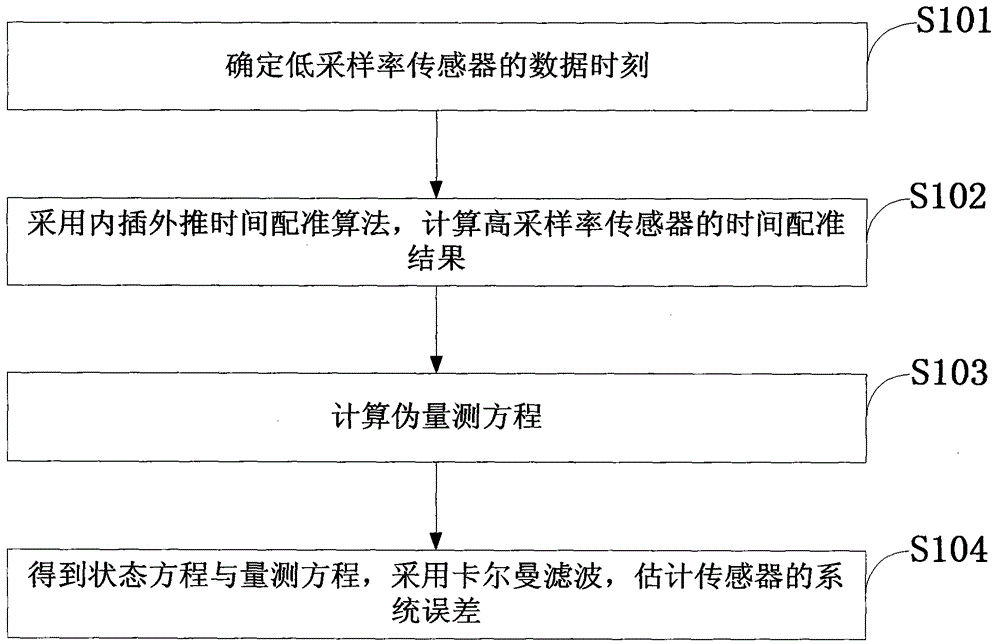
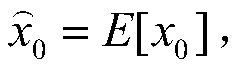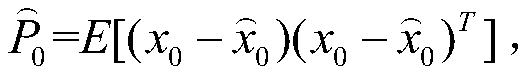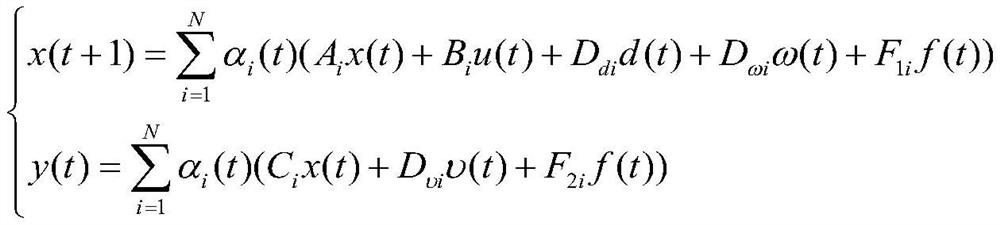Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
226 results about "State vector" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In navigation, a state vector is a set of data describing exactly where an object is located in space, and how it is moving. From a state vector, and sufficient mathematical conditions (e.g. the Picard-Lindelöf theorem), the object's past and future position can be determined.
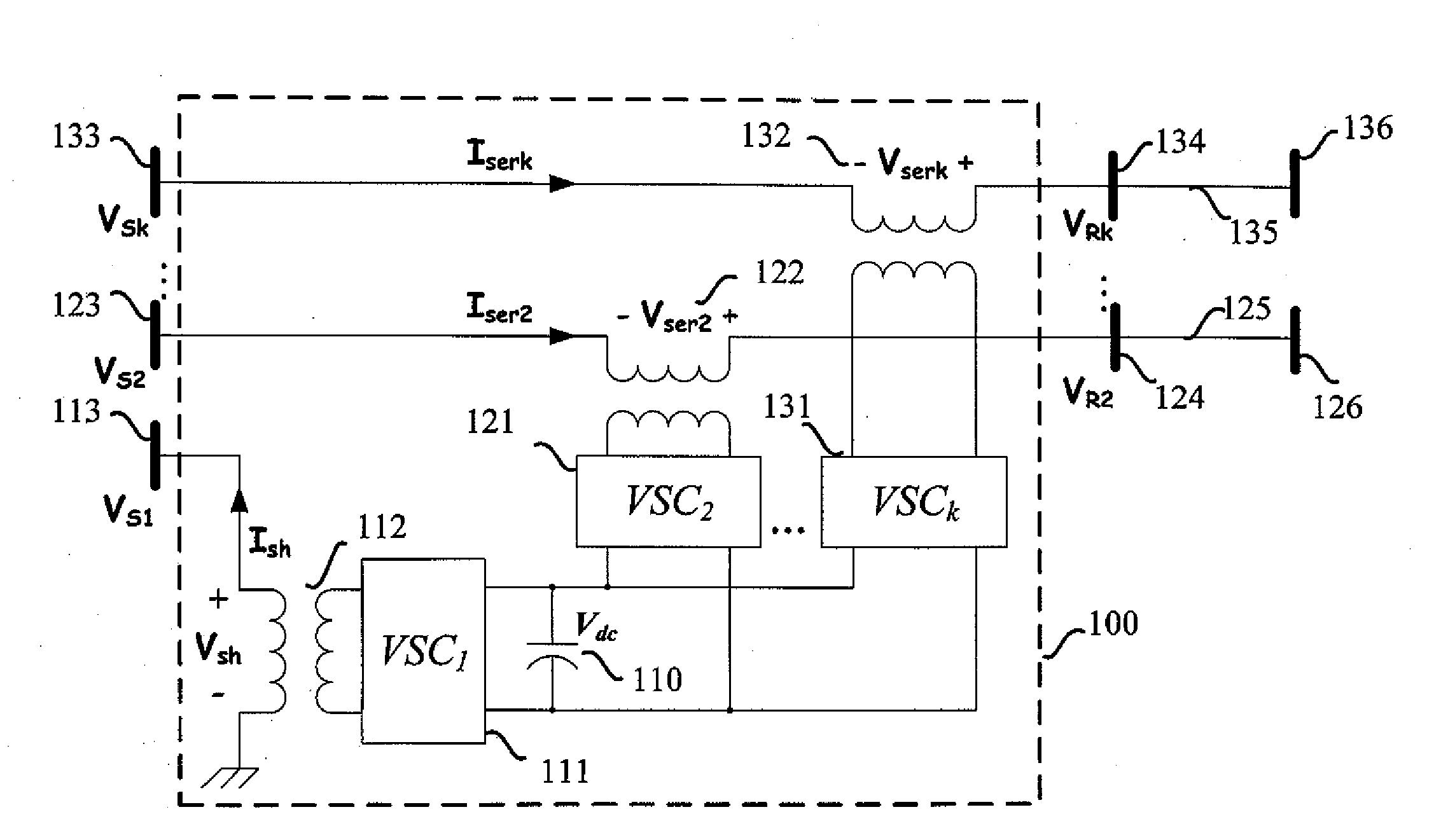
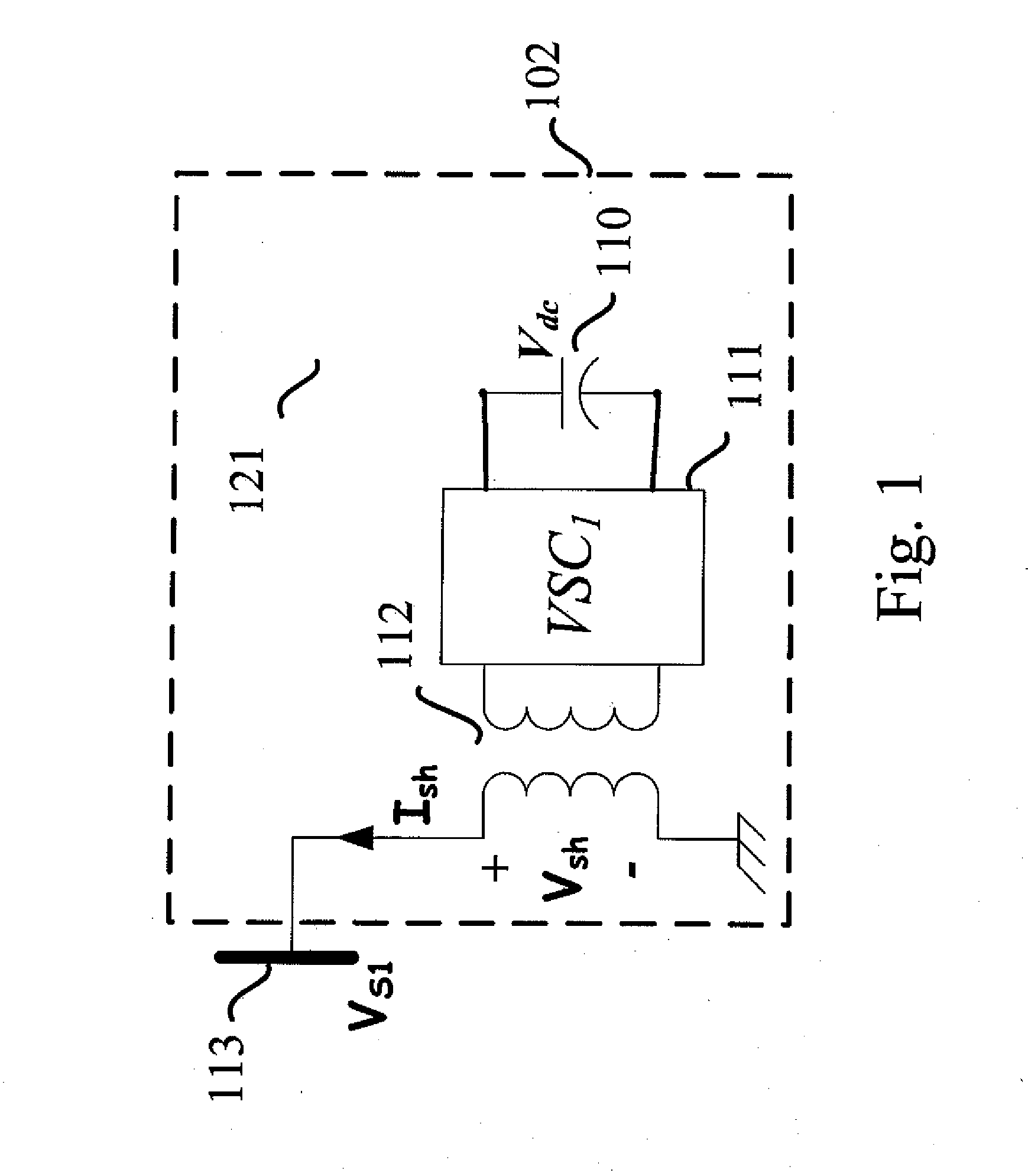
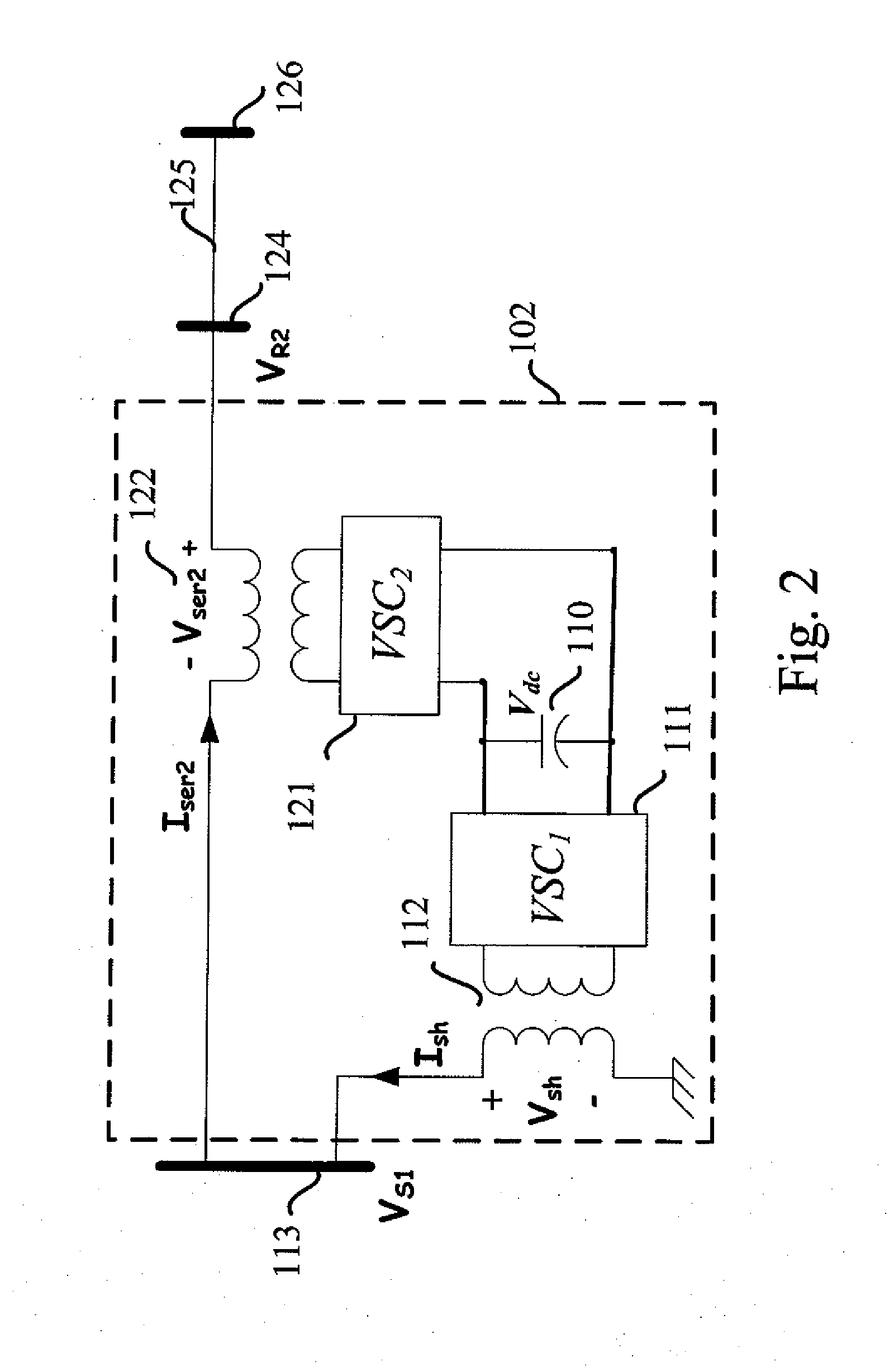
Method of Calculating Power Flow Solution of a Power Grid that Includes Generalized Power Flow Controllers
InactiveUS20090182518A1Fast convergenceFlexible structureFlexible AC transmissionBatteries circuit arrangementsConvertersPower flow
A method to incorporate the steady-state model of the generalized power flow controller into a Newton-Raphson power flow algorithm is disclosed. The disclosed method adopts a flexible steady-state model of the generalized power flow controller, which can be applied to calculate the power flow solution of a power grid embedded with STATCOM, UPFC, GUPFC and the generalized power flow controller in a single framework. The disclosed method only incorporates the control variables of the shunt voltage sourced converter into the state vector of Newton-Raphson power flow algorithm. The increment of state variables due to incorporating the generalized power flow controller is less than the prior art. Further, the method can preserve the quadratic convergence characteristic of the Newton-Raphson power flow algorithm after embedding the generalized power flow controller into a power grid.
Owner:CHANG GUNG UNIVERSITY
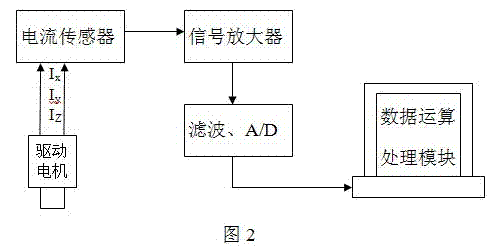
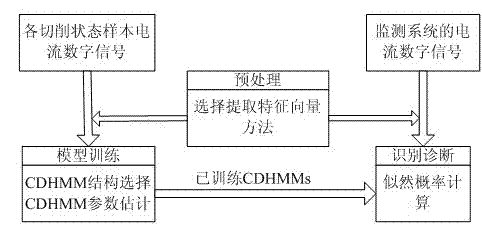
An online monitoring method for turning stability of CNC machine tools
InactiveCN102284888ARealize online monitoringReal-time online monitoringMeasurement/indication equipmentsMetal working apparatusNumerical controlMathematical model
The invention provides a monitoring method for the turning stability of a digital control machine tool, relating to the monitoring technical field. As the performance of a servo system is continuously improved, a response speed, the sensibility and the like of the servo system are also continuously improved, thus, states of the machine tool can be reflected on a current of a driving motor during a cutting process. In the invention, through various signal processing methods, a plurality of characteristic values of current signals are extracted, a characteristic status vector is established as an input of a mathematical model, and a cutting status of the machine tool is output through analysis and calculation of the mathematical model. As the invention has the characteristics that the current signal has high anti-interference performance and is easy to be acquired, assistant tools are fewer, and the like, compared with a plurality of existing monitoring methods, the invention has the advantages of simple and feasible operation, good monitoring effects and the like; thereby, the invention can more easily realize the online monitoring for the processing states, and can effectively guarantee the processing security and the product quality.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
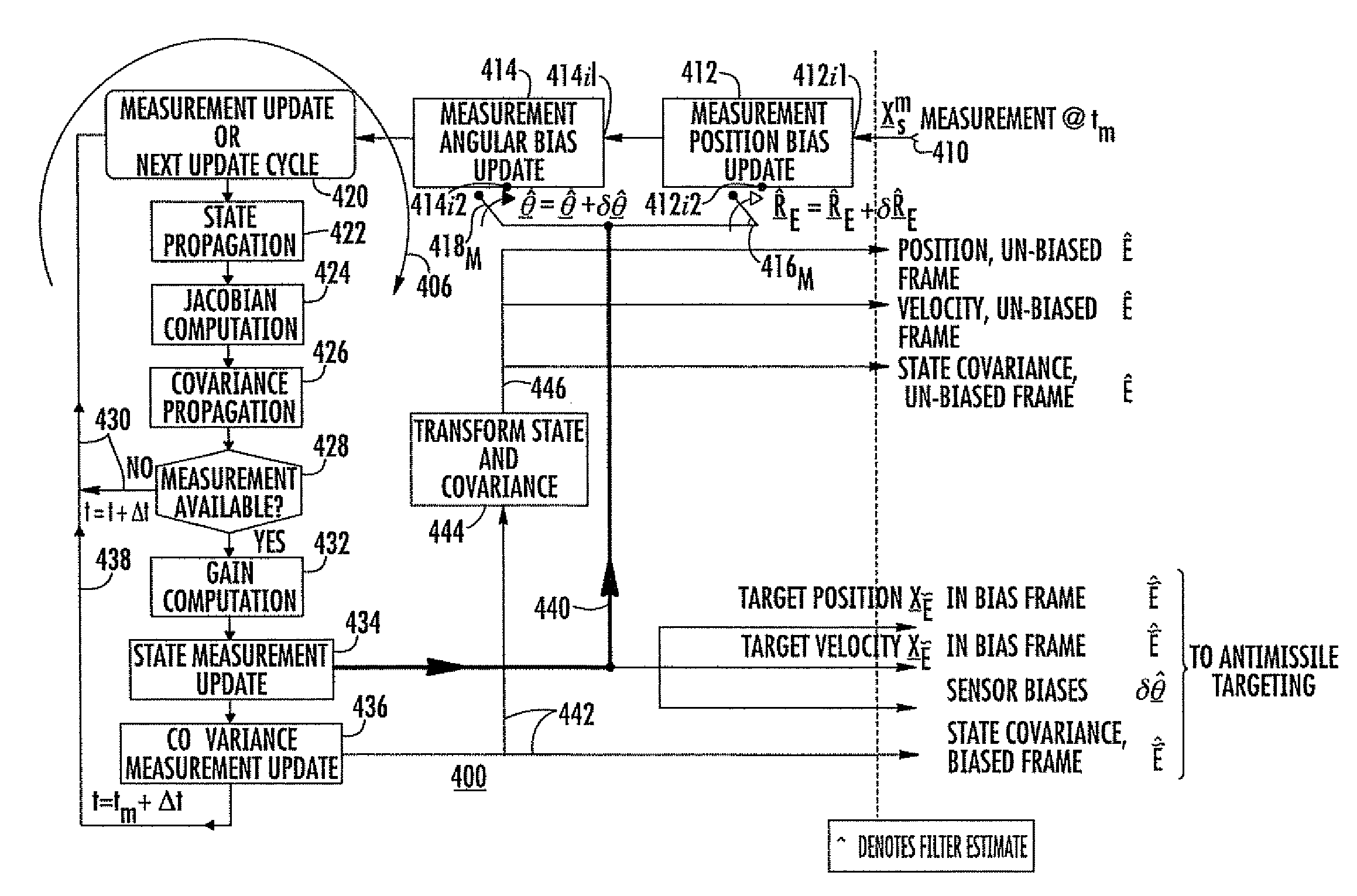
Unified navigation and inertial target tracking estimation system
InactiveUS7626534B1Direction finders using radio wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTarget signalMarine navigation
A target tracking method uses sensor(s) producing target signals subject to positional and / or angular bias, which are updated with sensor bias estimates to produce updated target-representative signals. Time propagation produces time-updated target states and sensor positional and angular biases. The Jacobian of the state dynamics of a target model produces the state transition matrix for extended Kalman filtering. Target state vector and bias covariances of the sensor are time propagated. The Kalman measurement residual is computed to produce state corrections, which are added to the time updated filter states to thereby produce (i) target state updates and (ii) sensor positional and angular bias updates. The covariance of a state vector comprising target states and sensor positional and angular biases is propagated, producing measurement updated state covariance including (i) target position and velocity measurement covariance updates and (ii) the sensor positional and angular bias measurement covariance updates.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Asynchronous sensor space alignment algorithm
InactiveCN104809326ASolving Spatial Registration ProblemsMeasurement devicesSpecial data processing applicationsState vectorMeasurement equations
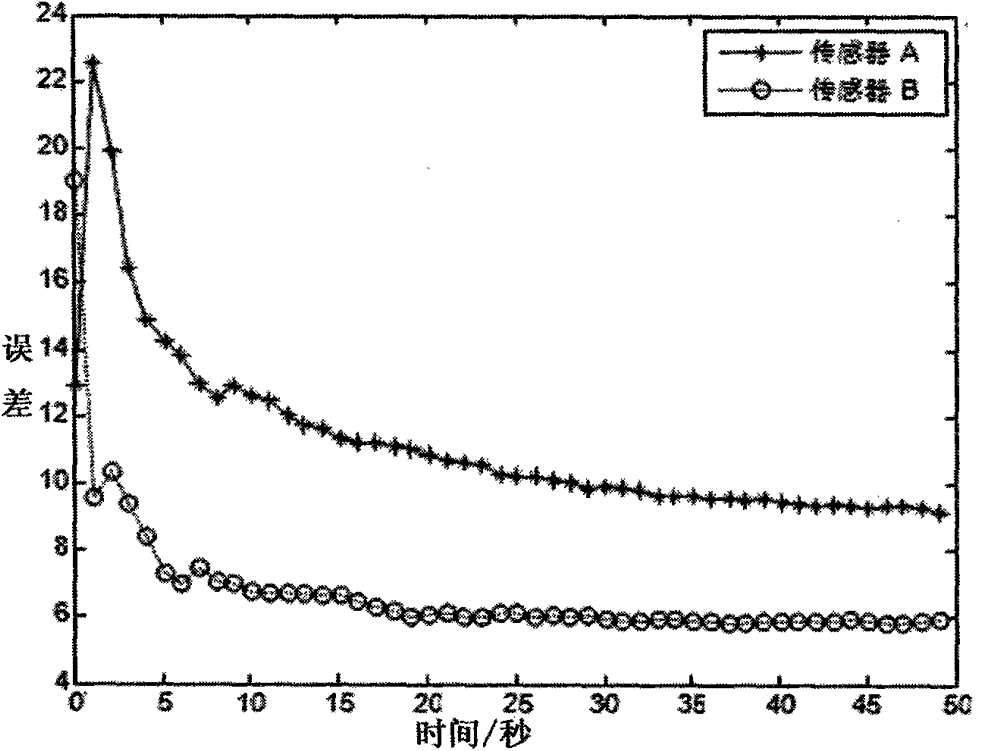
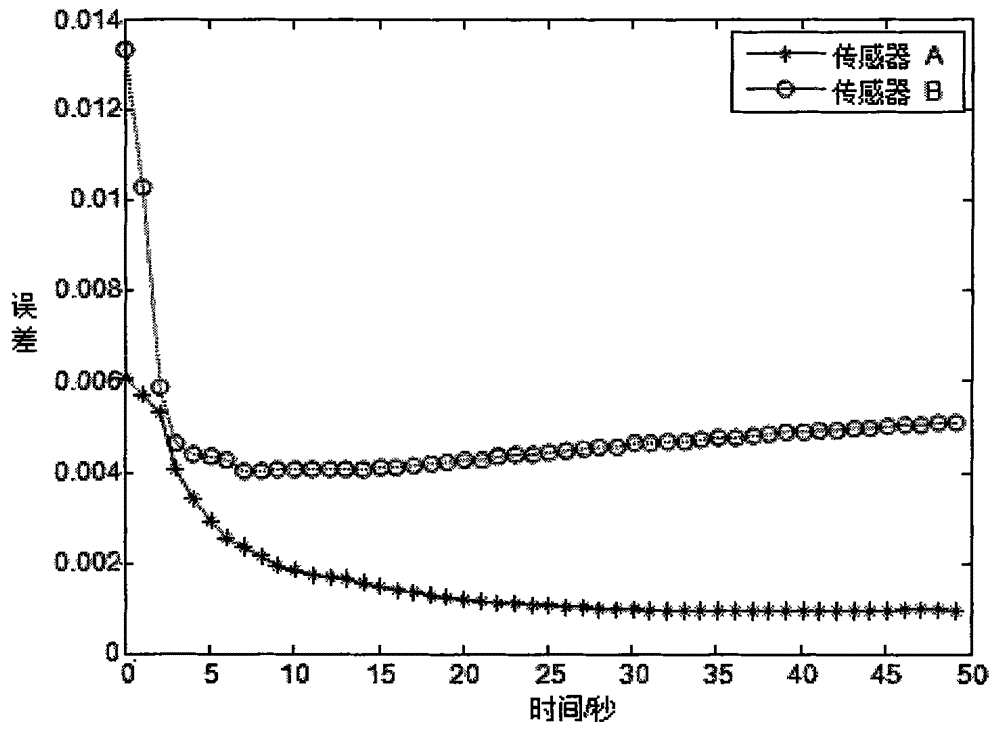
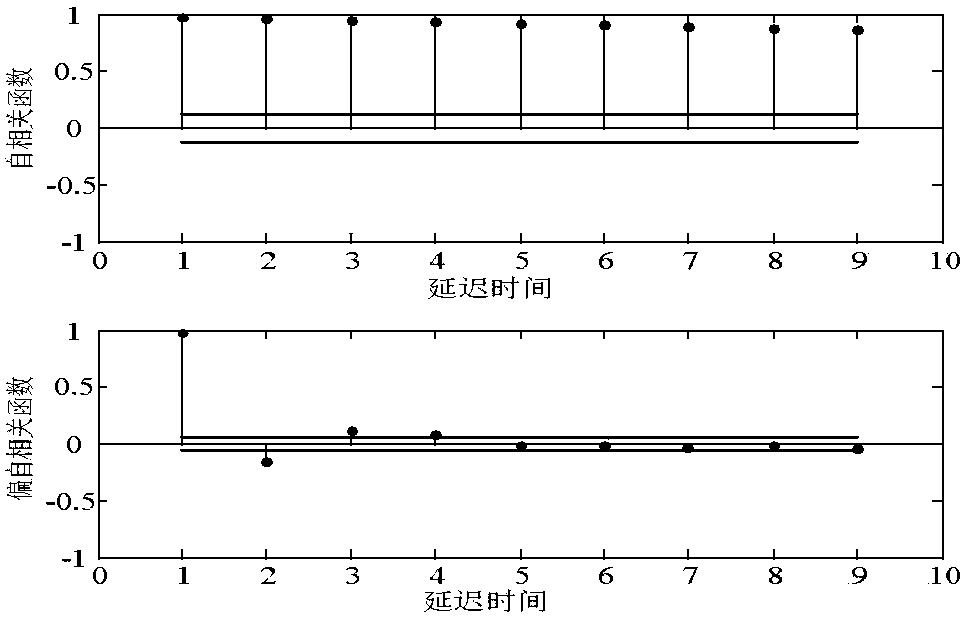
The invention discloses an asynchronous sensor space alignment algorithm. Data of two sensors are synchronized by the aid of an interpolation and extrapolation time alignment algorithm, a pseudo measurement equation is built according to time alignment results, and the asynchronous sensor space alignment algorithm based on the interpolation and extrapolation time alignment algorithm and a geocentric earth fixed coordinate system is provided to solve the problem of space alignment under target maneuvering conditions. The building process of the pseudo measurement equation is unrelated to a target state vector, and pseudo measurement built by the time alignment results can be proved to be unrelated to the target state vector, so that the algorithm can effectively solve the problem of asynchronous sensor space alignment under the target maneuvering conditions. Simulation experiments confirm that the algorithm can still accurately estimate system errors of the sensors under the condition of snakelike maneuvering of a target, and the influence of the sampling period ratio of the sensors and random errors on system error estimation precision is analyzed by simulation.
Owner:方洋旺 +1
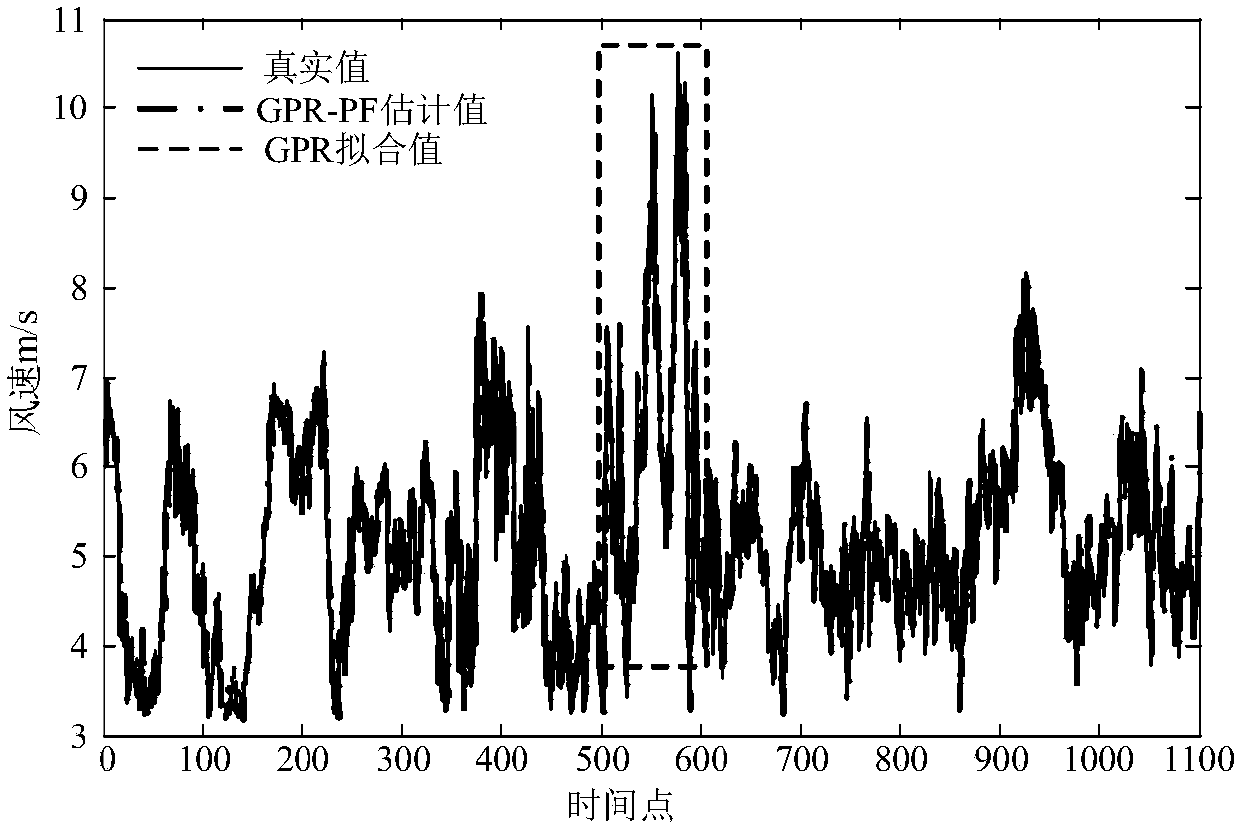
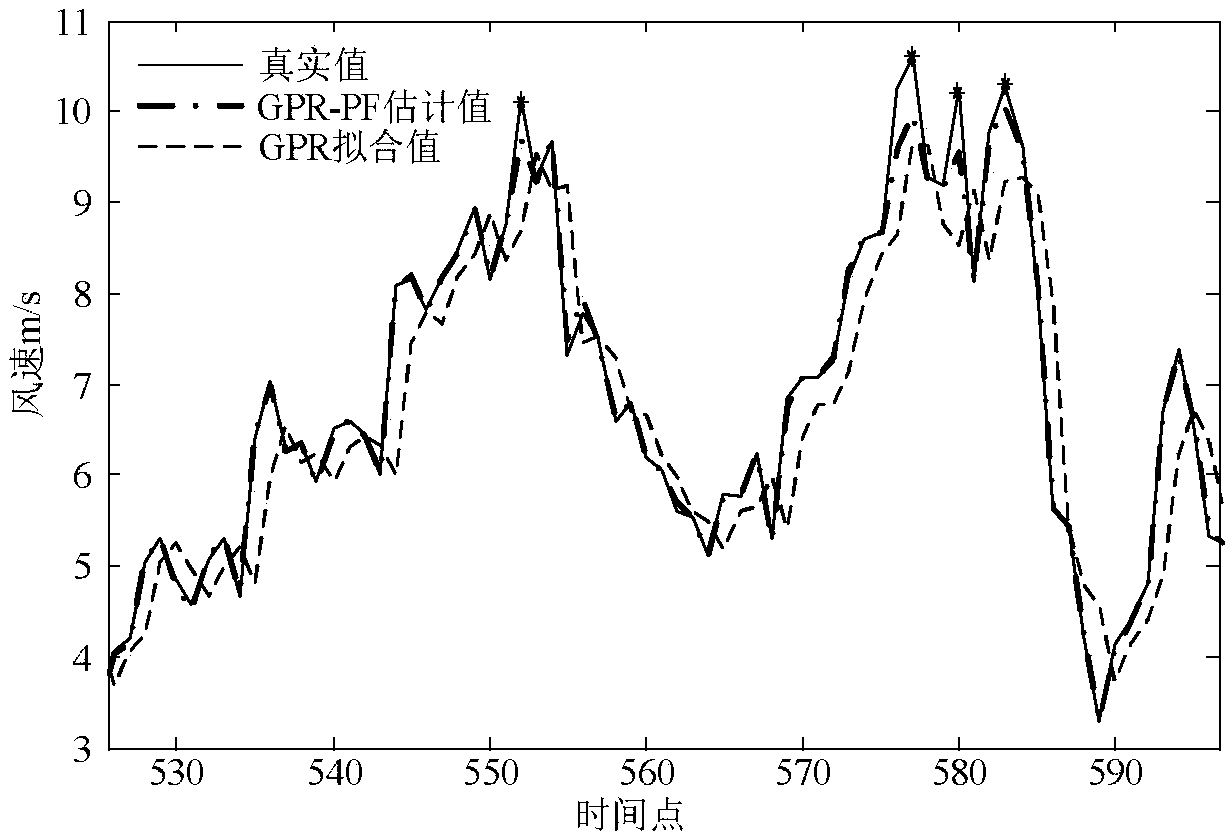
Short-term wind speed prediction method of Gaussian process regression and particle filtering
ActiveCN107765347AImprove forecast accuracyImprove predictive performanceWeather condition predictionElectric power systemAlgorithm
The invention discloses a short-term wind speed prediction method of Gaussian process regression and particle filtering, thereby realizing on-line dynamic detection and correction of abnormal values and improving wind speed prediction accuracy. According to the method, an input variable set having the highest correlation with a wind speed value at a to-be-predicted time is determined by using a partial autocorrelation function, a state vector is determined, and a proper training sample set is constructed; a Gaussian-process-regression-based short-term wind speed prediction model is establishedin the training sample set and a fitting residue during the training process is given; on the basis of combination of the state vector and the Gaussian process regression model, a particle filteringstate space equation is established and state estimation is carried out on a current measurement value by using a particle filtering algorithm; and the estimation value and the measurement value residual of particle filtering are analyzed, determination is carried out based on a 3 sigma principle, and an abnormal value is corrected. According to the method provided by the invention, the abnormal value can be detected and corrected effectively; the short-term wind speed prediction precision is improved; and a wind speed prediction problem of the power system is solved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
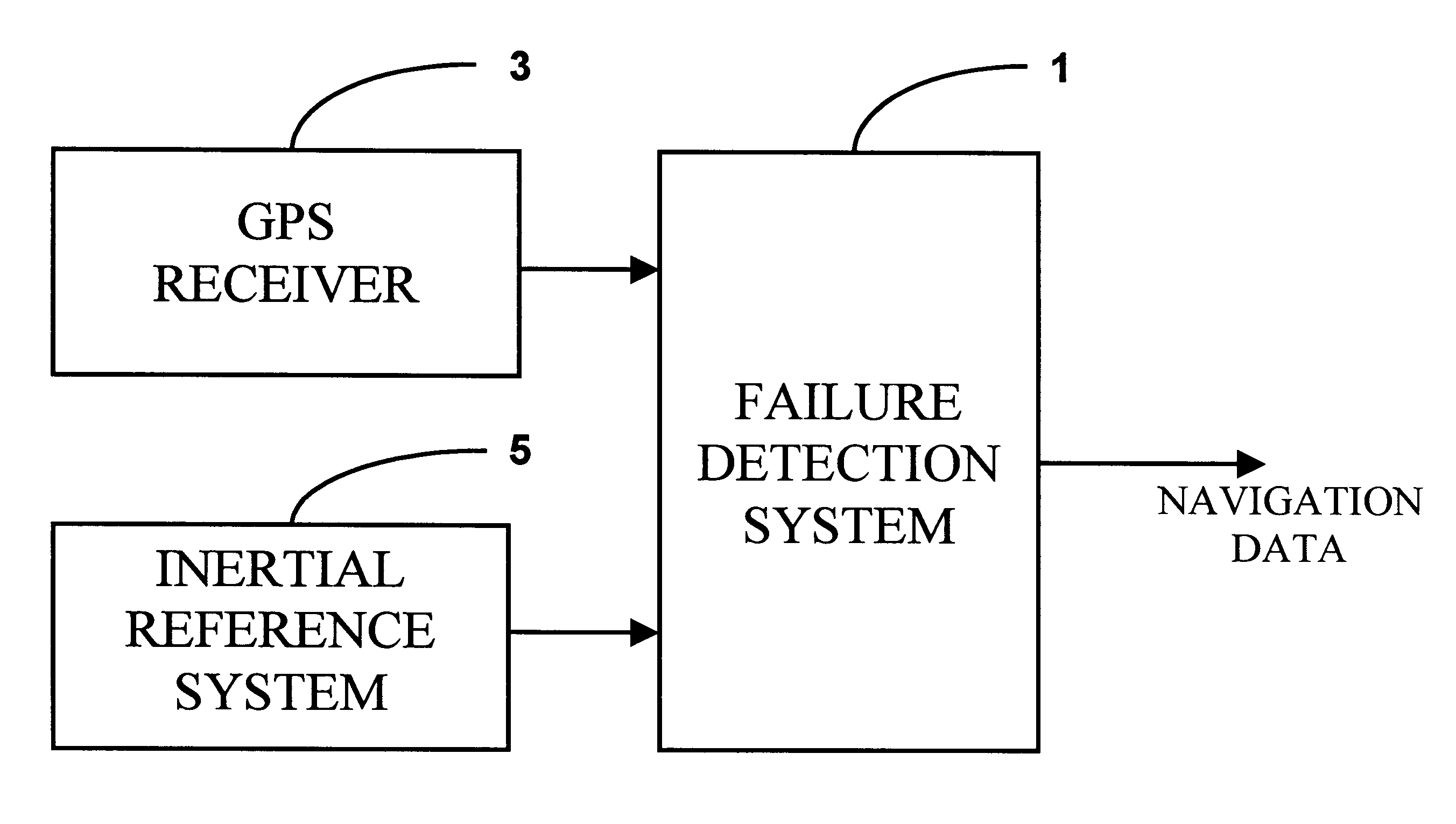
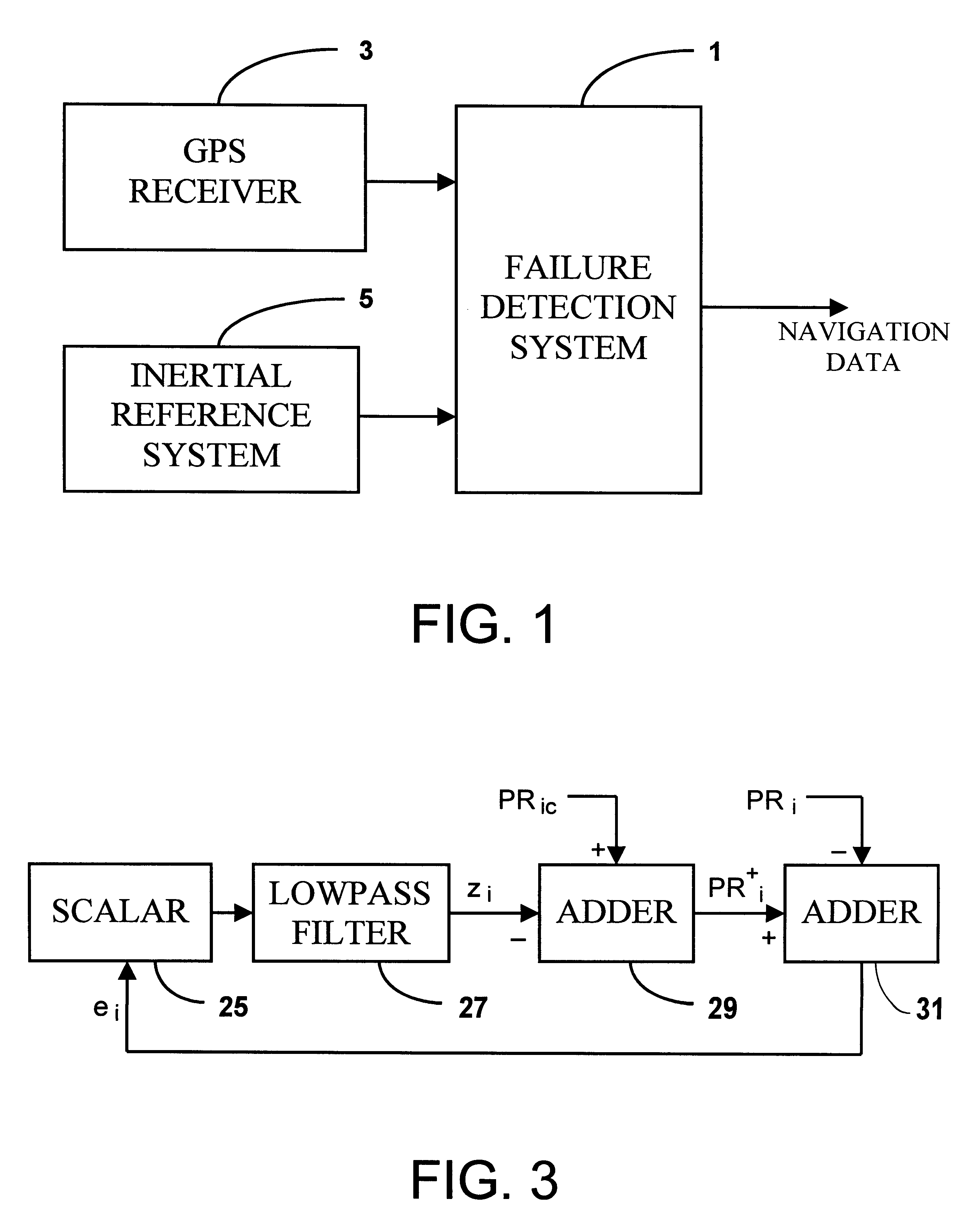
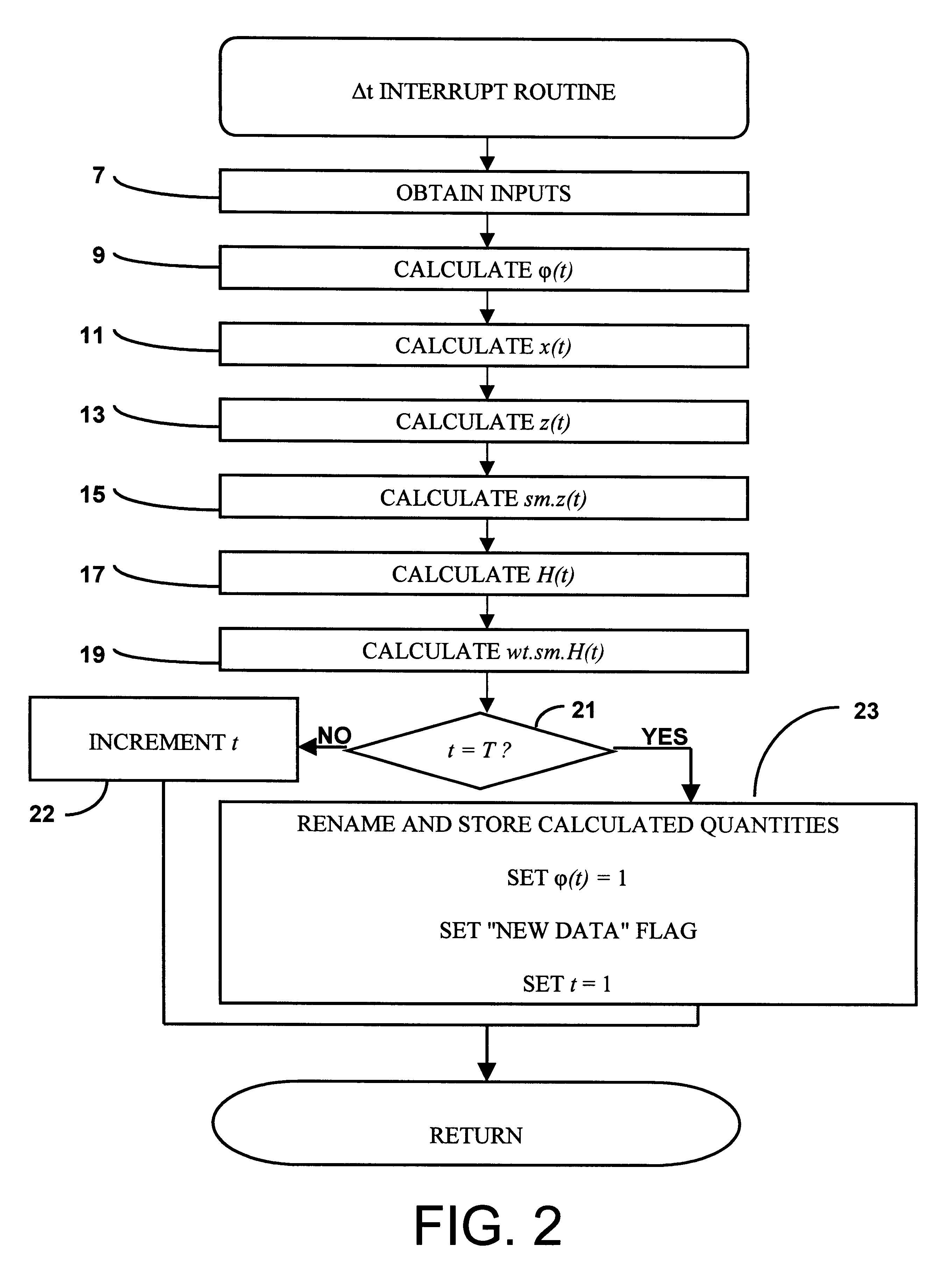
Failure detection system
InactiveUS6298316B1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceError detection/correctionAlgorithmState vector
The invention is a method and apparatus for determining a failure in a subsystem that is part of a system, the system being characterized in terms of a state vector comprising a plurality of state variables. The state vector is updated at times (jK+k)TDELTAt using one or more Kalman filter processes, j taking on integer values, K being a predetermined integer, k taking on integer values between 1 and K for each value of j, T being a predetermined integer, and DELTAt being a predetermined time interval. The method comprises the steps: (a) executing at present time a plurality of Kalman filter processes where one of the Kalman filter processes determines the state vector at present time minus (K-1)TDELTAt using data from subsystems without failures; (b) determining the values of one or more statistical measures of one or more residuals for each of one or more Kalman filter processes for one or more time periods equal to or greater than TDELTAt; and (c) determining a subsystem failure from the one or more values of the statistical measures.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP +1
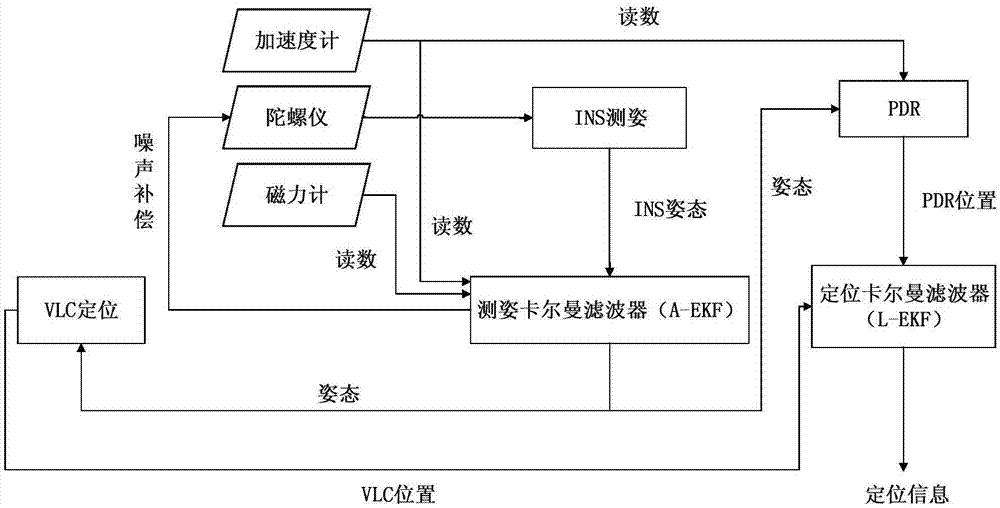
Fused dual-Kalman filter navigation device based on MEMS sensor and VLC positioning, and navigation method
ActiveCN107289933ASimple structureEliminate positioning effectsNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsKaiman filterAccelerometer
The invention discloses a fused dual-Kalman filter navigation device based on an MEMS sensor and VLC positioning, and a navigation method. The navigation device comprises an MEMS sensor, an inertial navigation system (INS) module, a pedestrian dead reckoning (PDR) positioning module, a visible light communication (VLC) positioning module, an attitude extended Kalman filter (A-EKF), and a location extended Kalman filter (L-EKF); for the A-EKF, an error equation edited mechanically based on the INS is used as a system equation, an observation equation comprises update of observation of an accelerometer and a magnetometer, and attitude information is output to the VLC positioning module and the PDR positioning module so as to correct attitude impact; and for the L-EKF, position information of a two-dimensional plane is used as a system state vector, a pedestrian dead reckoned error equation is used as a system equation, and a VLC positioning result is an observation equation. The navigation device and navigation method solve a problem that VLC positioning is easy to be affected by device attitude and cannot keep positioning continuously if an optical signal is blocked, and eliminate the influence of attitude on VLC positioning.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
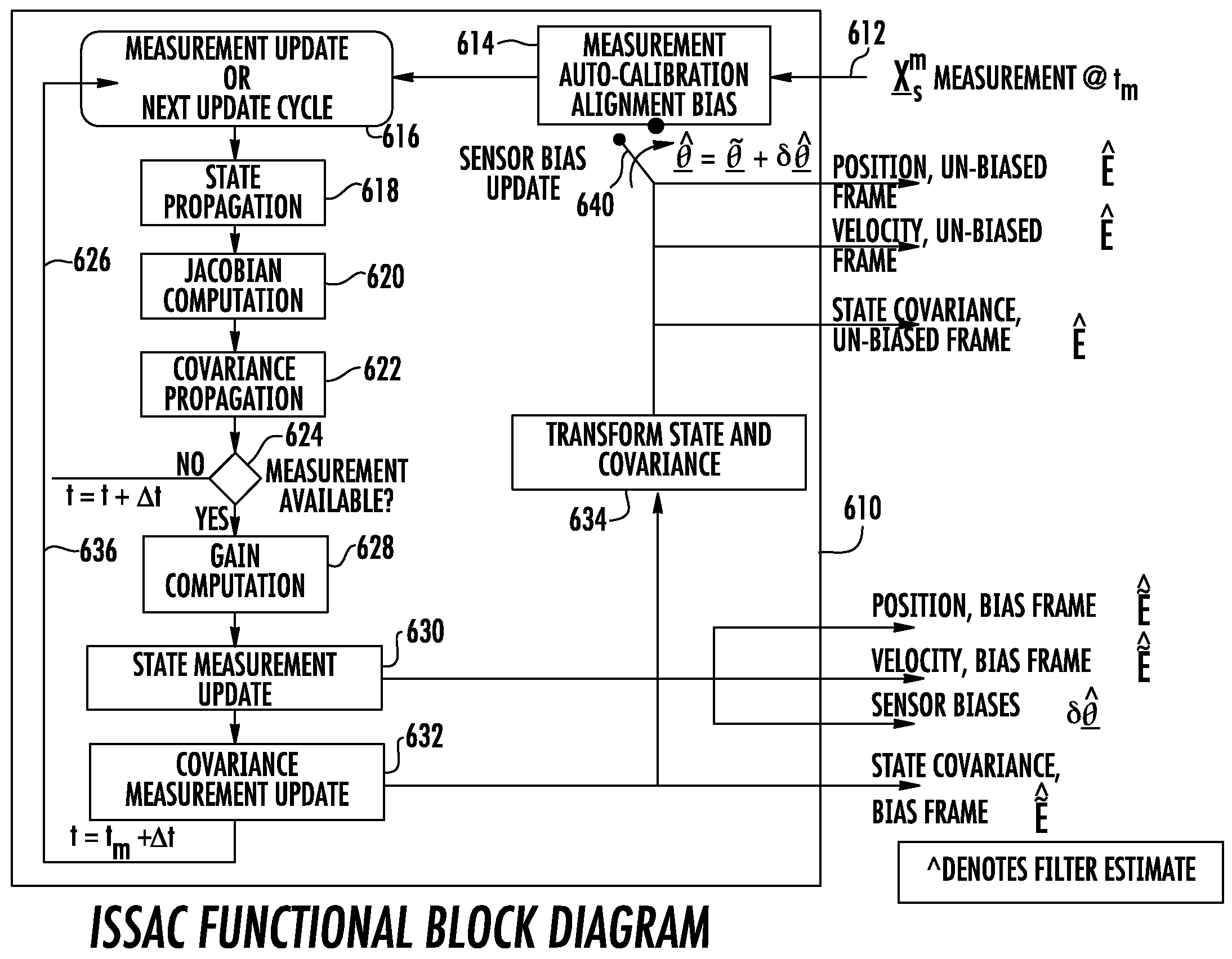
Instantaneous multisensor angular bias autoregistration
ActiveUS7248206B1Direction finders using radio wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDynamic equationCovariance
Unknown alignment biases of sensors of a tracking system are estimated by an iterative Kalman filter method. Current measurements are corrected for known alignment errors and previously estimated alignment biases. The filter time reference is updated to produce estimated target state derivative vectors. A Jacobian of the state dynamics equation is determined, which provides for observability into the sensor alignment bias through gravitational and coriolis forces. The target state transition matrix and the target error covariance matrix are propagated. When a new measurement becomes available, the Kalman gain matrix is determined, the state vector and covariance measurements are updated, and sensor alignment biases are estimated. The state vector, covariance measurements, and estimated sensor alignment biases are transformed to an estimated stable space frame for use in tracking the target and updating the next iteration.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
A generalized instruction generator and instruction generation method for variable flight mode unmanned aerial vehicle
InactiveCN102289207AReasonable conversion strategySmooth transition strategySimulator controlVehicle position/course/altitude controlControl vectorCurve fitting
The invention provides a macro instruction generator for an unmanned aerial vehicle with a variable flying mode and an instruction generation method for the macro instruction generator. The instruction generator comprises a guide instruction generator, a controlled state instruction generator, a state reference value generator and a macro control surface reference instruction generator. Balancing of a mode conversion process is equivalent to the balancing of various combined states in a sequence consisting of tilt angles and desired pitching angles; and in a specific tilt angle and desired pitching angle combined state, iterative optimization balancing is instructed by a cost function, so that balanced values of a state vector and a control vector of the macro control surface are changed stably along with the tilt angle and an air speed instruction. All inner functions of the guide instruction generator, the controlled state instruction generator, the state reference value generator and the macro control surface reference instruction generator are established by adopting a segmental curve fitting method according to a balanced result sequence. The iterative optimization balancing and the curve fitting are realized efficiently and accurately by using matrix laboratory (matlab) math software.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
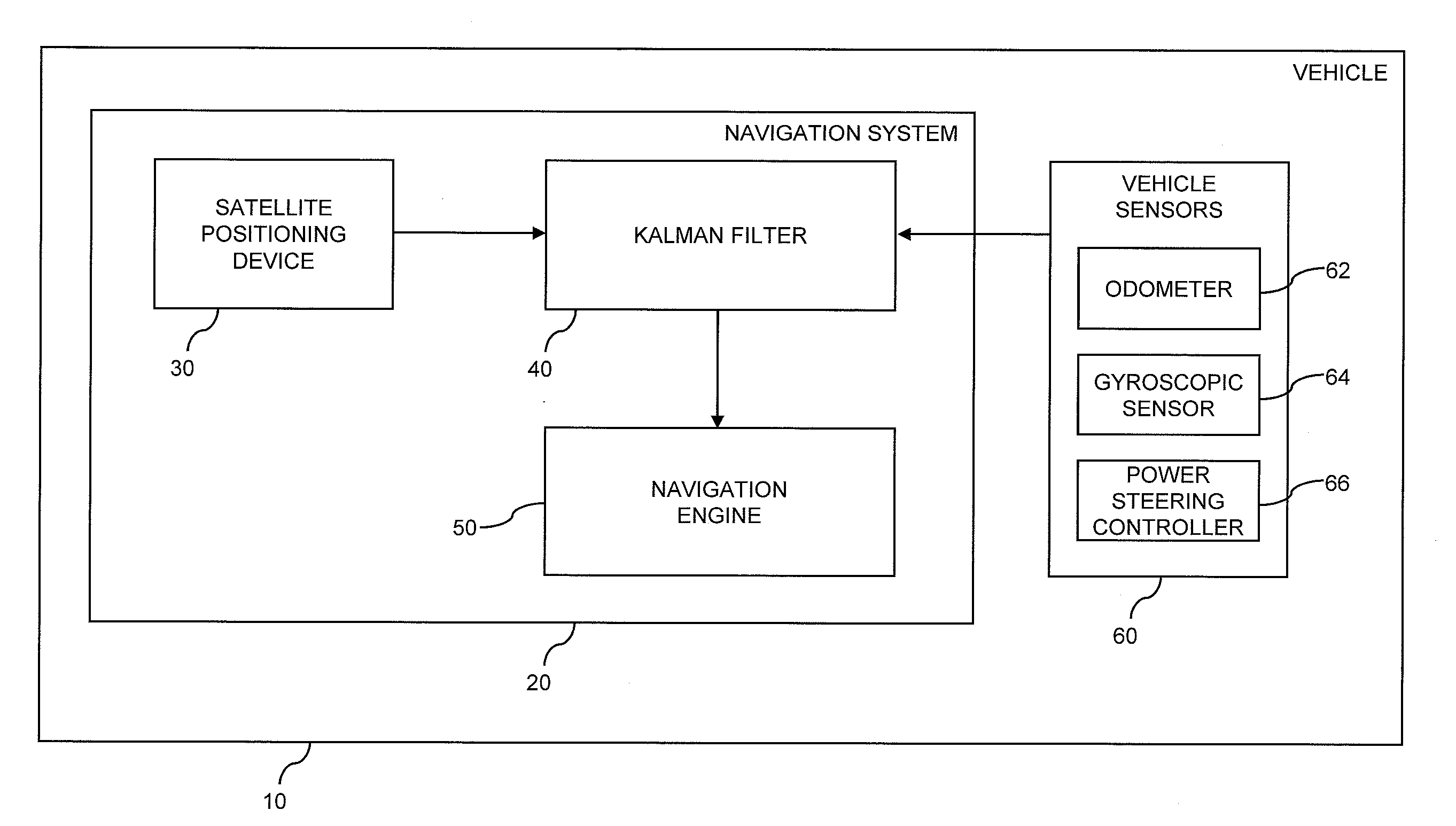
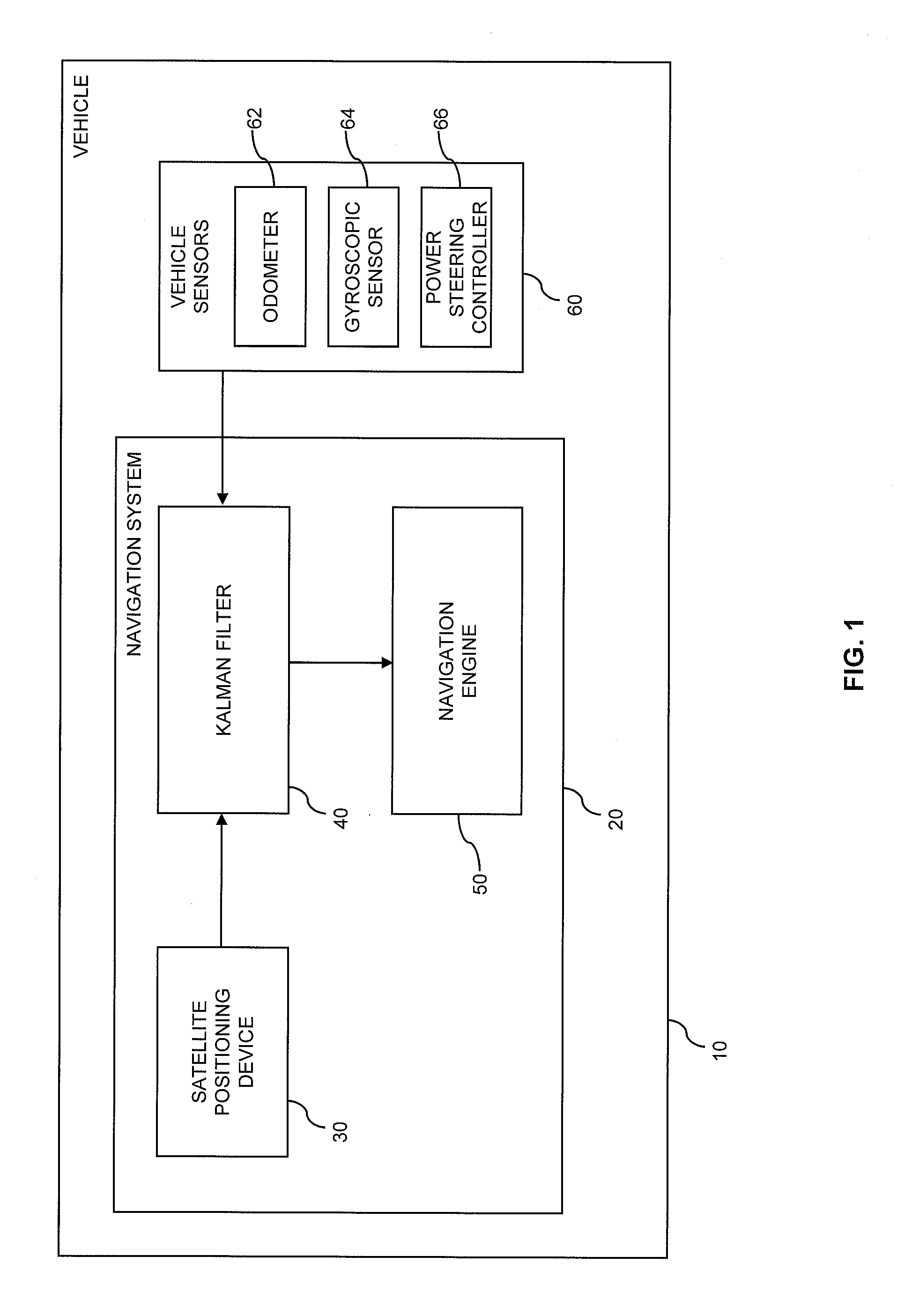
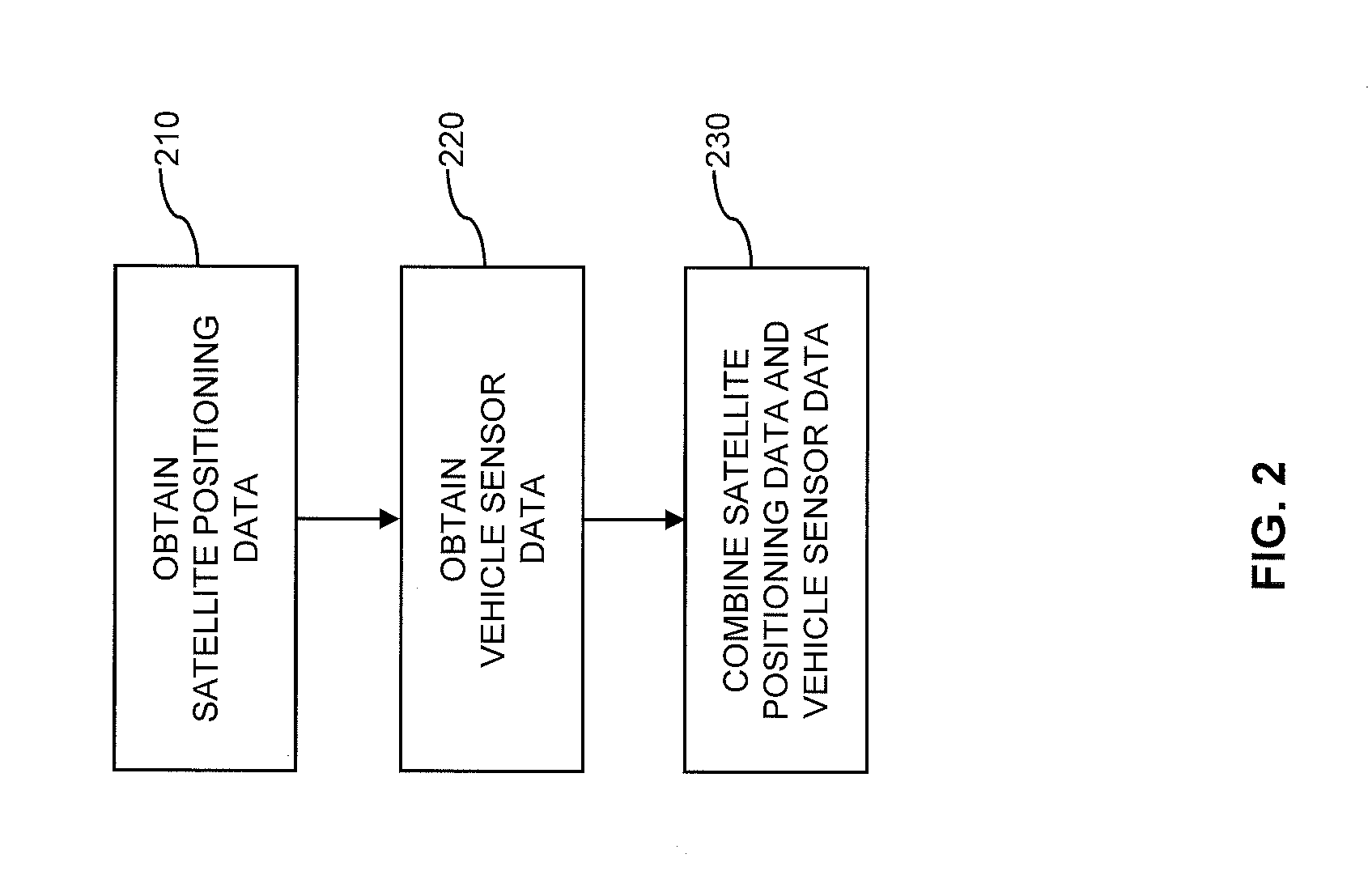
Vehicle navigation on the basis of satellite positioning data and vehicle sensor data
ActiveUS20130035855A1High positioning accuracyEfficient combinationInstruments for road network navigationPosition fixationState vectorKalman filter
A vehicle navigation system includes a Kalman filter having a first filter receiving satellite positioning data and a second filter receiving vehicle sensor data. The first filter generates a first state vector estimate and a corresponding first state error covariance matrix. The second filter generates a second state vector estimate and a corresponding second state error covariance matrix. A third filter receives the first and second state vector estimates and the first and second state error covariance matrices, and generates a combined state vector estimate and a corresponding combined state error covariance matrix. A prediction processor generates a predicted state vector estimate and a predicted state error covariance matrix from the combined state vector estimate and the combined state error covariance matrix. The predicted state vector estimate and the predicted state error covariance matrix are provided to the first filter, the second filter, and the third filter.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
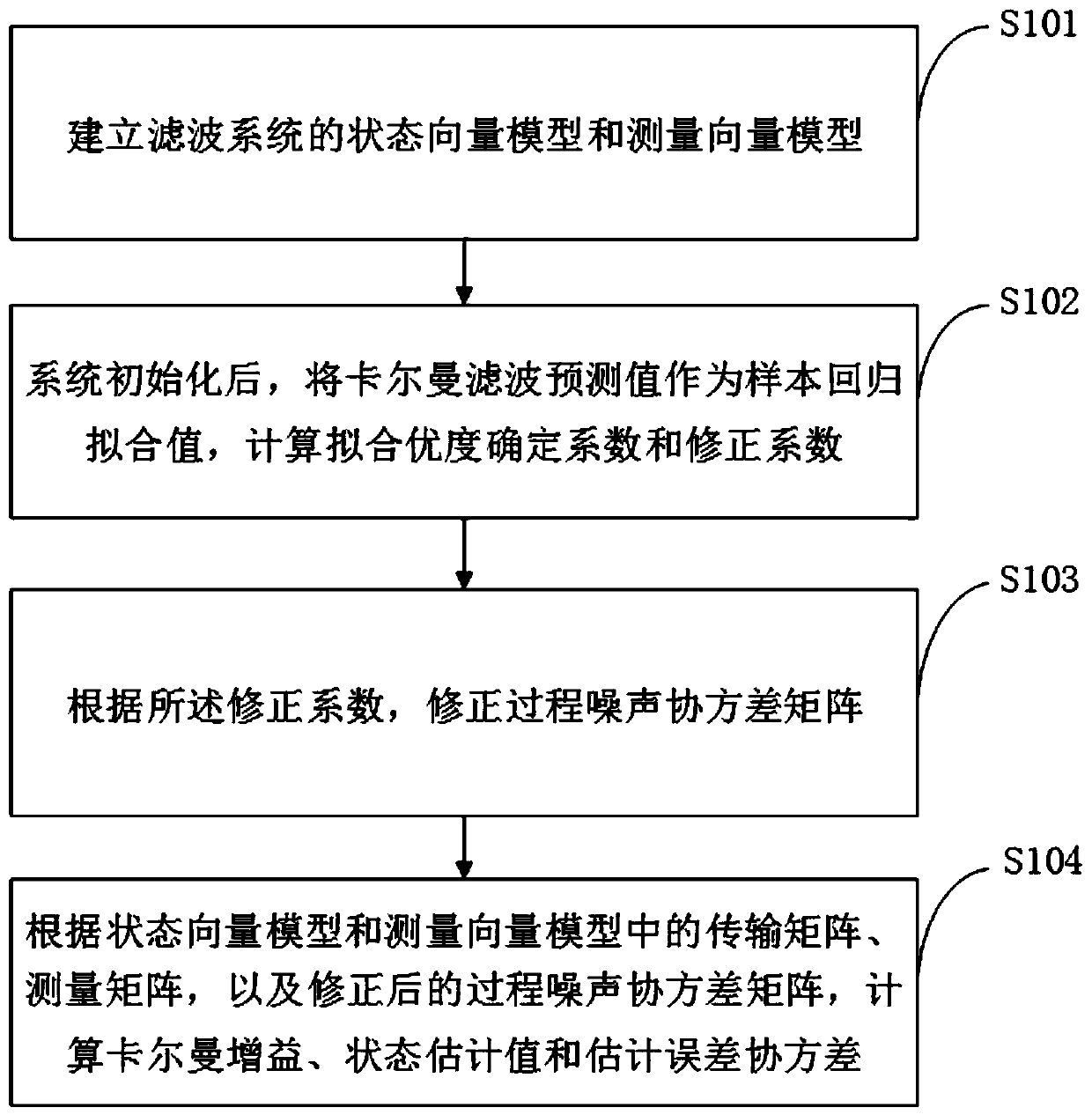
A self-adaptive Kalman filtering algorithm
InactiveCN109902568AGuaranteed filtering accuracyQuick responseCharacter and pattern recognitionComplex mathematical operationsProcess noiseTransmission matrix
The invention discloses a self-adaptive Kalman filtering algorithm, which is used for removing noise. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: establishing a state vector model and a measurement vector model of a filtering system; After the system is initialized, taking a Kalman filtering prediction value as a sample regression fitting value, and calculating a fitting goodness determination coefficient and a correction coefficient; Correcting a process noise covariance matrix according to the correction coefficient; And according to the transmission matrix, the measurement matrix and the corrected process noise covariance matrix in the state vector model and the measurement vector model, calculating Kalman gain, and calculating a state estimation value and an estimation error covariance. Through the technical scheme provided by the invention, real-time and efficient filtering can be realized, and the filtering precision is ensured.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
Robot vision semantic navigation method, device and system
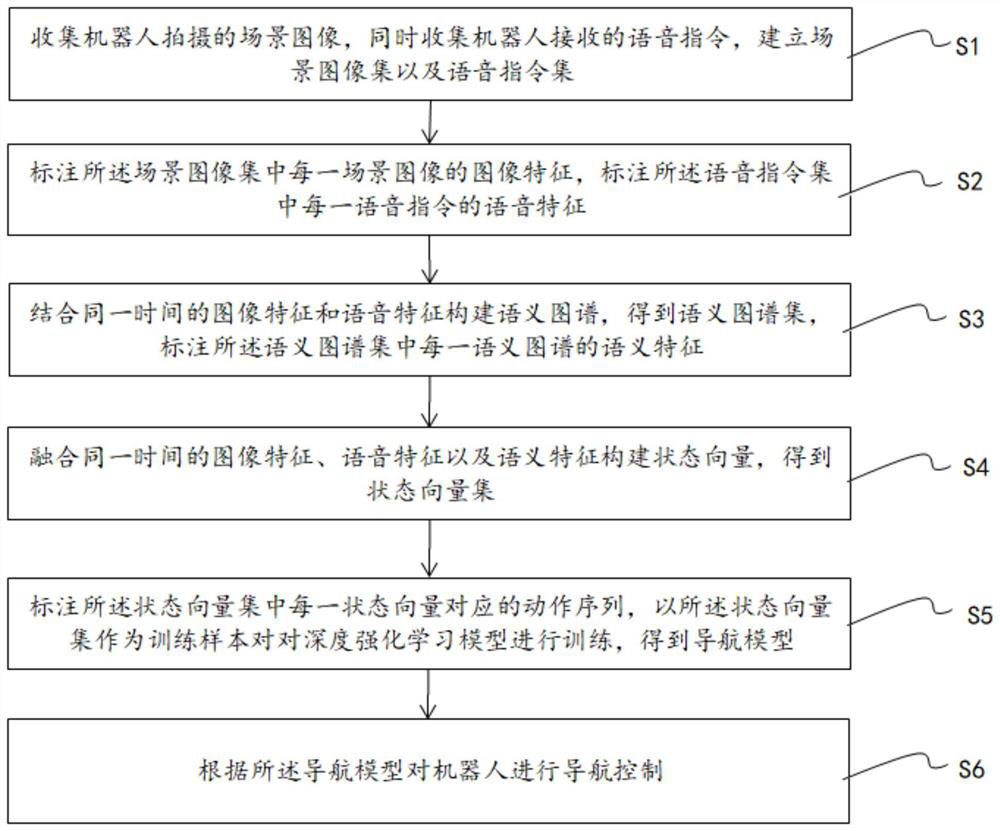
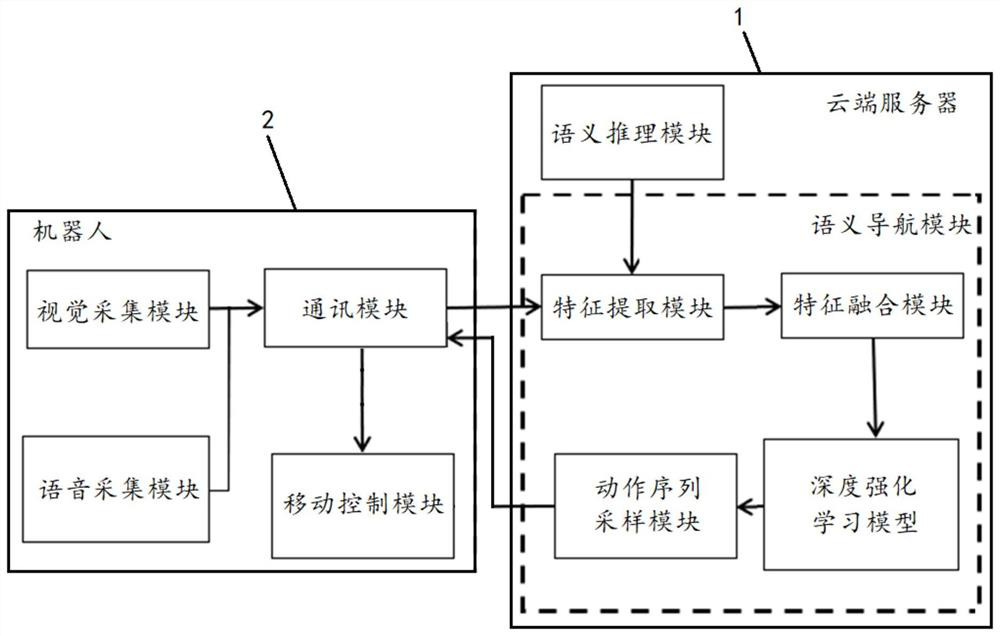
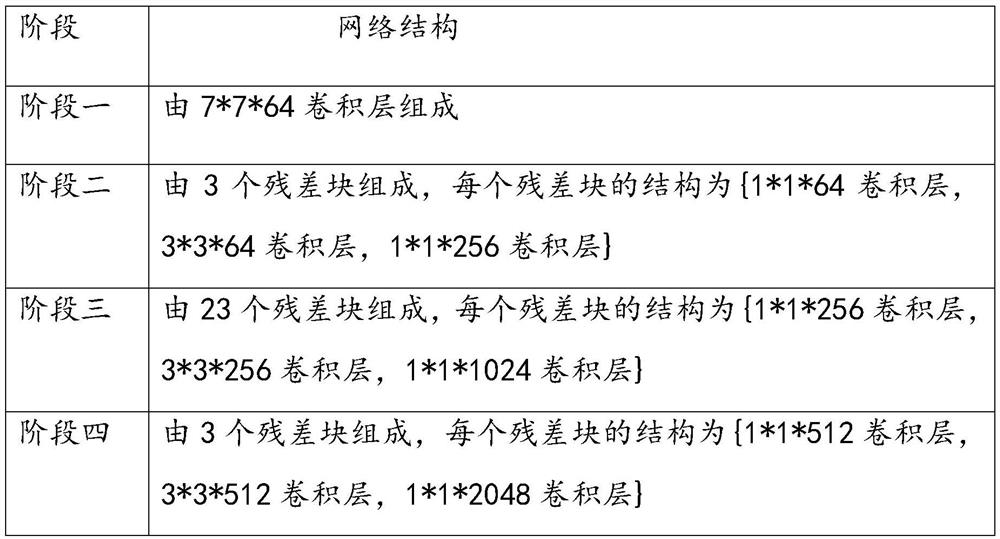
The invention relates to the technical field of robot navigation, and discloses a robot vision semantic navigation method. The robot vision semantic navigation method comprises the following steps that a scene image set and a voice instruction set are established; image features of each scene image in the scene image set are marked, and voice features of each voice instruction in the voice instruction set are marked; semantic graphs are construction by combining the image features and the voice features at the same time to obtain a semantic graph set, and semantic features of each semantic graph in the semantic graph set are marked; state vectors are constructed by fusing the image features, the voice features and the semantic features at the same time to obtain a state vector set; actionsequences of each state vector in the state vector set are marked, a deep strength learning model is trained with the state vector set as a training sample, and a navigation model is obtained; and a robot is subjected to navigation control according to the navigation model. According to the robot vision semantic navigation method, the navigation of objects not in the scope of robot vision can be achieved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
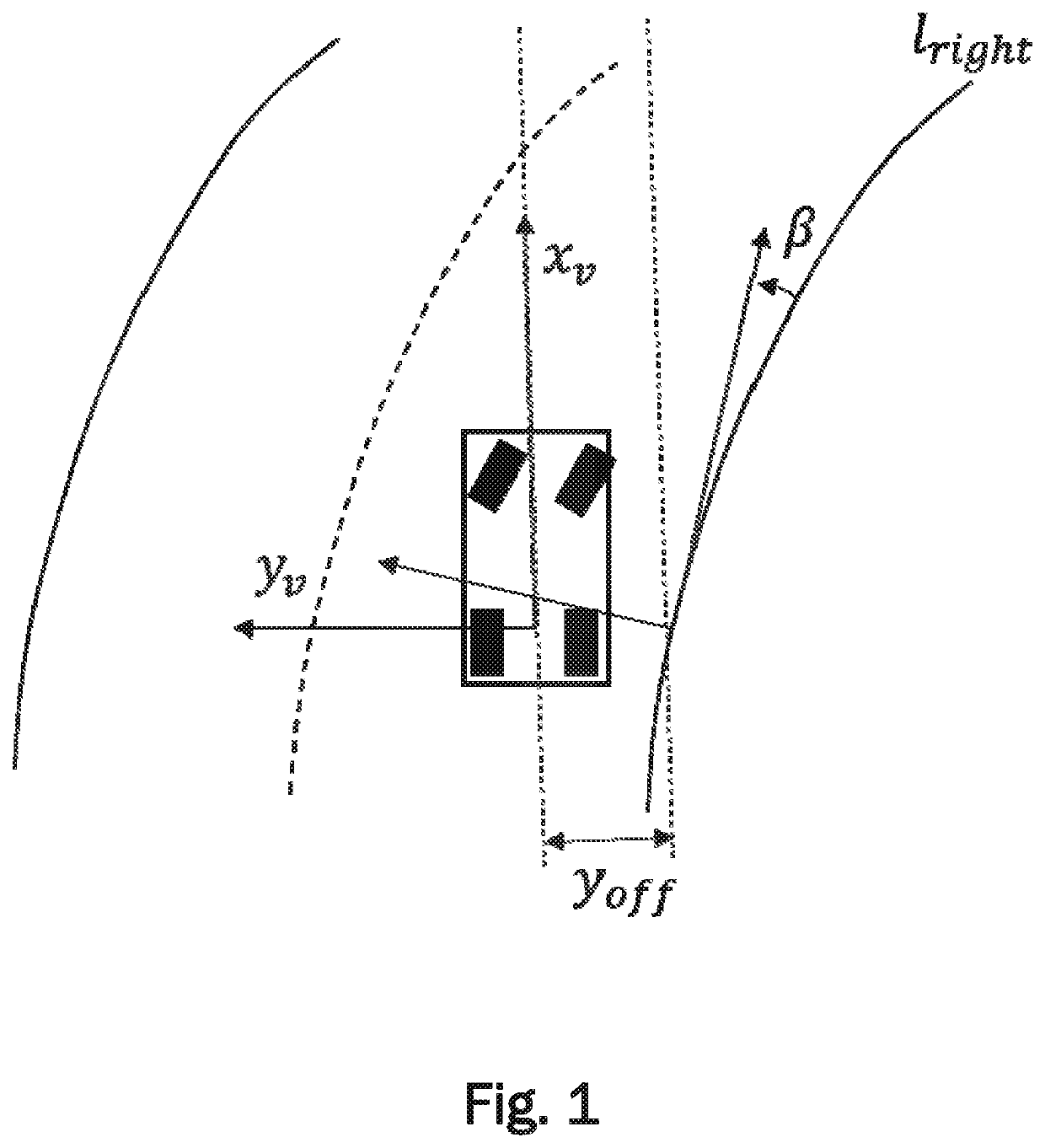
Method for determining the location of an ego-vehicle
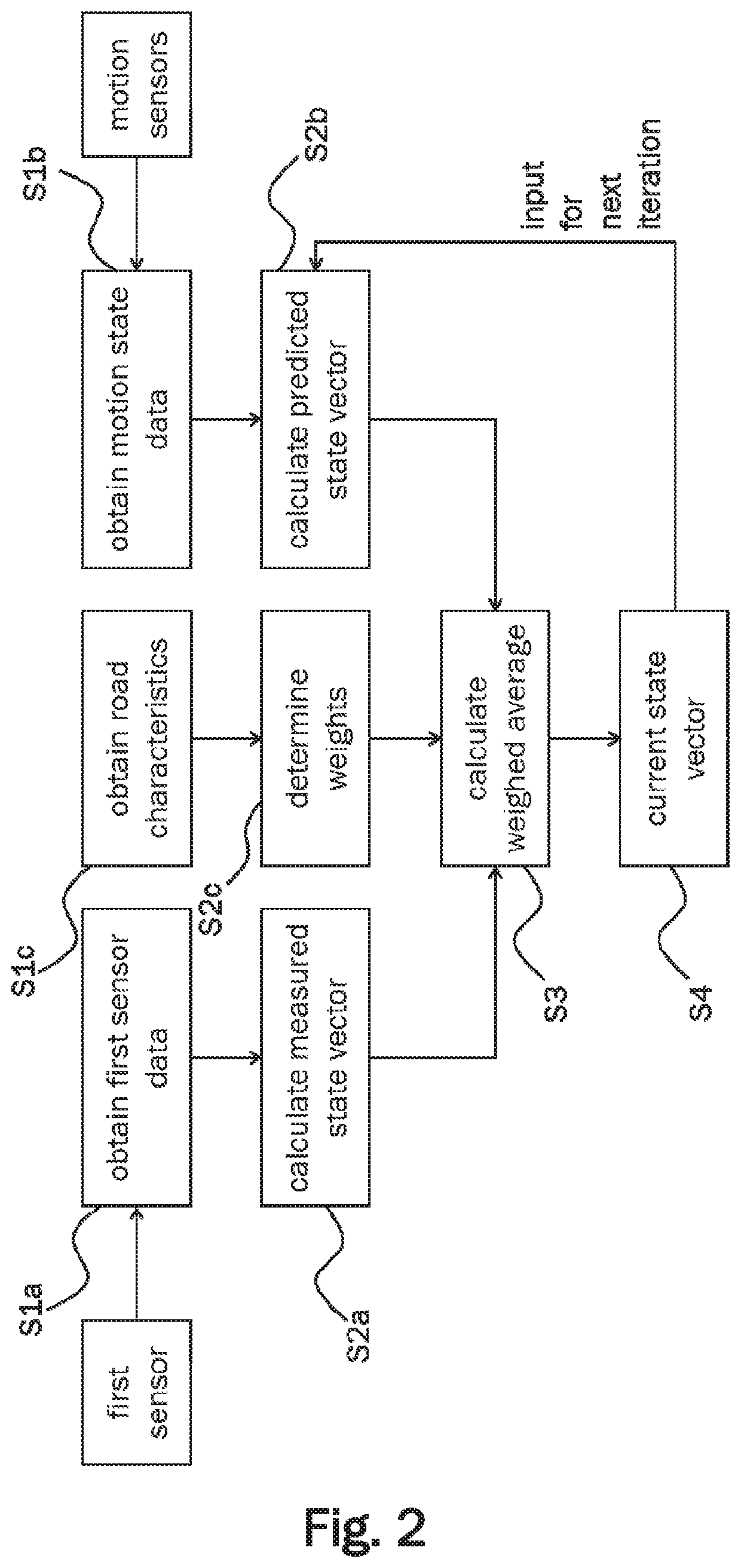
InactiveUS20200216076A1Improve image processing capabilitiesHigh positioning accuracyRoad vehicles traffic controlCharacter and pattern recognitionState vectorSimulation
A method for determining a current state vector describing location and heading of an ego-vehicle with respect to a lane boundary of a road comprises a step of obtaining road sensor data from at least one road sensor of the ego-vehicle detecting the lane boundaries of the road. In another step, a measured state vector of the ego-vehicle is calculated from the road sensor data. Furthermore, motion state data related to current heading and velocity of the ego-vehicle is obtained and a predicted state vector of the ego-vehicle is calculated based on the motion state data of the ego-vehicle and a previous state vector of the ego-vehicle. Finally a current state vector is determined by calculating a weighted average of the measured state vector and the predicted state vector of the ego-vehicle. The weights are determined based on characteristics of an upcoming section of the road.
Owner:VISTEON GLOBAL TECH INC
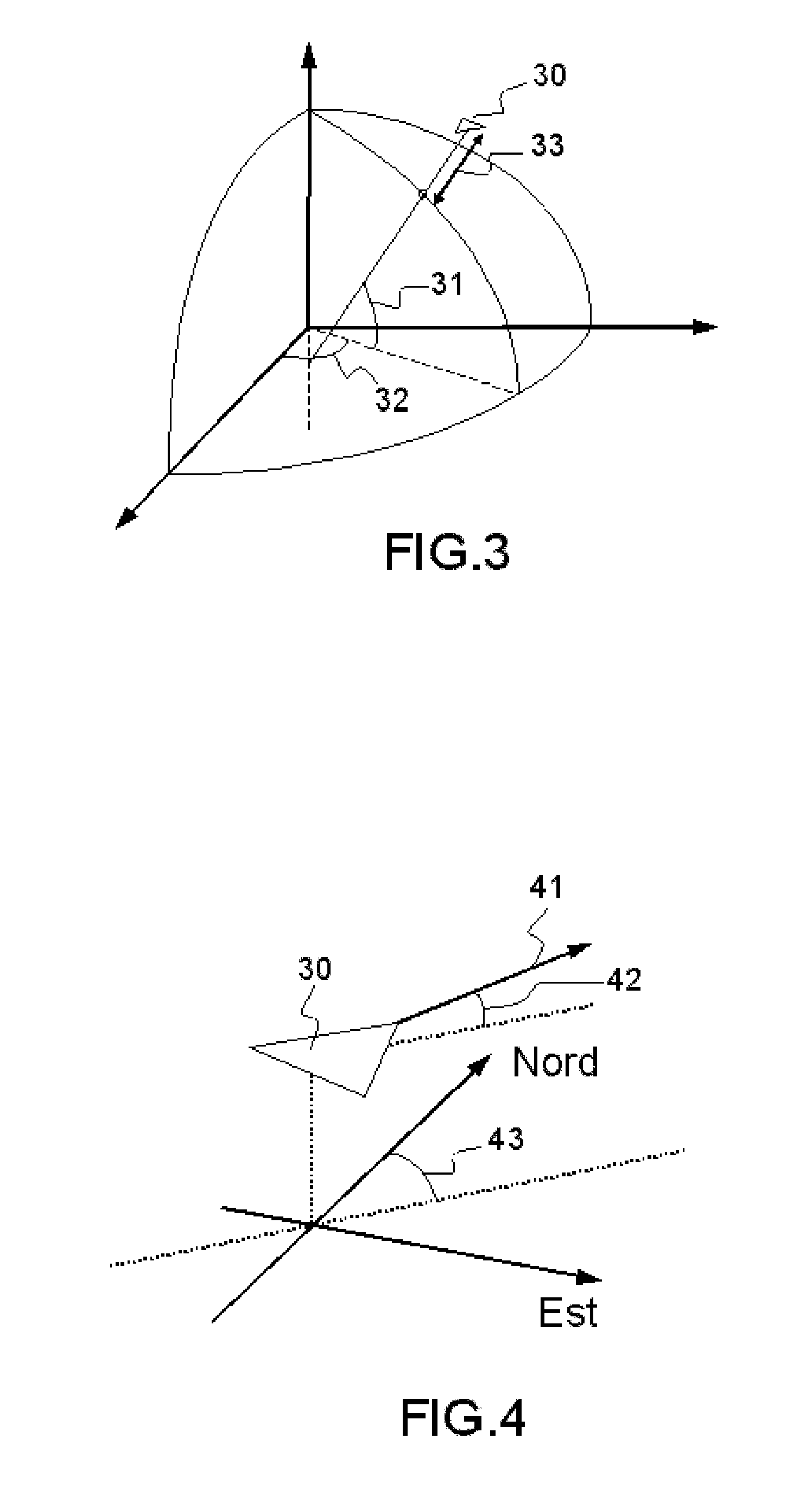
Method for constructing a trajectory of an aircraft by state vector
ActiveUS20140032095A1Navigation instrumentsVehicle position/course/altitude controlMarine navigationAirplane
A method for constructing a flight trajectory of an aircraft, comprises a step of computing a sequence of state vectors (Ei) representing the trajectory of the aircraft; a state vector (Ei+1) being determined on the basis of the state vector (Ei) preceding it by means of: a step of computing the speed components (Vi+1), consisting in determining: a flight setpoint, by selecting an objective navigation point, a joining strategy adapted to the flight setpoint and to the flight domain (DV) by means of a predefined library (LSr) of joining strategies, a manoeuvre by means of the flight domain (DV), making it possible to follow the joining strategy towards the flight setpoint; a step of computing the other components of the state vector (Ei+1), on the basis of the components of the speed vector (Vi+1) and of the preceding state vector (Ei).
Owner:THALES SA
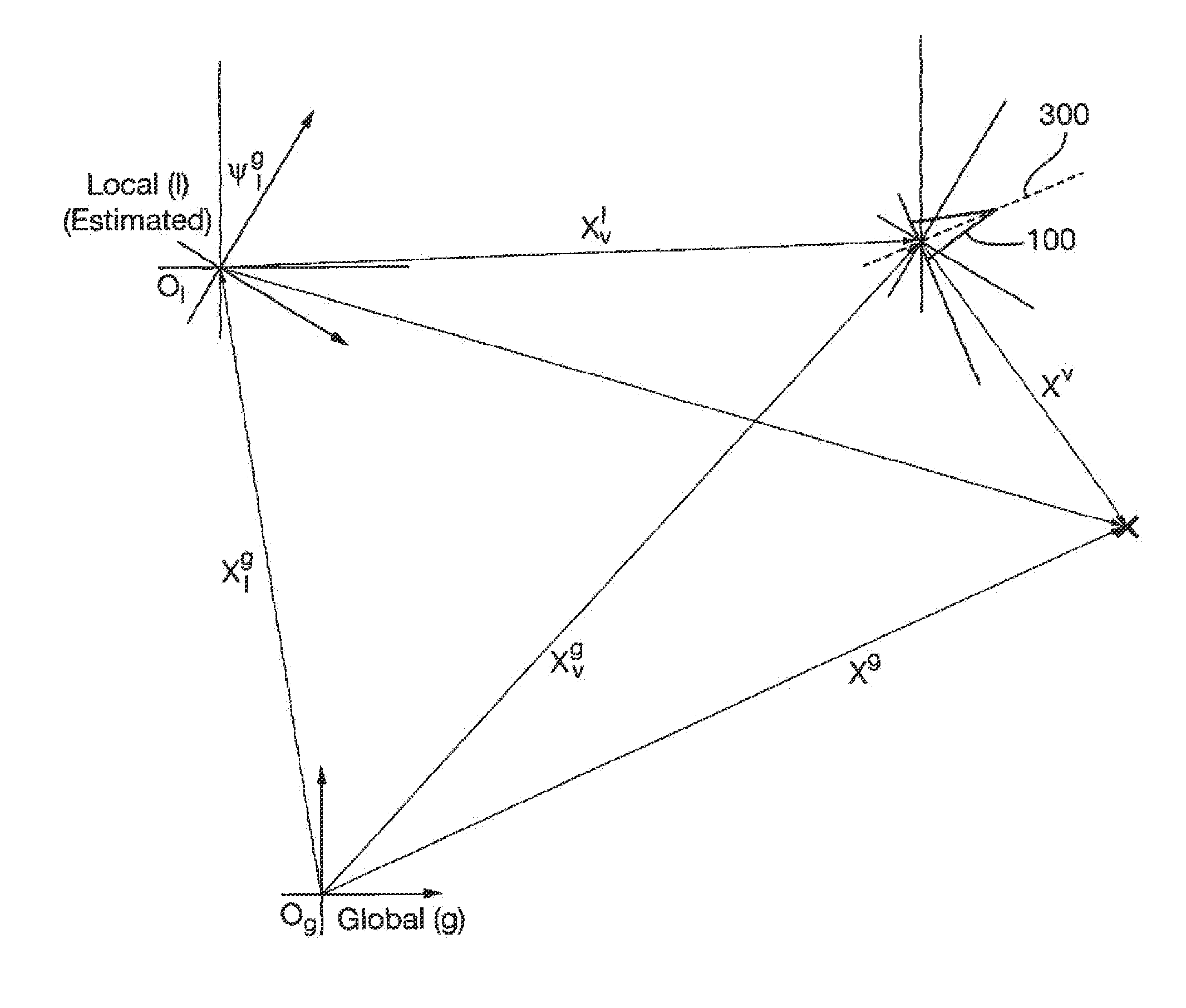
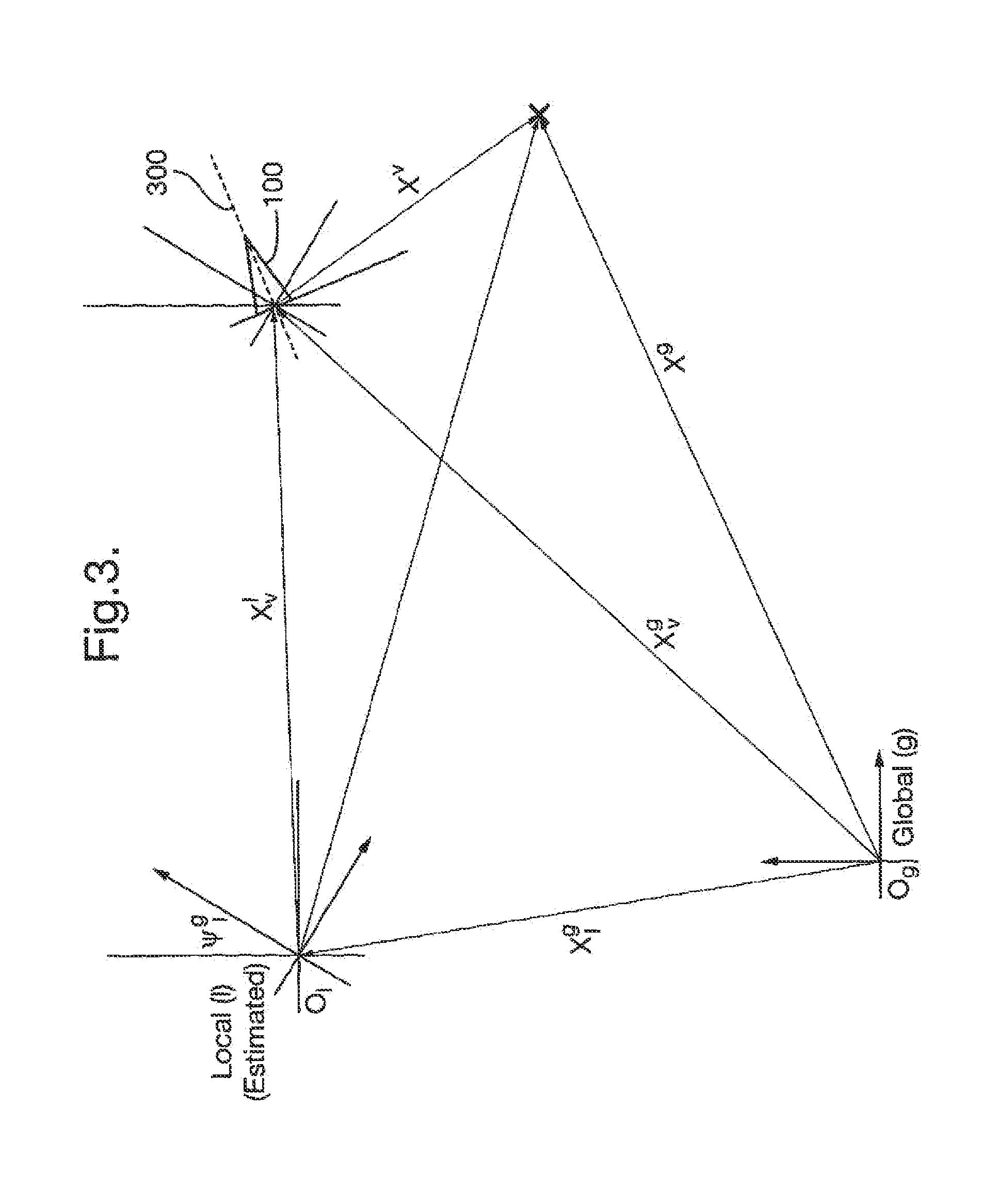
Estimating positions of a device and at least one target in an environment
ActiveUS20120122486A1Vehicle position/course/altitude controlWireless communicationState vectorEngineering
A method / system for estimating a state of a device and at least one target in an environment. The process involves computing a state vector using an error state form of the position of the device in a local coordinate reference frame.
Owner:BAE SYSTEMS PLC
Asynchronous multi-sensor space-time deviation joint estimation and compensation method and device
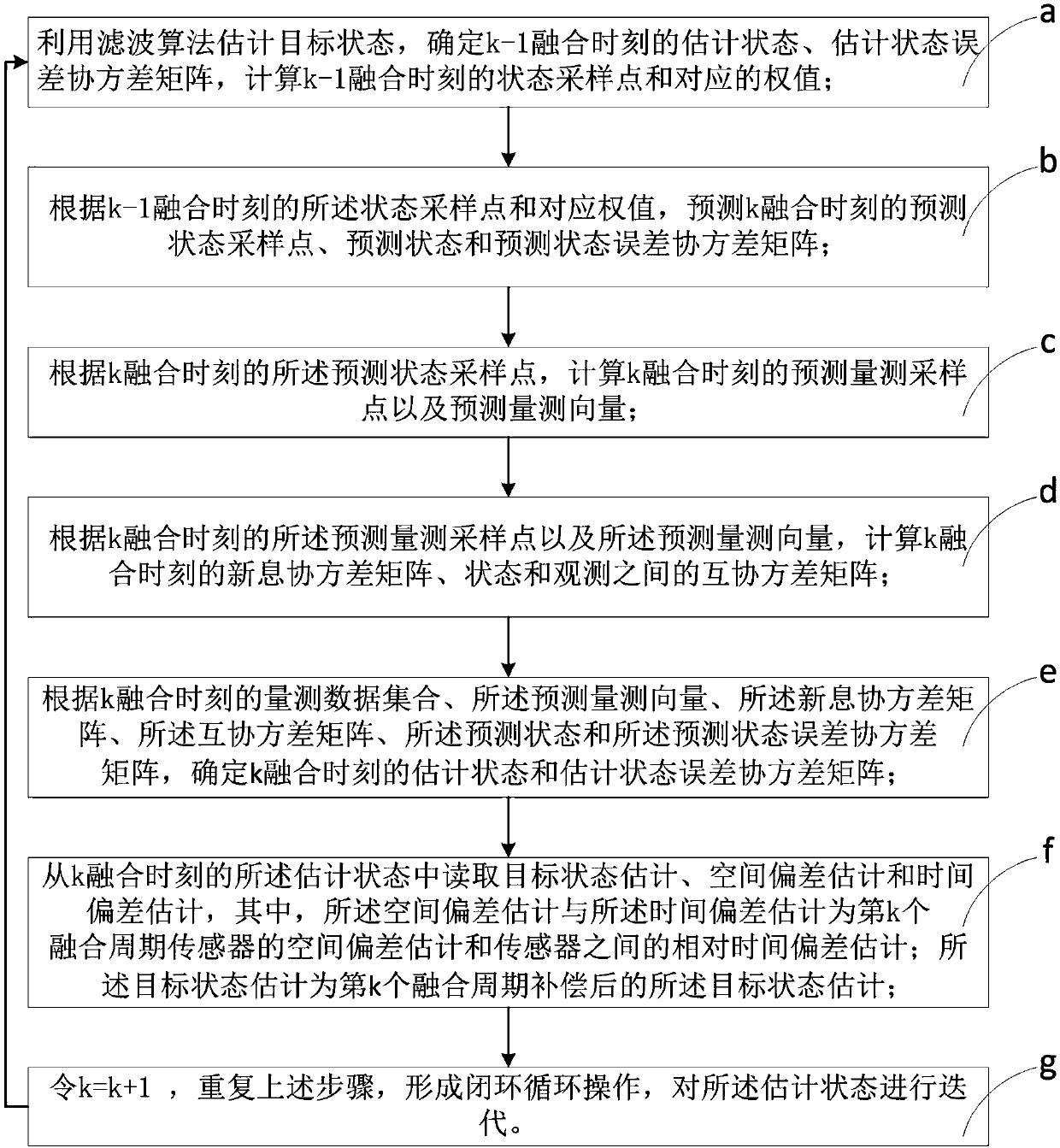
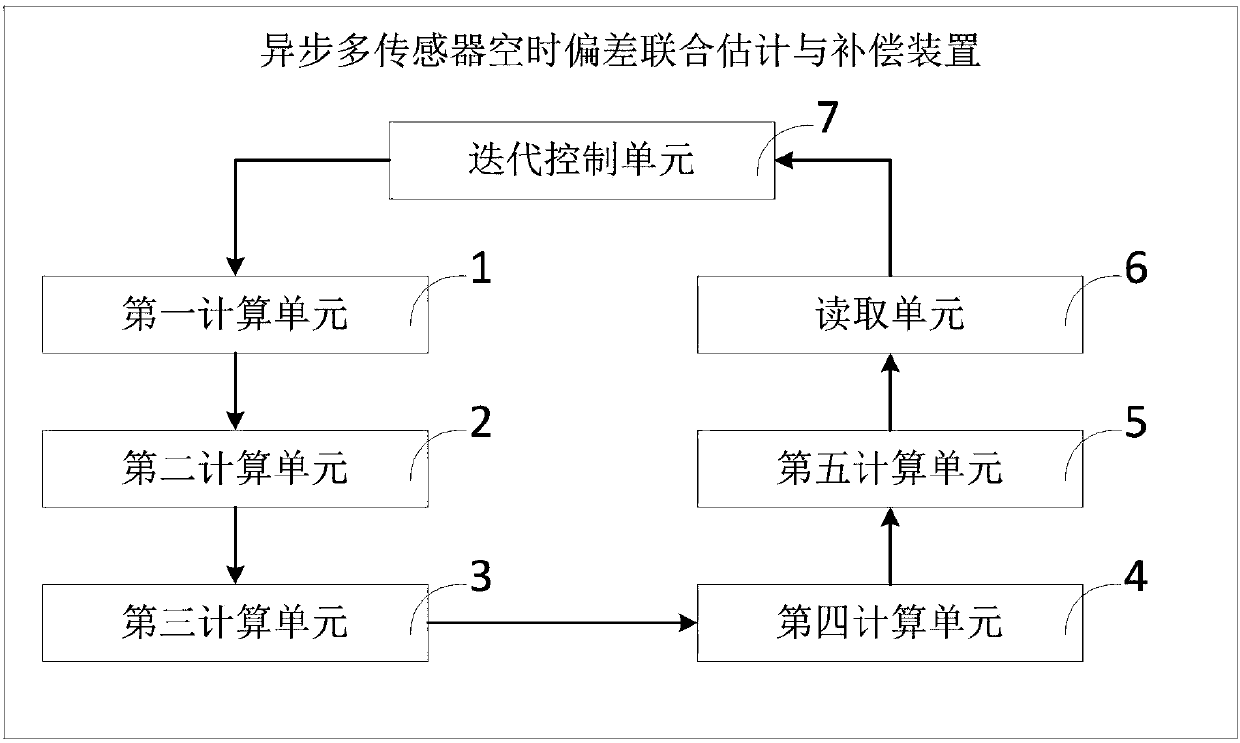
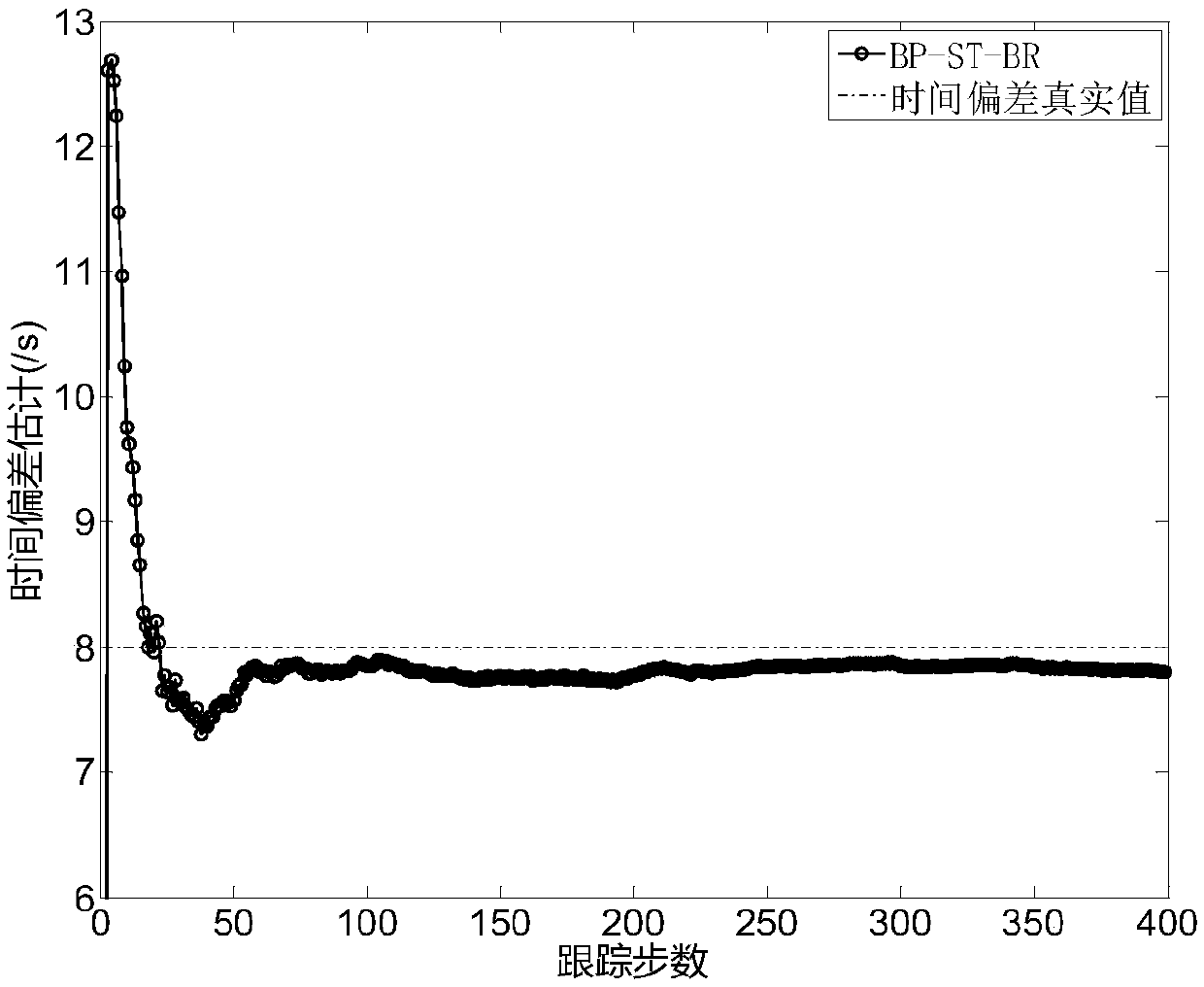
ActiveCN108319570AEffective estimateEffective compensationComplex mathematical operationsTime deviationAlgorithm
The invention discloses an asynchronous multi-sensor space-time deviation joint estimation and compensation method and device. The method includes the steps of a, calculating a state sampling point and a corresponding weight value at a k-1 fusion moment; b, calculating a prediction state sampling point, a prediction state and a prediction state deviation covariance matrix at a k fusion moment; c,calculating a predicted measurement sampling point and a predicted measurement vector; d, calculating an innovation covariance matrix and a cross covariance matrix between states and observation; e, determining an estimation state and an estimation state deviation covariance matrix at the k fusion moment; f, reading target state estimation, space deviation estimation and time deviation estimation;g, making k equal to the sum of k and 1 and repeating the procedures above to form a closed-loop cyclic operation, wherein the device corresponds to the method. In this way, under the situation thatthe data rates of sensors are different, state vectors after dimensional expansion are estimated, and the target state estimation is obtained through iteration while effective estimation and compensation of space-time deviations are achieved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
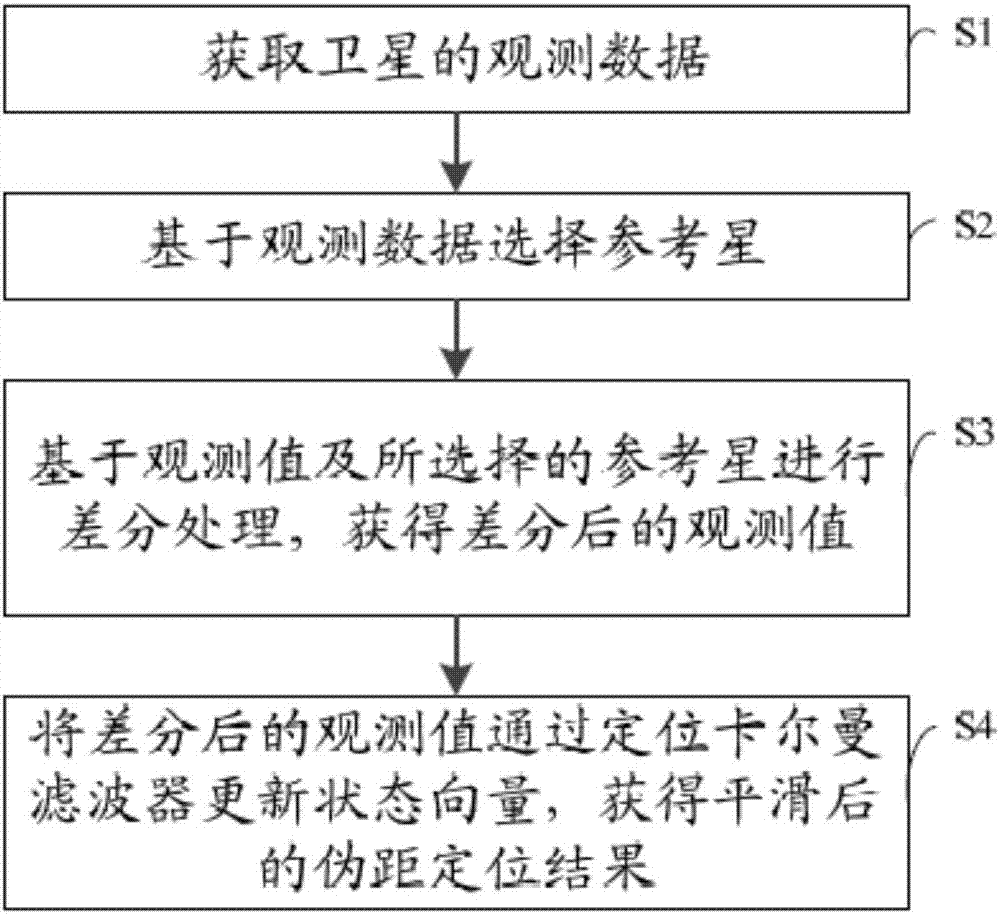
Pseudorange positioning smoothing method and system, and positioning terminal
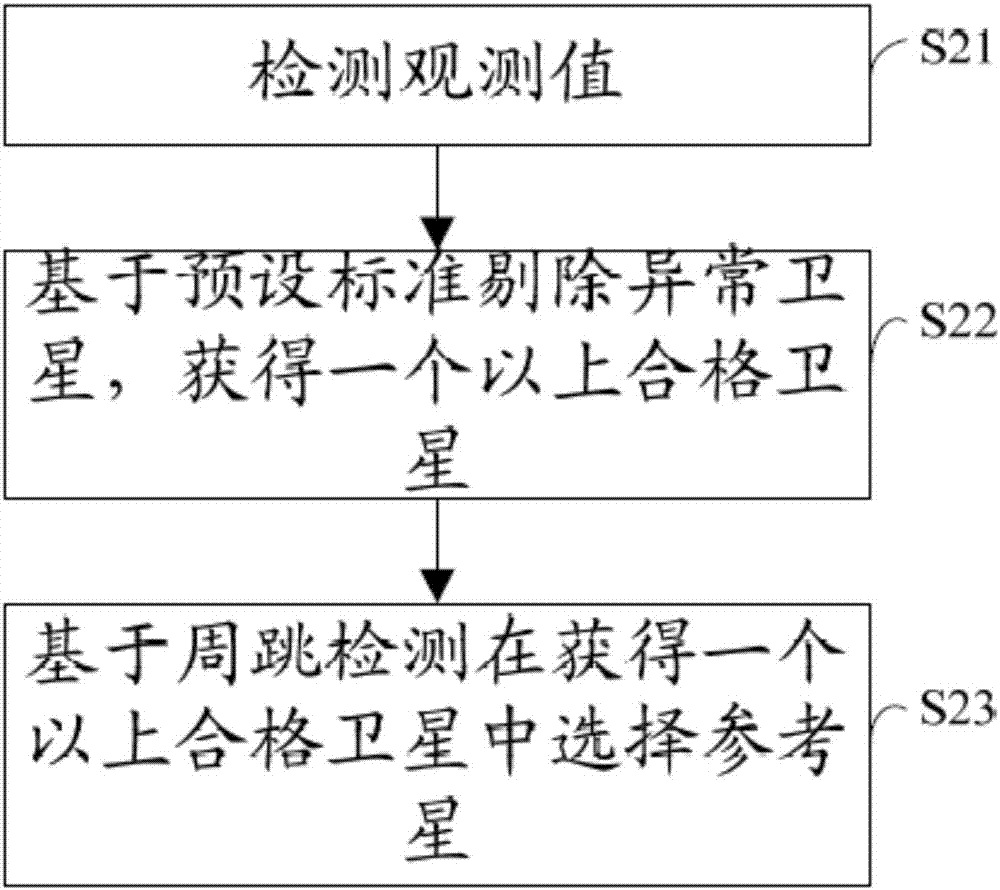
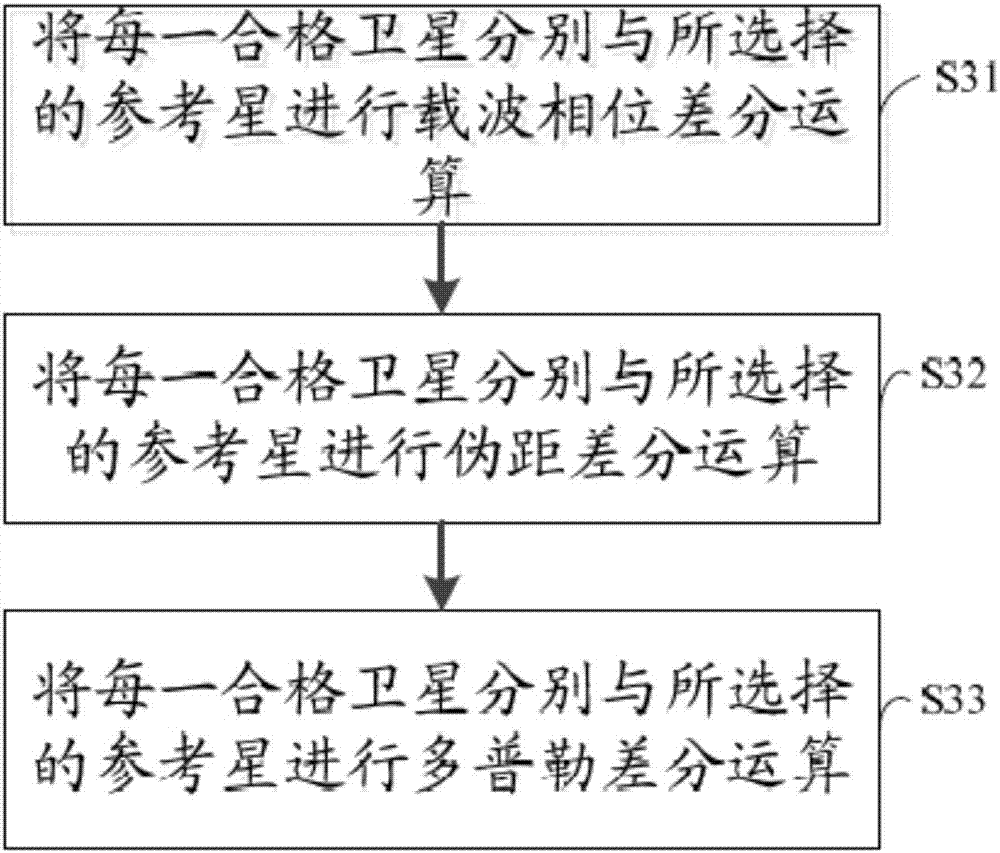
InactiveCN107193026AReduce mistakesHigh positioning accuracySatellite radio beaconingKaiman filterData selection
The invention discloses a pseudorange positioning smoothing method, a pseudorange positioning smoothing system and a positioning terminal. The pseudorange positioning smoothing method comprises the steps of: acquiring observation data of a satellite, wherein the observation data comprises an observed value; selecting a reference star based on the observation data; determining; conducting differential processing based on the observed value and the selected reference star to obtain an observed value after differencing, wherein the observed value after differencing comprises a pseudorange; and updating a state vector of the observed value after differencing through positioning a Kalman filter, so as to obtain a smoothed pseudorange positioning result. According to the pseudorange positioning smoothing method, the pseudorange positioning smoothing system and the positioning terminal, the observation data is acquired, the state vector is updated by using carrier phase increment, Doppler and eudorange after differencing at a positioning end directly without considering local clock skew, the pseudorange positioning error can be effectively reduced, and the positioning precision can be improved.
Owner:QIANXUN SPATIAL INTELLIGENCE INC
EKF (extended Kalman filter)-based alignment method for inertia/polarized light integrated navigation system under large misalignment angle
ActiveCN110672130AHigh precisionHigh precision attitude correction capabilityMeasurement devicesAccelerometerState vector
The invention relates to an EKF (extended Kalman filter)-based alignment method for an inertia / polarized light integrated navigation system under a large misalignment angle. According to the method, the state vectors of the initial alignment of the inertia / polarized light integrated navigation system are selected to build the nonlinear error state equation of the inertia / polarized light integratednavigation system under the large misalignment angle; a solar vector is calculated according to a polarization azimuth angle measured by a polarized light sensor, and a polarized light nonlinear measurement equation is established; a speed error measurement equation is established according to the speed output of an inertial navigation system; the unified nonlinear measurement equation of the inertia / polarized light integrated navigation system is established by using an augmentation technology; the nonlinear equation of the inertia / polarized light integrated navigation system is discretized;an extended Kalman filter is designed to estimate the error states such as misalignment angle, speed error, gyroscopic drift and accelerometer constant bias of the inertia / polarized light integratednavigation system; feedback correction is carried out on the attitude and speed of the inertia / polarized light integrated navigation system, and the initial alignment estimation precision and speed ofthe inertia / polarized light integrated navigation system under the large misalignment angle are improved. The method has the advantages of high precision, high speed and high autonomy.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Control method for state compensation model during batch processing
ActiveCN107544255AImprove performanceImprove control effectAdaptive controlBatch processingState model
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV +1
Method and in-vehicle device for correcting alignment information representative of the alignment of an in-vehicle camera
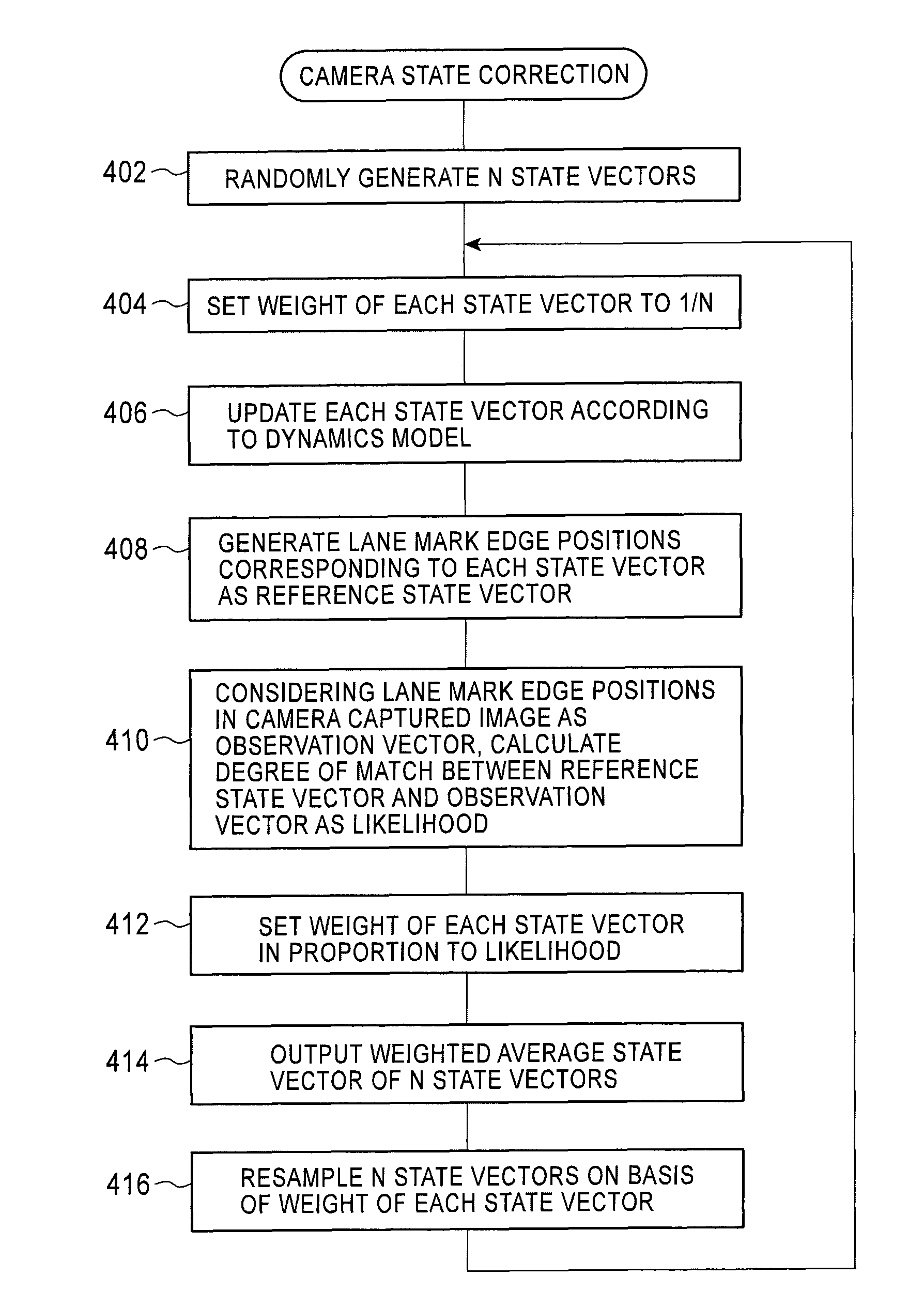
ActiveUS8350909B2Generate accuratelyAccurate informationCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsAs elementDynamic models
A process is repeated in which N state vectors each including, as elements, the position of a camera with respect to a vehicle, the posture of the camera, the width of a lane where the vehicle is driving, and the orientation of the vehicle with respect to the lane are changed according to a predetermined dynamics model, a reference state vector representing the positions of edges of lane marks included in an image captured by the camera is generated when each of the changed state vectors is true, considering the positions of edges of lane marks in the image as an observation vector, the degree of match between the reference state vector and the observation vector is calculated as the weight of the state vector, a weighted average vector of the state vectors is calculated, and N state vectors are resampled on the basis of the calculated weights.
Owner:ALPINE ELECTRONICS INC
Robot pose positioning method and system
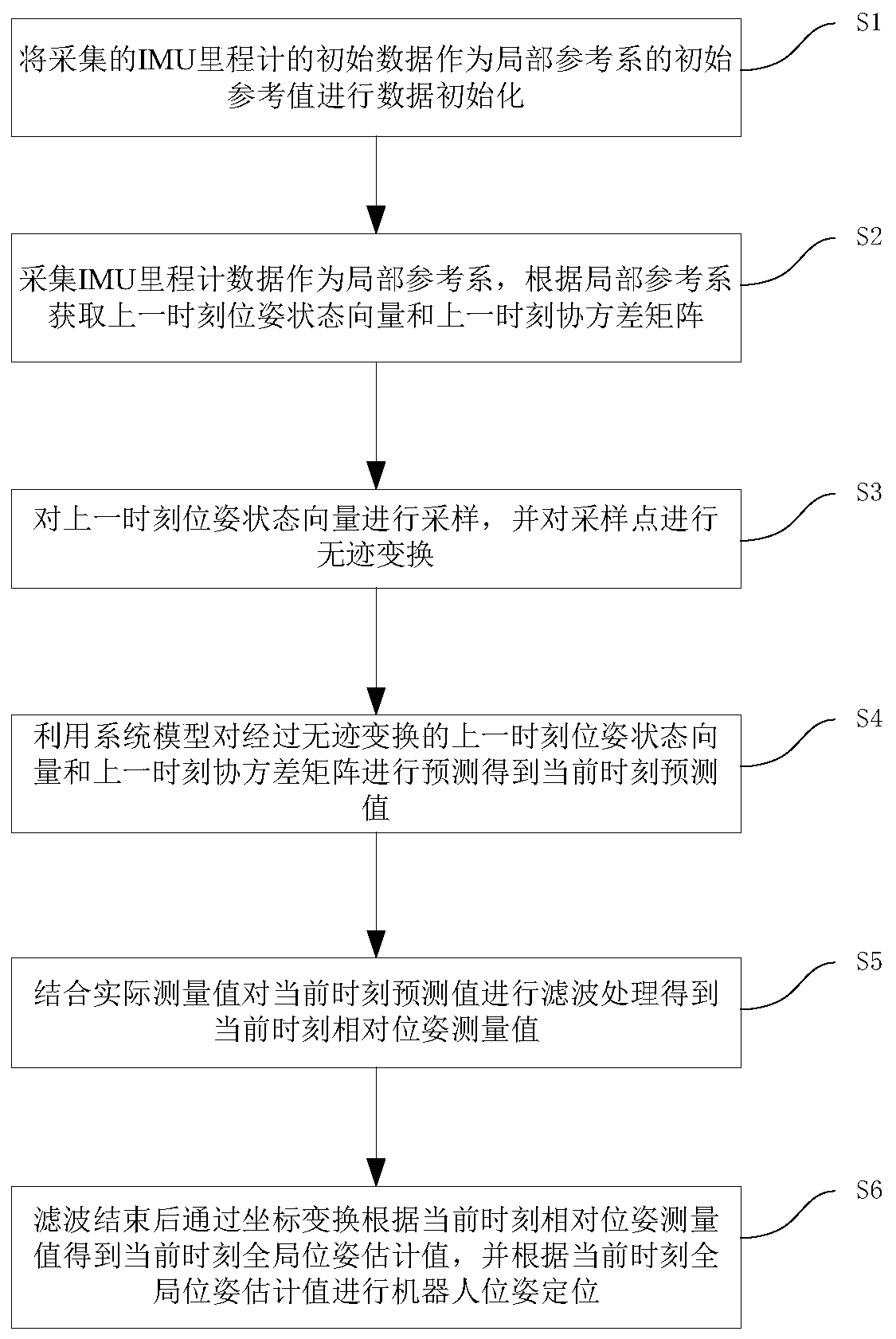
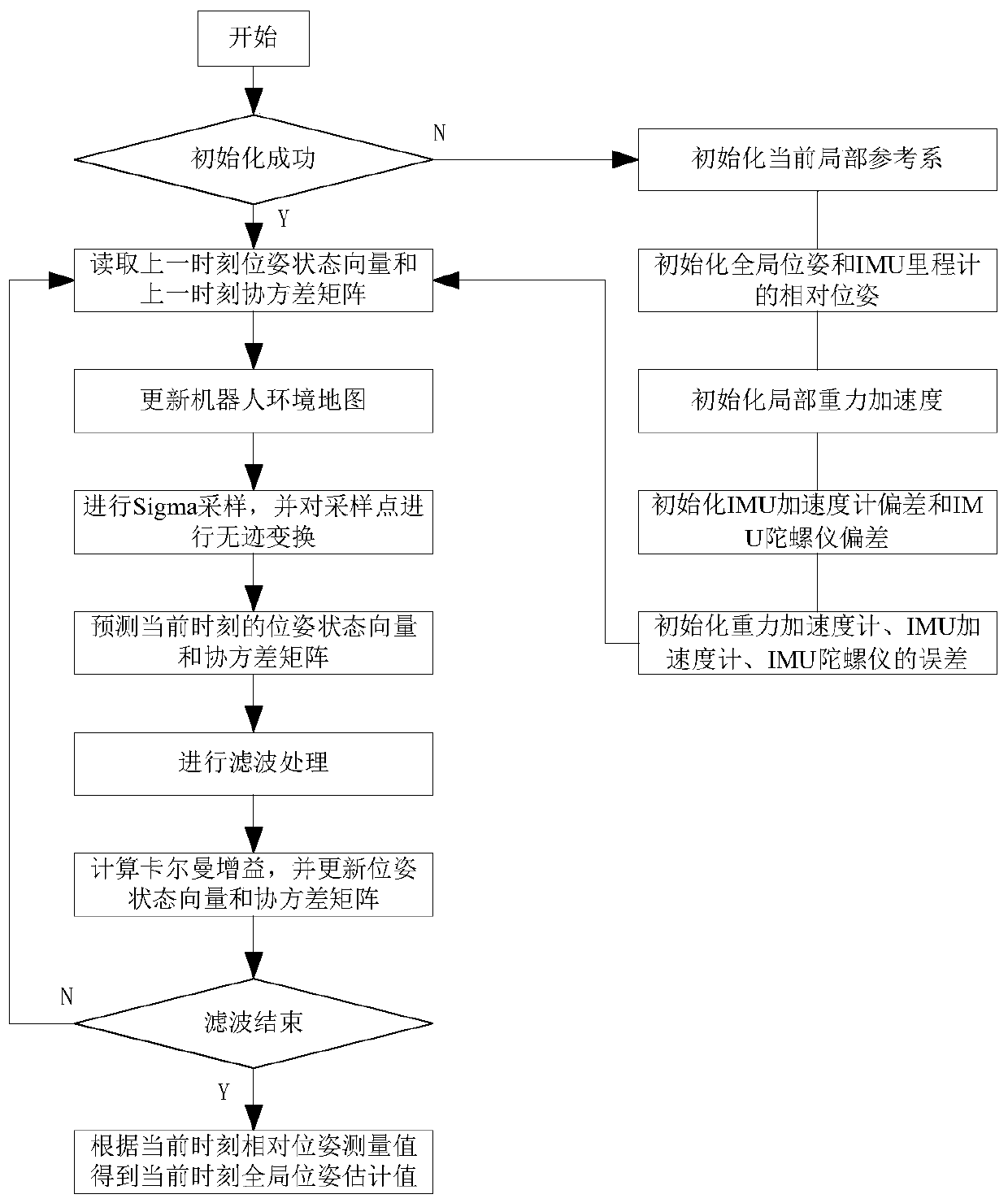
ActiveCN111136660ARobustHigh positioning accuracyProgramme-controlled manipulatorPattern recognitionState vector
The invention discloses a robot pose positioning method and a system, and relates to the field of robot positioning, wherein the method comprises the following steps of: acquiring IMU odometer data asa local reference system, acquiring a pose state vector and a covariance matrix at the previous time according to the local reference system, sampling the pose state vector at the previous time, performing unscented transformation to sampling points, predicting the pose state vector and the covariance matrix at the previous time subjected to unscented transformation by using a system model to obtain a prediction value at the current time, carrying out filtering treatment to the prediction value at the current time according to the actual measurement value to obtain the relative pose measurement value at the current time; after filtering, obtaining the global pose estimation at the current time according to the relative pose measurement value at the current time through coordinate transformation; and carrying out robot pose positioning according to the global pose estimation value at the current time. The unscented Kalman filter algorithm is combined with IMU odometer data and actual measurement values collected by GPS satellites or vision systems to obtain global pose estimation values, which are robust to complex environments and improve positioning precision.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
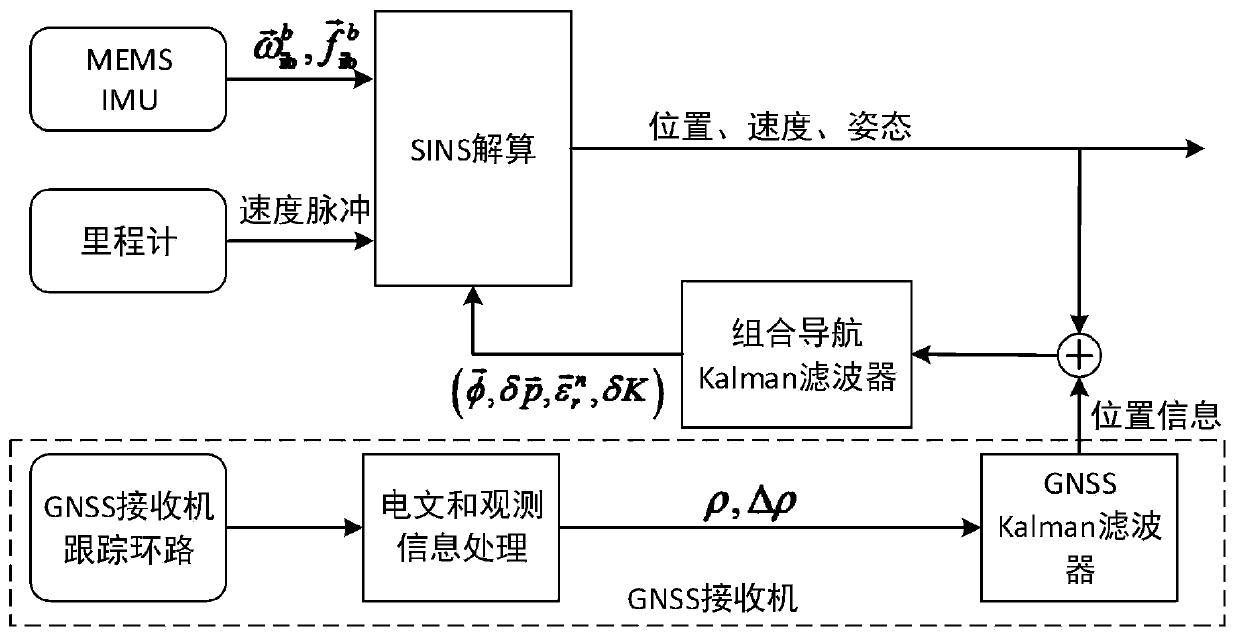
INS/DR & GNSS loosely integrated navigation method based on MEMS inertial component
PendingCN111156994AReduce selection requirementsEffective precisionNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSatellite radio beaconingGyroscopeState vector
The invention discloses an INS / DR & GNSS loosely integrated navigation method based on an MEMS inertial component. The INS / DR & GNSS loosely integrated navigation method comprises the following steps:establishing a state differential equation by taking a position error, a misalignment angle and gyro zero offset of an INS / DR system and a scale factor of a speedometer as state vectors; establishingan observation equation according to the position information of the GNSS system and the position information of the INS / DR system; enabling the state differential equation and the observation equation to enter a Kalman filter iteration process to calculate a state vector of the INS / DR system; correcting the position, the speed, the attitude angle and the gyro zero offset error of the INS / DR system by using the state vector to obtain corrected position, speed and attitude information. According to the invention, the performance of a navigation-level device is achieved by adopting a consumption-level IMU, and the gyroscope thermally-induced zero offset estimation method can be used for autonomous learning and adaptive compensation in the system operation process without any offline calibration; the installation error estimation algorithm provided by the invention can be used for autonomous estimation, and strict requirements on assembly are not needed any more.
Owner:SHANGHAI CYGNUS SEMICON CO LTD
UKF (unscented Kalman filter)-based alignment method for inertia/polarized light integrated navigation system under large misalignment angle
ActiveCN110672131AHigh precisionHigh precision attitude correction capabilityMeasurement devicesComputational physicsState vector
The invention relates to a UKF (unscented Kalman filter) alignment method for an inertia / polarized light integrated navigation system under a large misalignment angle. According to the method, the state vectors of the initial alignment of the inertia / polarized light integrated navigation system are selected to build the nonlinear error state equation of the inertia / polarized light integrated navigation system under the large misalignment angle; a solar vector is calculated according to a polarization azimuth angle measured by a polarized light sensor, and a polarized light nonlinear measurement equation is established; a speed error measurement equation is established according to the speed output of an inertial navigation system; the unified nonlinear measurement equation of the inertia / polarized light integrated navigation system is established by using an augmentation technology; the nonlinear equation of the inertia / polarized light integrated navigation system is discretized; an unscented Kalman filter is designed to estimate the error states such as misalignment angle, speed error, gyroscopic drift and accelerometer constant bias of the inertia / polarized light integrated navigation system; feedback correction is carried out on the attitude and speed of the inertia / polarized light integrated navigation system, and the initial alignment estimation precision and speed of theinertia / polarized light integrated navigation system under the large misalignment angle are improved. The method has the advantages of high precision, high speed and high autonomy.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
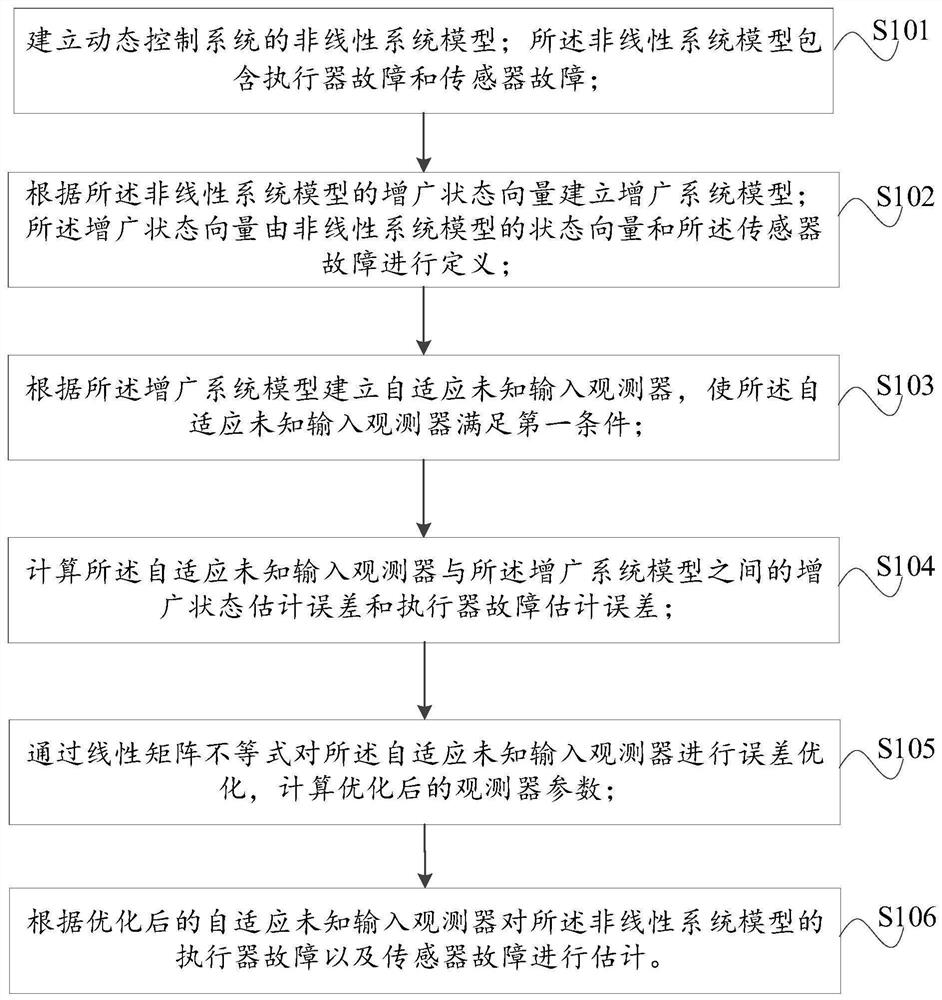
Rapid fault estimation method and device based on adaptive unknown input observer
ActiveCN113031570AAvoid restrictionsReduce the impact of disturbanceProgramme controlElectric testing/monitoringState vectorActuator fault
The embodiment of the invention provides a rapid fault estimation method and device based on an adaptive unknown input observer. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a nonlinear system model of the dynamic control system; establishing an augmented system model according to the augmented state vector of the nonlinear system model; establishing a self-adaptive unknown input observer according to the augmented system model, and enabling the self-adaptive unknown input observer to meet a first condition; calculating an augmented state estimation error and an actuator fault estimation error; performing error optimization on the adaptive unknown input observer through a linear matrix inequality, and calculating optimized observer parameters; and estimating an actuator fault and a sensor fault of the nonlinear system model. In this way, after the dynamic control system breaks down, fault information and specific fault conditions can be obtained in time, and the influence of external interference on a fault estimation result is restrained while the fault amplitude is estimated as accurately as possible.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Automatic driving method and system and vehicle
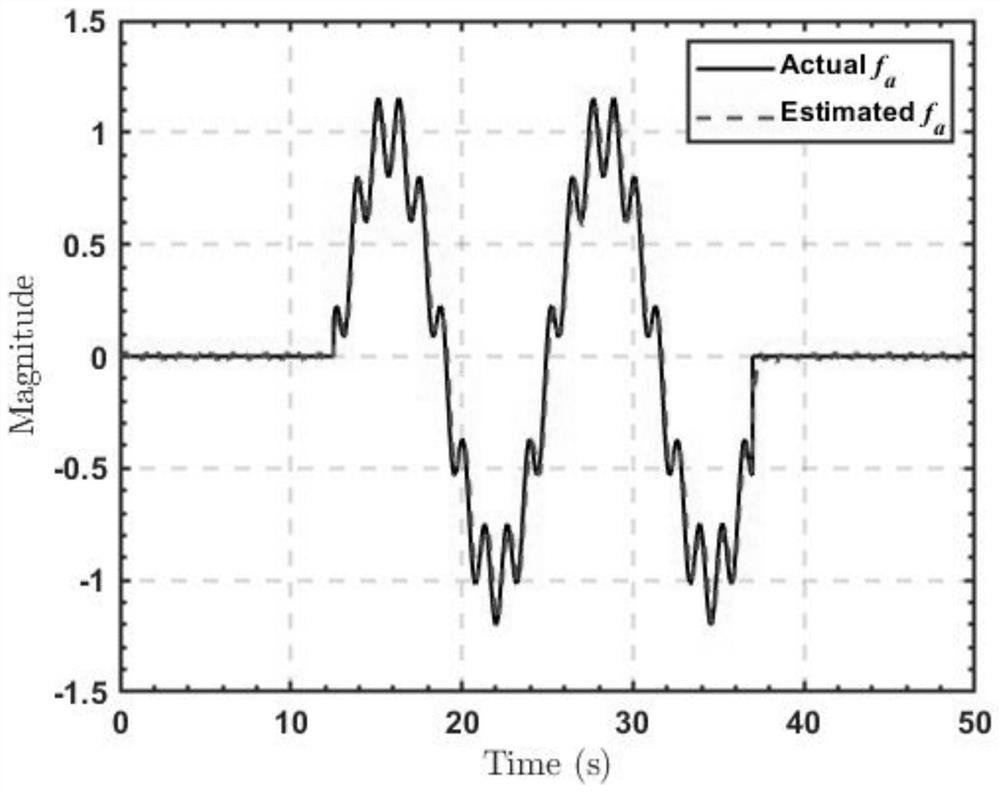
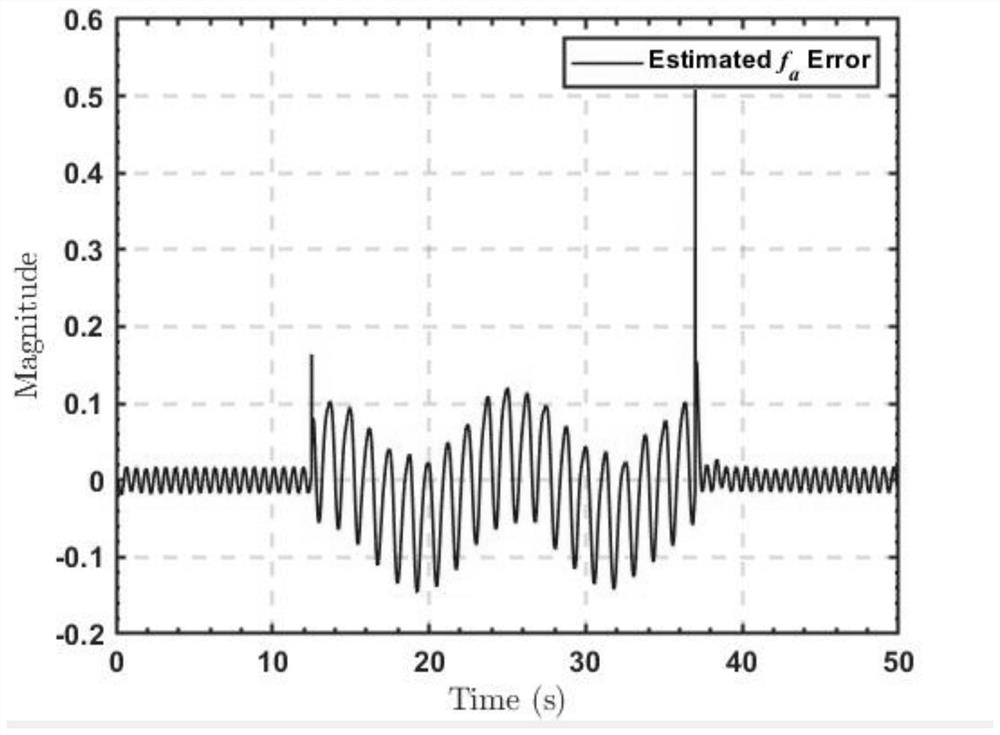
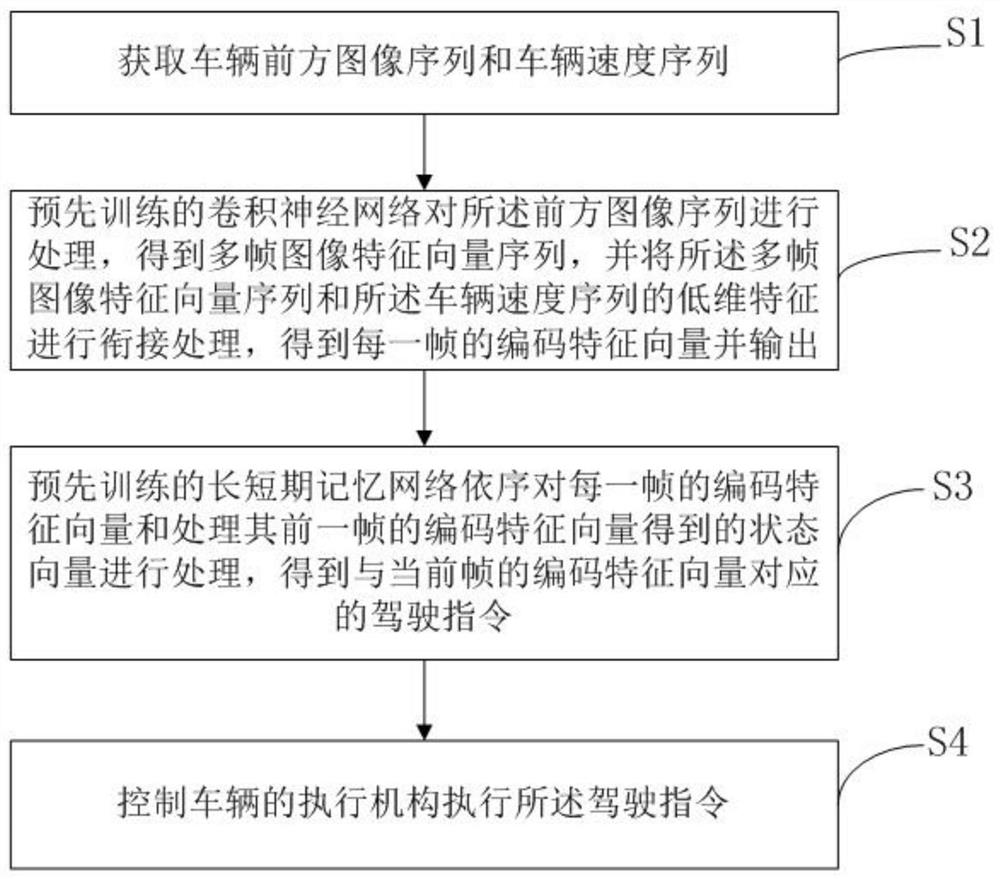
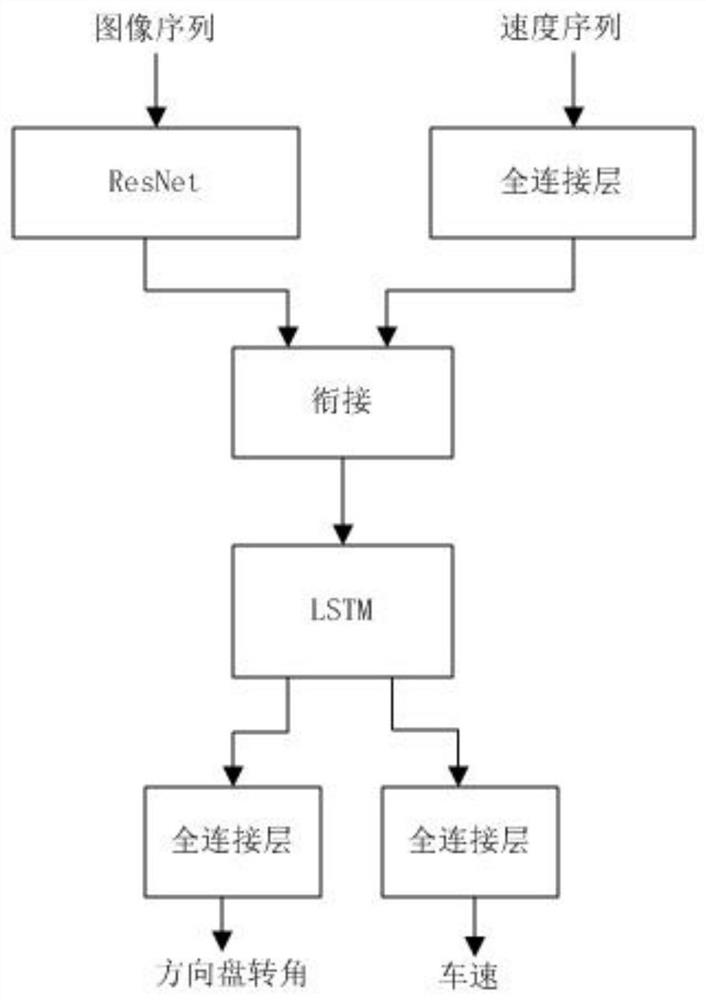
PendingCN111738037APreserve predictive powerShorten the timeCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesFeature vectorState vector
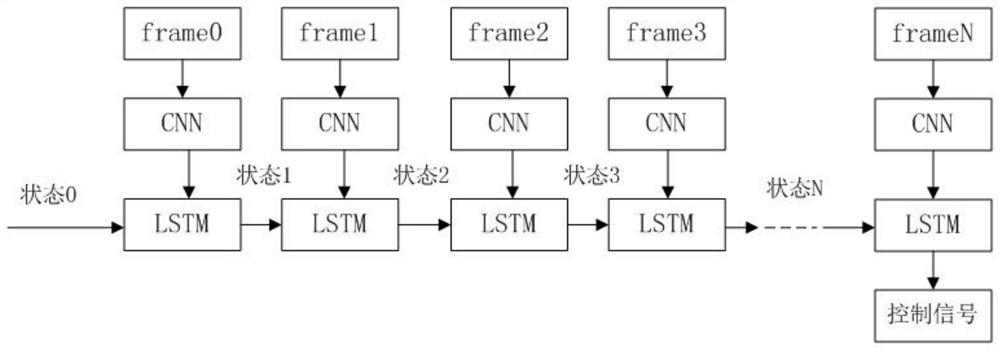
The invention relates to an automatic driving method and system and a vehicle. The method comprises the following steps that a vehicle front image sequence and a vehicle speed sequence are obtained; processing the front image sequence by a pre-trained convolutional neural network to obtain a multi-frame image feature vector sequence, and connecting the multi-frame image feature vector sequence with low-dimensional features of the vehicle speed sequence to obtain and output a coding feature vector of each frame; a pre-trained long-term and short-term memory network processes the coding featurevector of each frame and a state vector obtained by processing the coding feature vector of the previous frame in sequence to obtain a driving instruction corresponding to the coding feature vector ofthe current frame; and controlling an executing mechanism of the vehicle to execute the driving instruction. The system is a carrier for implementing the method, and the vehicle comprises the system.According to the invention, the accuracy and the real-time performance of vehicle anthropomorphic automatic driving can be improved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU AUTOMOBILE GROUP CO LTD
Beidou deformation monitoring real-time processing method based on novel Kalman filtering
InactiveCN111623703AReduce pollutionFast convergenceCharacter and pattern recognitionElectrical/magnetic solid deformation measurementState vectorEngineering
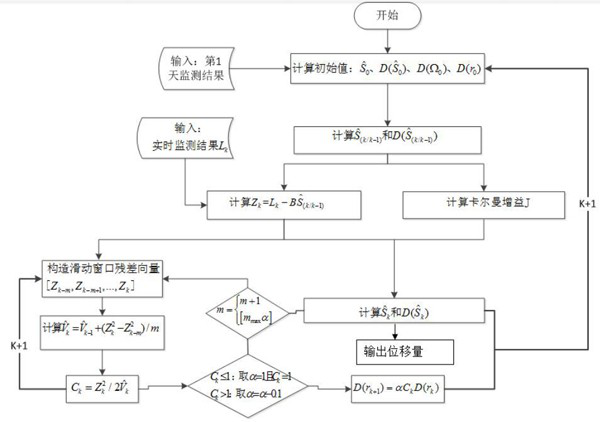
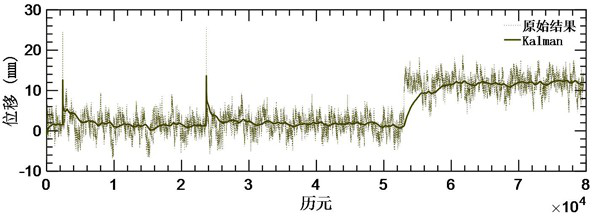
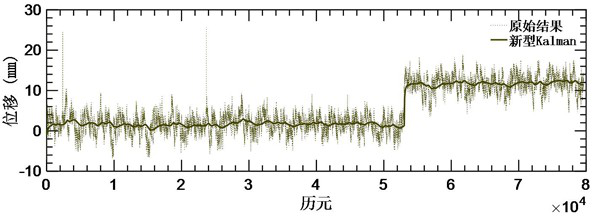
The invention provides a Beidou deformation monitoring real-time processing method based on novel Kalman filtering. The Beidou deformation monitoring real-time processing method comprises the steps ofobtaining an optimal estimation value of an initial state vector and the like; obtaining a one-step prediction value and a one-step prediction variance of the state vector based on Kalman filtering;acquiring real-time monitoring data; obtaining a standard deviation and a Kalman gain of the time period data; calculating an optimal estimation value of the state vector and a variance matrix of theoptimal estimation value; constructing a sliding window residual vector, dynamically adjusting the size of a sliding window, and updating an observation noise variance matrix in real time; and calculating and outputting displacement. According to the invention, gross error detection is realized through the ratio of the residual error to the standard deviation and is corrected by scaling and measuring the value of the noise variance matrix in real time, and the pollution of the gross error to an observation result is weakened; on the basis of gross error detection, the convergence of a monitoring result is accelerated by updating an observation noise variance matrix in real time and dynamically adjusting the size of a sliding window, the real displacement of a monitoring point is quickly reflected, and the monitoring requirement of deformation can be met.
Owner:HUNAN LIANZHI BRIDGE & TUNNEL TECH
Robust fault estimation method for discrete switching system based on unknown input observer
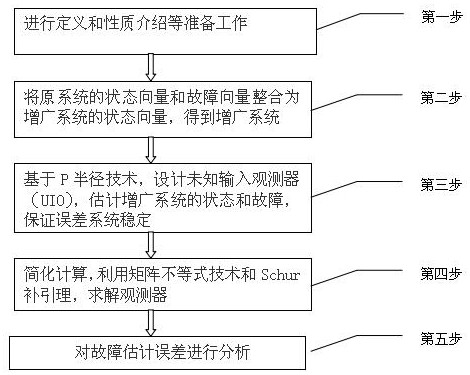
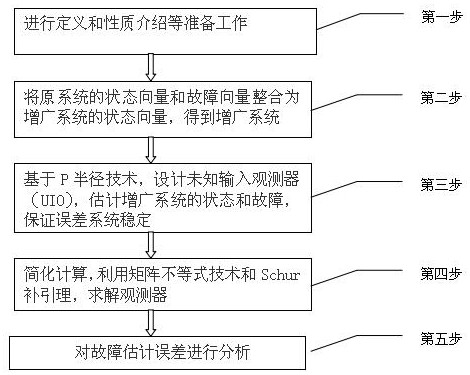
The invention relates to the technical field of fault diagnosis, and discloses a robust fault estimation method for a discrete switching system based on an unknown input observer. The method comprisesthe following steps: enabling a state vector and a fault vector of an original discrete switching system to be integrated into a state vector of an augmentation system in order to obtain an augmentation system; based on a P radius technology, designing an unknown input observer (UIO) to estimate the state and fault of the augmentation system; giving assumed conditions, and solving the observer through a linear matrix inequality technology and a Schur complementary leader; and analyzing the fault estimation error. Compared with the prior art, the method has the following advantages that the unknown input robust fault estimation observer is designed for the discrete switching system based on the P radius technology, the linear matrix inequality technology and the Schur complementary leaderare used for solving the observer and analyzing the fault estimation error, so that the stability of the error system is ensured, the fault estimation has complete robustness for unknown input interference; and compared with other traditional methods, the method has more accurate boundary and higher efficiency.
Owner:HUAIYIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Inverter model parameter self-adaptive identification method based on steepest descent method
ActiveCN111740575AImprove robustnessAc-dc conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsGrid connected inverterAdaptive identification
The invention provides an inverter model prediction control parameter self-adaptive identification method based on a steepest descent method in order to solve the problem that inverter control robustness is affected by parameter mismatch of an LCL type grid-connected inverter filter. According to the method, an error between a state vector prediction value and a sampling value at the current moment is calculated; an objective function is established with the purpose of minimizing the error vector; gradient derivation is conducted on the objective function in the parameter matrix direction based on a steepest descent method; and the minimum value of the objective function is searched, and the parameter matrix is adjusted in real time through an adaptive algorithm, so that the parameter matrix is gradually converged to be close to the true value of the parameter matrix, and therefore, the inductance and capacitance parameters of the filter can be identified online, the filter parametersin the controller can be corrected online, and the robustness of the grid-connected inverter can be improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Underwater robot monocular vision positioning method
ActiveCN105890589AMake up for the defect that only the position information can be estimatedNavigational calculation instrumentsPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryGyroscopeState vector
The invention provides an underwater robot monocular vision positioning method. A Doppler instrument and a gyroscope are combined o measure the linear speed and the angular speed of an underwater robot under a load system, and a state equation is obtained; four known static feature points of coordinates under an overall system are obtained, the positions of the feature points under an image system are obtained according to coordinate system changes, and a measuring equation is obtained; the state vector at the k-1 time and a covariance matrix of the state vector are known, and a Sigma point is obtained through an Unscented transform method; the measuring value at the k time is estimated through time update again; the Doppler instrument and the gyroscope are combined to measure the linear speed and the angular speed of an aircraft under the load system and the positions of the feature points under the overall system under the image system, the measuring value at the k time can be obtained, the state vector of the k time is estimated through measurement update, and a covariance matrix of the state vector at the k time is obtained. The limitation that layout of feather points in a geometric method must meet specific conditions is broken through, the defect that EKF filter can only estimate position information is overcome, and position information and the euler angle can be estimated at the same time.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Distributed kalman filter architecture for carrier range ambiguity estimation
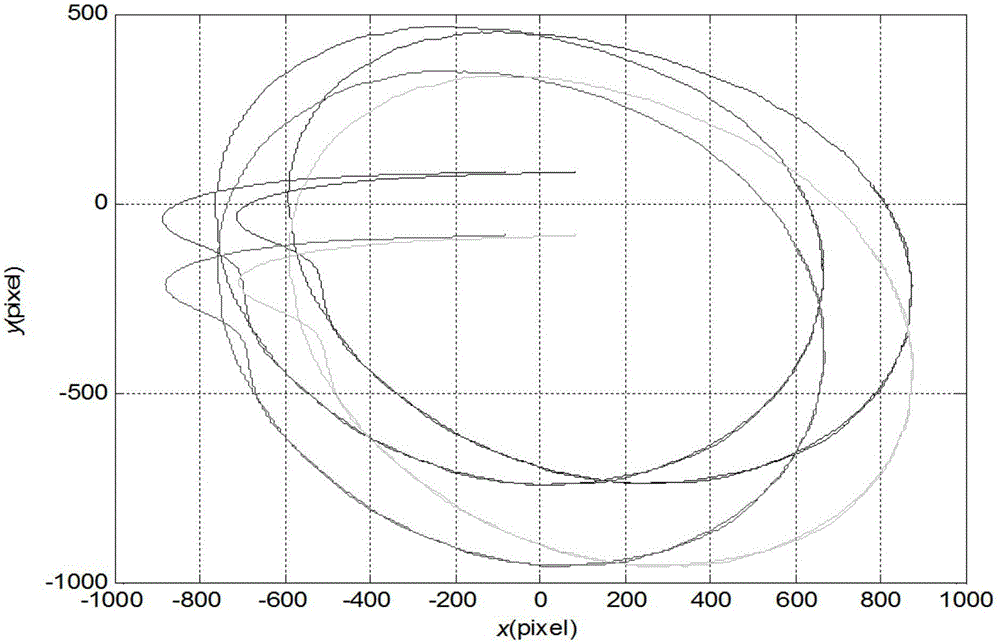
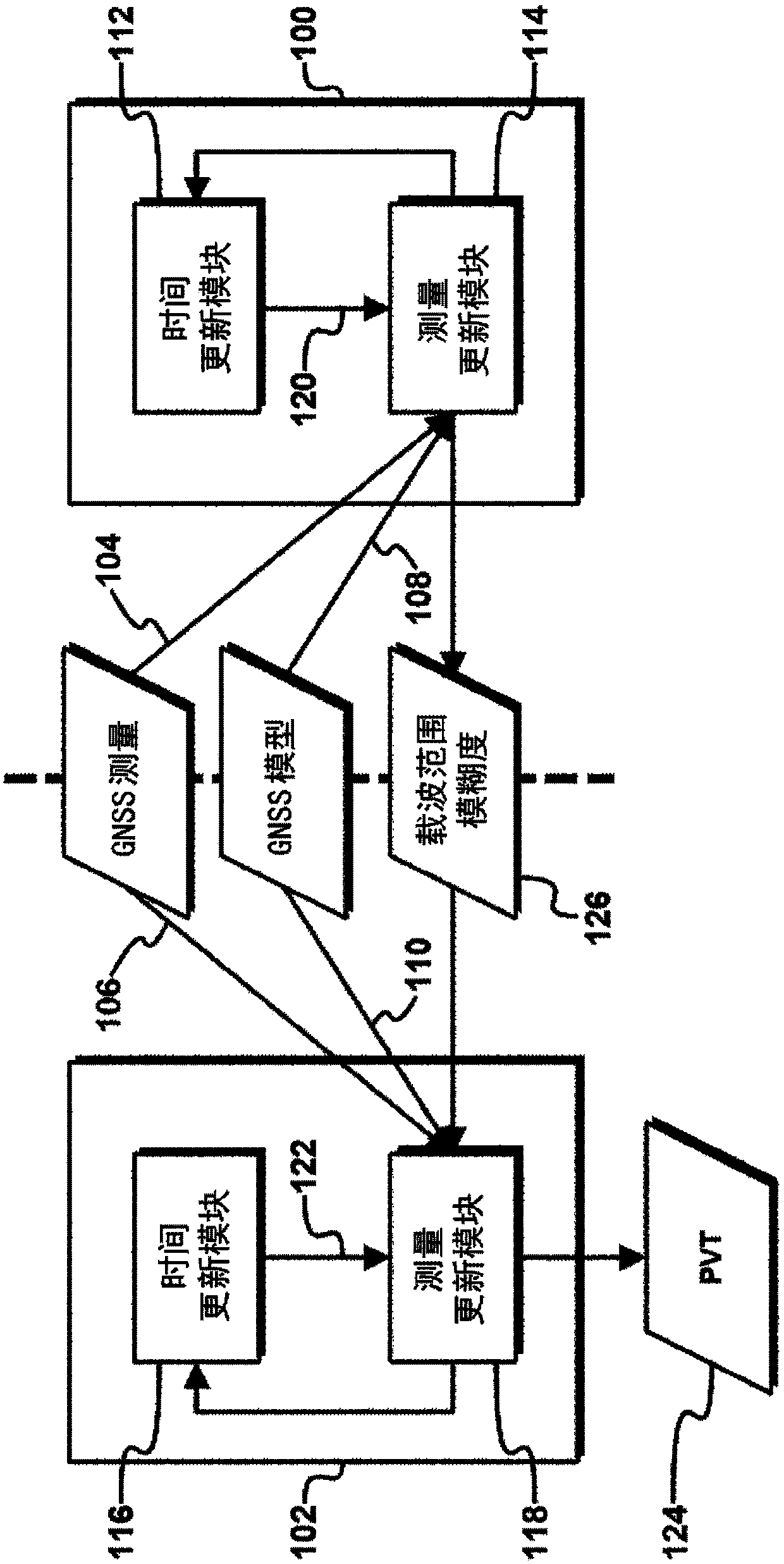
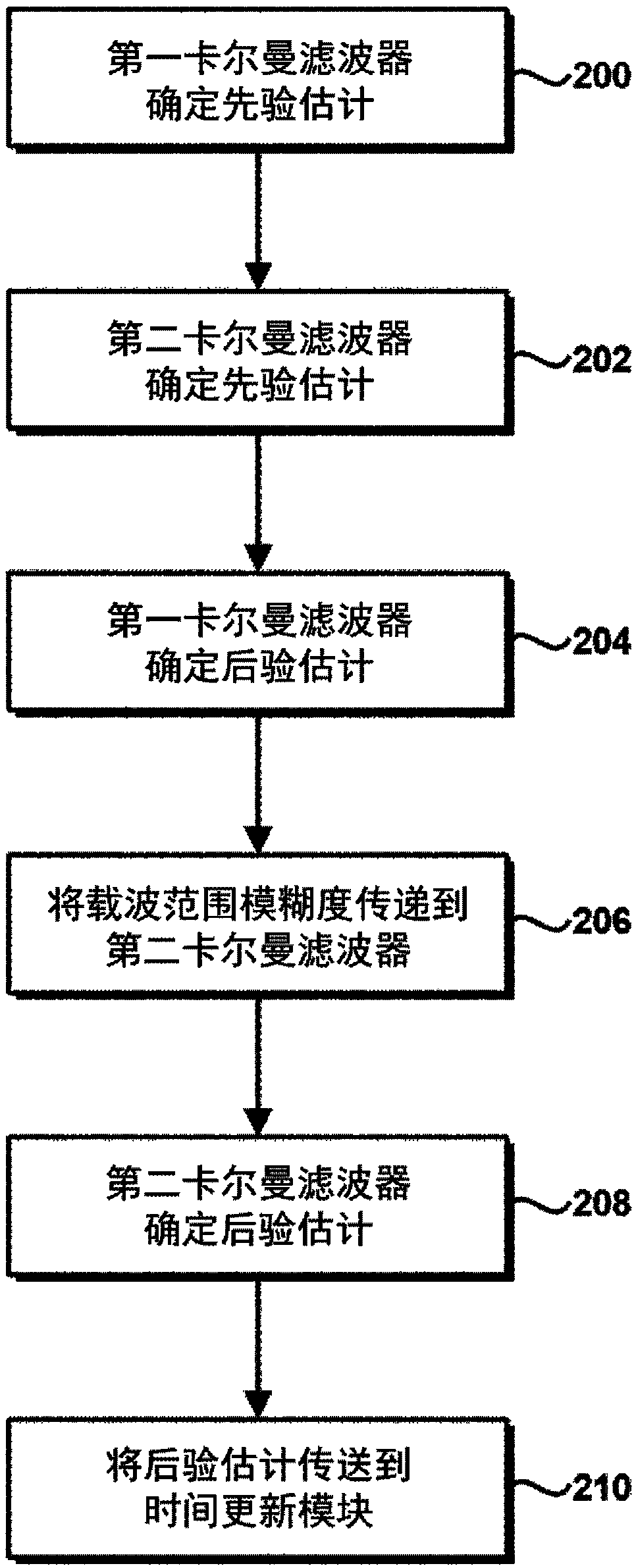
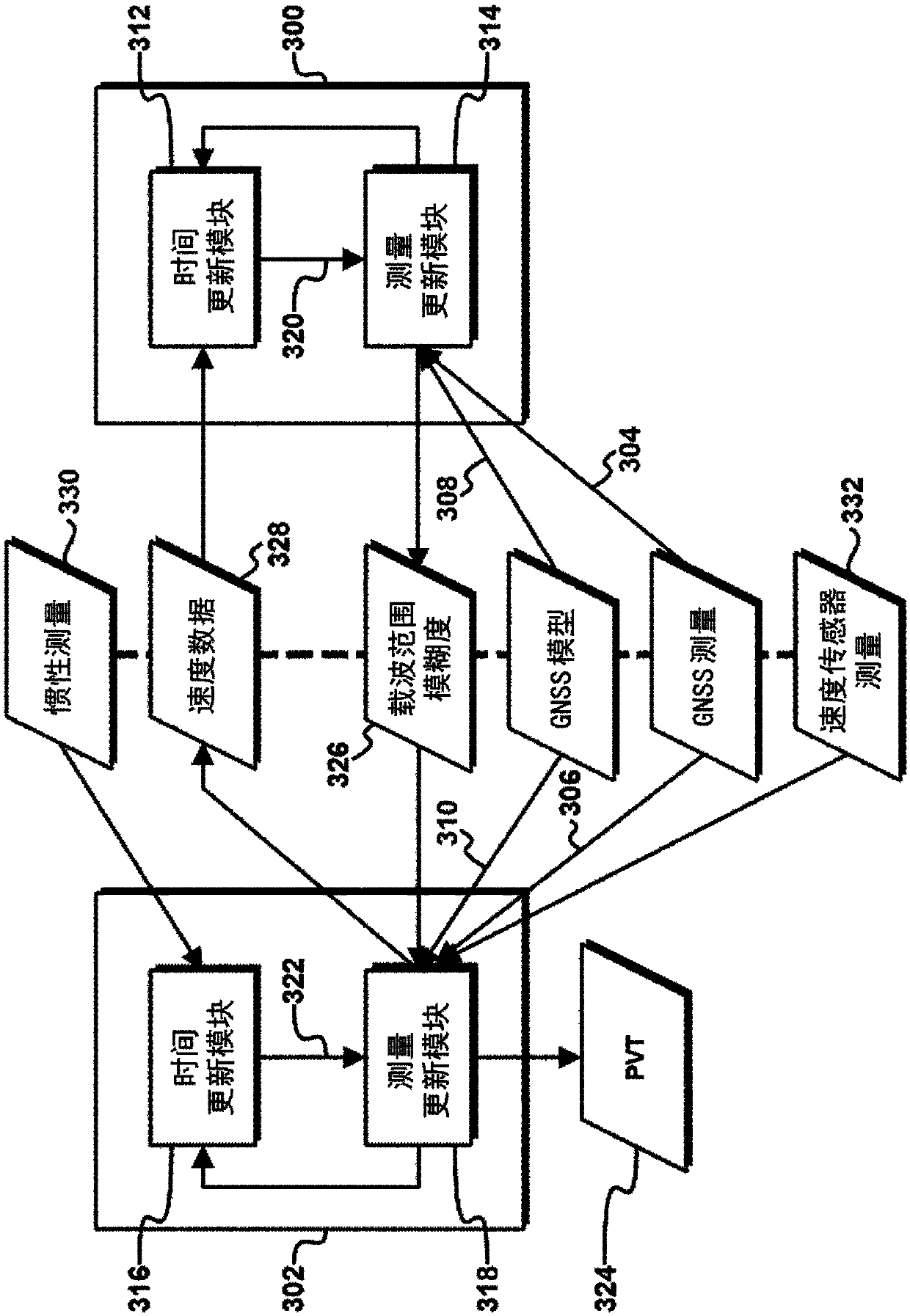
Methods and apparatus for determining navigation data (124) using carrier range measurements obtained by a GNSS receiver for a plurality of GNSS satellites, the apparatus comprising: a first Kalman filter (100) configured to determine an a posteriori estimate of a first state vector based at least in part on a first set of GNSS measurements (104) obtained by the, and / or a further, GNSS receiver and an a priori estimate of the first state vector, the first state vector comprising carrier range ambiguity values relating to the plurality of GNSS satellites and a position of the, and / or the further, GNSS receiver; and a second Kalman filter (102) configured to determine an a posteriori estimate of a second state vector, which comprises the navigation data (124), based at least in part on a second set of GNSS measurements (106) obtained by the, and / or a further, GNSS receiver, an a priori estimate of the second state vector, and carrier range ambiguity data (126) based on the carrier rangeambiguity values determined in the a posteriori estimate of the first state vector.
Owner:U-BLOX
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com