Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
166 results about "Geosynchronous orbit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
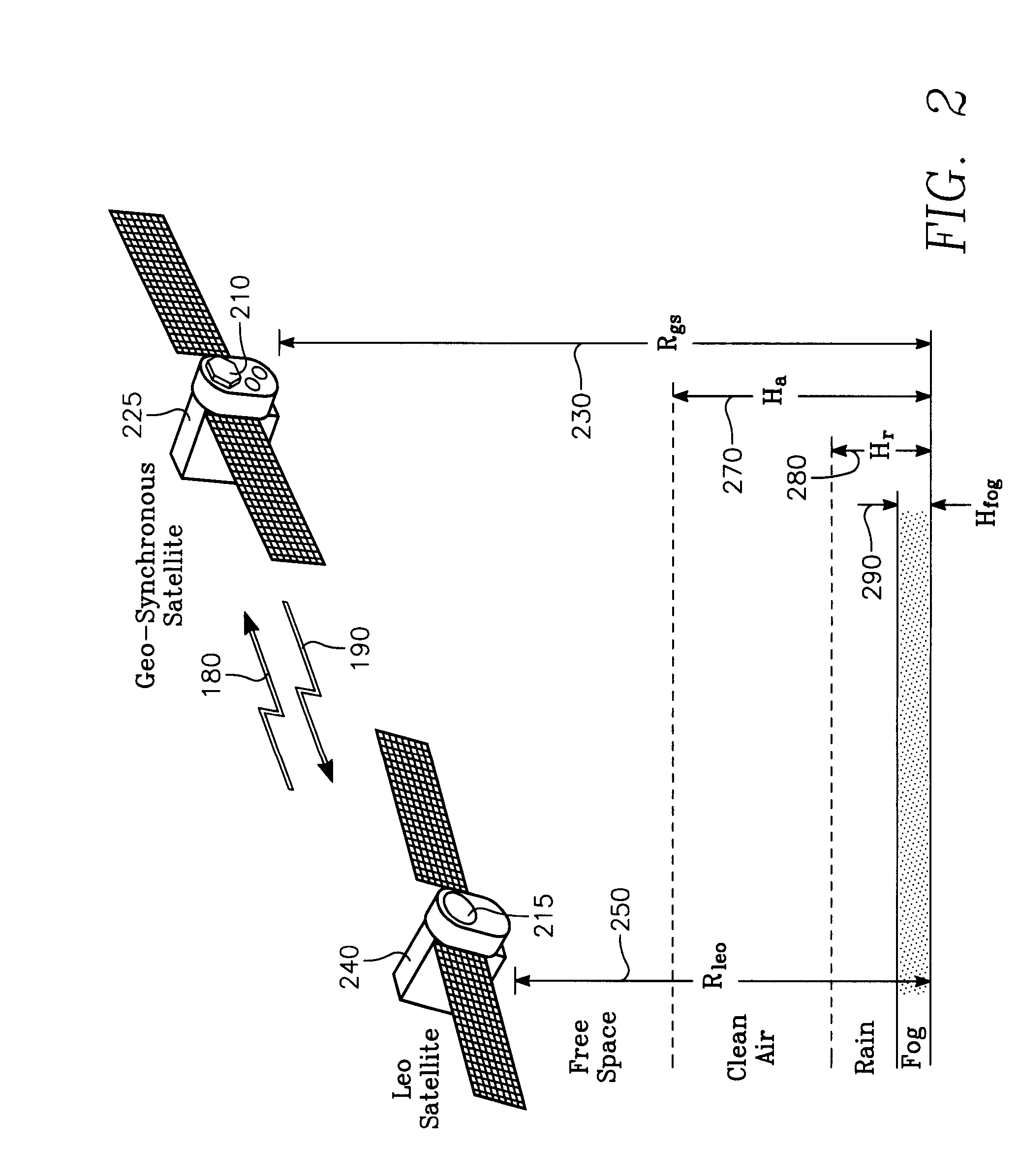
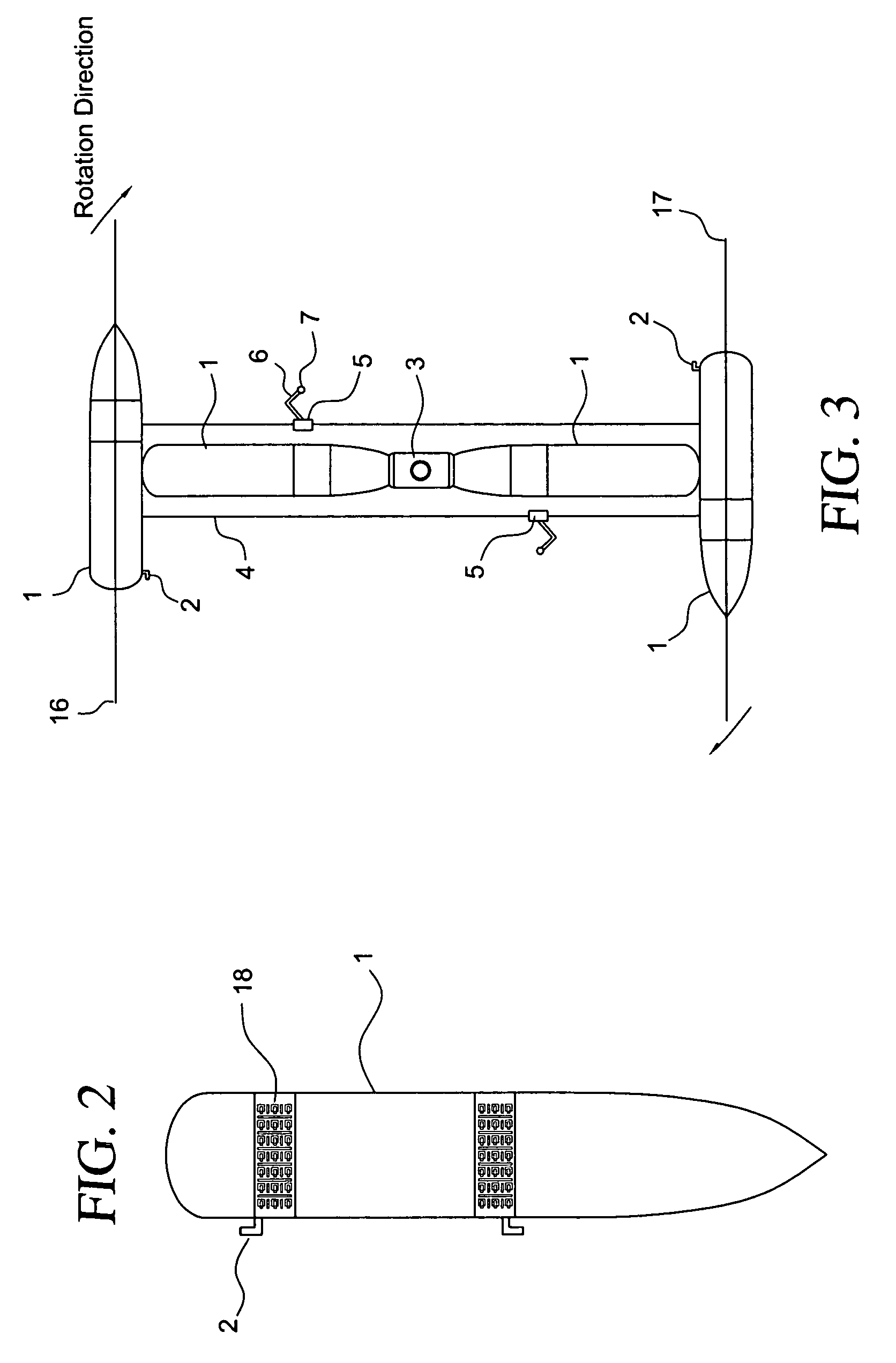
A geosynchronous orbit (sometimes abbreviated GSO) is an orbit around Earth of a satellite with an orbital period that matches Earth's rotation on its axis, which takes one sidereal day (about 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4 seconds). The synchronization of rotation and orbital period means that, for an observer on Earth's surface, an object in geosynchronous orbit returns to exactly the same position in the sky after a period of one sidereal day. Over the course of a day, the object's position in the sky may remain still or trace out a path, typically in a figure-8 form, whose precise characteristics depend on the orbit's inclination and eccentricity. Satellites are typically launched in an eastward direction. A circular geosynchronous orbit is 35,786 km (22,236 mi) above Earth's surface. Those closer to Earth orbit faster than Earth rotates, so from Earth, they appear to move eastward while those that orbit beyond geosynchronous distances appear to move westward.
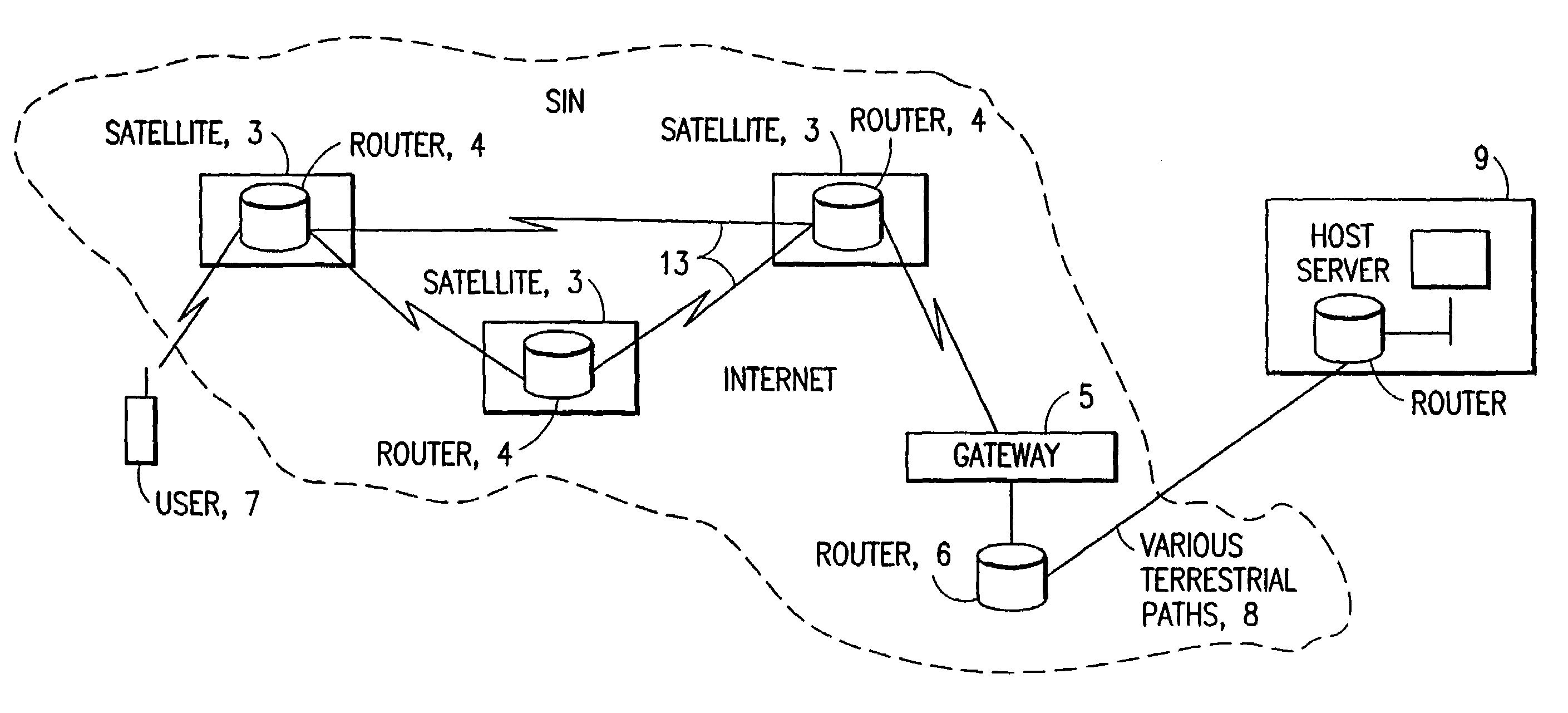
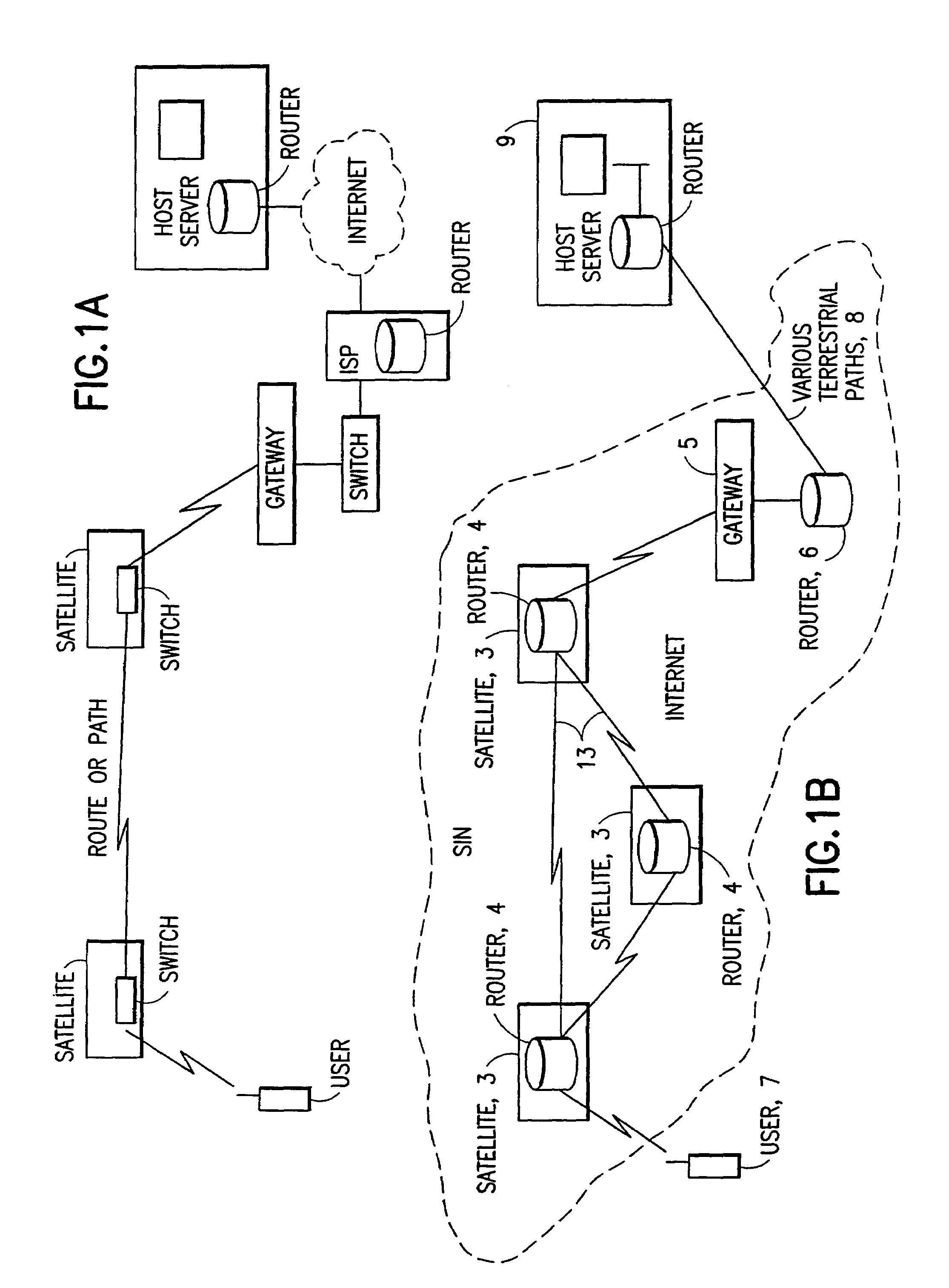
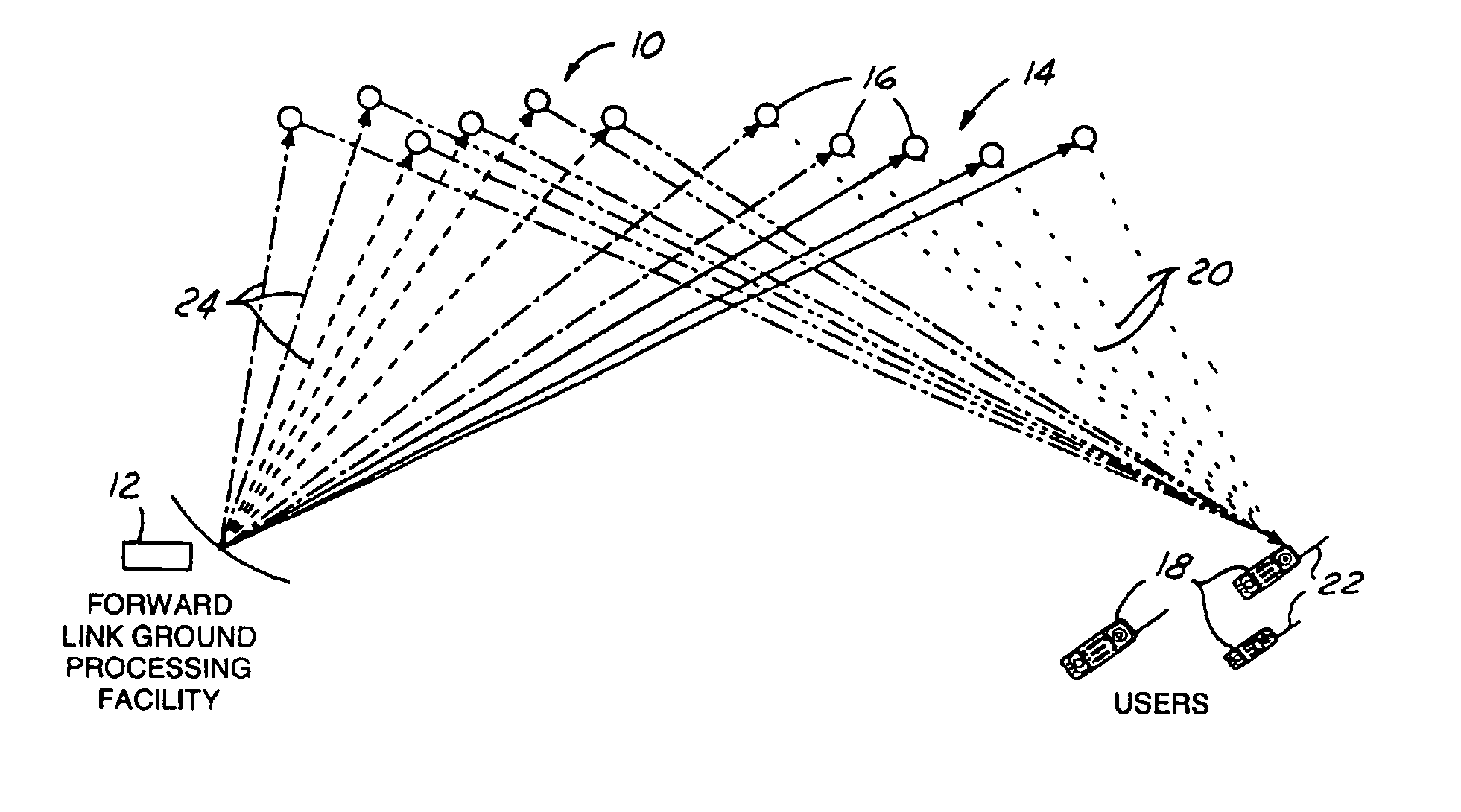
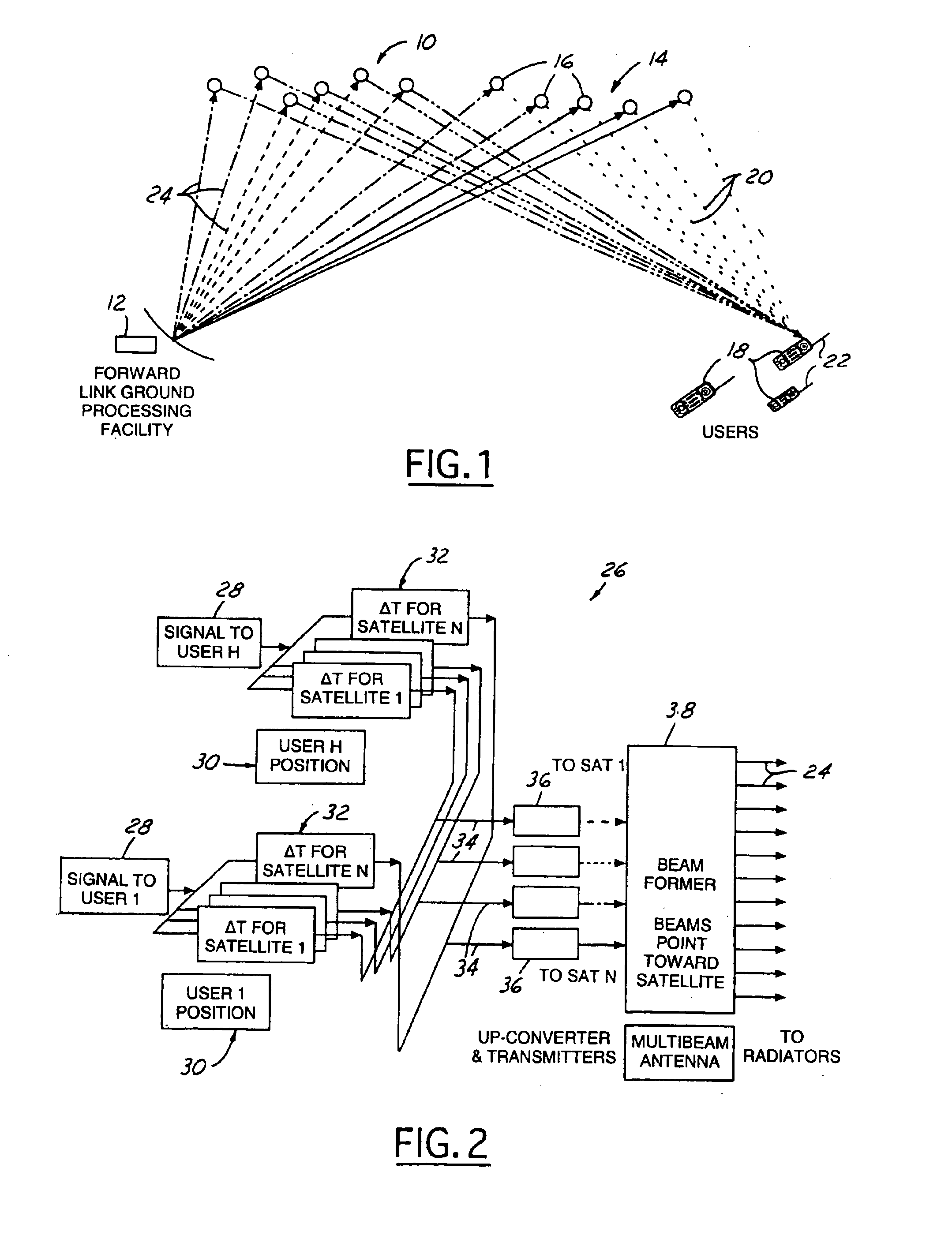
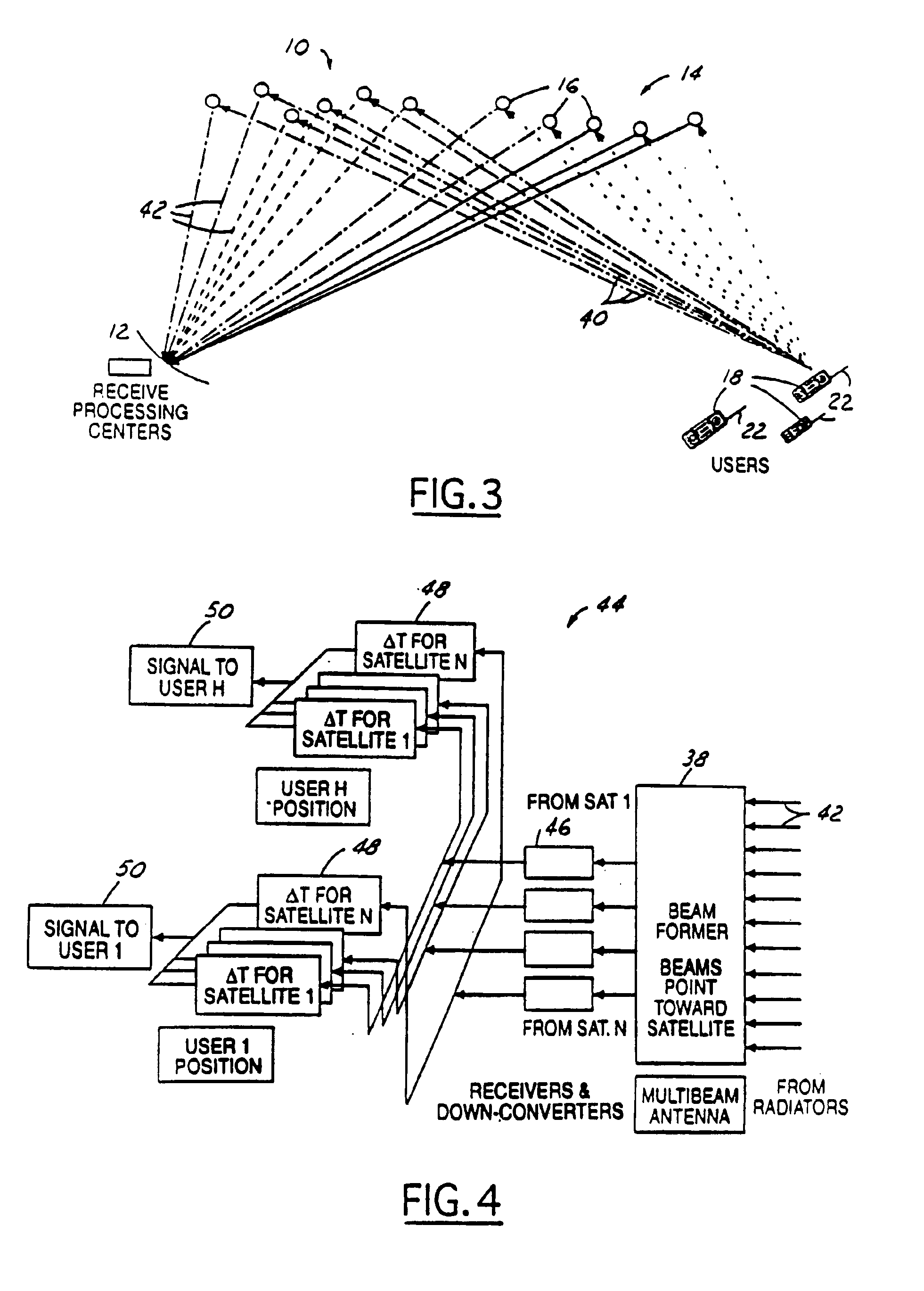
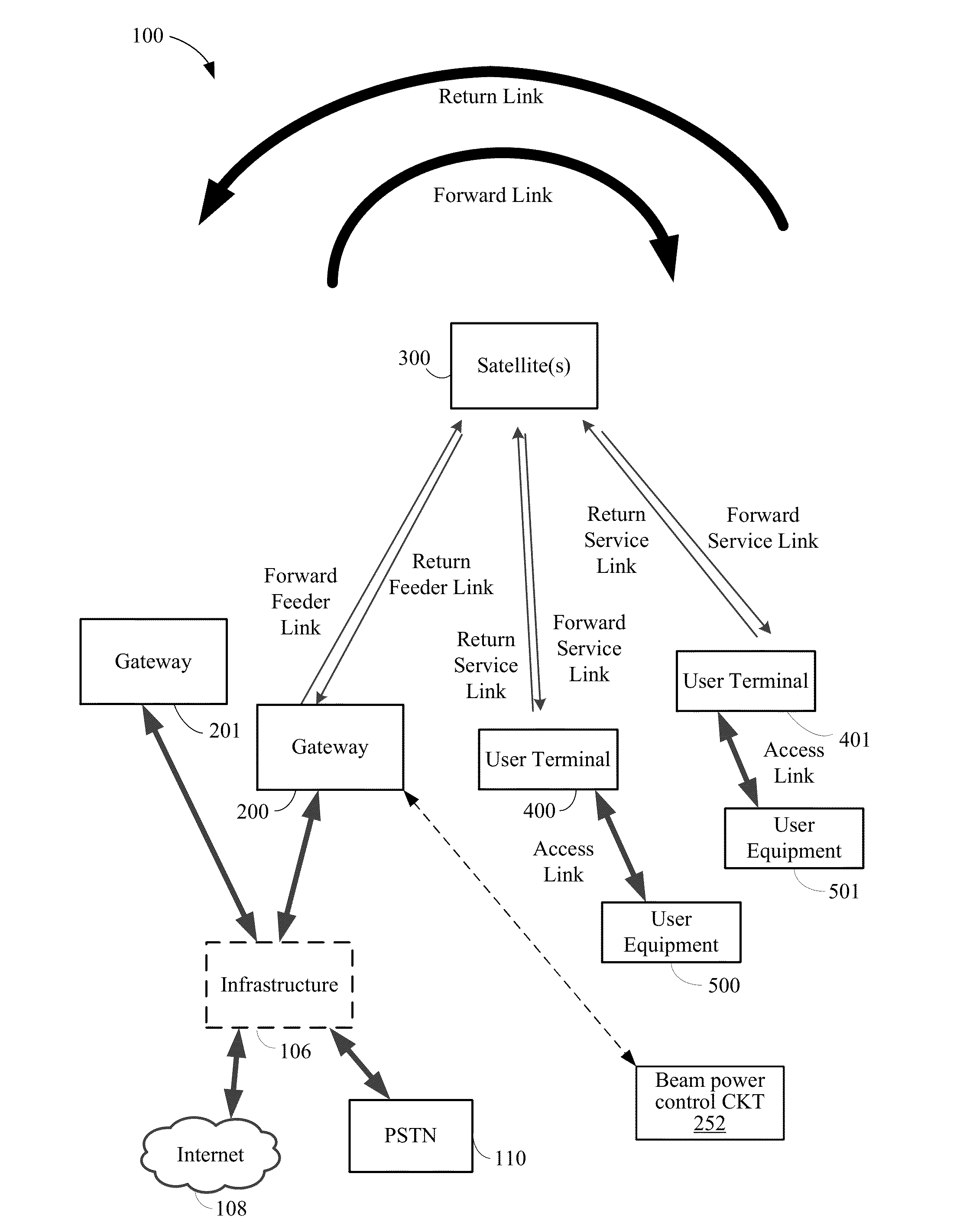
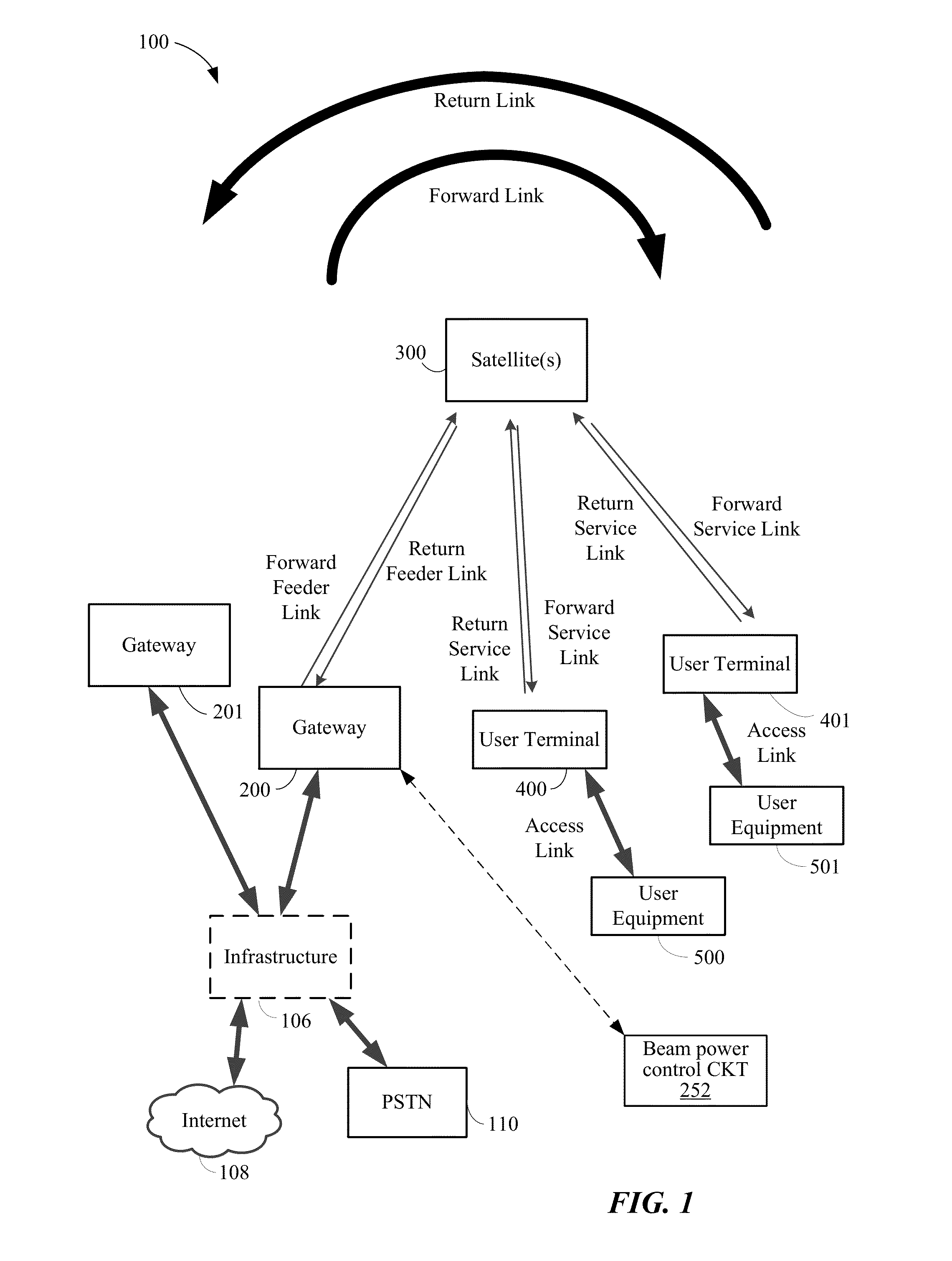
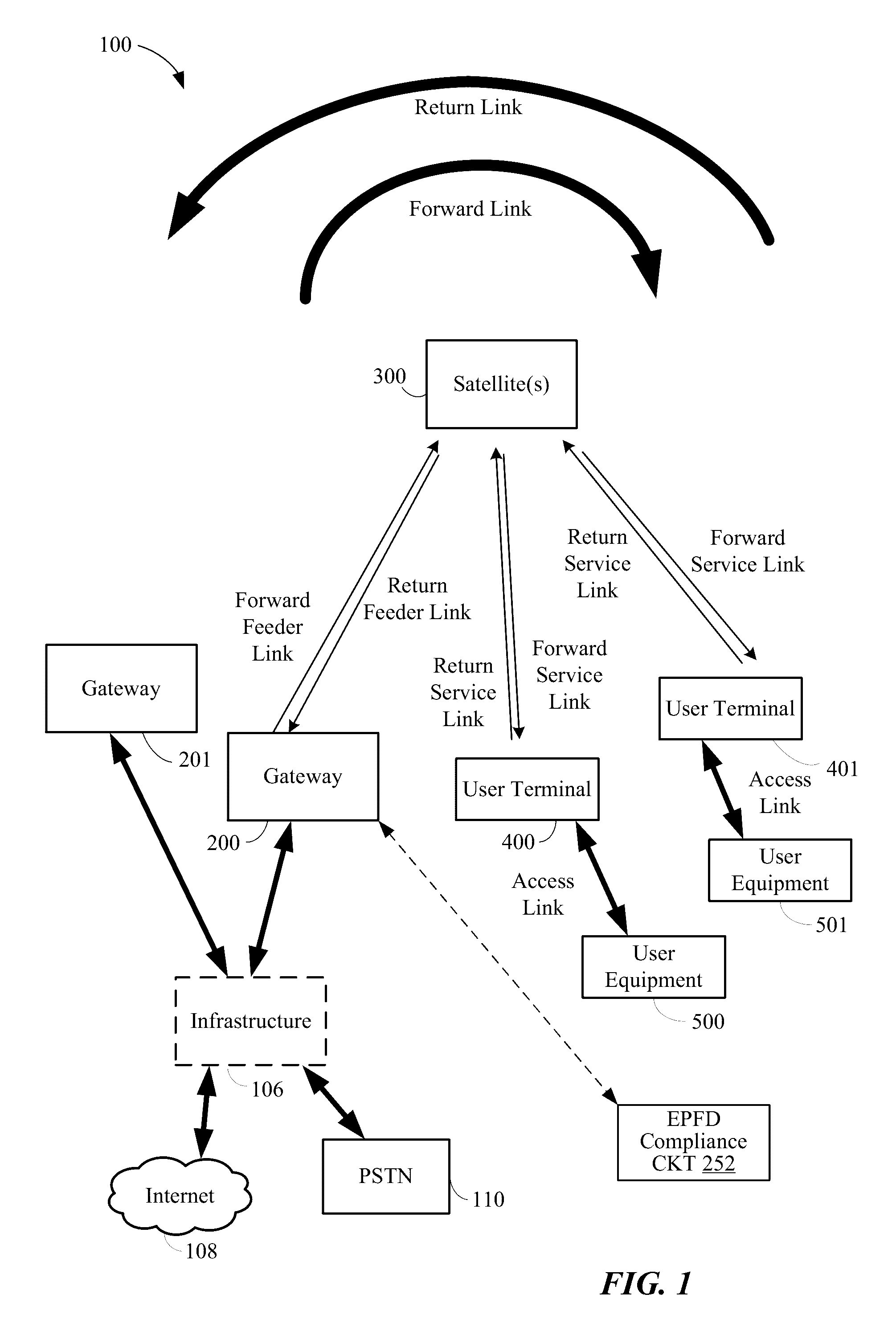
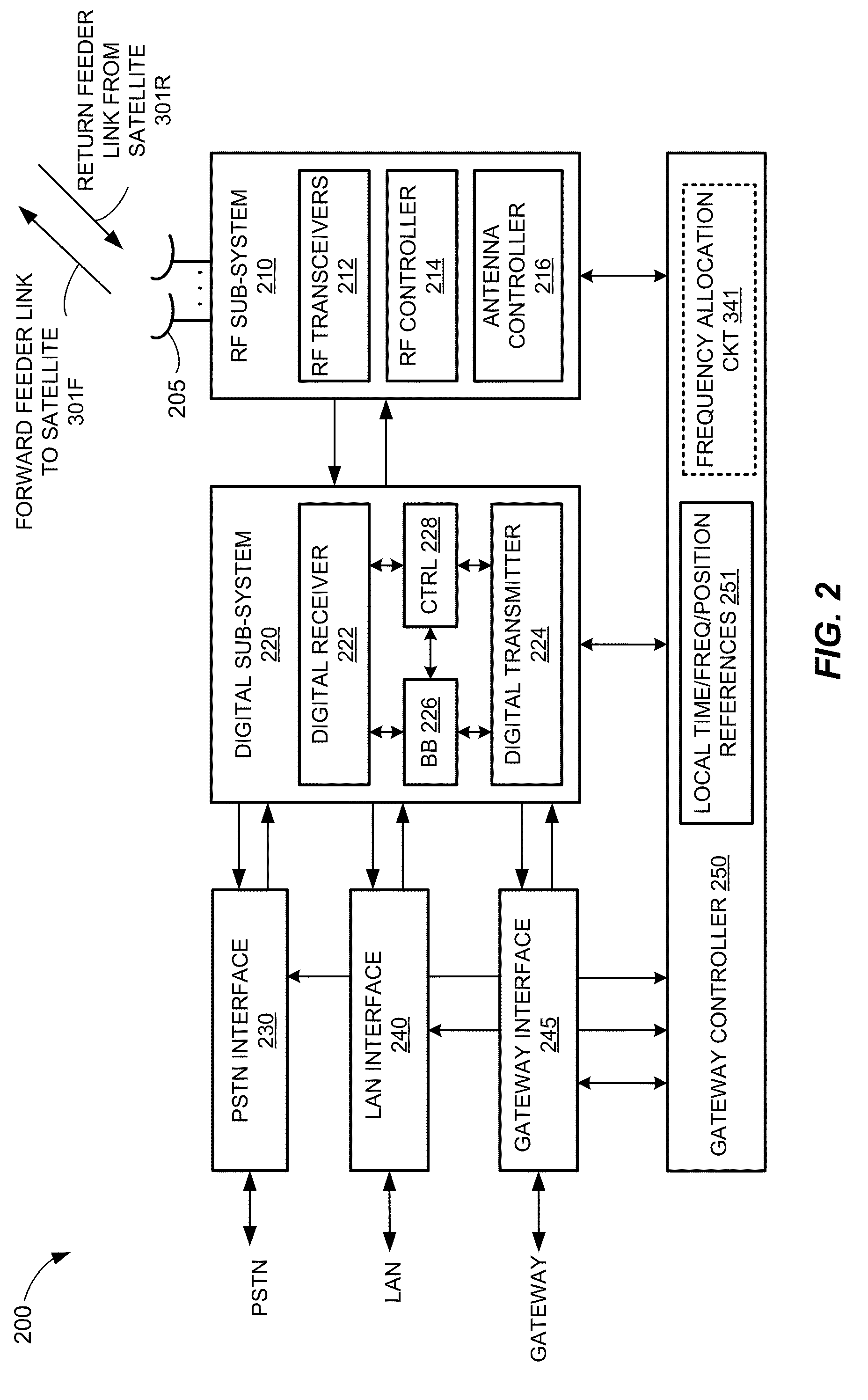
ISP system using non-geosynchronous orbit satellites
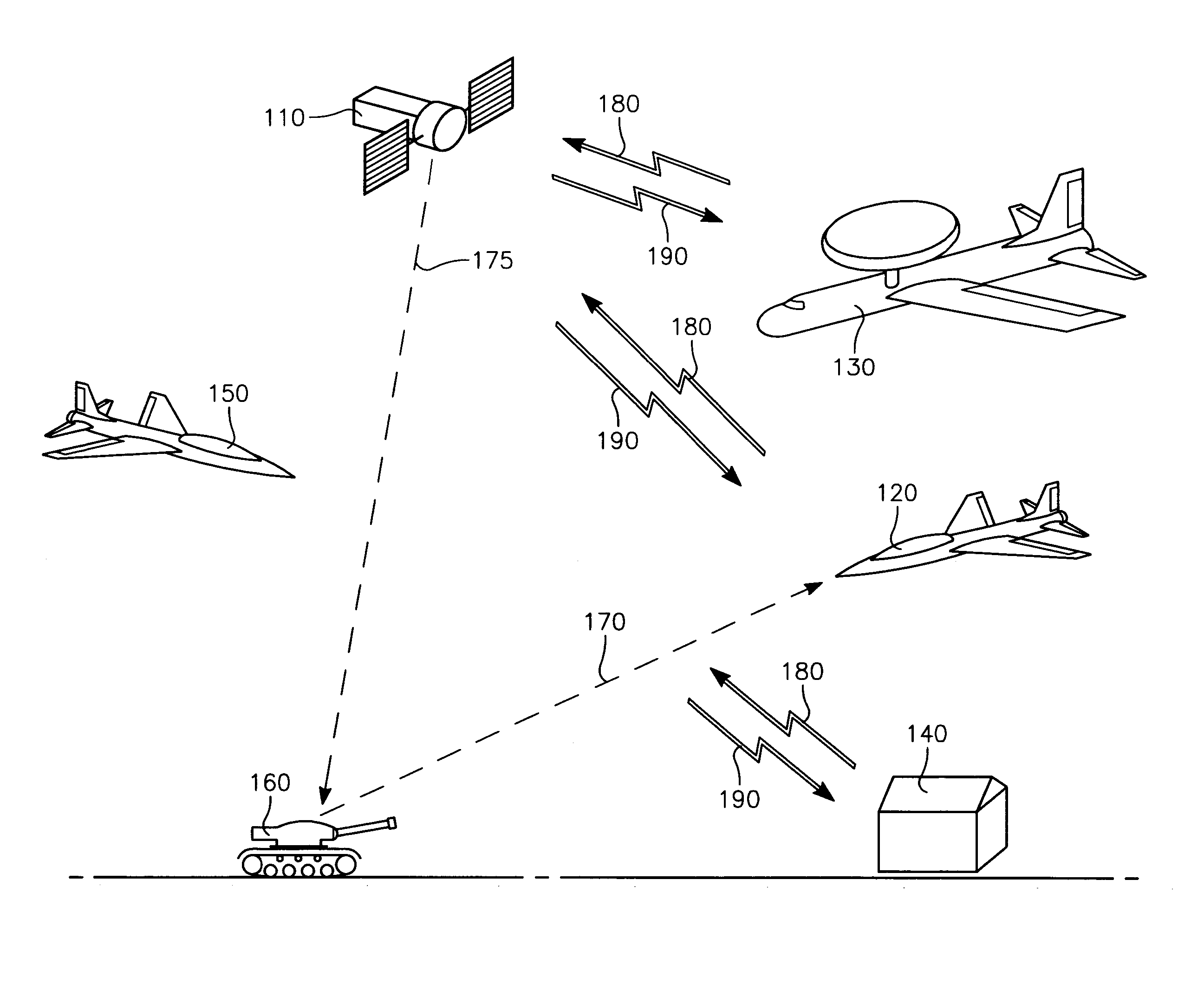
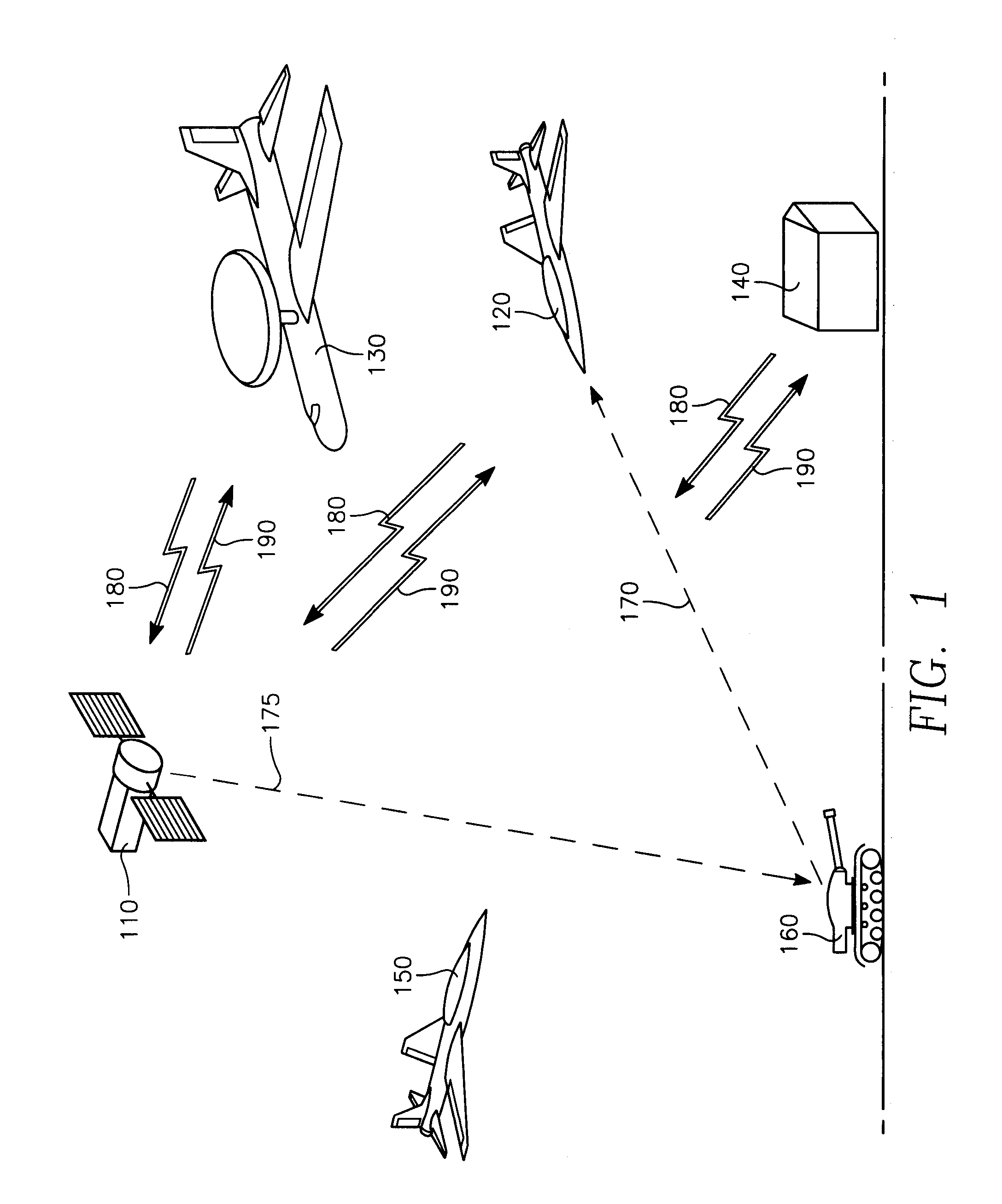
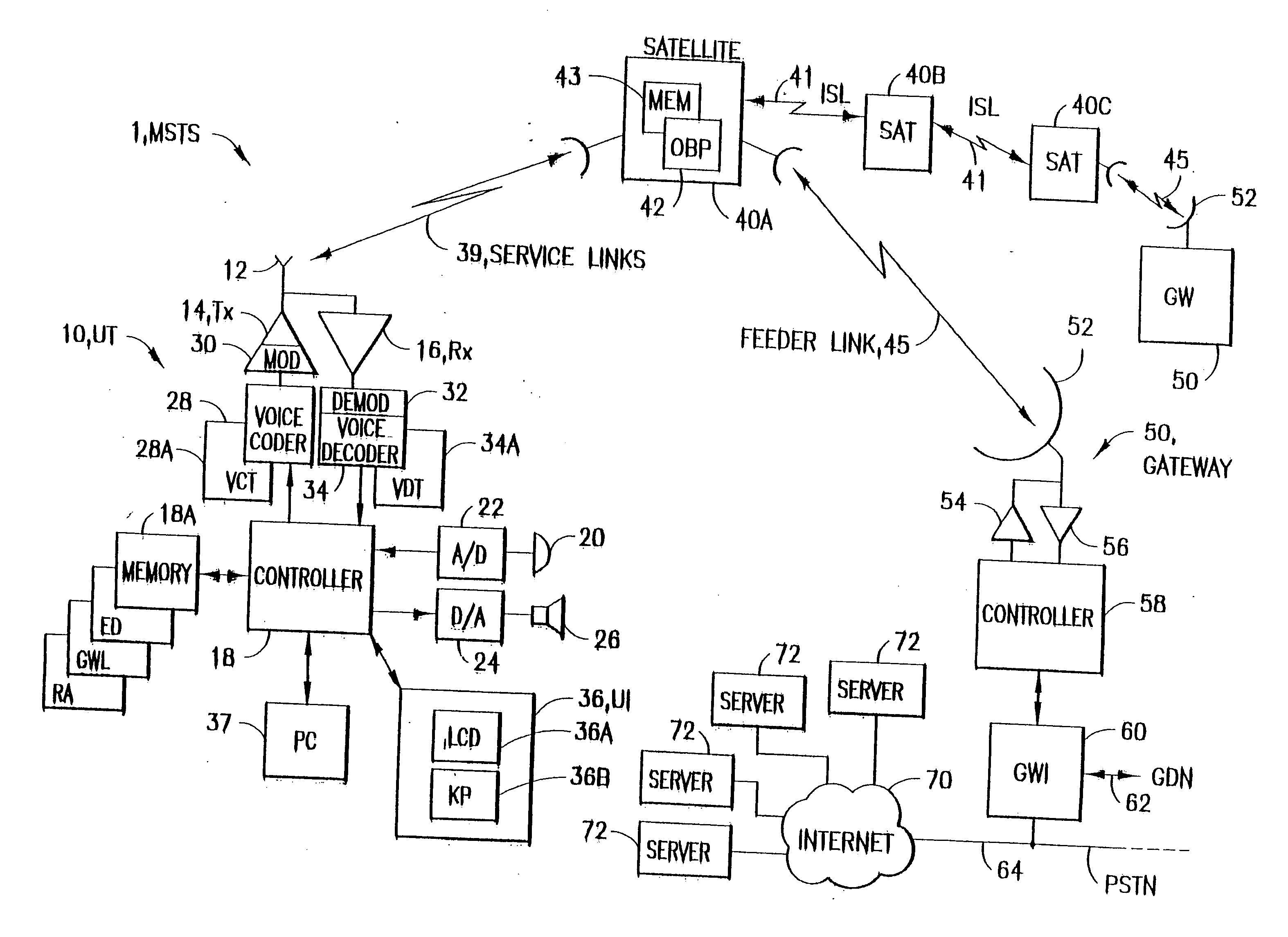
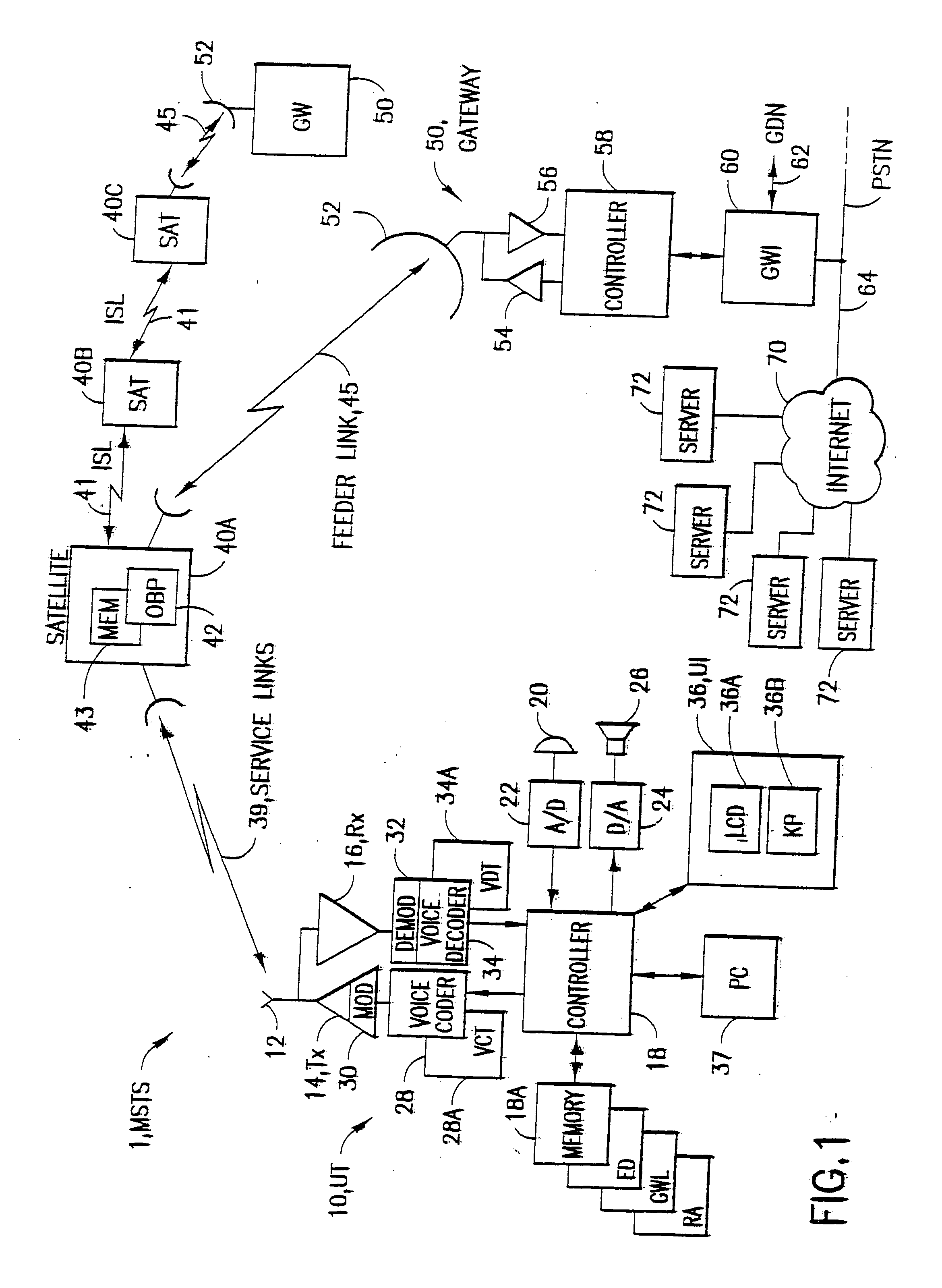
A satellite communication system includes a plurality of satellites, such as low earth orbit satellites, and a plurality of gateways. The satellite communication system is bidirectionally coupled to a terrestrial communication system through at least the plurality of gateways. The satellite communication system and the terrestrial communications system together form a data communication network having a plurality of nodes including source nodes, destination nodes and intermediate nodes. Multiple copies of a packet can coexist within the data communication network, and the packet and its one or more copies are routed, using at least in part satellite-resident routers and gateway-resident routers, over a plurality of different paths between a particular source node and a particular destination node. At least one duplicate copy of a given packet is simply not used during the execution of a packet reordering procedure in the destination node, or at an intermediate node. Certain of the paths are carried over satellite-to-satellite cross-links, while certain other ones of the paths are carried over satellite-to-gateway uplinks and downlinks, and at least one path exists between a user terminal and at least one satellite. In a preferred embodiment the packets are TCP / IP (or equivalent protocol) packets containing information for enabling the selective destruction of a duplicate packet to occur.
Owner:GLOBALSTAR INC
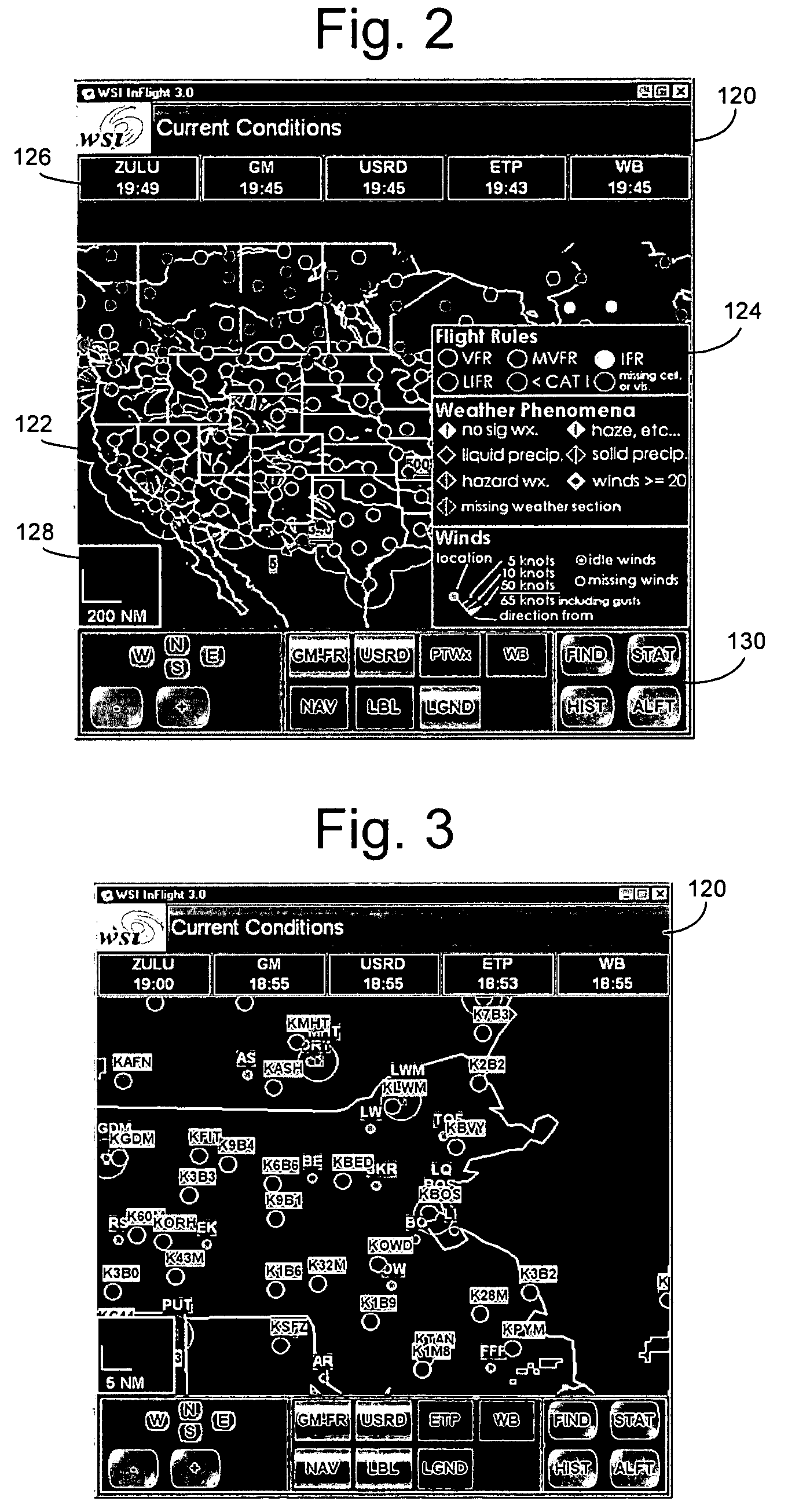
Inflight weather service
InactiveUS7612688B1Easy to understandImprove securityNavigation instrumentsAlarmsGraphicsData stream
A weather briefing system that may be used in the cockpit to provide near real-time graphic and text weather information. Weather information and pilot reports are fed to the cockpit from, e.g., a satellite in geosynchronous orbit. Once delivered to the aircraft, the system processes the data stream and formats it for delivery to an end user device. The data is collected from an extensive network of sources. The end user device may be a portable electronic flight bag (EFB), panel-mounted display (MFD), or similar device programmed to display the formatted data. The system provides timely and accurate weather information to pilots of all types of aircraft. This information may be used for pre-flight planning and in-flight decision-making.
Owner:DTN LLC
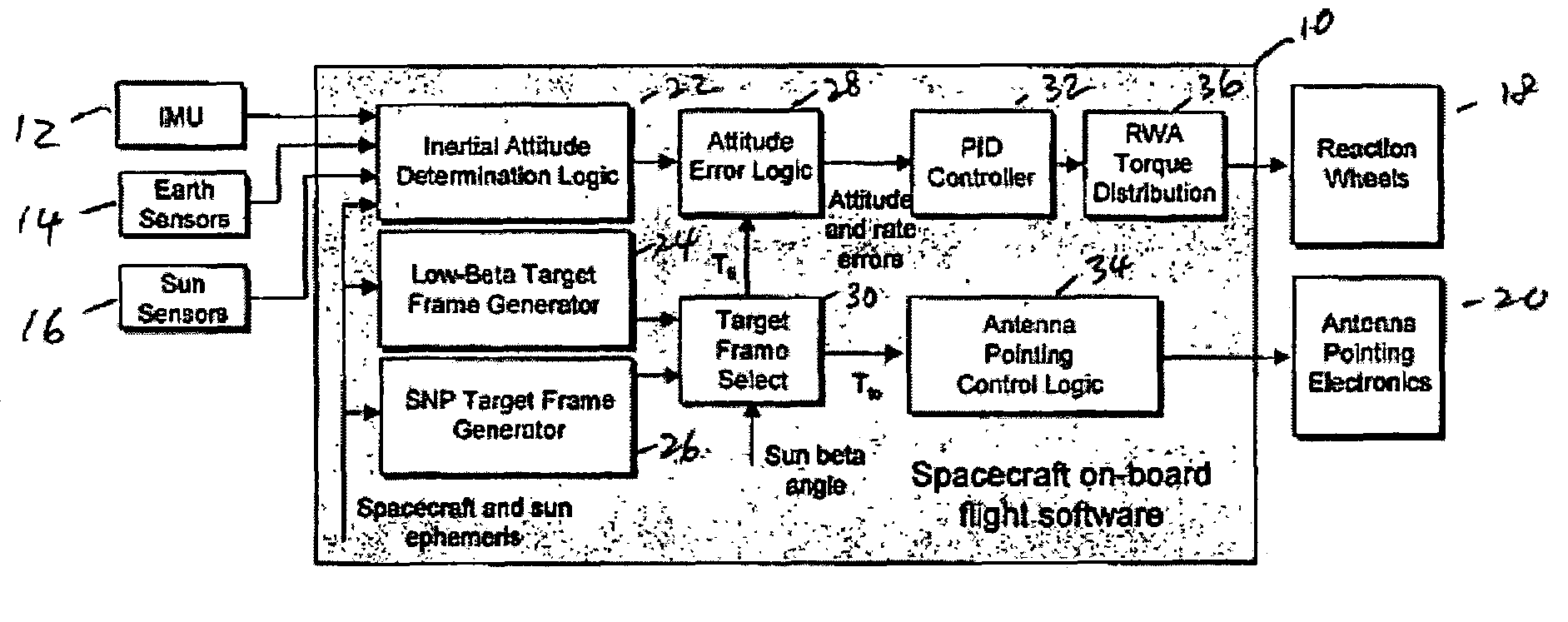
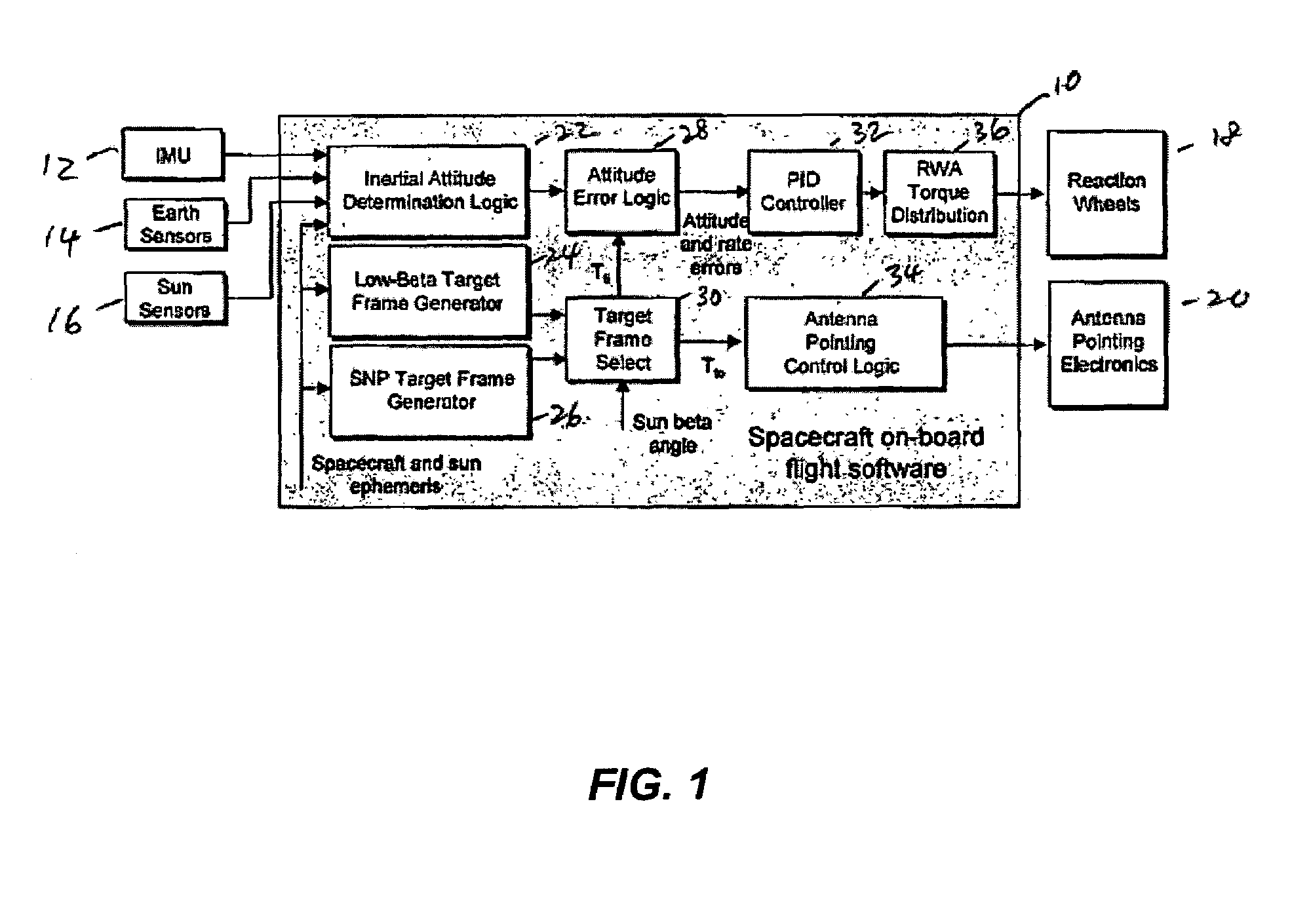
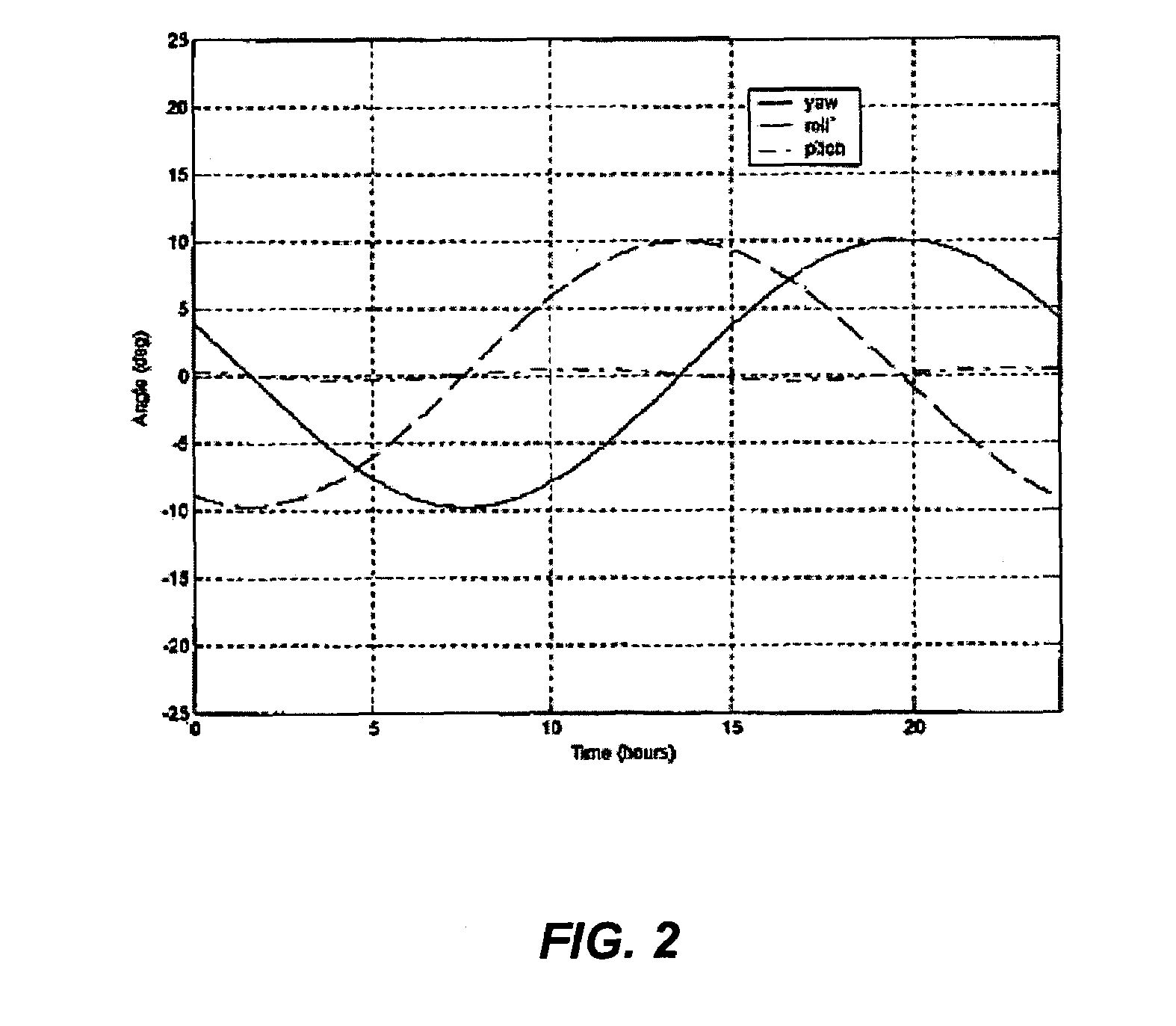
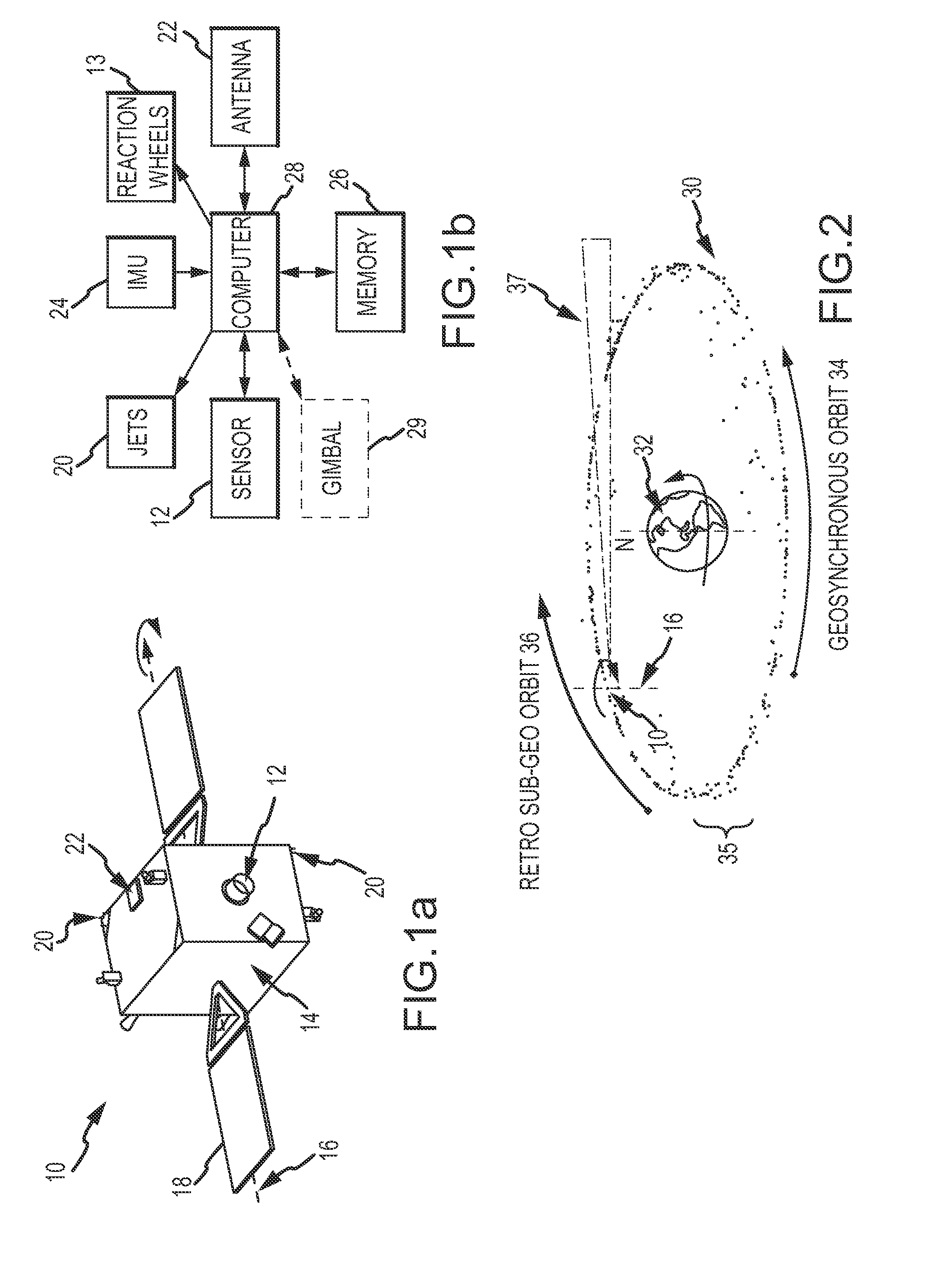
Attitude and antenna steering system for geosynchronous earth orbit (GEO) spacecraft
ActiveUS7357356B1High rateLarge rotation angleCosmonautic vehiclesRadio transmissionBeta angleGeosynchronous orbit
A system for providing attitude and antenna steering for a spacecraft is disclosed. The spacecraft has a number of reaction wheels and a number of antennas. The system includes control logic configured to: determine a beta angle, the beta angle being the angle between a sun vector and an orbit plane of the spacecraft, and alternately engage either a first mode or a second mode to provide attitude and antenna steering based on the beta angle.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
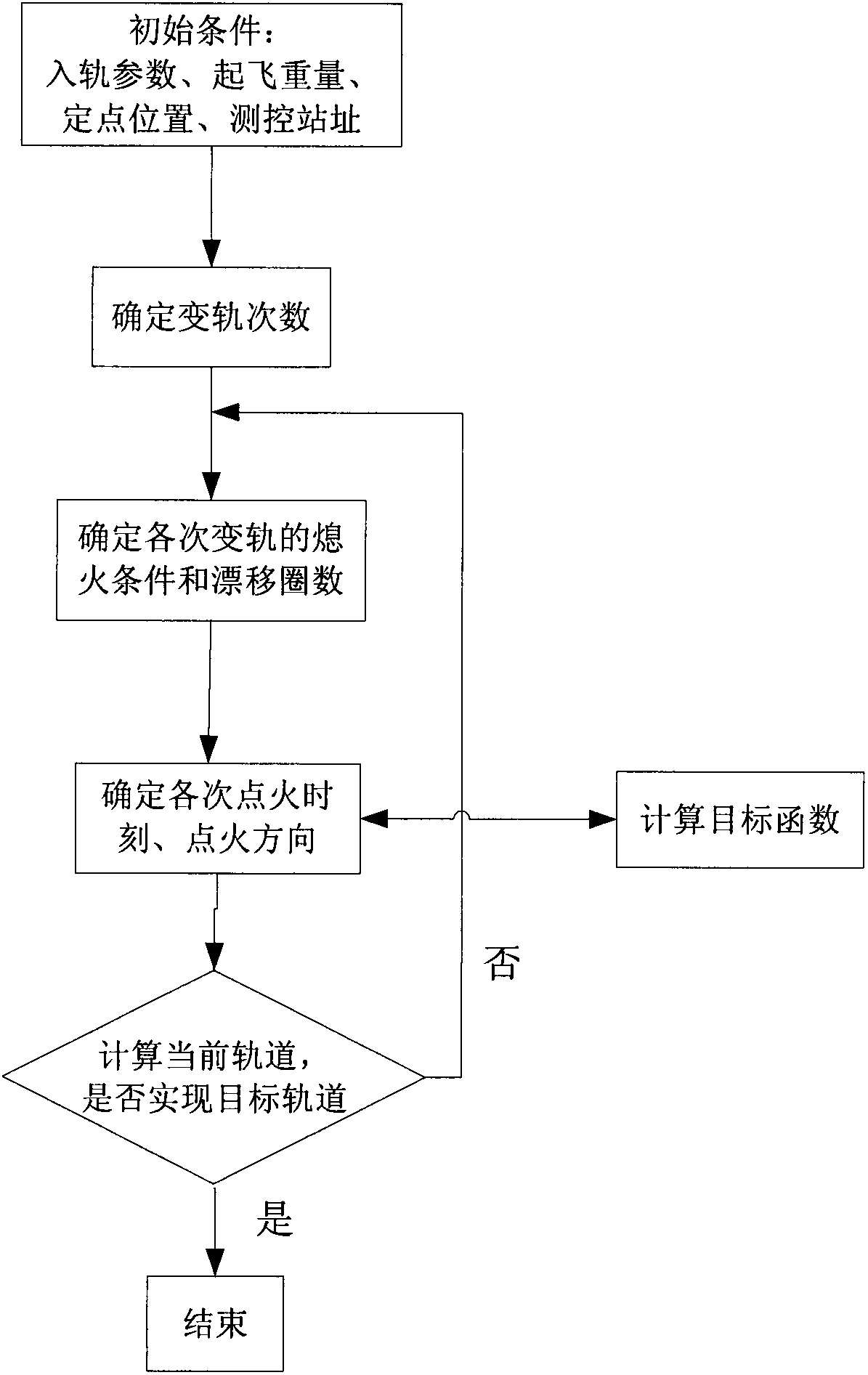
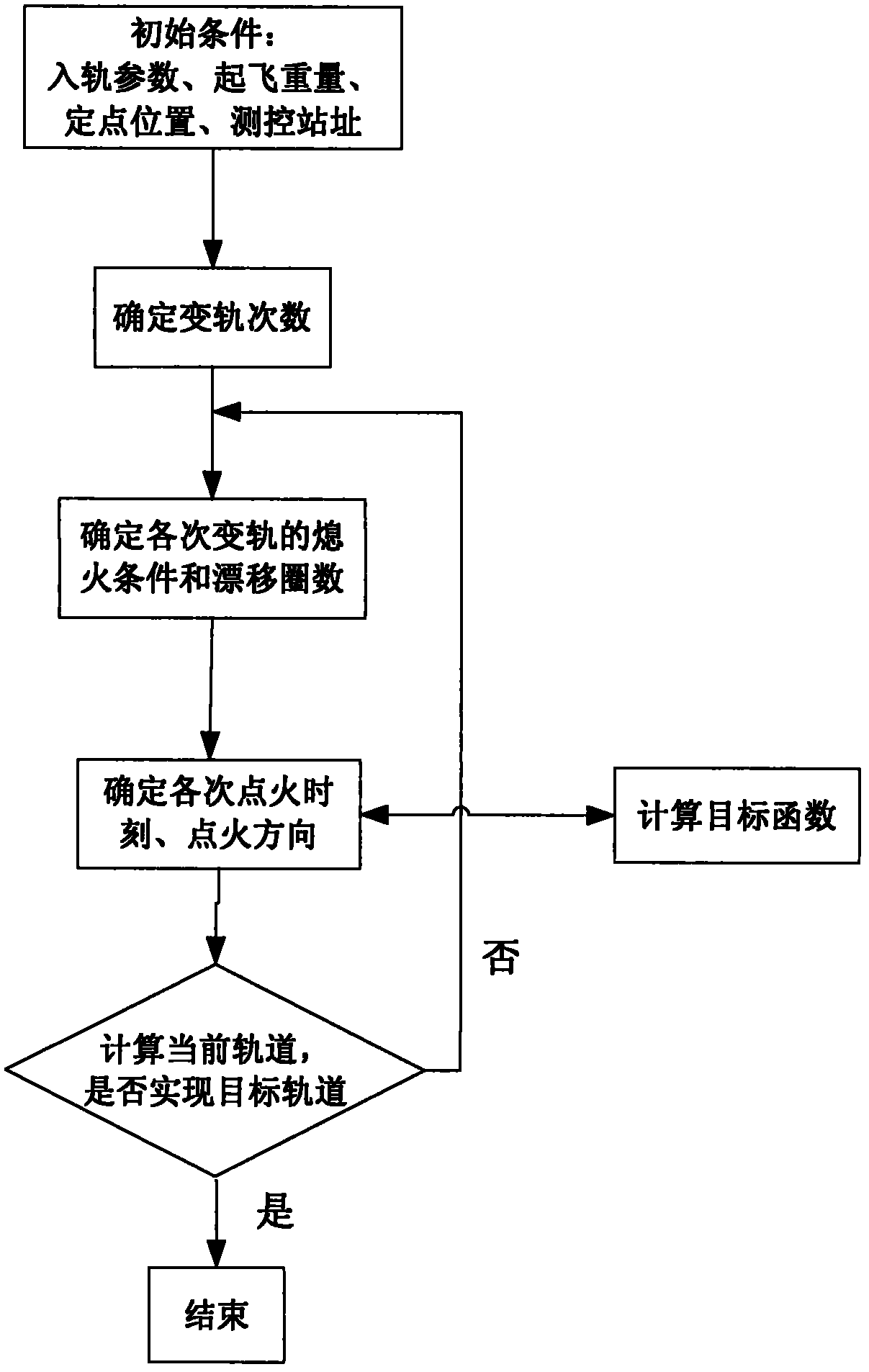
Method for optimizing orbital transfer strategy of geostationary orbit satellite
ActiveCN102424116ASmall amount of calculationShort calculation timeArtificial satellitesGeostationary orbitGeosynchronous orbit
The invention relates to a method for optimizing an orbital transfer strategy of a geostationary orbit satellite, which comprises the following steps of: 1, determining orbital transfer times, orbital transfer circle times and the controlled variable of each-time orbital transfer; and 2, determining time and a thrust direction in each-time orbital transfer. The process of launching the geostationary orbit satellite at present generally comprises the following steps of: launching the satellite into a highly elliptic transfer orbit with an inclination angle by using a carrier rocket; performing apogee / perigee orbital transfer for several times by using a self-contained liquid engine of the satellite, and transferring to a geosynchronous orbit; and correcting and rounding the inclination angle of the orbit to realize a geostationary orbit. For the satellite, operation for changing the transfer orbit into the geostationary orbit by performing apogee / perigee orbital transfer for several times is complex, so too many orbital transfer times is not suitable, and orbital transfer complexity and risk are prevented from being increased; in addition, factors such as the capacity of the liquid engine of the satellite, arc segment loss in an orbital transfer period, and the like are considered, so too few orbital transfer times is not suitable.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
Fire urgency estimator in geosynchronous orbit (FUEGO)
ActiveUS20160132714A1Quality improvementEliminate artifactsTelevision system detailsImage enhancementFire detectorSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A fire detector is disclosed that successively images a particular area from geosynchronous Earth orbit satellite to attain very good signal-to-noise ratios against Poisson fluctuations within one second. Differences between such images allow for the automatic detection of small fires greater than 12 square meters. Imaging typically takes place in transparent bands of the infrared spectrum, thereby rendering smoke from the fire and light clouds somewhat transparent. Several algorithms are disclosed that can help reduce false fire alarms, and their efficiencies are shown. Early fire detection and response would be of great value in the United States and other nations, as wild land fires destroy property and lives and contribute around five percent of the US global carbon dioxide contribution. Such apparatus would incorporate modern imaging detectors, software, and algorithms able to detect heat from early and small fires, and yield detection times on a scale of minutes.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Multi-node point-to-point satellite communication system employing multiple geo satellites
InactiveUS6990314B1Reduce restrictionsReduce complexityActive radio relay systemsWireless commuication servicesEarth satelliteCommunications system
A wireless communication system includes a satellite constellation consisting of a plurality of satellites. Each of the plurality of satellites is in an orbit whose eccentricity and inclination are perturbed relative to the same geosynchronous orbit. Each of the satellites in the constellation is capable of relaying signals in either direction between a central ground hub and a plurality of mobile user terminals. The plurality of satellites are configured such that the period of their geosynchronous orbit remains substantially constant at one sidereal day.
Owner:HUGHES ELECTRONICS
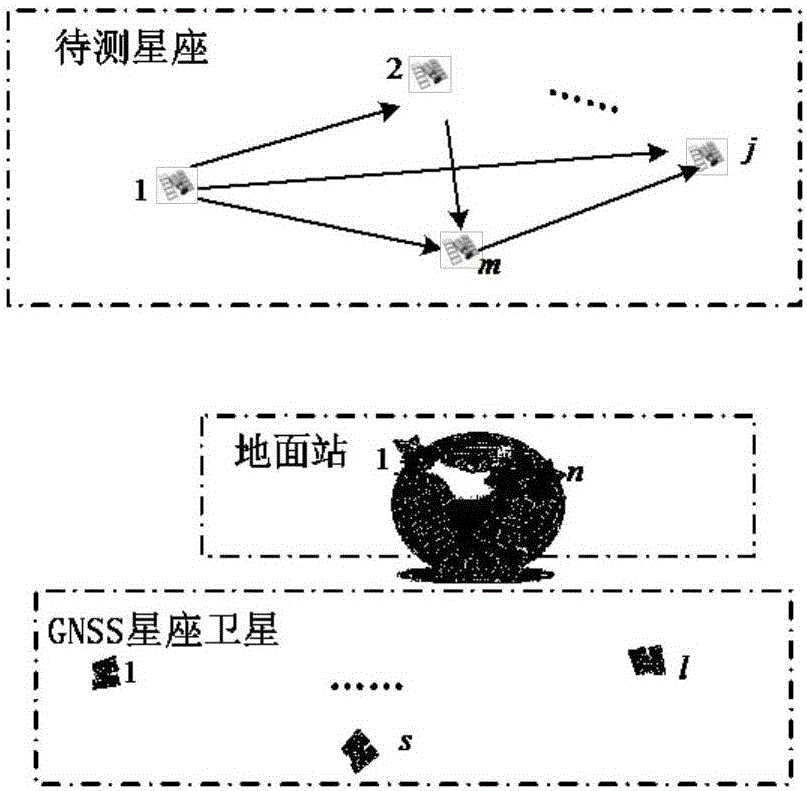
Geosynchronous orbit constellation orbit determination method based on ground station/satellite link/GNSS combined measurement
ActiveCN106338753AGuarantee the accuracy of orbit determinationSmall amount of calculationInstruments for comonautical navigationSatellite radio beaconingGeosynchronous orbitGround station
The invention discloses a geosynchronous orbit constellation orbit determination method based on ground station / satellite link / GNSS combined measurement. The method comprises the steps of (1) establishing the state equation of a GSO constellation orbit determination system in a centralized structure, (2) establishing the measurement equation of the GSO constellation orbit determination system in a centralized structure, (3) carrying out combined optimization of a ground station for orbit determination and GNSS measurement combination, (4) determining the filtering method for realizing orbit parameter estimation according to the above established GSO constellation combined orbit determination system model based on ground station / satellite link / GNSS, and (5) carrying out the concrete realization of a GSO constellation orbit determination method based on ground station / satellite link / GNSS in the centralized structure. According to the method, the combined distribution optimization strategy of ground station and GNSS measurement is established based on a precision factor, and the calculation amount is reduced while the orbit determination precision is ensured.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
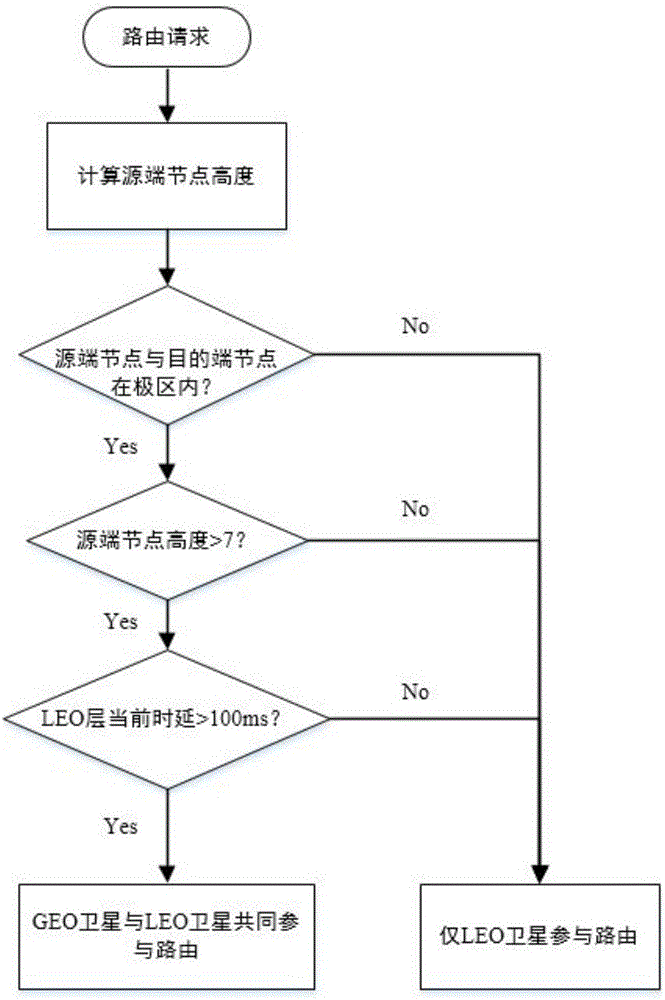
Double-layer topology routing method based on satellite communication network design
InactiveCN106792961AImprove throughputImprove transmission efficiencyActive radio relay systemsWireless communicationGeolocationGeosynchronous orbit
The invention discloses a double-layer topology routing method based on a satellite communication network design. The method comprises the steps of: constructing a double-layer satellite network constellation system, grouping satellites, calculating a routing path in a geosynchronous orbit and a low earth orbit, and assessing the performance of inter-satellite link routing via end-to-end delay and packet loss rate of data sent via the routing path; calculating a valid link and an availability weight of a satellite network according to the geographic position of a satellite node, the number of hops required by a source-to-destination calculation path and the congestion situation of the inter-satellite link; calculating the total cast for inter-satellite link data transmission in combination with the weight of a low earth orbit satellite initial calculation link and the availability weight of the source-to-destination satellite node; and screening a geosynchronous orbit satellite meeting the service requirement according to the business of low earth orbit satellites and the complexity of the routing path to participate in data transmission. The method can establish a valid path and balance the data transmission demand and the end-to-end delay, thereby optimizing the network performance.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV +1
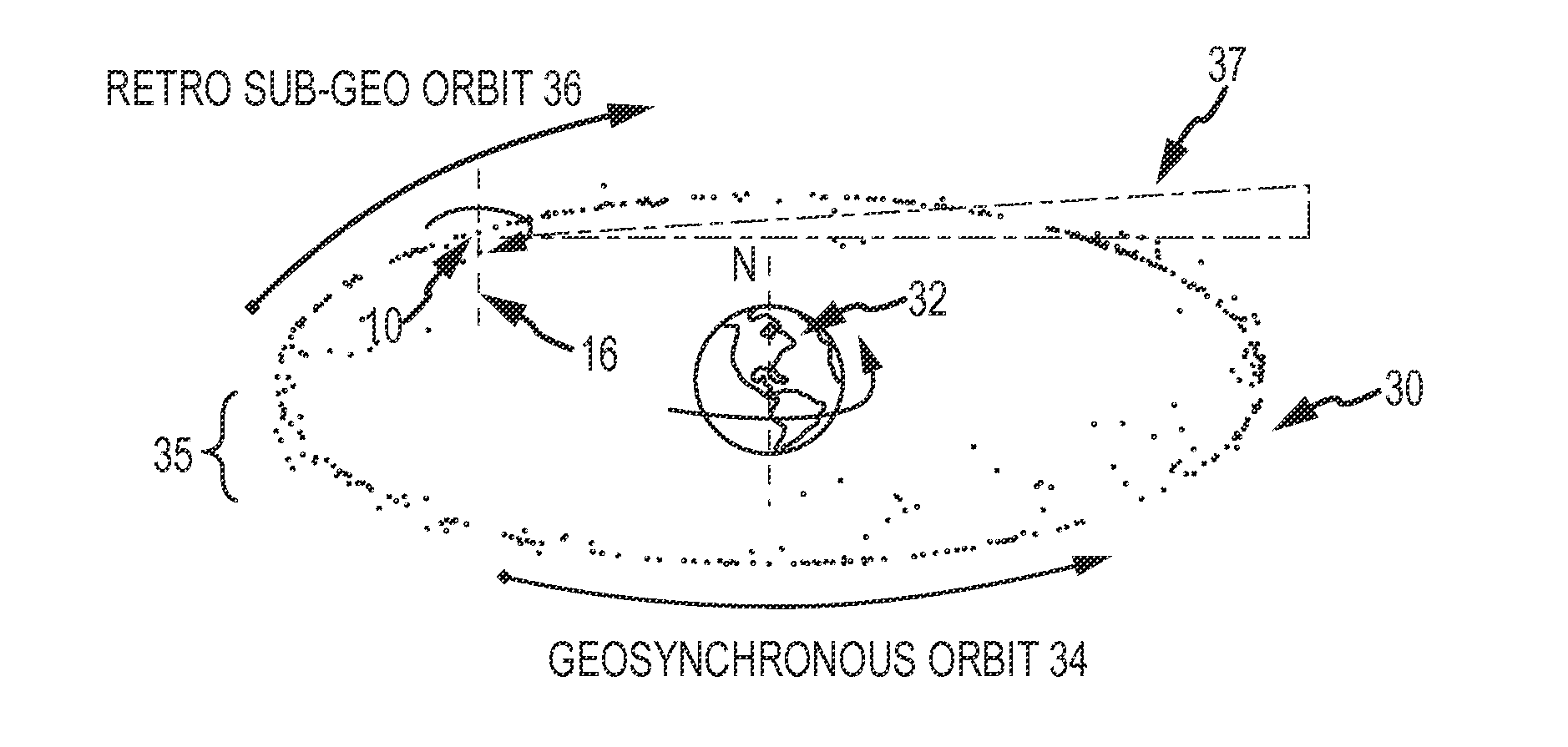
Retro-Geo Spinning Satellite Utilizing Time Delay Integration (TDI) for Geosynchronous Surveillance
ActiveUS20110049302A1Quick scanLow-cost solutionDigital data processing detailsArtificial satellitesNatural satelliteTime delays
Geosynchronous surveillance is conducted by injecting one or more observer satellites into a retro sub or super geosynchronous orbit at approximately zero inclination. The observer satellite spins about an approximately North-South axis in an Earth frame of reference to sweep a sensor's FOV around the geobelt. Sensor time delay integration (TDI) is synchronized to the observer satellite's spin-rate and possibly the sum of the spin-rate and the target inertial LOS rate to realize longer integration times. This approach facilitates faster scans of the entire geobelt, more timely updates of the catalog of tracked objects and resolution of small and closely spaced objects. An inexpensive small-aperture body-fixed visible sensor may be used.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
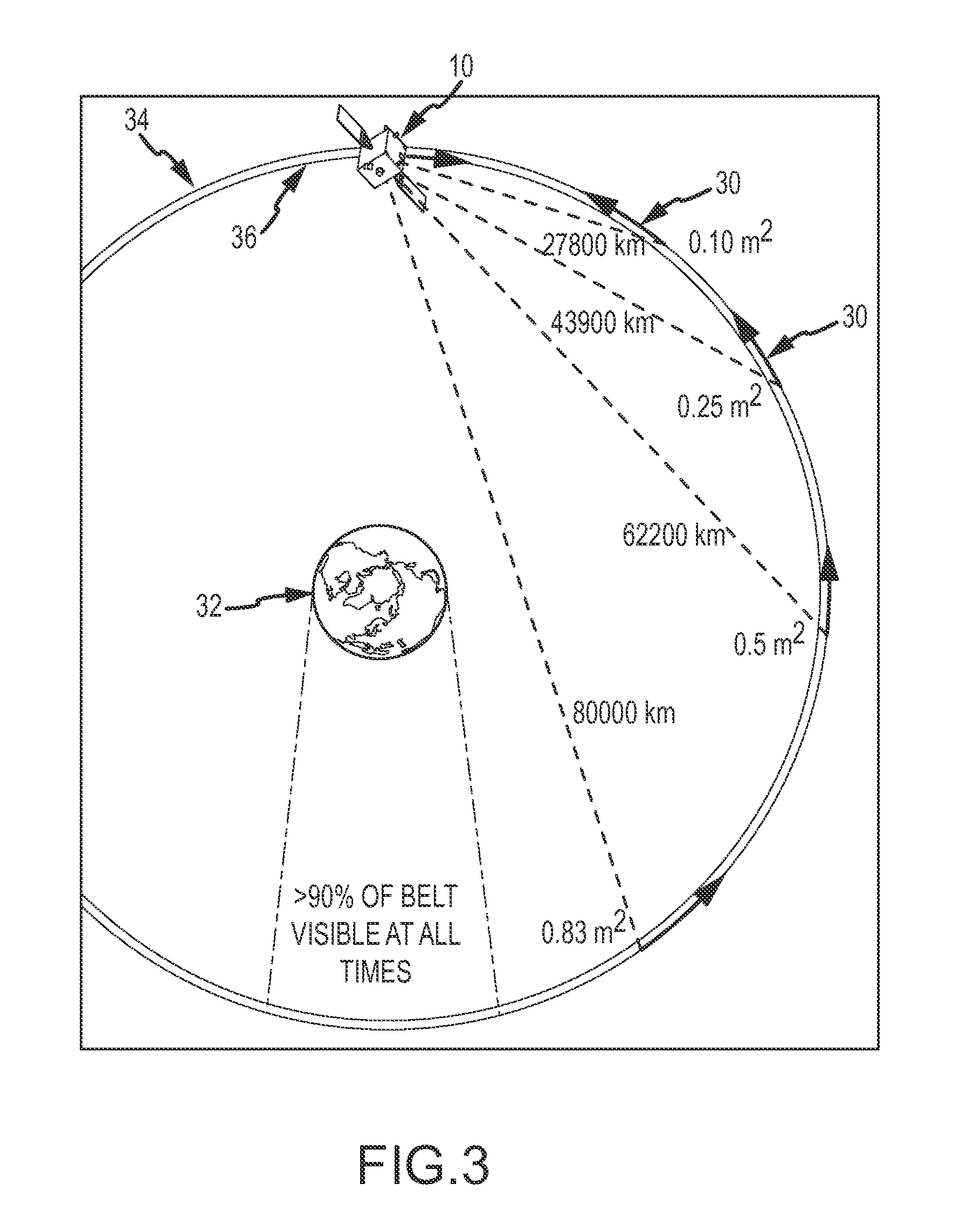
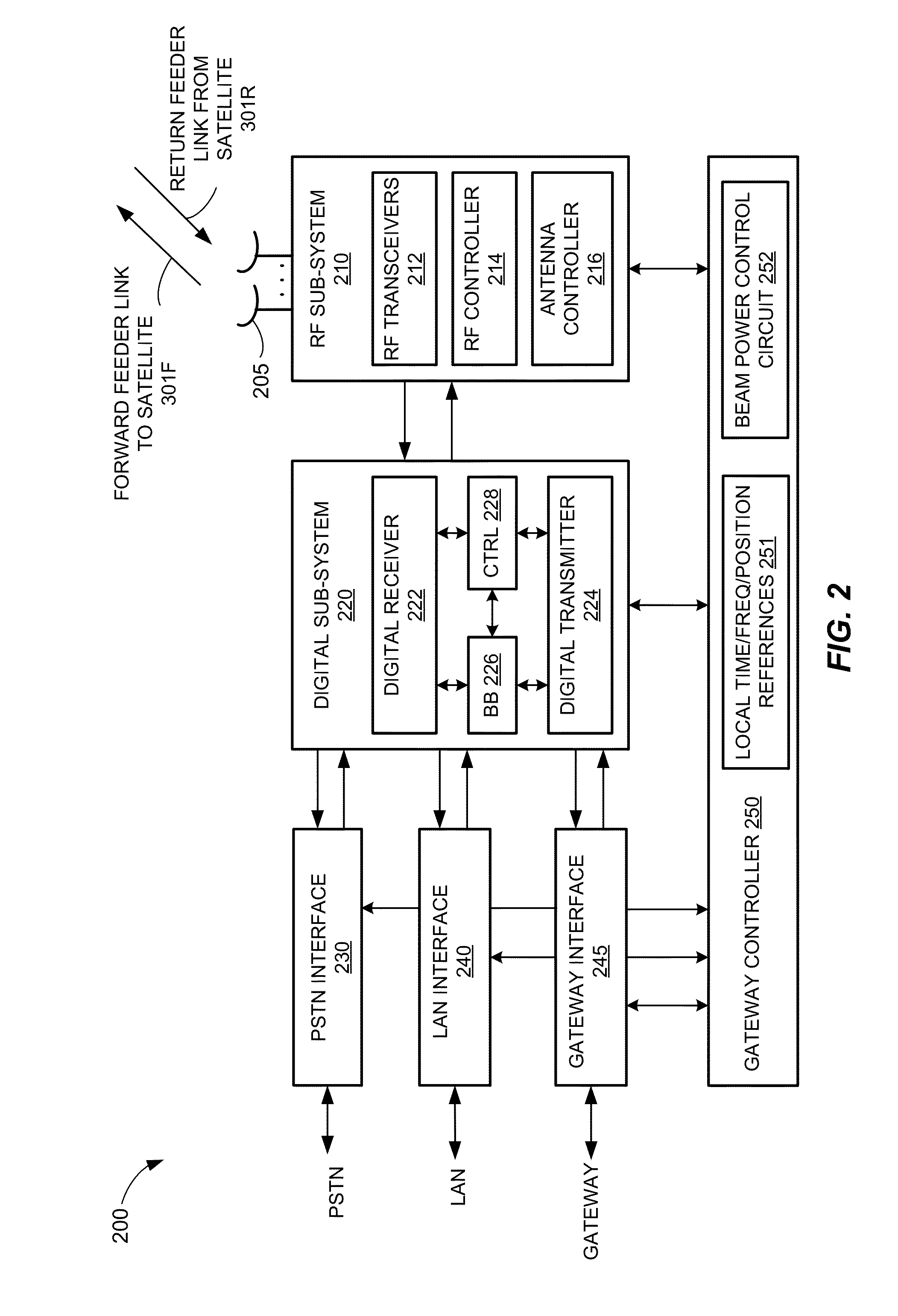
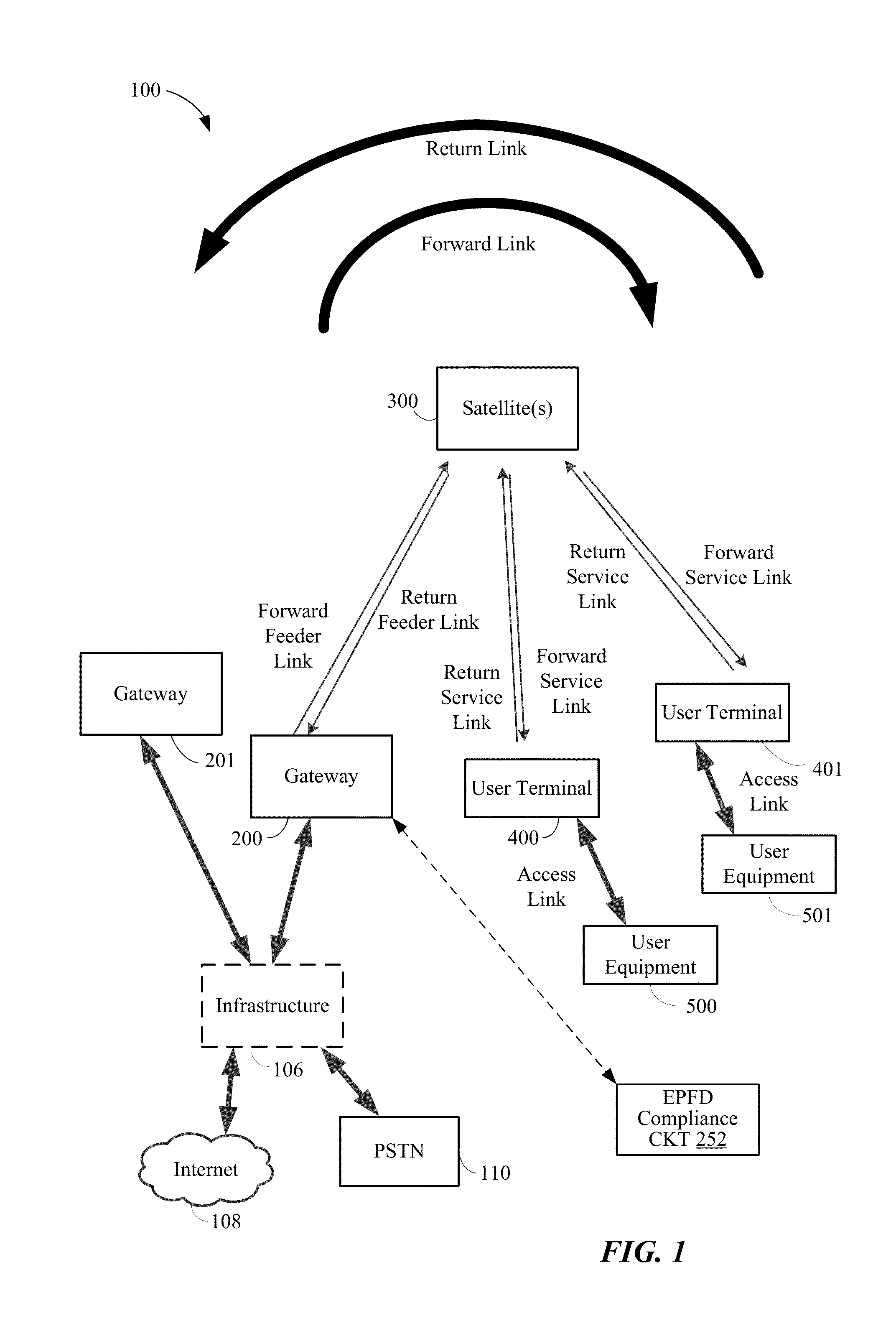
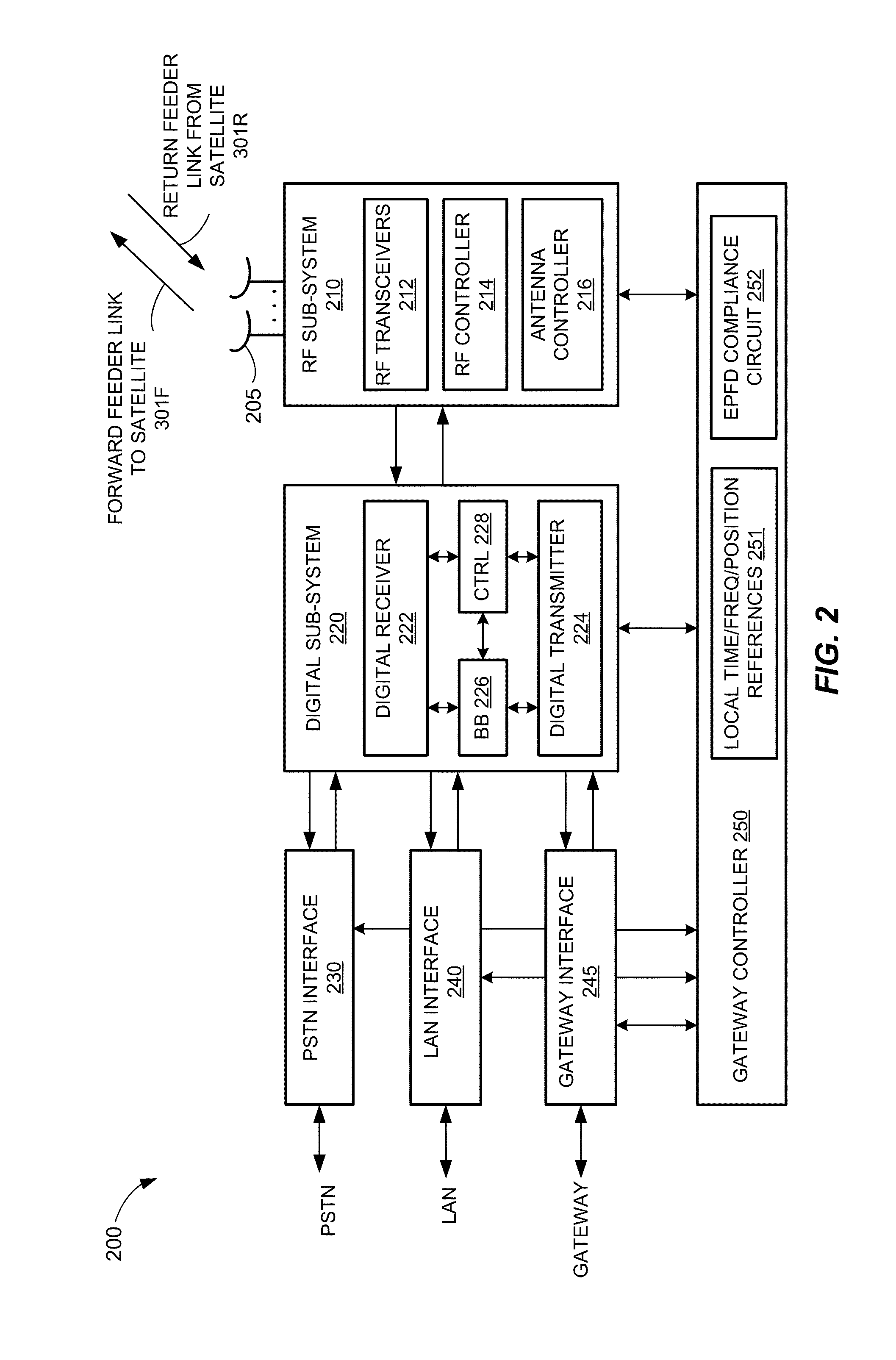
Satellite beam power backoff
A method and apparatus for a non-geosynchronous orbit (NGSO) satellite to comply with equivalent power flux density (EPFD) limits are disclosed. The example implementations may allow a constellation of NGSO satellites to comply with EPFD limits without disabling beams transmitted from the NGSO satellites. The power level of one or more beams to be transmitted from the NGSO satellites may be dynamically adjusted according to a beam power back-off schedule. In some aspects, the beam power back-off schedule may specify beam power back-off values as a function of latitude on Earth, and may allow for maximum allowable power levels for beams transmitted from the NGSO satellites without violating any of the EPFD percentile limits.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
EPFD coverage for NGSO satellites
ActiveUS9585150B2Gap minimizationAvoid interferencePower managementBroadcast transmission systemsGeosynchronous orbitSatellite constellation
A method and apparatus for operating one or more satellites in a non-geosynchronous orbit (NGSO) satellite constellation are disclosed. In some aspects, a coverage area on Earth for a first beam transmitted from a first satellite in the NGSO satellite constellation may be determined, a cone may be projected onto a first region of the beam coverage area, a second region of the beam coverage area may be defined as including portions of the beam coverage area lying outside the first region, and a minimum arc angle for each of a plurality of points within the first region but not the second region of the beam coverage area may be determined.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
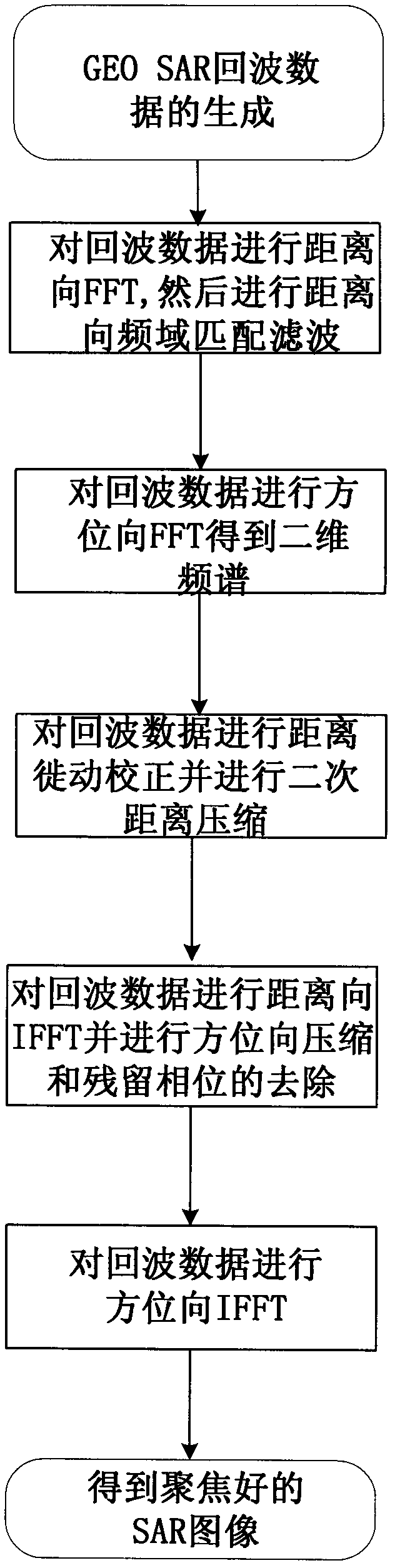
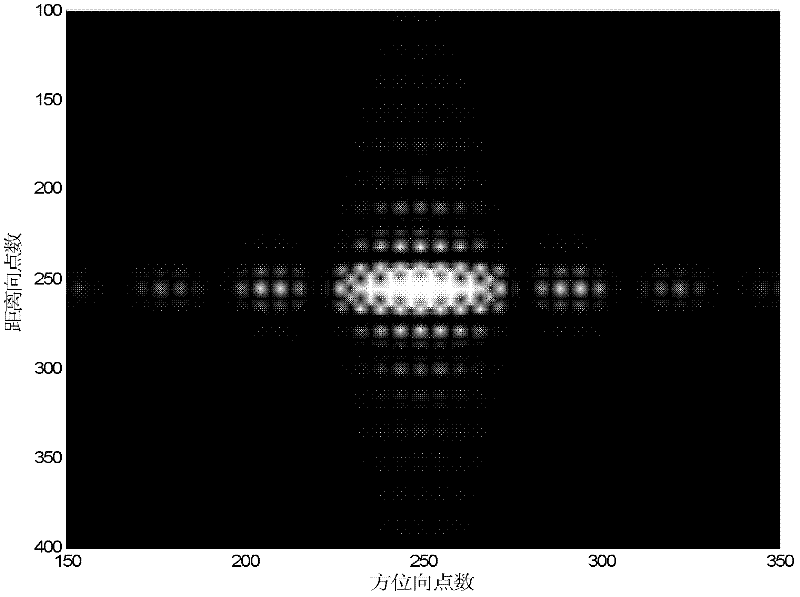
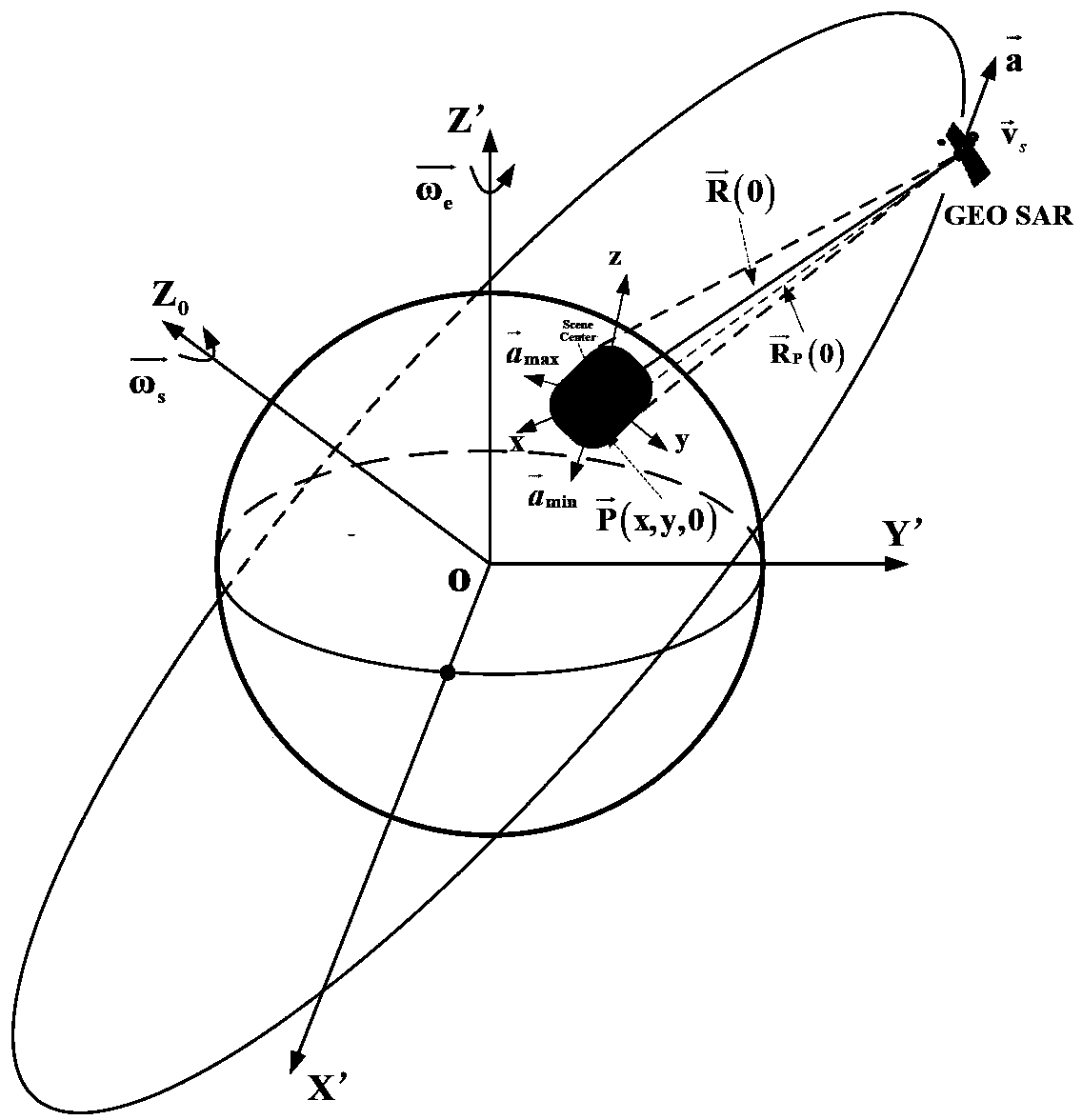
Method for focusing geo-synchronization orbit synthetic aperture radar in high precision
InactiveCN102169174AOvercome limitationsImproving Imaging AccuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionImaging algorithmSynthetic aperture radar
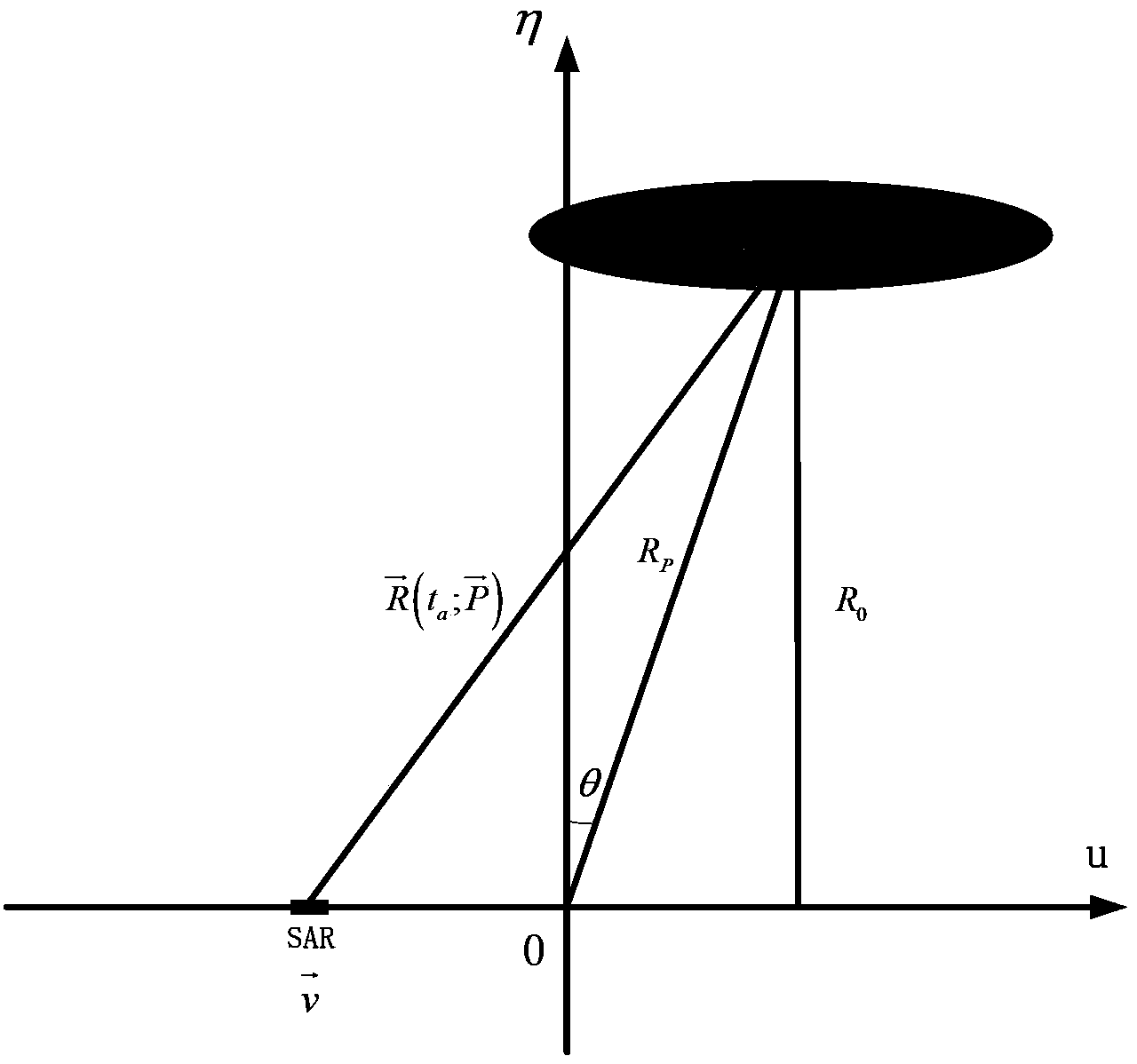
The invention relates to a method for focusing a geo-synchronization orbit synthetic aperture radar (GEO SAR) in high precision, and belongs to the technical field of radar signal processing. An error of a 'Stop-and-Go' supposition is taken into consideration and applied to a deduction process of an algorithm. Aiming at the problem that a typical low earth orbit synthetic aperture radar (LEO SAR) algorithm cannot process a false equivalent linear model, a norm is adopted to express an inclined distance and high-precision approximation is executed. By the method, the imaging precision is high; the method is applicable to imaging at an ultralong synthetic aperture time; high distance migration and boundedness of the equivalent linear model are overcome; and the problem that the LEO SAR imaging algorithm cannot process the 'Stop-and-Go' supposition is solved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
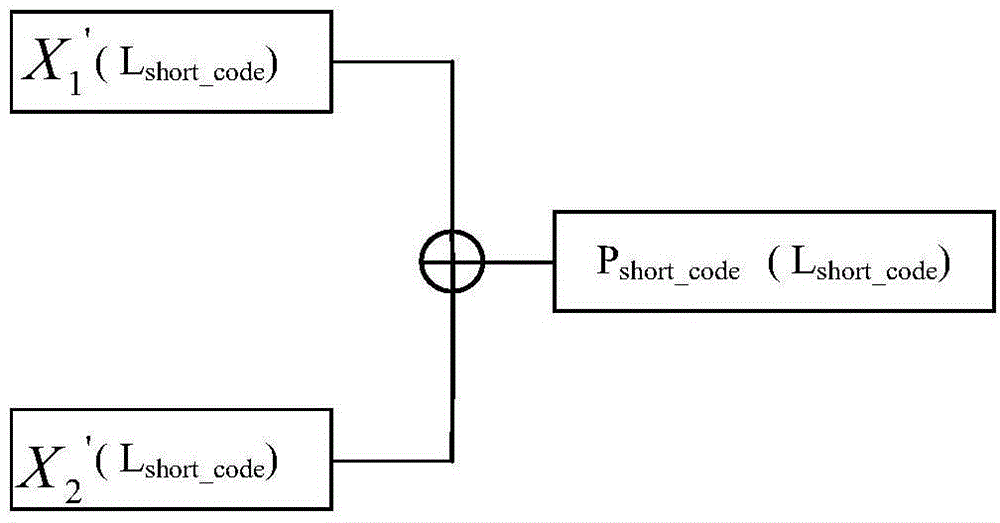
Beidou space-based high-precision real-time positioning method
InactiveCN104570024AImprove and enhance location services performanceEnhanced Location Services PerformanceSatellite radio beaconingSatellite observationCarrier signal
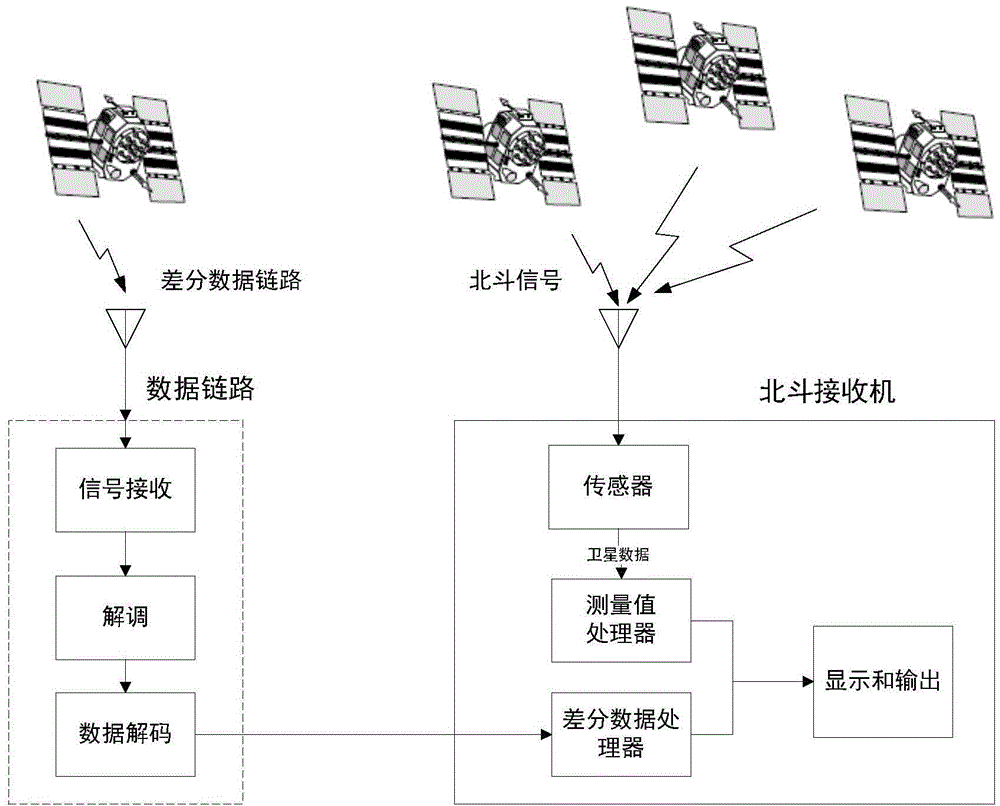
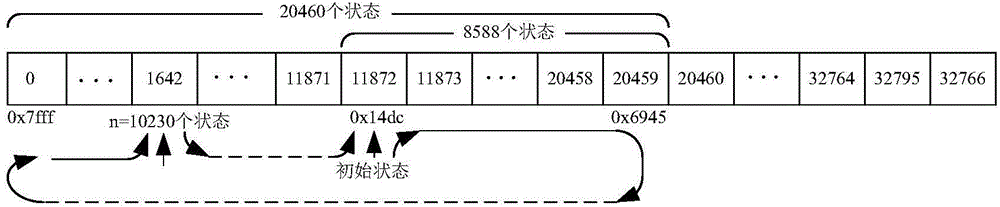
The invention provides a Beidou space-based high-precision real-time positioning method. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, generating difference revised data, then generating a difference broadcast telegraph text, adopting two pseudorandom sequences to generate a short precise code, and conducting spectrum spread and carrier modulation on the difference broadcast telegraph text and the short precise code so as to generate a difference broadcast signal; a user positioning terminal combines difference broadcast data of the difference broadcast signal and Beidou navigation satellite observation data to conduct positioning calculation so as to realize high-precision real-time positioning. The method can effectively realize decimeter-degree high-precision real-time positioning in the coverage area of a geosynchronous orbit satellite, and quickly improves and enhances the positioning service performance of a Beidou satellite navigation system.
Owner:NAT TIME SERVICE CENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Microwave and Millimeter Frequency Bistatic Radar Tracking and Fire Control System
InactiveUS20080042897A1Active radio relay systemsSatellite radio beaconingFire-control systemPassive radar
A bistatic passive radar system for tracking at least one target utilizing means for transmitting radar signals from at least one satellite platform in a geosynchronous orbit with the earth, means for receiving radar signals from a reflection from each target, means for tracking a position of each target over time, and means for computation of a fire control solution of each target.
Owner:USA REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY
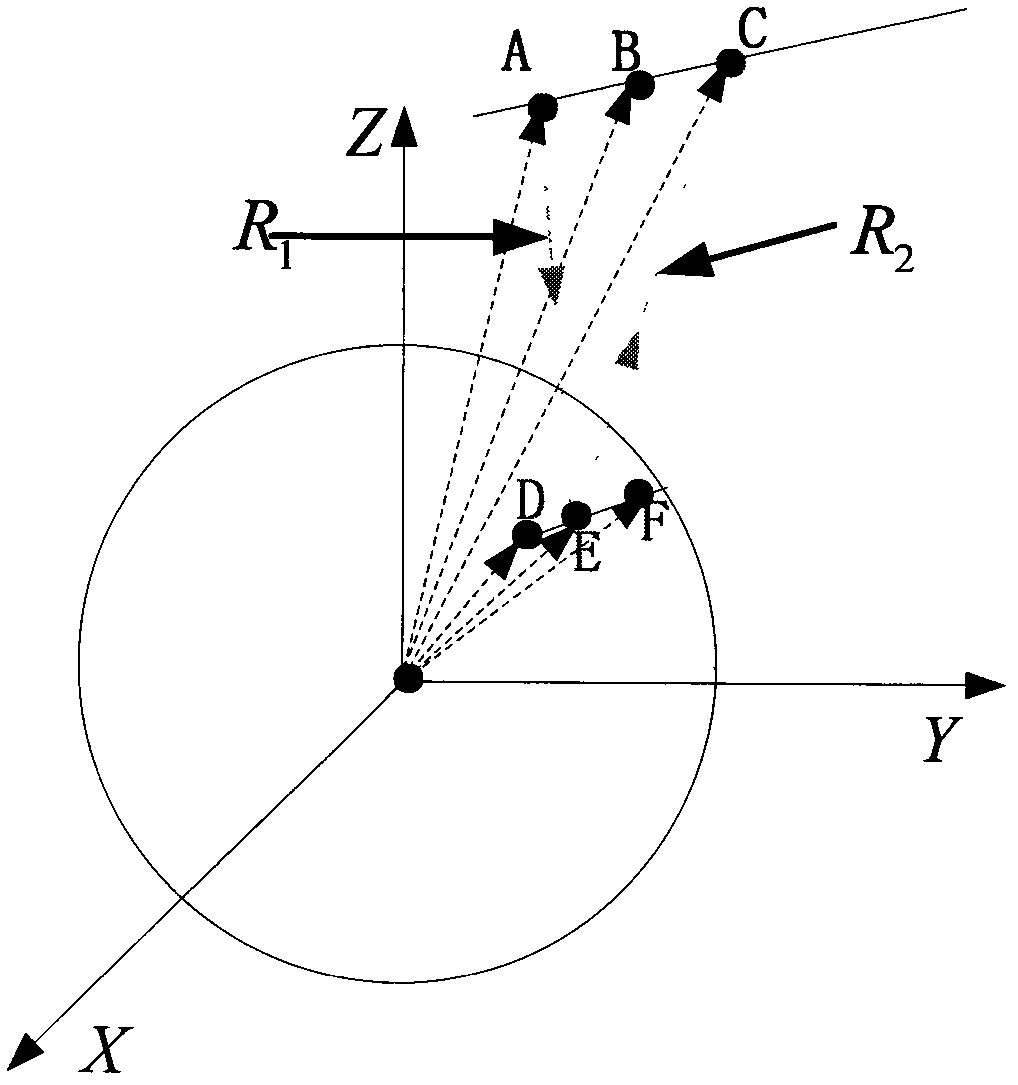
Elevation inversion method for geosynchronous orbit synthetic aperture radar interference
ActiveCN103543453ARealize elevation inversionGood effectRadio wave reradiation/reflectionImaging processingSynthetic aperture radar
The invention provides an elevation inversion method for geosynchronous orbit synthetic aperture radar interference. The method comprises the steps that step 1, GEO SAR is selected to obtain a track of interference data, and the interference data on the track are collected; step 2, GEO SAR imaging processing is conducted through a BP algorithm according to the interference data obtained in step 1; step 3, a GEO interference model is built according to the GEO SAR image processed in step 2, and when a phase position vector is separated from an imaging plane, the GEO SAR interference elevation inversion is conducted according to the GEO interference model. According to the elevation inversion method for the geosynchronous orbit synthetic aperture radar interference, due to the fact that the reasonable GEO SAR interference model is built, the effective elevation inversion processing under the condition that the phase position vector and the imaging plane are separated is achieved, the core problem of the elevation inversion of the GEO SAR interference processing, namely, the separation problem of the effective phase position vector and the imaging plane is solved, and the elevation inversion of the GEO SAR interference processing at any position is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY +1
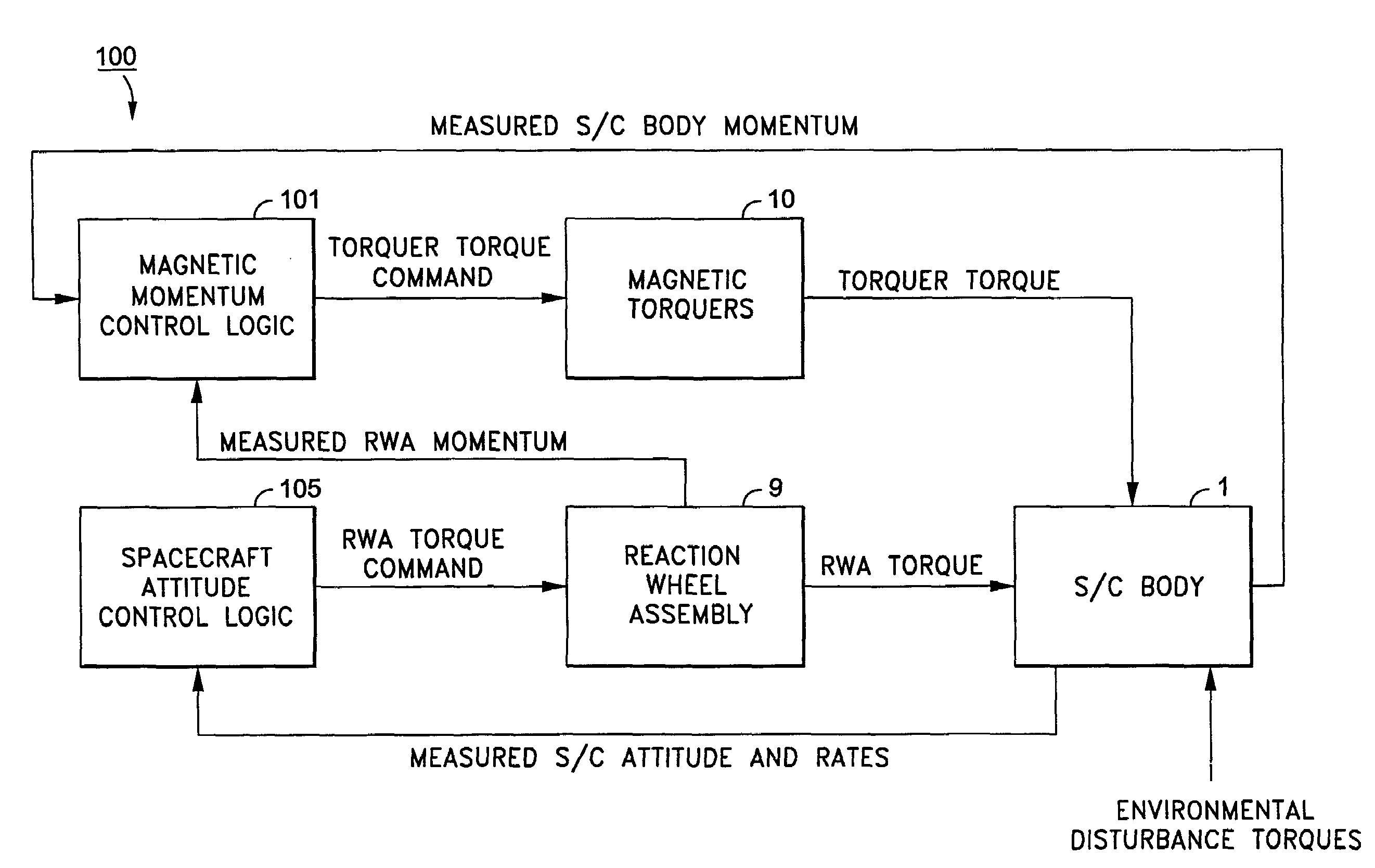
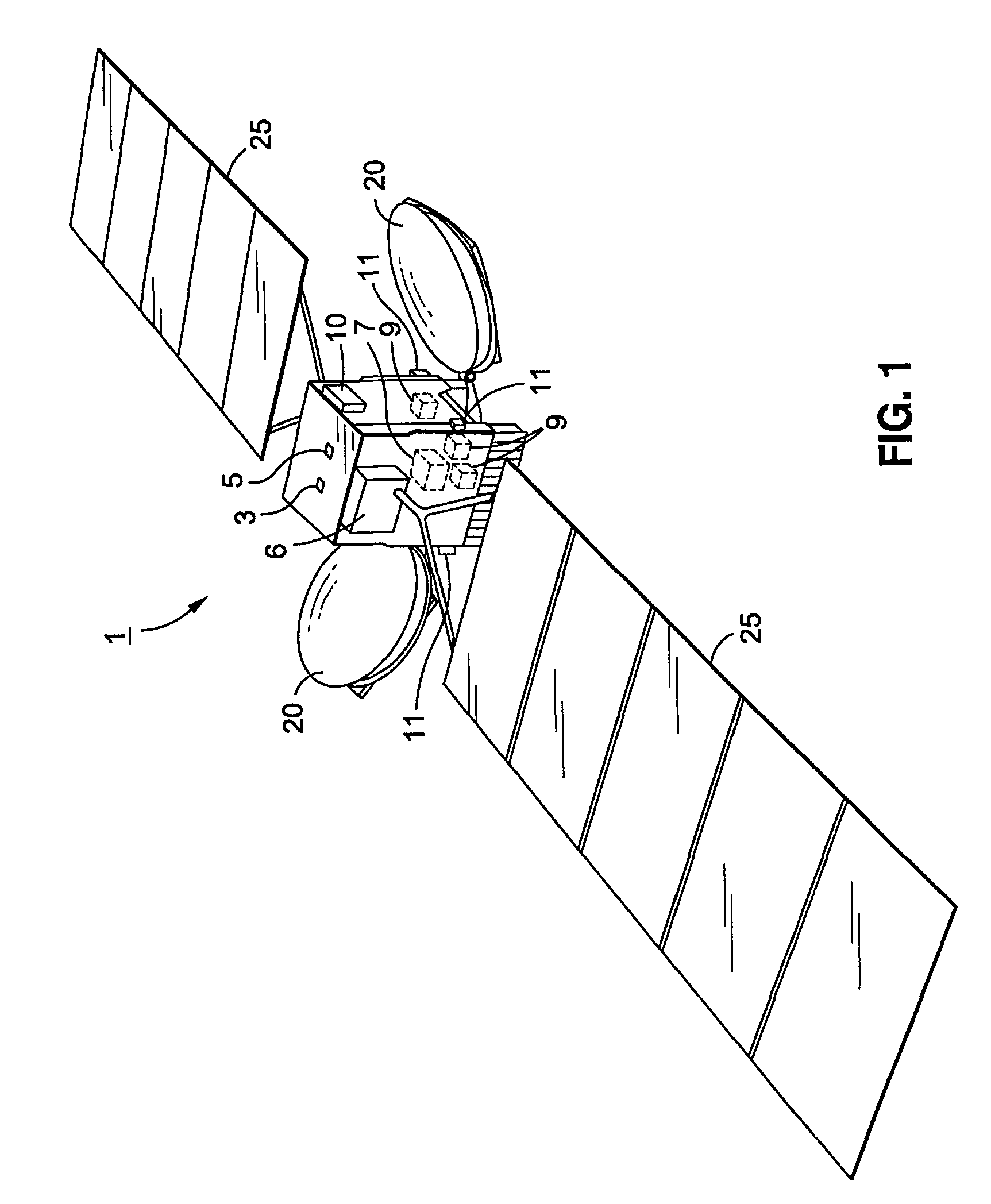
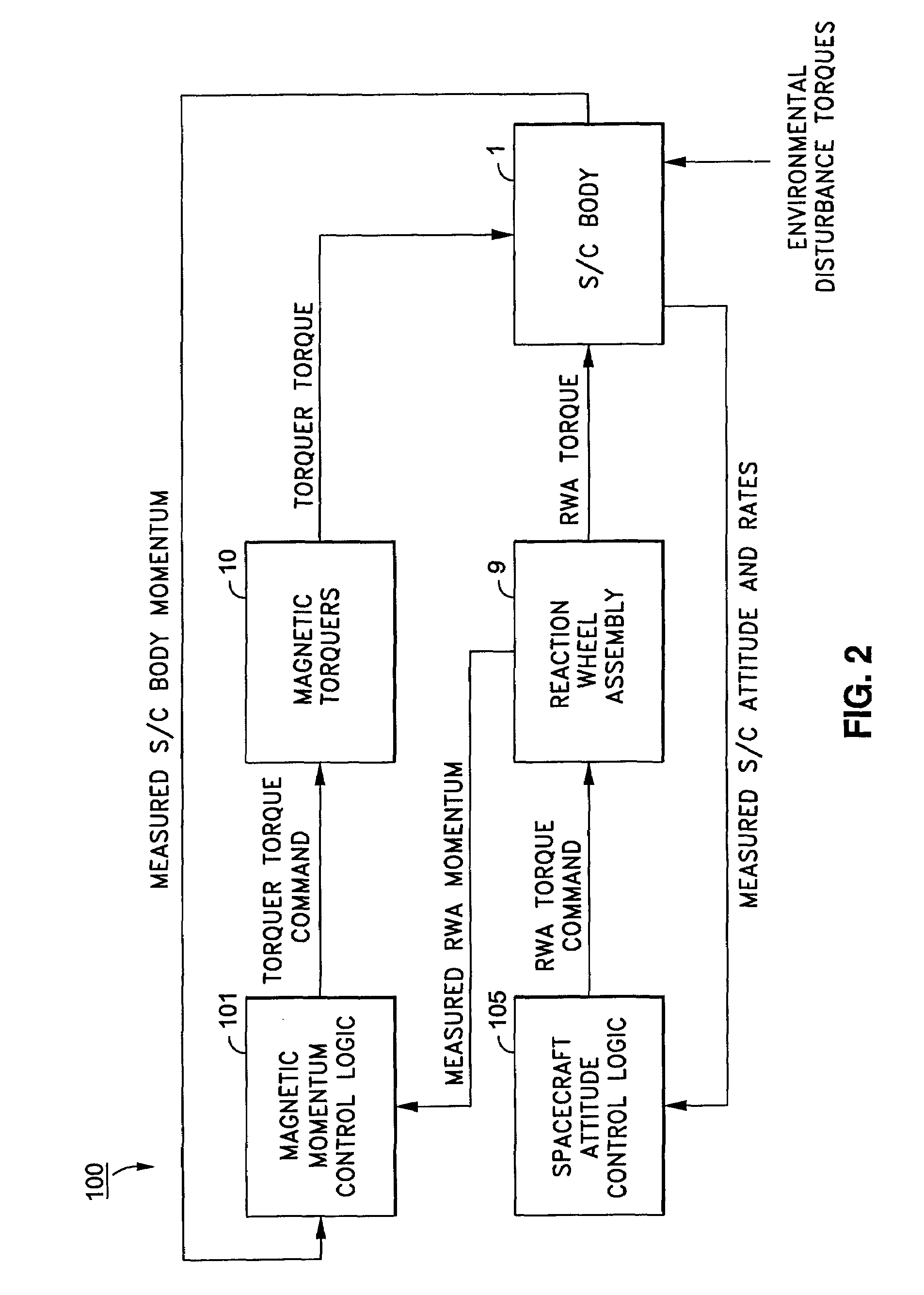
Spacecraft magnetic momentum control system
ActiveUS7376496B1Reduced torquer duty cycleReduce power consumptionCosmonautic vehiclesDigital data processing detailsMomentumControl system
Momentum control is maintained in a geosynchronous orbiting spacecraft that uses a plurality of reaction wheel assemblies and a plurality of magnetic torquers to control the spacecraft momentum, each orbit of the spacecraft being comprised of a set of time steps, by determining a current momentum error for a current time step of a current orbit by adding a system momentum change determined for an immediately preceding orbit to an average system momentum determined for the immediately preceding orbit, and then subtracting a magnetic control torque momentum change determined for the immediately preceding orbit, determining a current duty cycle for each of the magnetic torquers based on the current momentum error and on a torque value applied by each magnetic torquer at each time step of the immediately preceding orbit, and commanding each magnetic torquer to operate at the current time step in accordance with its respective determined current duty cycle, wherein the magnetic torquers apply a magnetic momentum control torque to the spacecraft to offset the current momentum error.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Method for manufacturing a solar module in orbit
InactiveUS20090173831A1Cosmonautic environmental control arrangementCosmonautic power supply systemsFuel tankGeosynchronous orbit
A geosynchronous Solar Power Satellite System is created by an artificial gravity, closed ecology, multiple use structure in low earth orbit that manufactures modular solar power panels and transmitter arrays. This facility takes empty fuel tanks and expended rocket boosters from launch vehicles that are sent into low earth orbit, and re-manufactures them into structural components. These components are mated to solar cells that are launched from earth. The modular solar panels are transported to geosynchronous orbit by vehicles with ion engines, where the panels are mated to other solar panels to collect power. Structural components are also mated to transmitter elements launched from earth. These are likewise transported to geosynchronous orbit. They are mated to the solar power collecting panels and they beam the collected power back to earth.
Owner:ROSEMAN PAUL
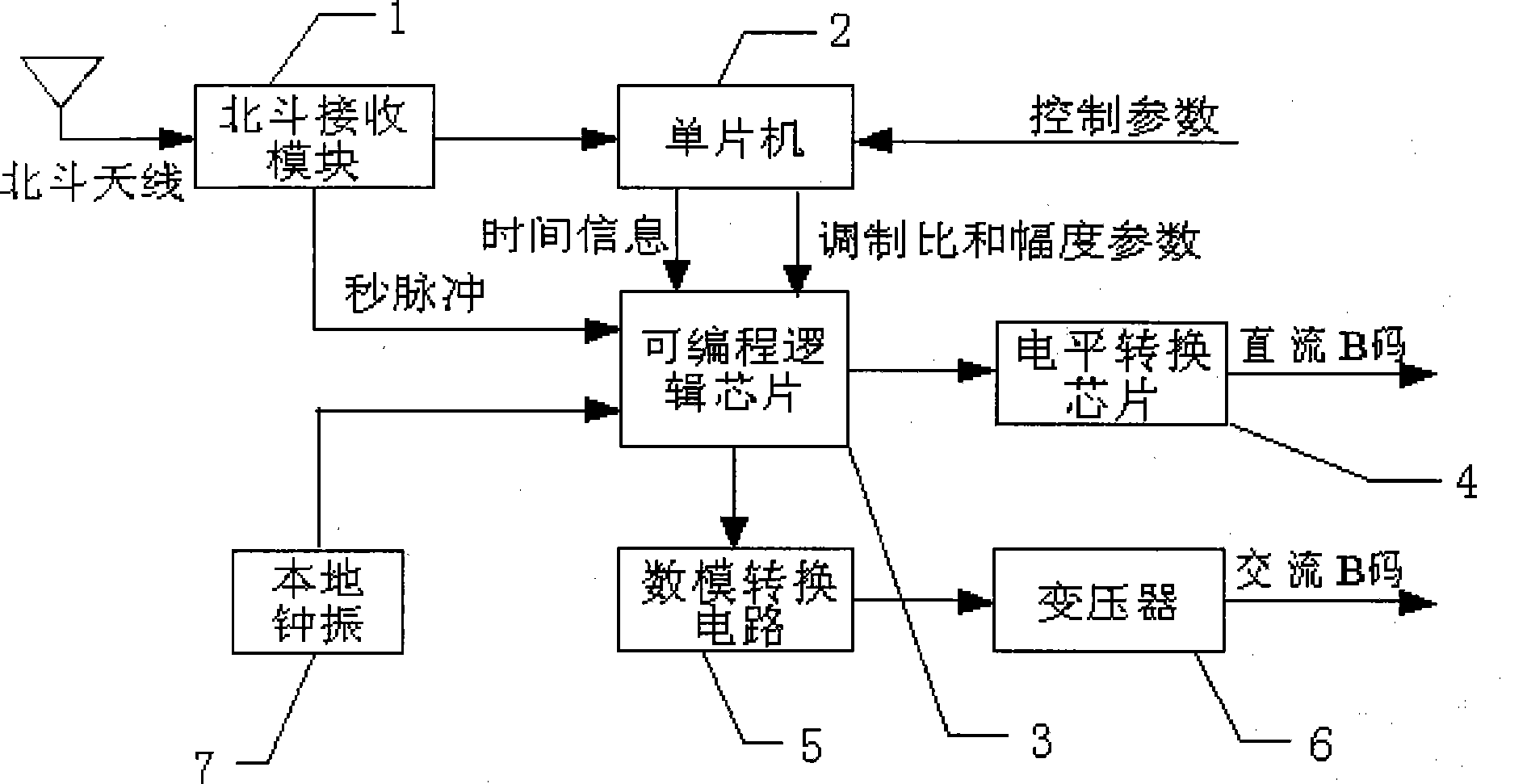
Big dipper satellite synchronizing clock time signal B code generating method and apparatus
InactiveCN101398666AImprove securityDoes not involve intersatellite switchingPreselected time interval producing apparatusClock timeTemporal information
The invention discloses a method for generating a B code of a time signal of a synchronizing clock of Beidou satellite. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: a. a Beidou satellite signal is received as the time source of a time synchronizing clock; b. the time signal is subject to maintenance processing to generate a DC B code signal; and c. the generated DC B code is utilized to perform amplitude modulation to generate an AC B code signal. The method has the advantages that as IRIG-B receives the Beidou satellite signal and Beidou navigation system is completely controlled by China, devices have high safety; as the Beidou satellite is positioned on a geosynchronous orbit and does not involve inter-satellite switching, the time service system is good and the time service precision is high; as the time processing part of the IRIG-B adopts a time maintenance technology, the IRIG-B can judge the correctness of the time information output by a Beidou receiving module and maintain the time by self when the Beidou satellite signal is unavailable, therefore the correctness of the time information generated by the IRIG-B can be ensured, and the availability of the system is improved.
Owner:郑州威科姆技术开发有限公司
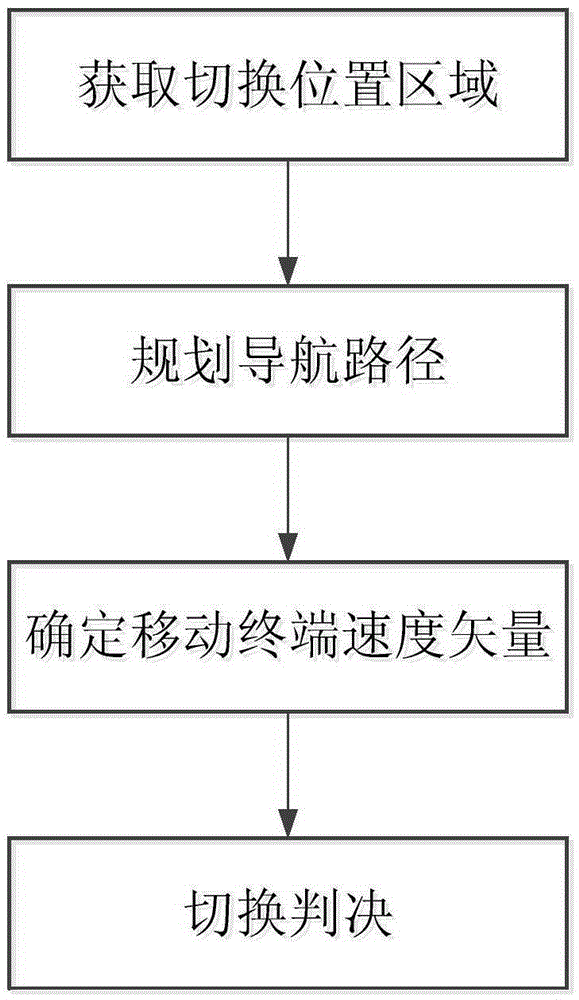
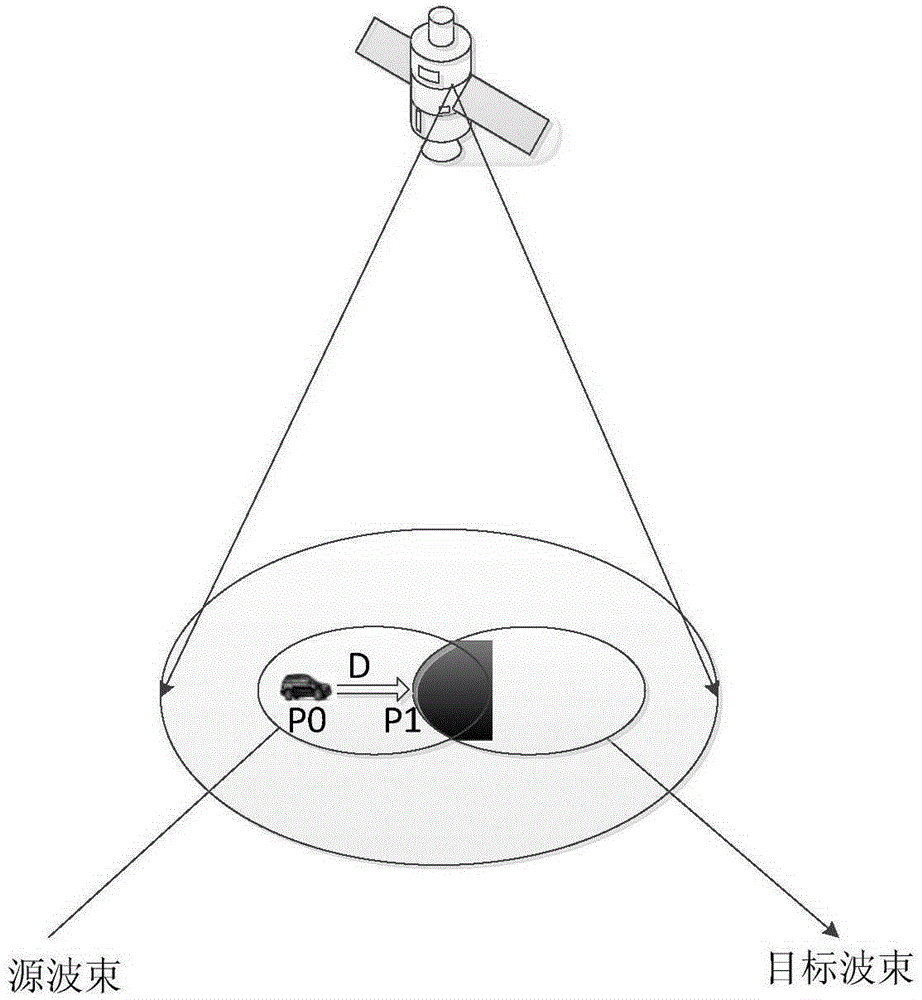
Method for reducing satellite communication system switching delay
ActiveCN105357725AReduce latencyReduce the ping-pong effectRadio transmissionWireless communicationGeostationary orbitGeosynchronous orbit
The invention relates to a method for reducing satellite communication system switching delay, in particular to a switching method for spot beams in the same gateway station of a geostationary orbit satellite. In the method, a switching position area is acquired by using the position information of a mobile terminal of a satellite communication system and combining historical measurement information; the possibly-spanned switching position area is pre-judged according to a navigation path; a velocity vector of the current mobile terminal is acquired by combining a digital map, if the time when the mobile terminal travels to the switching position area from the current position is less than a certain threshold value, pre-switching is completed and finally, switching confirmation is carried out through measurement. Through the adoption of the method, the satellite beam switching delay can be reduced greatly, and in addition, the switching ping-pong effect can be reduced.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
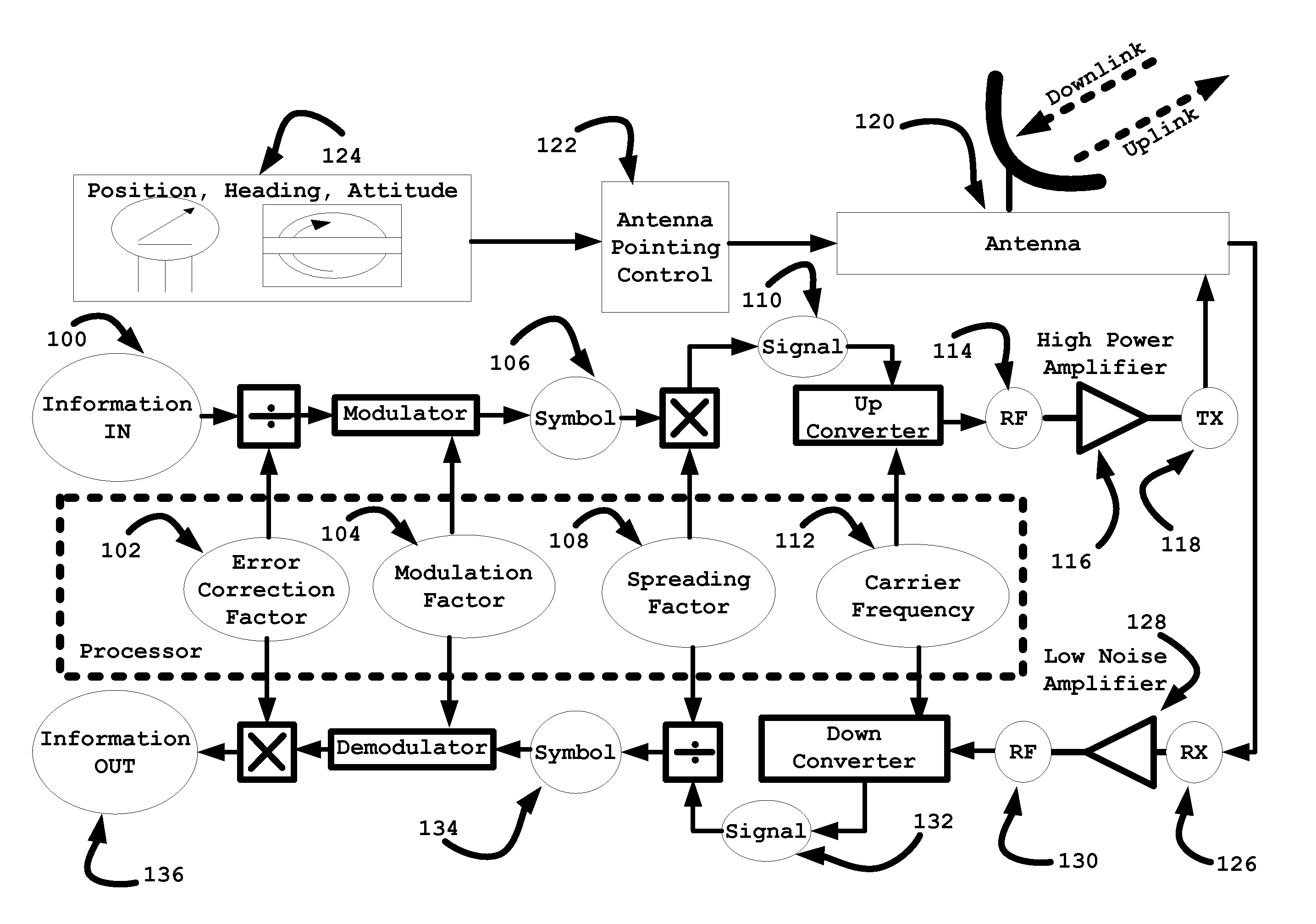
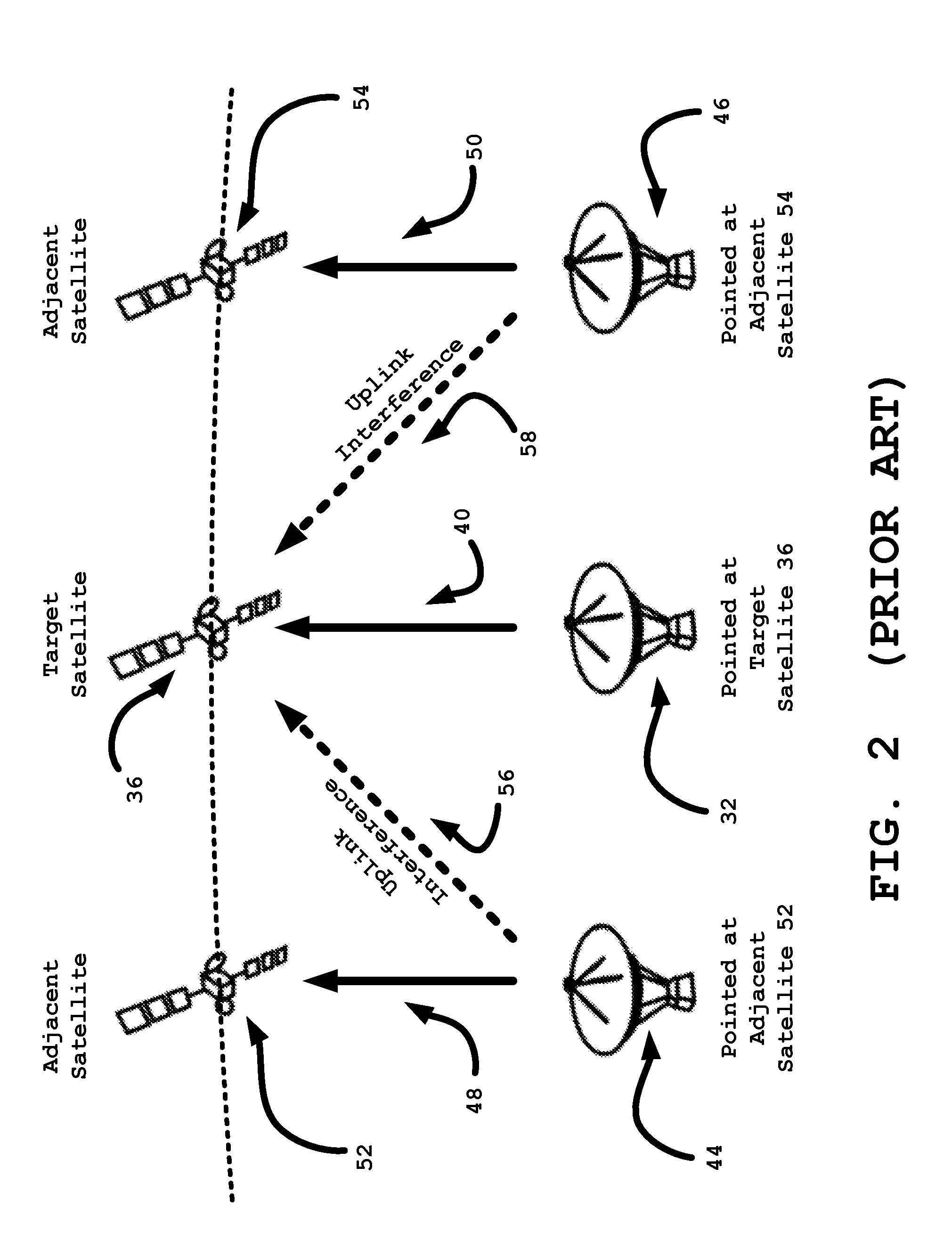
System and method for communicating via a satellite in an inclined geosynchronous orbit
ActiveUS20150215029A1Reduce distractionsEasy to separateAntenna arraysRadio transmissionFrequency spectrumSpectral efficiency
A hub terminal and remote client communicate via a target satellite in an inclined geosynchronous orbit. As the target satellite ascends or descends away from the geostationary arc, the signal strength of the uplink channel is increased without increasing the level of interference with adjacent geostationary satellites. The increased angular separation from adjacent satellites also decreases downlink interference. The resulting increase in signal to interference ratio permits adjustment of the modulation and coding parameters to increase spectral efficiency. The antenna gain pattern is modeled based on antenna characteristics and the model may be supplemented with measurements of a signal relayed by adjacent satellites. The method permits intermittent communication from locations where the geostationary arc is blocked or using disadvantaged antennas that would be impractical for use with geostationary satellites. In some circumstances, it is desirable to deliberately mis-steer the antenna slightly away from the target satellite.
Owner:LEMME PETER
Sub-satellite point circular geosynchronous orbit design method
InactiveCN103678787AMeet the needs of multi-angle earth observationSpecial data processing applicationsNatural satelliteGeosynchronous orbit
Disclosed is a sub-satellite point circular geosynchronous orbit design method. The method includes: (1) analyzing and determining sub-satellite point circular geosynchronous orbit generating conditions including that (1.1) an orbital semi-major axis is 42164km, (1.2) a satellite drifts back and forth in the north-south direction every day, (1.3) the satellite drifts back and forth in the east-west direction every day, (1.4) the distance of north-south direction drift is equal to that of east-west direction drift, and (1.5) the satellite passes the equator twice every day with relative distance of sub-satellite points when the satellite passes the equator twice equal to east-west direction drift distance of the satellite; (2) according to the conditions in the step (1), determining orbital parameters, satisfying the five conditions at the same time, namely the orbital semi-major axis a, eccentricity ratio e, inclination angle i, right ascension of ascending node Omega, argument of perigee omega and true anomaly theta. Design of a sub-satellite point circular geosynchronous orbit is completed by utilizing the determined orbital parameters.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
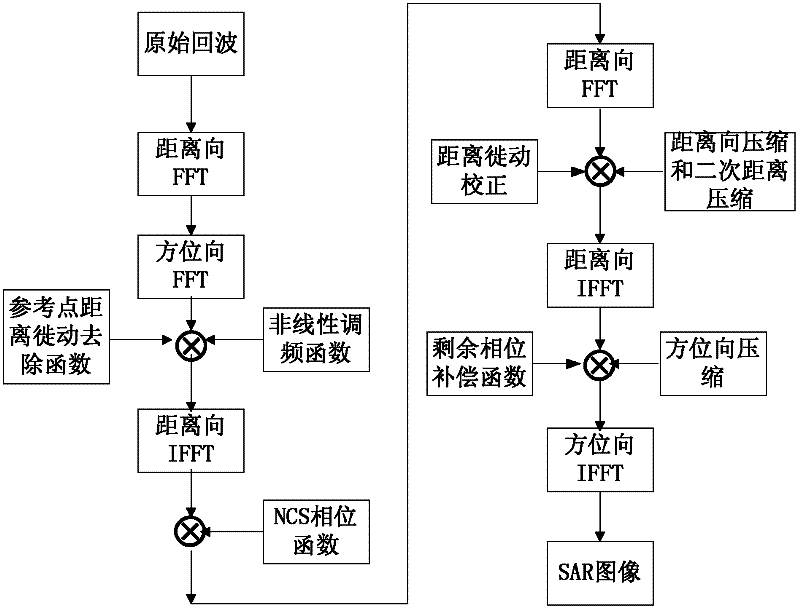
Improved NCS (Nonlinear Chirp Scaling) imaging algorithm suitable for geosynchronous orbit (GEO) SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar)
InactiveCN102331577ARealize the requirements of large scene imagingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency spectrumAlgorithm
The invention relates to an improved NCS (Nonlinear Chirp Scaling) imaging algorithm suitable for a geosynchronous orbit (GEO) SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar), belonging to the technical field of SAR imaging. The NCS imaging algorithm is improved by establishing a curved locus signal model for replacing an equivalent linear model in an original NCS imaging algorithm and evaluating a two-dimensional resolving spectrum expression suitable for the NCS imaging algorithm on the basis of the established curved locus signal model. Compared with the prior art, the improved NCS imaging algorithm has the advantages that: a novel curved locus model suitable for the GEO SAR is obtained with a high-order Taylor expansion method, and the defects of large error of a near equivalent linear model, completely unavailable application of a far equivalent linear model and the like of the GEO SAR can be overcome by adopting the locus model; and meanwhile, a two-dimensional resolving spectrum suitable for the NCS algorithm is obtained on the basis of the equivalent linear model, and various compensation functions of the NCS algorithm can be resolved by using the spectrum, so that the requirement on large-scene imaging of the GEO SAR is met.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Epfd coverage for ngso satellites
ActiveUS20160278064A1Minimizing (or eliminating) satellite service gapAvoid interferencePower managementRadio transmissionGeosynchronous orbitSatellite constellation
A method and apparatus for operating one or more satellites in a non-geosynchronous orbit (NGSO) satellite constellation are disclosed. In some aspects, a coverage area on Earth for a first beam transmitted from a first satellite in the NGSO satellite constellation may be determined, a cone may be projected onto a first region of the beam coverage area, a second region of the beam coverage area may be defined as including portions of the beam coverage area lying outside the first region, and a minimum arc angle for each of a plurality of points within the first region but not the second region of the beam coverage area may be determined.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
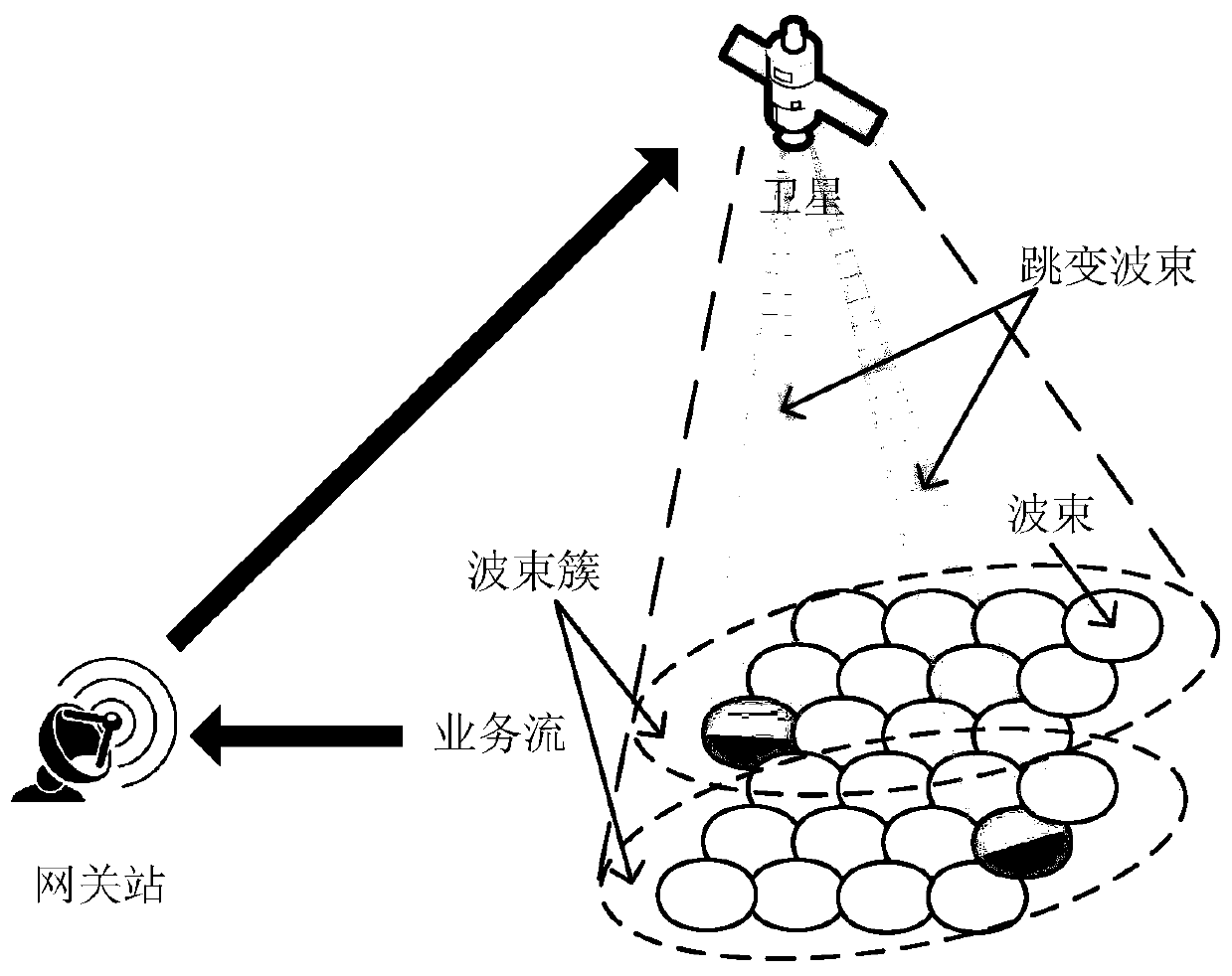
Hopping pattern optimization method and device based on time slot allocation algorithm and storage medium
ActiveCN110518956AIncrease capacityImprove resource allocation efficiencyTransmission monitoringRadio transmissionSignal qualitySystem capacity
The invention discloses a hopping pattern optimization method and device based on a time slot allocation algorithm, and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: determining a distance threshold according to a relationship between a calculated signal to interference plus noise ratio (SINR) and a distance between beams; constructing a time slot allocation model according to the relationship between the capacity resources and the time slot resources in the downlink of the hopping beam satellite system; obtaining the request capacity of a user in each beam coverage range, and converting the request capacity into the number of request time slots; and for the number of request time slots, adopting a time slot allocation model to allocate the number of time slots for each beam,and completing optimization of a hopping beam pattern according to an interference avoidance principle. By adopting the method and the device, efficient time slot resource allocation can be realizedin a GEO (Geosynchronous Orbit) satellite communication system, and the influence of interference on signal quality is effectively eliminated while the system capacity is improved.
Owner:ARMY ENG UNIV OF PLA
Satellite network architecture with network reconstruction capability
ActiveCN110012558ARealize integrated utilizationHas flexible refactoring capabilitiesNetwork topologiesRadio transmissionAccess networkInformation networks
The invention provides a satellite network architecture with a network reconstruction capability. The architecture comprises a space-based network and a land backbone network, the space-based networkcomprises a space-based backbone network, a space-based access network and a space-based sensing network, wherein the space-based backbone network is mainly composed of geosynchronous orbit satellites, the space-based access network is mainly composed of low-orbit satellite constellations, and the space-based sensing network is mainly composed of any one or any combination of remote sensing satellites, meteorological satellites and navigation satellites. The method has the beneficial effects that the architecture design problem of a space-based information network for joint networking and fusion utilization of high, medium and low orbit satellites and cooperative work of communication, navigation and remote sensing satellites is solved, integrated utilization of various satellite resourcesin the existing space is realized, and a hybrid heterogeneous satellite network architecture with a satellite network flexible reconstruction function is built.
Owner:亚太卫星宽带通信(深圳)有限公司
GEO-UAV Bi-SAR route planning method based on differential evolution
InactiveCN105279581AMeeting Imaging Performance NeedsStrong global search capabilityForecastingSynthetic aperture radarSimulation
The invention discloses a GEO (Geosynchronous orbit)-UAV (unmanned aerial vehicle) Bi-SAR (synthetic aperture radar) route planning method based on differential evolution. The GEO-UAV Bi-SAR route planning method based on differential evolution comprises 1) generating a three dimensional landform; 2) modeling a UAV accepting station route; 3) modeling the route planning as a multiobjective optimization problem for a constraint condition; 4) utilizing a multiobjective differential evolution algorithm to solve; and 5) obtaining the optimal solution, generating a UAV optimal path, and realizing autonomous navigation and Bi-SAR imaging of the UAV in the three dimensional complicated landform. The GEO-UAV Bi-SAR route planning method based on differential evolution models the UAV route planning problem which comprehensively considers the route length, the flight safety and the SAR imaging performance as a multiobjective optimization problem, and utilizes the improved differential evolution algorithm to solve and obtain a set of optimal UAV accepting station flight routes.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
User terminal employing quality of service path determination and bandwidth saving mode for a satellite ISP system using non-geosynchronous orbit satellites
InactiveUS20070109985A1Reduce the amount of informationNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesQuality of serviceGeosynchronous orbit
A mobile satellite telecommunications system is disclosed including at least one user terminal, at least one satellite in earth orbit, and at least a gateway bidirectionally coupled to a data communications network wherein a user terminal comprises a controller responsive to applications for selecting individual ones of a plurality of Quality of Service modes for servicing different application requirements.
Owner:WIEDEMAN ROBERT A +1
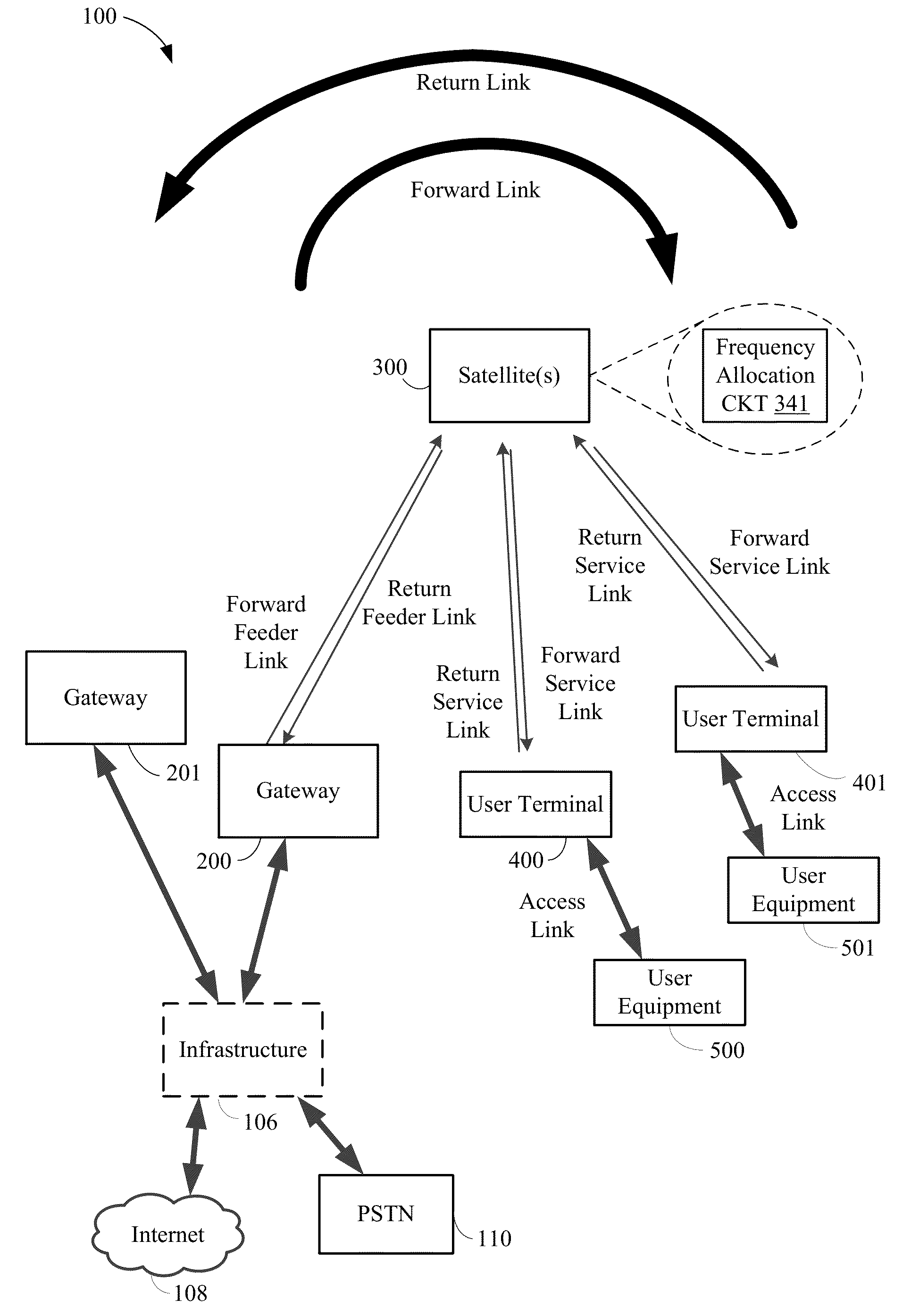
Dynamic frequency allocation of satellite beams
A method and apparatus for operating one or more satellites in a non-geosynchronous orbit (NGSO) satellite constellation are disclosed. In some aspects, the satellite may allocate a first frequency band to a first beam, and may allocate a second frequency band to a second beam. Then, if the first beam is disabled, the satellite may re-map the first frequency band from the first beam to the second beam. In this manner, frequency resources initially allocated to a disabled beam may be re-mapping to another, non-disabled beam.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Geosynchronous orbit synthetic aperture radar velocity spatial variability compensating method
InactiveCN103364782AImplement focus processingSolved - speed space variation compensation problemRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture radarClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a geosynchronous orbit synthetic aperture radar velocity spatial variability compensating method. According to the method, the velocity spatial variability is compensated through self-adaptive phase compensation processing, so that a core problem, i.e. a velocity spatial variability compensation problem, of geosynchronous orbit synthetic aperture radar (GEO SAR) large-scale scene imaging is solved, the GEO SAR large-scale scene imaging focusing processing of arbitrary position is realized, and a good effect is obtained.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
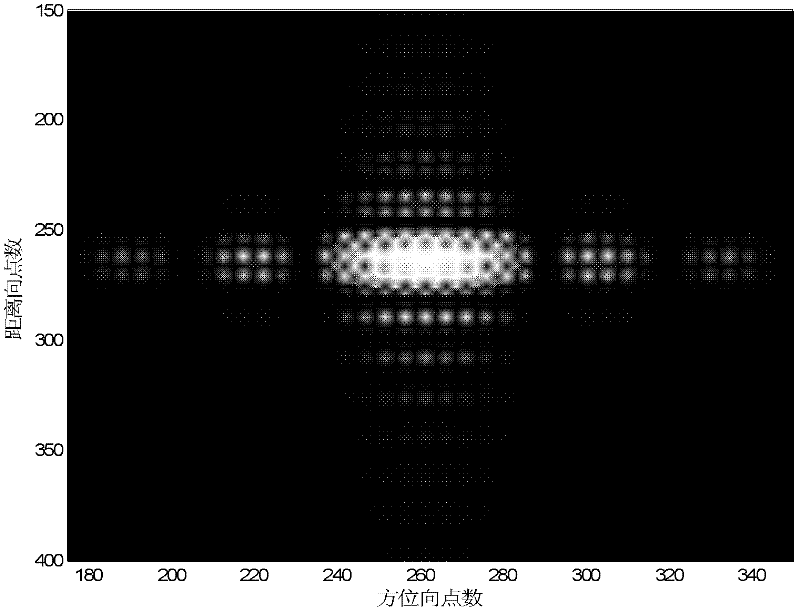
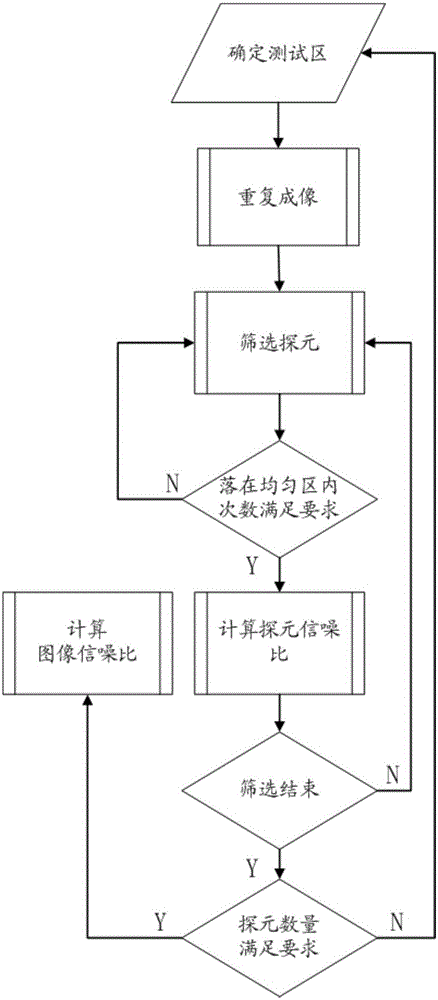
Staring-imaging-based in-orbit signal-to-noise ratio test method of satellite
ActiveCN105096319AObjective evaluation of imaging capabilitiesImage enhancementImage analysisImaging qualityGeosynchronous orbit
The invention relates to a staring-imaging-based in-orbit signal-to-noise ratio test method of a satellite. Repeated imaging of an earth surface uniform region is carried out by a satellite with an ultra-high time resolution and a high spatial resolution; on the premise that the illumination condition and the surface radiation characteristic are consistent basically, statistics of mean values of detector cells and standard differences of the imaging at the uniform region is carried out and ratios of the mean values and to standard differences are used as pixel signal to noise ratios; and then a mean value of a plurality of pixel signal to noise ratios is used as an image signal-to-noise ratio. With the method, an influence caused by inconsistency of the pixel response spaces can be eliminated. When statistics of the standard differences of imaging data of each pixel at multiple times is carried out, uncertainty of repeated sampling is mainly reflected; and thus the noises can be effectively retrained in terms of numerical value and the actual signal to noise ratio of the satellite image can be reflected, thereby evaluating the remote sensing satellite imaging capability of the geosynchronous orbit objectively. Therefore, the method has the practical application value in development of in-orbit testing and in-orbit operation state image quality evaluation in satellite ground system engineering.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com