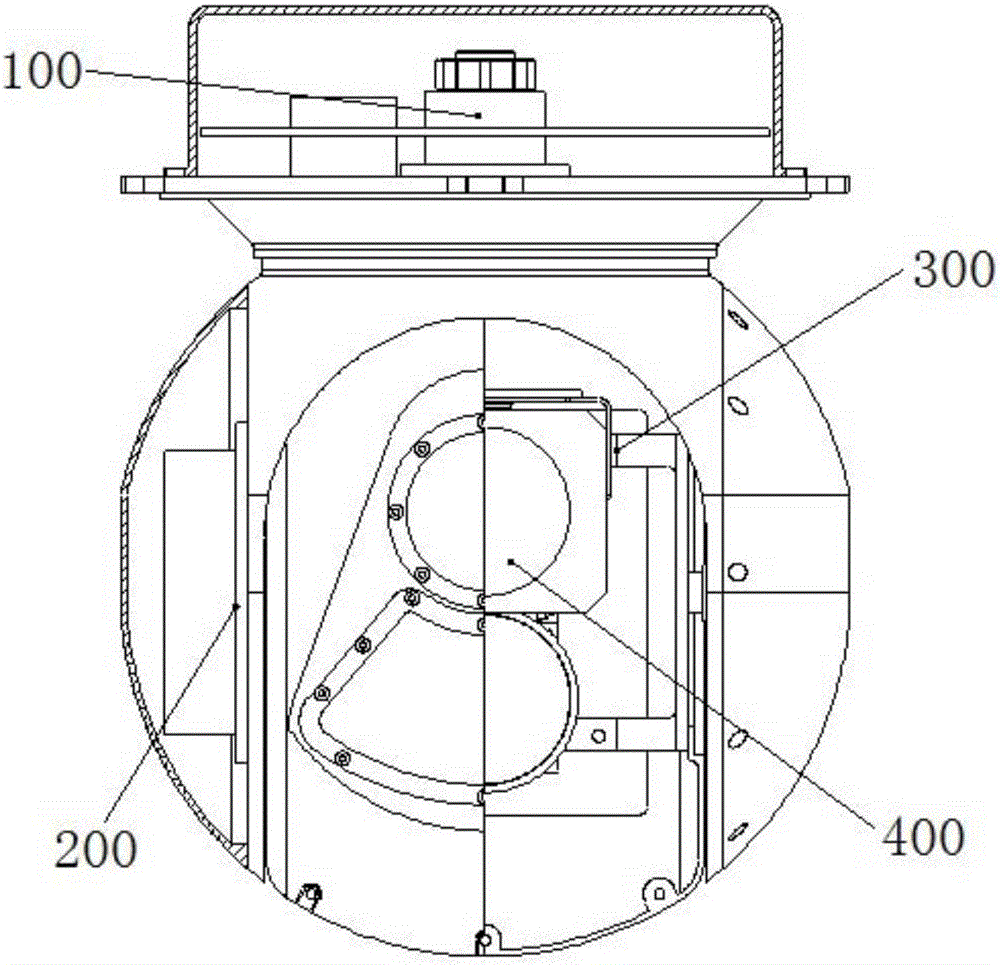
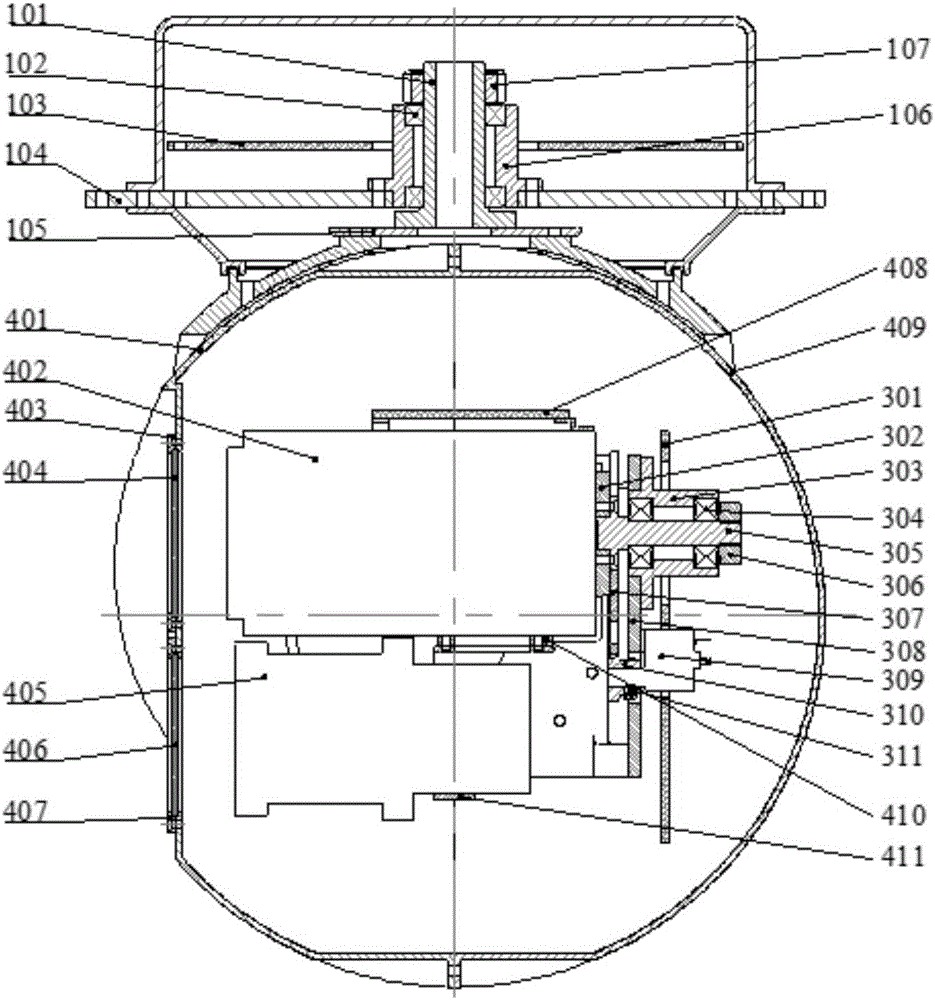
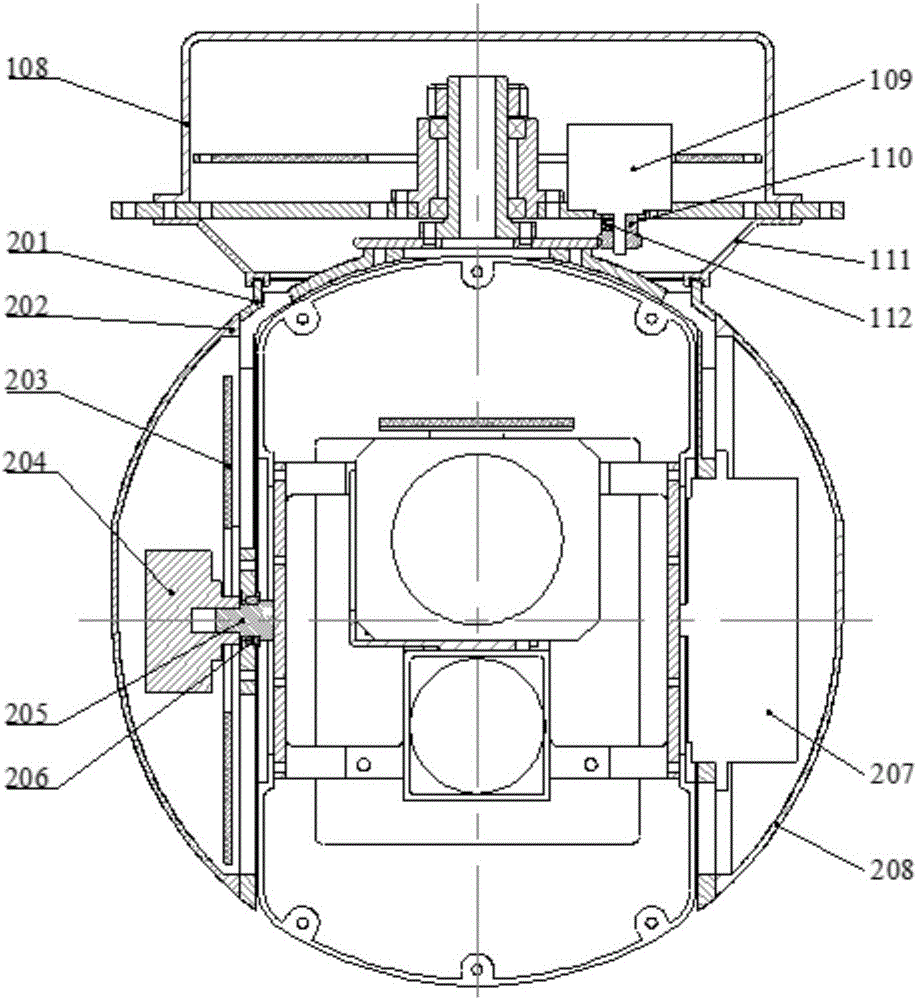
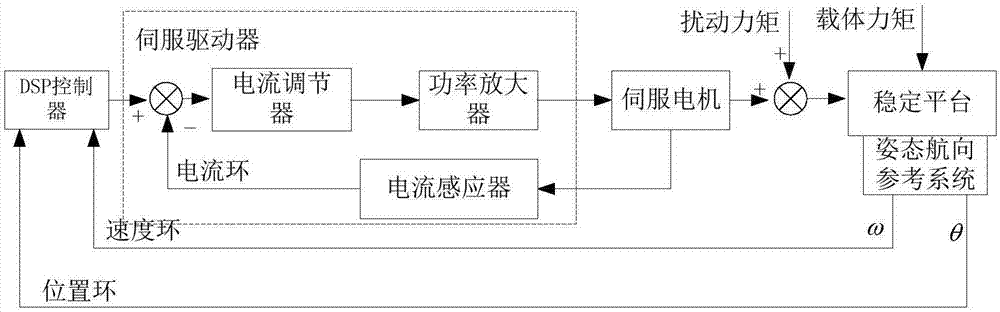
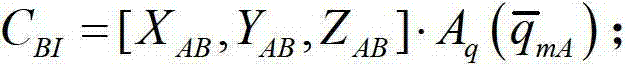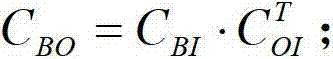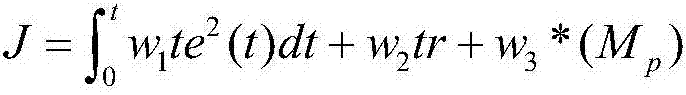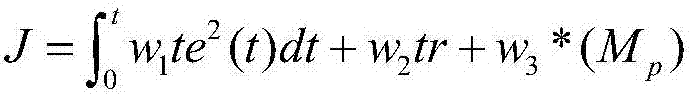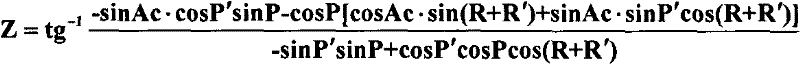Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
68 results about "Three-axis stabilisation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Three-axis stabilisation involves the use of three gyroscopes—one for each axis —to keep satellites correctly oriented in space. The same technology is used to 'steer' guided missiles, but it involves only 2 gyroscopes. This is normally accomplished by use of Reaction wheels.
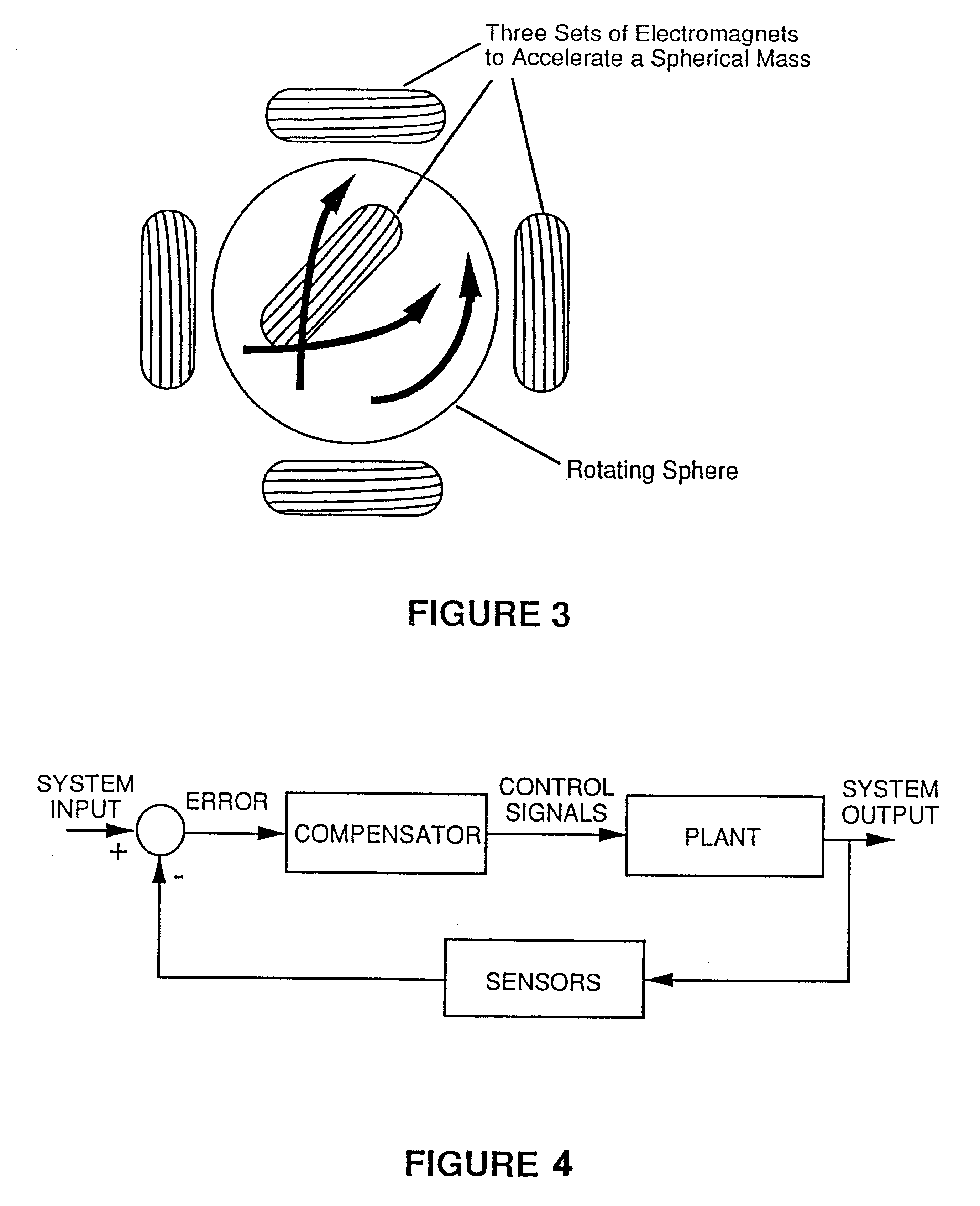
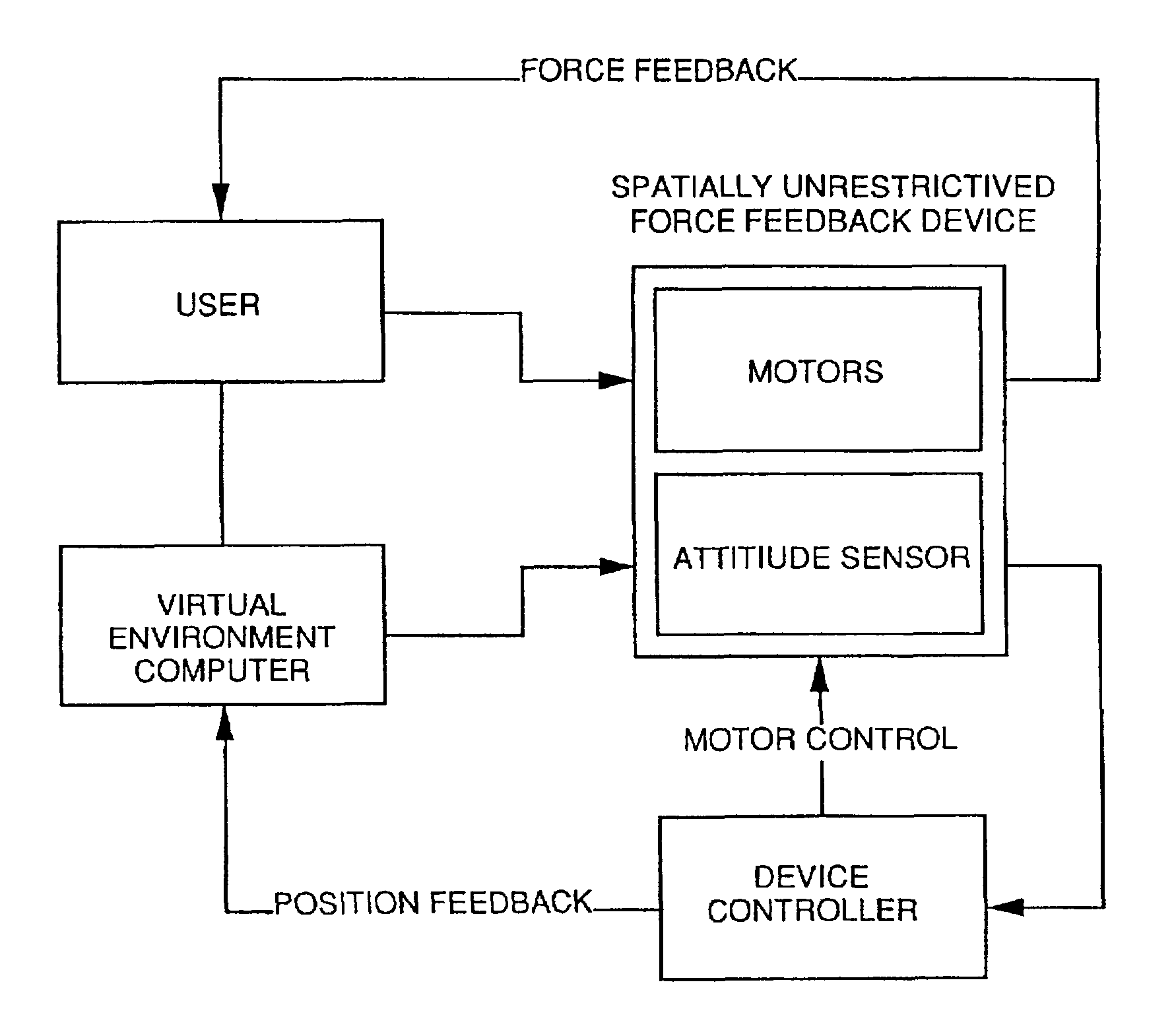
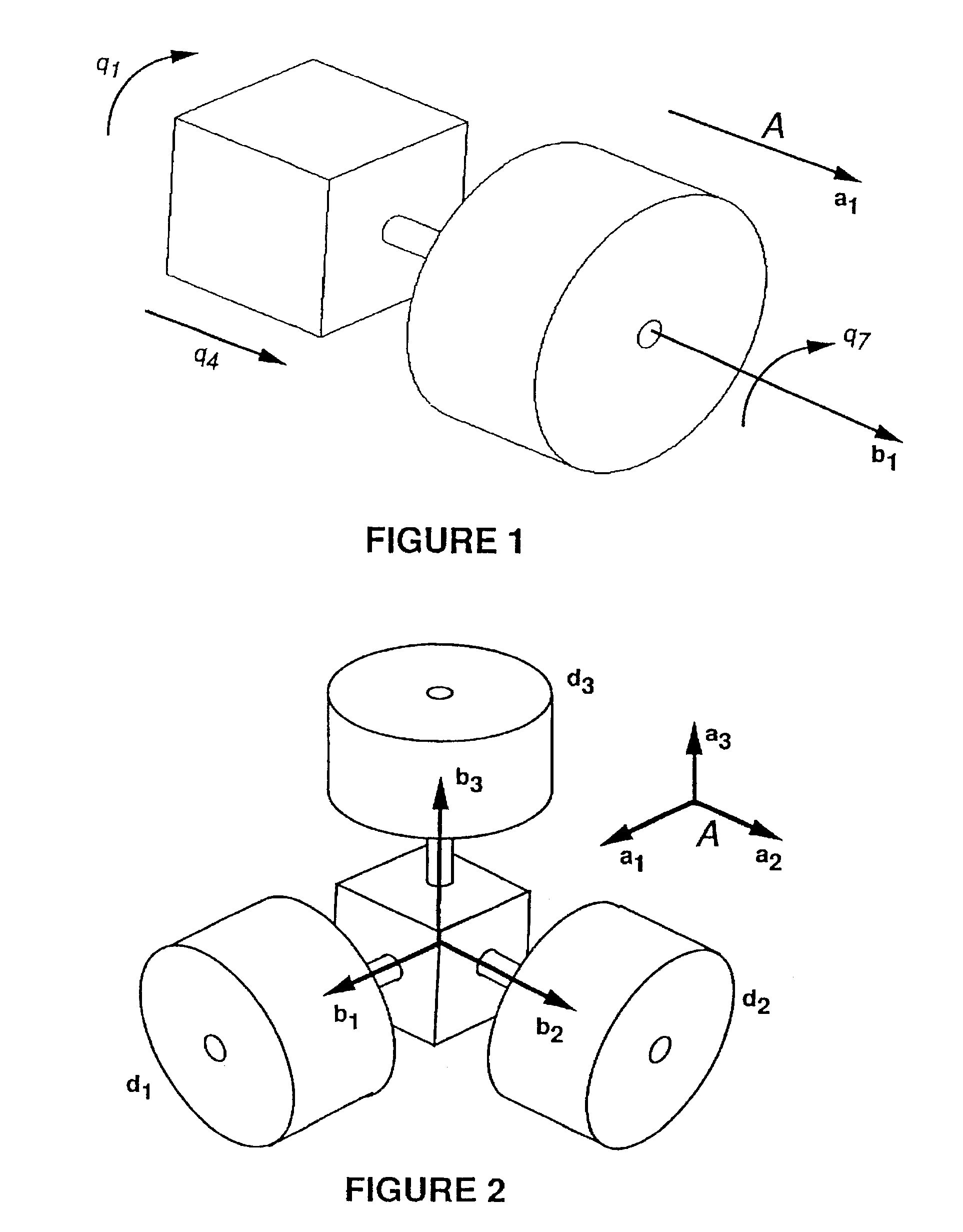
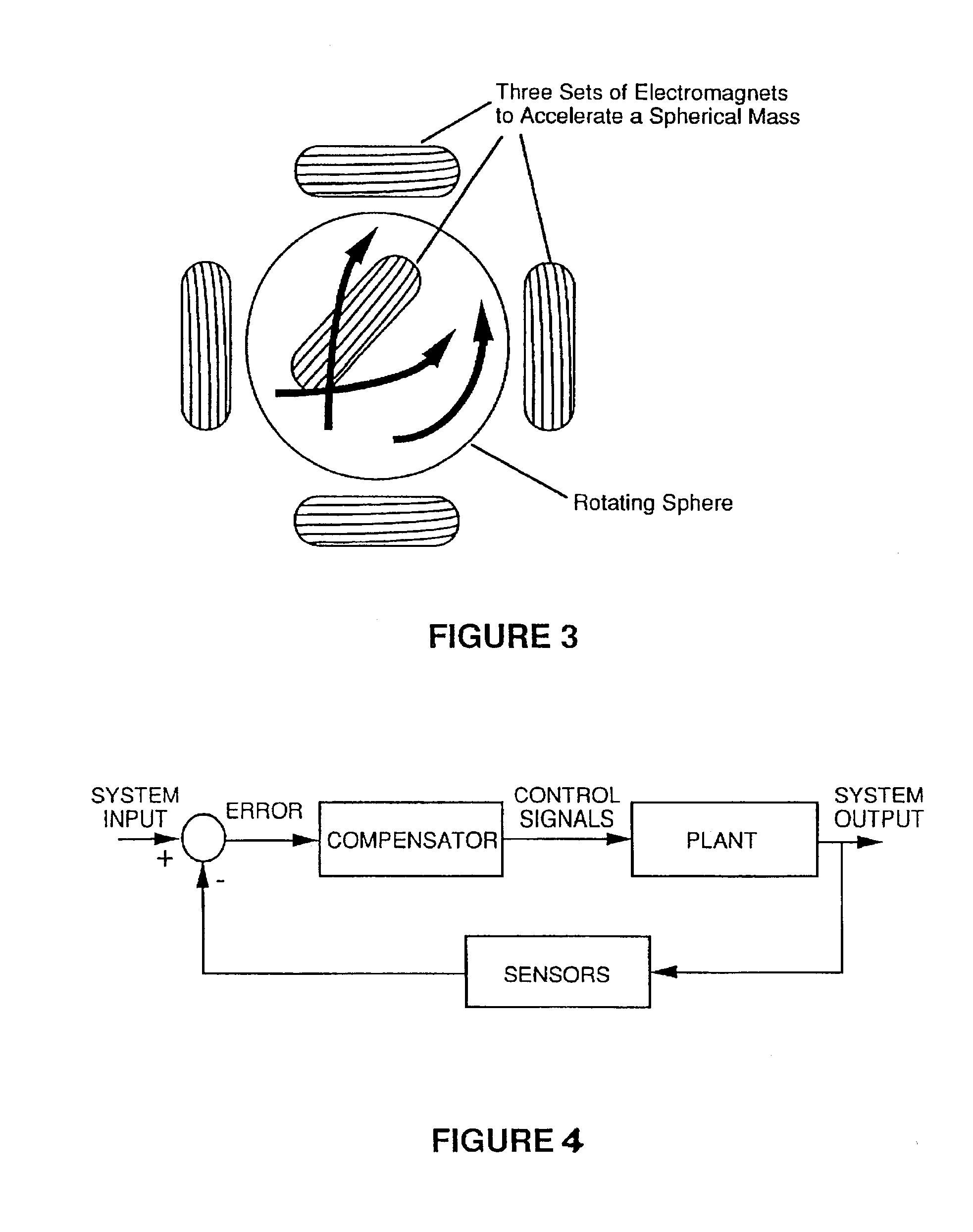
Gyro-stabilized platforms for force-feedback applications
InactiveUSRE37374E1Input/output for user-computer interactionProgramme-controlled manipulatorJoystickGyroscope
Force feedback in large, immersive environments is provided by device which a gyro-stabilization to generate a fixed point of leverage for the requisite forces and / or torques. In one embodiment, one or more orthogonally oriented rotating gyroscopes are used to provide a stable platform to which a force-reflecting device can be mounted, thereby coupling reaction forces to a user without the need for connection to a fixed frame. In one physical realization, a rigid handle or joystick is directly connected to the three-axis stabilized platform and using an inventive control scheme to modulate motor torques so that only the desired forces are felt. In an alternative embodiment, a reaction sphere is used to produce the requisite inertial stabilization. Since the sphere is capable of providing controlled torques about three arbitrary, linearly independent axes, it can be used in place of three reaction wheels to provide three-axis stabilization for a variety of space-based and terrestrial applications.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
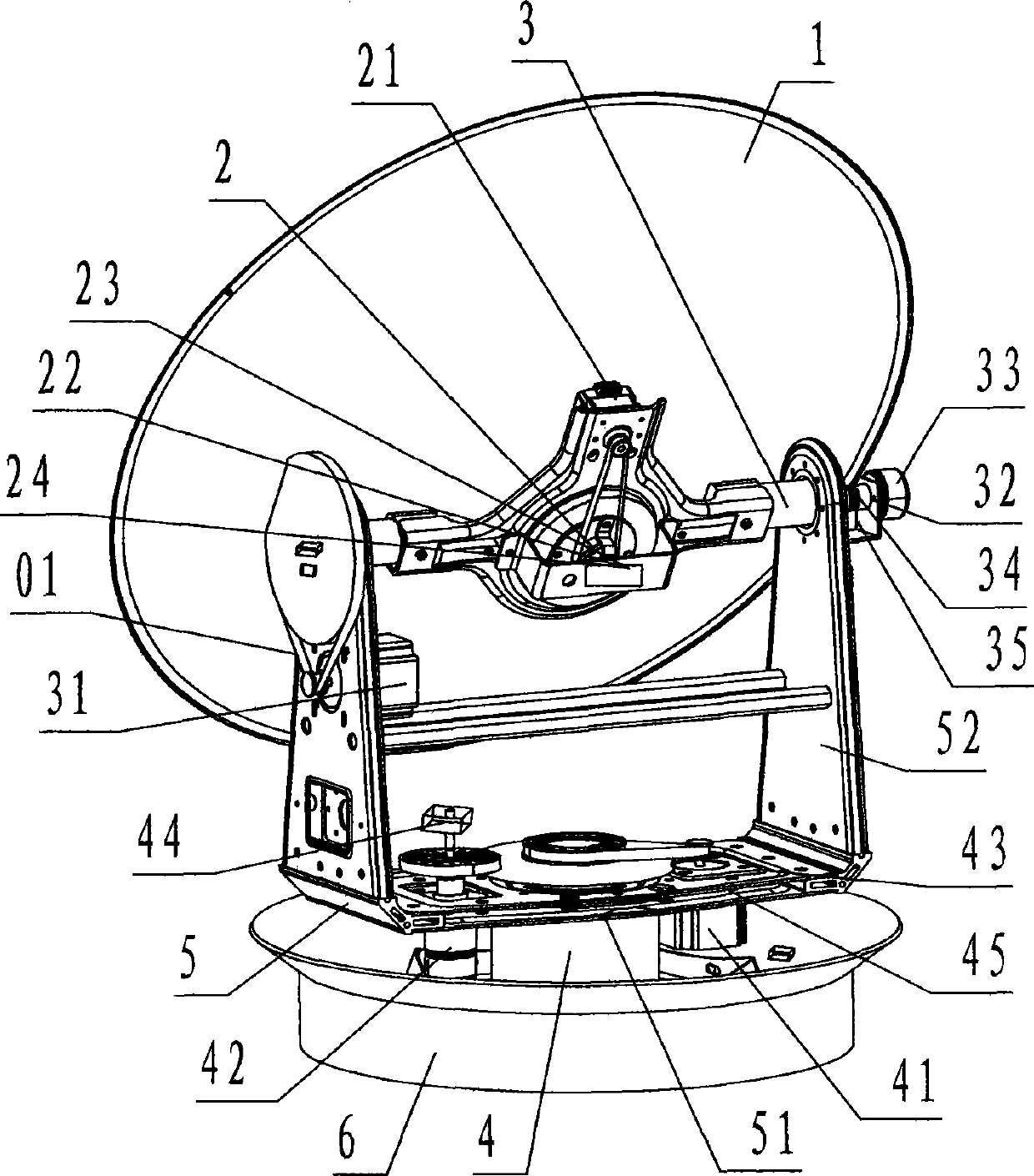
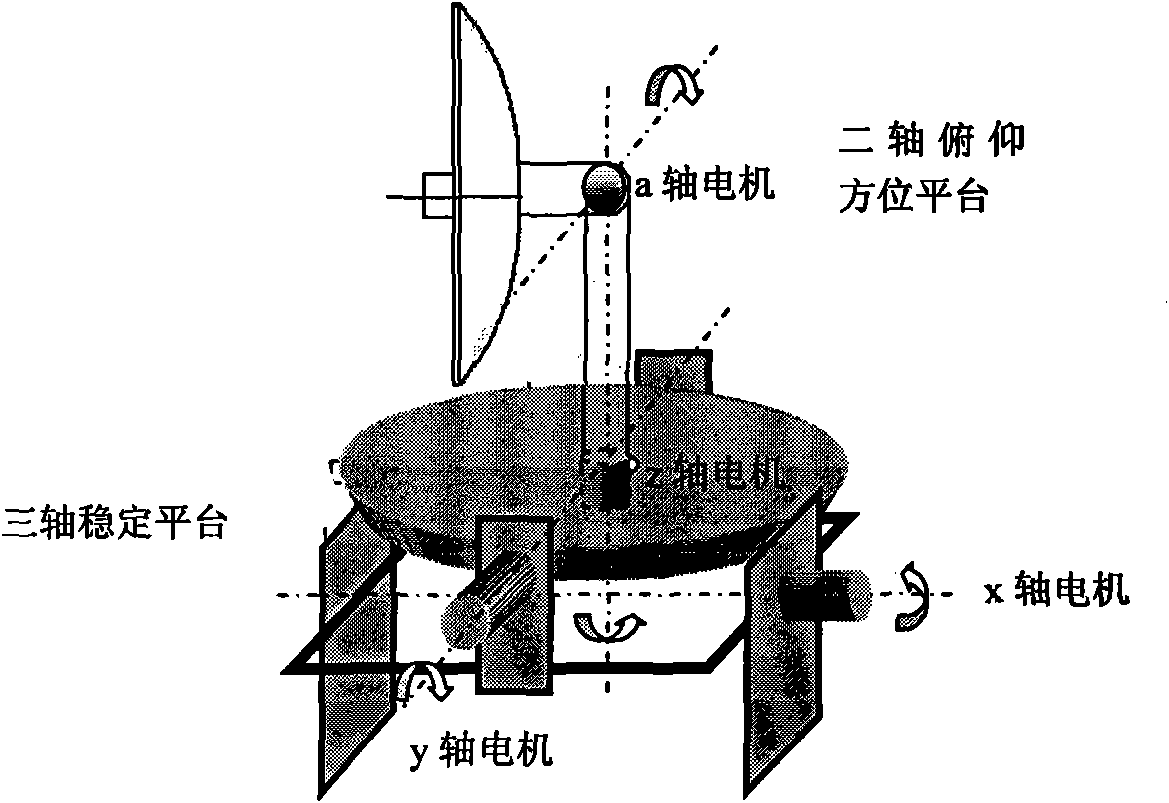
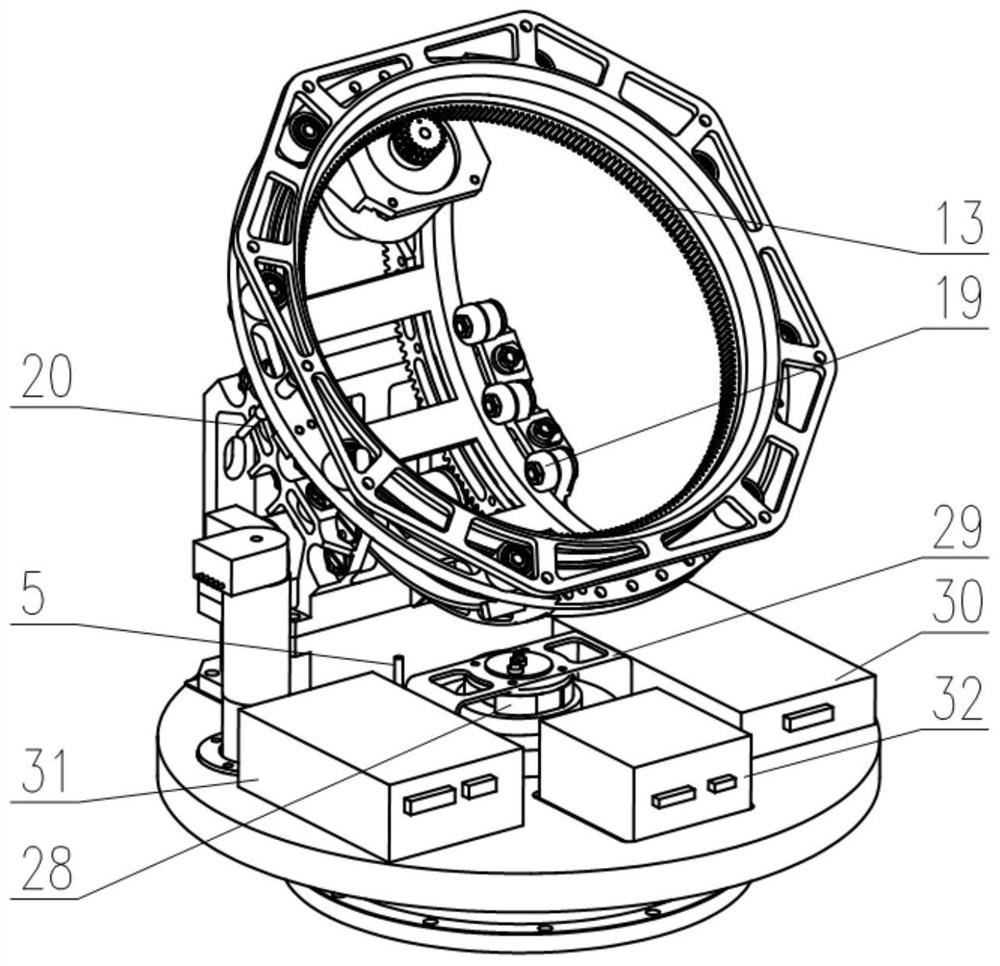
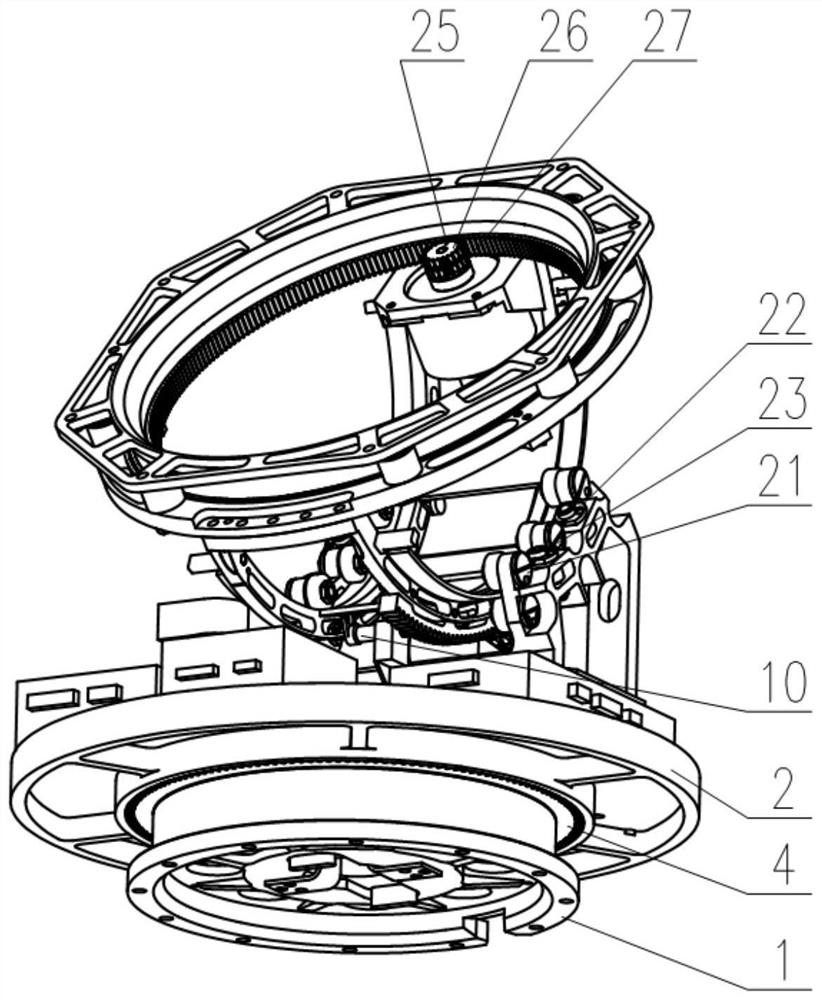
Three-axis stable follow-up tracking device of shipborne satellite antenna
InactiveCN103138050AKeep moving parallelLow costAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesNatural satelliteDevice form
The invention discloses a three-axis stable follow-up tracking device of a shipborne satellite antenna. The three-axis stable follow-up tracking device of the shipborne satellite antenna comprises a parabolic antenna (1), a roll rotary shaft (2), a pitching rotary shaft (3), as azimuth rotary shaft (4), a support (5) and a base seat (6). Due to the adoption of a three-axis rotation device formed by the components and the technical scheme including that the azimuth rotary shaft is fixedly connected in the center of the bottom of the base seat in a vertically upward mode, the center of a cross beam of the support is rotationally connected at the upper end of the azimuth rotary shaft, the pitching rotary shaft is rotationally and horizontally arranged on the upper portions of two stand supports of the support, the roll rotary shaft is located above the center position of the pitching rotary shaft and in rotational orthogonality connection with the pitching rotary shaft, the parabolic antenna is fixedly connected on the roll rotary shaft, and a feedback system composed of a photoelectric sensor, a position potentiometer, an angular velocity sensor, an electronic compass, a rotary encoder and a global position system (GPS) receiver is adopted to replace a gyro system, the shipborne satellite antenna is enabled to achieve the purposes of being simplified in structure, lowered in cost, and easy to civilianize.
Owner:NINGBO SENFU MACHINERY & ELECTRIC MFG
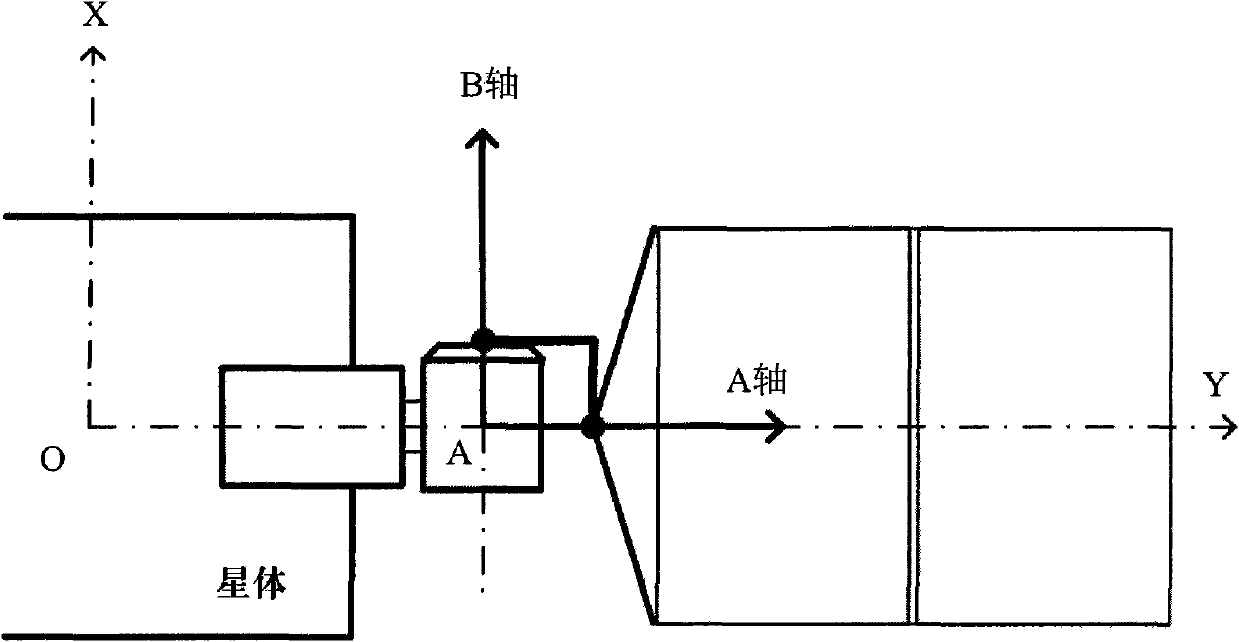
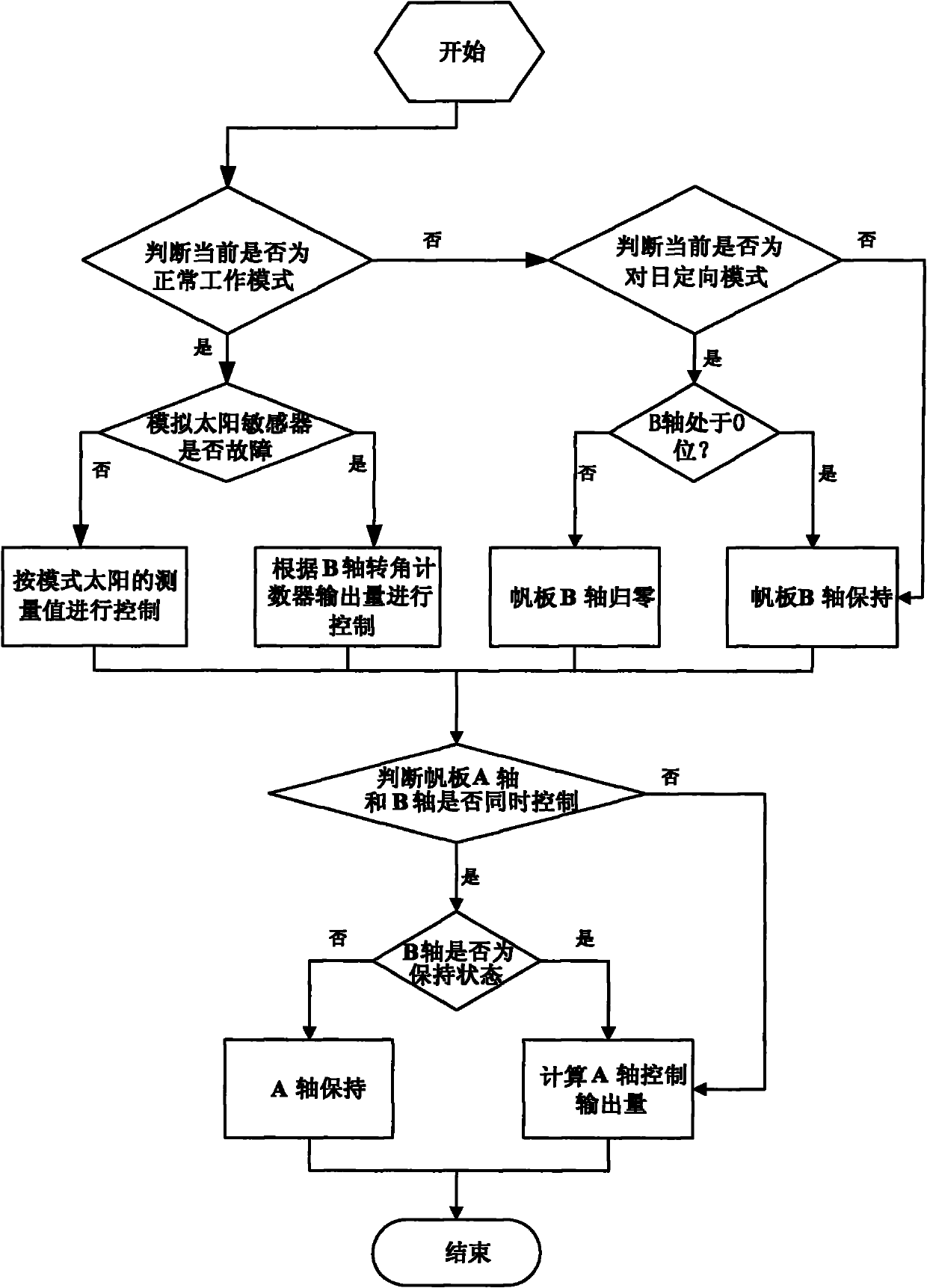
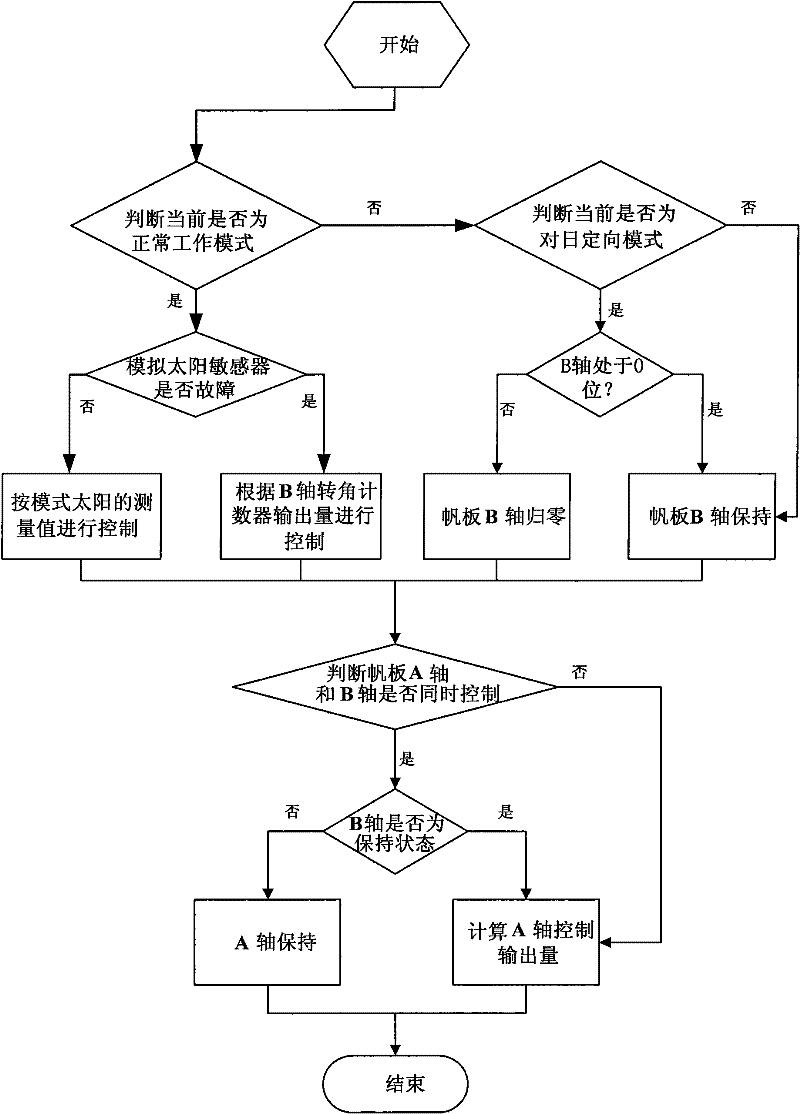
Non-sun-synchronous orbit satellite double-shaft sailboard control method
ActiveCN102004492ASimplify flight proceduresLow costPosition/course control in three dimensionsEnergy supplyRotational degrees of freedom
The invention discloses a non-sun-synchronous orbit satellite double-shaft sailboard control method. A double-shaft sailboard is a solar sailboard structure which has two rotational degrees of freedom and of which the two rotating shafts can independently control work. The double-shaft sailboard control method comprises a control method of each single-shaft sailboard in the double-shaft sailboard and an implementation method during double-shaft cooperative work of the sailboard. In the single-shaft control method of the sailboard, measurement modes and rotation strategies for the sailboard in different work modes of the satellite are mainly designed. In the double-shaft cooperative work method, the working order of each single shaft and the rotation logic are specified. The inconvenience that a non-sun-synchronous orbit satellite needs to frequently perform attitude maneuver to ensure the sailboard tracks the sun is solved by applying the double-shaft sailboard control method on a satellite. By the method, the satellite can track the sun in real time on orbit by controlling the rotation of the sailboard, so that the energy supply on the satellite is guaranteed, and the requirement of the satellite over the ground directional triaxial stability is met.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Antenna tracking system used for mobile satellite communication system
The invention relates to an antenna tracking system used for a mobile satellite communication system. The antenna tracking system is based on combination of multiple sensors for performing posture measurement, and fusion and estimation are performed on the combination of magnetic strength information, acceleration information and angular speed information. The method of three-axis stabilization plus dynamic search is adopted, and an inner ring for combined posture measurement compensation is used for realizing the three-axis stabilization, so as to prevent the posture of a carrier from being affected by the environment; and a strength signal output by a digital receiver is introduced into a controller as a feedback signal for constituting an outer ring for tracking a level signal, so that the way of double-ring nestification dynamic search of the maximum point in the signal can be formed for performing error compensation. The specific algorithm is as follows: utilizing a carrier rotation angular speed component measured by a three-axis gyroscope to perform Kalman filtering on a measured gravitational acceleration component and a geomagnetism induction density component, removing interferences caused by accelerated motion and an external magnetic field, further getting a true value, and finally utilizing the value to perform the posture resolution.
Owner:宗鹏 +1
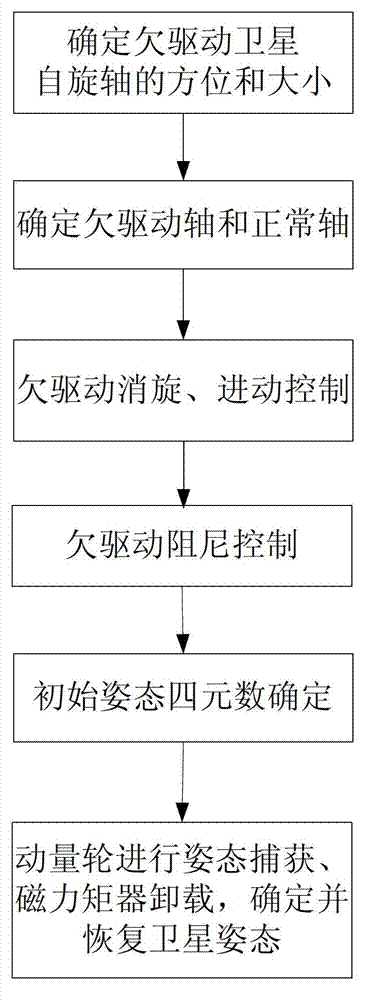
Method for building normal gestures of under-actuated high-speed spinning satellite
ActiveCN103112603AStrong engineering achievabilityPromote engineering applicationSpacecraft guiding apparatusMagnetic tension forceMomentum
The invention discloses a method for building normal gestures of an under-actuated high-speed spinning satellite. The method for building the normal gestures of the under-actuated high-speed spinning satellite comprises the following steps: (1) a spinning shaft of the under-actuated satellite is confirmed by means of output data of a gesture sensor; (2) an under-actuated shaft and a normal shaft are confirmed; (3) under-actuated spinning counteraction of the satellite is conducted and the satellite is controlled until the spinning top breaks away from saturation; (4) after the spinning top breaks away from saturation, under-actuated control is conducted on triaxial angle speeds; (5) quaternions of initial gestures are confirmed and renewed; (6) a momentum wheel is adopted to conduct gesture capture and magnetic torquer unloading, the satellite gestures are confirmed, and the satellite is recovered to normal triaxial stable gestures to the earth. The method for building the normal gestures of the under-actuated high-speed spinning satellite solves the problem that an under-actuated satellite with a certain channel losing air-injecting control ability recovers normal gestures.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Three-axis sun-oriented control method of satellite for guaranteeing satellite-earth link
ActiveCN106155074AGuarantee unimpededGuaranteed demand for Japanese orientationAttitude controlQuaternionSatellite orbit
The invention discloses a three-axis sun-oriented control method of a satellite for a guaranteeing satellite-earth link. The three-axis sun-oriented control method comprises the following steps: solving a projection of a sun vector under a satellite orbit coordinate system according to the sun vector calculated according to a satellite orbit; establishing a sun-oriented reference coordinate system according to the satellite orbit and the definition of the satellite polarity, and calculating an attitude quaternion of the sun-oriented reference coordinate system relative to the satellite orbit coordinate system; calculating an error quaternion between an attitude quaternion of a star relative to the satellite orbit coordinate system and the attitude quaternion of the sun-oriented reference coordinate system relative to the satellite orbit coordinate system; carrying out attitude reference tracking according to a symbol of the error quaternion; and when continuously meeting that the error quaternion is smaller than a preset threshold value, establishing a star sensor sun-oriented sign, carrying out three-axis stabilization sun-oriented control by virtue of a star sensor, and otherwise, continuing to carry out two-axis sun-oriented control based on sun sensor. By virtue of the three-axis sun-oriented control method, the smoothness of the satellite-earth link after the sun orientation of a sailboard can be guaranteed, and a near-optimal maneuvering path is guaranteed when a sun-oriented maneuvering manner is changed into a ground-oriented maneuvering manner.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
Method for determining and compensating full-field drift angle of space-based camera
ActiveCN104567819AImprove calculation accuracyWide applicabilityPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryEarth observationDrift angle
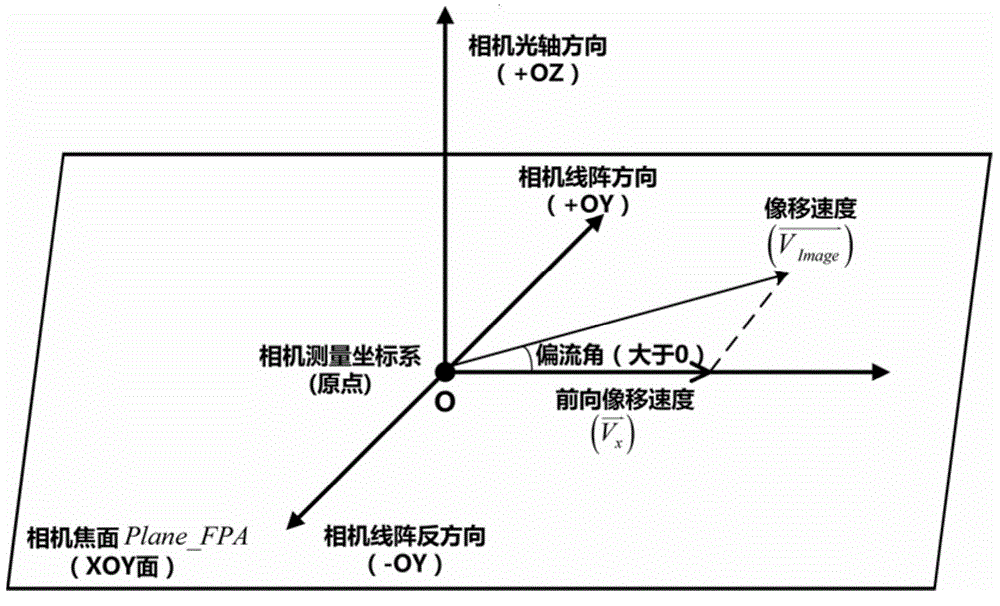
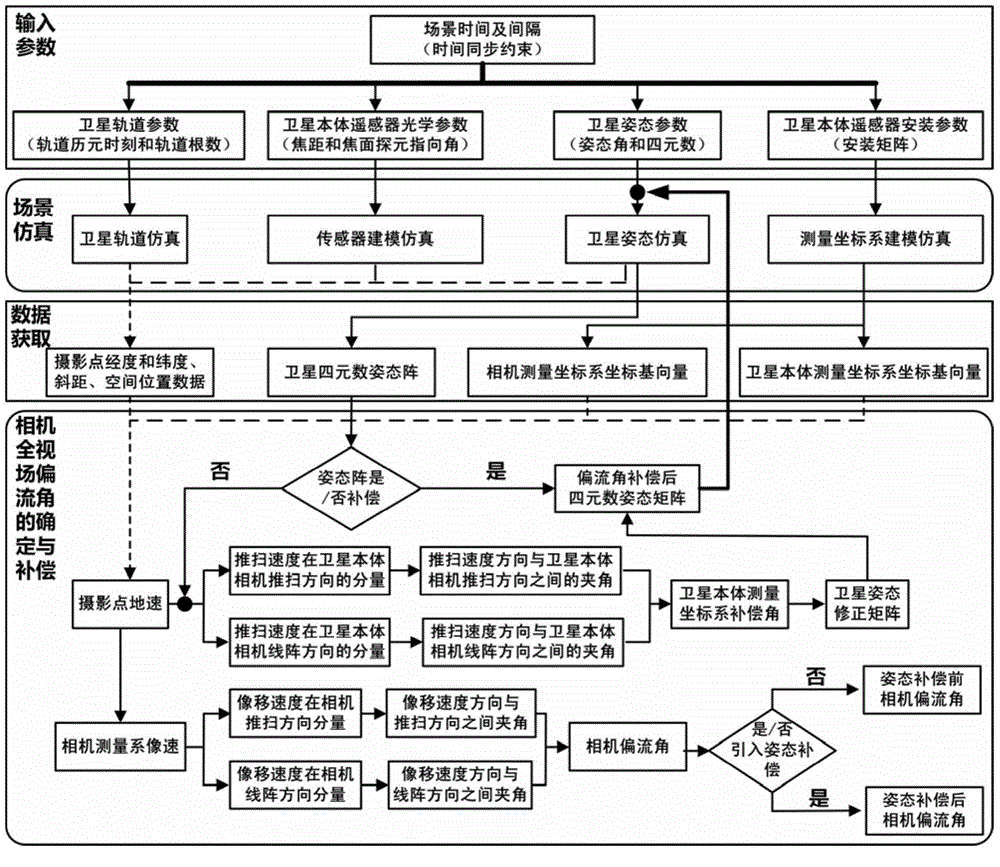
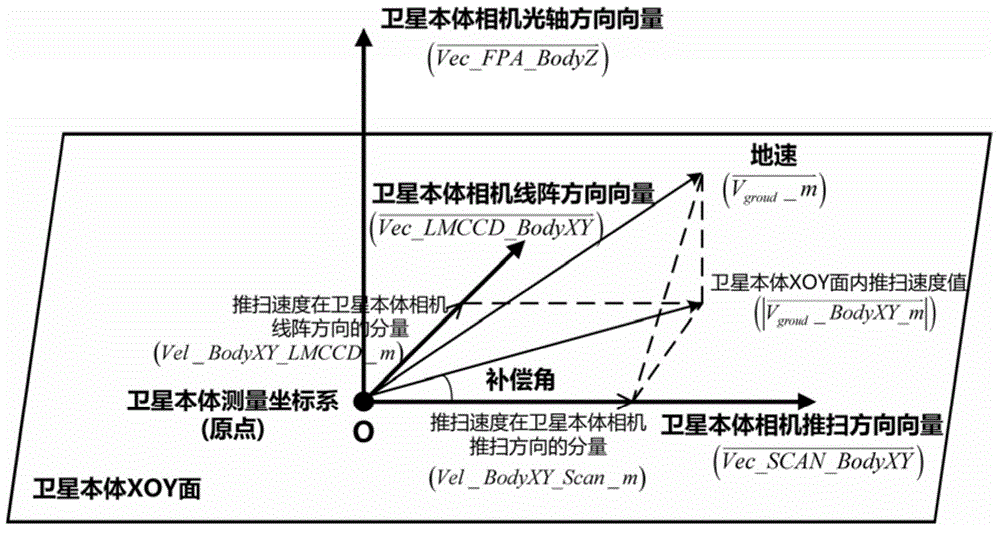
The invention discloses a method for determining and compensating a full-field drift angle of a space-based camera. The method comprises the following steps: (1) performing scene simulation and modeling, comprising performing high-precision modeling and simulation on the satellite orbit, attitude, camera measurement coordinate system, satellite body measurement coordinate system and different field sensors of the camera; (2) calculating the full-field drift angle of the camera under a geocentre terrestrial reference frame; (3) calculating a compensation angle of the satellite body measurement coordinate system; (4) calculating a compensation attitude quaternion matrix on the satellite drift angle; and (5) calculating the full-field drift angle of the camera subjected to attitude compensation. According to the method disclosed by the invention, after a three-axis stability satellite rotates around three axes of the satellite body, the problem that the full-field drift angle of the camera cannot be determined and compensated during earth observation of the satellite in a specific attitude can be solved, and the method can be used for determining the drift angle of a satellite-borne large-field camera, designing and verifying the drift angle compensation method and optimizing the satellite design in the satellite development process.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG SATELLITE
Optical imaging minisatellite attitude control system and in-orbit working mode switching method
ActiveCN104326093ASolve the problem of on-orbit switchingWide range of usesSpacecraft guiding apparatusGyroscopeEngineering
The invention discloses an optical imaging minisatellite attitude control system and an in-orbit working mode switching method, belongs to the field of satellite attitude control and aims at solving the problem that existing optical imaging satellites cannot be simply and effectively switched in the orbit. The optical imaging minisatellite attitude control system comprises an attitude measurement sensor, an actuating mechanism and an attitude controller, wherein the attitude measurement sensor comprises a sun sensor, a star sensor and a gyroscope; the actuating mechanism comprises a counteraction flywheel and a magnetorquer. According to an in-orbit working mode switching method of the optical imaging minisatellite attitude control system, the optical imaging minisatellite attitude control system has six working modes, namely a rate damping mode, a sun capture mode, a sun-orientated three-axis stabilization mode, an earth-orientated three-axis stabilization mode, a data transmission mode and a safety mode. The optical imaging minisatellite attitude control system and the in-orbit working mode switching method are suitable for all the optical imaging minisatellites.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Mars self-orientating method of large elliptical orbit Mars probe
ActiveCN103017760ARealize autonomous fire directional controlNavigation by astronomical meansAttitude controlShort termsOrbital elements
The invention discloses a Mars self-orientating method of a large elliptical orbit Mars probe, to enable a Mars probe to accomplish three-axis stable control to Mars orientation under the condition that the Mars probe does not completely depend on ground monitoring and control and self-orientation sensors are not available. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out corresponding short-term orbit recursion calculation according to the number of initial orbits and a reference coordinate system for describing the number of the orbits; adopting a simplified analysis method for Mars self-recursion, and adopting a high precision numerical method for orbit recursion on the ground; establishing a Mars orientation reference coordinate system by taking a Mars center-probe position vector as the Z-axis direction; and turning to a posture working mode for Mars-orientation after the Mars receives remote control instructions. Compared with the prior art, the Mars self-orientating method has the beneficial effects that under the condition that the ground communication has time delay and the self-orientation sensors cannot achieve engineering application, the Mars self-orientation control of the Mars probe is reliably realized through the orbit recursion and the establishment of the orientation reference coordinate system.
Owner:上海航天控制工程研究所
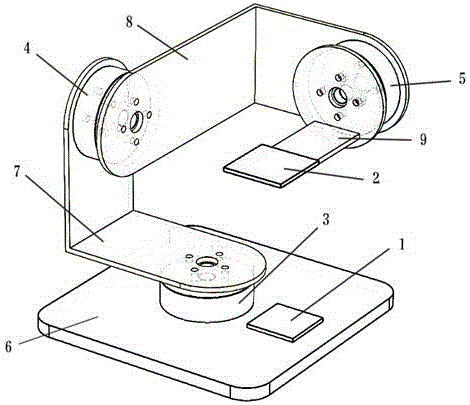
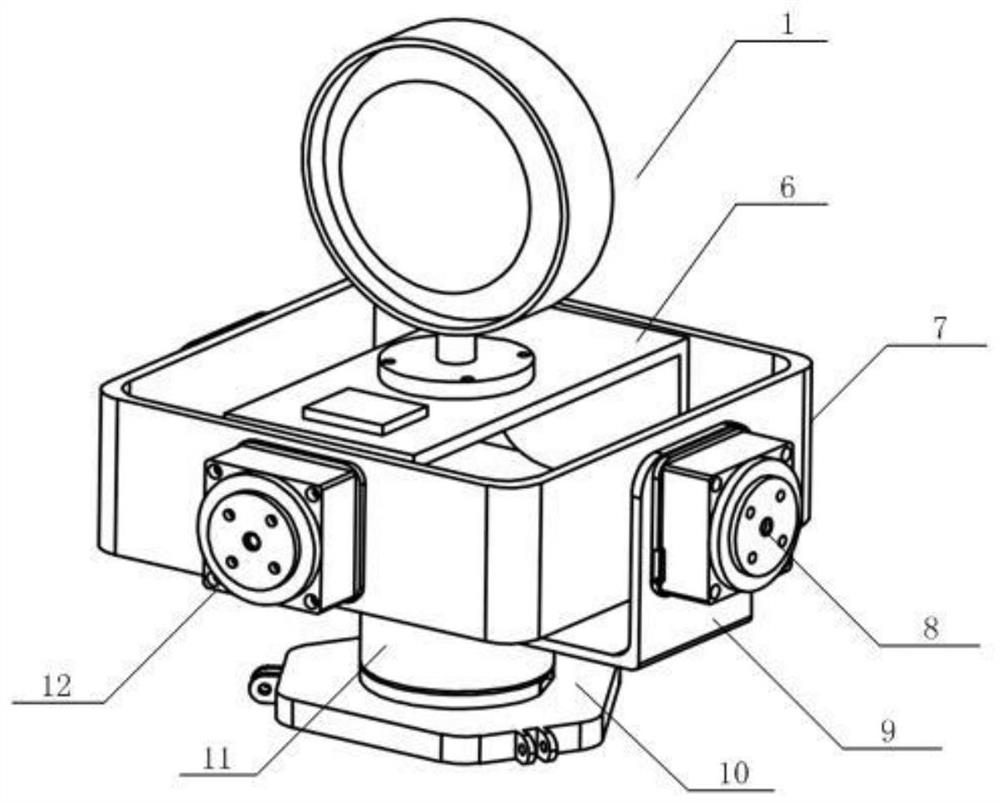
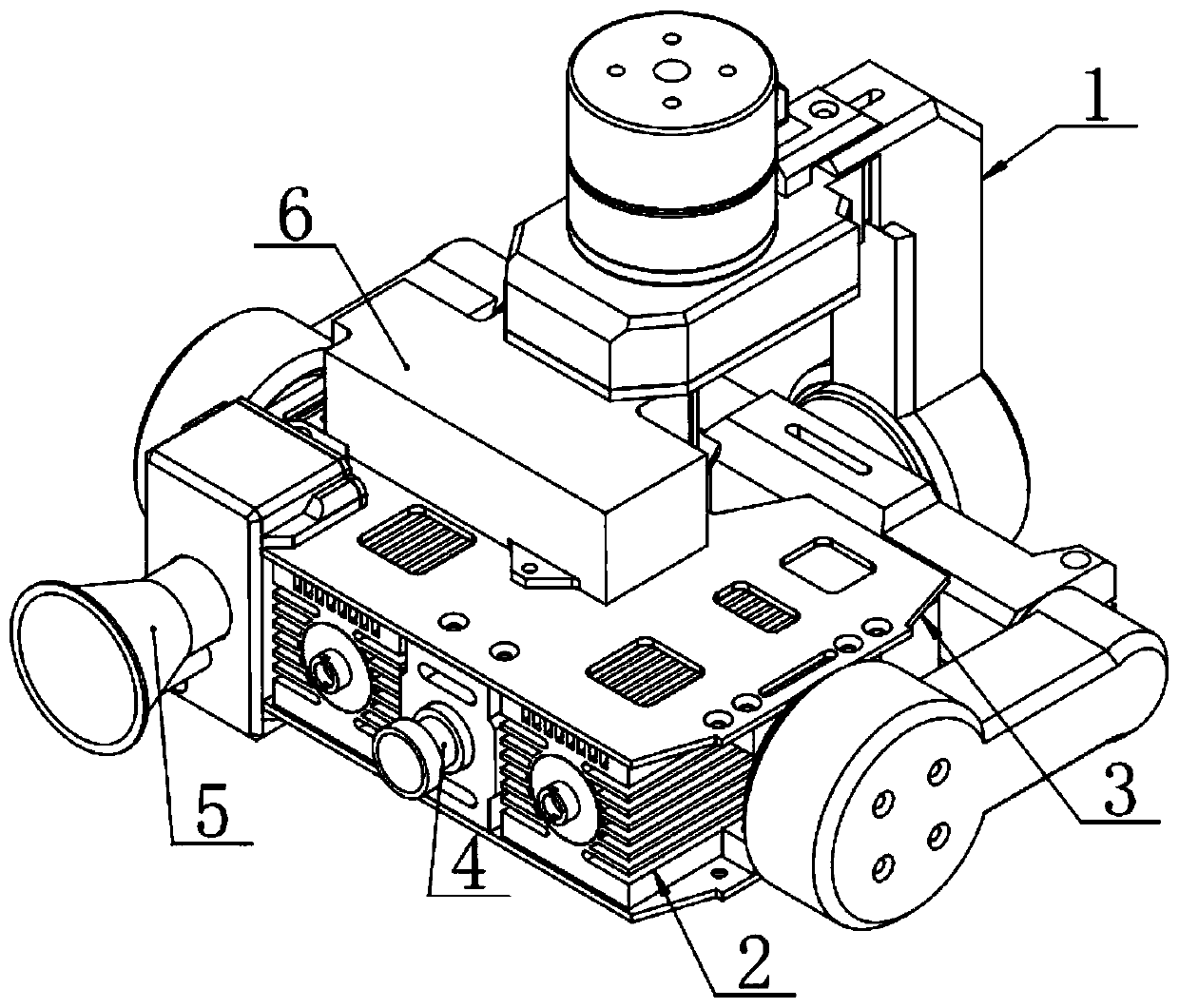
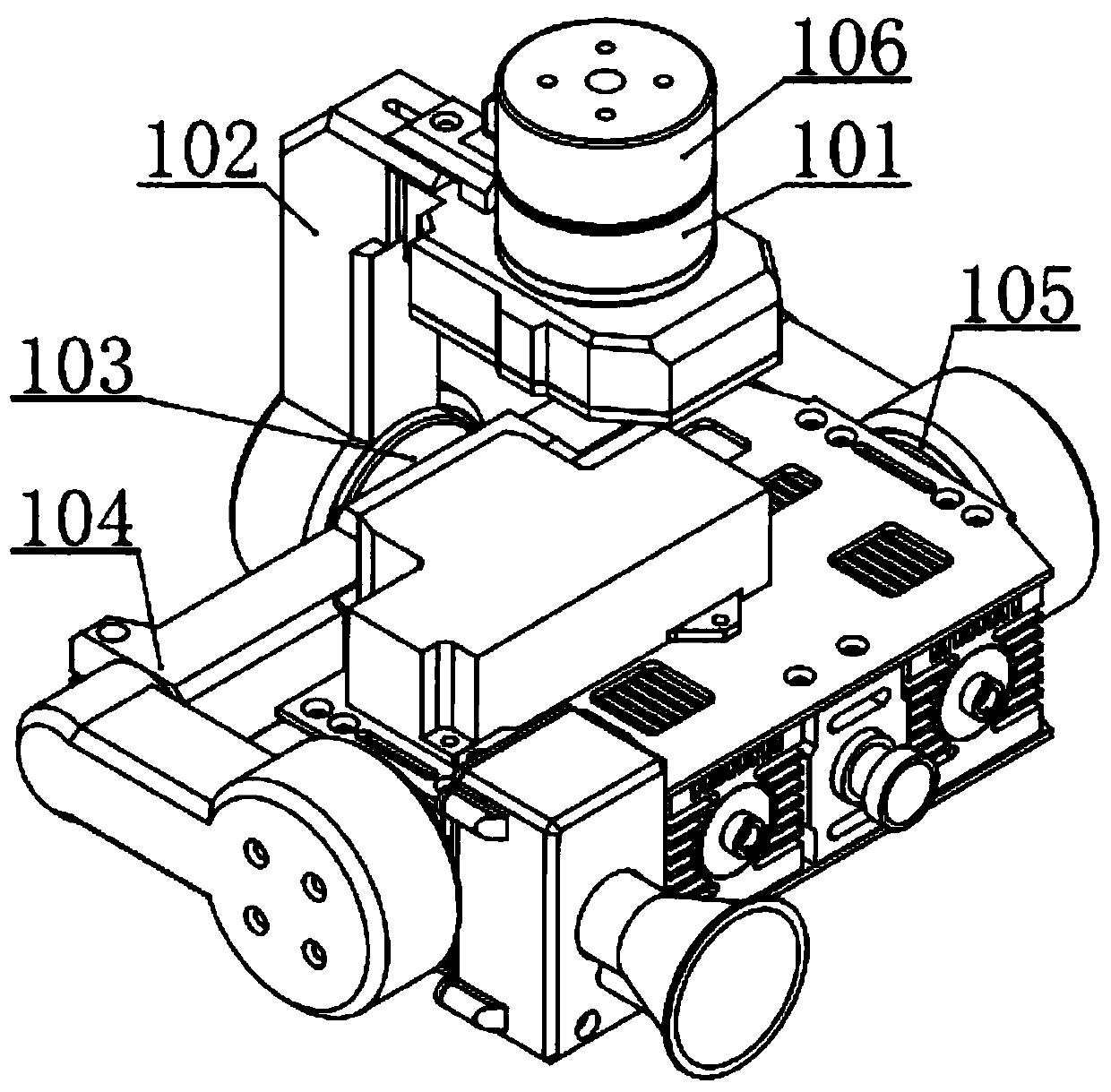
Three-axis stable pan-tilt
InactiveCN106090549AReduced precision requirementsImprove maneuverabilityStands/trestlesCamera body detailsBrushless motorsDevices fixation
The invention relates to a three-axis stable pan-tilt. The three-axis stable pan-tilt comprises a base, wherein a yaw axis control brushless motor is arranged on the base and connected with a roll axis control brushless motor through an inter-axis connection support I; the roll axis control brushless motor is connected with a pitching axis control brushless motor through an inter-axis connection support II; an equipment fixing platform is arranged on a rotor of the pitching axis control brushless motor; a feedback control module is arranged on the equipment fixing platform; and a master control module is arranged on the base. The three small-sized DC brushless motors in orthogonal connection are adopted to adjust the stability of three axes of the pan-tilt, feed-forward and feedback composite control is utilized to realize stable feedback control and rapid feed-forward control and can guarantee that the pan-tilt system is more stable, and the three-axis stable pan-tilt is stronger in controllability and is suitable for popularization and practical application.
Owner:NANJING INST OF TECH
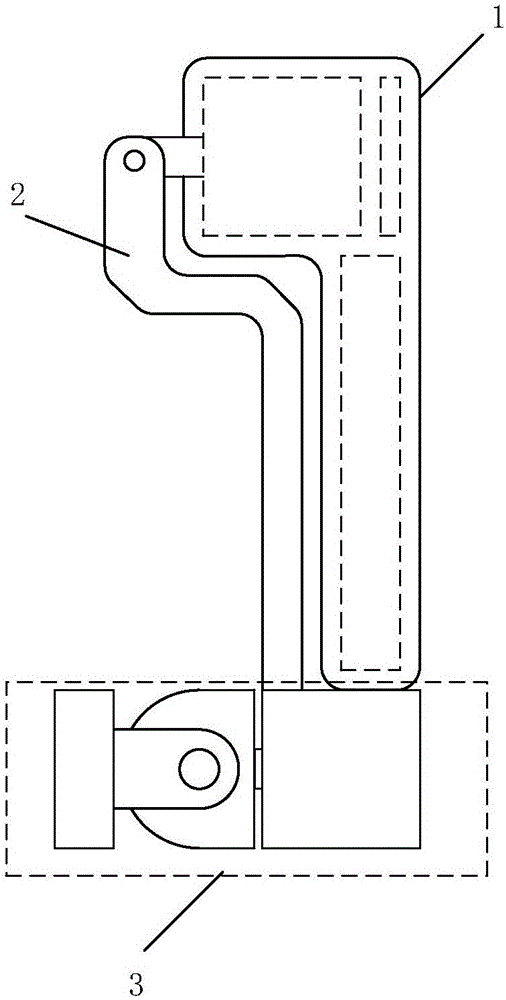
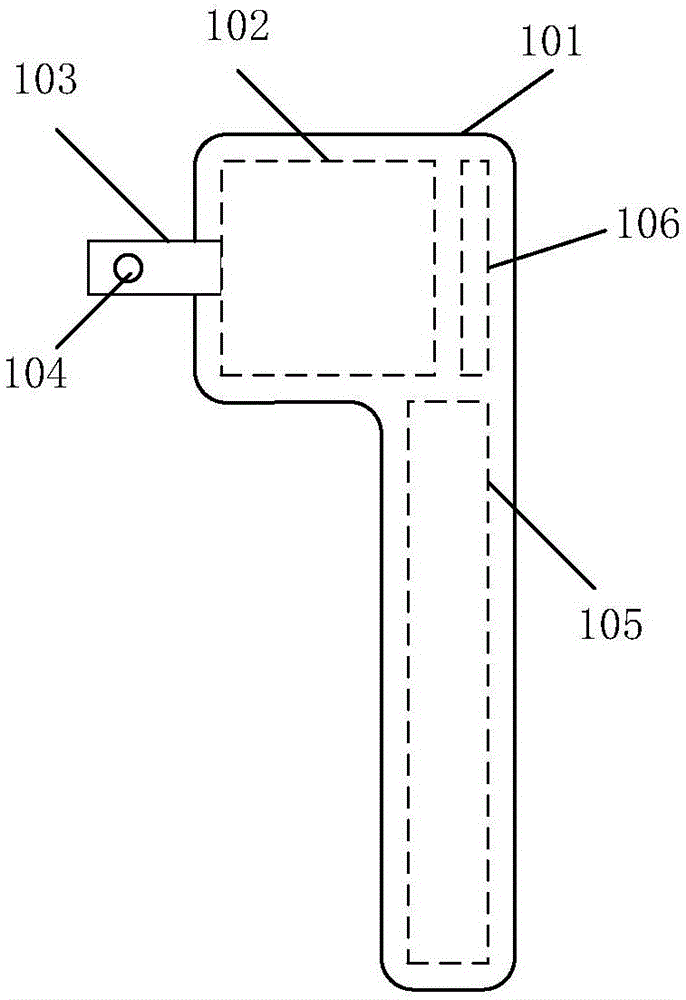
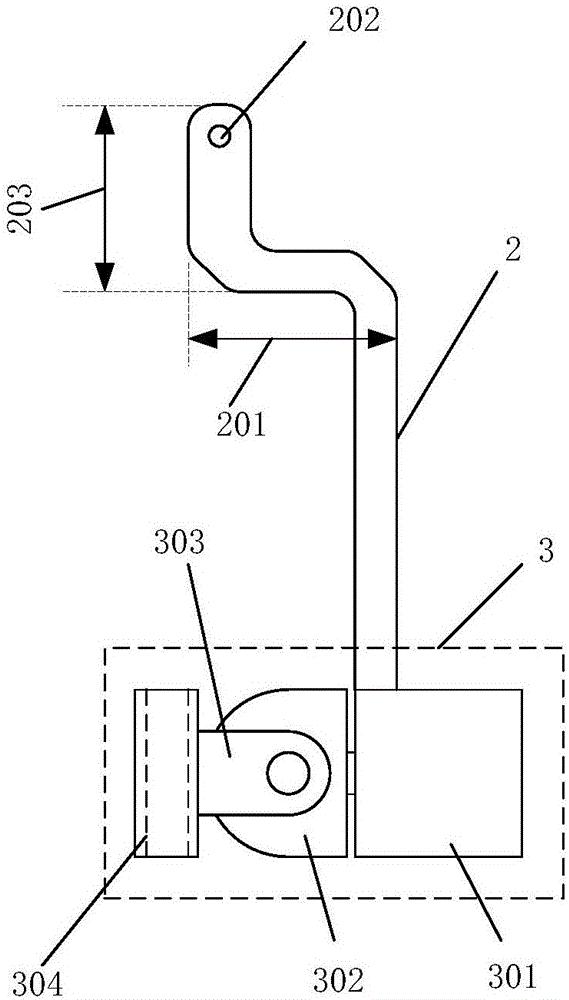
Foldable three-axis stable tripod head
ActiveCN106764305AGuaranteed Auto-TrimEasy to trimStands/trestlesTelephone set constructionsEngineeringCantilever
The invention provides a foldable three-axis stable tripod head for overcoming the shortcomings existing in the prior art. The foldable three-axis stable tripod head comprises a handle, a crankshaft and an end assembly, wherein the handle comprises a shell, a pitching motor, a pitching shaft and crankshaft rotating shafts; the pitching motor is mounted at the top end of the handle; the pitching shaft is connected with the crankshaft by the crankshaft rotating shafts; and the other end of the crankshaft is fixed on the end assembly. The foldable three-axis stable tripod head is provided with the three controllable rotating shafts, shaking in any directions can be compensated, and therefore, shot pictures are stable and smooth. In addition, the foldable three-axis stable tripod head is provided with a foldable cantilever, and can be stored when shooting stops, so that the foldable three-axis stable tripod head is quite small in size; and automatic balancing of centers of gravity of mobile phones with different weights in two axes of azimuth and roll is guaranteed.
Owner:中山市紫科智能科技有限公司
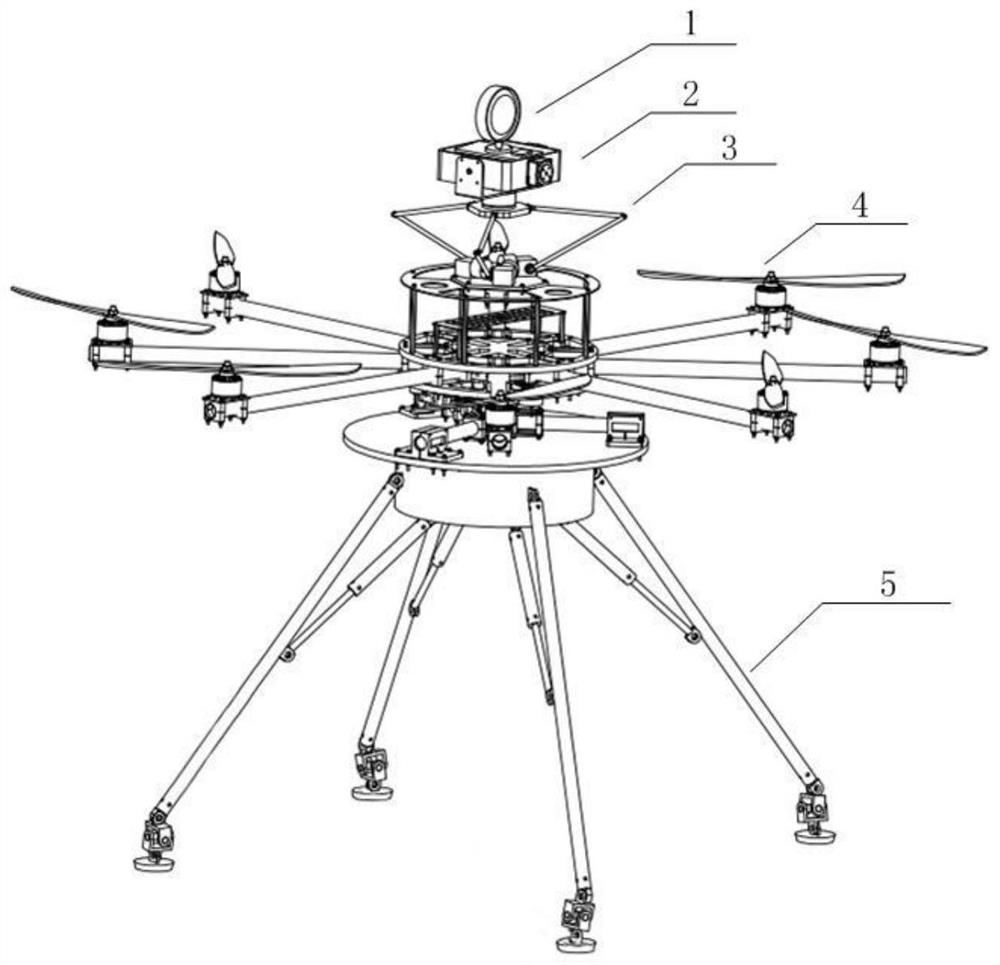
Three-axis stable electro-optical pod for unmanned aerial vehicle
ActiveCN106005460AWith three-axis adjustment functionTwisted and rotatedAircraft componentsAzimuth directionEngineering
The invention discloses a three-axis stable electro-optical pod for an unmanned aerial vehicle. The three-axis stable electro-optical pod comprises a shell, an azimuth axis assembly, a pitch axis assembly, a horizontal roller and an image assembly, wherein the azimuth axis assembly is arranged in the shell and provides rotation of -180 degrees to +180 degrees in the azimuth direction, the pitch axis assembly is arranged in the shell and provides rotation of -180 degrees to +180 degrees in the pitching direction, the horizontal roller provides rotation of -30 degrees to +30 degrees in the horizontal rolling direction, and the image assembly is used for shooting pictures. The three-axis stable electro-optical pod for the unmanned aerial vehicle is small in volume and light in weight and has a three-axis adjustment function, the pictures taken by the image assembly are clear and free of twist rotation.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST +1
Control method of shipborne three-axis stable platform
The invention, which belongs to the technical field of instrument science, provides a control method of a shipborne three-axis stable platform, so that a problem that the ship shakes and can not sail stably when being affected by sea waves or wind is solved. The control method comprises: step one, constructing a stable platform control system model; step two, constructing an auto-disturbance rejection controller (ADRC)of a gyroscope stable platform; step three, constructing an objective function equation and designing a simulation experiment; and step four, completing stable control of a shipborne three-axis stable platform. According to the control method provided by the invention, disturbance estimation is carried out and active compensation is carried out, so that the anti-interference capability of the platform position is enhanced and stable tracking on the target position is improved.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Gyro-stabilized platforms for force-feedback applications
InactiveUSRE44396E1Input/output for user-computer interactionProgramme-controlled manipulatorJoystickGyroscope
Force feedback in large, immersive environments is provided by device which a gyro- stabilization to generate a fixed point of leverage for the requisite forces and / or torques. In one embodiment, one or more orthogonally oriented rotating gyroscopes are used to provide a stable platform to which a force-reflecting device can be mounted, thereby coupling reaction forces to a user without the need for connection to a fixed frame. In one physical realization, a rigid handle or joystick is directly connected to the three-axis stabilized platform and using an inventive control scheme to modulate motor torques so that only the desired forces are felt. In an alternative embodiment, a reaction sphere is used to produce the requisite inertial stabilization. Since the sphere is capable of providing controlled torques about three arbitrary, linearly independent axes, it can be used in place of three reaction wheels to provide three-axis stabilization for a variety of space-based and terrestrial applications.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
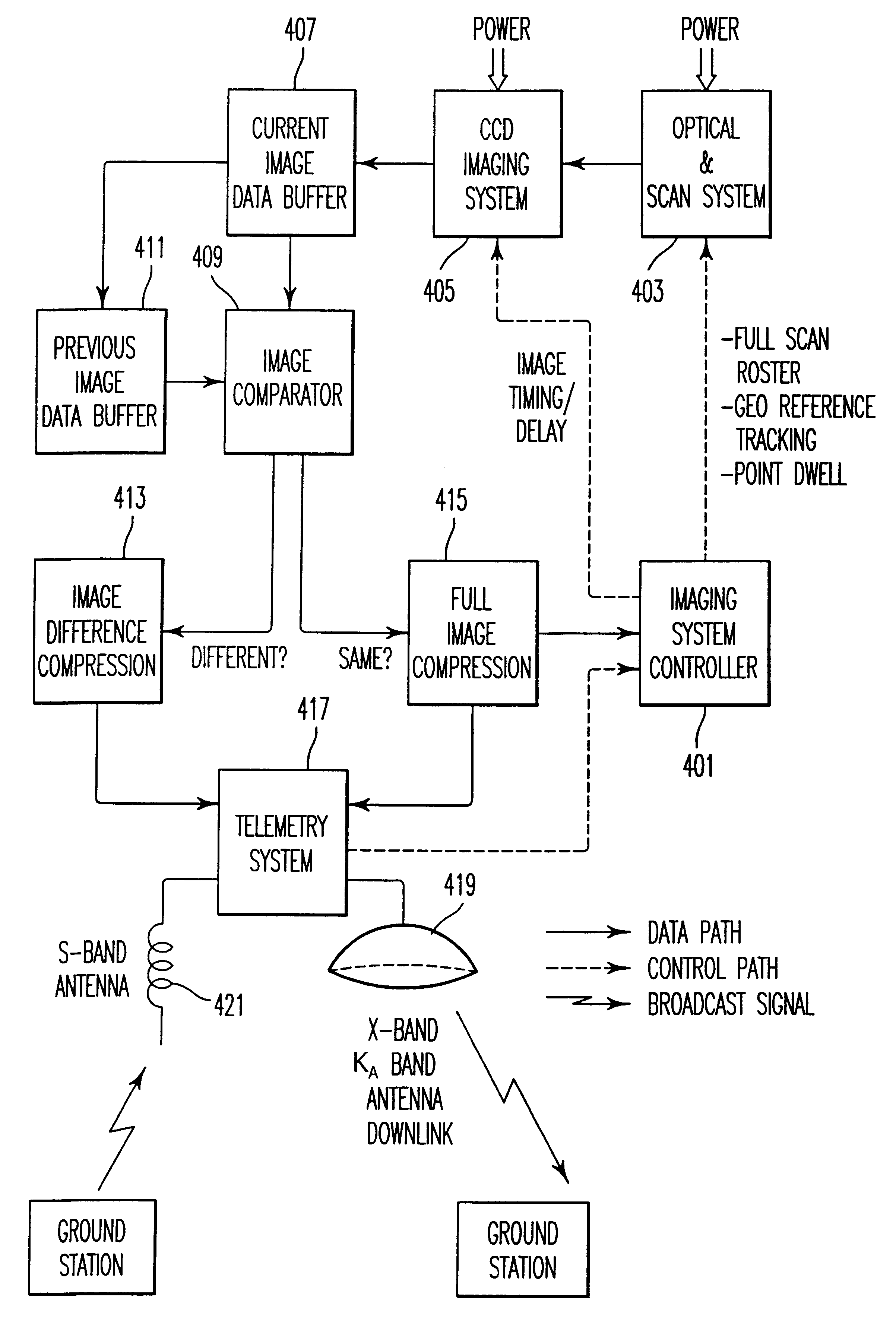
Direct broadcast imaging satellite system apparatus and method for providing real-time, continuous monitoring of Earth from geostationary Earth orbit
InactiveUS6504570B2Picture taking arrangementsColor television detailsNatural satelliteTelecommunications link
A system, method and apparatus for collecting an distributing real-time, high resolution images of the Earth from GEO include an electro-optical sensor based on multi-megapixel two-dimensional charge coupled device (CCD) arrays mounted on a geostationary platform. At least four, three-axis stabilized satellites in Geostationary Earth orbit (GEO) provide worldwide coverage, excluding the poles. Image data that is collected at approximately 1 frame / sec, is broadcast over high-capacity communication links (roughly 15 MHZ bandwidth) providing real-time global coverage of the Earth at sub-kilometer resolutions directly to end users. This data may be distributed globally from each satellite through a system of space and ground telecommunication links. Each satellite carries at least two electro-optical imaging systems that operate at visible wavelengths so as to provide uninterrupted views of the Earth's full disk and coverage at sub-kilometer spatial resolutions of most or selected portions of the Earth's surface.
Owner:ASTROVISION INT
Three-axis stabilized and four-axis tracked shipborne on-the-move antenna
ActiveCN105161825AOvercoming technical issues with interruptionsImprove stabilityAntenna supports/mountingsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesShaped beamSatellite tracking
The invention discloses a three-axis stabilized and four-axis tracked shipborne on-the-move antenna which comprises a transverse rolling transmission part, wherein the transverse rolling transmission part comprises a transverse rocking arm, a transverse rolling big belt pulley, a transverse synchronous belt and a transverse rolling small belt pulley, the transverse rocking arm is of an U-shaped beam structure, the U-shaped beam structure comprises a cross beam, the top of a web plate of an U-shaped beam body is provided with a lug in an outward extension way, one end of a transverse rocking arm support is fixedly arranged on a directional rotation support, the other end of the transverse rocking arm support is connected with the cross beam of the transverse rocking arm through a rotation shaft, the transverse rolling big belt pulley is fixedly arranged on the cross beam of the transverse rocking arm, and the transverse rolling big belt pulley and the transverse rolling small belt pulley synchronously and positively / inversely rotate through the transverse rolling synchronous belt to lead the transverse rocking arm to shake from side to side. The rotation of a transverse rocking shaft is added on the basis of the traditional directional, pitching and polarization rotation to lead a boat body to face with composite motion such as rolling, pitching and steering, the composite motion, adaptive to the boat body, of the on-the-move antenna is achieved by the transverse rolling transmission part, and the satellite tracking stability of the shipborne on-the-move antenna during the extreme swinging of the boat body is improved.
Owner:NANJING CHINA SPACENET SATELLITE TELECOM
Satellite configuration design method adapting to one-rocket multi-satellite launching
ActiveCN106043741AReduce weightImprove reliabilityCosmonautic power supply systemsArtificial satellitesNatural satelliteConfiguration design
The invention relates to the field of satellite development, in particular to a satellite configuration design method adapting to one-rocket multi-satellite launching. According to the method, for the illumination characteristic that the solar angle of a low-dip-angle orbit changes in a large range, an outer surface corresponding to the lower bottom of a satellite trapezoidal cross section is improved to be an arch formed by three panels in an enclosing mode to serve as an installing surface for fixing a solar cell array, and iterative optimization is conducted on included angles of the three cell panels. A satellite configuration designed through the method can be equivalent to the satellite configuration formed by a prismoid with a trapezoidal cross section and two slant prismoids with trapezoidal cross sections. The satellite configuration design method adapting to one-rocket multi-satellite launching has the main advantages that a solar wing spreading and driving mechanism is not arranged for each satellite, the weights of the satellites are reduced, and the reliability of the satellites is improved; a flight mission of long-time over-the-ground three-axis stable operation of a low-oblique-angle orbit can be met.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG DEV LTD
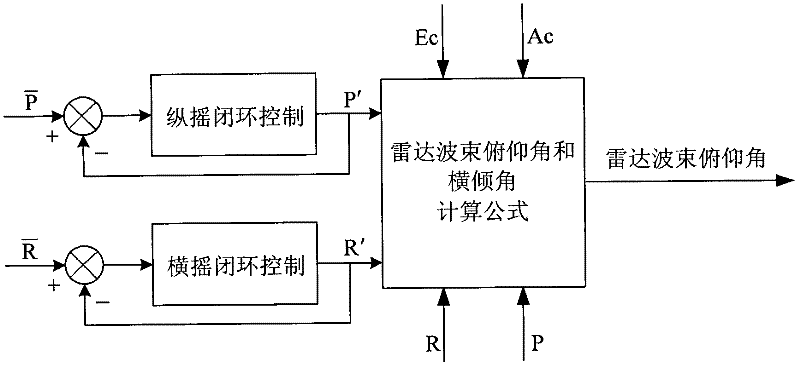
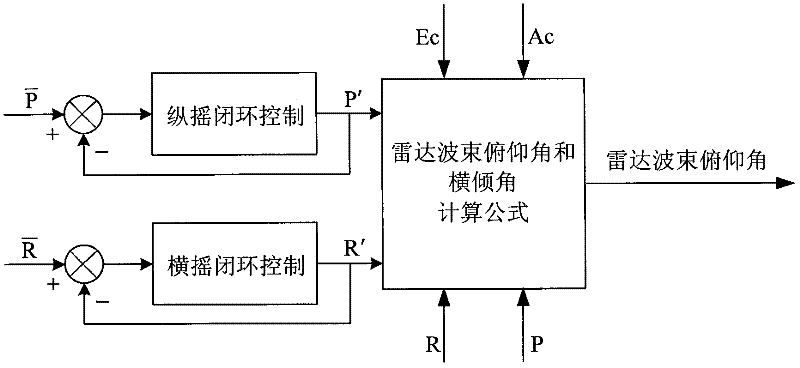
Method for controlling radar beam elevation angle of shipbased radar by utilizing position-pitching-rolling tri-axial stabilization system
InactiveCN102541086AEasy to controlReduce complexityControl using feedbackElevation angleThree-axis stabilisation
The invention relates to a method for controlling a radar beam elevation angle of a shipbased radar by utilizing a position-pitching-rolling tri-axial stabilization system, which is used for accurately controlling the radar beam elevation angle at a specified position by controlling the pitching and the rolling of a mechanical stabilization platform, and can achieve an elevation angle control function based on the position-pitching-rolling tri-axial stabilization system instead of a position-pitching-rolling-pitch four-axial stabilization system used by a conventional method. The shipbased radar utilizing the position-pitching-rolling tri-axial stabilization system needs to control the radar beam elevation angle in use, but the tri-axial stabilization system has no elevation shaft. Therefore, if the control on the radar beam elevation angle is achieved, the commonly-used method is that an elevation shaft is arranged on the tri-axial mechanical stabilization platform, namely the position-pitching-rolling-pitch four-axial stabilization system, thereby greatly improving complex of the system, increasing the weight of the mechanical stabilization platform and reducing adaptability of the radar. By controlling the pitching and the rolling of the mechanical stabilization platform, the accuracy control on the radar beam elevation angle is achieved, accuracy control on the radar beam elevation angle at the specified position is ensured, and the condition that radar beam pointing is free of rolling is ensured. Therefore, the elevation angle control function is achieved by utilizing the position-pitching-rolling tri-axial stabilization system instead of the position-pitching-rolling-pitch four-axial stabilization system, thereby reducing complex of the mechanical system and the weight of the radar and increasing adaptability of the radar.
Owner:THE 724TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND
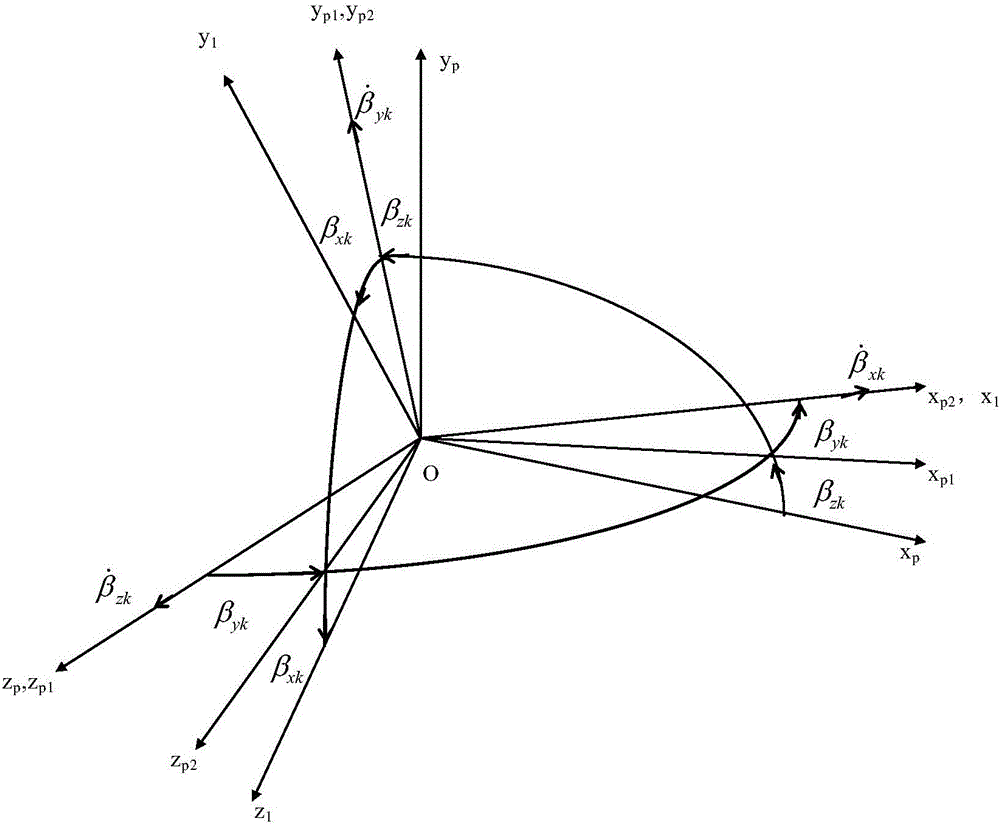
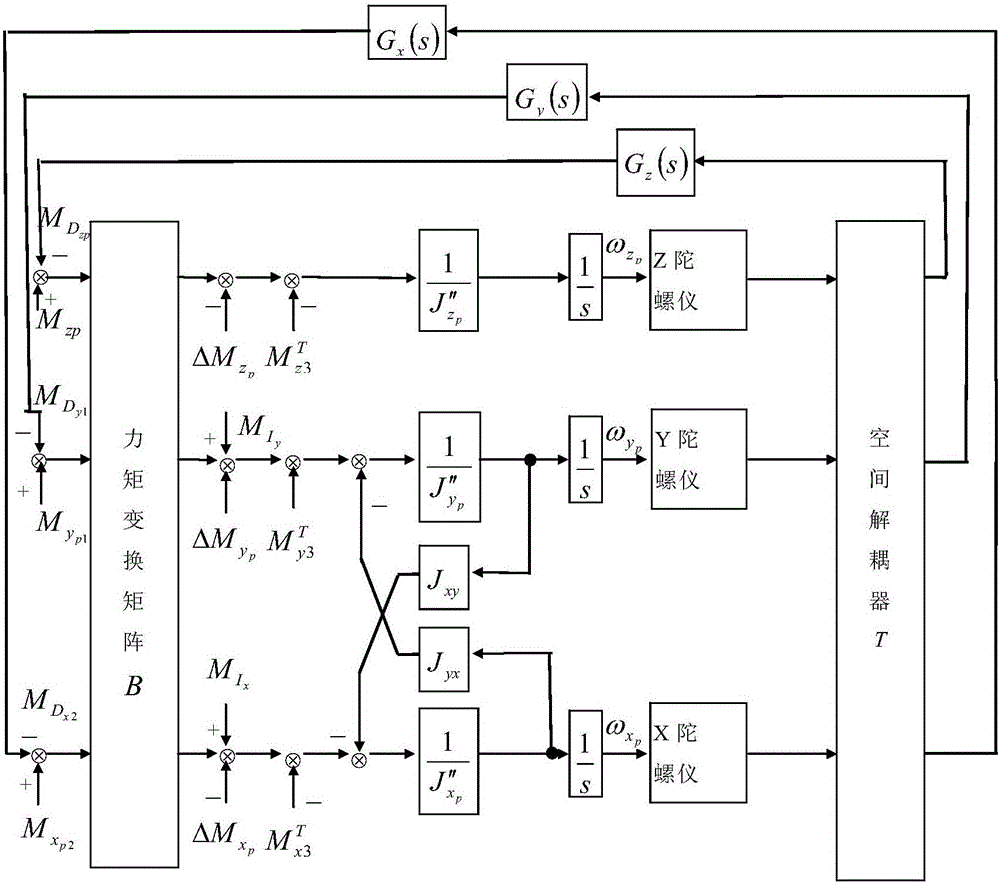
Servo loop decoupling method for three-axis stabilization platform system
ActiveCN105115503AOvercome the singular value problemAvoid problems with gains tending to infinityNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsTurn angleBody axis
The invention discloses a servo loop decoupling method for a three-axis stabilization platform system. The servo loop decoupling method comprises the following steps: taking four variables as input information of a decoupling link, wherein the four variables are as follows: output angular rates Omega xp, Omega yp and Omega zp of three gyroscopes orthogonally mounted on a platform body, and a turning angle Beta zk of an inner frame relative to the platform body; and outputting three axis-end torque motors respectively acting on a platform body axis, an inner ring axis and an outer ring axis after information fusion. The invention firstly provides the method for controlling a servo loop in a single-input single-output manner instead of multi-variable manner when a carrier is in any posture relative to the platform body; no strange value phenomenon occurs; the unengaged track motion of the carrier after the three-axis stabilization platform system is adopted is realized.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF AEROSPACE CONTROL DEVICES
Real-time compensation decoupling method and compensation decoupling system for spacecraft platform disturbance by spaceborne radar
ActiveCN104201458ANo need to occupy volumeRealize real-time compensationAntenna supports/mountingsGyroscopeControl theory
The invention discloses a real-time compensation decoupling method for spacecraft platform disturbance by a spaceborne radar. The method includes that when the spaceborne radar searches, a three-axis stabilization rate gyroscope real-timely detects changing amount and changing direction of a spacecraft platform attitude angle; the changing amount and the changing direction of the spacecraft platform attitude angle are subjected to transformation of coordinates to obtain changing amount and changing direction of a spaceborne radar attitude angle; when the changing amount of the spaceborne radar attitude angle exceeds a preset threshold value, the spaceborne radar sets a searching compensatory angle; the value of the searching compensatory angle is the changing amount of the spaceborne radar attitude angle; the compensation direction of the searching compensatory angle is vertical to the searching direction of the spaceborne radar and opposite to the changing direction of the spaceborne radar attitude angle; a servo mechanism of the spaceborne radar performs real-time compensation controlling on the spaceborne radar attitude angle according to the searching compensatory angle. According to the real-time compensation decoupling method and a compensation decoupling system for spacecraft platform disturbance by the spaceborne radar, own resources of a spacecraft platform are utilized, real-time compensation of the servo mechanism of the spaceborne radar is achieved, valuable volume, weight, and power consumption resources of a spacecraft can not be occupied, and resources are saved.
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIO EQUIP RES INST
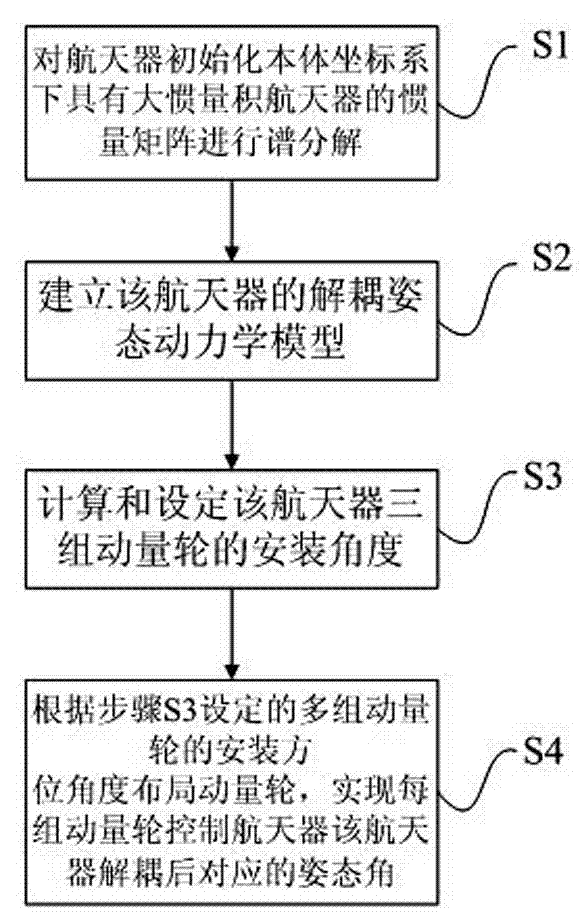
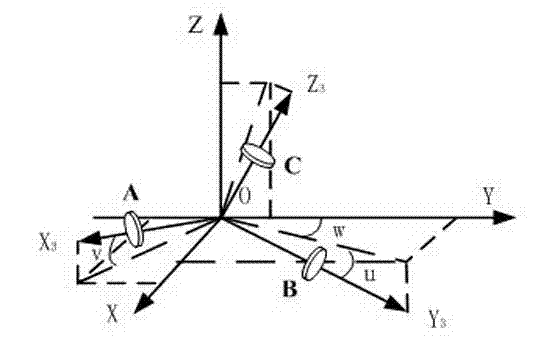
Momentum wheel layout configuration method for spacecraft with large inertia product
ActiveCN104850128AAchieve independent controlSolve the attitude coupling problemAttitude controlMomentumDynamic models
The invention discloses a momentum wheel layout configuration method for a spacecraft with a large inertia product. Through spectral decomposition on an inertia matrix with the spacecraft with the large inertia product, a decoupling attitude dynamics model of the spacecraft is established, the installation angle position of a momentum wheel set and arranged on the spacecraft is calculated, and decoupling control of the attitude angle of the spacecraft is finally realized. The method provided by the invention can prevent coupling existing in attitude motion in two or three directions on a body coordinate axis of the spacecraft, caused by the large inertia product, realizes decoupling control of large-inertia-product triaxial stable zero momentum and realizes independent control of each attitude of the spacecraft.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINYUE METER FACTORY
Engineering surveying and marking device and method based on unmanned flying platform
PendingCN112180384AReduce security risksTackling Difficult Measurement JobsUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansSurveying instrumentsLight beamPrism
The invention provides an engineering surveying and marking device and method based on an unmanned flying platform. The engineering surveying and marking device is mainly composed of a multi-rotor flying platform, a three-axis stable holder, a servo lifting frame, an all-terrain foot stand, a reflecting prism and the like, wherein the reflecting prism is fixed at the top end of the three-axis stable holder and is used for reflecting a light beam emitted by a photoelectric range finder; the three-axis stable holder is fixed on the servo lifting frame and can drive the reflecting prism to rotateto a specified attitude angle; the servo lifting frame is installed on the flying platform, stretching is achieved through a two-section type folding structure, the stretching length of the servo lifting frame is controlled, and then the height of the reflecting prism is controlled; the flying platform is a carrier for realizing flying movement and fixed-point hovering of the whole device, and carries the reflecting prism to move across terrain obstacles in a large range in a horizontal plane; and the all-terrain foot stand is installed below the flying platform and is mainly used for observing and measuring the ground condition of an undetermined landing point and achieving horizontal landing and stabilization of a flight marking device on different terrains.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
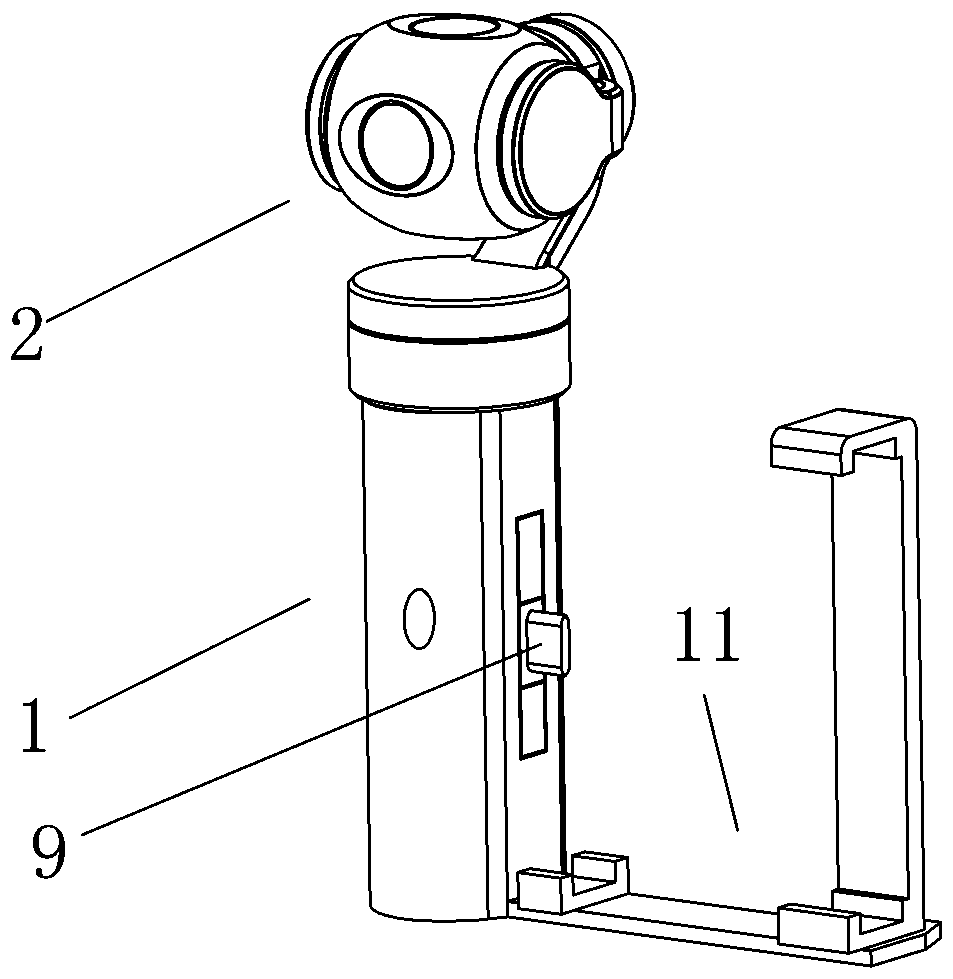
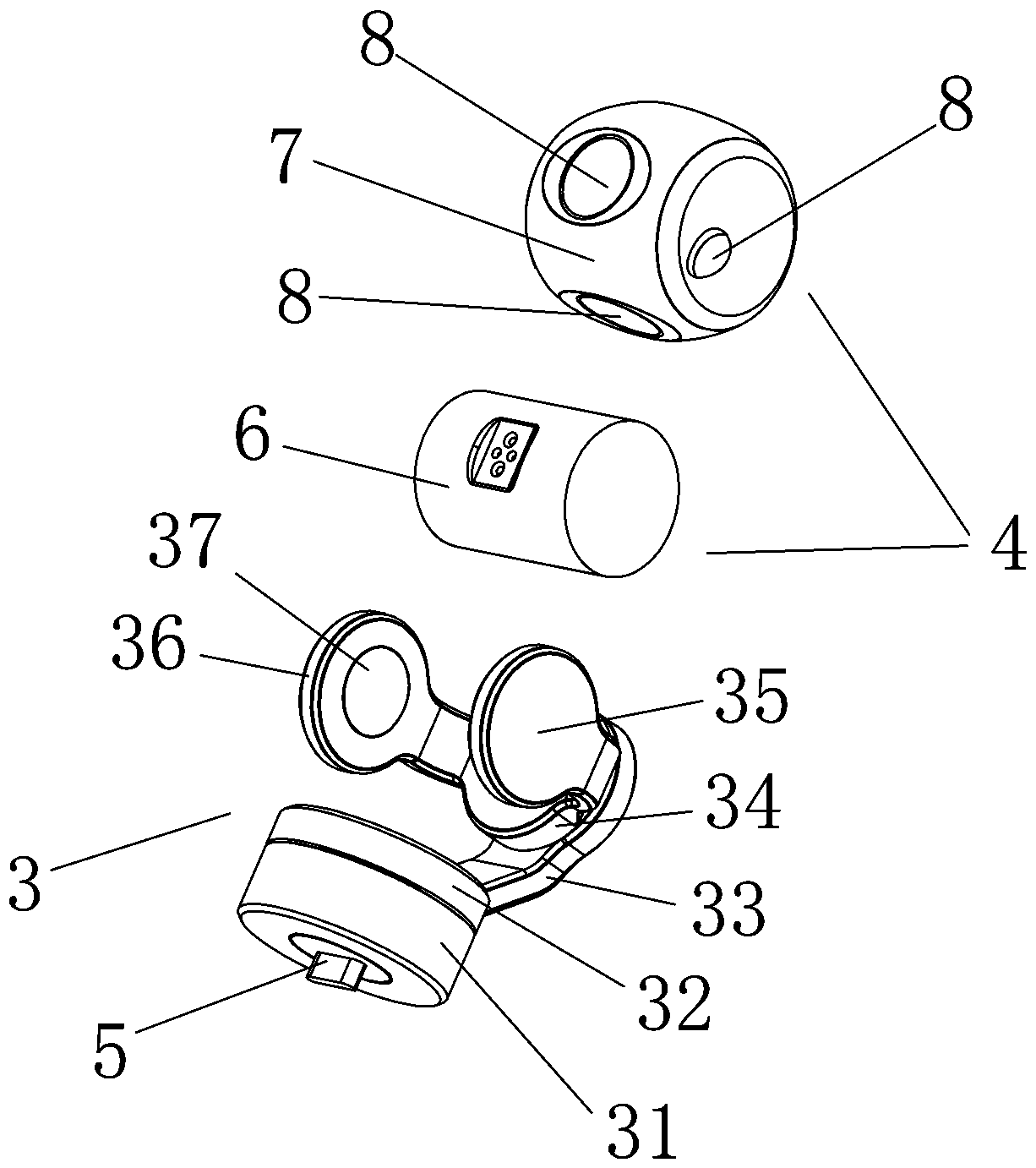
Portable multifunctional combined three-axis stable shooting device
PendingCN109561187AIncrease flexibilityFunction increaseTelevision system detailsColor television detailsVertical planeEngineering
The invention discloses a portable multifunctional combined three-axis stable shooting device. The device comprises a three-axis shooting platform assembly and a selfie stick which are connected up and down in a detachable manner, wherein the three-axis shooting platform assembly includes a three-axis electric cradle head, a camera assembly and a control circuit, the camera assembly includes a camera, a housing and lenses mounted on the surface of the housing, the lower end of the selfie stick is provided with a second data joint, the selfie stick is connected with a hidden bracket, the three-axis shooting platform assembly is controlled by a control program of a smart phone, a plurality of different lenses are used for shooting different effects, and the three-axis shooting platform assembly can rotate freely by 360 degrees in a horizontal plane, a vertical plane and a front-back plane. The portable multifunctional combined three-axis stable shooting device controls the stability of the camera assembly and selects the desired shooting angle and the shooting effect presented by various physical lenses through the control program on the smart phone. The hidden bracket can enable thesmart phone to obliquely stand on the desktop. The device not only can serve as a selfie stick, but also can be used as a phone holder, thereby being diversified in function, and meeting various demands.
Owner:张奉果
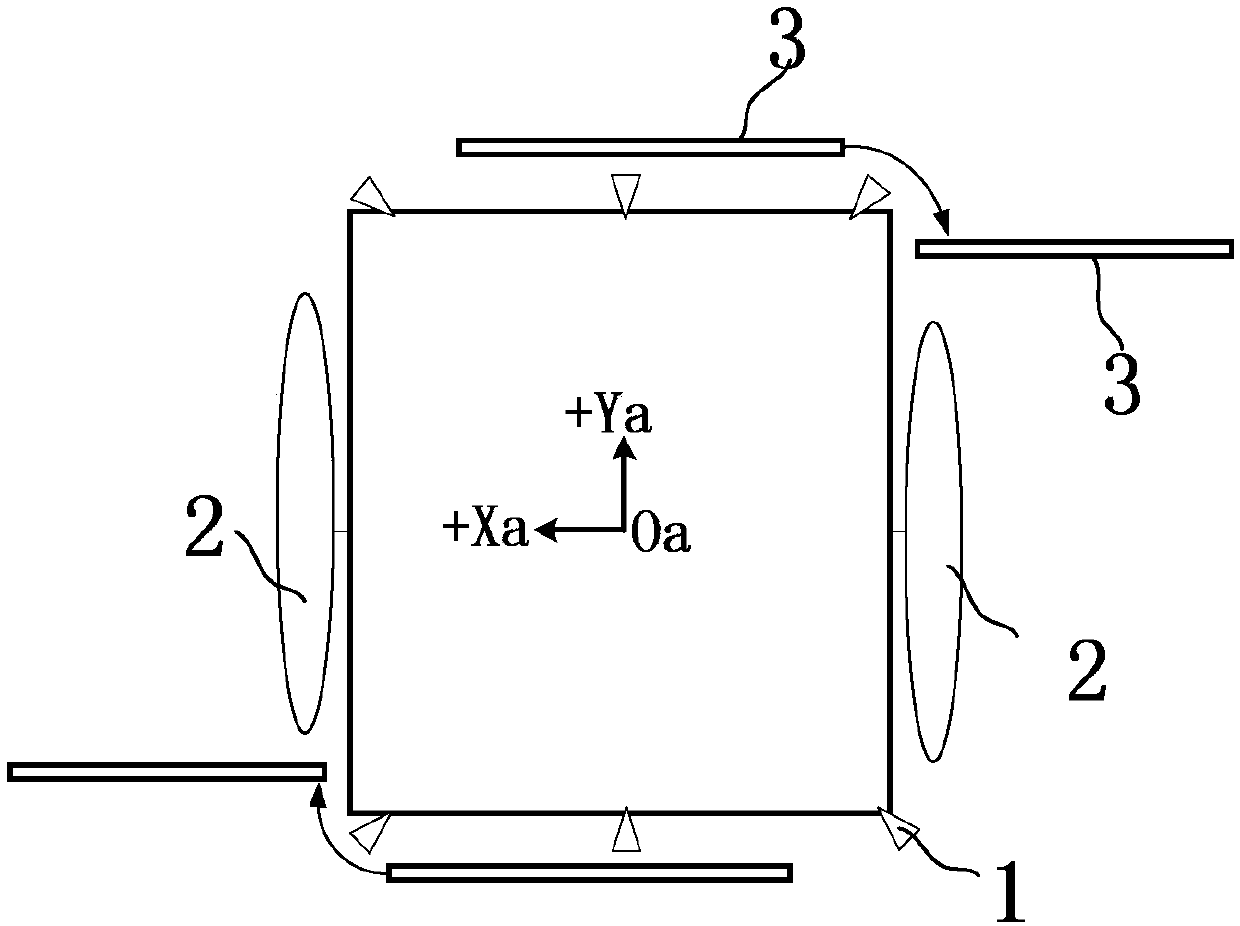
Formation layout and installation system for three-axis stabilization satellite
ActiveCN107839900AGuaranteed craftsmanshipSolve the installation accuracyArtificial satellitesSpacecraft guiding apparatusFlight directionSolar battery
The invention discloses a formation layout and installation system for a three-axis stabilization satellite. In order to meet the formation requirement for the satellite, formation thrusters need to be added to the satellite on the basis of a posture control thruster and a track control thruster; under a launching state, effective load and solar battery arrays of the satellite are drawn to the periphery of the satellite; when the satellite stays on the track, the effective load and the solar battery arrays are all spread in the Xa direction of the flight direction of the satellite to ensure that plumes of the formation thrusters do not intervene in the solar battery arrays and the effective load, and guarantee the maximization of the efficiency of the formation thrusters; according to theflight posture of the satellite, the formation thrusters are divided into two groups, the two groups are distributed at a +- Ya side of the satellite separately, the planes of the thrusters are perpendicular to the direction, pointing to the ground, of the satellite, and the formation thrusters cooperate with one another to pass through an average centroid of the satellite when the satellite staysat an on-track flight state. By adopting the formation layout and installation system, the satellite installation accuracy of the formation thrusters and the manufacturability of operation implementation are ensured; the demands of the formation thrusters for installation, accuracy measurement and formation control in the satellite can be effectively met.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
Non-sun-synchronous orbit satellite double-shaft sailboard control method
ActiveCN102004492BSimplify flight proceduresLow costPosition/course control in three dimensionsEnergy supplyRotational degrees of freedom
The invention discloses a non-sun-synchronous orbit satellite double-shaft sailboard control method. A double-shaft sailboard is a solar sailboard structure which has two rotational degrees of freedom and of which the two rotating shafts can independently control work. The double-shaft sailboard control method comprises a control method of each single-shaft sailboard in the double-shaft sailboard and an implementation method during double-shaft cooperative work of the sailboard. In the single-shaft control method of the sailboard, measurement modes and rotation strategies for the sailboard indifferent work modes of the satellite are mainly designed. In the double-shaft cooperative work method, the working order of each single shaft and the rotation logic are specified. The inconvenience that a non-sun-synchronous orbit satellite needs to frequently perform attitude maneuver to ensure the sailboard tracks the sun is solved by applying the double-shaft sailboard control method on a satellite. By the method, the satellite can track the sun in real time on orbit by controlling the rotation of the sailboard, so that the energy supply on the satellite is guaranteed, and the requirement of the satellite over the ground directional triaxial stability is met.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Wheel track type three-axis stable following radar antenna pedestal
PendingCN114267933AThick loadImprove consistencyAntenna supports/mountingsRadar antennasBall bearing
The invention relates to a wheel track type three-axis stable following radar antenna pedestal, and relates to the field of radar equipment. The azimuth dimension is supported by a turntable bearing to drive the azimuth turntable, the pitching dimension and the rolling dimension to rotate; in the pitching dimension, radial and axial support is realized by a cam bearing consisting of 16 deep groove ball bearings, and the pitching frame and the transverse rolling dimension are driven to move; the transverse rolling dimension is supported by a combined cam bearing composed of eight groups of deep groove ball bearings and drives the transverse rolling frame to move. The supporting mode adopted in the pitching dimension saves the position space of traditional pitching two-side supports, and reduces the radial space and the rotation space occupied by the antenna pedestal. A supporting form adopted in the rolling dimension and an arc-shaped track adopted in the pitching dimension are beneficial to installation of a thicker antenna load; and the adjustment and clearance elimination processing of the last-stage transmission backlash satisfy the high consistency of the tracking precision of the antenna pedestal.
Owner:CNGC INST NO 206 OF CHINA ARMS IND GRP
Triaxial self-stabilization controllable foreign matter removing device of multi-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle
PendingCN110620350AEasy to removeMake sure to position the cutAircraft componentsLaser beam welding apparatusForeign matterMiniaturization
The invention discloses a triaxial self-stabilization controllable foreign matter removing device of a multi-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle. The multi-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle comprises a three-axis stable holder and a laser module, wherein a top end of the three-axis stable holder is fixedly connected with the multi-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle, the laser module is fixedly connected with a rack, and the rack is fixedly connected with a pitching output end of the three-axis stable holder. The multi-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle is advantaged in that the laser module is mounted on a multi-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle in the prior art through the three-axis stable holder, foreign matters on a power transmission line can be efficiently and quickly removed under the condition of no powerfailure, the equipment achieves goals of no fire, miniaturization, high efficiency and simplicity and convenience in operation; the three-axis stable holder is adopted, free control over a spraying angle can be achieved, the stable airborne laser aerial shooting direction is achieved, that laser conducts positioning cutting of foreign matters and laser long-distance cutting is ensured, long-distance cutting can be achieved, operation difficulty of operators is greatly lowered, cutting efficiency and foreign matter removing efficiency are improved, long-distance removing is achieved, and safety is higher.
Owner:GUIZHOU POWER GRID CO LTD
Method for achieving satellite three-axis stable control through single control moment gyroscope and two flywheels
ActiveCN110697086AStable controlStable postureCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusStabilization controlClassical mechanics
The invention relates to a method for achieving satellite three-axis stable control through a single control moment gyroscope and two flywheels. A ground measurement and control station remotely controls a satellite to control the attitude through a thruster. Angular momentum corresponding to the rotating speed of the CMG inner rotor is obtained according to the rotating speed instruction of the CMG inner rotor; a magnetic unloading target angular momentum is set according to the CMG outer frame position and the effective rotating speed instructions of the two flywheels; a changed angular momentum control instruction is calculated according to the instruction torque, the CMG frame angular position, the frame rotating speed, the system control period, the effective angular momentum controlinstructions of the two flywheels and the like, and the CMG frame angle is resolved: allowing single CMG control, selecting single CMG access, effectively connecting the two flywheels, and controllingthe satellite attitude by using the flywheels. For satellites adopting flywheels and control moment gyroscopes as attitude control main actuating mechanisms, stable attitude control can be realized under the condition that only one control moment gyroscope and two reaction flywheels are effective on the satellite.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
Five-axis gyroscope stabilizer for unmanned aerial vehicle
ActiveCN110203394AReduce the burden onEasy to adjustAircraft componentsAircraftsGyroscopeEngineering
The invention discloses a five-axis gyroscope stabilizer for an unmanned aerial vehicle. The five-axis gyroscope stabilizer comprises conical belt wheels and spiral rotating shafts, wherein the conical belt wheels are arranged on a first mounting frame and a second mounting frame through the spiral rotating shafts, and electromagnetic valves are mounted on the side surfaces of the two spiral rotating shafts. The electromagnetic valves are arranged in the first mounting frame and the second mounting frame, wherein the first mounting frame, the second mounting frame and a third installation frame are vertically arranged in a paring mode, and the third mounting frame is provided with a synchronous belt wheel through a third rotation shaft, the two conical belt wheels and the synchronous beltwheel are arranged on a first motor wheel, a second motor wheel and a third motor wheel through a synchronous belt. According to the five-axis gyroscope stabilizer for the unmanned aerial vehicle, axes of two directions are added by increasing the linear movement of a three-axis stabilizer in the horizontal direction and the vertical direction, and the linear movement mode can be electrically connected and controlled, thus achieving the remote signal control and the application of the five-axis stabilizer in the unmanned aerial vehicle.
Owner:南京华特莱思模塑有限公司
Space floating island for service space station
The invention discloses a space floating island for a service space station. The space floating island for the service space station comprises a main body (1) and a flexible rope way (2) connected with the space station (A); the main body (1) comprises a three-axis stabilized earth part (1a) and a spinning part (1b) connected with each other; and a first booster (11) used for adjusting an attitudeof the main body (1) and a second booster (12) used for keeping a track height of the main body (1) and a phase difference between the main body (1) and the space station (A) are arranged on the three-axis stabilized earth part (1a). By using a freight airship to build the space floating island, the utilization rate of the freight airship is greatly increased; after the freight airship is dockedwith the space station, the freight airship does not need to crash; and therefore, the launching cost of a space flying task is effectively reduced, and the possibility of generating space garbage isalso reduced.
Owner:BEIJING SPACE TECH RES & TEST CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com