Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
762results about "Error avoidance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
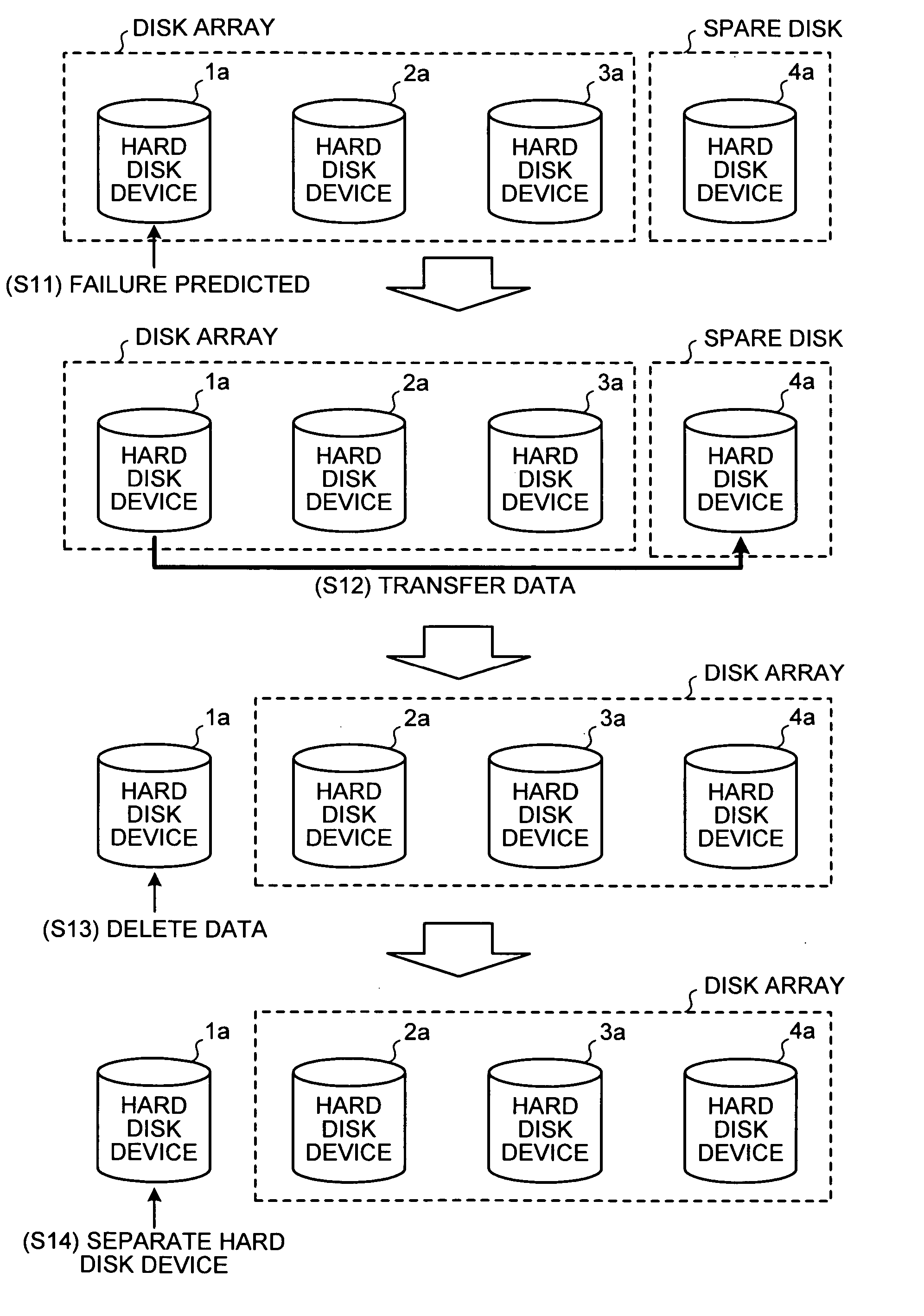
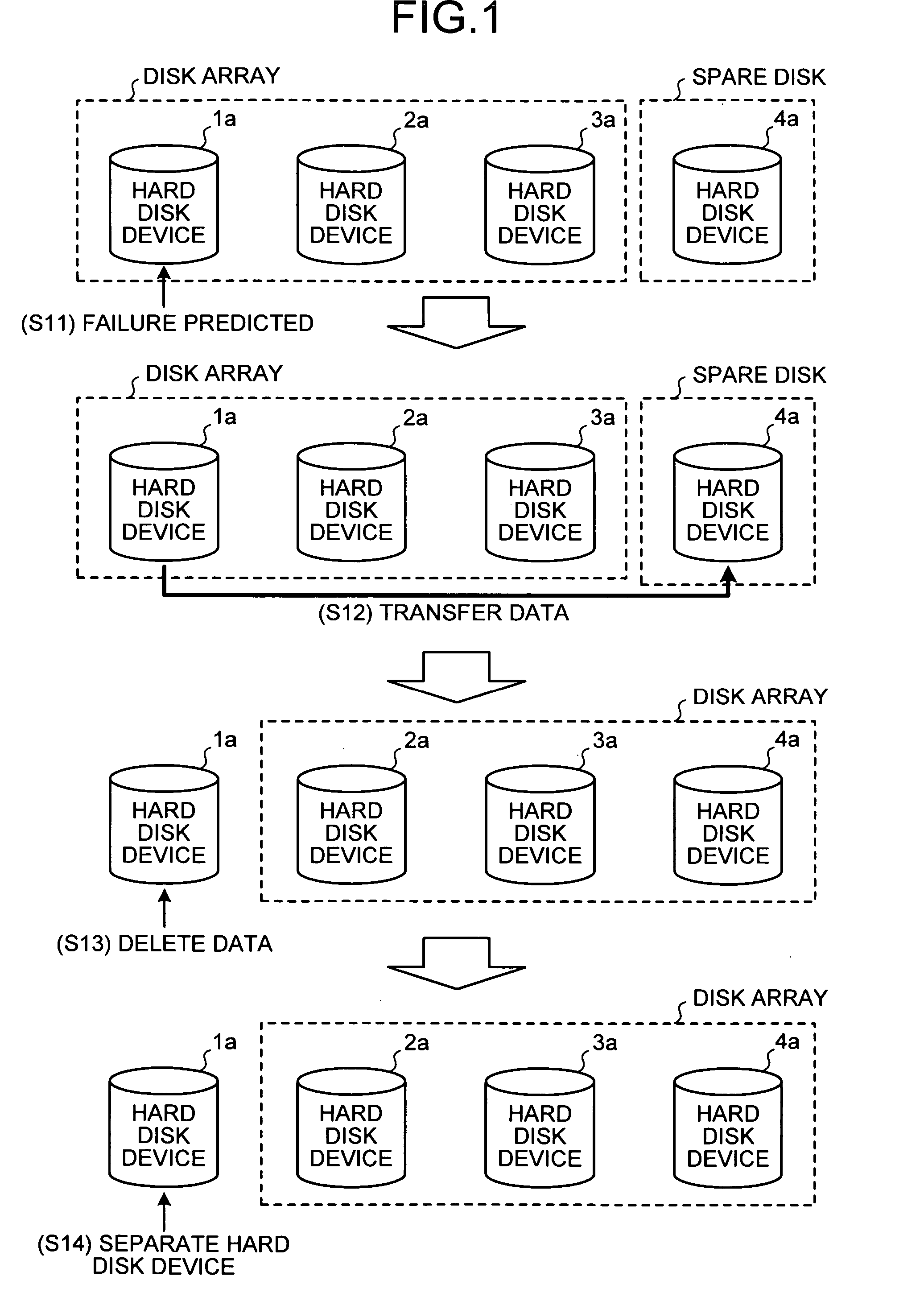
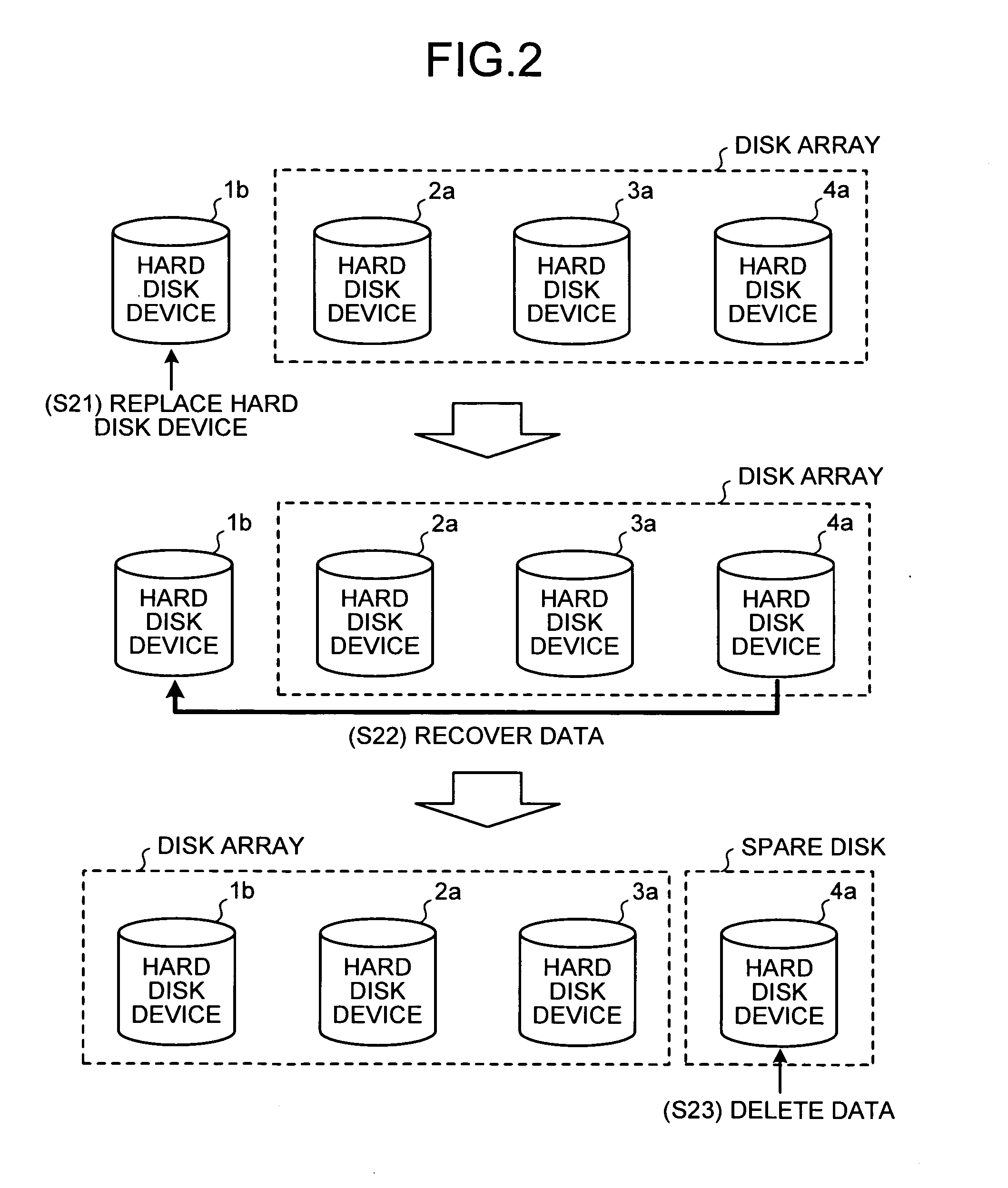
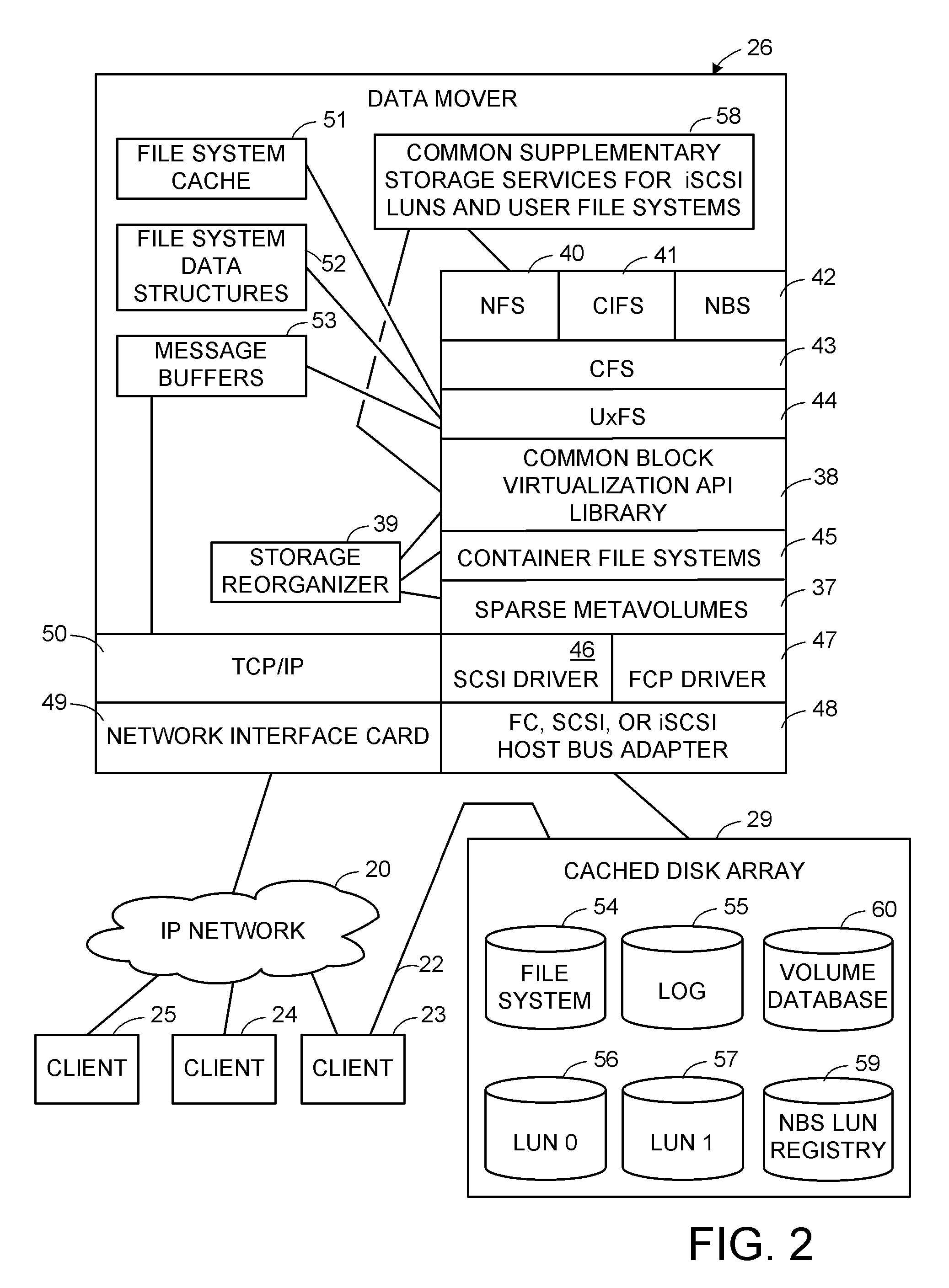
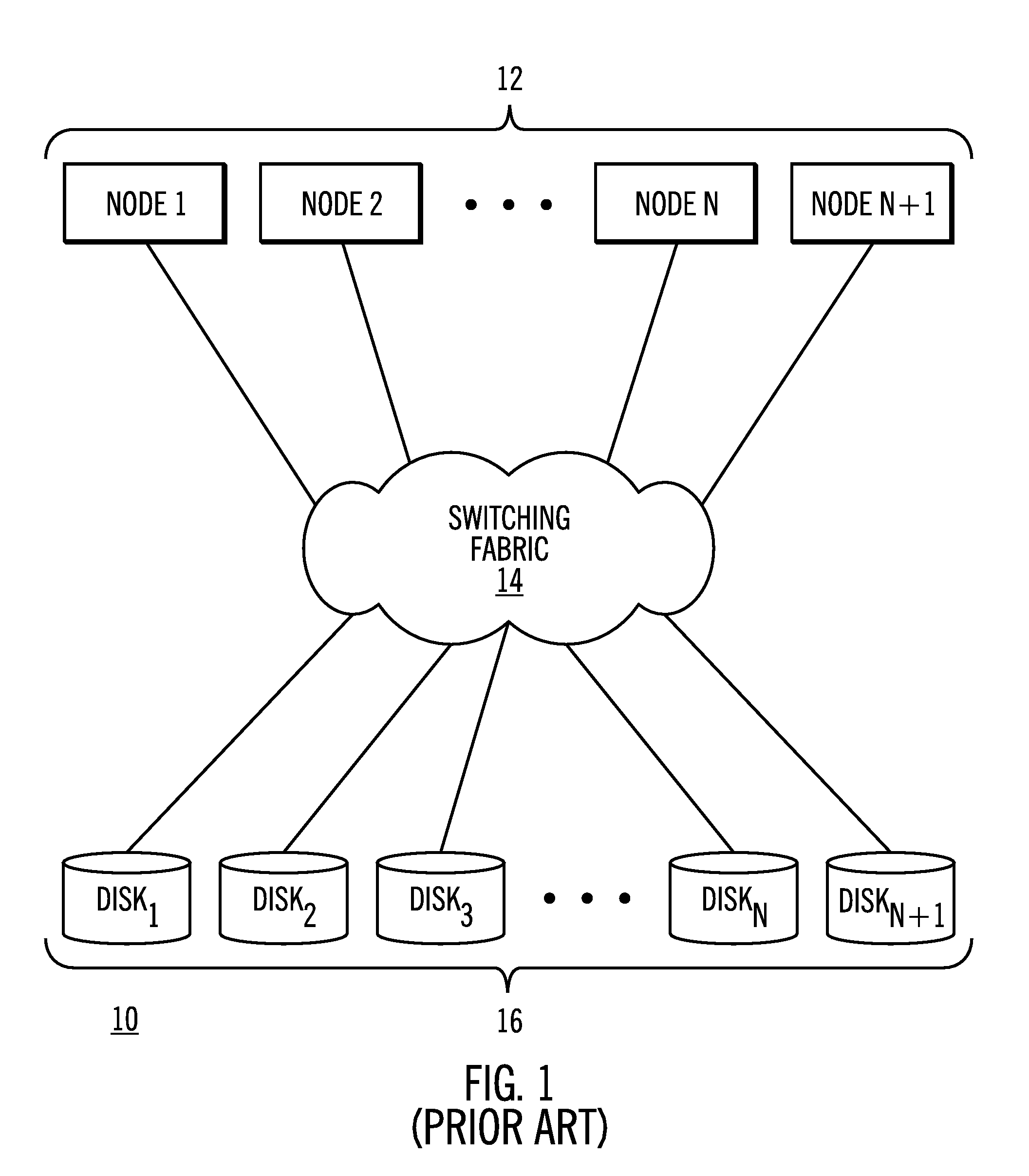
Disk array apparatus and disk-array control method
InactiveUS20070171562A1Solve problemsRedundant array of inexpensive disk systemsFilamentary/web record carriersData shippingDisk array
A failure predicting unit predicts a failure in a hard disk device that forms a disk array. A data transferring unit transfers data from a failure-predicted hard disk device for which the failure is predicted by the failure predicting unit to a spare disk. A data deleting unit deletes the data from the failure-predicted hard disk device after the data transferring unit completes transferring the data.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
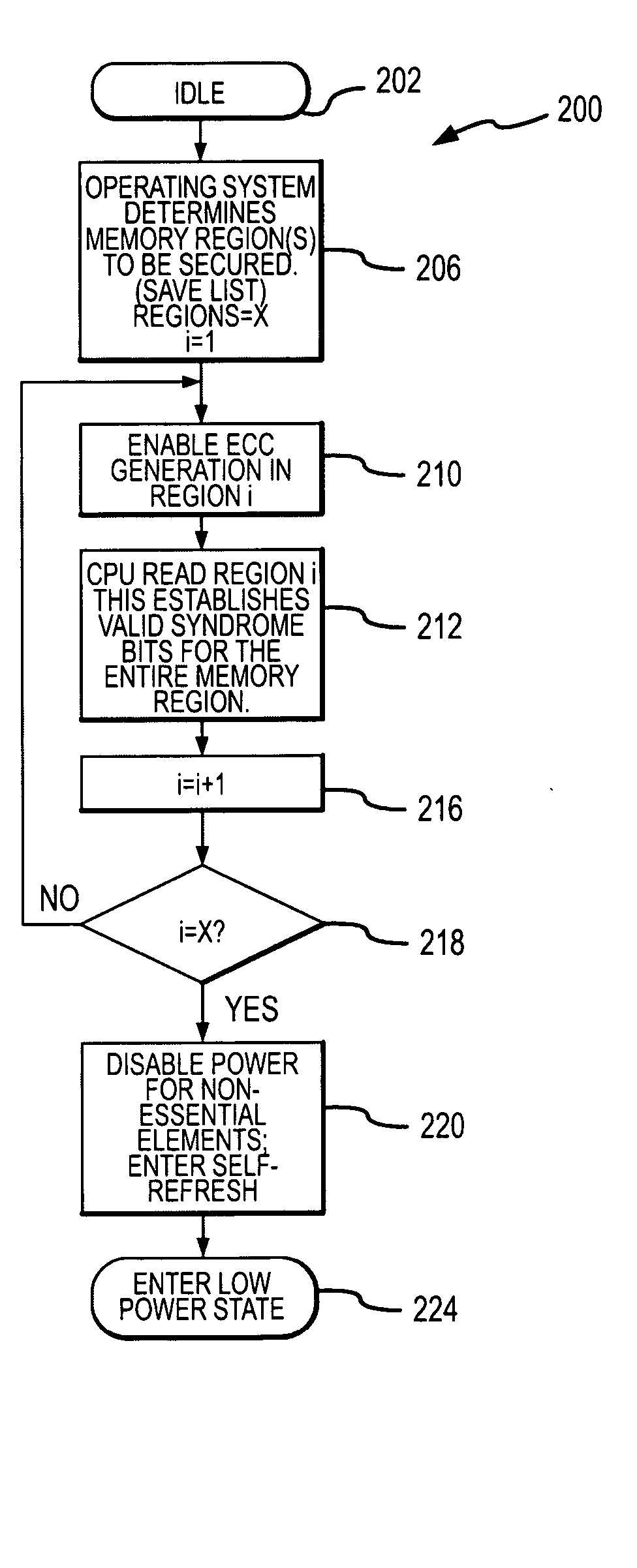
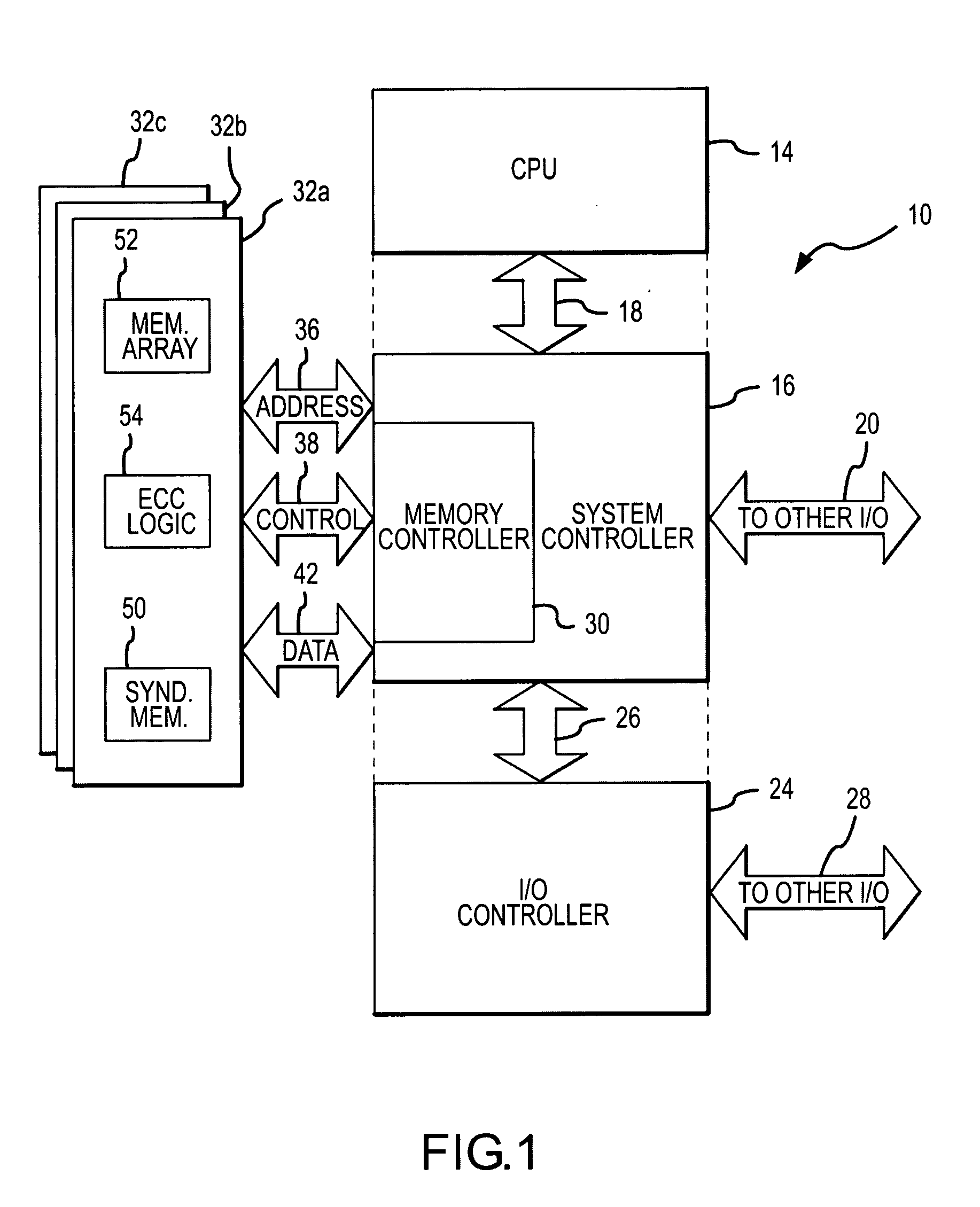
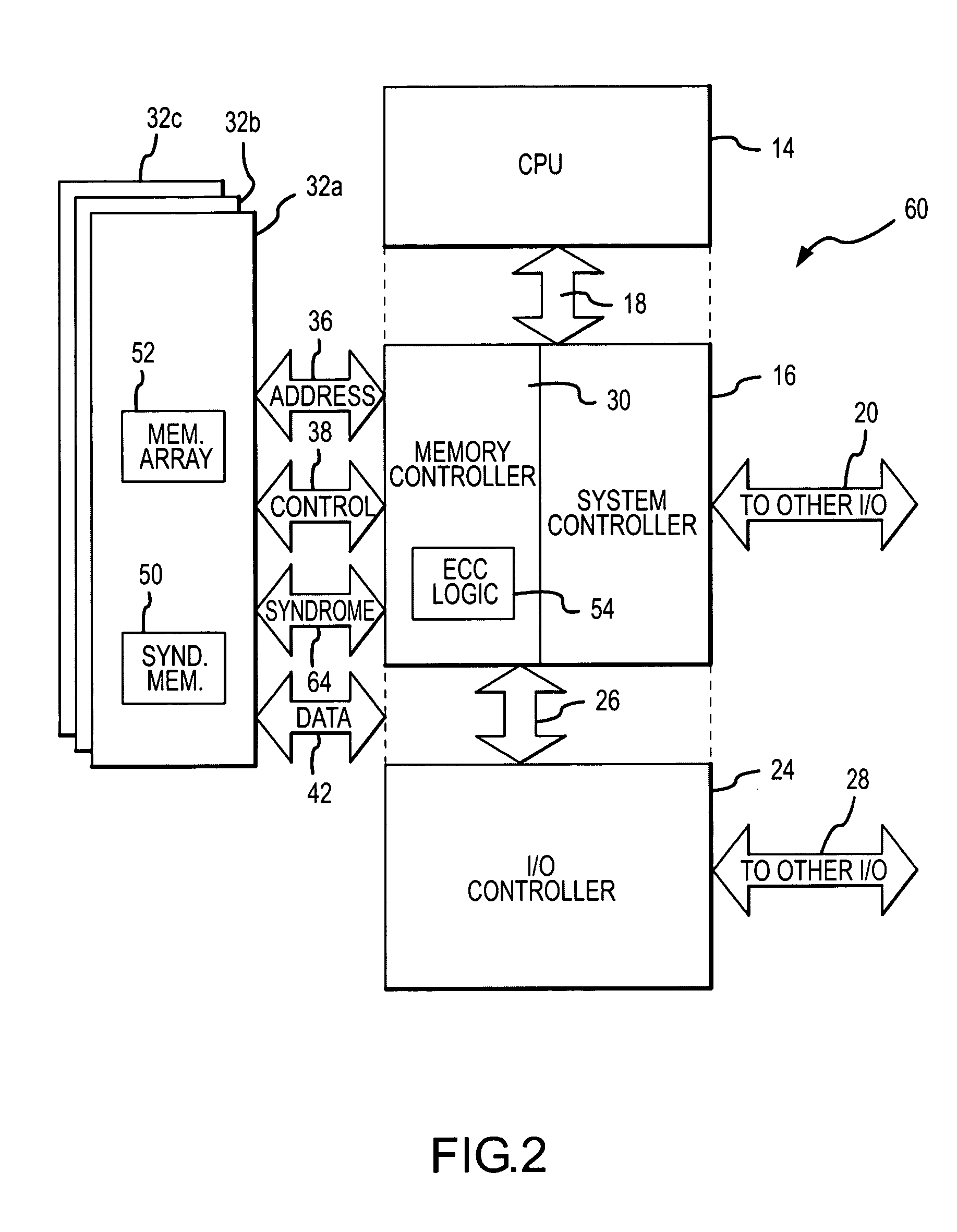
Memory system and method having selective ECC during low power refresh
InactiveUS20060010339A1Reduced power ratingMemory loss protectionError avoidanceError checkingMemory controller
A computer system includes a processor coupled to a DRAM through a memory controller. The processor switches the DRAM to a low power refresh mode in which DRAM cells are refreshed at a sufficiently low rate that data retention errors may occur. Prior to switching the DRAM to the low power refresh mode, the processor identifies a region of an array of DRAM cells that contains essential data that needs to be protected from such data retention errors. The processor then reads data from the identified region, and either the DRAM or the memory controller generates error checking and correcting syndromes from the read data. The syndromes are stored in the DRAM, and the low power refresh mode is then entered. Upon exiting the low power refresh mode, the processor again reads the data from the identified region, and the read data is checked and corrected using the syndromes.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
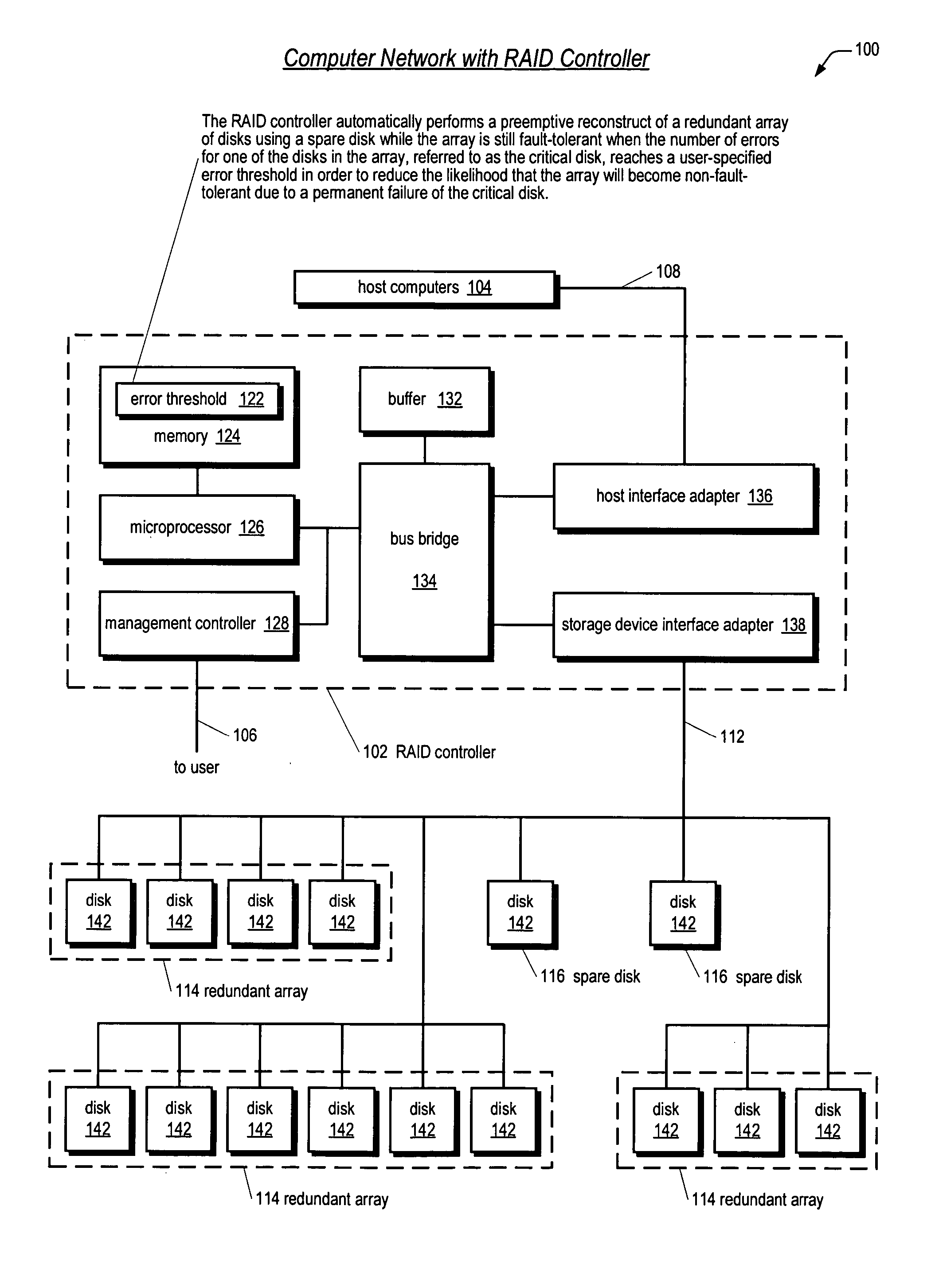
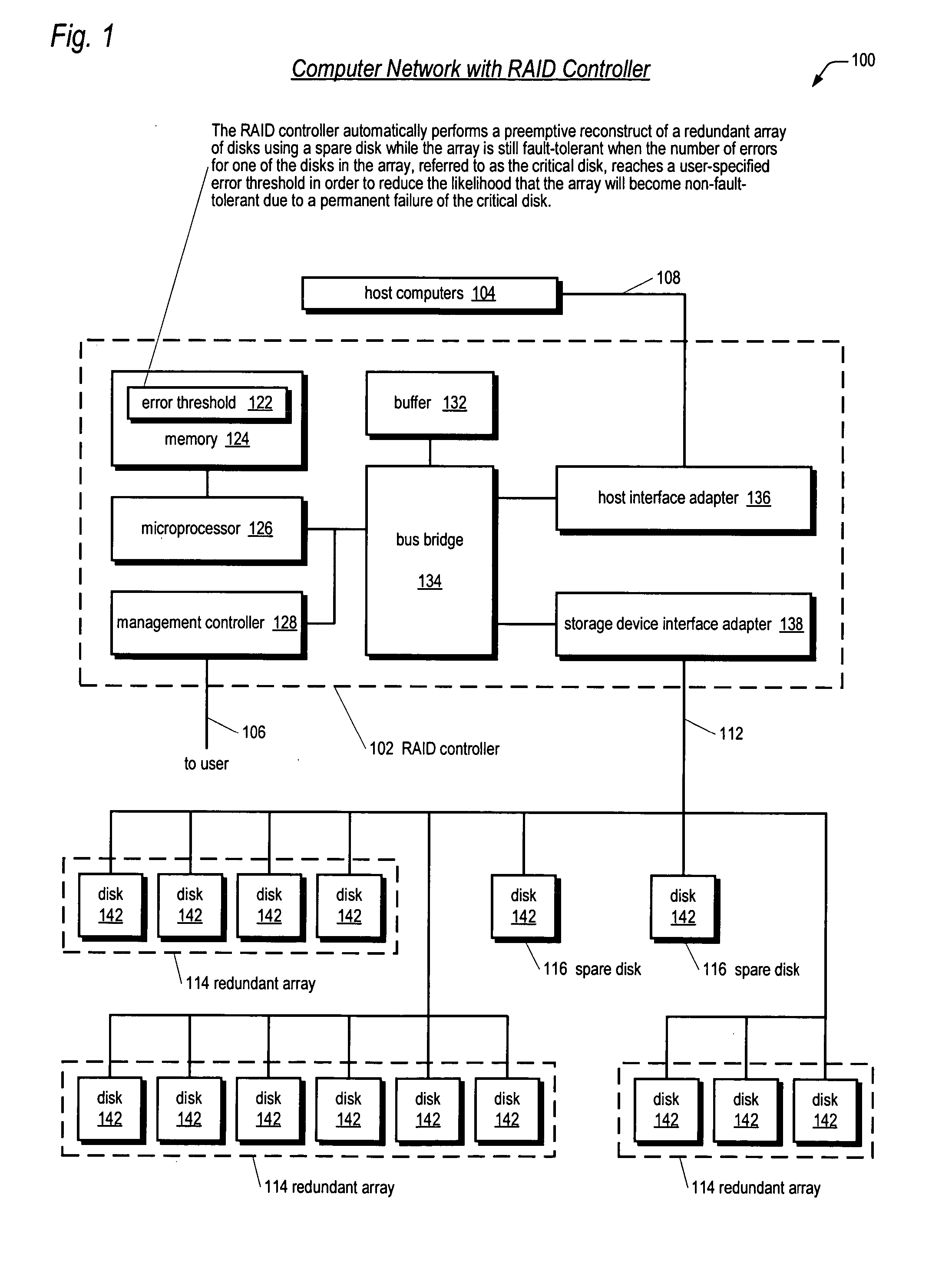
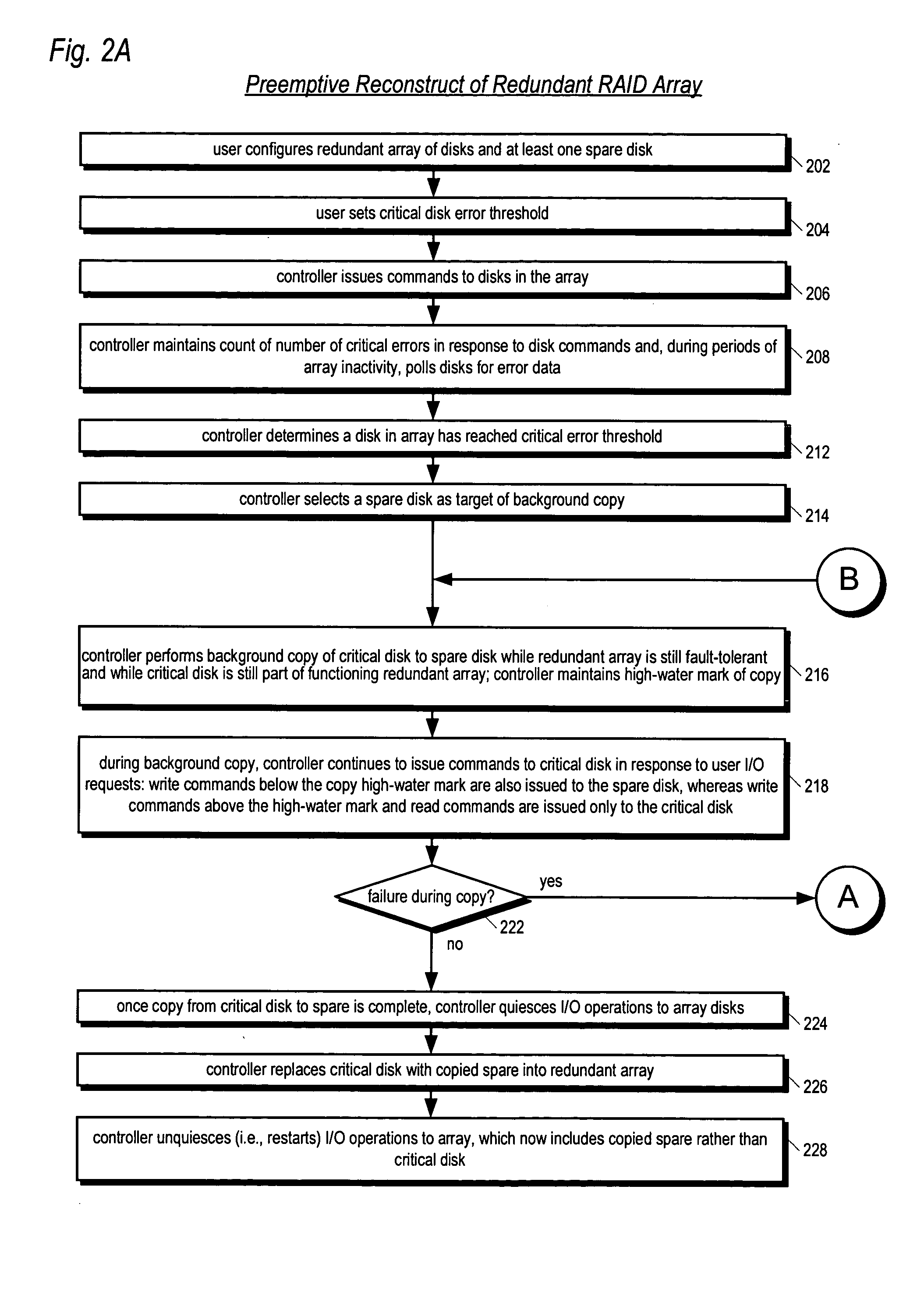
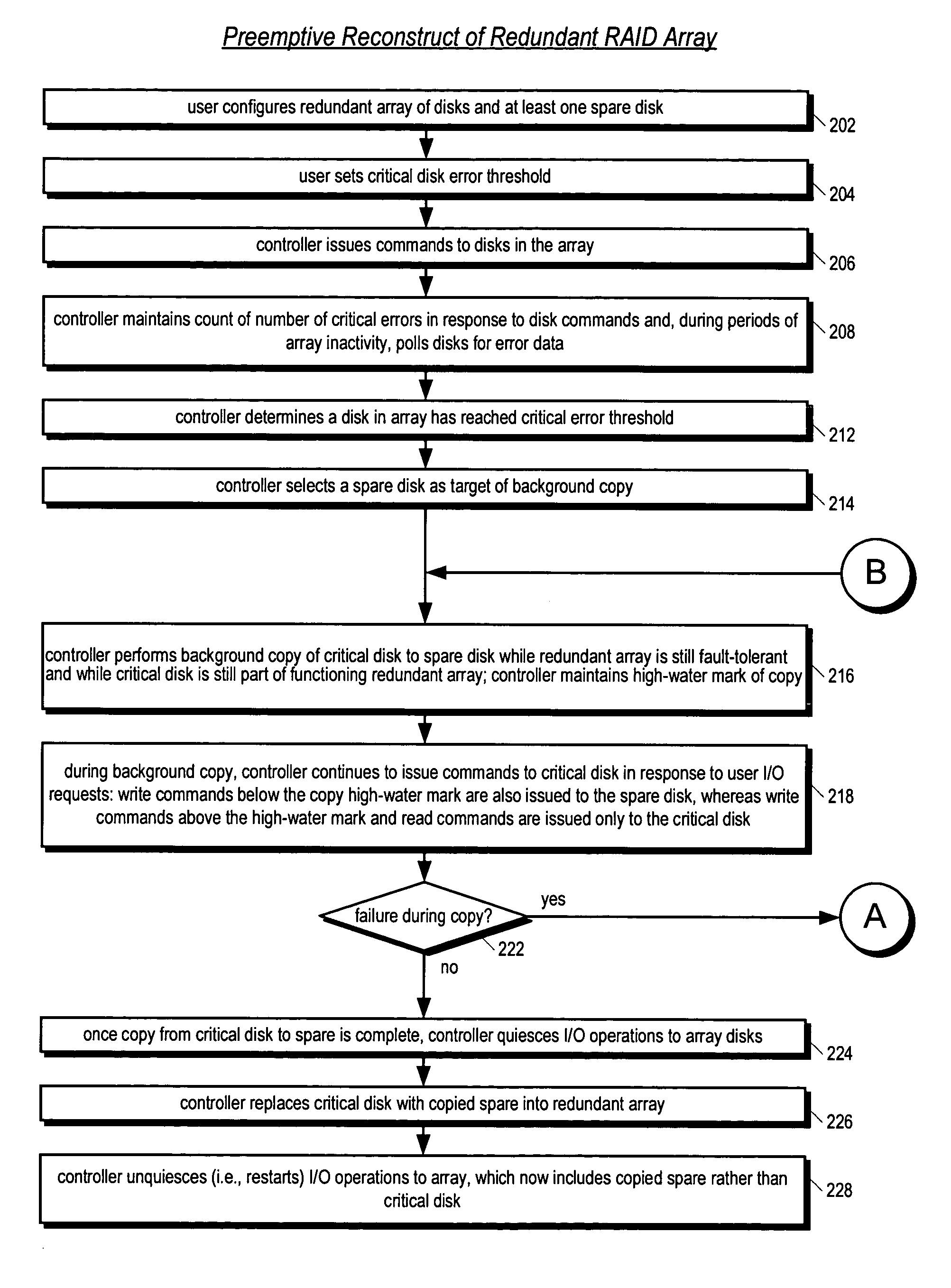
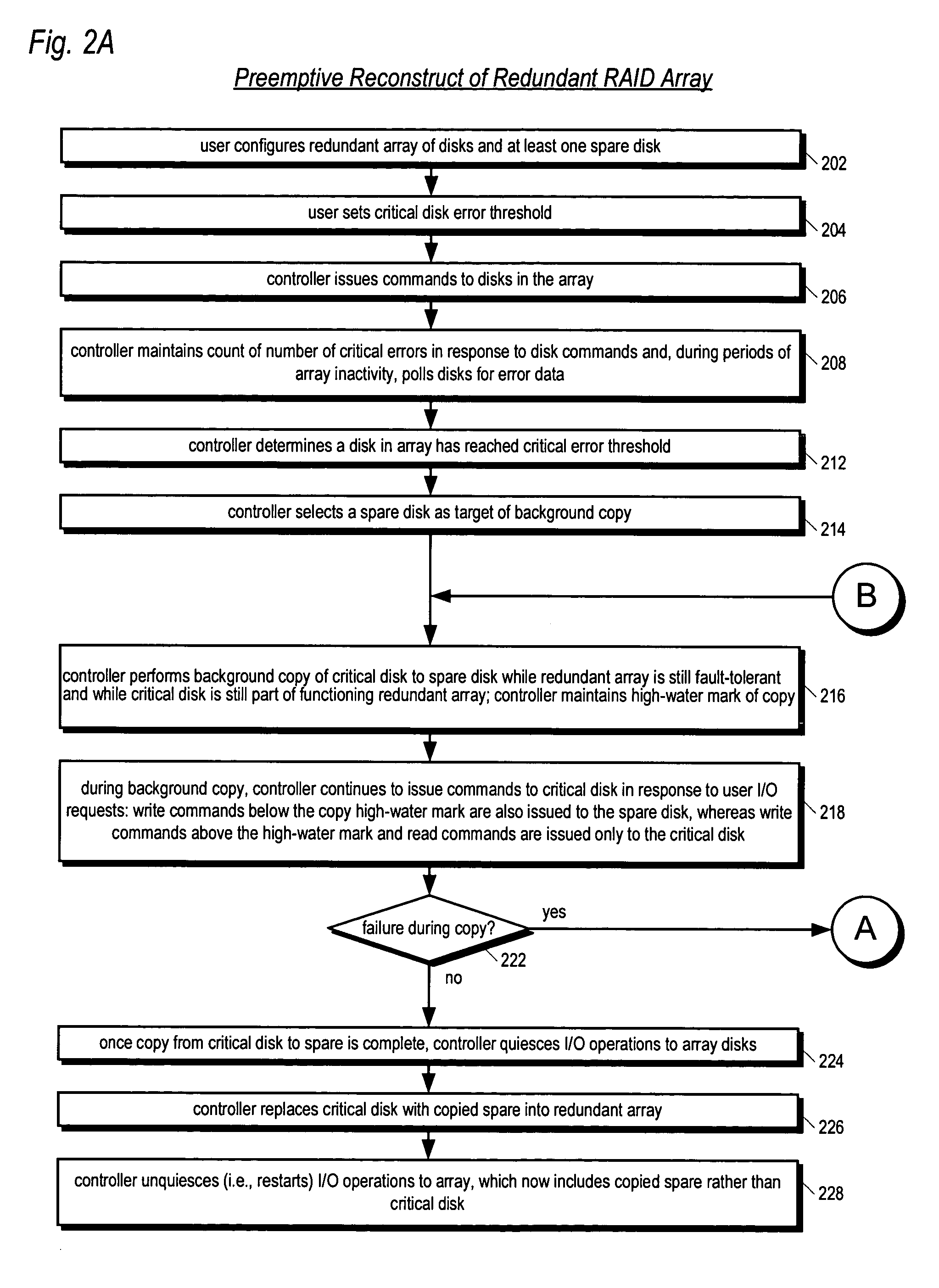
Apparatus and method for performing a preemptive reconstruct of a fault-tolerand raid array
ActiveUS20050283655A1Reduce the possibilityLess timeReliability/availability analysisError avoidanceRAIDUser input
A RAID controller performing a preemptive reconstruct of a redundant array of disks while the array is still fault-tolerant is disclosed. The controller receives user input specifying an error threshold. When a disk in the array (critical disk) exceeds the error threshold, the controller copies the critical disk data to a spare disk. After the copy completes, the controller replaces the critical disk with the spare disk in the array. The controller keeps the critical disk as part of the redundant array during the copy, i.e., continues to read and write the critical disk in response to user I / O requests. Hence, the array remains fault-tolerant during the preemptive reconstruct. In one embodiment, the controller automatically performs the reconstruct without user intervention. If the critical disk fails during the copy, the controller performs a conventional reconstruct to the spare disk starting where the copy left off.
Owner:DOT HILL SYST
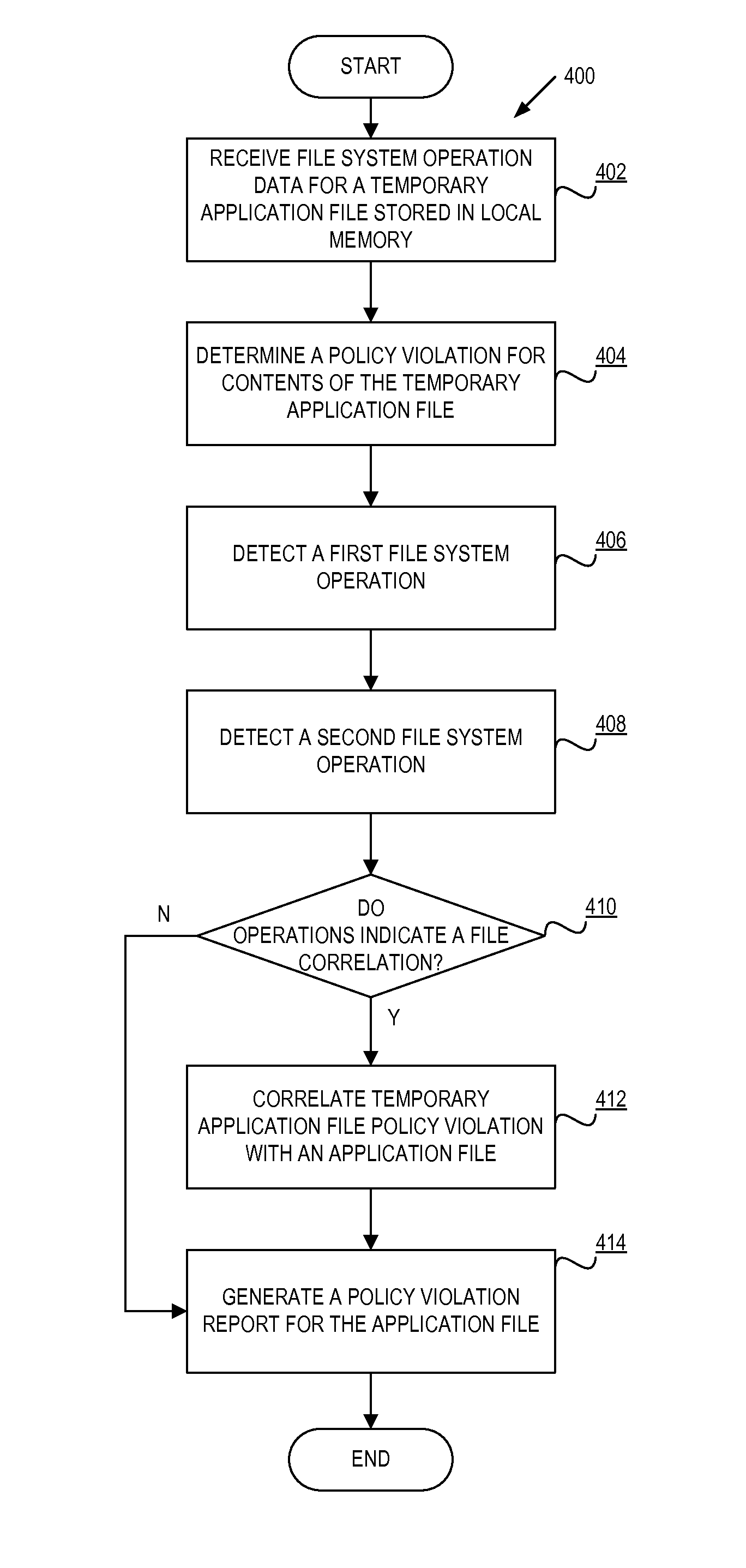
System and method for managing data loss due to policy violations in temporary files
InactiveUS7991747B1Memory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsClient agentApplication software
A method and apparatus for managing data loss due to policy violations in temporary files is described. In one embodiment, the method includes monitoring, by a client agent, information content on a client for violations of a policy. The method further includes determining, by the client agent, that a violation of the policy has occurred for content of a temporary file of an application. In one embodiment, the policy violation of the temporary file is correlated, by the client agent, with an original file of the application.
Owner:CA TECH INC
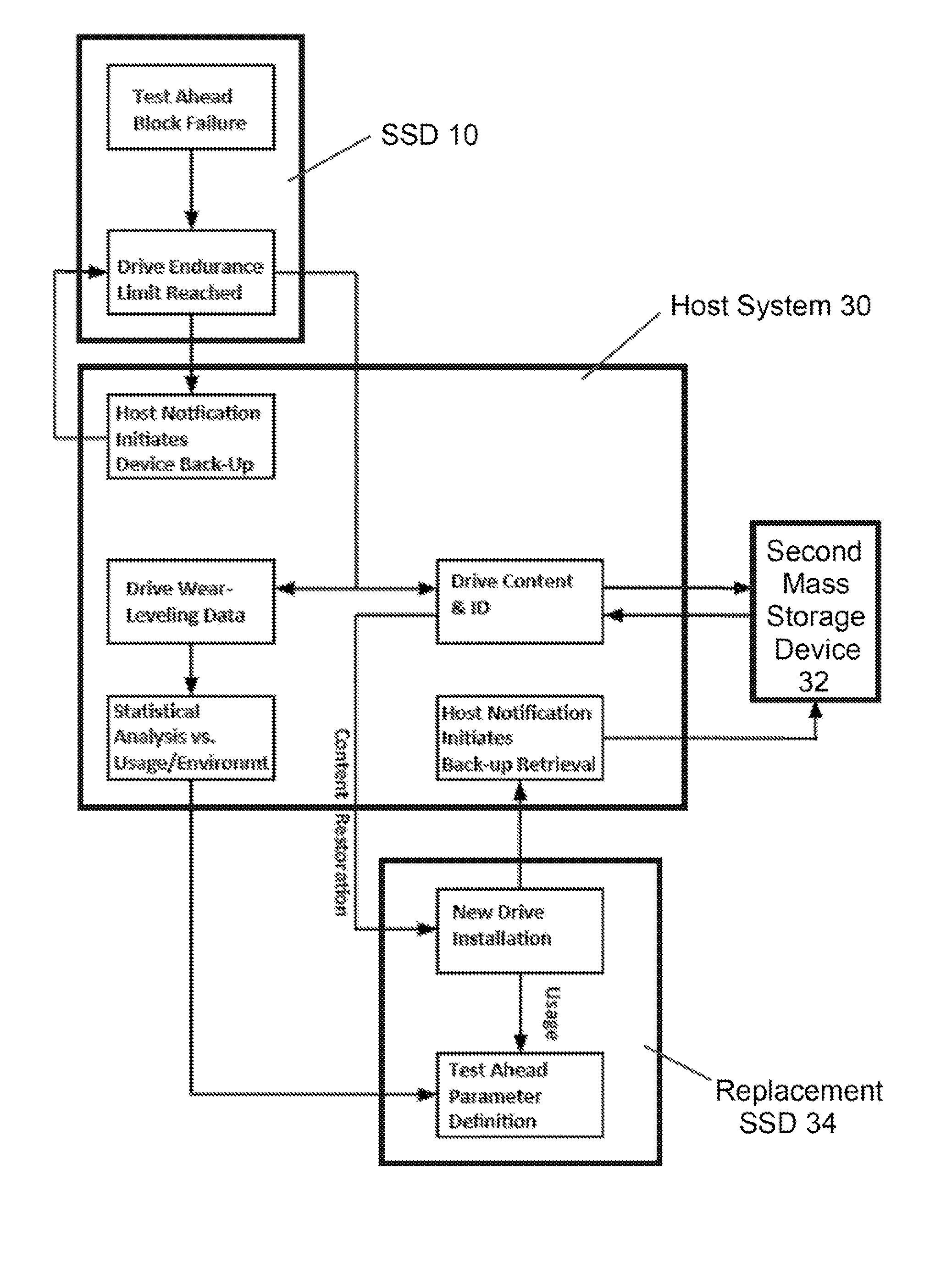
Computer system with backup function and method therefor
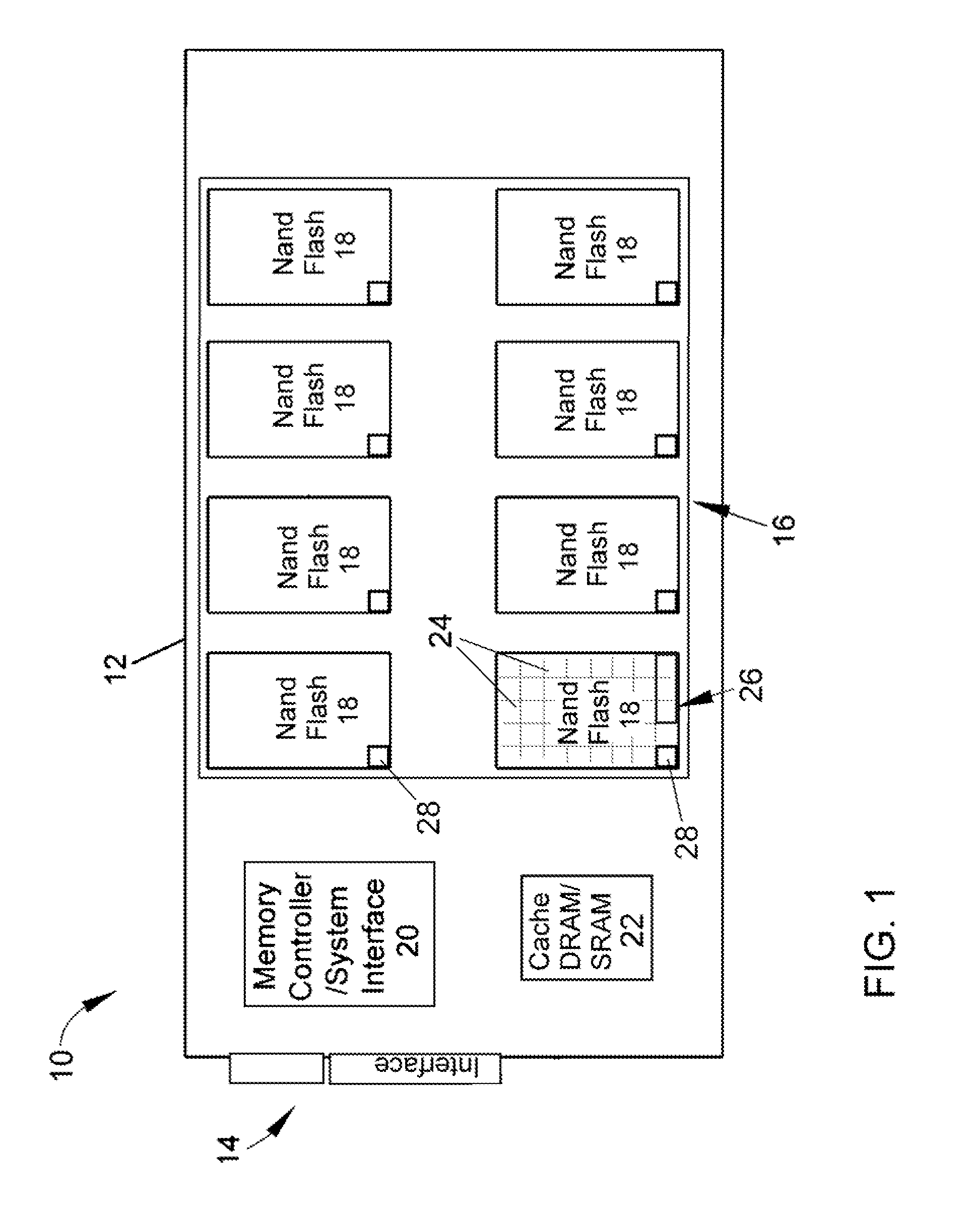
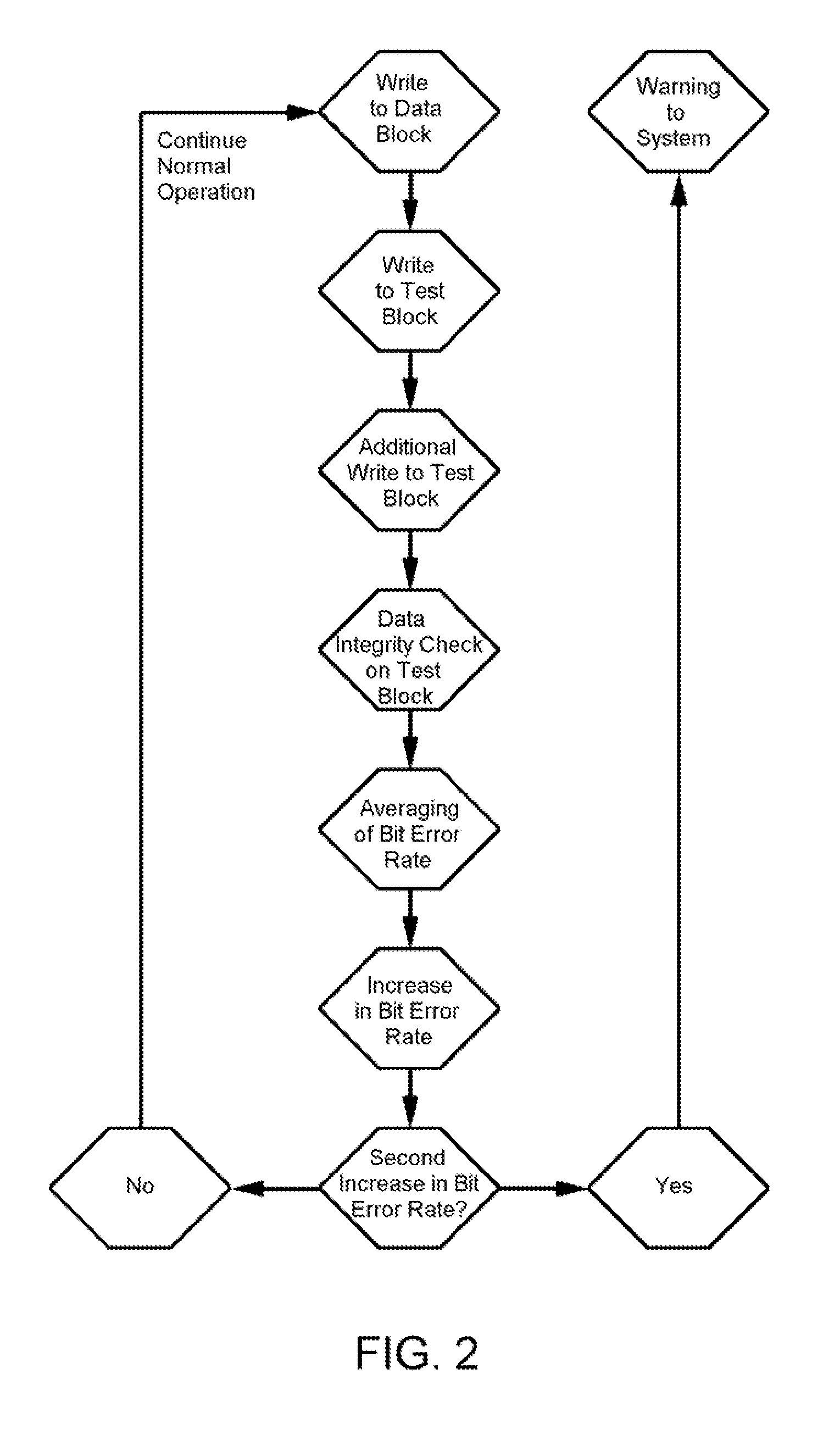
ActiveUS20110173378A1Avoid lostIncrease chanceMemory loss protectionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMass storageDevice failure
A solid-state mass storage device and method of anticipating a failure of the mass storage device resulting from a memory device of the mass storage device reaching a write endurance limit. A procedure is then initiated to back up data to a second mass storage device prior to failure. The method includes assigning at least a first memory block of the memory device as a wear indicator, using other memory blocks of the memory device as data blocks for data storage, performing program / erase (P / E) cycles and wear leveling on the data blocks, subjecting the wear indicator to more P / E cycles than the data blocks, performing integrity checks and monitoring the bit error rate of the wear indicator, and taking corrective action if the bit error rate increases, including the initiation of the backup procedure and generating a request to replace the device.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
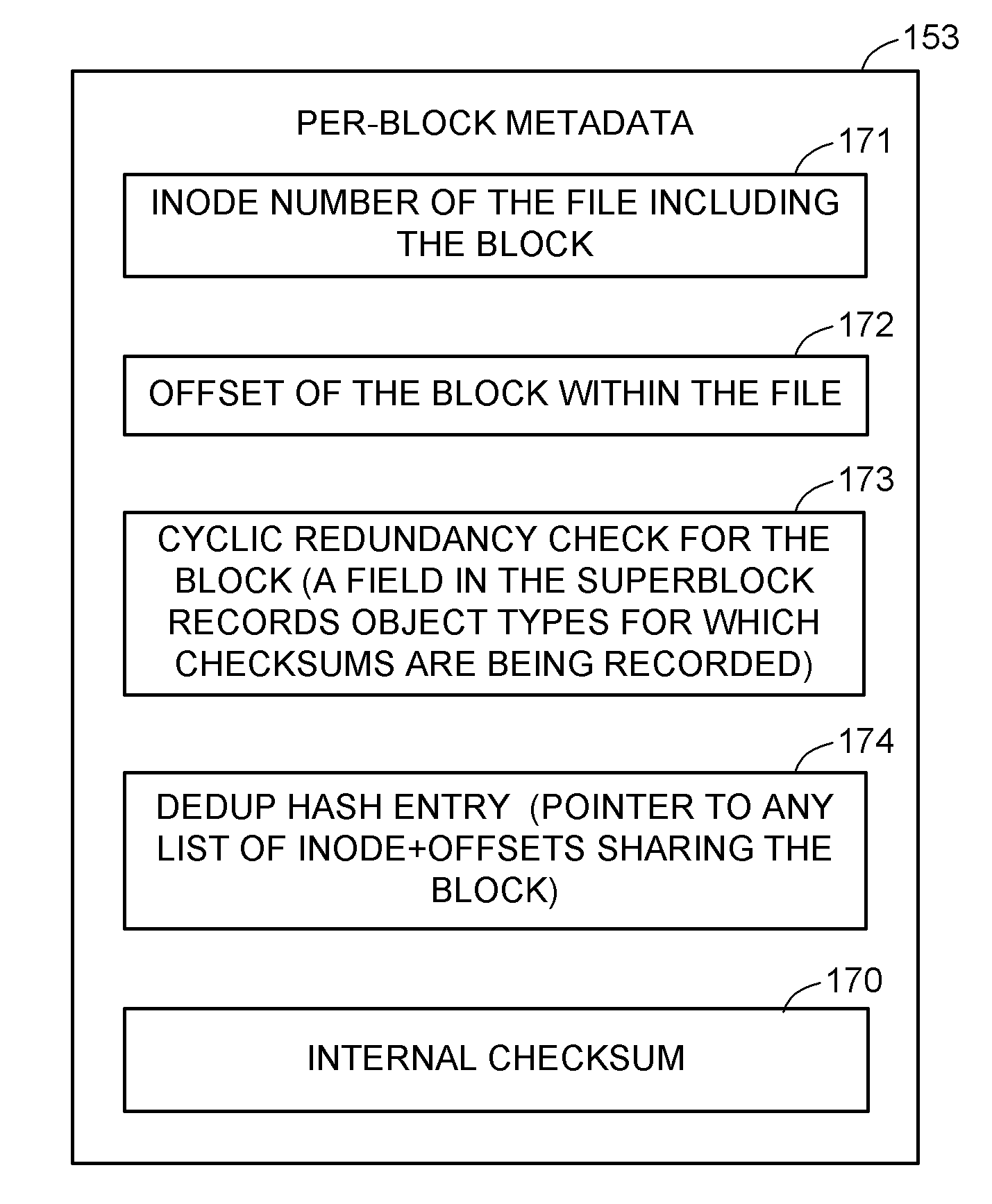
Self healing file system
A self healing file system is designed for proactive detection and containment of faults, errors, and corruptions, in order to enable in place (online) and non-intrusive recovery. For proactive fault detection, the file system maintains certain per-block metadata of each file system block. The per-block metadata includes a redundancy check, and for file system data blocks, an inode identifier, and an offset of the file system data block in the file including the file system data block. The redundancy check is used to detect and mark bad file system blocks. The inode identifier and offset is used for validating connectivity of the file system blocks to the inodes, and for tracing bad blocks to files that contain the bad blocks.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Method and system for maintaining information about modified data in cache in a storage system for use during a system failure
InactiveUS6513097B1Avoid problemsSave resourcesMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSystem failureData storing
Disclosed is a system and method for caching data. A processor receives data from a host to modify a track in a first storage device. The processor stores a copy of the modified data in a cache and indicates in a second storage device the tracks for which there is modified data in cache. During data recovery operations, the processor processes the second storage device and data therein to determine the tracks for which there was modified data in cache. The processor then marks the determined tracks as failed to prevent data at the determined tracks in the first storage device from being returned in response to a read request until the failure is resolved. In further embodiments, in response to detecting a partial failure within the storage system, the processor would scan the cache to determine tracks for which there is modified data stored in the cache. The processor then stores in the second storage device information indicating the tracks having modified data in cache and schedules the destaging of the modified data from the cache to the first storage device. The processor is further capable of receiving and processing read / write requests directed to the first storage device before all the modified data is destaged from cache.
Owner:IBM CORP
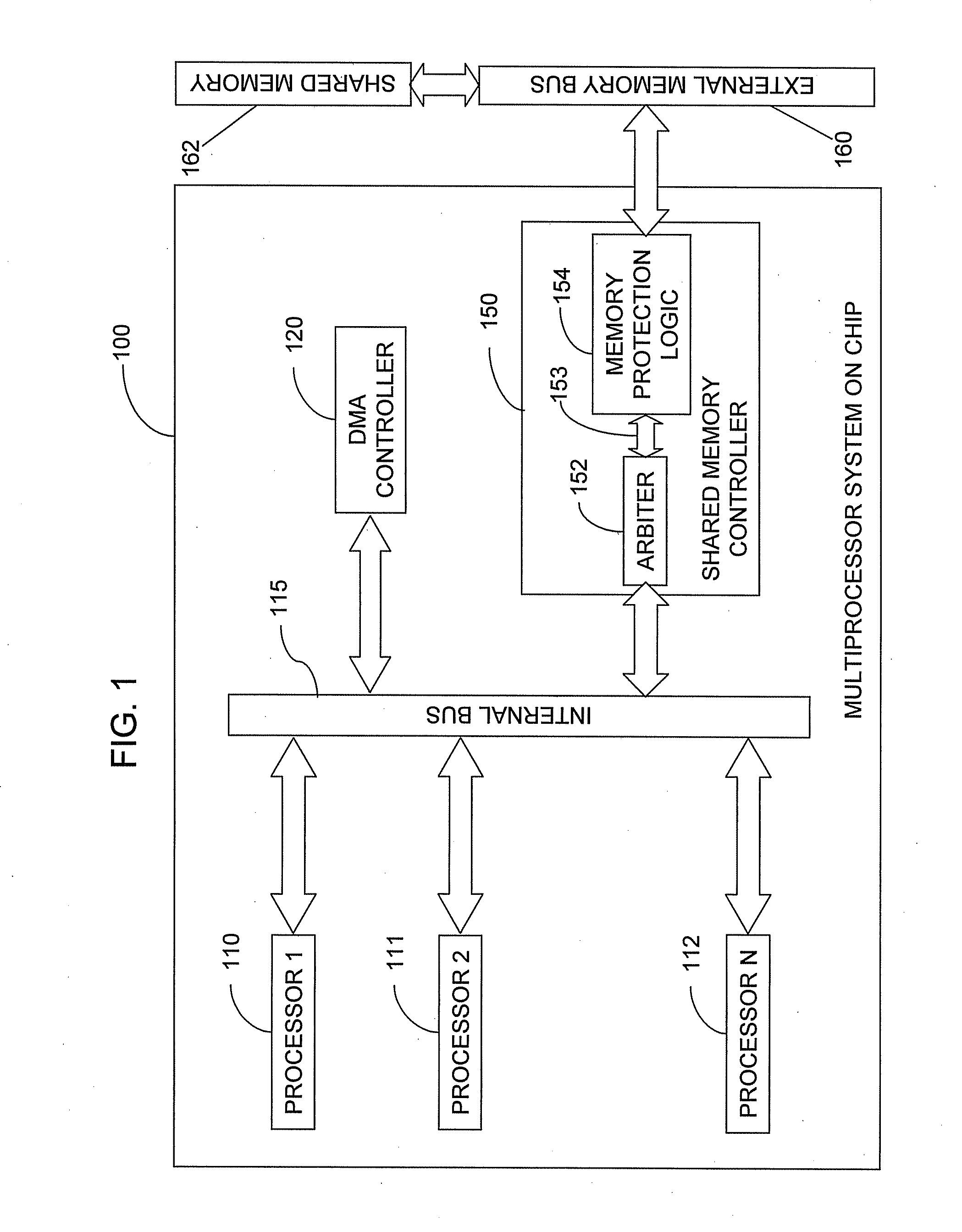
Memory protection system and method
A shared memory controller is provided for controlling access to a shared memory by a plurality of processors. At least one device includes a storage area for storing a respective address range for each of a plurality of memory regions. The at least one device further includes a permission table containing, for each of the plurality of memory regions, read and write permission data for each of the plurality of processors. A memory fault detector is coupled to the at least one device and has an input for receiving a memory access request including a memory address, a processor identification and a read / write indicator. The memory fault detector includes logic for determining whether a memory access according to the memory access request would conflict with the read and write permission data in the permission table.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Preventive recovery action in hard disk drives
InactiveUS6401214B1Not easy to failError minimizationRecord information storageHardware monitoringData processing systemHard disc drive
A method in a data processing system for minimizing read / write errors caused by impaired performance of a hard disk drive during runtime operation of the hard disk drive. The runtime operation includes an active mode during which read / write operations are conducted and a standby mode which occurs while no read / write operation is underway. First, at least one performance parameter of a hard disk drive is monitored during a standby mode of operation. Next, in response to detecting a degraded value of the at least one performance parameter, performing preventive recovery action only during the standby mode of operation, such that the performance parameter is restored to an acceptable value without interfering with hard disk drive operation during an active mode.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Integrated circuit having hardware circuitry to prevent electrical or thermal stressing of the silicon circuitry
InactiveUS6330668B1Digital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsElectricityEngineering
An integrated circuit, such as a microprocessor, which incorporates hardware mechanisms to prevent the circuitry from operating outside the proper bounds of design. The hardware circuitry prevents the microprocessor circuitry from being forced to operate at clock speeds that are greater than it is designed for, from operating at temperatures above or below that which it is designed for, and from being forced to operate at voltages that are above or below voltages that the microprocessor is designed to operate at.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
Storage system
In a storage system having a plurality of virtualization apparatuses that allocate a storage area which a storage device has, form a plurality of virtual volumes, and process input-output from a host processor to one of the virtual volumes, a request for completing all the input-output being processed that is received from the host processor and temporarily holding the input-output processing received subsequently is issued to the plurality of virtualization apparatuses, when a completion report of the processing of the input-output in response to the request is received from the plurality of virtualization apparatuses and the completion report is received from all the virtualization apparatuses to which the request was issued, an instruction of an allocation change of the storage area of the storage device is sent to all the virtualization apparatuses, and when the completion report of the allocation change is received from all the virtualization apparatuses, the storage area of the storage device is allocated to the virtual volume by sending an instruction for releasing a state of the input-output held temporarily to all the virtualization apparatuses.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Systems and methods for a read only mode for a portion of a storage system
In general, embodiments of the invention relate to reading data from and writing data to a storage system. Specifically, embodiments of the invention relate to a read only mode for a portion of a storage system. In one embodiment, a selective read-only mode for a portion of a storage system is implemented by monitoring a condition that may affect a subset of persistent storage in a storage system, by detecting the condition, by entering a read-only mode for the subset, and by enforcing a policy of processing write requests and read requests to the storage system, which includes processing the write requests without modifying user data stored on the subset and processing the read requests, including requests for user data stored on the subset.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
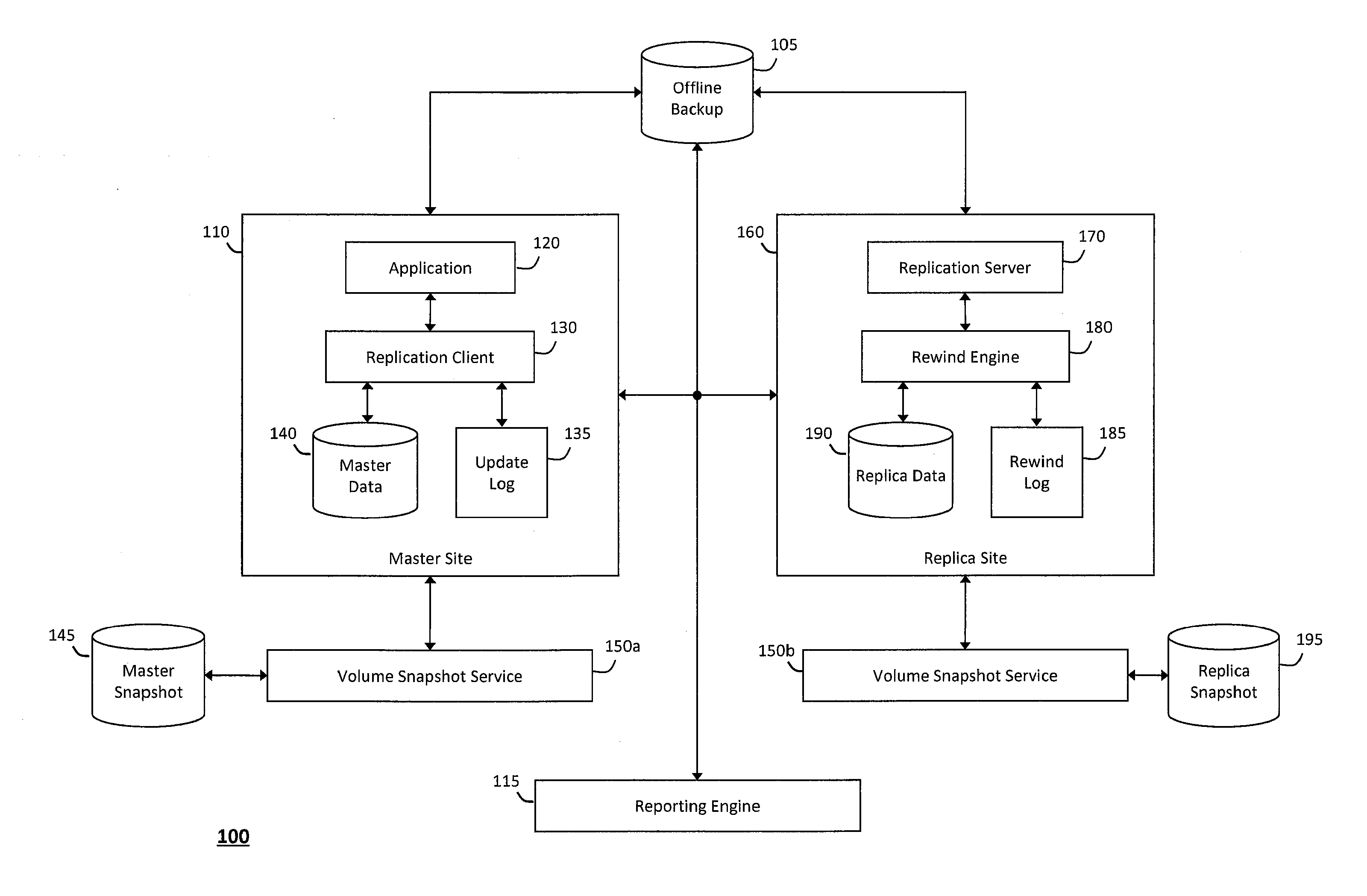
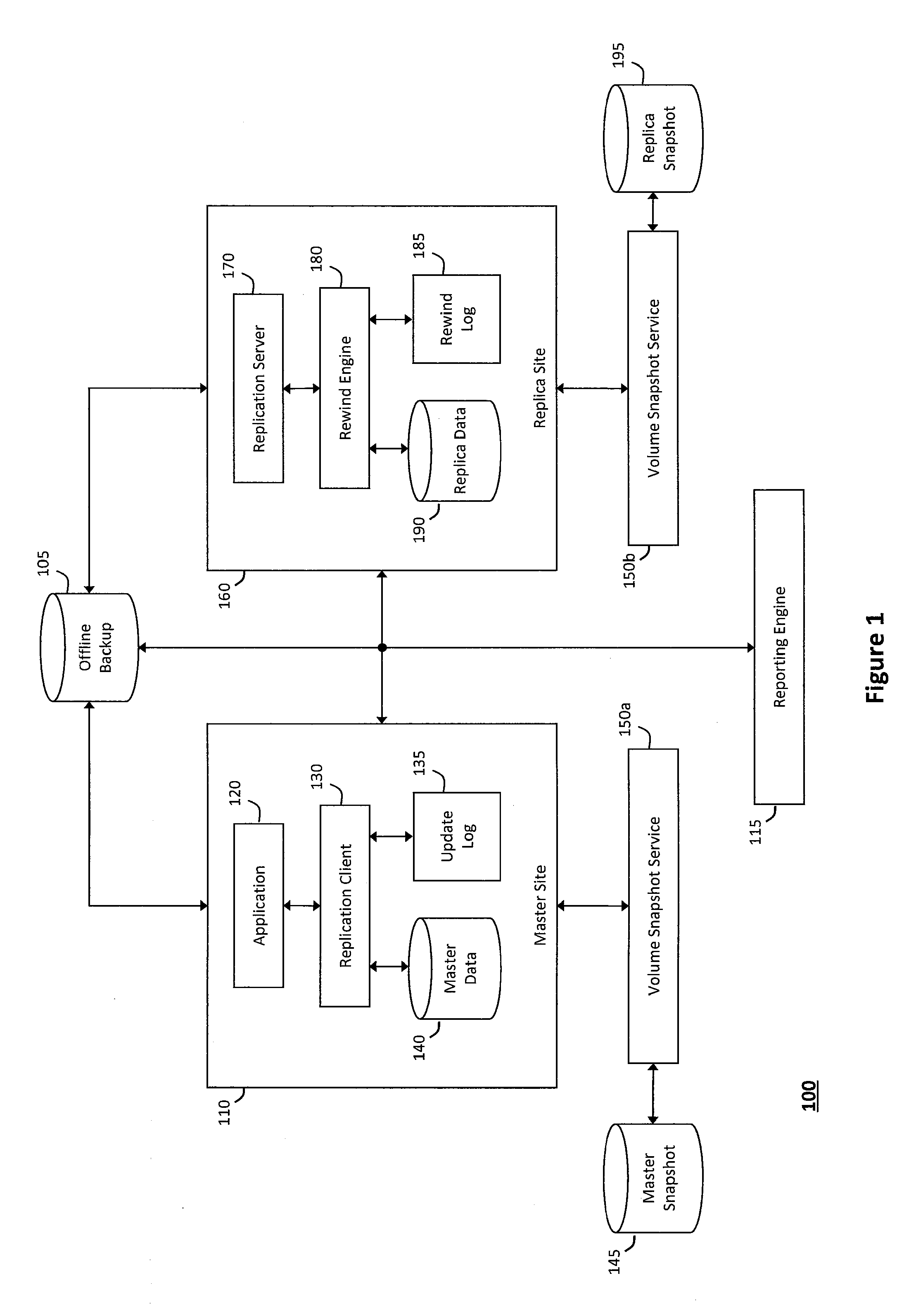
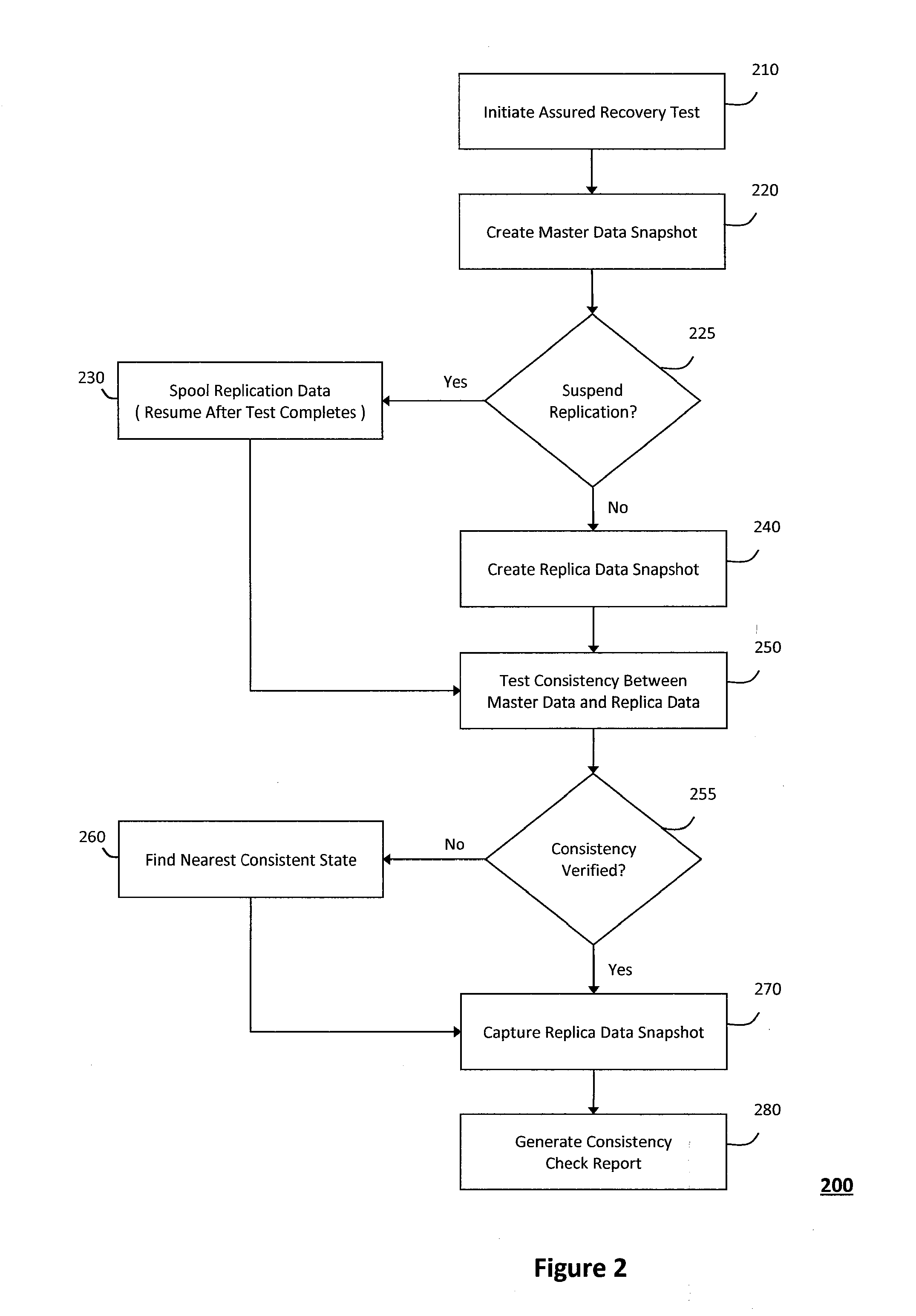
System and method for providing assured recovery and replication
ActiveUS20120233123A1Reliably utilizedDigital data processing detailsError avoidanceData sourceApplication software
The system and method for providing assured recovery and replication described herein may recover a master data source from a replica data source without impacting the master data source or the replica data source, and without having to install a standby version of an application associated with the master data source. In particular, a master snapshot may be created to copy application data stored in the master data source, wherein a replication server confirms that the replica data source can recover the master data source if the master snapshot and the replica data source are consistent. The replication server may create a replica snapshot to copy the replica data source and assign an identity associated with the master data source to the replica data source to recover the master data source. As such, replication may be resumed on a virtual machine disk file associated with the replica snapshot.
Owner:CA TECH INC
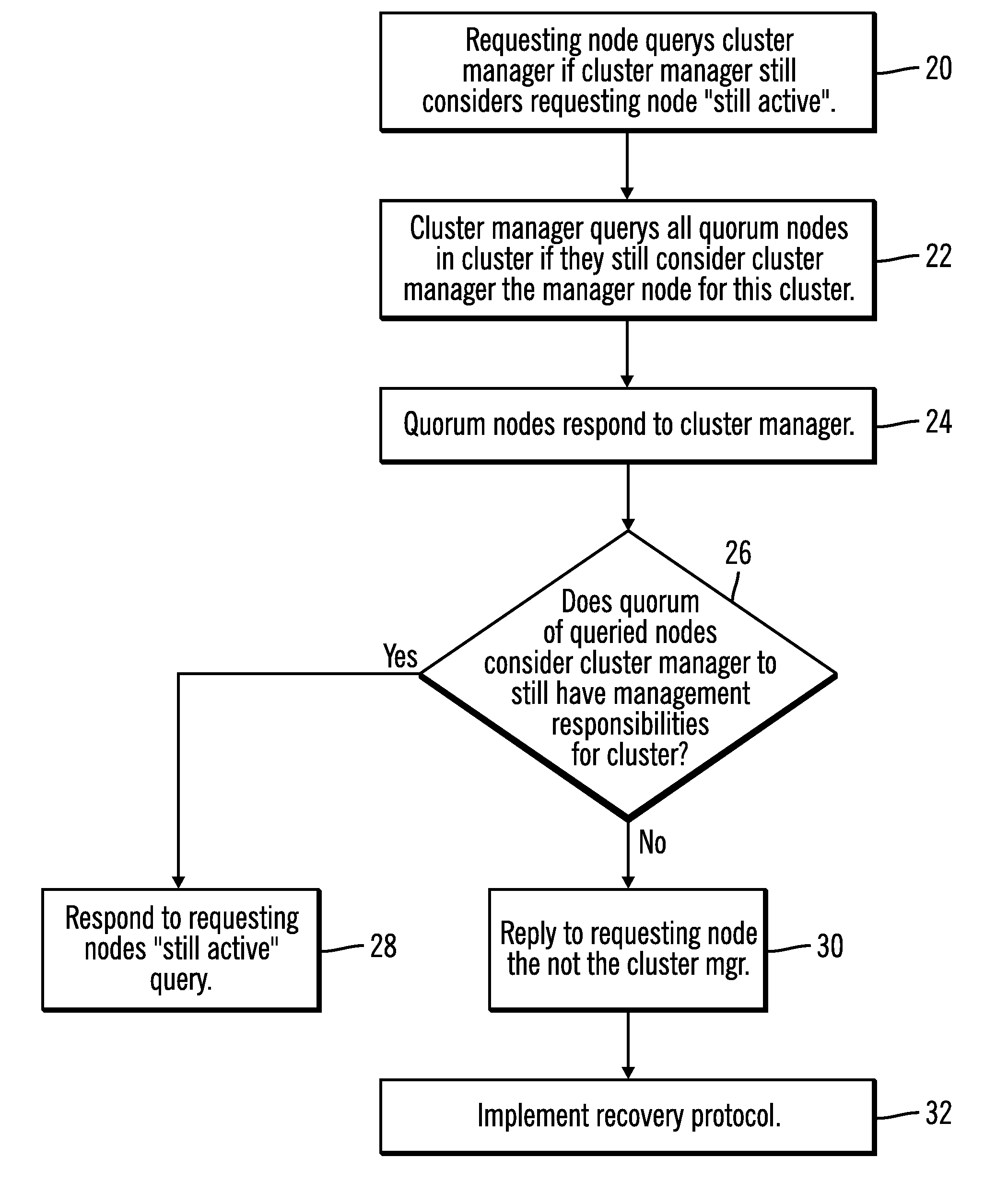
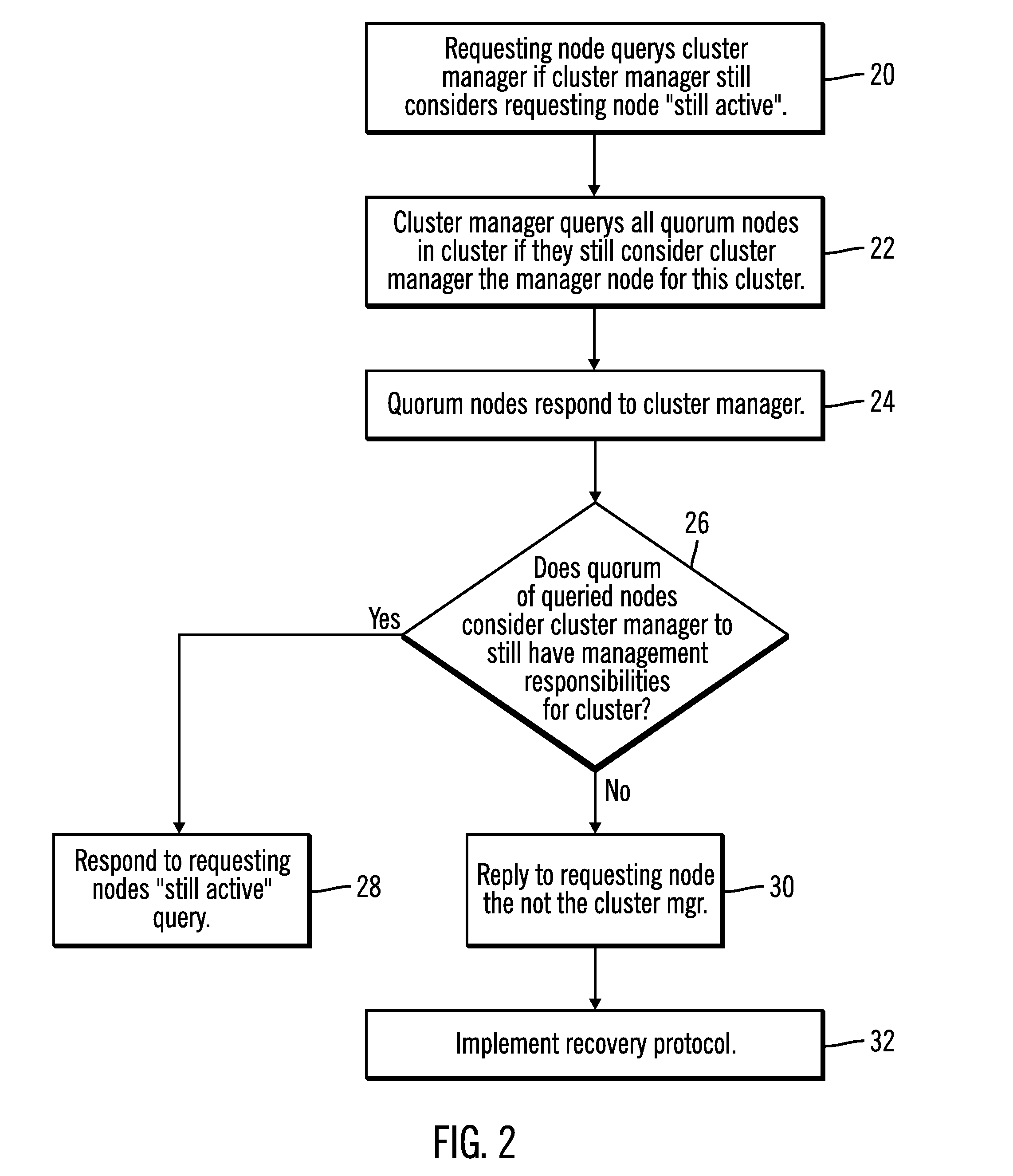
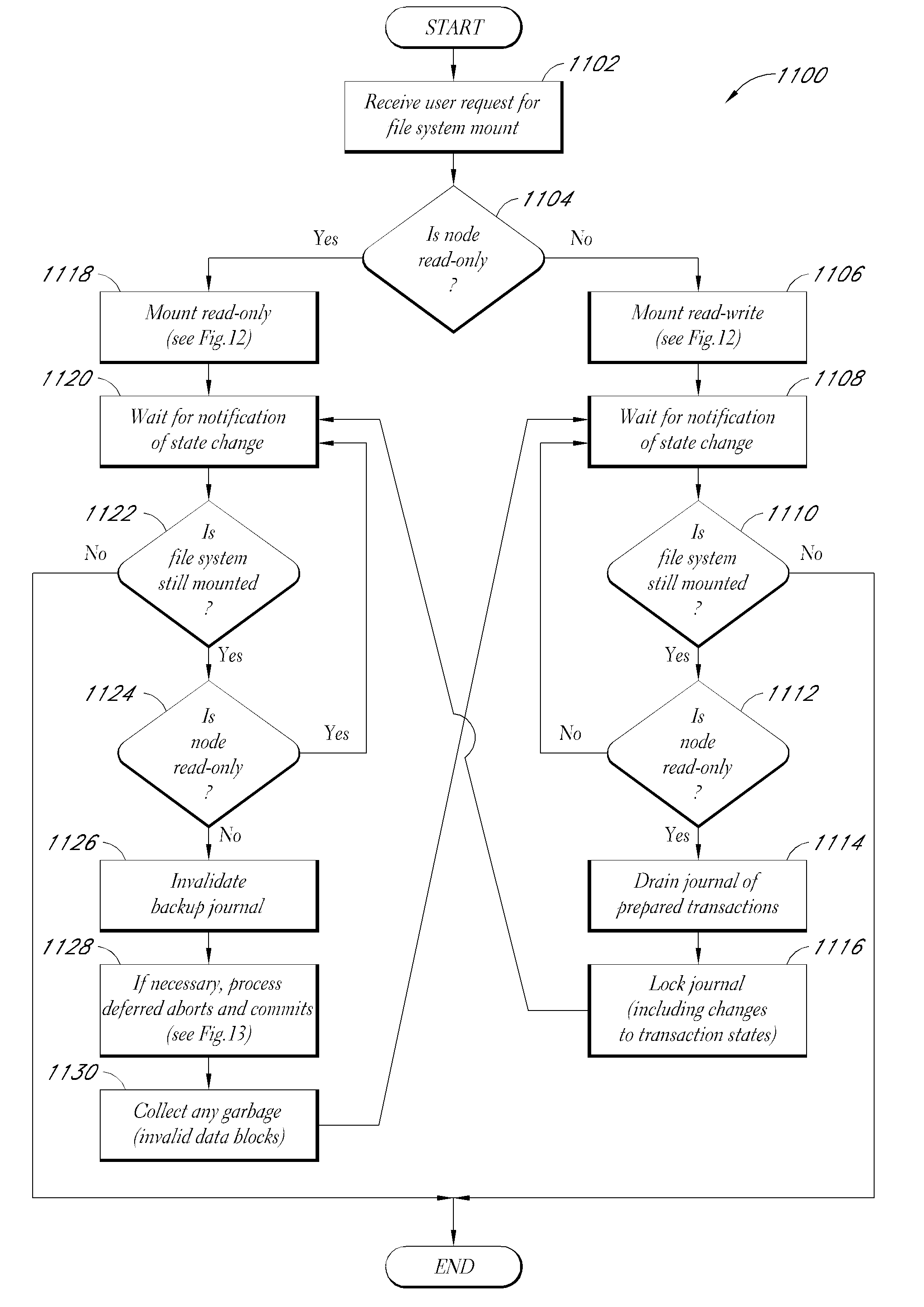
File system mounting in a clustered file system
InactiveUS20090019098A1Quickly and efficiently prevented from mounting a file systemDigital computer detailsError avoidanceFile systemClustered file system
A method effectively preventing a requesting node from unfencing and mounting a file system subsequent to a failure in a cluster file system having a plurality of active nodes. The method comprising first upgrading one active node in the cluster to function as a cluster manager node. The cluster manager is in communication with all nodes. The cluster manager is assigned manager responsibilities, in part, comprising first receiving an active status request from the node requesting to mount a file system. The cluster manager first queries the quorum nodes to determine whether each node considers the cluster manager to still have cluster management responsibilities for the file system. If a majority of quorum nodes consider the cluster manager to still have cluster management responsibilities for the file system then the cluster manager responds to the requesting node's active status request. Thereafter, the requesting node proceeds with mounting the file system.
Owner:IBM CORP
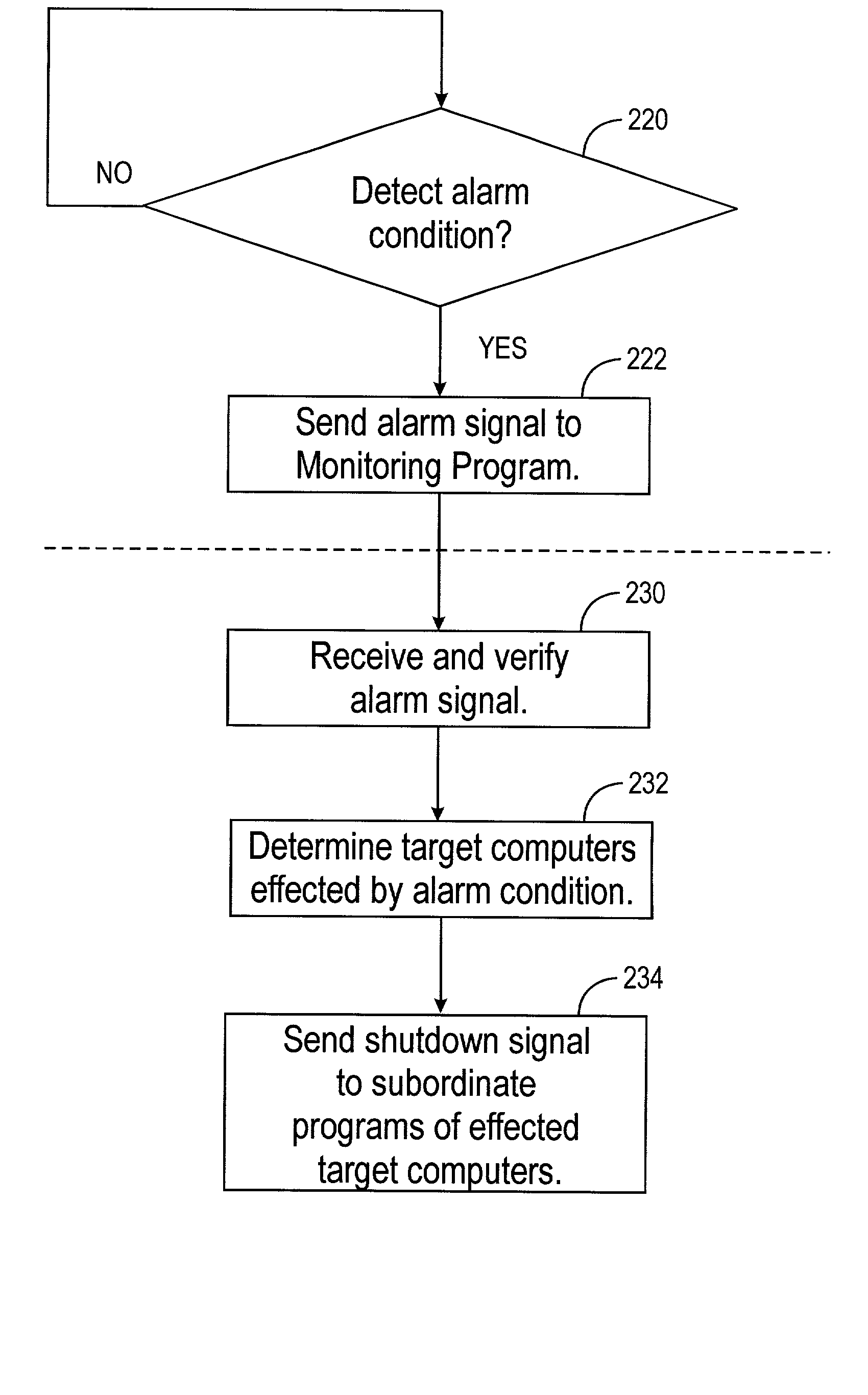
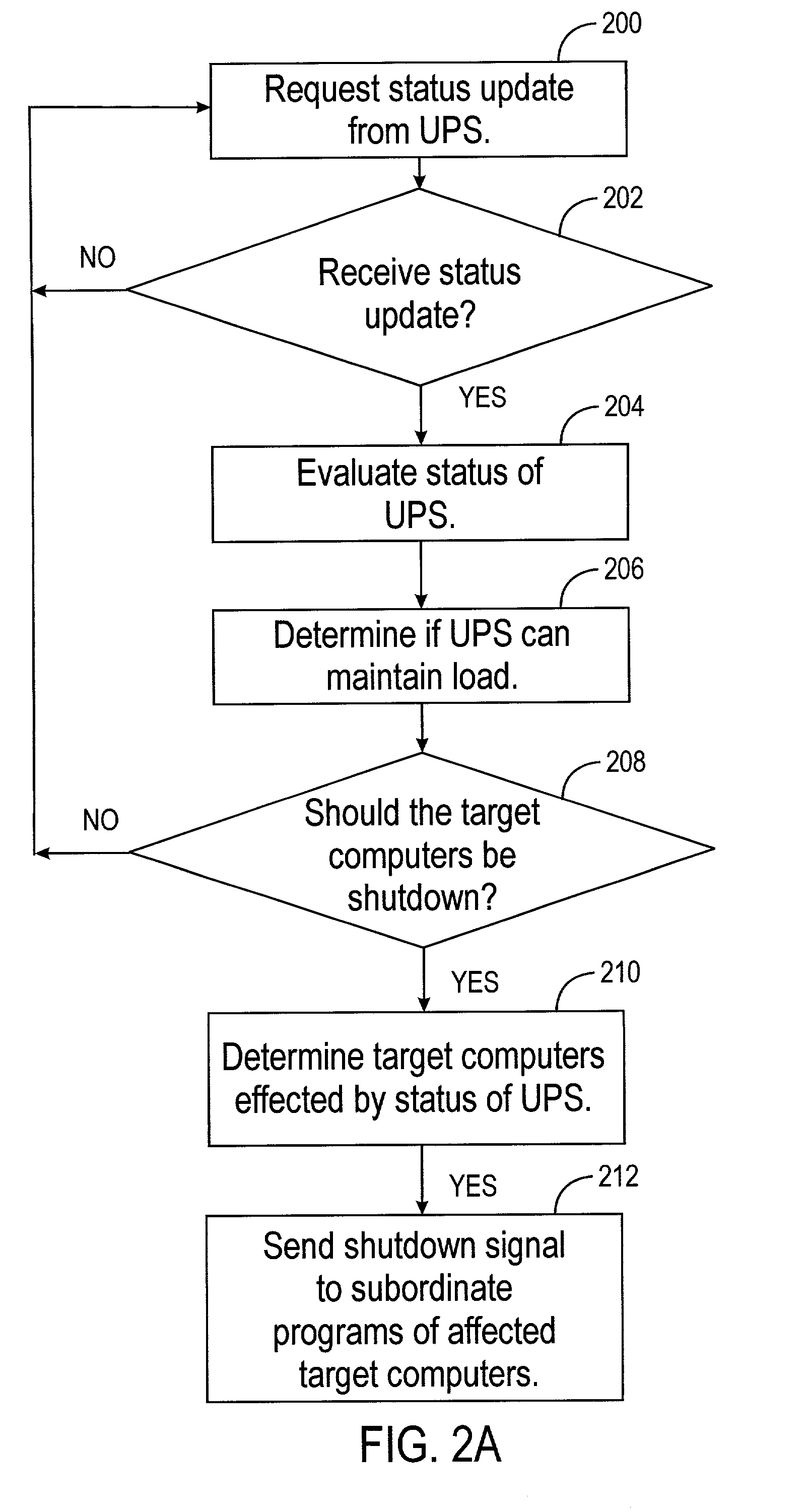
Method and system for monitoring an apparatus for a computer
A system for monitoring various support devices of a computer network is disclosed. The network has a monitoring computer with a monitoring program that monitors the devices. The monitoring program is used to configure a subordinate program. Using push technology, the subordinate program is installed on and is run on target computers in the network. The monitoring program monitors operating parameters and alarm signals from the devices. When the monitoring program determines that the devices can no longer support its load, the monitoring computers sends a shut down instruction to the affected target computers. The subordinate program executes a shutdown routine for the target computer based on the shutdown instruction sent from the monitoring program. The subordinate program has minimal or no graphical user interface on the target computer and requires no local configuration by the user of the target computer.
Owner:LIEBERT
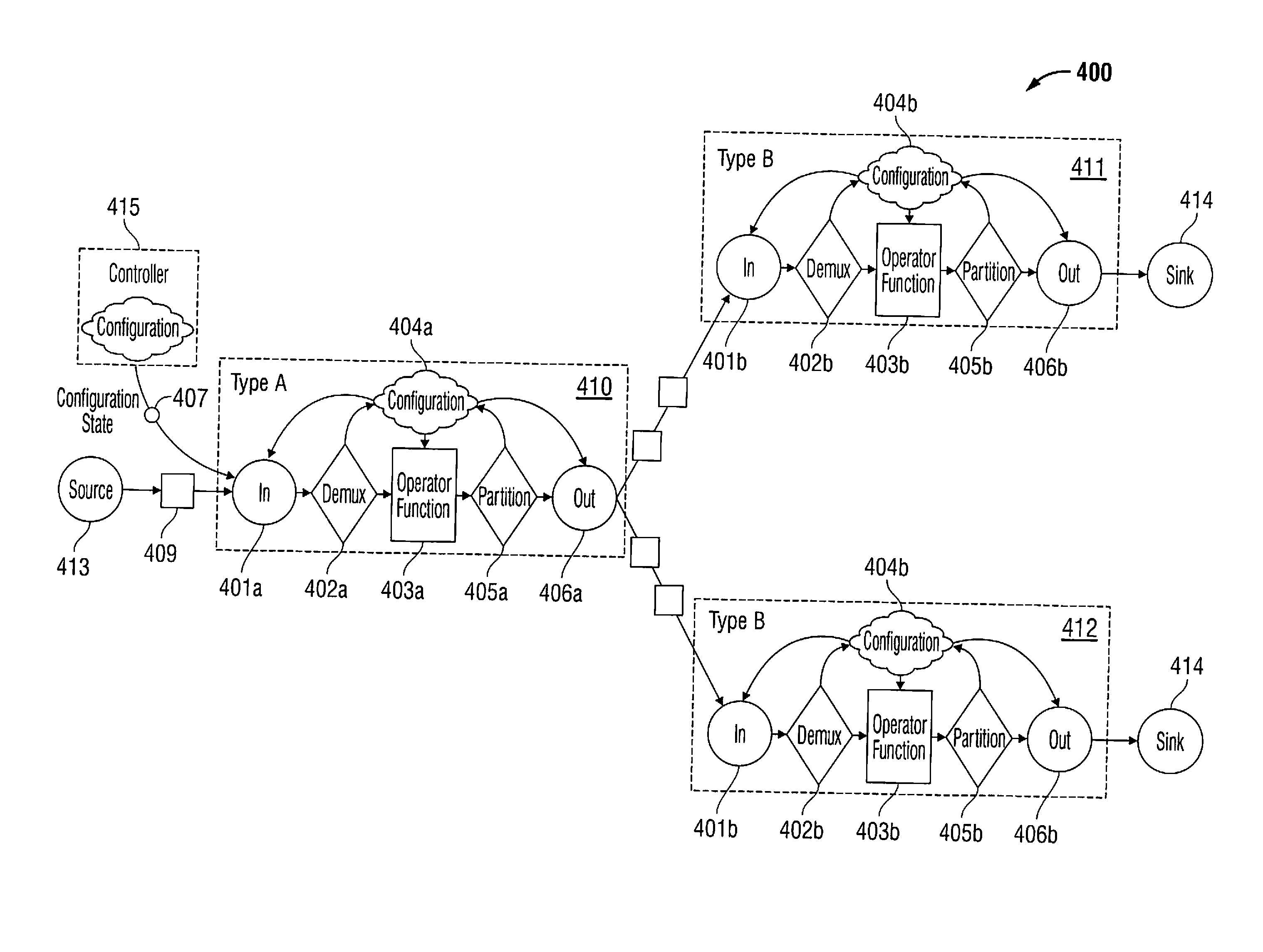
Methods and systems for reconfiguration and repartitioning of a parallel distributed stream process
ActiveUS20120137018A1Multiple digital computer combinationsError avoidanceSecure stateStream processing
A method of reconfiguring a stream process in a distributed system includes the initial step of managing a stream process including one or more operators. The one or more operators are communicatively associated with one or more stream targets. The one or more operators use a partition function to determine the routing of messages to the one or more stream targets. The method includes the steps of determining a safe state within the stream process, and configuring a configuration state of the one or more operators during the safe state.
Owner:ADELLO
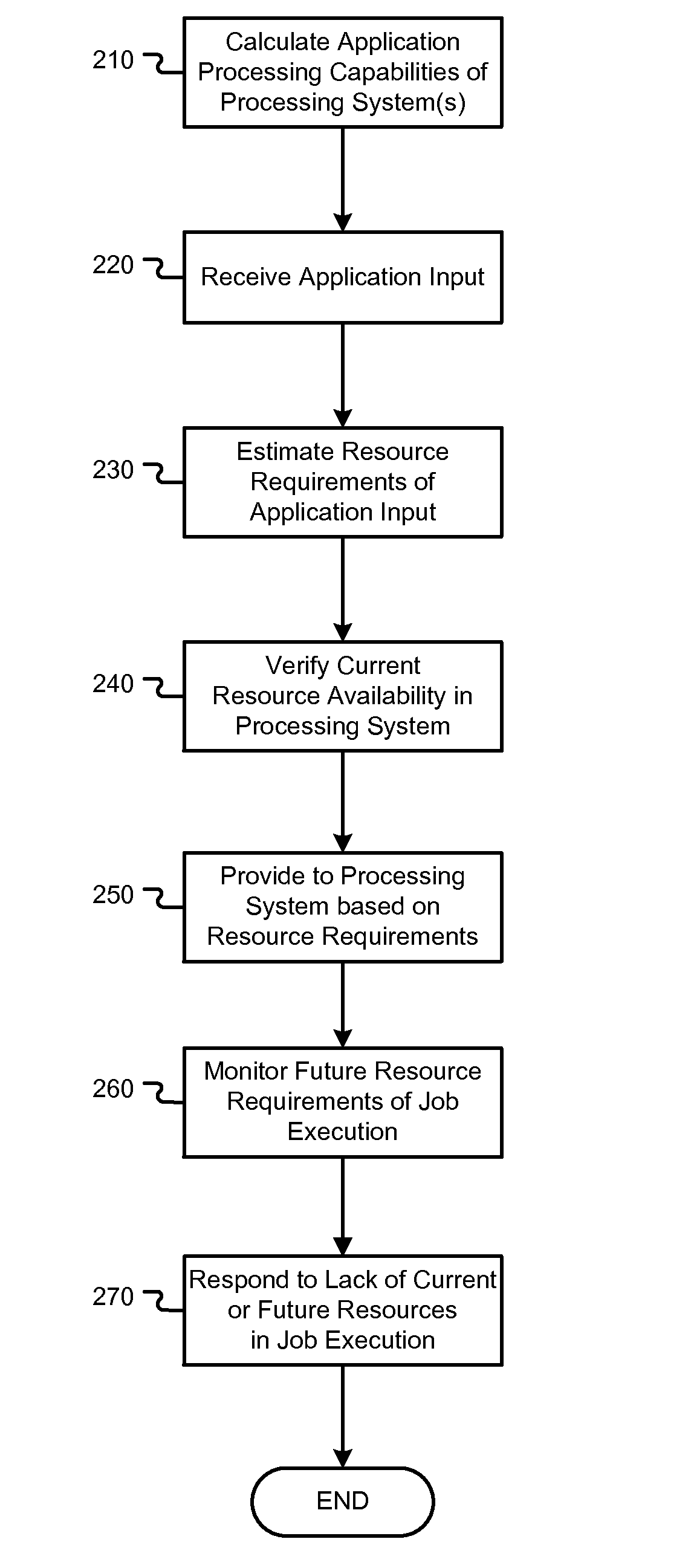
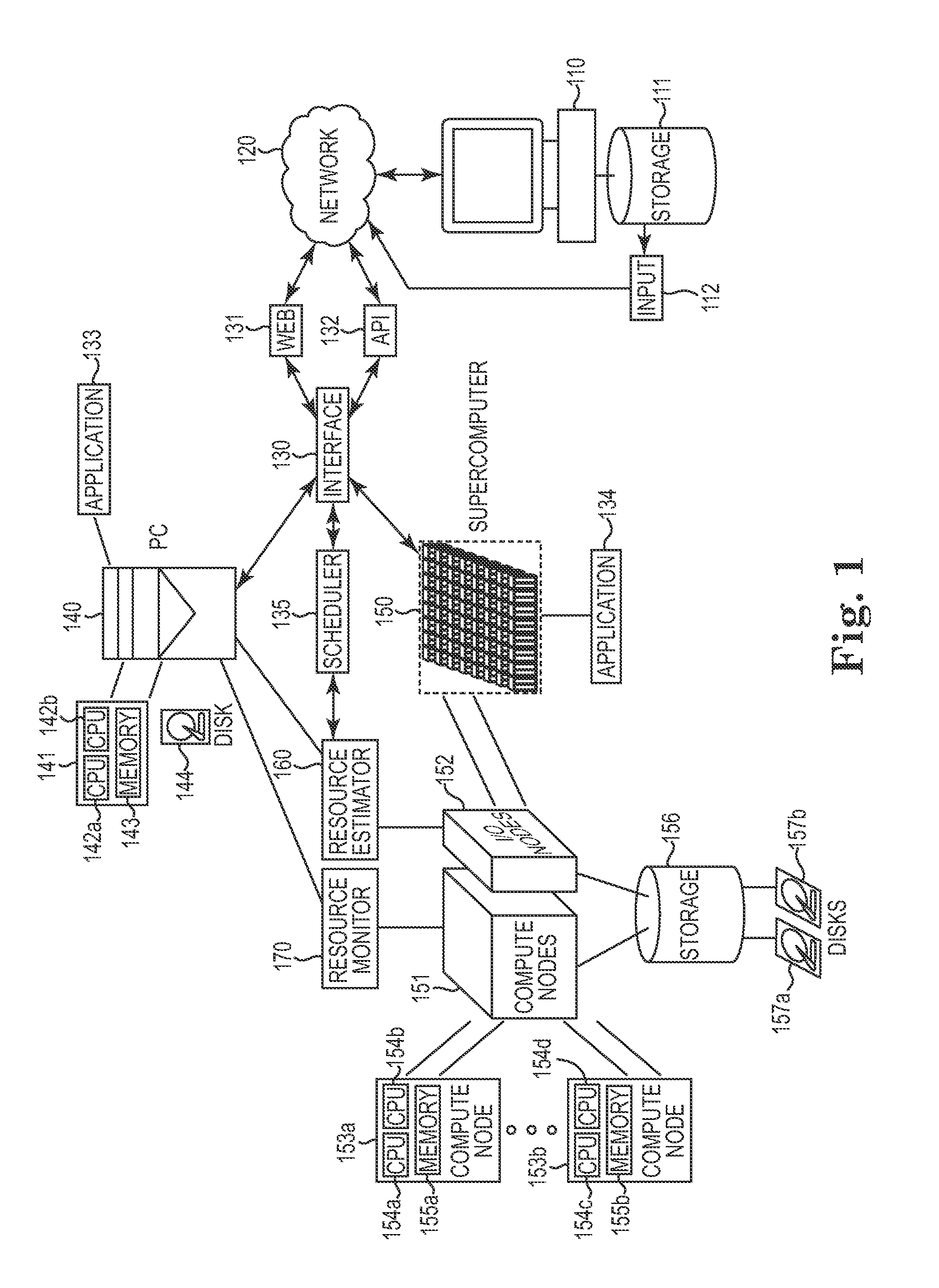
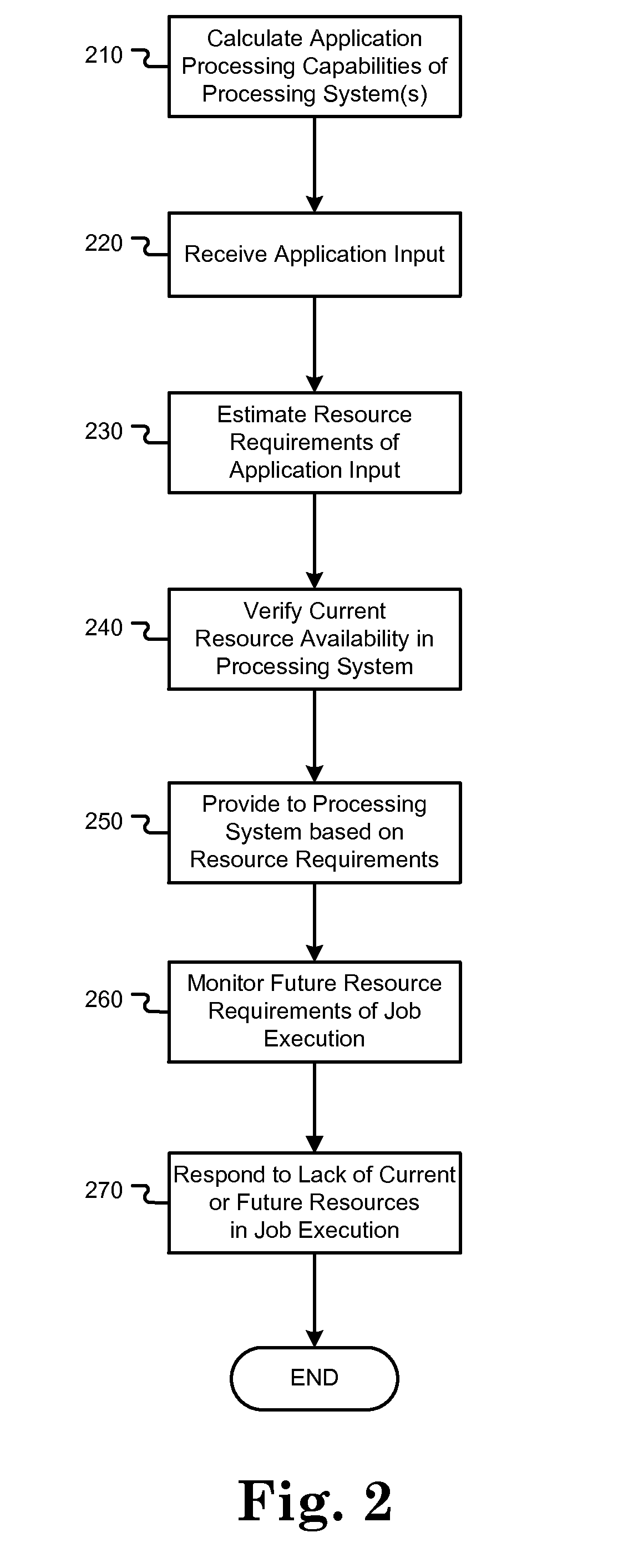
Real-time computing resource monitoring
InactiveUS20120110582A1Avoid failureSave resourcesResource allocationError avoidanceComputerized systemResource based
Techniques used to enhance the execution of long-running or complex software application instances and jobs on computing systems are disclosed herein. In one embodiment, a real time, self-predicting job resource monitor is employed to predict inadequate system resources on the computing system and failure of a job execution on the computing system. This monitor may not only determine if inadequate resources exist prior to execution of the job, but may also detect in real time if inadequate resources will be encountered during the execution of the job for cases where resource availability has unexpectedly decreased. If a resource deficiency is predicted on the executing computer system, the system may pause the job and automatically take corrective action or alert a user. The job may resume after the resource deficiency is met. Additional embodiments also integrate this resource monitoring capability with the adaptive selection of a computer system or application execution environment based on resource capability predictions and benchmarks.
Owner:IBM CORP
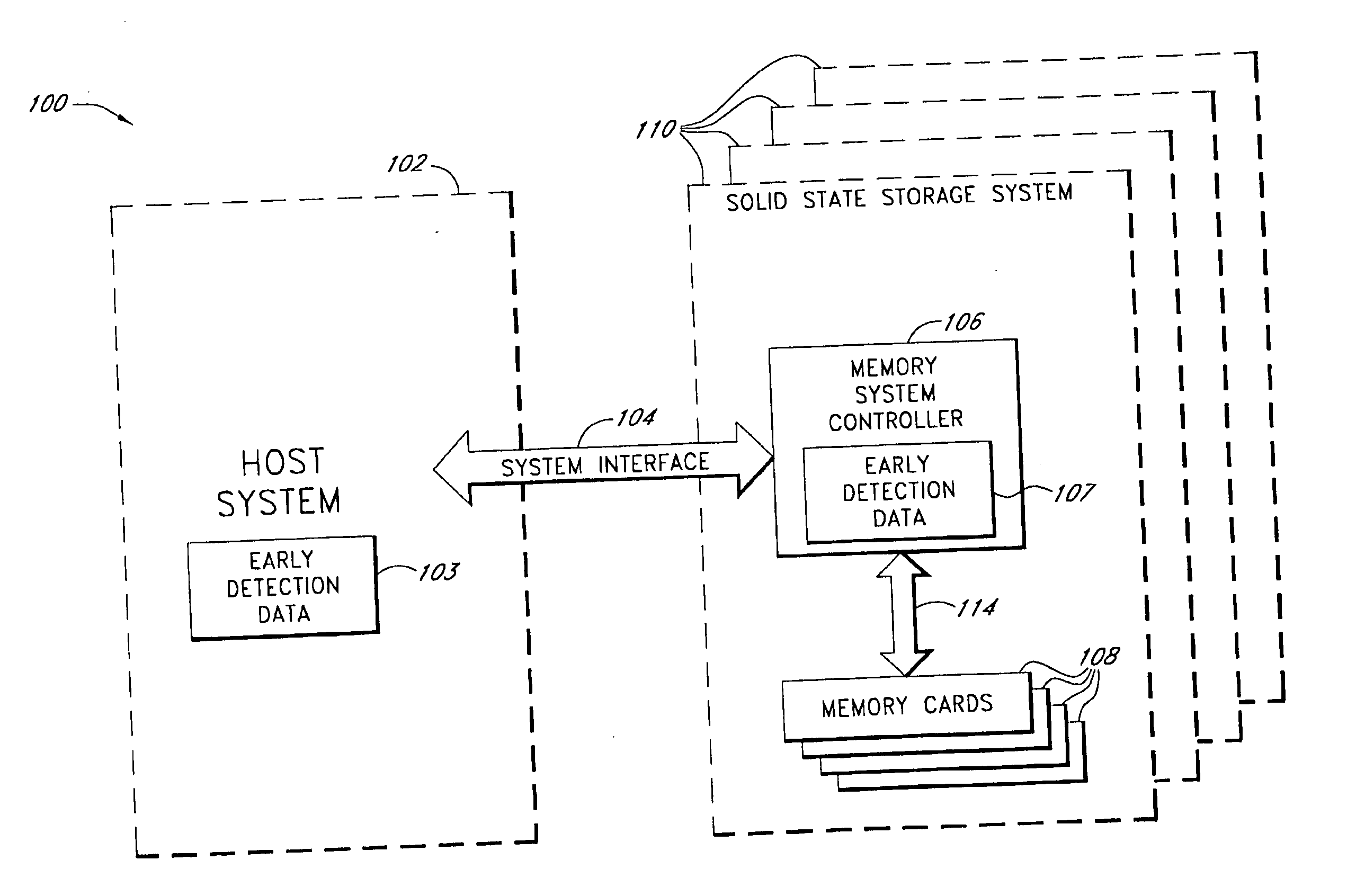
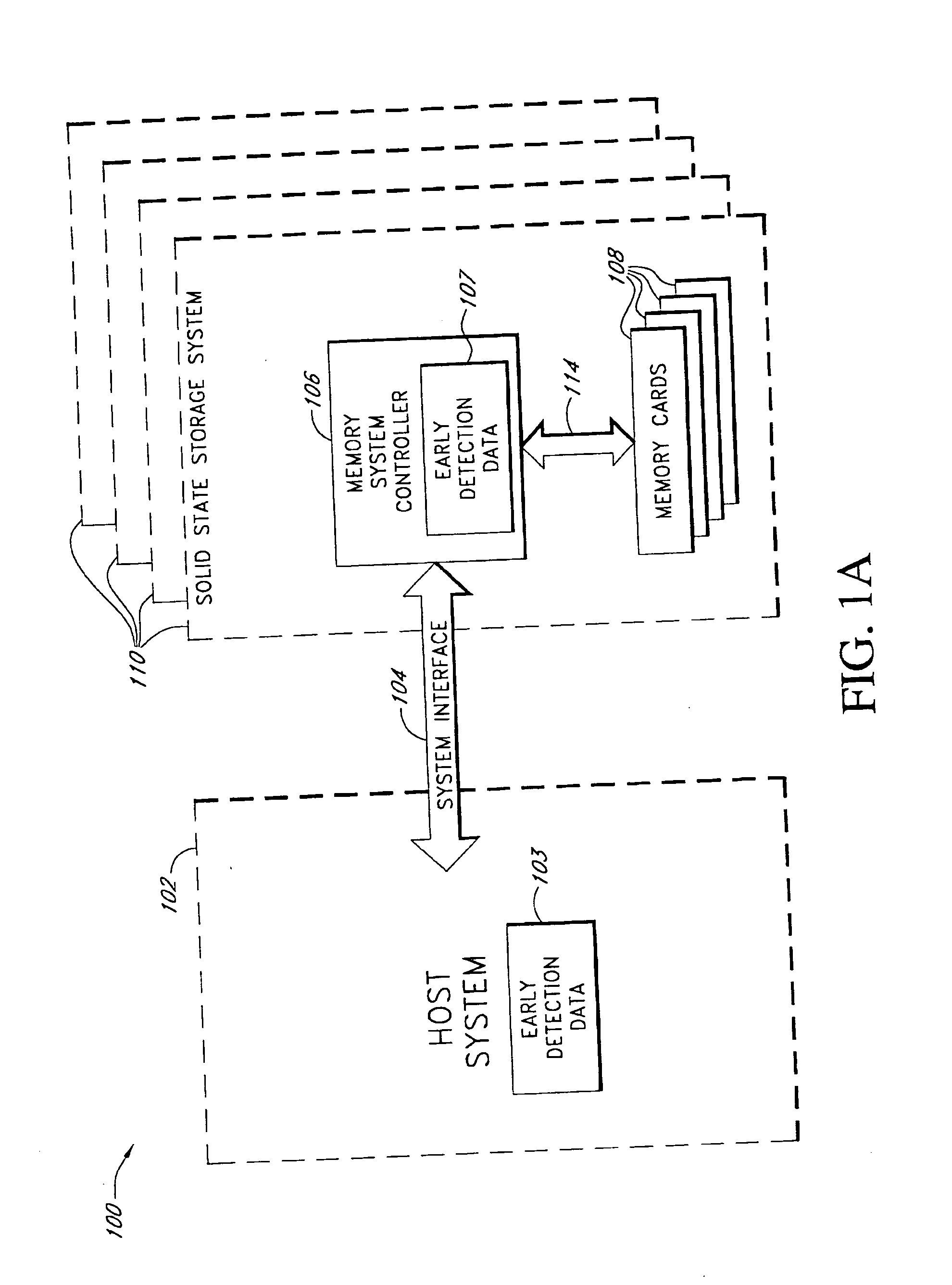
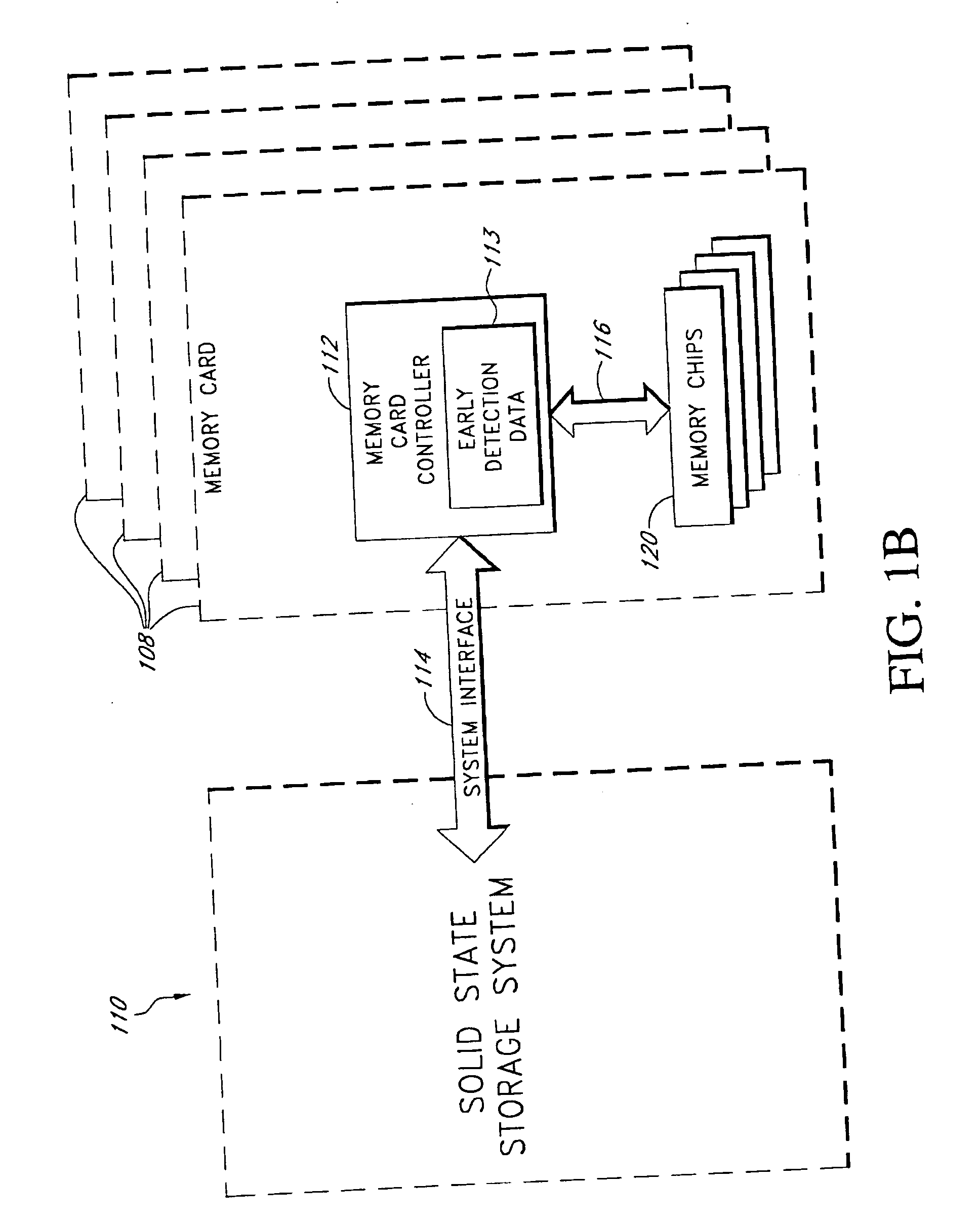
System and method for early detection of failure of a solid-state data storage system
InactiveUS20050044454A1Inhibiting consequenceError avoidanceNon-redundant fault processingData integritySystem failure
Various embodiments are disclosed of a failure detection system for a solid-state data storage system that can experience difficulties, such as system failure or loss of data integrity, when it runs out of spare storage locations. Spare storage locations can be used by a solid-state data storage system to replace storage locations that have become defective. In one embodiment, a count is kept of the available spare storage locations in a system, or sub-system, and when the amount of available spare locations drops to a threshold value, an action can be taken to avoid the consequences of an impending failure. In other embodiments, the available spare storage locations are monitored by keeping track of the percentage of initially available spare locations still remaining, by keeping track of the rate of new spare locations being used, or by other techniques. In various embodiments, the early failure detection system responds to detection of a possible impending failure by taking one or more of a variety of actions, including, for example, sending an alert notification, enabling additional storage capacity, copying portions of the data stored in the system to other secure storage locations, shutting the system down, and taking no action.
Owner:INNOVATIVE MEMORY SYST INC
Method and apparatus for copying and backup in storage systems
InactiveUS20050166022A1Improve reliabilityImproving replication and backup operationMemory loss protectionError avoidanceCopyingBackup
A technique is described for controlling a storage system in which primary storage volumes and replication storage volumes are present. A boundary of a potential failure of the primary storage volumes and the replication storage volumes is determined, and using that boundary, replication storage volumes are assigned to assure that at least some of them are outside the failure boundary.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Systems and methods for a read only mode for a portion of a storage system
ActiveUS20090248765A1Memory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsHybrid storage systemData storing
In general, embodiments of the invention relate to reading data from and writing data to a storage system. Specifically, embodiments of the invention relate to a read only mode for a portion of a storage system. In one embodiment, a selective read-only mode for a portion of a storage system is implemented by monitoring a condition that affects a subset of persistent storage in a storage system, by detecting the condition, by entering a read-only mode for the subset, and by enforcing a policy of processing write requests and read requests to the storage system, which includes processing the write requests without modifying user data stored on the subset and processing the read requests, including requests for user data stored on the subset.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Reducing application downtime in a cluster using user-defined rules for proactive failover
Owner:UNISYS CORP
Apparatus and method for performing a preemptive reconstruct of a fault-tolerant RAID array
ActiveUS7313721B2Reduce the possibilityLess timeReliability/availability analysisError avoidanceFault toleranceRAID
A RAID controller performs a preemptive reconstruct of a redundant array of disks while it is still fault-tolerant by determining the errors by a first disk exceeded the error threshold, and reading data from a second disk, and writing the data to a spare disk. The second disk's data is a mirrored copy of the first disk's data. The controller also replaces the first disk with the spare disk, after completing the reading and writing. Additionally, while performing the reading and writing, the controller writes second data to the first disk in response to a user write request including the second data, thereby maintaining the fault-tolerance of the redundant array. In another embodiment, the controller creates the data of the first disk from second data read from two or more of the other disks in the array and writes the created data to the spare disk.
Owner:DOT HILL SYST
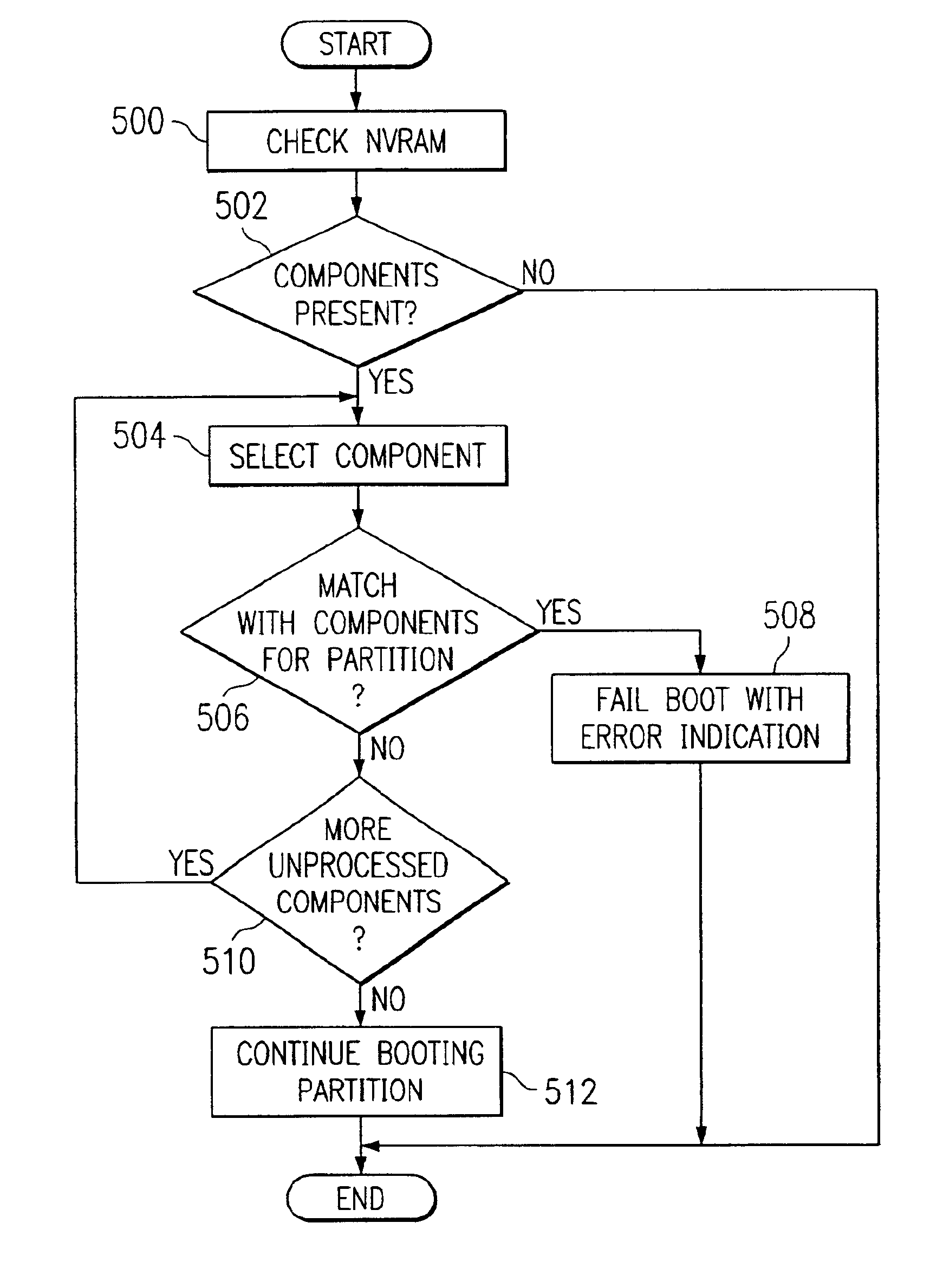
Method and apparatus for preventing the propagation of input/output errors in a logical partitioned data processing system
A method, apparatus, and computer instructions for halting input / output error propagation in the logically partitioned data processing system. All components associated with the bridge are identified to form a set of failed components in response to detecting an error state in a bridge within a set of bridges in the logical partitioned data processing system. An identification of the failed components is stored in which the identification is used by each partition during a boot process.
Owner:IBM CORP
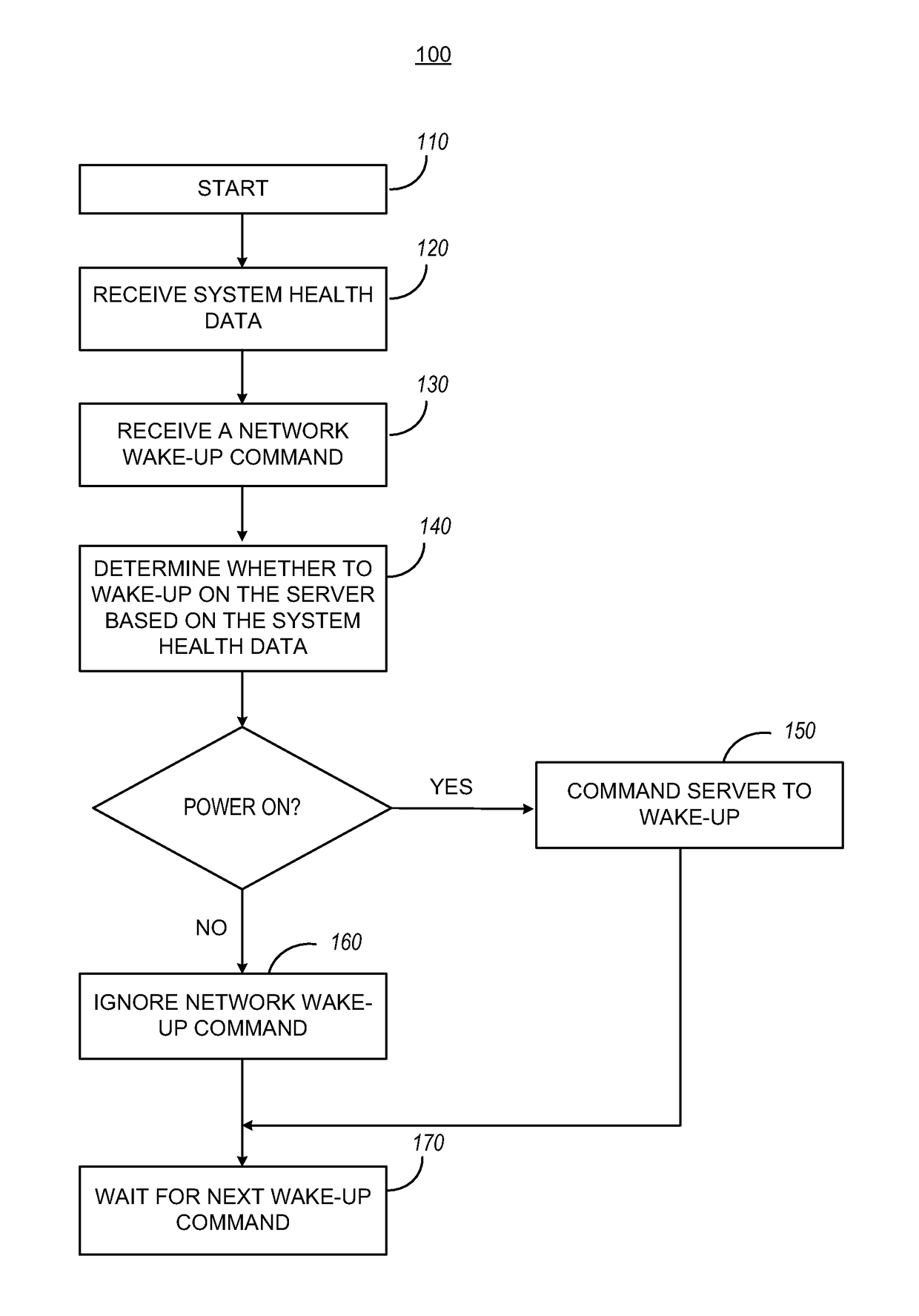
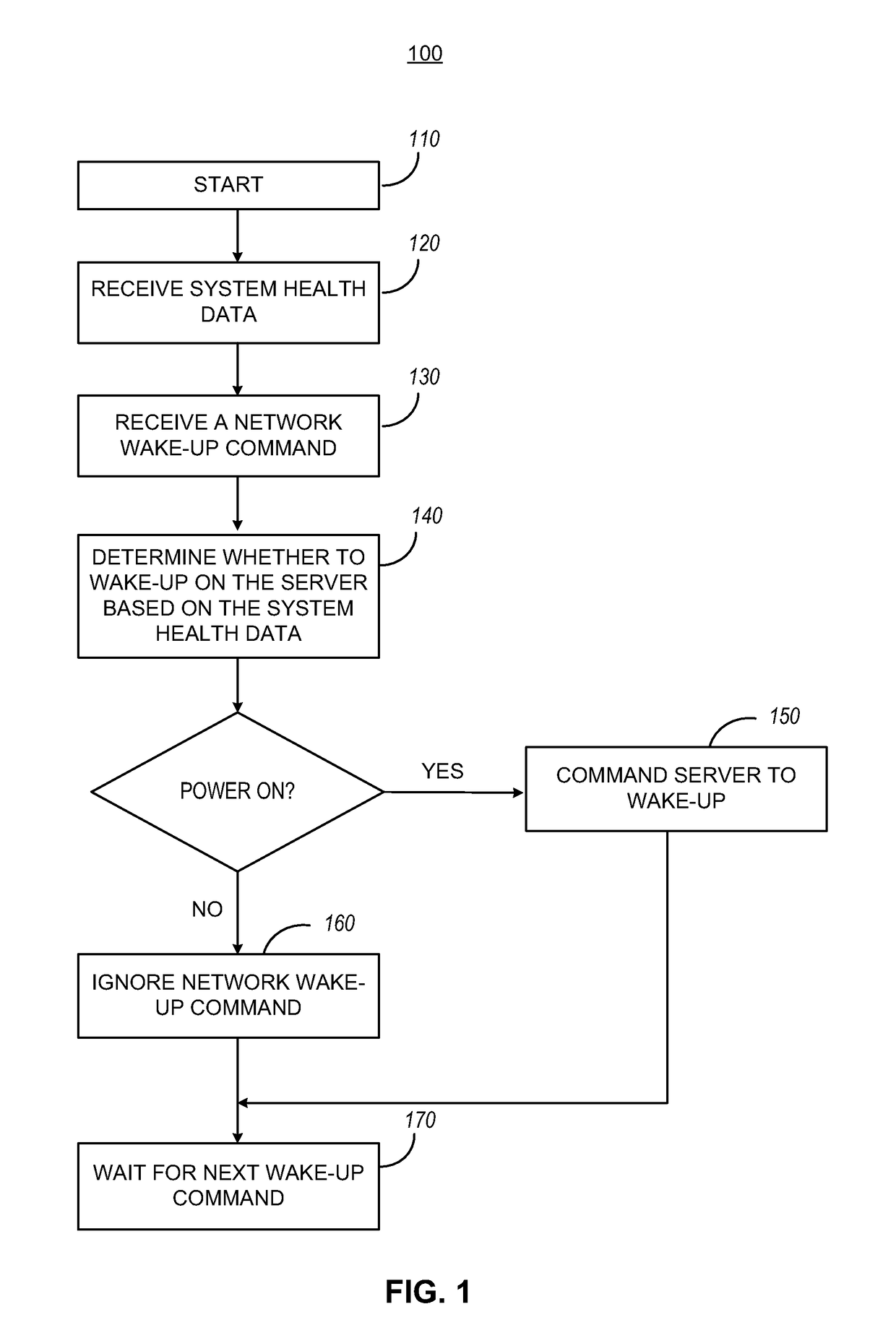
Managing network wake-up commands
ActiveUS20170108912A1Substation remote connection/disconnectionPower supply for data processingNetwork interface controllerNetwork interface
A method for managing network wake-up commands by a controller of a server includes receiving a system health data. The method includes receiving a network wake-up command from a network interface controller of the server. The method further includes the determining whether to wake-up the server based on the system health data to yield a determination, and commanding the server to wake-up, when the determination is to wake-up the server.
Owner:QUANTA COMPUTER INC
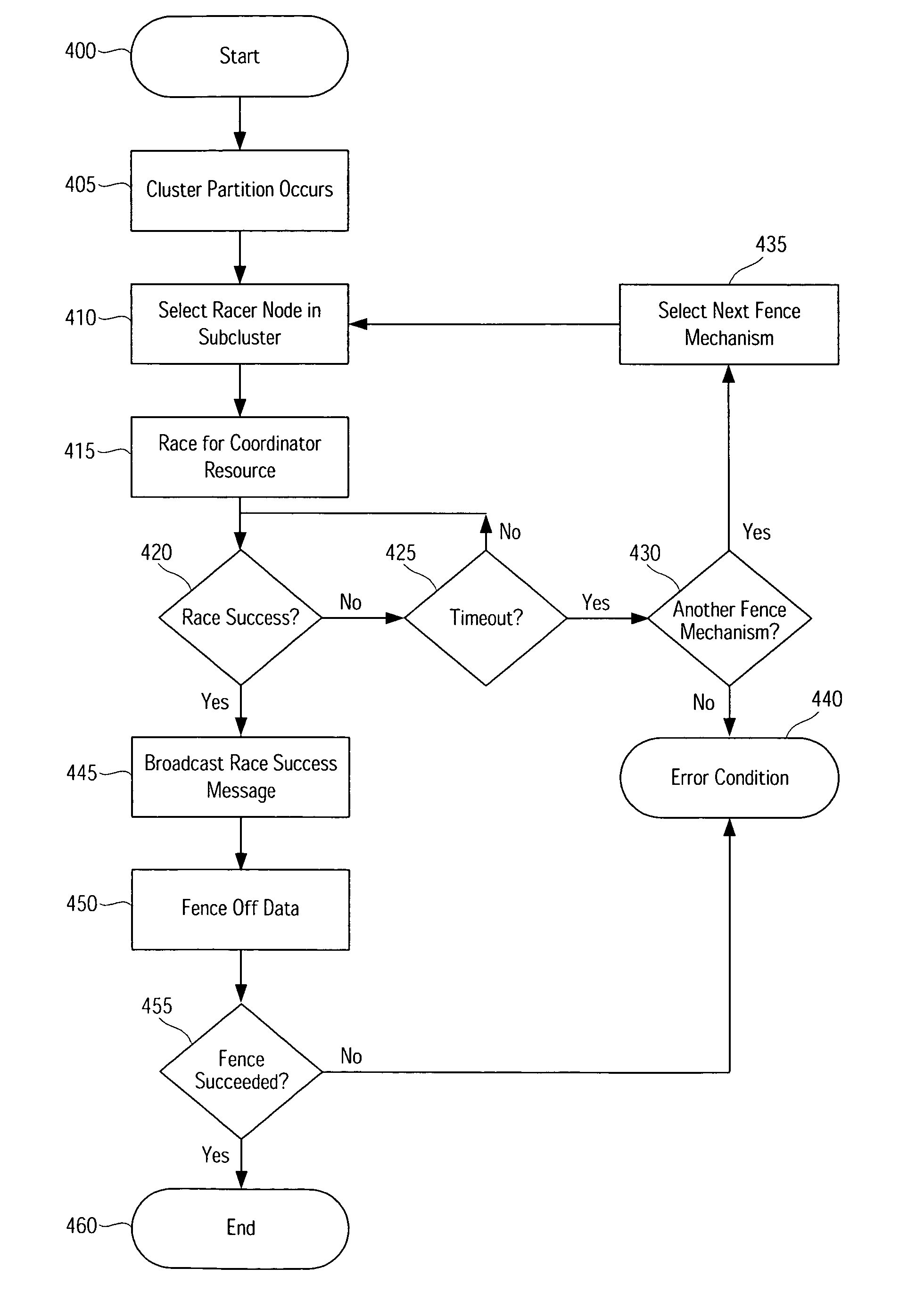
System and method for customized I/O fencing for preventing data corruption in computer system clusters
ActiveUS7590737B1Easy to useDigital computer detailsError avoidanceCluster systemsComputerized system
Systems, methods, apparatus and software can implement a flexible I / O fence mechanism framework allowing clustered computer systems to conveniently use one or more I / O fencing techniques. Various different fencing techniques can be used, and fencing mechanism can be customized.
Owner:SYMANTEC OPERATING CORP
Computer system with backup function and method therefor
ActiveUS8464106B2Avoid lostPredict the fatigue threshold of a solid-state mass storage deviceRead-only memoriesError avoidanceMass storageComputerized system
A solid-state mass storage device and method of anticipating a failure of the mass storage device resulting from a memory device of the mass storage device reaching a write endurance limit. A procedure is then initiated to back up data to a second mass storage device prior to failure. The method includes assigning at least a first memory block of the memory device as a wear indicator, using other memory blocks of the memory device as data blocks for data storage, performing program / erase (P / E) cycles and wear leveling on the data blocks, subjecting the wear indicator to more P / E cycles than the data blocks, performing integrity checks and monitoring the bit error rate of the wear indicator, and taking corrective action if the bit error rate increases, including the initiation of the backup procedure and generating a request to replace the device.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Proactive controller for failure resiliency in communication networks
ActiveUS20150195190A1Reduce the impact of failureHardware monitoringReliability/availability analysisTraffic capacityReal-time data
Network devices and systems relating to prevention of large-scale network failure and determining a probability of a large-scale network failure for a network. The network devices may control rerouting of network traffic from failed network paths to preventative paths with probabilities of failure below determined thresholds. The network devices monitor and process real time data for dynamic and proactive rerouting when large-scale network failure occurs or is likely to occur.
Owner:UNIV OF ONTARION INST OF TECH
Apparatus, system and method for healthcheck of information technology infrastructure based on log data
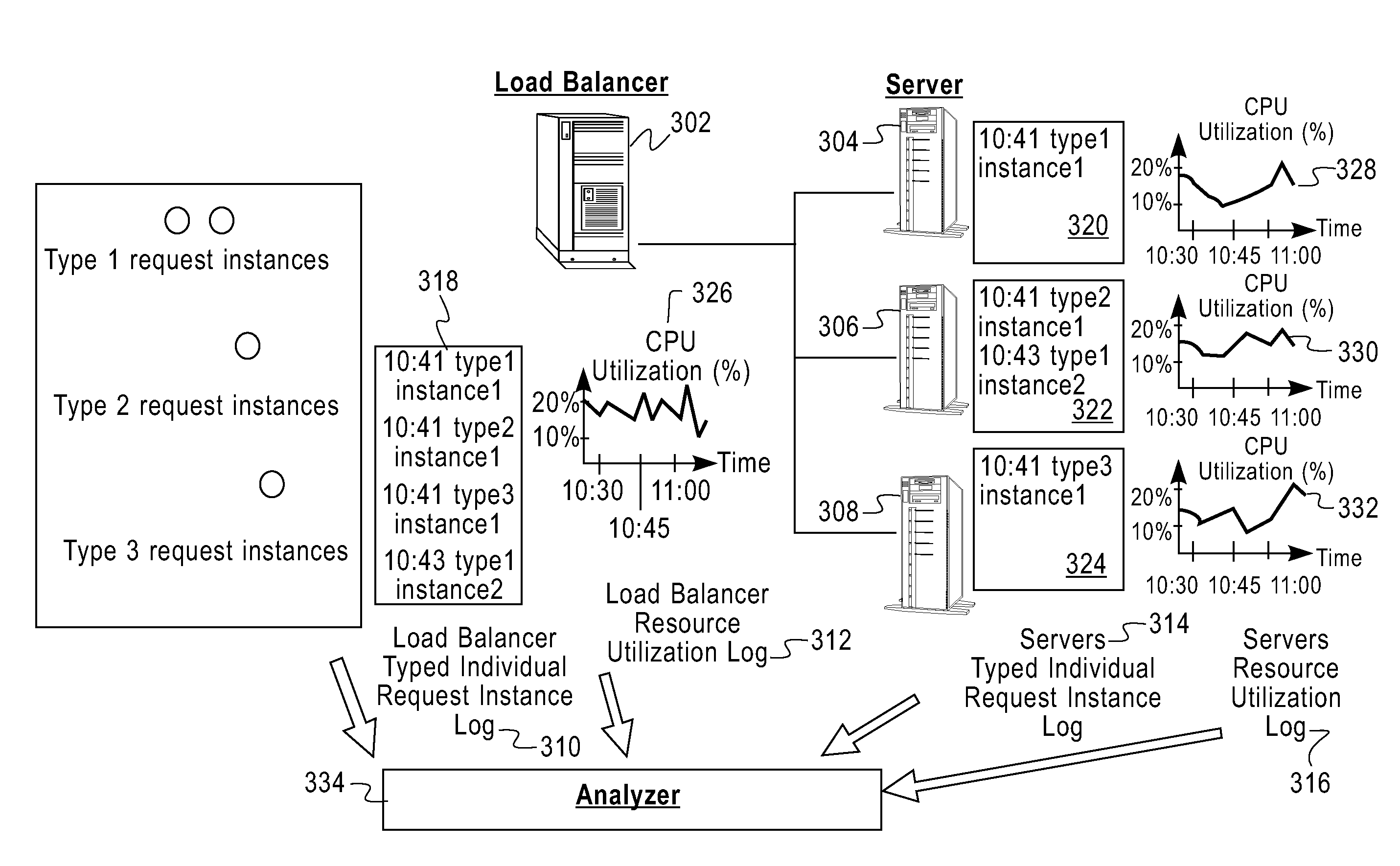
InactiveUS20090287744A1Database updatingDigital data processing detailsResource utilizationPredicting performance
A method and system for checking health of information technology infrastructure based on log data, in one aspect, collect log data non-intrusively from a production system, said log data at least associated with transactions occurring in the production system and resource utilization of the production system, normalize said log data into a plurality of log data types, perform data regression analysis using said plurality of log data types to estimate resources consumed by each of said transactions and throughput of each of said transactions, and use a queuing model to predict performance of the information technology infrastructure under various workloads.
Owner:IBM CORP
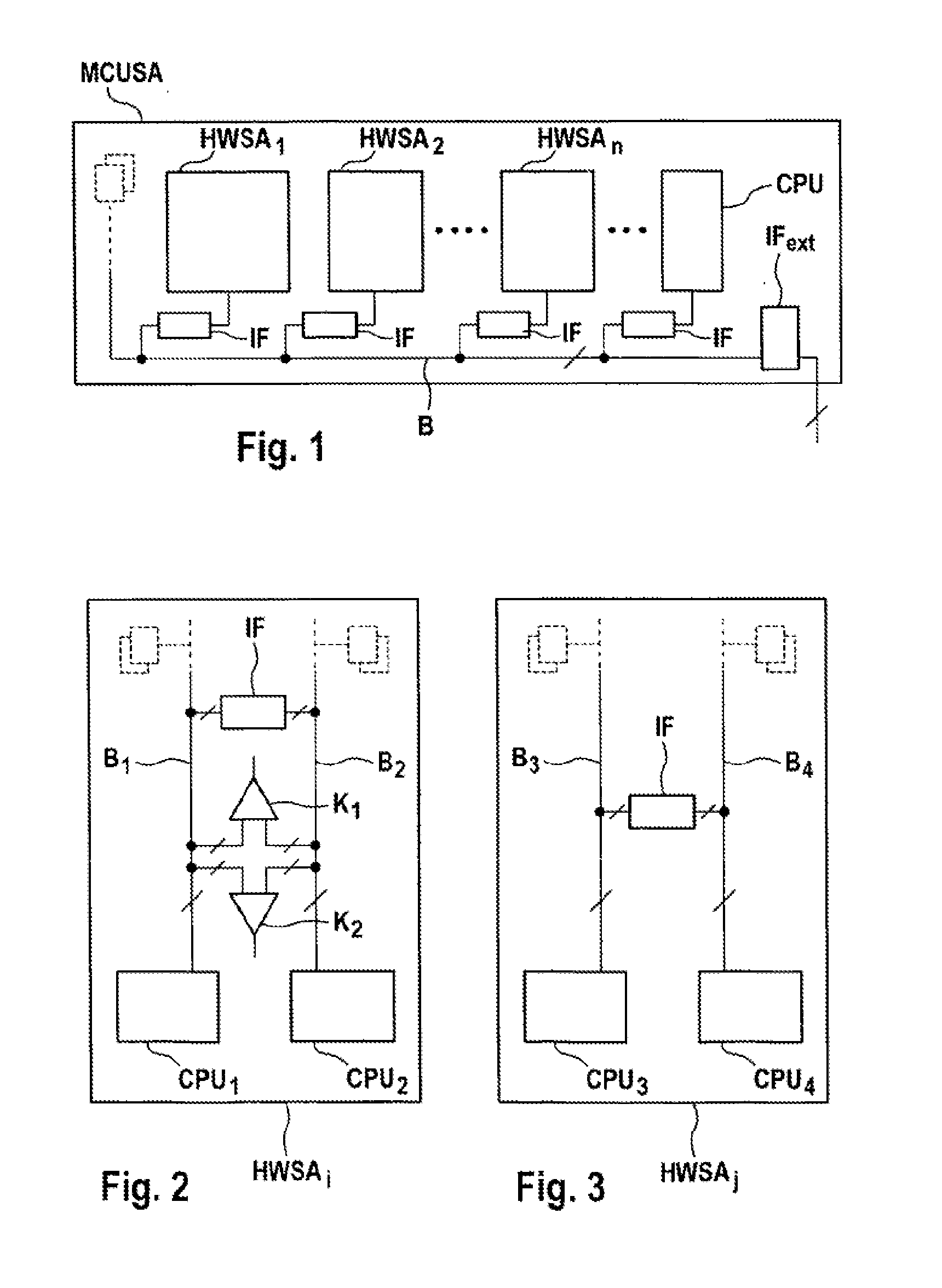
Microprocessor System Having Fault-Tolerant Architecture
InactiveUS20130268798A1Improve robustnessFurther-increased robustnessSafety arrangmentsError avoidanceFault tolerant architectureIntrinsic safety
The invention relates to a microprocessor system for executing software modules, at least some of which are security critical, within the scope of controlling functions or tasks assigned to the software modules, comprising an intrinsically safe microprocessor module having at least two microprocessor cores. At least one further intrinsically safe microprocessor module having at least two microprocessor cores is provided. At least two microprocessor modules are connected via a bus system, at least two software modules are provided which execute functions, at least some of which overlap, the software modules having at least partially overlapping functions are distributed on a microprocessor module or n at least two microprocessor modules, and means for comparing or arbitrating events generated with the software modules for the identical functions are provided in order to detect software or hardware faults.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Predictive failure analysis for storage networks
InactiveUS6948102B2Improve reliabilityImprove availabilityDigital computer detailsBiological neural network modelsStorage area networkPredictive failure analysis
A method of predicting failures of data storage devices in a data storage network. In predicting failures, birth and / or health records of data storage devices in the data storage network are requested. The records are then scaled and thresholded and processed using a probabilistic neural network to classify the data storage devices. Based on the classification, an action is taken to improve the reliability and availability of the data storage network.
Owner:IBM CORP
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com