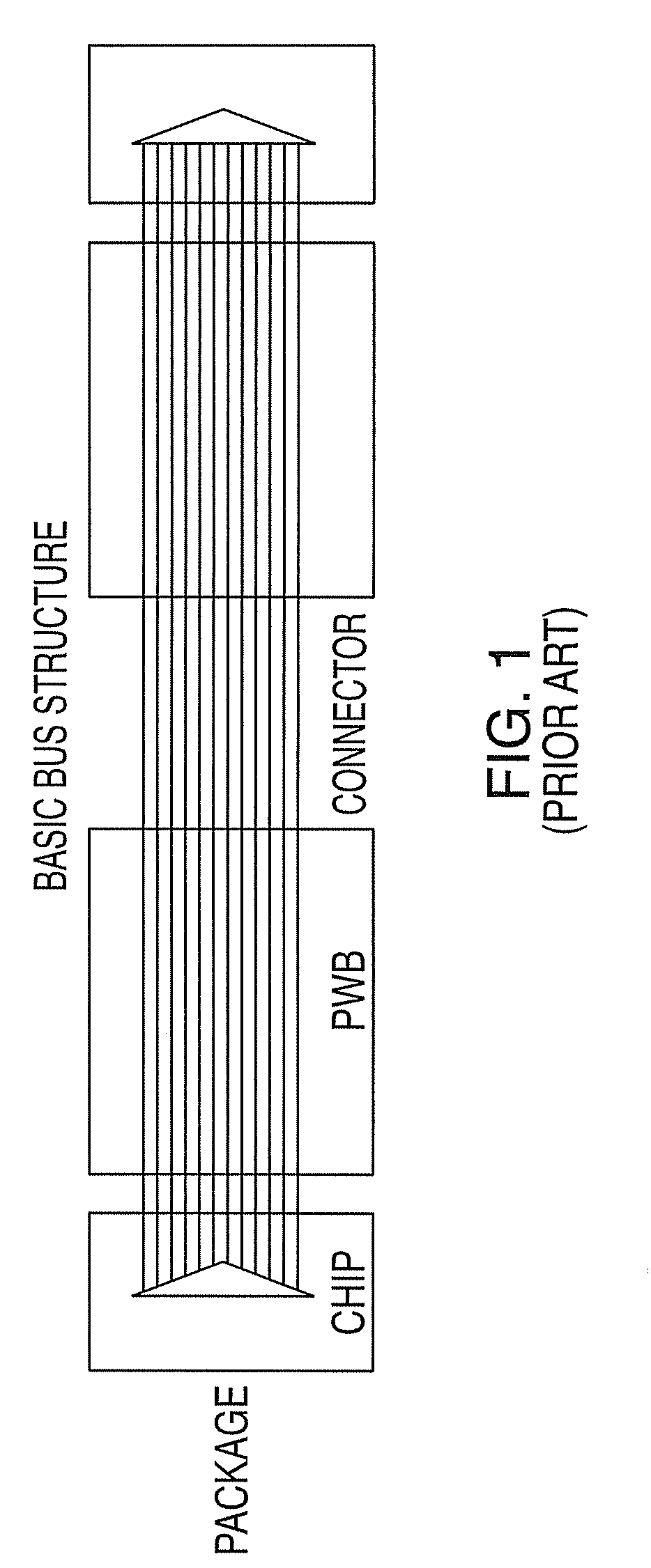
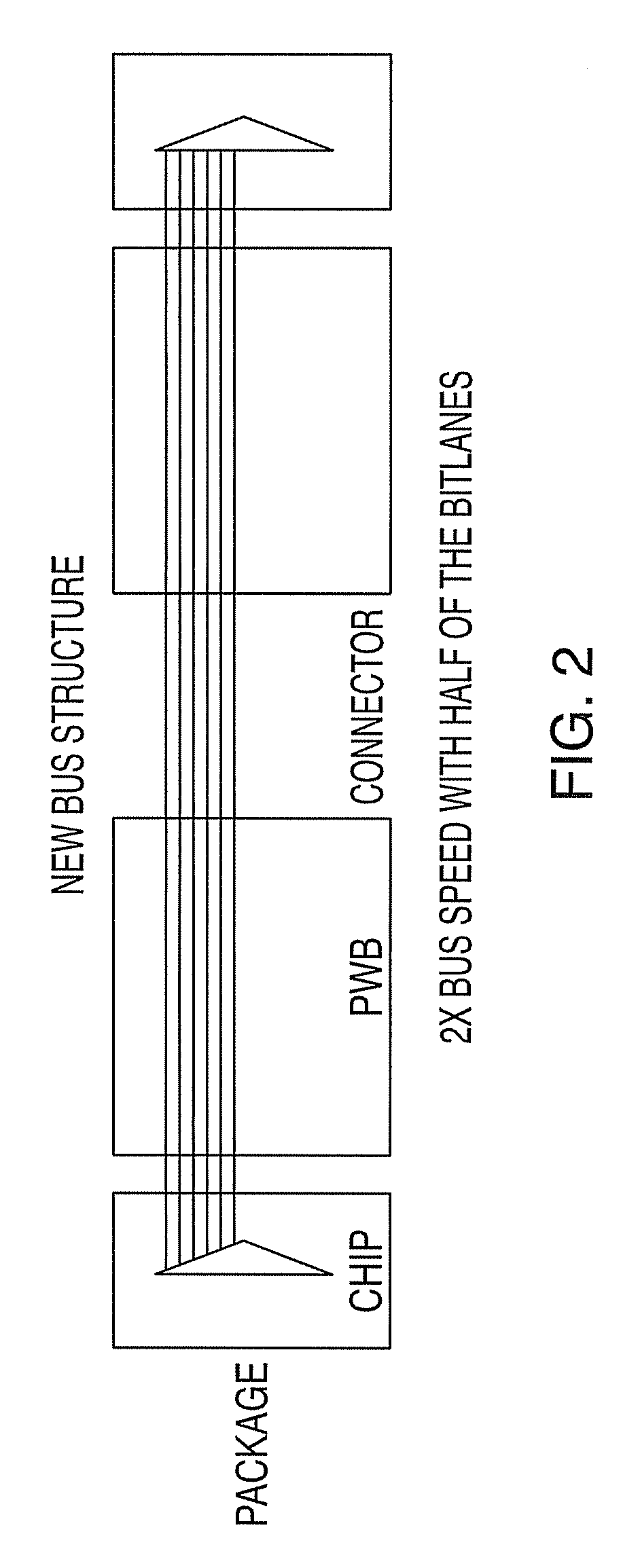
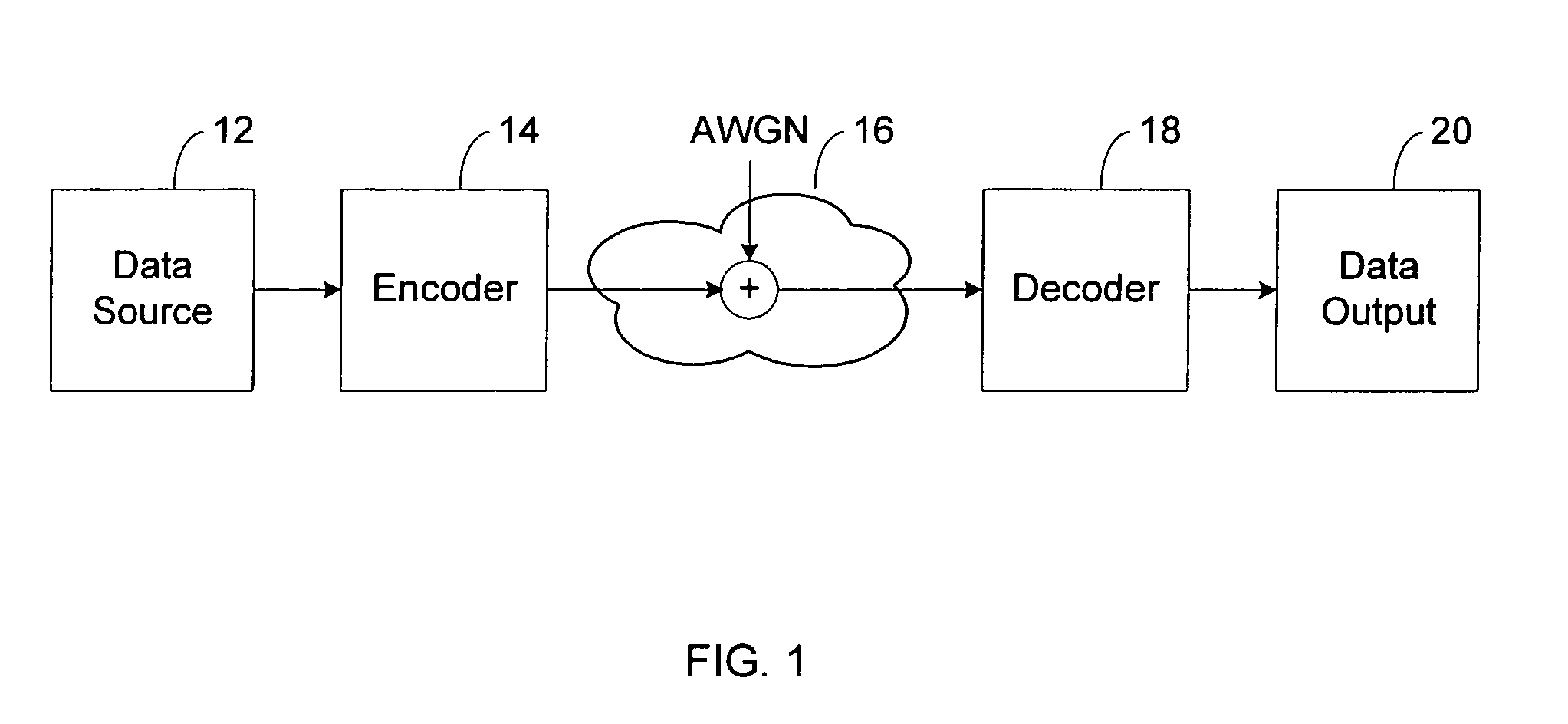
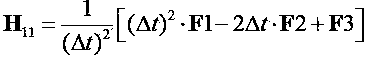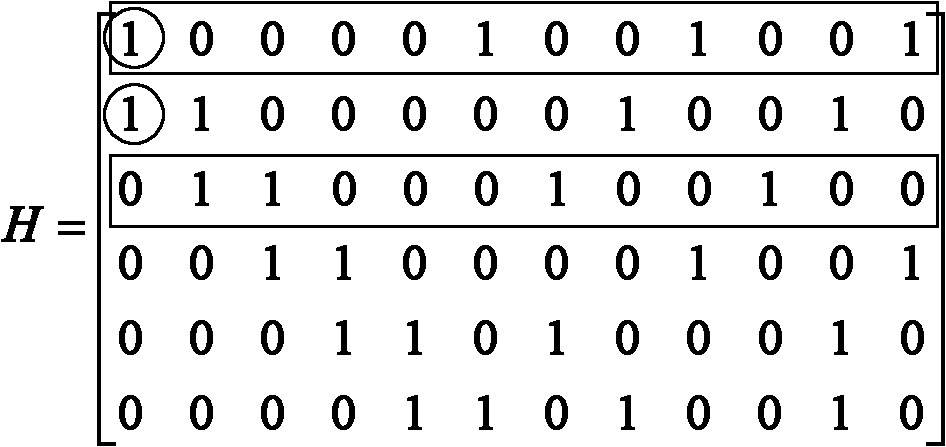Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
67 results about "H matrix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Compensation of I/Q gain mismatch in a communications receiver
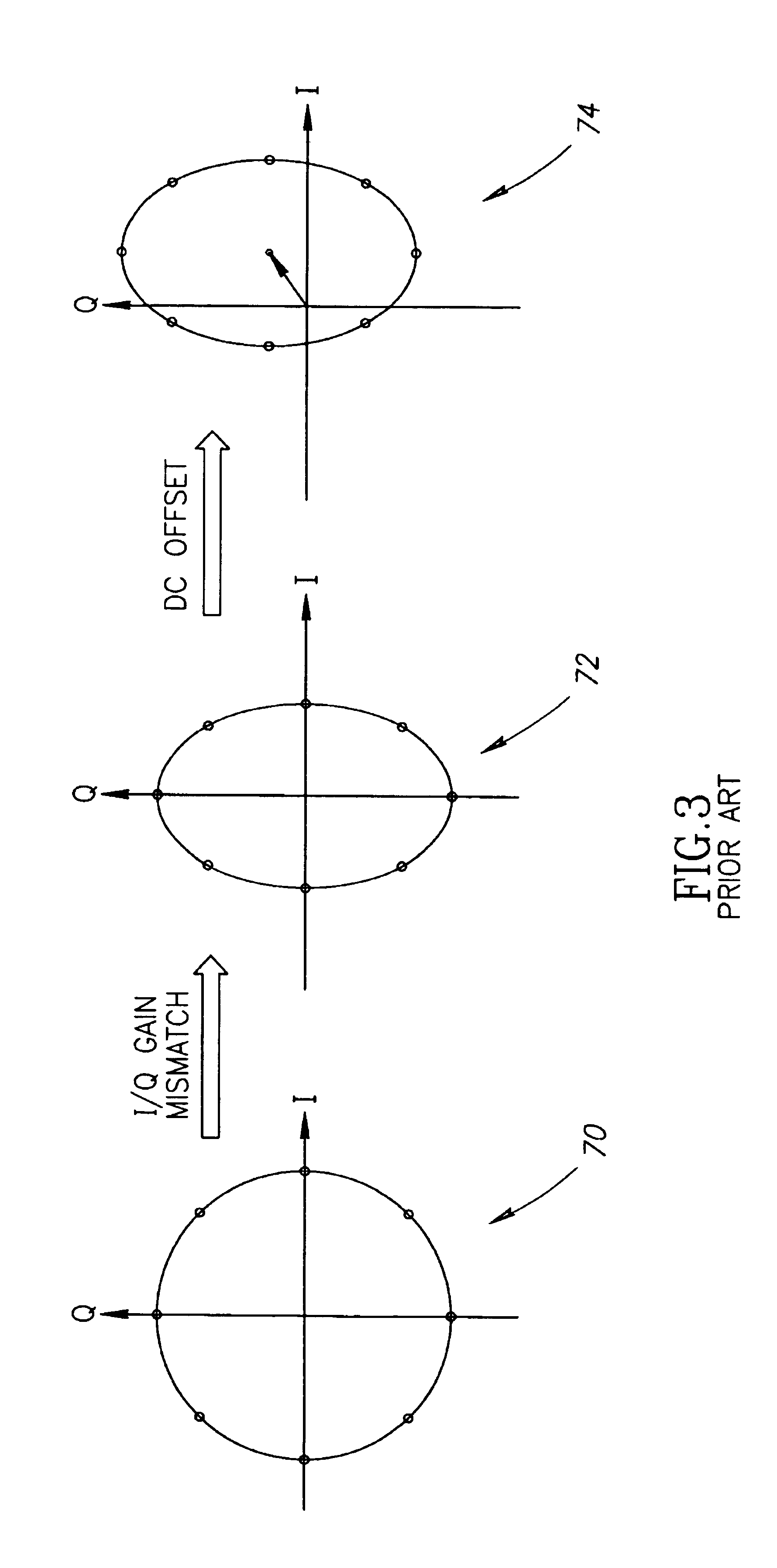
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of I / Q gain mismatch compensation for use in a communications receiver. The invention is operative to calculate an estimate of the I / Q gain mismatch. Each input sample is subsequently multiplied by the inverse of the estimate to generate compensated samples. The training sequence portion of the uncompensated input samples is used to generate the I / Q gain mismatch estimate. In accordance with the present invention, the H matrix used in calculating the gain mismatch estimate is pre-calculated for several channel lengths and stored in memory. An estimate of the channel is generated which provides the channel length and the location in the input sample buffer of the first training sequence sample to be used in calculating the gain mismatch estimate. The channel length is used to determine the number of training sequence samples to be used and to select one of the previously calculated H matrices.
Owner:COMSYS COMM & SIGNAL PROC
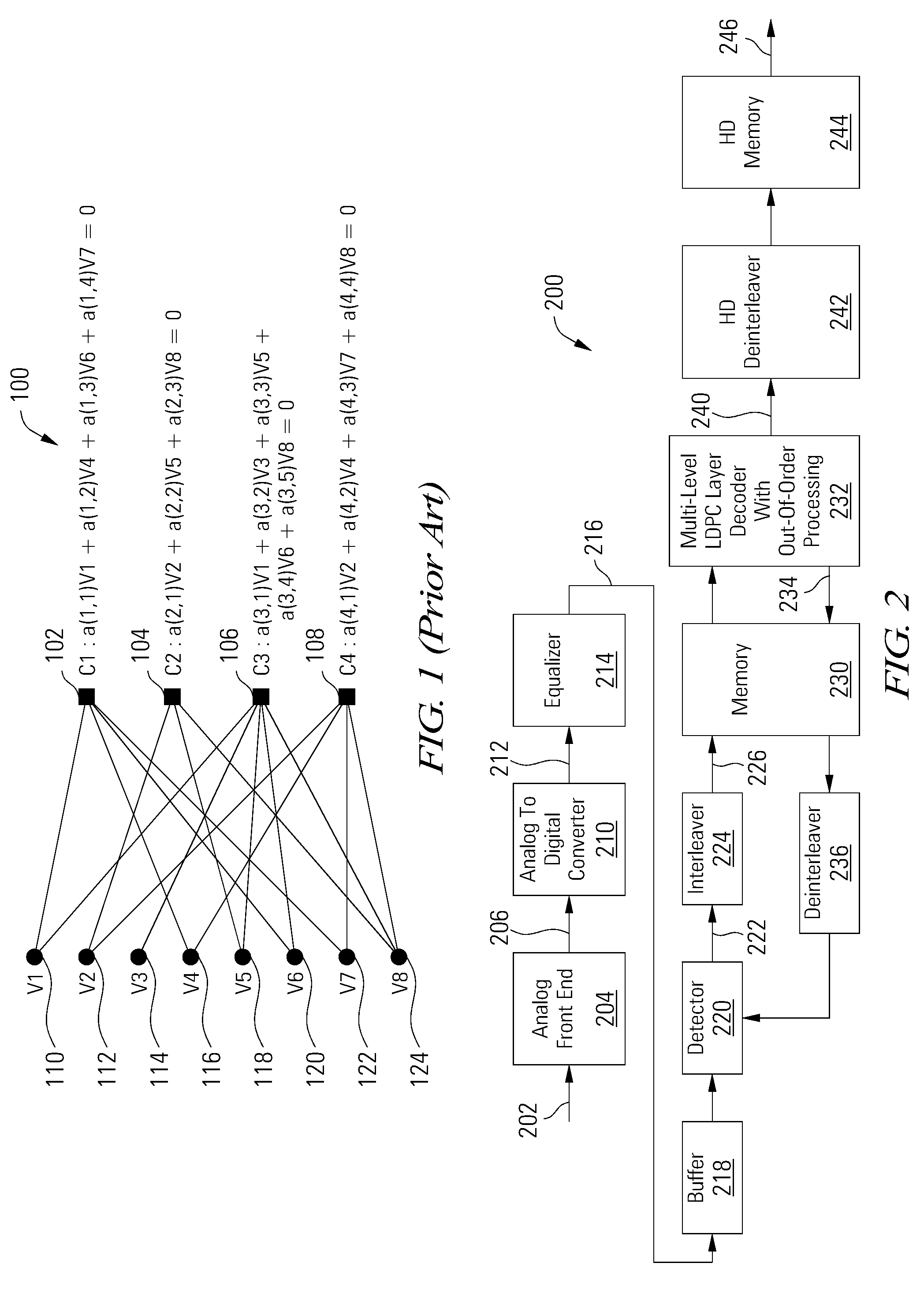
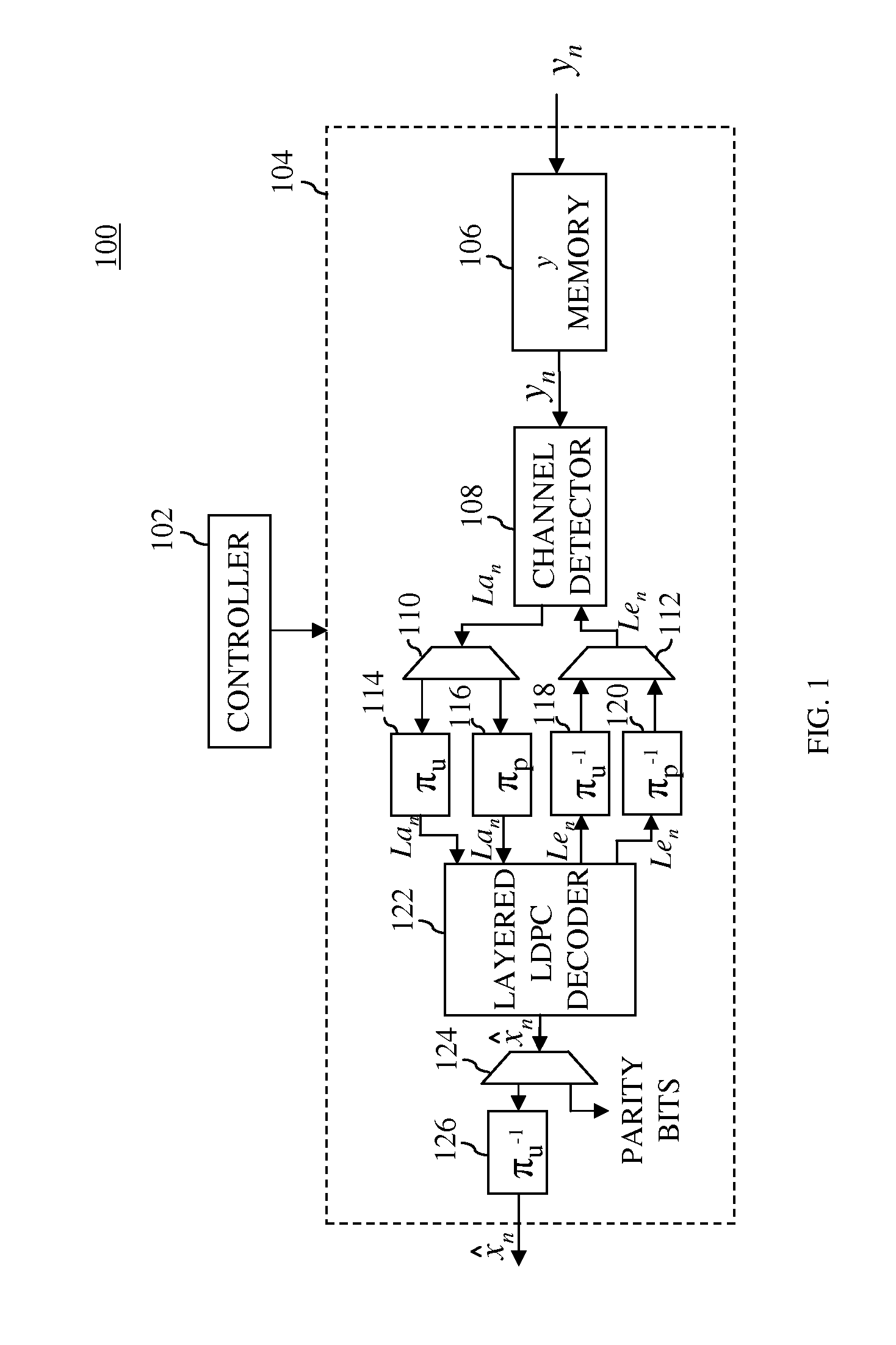
Conditional skip-layer decoding
ActiveUS20110320902A1Code conversionError correction/detection using block codesComputer hardwareH matrix
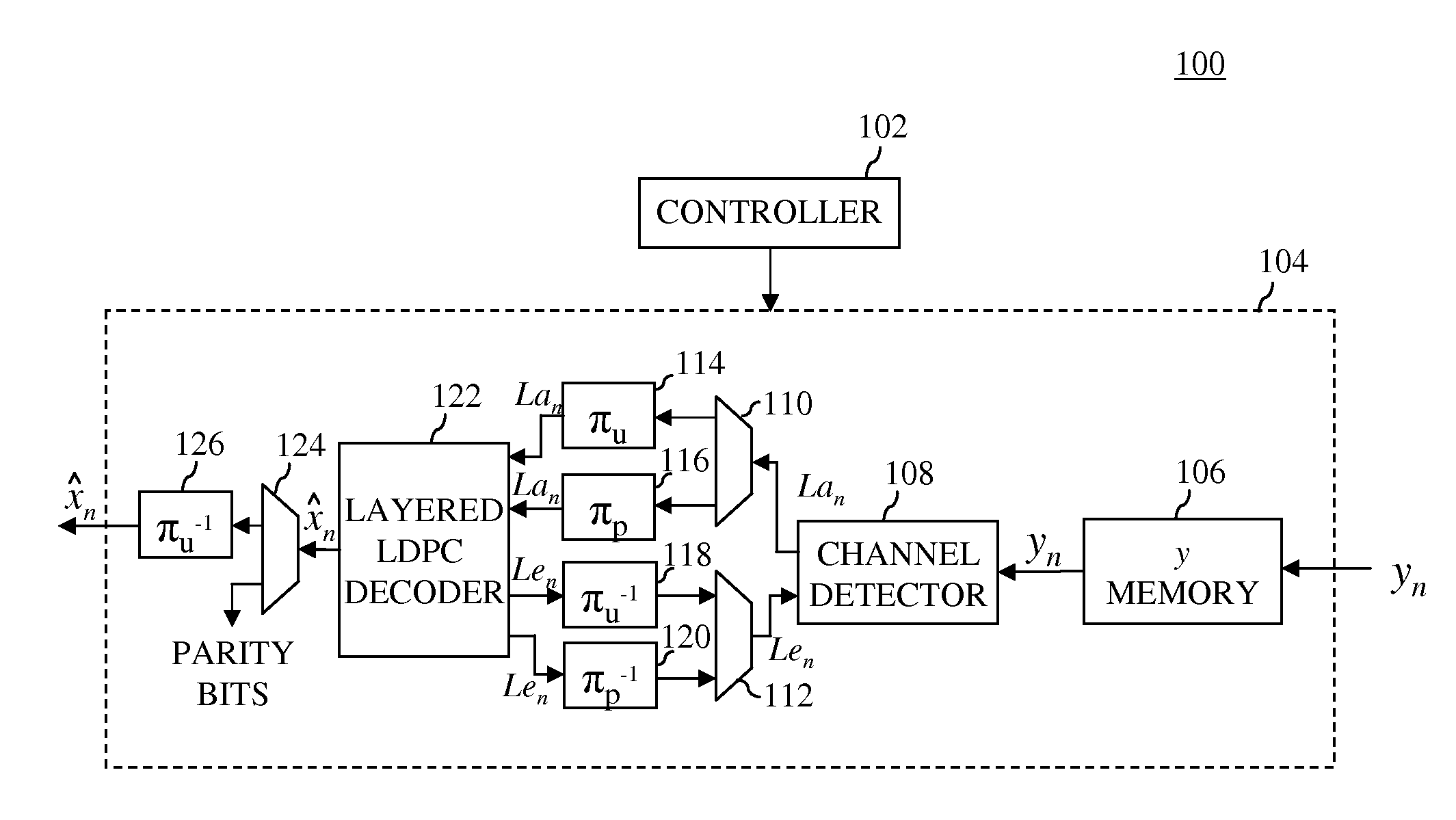
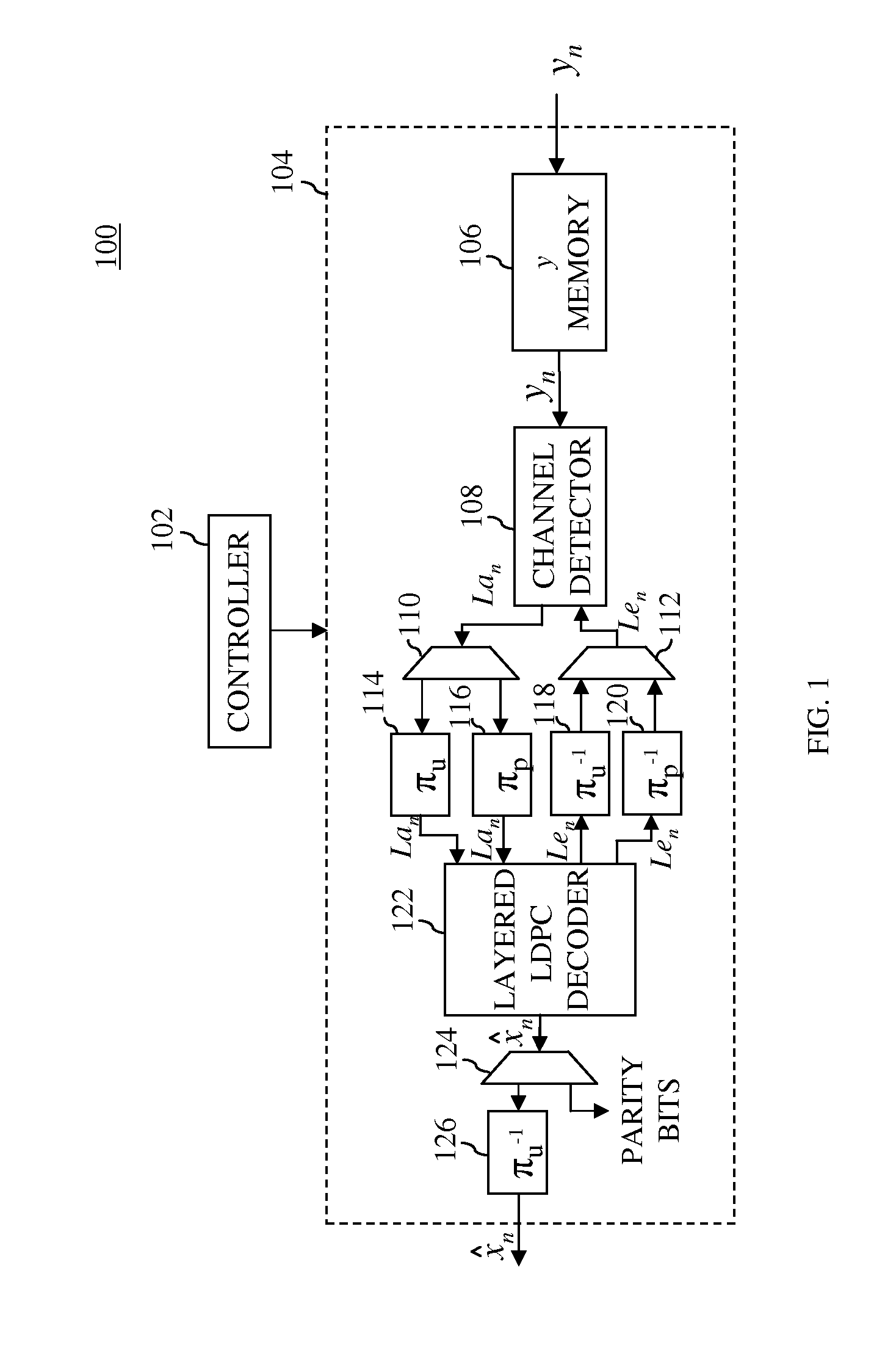
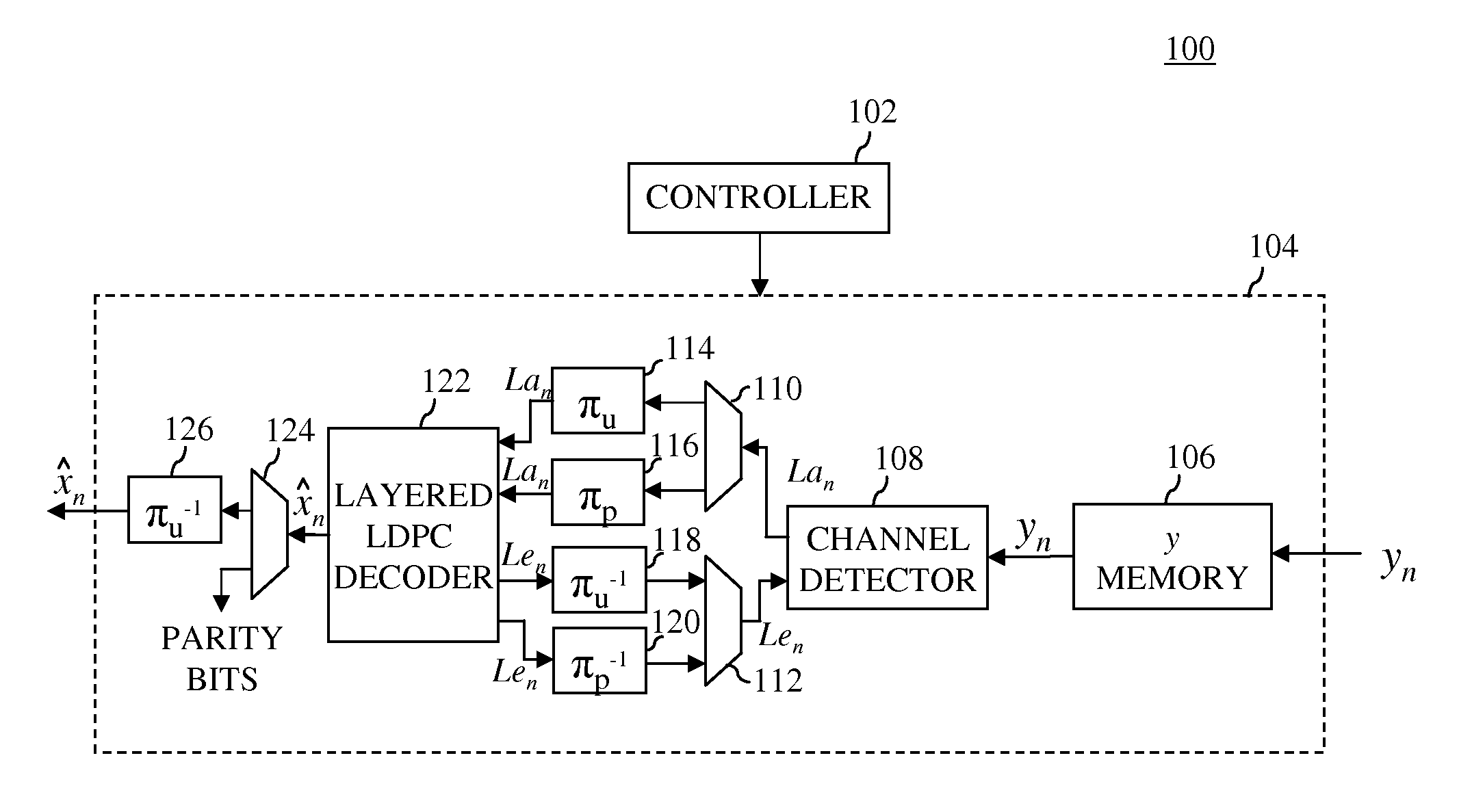
In one embodiment, a turbo equalizer is selectively operable in either first or second modes. In the first mode, layered (low-density parity-check (LDPC)) decoding is performed on soft-output values generated by a channel detector, where, for each full local decoder iteration, the updates of one or more layers of the corresponding H-matrix are skipped. If decoding fails to converge on a valid LDPC-encoded codeword and a specified condition is met, then LDPC decoding is performed in a second mode, where the updates of all of the layers of the H-matrix are performed for each full local decoder iteration, including the one or more layers that were previously skipped in the first mode. Skipping one or more layers in the first mode increases throughput of the decoder, while updating all layers in the second mode increases error correction capabilities of the decoder.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Low-density parity-check (LDPC) encoder
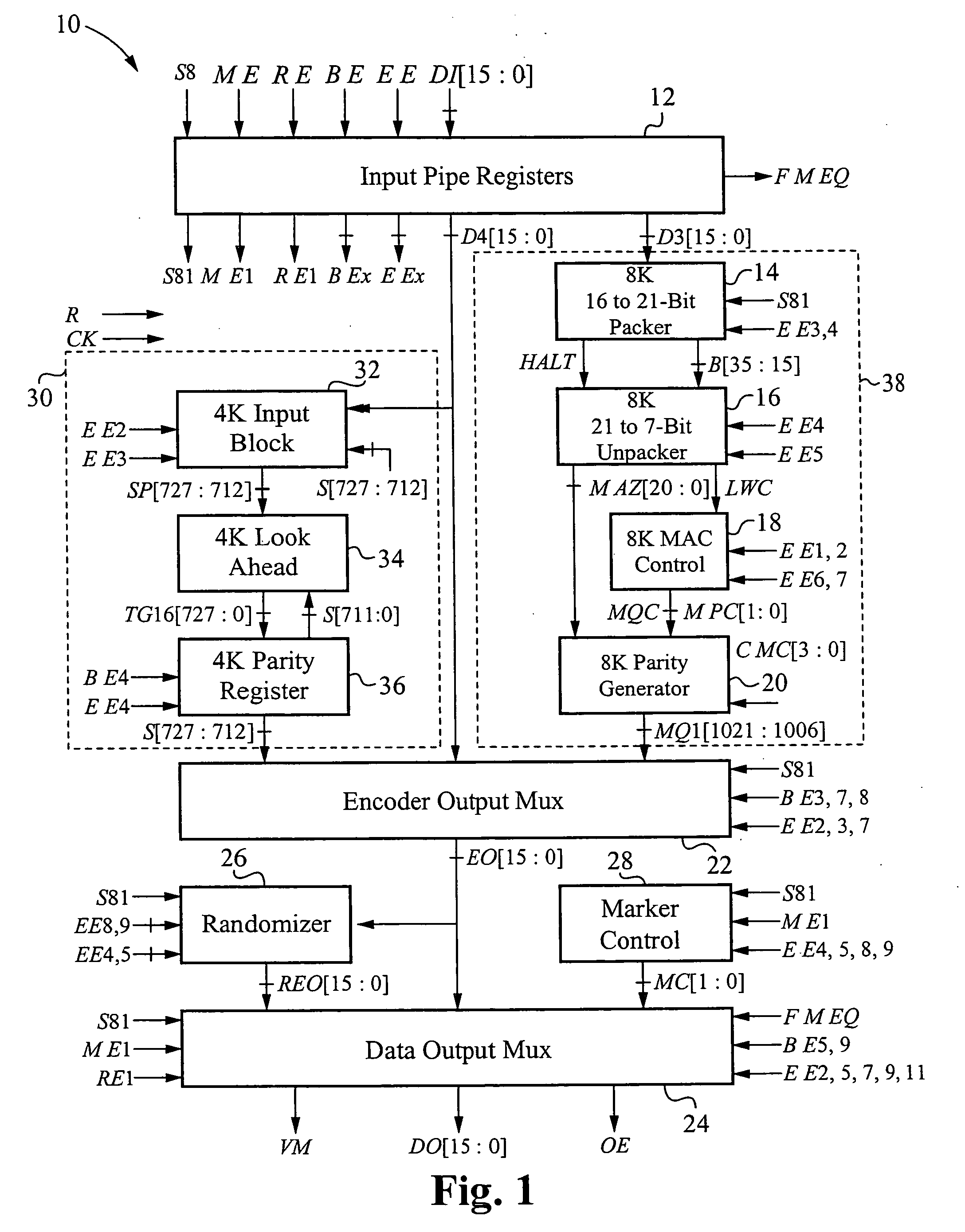
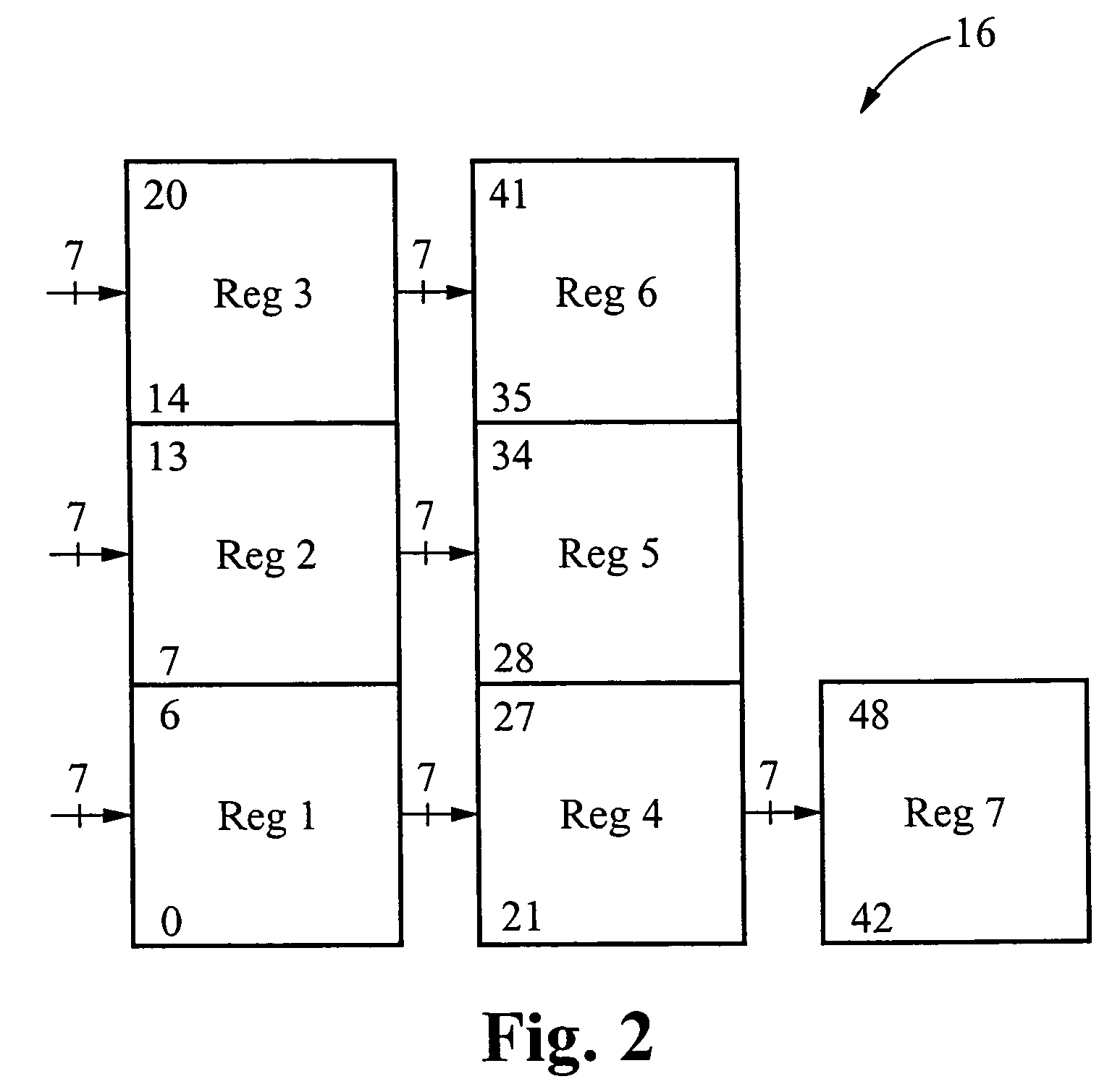
The encoder chip of the present invention uses LDPC codes to encode input message data at a transmitting end, thereby generating a series of codewords. The encoder chip implements two low-density parity-check (LDPC) codes. The first LDPC code is a (4088,3360) code (4K) which is shortened from a (4095,3367) cyclic code. The second LDPC code is a quasi-cyclic (8158,7136) code (8K). The message data and the generated codewords are transmitted to a receiving end where the received codewords are decoded and checked for errors. To generate the codewords, the encoder applies a generator matrix G to the input message data. The G matrix is generated by first defining an H matrix. An H matrix is initially defined as 16×2 array of right-circulant sub-matrices. The G matrix is formed by manipulating the H matrix according to a 4-step algorithm. A randomizer and a synchronization marker are also included within the encoder.
Owner:IDAHO RESARCH FOUNDATION INC
Pattern recognition method of substation switch based on infrared detection
ActiveCN102289676AImprove match stabilityImprove noise immunityCircuit arrangementsCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionSmart substation
The invention discloses a method for identifying the mode of a switch of a substation based on infrared detection. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, inputting an image to be identified, acquiring a switch area of the image by image registration, and sequentially graying, binarizing and thinning the switch area; 2, linearly detecting the image of the thinned switch area by using a Hough transformation algorithm; and 3, determining a detection result, and identifying the state of the switch by using a switch state determination condition. An H matrix between two images is obtainedby matching of the features of scale invariant feature transform (SIFT), the switch area in the image is found, and then the state of the switch is identified. Experiments show that: by the method, the problem of identification of a power switch can be effectively solved; an important significance is provided for automatic monitoring of the power equipment of an intelligent substation; the burdens on an inspector of the substation can be reduced; and detection efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:STATE GRID INTELLIGENCE TECH CO LTD
Construction method of multi-code rate compatible LDPC code and its decoder
InactiveCN101047387AChange the maximum read and write depthSave storage resourcesError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionH matrixTheoretical computer science
A method for structuring multi-code rate compatible LDPC code includes carrying out sequencing from high to low as per code rate, distributing dimensionality in following to constraint conditions, using block-PEG algorithm to structure out H matrix of LDPC code with highest code rate, utilizing said matrix as reference to restructure H matrix with different code rate as per code rate order from high to low, making said restructuring obey on constraint conditions and setting zero element position in H matrix of high code rate LDPC code still to be zero element in H matrix of low code rate.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
High-efficiency time domain electromagnetic simulation method based on H matrix algorithm
InactiveCN102033985AQuick solveDiscrete Fit ExactSpecial data processing applicationsComputation complexityDecomposition
The invention discloses a high-efficiency time domain electromagnetic simulation method based on an H matrix algorithm, which can realize electromagnetic simulation on a large three-dimensional target. In the method, a time domain finite element method (TDFEM) is used as a background, a low-rank compression technique is used as a core, and a tree structure is used as a basis for carrying out logical unit (LU) decomposition on a sparse matrix generated by the TDFEM by a four arithmetic algorithm corresponding to the H matrix. The acquired upper and lower triangular factors have low-rank compressible characteristics, and the compressed matrix equation can realize quick solution of high-efficiency time domain electromagnetic simulation by the H matrix algorithm. The high-efficiency time domain electromagnetic simulation method has the advantages of fast computation speed, low memory consumption, controllable computation accuracy, good stability and the like, can reduce the complexity of computation to O(Nlog<2>N) and reduce the memory consumption to O(NlogN), can be widely applied to the solution of a large sparse linear system of equations during high-efficiency time domain electromagnetic simulation, and can provide important reference for analyzing the electromagnetic property of the large three-dimensional target.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Multi-Section Non-Binary LDPC Decoder
InactiveUS20130275827A1Redundant array of inexpensive disk systemsCode conversionH matrixDistributed computing
Various embodiments of the present invention provide systems and methods for decoding codewords in a multi-section non-binary LDPC decoder. For example, an LDPC decoder is disclosed that includes a variable node processor operable to perform variable node updates based at least in part on check node to variable node messages and to generate variable node to check node messages, and a check node processor operable to process the variable node to check node messages in groups across each of a plurality of sections of an H matrix and to generate the check node to variable node messages.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Method and apparatus for parallel processing in a gigabit LDPC decoder
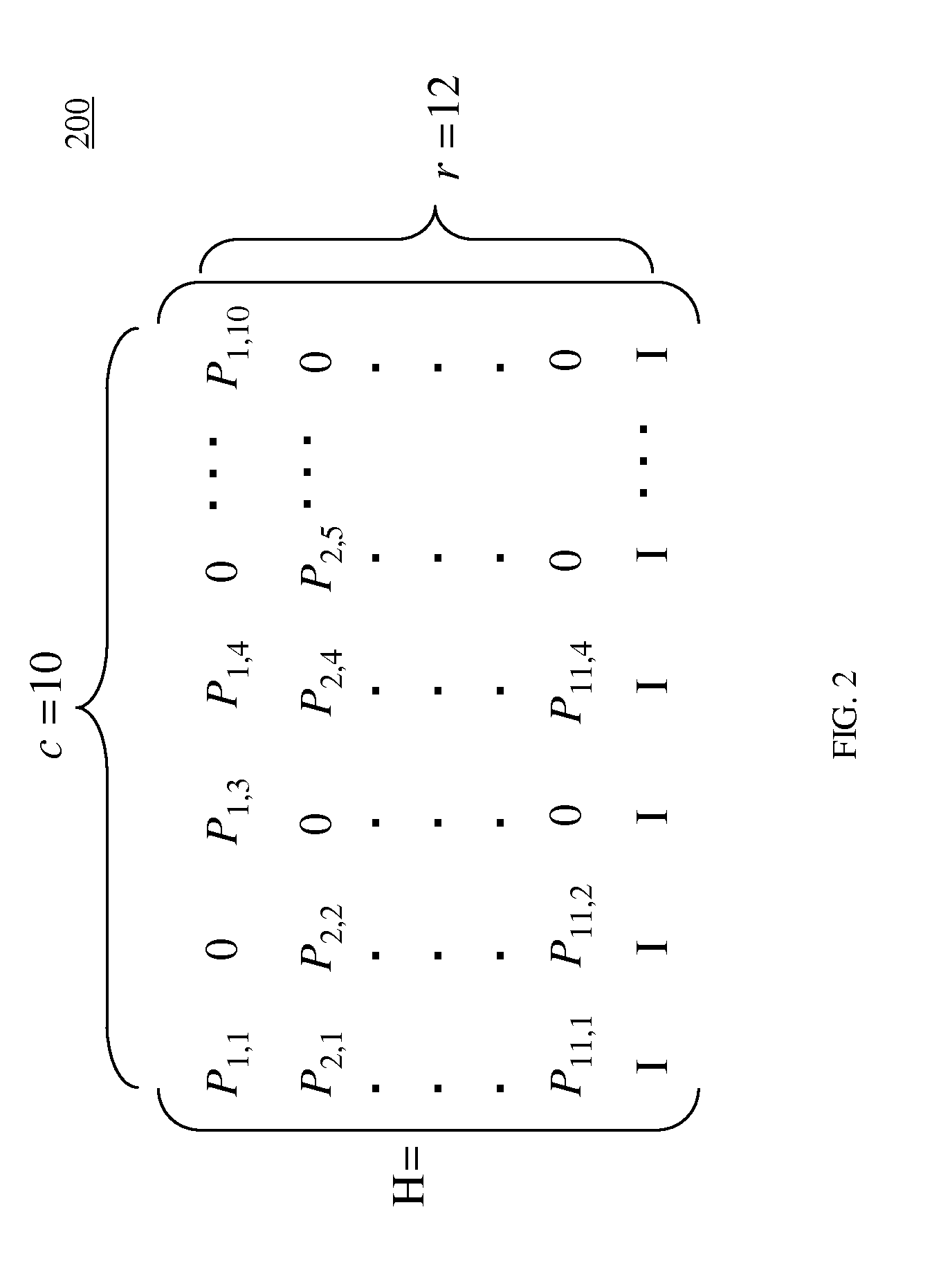
ActiveUS20110307760A1Improve design efficiencyError preventionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsGigabitParity-check matrix
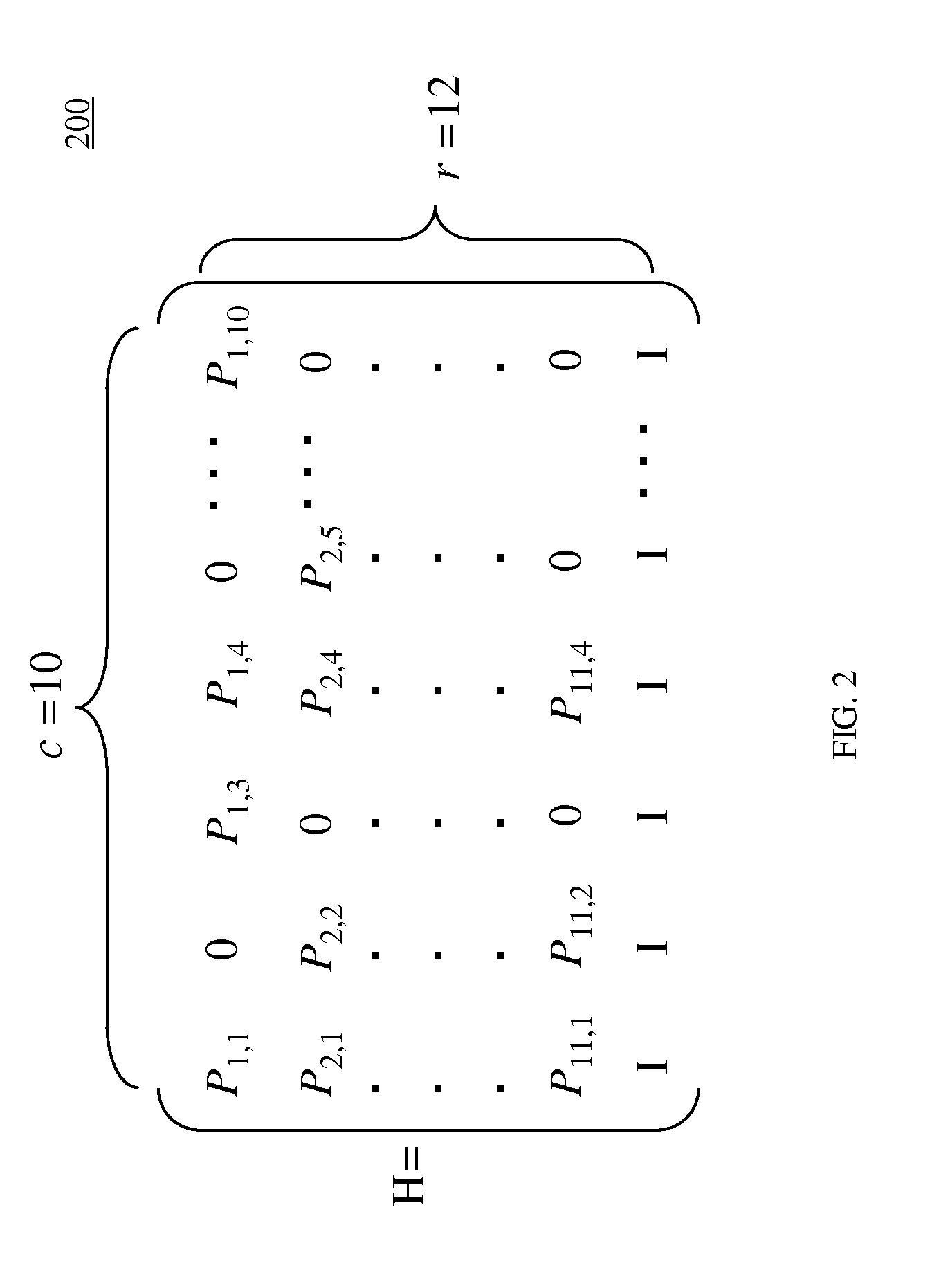
A receiver for use in a wireless communications network capable of decoding encoded transmissions. The receiver comprises receive path circuitry for receiving and downconverting an incoming radio frequency (RF) signal to produce an encoded received signal; and a low-density parity check (LDPC) decoder associated with the receive path circuitry for decoding the encoded received signal. The LDPC decoder further comprises a memory for storing a parity check H matrix comprising R rows and C columns, where each element of the parity check H matrix comprises one of a shift value or a −1 value; and a plurality of processing elements for performing LDPC layered decoding, wherein at least one processing element is operable to process in the same cycle a first row and a second row of the parity check H matrix.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Construction method of non-regular permutation matrix LDPC code and its device
InactiveCN1794621ASimple designSimplify implementation complexityError preventionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsRing circuitH matrix
This invention relates to a method for constructing new non-standard replacement matrix LDPC codes characterizing that under the principle of optimizing the smallest ring circuit, it takes each sub-block as the smallest unit and utilizes a binary chart with weight to determine the position of the sub-block and the deviation of circulation shift: simplifying the binary chart with bit as the unit of the LDPC code to that with a sub-block as the unit based on the property of the matrix of a replacement unit, then applying the traditional PEG algorithm with the bit as the unit to the new chart with the sub-block as the unit to determine the position of every replacement unit matrix of the H matrix and finally utilizing the ring circuit property of the LDPC code to decide the deviation of circular shift of each replacement unit matrix.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Clash-free irregular-repeat-accumulate code
ActiveUS20070011566A1Error detection/correctionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsTheoretical computer scienceDiagonal matrix
Methods, apparatuses, and systems are presented for performing data encoding involving receiving a sequence of data bits, encoding the sequence of data bits in accordance with a parity check matrix (H-matrix) to generate a sequence of encoded bits, wherein the H-matrix is capable of being partitioned into a first matrix and a second matrix, the first matrix being a dual-diagonal matrix, the second matrix comprising one or more vertically stacked sub-matrices, each sub-matrix consisting of a plurality of columns, each column having a column weight of no more than 1, wherein the second matrix is capable of being expressed as a product of a parity check matrix, an interleaver permutation matrix, and a repeat block matrix, and the interleaver permutation matrix satisfies a clash-free interleaver constraint, and outputting the sequence of encoded bits.
Owner:TRELLIS WARE TECH
Systems, methods, and computer program products for providing a two-bit symbol bus error correcting code with all checkbits transferred last
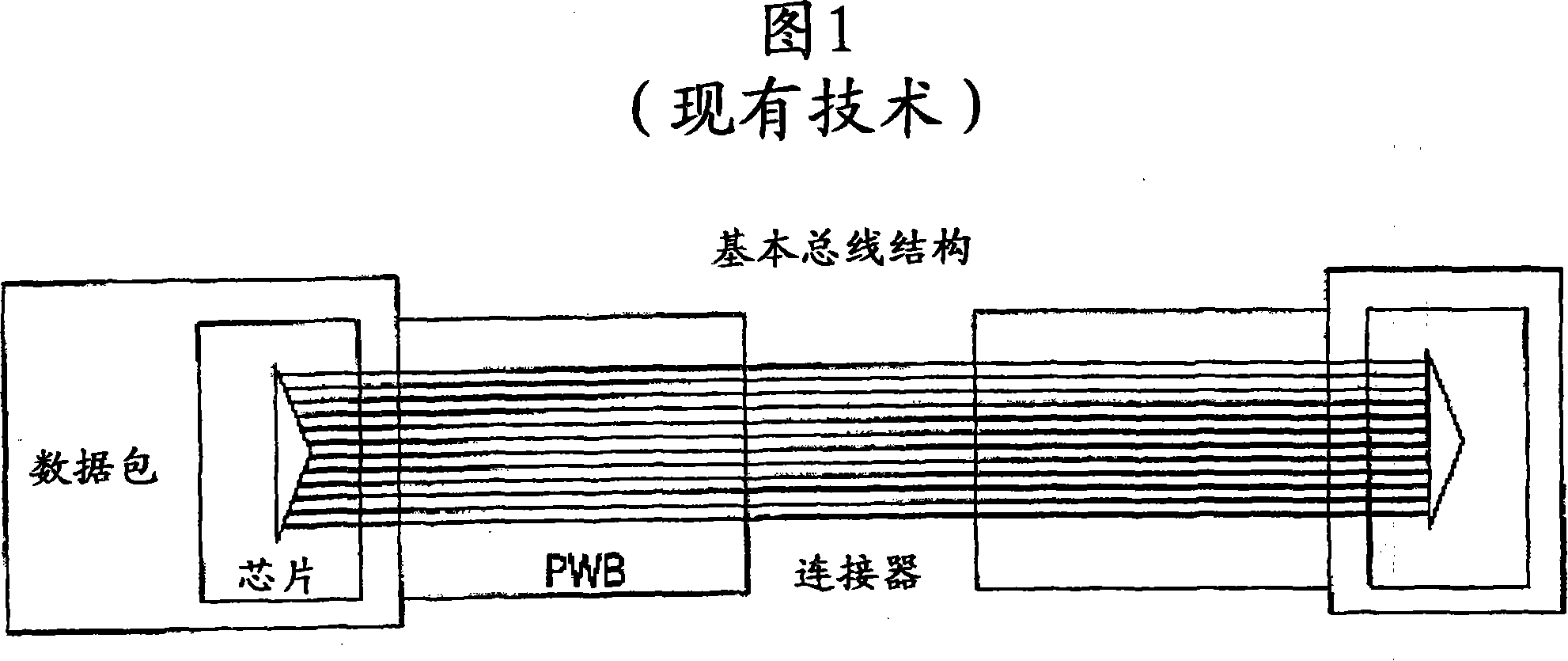
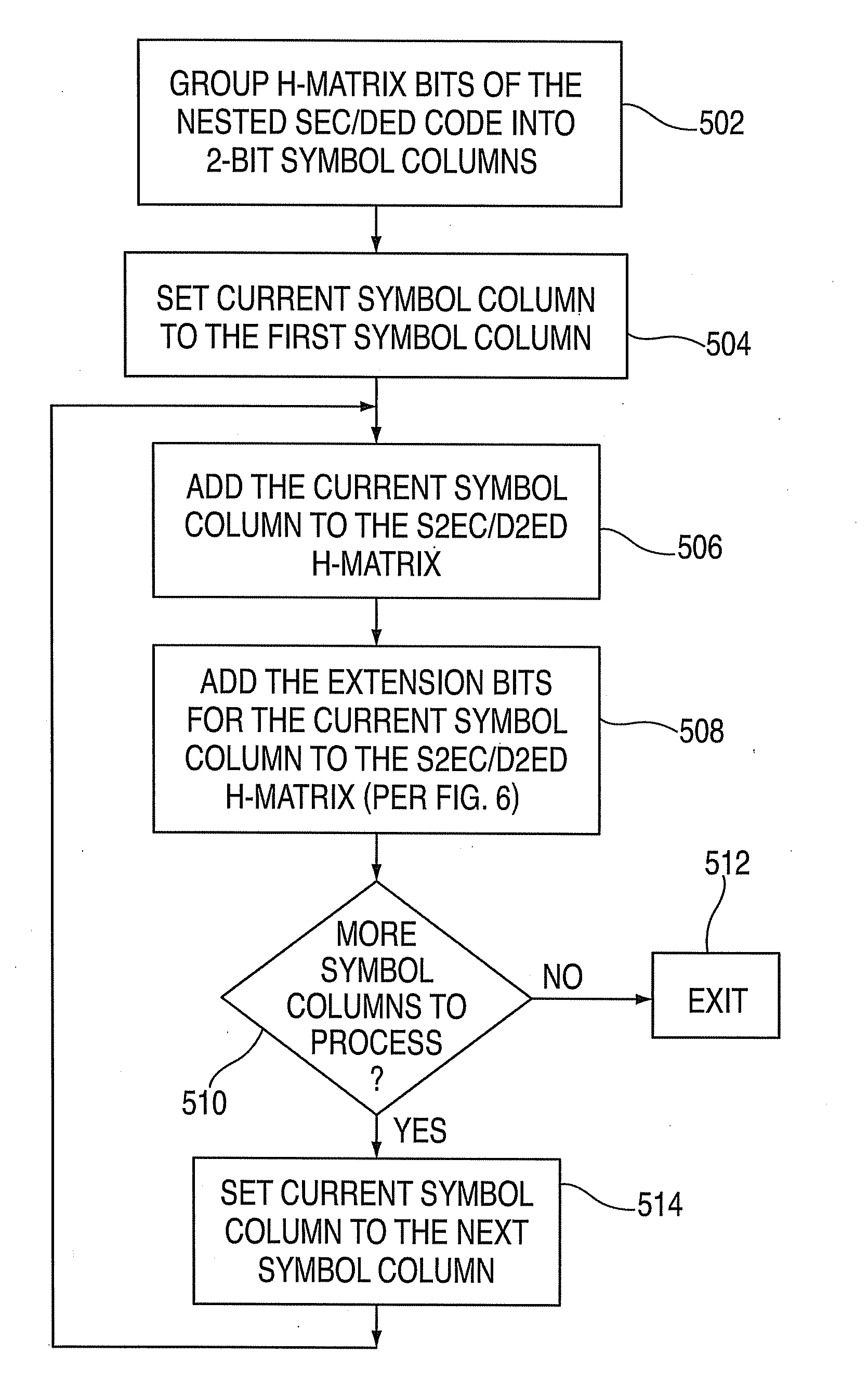
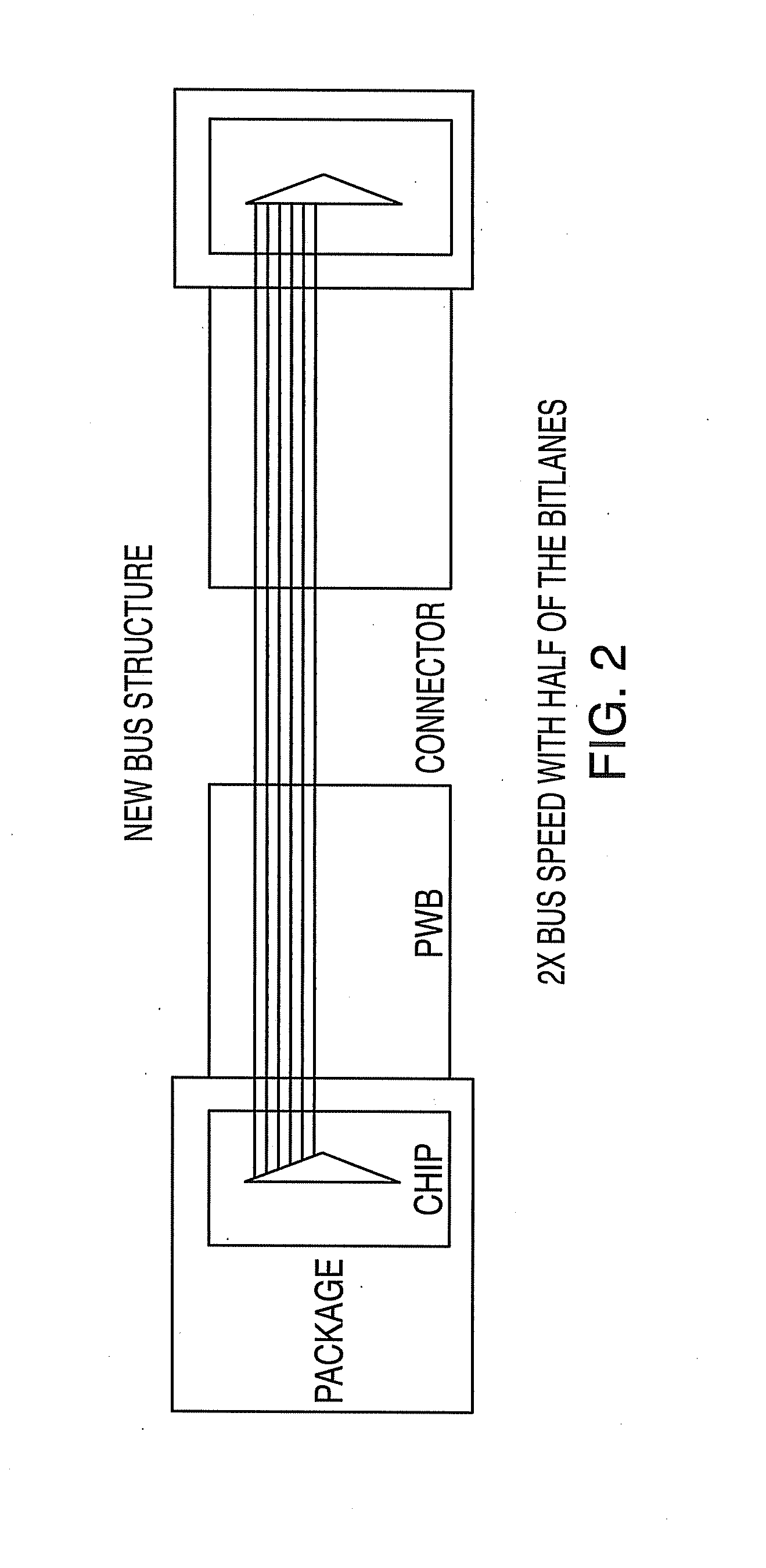
Systems, method, and computer program products for providing a nested two-bit symbol bus error correcting code scheme for transfer over a bus in two or more transfers. Methods include constructing a nested error correcting code (ECC) scheme. The method includes receiving a Hamming distance n code including original checkbits. A symbol correcting code H-matrix framework is defined including specifying bit positions for the original checkbits and for additional checkbits associated with a symbol correcting code. The bit positions are specified such that the original checkbits and the additional checkbits are in bit positions that are transferred over a bus in a transfer subsequent to a first transfer. A symbol correcting code H-matrix is created using the bit positions indicated by the framework by iteratively adding rows of H-matrix bits on a symbol column basis such that the symbol correcting code H-matrix describes the symbol correcting code, and the Hamming distance n code is preserved as a subset of the symbol correcting code H-matrix.
Owner:IBM CORP
Clash-free irregular-repeat-accumulate code
ActiveUS7584400B2Error detection/correctionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsAlgorithmParity-check matrix
Methods, apparatuses, and systems are presented for performing data encoding involving receiving a sequence of data bits, encoding the sequence of data bits in accordance with a parity check matrix (H-matrix) to generate a sequence of encoded bits, wherein the H-matrix is capable of being partitioned into a first matrix and a second matrix, the first matrix being a dual-diagonal matrix, the second matrix comprising one or more vertically stacked sub-matrices, each sub-matrix consisting of a plurality of columns, each column having a column weight of no more than 1, wherein the second matrix is capable of being expressed as a product of a parity check matrix, an interleaver permutation matrix, and a repeat block matrix, and the interleaver permutation matrix satisfies a clash-free interleaver constraint, and outputting the sequence of encoded bits.
Owner:TRELLIS WARE TECH
Low-density parity-check (LDPC) encoder
The encoder chip of the present invention uses LDPC codes to encode input message data at a transmitting end, thereby generating a series of codewords. The encoder chip implements two low-density parity-check (LDPC) codes. The first LDPC code is a (4088,3360) code (4K) which is shortened from a (4095,3367) cyclic code. The second LDPC code is a quasi-cyclic (8158,7136) code (8K). The message data and the generated codewords are transmitted to a receiving end where the received codewords are decoded and checked for errors. To generate the codewords, the encoder applies a generator matrix G to the input message data. The G matrix is generated by first defining an H matrix. An H matrix is initially defined as 16×2 array of right-circulant sub-matrices. The G matrix is formed by manipulating the H matrix according to a 4-step algorithm. A randomizer and a synchronization marker are also included within the encoder.
Owner:IDAHO RESARCH FOUNDATION INC
Encoding method for low code rate LDPC code
InactiveCN101488760AReduce in quantityImprove performanceError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsComputation complexitySignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
The invention discloses an encoding method of low bit-rate LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) code, including the following steps: step 1, matrixes H and H are respectively constructed, the H matrix is a diagonal matrix, H is an array matrix with q multiplied by 1 and consists of q end-around-shift permutation matrixes Q; the permutation matrix Q consists of b multiplied by b step permutation matrixes Q having row weight and line weight of 1, at most one element of 1 on each diagonal line and the rest elements of 0; step 2, an H matrix with the size of equal to bq multiplied b(q+1) is constructed; step 3, check vector c is constructed, c is equal to (p1, 1=1, 2, ..., M), p1 represents the value of any first check bit, and M is the length of check bit; step 4, according to the check vector c=(p1), the inputted information vector c is equal to (dj), and coded code word c=(cc) is obtained. In the method of the invention, an algebraic method used by end-around-shift value of Q permutation matrix leads belief propagation iterative decoding algorithm to be more easily realized in parallel; bidiagonal matrix structural characteristic of H matrix can encode low rate LDPC code in a recursion manner, and has linear time computing complexity. The simulation performance is superior to the performance of the existing low rate error correcting code, thereby being capable of reaching a signal noise ratio of 0.4 dB and having ratio compatibility.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Orthogonal polynomial-based milling stability prediction method
InactiveCN104680000AReduce local errorReduce the number of iterationsSpecial data processing applicationsKinetics equationH matrix
The invention relates to the field of advanced manufacturing, in particular to an orthogonal polynomial-based milling stability prediction method. The orthogonal polynomial-based milling stability prediction method adopts orthogonal polynomials to approach a state term, a delay term and a periodical coefficient term in a kinetic equation, and adopts a plurality of known time points and responses thereof to fit the needed terms, so that the local errors of the calculation method are reduced, and thereby the precision of the prediction method is increased; meanwhile, in the process of obtaining a stability lobe diagram, an H matrix is introduced instead of directly substituting an F matrix for calculation, so that the number of iterations in the F matrix calculation process is reduced, consequently, the time of the calculation method is saved, and the efficiency of calculation is increased.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Obstacle avoidance solution applied to redundant manipulator
The invention discloses an obstacle avoidance solution applied to a redundant manipulator. The obstacle avoidance solution comprises the steps of: S1, acquiring a forward kinematics model of the manipulator through establishing a D-H matrix of the manipulator, and establishing a target track equality constraint index of a speed layer after performing derivation processing on the forward kinematicsmodel; S2, establishing a vector-based obstacle avoidance inequality constraint index; S3, writing the target track equality constraint index of the speed layer established in the step S1 and the vector-based obstacle avoidance inequality constraint index established in the step S2 into quadratic programming problems in the unified form; S4, transforming the quadratic programming problems in theunified form in the step S3 into a linear variational inequality; S5, solving the linear variational inequality in the step S4 by means of a primal-dual neural network solver; S6, and outputting manipulator joint angle control variables solved by means of the primal-dual neural network solver in the step S5 to the manipulator, so as to realize the effect of controlling the redundant manipulator toavoid obstacles.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for constructing LDPC (low density parity check) codes based on row-column combined iterative decoding
InactiveCN102185616AExcellent performance in different parametersLower latencyError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsAlgorithmLow-density parity-check code
The invention provides a method for constructing LDPC (low density parity check) codes based on row-column combined iterative decoding, comprising the following steps: 1, initializing parameters of the LDPC codes; 2, setting an operation sequence of rows (block rows); and 3, using a Peg or (Block-Peg) algorithm to construct an H matrix of the LDPC codes [QC (quasi-cyclic)-LDPC codes], wherein when positions of nonzero elements (sub-blocks) are determined, that is, when the connection of bipartite graphs of the H matrix is determined, the condition met: any two check nodes in all connected check nodes at the same variable node are not adjacent under an arrangement sequence determined in the step 2. The nonzero blocks in the two adjacent rows under the operation sequence of the rows of the constructed LDPC codes are not in the same column, thus reducing the time delay of information updating between the rows when hardware is realized, and improving the decoding rate.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
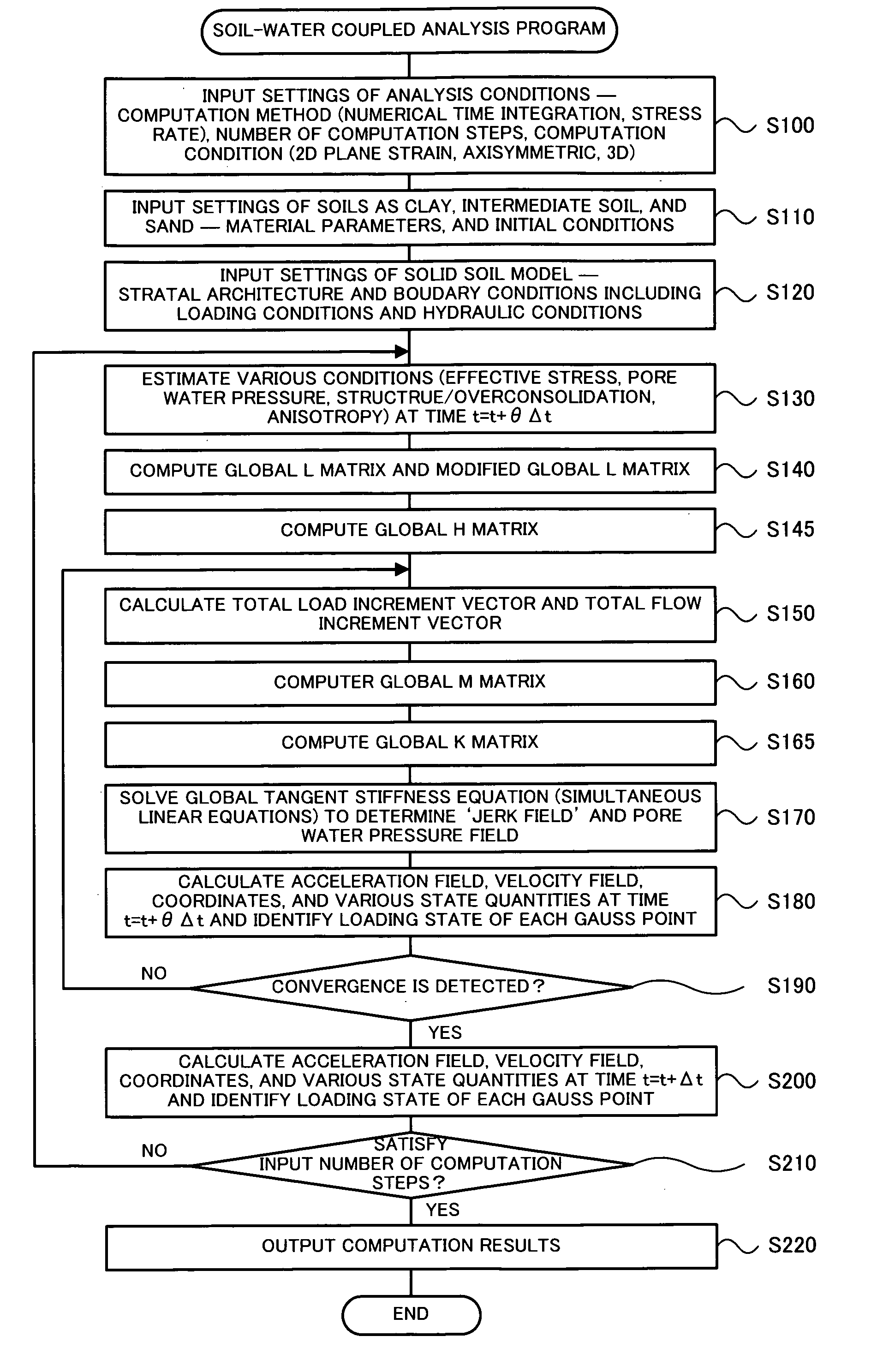
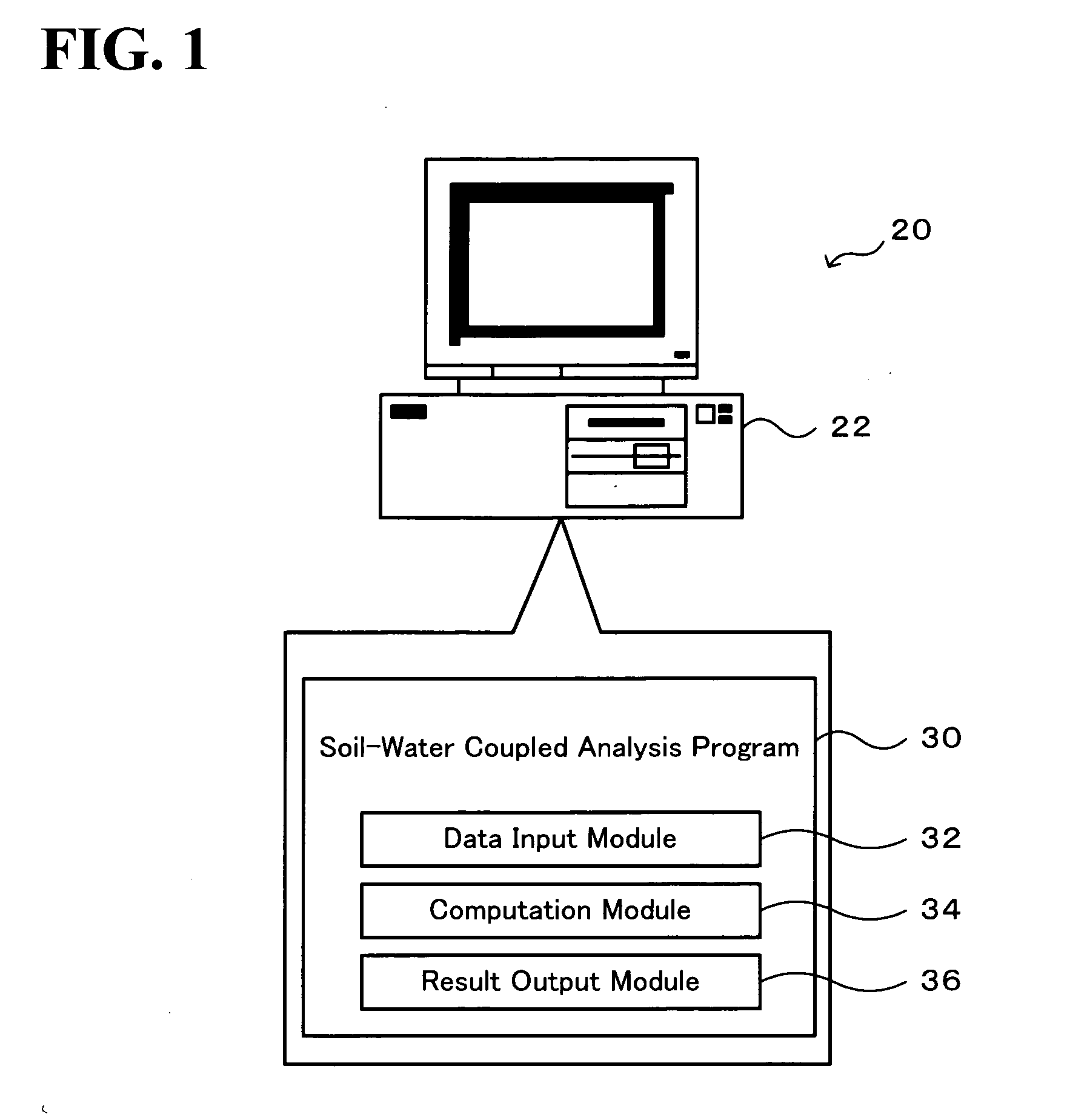
Soil-Water Coupled Analyzer and Soil-Water Coupled Analysis Method
InactiveUS20090164179A1Easy to calculateForecastingComputation using non-denominational number representationSoil skeletonH matrix
The soil-water coupled analysis program of the invention computes a global L matrix and a modified global L matrix regarding a volume change rate of a soil skeleton over time, a global H matrix regarding a water permeability of soil, a global M matrix regarding a mass, and a global K matrix regarding a tangent stiffness of the soil skeleton, based on input settings of soils, such as clay, intermediate soil, and sand, to respective elements of a soil foundation, input settings of a solid soil model, and input settings of analysis conditions (steps S140 to S165). The soil-water coupled analysis program formulates a global tangent stiffness equation (simultaneous linear equations) using all these computed matrixes and determines an unknown ‘jerk field’ and a ‘pore water pressure field’ under given boundary conditions, for example, a given deformation condition and a given stress rate condition (step S170). This enables highly-accurate dynamic and static analyses in soil foundations of various soils from sand to intermediate soils and clay.
Owner:NAGOYA UNIVERSITY
Nonlinear dynamic process monitoring method based on canonical variable nonlinear principal component analysis
ActiveCN109145256ALess nonlinear characteristicsReduce the impact of dynamic characteristicsCharacter and pattern recognitionComplex mathematical operationsDecompositionNon linear dynamic
The invention discloses a non-linear dynamic process monitoring method based on the non-linear principal component analysis of a normalized variable, which comprises the following steps: acquiring a data matrix Y, pre-specifying a value of p and a system order n; the Hankel matrix of the past and future observational side values being combined according to the formula; calculating covariance and cross-variance matrices of past and future observations; singular value decomposition of H matrix; calculating a state vector and a residual vector; the state vector being projected onto the high dimensional feature space by explicit second order polynomial mapping; the first k principal components being determined by eigenvalue decomposition in principal component analysis; finally, the T2 statistic, the combined statistic Qc and their corresponding control limits being calculated. The method of the invention is used for monitoring three different types of faults in the Eastman chemical process of Tennessee, and the simulation results show that the proposed CV-NPCA method has high fault detection rate and relatively low fault false alarm rate.
Owner:保控(南通)物联科技有限公司
Low density parity check (LDPC) decoder and implementation method thereof
ActiveCN103166648ASave storage spaceSave resourcesError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsComputer architectureProcess module
The invention discloses a low density parity check (LDPC) decoder and an implementation method thereof. The LDPC decoder comprises an input buffer cell, a state control and address generation module, a check node processing module, a variable node processing module and a decision codon storage unit. The input buffer cell comprises an H matrix array unit, a V matrix array unit and an initial information storage unit. Storage of results of row matrix and column matrix is carried out on only 57 ransom access memory (RAM), the number of the RAM is reduced by nearly 50%, and storage space in an implementation process of the LDPC decoder is reduced. At the same time, check node operation is carried out on an arithmetic unit of 5 CNU nodes, variable node operation is carried out on an arithmetic unit of 9 VNU nodes, a needed arithmetic unit in the implementation process of the LDPC decoder is reduced, and the goal of saving chip resources is achieved.
Owner:LEADCORE TECH
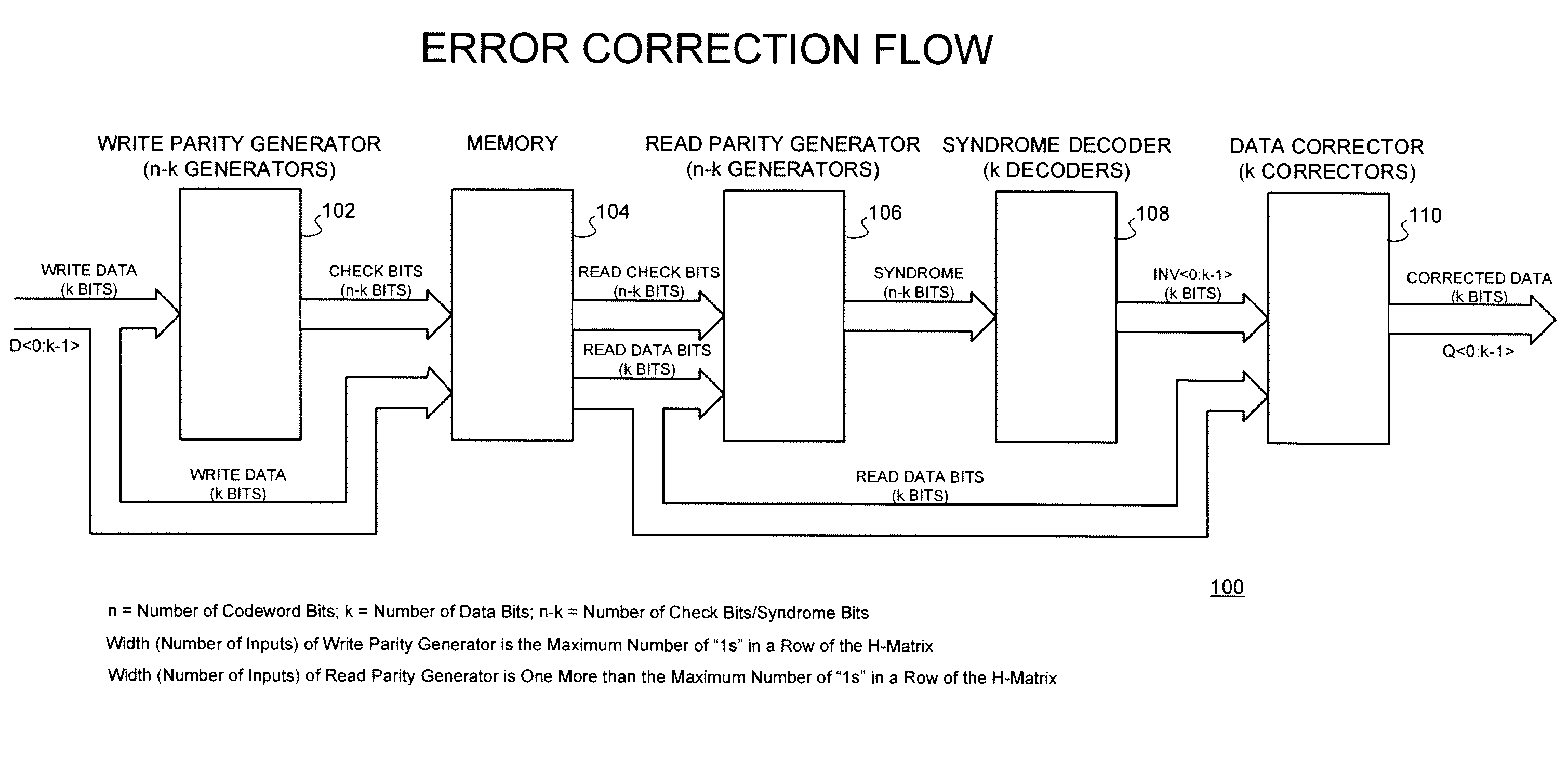
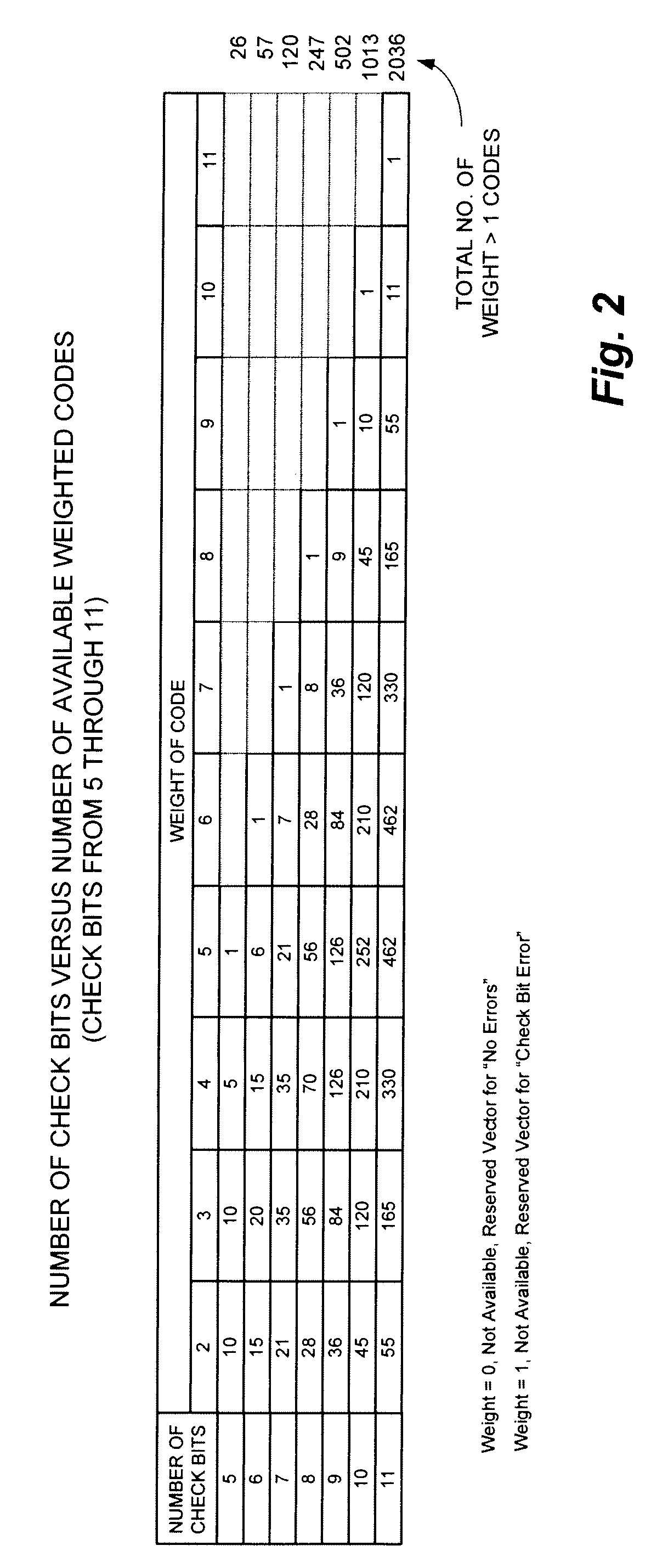
Technique for reducing parity bit-widths for check bit and syndrome generation for data blocks through the use of additional check bits to increase the number of minimum weighted codes in the hamming code h-matrix
ActiveUS20090077453A1Increase the number ofReduce in quantityError detection/correctionCode conversionHamming codeMinimum weight
A technique for reducing parity bit-widths for check bit and syndrome generation through the use of additional check bits to increase the number of minimum weighted codes in the Hamming Code H-Matrix. The technique of the present invention may be implemented while adding no additional correction / detection capability, in order to reduce the number of data bits that are used for each check bit / syndrome generation and to reduce the width of the parity generating circuitry.
Owner:INVENSAS CORP +1
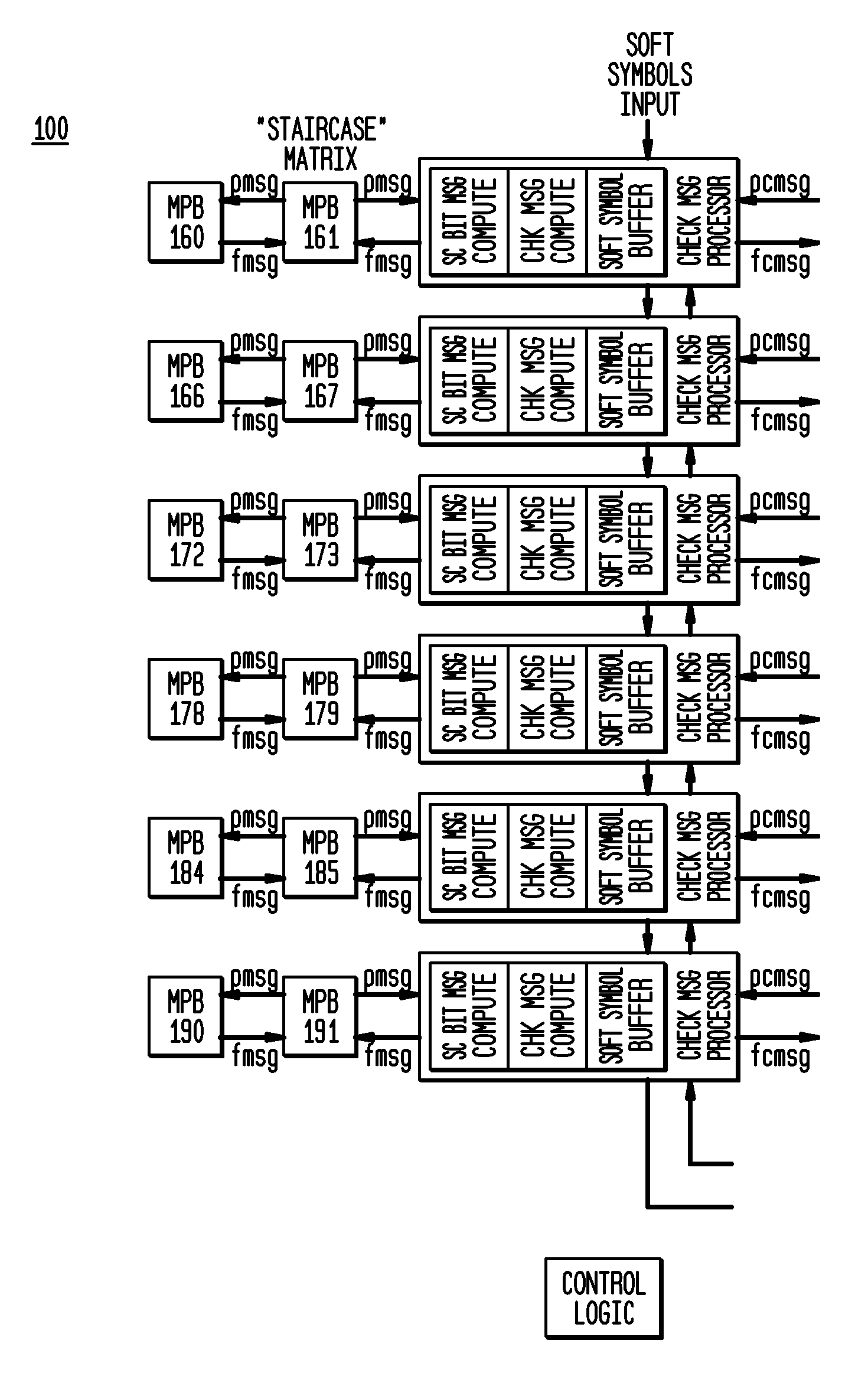
Efficient, programmable and scalable low density parity check decoder
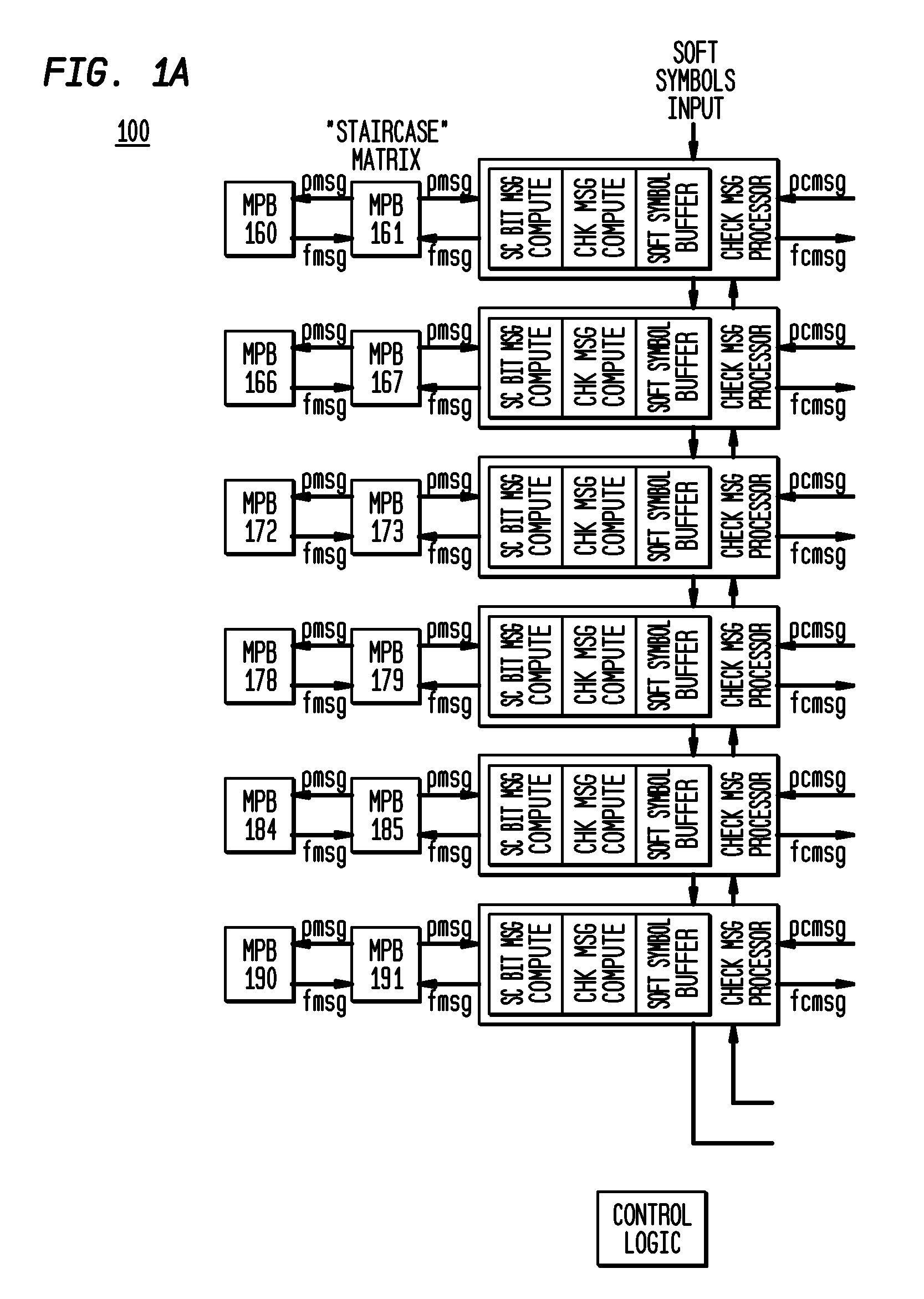
InactiveUS20100064199A1Minimize processing cycleEfficient designData representation error detection/correctionError detection/correctionCoding blockFpga implementations
In exemplary embodiments of the present invention, methods and apparatus allowing for an efficient design of an LDPC decoder suitable for a range of code-block sizes and bit-rates, which is also suitable for both ASIC and FPGA implementations, are provided. In exemplary embodiments of the present invention, the overhead associated with correction data sent along the transmission channel can be minimized. In exemplary embodiments of the present invention, an LDPC decoder is suitable for both ASIC and FPGA implementations. Method and apparatus allowing for an efficient design of an LDPC decoder suitable for a range of code-block sizes and bit-rates are presented. In exemplary embodiments of the present invention, such an LDPC decoder can be implemented in both ASIC and FPGA implementations. In exemplary embodiments of the present invention such an LDPC decoder can be optimized for either eIRA based H matrices or for general H matrices, as may be desirable. In exemplary embodiments of the present invention, an H parity matrix can be constructed and / or manipulated to arrange the bit-node message “columns” to facilitate mapping to MPB “columns” and corresponding access via LUT pointer tables to minimize processing cycles so as to, for example: (i) minimize address conflicts within the same MPB that will take multiple access cycles to resolve; (ii) minimize splitting of bit-node messages across MPB “columns” that will take multiple access cycles to resolve; and (iii) balance the bit-node computations across all the MPB / LUT “columns” so that they will complete their computations at nearly the same time.
Owner:SIRIUS XM RADIO INC
Systems, methods, and computer program products for providing a two-bit symbol bus error correcting code
Systems, methods and computer program products for providing a nested two-bit symbol bus error correcting code. Methods include constructing a nested error correcting code (ECC) scheme. The method includes receiving a Hamming distance n code. A symbol correcting code H-matrix is created by iteratively adding rows of H-matrix bits on a symbol column basis such that the symbol correcting code H-matrix describes a symbol correcting code, and the Hamming distance n code is preserved as a subset of the symbol correcting code H-matrix.
Owner:IBM CORP
Coding method of low density oven odd check code
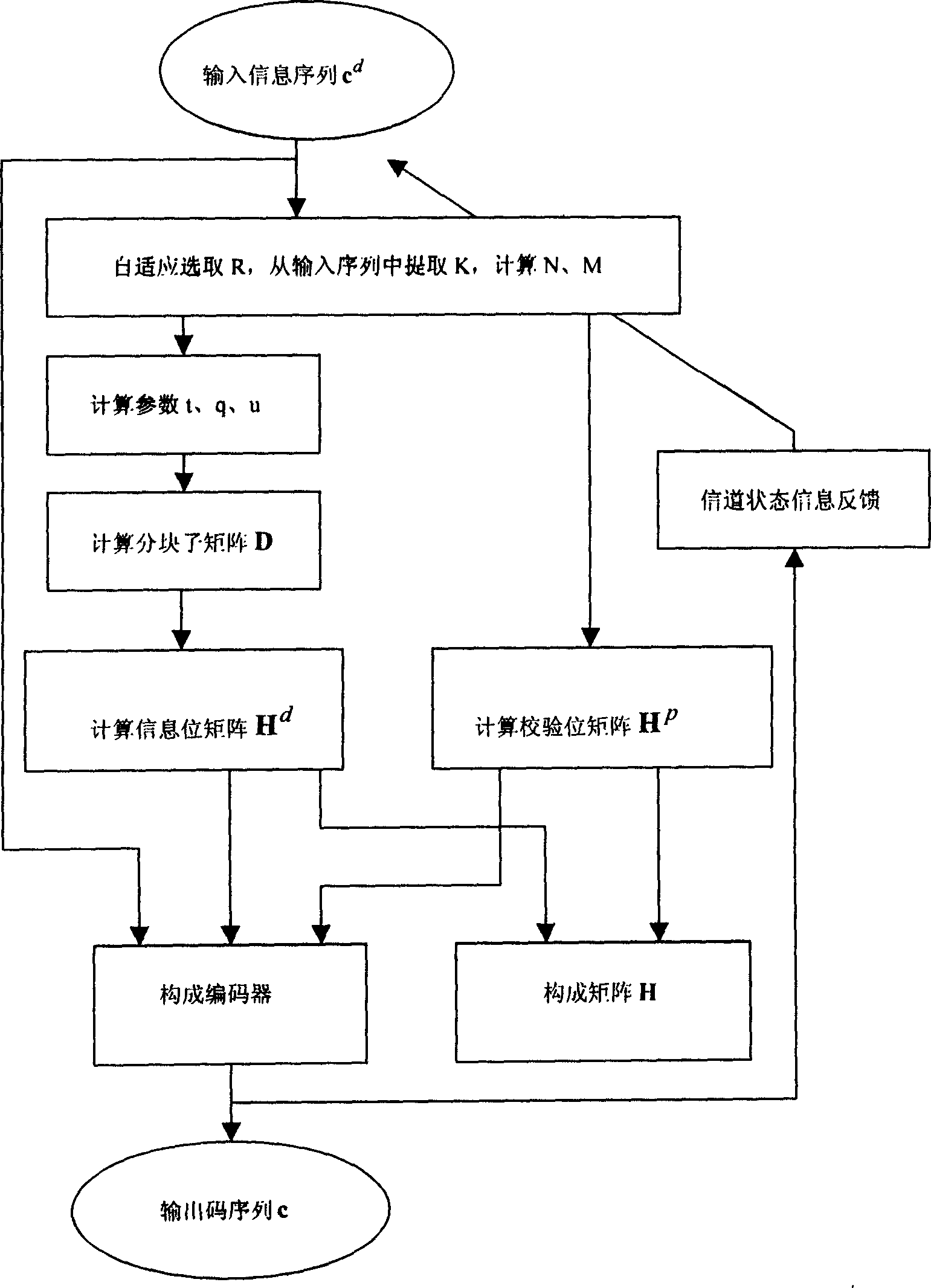
InactiveCN1753315AFlexible designGreat application potentialError preventionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsComputation complexityMatrix group
This invention discloses an encoding method for a low density odd-even check code including: 1, determining code rate R and a code length N and computing the check bit length M, 2, constructing the H to the power p matrix of MxM, 3, determining the structure parameter line weight t of the H to the power d, rank weight q and a sub-matrix dimension u, 4, utilizing the arithmetic sequence to comprise the vector v to constitute matrix D finally, 5, the D matrix and a group of its orthogonal D matrix group constitute matrix H to the power d, 6, evaluating the code sequence c and construct the H matrix, H=H to the power p:H to the power d.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
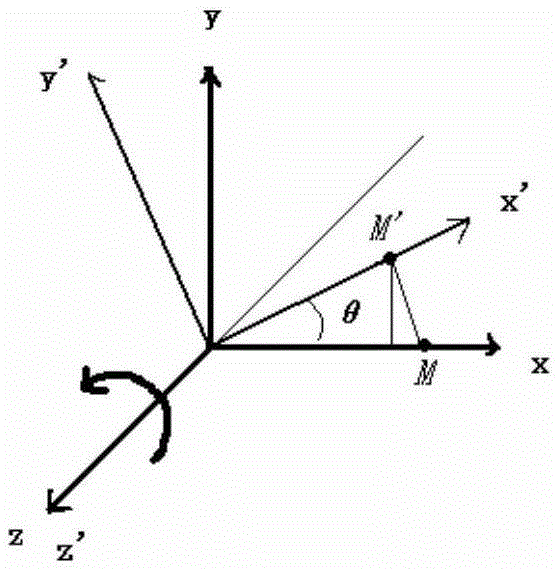
Kinematic performance analysis method of irregular RPR, RP and PR type mechanical arm connecting rod coordinate systems
The invention provides a kinematic performance analysis method of irregular RPR, RP and PR type mechanical arm connecting rod coordinate systems. The kinematic performance analysis method includes the specific steps of distinguishing rotating rod pieces and stretchable rod pieces in irregular mechanical arm connecting rods; determining rotating points and rotating axes of the rotating rod pieces and stretchable points and stretchable axes of the stretchable rod pieces, and establishing coordinate systems of all the rotating points and all the stretchable points; obtaining auxiliary articulation points, and establishing coordinate systems of the auxiliary articulation points; constructing D-H matrix parameters of the auxiliary articulation points; deducing translational transformation matrixes and rotating transformation matrixes; correspondingly substituting the D-H matrix parameters of the auxiliary articulation points into the translational transformation matrixes and the rotating transformation matrixes, and obtaining transformational matrixes of the irregular mechanical arm connecting rods; and inserting the obtained transformational matrixes into coordinate systems of front-and-back regular connecting rods corresponding to the irregular mechanical arm connecting rods. The method is simple and effective, modeling of the irregular mechanical arm connecting rod coordinate systems can be rapidly and accurately completed, and kinematic analysis becomes possible.
Owner:CHINA GEZHOUBA GRP YIPULI CO LTD
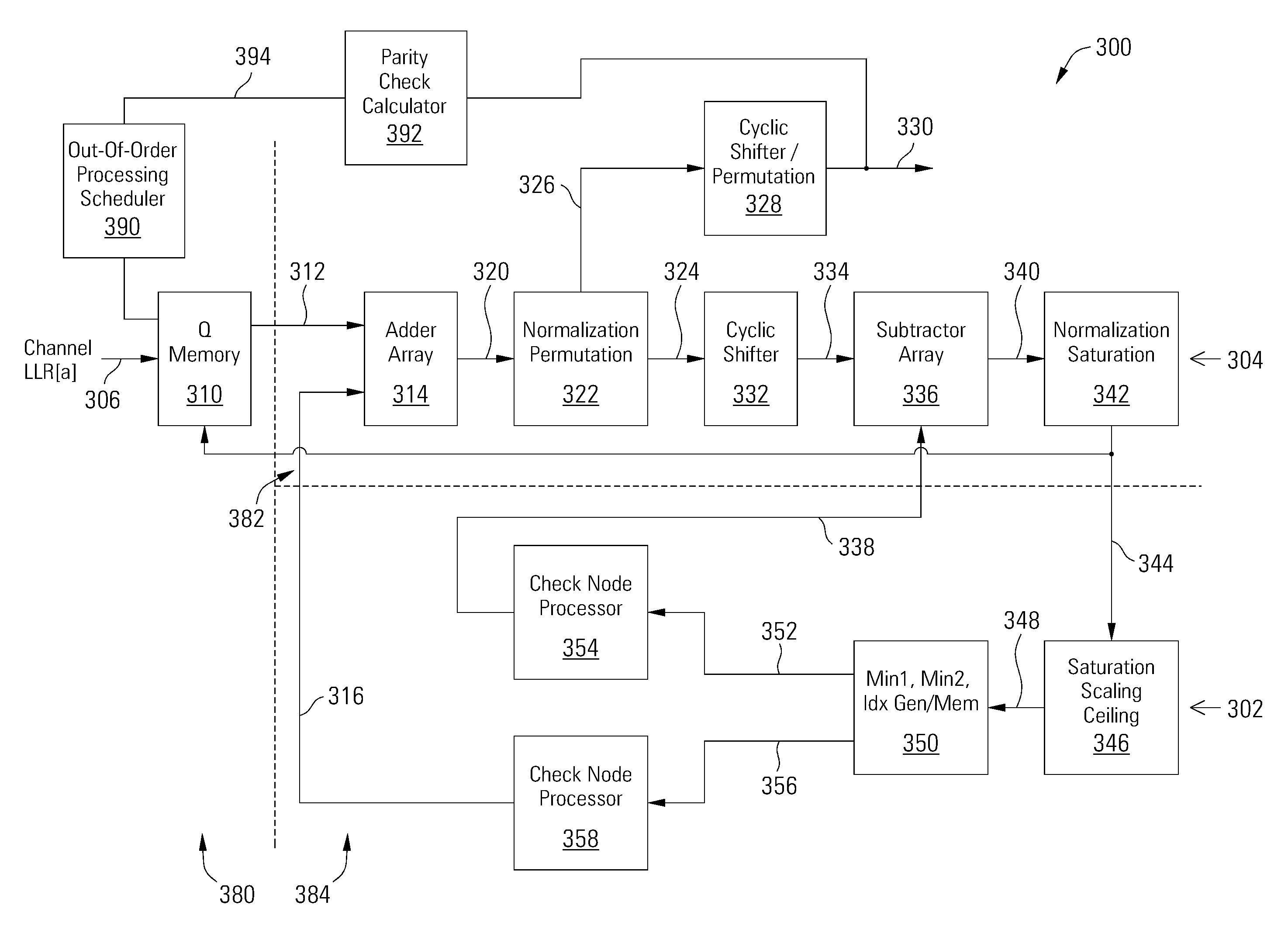
Multi-level LDPC layered decoder with out-of-order processing
ActiveUS9015547B2Reduce memory requirementsReduce bit widthSignal processing to reduce distortionsError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsParallel computingH matrix
An apparatus for low density parity check decoding includes a variable node processor operable to generate variable node to check node messages and to calculate perceived values based on check node to variable node messages, a check node processor operable to generate the check node to variable node messages and to calculate checksums based on the variable node to check node messages, and a scheduler operable to determine a layer processing order for the variable node processor and the check node processor based at least in part on the number of unsatisfied parity checks for each of the H matrix layers.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method for fast state estimation of power distribution network based on three pieces of measurement data
InactiveCN108649574AFix alignment issuesImprove ObservabilitySystems intergating technologiesInformation technology support systemObservabilityOccurrence time
The invention belongs to the technical field of power distribution network scheduling automation, and particularly relates to a method for fast state estimation of a power distribution network based on three pieces of measurement data. The method comprises the following steps of setting the taking time of SCADA measurement to be Eb+Tk in order to enable the sampling time of the SCADA measurement data to be consistent with the time of PMU data, wherein Eb is an expectation of SCADA measurement delay, and Tk is the occurrence time of the PMU data; adopting a linear extrapolation method to supplement high-precision pseudo measurement data in order to fuse PMU, SCADA and AMI measurement data; and establishing a mixed measurement state estimation model, computing a Jacobi equation H matrix, adding the active power and the reactive power for compensation decoupling, and obtaining a state estimation result after iteration solution. According to the method, a problem of data alignment of time-scale-free measurement and long-delay measurement is solved, the observability, the estimated accuracy and the computation convergence of the system are improved, and the problems of high mixed measurement dimension and slow convergence are solved.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING) +2
Systems, methods, and computer program products for providing a two-bit symbol bus error correcting code with bus timing improvements
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Systems, methods, and computer program products for providing a two-bit symbol bus error correcting code with bus timing improvements
Systems, method, and computer program products for providing a nested two-bit symbol bus error correcting code scheme for transfer over a bus in two or more transfers. Methods include constructing a nested error correcting code (ECC) scheme. The method includes receiving a Hamming distance n code including original checkbits. A symbol correcting code H-matrix framework is defined including specifying bit positions for the original checkbits and for additional checkbits associated with a symbol correcting code. The bit positions are specified such that the additional checkbits are in bit positions that are transferred over a bus in a transfer subsequent to a first transfer. A symbol correcting code H-matrix is created using the bit positions indicated by the framework by iteratively adding rows of H-matrix bits on a symbol column basis such that the symbol correcting code H-matrix describes the symbol correcting code, and the Hamming distance n code is preserved as a subset of the symbol correcting code H-matrix.
Owner:IBM CORP
Multi-mode layered decoding
ActiveUS8499226B2Data representation error detection/correctionCode conversionComputer hardwareH matrix
In one embodiment, a turbo equalizer is selectively operable in either first or second modes. In the first mode, layered (low-density parity-check (LDPC)) decoding is performed on soft-output values generated by a channel detector, where, for each full local decoder iteration, the updates of one or more layers of the corresponding H-matrix are skipped. If decoding fails to converge on a valid LDPC-encoded codeword and a specified condition is met, then LDPC decoding is performed in a second mode, where the updates of all of the layers of the H-matrix are performed for each full local decoder iteration, including the one or more layers that were previously skipped in the first mode. Skipping one or more layers in the first mode increases throughput of the decoder, while updating all layers in the second mode increases error correction capabilities of the decoder.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com