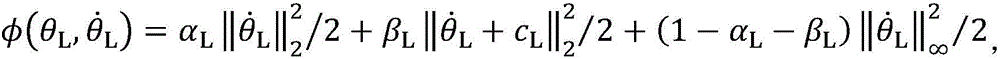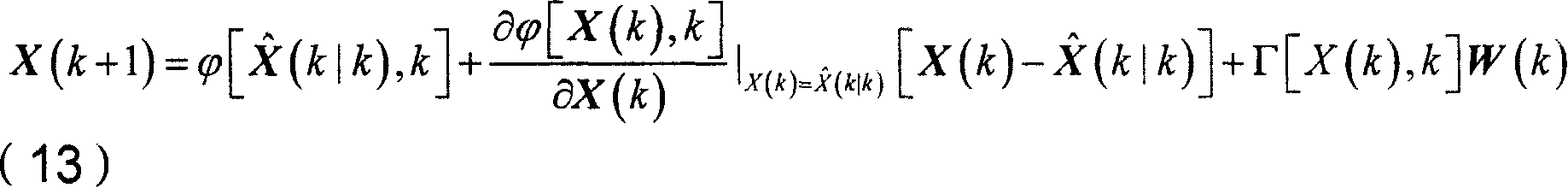Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
461 results about "Kinematics equations" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Kinematics equations are the constraint equations of a mechanical system such as a robot manipulator that define how input movement at one or more joints specifies the configuration of the device, in order to achieve a task position or end-effector location. Kinematics equations are used to analyze and design articulated systems ranging from four-bar linkages to serial and parallel robots.
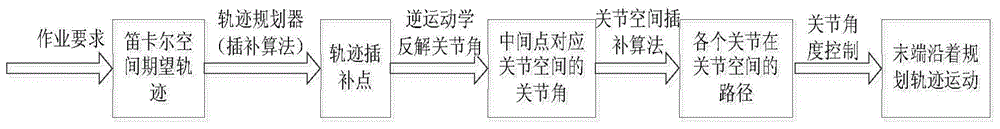
Robot cartesian space trajectory planning method
ActiveCN104965517AGuaranteed SolvableEasy to operateAttitude controlAdaptive controlGeometric propertyKinematics equations
The invention discloses a robot cartesian space trajectory planning method. The method includes establishing a connecting rod coordinate system and obtaining a forward kinematic equation through a kinetic modeling analysis method; solving the rotating angles of a master control joint and a middle joint according to the vector geometric property and trajectory planning requirement of the robot; seeking a relation equation including introduced variables and solving the rotating angle of the corresponding joint by means of the kinetic modeling analysis method and the solved joint rotating angle; determining whether the pose position can be reached through a vector geometric method when the trajectory planning is carried out in a task space with obstacles; and planning the continuous time variant attitudes of coupled position information to complete the planning tasks. According to the method, extraneous roots can be prevented, efficient solutions can be screened and matched, strange paths can be effectively avoided, and meanwhile, the defects of complex end trajectory planned by the joint space can be prevented and optimized.
Owner:张耀伦
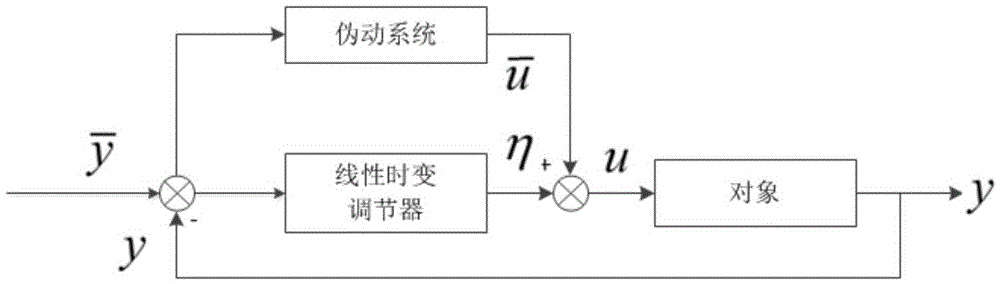
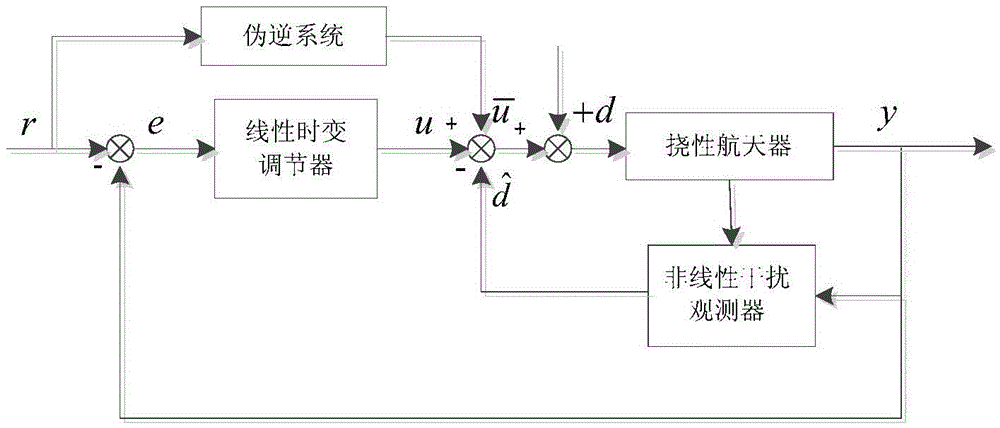
Flexible satellite locus linearization attitude control method based on disturbance observer
ActiveCN105468007ATracking error converges asymptoticallyEasy to implementAttitude controlDifferentiatorKinematics equations
The invention relates to a flexible satellite locus linearization attitude control method based on a disturbance observer. The invention aims at solving problems that a single locus linearization control method is poor in capability of inhibiting interference, is poorer in robustness, and does not consider external interference and the impact from flexible accessories. The method comprises the steps: employing Euler angles for describing attitudes of a spacecraft, employing an idea of equivalent disturbance, and building a flexible spacecraft dynamics and kinetics equation; solving the pseudo-inverse of a controlled object under the condition of neglecting equivalent disturbance, designing a quasi-differentiator of a specific type, and obtaining the nominal control of an expected locus; and designing a linear time varying adjuster through proportion-integration control. The method gives consideration to the influence of equivalent disturbance, designs the disturbance observer, and guarantees the asymptotic convergence of a tracking error of a flexible spacecraft. The method improves the anti-interference capability of a system, and improves the robustness of the system. The method is used in the attitude control field of flexible satellites.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Sensor Fusion System and Method for Estimating Position, Speed and Orientation of a Vehicle, in Particular an Aircraft
InactiveUS20070213889A1Increase computational costOptical rangefindersDigital data processing detailsBody axisKinematics equations
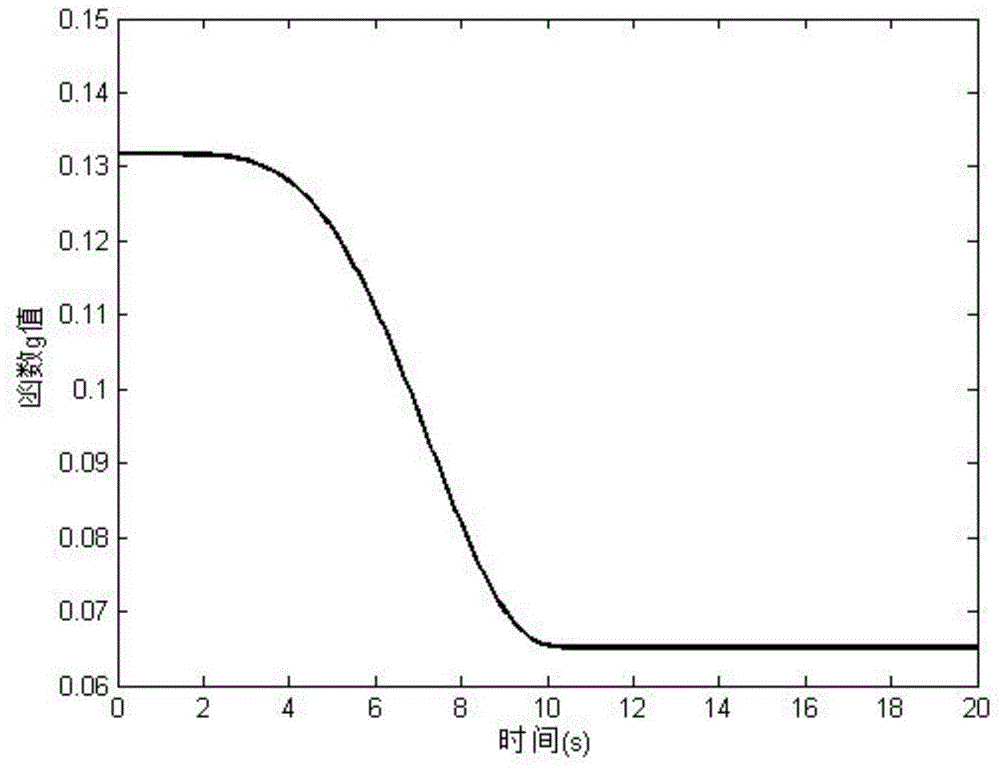
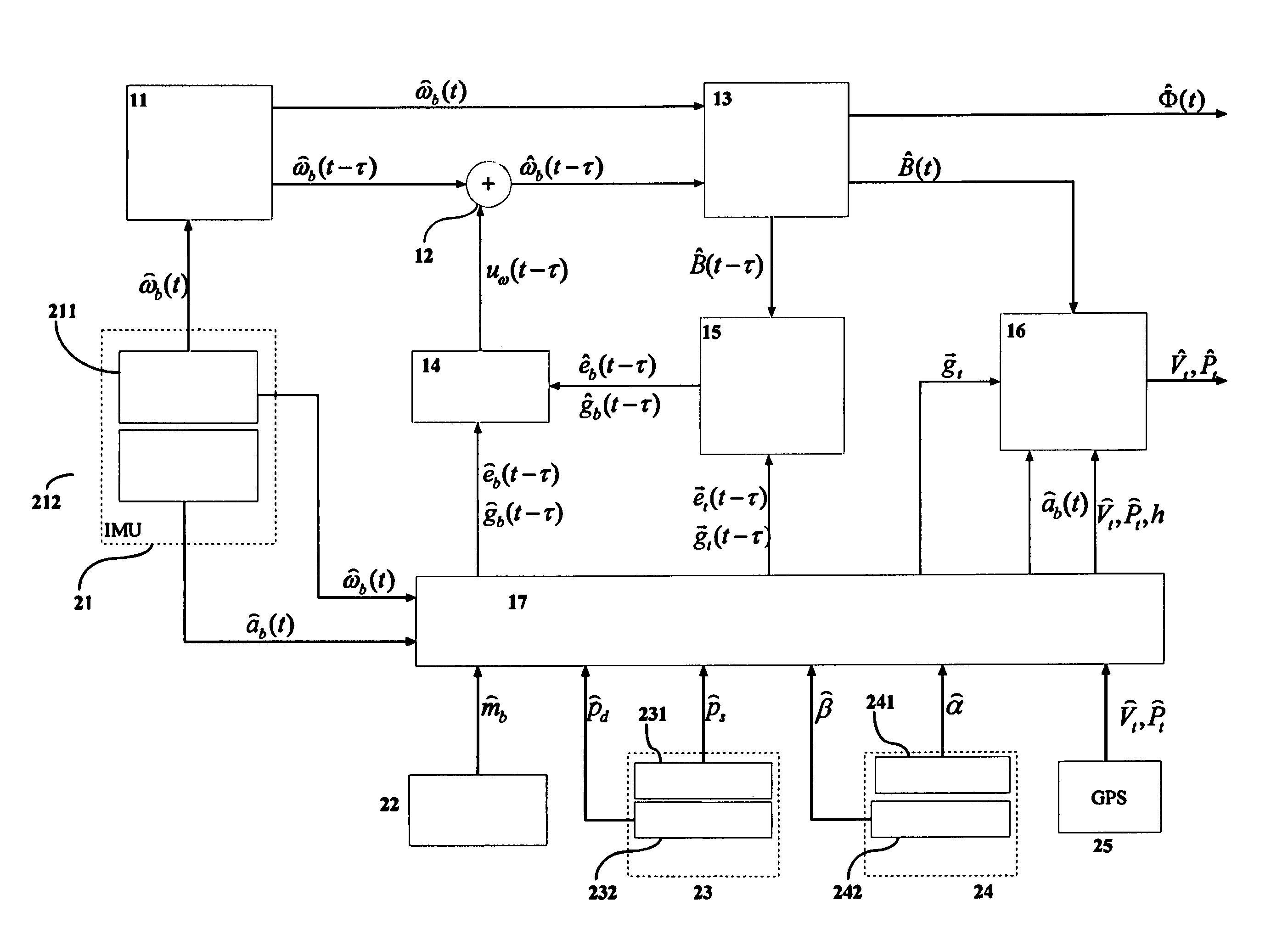
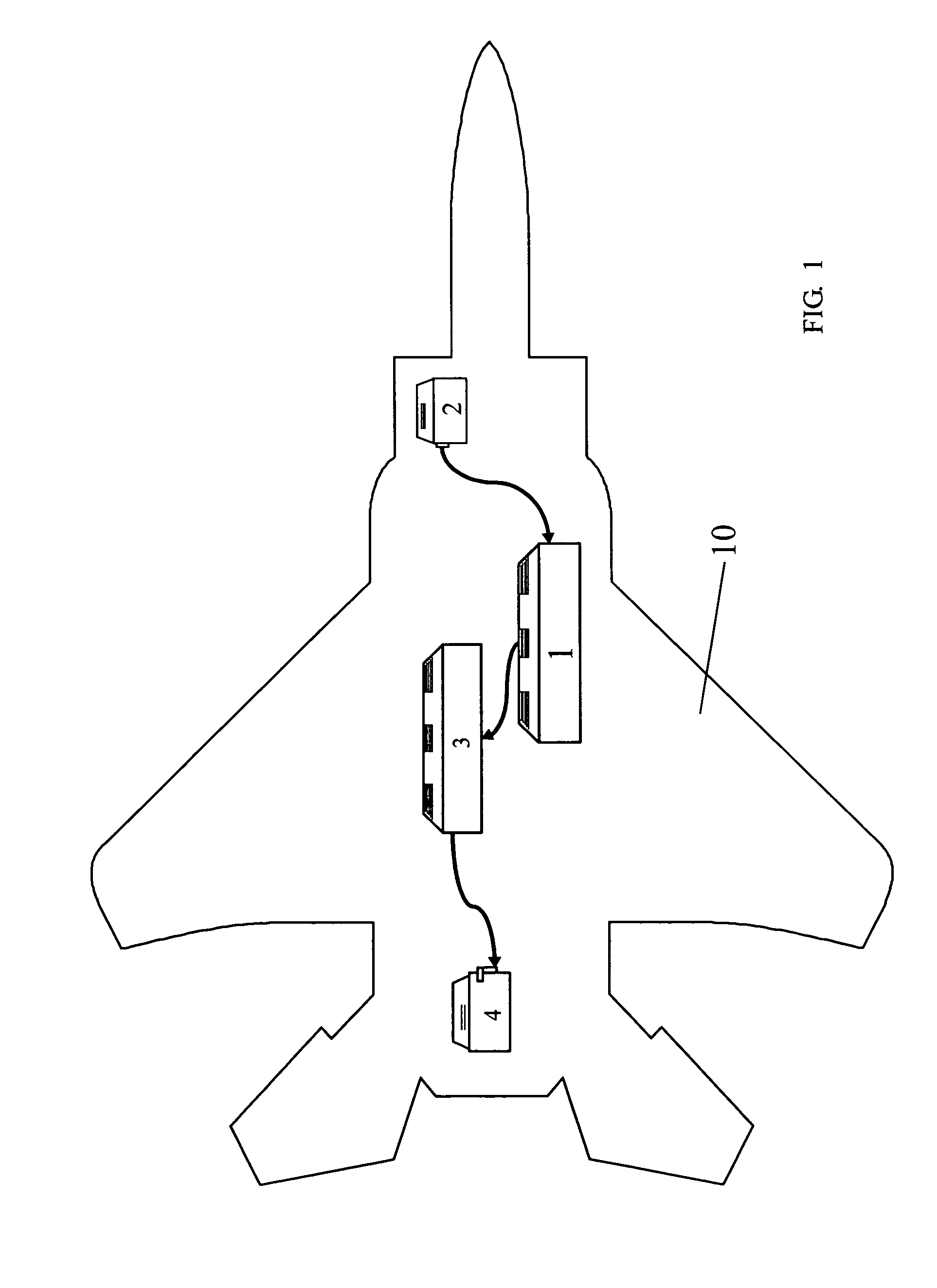
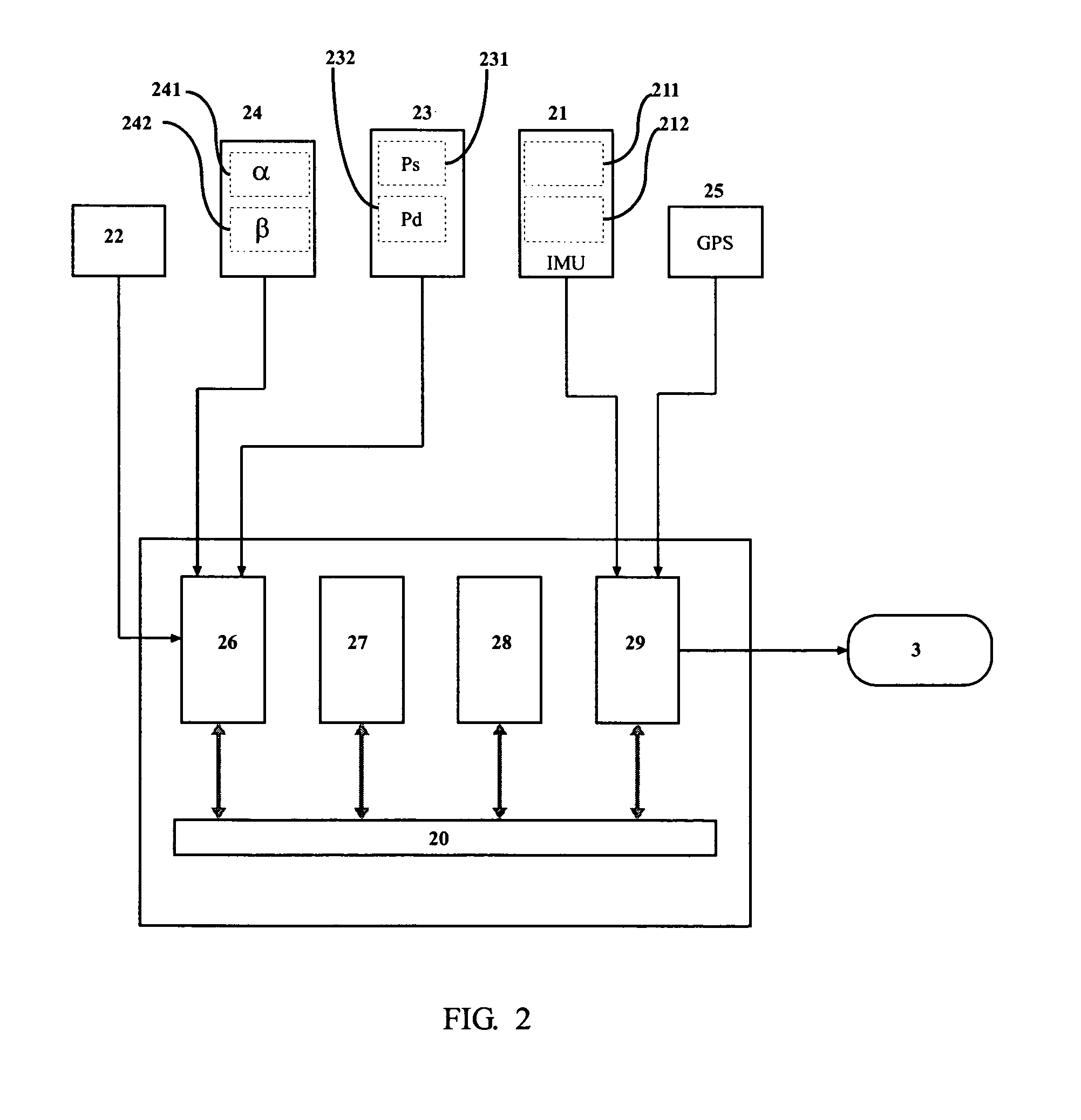
This invention relates to a system for estimating the position, speed and orientation of a vehicle (10), comprising means for determining the components of two noncollinear constant unit vectors b, b according to vehicle body axes; means for determining the components of said noncollinear constant unit vectors {right arrow over (g)}t, {right arrow over (e)}t according to Earth's axes; means for determining the three components of angular velocity b of the vehicle in body axes; means for correcting said angular velocity b with a correction uω and obtaining a corrected angular velocity {circumflex over (ω)}b=b+uω; a control module (14) implementing a control law to calculate said correction uω, where said control law is: uω=σ(b×ĝb+<?img id="custom-character-00007" he="3.13mm" wi="1.78mm" file="US20070213889A1-20070913-P00901.TIF" alt="custom character" img-content="character" img-format="tif" ?>b×êb) [1]where σ is a positive scalar, such that upon using said corrected angular velocity {circumflex over (ω)}b=b+uω as input to a module for integrating the kinematic equations, the latter are stable in the ISS sense and the error in the estimation of the direction cosine matrix {circumflex over (B)} and of the Euler angles {circumflex over (Φ)} is bounded.
Owner:INST NACIONAL DE TECNICA AEROESPACIAL
Spacecraft fault tolerance attitude cooperation tracking control method based on normalized neural network
ActiveCN105404304AReduce estimation errorEliminate Aggregation InterferenceAttitude controlFault toleranceKinematics equations
The invention relates to a spacecraft fault tolerance attitude cooperation tracking control method based on a normalized neural network, and belongs to the technical field of spacecraft formation flight. According to the method, an attitude motion model of a single spacecraft is built, errors are defined, a control law is designed for the model, a sliding mode function is designed, the derivative of the sliding mode function is solved, an error model is obtained, a control law based on an input normalized neural network is designed, and the states of the spacecrafts are cooperative and consistent; each spacecraft calculates the required control torque according to attitude information of itself and the adjacent spacecraft, the calculated control torque is acted on the corresponding spacecraft via an execution mechanism of each spacecraft, the angular velocity is solved via an obtained attitude dynamic equation, a unit quaternion attitude tracks an expected attitude via the attitude dynamic equation, and consistent attitude of the spacecraft formation is finally realized. According to the method, estimation errors of non-linear function approximation are reduced, the calculating time is reduced, and the convergence rate and the control precision of the system are increased.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Space manipulator track planning method for minimizing base seat collision disturbance
InactiveCN104526695AAccurate pose captureReduce base attitude disturbanceProgramme-controlled manipulatorKinematics equationsEngineering
The invention discloses a space manipulator track planning method for minimizing base seat collision disturbance, and belongs to the technical field of manipulator control. The space manipulator track planning method for minimizing the base seat collision disturbance includes: deriving a manipulator base seat attitude disturbance equation on the basis of establishing a space manipulator kinematical equation and a dynamical equation; designing a comprehensive optimized operator on the premise of considering tail capture pose accuracy and joint displacement limiting of a space manipulator, and optimizing manipulator configuration in a null space so as to achieve minimization of the base seat disturbance caused by collision; finally, using a particle swarm optimization algorithm to achieve track planning before the collision of the space manipulator from an initial pose to an ideal pose. The space manipulator track planning method for minimizing the base seat collision disturbance solves problems in the track planning before the collision of the space manipulator, achieves a simple and pellucid control process, performs novel and practical design of the comprehensive optimized operator, can achieve the purpose of reducing the base seat pose disturbance caused by the collision to the utmost on the premise of guaranteeing the accurate tail capture pose of the manipulator and preventing joint angles from exceeding limits.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Sensor fusion system and method for estimating position, speed and orientation of a vehicle, in particular an aircraft
InactiveUS7970500B2Increase computational costInstruments for road network navigationOptical rangefindersBody axisKinematics equations
This invention relates to a system for estimating the position, velocity and orientation of a vehicle, by determining the components of two noncollinear constant unit vectors b,b according to vehicle body axes; and determining the components of the noncollinear constant unit vectors {right arrow over (g)}t,{right arrow over (e)}t according to Earth's axes. The system further determines the three components of angular velocity b of the vehicle in body axes; corrects the angular velocity b with a correction uω and obtains a corrected angular velocity {circumflex over (ω)}b=b+uω; a control module implementing a control law to calculate the correction uω, where the control law is:uω=σ(b×ĝb+b×êb) [1]where σ is a positive scalar,such that upon using the corrected angular velocity {circumflex over (ω)}b=b+uω as input to a module for integrating the kinematic equations, the latter are stable in the ISS sense and the error in the estimation of the direction cosine matrix {circumflex over (B)} and of the Euler angles {circumflex over (φ)} is bounded.
Owner:INST NACIONAL DE TECNICA AEROESPACIAL
Method for real-time estimation of queuing length of signalized intersection based on vehicle track
ActiveCN106355907AStrong real-timeImplementing Quadratic Queue EstimationControlling traffic signalsKinematics equationsSelf estimation
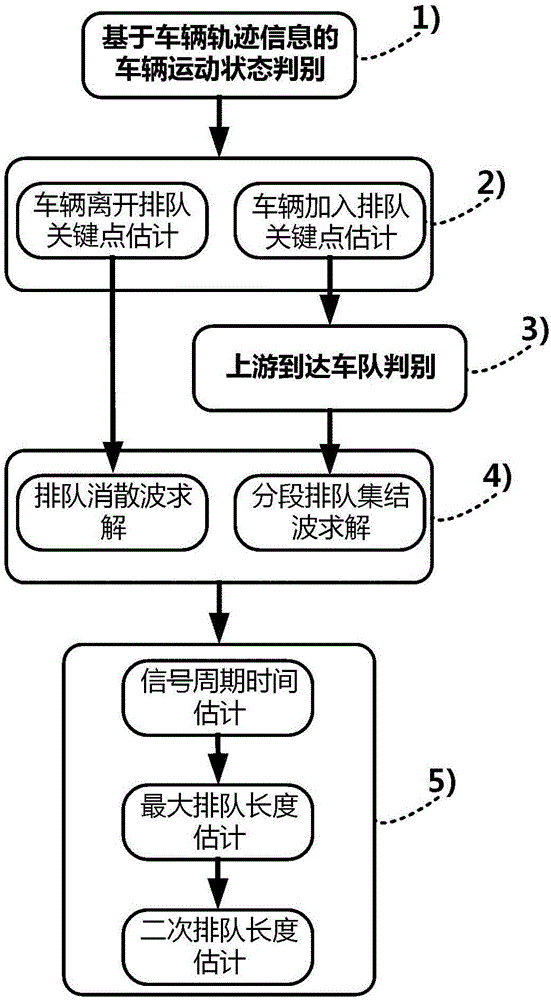
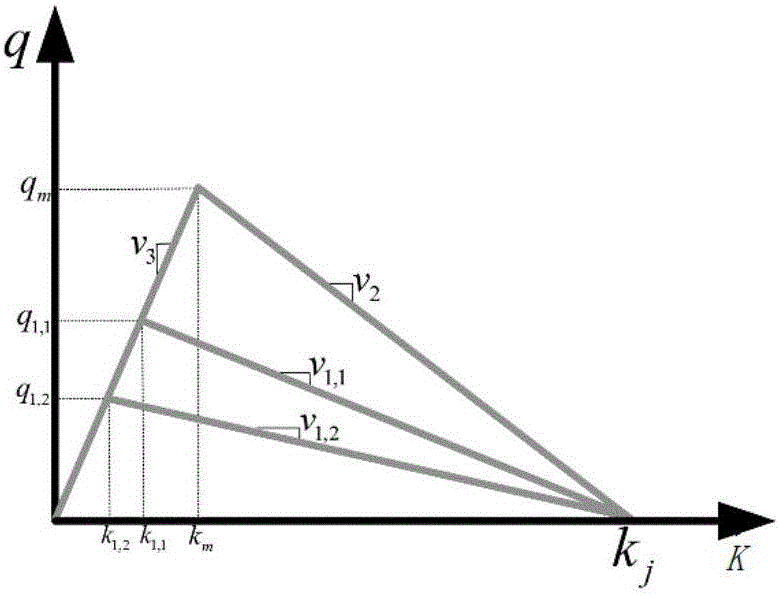
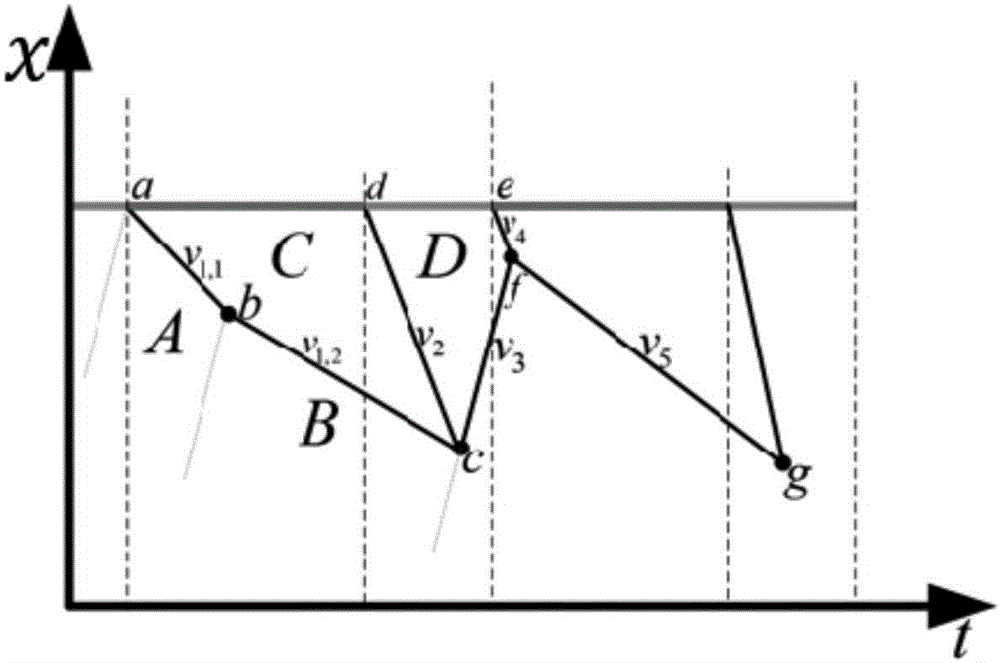
The invention relates to a method for real-time estimation of the queuing length of a signalized intersection based on a vehicle track. The method comprises the following steps: (1) judging a vehicle traffic state according to real-time vehicle traffic information; (2) estimating a vehicle queue-joining key point and a vehicle queue-leaving key point according to the real-time vehicle track information, vehicle traffic state and kinematical equation; (3) identifying an upstream reached fleet according to the estimated vehicle queue-joining key point; (4) performing queuing wave and evanescent wave estimation according to the estimated vehicle queue-joining key point, the queue-leaving key point and the identified fleet; and (5) estimating the intersection signal parameter and the queuing length according to the estimated queuing wave and evanescent wave. Compared with the prior art, the method is adaptive to a data environment with low sampling frequency and low sampling rate, and has the advantages of strong robustness, high real-time performance, good accuracy and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Accurate track tracking control method based on finite time expansion state observer
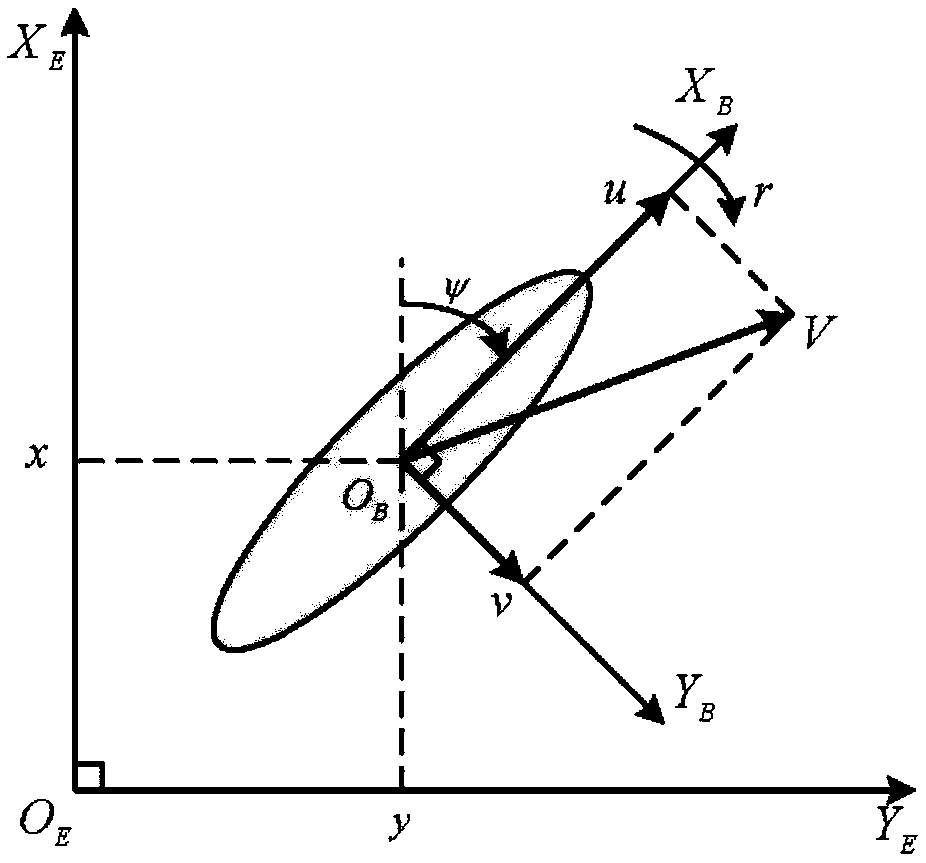
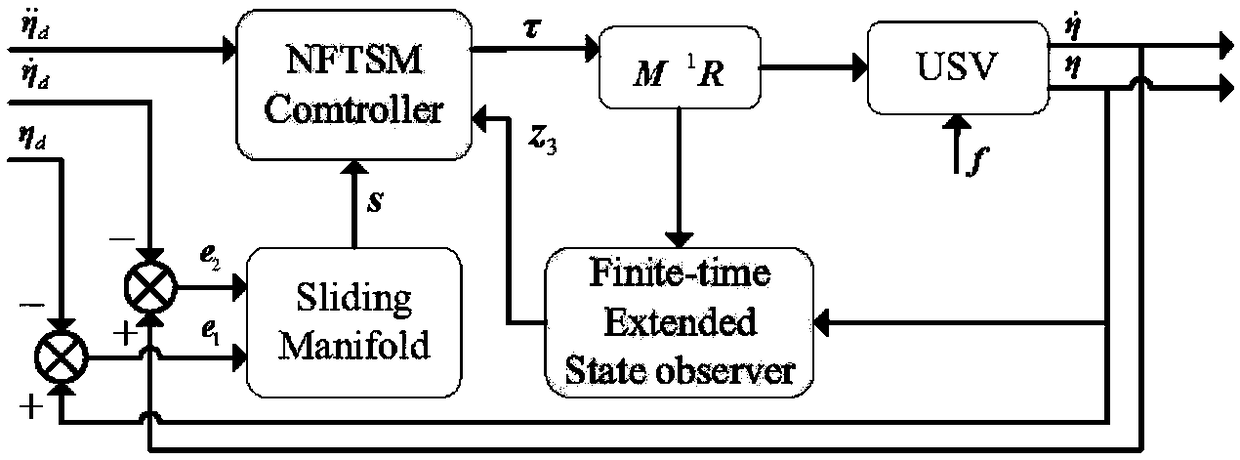
ActiveCN108828955AOvercome limitationsPrecise track tracking control performanceAdaptive controlKinematics equationsMathematical model
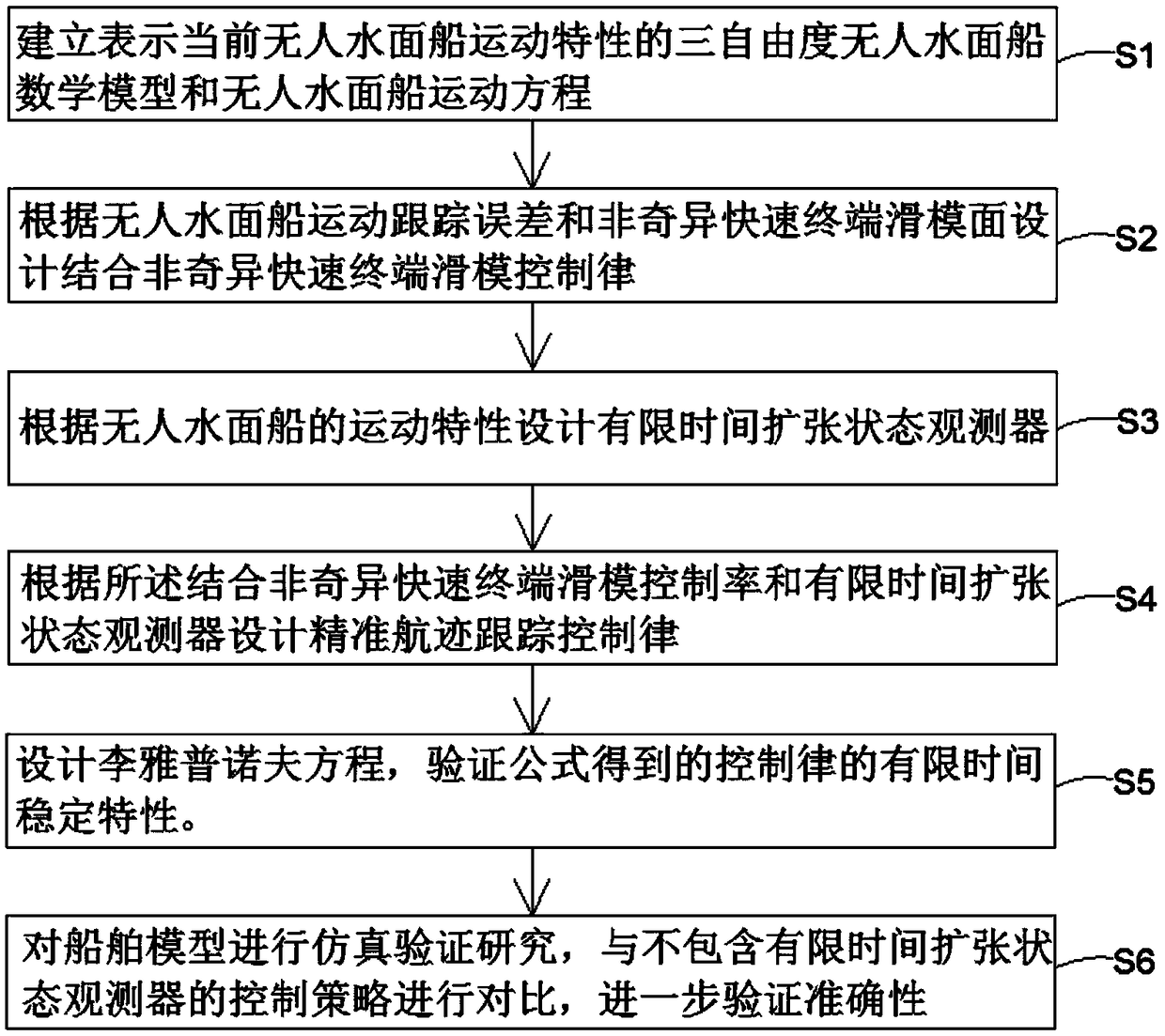
The present invention provides an accurate track tracking control method based on a finite time expansion state observer. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a mathematical modeland a kinematic equation representing current unmanned ship motion features, designing a combined nonsingular rapid terminal sliding-mode control law according to the unmanned surface ship motion tracking errors and a nonsingular rapid terminal sliding-mode surface, designing a finite time expansion state observer according to the unmanned ship motion features, and designing an accurate track tracking control law according to the combined nonsingular rapid terminal sliding-mode control law and the finite time expansion state observer. Through design of the finite time expansion state observer, the lump interference comprising external interference and a complex nonlinear term can be observed by the finite time to a small enough range to avoid the limitation of the approximation observation. Through the designed combined nonsingular rapid terminal sliding-mode control law and the nonsingular rapid terminal sliding-mode unmanned ship track tracking controller, the accurate track tracking control method achieves the accurate track tracking control performance in a complex external interference.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
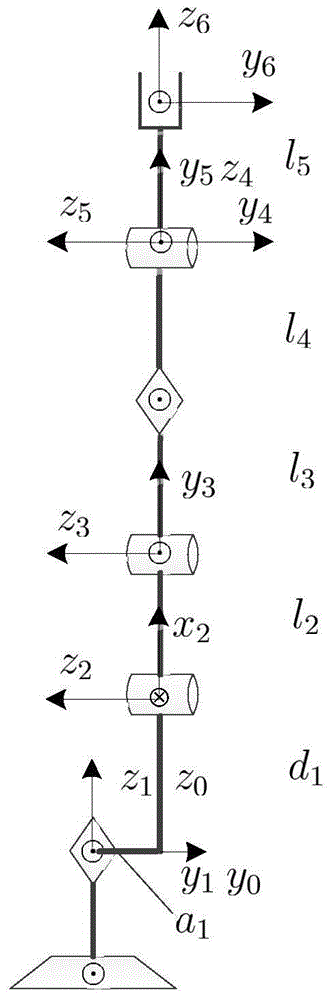
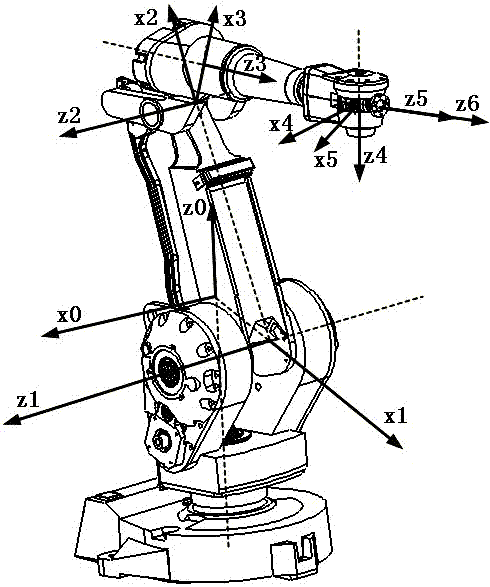
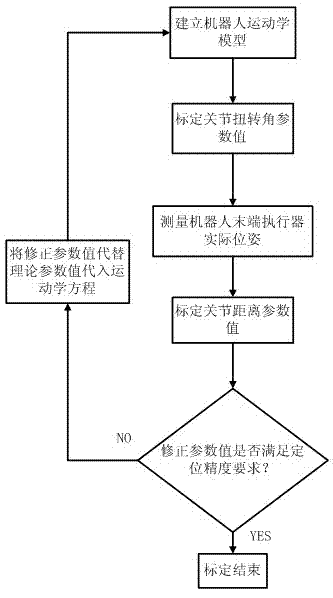
Industrial robot positioning precision calibration method
InactiveCN102692873AImprove absolute positioning accuracyImprove performanceAdaptive controlKinematics equationsEngineering
The invention relates to an industrial robot positioning precision calibration method used for improving robot absolute positioning precision. The method comprises the steps that: a robot kinetics model is established; a rotary joint equation is established by using a circumferential method; joint torsion angle parameter values are calculated; the actual pose of a robot end is measured accurately by utilizing a laser tracker; D-H algorithm inversion kinetics equation is improved to obtain geometrical structural parameters; calibration of joint distance parameter values and calibration of joint offset are realized, and thereby first calibration is completed. Error correction is carried out on D-H parameters based on first calibration results, and if positioning precision can not meet requirements, second calibration can be carried out by substituting parameter correction values, instead of theoretical parameter values, into the kinetics equation. Absolute positioning precision of the robot is improved with the calibration method, which is proved in experiments. According to the invention, the calibration method is advantaged in that the method is simple and practical and introduces small external errors.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
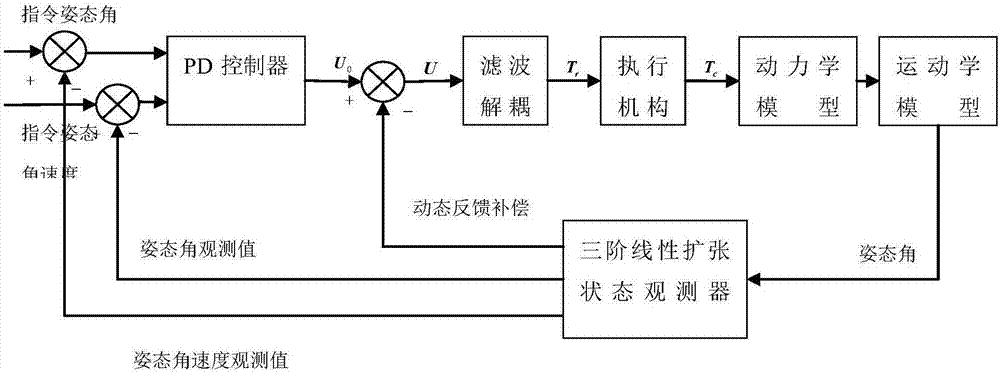
Method of designing multi-channel linear active disturbance rejection controller
The invention relates to a method of designing a multi-channel linear active disturbance rejection controller, comprising the following steps: S1, rewriting the dynamics and kinematics equations of a flexible spacecraft, and getting a form suitable for designing an active disturbance rejection controller; S2, designing a third-order linear extended state observer to estimate the system state quantity and the total internal and external disturbances; and S3, designing a multi-channel linear active disturbance rejection controller by use of generalized disturbance estimated by the observer. The method has the advantages possessed by the traditional active disturbance rejection control method, does not need to know the accurate mathematical model of the system, and has characteristics such as less overshoot, high precision, strong adaptability, high stability and strong robustness. In addition, the control law is improved for spacecrafts with inertial gyro failure on the basis of an active disturbance rejection controller, the control law is designed by using the observed state of the observer to replace the attitude angle and attitude angular velocity information of a spacecraft, and a fault-tolerant control method is provided for the condition of gyro failure.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
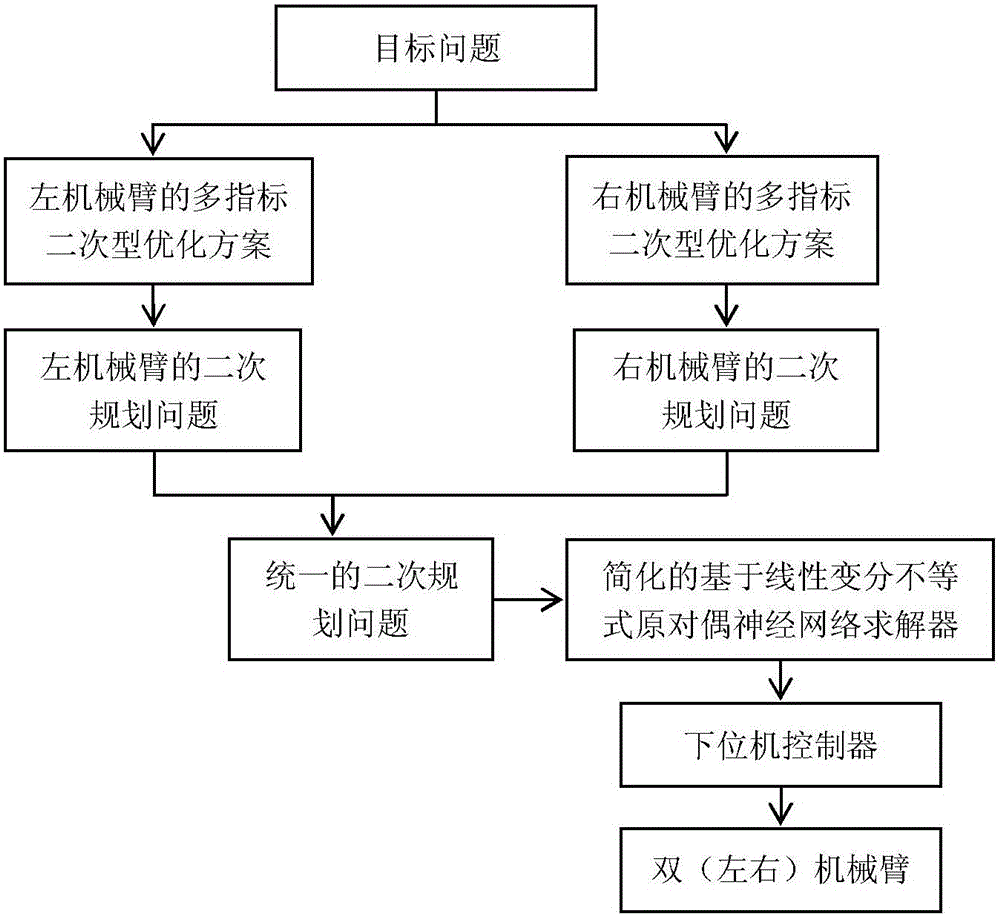
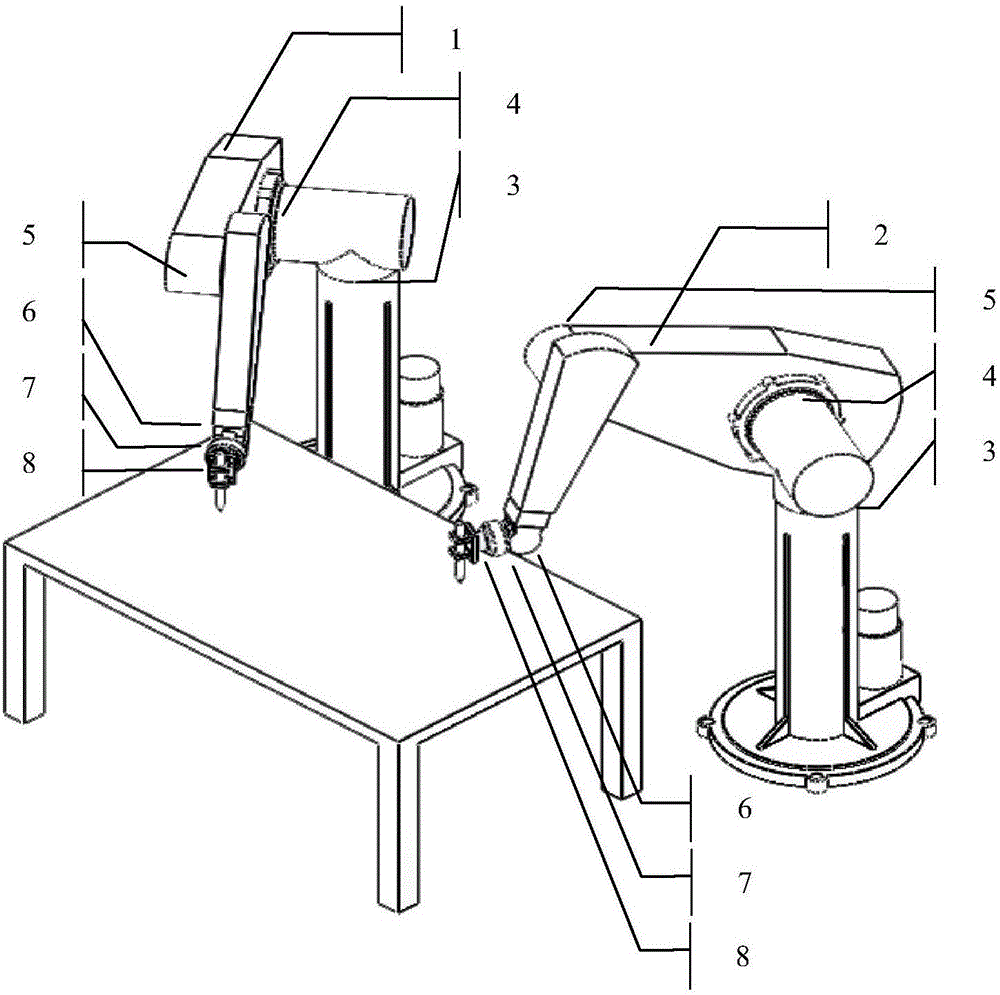
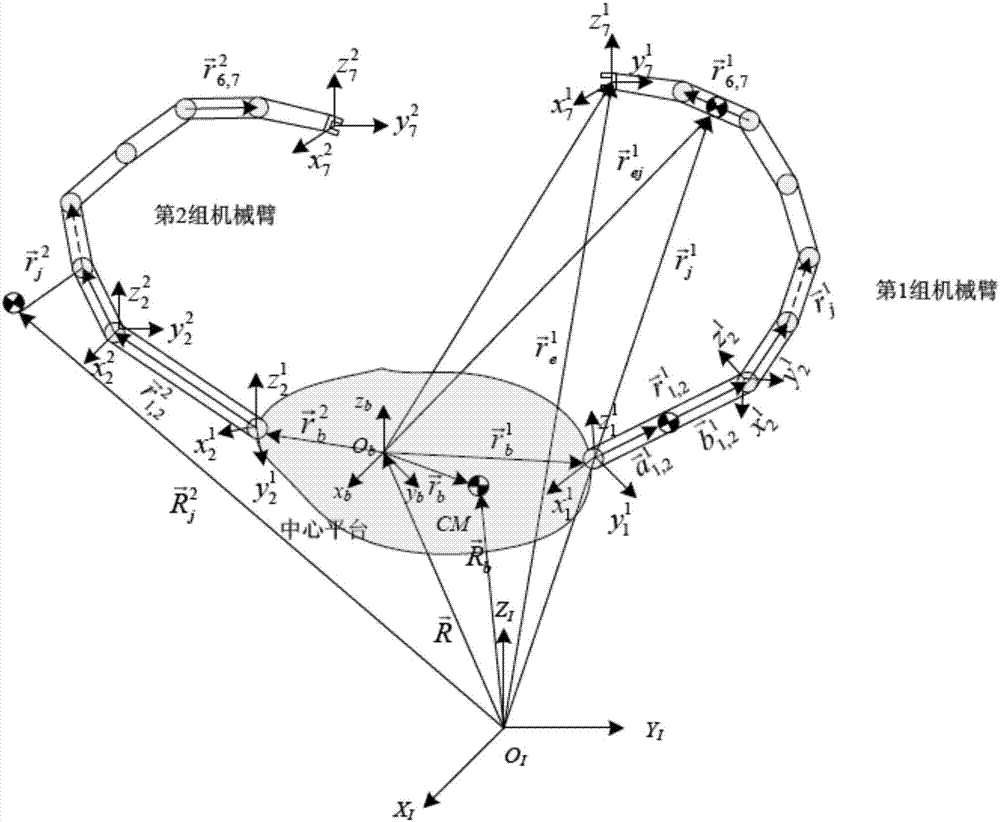
Redundancy dual-mechanical-arm multi-index coordinate exercise planning method
ActiveCN106426164AMeet the needs of different tasksImprove work efficiencyProgramme-controlled manipulatorKinematics equationsPerformance index
The invention discloses a redundancy dual-mechanical-arm multi-index coordinate exercise planning method. The method includes the steps that (1) based on a target problem, quadric form prioritization schemes are adopted for an upper computer to conduct inverse kinematics analysis on double mechanical arms on the speed layer, designed performance indexes are formed by the weighted array of three indexes including a minimum velocity two-norm, repeating motion and a minimum velocity infinite norm, and the performance indexes are limited to the kinematical equations, the joint angle extremities and the joint angle velocity extremities of the double mechanical arms correspondingly; (2) the quadric form prioritization schemes of the double mechanical arms in the step (1) are converted into standard quadratic programming problems; (3) the quadratic programming problems of the double mechanical arms in the step (2) are unified into one quadratic programming problem; (4) the unified quadratic programming problem in the step (3) is solved with a simplified original dual neural network solver based on the linear variational inequality; and (5) a solving result in the step (4) is transmitted to a lower computer controller to drive the double mechanical arms to move.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Motion coordination control method for space dual-manipulator system
ActiveCN106945020AFast trackImprove operating precisionProgramme-controlled manipulatorKinematics equationsControl system
The invention relates to a motion coordination control method for a space dual-manipulator system, and belongs to the technical field of space manipulators. In order to overcome the defects that no space manipulator system specific to dual manipulators exists at present, the coordinated relation between a manipulator and a satellite body is not considered in an existing space manipulator system and tracking errors are high, the motion coordination control method for the space dual-manipulator system is provided. The motion coordination control method for the space dual-manipulator system includes the steps that a kinematical equation and kinetic equation of the space dual-manipulator system are established; the space dual-manipulator system is subjected to trajectory planning according to the initial postures and tail-end postures of the manipulators; and trajectories of the space dual-manipulator system are subjected to tracking control through a PD controller. The motion coordination control method for the space dual-manipulator system is suitable for a space manipulator control system.
Owner:黑龙江省工研院资产经营管理有限公司
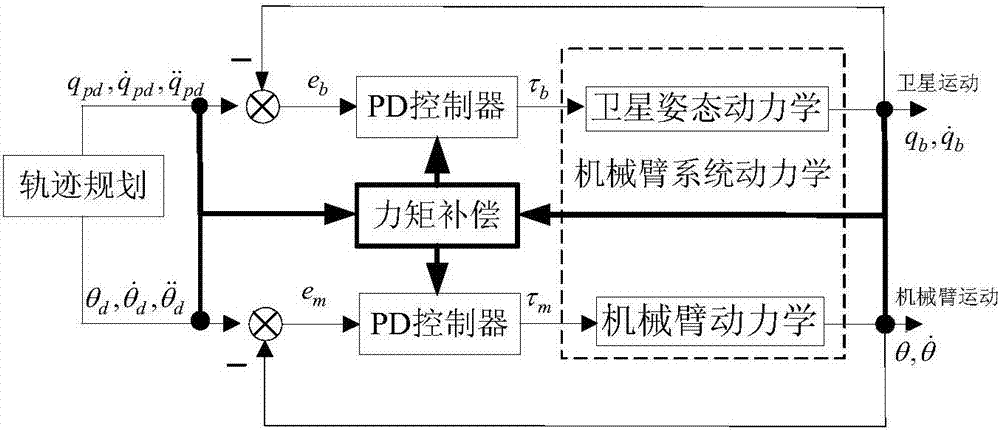
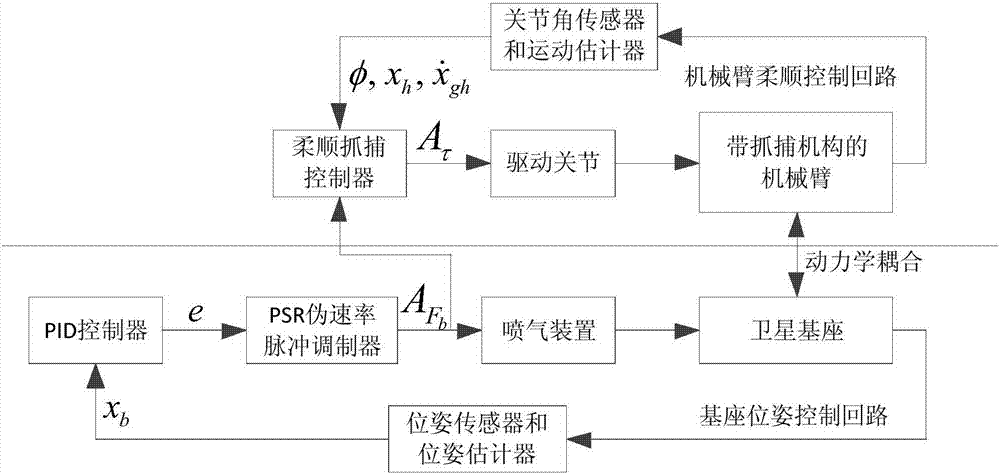
Compliant and coordinated control method for in-orbit capturing process of space robot
ActiveCN106891335ACatch stableGuaranteed stabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorRobotic systemsKinematics equations
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
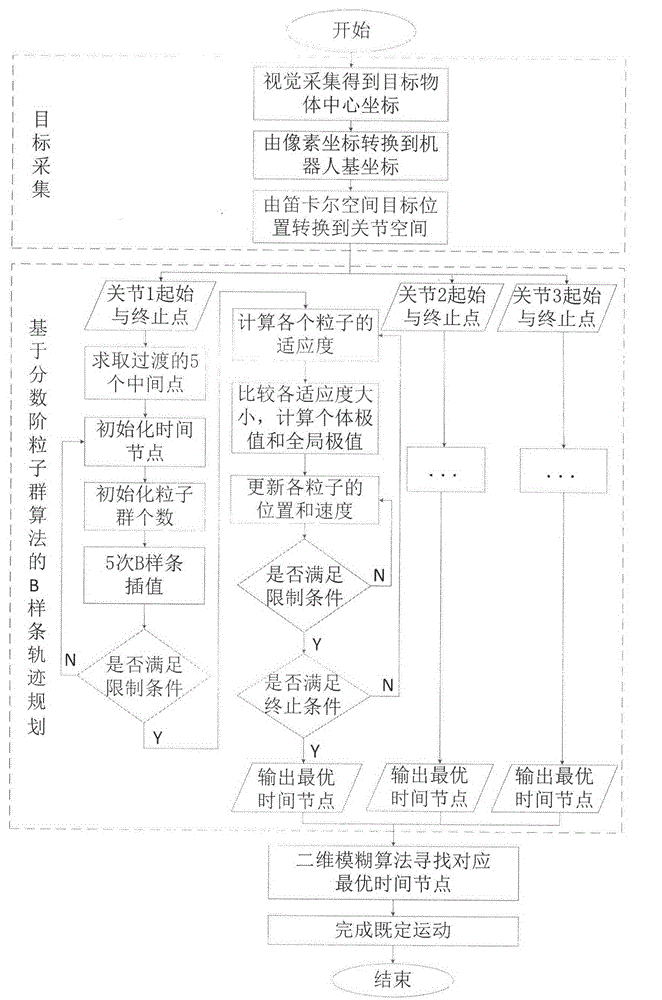
Delta robot time optimal trajectory planning method
ActiveCN104062902AImprove control efficiencyImprove control stabilityAdaptive controlNODALKinematics equations
The invention provides a vision-guided trajectory planning method on the basis of a Delta robot joint space. The method is applied to the optimal time motion of a Delta robot. The method comprises the following steps: solving a kinematic relation of the Delta robot; establishing an inverse kinematical equation for a motion from an end effector to each joint; acquiring a target position through an industrial intelligent camera; updating the target position on real time through an encoder; dividing a working area of the Delta robot into 9*13 subareas; planning the motion route of each joint at different areas through a B spline offline; maintaining smooth and continuous speed, acceleration and jerk; reducing the impact of a servo motor to a mechanical structure; improving the typical particle swarm optimization; speeding up to search time nodes with optimal solution by the fractional order particle swarm optimization in order to avoid local optimal solution; then performing the two-dimensional fuzzy method to select the optimal time node corresponding to the working area of the robot on line, and thus finishing control.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
Combination automatic control method with single-joint manipulator under mixed suspension microgravity environments
InactiveCN104589349AAchieve autonomous controlAchieve estimatesProgramme-controlled manipulatorAdaptive controlAutomatic controlKinematics equations
The invention provides a combination automatic control method with a single-joint manipulator under mixed suspension microgravity environments. The combination automatic control method comprises the following steps of 1, enabling a combination to be equivalent to an underwater robot, and establishing a kinematics equation and a dynamics equation; 2, approximating the dynamics equation of the combination by a radial basis function neural network, so as to obtain control force and control torque corresponding to the radial basis function neural network; 3, using a sliding mode control method, so as to obtain control force and control torque corresponding to sliding model control; 4, synthesizing the control force and control torque corresponding to the neural network and the control force and control torque obtained by the sliding model control method, and distributing thrust, so as to obtain a general vector which consists of thrust and joint torque of each propeller; approximating the thrust deviation of the corresponding thruster through the radial basis function neural network, so as to obtain the estimation value of the thrust deviation; 5, combining the results obtained in step 2, step 3 and step 4, obtaining the general vector consisting of the thrust and the joint torque of the corresponding propeller, and further obtaining the thrust and the joint torque of the corresponding propeller, so as to realize the automatic control.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
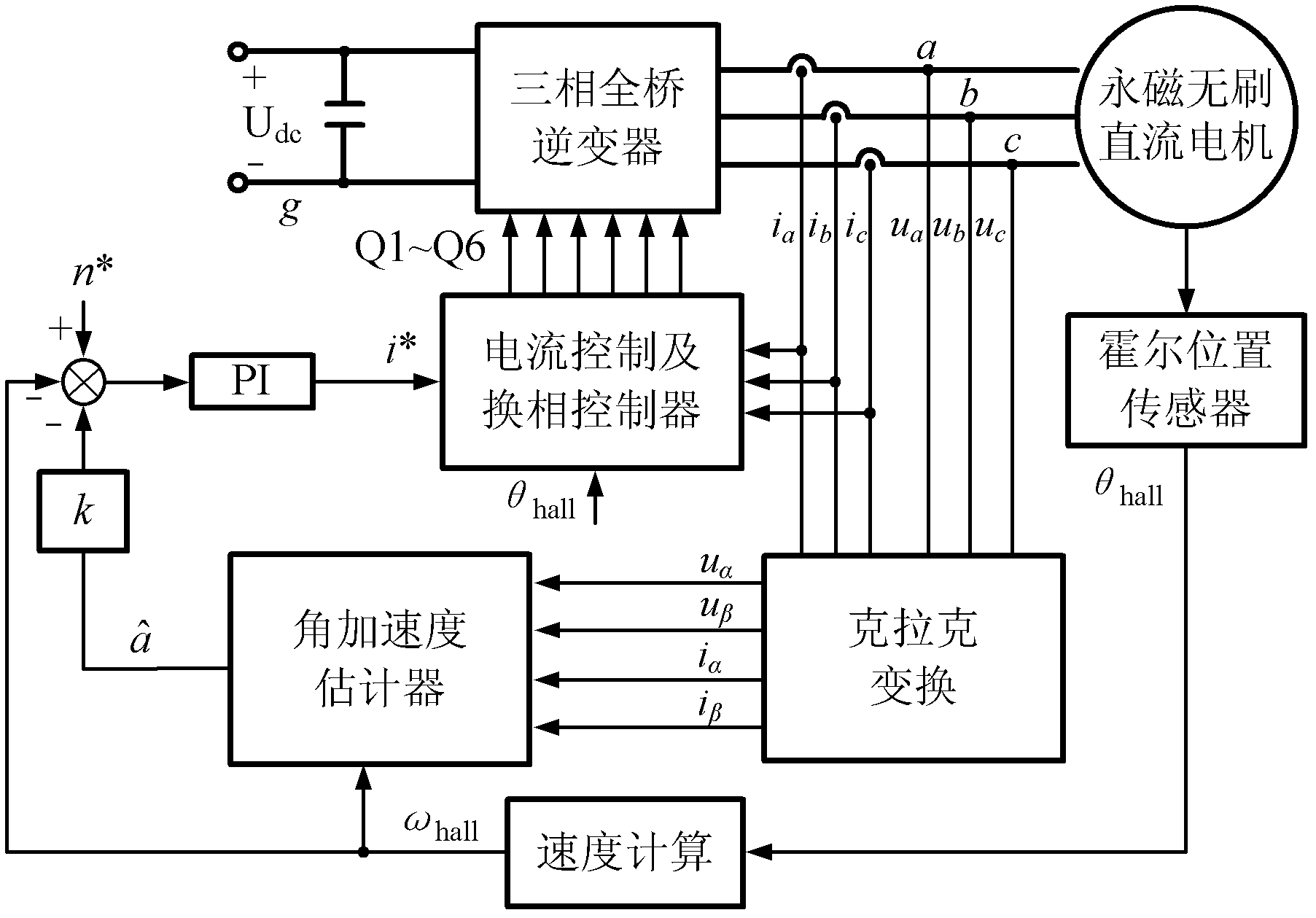
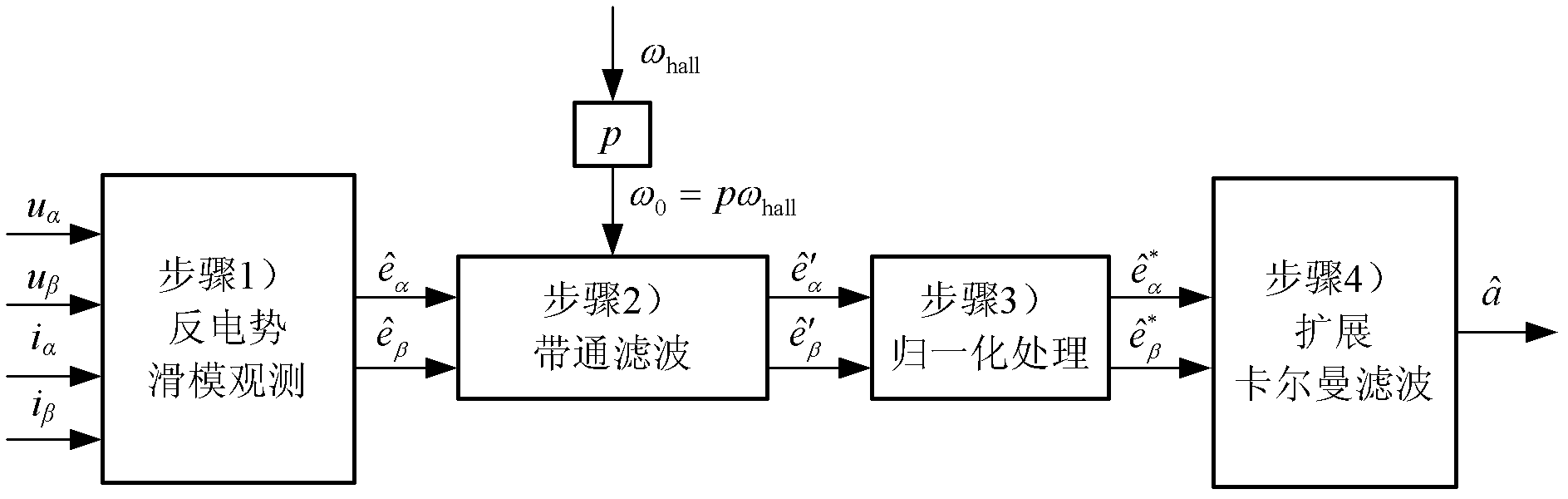
Method for estimating angular acceleration of permanent magnet brushless direct-current motor
InactiveCN102624303AGuaranteed accuracyFast convergenceVector control systemsDynamo-electric converter controlKinematics equationsFiltration
The invention discloses a method for estimating angular acceleration of a permanent magnet brushless direct-current motor, which includes establishing a sliding mode observer and observing components of counter potential of the brushless direct current motor to obtain a counter potential observed value; performing filtration through a band-pass filter and filtering direct current offset and high-frequency components of the counter potential observed value to obtain a filtered value of the counter potential observed value; normalizing the filtered counter potential observed value; and establishing an extended Kalman filter according to a kinematical equation of the brushless direct current motor, extracting location information from a normalized value of the counter potential and then estimating to obtain an angular acceleration value. The method uses the location information included in the counter potential to estimate the angular acceleration of the permanent magnet brushless direct-current motor, so that the problems of long delay and poor precision in computed results caused by the fact that the angular acceleration computation of the permanent magnet brushless direct current motor in prior art is influenced by processing precision of Hoer position sensors and is restricted by resolution ratios are solved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Spacecraft attitude tracking control method based on discontinuous adaptive control
ActiveCN110347173AImplement trackingHigh steady-state control accuracyAttitude controlAdaptive controlKinematics equationsInertial coordinate system
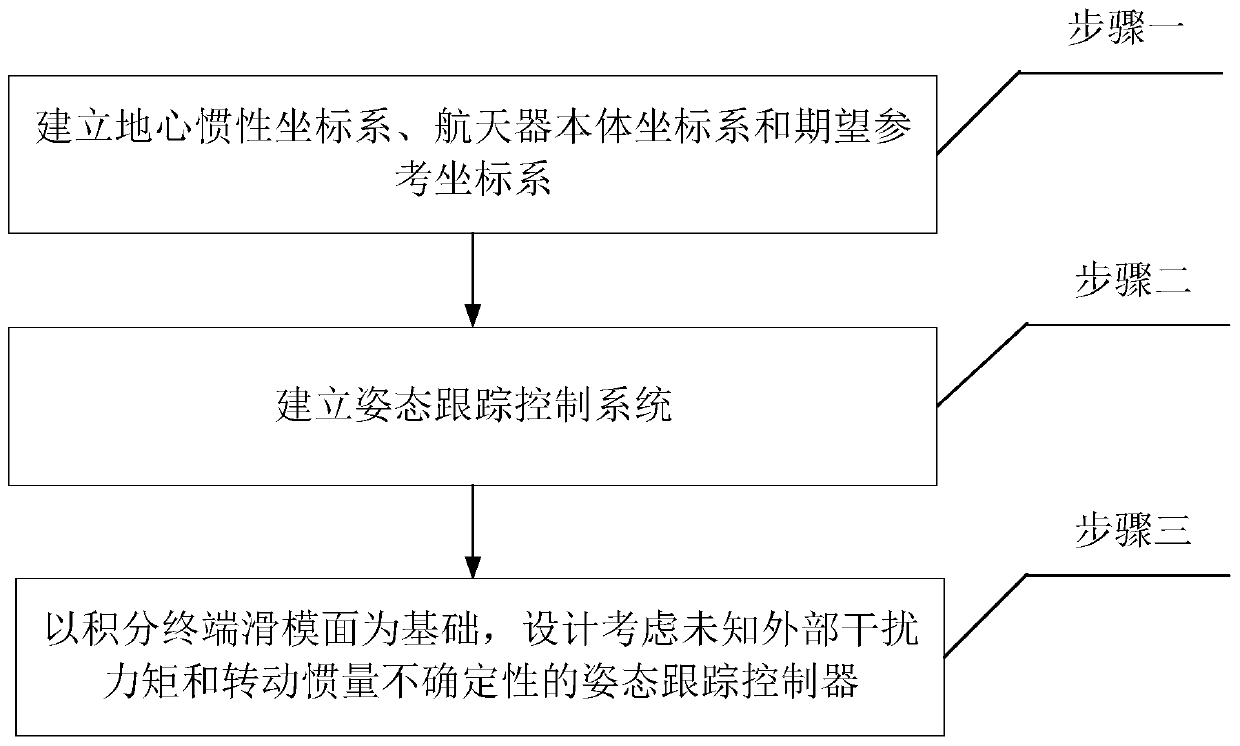
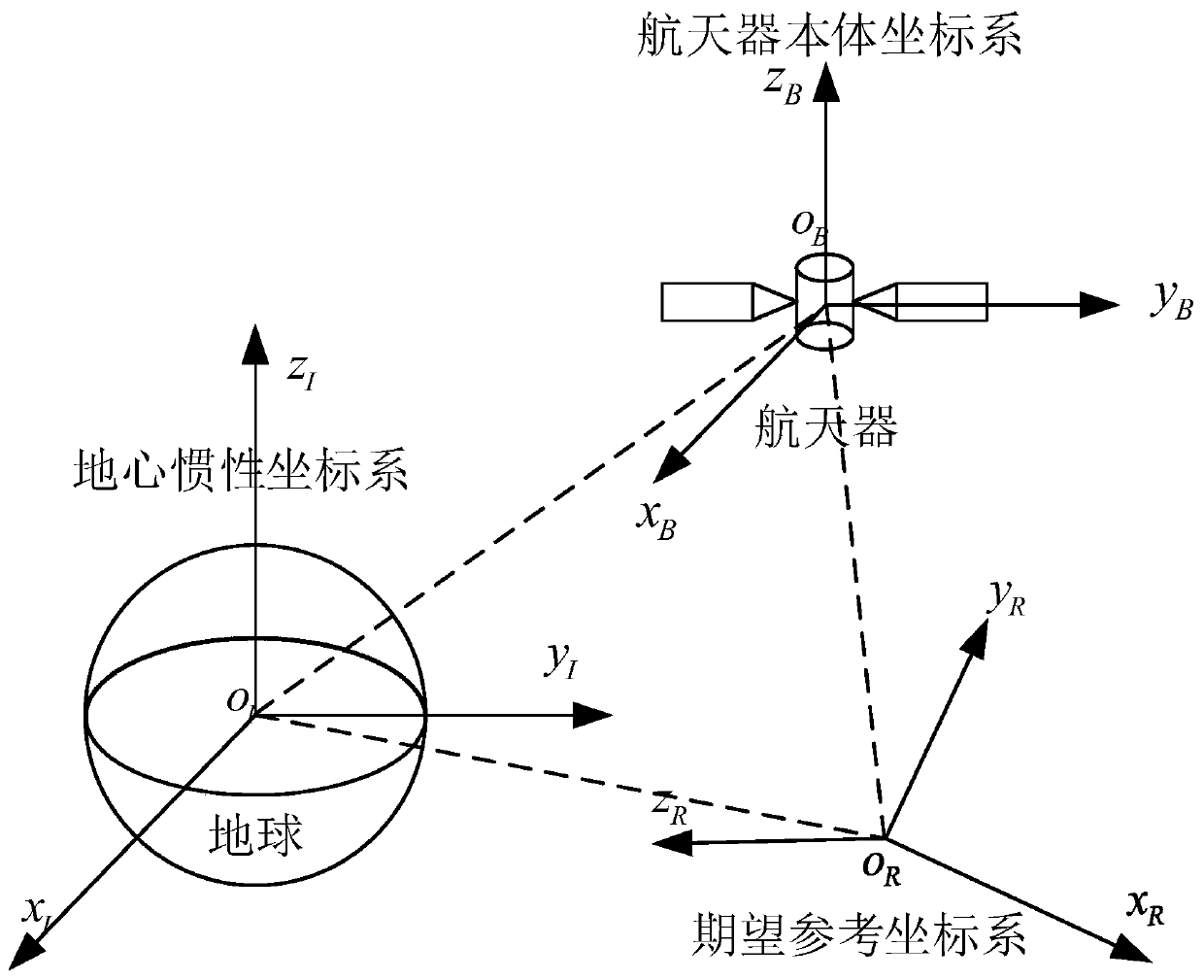
The invention provides a spacecraft attitude tracking control method based on discontinuous adaptive control, belongs to the technical field of spacecraft attitude tracking control, and solves the problem that a spacecraft attitude tracking control system is poor in robustness so that a spacecraft attitude tracking control effect is poor in the case of modeling uncertainty, external disturbances and input saturation effects. The spacecraft attitude tracking control method comprises the following specific steps of step 1, establishing an earth centered inertial oIxIyIzI, a spacecraft body coordinate system oBxByBzB and an expected reference coordinate system oRxRyRzR; step 2, according to the coordinate systems established in step 1, obtaining the spacecraft attitude kinematics and a kinetic equation described by using an attitude quaternion, and a spacecraft error attitude kinematics equation and the kinetic equation, namely the attitude tracking control system; and step 3, based on the step 2, based on a sliding mode surface of an integral terminal, designing an attitude tracking controller considering an unknown external disturbance torque and the rotational inertia uncertainty.The spacecraft attitude tracking control method based on the discontinuous adaptive control provided by the invention can be applied to spacecraft attitude tracking control.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
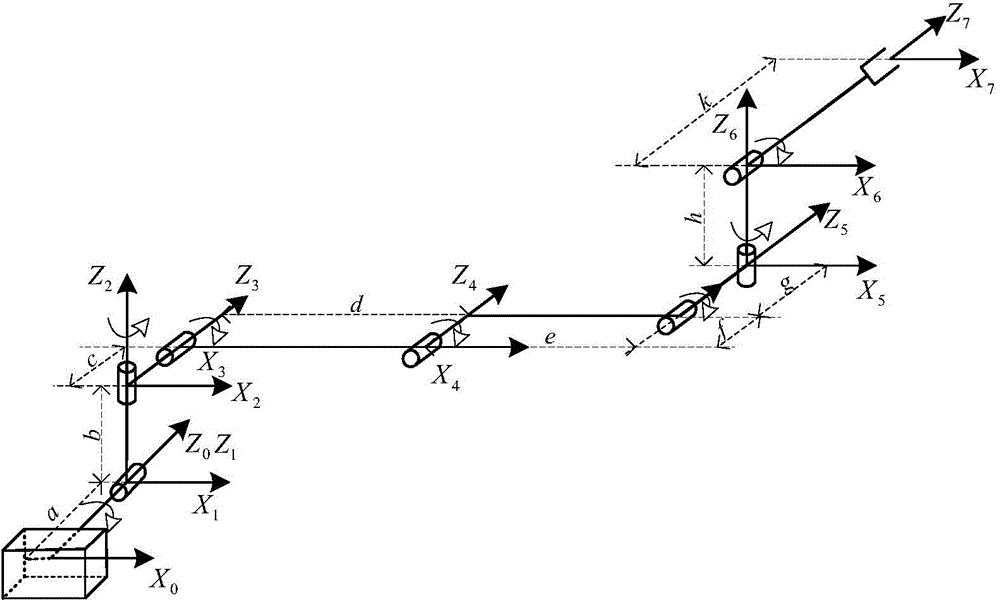
Inverse-kinematics universal solving method of robot with multi-degree of freedom
InactiveCN103901898AOvercome limitationsOvercoming real-timePosition/direction controlWeighted spaceKinematics equations
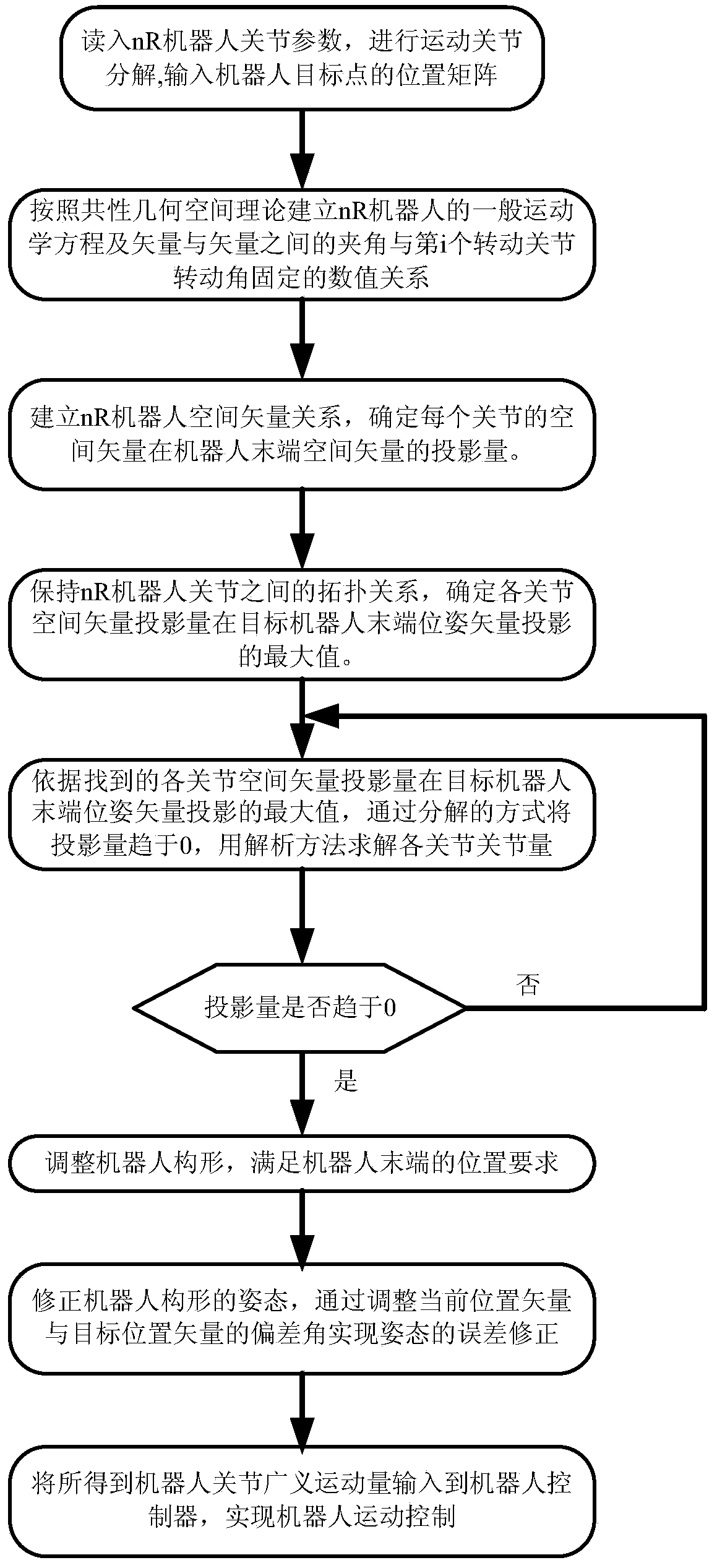
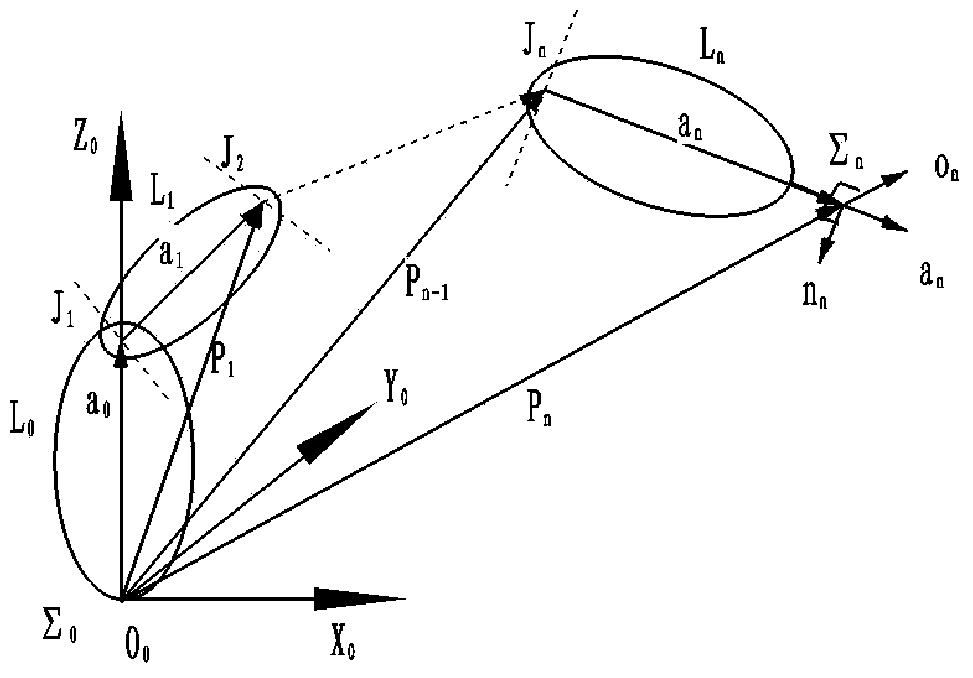
The invention provides an inverse-kinematics universal solving method of a robot with multi-degree of freedom. The common space theory is used for setting a universal kinematical equation of an nR robot, the weighted space vector projection method is used for analyzing the relationship between space vector projection values and revolute joint angles of a space robot, projection weighted values of joint vectors on robot tail end vectors are used as the basis for regulating the tail end pose of the robot, and projection weighted values of joint vectors are determined to achieve half-analytic solution of the inverse kinematics. The method achieves kinematical salvation of the nR robot and also finishes the space obstacle avoidance task. The method can be widely applied to series type space nR robots, has the advantages of being high in calculation speed and high in solving precision, provides control input parameters for series type robots, and meets the requirement for robot kinematics solving operation on industrial sites.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Spacecraft posture fault tolerance control method of single gimbal control moment gyroscope groups
ActiveCN105867401AApplicable fault-tolerant controlNo total failureAttitude controlFault toleranceGyroscope
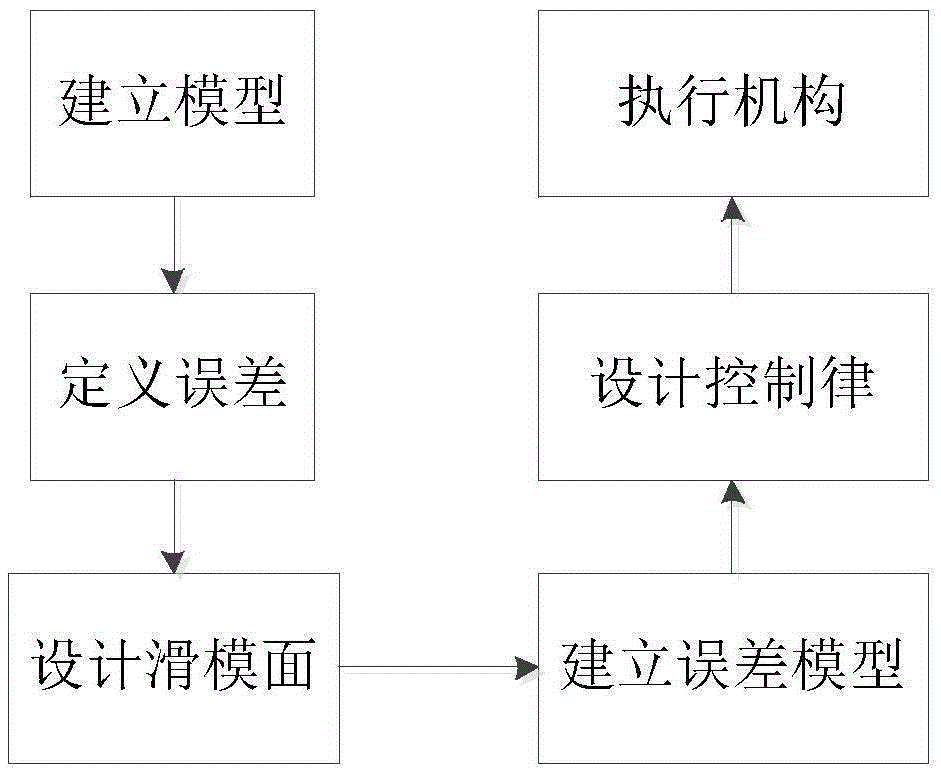
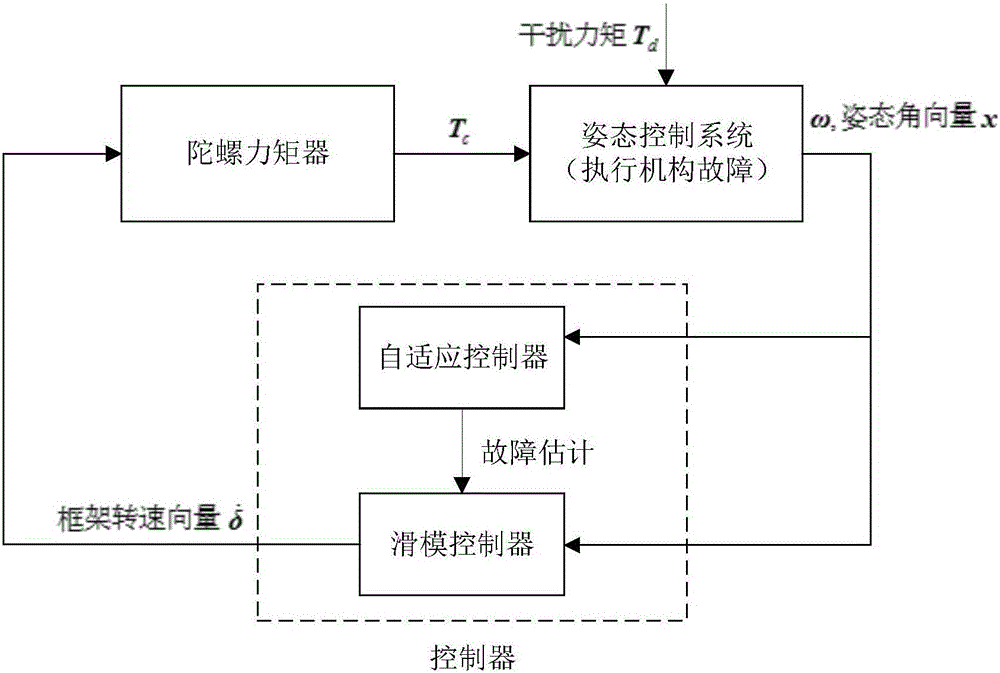
A spacecraft posture fault tolerance control method of single gimbal control moment gyroscope groups includes the following steps that firstly, a kinetic equation and a kinematical equation are established when partial failures exist in the single gimbal control moment gyroscope groups (SGCMGs), wherein a coordinate system is defined, and a control system state equation is established; secondly, on the basis of in-orbit operation characteristics of a spacecraft, the spacecraft posture fault tolerance control method of the single gimbal control moment gyroscope groups is adopted; thirdly, the sliding mode control law is designed, wherein a sliding mode face is designed, the control law is primarily designed and the control law is improved. The method has the advantages that the designed control law is also applicable to fault tolerance control of aircrafts with flywheels as execution mechanisms; people do not need to learn about prior information of faults, real-time estimation of fault information and interference information is achieved through self-adaptation control, and fault time varying is allowed; the method is applicable to SGCMGs of any structure or partial failure modes of flywheels; the method is used in aircrafts of the SGCMGs, the rotation speed of a gyroscope frame serves as direct control amount, and the method conforms to engineering practice.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Finite time fault-tolerant control method for approaching and tracking space non-cooperative target
ActiveCN105159304AAchieve attitude controlHigh precisionAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsKinematics equationsAttitude control
A finite time fault-tolerant control method for approaching and tracking a space non-cooperative target belongs to the field of orbit control and attitude control, and aims to solve the problem of low tracking supervision precision caused by big tracking control error of an existing tracking spacecraft which performs line-of-sight tracking for a non-cooperative target. The finite time fault-tolerant control method is characterized in that dynamical and kinematical equations are established under a line-of-sight coordinate system, the situations such as nondeterminacy of a system, partially unknown motion parameters of the non-cooperative target, control input saturation and dead zone are taken into consideration, self-adaptive estimation and compensation can be performed through adoption of an RBF neural network, and a back-stepping thought is adopted to design a controller so that the tracking spacecraft can converge to an expected attitude and orbit within finite time and can keep the attitude and the orbit. The finite time fault-tolerant control method of the present invention has the advantages of quick control convergence, good robustness and high tracking control precision.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Collaborative path planning method for kinematic redundant two-arm space robot
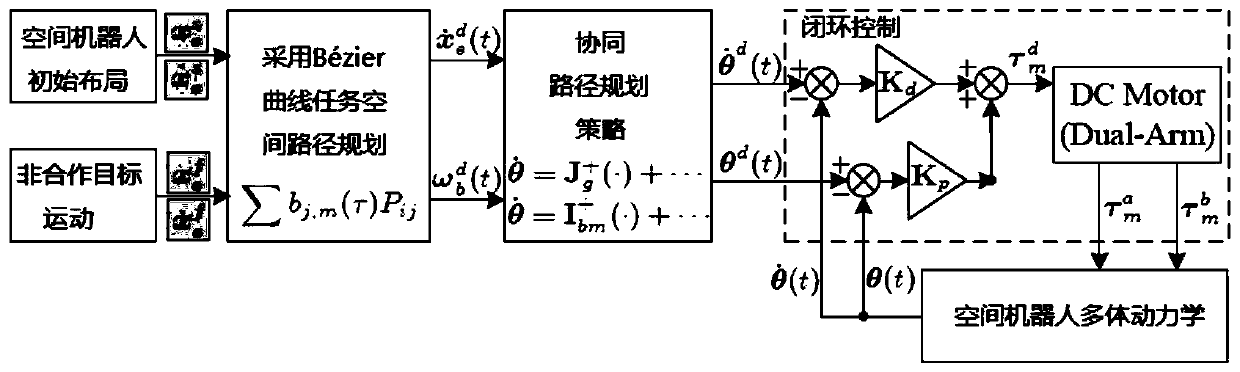
ActiveCN110104216AImplementing a collaborative path planning methodSmall attitude disturbanceProgramme-controlled manipulatorCosmonautic vehiclesKinematics equationsDynamic balance
The invention discloses a collaborative path planning method for a kinematic redundant two-arm space robot. The collaborative path planning method for the kinematic redundant two-arm space robot comprises the following steps that a dynamic equation and a kinematic equation of a space robot system are established; a redundant solution of an inverse kinematics equation of an end-effector is solved,and a system non-holonomic constraint equation is obtained through a momentum conservation equation; a task space constraint equation of the relationship between the end-effector motion and the attitude of a base is obtained through the system non-holonomic constraint equation; the path planning of the end-effector in a task space is obtained by using a quintic bezier curve, and path execution time is determined by the velocity and acceleration boundary of the end-effector; and the joint motion trajectory planning corresponding to different task priorities is obtained through the end-effectormotion equation and the task space constraint equation. The collaborative path planning method of the space two-arm robot is implemented, various tasks can be performed according to the priorities ofthe tasks such as a multi-arm collaborative task and a dynamic balancing task, and the operation ability of a space manipulator is greatly expanded.
Owner:RES & DEV INST OF NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV IN SHENZHEN +1
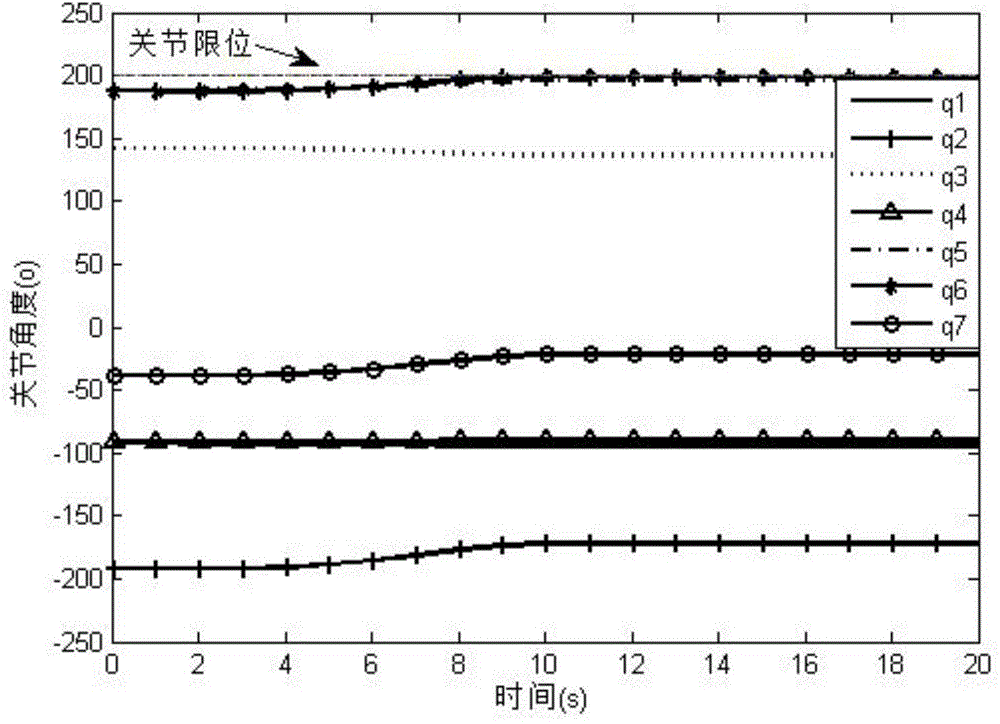
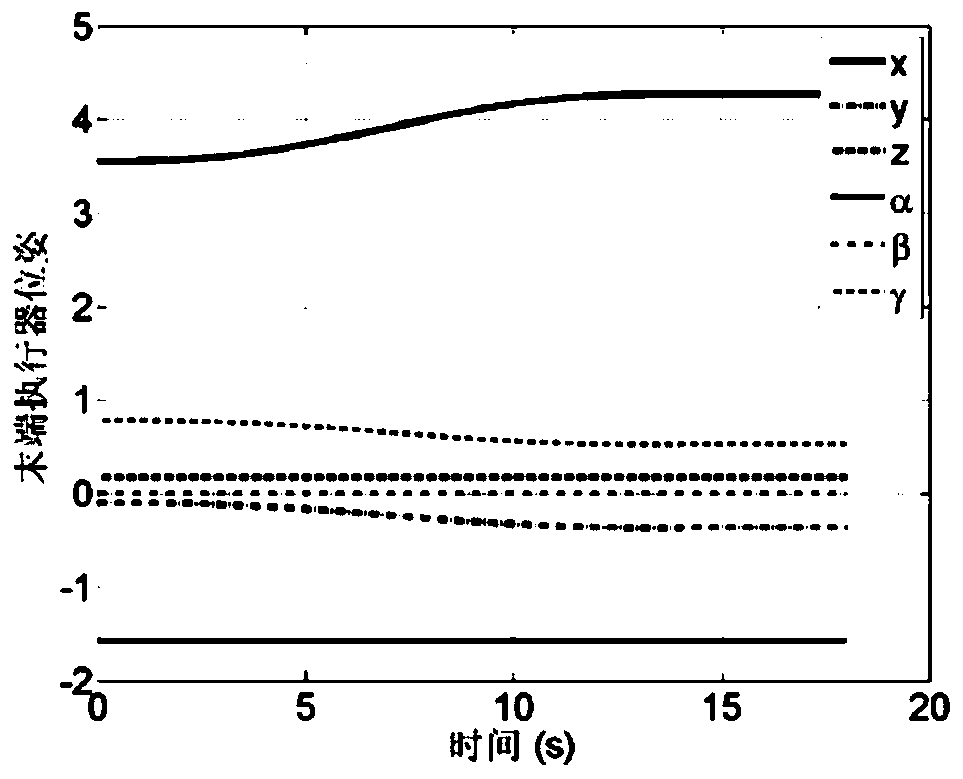
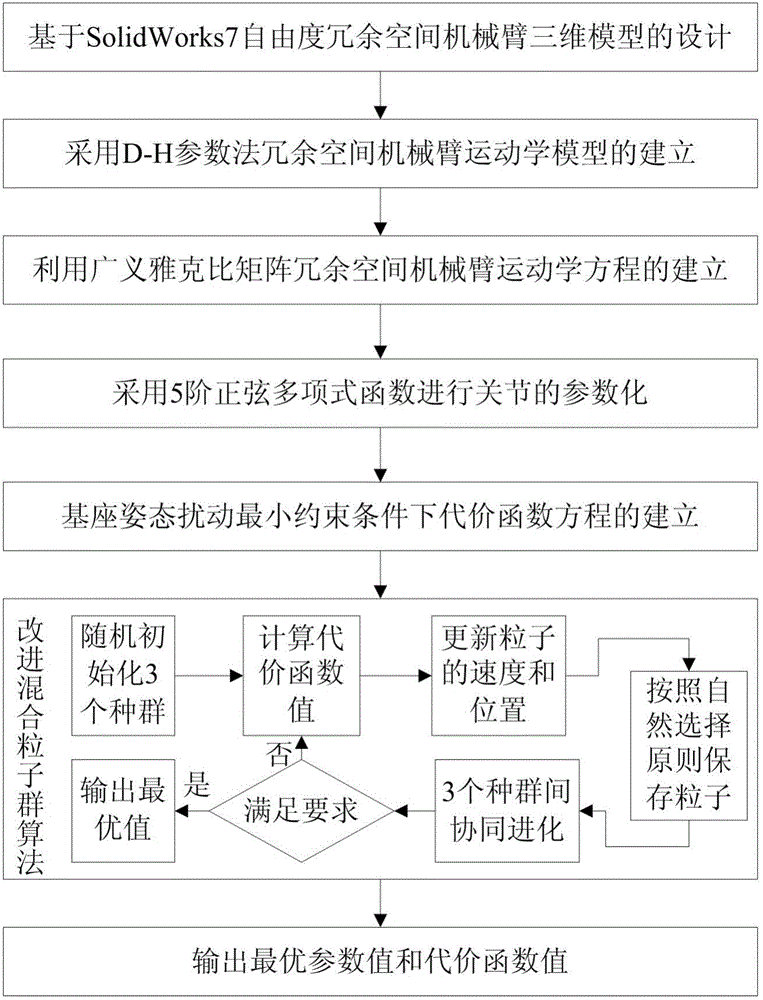
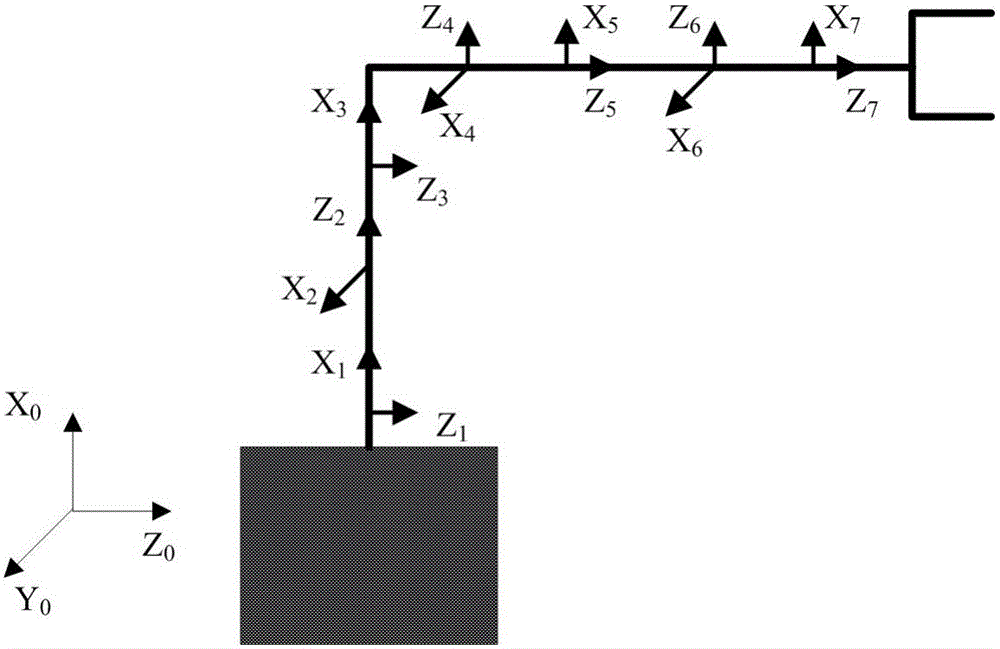
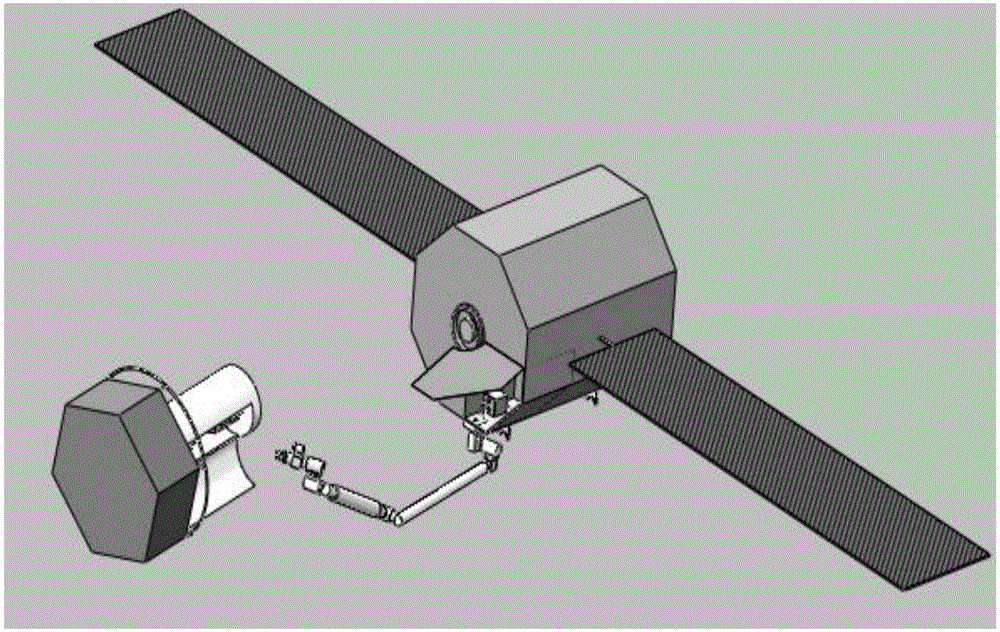
Minimum base attitude disturbance track planning method for redundant space manipulator
InactiveCN106055522ASolve the blockageHigh precisionProgramme-controlled manipulatorComplex mathematical operationsAviationKinematics equations
The invention relates to a minimum base attitude disturbance track planning method for a redundant space manipulator, and belongs to the technical field of aerospace. The method comprises the steps of (1), designing a three-dimensional model of the redundant space manipulator; (2), establishing a kinematic model of the redundant space manipulator; (3) establishing a kinematic equation of the redundant space manipulator by employing a generalized Jacobian matrix; (4), parameterizing joints by employing a 5-order sine polynomial function; (5), establishing a cost function equation under a minimum constraint condition of base attitude disturbance; (6), providing an improved hybrid particle swarm optimization; and (7), carrying out optimization solution to the cost function by employing the hybrid particle swarm optimization, thereby obtaining planning tracks under the constraint condition. According to the method, the track planning problem of the redundant space manipulator under the minimum constraint condition of the base attitude disturbance is solved, and the planning tracks solved by the improved hybrid particle swarm optimization is high in precision and good in effect and is steady.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
SLAM-based visual perception mapping algorithm and mobile robot
The invention discloses an SLAM-based visual perception mapping algorithm and a mobile robot. The algorithm comprises the steps of obtaining image data of a to-be-mapped area environment and rotatingspeed data of a driving wheel; performing feature extraction on a color image in the image data; after the rotating speed data is calculated and processed according to a kinematics equation, fusing and optimizing the rotating speed data and a depth image in the image data by using a method of minimizing an encoder and a re-projection error to obtain a current frame pose of the robot; screening current frame image data acquired when a robot walks in a to-be-mapped area to obtain a key frame, identifying and classifying objects in an environment by utilizing a color image of the key frame, deleting the classified dynamic objects from the key frame, carrying out sparse processing on static objects, and carrying out local loopback for correction; taking pixel points of the color image and thecorresponding depth image in the key frame as map points, storing the map points through an octree, and carrying out mapping.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
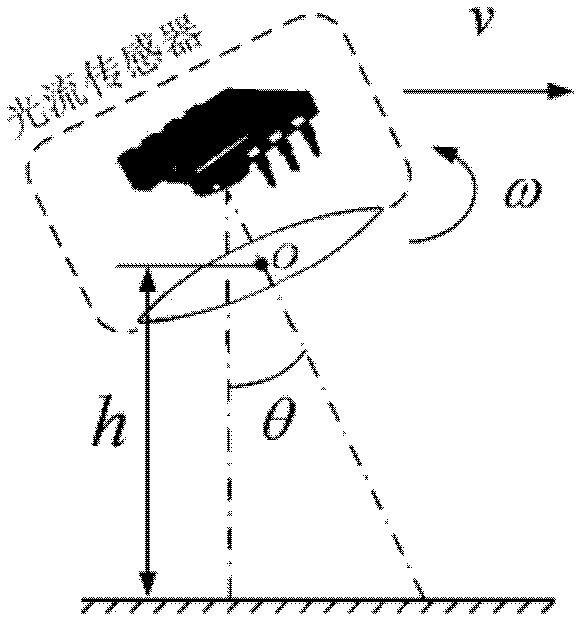
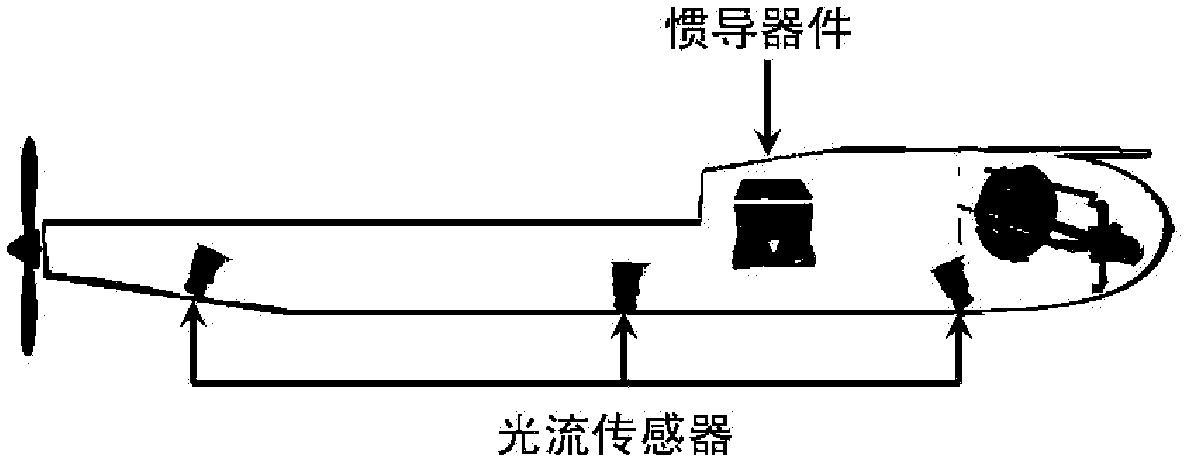
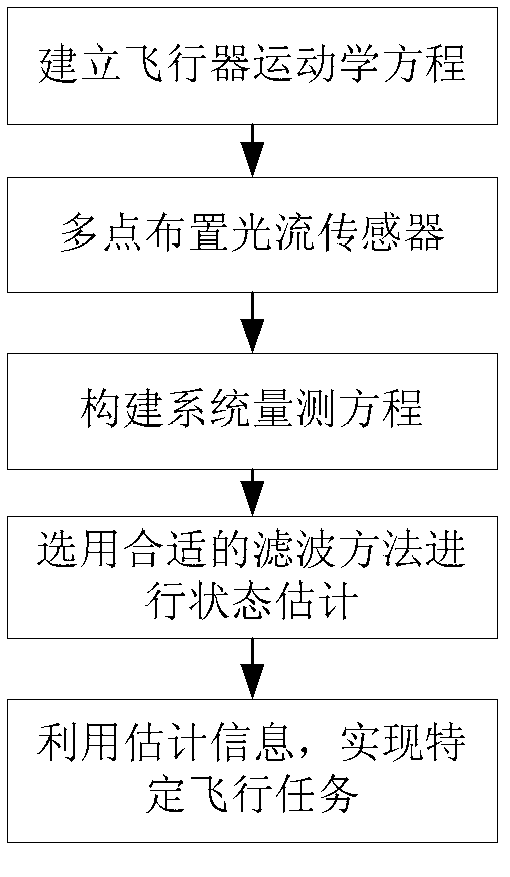
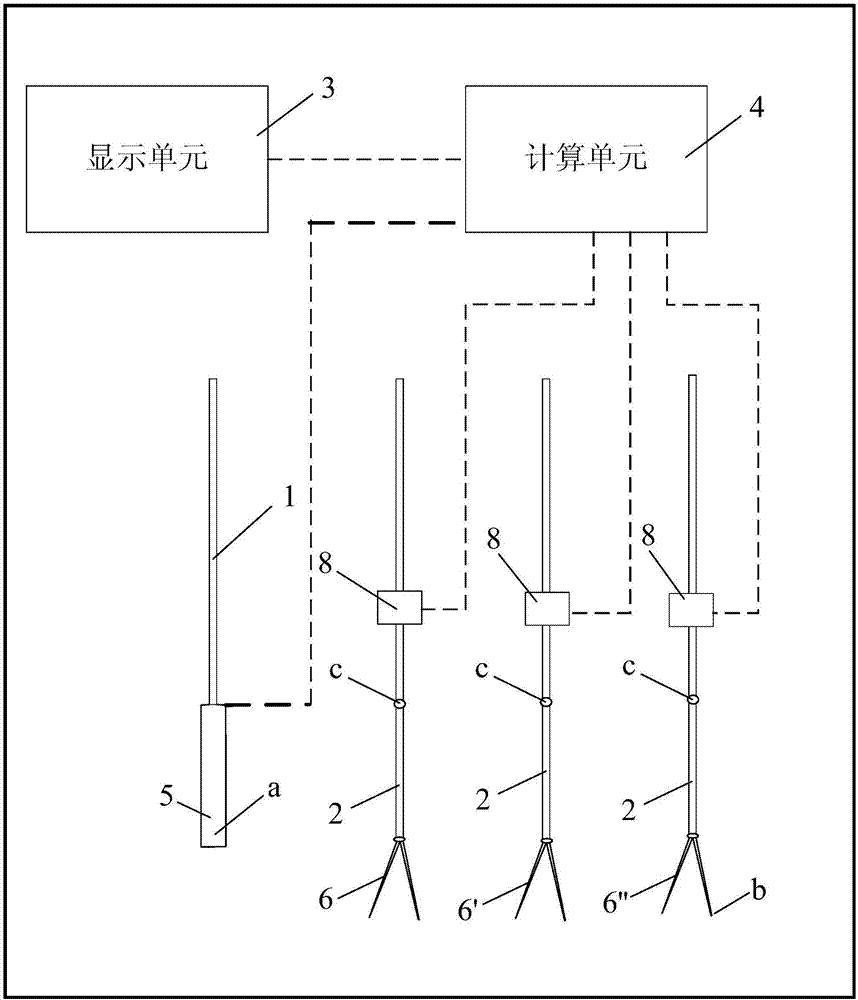
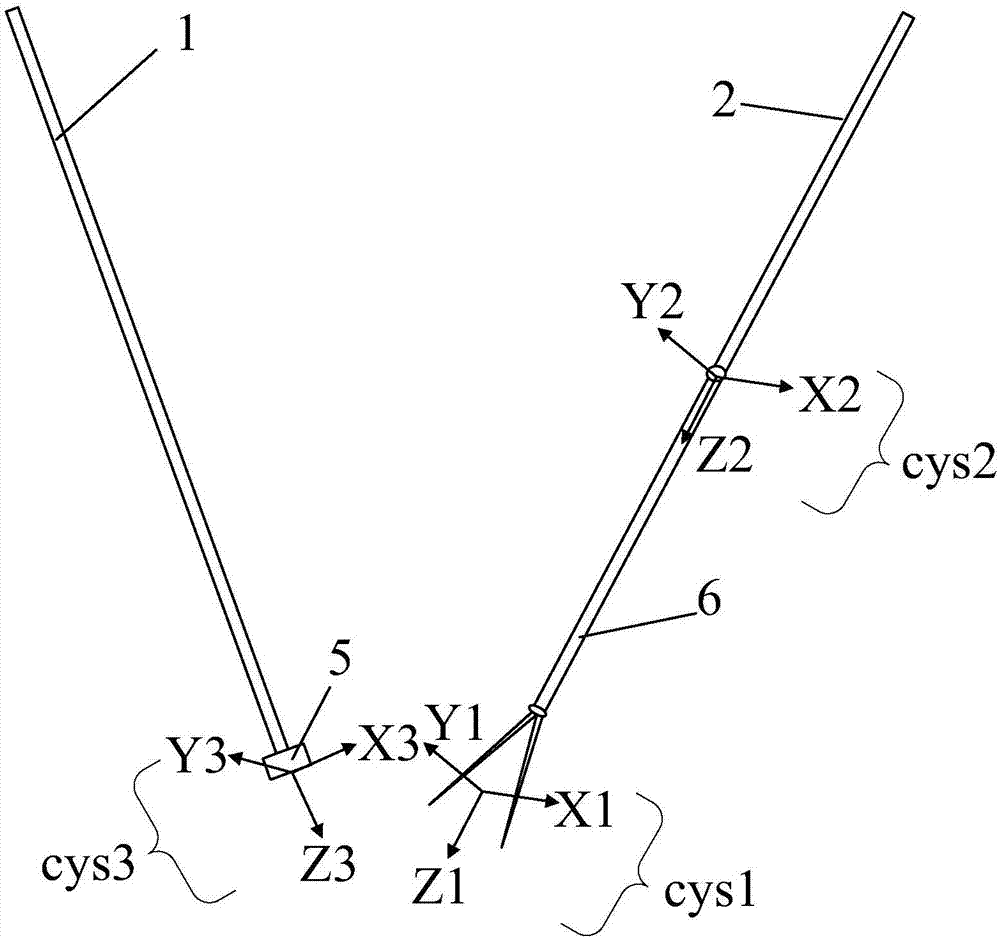
Configuration method for information fusion of a plurality of optical flow sensors and inertial navigation device
A configuration method for the information fusion of a plurality of optical flow sensors and an inertial navigation device is disclosed, which comprises the following five steps of: 1, establishing a linear disturbance kinematical equation aiming at an aircraft needing to be installed with optical flow sensors; 2, arranging the optical flow sensors on the aircraft in all directions and at a plurality of points; 3, establishing the measurement equation of the optical flow sensors according to the installation position and direction of each optical flow sensor on the aircraft; 4, estimating the flight state of the aircraft by utilizing EKF, that is, extended Kalman filter method and UKF, that is, unscented Kalman filter method respectively; and 5, realizing the specific flight mission of the aircraft by the estimated state information. In the configuration method for the information fusion of a plurality of optical flow sensors and an inertial navigation device, a plurality of optical flow sensors and an inertial navigation device are used; and the optical flow sensors and the inertial navigation device are light in weight, small in volume, low in power consumption, convenient to install and arrange on the aircraft, and unable to radiate electromagnetic signal outwards, thereby enhancing the concealment of the aircraft. The configuration method for the information fusion of a plurality of optical flow sensors and an inertial navigation device has practical value and wide application prospect in the technical fields of measurement and estimation for the attitude, flight speed and height of aircraft.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
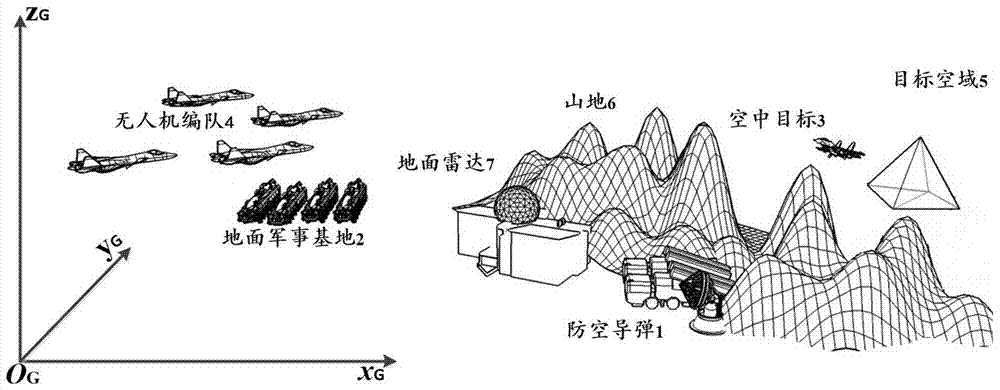
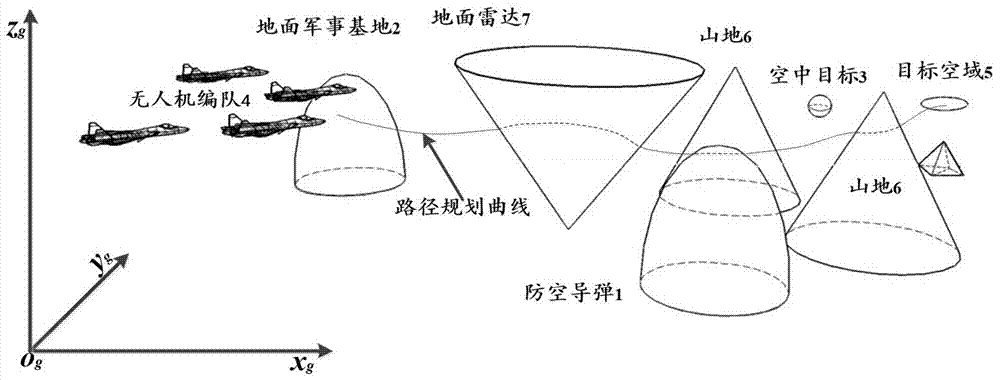
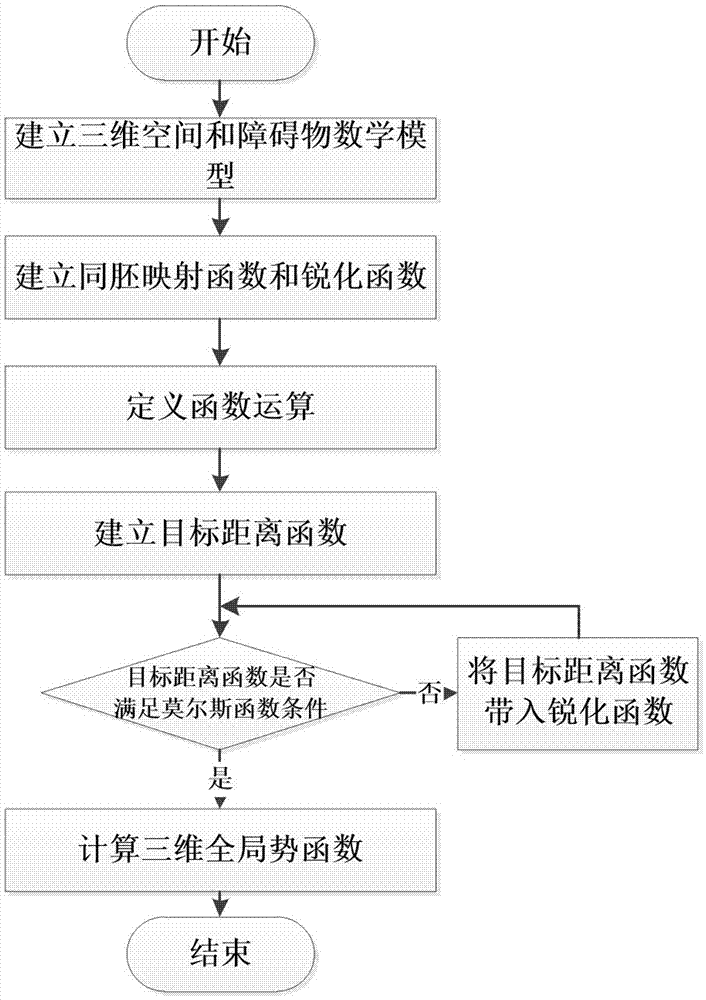
Unmanned aerial vehicle formation path planning algorithm based on three-dimensional global artificial potential function
ActiveCN107219857AAddress limitationsSolve the real problemPosition/course control in three dimensionsKinematics equationsGeometric relations
The invention discloses an unmanned aerial vehicle formation path planning algorithm based on a three-dimensional global artificial potential function. The algorithm is mainly used to solve problems of formation maintenance of an unmanned aerial vehicle, path planning, three-dimensional obstacle avoidance and the like under a three-dimensional space environment. The algorithm comprises the following steps of firstly establishing a mathematic model of a global potential function under a three-dimensional space; then according to an expected formation, establishing a formation geometry equation of the unmanned aerial vehicle under the three-dimensional space; and finally, establishing a formation unmanned aerial vehicle kinematics equation containing a formation constraint. In the method, through the formation geometry equation, a geometric relation of the plurality of unmanned aerial vehicles under the three-dimensional space is established; and a penalty function method is used to solve a constraint dynamics equation so as to acquire a flight path of the formation unmanned aerial vehicle. Compared to a traditional classic artificial potential function, by using the algorithm of the invention, a two-dimensional space limitation problem of a two-dimensional classic artificial potential function can be solved and problems that a local minimum value exists in a classic potential function and so on can be solved too. By using the algorithm of the invention, limitation of the two-dimensional classic potential function and path planning of the formation unmanned aerial vehicle can be effectively solved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Earth satellite self astronomical navigation method based on self adaptive expansion kalman filtering
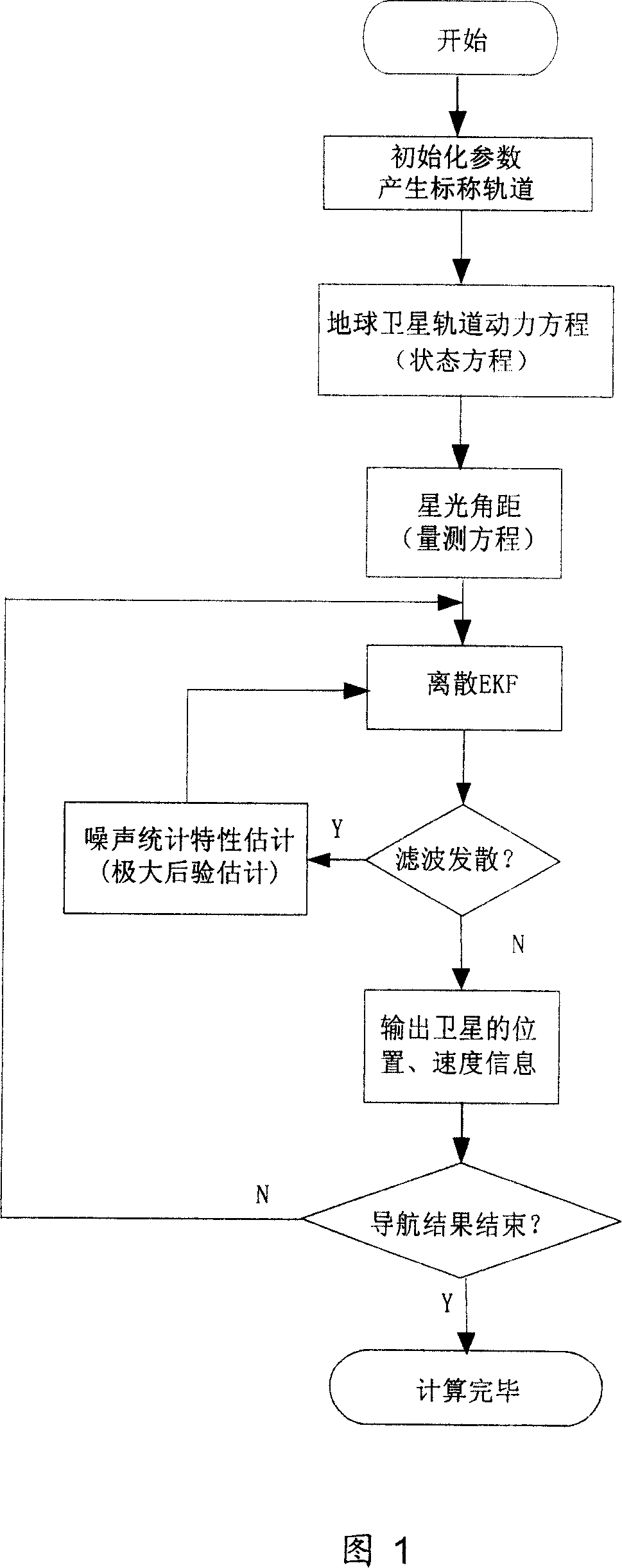
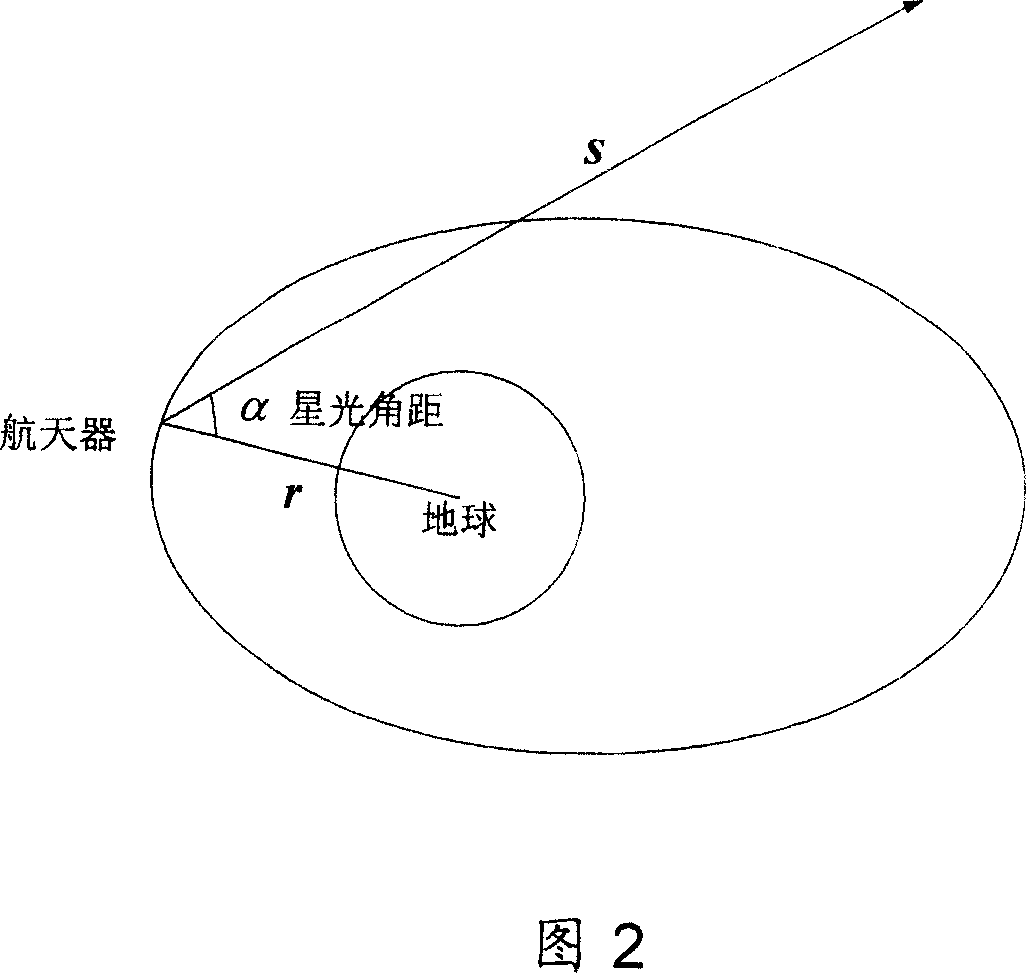
InactiveCN1987355AImprove navigation accuracyOvercome the problem of divergenceNavigational calculation instrumentsInstruments for comonautical navigationEarth satelliteKinematics equations
The method includes steps: building up kinematical equation of earth satellite orbit based on rectangular coordinate system; building up measurement equation based on angular distance of starlight as measuring quantity; building up discrete type extended Kalman filtering equation to determine whether extended Kalman filtering is divergent; using prognostic filtering residual to determine whether extended Kalman filter is divergent; if yes, then the method carries out estimating statistic characteristics of noise; otherwise, carrying out calculation according to standard extended Kalman filtering program. The invention solves issue that divergence of noise filter caused by inaccurate determination of statistic characteristics of noise influences on navigation accuracy. Advantages are: independent, flexible and simple, and high precision. The invention is especially suitable to earth application satellite needed high navigation accuracy in resource, weather areas etc.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
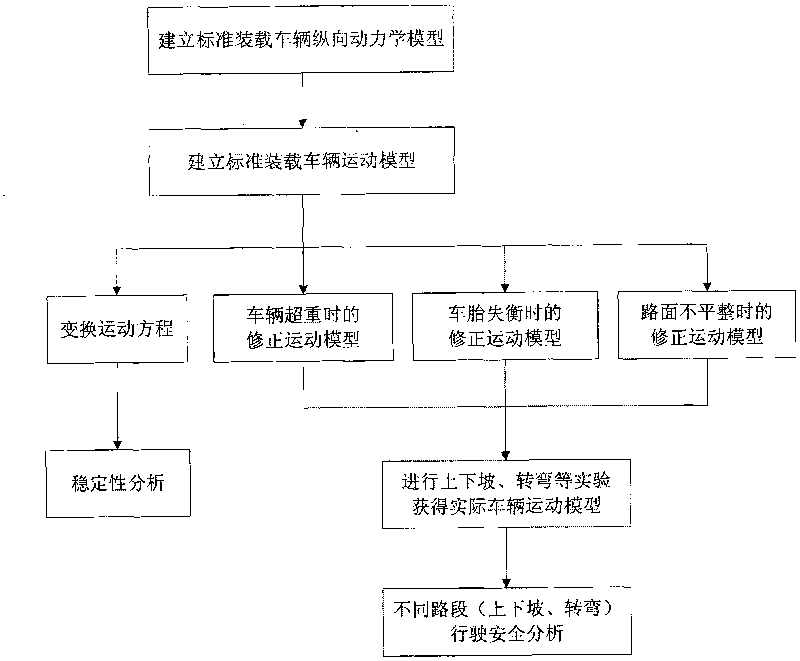
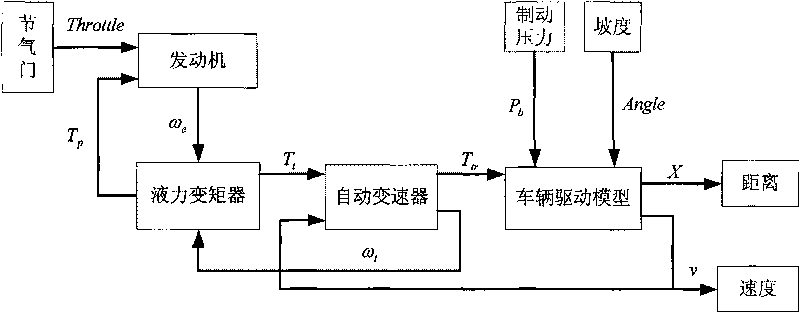
Method for analyzing driving safety of vehicles
InactiveCN101739816ADriving Safety JudgmentDetection of traffic movementSpecial data processing applicationsKinematicsKinematics equations
The invention discloses a method for analyzing driving safety of vehicles, belongs to the technical field of driving safety of vehicles, and analyzes the driving safety of different vehicles on road sections in mountainous area or on a bridge, and the like. The method for analyzing driving safety of vehicles of the invention comprises the following steps of: establishing a longitudinal kinetic model of a vehicle by establishing an engine model, a hydraulic torque converter model, an automatic transmission model, a vehicle driving model and a brake system model respectively and combining the models; building a standard loading vehicle movement model in a common state by combining a vehicle kinetic equation, modifying movement models of light loaded, heavy loaded and overloaded vehicles based on the standard loading vehicle movement model in a common state, and analyzing a corresponding motion law. The method realizes the judgment of the driving safety of vehicles on specific road section by establishing the kinetic models of the vehicles, acquiring driving data of vehicles, verifying and modifying the models by designed tests.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Surgical robot system and surgical instrument position display method
ActiveCN107049492AImprove securityIncrease success rateSurgical navigation systemsEndoscopesSurgical robotKinematics equations
The invention relates to a surgical robot system and a surgical instrument position display method. The surgical robot system comprises an image arm, a tool arm, a display unit and a computing unit, wherein the image arm can be used for clamping an endoscope used for collecting image information; the tool arm is a fixed point mechanism and used for clamping a surgical instrument, and the surgical instrument comprises at least one feature point identifying surgical instrument position information; the display unit is connected with the computing unit in a communication mode, and an endoscope coordinate system is arranged at the tail end of the endoscope; the computing unit is used for obtaining coordinate values of the feature points under the endoscope coordinate system according to the forward kinematical equation, obtaining position information of the surgical instrument under the plane of an endoscope camera according to coordinate values and conducting imaging processing on the position information; the display unit receives the position information after imaging processing and displays the position information to improve surgical safety and efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICROPORT MEDBOT (GRP) CO LTD
Obstacle avoidance path optimal successive operation planning method for spatial multiplexing
The invention discloses an obstacle avoidance path optimization successive operation planning method for spatial multiplexing. The obstacle avoidance path optimization successive operation planning method comprises the steps of finding a path optimization task sequence, finding a shortest obstacle avoidance path among adjacent task points, then finding joint movements with minimum disturbance to body attitudes, and realizing planning of path optimization successive operation for spatial multiplexing. The obstacle avoidance path optimization successive operation planning method utilizes a kinematical equation of a free-floating space robot system, adopts a hybrid particle swarm optimization algorithm, performs successive operation planning of path optimization for spatial multiplexing, is simple in algorithm, has few calculation workload, and is high in operation result precision. The obstacle avoidance path optimization successive operation planning method is suitable for a spatial operation system to execute multiple tasks continuously, saves time and fuel, is conductive to prolonging the service life of the spacecraft, and provides a new idea for the continuous execution problem of multiple tasks by the spatial operation system. The obstacle avoidance path optimization successive operation planning method is further elaborated by combining the drawings and embodiments.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Method for simultaneous performing visual servo and adaptive depth identification through robot
InactiveCN106774309ASolve the problem of identifying depth informationSolve the global stability problemPosition/course control in two dimensionsStabilization controlSimulation
A method for simultaneous performing visual servo and adaptive depth identification through a robot belongs to the computer vision and mobile robot technology field. The method comprises: obtaining an open loop kinematical equation with stable error according to a robot pose position polar coordinate representation method; and designing an adaptive updating rule capable of identifying depth information according to a concurrence learning strategy, and constructing a vision stabilization control rule of a mobile robot. The parameter adaptive updating rule designed by the invention can perform learning at the initial stage of the robot performing stabilization motion and perform online identification of the depth information in the robot motion process. The method for simultaneous performing visual servo and adaptive depth identification through the robot can prove the simultaneous convergence of the pose posture errors and the depth identification errors according to a Lyapunov method and a LaSalle invariance principle. The method for simultaneous performing visual servo and adaptive depth identification through the robot can accurately and reliability identify the depth information while the mobile robot completes the vision stabilization control so as to prove the simultaneous convergence of the controller and the identification module.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com