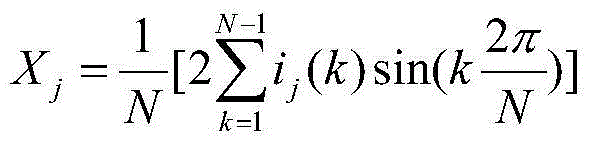Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
66 results about "Maximum magnitude" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An important parameter in the calculation of seismic hazard, maximum magnitude (expressed as Moment magnitude scale) is also one of the more contentious. The choice of the value can greatly influence the final outcome of the results, yet this is most likely a size of earthquake that has not yet occurred in the region under study.
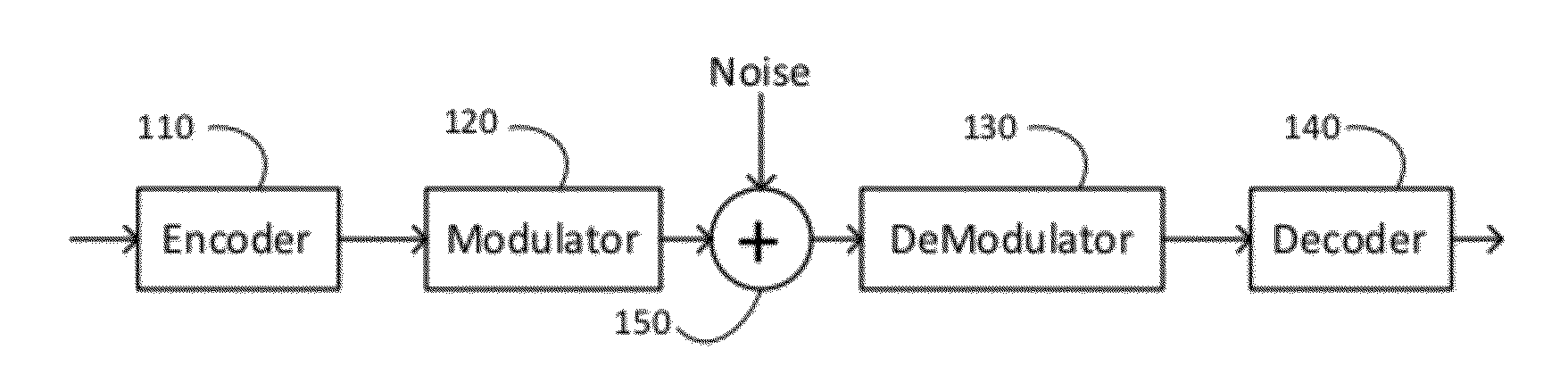
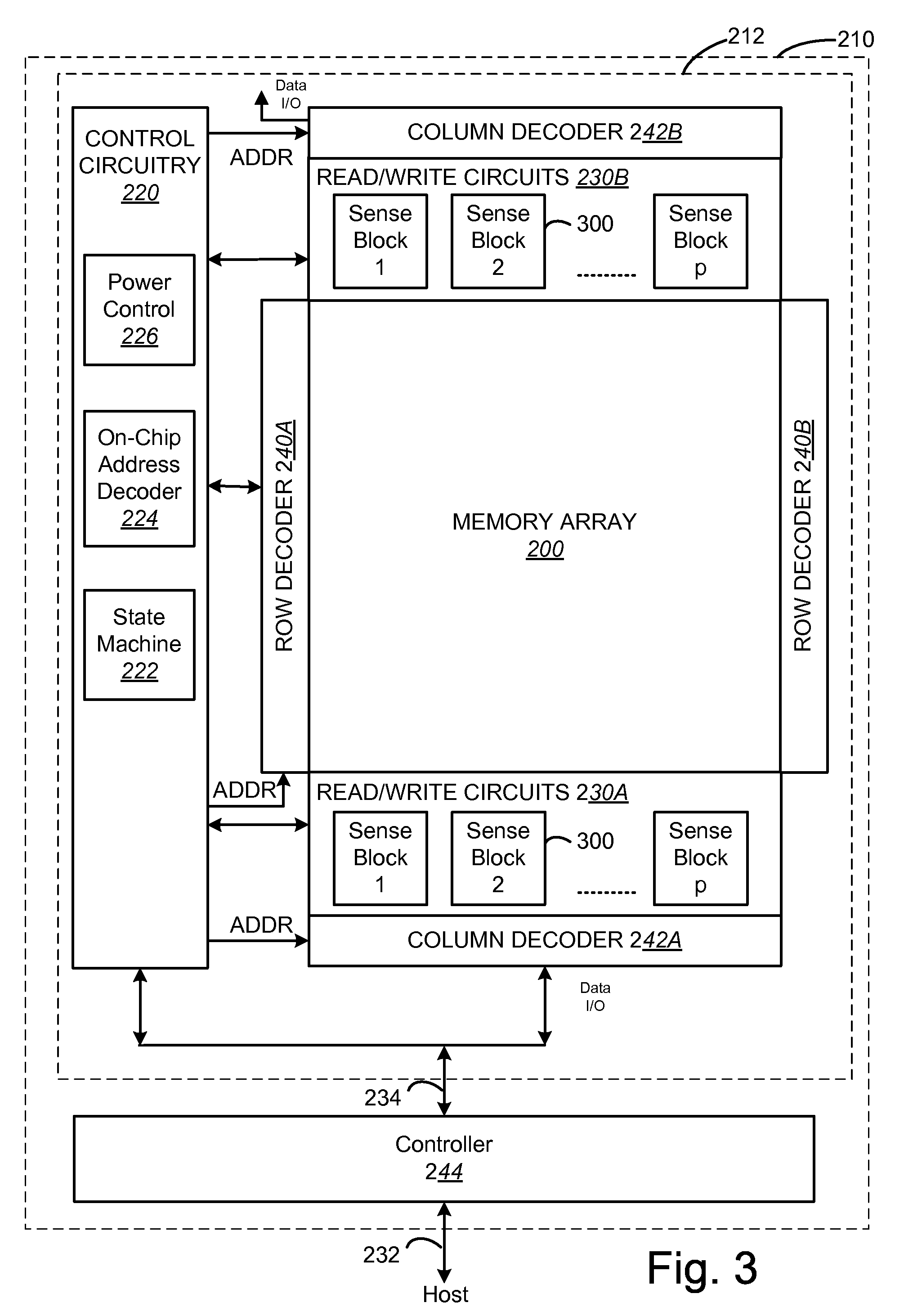
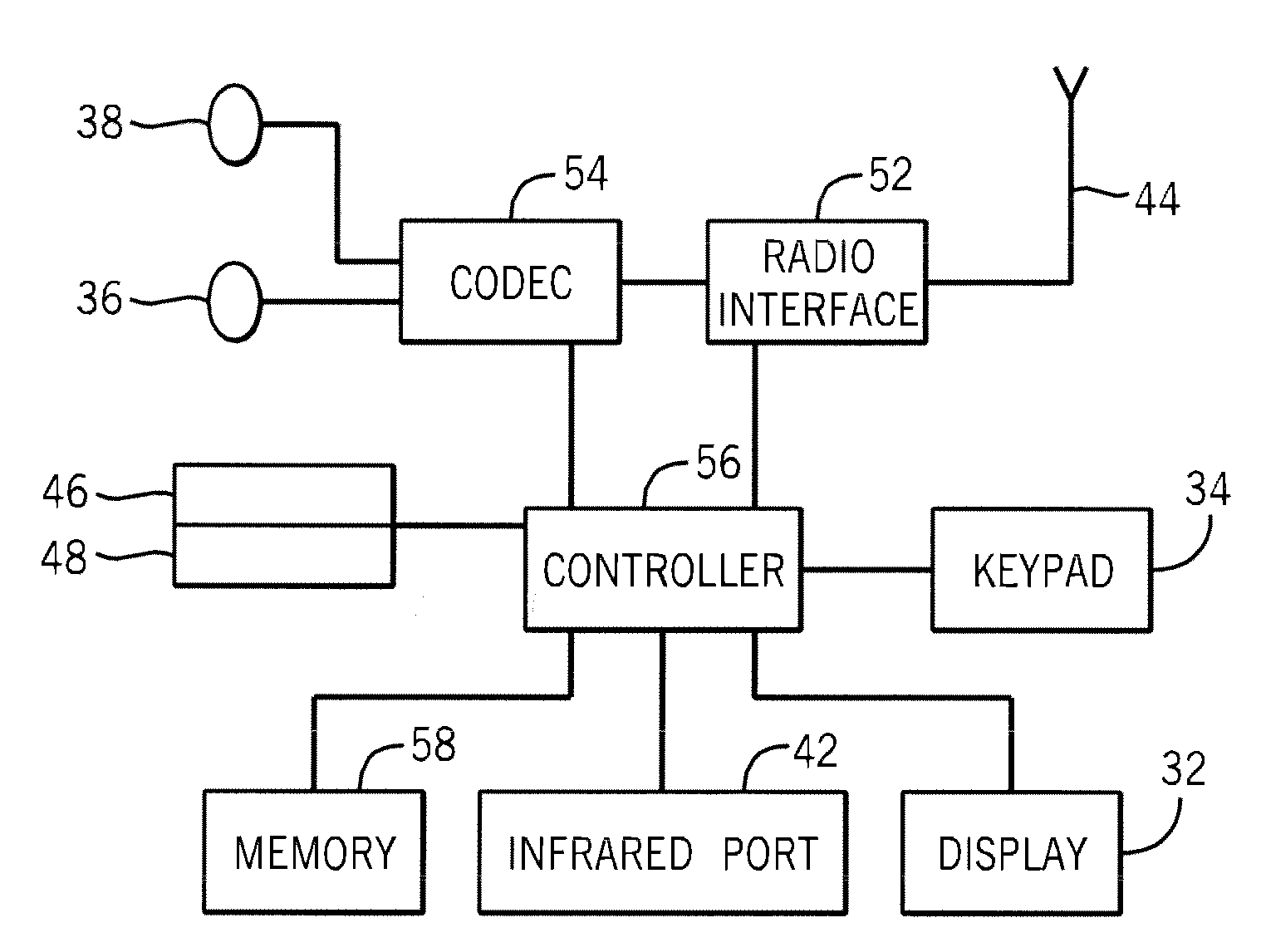
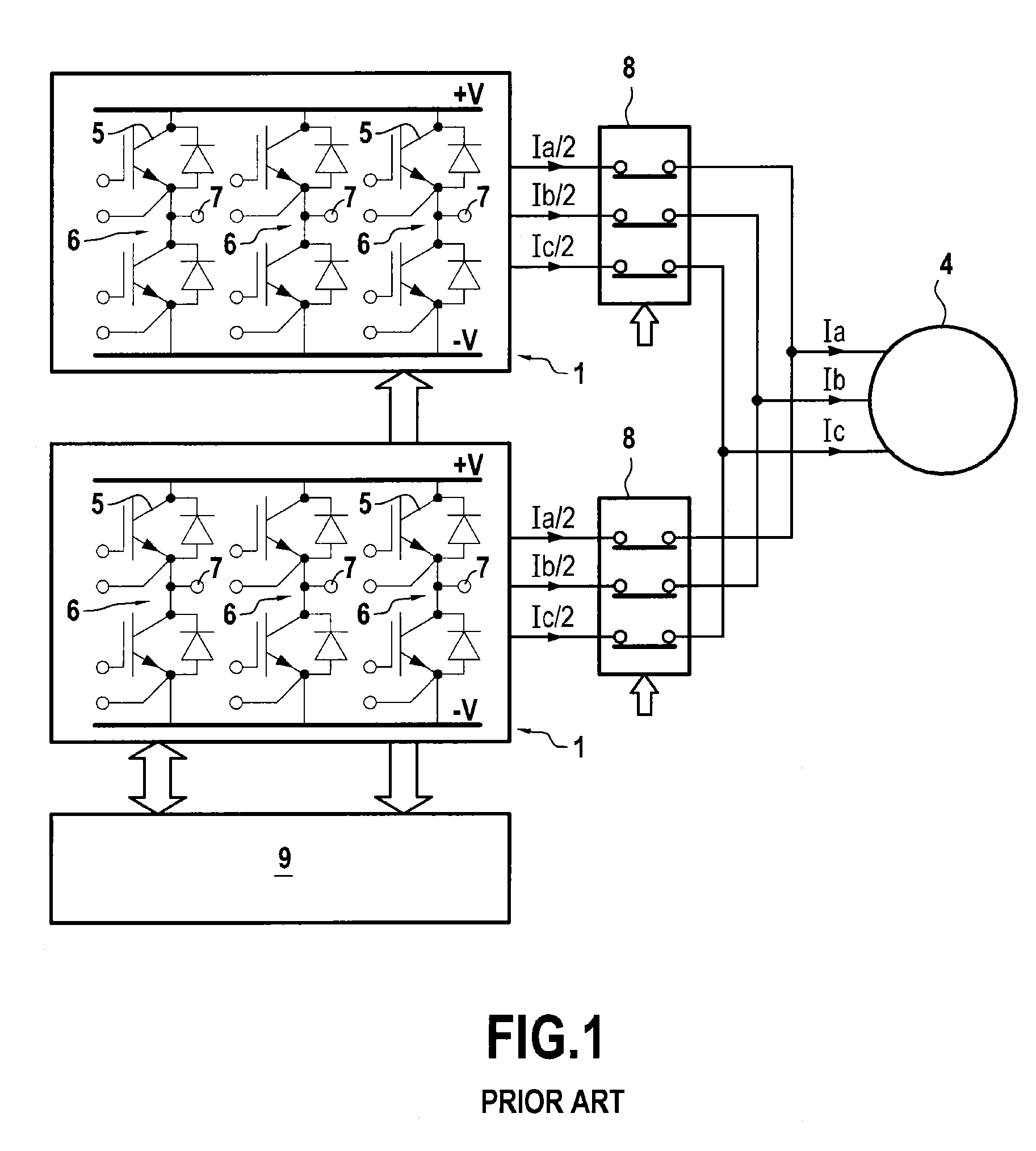
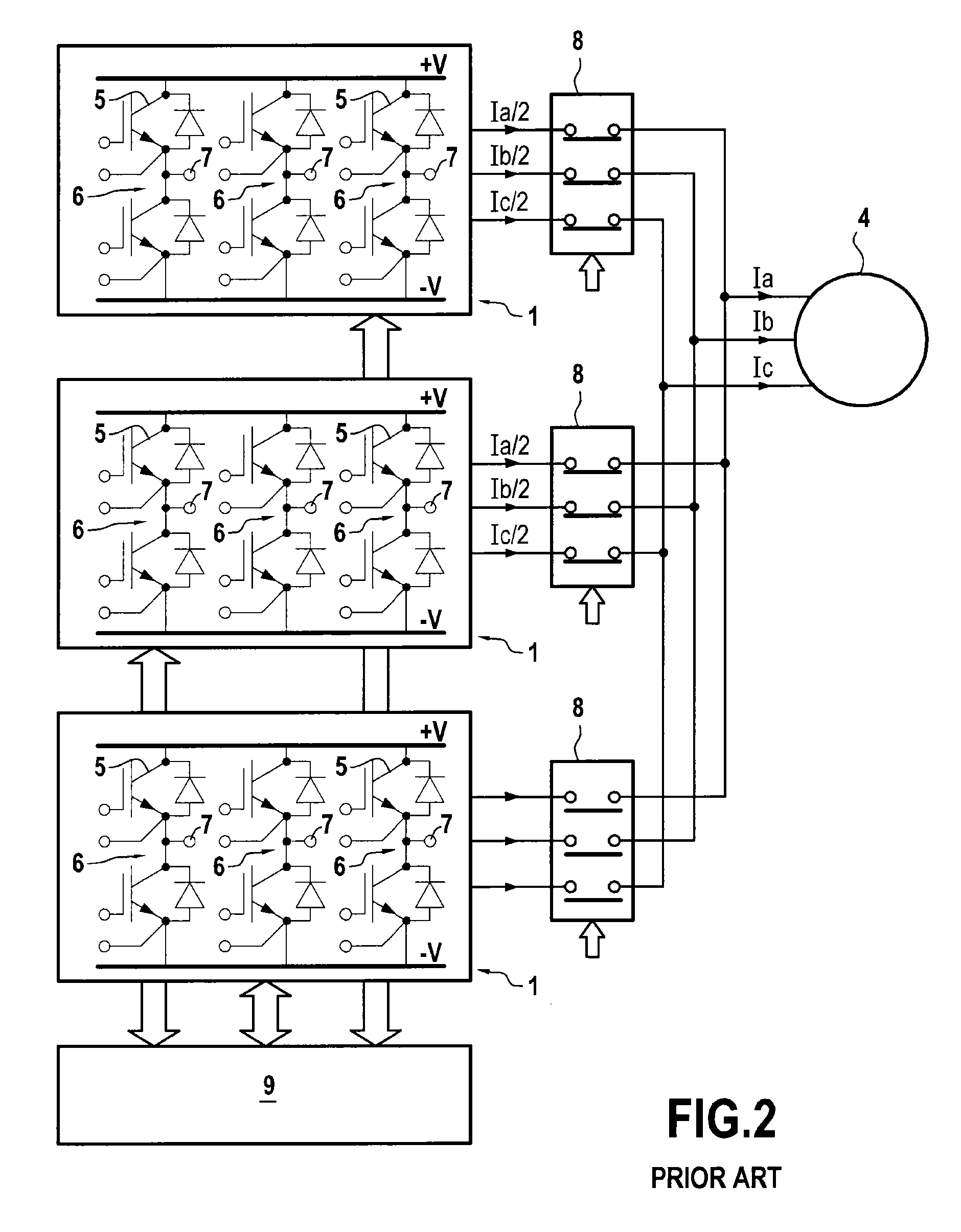
Block floating point compression of signal data
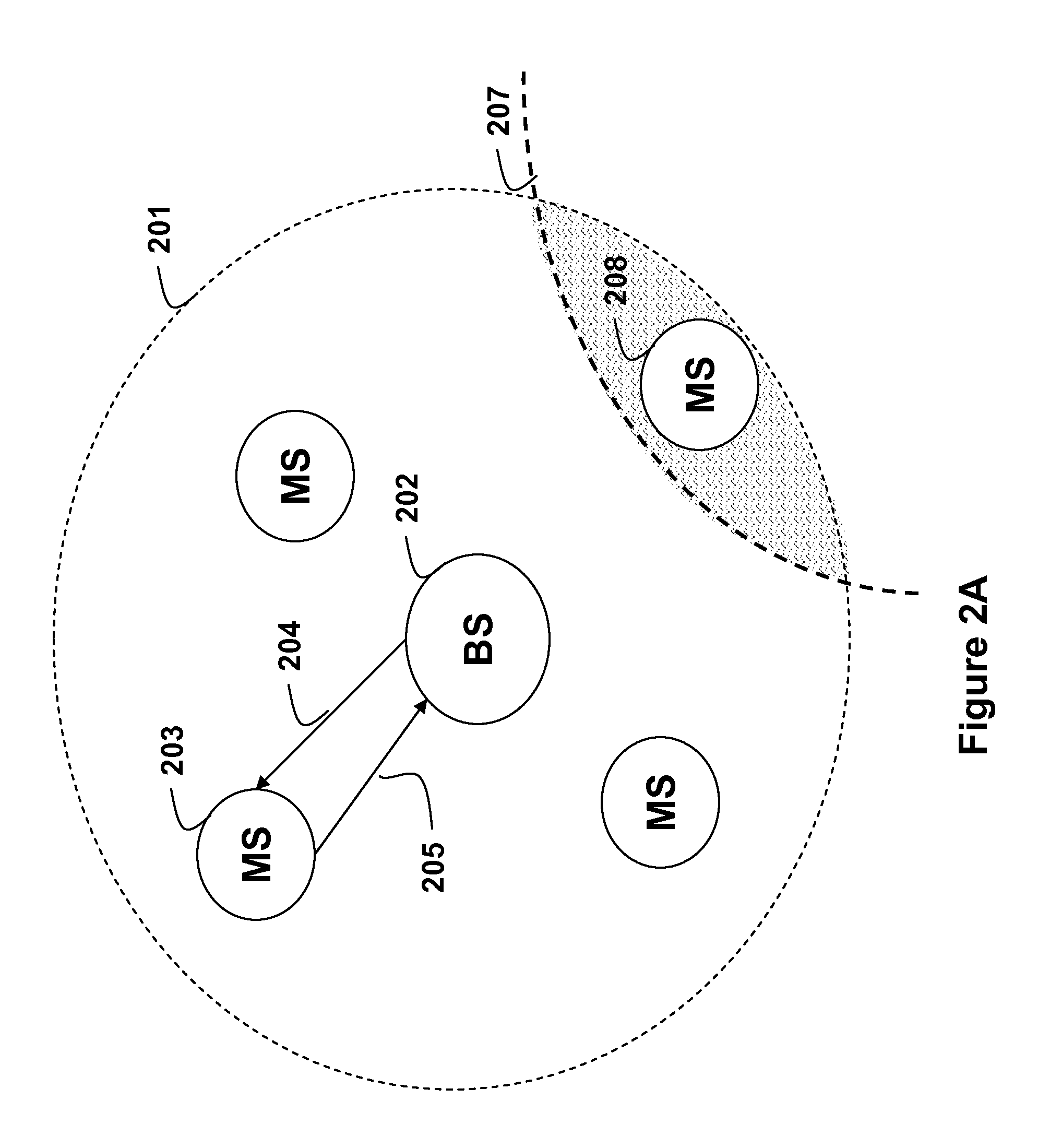
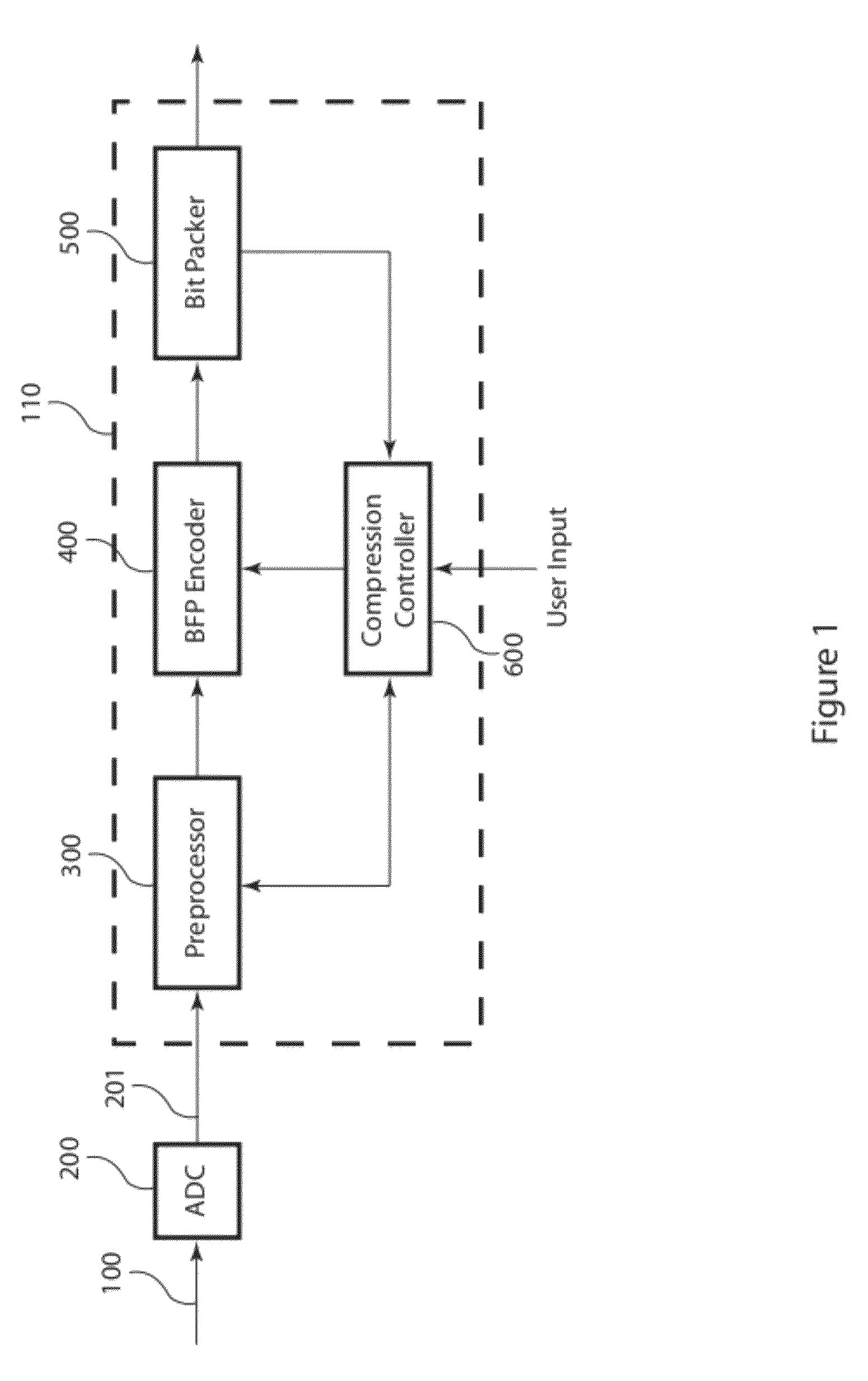
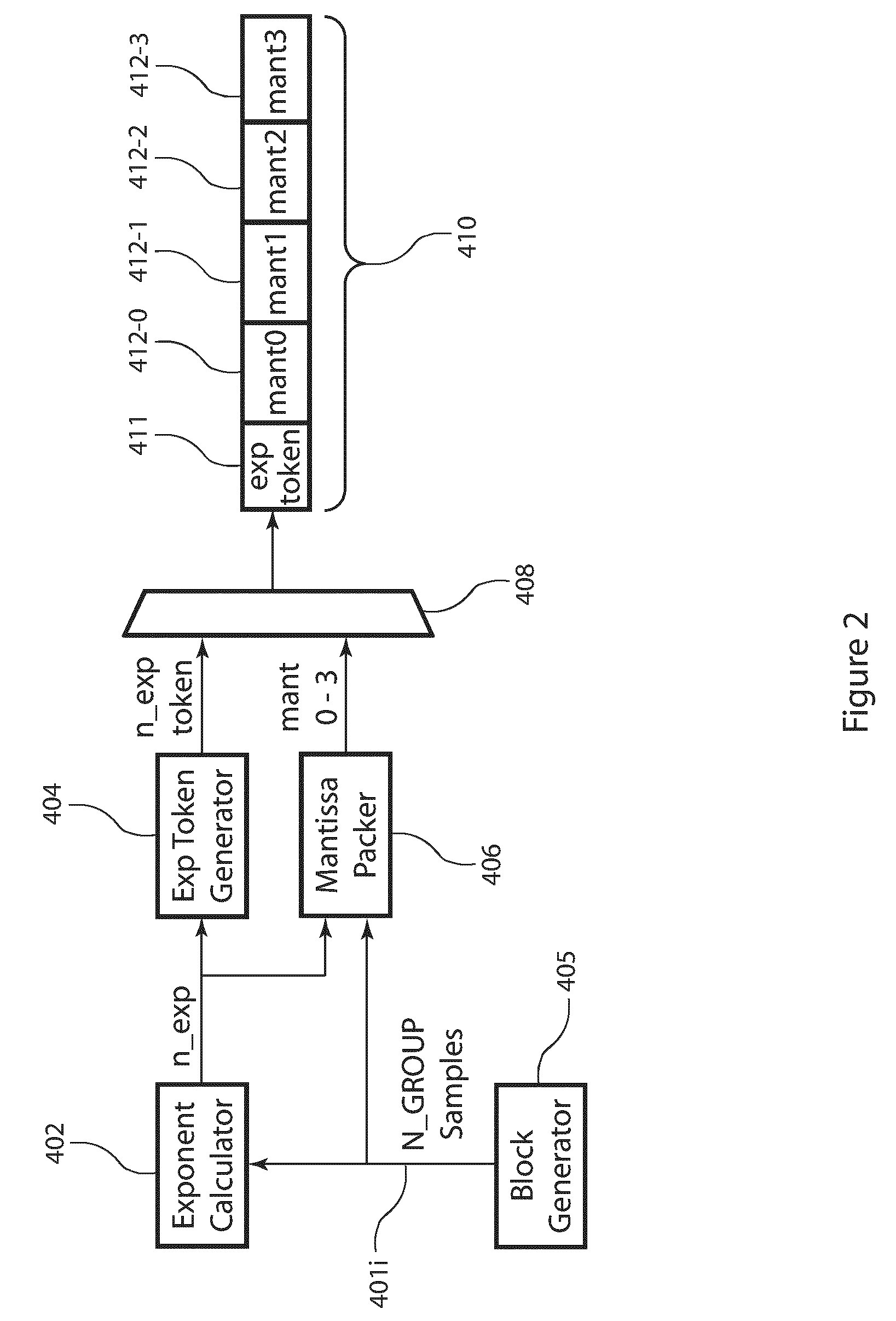
ActiveUS20110099295A1Enhanced block floating point compressionDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationMaximum magnitudeAlgorithm
A method and apparatus for compressing signal samples uses block floating point representations where the number of bits per mantissa is determined by the maximum magnitude sample in the group. The compressor defines groups of signal samples having a fixed number of samples per group. The maximum magnitude sample in the group determines an exponent value corresponding to the number of bits for representing the maximum sample value. The exponent values are encoded to form exponent tokens. Exponent differences between consecutive exponent values may be encoded individually or jointly. The samples in the group are mapped to corresponding mantissas, each mantissa having a number of bits based on the exponent value. Removing LSBs depending on the exponent value produces mantissas having fewer bits. Feedback control monitors the compressed bit rate and / or a quality metric. This abstract does not limit the scope of the invention as described in the claims.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Method of error floor mitigation in low-density parity-check codes
ActiveUS20120266040A1Improve performanceError correction/detection using LDPC codesCode conversionComputer hardwareMaximum magnitude
A digital communication decoding method for low-density parity-check coded messages. The decoding method decodes the low-density parity-check coded messages within a bipartite graph having check nodes and variable nodes. Messages from check nodes are partially hard limited, so that every message which would otherwise have a magnitude at or above a certain level is re-assigned to a maximum magnitude.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
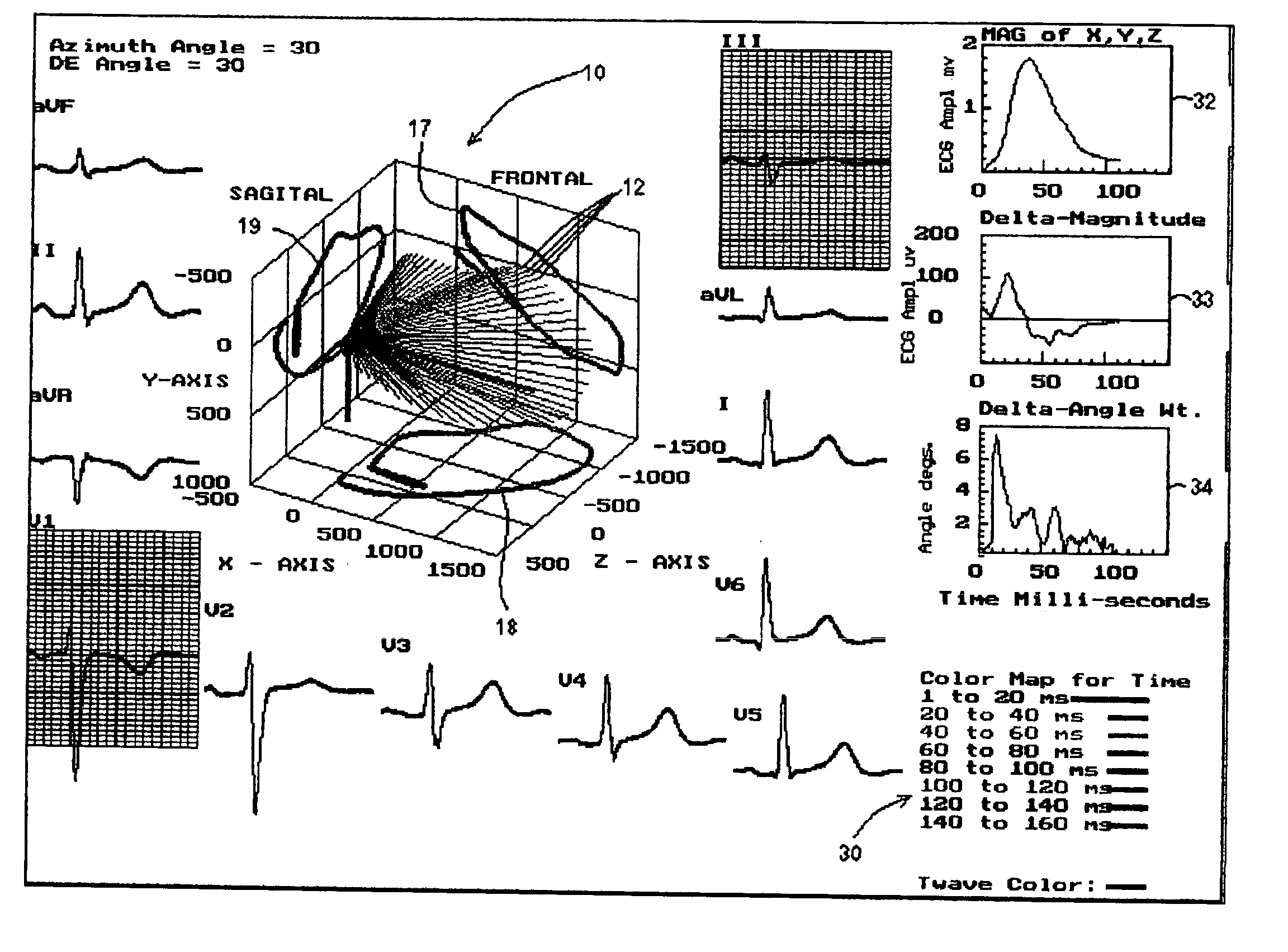
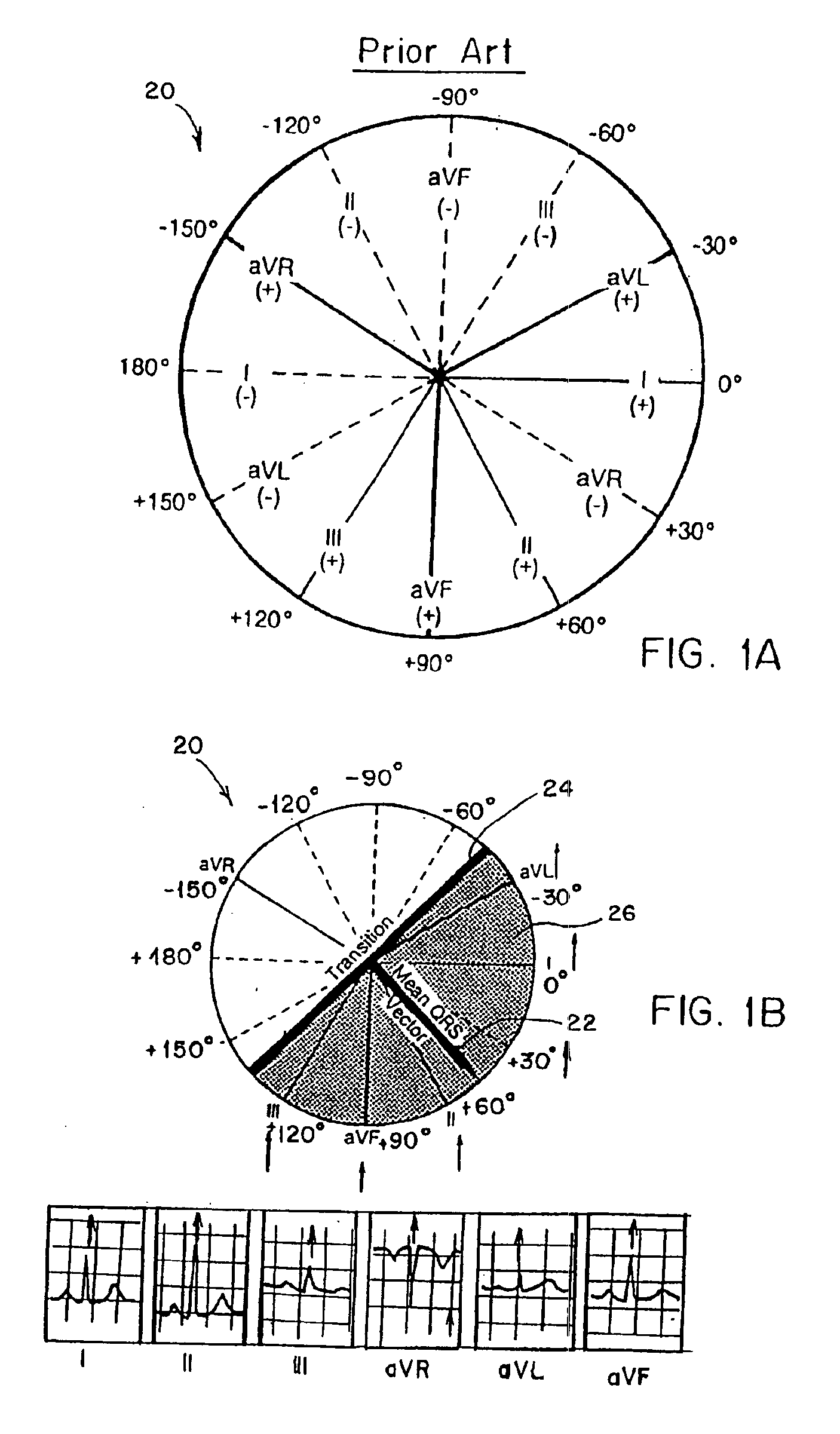
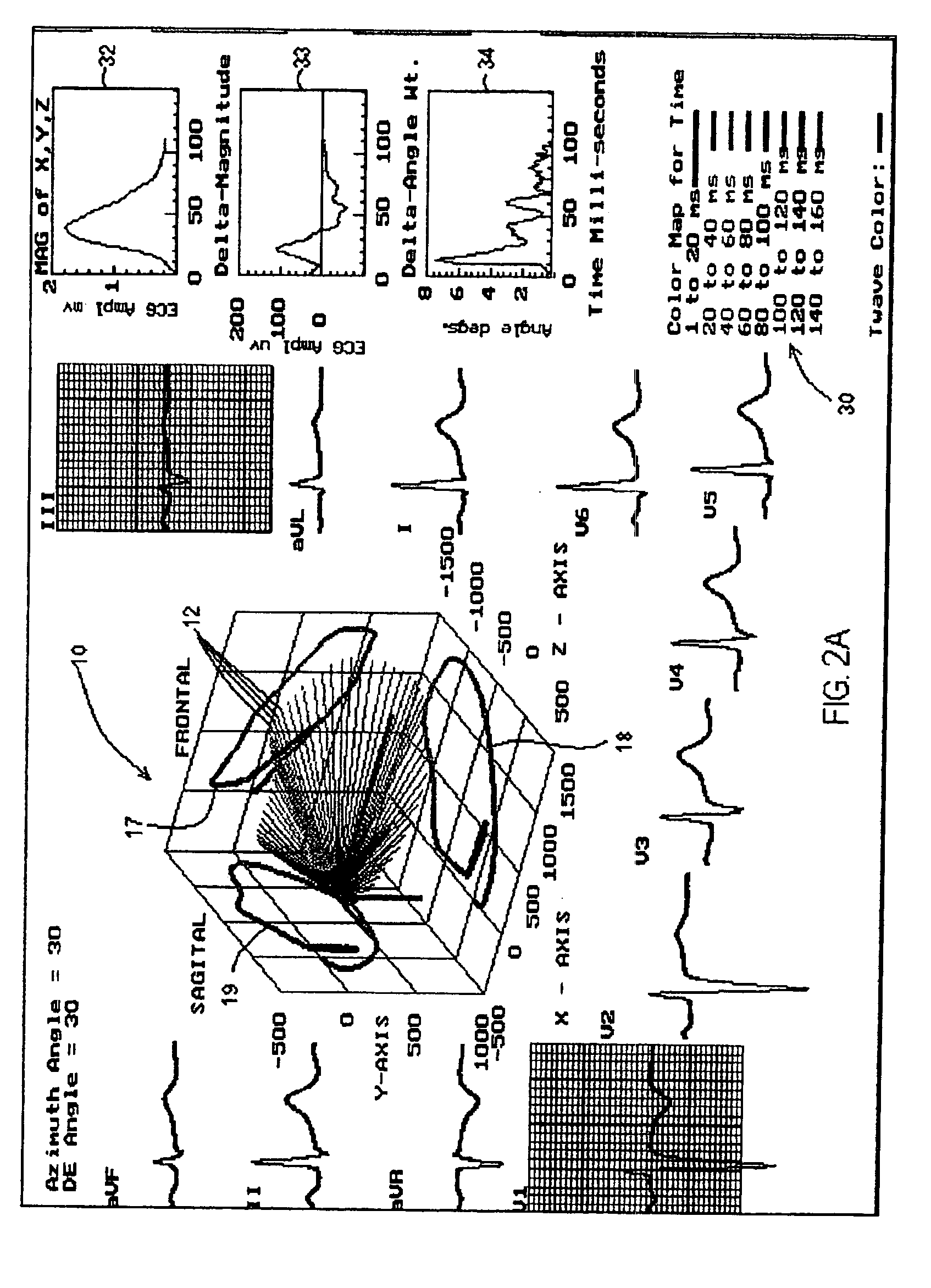
Three dimensional vector cardiograph and method for detecting and monitoring ischemic events
InactiveUS6884218B2Easy to analyzeGood techniqueElectrocardiographyBlood flow measurement devicesMaximum magnitudeT wave
A method of determining an ischemic event includes the steps of: monitoring and storing an initial electrocardiogram vector signal (x, y, z) of a known non-ischemic condition over the QRS, ST and T wave intervals; calculating and storing a J-point of the vector signal and a maximum magnitude of a signal level over the T wave interval; monitoring a subsequent electrocardiogram vector signal over the QRS, ST and T wave intervals; measuring and storing the magnitude (Mag.) of the vector difference between a subsequent vector signal and the initial vector signal; measuring and storing the angle (Ang.) difference between a subsequent vector and the initial vector at points; regressing a line from points about 25 milliseconds prior to the J point and about 60 milliseconds after the J-point and determining the slope of the regression line and the deviation of the angle difference of the regression line; regressing a line from points about 100 milliseconds prior to the maximum magnitude of the signal level over the T wave interval and determining the slope of the regressing line and the deviation of the angle difference of the regression line; and comparing the slope and deviation of the lines from the J point and the T wave interval to a set of known values to determine the presence of an ischemic event.
Owner:ECG TECH CORP
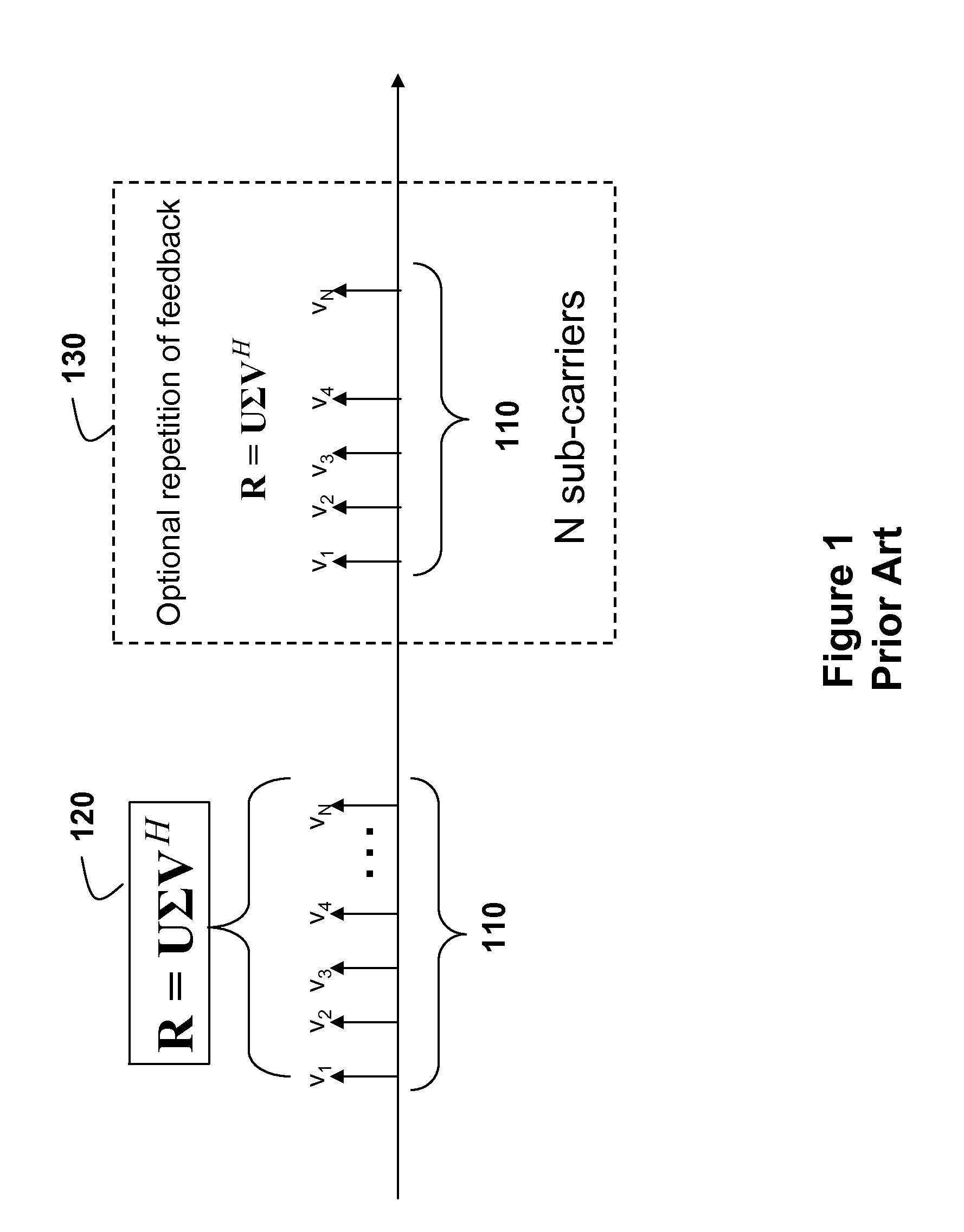
Parametric Compression of Rank-1 Analog Feedback
InactiveUS20100272014A1Radio transmissionWireless commuication servicesSingular value decompositionCarrier signal
Channel state information in a closed-loop, multiple-input, multiple-output wireless networks is fed back from each mobile station to a base station by first determining a transmit covariance matrix R, and applying a singular value decomposition (SVD) R=UΣVH, where U, V are left and right singular vector matrices, Σ is a diagonal matrix with singular values. The matrix V includes column vectors V. A beamforming vector vmax=[1 exp(jΦ)exp(j2Φ) . . . exp(jΦ)] / √{square root over (N)}] is approximated by the column vector V having a maximum magnitude, where Φ is a real number. Then, only the angle Φ is fed back using a phase modulation mapping of the components exp(jΦ) onto the associated subcarrier.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Block floating point compression of signal data
ActiveUS8301803B2Enhanced block floating point compressionDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationMaximum magnitudeAlgorithm
A method and apparatus for compressing signal samples uses block floating point representations where the number of bits per mantissa is determined by the maximum magnitude sample in the group. The compressor defines groups of signal samples having a fixed number of samples per group. The maximum magnitude sample in the group determines an exponent value corresponding to the number of bits for representing the maximum sample value. The exponent values are encoded to form exponent tokens. Exponent differences between consecutive exponent values may be encoded individually or jointly. The samples in the group are mapped to corresponding mantissas, each mantissa having a number of bits based on the exponent value. Removing LSBs depending on the exponent value produces mantissas having fewer bits. Feedback control monitors the compressed bit rate and / or a quality metric. This abstract does not limit the scope of the invention as described in the claims.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Transmitter With Peak-Tracking PAPR Reduction and Method Therefor
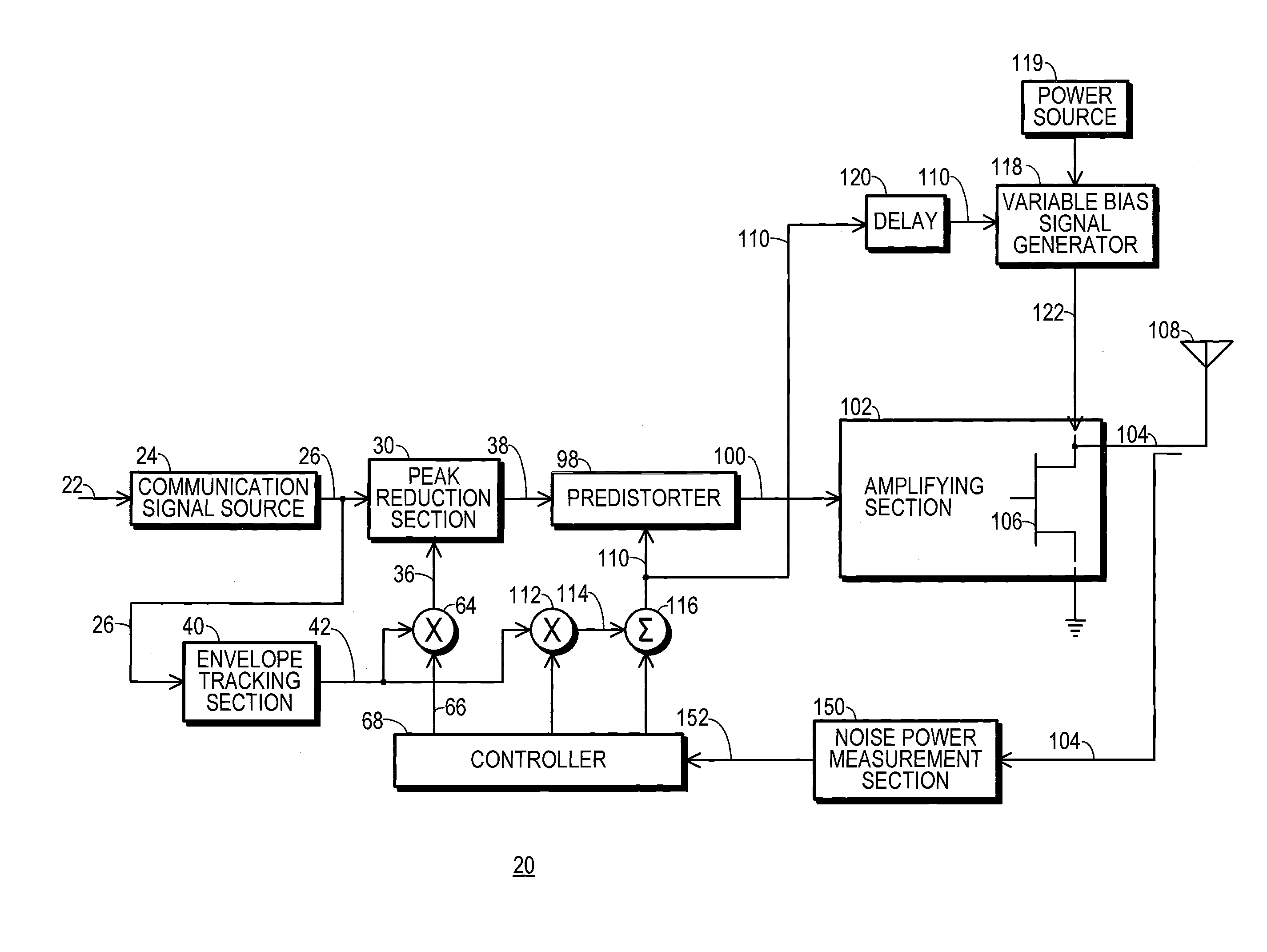
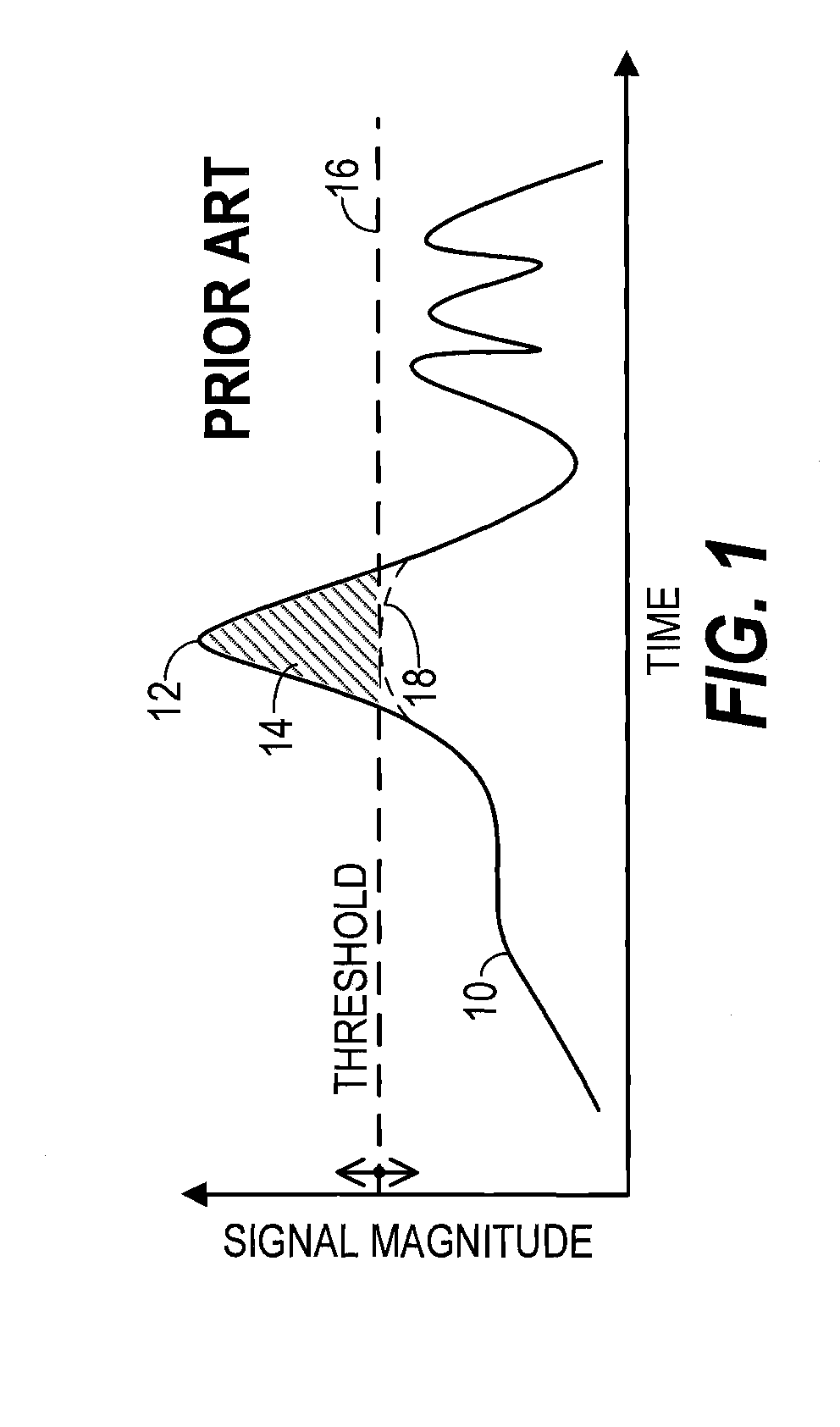
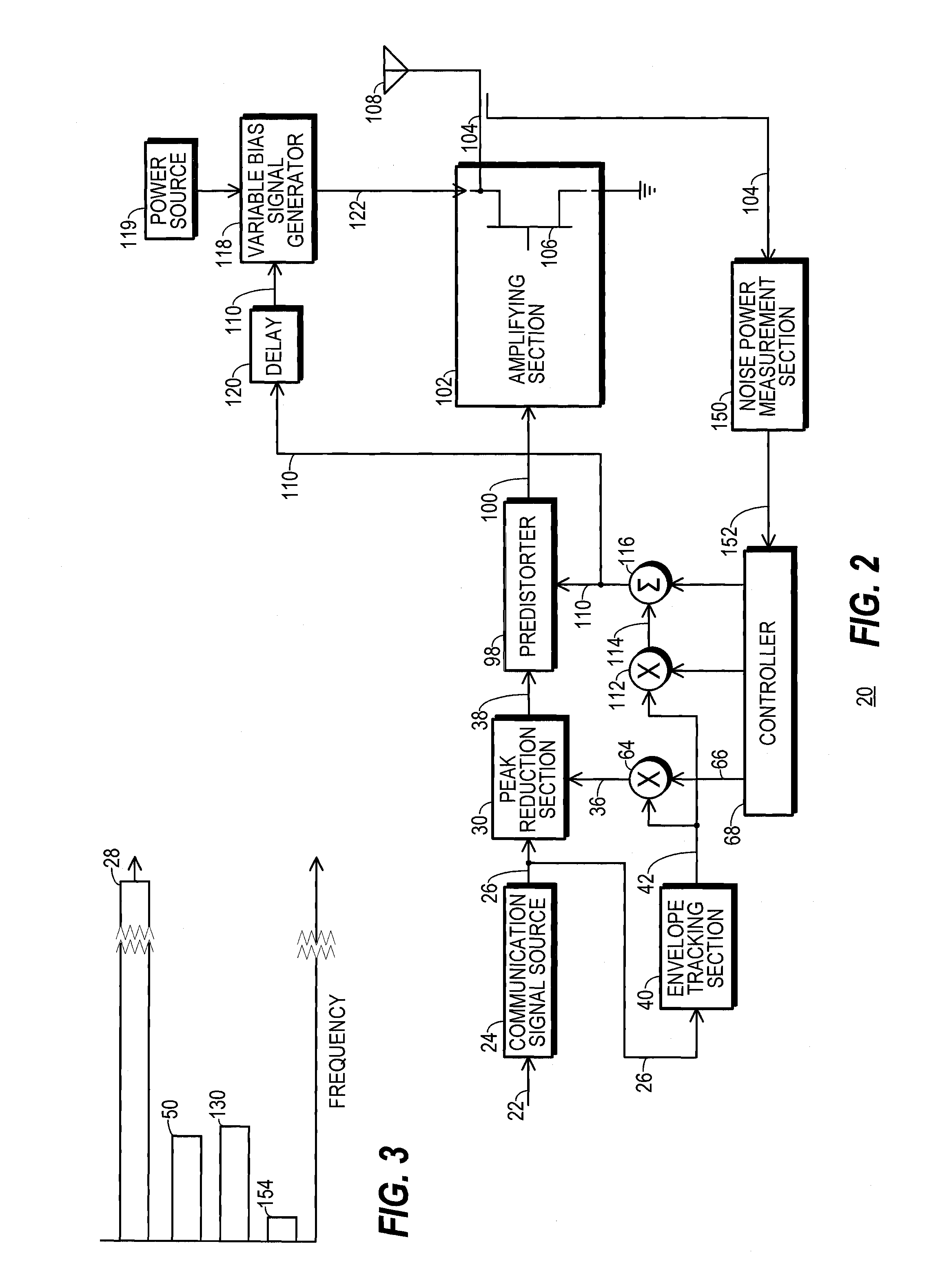
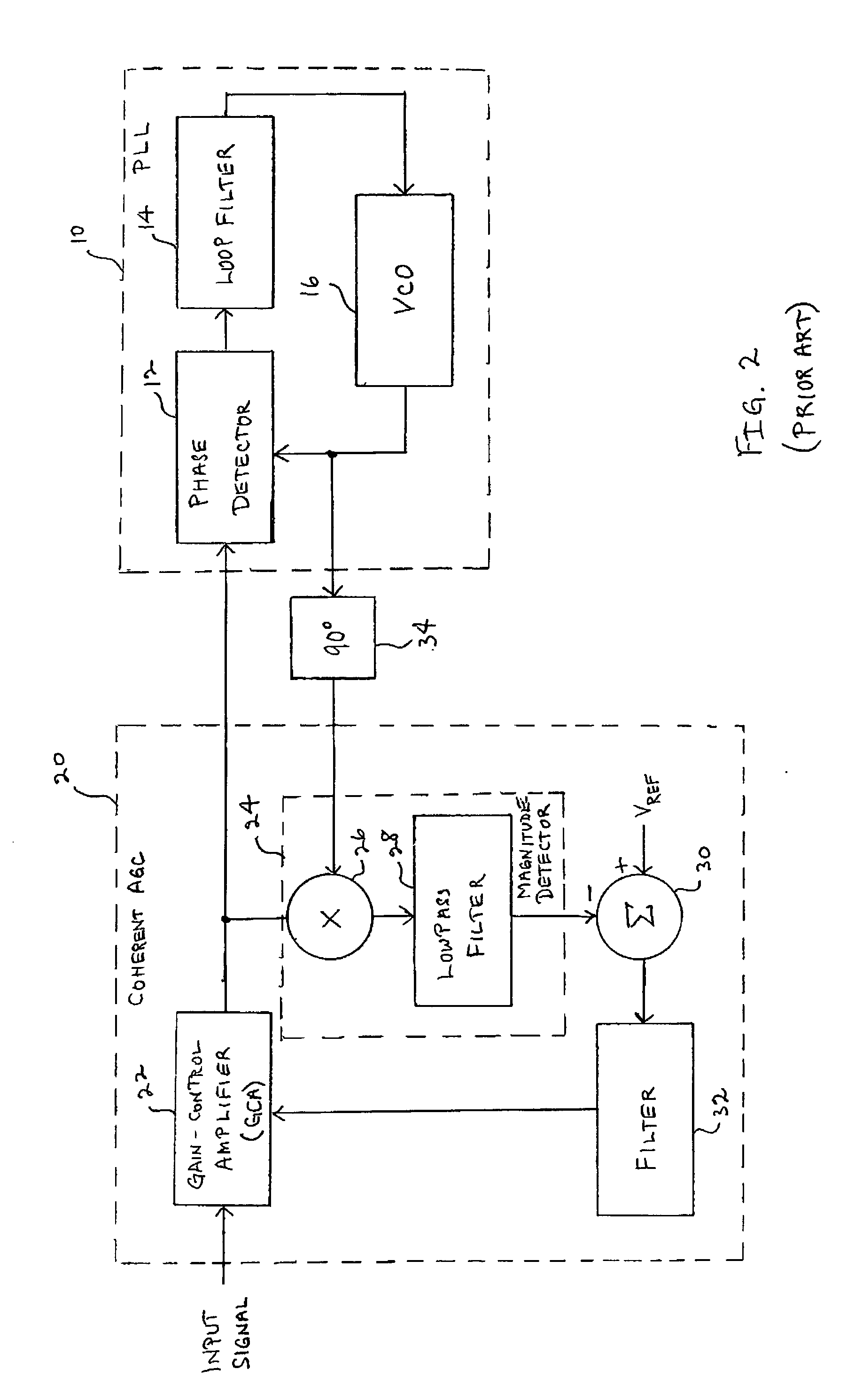
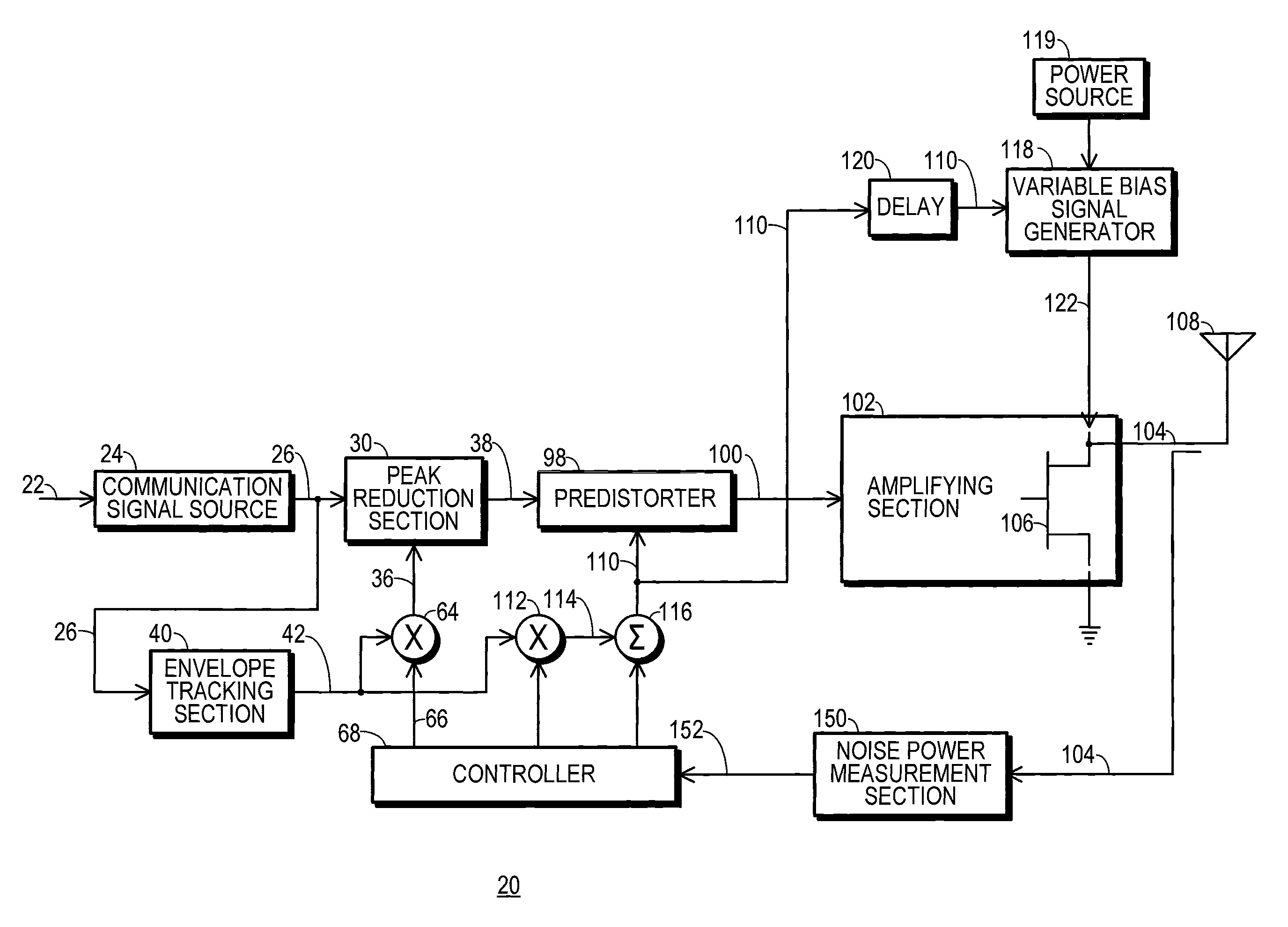
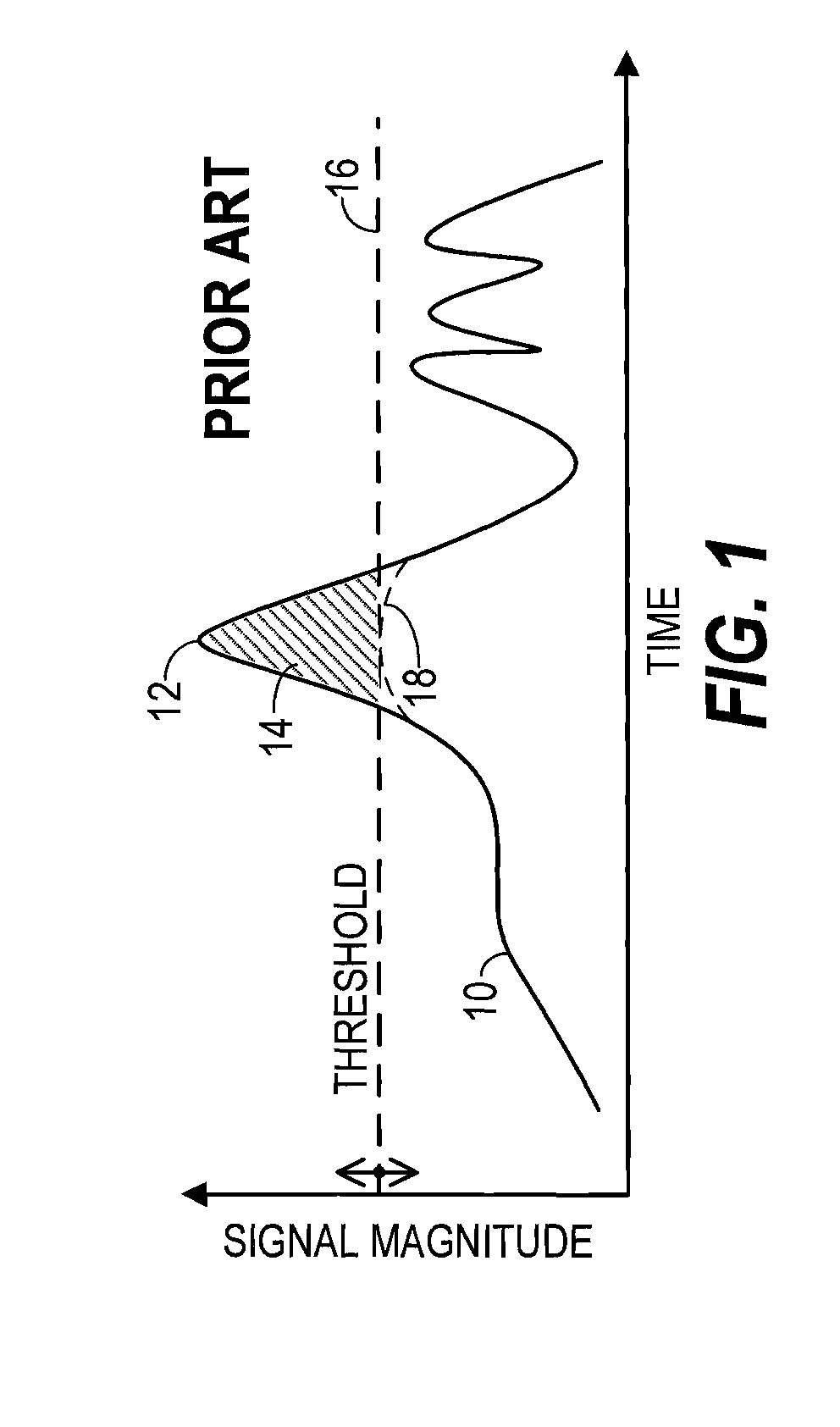
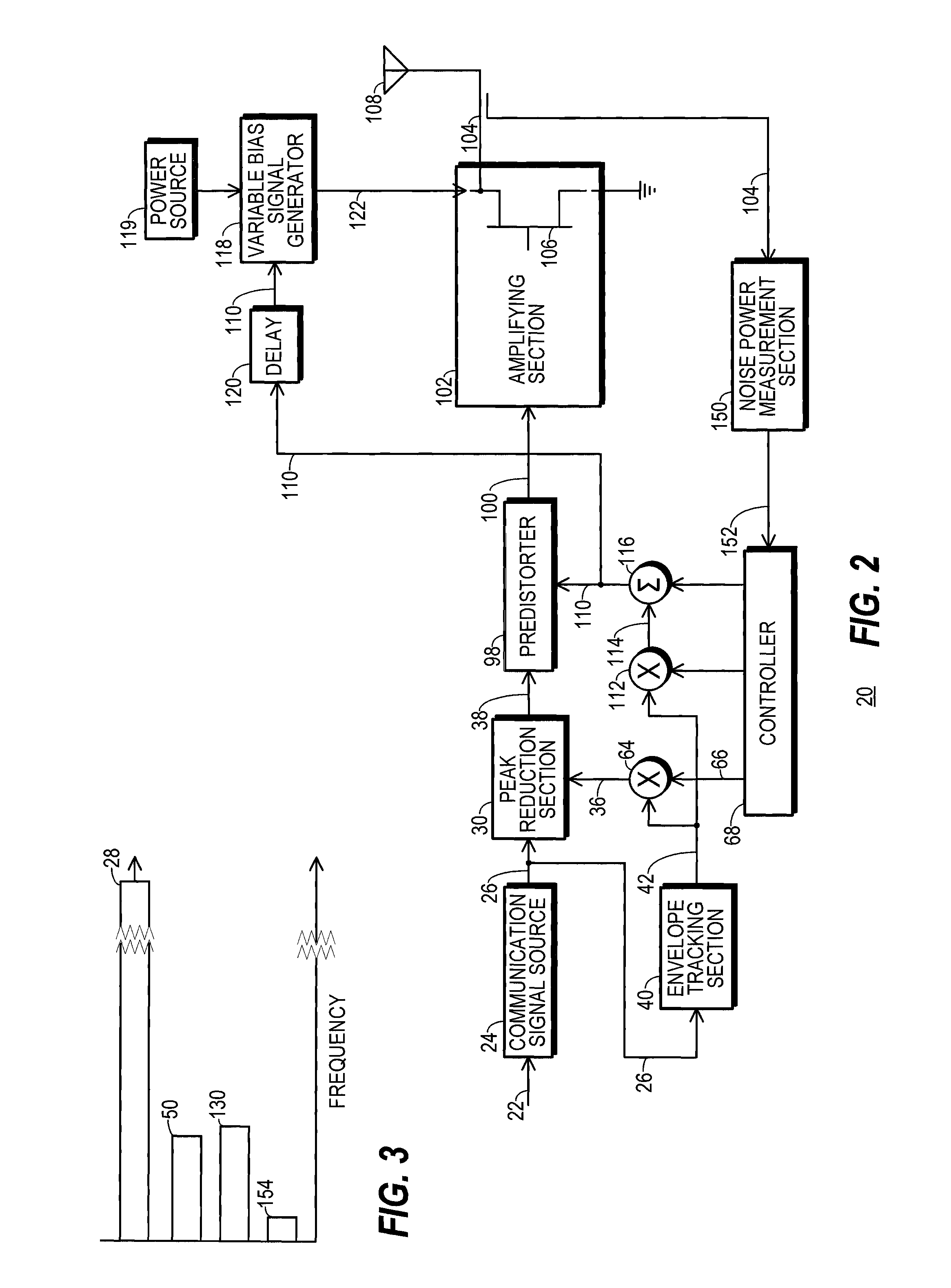
InactiveUS20140065986A1Amplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesTransmissionMaximum magnitudeControl signal
A transmitter (20) includes a peak reduction section (30), a predistorter (98), and an amplifying section (102) biased by a variable bias signal generator (118). The peak reduction section (30) is controlled by a signal magnitude threshold (36) that defines maximum magnitudes for local peaks (32) of a reduced-peak communication signal (38). The bias signal generator (118) is controlled by a bias control signal (110). Both the signal magnitude threshold (36) and the bias control signal (110) are derived from a common reduced bandwidth (50) peak-tracking signal (42). The peak-tracking signal (42) is derived from an inflated-peak communication signal (26). The predistorter (98) applies distortion to the reduced-peak communication signal (38) that is configured, at least in part, by the bias control signal (110).
Owner:CRESTCOM INC
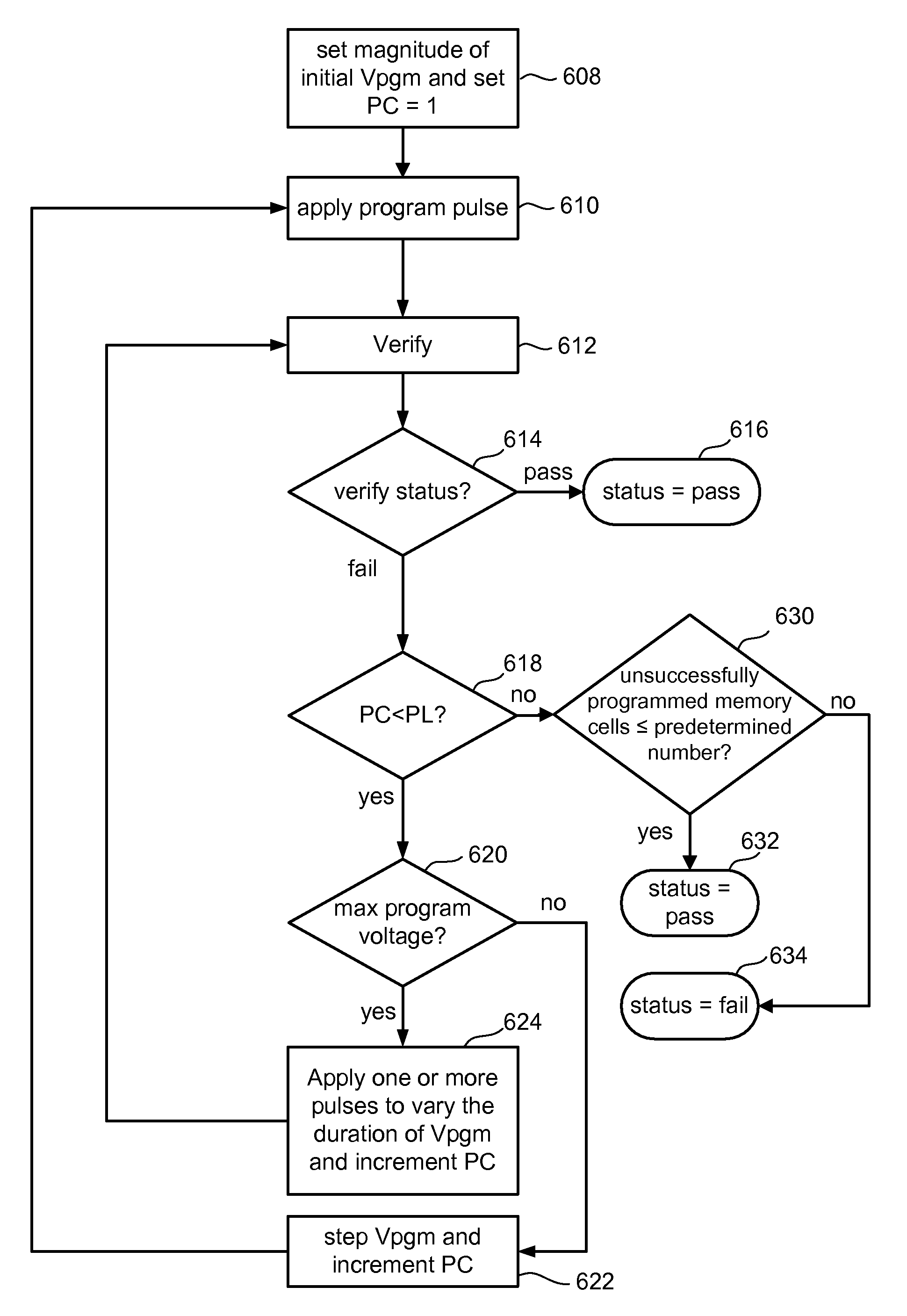
Intelligent control of program pulse duration
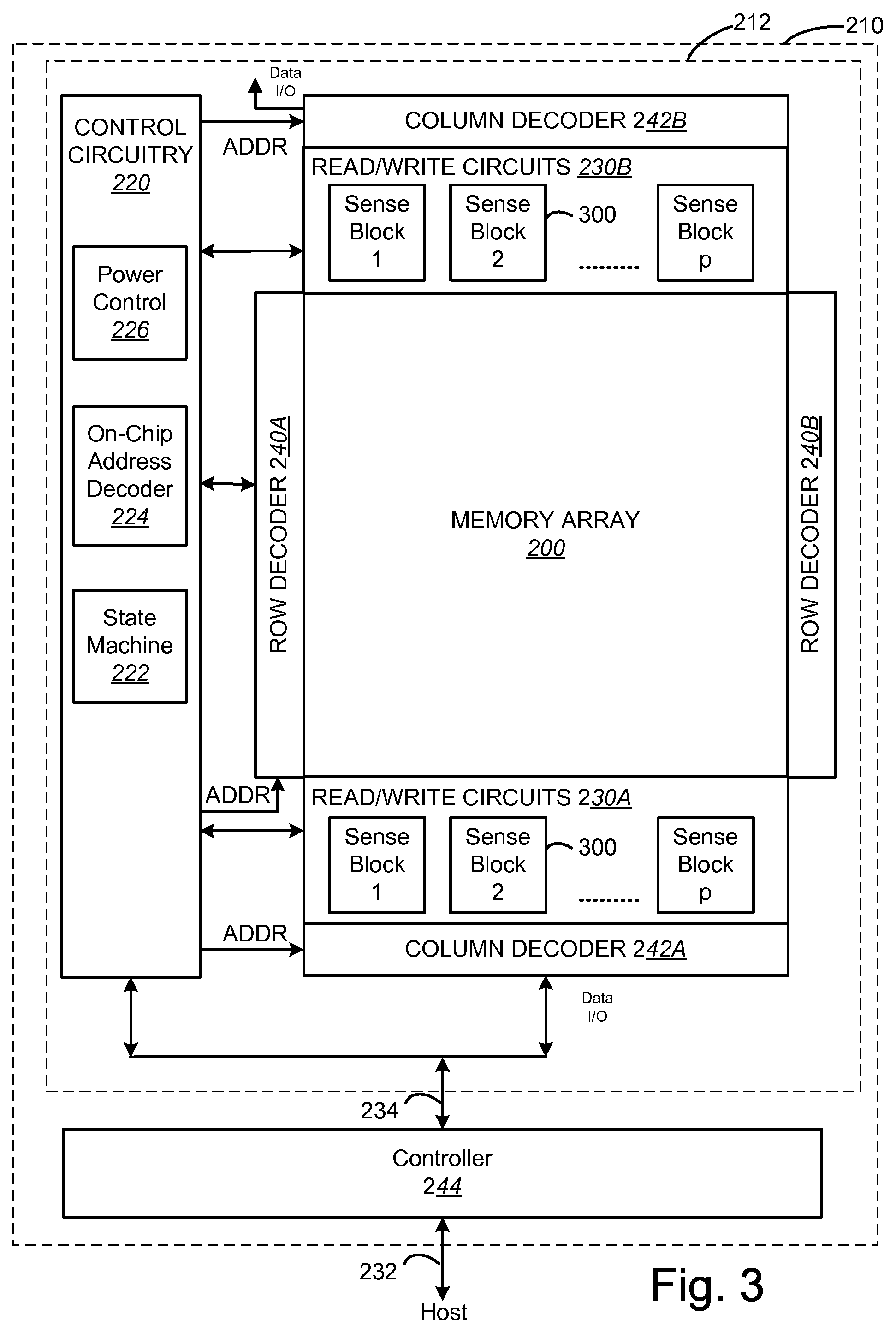
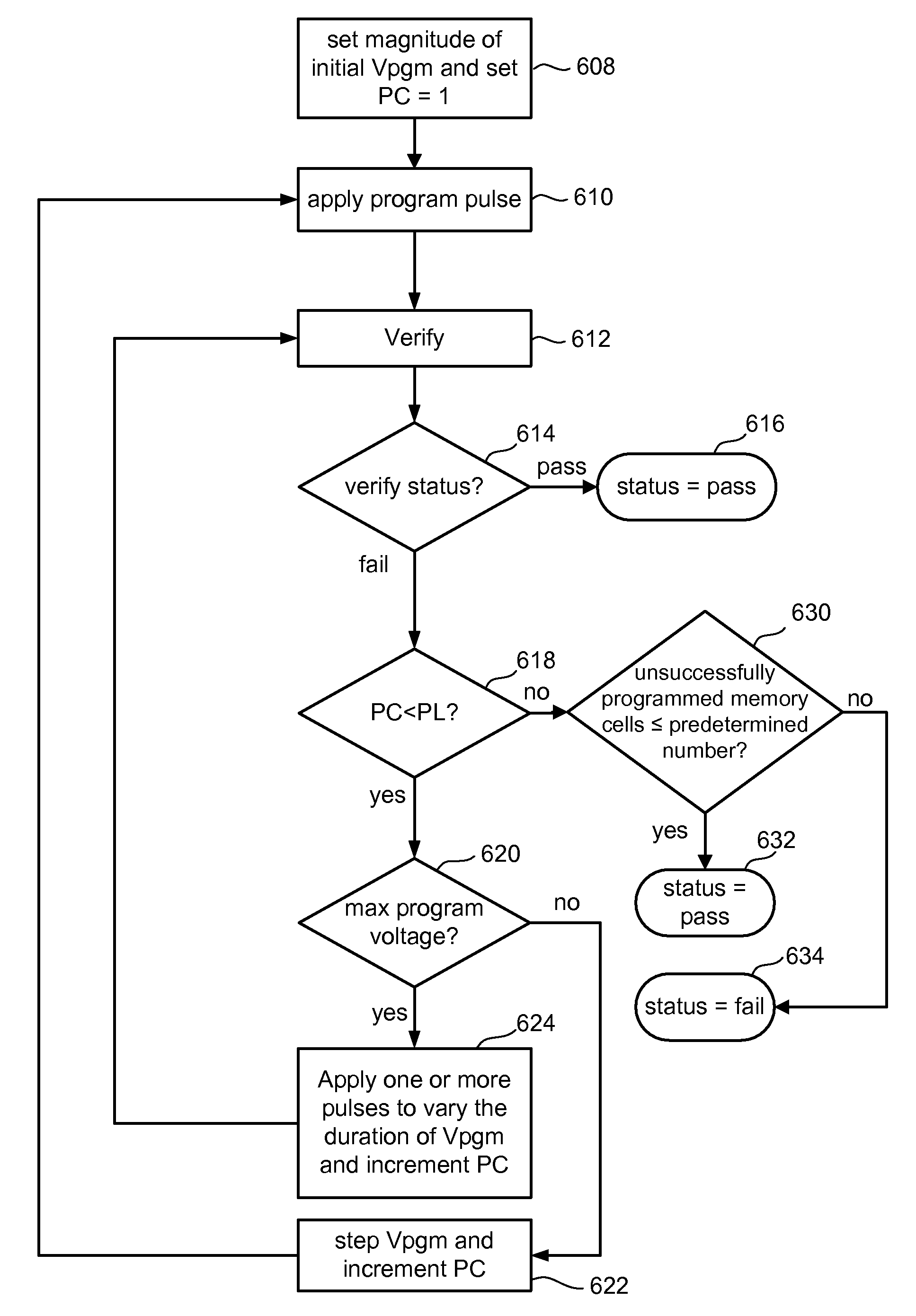
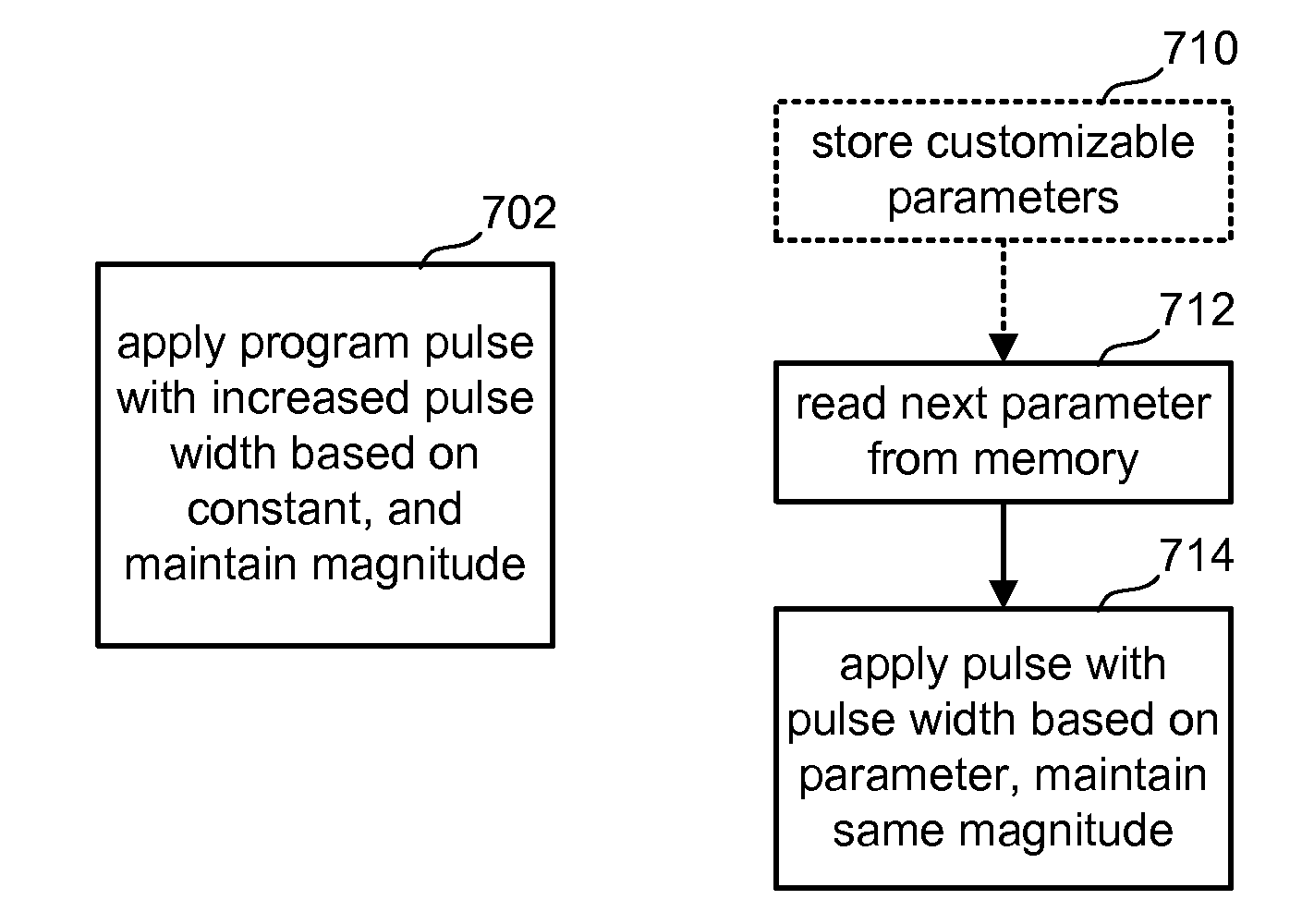
To program a set of non-volatile storage elements, a set of programming pulses are applied to the control gates (or other terminals) of the non-volatile storage elements. The programming pulses have a constant pulse width and increasing magnitudes until a maximum voltage is reached. At that point, the magnitude of the programming pulses stops increasing and the programming pulses are applied in a manner to provide varying time duration of the programming signal between verification operations. In one embodiment, for example, after the pulses reach the maximum magnitude the pulse widths are increased. In another embodiment, after the pulses reach the maximum magnitude multiple program pulses are applied between verification operations.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
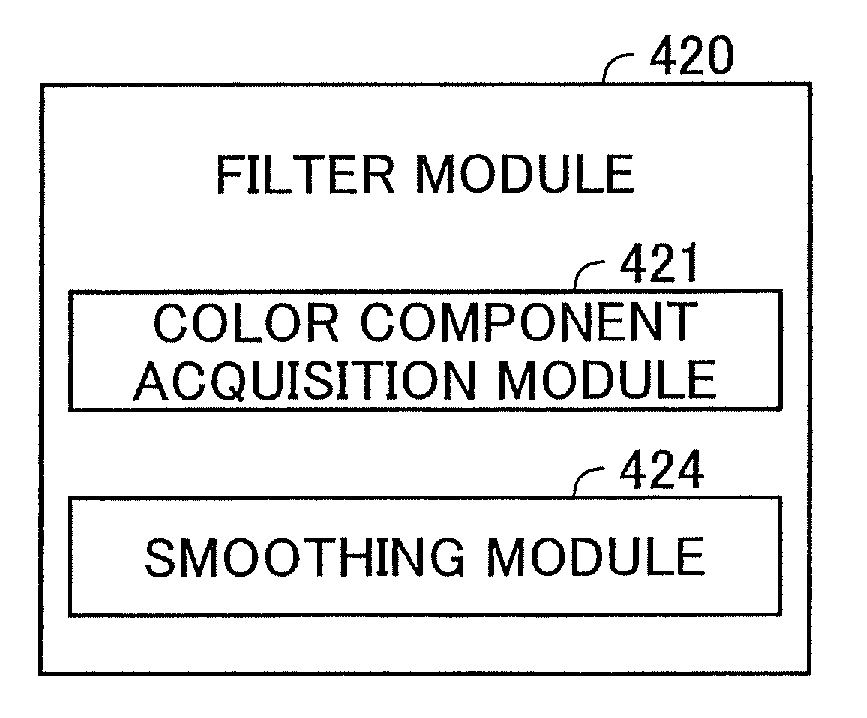
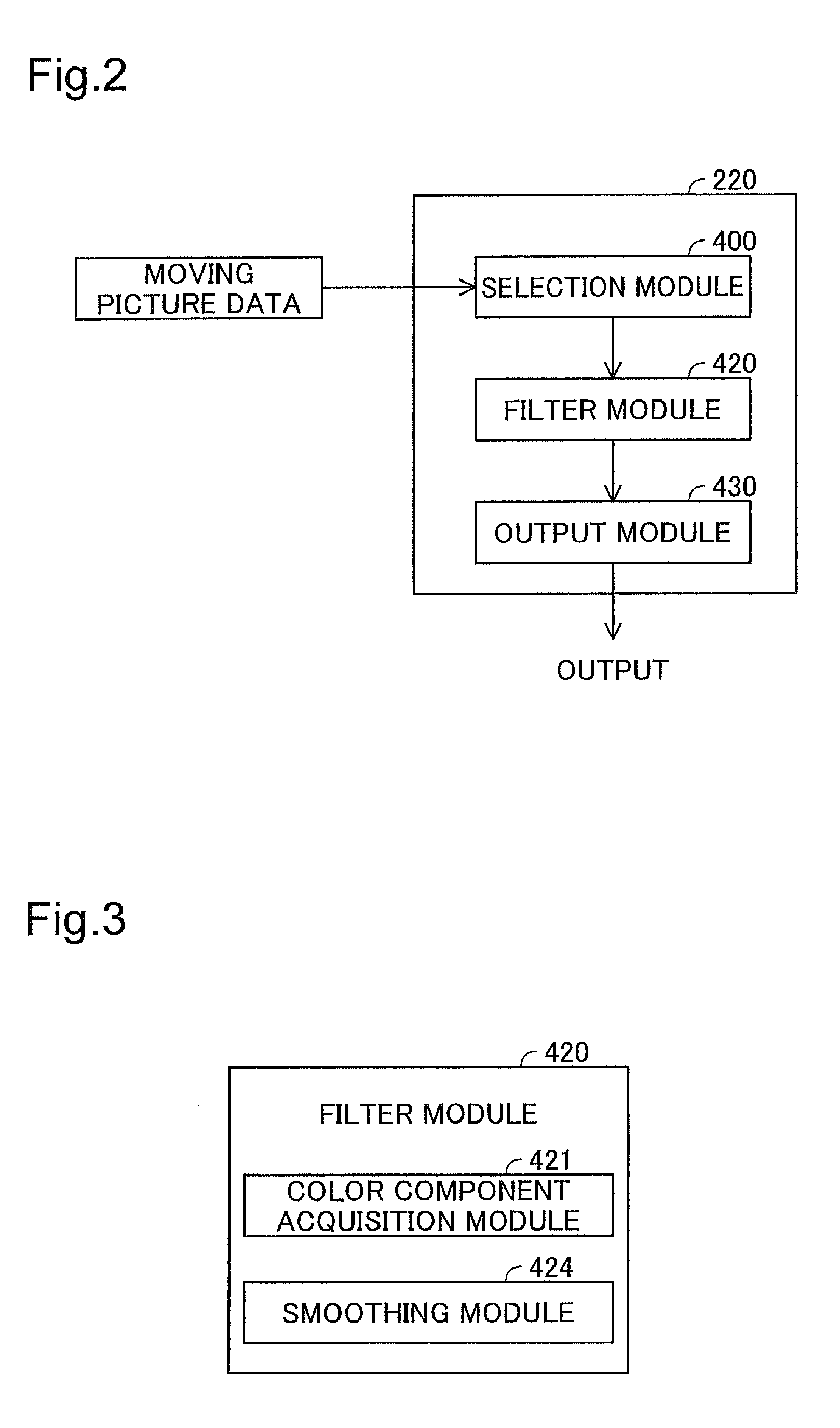
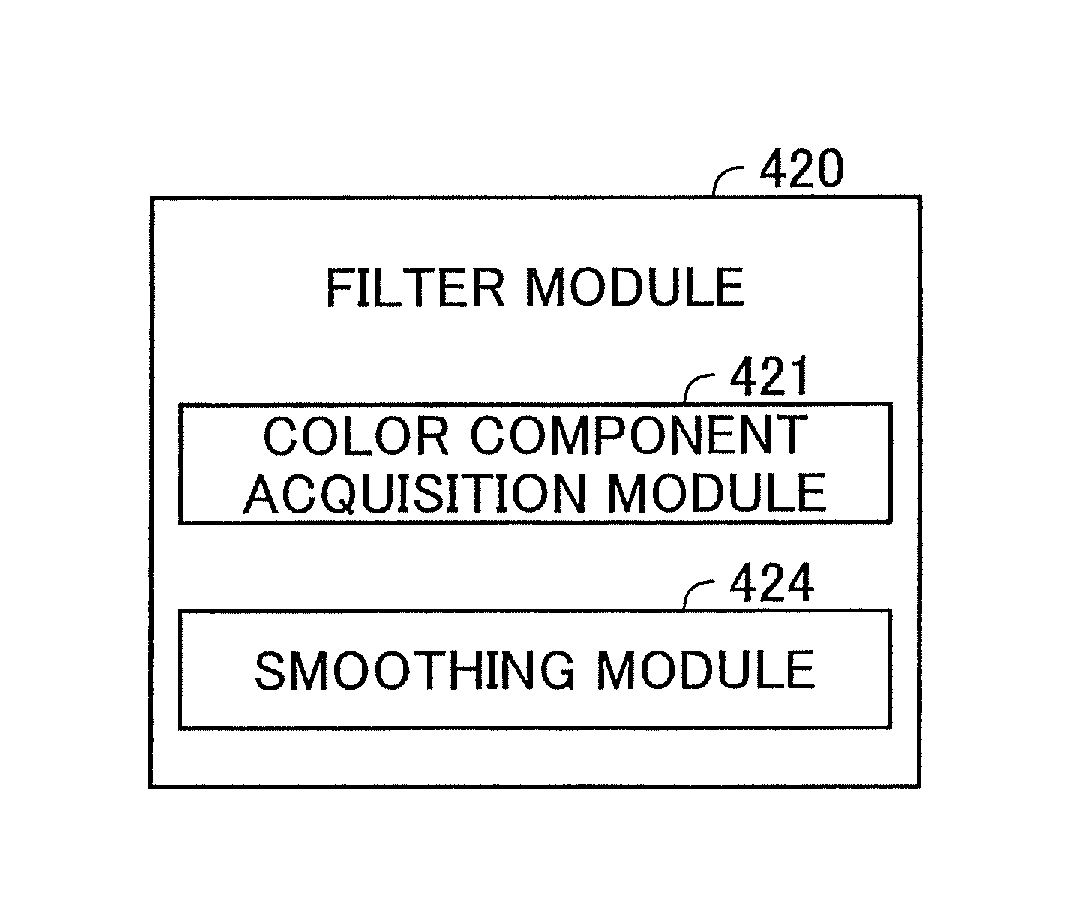
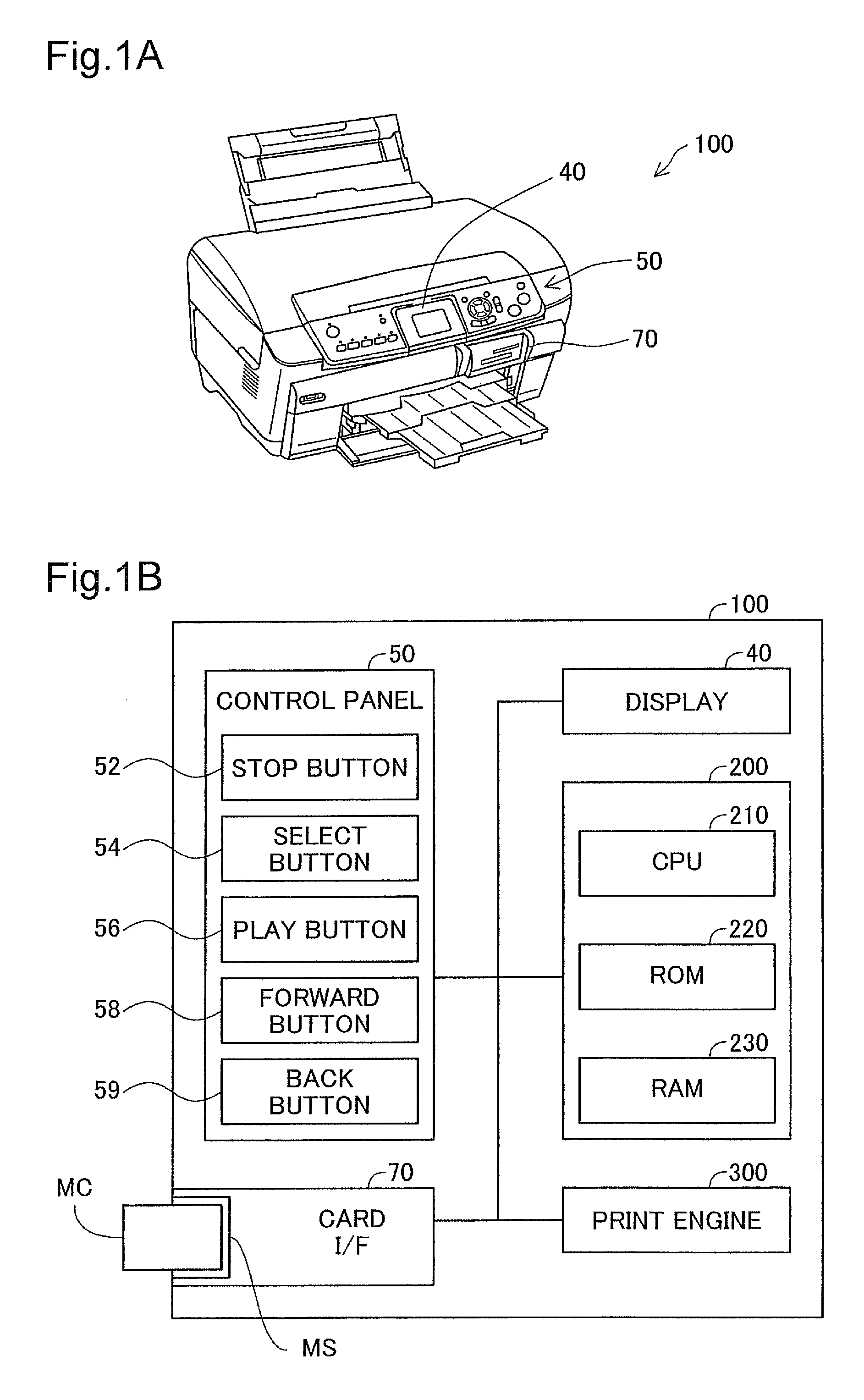
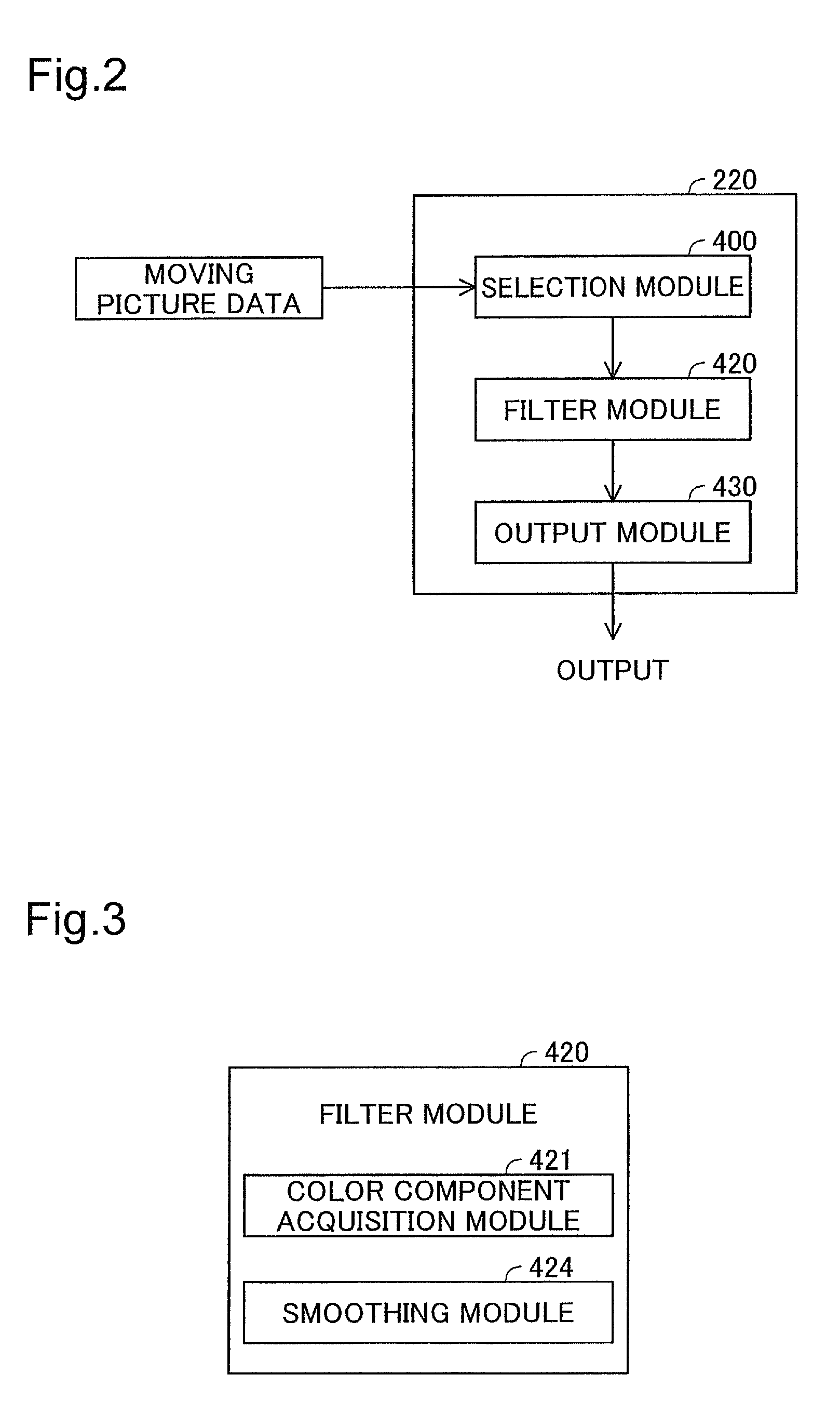
Apparatus, method, and program product for image processing
InactiveUS20090226085A1Excessive blurring of image can be suppressedReduce noiseImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingMaximum magnitude
From the target image data, a luminance component, a first color difference component, and a second color difference component which represent color of respective pixels are acquired; and a maximum magnitude smoothing process is carried out on the first color difference component.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Scalable video coding and decoding
InactiveUS20080048894A1Improve coding efficiencyRaise the possibilityPulse conversionDigital video signal modificationVariable-length codeVideo encoding
A system and method for improved video encoding and decoding. The present invention addresses issues that arise in the H.264 / AVC standard involving “high magnitude coefficients.” According to various embodiments of the present invention, an encoded end of block (EOB) symbol provides information comprising at least one of the maximum magnitude of values in a block, the number of values in the block with a magnitude greater than 1, and a variable length code (VLC) index indicating a VLC to be used in decoding precise magnitudes for non-zero values in the block. By including this information in the EOB symbol, improved coding efficiency is achieved.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
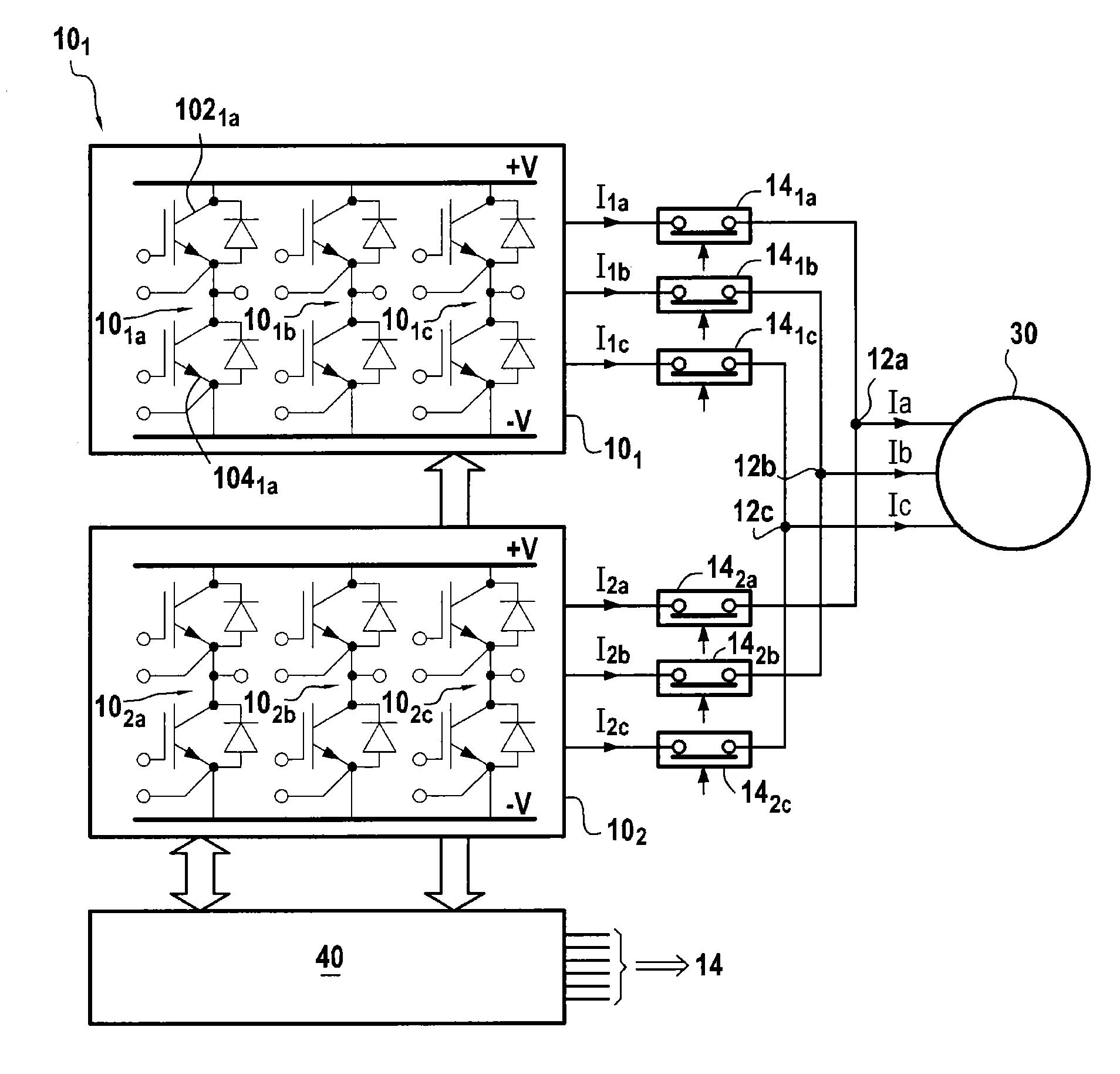
Method and device for controlling a polyphase electrical machine
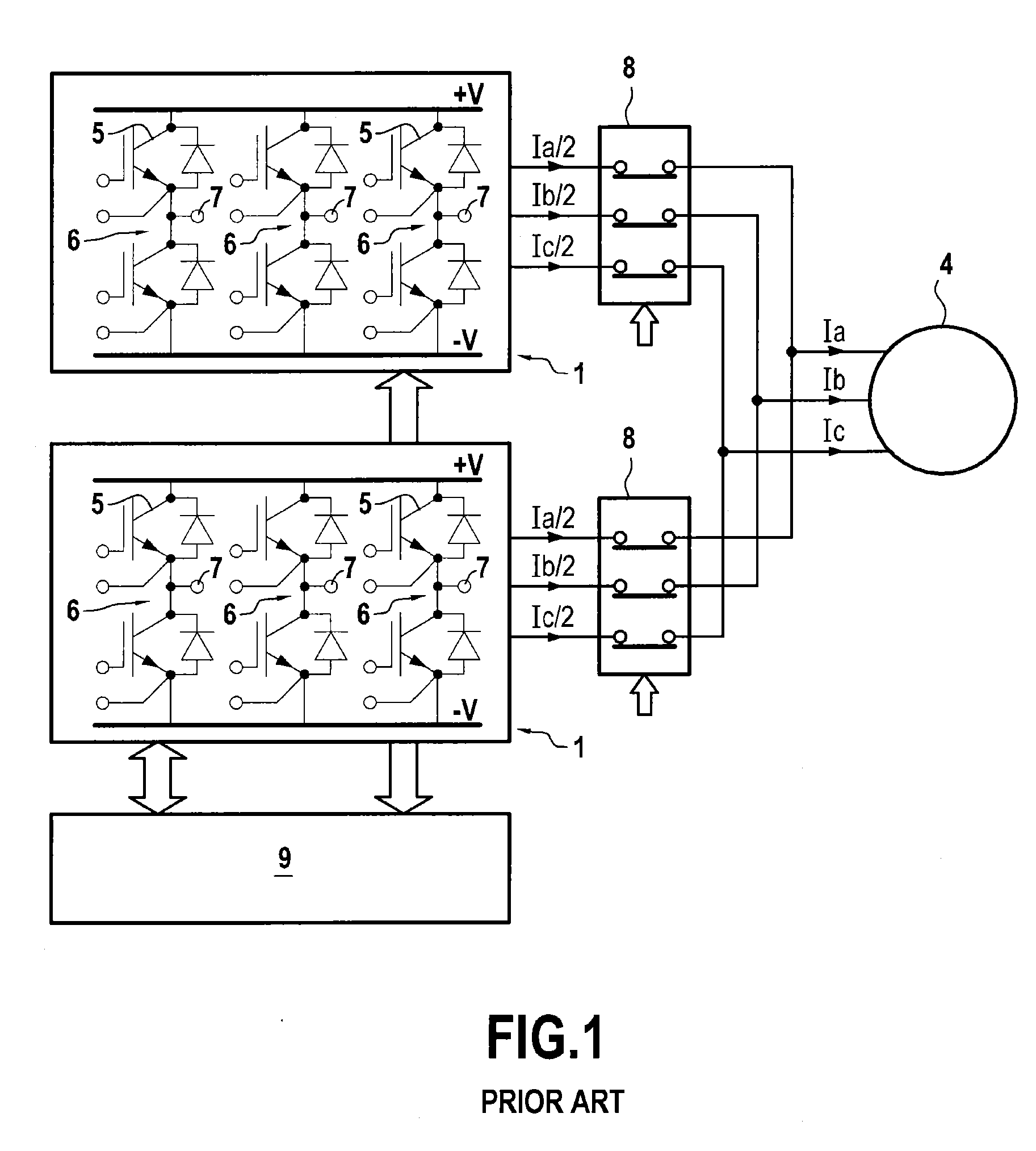
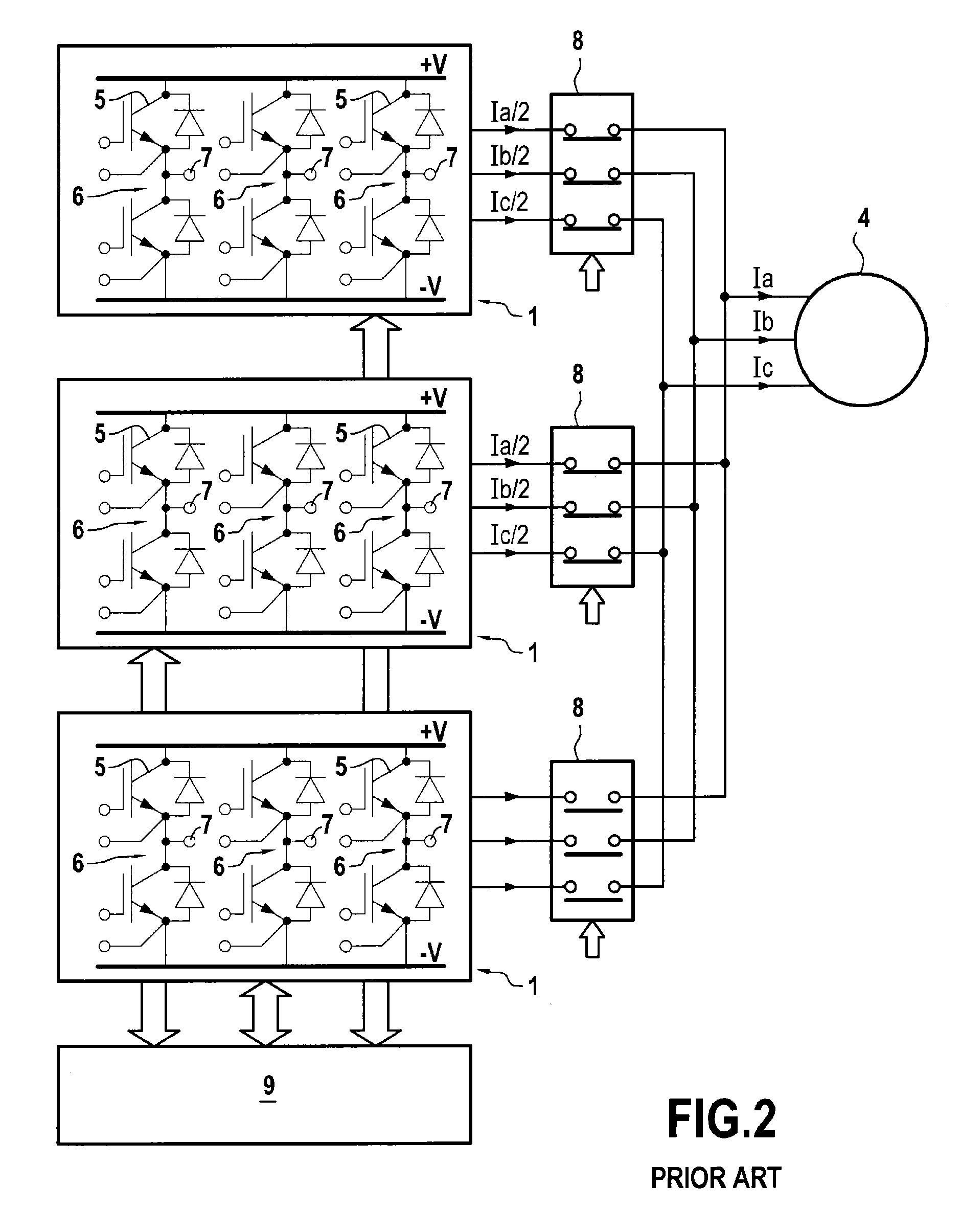
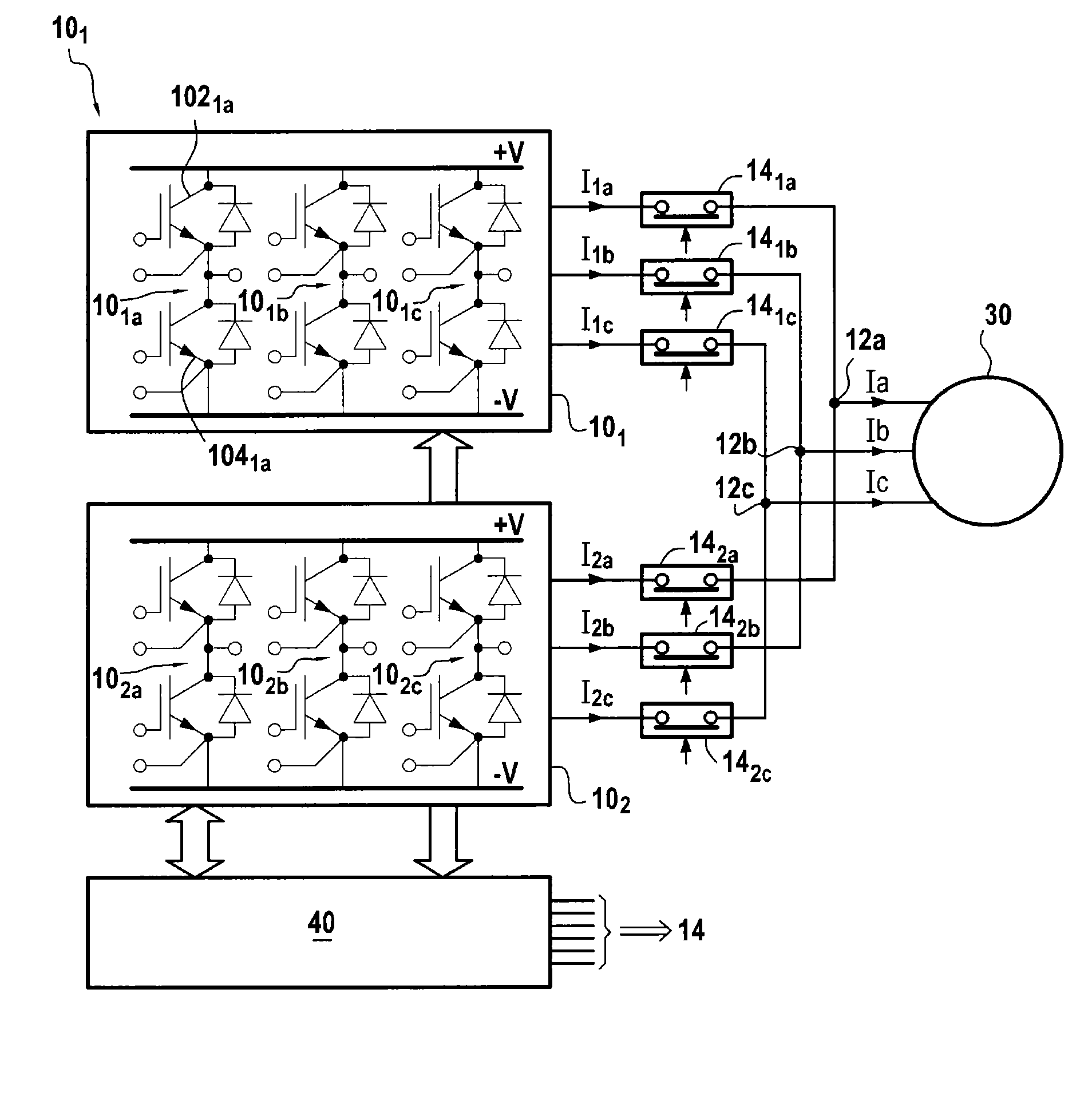
ActiveUS20130009580A1Improve reliabilityReduce failureMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersPhase currentsMachine control
A polyphase electrical machine controlled by at least two parallel inverters, each including a number of branches equal to a number of phases of the machine and controlled by PWM. When detecting an inverter branch is faulty, the faulty branch is isolated and the phase in question is powered by each corresponding other inverter branch. The PWM is modified to make power switches of each other branch conductive in succession, without switching while absolute value of the current of the phase in question is greater than or equal to a threshold of 80% to 120% of (n−1)Imax / n, n is number of inverters and Imax is maximum magnitude of the phase current. It is thus possible to continue generating substantially sinusoidal voltages on each of the phases, while avoiding overdimensioning the power switches to ensure in event of a fault they can deliver currents of amplitude higher than in normal operation.
Owner:SAFRAN ELECTRICAL & POWER
Non-volatile storage system with intelligent control of program pulse duration
To program a set of non-volatile storage elements, a set of programming pulses are applied to the control gates (or other terminals) of the non-volatile storage elements. The programming pulses have a constant pulse width and increasing magnitudes until a maximum voltage is reached. At that point, the magnitude of the programming pulses stops increasing and the programming pulses are applied in a manner to provide varying time duration of the programming signal between verification operations. In one embodiment, for example, after the pulses reach the maximum magnitude the pulse widths are increased. In another embodiment, after the pulses reach the maximum magnitude multiple program pulses are applied between verification operations.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Utility for full wave rectified current-fed class of DC galvanically isolated DC-to-DC power conversion topologies allows reduction of working voltage magnitudes and improvement to efficiency for secondary circuits
InactiveUS20110211378A1Reduce manufacturing costImprove reliabilityAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcPower flowFull wave
New utility of an existing class of DC galvanically isolated current sourcing circuit topologies for power conversion simultaneously allows improvement in its secondary circuit(s) to power conversion efficiency and reduction in working voltage magnitudes, or simply reduction in working voltage magnitudes, with resulting benefits for reduction in manufacturing cost, reduction in size and weight, and increase in market acceptance, or may simply allow secondary circuit(s) to enable easier provisioning of safety, improvement in reliability, or improvement in efficiency. The magnitude of DC output voltage is optimized at higher value for greater efficiency, while simultaneously optimizing the secondary circuit's working voltage maximum magnitude at a lower value for greater safety. The method requires full cycle current-compliant input impedance of the secondary power source whereby the secondary of the DC galvanically isolating device behaves in a mode of being a full cycle voltage-compliant current source.
Owner:MAROON RAYMOND PETER
Low voltage differential signal (LVDS) transmitter with output power control
ActiveUS7719324B1Multiple input and output pulse circuitsElectric pulse generatorMaximum magnitudeLow voltage
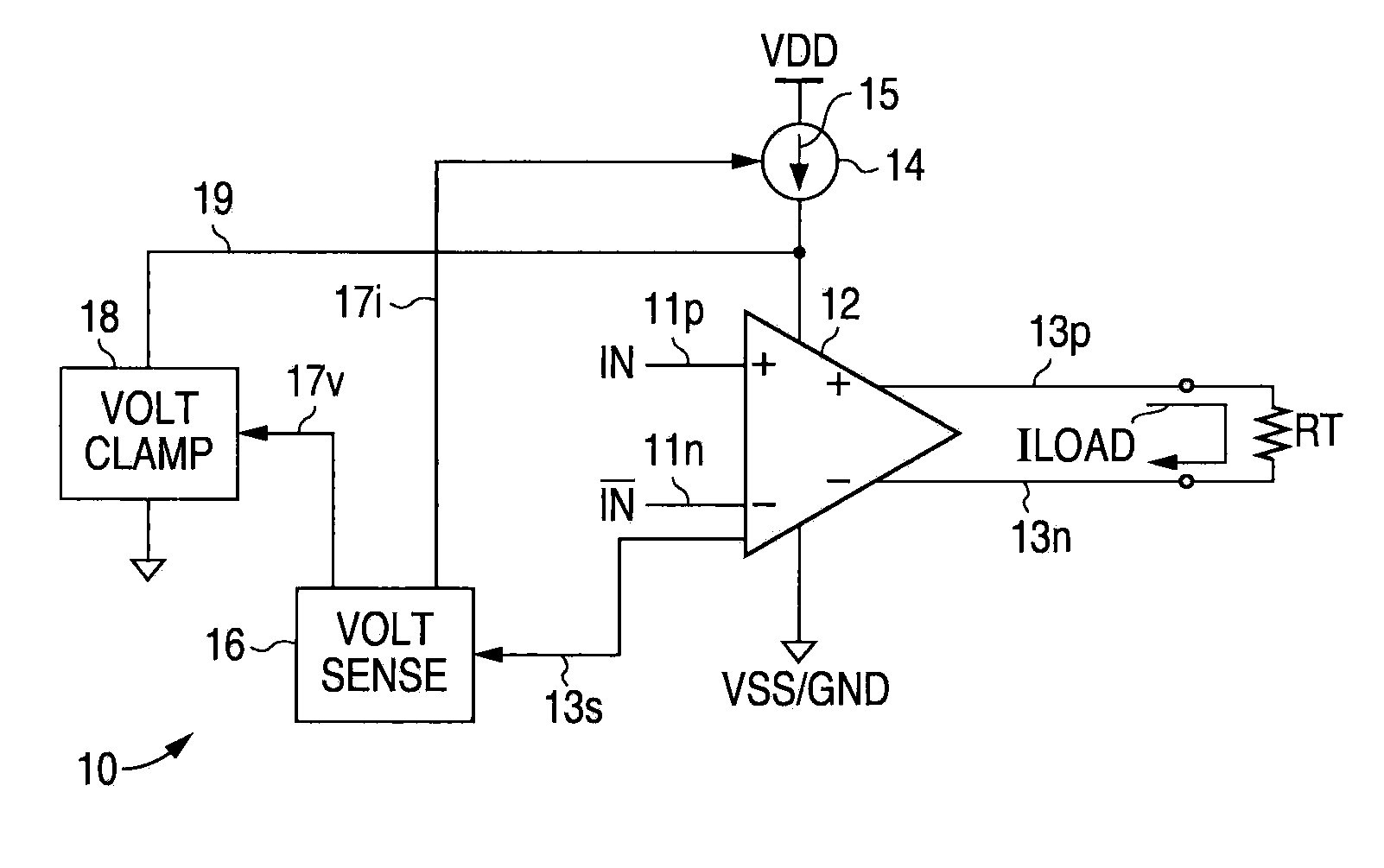
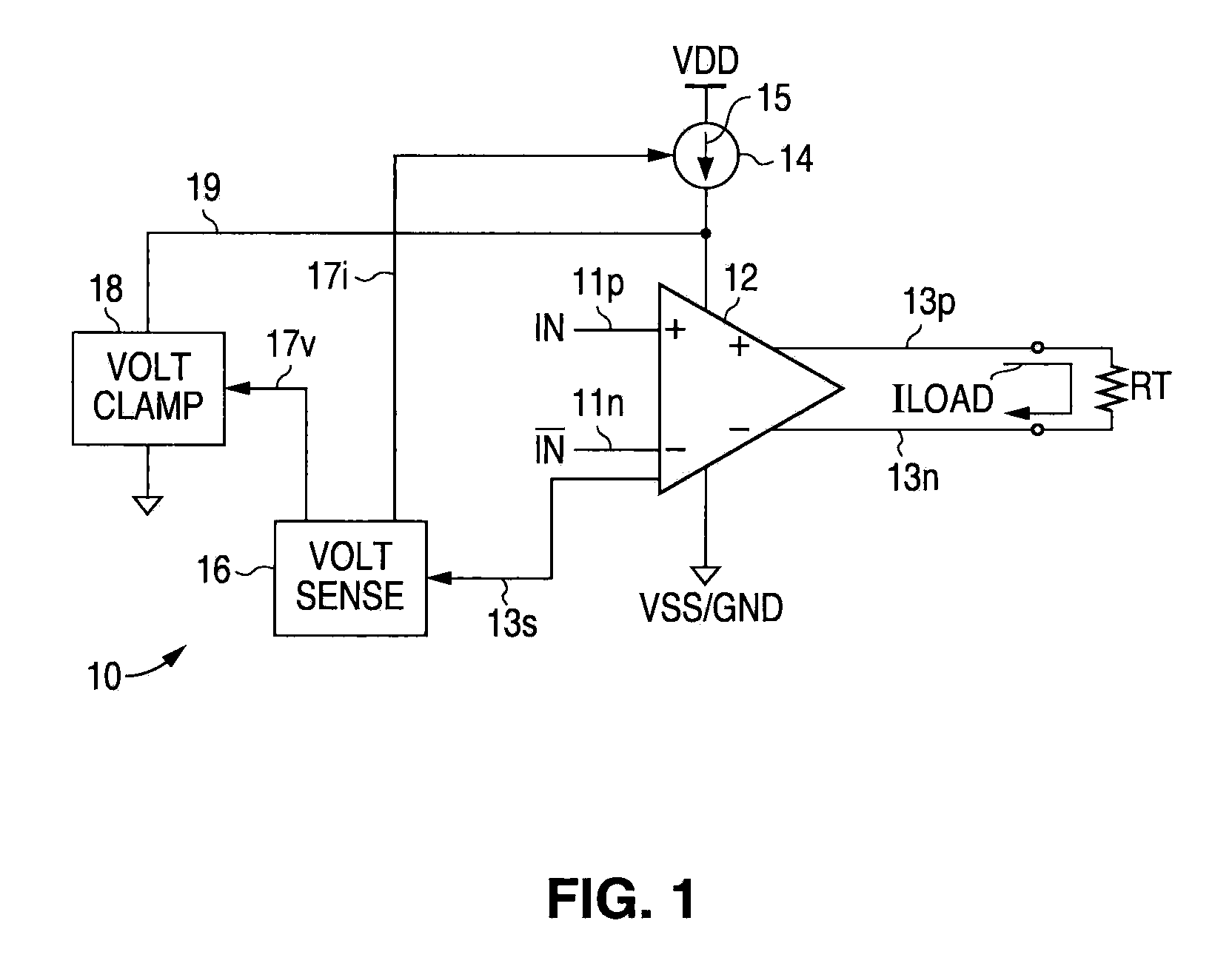
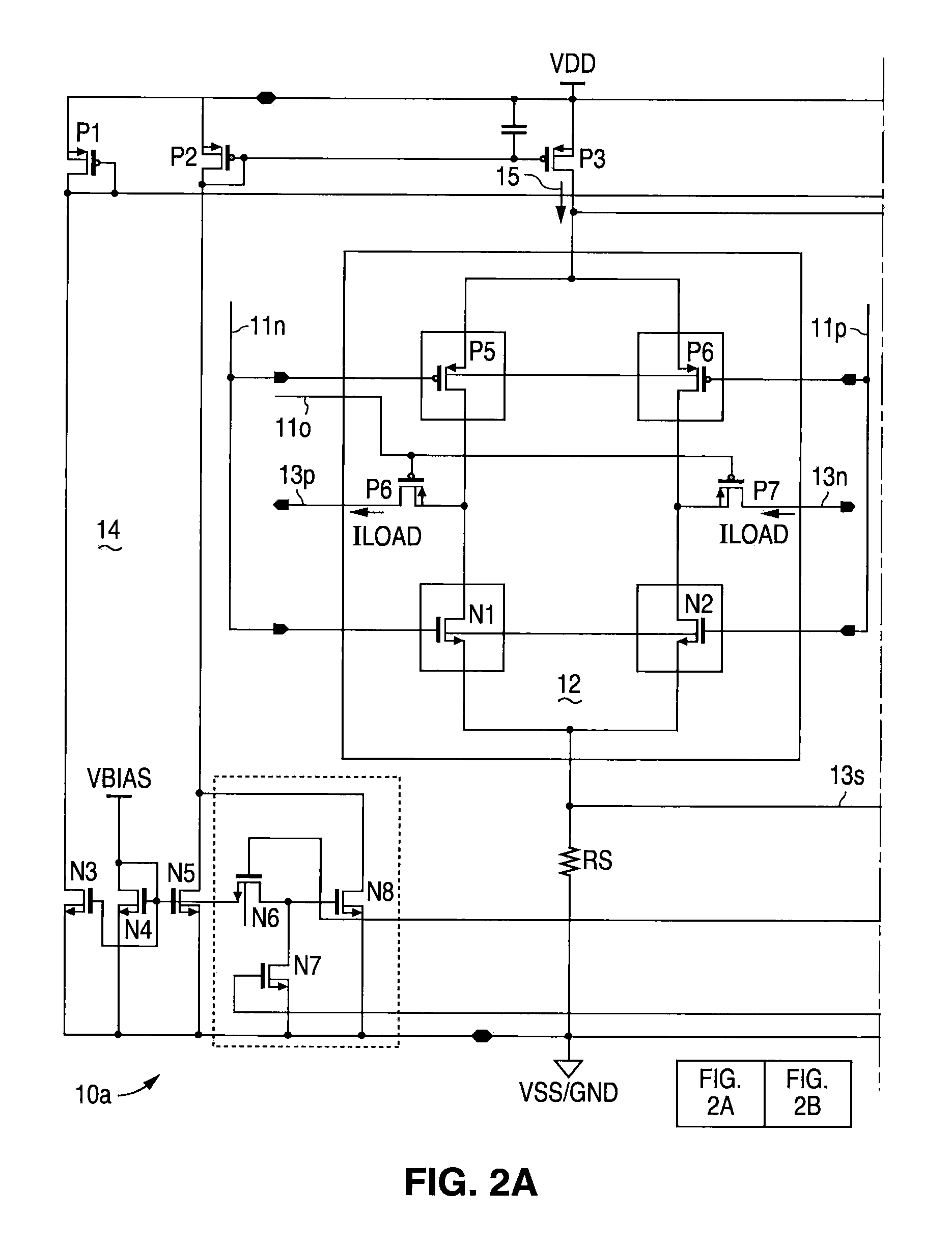
A low voltage differential signal (LVDS) transmitter with output power control. Internal sensing circuitry monitors output current flow through the termination impedance. When a proper termination impedance is not connected to the output, the resulting improper output current flow (e.g., zero output current when no termination impedance is connected) is detected by the sensing circuitry, which causes the supply current to the output driver circuitry to be reduced. Additionally, further in response to such detection of improper output current flow, the sensing circuitry can cause the output voltage to be limited, e.g., clamped, at a predetermined maximum magnitude.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Wind power system and method of operating it
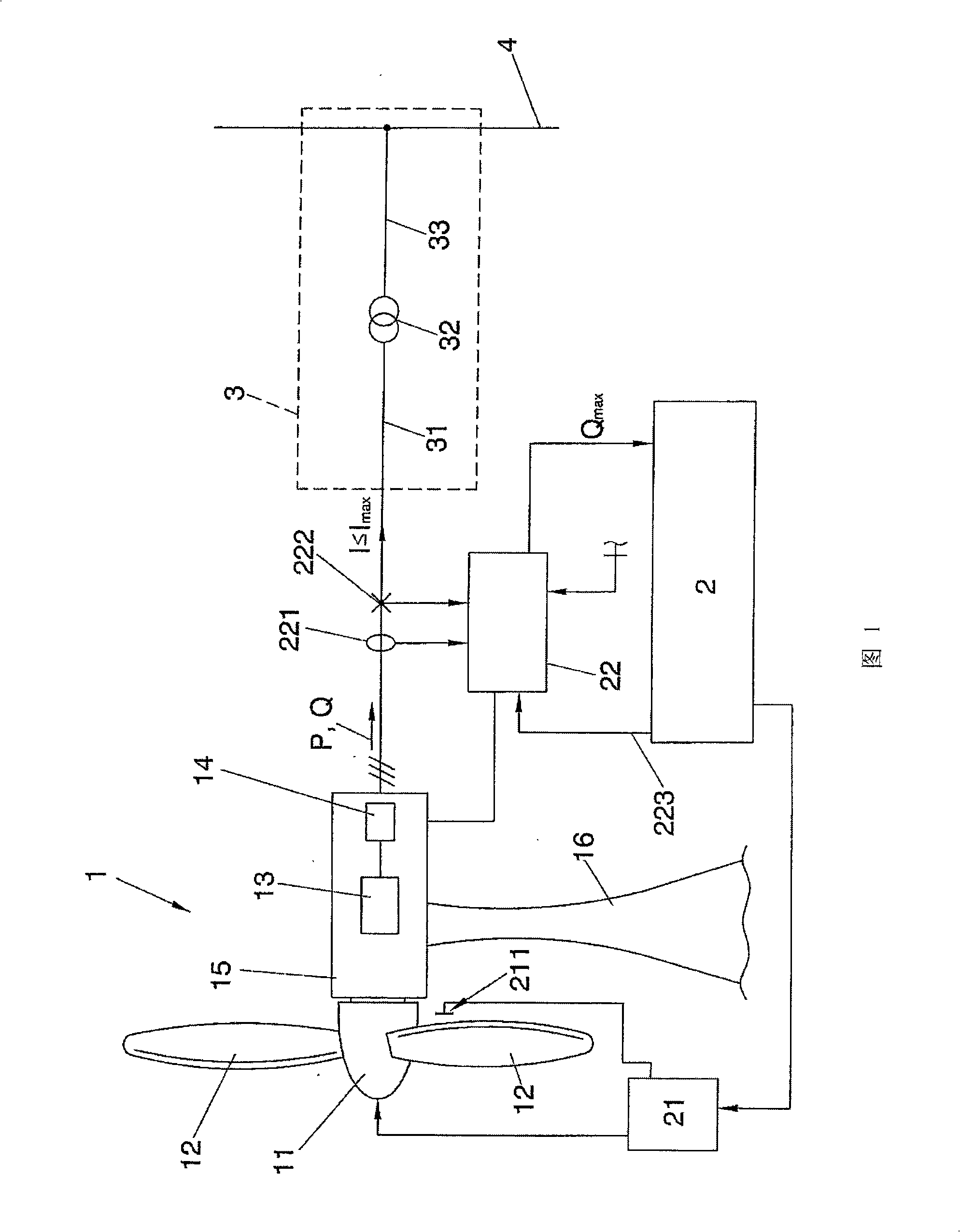
ActiveCN101350528AIncrease reactive powerWind motor controlSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower controllerControl system
The wind power system comprises an installation (1) for generating electrical power from wind by means of at least one power generating turbine arranged to be rotated by wind, and a control system (2) including a power controller (22). The power controller (22) is configured to keep the magnitude of the total current below a pre-set maximum magnitude (Imax).
Owner:GAMESA INNOVATION & TECH SA
Apparatus and method for radio frequency tracking and acquisition
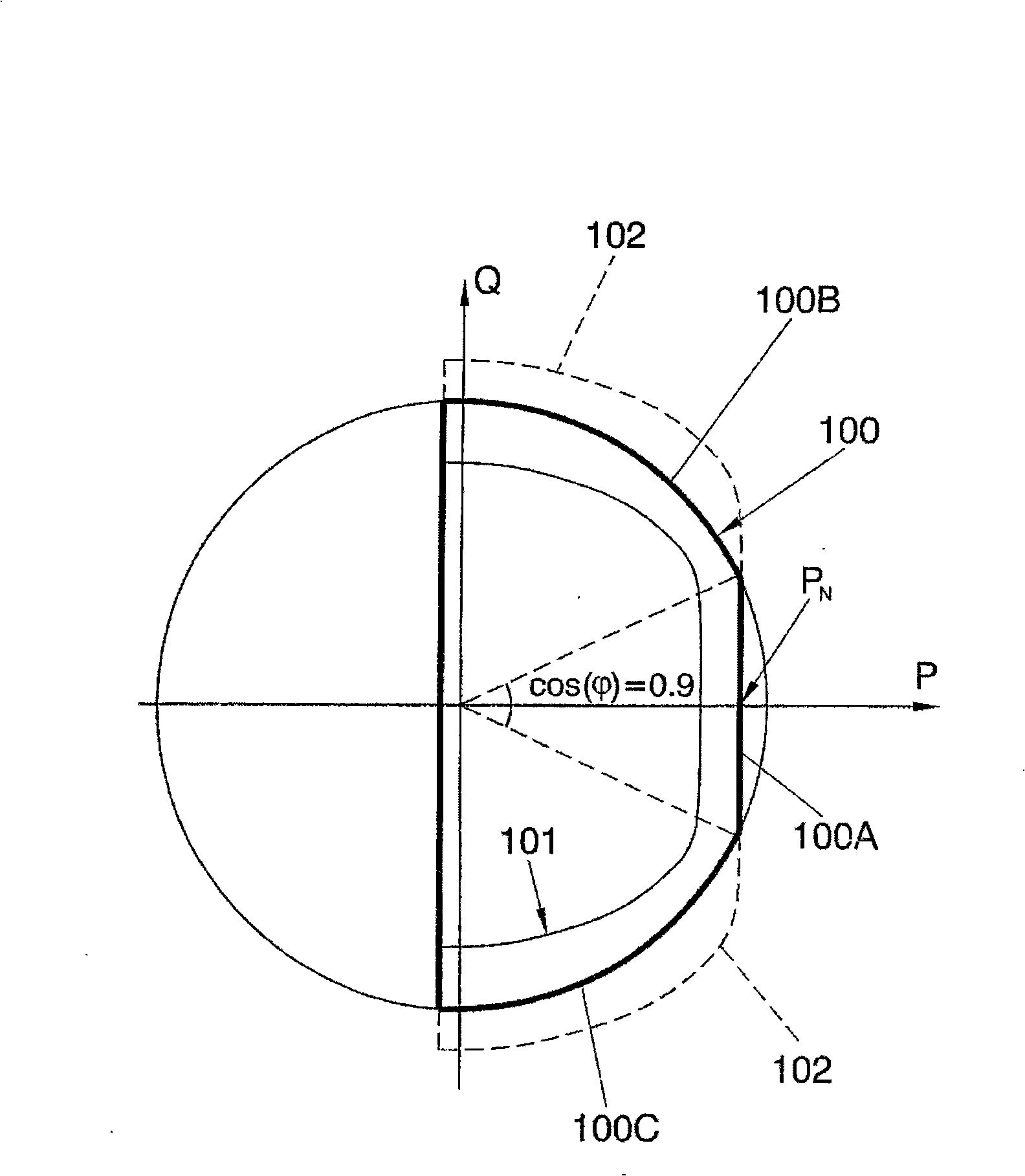
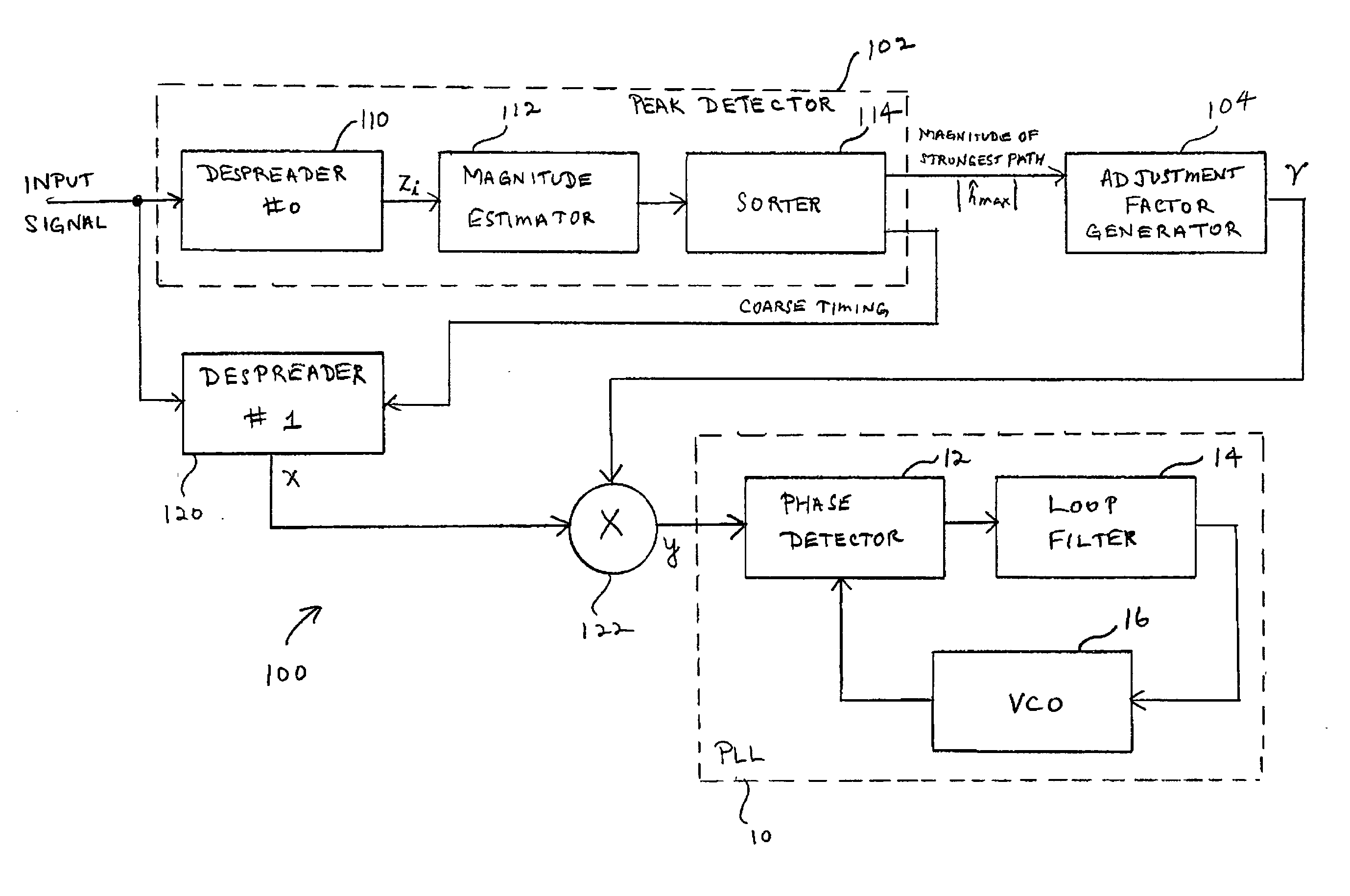
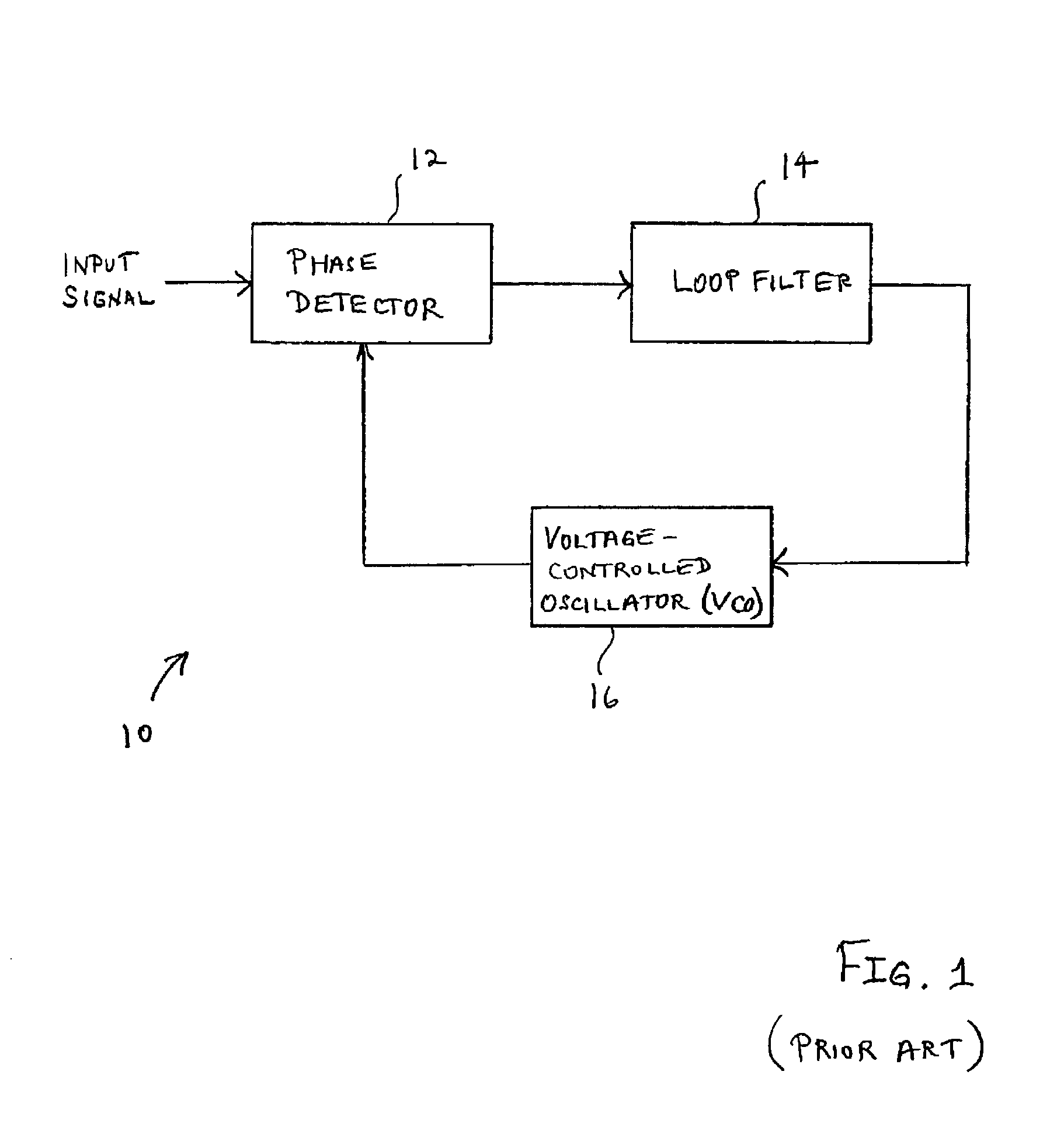
InactiveUS20040004962A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsCircuit switching systemsRadio receptionMaximum magnitude
A system and method for adjusting loop bandwidth in a synchronization loop of a radio receiver uses a noncoherent peak detector to determine the maximum magnitude and timing of incoming data at various code phase offsets. The maximum magnitude and timing are used in subsequent processing with the maximum magnitude value used to determine an adjustment factor. The timing information associated with the maximum signal value is used to despread the incoming signal. The despread incoming signal is subsequently scaled in accordance with the determined adjustment factor such that the input to the synchronization loop is scaled to produce the desired loop bandwidth.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Transmitter with peak-tracking PAPR reduction and method therefor
A transmitter (20) includes a peak reduction section (30), a predistorter (98), and an amplifying section (102) biased by a variable bias signal generator (118). The peak reduction section (30) is controlled by a signal magnitude threshold (36) that defines maximum magnitudes for local peaks (32) of a reduced-peak communication signal (38). The bias signal generator (118) is controlled by a bias control signal (110). Both the signal magnitude threshold (36) and the bias control signal (110) are derived from a common reduced bandwidth (50) peak-tracking signal (42). The peak-tracking signal (42) is derived from an inflated-peak communication signal (26). The predistorter (98) applies distortion to the reduced-peak communication signal (38) that is configured, at least in part, by the bias control signal (110).
Owner:CRESTCOM INC
Intelligent control of program pulse duration
To program a set of non-volatile storage elements, a set of programming pulses are applied to the control gates (or other terminals) of the non-volatile storage elements. The programming pulses have a constant pulse width and increasing magnitudes until a maximum voltage is reached. At that point, the magnitude of the programming pulses stops increasing and the programming pulses are applied in a manner to provide varying time duration of the programming signal between verification operations. For example, after the pulses reach the maximum magnitude the pulse widths are increased. Alternatively, after the pulses reach the maximum magnitude multiple program pulses are applied between verification operations.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Apparatus, method, and program product for image processing
InactiveUS8175383B2Reduce noiseExcessive blurring of image can be suppressedImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingMaximum magnitude
From the target image data, a luminance component, a first color difference component, and a second color difference component which represent color of respective pixels are acquired; and a maximum magnitude smoothing process is carried out on the first color difference component.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
High-speed low-voltage programming and self-convergent high-speed low-voltage erasing schemes for EEPROM
InactiveUS20070158733A1Disturb chargeIncreasing EEPROM cell densityTransistorRead-only memoriesTemperature controlProgrammable read-only memory
The present invention provides a high-speed low-voltage programming scheme and self-convergent high-speed low-voltage erasing schemes for Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memories (EEPROM). For the N-type Field Effect Transistor (NFET) based NVM programming, an elevated source voltage to the substrate can achieve high efficient Drain-Avalanche-Hot-Electron Injection (DAHEI) into the floating gate resulting in high-speed and low-voltage operations. The self-convergent and low-voltage erasing can be achieved by applying Drain-Avalanche-Hot Hole Injection (DAHHI) with the conditions of restricted maximum drain current and a moderate control gate voltage enough to turn on the NFET. For the p-type FET (PFET) based EEPROM programming, a negative source voltage relative to the substrate can achieve high efficient Drain-Avalanche-Hot-Hole Injection (DAHHI) into the floating gate resulting in high-speed and low voltage operations. The self-convergent and low voltage erasing can be achieved by applying Drain-Avalanche-Hot-Electron Injection (DAHEI) with the conditions of restricted maximum magnitude of drain current and a negative moderate control gate voltage enough to turn on the PFET.
Owner:YIELD MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Complementary Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) imaging sensor
ActiveCN102820313AGuaranteed captured image qualityImprove dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCMOSMaximum magnitude
The invention provides a complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) imaging sensor which at least comprises a semiconductor substrate and a plurality of pixel units located in the semiconductor substrate. Each pixel unit at least comprises a first sensitization device, a second sensitization device, a pixel reading circuit and an isolation structure. Compared with the existing CMOS imaging sensor, the second sensitization devices are added in the traditional CMOS imaging sensor, so that an output response curve of the sensitization devices is nonlinearity, corresponding to the same output voltage swing, maximum magnitudes of the CMOS imaging sensor to sense light are increased, namely a maximum value of lighting levels is increased, and accordingly a dynamic range of the imaging sensor is improved. Simultaneously, a connection mode of the pixel reading circuits of the existing CMOS imaging sensor is kept to guarantee image capture quality of the CMOS imaging sensor.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Non-volatile storage system with intelligent control of program pulse duration
To program a set of non-volatile storage elements, a set of programming pulses are applied to the control gates (or other terminals) of the non-volatile storage elements. The programming pulses have a constant pulse width and increasing magnitudes until a maximum voltage is reached. At that point, the magnitude of the programming pulses stops increasing and the programming pulses are applied in a manner to provide varying time duration of the programming signal between verification operations. In one embodiment, for example, after the pulses reach the maximum magnitude the pulse widths are increased. In another embodiment, after the pulses reach the maximum magnitude multiple program pulses are applied between verification operations.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Method and device for controlling a polyphase electrical machine
ActiveUS8810179B2Improve reliabilityReduce failureMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersPhase currentsMachine control
A polyphase electrical machine controlled by at least two parallel inverters, each including a number of branches equal to a number of phases of the machine and controlled by PWM. When detecting an inverter branch is faulty, the faulty branch is isolated and the phase in question is powered by each corresponding other inverter branch. The PWM is modified to make power switches of each other branch conductive in succession, without switching while absolute value of the current of the phase in question is greater than or equal to a threshold of 80% to 120% of (n−1)Imax / n, n is number of inverters and Imax is maximum magnitude of the phase current. It is thus possible to continue generating substantially sinusoidal voltages on each of the phases, while avoiding overdimensioning the power switches to ensure in event of a fault they can deliver currents of amplitude higher than in normal operation.
Owner:SAFRAN ELECTRICAL & POWER
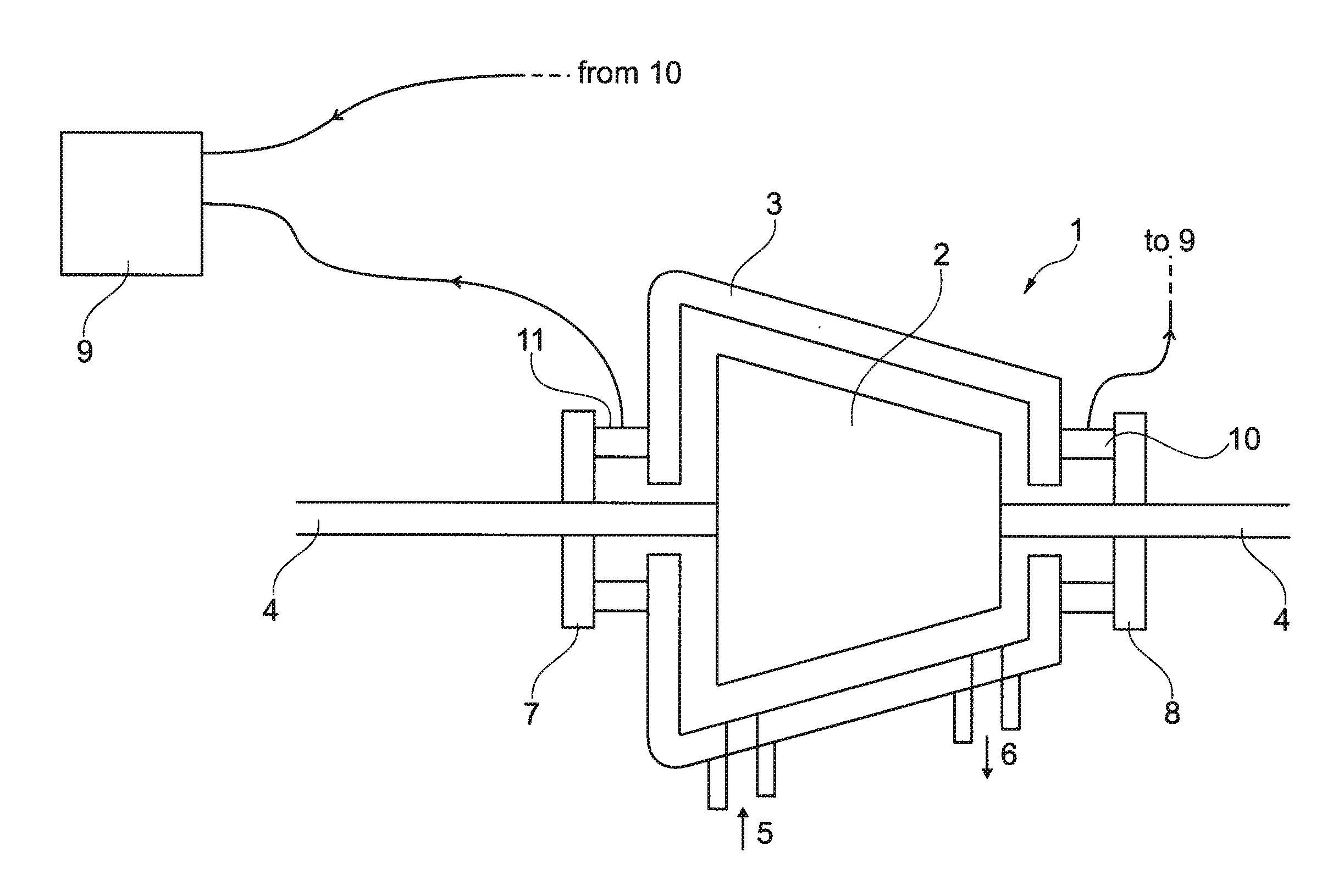
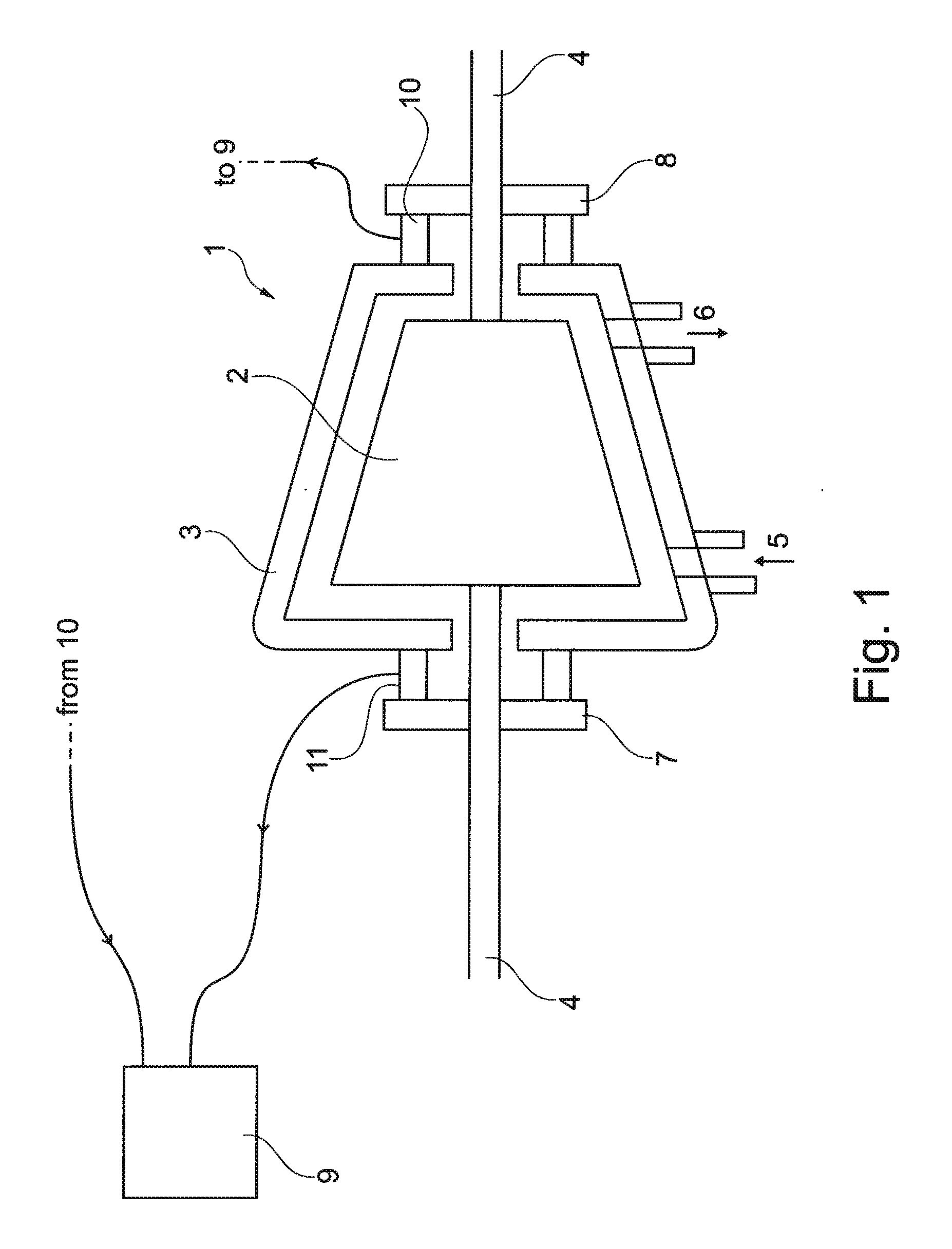
Method and equipment for detecting rotating stall and compressor
A method for detecting rotating stall in a compressor is disclosed herein. The method comprises measuring radial vibration of the rotor relative to the stator and generating a vibration measurement signal, calculating a frequency spectrum of the vibration measurement signal, identifying a plurality of frequency bandwidths of the frequency spectrum, neglecting one first frequency bandwidth of the plurality of frequency bandwidths if the rotation frequency of the rotor falls within the first frequency bandwidth, neglecting at least one second frequency bandwidth of the plurality of frequency bandwidths if the rotation frequency of the rotor falls below the second frequency bandwidth, determining the maximum magnitude of the spectrum in each of the non-neglected frequency bandwidths, and comparing each determined maximum magnitude and a predetermined value. Rotating stall is considered occurring if at least one of the comparisons shows that the corresponding determined maximum magnitude is greater than the predetermined value.
Owner:NUOVO PIGNONE TECH SRL
Method of, and apparatus for, determining position
A method of, and apparatus for, determining position, comprises a receiver ( 14 ) receiving a signal from a remote transmitter ( 22 ) whose position has to be determined. The Fourier transform of a power spectrum density of the received signal is determined and a check is made to see if a line-of-sight (LOS) signal is present. If so, a multipath mitigation technique is implemented to identify the LOS signal and once identified the position of the remote transmitter is determined by deriving the propagation time of the LOS signal. Current can be saved by inhibiting the multipath mitigation technique in the absence of detecting a LOS signal. In one embodiment the presence or absence of the LOS signal is determined by dividing the magnitude of the peak at zero frequency by the maximum magnitude of all the other peaks and if the answer is less than unity, LOS is not present.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
LDMOS having a field plate
Laterally diffused metal oxide semiconductor transistor for a radio frequency-power: amplifier comprising a drain finger (25,27) which drain finger is connected to a stack of one or more metal interconnect layers, (123,61,59,125) wherein a metal interconnect layer (123) of said stack is connected to a drain region (25) on the substrate, wherein said stack comprises a field plate (123, 125, 121) adapted to reduce the maximum magnitude of the electric field between the drain and the substrate and overlying the tip of said drain finger.
Owner:AMPLEON NETHERLANDS
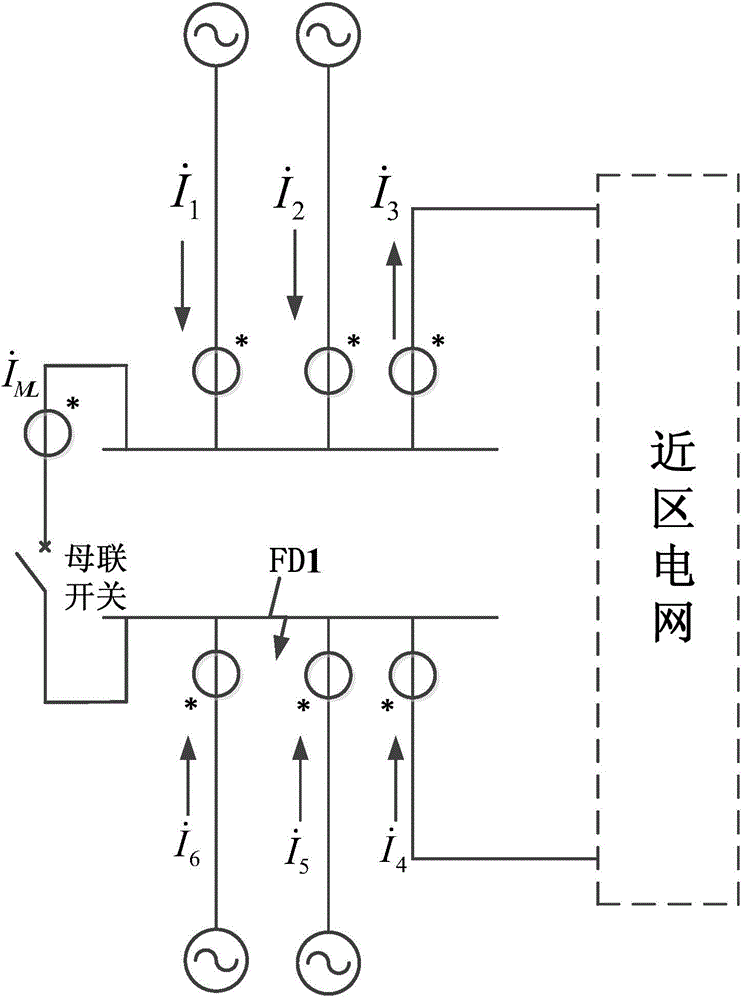
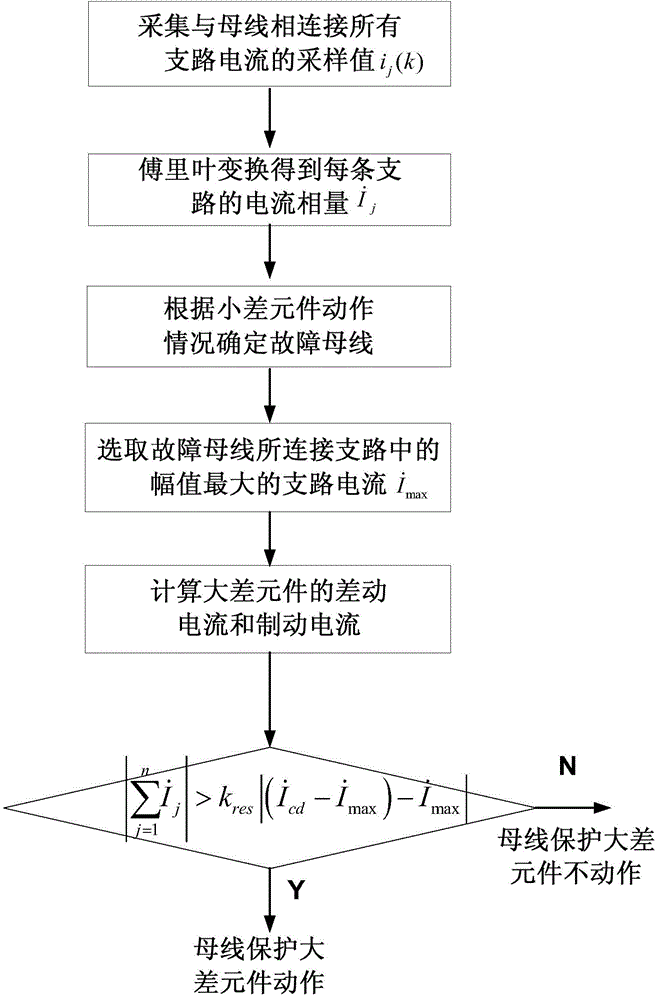
Method for overcoming influence of outgoing current on busbar differential protection
ActiveCN104393579AEliminate the effects ofHigh sensitivityEmergency protective circuit arrangementsElectrical testingMaximum magnitudeBusbar
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Method of error floor mitigation in low-density parity-check codes
ActiveUS8656245B2Improve performanceError correction/detection using LDPC codesCode conversionComputer hardwareMaximum magnitude
A digital communication decoding method for low-density parity-check coded messages. The decoding method decodes the low-density parity-check coded messages within a bipartite graph having check nodes and variable nodes. Messages from check nodes are partially hard limited, so that every message which would otherwise have a magnitude at or above a certain level is re-assigned to a maximum magnitude.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
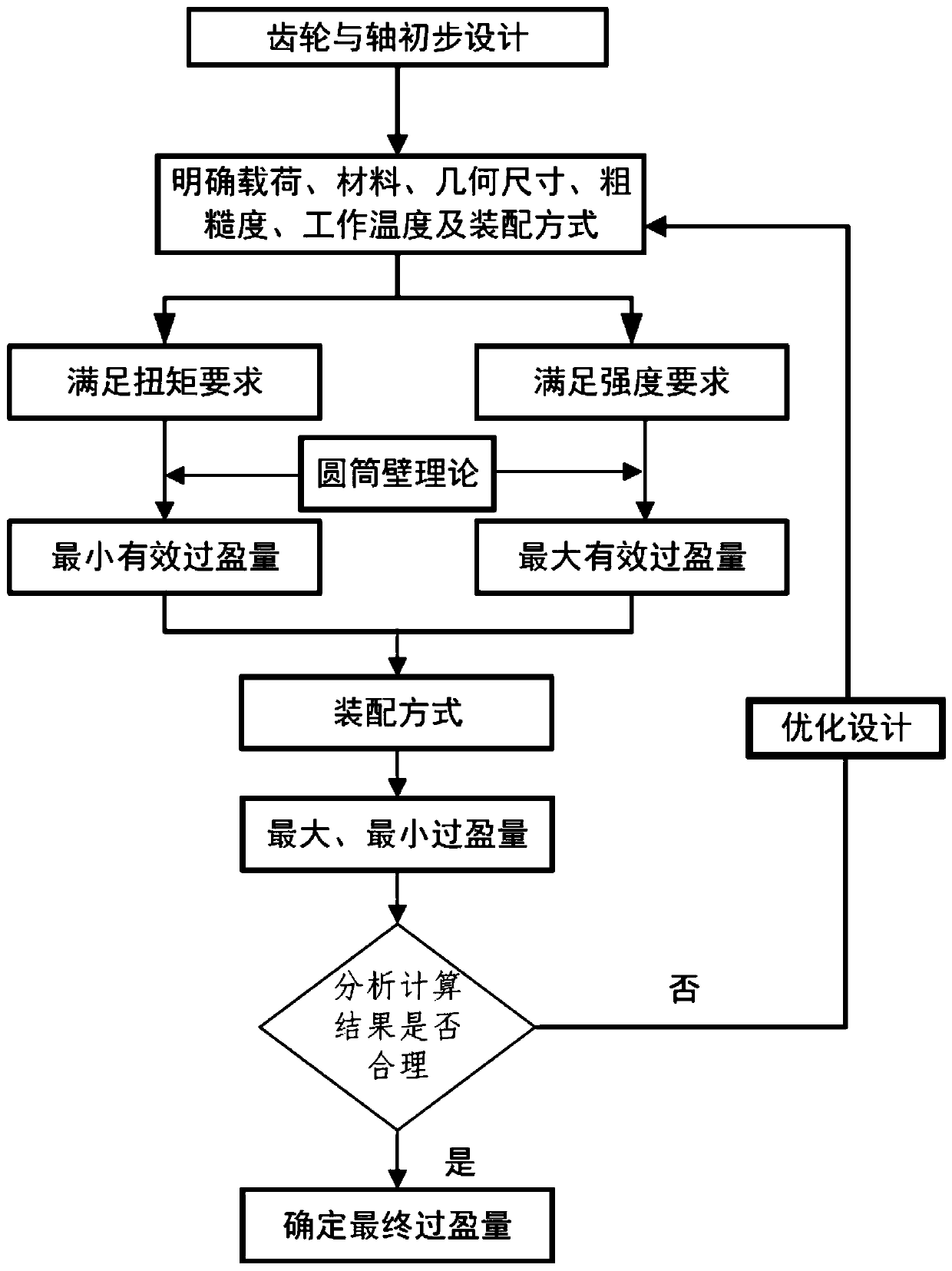
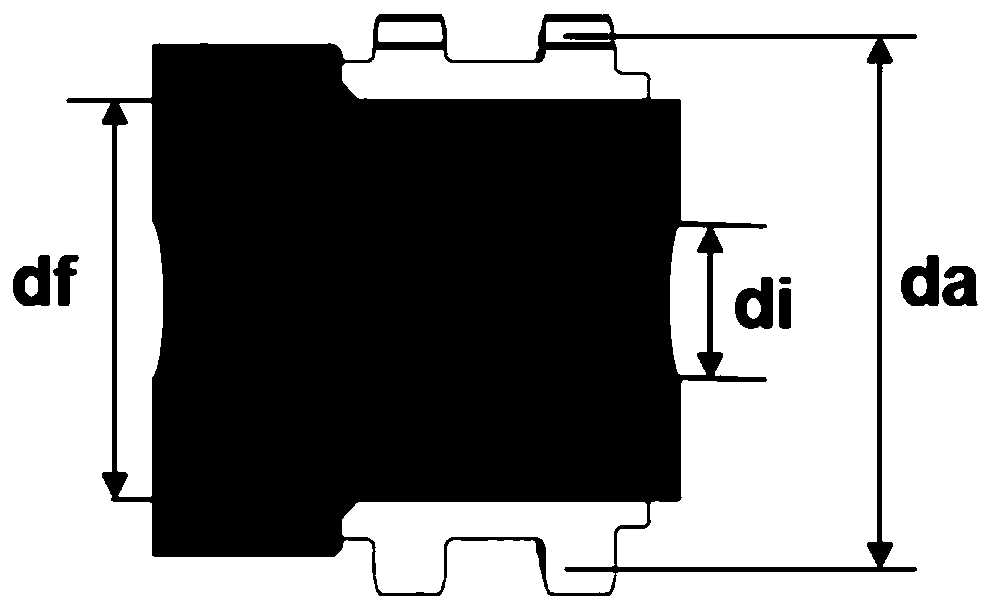
Design method for interference fit between engine gear and shaft
PendingCN110263440AEfficient designRealize the designGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsInterference fitMaximum magnitude
The invention discloses a design method for interference fit between an engine gear and a shaft. The design method comprises the steps of S1, clearing the basic size, the material parameters, the junction surface roughness, the working temperature and the assembly mode of the gear and the shaft; S2, calculating the minimum magnitude of interference; S3, calculating the maximum magnitude of interference; S4, determining the selection range of the magnitude of interference between the gear and the shaft; S5, analyzing and evaluating whether the calculation result meets the expected design index or not; and S6, determining the magnitude of interference between the final gear and the shaft, and designing the size and the tolerance of the gear and the shaft. According to the design method for the interference fit of the engine gear and the shaft, the optimization design of the interference fit of the gear and the shaft can be simply and efficiently completed, and the design period is shortened, the design cost is saved, so that the design of the engine parts is better achieved.
Owner:安徽航瑞航空动力装备有限公司
Intelligent control of program pulse for non-volatile storage
To program a set of non-volatile storage elements, a set of programming pulses are applied to the control gates (or other terminals) of the non-volatile storage elements. The programming pulses have a constant pulse width and increasing magnitudes until a maximum voltage is reached. At that point, the magnitude of the programming pulses stops increasing and the programming pulses are applied in a manner to provide varying time duration of the programming signal between verification operations. In one embodiment, for example, after the pulses reach the maximum magnitude the pulse widths are increased. In another embodiment, after the pulses reach the maximum magnitude multiple program pulses are applied between verification operations.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
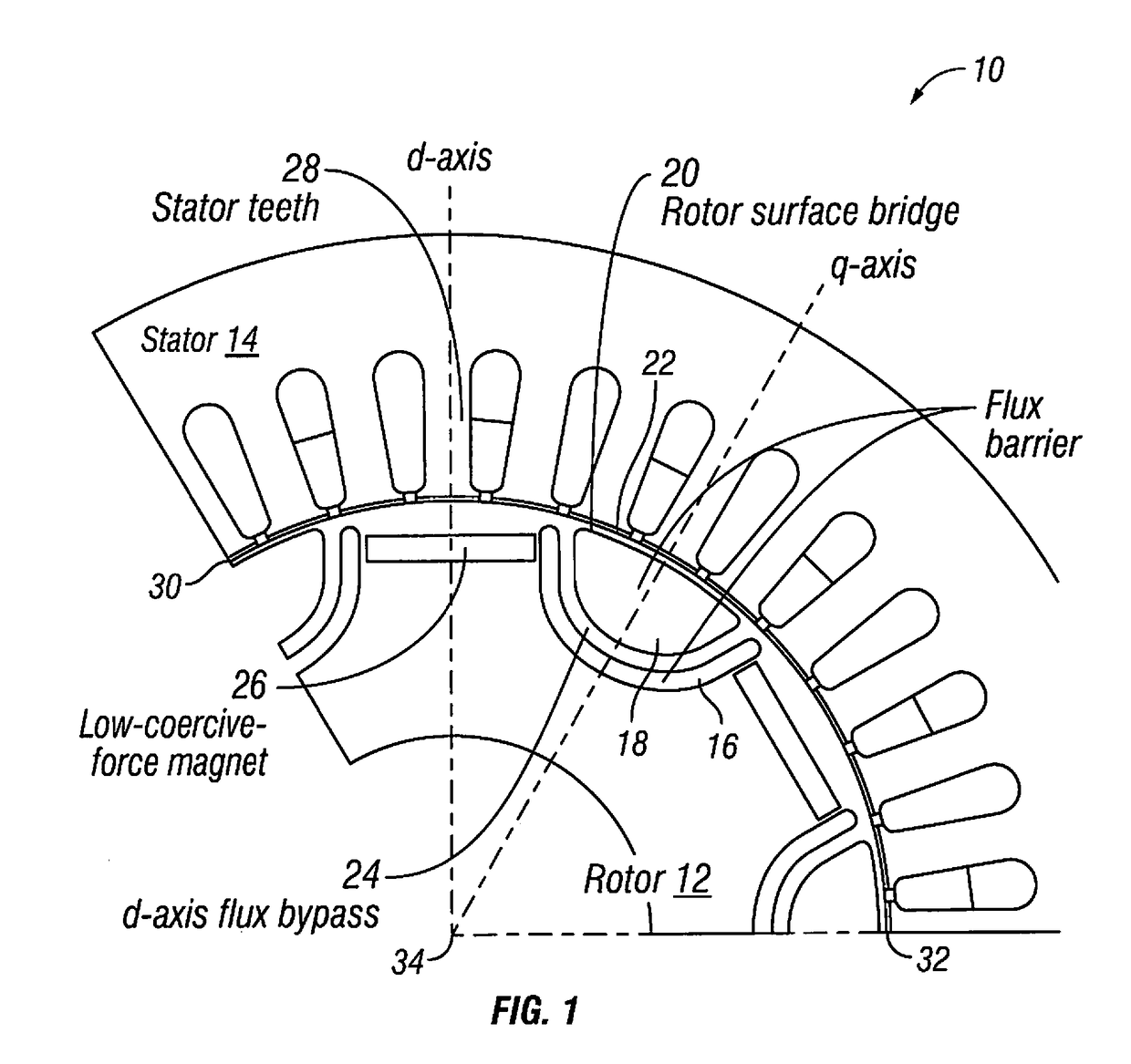
Variable magnetization machine controller
ActiveUS20170279392A1High voltageReduce voltageElectronic commutation motor controlSpeed controllerMachine controlControl system
A variable magnetization machine control system comprising a controller configured to generate a reversely rotating d-axis / q-axis current vector trajectory during a change in a magnetization state of a variable magnetization machine to drive the variable magnetization machine at a predetermined speed while maintaining the driving voltage below a predetermined maximum magnitude.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com