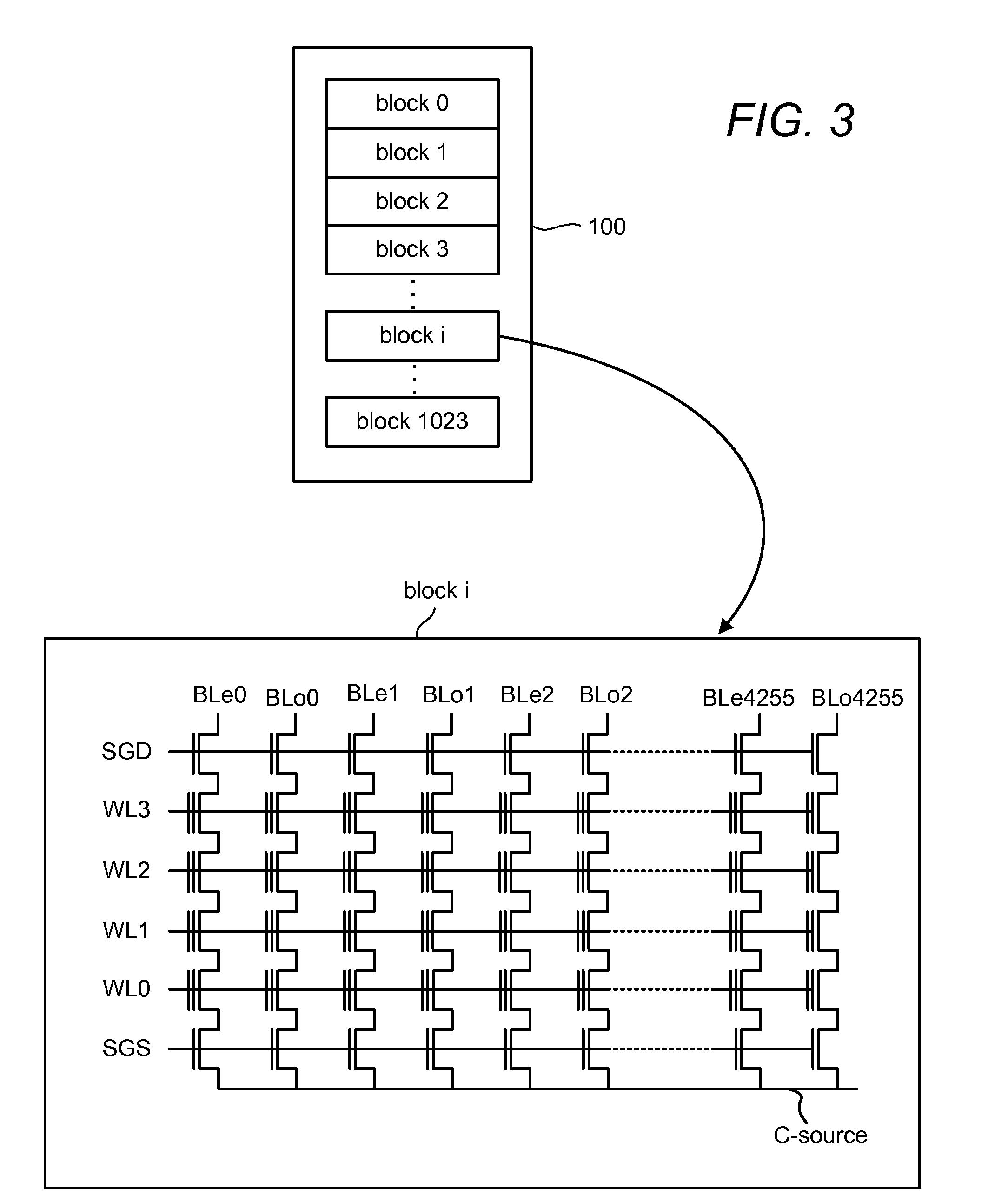
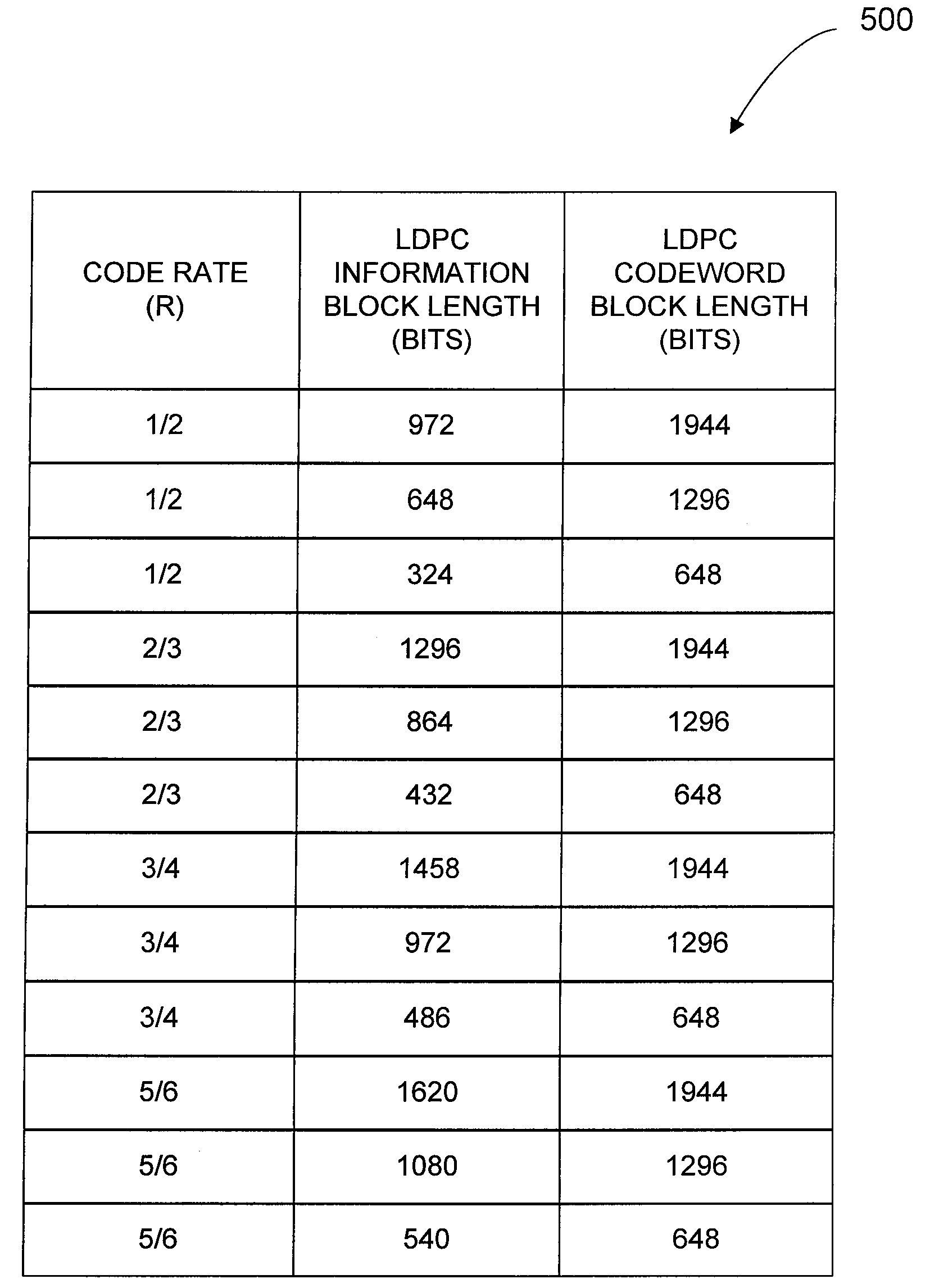
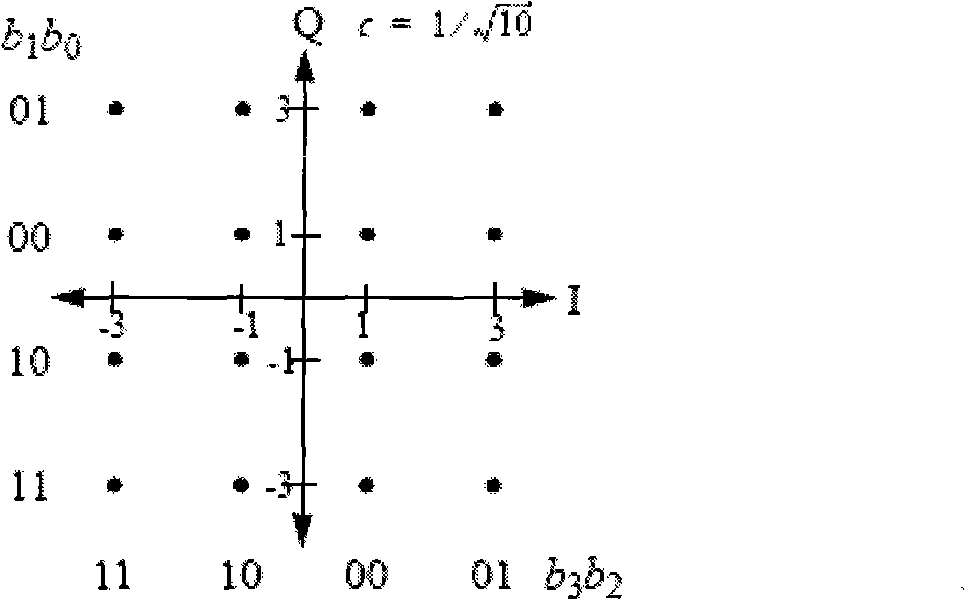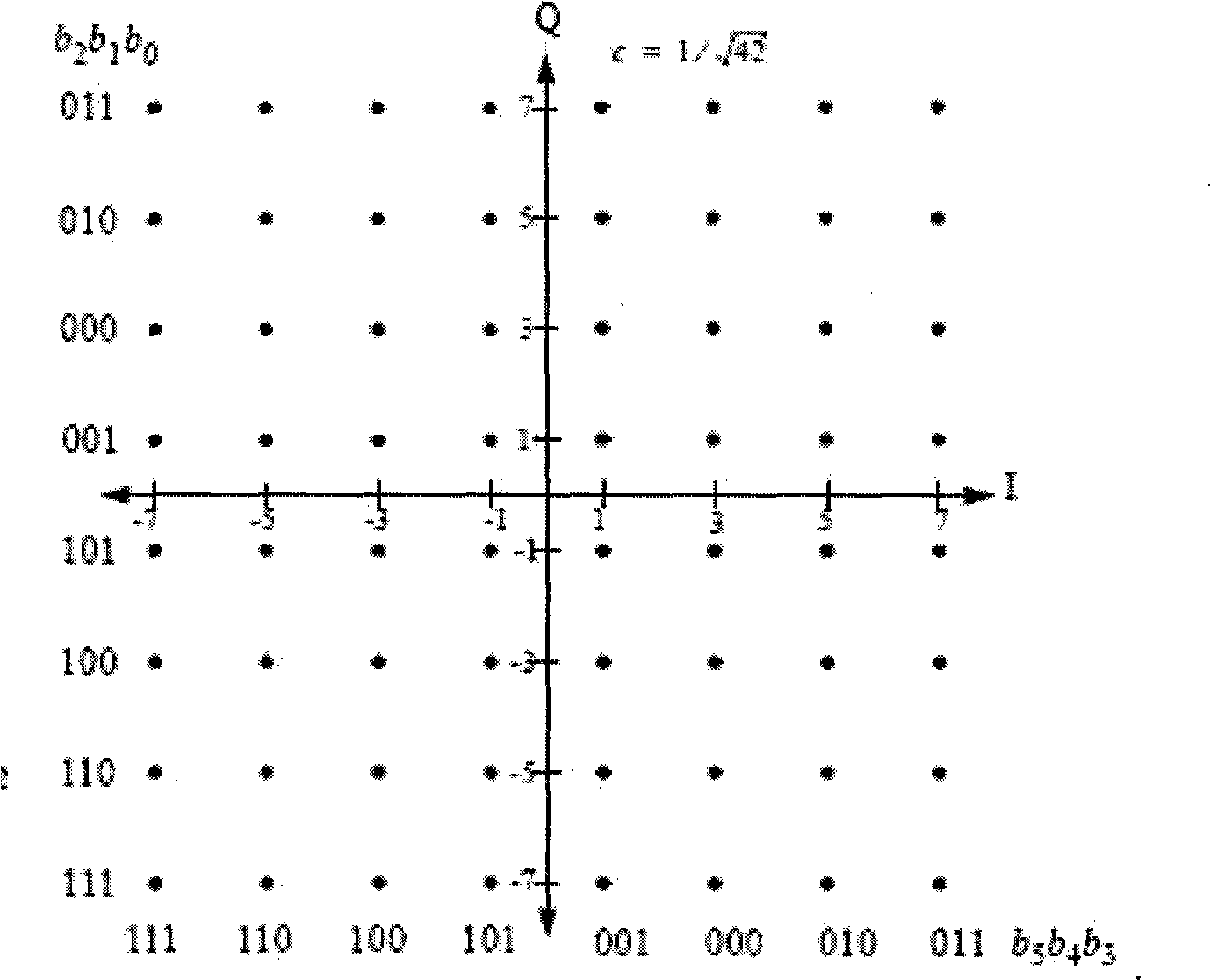Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
759 results about "Low-density parity-check code" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
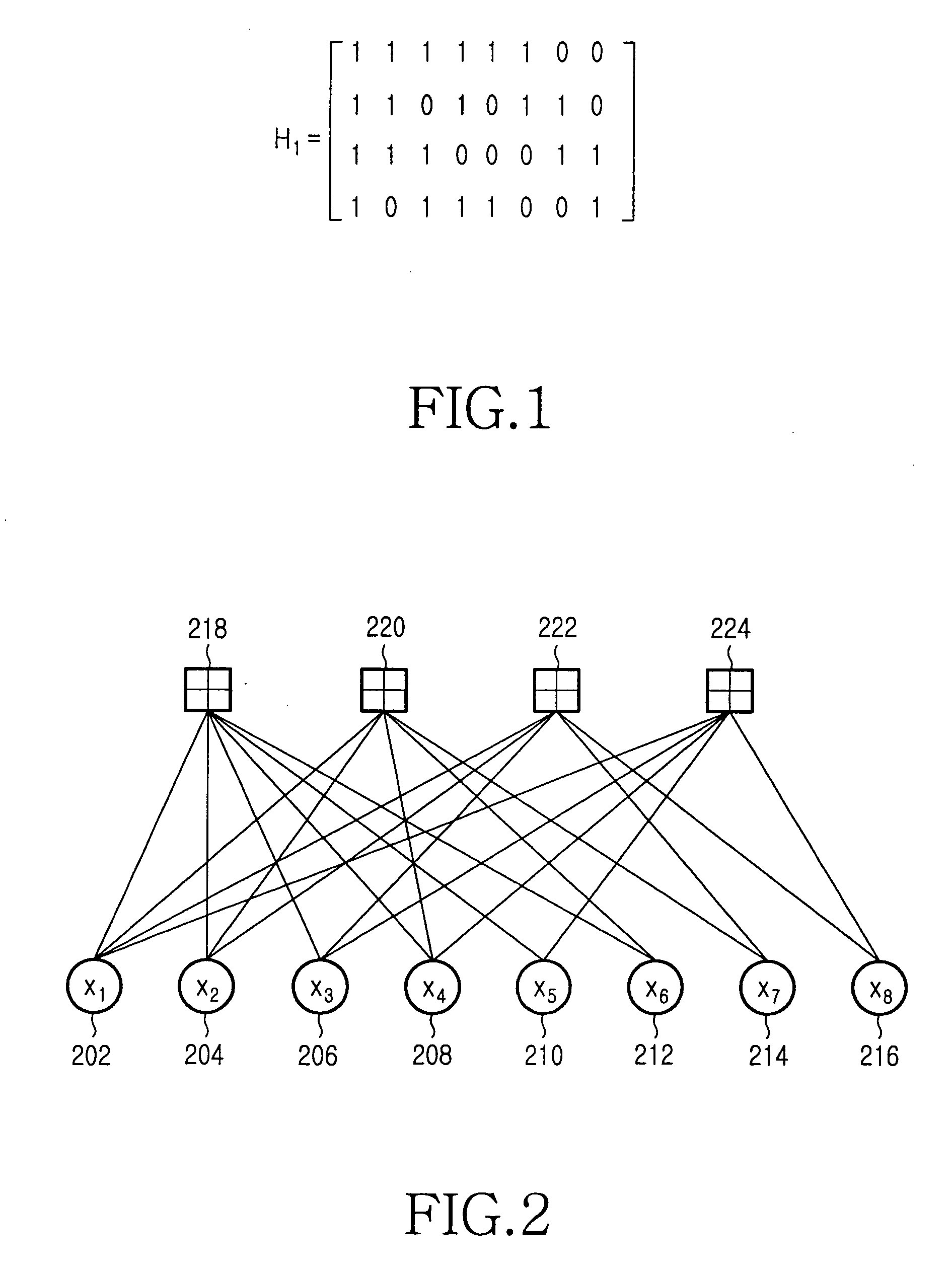
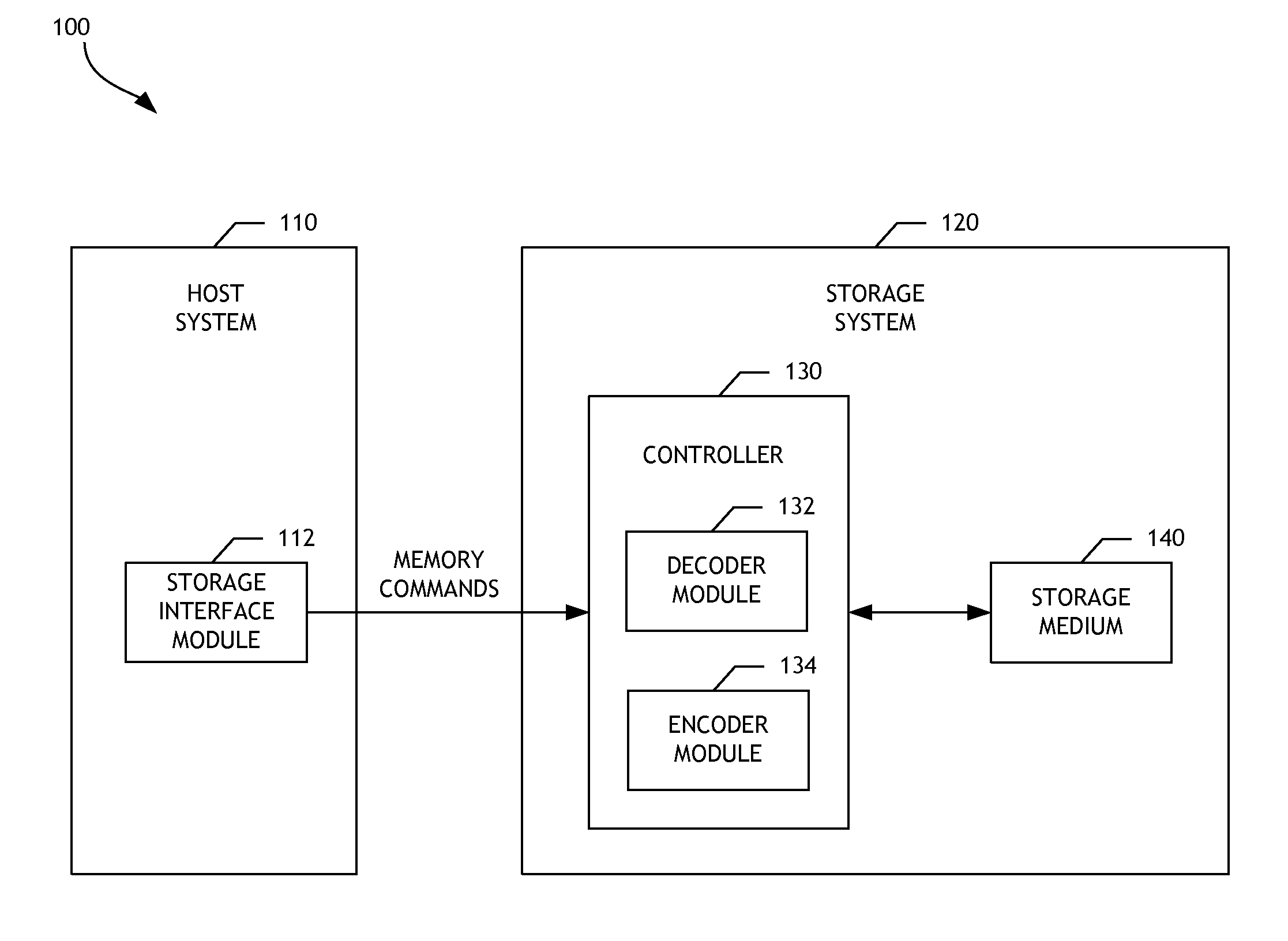
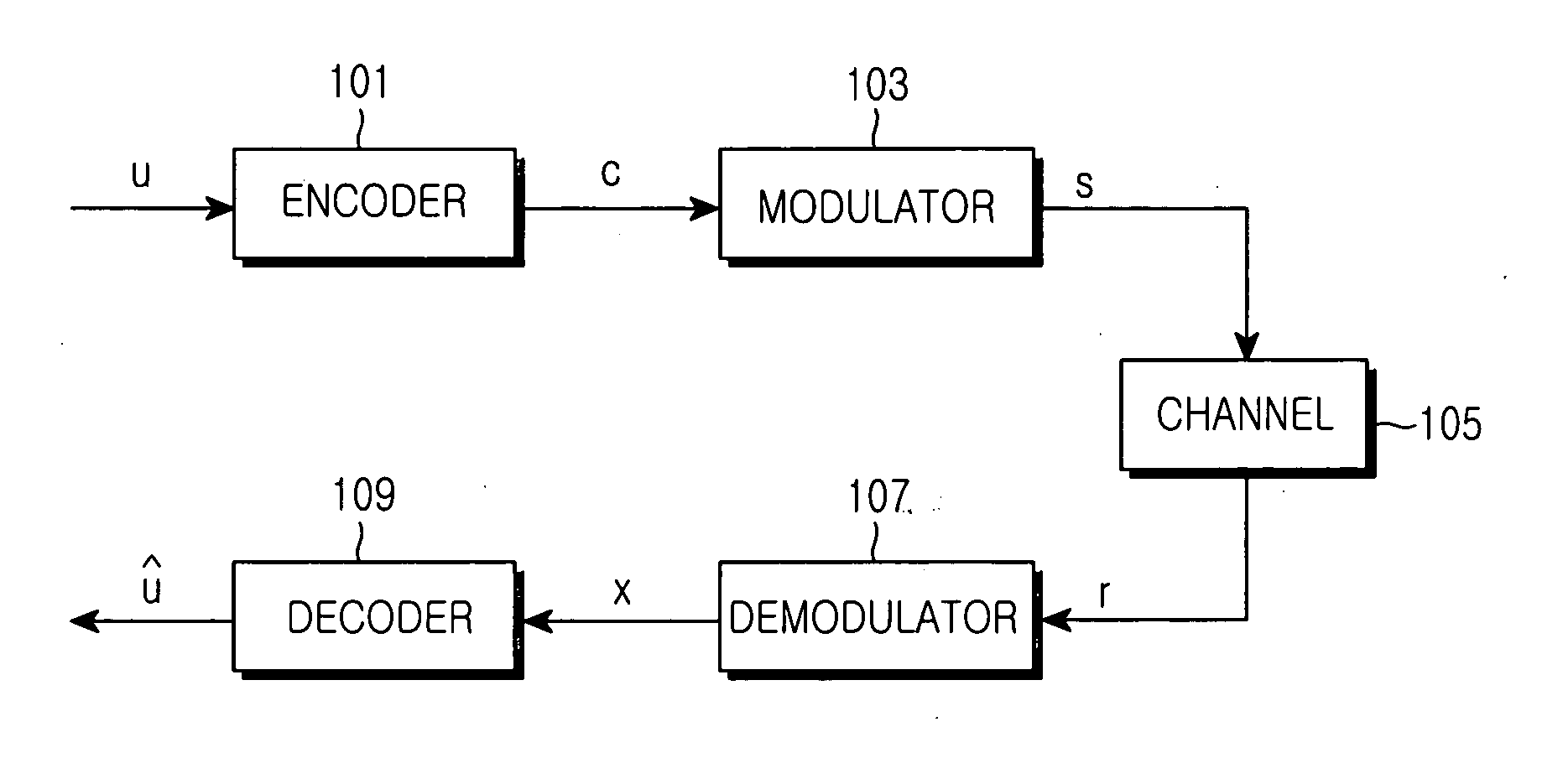
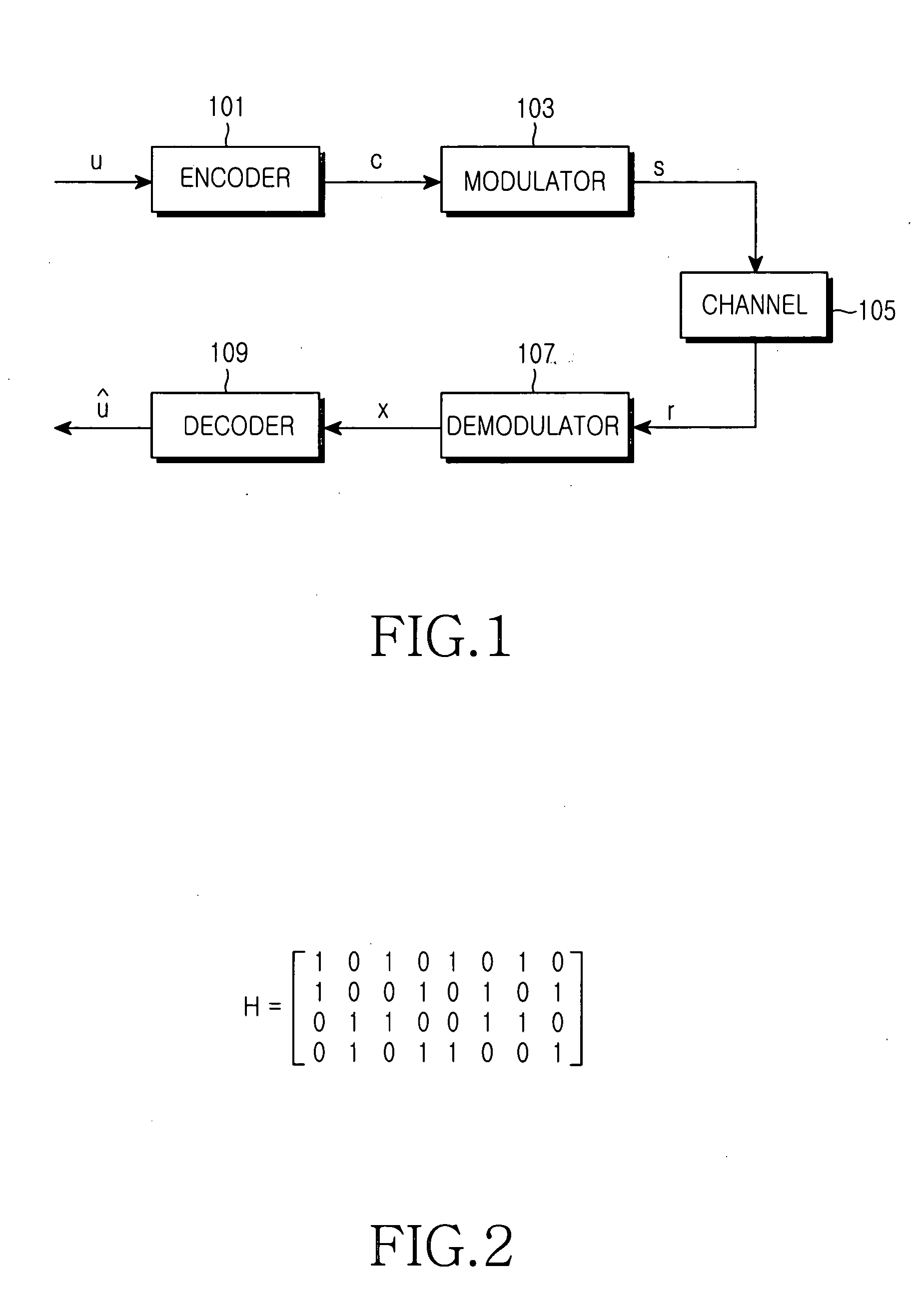
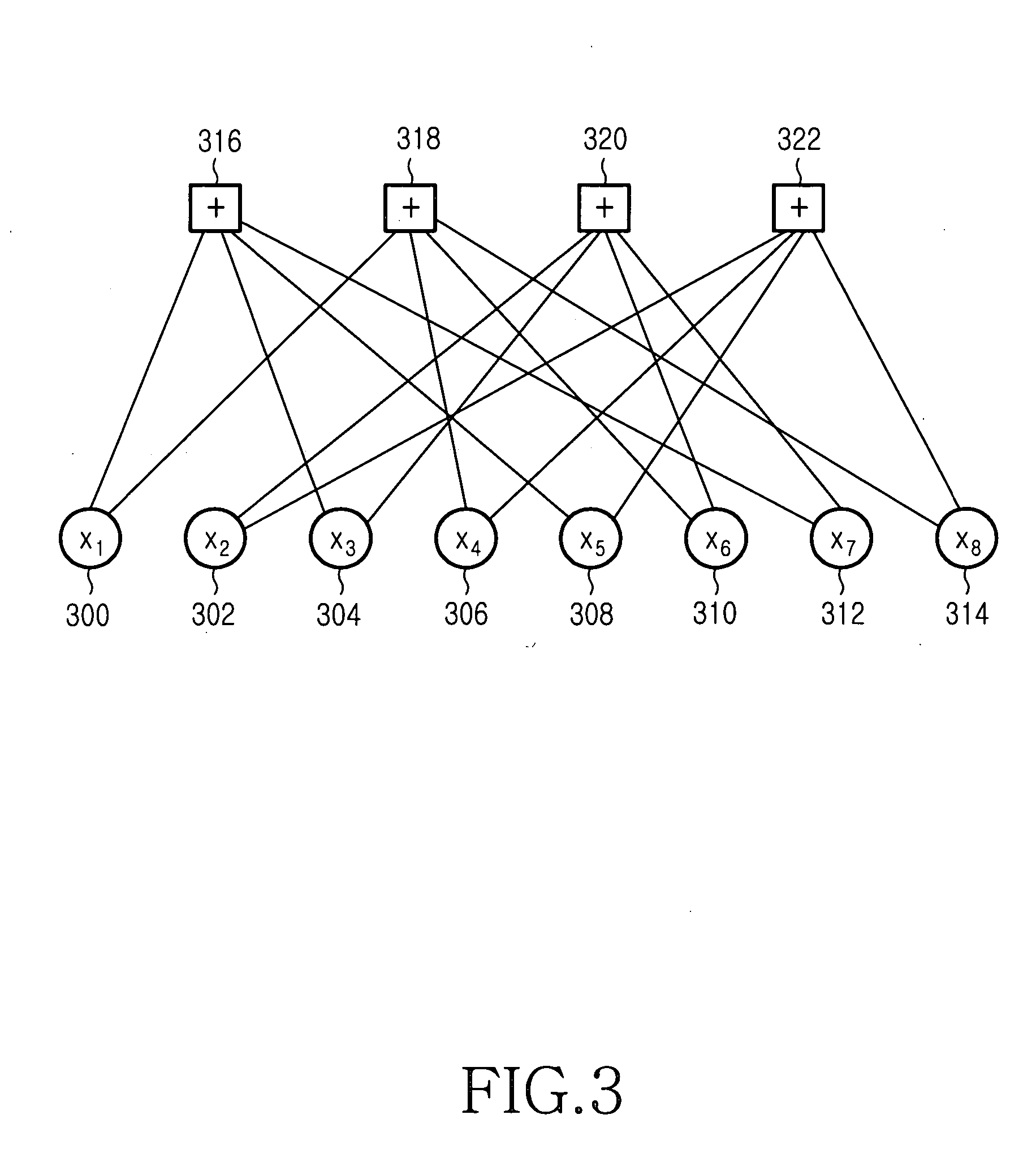
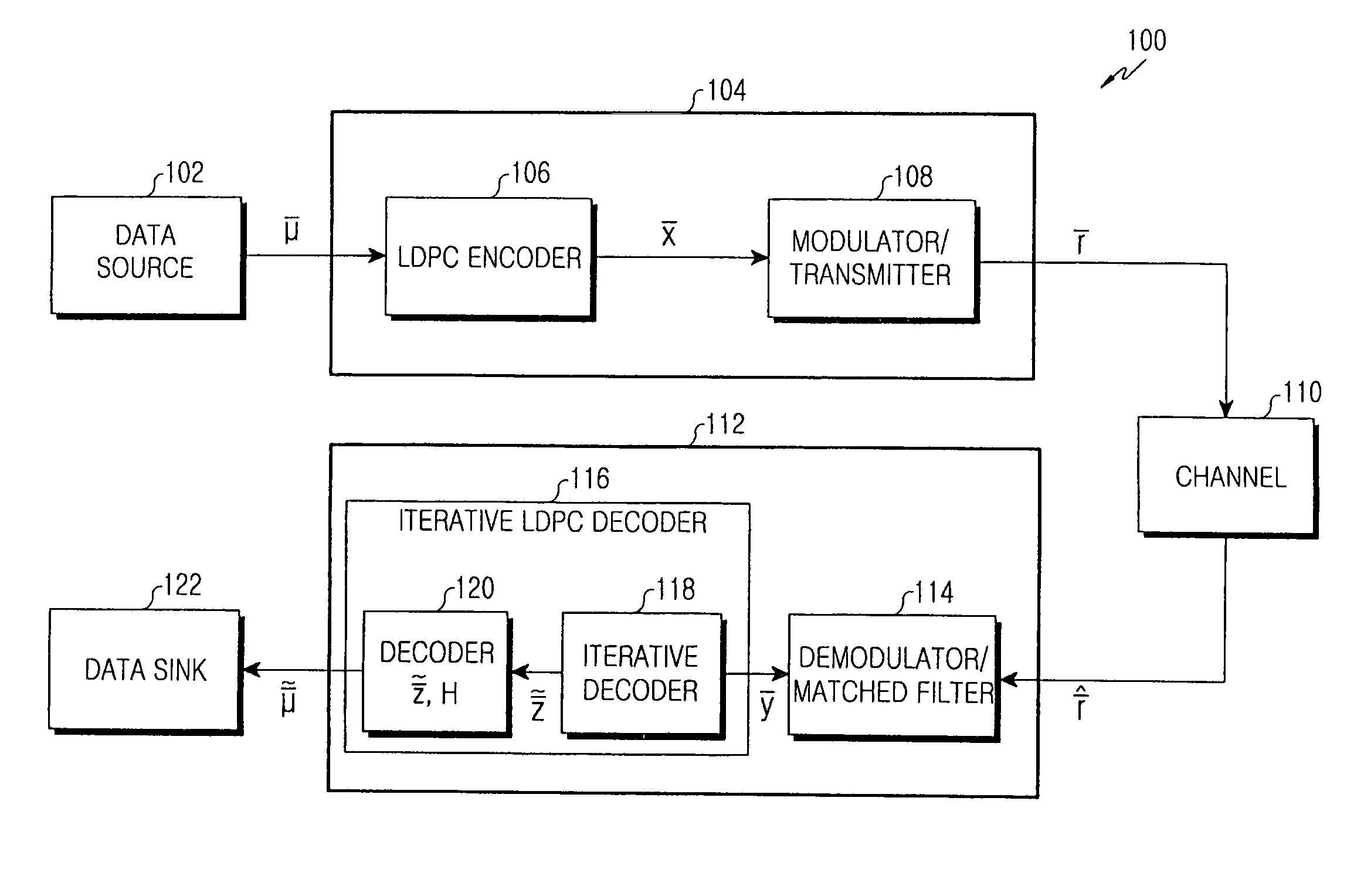
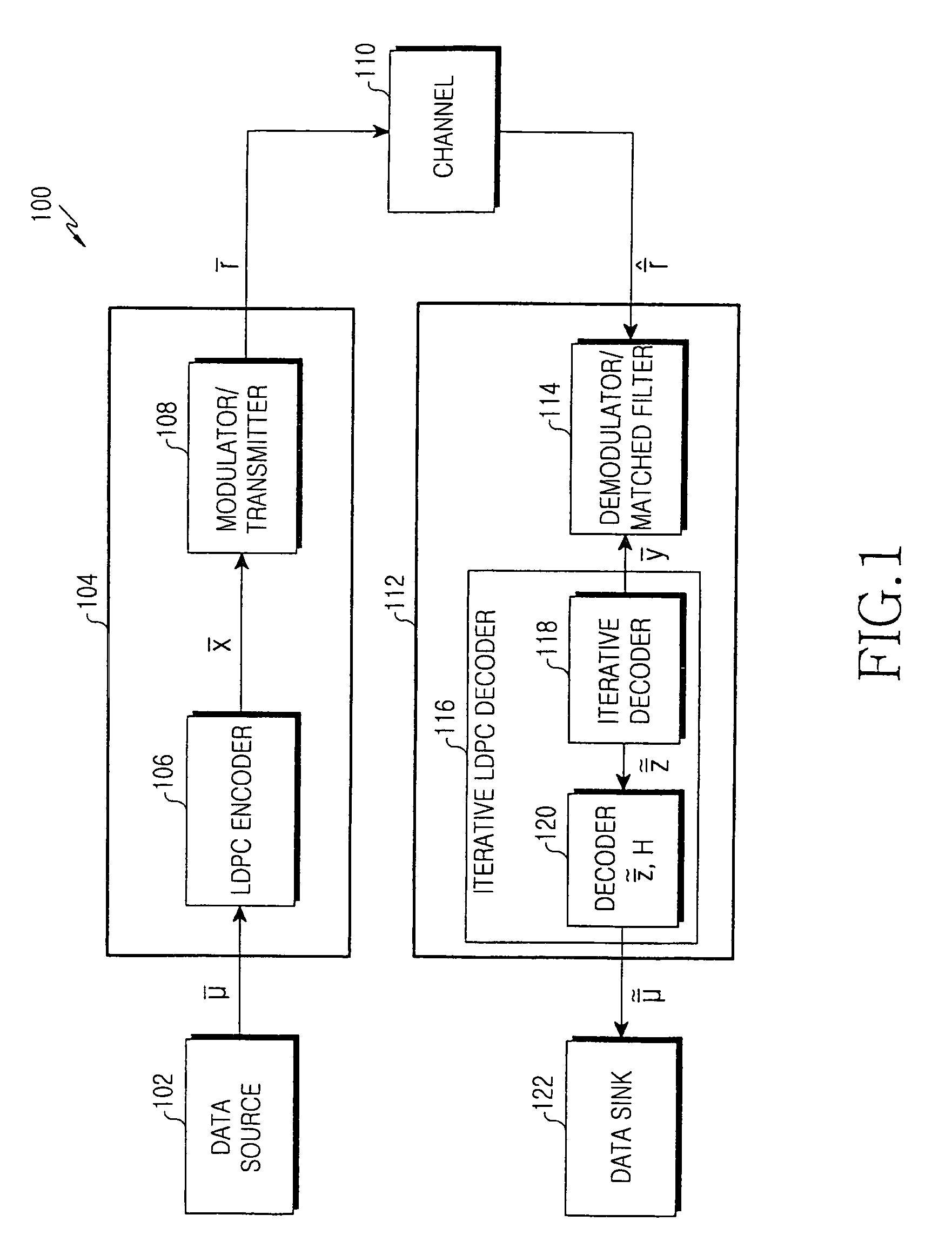
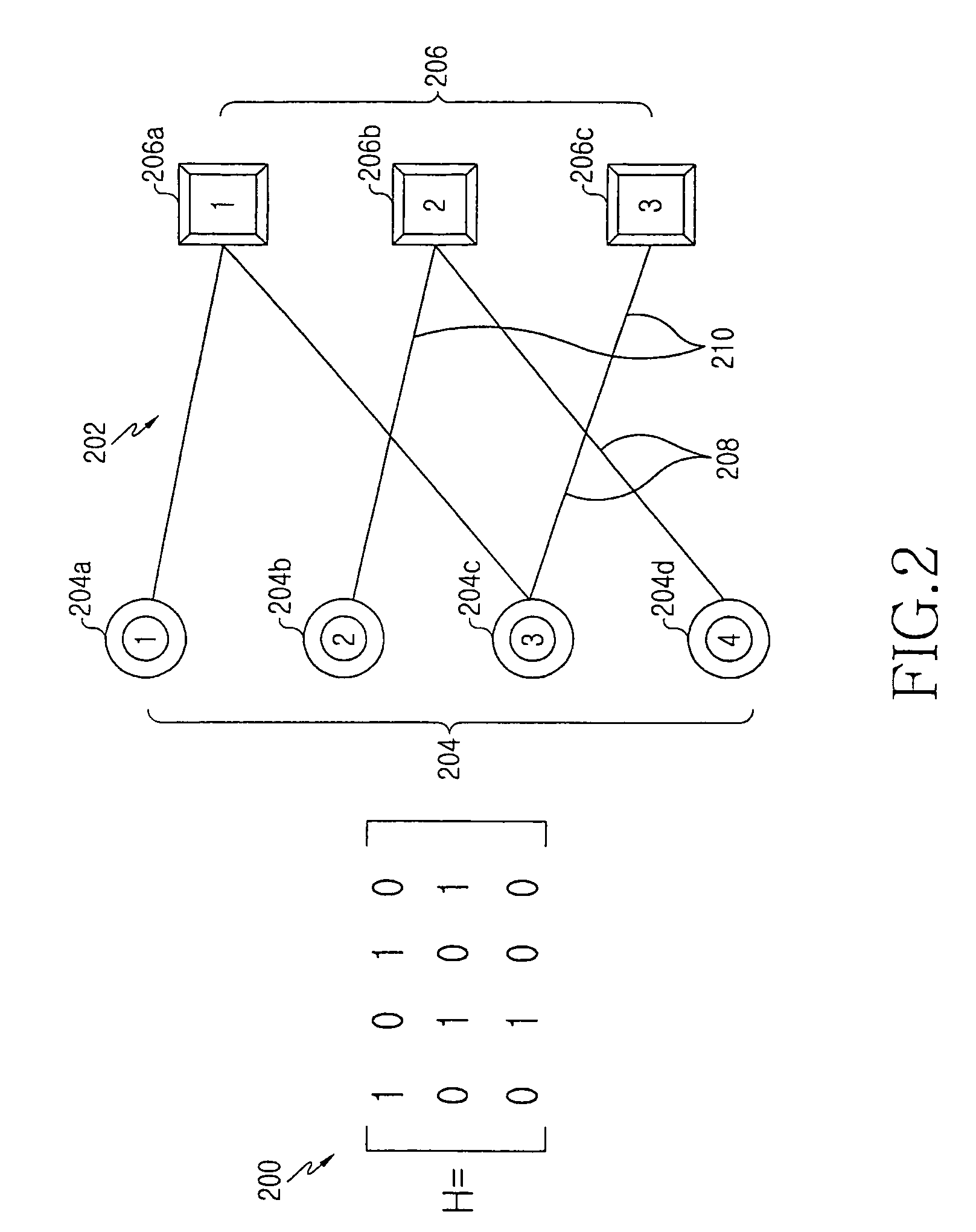
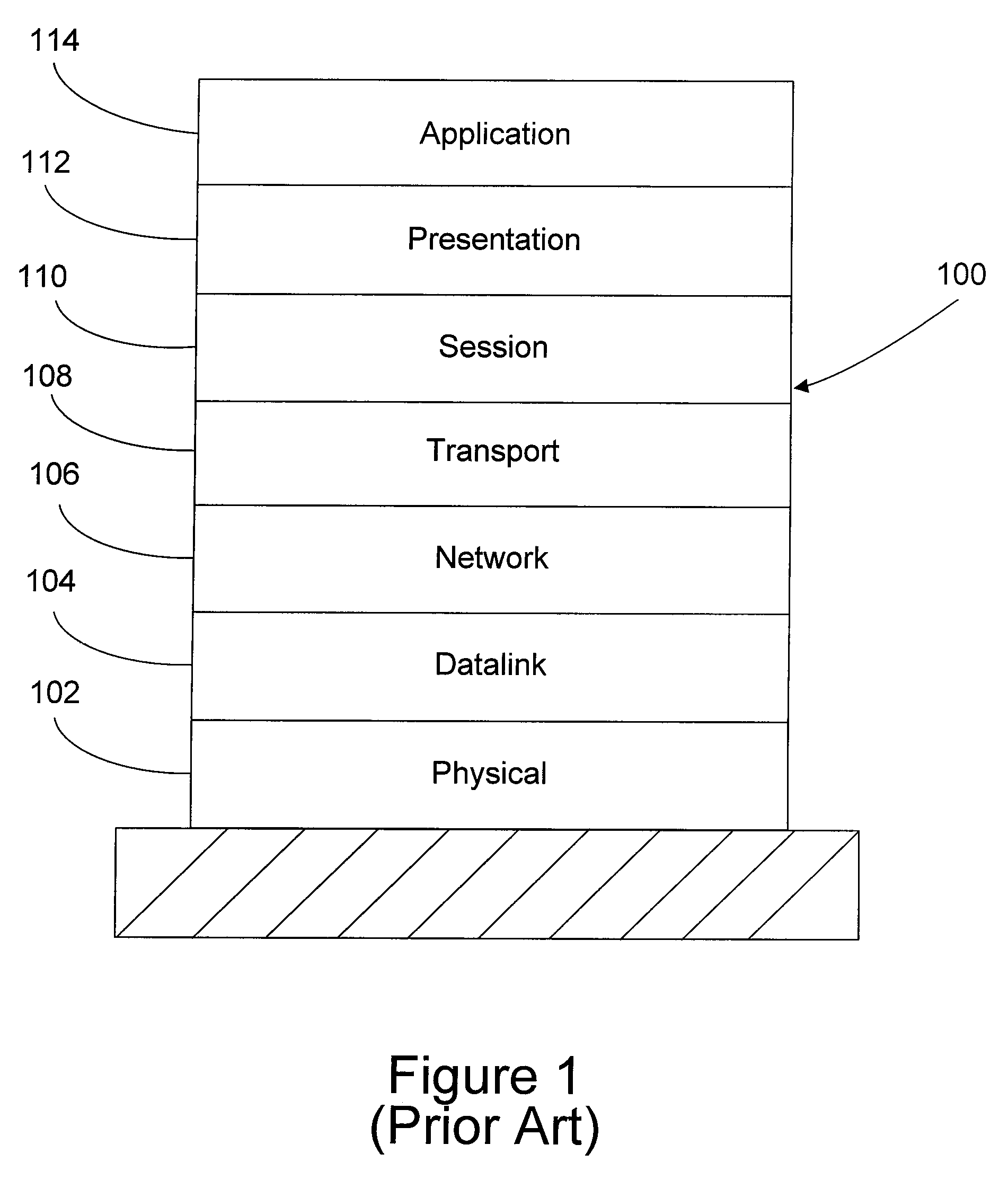
In information theory, a low-density parity-check (LDPC) code is a linear error correcting code, a method of transmitting a message over a noisy transmission channel. An LDPC is constructed using a sparse bipartite graph. LDPC codes are capacity-approaching codes, which means that practical constructions exist that allow the noise threshold to be set very close (or even arbitrarily close on the binary erasure channel) to the theoretical maximum (the Shannon limit) for a symmetric memoryless channel. The noise threshold defines an upper bound for the channel noise, up to which the probability of lost information can be made as small as desired. Using iterative belief propagation techniques, LDPC codes can be decoded in time linear to their block length.
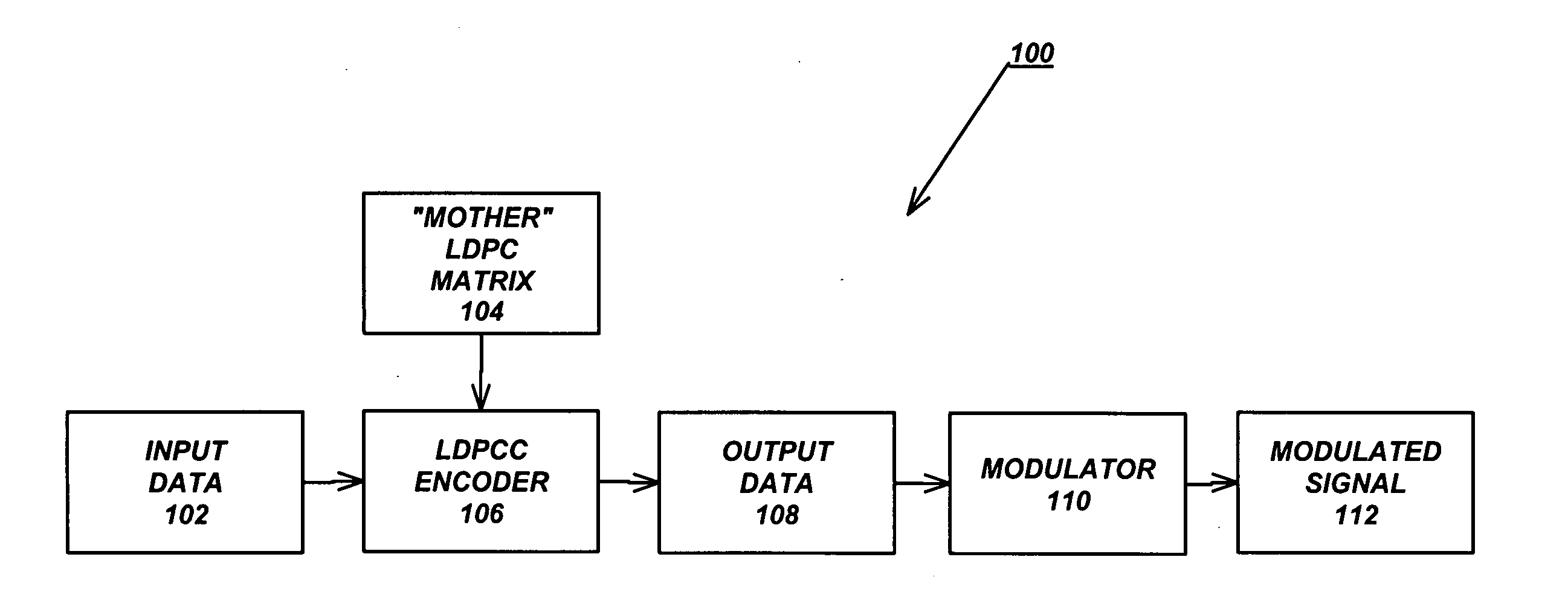
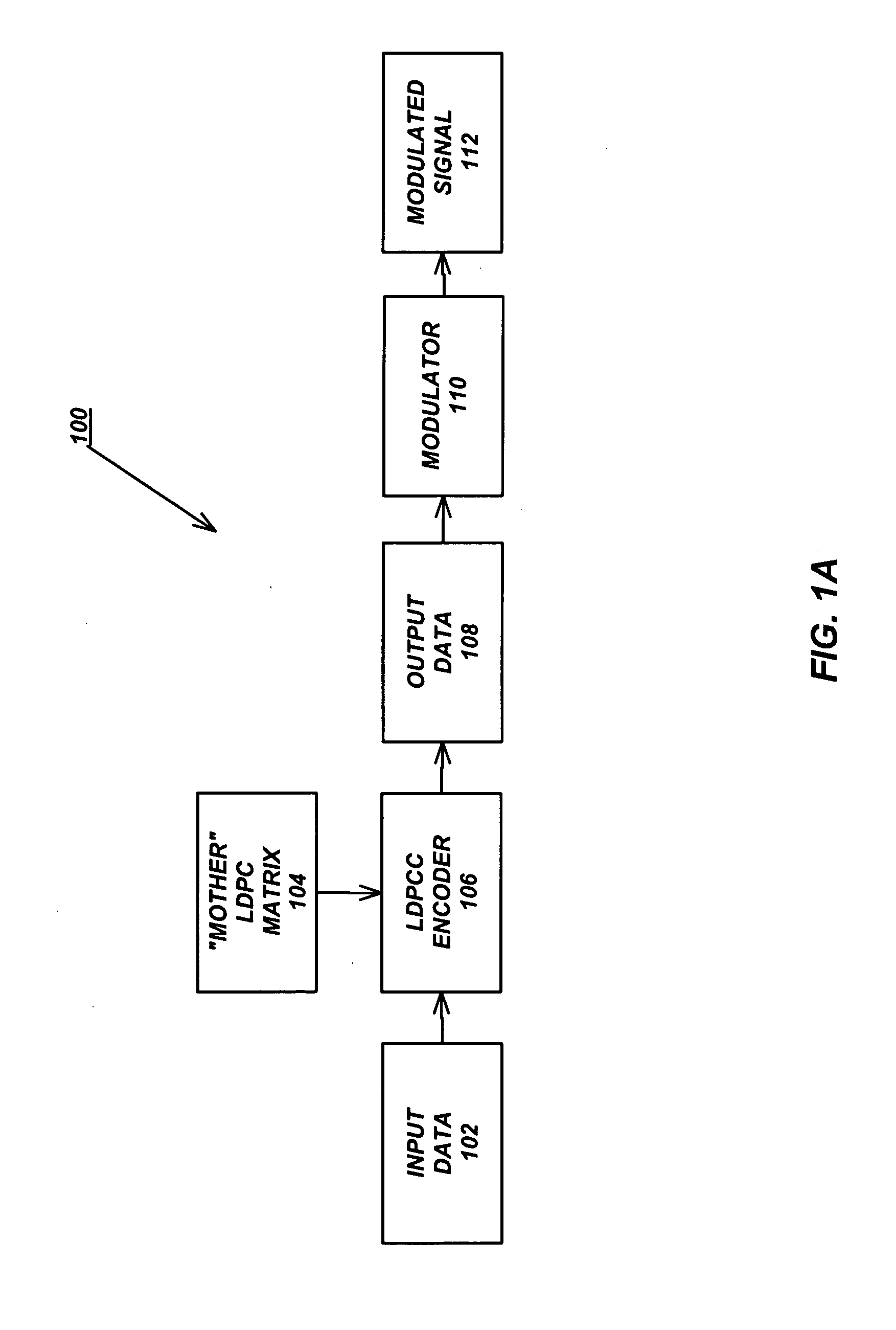
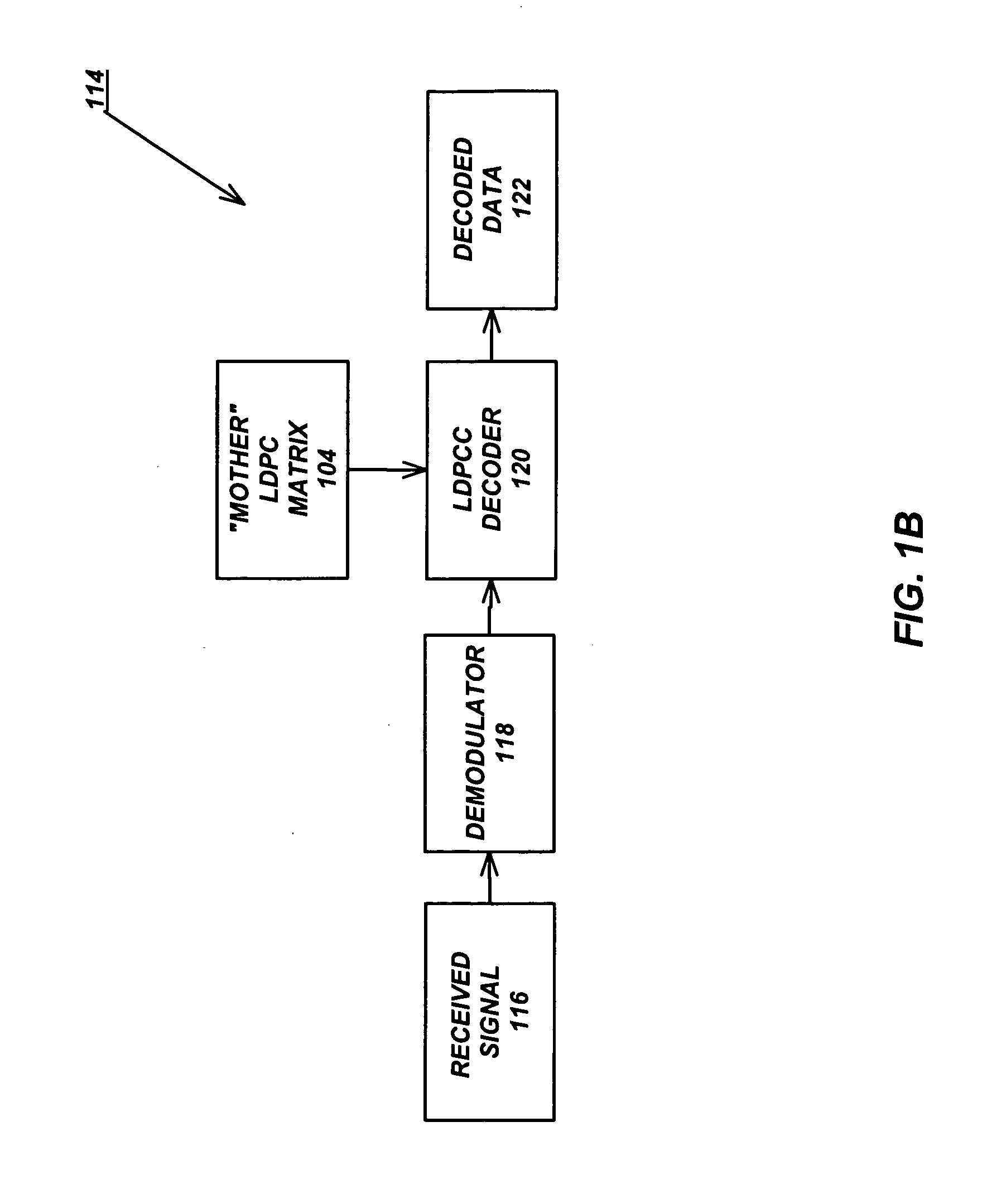
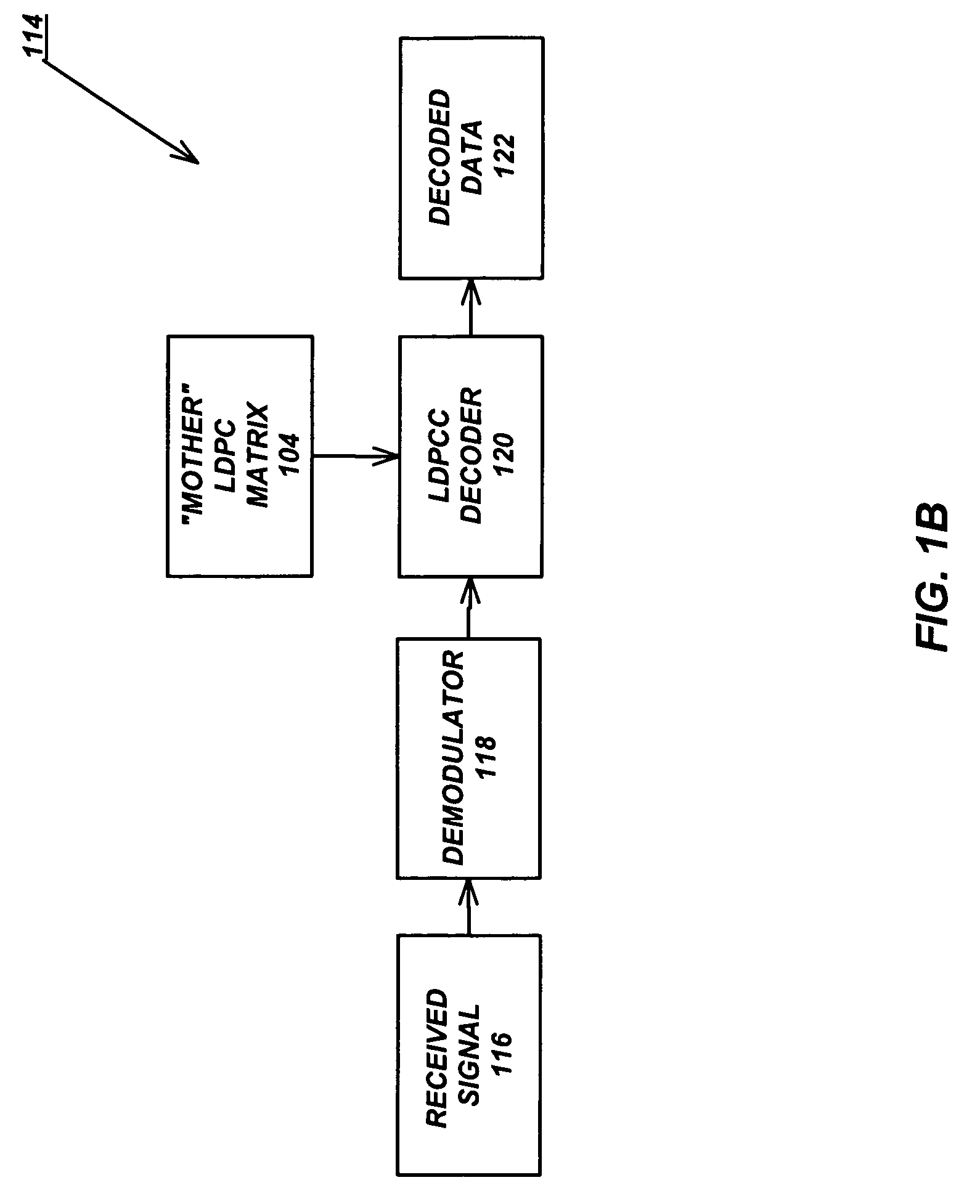
Variable-rate low-density parity check codes with constant blocklength
Low density parity check (LDPC) codes (LDPCCs) have an identical code blocklength and different code rates. At least one of the rows of a higher-rate LDPC matrix is obtained by combining a plurality of rows of a lower-rate LDPC matrix with the identical code blocklength as the higher-rate LDPC matrix.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Interleaving method and deinterleaving method
ActiveUS20130216001A1Improve reception performanceError correction/detection using LDPC codesChecking code calculationsCommunications systemLow-density parity-check code
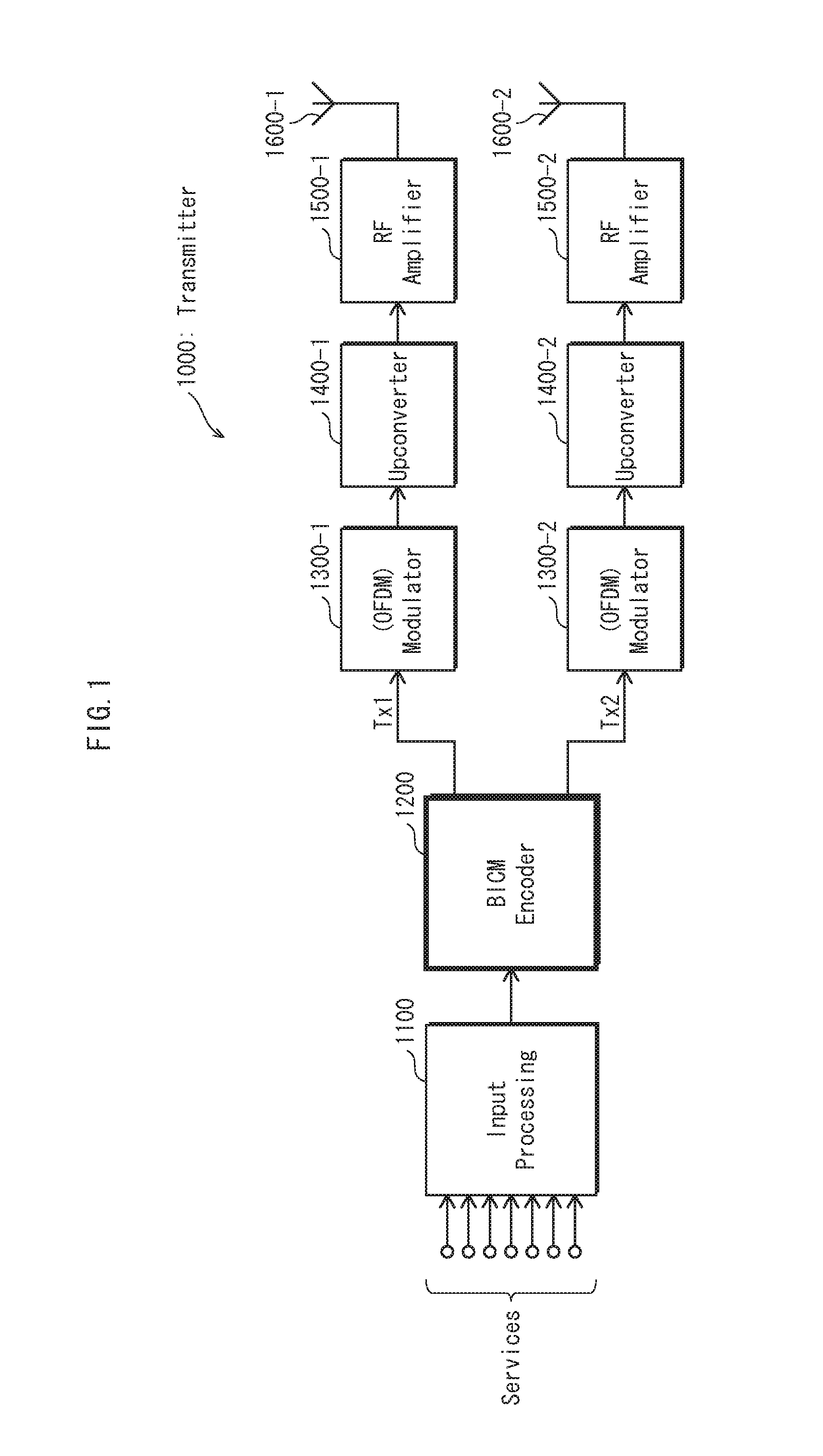
An interleaving method performed by a transmitter for a communication system with quasi-cyclic low-density parity-check codes, spatial multiplexing, and T transmit antennas is used for applying permutation to N cyclic blocks of a codeword in order to map bits of the permutated cyclic blocks onto T constellation words constituting multiple spatial-multiplexing blocks from the codeword. Each cyclic block consists of Q bits.
Owner:SUN PATENT TRUST
Apparatus and method for transmitting and receiving data in a communication system using low density parity check codes
ActiveUS20090063929A1Reduce signal distortionImprove performanceError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsCommunications systemLow-density parity-check code
An apparatus for transmitting data in a communication system using a Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) matrix is provided. The apparatus includes an interleaver for interleaving a descending bit-ordered codeword having a predetermined size and in accordance with a predetermined modulation scheme; and a bit mapper for mapping codeword bits constituting the interleaved codeword in accordance with a predetermined mapping scheme that takes into account degrees of the codeword bits and reliability characteristics of modulation symbol-constituting bits based on the predetermined modulation scheme.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
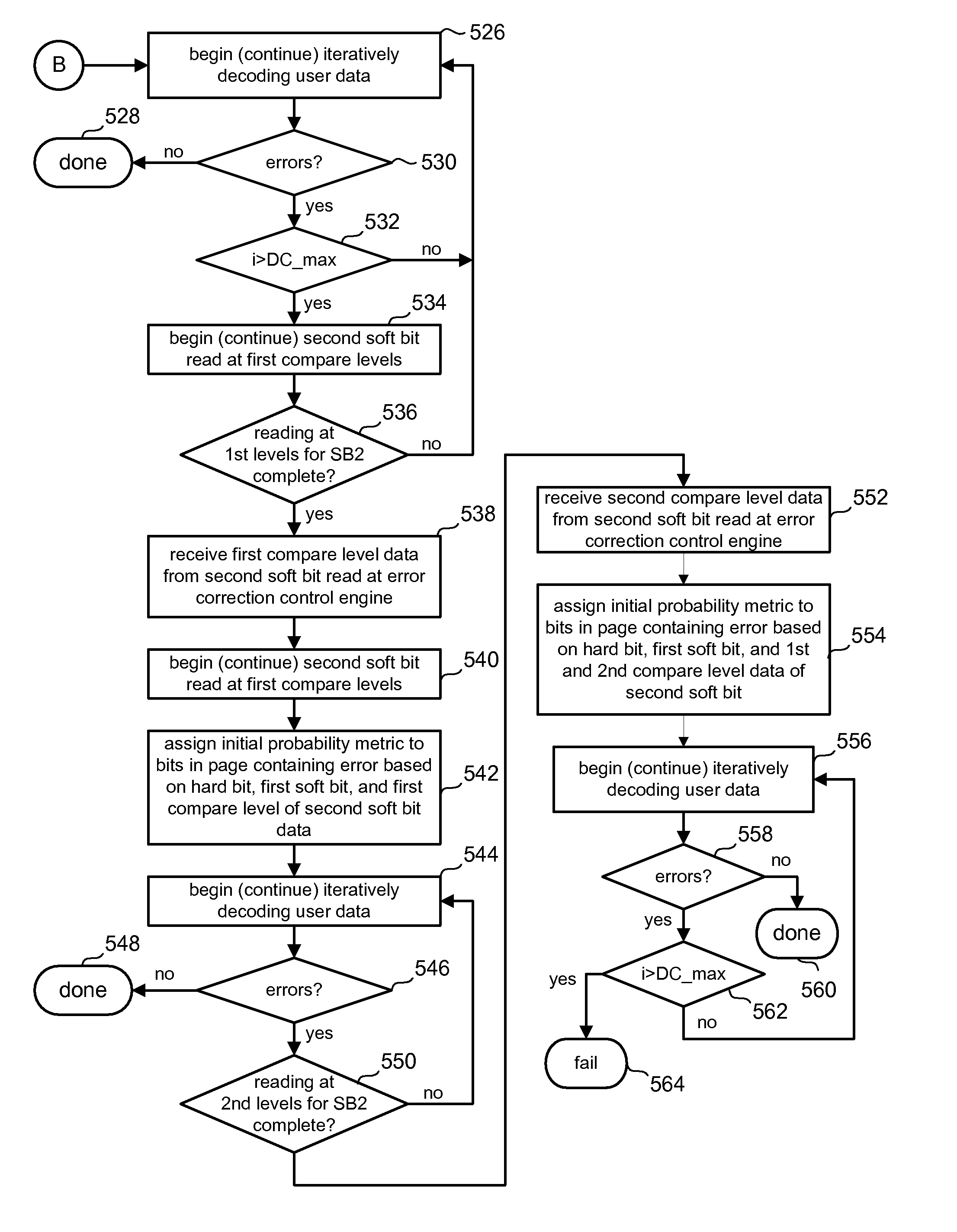
Soft bit data transmission for error correction control in non-volatile memory
ActiveUS20080244338A1High resolutionError detection/correctionCode conversionLow-density parity-check codeSoft data
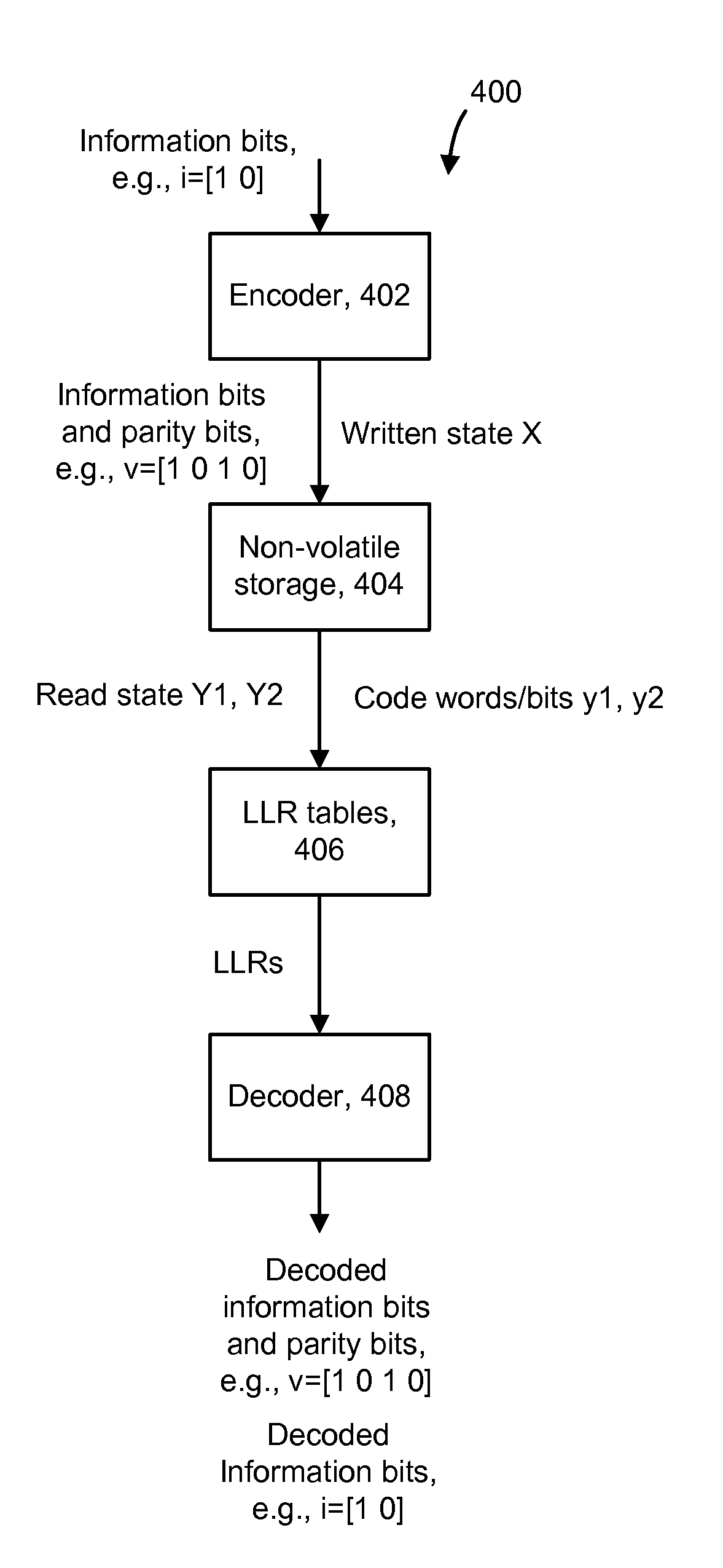
Data stored in non-volatile storage is decoded using iterative probabilistic decoding. An error correcting code such as a low density parity check code may be used. In one approach, initial reliability metrics, such as logarithmic likelihood ratios, are used in decoding sensed states of a set of non-volatile storage element. The decoding attempts to converge by adjusting the reliability metrics for bits in code words which represent the sensed state. Soft data bits are read from the memory if the decoding fails to converge. Initial reliability metric values are provided after receiving the hard read results and at each phase of the soft bit operation(s). In one embodiment, a second soft bit is read from the memory using multiple subsets of soft bit compare levels. While reading at the second subset of compare levels, decoding can be performed based on the first subset data.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Decoder having early decoding termination detection
InactiveUS20140223255A1Code conversionCoding detailsComputer architectureLow-density parity-check code
Embodiments of decoders having early decoding termination detection are disclosed. The decoders can provide for flexible and scalable decoding and early termination detection, particularly when quasi-cyclic low-density parity-check code (QC-LDPC) decoding is used. In one embodiment, a controller iteratively decodes a data unit using a coding matrix comprising a plurality of layers. The controller terminates decoding the data unit in response to determining that the decoded data units from more than one layer decoding operation satisfy a parity check equation and that the decoded data units from more than one layer decoding operation are the same. Advantageously, the termination of decoding of the data unit can reduce a number of iterations performed to decode the data unit.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Simplified decoding using structured and punctured LDPC codes
ActiveUS20060123277A1Improve performanceAvoid interferenceData representation error detection/correctionError preventionProgramming languageTransceiver
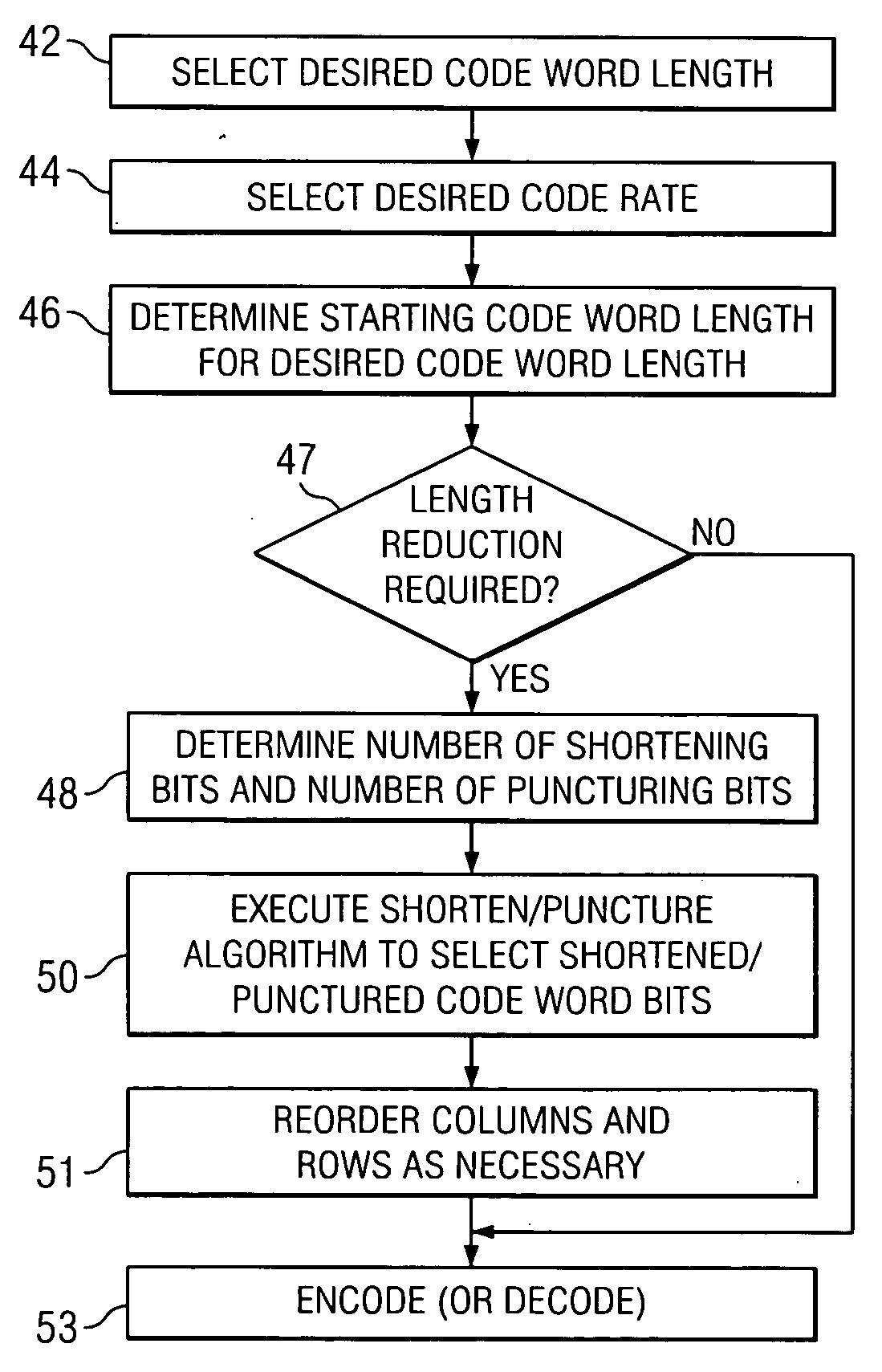
A communications transceiver for transmitting and receiving coded communications, with the coding corresponding to a low-density parity check code, is disclosed. A set of available code word lengths and code rates are to be supported by the transceiver. These available code word lengths and code rates are implemented as a subset of starting code word lengths, which are length-reduced by shortening and puncturing selected bit positions in the starting code word length to attain the desired one of the available code word lengths and code rates. The bit positions to be shortened and punctured are selected in a manner that avoids interference between the shortened and punctured bit positions, and that attains excellent code performance.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method for decoding data in non-volatile storage using reliability metrics based on multiple reads
ActiveUS20080250300A1Other decoding techniquesError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsLow-density parity-check codeDependability
Data stored in non-volatile storage is decoded using iterative probabilistic decoding and multiple read operations to achieve greater reliability. An error correcting code such as a low density parity check code may be used. In one approach, initial reliability metrics, such as logarithmic likelihood ratios, are used in decoding read data of a set of non-volatile storage element. The decoding attempts to converge by adjusting the reliability metrics for bits in code words which represent the sensed state. If convergence does not occur, e.g., within a set time period, the state of the non-volatile storage element is sensed again, current values of the reliability metrics in the decoder are adjusted, and the decoding again attempts to converge. In another approach, the initial reliability metrics are based on multiple reads. Tables which store the reliability metrics and adjustments based on the sensed states can be prepared before decoding occurs.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Method for decoding data in non-volatile storage using reliability metrics based on multiple reads
ActiveUS7904793B2Other decoding techniquesRead-only memoriesLow-density parity-check codeDependability
Data stored in non-volatile storage is decoded using iterative probabilistic decoding and multiple read operations to achieve greater reliability. An error correcting code such as a low density parity check code may be used. In one approach, initial reliability metrics, such as logarithmic likelihood ratios, are used in decoding read data of a set of non-volatile storage element. The decoding attempts to converge by adjusting the reliability metrics for bits in code words which represent the sensed state. If convergence does not occur, e.g., within a set time period, the state of the non-volatile storage element is sensed again, current values of the reliability metrics in the decoder are adjusted, and the decoding again attempts to converge. In another approach, the initial reliability metrics are based on multiple reads. Tables which store the reliability metrics and adjustments based on the sensed states can be prepared before decoding occurs.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Channel coding/decoding apparatus and method using a parallel concatenated low density parity check code
InactiveUS20050149841A1Reduce complexityError prevention/detection by using return channelError detection/correctionComputer hardwareLow-density parity-check code
A parallel concatenated low density parity check (LDPC) code having a variable code rate is provided by generating, upon receiving information bits, a first component LDPC code according to the information bits, interleaving the information bits according to a predetermined interleaving rule, and generating a second component LDPC code according to the interleaved information bits. With use of the parallel concatenated LDPC code, a mobile communication system can use a Hybrid Automatic Retransmission Request (HARQ) scheme and an Adaptive Modulation and Coding (AMC) scheme without restriction.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Transmitting apparatus and puncturing method thereof
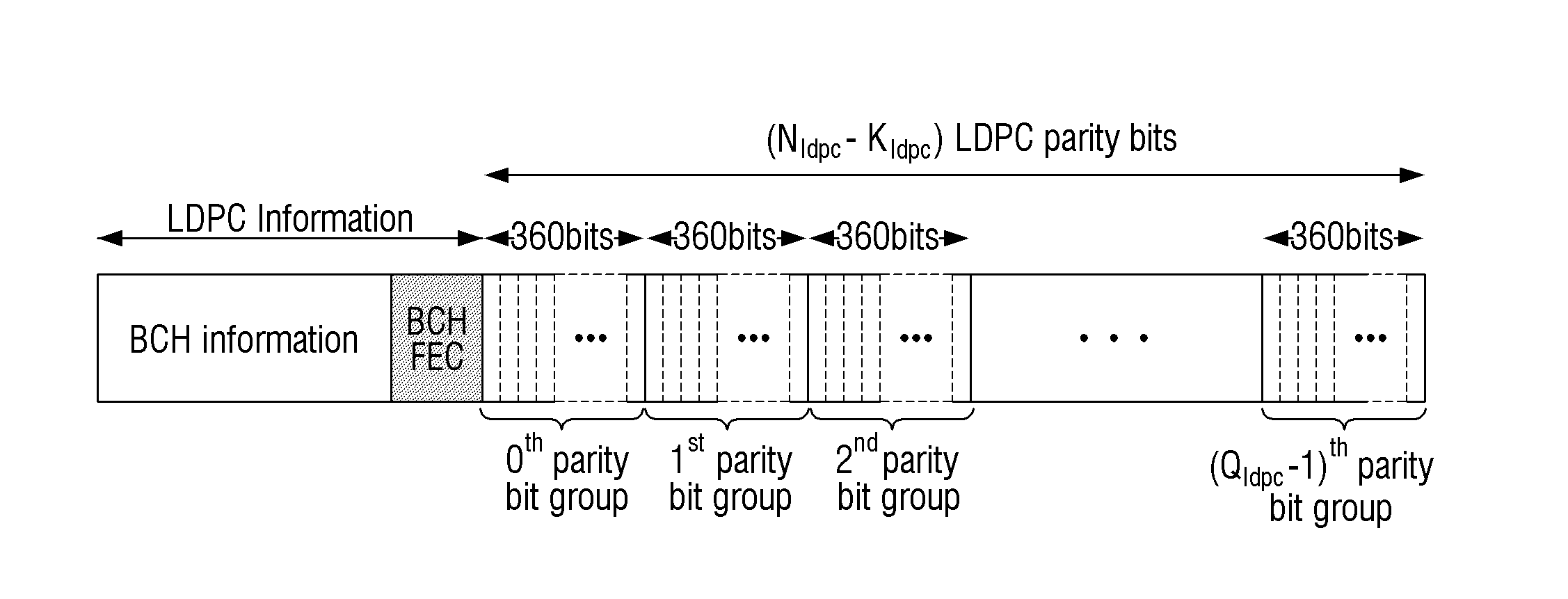
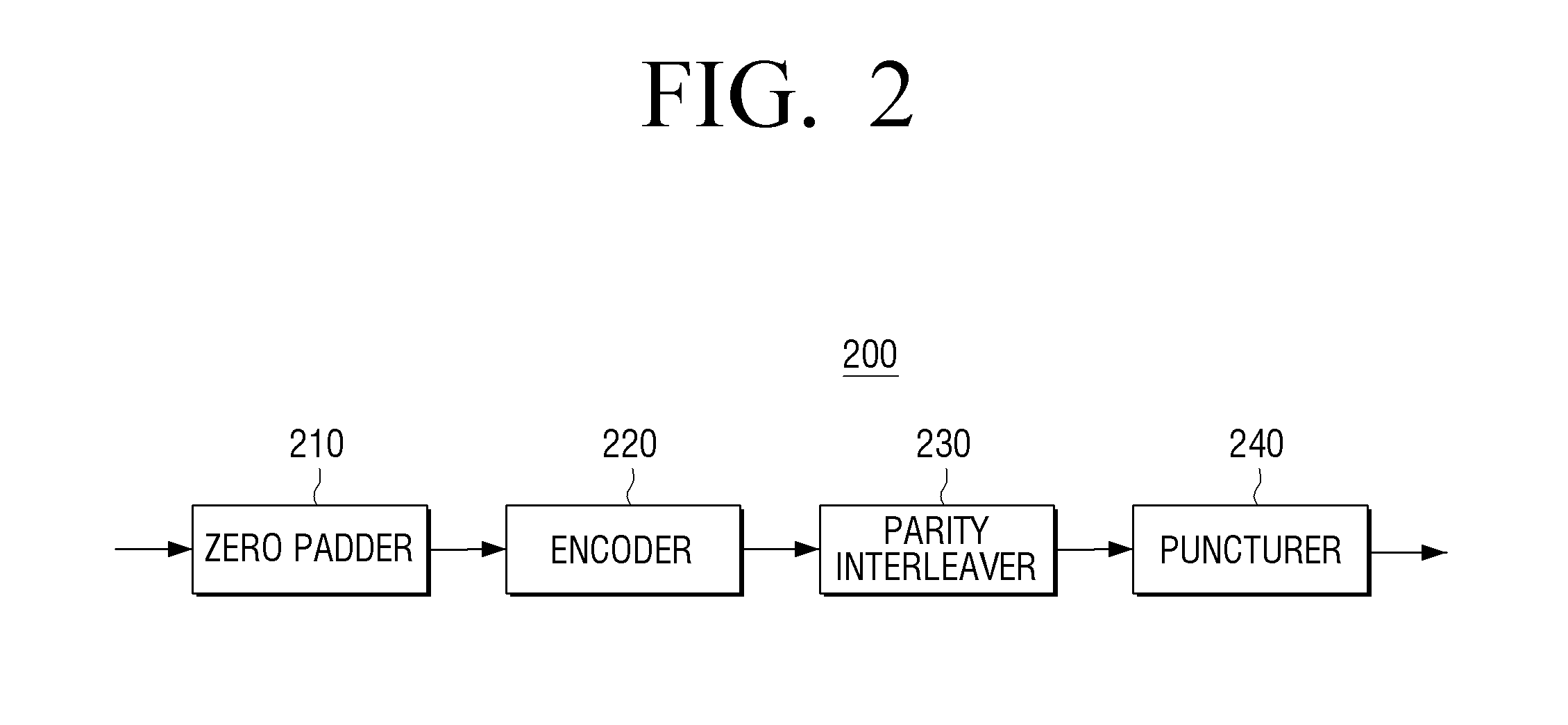
InactiveUS20150082118A1Improve decoding performanceError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionLow-density parity-check codeLow density
Provided are a transmitting apparatus, a receiving apparatus and methods of puncturing and depuncturing of parity bits. The transmitting apparatus includes: a zero padder configured to pad at least one zero bit to input bits; an encoder configured to generate a Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) codeword by performing LDPC encoding with respect to the bits to which the at least one zero bit is padded; a parity interleaver configured to interleave LDPC parity bits constituting the LDPC codeword; and a puncturer configured to puncture at least a part of the interleaved LDPC parity bits based on a pre-set puncturing pattern.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Apparatus and method for receiving signal in a communication system using a low density parity check code
ActiveUS8006161B2Reduce coding complexityData representation error detection/correctionError preventionCommunications systemLow-density parity-check code
An apparatus and a method for receiving a signal in a communication system using a Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) code. The apparatus and the method includes decoding a received signal according to a hybrid decoding scheme, wherein the hybrid decoding scheme is generated by combining two of a first decoding scheme, a second decoding scheme, and a third decoding scheme.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Apparatus and method for transmitting/receiving a signal in a communication system using a low density parity check code
InactiveUS7954041B2Performance maximizationError prevention/detection by using return channelData representation error detection/correctionCommunications systemLow-density parity-check code
An apparatus and method are provided for transmitting a signal in a communication system using a low density parity check (LDPC) code. An LDPC codeword is generated by encoding an information word at a coding rate. A puncturing pattern is generated when a hybrid automatic repeat request (HARQ) scheme to be applied to the LDPC codeword is an incremental redundancy (IR) scheme. An additional pattern is generated when the HARQ scheme to be applied to the LDPC codeword is a partial chase combining (CC) scheme. A signal is transmitted by applying the puncturing pattern to the LDPC codeword at an associated coding rate when the HARQ scheme to be used is the IR scheme. A signal is transmitted by applying the additional pattern to the LDPC codeword at an associated coding rate when the HARQ scheme to be used is the partial CC scheme.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Variable-rate low-density parity check codes with constant blocklength
Low density parity check (LDPC) codes (LDPCCs) have an identical code blocklength and different code rates. At least one of the rows of a higher-rate LDPC matrix is obtained by combining a plurality of rows of a lower-rate LDPC matrix with the identical code blocklength as the higher-rate LDPC matrix.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Method and apparatus for receiving data
ActiveUS20120134446A1Amplitude demodulation by homodyne/synchrodyne circuitsCode conversionData streamModem device
Modem coding and modulation techniques have greatly improved the transmission and reception of signals. A method is described including receiving a signal de-mapping the signal into a first and second substream, decoding the first and second substream using a low density parity check decoding process, and combining the first and second decoded substream into a single data stream. An apparatus is described including a symbol de-mapper that receives a signal de-maps the modulation symbols in the signal into a first and second substream, a first decoder that decodes the first substream using a low density parity check coding process at a first decoding rate, a second decoder that decodes the second substream at a second encoding rate, and a combiner that combines the first substream and the second substream into a single data stream.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
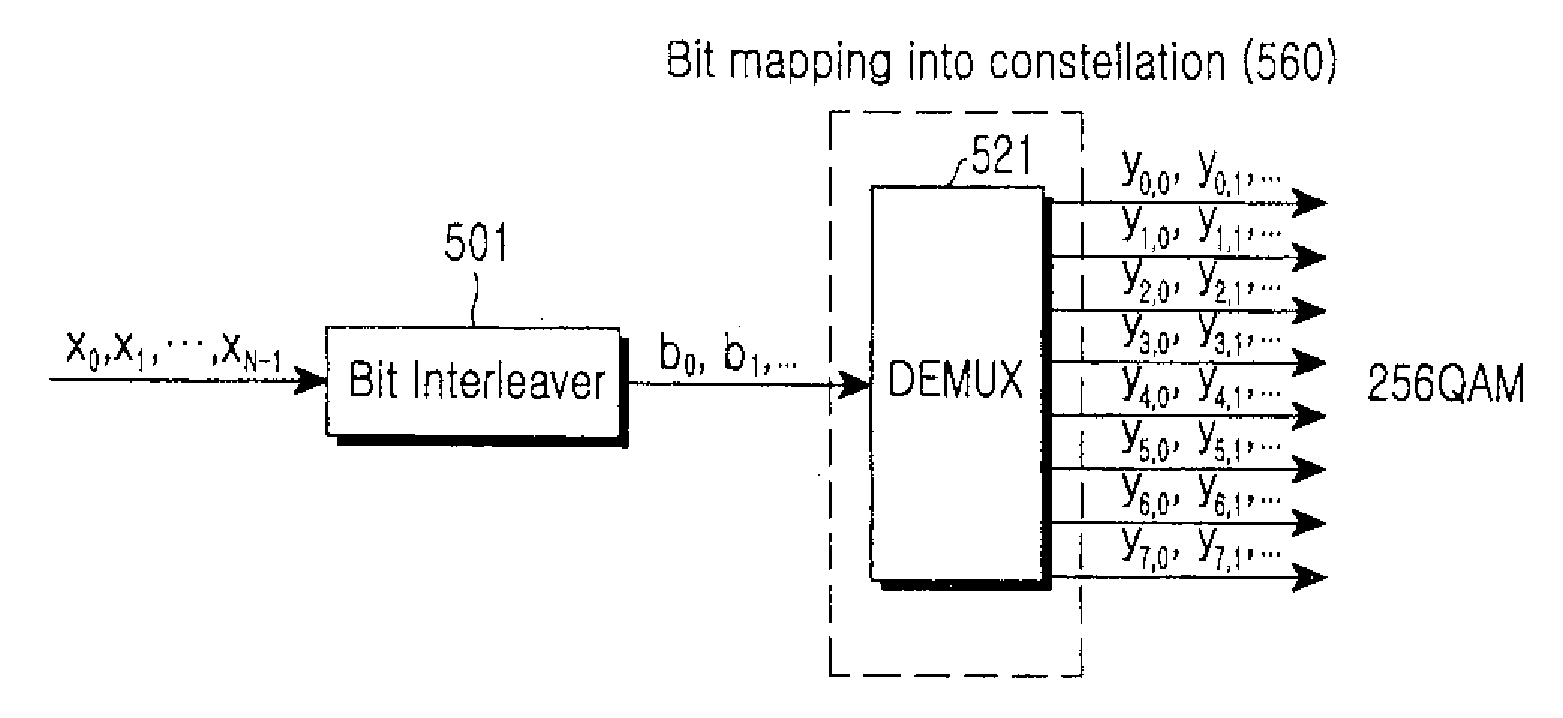
LDPC code encoding modulation method and apparatus
ActiveCN101488819APremium Coded Modulation GainError preventionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsLow-density parity-check codeTheoretical computer science
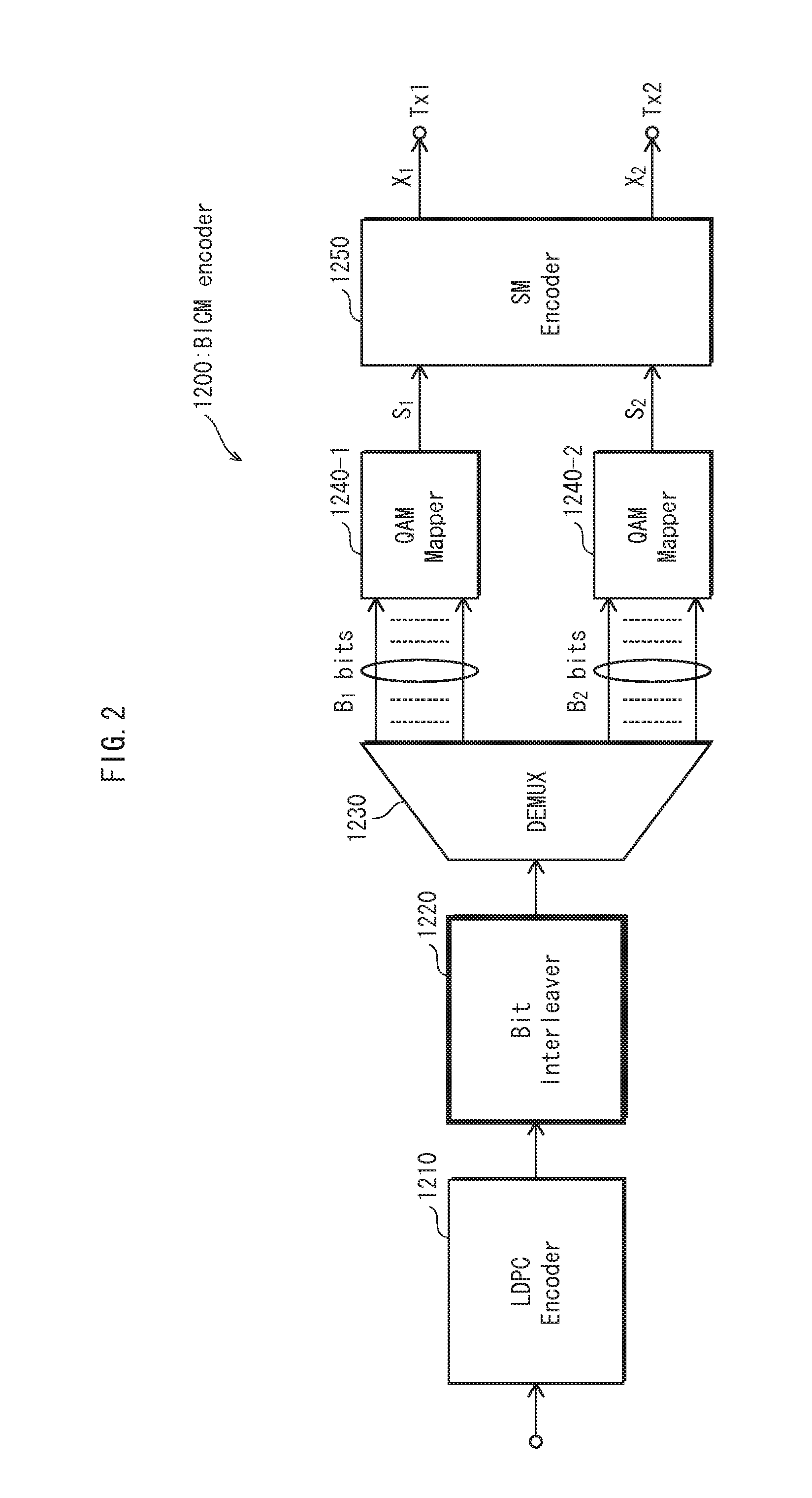
The invention embodiment provides a coded modulation method for low density parity check code, a low density parity check code coded processing can be performed for an information sequence to obtain a code word, and the interweave processing can be performed for the code word, then the modulated processing can be performed for the code word by interweave processing; meanwhile, the invention embodiment also provides a coded modulation apparatus for the low density parity check code. The technical scheme disclosed by the invention embodiment is based on the importance of low density parity check code degree distribution, and the different bits on a star map in high order modulation have different reliabilities, and the excellent coded modulation gain can be obtained.
Owner:XFUSION DIGITAL TECH CO LTD
Apparatus and method for transmitting and receiving data in a communication system using low density parity check code
ActiveUS20090125781A1Reduce signal distortionImprove performanceModulated-carrier systemsError correction/detection using LDPC codesCommunications systemLow-density parity-check code
A method for transmitting data in a communication system using a Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) matrix includes generating an LDPC codeword by encoding information data bits, interleaving the LDPC codeword, mapping the interleaved LDPC codeword to a modulation signal, and generating a mapped signal by mapping the LDPC codeword bits separately to a bit corresponding to a real part and a bit corresponding to an imaginary part of said modulation signal, among bits constituting the modulation signal, generating a modulation signal by high-order-modulating the mapped signal and Radio Frequency (RF)-processing the modulation signal, and transmitting the RF-processed signal via a transmission antenna.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND +1
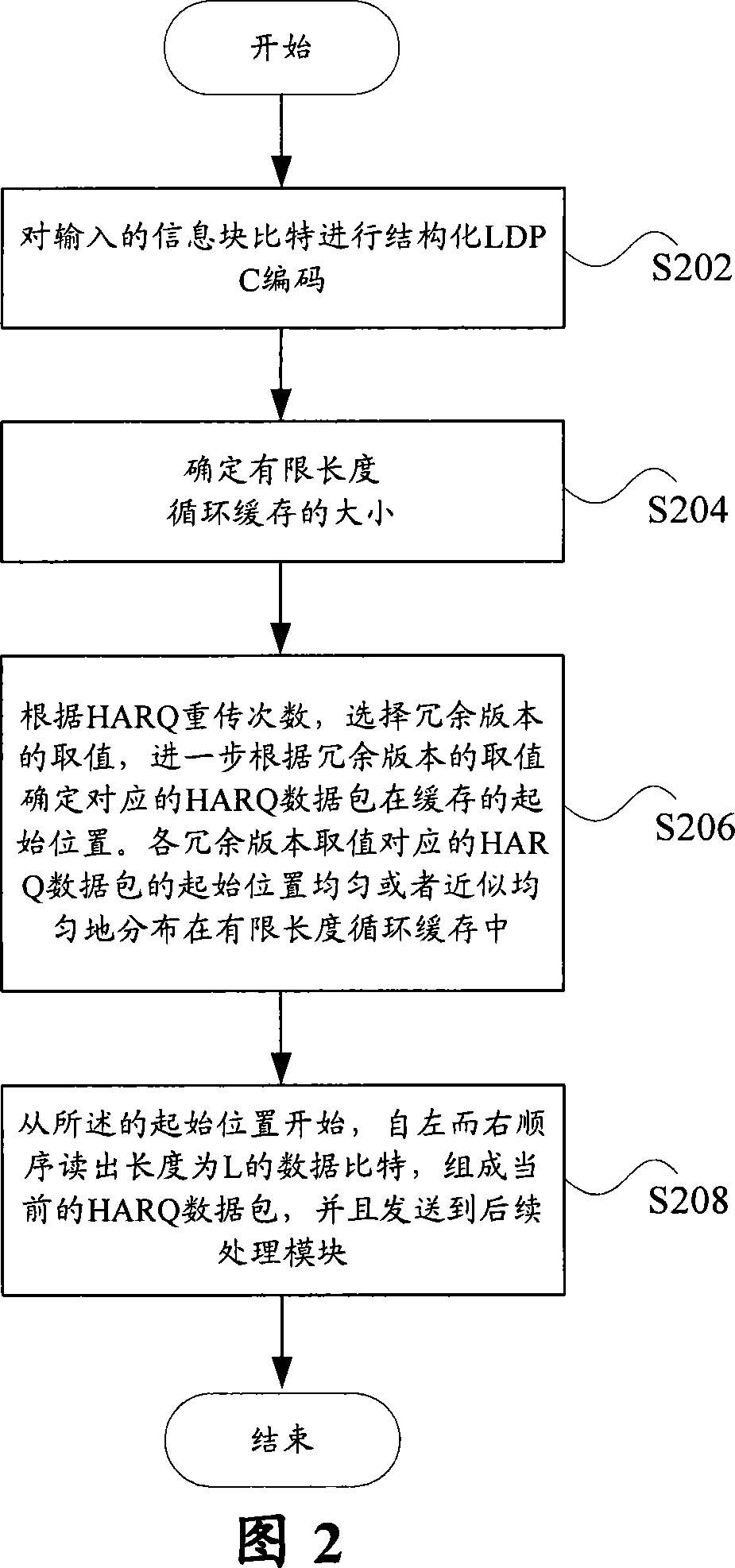
Speed matching method of limited length circular buffer of LDPC code
ActiveCN101188428AImprove retransmission performanceSave cache spaceError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsNetwork packetLow-density parity-check code
The invention discloses a speed matching method of the limited-length circular cache of a low-density parity-check code. The method includes the following steps of conducting a structured low-density parity-check code encoding on the data bit of an inputted information block, and determining the size of the one-dimensional limited-length circular cache according to the encoding result; selecting a redundant version value from a plurality of preset redundant version values according to the retransmission times of the mixed retransmission request, and determining the initial position of the data bit of the formed mixed retransmission request data packet read from the one-dimensional limited-length circular cache according to the selected redundant version value; and reading the mixed automatic retransmission request data packet composed of specific-length data from the initial position in order, and sending the mixed automatic retransmission request data packet out. The respective corresponding initial positions of the multiple preset redundant version values are evenly or almost evenly distributed on the one-dimensional limited-length circular cache.
Owner:ZTE CORP
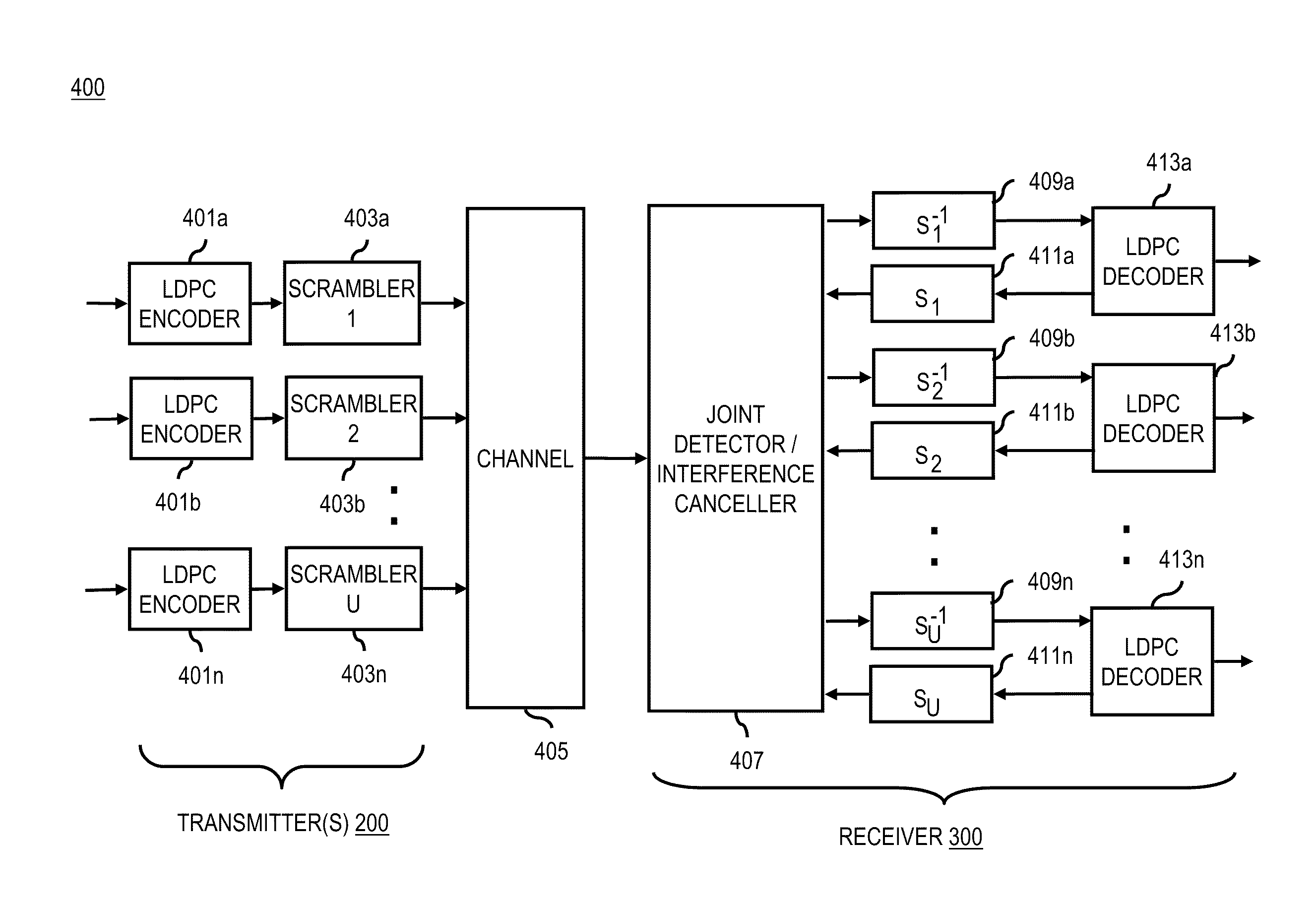
Method and system for providing low density parity check (LDPC) coding for scrambled coded multiple access (SCMA)
InactiveUS20100122143A1Joint error correctionCode conversionComputer architectureLow-density parity-check code
A multiple access scheme is described. One or more encoders are configured to encode a plurality of bit streams using Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) coding. The bit streams correspond to a respective plurality of terminals. The plurality of bit streams are converted to provide a multiple access scheme for the terminals.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
LDPC encoder and method thereof
InactiveUS7072417B1Reduces row weightReduce weightError detection/correctionCode conversionLow-density parity-check codeMachine learning
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Non-Volatile Memory with Soft Bit Data Transmission for Error Correction Control
ActiveUS20080244360A1High resolutionData representation error detection/correctionError detection/correctionLow-density parity-check codeSoft data
Data stored in non-volatile storage is decoded using iterative probabilistic decoding. An error correcting code such as a low density parity check code may be used. In one approach, initial reliability metrics, such as logarithmic likelihood ratios, are used in decoding sensed states of a set of non-volatile storage element. The decoding attempts to converge by adjusting the reliability metrics for bits in code words which represent the sensed state. Soft data bits are read from the memory if the decoding fails to converge. Initial reliability metric values are provided after receiving the hard read results and at each phase of the soft bit operation(s). In one embodiment, a second soft bit is read from the memory using multiple subsets of soft bit compare levels. While reading at the second subset of compare levels, decoding can be performed based on the first subset data.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC +1
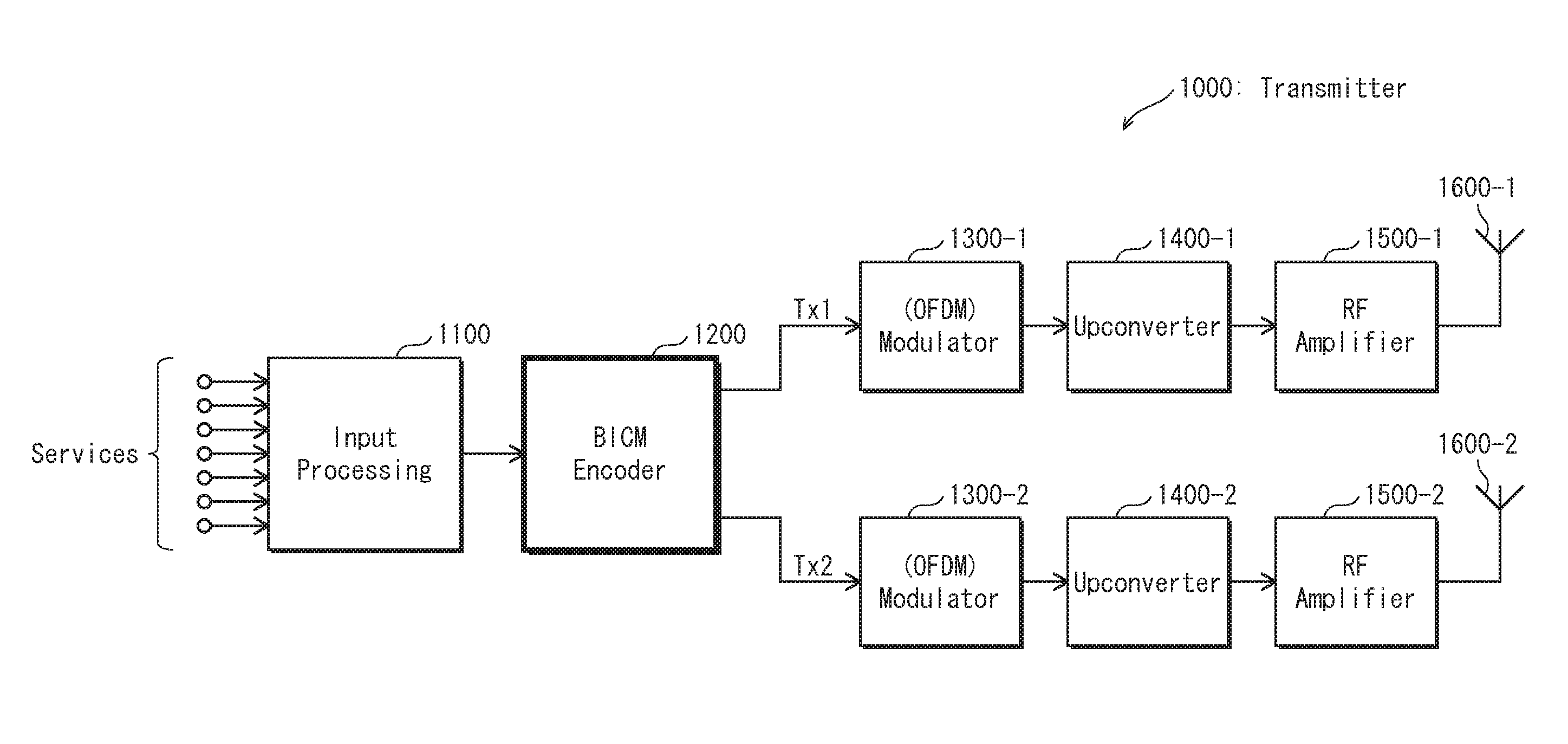
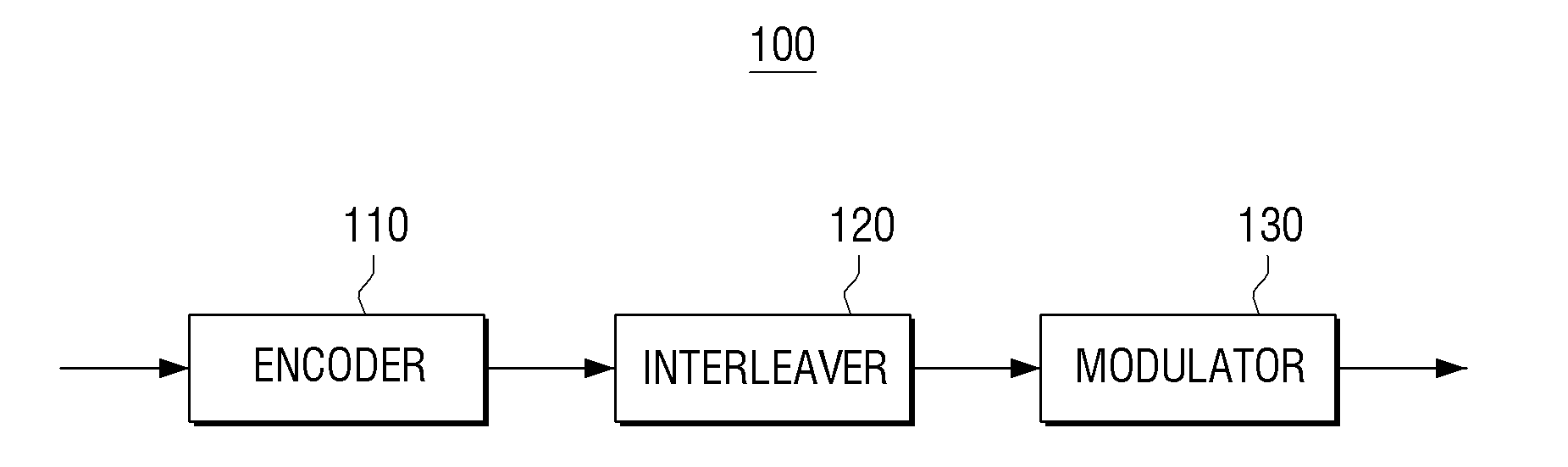
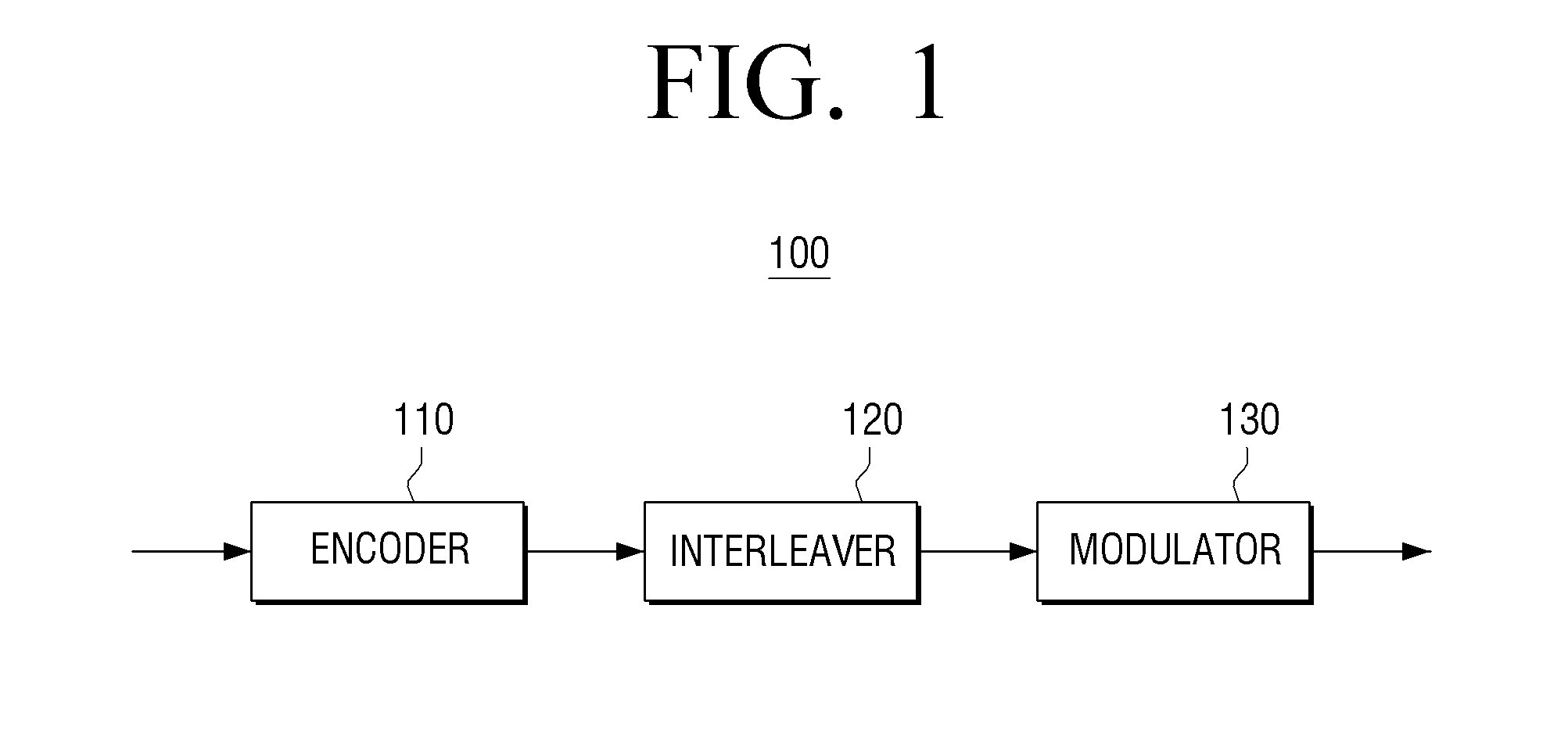
Transmitting apparatus and signal processing method thereof
ActiveUS20150082131A1Improve decoding performanceImprove reception performanceError correction/detection using LDPC codesError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsLow-density parity-check codeLow density
A transmitting apparatus and a receiving apparatus are provided. The transmitting apparatus includes: an encoder configured to generate a low density parity check (LDPC) codeword by performing LDPC encoding; an interleaver configured to interleave the LDPC codeword; and a modulator configured to modulate the interleaved LDPC codeword according to a modulation method to generate a modulation symbol. The interleaver includes a block interleaver formed of a plurality of columns each comprising a plurality of rows, and the block interleaver is configured to divide the plurality of columns into at least two parts and interleave the LDPC codeword.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
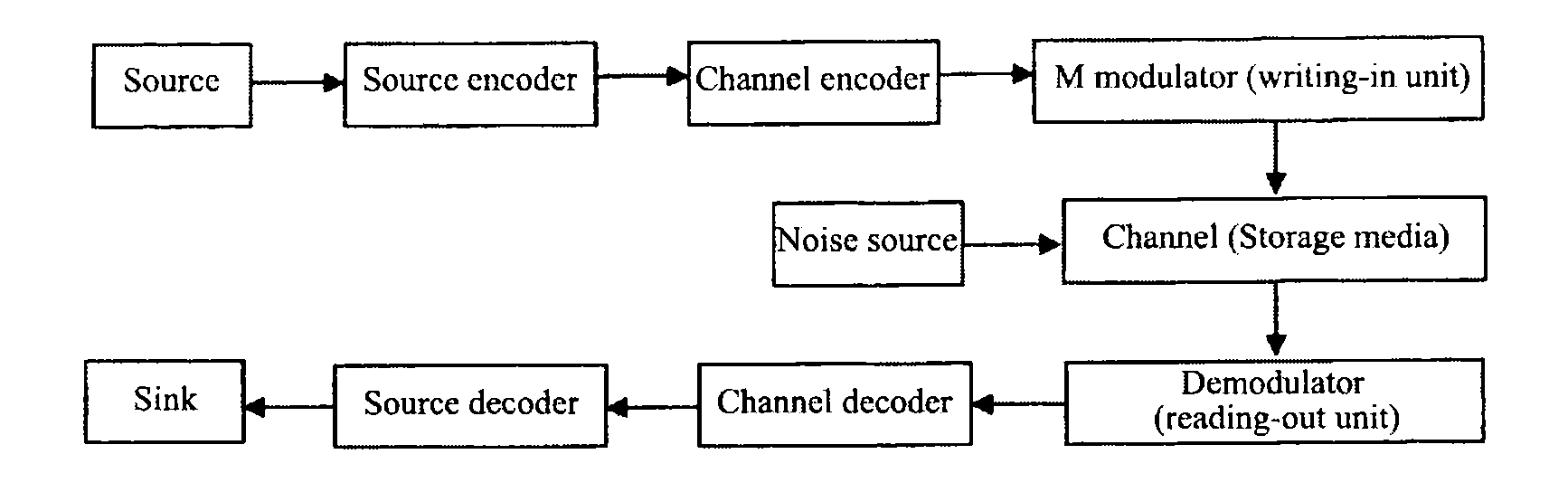
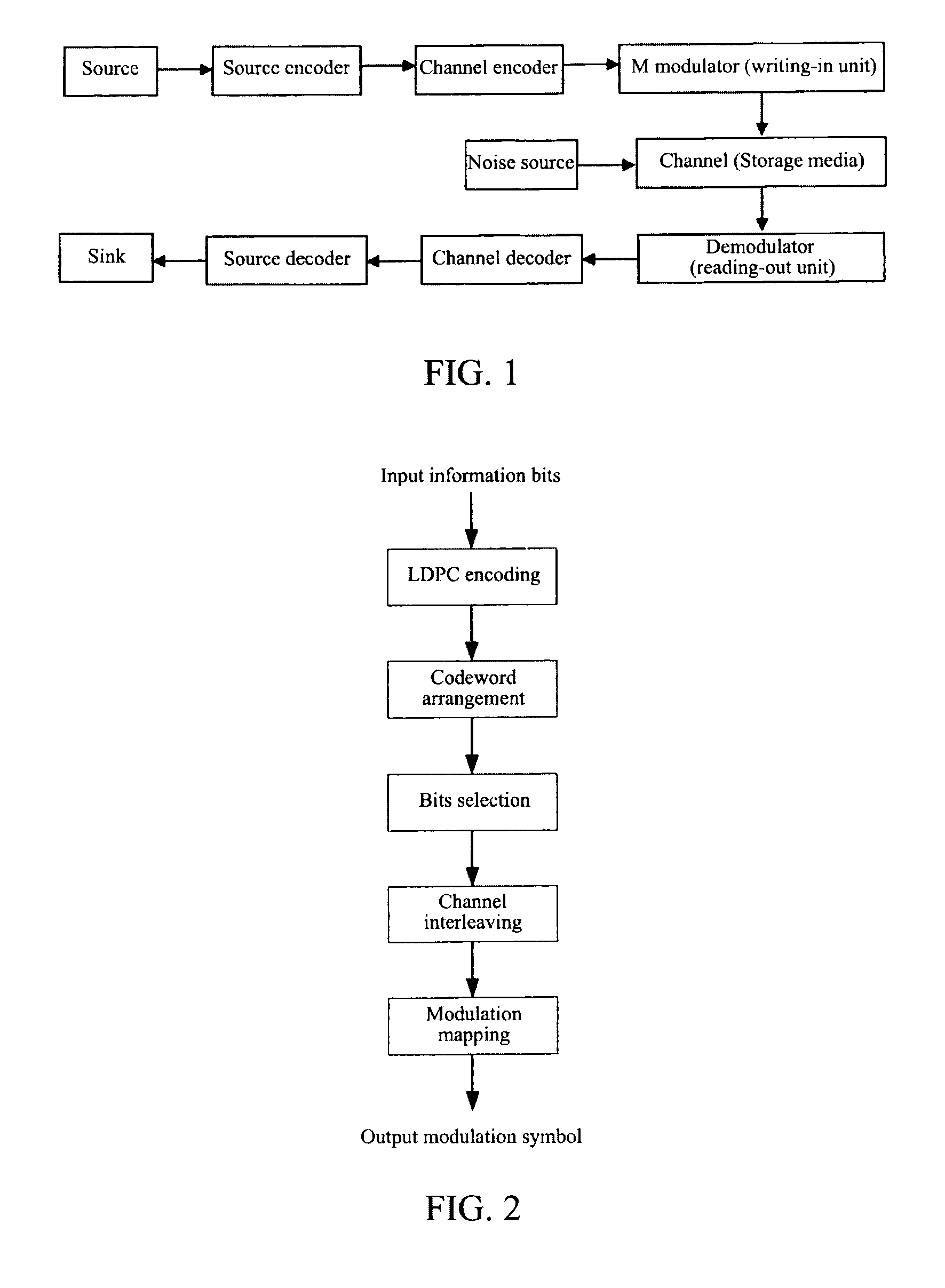
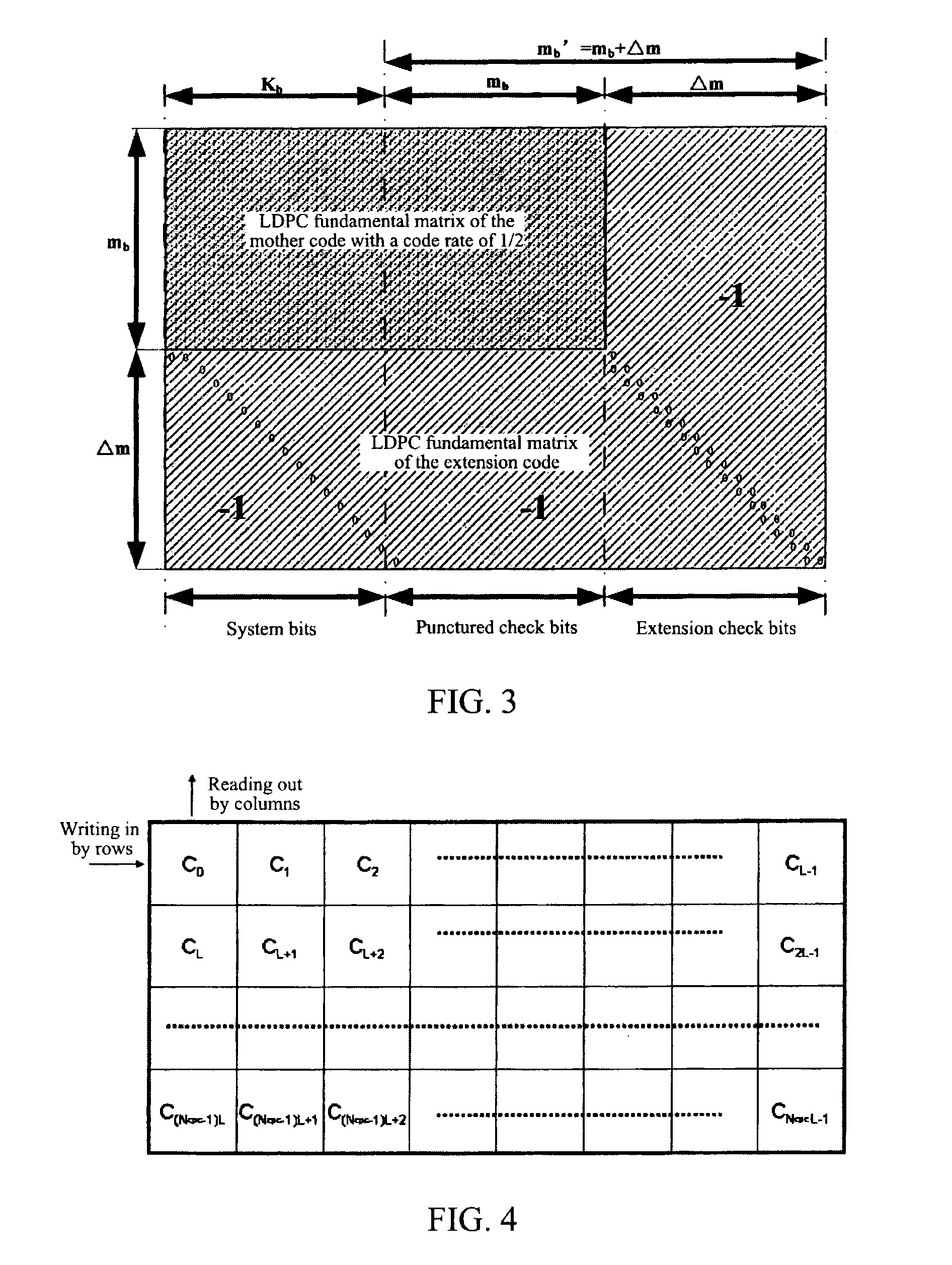
Methods and Systems for LDPC Coding
ActiveUS20080204286A1Data representation error detection/correctionCode conversionReliable transmissionLow-density parity-check code
Methods and systems of low density parity check coded (LDPCC) coding are disclosed herein in which a set of LDPC codes ensure reliable transmission for channels in which modulation symbols may undergo attenuation in a random fashion. Methods and systems of LDPC coding disclosed herein include choosing a code blocklength and concatenating codewords into which a data packet can be encoded. To optimize the coding scheme, first, codeword shortening is performed to ensure an integer number of codewords for a desired packet length. The codewords may then be punctured or repeated to ensure an integer number of channel symbols per codeword. Shortening and puncturing repetition methods are implemented to yield minimum overhead while keeping the effective coding rate low.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
Transmitting apparatus and signal processing method thereof
ActiveUS20150128005A1Overcome disadvantagesError correction/detection using LDPC codesError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsLow-density parity-check codeLow density
A transmitting apparatus and a receiving apparatus are provided. The transmitting apparatus includes an encoder configured to generate a low density parity check (LDPC) codeword by performing LDPC encoding, an interleaver configured to interleave the LDPC codeword, and a modulator configured to modulate the interleaved LDPC codeword according to a modulation method to generate a modulation symbol. The interleaver performs interleaving by dividing the LDPC codeword into a plurality of groups, rearranging an order of the plurality of groups in group units, and dividing the plurality of rearranged groups based on a modulation order according to the modulation method.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of error floor mitigation in low-density parity-check codes
ActiveUS20120266040A1Improve performanceError correction/detection using LDPC codesCode conversionComputer hardwareMaximum magnitude
A digital communication decoding method for low-density parity-check coded messages. The decoding method decodes the low-density parity-check coded messages within a bipartite graph having check nodes and variable nodes. Messages from check nodes are partially hard limited, so that every message which would otherwise have a magnitude at or above a certain level is re-assigned to a maximum magnitude.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
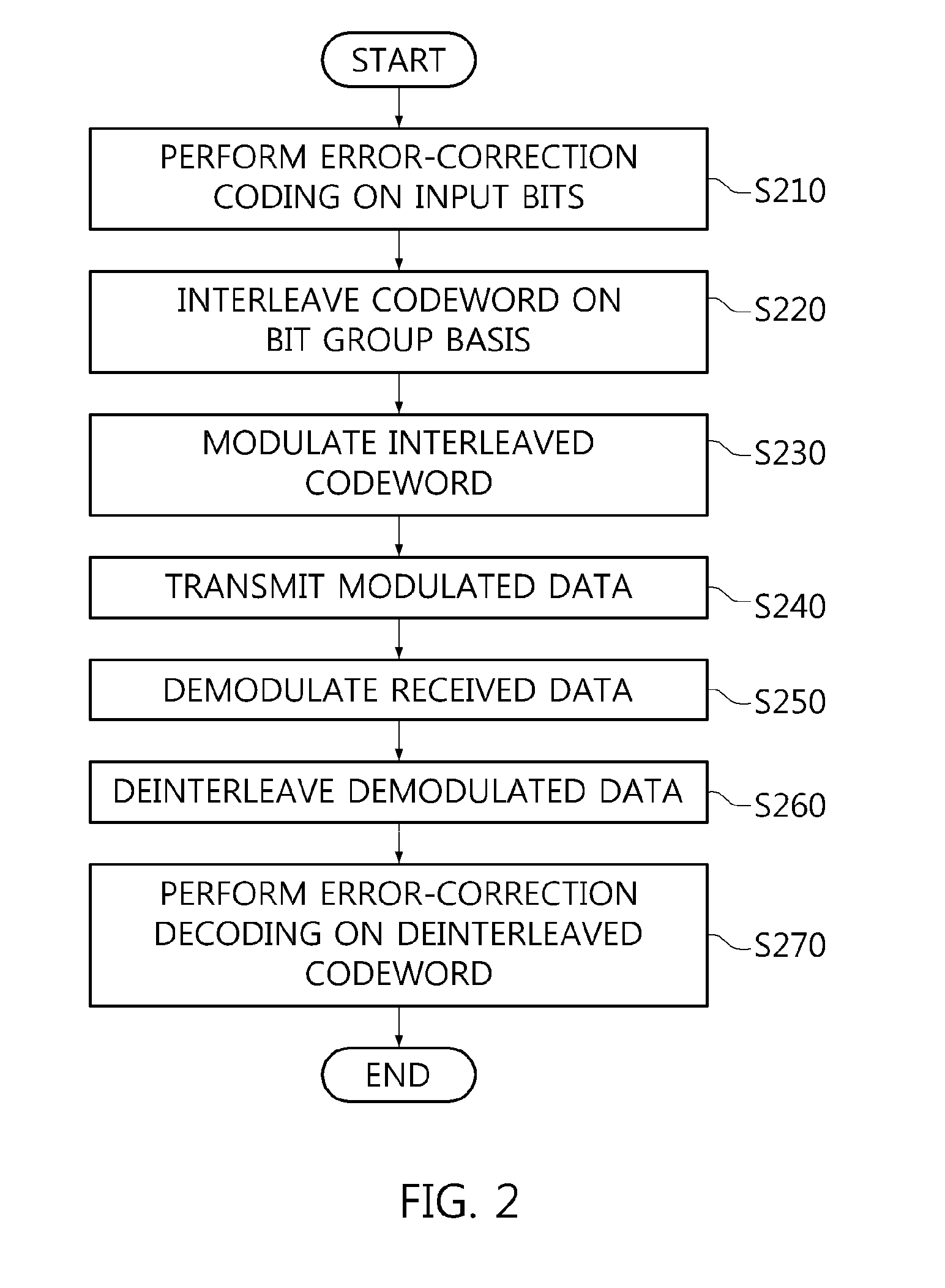
Bit interleaver for low-density parity check codeword having length of 64800 and code rate of 4/15 and 256-symbol mapping, and bit interleaving method using same
ActiveUS20150256202A1Effective distributionEfficiently distributedError correction/detection using LDPC codesBurst error correctionSymbol mappingParallel computing
A bit interleaver, a bit-interleaved coded modulation (BICM) device and a bit interleaving method are disclosed herein. The bit interleaver includes a first memory, a processor, and a second memory. The first memory stores a low-density parity check (LDPC) codeword having a length of 64800 and a code rate of 4 / 15. The processor generates an interleaved codeword by interleaving the LDPC codeword on a bit group basis. The size of the bit group corresponds to a parallel factor of the LDPC codeword. The second memory provides the interleaved codeword to a modulator for 256-symbol mapping.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Channel coding, modulating and mapping method for hybrid automatic repeat request of low density parity check code
ActiveUS20110239075A1Improve protectionLow reliabilityError prevention/detection by using return channelError correction/detection using LDPC codesLow-density parity-check codeComputer science
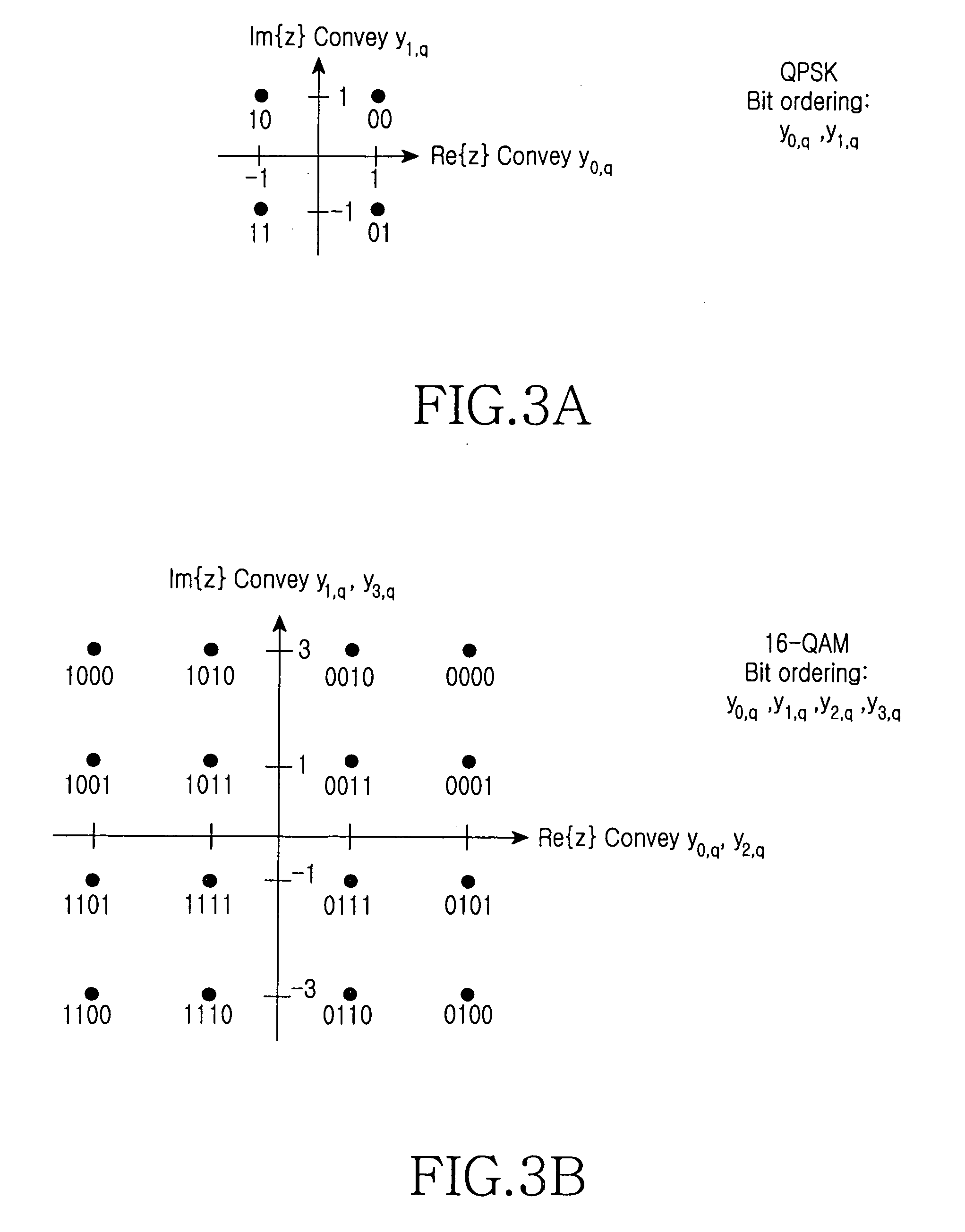
The present invention discloses a method for channel coding and modulation mapping in HARQ of the LDPC code, comprising: performing structural LDPC encoding of an information bit sequence with a length of K input by a channel encoder, and sending a generated codeword to a HARQ buffer; rearranging codeword bits of a LDPC HARQ mother code in the HARQ buffer, and sequentially selecting codeword bits to generate a binary sequence of a HARQ packet; mapping codeword bits of the HARQ packet to a constellation, and high-order bits in encoding blocks of the HARQ packet being mapped to high reliability bits in the constellation. The present invention provides the LDPC codeword with the maximal constellation gain, so that the LDPC HARQ channel encoding has the optimal performance.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Channel interleaving/deinterleaving apparatus in a communication system using low density parity check code and control method thereof
ActiveUS20070033486A1Error correction/detection using LDPC codesError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCommunications systemLow-density parity-check code
A channel interleaving method and apparatus in a communication system using a low density parity check (LDPC) code. Upon receipt of information data bits, an encoder encodes the information data bits into an LDPC codeword using a predetermined coding scheme. A channel interleaver interleaves the LDPC codeword according to a predetermined channel interleaving rule. A modulator modulates the channel-interleaved LDPC codeword into a modulation symbol using a predetermined modulation scheme.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
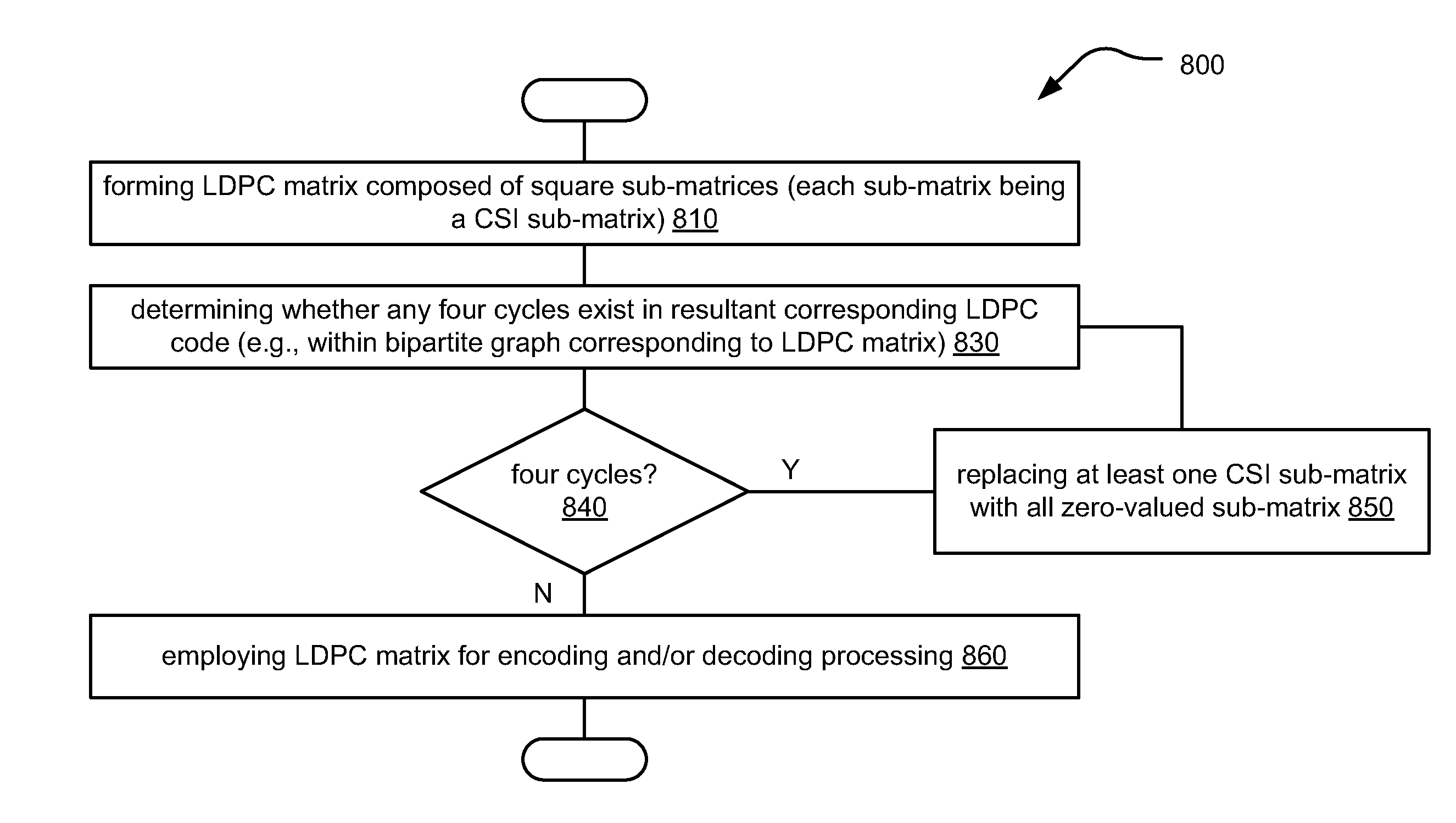
Quasi-cyclic LDPC (low density parity check) code construction
ActiveUS8341492B2Error preventionCode conversionLow-density parity-check codeTheoretical computer science
Quasi-cyclic LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) code construction is presented that ensures no four cycles therein (e.g., in the bipartite graphs corresponding to the LDPC codes). Each LDPC code has a corresponding LDPC matrix that is composed of square sub-matrices, and based on the size of the sub-matrices of a particular LDPC matrix, then sub-matrix-based cyclic shifting is performed as not only a function of sub-matrix size, but also the row and column indices, to generate CSI (Cyclic Shifted Identity) sub-matrices. When the sub-matrix size is prime (e.g., each sub-matrix being size q×q, where q is a prime number), then it is guaranteed that no four cycles will exist in the resulting bipartite graph corresponding to the LDPC code of that LDPC matrix. When q is a non-prime number, an avoidance set can be used and / or one or more sub-matrices can be made to be an all zero-valued sub-matrix.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
COFDM broadcasting with single-time retransmission of COFDM symbols
InactiveUS20140161209A1Facilitate transmissionPolarisation/directional diversityEqualisersLow-density parity-check codeRadio frequency
Transmitter apparatus to broadcast coded orthogonal frequency-division multiplexed (COFDM) radio-frequency carriers conveying digital television (DTV) signals encoded using Bose-Chaudhuri-Hocquenghem (BCH) coding concatenated with subsequent low-density parity-check coding (LPDC) transmits the same coded DTV signals twice some time apart. The coded DTV signals are mapped to quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) of the COFDM carriers. Preferably, the circular Fourier transforms of COFDM symbols in the earlier transmissions are rotated one half revolution respective to the circular Fourier transforms of corresponding COFDM symbols in the later transmissions. Receiver apparatus combines the earlier and later transmissions of twice-transmitted COFDM signals as part of iterative procedures for de-mapping QAM and decoding the concatenated BCH-LDPC coding of the DTV signals.
Owner:LIMBERG ALLEN LEROY
Method and device for encoding low-density parity check code
InactiveCN102412842AIncrease variabilityReduce complexityError preventionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsExpansion factorLow-density parity-check code
The invention provides a method and device for encoding a low-density parity check code. The method comprises the following steps of: comparing a mother code rate and a transmission code rate which are supported by a uniform basic matrix; determining the length K'of an input information grouping bit according to a comparison result; determining an encoding matrix of the low-density parity check (LDPC) code according to the uniform basic matrix and an expansion factor; determining an information bit to be encoded according to the received information grouping bit with the length of K'; and performing LDPC encoding on the information bit to be encoded by using the encoding matrix, and processing a mother code word bit obtained through encoding to acquire a code word bit to be transmitted. By the method and device for encoding the LDPC code, the basic matrix and the expansion factor are determined; the input information grouping length is determined or the encoding matrix is processed according to the received transmission code rate, so the code word which is in accordance with the transmission code rate can be acquired; on the basis of the optimal performance, the changeability of the code rate is realized; furthermore, the hardware design complexity is reduced and the cost is lower.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com