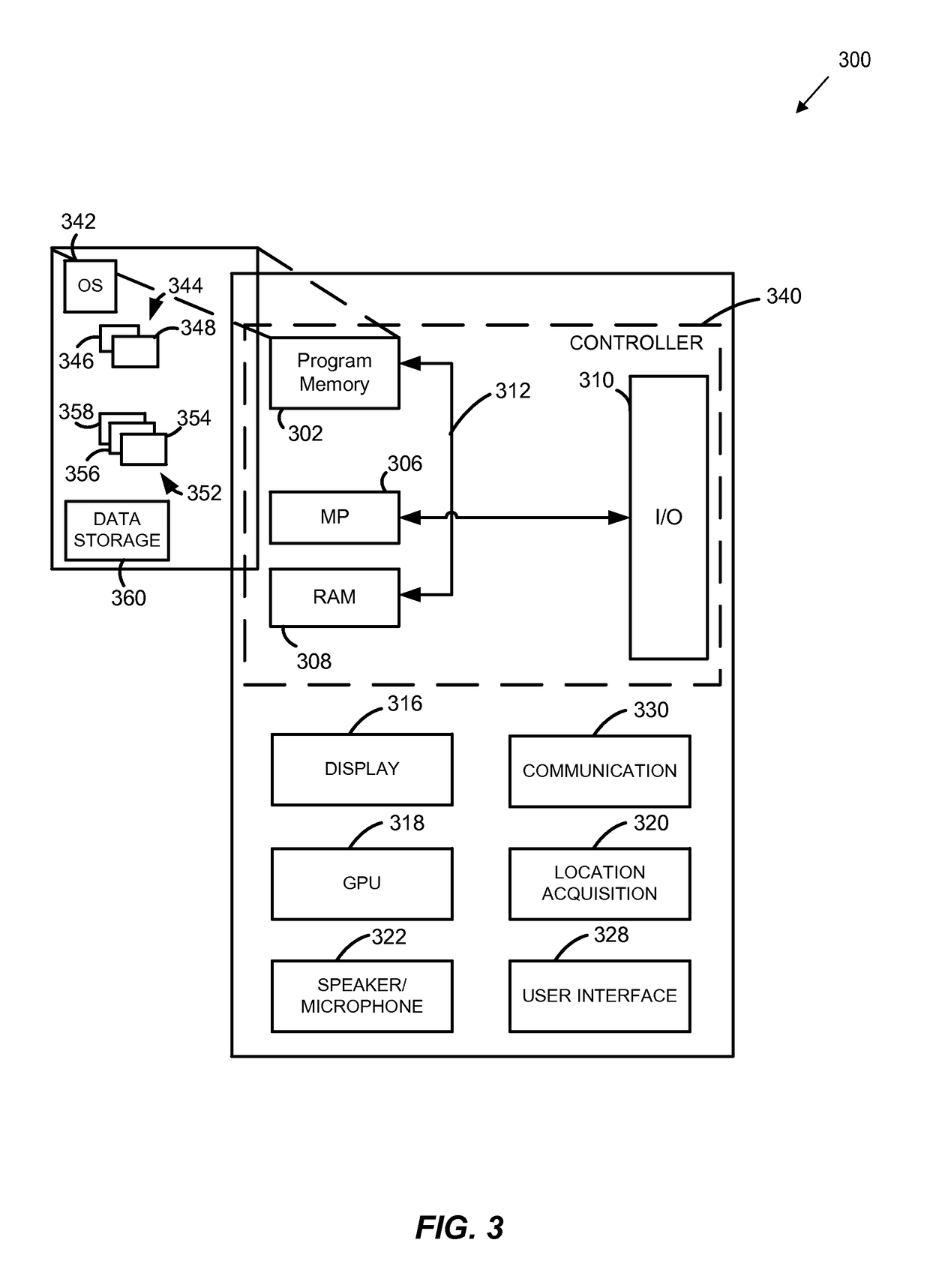
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2540results about "Picture taking arrangements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
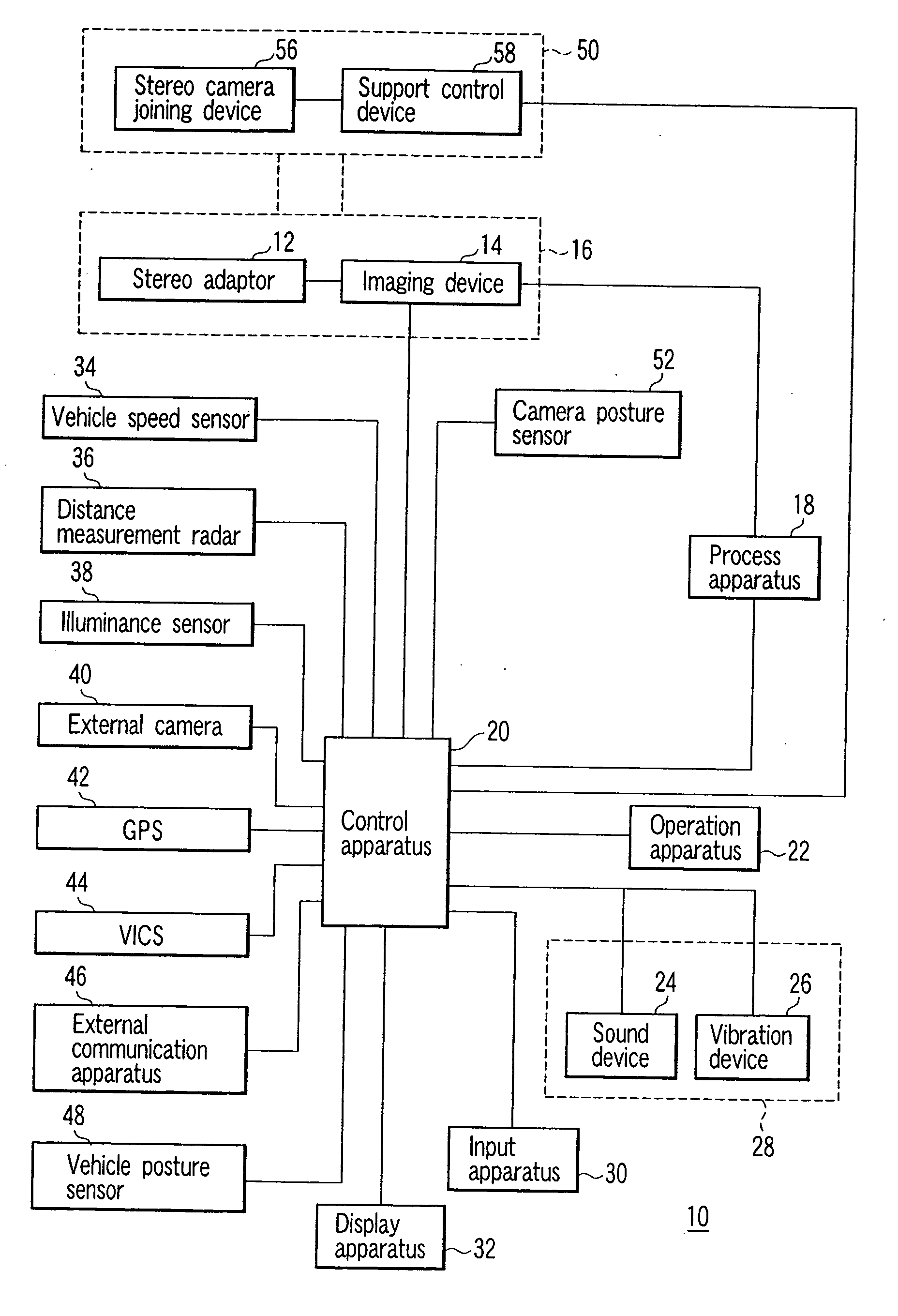
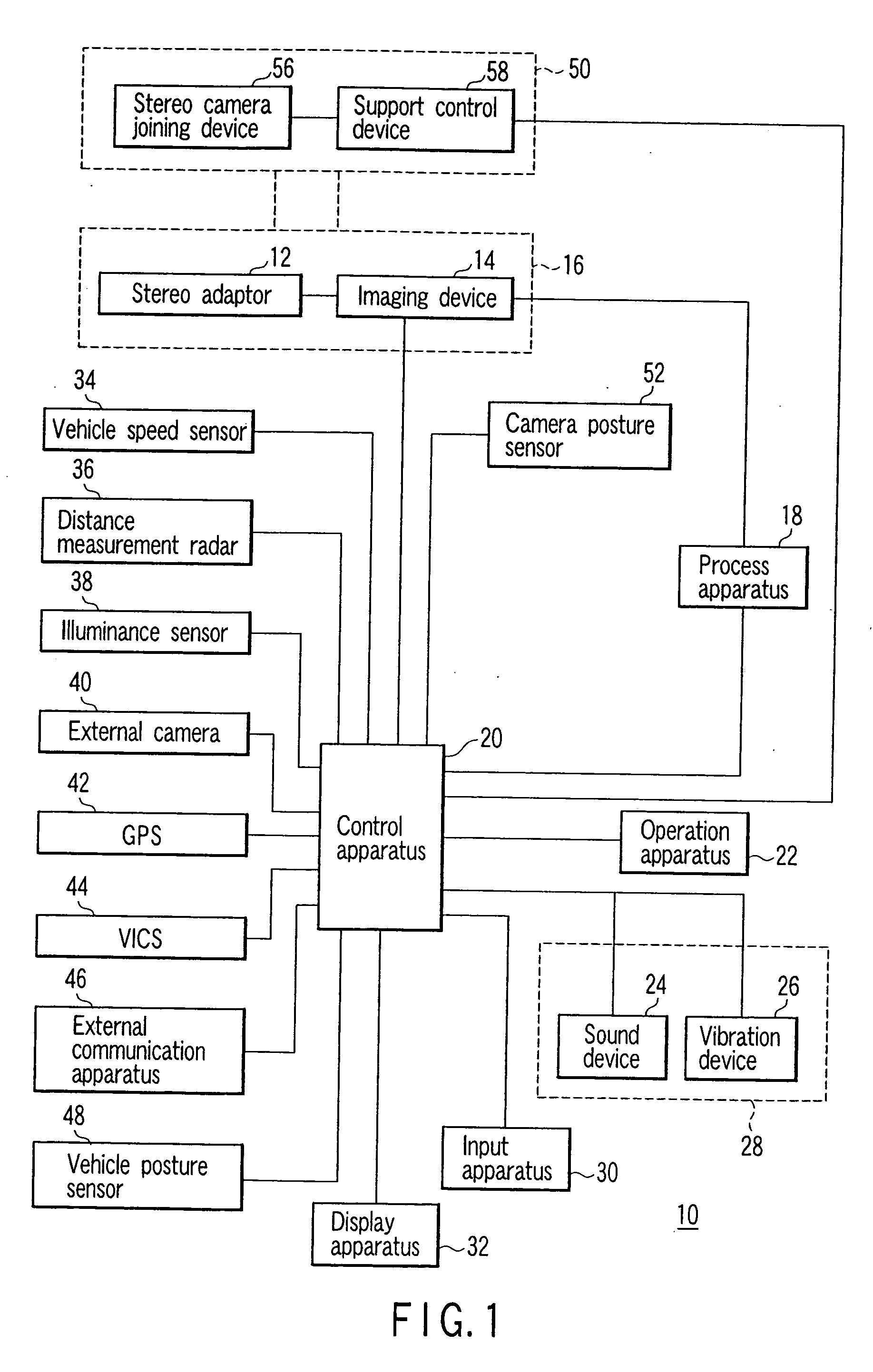
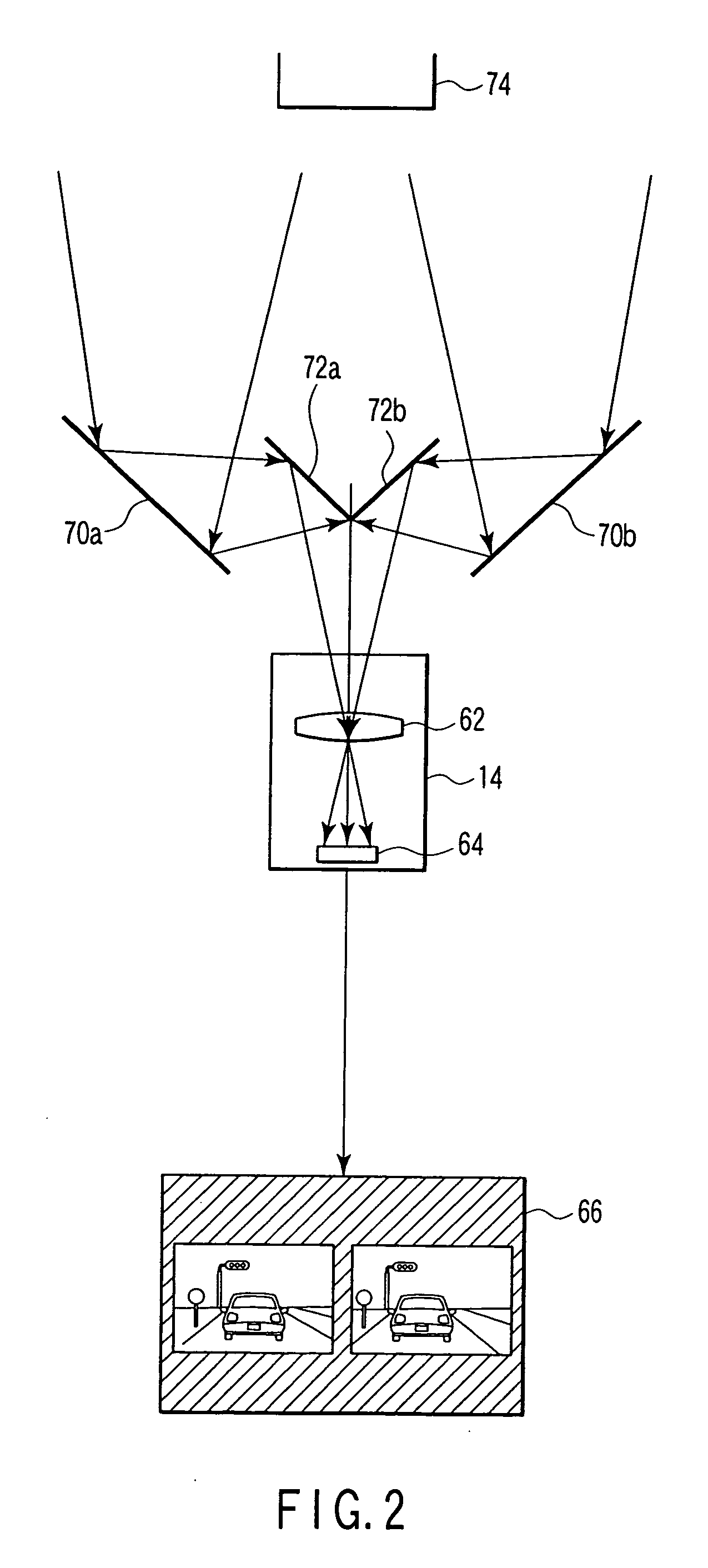
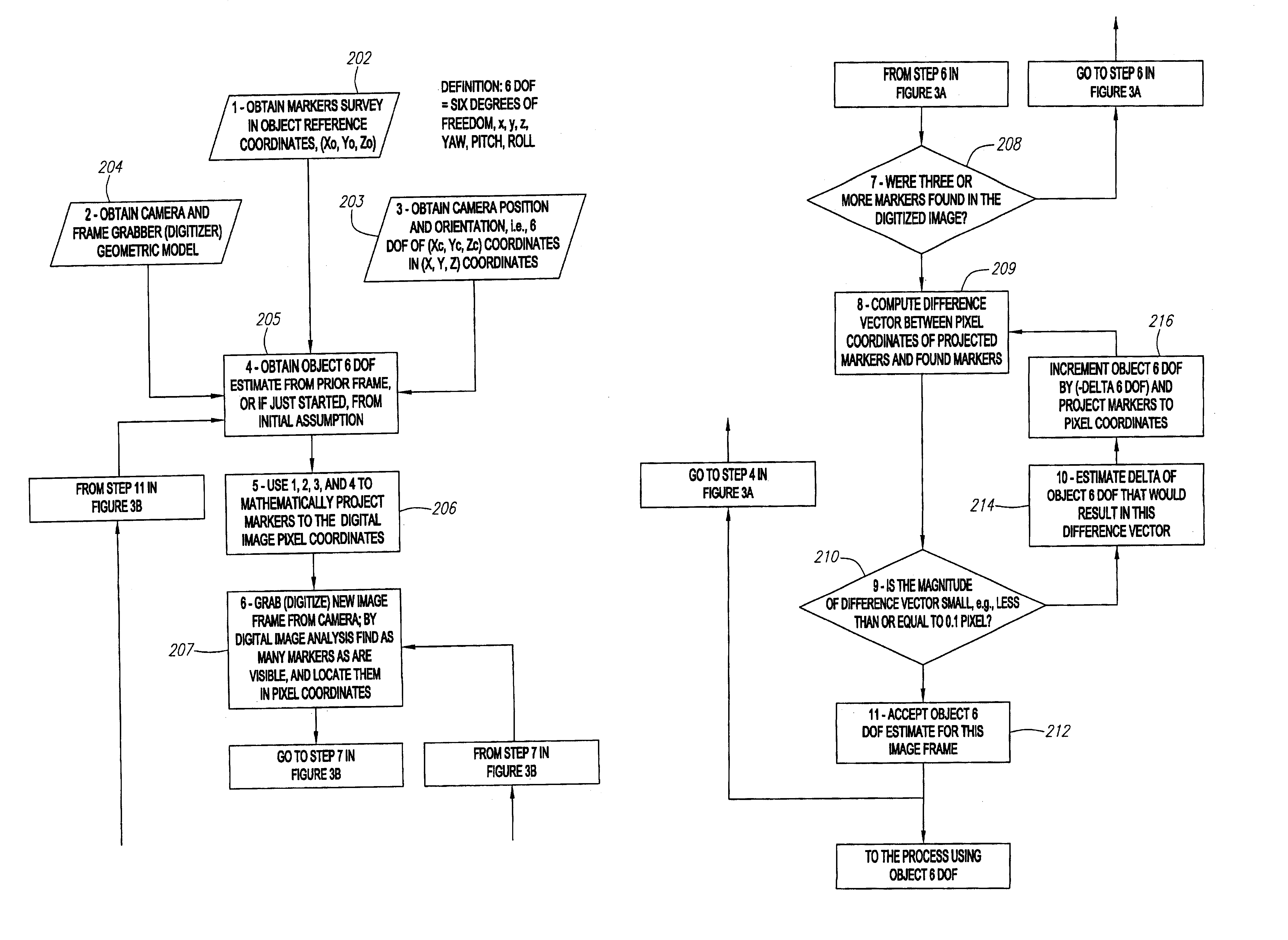
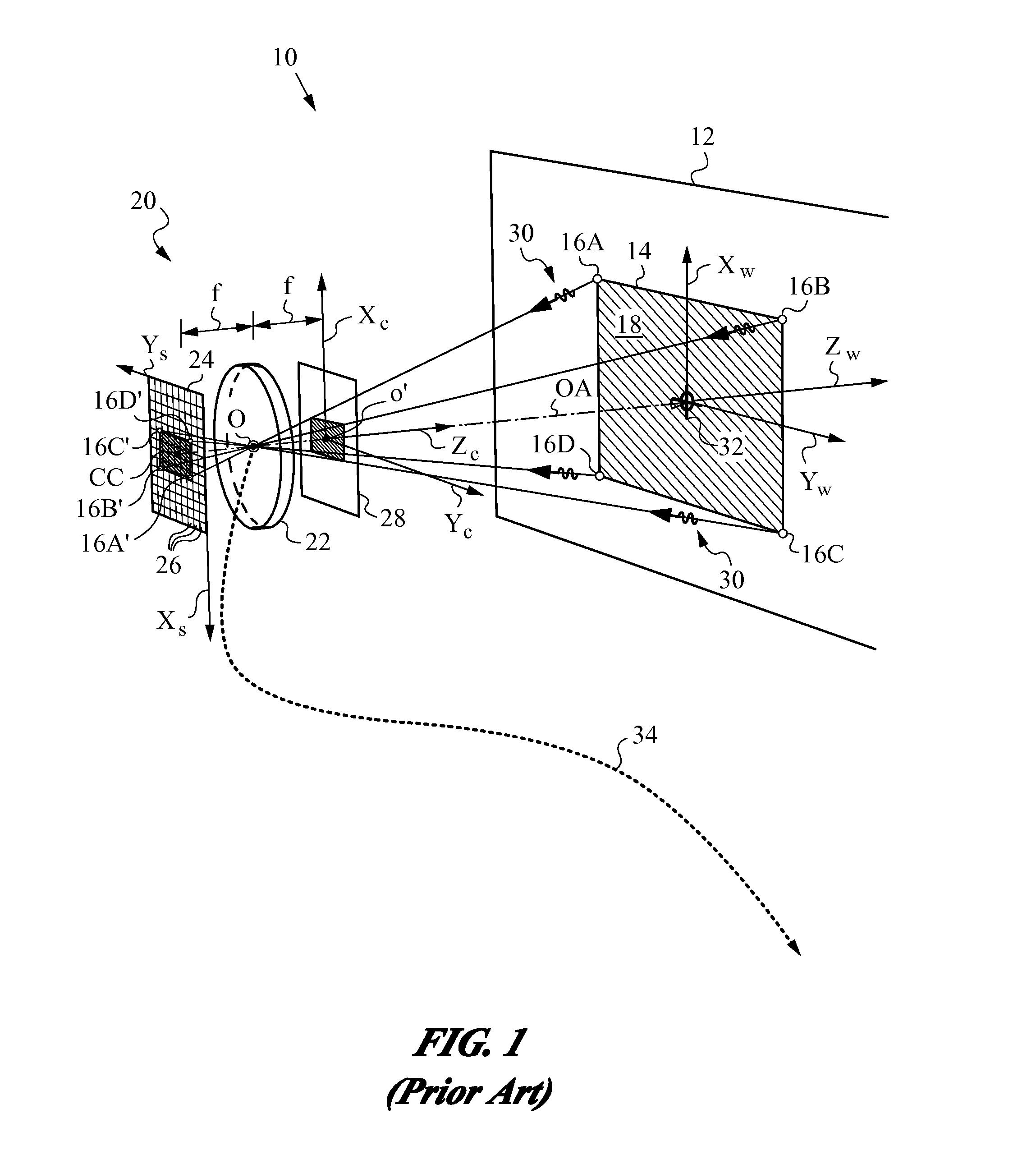
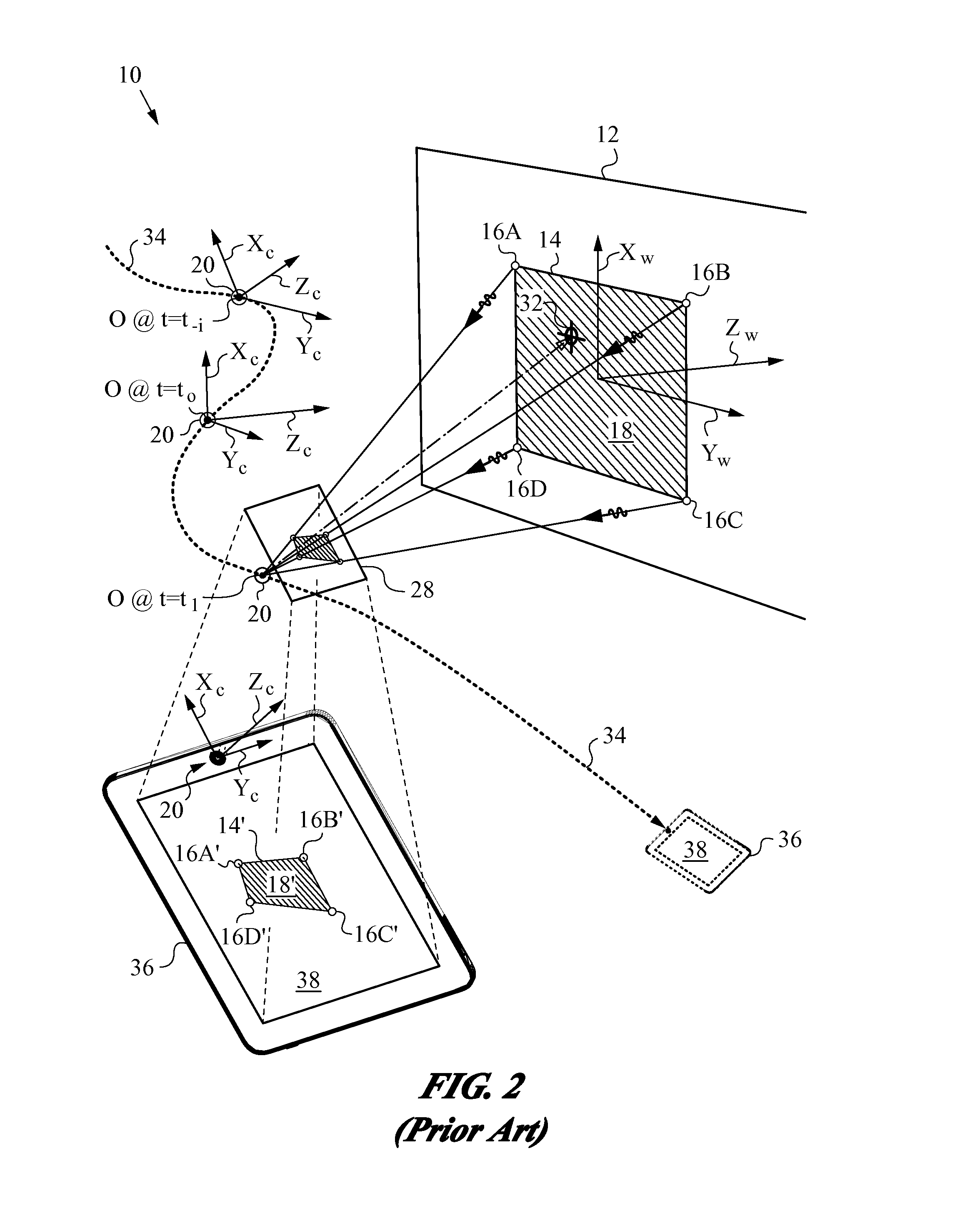
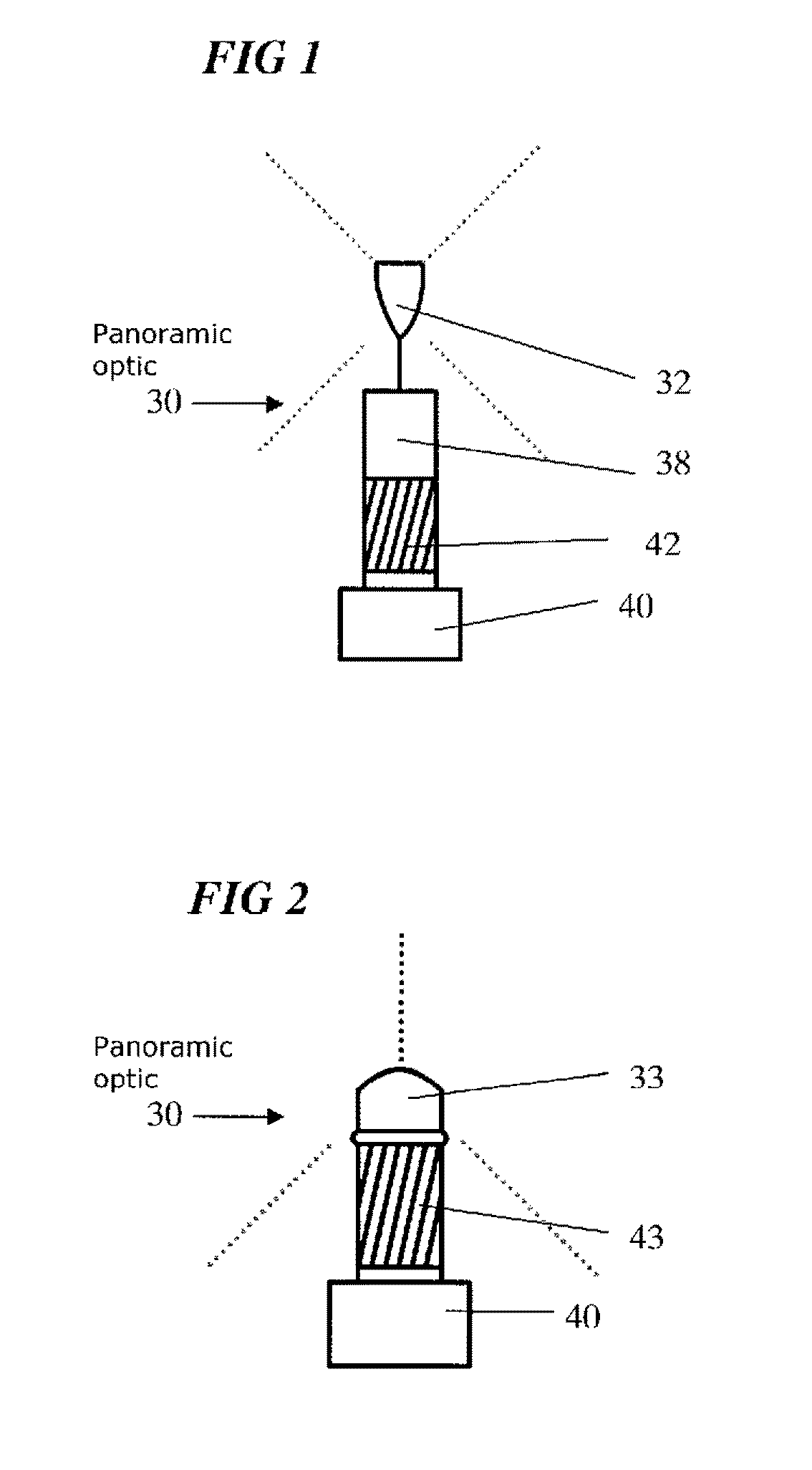
Stereo camera supporting apparatus, stereo camera supporting method, calibration detection apparatus, calibration correction apparatus, and stereo camera system
InactiveUS20050237385A1Efficient collectionImage analysisPicture taking arrangementsStereo camerasControl posture
A stereo camera supporting apparatus of the present invention comprises a joining member constituted in such a manner as to support a stereo camera on a vehicle, and a control device which controls posture or position of the stereo camera supported on the vehicle by the joining member. The control device controls the posture or position of the stereo camera with respect to video obtained by the stereo camera in such a manner that a contour portion present in the highest level position in a contour of a noted subject in the video is positioned in a frame upper end of the video or its vicinity irrespective of a change of the posture or position of the vehicle.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
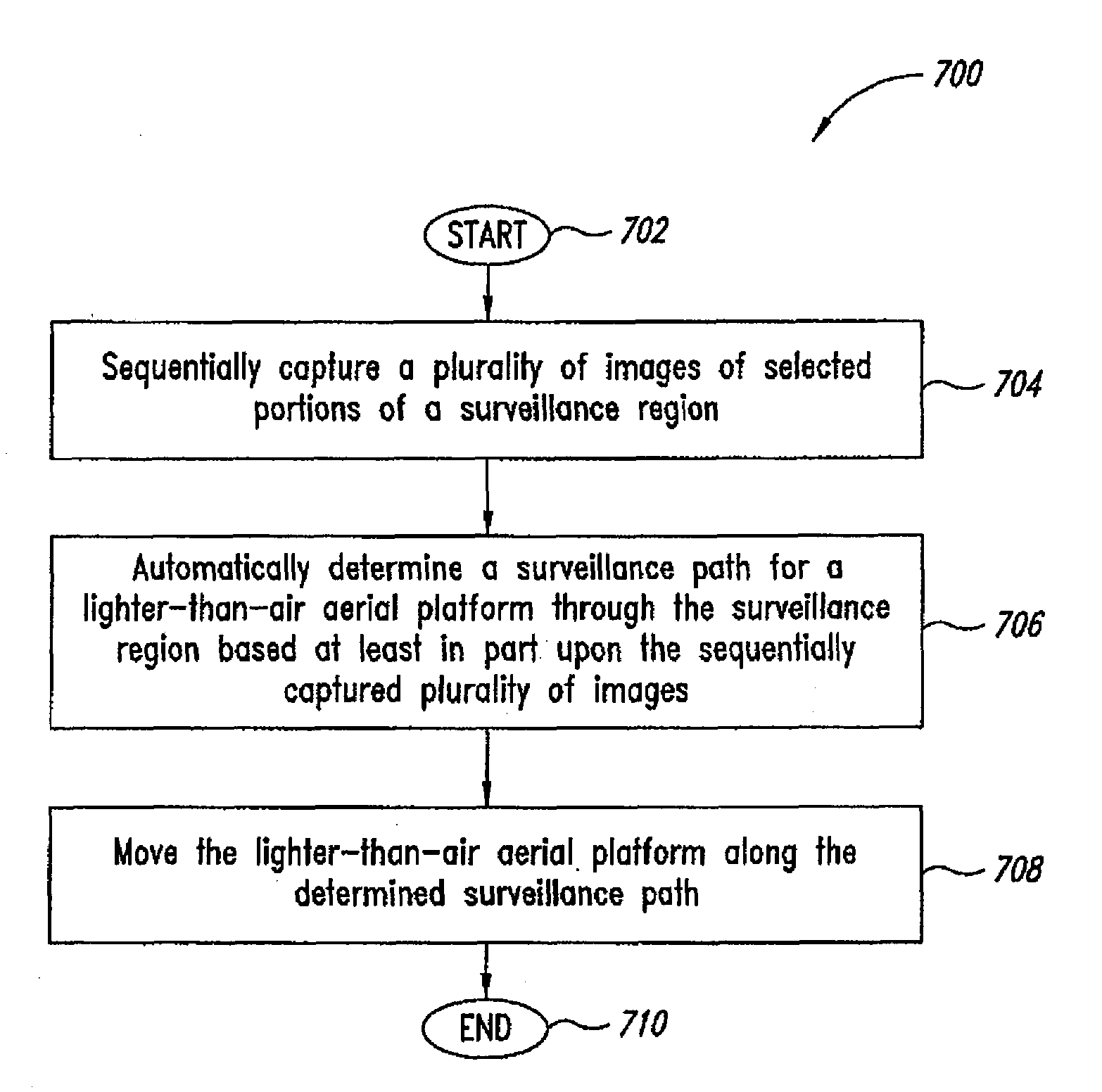
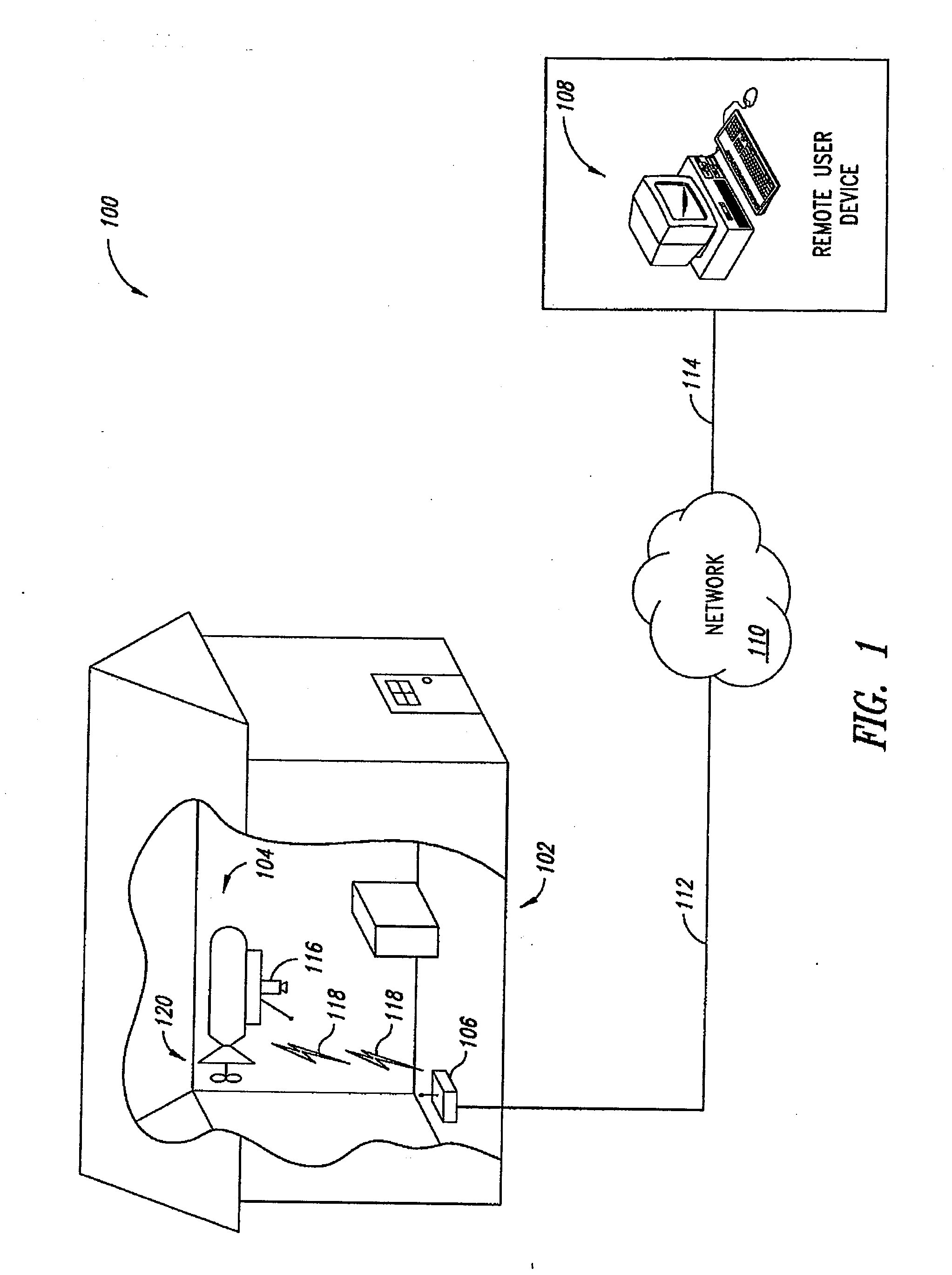
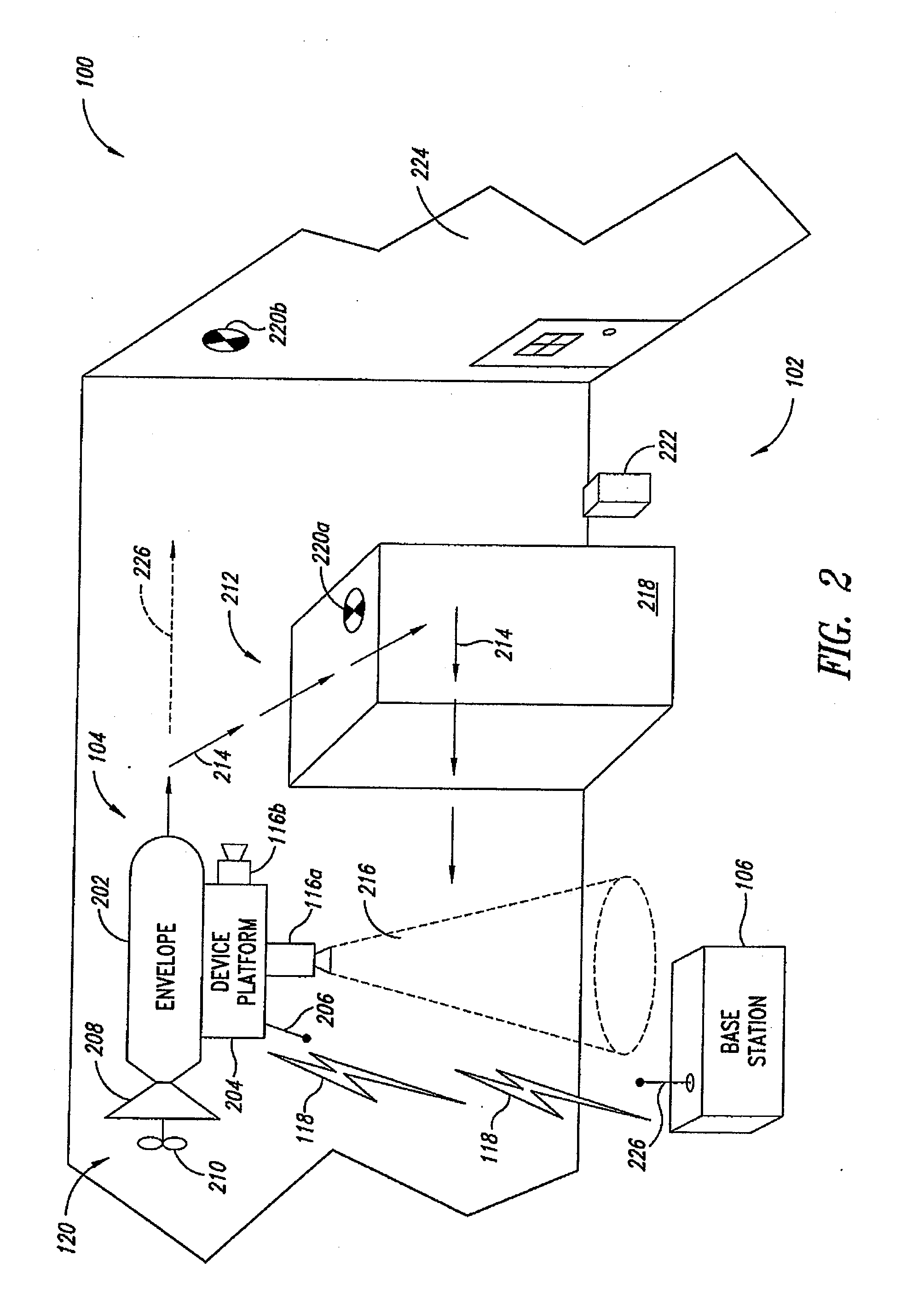
System and method of aerial surveillance
InactiveUS20080144884A1Improve drawing legibilityUnmanned aerial vehiclesPicture taking arrangementsGuidance controlEngineering
A system and method for an aerial surveillance system are disclosed. Briefly described, one embodiment comprises a lighter-than-air aerial platform, at least one image capture device carried by the lighter-than-air aerial platform and operable to sequentially capture a plurality of images, and at least one control surface physically coupled to the lighter-than-air aerial platform and operable to control direction of movement of the lighter-than-air aerial platform along a surveillance path in response to a guidance control signal determined in part upon the sequentially captured plurality of images.
Owner:ROBOTICVISIONTECH
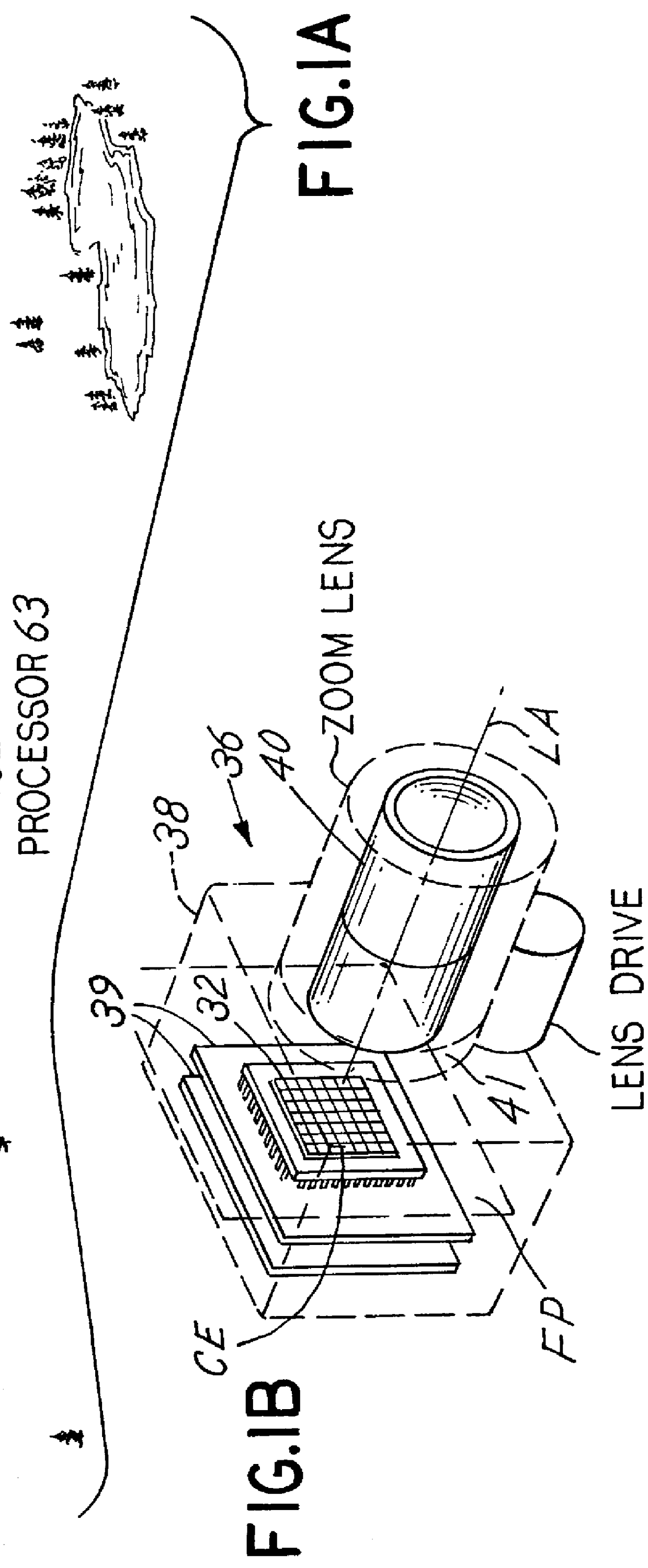
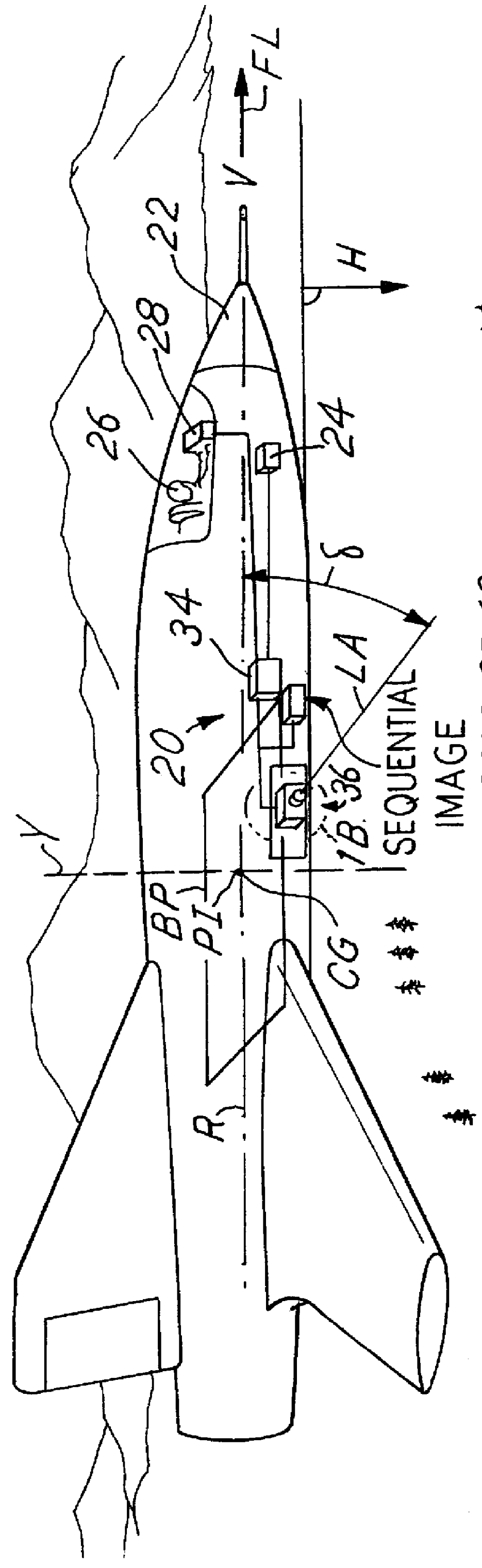
Autonomous electro-optical framing camera system with constant ground resolution, unmanned airborne vehicle therefor, and methods of use
InactiveUS6130705AReduce vibrationIncrease flexibilityTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersCamera imageImage resolution
An aerial reconnaissance system generates imagery of a scene that meets resolution or field of view objectives automatically and autonomously. In one embodiment, a passive method of automatically calculating range to the target from a sequence of airborne reconnaissance camera images is used. Range information is use for controlling the adjustment of a zoom lens to yield frame-to-frame target imagery that has a desired, e.g., constant, ground resolution or field of view at the center of the image despite rapid and significant aircraft altitude and attitude changes. Image to image digital correlation is used to determine the displacement of the target at the focal plane. Camera frame rate and aircraft INS / GPS information is used to accurately determine the frame to frame distance (baseline). The calculated range to target is then used to drive a zoom lens servo mechanism to the proper focal length to yield the desired resolution or field of view for the next image. The method may be performed based on parameters other than range, such as aircraft height and stand off distance.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
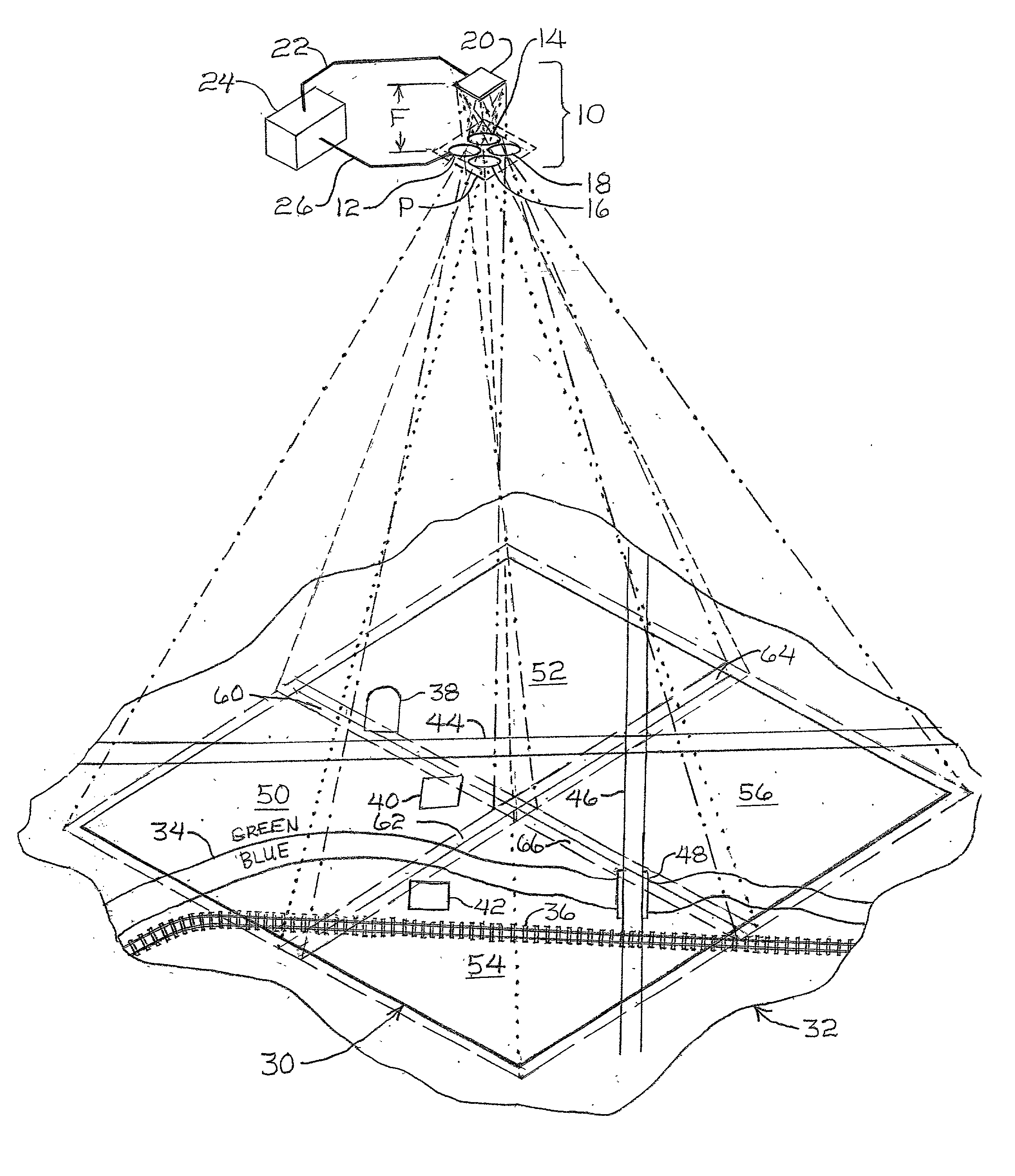
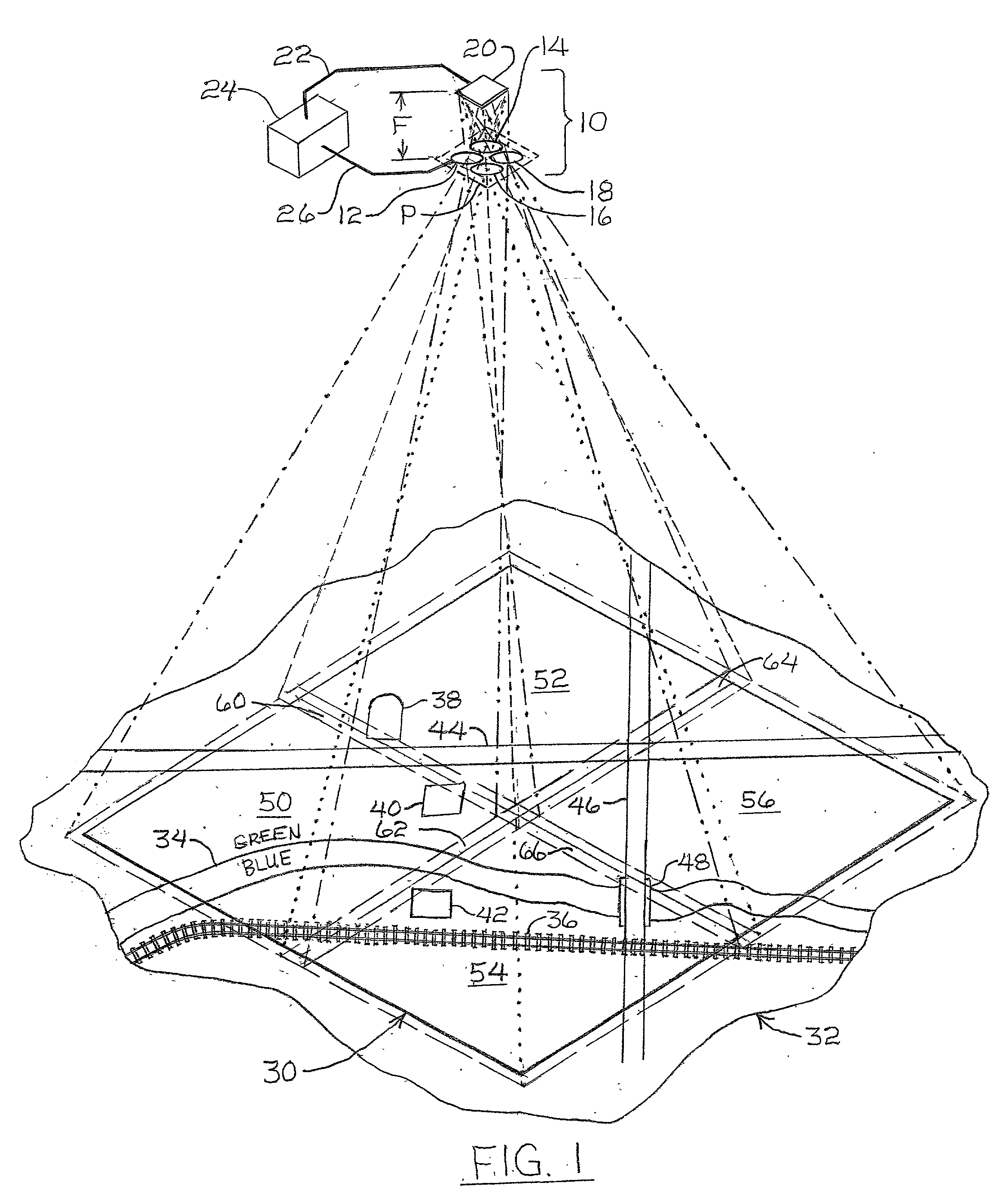
Self-calibrating, digital, large format camera with single or multiple detector arrays and single or multiple optical systems
InactiveUS7009638B2High resolutionTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationDigital signal processingAccelerometer
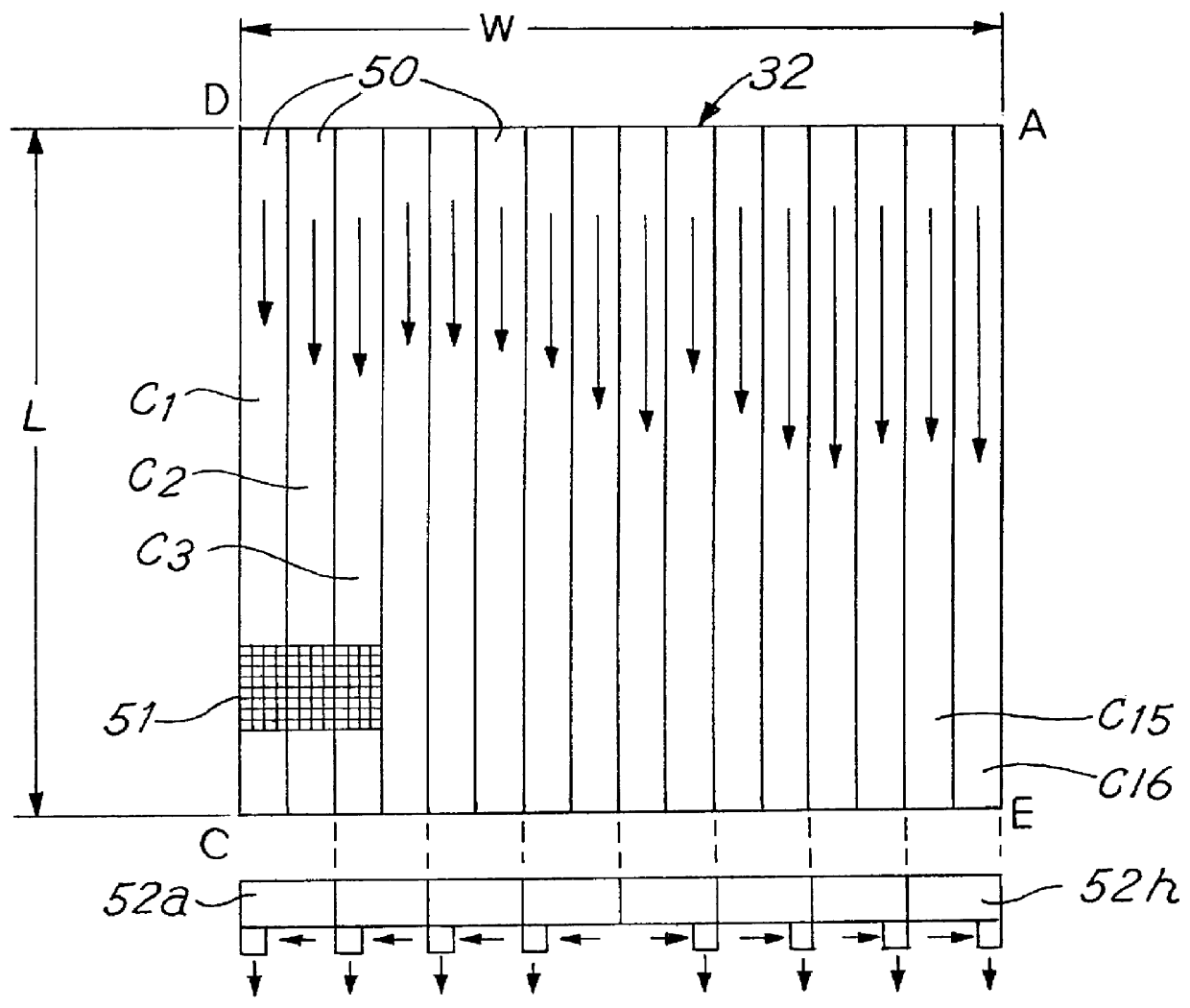
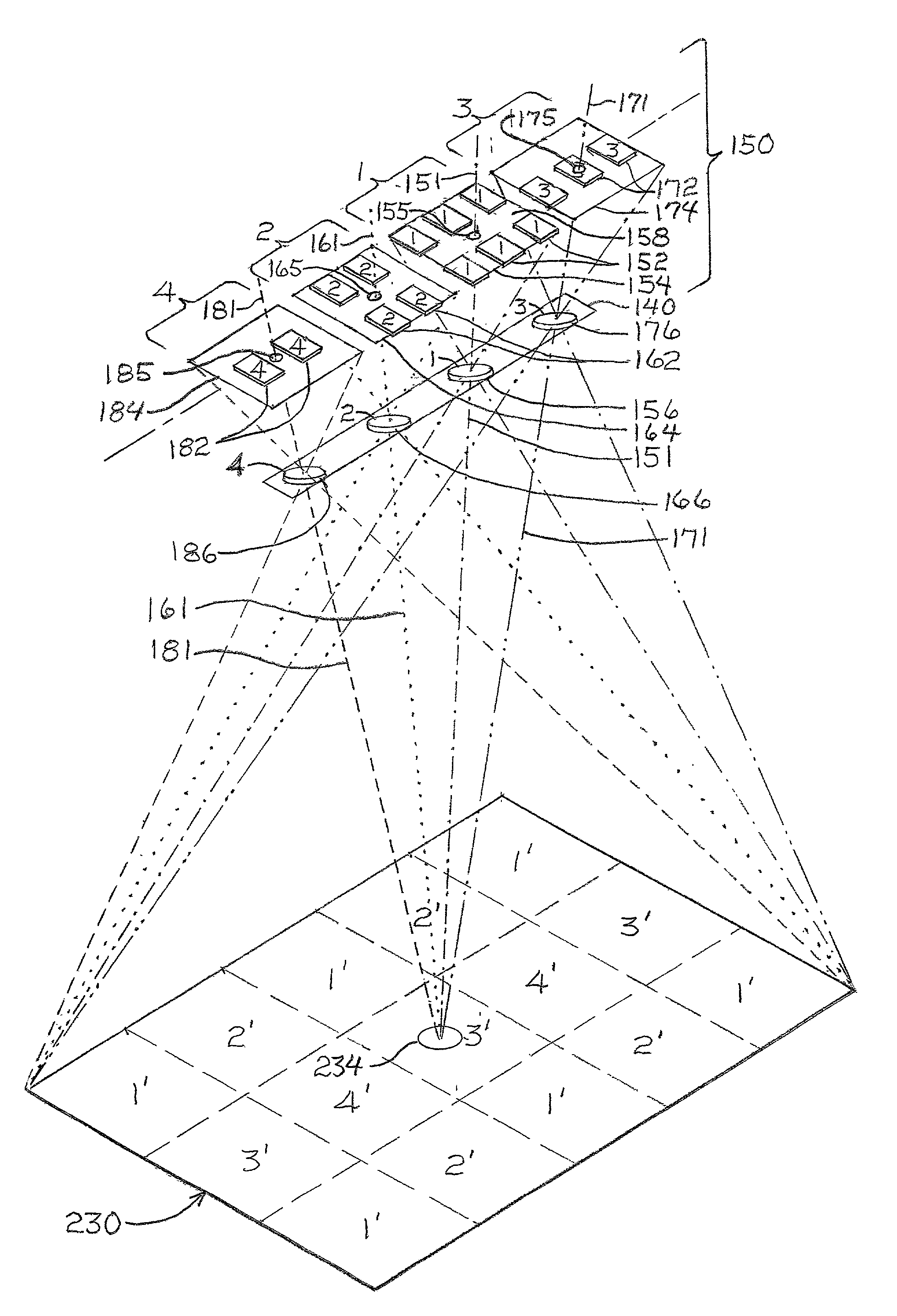
Large format, digital camera systems (10, 100, 150, 250, 310) expose single detector arrays 20 with multiple lens systems (12, 14, 16, 18) or multiple detector arrays (104, 106, 108, 110, 112, 114, 116, 118, 120, 152, 162, 172, 182, 252, 262, 272, 282, 322, 324) with one or more single lens systems (156, 166, 176, 186) to acquire sub-images of overlapping sub-areas of large area objects. The sub-images are stitched together to form a large format, digital, macro-image (80, 230″, 236″, 238″, 240″), which can be colored. Dampened camera carrier (400) and accelerometer (404) signals with double-rate digital signal processing (306, 308) are used.
Owner:VEXCEL IMAGING US INC
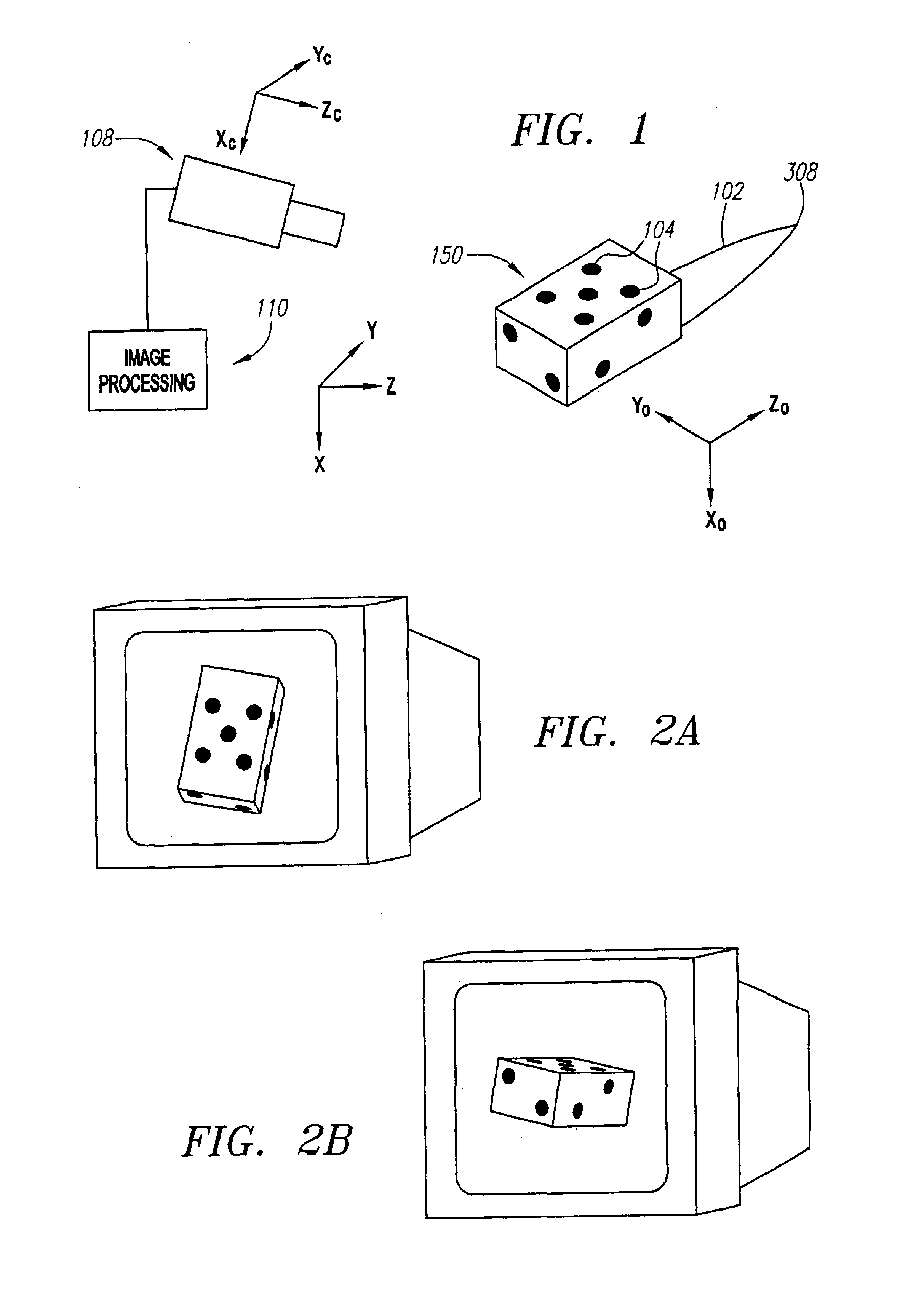
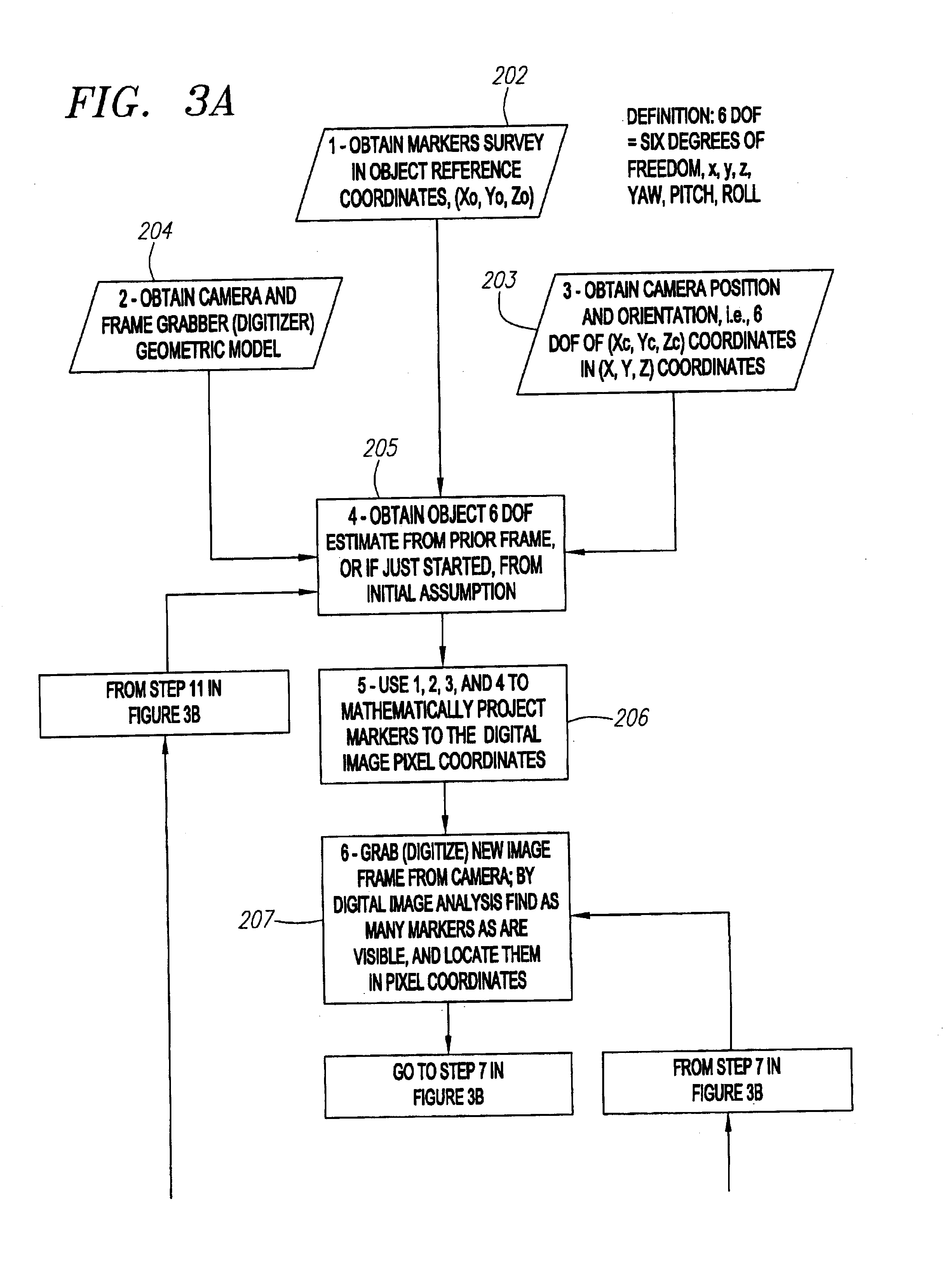
Single-camera tracking of an object
InactiveUS6973202B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementOptical trackingVideo camera
A method and system for determining the position and orientation of an object is disclosed. A set of markers attached or associated with the object is optically tracked and geometric translation is performed to use the coordinates of the set of markers to determine the location and orientation of their associated object.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
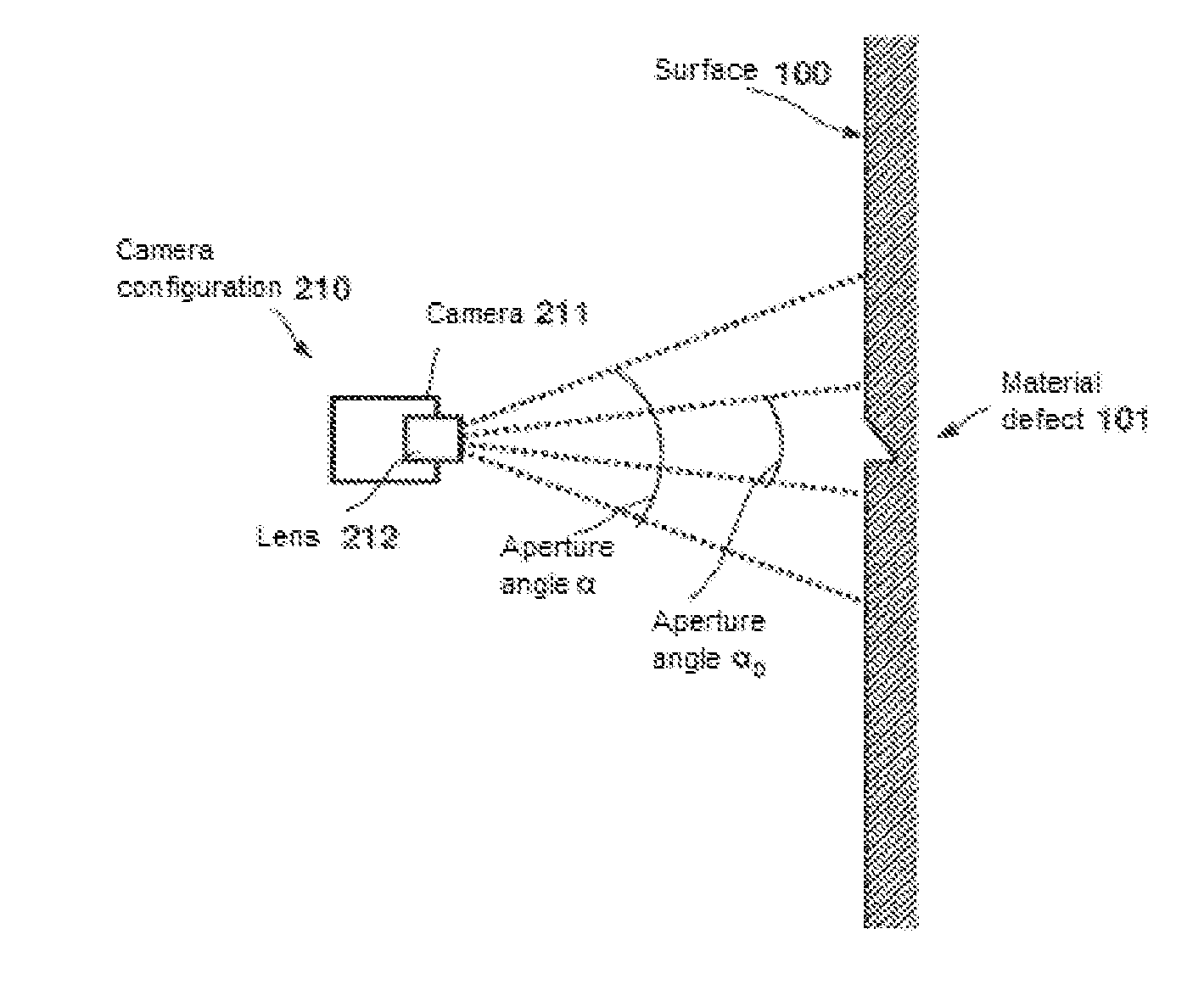
Method and System for Inspecting a Surface Area for Material Defects
ActiveUS20140168420A1Reduce associated effortReduce security risksPicture taking arrangementsColor television detailsMaterial defectEngineering
A camera assembly arranged on an unmanned and autonomously navigating aerial vehicle is employed to inspect a surface area of for material defects. The vehicle is automatically flown to the surface area from a launch site, wherein it can fly around obstacles using automatic obstacle detection and avoidance methods. A relative position of the aerial vehicle with respect to the surface area with the aid of a position sensor is continuously measured and a sequence of images of the surface area is recorded. Between the individual images, the aerial vehicle is moved along a flight path overlapping image details of the surface area. The images of the sequence are composed into an overall image of the surface area to allow for the surface area to be inspected for defects and the location of defects to be ascertained on the basis of the overall image.
Owner:EADS DEUT GMBH
Virtual billboards
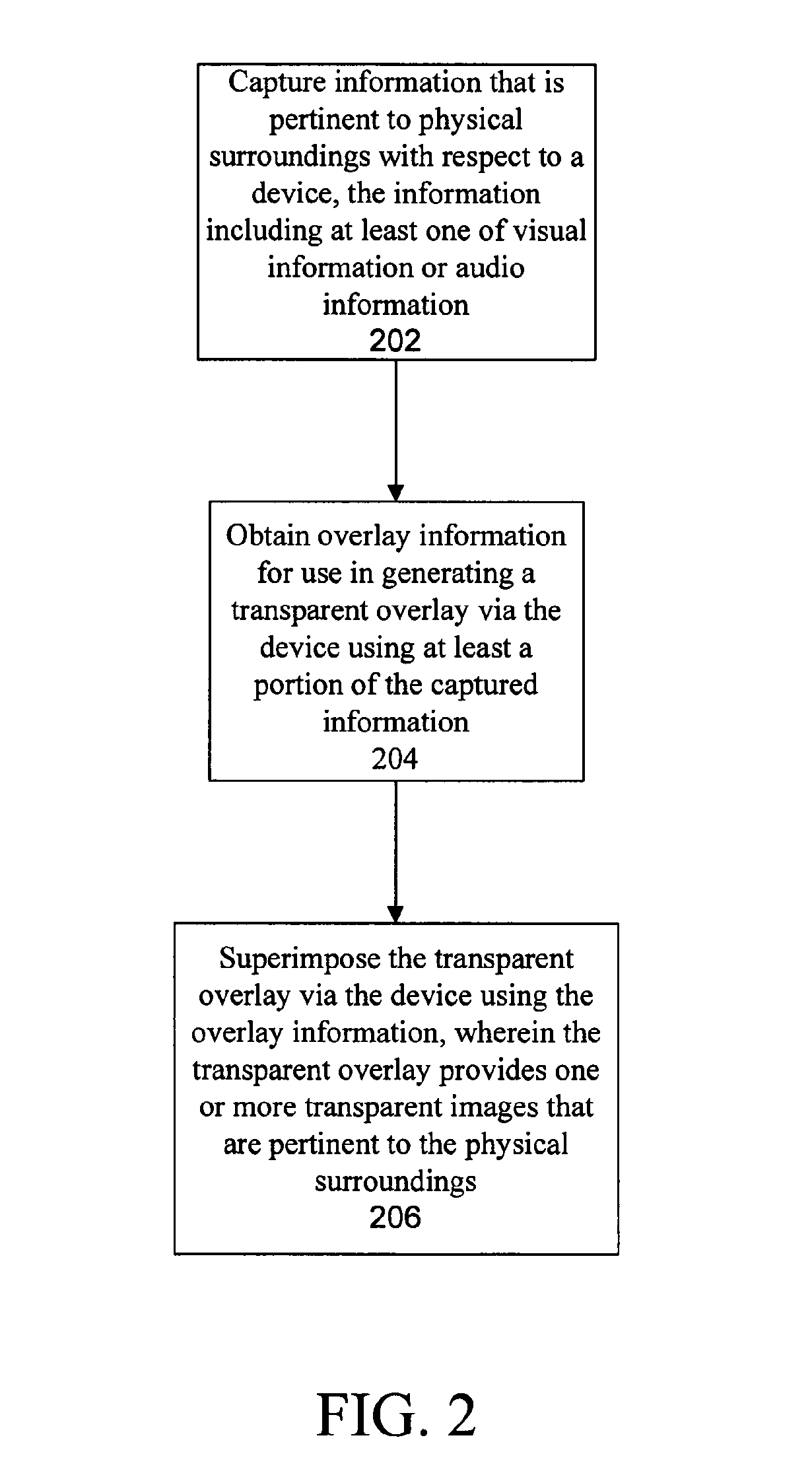
Disclosed are methods and apparatus for implementing a reality overlay device. A reality overlay device captures information that is pertinent to physical surroundings with respect to a device, the information including at least one of visual information or audio information. The reality overlay device may transmit at least a portion of the captured information to a second device. For instance, the reality overlay device may transmit at least a portion of the captured information to a server via the Internet, where the server is capable of identifying an appropriate virtual billboard. The reality overlay device may then receive overlay information for use in generating a transparent overlay via the reality overlay device. The transparent overlay is then superimposed via the device using the overlay information, wherein the transparent overlay provides one or more transparent images that are pertinent to the physical surroundings. Specifically, one or more of the transparent images may operate as “virtual billboards.” Similarly, a portable device such as a cell phone may automatically receive a virtual billboard when the portable device enters an area within a specified distance from an associated establishment.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Systems and methods for target tracking
The present invention provides systems, methods, and devices related to target tracking by UAVs. The UAV may be configured to receive target information from a control terminal related to a target to be tracked by an imaging device coupled to the UAV. The target information may be used by the UAV to automatically track the target so as to maintain predetermined position and / or size of the target within one or more images captured by the imaging device. The control terminal may be configured to display images from the imaging device as well as allowing user input related to the target information.
Owner:SZ DJI TECH CO LTD
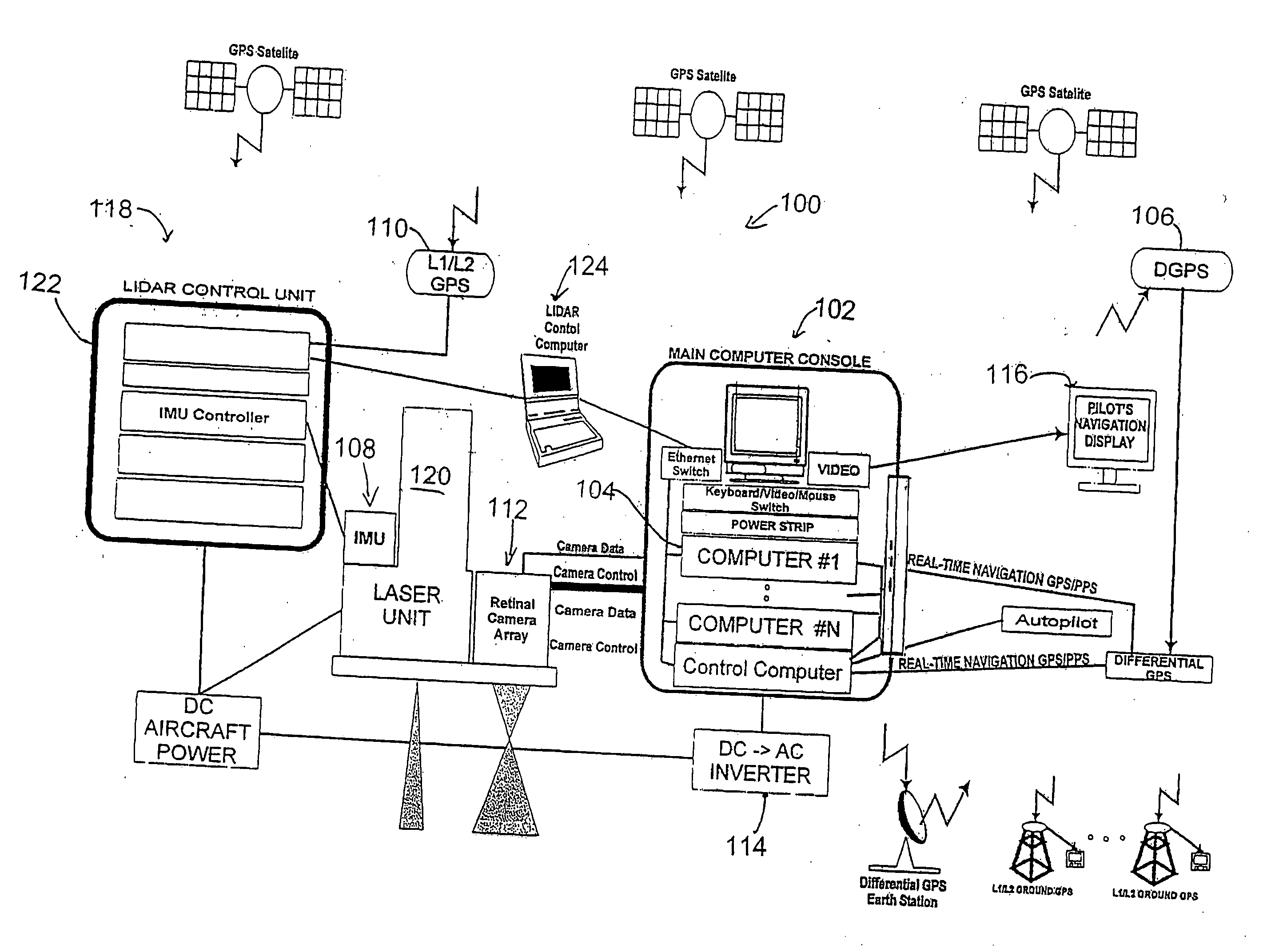
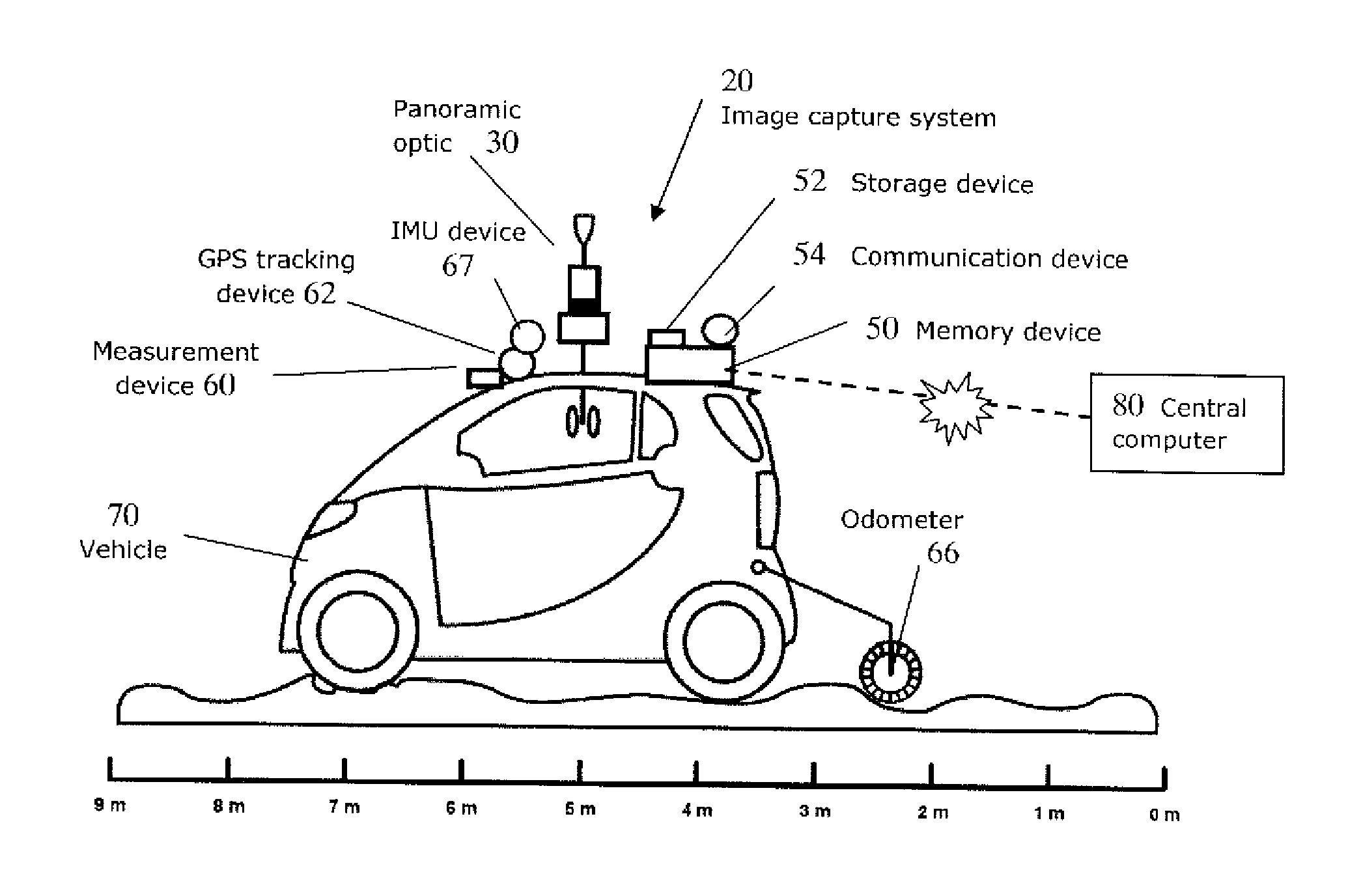
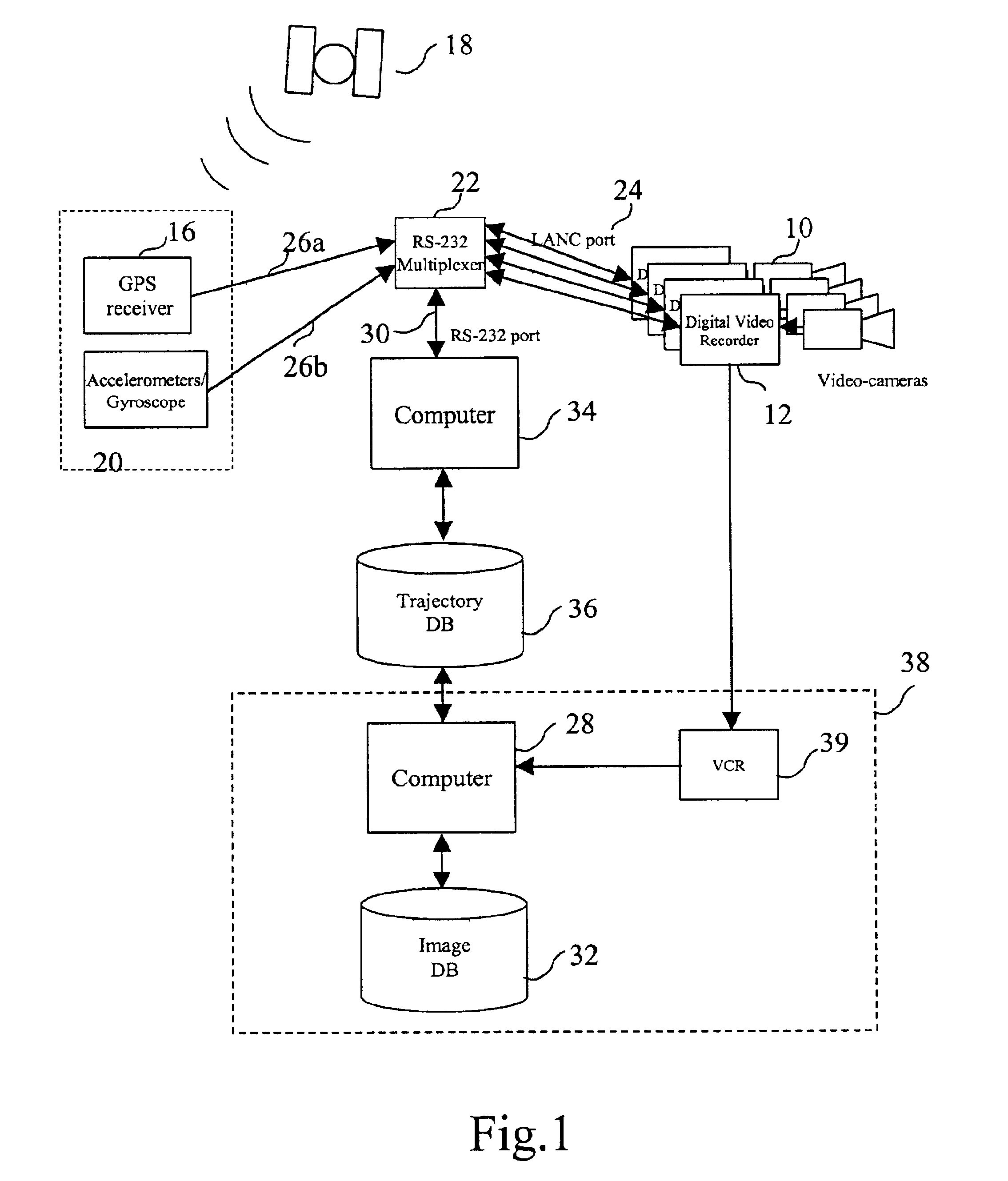
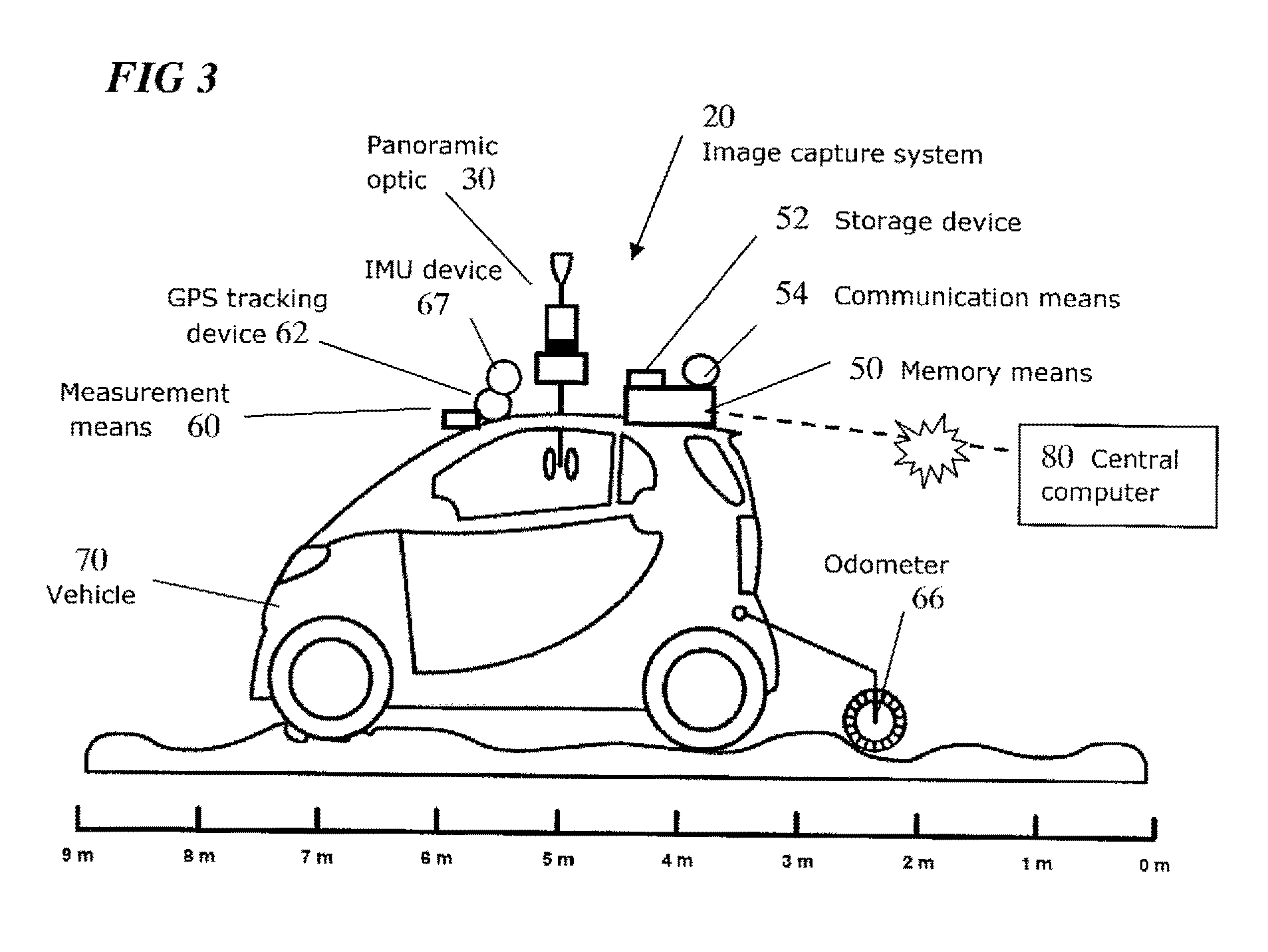
Vehicle based data collection and processing system and imaging sensor system and methods thereof
ActiveUS20070046448A1Picture taking arrangementsColor television detailsGlobal Positioning SystemData harvesting
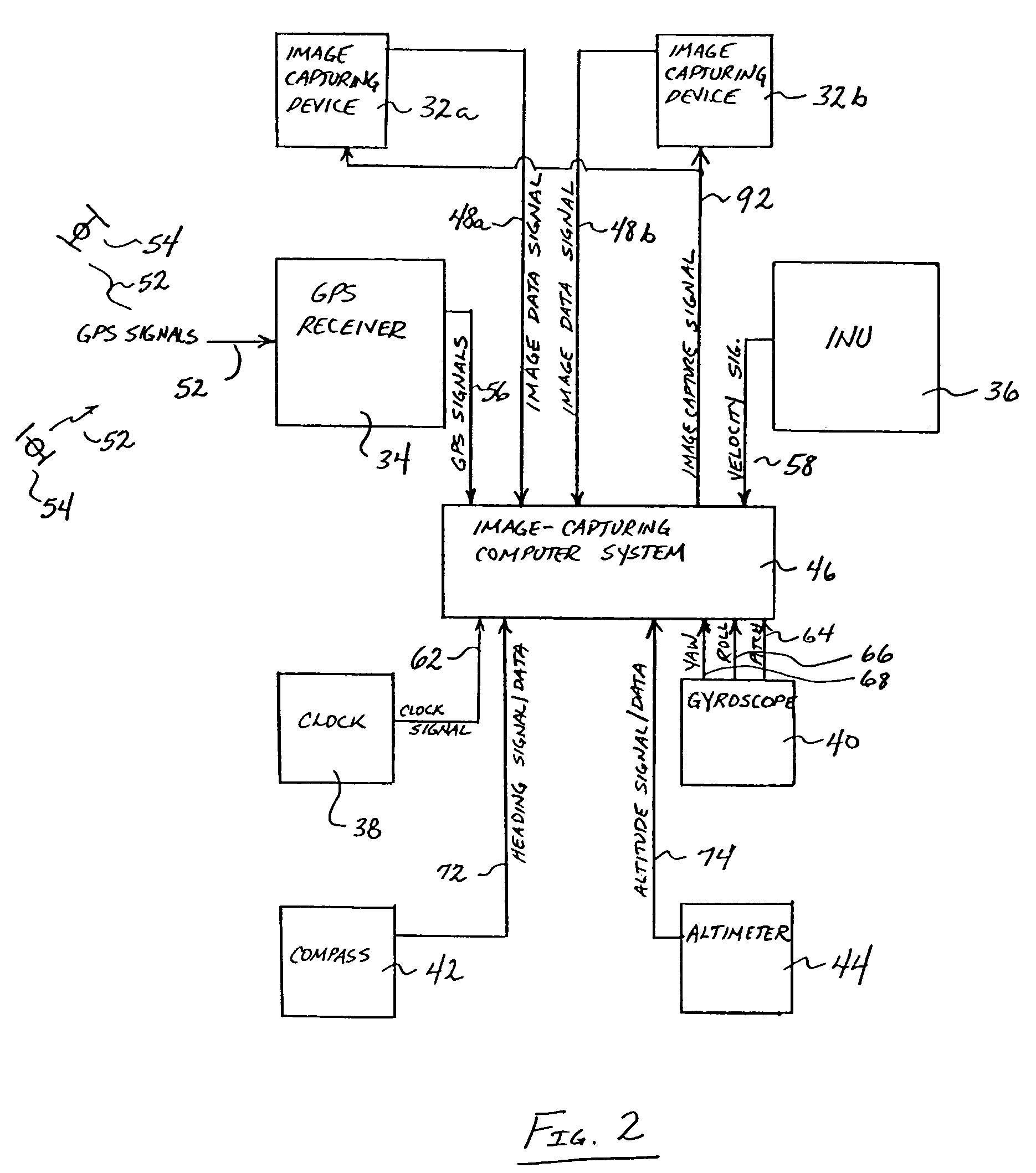
A vehicle based data collection and processing system which may be used to collect various types of data from an aircraft in flight or from other moving vehicles, such as an automobile, a satellite, a train, etc. In various embodiments the system may include: computer console units for controlling vehicle and system operations, global positioning systems communicatively connected to the one or more computer consoles, camera array assemblies for producing an image of a target viewed through an aperture communicatively connected to the one or more computer consoles, attitude measurement units communicatively connected to the one or more computer consoles and the one or more camera array assemblies, and a mosaicing module housed within the one or more computer consoles for gathering raw data from the global positioning system, the attitude measurement unit, and the retinal camera array assembly, and processing the raw data into orthorectified images.
Owner:VI TECH LLC
Self-calibrating, digital, large format camera with single or mulitiple detector arrays and single or multiple optical systems
InactiveUS20020163582A1High resolutionTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationDigital signal processingAccelerometer
Large format, digital camera systems (10, 100, 150, 250, 310) expose single detector arrays 20 with multiple lens systems (12, 14, 16, 18) or multiple detector arrays (104, 106, 108, 110, 112, 114, 116, 118, 120, 152, 162, 172, 182, 252, 262, 272, 282, 322, 324) with one or more single lens systems (156, 166, 176, 186) to acquire sub-images of overlapping sub-areas of large area objects. The sub-images are stitched together to form a large format, digital, macro-image (80, 230'', 236'', 238'', 240''), which can be colored. Dampened camera carrier (400) and accelerometer (404) signals with double-rate digital signal processing (306, 308) are used.
Owner:VEXCEL IMAGING US INC
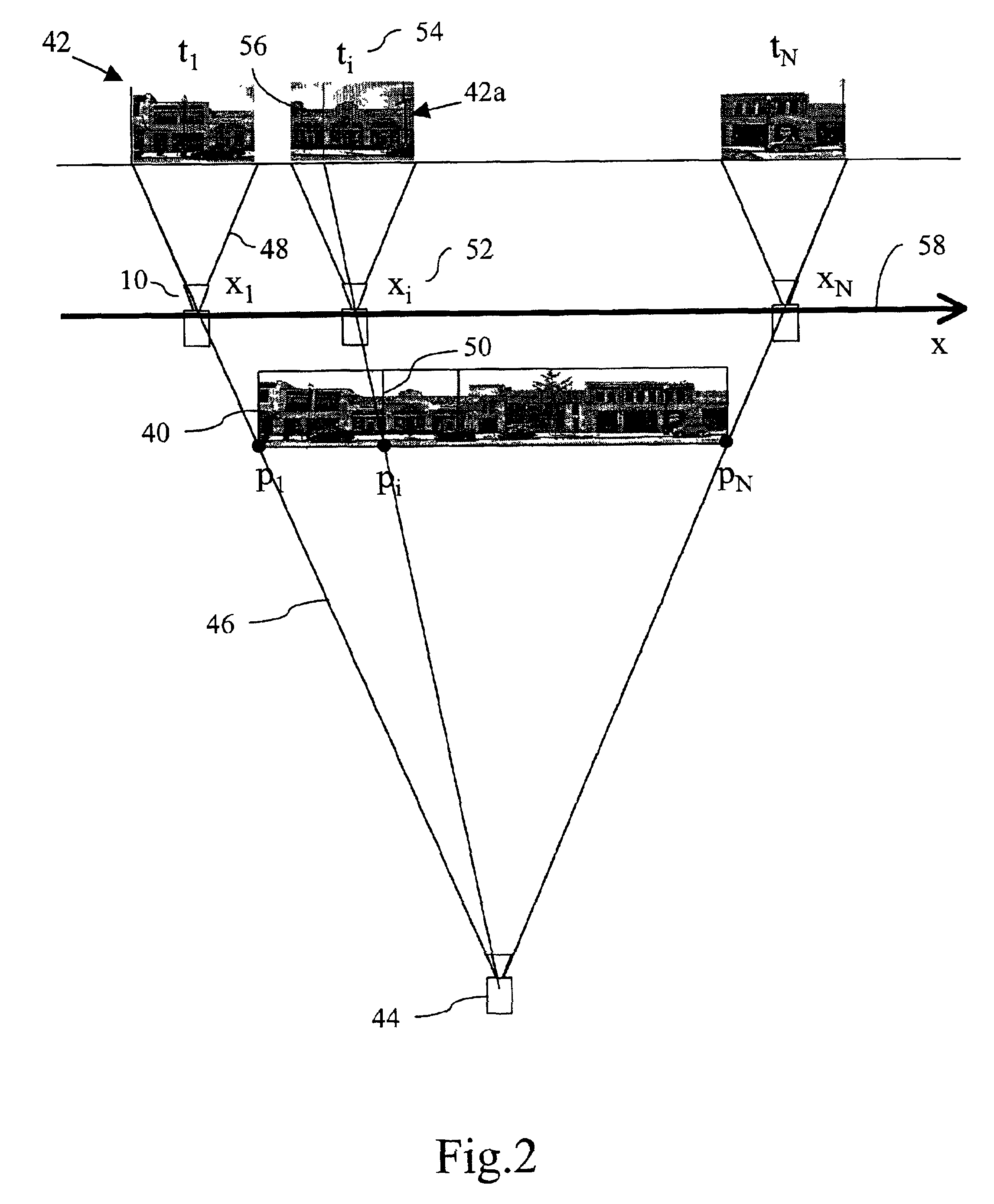
Method and apparatus for capturing, geolocating and measuring oblique images
A computerized system for displaying, geolocating, and taking measurements from captured oblique images includes a data file accessible by the computer system. The data file includes a plurality of image files corresponding to a plurality of captured oblique images, and positional data corresponding to the images. Image display and analysis software is executed by the system for reading the data file and displaying at least a portion of the captured oblique images. The software retrieves the positional data for one or more user-selected points on the displayed image, and calculates a separation distance between any two or more selected points. The separation distance calculation is user-selectable to determine various parameters including linear distance between, area encompassed within, relative elevation of, and height difference between selected points.
Owner:PICTOMERTRY INT CORP
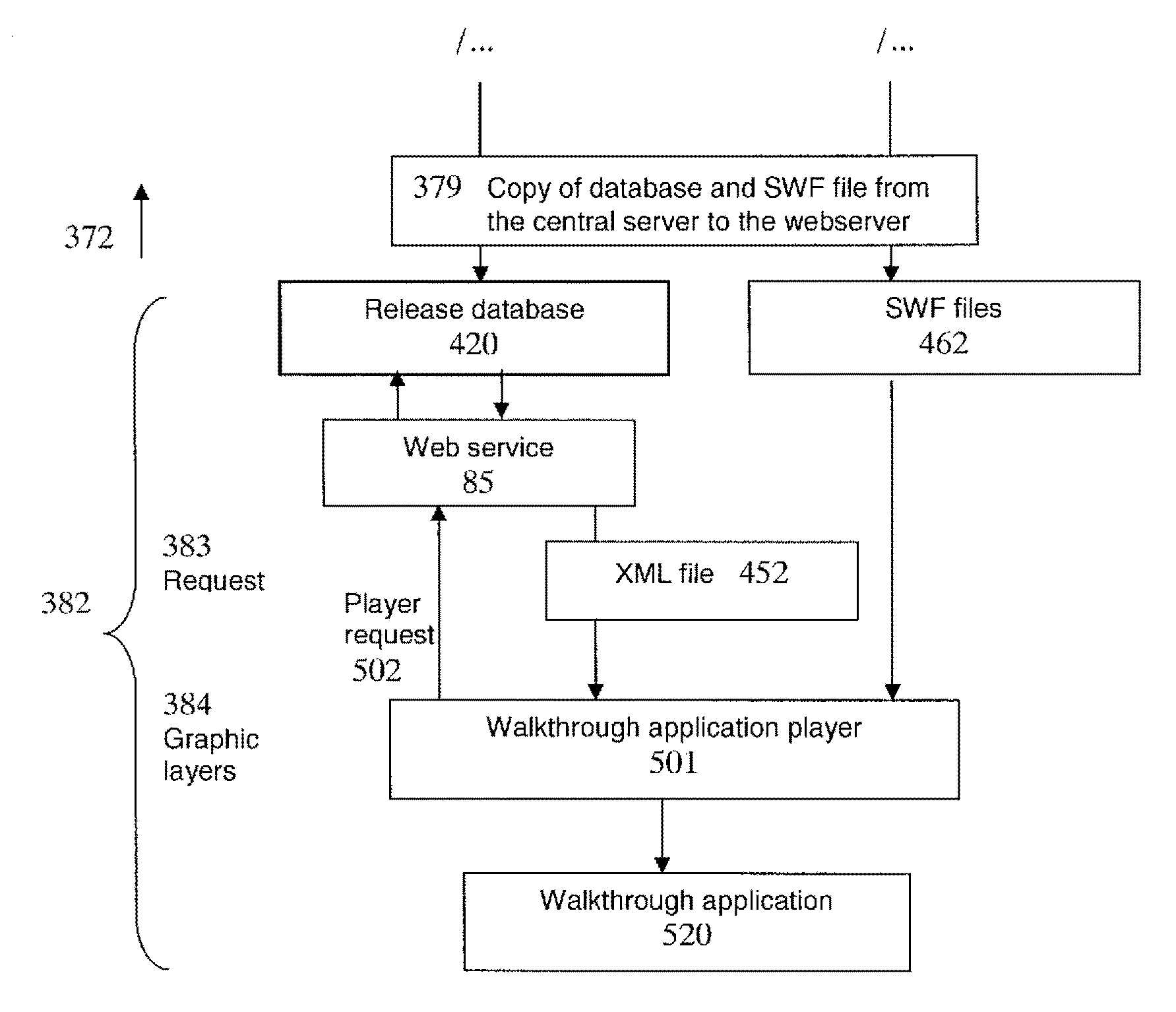
System and method for creating interactive panoramic walk-through applications
InactiveUS20110211040A1Quality improvementTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationComputer visionBroadcasting
System and method of the invention provides for creating, storing and broadcasting interactive panoramic walk-through applications. The combination of images is determined by the user's choice of direction of displacement at each intersection point and from each view point or geographical coordinate, in order to provide a complete view from a first person's point of view. The system provides a visual perspective comparable to a human visual experience.
Owner:LINDEMANN PIERRE ALAIN +2
System and method for creating, storing, and utilizing composite images of a geographic location
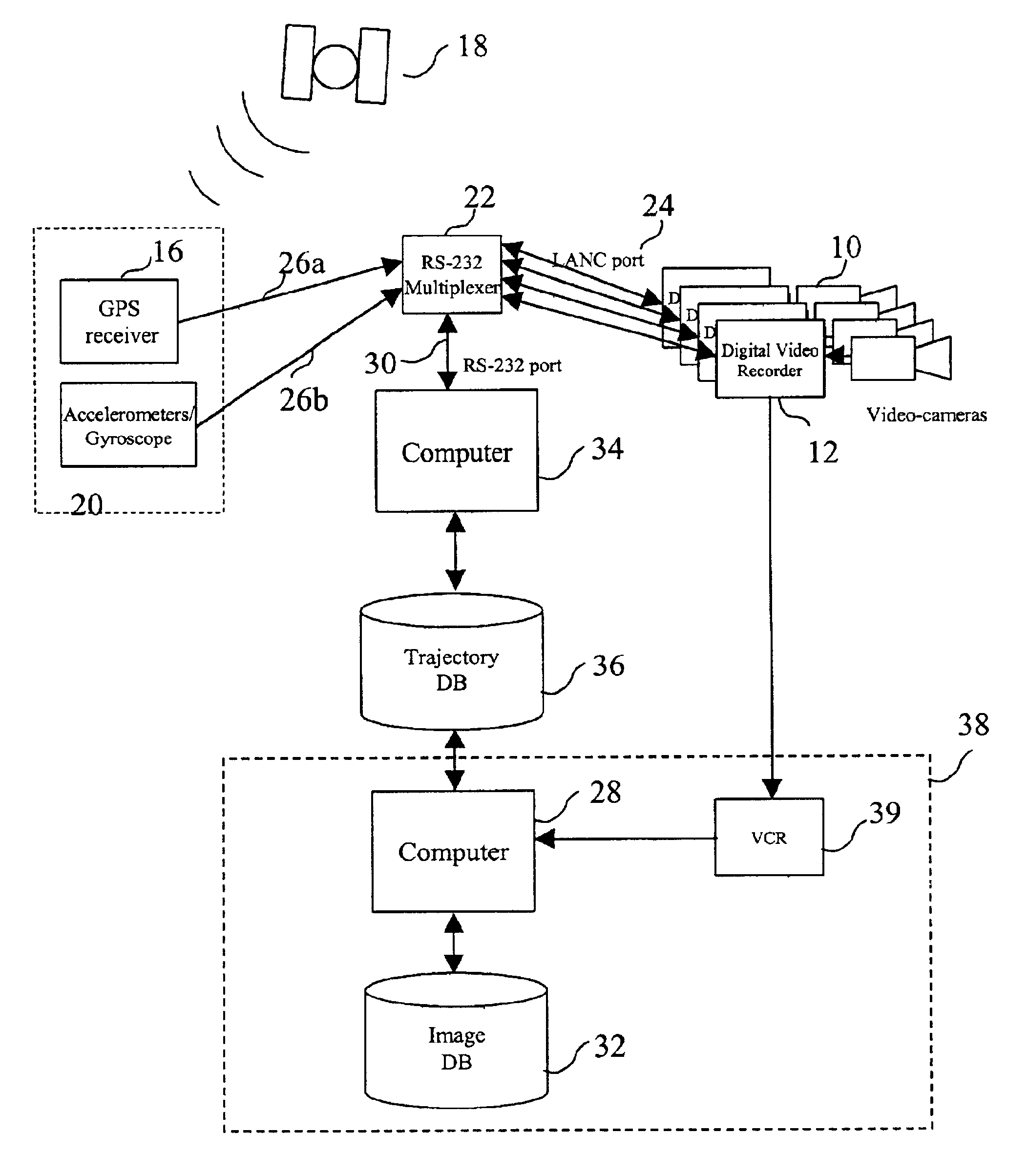
InactiveUS6895126B2Television system detailsInstruments for road network navigationGps receiverGeolocation
A system and method synthesizing images of a locale to generate a composite image that provide a panoramic view of the locale. A video camera moves along a street recording images of objects along the street. A GPS receiver and inertial navigation system provide the position of the camera as the images are being recorded. The images are indexed with the position data provided by the GPS receiver and inertial navigation system. The composite image is created on a column-by-column basis by determining which of the acquired images contains the desired pixel column, extracting the pixels associated with the column, and stacking the columns side by side. The composite images are stored in an image database and associated with a street name and number range of the street being depicted in the image. The image database covers a substantial amount of a geographic area allowing a user to visually navigate the area from a user terminal.
Owner:VEDERI
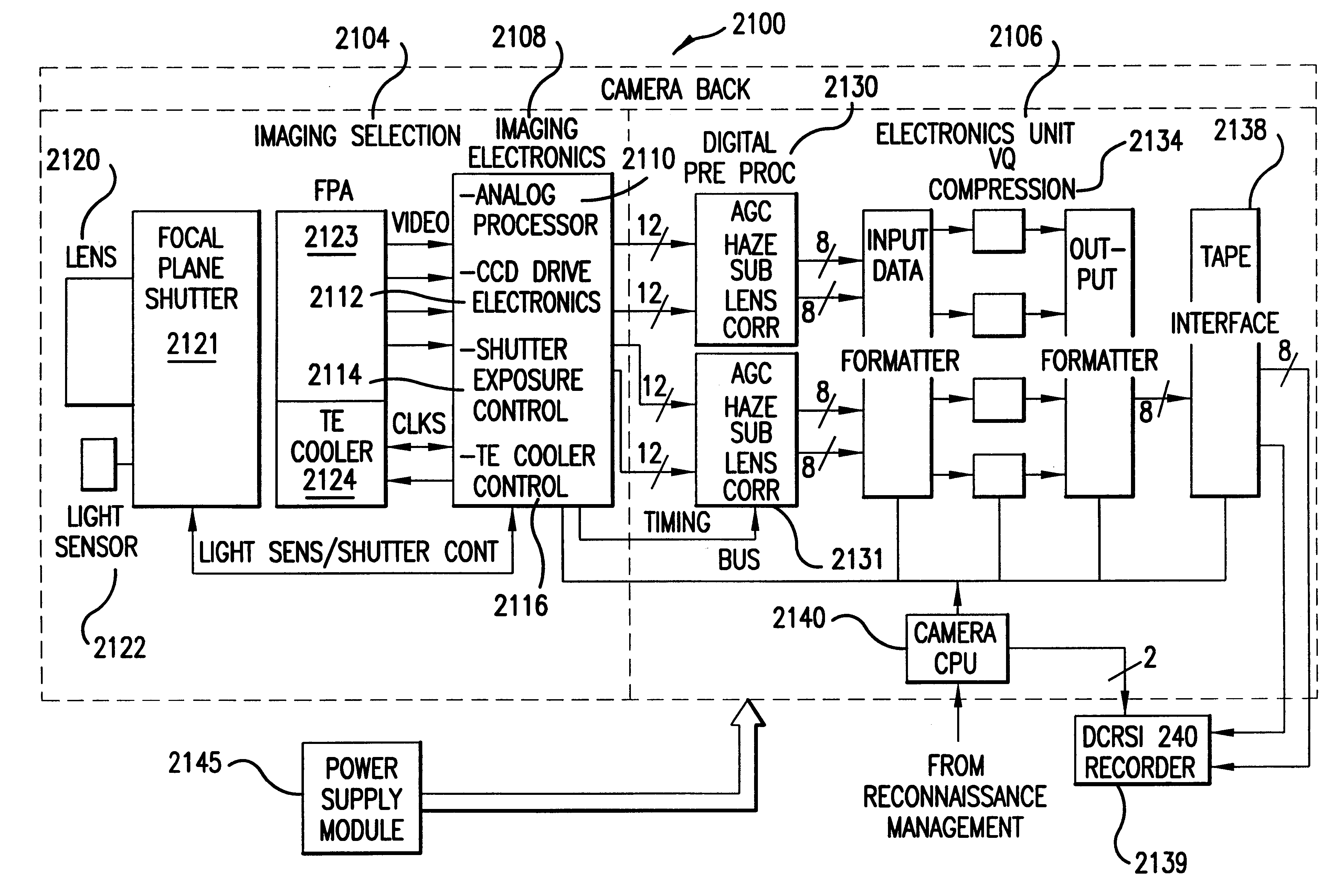
Electro-optical reconnaissance system with forward motion compensation
InactiveUS6256057B1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImage transferImage motion
An electro-optical framing camera forward motion compensation (FMC) reconnaissance system comprising a moving shutter and a full frame focal plane array detector is designed to minimize the variation of image motion from a target scene across the focal plane array. The full frame focal plane array, such as a Charge Coupled Device (CCD), is designed to transfer and add the image from pixel to pixel at a predetermined rate of image motion corresponding to the region exposed by the focal plane shutter. The focal plane shutter aperture and velocity are set to predetermined values coordinated with the available illumination. The CCD image transfer rate is set to minimize the smear effects due to image motion in the region of the scene exposed by the focal plane shutter. This rate is variable with line of sight depression angle, aircraft altitude, and aircraft velocity / altitude ratio. Further, a method of FMC utilizes a comparison of a measured light level to a standard value in order to determine the appropriate exposure time and shutter motion rate. An optimal FMC clocking signal is calculated based on image motion equations incorporated in the processing unit of the reconnaissance system.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Airborne inventory and inspection system and apparatus
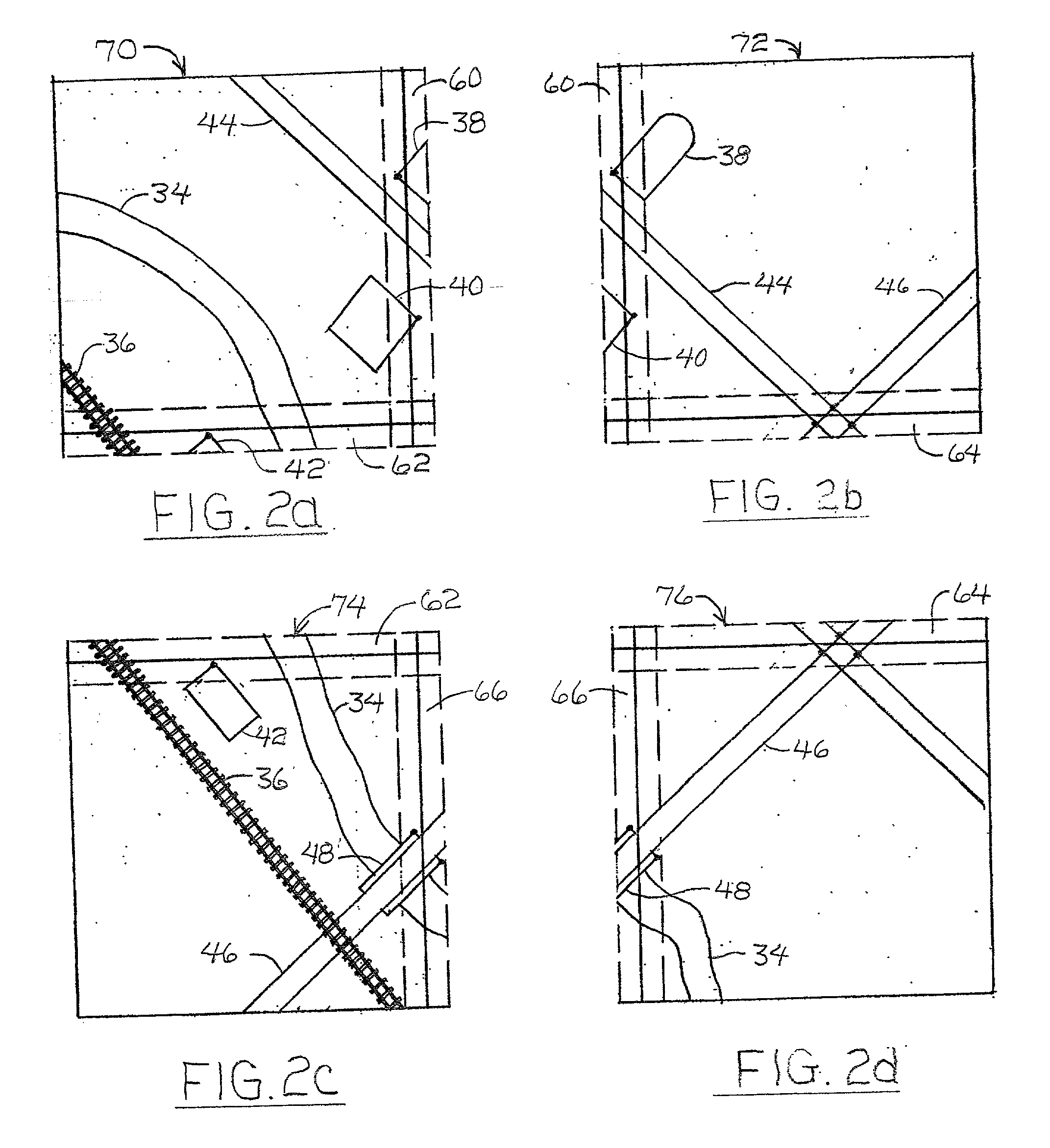
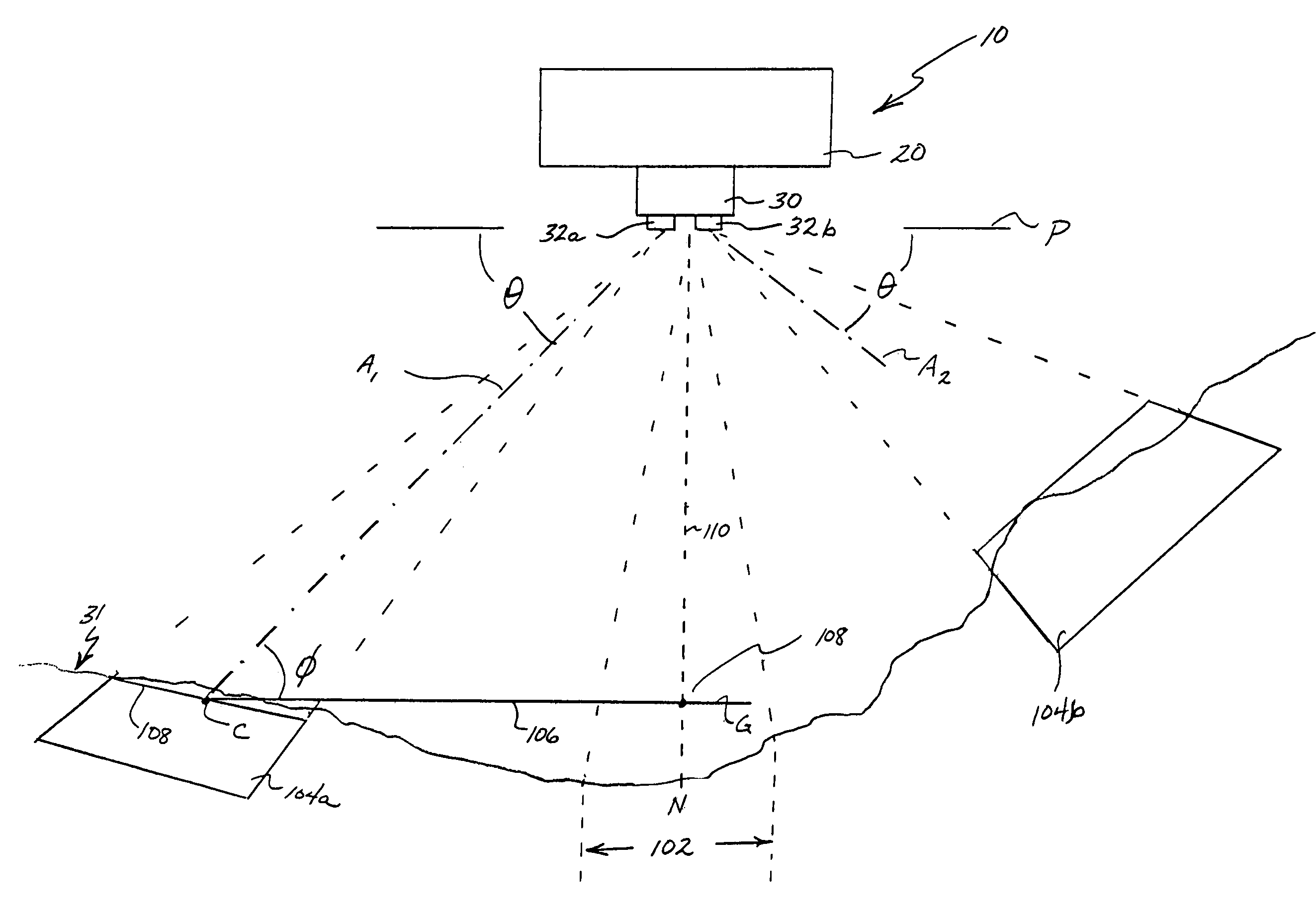
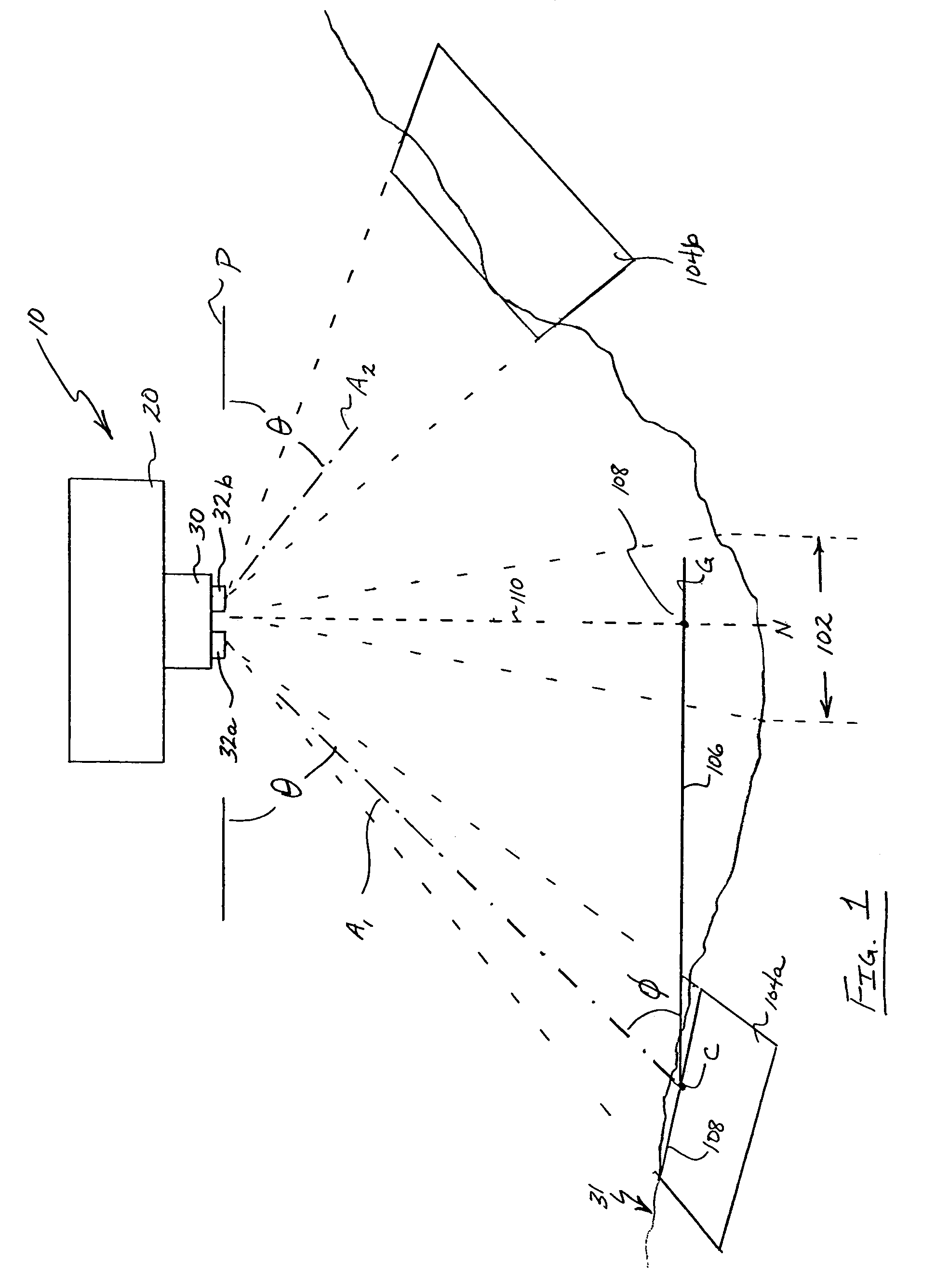
InactiveUS7184072B1Enhance the photos being takenDigital data processing detailsPicture taking arrangementsElectric power transmissionLongitude
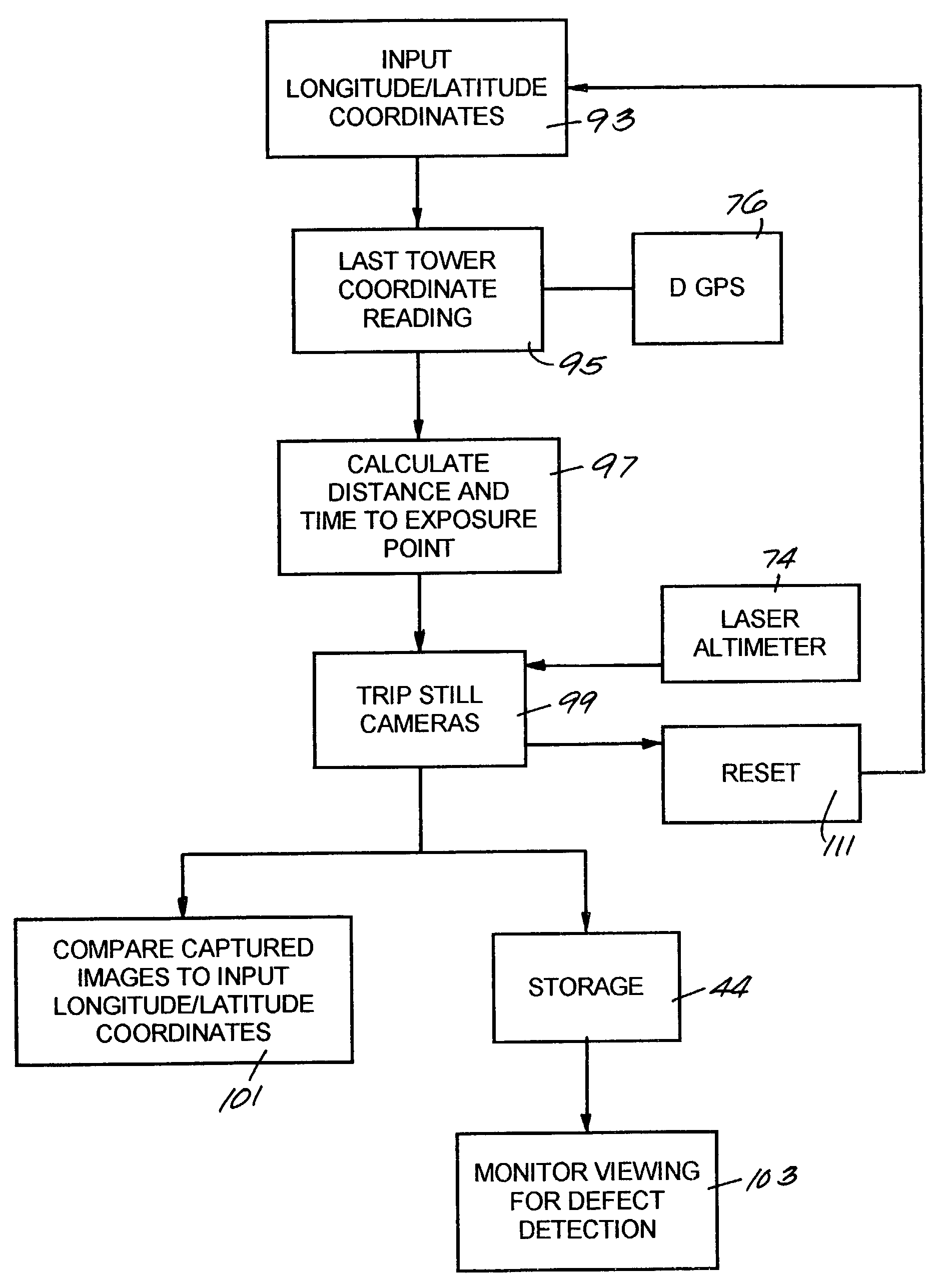
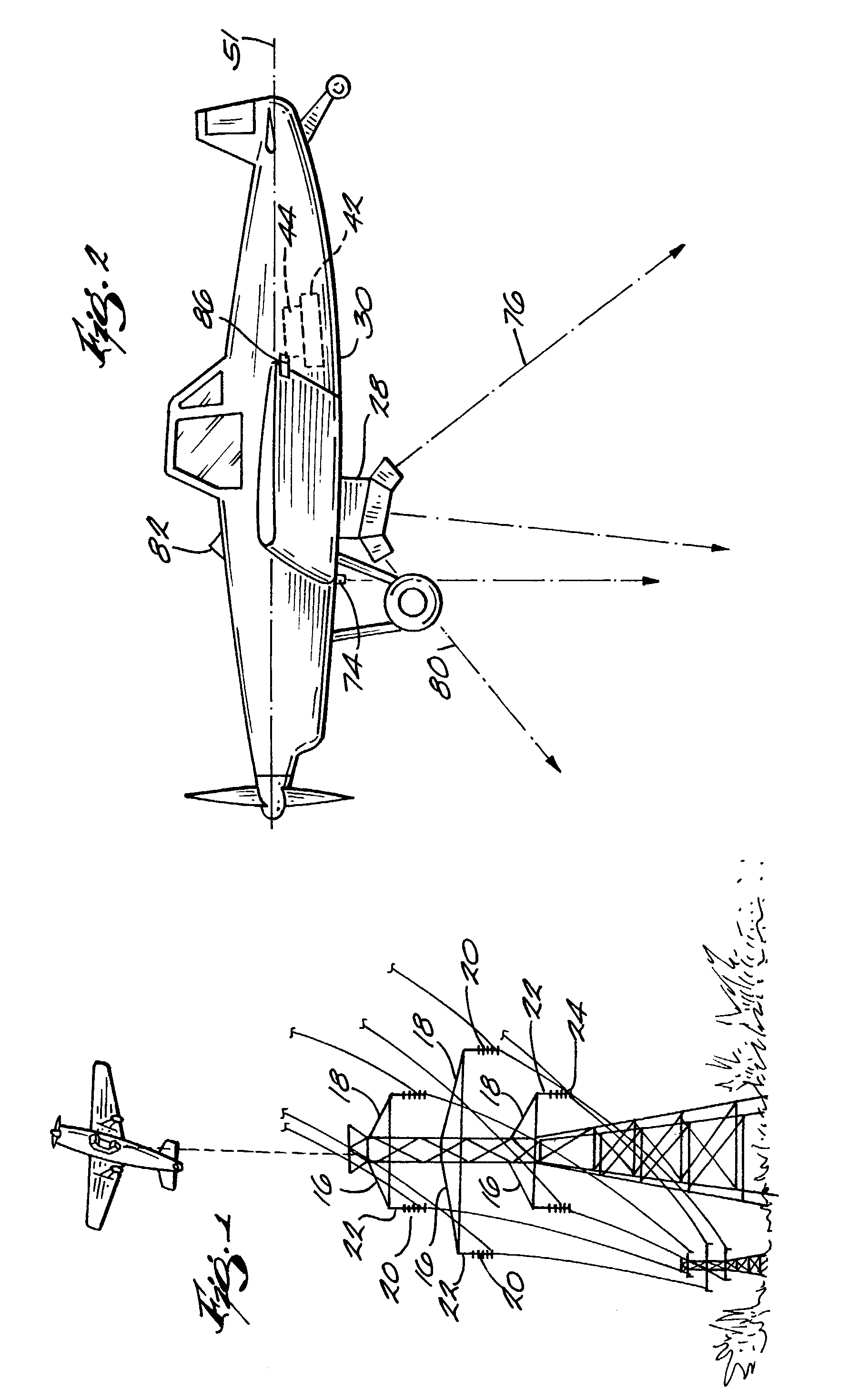
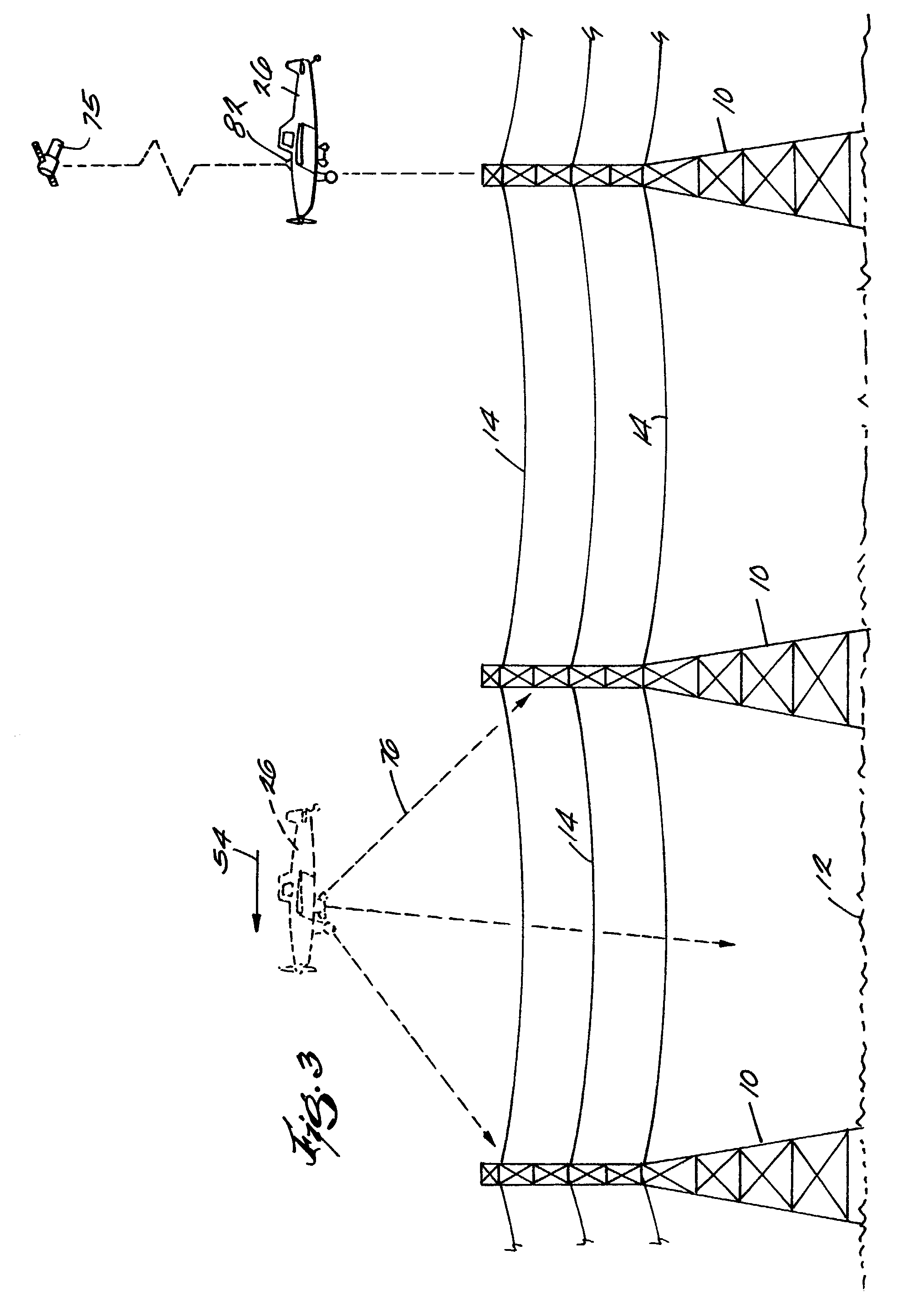
A system and apparatus for acquiring images of electric transmission line tower structures, equipment attached to said tower structures, and transmission lines suspended from said towers. The system uses a fixed wing aircraft and an arrangement of at least one still camera, means for detecting a tower structure, a data storage unit, and a central processing unit containing operational software. The central processing unit is connected to the camera, the means for detecting a tower structure, and the storage unit. The detection means is a laser altimeter or a combination of preset longitude / latitude coordinates for tower locations and a GPS unit which supplies continuous longitude / latitude coordinates for the aircraft location for comparison to those preset coordinates. The aircraft is flown along the transmission line at a predetermined altitude above the tops of said towers (60–100 feet). The still camera points rearwardly relative to the line of flight of the aircraft and take a picture from between two adjacent towers and along an exposure line directed downwardly at an angle to the line of flight, 30–60 degrees and preferably 45 degrees. The detecting means transmits a signal to the central processing indicative of the presence of a tower to be photographed. The central processing unit calculates the time delay necessary for said aircraft to fly past the tower to a predetermined exposure point located between the tower to be photographed and the next tower in said transmission line after the tower to be photographed. The still camera is activated at the exposure point to acquire an image of the tower structure. The data corresponding to the acquired image is transmitted to a data storage unit for later retrieval and examination to identify defects in the tower or the equipment or transmission lines suspended form the tower. The system is reset to continue acquiring images along the transmission lines. The system is also provided with a video capability to film the towers and transmission lines and the line right-of-way.
Owner:POWER VIEW COMPANY L L C
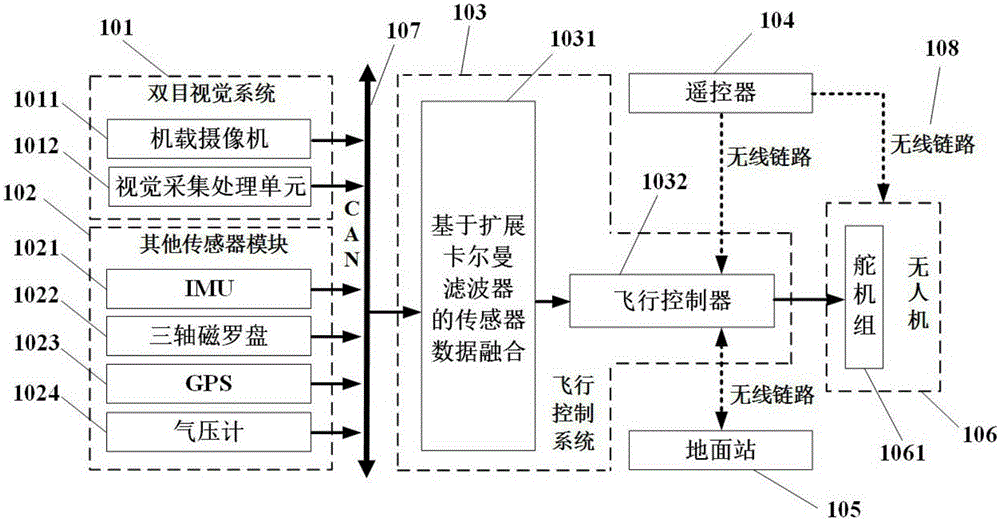
Unmanned aerial vehicle autonomous obstacle detection system and method based on binocular vision
InactiveCN105222760ARealize the function of effective obstacle avoidanceRealize the function of obstacle avoidanceTransmission systemsPicture taking arrangementsUncrewed vehicleObstacle avoidance
The invention relates to an unmanned aerial vehicle autonomous obstacle detection system and method based on binocular vision. The unmanned aerial vehicle autonomous obstacle detection system and method based on the binocular vision are characterized in that the system comprises a binocular visual system, other sensor modules and a flight control system which are mounted on an unmanned aerial vehicle; the method comprises the steps that the binocular visual system acquires visual information of the flight environment of the unmanned aerial vehicle, and obstacle information is obtained through processing; other sensor units acquire state information of the unmanned aerial vehicle; the flight control system receives the obstacle information and the state information of the unmanned aerial vehicle, establishes a flight path and generates a flight control instruction to send to the unmanned aerial vehicle; the unmanned aerial vehicle flies by avoiding obstacles according to the flight control instruction. According to the unmanned aerial vehicle autonomous obstacle detection system and method based on the binocular vision, the vision information is fused with other sensor information, the flight environment information is perceived, flight path control and path planning are conducted to avoid the obstacles, the problem of vision obstacle avoidance of the unmanned aerial vehicle is effectively solved, and the capacity of completing vision obstacle avoidance by means of a vehicle-mounted camera is achieved.
Owner:一飞智控(天津)科技有限公司
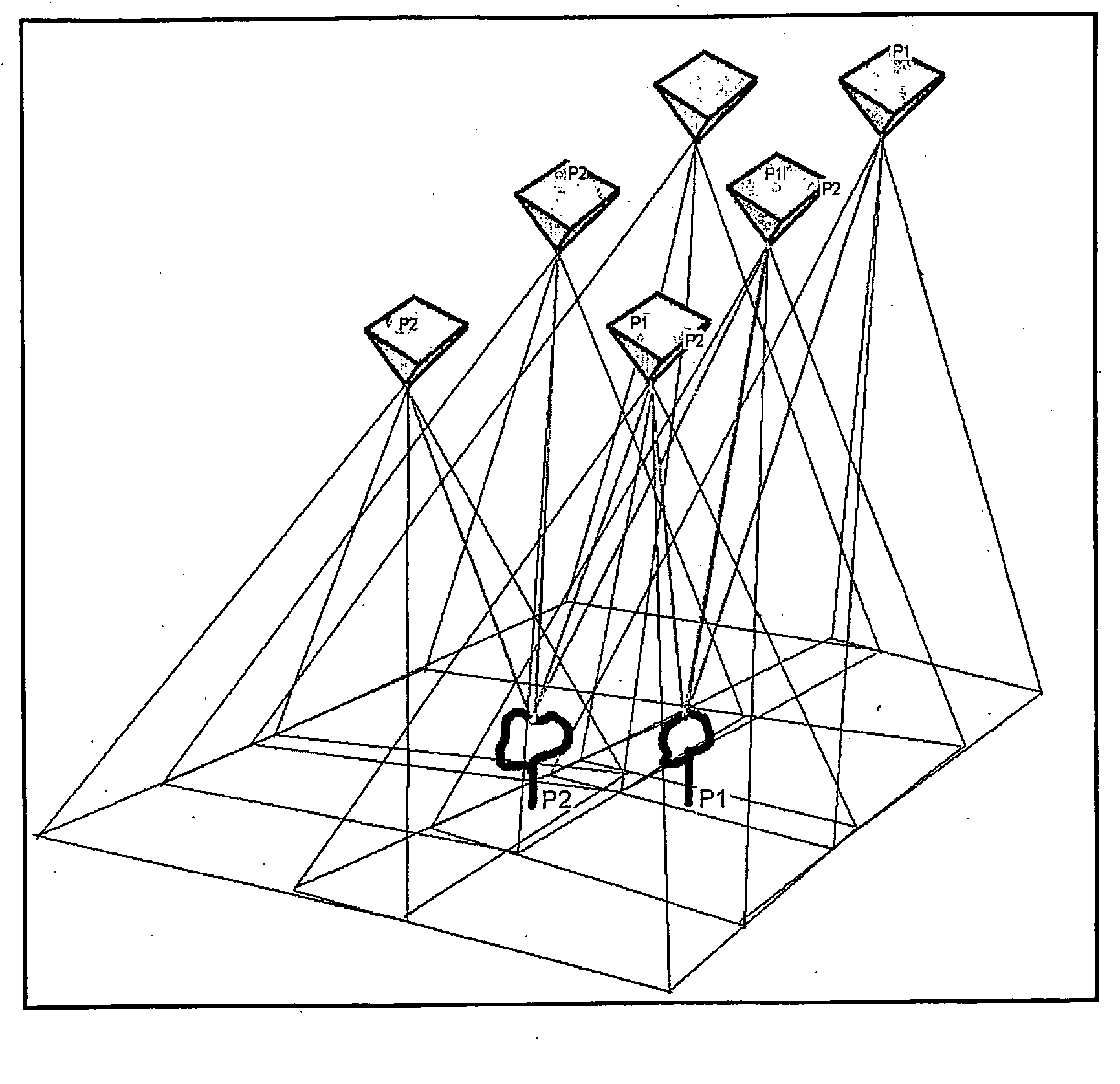
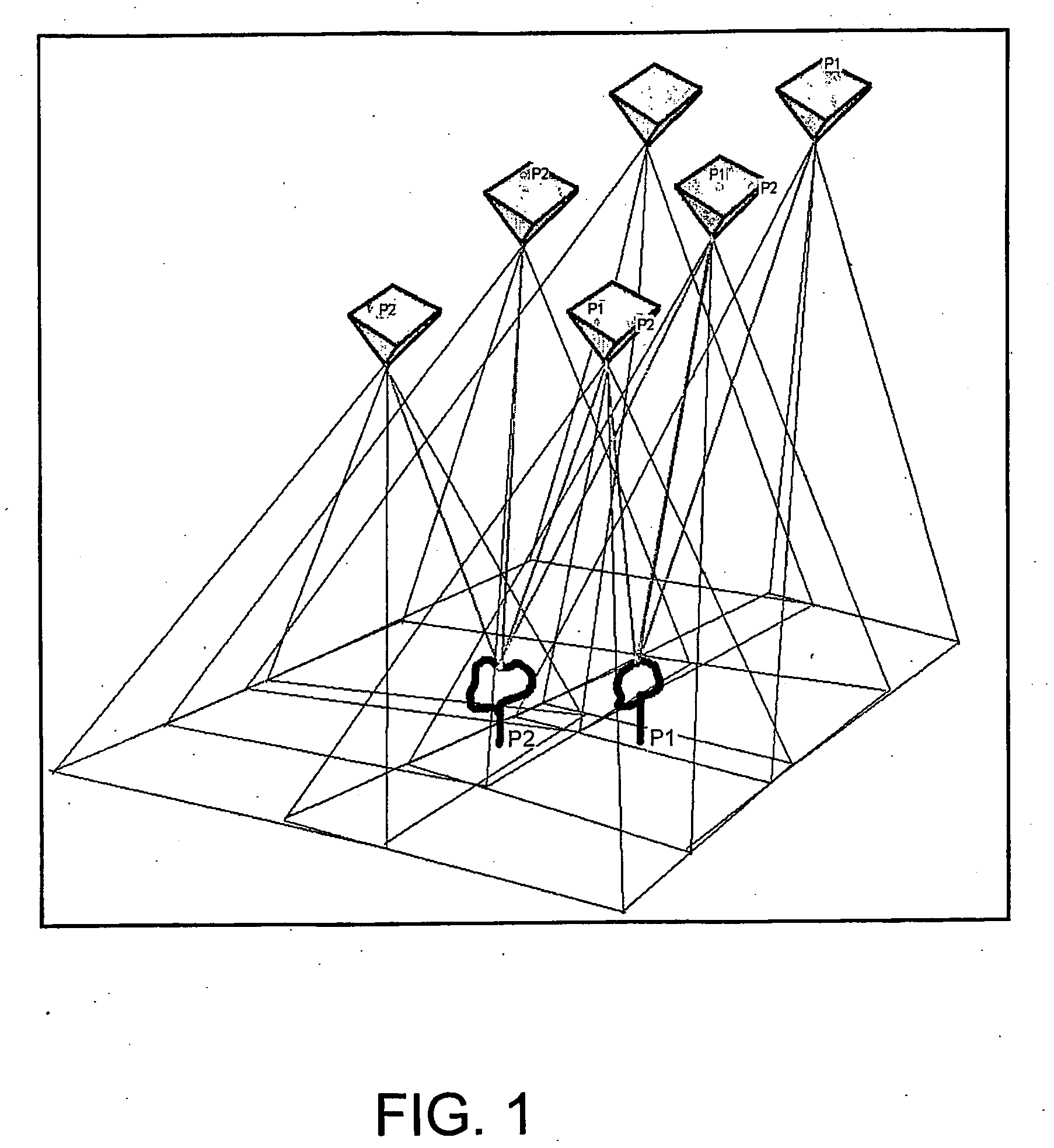
Reduced Homography for Recovery of Pose Parameters of an Optical Apparatus producing Image Data with Structural Uncertainty
A reduced homography H for an optical apparatus to recover pose parameters from imaged space points Pi using an optical sensor. The electromagnetic radiation from the space points Pi is recorded on the optical sensor at measured image coordinates. A structural uncertainty introduced in the measured image points is determined and a reduced representation of the measured image points is selected based on the type of structural uncertainty. The reduced representation includes rays {circumflex over (r)}i defined in homogeneous coordinates and contained in a projective plane of the optical apparatus. At least one pose parameter of the optical apparatus is then estimated by applying the reduced homography H and by applying a condition on the motion of the optical apparatus, the condition being consonant with the reduced representation employed in the reduced homography H.
Owner:ELECTRONICS SCRIPTING PRODS
Systems and methods for target tracking
The present invention provides systems, methods, and devices related to target tracking by UAVs. The UAV may be configured to receive target information from a control terminal related to a target to be tracked by an imaging device coupled to the UAV. The target information may be used by the UAV to automatically track the target so as to maintain predetermined position and / or size of the target within one or more images captured by the imaging device. The control terminal may be configured to display images from the imaging device as well as allowing user input related to the target information.
Owner:SZ DJI TECH CO LTD
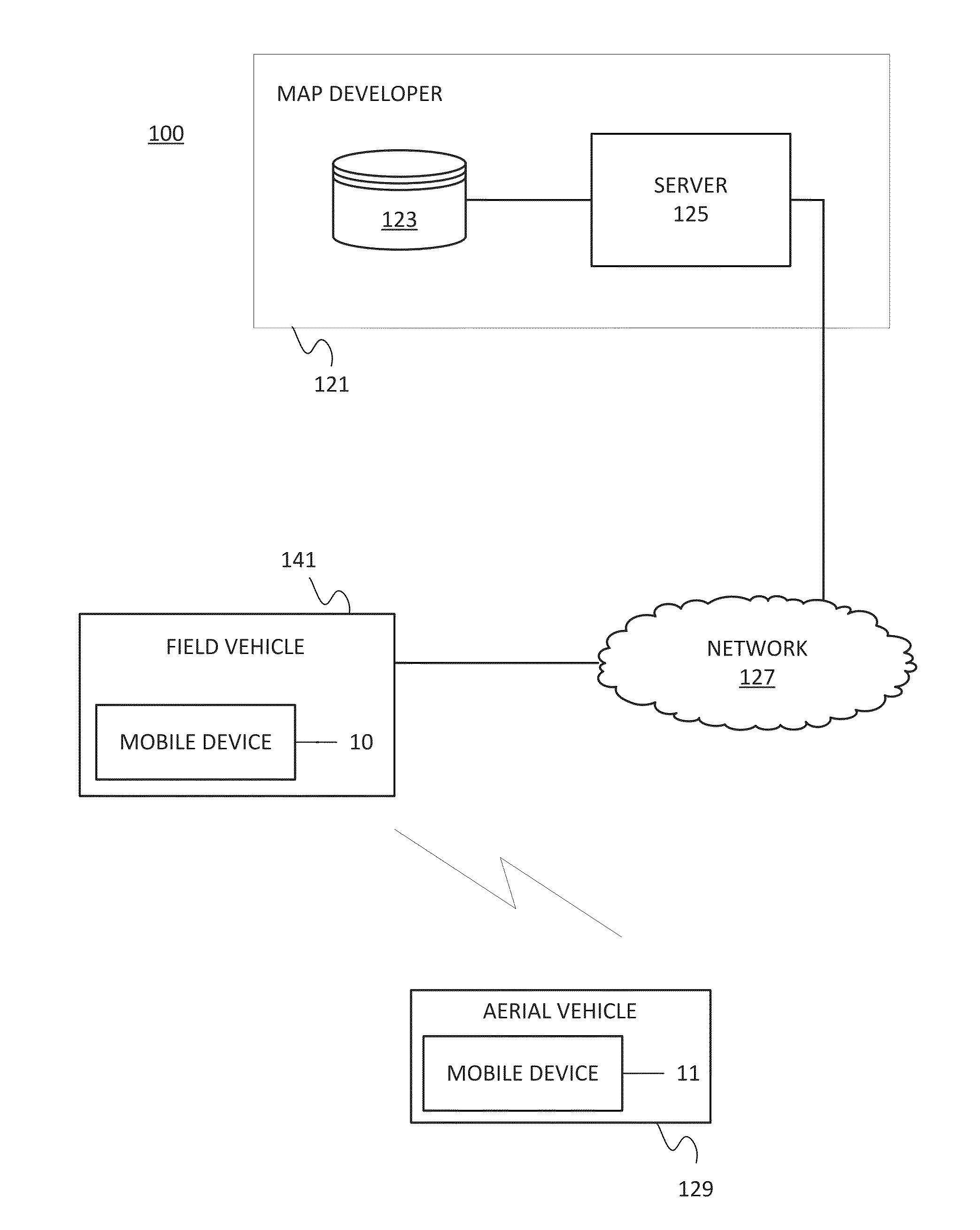
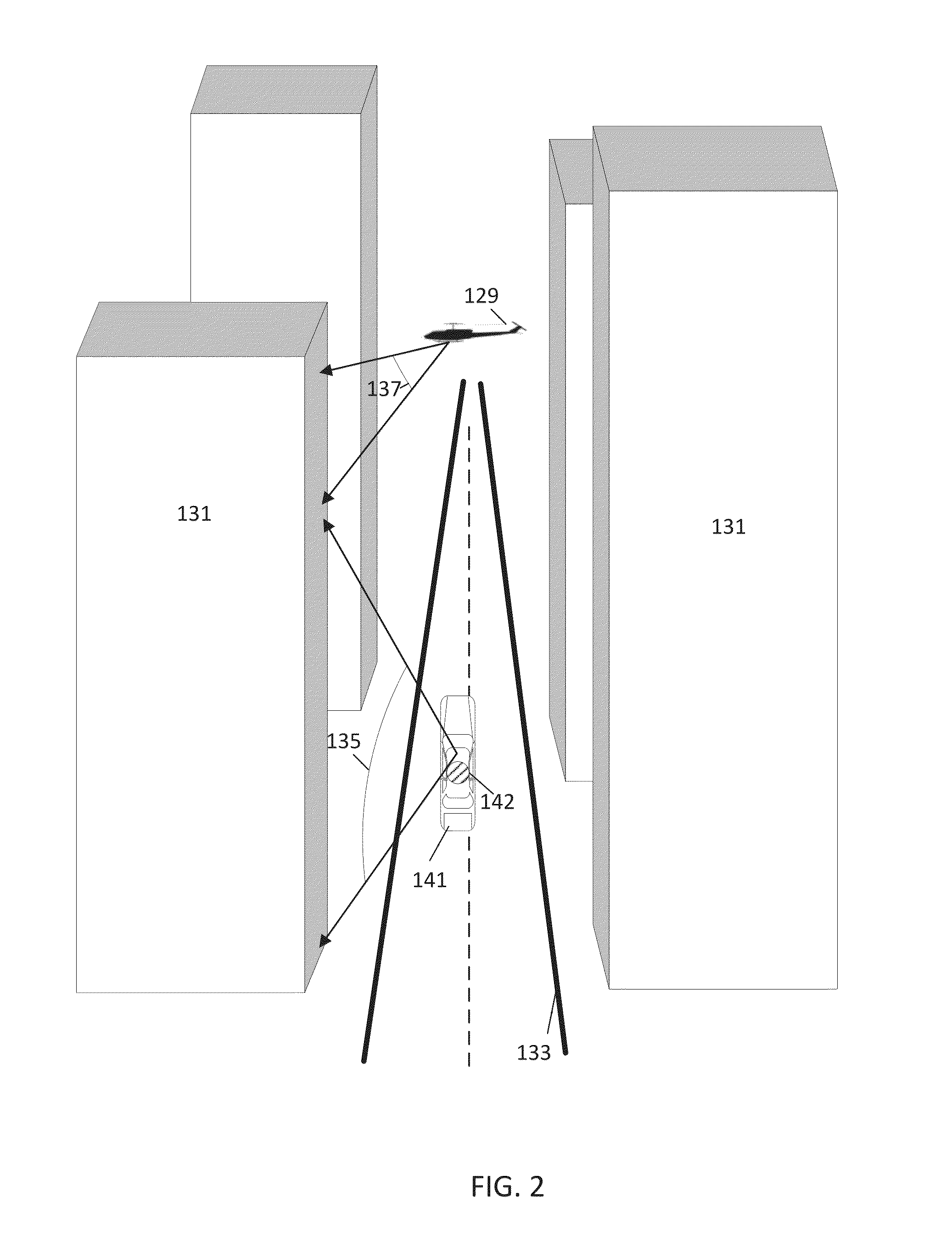
Aerial image collection
ActiveUS20140257595A1Aircraft controlDigital data processing detailsCollection systemAerial photography
In one embodiment, an aerial collection system includes an image collection field vehicle that travels at street level and an image collection aerial vehicle that travels in the air above the street. The aerial vehicle collects image data including at least a portion of the field vehicle. The field vehicle includes a marker, which is identified from the collected image data. The marker is analyzed to determine an operating characteristic of the aerial vehicle. In one example, the operating characteristic in the marker includes information for a flight instruction for the aerial vehicle. In another example, the operating characteristic in the marker includes information for the three dimensional relationship between the vehicles. The three dimensional relationship is used to combine images collected from the air and images collected from the street level.
Owner:HERE GLOBAL BV
System and method for creating and broadcasting interactive panoramic walk-through applications
InactiveUS20110214072A1Improve balanceTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationComputer visionBroadcasting
The system and method provides for creating, storing and broadcasting interactive panoramic walk-through applications. The combination of images is determined by the array of possibilities for the user to choose the direction of displacement at each intersection point and from each point or geographical coordinate, to have a complete view from a first person's point of view. The system uses geo-streaming methods to optimize broadcast and real-time construction of panoramic applications. The system provides a visual perspective which approaches that of human vision.
Owner:LINDEMANN PIERRE ALAIN +2
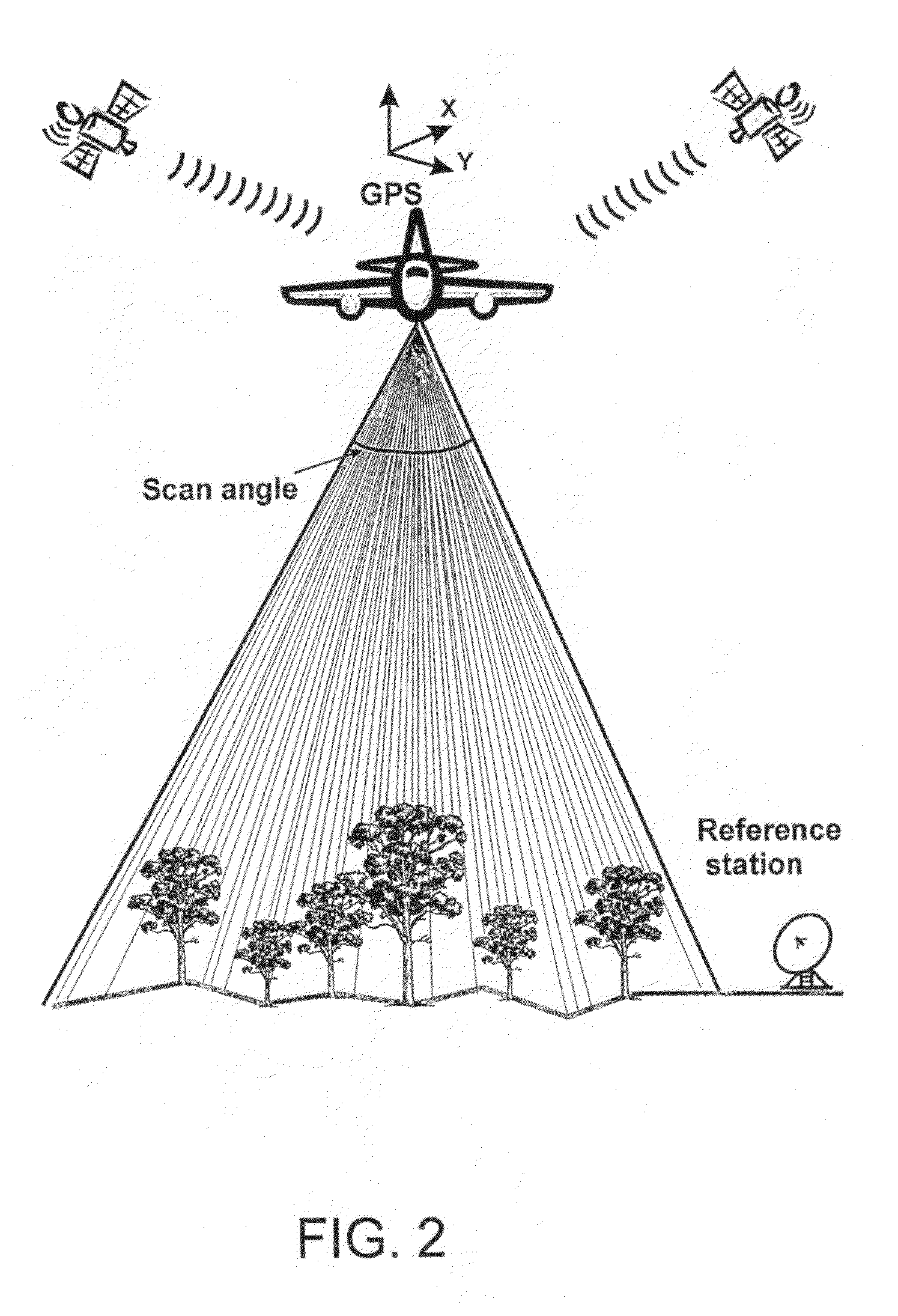
Method for Determination of Stand Attributes and a Computer Program for Performing the Method
ActiveUS20080260237A1Improve accuracyReduce the numberPicture taking arrangementsScene recognitionSample plotPoint cloud
The invention is concerned with a method for forest inventory and for determination of stand attributes. Stand information of trees, sample plots, stands and larger forest areas can be determined by measuring or deriving the most important attributes for individual trees. The method uses a laser scanner and overlapping images. A densification of the laser point clouds is performed and the achieved denser point clouds are used to identify individual trees and groups of trees. The invention is also concerned with a computer program for performing the method.
Owner:FM KARTTA +1
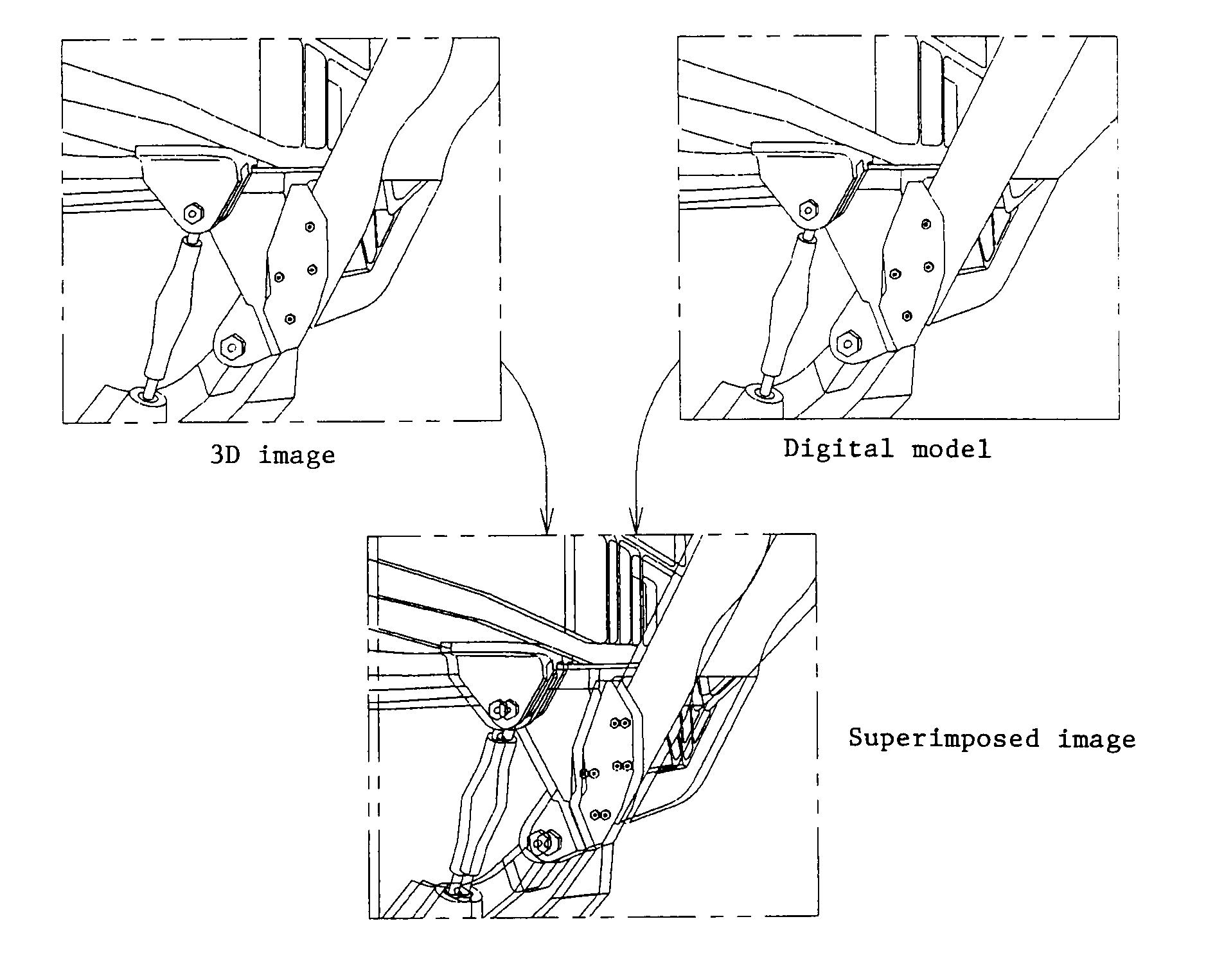
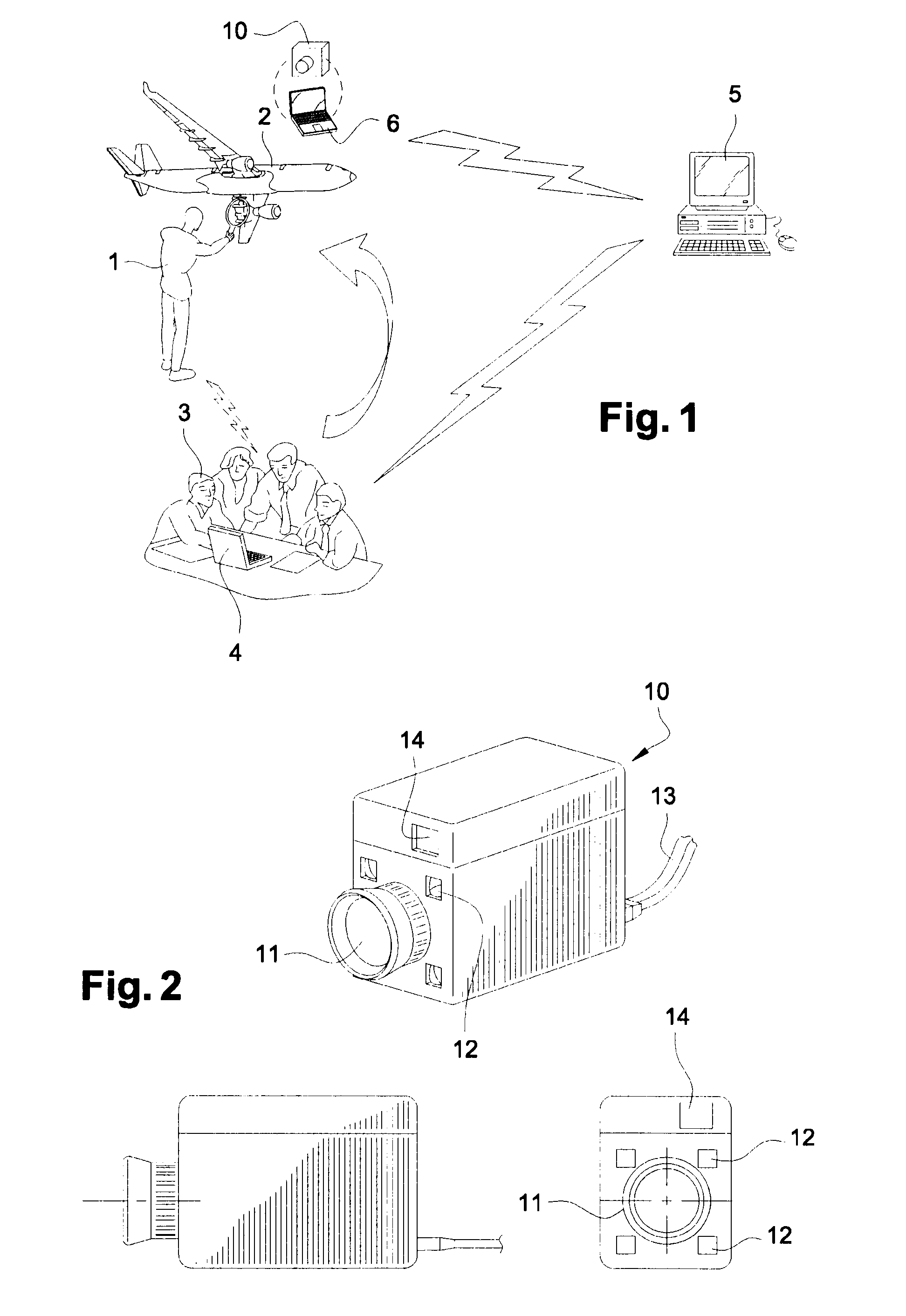
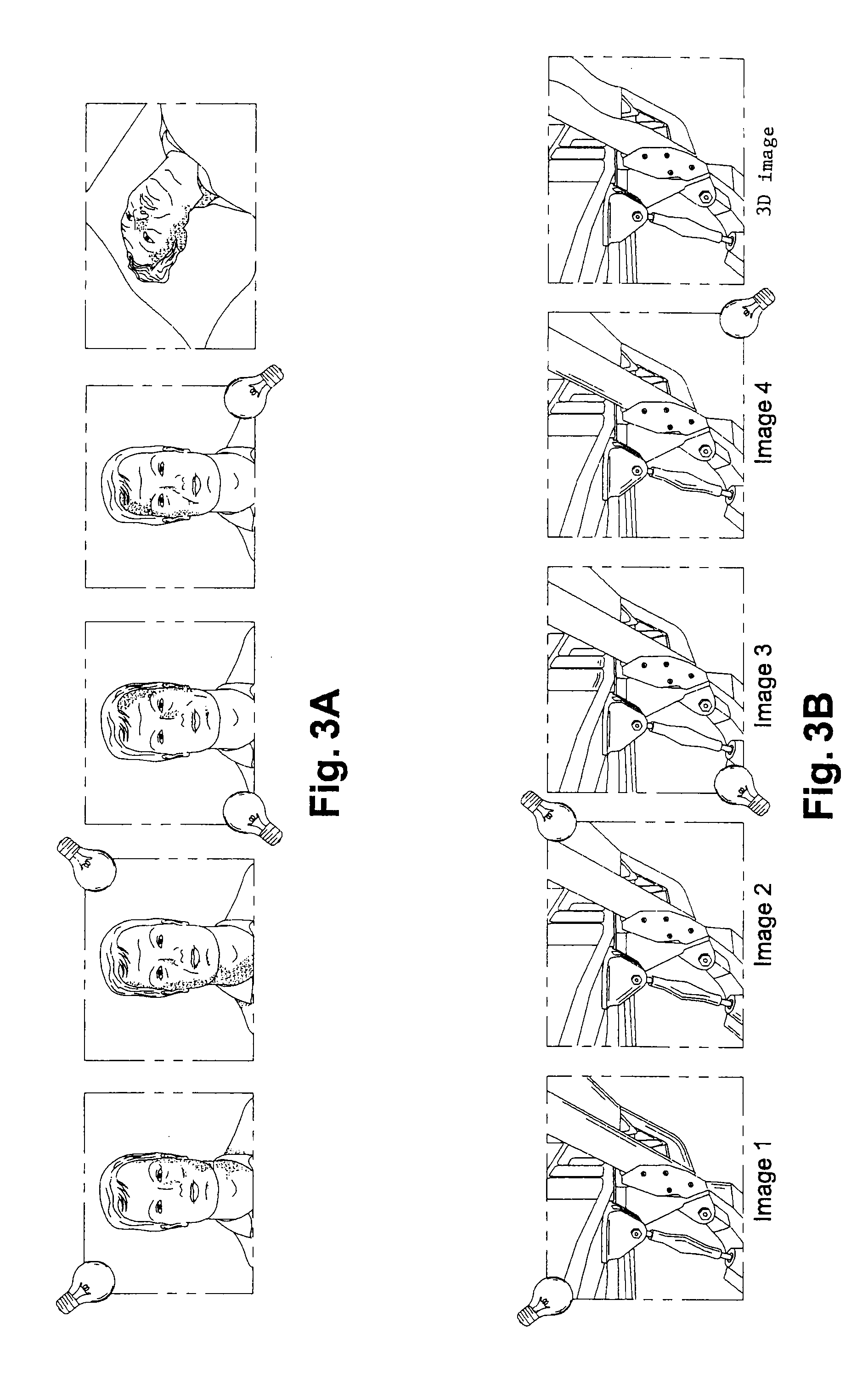
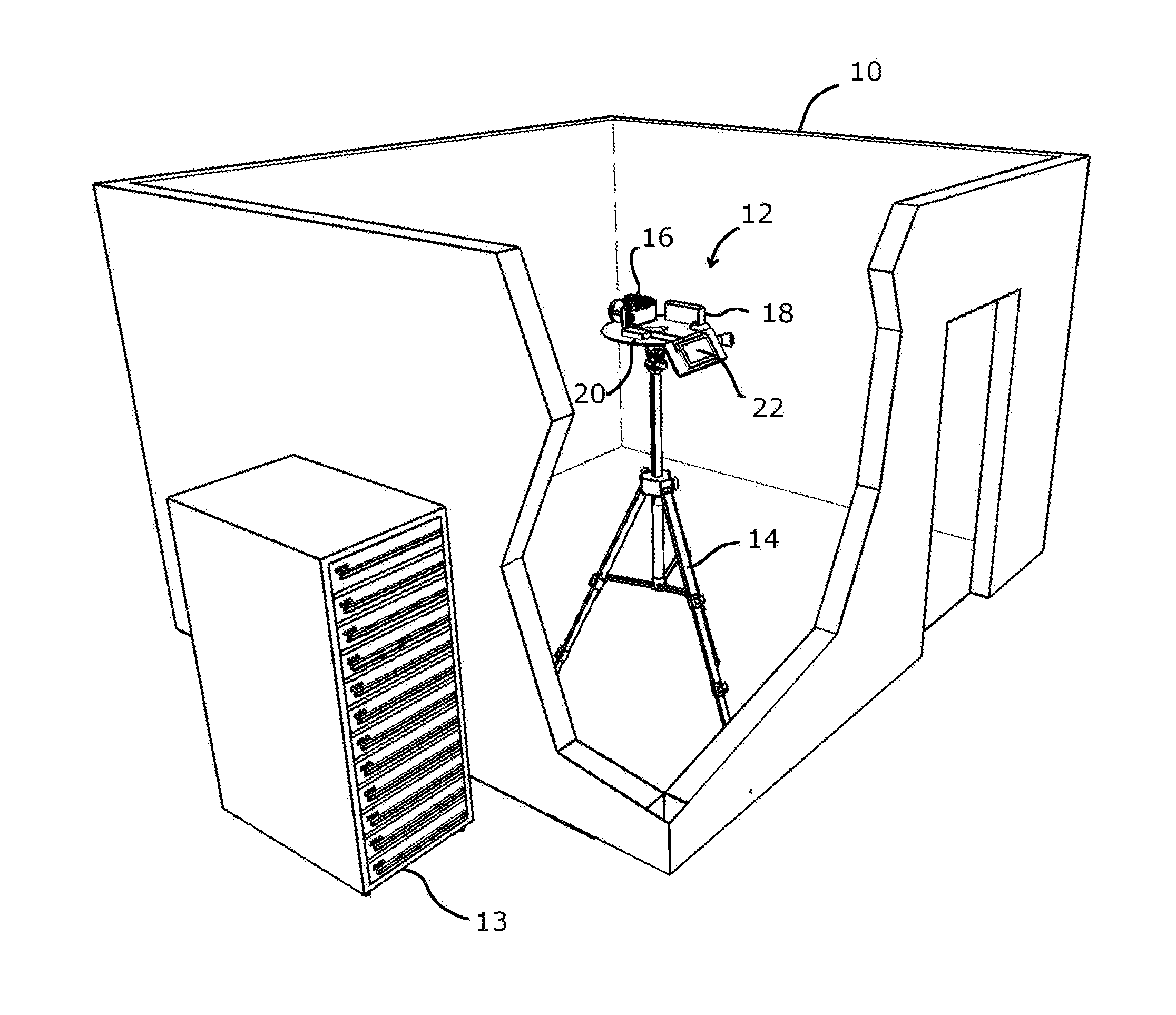
Method and system for the remote inspection of a structure
The invention relates to a method for the remote inspection of a structure, comprising the following operations:producing a 3D image of an area of the structure to be inspected,superimposing said 3D image with a previously stored digital model of the structure,geographically locating the area of the structure to be inspected on the structure model, andinspecting the area of the structure to be inspected on the 3D image superimposed with the digital model.The invention also relates to a system for implementing the method, comprising an imaging device (10) that can be installed in the vicinity of the area of the structure to be inspected (2), and an image-processing device (6) located remotely from the imaging device (10) in order to generate a 3D image from the images captured by the camera (11).
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
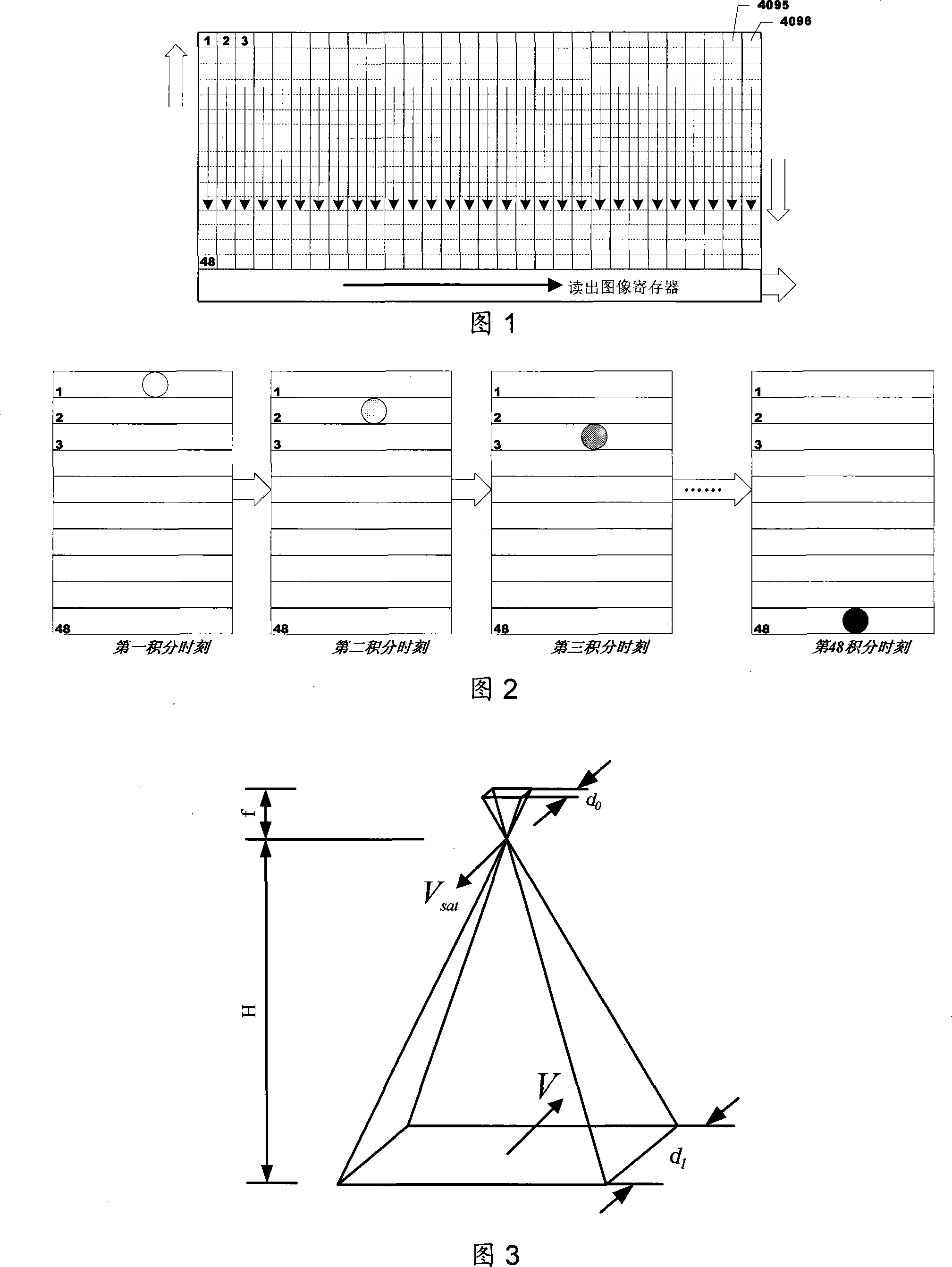
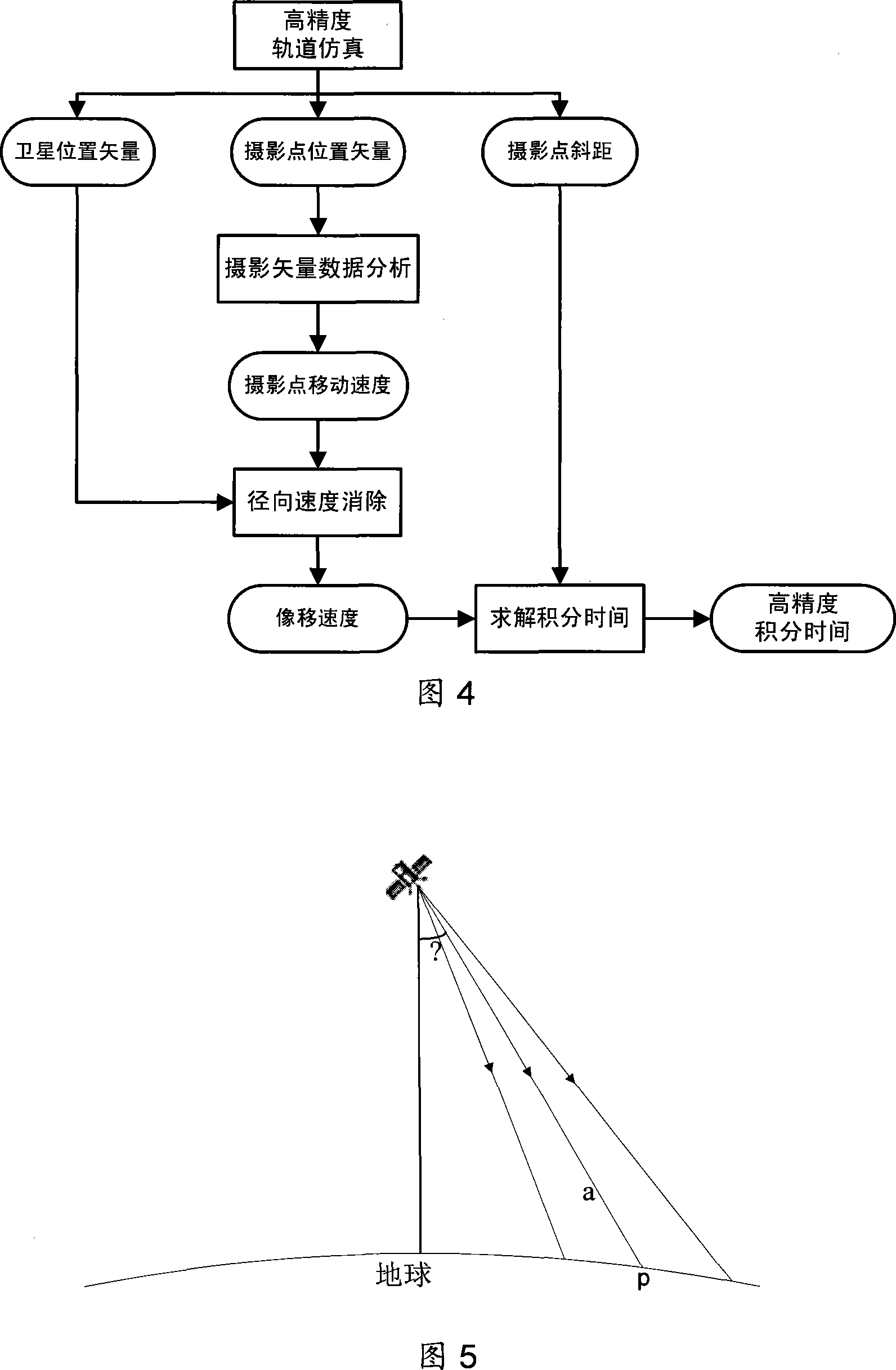
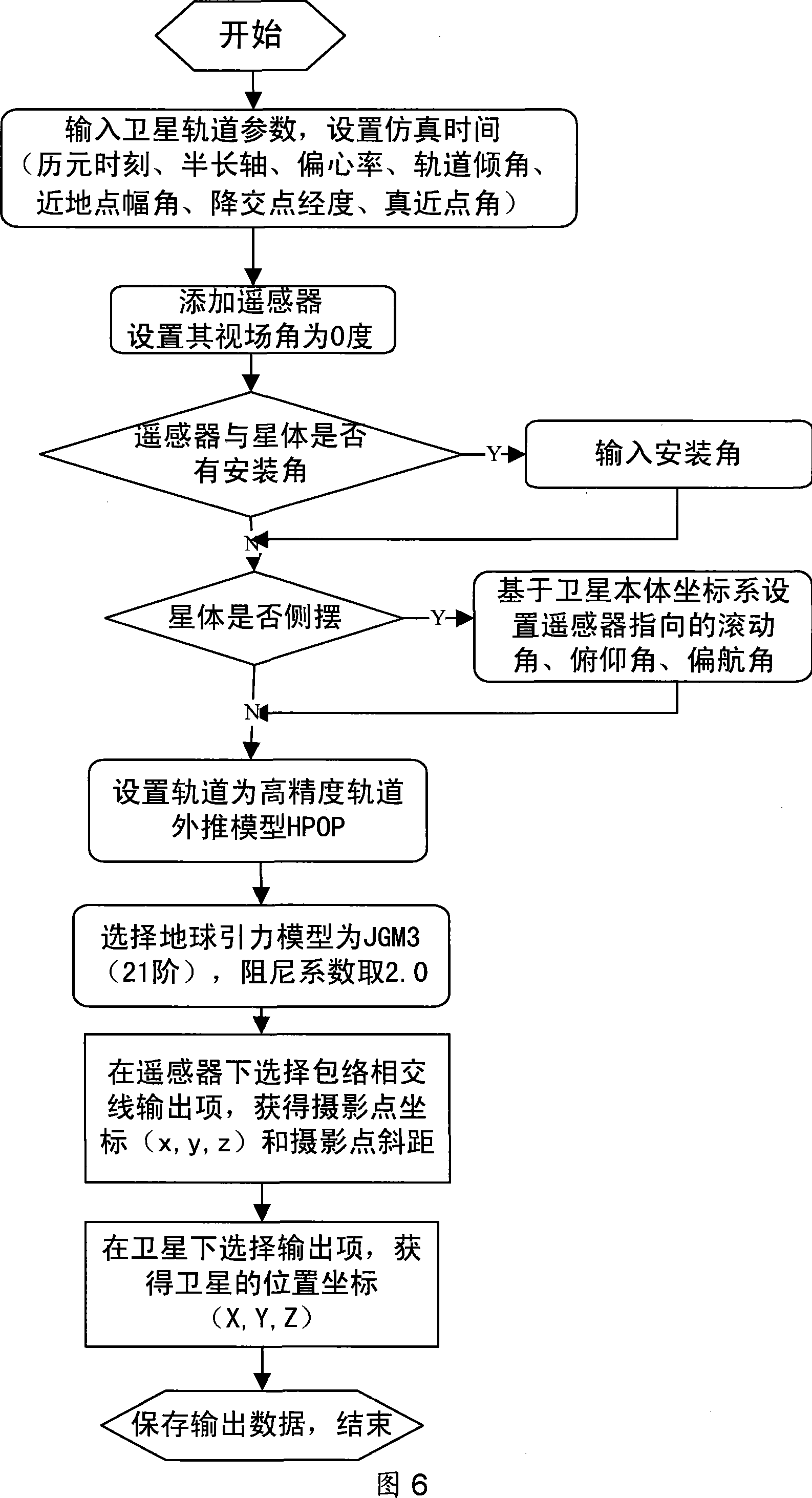
Method for calculation and regulation of integral time of star-loading TDICCD camera
ActiveCN101226059AImprove real-time performanceEliminate errorsPicture taking arrangementsComing outImage motion
The invention relates to a space borne TDICCD camera integral timing and adjusting method, which comprises the following steps: (1) the orbit is simulated with high precision in which positions parameters of photographed spots of the satellite under drift angle control or at different swinging angles are outputted such as vector coordinates and oblique distances of the photographed spots as well as vector simulation data for the satellite position; (2) the vector simulation data for the satellite position are analyzed to come out with the shift speeds of the photographed spots; (3) eliminate the radial-directional speeds from the shift speeds of the photographed spots to become the image motion speeds; (4) utilize the image motion speeds and the oblique distances of the photographed spots to obtain the integral times. The invention also provides a design method for TDICCD related parameters as well as a real-time adjusting method for integral times on the satellite under control of ground commands. The space borne TDICCD camera integral timing and adjusting method realizes an organic combination of simulation modeling with high precision and positional vector differential method, which eliminates errors introduced into the deduction process in traditional geometric analysis and calculation and controls error delivery to improve calculation precision; the arrival real-time adjusting method for integral times on the satellite ensures a reliable integral synchronous control.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG SATELLITE
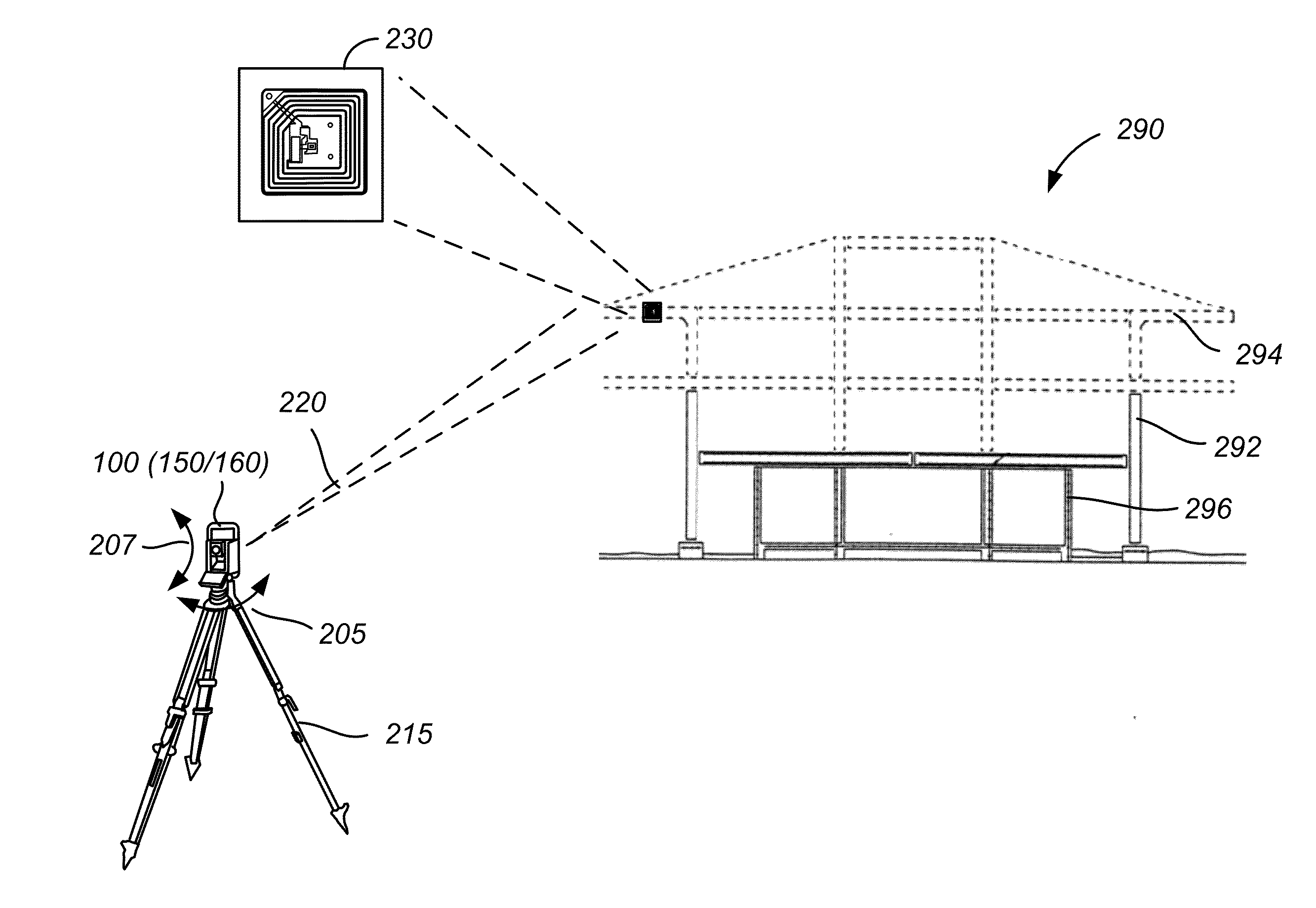
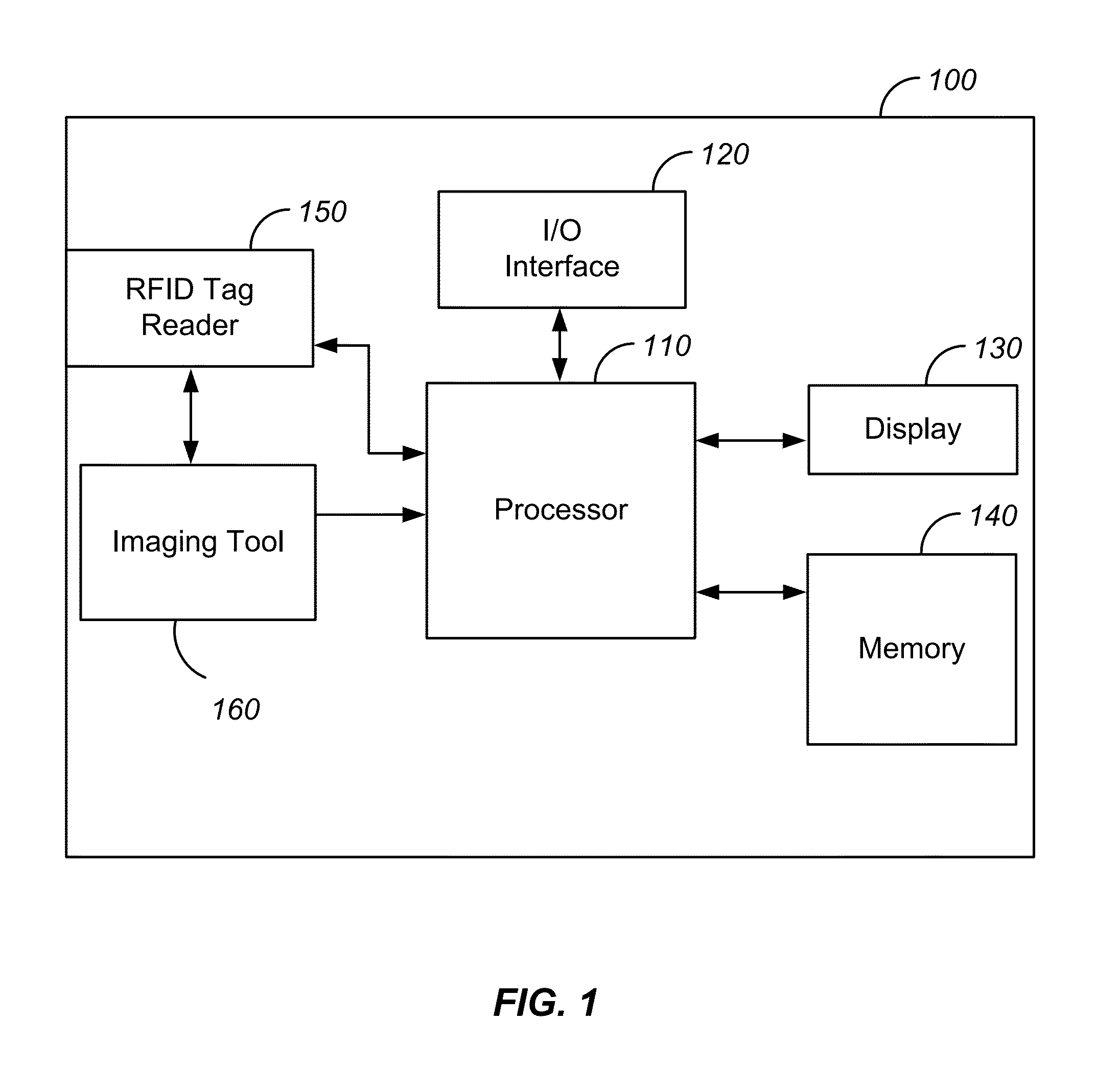
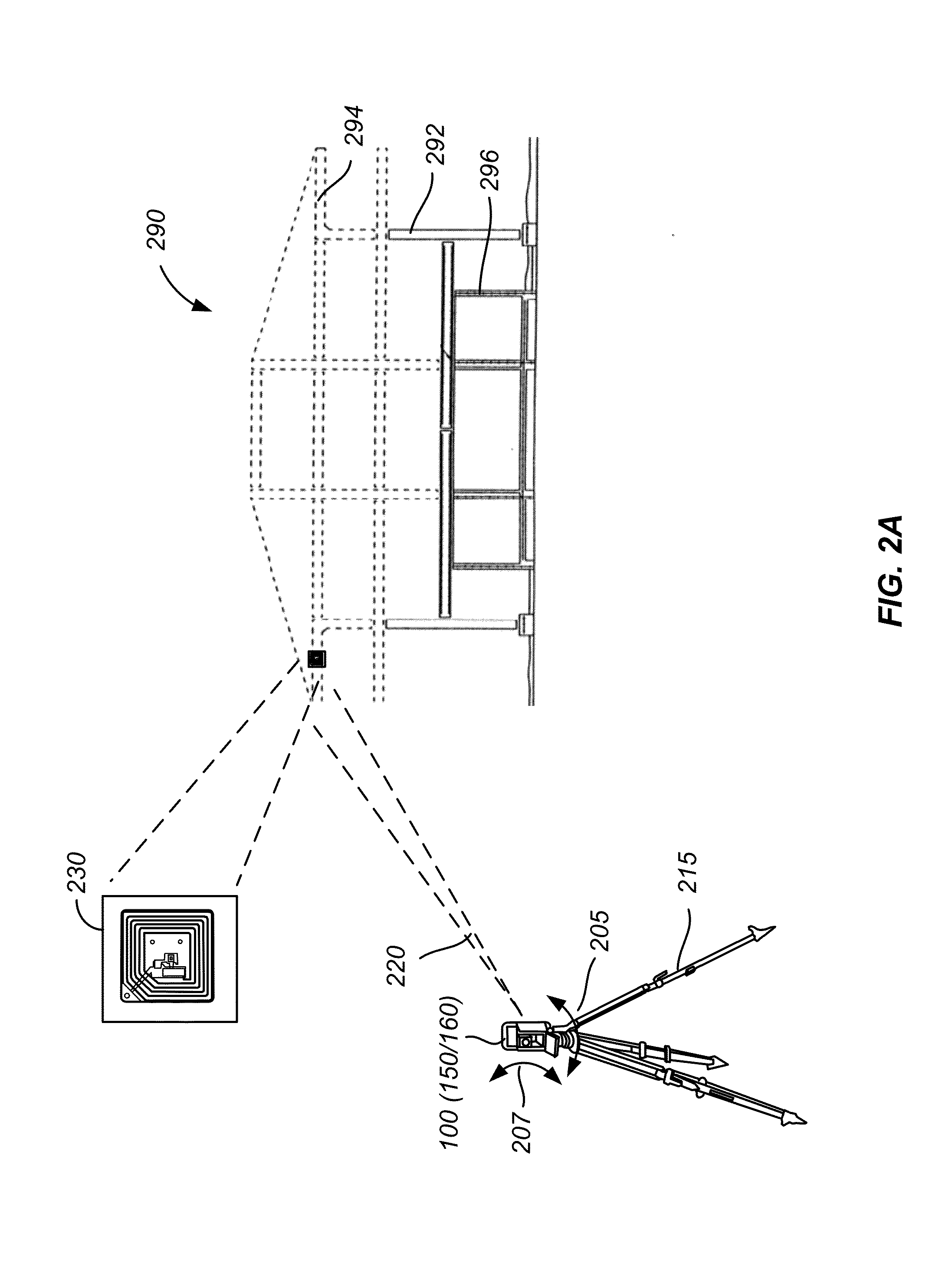
Method and system for rfid-assisted imaging
ActiveUS20130228620A1Reduce and eliminate errorLimited and no obscuringStill image data retrievalActive open surveying meansImaging ToolData storing
A method includes acquiring imaging data of a scene using an imaging tool. The method also includes extracting radio frequency identification (RFID) data stored in an RFID tag associated with the scene. The method further includes associating the RFID data with the imaging data.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
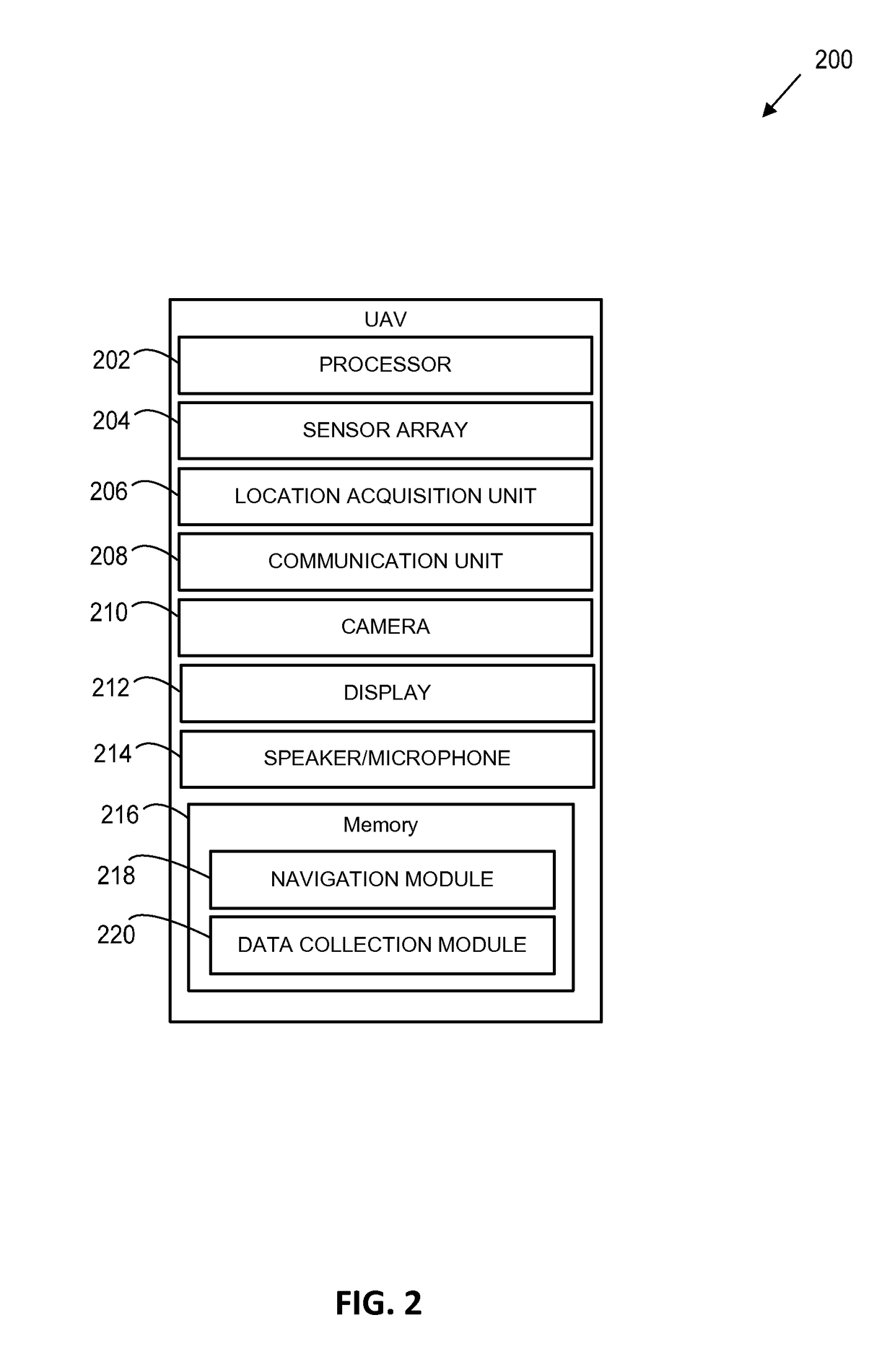
Accident reconstruction implementing unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs)
Owner:STATE FARM MUTAL AUTOMOBILE INSURANCE COMPANY
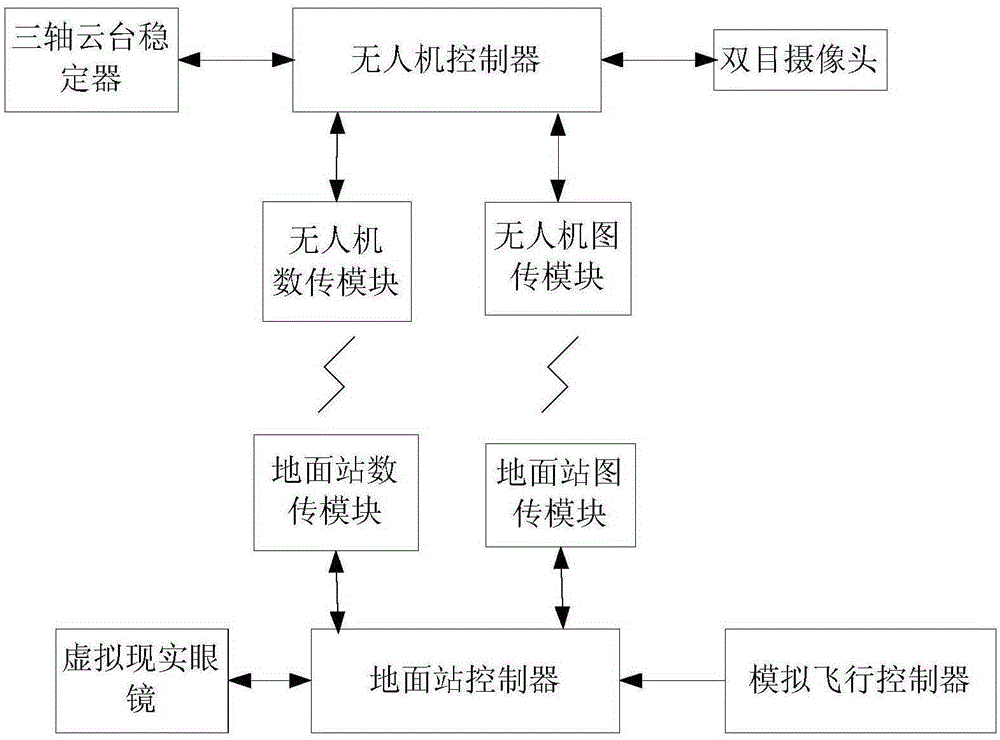
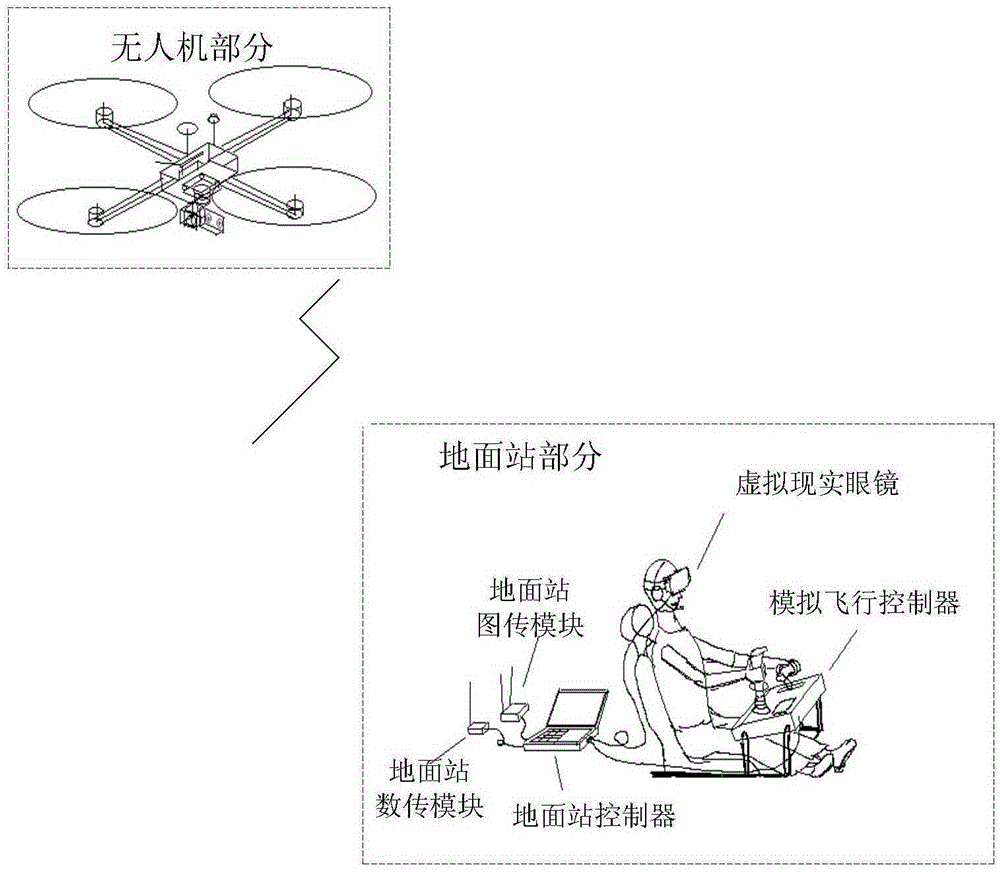
First-person immersive unmanned aerial vehicle driving system realized by virtue of virtual reality and binocular vision technology and driving method
InactiveCN105222761ARealize Virtual MigrationTrack syncSimulator controlPicture taking arrangementsUncrewed vehicleEyewear
A first-person immersive unmanned aerial vehicle driving system realized by virtue of virtual reality and a binocular vision technology and a driving method belong to the technical field of unmanned aerial vehicles and aim at solving the problems that a real-time flying state cannot be mastered through an existing unmanned aerial vehicle driving system, and errors are liable to occur. The driving system and the driving method are characterized in that an unmanned aerial vehicle body carries a binocular camera through an existing tri-axial cradle head stabilizer, an unmanned aerial vehicle image transmission module is equipped for image back transmission, and the tri-axial cradle head stabilizer and the actions of a driver on the ground are synchronized by virtue of a data transmission module and a pair of virtual reality goggles; the driver of the unmanned aerial vehicle on the ground wears the virtual reality goggles and sits in a simulating cabin approximate to a real helicopter driving cabin to feel pictures took by the binocular camera and aircraft flying information, and the flying of the unmanned aerial vehicle is controlled by adopting the data transmission module. The driving system and the driving method are suitable for manipulation of the unmanned aerial vehicle.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Apparatus and Method for Spatially Referencing Images
Provided is a method of spatially referencing a plurality of images captured from a plurality of different locations within an indoor space by determining the location from which the plurality of images were captured. The method may include obtaining a plurality of distance-referenced panoramas of an indoor space. The distance-referenced panoramas may each include a plurality of distance-referenced images each captured from one position in the indoor space and at a different azimuth from the other distance-referenced images, a plurality of distance measurements, and orientation indicators each indicative of the azimuth of the corresponding one of the distance-referenced images. The method may further include determining the location of each of the distance-referenced panoramas based on the plurality of distance measurements and the orientation indicators and associating in memory the determined locations with the plurality of distance-referenced images captured from the determined location.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
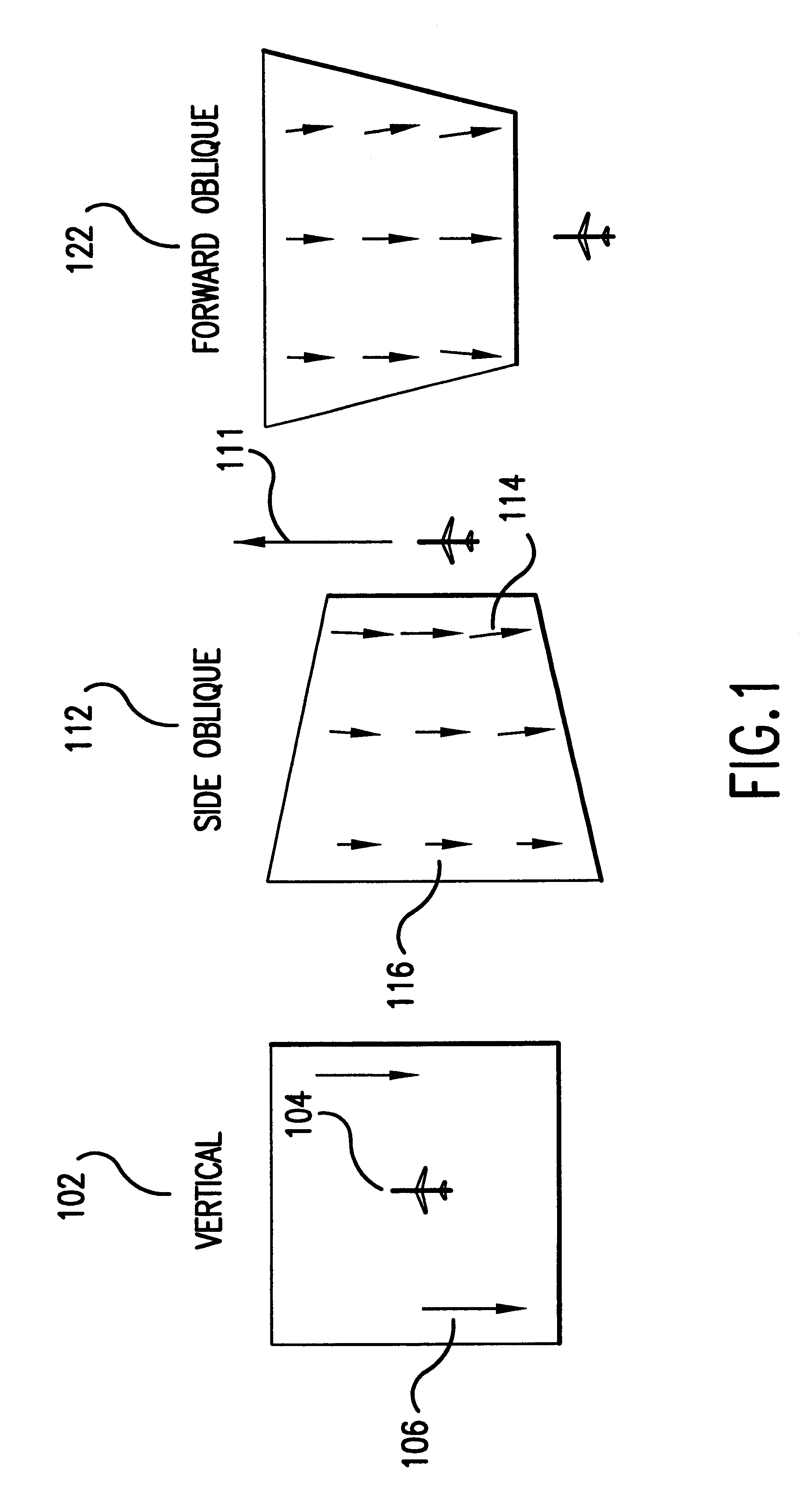
Aerial Photographing System
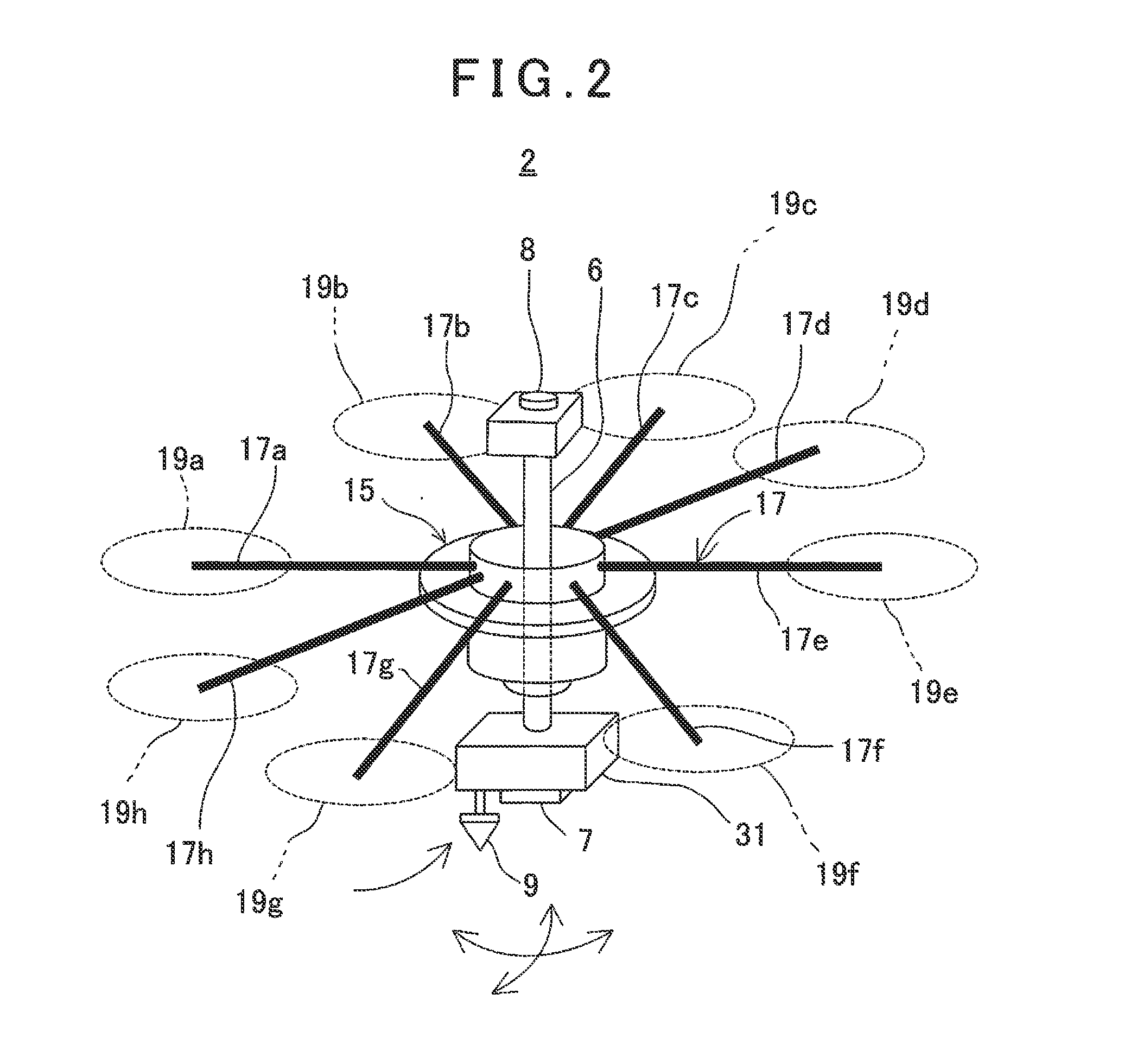
ActiveUS20140240498A1Easy to getHighly accurate photogrammetryAircraft componentsSurveying instrumentsTotal stationEngineering
An aerial photographing system, comprising a flying vehicle being remotely controlled, a camera (7, 8) tiltably supported in any direction via a gimbal (25), a retro-reflector (9) tilting integrally with the camera, being set in a known relation with the camera and used as an object to be measured, and a total station (3) for tracking the retro-reflector and for measuring position of the retro-reflector.
Owner:KK TOPCON
Photogrammetric measurement system and method
ActiveUS6990215B1Picture taking arrangementsCharacter and pattern recognitionGeometric elementPattern recognition
A method for characterizing a geometric element of an object includes positioning a calibrated target adjacent a calibration geometric element, the calibrated target having at least two differentially detectable features having a known geometric relationship to each other. Next a relationship of the calibrated target to the calibration geometric element is determined, and the calibrated target is moved adjacent a geometric feature of an object desired to be characterized. Then photogrammetry is applied to the calibrated target features and the desired geometric feature to spatially characterize the desired geometric feature. A system for characterizing a geometric element of an object includes the movable calibrated target and a photogrammetric analysis system for determining a relationship of the calibrated target to a calibration geometric element and for spatially characterizing the desired geometric feature using the calibrated target features.
Owner:GEODETIC SERVICES
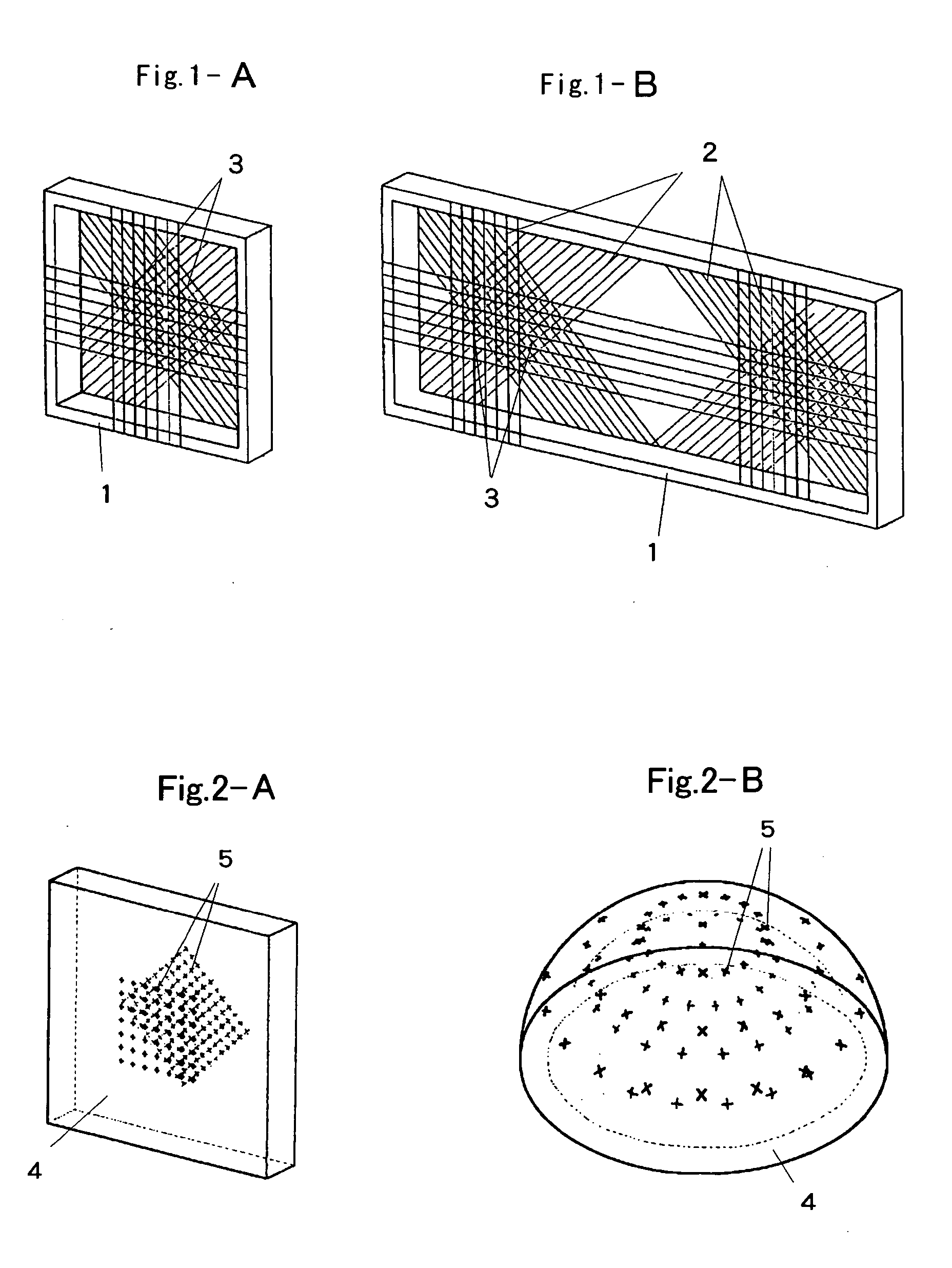
Transparent camera calibration tool for camera calibration and calibration method thereof
InactiveUS20050280709A1Accurate CalibrationTelevision system detailsImage analysisLight beamComputer vision
The calibration tool of the present invention is a transparent camera calibration tool in which a plurality of indicator points is spatially distributed and fixed, wherein the indicator points are formed as intersecting points of thin wires extended to the frame by varying the position of the thin wires in the thickness direction and the indicator points are formed as groups of intersecting points of thin wires rendered by extending a plurality of parallel thin wire groups in different directions. The indicator groups are arranged in at least two sets in a non-coplanar relationship and embodied by distributing distinguishable minute particles in a transparent raw material or by marks or similar in the surface of the raw material. Further, a plurality of cameras arranged separately from one another are calibrated in the same coordinate system by using the transparent camera calibration tool, plate tools that are added thereto, and light beams.
Owner:JAPAN AEROSPACE EXPLORATION AGENCY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com