Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5156 results about "Satellite positioning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
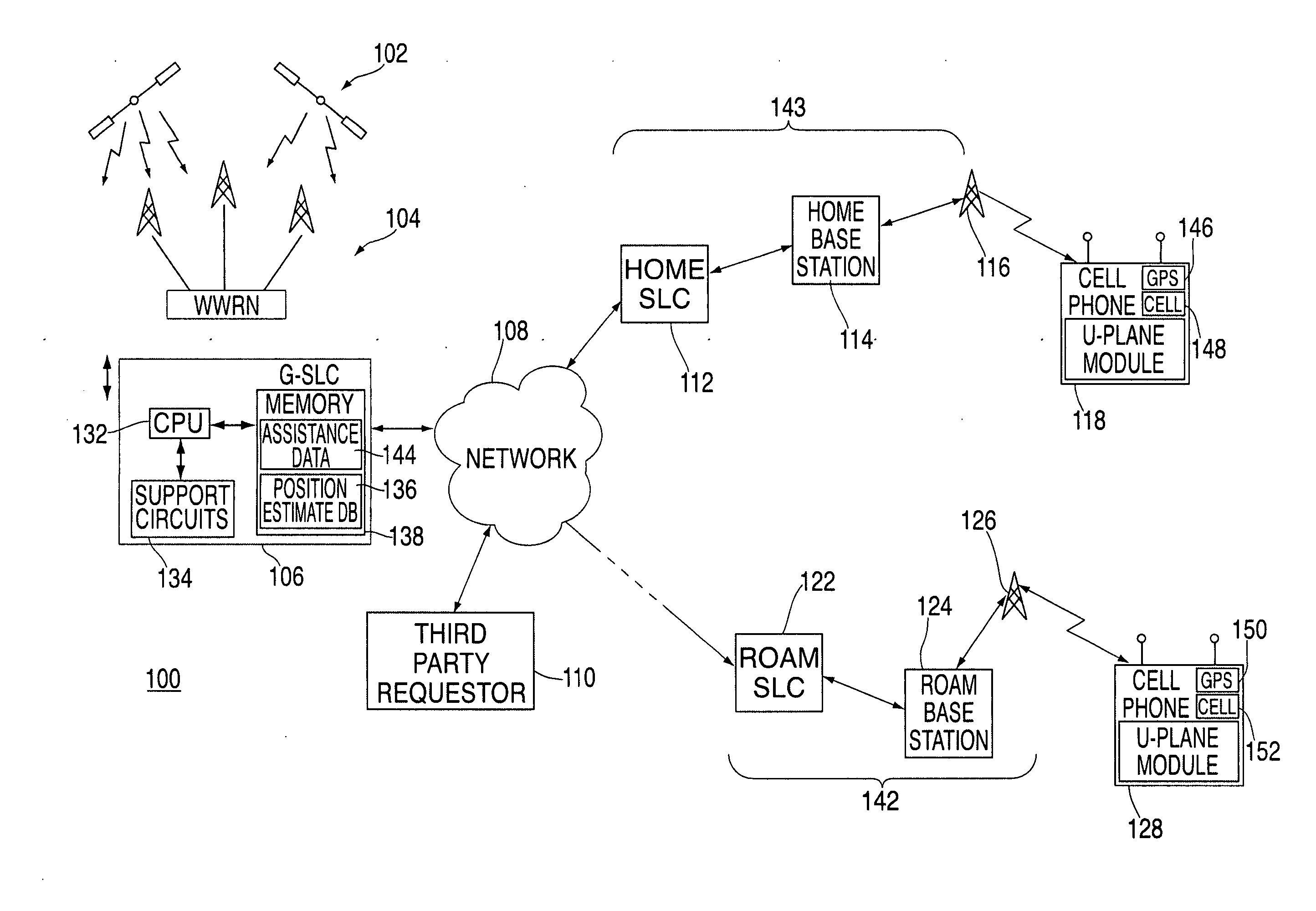
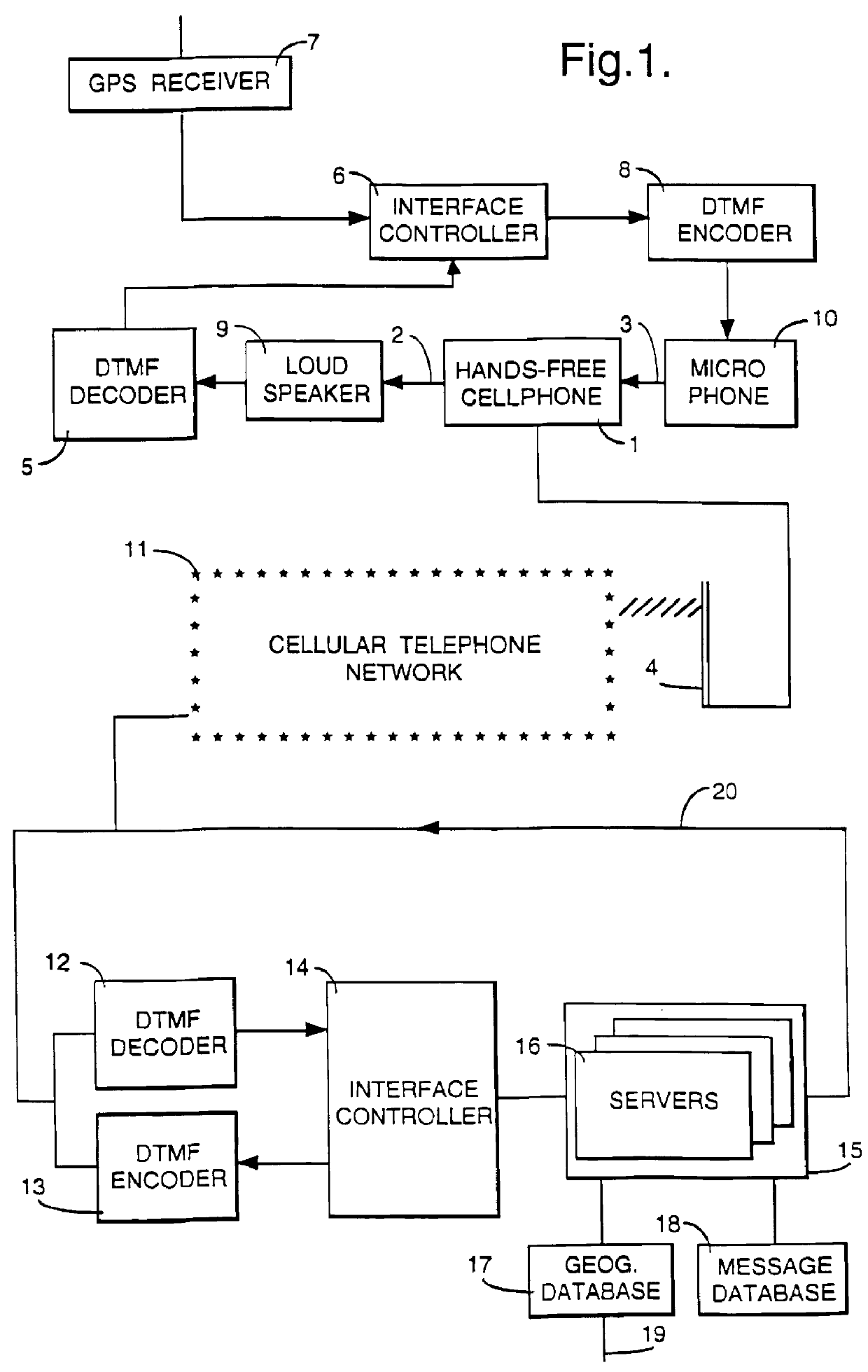
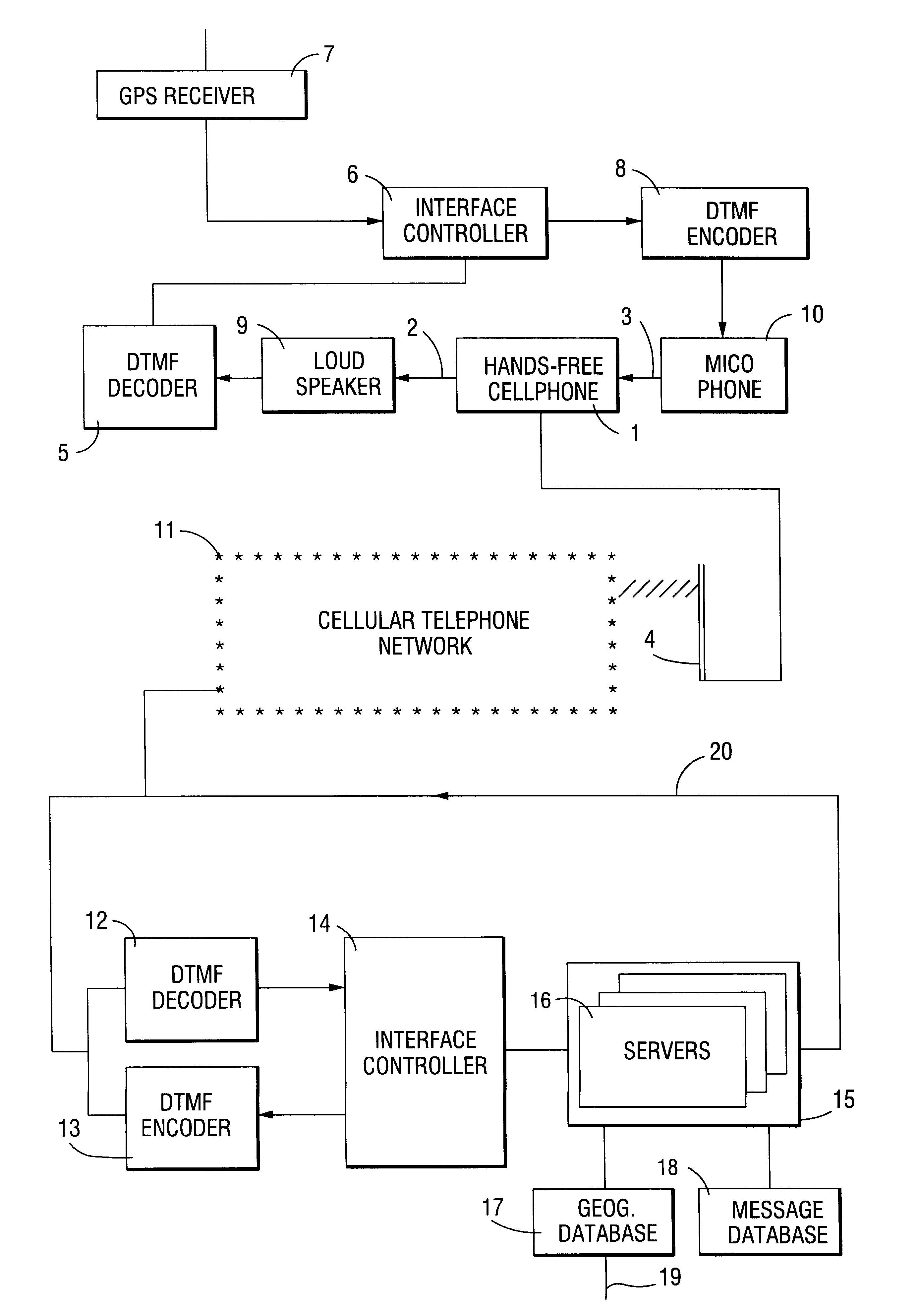
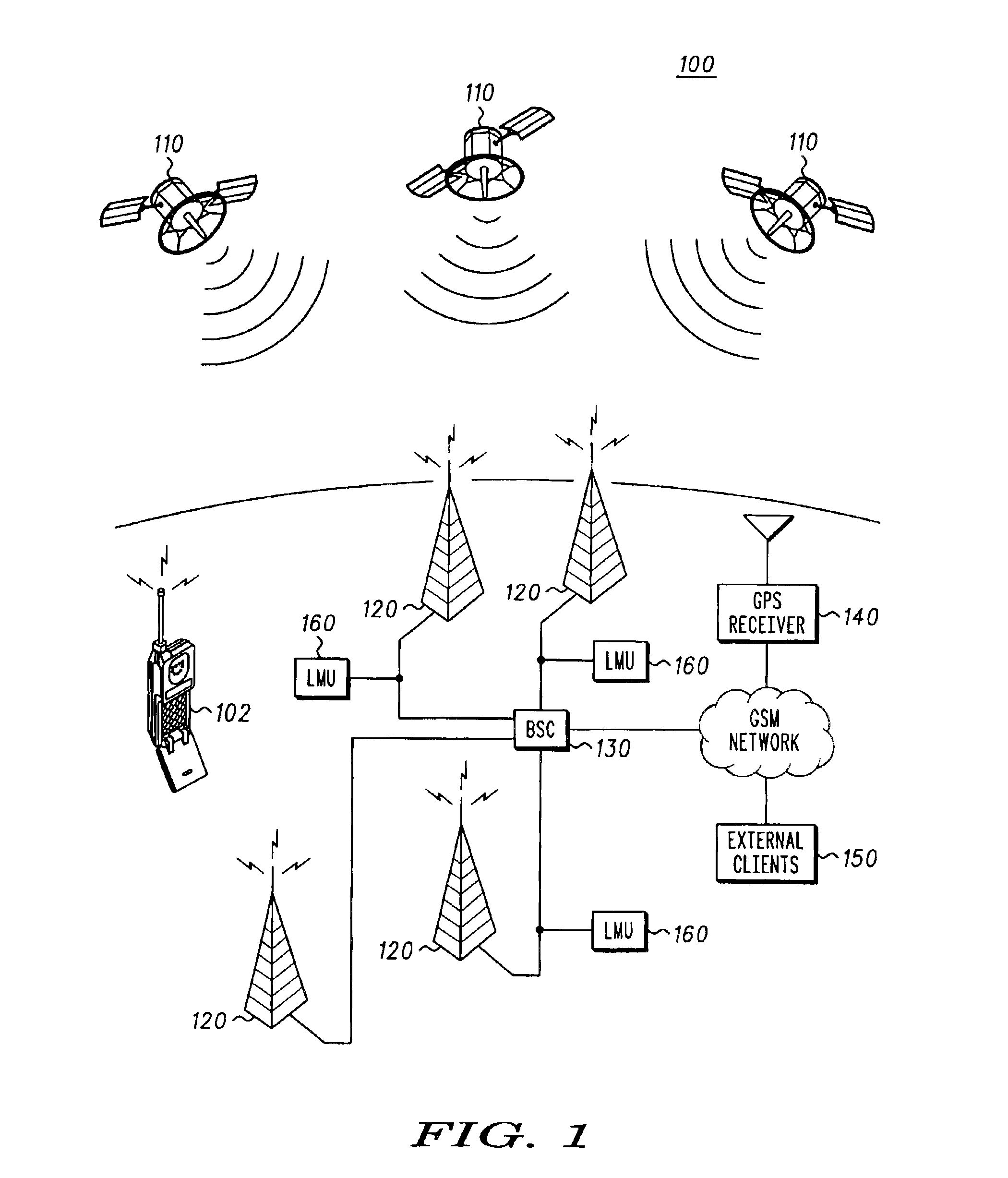
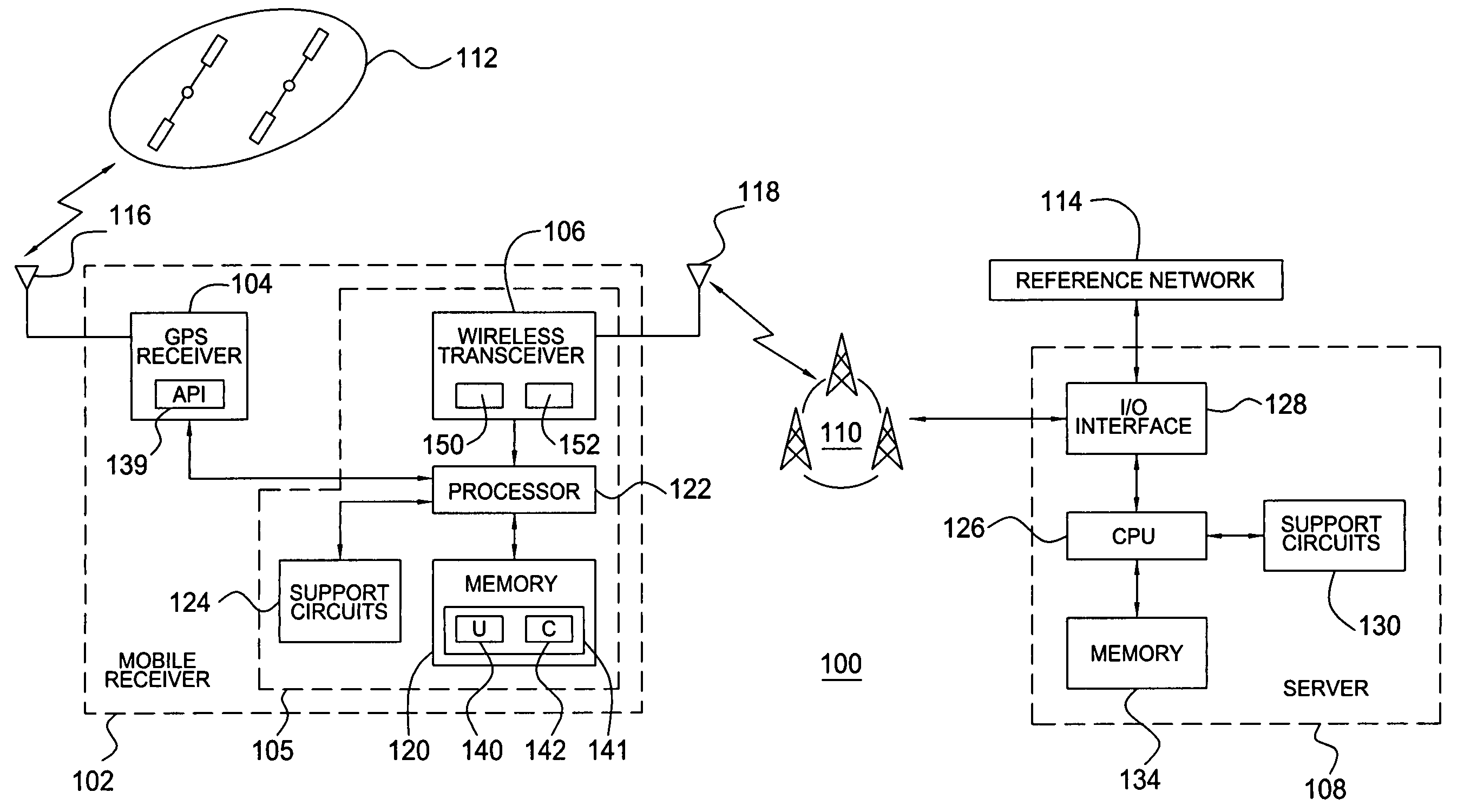
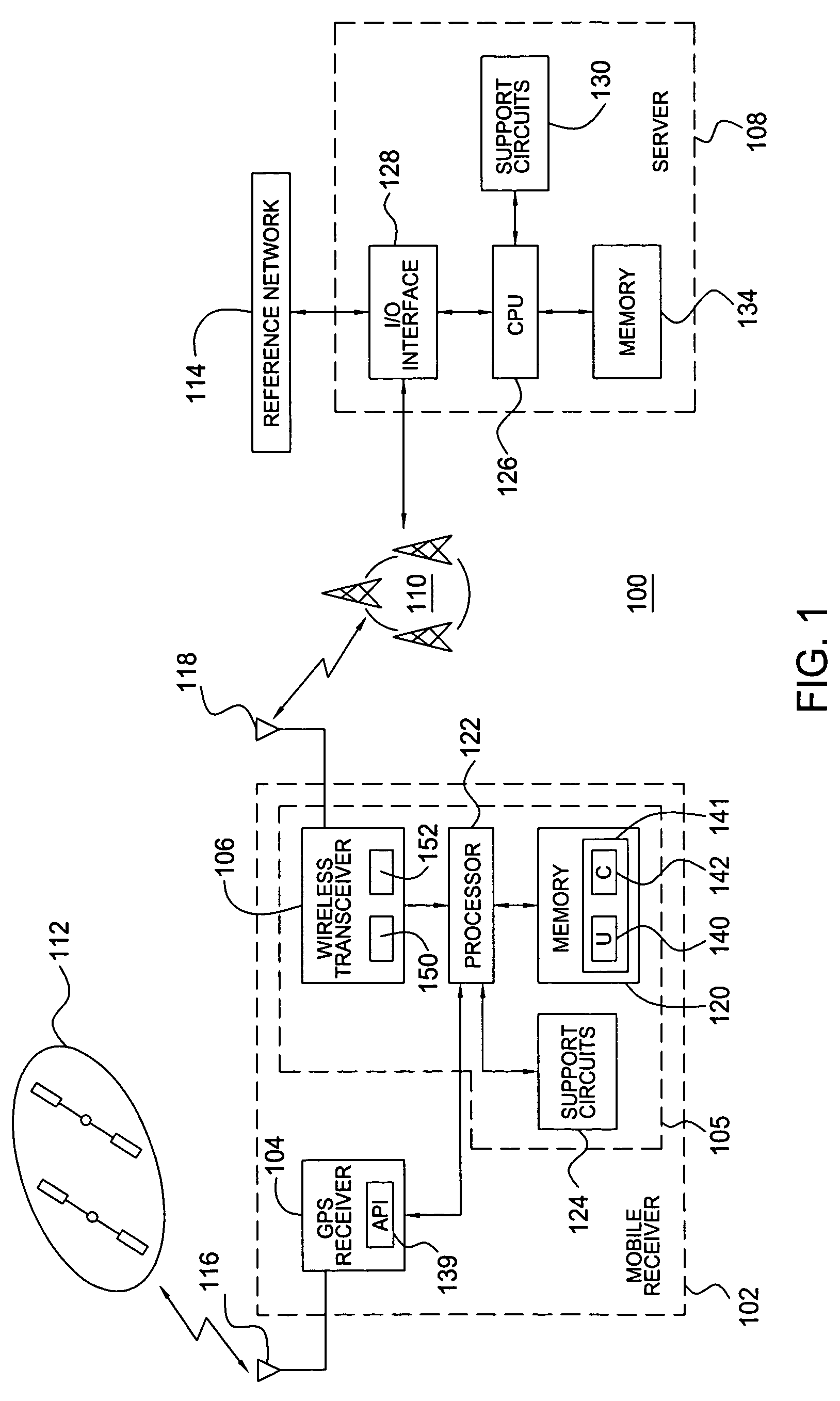
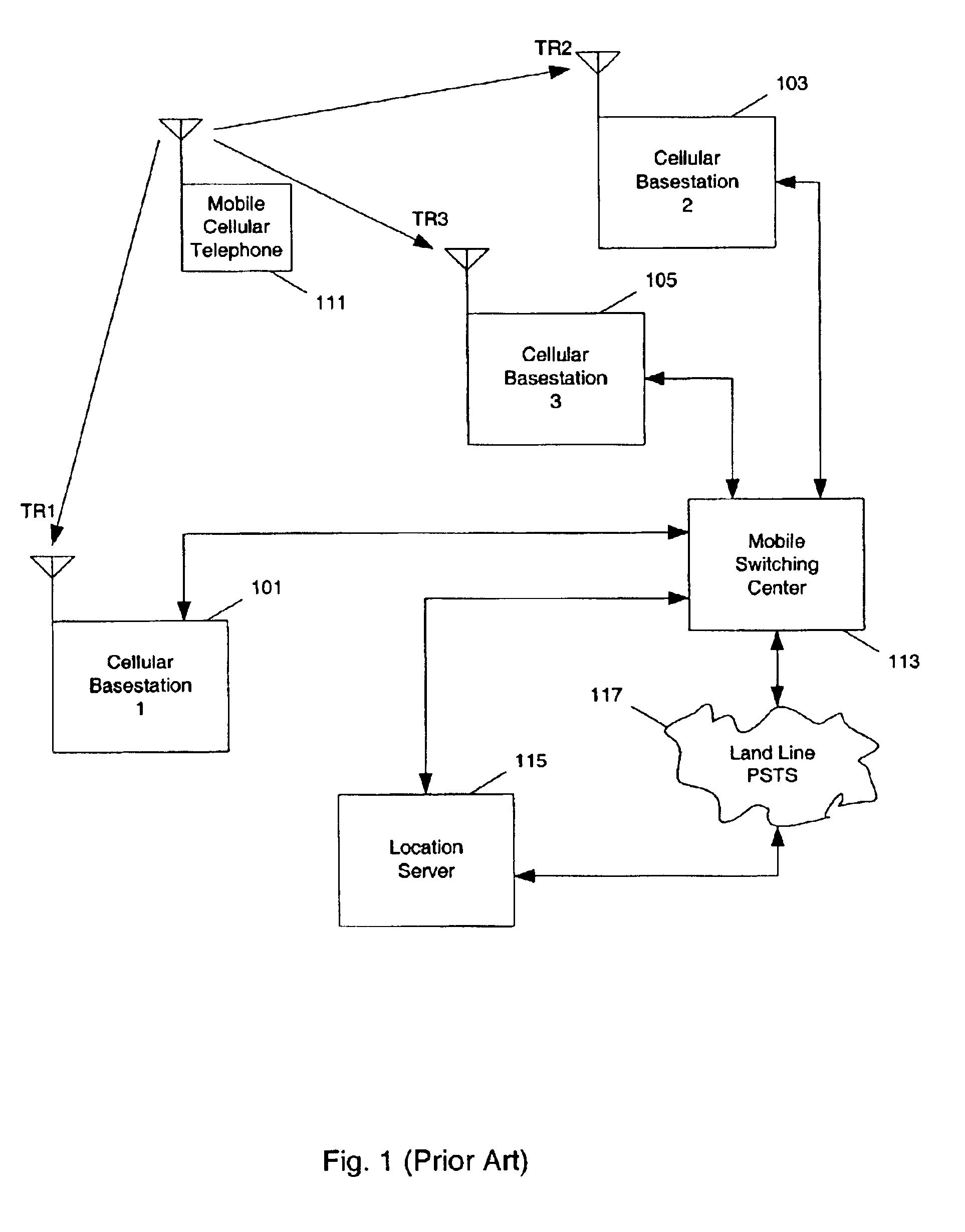
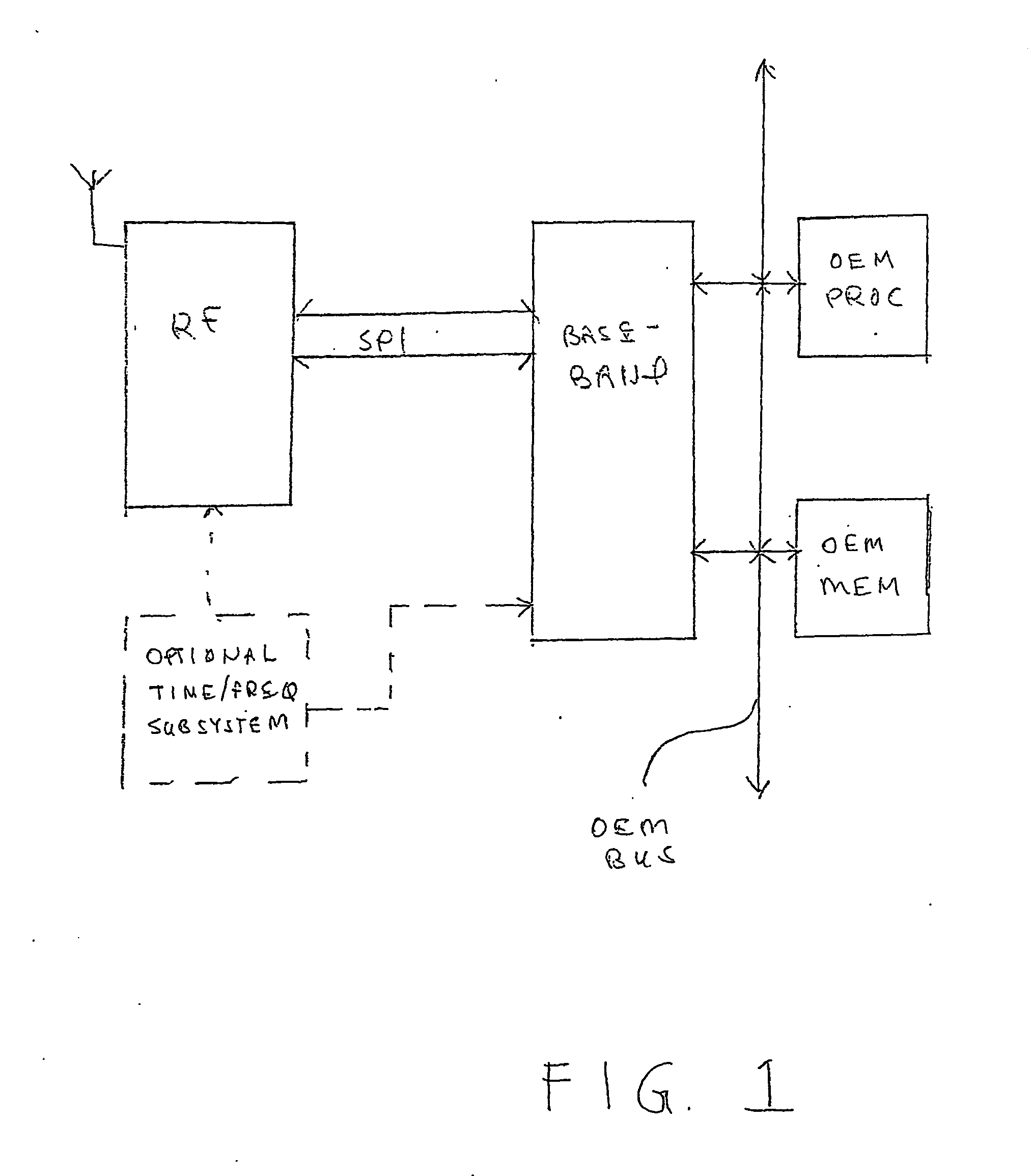
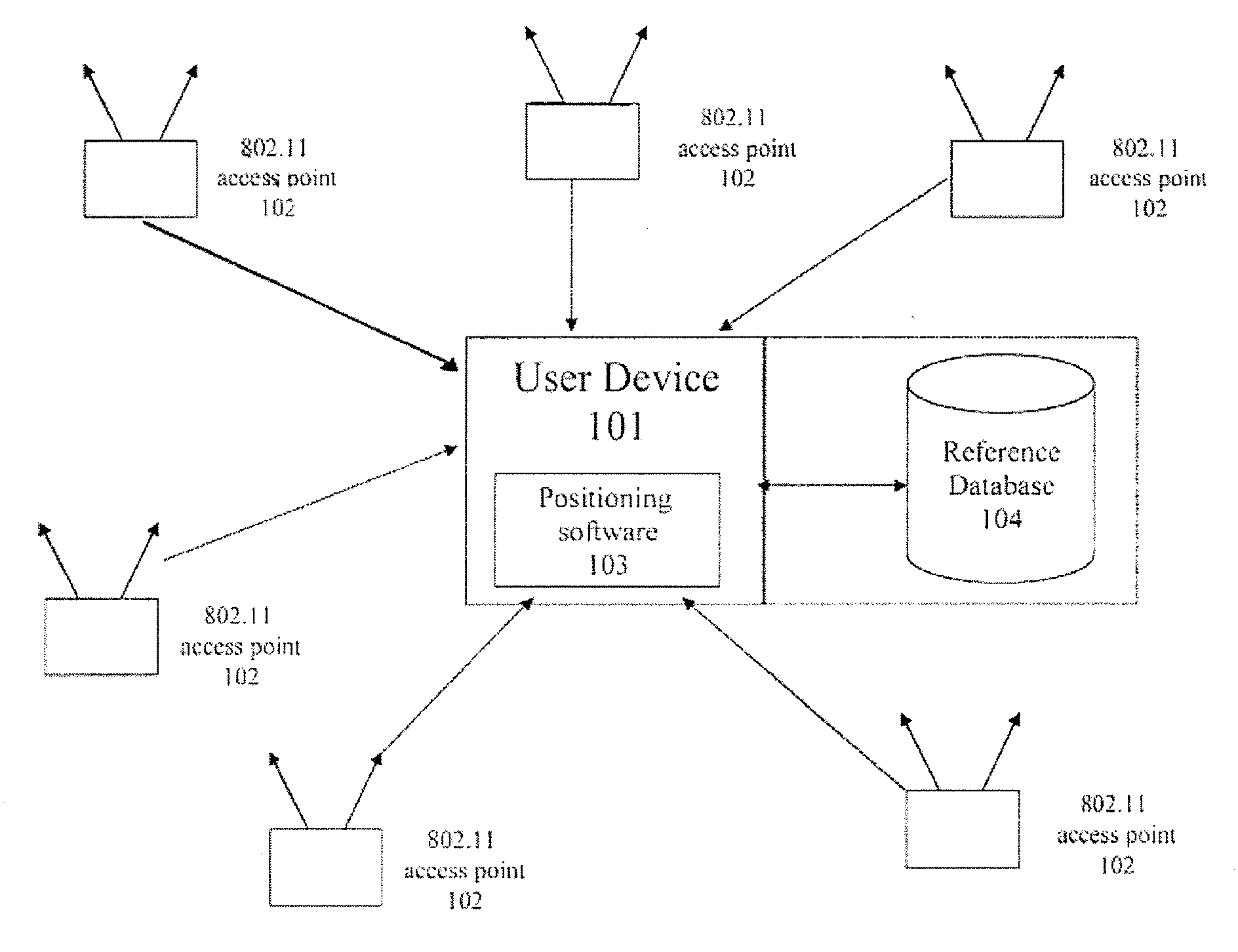
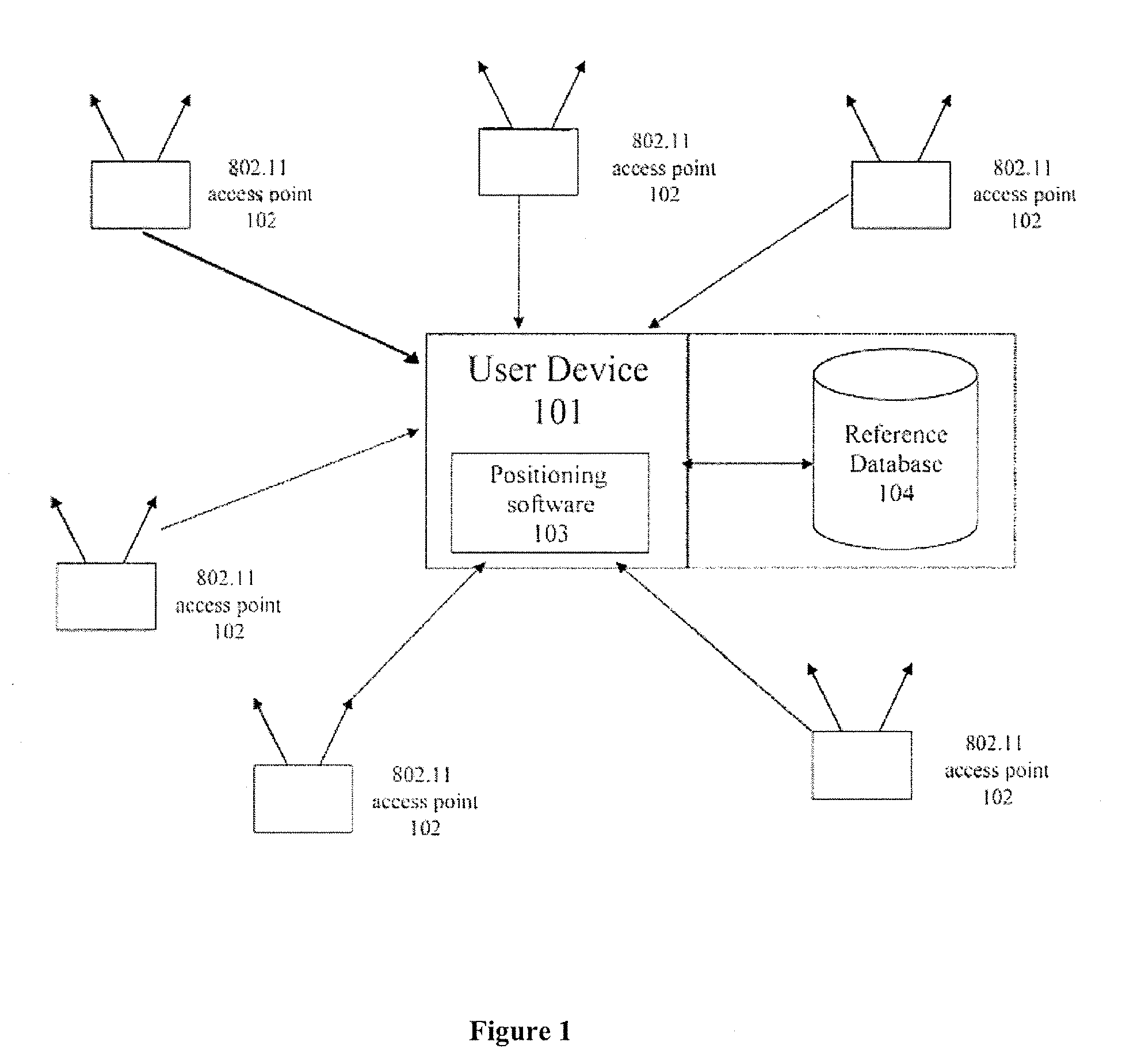
Method and apparatus for providing a global secure user plane location (SUPL) service
InactiveUS20070096981A1Avoid chargingPosition fixationServices signallingComputer networkSecure User Plane Location
A method and apparatus for providing assistance data for satellite positioning system receivers utilizing a secure user plane location (SUPL) service. In one embodiment, the assistance data is supplied by a global secure user plane location center that contains global assistance data.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
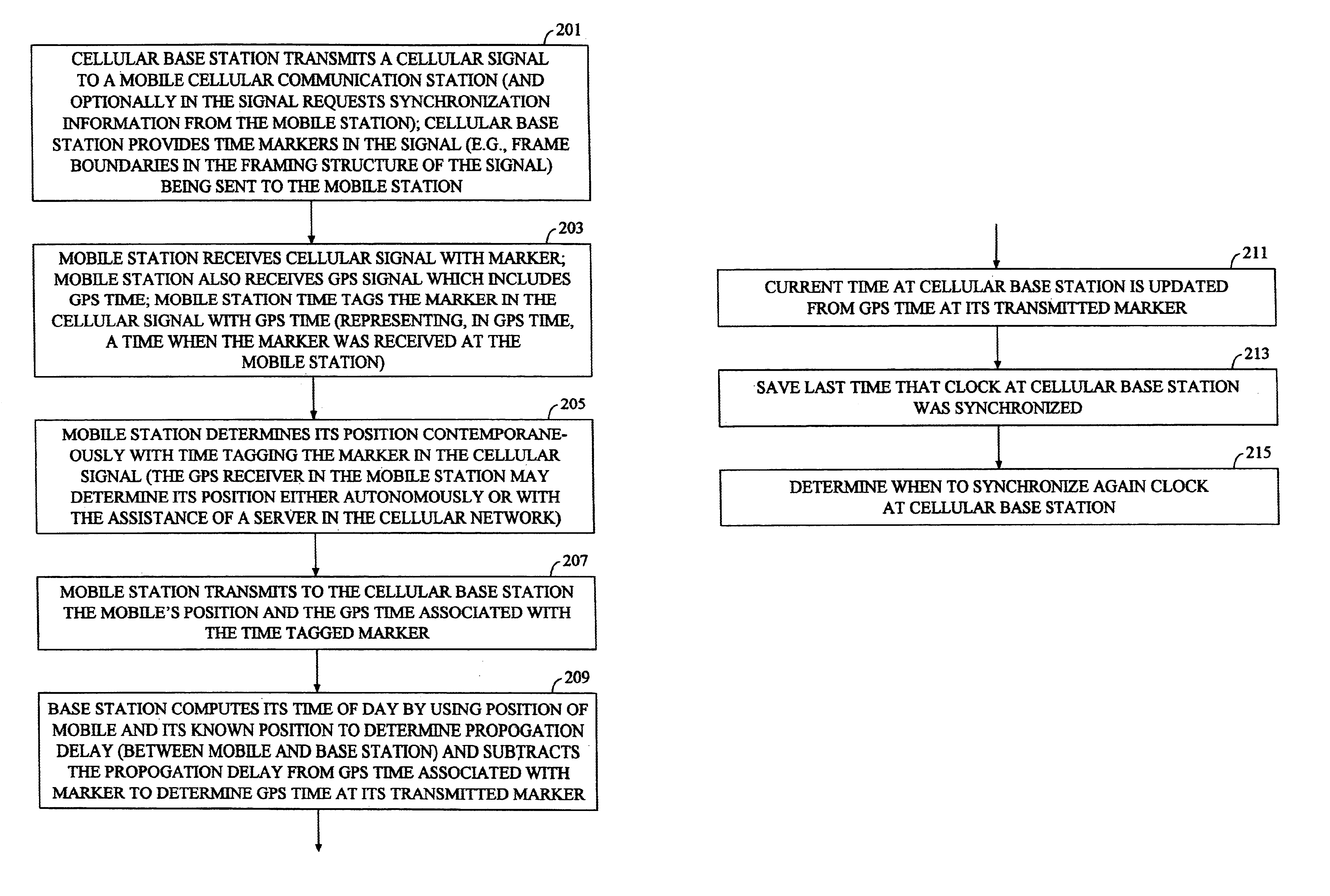
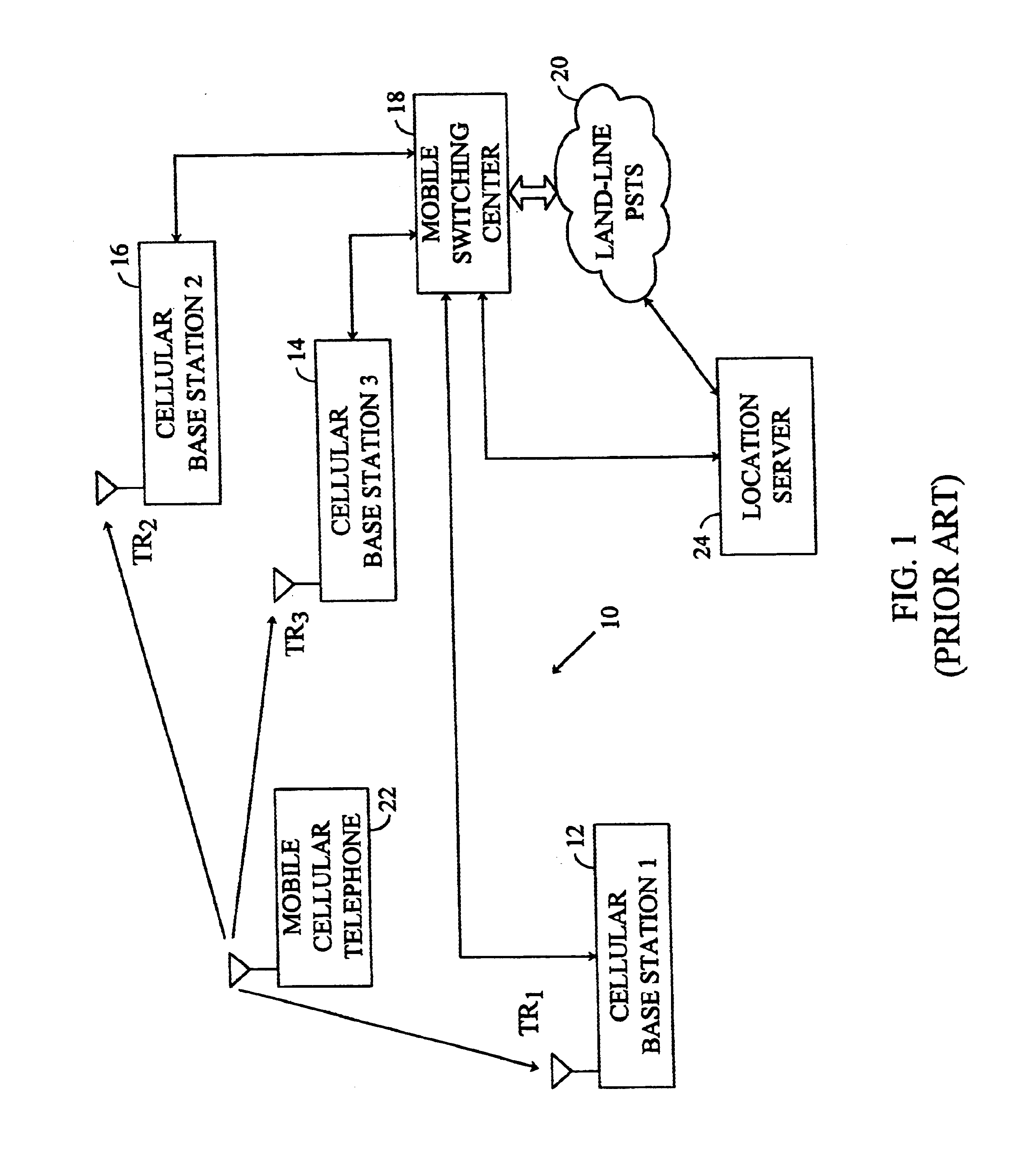
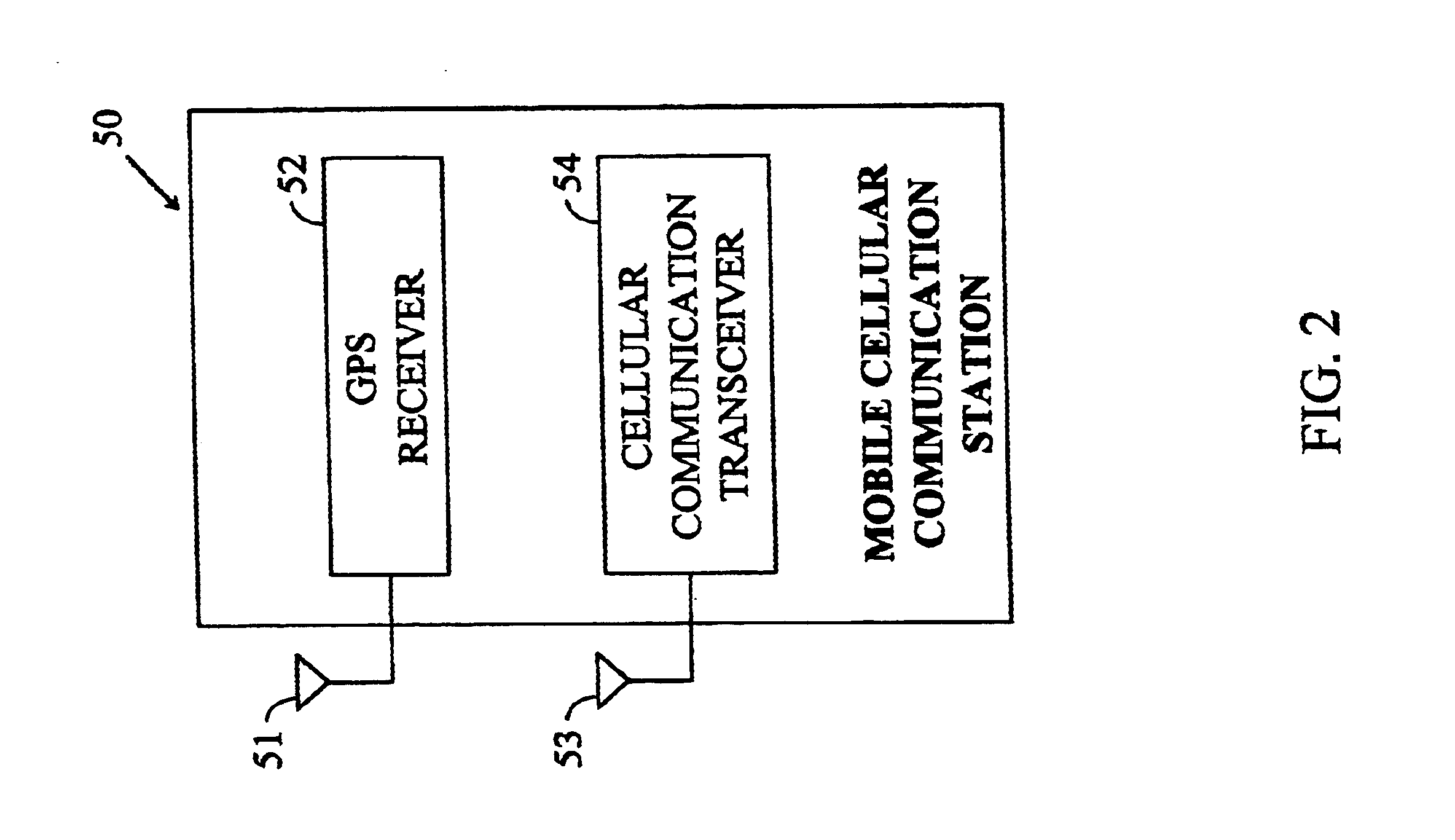
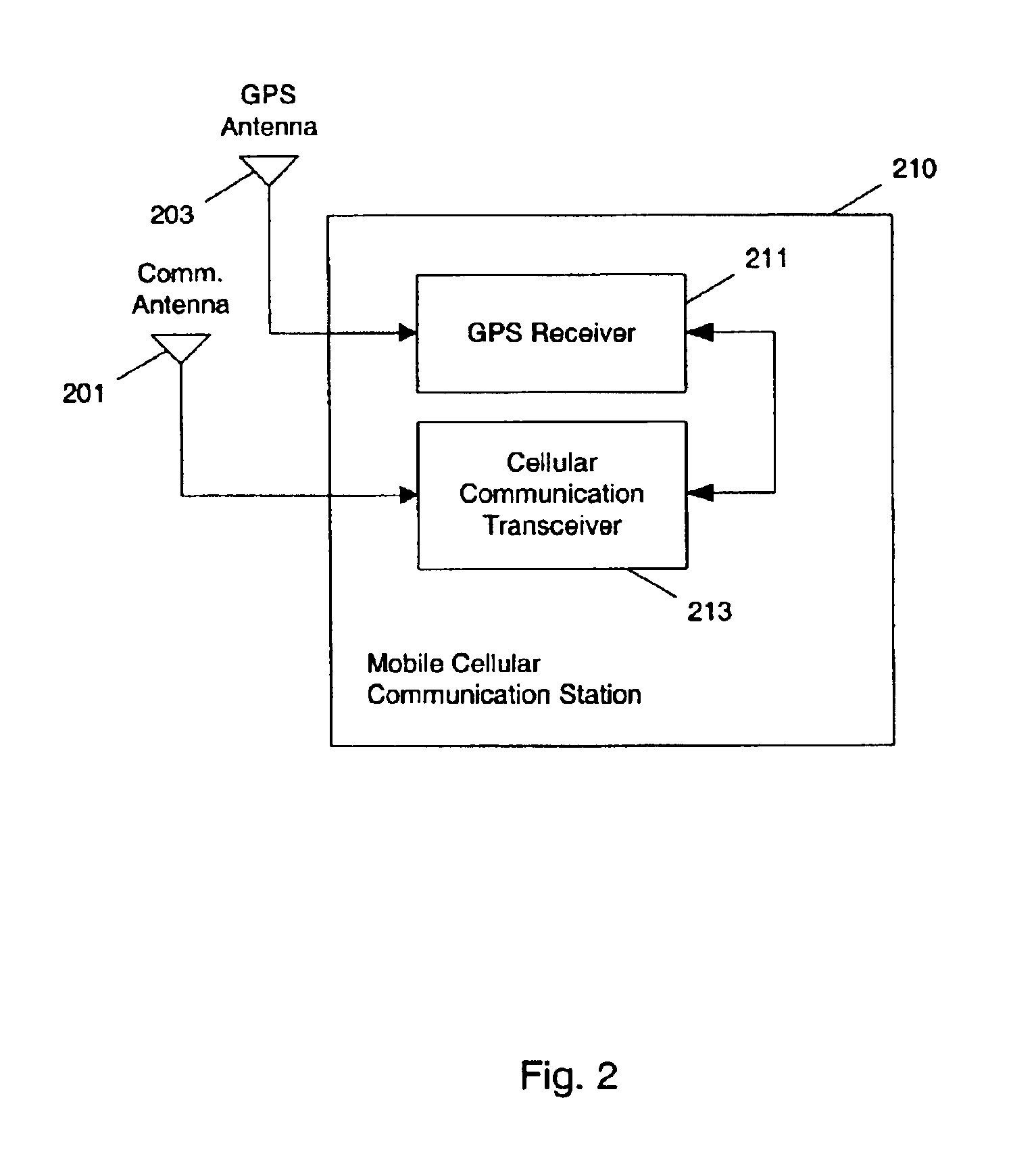
Methods and apparatuses for using mobile GPS receivers to synchronize basestations in cellular networks
InactiveUS6665541B1Low costSynchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexGeolocationGps receiver
Methods and apparatuses for synchronizing basestations in a cellular network. One exemplary method performs time synchronization between at least two basestations, a first basestation and a second basestation, of a cellular communication system. In this exemplary method, a first time-of-day and a first geographical location of a first mobile cellular receiver station (MS) are determined from a first satellite positioning system (SPS) receiver which is co-located with the first MS, and the first time-of-day and first location are transmitted by the first MS to a first basestation which determines a time-of-day of the first basestation from the first time-of-day and first location and from a known location of the first basestation. Also in this exemplary method, a second time-of-day and a second geographical location of a second MS are determined from a second SPS receiver which is co-located with the second MS, and the second time-of-day and the second location are transmitted to a second basestation which determines a time-of-day of the second basestation from the second time-of-day and the second location and a known location of the second basestation. Other methods and apparatuses are also described for synchronizing basestations in a cellular network.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
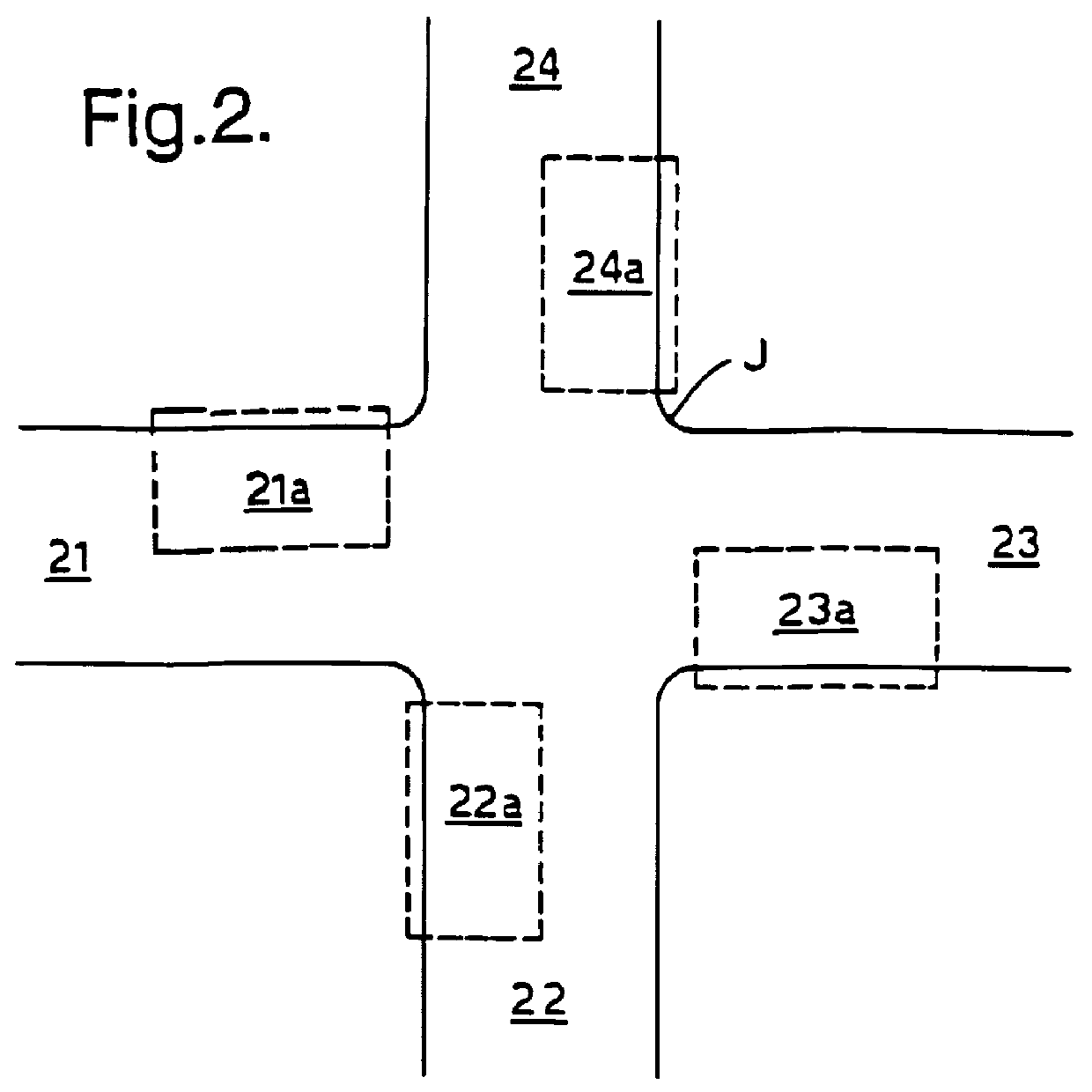
Navigation information system
InactiveUS6111539AInstruments for road network navigationArrangements for variable traffic instructionsCommunications systemIn vehicle
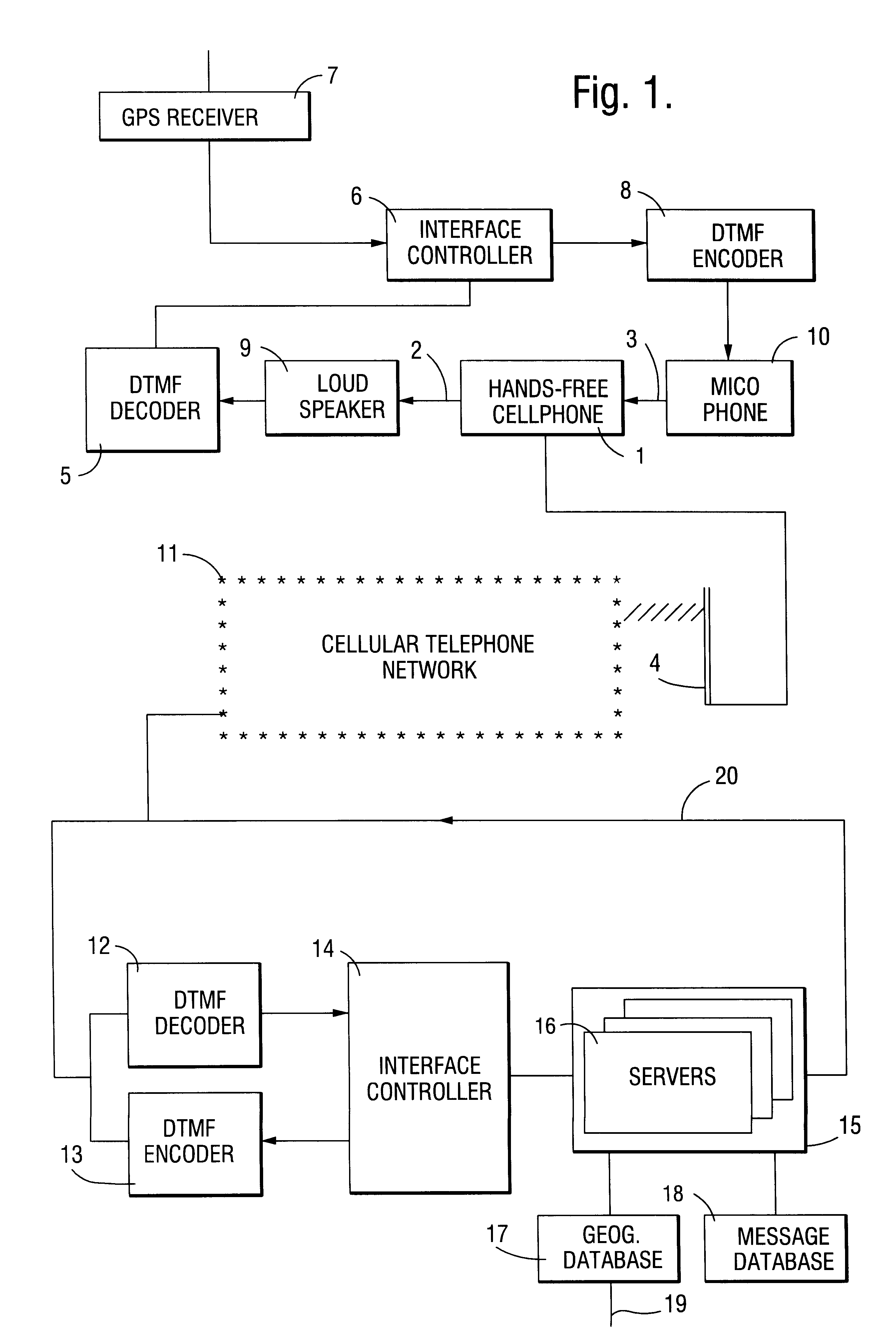
A navigation information system includes a communications system having a fixed part and at least one mobile part, the fixed part including data storage and processing for identifying the location of a mobile unit, generating guidance information appropriate to that location and transmitting it to the mobile unit. By locating most of the complexity with the service provider, in particular the navigation computer and geographical database, the system can be readily updated and the capital cost of the in-vehicle system, which in its simplest form may be a standard cellular telephone, can be minimized. The user makes a request for guidance information, and the system, having determined the user's present location, then transmits instructions to the user. The user's present location can be determined by a Satellite Positioning System.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
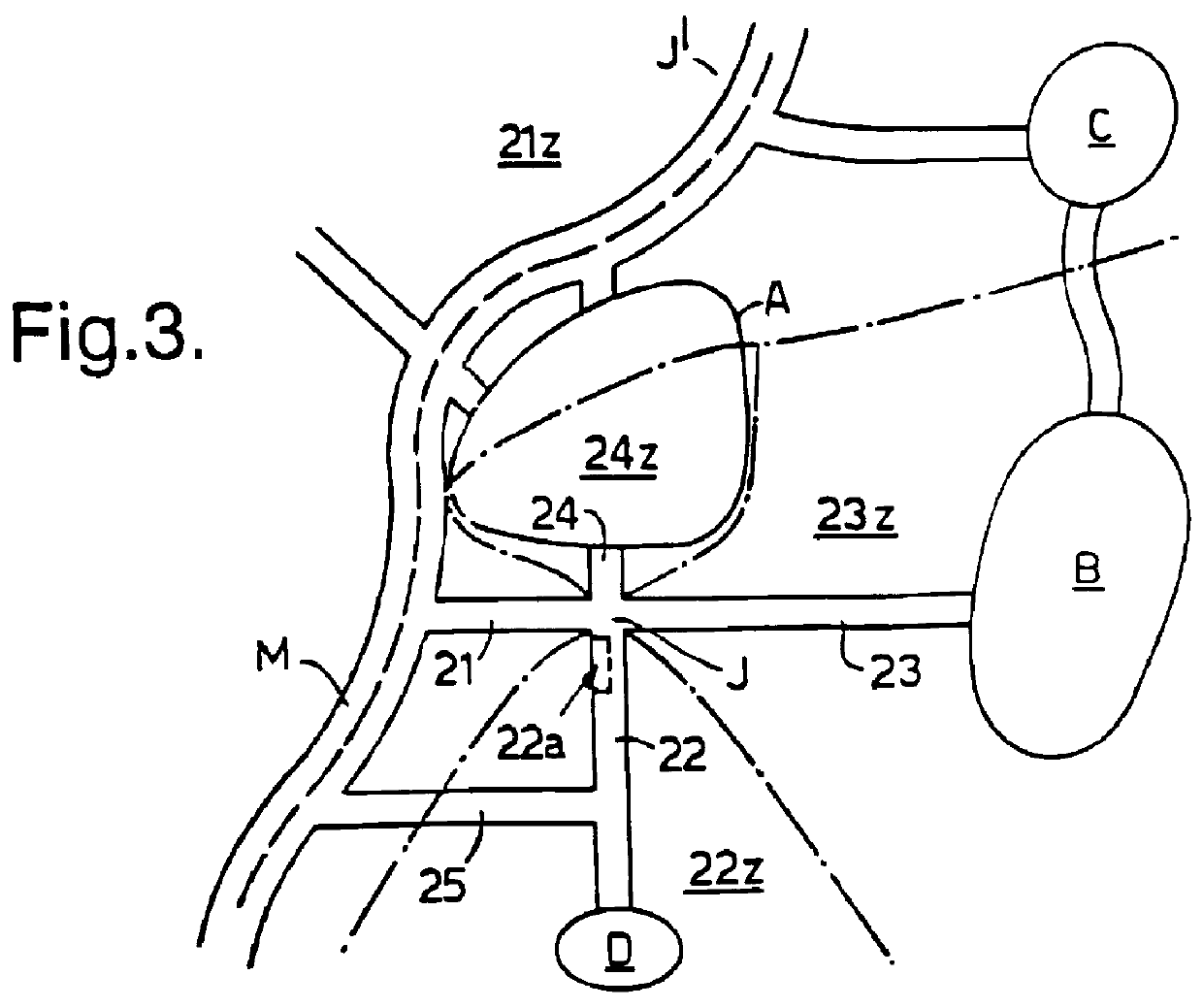
Navigation information system
InactiveUS6169515B1Instruments for road network navigationArrangements for variable traffic instructionsData memoryCapital cost
A navigation information system includes a communications system having a fixed part and at least one mobile part, the fixed part including data storage and a processor identifying the location of a mobile unit, generating guidance information appropriate to that location and transmitting it to the mobile unit. By locating most of the complexity with the service provider, in particular the navigation computer and geographical database, the system can be readily updated and the capital cost of the in-vehicle system, which in its simplest form may be a standard cellular telephone, can be minimized. The user makes a request for guidance information, and the system, having determined the user's present location, then transmits instructions to the user. The user's present location can be determined by a Satellite Positioning System or the like.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
Local emergency alert for cell-phone users
Local emergency alert service for cell-phone or pager users is provided using regional or localized broadcast to or polling of available, voluntary, or otherwise identified wireless communication devices or other network-accessible nodes operating using different protocol in proximate help area, thus allowing such alerted users to respond to nearby emergency request or condition. Wireless communicator location is determined using relative satellite positioning, radio signal triangulation, or manual entry technique. Sensor may alert wireless communicator automatically of emergency condition.
Owner:FERNANDEZ DENNIS SUNGA +2
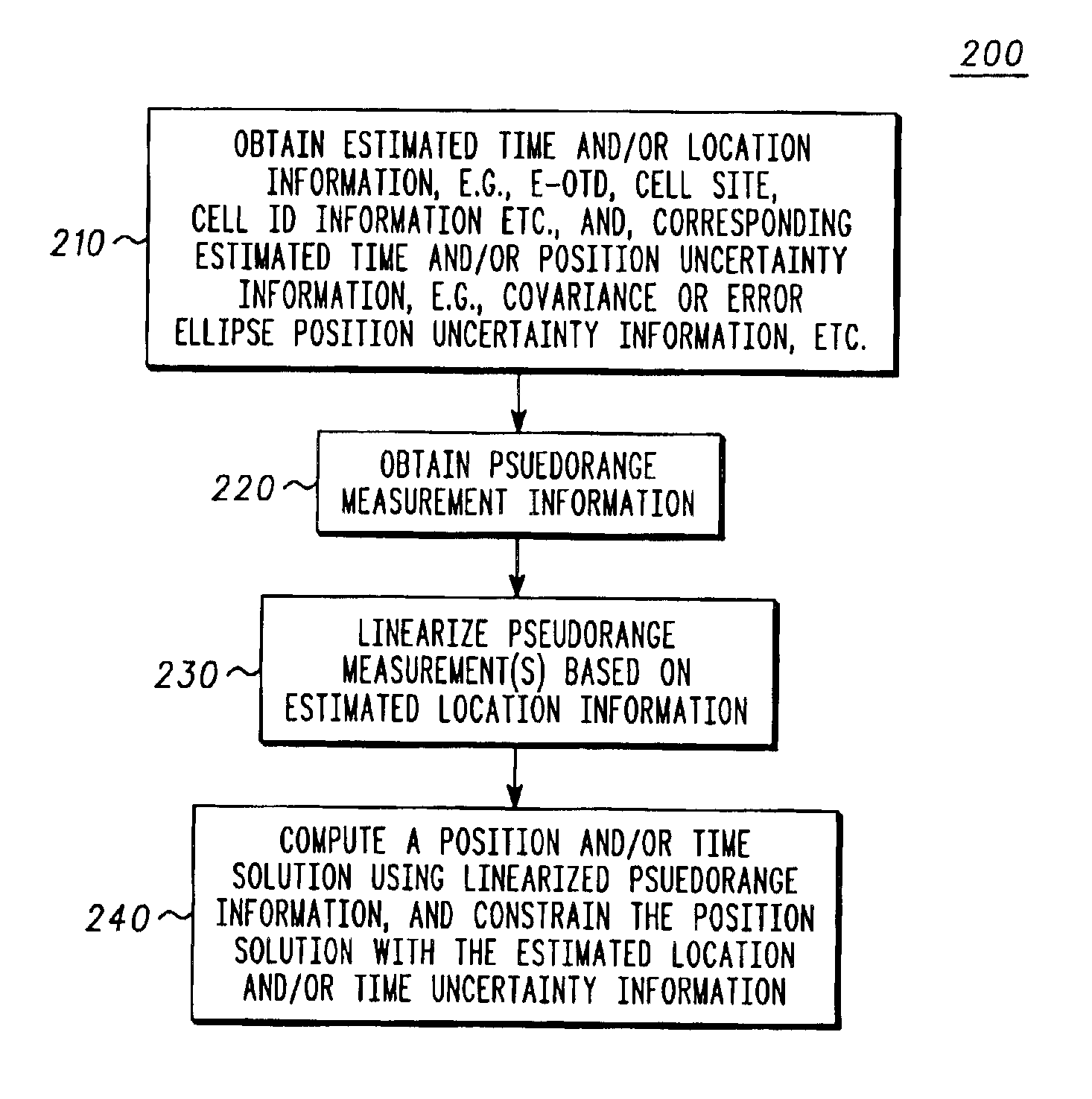
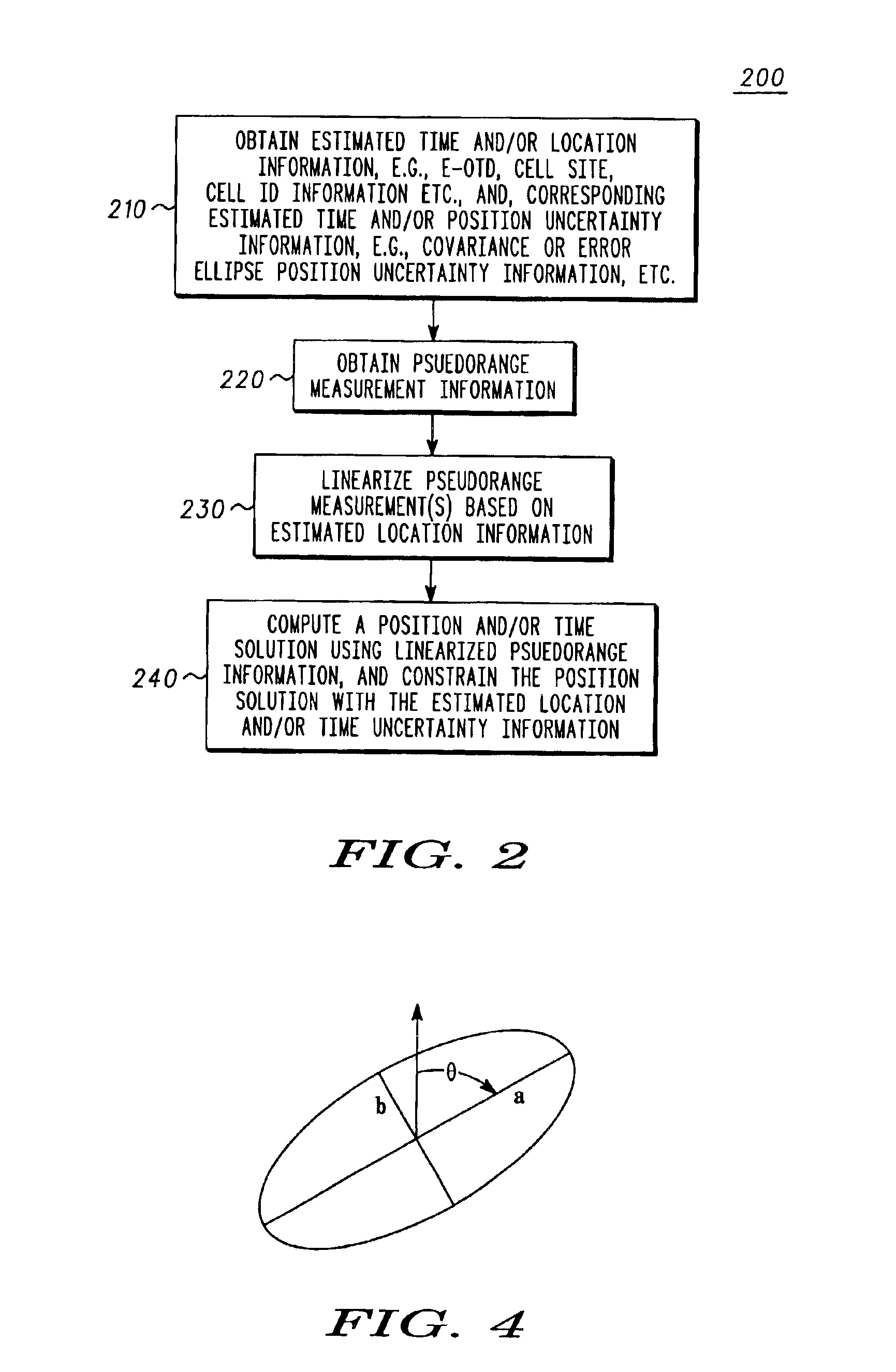
Aiding location determinations in satellite positioning system receivers
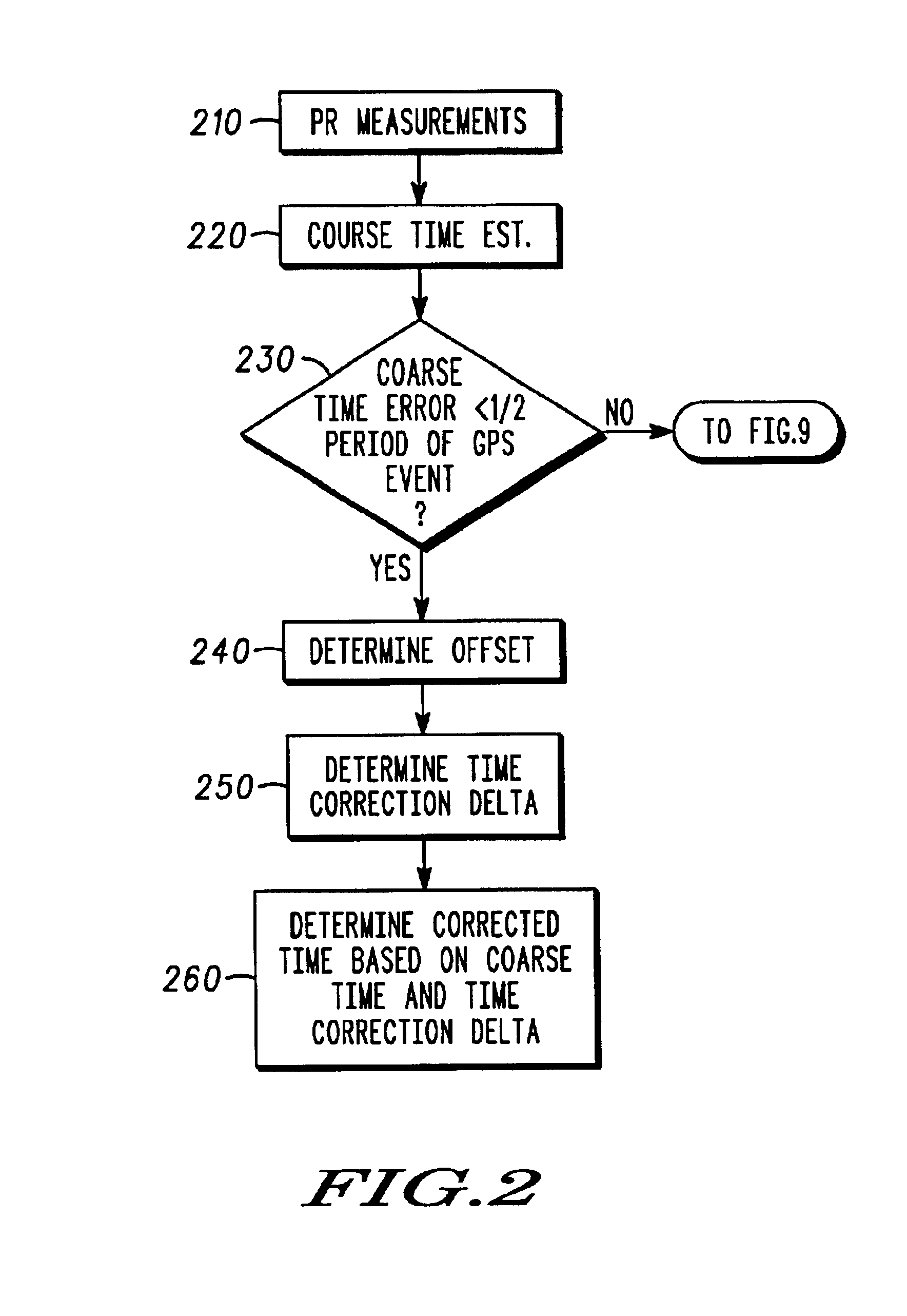
A method for locating a satellite positioning system receiver, for example, a satellite positioning system enabled wireless communications device in cellular network, including obtaining a coarse position and / or a time estimate (210), and computing a satellite positioning system based position and / or time solution (240) that is constrained by uncertainty information associated with the coarse position and / or a time estimate. The uncertainty constraints may also be used to identify erroneous measurements used to compute the position solution.
Owner:CSR TECH INC
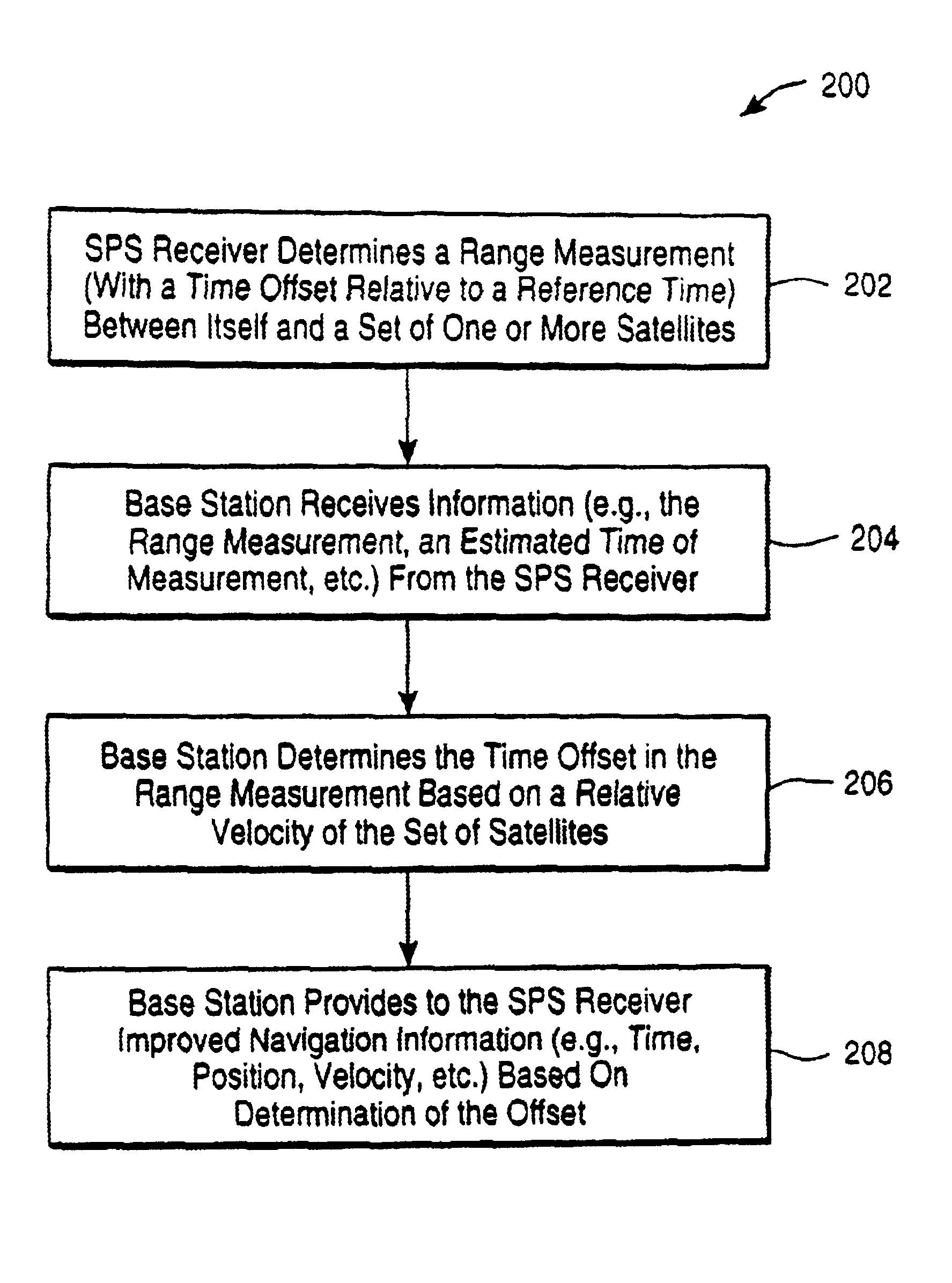
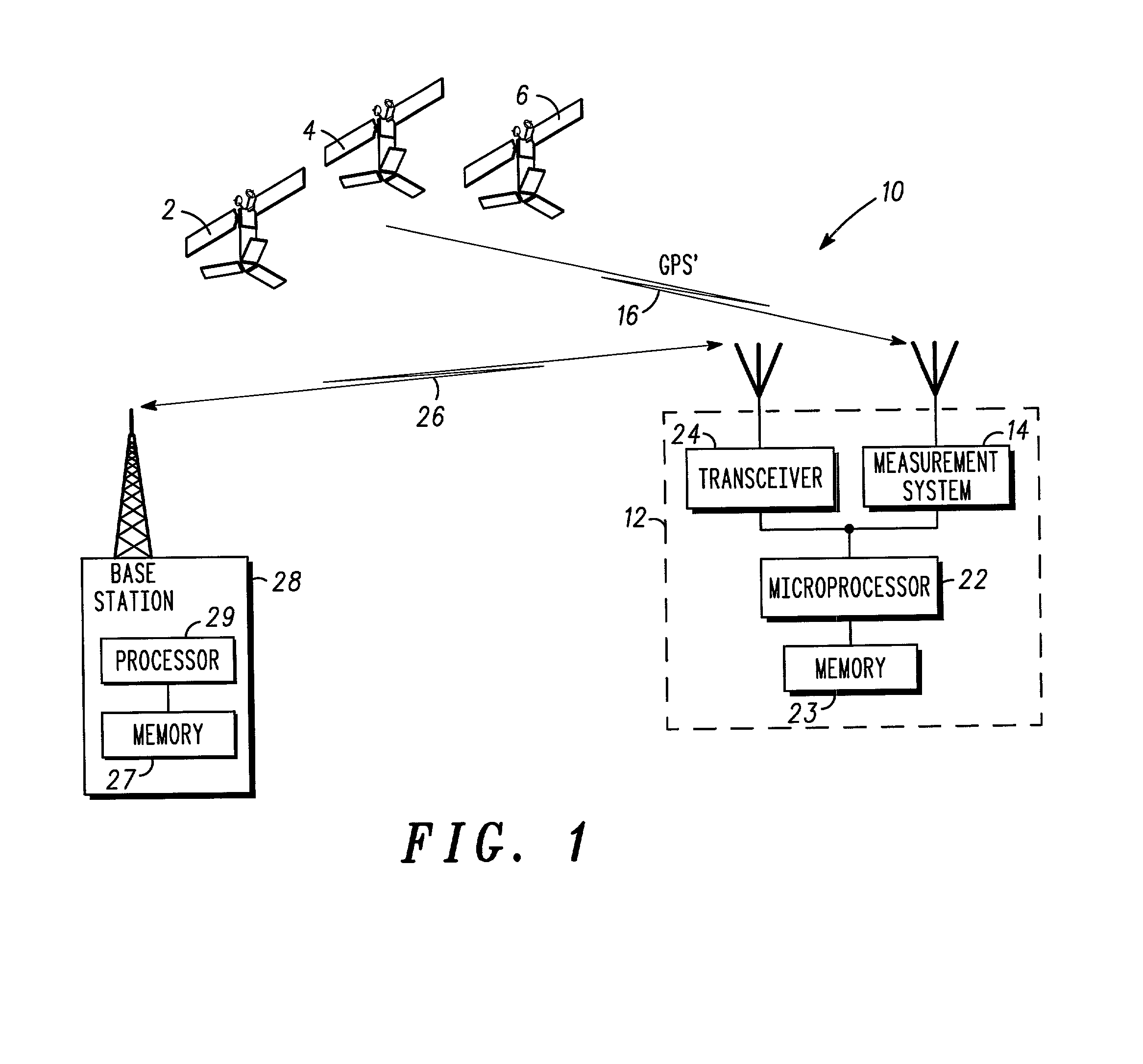
Method and apparatus for determining time in a satellite positioning system
InactiveUS6839021B2Beacon systems using radio wavesSynchronous motors for clocksSatellite positioningRelative velocity
A method and apparatus for determining a reference time associated with a satellite positioning system. In turn, the reference time, in one embodiment, may be used to determine other navigational information. Such navigational information may include, for example, the location / position of a satellite positioning system (SPS) receiver. In one embodiment, a relative velocity between an SPS receiver and a set of one or more satellites is used to determine an offset between time as indicated by the SPS receiver and the reference time. According to another embodiment of the invention, an error statistic is used to determine the reference time. According to yet another embodiment of the invention, two records, each representing at least a portion of a satellite message, are compared to determine time. In one implementation, the SPS receiver is mobile and operates in conjunction with a basestation to determine time and / or other navigational information according to one or a combination of the methods described.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
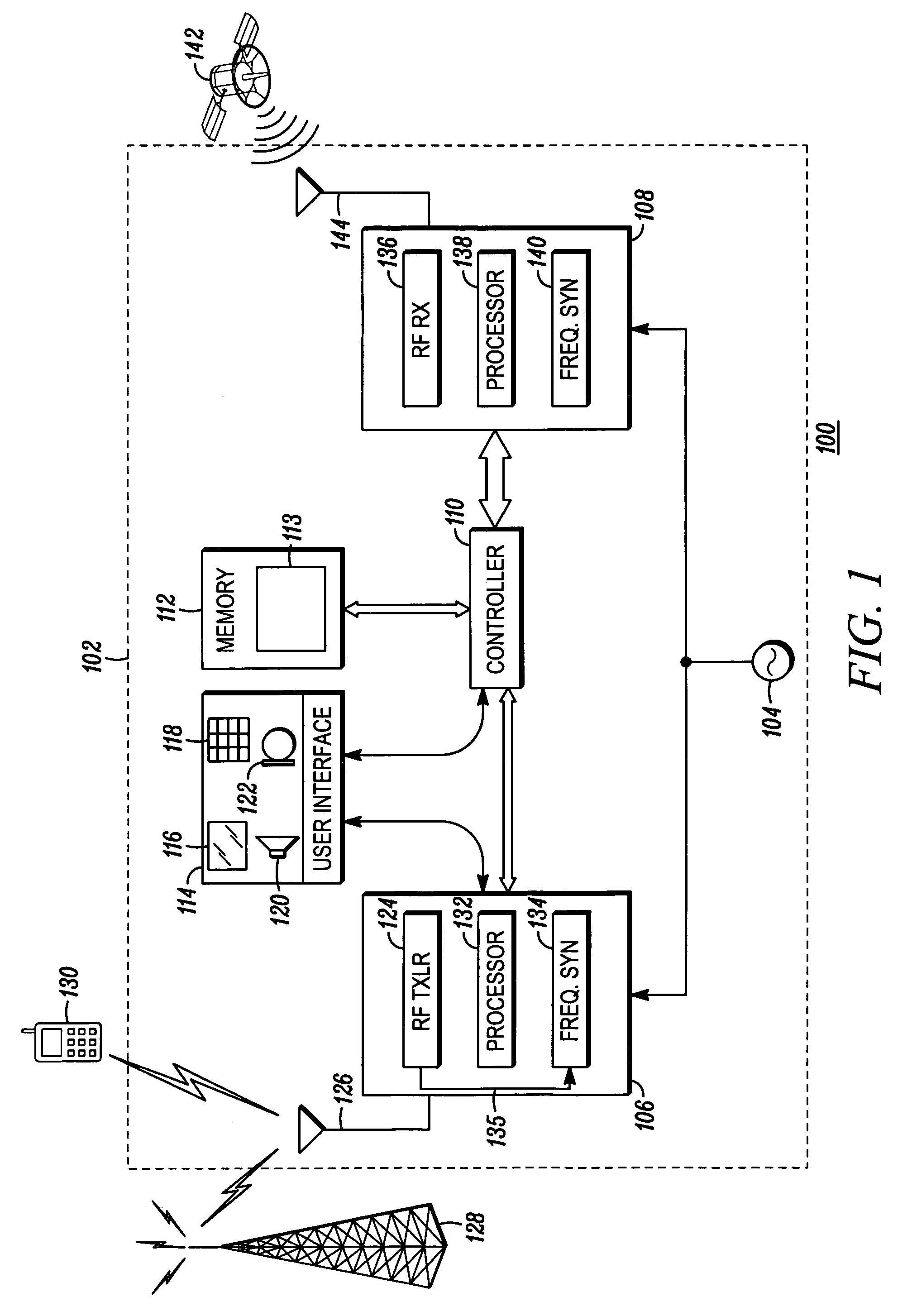
Method and apparatus for processing location service messages in a satellite position location system
Method and apparatus for processing location service messages in a satellite position location system is described. In one example, a mobile receiver includes a satellite signal receiver, wireless circuitry, and at least one module. The satellite signal receiver is configured to receive satellite positioning system signals, such as Global Positioning System (GPS) signals. The wireless circuitry is configured to communicate location service messages between the mobile receiver and a server through a cellular communication network. The location service messages may include any type of data related to A-GPS operation, such as assistance data, position data, request and response data, and the like. The at least one module is configured to provide a user-plane interface and a control-plane interface between the satellite signal receiver and the wireless transceiver. The at leat one module is capable of processing location service messages communicated using either the control-plane signaling or user-plane signaling mechanisms.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
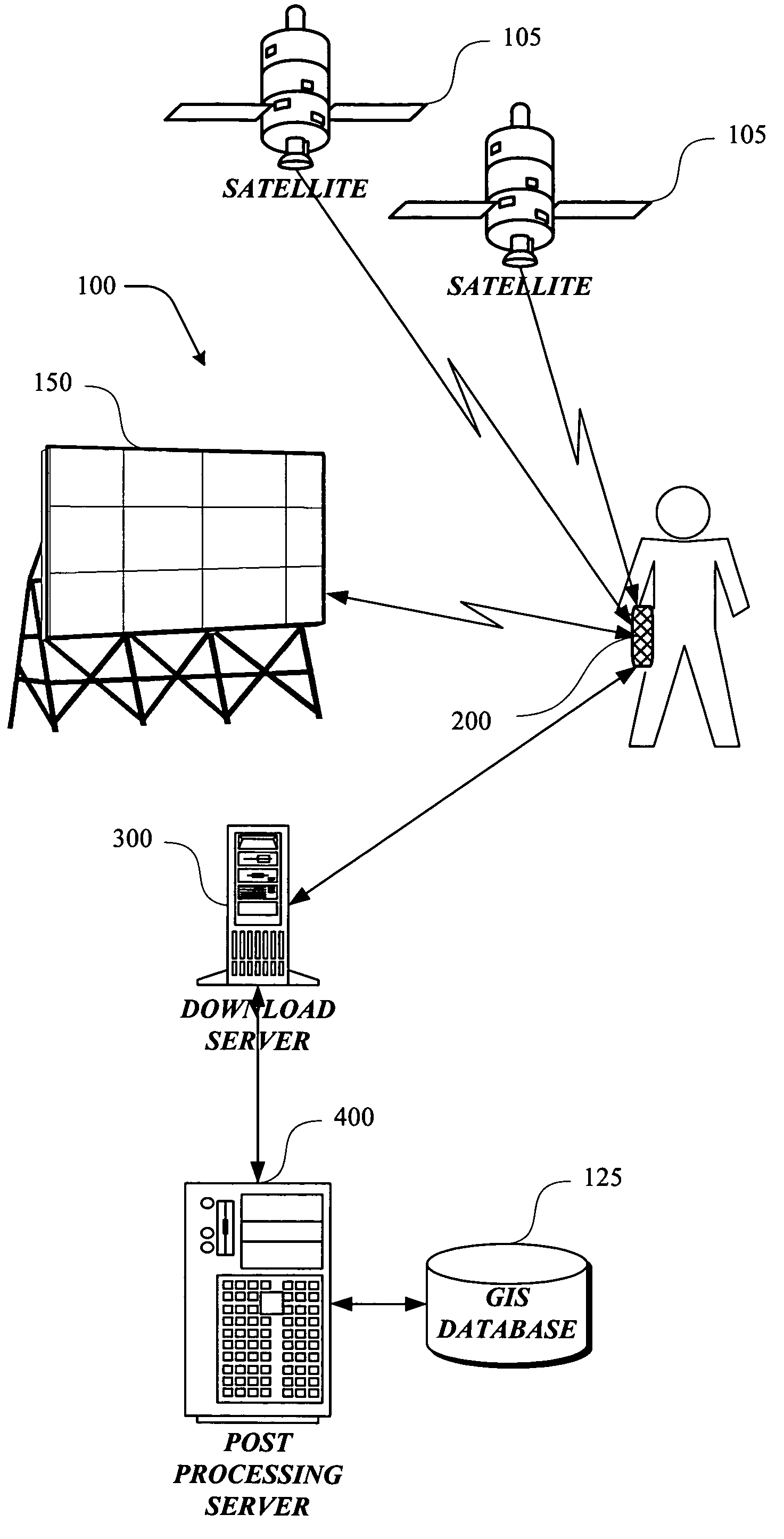
Satellite positioning system enabled media measurement system and method
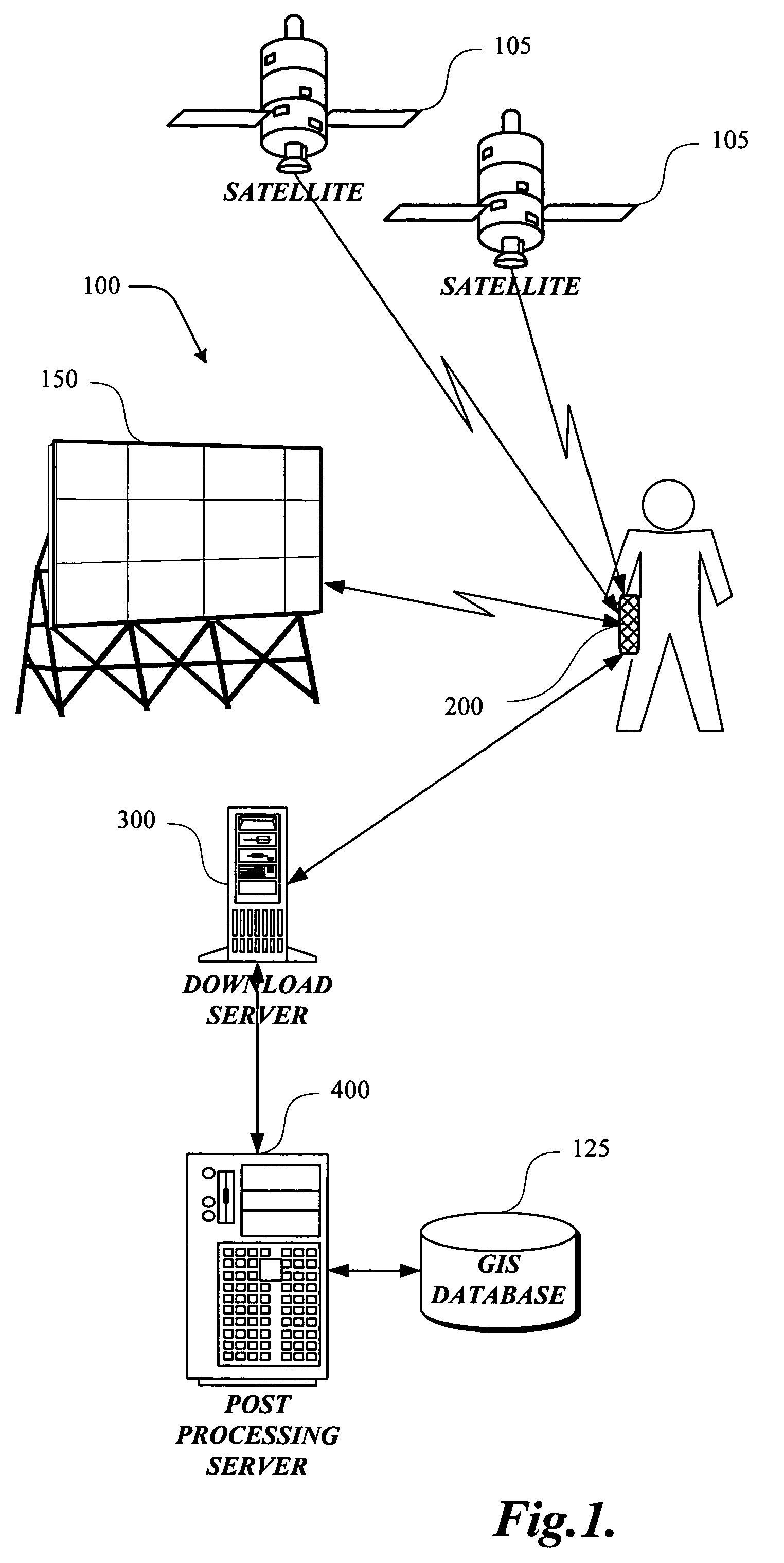
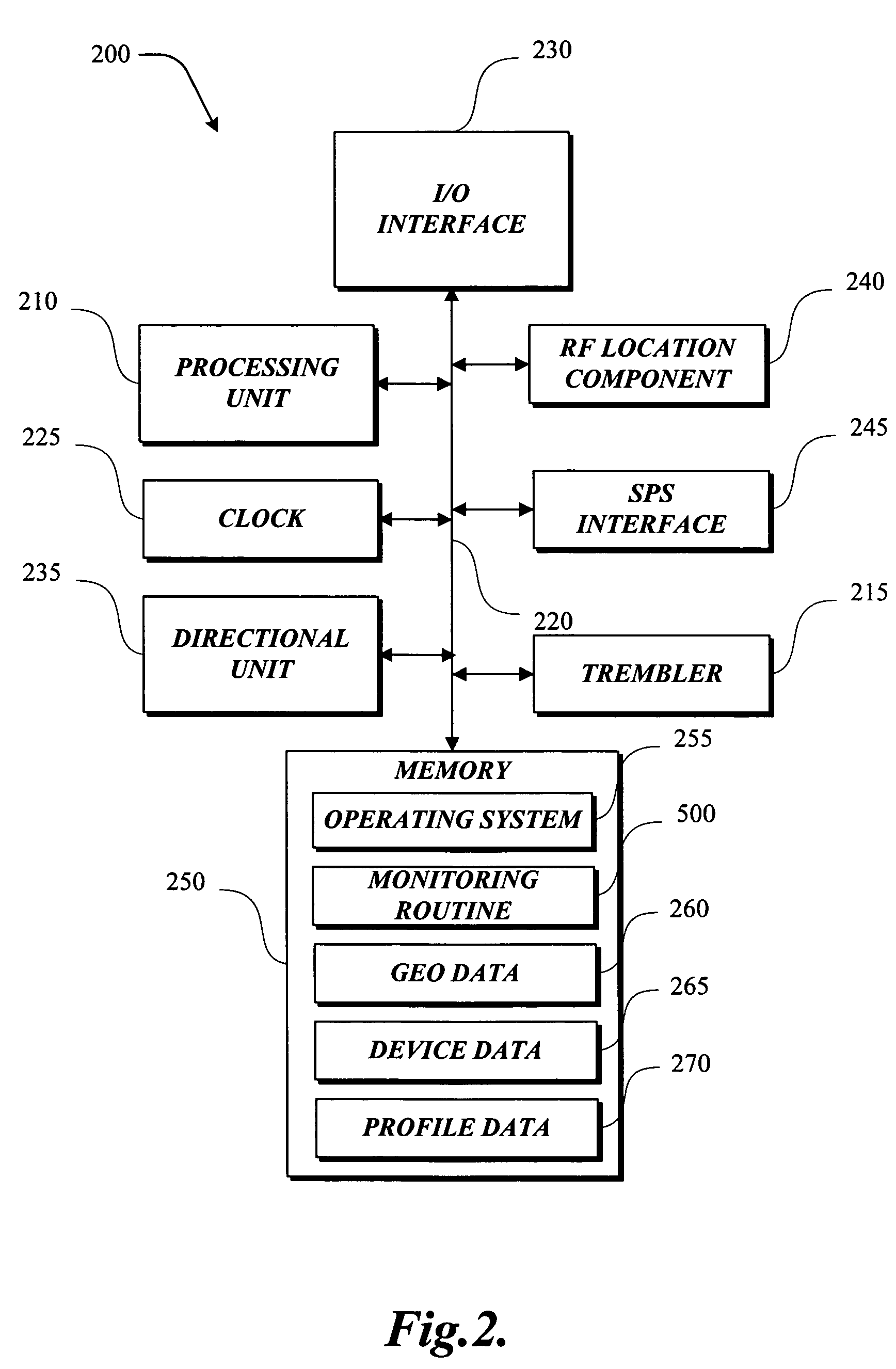
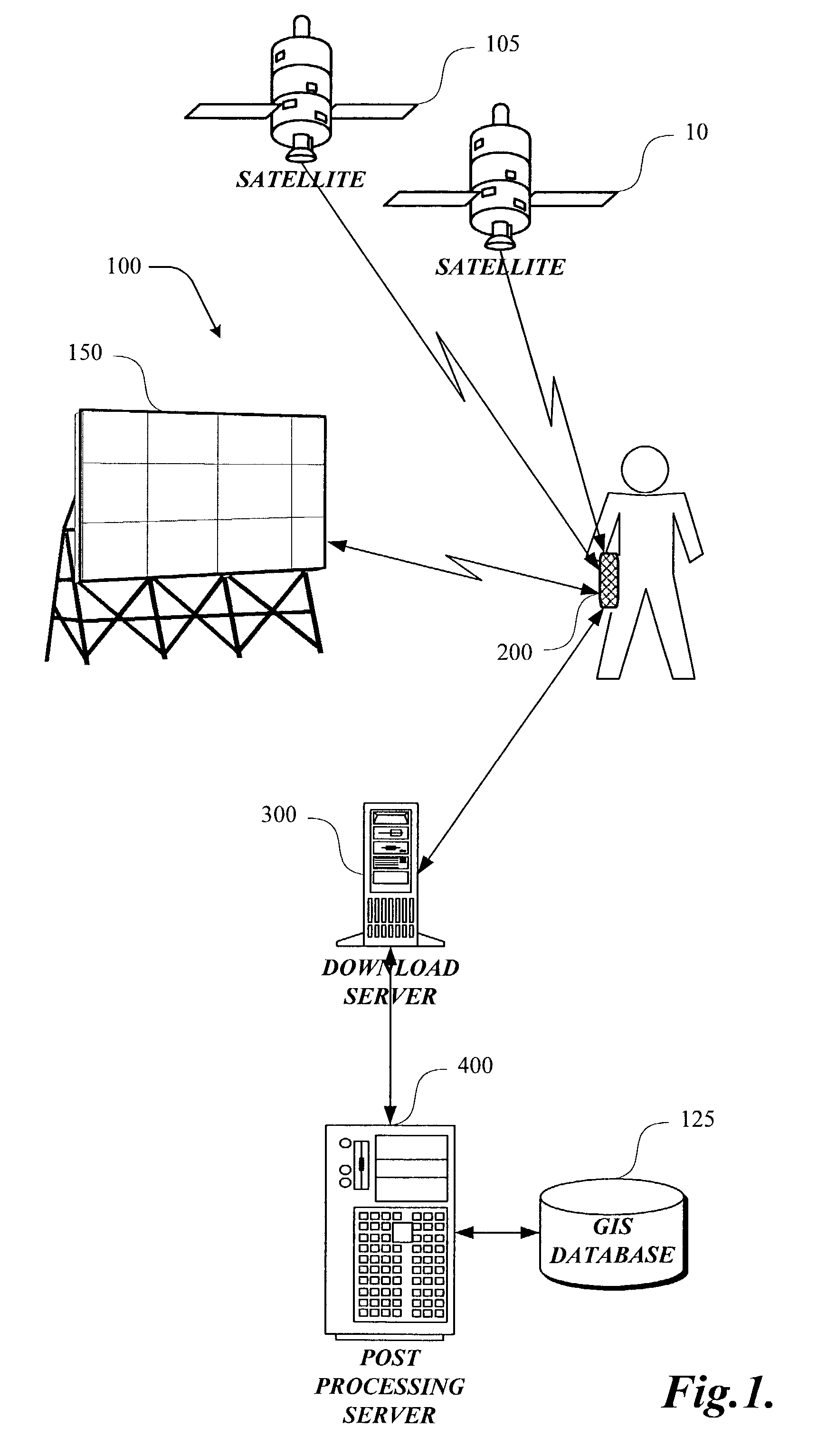
InactiveUS6970131B2Augment location and movement trackingBeacon systems using radio wavesPosition fixationLocation trackingDisplay device
The present invention is directed to utilizing monitoring devices (200) for determining the effectiveness of various locations, such as media display locations (150) for an intended purpose (media display exposure). The monitoring devices (200) are distributed to a number of study respondents. The monitoring devices (200) track the movements of the respondents. While various technologies may be used to track the movements of the respondents, at least some of the location tracking of the monitoring device (200) utilize a satellite (105) location system such as the global positioning system (“GPS”). These movements of the respondent and monitoring device (200) at some point coincide with exposure to a number of media displays (150). Geo data (movement data) collected by the monitoring devices, is downloaded to a download server (300), for determining which media displays (150) the respondent was exposed to. The exposure determinations are made by a post-processing server (400).
Owner:RDPA LLC
Methods and apparatuses for measuring frequencies of basestations in cellular networks using mobile GPS receivers
InactiveUS6937872B2Synchronisation arrangementSatellite radio beaconingCommunications systemGps receiver
Methods and apparatuses for frequency synchronizing basestations in a cellular communication system. In one aspect of the invention, a method to predict a timing of transmission of a basestation in a cellular communication system includes: receiving a first time tag for a first timing marker in a first cellular signal transmitted from the basestation; receiving a second time tag of a second timing marker in a second cellular signal transmitted from the basestation; and computing a frequency related to the basestation using the first and second time tags. Each of the time tags are determined using at least one satellite positioning system signal received at a mobile station which receives the corresponding time marker.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
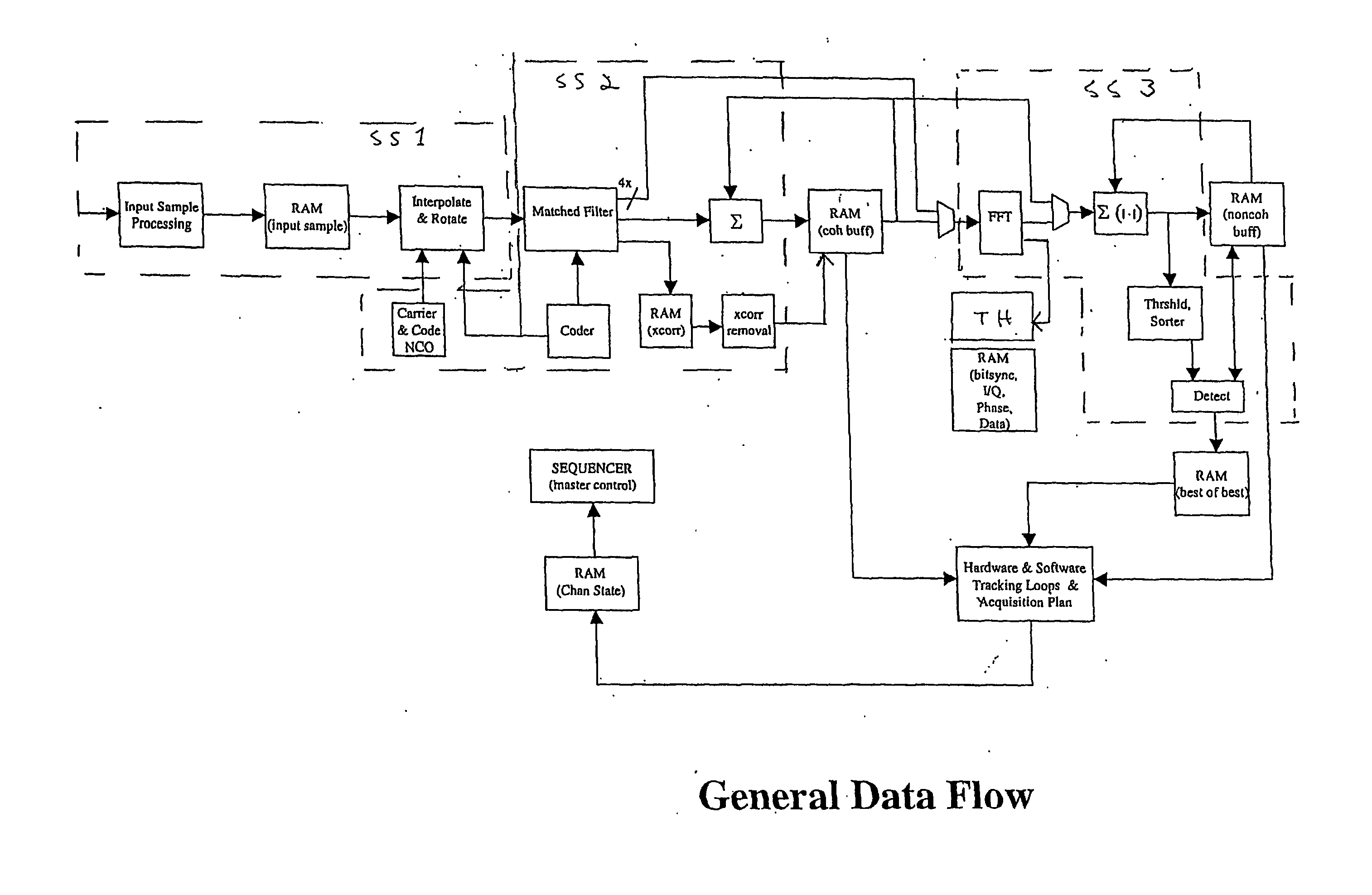
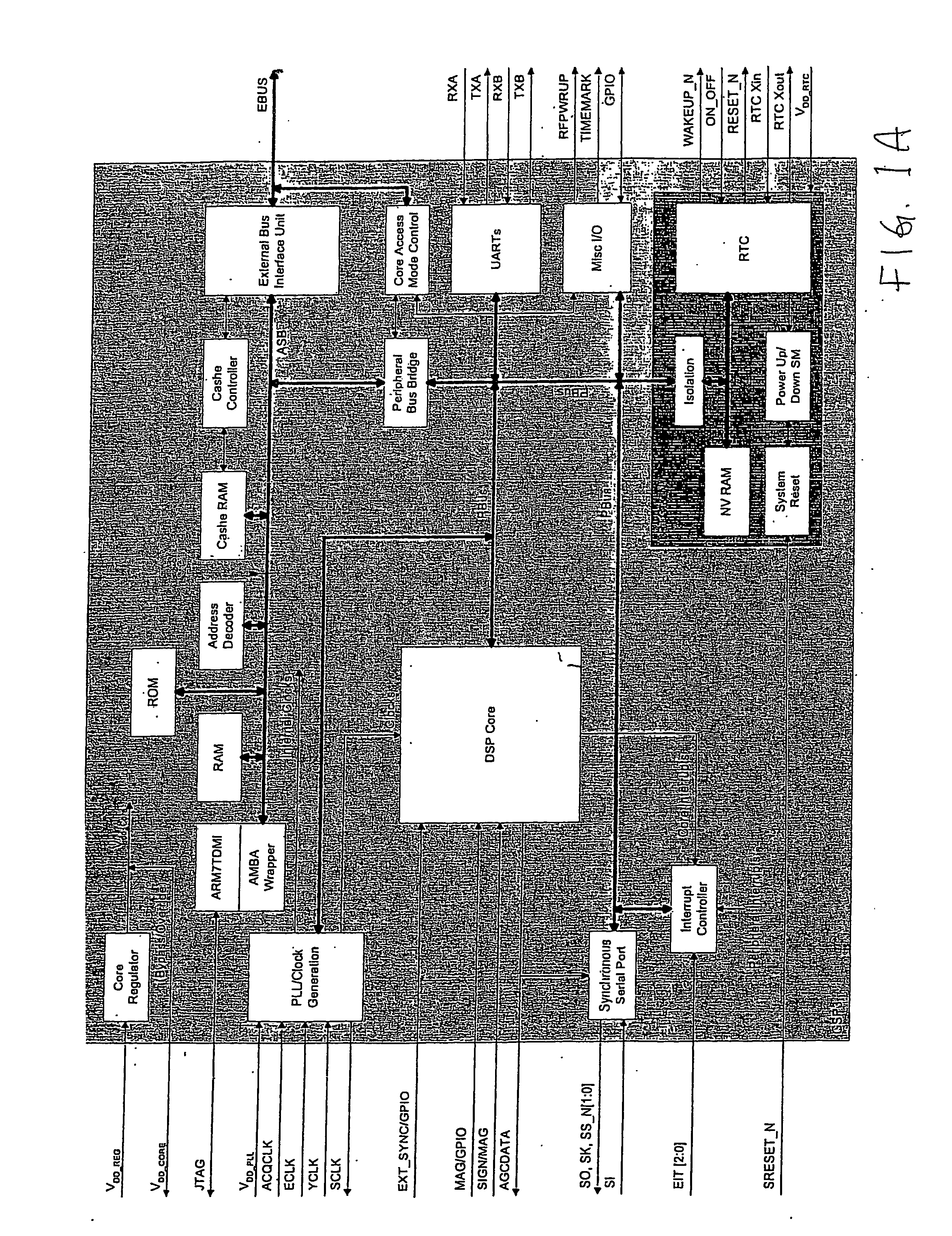
Signal Processing System for Satellite Positioning Signals
InactiveUS20110102258A1Beacon systemsSatellite radio beaconingControl signalFourier transform on finite groups
A signal processing system for processing satellite positioning signals is described. The system comprises at least one processor and a signal processor operating under a number of operational modes. The signal processor includes at last one of a signal processing subsystem, a fast Fourier transform (FFT) subsystem, and a memory subsystem that are each dynamically and independently configurable in response to the operational modes. Further, the system includes a controller that couples to control transfer of data among the signal processing subsystem and the FFT subsystem via the memory subsystem. Configurability of the memory subsystem includes configuring the memory subsystem into regions according to the operational modes where each region is accessible in one of a number of manners according to the operational modes.
Owner:CSR TECH INC
Aiding in a satellite positioning system
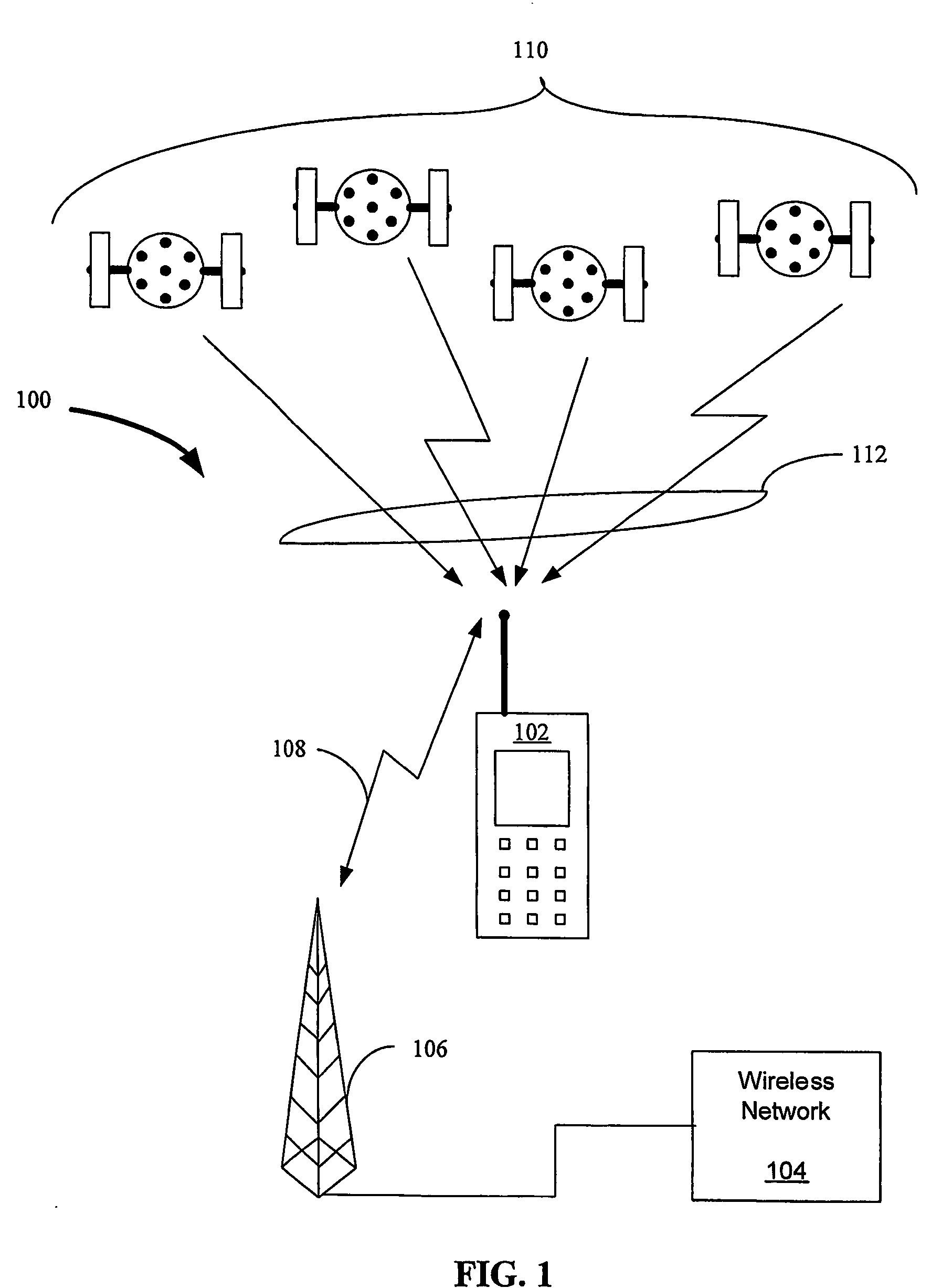
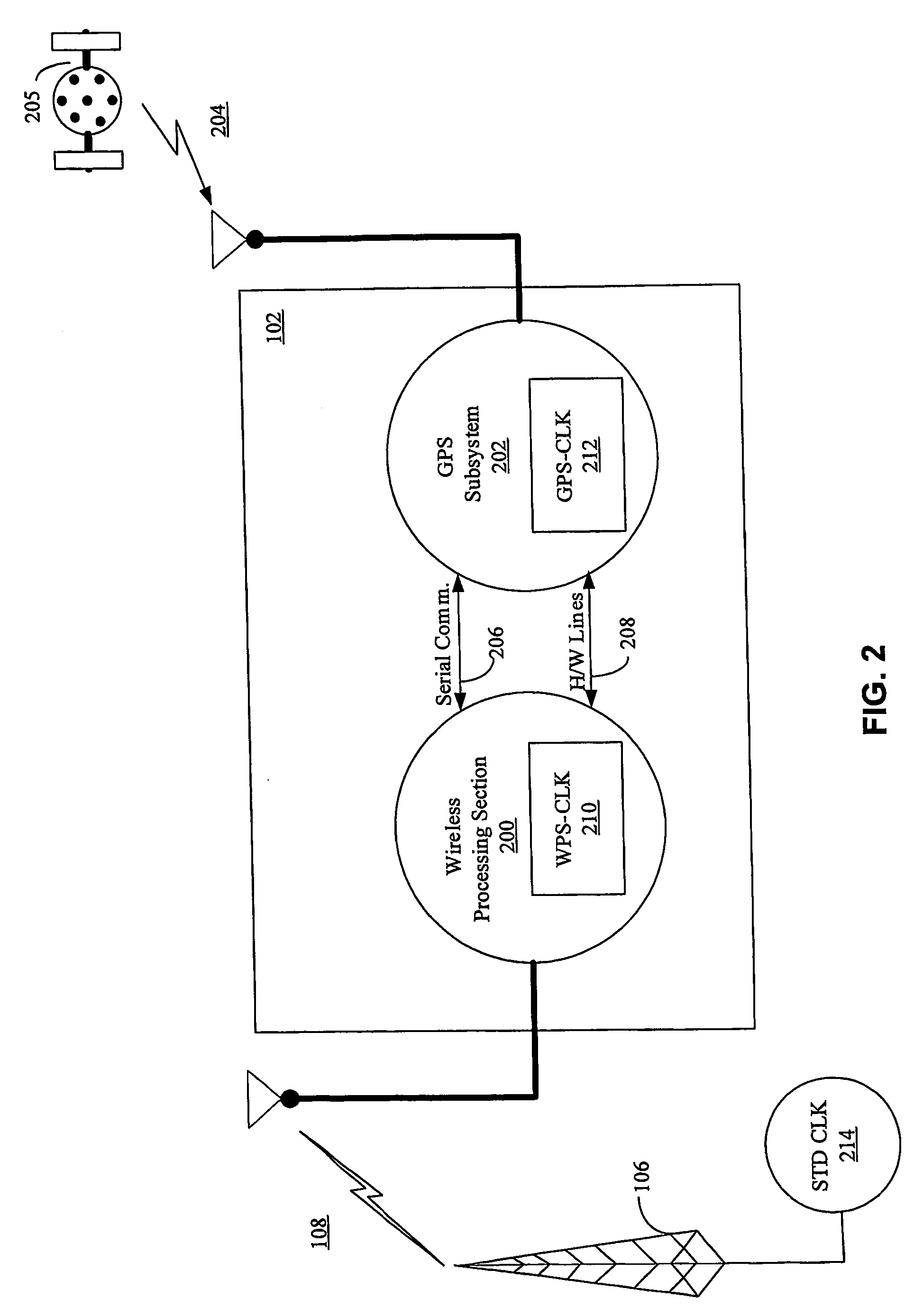
InactiveUS7236883B2Broadcast transmission systemsPosition fixationWireless mesh networkNetwork clock
The invention relates to an aided Global Positioning System (GPS) subsystem within a wireless device. The wireless device includes a wireless processing section capable of receiving signals from a wireless network and a GPS subsystem having a radio frequency (RF) front-end capable of receiving a GPS satellite signal. The wireless processing section of the wireless device receives an external clock and determines the offset between the clock in the wireless processing section and that of the external clock. The GPS subsystem then receives the offset information from the wireless processing section, information related to the nominal frequency of the wireless processing section clock and the wireless processing section clock. Using this information and the GPS clock in the GPS subsystem, the GPS subsystem determines an acquiring signal, which is related to a frequency offset between the GPS clock and the network clock. The GPS subsystem then acquires GPS satellite signals in an acquiring unit though the use of the acquiring signal.
Owner:CSR PLC
Time determination in satellite positioning system receivers and methods therefor
InactiveUS6944540B2Instruments for road network navigationSynchronous motors for clocksSatellite positioningPseudorange
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
On-board apparatus for avoiding restricted air space in non-overriding mode
InactiveUS6675095B1Minimize interferenceDigital data processing detailsAnti-collision systemsReal-time dataOn board
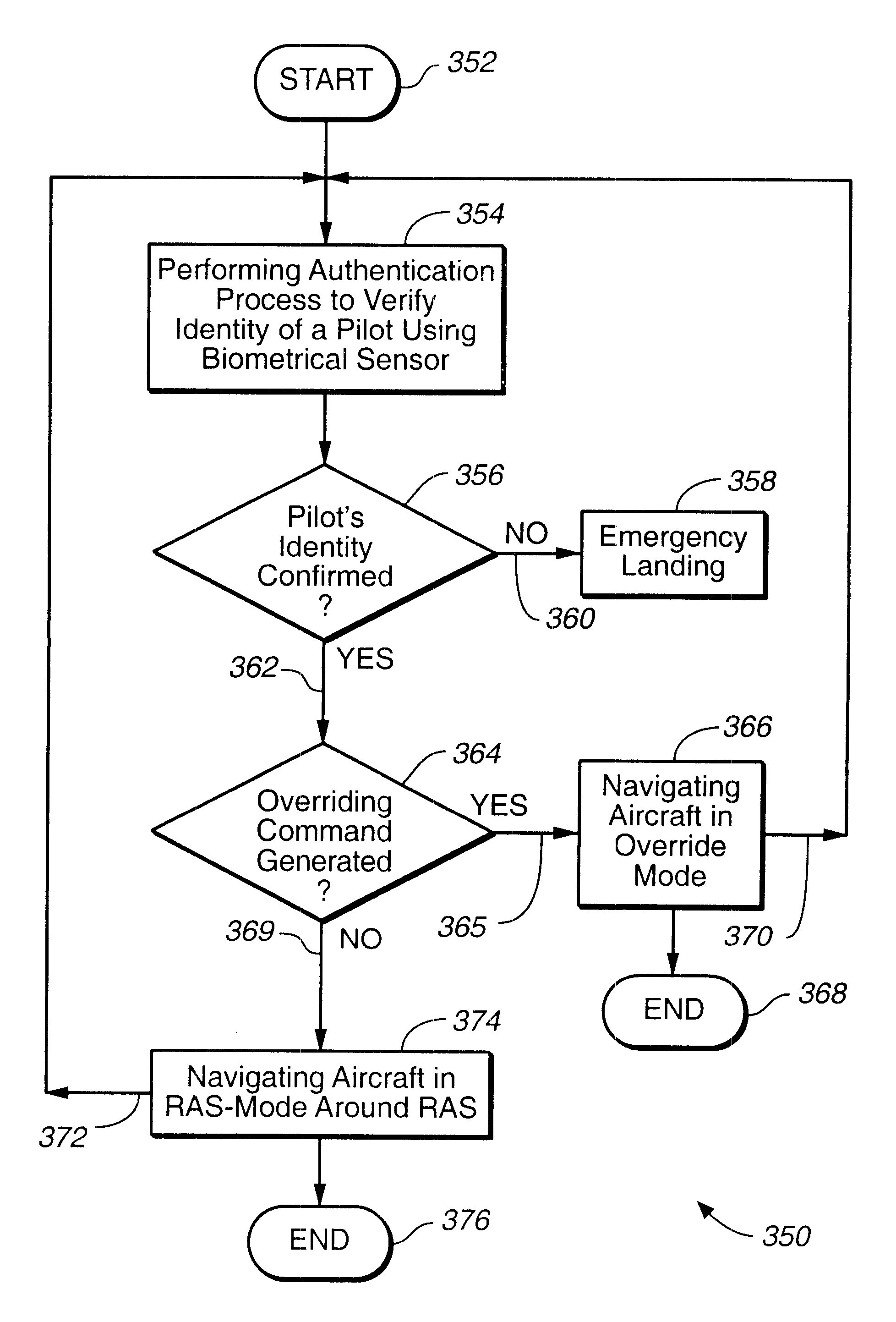
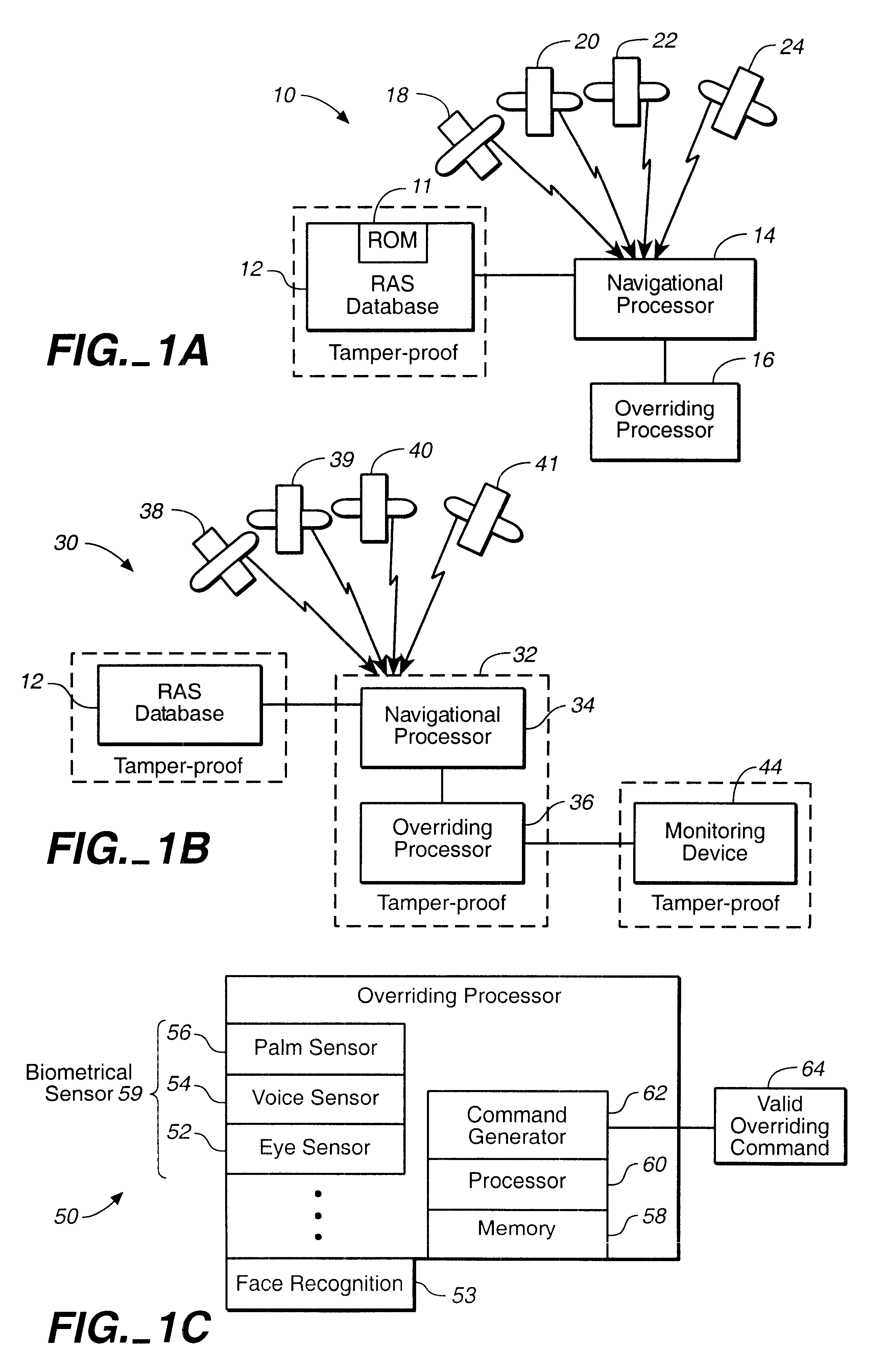
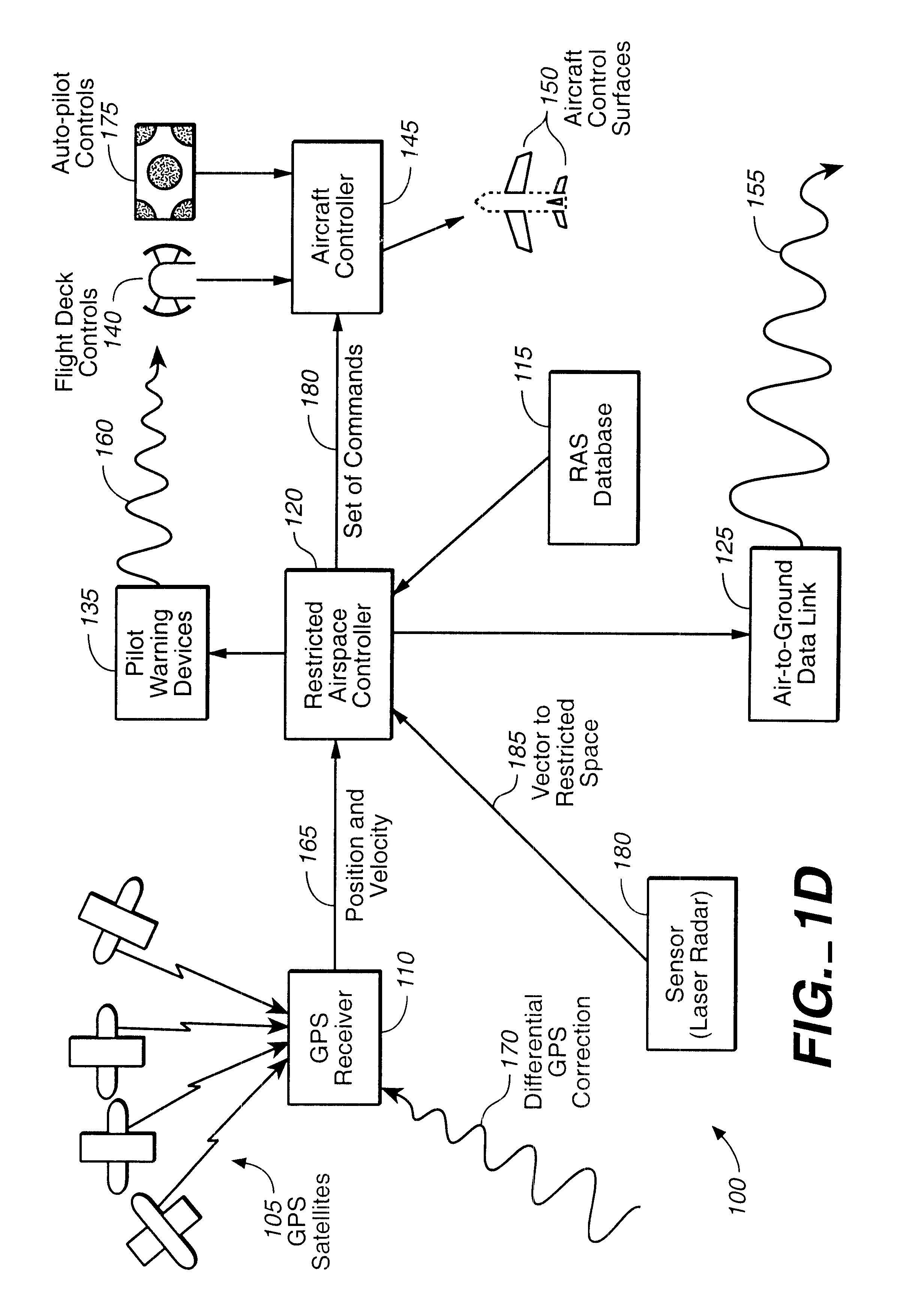
A tamper-resistant apparatus located on board of an aircraft for avoiding a restricted air space (RAS) comprising: (a) a tamper-resistant restricted air space (TAP-RAS) database configured to include a set of coordinates that determines the RAS; and (b) a navigational processor configured to navigate the aircraft around the RAS, if a valid overriding command is not generated. The navigational processor includes: a Satellite Positioning System (SATPS) configured to substantially continuously obtain a set of real time position coordinates of the aircraft; a restricted airspace controller configured to receive a set of real time data including the set of coordinates that determines the RAS, the set of real time position coordinates; and configured to analyze the set of real time data in order to substantially continuously generate a set of real time commands; and an aircraft controller configured to navigate the aircraft utilizing the real time set of commands around the RAS. The navigational processor is configured to navigate the aircraft in an overriding mode, if the valid overriding command is generated.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
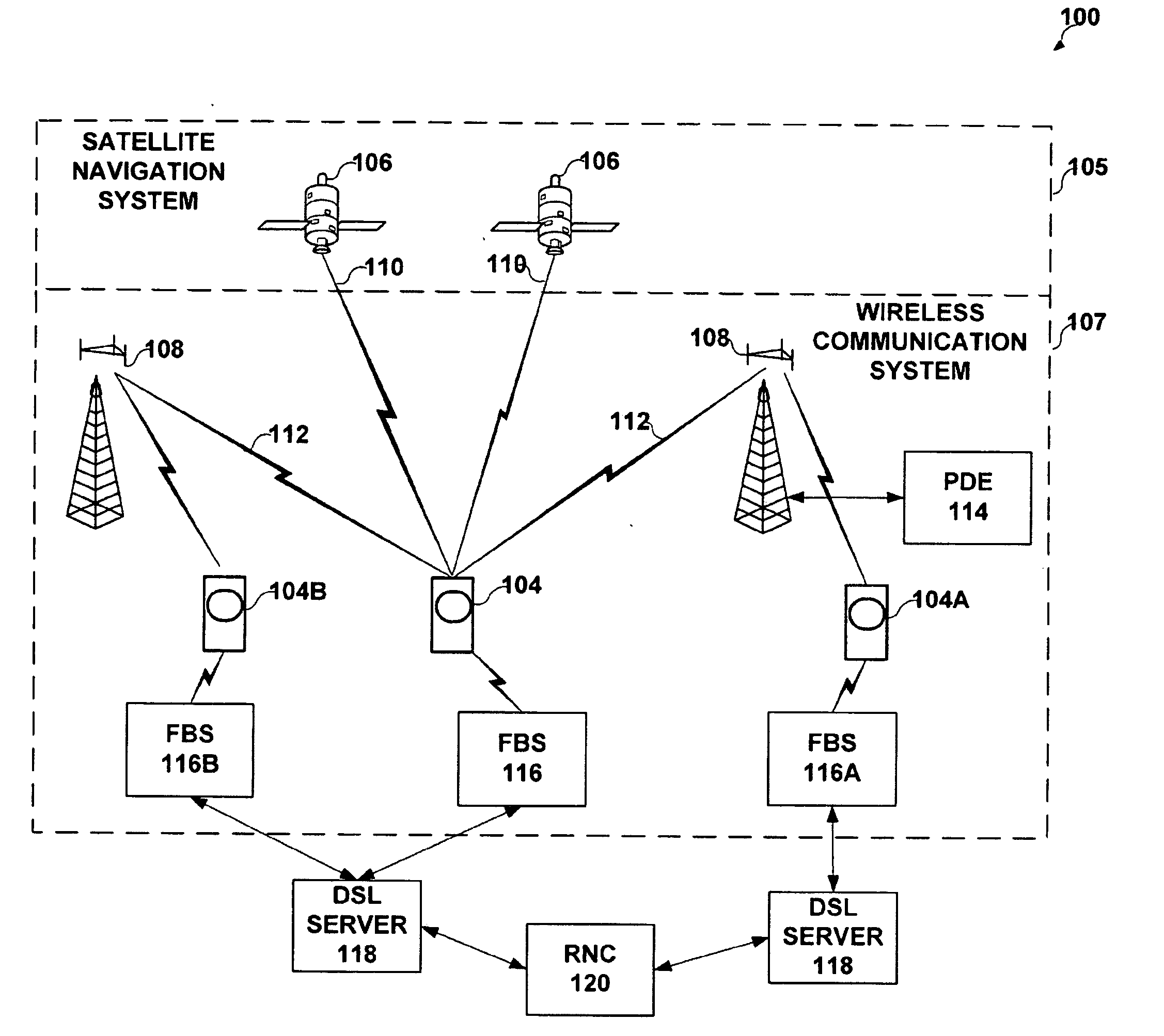
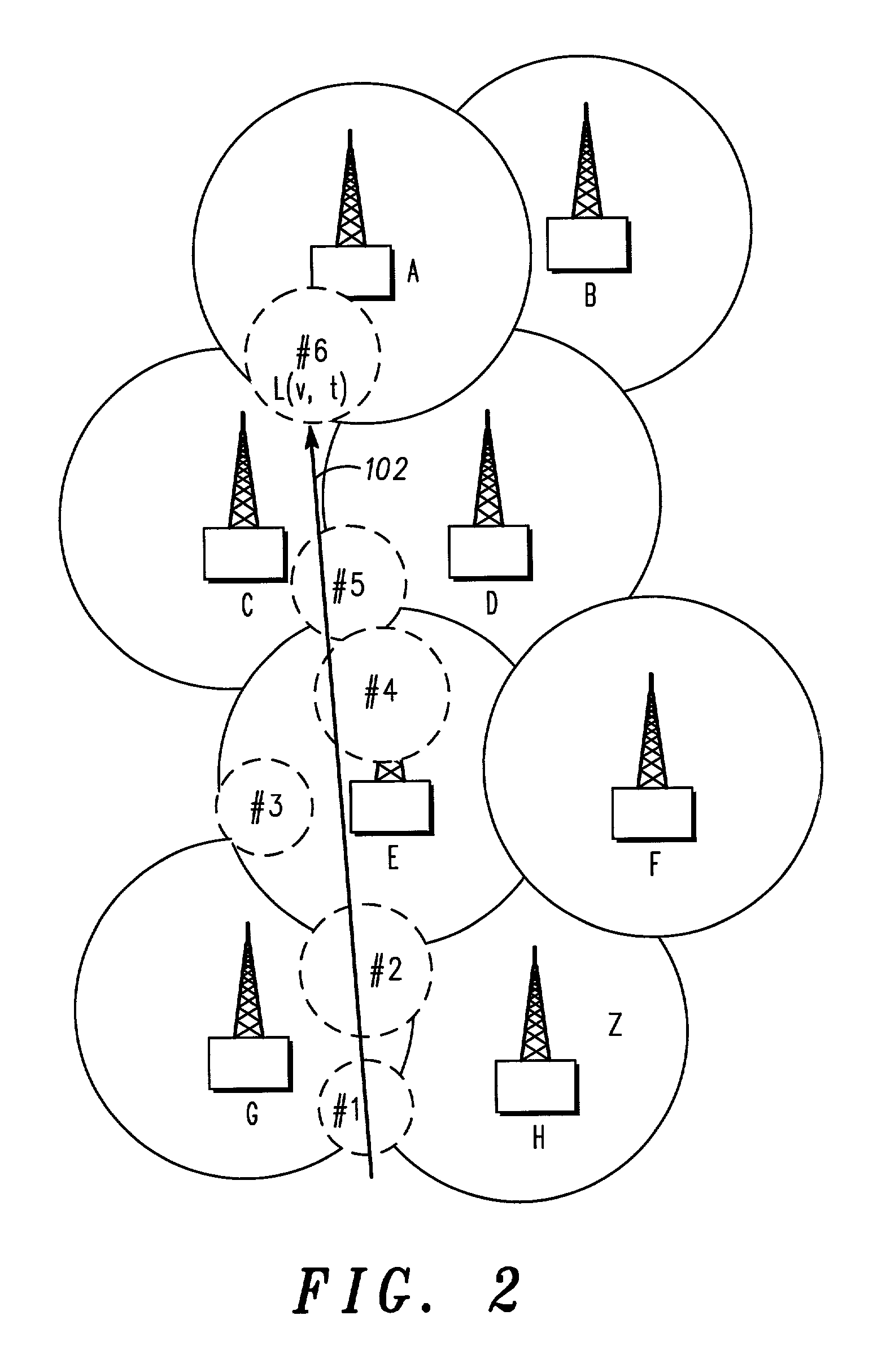
Methods and Apparatus for Determining FEMTO Base Station Location
A system and method for determining the location of a re-deployable base station is disclosed. The disclosed system and method allow for accurate determination of the location of a re-deployable base station, such as a femto base station (FBS), using position information obtained from a mobile station (MS) that is communicating with the FBS being located. The position information can include the location of the mobile device as estimated using one or more satellite positioning systems or cellular network based positioning systems. The position information can also include data identifying pilots from base stations and / or other FBS's that the MS is receiving. A determination of the propagation loss between the MS and the FBS is used to estimate the distance between the mobile device and the FBS. The location of the FBS is determined based on the received position information and the determined distance between the MS and the FBS.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
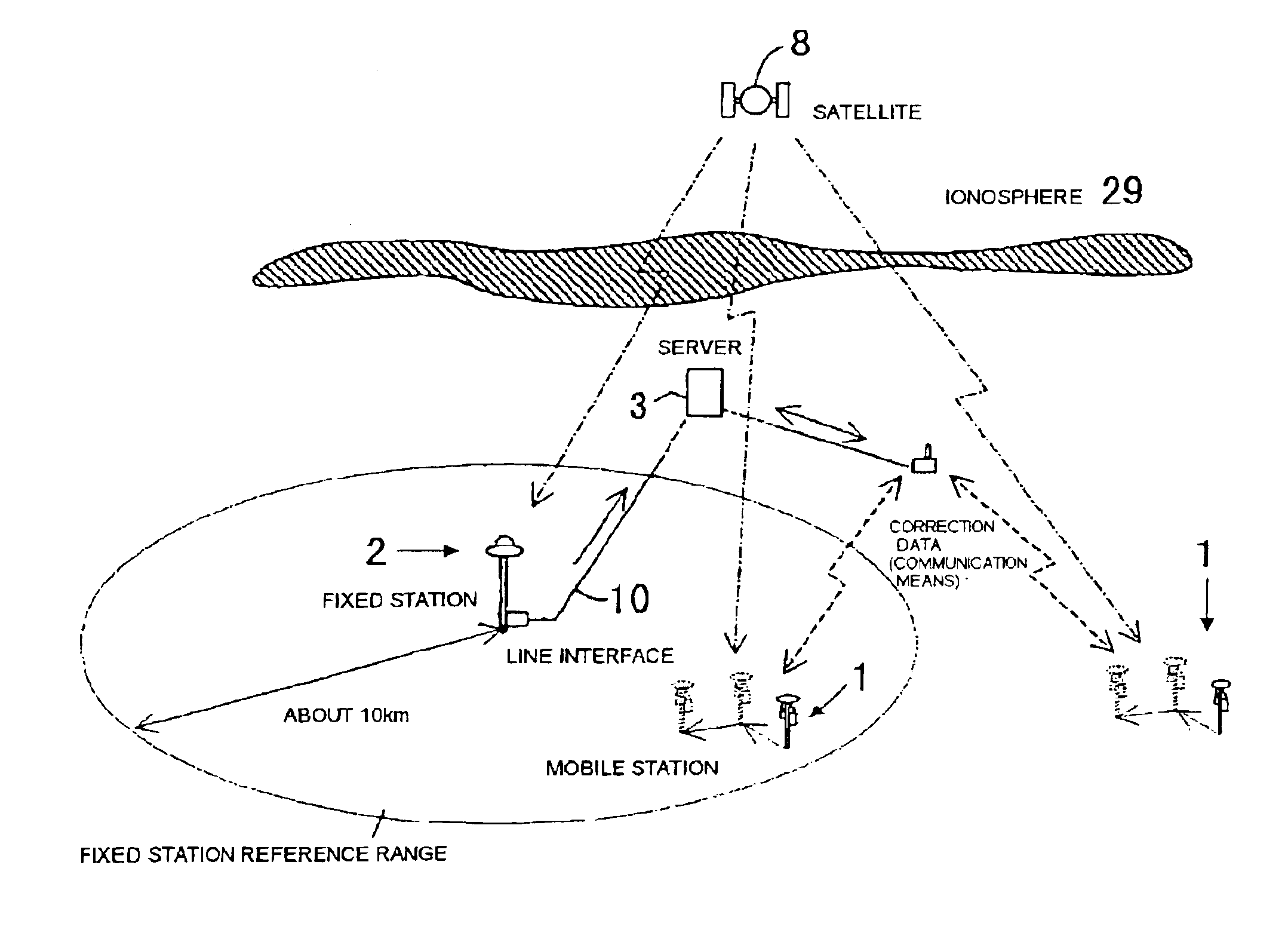
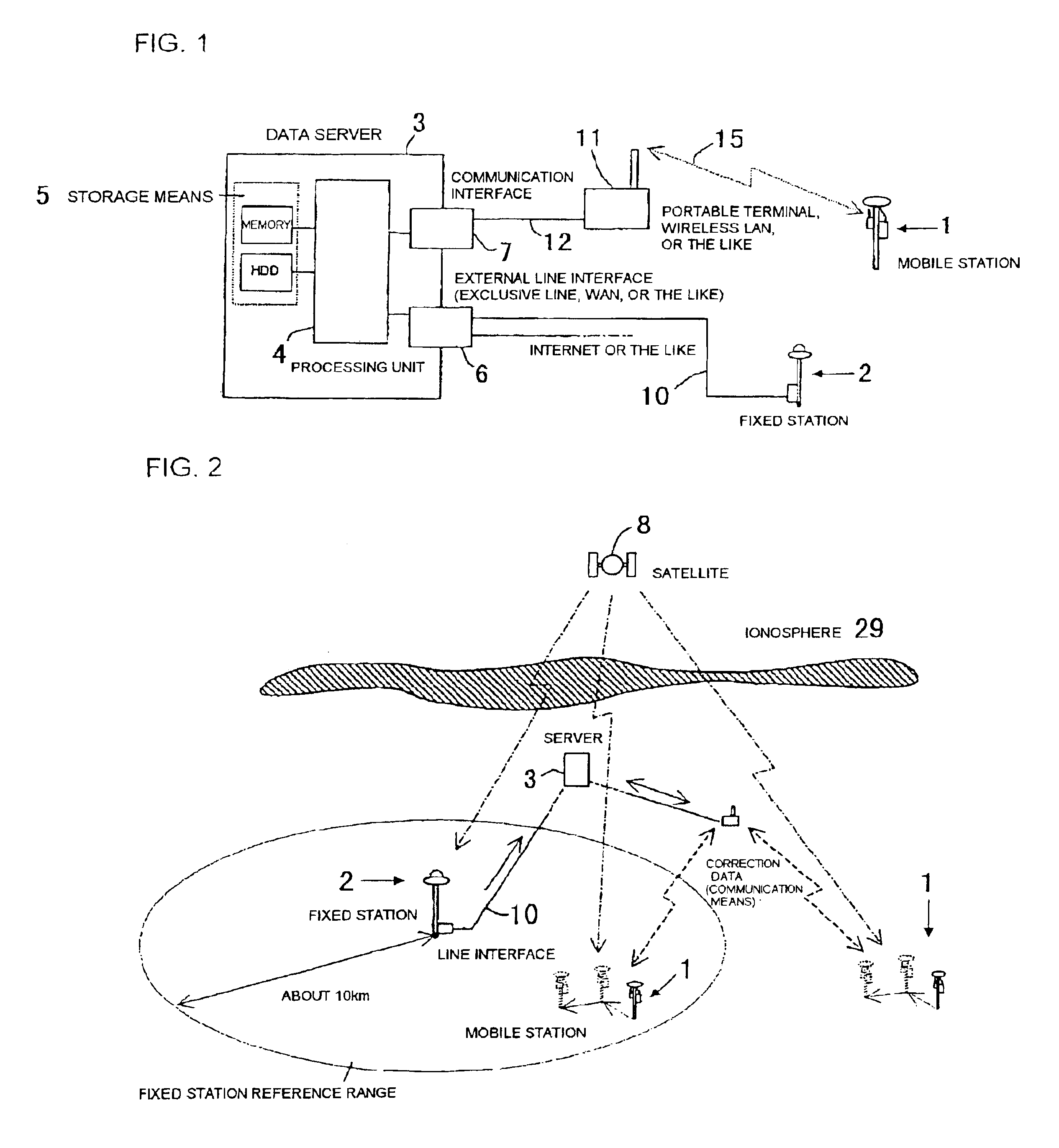
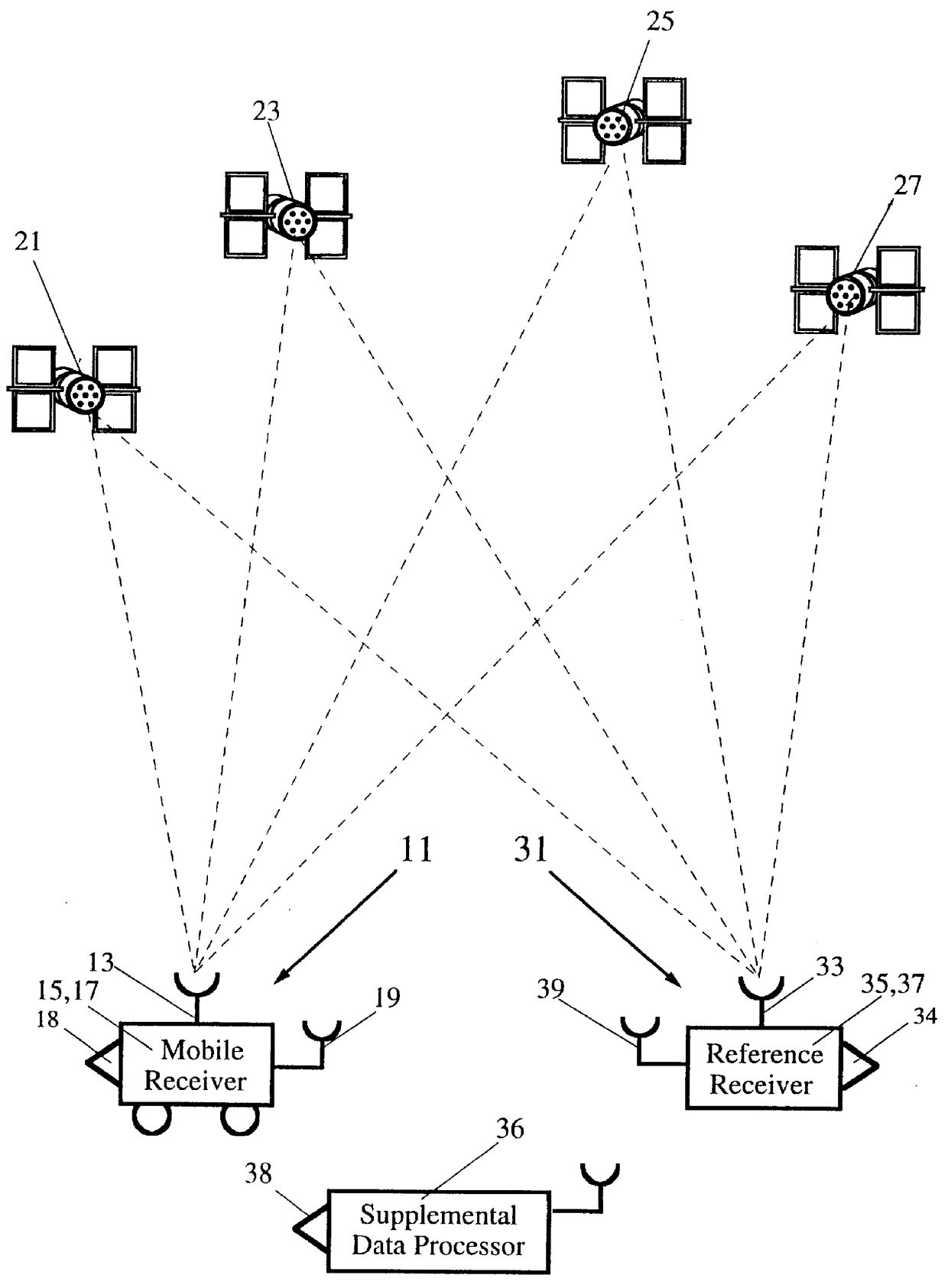
Satellite position measurement system
InactiveUS6865484B2Instruments for road network navigationCosmonautic vehiclesGps positioning systemMobile station
A GPS positioning system that has: at least one mobile station to measure a positional coordinate by receiving radio wave from a satellite; a plurality of fixed stations that have predetermined positional coordinates and receive radio wave from the satellite; and arithmetic processing means, which is connected with at least one mobile station and a plurality of fixed stations via communication, and that transmits correction data suitable for the mobile station to the mobile station based on positioning data transmitted from the mobile station.
Owner:KK TOPCON
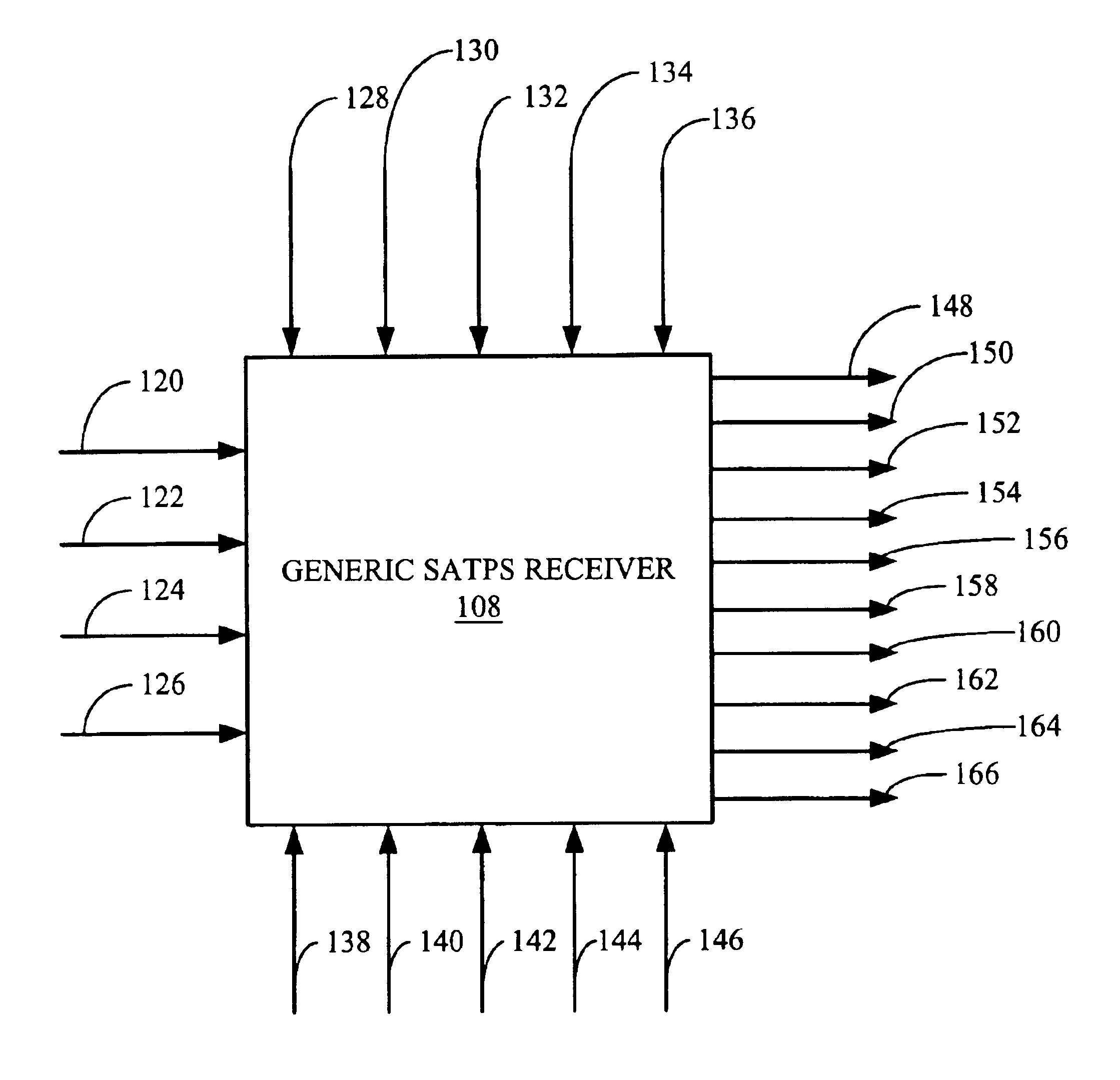
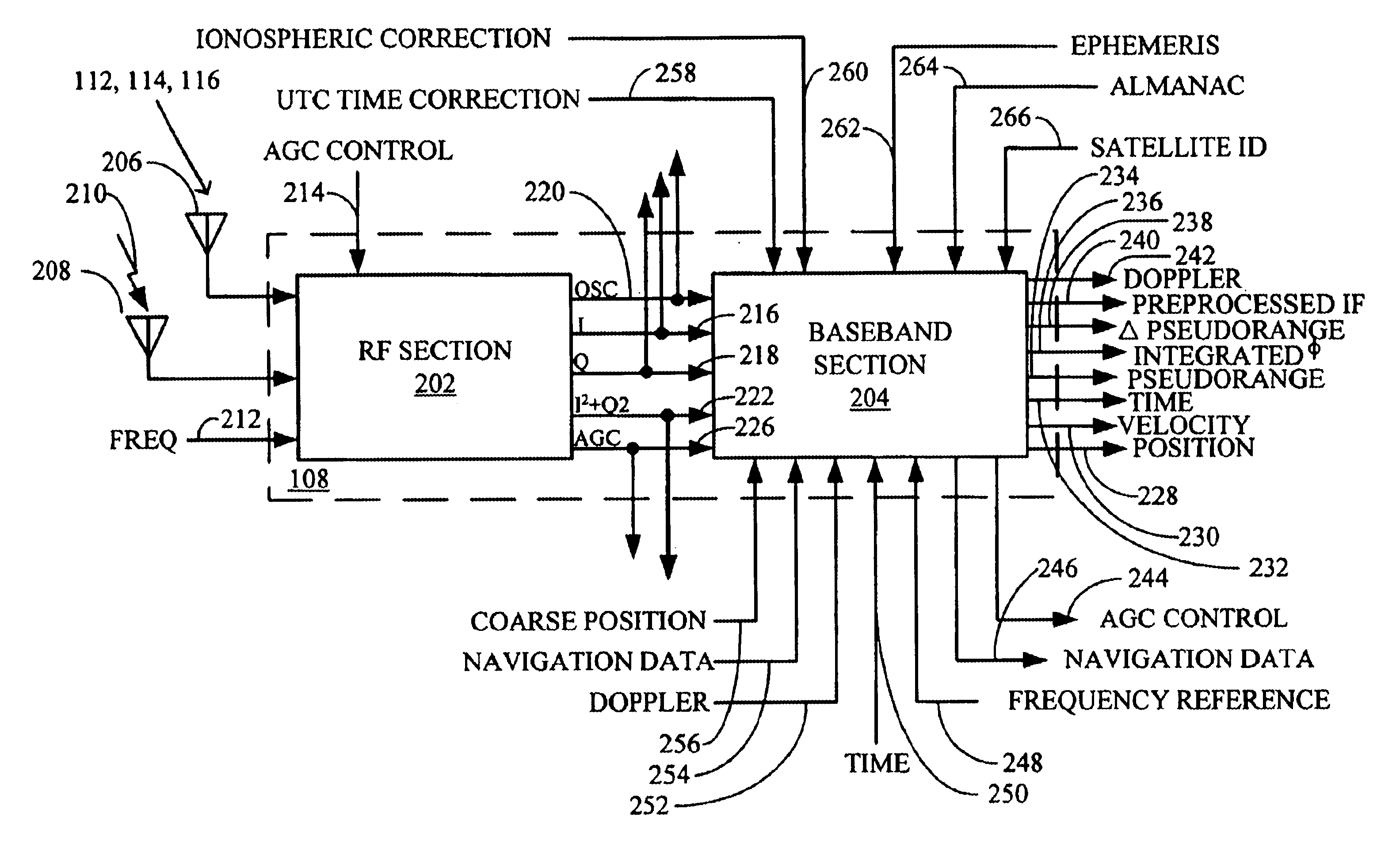
Generic satellite positioning system receivers with programmable inputs
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
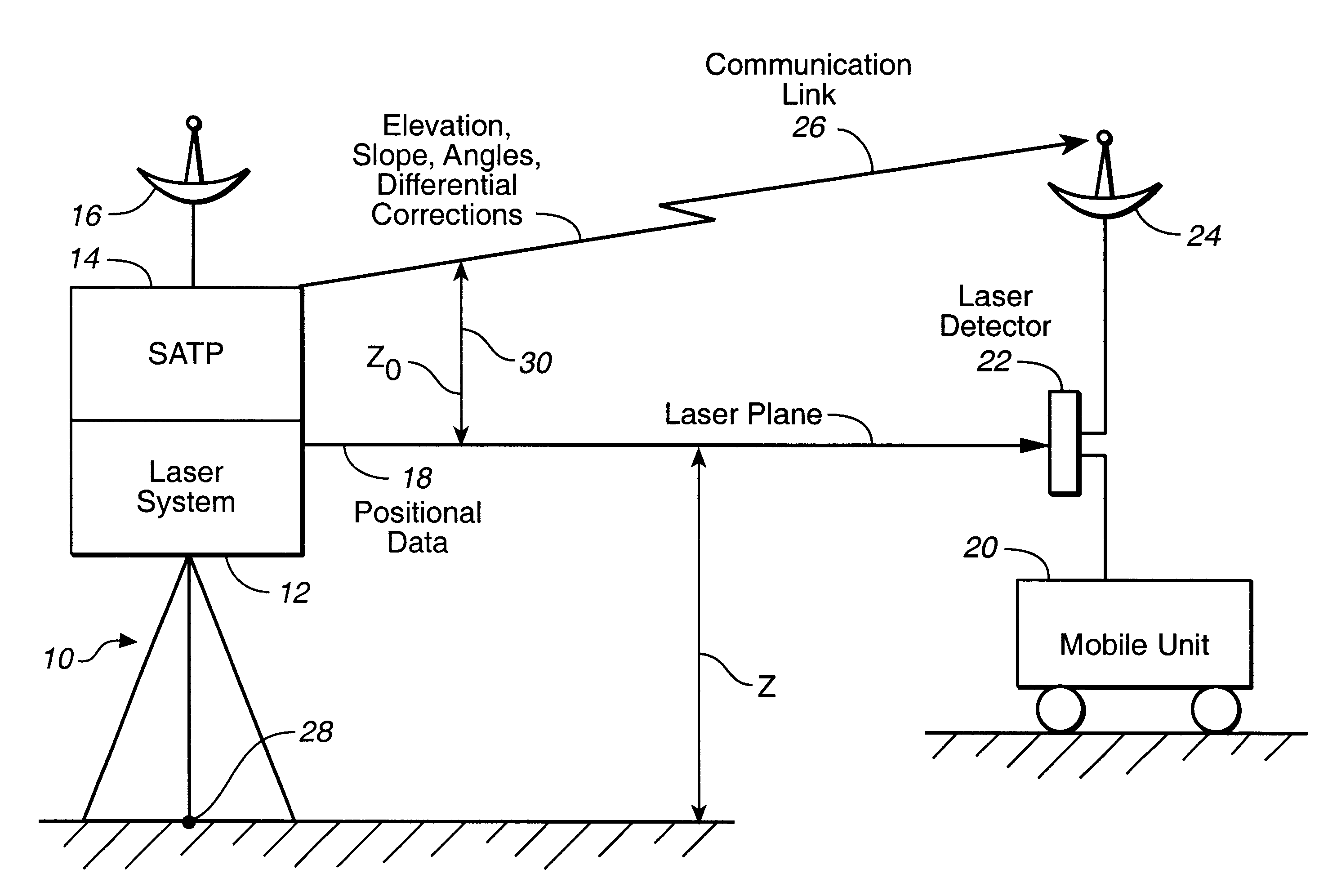
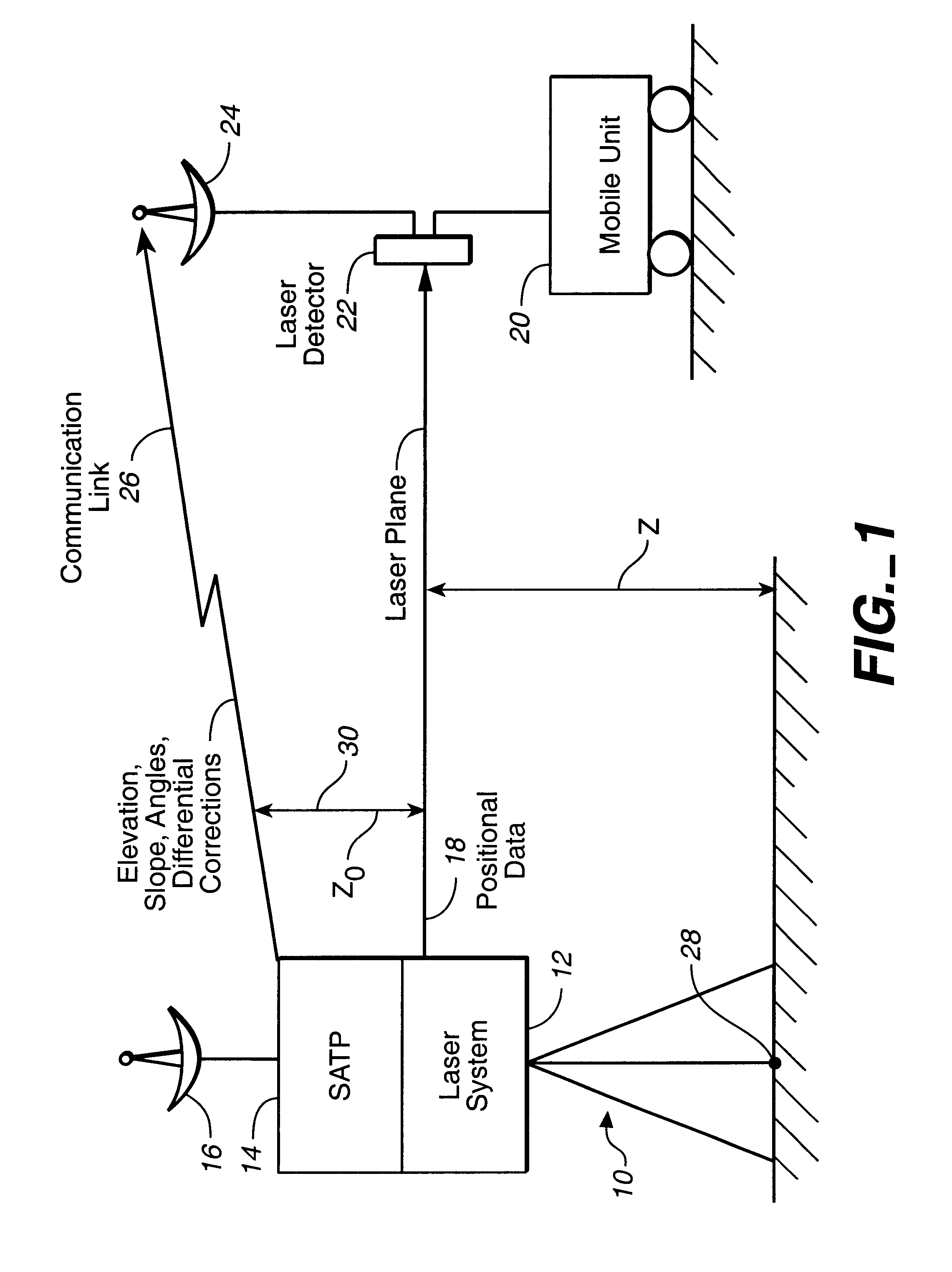
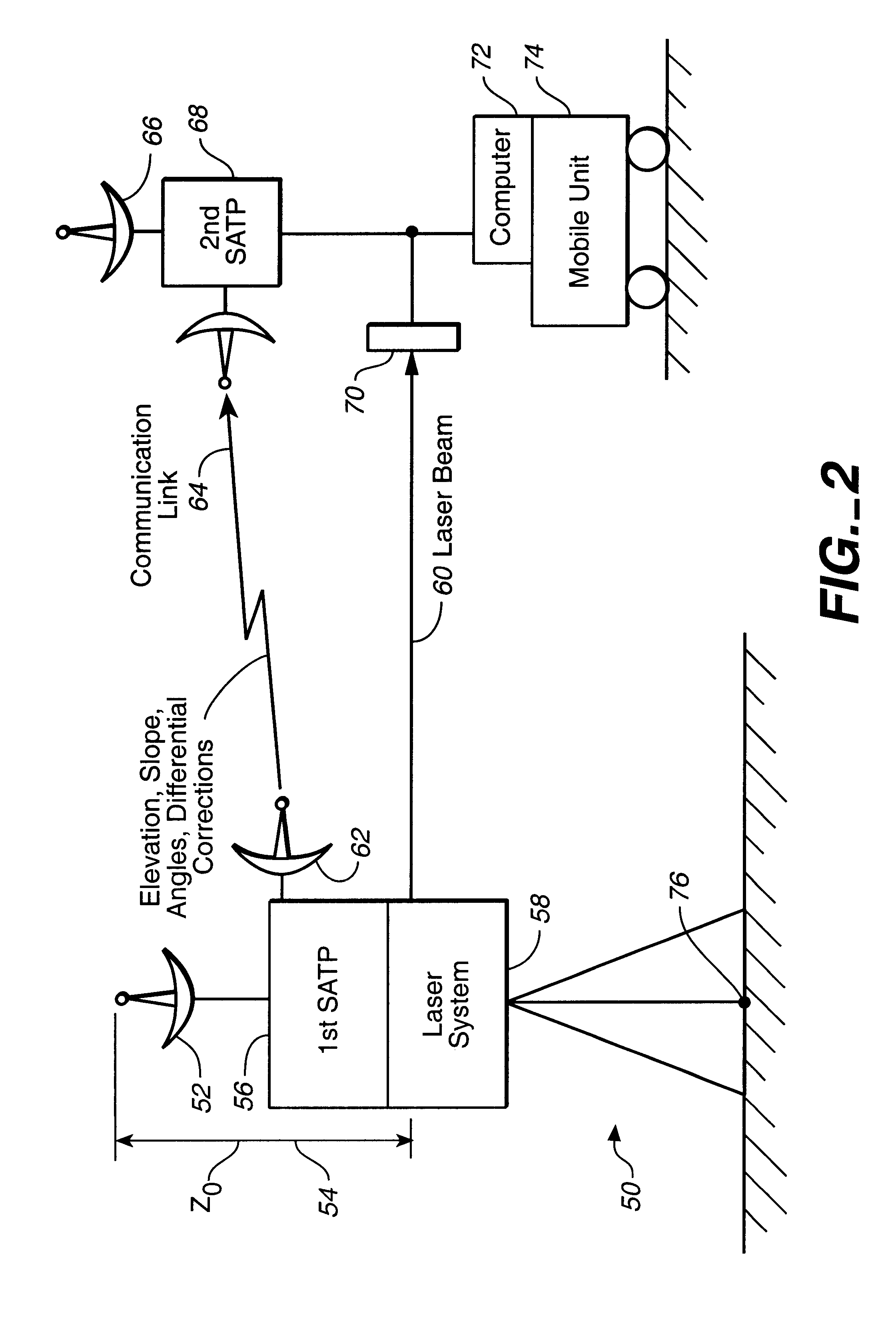
High precision GPS/RTK and laser machine control
InactiveUS6433866B1Angle measurementLaser using scattering effectsMachine controlDifferential correction
The integrated laser and satellite positional system receiver is disclosed. The integrated laser and satellite positioning system receiver can provide a plurality of mobile units with a laser plane data determined with a millimeter relative accuracy. The integrated laser and differential satellite positioning system receiver can also generate and transmit the differential correctional data to a plurality of mobile units. Each mobile unit equipped with a mobile satellite positioning system receiver can use the differential correction data and the high precision laser plane data to improve its position determination capabilities.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
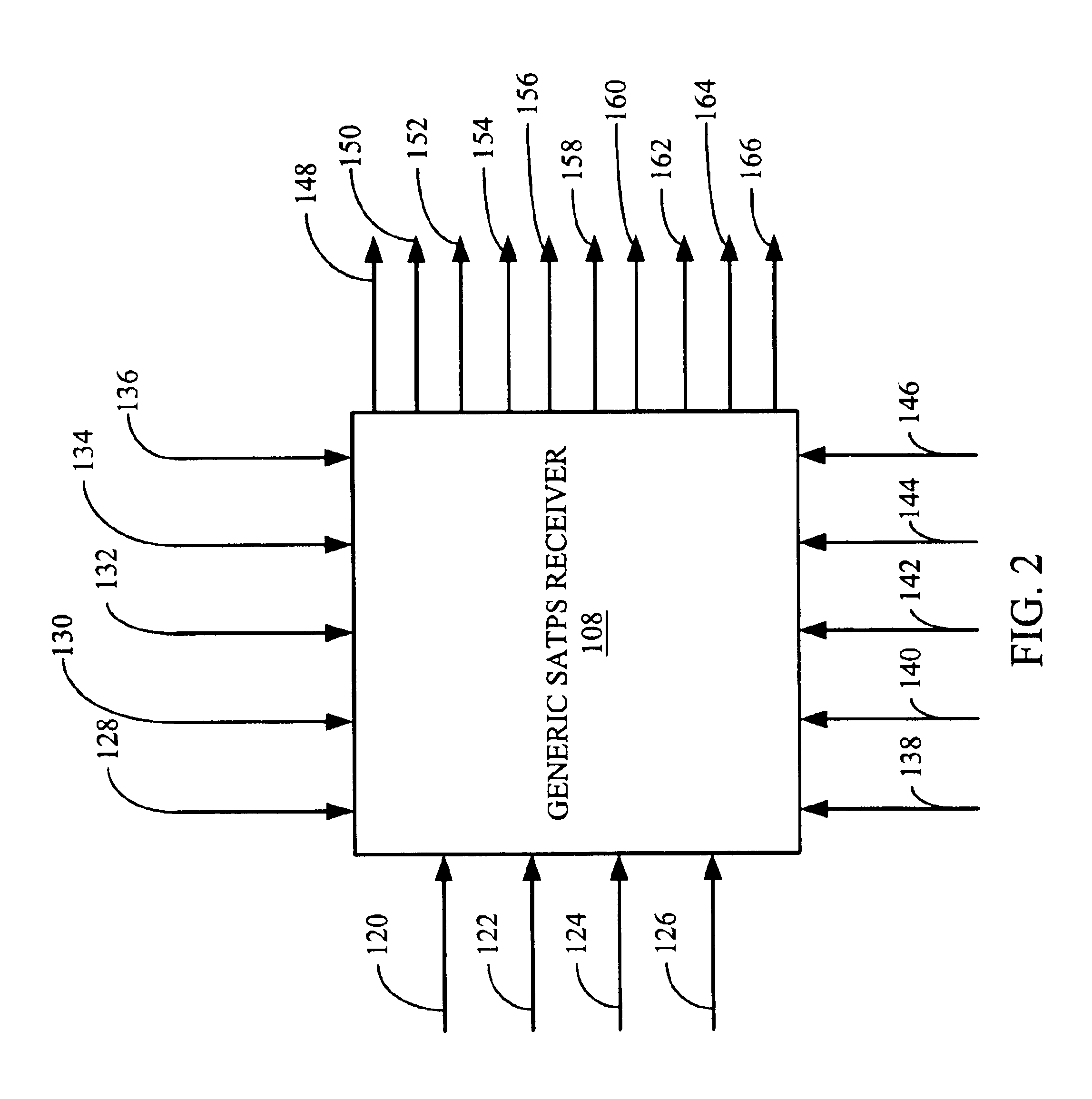
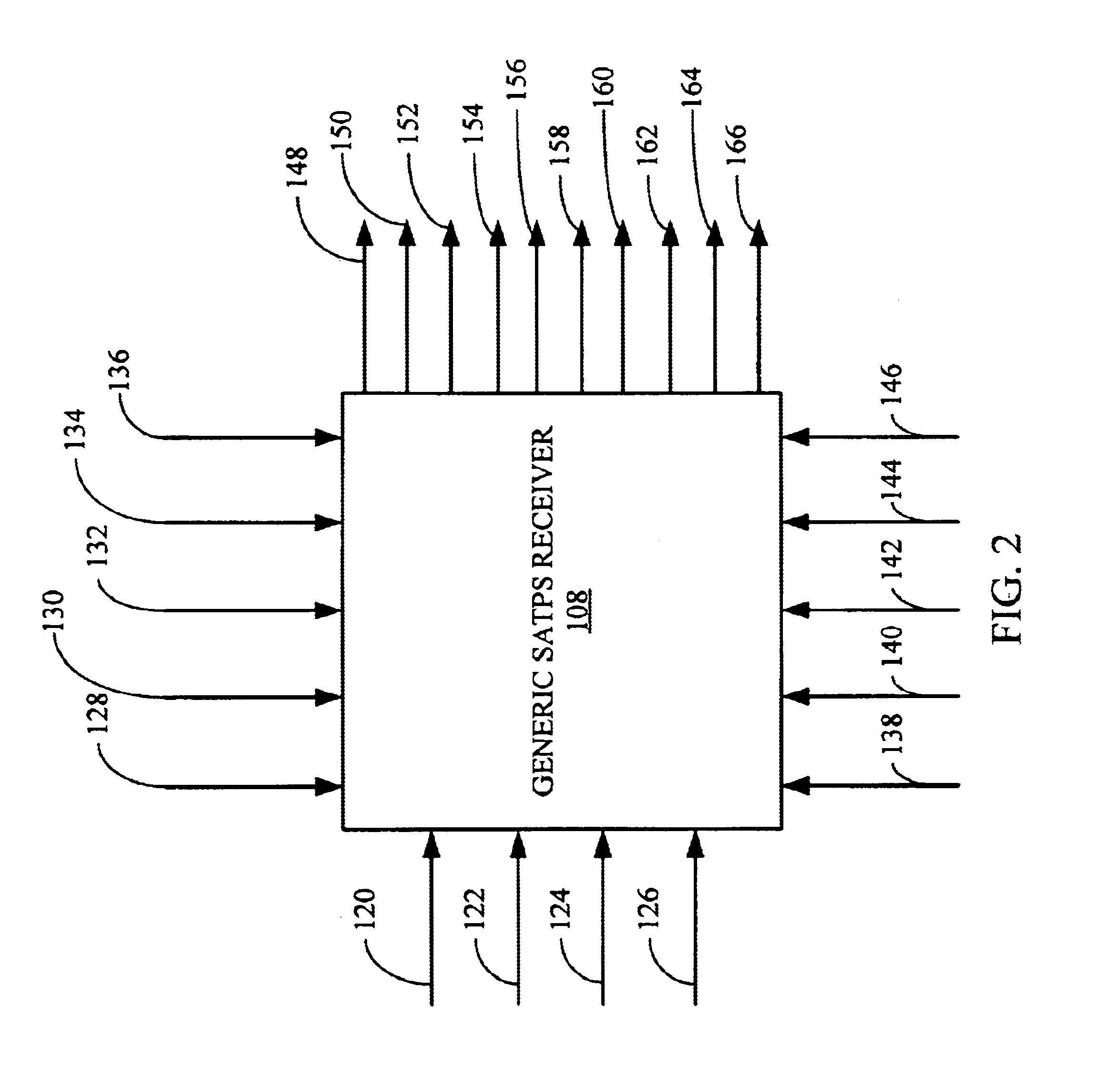
Generic satellite positioning system receivers with selective inputs and outputs
Generic SATPS receivers and methods for configuring generic SATPS receivers that include a plurality of outputs are provided. These configurable SATPS receivers are adapted to be utilized in at least one of a plurality of particular SATPS receiver applications, and can also include a plurality of input paths, and a means for generating selected ones of the plurality of possible outputs. Selected ones of the plurality of outputs are enabled / disabled based on at least one requirement of the particular receiver application to configure or program the generic SATPS receiver to function as a SATPS receiver used for a particular SATPS receiver application or operating environment. The selected ones of the plurality of outputs can be defined by and can be those utilized by the particular SATPS receiver application or operating environment. Thus, SATPS receivers are provided that can be used in multiple applications, that can accept multiple types of assistance data, and that have multiple types of outputs depending on the application and / or desires of the user. The SATPS receiver can be implemented in SATPS systems that include at least one satellite that provides SATPS information, a generic SATPS receiver, and a remote computer.
Owner:CSR TECH INC
Unmanned aerial vehicle obstacle avoidance controlling method
InactiveCN103116360ASimple methodEasy to operatePosition/course control in three dimensionsWireless dataGeolocation
The invention discloses an unmanned aerial vehicle obstacle avoidance controlling method. An unmanned aerial vehicle subsystem and a ground station subsystem are arranged, the unmanned aerial vehicle subsystem comprises an embedded flight controller and an airborne terminal of a wireless data chain, a satellite positioning receiver and a height sensor are arranged in the embedded flight controller, the ground subsystem comprises an embedded monitoring computer and a ground terminal of the wireless data chain, and an electronic map containing geographic information of obstacles is arranged in the embedded monitoring computer. On the electronic map in the embedded monitoring computer of the ground station subsystem, the geographic information of the obstacles in a flight area is determined, virtual obstacle polygonal cylinders are established, shape data of the virtual obstacle polygonal cylinders are downloaded in the embedded flight controller which obtains the current position of the unmanned aerial vehicle and calculates space correlation between the unmanned aerial vehicle and the obstacle polygonal cylinders, track-shifting instruction of the unmanned aerial vehicle is generated, and automatic obstacle avoidance of the unmanned aerial vehicle is realized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
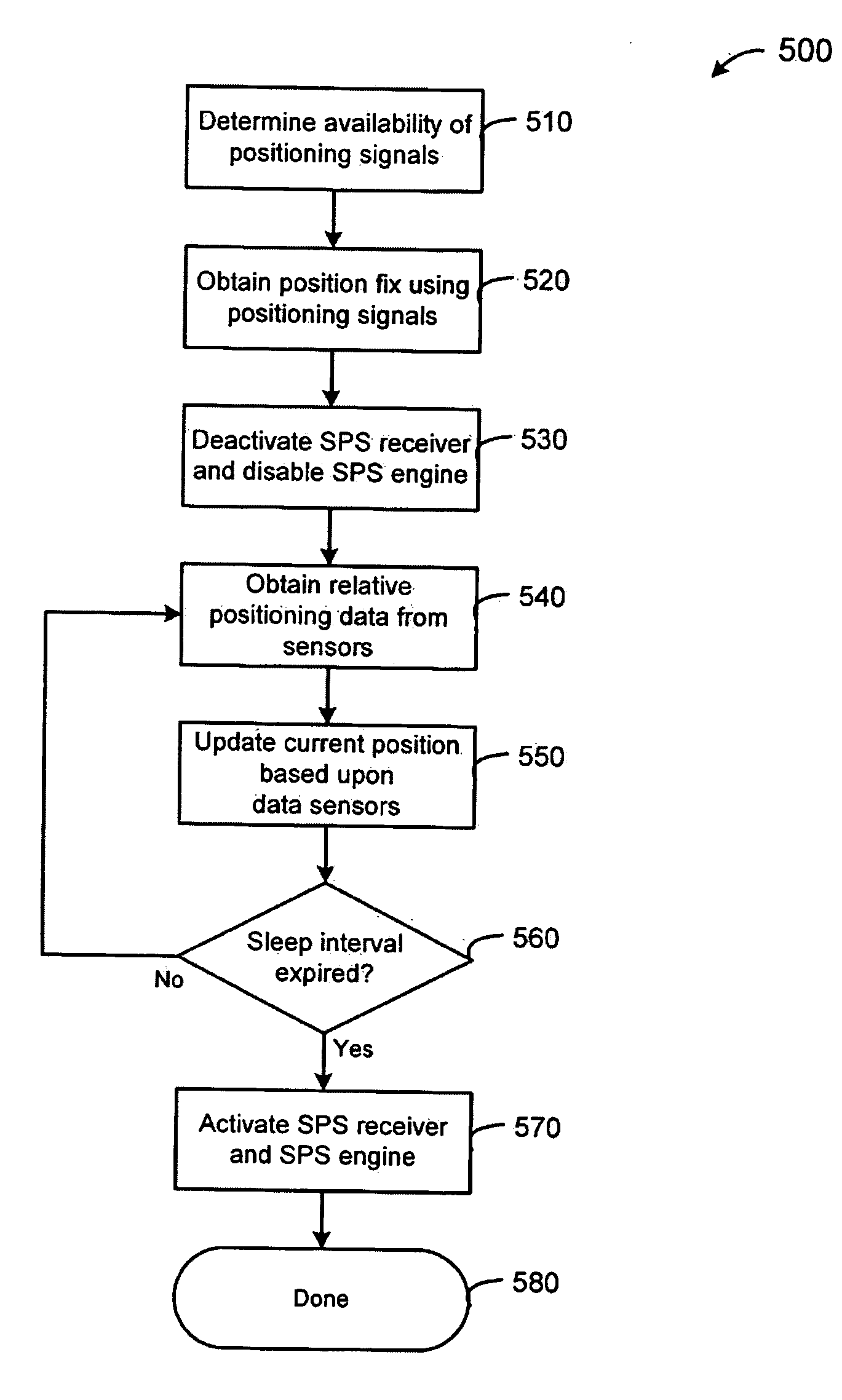
GPS power savings using low power sensors
ActiveUS20090278738A1Reduce power consumptionNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsBeacon systemsPower sensorEngineering
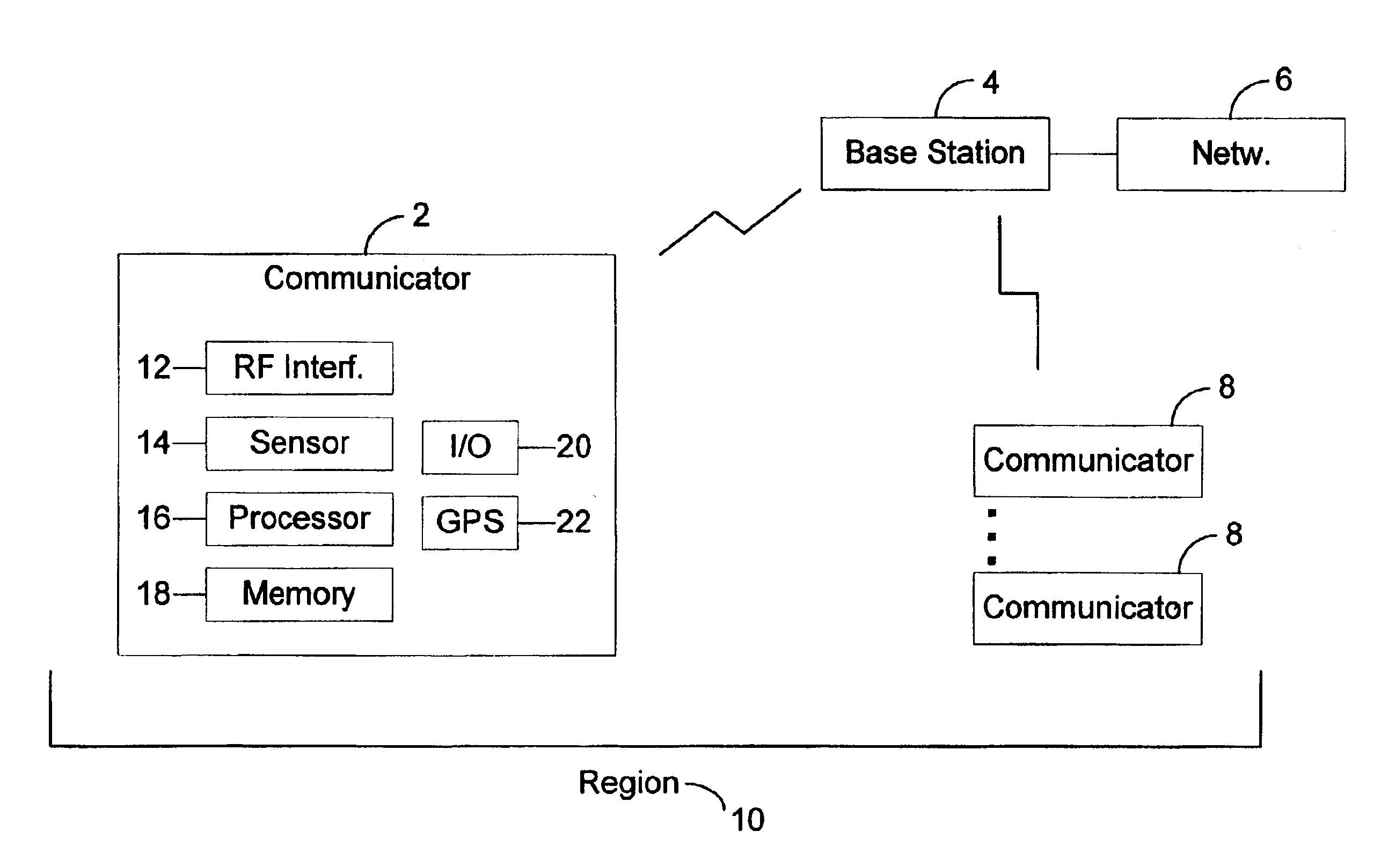
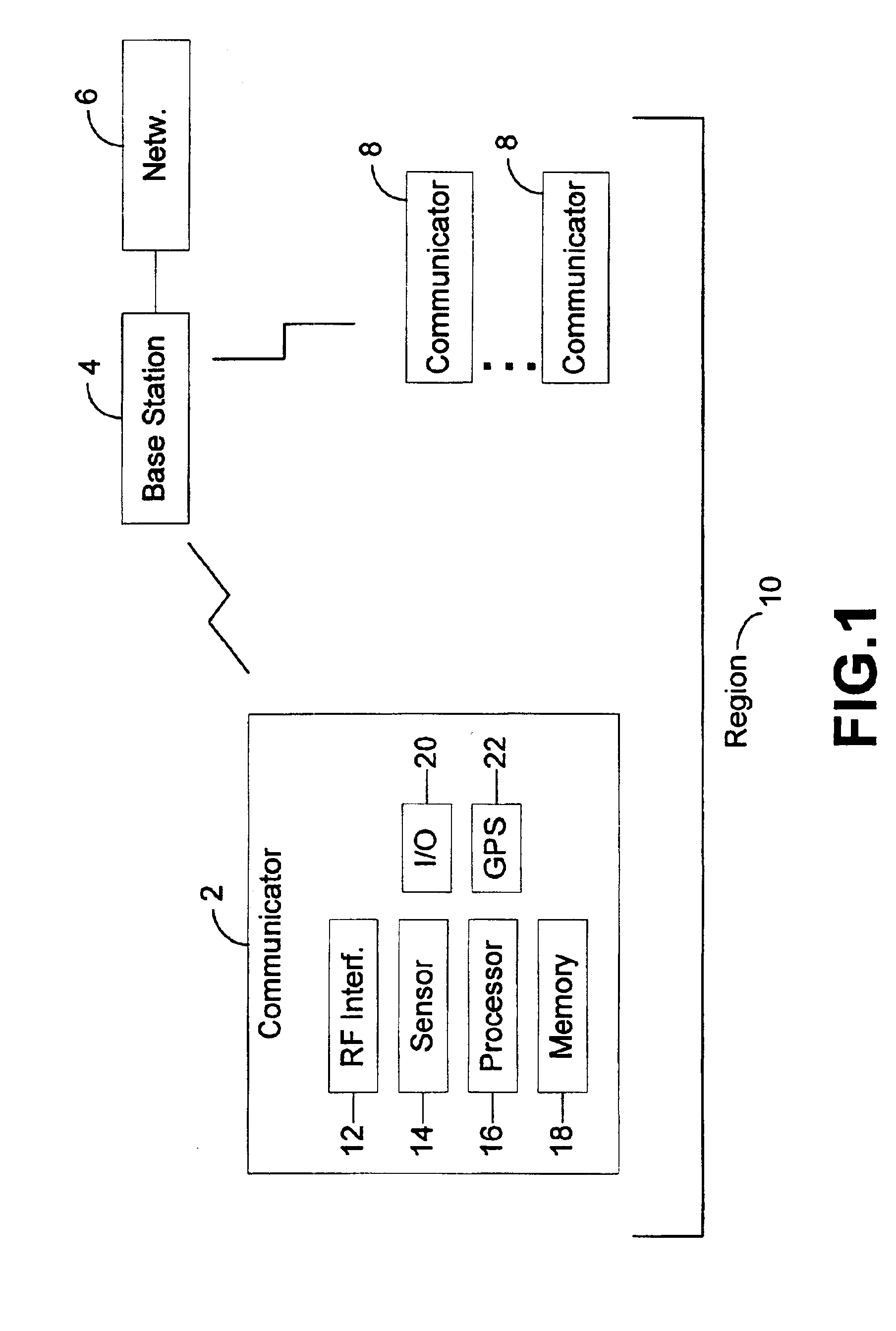
A position location system, apparatus, and method are disclosed. A wireless device includes a satellite positioning system (SPS) receiver and position location processor. The SPS receiver detects the availability of positioning signals and the position location processor determines an initial position of the wireless device based upon the positioning signals. A controller generates power saving events when the positioning signals are detected as being available. The controller determines the timing and duration of the power saving events. During a power saving event, the SPS receiver is deactivated and / or processing of the positioning signals is suspended to reduce power consumption of the wireless device. The initial position is updated based upon relative positioning information from one or more sensors during the power saving event. The controller activates the SPS receiver and resumes processing of the positioning signals following the power saving event.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
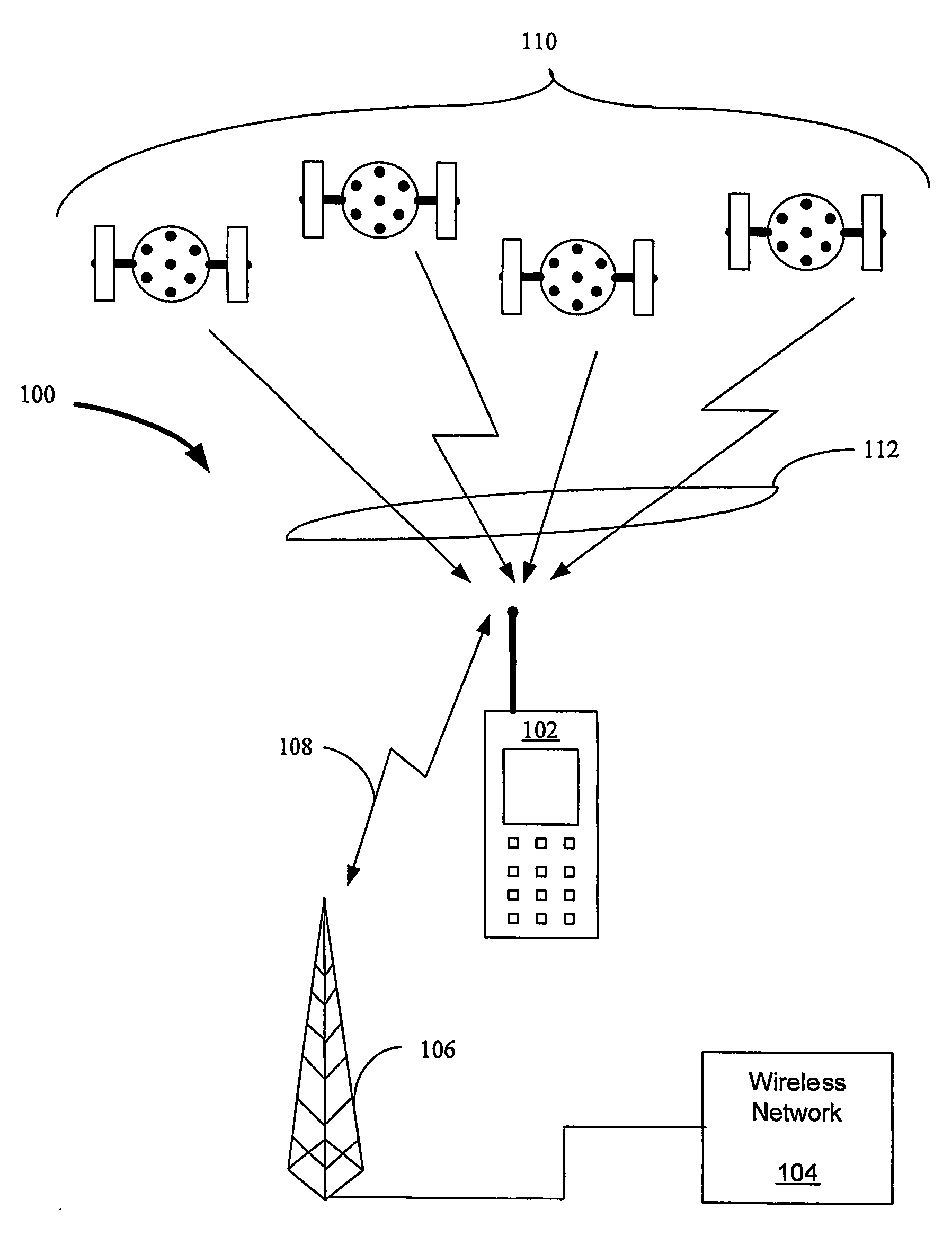
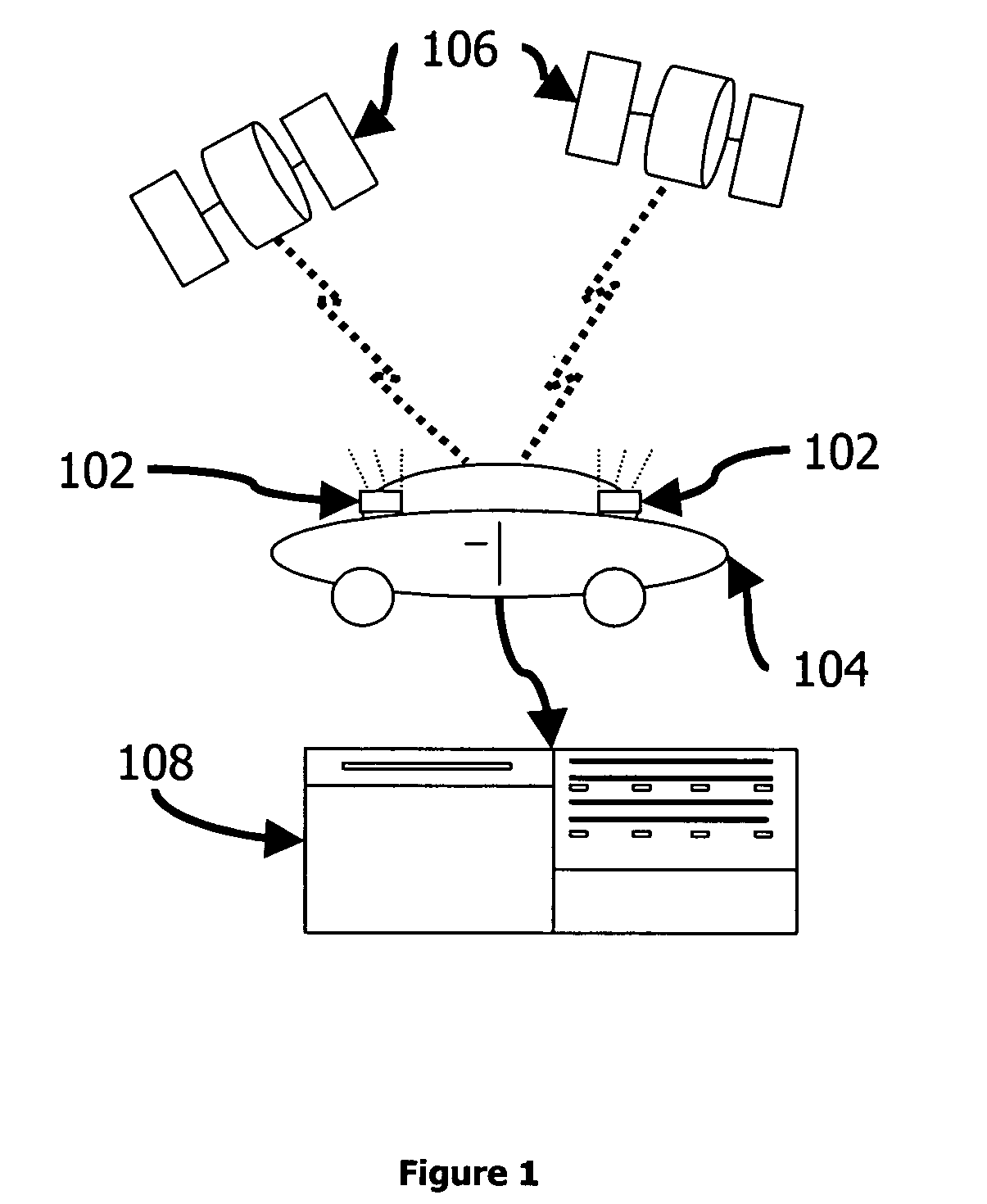
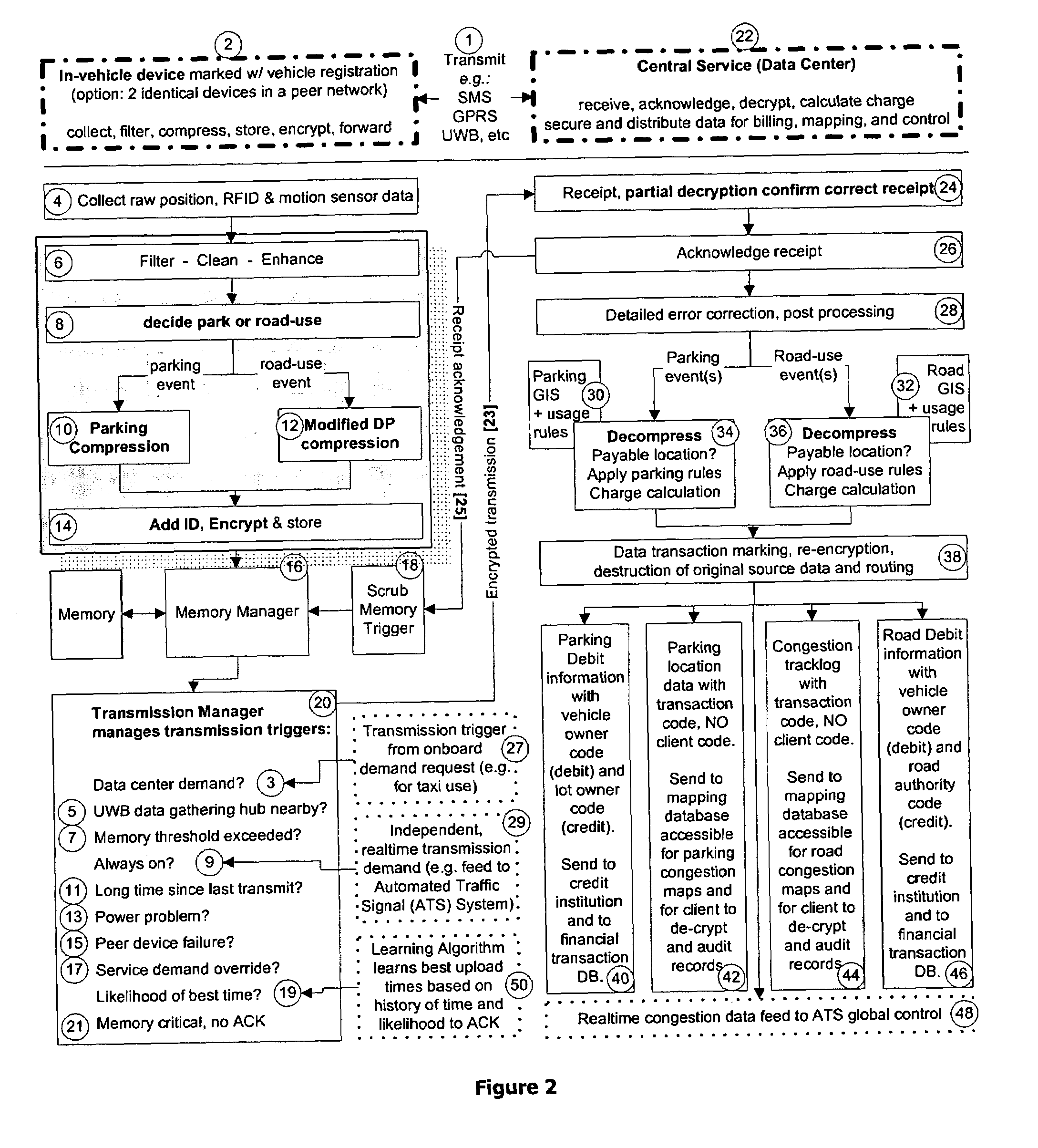
Method and apparatus for a satellite positioning-based metering system for use in transport-related applications
ActiveUS7215255B2Cheap for transmissionThin on-board environmentRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesDetection of traffic movementReal-time dataWireless transmission
A system and method for monitoring, measuring, and / or usage metering of a vehicle involving tracking continuous movement and position of the vehicle for priced parking spots, priced roads, and / or pay-as-you-drive insurance. The system comprises a vehicle-mounted apparatus incorporating positioning signal reception, filtering, compression, storage and wireless transmission, while a central processing system collects these position-logs for matching with digital maps and parking, road use, and insurance fee application schedules. Sufficient accuracy and precision enables billing of vehicle owners unambiguously, generating timely congestion and traffic maps, and providing real time data feeds to signal control and navigation systems. This invention may be used to meter parking, road use, or insurance, either alone or concurrently in combination.
Owner:SKYMETER
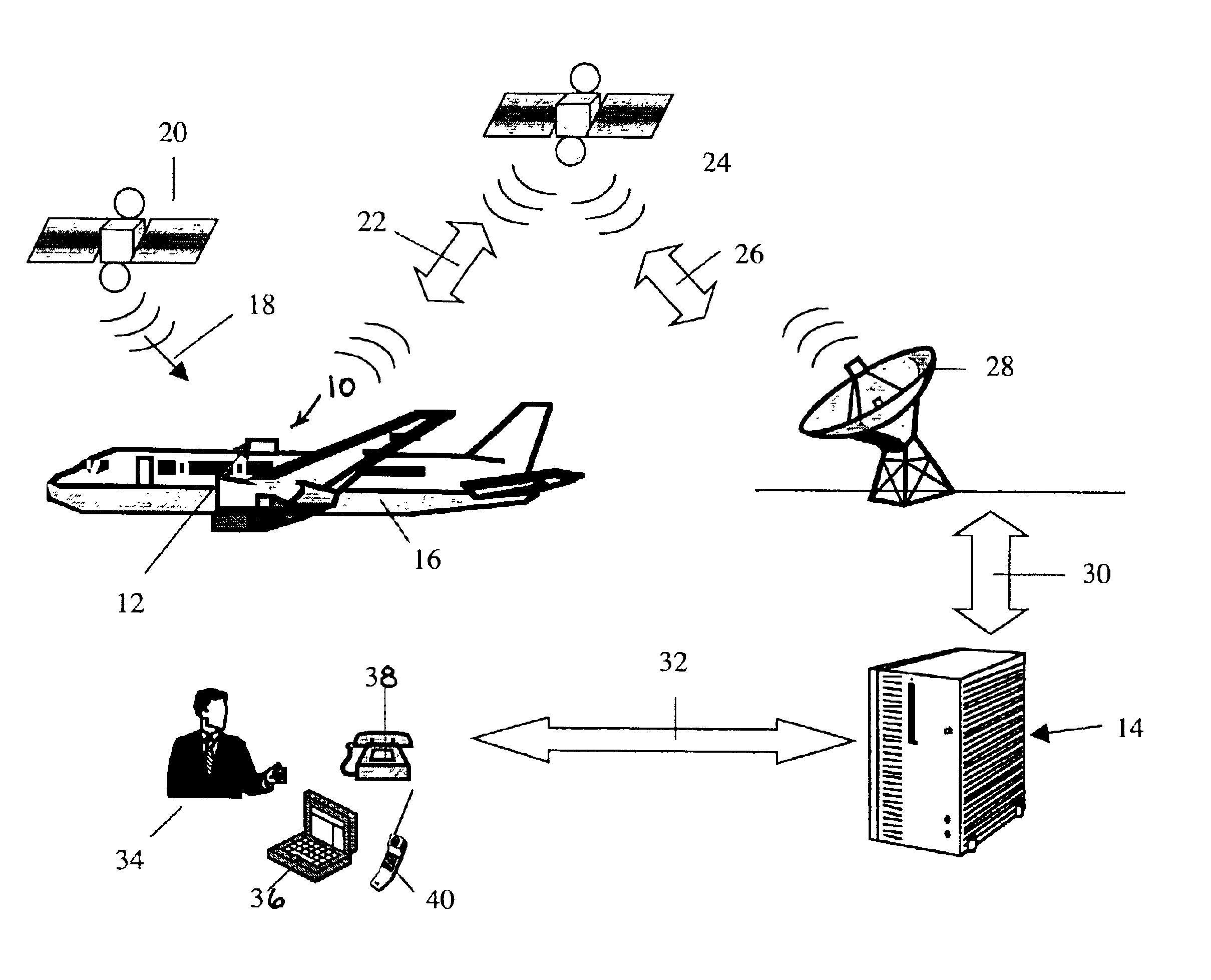
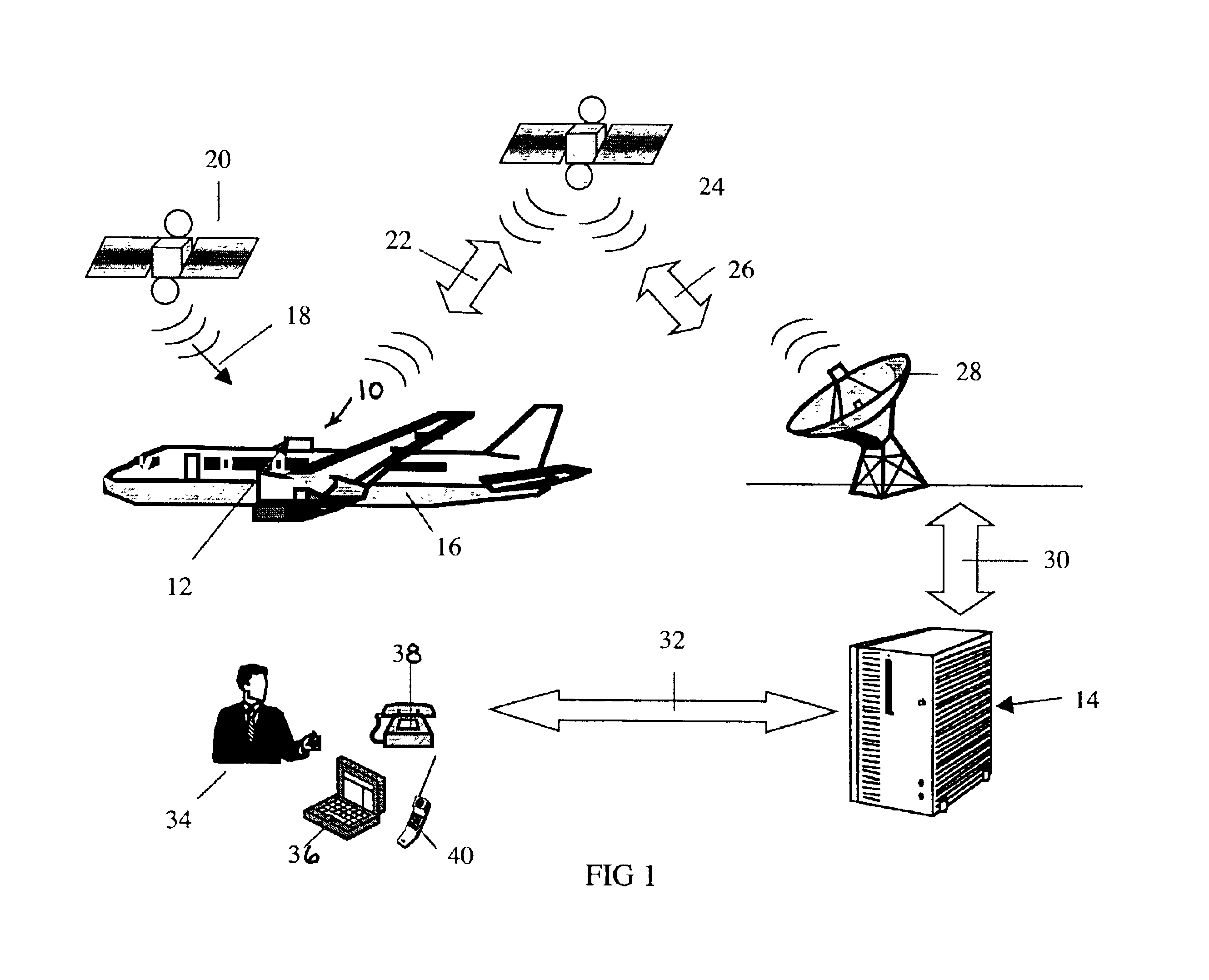
Aircraft location monitoring system and method of operation
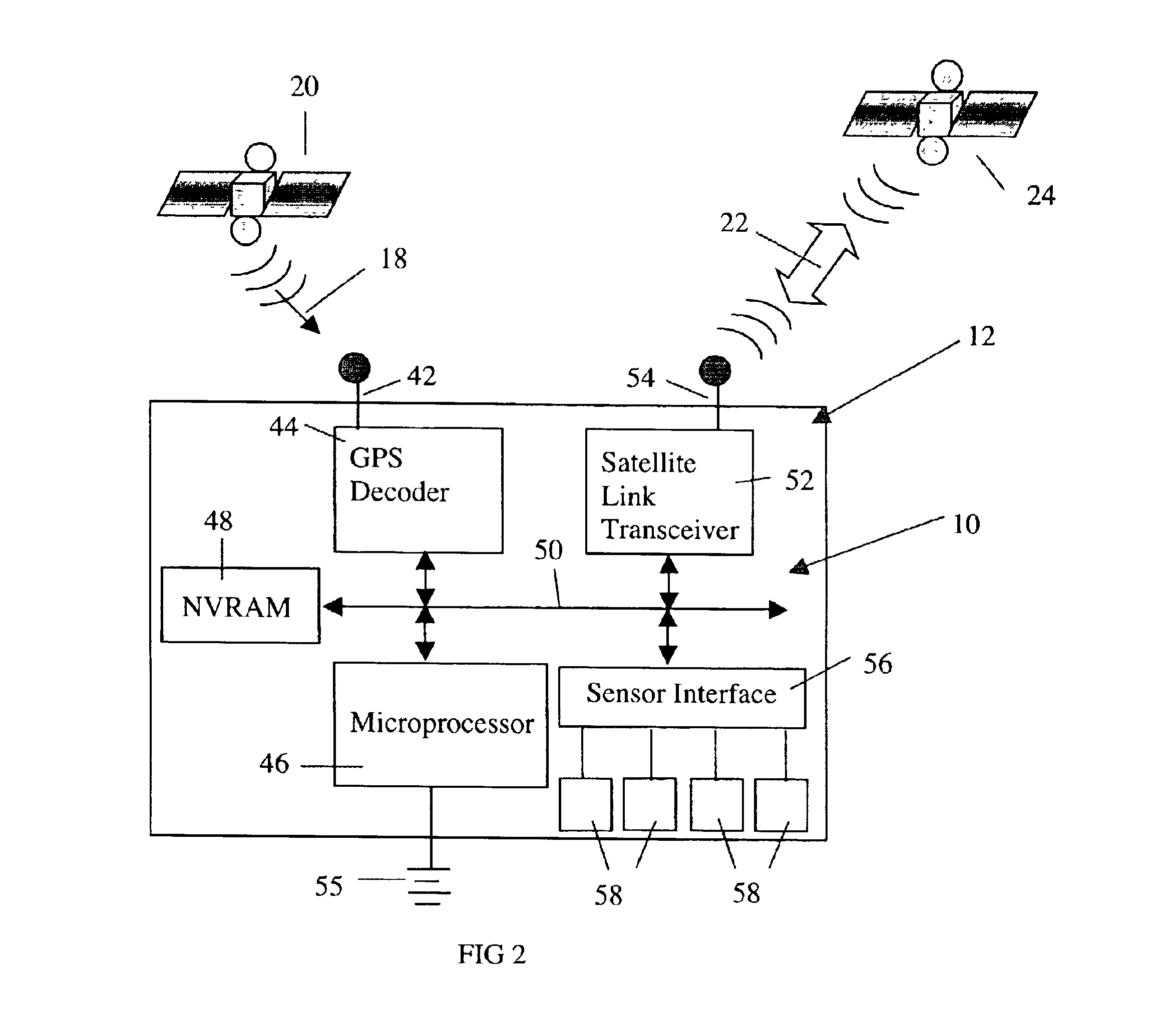
InactiveUS6799094B1Easy to adaptDigital data processing detailsPosition fixationTransceiverMonitoring system
An aircraft monitoring system adapted for mounting in an aircraft and at a location independent of the aircraft for providing information related to aircraft location and / or the current state of the operation of the aircraft. The monitoring system includes an aircraft-tracking device and a server computer adapted for communicating with an aircraft owner / operator. The device includes a signal receiving antenna for receiving signals from a satellite positioning system and a decoder connected to the antenna for decoding the location position coordinates (GPS or GLONASS). Further, the aircraft-tracking device includes a microprocessor connected to the decoder and a two-way satellite communication transceiver. The transceiver is connected to a two-way radio communication antenna. The radio communication antenna receives and sends two-way satellite communications between a satellite communication system. The satellite communication system communicates with a ground-based satellite communication service. The server computer is connected to the satellite communication service and is connected to a telecommunication system for alerting the owner / operator as to the aircraft's location and / or the current state of operation.
Owner:NORTHSTAR SYST LLC
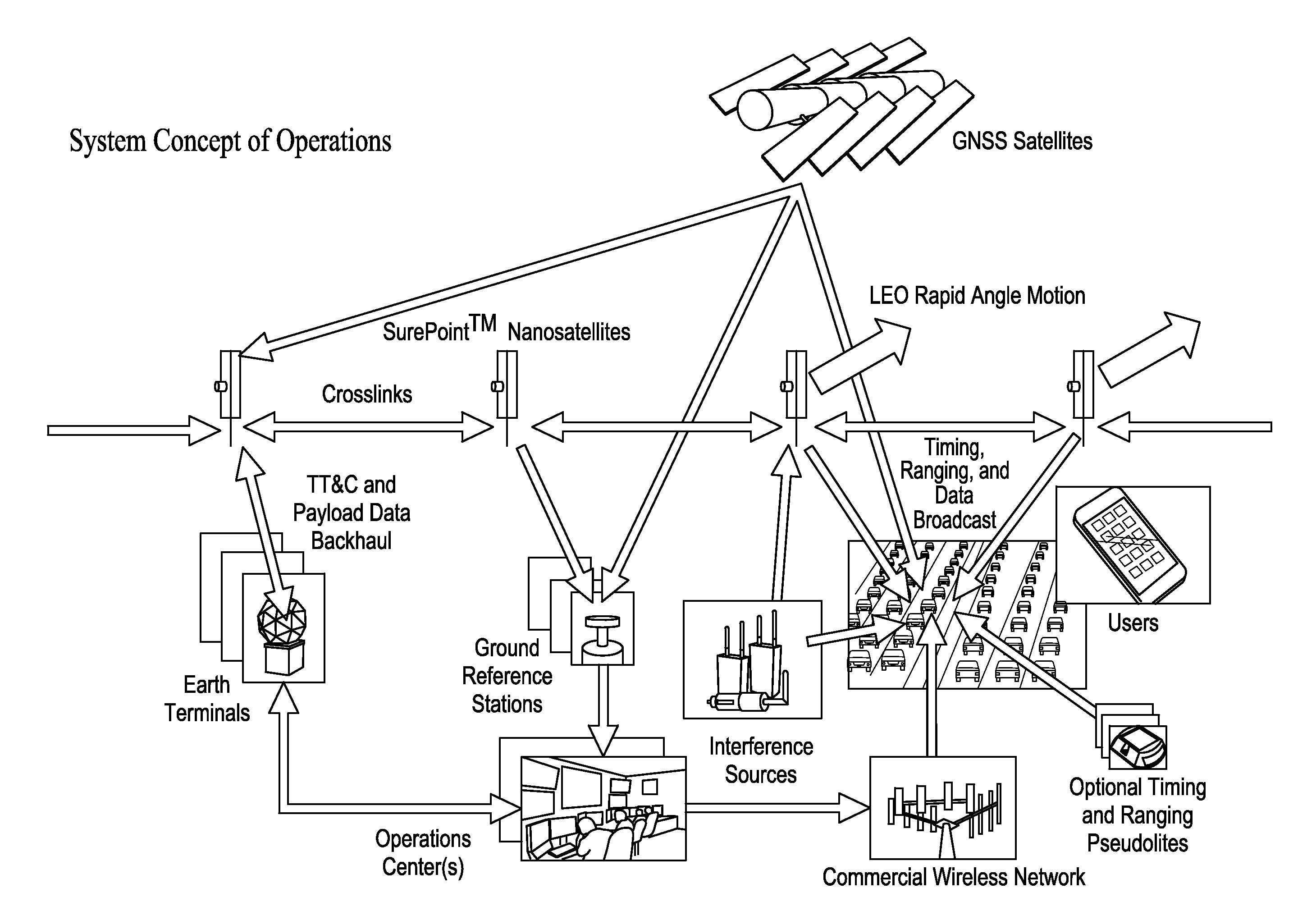
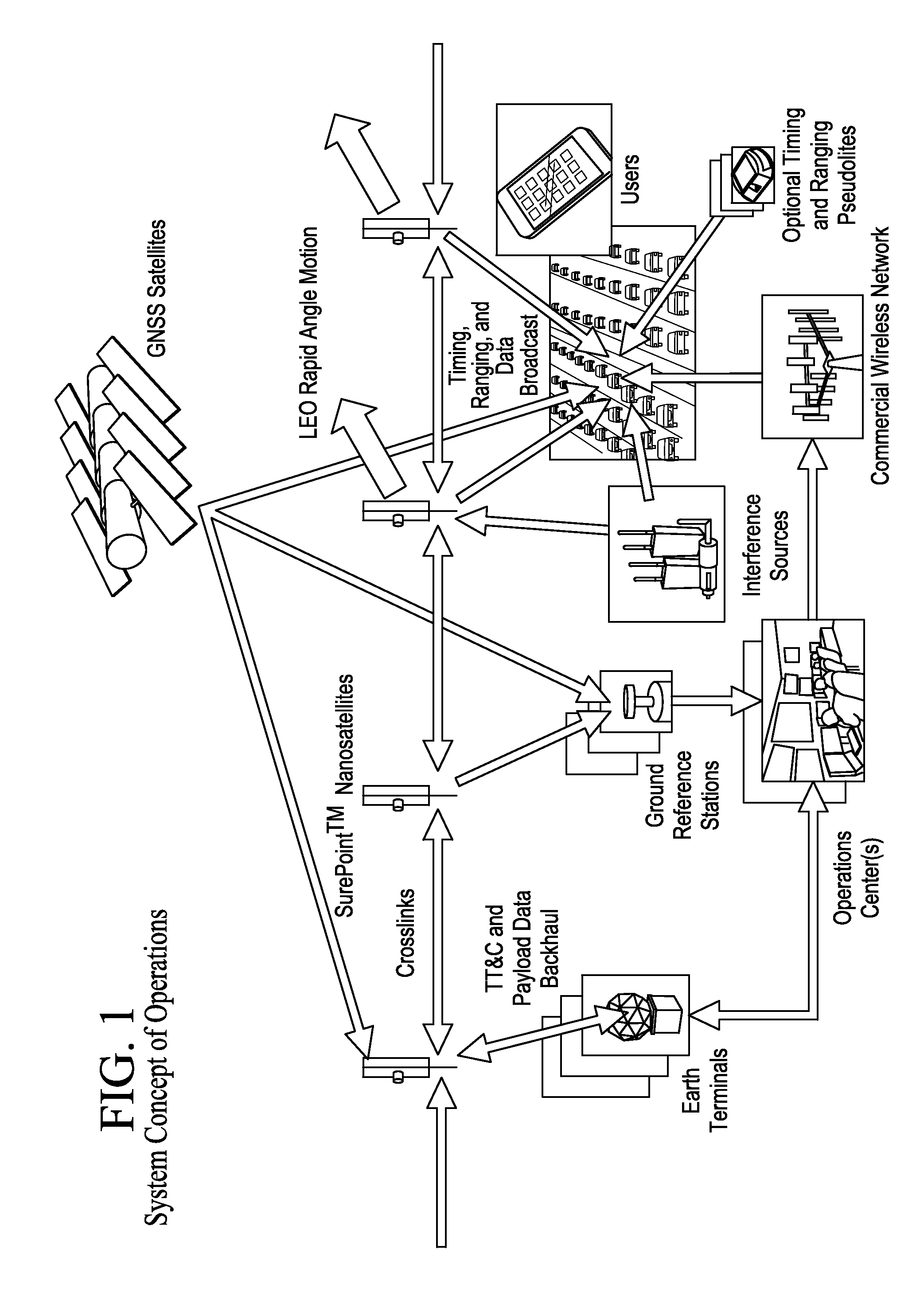
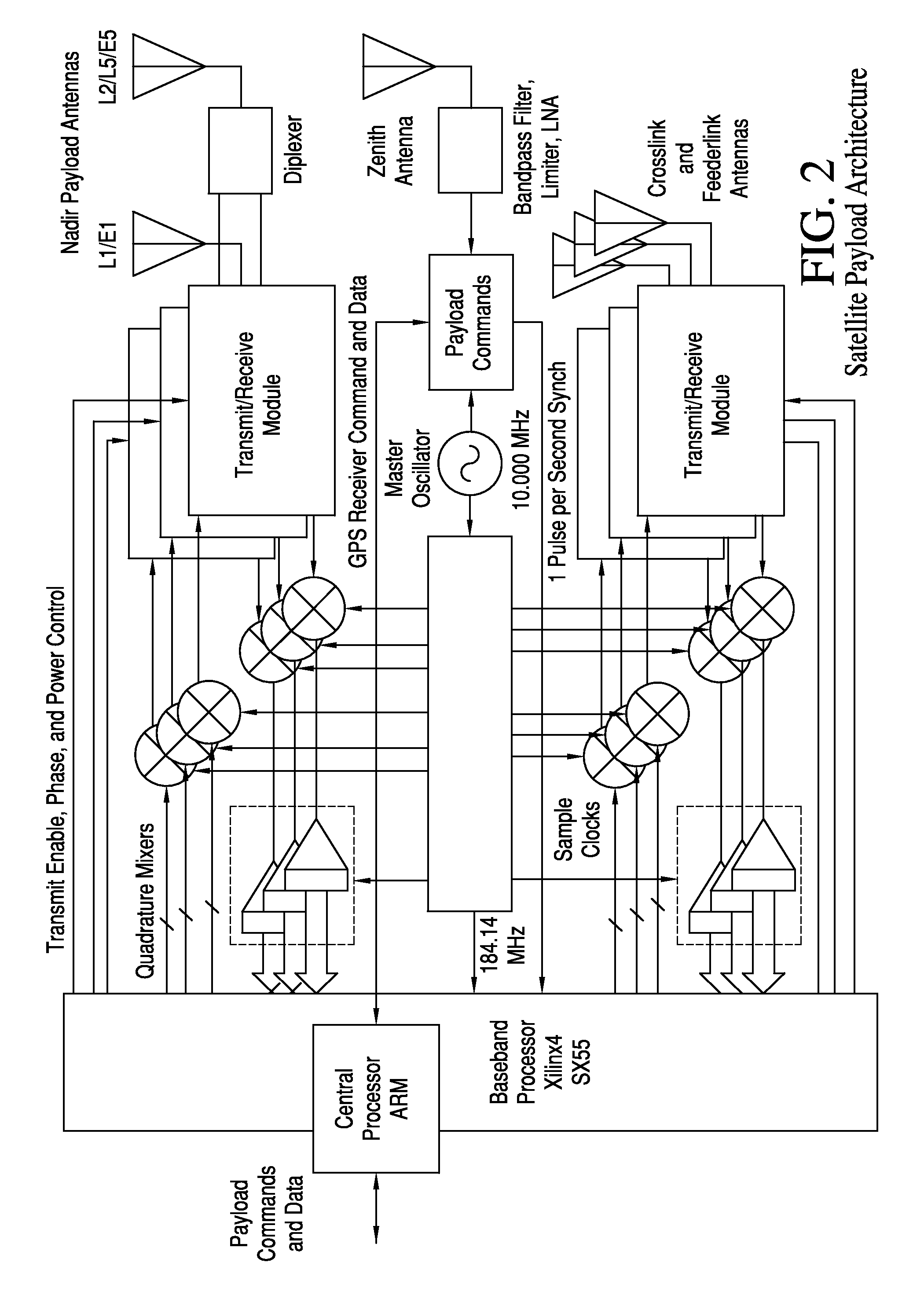
Performance and Cost Global Navigation Satellite System Architecture
ActiveUS20160011318A1Improve performanceCost effectiveSatellite radio beaconingAviationFrequency spectrum
Significant, cost-effective improvement is introduced for Position, Navigation, and Timing (PNT) on a global basis, particularly enhancing the performance of Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS), an example of which is the Global Positioning System (GPS). The solution significantly improves performance metrics including the accuracy, integrity, time to acquire, interference rejection, and spoofing protection. A constellation of small satellites employing a low-cost architecture combined with improved signal processing yields an affordable enabler for spectrum-efficient transportation mobility. As air traffic management modernization transitions to a greater dependence on satellite positioning, the solution provides aviation users new protections from both intentional and unintentional interference to navigation and surveillance. And in response to an era in which intelligent transportation is under development for automobiles, reliable where-in-lane positioning enables new applications in connected and autonomous vehicles. New military capability increases PNT availability.
Owner:PNT HLDG INC
Satellite positioning system enabled media measurement system and method
InactiveUS7038619B2Augment location and movement trackingBeacon systems using radio wavesPosition fixationLocation trackingDisplay device
The present invention is directed to utilizing monitoring devices (200) for determining the effectiveness of various locations, such as media display locations (150) for an intended purpose (media display exposure). The monitoring devices (200) are distributed to a number of study respondents. The monitoring devices (200) track the movements of the respondents. While various technologies may be used to track the movements of the respondents, at least some of the location tracking of the monitoring device (200) utilize a satellite (105) location system such as the global positioning system (“GPS”). These movements of the respondent and monitoring device (200) at some point coincide with exposure to a number of media displays (150). Geo data (movement data) collected by the monitoring devices, is downloaded to a download server (300), for determining which media displays (150) the respondent was exposed to. The exposure determinations are made by a post-processing server (400).
Owner:RDPA LLC
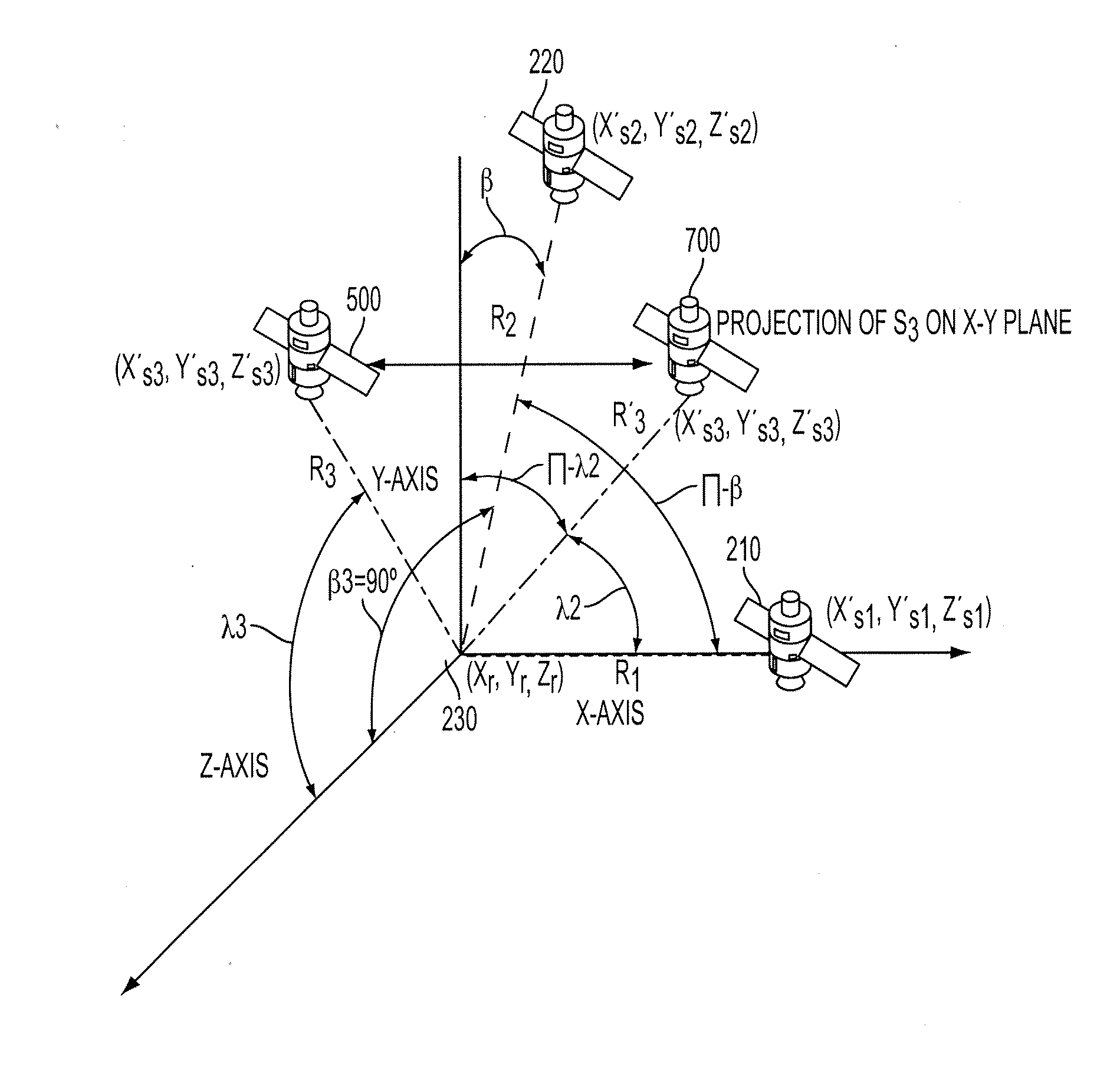
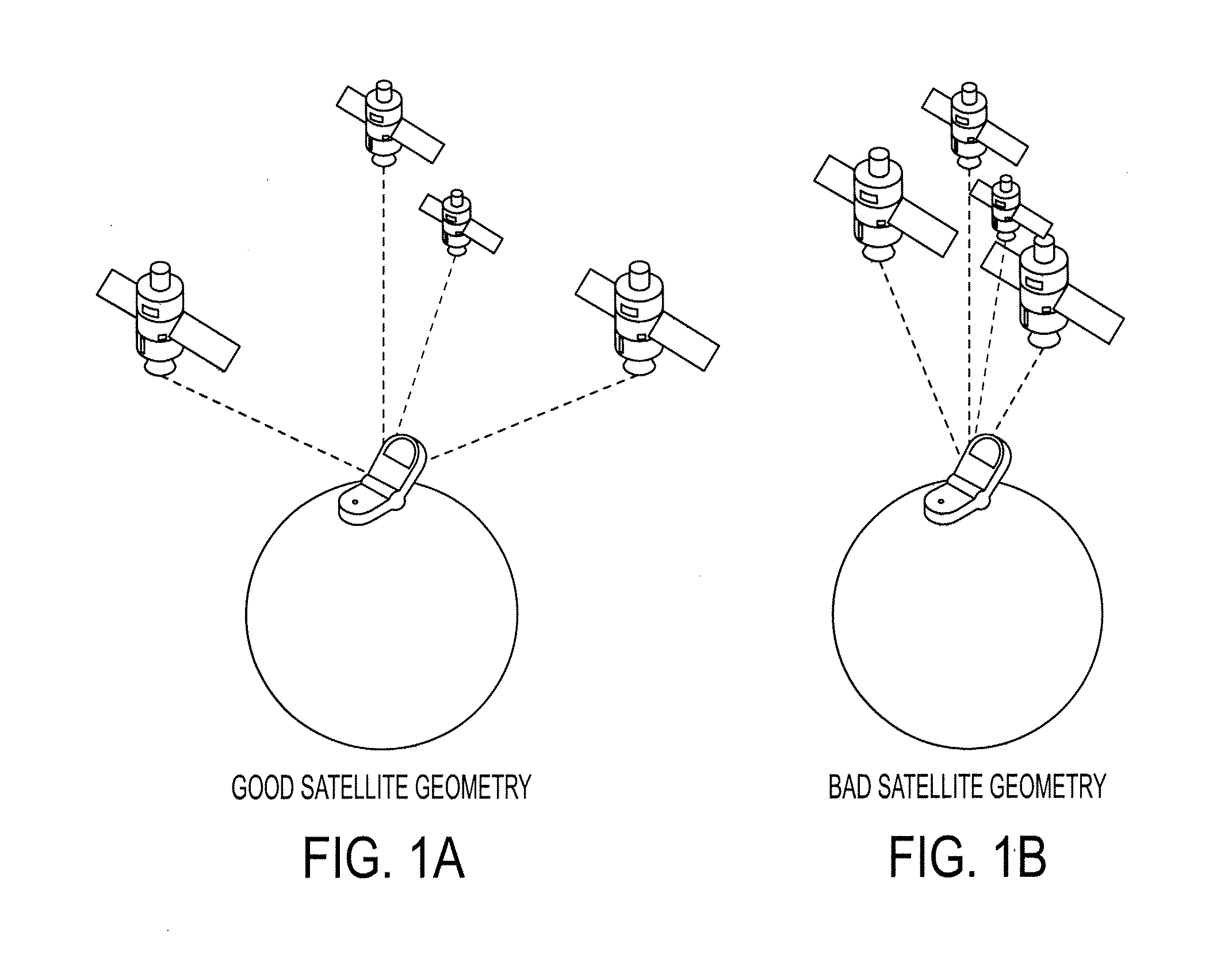
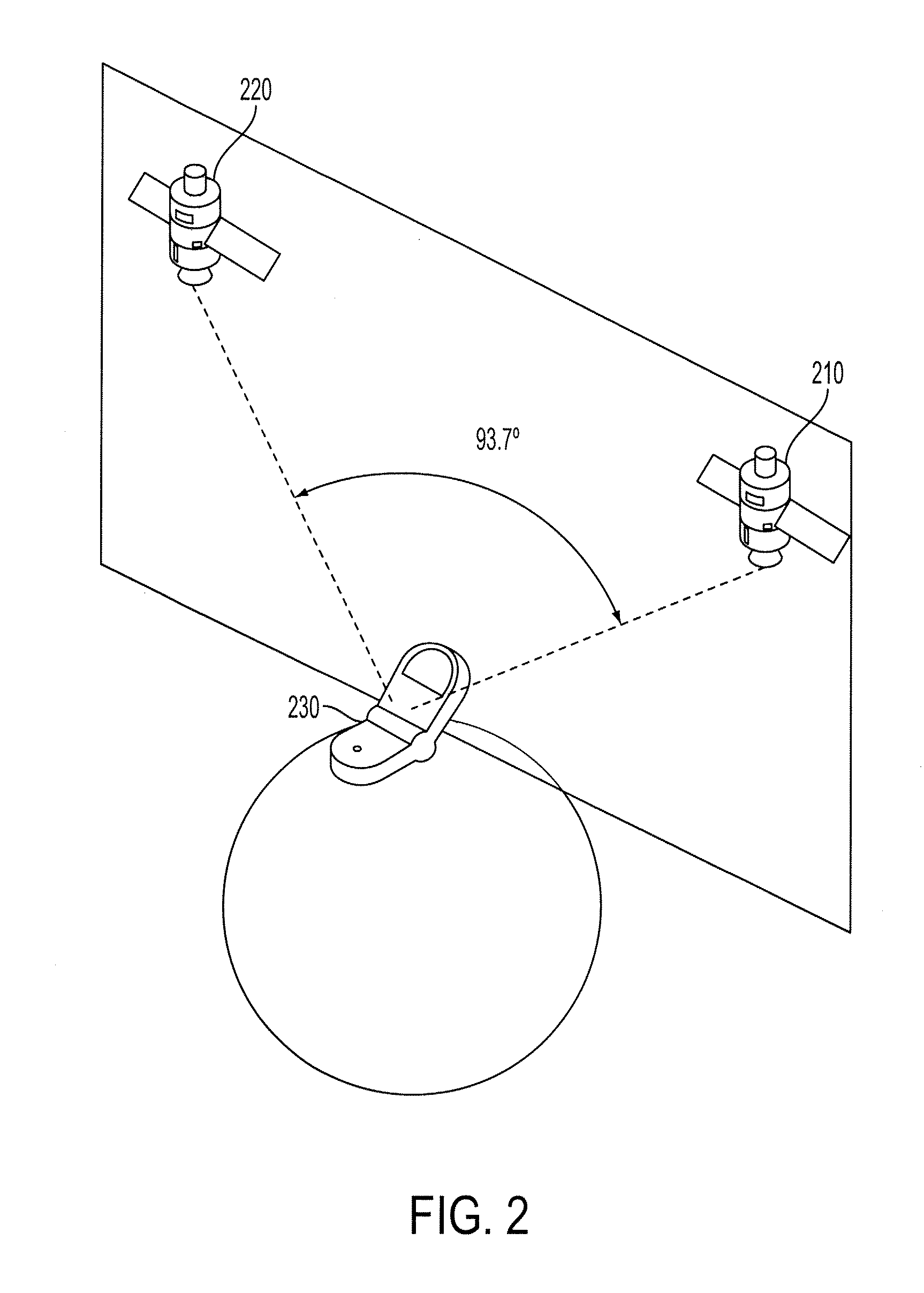
Determining A Dilution of Precision Metric Using Two or Three GPS Satellites
The disclosed subject matter relates to a method for determining a Dilution of Precision Metric (DOP) with less than four satellites in a hybrid positioning system. In some embodiments, the method includes determining an initial position estimate of a device using a non-satellite positioning system, obtaining satellite measurements from less than four satellites, wherein the measurements include each satellite's position with respect to the initial position estimate, constructing a geometry matrix corresponding to the measurements from the less than four satellites using each satellite's position and the initial position estimate, multiplying the geometry matrix by its transpose to construct an H matrix, determining an inverse of the H matrix, and determining the DOP based on a sum of the diagonal elements of the inverse H matrix. In some embodiments, the non-satellite positioning system is a WLAN positioning system.
Owner:SKYHOOK WIRELESS
Systems and methods for maintaining clock bias accuracy in a hybrid positioning system
InactiveUS20100052983A1Maintain its internal clock accuracyPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingHybrid positioning systemSatellite positioning
This disclosure describes systems and methods for maintaining clock bias accuracy in a hybrid positioning system. In some embodiments, the method to maintain the stability of an internal clock of an satellite positioning system receiver by using WLAN access points (APs) can include maintaining the internal clock accuracy of a satellite positioning system receiver by using one or more WLAN APs as a reference.
Owner:SKYHOOK WIRELESS
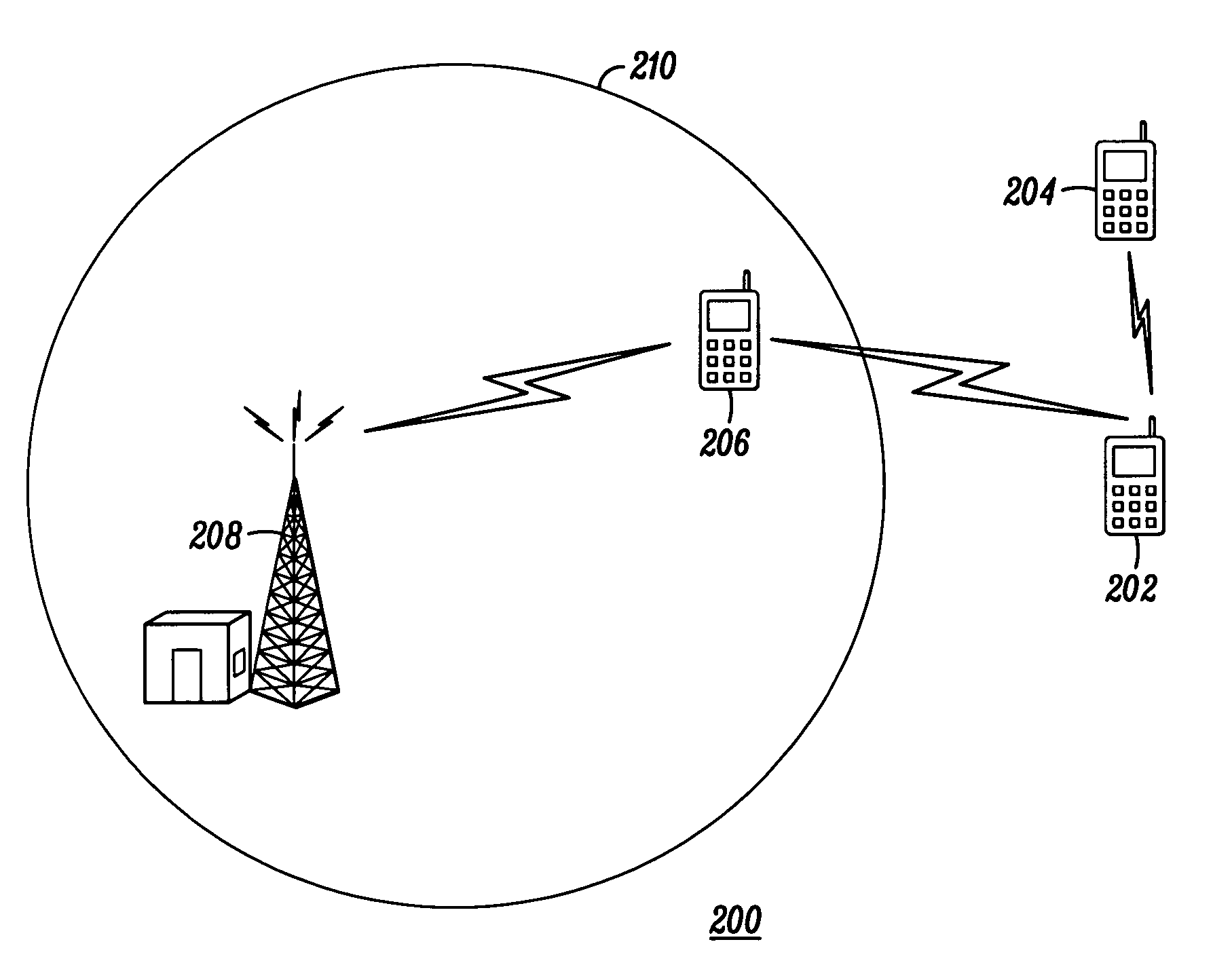
Method for providing location aiding among peers operating in a direct communication mode
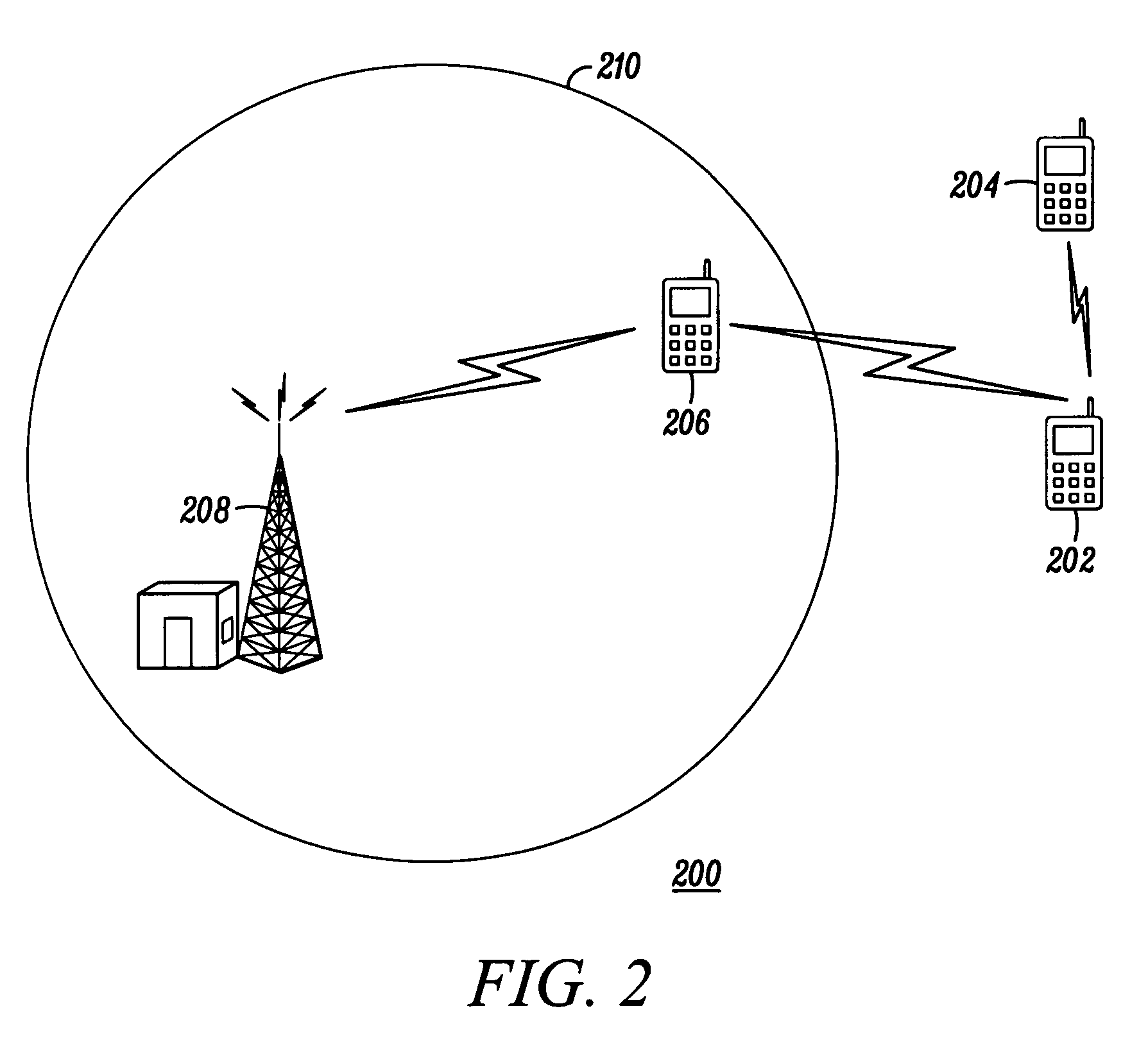
A mobile communication device (202) outside the service area of a communications network 210 in need of satellite positioning assistance information to perform a location determination (308). The mobile communication device receives the assistance information from a peer mobile communication device (204, 206) over a direct link.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
Method and system for validating a mobile station location fix
InactiveUS20020098851A1Special service for subscribersPosition fixationMobile stationSatellite positioning
A method and system for evaluating the validity of location fixes of a mobile station by comparison of a location fix for which a validity determination is desired with one or more prior reference location fixes. In one embodiment, a satellite positioning system based location fix of a satellite positioning system enabled cellular mobile station in a cellular communications network is validated by comparison of the satellite positioning system based location fix to one or more of a plurality of network based location fixes, or to an estimated future location fix of the mobile station.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Post-processing of inverse DGPS corrections
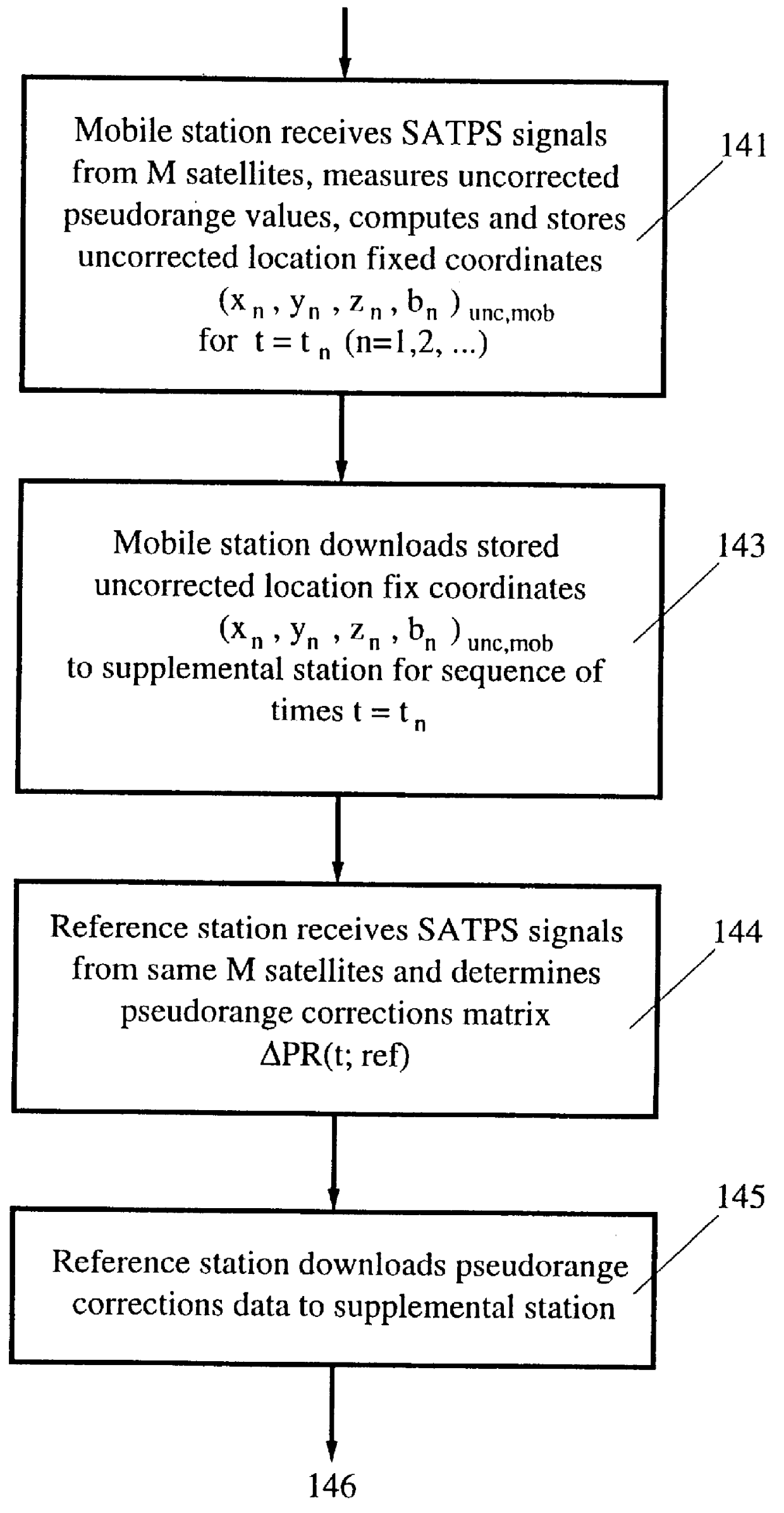
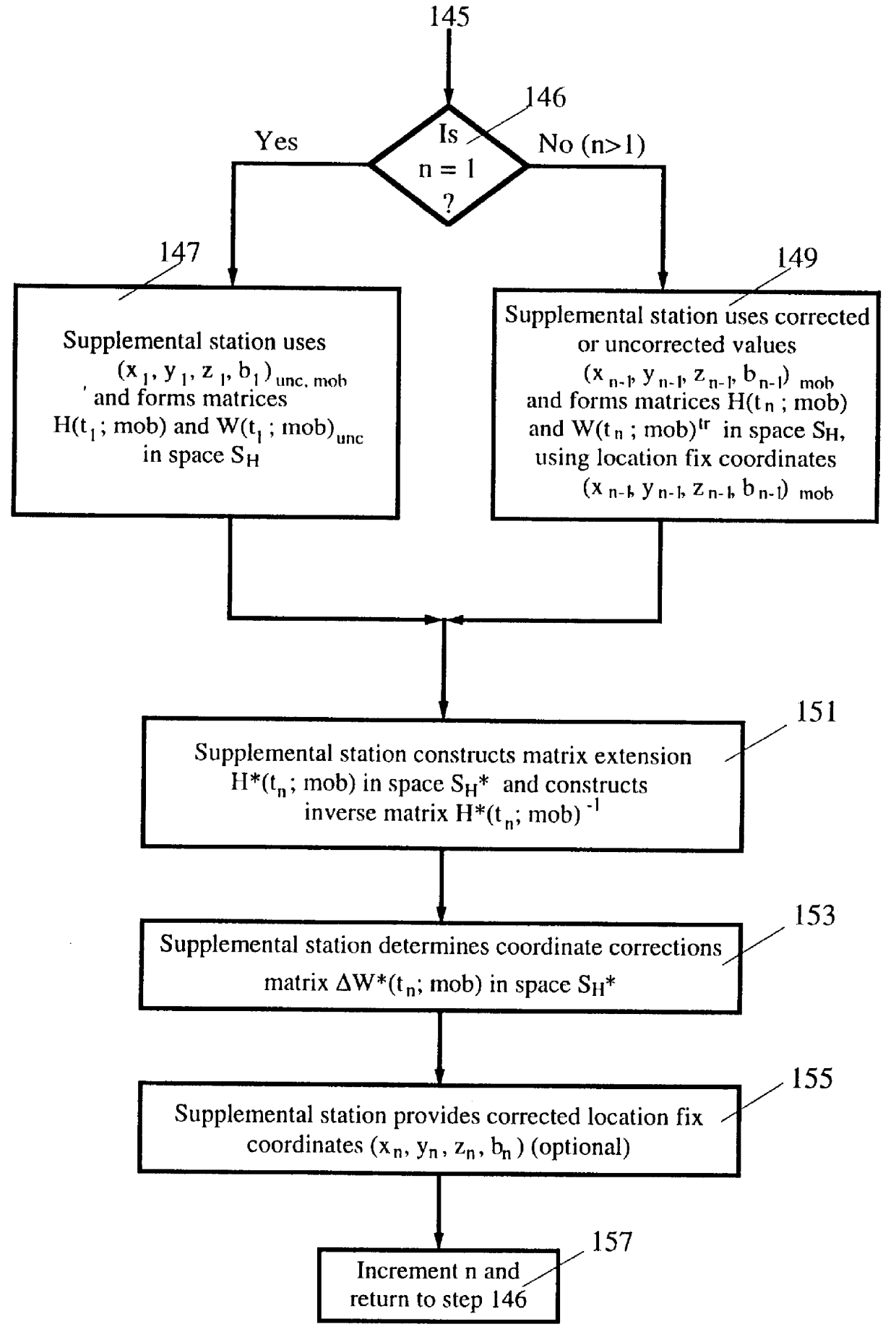
A method for enhancing the accuracy of location coordinates and / or clock bias computed for a mobile user station that is part of a Satellite Positioning System (SATPS), such as GPS or GLONASS. A data processing station is provided with pseudorange corrections PRC(t;j;ref) for an SATPS reference station for each of M SATPS satellites (j=1, . . . , M; M> / =3) and with uncorrected location fix coordinates x'(tf), y'(tf)', z'(tf)' and / or b'(tf) for the mobile station for a selected location fix time tf. A matrix equation H(tf;mob) DELTA W(tf;mob)=PRC(tf;ref) relates a matrix DELTA W of location fix coordinate corrections for the mobile station to a matrix PRC(t;ref) of the pseudorange correction values, where H(tf;mob) is an MxN matrix (M< / =N; N=3 or 4) with known entries computed from mobile station data. An inverse or pseudo-inverse matrix H(tf;mob)(-1) is formed satisfying the relation H(tf;mob)(-1)H(tf;mob)=the identity matrix I, and the matrix DELTA W(tf;mob)=H(tf;mob)(-1)PRC(tf;ref) is computed. The entries of the matrix DELTA W(tf) are interpreted as additive corrections for the location fix coordinates x'(tf), y'(tf)', z'(tf)' and / or b'(tf) for the mobile station. Post-processing can be performed to apply the pseudorange corrections to the mobile station data.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com