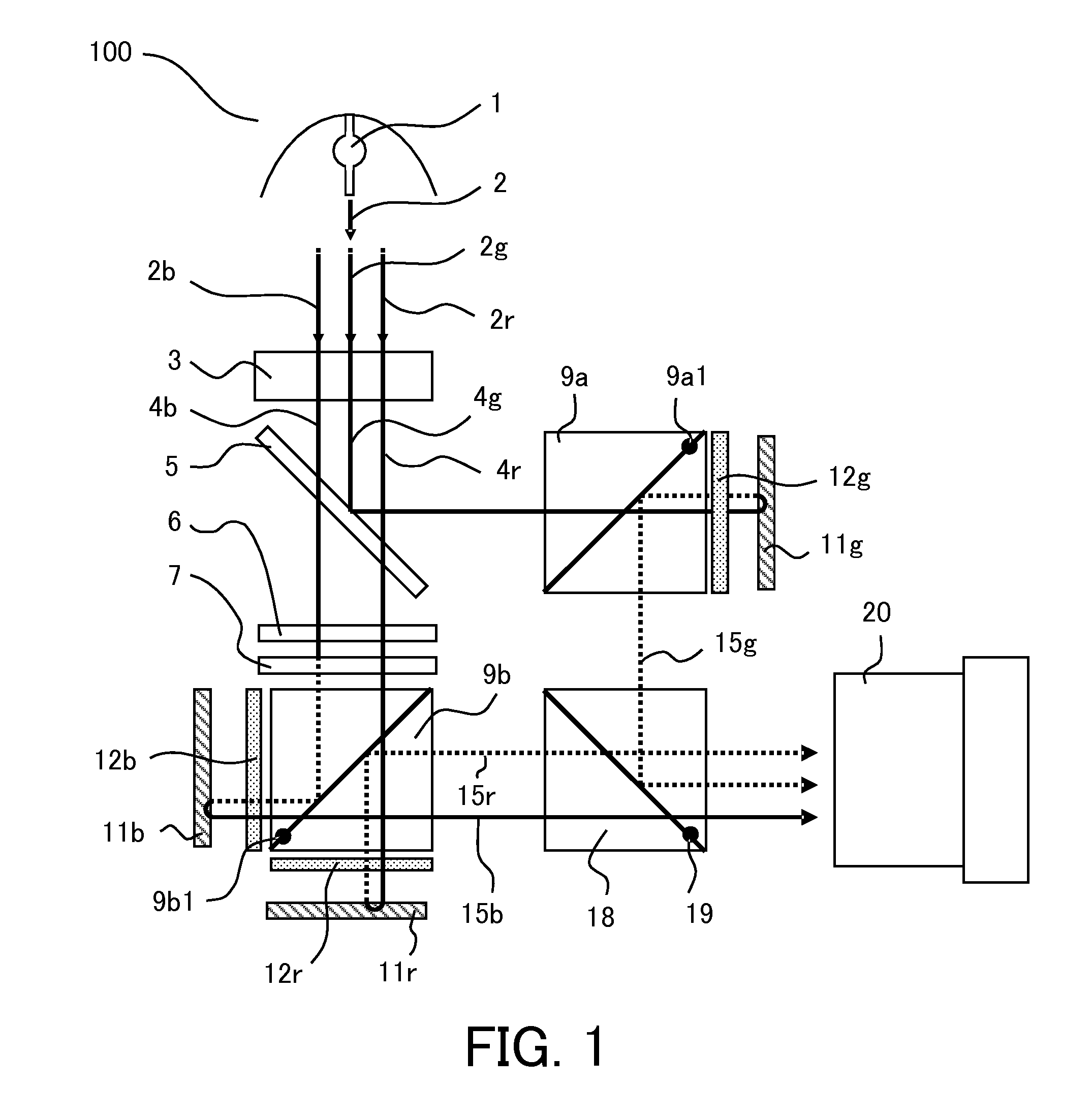
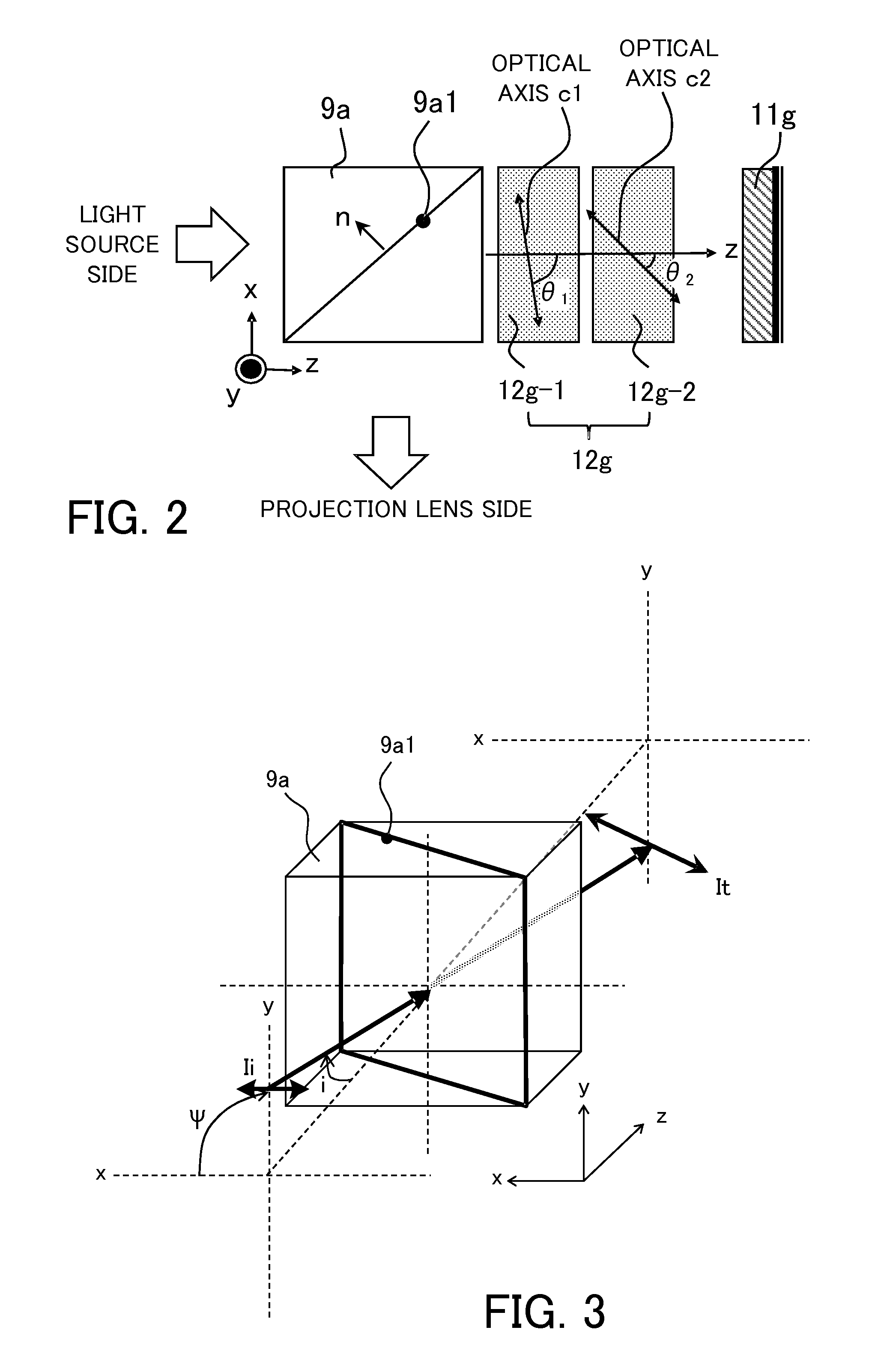
InactiveUS9235111B2Increase contrastProjectorsColor photographyAxis–angle representationOptical axis
A projection display apparatus includes a polarization beam splitter, a first phase compensation plate including two layers, and a light modulator. Each layer has a constant axial angle, and an optical axis of each layer inclines with respect to the x axis in an xz plane. The axial angle of the layer closer to the polarization beam splitter among the two layers is larger than the axial angle of the layer farther from the polarization beam splitter. 20°≦θmax−θmin≦80° is satisfied where θmax is a maximum value of the axial angle and θmin is a minimum value of the axial angle. 40°≦θave≦70° is satisfied where θave is an average value of axial angles of the two layers.
Owner:CANON KK
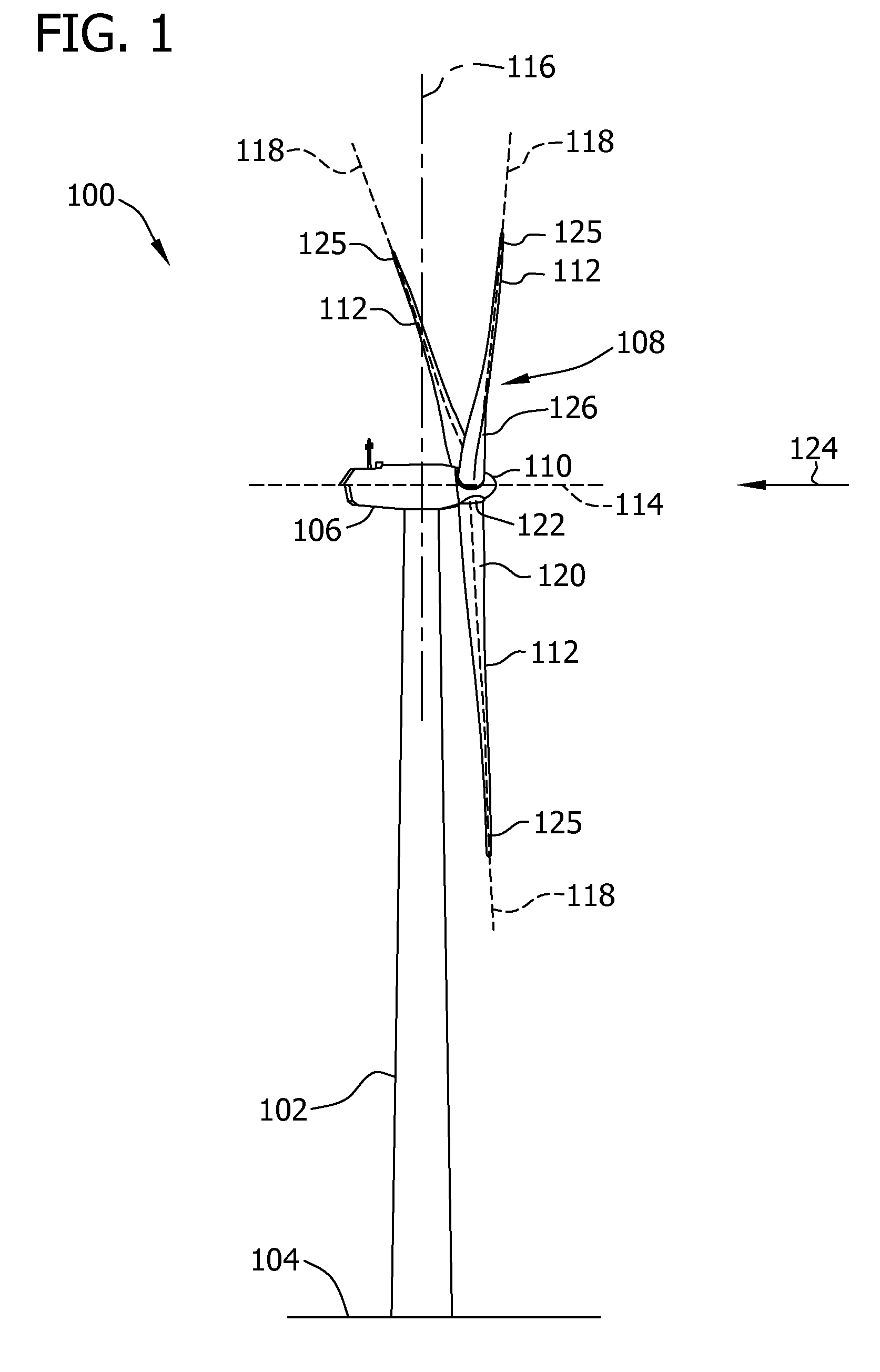
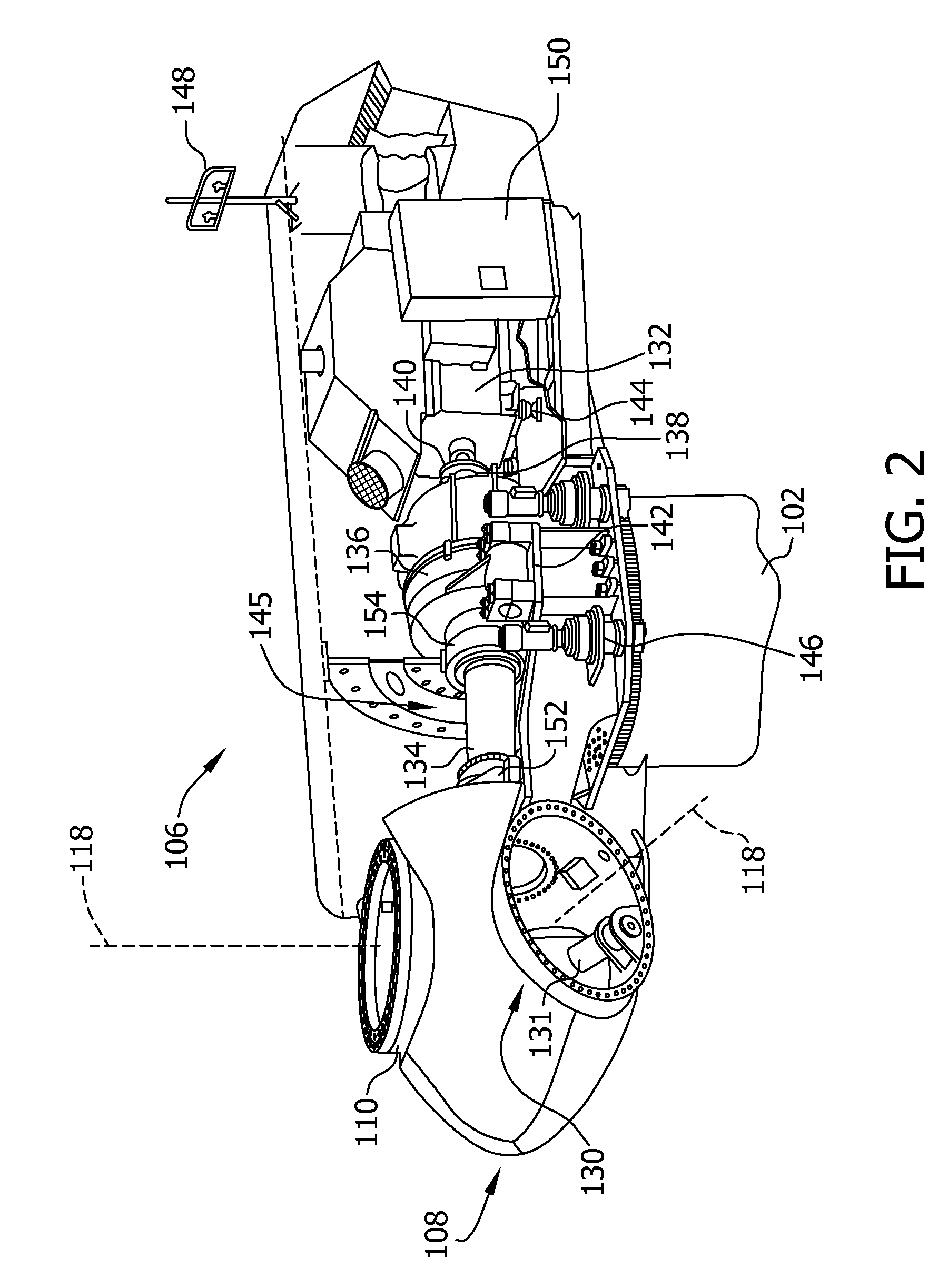
Condition monitoring system for wind turbine generator and method for operating wind turbine generator
A method for operating a wind turbine generator includes generating at least one of a plurality of rotor shaft angular displacement values, a plurality of rotor shaft angular velocity signals, and a plurality of rotor shaft angular acceleration signals. The method also includes determining a torsional moment within a rotor shaft, and modulating at least one of a wind turbine generator yaw orientation and a blade pitch orientation as a function of the determined torsional moment.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and device for detecting position of rotor of brushless motor
InactiveCN101719752AFunctionalImplement fault-tolerant detectionElectronic commutatorsBrushless motorsLocation detection
The invention relates to a method and a device for detecting the position of a rotor of a brushless motor, which are characterized in that a rotary transformer and the rotor of a tested brushless motor are arranged coaxially, the rotary transformer outputs two paths of orthogonal high-frequency sine-cosine signals containing information about the position of the rotor, and the information about the position of the rotor is obtained by the methods such as signal conditioning or resolving and the like. The most widely applied integrated chip at present adopting a special Resolver-to-Digital converter (RDC for short) and the like and a peripheral configuration circuit are used for performing resolving, and a special resolving chip of the type is sensitive to signals and has no fault-tolerant function, so the reliability is difficult to guarantee. The device of the invention is provided with a simple signal conditioning circuit on the basis of an RDC functional circuit to realize the detection of the position of the rotor of the brushless motor with self-monitoring and fault tolerance functions.
Owner:NANTONG WANBAO IND +1
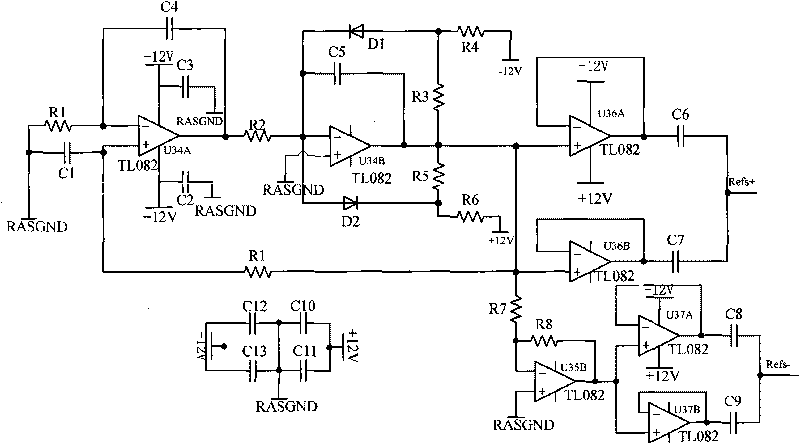
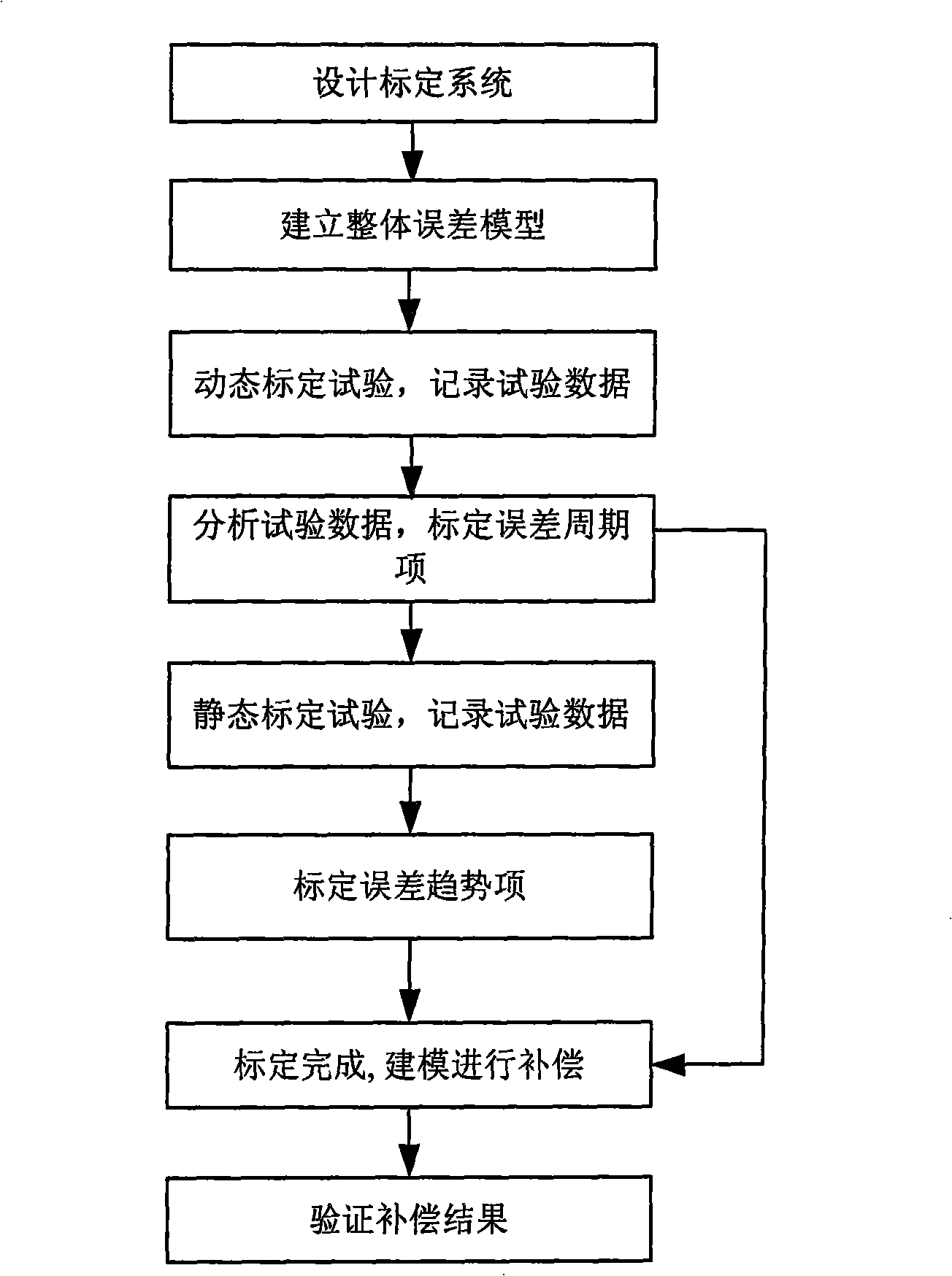
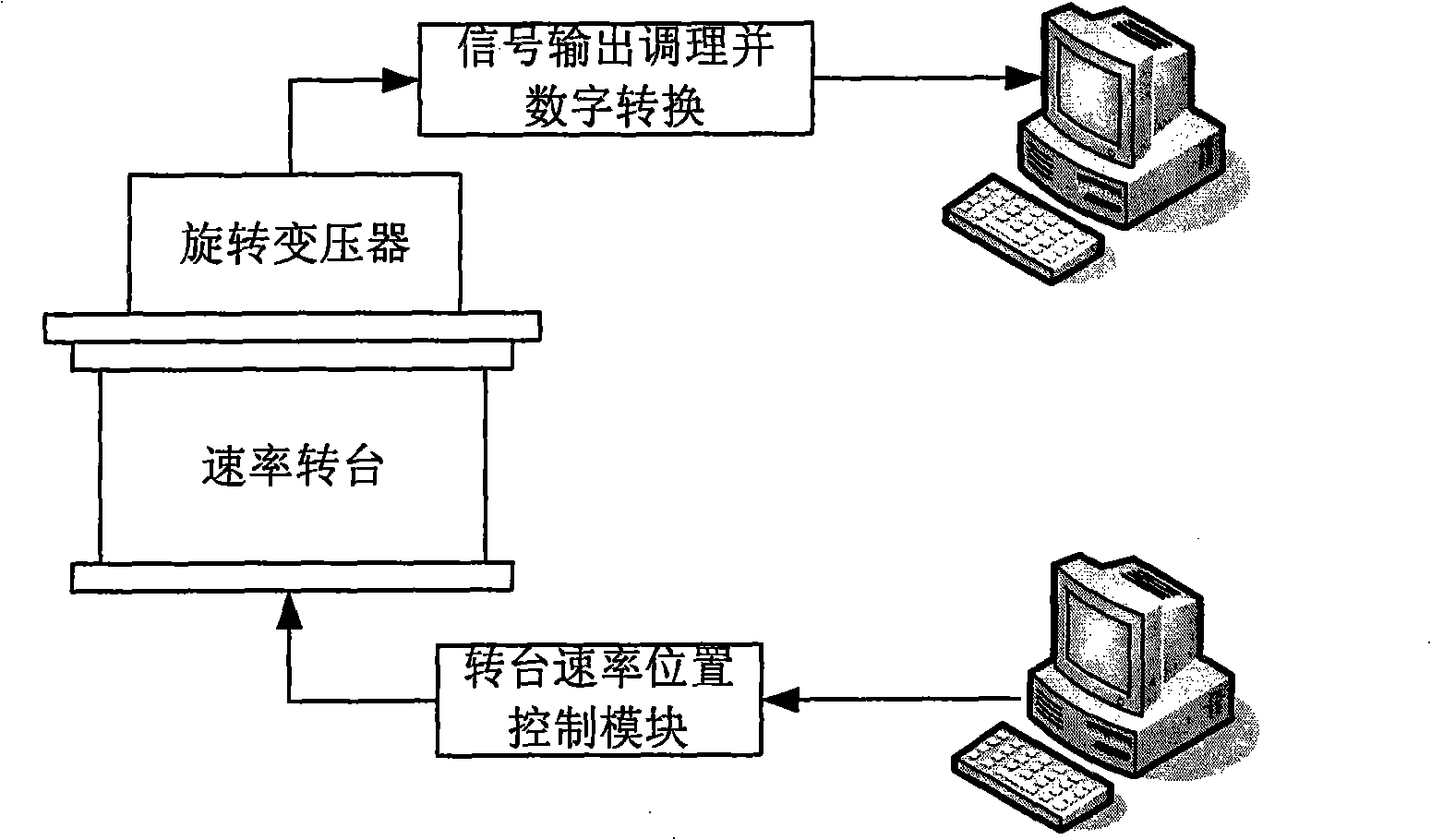
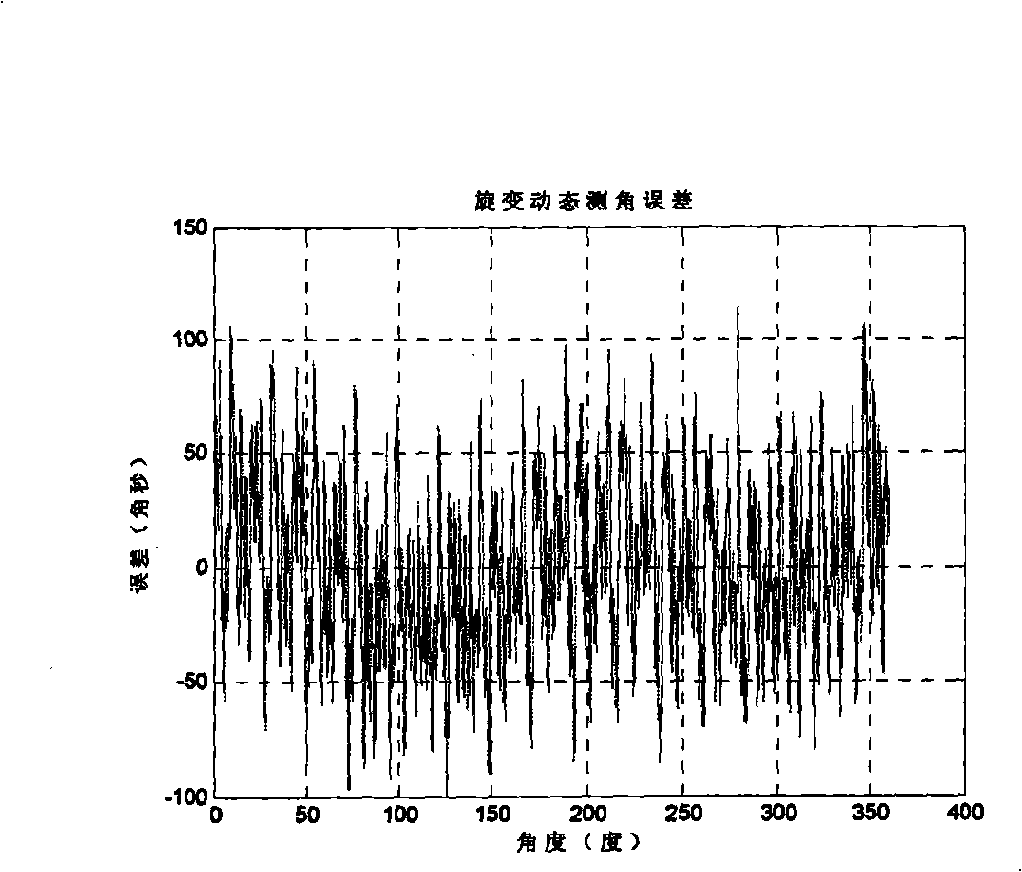
Calibration compensation method for rotating transformer angle observation error based on velocity rotating platform
InactiveCN101271007AAchieve precise calibrationImprove angle measurement accuracyConverting sensor output electrically/magneticallyAxis–angle representationEngineering
A calibration compensation method of angle-measurement error of a rotating transformer based on a rate rotary table; the calibration method obtains the dynamic continuous output of the rotating transformer through a dynamic calibration test of a digital calibration system, so as to calibrate the cycle error term coefficient of the rotating transformer; calibrates the one degree term and zero degree term errors of the rotating transformer through a static calibration test; completes precise error calibration of the rotating transformer through the dynamic and the static tests; and later, builds a model to compensate the calibrated rotary error. The invention integrates the advantages of the dynamic and the static calibration methods, is not restricted by precision of an angle measuring device, is easy and simple; the built error compensation model of the rotating transformer greatly improves the angle-measuring precision of the rotating transformer. The method is also applicable in calibration and compensation of all other shaft angle sensors as well as the angle-measuring precision.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Angle measurement precision detection apparatus of encoder and detection method thereof
InactiveCN102494710AMany measuring pointsShort measuring cycleUsing optical meansContinuous measurementObservational error
The invention relates to the precision shaft angle measuring instrument precision detection filed, more particularly to an angle measurement precision detection apparatus of an encoder and a detection method thereof. The apparatus comprises a coupling assembly, a precision main shaft, a motor, a precision encoder, a connection base, a rotary table, a workbench, and a computer system. The precision encoder is employed as a reference and is connected with the precision main shaft coaxially. The precision main shaft is driven by the motor; and an output shaft of the precision main shaft is connected with a detected encoder. The computer controls the rotating speed and the position of the motor as well as simultaneously collects angle measurement data of the precision encoder and the detected encoder; and an error value representing deviation of the position output of the detected encoder from the position output of a reference precision encoder is obtained in rotation angles from 0 degree to 360 degrees of the precision main shaft. And processing is carried out by the computer to provide various measurement errors of the detected encoder and error frequency spectrums. According to the invention, beneficial effects are as follows: there are lots of measurement points and measurement can be carried out continuously, so that various errors of a detected encoder can be reflected; a frequency spectrum analysis on an error source can be carried out; automatic measurement is carried out, the measuring period is short and efficiency is high; and electronization of data processing is realized as well as detection data are filed.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Attitude sensing device
InactiveUS20050144795A1Avoid problemsSuitable degree of accuracySeismic signal receiversPlumb lines for surveyingAxis–angle representationThree-dimensional space
The present invention provides an attitude sensing device and an attitude sensing method, and in particular techniques for determining an attitude in three-dimensional space of a reference axis of a package with which the attitude sensing device is associated. The attitude sensing device comprises an electromechanical sensor having a rotatable shaft operable to rotate about its axis to any shaft angle and a mass coupled to the shaft. The mass causes the shaft to rotate as the mass adopts a gravity-induced position. The electromechanical sensor is operable to provide an electrical signal in dependence on the shaft angle. The attitude of the reference axis being derivable from the electrical signal. By this approach, a simple arrangement is provided by which the attitude of the reference axis may easily be determined over the required operating range.
Owner:QINETIQ LTD
Vibrating Inertial Rate Sensor Utilizing Split or Skewed Operational Elements
InactiveUS20070256495A1Improved rate sense senseImproved sense drive sense signalAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsAxis–angle representationGyroscope
A vibrating inertial rate sensor has operational elements that define axes that are rotationally offset or “skewed” from a node or anti-node reference axis. The skew may be relative to separate node or anti-node reference axes, or take the form of an element that is “split” about the same node axis. Both the drive signal and the sense signal may be resolved from a common set of sensing elements. The drive elements may also operate on a skewed axis angle to rotationally offset the vibration pattern to affect active torquing of the gyroscope. Skewed drive elements may be combined with skewed or split elements on the same device. The skewed sensing scheme may be applied to vibratory systems having one or more node axes. The skewed drive scheme may be applied to vibratory systems having two or more node axes to affect active torquing.
Owner:WATSON INDUSRIES
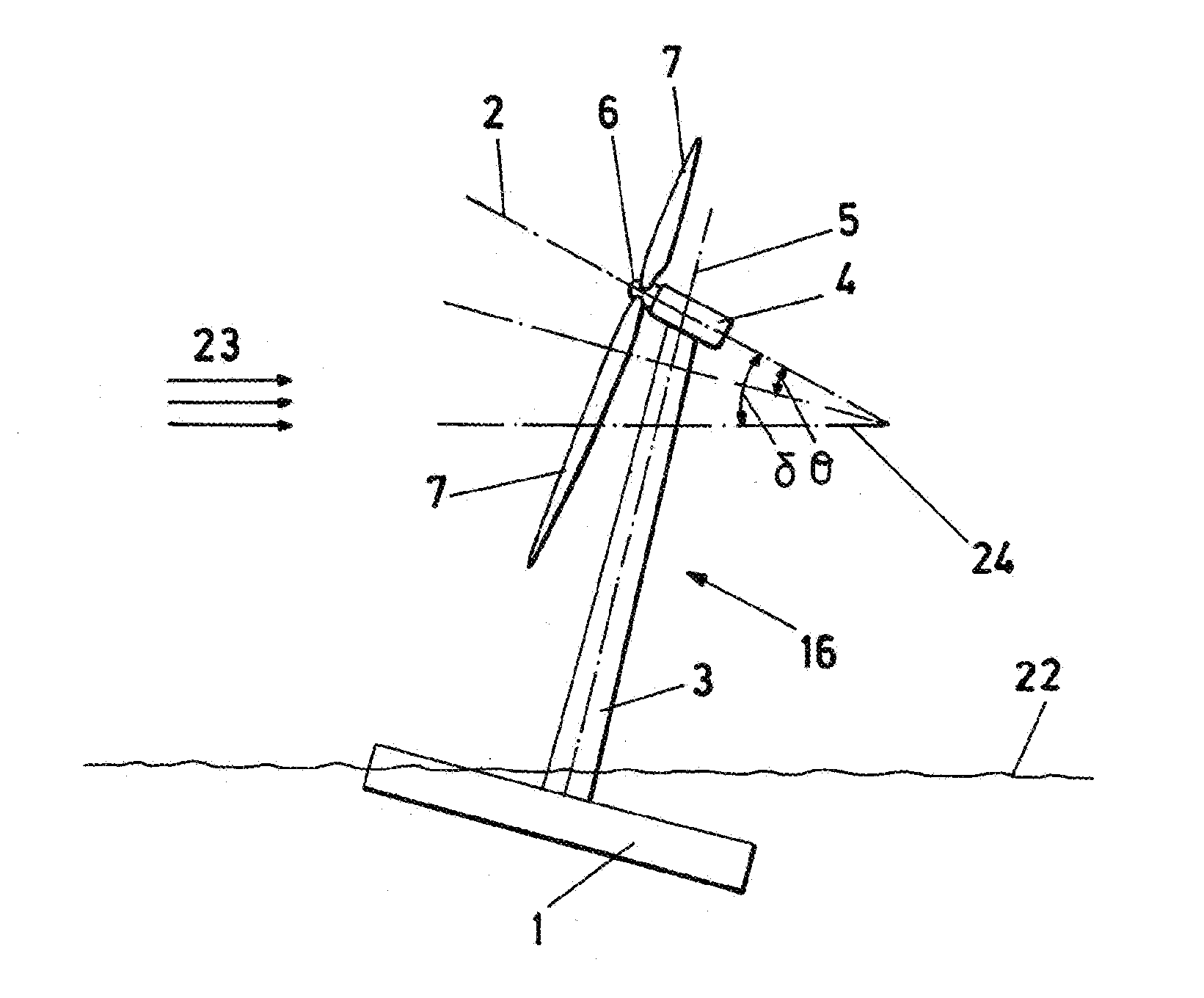
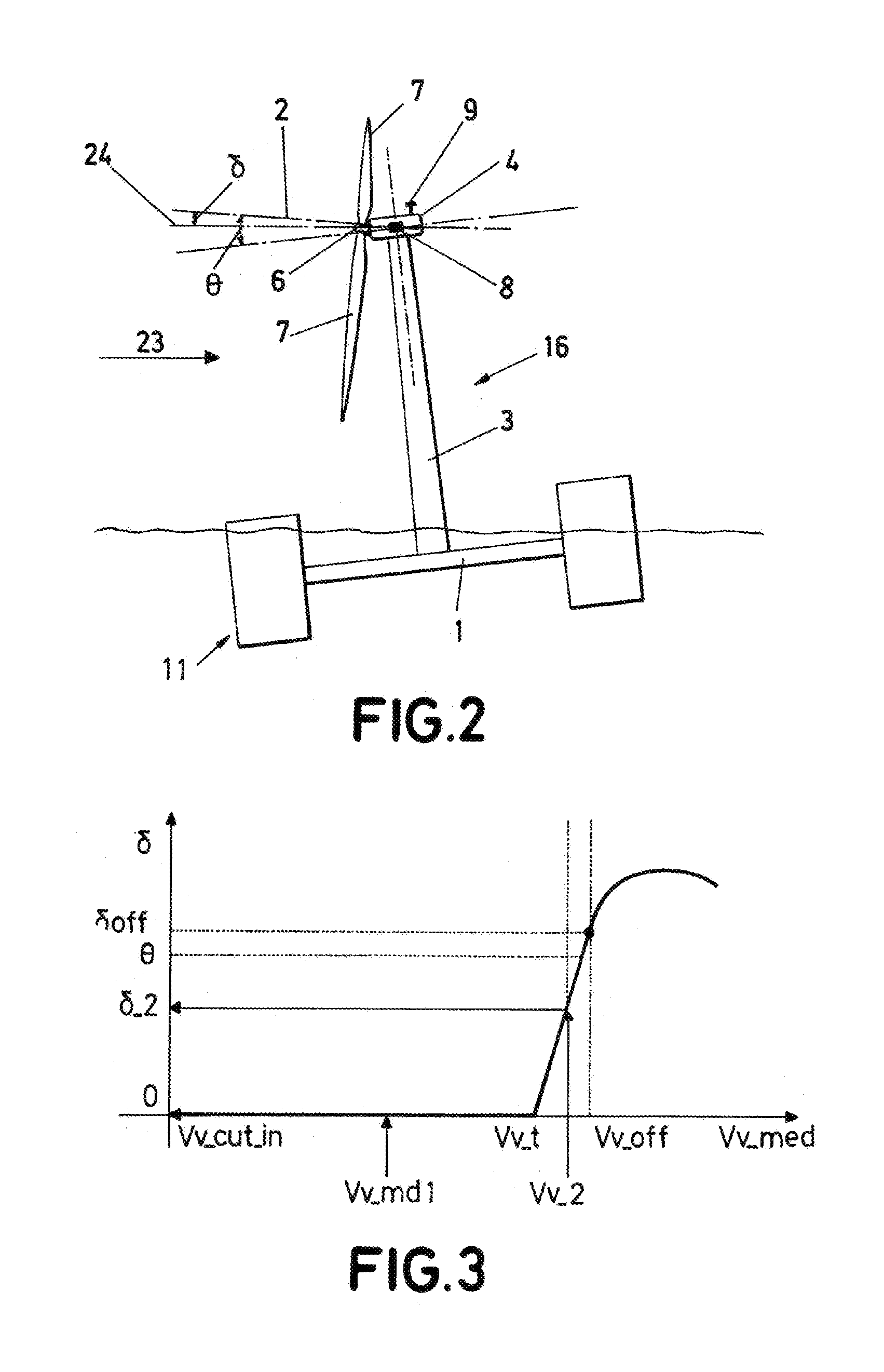
Wind turbine - floating platform assembly and method for orienting said assembly description
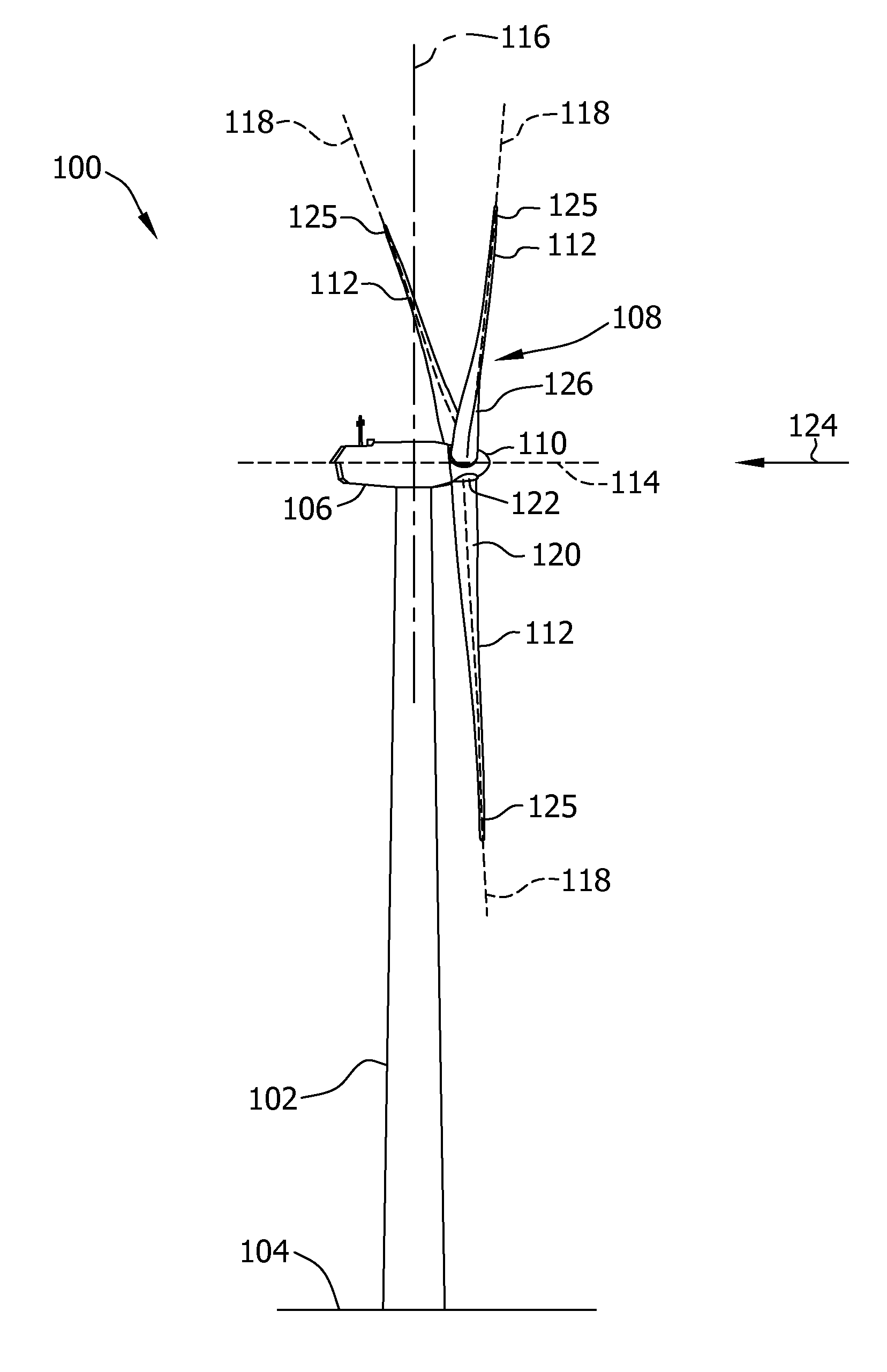
ActiveUS20120171034A1Low costMost efficientPropellersWind motor controlAxis–angle representationFloating platform
The invention allows orientation of the platform (1) in order to obtain conditions of maximum efficiency in the wind turbine (16). It comprises first sensors (8) for detecting an effective rotation axis angle (δ) formed between the rotation axis (2) and a horizontal plane (24); second sensors (9) for detecting wind direction (23); platform orientation means (11) for modifying the effective rotation axis angle (δ); and at least one control unit (12) adapted for receiving a first input (13) from the first sensors (8) and a second input (14) from the second sensors (9) and, based on said inputs (13, 14), transmitting orders to the platform orientation means (11) and yaw mechanism.
Owner:NORDEX ENERGY SPAIN SA
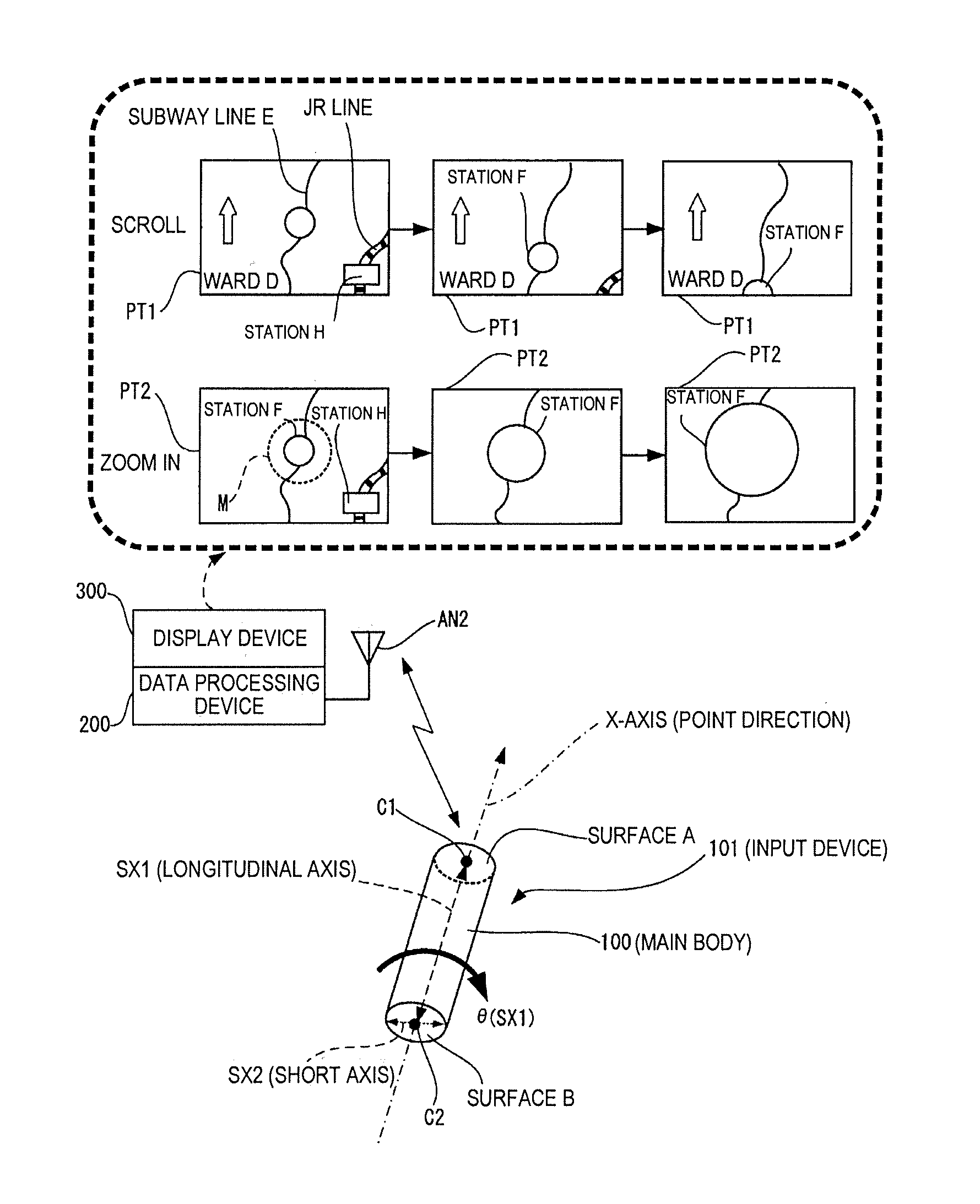
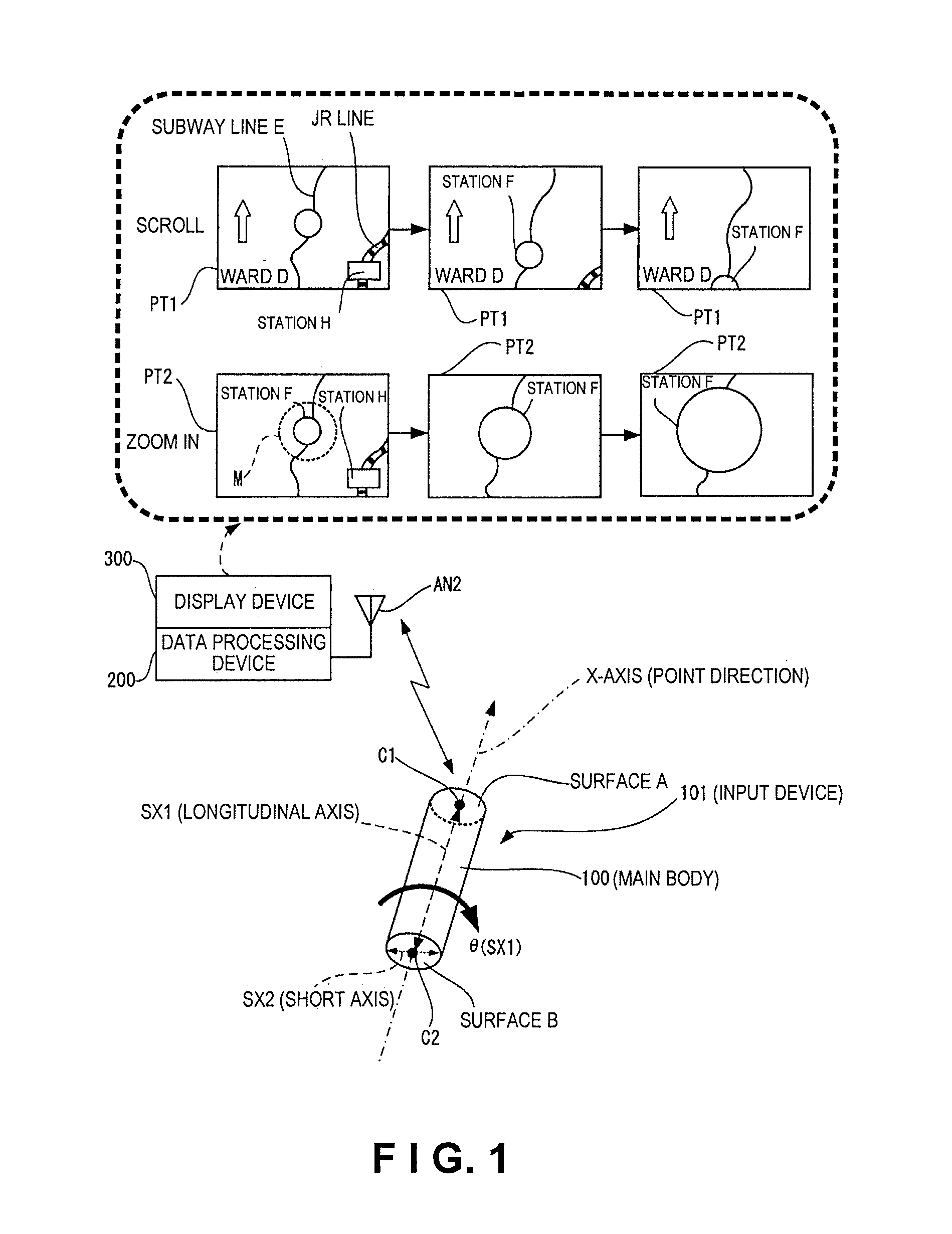
Input device and data processing system
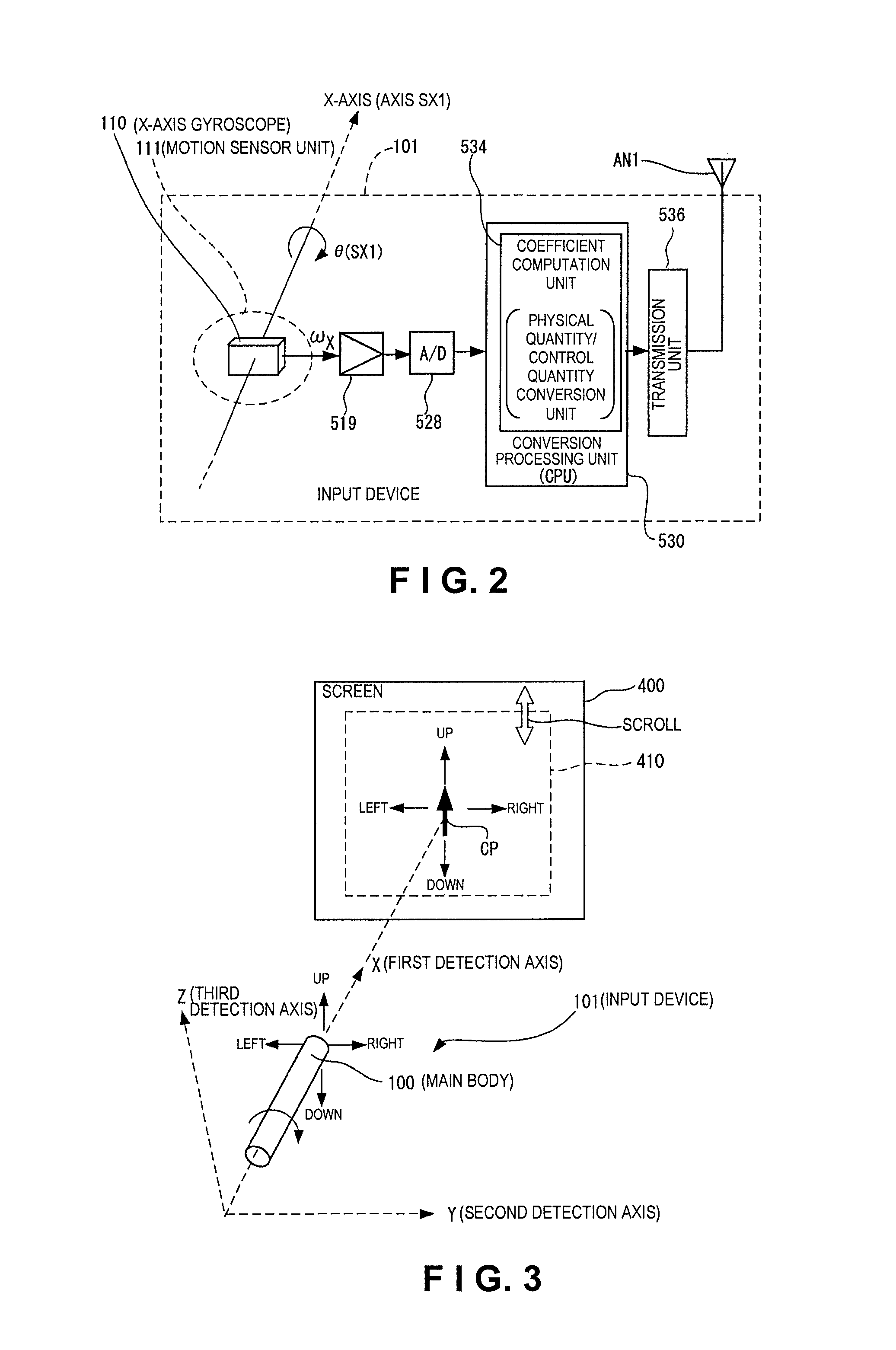
ActiveUS20100156785A1Easy to operateImprove convenienceDigital computer detailsSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsAxis–angle representationData processing system
An input device includes a main body and a motion sensor unit. The main body has a longitudinal axis. The motion sensor unit is configured and arranged to detect rotation of the main body about the longitudinal axis. The motion sensor unit has an X-axis angular velocity sensor configured and arranged to detect an angular velocity of the main body about an X-axis in a three-dimensional orthogonal coordinate system defined by the X-axis, a Y-axis and a Z-axis. The X-axis coincides with the longitudinal axis of the main body and the Y-axis and the Z-axis being orthogonal to each other in a first plane perpendicular to the X-axis.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
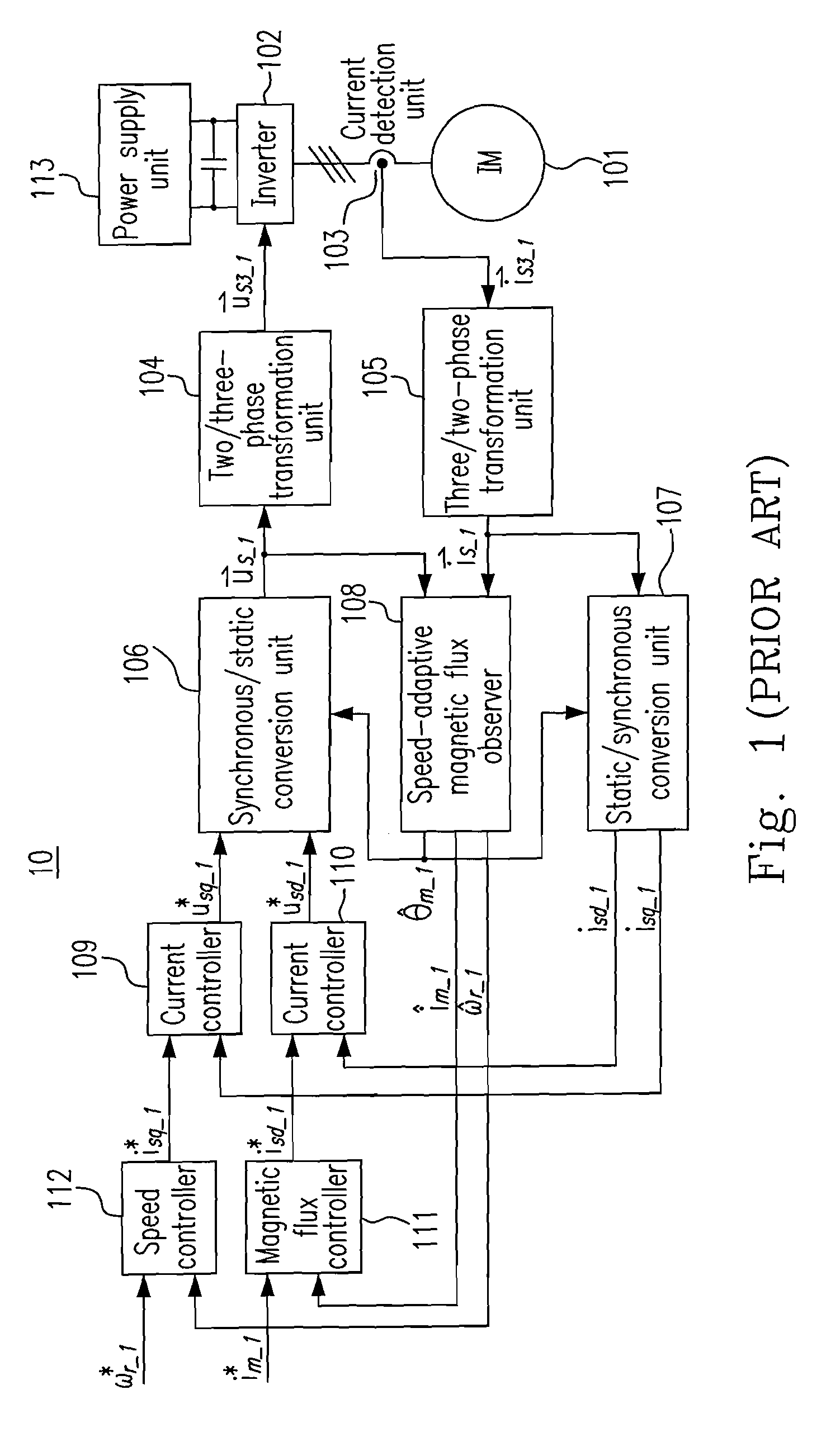
Sensorless control apparatus and method for induction motor
ActiveUS20090160394A1Motor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlAxis–angle representationPhase currents
A control apparatus for an induction motor is provided and includes a rotating-speed locked loop and a feed-forward magnetizing-axis angular position emulator. The rotating-speed locked loop emulates a speed control loop of the induction motor for producing an emulated torque current and an emulated rotor angular speed. The feed-forward magnetizing-axis angular position emulator receives the emulated torque current and the emulated rotor angular speed for producing a feed-forward estimated magnetizing-axis angular position, wherein according to the feed-forward estimated magnetizing-axis angular position, a first voltage controlling the induction motor is transformed from a synchronous reference coordinate system of the induction motor to a static reference coordinate system of the induction motor, and a two-phase current detected from the induction motor is transformed from the static reference coordinate system to the synchronous reference coordinate system. The state the stator angular frequency is at zero can be skipped through the apparatus.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Angular position pick up for measuring high linear flux density
InactiveCN1519536ADrop output voltage levelUsing electrical meansElectrical steeringAxis–angle representationVolumetric Mass Density
An angular position sensor is provided which is designed to an angular position of a rotary shaft. The angular position sensor has a magnet affixed to the rotary shaft. The magnet has an N-pole and an S-pole and is so geometrically shaped as to produce magnetic flux which is substantially uniform in amount within a range extending around each of centers of the N-pole and the S-pole. This improves the linearity of a change in sensor output upon rotation of the rotary shaft.
Owner:DENSO CORP
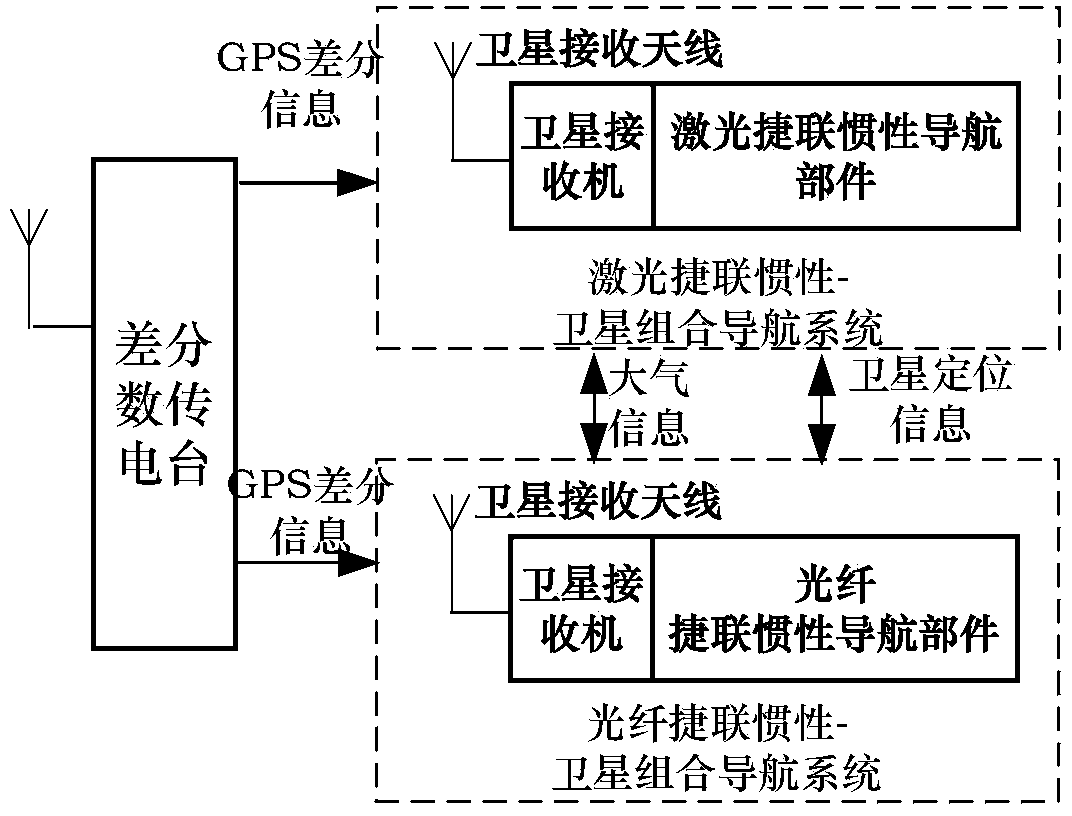
Non-similar dual-redundancy integrated navigation device applied to unmanned plane
InactiveCN104180803AImprove reliabilityImprove maintainabilityNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSatellite radio beaconingAxis–angle representationNavigation system
The invention discloses a non-similar dual-redundancy integrated navigation device applied to an unmanned plane, comprising main and standby combined navigation systems and a difference data transmission radio, wherein a laser strapdown inertia-satellite combined navigation system is adopted as the main combined navigation system which comprises a laser strapdown inertia navigation part and a satellite receiver; an optical fiber strapdown inertia-satellite combined navigation system is adopted as the standby combined navigation system which comprises an optical fiber strapdown inertia navigation part and a satellite receiver; the satellite receivers are both used for receiving GPS difference information, carrying out difference correction resolving and outputting satellite positioning information; the strapdown inertia navigation parts are both used for receiving atmosphere information and control commands and simultaneously outputting navigation information; the main and standby combination navigation systems transmit respectively received atmosphere information and satellite positioning information via serial interfaces. The device has the advantages of high reliability, good maintenance and lowering of requirements on a power supply caused by volume, weight and cost, providing of plane shaft angular rate information, high navigation precision and practicability.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
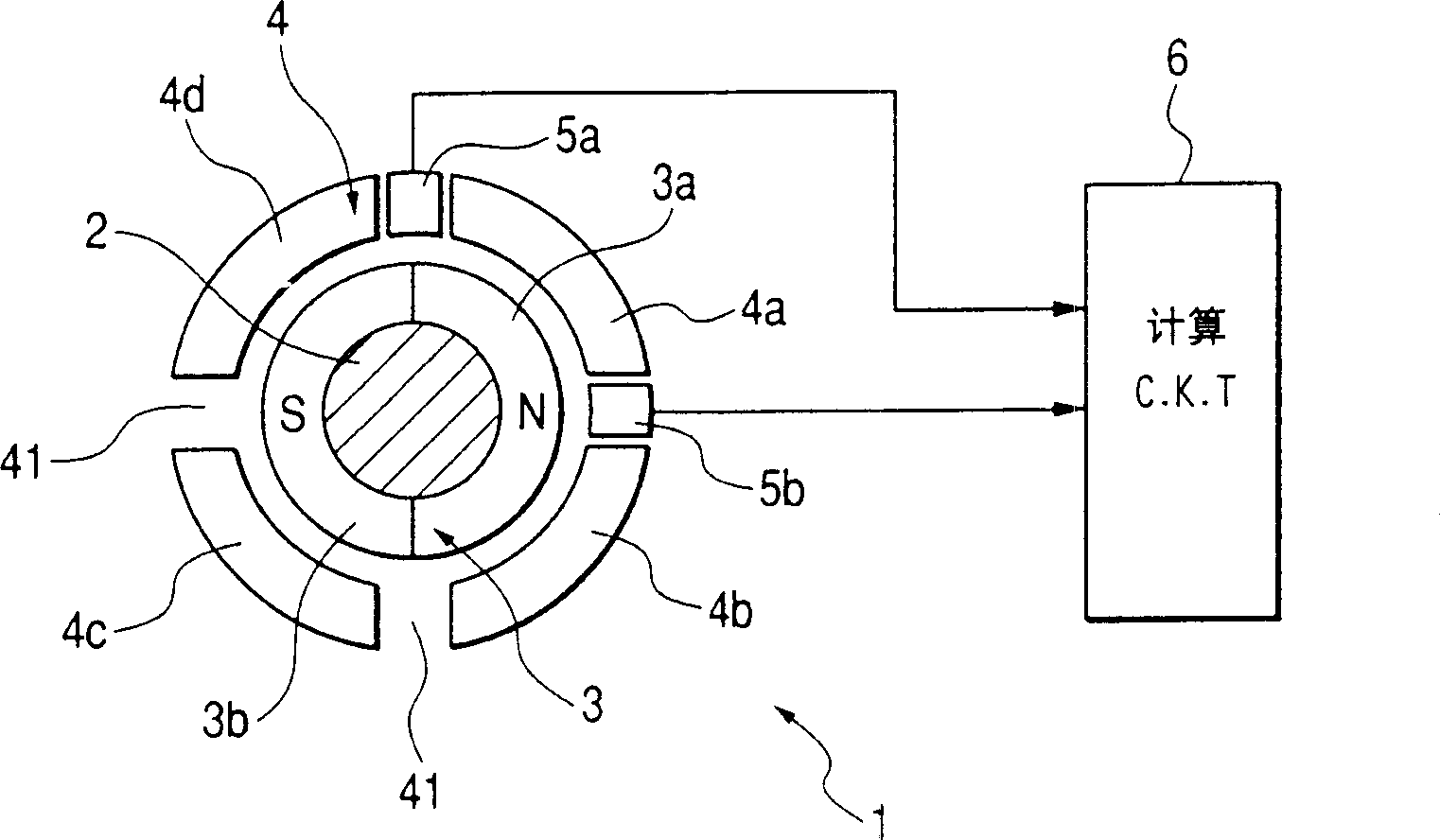
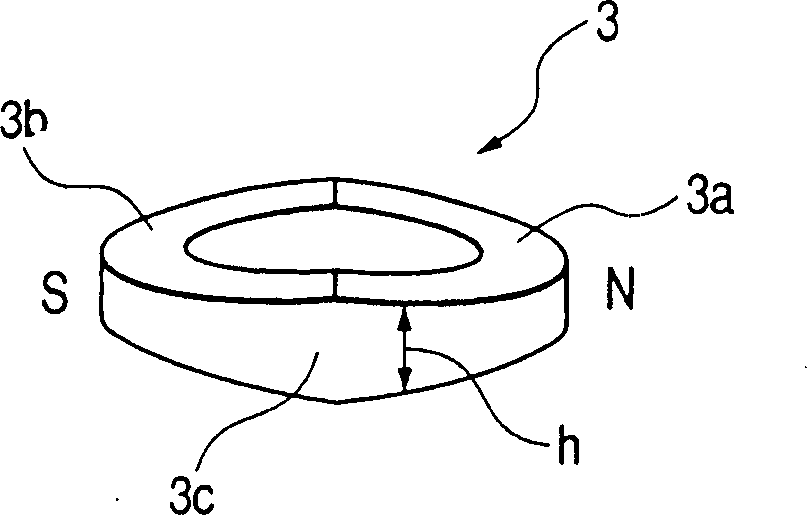
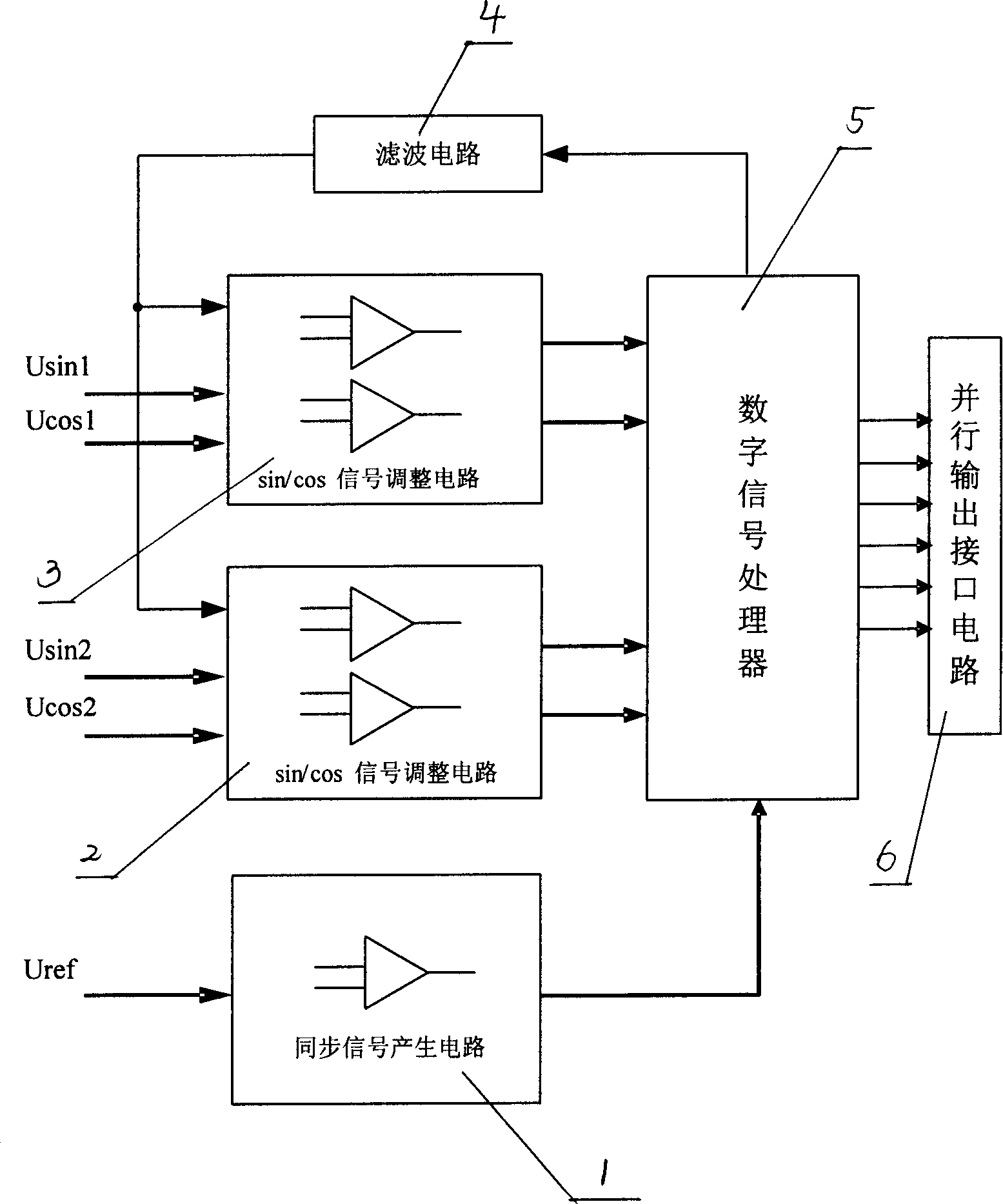
Double speed angle-digital converter
ActiveCN1825054ALow costImprove conversion performanceUsing electrical meansControl using feedbackAxis–angle representationDigital down converter
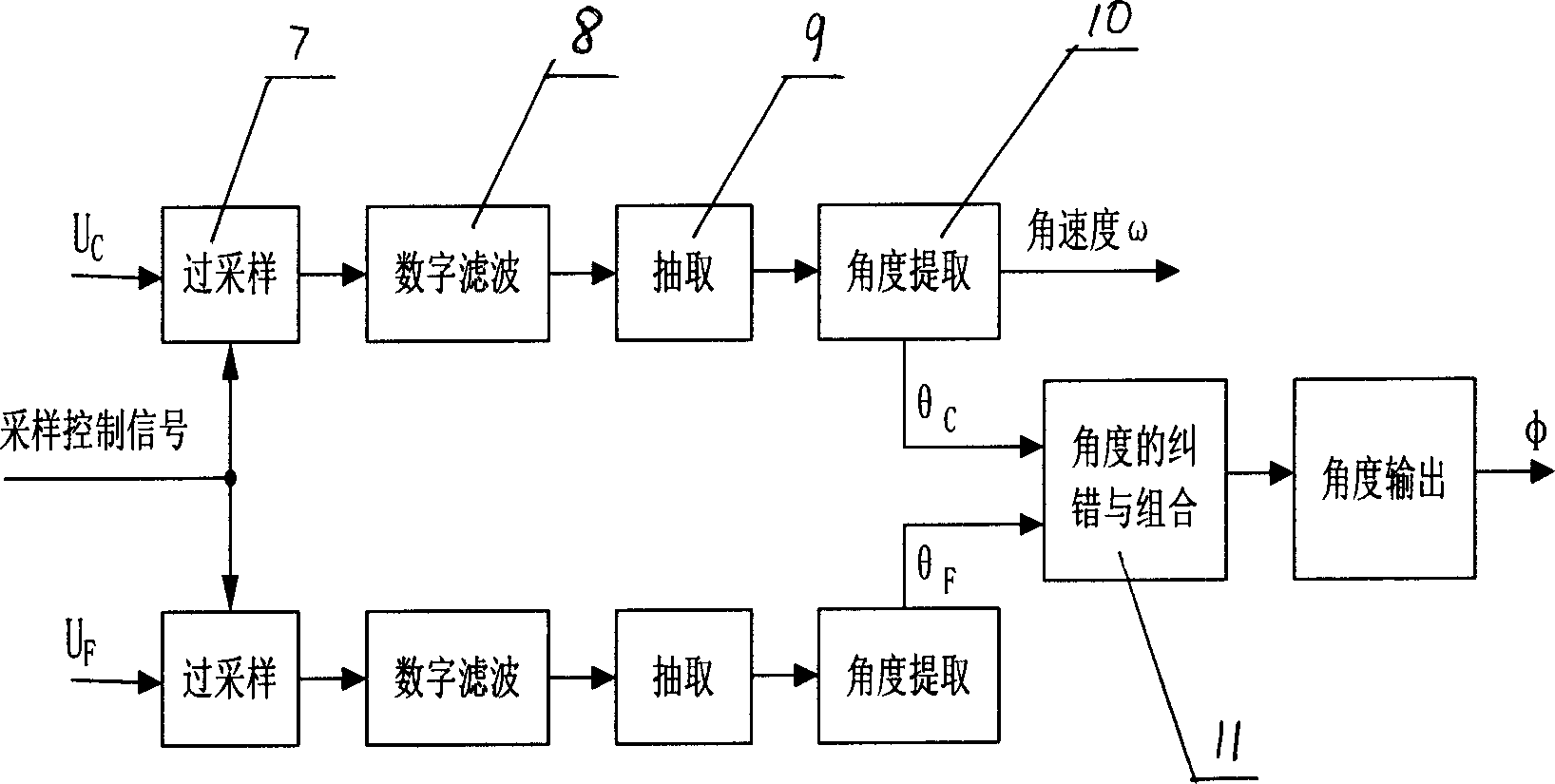
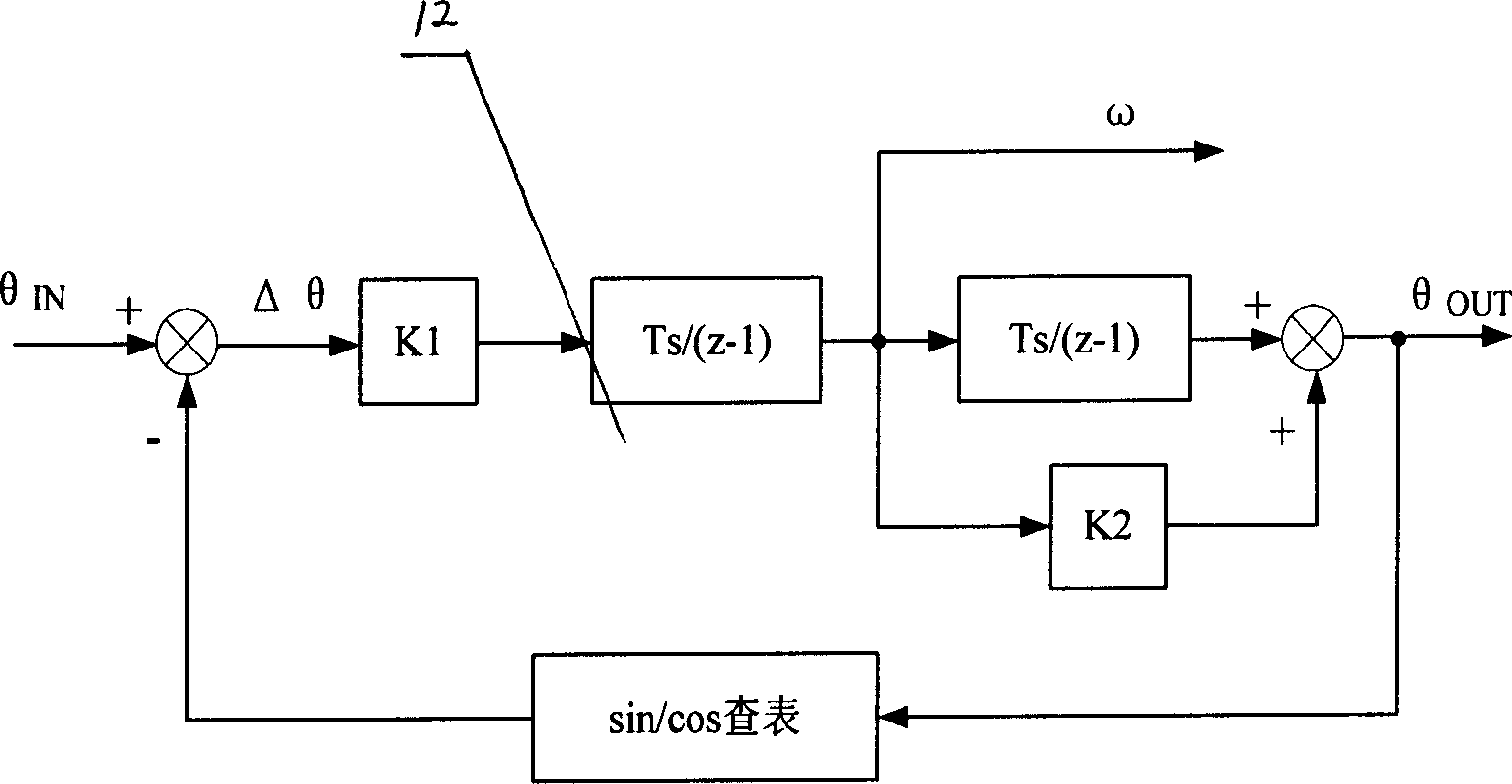
The invention relates to a double speed axial angle digital converter that uses DSP as central process unit. The process includes the following steps: the excitation signal of rotating transformer accessing to DSP through synchronizing signal generating circuit, and the rotating transformer signal of raw and fined channels accessing to DSP through signal adjusting circuit, the DSP first gaining compounding axial angle location and speed, and realizing digital quantity output through interface circuit after taking angle error correction and combining, the random dither signal generated by DSP would be accessed to signal adjusting circuit through filtering circuit and rotating transformer. The speed ratio and converting accuracy could be adjusted. The whole converting process could be realized by software arithmetic. Thus, it could not only reduce hardware circuit, lower cost, but also could adjust diameter by software and improve adaptability.
Owner:连云港杰瑞电子有限公司
Open-loop control method for rotation speed change of reaction wheels and unloading method
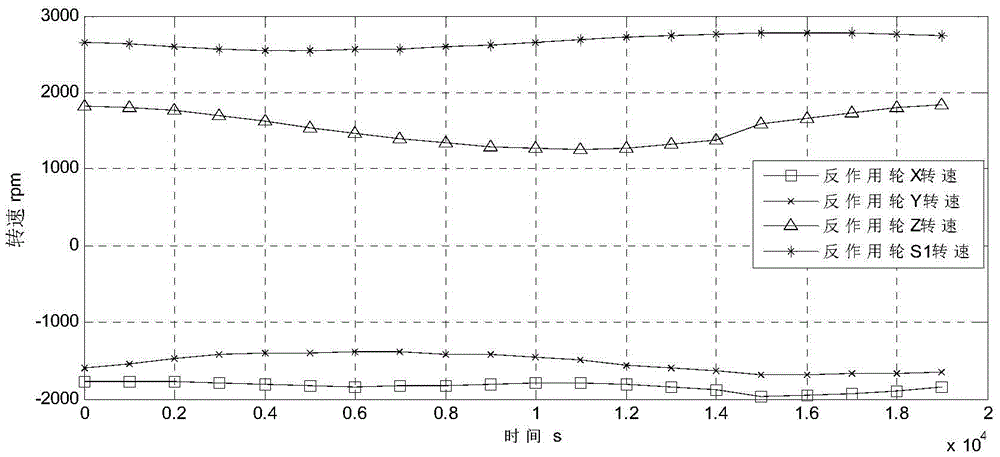
InactiveCN105644810AEasy to controlEasy to use and flexibleCosmonautic vehiclesAttitude controlDistribution matrixAxis–angle representation
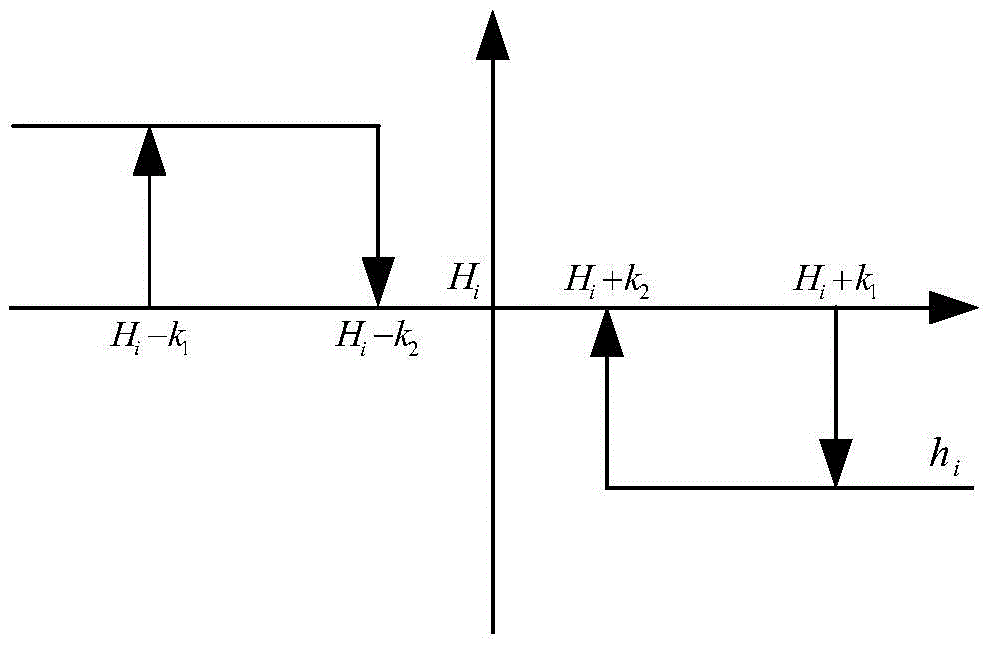
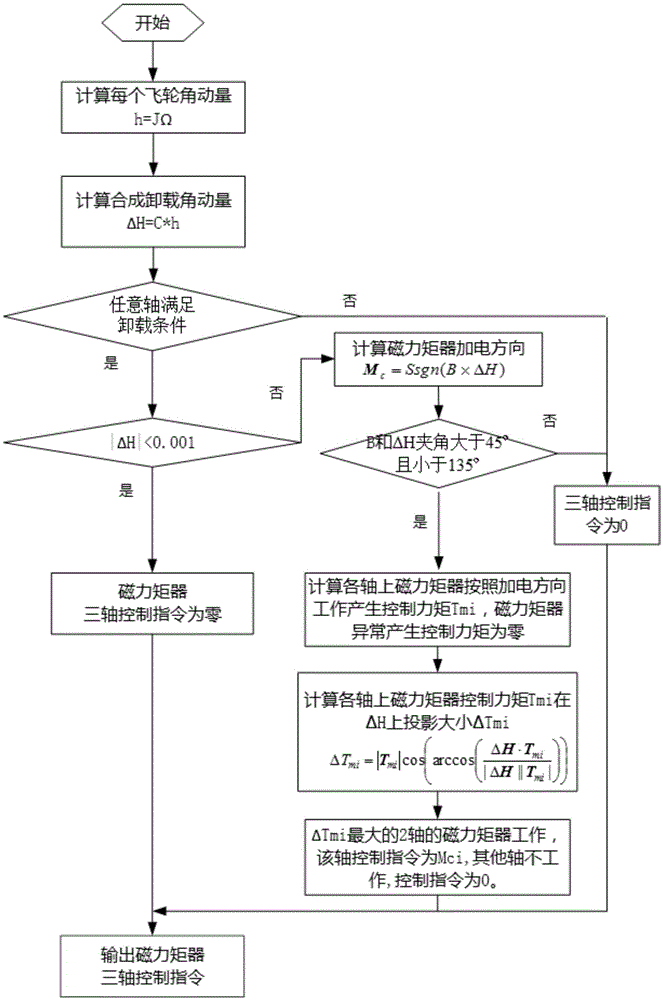
The invention provides an open-loop control method for the rotation speed change of reaction wheels (hereinafter referred to as flywheels) and an unloading method. The open-loop control method for the rotation speed change of the reaction wheels and the unloading method comprise the following specific steps that 1, controlling is conducted through the four flywheels, and the instruction of the magnitude of the reaction wheel control torque of the fourth flywheel is adjusted to be consistent with the magnitude of the theoretical nominal rotation speed friction torque; 2, a control instruction output by a controller is limited within the maximum output torque, the control torque of each flywheel is distributed according to a flywheel distribution matrix, after the control torque of each flywheel is distributed, the flywheel with the maximum output torque is limited within the maximum torque, and the control torque of the other two flywheels is decreased and increased proportionally; 3, the momentum of a synthetic angle of the four flywheels is calculated, and when any axial angle momentum reaches the unloading threshold range and the relationship between the magnetic field intensity and an angular momentum included angle during unloading is met, magnetic torquers are started to be uninstalled; and 4, the magnetic torquer with the maximum unloading capacity is selected to work, and the flywheels are unloaded by adopting a switch control mode.
Owner:SHANGHAI ENG CENT FOR MICROSATELLITES
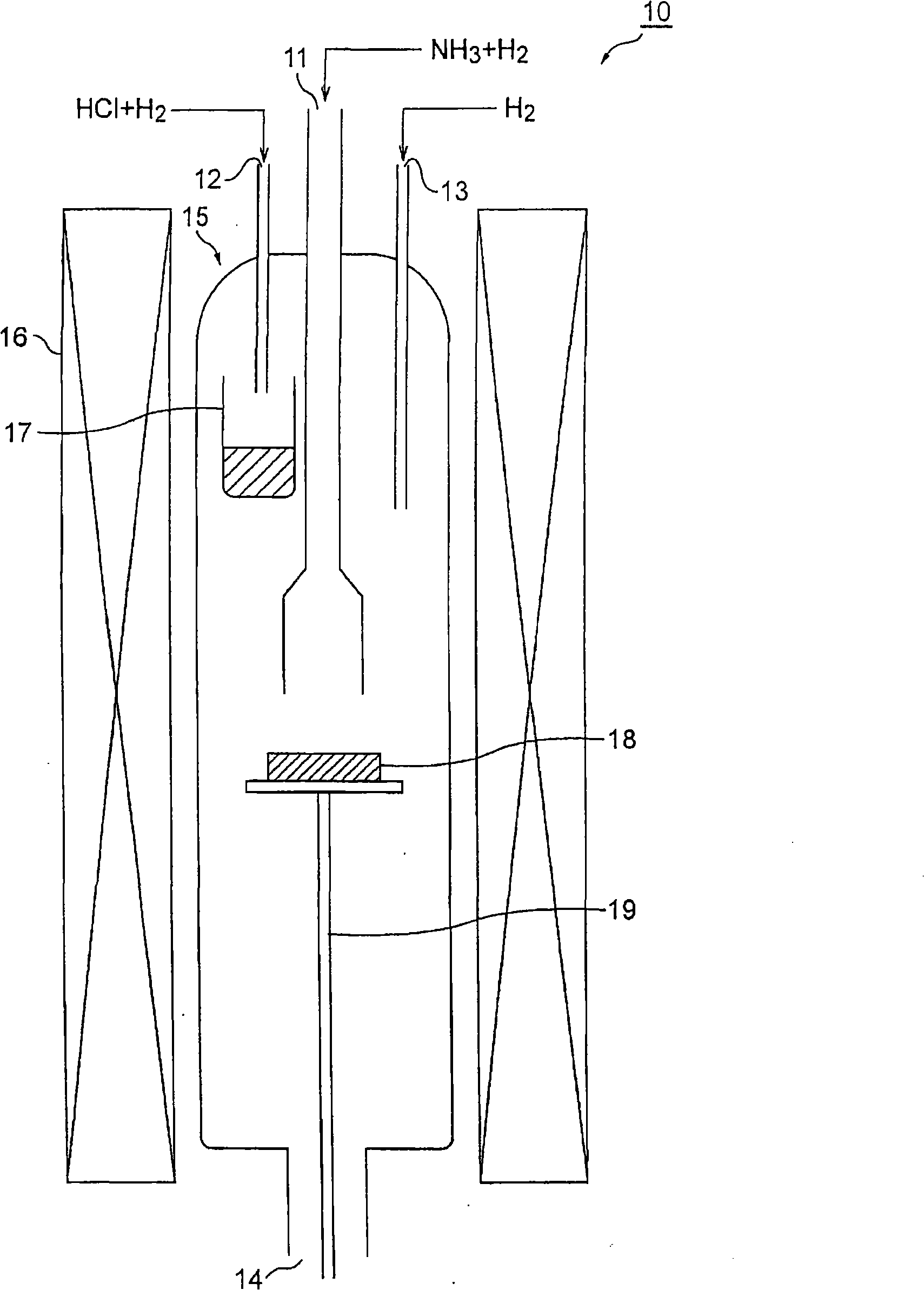
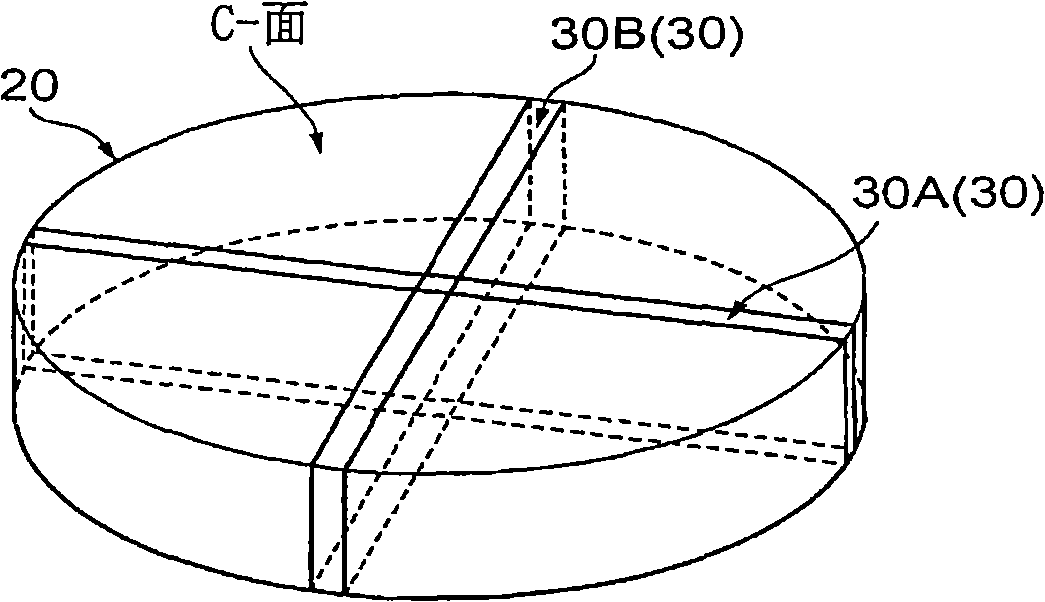
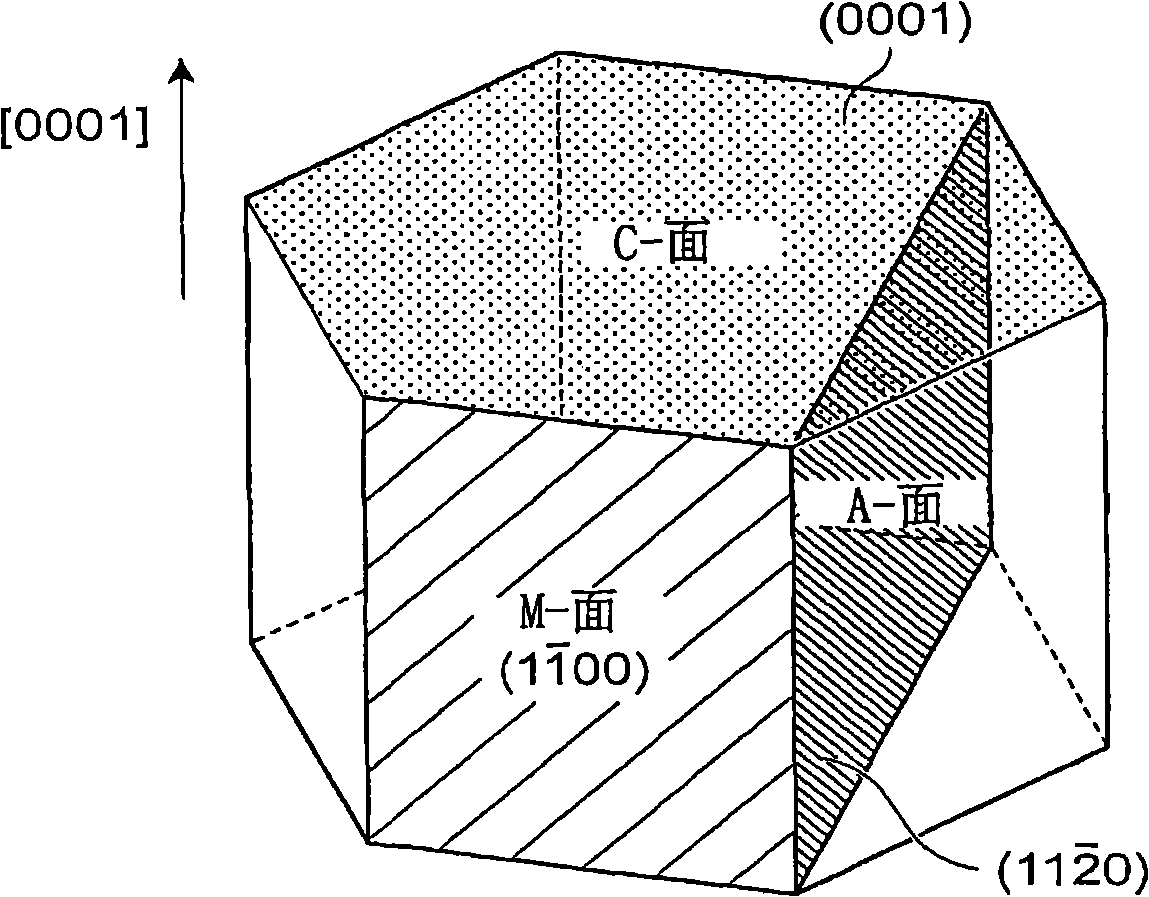
Gan substrate, and epitaxial substrate and semiconductor light-emitting device employing the substrate
InactiveCN101308896AImprove emission efficiencyPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAxis–angle representationEmission efficiency
The invention relates to a GaN substrate, an epitaxial substrate adopting the GaN substrate and semiconductor light-emitting devices. A growth plane (30a) of the GaN substrate (30) is oriented off-axis relative to an m-plane or an a-plane, namely in the GaN substrate (30), the growth plane (30a) is either the m-plane or the a-plane which has been misoriented. Because the m-plane and the a-plane are nonpolar planes, the GaN substrate (30) is utilized to manufacture the semiconductor light-emitting devices, so as to avoid the influence of piezoelectric fields so as to realize superior emission efficiency. The growth plane is imparted the off-axis angle according to the m-plane and the a-plane to realize high quality morphology in crystal grown on the substrate. Utilizing the GaN substrate to manufacture the semiconductor litght-emitting devices can further improve emission efficiency.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
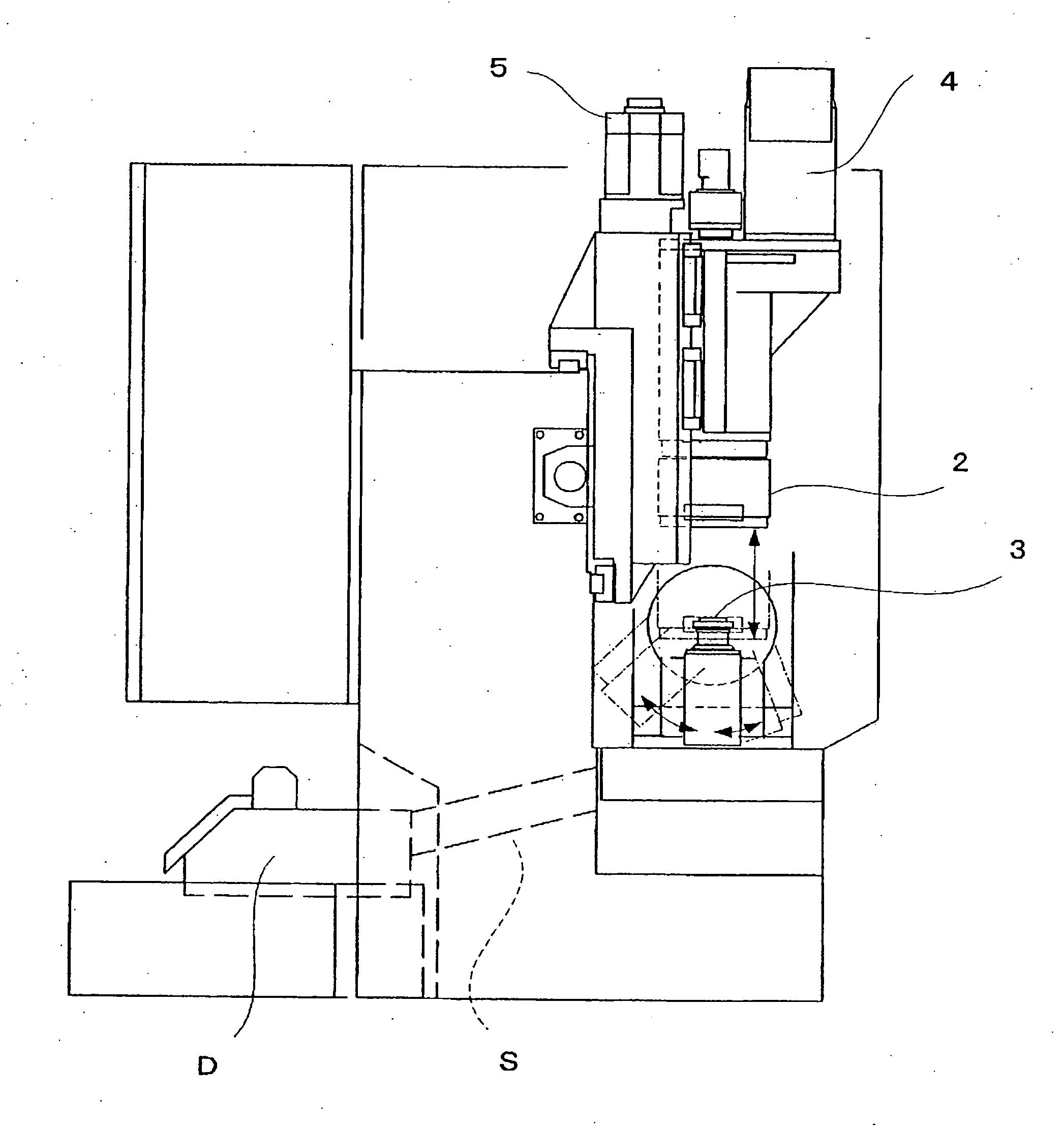
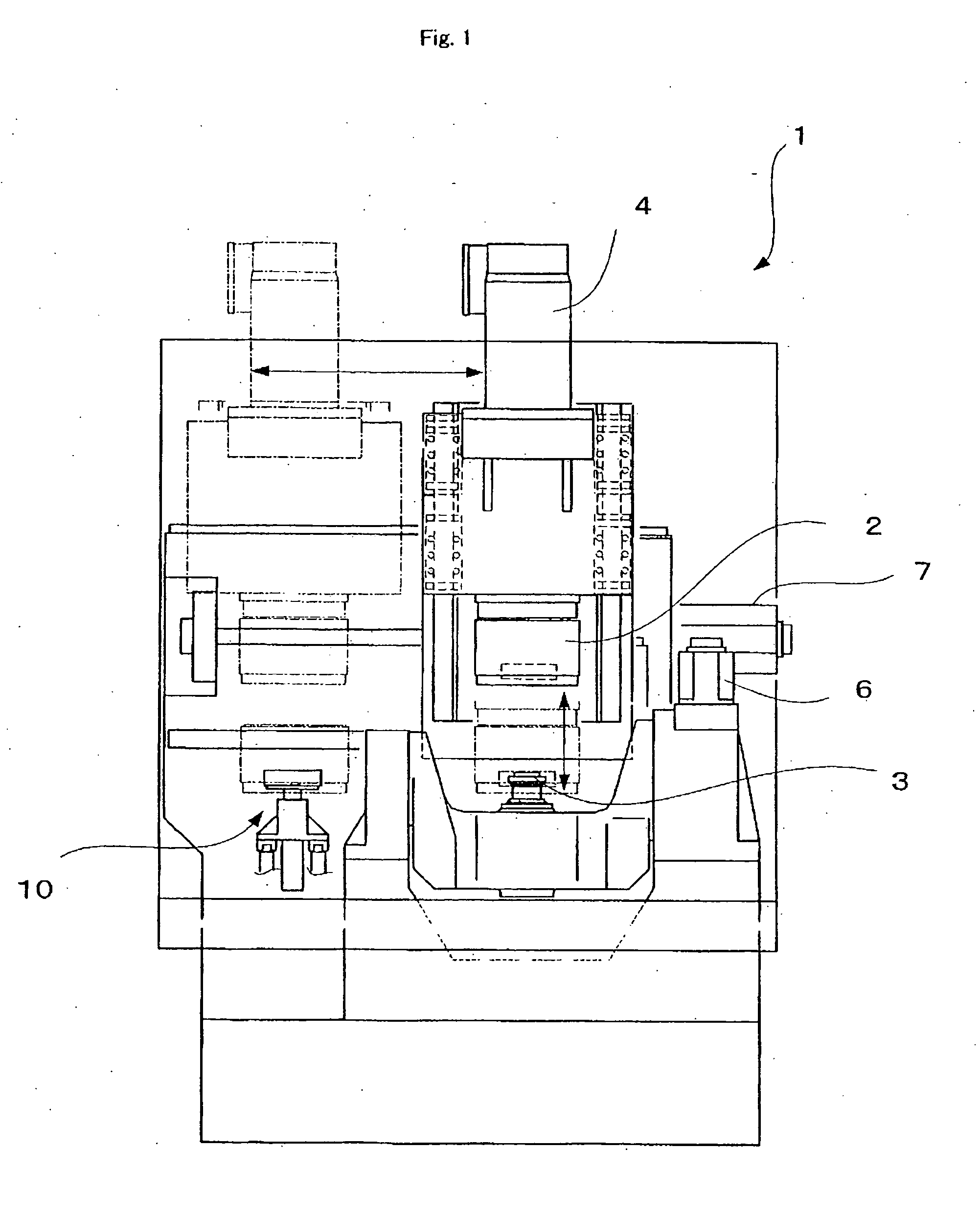
Internal gear shaving machine
An internal gear shaving machine 1 which brings a shaving cutter 3 and an internal gear held by a workpiece chuck 2 into engagement with a crossed axes angle, and subjects the tooth flanks of the internal gear to final machining while it rotationally drives at least one of the shaving cutter 3 and the workpiece chuck 2. The workpiece chuck 2 and shaving cutter 3 are supported movably toward and away from each other in a vertical direction with the workpiece chuck 2 higher and supported movably in the horizontal direction relative to each other. The workpiece chuck 3 is constituted to hold the outer circumferential surface of the internal gear with the axis of rotation of the internal gear oriented in a up-down direction so that shavings produced during processing by the shaving cutter can fall downwardly from the internal gear.
Owner:KANZAKI KOKYUKOKI MFG
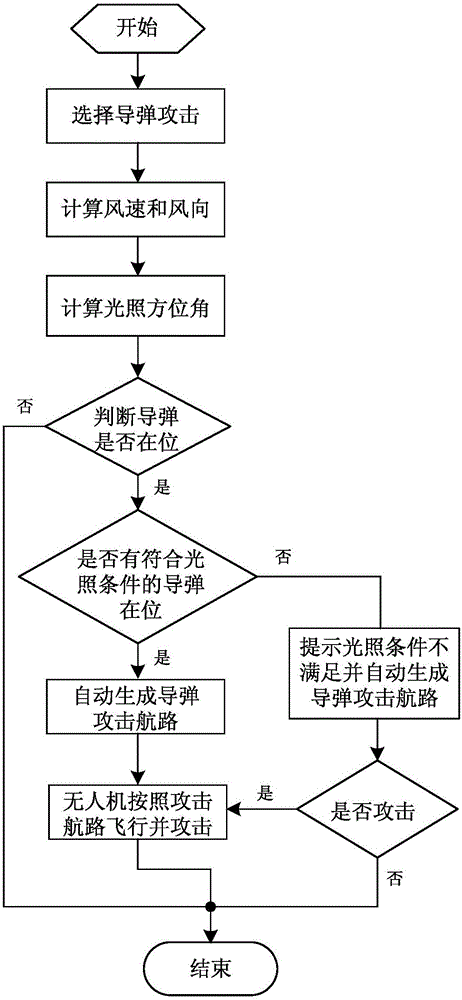
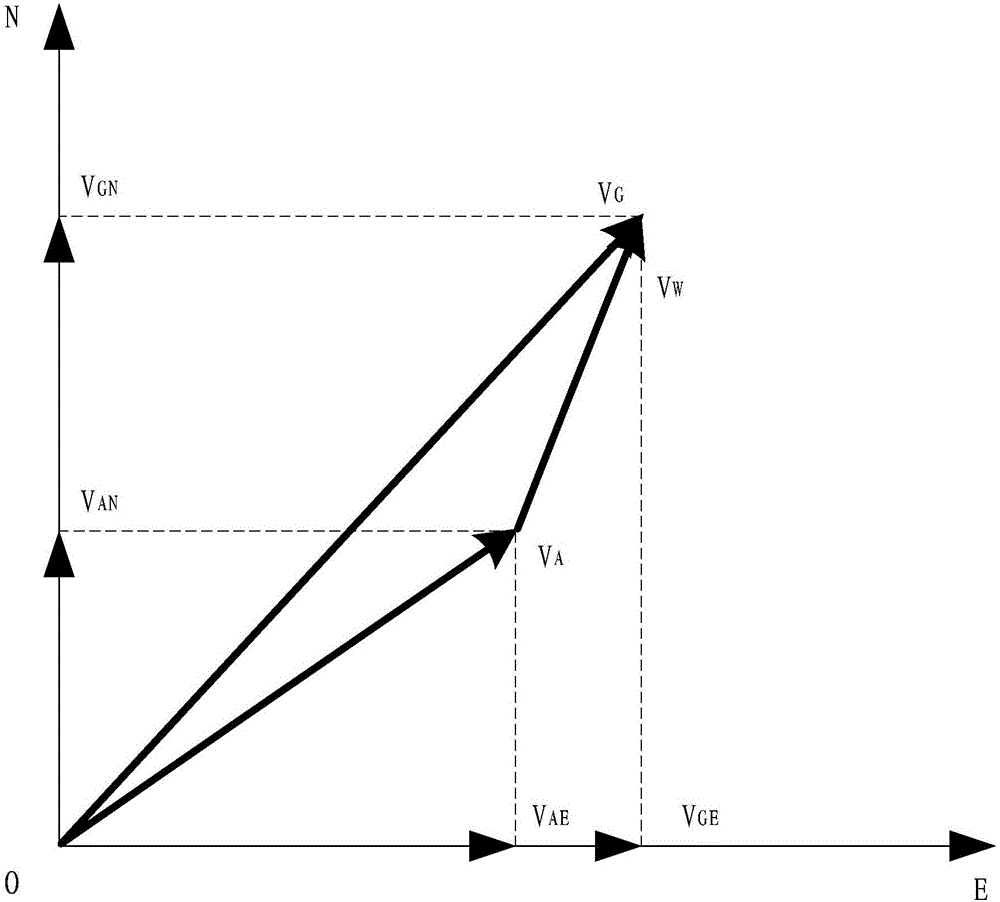
Unmanned aerial vehicle-based guided missile attack route planning method
ActiveCN105157488AMeet the requirements of tail smokeReduce the difficulty of manual flight lateral controlSelf-propelled projectilesAxis–angle representationUncrewed vehicle
The invention relates to an unmanned aerial vehicle-based guided missile attack route planning method which comprises the following steps: calculating to obtain the wind speed and the wind direction according to fight parameters of an unmanned aerial vehicle, and determining the sun illumination azimuth angle according to local time; calculating track angles of the unmanned aerial vehicle attacked by guided missiles from the left side and the right side according to the wind speed and the wind direction, and selecting the side having the relatively small absolute value of the difference value between the track angle of the unmanned aerial vehicle and the sun illumination azimuth angle to be used as the side suitable for being attacked by the guided missiles; determining the launching off-axis angles and launching axial distances of the guided missiles according to launching requirements and trajectories of the guided missiles so as to obtain the laterodeviation of the unmanned aerial vehicle; and calculating to obtain the coordinate of laterodeviation point stroke according to the track angle, at the side suitable to be attacked by the guided missiles, of the unmanned aerial vehicle, the laterodeviation of the unmanned aerial vehicle, and known impact point coordinates and further to obtain the attack route of the guided missiles, so that the unmanned aerial vehicle flies for attacking according to the attack route. According to the unmanned aerial vehicle-based guided missile attack route planning method, use requirements of all-weather attack of the unmanned aerial vehicle are met, and the automation degree, the rapidity and the real-time performance of the attack can be improved to the greatest extent.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF AEROSPACE AERODYNAMICS
Solid-state gyroscopes and planar three-axis inertial measurement unit
InactiveUS20050092085A1Simple manufacturing processLow costAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsAxis–angle representationCapacitance
The present invention relates to a z-axial solid-state gyroscope. Its main configuration is manufactured with a conductive material and includes two sets of a proof mass and two driver bodies suspended between two plates by an elastic beam assembly. Both surfaces of the driver bodies and the proof masses respectively include a number of grooves respectively perpendicular to a first axis and a second axis. The surfaces of the driver bodies and the proof masses and the corresponding stripe electrodes of the plates thereof are respectively formed a driving capacitors and a sensing capacitors. The driving capacitor drives the proof masses to vibrate in the opposite direction along the first axis. If a z-axial angular velocity input, a Coriolis force makes the two masses vibrate in the opposite direction along the second axis. If a second axial acceleration input, a specific force makes the two masses move in the same direction along the second axis. Both inertial forces make the sensing capacitances change. Two z-axial solid-state gyroscopes and two in-plane axial gyroscopes can be designed on a single chip to form a complete three-axis inertial measurement unit.
Owner:NAT CHUNG SHAN INST SCI & TECH
Method for measuring curved surface of workpiece, program and medium thereof
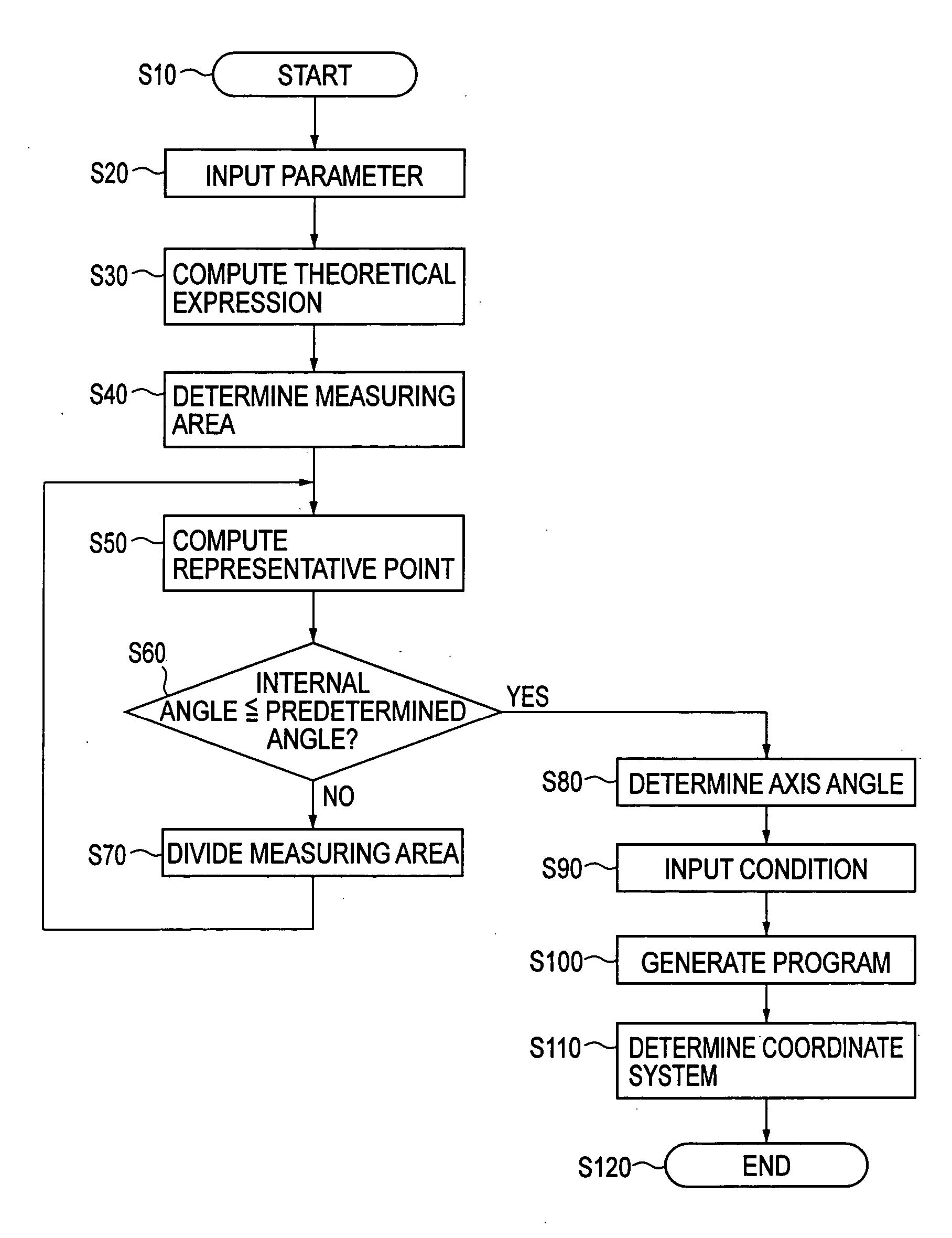
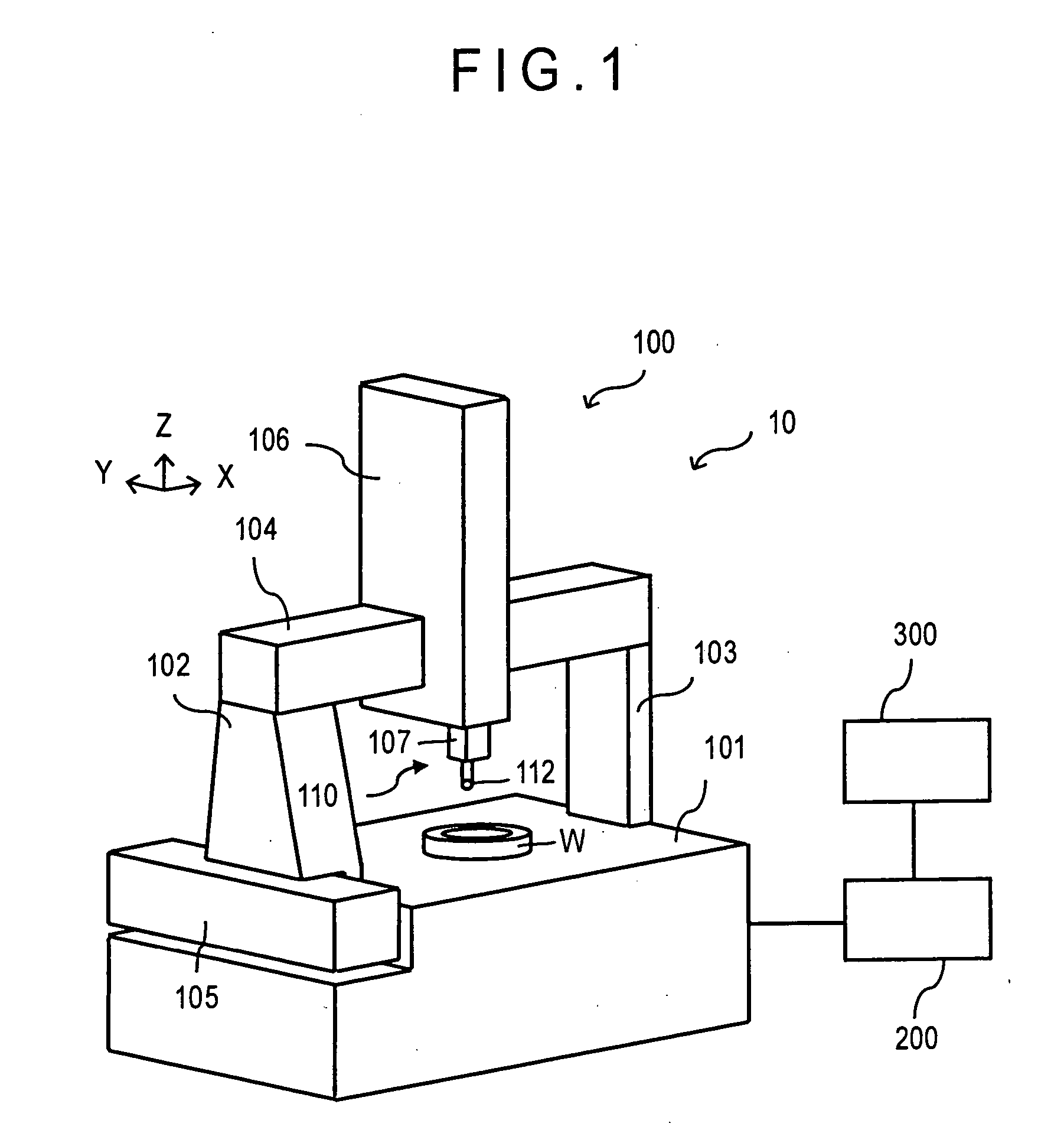
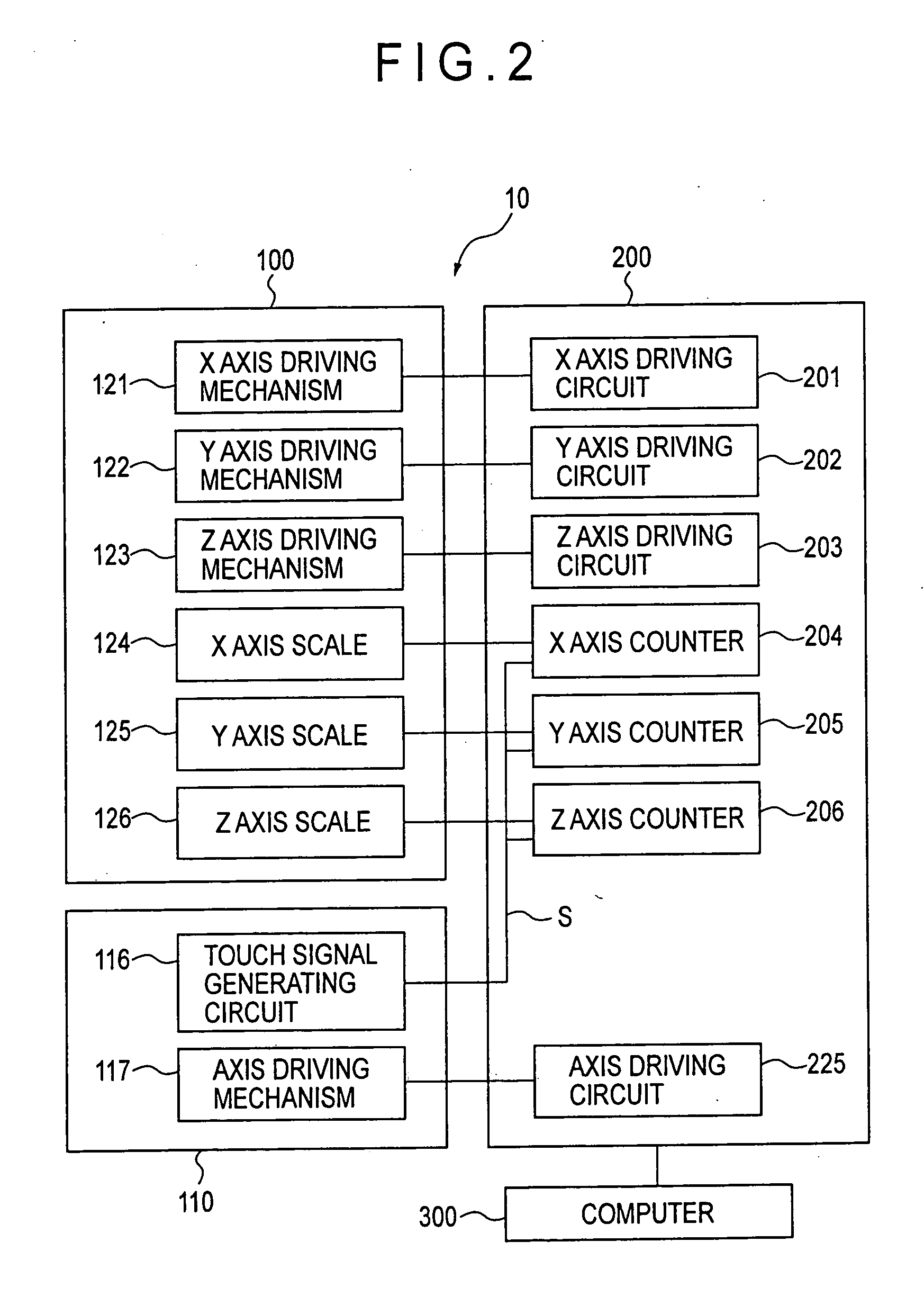
ActiveUS20050086025A1Simple calculationPromote generationFeeler-pin gaugesMechanical counters/curvatures measurementsAxis–angle representationPhysics
A theoretical expression of a workpiece (W) the curved surface of which is measured by a measuring probe (110) equipped with a stylus (111) is specified, a measuring area where the measurement is executed on the measuring surface of the workpiece (W) is determined, and the axis angles of the stylus (111) are determined based on the coordinate values and the normal vector of a representative point determined in the measuring area.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
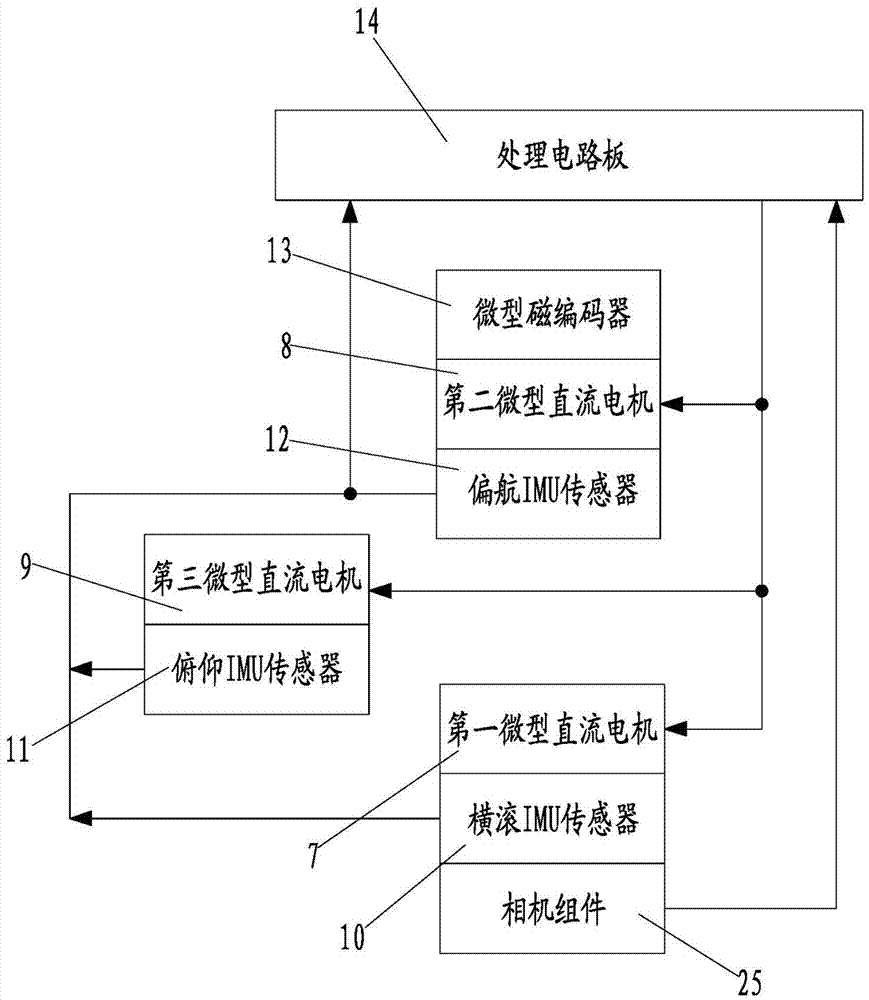
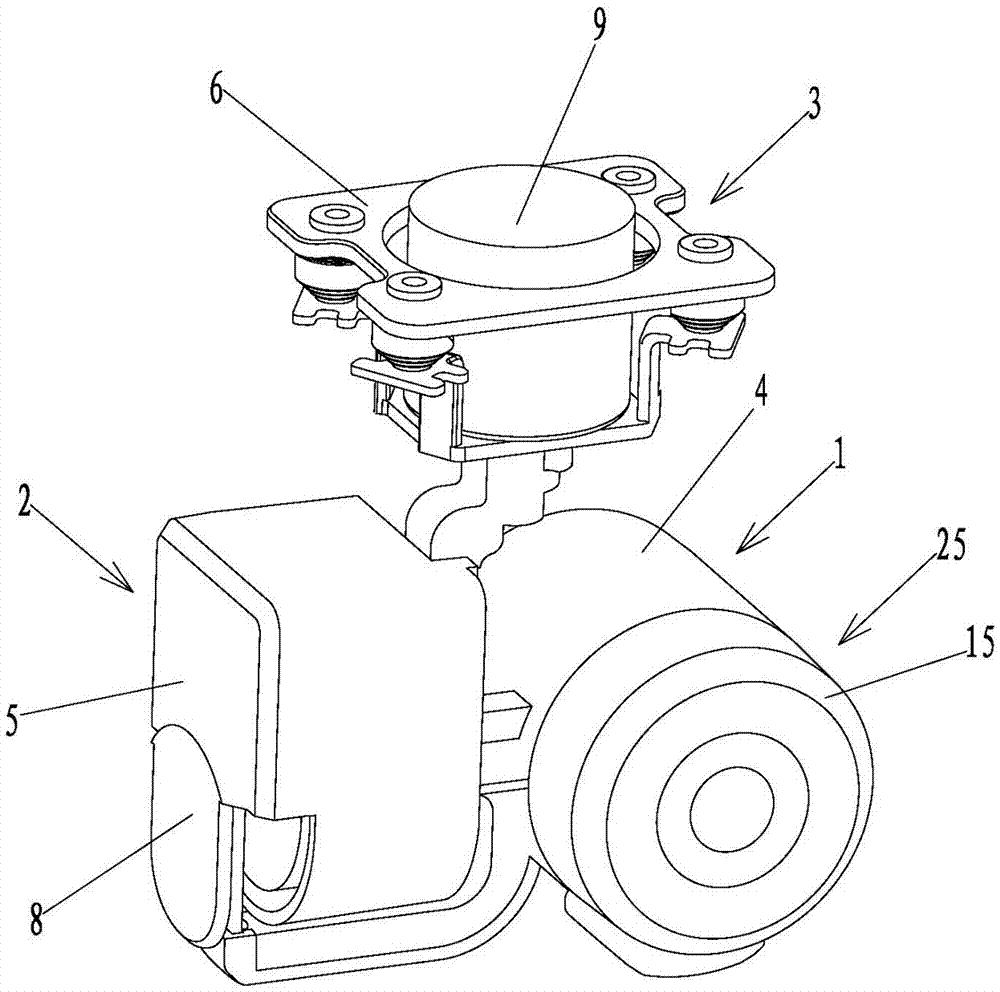
Three-axis micro pan/tilt and control method thereof
PendingCN106873641AReduce volumeSatisfied with high frequency and fast rotationControl using feedbackAxis–angle representationMiniaturization
The invention discloses a three-axis miniature pan-tilt and its control method. The miniature pan-tilt includes a roll axis assembly, a pitch axis assembly and a yaw axis assembly, and is characterized in that the roll axis assembly, the pitch axis assembly and the The yaw axis components are respectively equipped with micro DC motors and IMU sensors for collecting the angular velocity and acceleration of each axis. The three micro DC motors and the three IMU sensors are respectively electrically connected to the processing circuit device; the control method is through the processing circuit The microprocessor of the board receives the three-axis angular velocity and acceleration data collected by the three IMU sensors in real time, so as to control the rotation of the micro DC motor on the roll axis assembly and the pitch axis assembly in real time. The three-axis miniature pan / tilt of the present invention is small in size, realizes miniaturization, can be mounted on a miniature unmanned aerial vehicle or a pocket unmanned aerial vehicle, provides clear and stable video images for users, and its control mode is simple at the same time.
Owner:PRODRONE TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
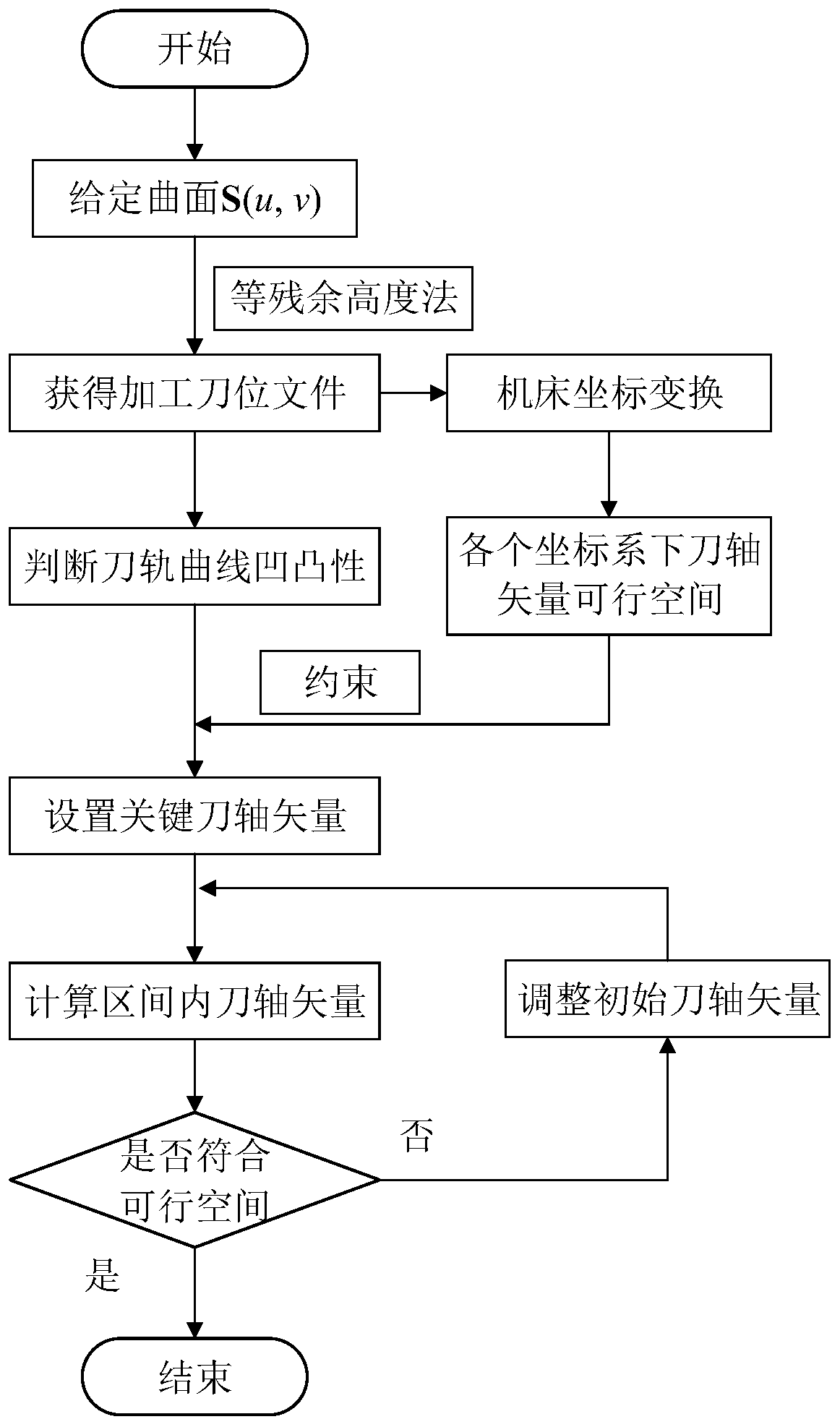
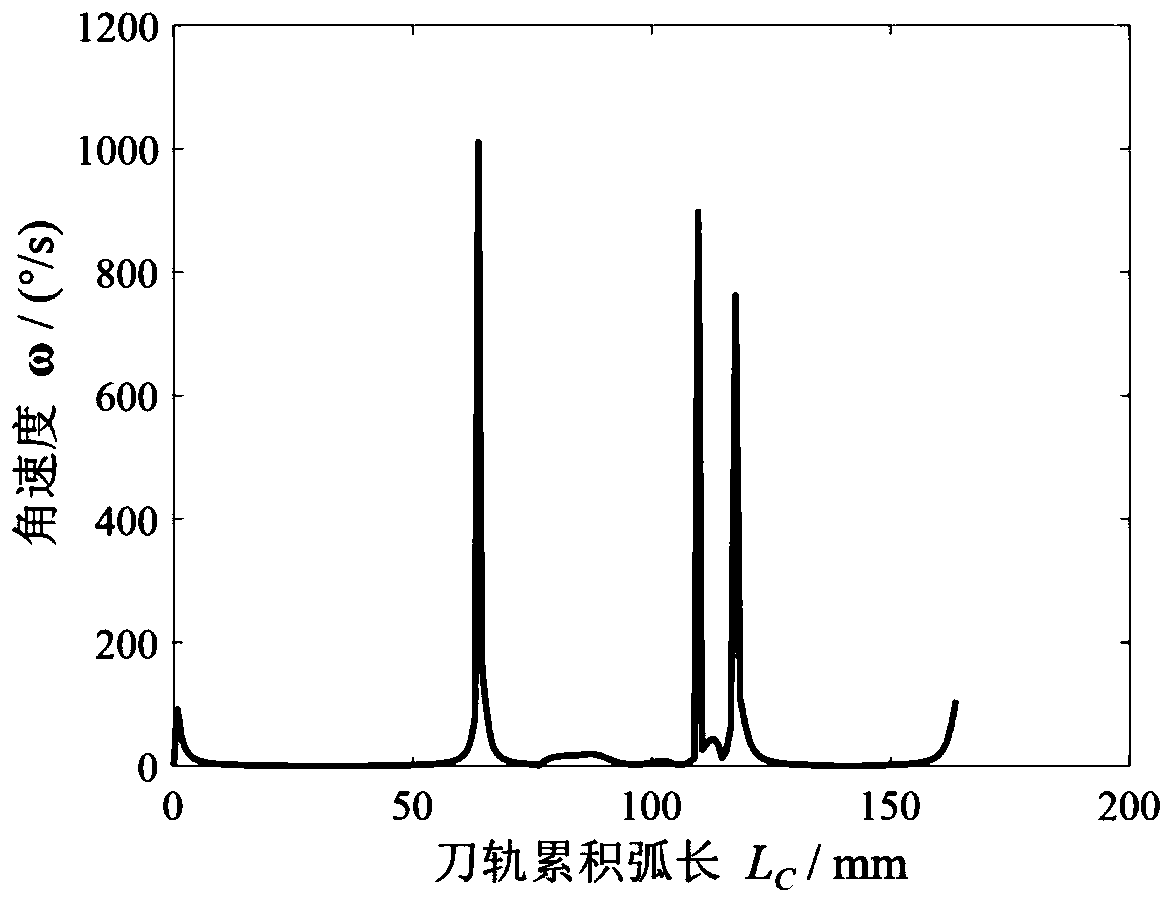
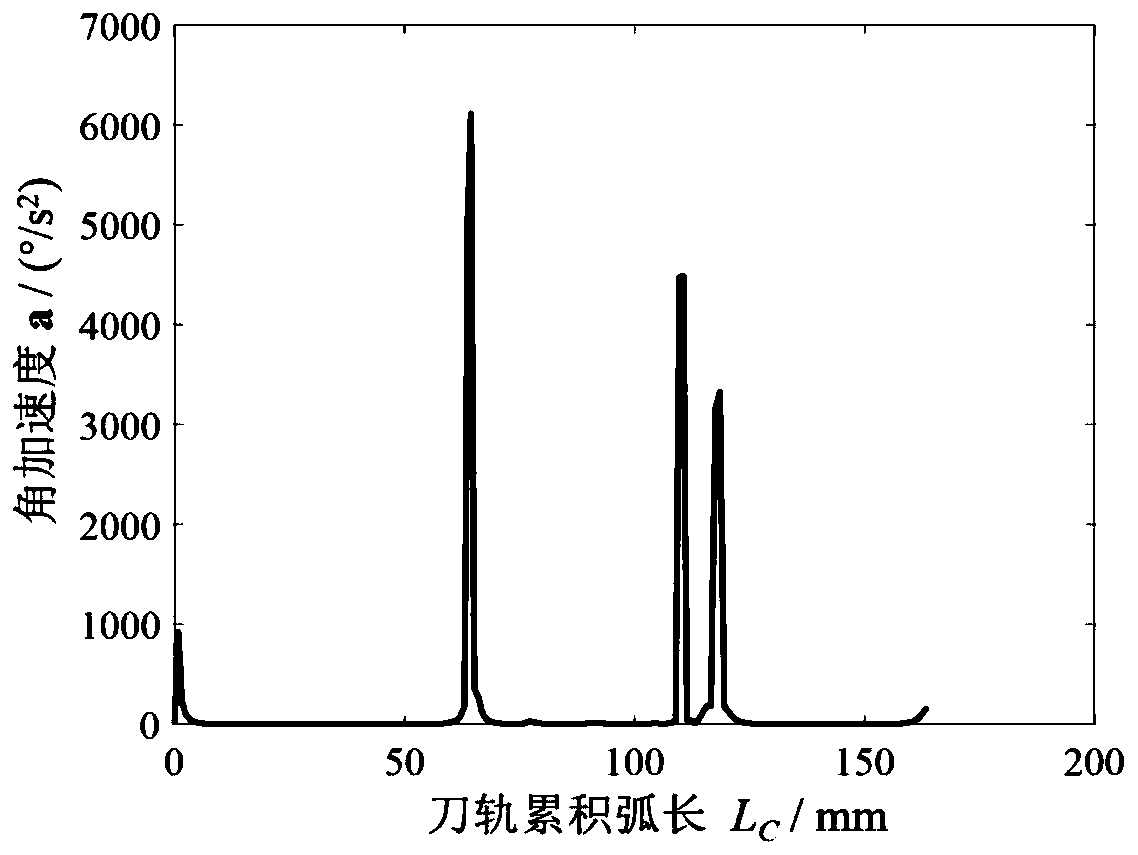
Global optimization method for cutter-axis vector based on minimum angular acceleration of machine tool rotating shaft
ActiveCN110488747AImprove machining accuracyRealize CNC machiningNumerical controlAxis–angle representationEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of high-quality and high-efficiency milling of complex curved surface parts, and relates to a global optimization method for a cutter-axis vector based onthe minimum angular acceleration of a machine tool rotating shaft. The method comprises the steps of generating a cutter track by using an equal residual height method according to the curved surfaceand cutter characteristics; establishing an inverse kinematics relation of a five-axis machine tool; converting the cutter-axis vector under the workpiece coordinate system into a rotation angle valueof rotary feeding shaft of the machine tool, calculating the angular speed and the angular acceleration of the rotary feeding shaft of the machine tool by using a finite difference method; calculating a feasible space of the cutter axis at the position of a cutter contact point by means of a C space method according to an interference judgment criterion, judging the concavity and convexity of a cutter path curve, and determining a key cutter-axis vector on the cutter path curve; and optimizing the cutter-axis vector by taking the minimum angular acceleration in each interval as an objective.The method can effectively reduce the angular acceleration of the rotary feeding shaft of the machine tool in the machining process, realize the stability of the machining process, improve the surfacemachining quality and reduce the machining contour error.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Planar 3-axis intertial measurement unit
InactiveUS20050217374A1Simple manufacturing processLow costAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsCapacitanceAxis–angle representation
The present invention relates to a z-axial solid-state gyroscope. Its main configuration is manufactured with a conductive material and includes two sets of a proof mass and two driver bodies suspended between two plates by an elastic beam assembly. Both surfaces of the driver bodies and the proof masses respectively include a number of grooves respectively perpendicular to a first axis and a second axis. The surfaces of the driver bodies and the proof masses and the corresponding stripe electrodes of the plates thereof are respectively formed a driving capacitors and a sensing capacitors. The driving capacitor drives the proof masses to vibrate in the opposite direction along the first axis. If a z-axial angular velocity input, a Coriolis force makes the two masses vibrate in the opposite direction along the second axis. If a second axial acceleration input, a specific force makes the two masses move in the same direction along the second axis. Both inertial forces make the sensing capacitances change. Two z-axial solid-state gyroscopes and two in-plane axial gyroscopes can be designed on a single chip to form a complete three-axis inertial measurement unit.
Owner:NAT CHUNG SHAN INST SCI & TECH
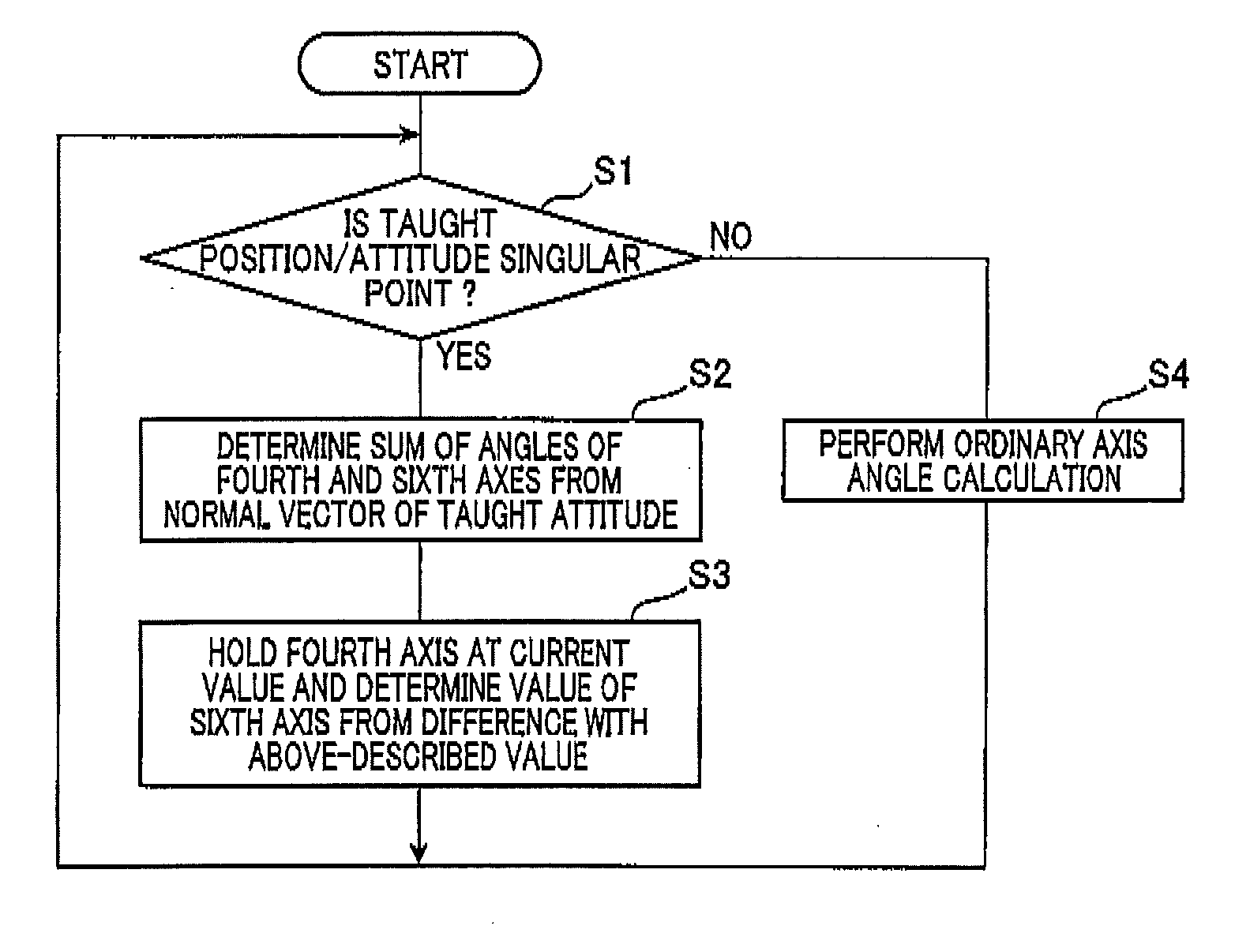
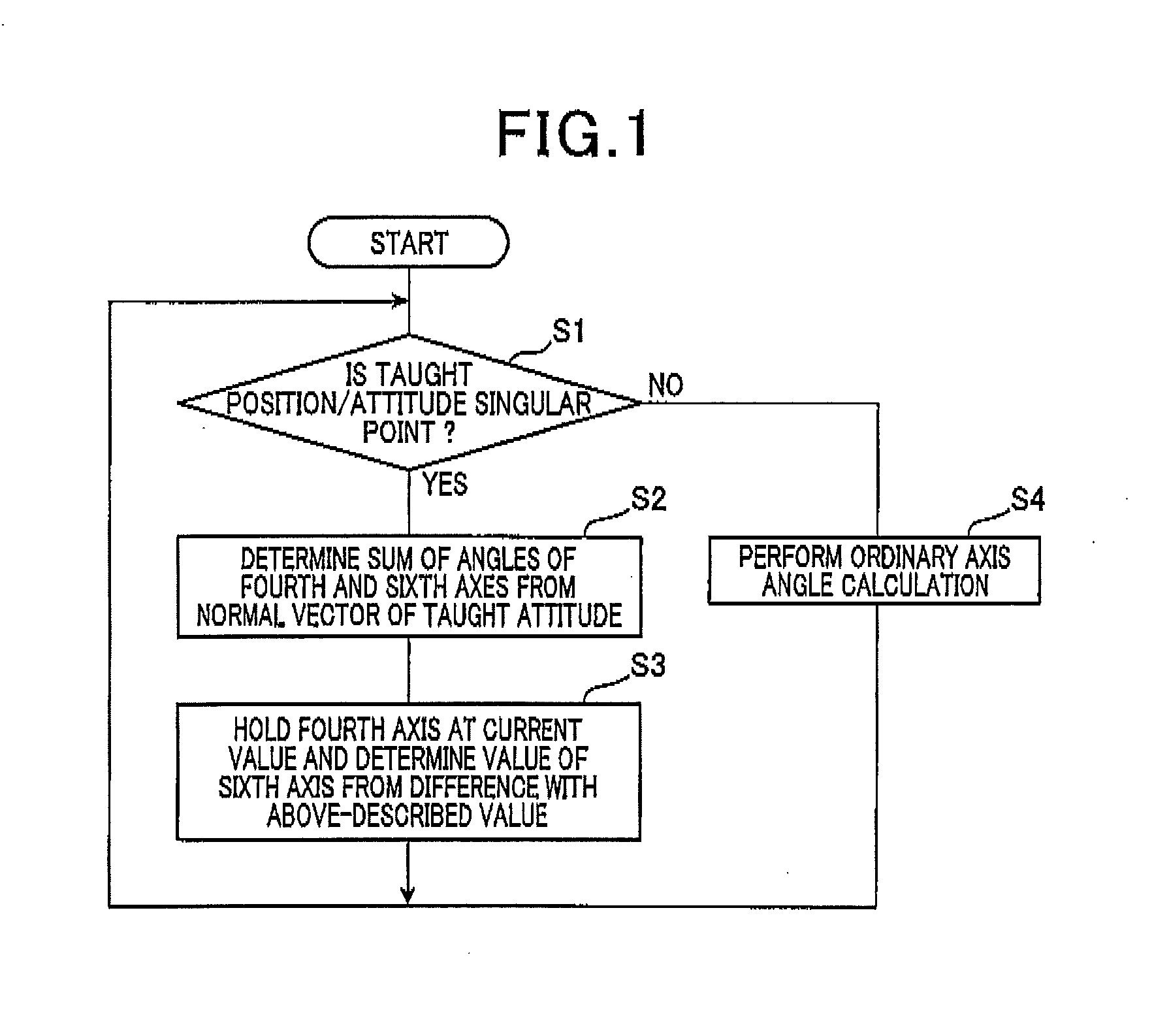
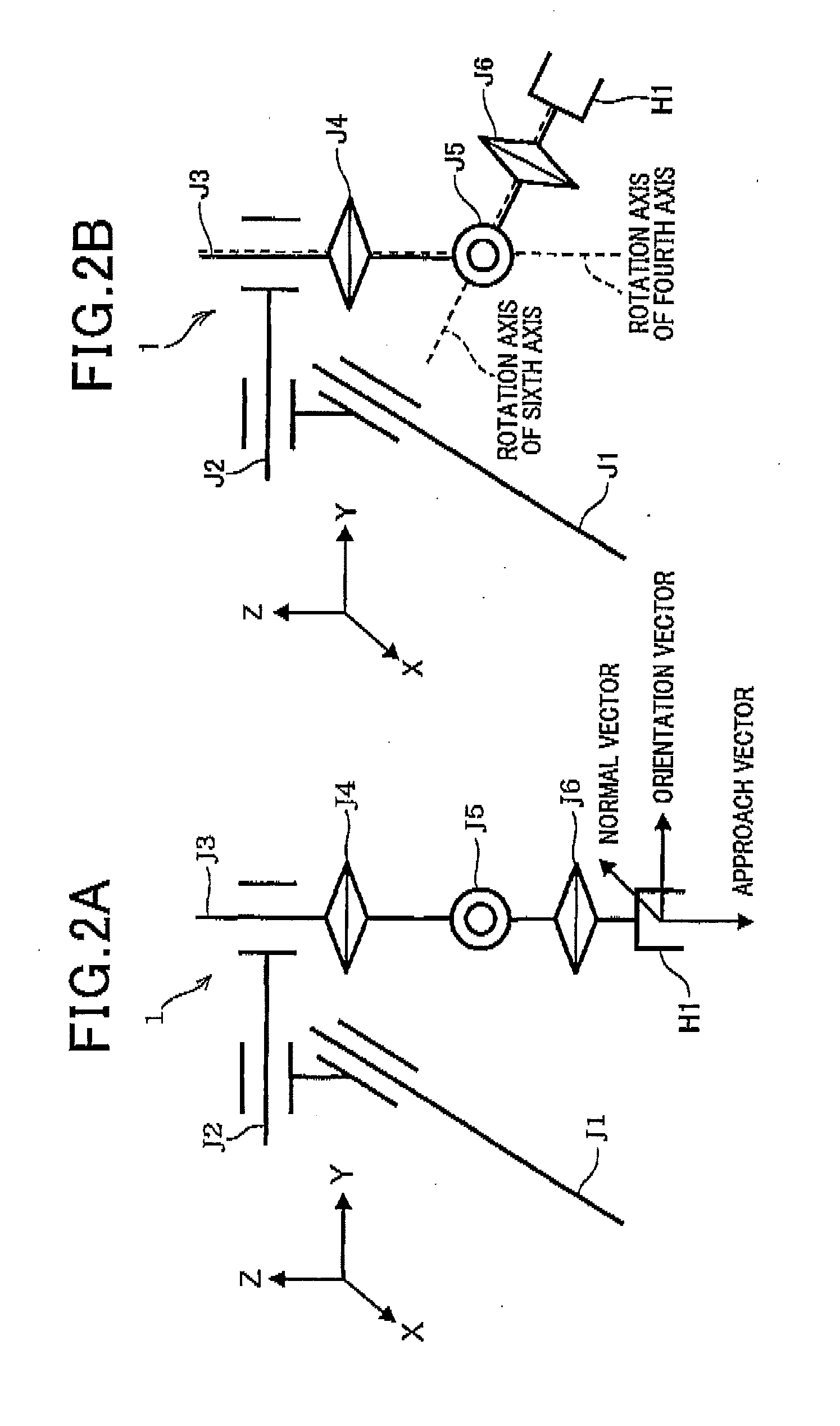
Axis angle determination method for six-axis robot and control apparatus for six-axis robot
ActiveUS20150120059A1Work load increaseIncreased work loadProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorRotational axisAxis–angle representation
In an axis angle determination method, an angle or a position of each axis of a six-axis robot is determined. The robot is capable of taking an attitude of a singular point being a state in which rotation axes of fourth and sixth axes match. Based on teaching results of a position and attitude of a hand by point-to-point teaching, the method judges whether an attitude of the robot in which the angle or the position of each angle is to be determined next is a singular point. If judged that the attitude is the singular point, angles of the fourth and sixth axes required for the six-axis robot to move to the singular point are determined such that an angle of one of the fourth and sixth axes is fixed to a current value and an angle of the other axis is determined based on the fixed angle.
Owner:DENSO WAVE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com