High-efficiency time domain electromagnetic simulation method based on H matrix algorithm
A time-domain electromagnetic and matrix algorithm technology, applied in computing, electrical digital data processing, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as high computational complexity, non-convergence, and low requirements for iterative stability, to achieve accurate fitting and ensure accuracy Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
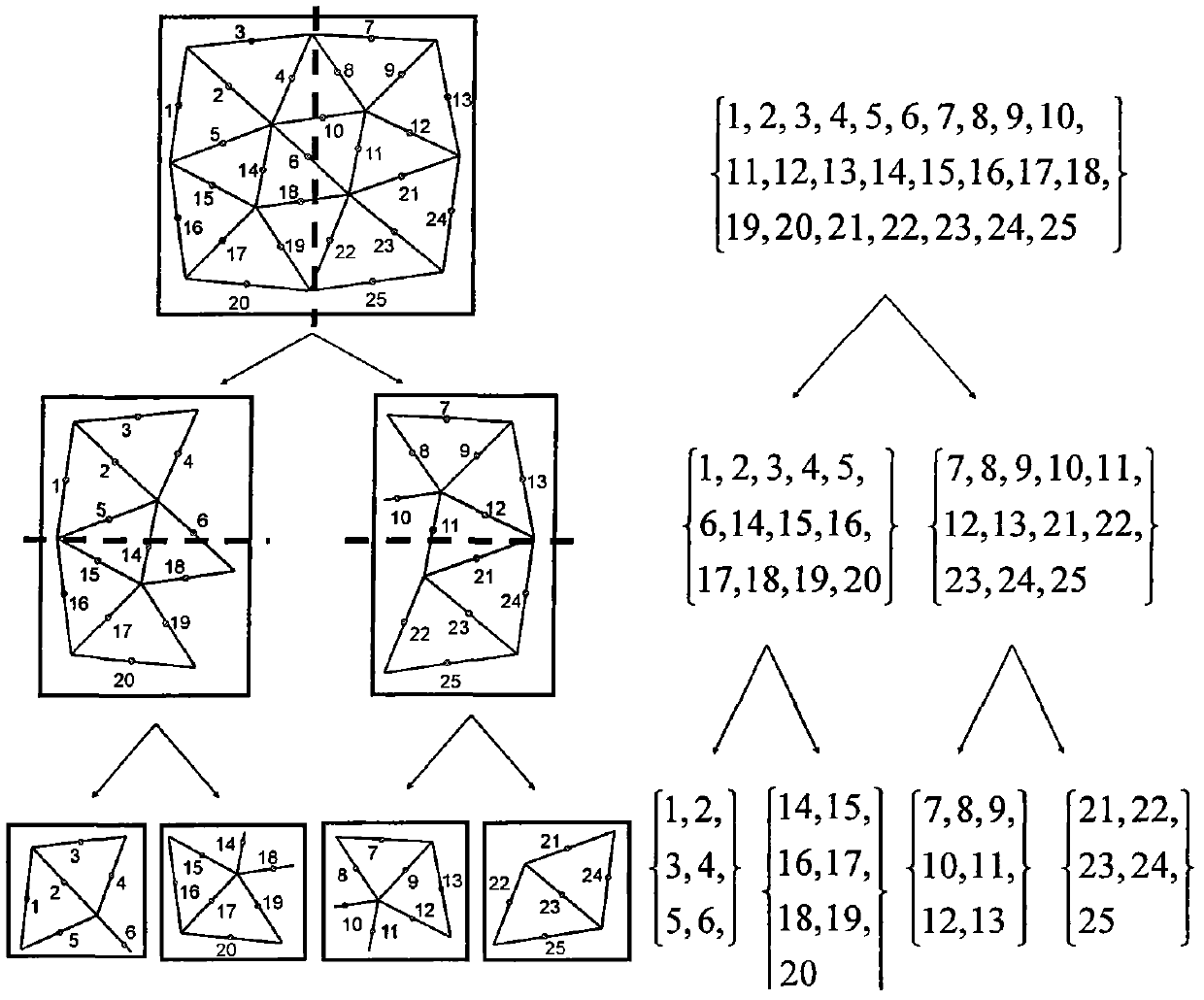
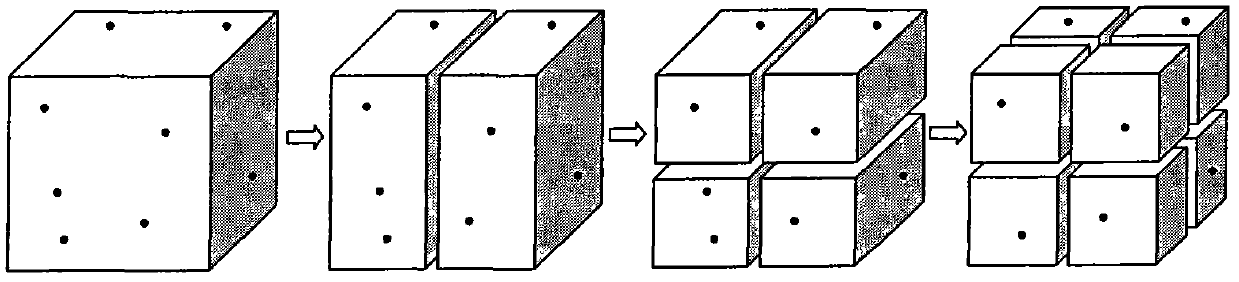
[0028] In the following, in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, an electromagnetic simulation analysis of a microstrip electromagnetic band gap structure (EBG) is taken as an example to further describe the specific steps of the present invention in detail.
[0029] According to the invention figure 1 The specific steps for electromagnetic simulation of the microstrip electromagnetic bandgap structure (EBG) are as follows:
[0030] The first step is to use ANSYS software to establish a three-dimensional geometric model of the microstrip electromagnetic bandgap structure (EBG). In order to cut off the entire simulation area, set a cutoff boundary (such as a perfectly matched layer) at both ends of the microstrip electromagnetic bandgap structure, and then The different materials in the model are numbered separately. The purpose of numbering is to give different properties to the tetrahedral elements in different materials in the time-domain finite element method. Finally, the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com