Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4903 results about "CCD - charge coupled device" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is a device for the movement of electrical charge, usually from within the device to an area where the charge can be manipulated, for example conversion into a digital value. This is achieved by "shifting" the signals between stages within the device one at a time.
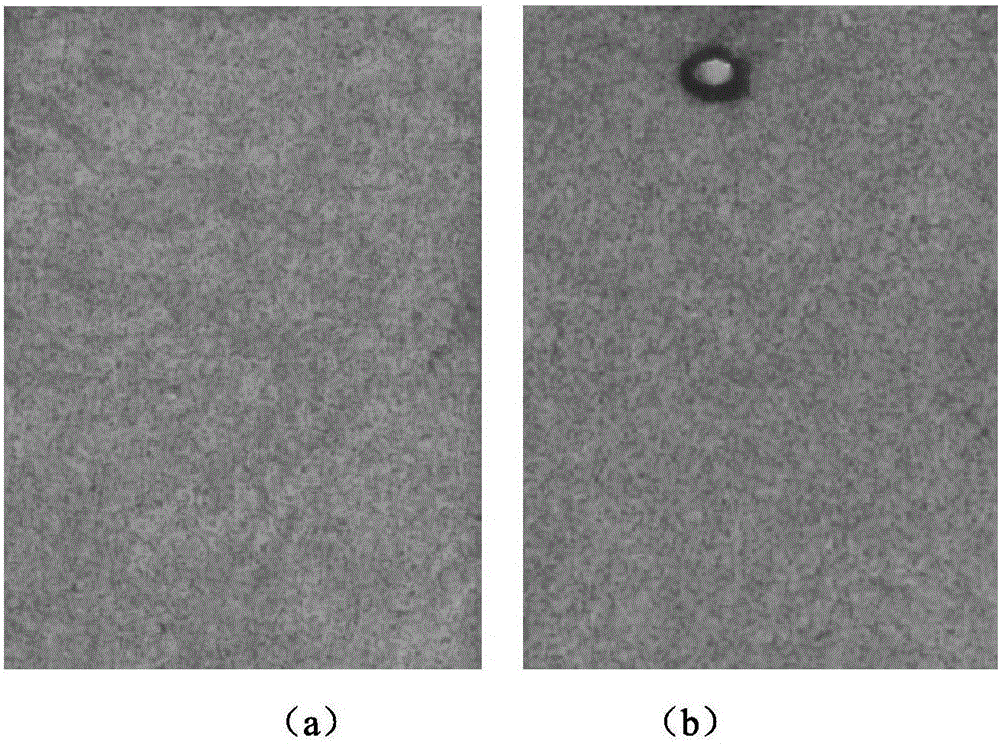
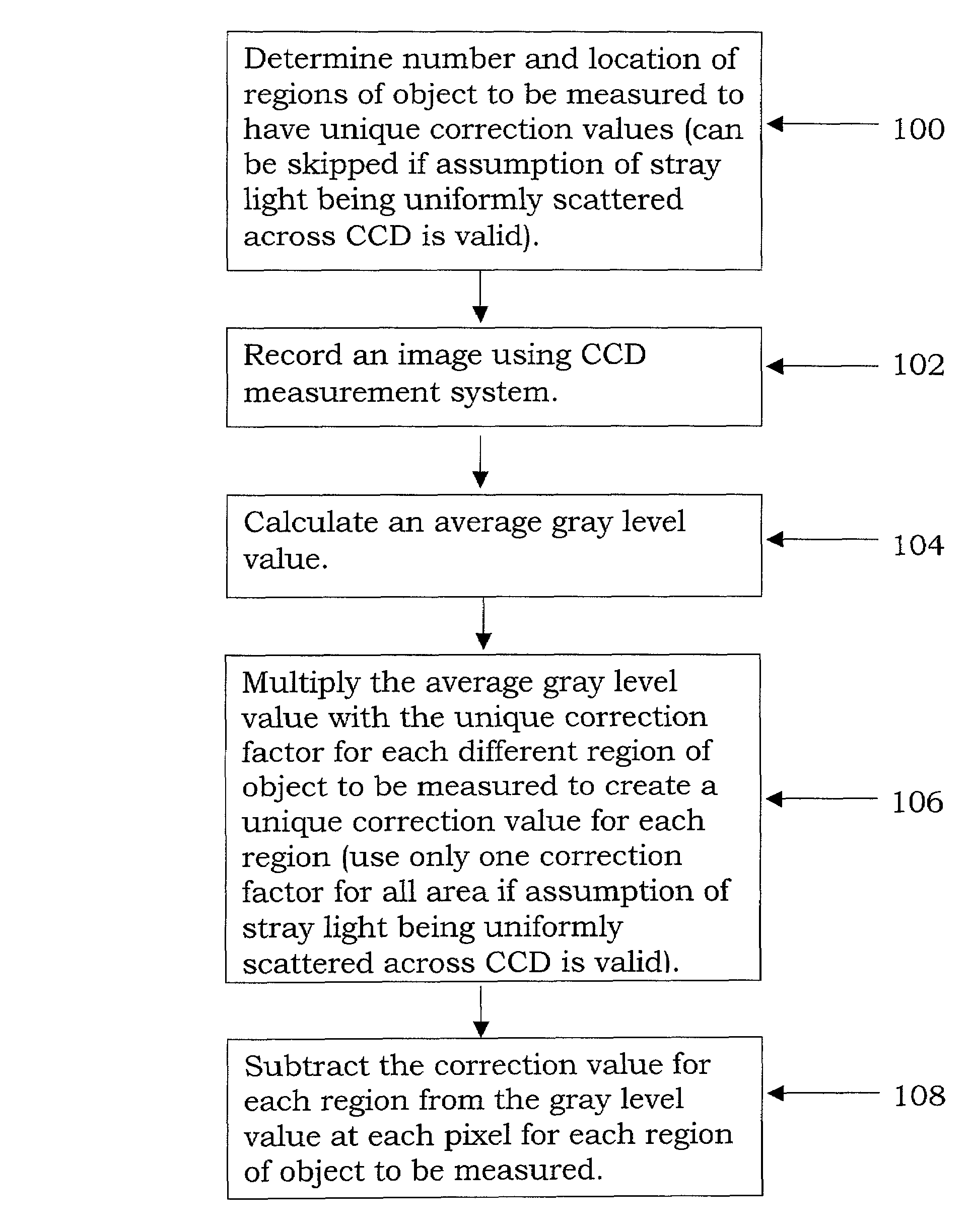
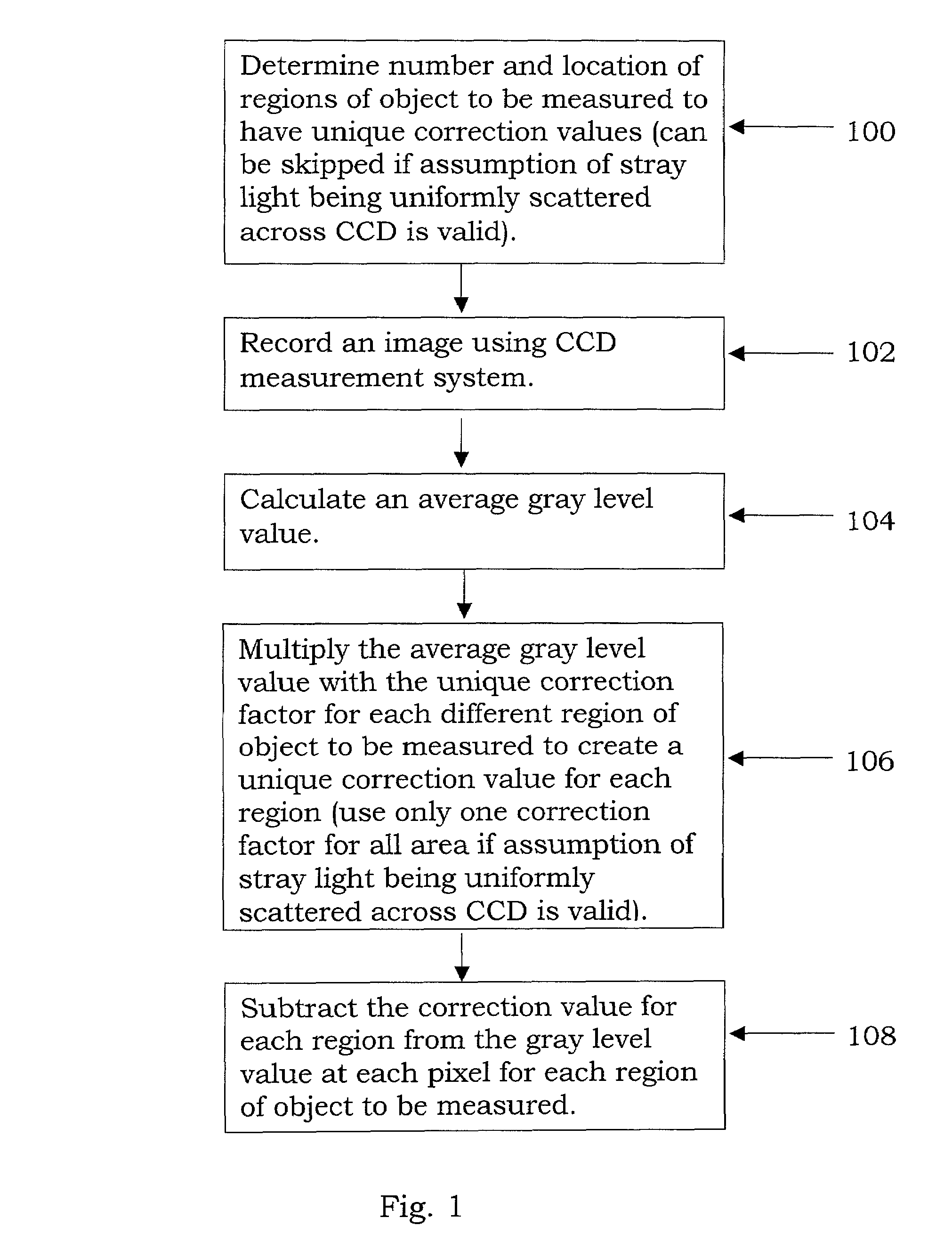
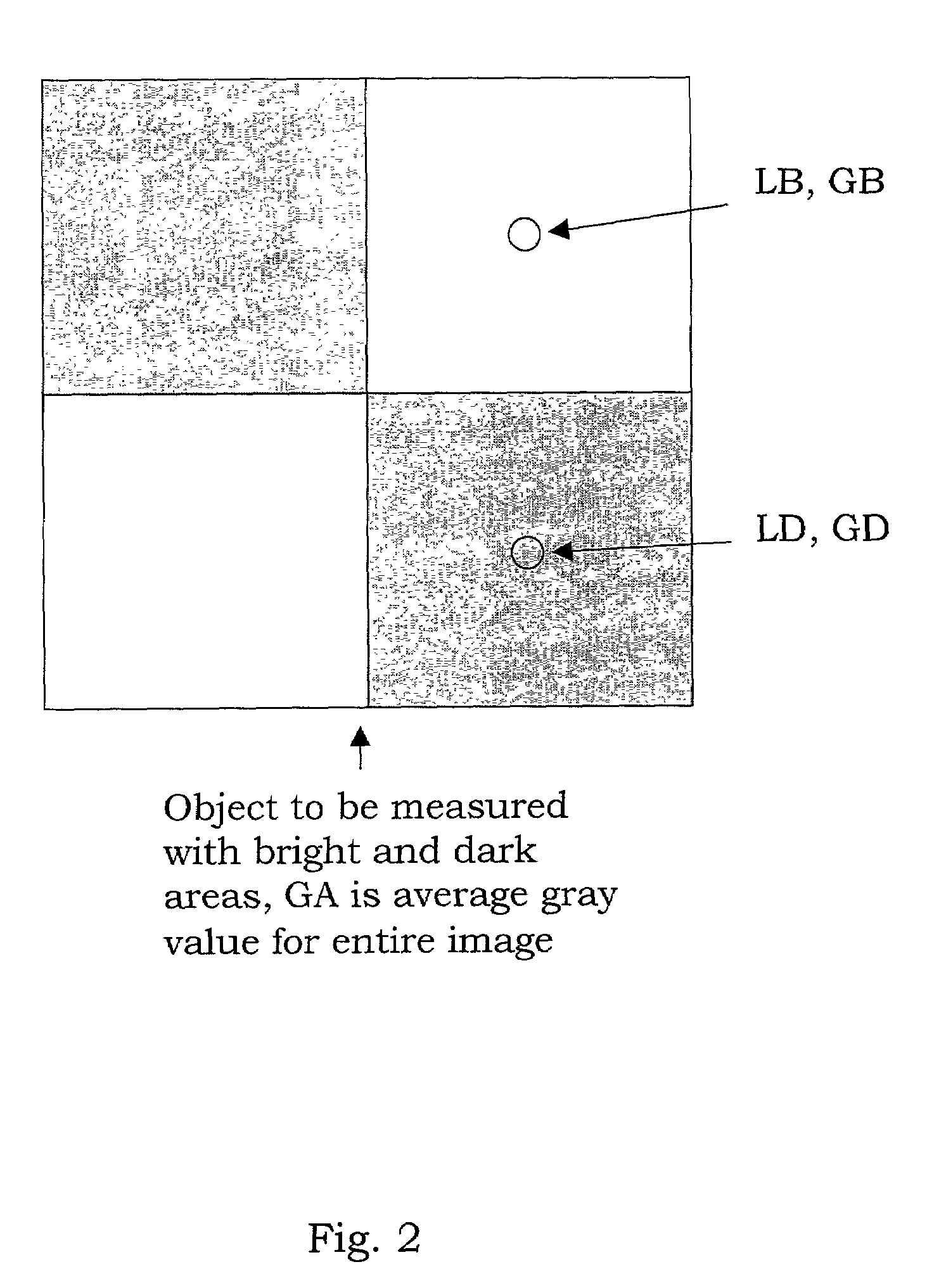
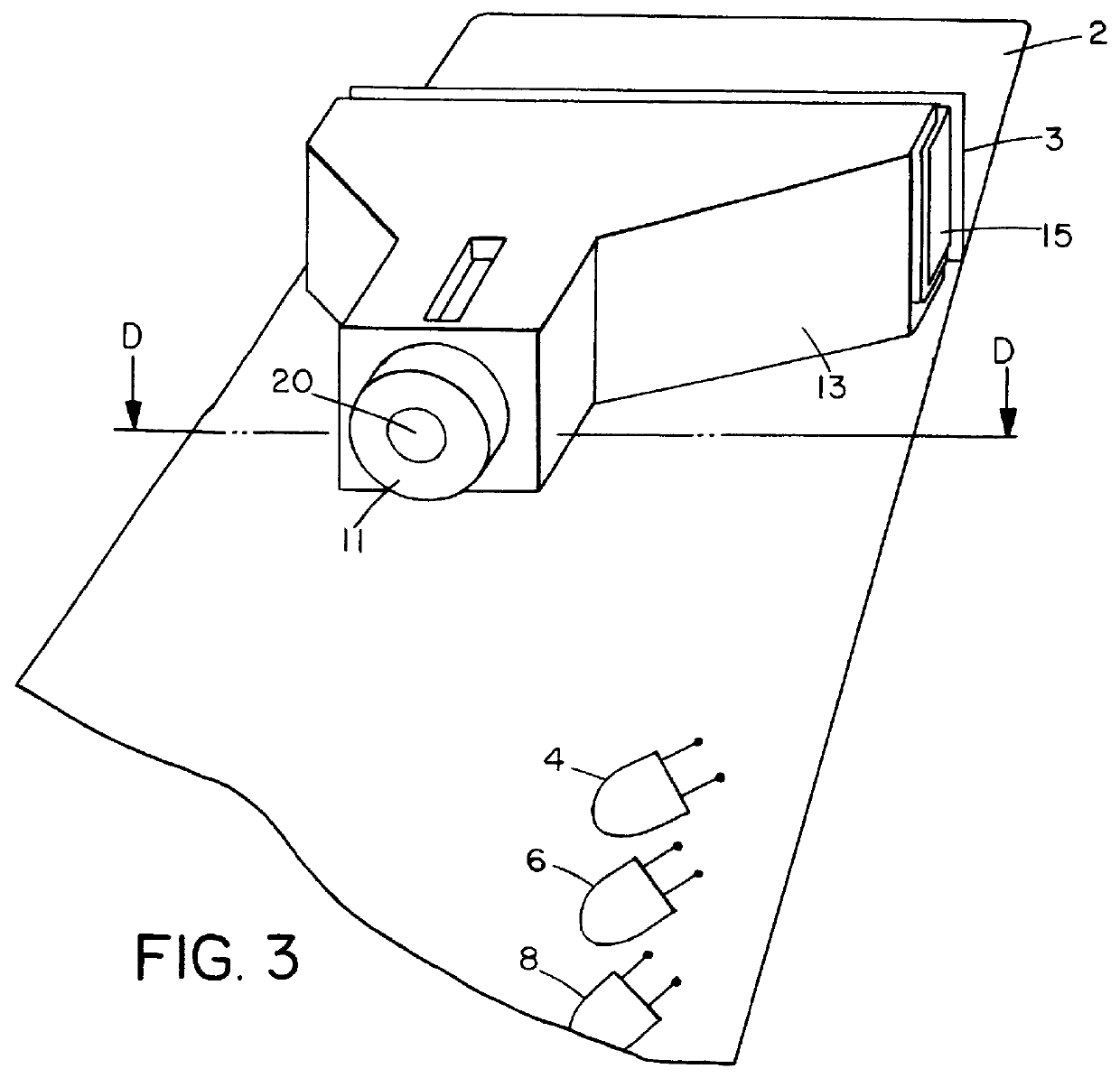
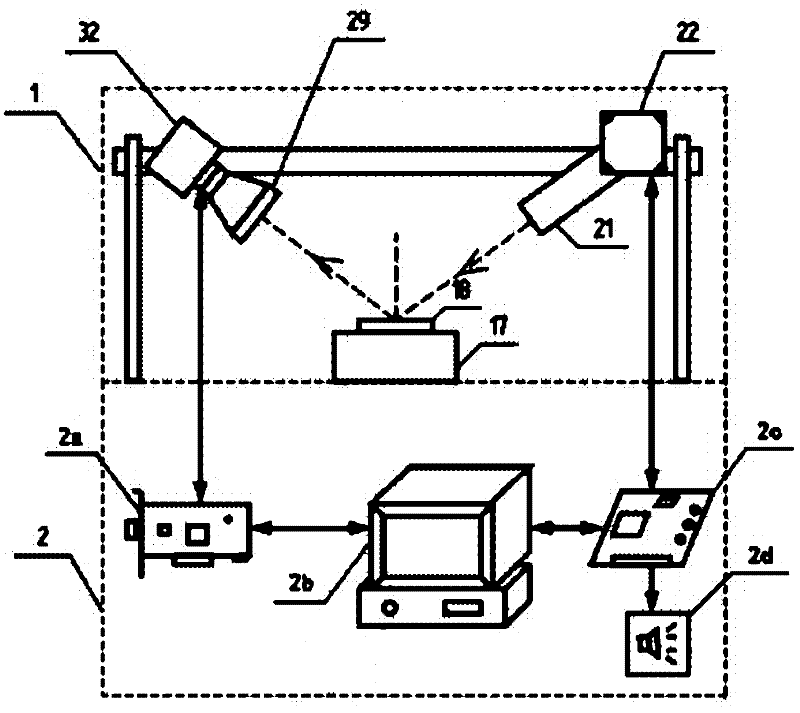
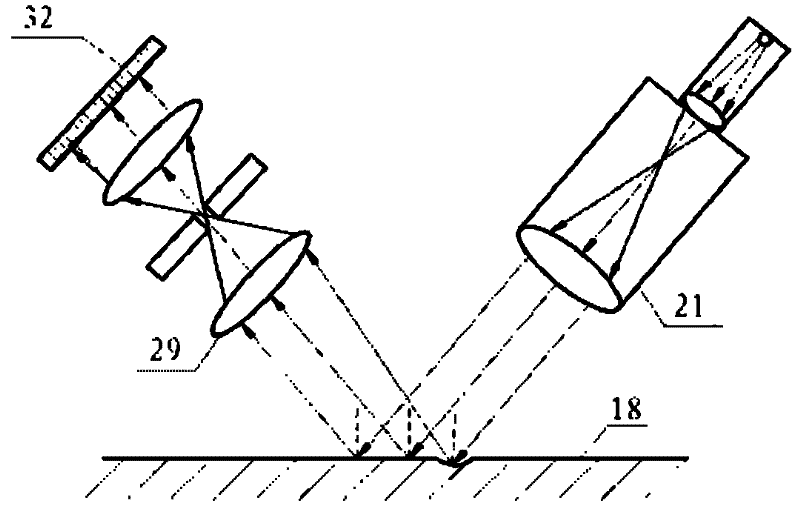
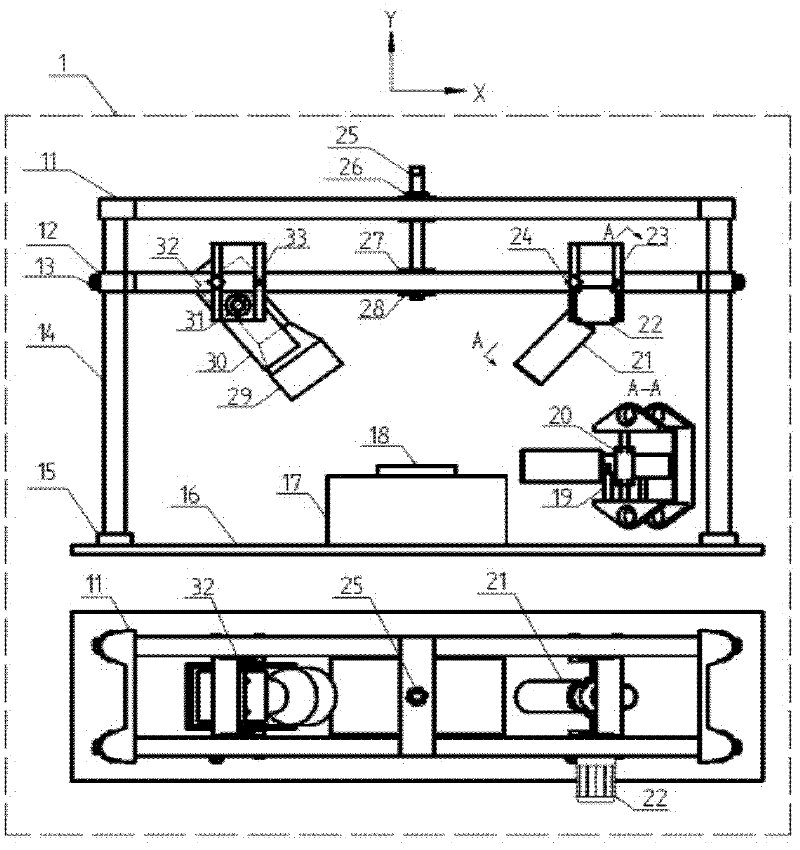
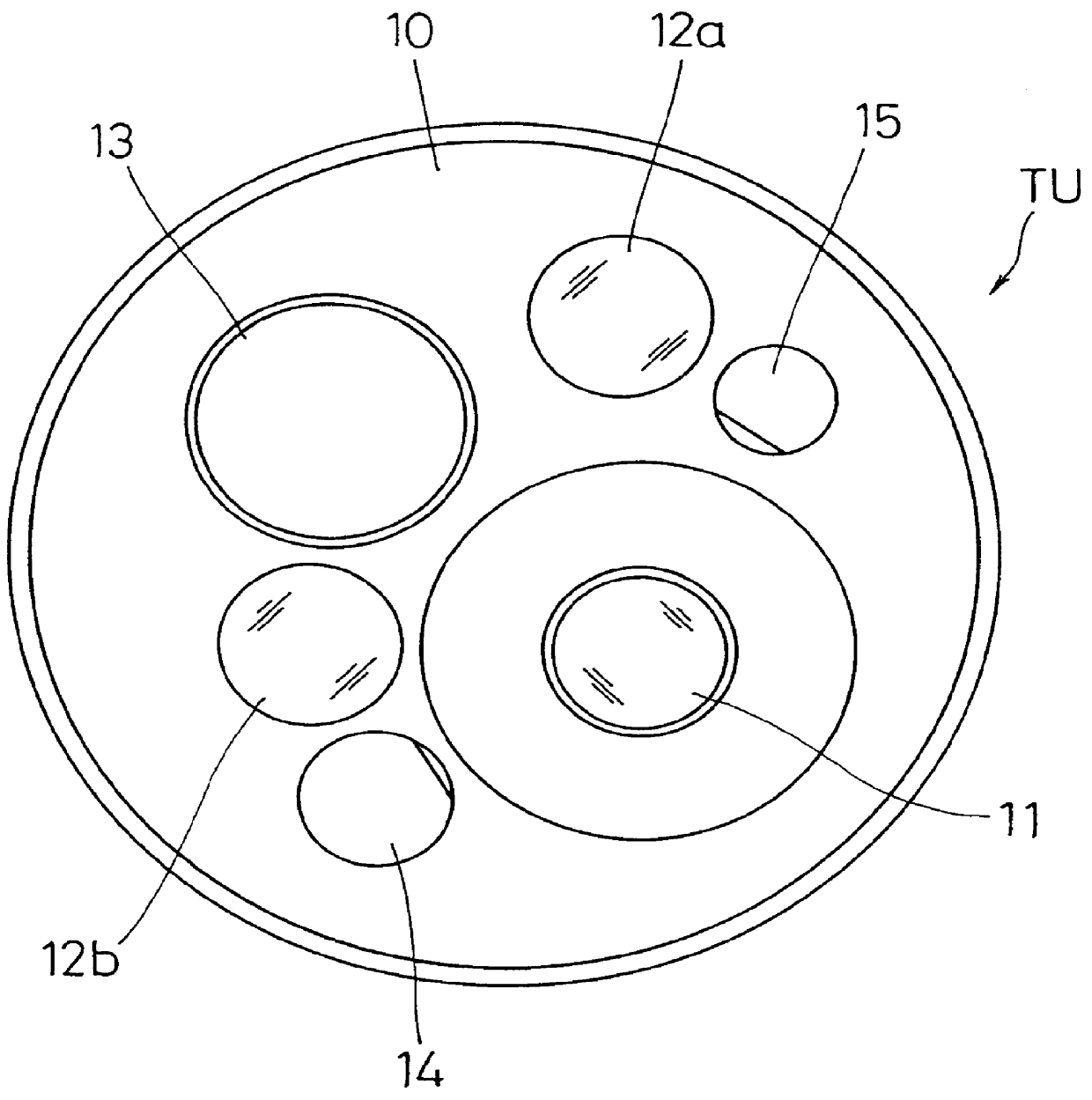
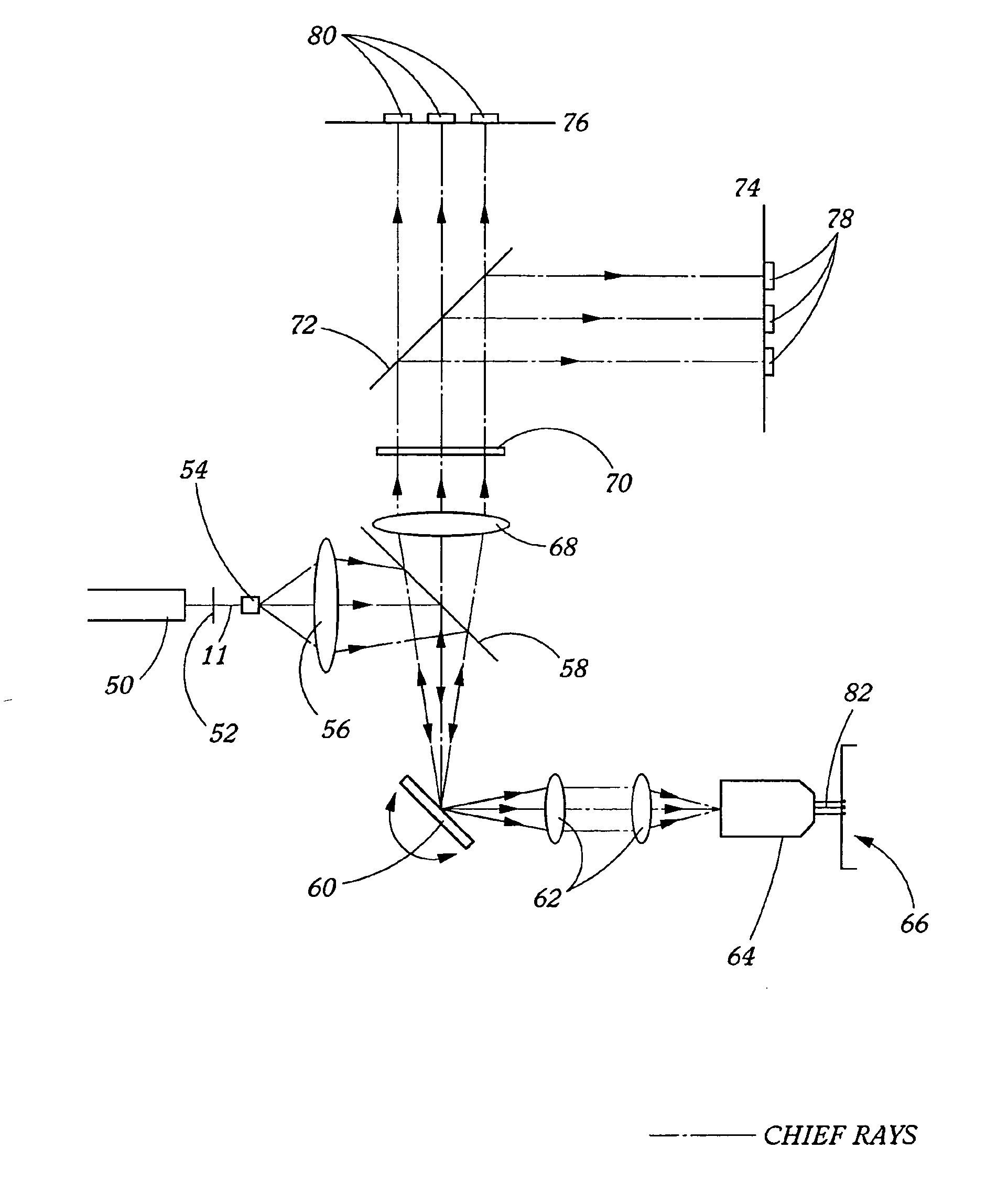
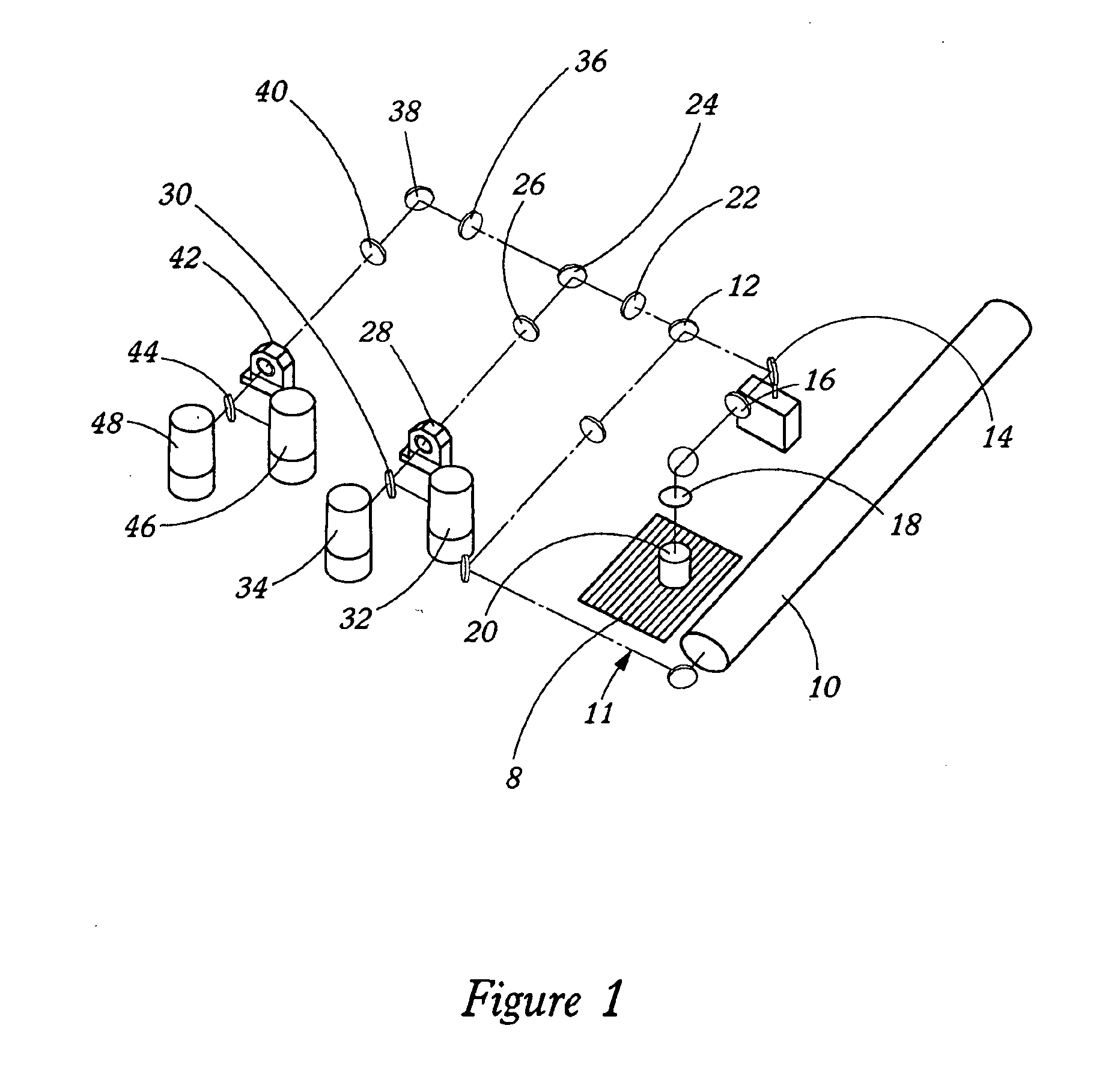
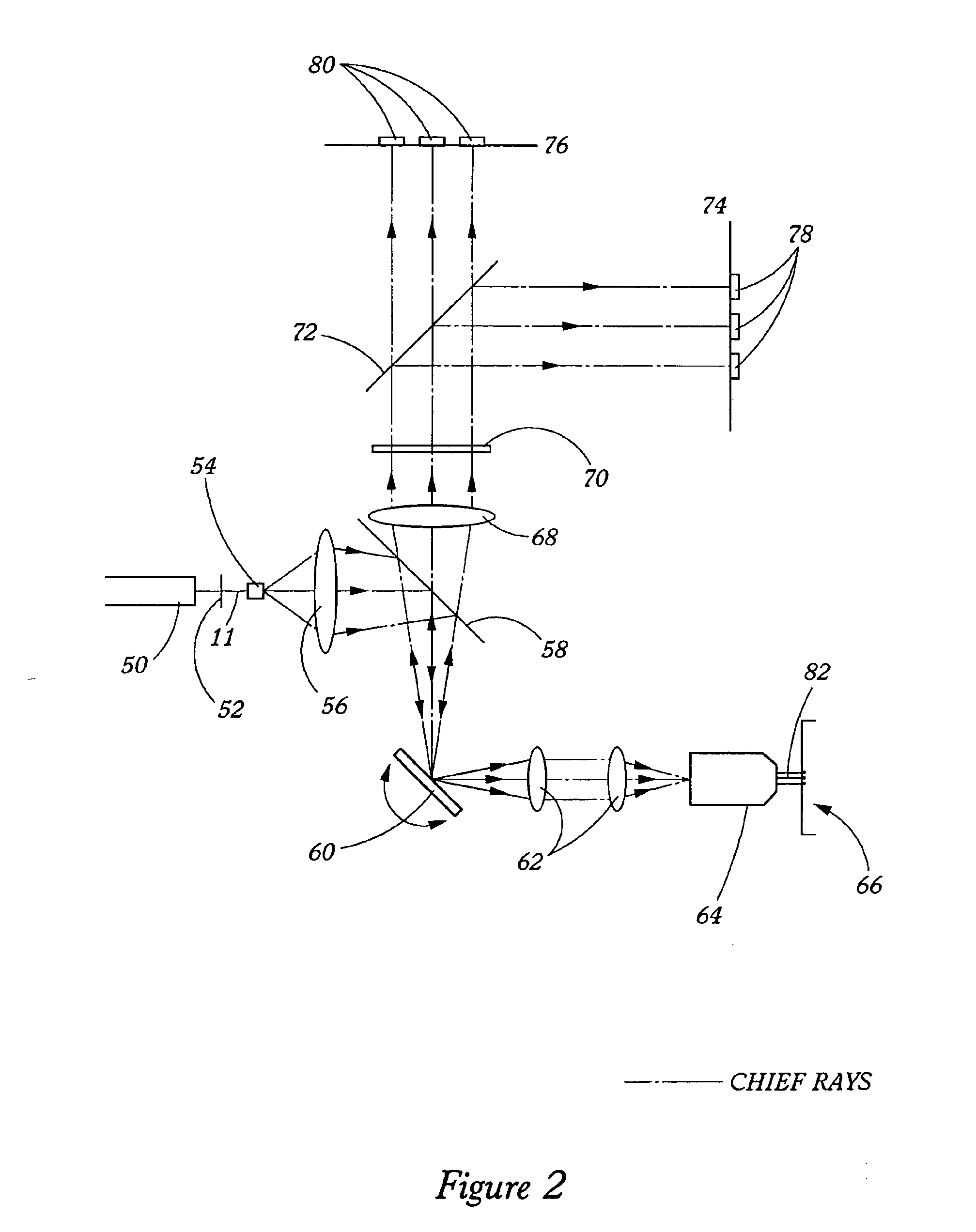
Stray light correction method for imaging light and color measurement system
ActiveUS6975775B2Eliminate the effects ofIncrease grayscaleTelevision system detailsImage enhancementGray levelOptoelectronics
A stray light correction method for image light and color measurement system, uses a solid-state light detector array such as a charge-coupled device to record an image, so that a gray level value for each pixel of the solid-state light detector array is obtained. An average gray level value of the solid-state light detector array is calculated based on the gray level value for each pixel. The average gray level value is further multiplied with a stray light factor to obtain a correction value. The gray level value of each pixel is then subtracted with the correction value, such that the stray light effect can be eliminated.
Owner:RADIANT ZEMAX
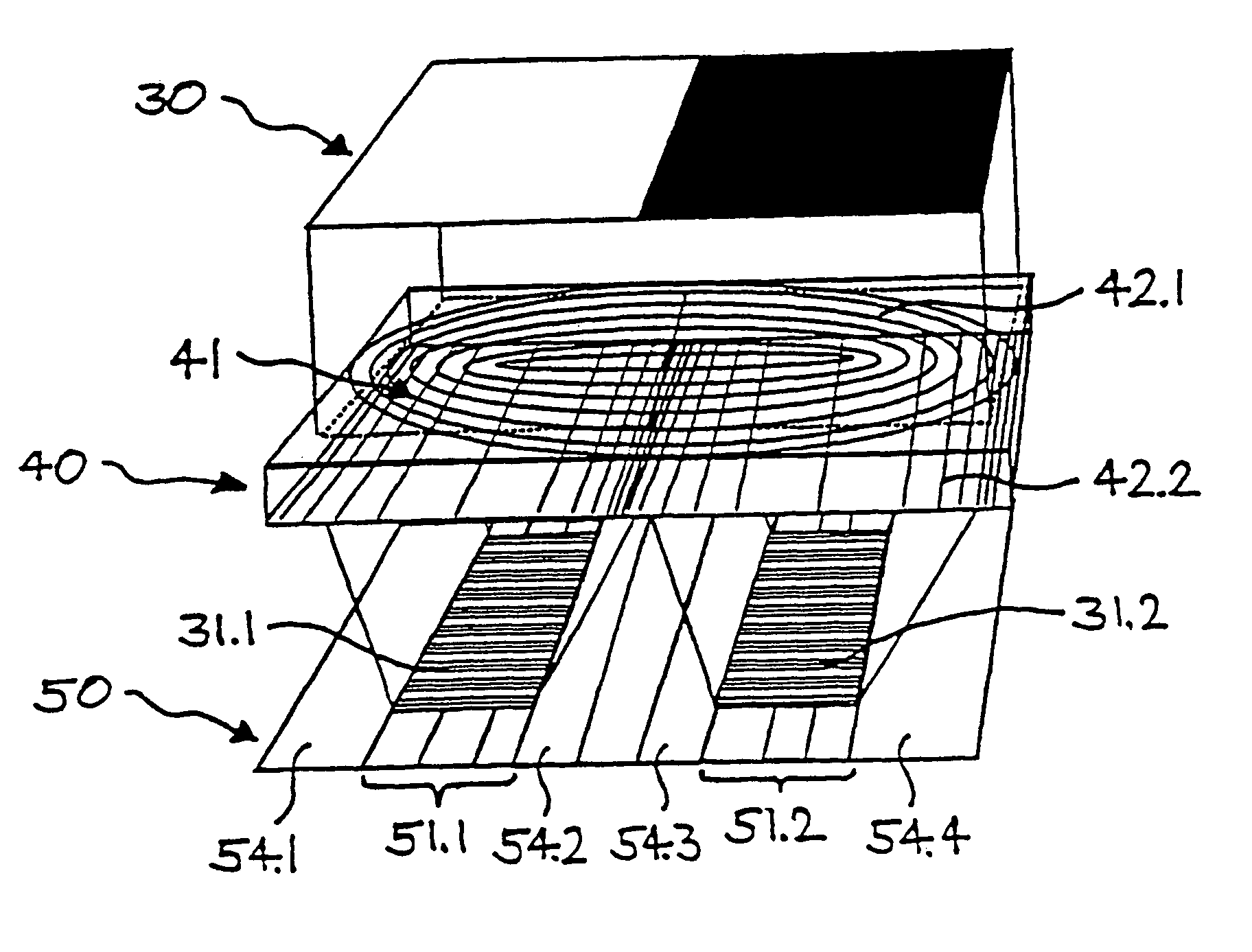
Device and method for spatially resolved photodetection and demodulation of modulated electromagnetic waves
InactiveUS7060957B2Low lighting powerExtend integration timePrismsSolid-state devicesPulse radiationData acquisition
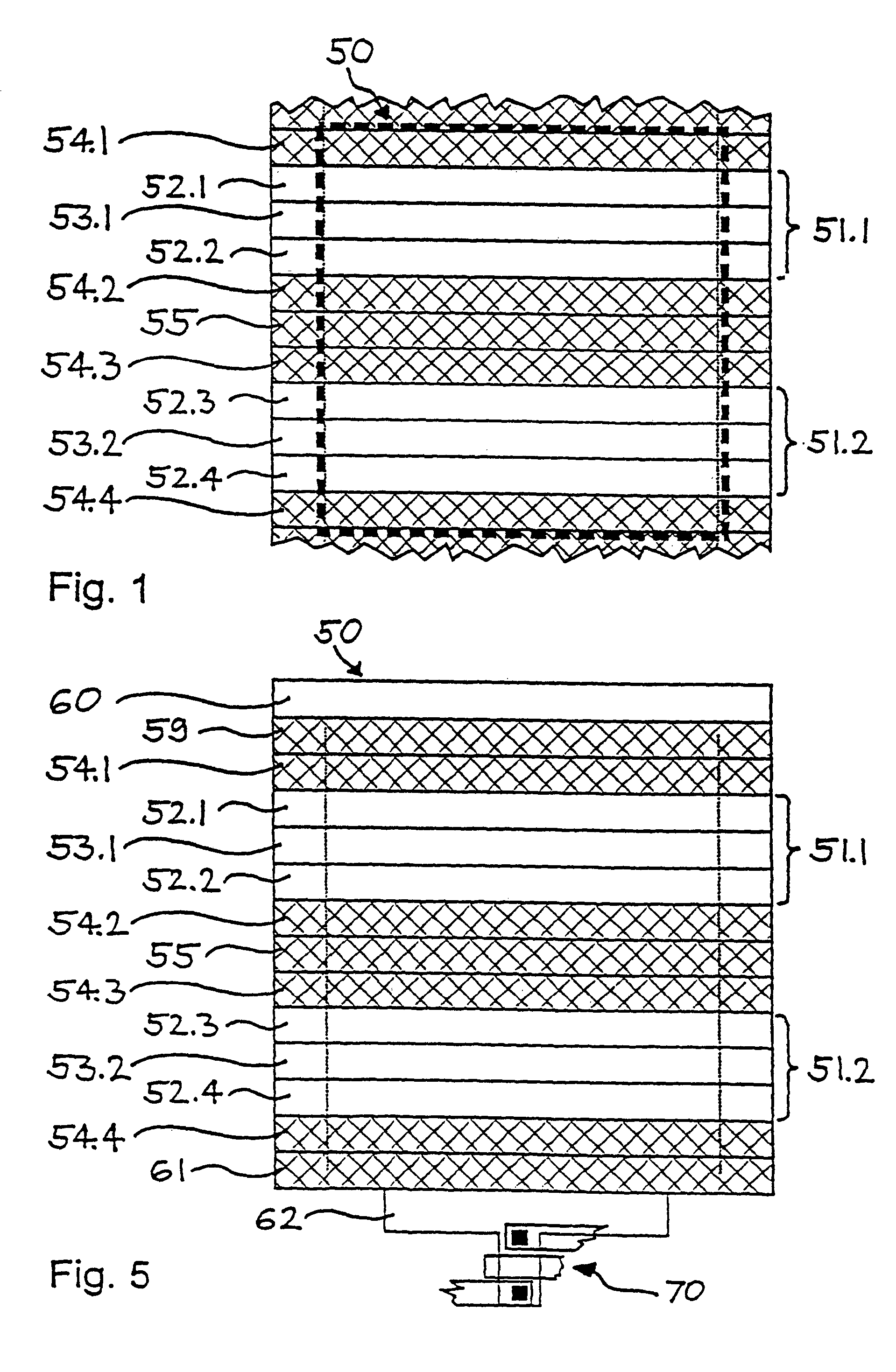
A device and method for spatially resolved photodetection and demodulation of temporally modulated electromagnetic waves makes it possible to measure phase, amplitude and offset of a temporally modulated, spatially coded radiation field. A micro-optical element (41) spatially averages a portion (30) of the scene and equally distributes the averaged intensity on two photo sites (51.1.51.2) close to each other. Adjacent to each of these photo sites (51.1) are two storage areas (54.1, 54.2) into which charge from the photo site can be moved quickly (with a speed of several MHz to several tens or even hundreds of MHz) and accumulated essentially free of noise. This is possible by employing the charge-coupled device (CCD) principle. The device combines a high optical fill factor, insensitivity to offset errors, high sensitivity even with little light, simultaneous data acquisition, small pixel size, and maximum efficiency in use of available signal photons for sinusoidal as well as pulsed radiation signals. The device and method may be used in a time-of-flight (TOF) range imaging system without moving parts, offering 2D or 3D range data.
Owner:AMS SENSORS SINGAPORE PTE LTD
Optical scanning head
InactiveUSRE36528E1Add depthIncrease distanceVisual representatino by photographic printingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusOptical scannersBarcode
The [ornamental] design for a bar code Scanner using the Light Emitting Diode (LED), Optical Scanner assembly and Charge-Coupled Devices (CCD) capable of reading the barcode symbols at the variable distance, as shown and described. The optical passive elements for increasing the depth of field and method of fabricating the scanning head by mass-production techniques are also disclosed.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH INC
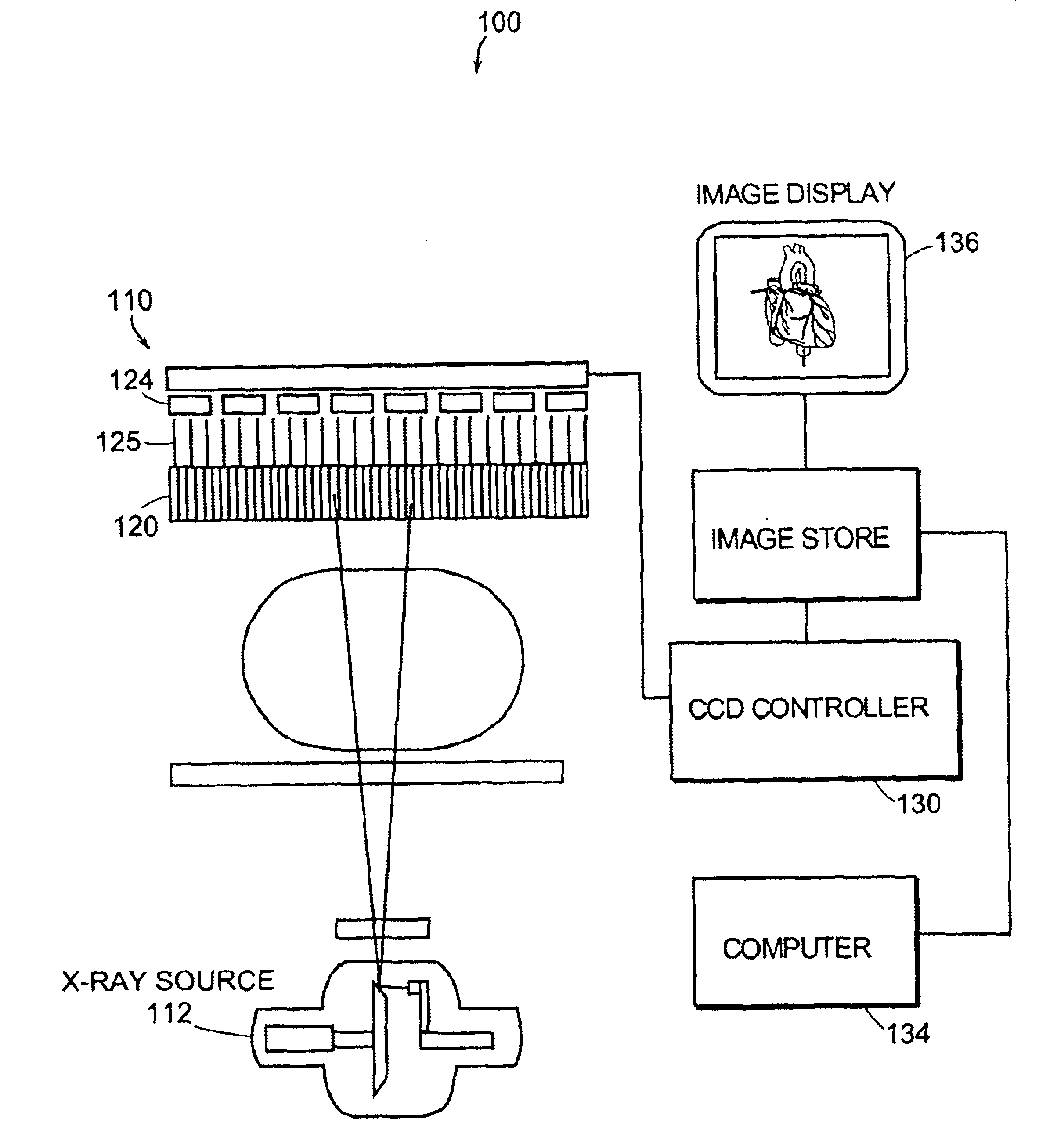
System and method for x-ray fluoroscopic imaging
InactiveUS6895077B2Increase frame rateAccurate imagingTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesFluorescenceX-ray
A system for x-ray fluoroscopic imaging of bodily tissue in which a scintillation screen and a charge coupled device (CCD) is used to accurately image selected tissue. An x-ray source generates x-rays which pass through a region of a subject's body, forming an x-ray image which reaches the scintillation screen. The scintillation screen re-radiates a spatial intensity pattern corresponding to the image, the pattern being detected by the CCD sensor. In a preferred embodiment the imager uses four 8×8-cm three-side buttable CCDs coupled to a CsI:T1 scintillator by straight (non-tapering) fiberoptics and tiled to achieve a field of view (FOV) of 16×16-cm at the image plane. Larger FOVs can be achieved by tiling more CCDs in a similar manner. The imaging system can be operated in a plurality of pixel pitch modes such as 78, 156 or 234-μm pixel pitch modes. The CCD sensor may also provide multi-resolution imaging. The image is digitized by the sensor and processed by a controller before being stored as an electronic image. Other preferred embodiments may include each image being directed on flat panel imagers made from but not limited to, amorphous silicon and / or amorphous selenium to generate individual electronic representations of the separate images used for diagnostic or therapeutic applications.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS MEDICAL CENT
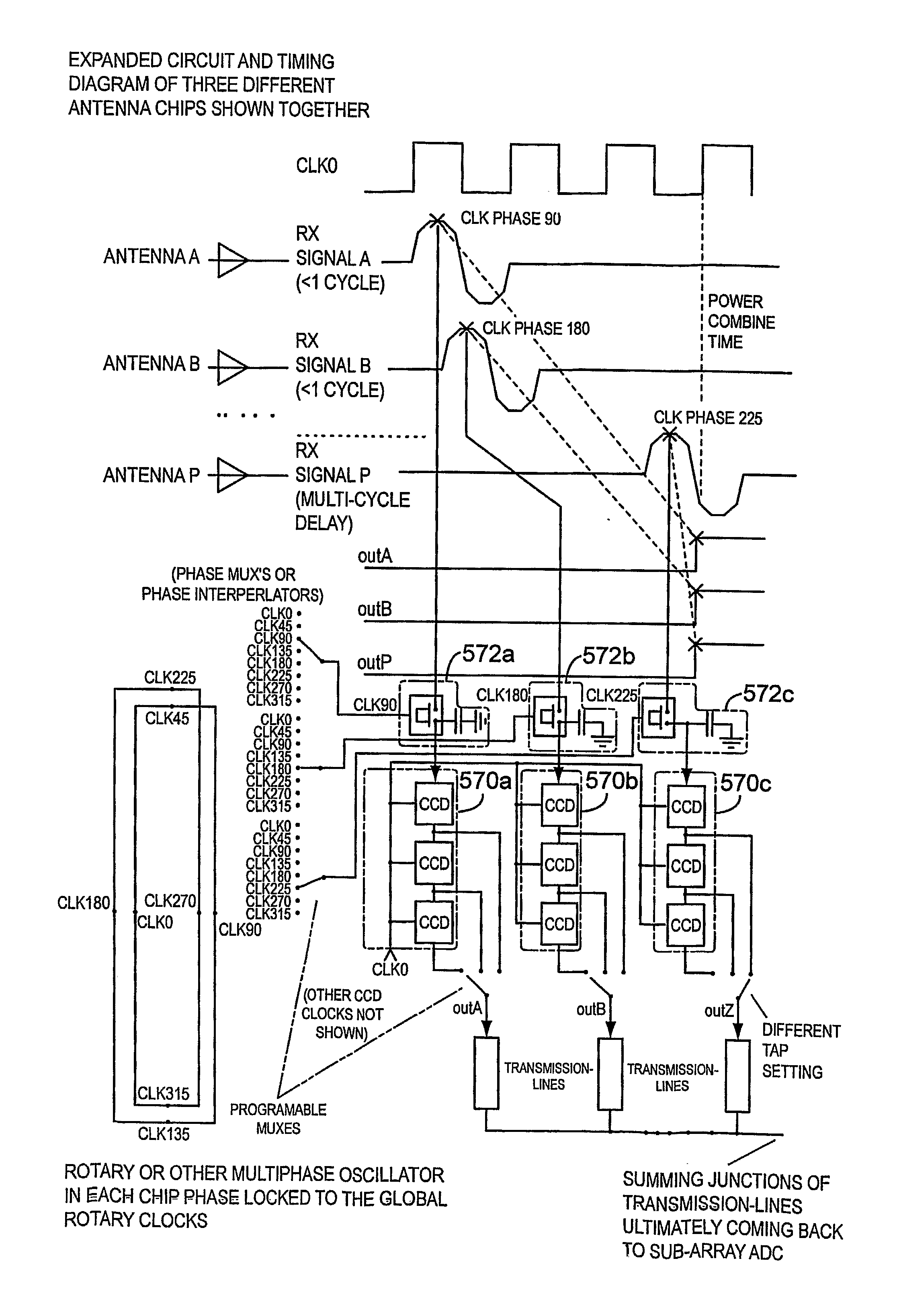
True time delay phase array radar using rotary clocks and electronic delay lines
ActiveUS20120039366A1Forming accuratelyEasy to moveAntenna arraysPulse automatic controlTime delaysAnalog delay line
Local oscillator circuitry for an antenna array is disclosed. The circuitry includes an array of rotary traveling wave oscillators which are arranged in a pattern over an area and coupled so as to make them coherent. This provides for a set of phase synchronous local oscillators distributed over a large area. The array also includes a plurality of phase shifters each of which is connected to one of the rotary oscillators to provide a phase shifted local oscillator for the array. The phase shifter optionally includes a cycle counter that is configured to count cycles of the rotary oscillator to which it is connected and control circuitry that is then operative to provide a shifted rotary oscillator output based on the count from the cycle counter. A system and method for operating a true-time delay phased array antenna system. The system includes a plurality of antenna element circuits for driving or receiving an rf signal from the elements of the array. Each element circuit has a transmit and a receive path and a local multiphase oscillator, such as a rotary traveling wave oscillator. Each path has an analog delay line for providing a true-time delay for the antenna element. Preferably, the analog delay line is a charge coupled device whose control nodes are connected to phases of the local multiphase oscillator to implement a delay that is an integer number local multiphase oscillator periods. A fractional delay is also included in the path by using a sample and hold circuit connected to a particular phase of the oscillator. By delaying each antenna element by a true time delay, broadband operation of the array is possible.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
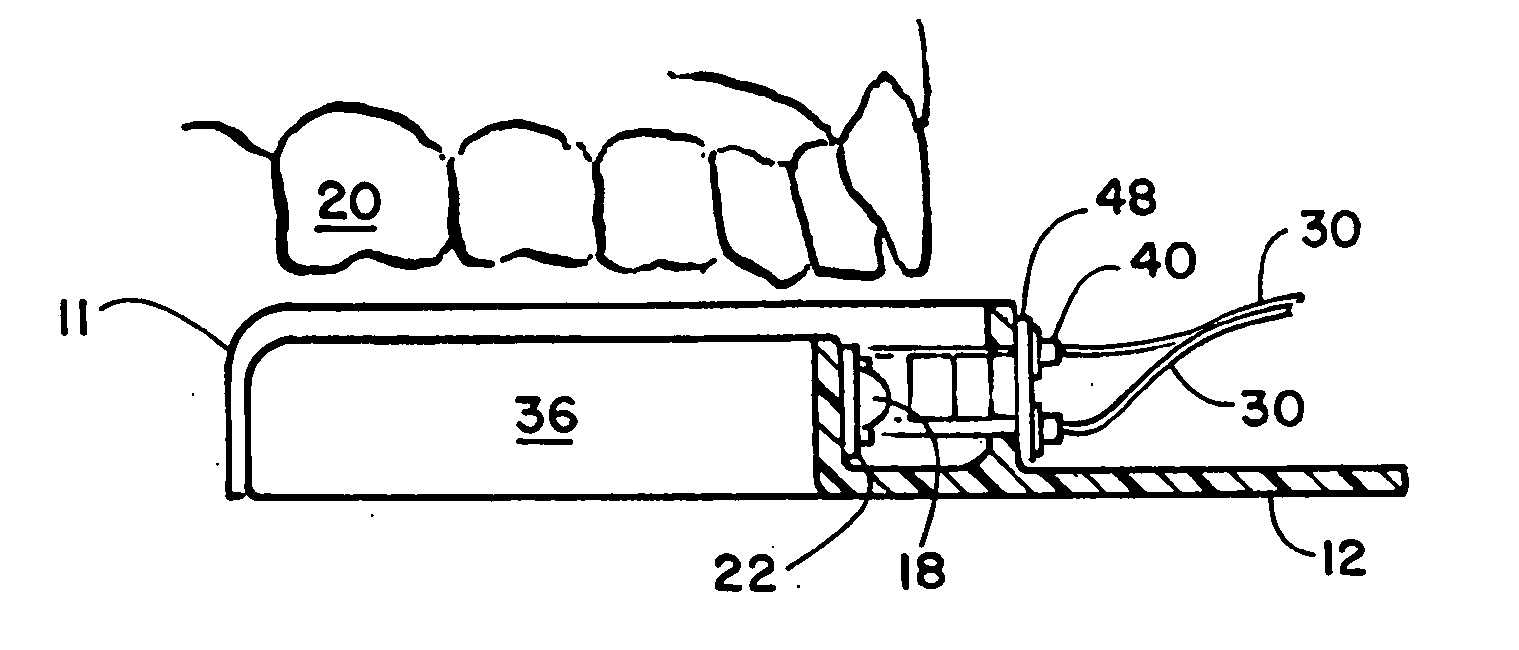
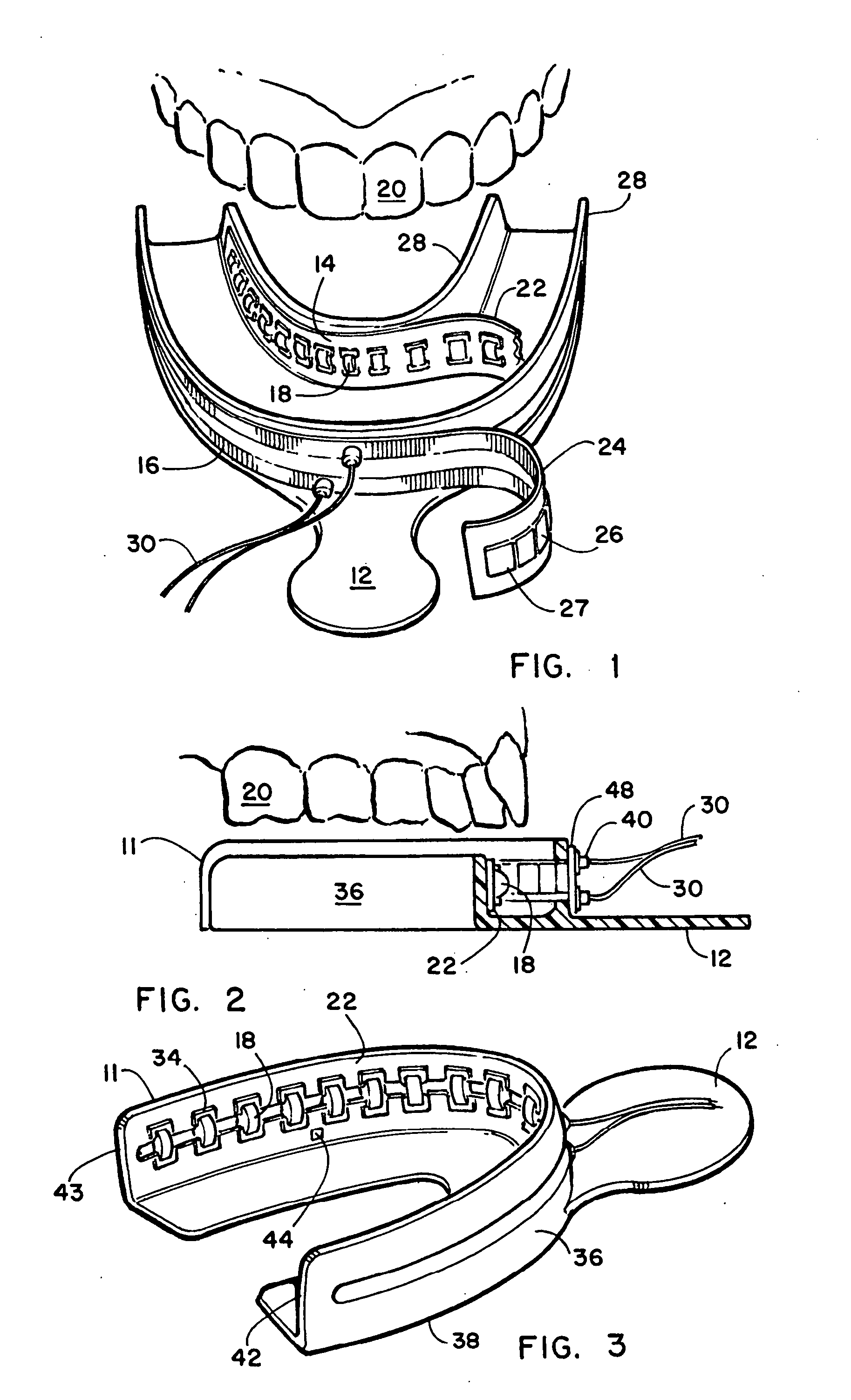
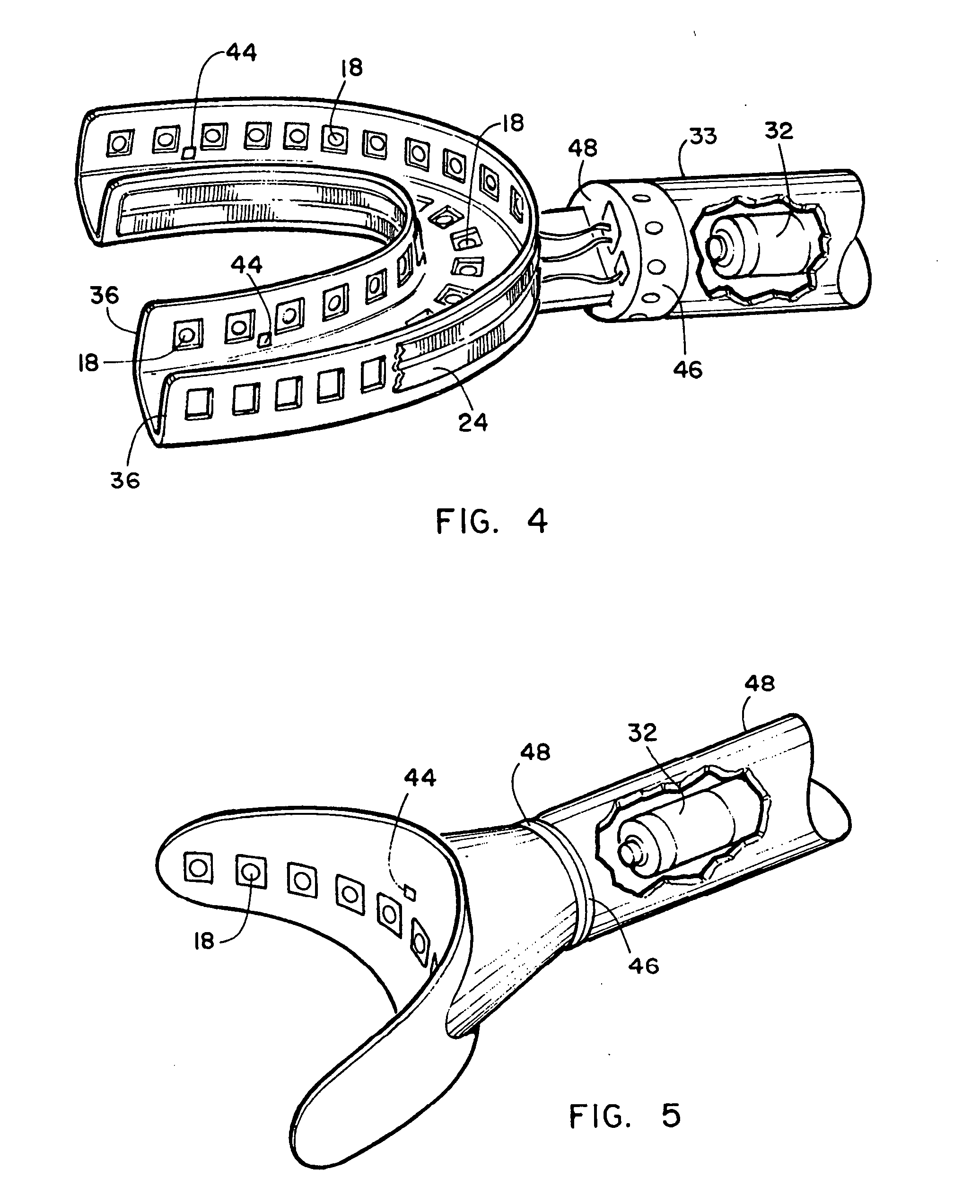
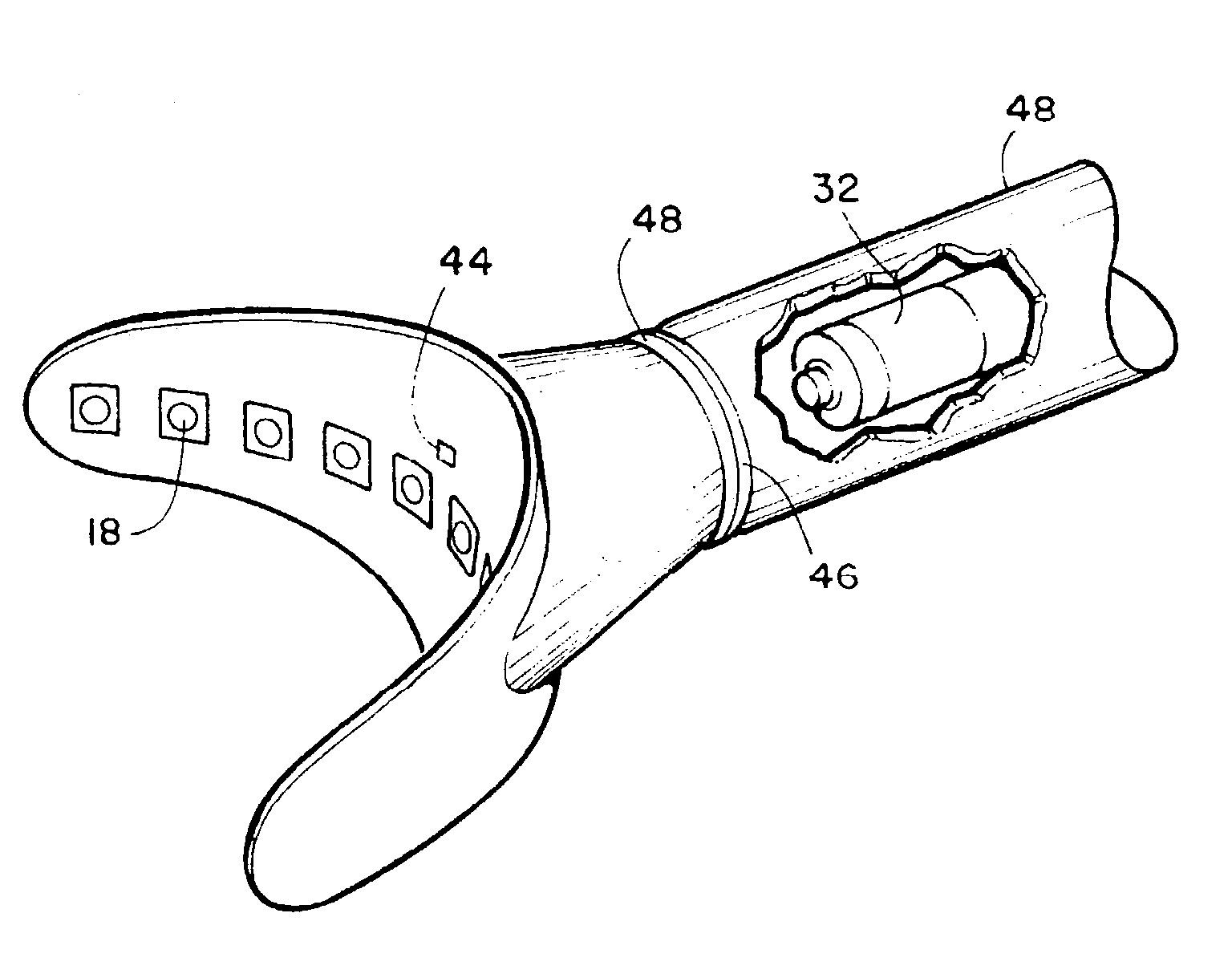
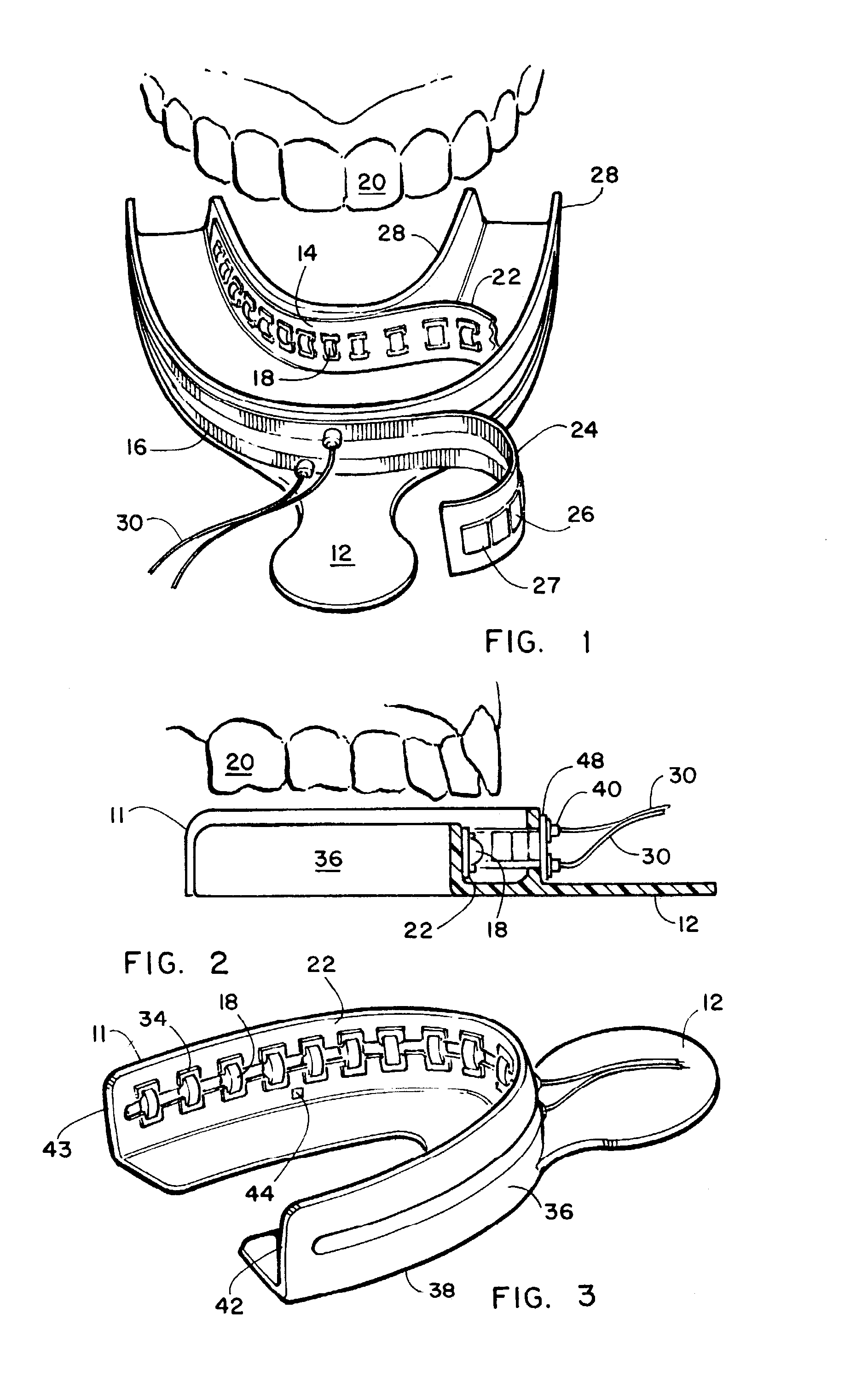
Dental imaging and treatment system
InactiveUS20050202363A1Good precisionShort curing timeImpression capsDental toolsTooth whiteningDental structure
An intra-oral dental irradiation device for use in dental procedures for whitening teeth, imaging teeth, and making impressions of tooth structures of a patient. The device features one or a plurality of LED devices mounted to an arched shaped structure which project light upon or through teeth. In the whitening mode the light of the proper spectrum to activate enamel whitening material is projected. In the imaging mode light projected by the LED devices is received by a charged coupled device which communicates the image of the light passing through the teeth from the LED devices, to a computer. In making dental impressions, the device projects light in a spectrum that provides the catalyst to material that hardens when exposed to that spectrum thereby hardening dental impression material when inserted over the teeth of a patient.
Owner:NOVA RANGER
Intra oral dental irradiation device for material curing and dental imaging
InactiveUS6976841B1Eliminate health hazardsStrong specificityImpression capsDental toolsDental impression materialDental procedures
An intra-oral dental irradiation device for use in dental procedures for whitening teeth, imaging teeth, and making impressions of tooth structures of a patient. The device features one or a plurality of LED devices mounted to an arched shaped structure which project light upon or through teeth. In the whitening mode the light of the proper spectrum to activate enamel whitening material is projected. In the imaging mode light projected by the LED devices is received by a charged coupled device which communicates the image of the light passing through the teeth from the LED devices, to a computer. In making dental impressions, the device projects light in a spectrum that provides the catalyst to material that hardens when exposed to that spectrum thereby hardening dental impression material when inserted over the teeth of a patient.
Owner:NOVA RANGER
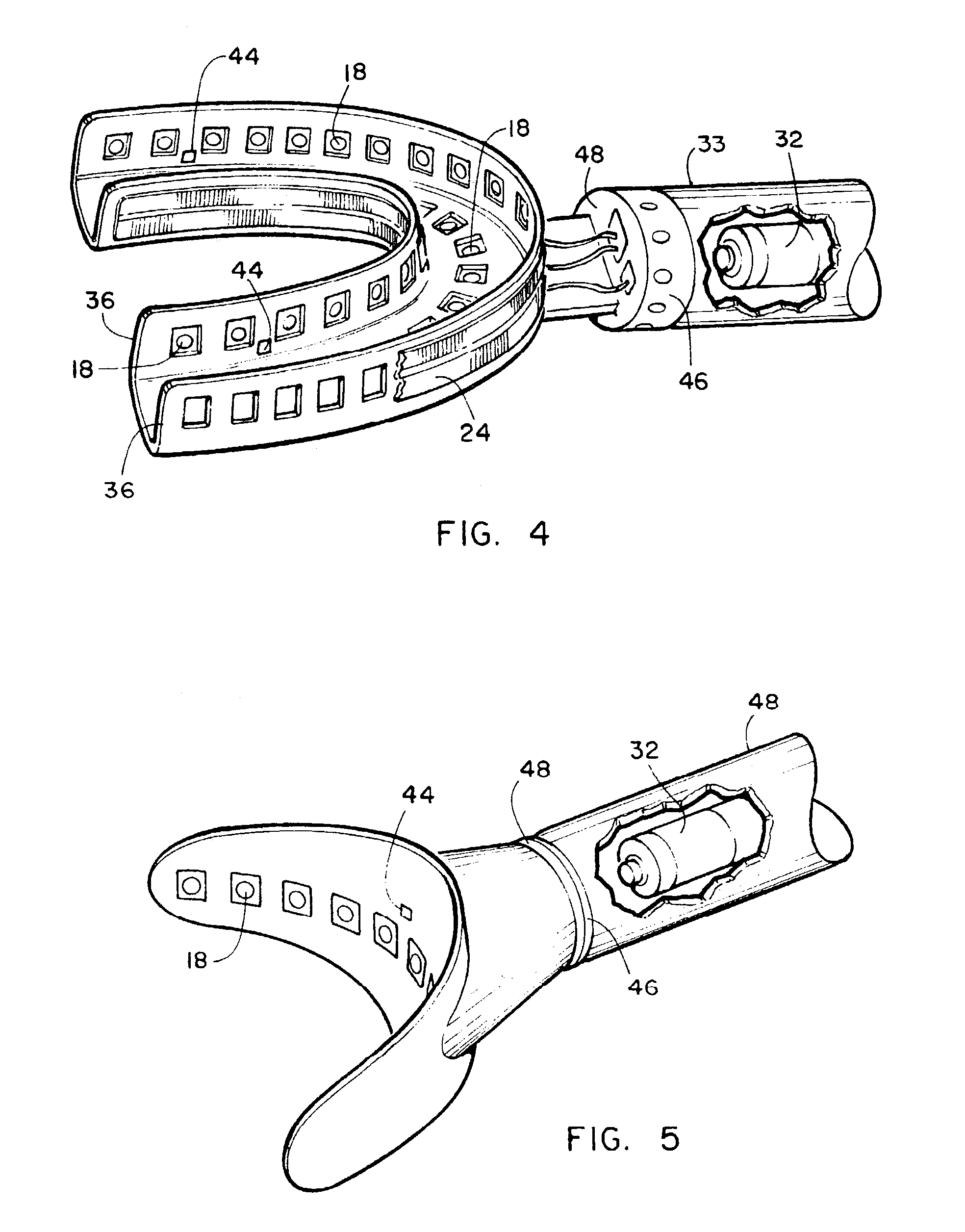
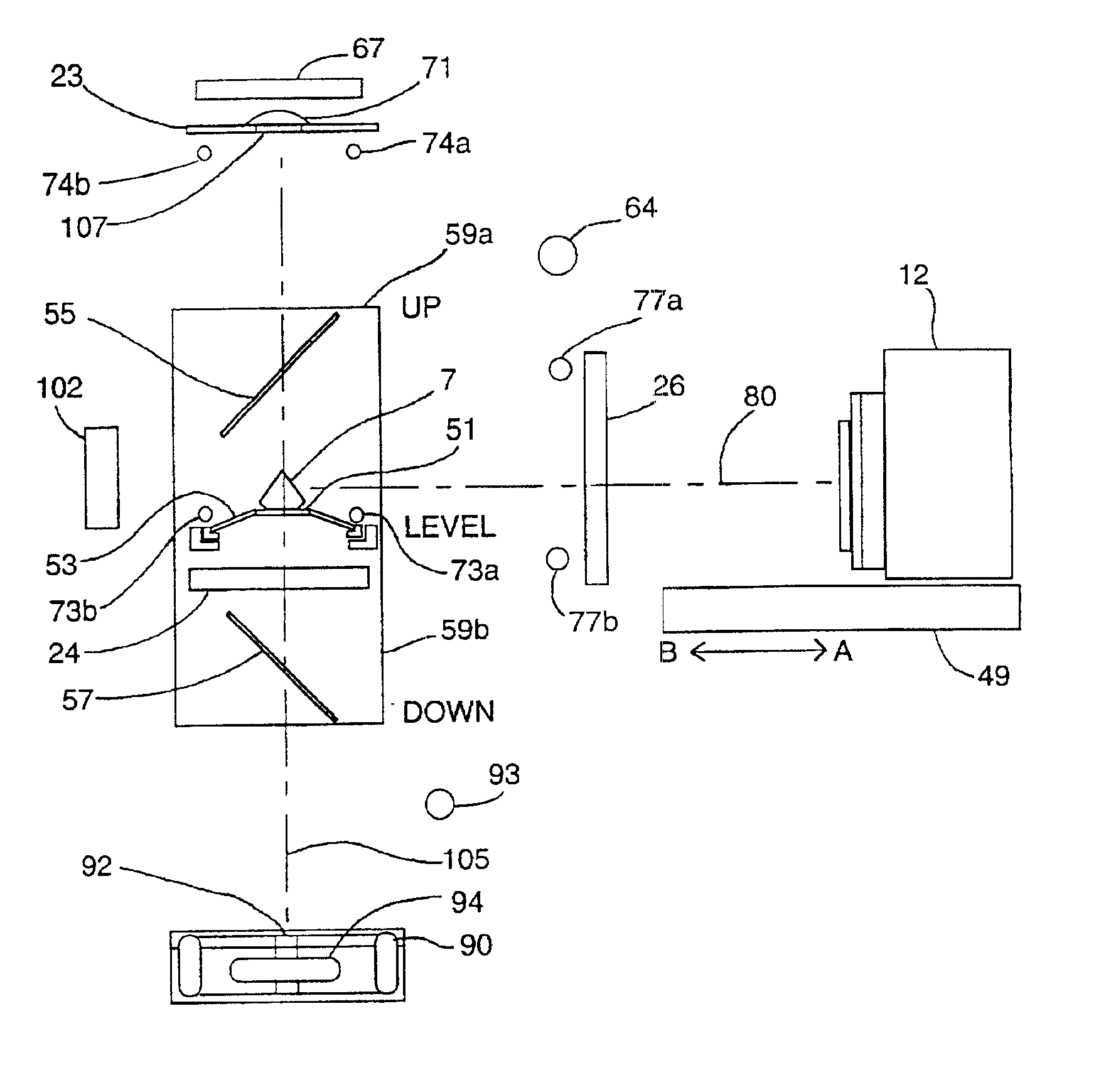
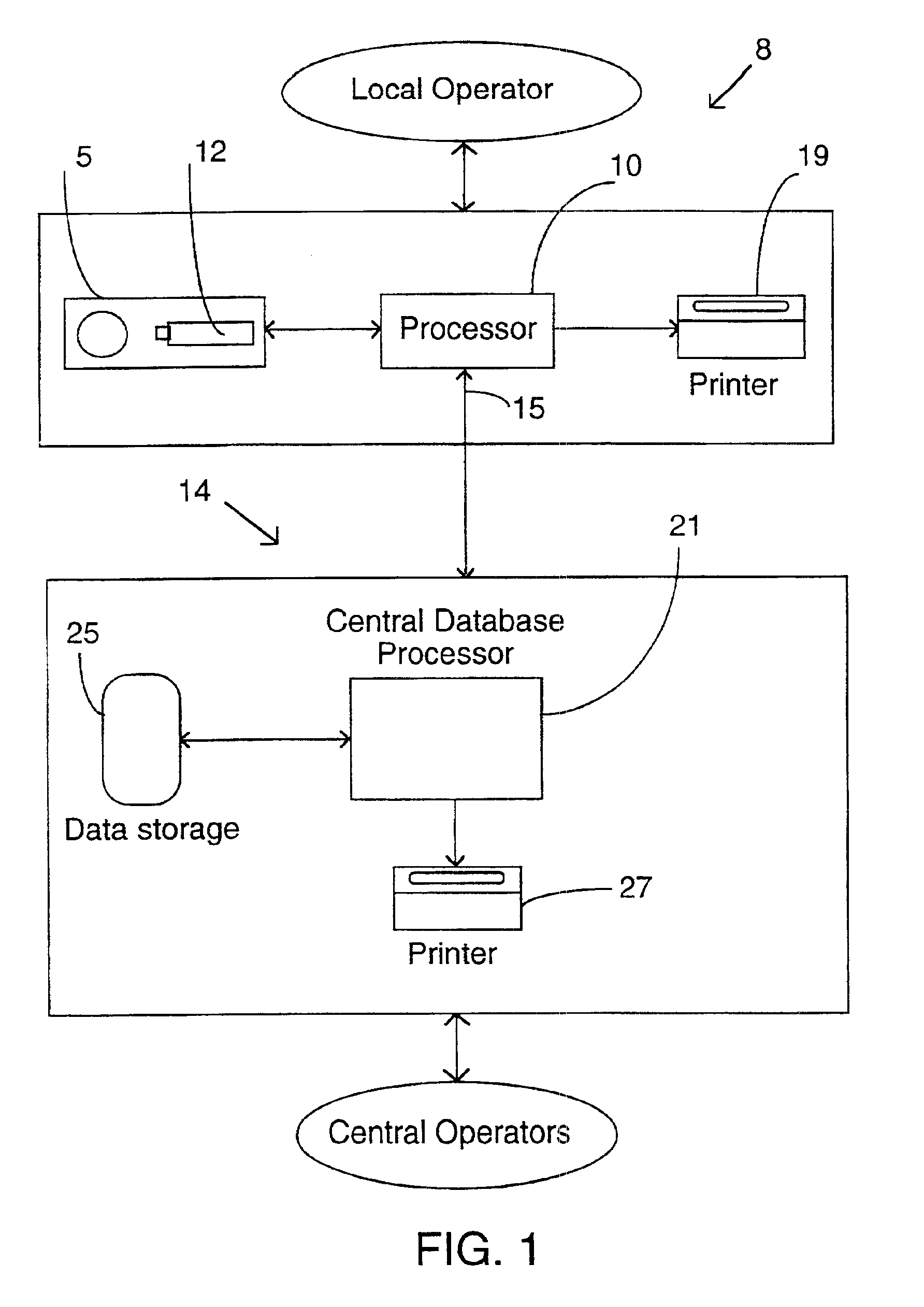
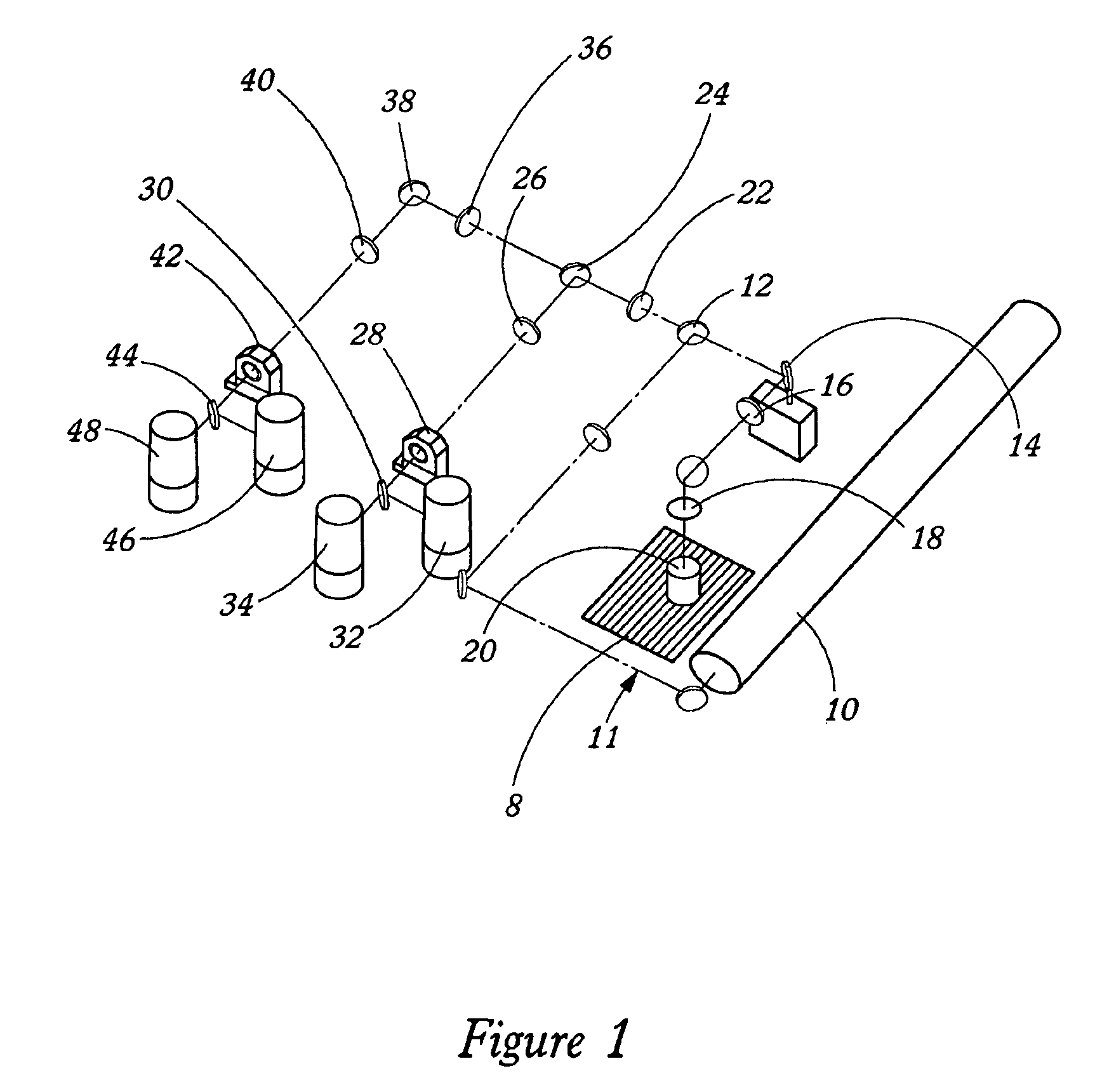
Method and associated apparatus for the standardized grading of gemstones
InactiveUS6980283B1Process safetyInvestigating jewelsSpecial data processing applicationsSpectral responseData set
A method and associated apparatus (5) for the standardized grading of gemstones is provided. The system gauges the spectral response of a gemstone subject to a plurality of incident light sources (77, 64, 90, 92, 102) within an imaging apparatus. The operation of the imaging apparatus is controlled by an instruction set of a local station control data processor (12). Light energy data is captured in the form of pixel data sets via a charge coupled device of the imaging apparatus of the local station (8). The control data processor data of the local station is operably linked to analysis station (14). Gemstones qualities are analyzed by the plurality of light sources (92, 90, 102) of the imaging apparatus (5) and quantified relative to model pixel data sets of the database and recorded for future reference therein.
Owner:IMAGESTATISTICS
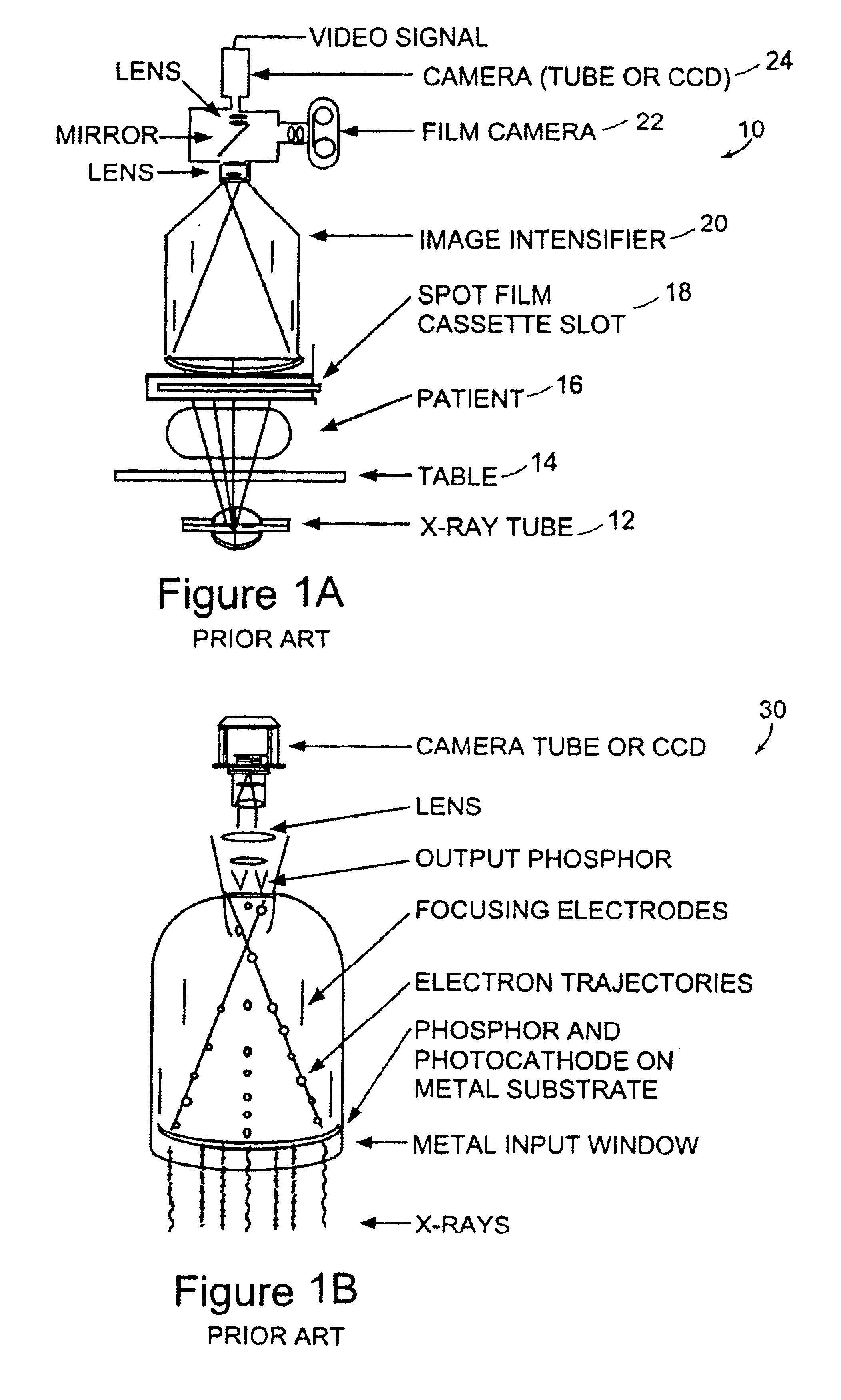
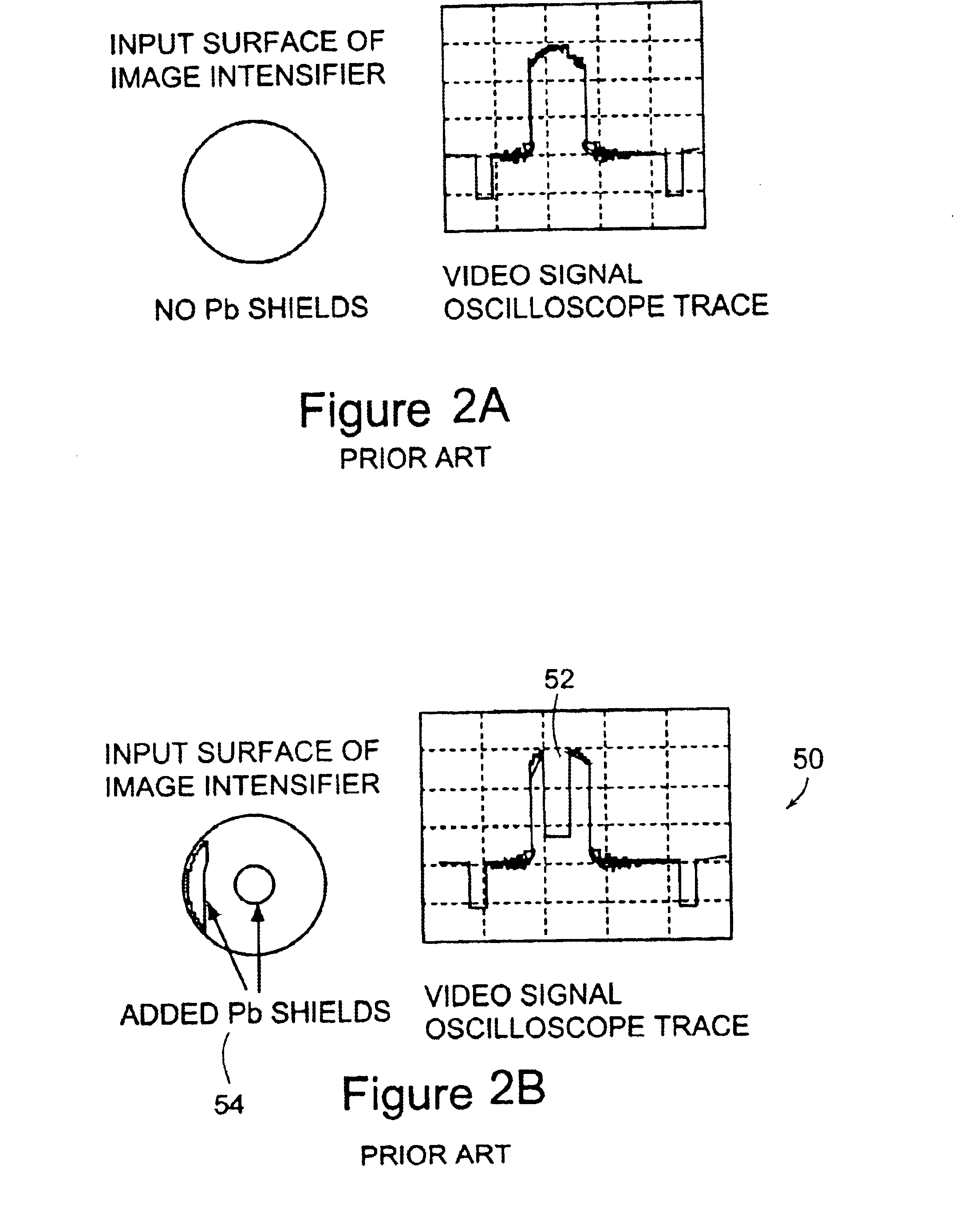
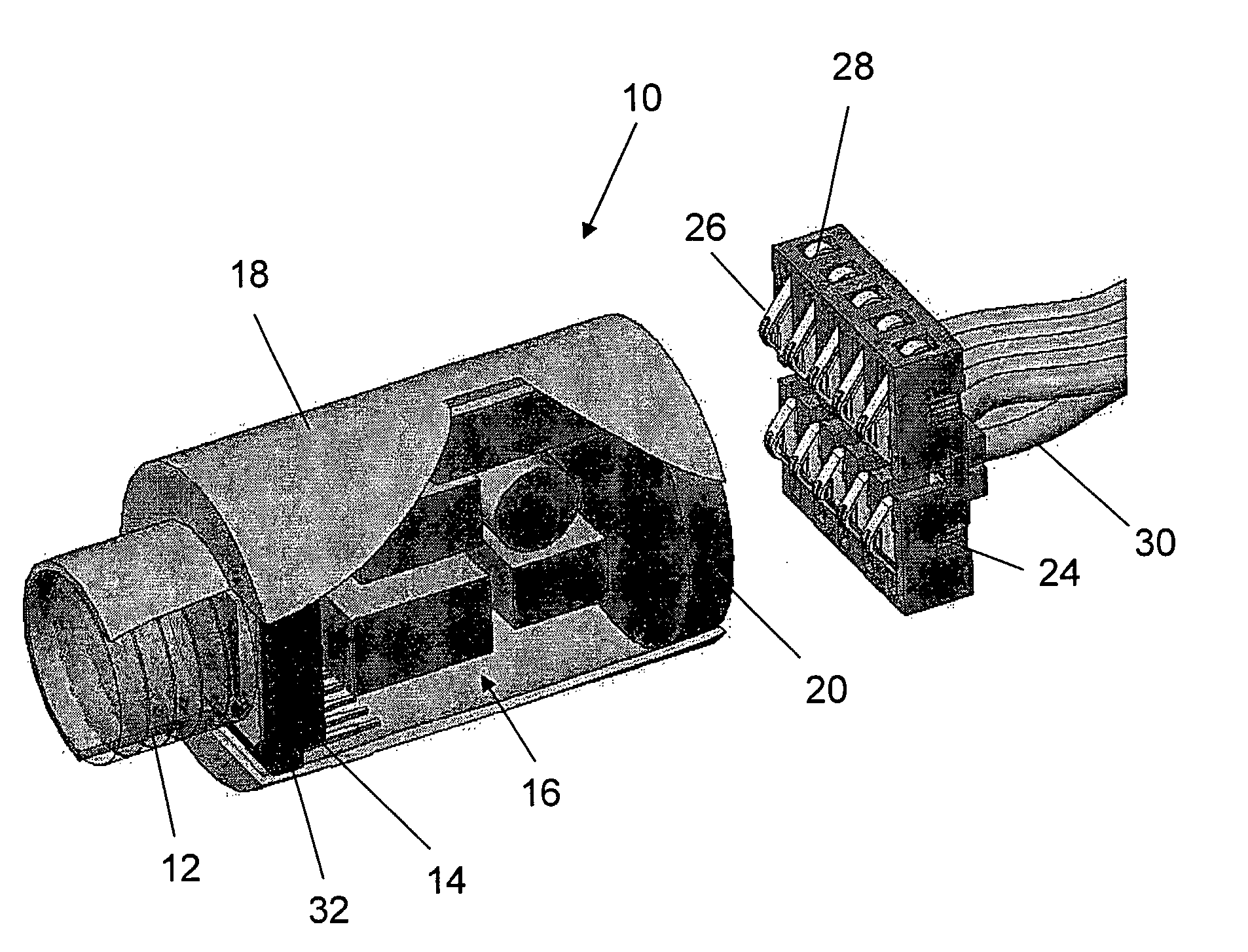
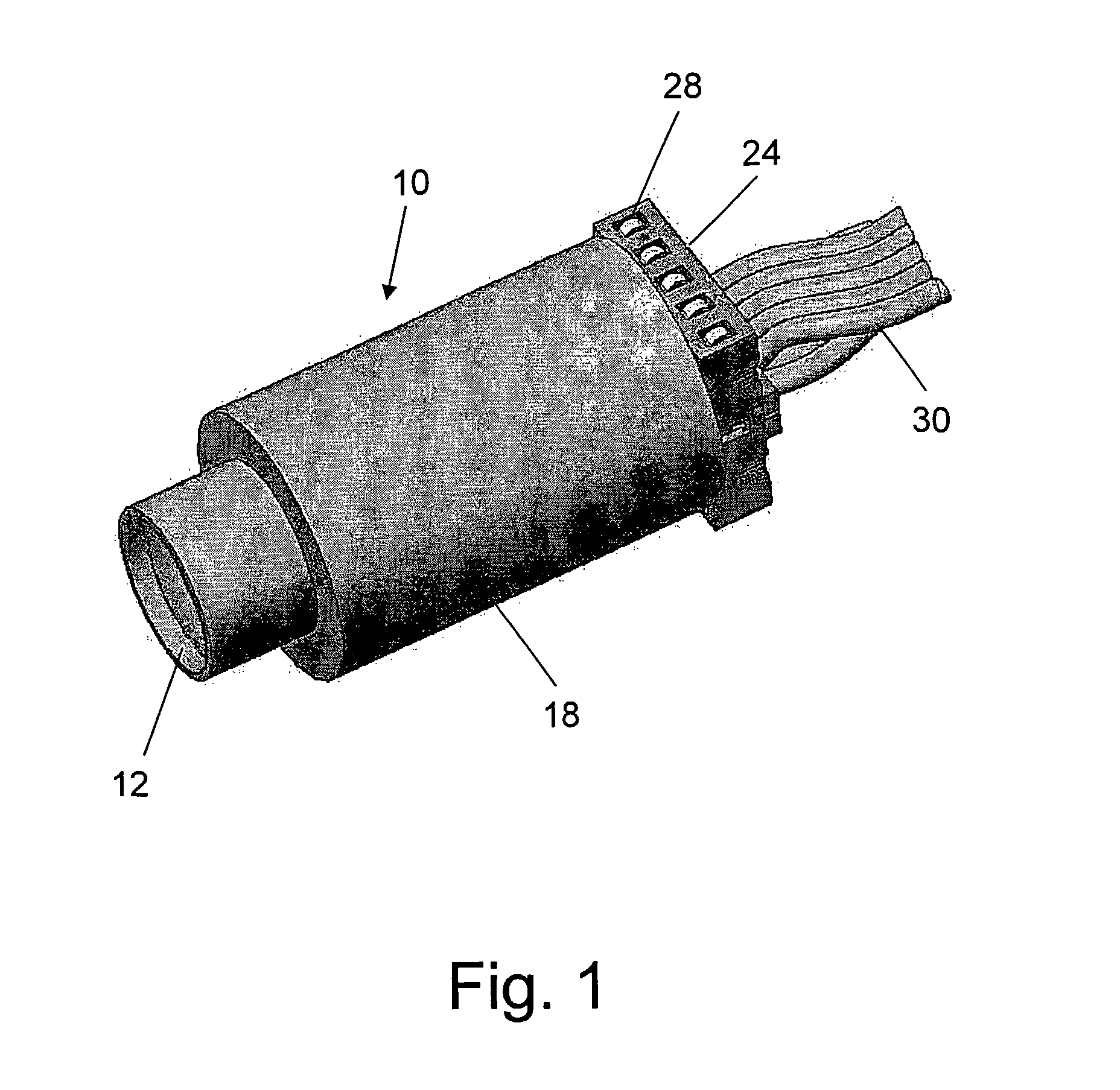
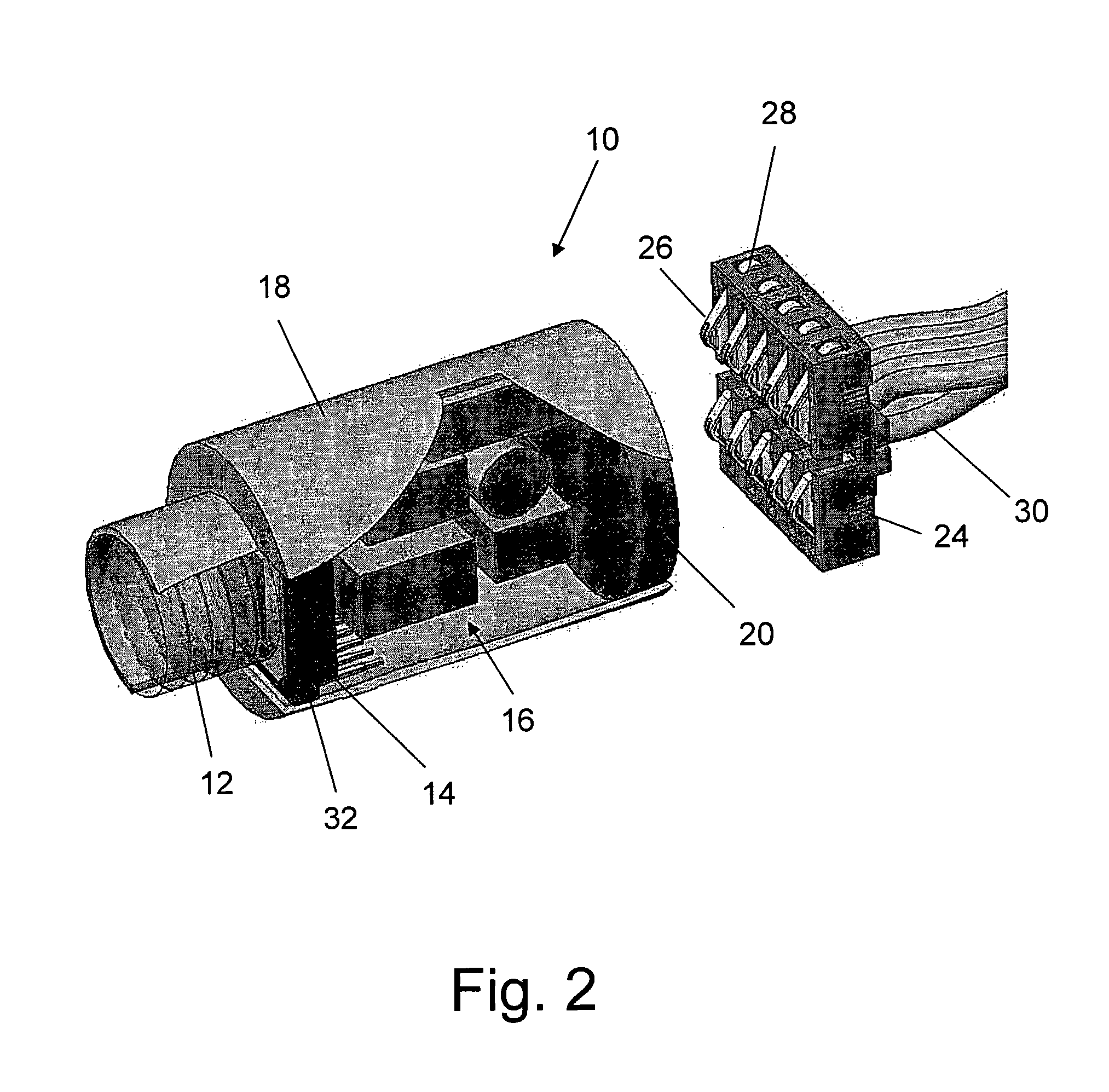
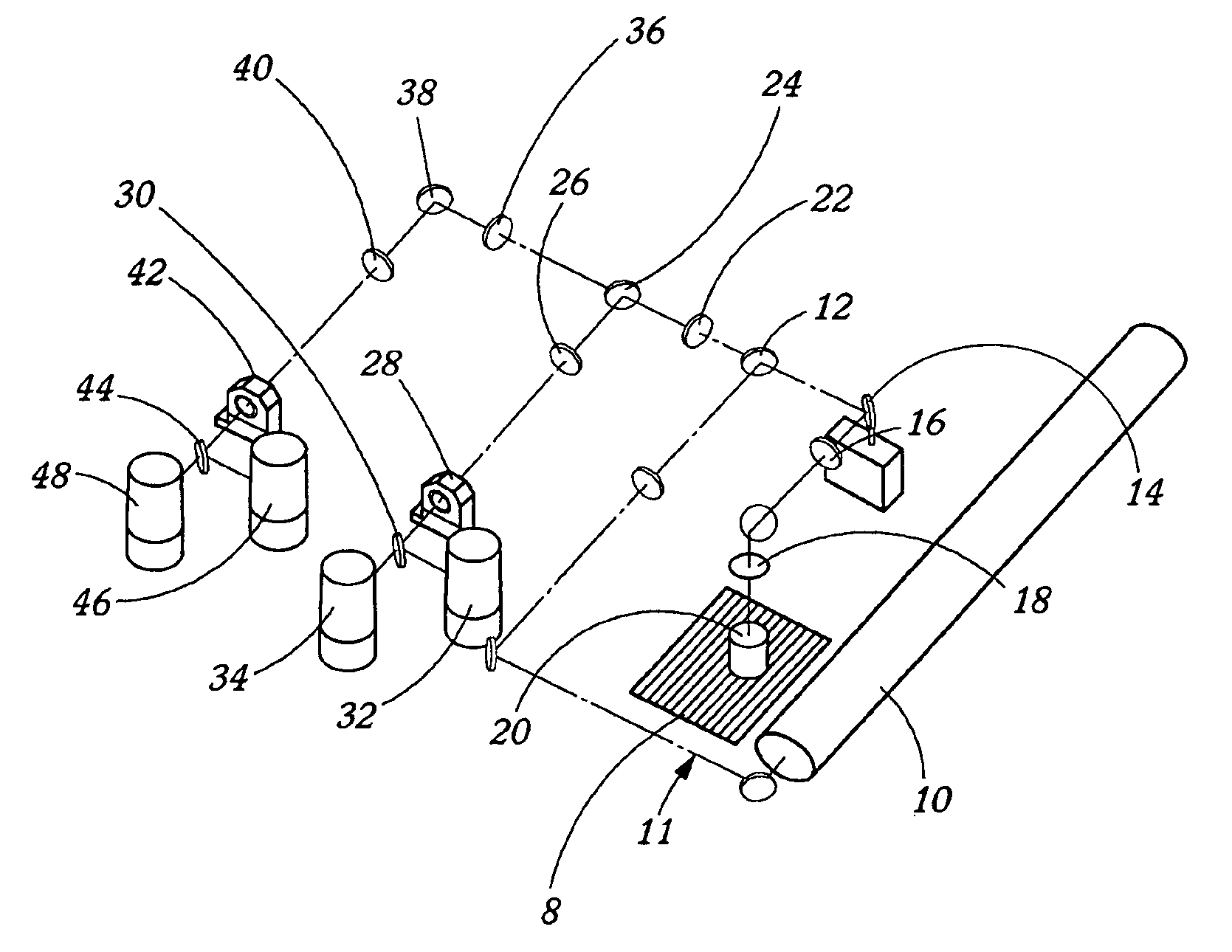
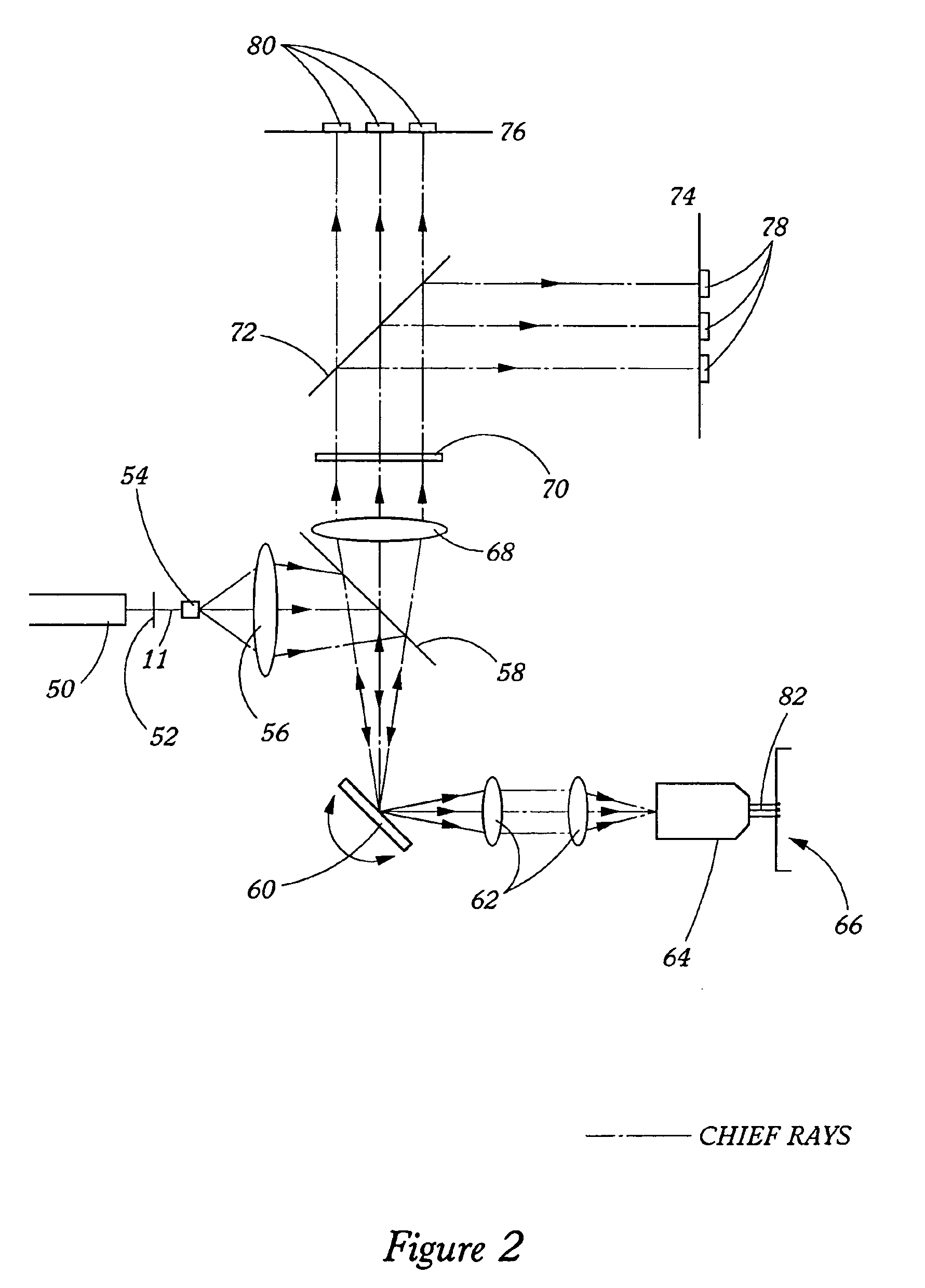
Reusable miniature camera head
The invention is a reusable miniature camera head (10) that can be attached to and detached from an object. The camera head comprises: a housing (18), a lens system (12), a solid-state sensor (14), components of an electronic driver (16), and an internal electrical connector (20) located at the proximal end of the housing and having a plurality of sockets (22) or pins (110) on its external face. The object has an external connector (24) for receiving the camera head. The internal and external electrical connectors comprise a plurality of pins or sockets arranged in matching patterns on opposing faces thereby allowing the camera head to be attached to or disconnected by engaging the two connectors. In preferred embodiments of the invention, the object to which the camera head is attached is an endoscopic or laparoscopic device, the solid-state sensor is a Charge Coupled Device (CCD), and the housing does not contain a printed circuit board.
Owner:MEDIGUS LTD
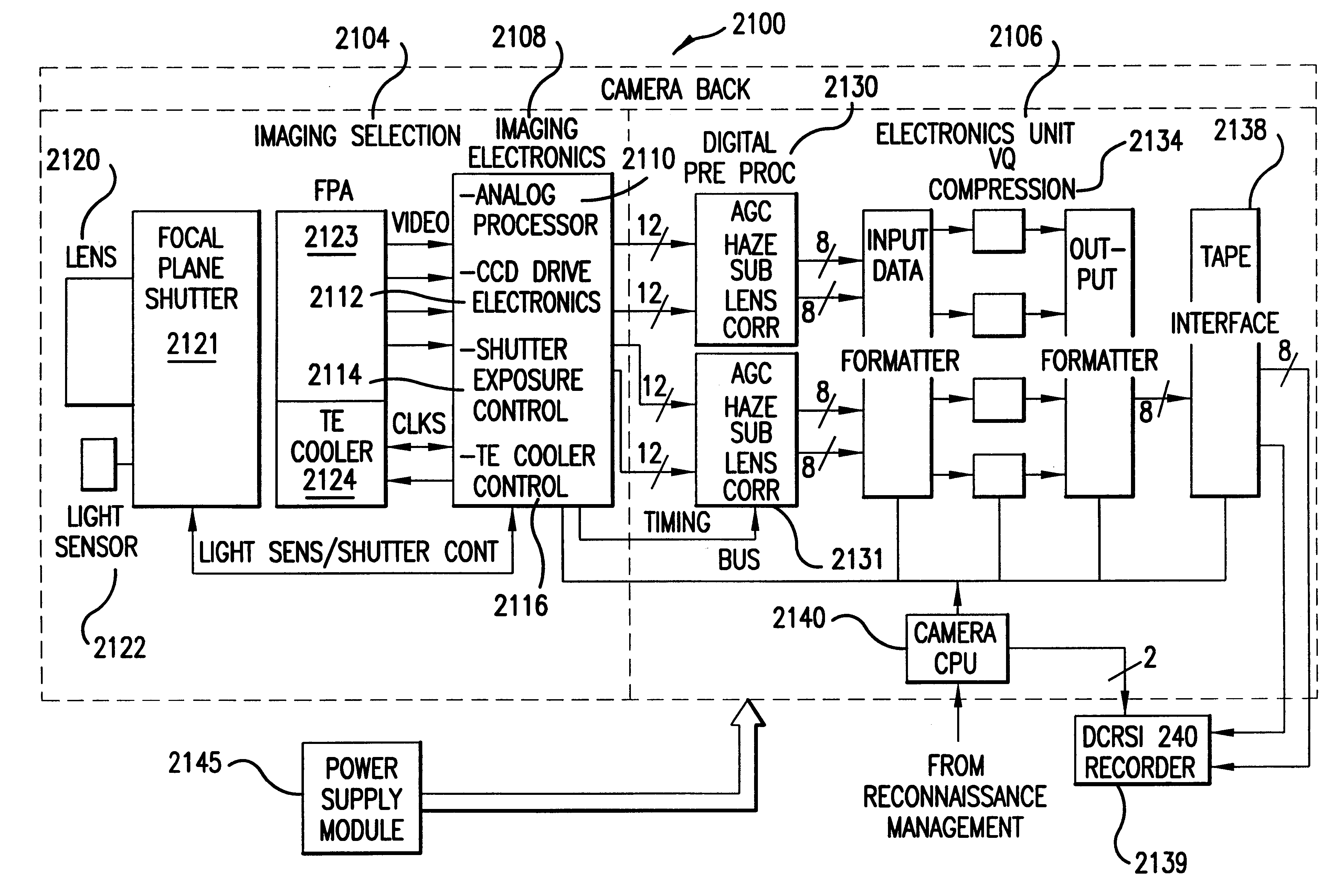
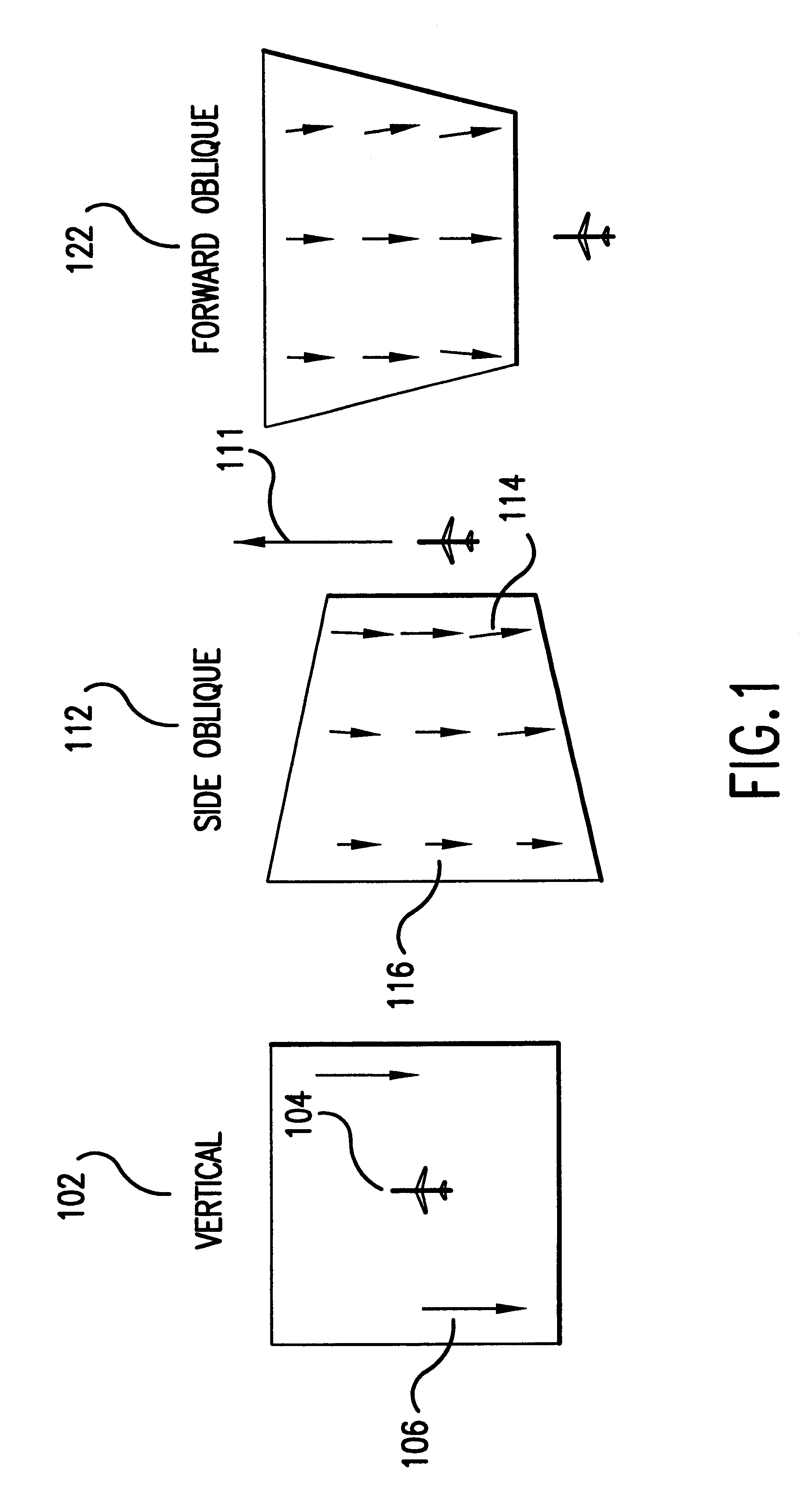
Electro-optical reconnaissance system with forward motion compensation
InactiveUS6256057B1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImage transferImage motion
An electro-optical framing camera forward motion compensation (FMC) reconnaissance system comprising a moving shutter and a full frame focal plane array detector is designed to minimize the variation of image motion from a target scene across the focal plane array. The full frame focal plane array, such as a Charge Coupled Device (CCD), is designed to transfer and add the image from pixel to pixel at a predetermined rate of image motion corresponding to the region exposed by the focal plane shutter. The focal plane shutter aperture and velocity are set to predetermined values coordinated with the available illumination. The CCD image transfer rate is set to minimize the smear effects due to image motion in the region of the scene exposed by the focal plane shutter. This rate is variable with line of sight depression angle, aircraft altitude, and aircraft velocity / altitude ratio. Further, a method of FMC utilizes a comparison of a measured light level to a standard value in order to determine the appropriate exposure time and shutter motion rate. An optimal FMC clocking signal is calculated based on image motion equations incorporated in the processing unit of the reconnaissance system.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Optically-based location system and method for determining a location at a structure
InactiveUS6865347B2Beacon systems using electromagnetic wavesPosition fixationDelayed timePositioning system
An optically based location system and method of determining a location at a structure include a lighting infrastructure having lights at a structure. Each light is configured to illuminate and to transmit a respective relative or absolute terrestrial position through modulation of emitted light. An optical receiver is configured to detect the lights, to demodulate the position of detected lights, and to determine from the detection a position of the receiver. The receiver can have a conventional optical detector for determining a two-dimensional position of the receiver relative to a detected light, or can have a three-dimensional spot collimating lens and charged couple device optical detector for determining a three-dimensional position of the receiver relative to a detected light. The receiver and lights can be synchronized for converting a delay time into a distance measurement to calculate a distance between a light and the receiver.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
System for determination of a location in three dimensional space
InactiveUS6141104AReduce the impact of interferenceNarrow downInput/output for user-computer interactionPosition fixationThree-dimensional spaceMathematical correlation
An optical improvement for angular position sensors, which may be used to determine the spatial coordinates of a small source of light (or other energy) in a 3-dimensional volume. Such sensors normally include a linear photosensitive image detector such as a photodiode array or a charge-coupled device (CCD). An irregular pattern of parallel slits is described which increases the amount of light gathered while avoiding the undesirable characteristics of lens optics for this application. One optimal type of irregular pattern is the uniformly redundant array. A mathematical correlation function together with a polynomial interpolation function can determine the displacement of the image on the detector and thereby the location of the source relative to one angular dimension. Given the locations and orientations of several sensors in a 3-dimensional coordinate system and given the angles measured by each, the location of the point source can be computed.
Owner:IMAGE GUIDED TECH
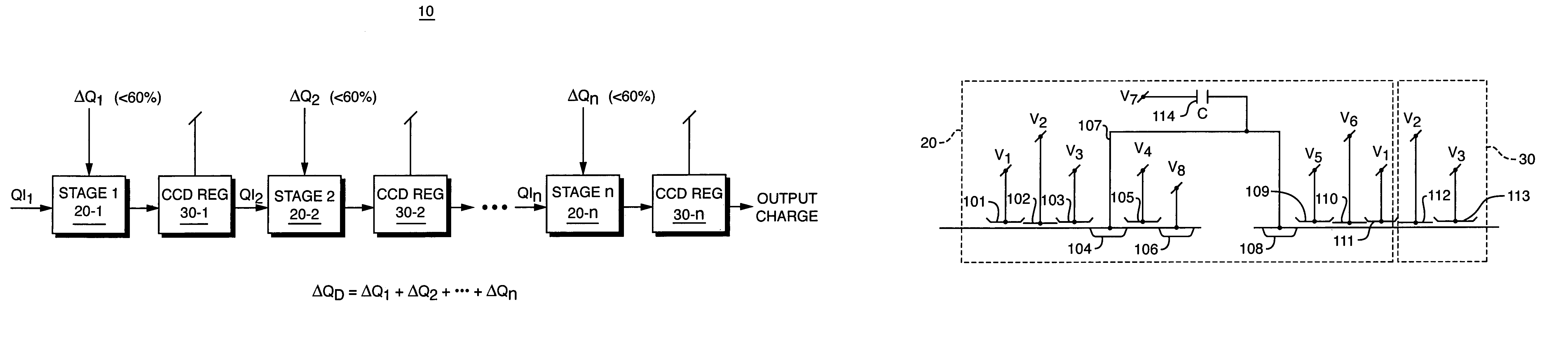
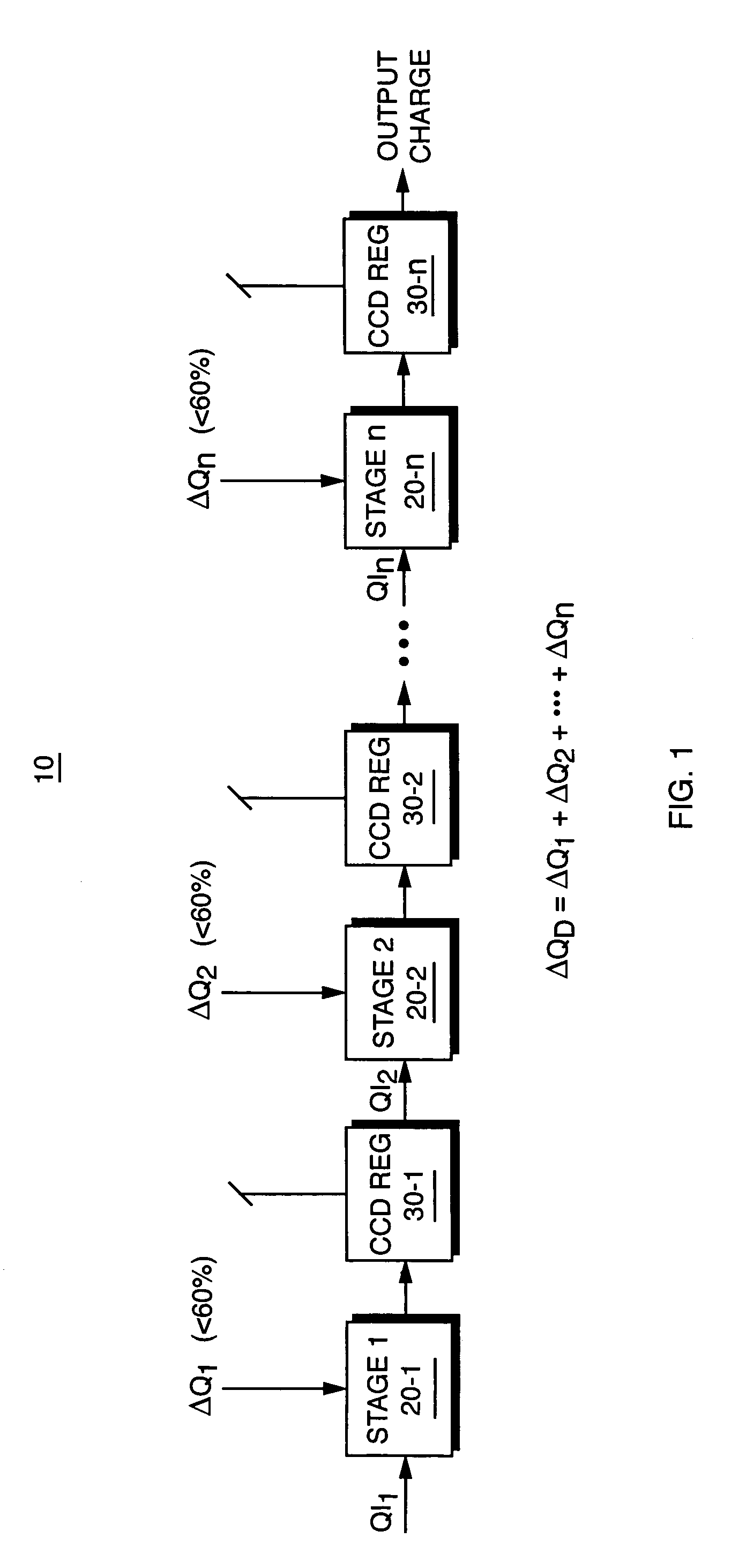
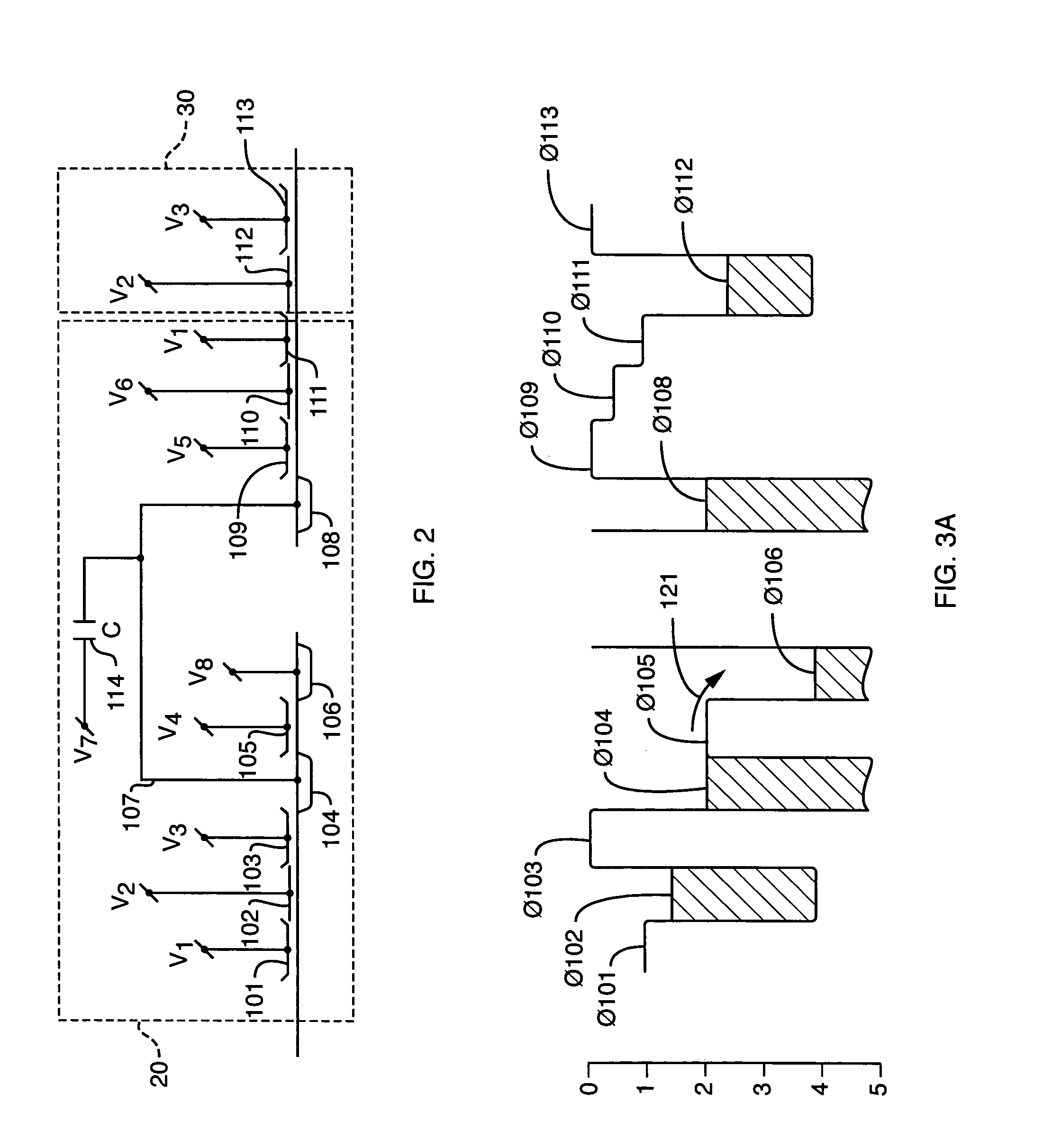
Device for subtracting or adding a constant amount of charge in a charge-coupled device at high operating frequencies
InactiveUS7003068B2Counting chain synchronous pulse countersSolid-state devicesMemory effectEngineering
Owner:KENET
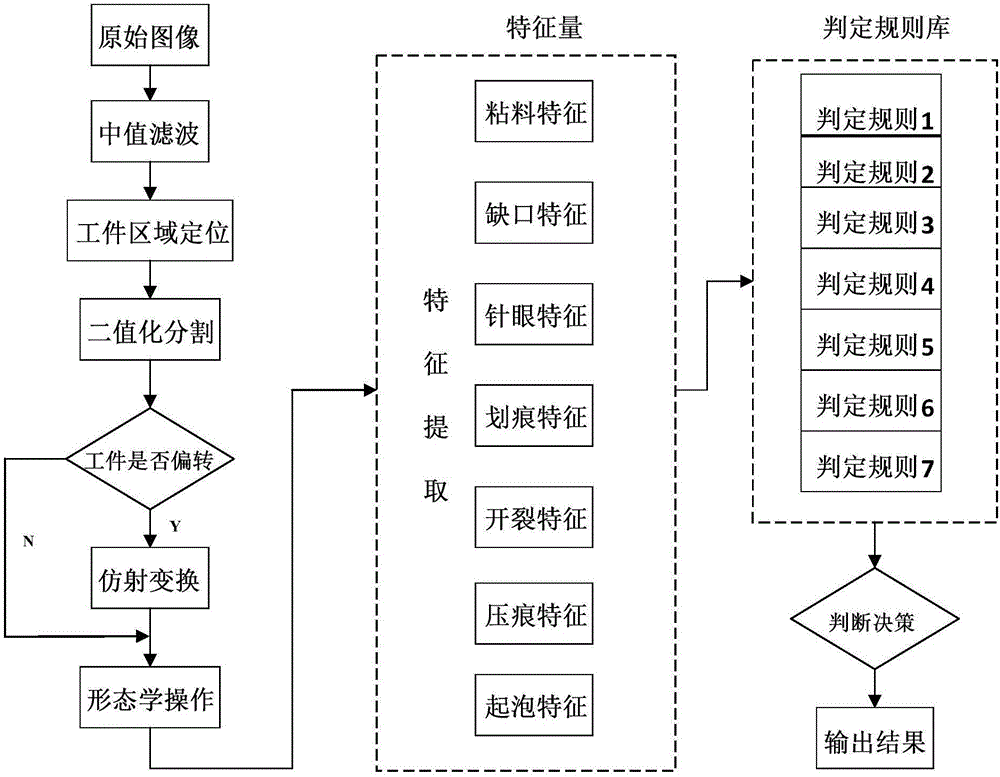
Device and method for detecting micro defects on bright and clean surface of metal part based on machine vision
ActiveCN102590218ARealize installation positioningEasy to operateOptically investigating flaws/contaminationEffect lightCcd camera
The invention relates to a device and method for detecting micro defects on the bright and clean surface of a metal part based on machine vision. The device comprises an imaging, positioning and adjusting mechanism and a processing unit, wherein the imaging, positioning and adjusting mechanism comprises a base plate, a guide rod, a fixed support, a sliding support, a stepping motor, a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) camera, a telecentric lens and parallel light sources, wherein the imaging and coaxial lighting of the CCD camera are primarily adjusted; an image collection card, an industrial personal computer, an equipment control card and an alarm are electrically connected in the processing unit and are used for collecting, transmitting, storing, processing, displaying and alarming image. The method comprises coaxial lighting adjustment and image processing, wherein coaxial lighting adjustment comprises the steps of triggering the equipment control card via software of the industrial personal computer to drive the stepping motor, and adjusting the rotating angles of the parallel light sources until the coaxial lighting condition is satisfied; and image processing comprises the steps of detecting defects on the internal surface of the detected part, respectively detecting large and small defects on the outer edge on the surface of the detected part, displaying the processing images in real time and judging the results.
Owner:安徽中科智能高技术有限责任公司
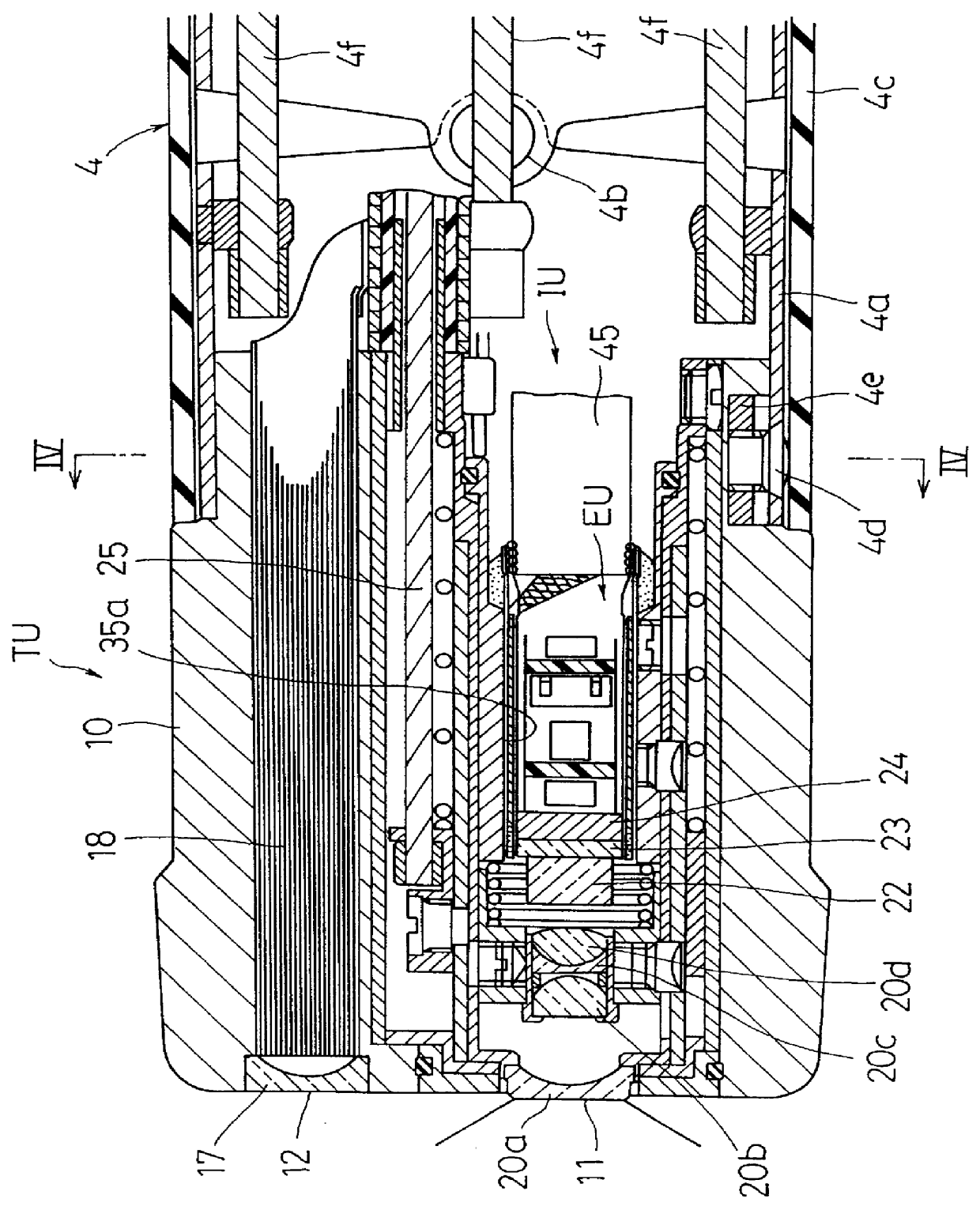
Endoscope with movable imaging unit for zooming or focusing
An electronic endoscope includes a charge coupled device and provides macro-zooming function. The endoscope comprises an imaging unit including a plurality of optical elements forming an optical system and a support and guide mechanism for supporting and / or guiding the optical elements. The optical elements include a fixed lens, movable lenses, and a CCD. The support and guide mechanism comprises a casing including inner and outer cylinders. The axis of the inner cylinder defines a reference axis. A cam cylinder is fitted over the inner cylinder and is guided for rotational movement with no axial movement. An axial slider is fitted over the cam cylinder and guided for axial movement with no rotational movement. The axial slider is driven for axial movement through a manipulating lever provided on a handpiece. First and second carriages are fitted in the inner cylinder and guided for axial movement with no rotational movement. The fixed lens is secured to the casing, the movable lens are carried on the first carriage, and the CCD is carried on the second carriage. A first cam mechanism is provided to producing rotational movement of the cam cylinder in response to axial movement of the axial slider. A second cam mechanism is provided for producing respective axial movements of the carriages in response to rotational movement of the cam cylinder.
Owner:HOYA CORP
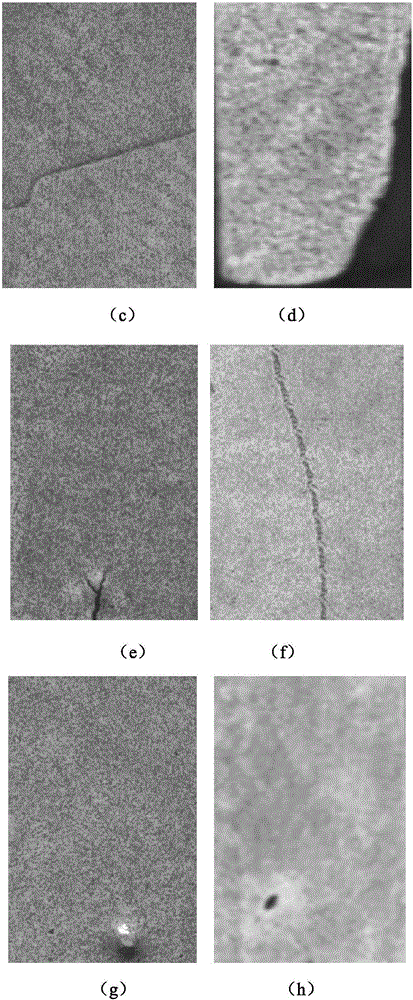
System for visually detecting workpiece appearance defects based on image processing
ActiveCN106053479AFast positioningHigh precisionImage enhancementImage analysisDiffuse reflectionVisual perception
The invention discloses a system for visually detecting workpiece appearance defects based on image processing, comprising an industrial personal computer, a coaxial light source, a CCD (charge coupled device) industrial camera, an image acquisition card and a rejecting mechanism; both the coaxial light source and the rejecting mechanism are connected with the industrial personal computer; the CCD industrial camera is connected with the industrial personal computer through the image acquisition card; wherein the coaxial light source is used for providing a diffuse reflection light source for a workpiece to be detected; the CCD industrial camera is used for taking an image of the workpiece at a detection station; the rejecting mechanism is used for rejecting from a production line, workpieces detected to be defective; the industrial personal computer has a defect detection module based on image processing; the system is high in detection efficiency and easy to implement.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Online monitoring system for infrared thermal imaging of converting station
InactiveCN102169017ARealize automatic inspectionRealize automatic warningRadiation pyrometryInformation processingSystems management
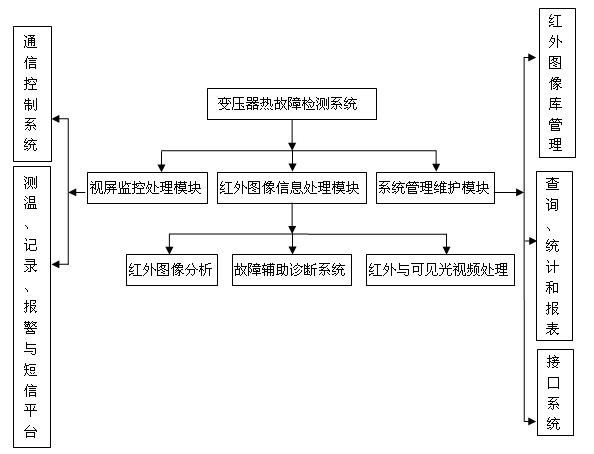
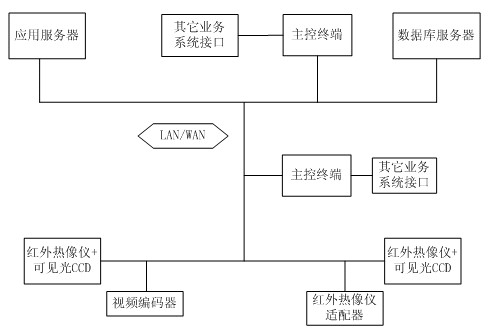
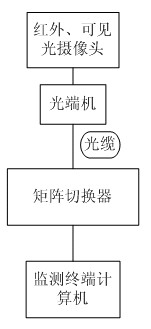
The invention discloses an online monitoring system for infrared thermal imaging of a converting station. The system comprises an online infrared thermal imaging instrument, a view screen monitoring and processing module, an infrared image information processing module and a system management and maintenance module, wherein the view screen monitoring and processing module comprises a communication and control subsystem and an infrared imaging and temperature measuring subsystem; the communication and control subsystem is used for controlling a field online infrared thermal imaging instrument, a visible light CCD (Charge Coupled Device) and a tripod head servo and setting and controlling a data link; the infrared imaging and temperature measuring subsystem comprises a temperature measuring, recording, alarming and short message platform system for realizing temperature measurement, alarming and transmission of alarm information through a short message platform; the infrared image information processing module comprises an infrared image analysis system, a failure auxiliary diagnosis system and an infrared and visible light video processing system; and the system management and maintenance module comprises an equipment thermal failure typical infrared image library management system, a management inquiry, statistic and report system and an interface system for an extant service system. By means of the online monitoring system in the invention, the defects of portable infrared imaging are overcome, artificial detection is combined with system detection, real-time monitoring of electric equipment is realized, and infrared thermal image monitoring of a monitored range or specified target equipment as well as data acquisition and recording, storage and analysis of a temperature field are ensured. The system has the characteristics of automatic routing inspection, automatic pre-warning, accuracy, high speed and remote monitoring.
Owner:JIANGXI JIUJIANG POWER SUPPLY +1
Optical architectures for microvolume laser-scanning cytometers
InactiveUS6979830B2Reduce power densityMinimizing limitationOptical radiation measurementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSpectroscopyLaser scanning
Methods and instrumentation for performing charge coupled device (CCD)-based confocal spectroscopy with a laser spot array are provided. The methods and instruments of the invention are useful in any spectroscopic application, including, but not limited to, microscopy and microvolume laser scanning cytometry (MLSC).
Owner:PPD BIOMARKER DISCOVERY SCI
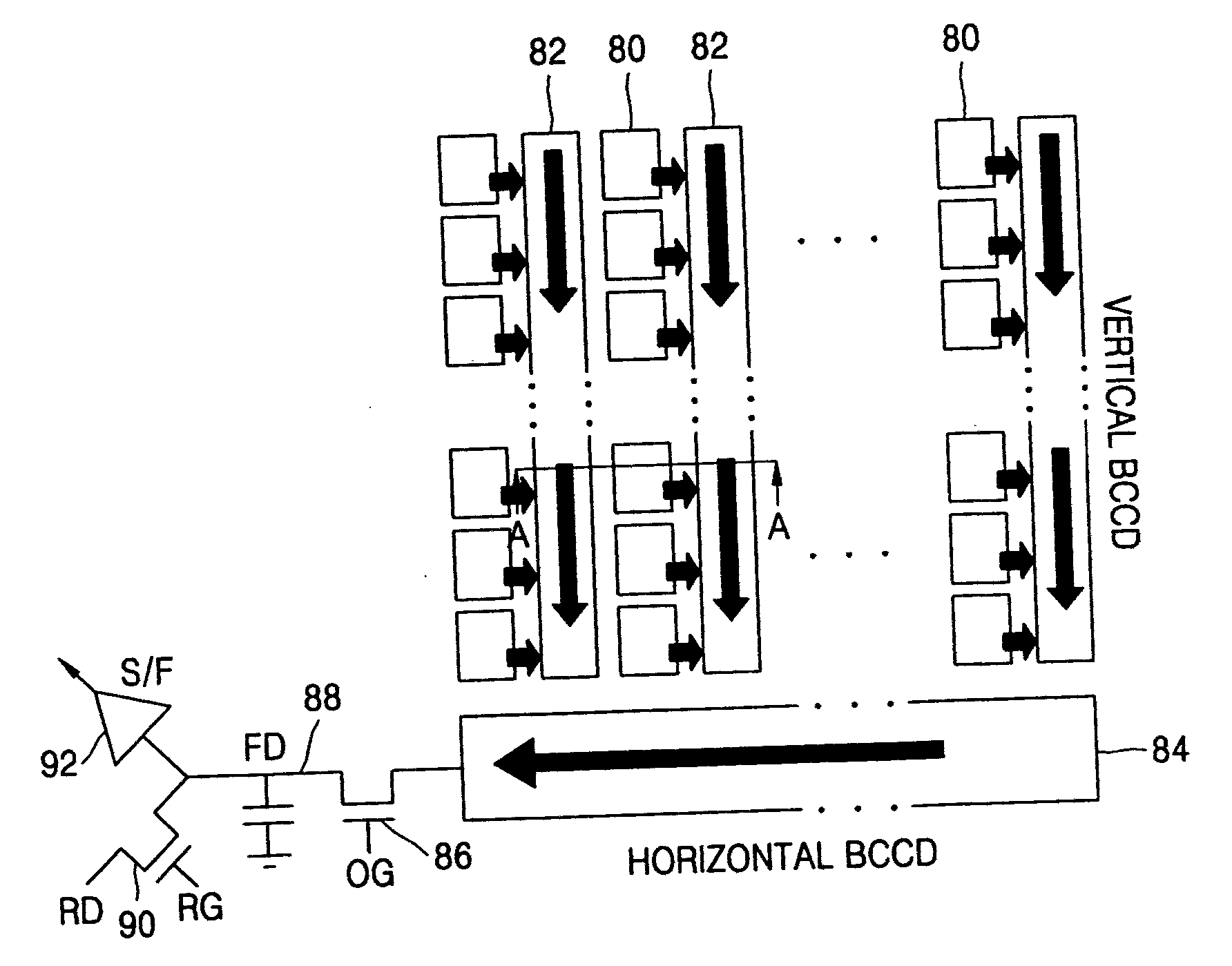
Method of acquiring an image from an optical structure having pixels with dedicated readout circuits
An imaging device formed as a monolithic complementary metal oxide semiconductor integrated circuit in an industry standard complementary metal oxide semiconductor process, the integrated circuit including a focal plane array of pixel cells, each one of the cells including a photogate overlying the substrate for accumulating photo-generated charge in an underlying portion of the substrate, a readout circuit including at least an output field effect transistor formed in the substrate, and a charge coupled device section formed on the substrate adjacent the photogate having a sensing node connected to the output transistor and at least one charge coupled device stage for transferring charge from the underlying portion of the substrate to the sensing node.
Owner:NASA
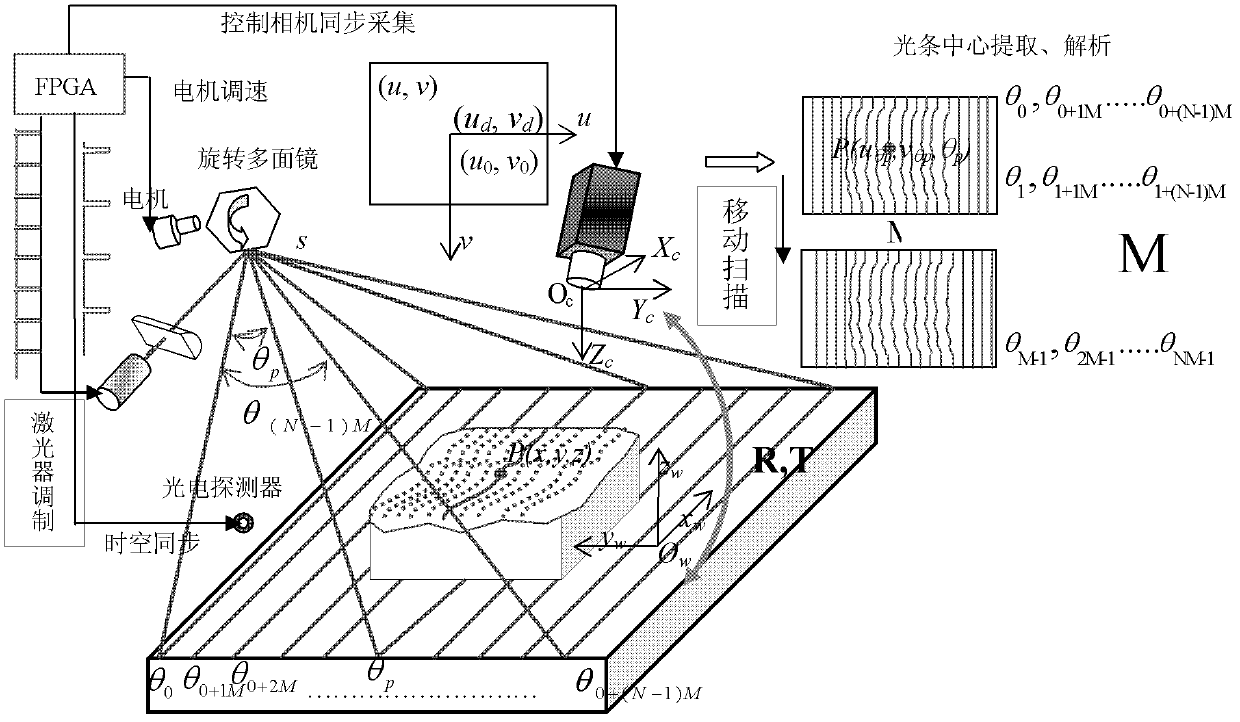
High-speed scanning and overall imaging three-dimensional (3D) measurement method
InactiveCN102589476AFast measurementLittle effect on reflectivityUsing optical meansThree dimensional measurementPrism
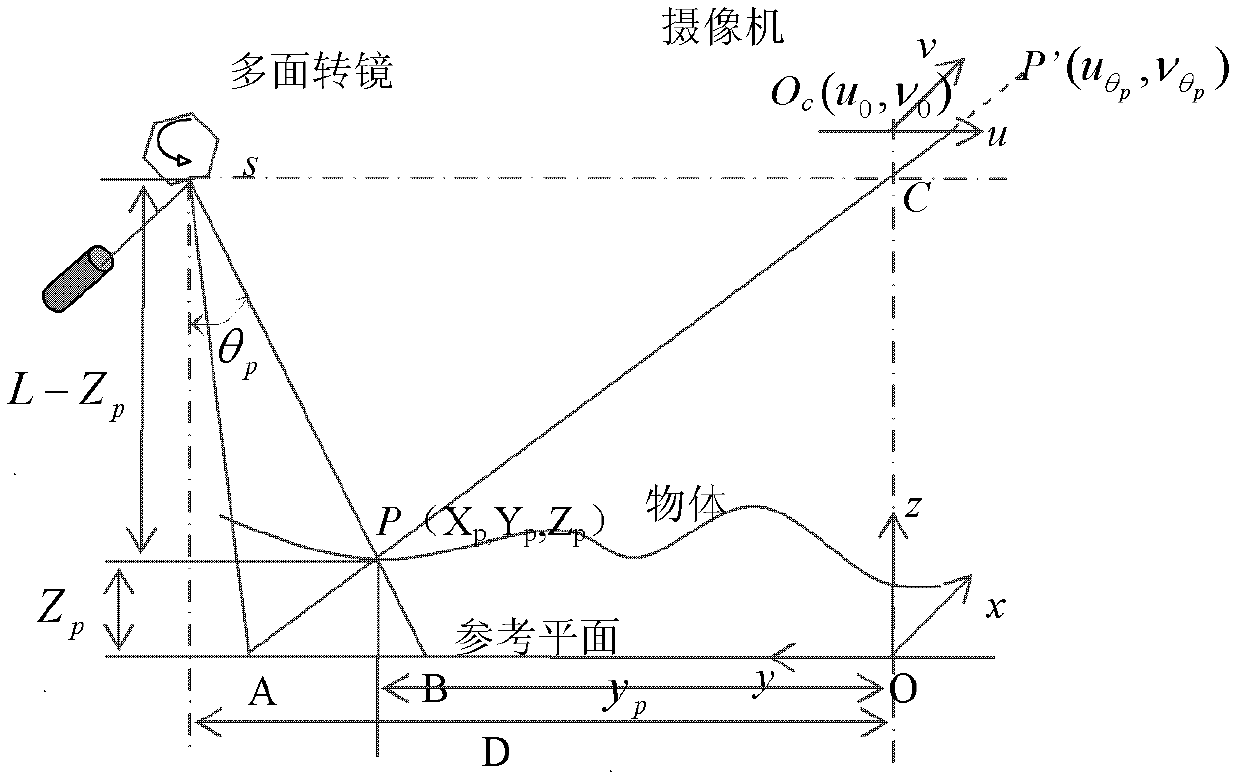
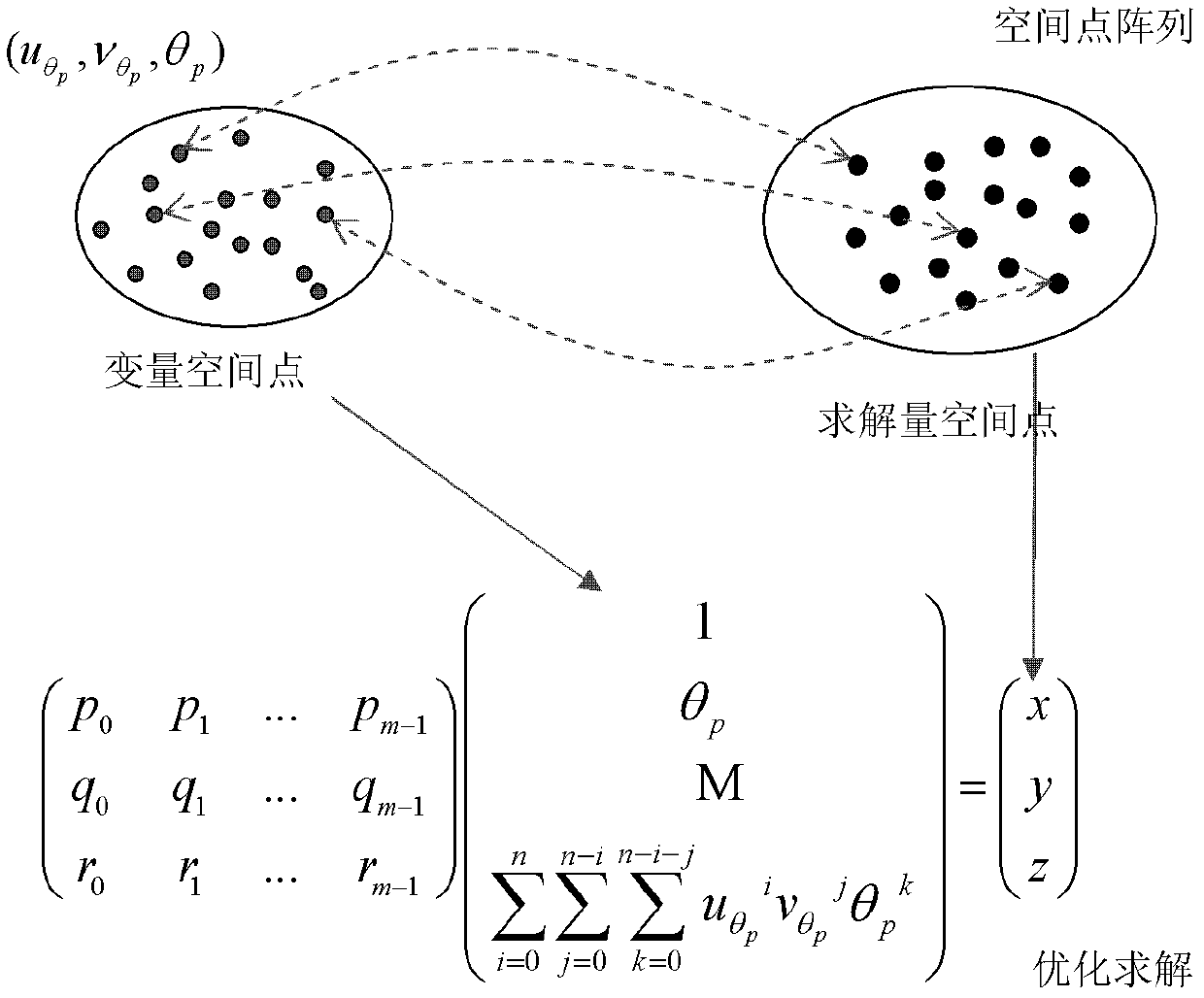
The invention relates to a visual inspection technology. In order to meet the requirements of fast and high-accurate surface three-dimensional (3D) topography online measurement and the detection requirements of a production line on intelligence, fastness, high accuracy and low cost, the invention adopts the technical scheme that: a high-speed scanning and overall imaging 3D measurement method comprises the following steps of: carrying out external modulation on a driving power supply by using a laser so as to control the output of a word line laser; rotating a multifaceted prism under the drive of a high-speed motor, wherein line-structured light outputted by the laser is reflected and projected to the surface of a measured object by the multifaceted prism; and placing a photoelectric detector at a position which is the limit position projected by the line-structured light during the rotating process of the multifaceted prism, carrying out exposure on an area-array CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) camera during the process that the line-structured light scans the whole area, and establishing a measurement model, wherein the 3D coordinate (xp, yp, zp) of the surface feature point of the measured object is obtained according to a formula by using an image coordinate (u[theta]p, v[theta]p) formed by the area-array CCD camera and [theta]p. The high-speed scanning and overall imaging 3D measurement method is mainly applied to the fast and high-accurate surface 3D topography online measurement.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
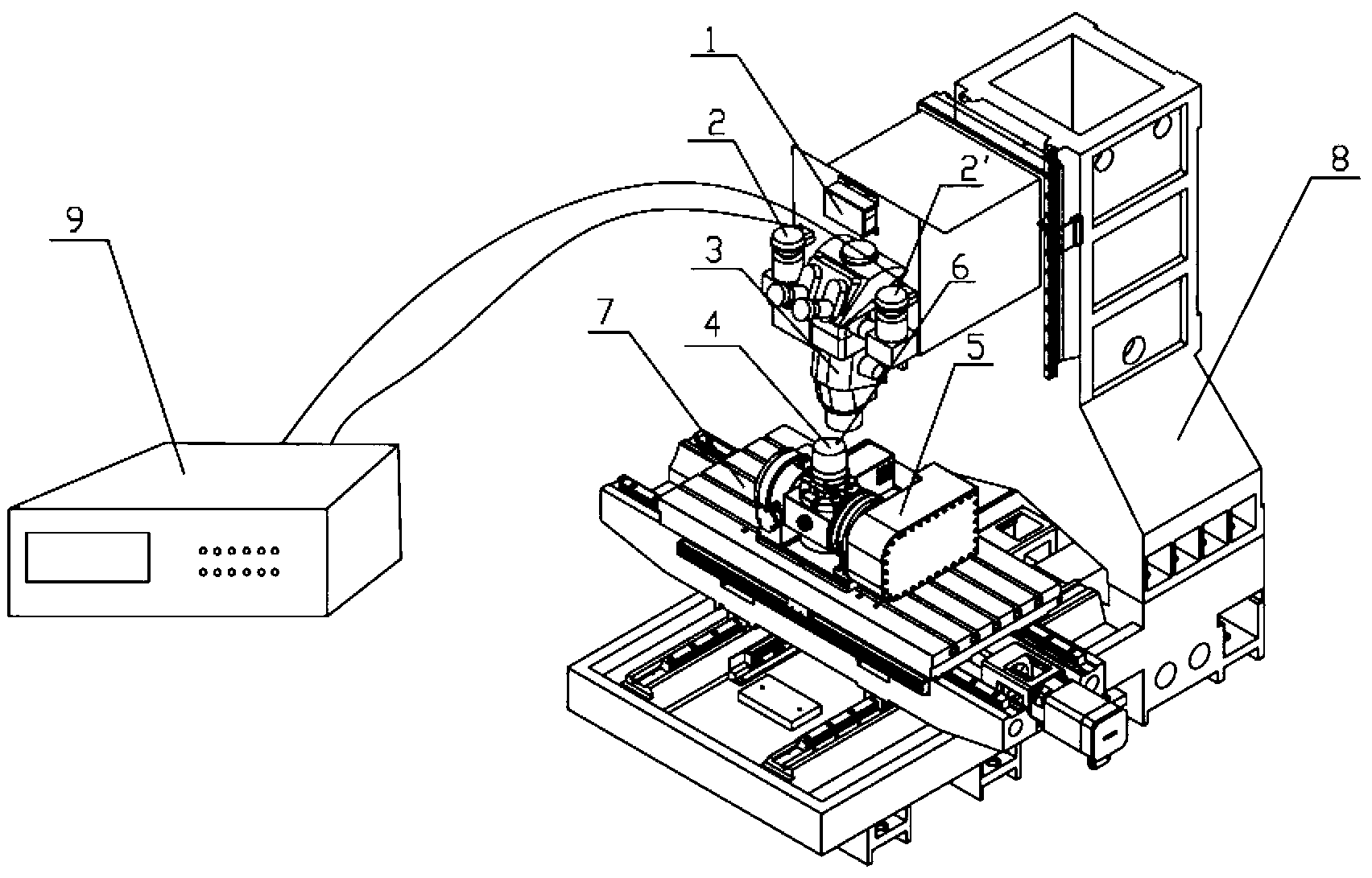
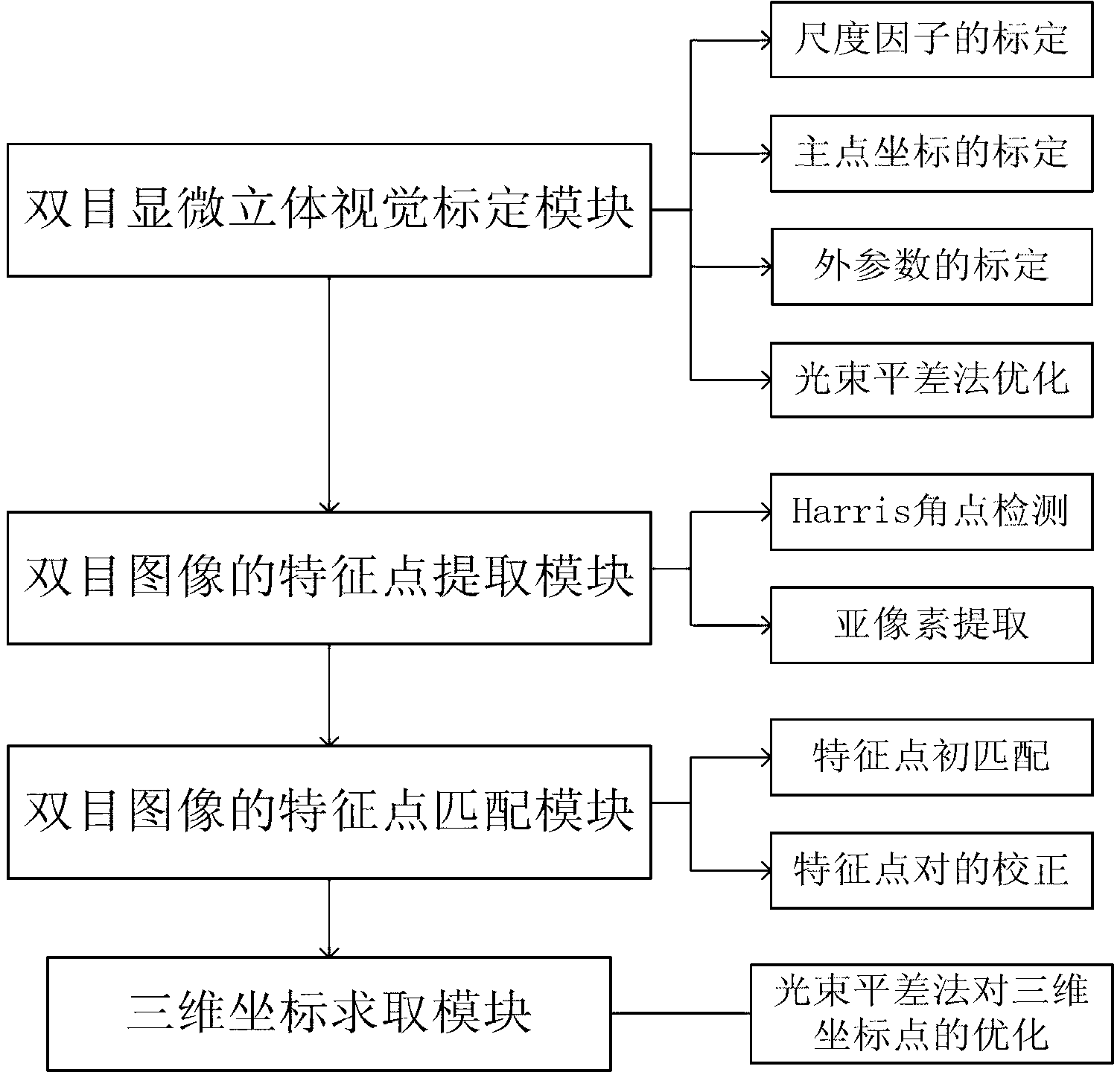
Accurate part positioning method based on binocular microscopy stereo vision
The invention discloses an accurate part positioning method based on binocular microscopy stereo vision, which belongs to the technical field of computer visual measuring and relates to an accurate precision part positioning method based on the binocular microscopy stereo vision. A binocular microscopy stereo vision system is adopted, two CCD (charge coupled device) cameras are adopted to acquire the images of the measured parts, the image information in the to-be-measured area on the measured part is amplified by a stereo microscope, a checkerboard calibrating board is adopted to calibrate the two CCD cameras, and a Harris corner point detecting algorithm and a sub-pixel extracting algorithm are adopted to extract feature points. The extracted feature points are subjected to the primary matching and correcting of matching point pairs, and the feature point image coordinates are inputted to a calibrated system to obtain the space actual coordinates of the feature points. The accurate part positioning method based on the binocular microscopy stereo vision solves the measuring difficult problems generated by the small size of the to-be-measured area, high positioning demand, non-contact and the like. The accurate positioning of the precision part is well finished by adopting the non-contact measuring method of the binocular microscopy stereo vision.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
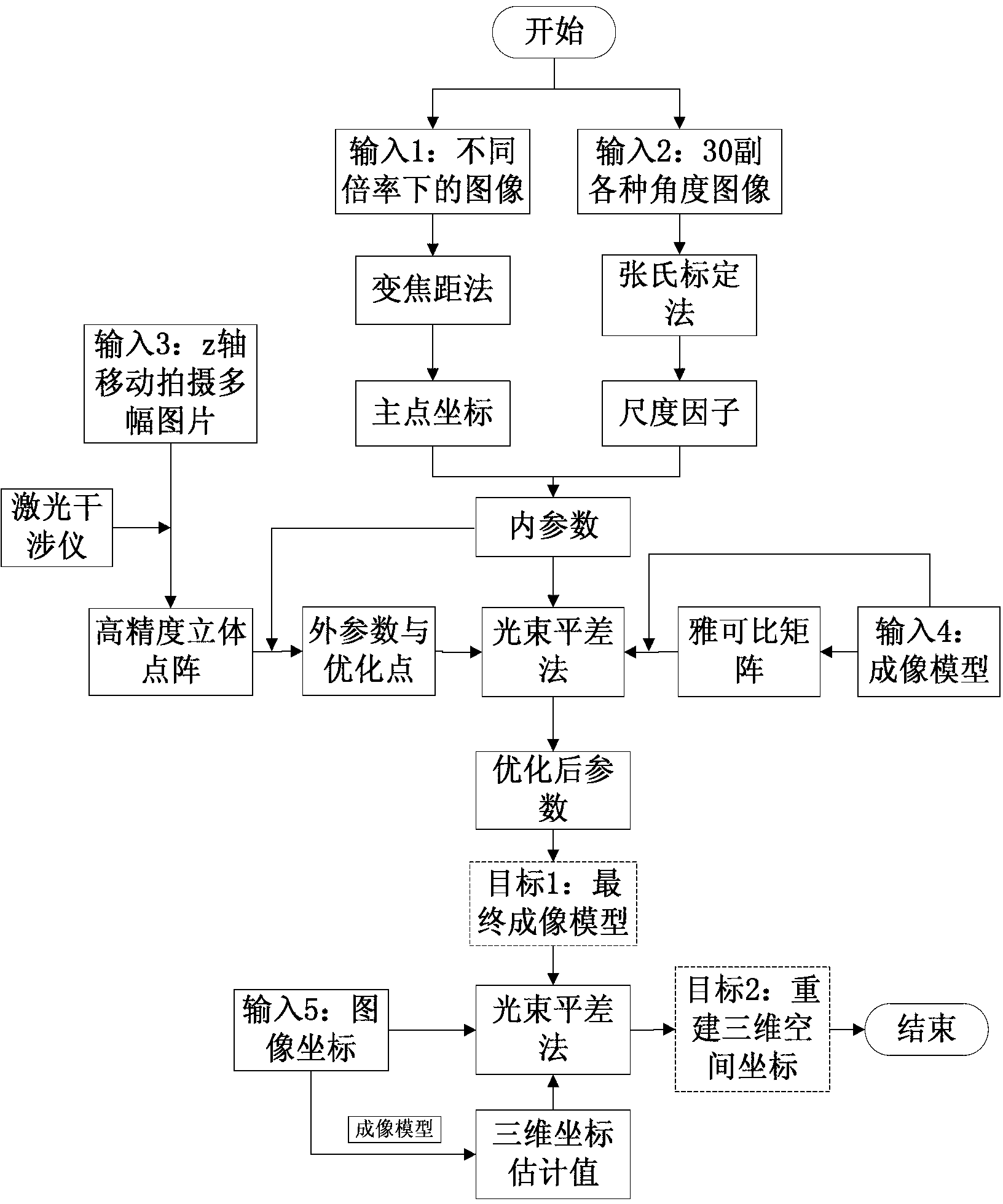
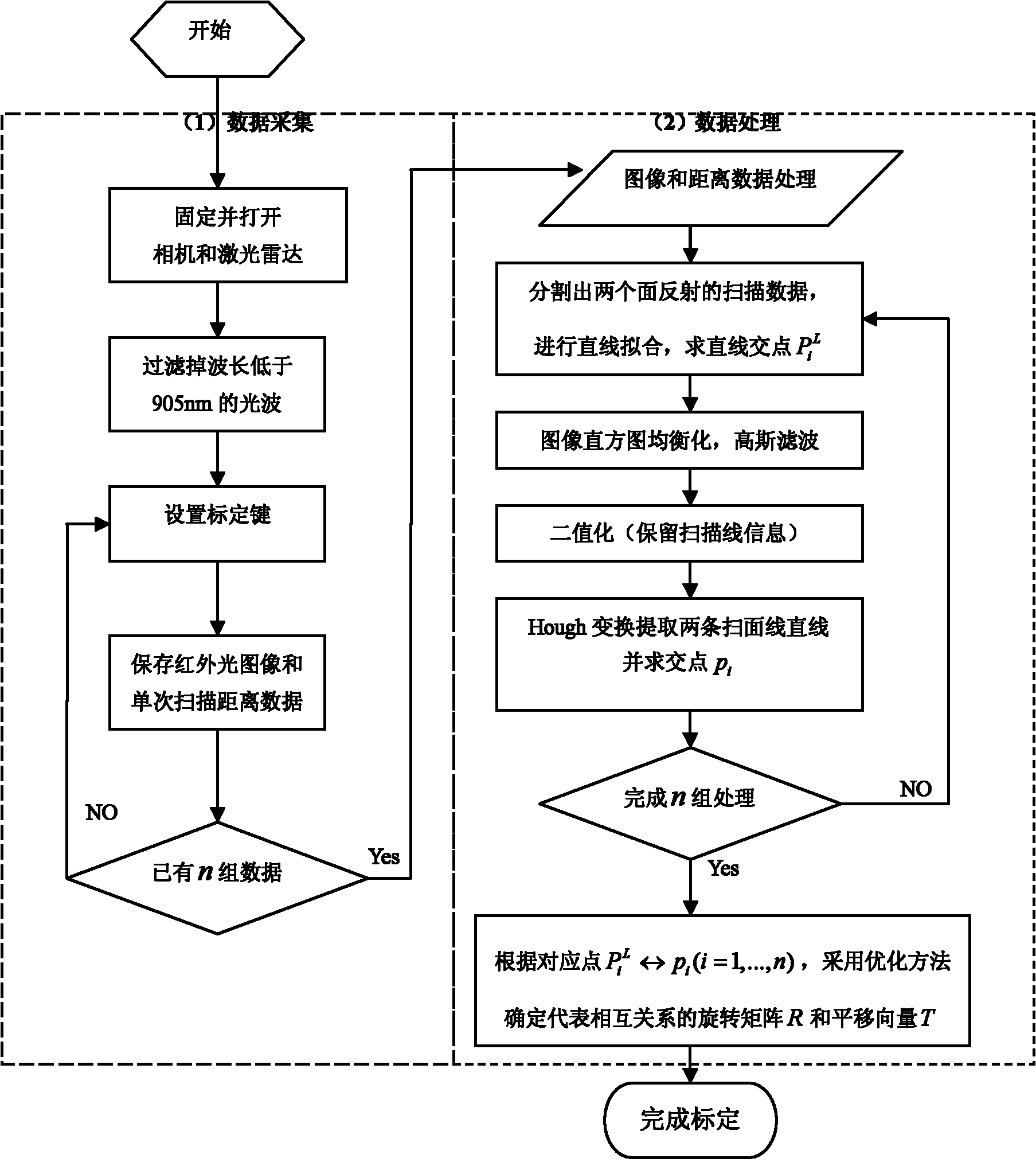
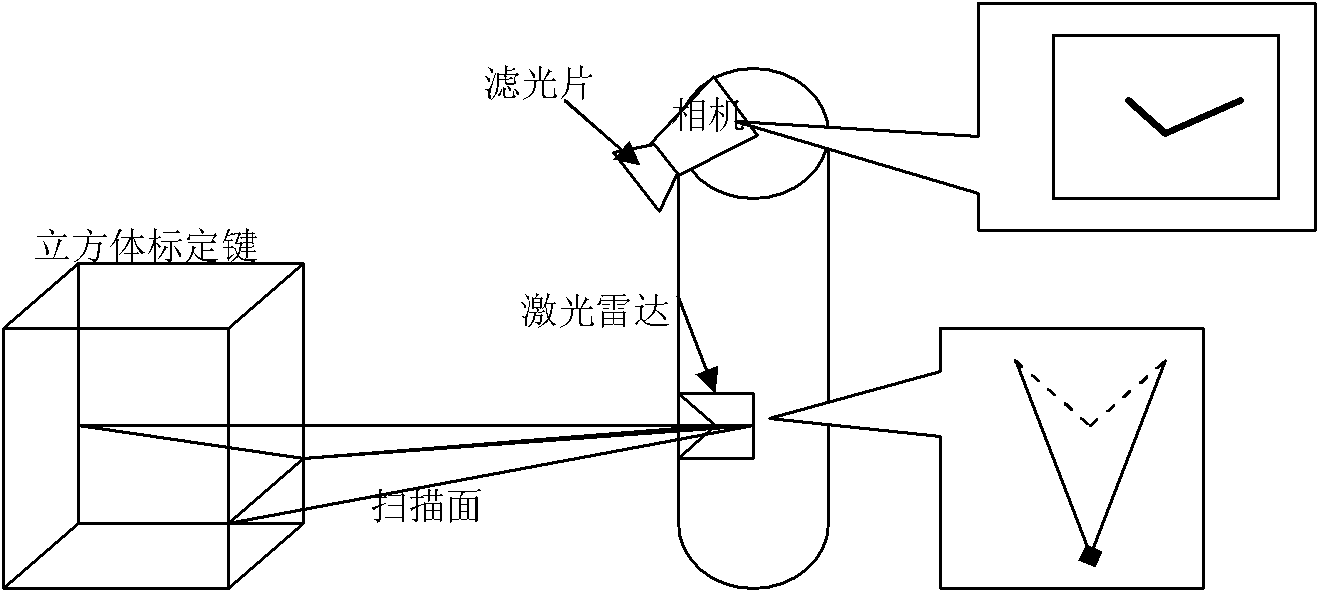
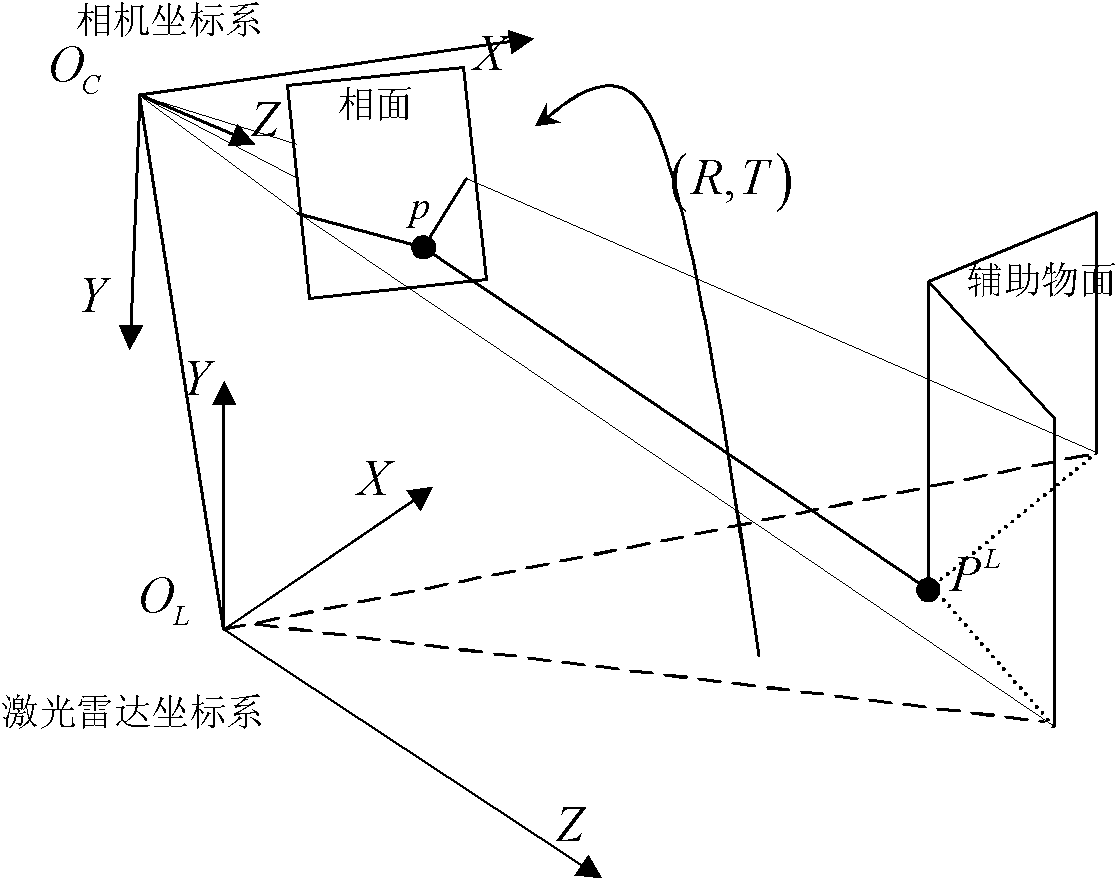
Calibration method of correlation between single line laser radar and CCD (Charge Coupled Device) camera
InactiveCN101882313AEasy to makeEasy to buyImage analysisElectromagnetic wave reradiationLaser scanningIntersection of a polyhedron with a line
The invention discloses a calibration method of correlation between a single line laser radar and a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) camera, which is based on the condition that the CCD camera can carry out weak imaging on an infrared light source used by the single line laser radar. The calibration method comprises the steps of: firstly, extracting a virtual control point in a scanning plane under the assistance of a cubic calibration key; and then filtering visible light by using an infrared filter to image infrared light only, carrying out enhancement, binarization treatment and Hough transformation on an infrared image with scanning line information, and extracting two laser scanning lines, wherein the intersection point of the two scanning lines is the image coordinate of the virtual control point in the image. After acquiring multiple groups of corresponding points through the steps, a correlation parameter between the laser radar and the camera can be solved by adopting an optimization method for minimizing a reprojection error. Because the invention acquires the information of the corresponding points directly, the calibration process becomes simpler and the precision is greatly improved with a calibrated angle error smaller than 0.3 degree and a position error smaller than 0.5cm.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Laser ablation apparatus and method
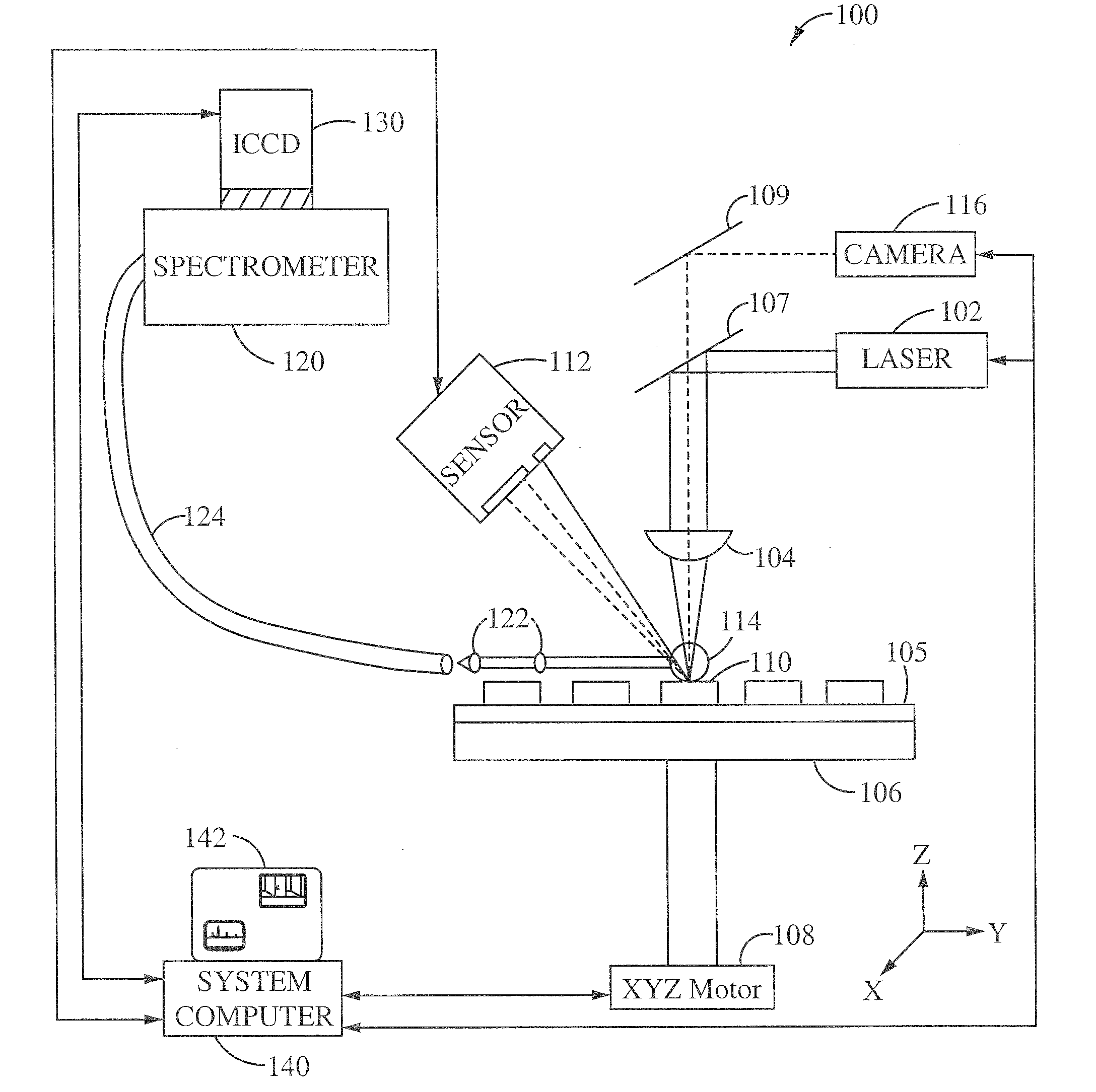
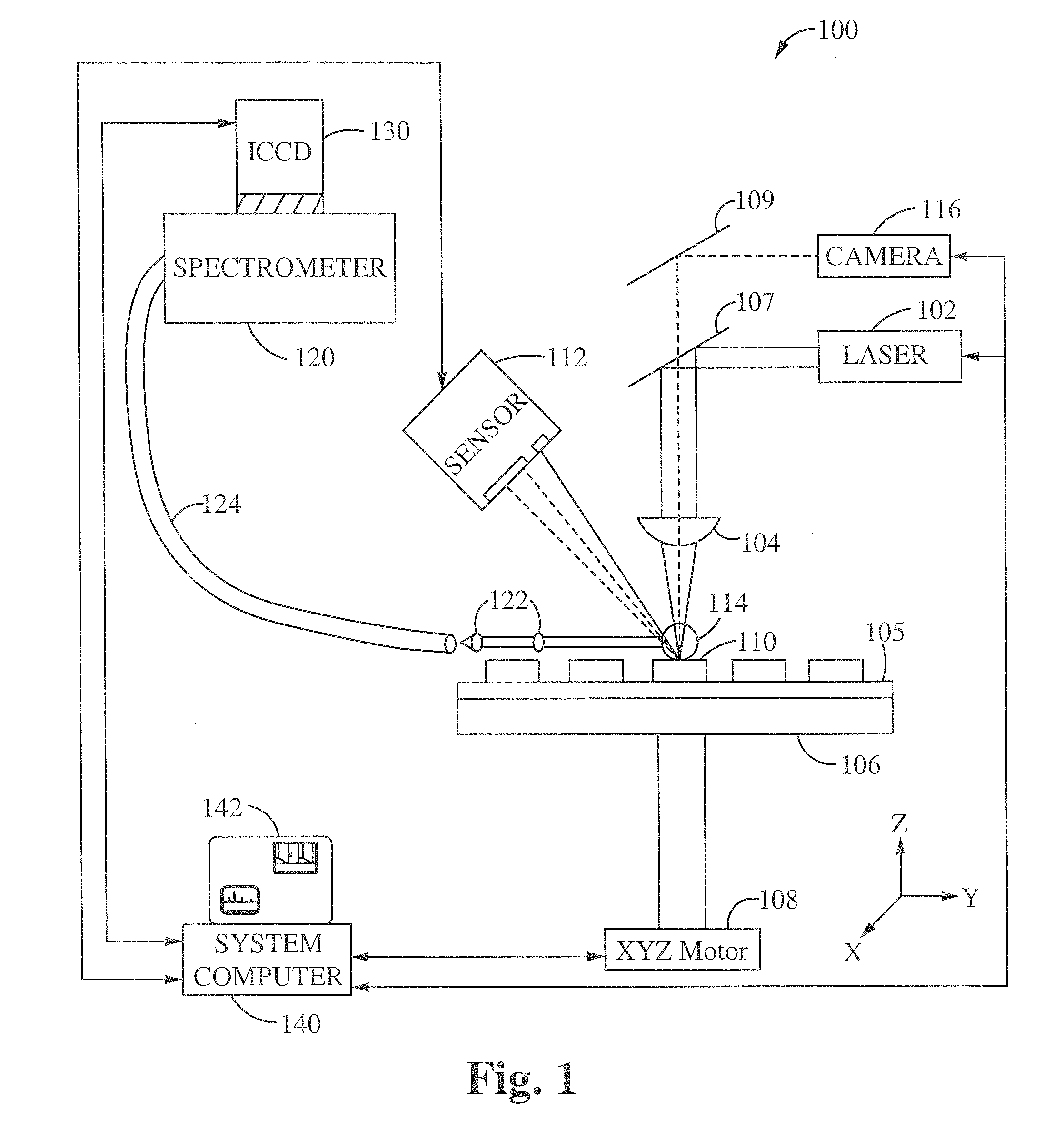
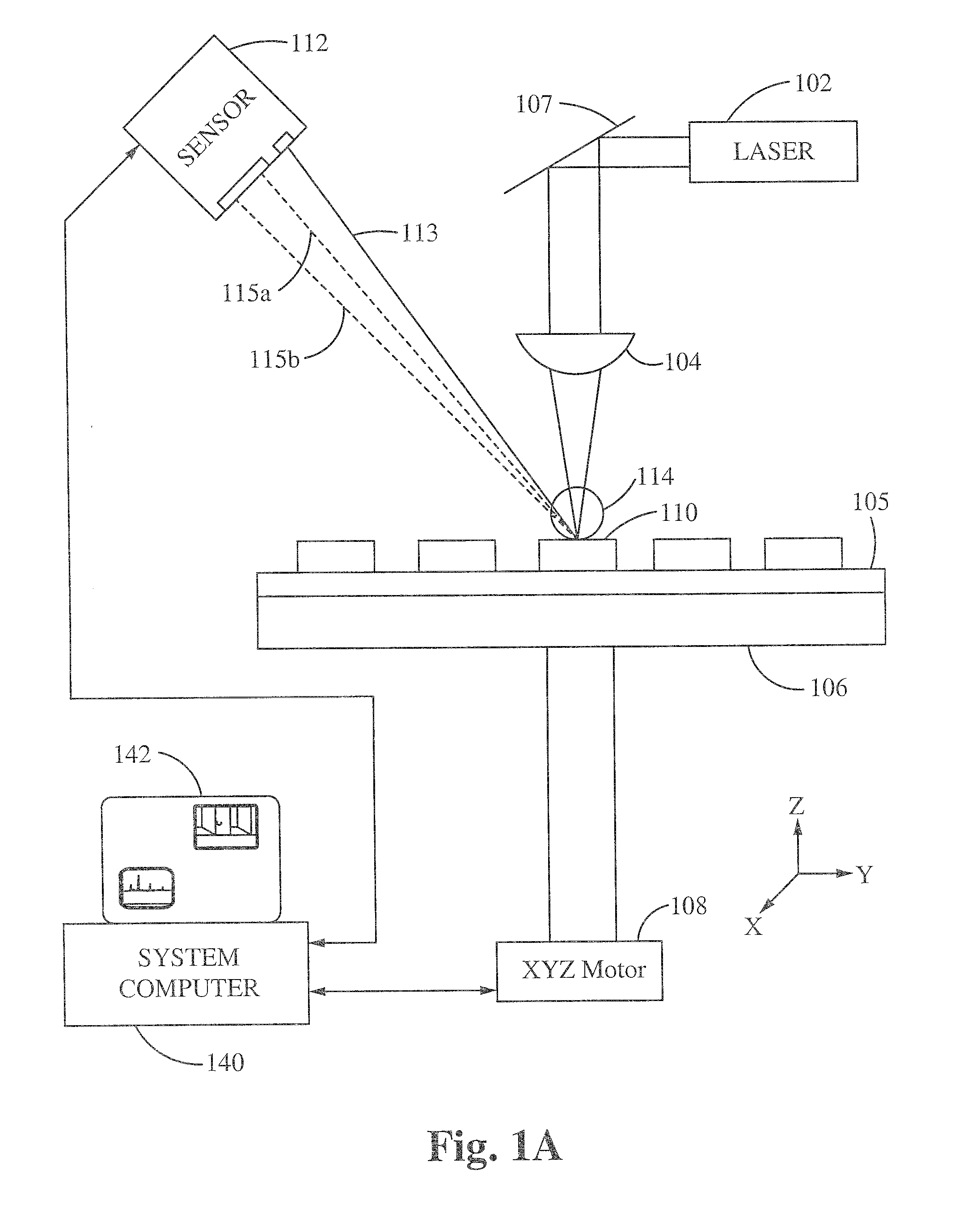
Provided is a laser ablation spectroscopy apparatus and method. A pulse laser is focused on the sample site to generate a plasma plume during a laser ablation process. The plasma plume is detected with a spectrometer and an intensified charge coupled device. A sample of material is coupled to a stage movable in the x, y and z directions using an array of x-y-z motors. A change in the height of the sample is detected using a triangulation sensor. The apparatus includes a system computer for synchronizing the movement of the stage in the x, y and z direction during the laser ablation process. The method includes a protocol of generating one or more laser ablations per sample site. The spectral data of the total number of laser ablations for each sample site are averaged together. The protocol includes laser ablating additional sample sites and averaging the spectral data of the total number of sample sites.
Owner:APPLIED SPECTRA
Low-resistivity photon-transparent window attached to photo-sensitive silicon detector
InactiveUS6025585ALow resistivityHigh resistivitySolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansCMOS sensorX-ray
The invention comprises a combination of a low resistivity, or electrically conducting, silicon layer that is transparent to long or short wavelength photons and is attached to the backside of a photon-sensitive layer of silicon, such as a silicon wafer or chip. The window is applied to photon sensitive silicon devices such as photodiodes, charge-coupled devices, active pixel sensors, low-energy x-ray sensors and other radiation detectors. The silicon window is applied to the back side of a photosensitive silicon wafer or chip so that photons can illuminate the device from the backside without interference from the circuit printed on the frontside. A voltage sufficient to fully deplete the high-resistivity photosensitive silicon volume of charge carriers is applied between the low-resistivity back window and the front, patterned, side of the device. This allows photon-induced charge created at the backside to reach the front side of the device and to be processed by any circuitry attached to the front side. Using the inventive combination, the photon sensitive silicon layer does not need to be thinned beyond standard fabrication methods in order to achieve full charge-depletion in the silicon volume. In one embodiment, the inventive backside window is applied to high resistivity silicon to allow backside illumination while maintaining charge isolation in CCD pixels.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Semiconductor package and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20070249095A1Reduce manufacturing costMinimized in sizeTelevision system detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCMOSSemiconductor package
Disclosed herein are a semiconductor package used in digital optical instruments and a method of manufacturing the same. The semiconductor package comprises a wafer made of a silicon material and having pad electrodes formed at one side surface thereof, an IR filter attached on the pad electrodes of the wafer by means of a bonding agent, terminals electrically connected to the pad electrodes, respectively, in via holes formed at the other side surface of the wafer, which is opposite to the pad electrodes, and bump electrodes, each of which is connected to one side of each of the terminals. The present invention is capable of minimizing the size of a semiconductor package having an image sensor, which is referred to as a complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) or a charge coupled device (CCD), through the application of a wafer level package technology, thereby reducing the manufacturing costs of the semiconductor package and accomplishing production on a large scale.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
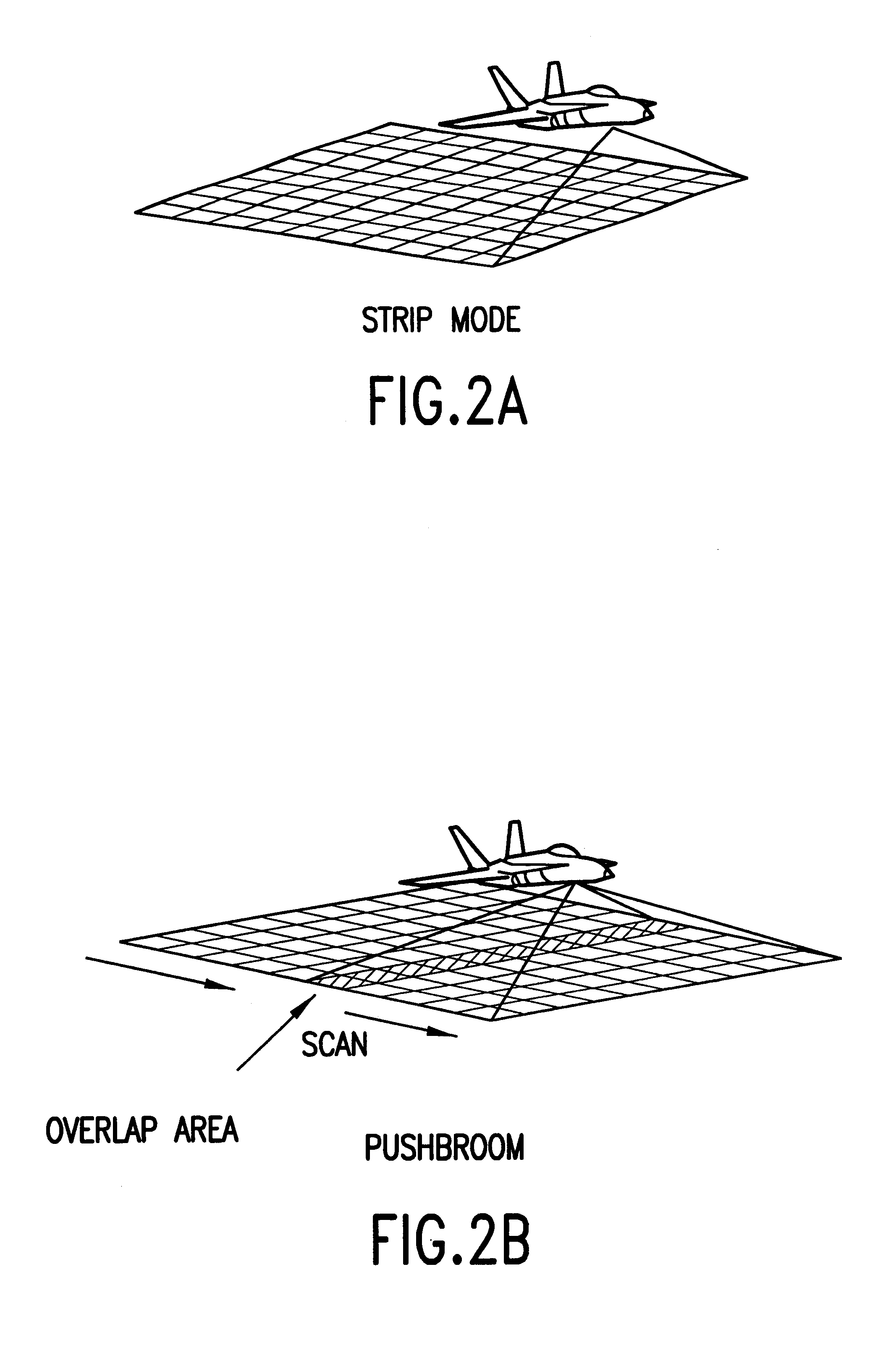
System for digitally capturing and recording panoramic movies
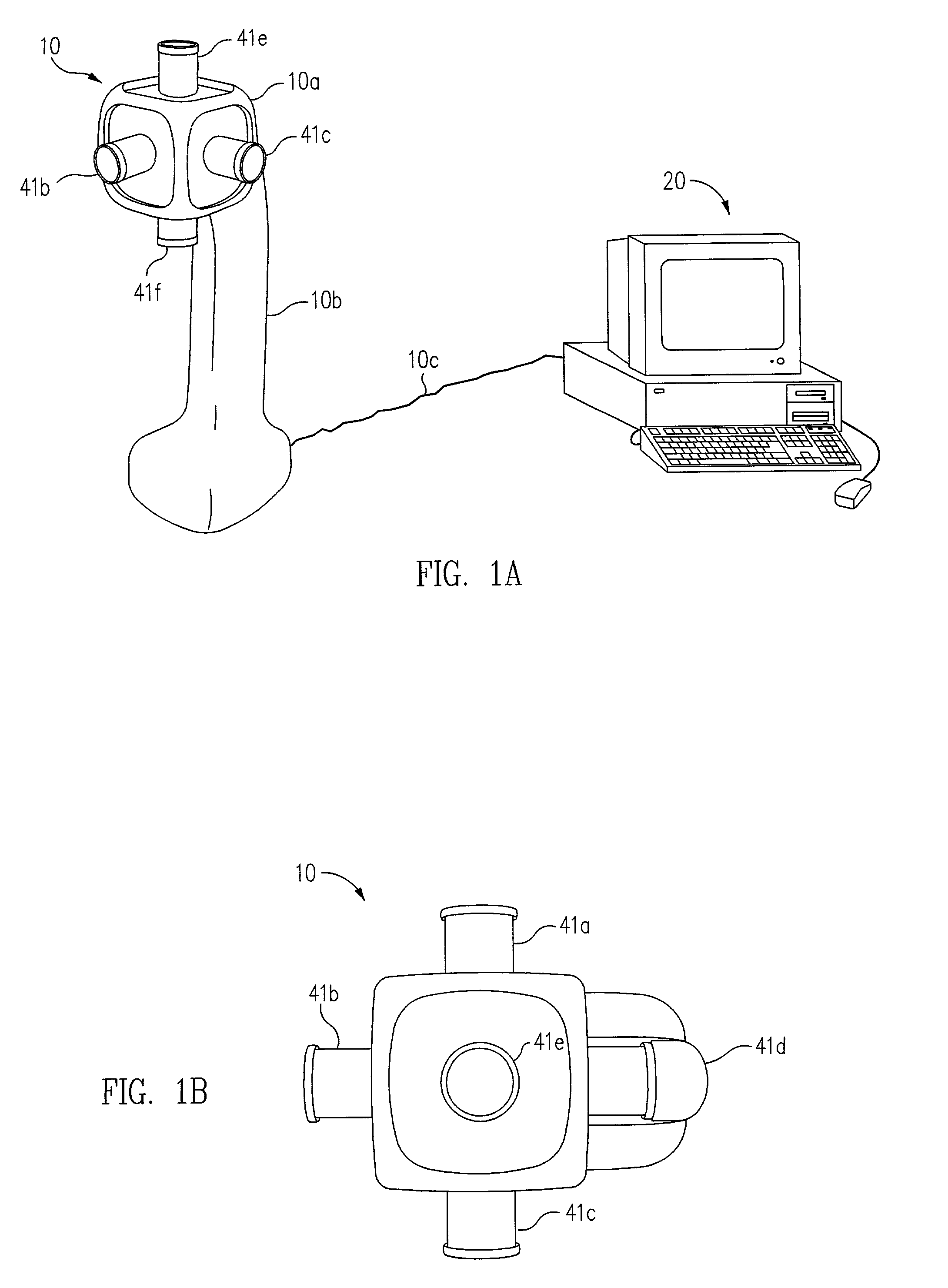
InactiveUS20020046218A1Flexible and convenient controlEffective apertureTelevision system detailsColor television signals processingCamera lensData compression
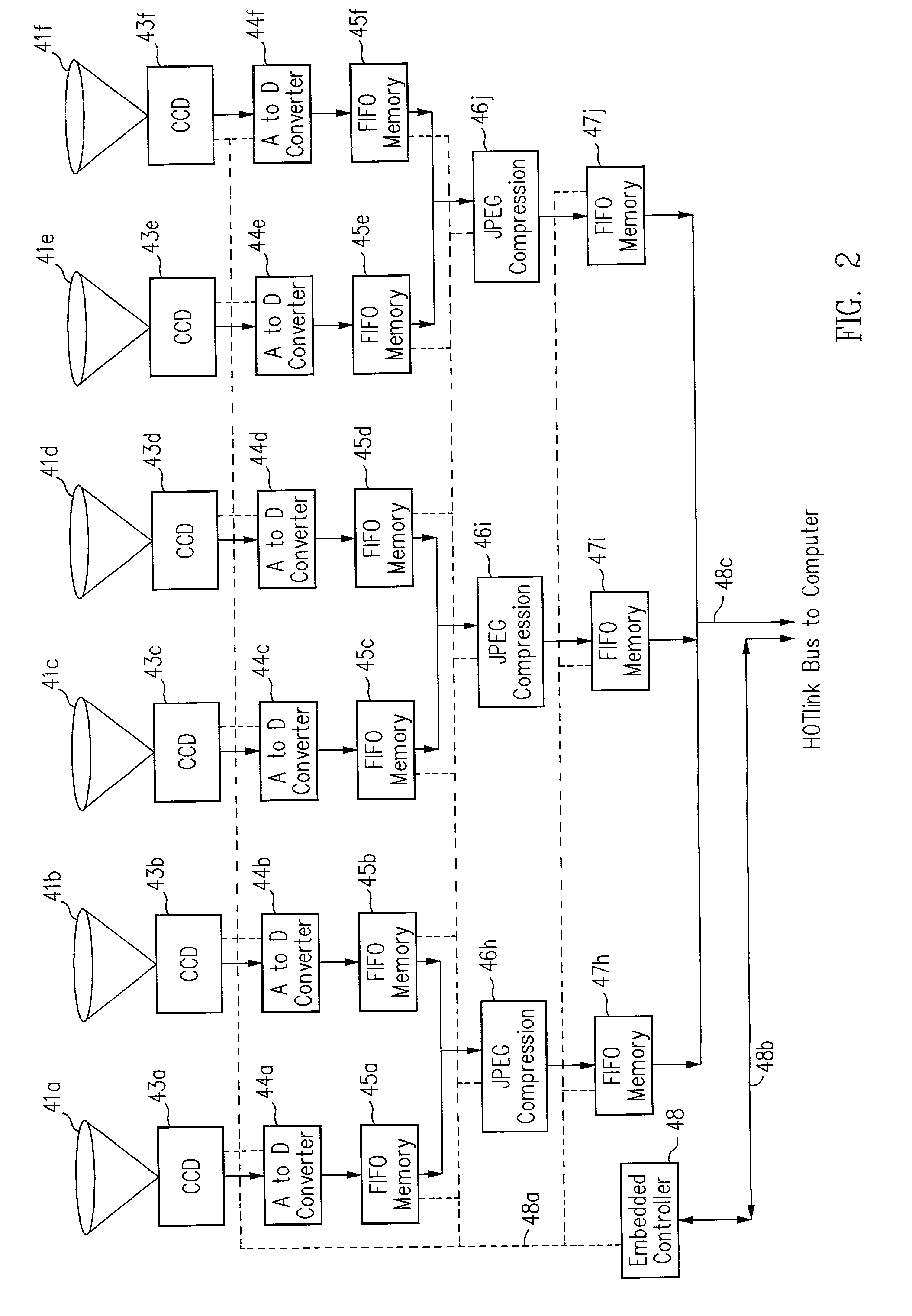
The present invention provides a very flexible, digital system for capturing and storing panoramic images using progressive scan (that is, non interlaced) technology. The system includes a digital image input device and an associated control computer. Since the image capture device is digital it can be easily and flexibly controlled by software in the control computer. The image input device has six lenses positioned on the six faces of a cube. While the image input system can have other lens configurations, the use of six lenses in a cubic configuration is optimal for a system that is used to capture a spherical panorama. The six lenses simultaneously focuses different images on six CCDs (Charge Coupled Devices). The image input device also includes an embedded controller, and data compression circuitry. The embedded controller controls the exposure time of the CCDs (i.e. the effective aperture and effective shutter speed) and reads image data from the CCDs. The image data read from the CCDs is compressed, multiplexed, and sent to the control computer. The control computer stores the images in frames, each of which have one image from each of the six lenses. Each frame includes six images that were simultaneously recorded and any associated information, such as audio tracks, textual information, or environmental information such as GPS (Global Position System) data or artificial horizon data. The control computer includes a user interface which allows a user to specify control information such as frame rate, compression ratio, gain, etc. The control computer sends control information to the embedded controller which in turn controls the CCDs and the compression circuitry. The images can be sent from the control computer to a real time viewer so that a user can determine if the correct images are being captured. The images stored at the control computer are later seamed into panoramas and made into panoramic movies.
Owner:GILBERT SCOTT +3
DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) sequencer
ActiveCN102703312AImprove sequencing efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatments3-deoxyriboseBiochemical engineering
The invention discloses a DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) sequencer which comprises a supporting table, a plurality of vibration dampers, a vibration damping plate, a reaction bin assembly, a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) camera, a two-dimensional regulation supporting device and a medicament supply assembly, wherein the vibration damping plate is connected with the supporting table by a plurality of vibration dampers; the reaction bin assembly is fixedly arranged on the vibration damping plate and is used for performing the DNA sequencing reaction; the CCD camera is used for acquiring an optical signal; the two-dimensional regulation supporting device is used for supporting the CCD camera; and the medicament supply assembly is arranged on the supporting table and is used for providing reagents and buffer solution for the reaction bin assembly. According to the DNA sequencer disclosed by the invention, by the arrangement of a plurality of reaction bins and the matching of the two-dimensional regulation supporting device capable of carrying out two-dimensional regulation and the medicament supply assembly capable of supplying the reagents for a plurality of reaction bins, the aim of simultaneously performing a plurality of reactions is fulfilled, a plurality of samples can be simultaneously sequenced and the DNA sequencing efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION +1
System and method for managing difficult airways
ActiveUS20070129603A1Easy to installEasy to replaceRespiratorsBronchoscopesVideo transmissionMedicine
A system and method for endotracheal intubation of airways are disclosed. A malleable stylet having a distal end and a proximal end, a charged coupled device (CCD) at the distal end and a transmitter, at or near the proximal end or connected to the proximal end of the stylet with connectors, transmits video to a visualization device comprising a receiver means, a display means, and a display support adapted to be worn on an operator in a position so that the operator can view the display with one eye while simultaneously viewing the airway directly. The display support is typically worn on the head of a physician. A second display can be worn by a student or observer. In some instances, the transmitter means and receiver means are wireless.
Owner:THE COOPER HEALTH SYST
Novel optical architectures for microvolume laser-scanning cytometers
InactiveUS20050057749A1Reduce power densityMinimizing limitationOptical radiation measurementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsLaser scanningSpectroscopy
Methods and instrumentation for performing charge coupled device (CCD)-based confocal spectroscopy with a laser spot array are provided. The methods and instruments of the invention are useful in any spectroscopic application, including, but not limited to, microscopy and microvolume laser scanning cytometry (MLSC).
Owner:PPD BIOMARKER DISCOVERY SCI
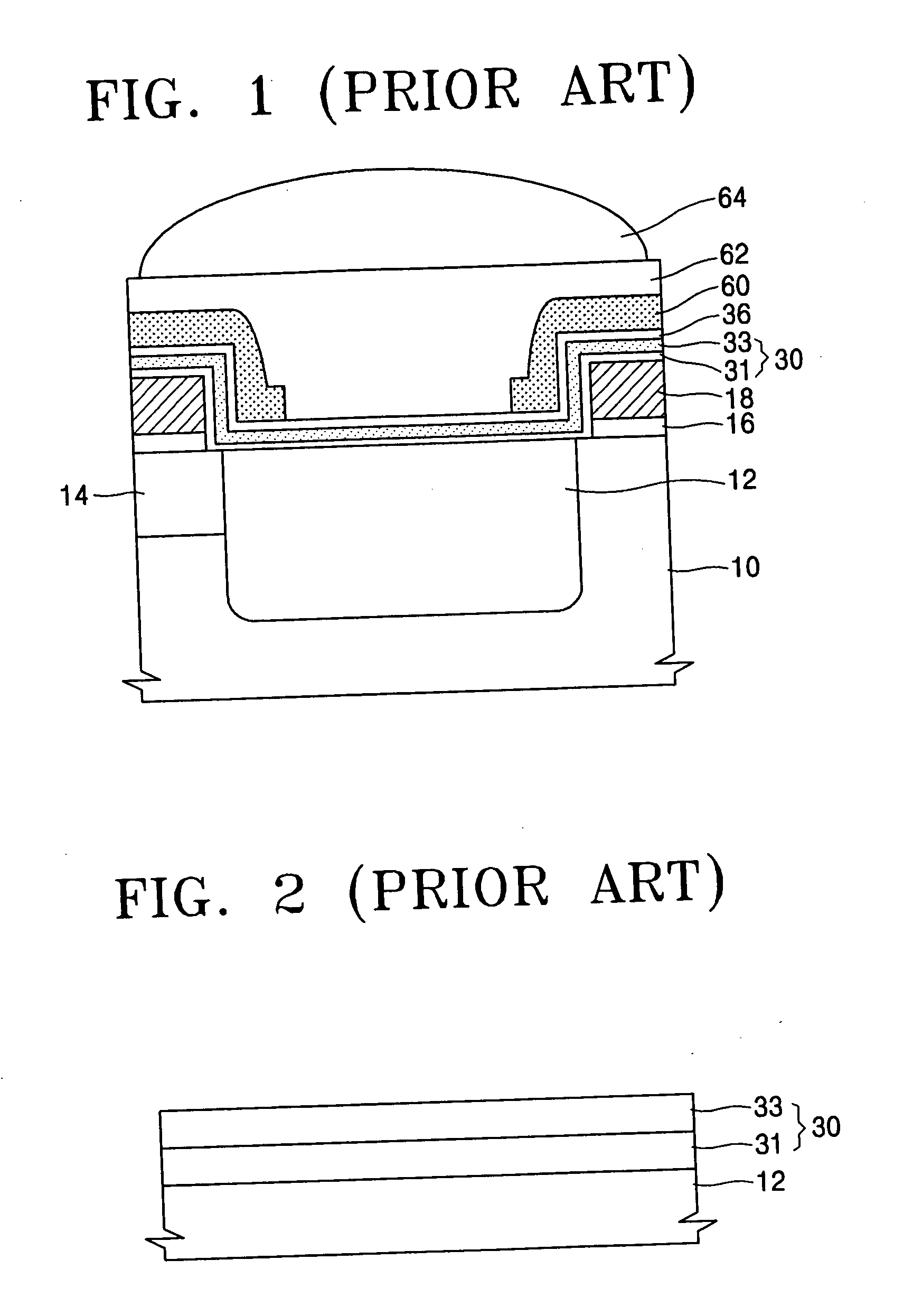
Image sensor and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20050287479A1Improve efficiencyHigh refractive indexSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesRefractive indexEngineering
In a solid state imaging device, and a method of manufacture thereof, the efficiency of the transfer of available photons to the photo-receiving elements is increased beyond that which is currently available. Enhanced anti-reflection layer configurations, and methods of manufacture thereof, are provided that allow for such increased efficiency. They are applicable to contemporary imaging devices, such as charge-coupled devices (CCDs) and CMOS image sensors (CISs). In one embodiment, a photosensitive device is formed in a semiconductor substrate. The photosensitive device includes a photosensitive region. An anti-reflection layer comprising silicon oxynitride is formed on the photosensitive region. The silicon oxynitride layer is heat treated to increase a refractive index of the silicon oxynitride layer, and to thereby decrease reflectivity of incident light at the junction of the photosensitive region.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com