Asynchronous sensor space alignment algorithm
A spatial registration and sensor technology, applied in the field of information fusion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
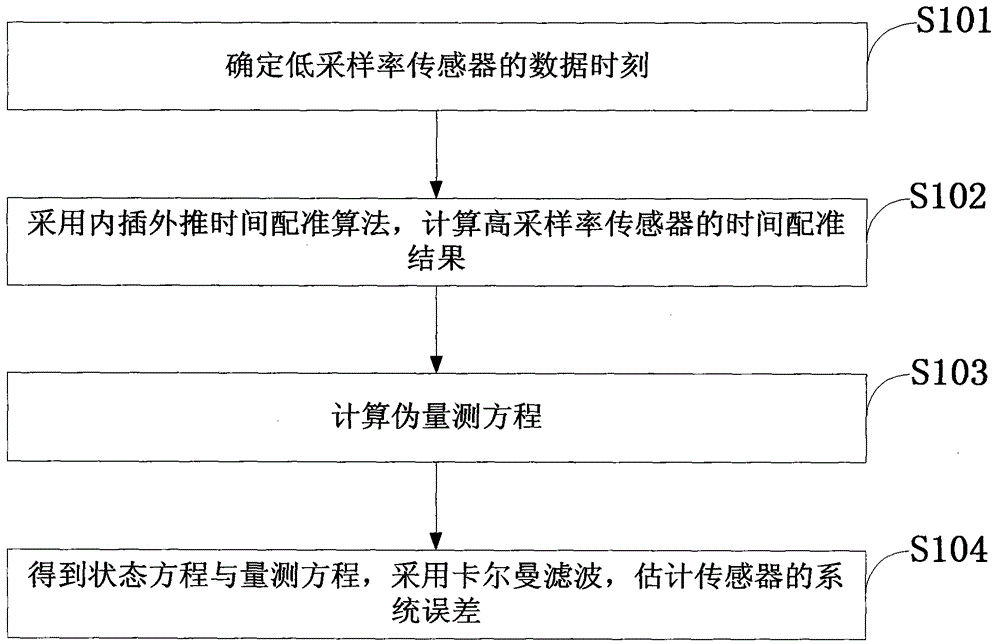
[0113] Embodiment 1, specifically includes the following steps:
[0114] Step 1: Initialize the target and sensor carrier parameters:
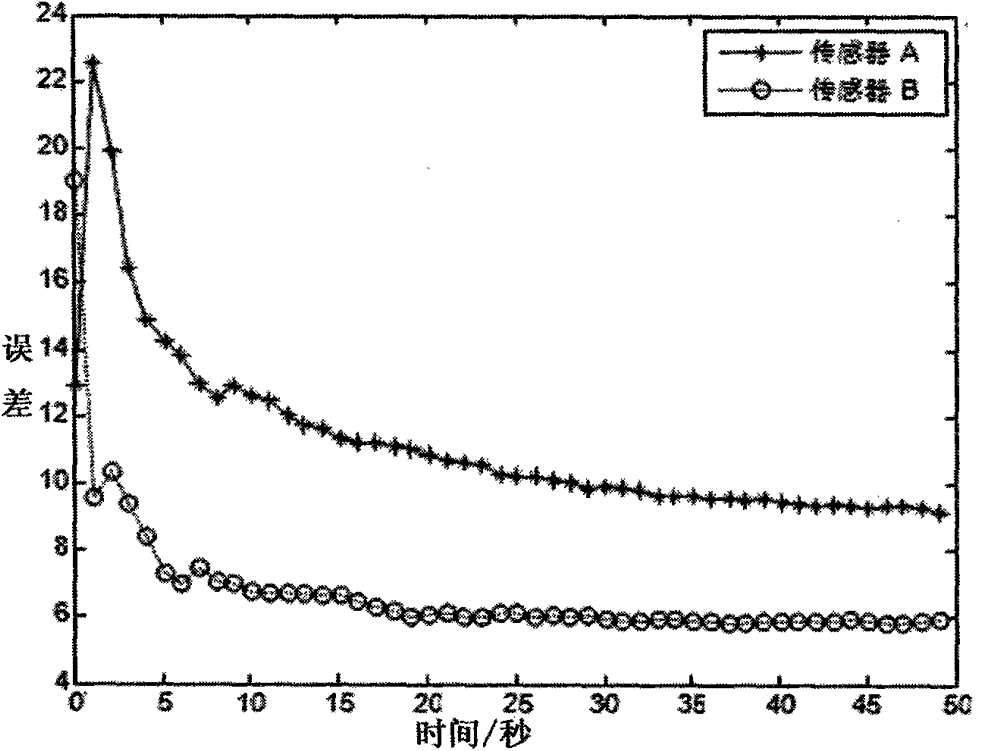
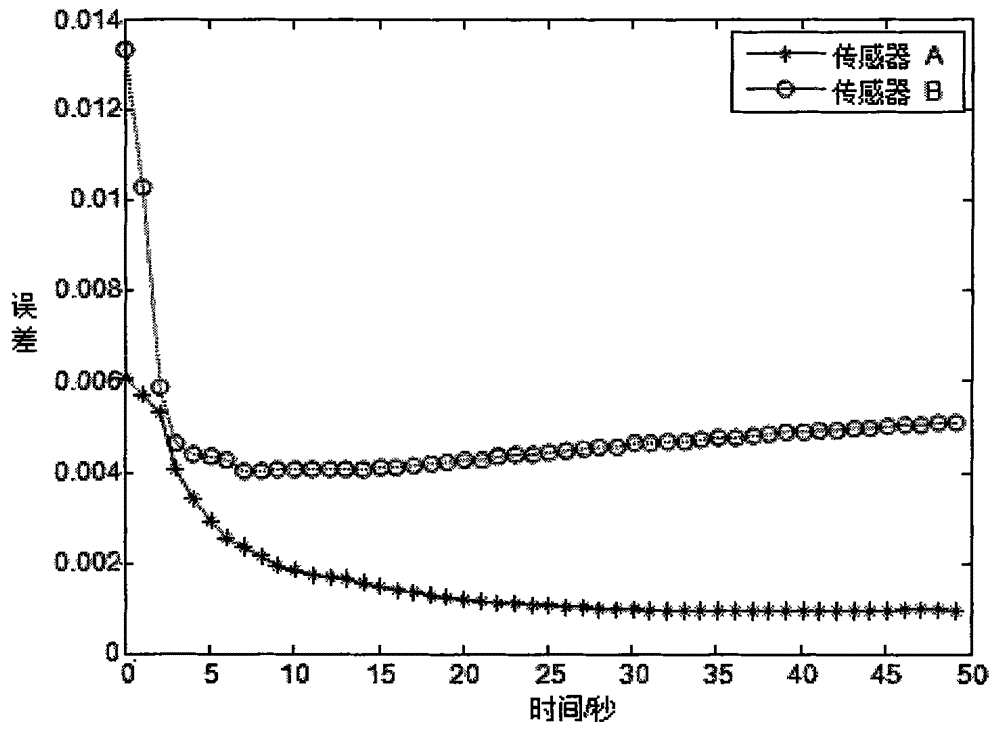
[0115] Assume that the systematic error of sensor A is ξ A (k)=[100m, 0.01rad, 0.01rad] T , Random noise has a mean value of 0, and a covariance of diag[10 2 0.002 2 0.002 2 ] White noise, the sampling period is 0.09s, and the system error of sensor B is ξ B (k)=[-150m, 0.05rad, -0.02rad] T , Random noise has a mean value of 0, and a covariance of diag[10 2 0.002 2 0.002 2 ] White noise, the sampling period is 0.1s, the position of sensor A in the ECEF coordinate system is (0, 0, 0), the position of sensor B in the ECEF coordinate system is (10000, 10000, 5000), and the target is in ECEF The initial position in the coordinate system is (5000, 5000, 2000);
[0116] Step 2: Calculate the time registration result of sensor A according to formula (5);
[0117] Step 3: Calculate the pseudo measurement equation according to formula (9);
[0118] Acco...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com