Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
202 results about "Forward kinematics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Forward kinematics refers to the use of the kinematic equations of a robot to compute the position of the end-effector from specified values for the joint parameters. The kinematics equations of the robot are used in robotics, computer games, and animation. The reverse process that computes the joint parameters that achieve a specified position of the end-effector is known as inverse kinematics.
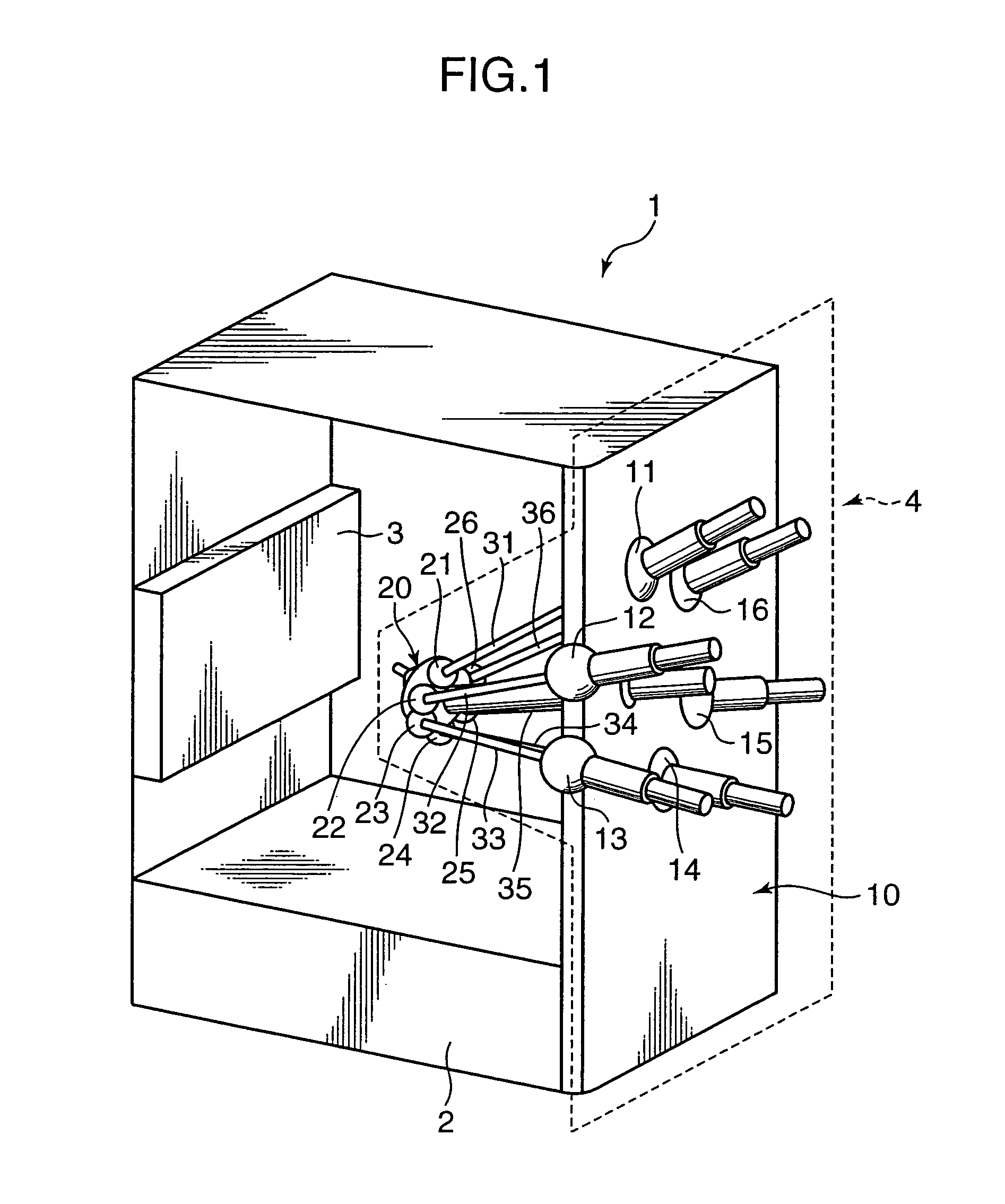
Parallel kinematic machine, calibration method of parallel kinematic machine, and calibration program product
InactiveUS20070138374A1Suppress numerical errorAccurate identificationControl mechanismProgramme-controlled manipulatorForward kinematicsCalculator
A parallel kinematic machine has a parallel kinematic mechanism including an end effecter and a parallel link mechanism. A numerical control device controls a position and orientation of the end effecter based on kinematics of the parallel kinematic mechanism. A posture setter sets an adjustment tool on the end effecter in a known posture in a reference coordinate system defined outside the parallel kinematic mechanism based on a measurement method. A data acquirer acquires data in accordance with a measurement method selecting code for designating the measurement method used by the posture setter in setting the adjustment tool in the known posture, and defines a correlation between kinematic parameters for the parallel kinematic mechanism and the reference coordinate system. A calculator calculates the kinematic parameters based on the acquired data by using a relational expression describing forward kinematics of the parallel kinematic mechanism.
Owner:SHINNIPPON KOKI
Three-dimensional posture fixing and local locating method for lunar surface inspection prober
ActiveCN101173858AOvercoming random noiseHigh precisionNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAttitude controlSteering wheelDrive wheel
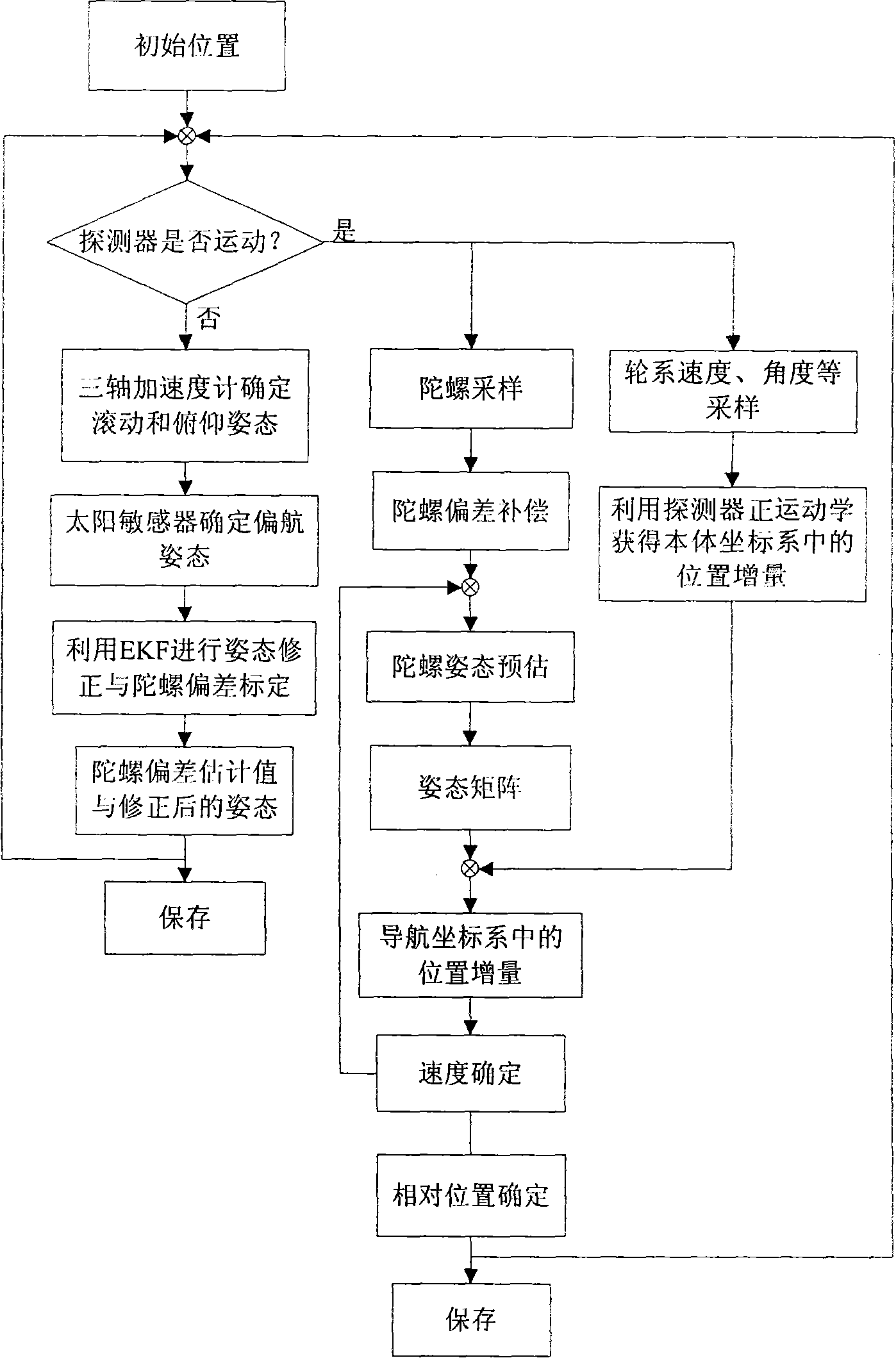
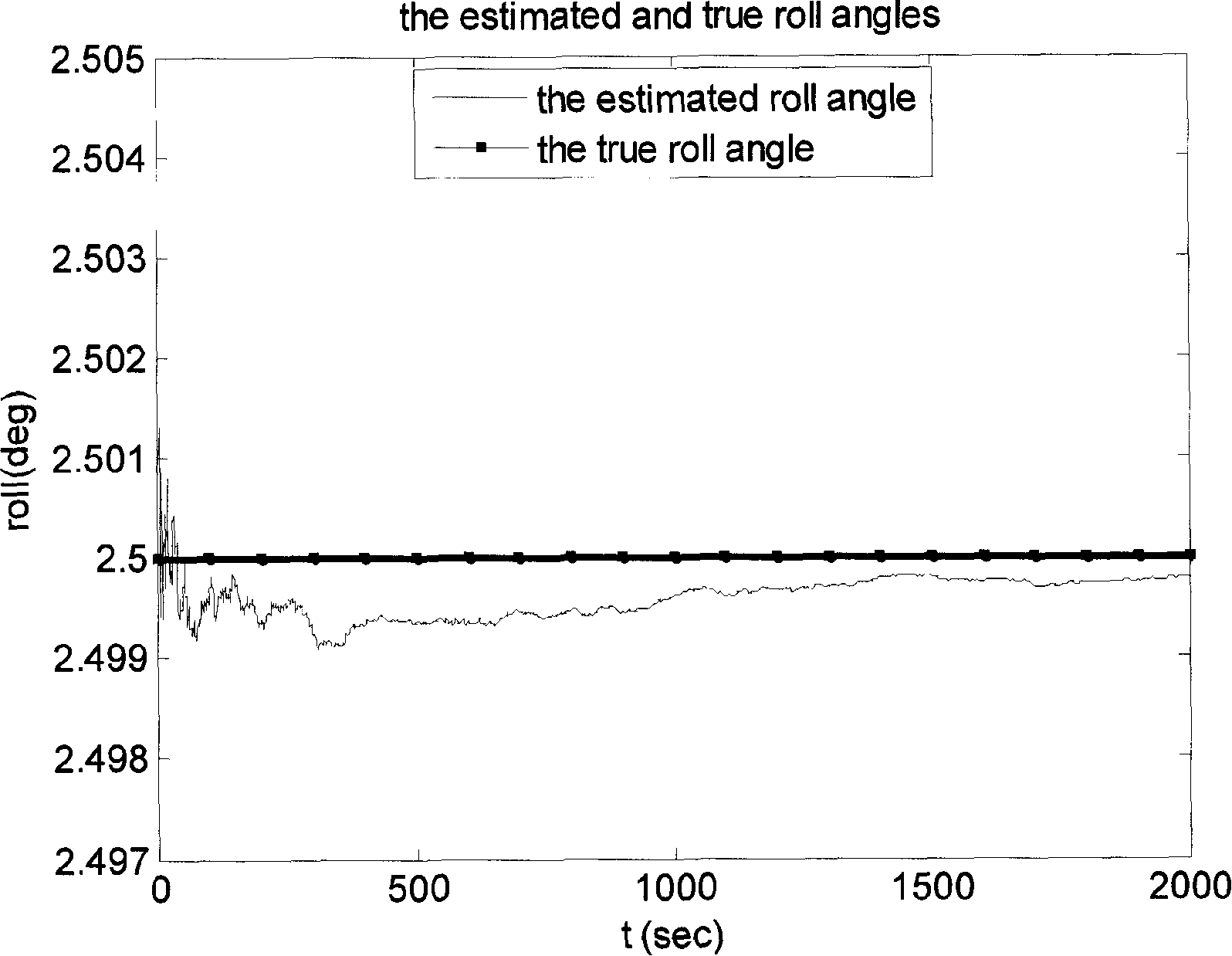
The invention relates to a three-dimensional gesture determining and local positioning method of a lunar surface rover, which comprises the following steps: (1) ascertaining the rolling and pitching angles by use of a triaxial accelerometer with sensitivity while the rover is still; (2) determining the drift angle gesture by means of a sun sensor; (3) using the axial gesture and the gyro deviation as the state quantity, the rolling and pitching angles established by the triaxial accelerometer, the drift angle determined by the sun sensor as well as three gyro outputs as the measuring information, building a state equation and a measuring equation, and estimating the triaxial and gyro deviations by means of extended Kalman filter; (4) after compensating the gyro outputs by virtue of the estimated gyro deviations while the rover is in motion, calculating the gesture changes of the rover, finishing the preestimation of the gyro gesture, and fulfilling gesture update; (5) acquiring the information about the rotation speed of the driving wheels of the rover, the rotating angle of the steering wheel, the rotating angle of the left and right rocker arms, and getting the position increment of the rover in the body coordinate system by use of the forward kinematics relationship. The invention has the advantages of high precision of gesture determining and positioning, simple calculation and easy implementation of the engineering.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Randomly topologically structured virtual role driving method based on skeleton
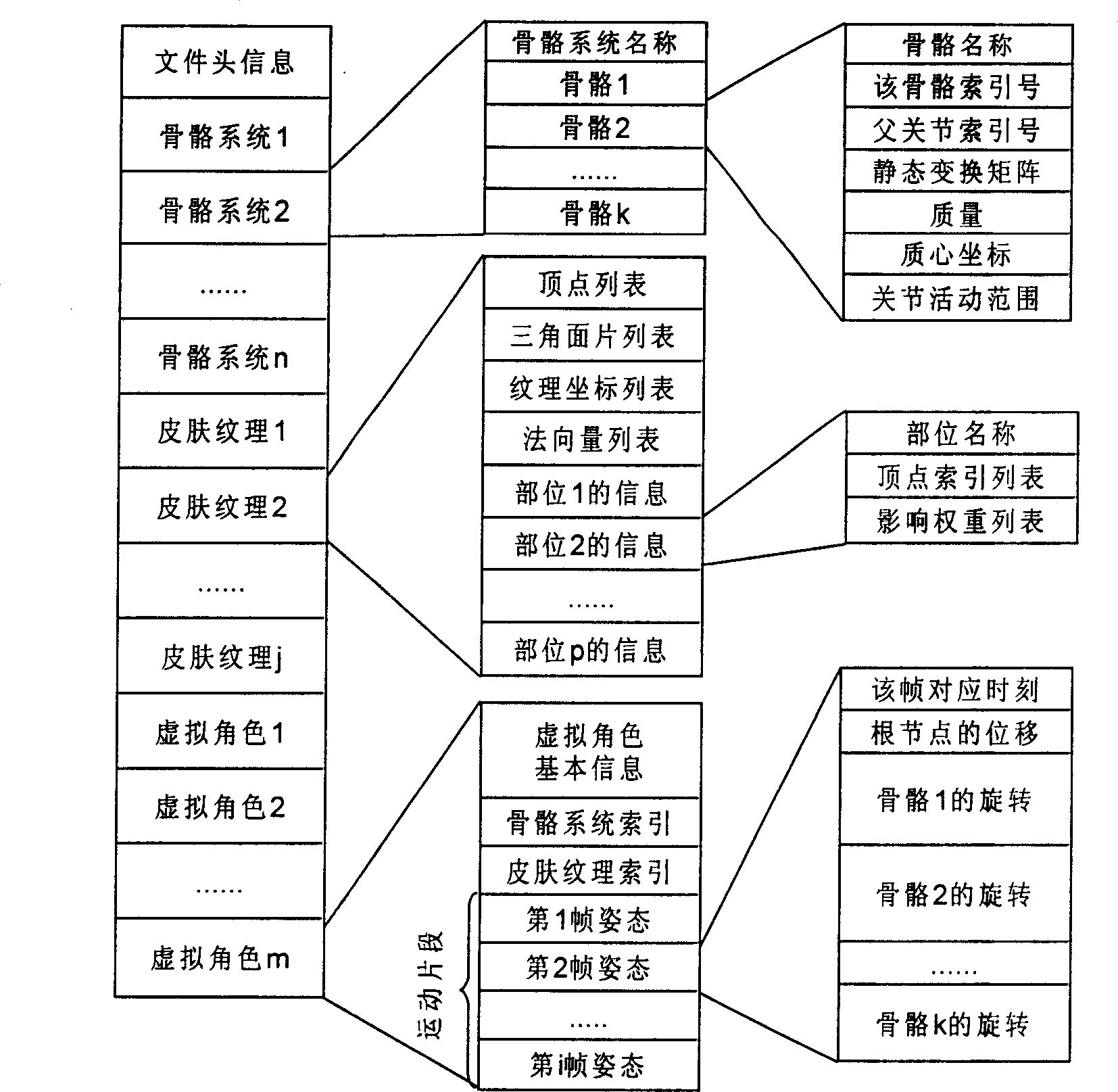
InactiveCN1885348AImplementation driveReduce space consumptionAnimation3D-image renderingKinematicsComputer science
The invention relates to a method for driving any topology virtual angle base on skeleton, which comprises: (1), classifying the information relative to the virtual angle into three kinds; (2), defining the disk storage format of said information; (3), based on real demand, fixing the virtual angle; (4), loading skeleton system; (5), loading skin pattern information; when loading, based on the name of each module in the skin pattern, building the relationship projected to the skeleton; (6), loading motion data to judge if the dimensions of freedom degree and the dimensions of skeleton system are same; (7), extracting the altitude at one time from the motion data; (8), calculating positive motion technique, to calculating the transform matrix of each skeleton local coordinate system relative to the globe coordinate system; (9), using the transform matrix between the skeleton local coordinate system and the globe coordinate system in the step (8) to calculate the coordinate at the top of skin; (10), romancing.
Owner:XIAOSHAN IND RES INST
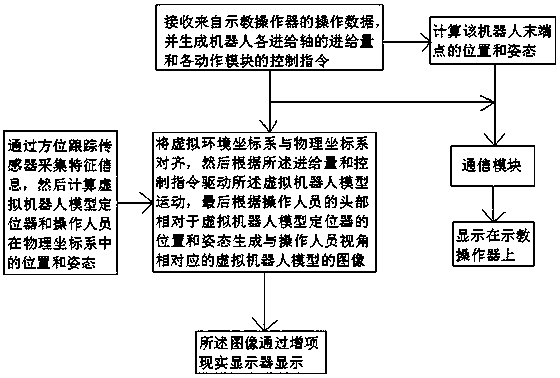
Robot online teaching device, system, method and equipment base on reality enhancing
The invention relates to a robot online teaching system based on reality enhancing. The robot online teaching system comprises a teaching manipulator, an orientation tracking sensor, a virtual robot model positioning device, a reality enhancing displayer and a computer. The computer comprises a storage, a processor and a communication module. Programs are stored in the storage, and the programs comprise a feeding calculation module, a robot forward kinematics model, a robot control logic and failure arrangement module, a virtual robot rendering module and an orientation tracking module. In therobot online teaching system, operation personnel can drive a virtual robot model to move through the physical teaching manipulator, and superpose the virtual robot model into a real scene by enhancing a reality technology, teaching training or teaching programming can be conducted without a physical robot, the safety of robot teaching training is improved, the cost is lowered, and the robot online teaching system can be widely applied to teaching and teaching programming.
Owner:QINGDAO TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
Visual mechanical arm control device and method based on Camshift visual tracking and D-H modeling algorithms
The invention discloses a visual mechanical arm control device based on Camshift visual tracking and D-H modeling algorithms. Image information acquired by a USB camera on a mechanical arm is analyzed by using a Camshift visual tracking algorithm to obtain precise positioning information of a workpiece to be grabbed and assembled; accurate positioning of such multiple targets as a visual mechanical arm, a target workpiece and a worktable is realized by using a robot forward kinematics D-H modeling algorithm; then, a multi-coordiate-system descriptive model with each steering engine joint as a coordinate system origin is built for the visual mechanical arm; and a closed analytic solution is derived through inverse dynamic calculation for different actions of the mechanical arm to determine unique control parameter of multiple steering engine joint movements of the mechanical arm, so that the precise control of the visual mechanical arm is realized, and such multiple actions as workpiece grabbing, machining, assembly and transportation by the mechanical arm are finished.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for adaptively tracking and controlling fingertip force of robot anthropomorphic finger
InactiveCN102363301AFast contact forceSmooth contact forceGripping headsContact forceDegrees of freedom
The invention discloses a method for tracking and controlling the fingertip force of a robot anthropomorphic finger. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) setting n joints and n degrees of freedom for the robot anthropomorphic finger; (2) measuring practical contact force of the anthropomorphic finger and the environment through a fingertip five-dimensional force sensor; (3) subtracting expected contact force Fr from the practical contact force to obtain a contact force error Fe; (4) multiplying the contact force error by a ratio factor eta, and adding with a practical fingertip position X to obtain a reference position Xr of a next fingertip control period; (5) resolving the reference position Xr according to the finger inverse kinematics L-1 (Xr) to obtain an expected reference joint angle theta r; and (6) subtracting the practical angle theta of each joint of the finger from the expected reference joint angle theta r to obtain a difference value serving as the input of a finger position controller, and resolving an output result of the finger position controller according to the finger forward kinematics L (theta) to obtain a practical fingertip position. The method has high control accuracy and a good control effect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Existing motion data-based realistic motion transfer and generation method and system
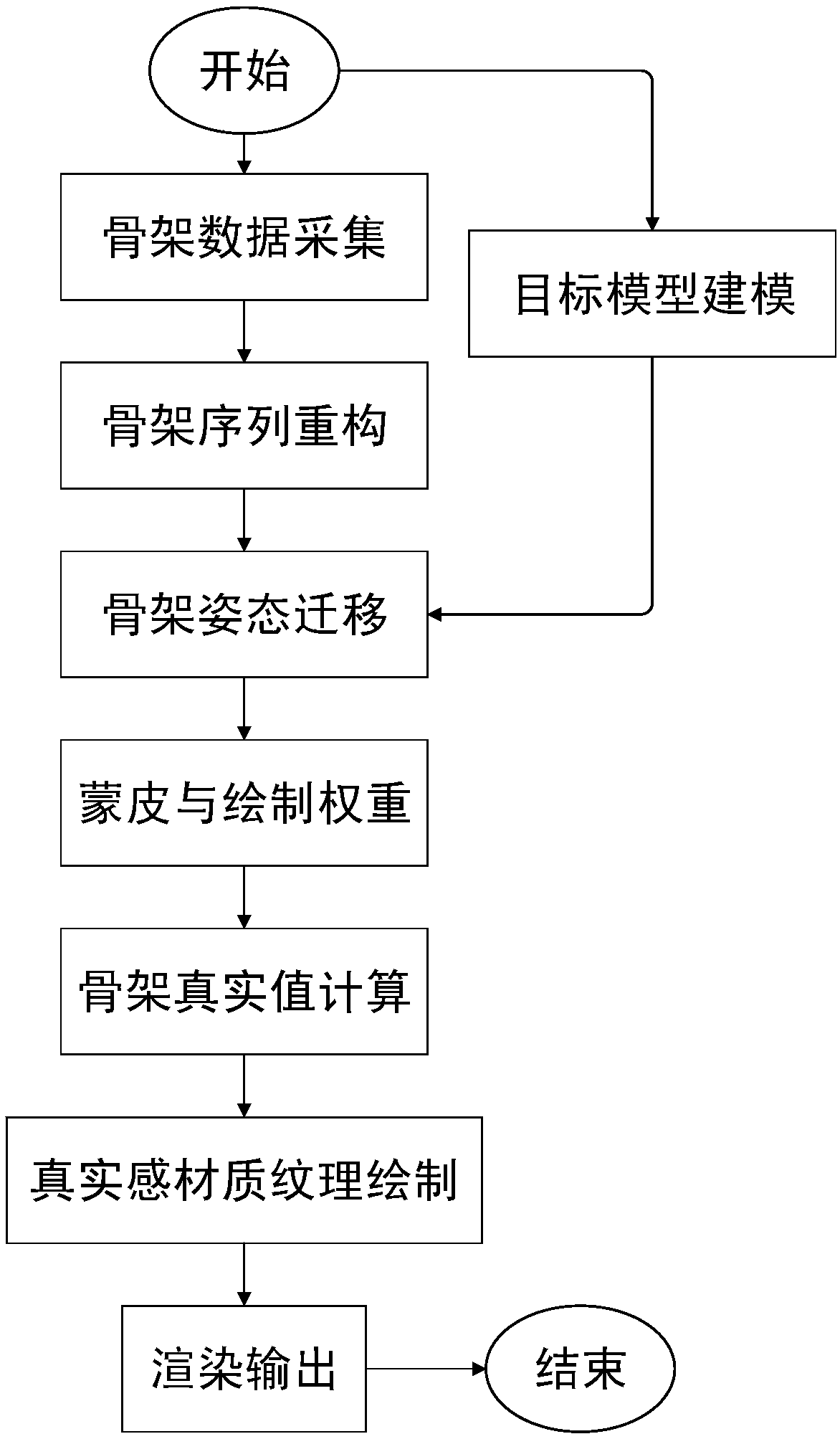
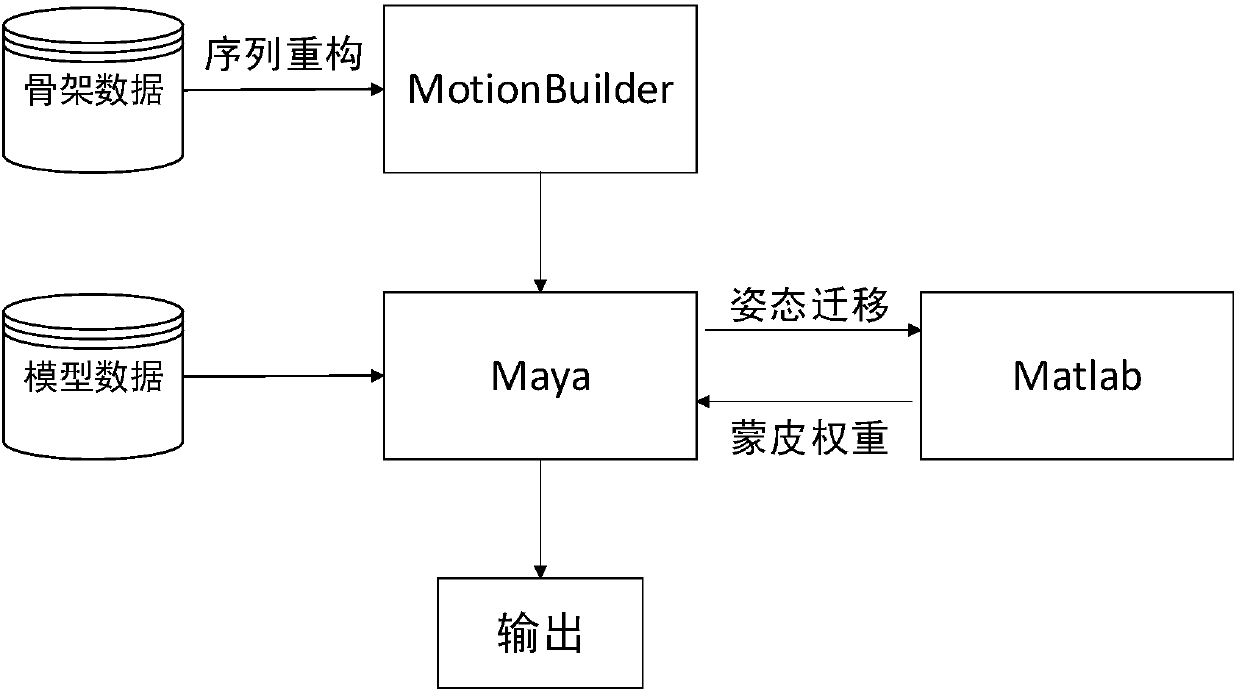
ActiveCN108510577AConforms to the topologyDetails involving processing stepsAnimationTransfer modelComputer science
The invention provides an existing motion data-based realistic motion transfer and generation method and system. The method includes the following specific steps that: a data glove is adopted to clearly and continuously shoot the motions of a measured object; a target transfer model is built; a skeleton sequence is reconstructed by means of inverse kinematics method; skeleton size is transferred by means of a forward kinematics method; skinning and drawing weighting operation is performed on a target skeleton and the target model; the real value of the three-dimensional position of the skeleton is calculated; realistic material texture is drawn on the model; and rendering is carried out, and a result is outputted. The method and system of the invention have the advantages of high automation degree, high precision, simple process and easiness in operation. With the method and system of the invention adopted, a lossless skeleton sequence can be obtained, and professional or popular motion transfer requirements can be satisfied.
Owner:INST OF SOFTWARE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Five-axis ball-end milling geometric error compensation method
ActiveCN108563186AGuaranteed Texture QualityImprove machining accuracyProgramme controlComputer controlForward kinematicsPositive direction
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Humanoid robot uneven ground walking stability control method
The invention discloses a humanoid robot uneven ground walking stability control method, and belongs to the technical field of robots. The method comprises four steps of maximum stability region based landing instep posture control, second-order spring damping impedance control, instep state estimation with forward kinematics calculation and instep inertial sensor measurement being combined and mass center acceleration control based on the supporting foot pressure center. The method disclosed by the invention uses landing compliance control, can effectively reduce impacts imposed on the instep by uneven ground, and enables the landing foot to have a large supporting region; and balance and stable control for the inclined instep enables the robot to realize stable walking of various supporting instep postures. Therefore, stable walking of a humanoid robot can be realized on the uneven ground, and the safety of the humanoid robot in the application process is effectively improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Control method for three-axis six-freedom hydraulic vibration table based on kinematics
InactiveCN101173876AAchieve precise position controlTo achieve the purpose of high-precision motion controlVibration testingPosition controlForward kinematics
The invention provides a controlling method for three-axle six-freedom hydraulic vibration table based on kinematics, which comprises the following steps: setting reference signal for the freedoms; three-state input filter; forward kinematics; speed and acceleration synthesis; three-state feedback; inverse kinematics solution; and output, wherein, all the steps can be realized with computer program. By adopting position solution method based on forward and inverse kinematics solution, the invention enables position control and decoupling control of the three-axle six-freedom hydraulic vibration table, and improves uniformity, transverse component and other indexes effectively; thereby, the invention has the advantages of enabling high-precision motion control of the three-axle six-freedom hydraulic vibration table, and improving uniformity, transverse component and other indexes effectively.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Space mechanical arm structure parameter optimization method based on operability
ActiveCN104331547ARealize numerical quantificationEasy to solveSpecial data processing applicationsKinematicsOperability
The invention provides a space mechanical arm structure parameter optimization method based on operability. The method comprises the following steps that (1) the freedom degree layout of a space mechanical arm and an initial parameter of an arm rod are determined; (2) the mechanical arm direct kinematics is applied, and the reachable work space of the space mechanical arm is determined by a numerical value method; (3) an upper half circle part is taken from a symmetrical surface of the reachable work space, and is divided into c*c sub regions, c is a positive integer, then, flexible posture probability coefficients are respectively calculated for each sub region, and a flexible work space chart of the whole reachable work space is obtained; (4) in the reachable work space, M work points are randomly selected, the respective corresponding flexible posture probability coefficients are calculated, in addition, the number m of work points greater than alpha in the posture probability coefficients is counted, and the mechanical arm operability is obtained; (5) the reciprocal number of the operability is used as an adaptability degree function, and the parameters of each arm rod of the space mechanical arm are optimized by a genetic algorithm.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Parallel mechanism based automated fiber placement system
ActiveUS20160250749A1Good kinematic performanceOptimization mechanismProgramme-controlled manipulatorDomestic articlesAviationFiber
The present invention introduces a new concept of applying a parallel mechanism in automated fiber placement for aerospace part manufacturing. The proposed system requirements are 4DOF parallel mechanism consisting of two RPS and two UPS limbs with two rotational and two translational motions. Both inverse and forward kinematics models are obtained and solved analytically. Based on the overall Jacobian matrix in screw theory, singularity loci are presented and the singularity-free workspace is correspondingly illustrated. To maximize the singularity-free workspace, locations of the two UPS limbs with the platform and base sizes are used in the optimization which gives a new design of a 4DOF parallel mechanism. A dimensionless Jacobian matrix is also defined and its condition number is used for optimizing the kinematics performance in the optimization process. A numerical example is presented with physical constraint considerations of a test bed design for automated fiber placement.
Owner:KHALIFA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Three-dimensional translational parallel mechanism based on motion decoupling
ActiveCN104959975AApplicable to remote control fieldDecouplingProgramme-controlled manipulatorKinematicsStrong coupling
The invention discloses a three-dimensional translational parallel mechanism based on motion decoupling with the purposes of overcoming problems of a parallel mechanism including difficulty in calculation of forward kinematics, small motion space, strong coupling between the position and the direction of a movable platform (II), low response speed and high cost. The three-dimensional translational parallel mechanism based on motion decoupling comprises a fixed platform (I), the movable platform (II), a first branched chain (III) of the parallel mechanism, a second branched chain (IV) of the parallel mechanism, a third branched chain (V) of the parallel mechanism. The movable platform (II) is located above the fixed platform (I). The first branched chain (III) of the parallel mechanism, the second branched chain (IV) of the parallel mechanism and the third branched chain (V) of the parallel mechanism are located between the movable platform (II) and the fixed platform (I). Upper ends of the first branched chain (III) of the parallel mechanism, the second branched chain (IV) of the parallel mechanism and the third branched chain (V) of the parallel mechanism are fixedly connected with the movable platform (II). Lower ends of the first branched chain (III) of the parallel mechanism, the second branched chain (IV) of the parallel mechanism and the third branched chain (V) of the parallel mechanism are fixedly connected with the fixed platform (I).
Owner:JILIN UNIV
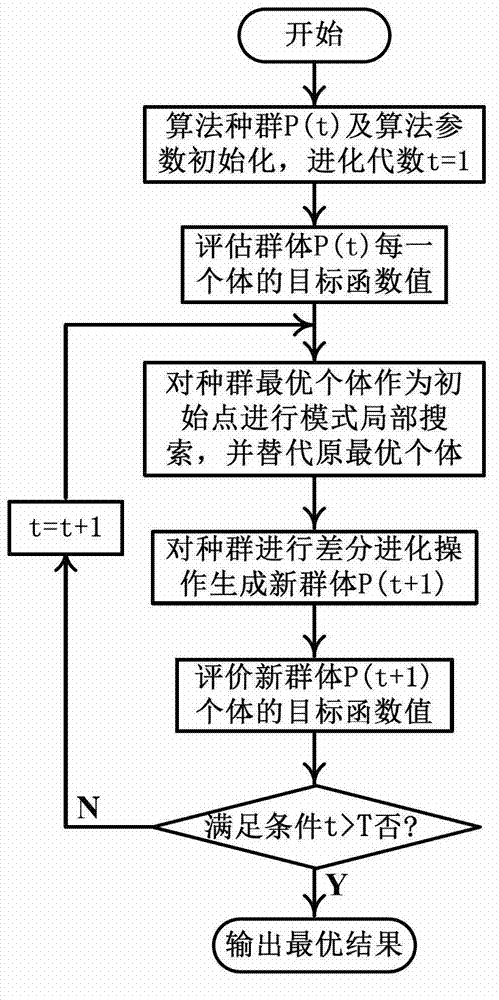
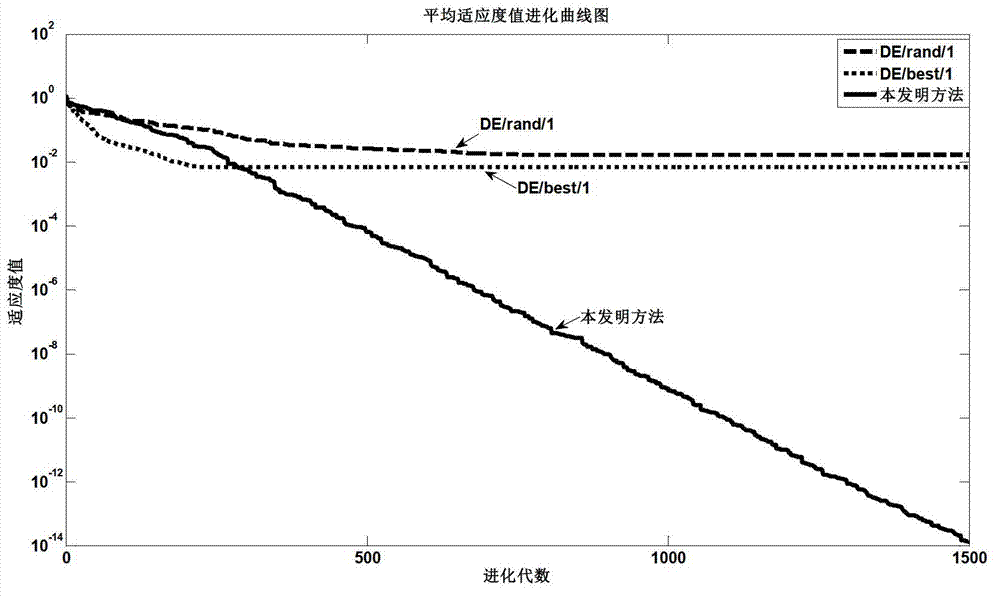
Forward kinematics solving method of parallel robot
ActiveCN102968665AImprove convenienceStrong global exploration abilityGenetic modelsHigh rateOptimization problem
The invention discloses a forward kinematics solving method of a parallel robot. When the method is applied to solve the forward kinematics problem of the parallel robot, the characteristic of easily solving inverse kinematics of the method is utilized, the forward kinematics solving problem of the parallel robot is converted into the equivalent minimal optimization problem, and the numerical optimization method is used for solving the problem. The method is integrated with the advantage of differential evolution having excellent global exploration performance on the solution space and the characteristic of pattern search having good local development capability on the solution space; and the mutual mechanisms of the two optimization algorithms are merged so that the search performance of the algorithms is improved. Compared with the traditional method, the method provided by the invention has high optimal solution searching accuracy and high rate of convergence while solving the forward kinematics problem of a 6-SPS type parallel robot; and simultaneously, the method also can be popularized to solve the forward kinematics problems of the parallel robots of other types.
Owner:SUZHOU SUXIANG ROBOT INTELLIGENT EQUIP CO LTD
Robot component based on parallel mechanism, optimum design method and robot
InactiveCN101564840AImprove stabilityLarge space for exerciseProgramme-controlled manipulatorHumanoid robot naoGait planning
The invention discloses a robot component based on a parallel mechanism, an optimum design method and a robot; the robot component comprises at least two parallel mechanisms; adjacent parallel mechanisms are connected with each other by an output converter; each parallel mechanism is provided with a fixed platform and a movable platform which moves correspondingly to the fixed platform, wherein the fixed platform of one parallel mechanism is movably connected with a motor. The robot with the parallel mechanism adopts the robot component and conducts optimum analysis and forward kinematics analysis on the initially selected parallel mechanism by inverse kinematics analysis to validate and debug the analysis results in the above steps so as to determine the component structure finally. By adjusting the motion types of the parallel mechanism, the space motion track of the robot in the motion process is realized, a genetic arithmetic is used to conduct the computation of inverse kinematics and gait planning to the parallel mechanism, the trajectory planning and motion form of the humanoid robot is improved, and the stability of the robot is improved during the motion process.
Owner:SHANGHAI XPARTNER ROBOTICS
Serial robot kinematics parameter calibration method based on vision
The invention provides a serial robot kinematics parameter calibration method based on vision. The optical axis of a camera serves as virtual straight line constraint, and a kinematics error model based on straight line constraint is built; a fixed point is selected from a calibration plate fixed to the tail end of a robot to serve as a feature point, motion of a mechanical arm is controlled through a visual control method based on images, and the feature point is made to arrive at the optical axis; according to joint angular data of the robot, the forward kinematics is used for calculating the nominal position of the feature point and the alignment error matrix; and the kinematics parameter error is estimated through the iterative least squares algorithm, and the actual kinematics parameter is calculated according to the nominal kinematics parameter. According to the serial robot kinematics parameter calibration method based on vision, the optical axis of the camera serves as virtualconstraint, calibration can be completed through only the joint angular data of the robot, the cost is low, operation is easy, expensive high-precision measuring equipment is not needed, and the method has the universality for serial robot calibration and can be widely applied to industrial, space and underwater environments to improve the absolute positioning precision of the mechanical arm.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Parallel kinematic machine, calibration method of parallel kinematic machine, and calibration program product
InactiveUS7386408B2Accurate identificationReduce the numberControl mechanismProgramme-controlled manipulatorNumerical controlParallel kinematics
A parallel kinematic machine has a parallel kinematic mechanism including an end effecter and a parallel link mechanism. A numerical control device controls a position and orientation of the end effecter based on kinematics of the parallel kinematic mechanism. A posture setter sets an adjustment tool on the end effecter in a known posture in a reference coordinate system defined outside the parallel kinematic mechanism based on a measurement method. A data acquirer acquires data in accordance with a measurement method selecting code for designating the measurement method used by the posture setter in setting the adjustment tool in the known posture, and defines a correlation between kinematic parameters for the parallel kinematic mechanism and the reference coordinate system. A calculator calculates the kinematic parameters based on the acquired data by using a relational expression describing forward kinematics of the parallel kinematic mechanism.
Owner:SHINNIPPON KOKI
Rapid solving method for failure workspace of six-degree-of-freedom parallel robot
InactiveCN103365249AReduce the number of iterationsFast convergenceProgramme controlComputer controlForward kinematicsSix degrees of freedom
The invention relates to a rapid solving method for the failure workspace of a six-degree-of-freedom parallel robot. The conventional methods have the defects that 1) a geometric method is high in engineering implementation difficulty and low in computational efficiency; and 2) a certain feasible pose solution capable of making a support leg corresponding to the pose solution right as long as that of a failing support leg is difficult to give by a kinematic inverse solution-based rapid searching method. The rapid solving method comprises the following steps of determining a minimum length value of each linear electrical executor and an extended stroke value which can be realized by each linear electrical executor according to the product performance of the adopted linear electrical executors; randomly generating N groups of support leg length data according to the data by using a pseudo-random method; solving the position of a motion platform according to known parallel robot pose parameters by utilizing a steepest descent position forward kinematics algorithm; and finally obtaining N motion platform pose points to obtain a motion space scatter diagram when the leg of the parallel robot fails. According to the method, the support leg failure workspace of a six-degree-of-freedom redundant drive parallel robot is more rapidly and accurately determined.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Six-freedom parallel robot decoupling method
InactiveCN101143443AHigh control precisionImprove controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorClosed loopDegrees of freedom
The invention provides a six-degree-of-freedom parallel robot decoupling method. The input signal of the six-degree-of-freedom parallel robot is an attitude signal, and the expansion range of an actuator is obtained by the inverse kinematics, and the control actuating quantity of the six-degree-of-freedom parallel robot is obtained by the action of a controller, and then the movement of the six-degree-of-freedom parallel robot can be driven, thus realizing the displacement closed loop of the actuator. The expansion range of the actual displacement of the actuator of the six-degree-of-freedom parallel robot is the actual attitude feedback quantity of the six-degree-of-freedom parallel robot by the forward kinematics. The invention is to conduct the output decoupling of the sinusoidal motion of the six-degree-of-freedom parallel robot, and to enhance the control accuracy of the parallel robot, thus improving the control results of the parallel robot. The invention facilitates the realization of computer digital control and has the advantages of high-degree automation, and high real-time performance. The method can be also used in the output decoupling of the parallel robot lower than six-degree-of-freedom.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
On-orbit calibration method and system for space manipulator based on hand-eye camera
ActiveCN107817682ASimple calculationEasy to implementAdaptive controlKinematics equationsNonlinear systems of equations
The invention relates to an on-orbit calibration method and system for a space manipulator based on a hand-eye camera. The on-orbit calibration method comprises the steps of (1) performing imaging ona target by using the hand-eye camera installed at the tail end of the space manipulator under multiple groups of different configurations; (2) recording angle measurement values of joints of the space manipulator and position and pose data, which is measured by the hand-eye camera, of the tail end of the space manipulator under each group of configurations; (3) substituting the joint angle data and the tail end position and pose data of the space manipulator under different configurations into a space manipulator forward kinematics equation, and building a nonlinear equation set related withstructural parameters of the space manipulator; and (4) solving the built nonlinear equation set by adopting a numerical iterative algorithm to obtain structural parameters of the space manipulator. The method can be applied to performing on-orbit calibration on the structural parameters of the space manipulator after a spacecraft is launched into the orbit, so that the control accuracy of the space manipulator is effectively improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Wearable high-precision data acquisition upper limb exoskeleton
The invention relates to a wearable high-precision data acquisition upper limb exoskeleton, comprising an adjustable base, a shoulder rotation pair mechanism, a shoulder slide ring mechanism, an upper arm connecting rod length sliding adjusting mechanism, an elbow parallel rotation pair mechanism, an elbow slide ring mechanism, a lower arm connecting rod length sliding adjusting mechanism, a wrist rotation pair mechanism, a tail end operation handle and a tool clamping device. A high-precision photoelectric encoder is mounted on each joint, the position and the posture of a tail end can be accurately acquired via forward kinematics, and a manipulator can be accurately controlled. The wearable high-precision data acquisition upper limb exoskeleton is compact in structure, light in weight and high in rigidity, is applicable to different operation heights and arm lengths, two control buttons are arranged on the handle to control procedures of an upper computer, and the exoskeleton further can be used as a guiding hand to be used for realizing upper limb exercise rehabilitation training of hemiplegia patients.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Obstacle avoidance solution applied to redundant manipulator
The invention discloses an obstacle avoidance solution applied to a redundant manipulator. The obstacle avoidance solution comprises the steps of: S1, acquiring a forward kinematics model of the manipulator through establishing a D-H matrix of the manipulator, and establishing a target track equality constraint index of a speed layer after performing derivation processing on the forward kinematicsmodel; S2, establishing a vector-based obstacle avoidance inequality constraint index; S3, writing the target track equality constraint index of the speed layer established in the step S1 and the vector-based obstacle avoidance inequality constraint index established in the step S2 into quadratic programming problems in the unified form; S4, transforming the quadratic programming problems in theunified form in the step S3 into a linear variational inequality; S5, solving the linear variational inequality in the step S4 by means of a primal-dual neural network solver; S6, and outputting manipulator joint angle control variables solved by means of the primal-dual neural network solver in the step S5 to the manipulator, so as to realize the effect of controlling the redundant manipulator toavoid obstacles.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
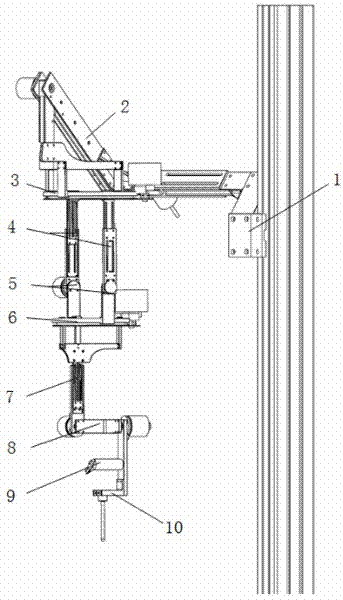
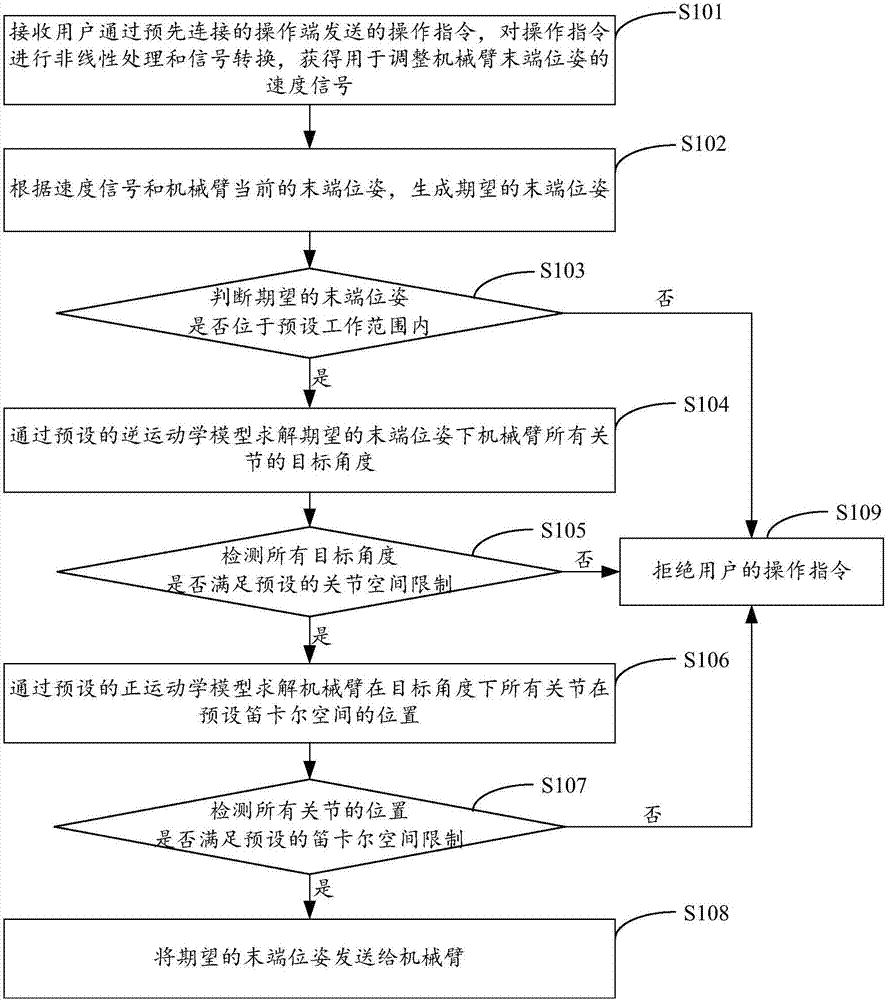
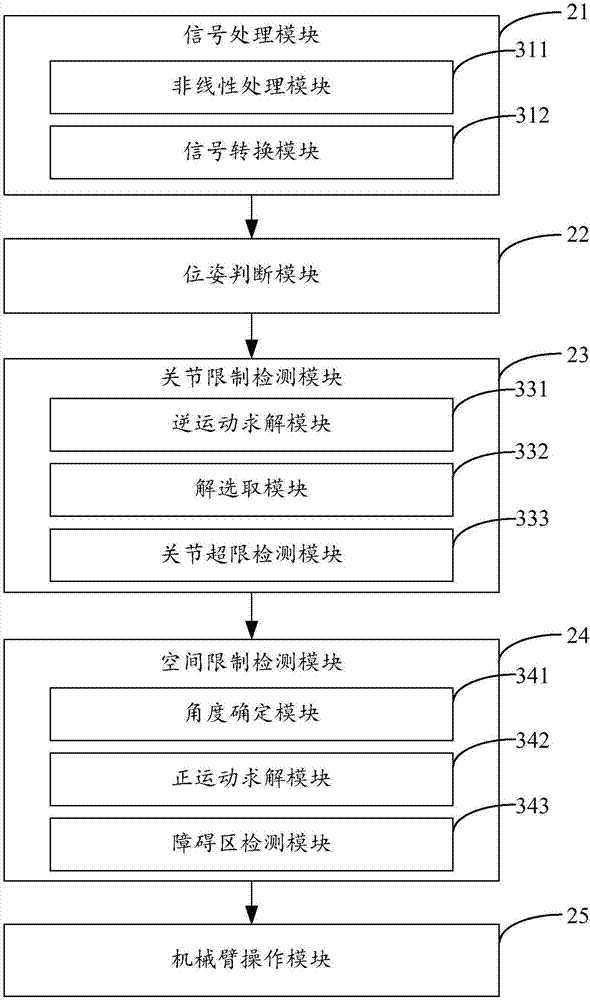
Operating method and device of mechanical arm
ActiveCN107116553AImprove securityReduce the number of operationsProgramme-controlled manipulatorOperating instructionAngular degrees
The invention is suitable for the technical field of computers, and provides an operating method and device of a mechanical arm. The method comprises the steps of receiving an operating instruction which is sent by a user through an operating end connected in advance, and performing nonlinear processing and signal conversion on the operating instruction so as to obtain a speed signal; generating an expected terminal position and pose according to the speed signal and the current terminal position and pose of the mechanical arm, and judging whether the expected terminal position and pose are within a working range; if the expected terminal position and pose are within the working range, solving target angles of all joints of the mechanical arm corresponding to the expected terminal position and pose through an inverse kinematics model, and detecting whether all the target angles satisfy joint space limitation; if all the target angles satisfy the joint space limitation, solving the positions of all the joints in Cartesian space at the target angles through a forward kinematics model, and detecting whether the positions of all the joints satisfy Cartesian space limitation; and if the positions of all the joints satisfy the Cartesian space limitation, sending the expected terminal position and pose to the mechanical arm. The operating stability of the mechanical arm is effectively increased, and the operating safety of the mechanical arm is effectively increased.
Owner:深拓科技(深圳)有限公司
Redundant freedom robot inverse kinematics method
InactiveCN108121833ADesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsMatrix solutionKinematics equations
The invention discloses a redundant freedom robot inverse kinematics method. The redundant freedom robot inverse kinematics method comprises the steps of establishing a forward kinematics equation; establishing an MP generalized inverse matrix equation; according to a generalized MP inverse matrix relationship, establishing a Newton iteration equation set; performing calculation according to the Newton iteration equation set to obtain partial joint position values; according to the partial joint position values, calculating residual joint position values; and performing selection on multiple joint solutions obtained by calculation. According to the redundant freedom robot inverse kinematics method provided by the invention, the time problem and the solution screening problem caused by seven freedom kinematics redundant axis calculation are solved by adopting an MP inverse matrix solution method, so that a mapping relationship between a pose of a gripper at the end of an operation arm of a robot and a joint vector is established.
Owner:SHENYANG SIASUN ROBOT & AUTOMATION
Manipulator servo control method, system and device based on screw theory
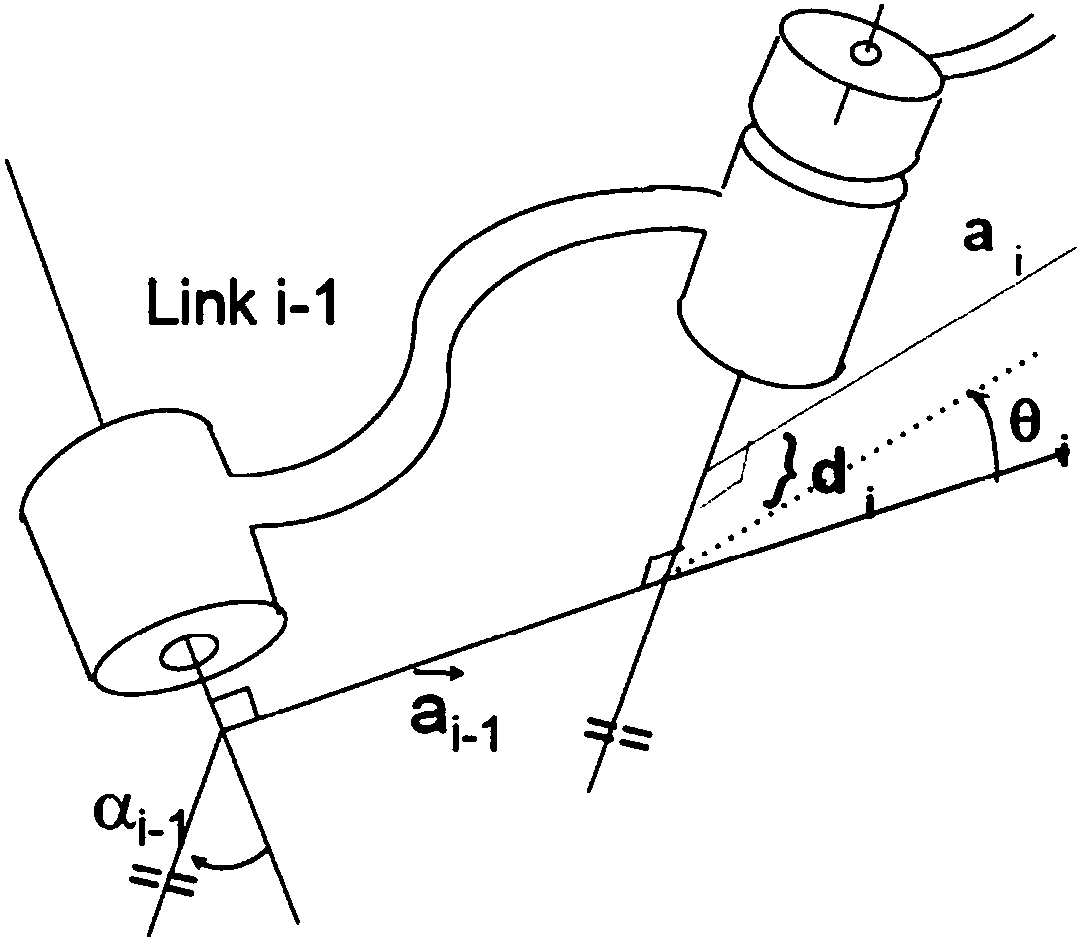
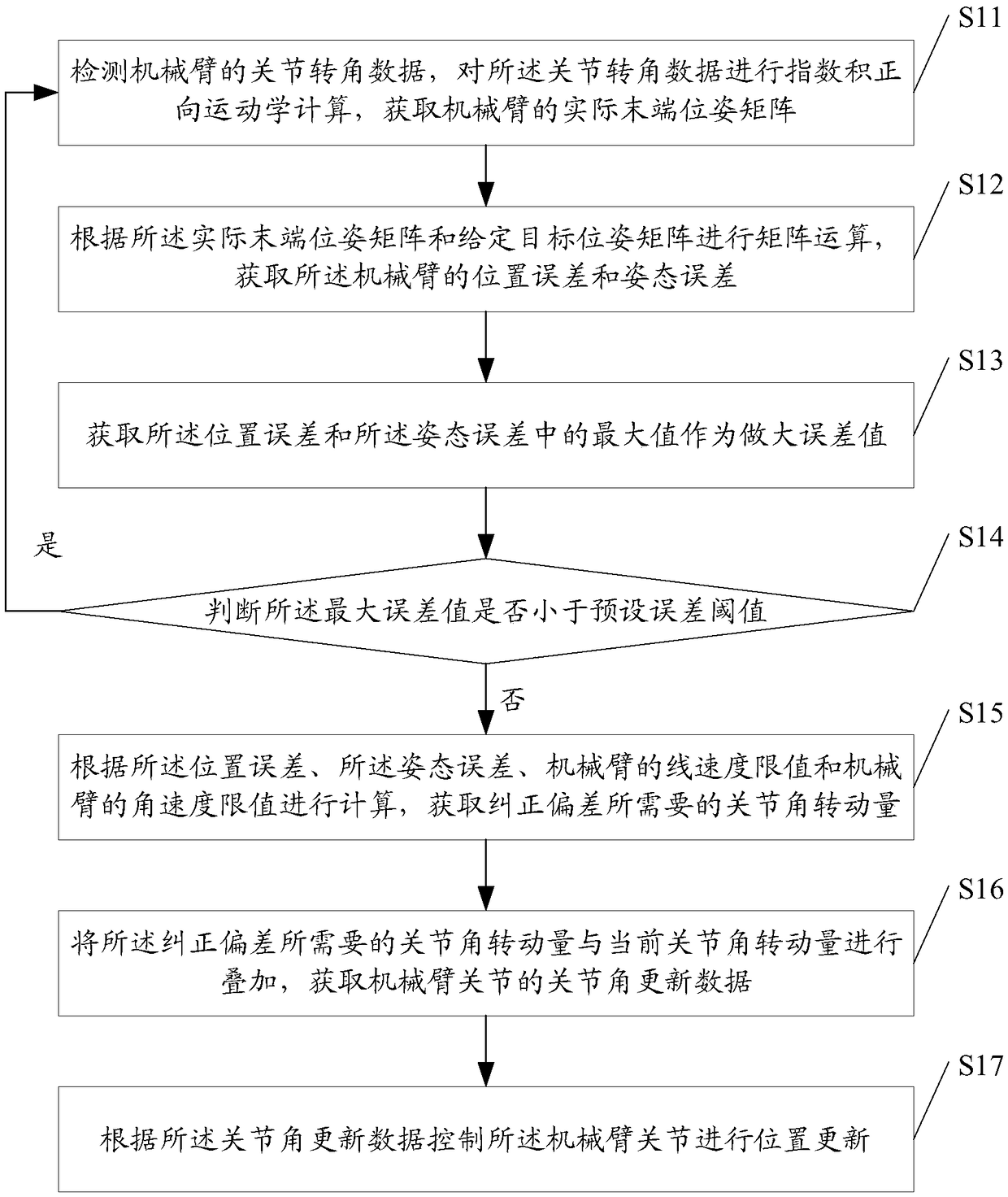
ActiveCN109483529AAvoid repeated calculationsSmall amount of calculationProgramme-controlled manipulatorData controlMaximum error
The invention discloses a manipulator servo control method, system and device based on a screw theory. The manipulator servo control method comprises the steps that joint rotating angle data of a manipulator are detected and subjected to exponential product direct kinematics calculation, and thus an actual tail end position-attitude matrix of the manipulator is obtained; matrix operation is conducted according to the actual tail end position-attitude matrix and a given target position-attitude matrix, and thus a position error and an attitude error of the manipulator are obtained; the maximumvalue in the position error and the attitude error is obtained to serve as the maximum error value, and whether the maximum error value is less than a preset error threshold value or not is judged; ifnot, calculation is conducted to obtain the joint angle rotating amount required by deviation correcting; joint angle updating data of manipulator joints are obtained; and the manipulator joints arecontrolled to be subjected to position updating according to the joint angle updating data. By adopting the manipulator servo control method, the advantages of small calculated amount, good real-timeperformance and accurate tracking are achieved, and the control precision of the manipulator can be effectively improved.
Owner:华南智能机器人创新研究院
Control method for multi-degree-of-freedom master-slave teleoperation manipulator
InactiveCN106112951ASolve the problem of slave manipulator control away from the siteReduce mental burdenProgramme-controlled manipulatorMulti degree of freedomVisual positioning
The invention discloses a control method for a multi-degree-of-freedom master-slave teleoperation manipulator. The control method comprises the following operation steps: step A, determining a pose matrix by a slave manipulator in the field by taking the current angles of joints as parameters according to a method of forward kinematics; step B, judging a grabbing target point (X, Y and Z) or the directions of X, Y and Z according to an actual target image or video; step C, manually setting a grabbing path track of the manipulator; step D, setting interpolation points, that is, a step length of each moving road section; step E, calculating the movement parameters of the joints, needed for the manipulator to arrive at the next interpolation point according to an inverse kinematics solution algorithm, and executing; and step F, feeding back through manual judgement and repeating the step A to enable the manipulator to arrive at a target position. According to the control method disclosed by the invention, manual single-joint control is replaced by a six-degree-of-freedom welding manipulator with a human vision location function and capable of realizing teleoperation, thus the mental burden of operating personnel is reduced, and the working efficiency is greatly increased.
Owner:广州霞光技研有限公司
Ultrasound Probe for Laparoscopy
ActiveUS20130338505A1Prevent fallingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterSonificationControl ultrasound
An intra-operative ultrasound probe for use with a robotic and laparoscopic surgical systems that allows for direct surgeon control over the position and orientation of the ultrasound image is presented. The transducer is designed to interface with the laparoscopic grasper so that it is easy to pick up in a locking, self-aligning and repeatable manner. The transducer is tracked in space using either forward kinematics or electromagnetic sensing, allowing multiple 2D images to be combined in order to create 3D ultrasound volumes. The 3D volumes can be further processed and displayed on the surgeon's console, or used to register and display acquired pre-operative images at the correct spatial location within the patient.
Owner:SCHNEIDER CAITLIN MARIE +3
Moving mechanical arm obstacle avoidance planning method based on random sampling
ActiveCN111761582ASimplify solving complexityReduce computational complexityProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputation complexitySimulation
The invention discloses a moving mechanical arm obstacle avoidance planning method based on random sampling. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, modeling a mobile platform into a special mechanical arm formed by connecting a rotating joint on a moving joint in the x and y directions and combining the special mechanical arm with an original mechanical arm model to establish a forward kinematics model of an n-degree-of-freedom moving mechanical arm; then, analyzing the constraints in the motion planning process, and then designing a moving mechanical arm vehicle-arm integrated path planning algorithm flow; and finally, designing a redundant path bidirectionally deleting method used for path smoothing processing to perform smoothing processing on the path obtain in the last step. According to the method, the whole moving mechanical arm is modeled to the special mechanical arm containing the moving joint, so that the kinematics solving complexity is greatly simplified; andmeanwhile, the redundant path bidirectionally deleting algorithm is designed, which greatly reduces and smoothes the path planned by the RRT algorithm with the low computational complexity.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Rapid solution method and rapid solution system for high-degree-of-freedom robot inverse kinematics
ActiveCN106844985AImprove real-time performanceAccelerated Inverse Kinematics SolvingProgramme-controlled manipulatorDesign optimisation/simulationKinematics equationsDegrees of freedom
The invention provides a rapid solution method and a rapid solution system for high-degree-of-freedom robot inverse kinematics. The method includes the steps of 1, substituting a joint variable theta into a robot kinematics equation to obtain a Jacobian matrix J, and transposing the Jacobian matrix J to obtain a transposed Jacobian matrix JT; 2, generating a group of speculative values, calculating corresponding joint variable update values for the speculative values, substituting each joint variable update value into a robot forward kinematics equation to obtain corresponding poses Pk, calculating pose deviation delta ek between each pose Pk and a target pose P and calculating a modulus errork of the pose deviation delta ek; 3, selecting a minimum value errormin, corresponding pose deviation delta emin and joint variable update values delta theta min from a set of the modulus errork, updating the pose deviation delta e=delta emin and updating a joint variable theta=theta+delta theta min; 4, judging whether the errormin meets errormin<threshold or not, outputting the joint variable theta and finishing if the errormin meets errormin<threshold, otherwise, returning to the step 1 and continuing execution.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Dual quaternion solution of six degrees of freedom parallel robot forward kinetics
ActiveCN105807712AQuick position calculationFast pose calculationNumerical controlRobotic systemsAlgebraic equation
The invention discloses a dual quaternion solution of six degrees of freedom parallel robot forward kinetics. According to the method, dual quaternions are taken as generalized coordinates of a parallel robot system, a forward kinetic equation set is a quadratic algebraic equation about the dual quaternions, a high-efficiency value algorithm is brought forward for the equation set, and least square solutions of the position and attitude of such a six degrees of freedom parallel robot motion platform can be rapidly calculated. For a parallel robot not including redundancy driving, a least square solution is also an exact solution.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com