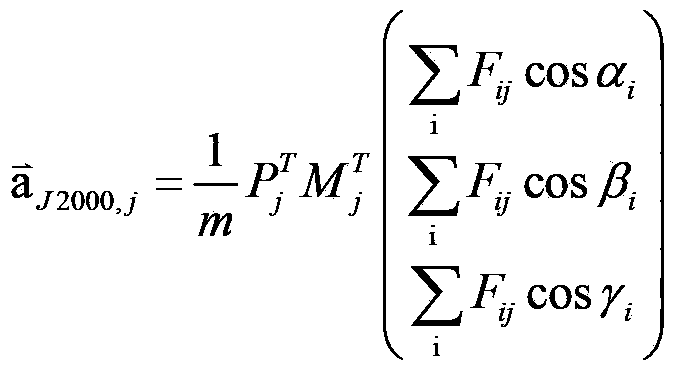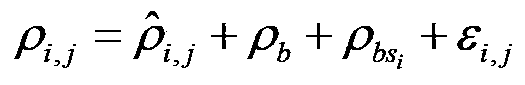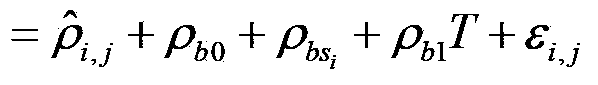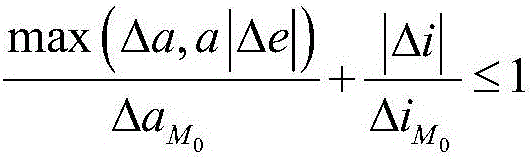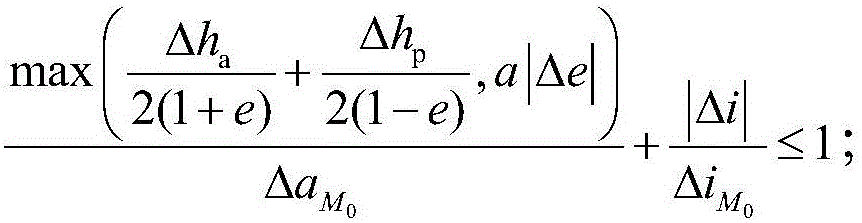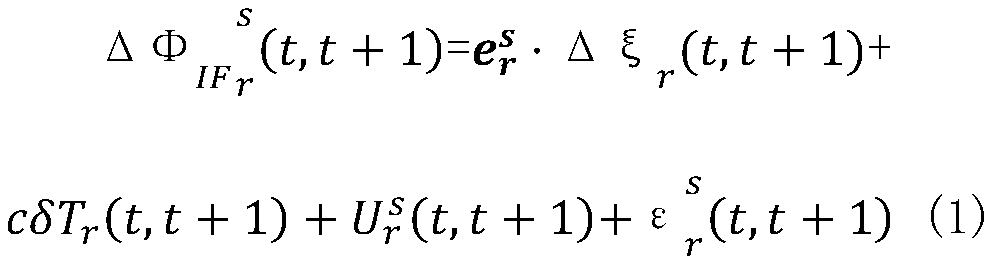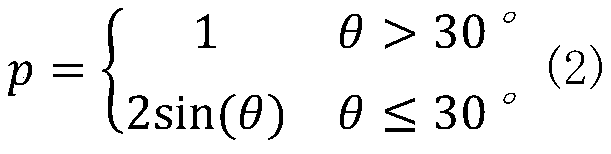Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
93 results about "Orbital maneuver" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In spaceflight, an orbital maneuver (otherwise known as a burn) is the use of propulsion systems to change the orbit of a spacecraft. For spacecraft far from Earth (for example those in orbits around the Sun) an orbital maneuver is called a deep-space maneuver (DSM).
Method and apparatus for propulsion and power generation using spinning electrodynamic tethers
InactiveUS6942186B1Economical and efficientImprove performanceCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusPower flowReverse current
The present invention improves the orbital maneuvering and power generation capabilities of a system of a satellite(s) connected with a conducting tether(s) by spinning the system about its mass center at an angular rate which is relatively high compared to the average orbital rate. An improvement in tether performance is achieved because at many times during rotation the tether is positioned at much better angles with the magnetic field and significantly higher currents are driven through the tether without destabilizing the system. The current can flow either in the direction of the EMF induced in the tether, or in the reverse direction, depending on the tether orientation with respect to the magnetic field and the mission goals. The reverse current is driven by the onboard power sources. Spinning electrodynamic tether systems can also be lighter and simpler in design and more flexible in operation.
Owner:STAR TECH & RES
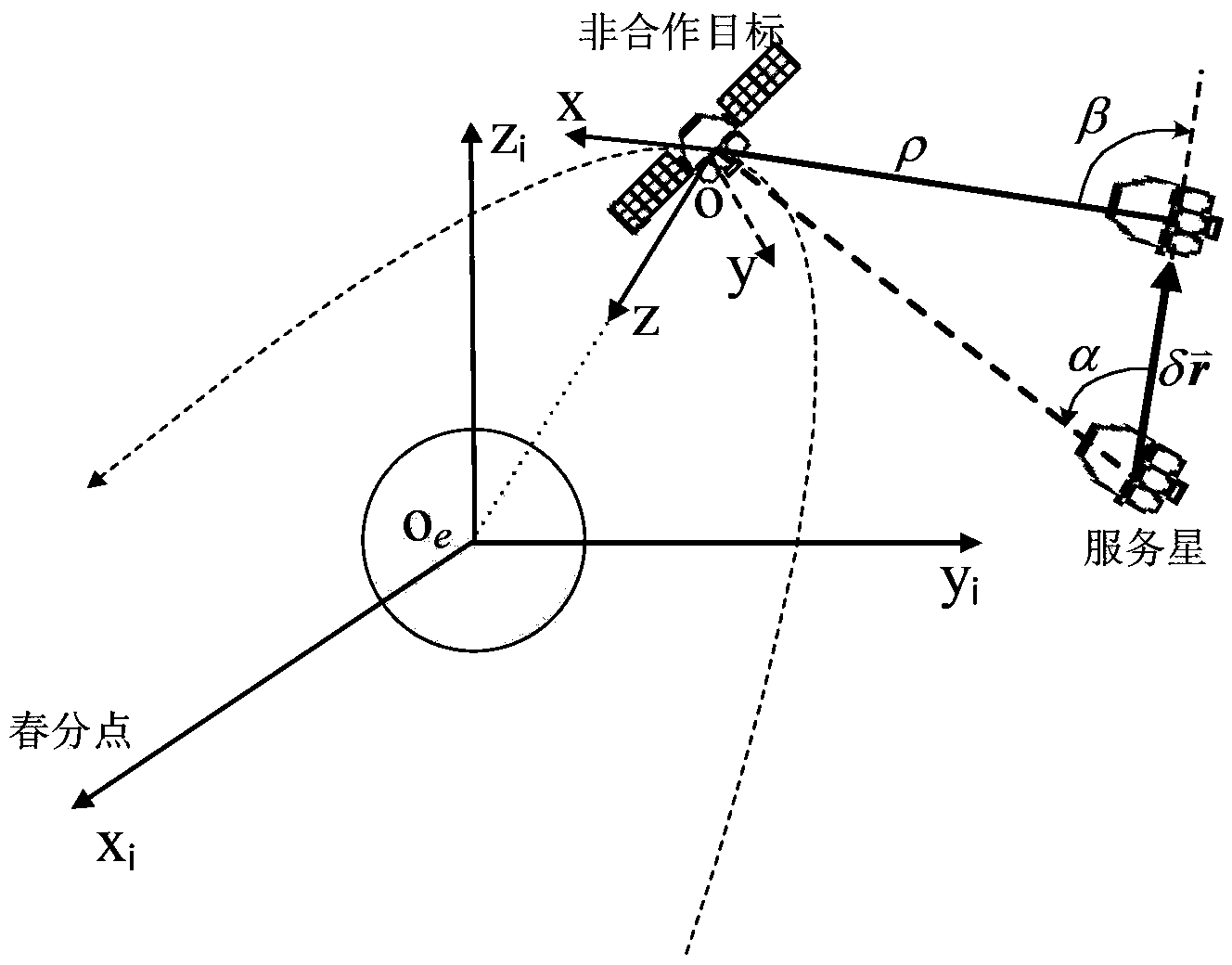
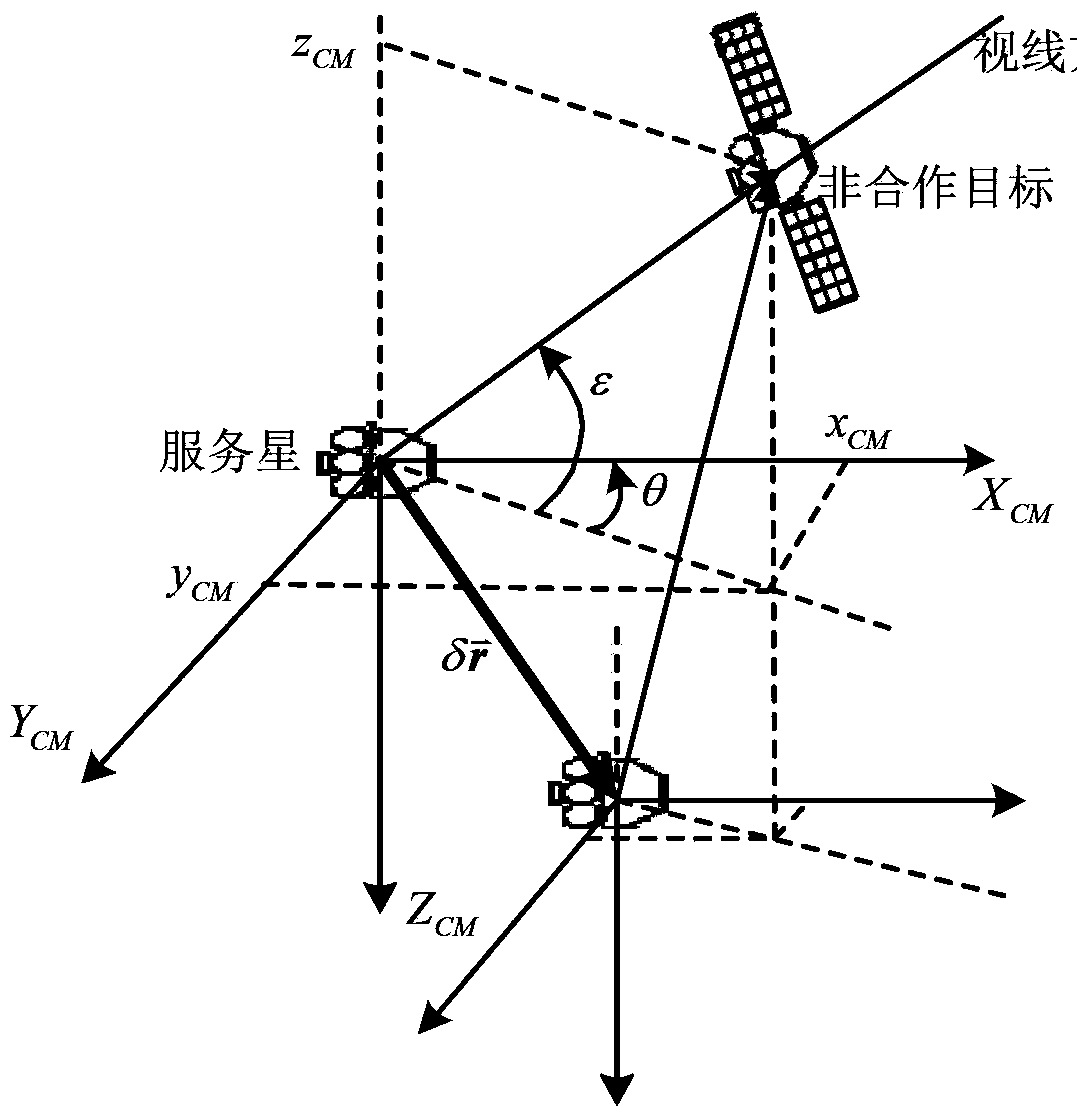
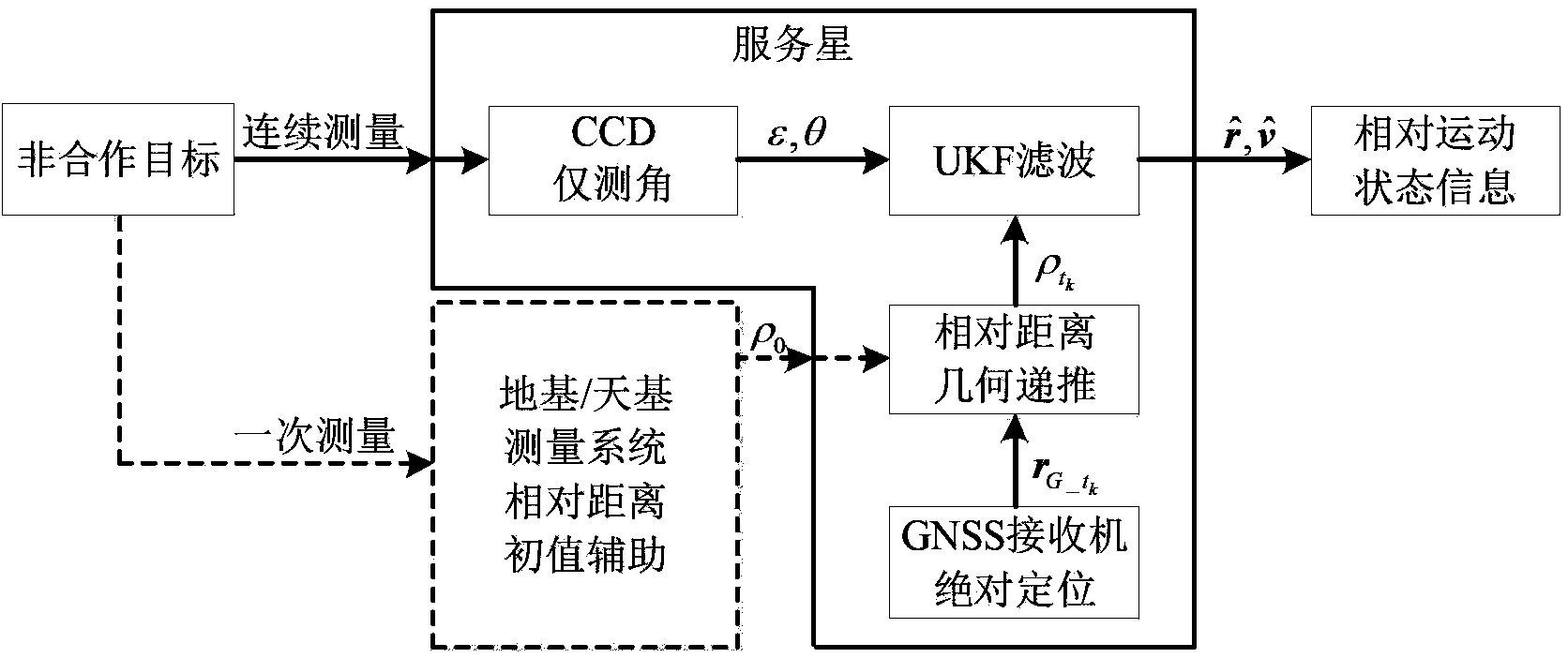
Relative navigation method for autonomous rendezvous of space non-operative target
InactiveCN103438888ARealize high-precision relative navigationInstruments for comonautical navigationFilter algorithmCcd camera
The invention relates to a relative navigation method for autonomous rendezvous of a space non-operative target. The relative navigation method comprises: taking a spacecraft relative orbital motion equation as a navigation state equation, taking relative visual angle information measured by a spaceborne CCD (Charge Coupled Device) camera, absolute positioning information output by a GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) receiver and relative distance rho information constructed by geometrical constraint as measure quantities, and employing UKF (Unscented kalman filter) filtering algorithm to accurately estimate the relative position and relative speed between a service satellite and the space non-operative target. The relative navigation method is applicable to relative navigation for remote autonomous rendezvous of space non-operative targets. The relative navigation method has the beneficial effects that: under the conditions that the service satellite has no special orbital maneuver and the number of the service satellite is not increased, the high-accuracy relative navigation for medium / long distance autonomous rendezvous of the space non-operative targets with the service satellite can be realized by only depending on the spaceborne CCD camera and the absolute positioning equipment GNSS receiver of the singular service satellite.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
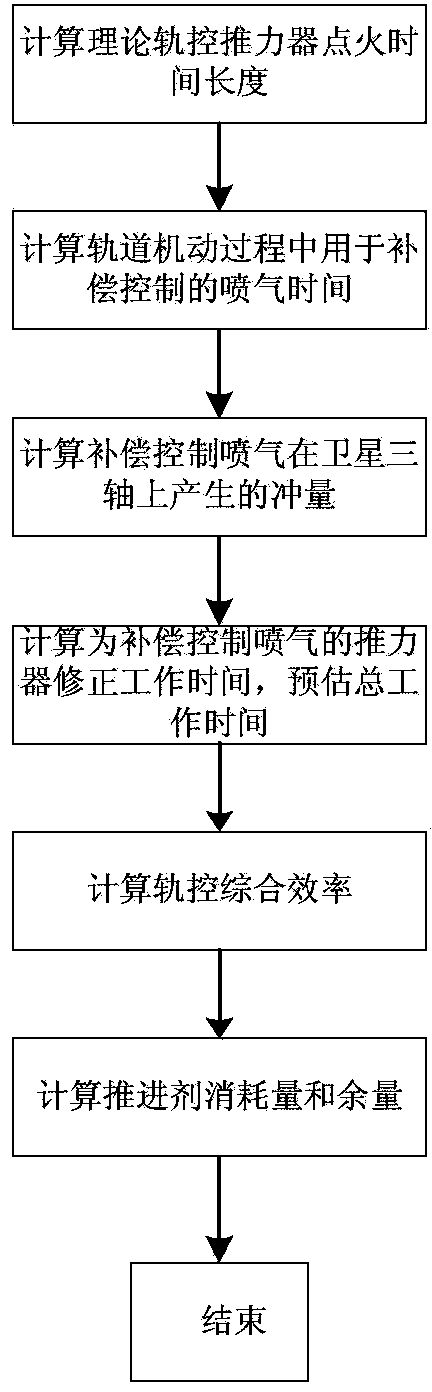
Method for estimating orbit control comprehensive efficiency and propellant consumption
ActiveCN103412563AImprove accuracyExtended cycleCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusVehicle position/course/altitude controlWork timeControl parameters
The invention relates to a method for estimating orbit control comprehensive efficiency and propellant consumption. Based on the in-orbit calibrated disturbance torque on a satellite by an orbit control thruster during working, the method for estimating the orbit control comprehensive efficiency and the propellant consumption calculates out unexpected influences on the position of an orbit when other thrusters compensate for the disturbance torque. According to the unexpected influences on the orbit, working time of the orbit control thruster is corrected and the orbit control comprehensive efficiency of the orbit control thruster of the satellite is worked out. Propellant consumption and propellant surplus of the orbital maneuver are estimated. According to the method for estimating the orbit control comprehensive efficiency and the propellant consumption, when the satellite performs orbital maneuver in the X direction of an orbital coordinate system, determination of control parameters and estimation of propellant consumption can be more accurate, the precision of orbital maneuver of a medium-to-high orbit satellite is effectively improved and the service life of the satellite in the orbit is prolonged.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Method for compositely controlling attitudes and orbits of in-orbit dragging combination spacecrafts
InactiveCN103970142AAchieving off-orbit maneuversClean operating environmentPosition/course control in three dimensionsMechanical engineeringOrbit/Orbital
The invention discloses a method for compositely controlling attitudes and orbits of in-orbit dragging combination spacecrafts. The method includes steps of identifying mass property parameters of the combination spacecrafts in an in-orbit manner; determining composite control on the attitudes and the orbits of the combination spacecrafts in orbit maneuver periods. The method has the advantages that abandoned spatial targets can be deorbited and maneuvered under the conditions of high disturbance torque and uncertain parameters; the method can be used for cleaning abandoned satellite or space debris in the earth orbit, and accordingly clean running environments can be provided for satellites which run normally.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINYUE METER FACTORY
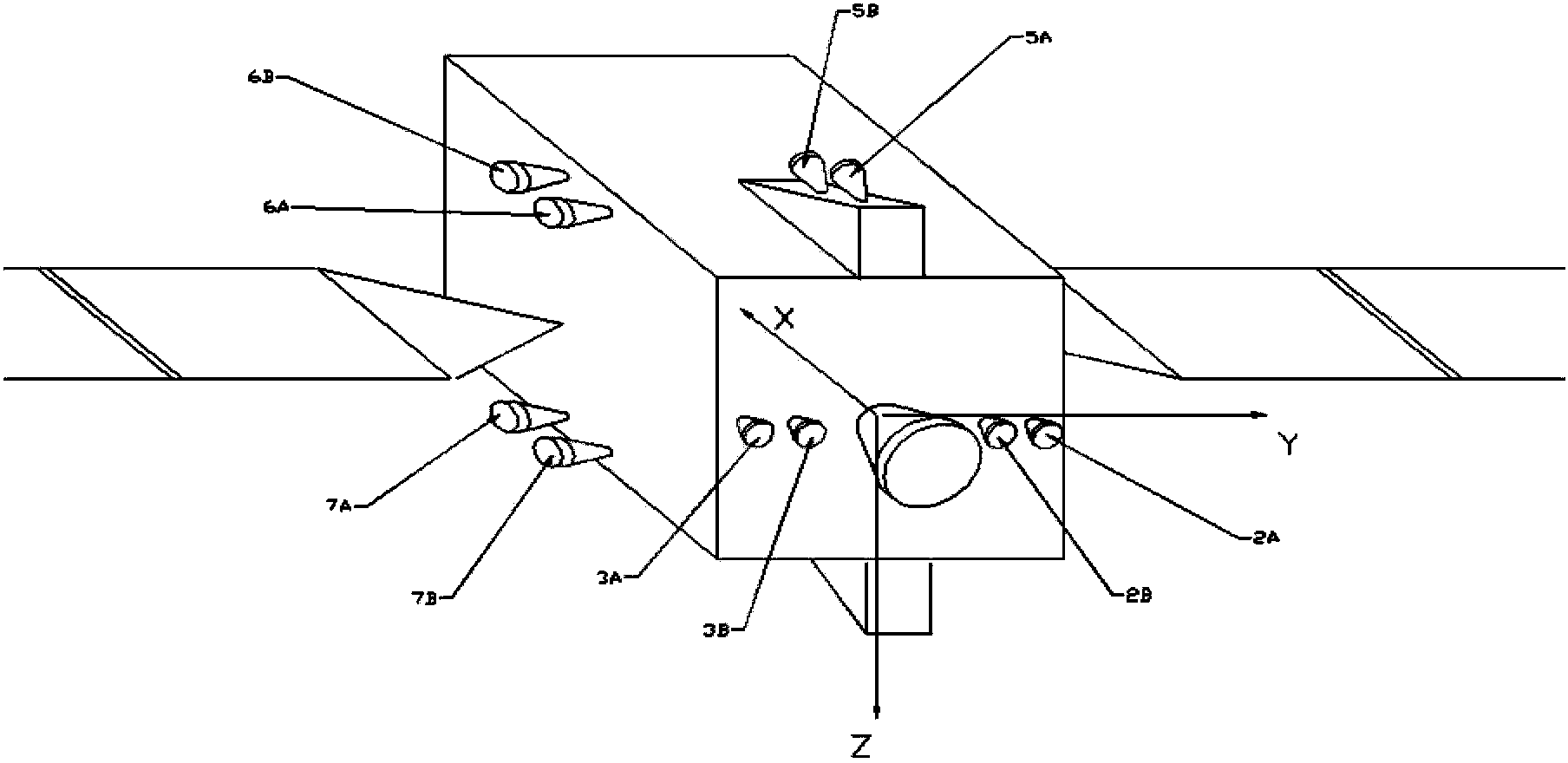
Thruster layout method for truss type GEO (geostationary orbit) satellite adopting subdivision optimization design
ActiveCN105197257ACorrect polarityAvoid disturbance torqueCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusNatural satelliteAttitude control
The invention discloses a thruster layout method for a truss type GEO (geostationary orbit) satellite adopting subdivision optimization design. Basic demands of truss type GEO satellite thrusters for subdivision modular design in thrusting service module layout are met, and layout azimuth angles of four 10N thrusters mounted at four corners of a thrusting service module back plate are designed according to demands of highest possible satellite orbital maneuver efficiency, enough capability of overcoming disturbance torque of a high-thrust orbit maneuver engine, combination of sedimentation of propellants and three-axis attitude control, angular momentum unloading and the like; under the adverse condition that the centroid of the whole satellite is remarkably higher than the upper end of a thrusting service module, a thrust vector slant and parallel layout method for 10N thrusters in pairs is adopted for layout of thrusters for east-west station keeping and south-north station keeping, so that layout of the thrusters for east-west station keeping combines functions of pitch attitude control and angular momentum unloading, layout of the thrusters for south-north station keeping combines functions of rolling, pitching, off-course attitude control and angular momentum unloading, and propellants for attitude control and angular momentum unloading are saved.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
Saw accessory for aerial work platform
InactiveUS7353817B2Easy to operateStreamlined operationMetal sawing devicesScaffold connectionsCoolant flowManipulator
A wall saw accessory is provided for an aerial work platform, where a wall saw is movably affixed on a track secured to a wall to be sawed. The accessory includes a saw / track manipulator fixable to the aerial work platform. The saw / track manipulator movably supports the track and saw and enables positioning of the saw and track to and from a working position. A hydraulic power source is coupled with a water supply to provide hydraulic power and coolant flow to the wall saw. In one arrangement, the accessory additionally incorporates an onboard pressure washer, which serves to streamline the process and maintain a clean work area. The accessory may be attached to a lift vehicle including a chassis supporting an onboard water supply.
Owner:JLG IND INC
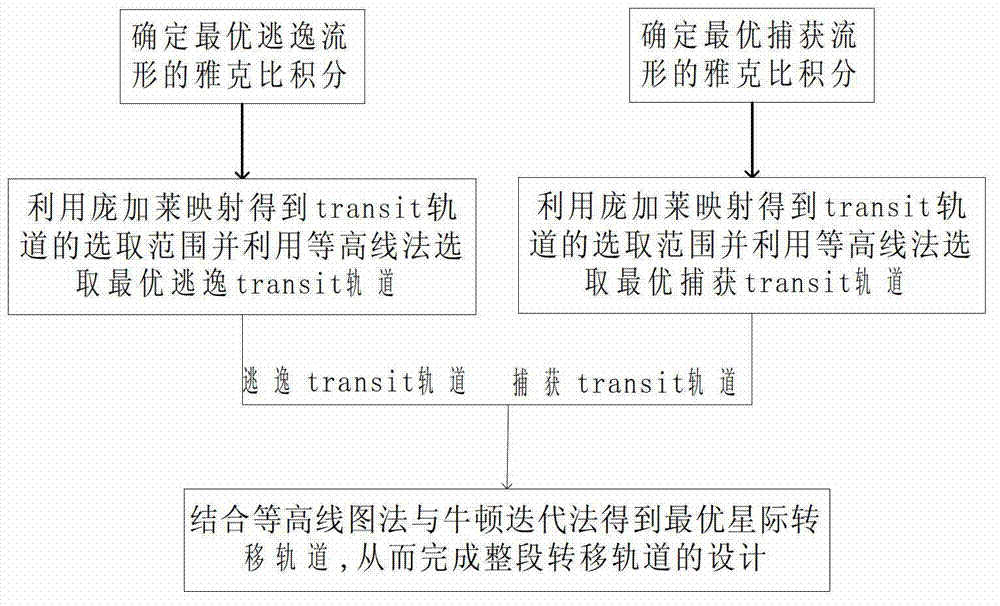
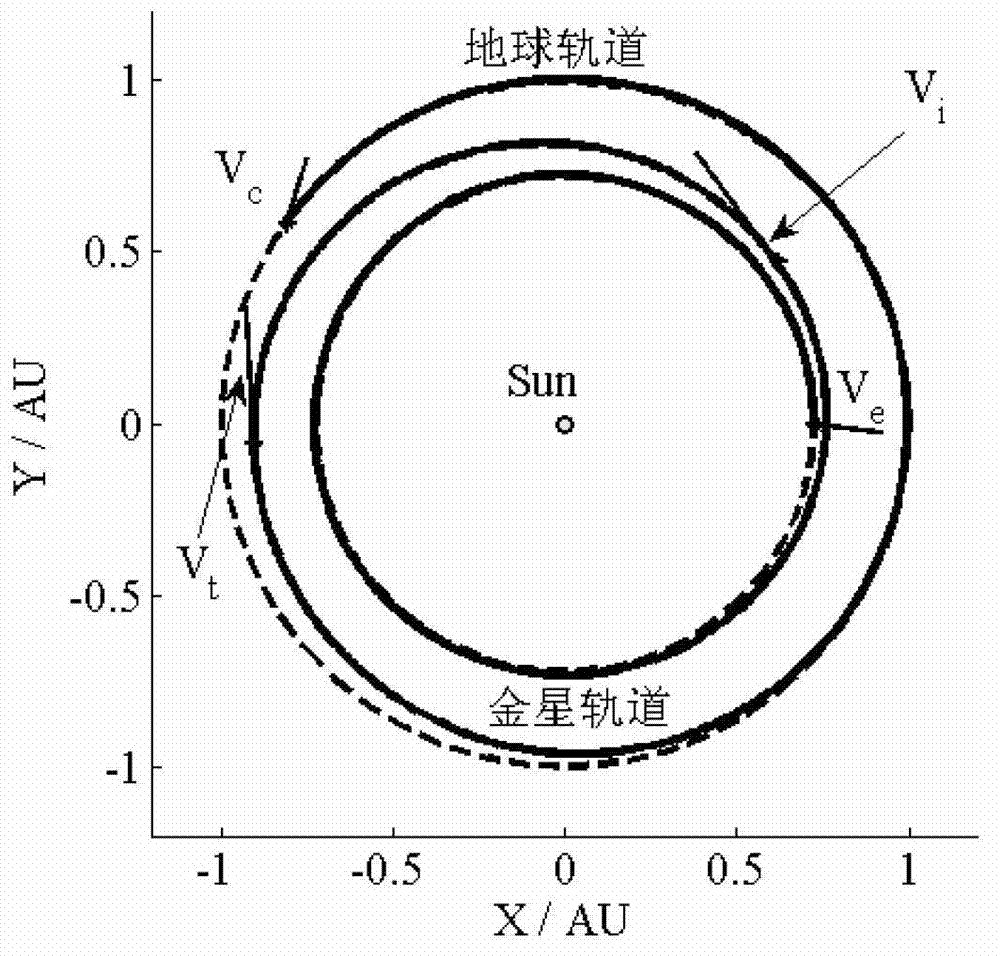
Design method for low-energy transit among interplanetary fixed orbits based on invariant manifold
InactiveCN102923323AImprove computing efficiencySimplify complexityCosmonautic componentsPoincaré mapFixed orbit
The invention relates to a design method for low-energy transit among interplanetary fixed orbits based on invariant manifold. The method is particularly suitable for transit between adjacent planetary orbits with approximate manifolds and belongs to the field of an orbital maneuver technology of spacecrafts. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly providing a pulse consumption assessment method and providing a judgment standard for selecting an appropriate invariant manifold; then determining the range of an invariant manifold transit orbit by calculating a poincare map of the invariant manifold on a fixed circular orbit, and obtaining a transit orbit with a minimum speed increment by using a contour map method; and splicing transit orbits at two ends of a heliocentric two-body model after finishing designing an escape transit orbit and a capture transit orbit, and finally finishing designing the design for low-energy transit among interplanetary fixed orbits based on invariant manifold. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple calculation, high calculation efficiency and the like and is suitable for the initial design of fixed orbits of different planets by using the low-energy transit orbit based on the invariant manifold.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
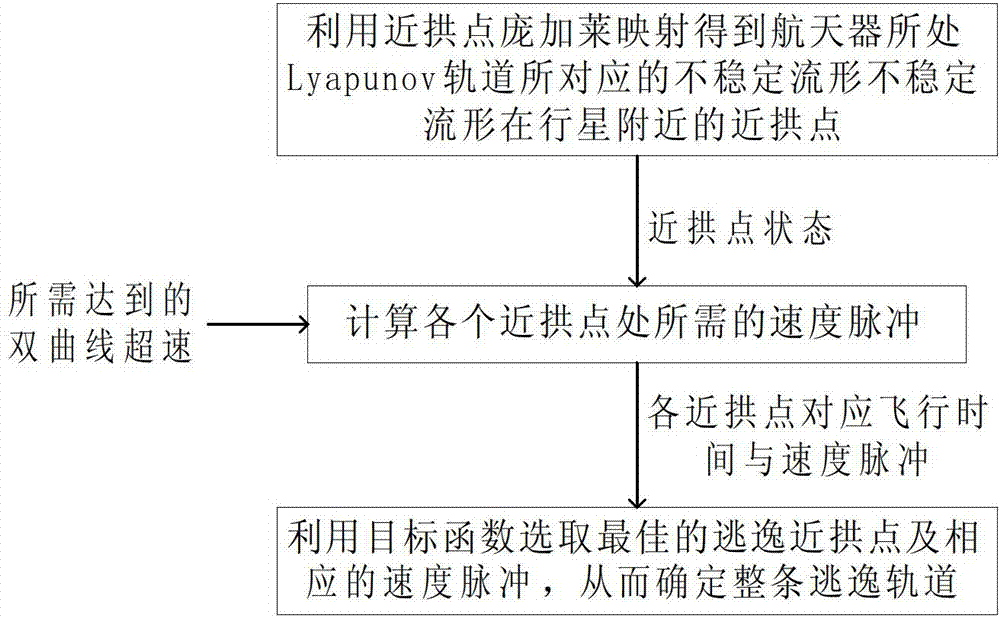
Low-energy planet escape orbit designing method based on invariant manifold and gravity assist
InactiveCN102923324ASimple algorithmImprove computing efficiencyCosmonautic componentsGravity assistDeep space exploration
The invention relates to low-energy planet escape orbit designing method based on an invariant manifold and a gravity assist, being particularly suitable for the design of a low-energy deep space exploration task orbit by using movable balance points and belonging to the field of an orbital maneuver technology of spacecrafts. The method is carried out by the following steps of: firstly obtaining an orbit state set of the invariant manifold at a periapsis place by introducing a periapsis poincare map based on sectional matching of the periapsis poincare map; and then calculating a maneuver pulse applied to each branch of the invariant manifold in the orbit state set by using a numeric iteration method according to an escape hyperbola excessive speed requirement needed for realizing interplanetary transit, and determining a branch of the invariant manifold corresponding to the escape with minimum fuel and the required maneuver pulse through the comparison of the maneuver pulses. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple calculation method, high calculation efficiency and the like and can provide reasonable and feasible initial value guess for a precise design.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Low-orbit constellation system phase keeping method, system and device and storage medium
ActiveCN111591469AReduce sample storage requirementsAchieve high precision phase holdCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusSatellite orbit determinationSatellite orbit
The invention discloses a low-orbit constellation system phase keeping method, system and equipment and a storage medium, wherein the method comprises the steps: determining the deviation between an actual semi-major axis and a reference semi-major axis of a satellite and the variation of the deviation along with time according to a reference flat phase angle and an actual flat phase angle of thesatellite; according to the deviation between the actual semi-major axis and the reference semi-major axis of the satellite and the variation of the deviation along with time, determining the orbit maneuvering time and the variation of the semi-major axis of the satellite; and adjusting the phase of the low-orbit constellation system in a satellite phase keeping task period by utilizing the satellite orbit maneuvering time and the semi-major axis variation. The technical scheme provided by the invention can be used for realizing high-precision phase retention of the low-orbit constellation system; under the conditions that the satellite position and speed determination precision is not high and the positioning data sampling rate is low, high-precision phase keeping (the precision requirement such as + / - 0.1 degree) can be achieved, and the requirements of high-precision phase keeping for satellite orbit determination precision and orbit determination data sampling storage are lowered.
Owner:航天科工空间工程发展有限公司
Orbit determination method for geostationary satellite adapting to orbital maneuver
ActiveCN103424116ASolve the difficulties caused by determiningAvoid difficultiesInstruments for comonautical navigationGeosynchronous satelliteSystematic deviation
The invention discloses a precision orbit determination method for a geostationary satellite adapting to orbital maneuver and belongs to the field of space metering and controlling. The method comprises the followings: firstly, maneuvering acceleration is calculated; observed quantity Rho i and observed residual error sequences delta Rho i and j are calculated; estimation to public system error Rho b is performed; the public system error Rho b is deducted from the observed residual error sequences delta Rho i and j, so as to obtain systematic deviations of all observation stations; the Rho b is deducted from the observed quantity, then orbit improvement is performed again on observation data of which system errors are deducted, and calculating is performed again on the improved initial state until orbit convergence, and precision orbit determination for the geostationary satellite is accomplished. The precision orbit determination method provided by the invention has the benefits as follows: difficulty in precision orbit determination caused by pushing force produced by air blast of an engine on a GEO satellite during orbital maneuver can be overcome, meanwhile, public systematic error appraisement and an all-station deviation adapting iteration eliminating method are adopted for solving the problem that systematic errors such as satellite clock errors and time delay of all observation station equipment are hard to separate is solved, and the orbit determination forecast accuracy of the GEO satellite during the orbital maneuver can be effectively improved.
Owner:CHINA XIAN SATELLITE CONTROL CENT
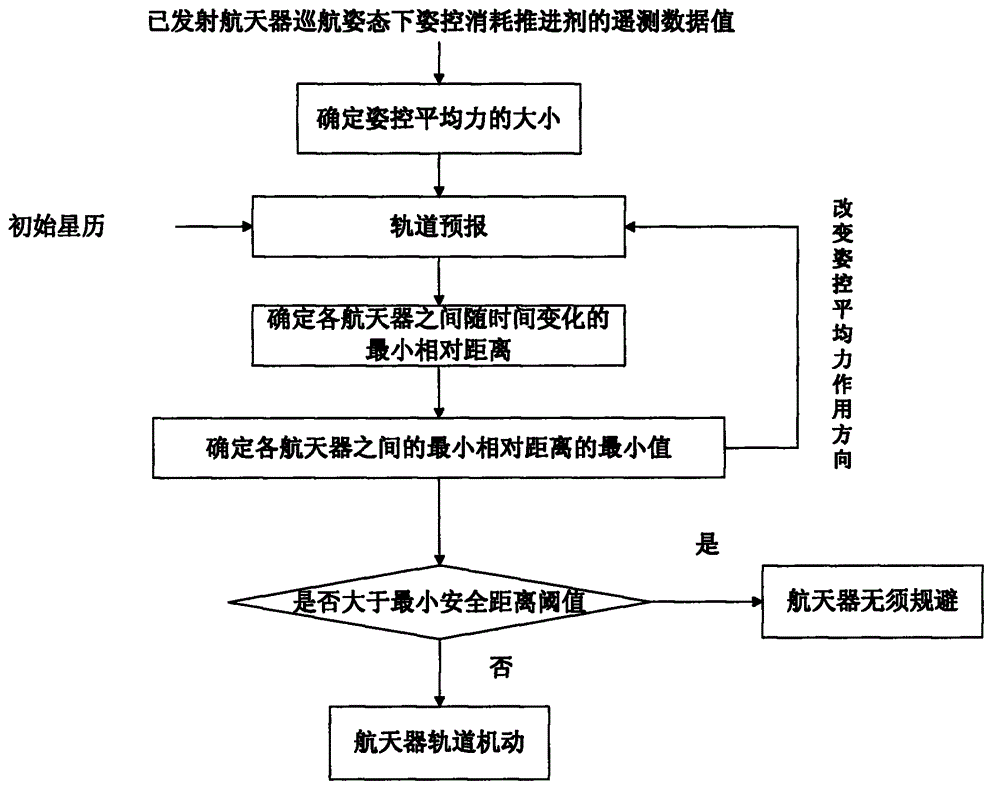
Multiple-constraint multi-spacecraft flight interval indicating and collision avoidance method
ActiveCN103064423AGuaranteed validityEnsure safetyPosition/course control in three dimensionsAttitude controlEngineering
A multiple-constraint multi-spacecraft flight interval indicating and collision avoidance method includes the following steps: (1) confirming magnitude of attitude control average force according to telemeasuring data value of propellant consumed by attitude control of launched spacecrafts on an orbit under the cruising attitude, (2) conducting high-accuracy orbit prediction according to initial ephemeris information of each spacecraft and the attitude control average force confirmed in the step one, calculating ephemeris of each spacecraft in an inertial frame at any time and relative distance between each spacecraft at any time, and confirming the minimum relative distance between the spacecrafts, (3) changing the direction of the attitude control average force, repeating the step one and the step two, calculating the minimum value of the minimum relative distance between each spacecraft, namely, the direction of the attitude control average force corresponding to the minimum value is the worst situation, (4) comparing the minimum value confirmed in the step three with the minimum safe distance, when the minimum value is greater than the minimum safe distance, the spacecrafts has no risk of collision, otherwise, within a first circle observation and controlling track segmental arc, one spacecraft which is selected conducts orbital maneuver, and thereby the distance between the spacecrafts is widened and the collision risk of the spacecrafts is avoided.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
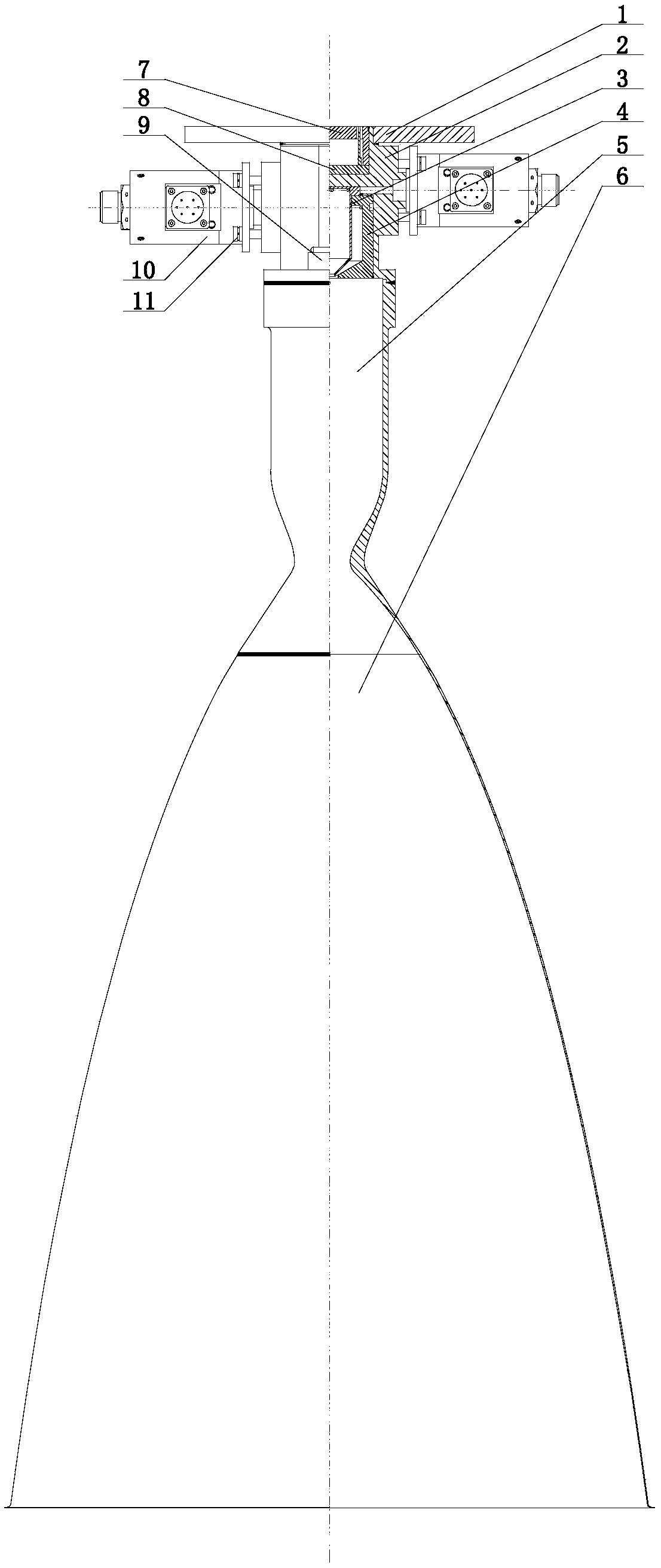
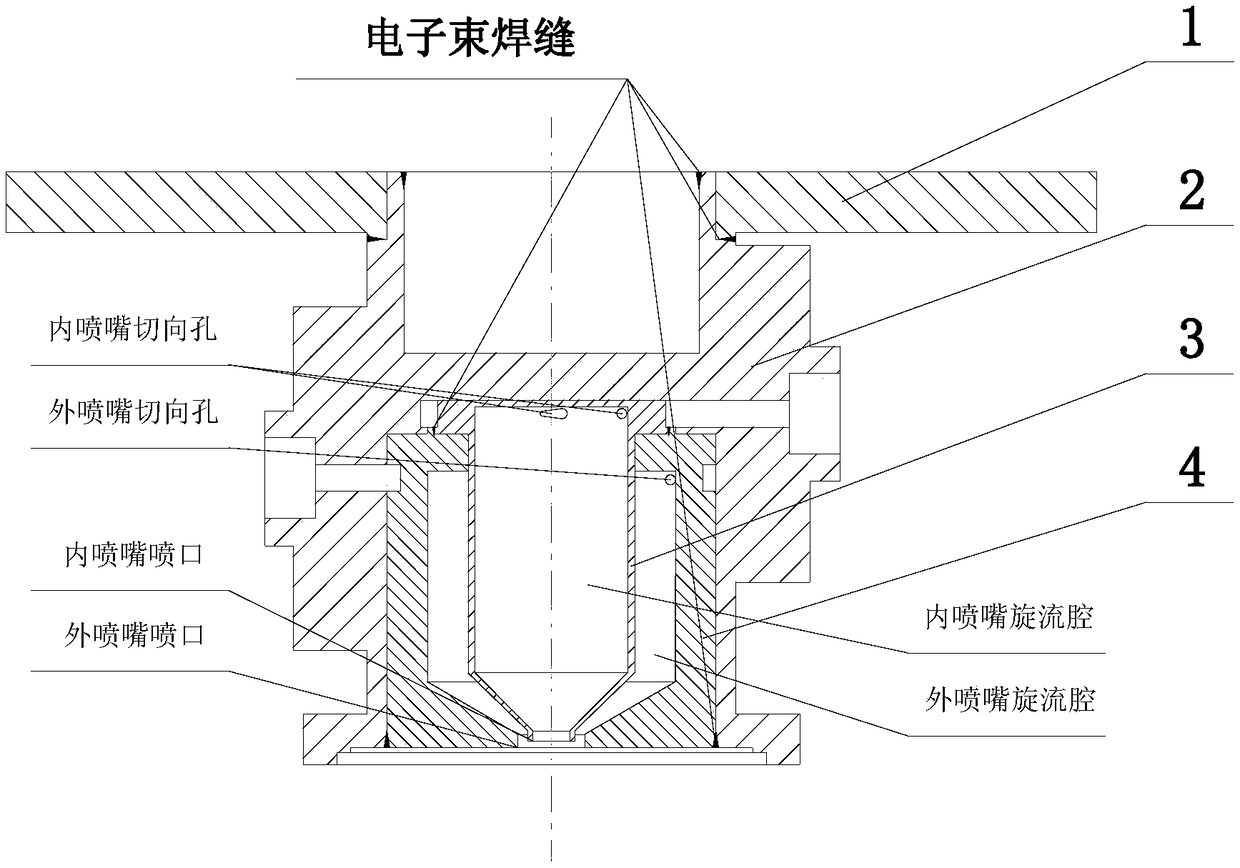
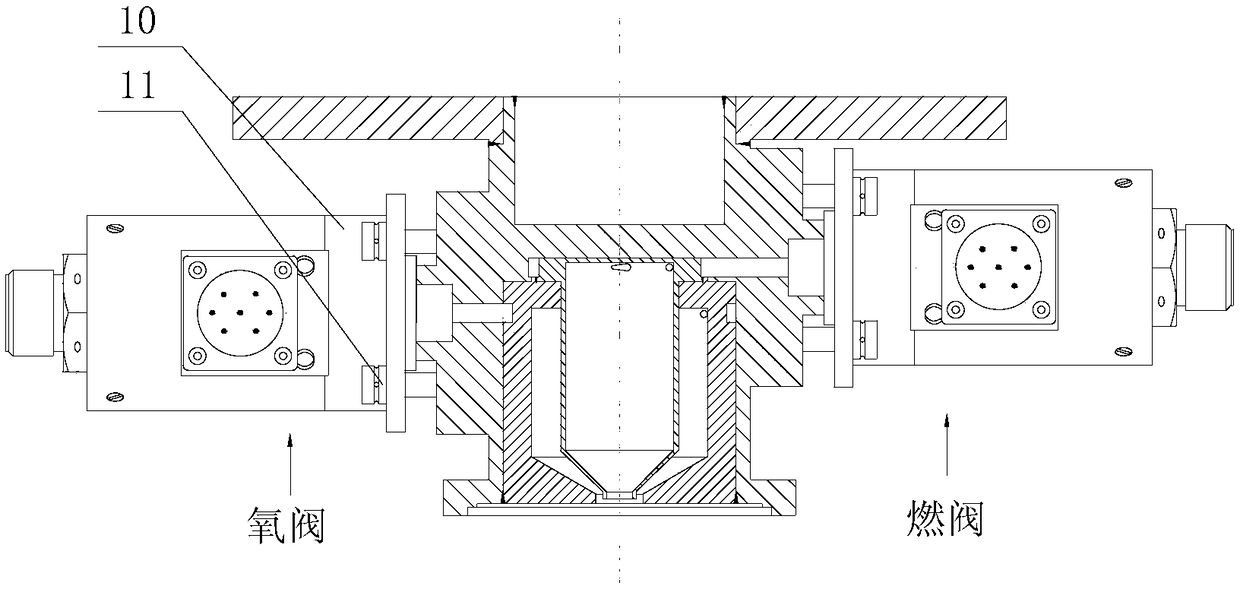
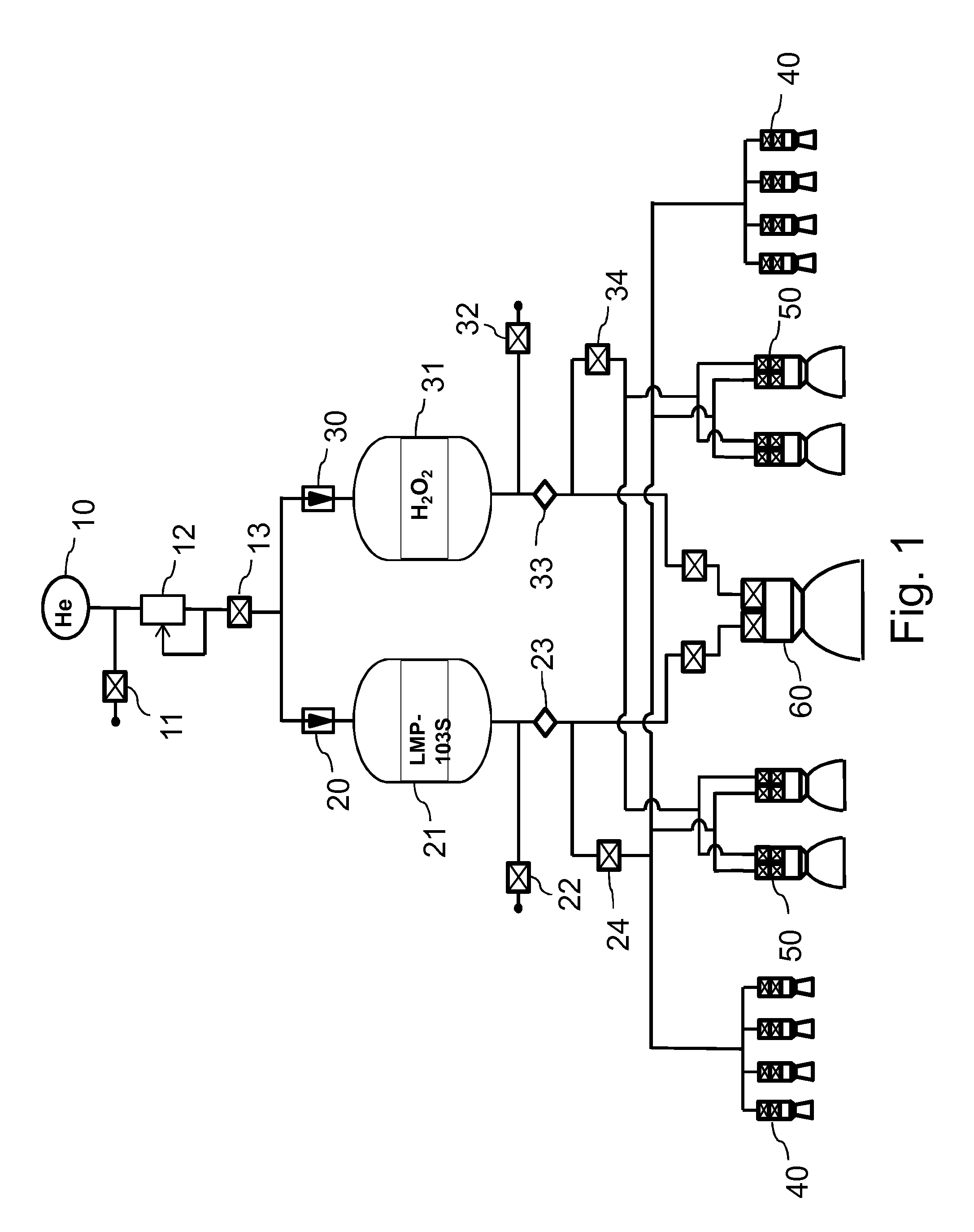
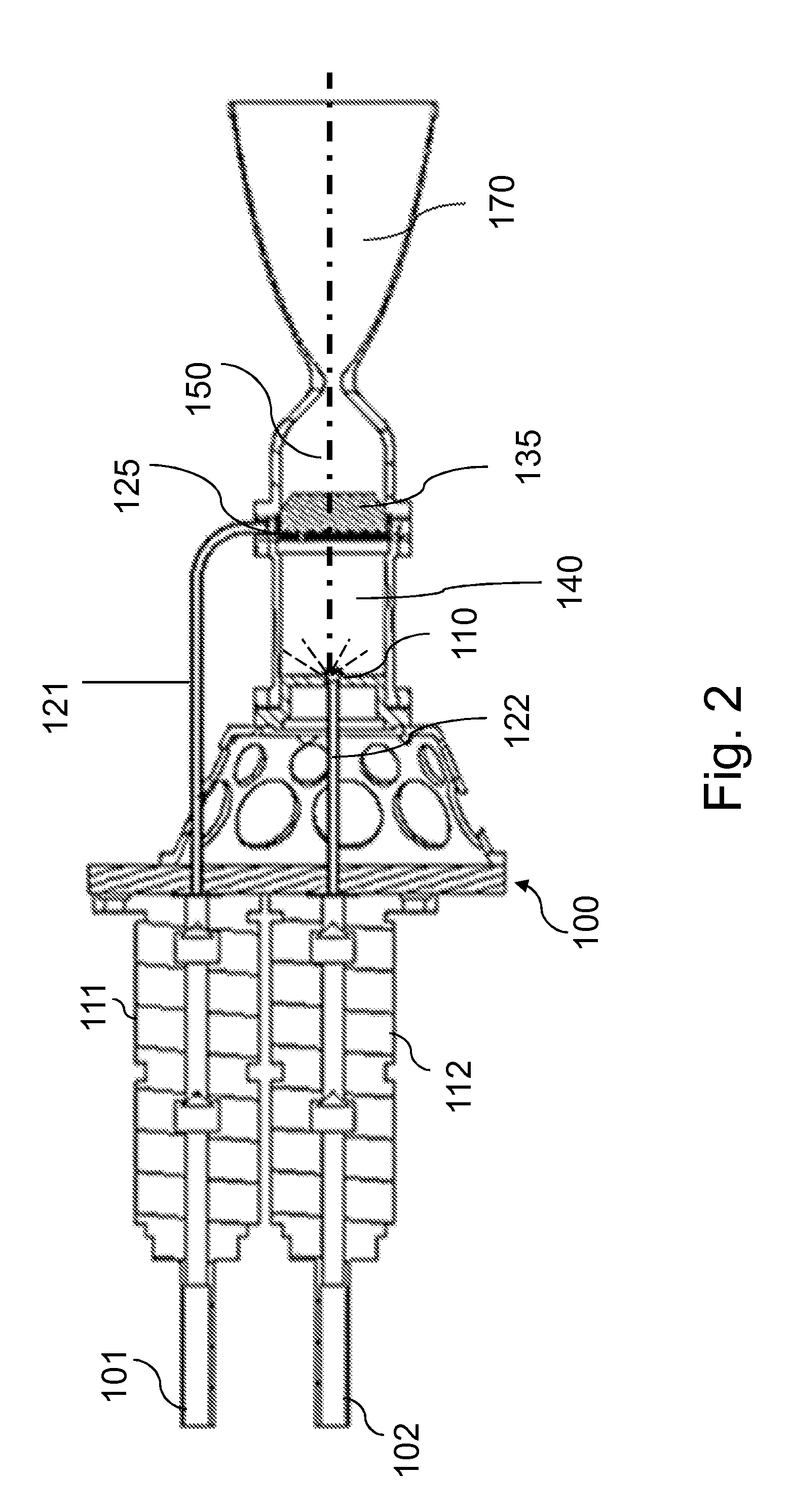
Space bipropellant orbit-control engine based on two-way single-nozzle centrifugal injector
The invention discloses a space bipropellant orbit-control engine based on a two-way single-nozzle centrifugal injector. The space bipropellant orbit-control engine is suitable for meeting the task requirements of orbital maneuver, orbital transfer and the like of aerospace crafts. The space bipropellant orbit-control engine comprises a mounting connection plate, a heating device, a control valve,screws, a body structure, an inner nozzle, an outer nozzle, a temperature measuring sensor, a combustion chamber and a jet pipe. After the control valve is started, the two propellants of an oxidizing agent and a combustion agent enter a swirling cavity of the outer nozzle and a swirling cavity of the inner nozzle of the centrifugal injector correspondingly to rotate at a high speed, rotational flow fog cones are formed on the nozzles and are further atomized and sprayed out according to a certain mass flow proportion, the two propellants are mixed for combusting in the combustion chamber coated with a high-temperature resistant and oxidation resistant coating, high-temperature fuel gas is formed ultimately and is further expanded and accelerated in the Laval jet pipe and accordingly thrust is formed.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Space-target positioning method based on multi-model filtering
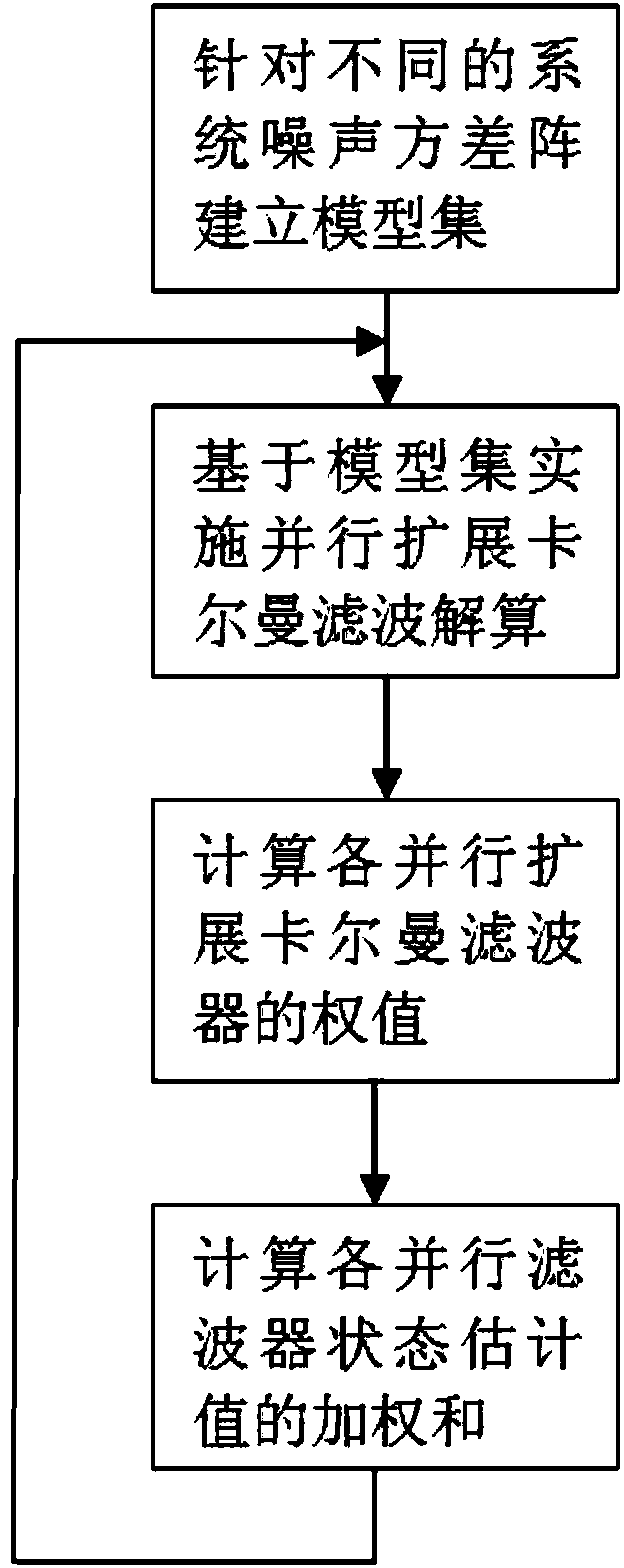
InactiveCN104296753AIncreased estimation errorImprove tracking performanceNavigational calculation instrumentsInstruments for comonautical navigationParallel ExtensionsState variable
The invention discloses a space-target positioning method based on multi-model filtering. The space-target positioning method comprises the following steps: firstly, selecting the position and the velocity vector of a space target as state variables, selecting different system noise variance matrixes, and establishing a plurality of models for describing the uncertainty of the orbital maneuver acceleration of the space target; secondly, establishing a plurality of parallel-extension Kalman filtering algorithms for the plurality of models, and respectively carrying out filtering to obtain a plurality of state estimated values; thirdly, calculating corresponding filtering weights according to the conforming degree of all the state estimated values and observed quantities; and finally, calculating the weighted sum of the state estimated values of all the parallel-extension Kalman filtering algorithms according to the filtering weights to obtain navigation filtering results, namely the estimated values of the position and the speed vector of the space target. The space-target positioning method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the system noise variance matrixes playing a leading role can be selected in a self-adaptive manner, so that the tracking and positioning capabilities of a filter to the maneuver target is enhanced, and the space-target positioning method is favorable for solving the problem that the uncertainty of the maneuver acceleration influences the positioning accuracy of the space target.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Spacecraft cluster only-ranging relative navigation method based on consistency filtering
PendingCN110186463AImplement relative orbit distribution estimationResolving Relative Orbital AmbiguityNavigational calculation instrumentsInstruments for comonautical navigationRelative orbitKaiman filter
The invention discloses a spacecraft cluster only-ranging relative navigation method based on consistency filtering. According to the method, measurement sensors are not added to members of the spacecraft cluster, and related orbital maneuvers are not performed. Under the condition that the absolute orbit is unknown, only only-ranging relative navigation of the spacecraft cluster can be realized by constructing the consistency expansion Kalman filter only by relying on the lever arm effect of the communication receiver antenna which is installed to deviate from the spacecraft mass center and the geometric topological constraint between cluster members. The method comprises: performing evolution of a relative orbit by taking a relative orbit motion equation among members of a spacecraft cluster as a navigation state equation; taking relative distance information measured in a receiver TOA mode installed in a manner of deviating from the mass center of the spacecraft as a measurement quantity; introducing geometric topology information among the members of the cluster as a consistency constraint; and designing a consistency-based extended Kalman filter to finish only-ranging relativenavigation of the spacecraft cluster.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Active-passive-combined rope net dragging safety orbit leaving control method
ActiveCN104407620AEnsure safetyTo achieve the purpose of anti-collision controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsIn planeActive tension
An active-passive-combined rope net dragging safety orbit leaving control method includes: tethered system mass center acceleration is designed according to tethered satellite orbit leaving task, and a propelling system applies corresponding push force on a primary satellite so as to track the designed orbital maneuver path in real time; tension control quality is designed, a tethered winch mechanism generates corresponding tension to be applied to the primary satellite so as to actively control the in-plane swing angle of a tether, and orbital maneuver of the tethered system is achieved by dragging secondary satellites through the orbital maneuver of the primary satellite and tether tension control. The method has the advantages that the large vibration of the in-plane swing angle of the tether is avoided during dragging, the in-plane swing angle of the tether is stabilized in a constraint range, and collision is prevented; meanwhile, the in-plane swing angle is restrained by the appropriate orbital maneuver path design and the active tension control applied to a combined body, and safety orbit leaving control of a target is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
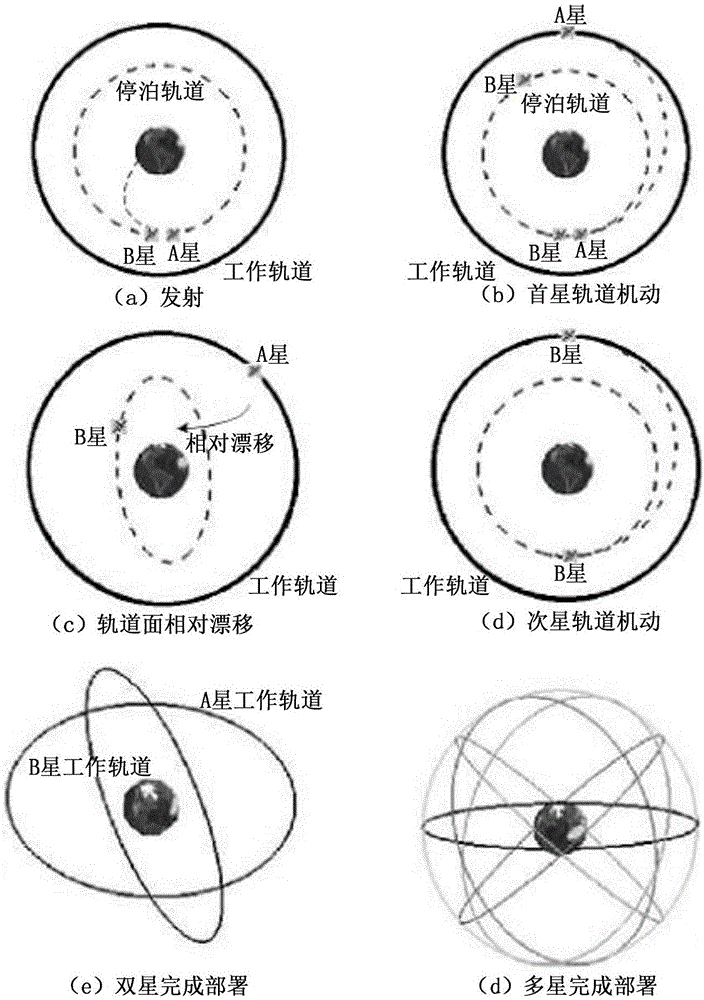
Walker constellation deployment method based on double berthing orbits
ActiveCN106802667ASolve the shortcomings of the long deployment cycle of different planesOptimizing Deployment Accuracy AnglePosition/course control in three dimensionsDeployment timeEngineering
The invention provides a Walker constellation deployment method based on double berthing orbits. The method comprises the following steps of: S1, delivering satellites for deploying a Walker constellation to a first berthing orbit and the second berthing orbit respectively; S2, enabling the first satellite to enter a working orbit through orbital maneuver and enabling the remaining satellites to remain in the first berthing orbit and the second berthing orbit; S3, waiting for the precessional motion of the orbital surface of the current berthing orbit relative to the orbital surface of a working orbit of an adjacent satellite until an ascending node of orbital surface and the right ascension have a preset angle, and then enabling the next satellite to enter the working orbit through orbital maneuver, and in the same way, enabling all the satellites for deploying the Walker constellation to enter the working orbits successively. The method can solve the limitation of a single-orbit plane deployment using one rocket with multi satellites, and solve the long single-berthing-orbit different-surface deployment period of the one rocket with multi satellites, and optimizes constellation deployment time and satellite deployment precision angle of the satellite relative position.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG DEV LTD
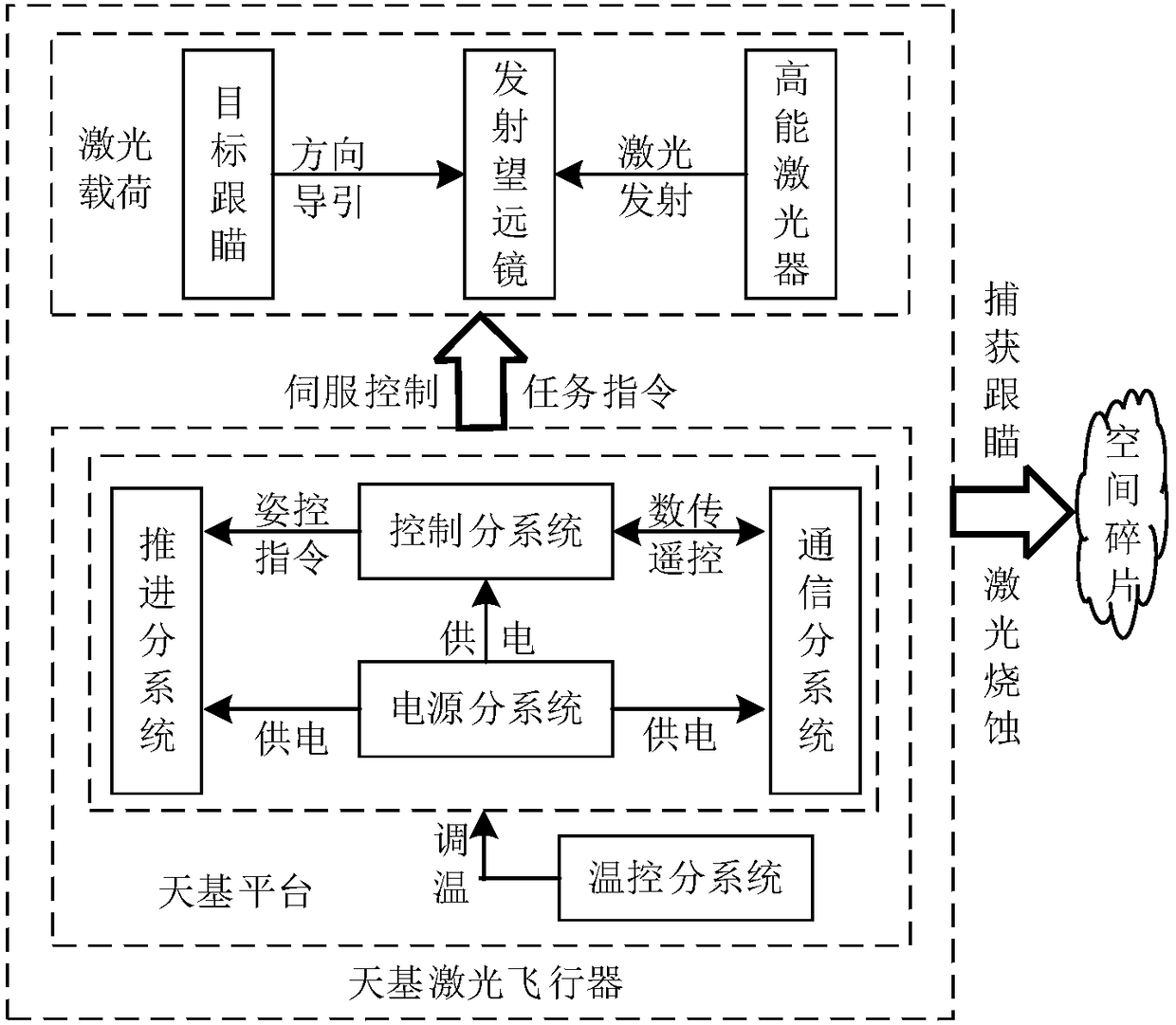
Space-based laser flight device
InactiveCN108263641AEfficient removalAvoid maneuveringCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic power supply systemsTemperature controlEngineering
The invention discloses a space-based laser flight device. The flight device comprises two parts of a space-based platform and a laser load. The space-based platform mainly comprises a propulsion subsystem, a power subsystem, a communication subsystem, a control subsystem and a temperature control subsystem. The laser load mainly comprises a high-energy laser device, a transmitter-telescope and atarget acquisition tracking and aiming subsystem. The flight device can remove space debris with high efficiency, meanwhile, a large-scale high-frequency orbital maneuver can be avoided, and the service life of the flight device is prolonged.
Owner:PLA PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY OF CHINA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE AEROSPACE ENG UNIV
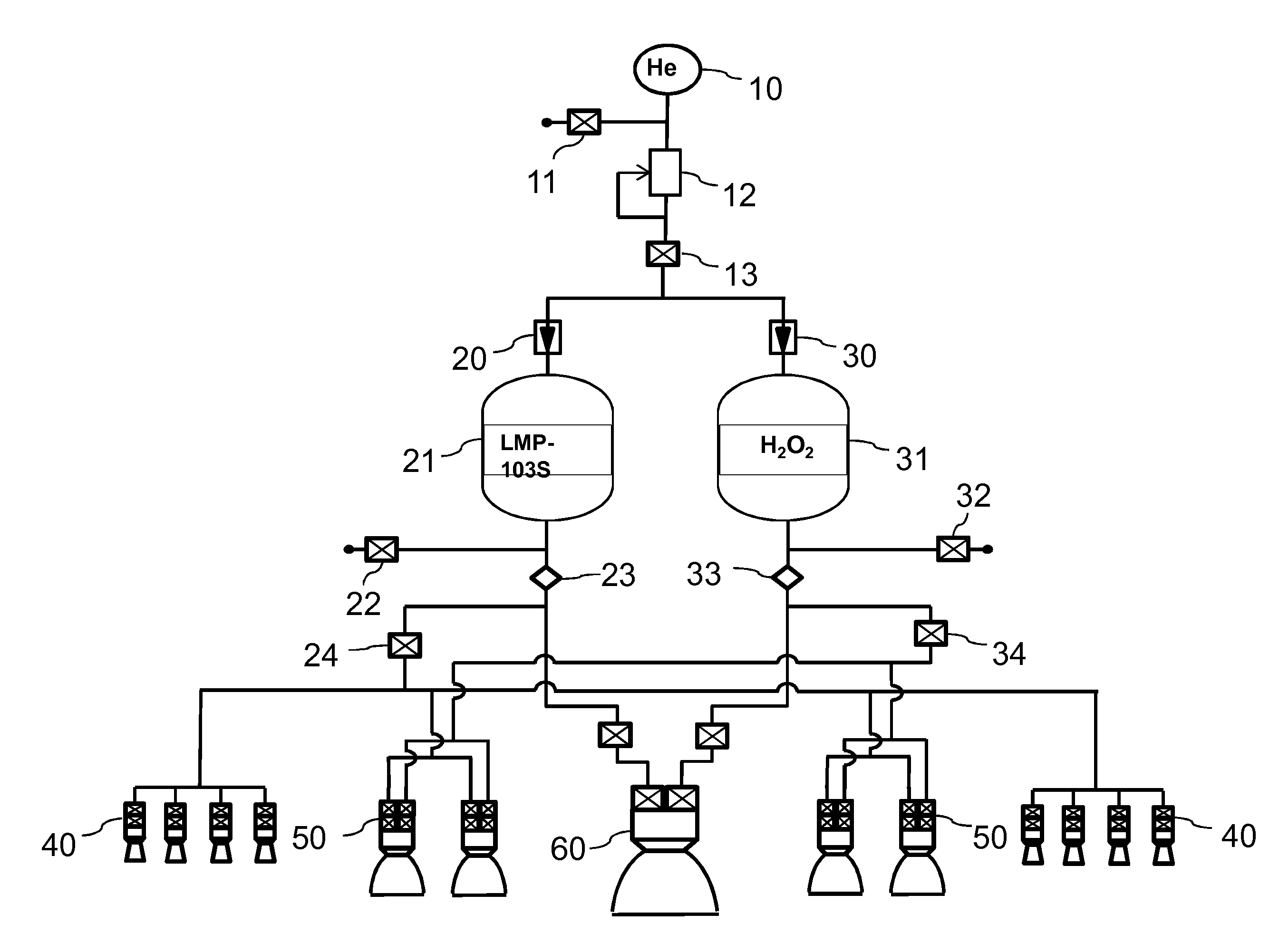
Dual mode chemical rocket engine, and dual mode propulsion system comprising the rocket engine
InactiveUS20160108855A1Improved density impulseReduce and facilitate propellant handlingCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusAviationDual mode
The invention relates generally to dual mode bipropellant chemical rocket propulsion systems to be used in aerospace applications for 1) orbit raising, orbit manoeuvres and maintenance, attitude control and deorbiting of spacecraft, and / or 2) propellant settling, attitude and roll control of missiles, launchers and space planes. The present invention also relates to a dual mode chemical rocket engine for use in such systems. The engine uses low-hazardous storable liquid propellants and can be operated either in monopropellant mode or in bipropellant mode. The monopropellants used are a low-hazard liquid fuel-rich monopropellant, and hydrogen peroxide, respectively.
Owner:ECAPS
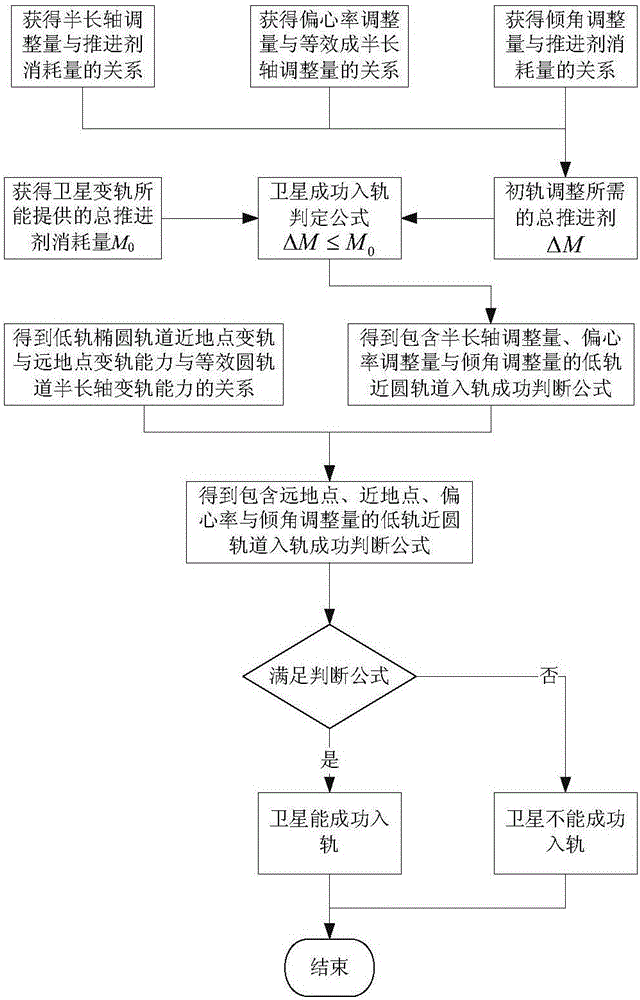
Propellant budget-based low orbit elliptic track satellite successful injection determining method
ActiveCN106570316AAnalytical calculation formulas are accurate and reasonableSimple methodSpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsSuccessful injectionRocket
A propellant budge-based low orbit elliptic track satellite successful injection determining method is provided. Through acquisition of relationships between propellant waste and apogee, perigee, eccentricity ratio and inclination angle adjustment amount, an injection success determination formula containing the apogee, perigee, eccentricity ratio and inclination angle adjustment amount can be achieved via total propellant waste provided by satellite orbital transferring; primary orbital transferring propellant amount allowed by a satellite can be determined according to limitations of each party; the apogee, perigee, eccentricity ratio and inclination angle deviation value of the satellite can be determined after separation of the satellite and a rocket; and whether the satellite successfully enters an orbit is determined via the determination formula. An orbital maneuver theory and formula are employed to achieve an analytic calculation formula, so accuracy, rationality, simplicity and high efficiency can be achieved; easy operation is provided and the method is in particular suitable for quick determination of success carry launch; and basis and instruction are provided for implements of emergency measures of the satellite upon problems during the carrying launch.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
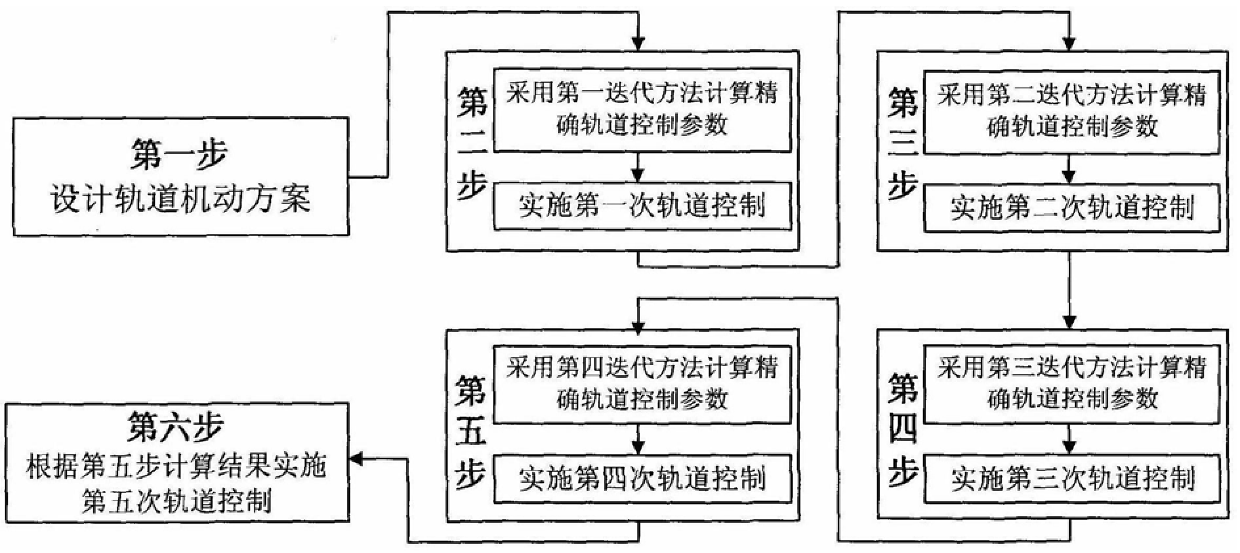
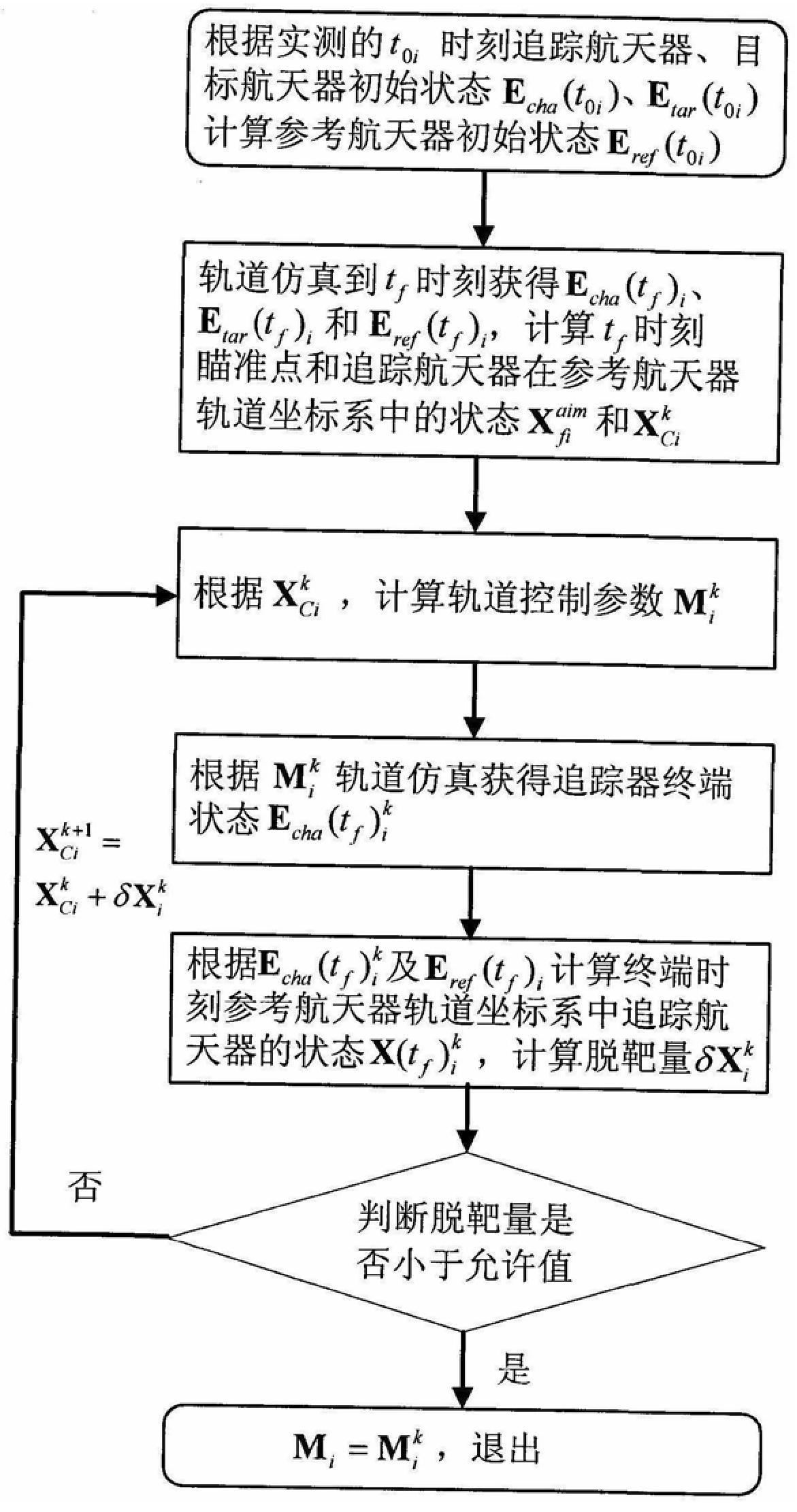
Orbit control method for ground guidance segment of space rendezvous with limited orbit maneuver
InactiveCN106507769BHigh control precisionCalculation speedSpacecraft guiding apparatusPosition/course control in three dimensionsSpace rendezvousControl system
The invention discloses a track control method for a space rendezvous ground guide section with limited orbit maneuvering, aiming to realize high-precision track control of the space rendezvous ground guide section under the condition of limited orbit maneuver. The technical solution is to first determine the orbital maneuvering scheme of the tracking spacecraft as five orbital maneuvering schemes, determine the orbital control parameters M1~M5 that need to be calculated; calculate the orbital control parameter M1 after the tracking spacecraft enters orbit, and upload it to the tracking spacecraft. The maneuvering system performs the first orbital maneuver; after the first, second, and third orbital maneuvers are completed, the orbital control parameters M2, M3, and M4 are calculated respectively, and uploaded to the tracking spacecraft, and the orbital maneuvering system performs the second, third, and fourth maneuvers Orbital maneuvering; finally implement the fifth orbital control according to the orbital control parameter M5 (obtained when calculating M4). The invention has less number of track maneuvers, lower requirements on the attitude control system, improves the track control accuracy of the ground guidance section under the condition of limited track maneuvers, and has fast calculation speed and good real-time performance.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
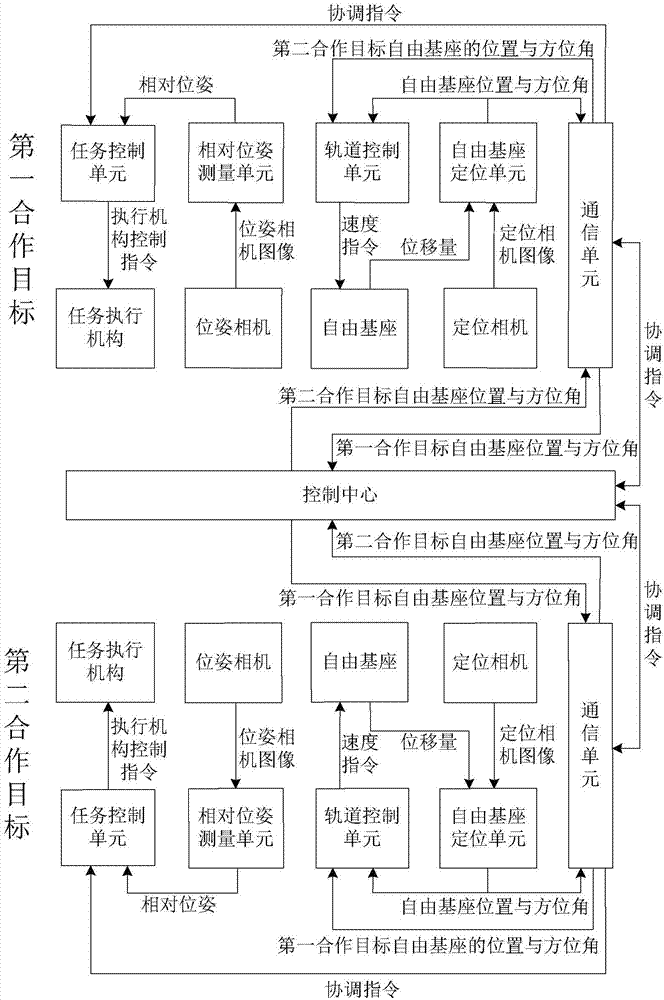
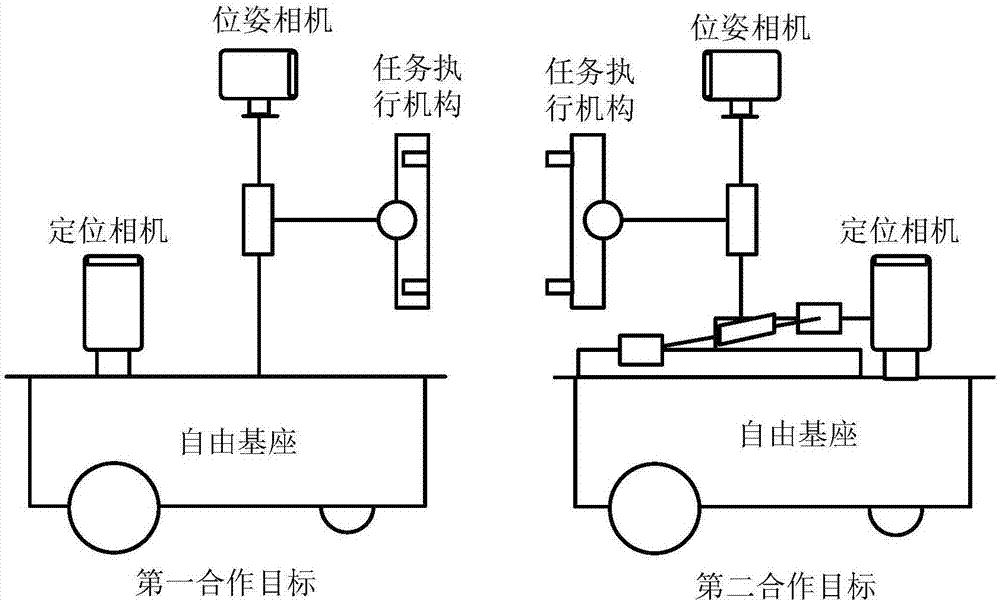
Free base space cooperation task motion reappearance experiment system
ActiveCN107244432AOvercome the inability to simulate the orbital motion of spacecraftVerify feasibilityCosmonautic condition simulationsComputer scienceTask control
The invention discloses a free base space cooperation task motion reappearance experiment system, and belongs to the field of space mission ground validation. In order to overcome the shortcoming that an existing space cooperation task ground validation system cannot simulate orbital motion of a spacecraft, orbital motion of the spacecraft is simulated by a free base, and a task execution mechanism is mounted on the free base and used for finishing cooperation tasks. The complete process of the space cooperation tasks from long distance navigation, orbital maneuver, target approaching to final task execution can reappear on ground motion, and feasibility of an orbital maneuver control scheme and a task control scheme is verified.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
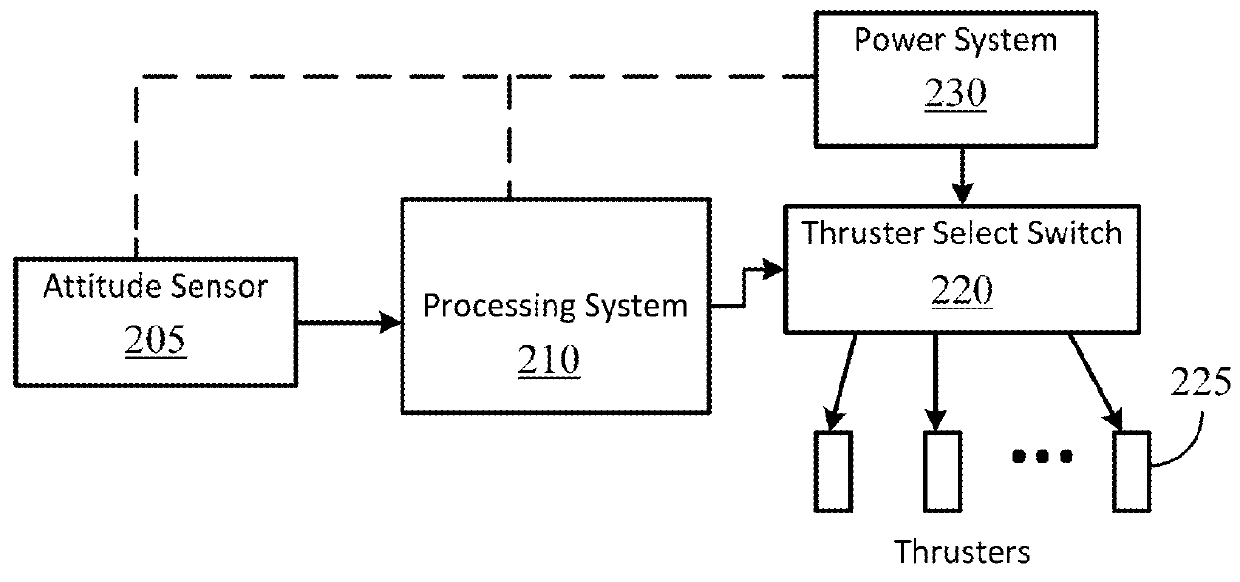
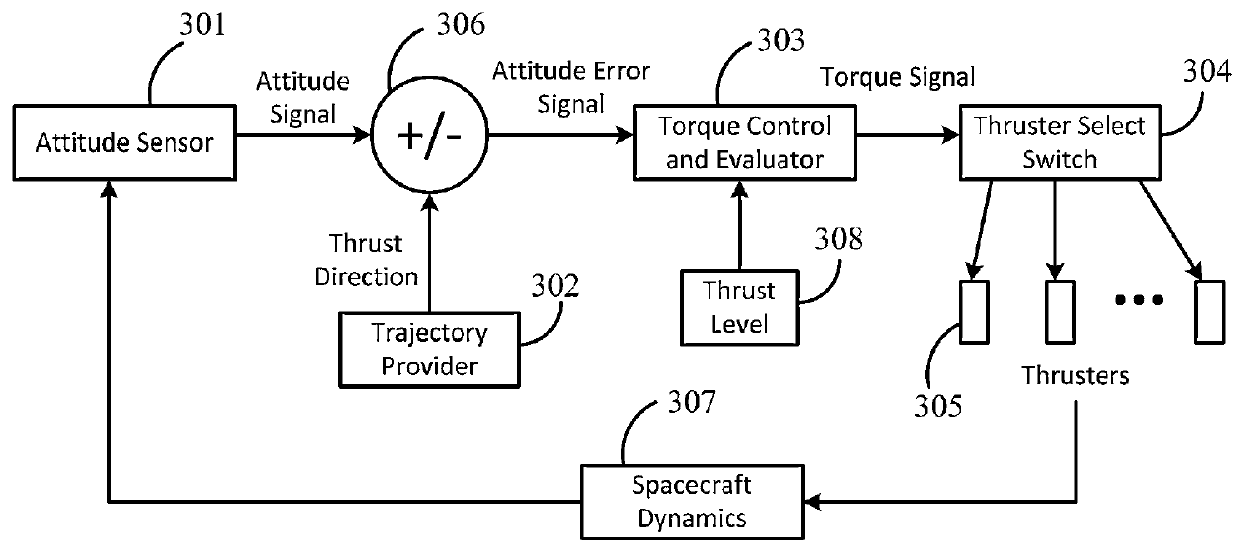
Unified orbit and attitude control for nanosatellites using pulsed ablative thrusters
ActiveUS9334068B2Saving massSave volumeInstruments for comonautical navigationArtificial satellitesControl systemAttitude control
Systems and methods for orbit and attitude control of nanosatellites are provided. A spacecraft can be equipped with a plurality of pulsed ablative thrusters (PAT), mounted on at least one of the spacecraft body orientations. The PATs are integrated with the spacecraft structure. The actual spacecraft attitude is measured by a sensor and compared with the desired thrust direction. In order to reduce attitude errors, a control system is used to determine the firing sequence of thrusters. During maneuvering the thrusters are continuously being fired. To conserve energy a thrust switch control is utilized, selecting a single PAT to be fired each pulse. The result of this operation is that the attitude of the spacecraft is adjusted continuously. Therefore, thrust deviation from a selected path can be minimized during orbital maneuvering.
Owner:KRONHAUS IGAL +1
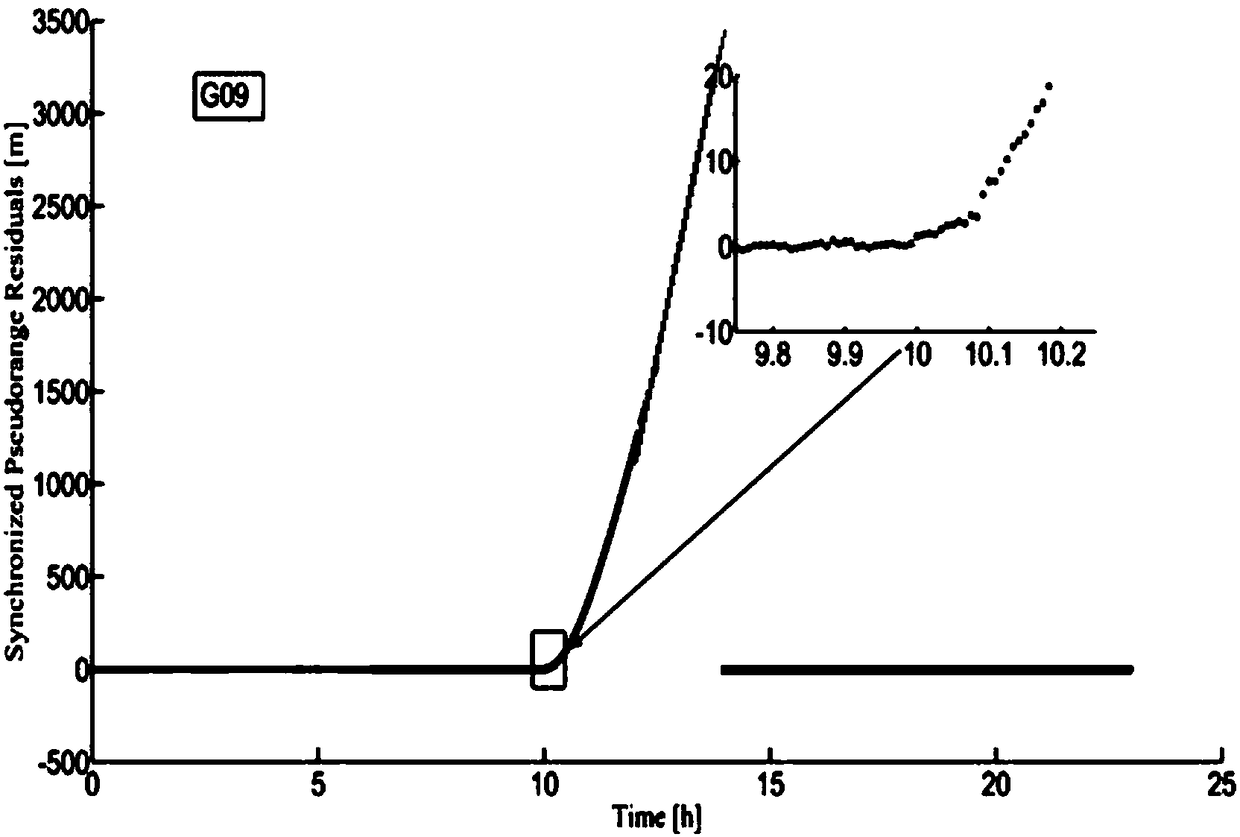
Method for detecting orbital maneuver of Beidou satellite in real time based on phase observation value
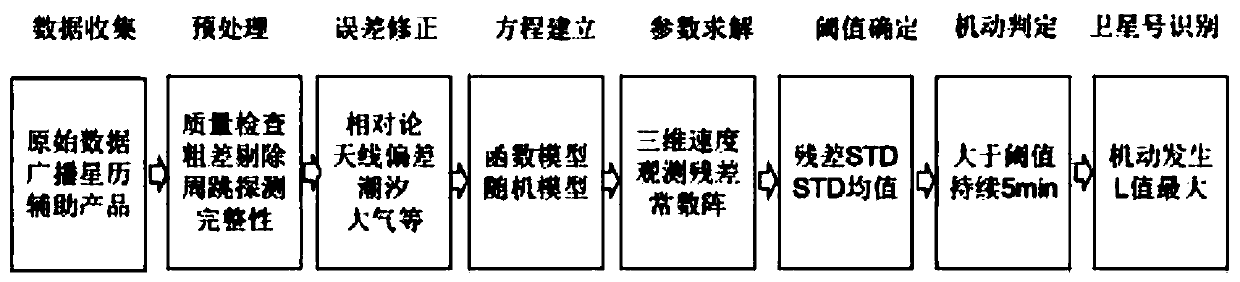
PendingCN111308504AReduce the impactImprove data qualitySatellite radio beaconingSimulationClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a method for detecting orbital maneuver of a Beidou satellite in real time based on a phase observation value. The method comprises eight steps of data acquisition, data preprocessing, error correction, equation establishment, parameter calculation, empirical threshold calculation, orbital maneuver judgment and maneuver satellite number judgment. According to the invention,epoch difference is directly carried out on an original phase observation value; an inter-epoch differential observation model is formed; the influence of partial common errors can be eliminated; theerror correction level is improved, meanwhile, an integer ambiguity parameter is eliminated; real-time estimation is carried out on the three-dimensional speed and the clock difference epoch change parameter; the three-dimensional speed and the corresponding parameter estimation information of an observation station can be directly obtained; the accuracy of orbital maneuver detection is improved,meanwhile, real-time operation is facilitated; orbital maneuver can be efficiently detected; the influence of satellite maneuver on precise orbit determination is reduced; the available observation time of a user side satellite is prolonged; and the method has an important value for improving precise navigation positioning time service.
Owner:NAT TIME SERVICE CENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-integration three-unit cubic satellite capable of maneuvering orbital transfer
InactiveCN112173171AIncrease functional densityHigh module integrationArtificial satellitesSpacecraft guiding apparatusSolar batteryRocket
The invention discloses a high-integration three-unit cubic satellite capable of maneuvering orbital transfer. The cubic satellite comprises a satellite basic platform, and the satellite basic platform comprises a main force bearing structure, a solar cell array, a satellite computer, a lithium battery pack, a power supply control panel, a UV antenna, a UV communication machine, an attitude measurement and control system, other related accessories and a propulsion and control system; and the control system comprises a double-pulse solid rocket thruster, an ignition control panel of the double-pulse solid rocket thruster, a cold air micro thruster, a pulse modulation module of the cold air micro thruster, a mass moment executing mechanism and a mass center adjusting mechanism. The three-unit cubic satellite has the thrust vector control capability and is high in integration degree, rapid orbital transfer and attitude orbit control of the cubic satellite can be conducted, large-range orbital maneuver of the satellite is achieved, and the application field of the cubic satellite is greatly expanded.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
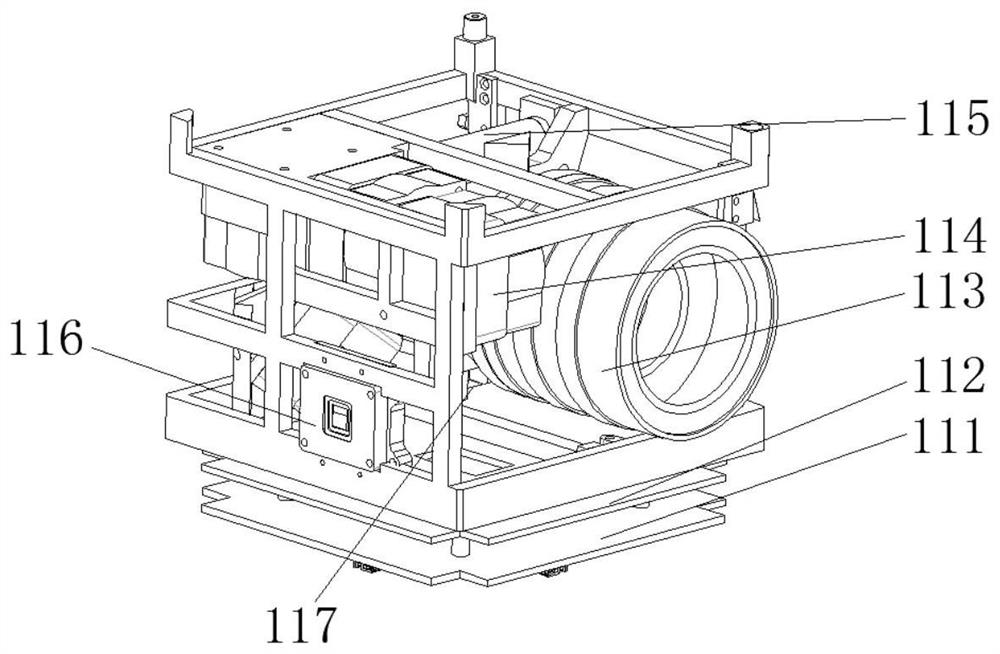
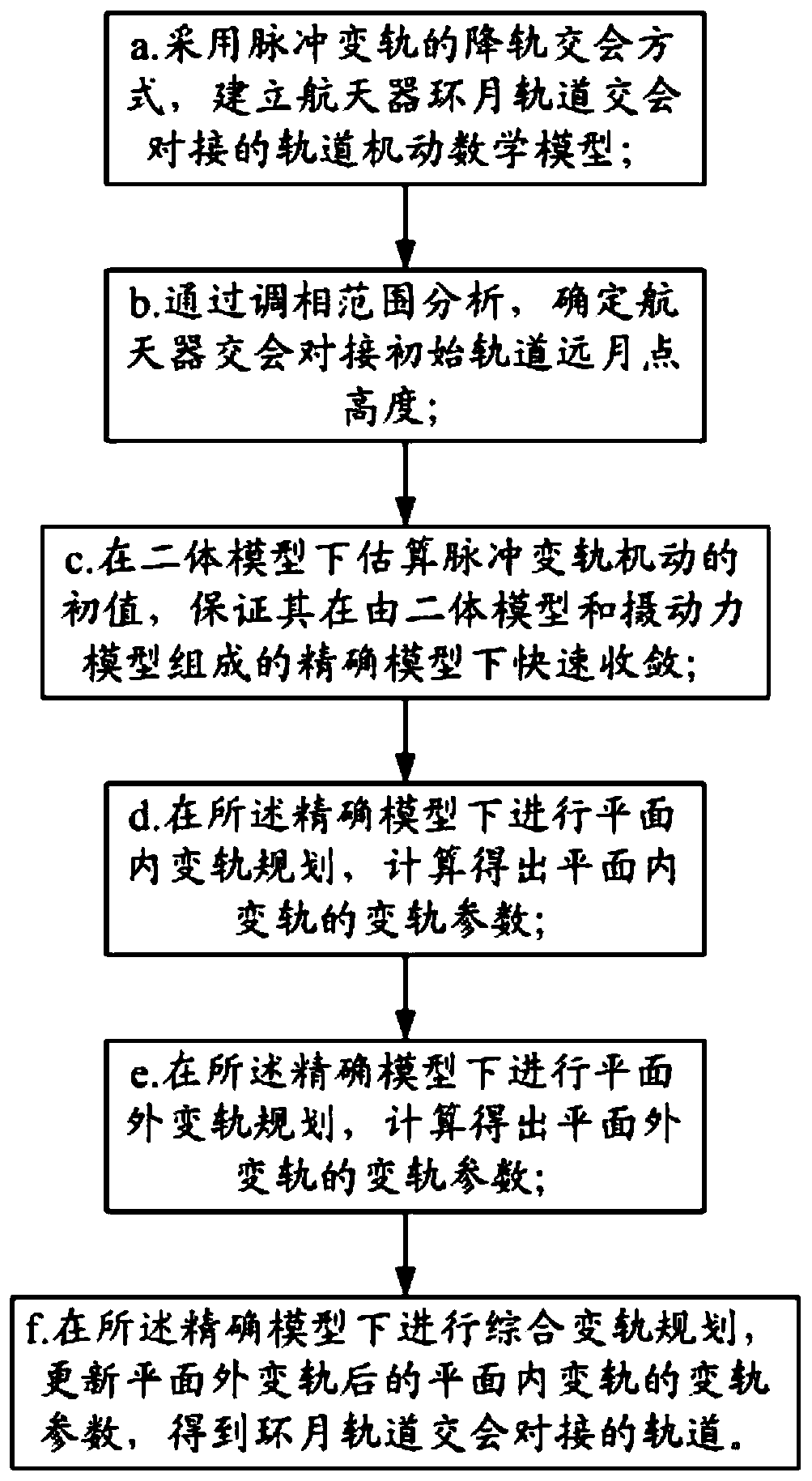
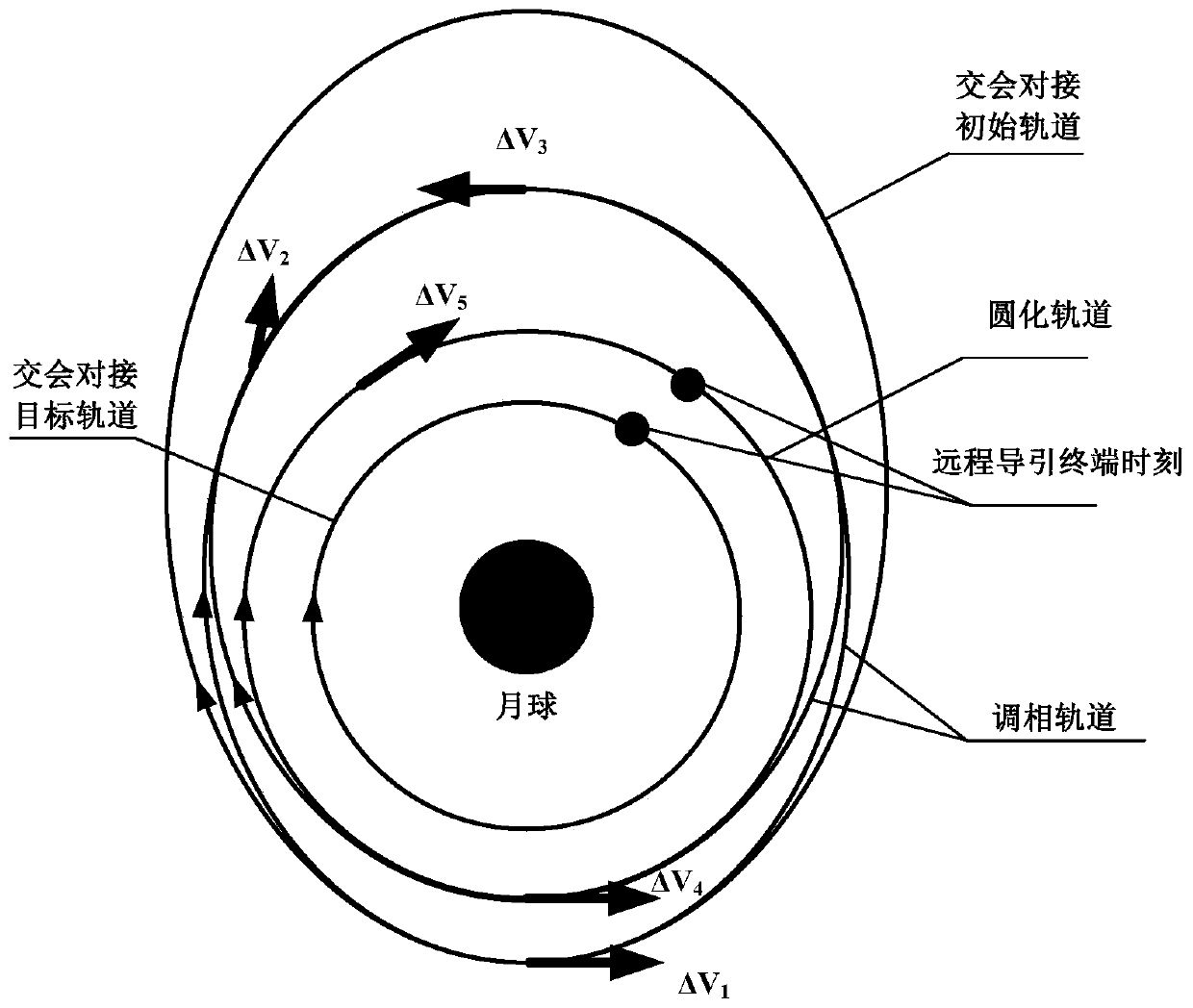
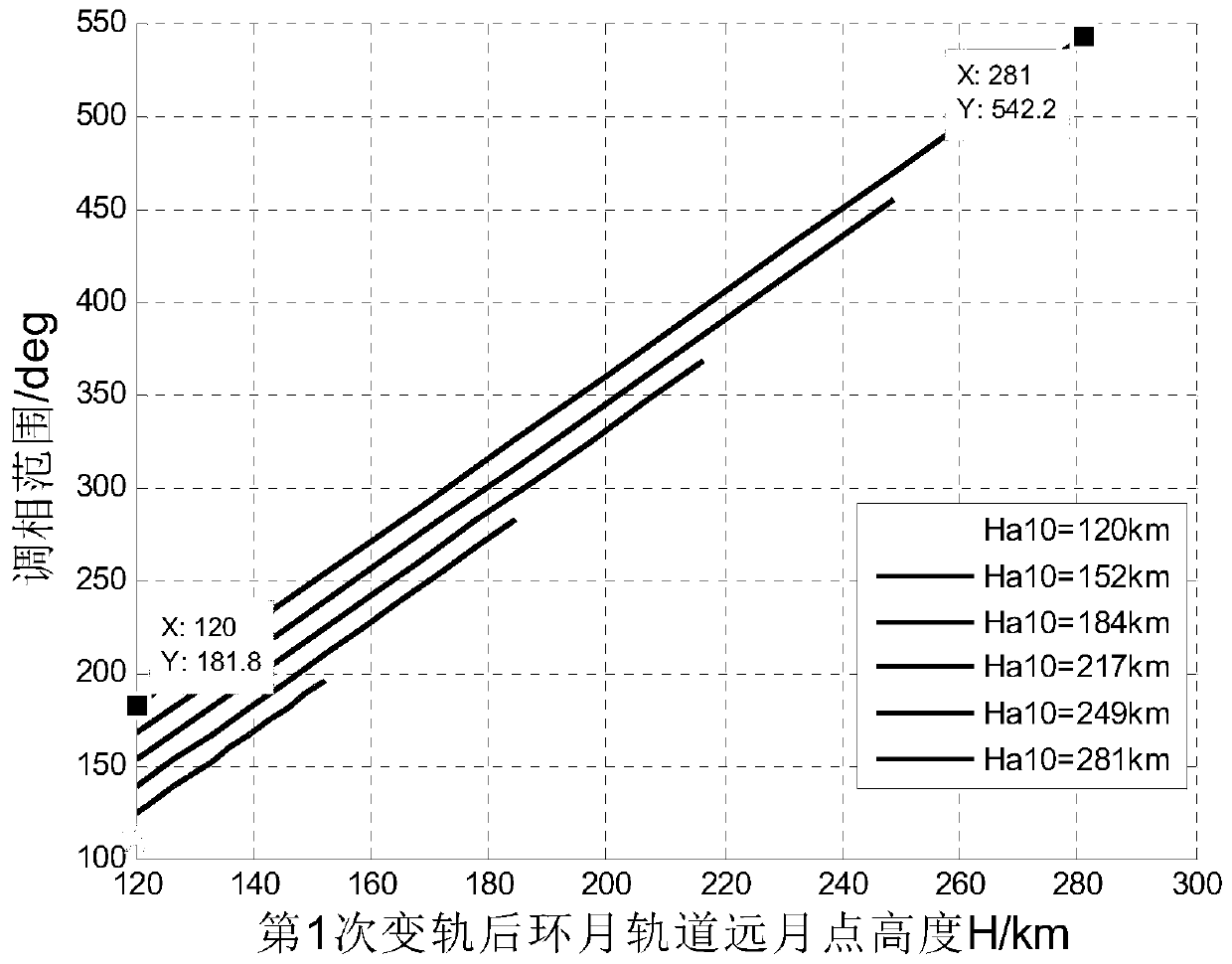
Orbit design method for spacecraft lunar orbit rendezvous and docking
ActiveCN110765504AFast solutionFast convergenceDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMathematical modelClassical mechanics
The invention relates to an orbit design method for spacecraft lunar orbit rendezvous and docking, which comprises the following steps: a, establishing an orbit maneuvering mathematical model for spacecraft lunar orbit rendezvous and docking by adopting an orbit descending rendezvous mode of pulse orbit transfer; b, determining the height of a spacecraft rendezvous and docking initial orbit lunarpoint through phase modulation range analysis; c, estimating an initial value of the pulse orbital transfer maneuver under the two-body model, and ensuring that the initial value is quickly convergedunder an accurate model consisting of the two-body model and a perturbation force model; d, performing in-plane orbital transfer planning under the accurate model, and obtaining orbital transfer parameters of in-plane orbital transfer through calculation; e, performing out-of-plane orbital transfer planning under the accurate model, and orbital transfer parameters of out-of-plane orbital transferare obtained through calculation; and f, performing comprehensive orbit transfer planning under the accurate model, updating orbit transfer parameters of in-plane orbit transfer after out-of-plane orbit transfer, and obtaining a lunar orbit rendezvous and butt joint orbit.
Owner:BEIJING SPACE TECH RES & TEST CENT
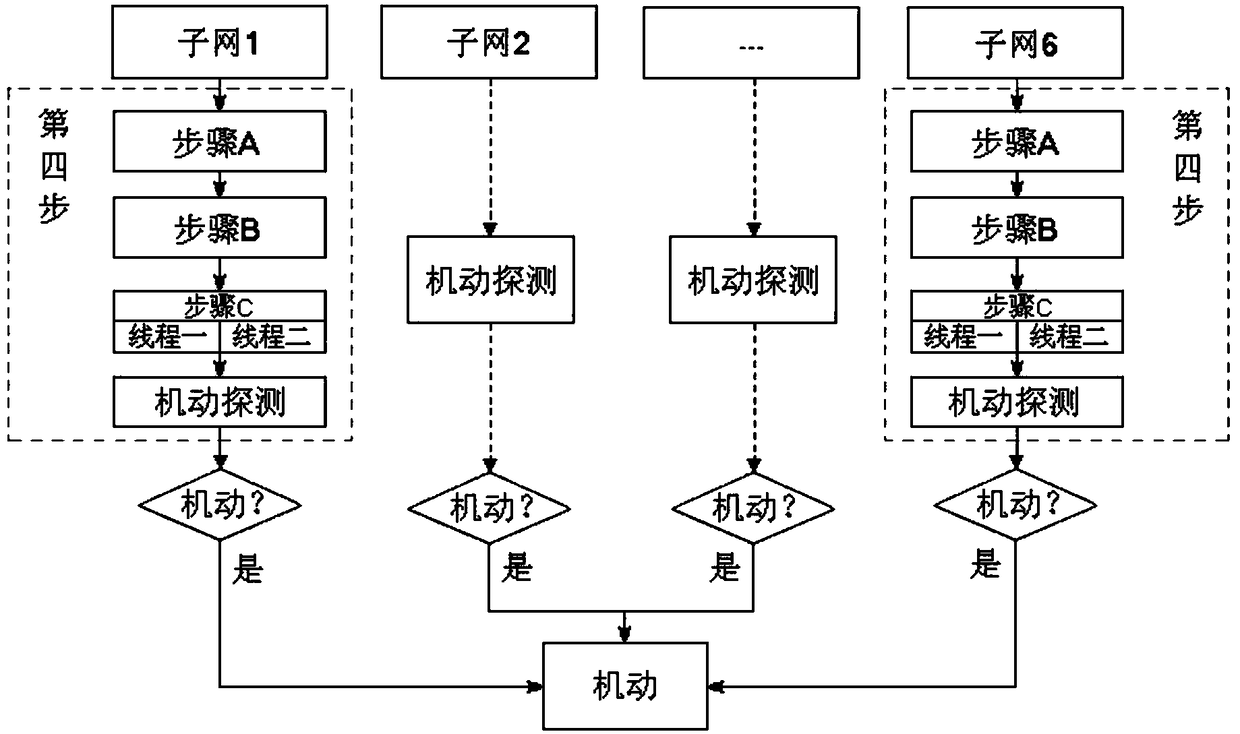
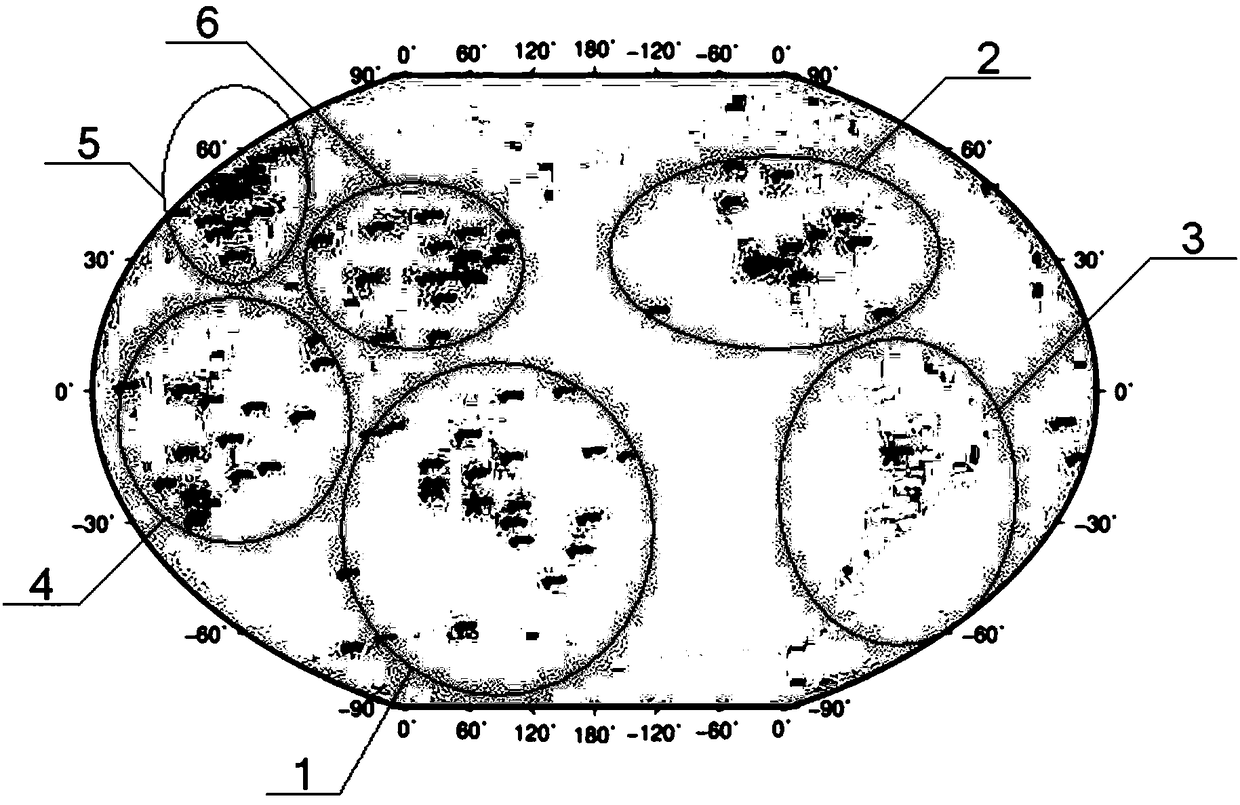
A method for detecting GNSS satellite orbital maneuver
ActiveCN108535746AReliable single-epoch maneuver detectionSatellite radio beaconingEphemerisLinearization
The invention provides a method for detecting GNSS satellite orbital maneuver. The method comprises the steps of: acquiring global observation station GNSS observation values and broadcast ephemeris through files or networks; dividing a global GNSS observation network into a plurality of sub-networks and selecting an observation station with an atomic clock for each sub-network as a base station,the other observation stations being reference stations; building a linearized ionosphere-free combination smooth pseudo-range observation equation for each observation station in the sub-networks, and then performing satellite maneuver judgment through two threads. The method can perform reliable all-weather single-epoch maneuver detection on all satellites and can provide a feasible thought forfuture real-time satellite maneuver.
Owner:INST OF GEODESY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Medium and long distance space non-cooperative target orbit maneuver detection method
PendingCN114018270AUniversalReduce complexityInstruments for comonautical navigationSustainable transportationCorrelation coefficientRelative motion
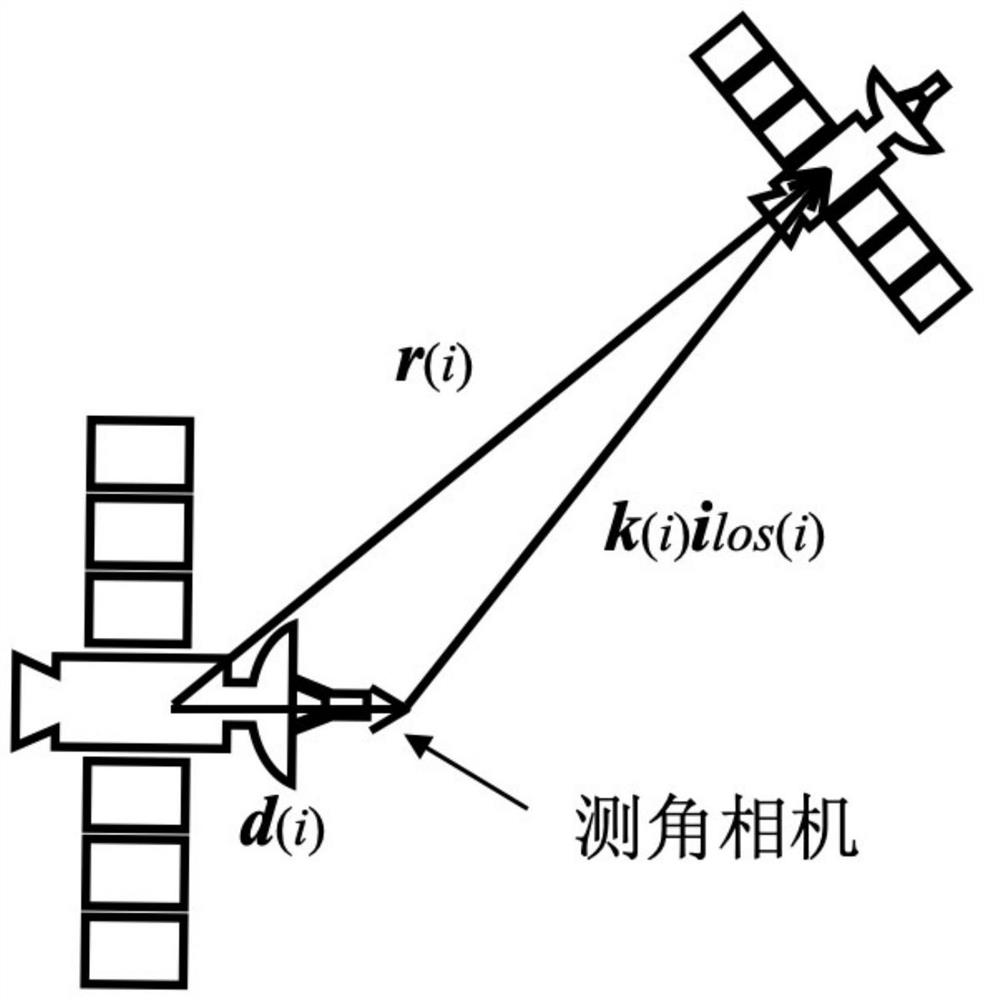
The invention discloses a medium and long distance space non-cooperative target orbit maneuver detection method, which comprises the following steps: taking relative angular momentum of a spacecraft as a center test parameter, establishing a relative kinetic model by a linearized relative motion equation, and carrying out relative measurement in a manner that an optical camera installed deviating from the mass center of a tracking satellite only measures an angle; setting a maneuver detection threshold value through a correlation coefficient of data in a sudden change simulation array and a sliding window, so that orbit maneuver detection of any in-orbit target satellite is realized, and measurement and tracking of any target satellite which may maneuver by a simple algorithm are realized through a mode of restarting a filter. According to the method, the calculation steps are simplified, the maneuvering detection accuracy of the short-range kilometer-level target satellite is improved, and improvement is carried out for the long-range hundred-kilometer-level target satellite.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Low-orbit spacecraft quasi-real-time orbital maneuver detection method based on measured data
ActiveCN111504330ASolve the problem of difficult trackingNavigational calculation instrumentsInstruments for comonautical navigationClassical mechanicsOrbital maneuver
The invention discloses a low-orbit spacecraft quasi-real-time orbital maneuver detection method based on measured data. Aiming at the characteristics of on-orbit operation rules and actual measurement data of a low-orbit spacecraft, the invention provides the low-orbit spacecraft quasi-real-time orbit maneuver detection method based on the measured data, and the method is characterized in that according to a preset detection threshold value, and after each arc section of the low-orbit spacecraft is tracked, whether an orbital maneuver phenomenon exists in the on-orbit flight process of the low-orbit spacecraft or not can be detected in a quasi-real-time mode, so that the problems that the iterative computation is difficult to converge during the orbital maneuver in the orbital determination process of the low-orbit spacecraft, and the spacecraft is difficult to track after orbital transfer, are effectively solved.
Owner:中国人民解放军63768部队
Flying-around orbit design method for continuous visible light detection of GEO space target
ActiveCN110647163ASatisfy situational awarenessSatisfy on-orbit servicing missionsAttitude controlSituation awarenessOrbital maneuver
The present invention discloses a flying-around orbit design method for continuous visible light detection of a GEO space target. The method comprises an approaching stage of a detection spacecraft toa target spacecraft and a flying-around stage of the detection spacecraft to the target spacecraft. Firstly, a flying-around orbit is designed, and for the designed flying-around orbit, the orbital maneuvering scheme in the approaching stage is designed by taking the most fuel-saving effect as an optimization goal; the key to the design of the flying-around orbit is to determine an initial phasewindow of the detection spacecraft flying around relative to the target spacecraft, an initial phase that meets the requirements is selected, and the flying-around orbit is designed according to the CW equation; and then an approaching-stage orbit is designed, and the key to the design of the approaching-stage orbit is to determine the two moments of the Lambert orbital maneuver. According to themethod provided by the present invention, the periodic factors of the GEO space target flying around are combined, the solar lighting conditions are fully considered, and the designed flying-around orbit can keep the detection spacecraft always facing the sun to perform visible light detection on the target spacecraft and can effectively meet situational awareness and on-orbit service missions ofthe GEO space target.
Owner:PLA PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY OF CHINA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE AEROSPACE ENG UNIV
Space target track maneuvering fusion detection method for only space-based angle measurement tracking
ActiveCN106501815AIncrease success rateOptimize detection resultsElectromagnetic wave reradiationComputer scienceOrbital maneuver
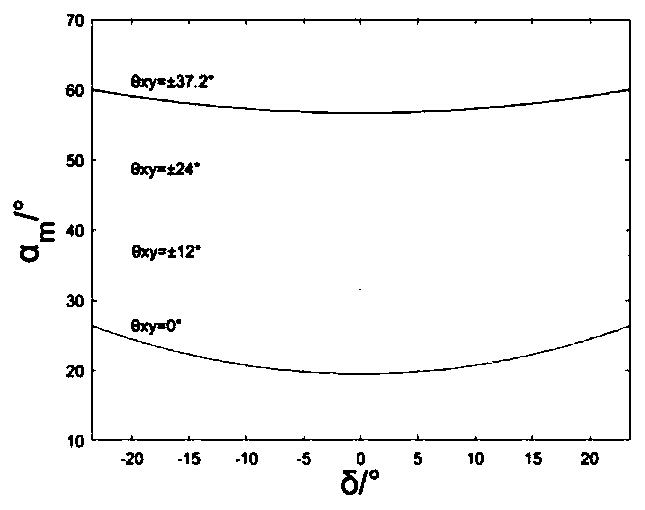
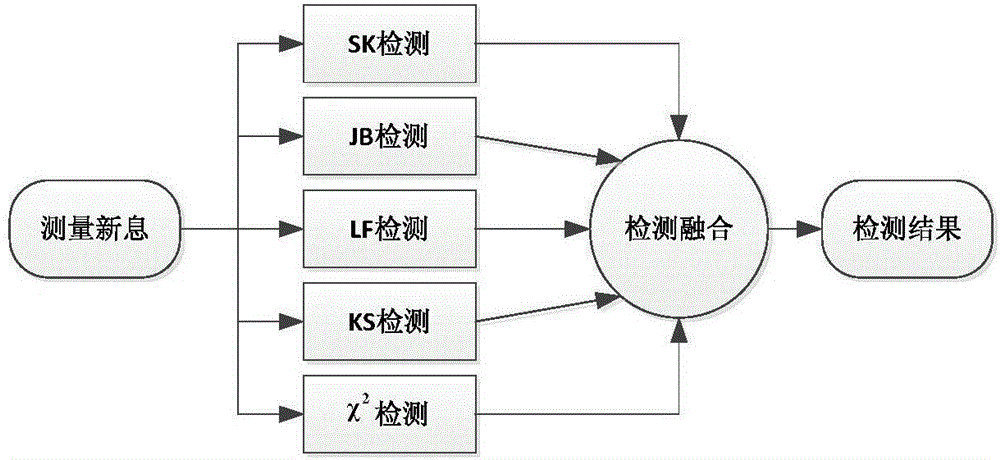
The invention discloses a space target track maneuvering fusion detection method for only space-based angle measurement tracking. The space target track maneuvering fusion detection method comprises a detection quantity selection method and a hypothesis test method. The detection quantity selection method takes measurement information in state estimation as detection quantity. The hypothesis test method performs hypothesis test by use of five test methods, namely, an X<2> test method, a skewness-kurtosis test method, a Jarque-Bera method, a Kolmogorov-Smirnov method, and a Lilliefors method. The space target track maneuvering fusion detection method further comprises a weighted fusion detection method. Linear weighted fusion is performed on the detection results of the five test methods to get a linear weighted detection fusion result. When the detection fusion result is greater than or equal to a maneuvering detection judgment threshold V-horizontal line, it can be judged that orbital maneuver occurs to a space target. According to the invention, the advantages of a variety of hypothesis test methods are fully utilized, the success rate of space target track maneuvering detection is improved, the detection result of a short detection window is improved, the demand for the length of a detection window is reduced, and the redundancy and robustness of the system are improved.
Owner:中国人民解放军63920部队
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com