Distributed kalman filter architecture for carrier range ambiguity estimation
A Kalman filter, ambiguity technology, applied in the direction of instruments, radio wave measurement systems, measurement devices, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
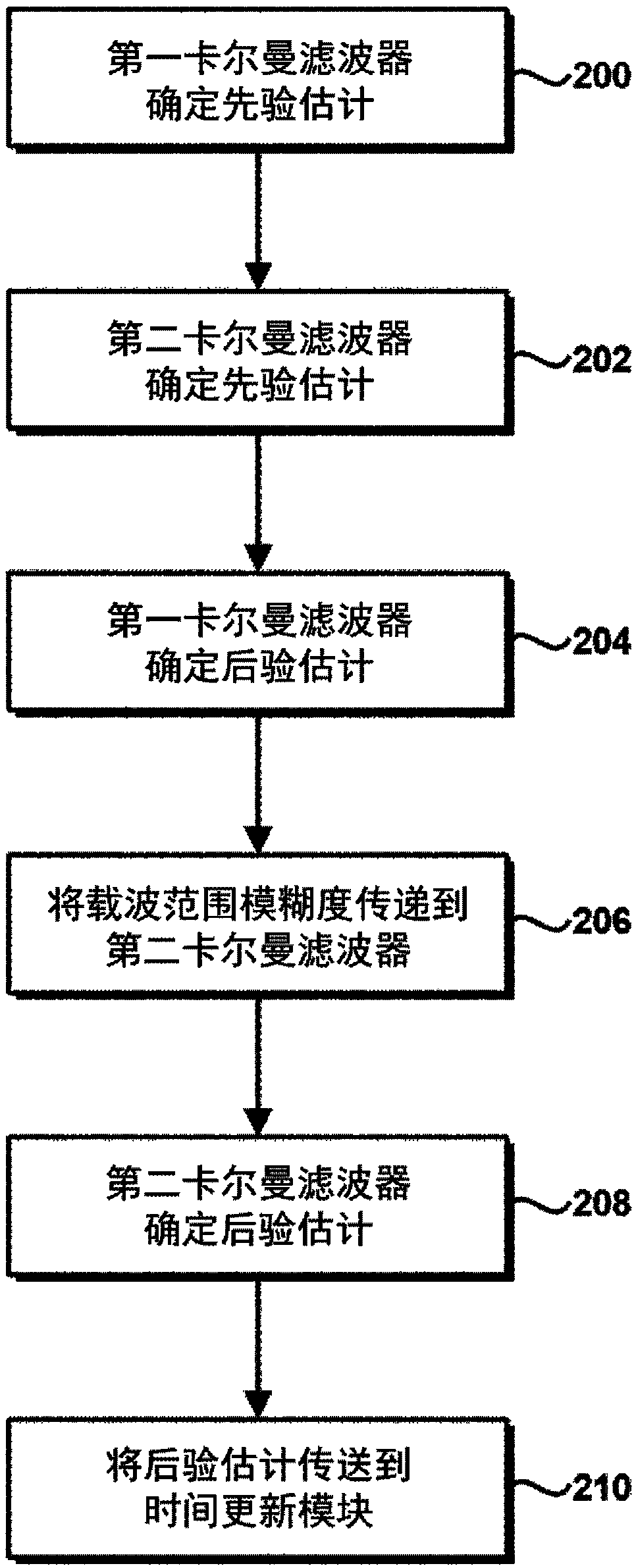
[0052] This paper describes methods for reducing the computational burden of Kalman filters that estimate carrier-wide ambiguities, allowing their implementation in resource-constrained environments.
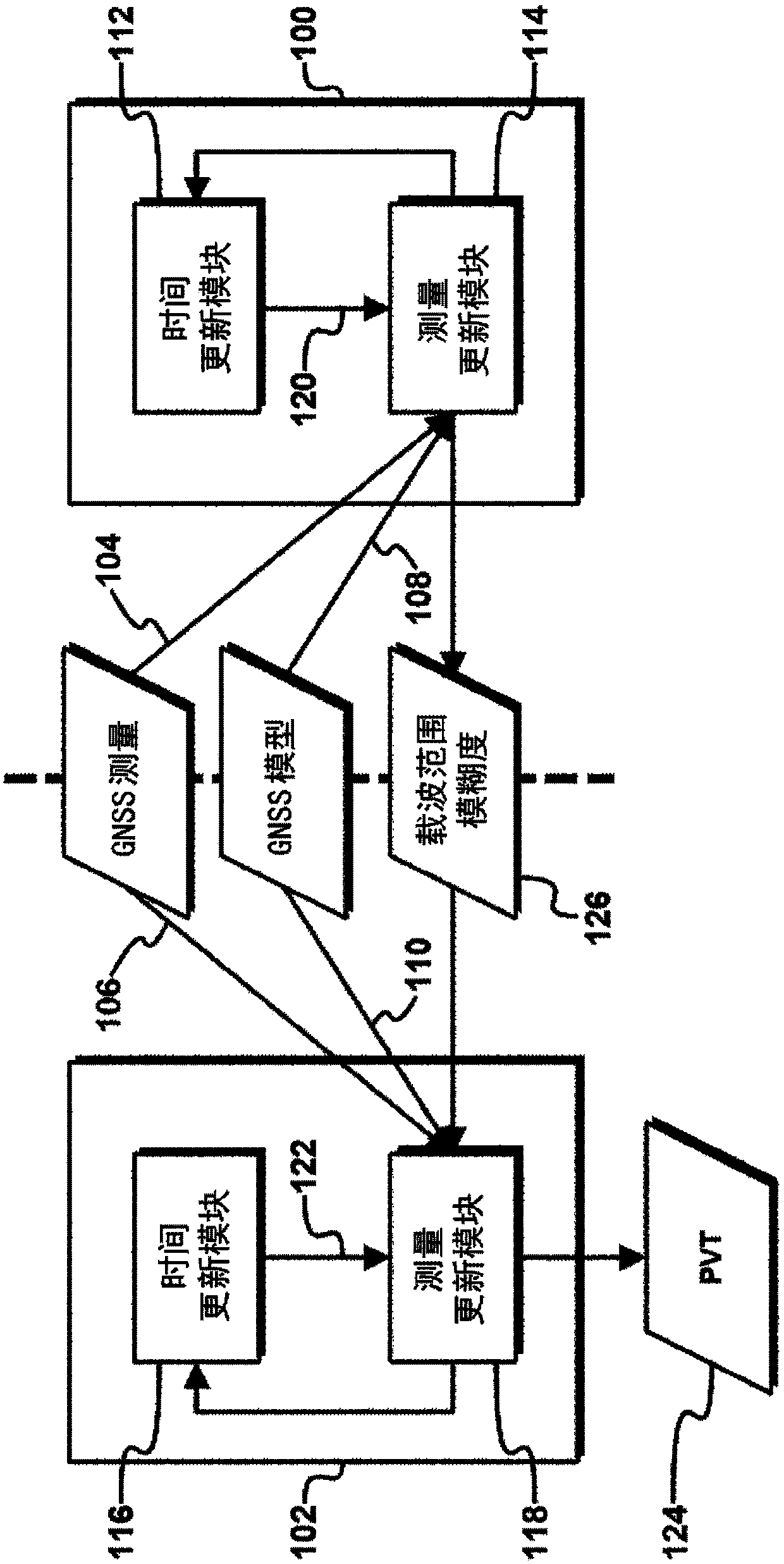
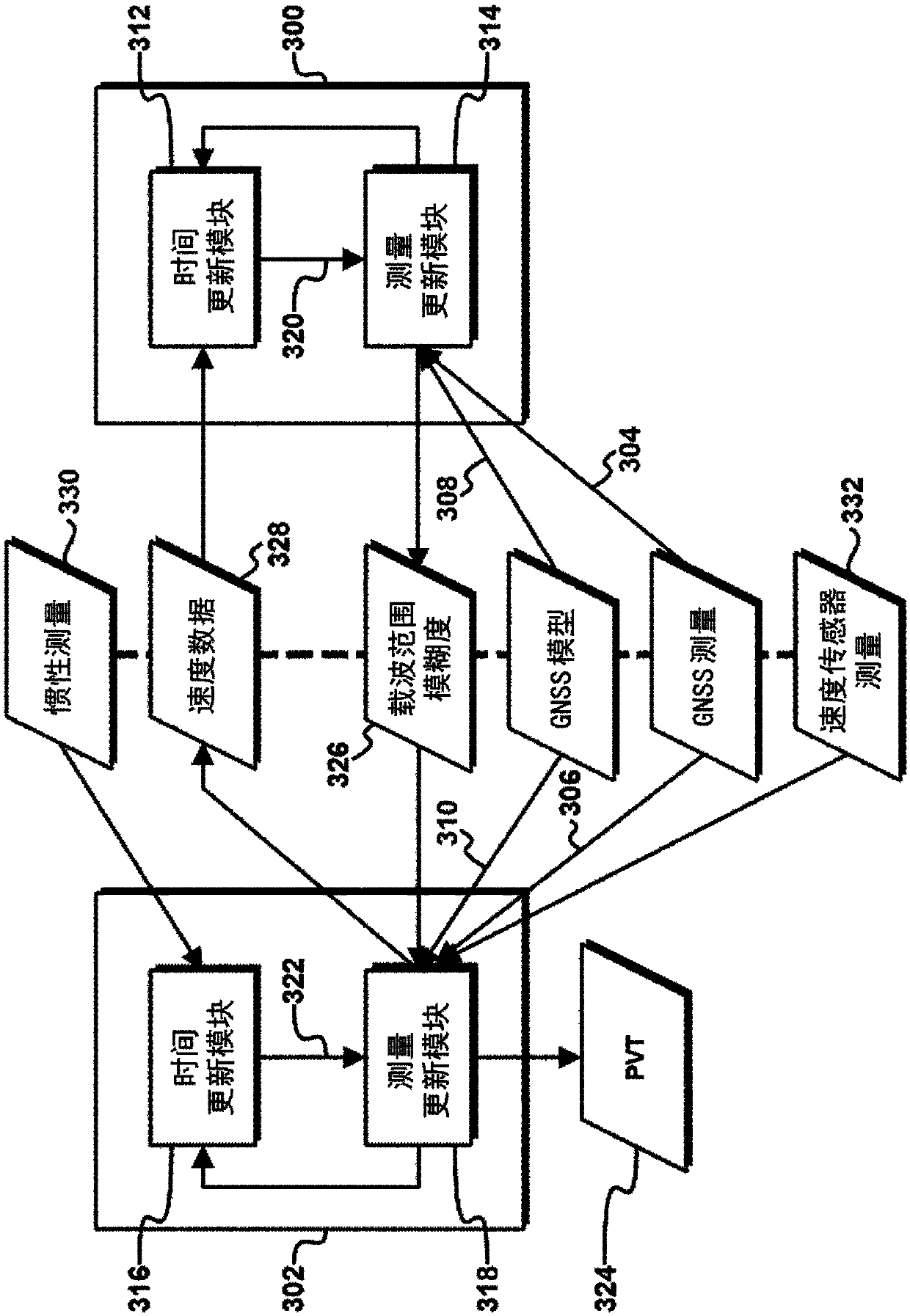
[0053] Separation of carrier range ambiguities
[0054] figure 1 is a block diagram of an exemplary apparatus capable of outputting a high precision navigation solution, eg, from GNSS measurements, without requiring computationally intensive implementation. The device comprises a first Kalman filter 100 and a second Kalman filter 102 . The first Kalman filter 100 and the second Kalman filter 102 receive GNSS measurements 104, 106 and GNSS model information 108, 110, respectively, and thus may enable the Kalman filters 100, 102 to estimate one or more states of the process, This will be discussed in this article.
[0055] The first Kalman filter 100 includes a time update module 112 and a measurement update module 114 , and the second Kalman filter 102 includes a time update m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com