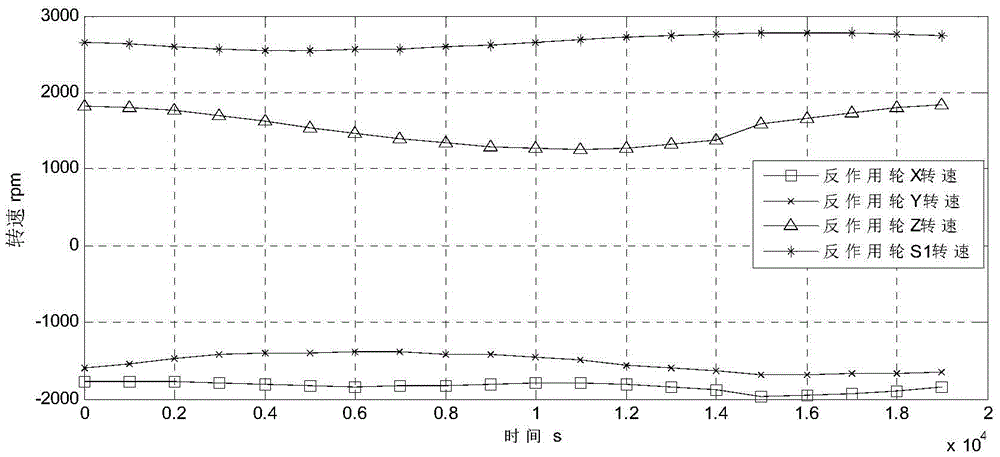
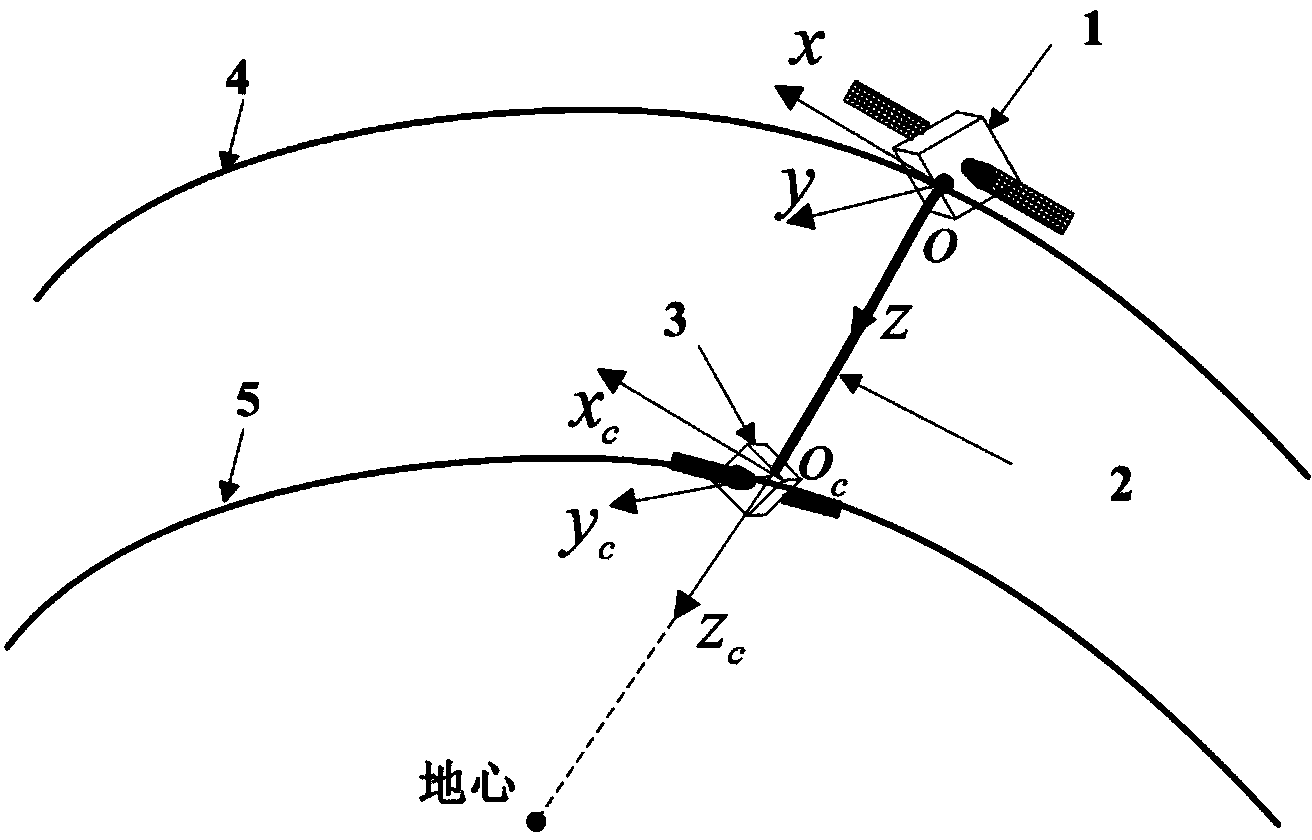
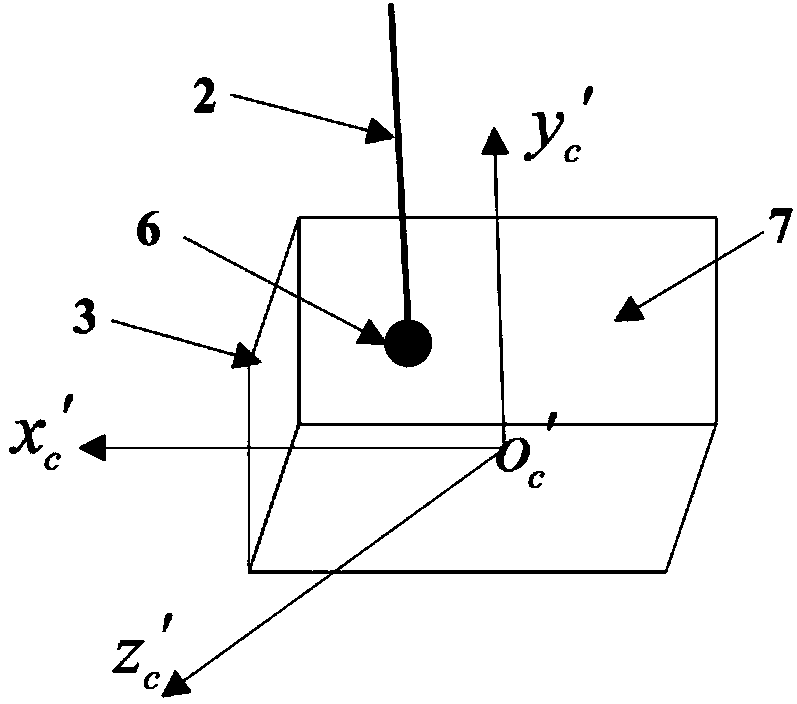
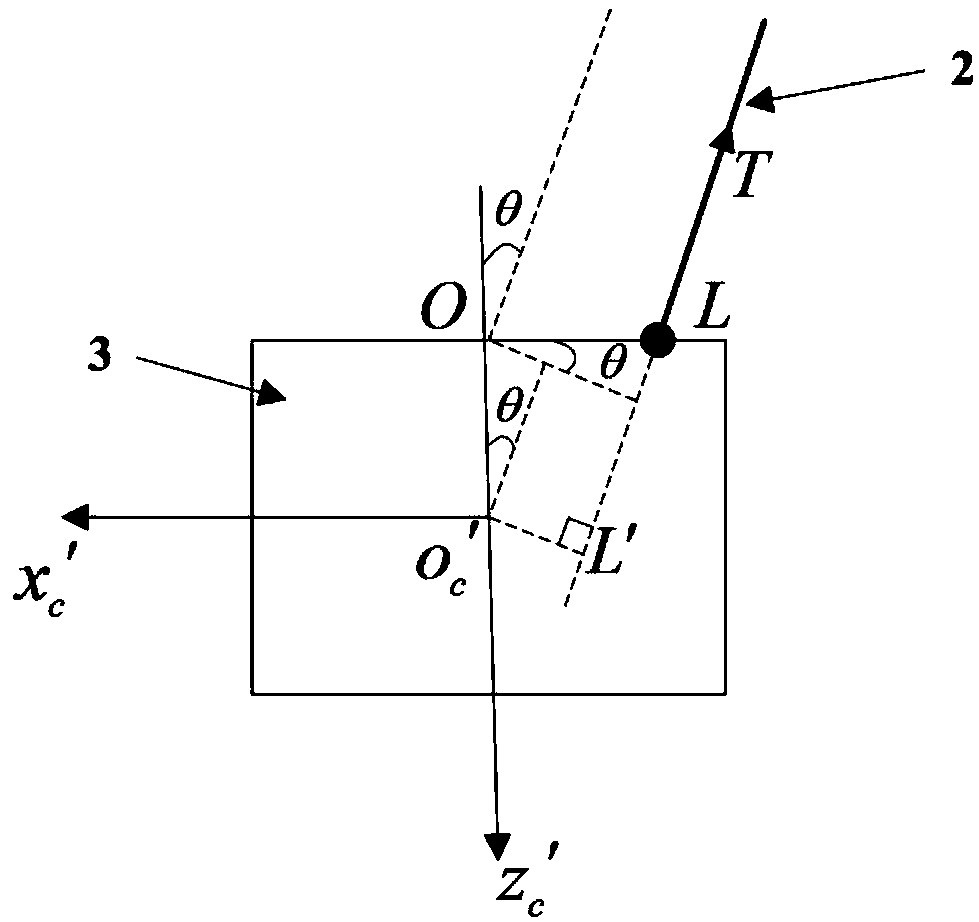
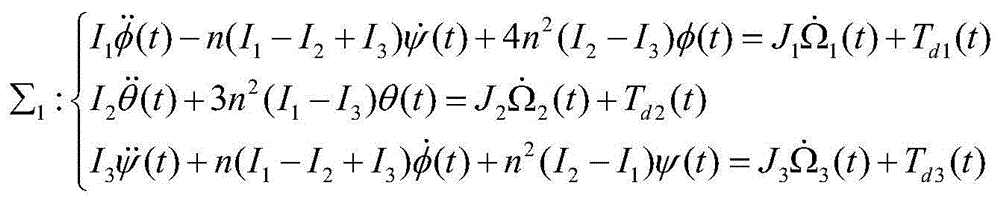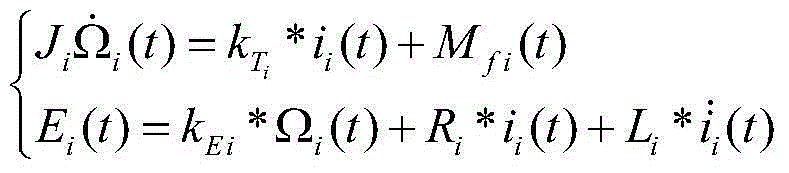Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
112 results about "Reaction wheel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A reaction wheel (RW) is a type of flywheel used primarily by spacecraft for three axis attitude control, which does not require rockets or external applicators of torque. They provide a high pointing accuracy, and are particularly useful when the spacecraft must be rotated by very small amounts, such as keeping a telescope pointed at a star.
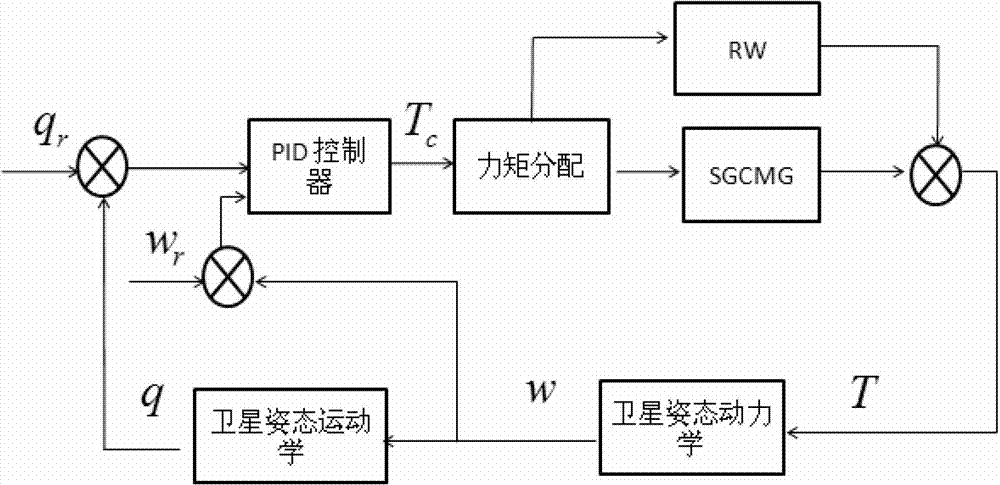
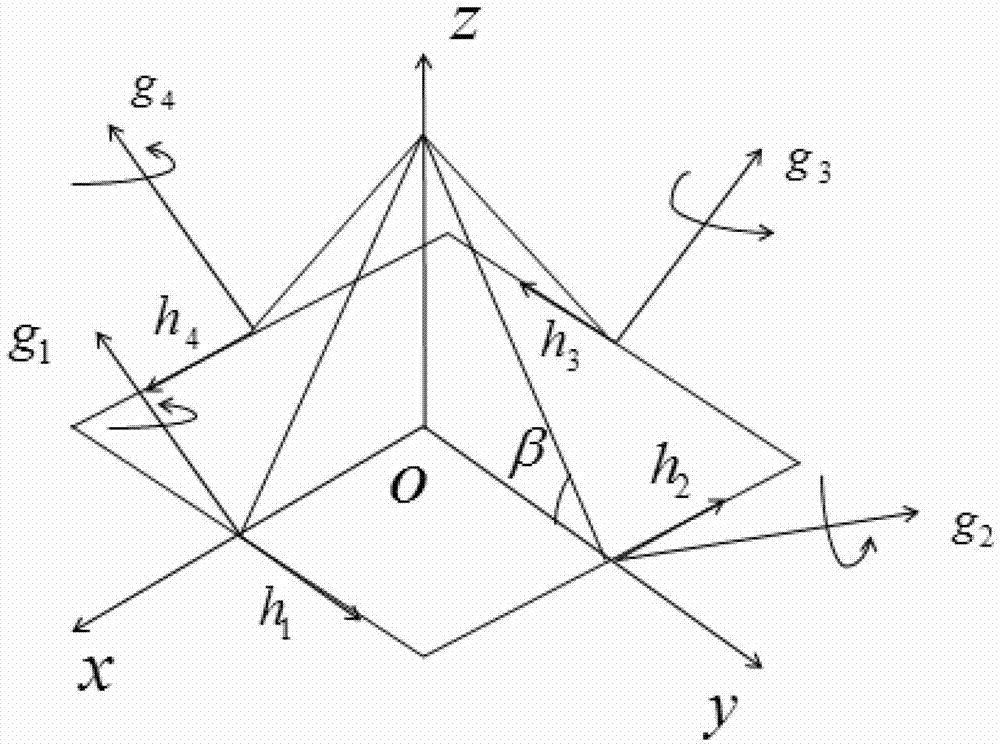
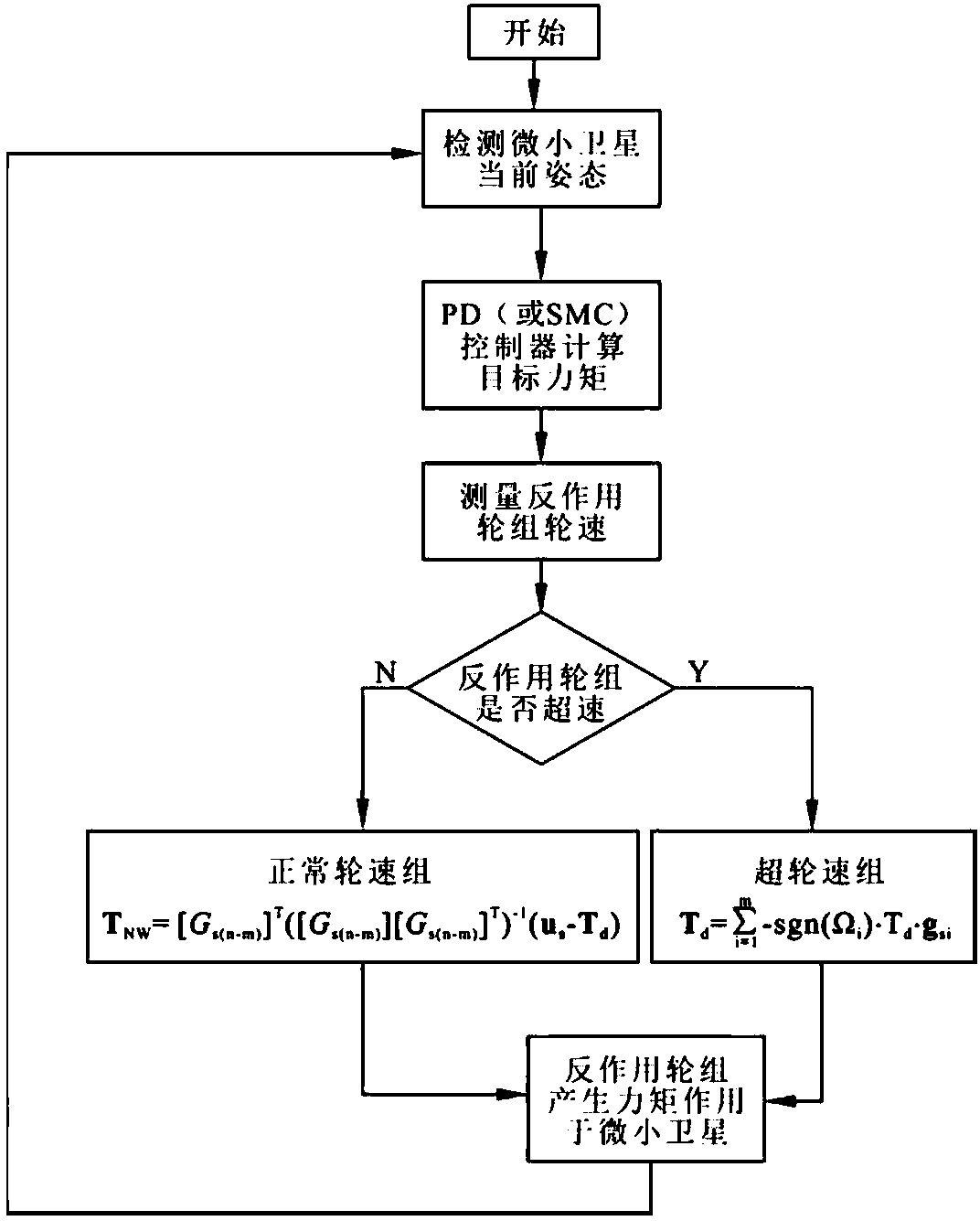
Spacecraft high-accuracy speediness attitude maneuver method based on single gimbal control moment gyro (SGCMG) and reaction wheel (RW)
ActiveCN103092208AHigh precisionReduce maneuvering timeAttitude controlAdaptive controlEngineeringFlywheel
The invention discloses a spacecraft high-accuracy speediness attitude maneuver method based on a single gimbal control moment gyro (SGCMG) and a reaction wheel (RW) and relates to a spacecraft high-accuracy speediness attitude maneuver method which is used for achieving spacecraft high-accuracy speediness attitude maneuver. According to the method, a control moment gyro (CMG) and the RW are used as a combination executing mechanism to achieve the spacecraft high-accuracy speediness attitude maneuver. Angular speed of winding around an Euler main shaft is divided into three sections. Needed controlling torque is generated through the CMG in an accelerating section and a braking section. After a constant speed section and the braking section are finished, a compensate torque generated by the RW is adopted to guarantee that the angular speed is kept near a steady state value so that the spacecraft high-accuracy speediness attitude maneuver is achieved. The method is suitable for the attitude maneuver condition that a spacecraft is provided with the CMG and the RW so that rapid maneuver of the spacecraft is achieved and attitude directing in high accuracy and stability are guaranteed. The method is suitable for maneuver control of the spacecraft.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
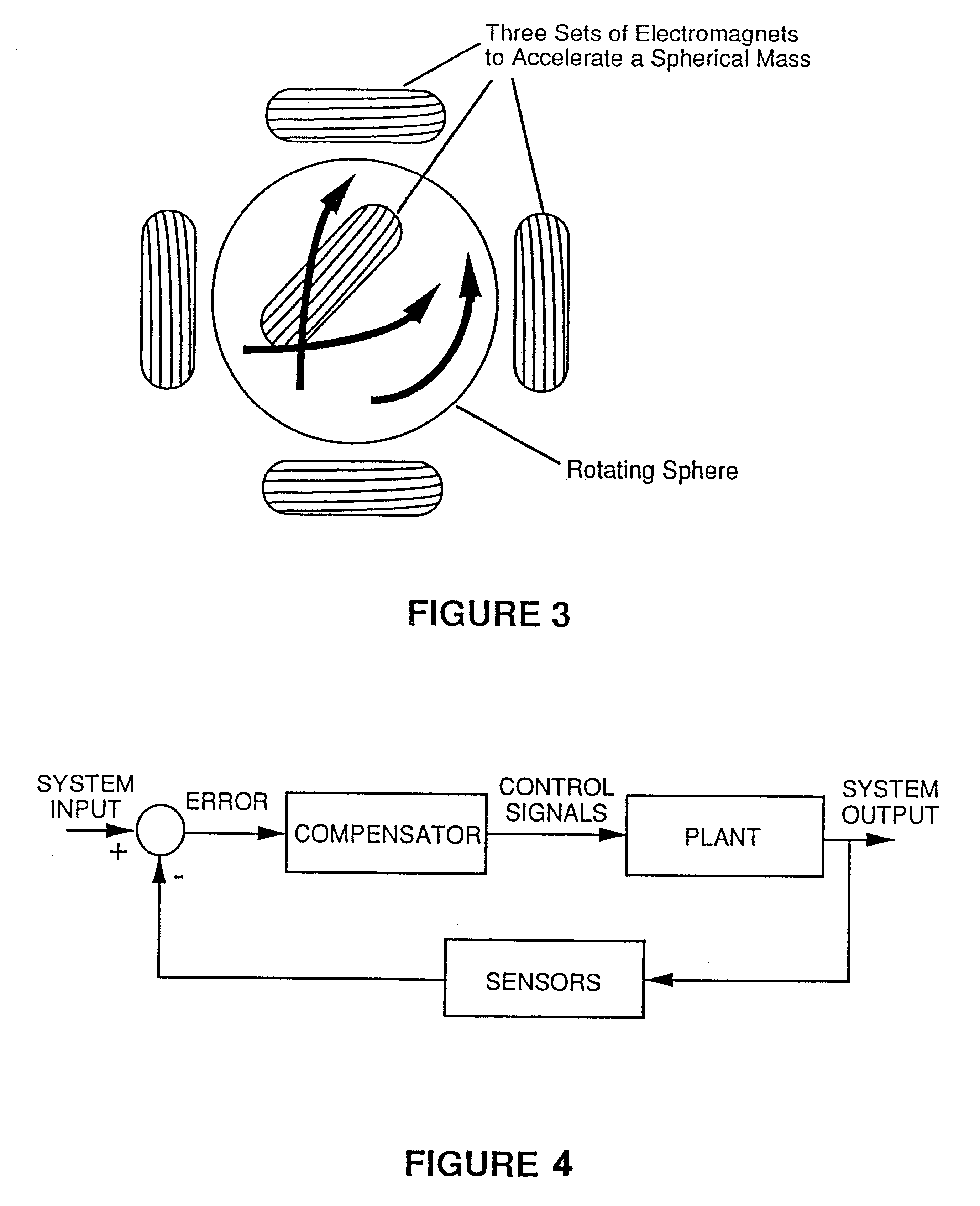
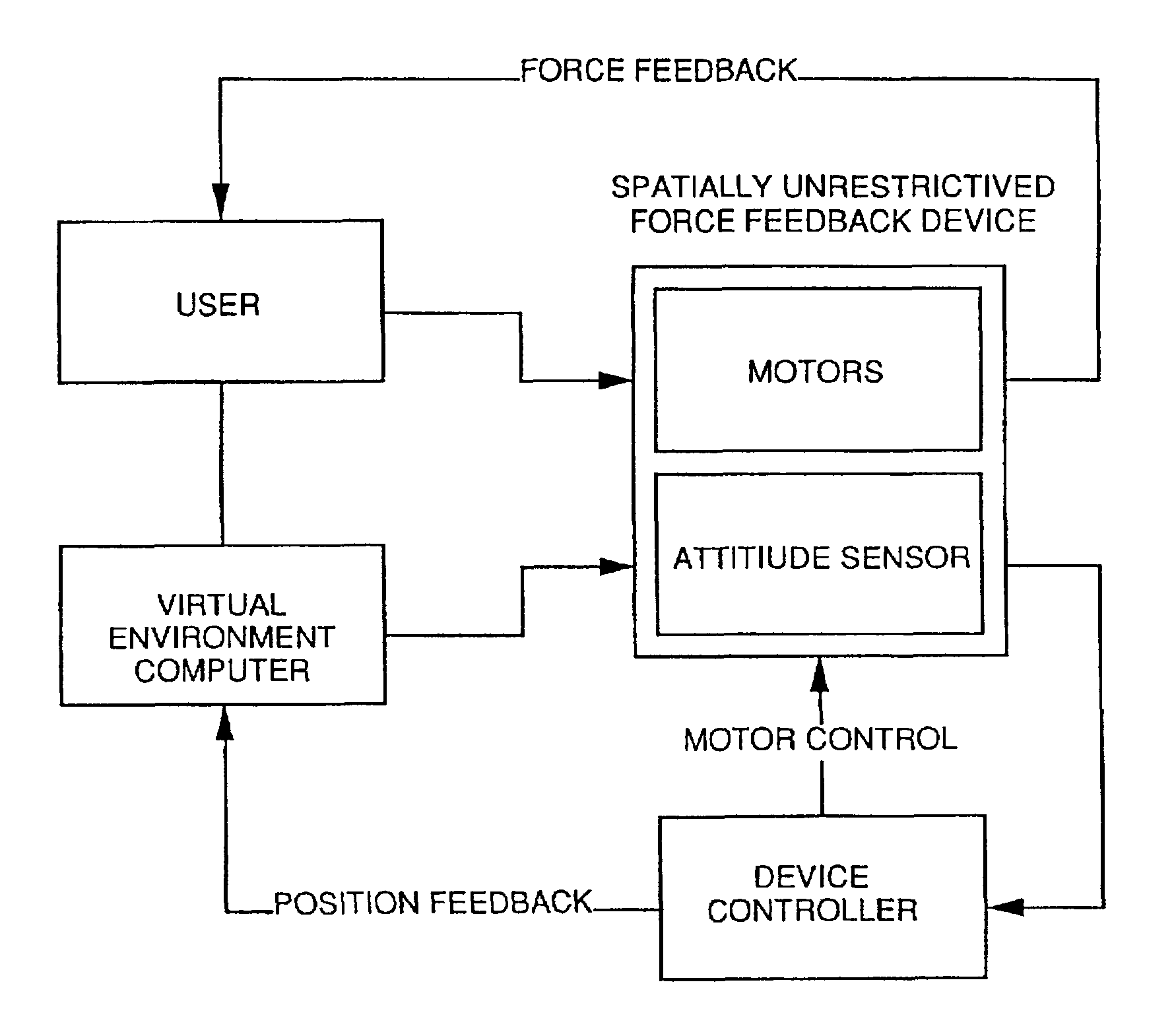
Gyro-stabilized platforms for force-feedback applications
InactiveUSRE37374E1Input/output for user-computer interactionProgramme-controlled manipulatorJoystickGyroscope
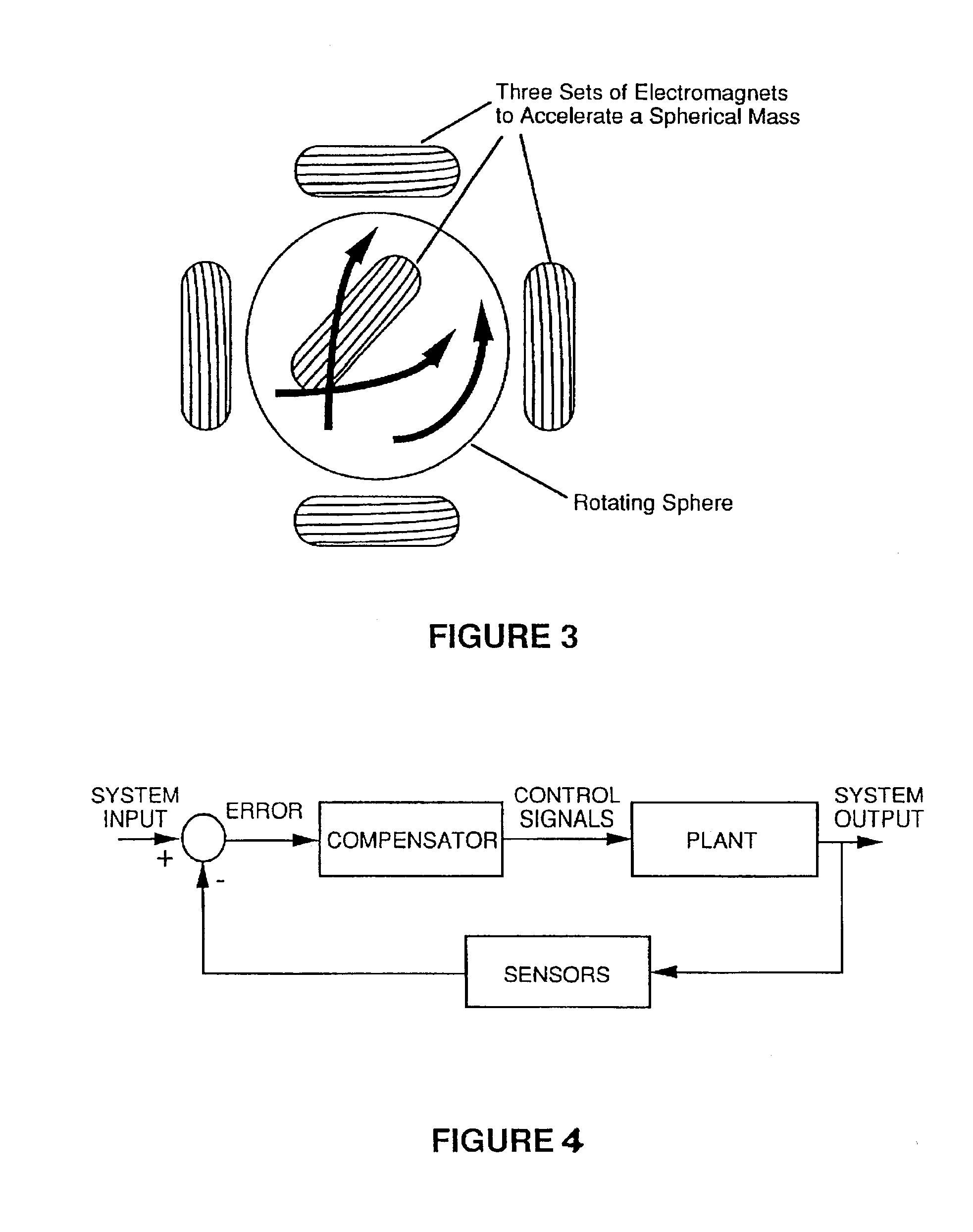
Force feedback in large, immersive environments is provided by device which a gyro-stabilization to generate a fixed point of leverage for the requisite forces and / or torques. In one embodiment, one or more orthogonally oriented rotating gyroscopes are used to provide a stable platform to which a force-reflecting device can be mounted, thereby coupling reaction forces to a user without the need for connection to a fixed frame. In one physical realization, a rigid handle or joystick is directly connected to the three-axis stabilized platform and using an inventive control scheme to modulate motor torques so that only the desired forces are felt. In an alternative embodiment, a reaction sphere is used to produce the requisite inertial stabilization. Since the sphere is capable of providing controlled torques about three arbitrary, linearly independent axes, it can be used in place of three reaction wheels to provide three-axis stabilization for a variety of space-based and terrestrial applications.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
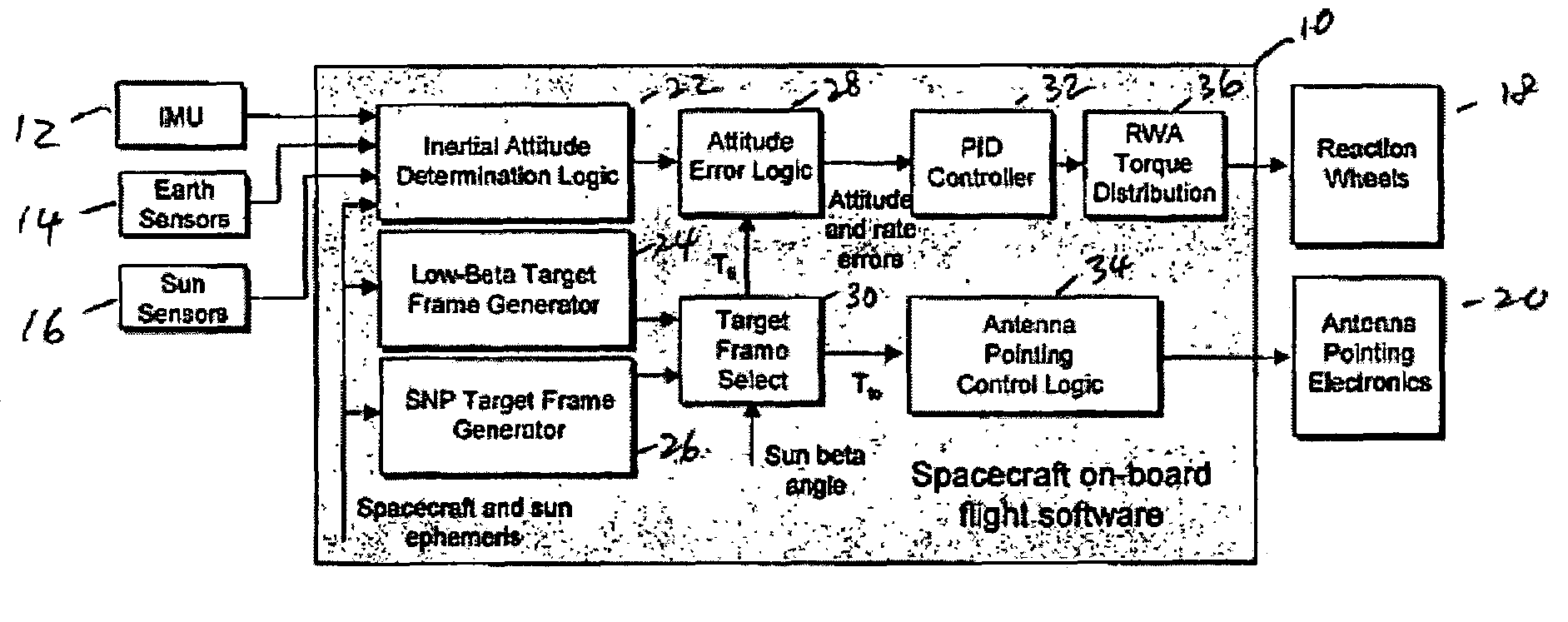
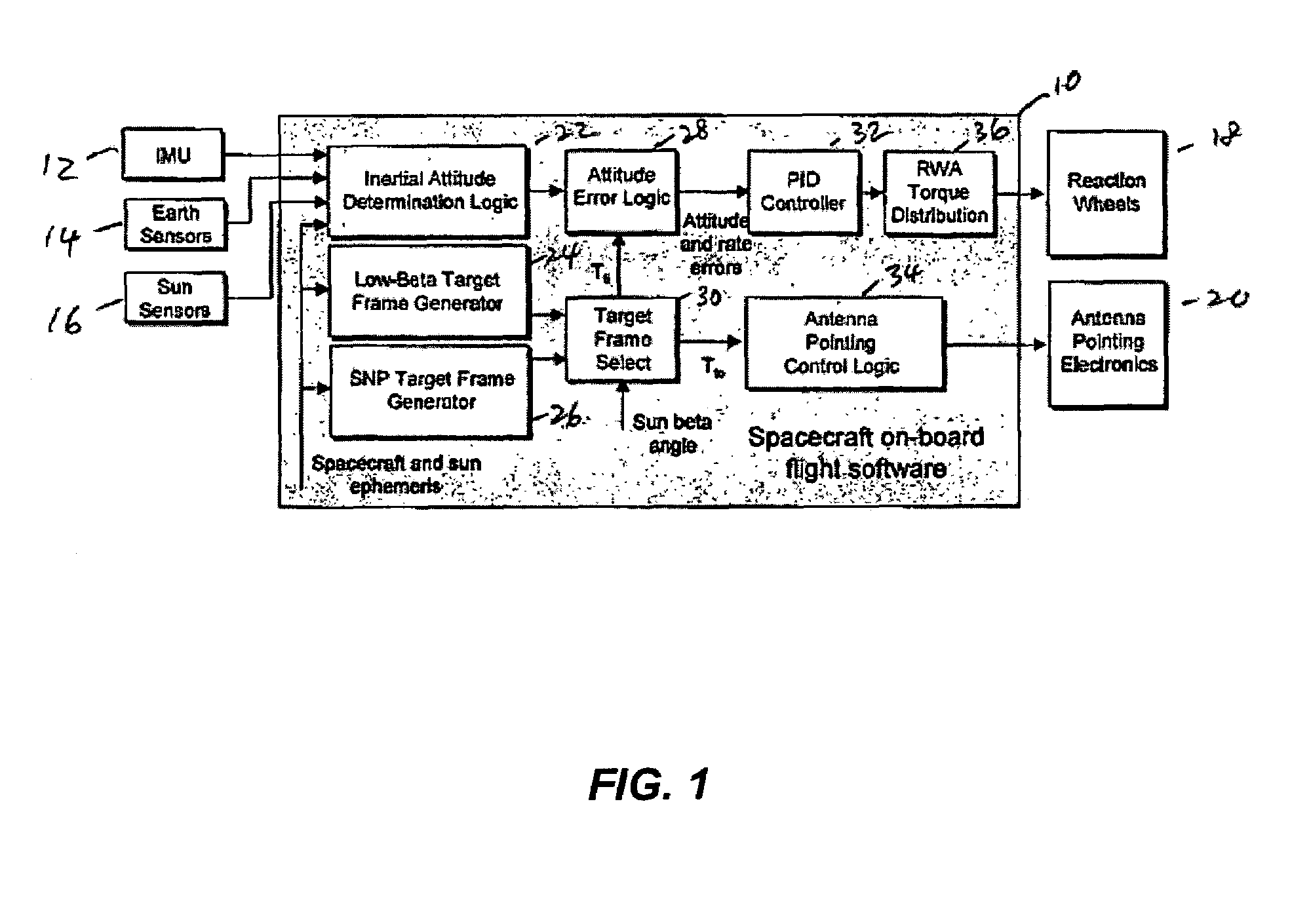
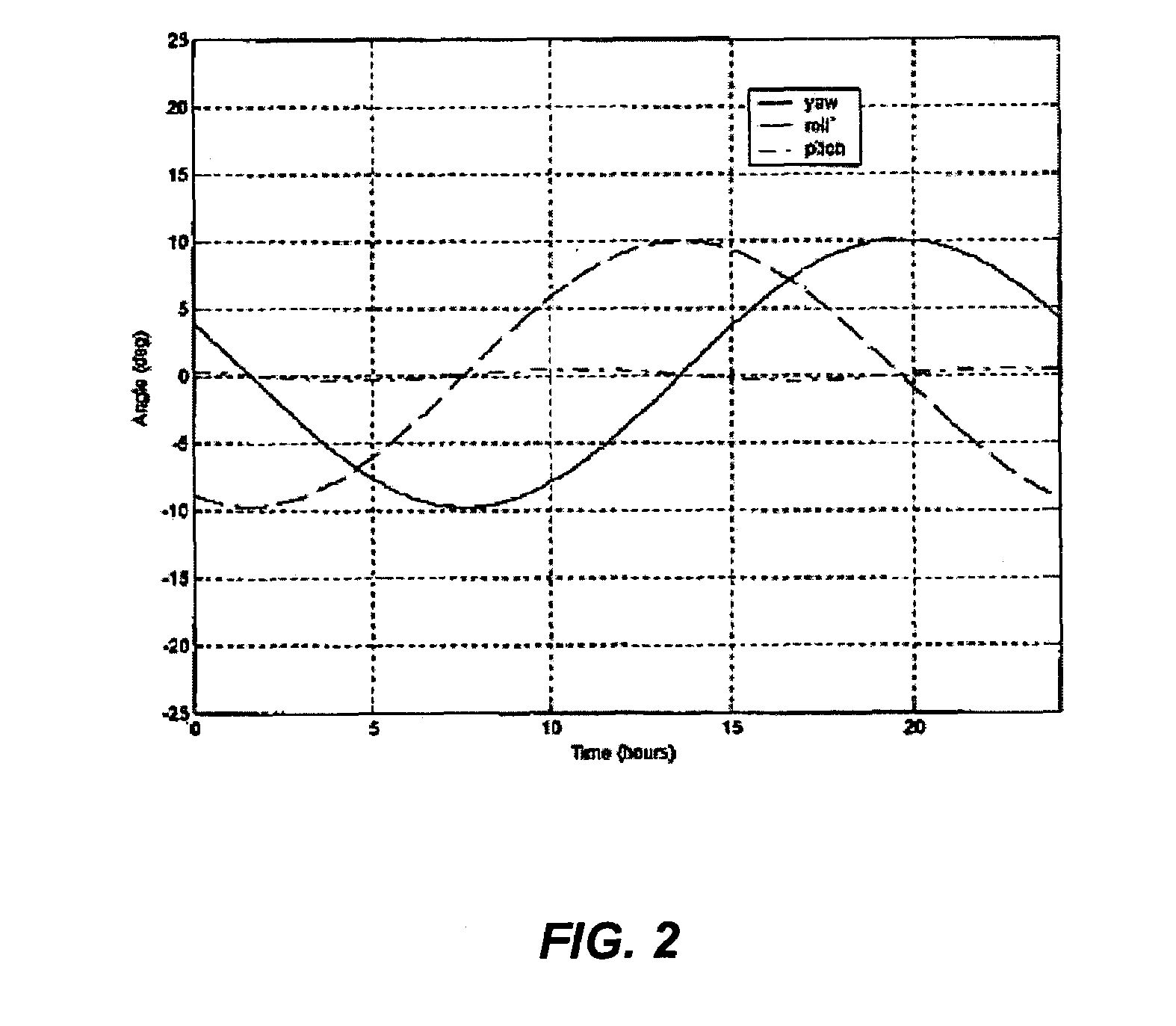
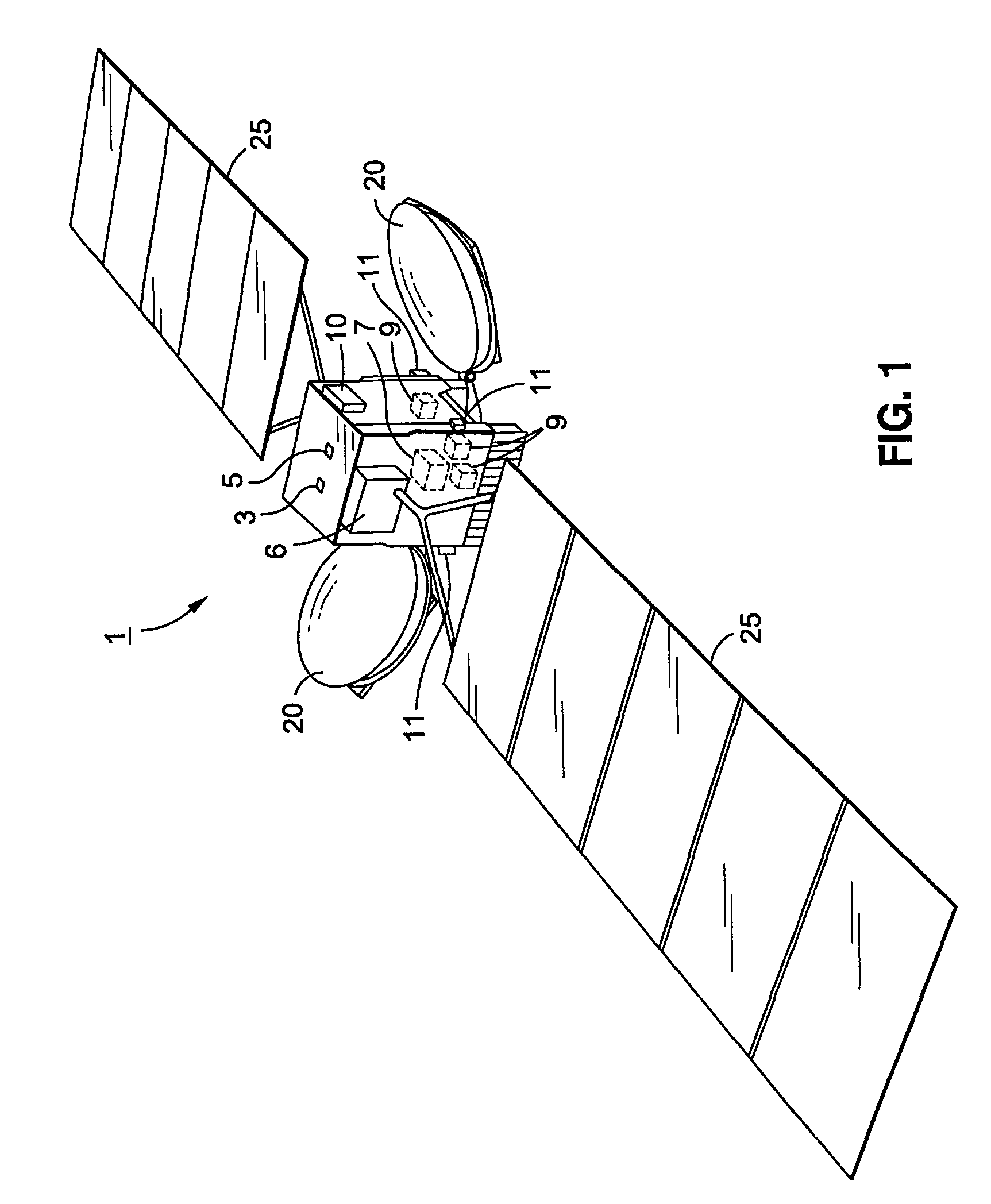
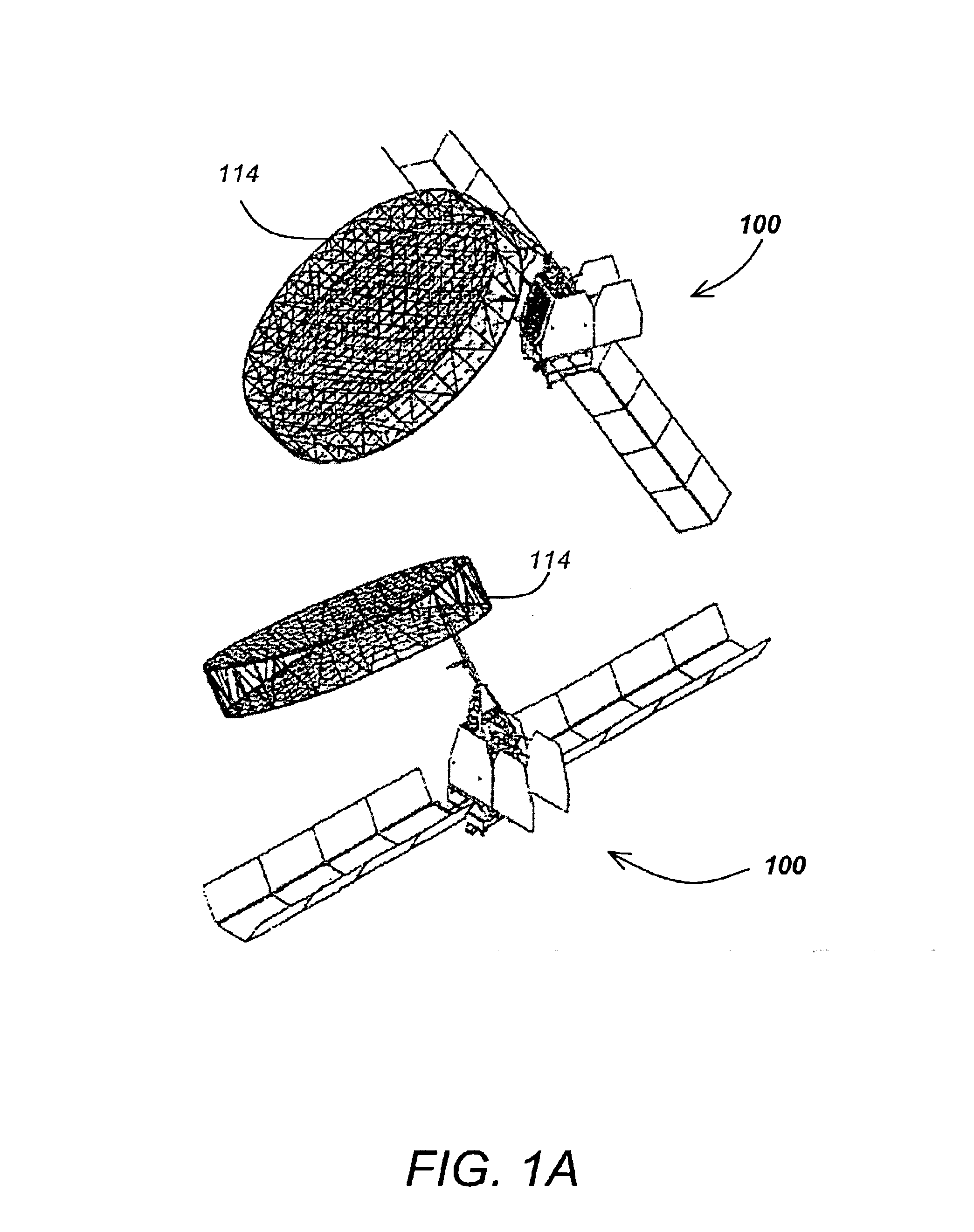
Attitude and antenna steering system for geosynchronous earth orbit (GEO) spacecraft
ActiveUS7357356B1High rateLarge rotation angleCosmonautic vehiclesRadio transmissionBeta angleGeosynchronous orbit
A system for providing attitude and antenna steering for a spacecraft is disclosed. The spacecraft has a number of reaction wheels and a number of antennas. The system includes control logic configured to: determine a beta angle, the beta angle being the angle between a sun vector and an orbit plane of the spacecraft, and alternately engage either a first mode or a second mode to provide attitude and antenna steering based on the beta angle.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
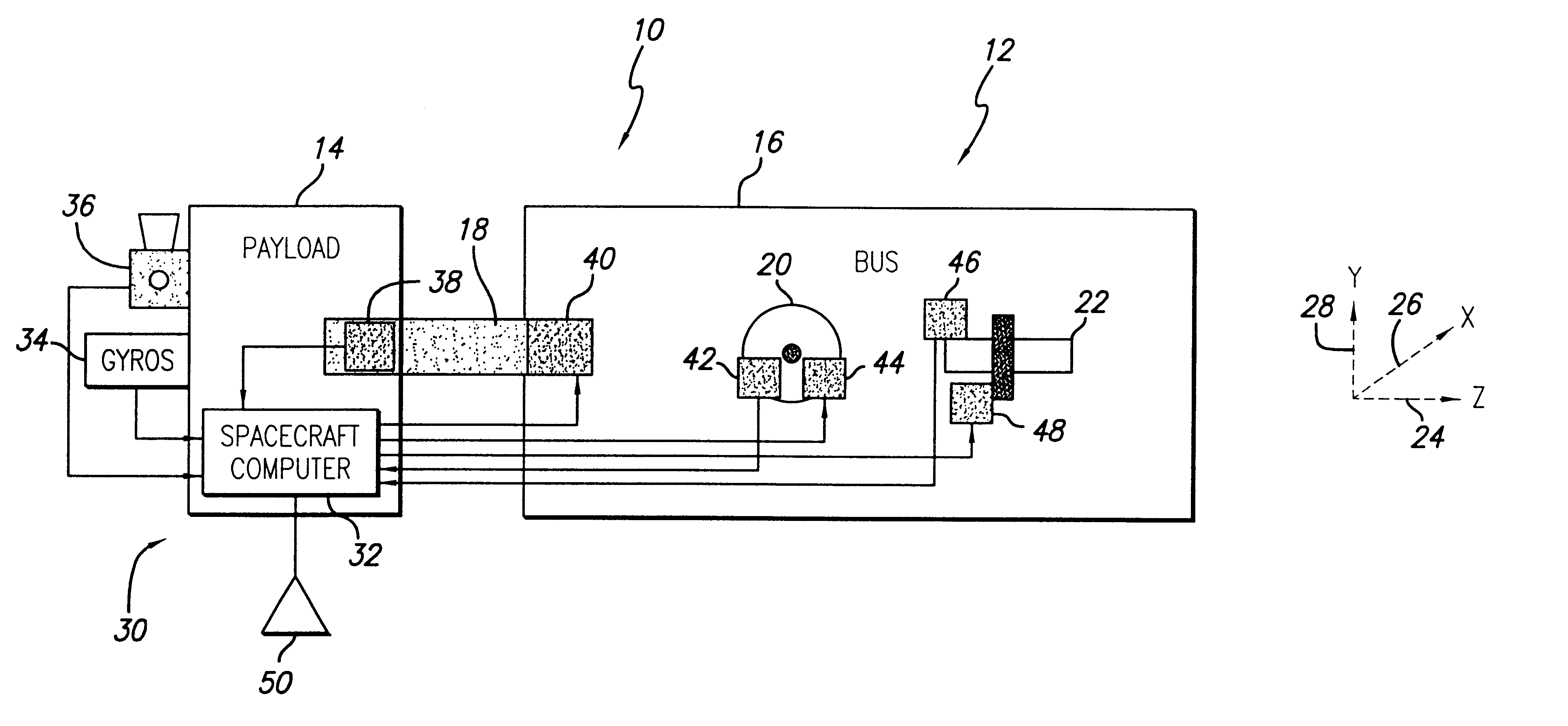
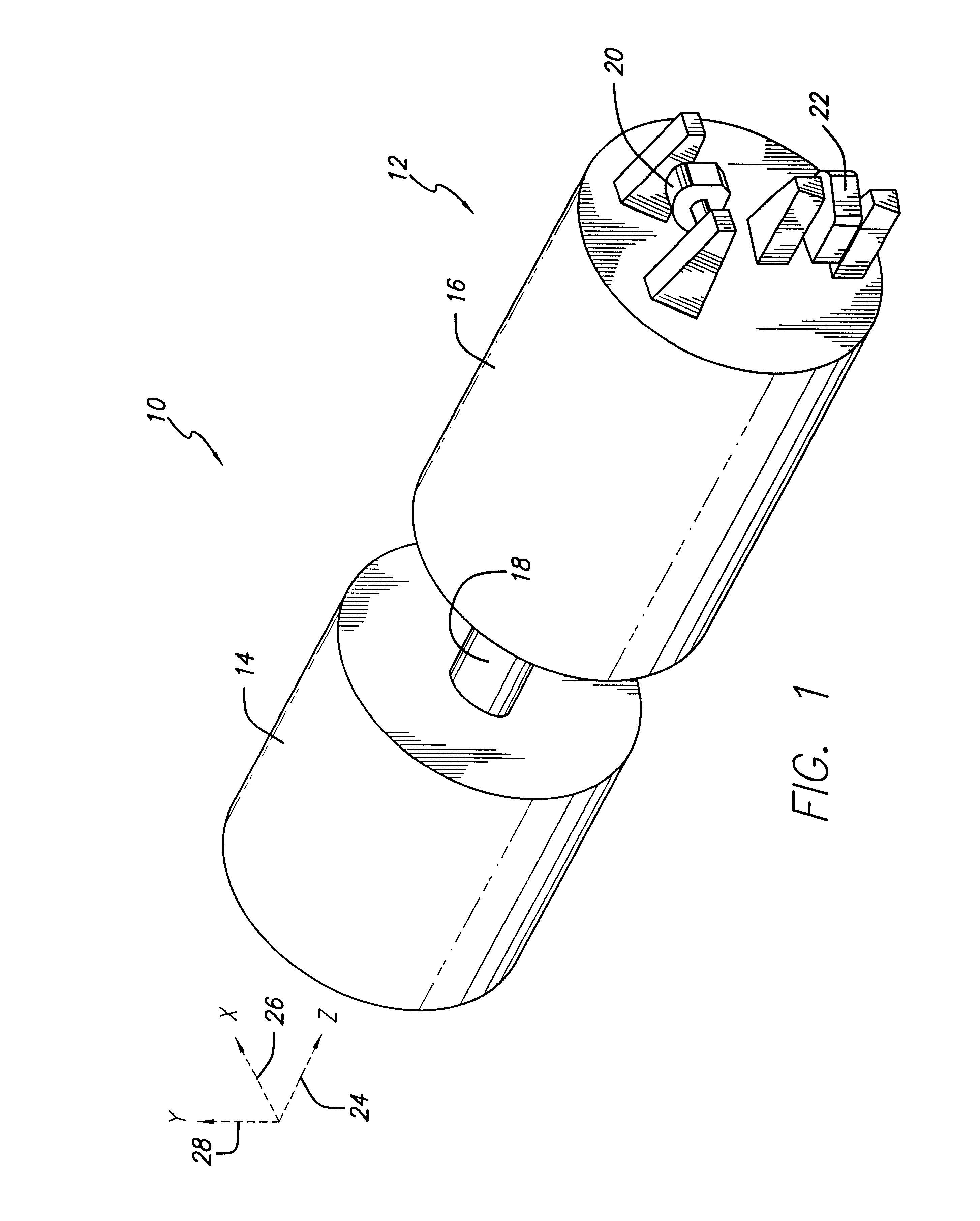
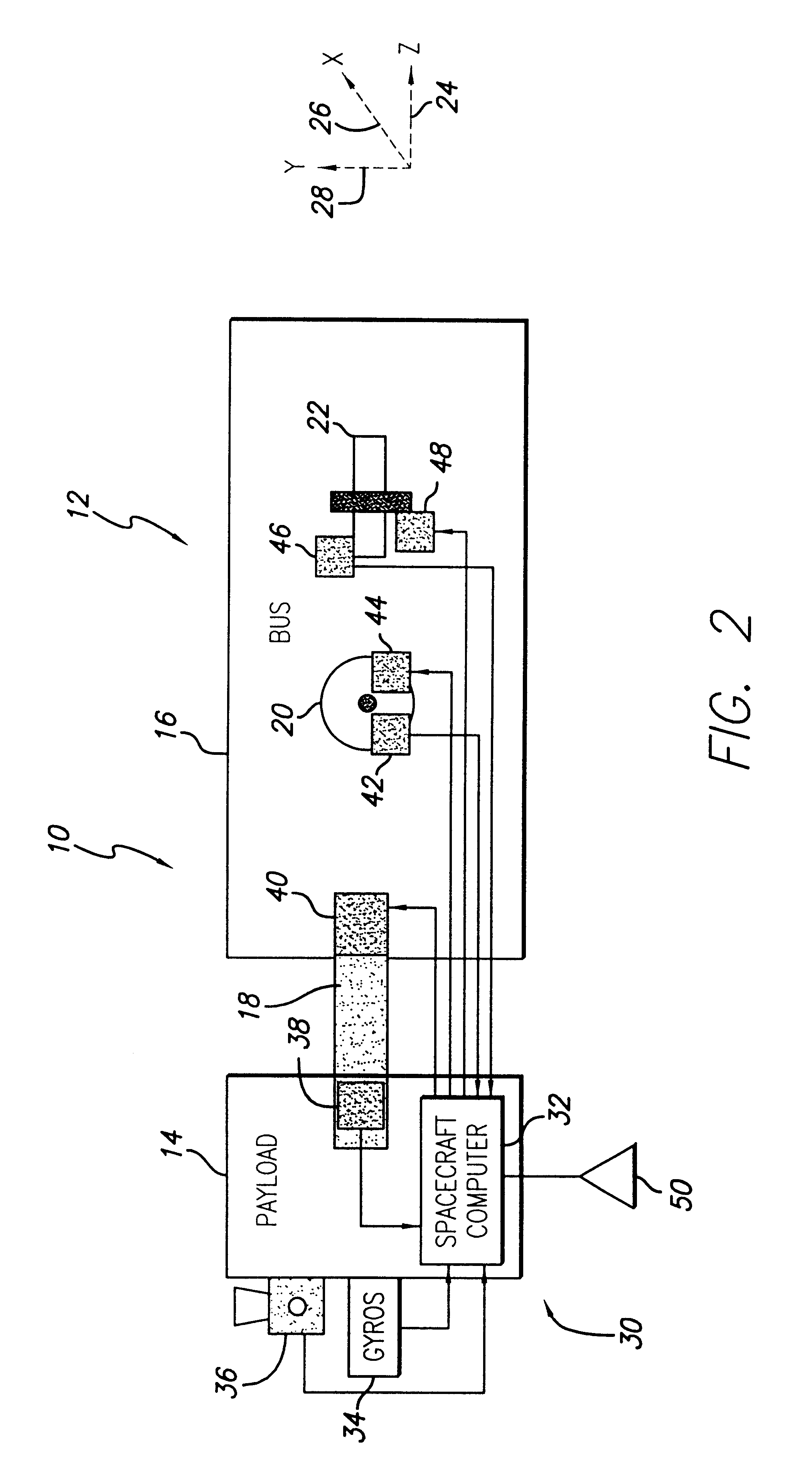
System and method for controlling the attitude of a space craft
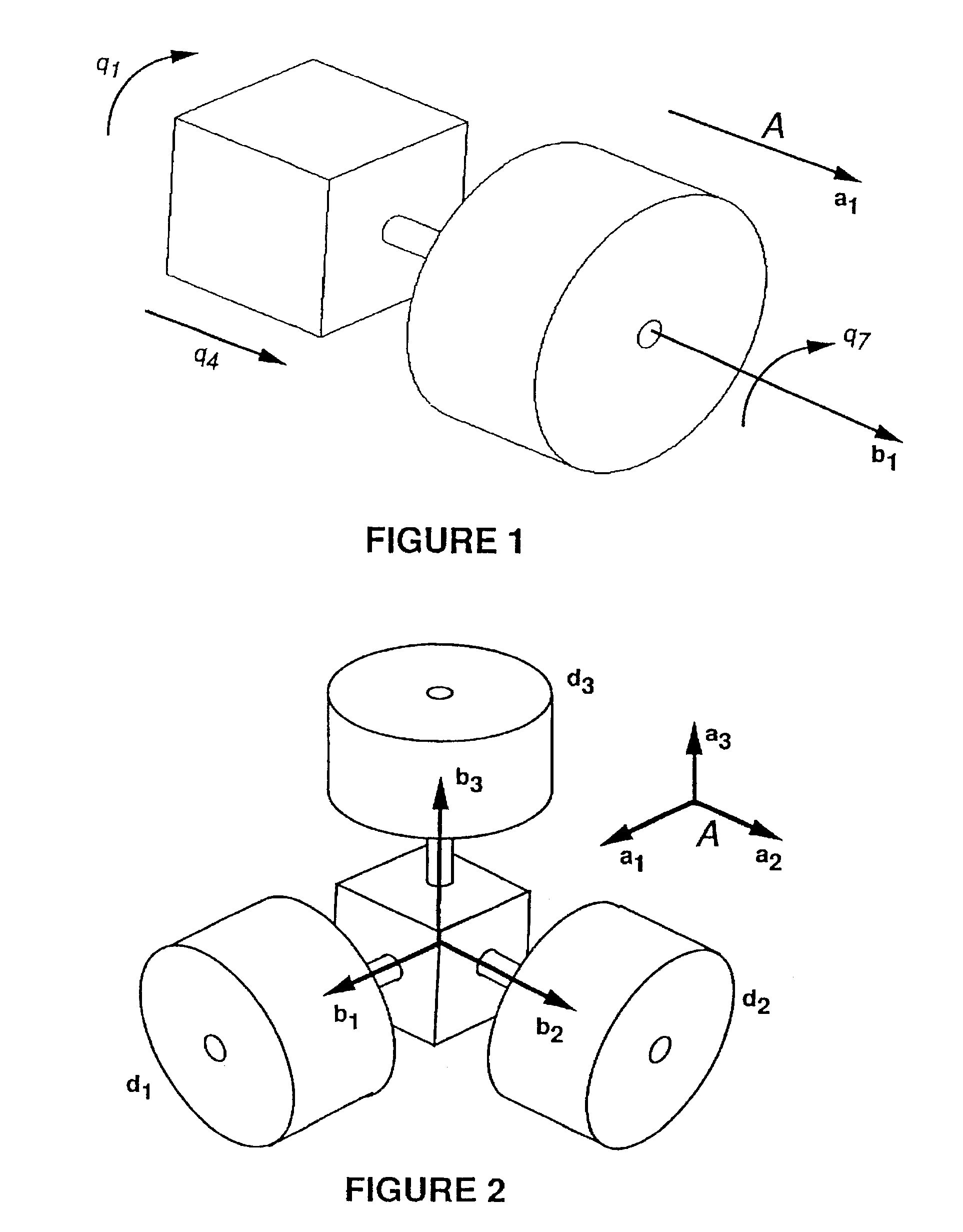
A system (30) for adjusting the orientation of a spacecraft adapted for use with a satellite (10). The system (30) includes a first control circuit (32, 38, 40) for canceling any momentum of the spacecraft via a counter-rotating spacecraft bus (16, 18). A second controller (32, 42, 44, 46, 48) orients the spacecraft via the application of internal spacecraft forces. In a specific embodiment, the spacecraft bus (16, 18) serves a dual use as storage section and includes a mass (16) having a moment of inertia on the same order as the moment of inertia of the satellite (10). The satellite (10) includes a bus section (16) and a payload section (14). The mass (16) includes the bus section (16). The first control circuit (32, 38, 40) runs software to selectively spin the mass (16) to cancel the momentum of the satellite (10). The software computes an actuator control signal, via a computer (32), that drives a first actuator (38) that spins the mass (16). The first control circuit (32, 38, 40) further includes a circuit for determining the inertial angular rate of the satellite (10) that includes a gyroscope sensor package (34) in communication with the computer (32). The gyroscope sensor package (34) provides a rate signal to the computer (32) that is representative of the momentum of the satellite (10). The computer (32) runs software for generating the actuator control signal in response to the receipt of the rate signal from the gyroscope sensor package (34). The second controller (32, 42, 44, 46, 48) includes a first reaction wheel (20) having an axis of rotation (26) approximately perpendicular to an axis of rotation (28) of a second reaction wheel (22). The first and second reaction wheels (20, 22) are rigidly mounted to the spacecraft bus (18, 16) and are free to spin about their respective axis. The first and second reaction wheels (20, 22) are selectively spun via first and second actuators (44, 48), respectively, in response to the receipt of first and second steering control signals, respectively.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
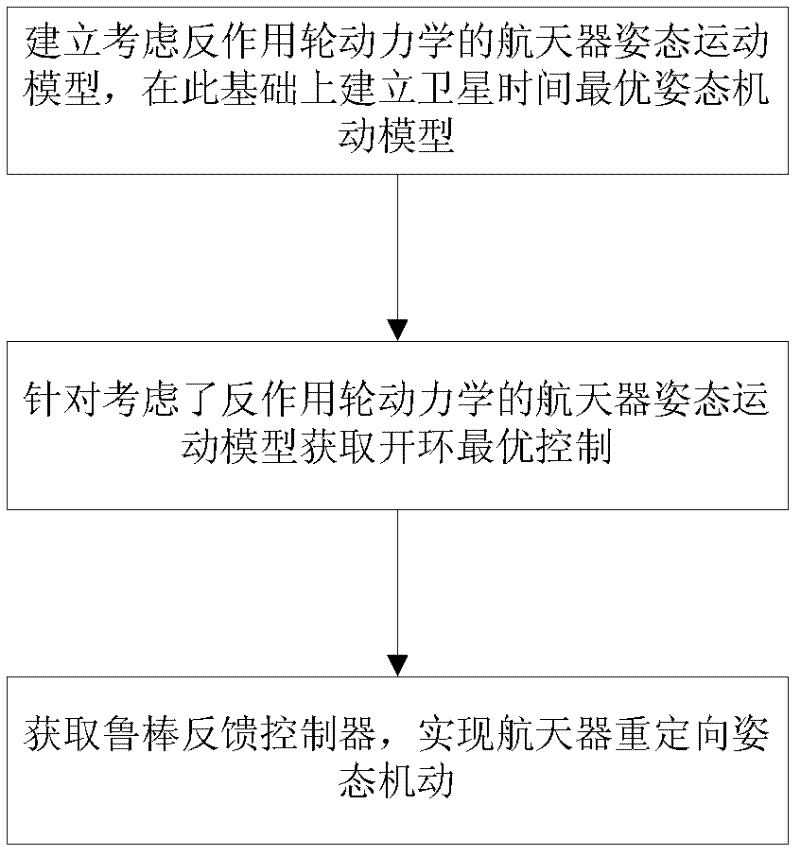
Satellite time optimal posture maneuvering method with reaction flywheel
InactiveCN102343985AHigh precisionAchieve fastest attitude maneuverSpacecraft guiding apparatusMomentumFeedback controller
The invention discloses a satellite time optimal posture maneuvering method with a reaction flywheel. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) establishing a spacecraft posture motion model considering reaction wheel dynamics, and establishing a satellite time optimal posture maneuvering model on this basis; (2) obtaining an open-loop optimal control for the spacecraft posture motion model considering reaction wheel dynamics; and (3) obtaining a robust feedback controller to realize spacecraft redirection posture maneuvering. According to the invention, fastest posture maneuvering of the spacecraft is realized; moreover, high accuracy and strong robustness of the maneuvering control are obtained; and moment saturation and momentum saturation restriction of an executing mechanism can be satisfied.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
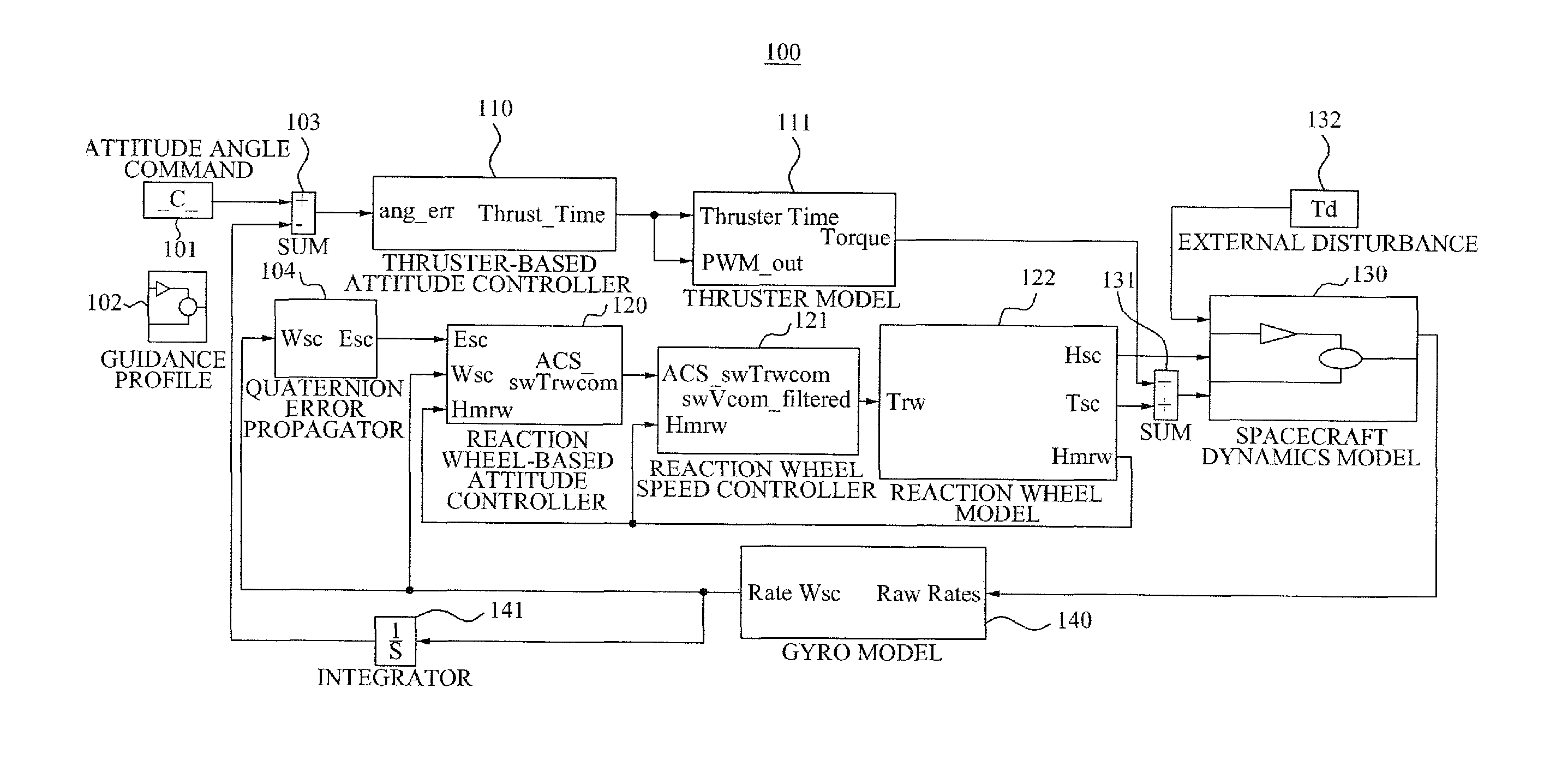
Method for improving maneuverability and controllability by simultaneously applying both reaction wheel-based attitude controller and thruster-based attitude controller
ActiveUS20100168938A1Cosmonautic vehiclesDigital data processing detailsControl systemAttitude control system
Provided are an attitude control system and method of a spacecraft of an artificial satellite that may enhance a maneuverability and a controllability by simultaneously applying a reaction wheel and a thruster among drive units used to maneuver an attitude of the spacecraft of the artificial satellite. The attitude control system may include: a thruster-based attitude controller which control firing time of thrusters mounted on the spacecraft; and a reaction wheel-based attitude controller controlling driving of a reaction wheel mounted on the spacecraft. The spacecraft may include a plurality of reaction wheels. When a defect occurs in the spacecraft due to a partial malfunction of the reaction wheels, an attitude maneuverability of the spacecraft may be corrected by simultaneously applying the thruster-based attitude controller and the reaction wheel-based attitude controller.
Owner:KOREA AEROSPACE RES INST
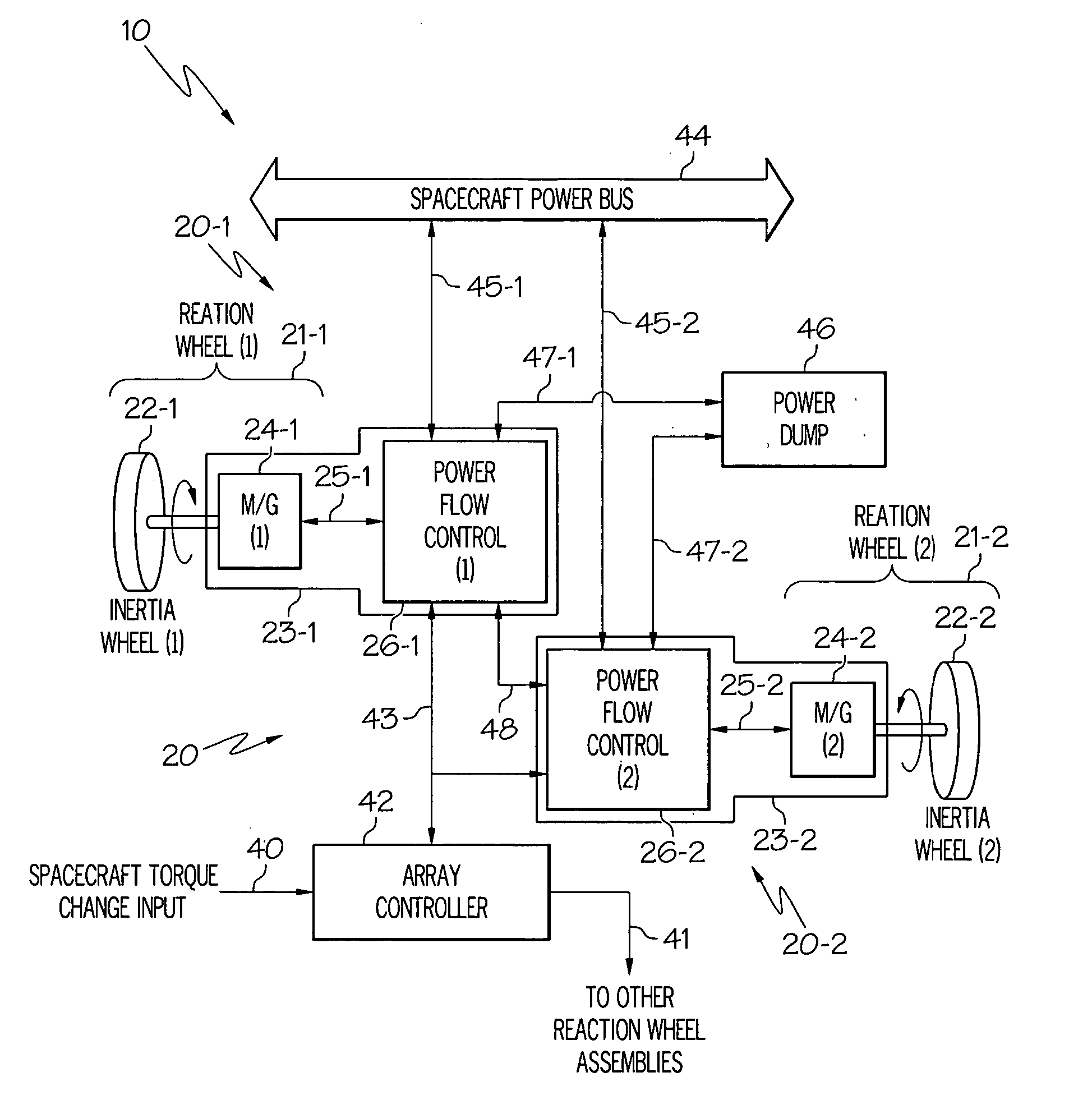
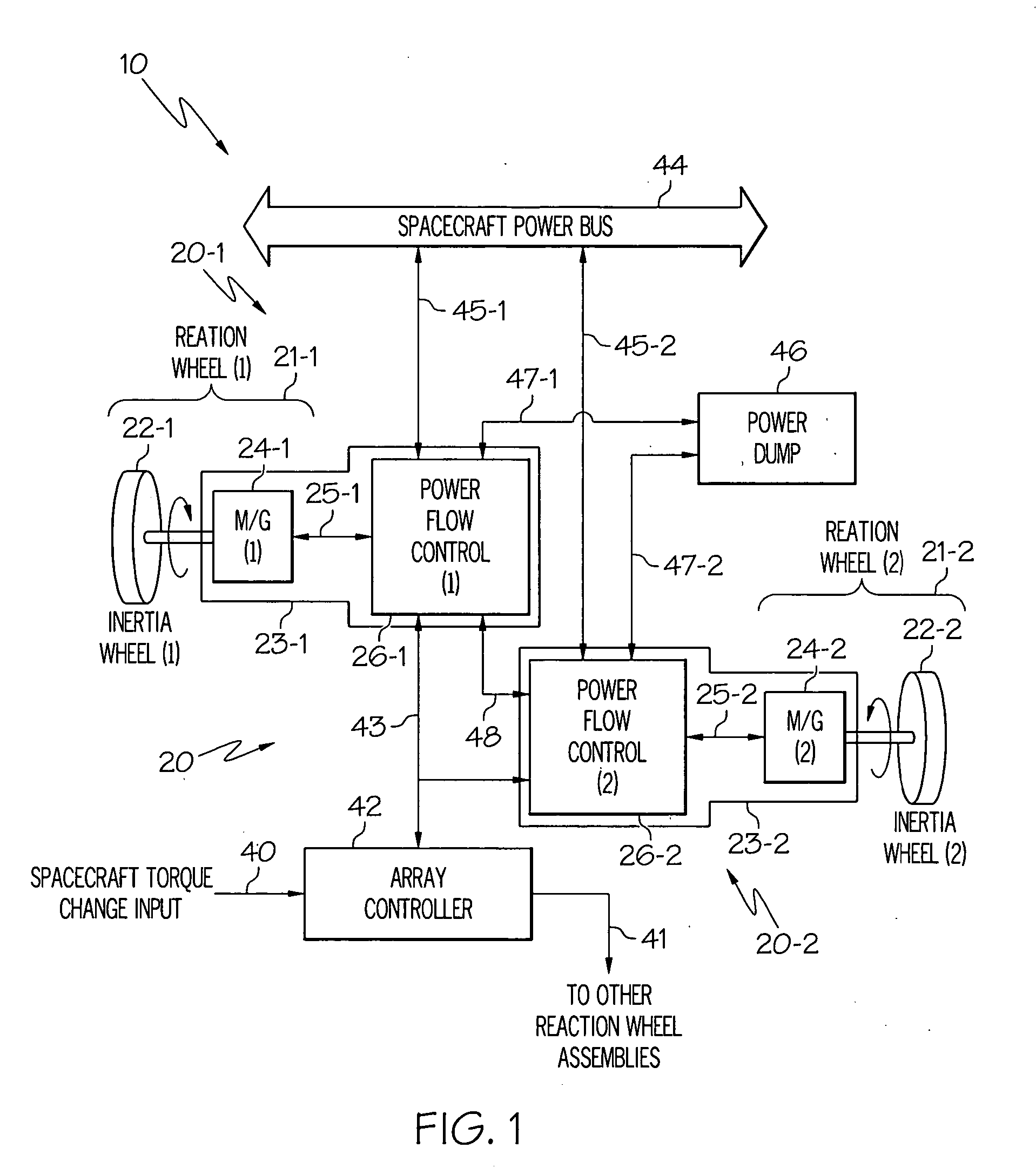
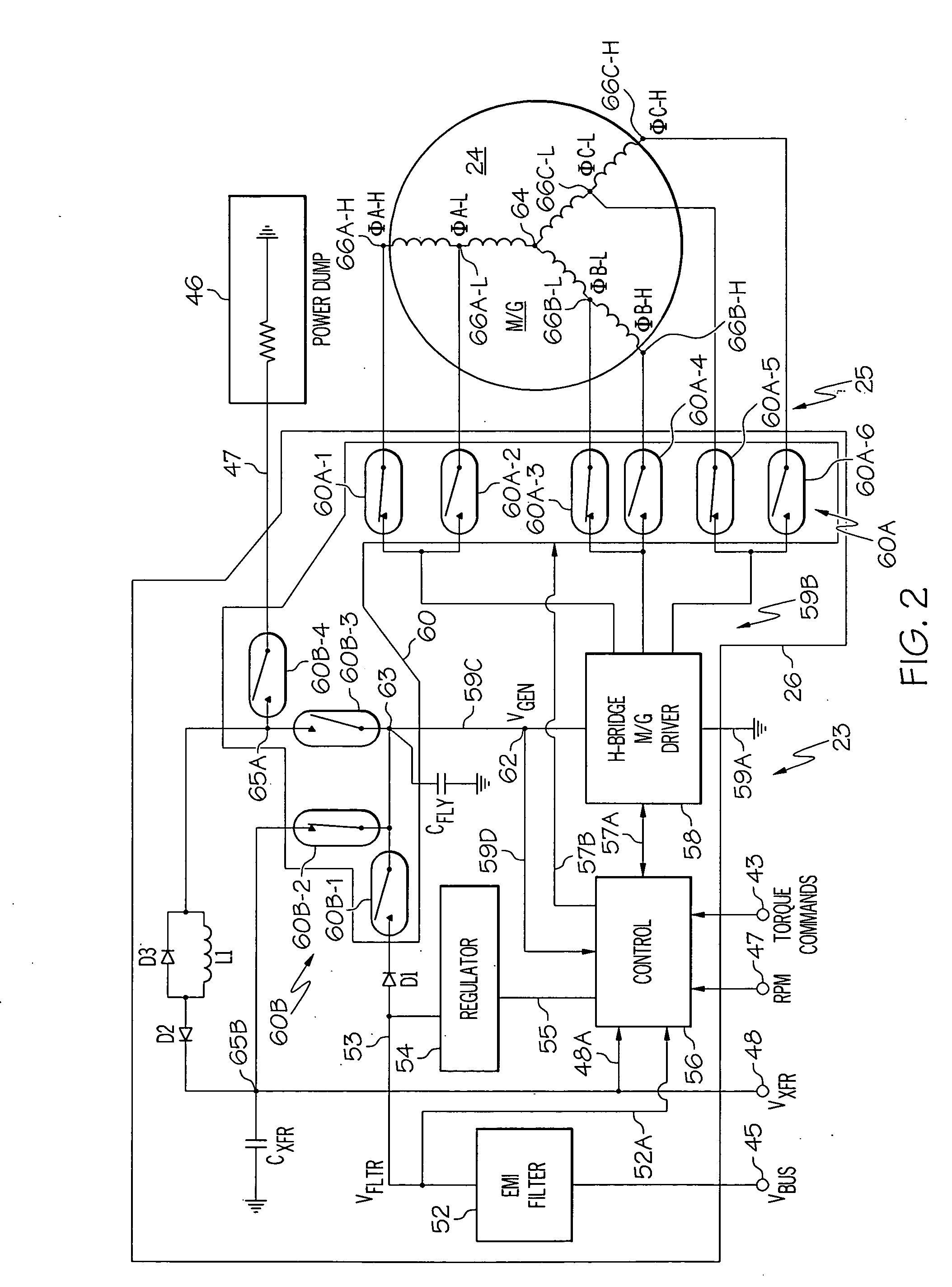
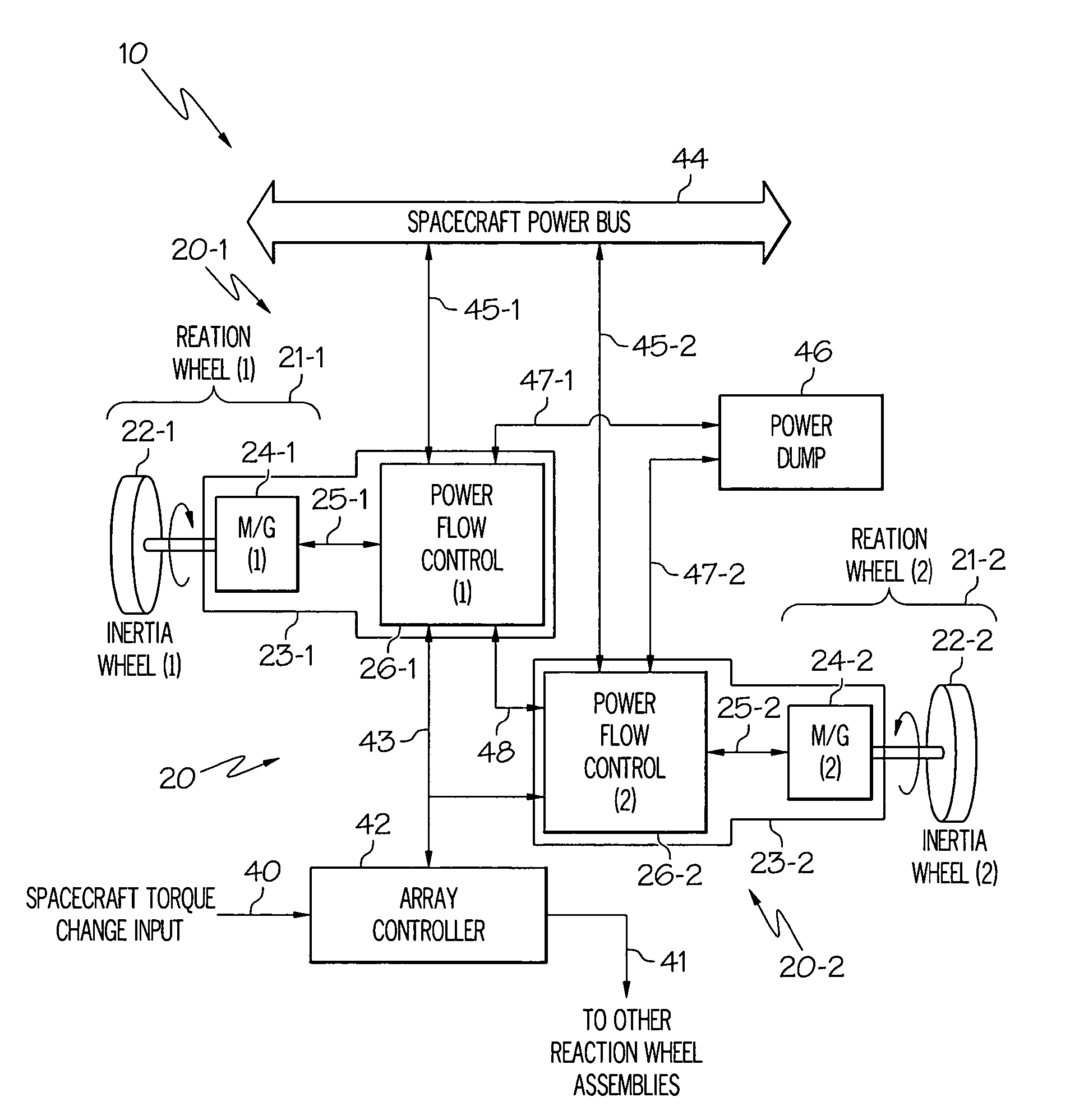
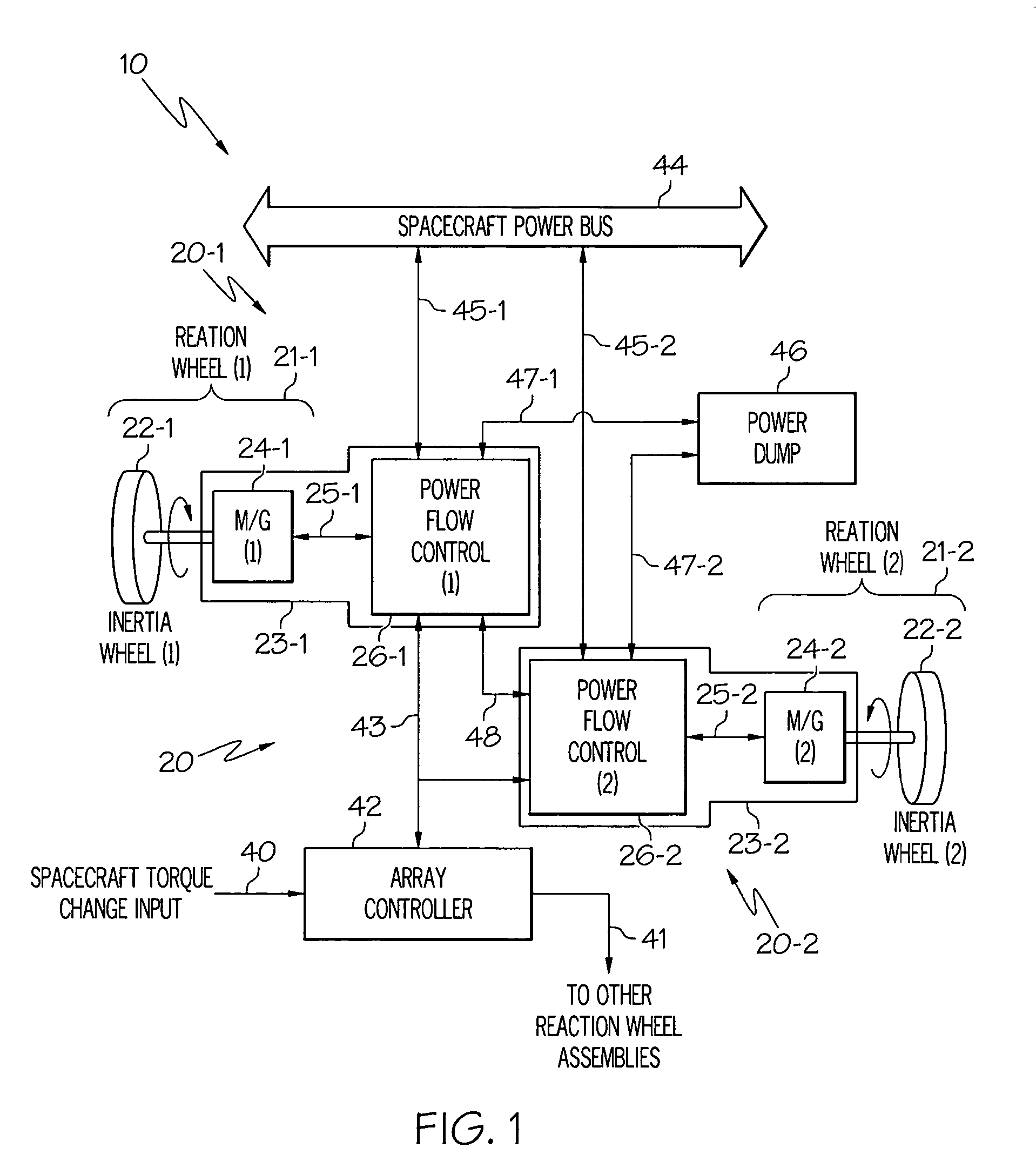
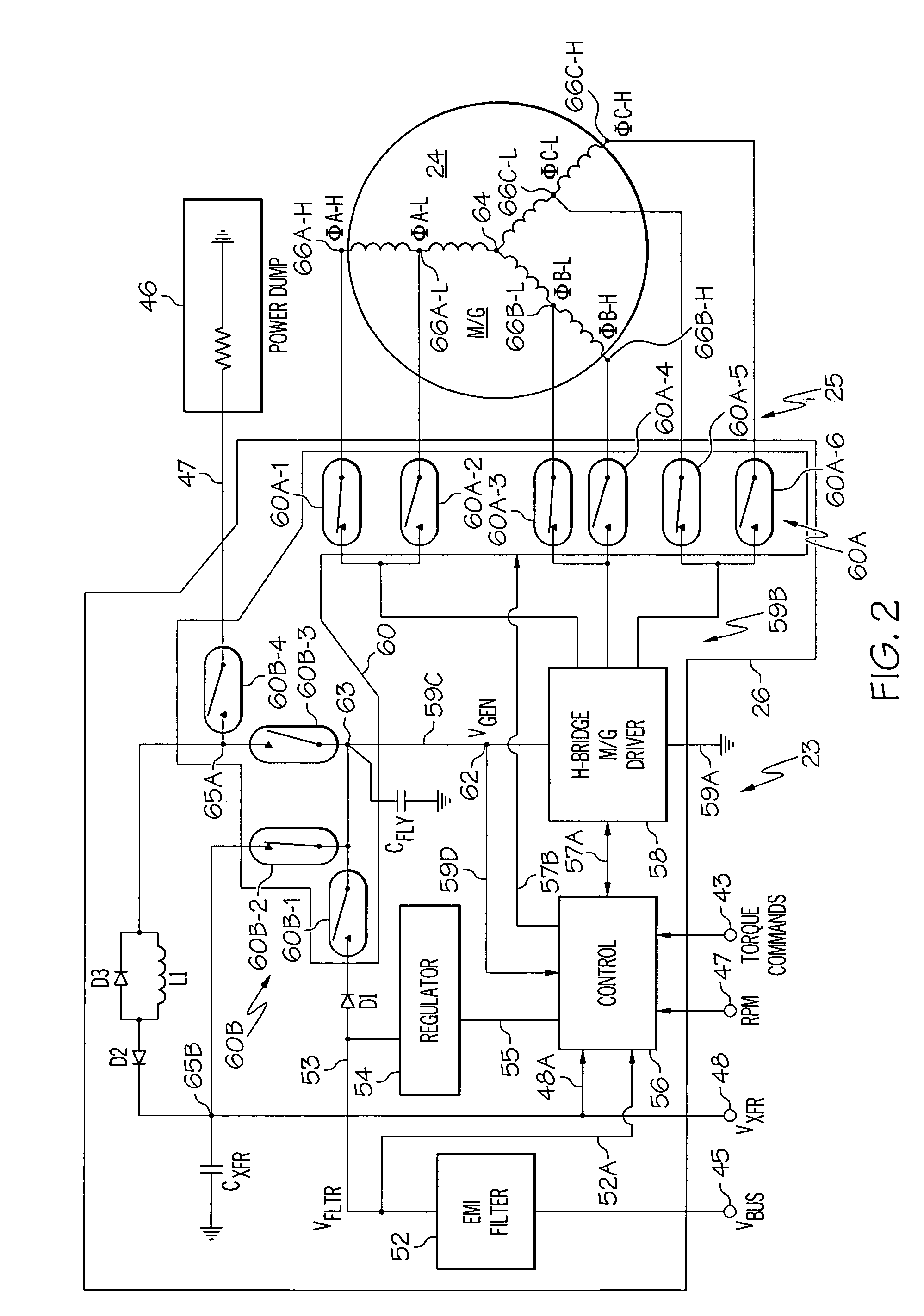
High-torque, low power reaction wheel array and method
ActiveUS20070023580A1Higher spacecraft steering torqueCosmonautic vehiclesDigital data processing detailsEnergy transferHigh torque
Methods and apparatus are provided for reaction wheel (RW) assemblies for spacecraft. The apparatus comprises a M / G coupled to an inertia wheel and a controller coupled to the M / G that, in response to commands it receives, couples power to or from an M / G of another RW assembly over a shared transfer connection (VXFR), so that one M / G acts as a generator powering another M / G acting as a motor. The controller compares generator voltage VGEN to the BEMF of the motor on VXFR and reconfigures a multi-winding M / G or steps-up the generated voltage to maintain VGEN>VXFR to maximize direct energy transfer from one RW to the other as long as possible. When VGEN declines sufficiently, the controller can couple the motor to the spacecraft power bus and / or the generator to a power dump so as to continue to provide the commanded torque if needed. Operation is automatic.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
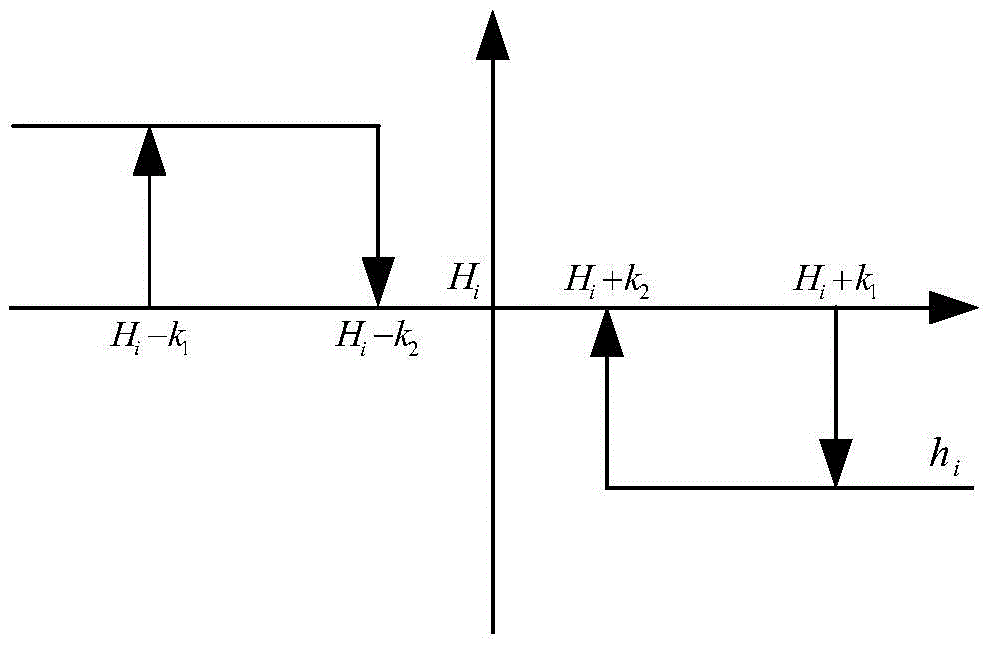
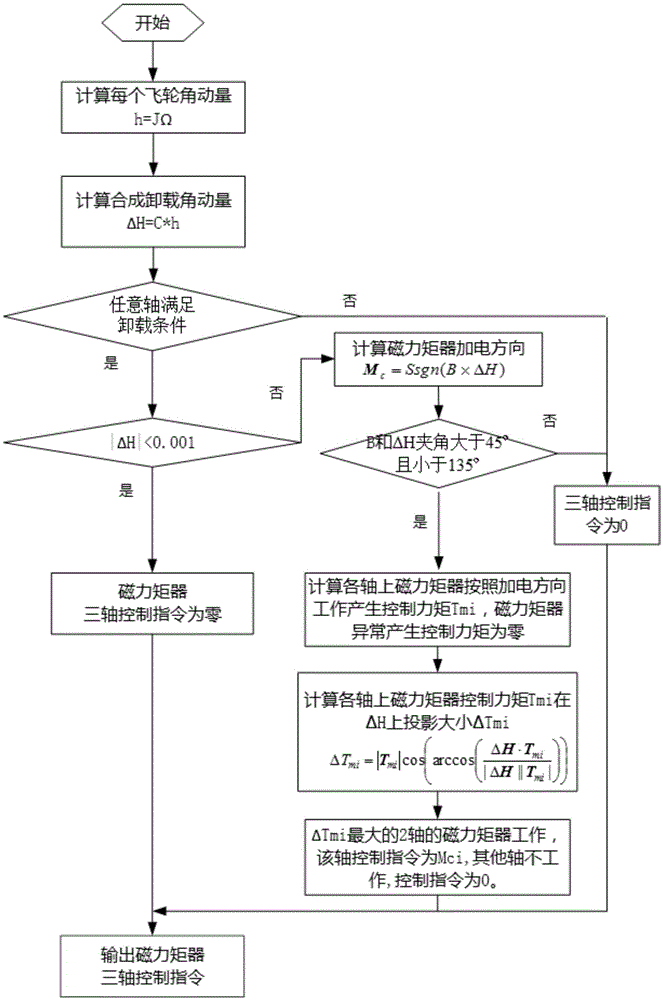
Open-loop control method for rotation speed change of reaction wheels and unloading method
InactiveCN105644810AEasy to controlEasy to use and flexibleCosmonautic vehiclesAttitude controlDistribution matrixAxis–angle representation
The invention provides an open-loop control method for the rotation speed change of reaction wheels (hereinafter referred to as flywheels) and an unloading method. The open-loop control method for the rotation speed change of the reaction wheels and the unloading method comprise the following specific steps that 1, controlling is conducted through the four flywheels, and the instruction of the magnitude of the reaction wheel control torque of the fourth flywheel is adjusted to be consistent with the magnitude of the theoretical nominal rotation speed friction torque; 2, a control instruction output by a controller is limited within the maximum output torque, the control torque of each flywheel is distributed according to a flywheel distribution matrix, after the control torque of each flywheel is distributed, the flywheel with the maximum output torque is limited within the maximum torque, and the control torque of the other two flywheels is decreased and increased proportionally; 3, the momentum of a synthetic angle of the four flywheels is calculated, and when any axial angle momentum reaches the unloading threshold range and the relationship between the magnetic field intensity and an angular momentum included angle during unloading is met, magnetic torquers are started to be uninstalled; and 4, the magnetic torquer with the maximum unloading capacity is selected to work, and the flywheels are unloaded by adopting a switch control mode.
Owner:SHANGHAI ENG CENT FOR MICROSATELLITES
Three-axis active posture control method for space tether-robot
The invention provides a three-axis active posture control method for a space tether-robot. The method includes the steps that according to the orbit dynamics characteristic of the space tether-robot, the nominal tension required by a space tether of the space tether-robot in the equilibrium state is calculated; according to posture kinematics and dynamical equations of the space tether-robot, a control moment variable is determined, a state equation and an output equation of posture kinematics of the space tether-robot are established, and posture control moments in three directions are calculated according to a feedback linearization control law; according to the relation among the control moments, the space tether connecting point positions and the rotating speed of a reaction wheel, the corresponding space tether connecting point positions and the rotating angular speed of the reaction wheel are obtained. By the adoption of the method, according to the posture of a target and with the use of the space tether and the reaction wheel, three-axis posture coordinated control is conducted on the posture of the space tether-robot, and the method is suitable for three-axis posture control of the space tether-robot when the space tether-robot is located on a connecting line of a space platform and the geocenter.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
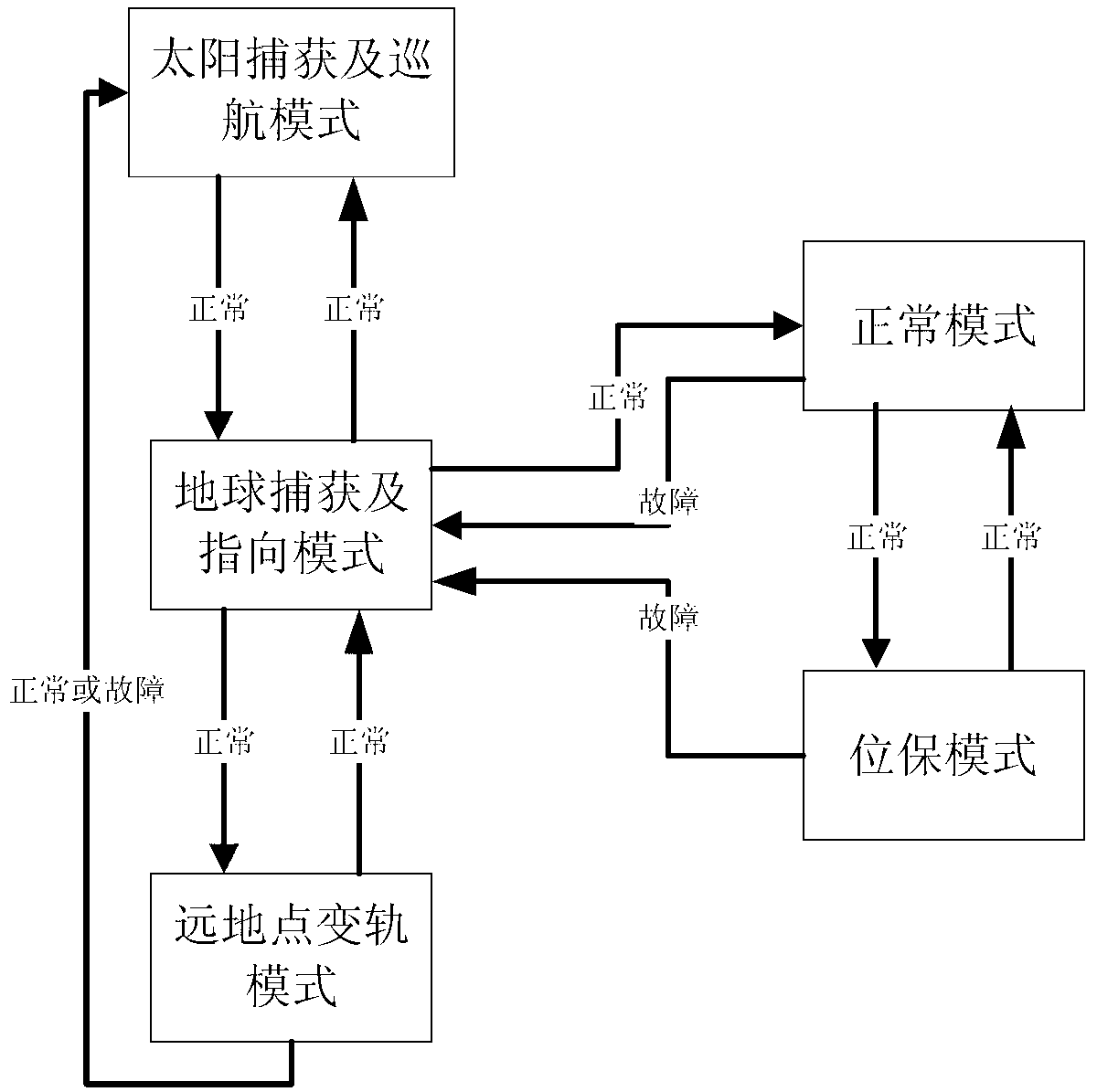
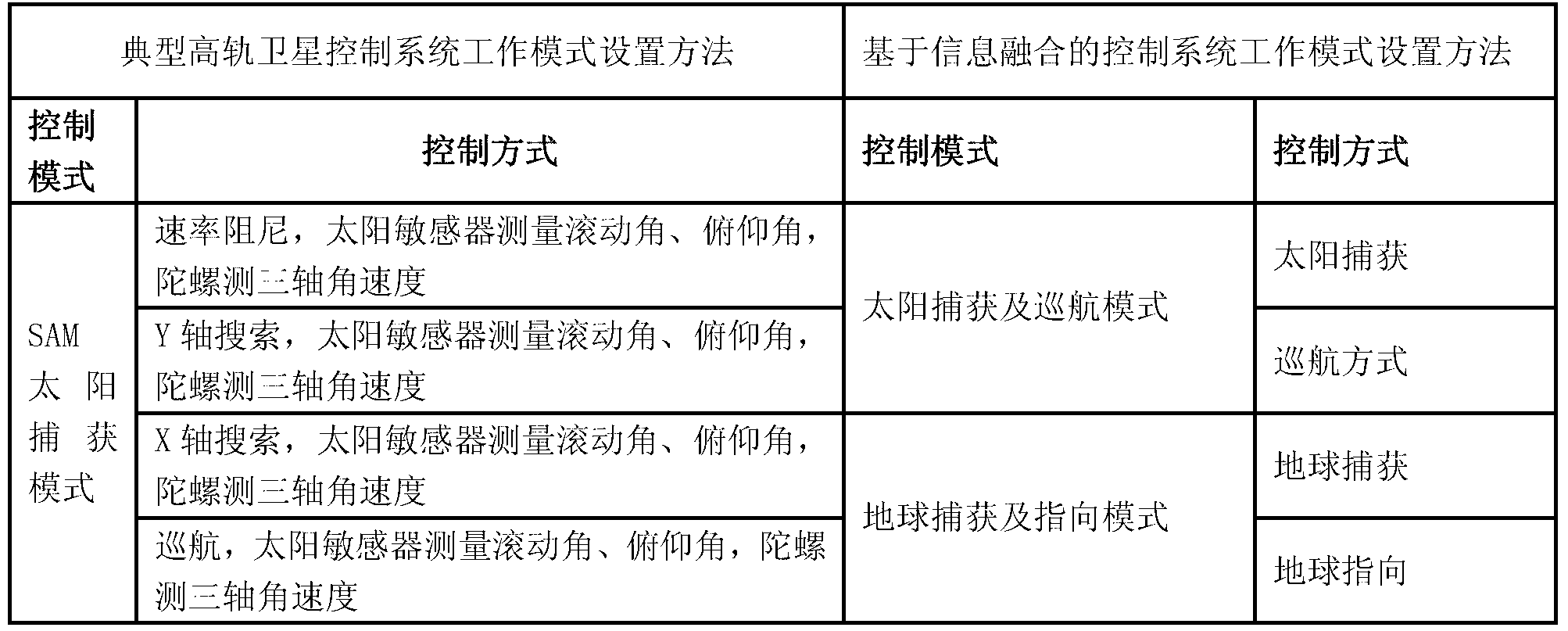
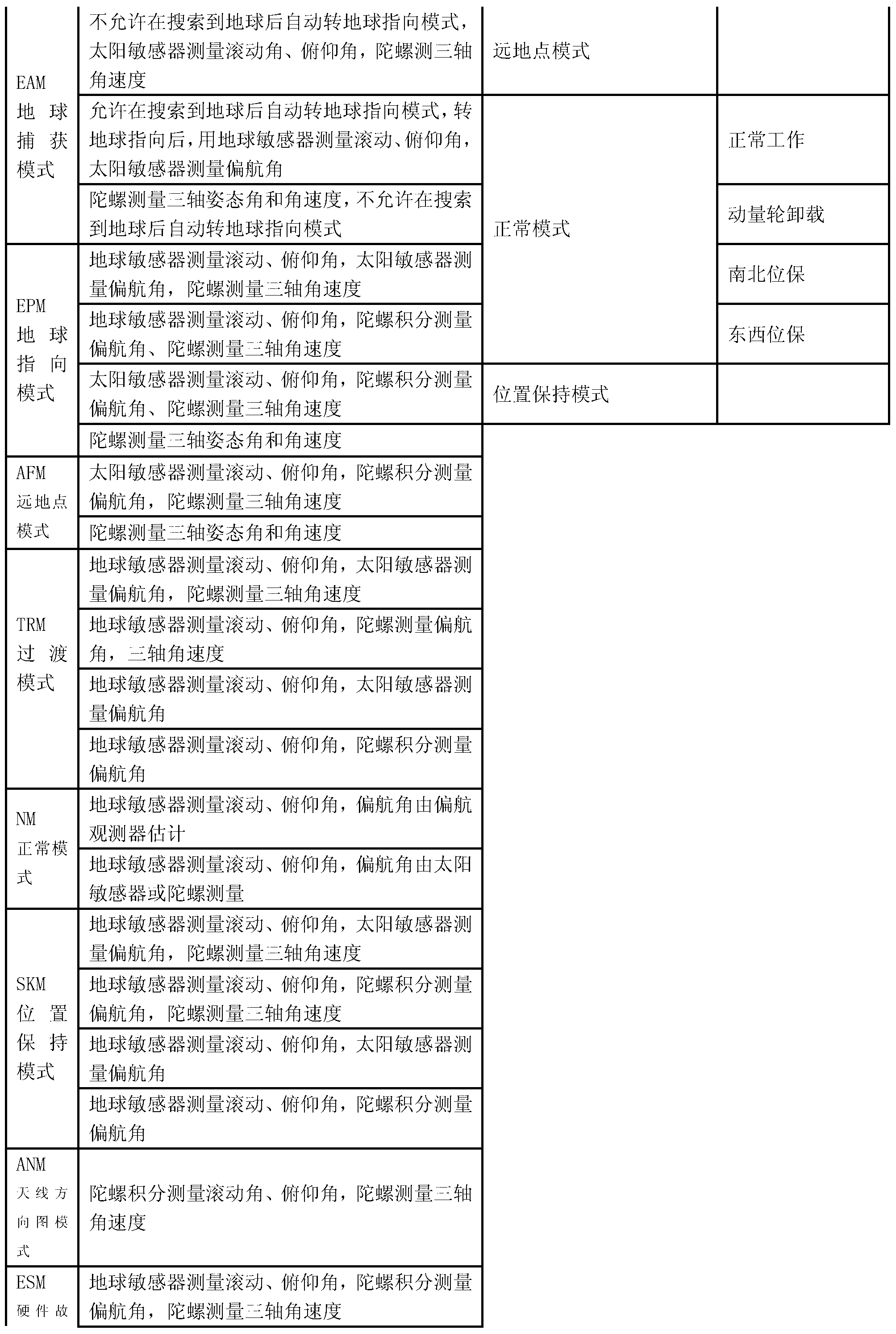
Control system working mode setting and switching method based on information fusion
ActiveCN103264776AReduce in quantityImprove performanceSpacecraft guiding apparatusWork patternControl system
Provided is a control system working mode setting and switching method based on information fusion. An existing method that a control system working pattern and mode is designed according to functions and the using conditions of a sensor is converted to a method that the control system working pattern and mode is determined according to the functions. The working pattern is designed as a sun capturing and cruising pattern, an earth capturing and pointing pattern, an apogee pattern, a position keeping pattern and a normal pattern (including a normal working mode, a counteractive wheel disassembling working mode, a north and south position keeping working mode and an east and west position keeping working mode). The patterns can be autonomously switched on a satellite or be switched in a remote-control mode from the ground. According to the method, pattern designing and switching conditions are optimized, the number of control patterns is reduced, conversion relation between the patterns is simplified, complex degree of ground observation and control is lowered, the using number of software codes is lowered, and the performance of a control system is improved.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
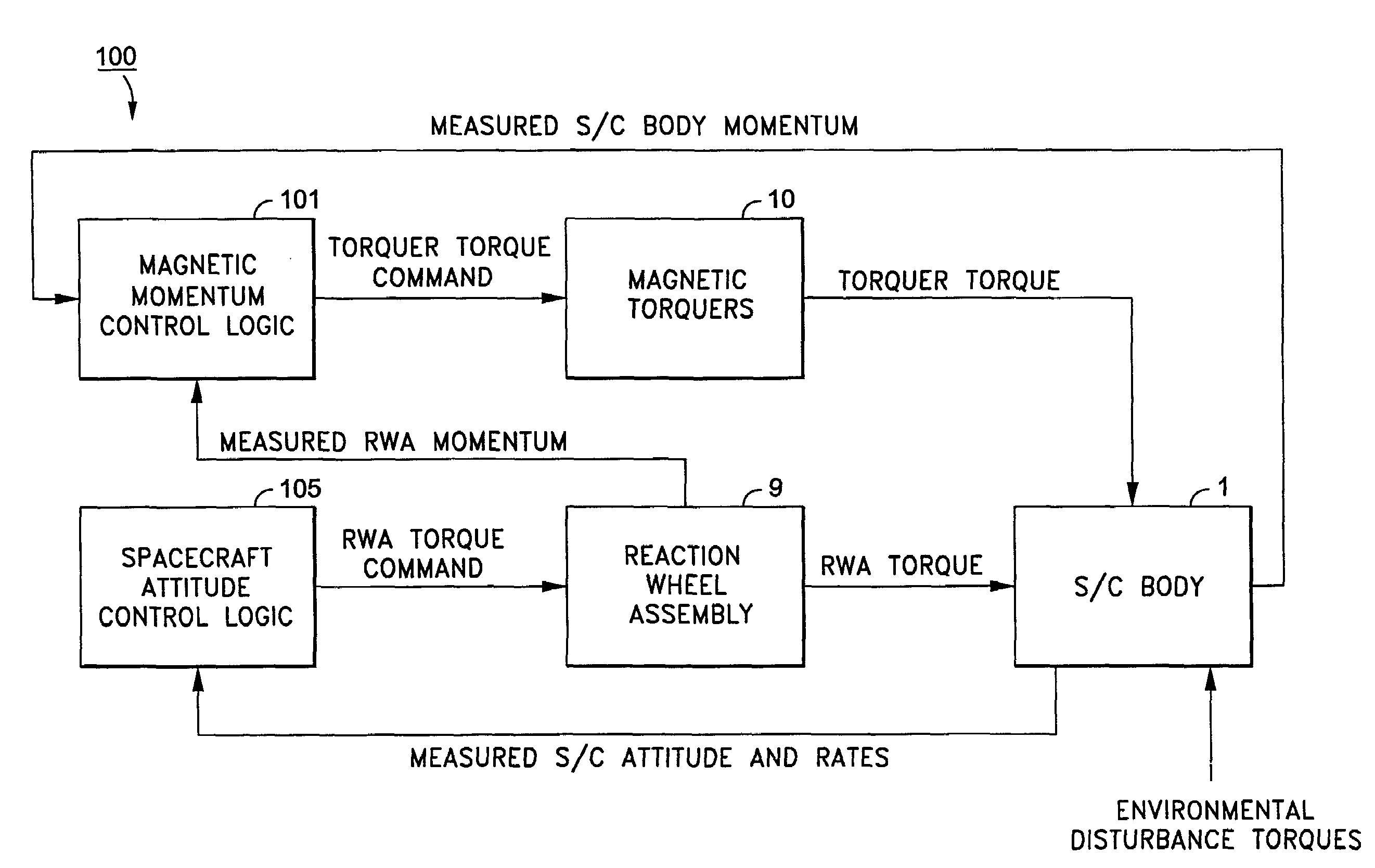
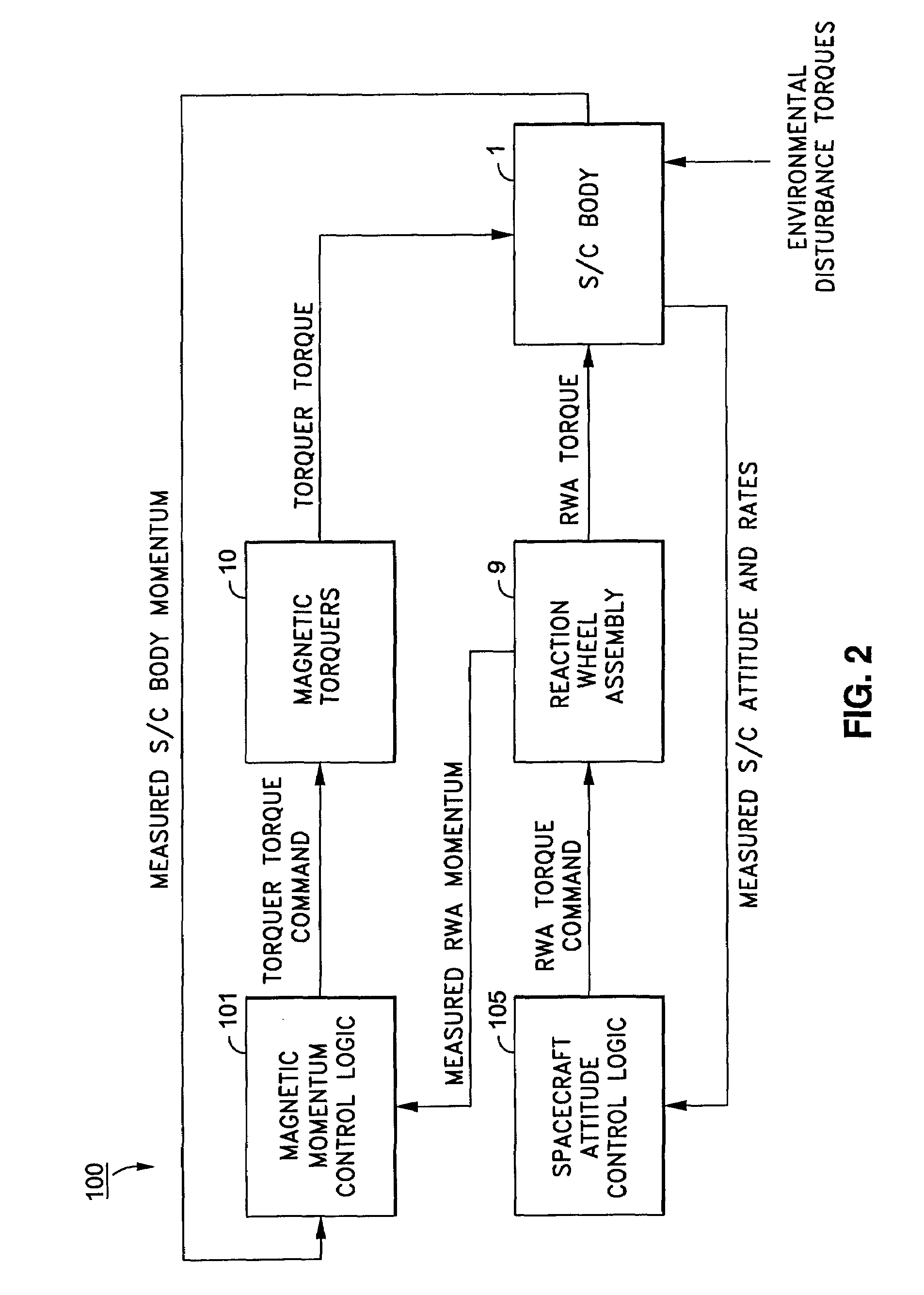
Spacecraft magnetic momentum control system
ActiveUS7376496B1Reduced torquer duty cycleReduce power consumptionCosmonautic vehiclesDigital data processing detailsMomentumControl system
Momentum control is maintained in a geosynchronous orbiting spacecraft that uses a plurality of reaction wheel assemblies and a plurality of magnetic torquers to control the spacecraft momentum, each orbit of the spacecraft being comprised of a set of time steps, by determining a current momentum error for a current time step of a current orbit by adding a system momentum change determined for an immediately preceding orbit to an average system momentum determined for the immediately preceding orbit, and then subtracting a magnetic control torque momentum change determined for the immediately preceding orbit, determining a current duty cycle for each of the magnetic torquers based on the current momentum error and on a torque value applied by each magnetic torquer at each time step of the immediately preceding orbit, and commanding each magnetic torquer to operate at the current time step in accordance with its respective determined current duty cycle, wherein the magnetic torquers apply a magnetic momentum control torque to the spacecraft to offset the current momentum error.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Reconfigurable reaction wheel for spacecraft
InactiveUS20080099626A1Cosmonautic vehiclesVehicle position/course/altitude controlFreewheelEngineering
The invention provides a reconfigurable reaction wheel for a spacecraft, a spacecraft, and a method of using the reconfigurable reaction wheel to control the movement of a spacecraft. The reaction wheel includes a reaction wheel housing, a flywheel rotatably disposed in the housing and an electric motor operably coupled to the flywheel. The electric motor includes a plurality of electrical windings. The motor is adapted and configured to operate in a first selectable operating state wherein the windings are arranged in a first electrical configuration, and a second selectable operating state wherein the windings are arranged in a second electrical configuration different from the first electrical configuration.
Owner:ITHACO SPACE SYST
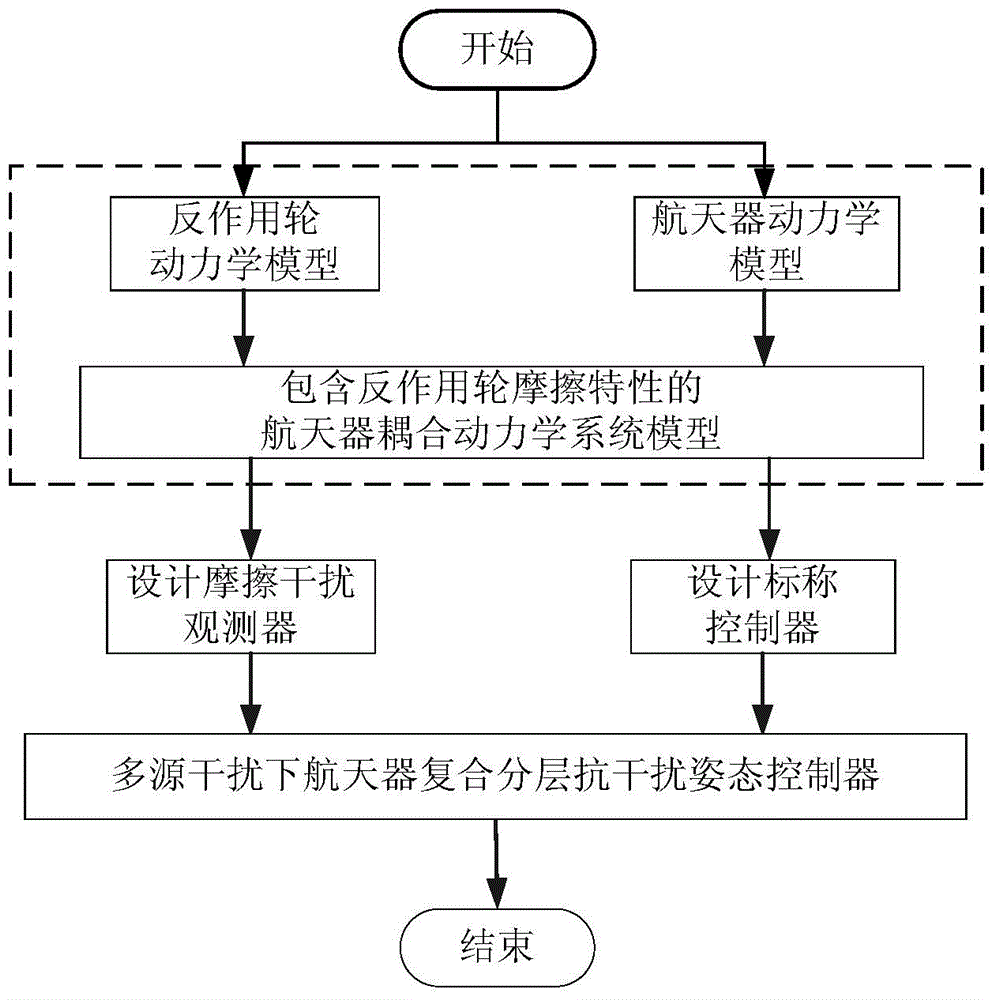
Anti-interference attitude control method based on the friction characteristics of a reaction wheel
Provided is an anti-interference attitude control method based on the friction characteristics of a reaction wheel. To solve the problems about zero-crossing friction and low attitude control precision of a reaction wheel, the method includes the steps: establishing a spacecraft coupling kinetic equation containing the friction characteristics of the reaction wheel, designing a friction interference estimator because the reaction wheel brings friction interference, and estimating the friction of the reaction wheel in real time; designing a norminal controller to inhibit friction interference estimated errors and environment interference in a spacecraft system; and combining the norminal controller with the friction interference estimator, and designing a composite layered anti-interference controller to achieve spacecraft anti-interference attitude control under the influence of multi-source interference. According to the method, actuating mechanism dynamics are additionally applied to the spacecraft kinetic equation so as to better analyze the problem of the decreased control precision due to the characteristics of an actuating mechanism. The method can be used for high-precision attitude control over high-precision earth observation satellites, space telescopes and other spacecrafts in the aerospace field.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
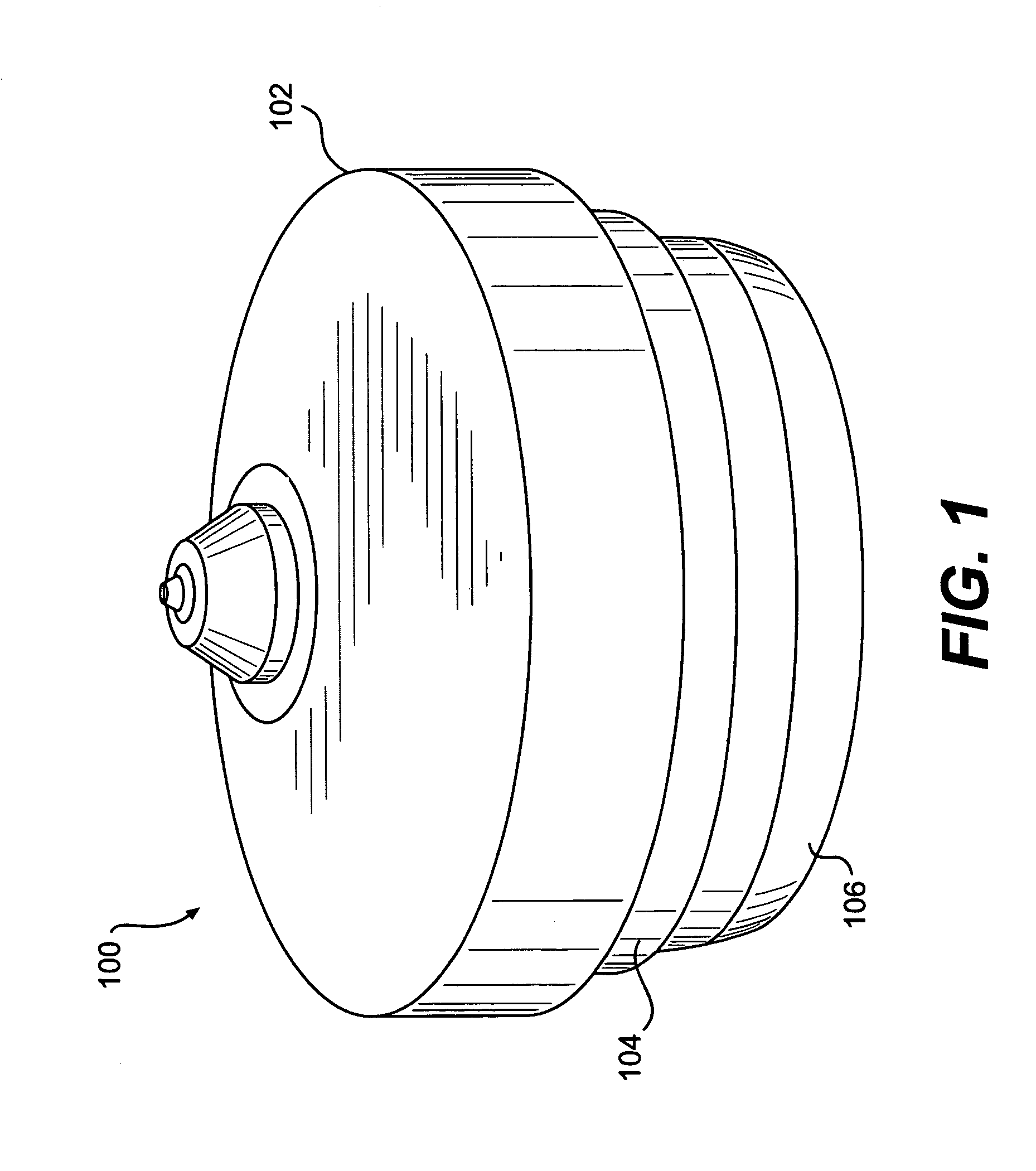
Clutch driven reaction wheel steering unit
InactiveUS20060032985A1Limited bandwidthReduce device complexityCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusFreewheelMomentum
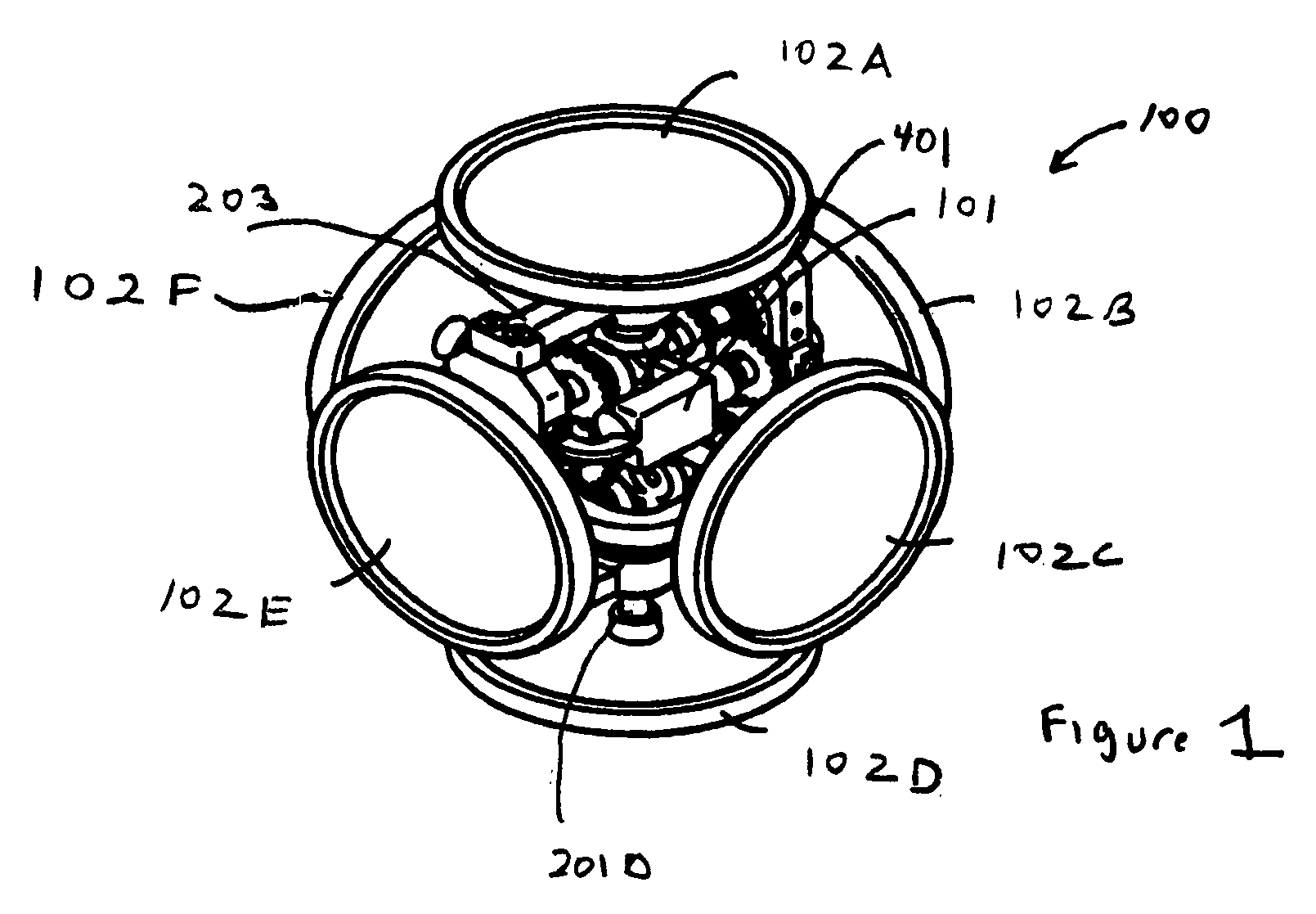
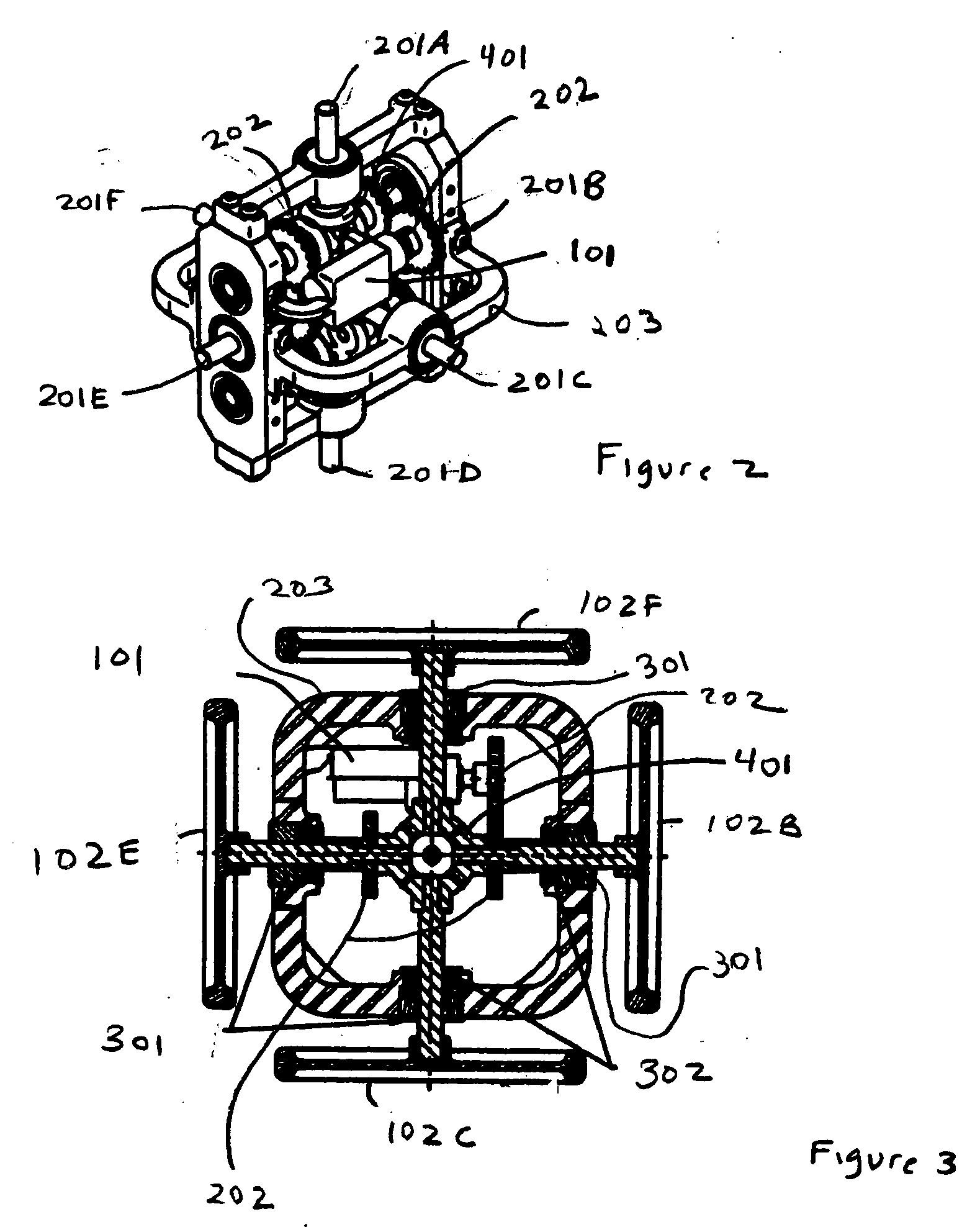
What is disclosed is a clutch driven reaction wheel steering unit having at least a single drive motor (101) coupled indirectly to a plurality of flywheels operable to provide momentum for all three axes in a single unit. In an exemplary embodiment, the drive motor (101) is mounted within a unit frame (203). A plurality of gears, including miter gears, are coupled directly or indirectly to the drive motor (101). Six flywheels (102A, 102B, 102C, 102D, 102E and 102F) are coupled to the ends of a plurality of shafts which extend through or are supported by the unit frame (203). Clutches are operable to selectively transmit rotational motion to the second plurality of shafts.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF NORTH TEXAS
A magnetic levitation counteractive flying wheel
InactiveCN101056079ASolve wear and tearSolve the friction problem when the speed crosses zeroAttitude controlMagnetic holding devicesMagnetic bearingEngineering
The present invention provides a magnetic bearing reaction wheel which can be used as an attitude control execution mechanism of the space vehicles such as a satellite, a geoelectric observation platform and a space telescope. The magnetic bearing reaction wheel mainly consists of a wheel body, a casing, an installing shaft, a radial magnetic suspension bearing, an axial magnetic suspension bearing, an upper protection bearing, a lower protection bearing, a bearing seat, a locknut, a displacement sensor, a displacement sensor support, an electric motor, a base etc. The radial magnetic suspension bearing controls the rotor to move in the radial direction, and the axial magnetic suspension bearing controls the radial rotation and the axial parallel movement of the rotor. In the present invention, the arrangement of the assembly is reasonable and compact, and the volume and the weight are reduced, and the over-zero friction force and the physical deterioration of the mechanic bearing flywheel are eliminated, and the control precision and the use lifetime of the flywheel are improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Methods and apparatus for tuned axial damping in rotating machinery with floating bearing cartridge
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
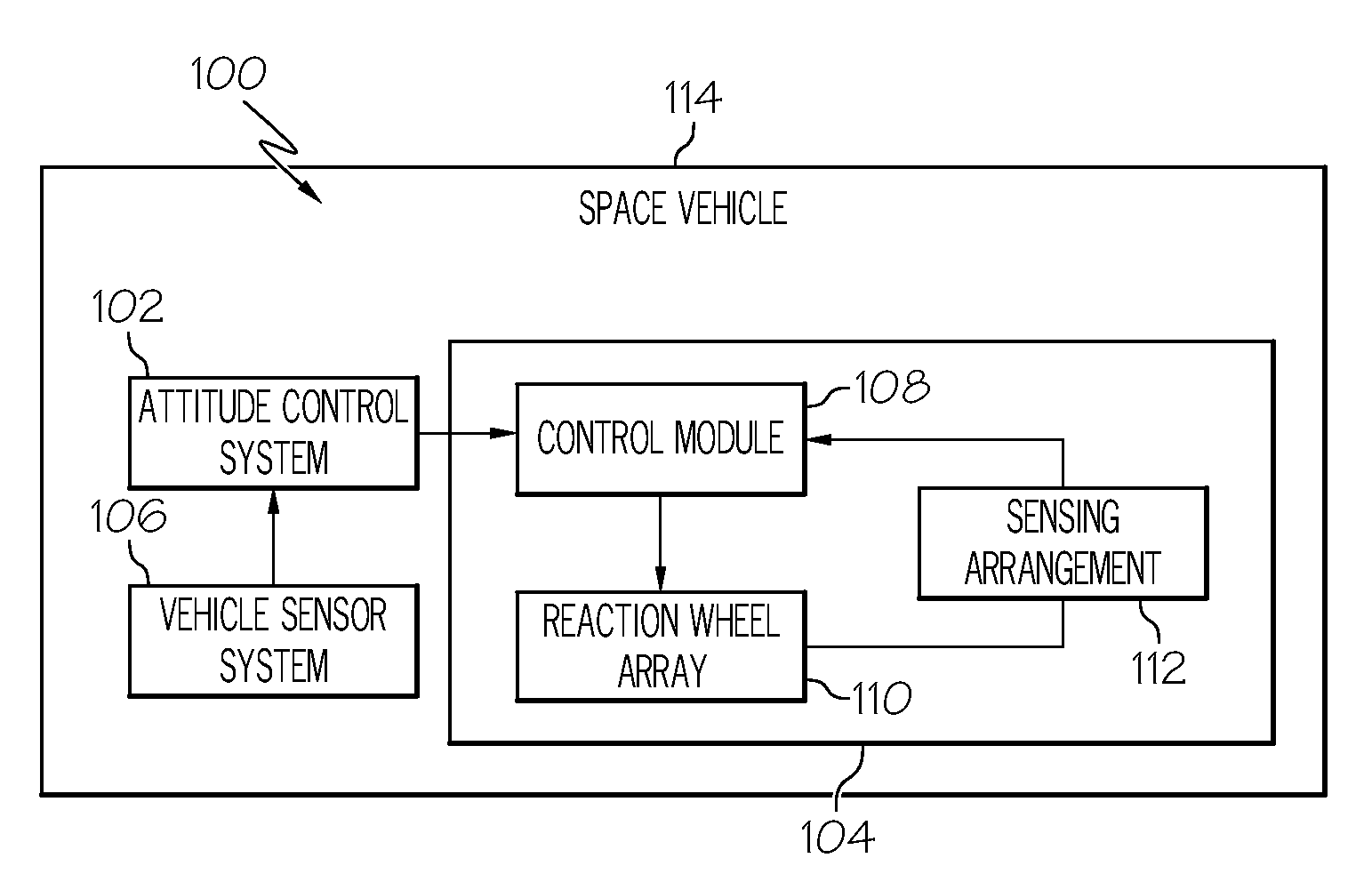
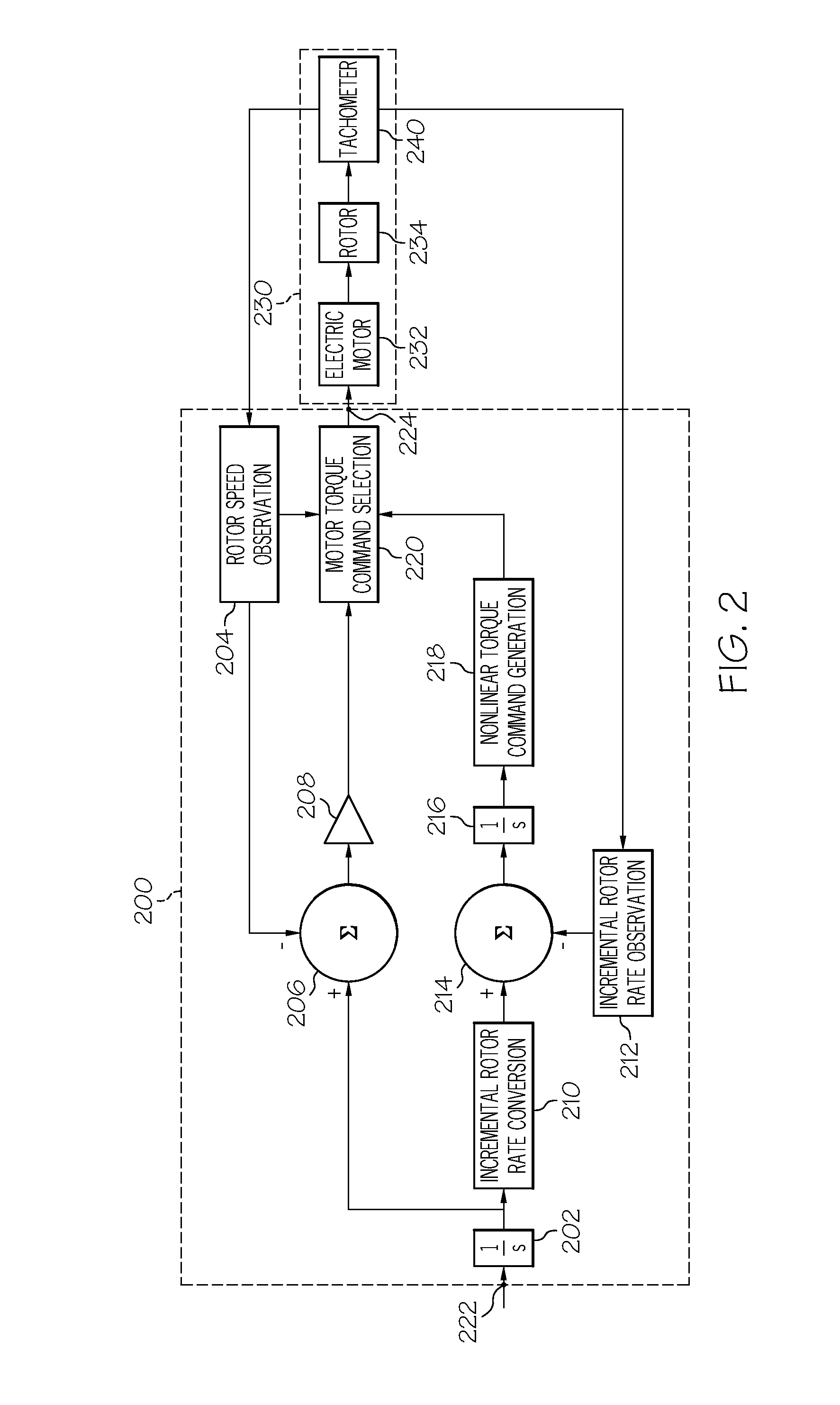
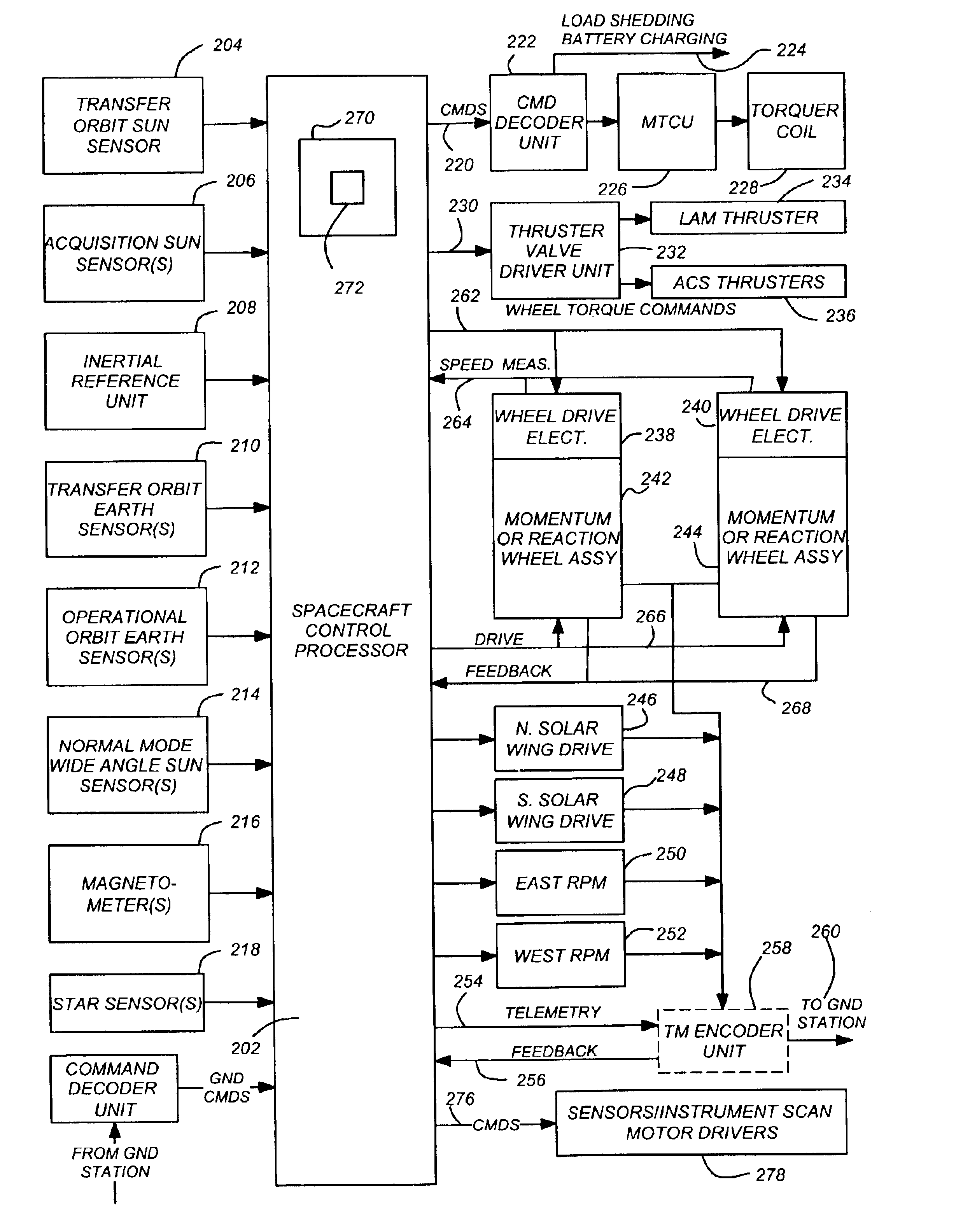
Methods and systems for adjusting attitude using reaction wheels
Methods and systems are provided for controlling attitude of a vehicle using a reaction wheel onboard the vehicle. One exemplary method involves receiving a torque command for adjusting the attitude of the vehicle using the reaction wheel, determining a phase error of the reaction wheel based at least in part on the torque command, and determining a motor torque command for the reaction wheel based on the phase error. The motor torque command is provided to an electric motor of the reaction wheel to apply a corresponding torque to the rotor of the reaction wheel. The relationship between the magnitude of the motor torque command and the magnitude of the phase error is nonlinear. In exemplary embodiments, the magnitude of the motor torque command exceeds the stiction torque, at least instantaneously, when the reaction wheel has fallen behind an expected position by more than a threshold amount.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
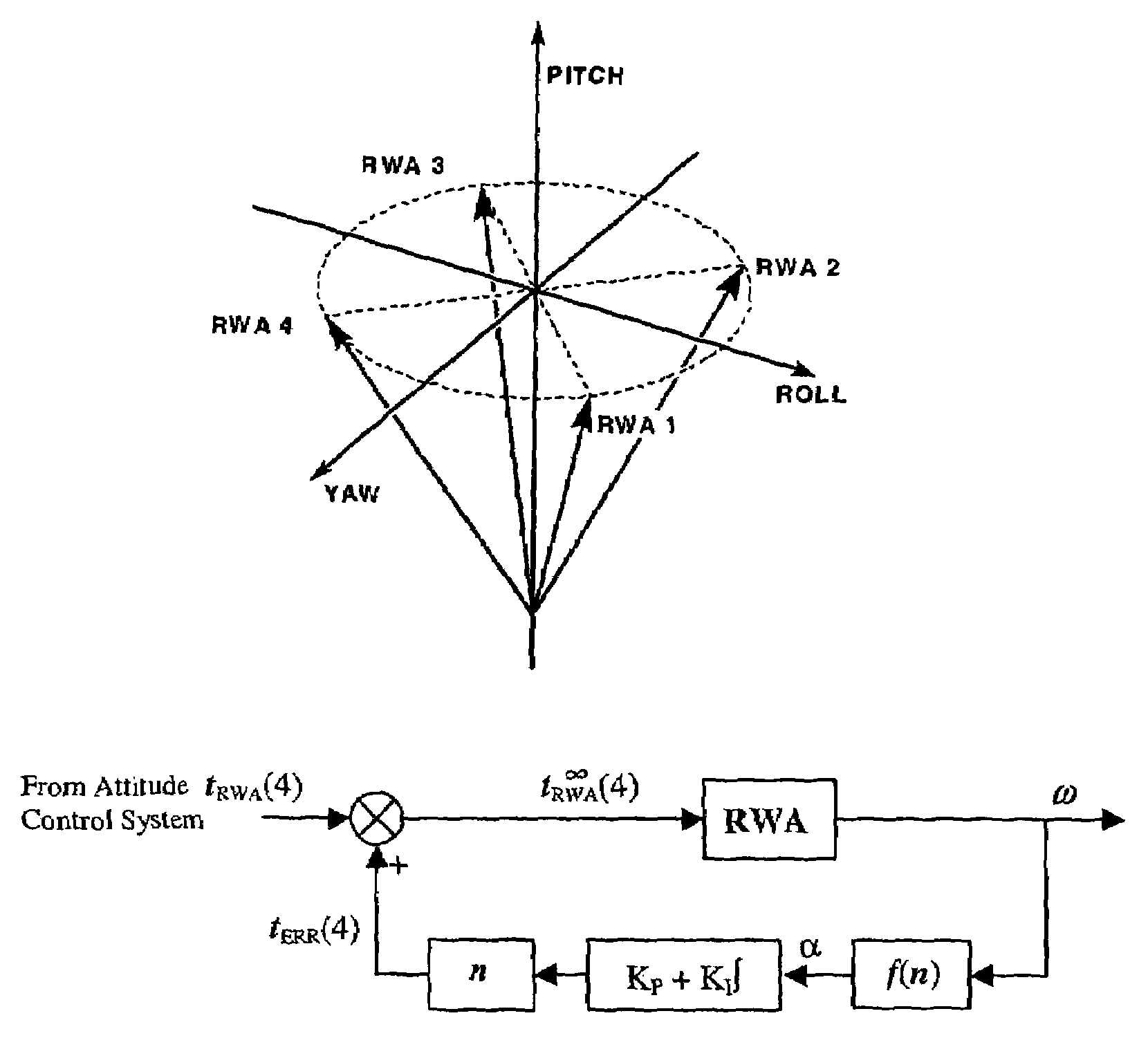
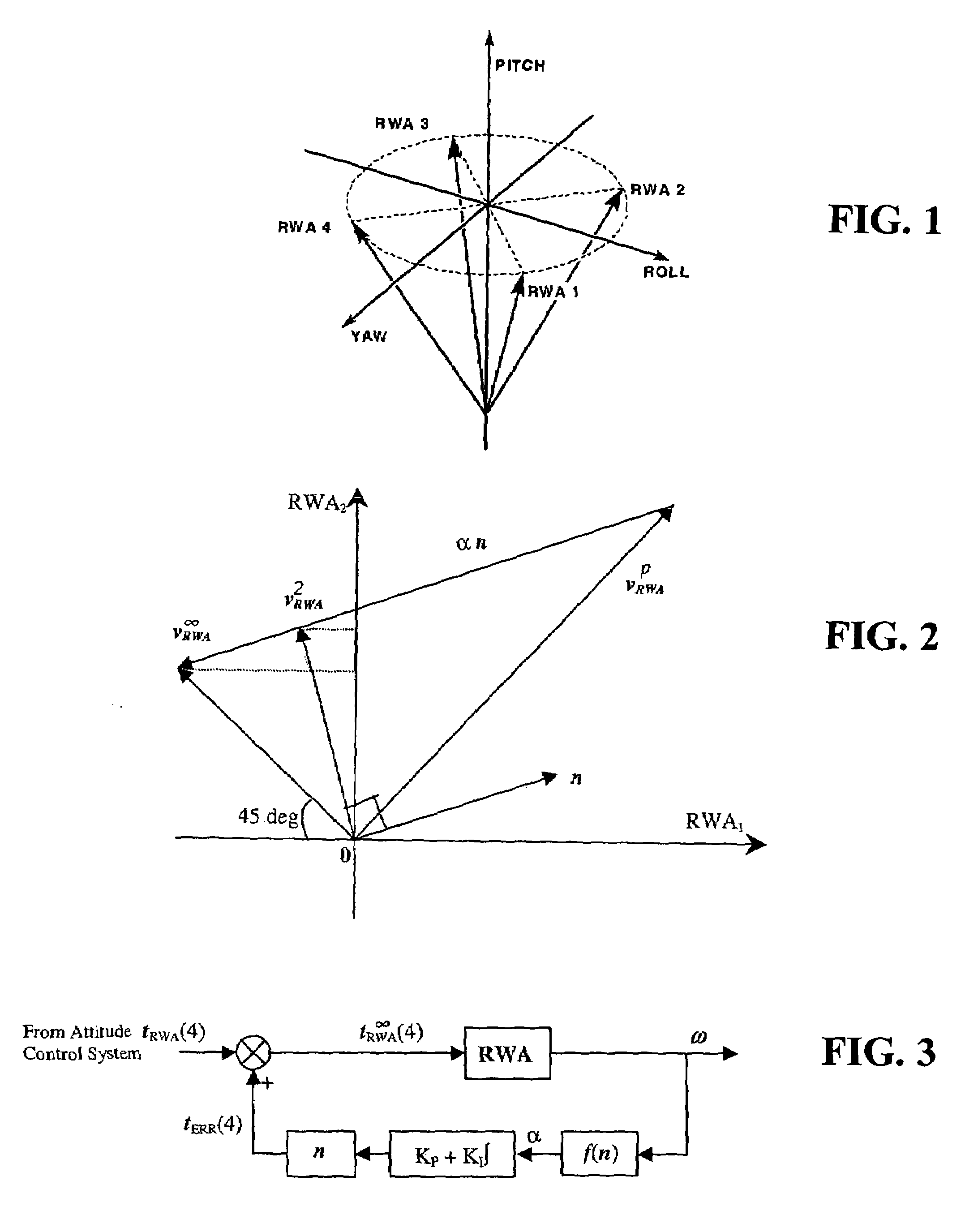
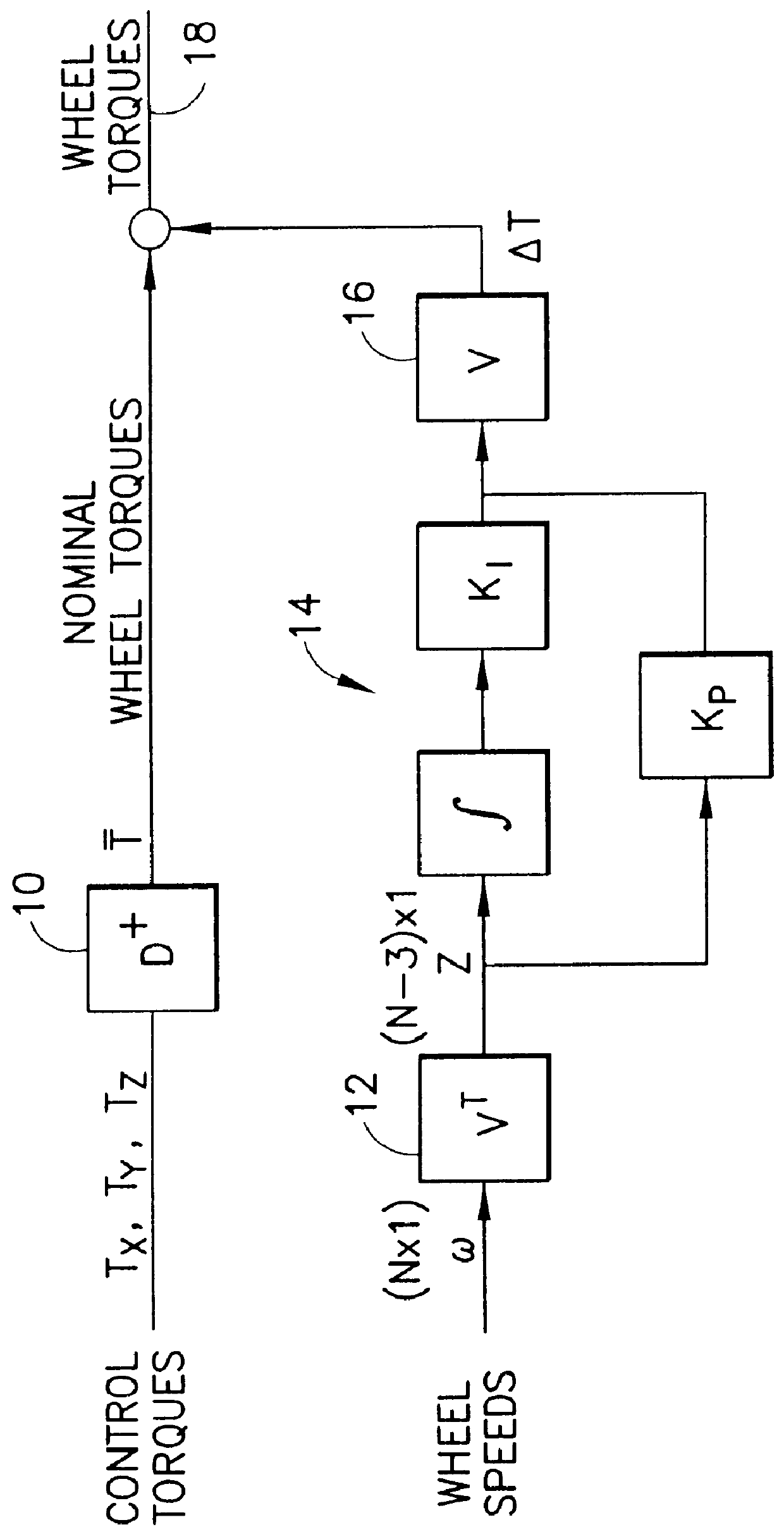
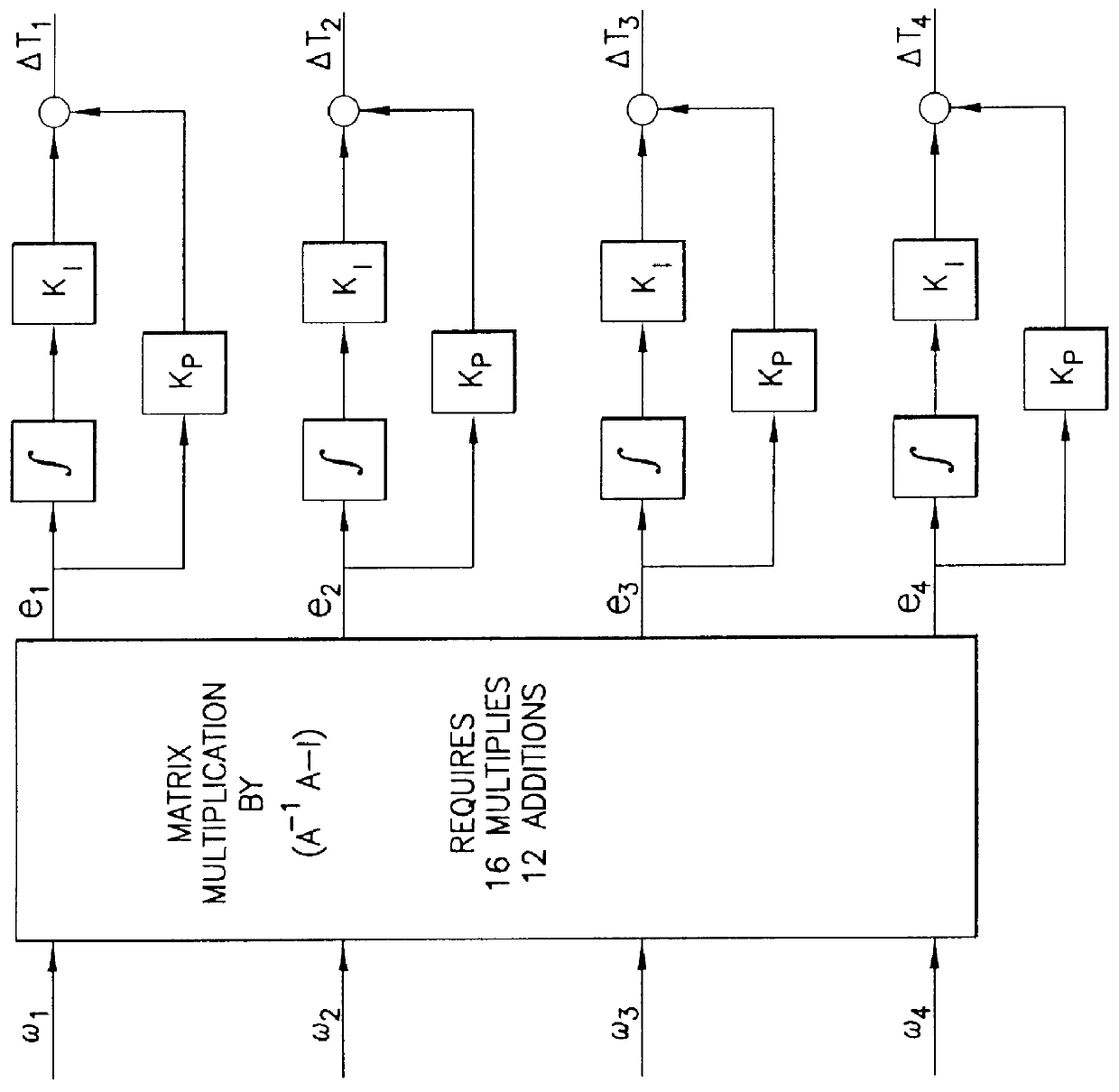
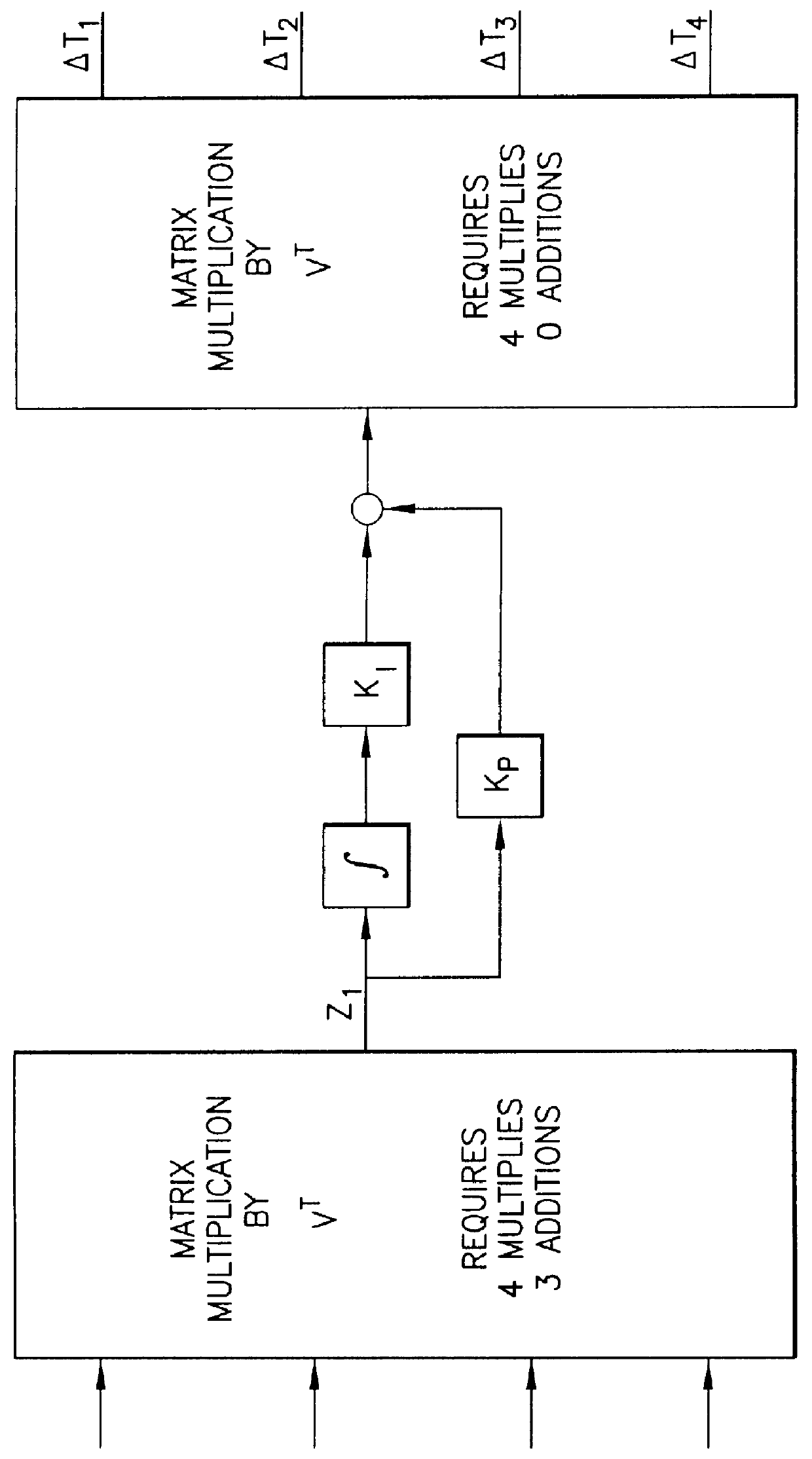
Optimal speed management for reaction wheel control system and method
ActiveUS7198232B1Minimization requirementsMaximum speedCosmonautic vehiclesDigital data processing detailsMomentumSpacecraft attitude control
A spacecraft attitude control system and method in which an attitude controller is configured for sensing three-dimensional attitude of the spacecraft, and producing torque signals for stabilizing the spacecraft in a prescribed attitude in space. At least four mutually skew reaction wheels are rotated in response to the torque control signals for storing three-dimensional angular momentum, and speeds of rotation of the wheels are measured. A reaction wheel speed control processor, responsive to reaction wheel torque and speed for producing reaction wheel spin control signals, implements an infinity-norm algorithm for causing the nullspace components of wheel speed to re-distribute a desired three-dimensional stabilizing momentum of the spacecraft in such a manner that the maximum speeds of rotation of all the reaction wheels is minimized. As a result, periods between successive momentum dumping maneuvers are prolonged to the maximum possible.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Satellite attitude control system and method
A satellite attitude control system includes a programmed processor system which includes a gyroscopic actuator first control stage for changing the attitude of the satellite and a reaction wheel second control stage for assuring that pointing of the satellite is accurate and stable. The method is intended to be used for a satellite including the two control stages indicated above, which it uses selectively for the operations indicated above.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
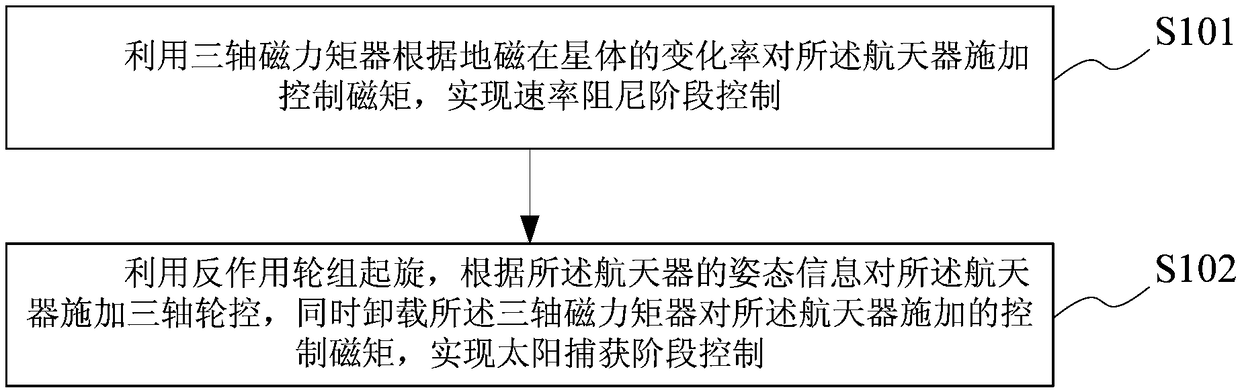
Initial attitude capture control method and system of spacecraft
InactiveCN108069050AEasy to controlSimple configurationCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusRocketReaction wheel
The invention provides an initial attitude capture control method and system of a spacecraft. The initial attitude capture control method of the spacecraft includes the steps that a three-shaft magnetmoment device is used for applying a control magnetic moment to the spacecraft according to the change rate of terrestrial magnetism on a satellite, and a speed damping stage is controlled; and a counteractive wheel set is used for spinning, three-shaft wheel control is applied to the spacecraft according to attitude information of the spacecraft, meanwhile, the control magnetic moment applied bythe three-shaft magnet moment device to the spacecraft is removed, and a sun capture stage is controlled. Only counteractive wheels and the magnet moment device are adopted as attitude control components, measures for dealing with the too large satellite and rocket separation deviation are considered, speed damping is applied firstly, the condition that the counteractive wheels are not saturatedserves as a precondition, meanwhile, in the sun capture stage, three-shaft wheel control is applied only depending on magnetometer information and sun sensor information, and initial capture control can be finished.
Owner:SHANGHAI ENG CENT FOR MICROSATELLITES
Gyro-stabilized platforms for force-feedback applications
InactiveUSRE44396E1Input/output for user-computer interactionProgramme-controlled manipulatorJoystickGyroscope
Force feedback in large, immersive environments is provided by device which a gyro- stabilization to generate a fixed point of leverage for the requisite forces and / or torques. In one embodiment, one or more orthogonally oriented rotating gyroscopes are used to provide a stable platform to which a force-reflecting device can be mounted, thereby coupling reaction forces to a user without the need for connection to a fixed frame. In one physical realization, a rigid handle or joystick is directly connected to the three-axis stabilized platform and using an inventive control scheme to modulate motor torques so that only the desired forces are felt. In an alternative embodiment, a reaction sphere is used to produce the requisite inertial stabilization. Since the sphere is capable of providing controlled torques about three arbitrary, linearly independent axes, it can be used in place of three reaction wheels to provide three-axis stabilization for a variety of space-based and terrestrial applications.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Reaction Flywheel Output Torque Measuring Circuit and Measuring Method
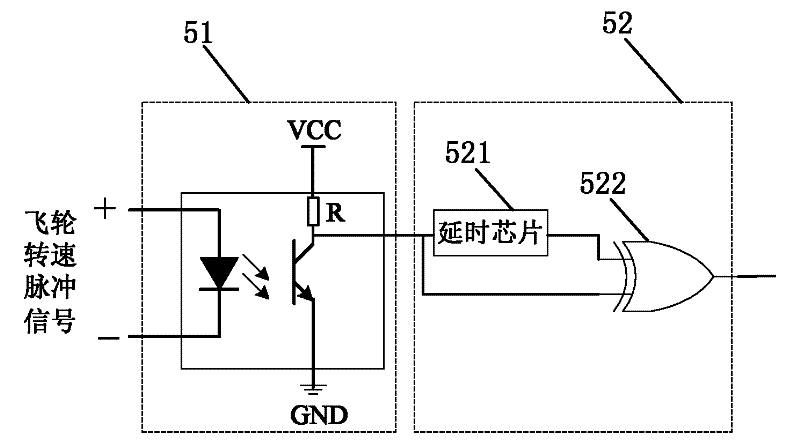
InactiveCN102288340ASimple designImprove calculation accuracyWork measurementTorque measurementCommunication interfaceControl system
The invention provides a reaction flywheel output torque measuring circuit and a measuring method thereof and relates to the field of measurement on output torque of a reaction flywheel, and solve the circuit and method provided by the invention can be used for solving the problems in measuring the output torque of the reaction flywheel in the calculation process of a dynamical model. The microprocessor of the circuit is connected to a communication interface, a counter and an integral module, and acquires a flywheel rotating speed direction signal and a 50ms pulse signal; the integral moduleacquires a flywheel rotating speed pulse signal; the counter is further connected to a crystal oscillator; and the communication interface outputs the signals of a dynamical calculation module. The method comprises the following steps of: initializing the microprocessor and the counter, wherein 50ms pulse interruption is superior to flywheel rotating speed pulse interruption; performing the 50ms pulse interruption: recording T50, setting flag to be equal to 1 and quitting the interruption; and performing the flywheel rotating speed pulse interruption: 1, adding 1 to the count value, performing a step 2 if the flag is equal to 1, otherwise, quitting the interruption; 2, reading Tflag, and calculating the rotating speed of the reaction flywheel within a current calculation cycle; 3, calculating moment; and 4, sending the moment to the dynamical model and quitting the interruption. The circuit and method disclosed by the invention are applied to dynamically testing a satellite attitude control system.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Remotely-operable reciprocating compactor
Embodiments of the present disclosure include a remotely-operable percussion compactor comprising: a primary power source; a plurality of electric motors coupled to the primary power source and attached to the compactor body; a plurality of reaction wheels coupled to respective electric motors; an inertial measurement unit (IMU); a remote control interface; and a controller configured to: receive one or more commands from the remote-control interface and a feedback signal from the IMU, and set a desired operating condition for at least one of the electric motors based on at least one of the feedback signal and the one or more commands. In some embodiments, the controller can be configured to determine an angular disturbance relative to at least one rotational axis of the compactor; and set the desired operating condition for one or more electric motors to generate a reactive force to at least partially counteract the angular disturbance.
Owner:WILLIAMS JASON A
Wheel speed control system for spacecraft with rejection of null space wheel momentum
InactiveUS6141606ACosmonautic vehiclesDigital data processing detailsMomentumSpacecraft attitude control
A spacecraft attitude control system uses at least four reaction wheels In order to minimize reaction wheel speed and therefore power, a wheel speed control means system is provided. The wheel speed control means monitors the wheel speeds and controls wheel speed nullspace components to keep the wheel speeds as small as possible.
Owner:SPACE SYST LORAL INC
Aircraft brake assembly
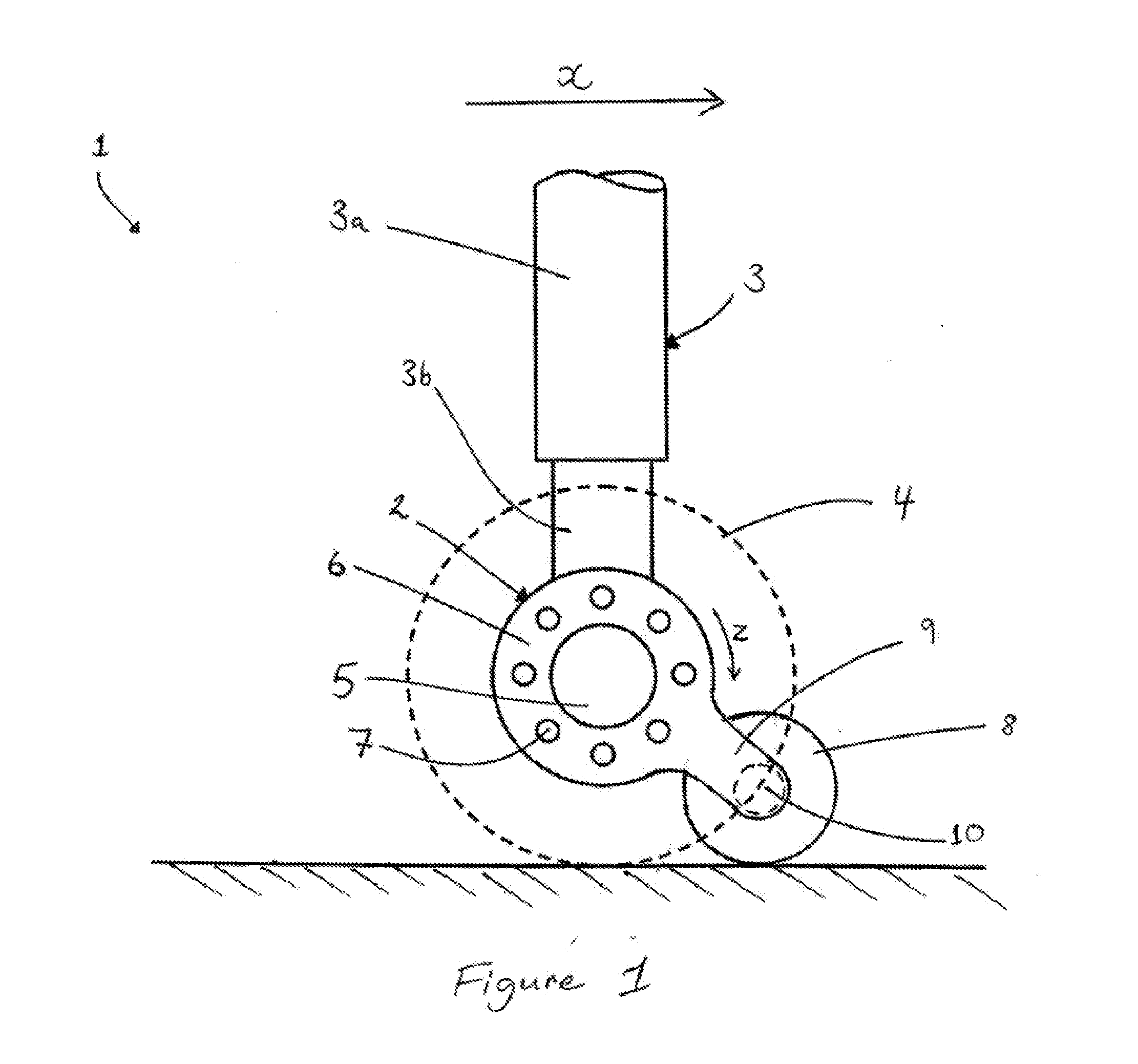
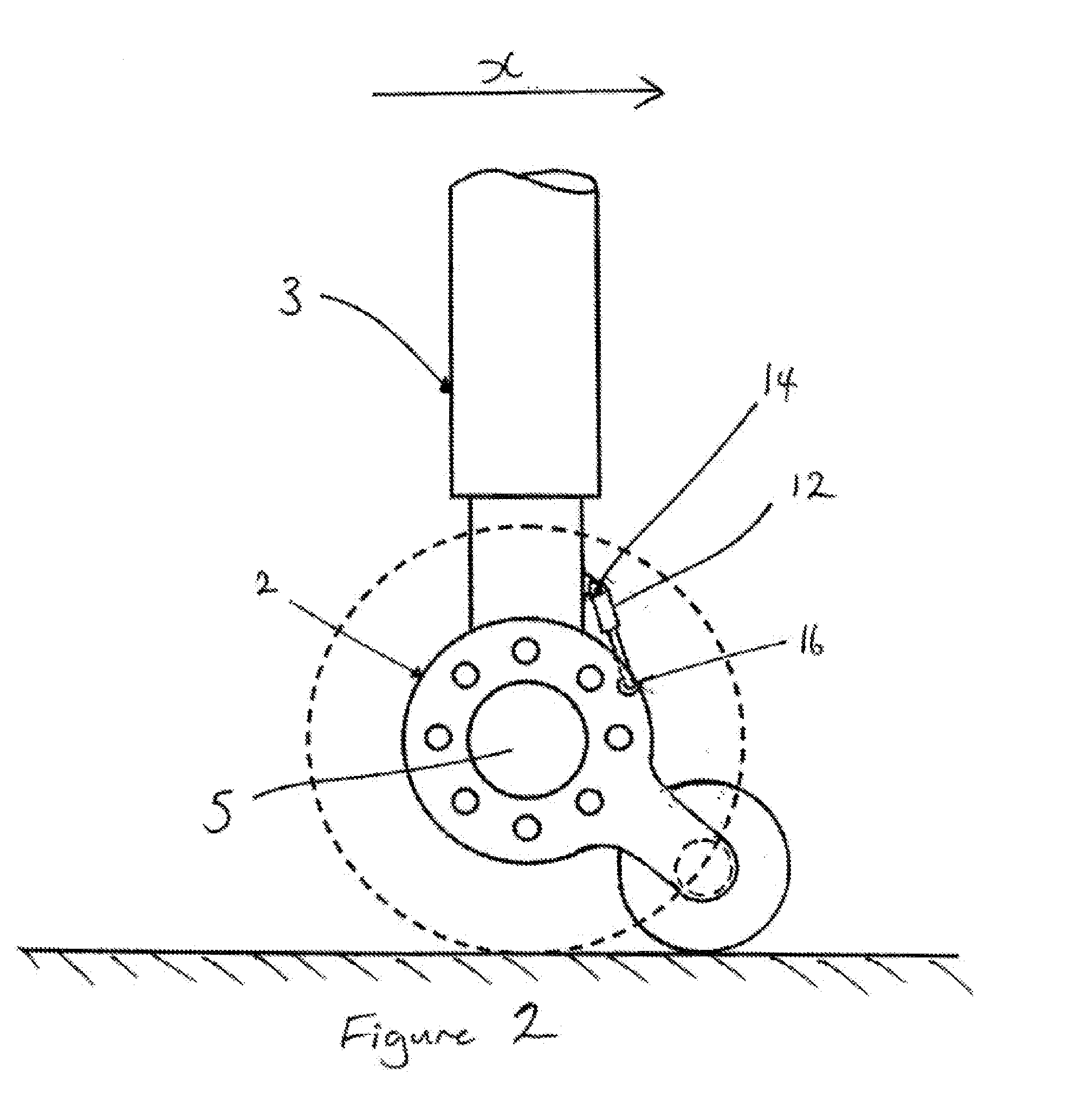
ActiveUS20150136902A1Avoid accidental movementOscillation be reduced and preventedAircraft braking arrangementsWheel arrangementsReaction wheelAirplane
Owner:MESSIER DOWTY
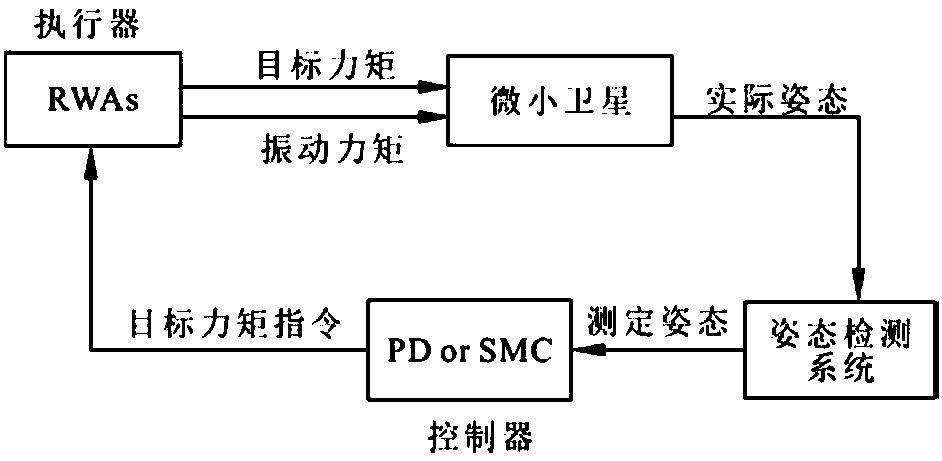
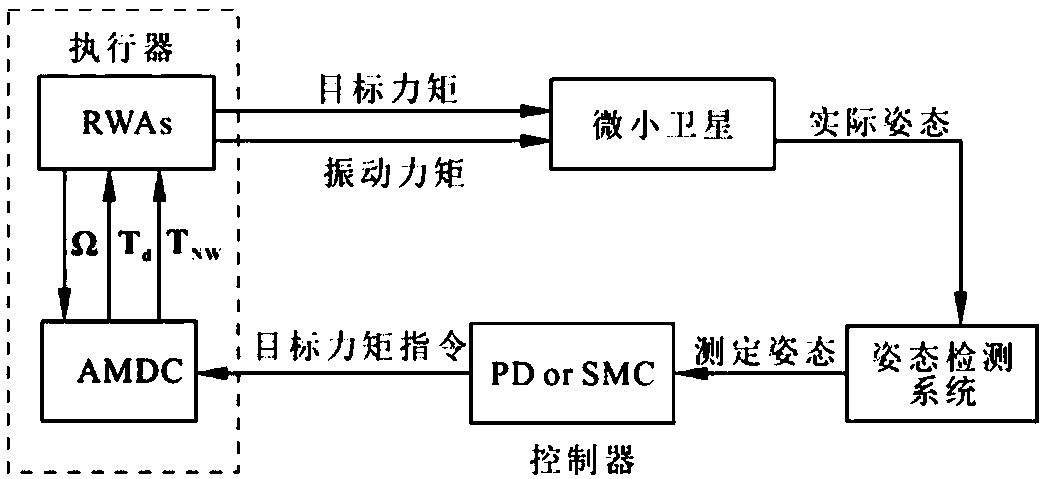
Counteractive wheel set adaptive moment distribution control method based on microsatellite
ActiveCN108327927AReduce the impactCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusDistribution controlMicrosatellite
The invention discloses a counteractive wheel set adaptive moment distribution control method based on a microsatellite. According to the method, after an attitude detecting system transmits a measured microsatellite attitude to a controller, the controller calculates targeted moment which should be applied according to the measured attitude, speeds of various counteractive wheels are used as feedback amounts, moments to be generated of the different counteractive wheels are distributed again, the various counteractive wheels carry out various distributed moments, and attitude regulation and control of the microsatellite are finished. According to the method, the counteractive wheel sets are arranged in a whole control loop, the moments are adaptively distributed according to the current rotating speed of the counteractive wheels, thus, the targeted moment can be generated by the counteractive wheels at low rotating speed, and influence of vibration of the counteractive wheels to attitudes of the satellite is relieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
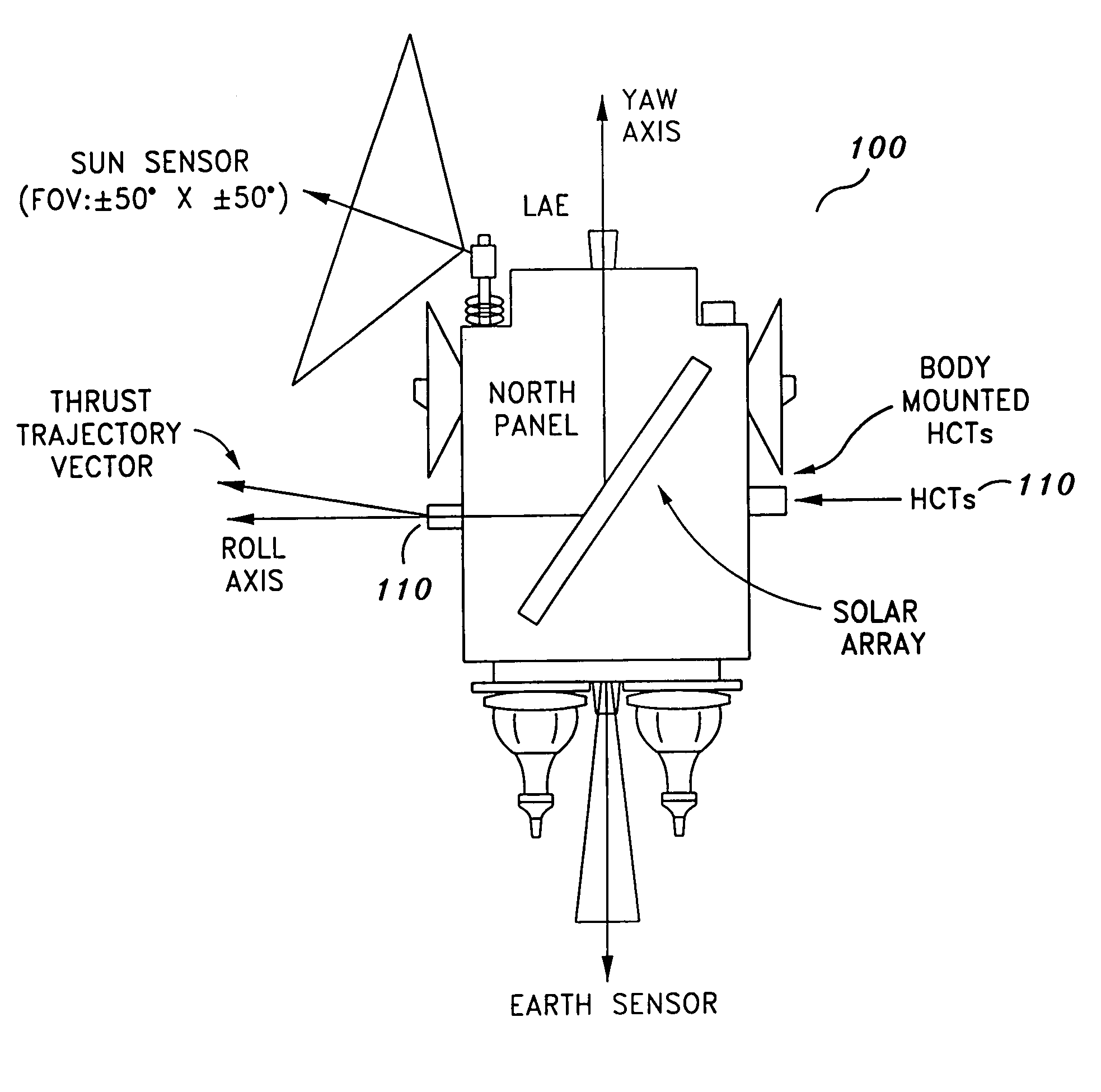
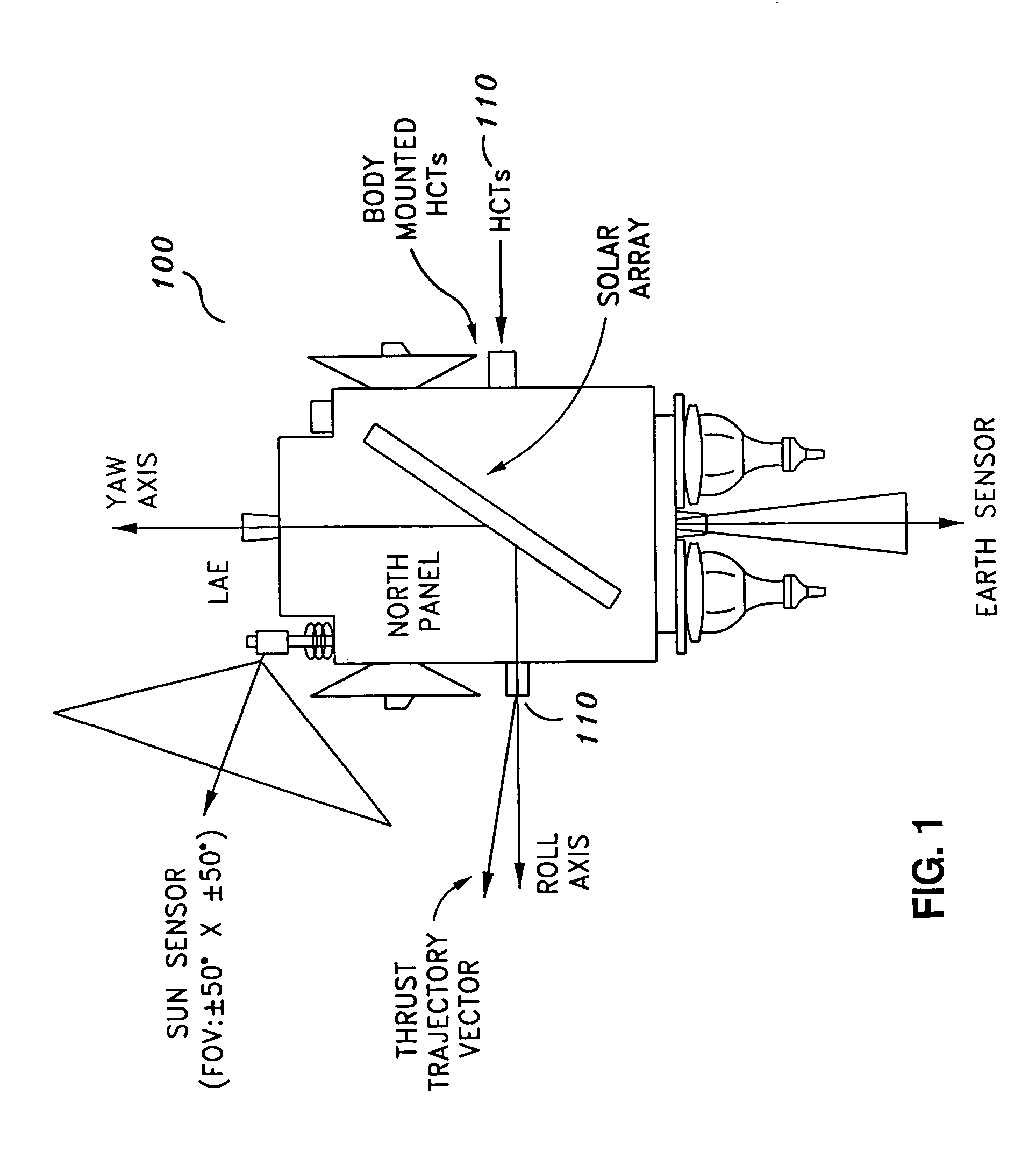
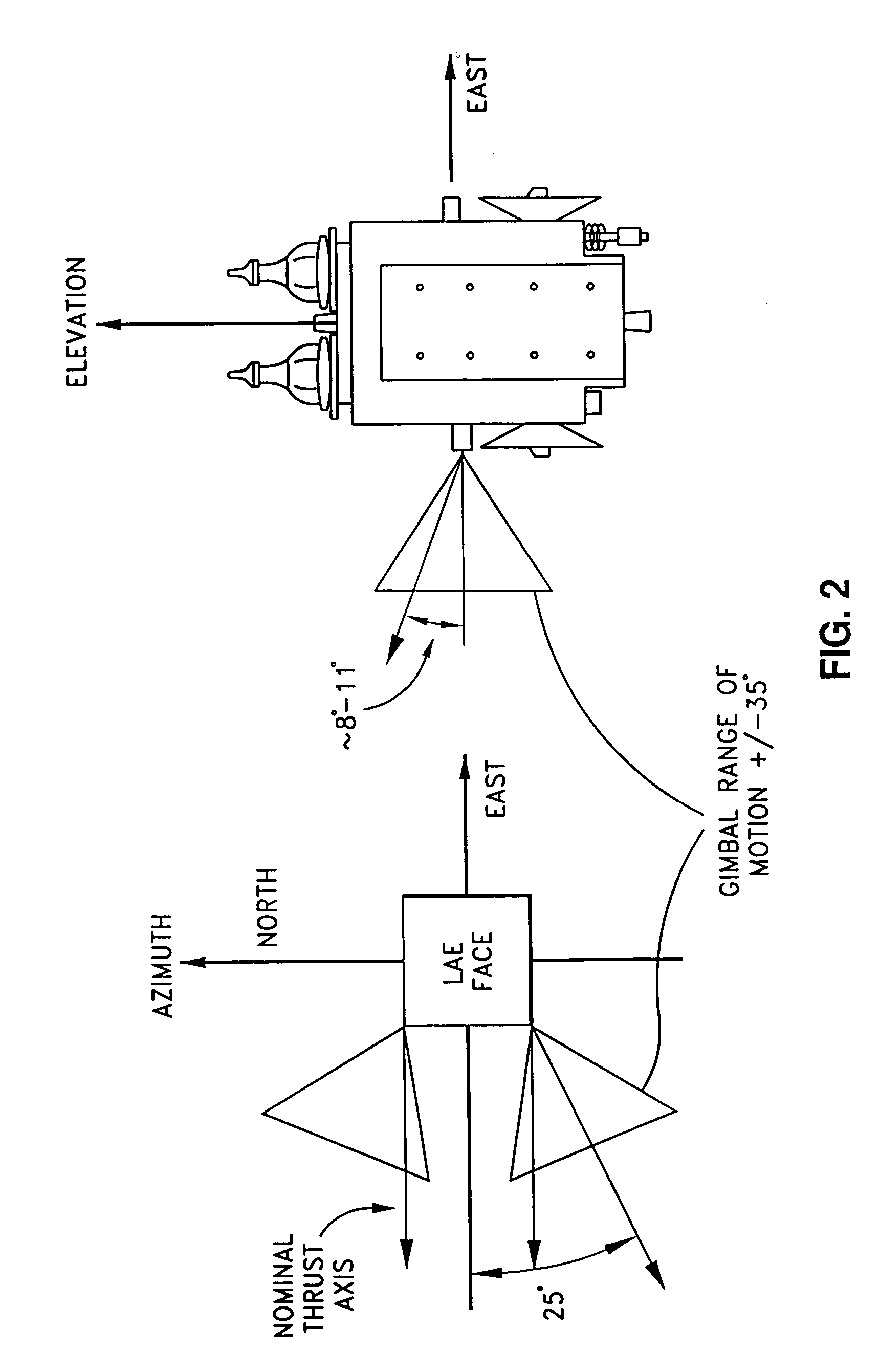
Precision attitude control system for gimaled thruster
ActiveUS20060049315A1Simple control arrangementPrecise attitude controlLaunch systemsRocket engine plantsMomentumControl system
A system for providing attitude control with respect to a spacecraft is provided. The system includes a reaction wheel control module configured to control a number of reaction wheel assemblies associated with the spacecraft in order to control attitude, and a maneuver control module configured to use a number of gimbaled Hall Current thrusters (HCTs) to control the total momentum associated with the spacecraft during an orbit transfer. The total momentum includes the momentum associated with the reaction wheel assemblies and the angular momentum of the spacecraft. Using the gimbaled HCTs to control the momentum associated with the reaction wheel assemblies during the orbit transfer results in minimal HCT gimbal stepping.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
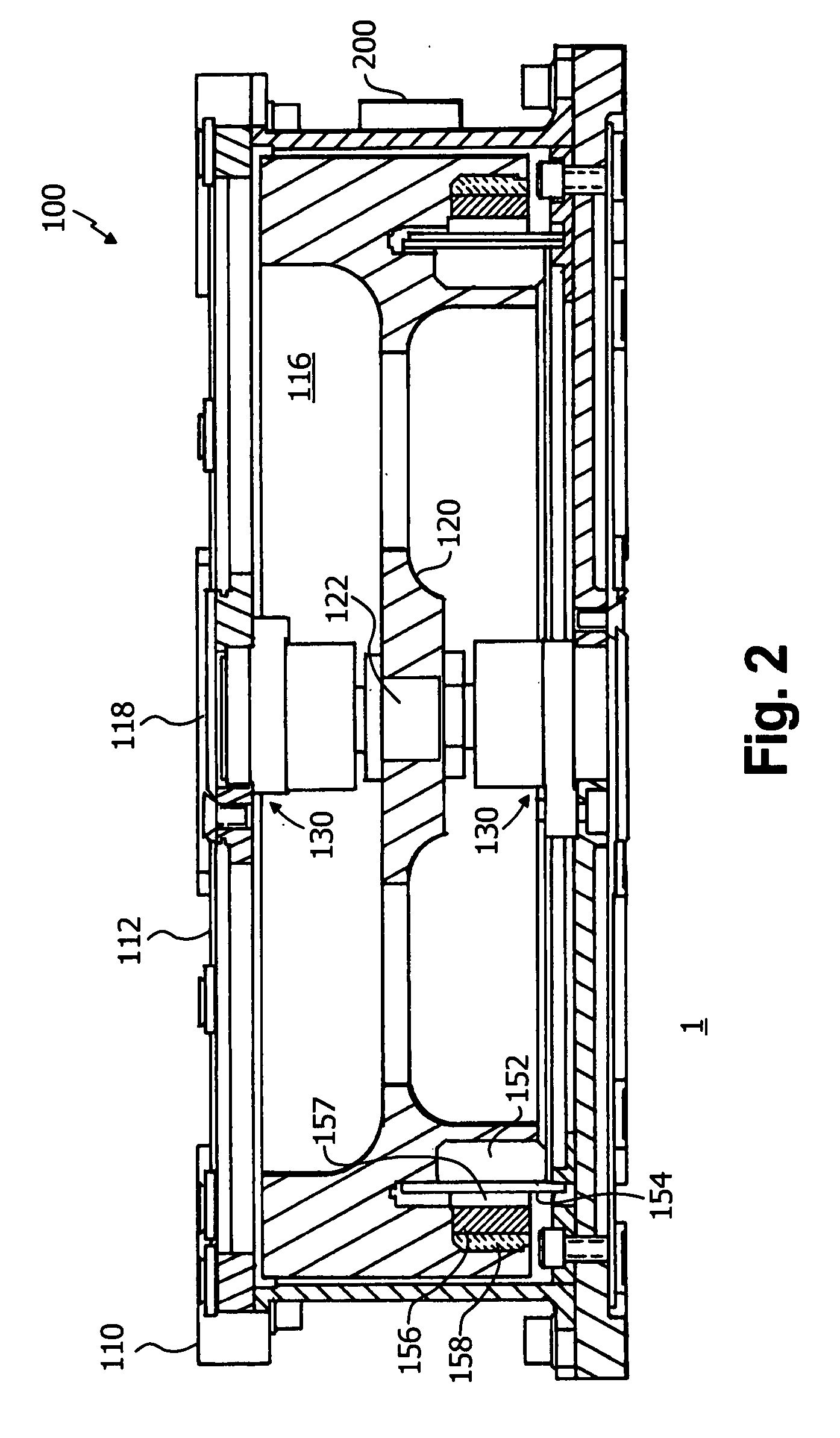
High-torque, low power reaction wheel array and method
Methods and apparatus are provided for reaction wheel (RW) assemblies for spacecraft. The apparatus comprises a M / G coupled to an inertia wheel and a controller coupled to the M / G that, in response to commands it receives, couples power to or from an M / G of another RW assembly over a shared transfer connection (VXFR), so that one M / G acts as a generator powering another M / G acting as a motor. The controller compares generator voltage VGEN to the BEMF of the motor on VXFR and reconfigures a multi-winding M / G or steps-up the generated voltage to maintain VGEN>VXFR to maximize direct energy transfer from one RW to the other as long as possible. When VGEN declines sufficiently, the controller can couple the motor to the spacecraft power bus and / or the generator to a power dump so as to continue to provide the commanded torque if needed. Operation is automatic.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
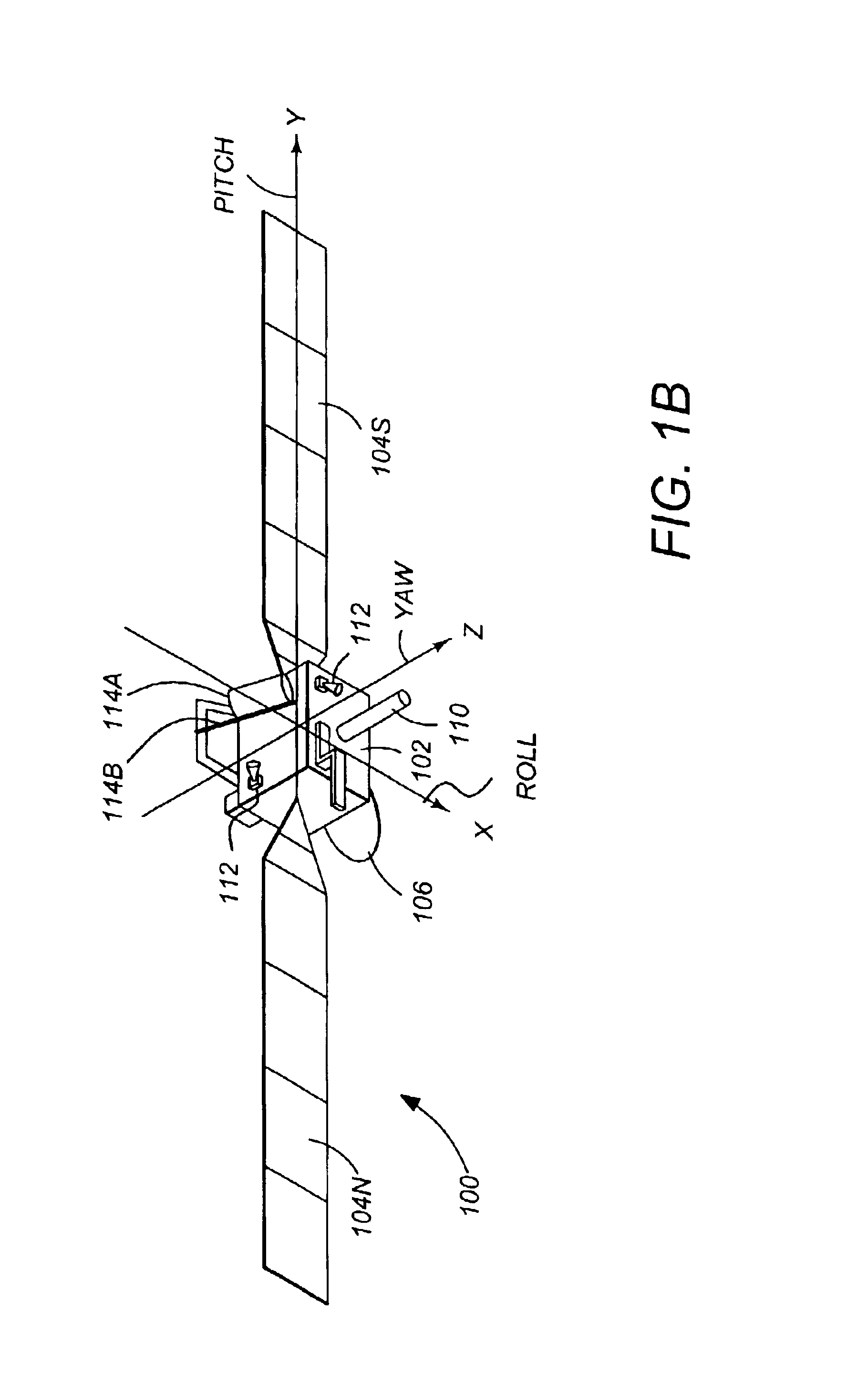
Method and apparatus for reaction wheel dynamic compensation in long-duration deployment of a large reflector
InactiveUS6990396B2Reduce heat dissipationReduce power consumptionCosmonautic vehiclesDigital data processing detailsMomentumEngineering
A method and an apparatus for controlling the attitude and momentum of a spacecraft while deploying an appendage from the spacecraft. The method comprises the steps of predicting an environmental torque the spacecraft will be subjected to during deployment of the appendage, computing a magnitude and a direction of momentum to add to the spacecraft to at least partially oppose the predicted environmental torque, and storing the computed magnitude and direction of momentum in at least one of the momentum wheels before deploying the appendage.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
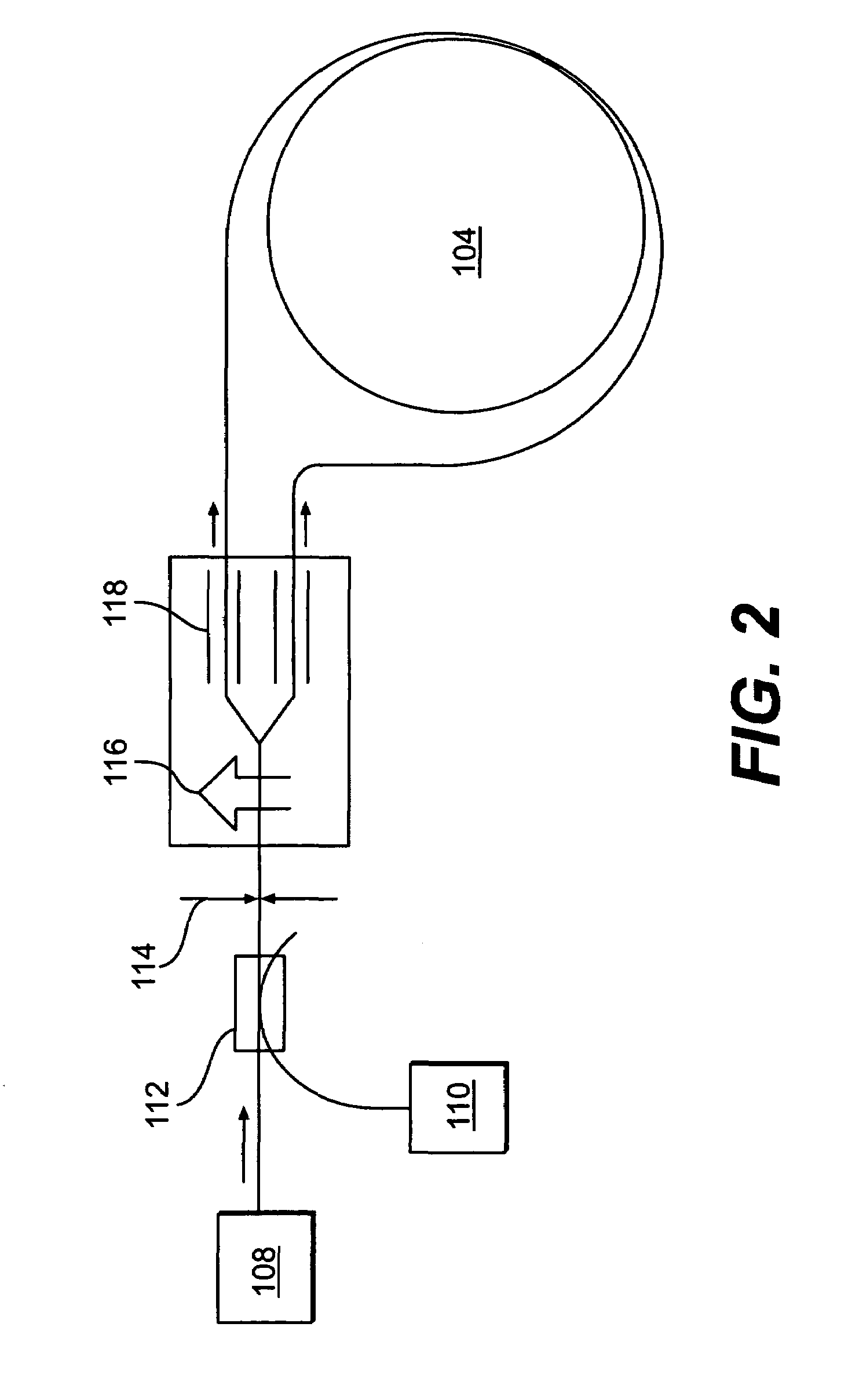
Integrated reaction wheel assembly and fiber optic gyro
The present invention relates to a reaction wheel assembly and fiber optic gyro device. The device includes a reaction wheel assembly having a reaction wheel assembly housing, a fiber optic gyro coil integrated with the reaction wheel assembly housing, and a fiber optic gyro electronics integrated with the reaction wheel assembly housing. The fiber optic gyro coil may be wound around the reaction wheel assembly housing. The gyro coil may also be located within the reaction wheel assembly housing.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com