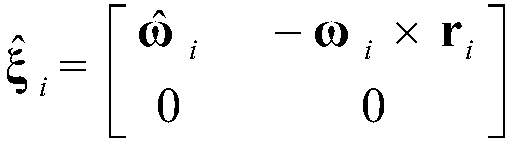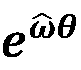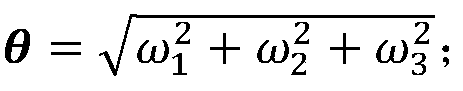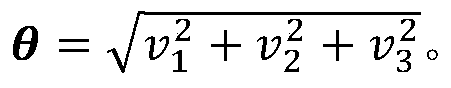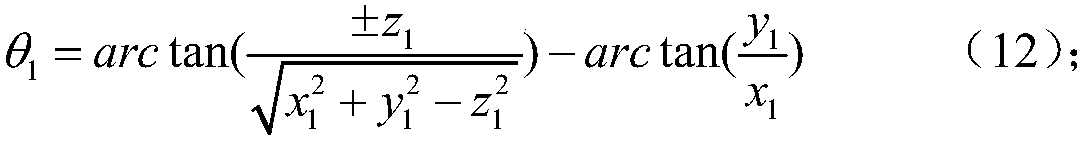Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35 results about "Screw theory" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
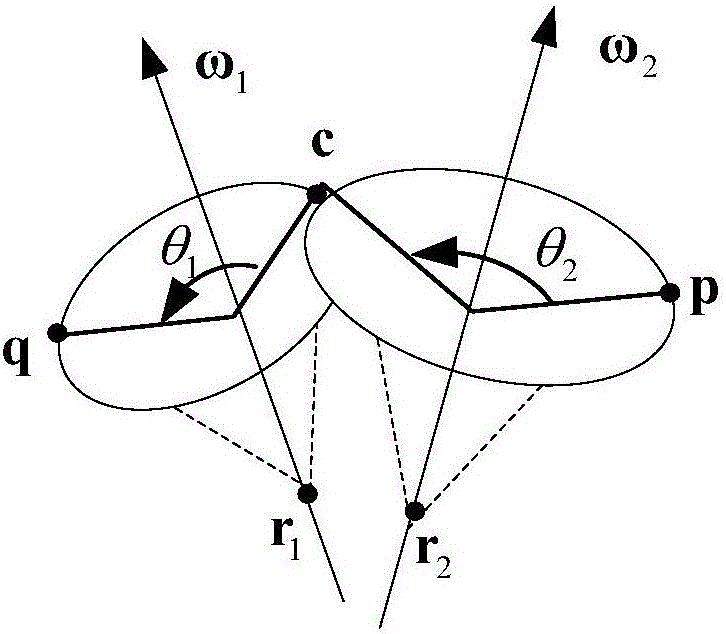
Screw theory is the algebraic calculation of pairs of vectors, such as forces and moments or angular and linear velocity, that arise in the kinematics and dynamics of rigid bodies. The mathematical framework was developed by Sir Robert Stawell Ball in 1876 for application in kinematics and statics of mechanisms (rigid body mechanics).
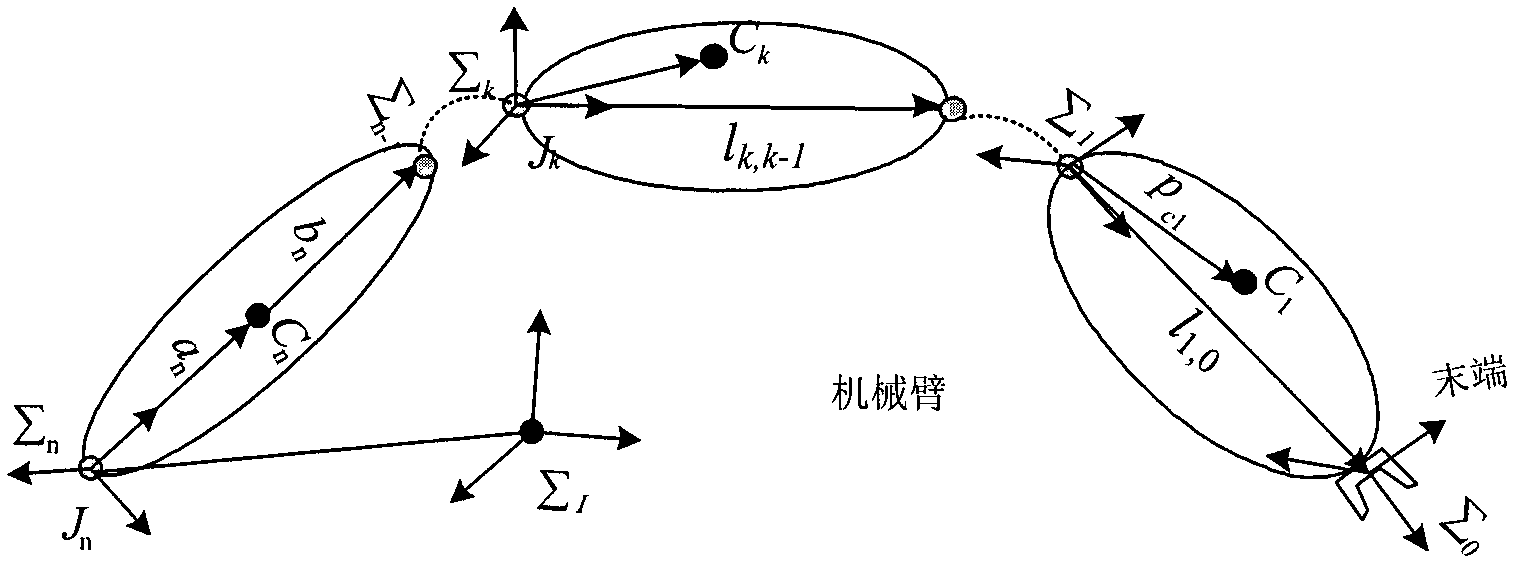
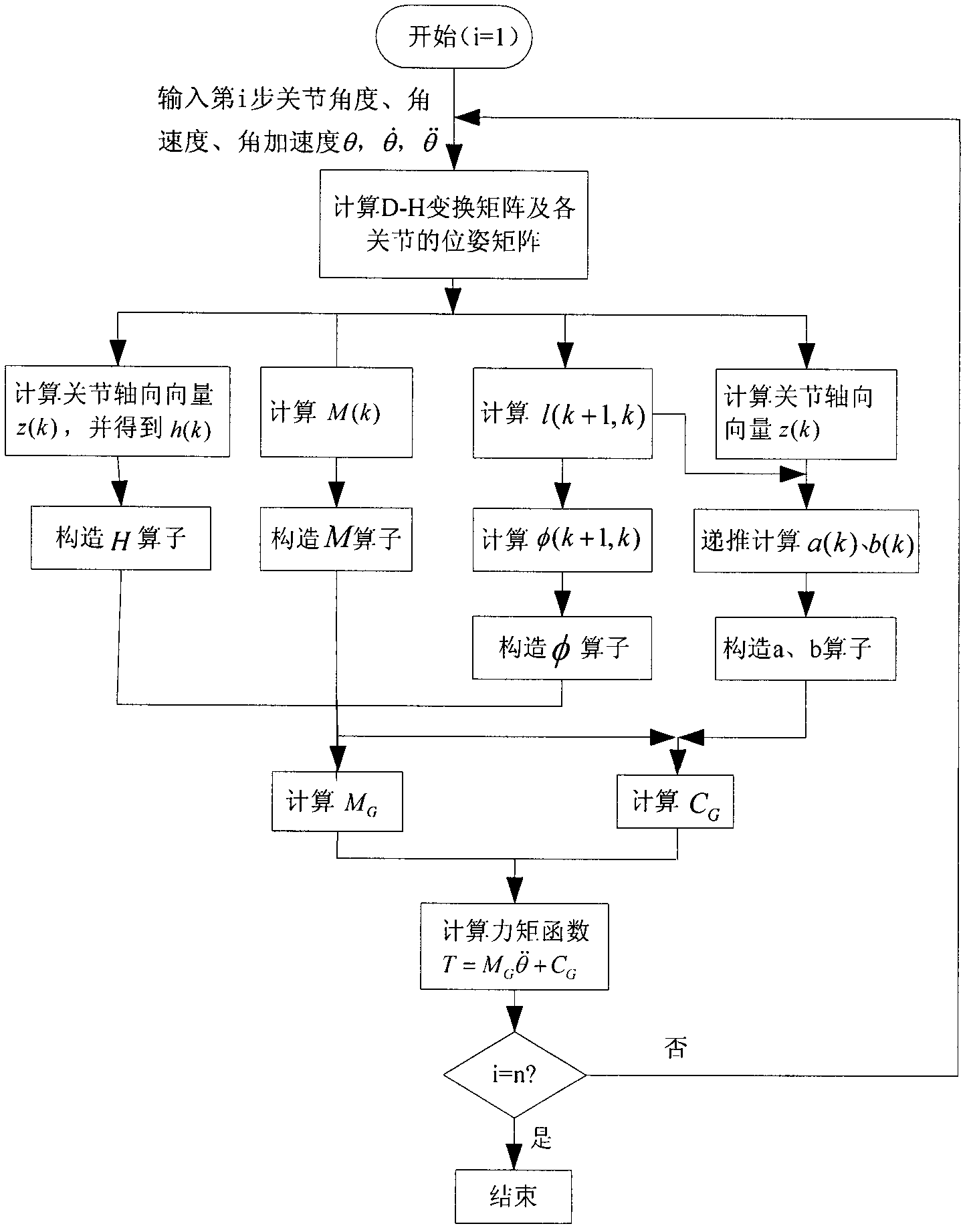
Efficient dynamic modeling method for multi-degree of freedom (multi-DOF) mechanical arm
InactiveCN102207988AReduce computational complexityImproving the efficiency of positive dynamics calculationsSpecial data processing applicationsComputational problemInertial mass
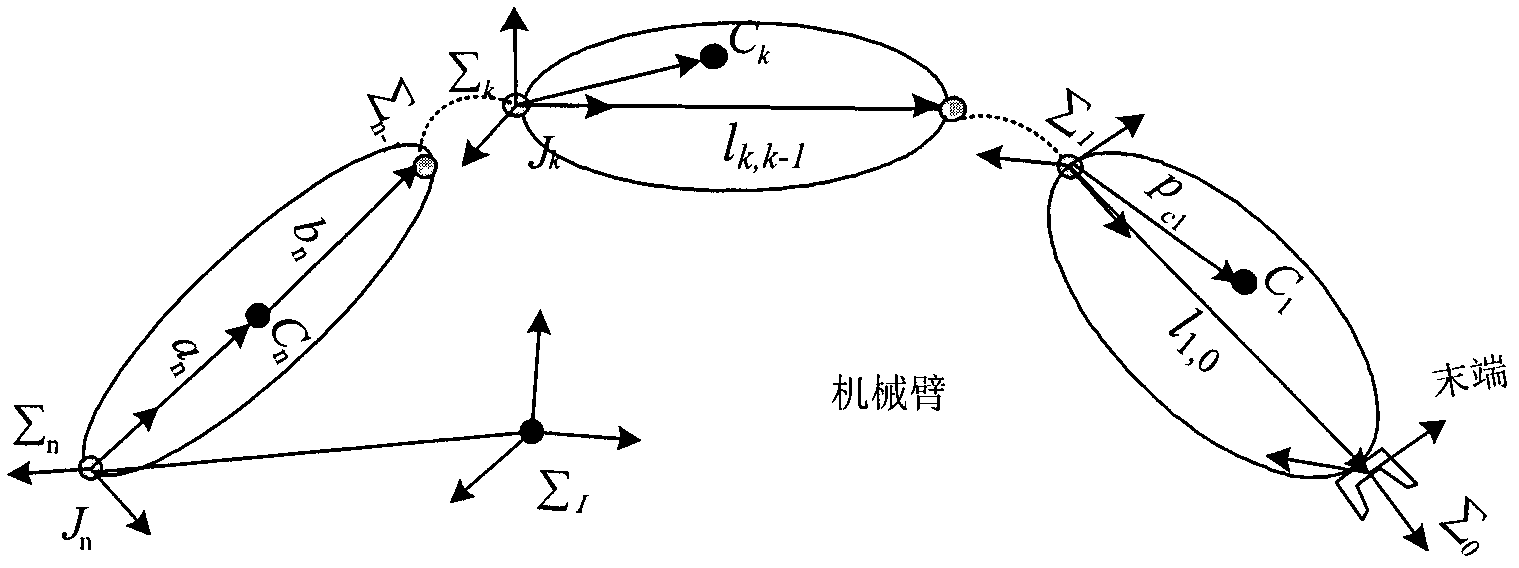
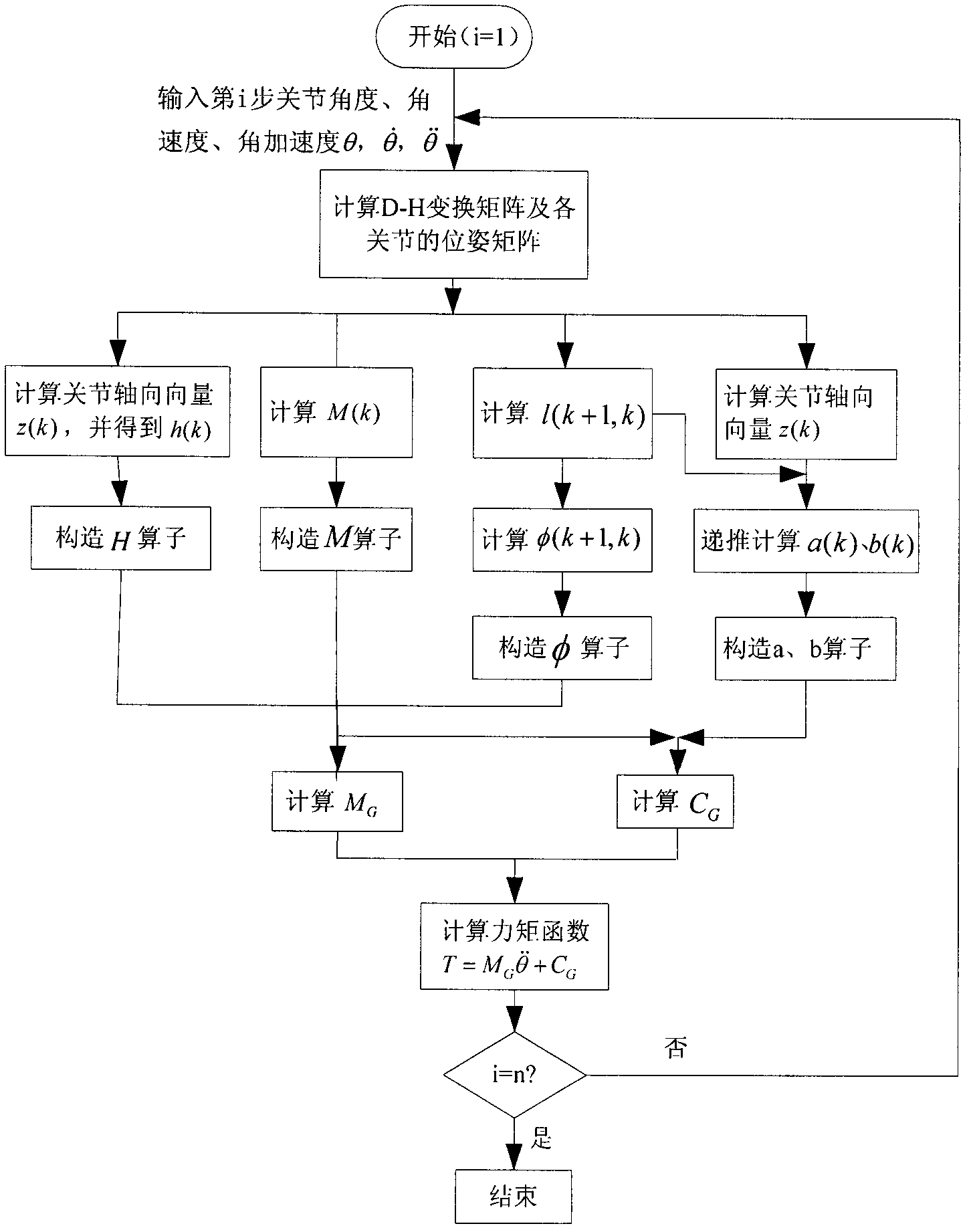
The invention discloses an efficient modeling method for a multi-degree of freedom (multi-DOF) mechanical arm. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: describing speed, acceleration, force and moment of each joint of the mechanical arm by using the screw theory; performing inverse dynamic modeling on the mechanical arm by using the spatial operator algebraic theory; and obtaining a generalized inertial mass matrix of the mechanical arm and a factorization form of the inverse matrix of the mechanical arm by using a Kalman filter smoothing method so as to obtain an efficient lower dynamic model. According to the method, the efficient dynamic calculation problem of the multi-DOF mechanical arm is solved, and the calculation efficiency of the method is first power magnitude order of the degree of freedom of the mechanical arm; meanwhile, the method has strong theoretical property, intuitive expression form and definite physical significance.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
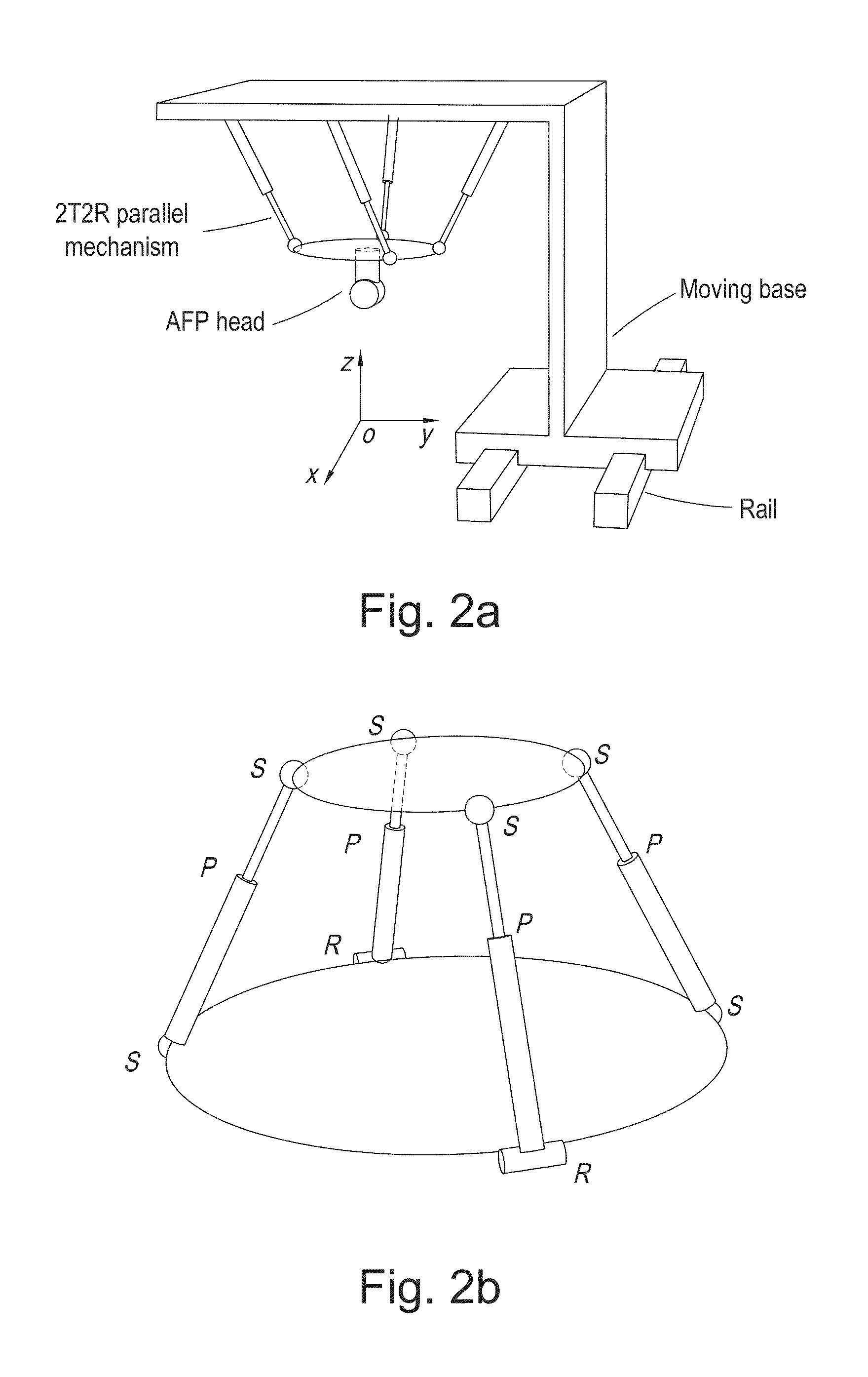
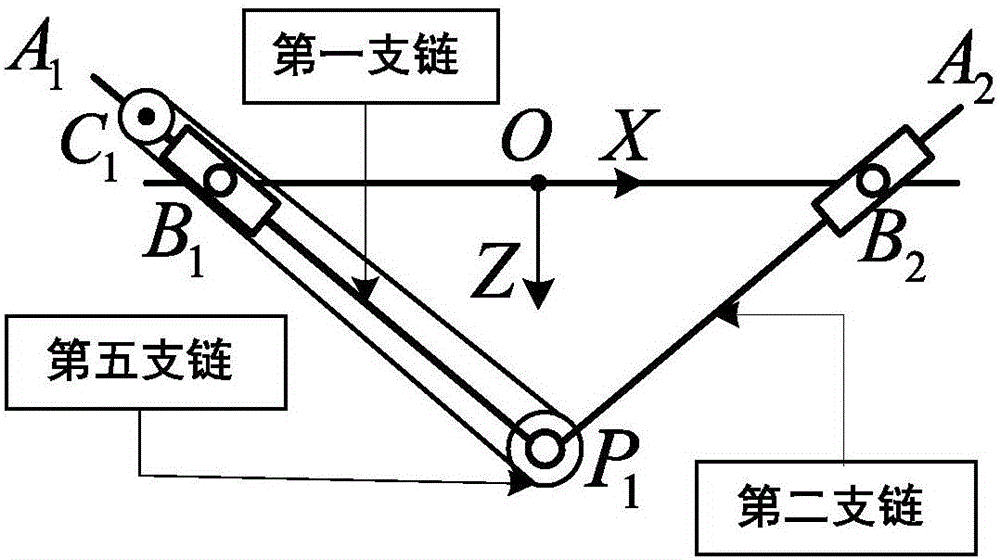
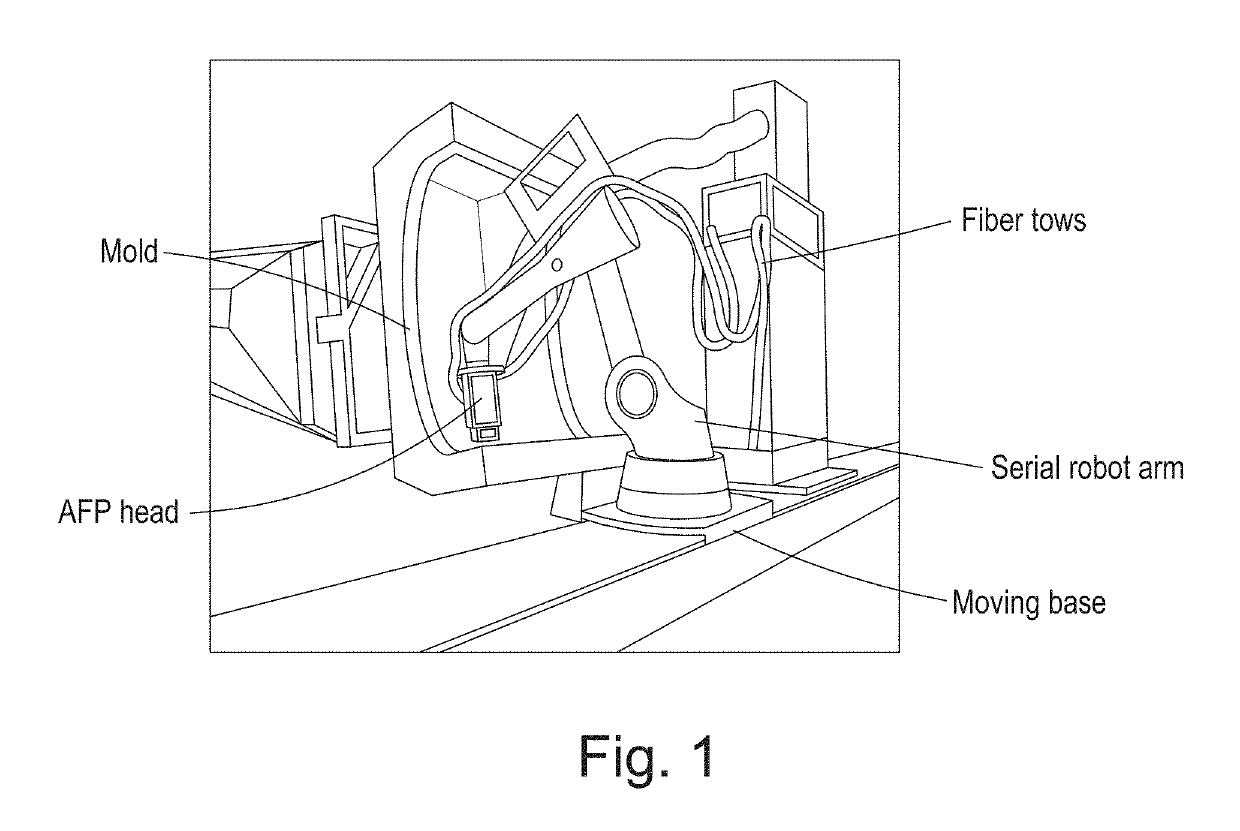
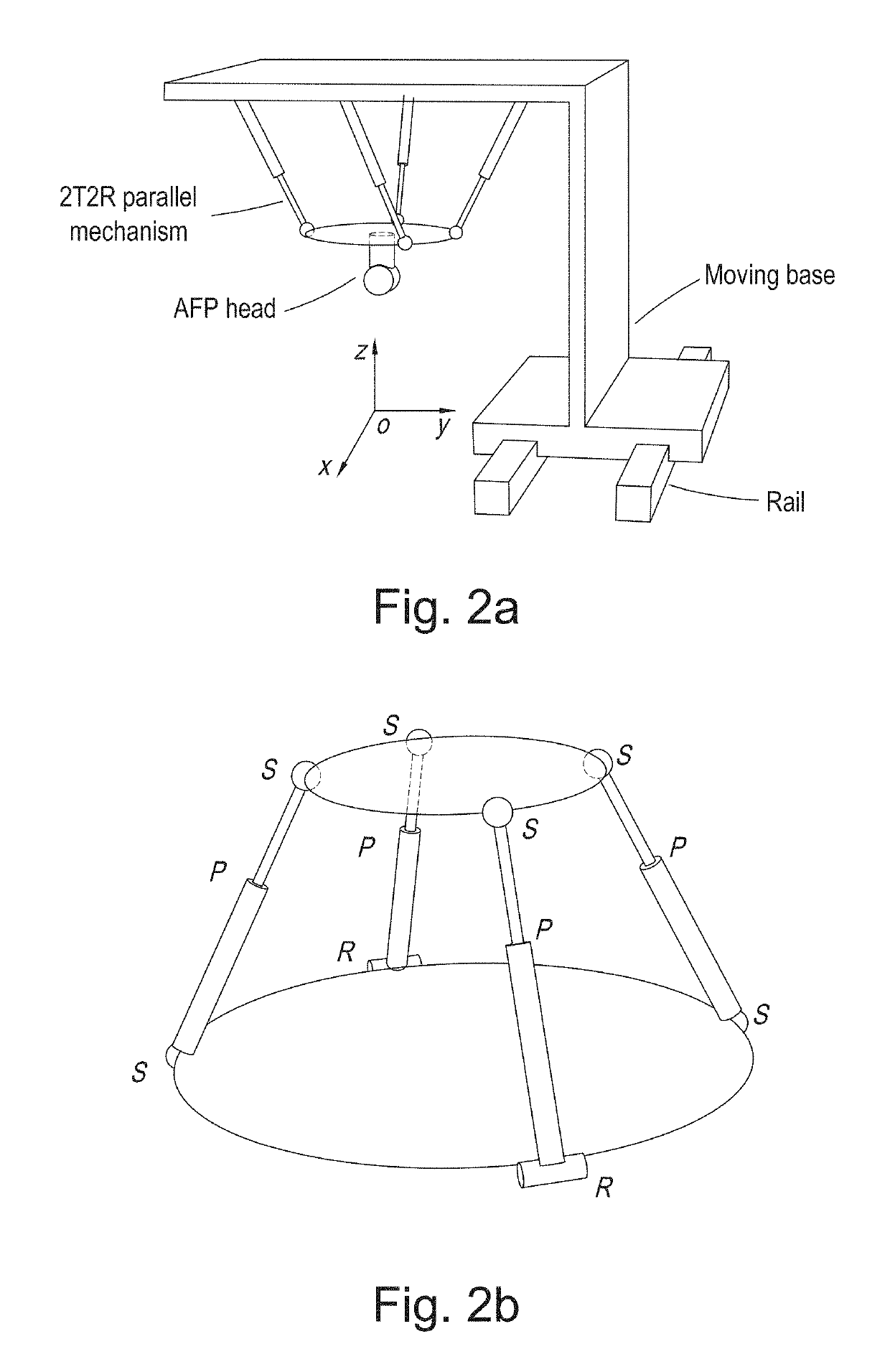
Parallel mechanism based automated fiber placement system
ActiveUS20160250749A1Good kinematic performanceOptimization mechanismProgramme-controlled manipulatorDomestic articlesAviationFiber
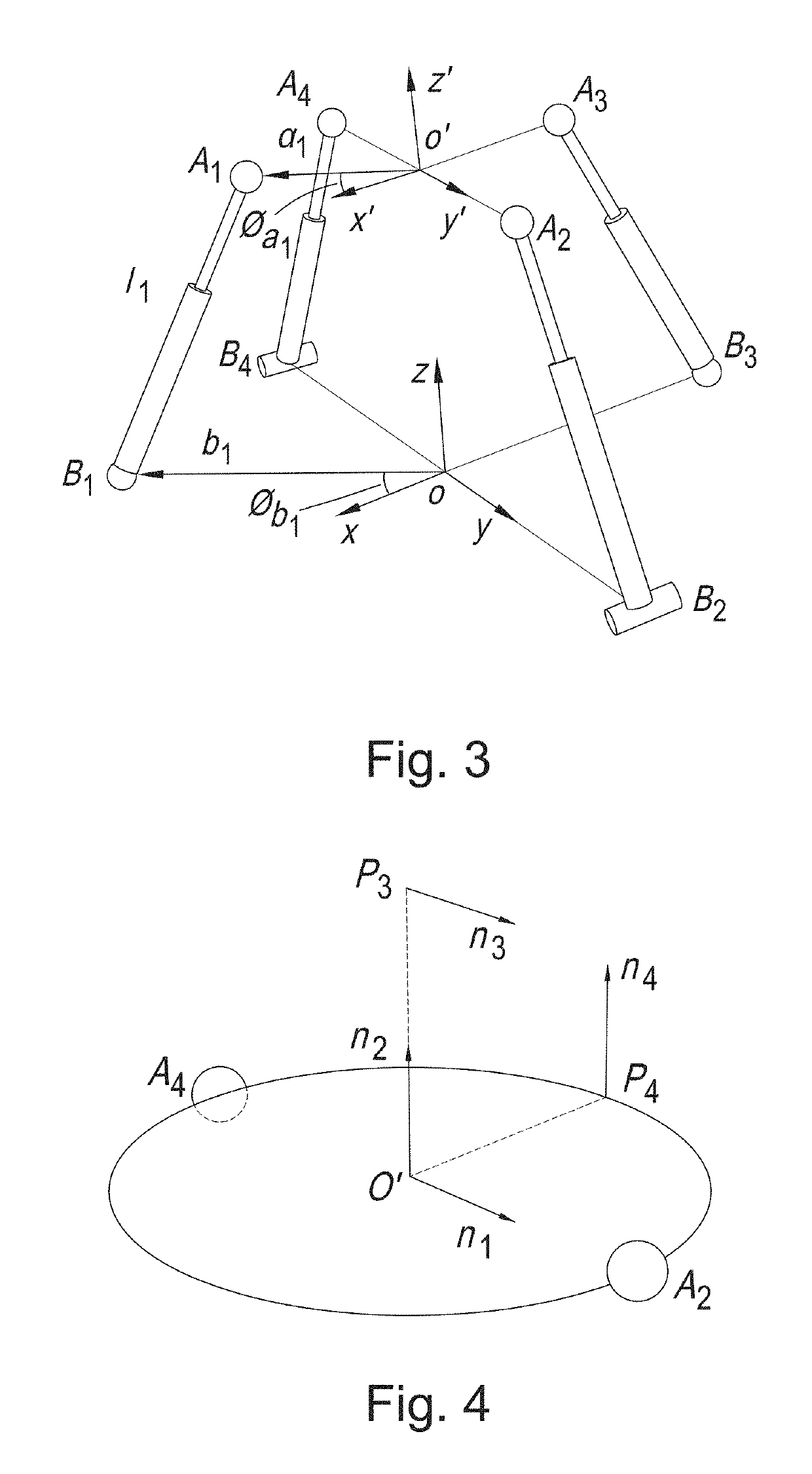
The present invention introduces a new concept of applying a parallel mechanism in automated fiber placement for aerospace part manufacturing. The proposed system requirements are 4DOF parallel mechanism consisting of two RPS and two UPS limbs with two rotational and two translational motions. Both inverse and forward kinematics models are obtained and solved analytically. Based on the overall Jacobian matrix in screw theory, singularity loci are presented and the singularity-free workspace is correspondingly illustrated. To maximize the singularity-free workspace, locations of the two UPS limbs with the platform and base sizes are used in the optimization which gives a new design of a 4DOF parallel mechanism. A dimensionless Jacobian matrix is also defined and its condition number is used for optimizing the kinematics performance in the optimization process. A numerical example is presented with physical constraint considerations of a test bed design for automated fiber placement.
Owner:KHALIFA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
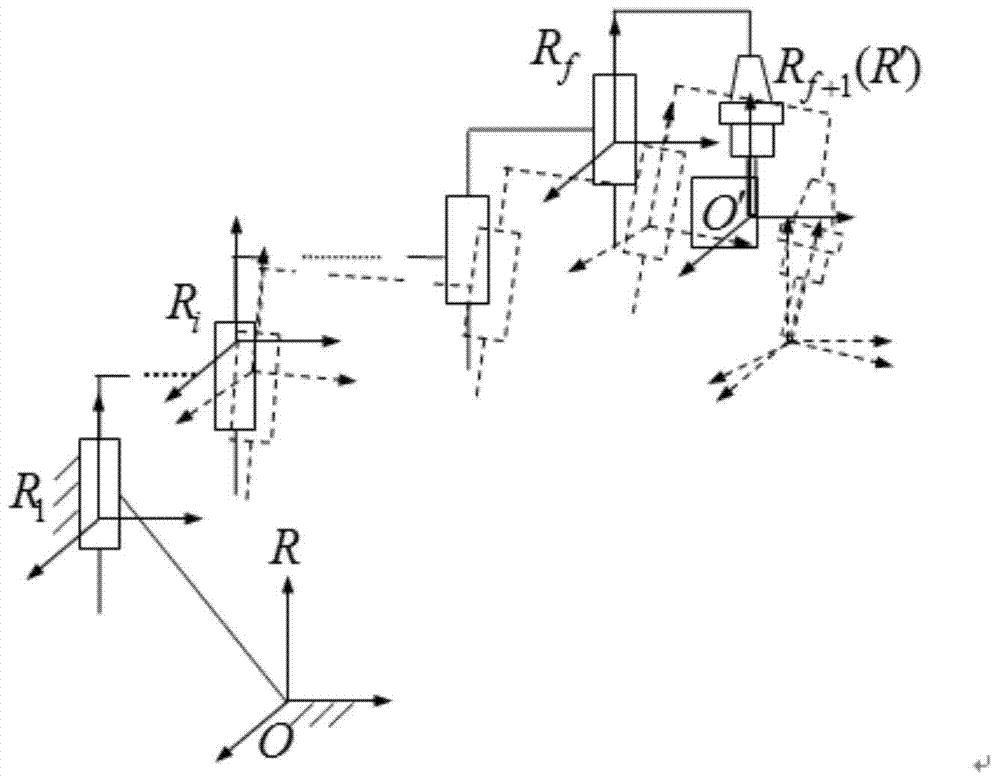
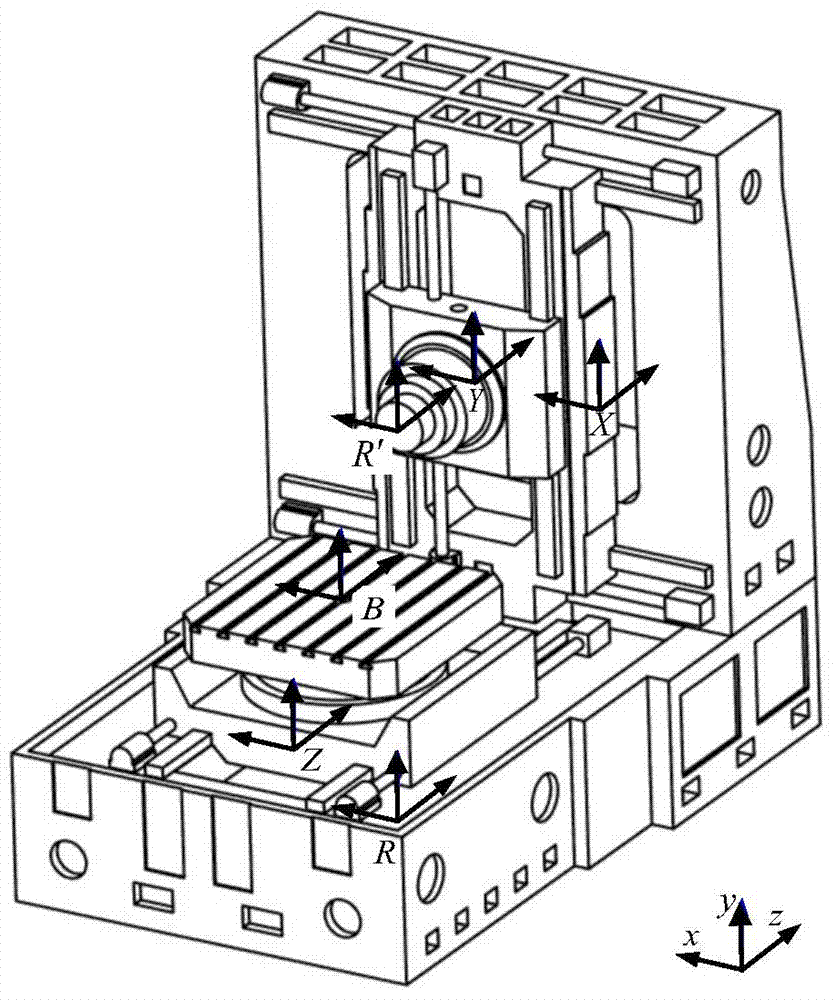
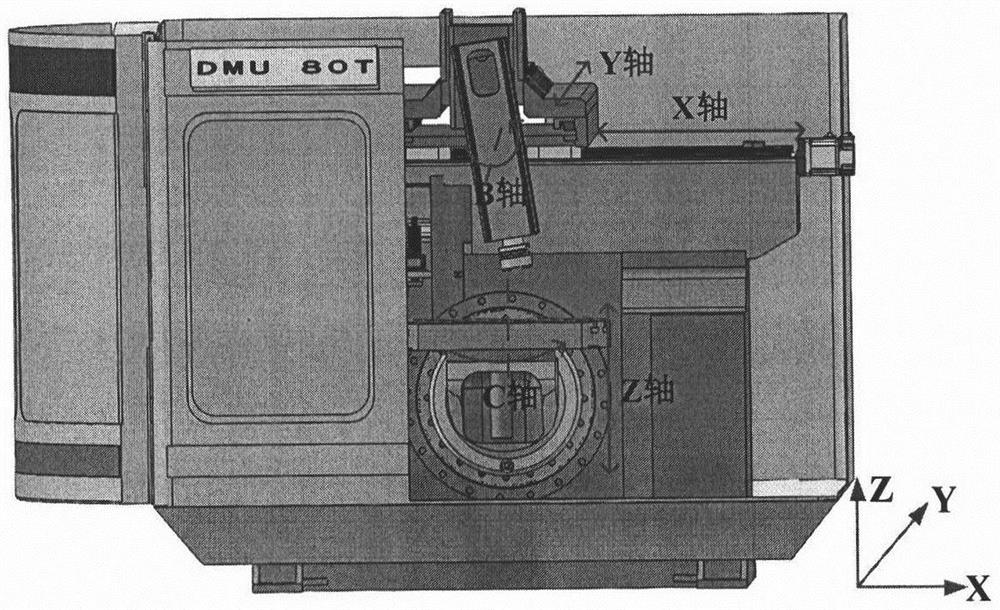
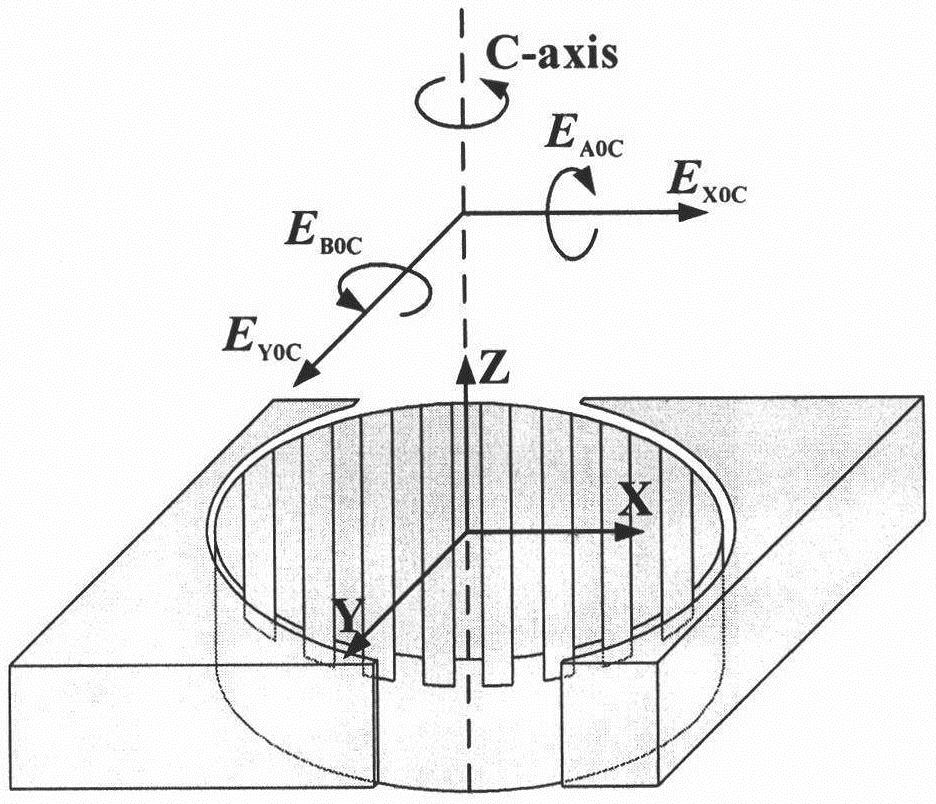
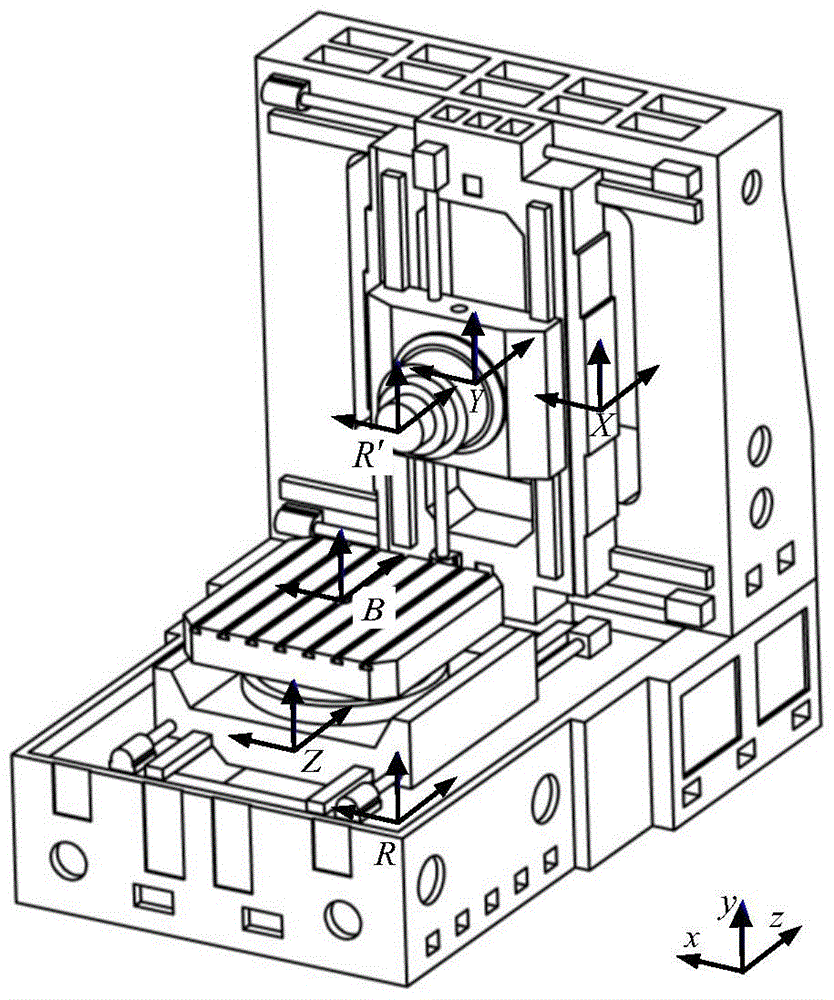
Geometric error screw theory modeling method for numerically-controlled machine tool
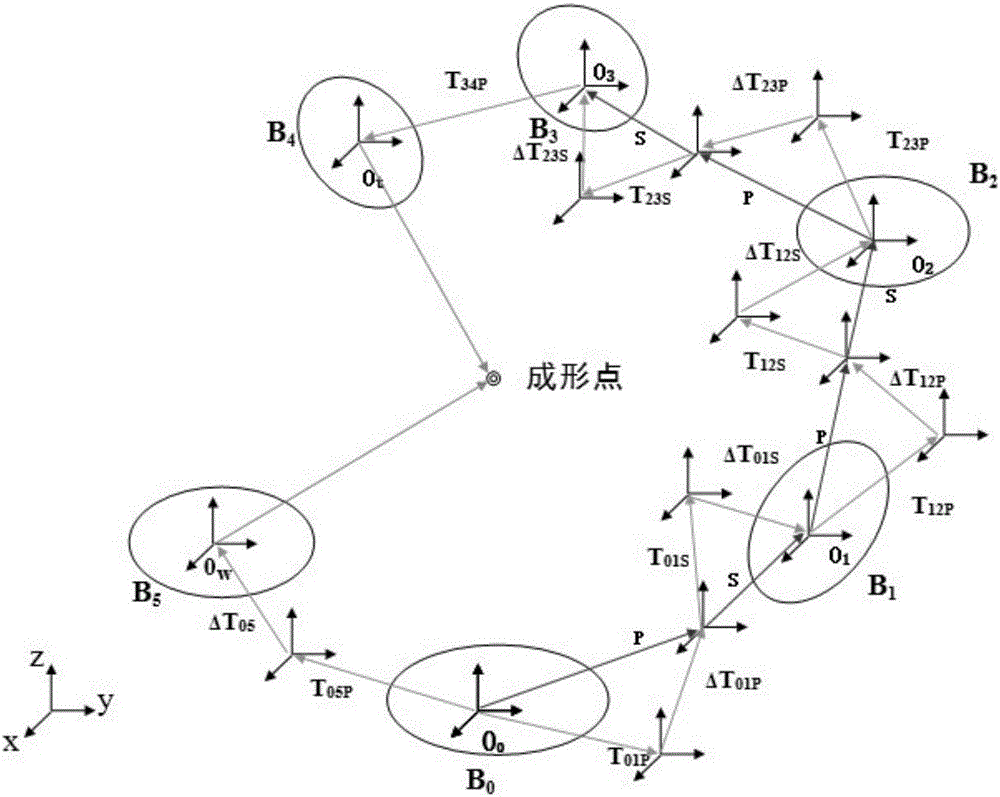
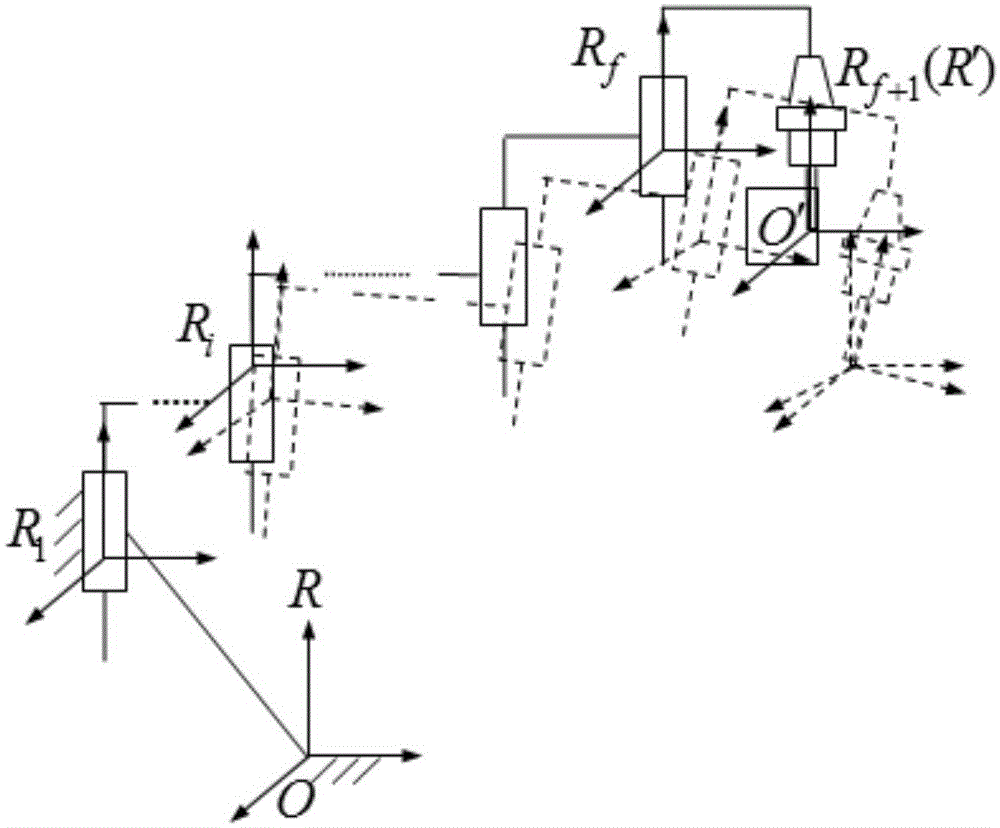
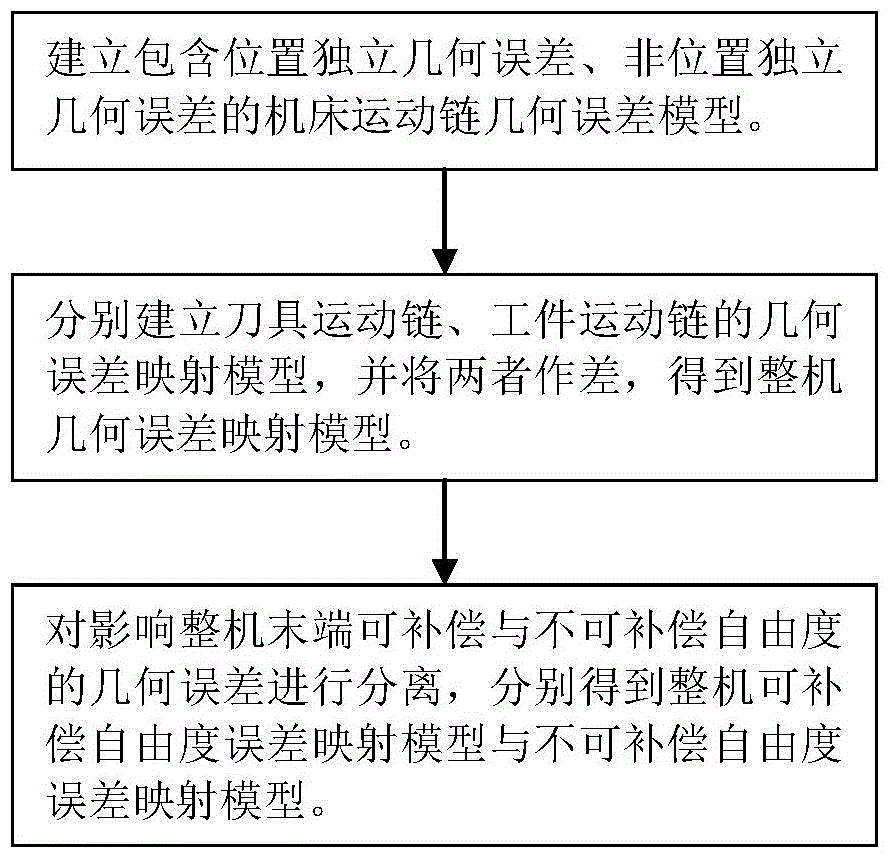
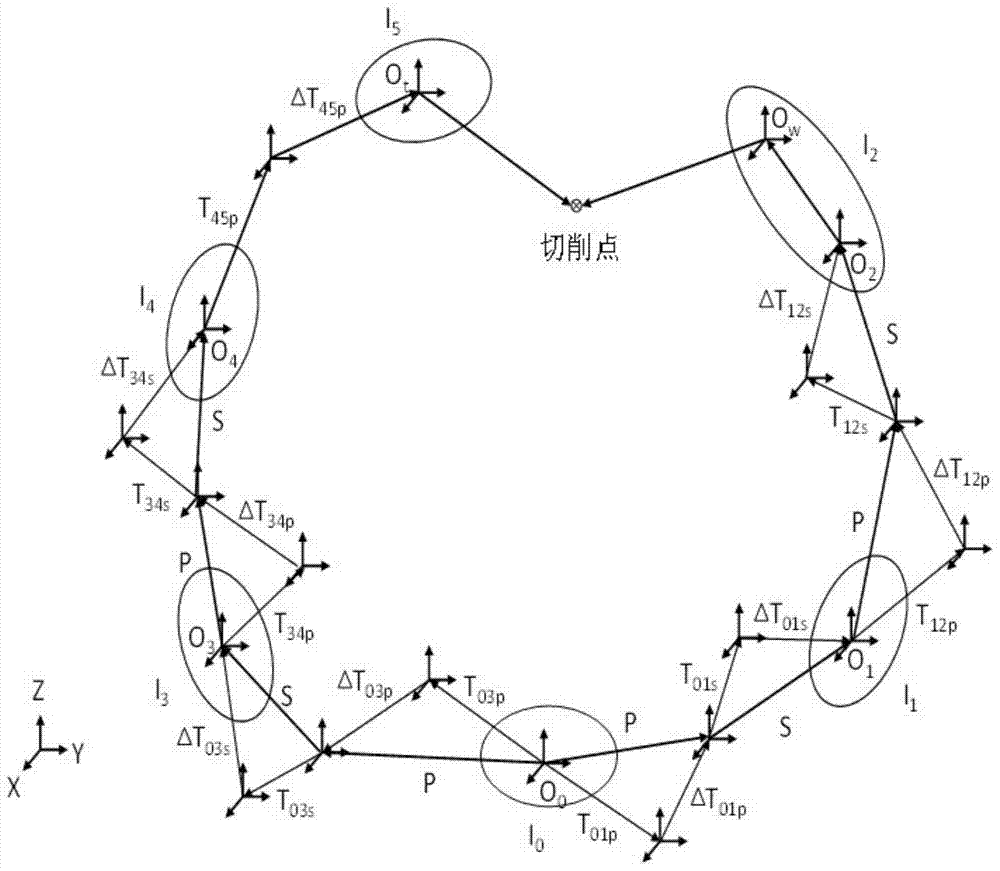
The invention discloses a geometric error screw theory modeling method for a numerically-controlled machine tool. The method includes the first step of establishing an overall coordinate system R at any point on a machine body, establishing instant reference coordinate systems R' at reference points of the tail ends of a kinematic chains and establishing cojoined coordinate systems R[i] on kinematic pairs according to the kinematic chains of the numerically-controlled machine tool, and establishing a machine tool kinematic chain geometric error model containing location independent geometric errors and non-location independent geometric errors, the second step of obtaining a whole machine geometric error mapping model through the machine tool machine tool kinematic chain geometric error modeling method in the first step, and the third step of carrying out separation on compensable freedom degree geometric errors and non-compensable freedom degree geometric errors influencing the tail end of the complete machine according to the properties of a variation space of a restrained rigid body, the properties of a force space of the restrained rigid body, the properties of subspaces of the variation space and the properties of subspaces of the force space to respectively obtain a compensable freedom degree error mapping model and a non-compensable freedom degree error mapping model of the whole machine. Through the method, the mathematical models are provided for error compensation, and an important instructional theoretical basis is provided for error prevention and the precision matching design of the machine tool.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
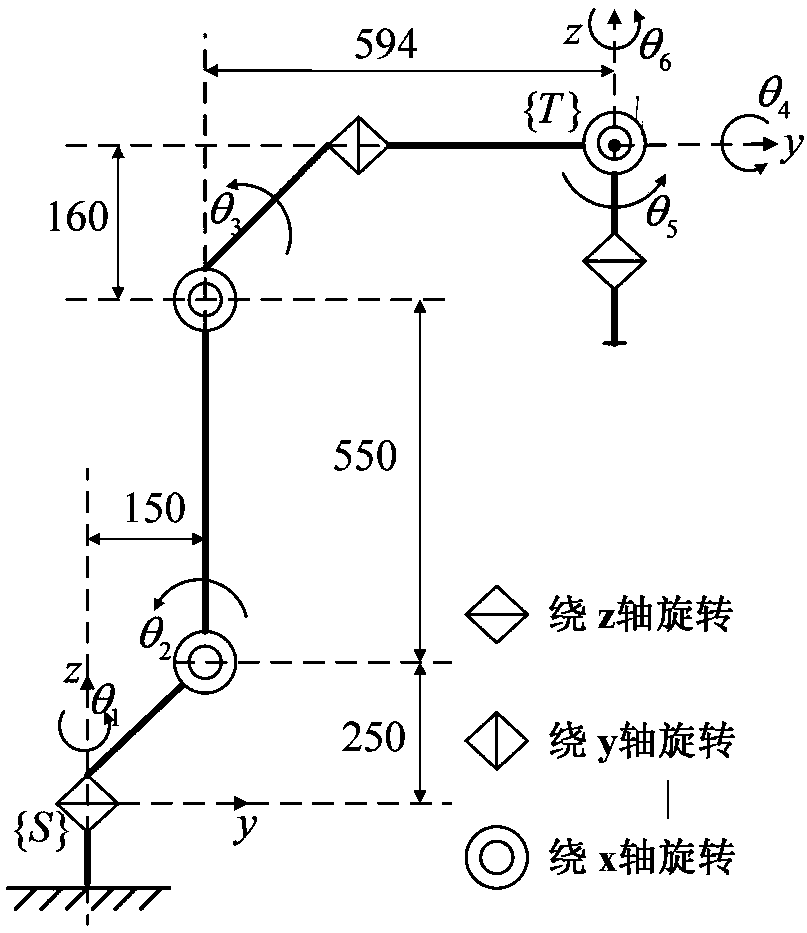
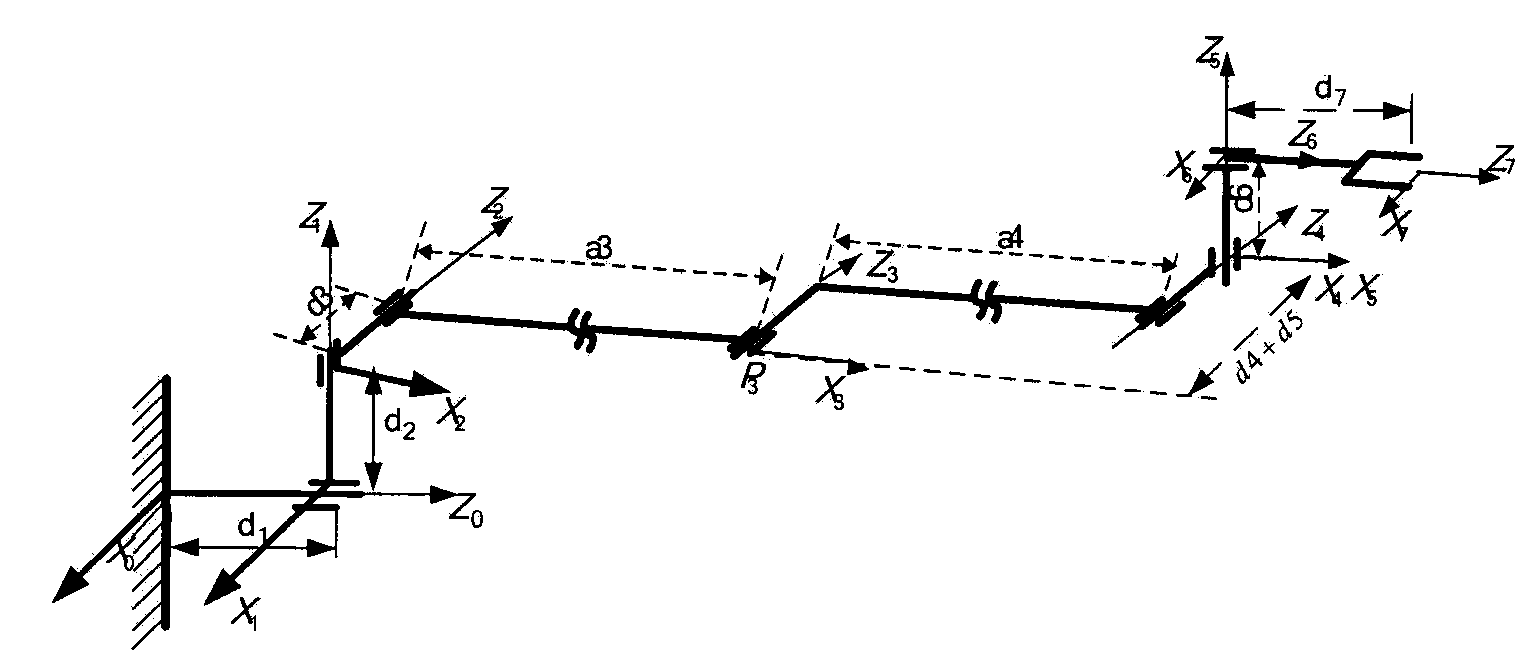
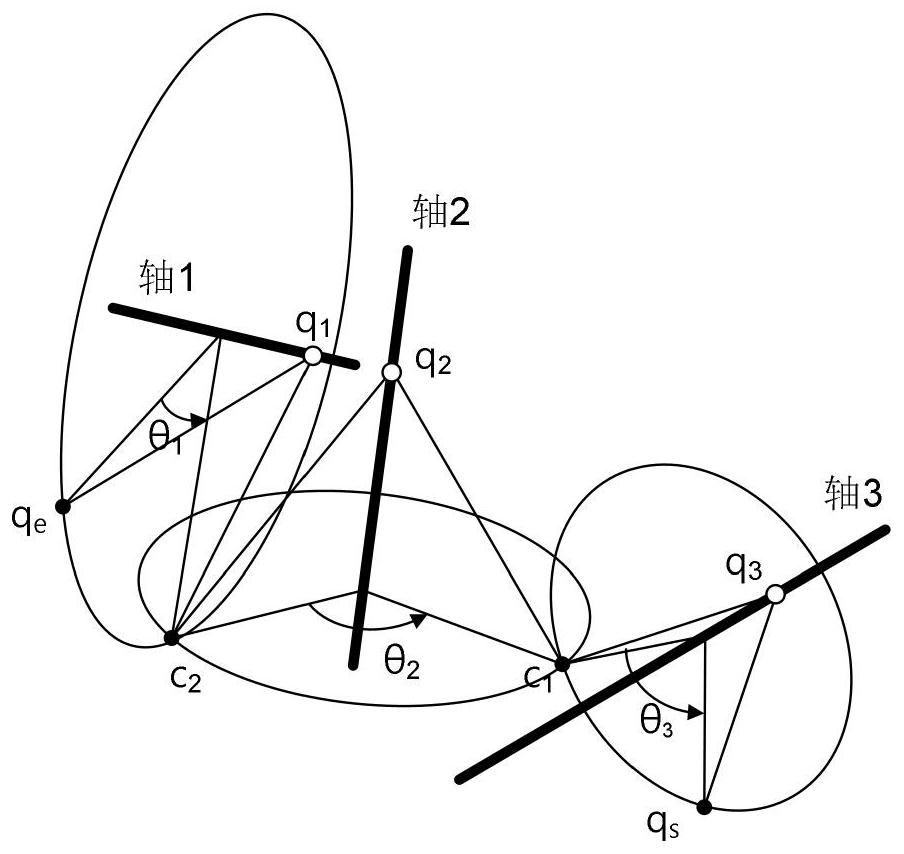
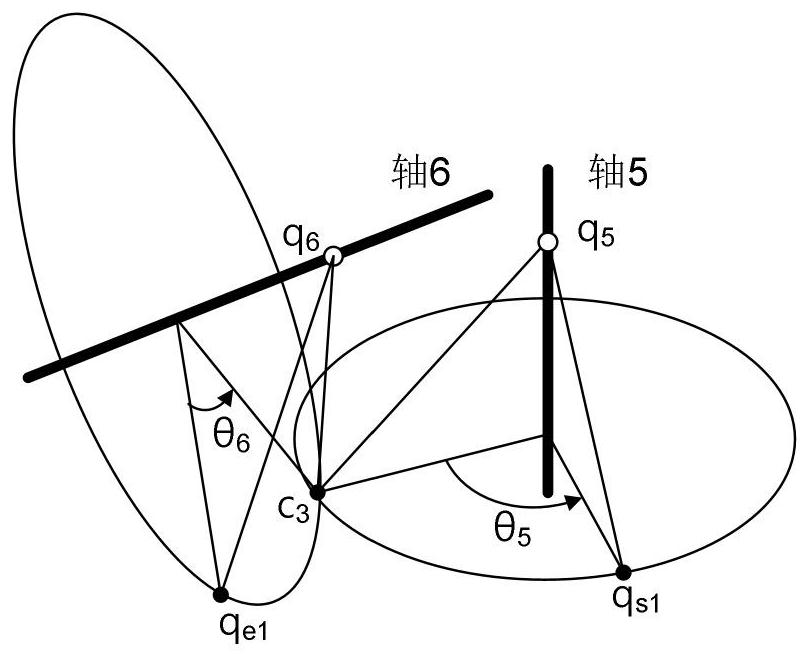
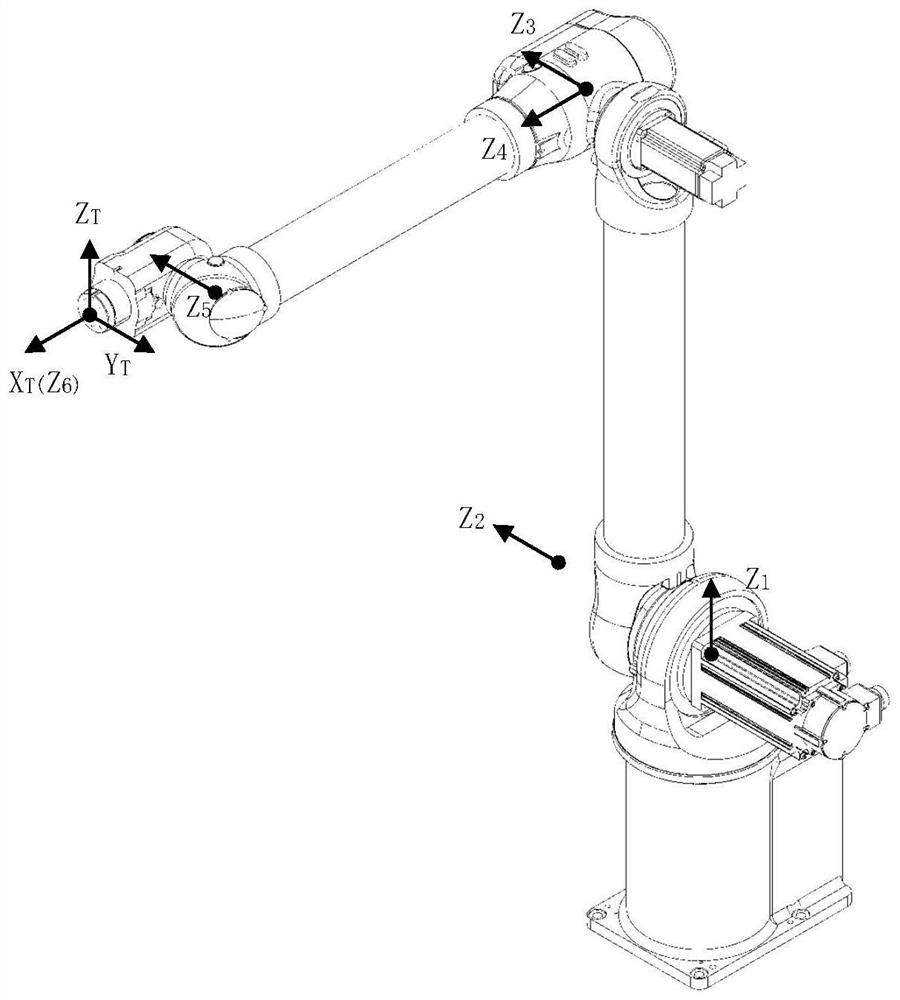
6R robot inverse kinematic geometry solving method based on screw theory
ActiveCN107756400ASimplified inverse modelGeometric meaning is clearProgramme-controlled manipulatorComplex mathematical operationsAlgebraic equationRobot kinematics
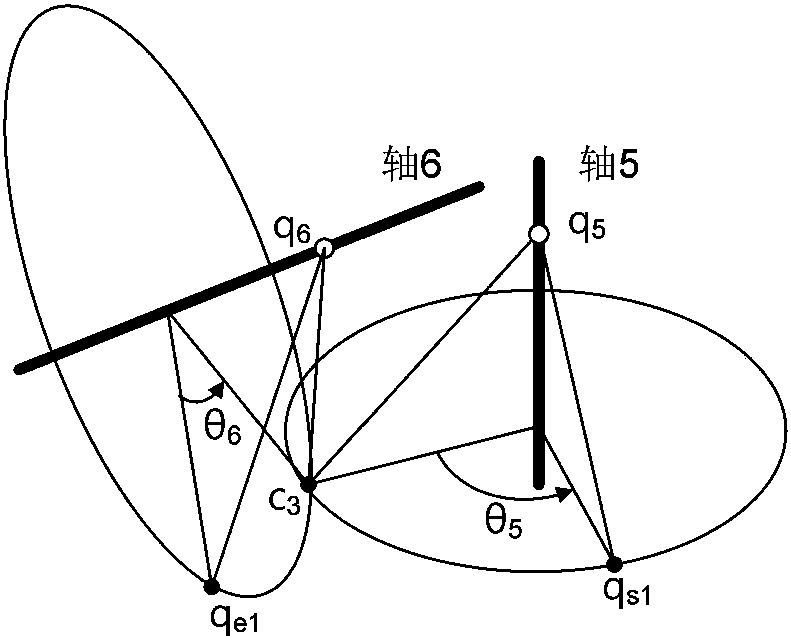
The invention discloses a 6R robot inverse kinematic geometry solving method based on a screw theory and belongs to the field of robot kinematic inverse solution research. A basal coordinate system and a tool coordinate system are established, kinematic parameters of a 6R robot are determined through the basal coordinate system and the tool coordinate system, and a forward kinematic model is established; inverse solution motion of first three joints of the 6R robot is descripted in a decomposed mode, and a six-variable quadratic equation set is established; and a target position qe1 corresponding to an initial position qs1 is solved based on a screw forward kinematic model. Through the method, geometric description is combined with the screw theory, the geometrical significance is more explicit, the algebraic equation set is solved through a simplified inverse kinematic algorithm, the calculation efficiency is effectively improved, and a new inverse kinematics processing method is provided for real-time control over robot movement.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Machine tool machining precision retaining ability prediction method based on rough set theory and least squares support vector machine
The invention relates to a machine tool machining precision retraining ability prediction method based on a rough set theory and a least squares support vector machine. Generally, complex and great data error are generated if error data is required to be measured in a long term and detection and analysis are required to be carried out on the machining precision within the specified time for multiple times. The invention provides a machining procession retaining ability prediction method on the basis of the error data, which comprises the steps of firstly establishing a spatial error model of the overall machine tool on the basis of a topological structure of the machine tool by using an exponential matrix mode of a screw theory so as to carry out topological structure based screw theory error modeling and carry out measurement on the error data; secondly, carrying out reduction on the error data based on the rough set (RS) theory, and then carrying out machining precision retaining ability prediction based on a least squares support vector machine (LS-SVM) method; and finally, proving the effectiveness of the prediction method provided by the invention by using a simulation method.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Manipulator servo control method, system and device based on screw theory
ActiveCN109483529AAvoid repeated calculationsSmall amount of calculationProgramme-controlled manipulatorData controlMaximum error
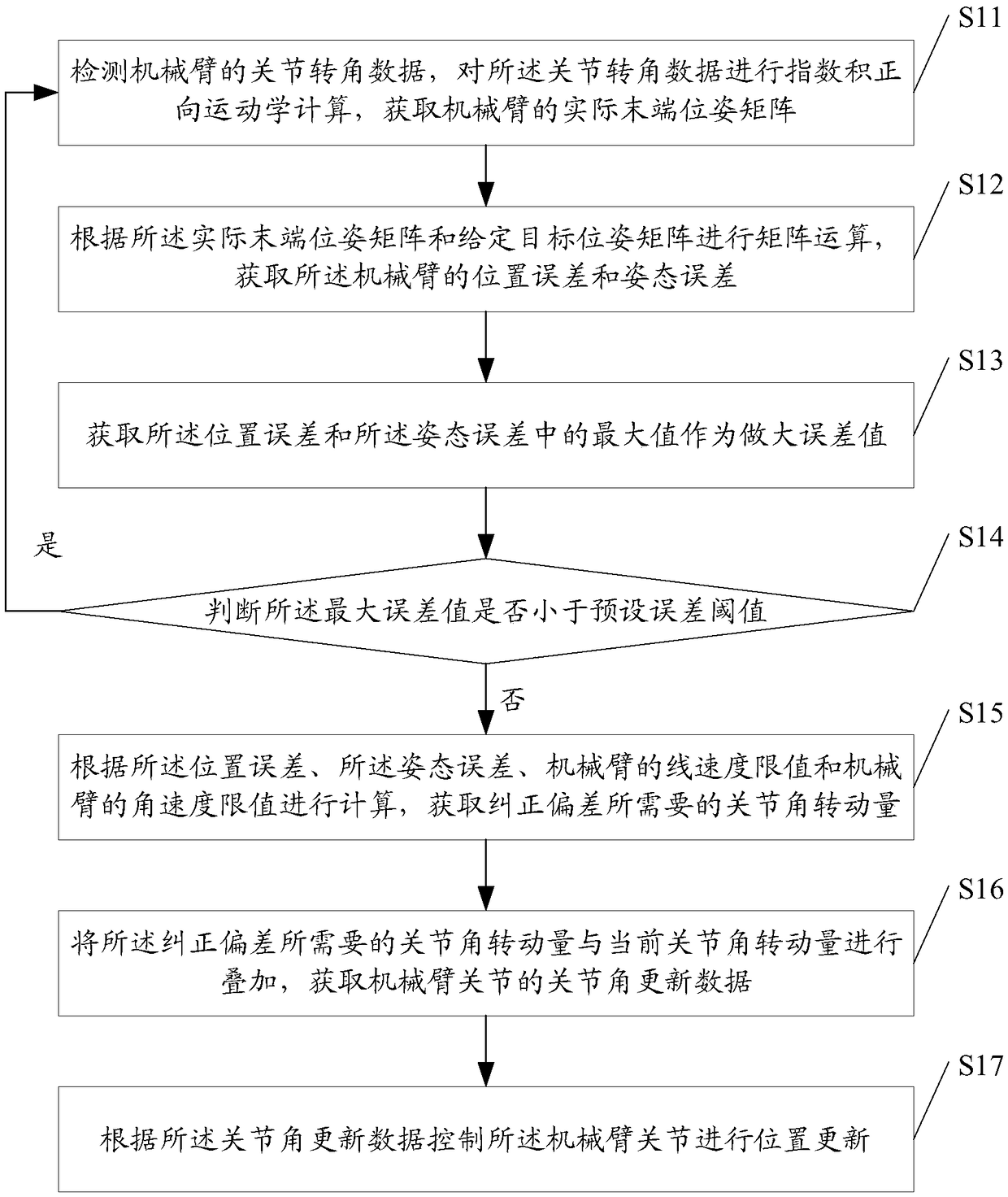
The invention discloses a manipulator servo control method, system and device based on a screw theory. The manipulator servo control method comprises the steps that joint rotating angle data of a manipulator are detected and subjected to exponential product direct kinematics calculation, and thus an actual tail end position-attitude matrix of the manipulator is obtained; matrix operation is conducted according to the actual tail end position-attitude matrix and a given target position-attitude matrix, and thus a position error and an attitude error of the manipulator are obtained; the maximumvalue in the position error and the attitude error is obtained to serve as the maximum error value, and whether the maximum error value is less than a preset error threshold value or not is judged; ifnot, calculation is conducted to obtain the joint angle rotating amount required by deviation correcting; joint angle updating data of manipulator joints are obtained; and the manipulator joints arecontrolled to be subjected to position updating according to the joint angle updating data. By adopting the manipulator servo control method, the advantages of small calculated amount, good real-timeperformance and accurate tracking are achieved, and the control precision of the manipulator can be effectively improved.
Owner:华南智能机器人创新研究院
Extended Fourier amplitude based extraction method of machine tool important geometric error source
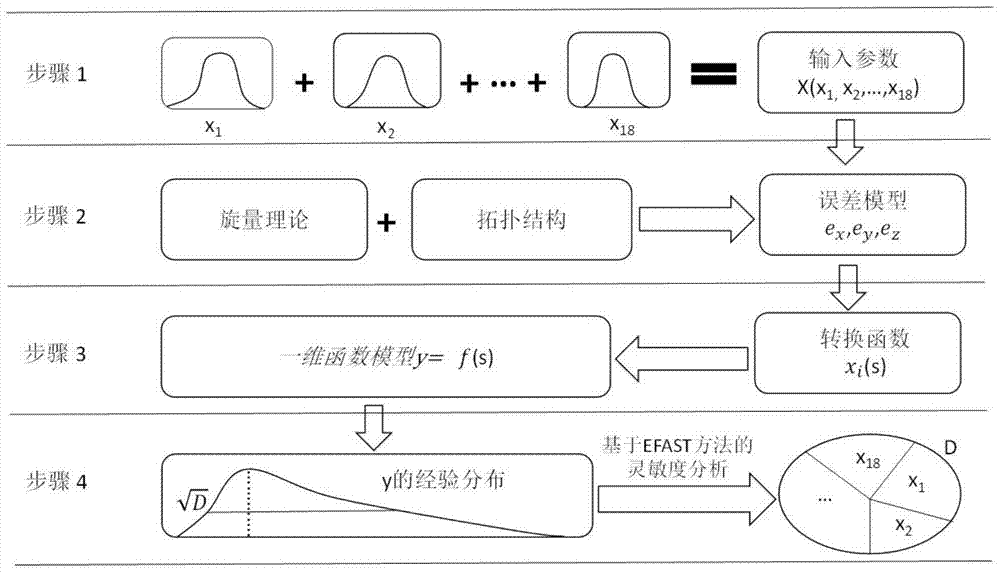
The invention discloses an extended Fourier amplitude based extraction method of a machine tool important geometric error source. Based on error measuring data, by use of an index matrix form of a screw theory, on the basis of the topology structure of a machine tool, an integral space error model of the machine tool is established, a high-order term of the error model is eliminated, and a basis equation of the error model is obtained. According to an EFAST global sensitivity analysis method, through selecting a proper conversion function, the error model is converted into a one-dimensional function from an eighteen-dimensional function, Fourier series expansion is carried out on the one-dimensional function, and a model caused by each parameter and a total variance of model output can be obtained. The EFAST method can simultaneously examine the influences exerted by change of multiple geometric errors on the result of a spinor error model and can also analyze the direct and indirect influences exerted by change of each geometric error on the model result, and the method provided by the invention can be applied to extraction of key geometric error terms having quite large influences on processing precision of the machine tool.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Inverse kinematics general solving method of five-degree-of-freedom serial robot
ActiveCN106845037ASimple form of expressionSimple and easy to understandDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsAngular degreesDegrees of freedom
The invention discloses an inverse kinematics general solving method of a five-degree-of-freedom serial robot and belongs to the field of inverse kinematics of the robot. The invention provides the inverse kinematics general solving method, which has a simple form and is easy to calculate, on the basis of an exponential product model; basic properties of a screw theory and Rodrigues rotary expression are mainly combined to simplify an inverse solution solving process; under the condition of meeting Pieper constraints, an angle value of each joint can be directly obtained without the need of considering a relation between former two joint axes; five joint angles can be uniformly expressed through only two expression formulas, and convenience is provided for robots in actual application.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Hybrid type automobile electrophoresis coating conveying mechanism dynamics modeling method
ActiveCN105159137AHas coordinate invarianceNeat and concise expressionProgramme controlSimulator controlHybrid typeDynamic models
The invention discloses a hybrid type automobile electrophoresis coating conveying mechanism dynamics modeling method. First of all, the symmetrical structure characteristic of a mechanism is fully utilized, the speed and the accelerated speed of each passive joint in the mechanism are analyzed through an analytical geometry method, and then the speed and the accelerated speed of each active joint of the mechanism are obtained by introducing a screw theory; secondly, based on this, a kinetic equation in a mechanism spinor form is established by use of virtual work principle; and finally, axial driving power of each active joint of the conveying mechanism capable of directly realizing control is obtained through calculation so that construction of a dynamics model capable of realizing high-performance control is completed. According to the invention, the analytical geometry method, the screw theory and the virtual work principle are combined together, so that the problem of coordinate transformation due to lack of coordinate invariance during dynamics modeling of a complex special mechanism is solved, the calculation complexity is reduced, and at the same time, the dynamics modeling method brought forward by the invention is quite simple, is tidy in form and is easy in programmed realization.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Machine tool geometric error measurement method based on ball rod instrument
InactiveCN111872748AImprove detection efficiencyHigh measurement accuracyMeasurement/indication equipmentsGeometric errorAlgorithm
The invention discloses a machine tool geometric error measurement method based on a ball rod instrument. The method comprises the following steps of establishing a five-axis machine tool geometric error model based on a spiral theory; establishing a mathematical model of constant-speed linkage of an X axis and a C axis of a machine tool, ensuring that constant-speed acquisition data of the ball rod instrument is synchronous with actual motion in the measurement process, and calculating machine tool codes through the mathematical model; and using the machine tool codes for carrying out a measurement experiment, performing error decoupling on the data measured by the ball rod instrument based on a particle swarm algorithm, and obtaining six geometric errors in a two-axis linkage measurementprocess. The method can measure the geometric errors of a linear shaft and a rotating shaft at the same time, and is high in measurement precision and good in practicability.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
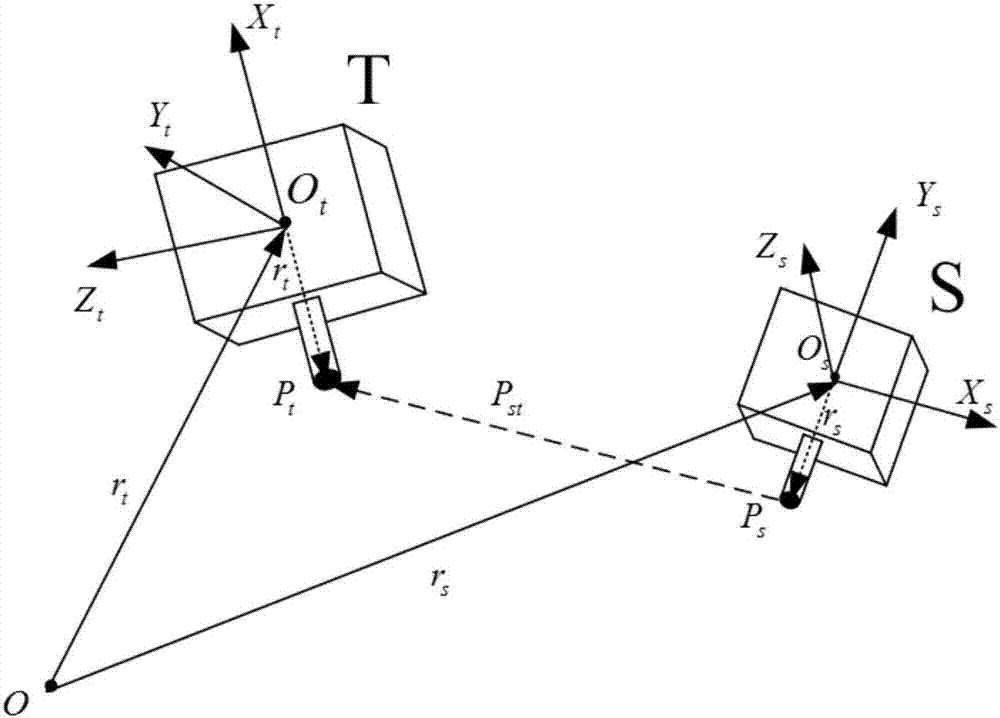
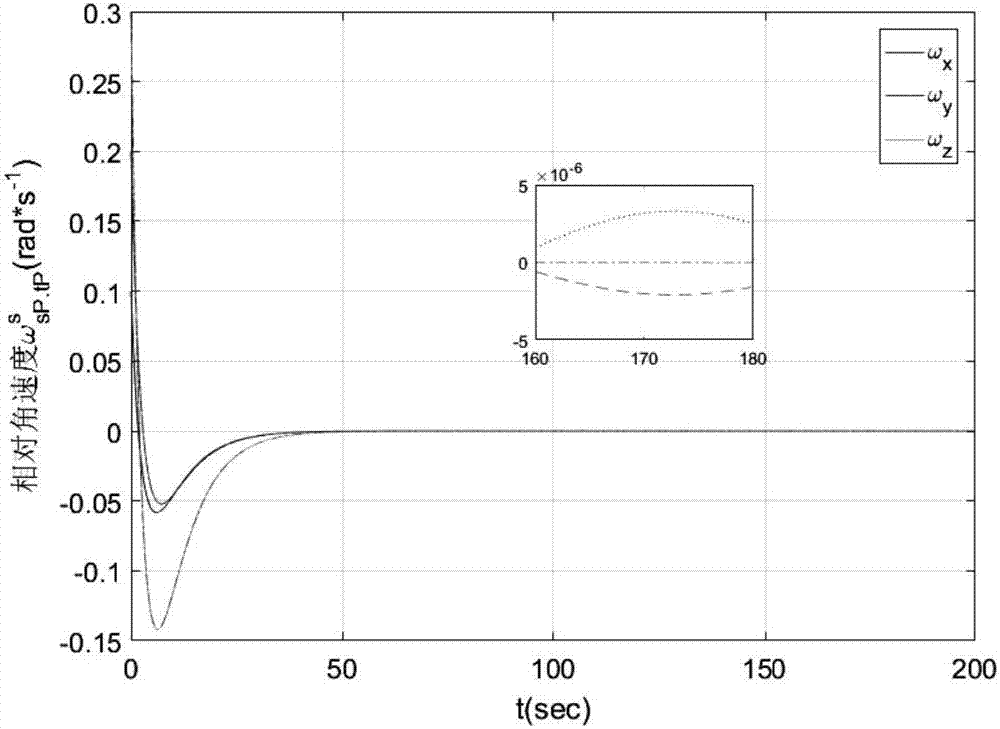
Spacecraft non-centroid relative movement modeling method
The invention discloses a spacecraft non-centroid relative movement modeling method. By introducing the appropriate conversion operator, the relative speed screw between the non-centroid docking points is established, and then based on the basic mechanics principle and screw theory, the derivation is carried out to obtain a non-centroid point relative movement attitude and trajectory coupled model. The modeling method has the characteristics of concise and convenient operation, and is compact in formula expression and easy to analyze and understand.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
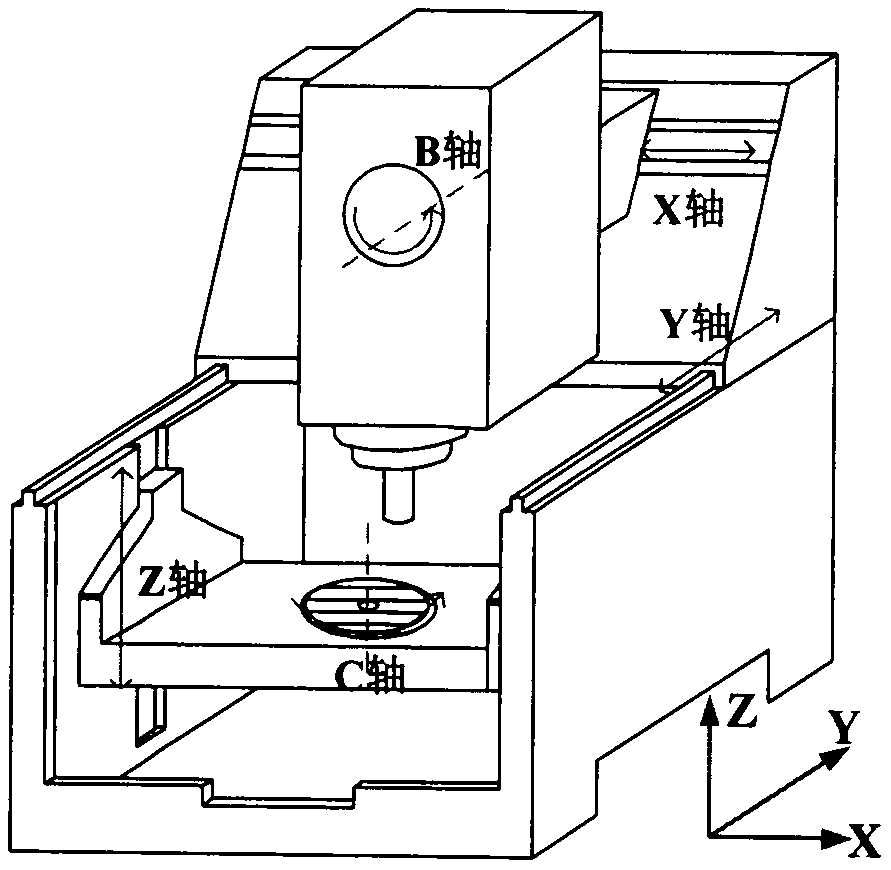
Five-axis machine tool error measurement method based on ball rod instrument
InactiveCN111872742ARealize simultaneous measurementImprove measurement efficiencyMeasurement/indication equipmentsGeometric errorMathematical model
The invention discloses a five-axis machine tool error measurement method based on a ball rod instrument. The method comprises the following steps of constructing a machine tool error model based on aspiral theory; establishing a mathematical model of constant-speed linkage of a Z axis and a B axis of a machine tool so as to ensure that data acquired by the ball rod instrument is synchronous withactual motion in the measurement process, and calculating machine tool codes based on the mathematical model; measuring machine tool errors. and performing error decoupling on the data measured by the ball rod instrument, so that geometric errors in a two-axis linkage measurement process can be solved. According to the method, simultaneous measurement of the geometric errors of the Z axis and theB axis of the machine tool is realized, so that the measurement efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
System and Method For Medical Imaging Calibration and Operation
InactiveUS20160081668A1Medical imagingOrgan movement/changes detectionData streamVolumetric Mass Density
A system and method is provided for solving the AX=XB calibration problem. A calibration method is presented to determine the unknown X in the AX=XB calibration problem. Sensor data is filtered, such that data without the desired screw theory invariants are discarded. The correspondence between A and B is then computed, either through a probabilistic Batch method that treats the data streams as probability density functions, or by formulating the data streams as a time-evolving differential equation which allows for online calibration of the device. Also, a calibration phantom and software is also provided. The phantom is an extension of known Z-fiducial phantoms, in which the Z-fiducials are oriented based on consideration of imaging physics. An additional phantom is designed that does not utilize rods within the phantom to perform the calibration.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
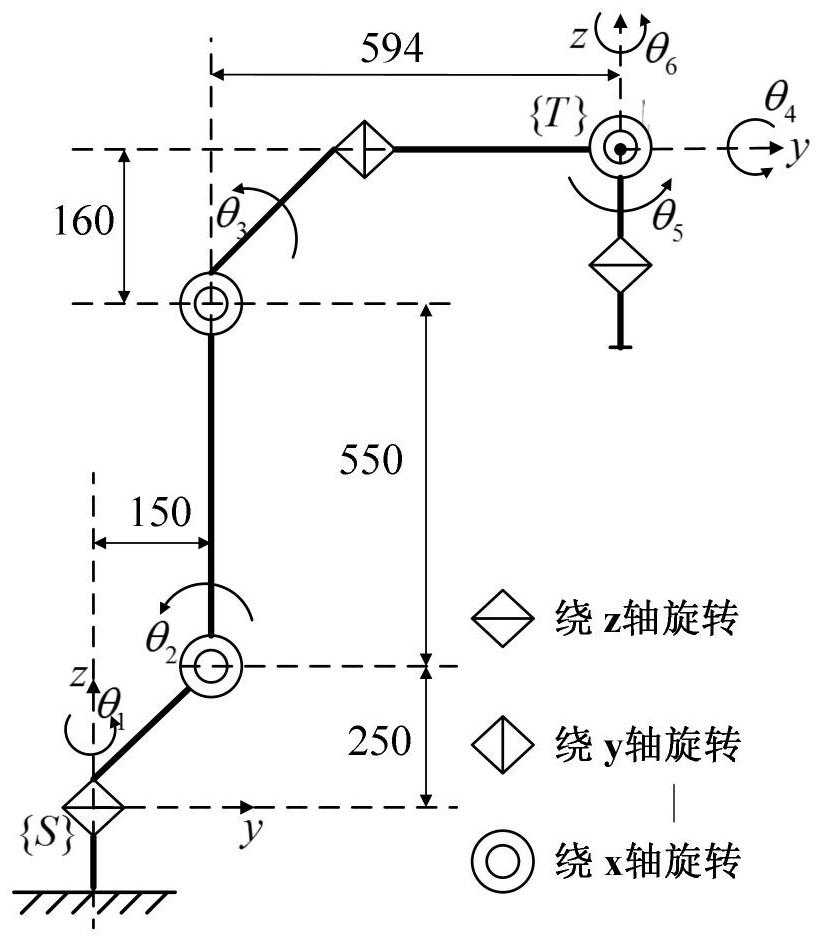
Non-spherical-wrist 6R robot inverse kinematics obtaining method
ActiveCN111452041AClarify the geometric meaningEasy to deriveProgramme-controlled manipulatorSimulationControl theory
The invention provides a non-spherical-wrist 6R robot inverse kinematics obtaining method. The method comprises the following steps that S1, a robot forward kinematical equation of a robot is built onthe basis of the screw theory exponential product formula; S2, a robot dissoluble conclusion is obtained through transformation of the robot forward kinematical formula; S3, robot decomposition pointselection and reconnection geometric constraint conditions are obtained; S4, a solution formula of all joint angles of the nonlinear closure equation is deduced, and a binary method is used for solution; S5, the effectiveness of the method is verified through simulation. Compared with a traditional method, the non-spherical-wrist 6R robot inverse kinematics obtaining method has the clearer geometric meaning, the deduction process is easier and more convenient, and real-time and high-precision control is achieved in the solving process.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF TECH
Parallel mechanism based automated fiber placement system
ActiveUS10414042B2Improve performanceDemonstrated effectProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsFiberAviation
Owner:KHALIFA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Modeling Method of Geometric Error Screw Theory for CNC Machine Tool
The invention discloses a geometric error screw theory modeling method of a numerical control machine tool, comprising: step 1, establishing a global coordinate system R at any point of the bed for the kinematic chain of the numerical control machine tool, and establishing an instantaneous reference coordinate at a reference point at the end of the kinematic chain System R', establish a conjoined coordinate system Ri on each kinematic pair; establish a geometric error model of the machine tool kinematic chain that includes position-independent geometric errors and non-position-independent geometric errors; The model method is used to obtain the geometric error mapping model of the whole machine; step 3, using the properties of the variational space, force space and their subspaces of the constrained rigid body, to separate the geometric errors that affect the compensable and non-compensable degrees of freedom at the end of the machine, The error mapping models of compensable degrees of freedom and non-compensable degrees of freedom of the whole machine are respectively obtained. The invention not only provides a mathematical model for error compensation, but also provides an important guiding theoretical basis for error prevention and machine tool precision matching design.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
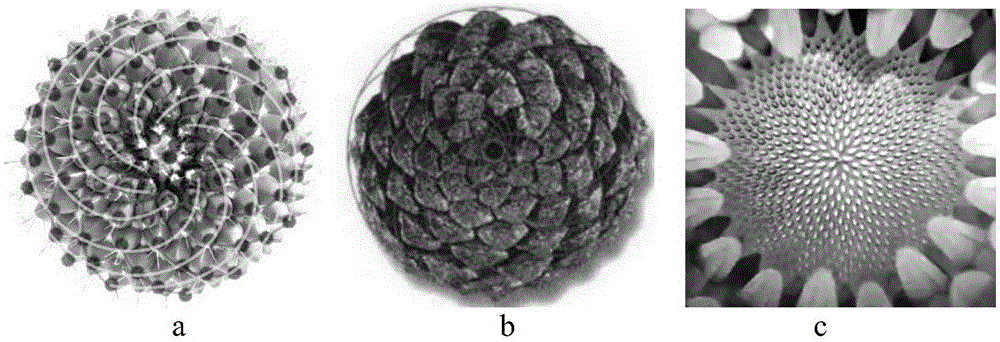
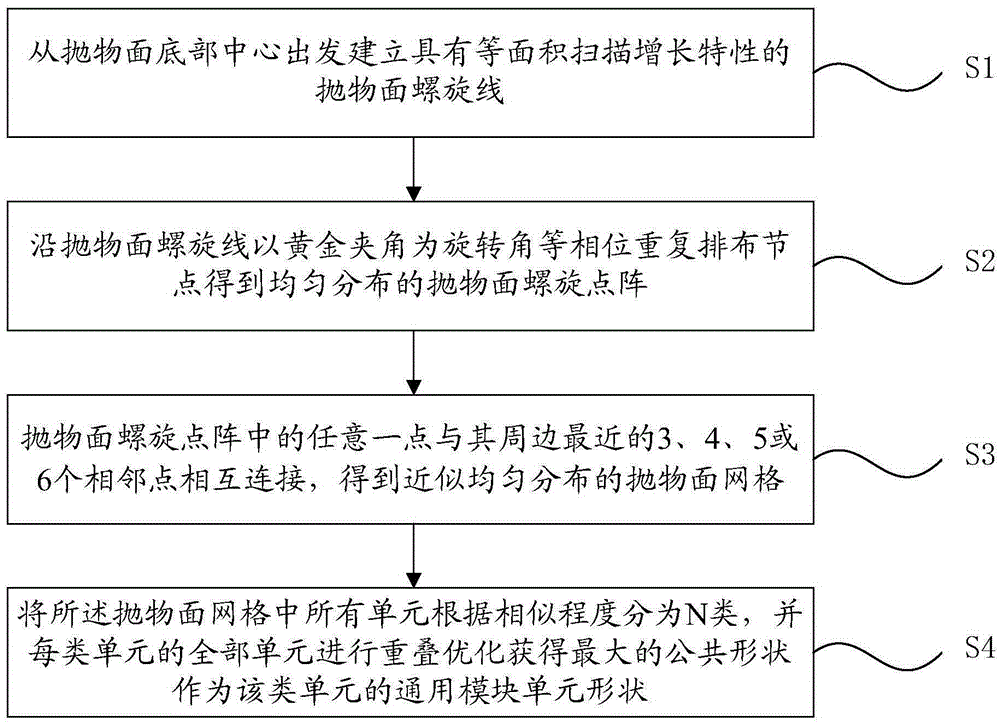
Paraboloid module division method based on screw theory
ActiveCN105335551ASolve the problem of customizing different modular unitsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDot matrixEngineering
The invention provides a paraboloid module division method based on a screw theory. The method comprise: starting from the center of the bottom of a paraboloid, establishing a paraboloid spiral line in an equal area scanning increase characteristic, repeatedly arranging nodes along the spiral line in equal phase, with a golden included angle as the rotation angle, to obtain a uniformly distributed paraboloid spiral dot matrix, connecting any dot in the dot matrix with two or three adjacent dots under the dot, to obtain paraboloid quadrangles or triangular grids approximate to uniform distribution, classifying all units in the paraboloid grids into N kinds (such as 3,5,6,7,or 9 kinds) according to level of similarity, and performing overlaying optimization on all the units in each kind of units, to obtain a largest common shape, and a module unit which can be used to assemble paraboloids in different diameters is obtained. The method can realize universalization of a module unit among different paraboloids, and creates conditions for universalization of an in-orbit assembling system and supporting facilities.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE SYST ENG INST
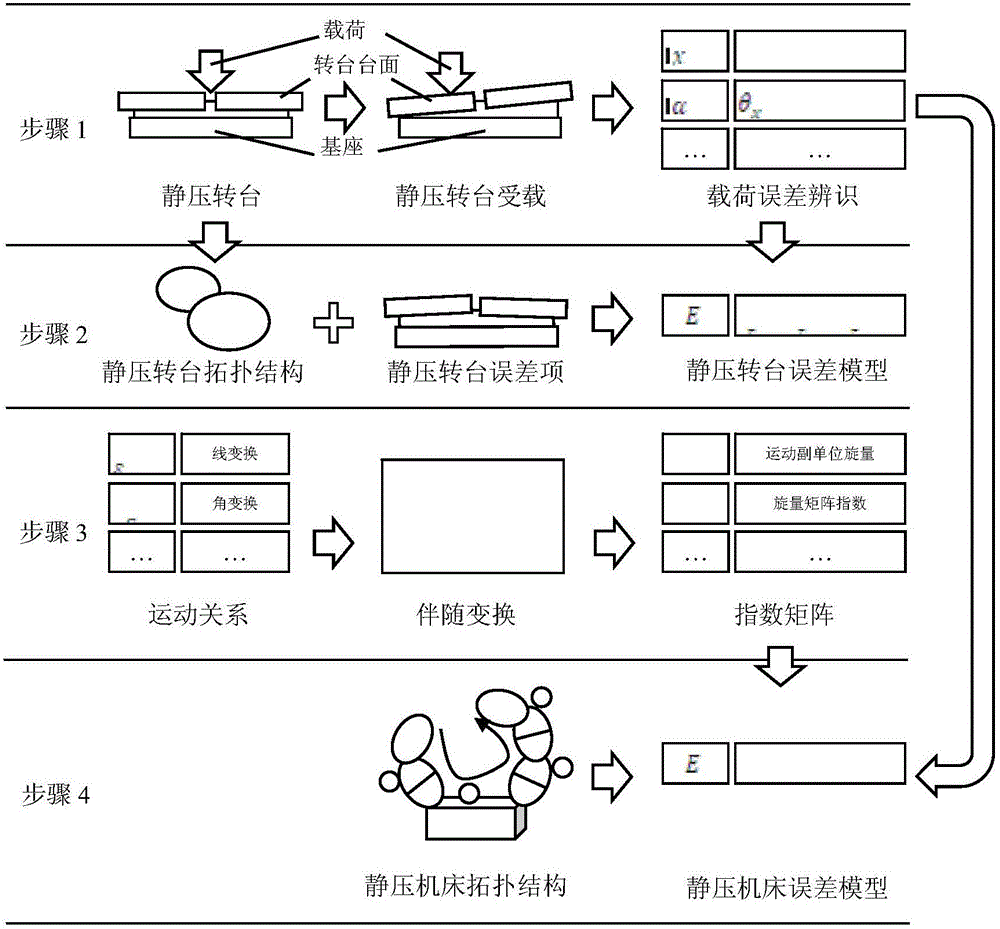
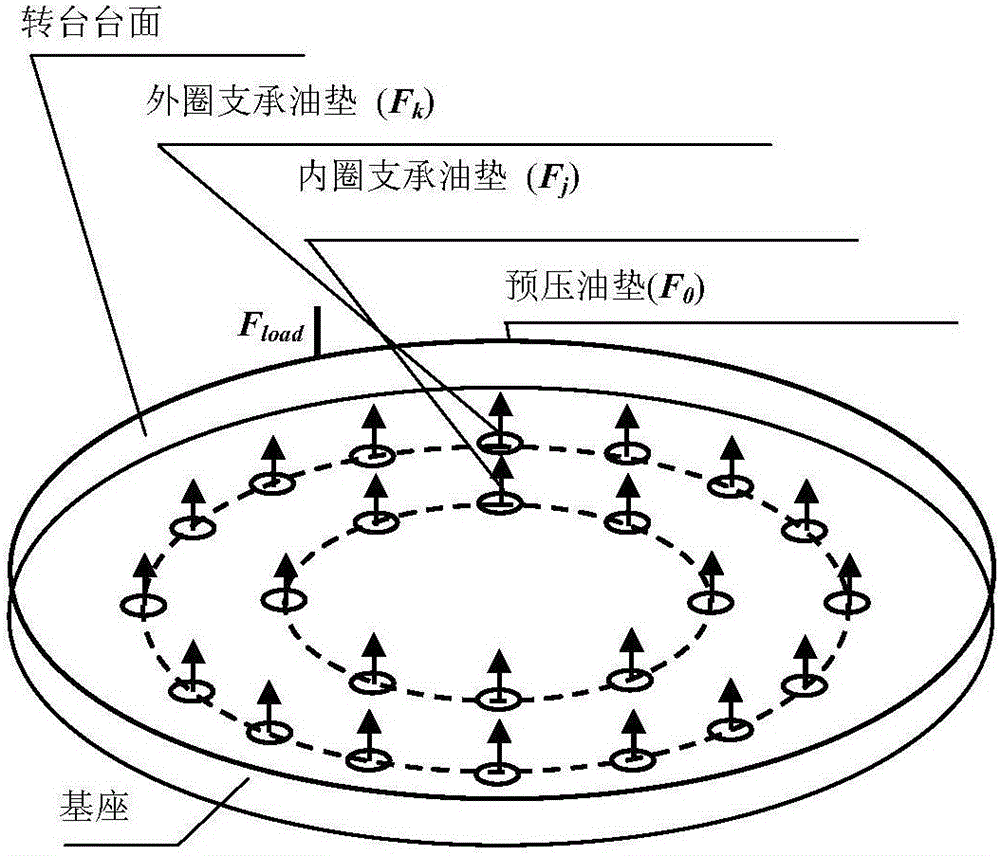
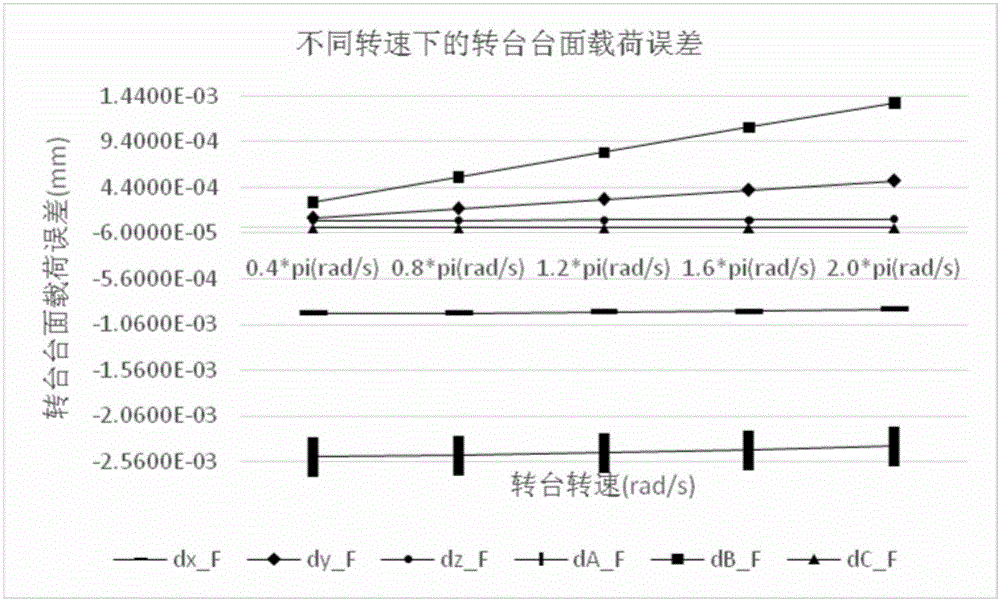
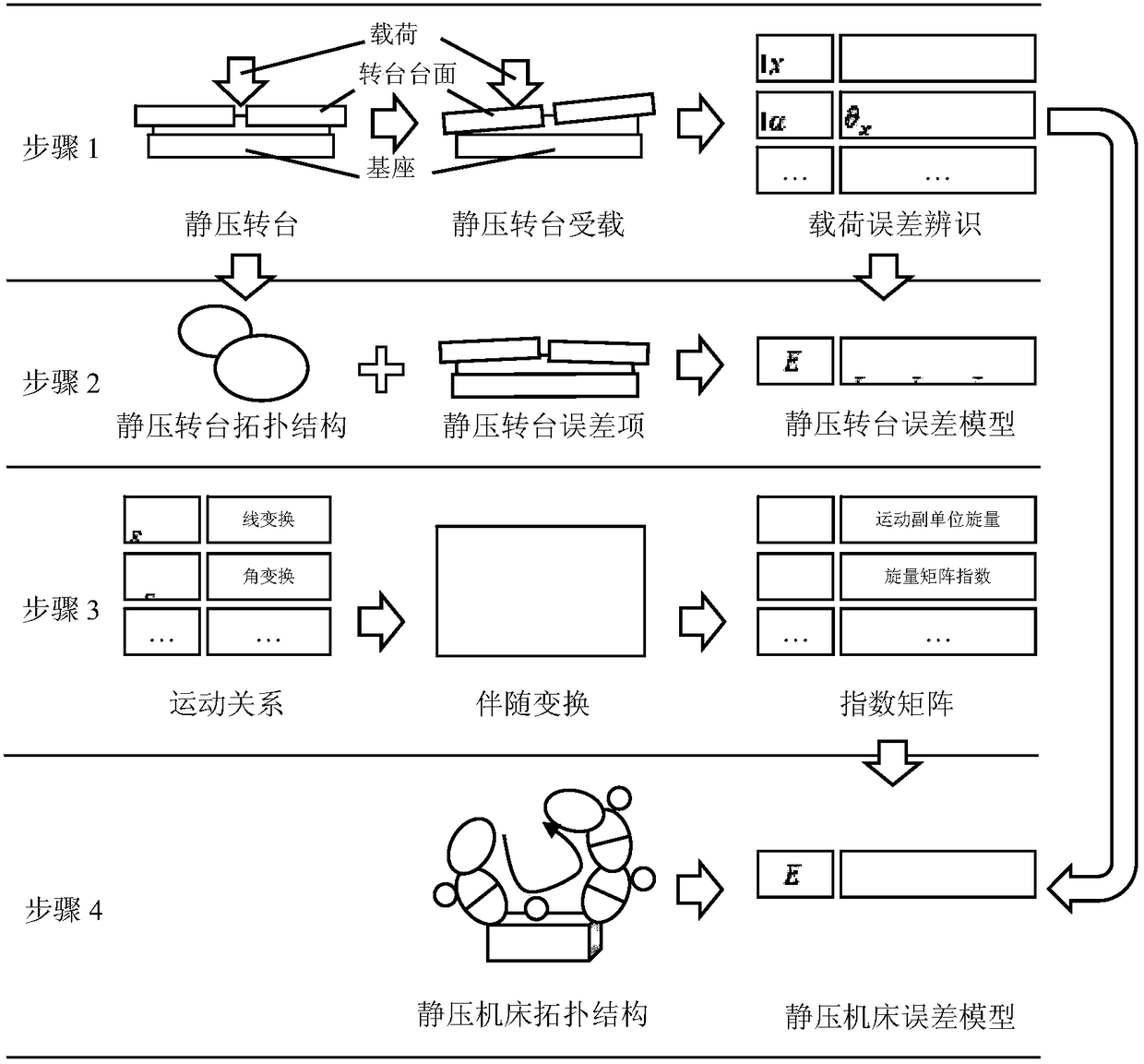
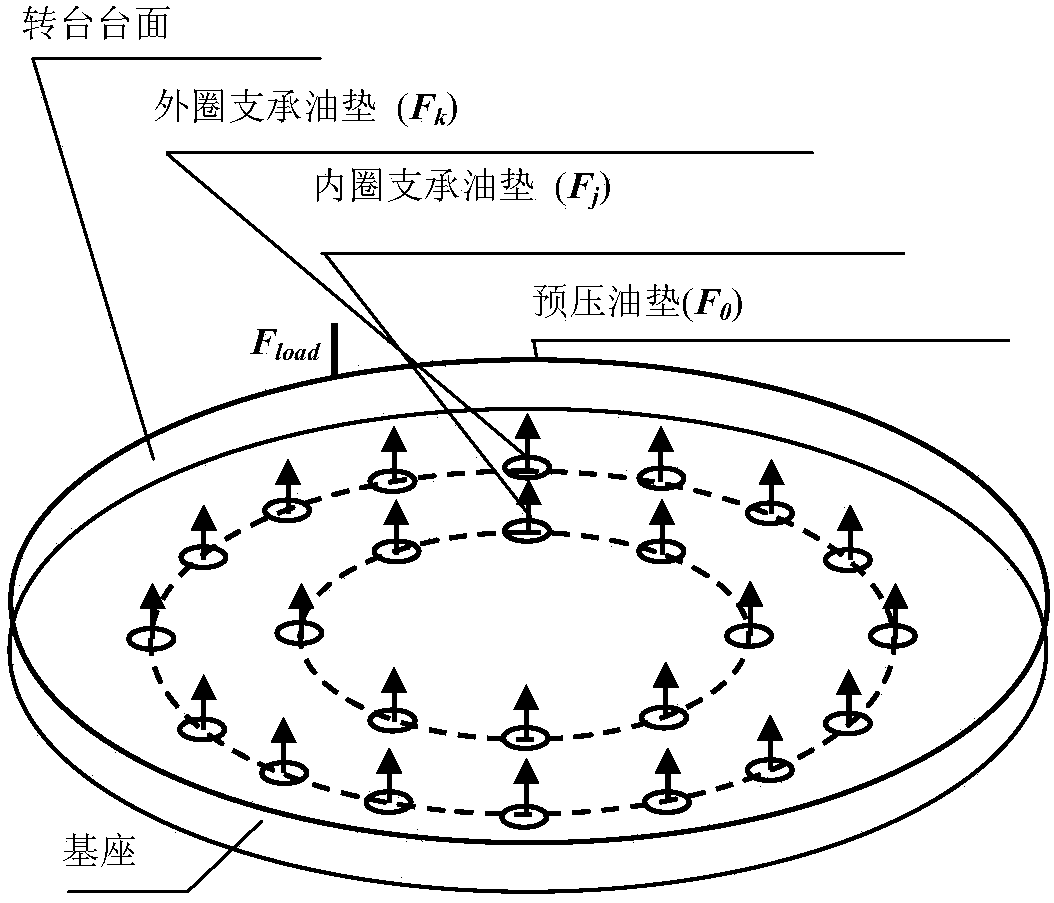
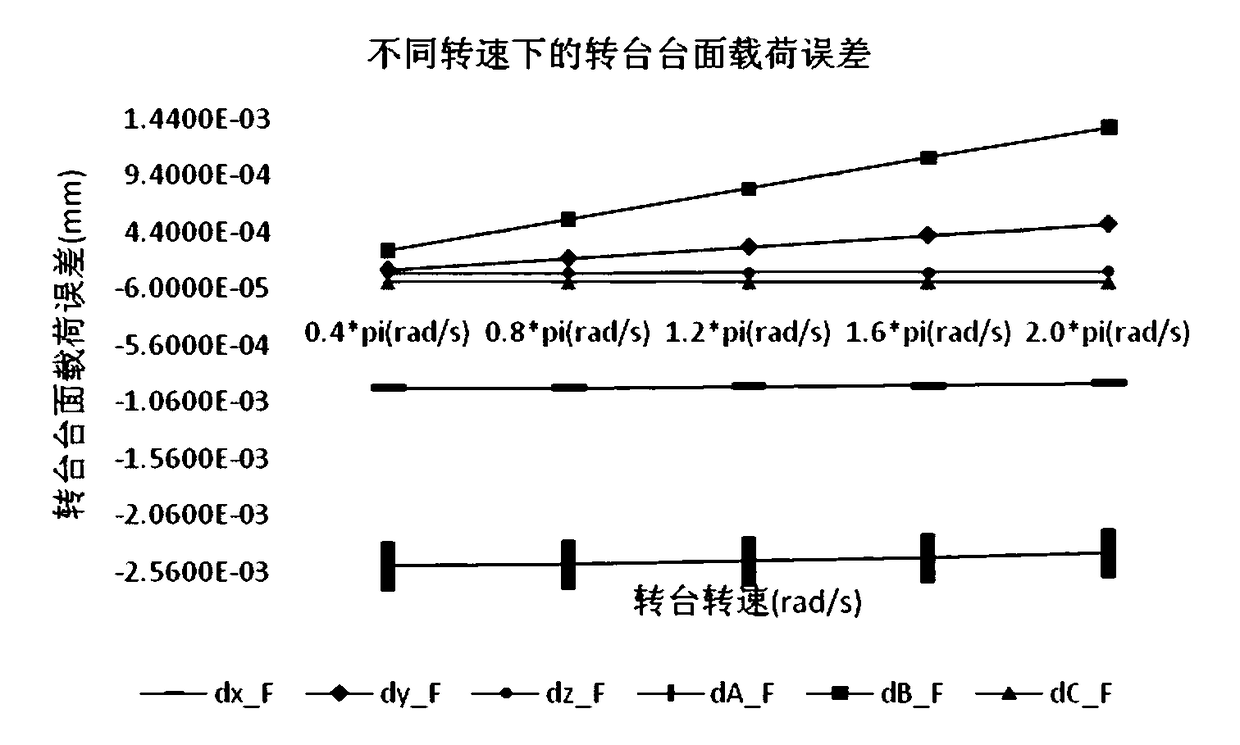
Influence analytical method for identifying load error of static-pressure rotary table and analyzing influence of load error on machining error of machine tool
The invention provides an influence analytical method for identifying the load error of a static-pressure rotary table and analyzing the influence of the load error on the machining error of a machine tool, and belongs to the accurate design field of numerical control machine tools. On the premise that the load error of a machine tool is taken into account, an N-S equation and a film hypothesis theory are adopted to derive the table-board load error recognition of the static-pressure rotary table. Based on error measurement data, a space error model of the entire machine tool is established based on the topological structure of the machine tool in the index matrix form of the screw theory. The above method comprehensively considers load parameters and is reliable and efficient in calculation. The accuracy model of the machine tool is established based on the index matrix of the screw theory, so that the influence effect of each load error can be accurately calculated through quantitatively considering a fluid dynamics equation. That means, the above method is capable of not only simultaneously detecting the combined effect of the variation of multiple load parameters on the result of the error model, but also analyzing the individual effect of the variation of each load parameter on the result of the error model. The results of actual cases show that, the above method is effective.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Inverse kinematics solving method for any three joints
InactiveCN108763151AImprove computing efficiencyEasy to implementComplex mathematical operationsInverse kinematicsComputer science
The invention discloses an inverse kinematics solving method for any three joints, and belongs to the field of robot inverse kinematics. On the basis of an exponential product model, a simple geometric constraint equation, the basic property of a screw theory and the Rodrigues expression of a rotation matrix are used for converting questions into a linear equation which relates to a trigonometricfunction to be solved, the inverse solution of any three joint axes is realized, the solving of a robot inverse solution is not limited to a constraint relationship of intersection, parallelism and verticality, a structure can be designed according to requirements, and errors in installation or processing do not affect a final calculation result. The method disclosed by the invention is a flexible, convenient and practical robot inverse solution method, and convenience is provided for the practical application of the robot.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
An efficient dynamic modeling method for multi-degree-of-freedom manipulators
InactiveCN102207988BReduce computational complexityImproving the efficiency of positive dynamics calculationsSpecial data processing applicationsDynamic modelsScrew theory
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
A geometric solution method for inverse kinematics of 6r robot based on screw theory
ActiveCN107756400BSimplified inverse modelGeometric meaning is clearProgramme-controlled manipulatorComplex mathematical operationsAlgebraic equationRobot kinematics
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
A prediction method of machining accuracy retention of machine tool based on rough set theory and least squares support vector machine
The invention relates to a machine tool machining precision retraining ability prediction method based on a rough set theory and a least squares support vector machine. Generally, complex and great data error are generated if error data is required to be measured in a long term and detection and analysis are required to be carried out on the machining precision within the specified time for multiple times. The invention provides a machining procession retaining ability prediction method on the basis of the error data, which comprises the steps of firstly establishing a spatial error model of the overall machine tool on the basis of a topological structure of the machine tool by using an exponential matrix mode of a screw theory so as to carry out topological structure based screw theory error modeling and carry out measurement on the error data; secondly, carrying out reduction on the error data based on the rough set (RS) theory, and then carrying out machining precision retaining ability prediction based on a least squares support vector machine (LS-SVM) method; and finally, proving the effectiveness of the prediction method provided by the invention by using a simulation method.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
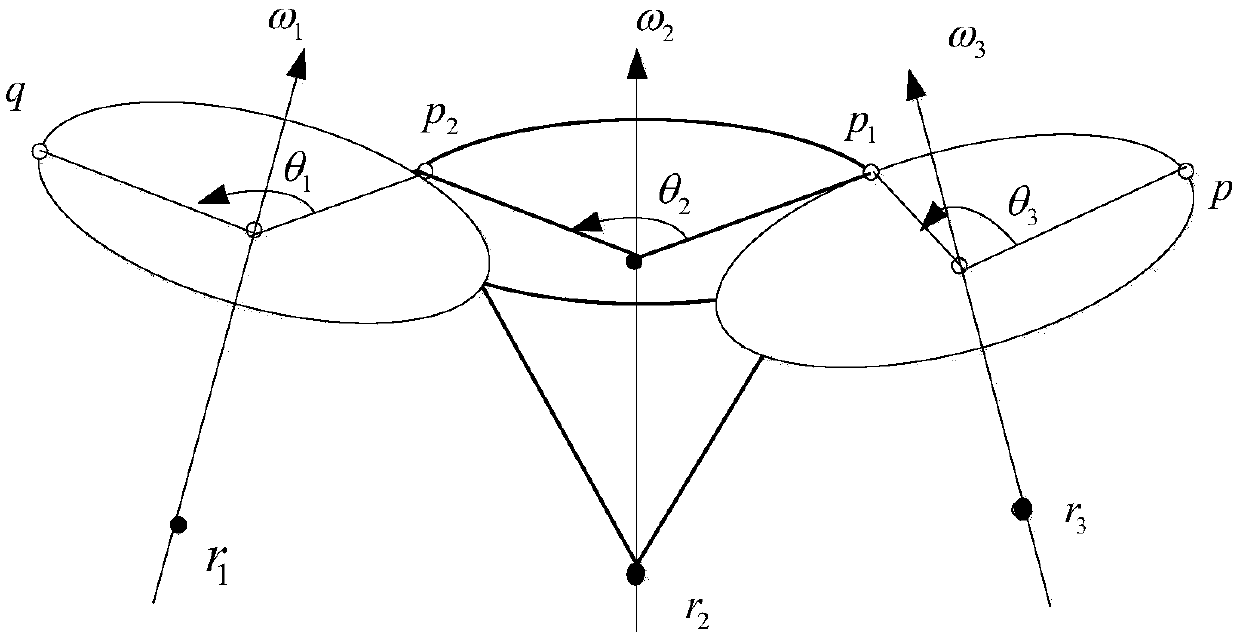
An Inverse Kinematics Method for Solving Second-Order Subproblems with Arbitrary Relation
ActiveCN106991277BSimple and easy to understandImprove computing efficiencyInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmInverse kinematics
The invention discloses a second-order subproblem inverse kinematics solution method for any relation, which belongs to the field of robot inverse kinematics. The invention relates to an inverse solution method for the second-order subproblem RR. The basic properties of the screw theory and the Rodrigues rotation matrix expression combine the geometric method with the algebraic method to give a general joint angle solution formula, which does not need to consider the relationship between the joint axes, whether it is intersecting, parallel, or different planes can be obtained directly by this method. The invention expands the solution method of the inverse solution of the robot, expands the scope of application, simplifies the solution process, and provides convenience for the actual development and application of the robot.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Static pressure rotary table load error identification and its influence analysis method on machine tool machining error
The invention provides an influence analytical method for identifying the load error of a static-pressure rotary table and analyzing the influence of the load error on the machining error of a machine tool, and belongs to the accurate design field of numerical control machine tools. On the premise that the load error of a machine tool is taken into account, an N-S equation and a film hypothesis theory are adopted to derive the table-board load error recognition of the static-pressure rotary table. Based on error measurement data, a space error model of the entire machine tool is established based on the topological structure of the machine tool in the index matrix form of the screw theory. The above method comprehensively considers load parameters and is reliable and efficient in calculation. The accuracy model of the machine tool is established based on the index matrix of the screw theory, so that the influence effect of each load error can be accurately calculated through quantitatively considering a fluid dynamics equation. That means, the above method is capable of not only simultaneously detecting the combined effect of the variation of multiple load parameters on the result of the error model, but also analyzing the individual effect of the variation of each load parameter on the result of the error model. The results of actual cases show that, the above method is effective.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
A Dynamic Modeling Method for Conveying Mechanism of Hybrid Automobile Electrophoretic Coating
ActiveCN105159137BHas coordinate invarianceNeat and concise expressionProgramme controlSimulator controlHybrid typeDynamic models
The invention discloses a hybrid type automobile electrophoresis coating conveying mechanism dynamics modeling method. First of all, the symmetrical structure characteristic of a mechanism is fully utilized, the speed and the accelerated speed of each passive joint in the mechanism are analyzed through an analytical geometry method, and then the speed and the accelerated speed of each active joint of the mechanism are obtained by introducing a screw theory; secondly, based on this, a kinetic equation in a mechanism spinor form is established by use of virtual work principle; and finally, axial driving power of each active joint of the conveying mechanism capable of directly realizing control is obtained through calculation so that construction of a dynamics model capable of realizing high-performance control is completed. According to the invention, the analytical geometry method, the screw theory and the virtual work principle are combined together, so that the problem of coordinate transformation due to lack of coordinate invariance during dynamics modeling of a complex special mechanism is solved, the calculation complexity is reduced, and at the same time, the dynamics modeling method brought forward by the invention is quite simple, is tidy in form and is easy in programmed realization.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
A Method for Extracting Important Geometric Error Sources of Machine Tool Based on Extended Fourier Amplitude
The invention discloses an extended Fourier amplitude based extraction method of a machine tool important geometric error source. Based on error measuring data, by use of an index matrix form of a screw theory, on the basis of the topology structure of a machine tool, an integral space error model of the machine tool is established, a high-order term of the error model is eliminated, and a basis equation of the error model is obtained. According to an EFAST global sensitivity analysis method, through selecting a proper conversion function, the error model is converted into a one-dimensional function from an eighteen-dimensional function, Fourier series expansion is carried out on the one-dimensional function, and a model caused by each parameter and a total variance of model output can be obtained. The EFAST method can simultaneously examine the influences exerted by change of multiple geometric errors on the result of a spinor error model and can also analyze the direct and indirect influences exerted by change of each geometric error on the model result, and the method provided by the invention can be applied to extraction of key geometric error terms having quite large influences on processing precision of the machine tool.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Robot external active gravity compensation system and simulation verification method
The invention discloses a robot external active gravity compensation system and a simulation verification method, including a gravity compensation device and a gravity compensation rope. It is connected with the force application end of the series robot, and the force application end of the series robot is connected with the end load at the same time. Realize the use of small load robots to complete large load tasks. According to the structure of the robot and the gravity compensation device, the kinematics model is established based on the screw theory, and the dynamic model of the closed-chain mechanism with passive joints is established by using the Newton-Euler method. The linear trajectory of the simulation experiment was designed, and the passive joint friction and constant moment gravity compensation were simulated in the dynamics simulation environment Coppeliasim. Effect of gravity compensation torque on robot joint torque.
Owner:GUANGDONG TOPSTAR TECH +1
A general solution method of inverse kinematics for five-degree-of-freedom tandem robot
ActiveCN106845037BImprove calculation accuracySimple and easy to understandDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsAngular degreesDegrees of freedom
The invention discloses a general solution method for inverse kinematics of a five-degree-of-freedom series robot, which belongs to the field of robot inverse kinematics. The invention proposes a simple and easy-to-calculate general solution method for inverse kinematics on the basis of an exponential product model , the invention mainly combines the basic properties of the screw theory with the Rodrigues rotation expression to simplify the inverse solution solution process, and realizes that under the condition of satisfying the Pieper constraint, the relationship between the first two joint axes can be obtained directly without considering the relationship between the first two joint axes The angle values of each joint, and the five joint angles only need two expressions to be expressed uniformly, which provides convenience for the practical application of this type of robot.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A Kinematics Calibration Method for Hybrid Robot
ActiveCN108015808BImprove recognition accuracyImprove stabilityDesign optimisation/simulationManipulatorAlgorithmKinematic calibration
The invention discloses a hybrid robot kinematics calibration method, comprising the following steps: step 1: establishing a hybrid robot geometric error model based on the screw theory; step 2: obtaining the end position of the hybrid robot based on the spatial position detection information of a laser tracker Attitude error; Step 3: Identify the geometric error source based on the Liu estimation method; Step 4: Implement error compensation step by step based on the modified controller output method. The present invention is a kinematics calibration method of a hybrid robot that is accurate, high in efficiency, convenient for industrial field application, and can be implemented based on the full-dimensional or less-dimensional pose error detection information at the end of the robot. The method of the present invention can establish an error model that satisfies completeness, minimalism, and continuity, and the model variables have clear physical meanings, effectively solves the problem of ill-conditioned identification matrix, improves the accuracy of error source identification and the stability of identification results, and further improves the compensation accuracy. .
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
A general solution method of inverse kinematics for a six-degree-of-freedom tandem robot
ActiveCN107203653BSimple form of expressionSimple and easy to understandDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsRodrigues' rotation formulaMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a general solution method for the inverse kinematics of a six-degree-of-freedom serial robot, which belongs to the field of robot inverse kinematics. The method is based on an exponential product model and proposes a closed solution with a simple calculation process and easy realization. The solution method, which mainly uses the basic properties of the screw theory, the Rodrigues rotation formula and the special geometric structure, transforms the complex inverse solution problem into a simple trigonometric function equation for solution, so that only two expressions are needed for the 6 joint angles That is to say, the form is simple and easy to remember. The invention has a wide range of applications and can be applied to any robot that satisfies the Pieper principle and has an intersecting or parallel relationship between two adjacent axes in the first three joints. The invention promotes the application of the robot and simplifies the application process.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com