Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
187results about "Redundant array of inexpensive disk systems" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
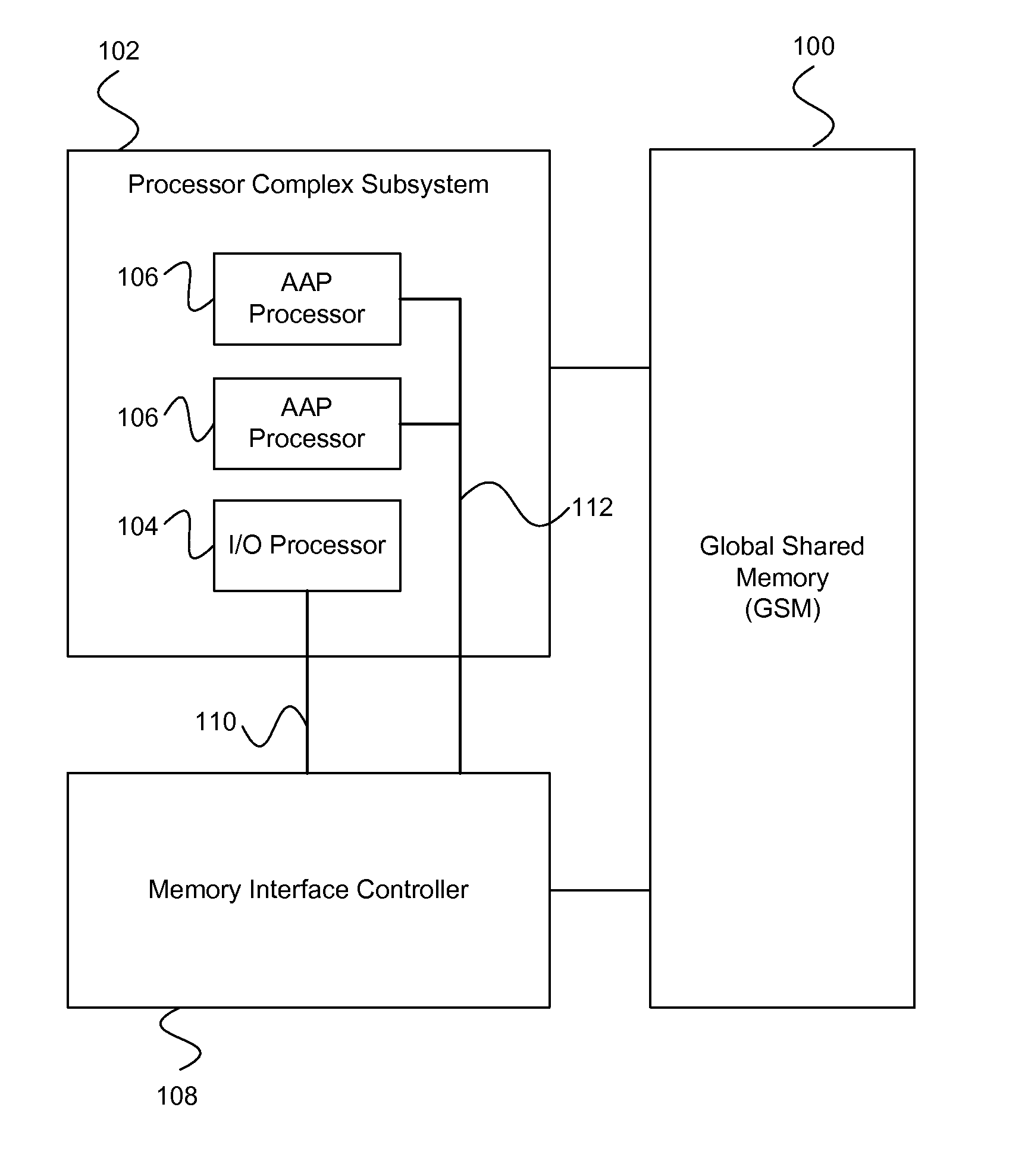
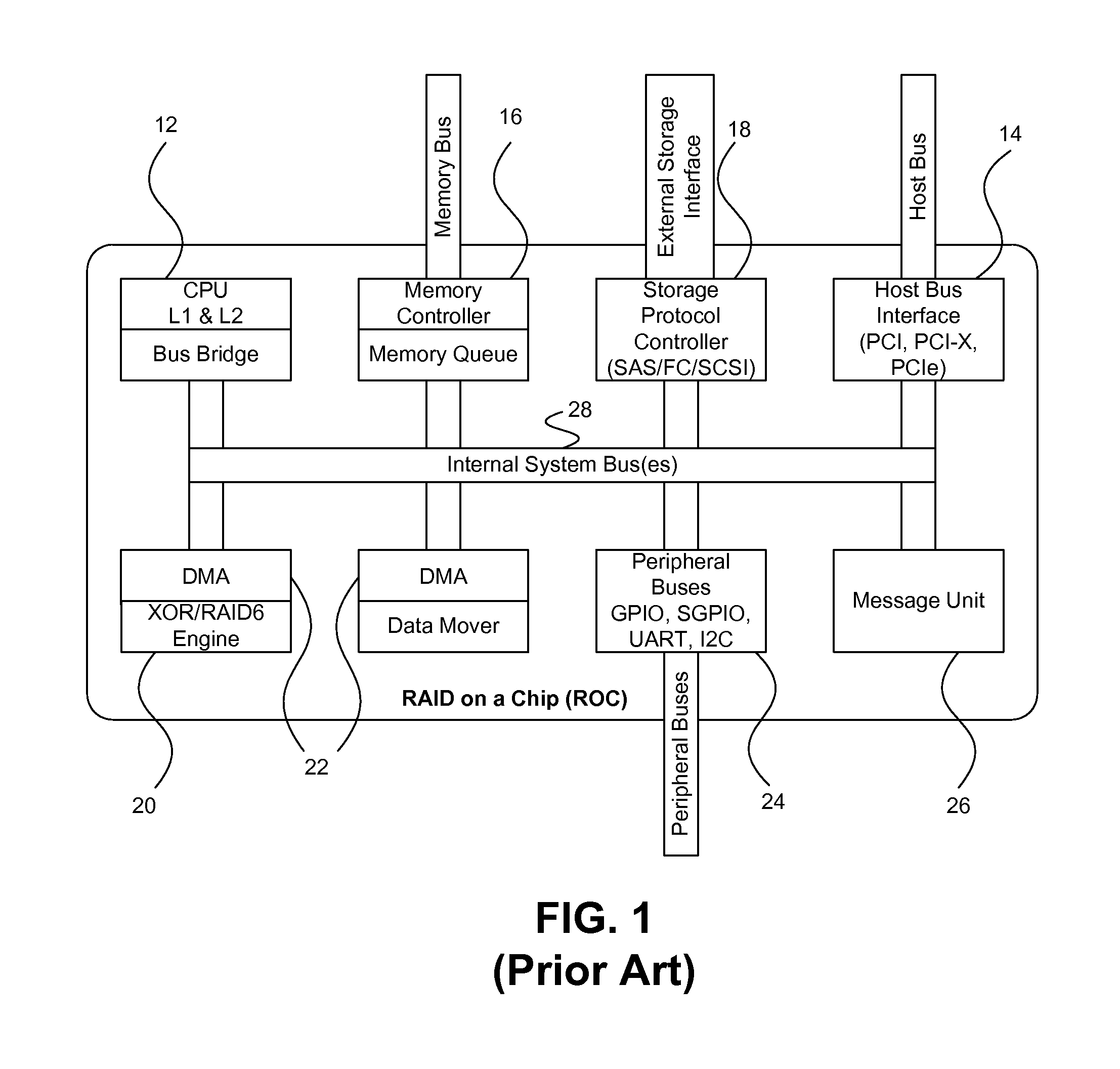
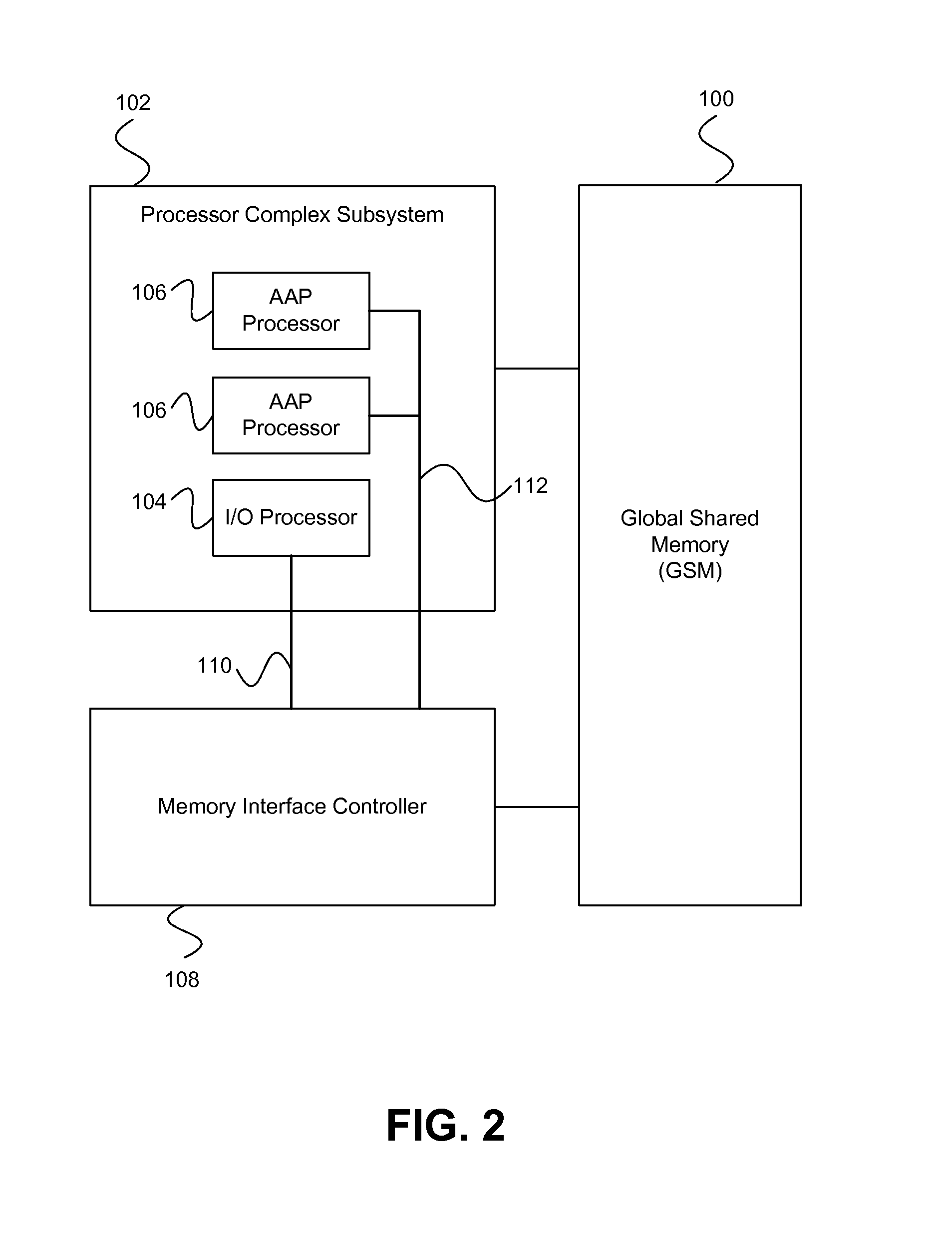
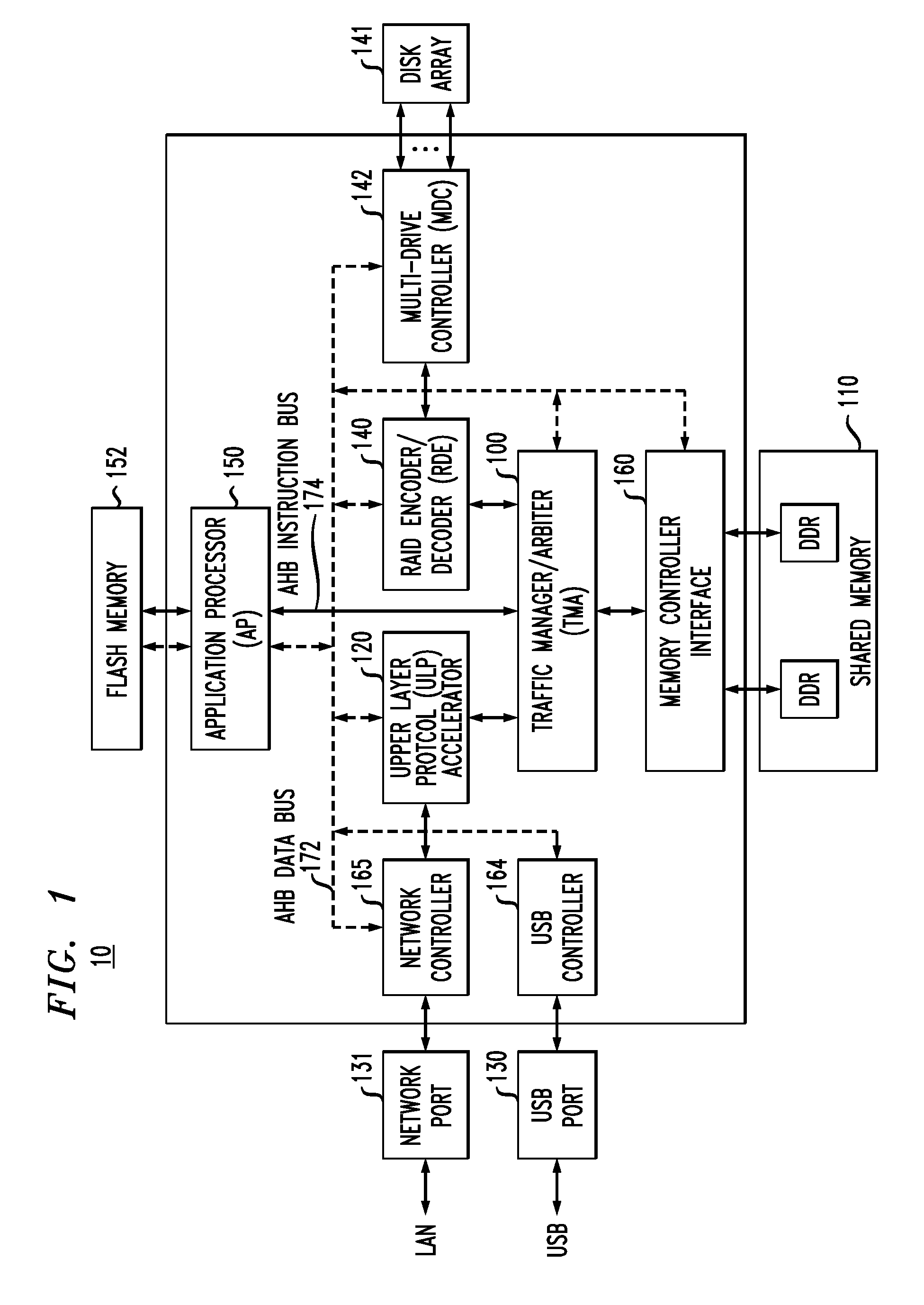
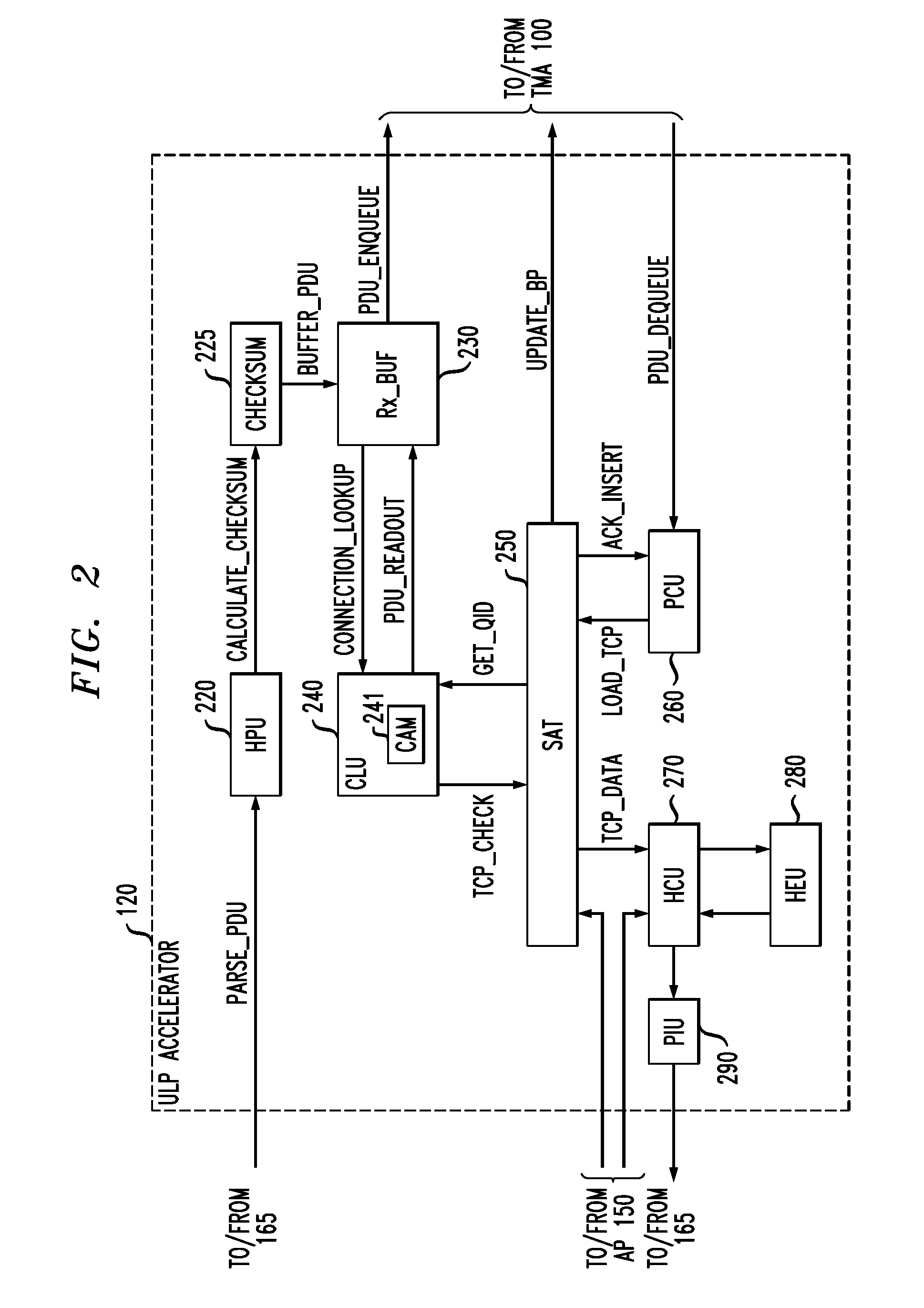
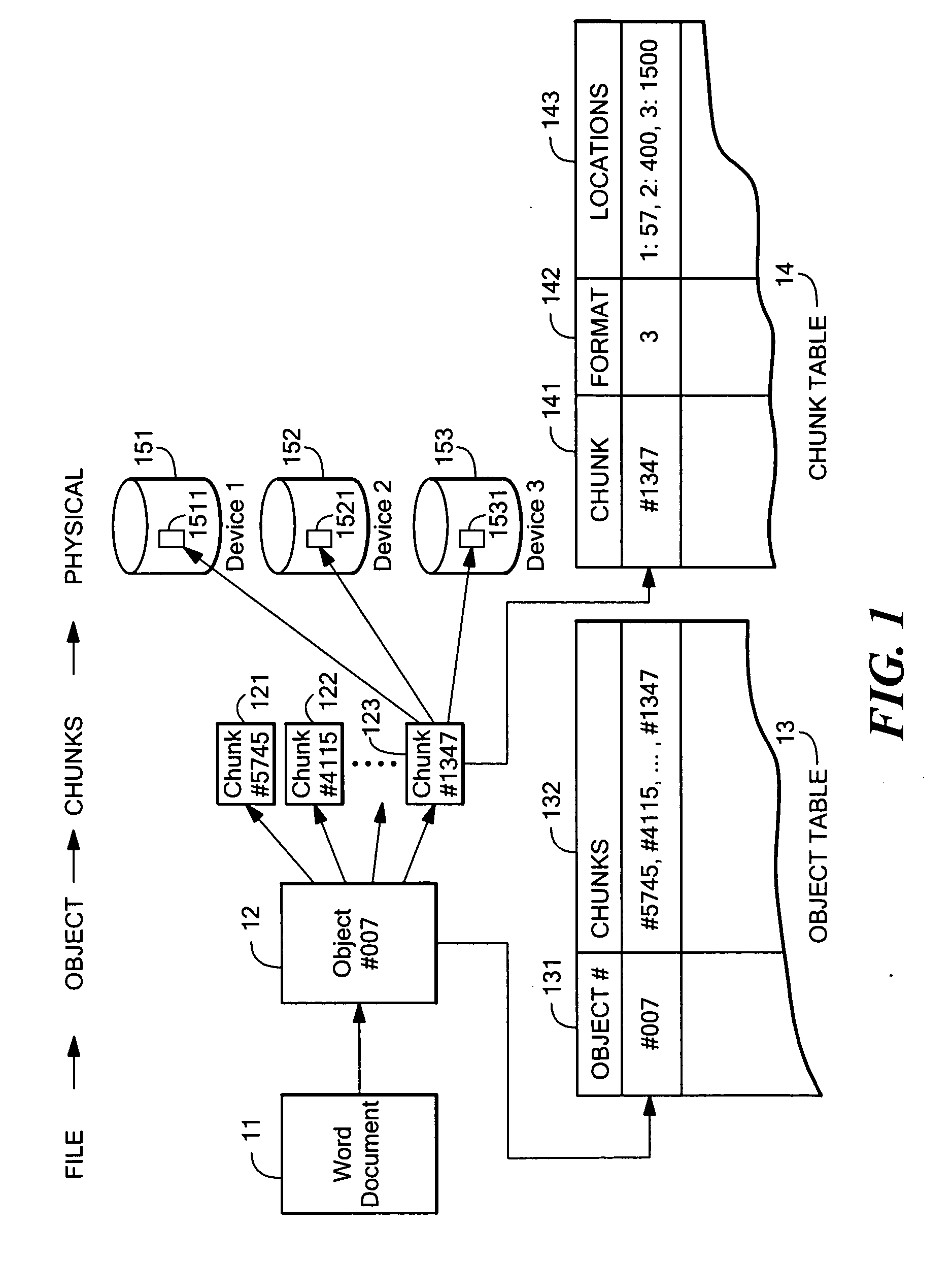
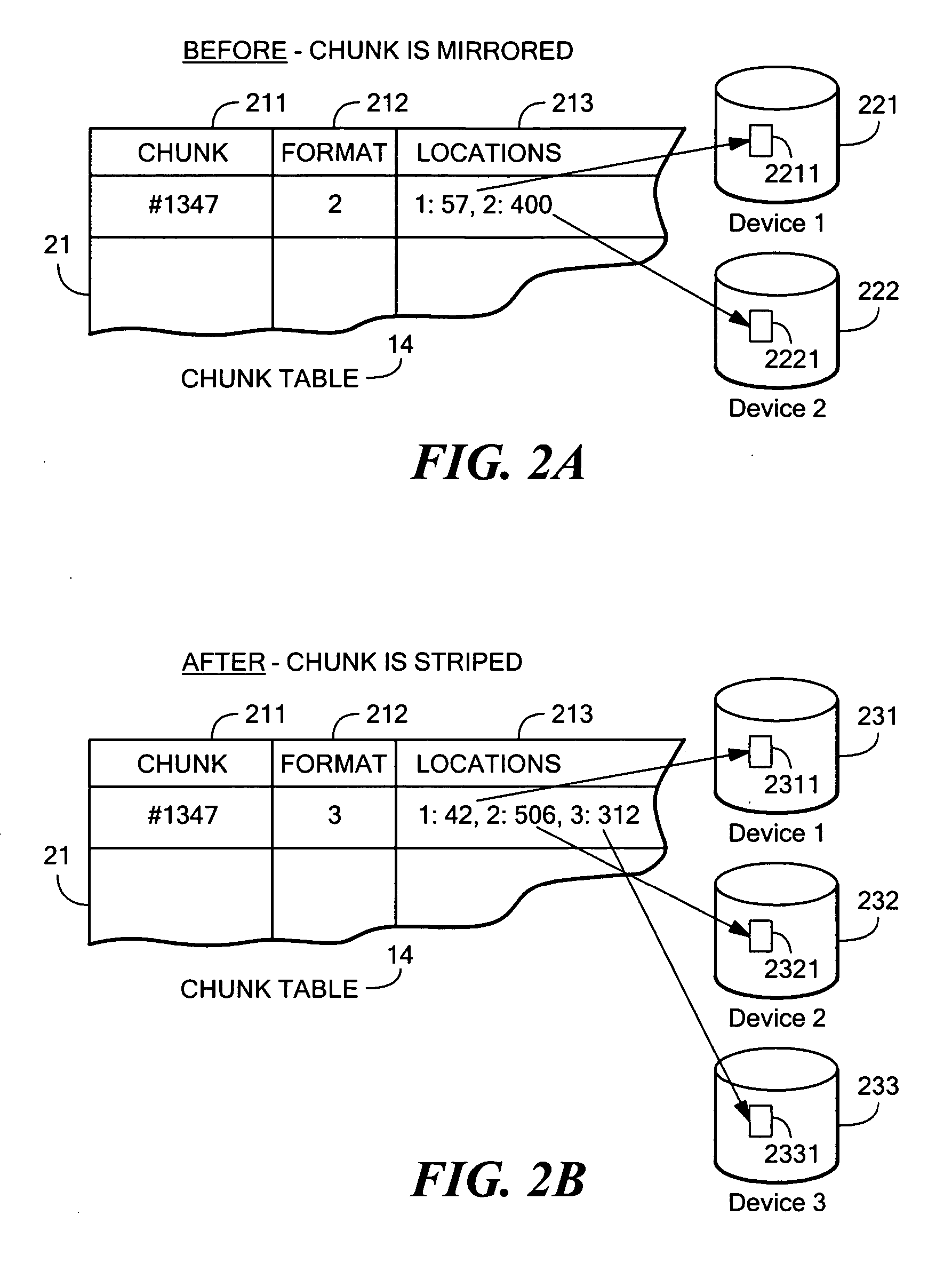
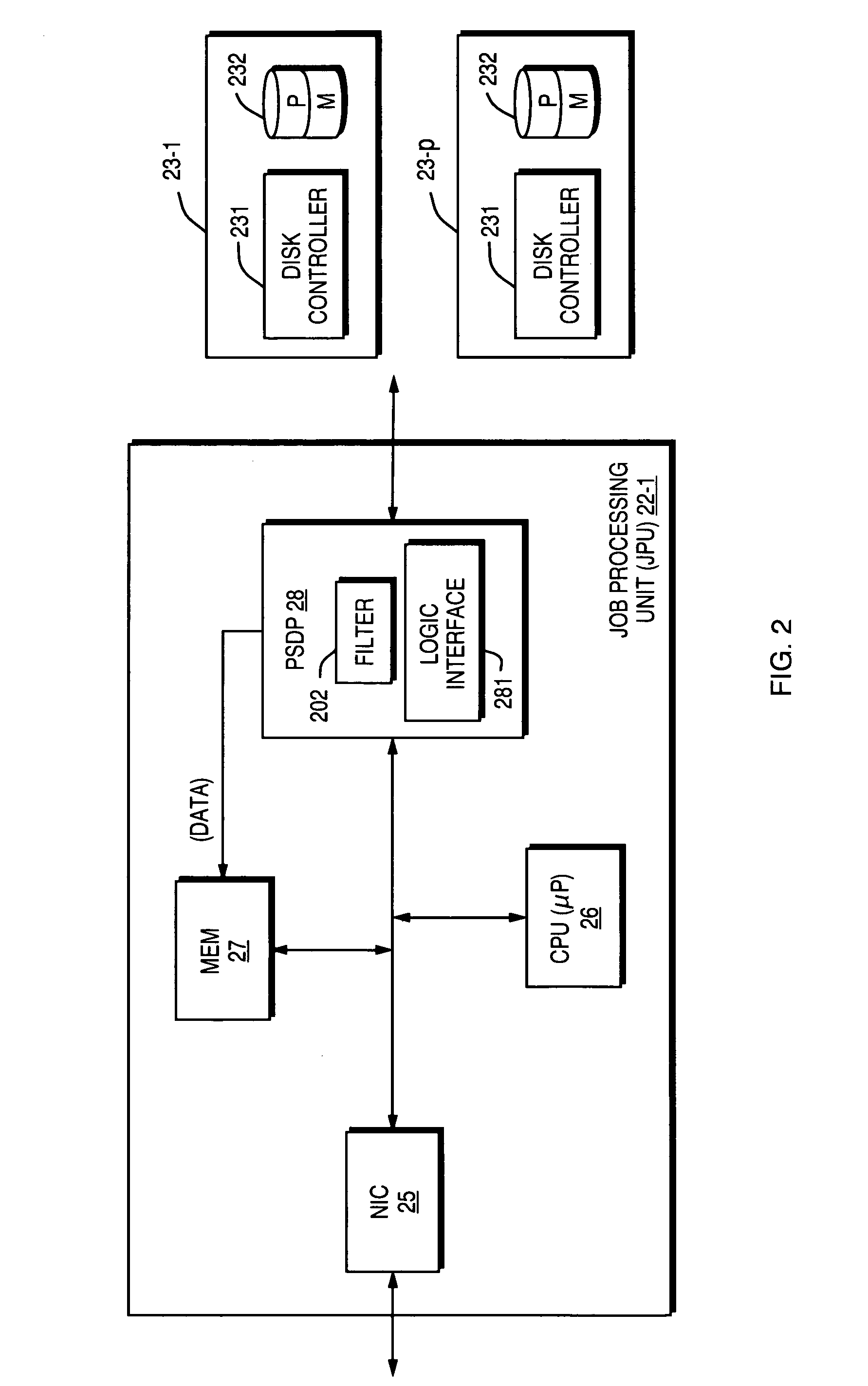
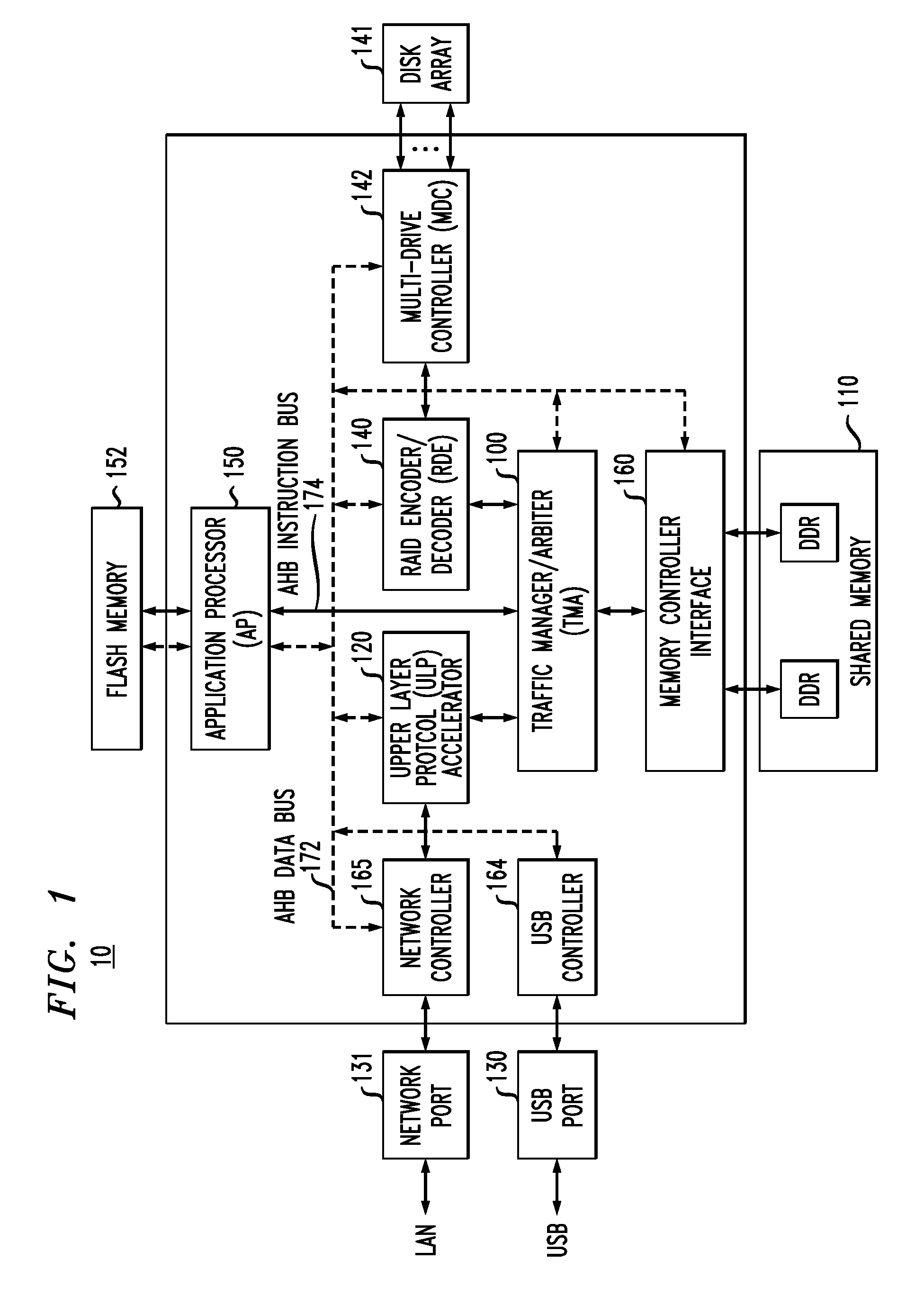
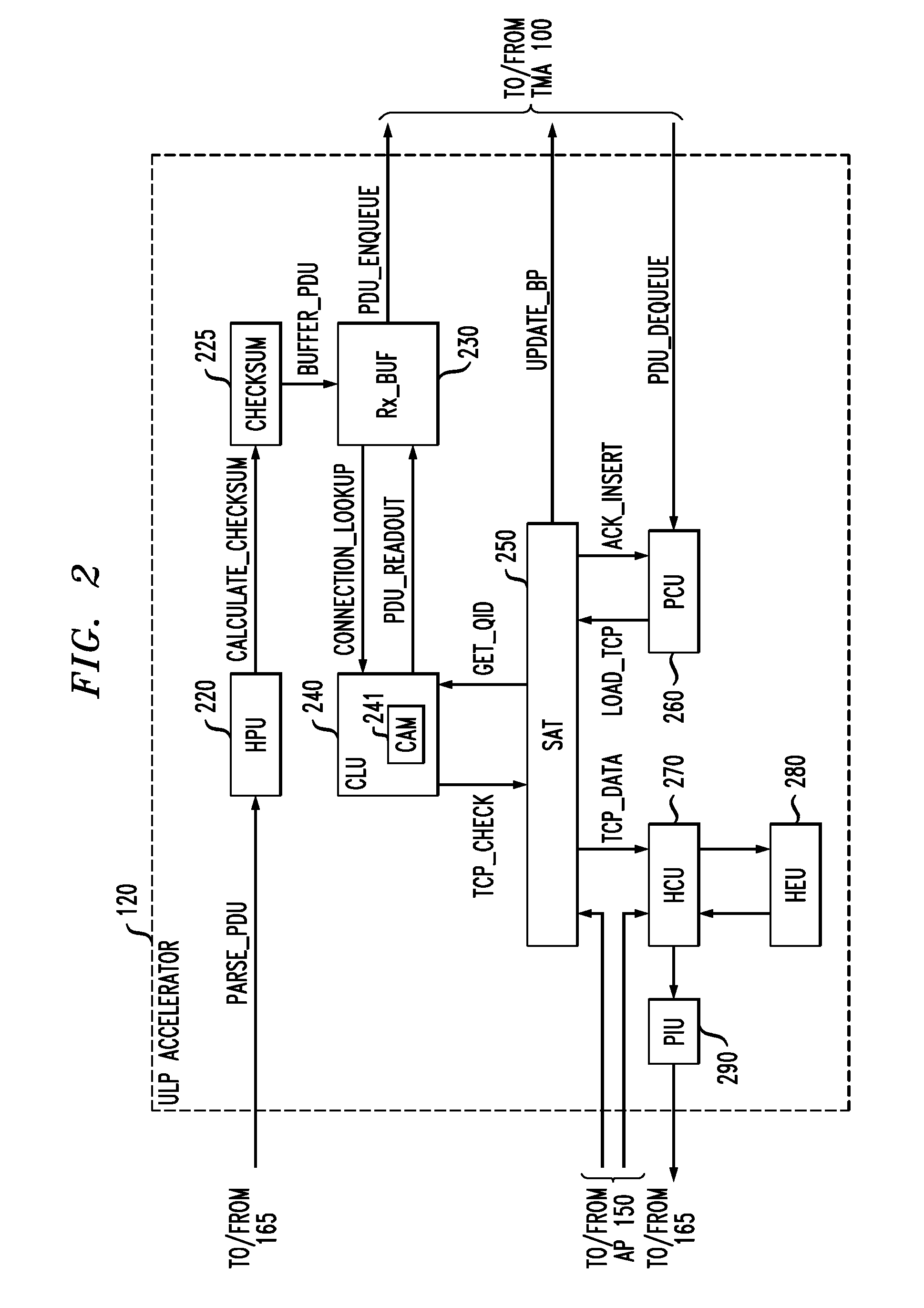
On-chip shared memory based device architecture
ActiveUS7743191B1Reduce disadvantagesLow costRedundant array of inexpensive disk systemsRecord information storageExtensibilityRAID
A method and architecture are provided for SOC (System on a Chip) devices for RAID processing, which is commonly referred as RAID-on-a-Chip (ROC). The architecture utilizes a shared memory structure as interconnect mechanism among hardware components, CPUs and software entities. The shared memory structure provides a common scratchpad buffer space for holding data that is processed by the various entities, provides interconnection for process / engine communications, and provides a queue for message passing using a common communication method that is agnostic to whether the engines are implemented in hardware or software. A plurality of hardware engines are supported as masters of the shared memory. The architectures provide superior throughput performance, flexibility in software / hardware co-design, scalability of both functionality and performance, and support a very simple abstracted parallel programming model for parallel processing.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS
Filesystem-Aware Block Storage System, Apparatus, and Method
ActiveUS20070266037A1Improve accessibilityImprove storage efficiencyDigital data processing detailsError detection/correctionOperational systemFile system
A filesystem-aware storage system locates and analyzes host filesystem data structures in order to determine storage usage of the host filesystem. To this end, the storage system might locate an operating system partition, parse the operating system partion to locate its data structures, and parse the operating system data structures to locate the host filesystem data structures. The storage system manages data storage based on the storage usage of the host file system. The storage system can use the storage usage information to identify storage areas that are no longer being used by the host filesystem and reclaim those areas for additional data storage capacity. Also, the storage system can identify the types of data stored by the host filesystem and manage data storage based on the data types, such as selecting a storage layout and / or an encoding scheme for the data based on the data type.
Owner:STORCENTRIC DIP LENDER LLC
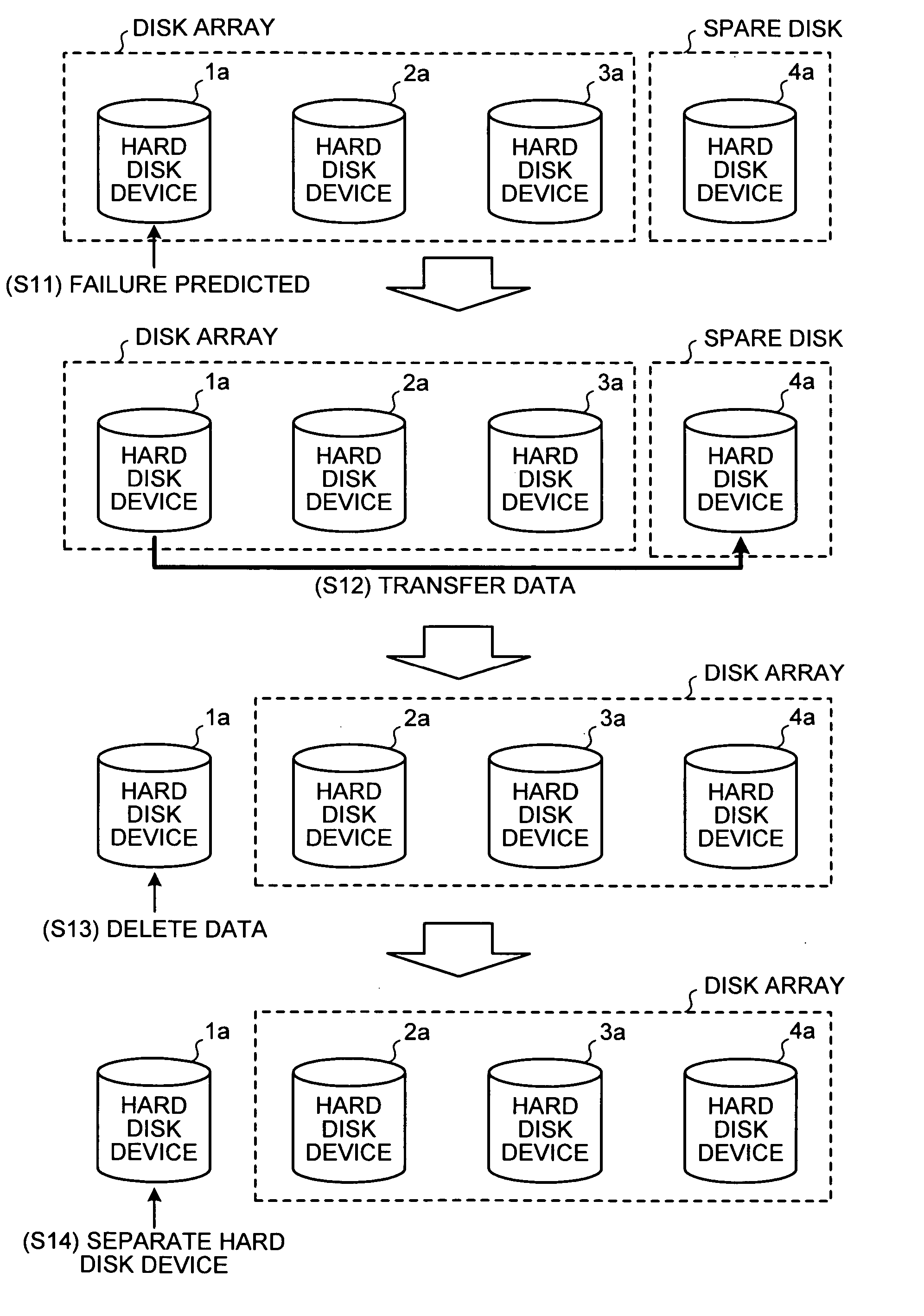
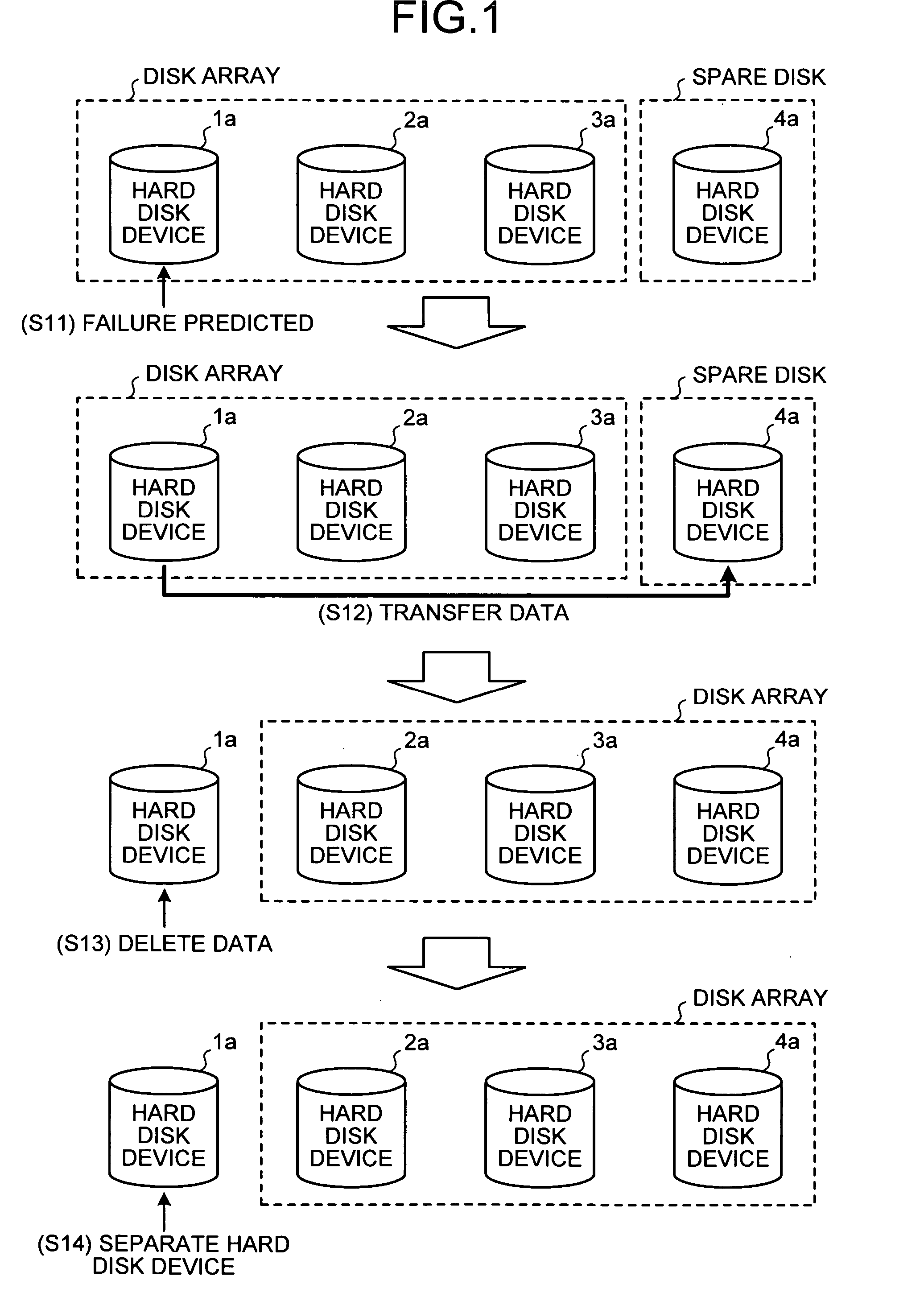
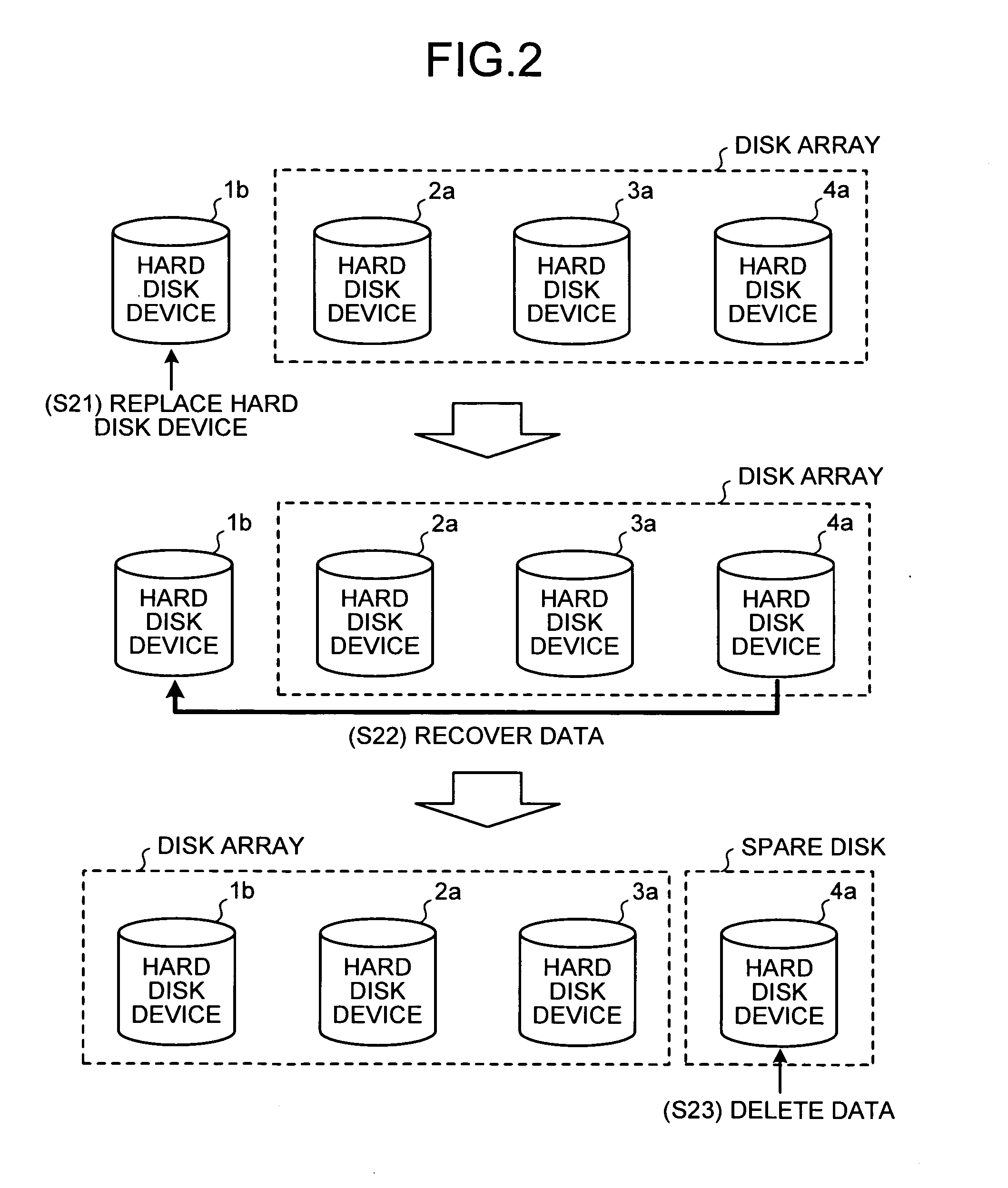
Disk array apparatus and disk-array control method
InactiveUS20070171562A1Solve problemsRedundant array of inexpensive disk systemsFilamentary/web record carriersData shippingDisk array
A failure predicting unit predicts a failure in a hard disk device that forms a disk array. A data transferring unit transfers data from a failure-predicted hard disk device for which the failure is predicted by the failure predicting unit to a spare disk. A data deleting unit deletes the data from the failure-predicted hard disk device after the data transferring unit completes transferring the data.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
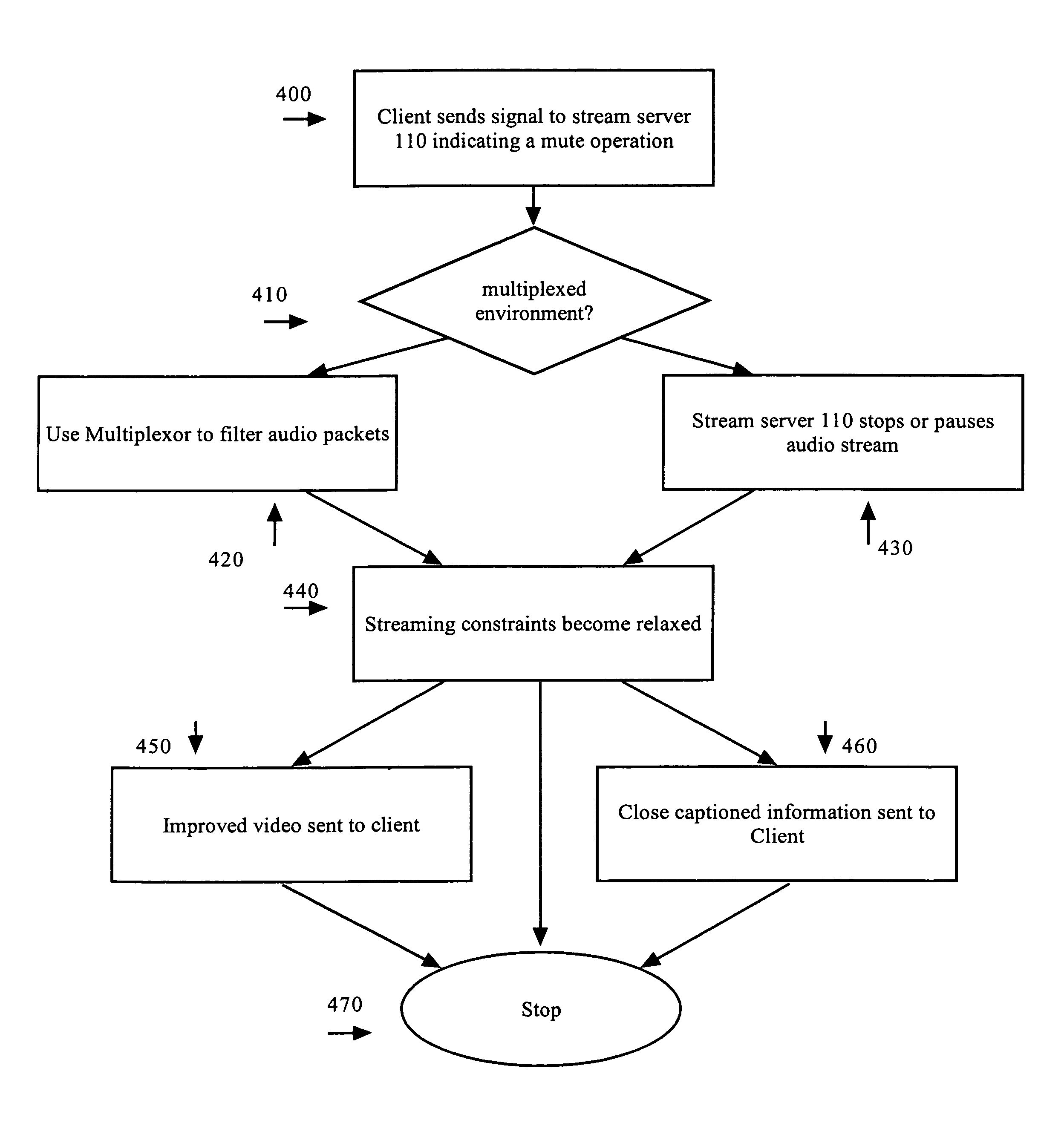
Dynamic quality adjustment based on changing streaming constraints
InactiveUS7058721B1Quality improvementReduce constraintsDisc-shaped record carriersRedundant array of inexpensive disk systemsQuality adjustmentSlow motion
A method and apparatus for dynamic quality adjustment based on changing streaming constraints is provided. According to one aspect of the present invention, a video stream is sent to a client according to a set of streaming constraints. At least a subset of the video information in the video stream is sent from a first source. Next, a signal is received indicating a relaxation of streaming constraints corresponding to the video stream. In one embodiment, the signal is a freeze frame signal. In another embodiment, the signal is a slow motion signal. In response to the signal, a set of improved quality video information from a second source is accessed and sent to the client. According to one embodiment, the set of improved quality video information comprises a still image. According to another embodiment, the set of improved quality video information comprises a set of preprocessed video information ready to be streamed. As a result of the techniques described herein, an improved quality visual image is available for presentation on the client and, consequently, when a viewer requests a presentation rate that reduces the streaming constraints on a video streaming service, the improved quality video information may be sent using the freed-up portion of the bandwidth previously allocated to the client.
Owner:ARRIS SOLUTIONS +1
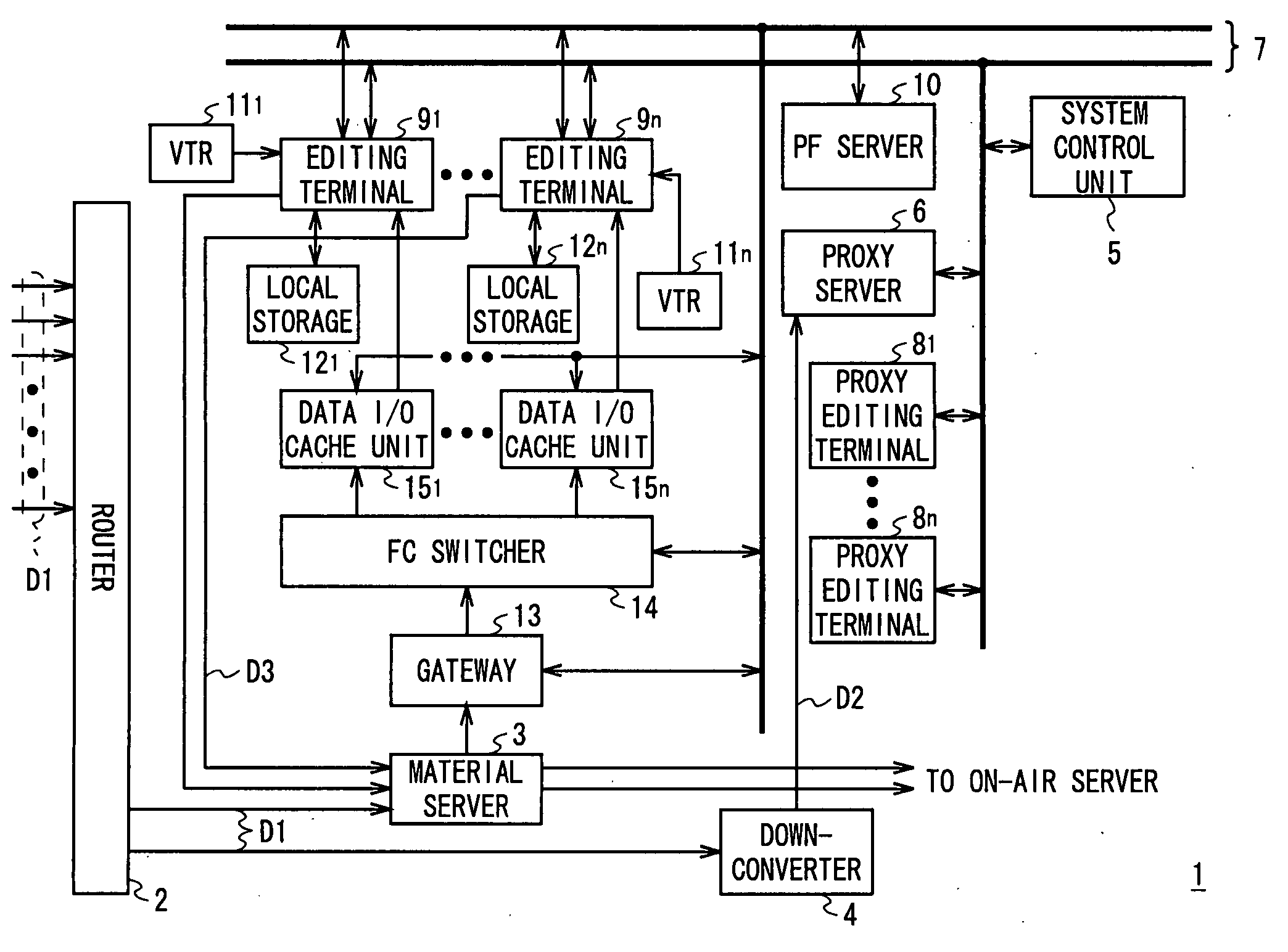
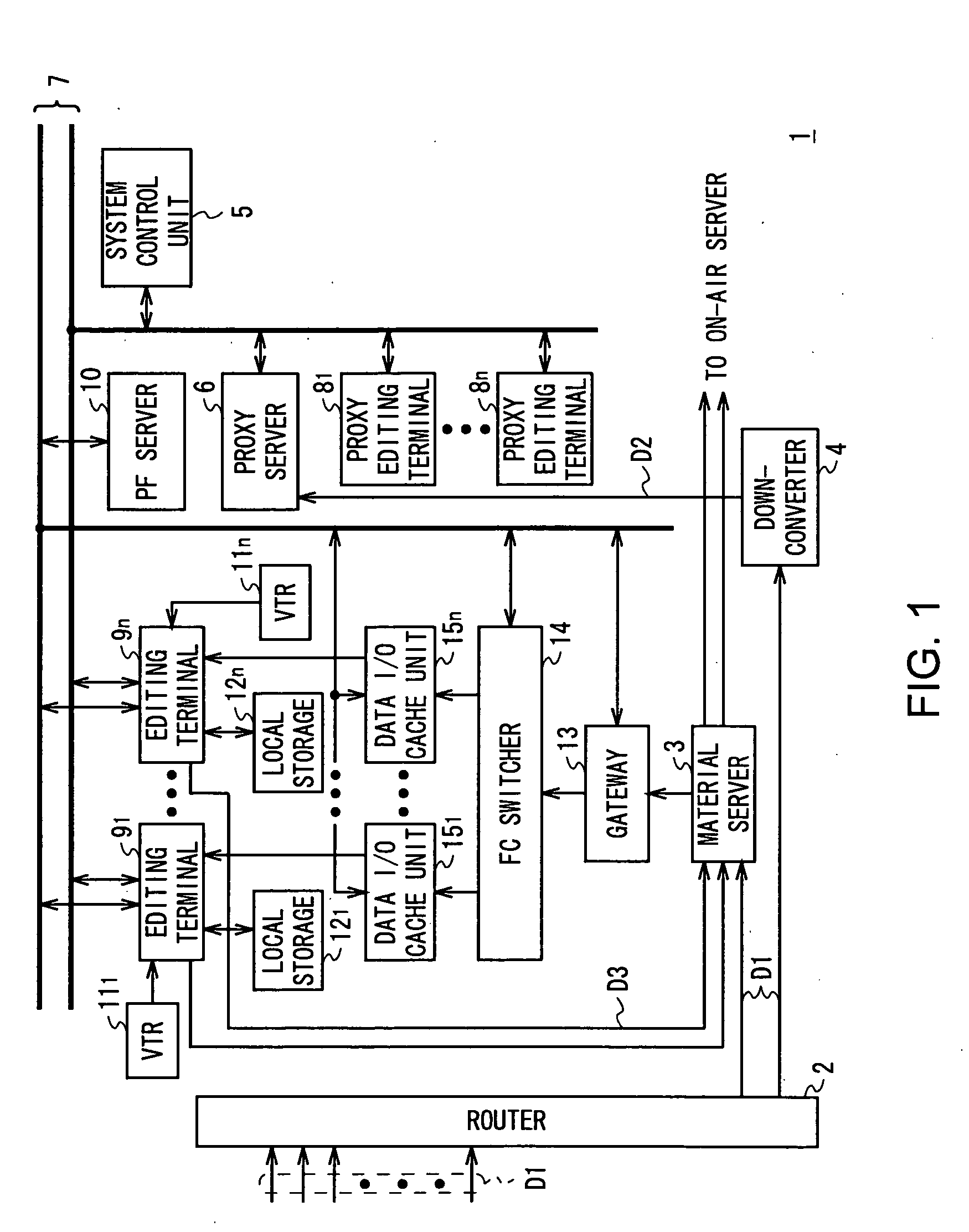
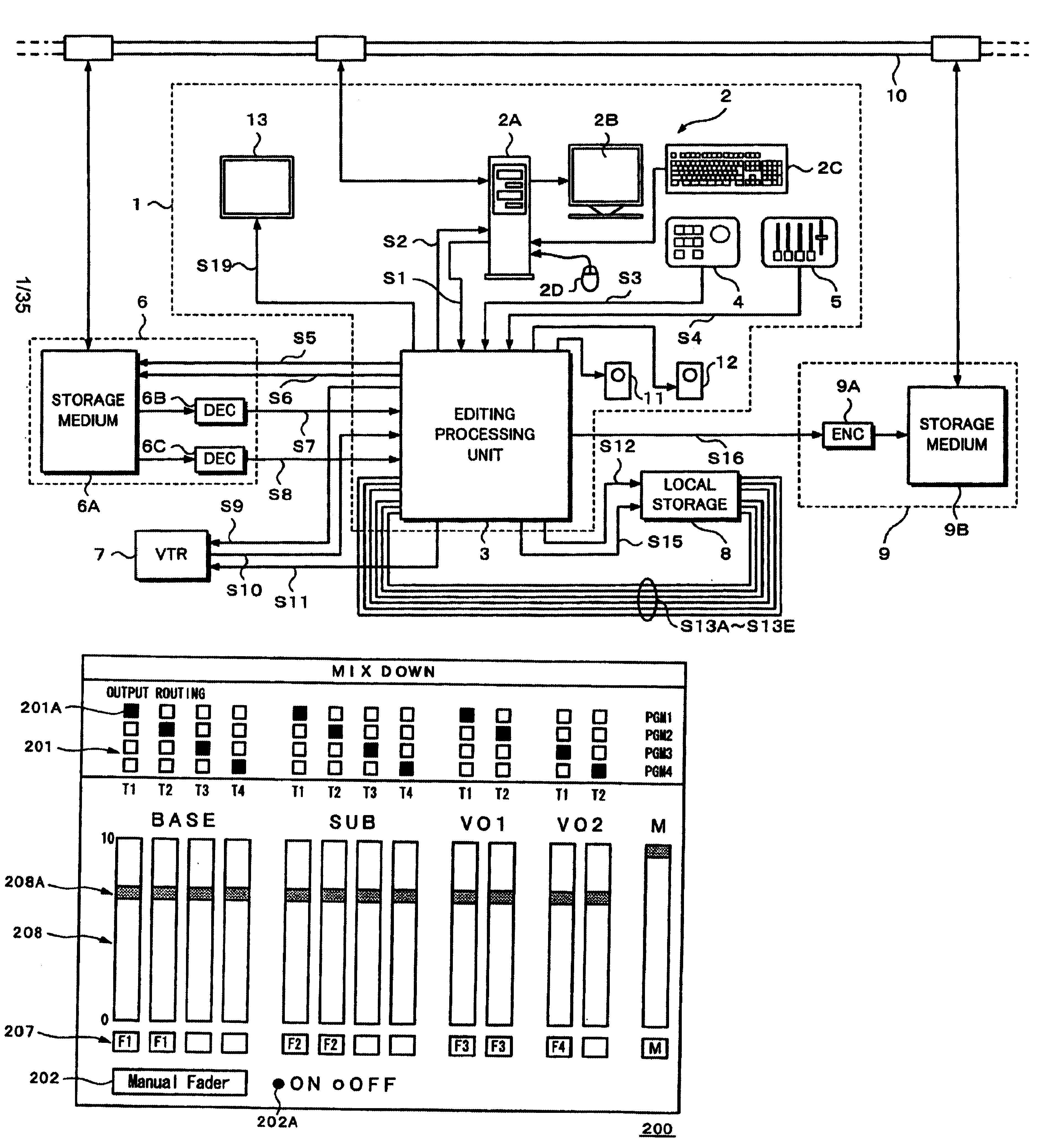
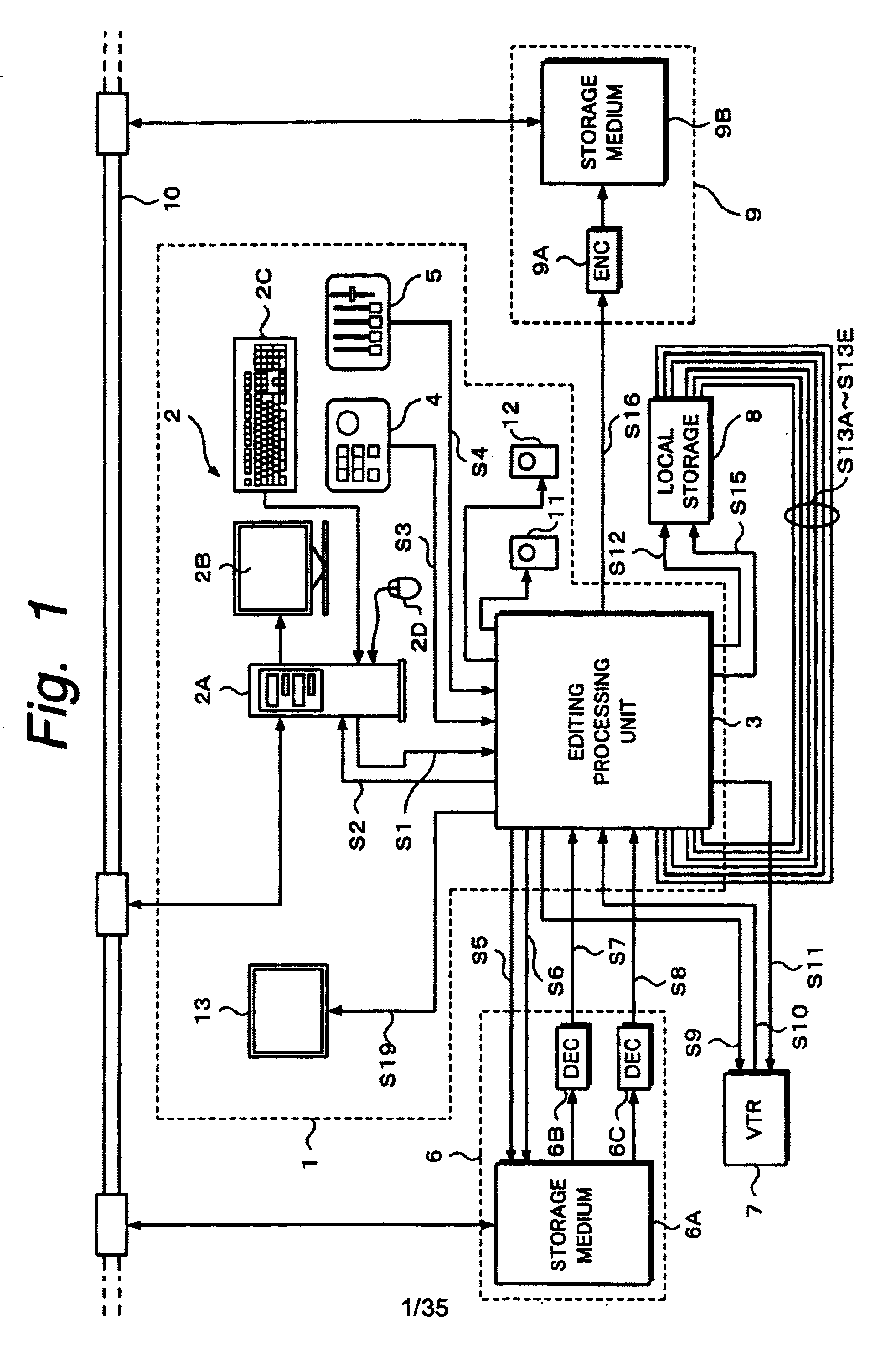
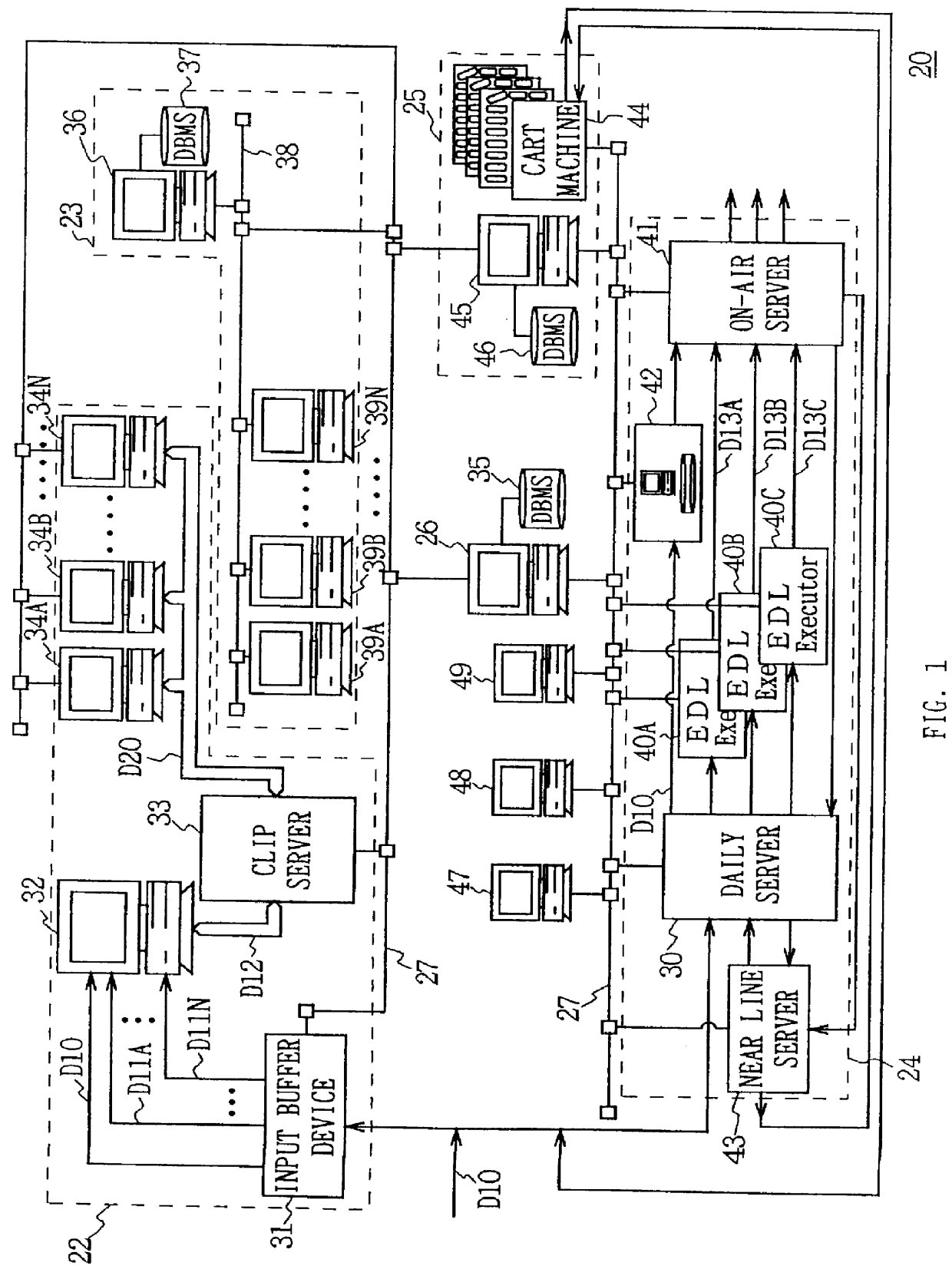
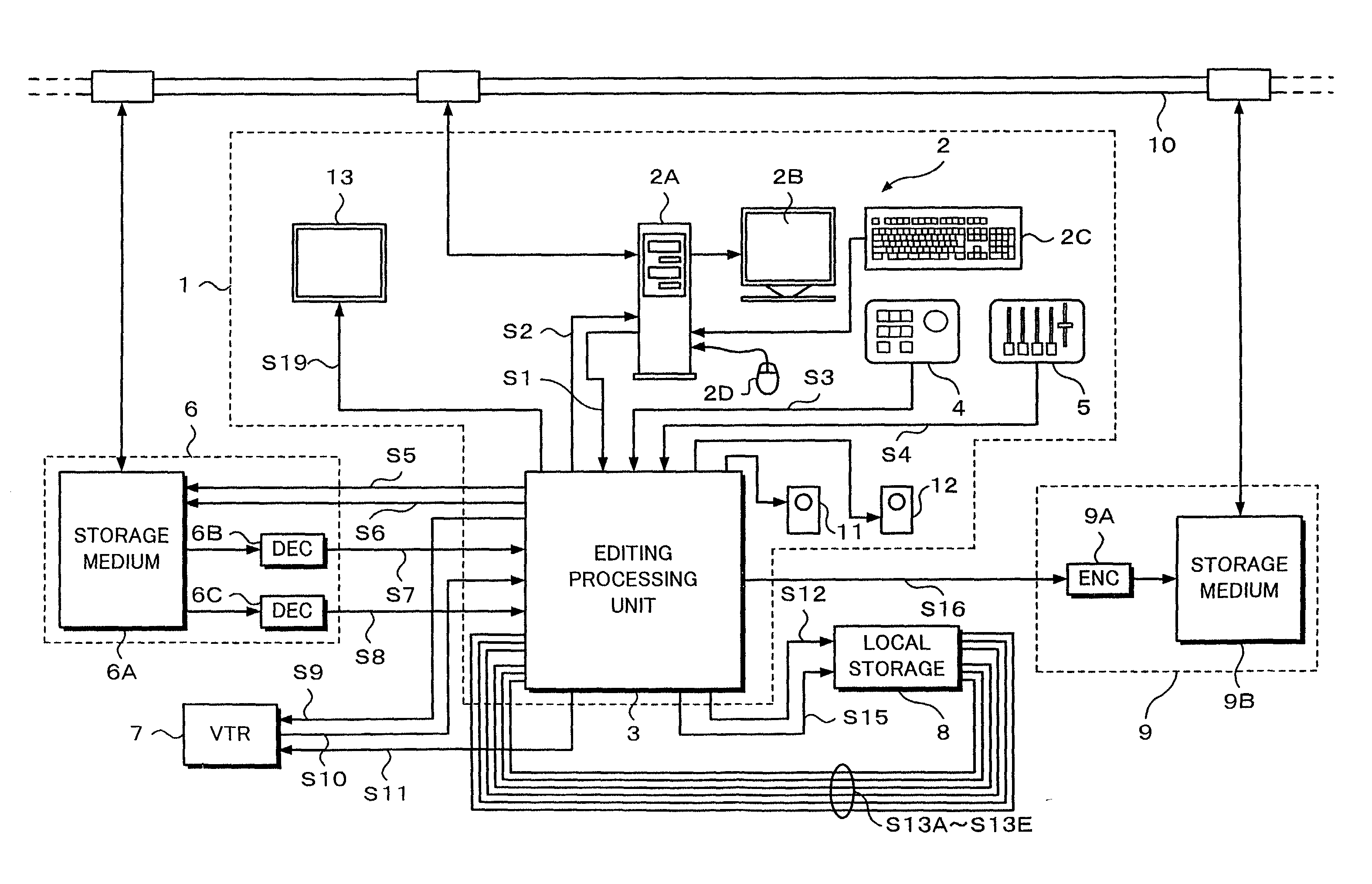
Editing system and control method thereof
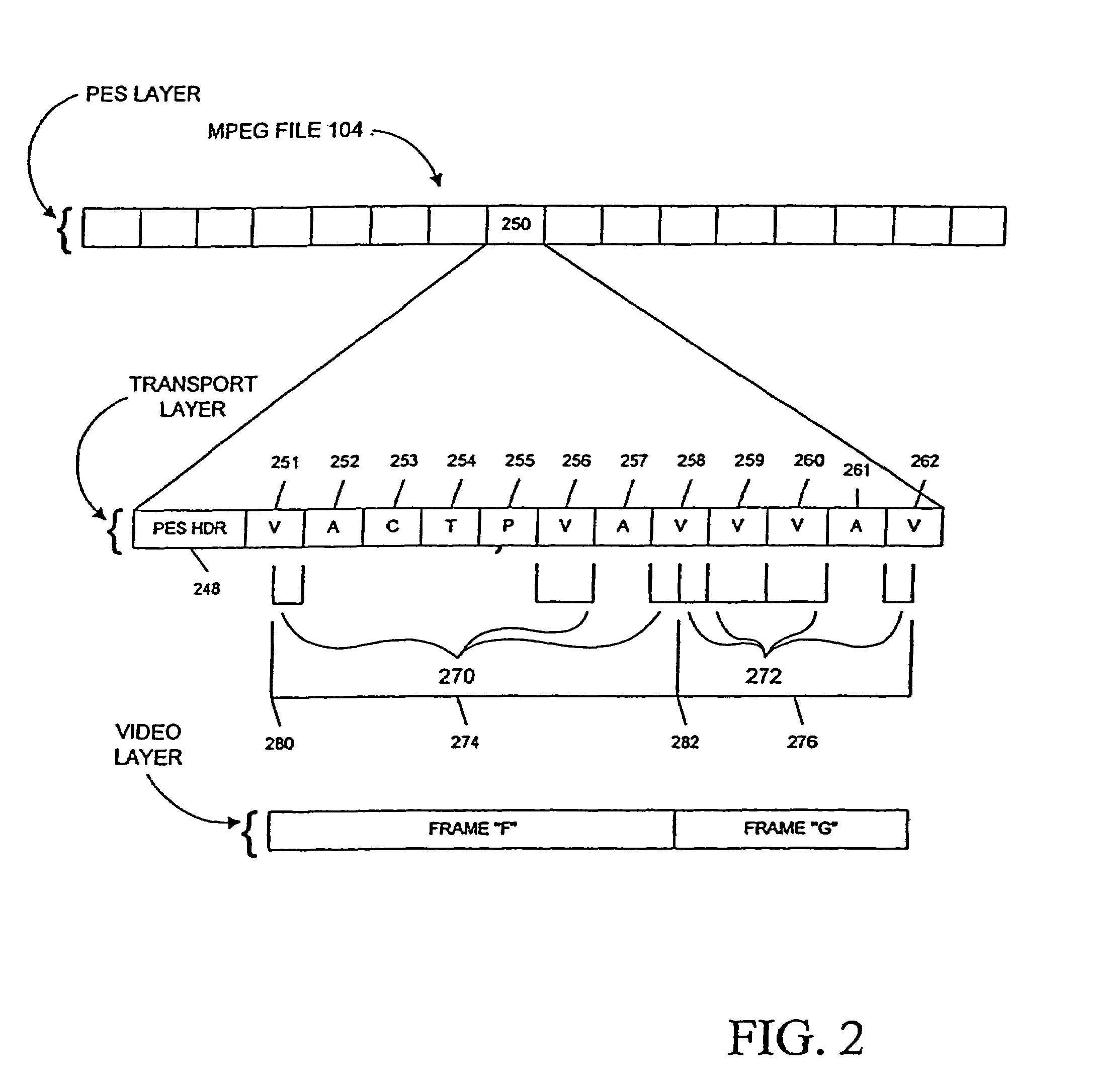
ActiveUS20050025454A1Improve work efficiencyShorten the timeTelevision system detailsRedundant array of inexpensive disk systemsComputer graphics (images)Image resolution
This invention realizes an editing system and control method thereof capable of significantly improving working efficiency of editing work. A proxy editing terminal device creates an EDL with low-resolution video / audio data, resulting in reducing time to create the EDL. Further, the low-resolution video / audio data and high-resolution video / audio data having the same contents and different resolutions are previously stored, so that the creation of a final edit list with the high-resolution video / audio data based on the EDL can be started in a short time after the EDL is created with the low-resolution video / audio data. Thus working efficiency of the editing work can be significantly reduced with reducing time to create the EDL and the final edit list.
Owner:SONY CORP
Filesystem-aware block storage system, apparatus, and method
ActiveUS7873782B2Improve accessibilityImprove storage efficiencyRedundant array of inexpensive disk systemsError detection/correctionOperational systemFile system
A filesystem-aware storage system locates and analyzes host filesystem data structures in order to determine storage usage of the host filesystem. To this end, the storage system might locate an operating system partition, parse the operating system partion to locate its data structures, and parse the operating system data structures to locate the host filesystem data structures. The storage system manages data storage based on the storage usage of the host file system. The storage system can use the storage usage information to identify storage areas that are no longer being used by the host filesystem and reclaim those areas for additional data storage capacity. Also, the storage system can identify the types of data stored by the host filesystem and manage data storage based on the data types, such as selecting a storage layout and / or an encoding scheme for the data based on the data type.
Owner:STORCENTRIC DIP LENDER LLC
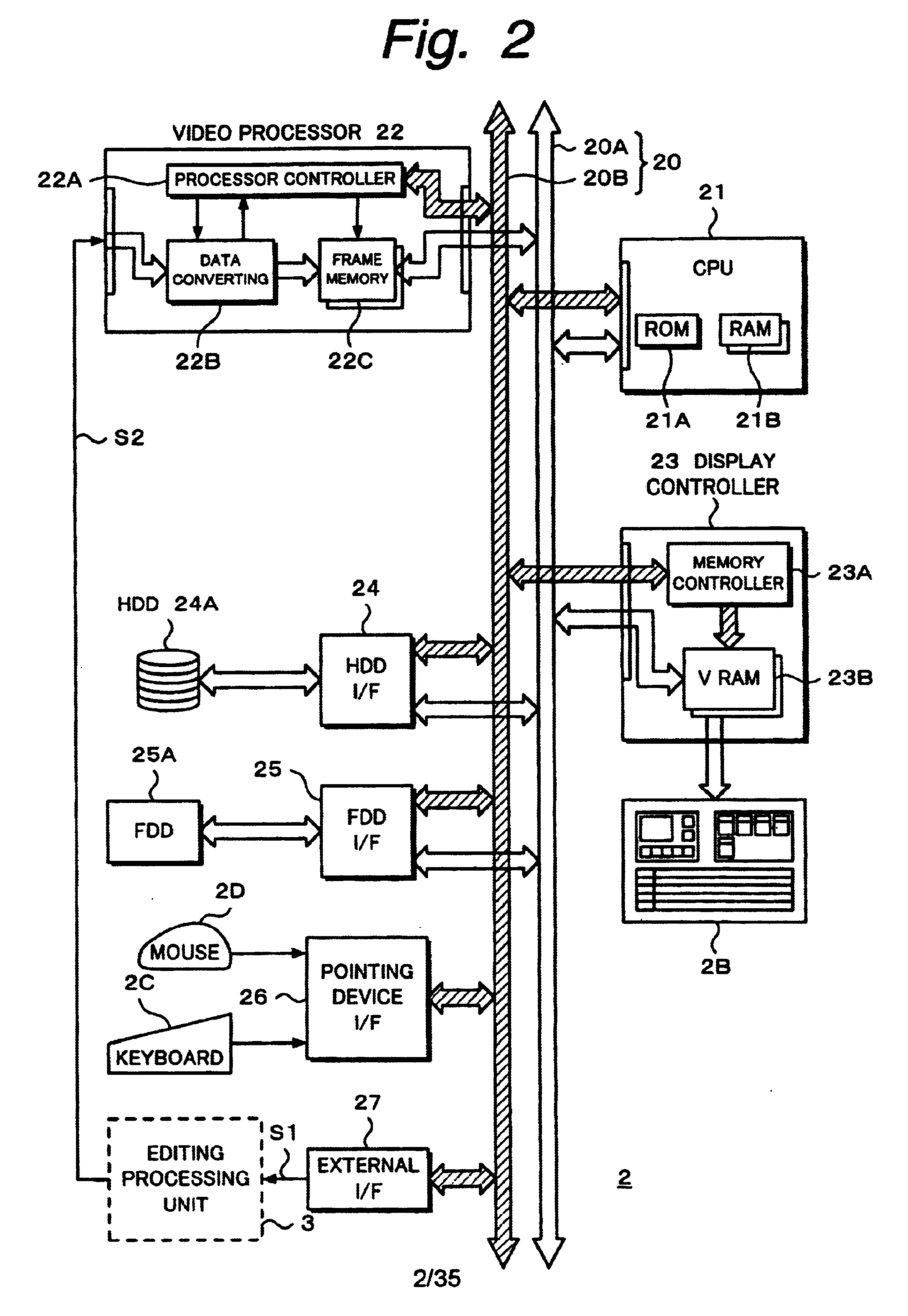
Editing device and editing method
InactiveUS6674955B2Secure performanceRemove background noiseTelevision system detailsRedundant array of inexpensive disk systemsComputer graphics (images)Source material
An editing apparatus comprises an editing processing unit for processing a video signal and an audio signal supplied as source materials, and a computer for controlling the editing processing unit, wherein the computer comprises a controlling means for displaying a viewer window, a log window, and a program window on a display of the computer, the viewer window allowing the editing operator to decide an edit point while viewing a video image of a source material so as to produce an event, the log window displaying a clip image corresponding to an event that is set on the viewer window, the program window allowing the editing operator to arrange a plurality of events on a time line in a desired order so as to produce a program list, and wherein the controlling means displays an icon that represents by what source device each event arranged on the time line is produced.
Owner:SONY CORP
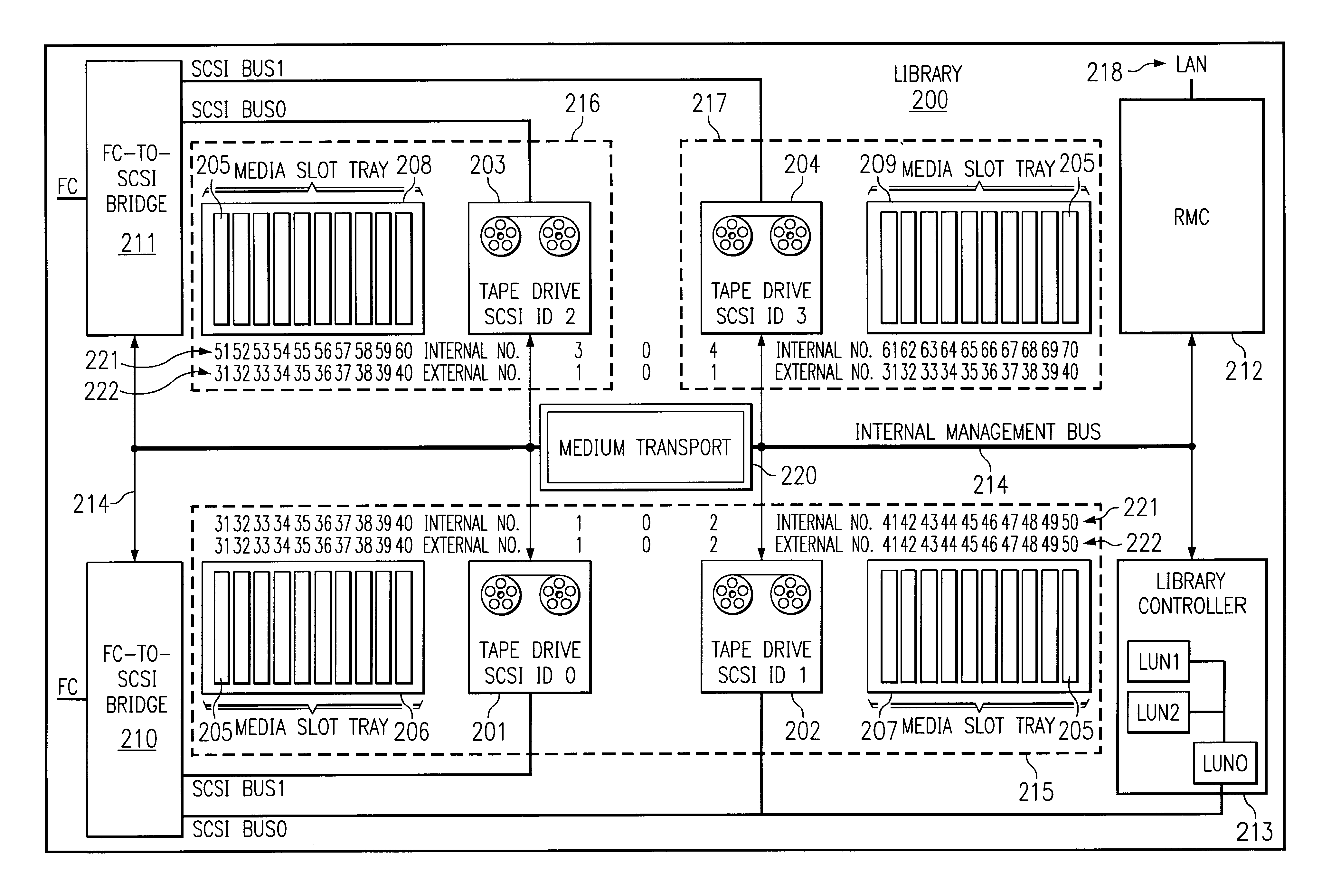
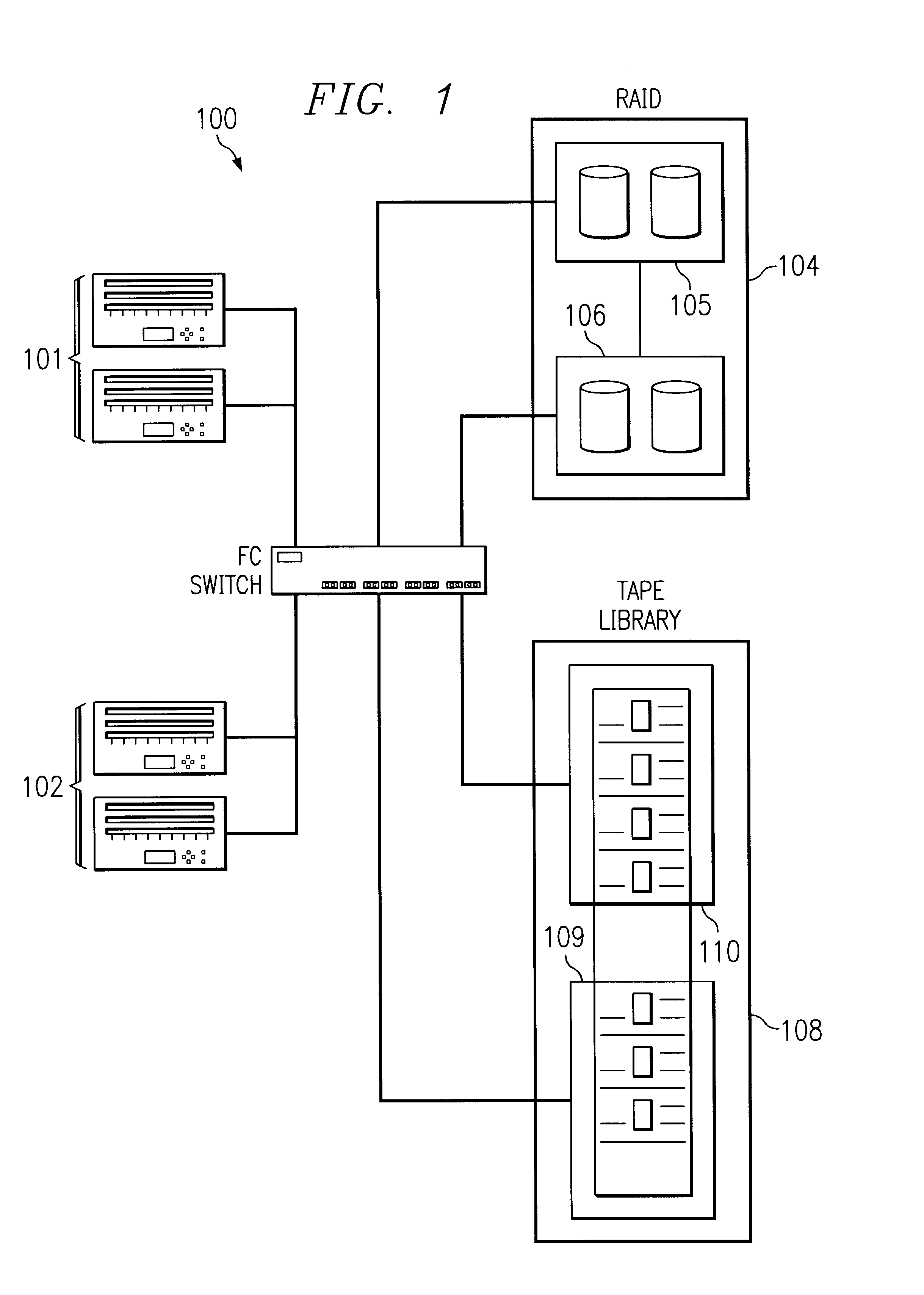
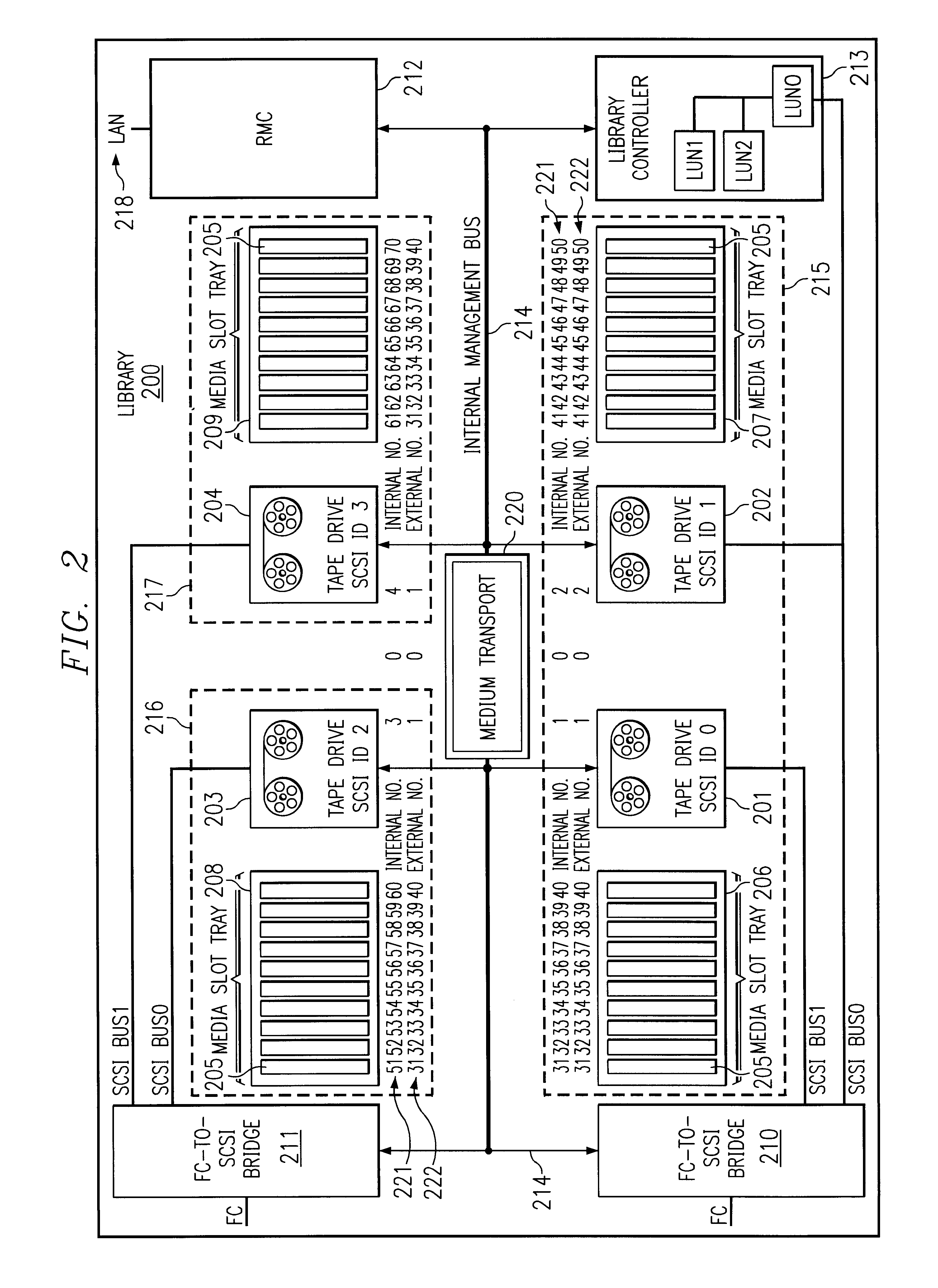
System and method for partitioning a storage area network associated data library employing element addresses
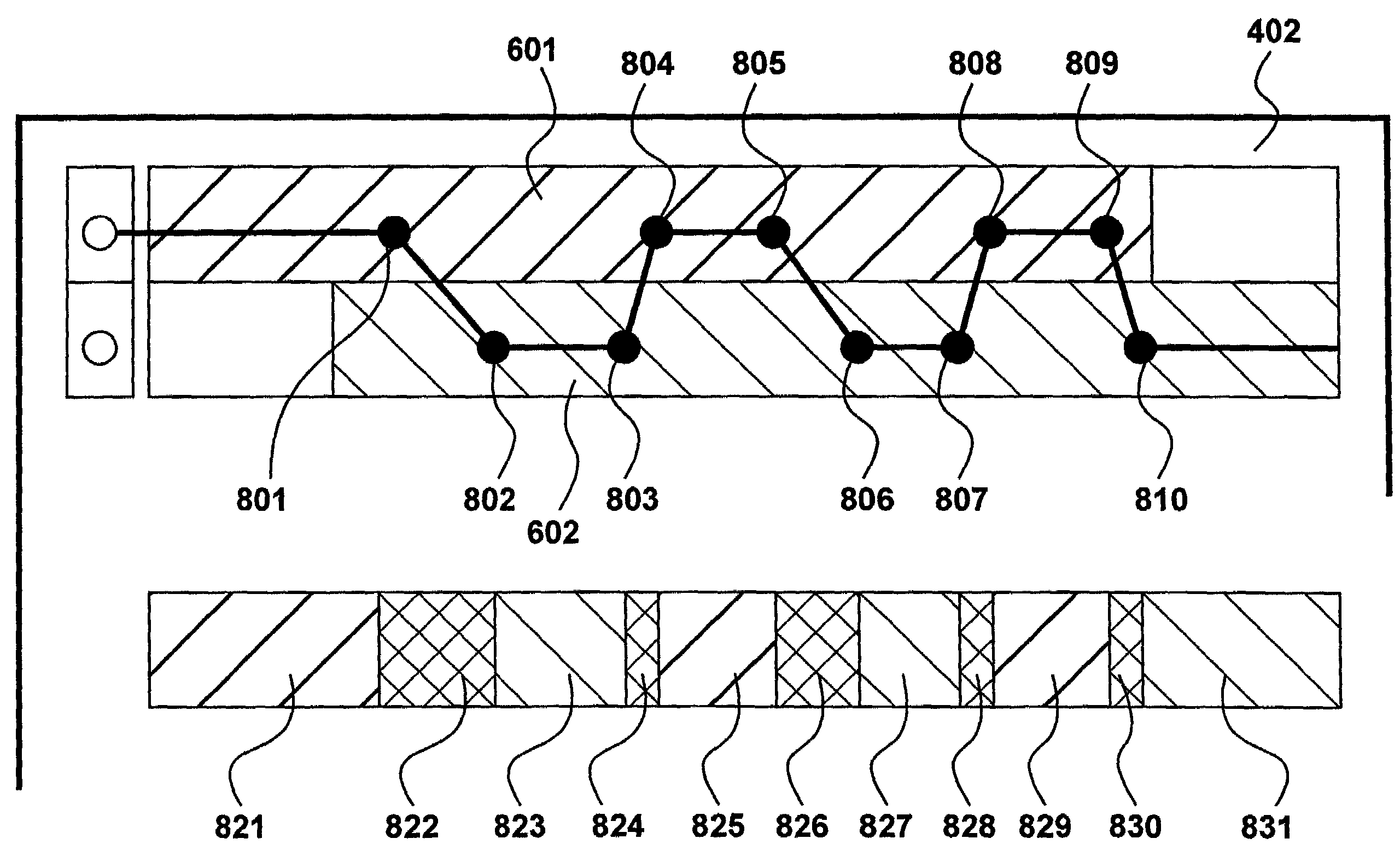
InactiveUS6839824B2Flat record carrier combinationsInput/output to record carriersStorage area networkLogic cell
A data library comprising a plurality of partitions, at least one data transfer element, each of the data transfer elements assigned to one of the partitions and assigned an internally unique element address, a plurality of data storage element slots, each of the slots assigned to a partition and assigned an internally unique element address, at least one media transport element shared by the partitions to move media between the slots and the at least one data transfer elements, the transport assigned an internally unique element address, and a library controller that assigns a different logical unit designation to each of the partitions and that assigns external element addresses to the transport, the data transfer elements, and the slots for each of the partitions and maps the internally unique addresses to the external addresses, the controller restricting movement of media to and from the slots assigned to a same of the partitions.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
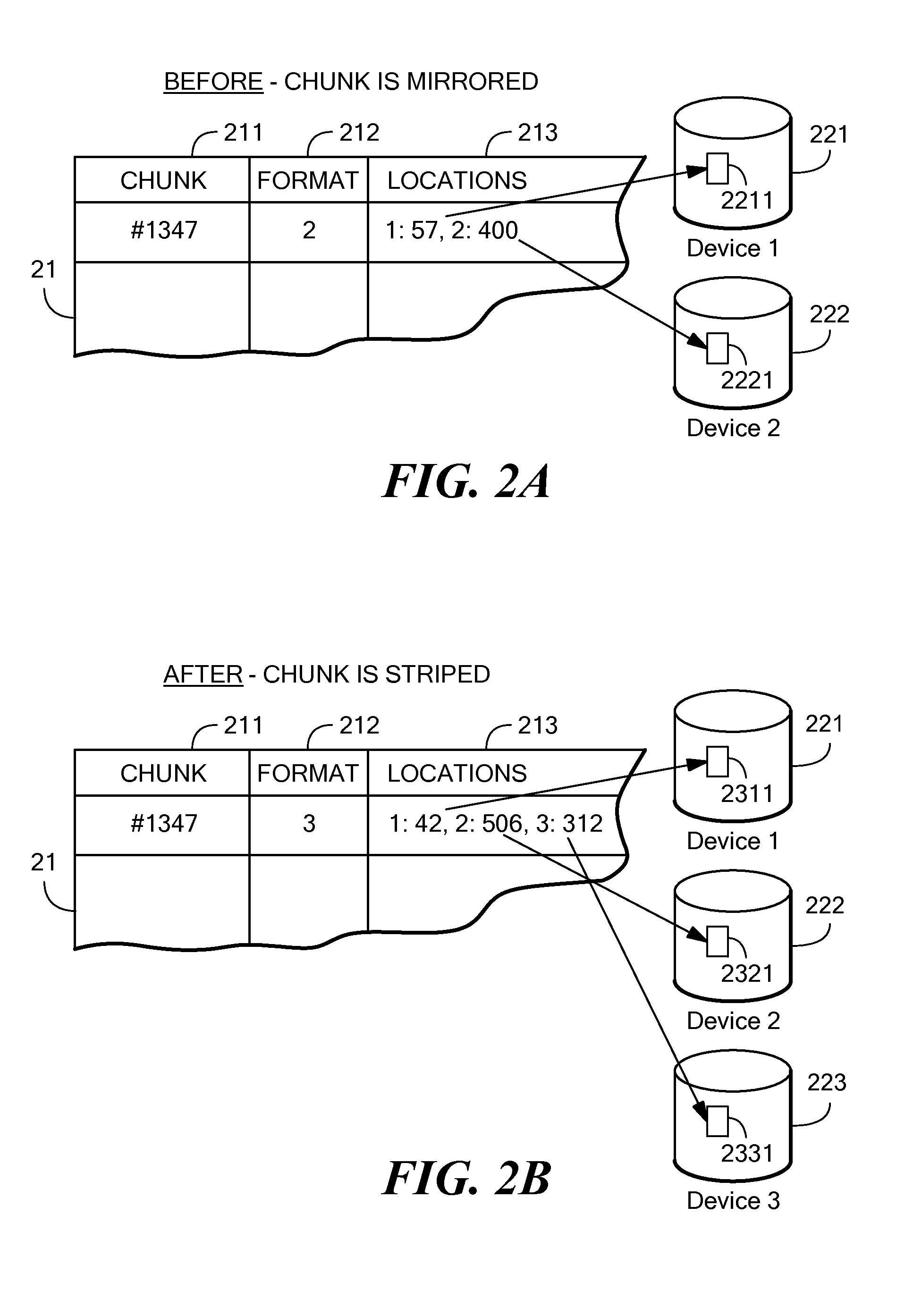
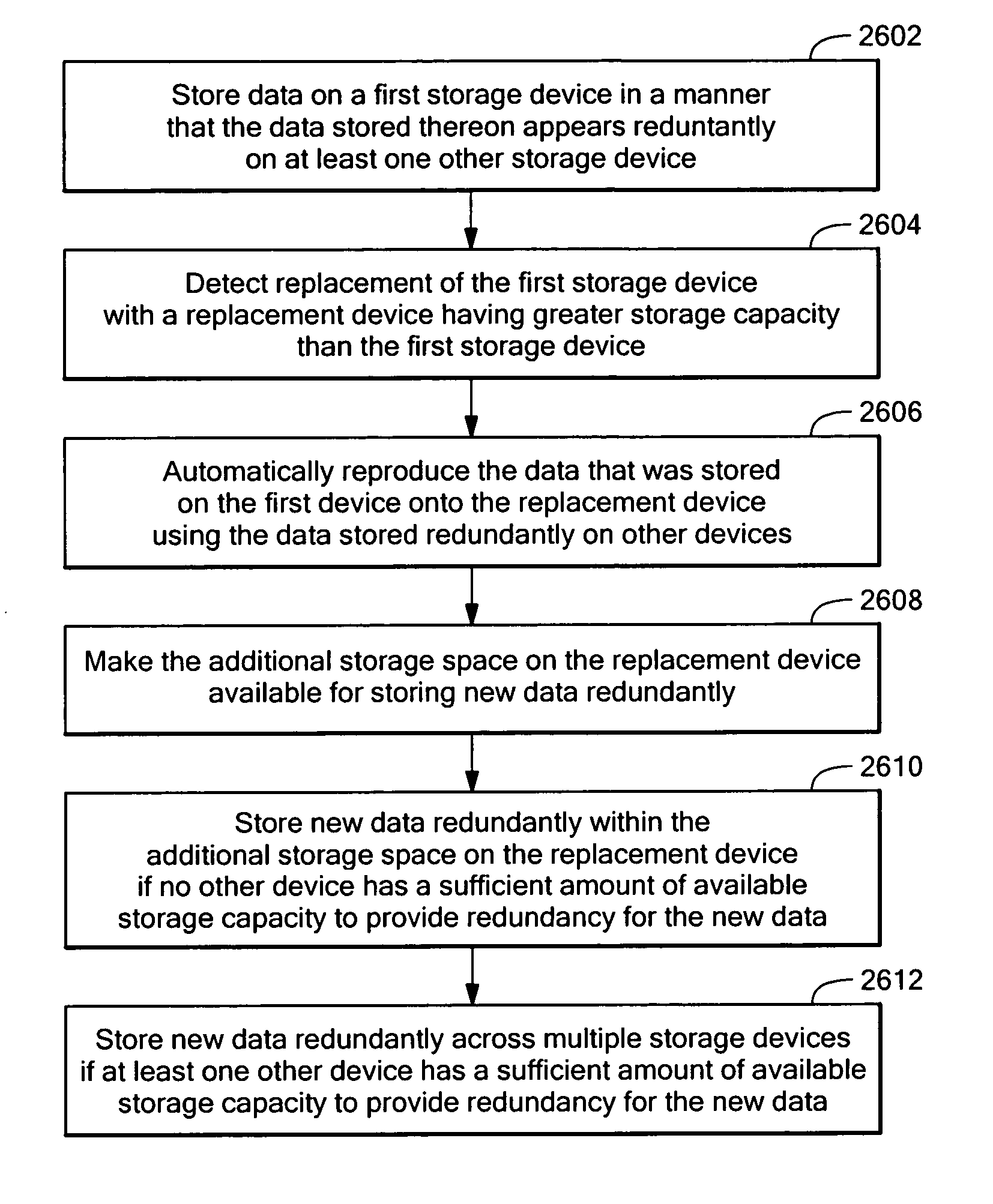
Dynamically expandable and contractible fault-tolerant storage system permitting variously sized storage devices and method
ActiveUS20060112222A1Improve storage efficiencyInput/output to record carriersMemory loss protectionData layoutOperating system
A dynamically expandable and contractible fault-tolerant storage system permits variously sized storage devices. Data is stored redundantly across one or more storage devices if possible. The layout of data across the one or more storage devices is automatically reconfigured as storage devices are added or removed in order to provide an appropriate level of redundancy for the data to the extent possible. A hash-based compression technique may be used to reduce storage consumption. Techniques for freeing unused storage blocks are also disclosed.
Owner:STORCENTRIC DIP LENDER LLC
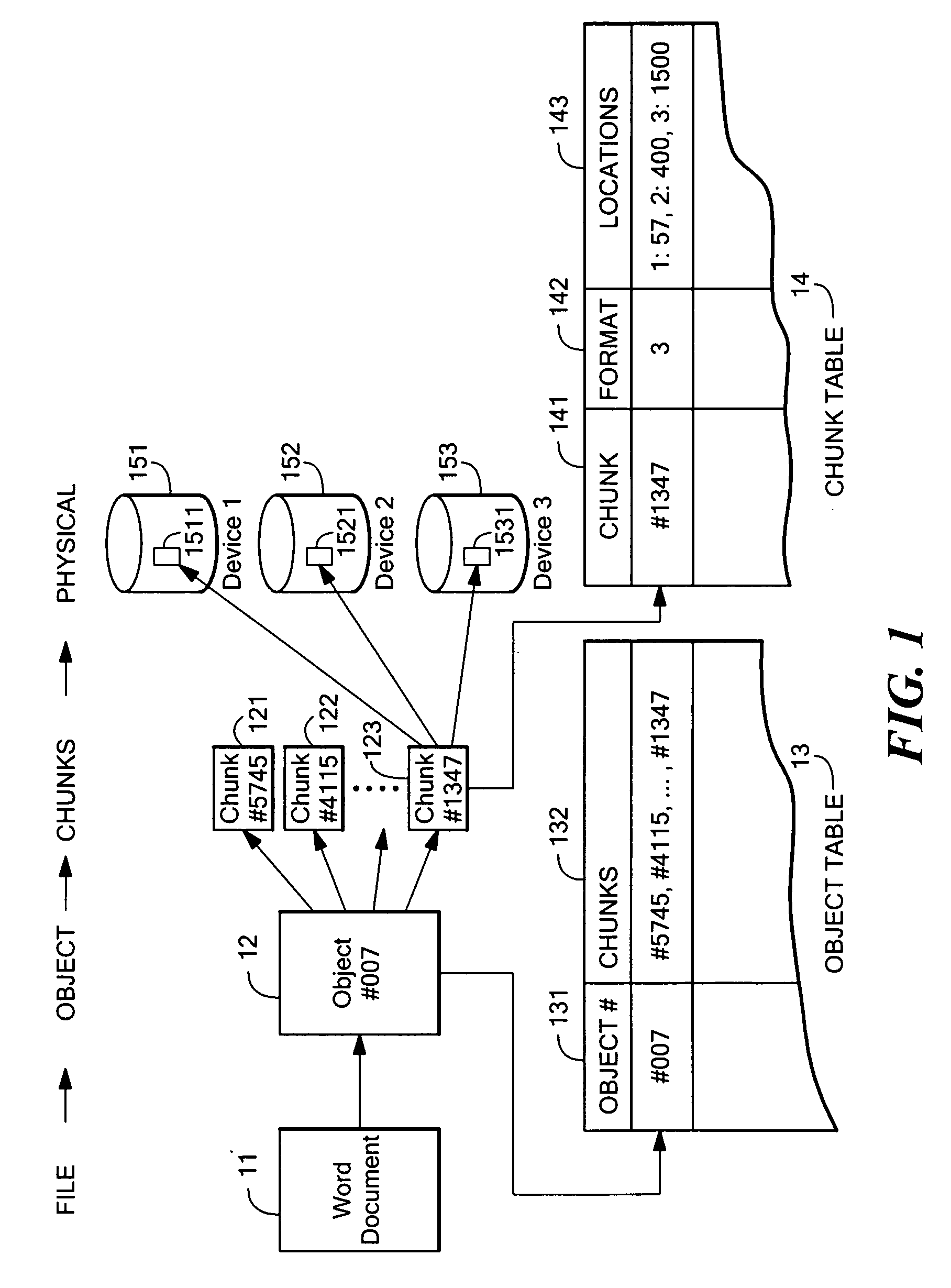
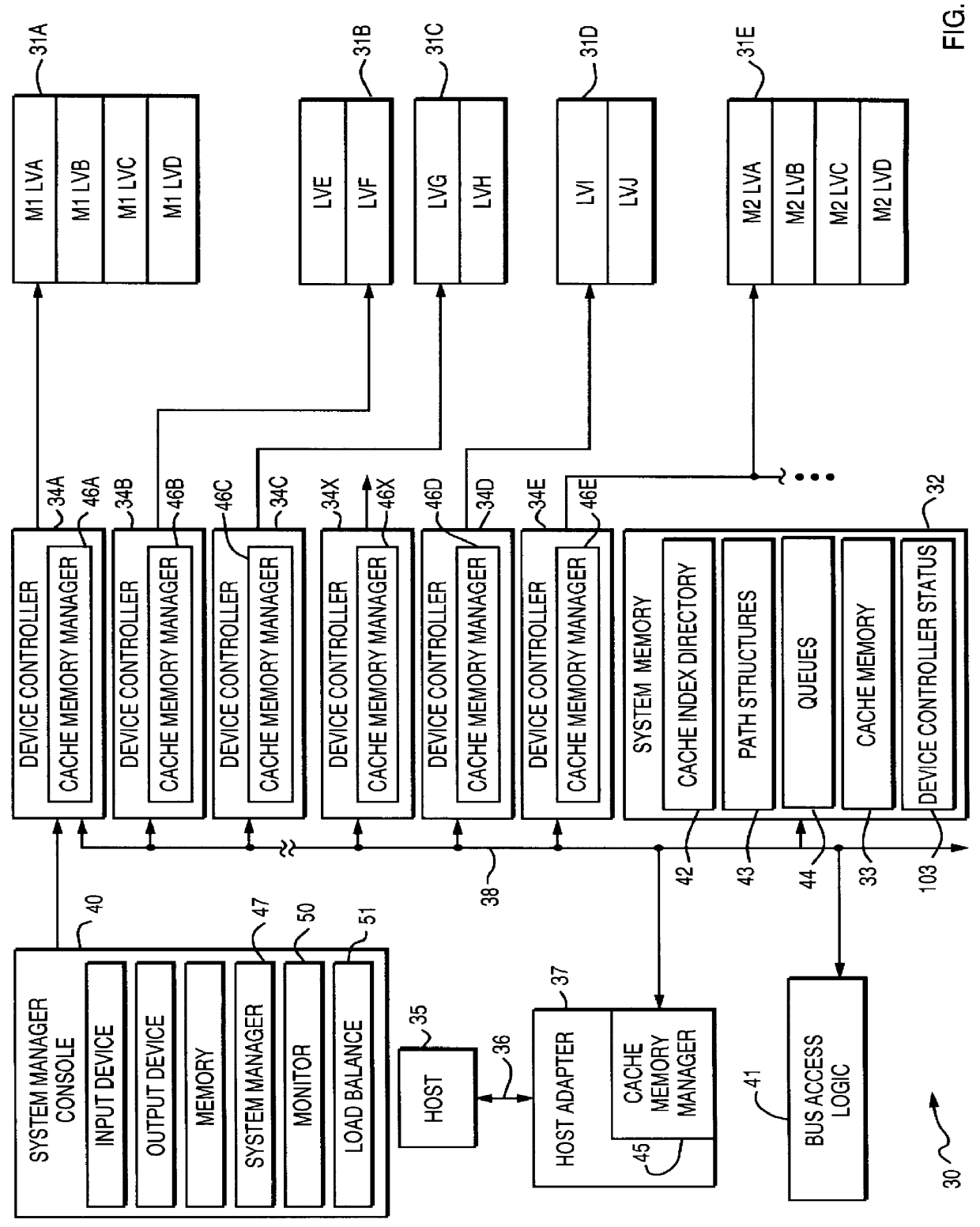
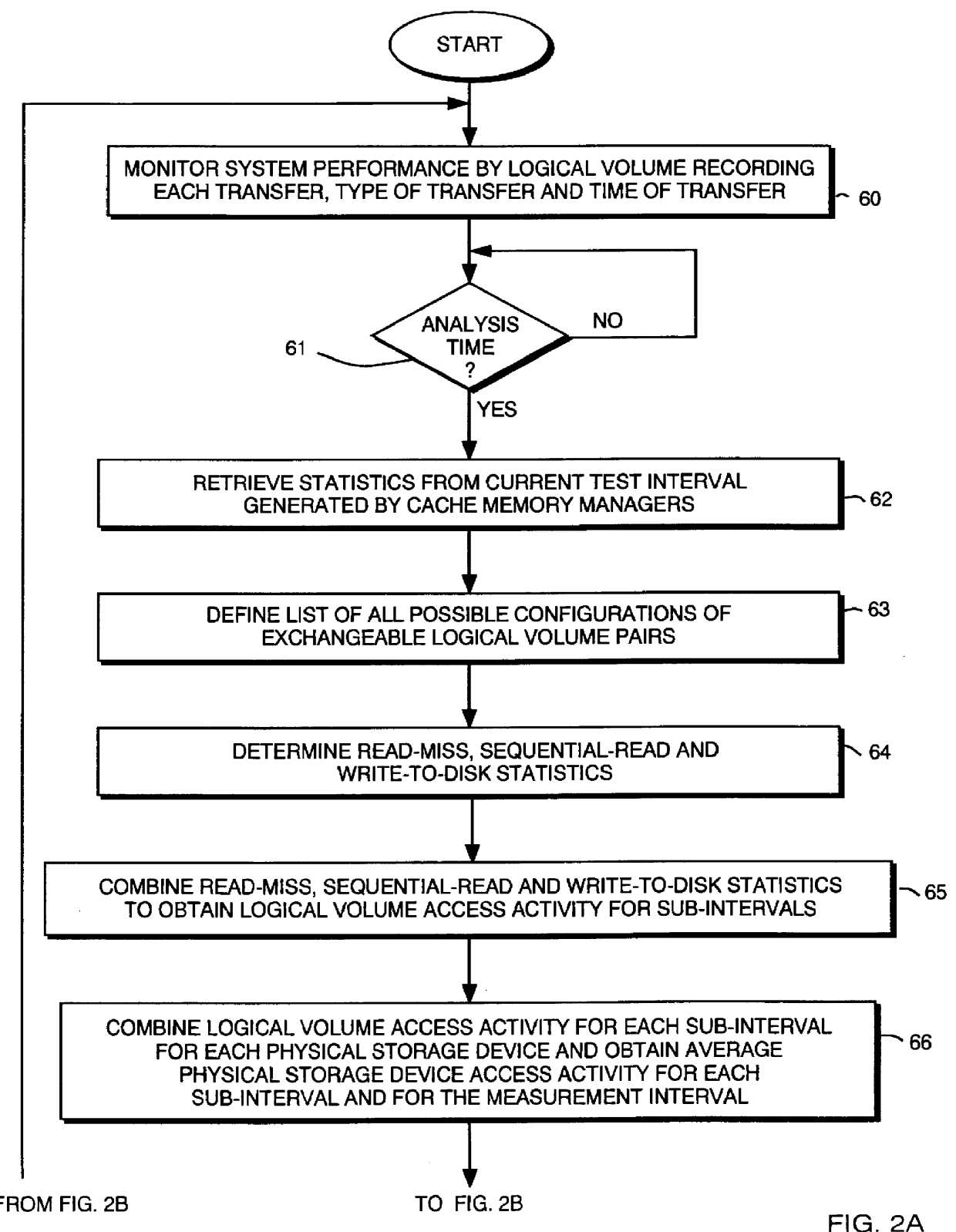
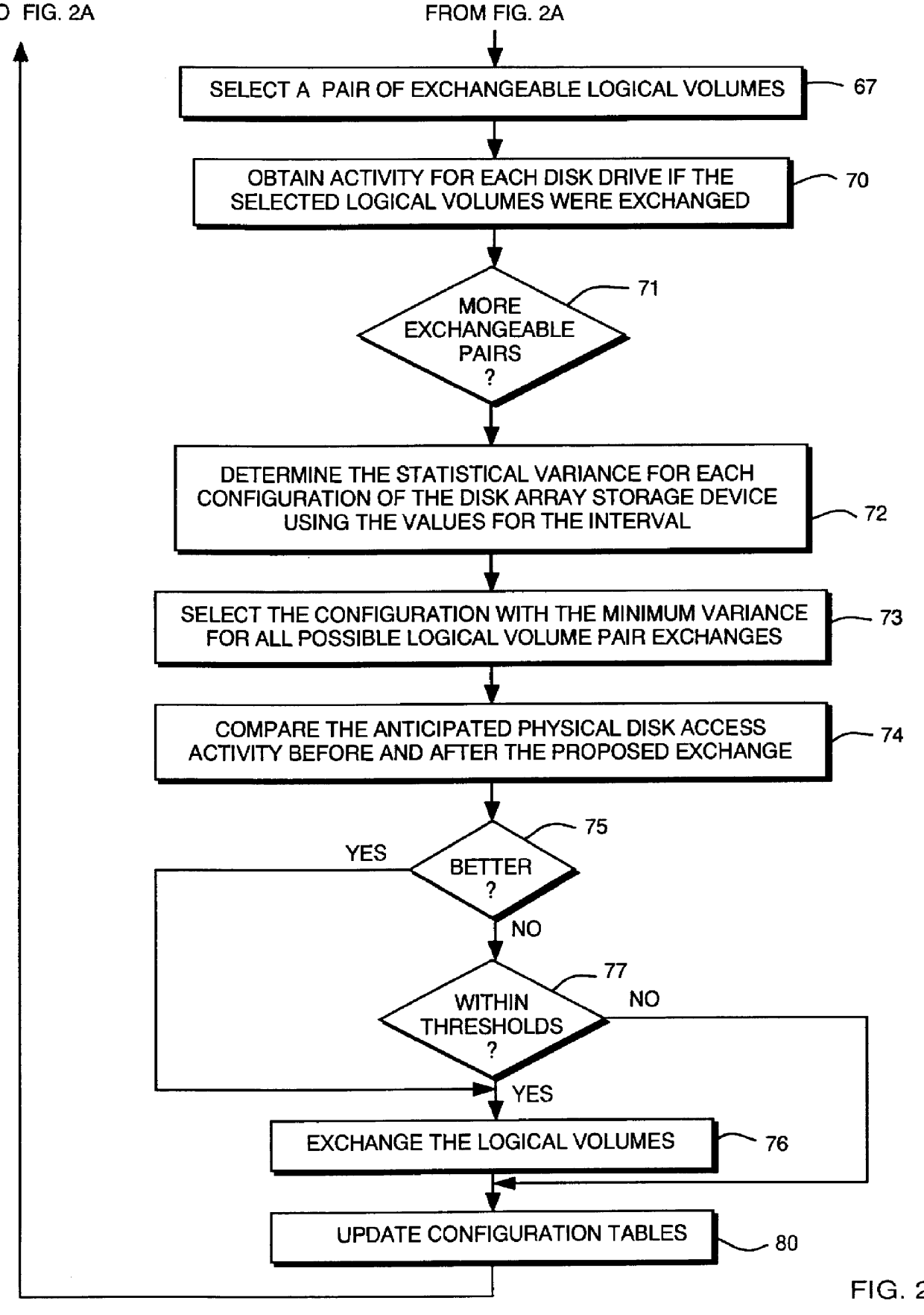
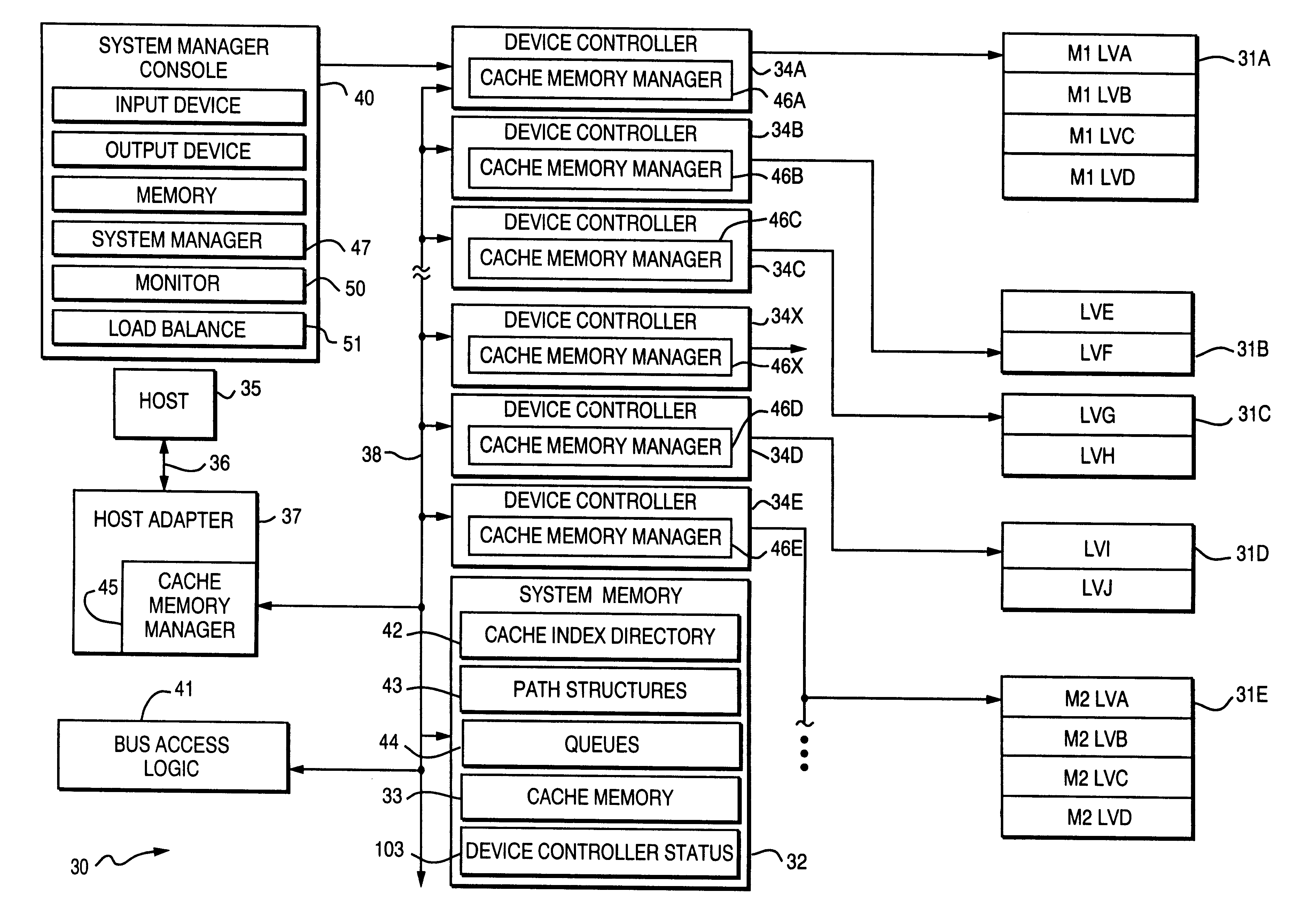
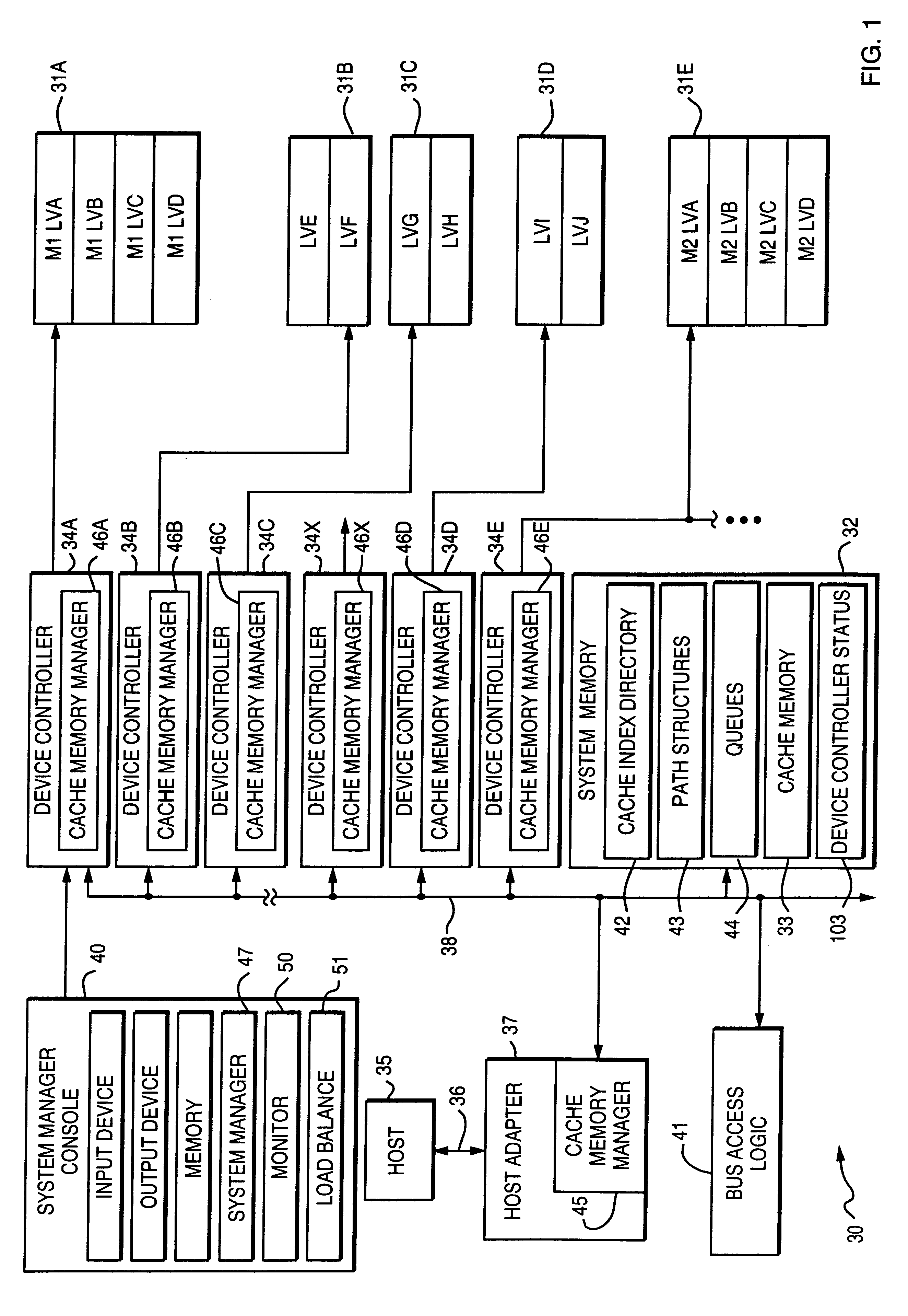
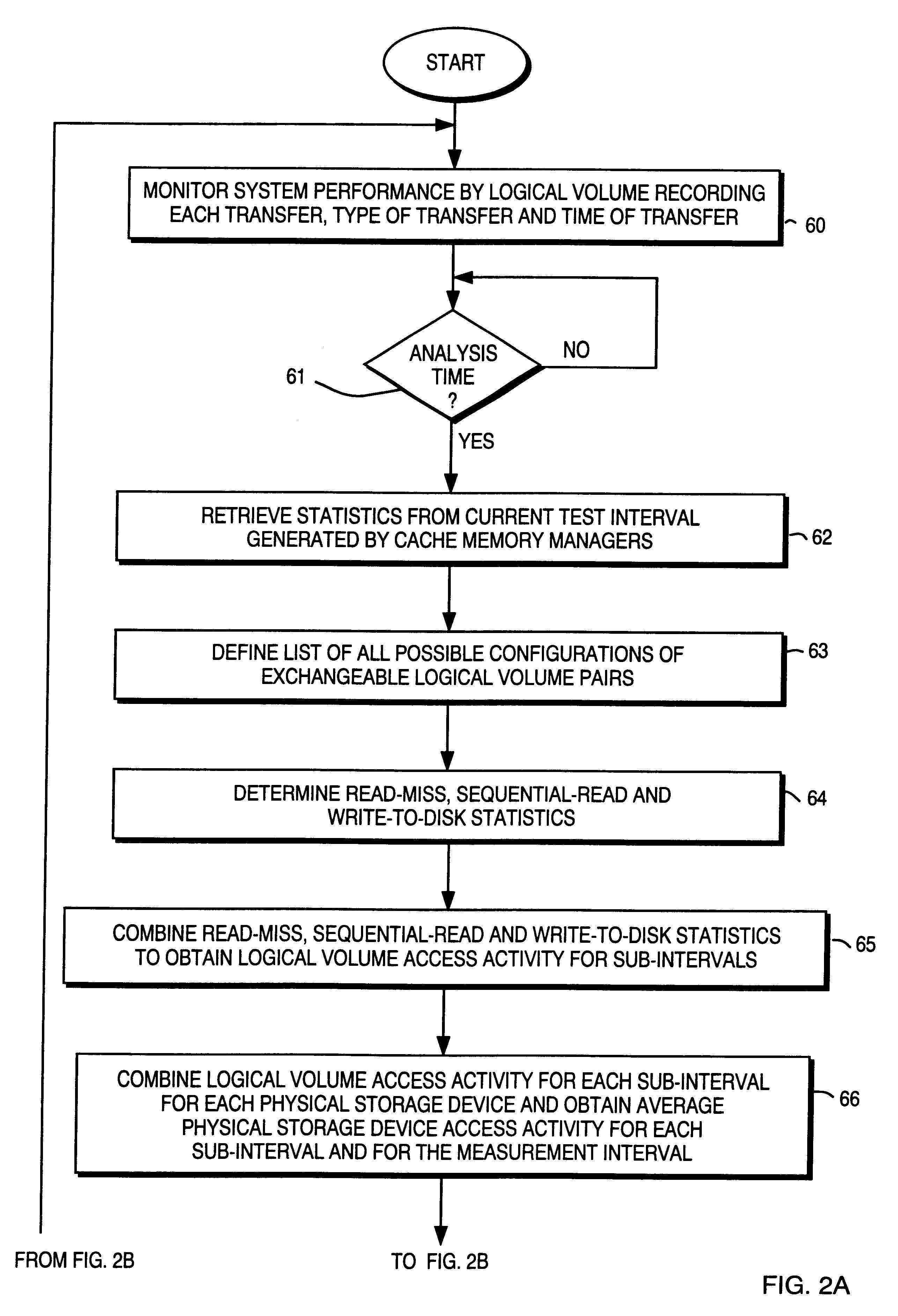
Method for exchanging logical volumes in a disk array storage device in response to statistical analyses and preliminary testing
InactiveUS6061761AInput/output to record carriersRedundant array of inexpensive disk systemsStatistical analysisDisk array
Load balancing of activities on physical disk storage devices is accomplished by monitoring reading and writing operations to logical volumes on the physical disk storage devices. A list of exchangeable pairs of logical volumes is developed based on size and function. Statistics accumulated over an interval are then used to obtain access activity values for each logical volume and each physical disk drive. A statistical analysis selects one logical volume pair. After testing to determine any adverse effect of making that change, the exchange is made to more evenly distribute the loading on individual physical disk storage devices.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
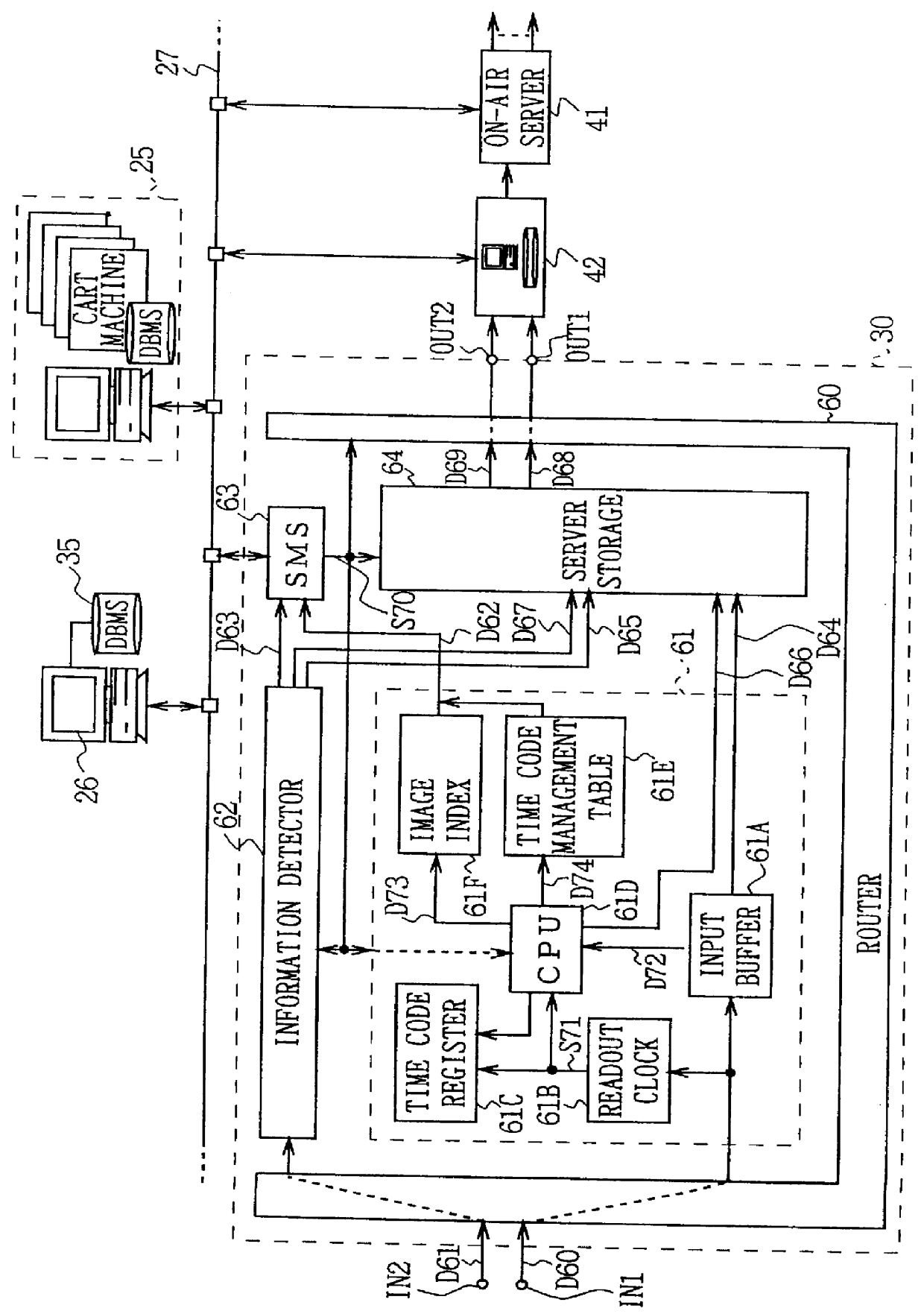
Video signal processing device that facilitates editing by producing control information from detected video signal information
InactiveUS6134378AEasy to set upEasy to operateTelevision system detailsFlat record carrier combinationsComputer hardwareUsability
In the video signal processing device which records video signal (D60) as the material by the predetermined recording reproducing means (64) and conducts the desired editing processing upon reading out the video signal recorded in said recording reproducing means, the detection means (61) for detecting the material information (D72) added to the video signal in the case of recording the video signal by the recording reproducing means and for forming the predetermined control information (D62) based on said material information, and the memory means (35) for storing the control information formed by the detection means are provided. And thus, even if the operator would not enter the control information, it can be easily set and the editing processing based on this control information can be conducted. And thereby, the video signal processing device having further improved usability can be realized.
Owner:SONY CORP
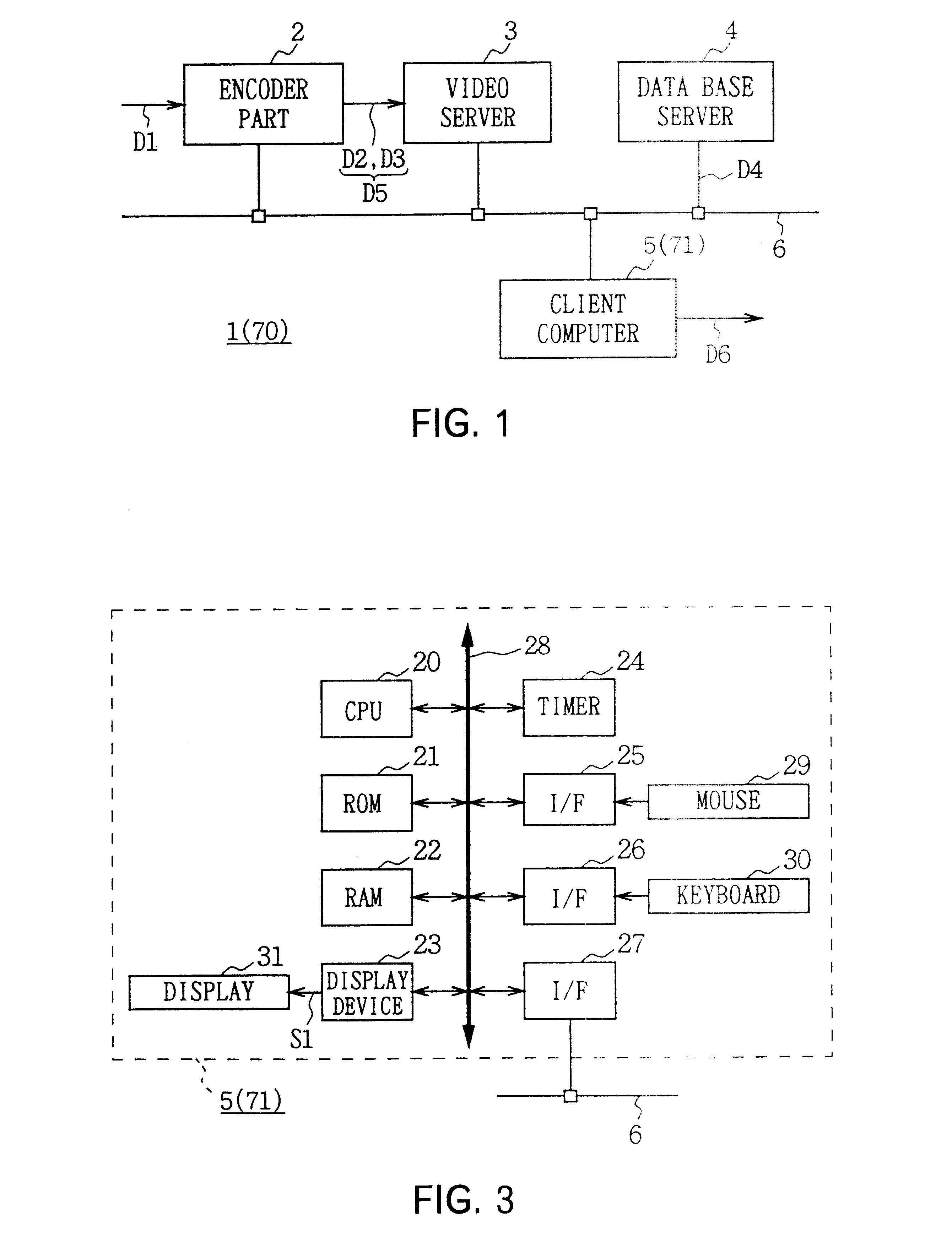
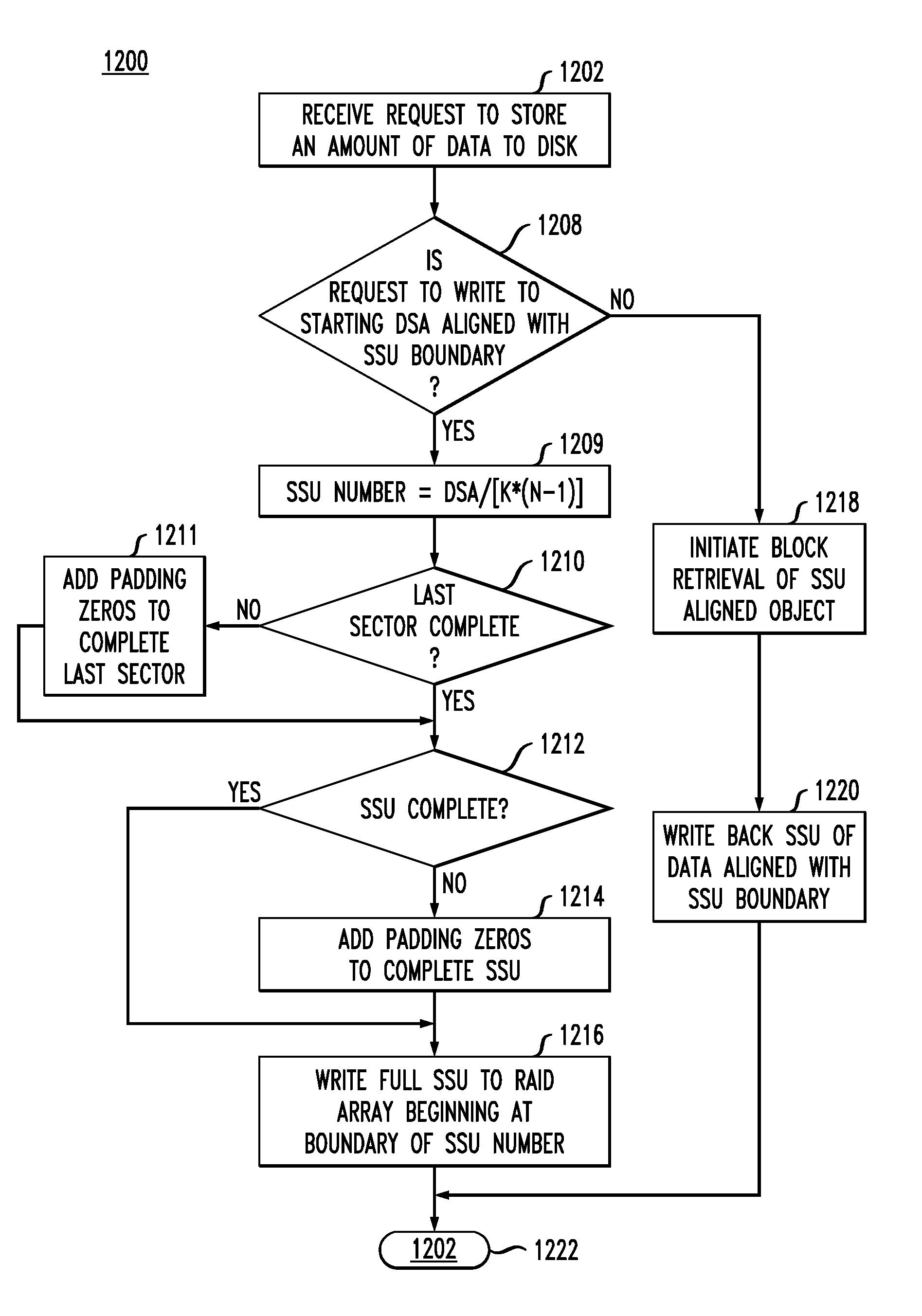
Aligned Data Storage for Network Attached Media Streaming Systems
InactiveUS20130091237A1Redundant array of inexpensive disk systemsDigital computer detailsRAIDNetwork connection
Described embodiments provide a server for transferring data packets of streaming data sessions between devices. A redundant array of inexpensive disks (RAID) array having one or more stripe sector units (SSU) stores media files corresponding to the one or more data sessions. The RAID control module receives a request to perform the write operation to the RAID array beginning at a starting data storage address (DSA) and pads the data of the write operation if the amount of data is less than a full SSU of data, such that the padded data of the write operation is a full SSU of data. The RAID control module stores the full SSU of data beginning at a starting data storage address (DSA) that is aligned with a second SSU boundary, without performing a read-modify-write operation.
Owner:BROADCOM INT PTE LTD
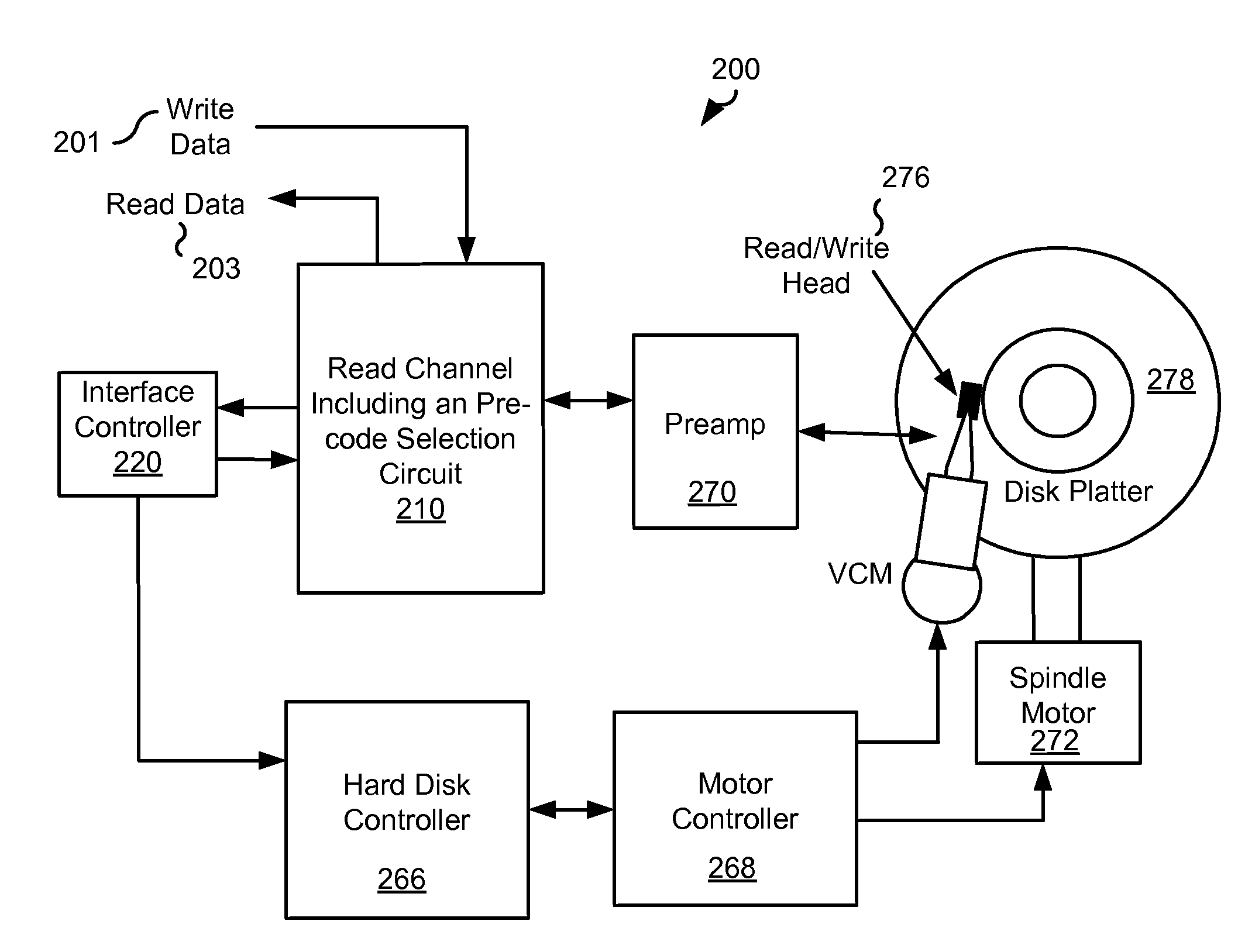
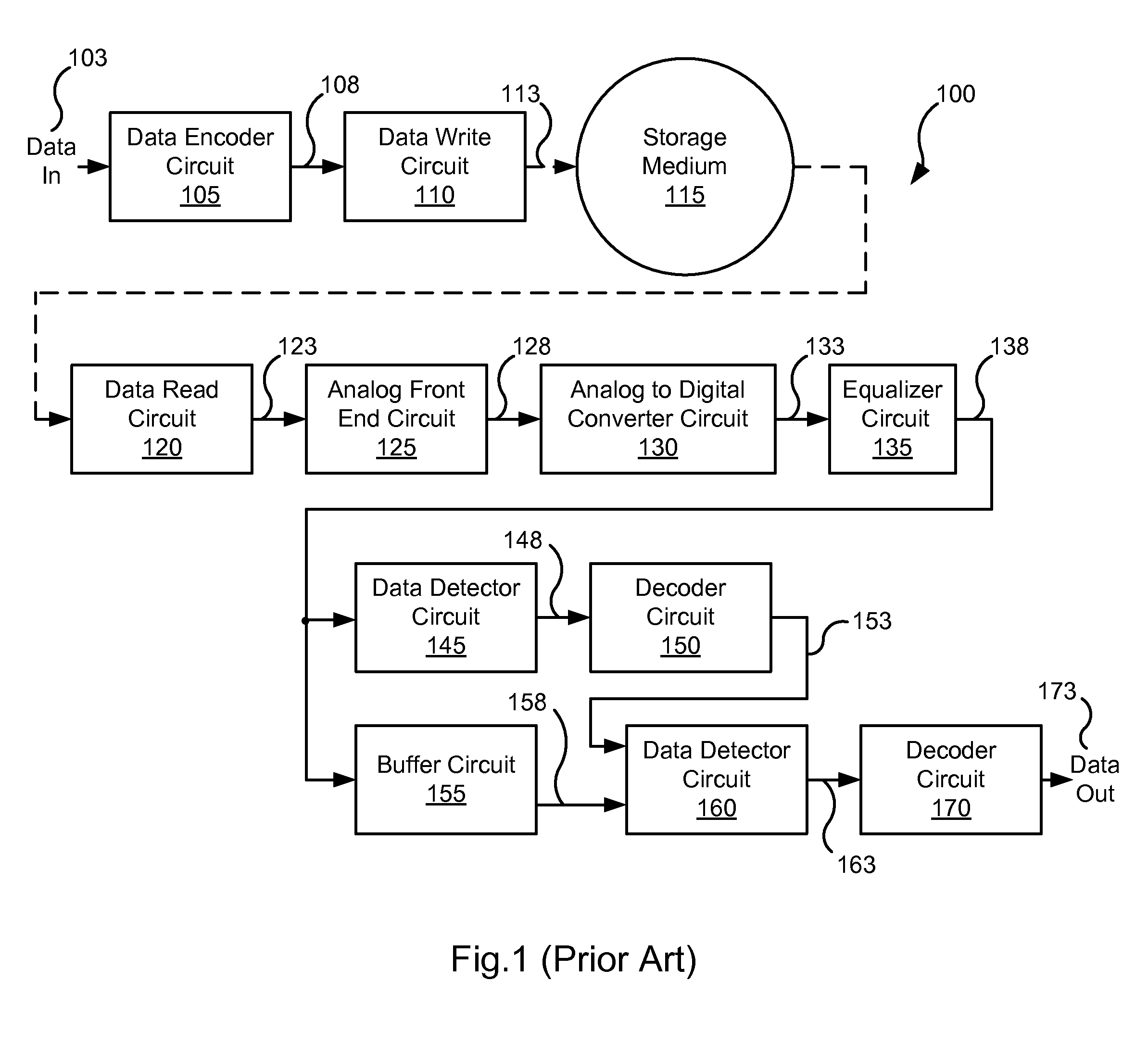
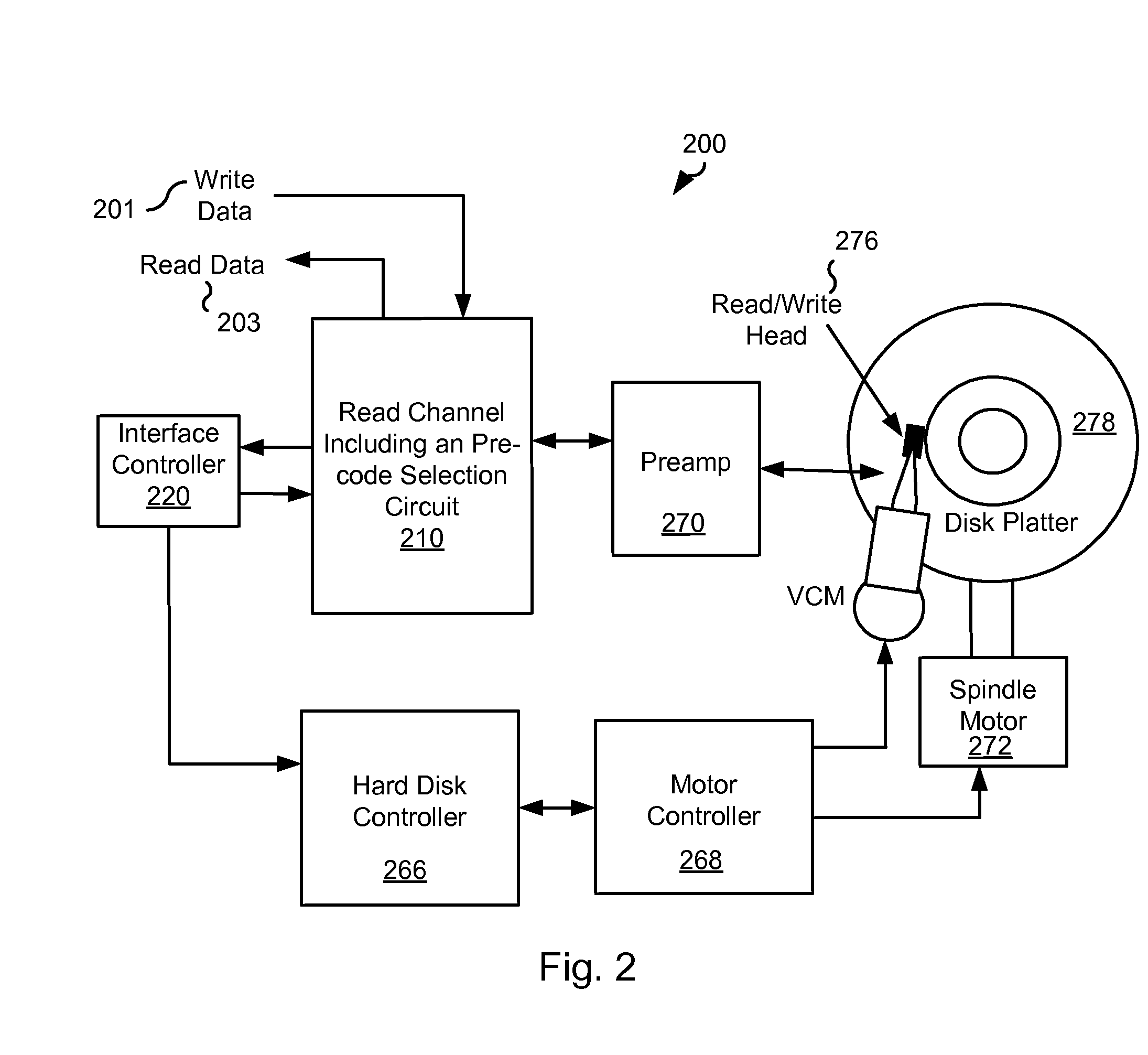
Systems and Methods for Data Pre-Coding Calibration
ActiveUS20120212849A1Multiple-port networksData representation error detection/correctionPrecodingDetector circuits
Various embodiments of the present invention provide systems and methods for selecting between pre-coding and non-pre-coding. As an example, a data processing circuit is disclosed that includes: a first data detector circuit, a second data detector circuit, a first comparator circuit, a second comparator circuit, and a pre-code selection circuit. The first data detector circuit is selectably configurable to operate in a pre-coded state, and operable to apply a data detection algorithm on a data input to yield a first detected output. The second data detector circuit operable to apply the data detection algorithm to the data input to yield a second detected output without compensating for pre-coding. The first comparator circuit operable to compare the first detected output against a known input to yield a first comparison value, and the second comparator circuit operable to compare the second detected output against the known input to yield a second comparison value. The pre-code selection circuit is operable to determine a selectable configuration of the first data detector circuit based at least in part on the first comparison value and the second comparison value.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Editing apparatus having dedicated processing unit for video editing
InactiveUS20030086686A1Secure performanceRemove background noiseTelevision system detailsRedundant array of inexpensive disk systemsSource materialDisplay device
An editing apparatus is disclosed, that comprises an editing processing unit for processing a video signal and an audio signal supplied as source materials, and a computer for controlling the editing processing unit, wherein the computer comprises a controlling means for displaying a viewer window, a log window, and a program window on a display of the computer, the viewer window allowing the editing operator to decide an edit point while viewing a video image of a source material so as to produce an event, the log window displaying a clip image corresponding to an event that is set on the viewer window, the program window allowing the editing operator to arrange a plurality of events on a time line in a desired order so as to produce a program list, and wherein the controlling means displays an icon that represents by what source device each event arranged on the time line is produced.
Owner:SONY CORP
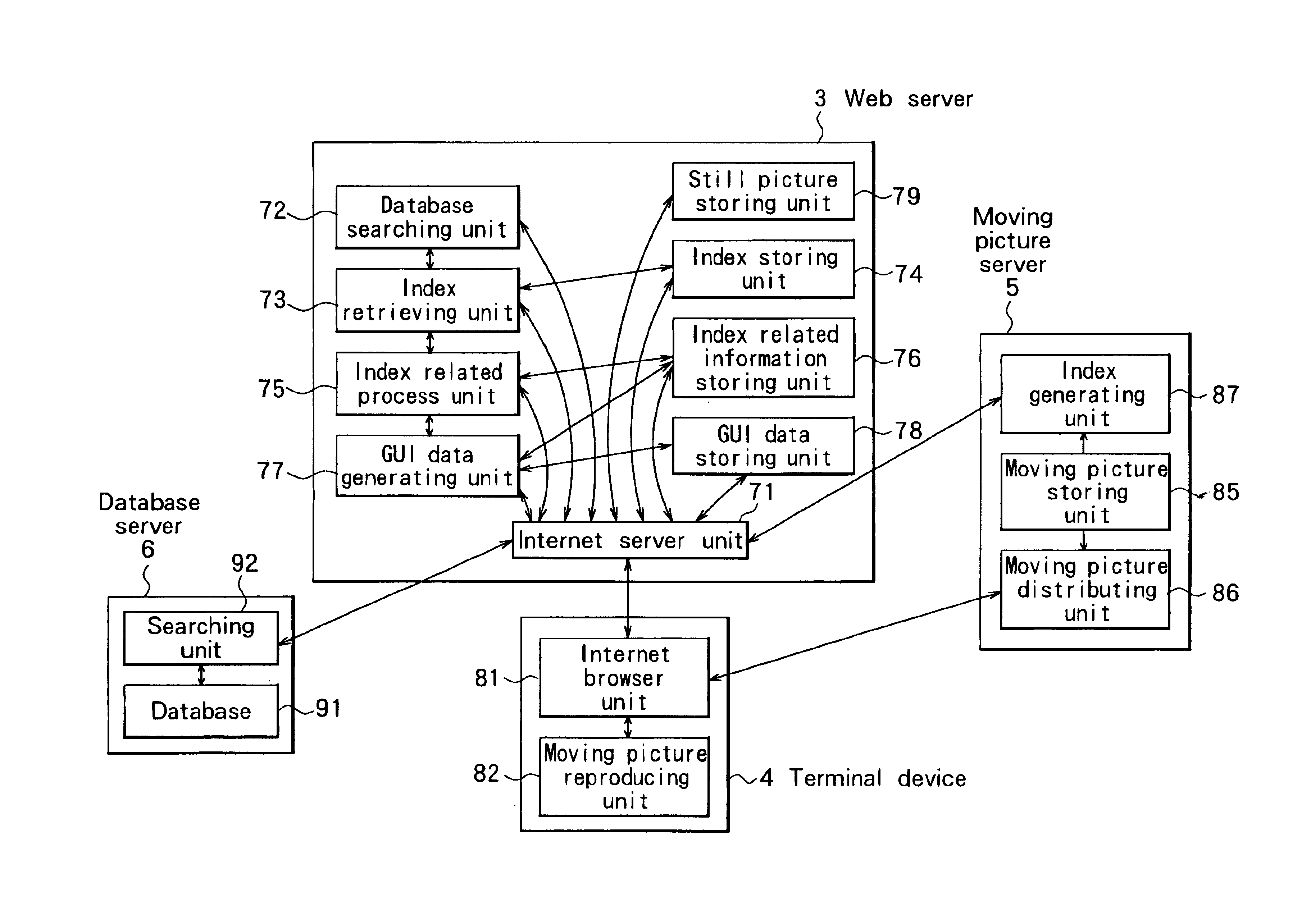
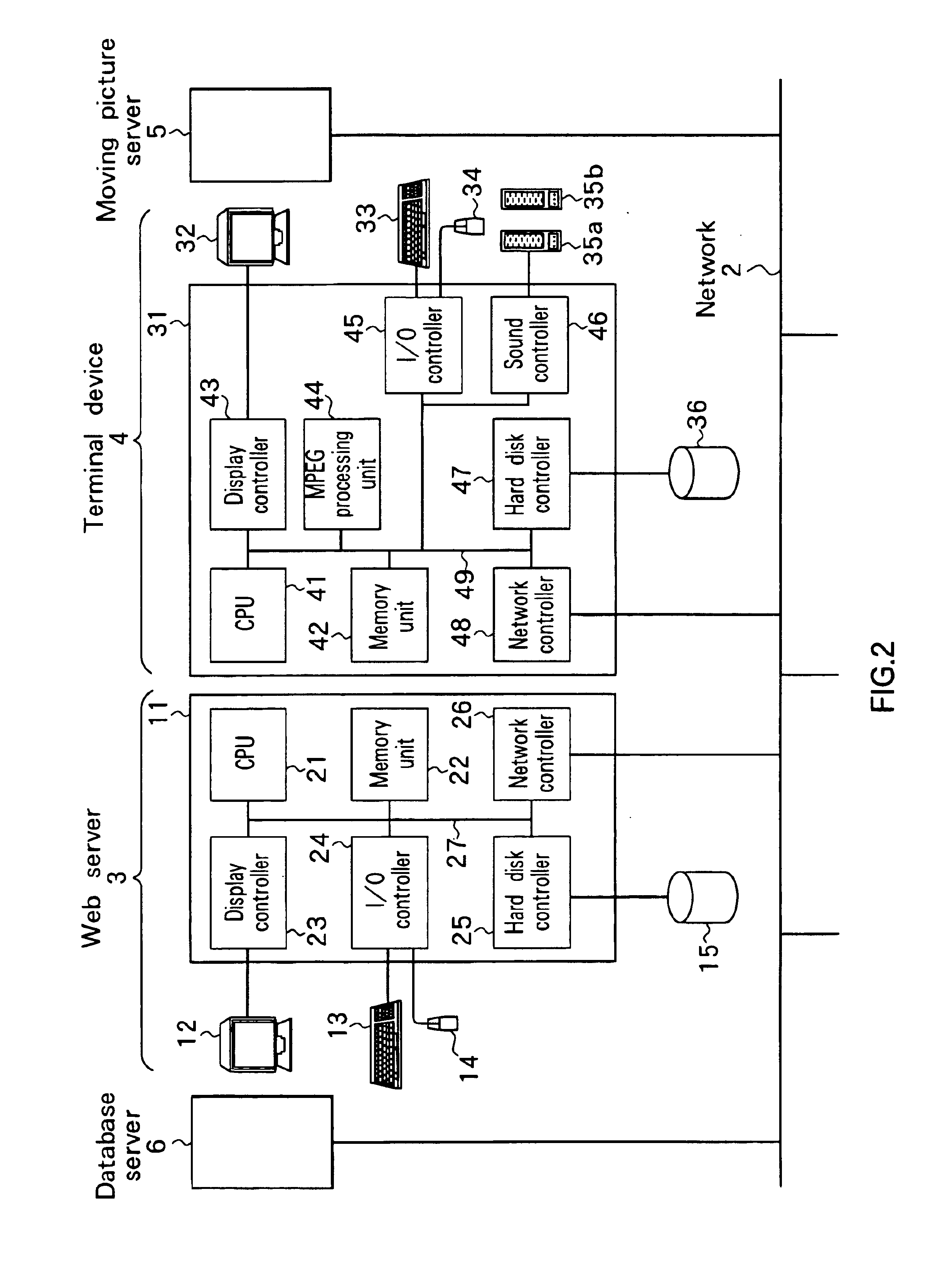
Image display apparatus and method
InactiveUS6851091B1Accurate startDigital data information retrievalRedundant array of inexpensive disk systemsComputer graphics (images)Image display
An imaging device capable of displaying an outline of a moving picture as a still picture is realized. Further, reproduction of a moving picture that is started from any desired scene by using an index picture can be realized. When VD index pictures displayed on a browser screen are selected, a corresponding index representative still picture is displayed. Therefore, a moving picture such as a moving picture of a quick motion whose contents cannot be easily grasped only by the VD index picture, can be easily recognized with the addition of the corresponding index representative still picture. By selecting the VD index pictures displayed on the browser screen, display of the corresponding moving picture is started from a portion corresponding to the selected VD index picture.
Owner:SONY CORP
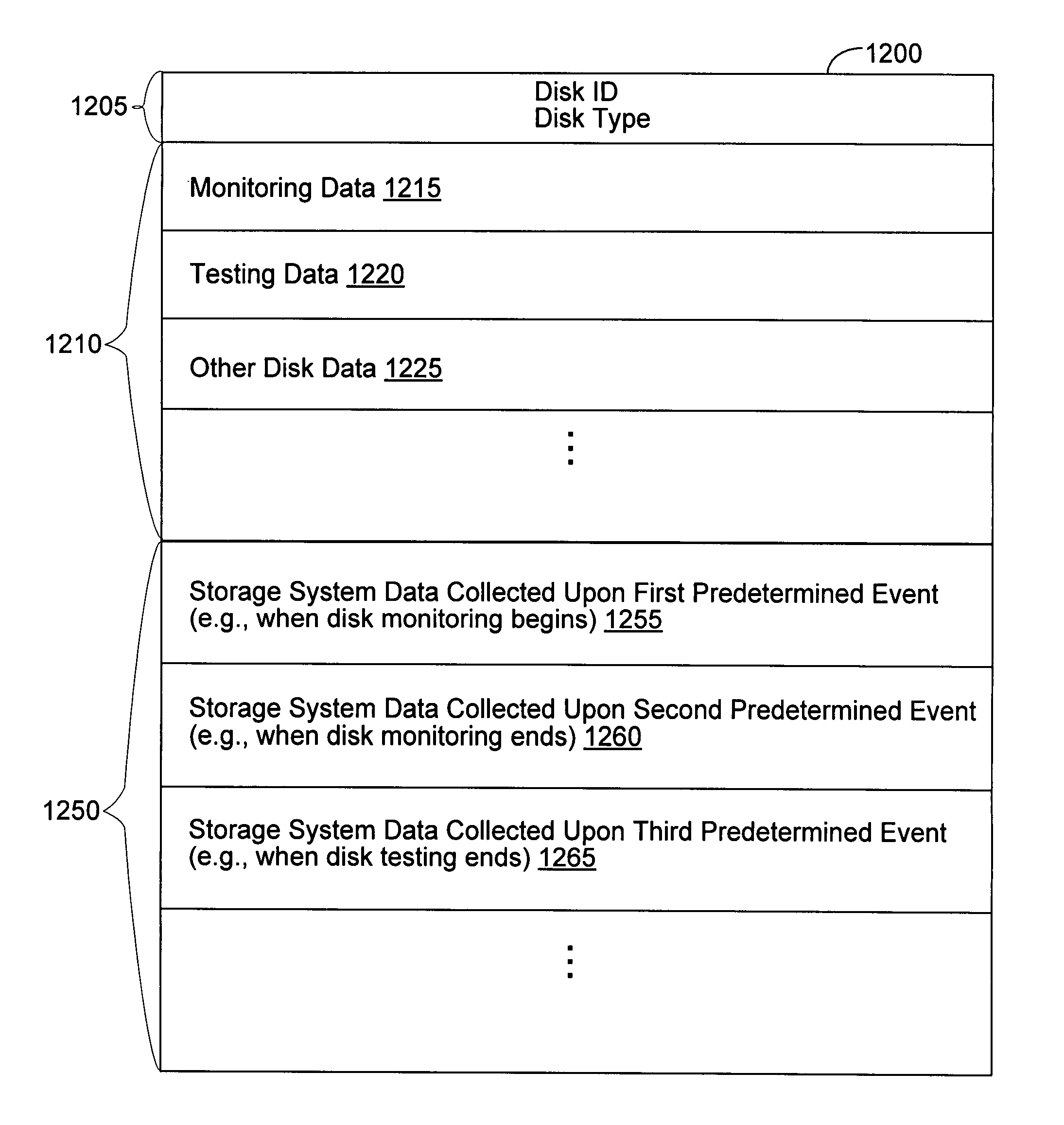
Method and apparatus for reporting storage device and storage system data
ActiveUS7743284B1Conveniently performedRedundant array of inexpensive disk systemsError detection/correctionOperational systemStorage management
A method for providing data regarding a storage system comprising storage devices is described herein. A storage management module of an operating system of the storage system may be used for servicing (e.g., monitoring or testing) storage devices according to servicing parameters. For each serviced storage device, a reporting module of the storage management module may collect storage device and storage system data upon the occurrence of predetermined events (e.g., when a storage device exhibits an error and monitoring begins, when monitoring ends, and when testing of the storage device ends). The collected data may be saved to a report file in a predetermined format and received by a program configured to automatically extract the data according to the predetermined format for use in storage device and storage system analysis and to determine modified servicing parameters used by the storage management module to service storage devices.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Storage system condition indicator and method
ActiveUS20060129875A1Input/output to record carriersMemory loss protectionOperant conditioningDatabase
A storage system condition indicator and method provides a visual display representing the operating condition of a set of storage devices. Various operating conditions may be defined based on available storage capacity and capacity to store data redundantly. One or more indicators may be used to represent the operating condition of the set of storage devices. The indicator(s) may be used to indicate whether additional storage capacity is recommended and, in a storage array, which slot in the array should be updated with additional storage capacity.
Owner:STORCENTRIC DIP LENDER LLC
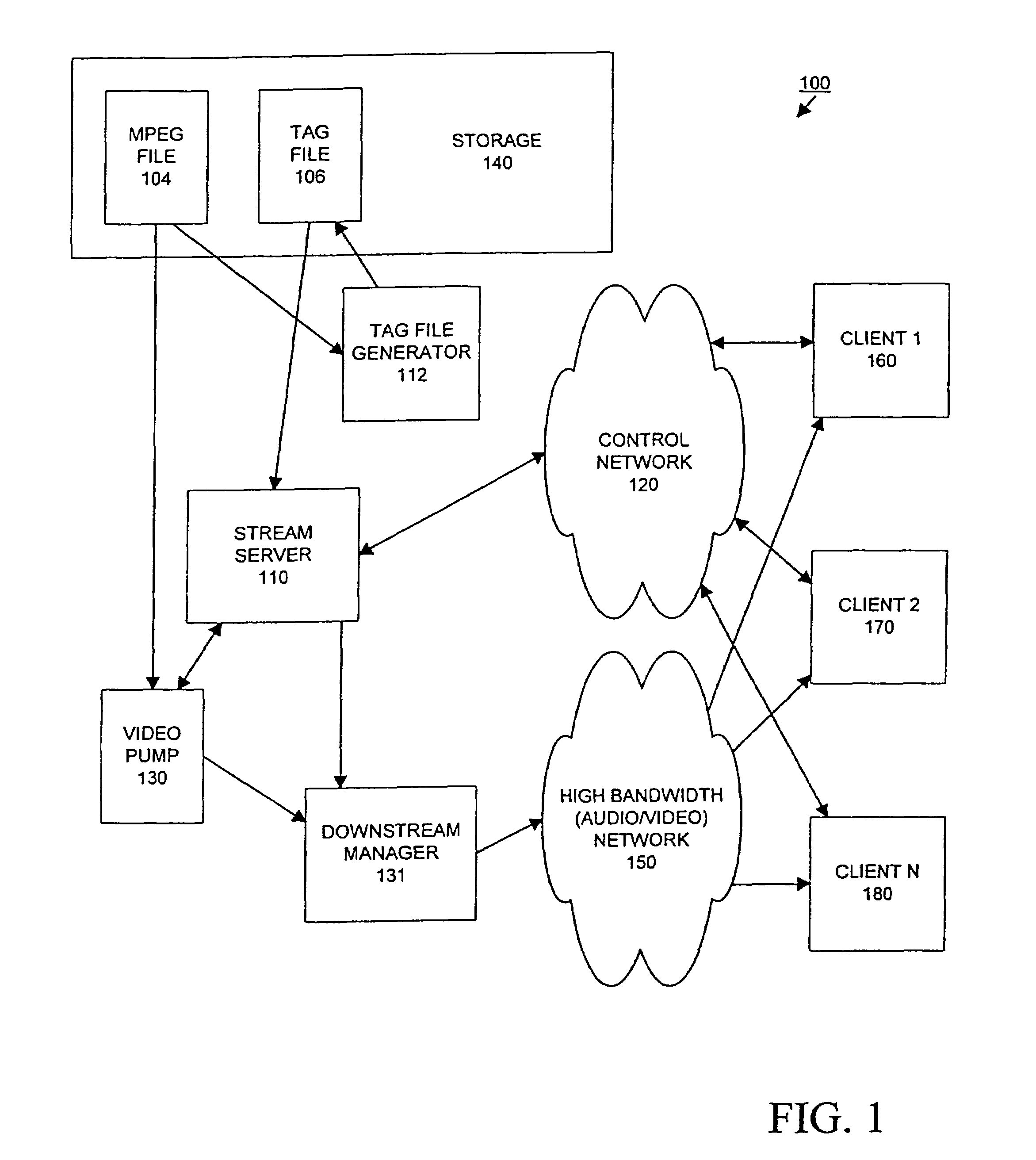
Dynamic quality adjustment based on changing streaming constraints
InactiveUS7512698B1Reduces streaming constraintEliminating waste in bandwidthDisc-shaped record carriersRedundant array of inexpensive disk systemsClient-sideComputer science
A method and apparatus for dynamic quality adjustment of digital media based on changing streaming constraints is provided. A digital media server sends a digital media stream according to a set of streaming constraints to a requesting client. Audio and visual information may be sent to a requesting client together in a single stream, or separately in multiple streams. A client sends a request over a control network to the digital media server indicating information of a particular type is no longer desired. In response to receiving the signal, the video server ceases transmission of that particular type of information to the signaling client, thus relaxing streaming constraints. As a result of the techniques described herein, an improved quality digital presentation is available for the client and, consequently, when a viewer signals that a particular type of information is not desired, that particular type of information is not transmitted to the client, which thereby reduces the streaming constraints on a video streaming service, and improved quality digital media information may be sent to any client using the freed-up portion of the bandwidth previously allocated to the signaling client.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS +1
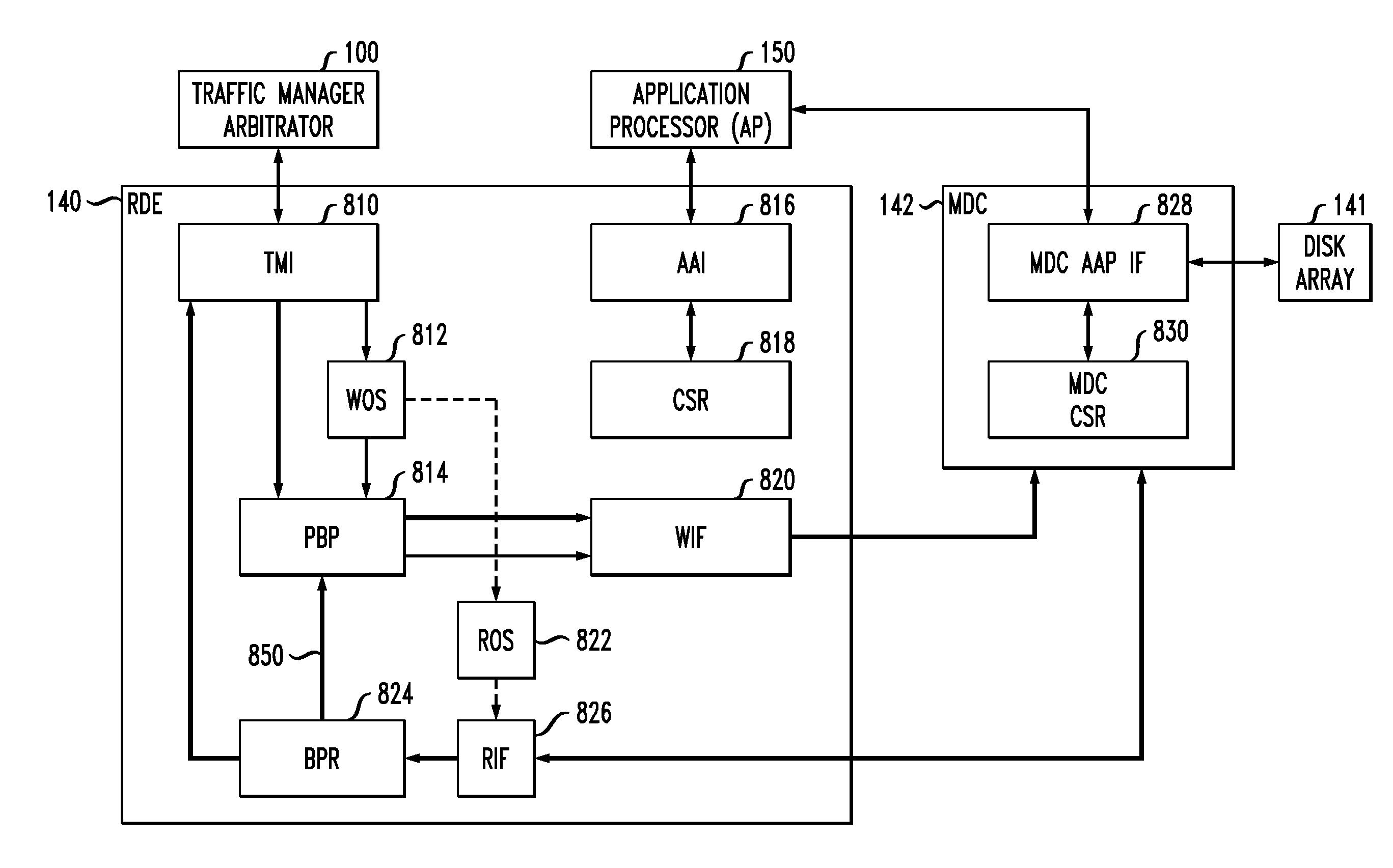
Storage controller and method for storage control
ActiveUS20060143508A1Improving sequential read performanceData redundancyInput/output to record carriersRedundant array of inexpensive disk systemsControl store
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Rapid regeneration of failed disk sector in a distributed database system
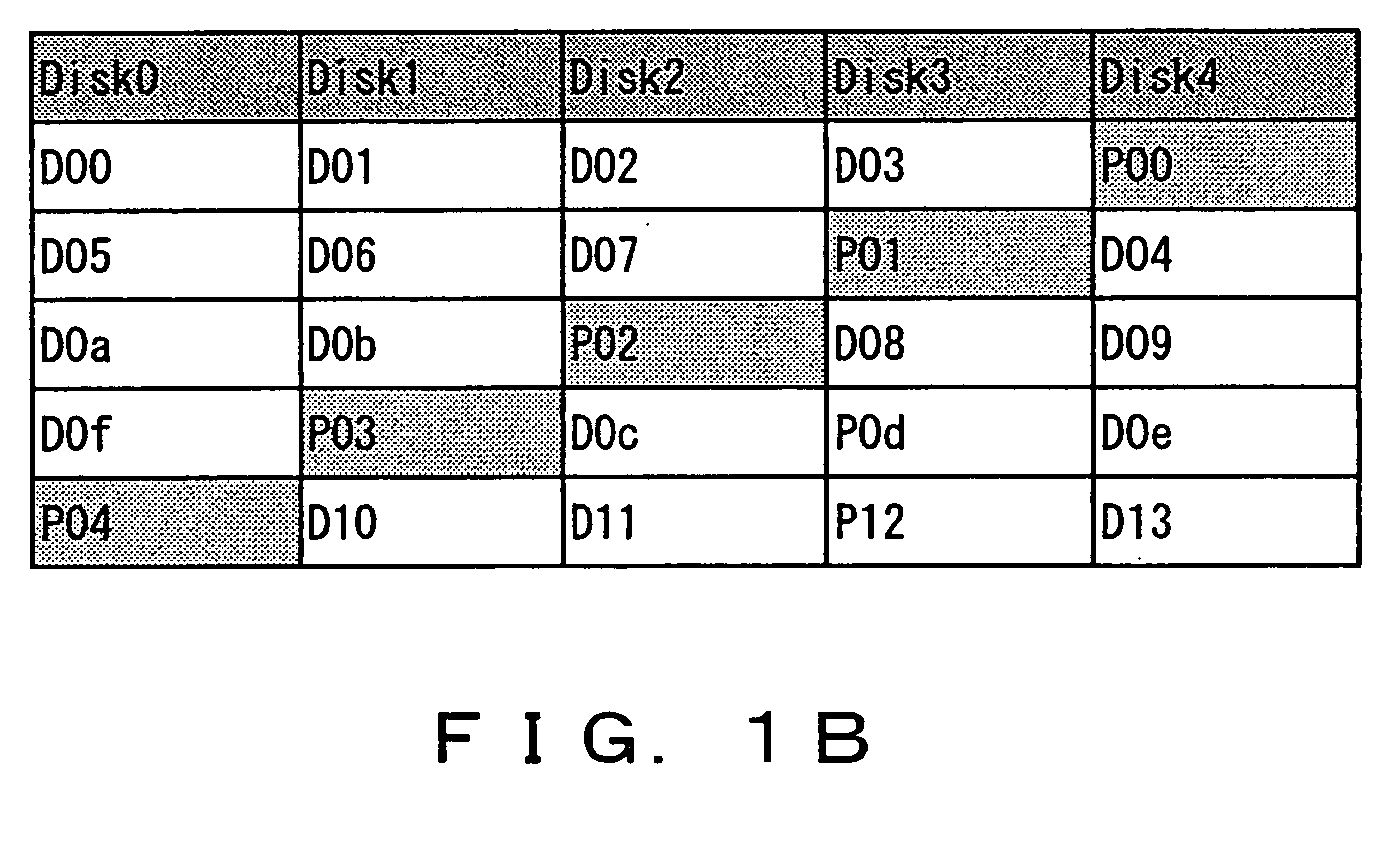
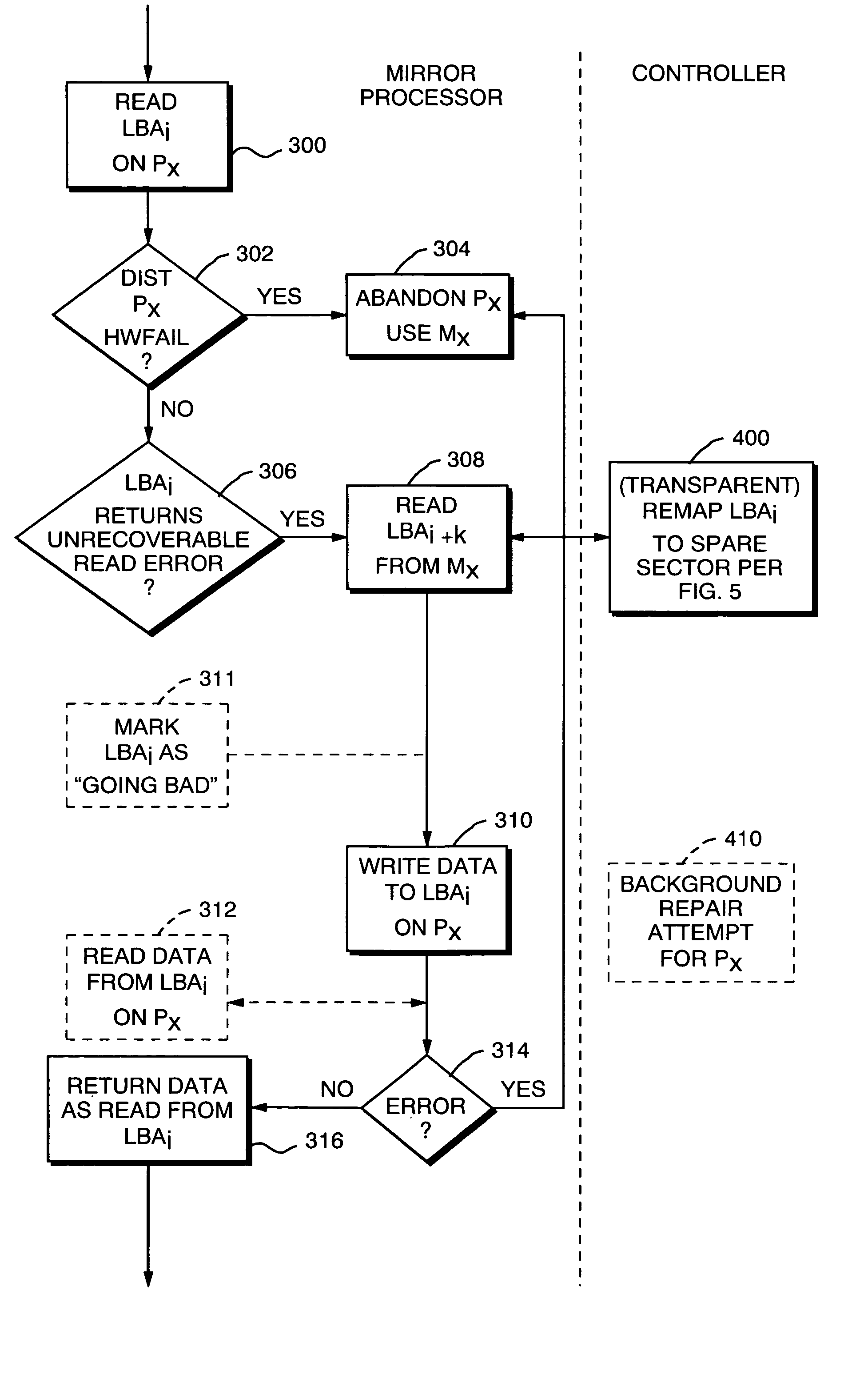
ActiveUS7281160B2Avoid the needPromote recoveryRedundant array of inexpensive disk systemsRecord information storageFailoverRAID
A technique for read error failover processing in a mirrored disk system such as a Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks (RAID) system, where individual disk units perform Logical Block Address (LBA) remapping. A read error causes a disk controller to report an “unrecoverable” read error to a RAID controller. After receiving this report of an unrecoverable read error, rather than simply switching over to a mirror, the RAID controller first checks to see whether the disk that caused the error can successfully reassign an LBA. In particular, the RAID controller can retrieve the data that was associated with the failed LBA from the mirror, and then write that data to the offending disk. The disk controller for that disk will then perform its standard LBA remapping, and write the data to a new, good sector. Only if this process does not succeed is the offending disk then treated by the RAID controller as having failed sufficiently to require failover to the mirror.
Owner:IMB INT GRP BV
Displaying control points over a timeline
ActiveUS7062713B2Television system detailsRedundant array of inexpensive disk systemsComputer graphics (images)Time line
Owner:AUTODESK INC
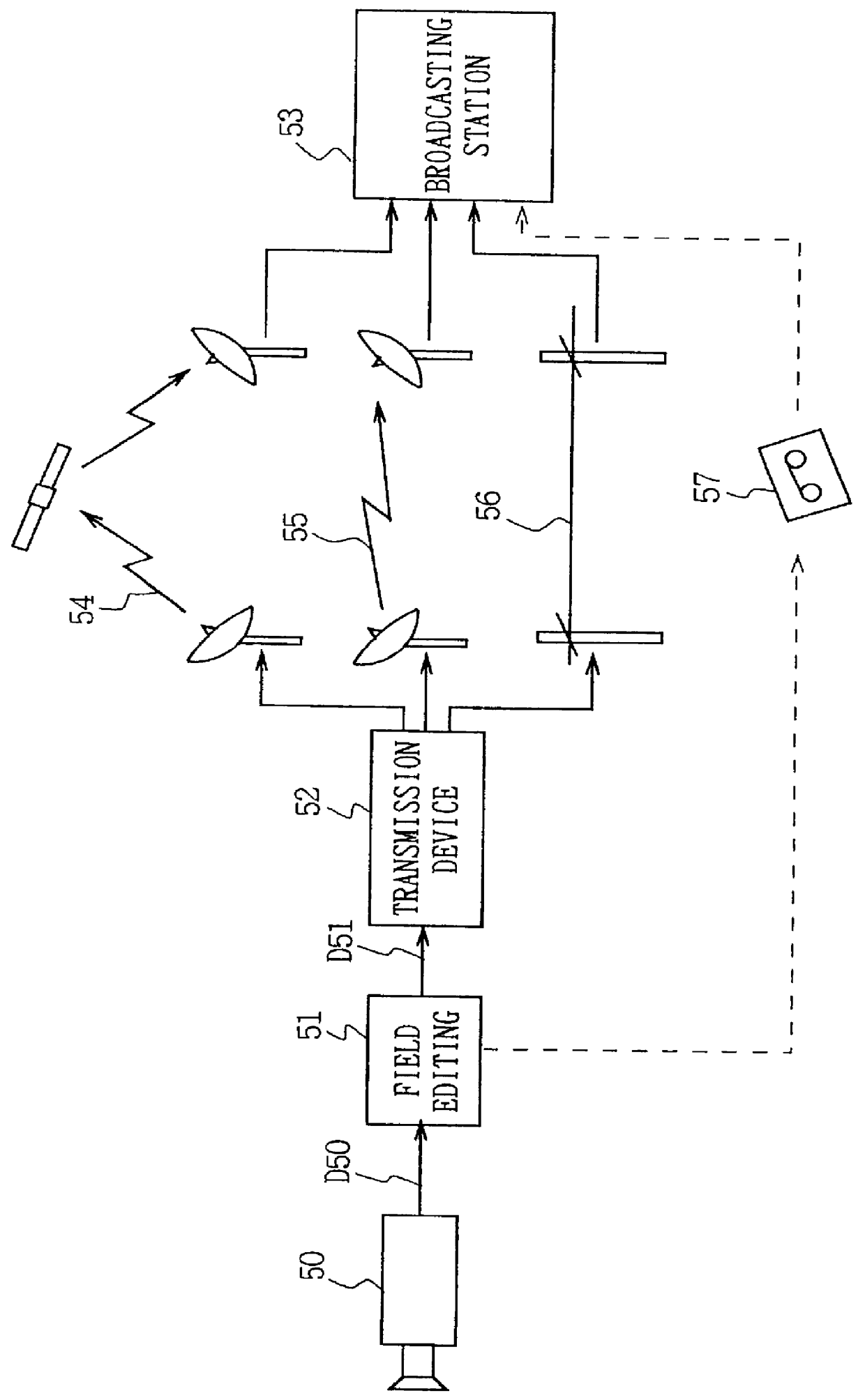
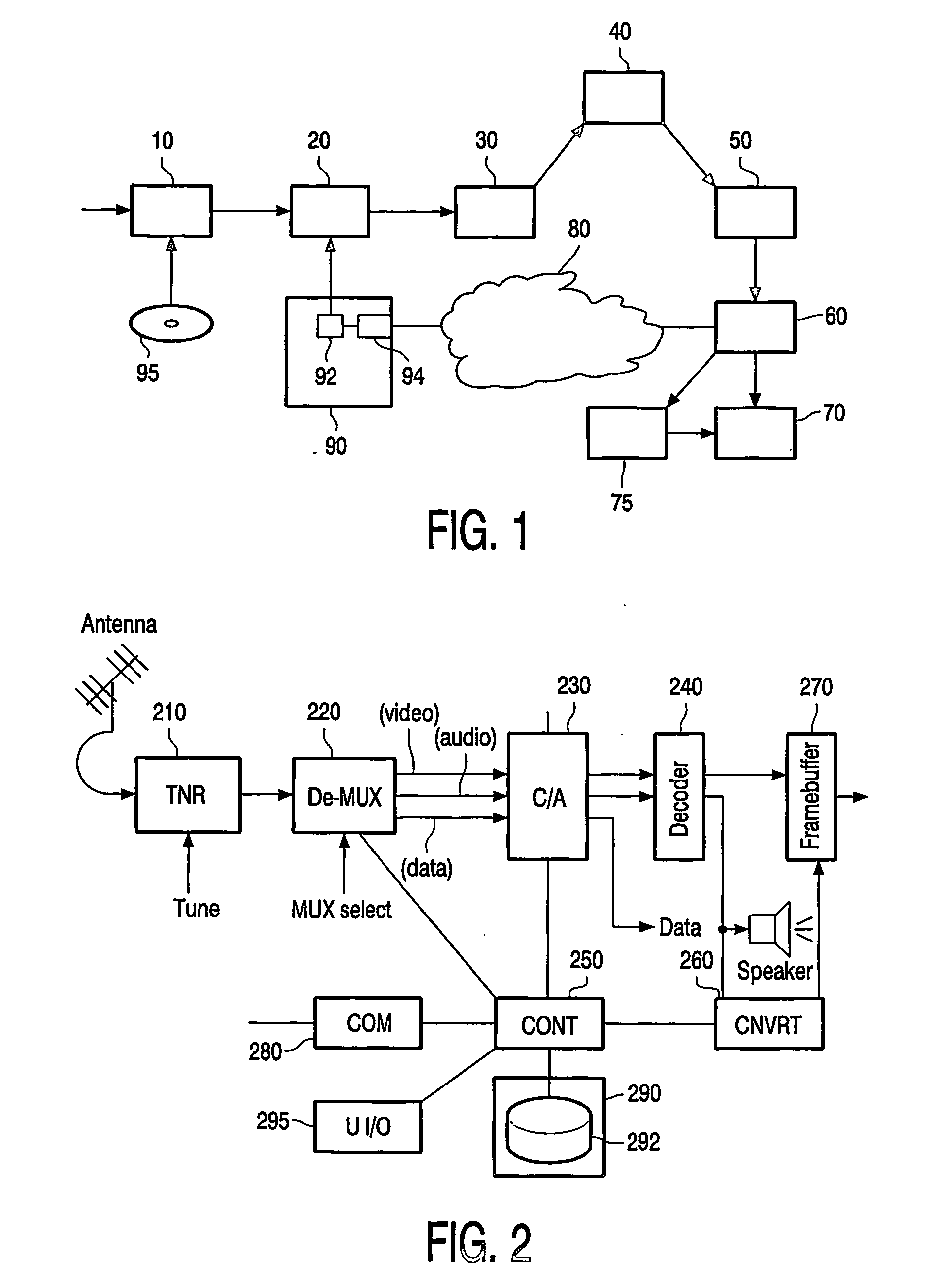
Recording of broadcast programmes
InactiveUS20060215988A1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionTelecommunicationsComputer science
A recording system (75) includes a broadcast receiver (210) for receiving broadcast programmes, and a download receiver (280) for requesting and receiving content parts of a broadcast programme from a server (90). A controller (250) determines whether an instruction for recording a broadcast programme would exceed a capacity for recording and playback of programmes during at least part of the corresponding broadcast period. If so, the controller instructs a recorder (290) to record content parts of the broadcast programme during a part of the broadcast period in which the capacity is not exceeded and stores an identification of a content part of the broadcast programme that could not be recorded. It determines a period in which the capacity of the recorder is not exceeded and ensures that the not recorded content parts are downloaded from the server in the determined period and recorded.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
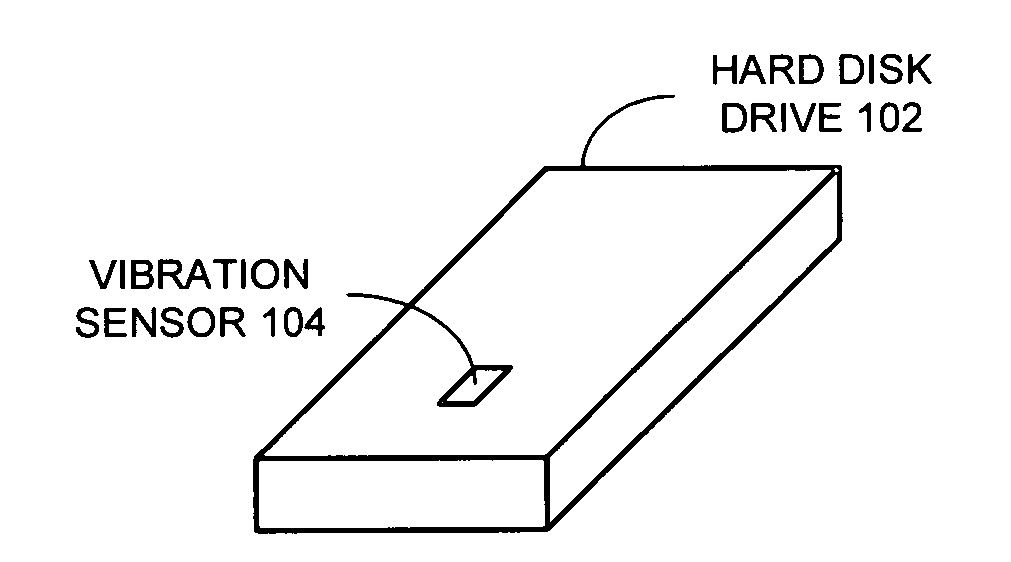
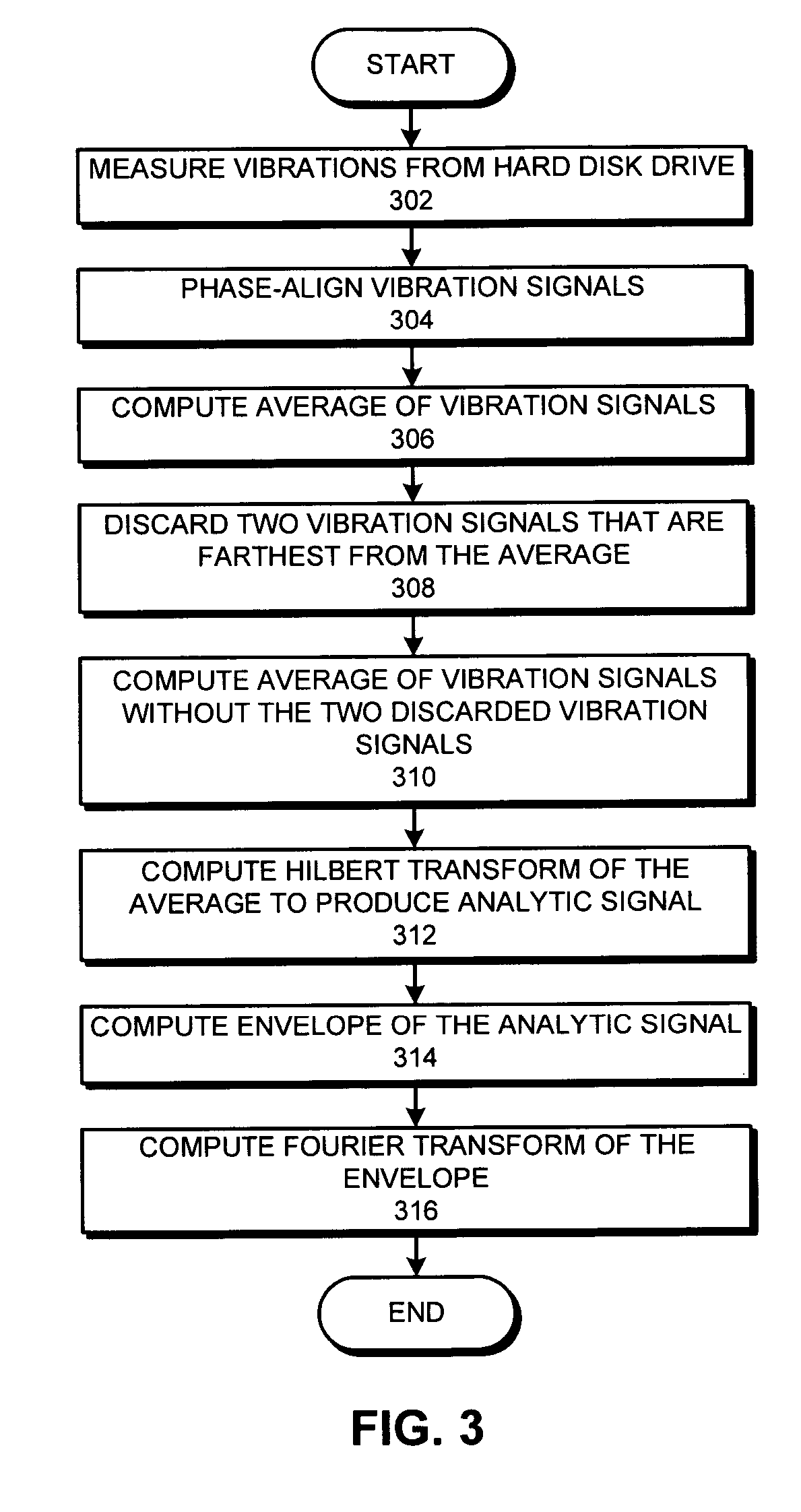
Method and apparatus for detecting the onset of hard disk failures
A system that detects the onset of hard disk drive failure. During operation, the system measures vibrations from the hard disk drive to produce one or more vibration signals. Next, the system generates a vibration signature for the hard disk drive from the measured vibration signals. The system then determines if the vibration signature indicates the onset of hard disk failure by comparing the vibration signature with a reference vibration signature for the hard disk drive. If so, the system generates a warning or takes a remedial action.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Video material selecting apparatus and method for selecting video material
InactiveUS6587123B2Television system detailsRedundant array of inexpensive disk systemsRelevant informationReference image
A video material selecting apparatus and a method for selecting a video material are proposed, which can remarkably improve the operating efficiency of the selecting operation for the video material. The video data and associated data of each video materials which satisfy requirements inputted through an inputting means, out of the plurality of video materials from a storing means, and the reference image and associated information of each video material are displayed on a screen based on the video data and the associated data.
Owner:SONY CORP
Aligned data storage for network attached media streaming systems
InactiveUS8521955B2Redundant array of inexpensive disk systemsDigital computer detailsStreaming dataRAID
Owner:BROADCOM INT PTE LTD
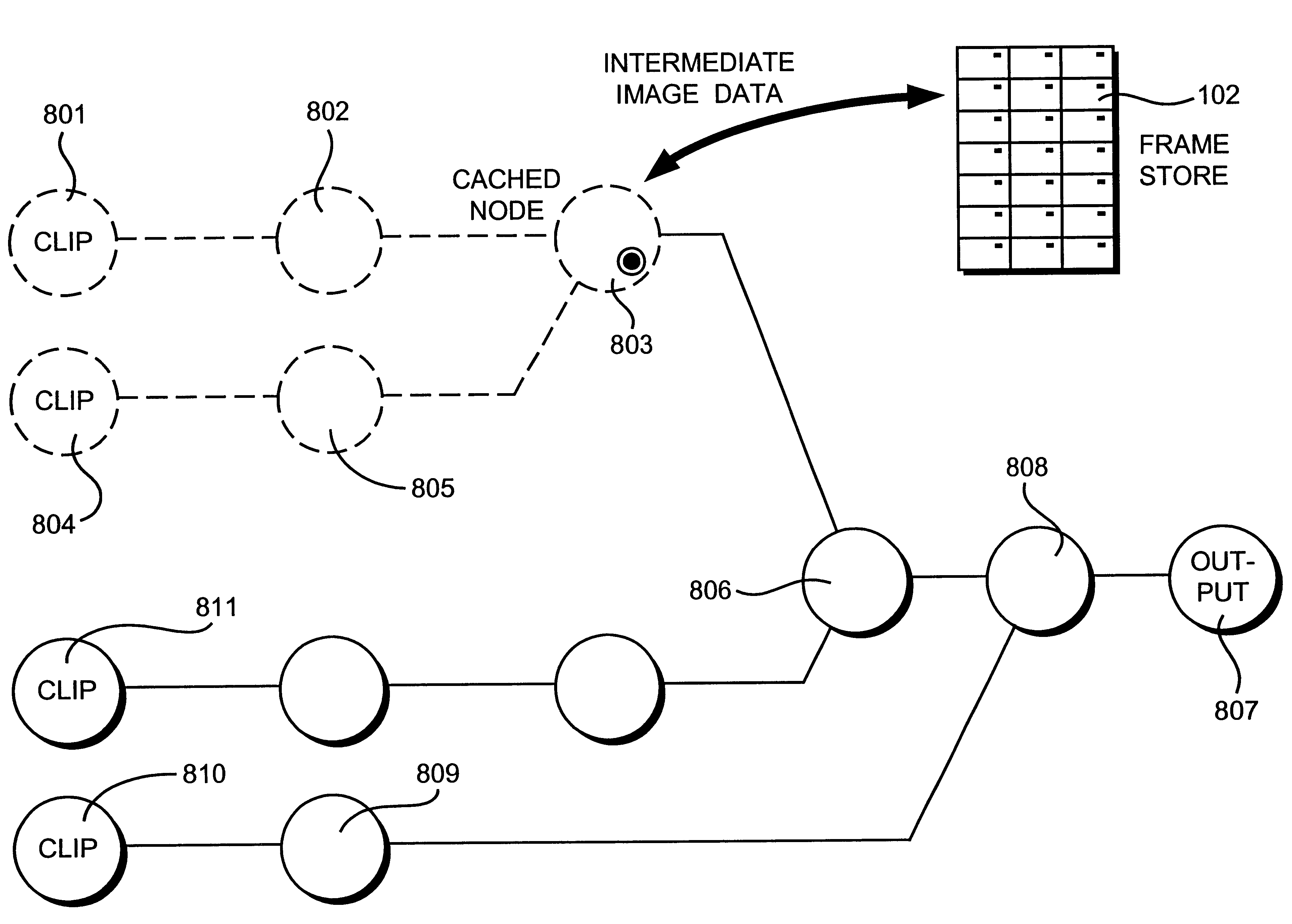
Caching data in a processing pipeline
InactiveUS6867782B2Optimize data structureFacilitate present inventionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
An image processing system processes image data in response to a sequence of image processing steps defined by a process tree data structure. The process tree comprises a plurality of interconnected nodes, including input nodes and at least one output node. Output rendering is performed a frame at a time, and each frame is rendered in a time determined by the amount of processing defined by the process tree. The process tree may comprise many branches of interconnected nodes, and the user can selectively cache intermediately rendered frames at nodes where the contributing process tree branches are relatively stable in their configuration. The user may then make modifications to processes in other parts of the process tree, without having to wait for image data to be rendered from unchanged parts of the process tree.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
Program and apparatus for balancing activity of disk storage devices in response to statistical analyses and preliminary testing
InactiveUS6487634B1Input/output to record carriersRedundant array of inexpensive disk systemsStatistical analysisLoad distribution
Load balancing of activities on physical disk storage devices is accomplished by monitoring reading and writing operations to logical volumes on the physical disk storage devices. A list of exchangeable pairs of logical volumes is developed based on size and function. Statistics accumulated over an interval are then used to obtain access activity values for each logical volume and each physical disk drive. A statistical analysis selects one logical volume pair. After testing to determine any adverse effect of making that change, the exchange is made to more evenly distribute the loading on individual physical disk storage devices.
Owner:EMC CORP
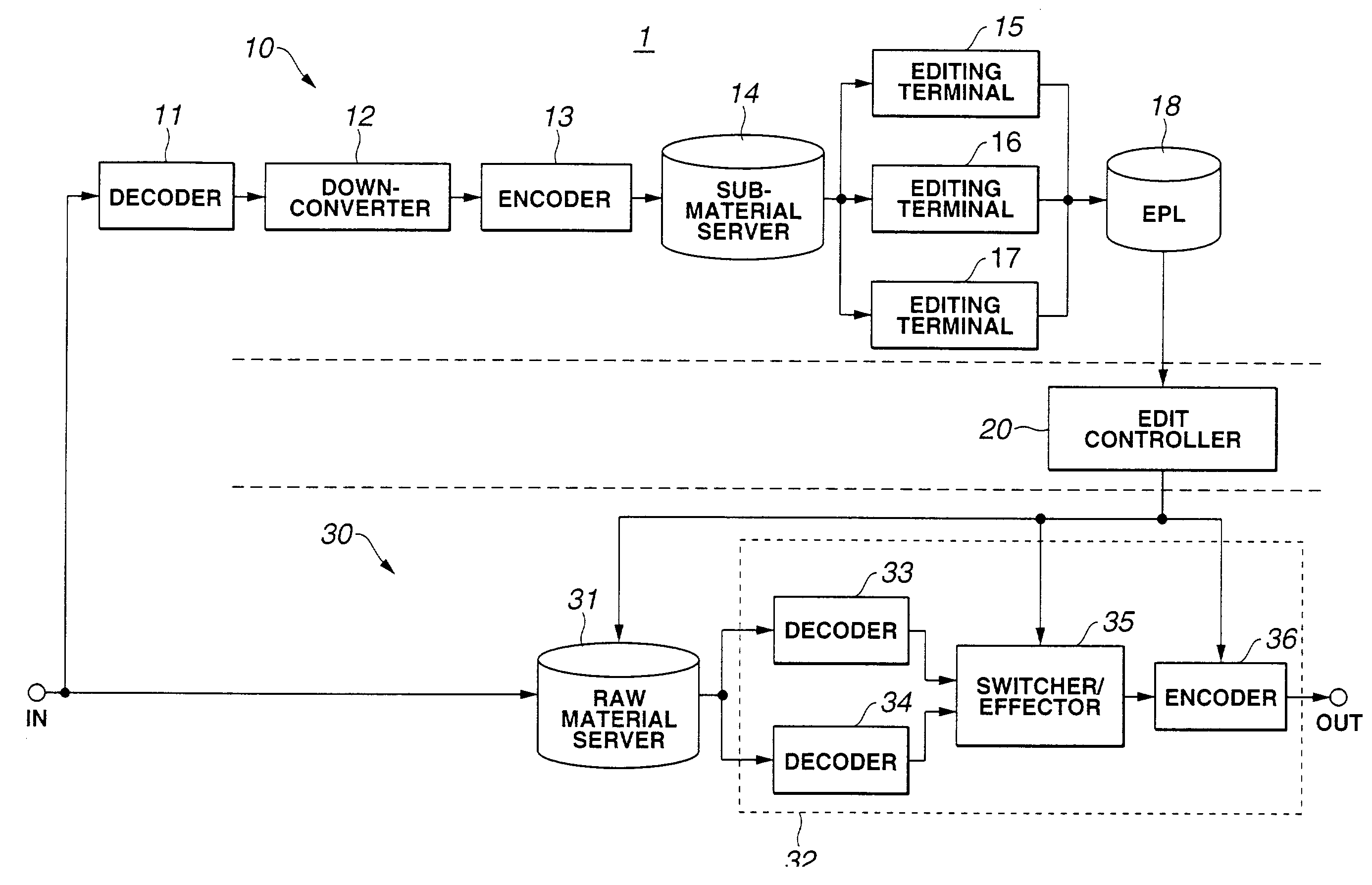
Device for creating content from multiple video and/or audio materials and method therefor
InactiveUS7660510B2Less costLess laborTelevision system detailsRedundant array of inexpensive disk systemsComputer graphics (images)Control signal
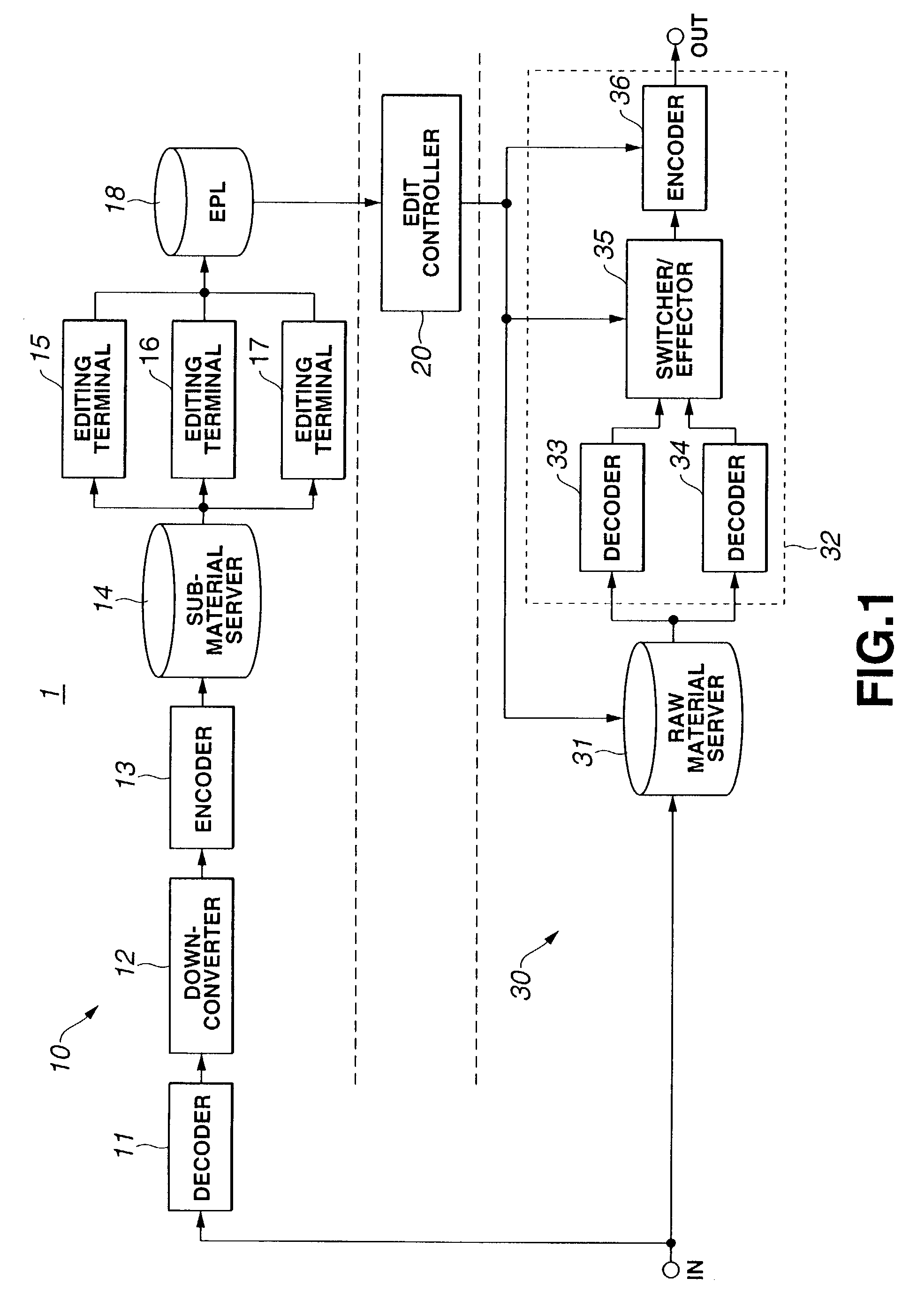
An EPL maker (10) is composed mainly of editing terminals (15), (16) and (17) each reading and decoding each of highly compressed sub materials to produce a material data and make an EPL while displaying, on a monitor, a video based on the material data. The EPL includes identification information for identification of a material used in editing and a format declare state for defining a format of at least a certain material. The EPLs made by the editing terminals (15), (16) and (17) are stored into an EPL storage unit (18). The EPLs stored in the EPL storage unit (18) are read by an edit controller (20). The edit controller (20) makes an edit control signal based on the EPLs, and supplies the signal to a content maker (30). Thus, an editing can be executed with having not to pool the materials once on hand and with labors and costs.
Owner:SONY CORP
Digital-cinema processing apparatus, ingesting method, and program
ActiveUS20080281872A1Easy to separateTelevision system detailsRedundant array of inexpensive disk systemsComputer science
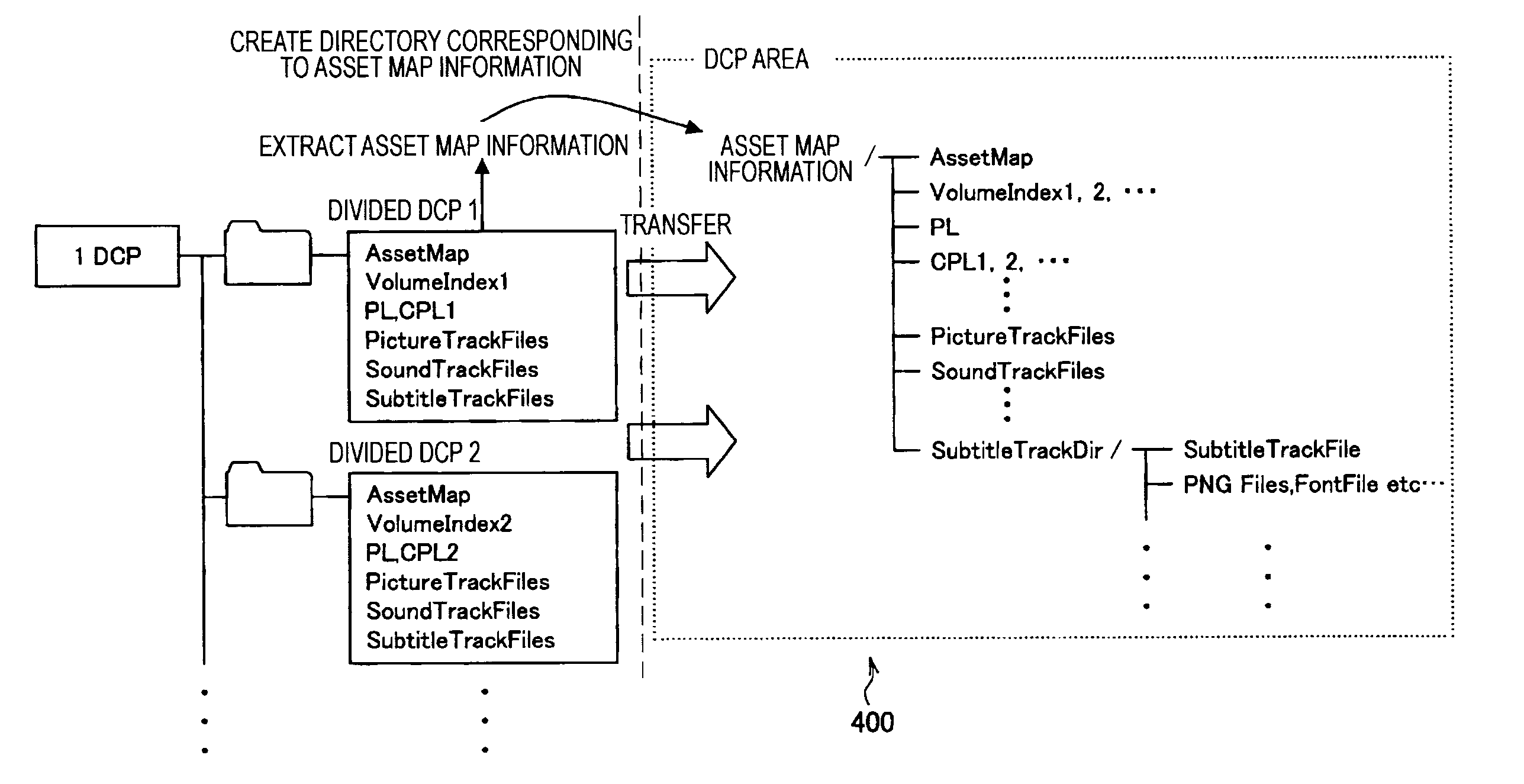
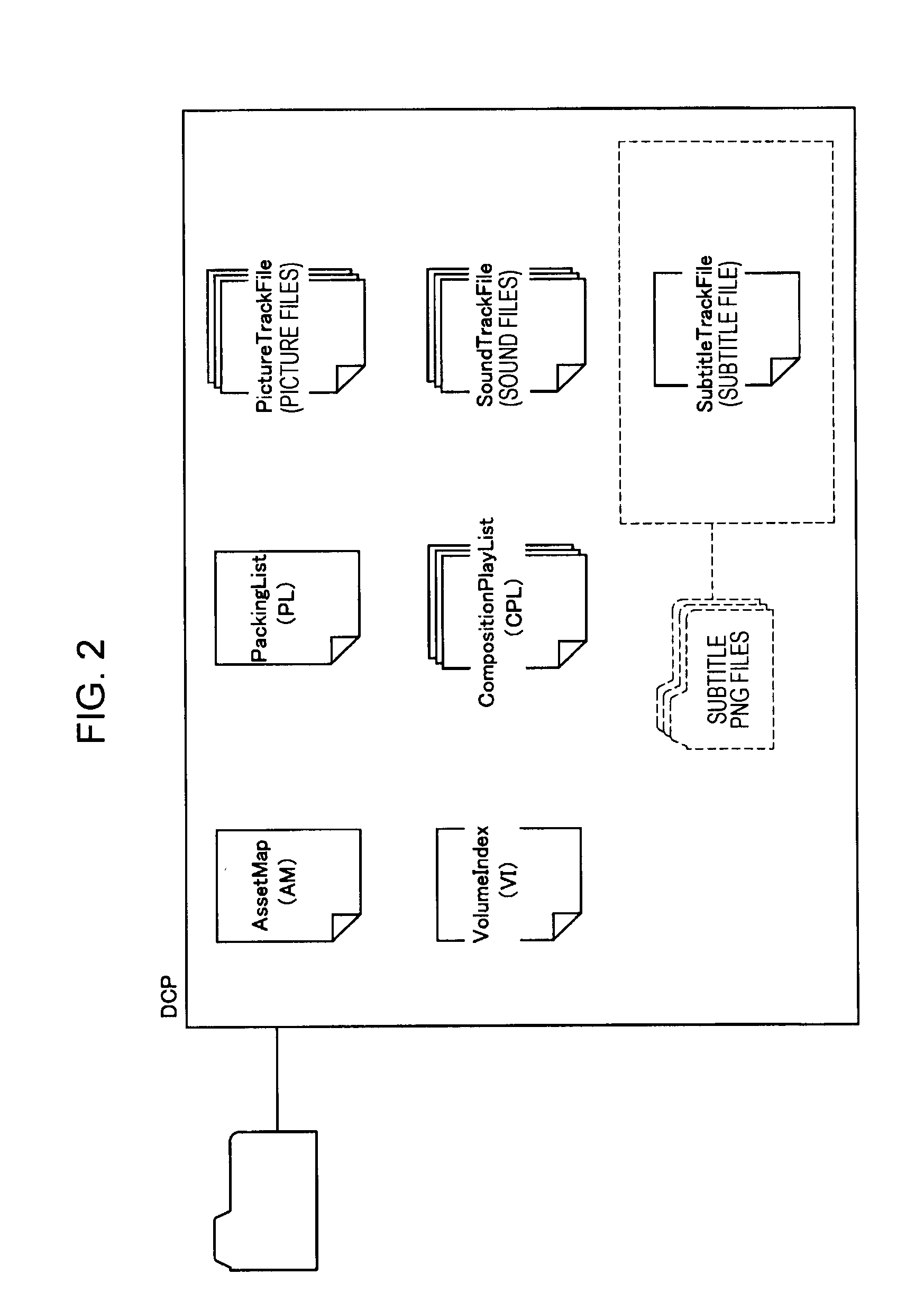
A digital-cinema processing apparatus for ingesting a digital cinema package (DCP) in a storage device includes a DCP obtaining unit configured obtain at least one divided DCP to be ingested among divided DCPs including a common asset map corresponding to a digital cinema, the divided DCPs having allocated thereto one or more picture track files, sound track files, and / or subtitle track files for the digital cinema; an asset-map-information extracting unit configured to extract asset map information from the asset map included in the divided DCP to be ingested, the asset map information being information unique to the asset map; a directory determining unit configured to determine an ingestion destination directory for the divided DCP in the storage device on the basis of the asset map information; and an ingesting unit configured to ingest the divided DCP in the ingestion destination directory of the storage device.
Owner:SONY CORP
Editing system and control method thereof
ActiveUS20050058430A1Improve efficiencyTelevision system detailsElectronic editing analogue information signalsComputer graphics (images)Video based
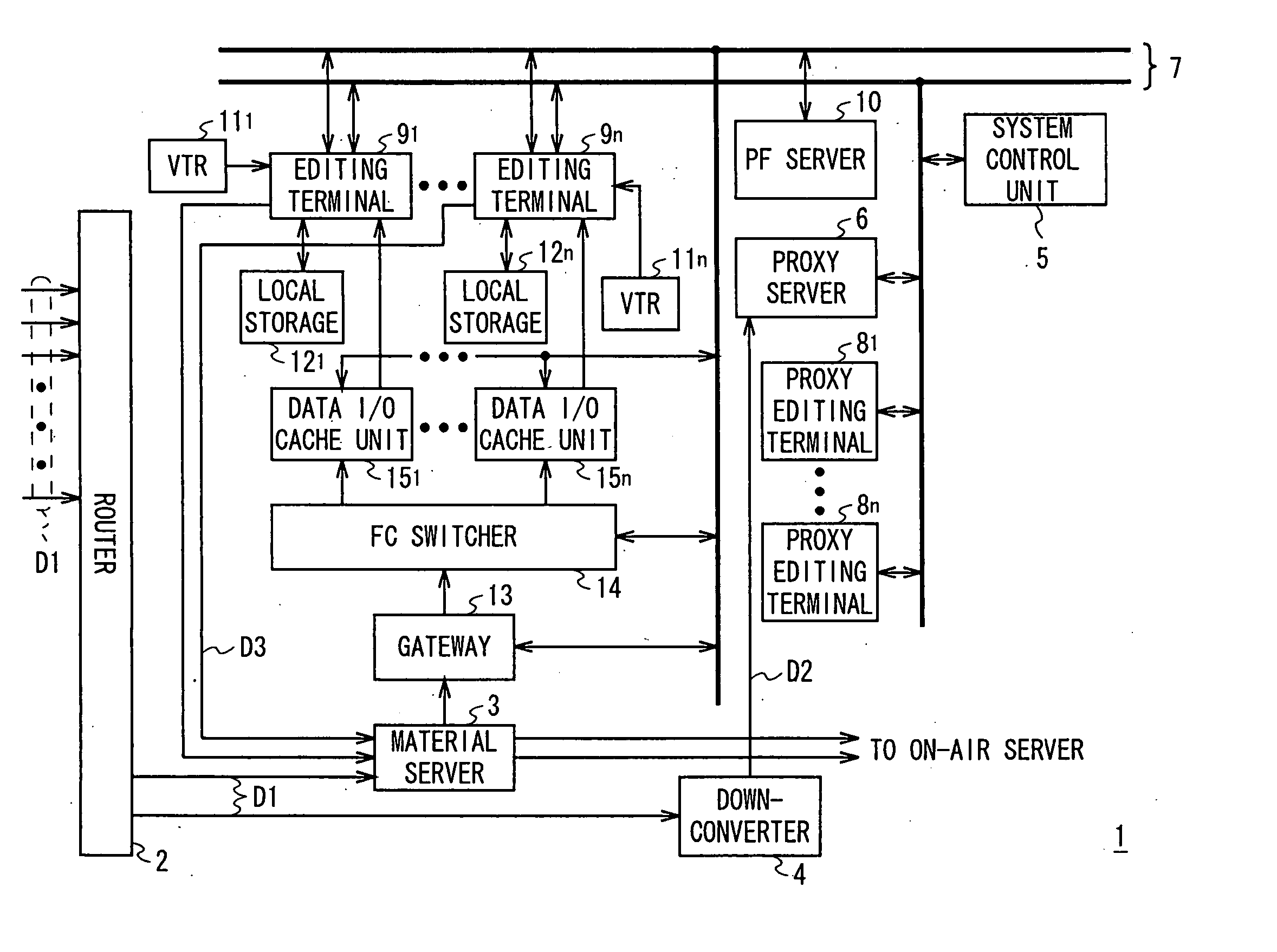
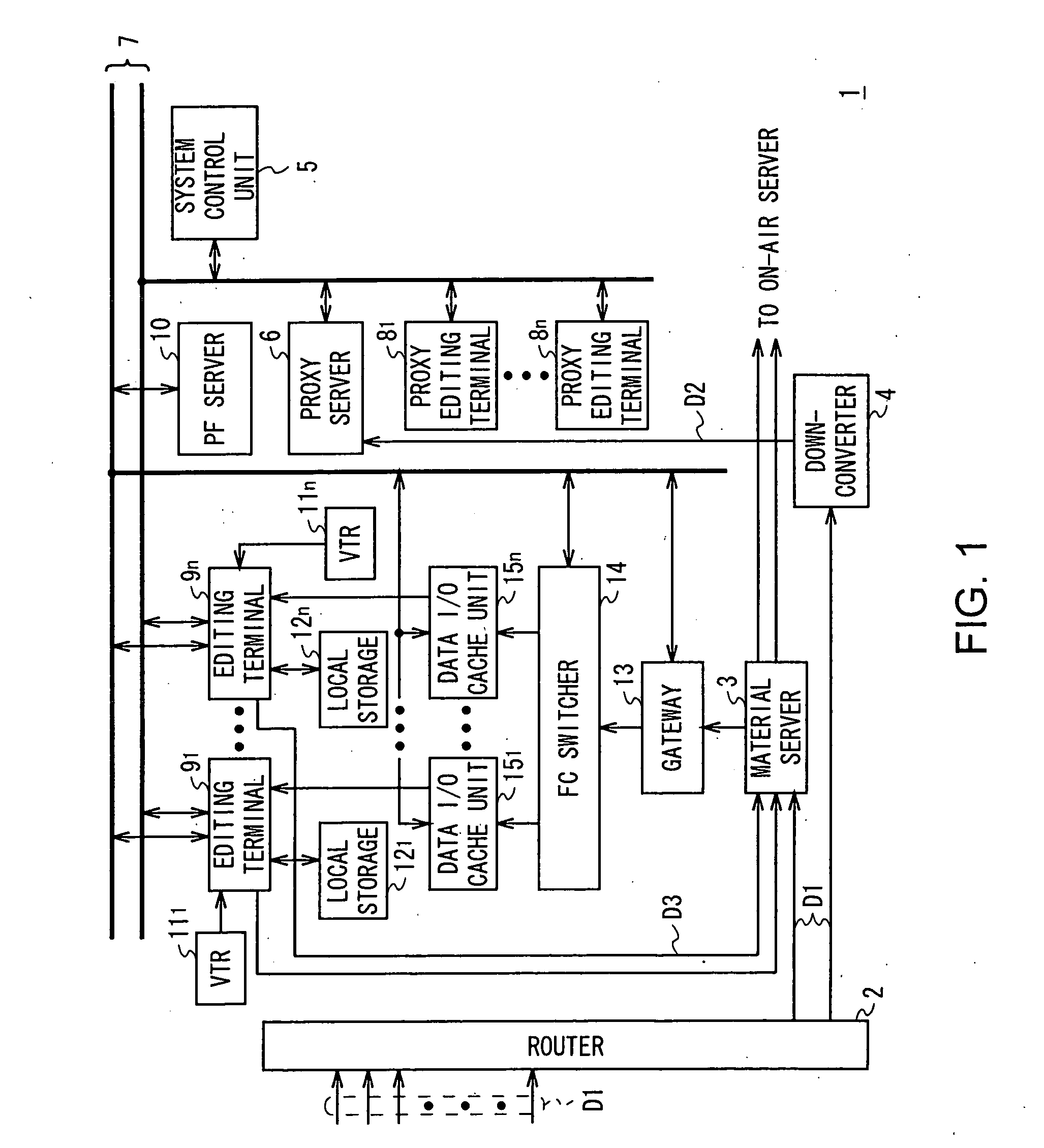
This invention proposes to an editing system and a control method thereof capable of significantly improving efficiency of editing work. The editing system is provided with: a server for storing and keeping the video data of edit material; a memory for storing and keeping video data read from the server, the memory having accessibility faster than the server; and an editing terminal for reading, processing, and editing required video data from the memory based on an edit list stored in a selected file, in order to create edited video based on the edit list. When opening the selected file, the editing terminal makes the server read the video data required for creating the edited video based on the edit list being stored in the file and makes the memory store and keep the video data.
Owner:SONY CORP
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com