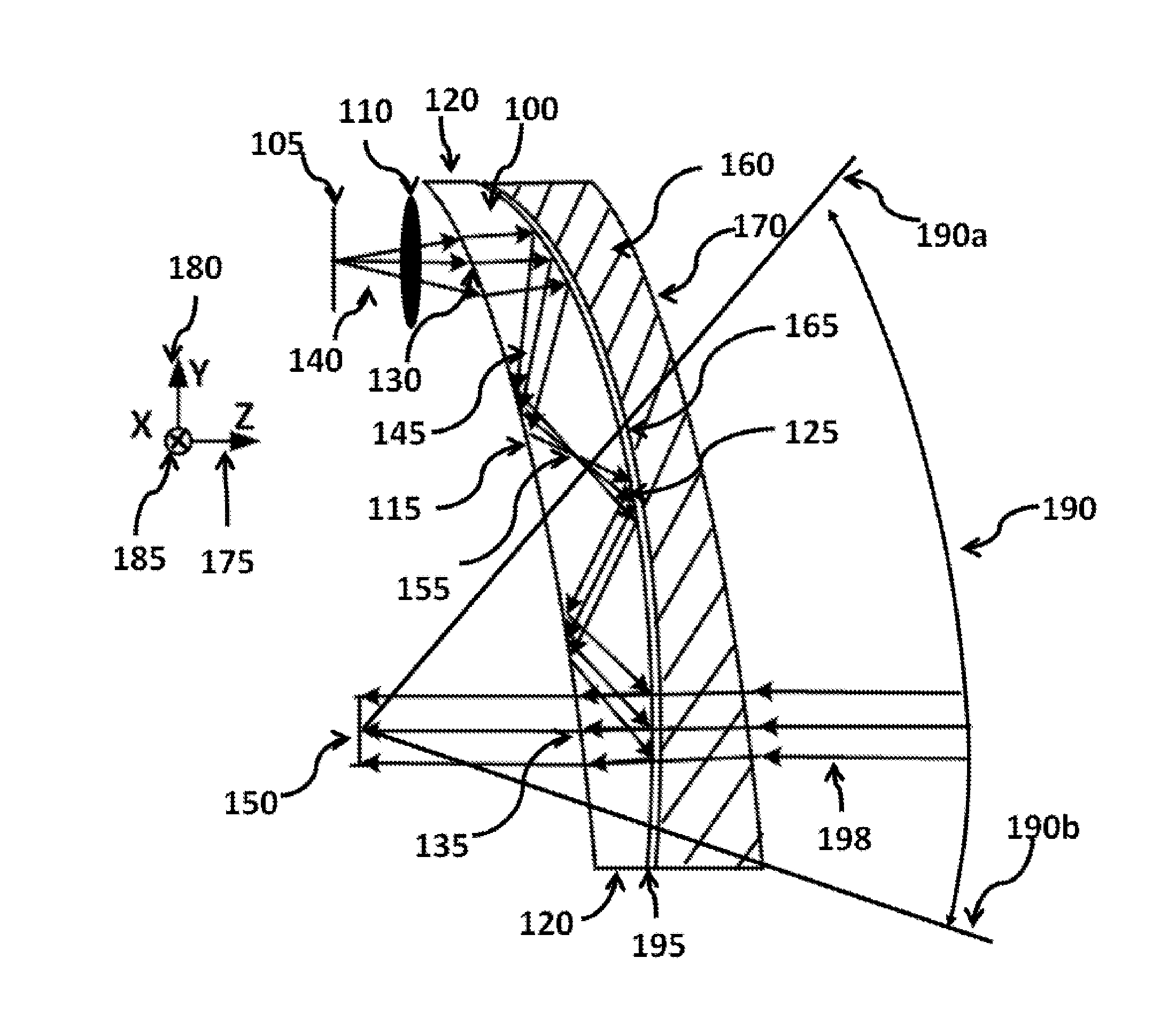
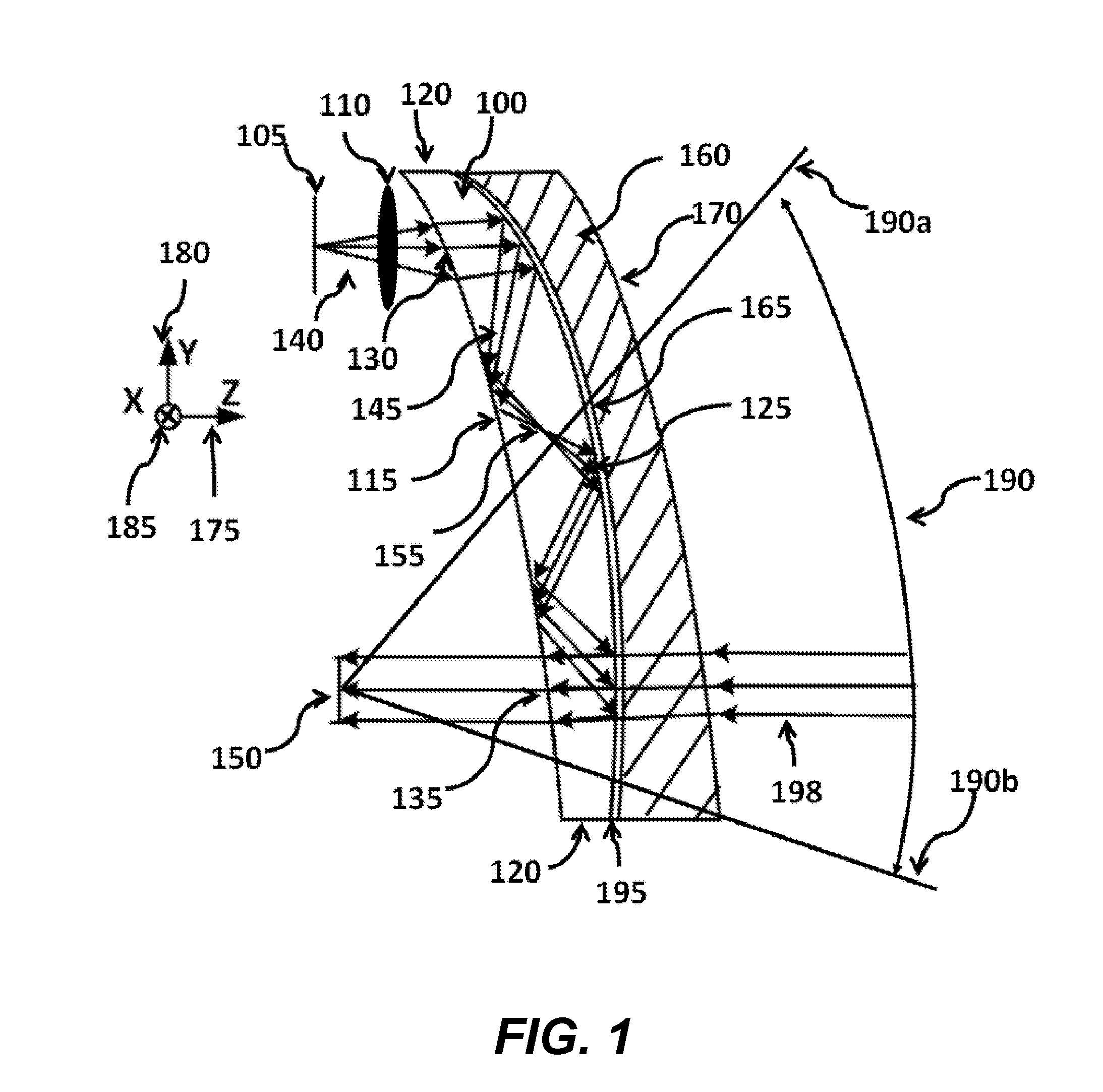
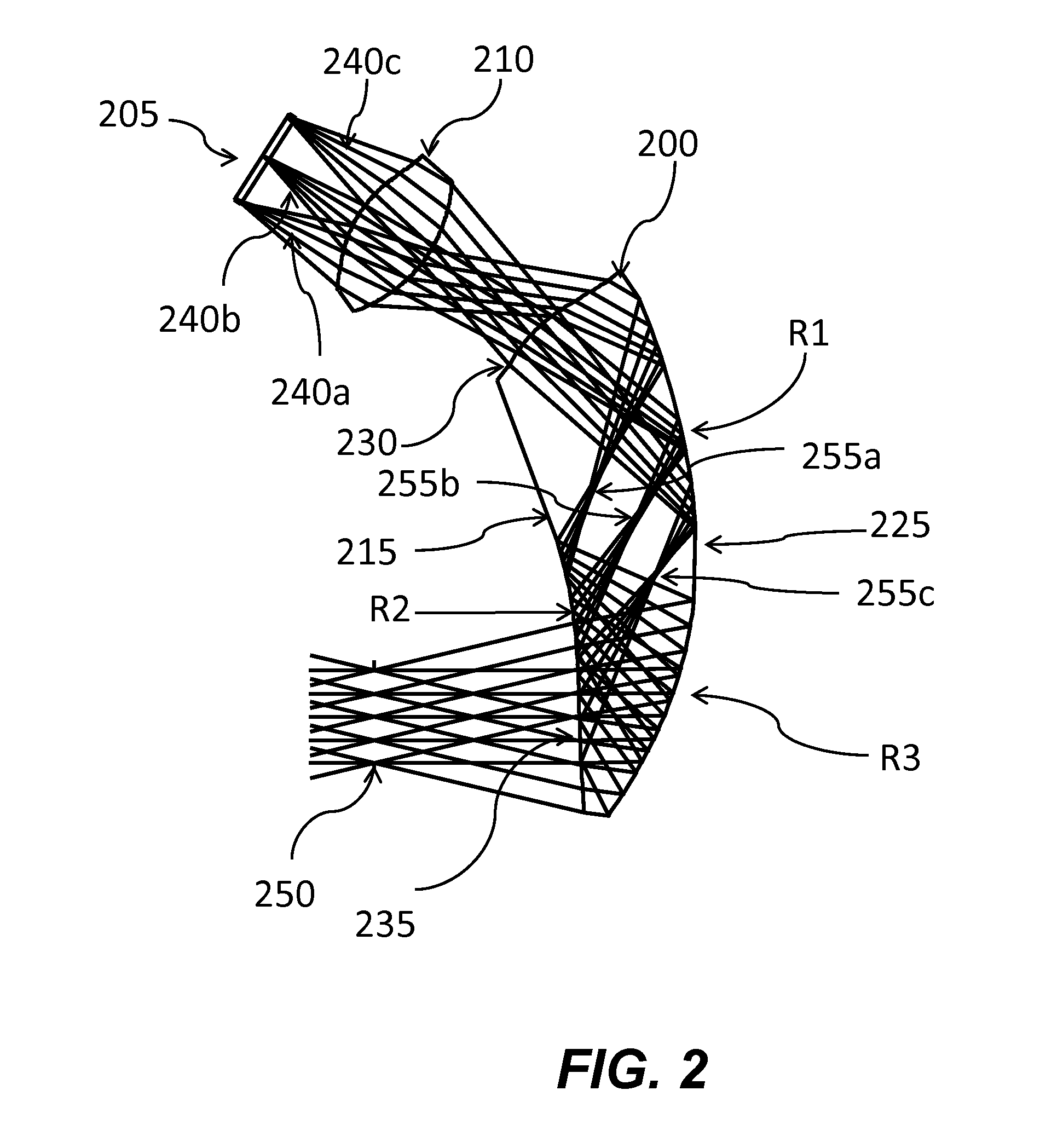
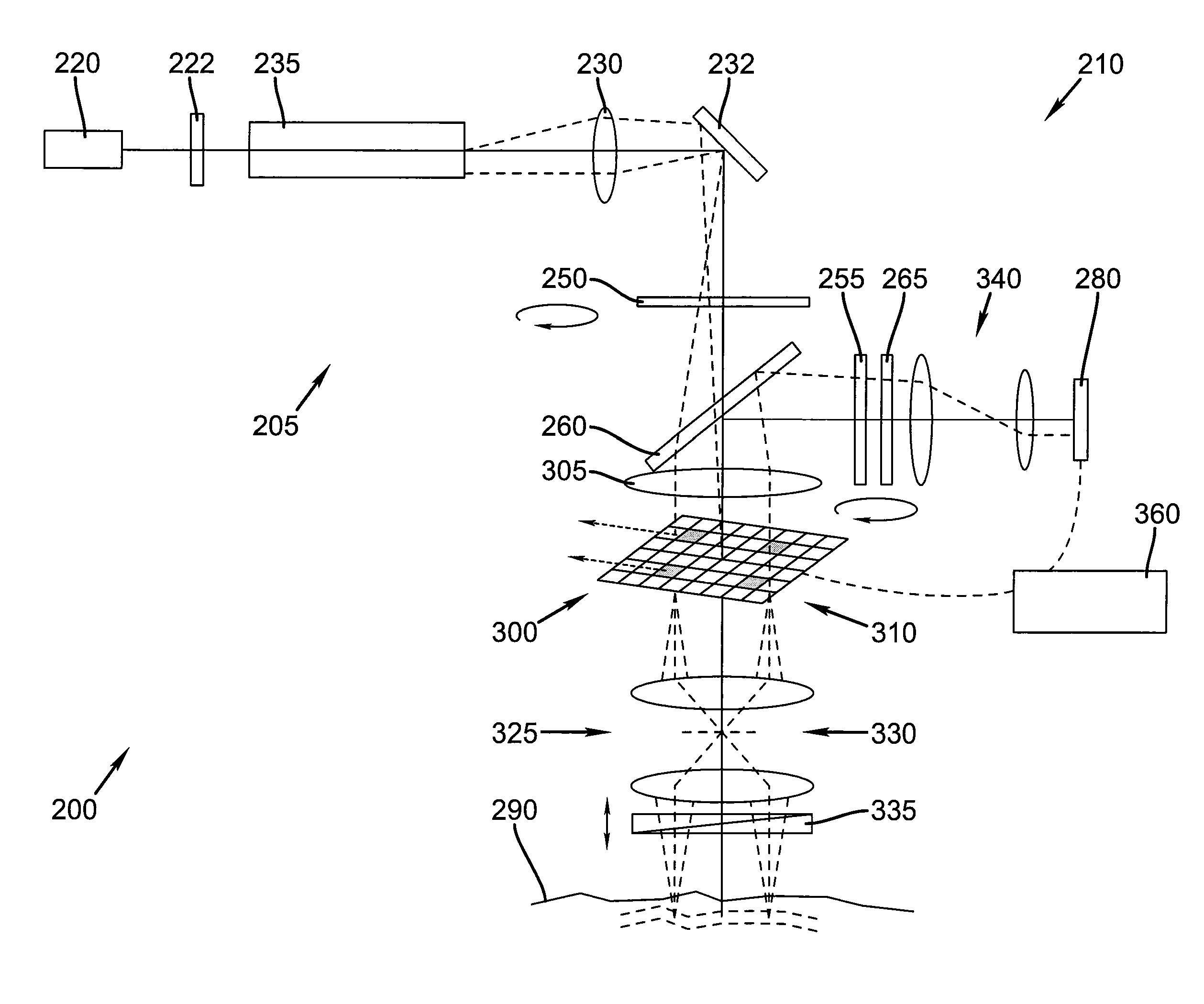
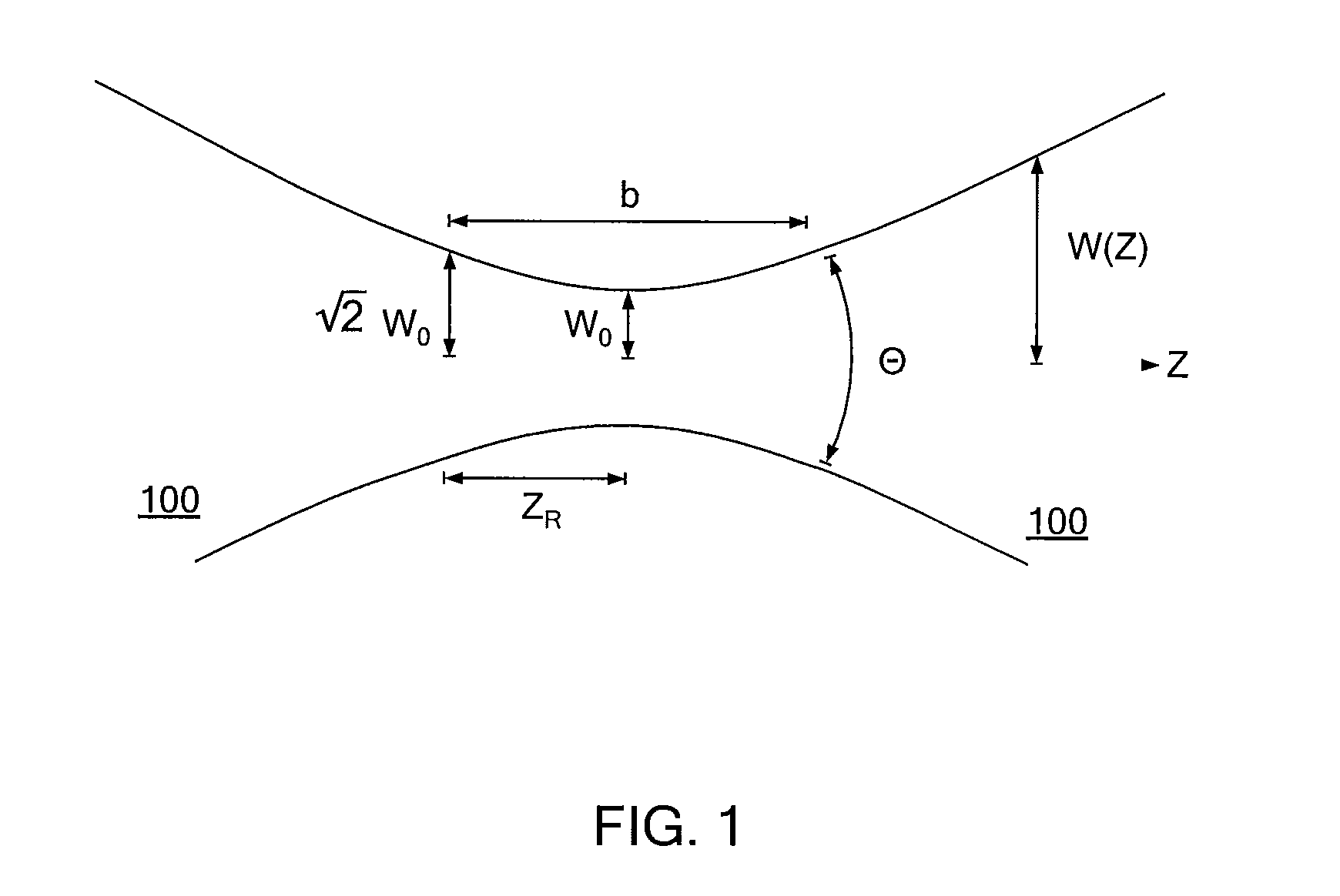
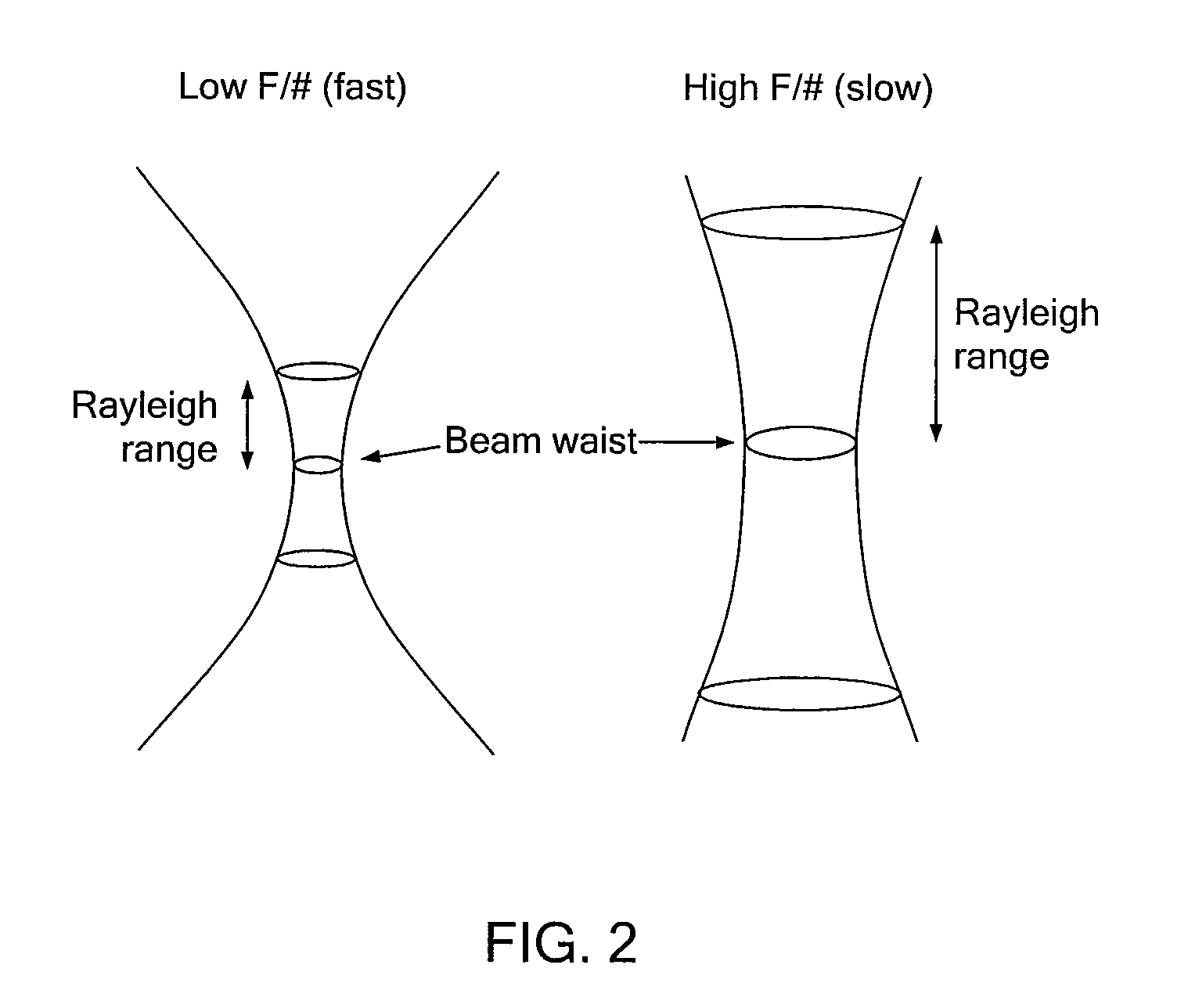
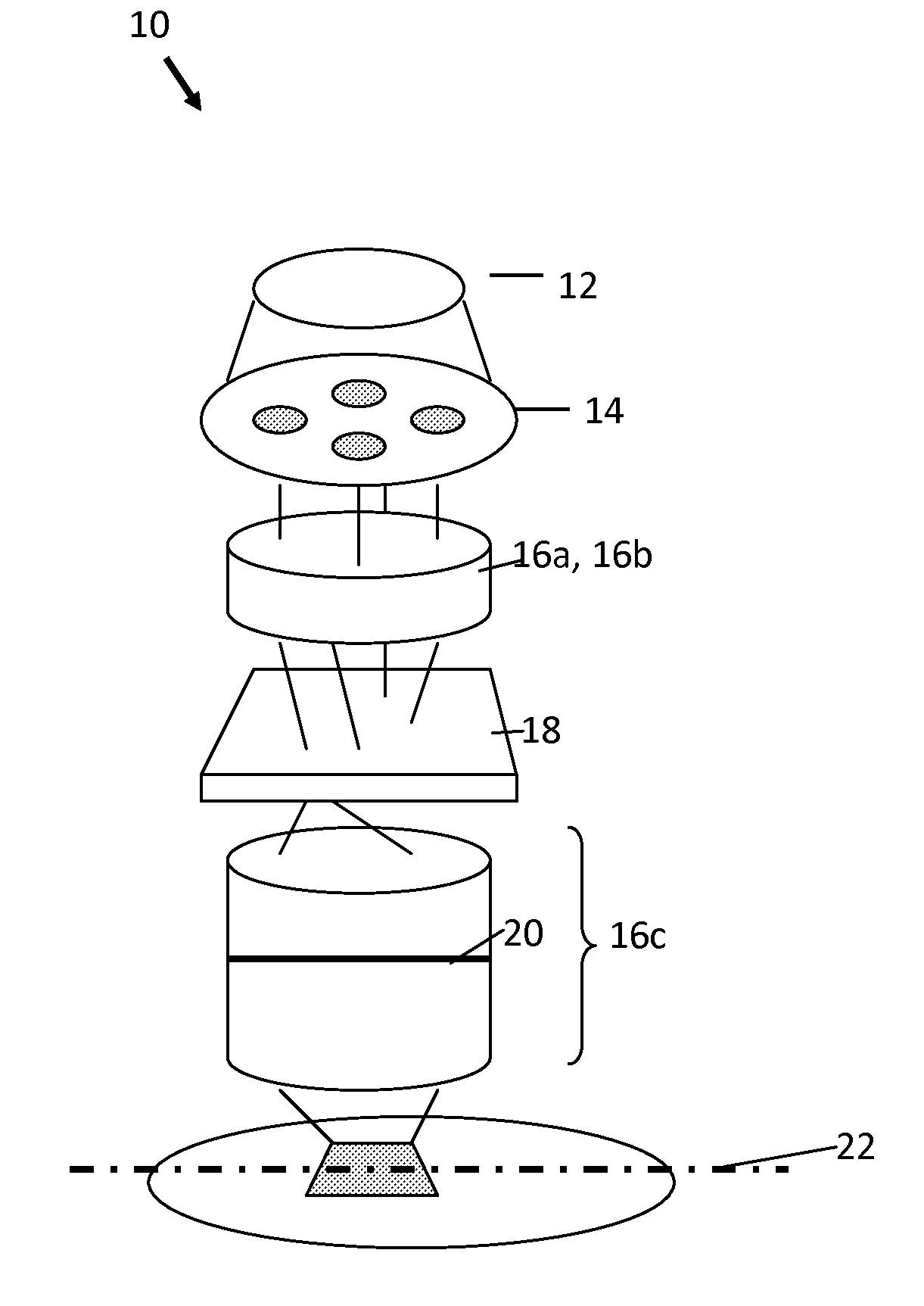
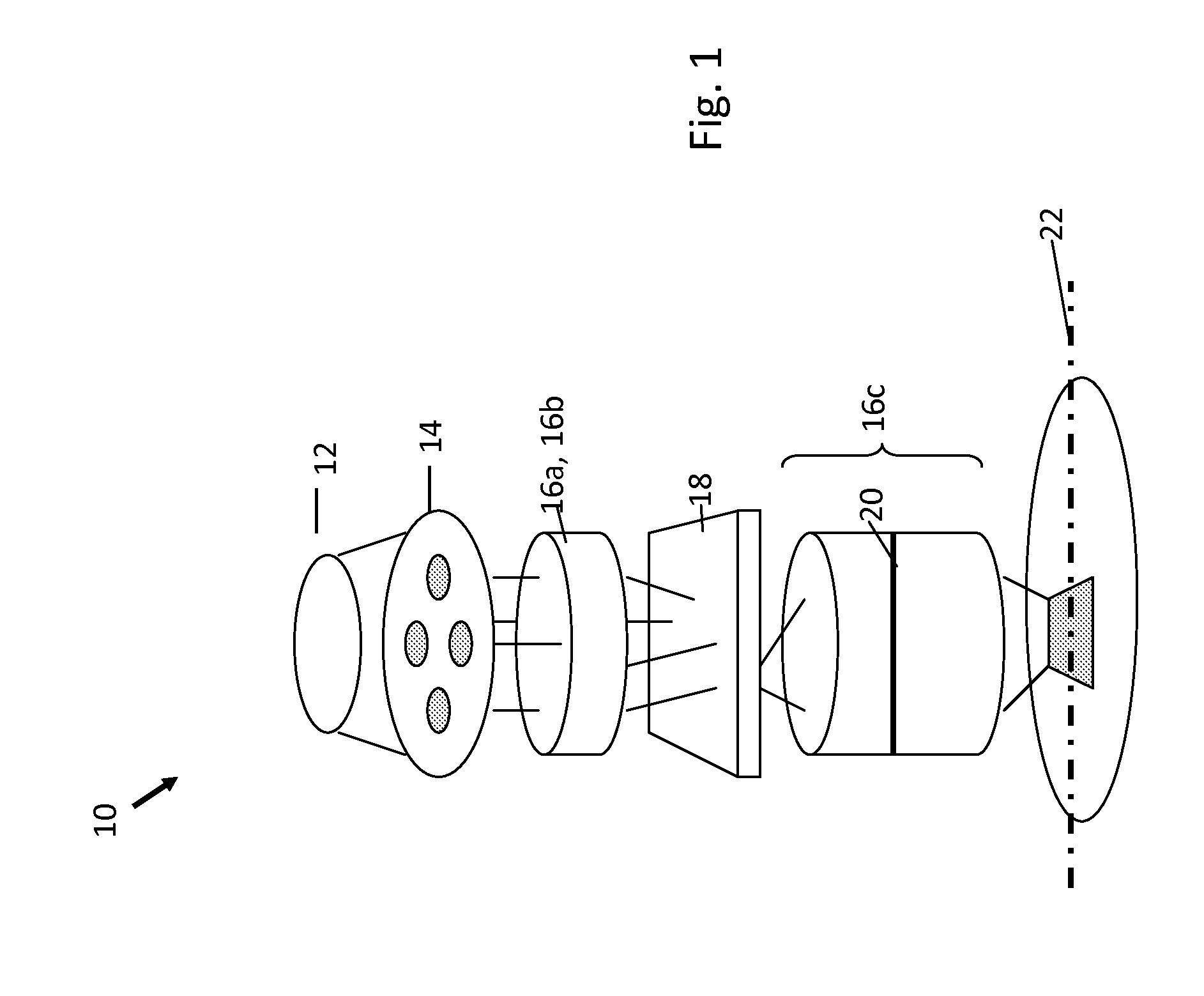
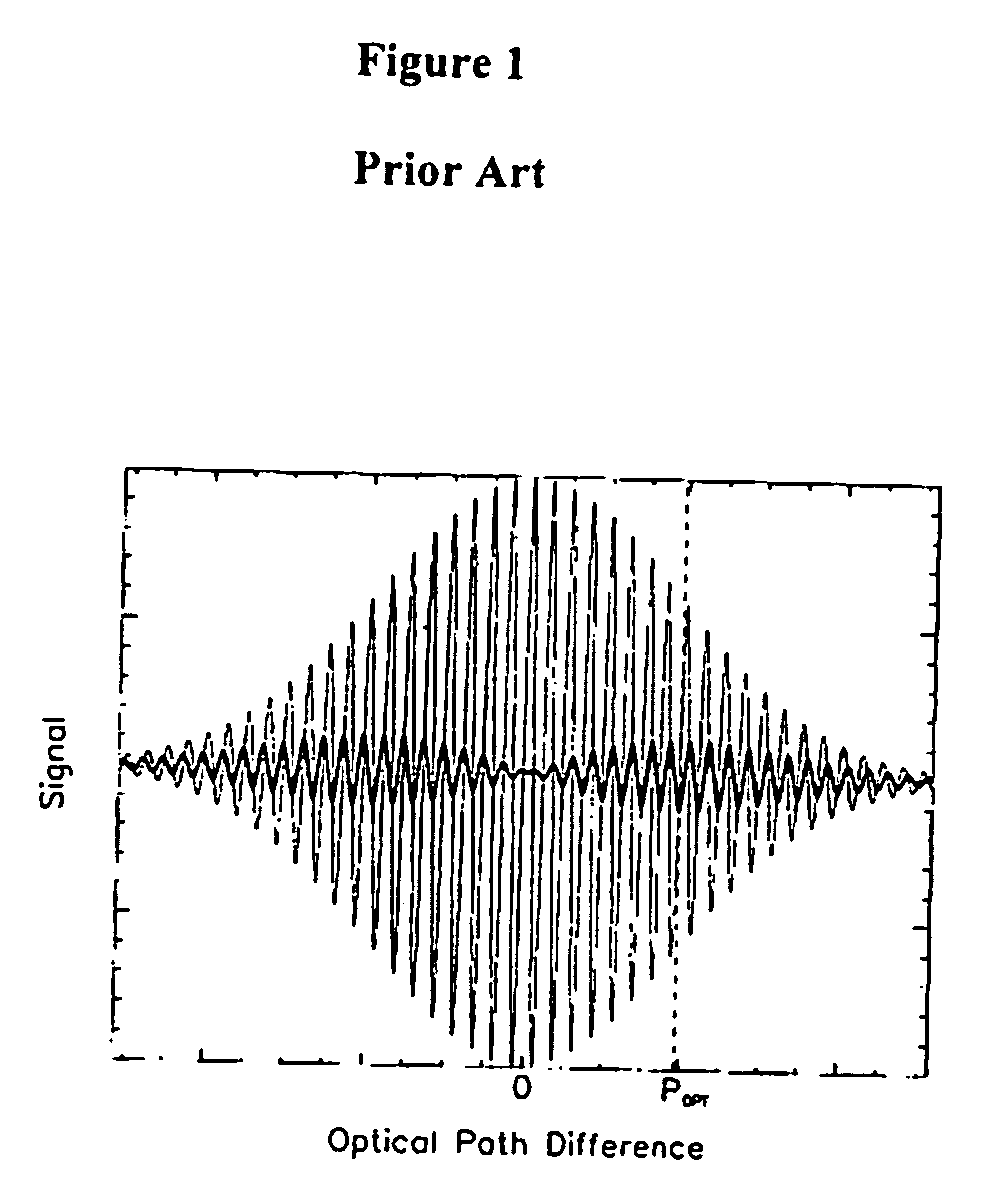
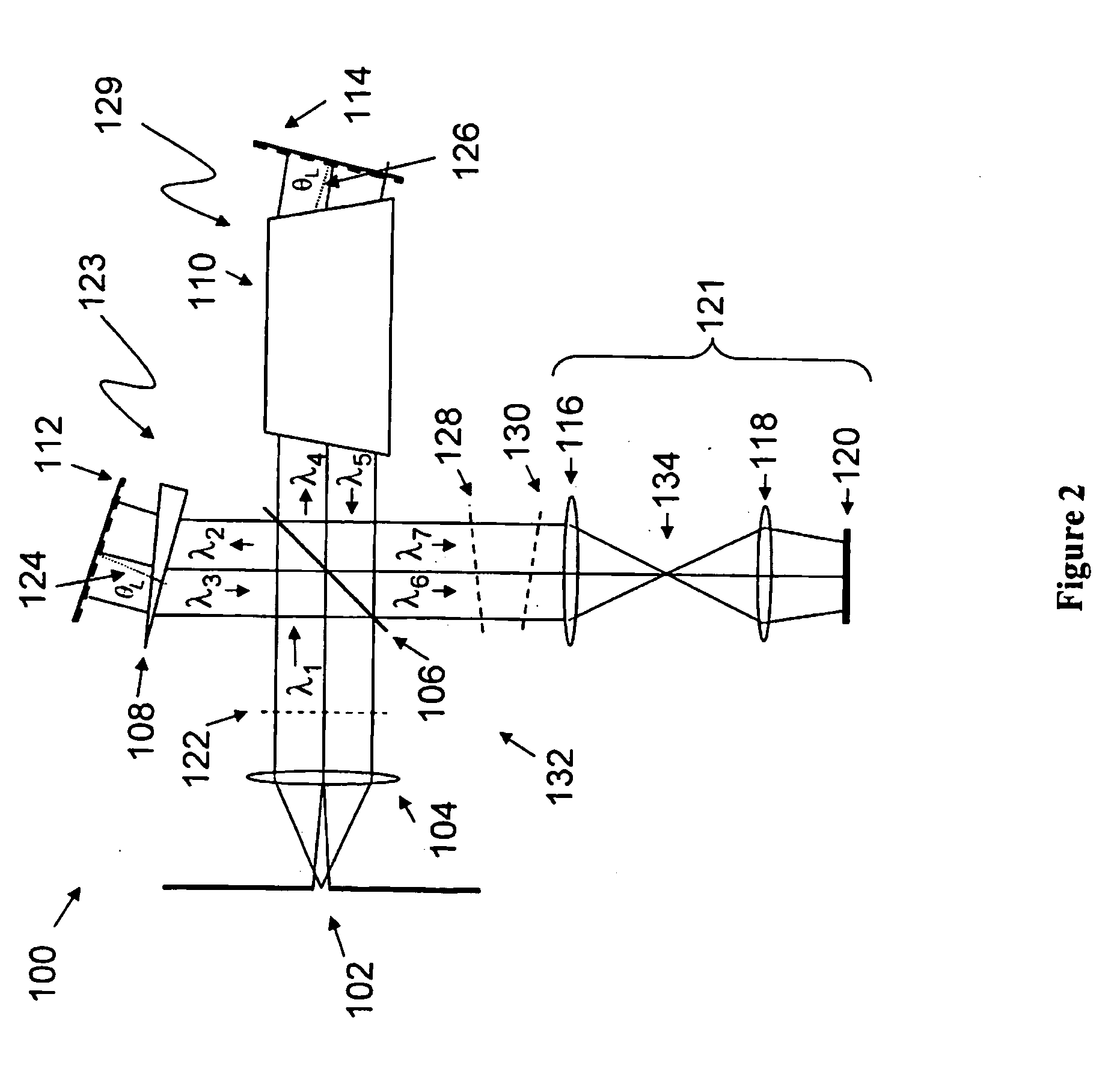
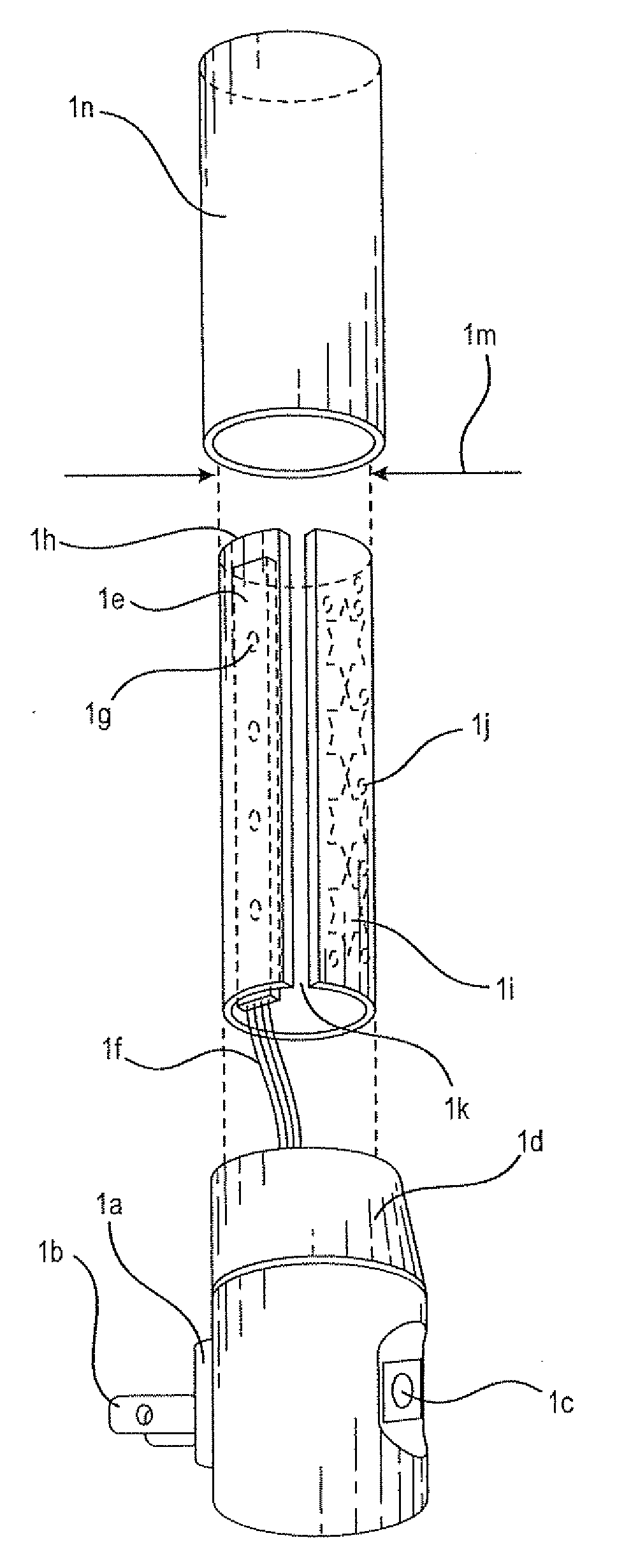
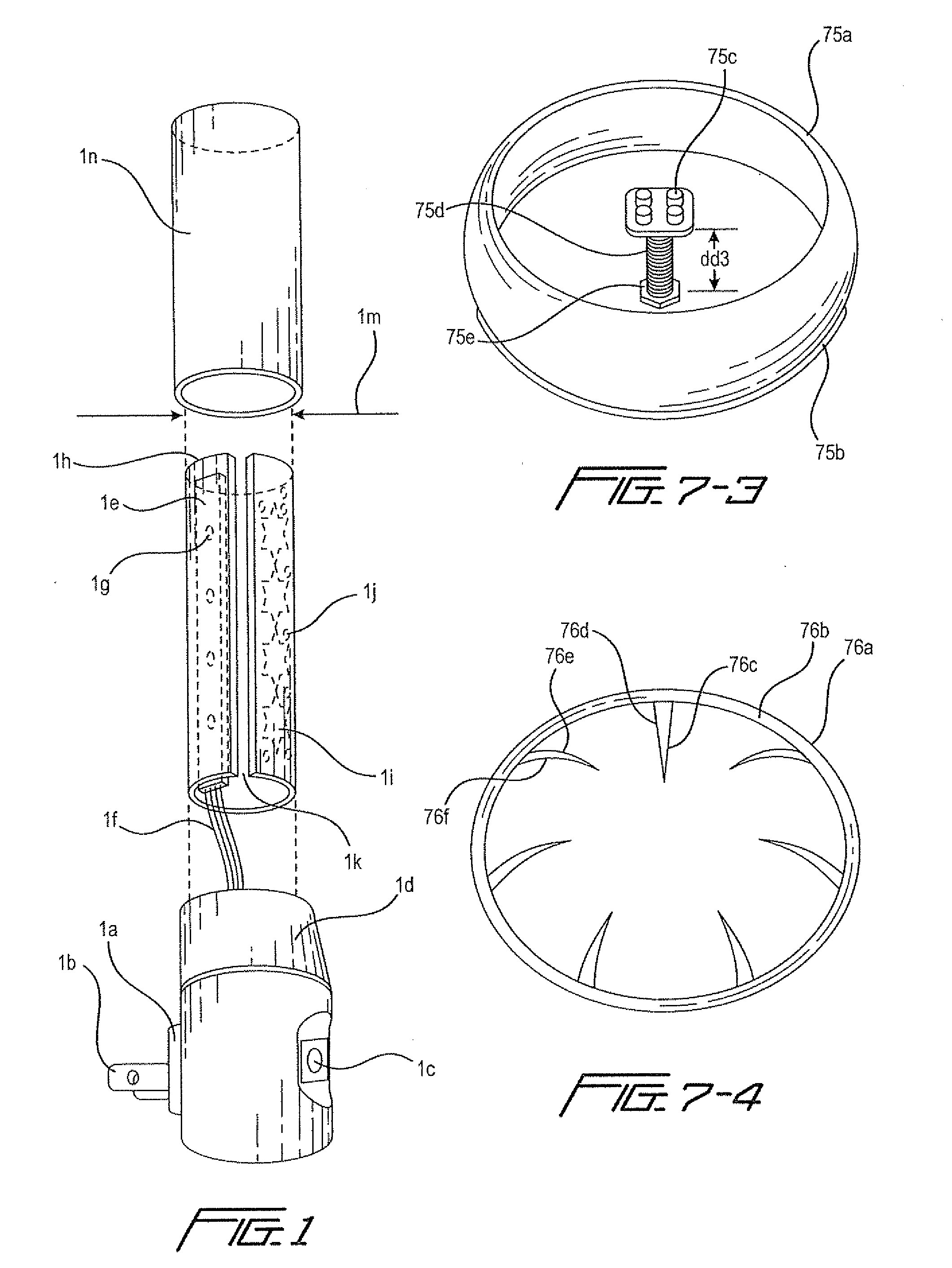
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
512 results about "Lens (optics)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
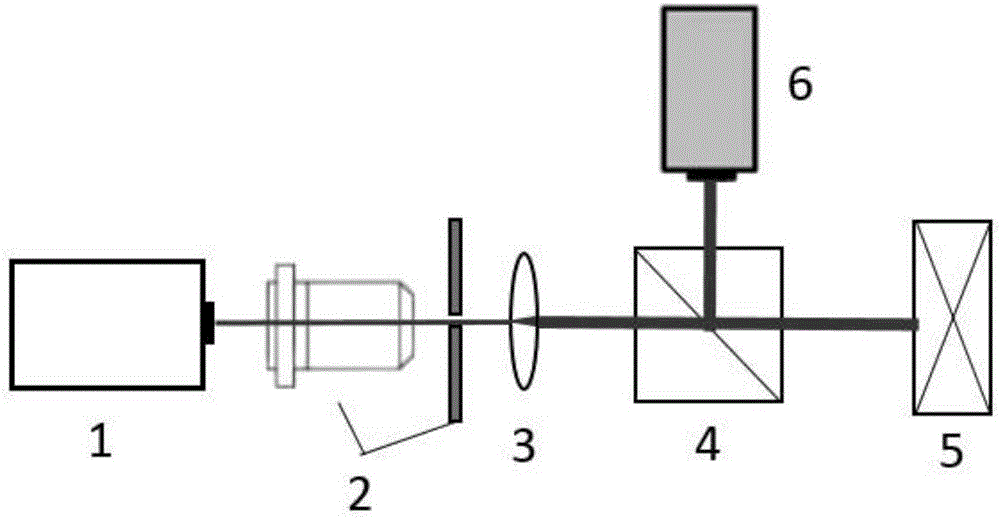
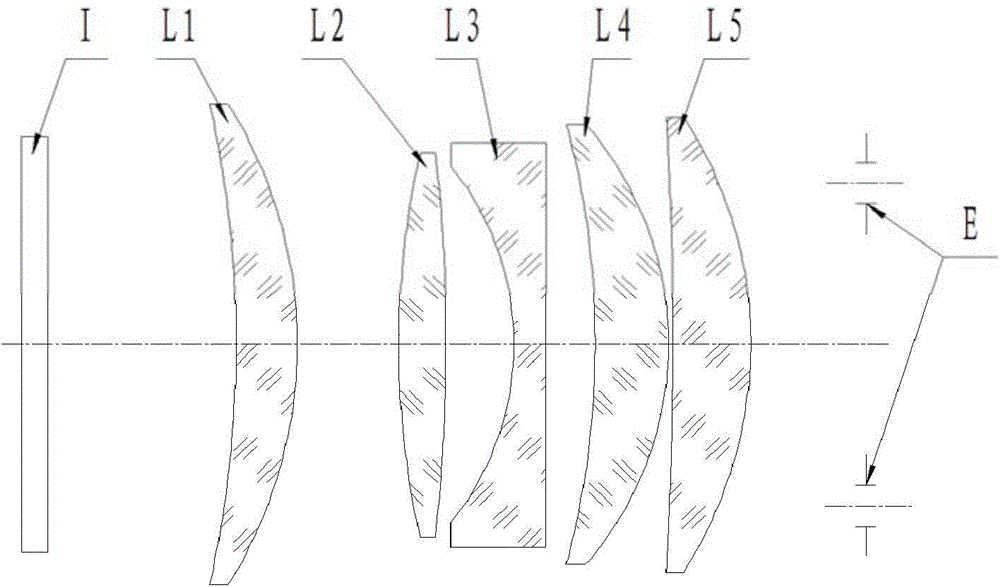
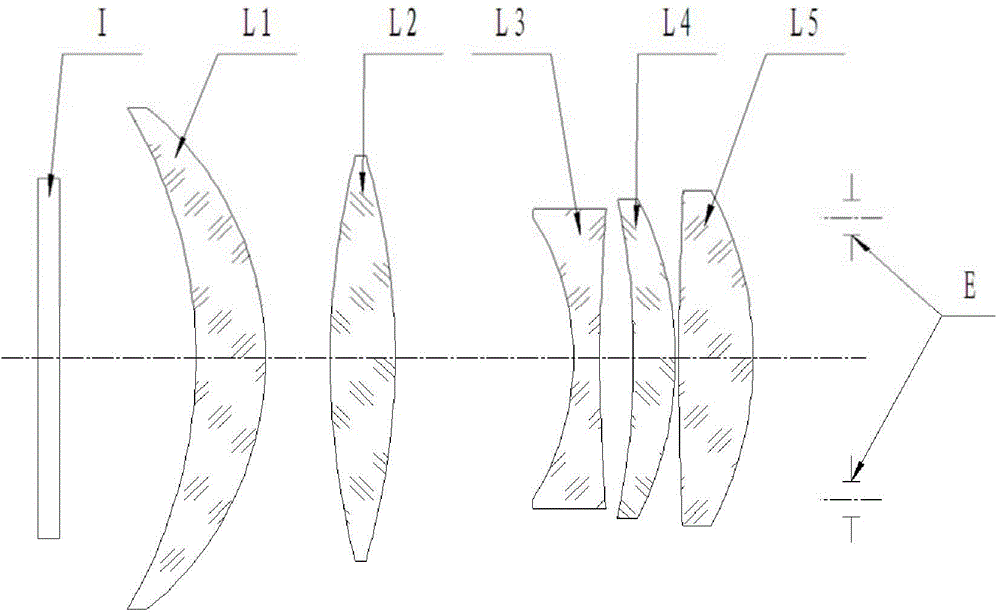
A lens is a transmissive optical device that focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (elements), usually arranged along a common axis. Lenses are made from materials such as glass or plastic, and are ground and polished or molded to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly focus or disperse waves and radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses, electron lenses, acoustic lenses, or explosive lenses.
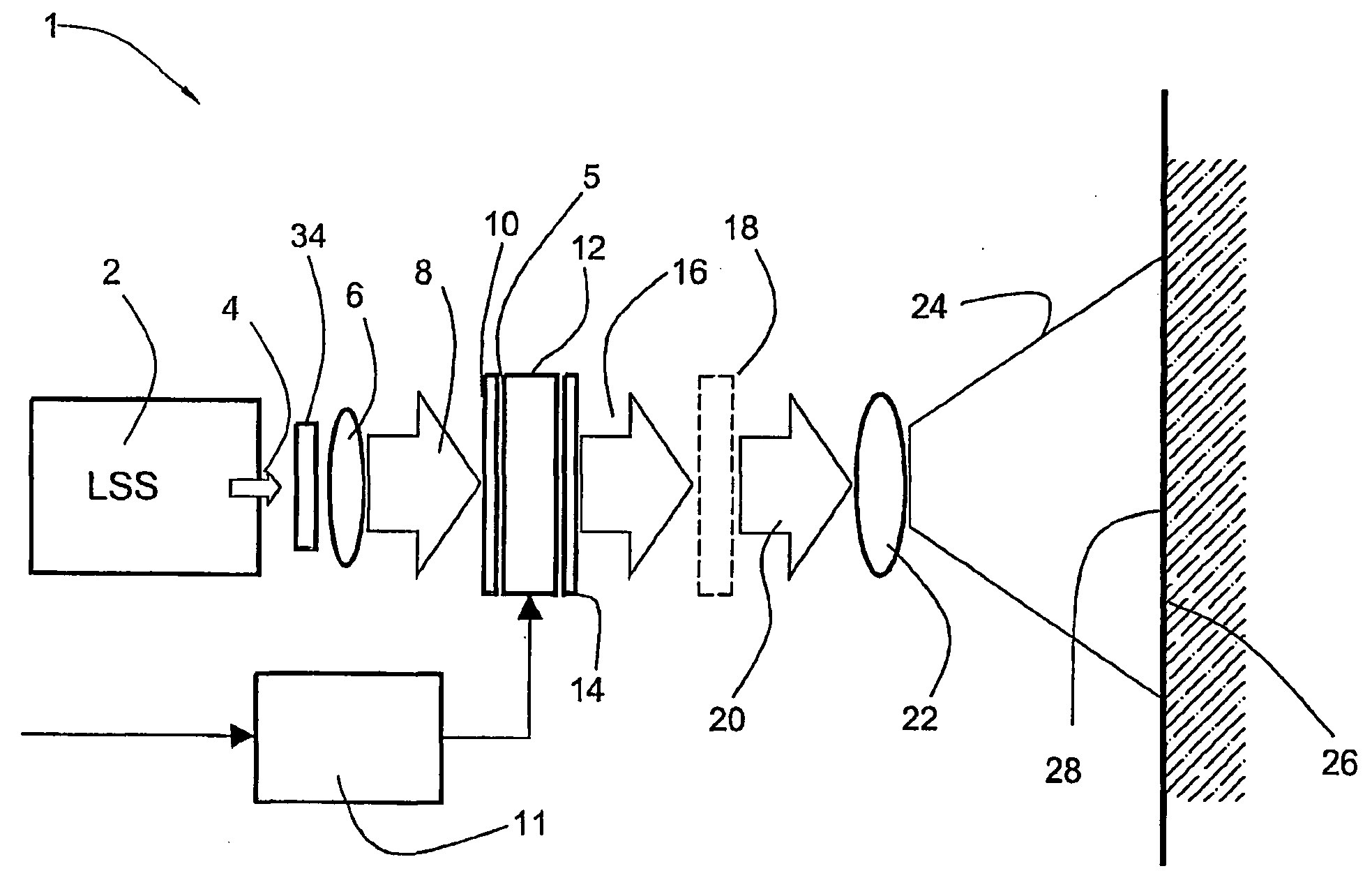
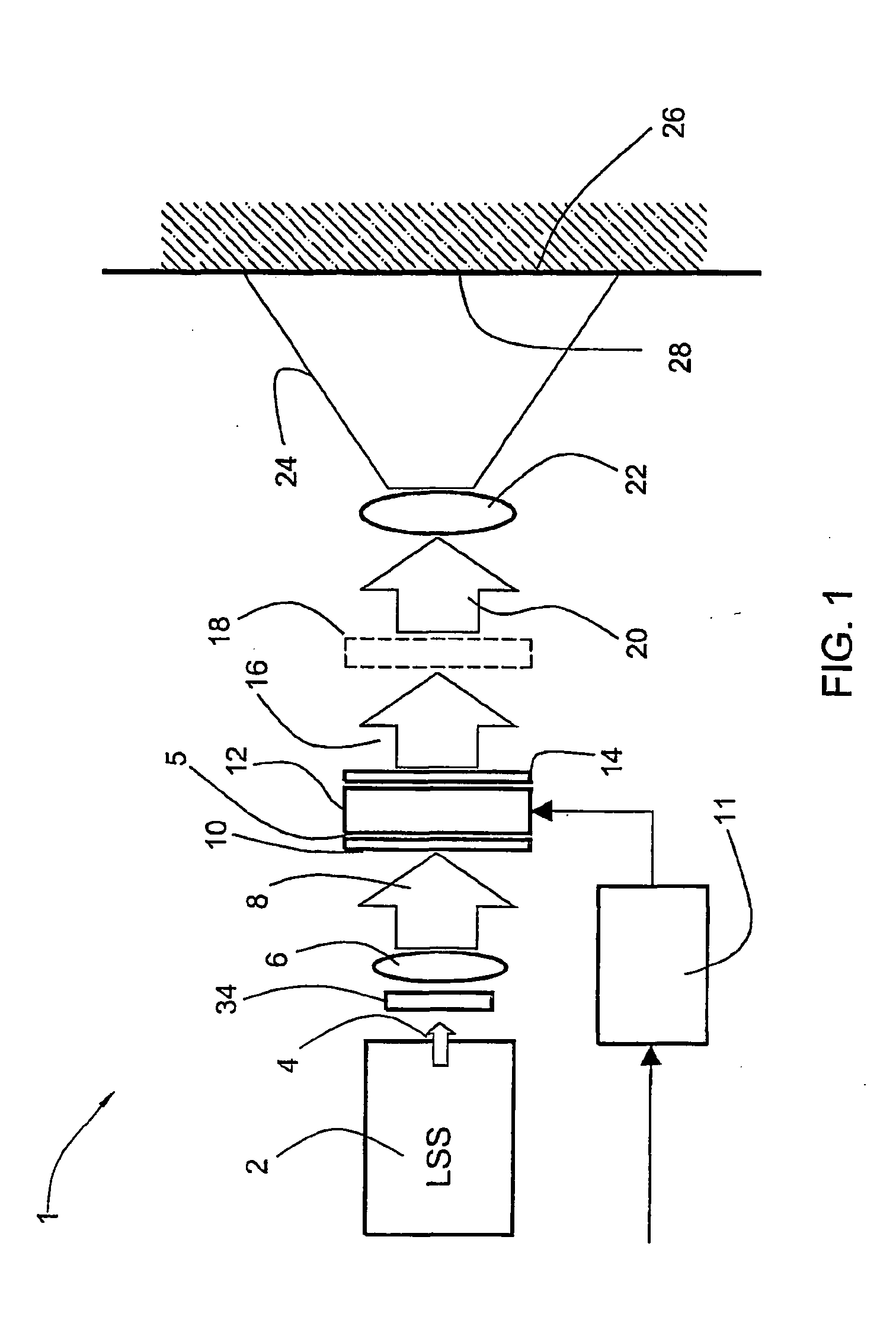
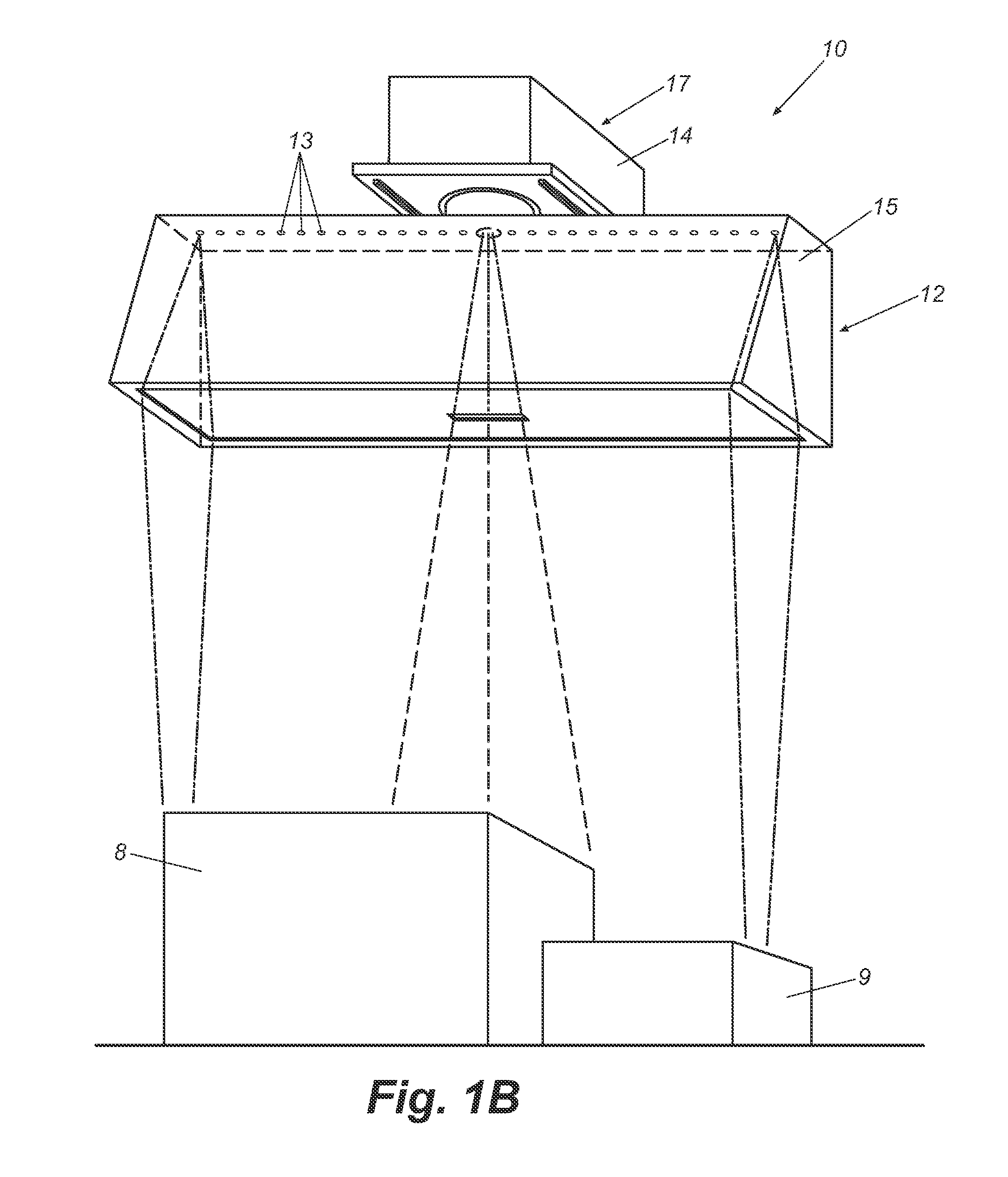
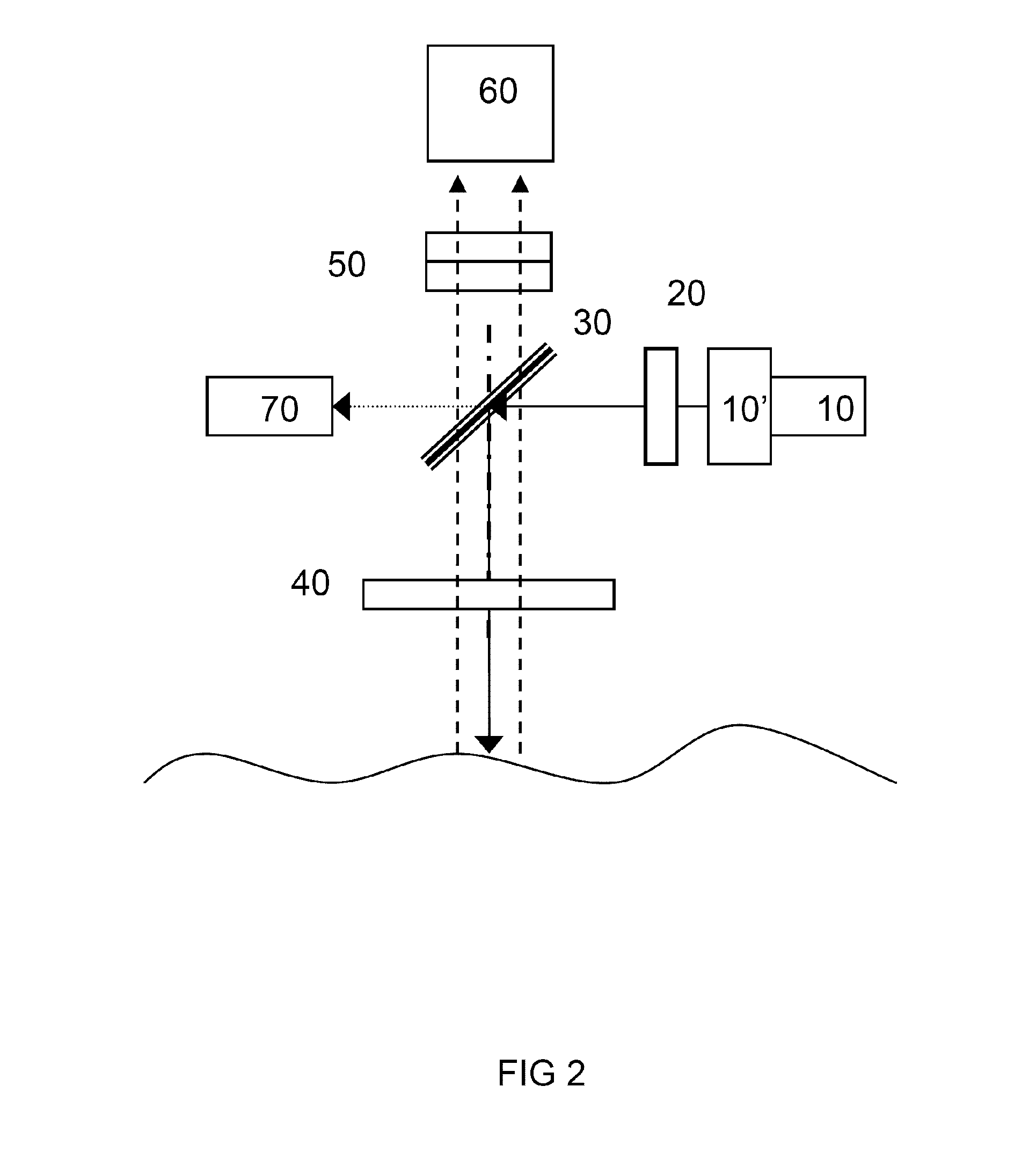
Ergonomic head mounted display device and optical system
Optical systems such as image display systems include a freeform optical waveguide prism and a freeform compensation lens spaced therefrom by a gap of air or index cement. The compensation lens corrects for aberrations which the optical waveguide prism will introduce in light or images from an ambient real-world environment. The optical waveguide prism receives actively projected images at an entry location, and emits the projected images at an exit location after internally reflecting the images along an optical path therein. The image display system may include an image source and coupling optics. The approach permits design of an optical viewing device, for example in optical see-through HMDs, achieving an eyeglass-form appearance and a wide see-through field of view (FOV).
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
Tissue imaging system
InactiveUS7460248B2Diagnostics using lightPolarisation-affecting propertiesSpatial light modulatorDirect illumination
A tissue imaging system (200) for examining the medical condition of tissue (290) has an illumination optical system (205), which comprises a light source (220), having one or more light emitters, beam shaping optics, and polarizing optics. An optical beamsplitter (260) directs illumination light to an imaging sub-system, containing a spatial light modulator array (300). An objective lens (325) images illumination light from the spatial light modulator array to the tissue. An optical detection system (210) images the spatial light modulator to an optical detector array. A controller (360) drives the spatial light modulator to provide time variable arrangements of on-state pixels. The objective lens operates in a nominally telecentric manner relative to both the spatial light modulator and the tissue. The polarizing optics are independently and iteratively rotated to define variable polarization states relative to the tissue. The modulator pixels optically function like pinholes relative to the illumination light and the image light.
Owner:CARESTREAM DENTAL TECH TOPCO LTD
Beam spreading optics for light emitting diodes
ActiveUS20100195335A1Discharge tube luminescnet screensPoint-like light sourceControl electronicsLight beam
An optical element is disclosed, for receiving relatively narrow light from a planar light-emitting diode (LED) source, and for redistributing the light into a relatively wide range of output angles that span a full 360 degrees. The element may be used to retrofit existing fixtures that were originally designed for incandescent bulbs with LED-based light sources that have similar emission profiles. The element is small enough so that it may be packaged along with an LED module and its control electronics in the volume envelope of an incandescent light bulb. An exemplary element is a single, transparent, rotationally-symmetric lens that has a batwing shape in cross-section, extending angularly away from a longitudinal axis. The lens also includes a variety of curved, straight, specular and optionally diffuse portions on its longitudinal and transverse faces, all of which cause a variety of internal and external reflections, refractions, and optionally scattering. As such, many of the specific lens features cannot be directly linked to specific optical effects at a particular angle; rather, the features all interact with each other to produce the wide-angle light output.
Owner:ABL IP HLDG
Method of and system for producing digital images of objects with subtantially reduced speckle-noise patterns by illuminating said objects with spatially and/or temporally coherent-reduced planar laser illumination
InactiveUS20020043561A1Reducing speckle-noise patternSemiconductor laser arrangementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSystems designHand held
Methods of and systems for illuminating objects using planar laser illumination beams having substantially-planar spatial distribution characteristics that extend through the field of view (FOV) of image formation and detection modules employed in such systems. Each planar laser illumination beam is produced from a planar laser illumination beam array (PLIA) comprising an plurality of planar laser illumination modules (PLIMs). Each PLIM comprises a visible laser diode (VLD, a focusing lens, and a cylindrical optical element arranged therewith. The individual planar laser illumination beam components produced from each PLIM are optically combined to produce a composite substantially planar laser illumination beam having substantially uniform power density characteristics over the entire spatial extend thereof and thus the working range of the system. Preferably, each planar laser illumination beam component is focused so that the minimum beam width thereof occurs at a point or plane which is the farthest or maximum object distance at which the system is designed to acquire images, thereby compensating for decreases in the power density of the incident planar laser illumination beam due to the fact that the width of the planar laser illumination beam increases in length for increasing object distances away from the imaging optics. Advanced high-resolution wavefront control methods and devices are disclosed for use with the PLIIM-based systems in order to reduce the power of speckle-noise patterns observed at the image detections thereof. By virtue of the present invention, it is now possible to use both VLDs and high-speed CCD-type image detectors in conveyor, hand-held and hold-under type imaging applications alike, enjoying the advantages and benefits that each such technology has to offer, while avoiding the shortcomings and drawbacks hitherto associated therewith.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
Image projecting device and method
InactiveUS20040239880A1Improve efficiencyReduce impactTelevision system detailsProjectorsSpatial light modulatorEffective surface
An image projecting device and method are presented. The device comprises a light source system operable to produce a light beam to impinge onto an active surface of a spatial light modulator (SLM) unit formed by an SLM pixel arrangement; and a magnification optics accommodated at the output side of the SLM unit. The light beam impinging onto the SLM pixel arrangement has a predetermined cross section corresponding to the size of said active surface. The SLM unit comprises first and second lens' arrays at opposite sides of the pixel arrangement, such that each lens in the first array and a respective opposite lens in the second array are associated with a corresponding one of the SLM pixels
Owner:EXPLAY
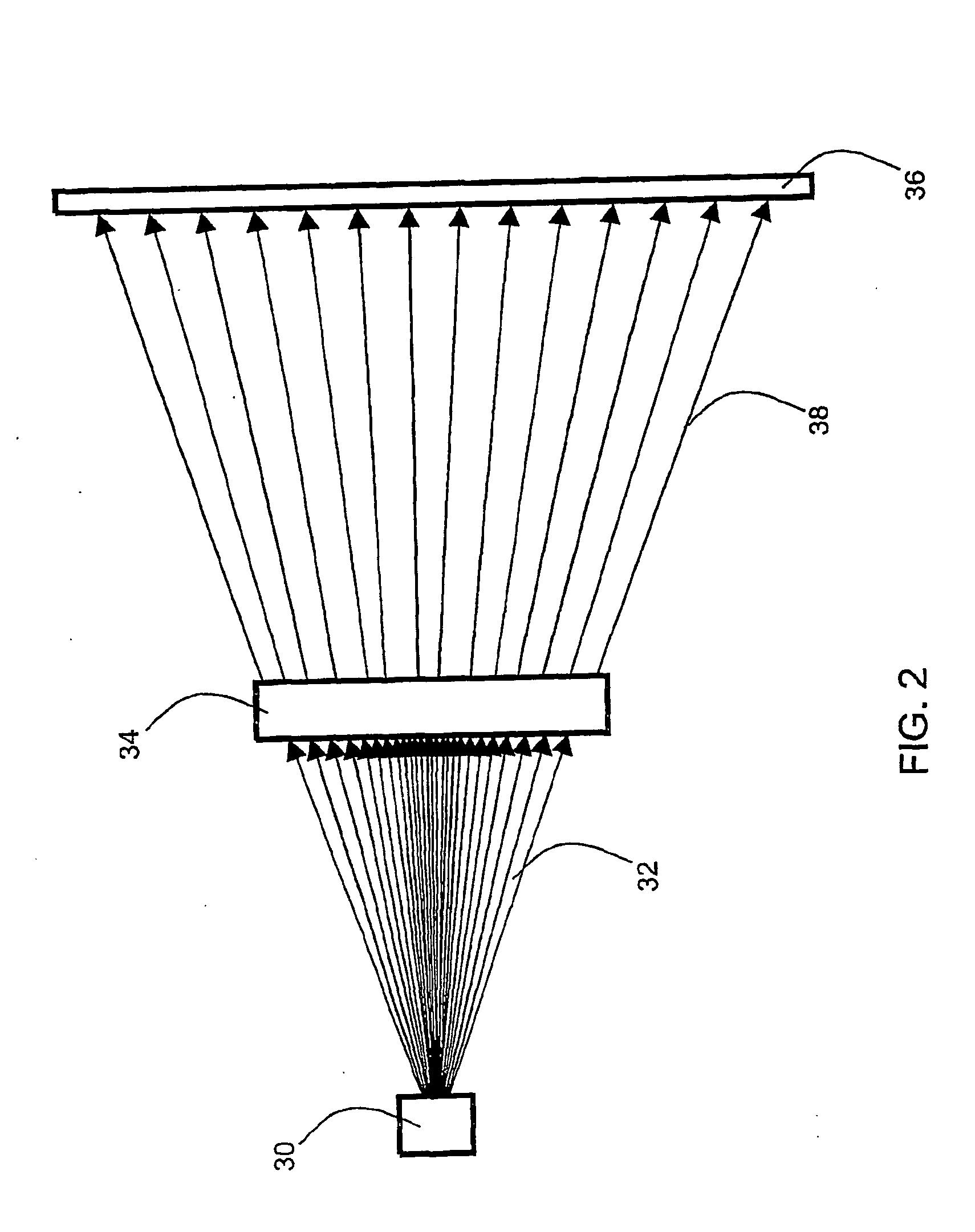
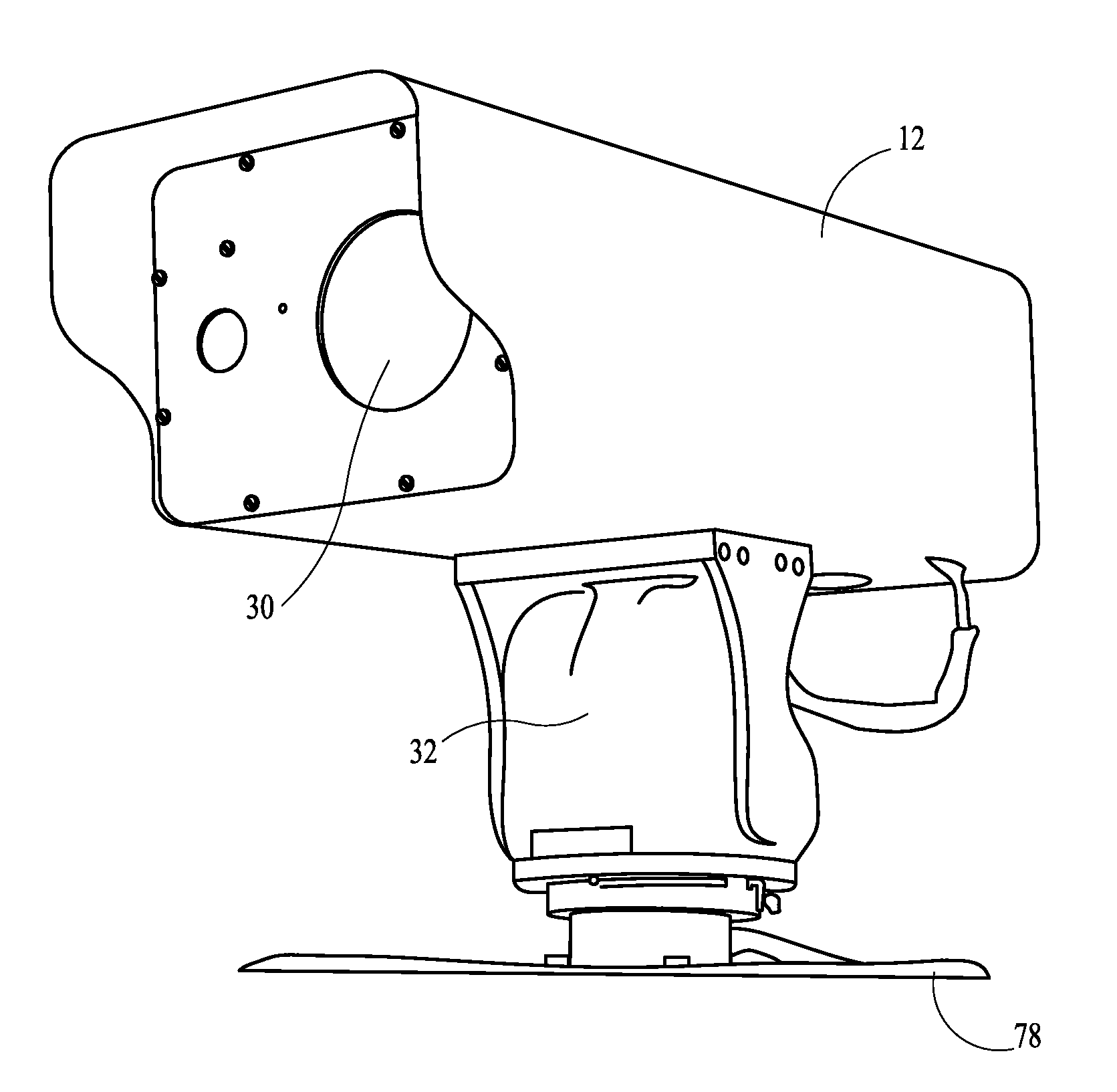
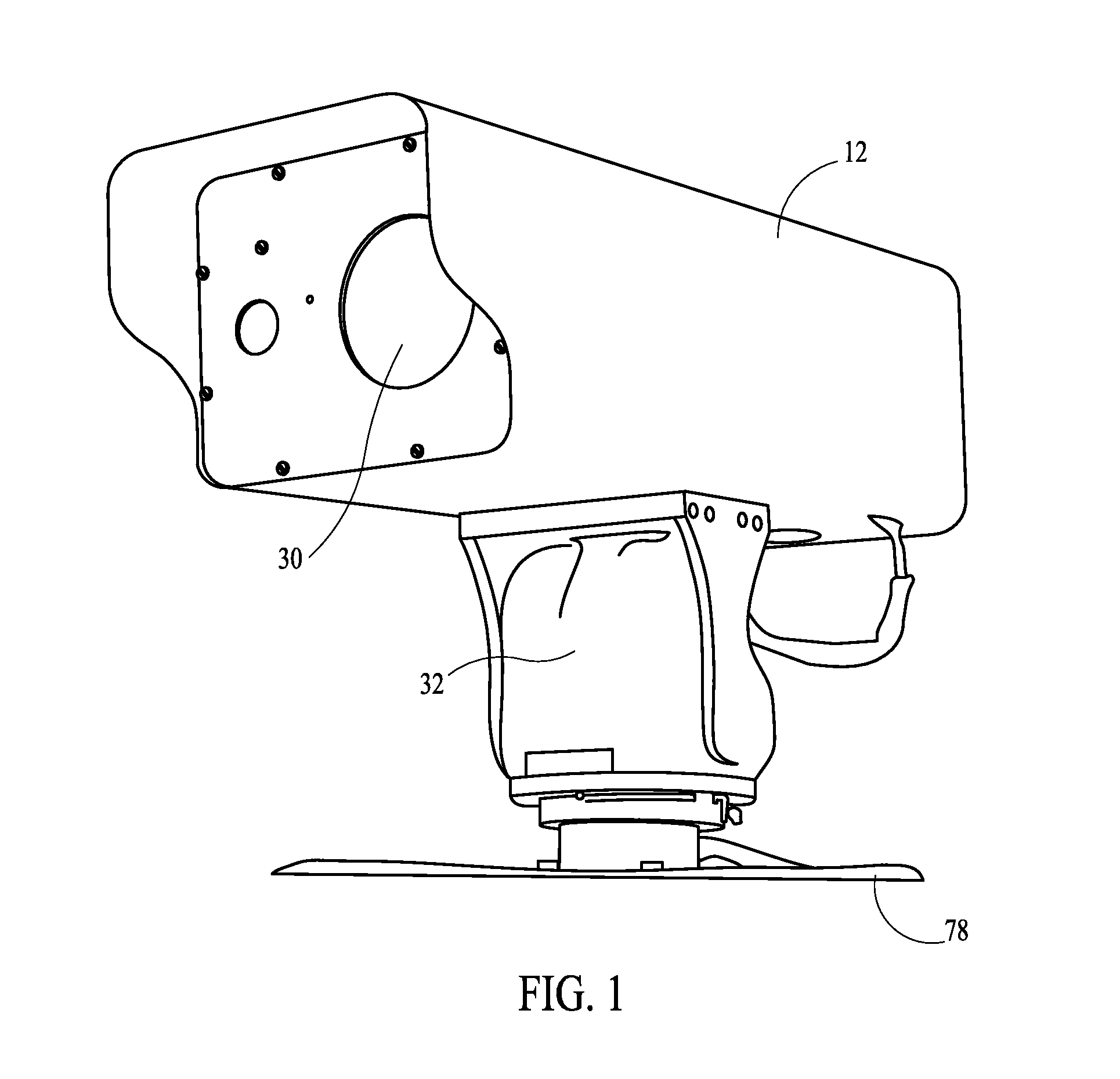
Long Range Day/Night Surveillance Video Camera
InactiveUS20110199482A1Low lightTelevision system detailsColor television detailsPower stationDiode-pumped solid-state laser
This invention relates to video cameras and, more specifically, to a high-resolution day / night video camera with a long lens, fast optics and pan / tilt / zoom electronics, coupled with a diode-pumped solid state laser illuminator for long range low light illumination. Potential applications include ports, borders, pipelines, power stations, communication transmitters and prisons.
Owner:MORGAN ARTHUR C
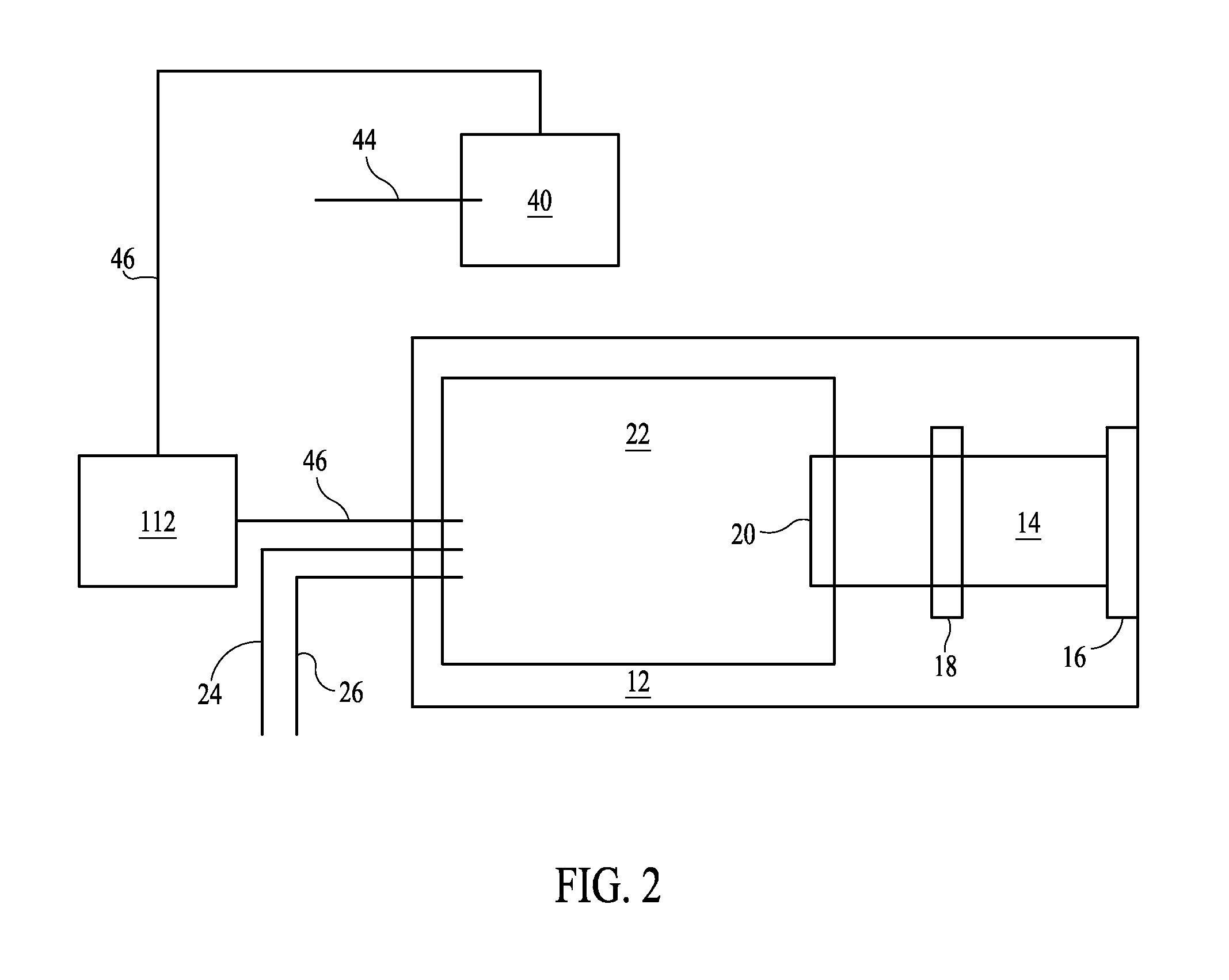
Data storage system and methods using diffractive near-field optics
InactiveUS6396789B1Minimize aberrationLow costOptical flying-type headsNanoinformaticsOptical pathOptical radiation
An optical assembly suitable for use with an optical medium for the storage and retrieval of data, the optical assembly comprising: a source of illumination for providing a beam of optical radiation, an objective lens disposed in the optical path of the beam for redirecting the beam to the optical medium, and a diffractive optical element disposed between the redirected beam of radiation and the optical medium such that at least a portion of the redirected beam of radiation passes through a surface of the diffractive optical element and is reflected to the objective lens.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
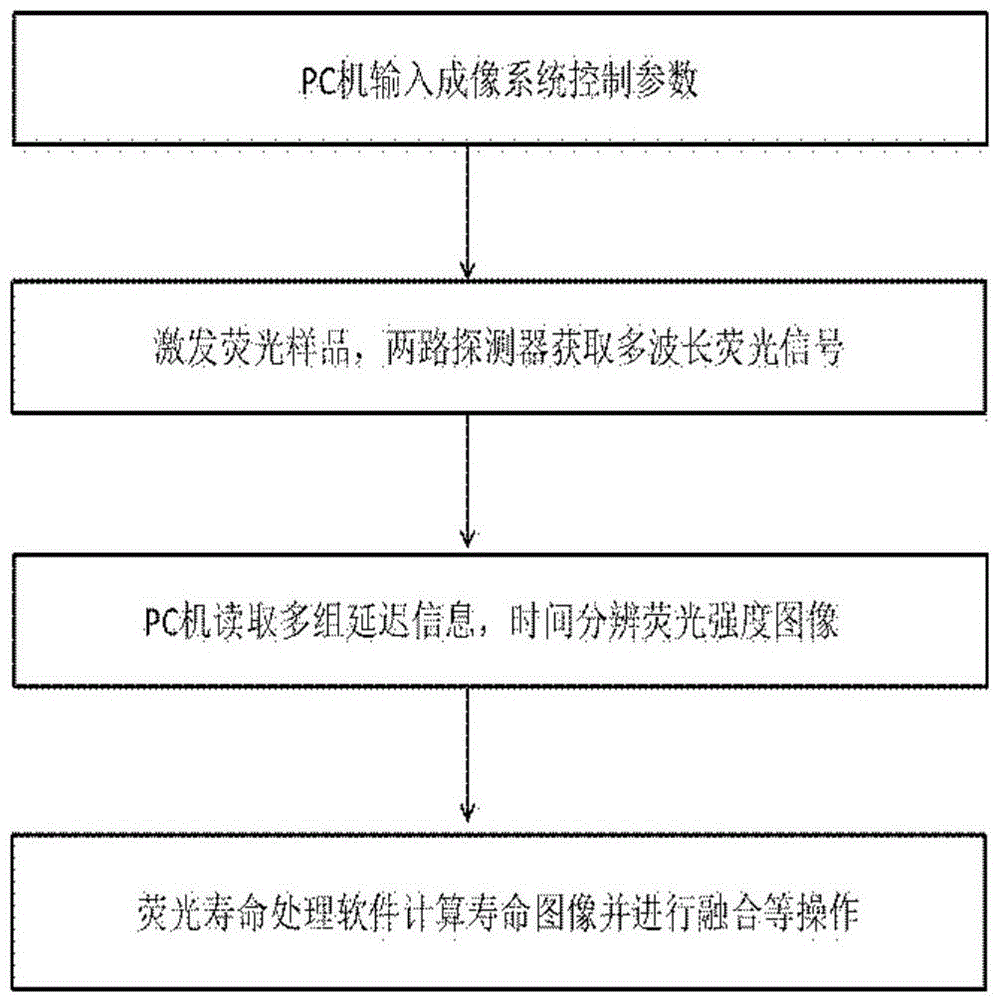
Two channel-based multi-spectrum fluorescent imaging microscopic system and method
ActiveCN104614353AFluorescence Imaging RealizationMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescencePicosecond pulsed laserFluorescence microscope
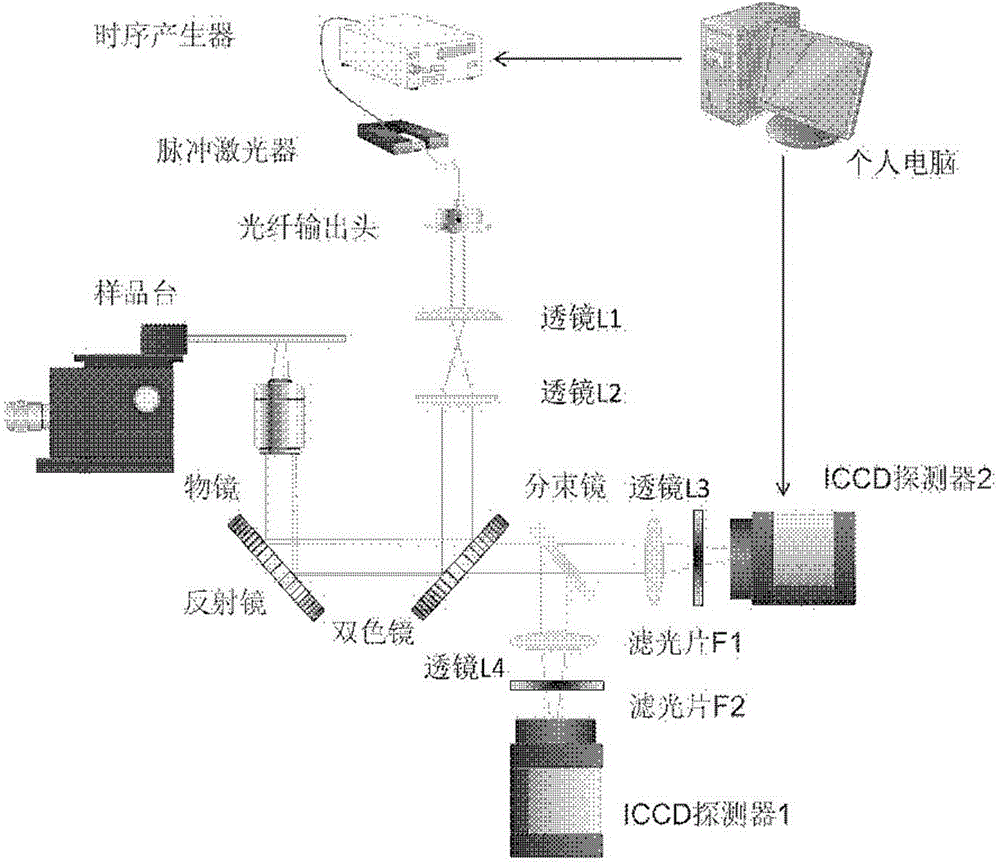
The invention is applicable to the field of optics, biomedicine, life science and the like, and provides a two channel-based multi-spectrum fluorescent imaging microscopic system and method, wherein the two channel-based multi-spectrum fluorescent imaging microscopic system comprises a picosecond pulse laser device, a fluorescent excitation and collection light path, a microscopic objective lens, a light beam lens, a double-ICCD detector, and a control and processing module. The invention further discloses a method for performing multi-spectrum imaging by utilizing the two channel-based multi-spectrum fluorescent imaging microscopic system. According to the two channel-based multi-spectrum fluorescent imaging microscopic system and method, the limitation of the existing fluorescent microscope and a fluorescent life imaging microscopic system only can acquire single wavelength fluorescent signal with one-time detection can be effectively solved, the simultaneous acquisition of the multi-spectrum fluorescent strength and fluorescent light image aiming at the dynamic process of fluorescent intensity-related detection limited in biomedicine and life science can be performed, so that the research and application ranges of biophotonics can be extended.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical collimator for LED lights
ActiveUS20140316742A1Improve cbcp per lumen performanceImprove sizingPlanar light sourcesPoint-like light sourceCollimatorOptoelectronics
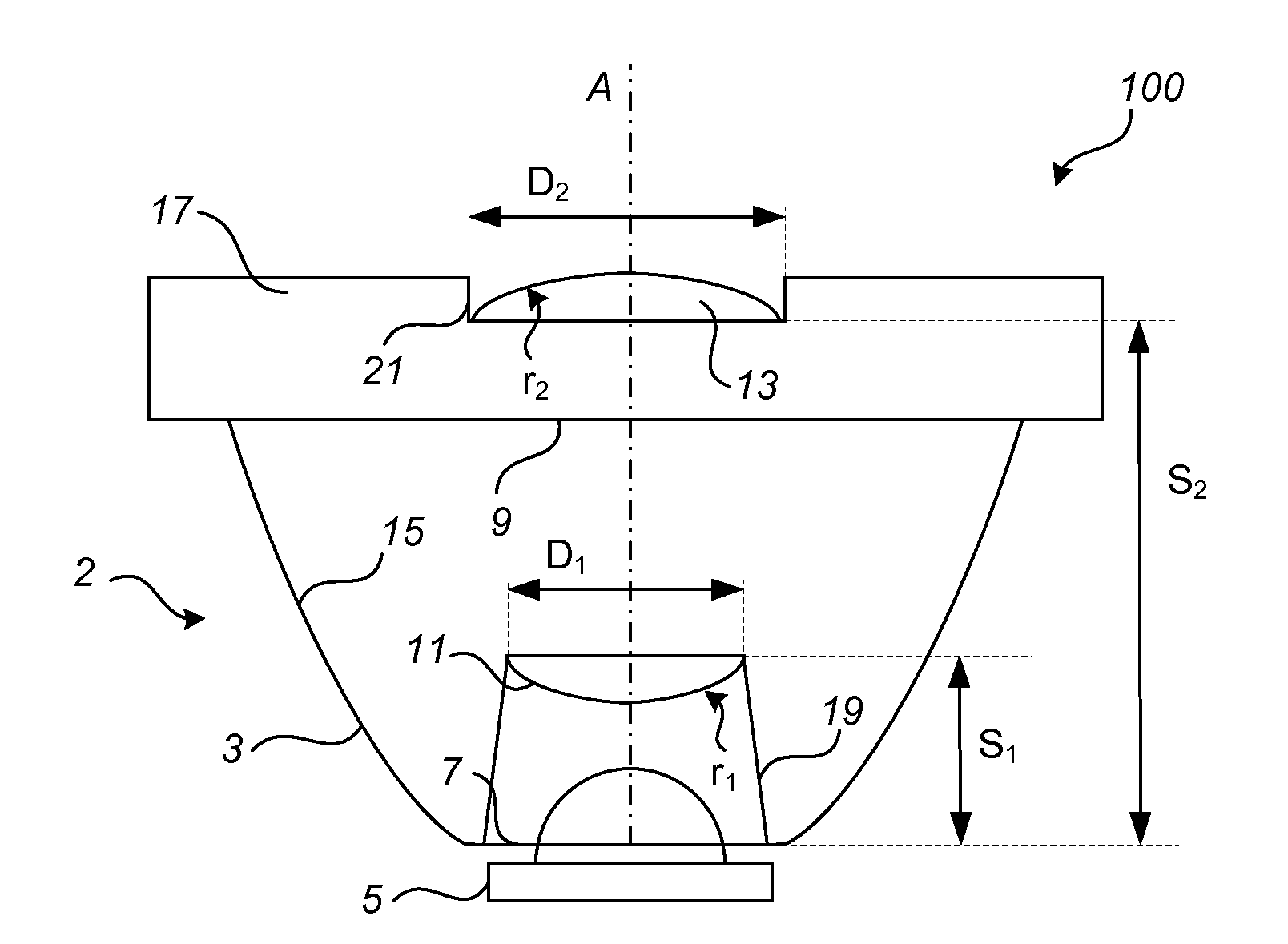
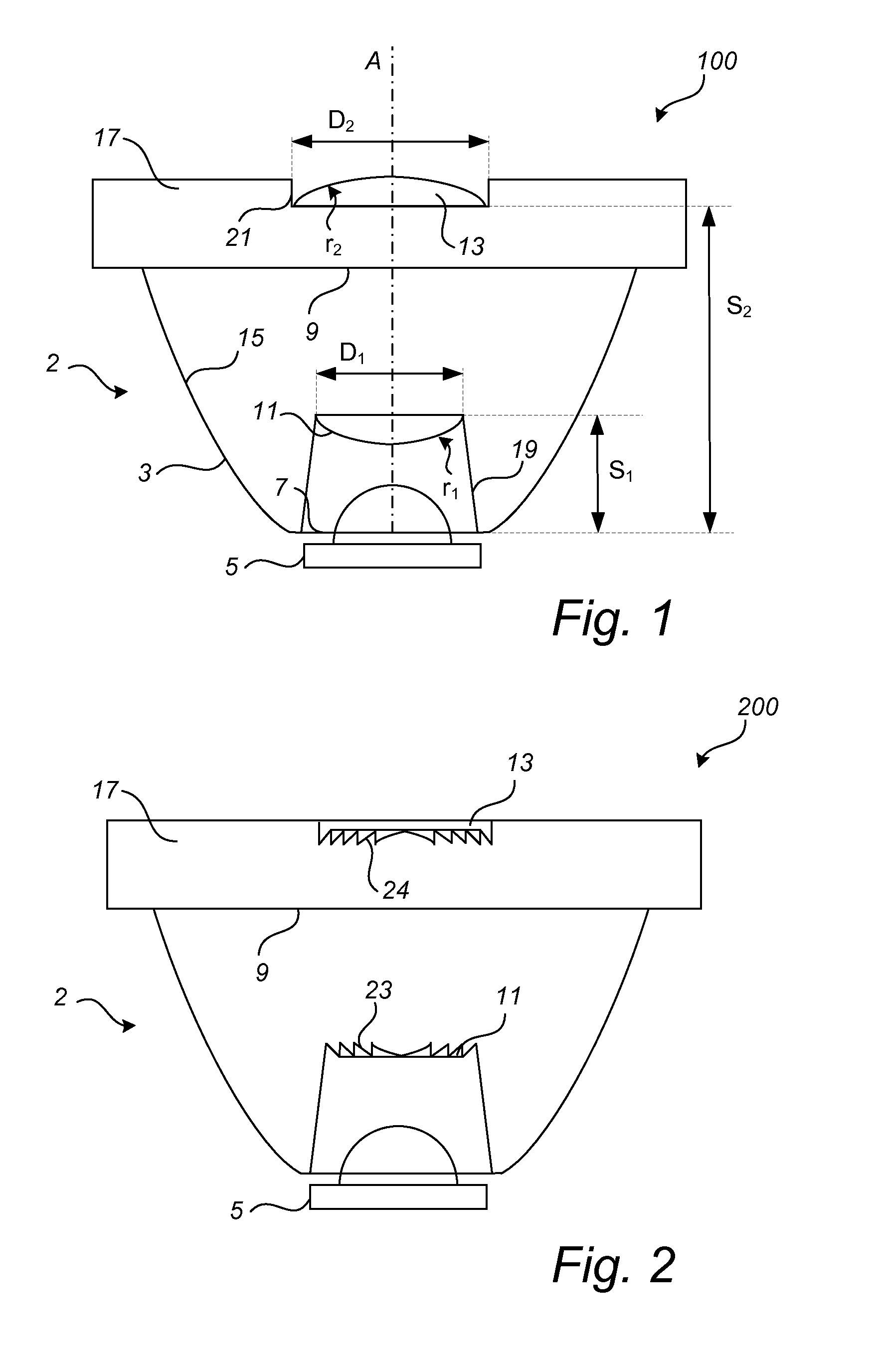
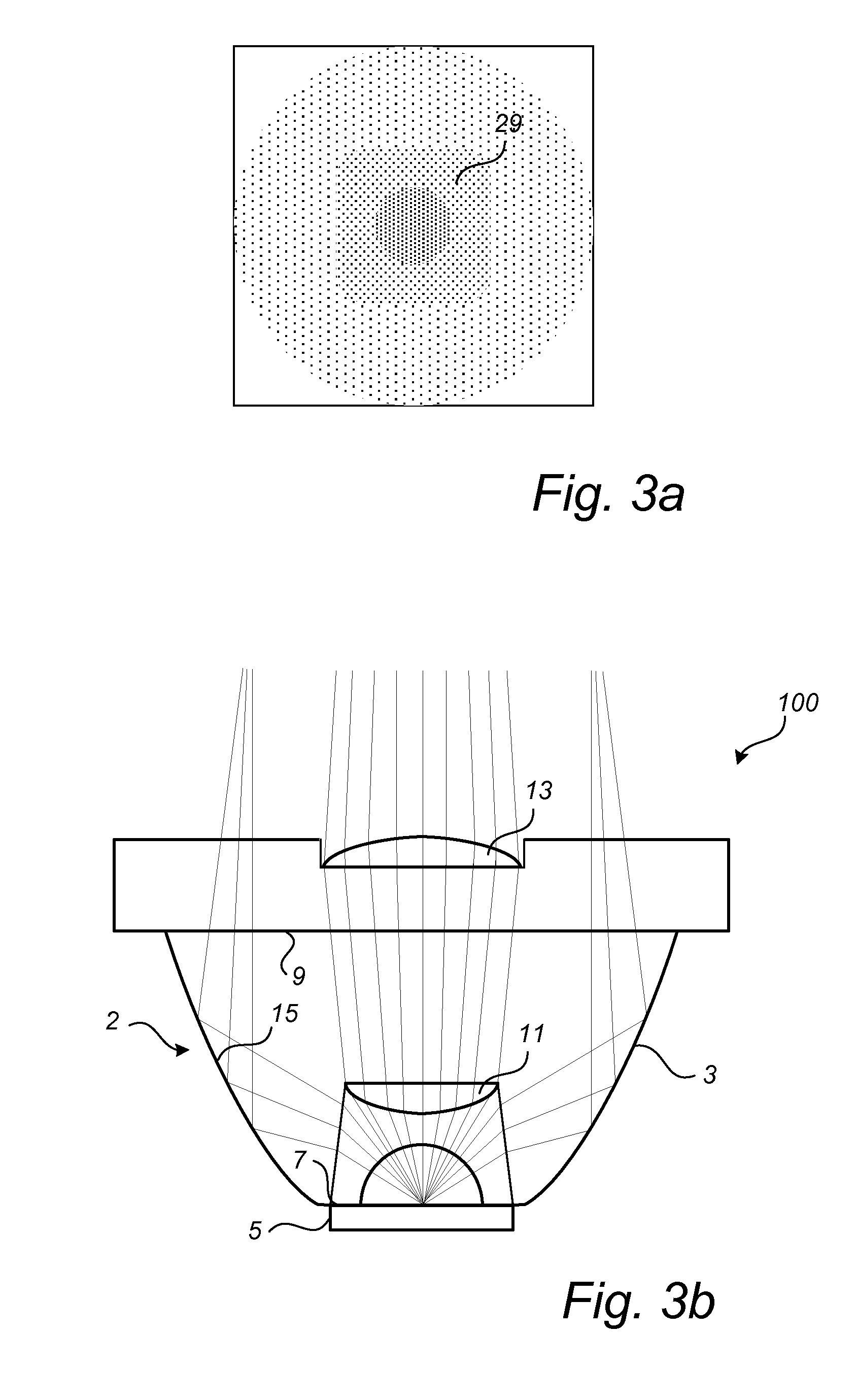
There is provided a luminaire (1) and a collimating optics (2) for LED lights (5). The collimating optics (2) comprises a reflection collimator (3) having a first aperture (7) for allowing incoming light from a LED light (5) to enter the collimator (3) and a second aperture (9) for allowing outgoing light to exit the collimator (3). The reflection collimator (3) further has a wall (15) with a reflective inner surface for guiding the incoming light from the first aperture (7) towards the second aperture (9). A first convex lens (11) is arranged at a distance from the first aperture (7) for refracting the incoming light, and a second convex lens (13) is arranged at the second aperture (9) for refracting and collimating the outgoing light. With the disclosed collimating optics the collimating capability is improved without the size of the optics being increased.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and apparatus for controlling a lens, and camera module incorporating same
InactiveUS20060045504A1Reduce the amount requiredShorten the timeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsEngineeringFlash light
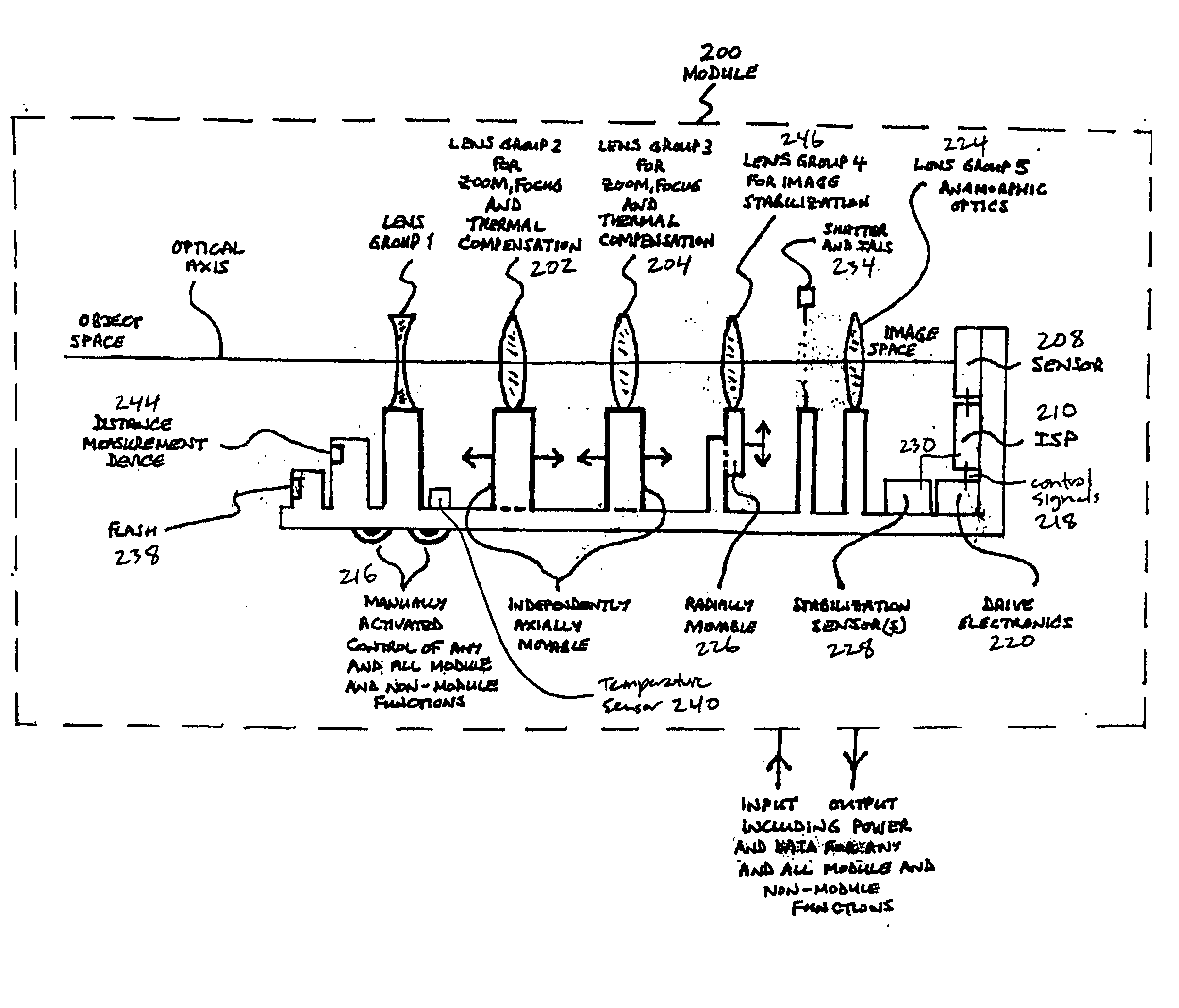
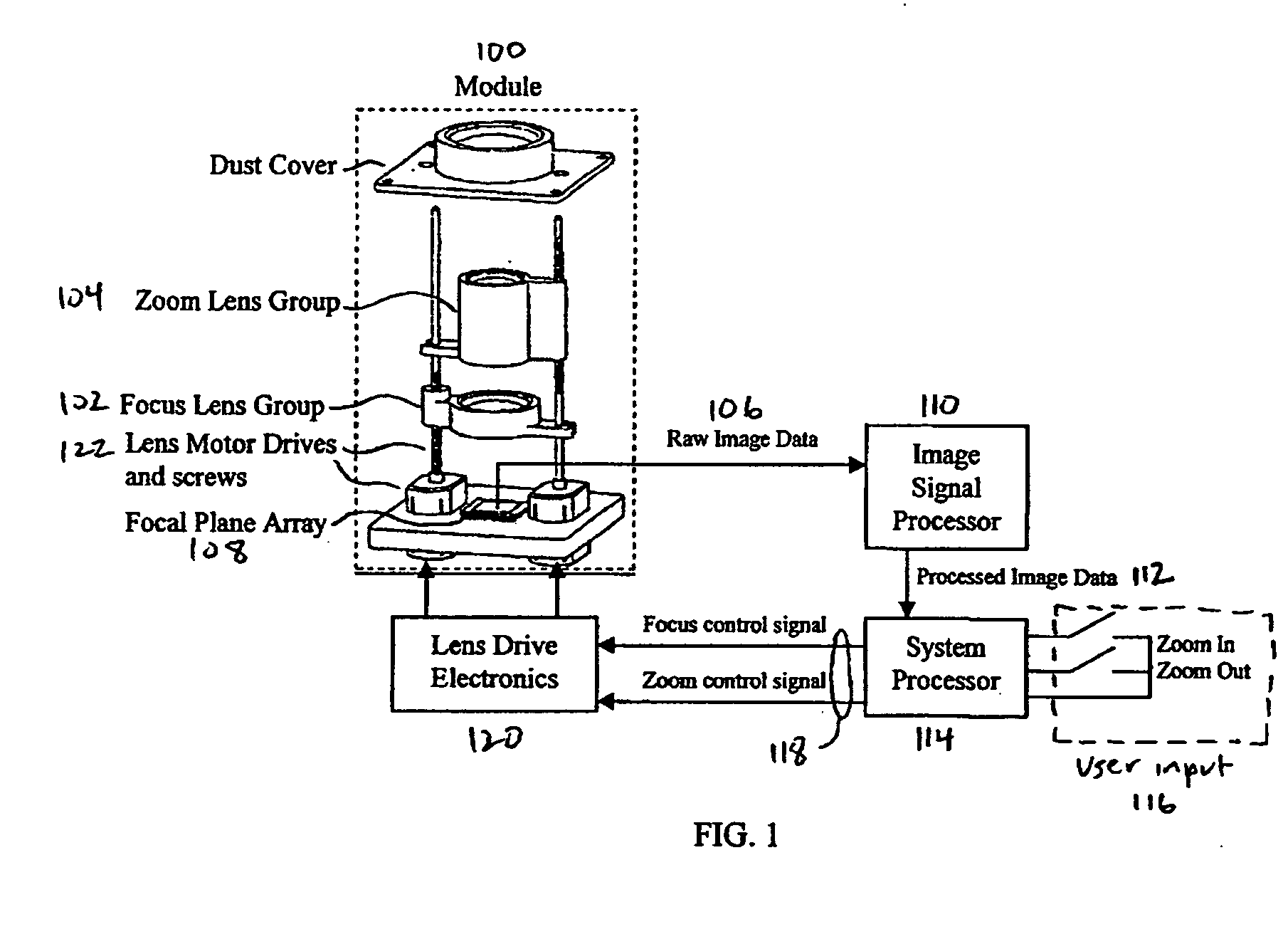
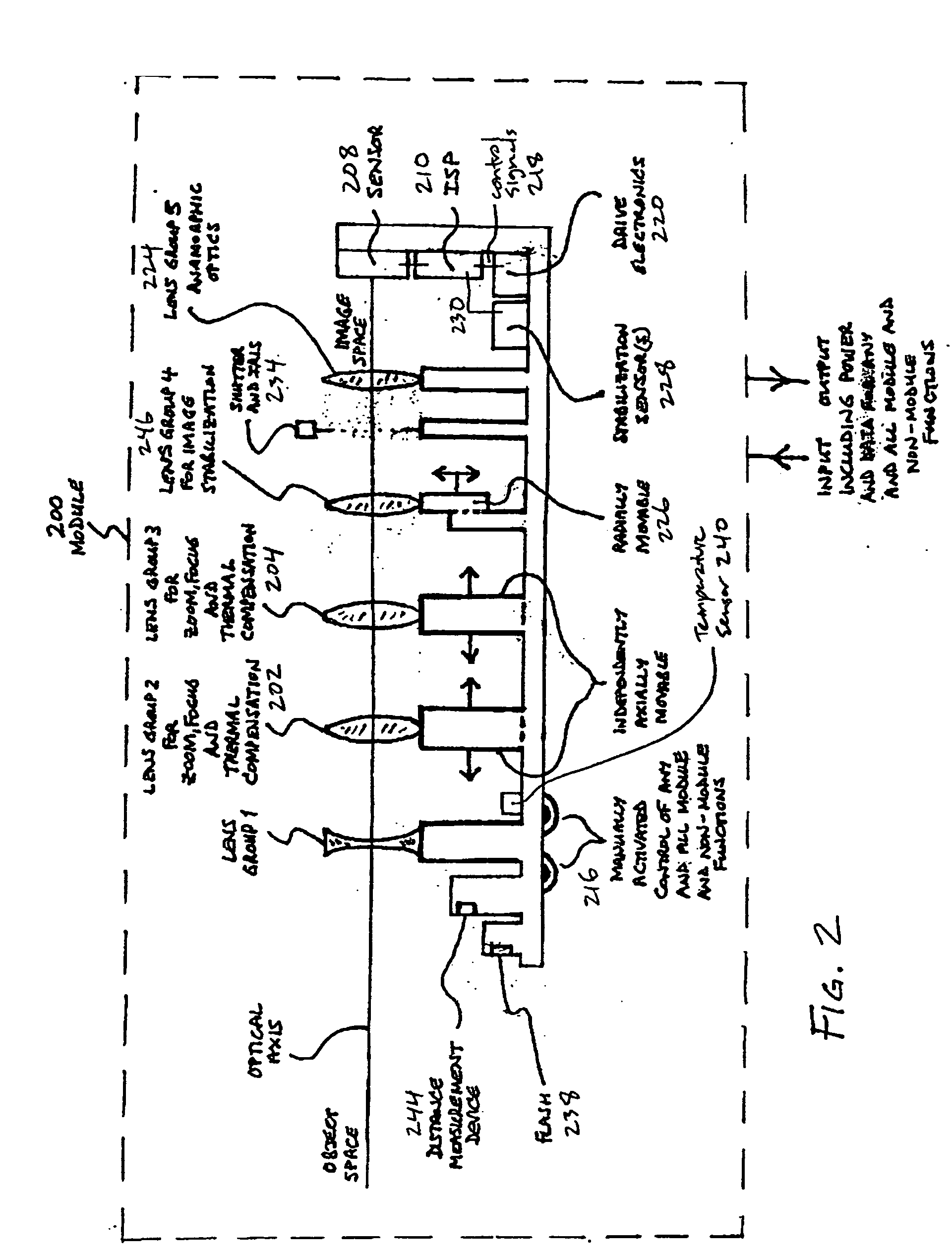
An efficient image capture system is disclosed that integrates functions to control a lens including one or more of focus or object distance, zoom, temperature compensation, and stabilization within an image signal processor (ISP) with appropriate algorithms. In particular, the integrated ISP circuitry may control the motion of the focus and zoom optics of an optical assembly, control stabilization, control the flash, provide enhanced functions and features for controlling the zoom and focus lenses to enable enhanced image capture sequences and / or tracking lens data, provide a set of algorithms within the ISP to alter the aspect ratio (both height and width of an image) of the image, for example to compensate for the addition of an anamorphic lens, and integrate an anamorphic lens into the module to alter an image's projected aspect ratio onto the focal plane array.
Owner:DYNAMAX IMAGING
System and method for laser generated corneal and crystalline lens incisions using a variable f/# optical system with aspheric contact interface to the cornea or rotating and adaptive optics
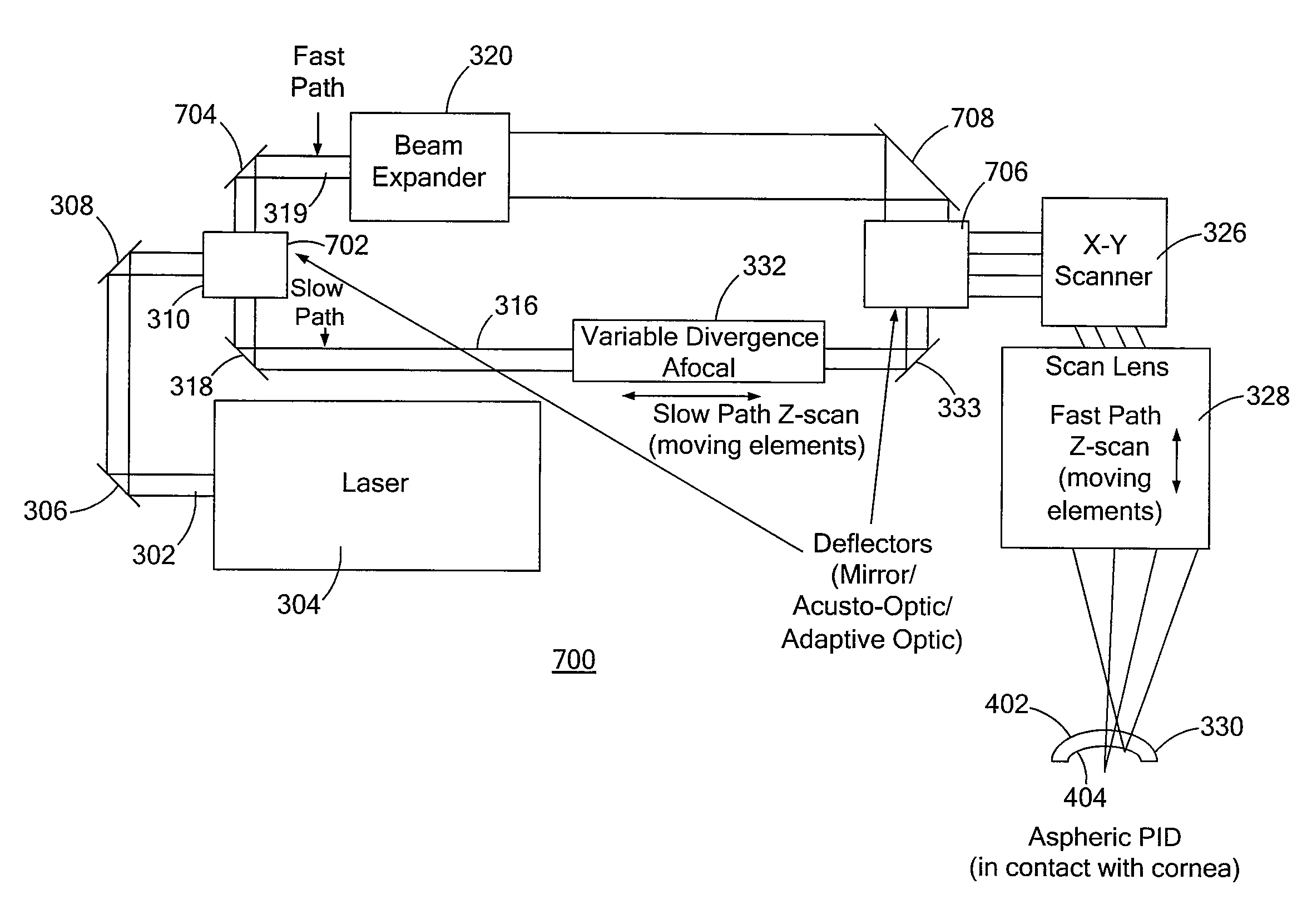
ActiveUS20120271286A1Reduce complexityMaximum flexibilityLaser surgeryPolarising elementsFast pathSelf adaptive
A laser system including a laser source that generates a laser beam and an optical switch that receives the laser beam and sends the laser beam to either a fast path or a slow path, wherein the F / # of the fast path is lower than the F / # of the slow path. The laser system includes an afocal optical system in the slow path and receives the laser beam from the optical switch and an x-y scanner that receives either a laser beam from the slow path or a laser beam from the fast path. The laser system including a scan lens system that performs a z-scan for the scanning laser beam only in the case wherein the scanning laser beam is generated from the laser beam in the fast path. The laser system including an aspheric patient interface device that receives a laser beam from the scan lens system.
Owner:LENSAR LLC
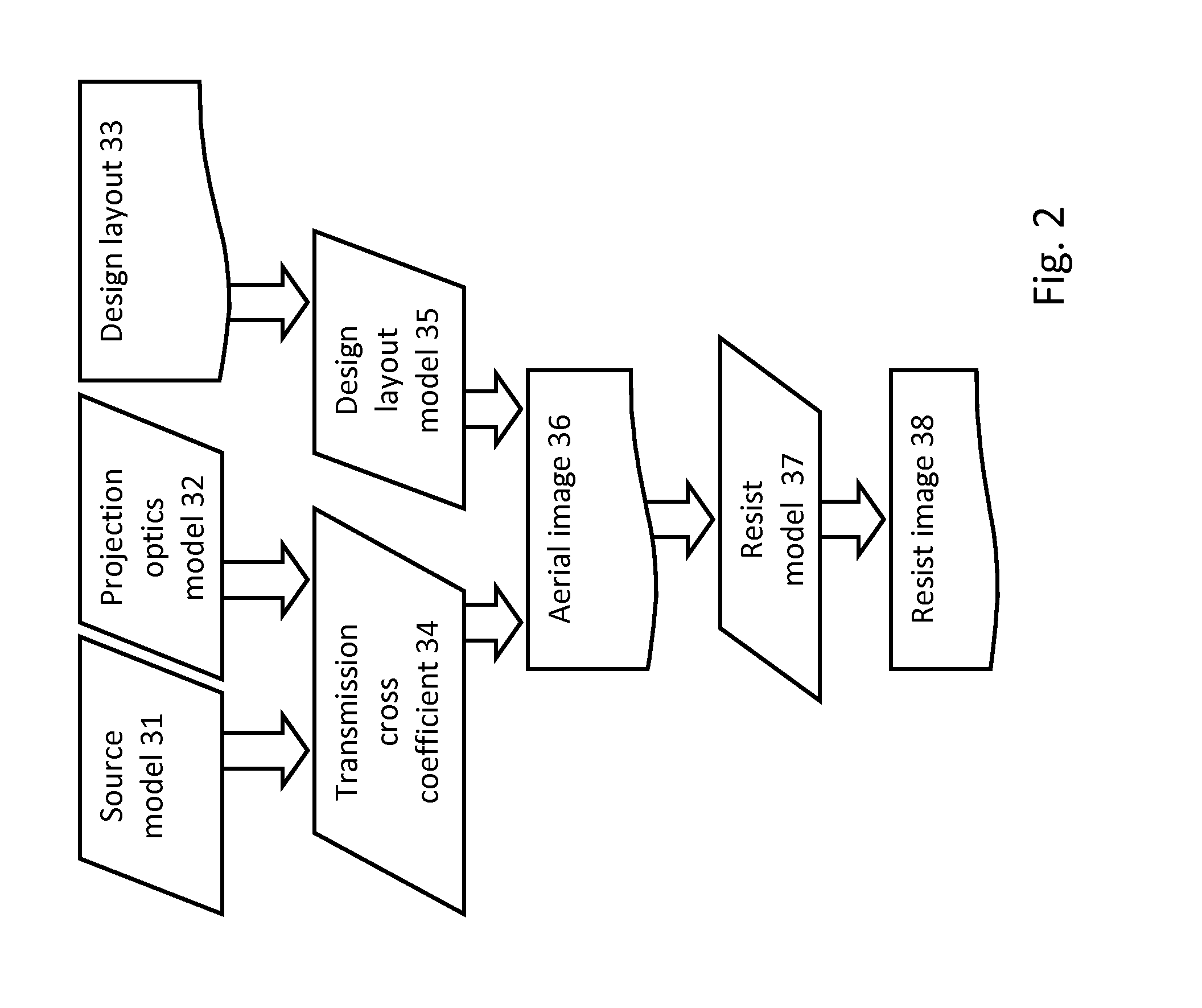
Optimization Flows of Source, Mask and Projection Optics
ActiveUS20120113404A1Improve or optimize the lithographic projection apparatusPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProjection opticsWavefront
Embodiments of the present invention provide methods for optimizing a lithographic projection apparatus including optimizing projection optics therein. The current embodiments include several flows including optimizing a source, a mask, and the projection optics and various sequential and iterative optimization steps combining any of the projection optics, mask and source. The projection optics is sometimes broadly referred to as “lens”, and therefore the optimization process may be termed source mask lens optimization (SMLO). SMLO may be desirable over existing source mask optimization process (SMO) or other optimization processes that do not include projection optics optimization, partially because including the projection optics in the optimization may lead to a larger process window by introducing a plurality of adjustable characteristics of the projection optics. The projection optics may be used to shape wavefront in the lithographic projection apparatus, enabling aberration control of the overall imaging process.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
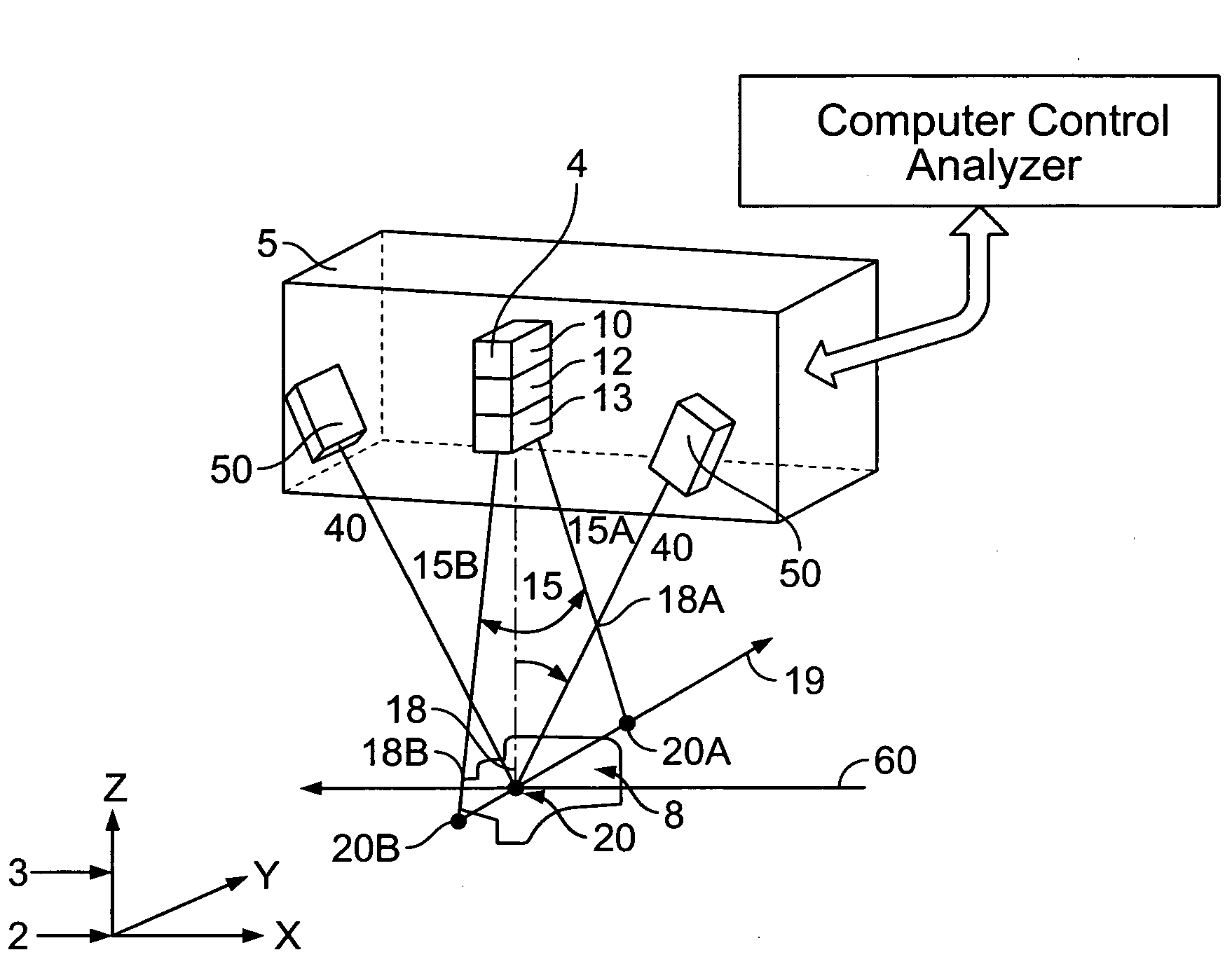
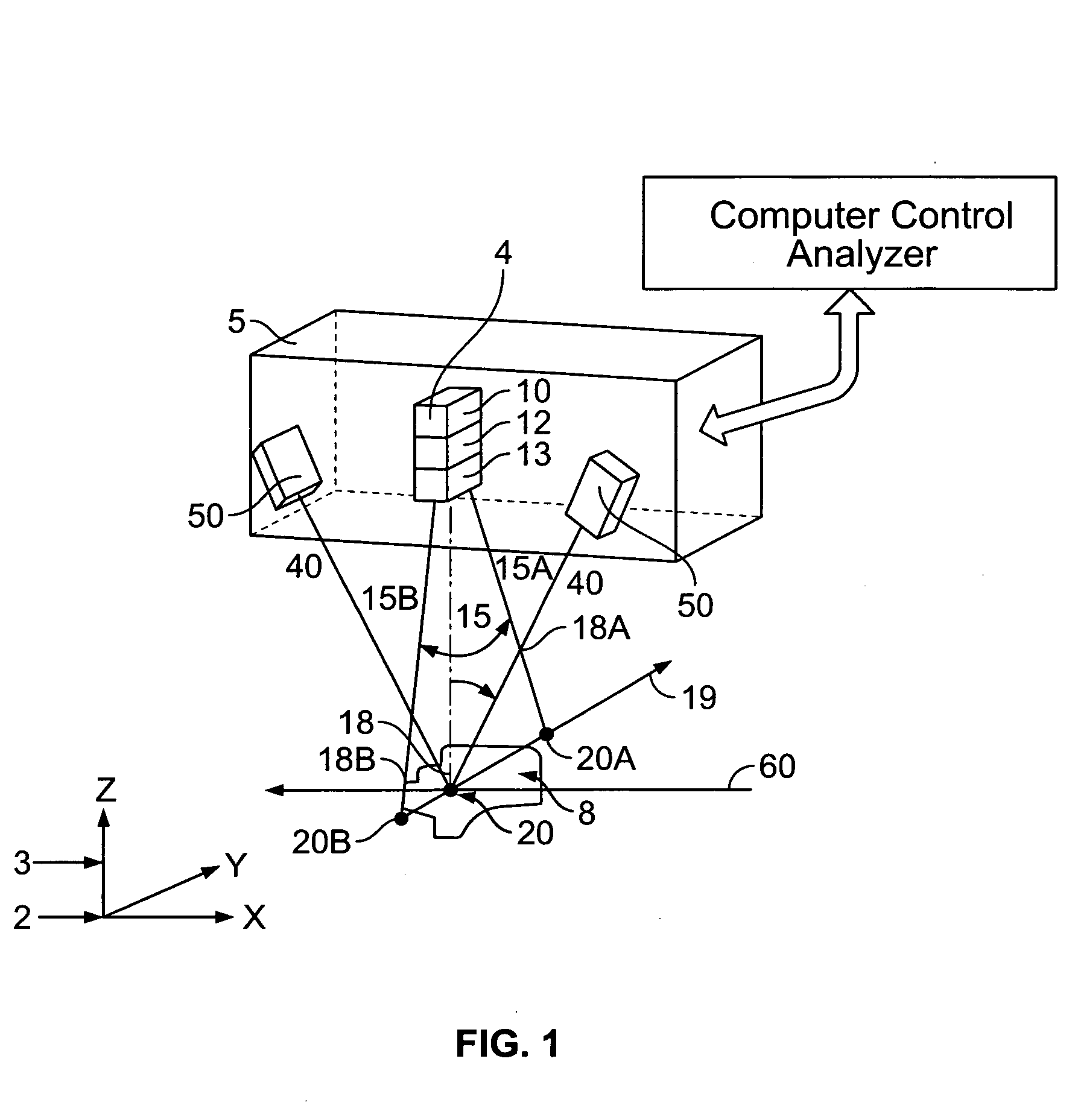
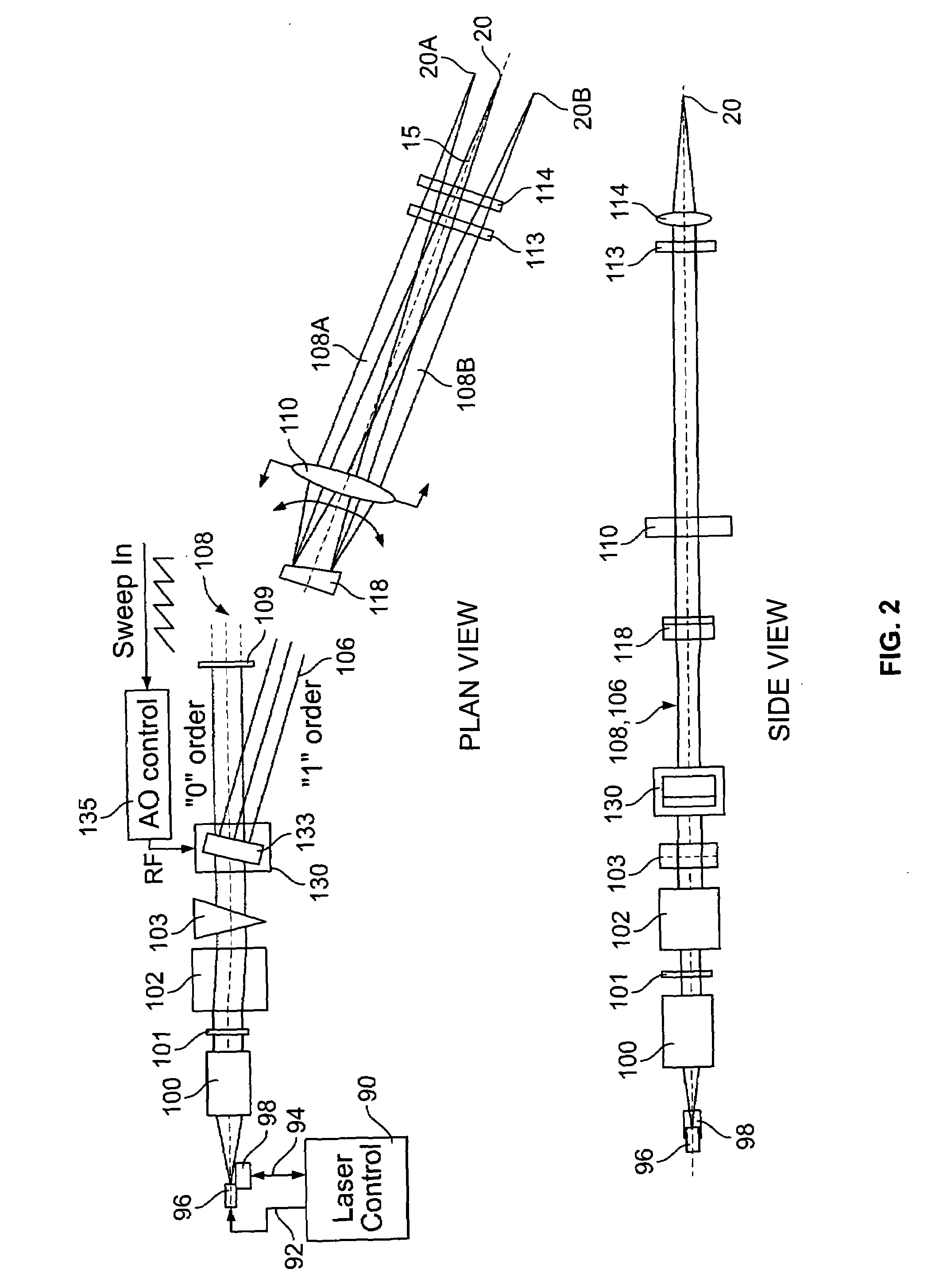
Method and system for providing a high definition triangulation system
ActiveUS20080165357A1Precise positioningSmall spot sizeScattering properties measurementsUsing optical meansOphthalmologyTriangulation
A triangulation system including a laser beam, optics focusing the laser beam on an object, a light detection unit detecting light reflected from the object due to impingement of the beam on the object, and an arrangement for determining, based on the detected light, object feature dimensions. The wavelength of the laser beam may be shorter than of infrared radiation, which allows for a reduced spot size without significant loss of depth of field. So as to reduce aberrations or a sensitivity to aberrations due to the shortened wavelength, the system may include (i) a polarization dependent coating matching the index of refraction of an element of the light detection unit to that of air for a range of angles, (ii) tilted projection optics, (iii) a prism wavefront corrector, and / or (iv) a positioning assembly, which provides for increased precision in positioning the laser diode with respect to a collimator lens.
Owner:ONTO INNOVATION INC
System and method of an integrated fiber optic inspection and cleaning apparatus
ActiveUS20130229650A1Rapid positioningHigh resolutionOptically investigating flaws/contaminationFlexible article cleaningFiberWide field
This disclosure concerns a cleaning and inspection system for fiber optics that is rapid, reliable and useful for various types of fiber optics. In an embodiment, the system includes a wide field of view (FOV) camera to image the ferrule and rapidly locate the fiber ends and a narrow FOV camera to provide detailed inspection of fiber ends. A cleaning module with a cleaning tip and a cleaning media that is drawn through the tip is used to clean the fiber ends. Images captured by the dual cameras are automatically enhanced and analyzed to determine the effectiveness of the cleaning process and to identify the types and quantity of defects present. In another embodiment, a single higher resolution camera is provided with a lens that can image an entire fiber array and yet enable defects to be detected by analysis of sub-images of each fiber in the fiber array.
Owner:FIBERQA
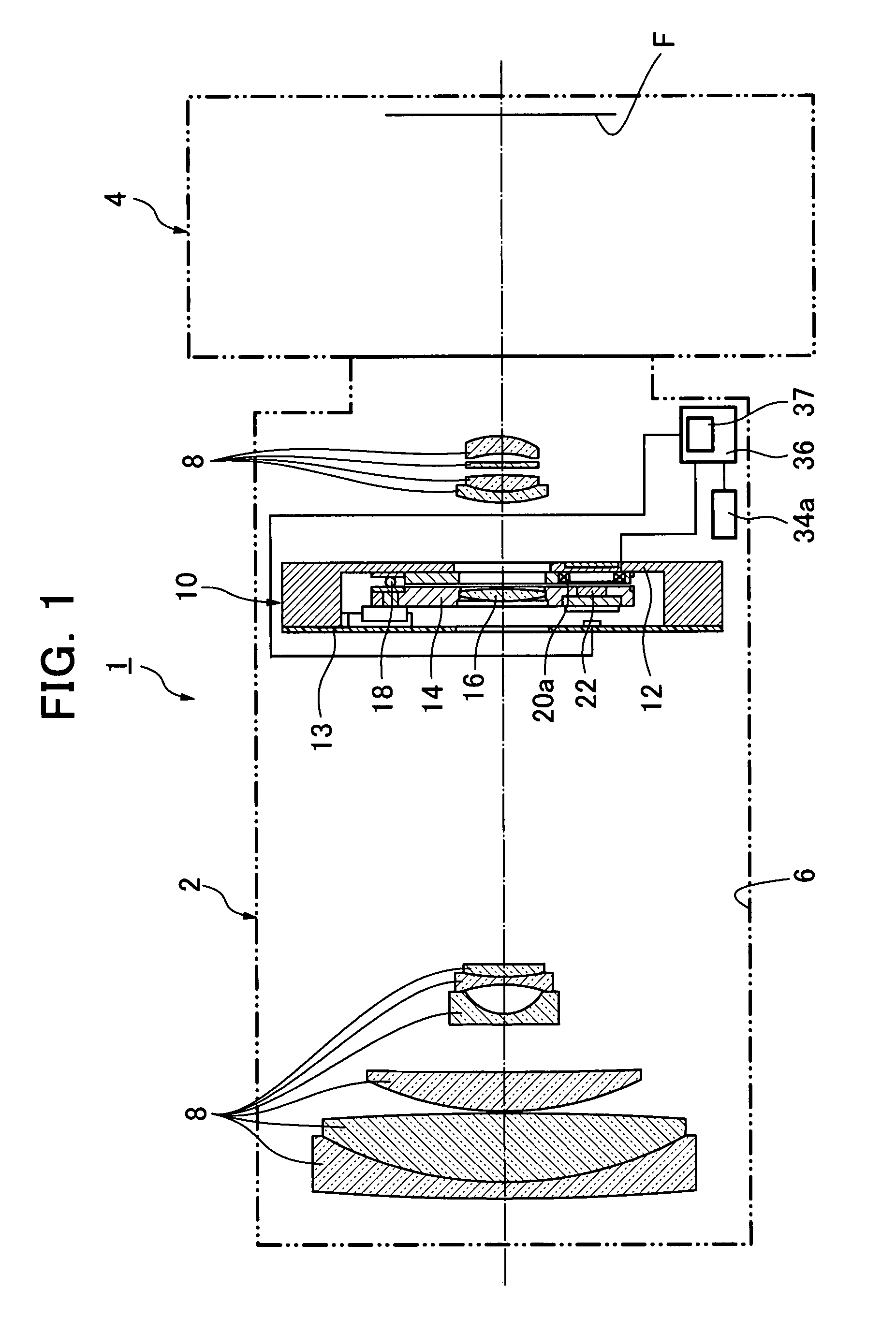
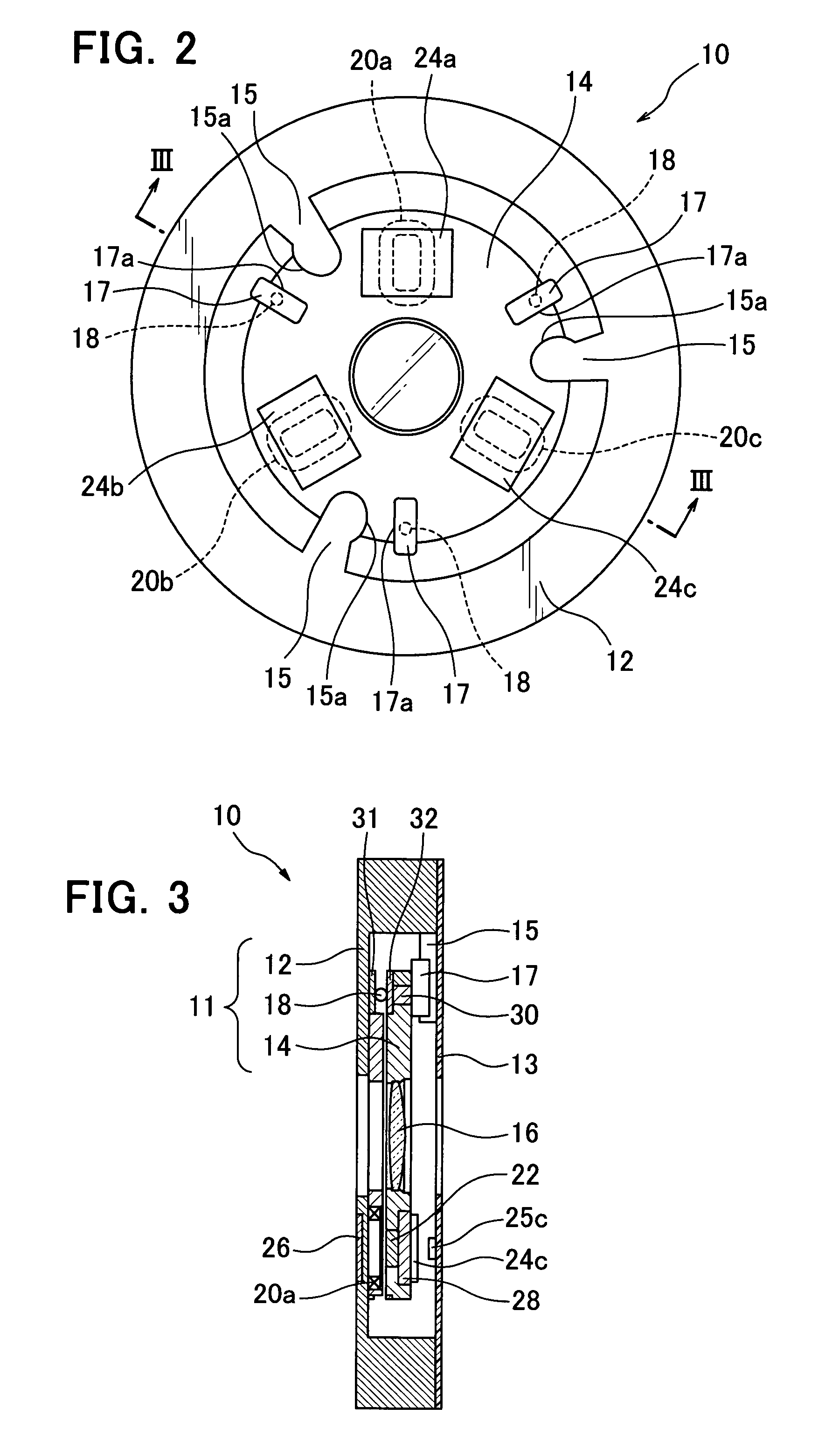
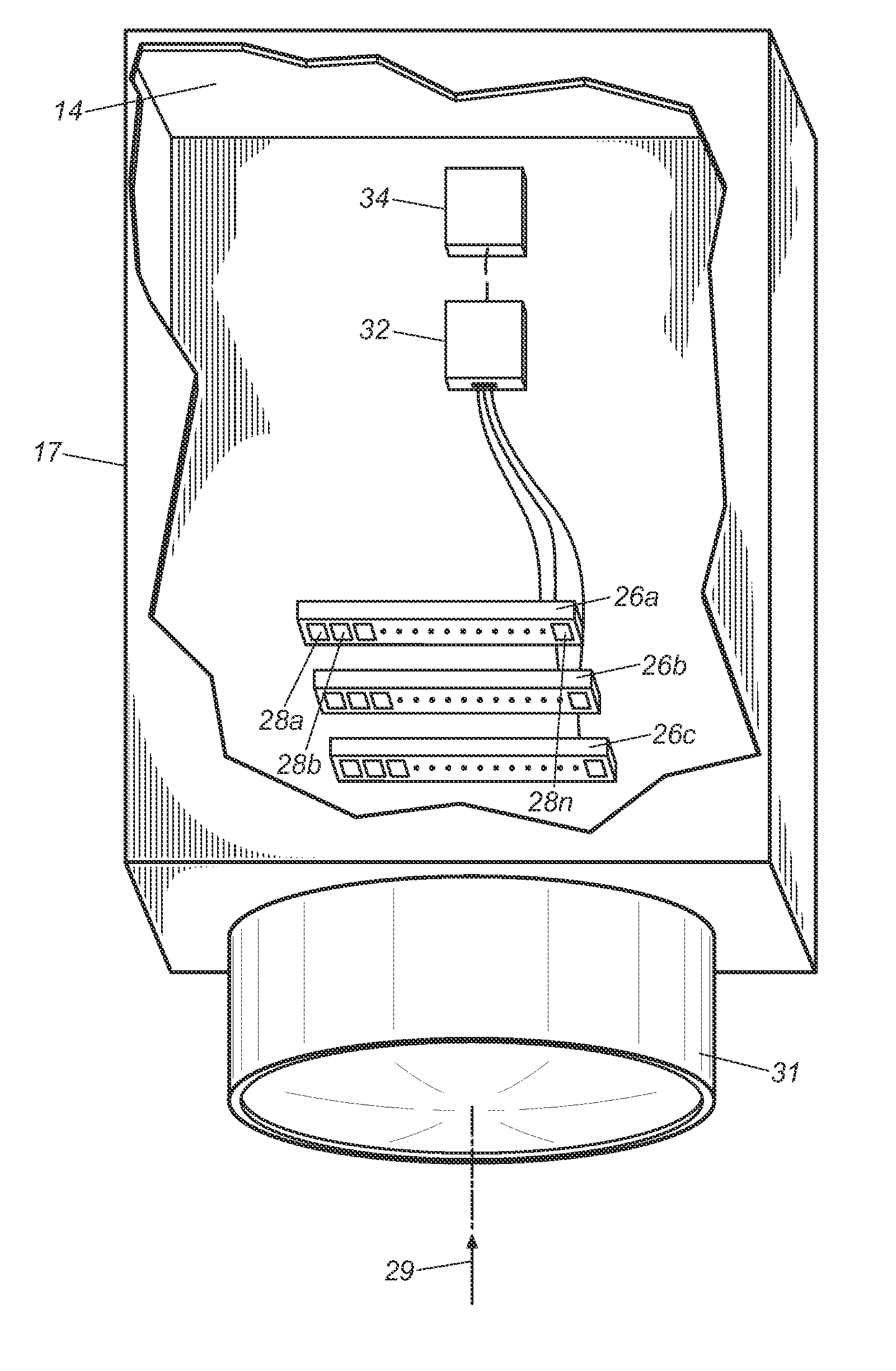
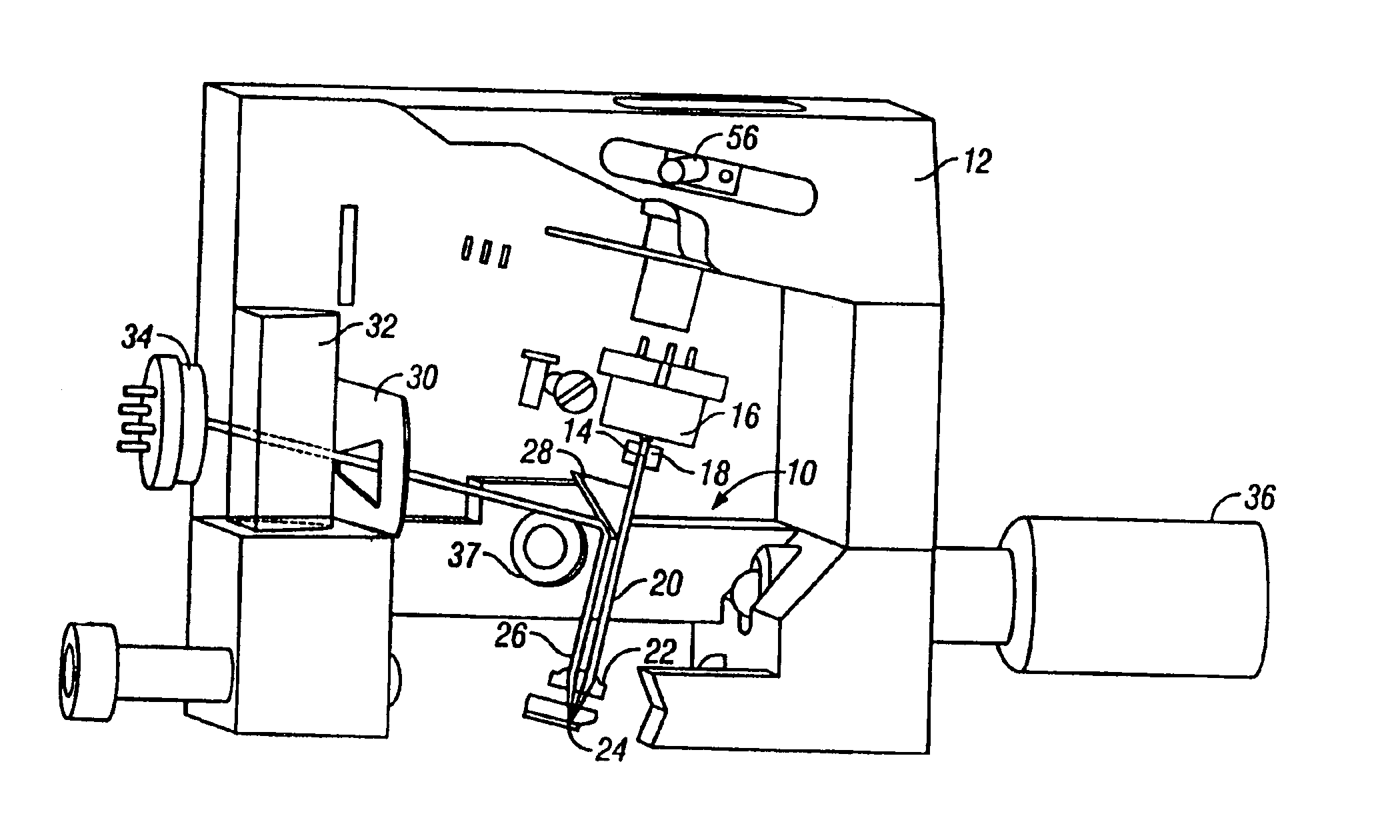
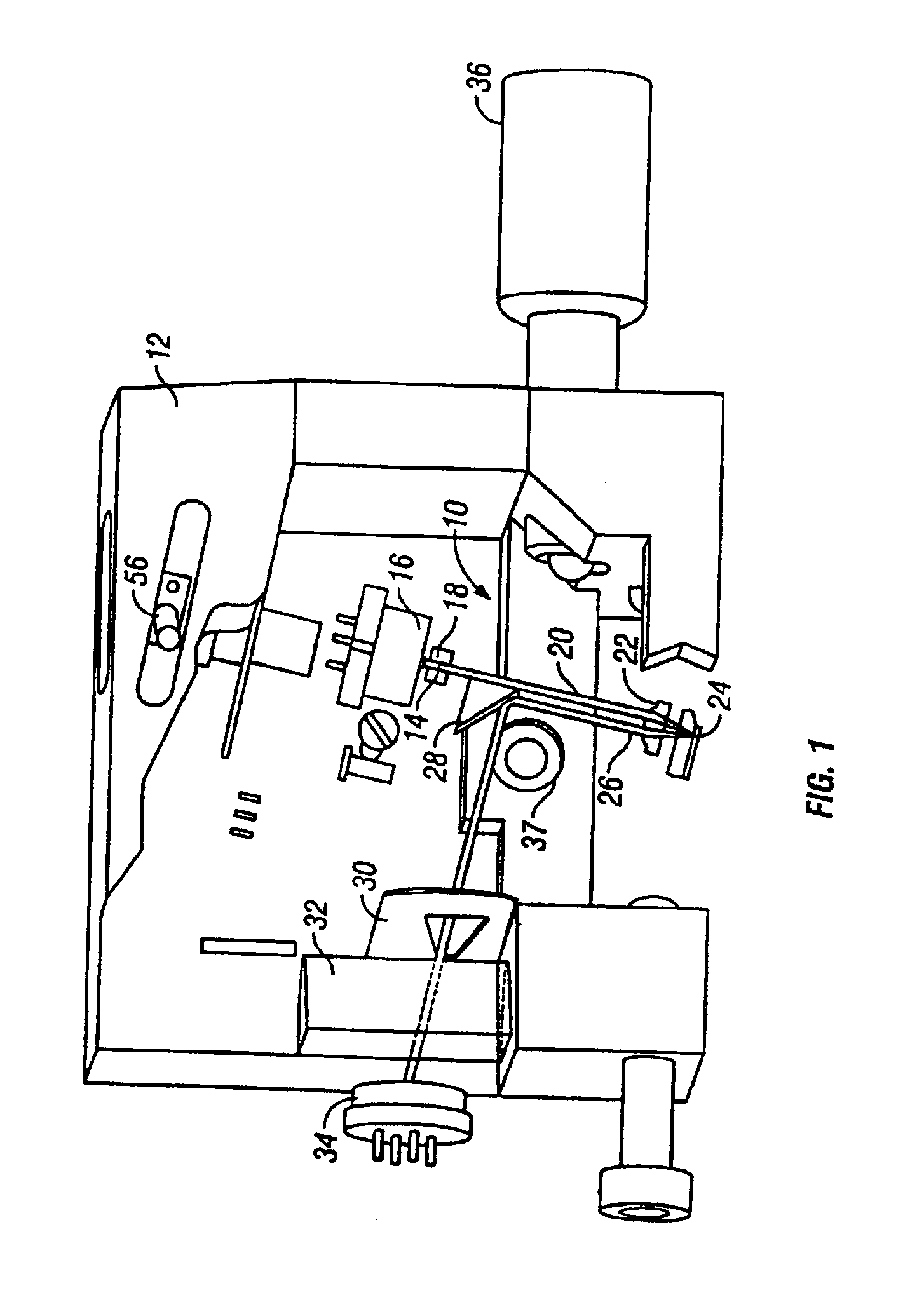
Actuator, and lens unit and camera with the same
The present invention is directed to an actuator capable of retaining an image-shake correcting lens in a position(s) at which a calibration of lens optics can be affected, without additional locking means. The actuator (10) is capable of translating an image-shake correcting lens (16) so as to prevent an image from shaking, and the actuator is comprised of a fixed member (12), a movable member (14) provided with the image-shake correcting lens, supporting means (18) for supporting the movable member, a position detecting means (24, 25) for detecting a position of the movable member, a driving means (20, 22) for translating and rotating the movable member, a plurality of positioning receiving portions (15a) provided on the fixed member, a plurality of positioning contact surfaces (17a) disposed on the movable member and forced by a rotational movement of the movable member to mate and come in contact with the positioning receiving portions so that the movable member can be moved to a calibration position, and a calibrating means (37) for calibrating the position detecting means in response to detection values from the position detecting means that are received when the movable member is positioned at the calibration position.
Owner:TAMRON
Large depth of field line scan camera
InactiveUS20070164202A1Material analysis by optical meansPhotoelectric discharge tubesDepth of fieldLinearity
A system for imaging an object comprising a surface for receiving the object to be imaged and an imaging device. The imaging device comprises a housing and a fixed focusing optical device mounted to the housing, whereby the fixed focusing optics comprises a lens for focusing light reflected from the object. A plurality of independent linear imaging sensors are positioned in the housing at different distances from the fixed focusing lens so that a face of each of the plurality of independent linear imaging sensors is aligned parallel to the surface. A processor is coupled to the plurality of independent linear imaging sensors for receiving an output signal from each of the plurality of independent linear imaging sensors representative of the reflected light. The lens defines a plane parallel to the surface, and the plurality of independent linear imaging sensors are adapted to receive reflected light from the object.
Owner:ACCU SORT SYST
High-collimation solar simulator optical system with auto-collimation aiming system
InactiveCN101907773AAccurate zero calibrationEliminate human influenceIndividual semiconductor device testingOptical elementsEyepiecePlane mirror
The invention relates to a high-collimation solar simulator optical system with an auto-collimation aiming system, belonging to a solar simulator optical system in the technical field of optics design and aiming at solving the technical problem of providing a high-collimation solar simulator optical system with the auto-collimation aiming system. The high-collimation solar simulator optical system with the auto-collimation aiming system comprises a xenon lamp source, an ellipsoid condenser, a plane mirror, an optics integrator assembly, a first dispersion prism, a second dispersion prism, an emission reticle, an LED light source, an aiming reticle, an ocular lens and a collimator objective. On the basis of the traditional high-collimation solar simulator optical system, an auto-collimation aiming system is added on an optical path of the optical integrator assembly, wherein the auto-collimation optical system comprises a first dispersion prism, a second dispersion prism, an emission reticle, an LED light source, an aiming reticle and an ocular lens. The invention can ensure more accurate zero calibration so as to eliminate the man-made influence and achieve better experimental effect.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
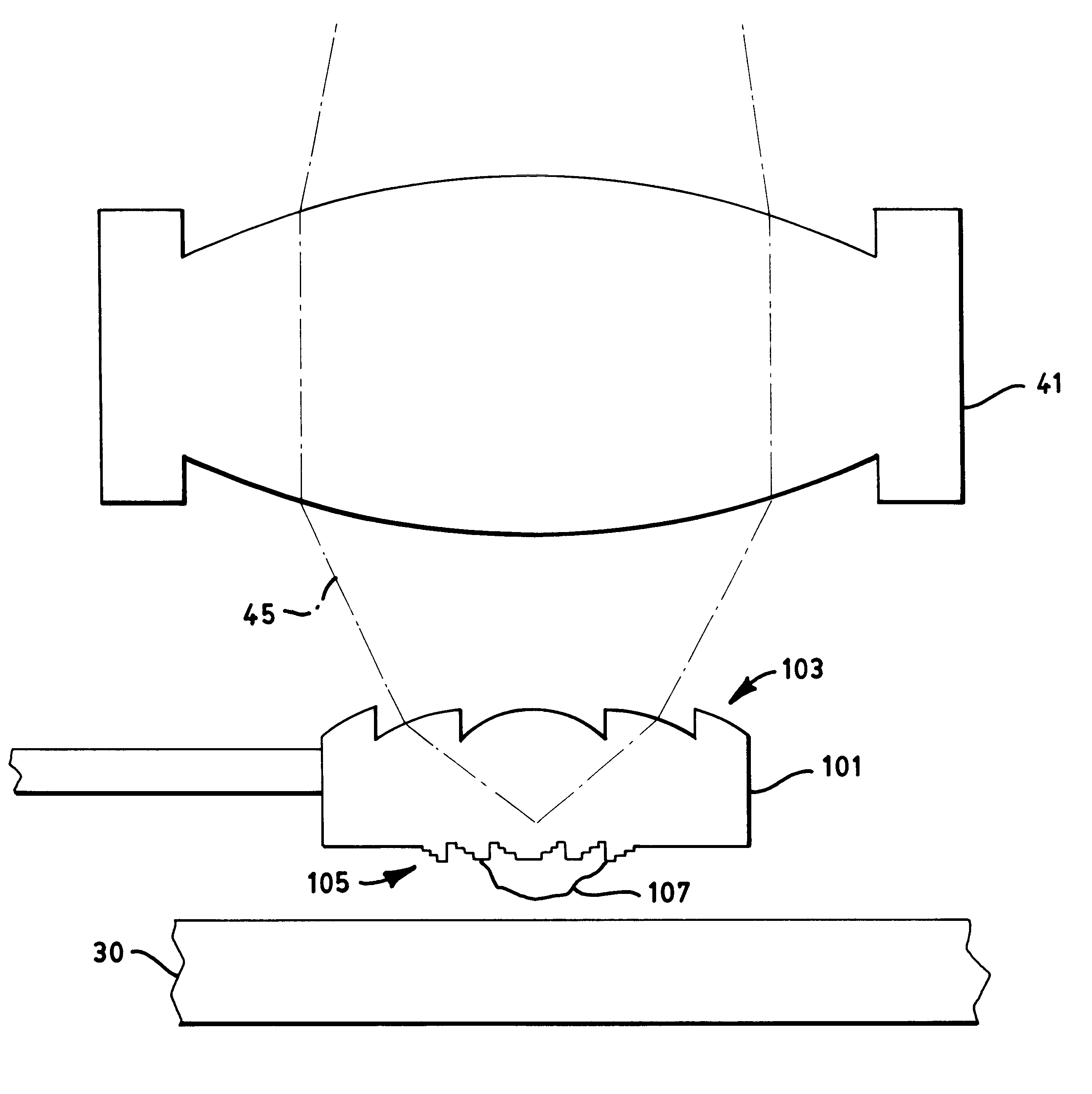
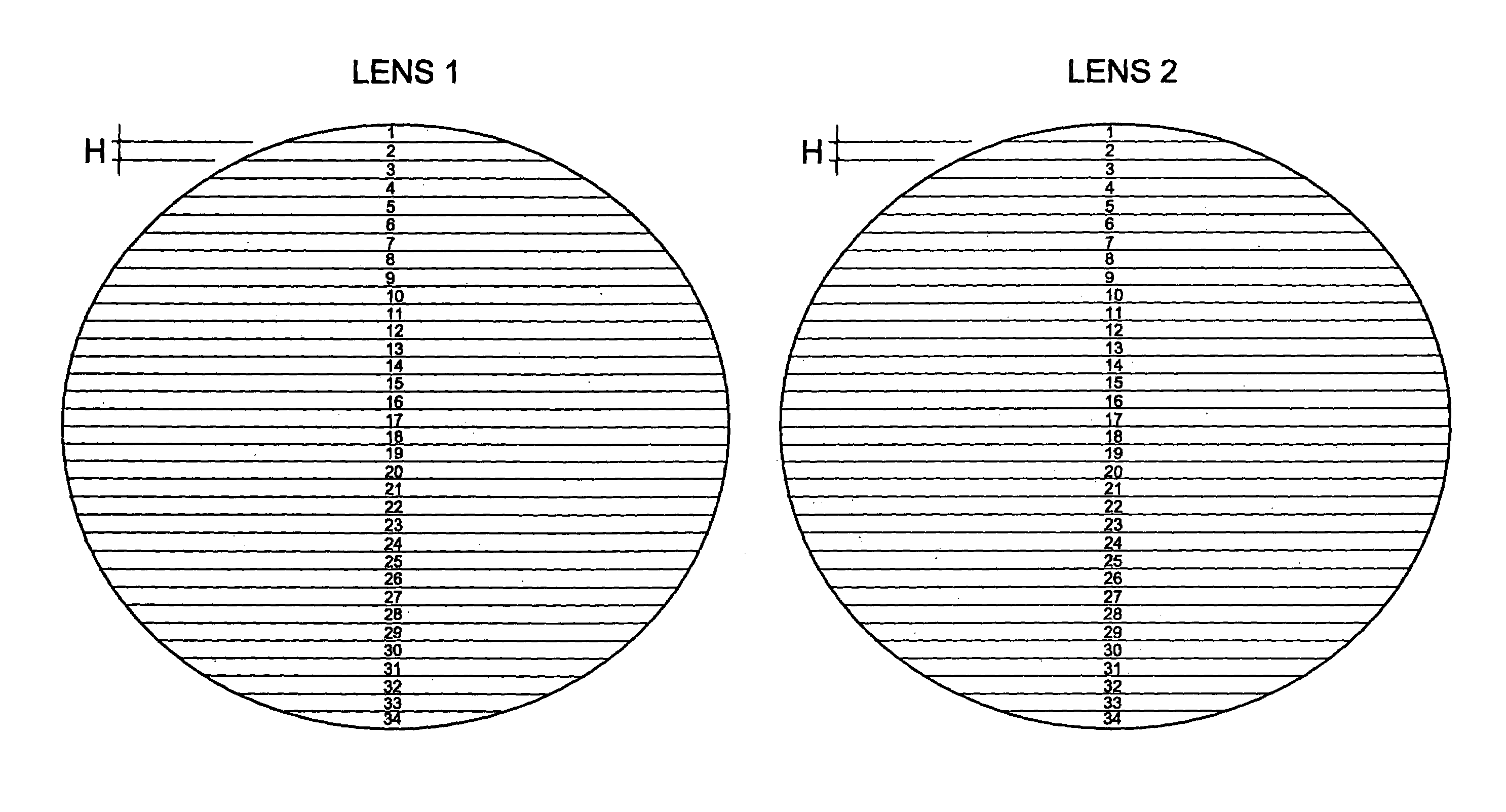
Dual complementary two-color optics which enables a user to see true neutral color, with improved shading design and shadow detail
InactiveUS6932472B2Improved shadow detailImprove shadingEye diagnosticsOptical partsCamera lensColor correction
A pair of dual complementary optics having a first lens and a second lens wherein the first lens has a gradient of a multiplicity of bands, the uppermost series of bands having a primary color embedded therein and the lowermost series of bands having a complementary secondary color embedded therein, the second lens having the inverse color embedded therein so that a primary color in the first lens is aligned with a secondary color in the second lens and a secondary color in the first lens is aligned with a primary color in the second lens. The color correction units are created such that the uppermost band has the largest amount of color correction units gradually decreasing to the lowermost band of the same color having the least amount of color correction units and thereafter, the second lower color has the lowest amounts of color correction units in the uppermost band of the secondary color gradually increasing to the greatest amount of color correction units in the secondary color in the lowermost band with the inverse in the second lens so that the lens is darkest on top and on the bottom and is lightest in the middle. Each lens is capable of either transmitting more than fifty percent of visible light in both wavelength ranges 400–550 nm and 550–750 nm or is capable of transmitting less than fifty percent of the visible length in both wavelength ranges 400–500 nm and 550–750 nm.
Owner:PACIFIC BEACH
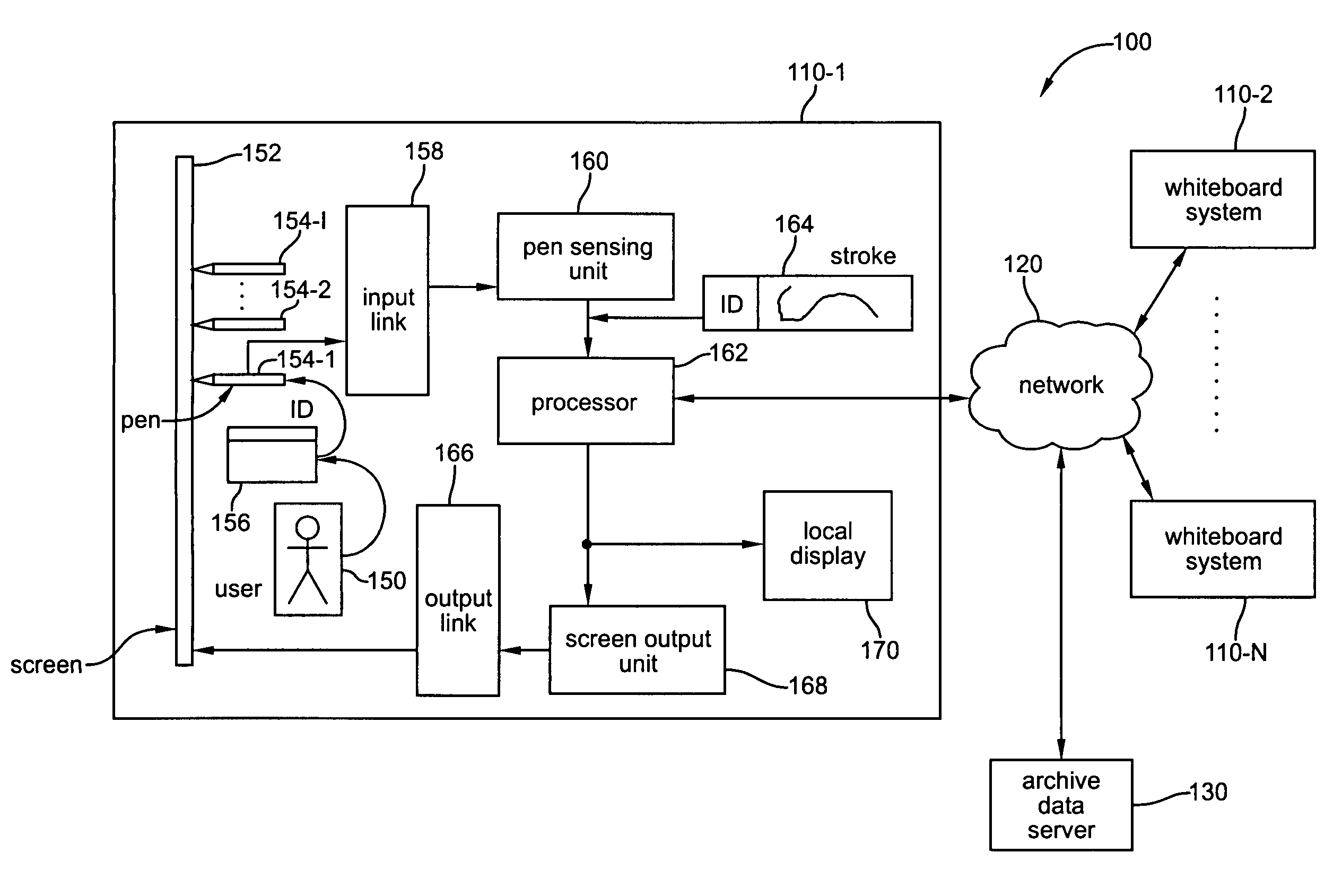
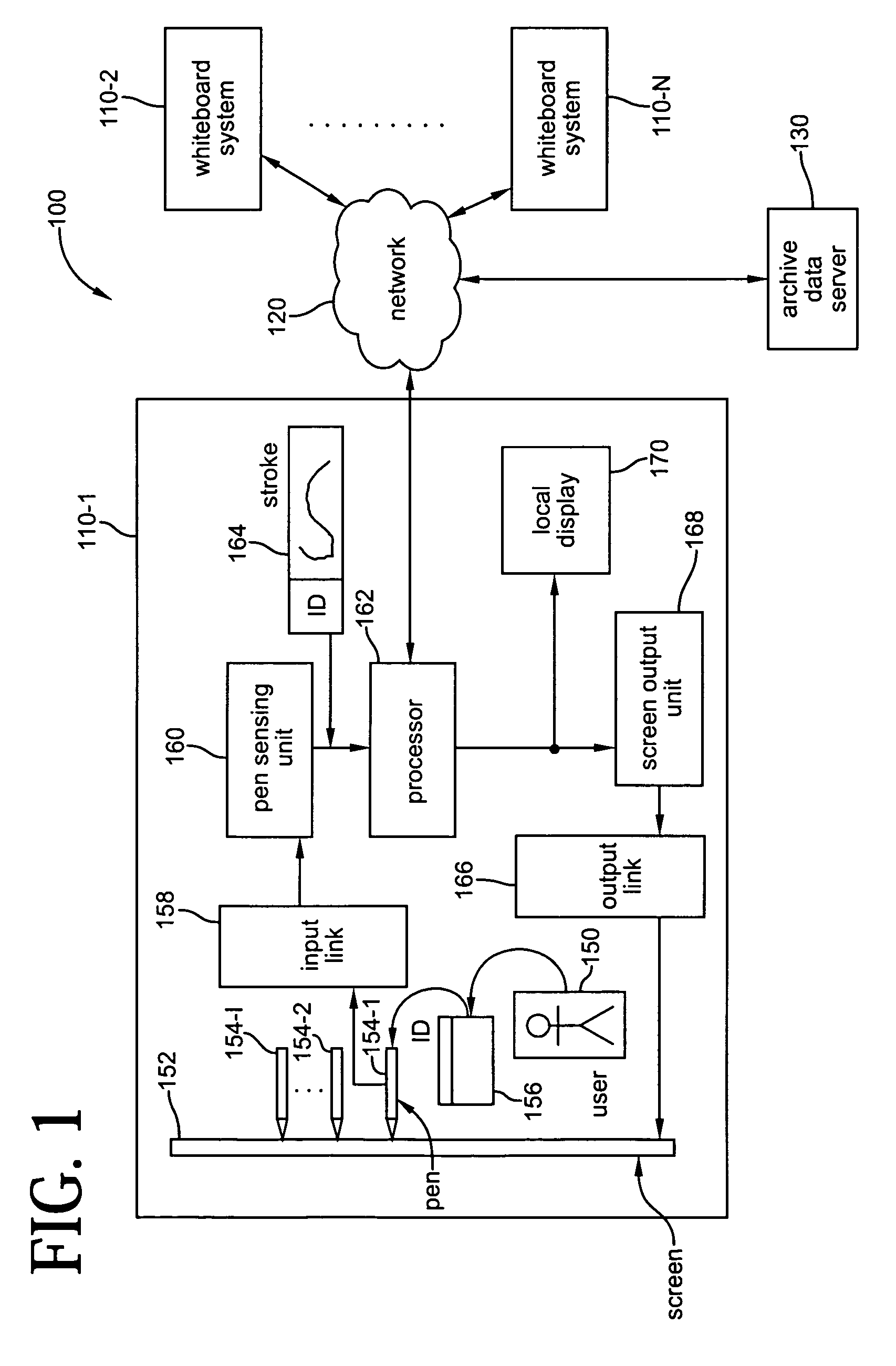
Methods and apparatus for associating a user with content in a collaborative whiteboard system
ActiveUS7219233B1Random number generatorsUser identity/authority verificationComputer graphics (images)Radiology
Projector and camera arrangements are provided for use in electronic whiteboard systems. Specifically, the present invention provides projector and camera arrangements wherein the projector and camera share the same imaging optics. By sharing the same projection and camera optics, the distortions that affect the projection system are the same as those of the camera system. Thus, the calibration step required in conventional whiteboard systems where the projector and camera are separate, i.e., each having their own distinct optics and settings, is no longer needed. Further, the arrangements provided in accordance with the invention are self-aligning, even when lens distortions are large and even in the presence of strong perspective effects. The shared optics projector and camera arrangements of the invention also provide for dynamic zooming. In addition, various active and passive optical marker or lightpen designs are provided for use in electronic whiteboard systems.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Camera system with exchangeable illumination assembly
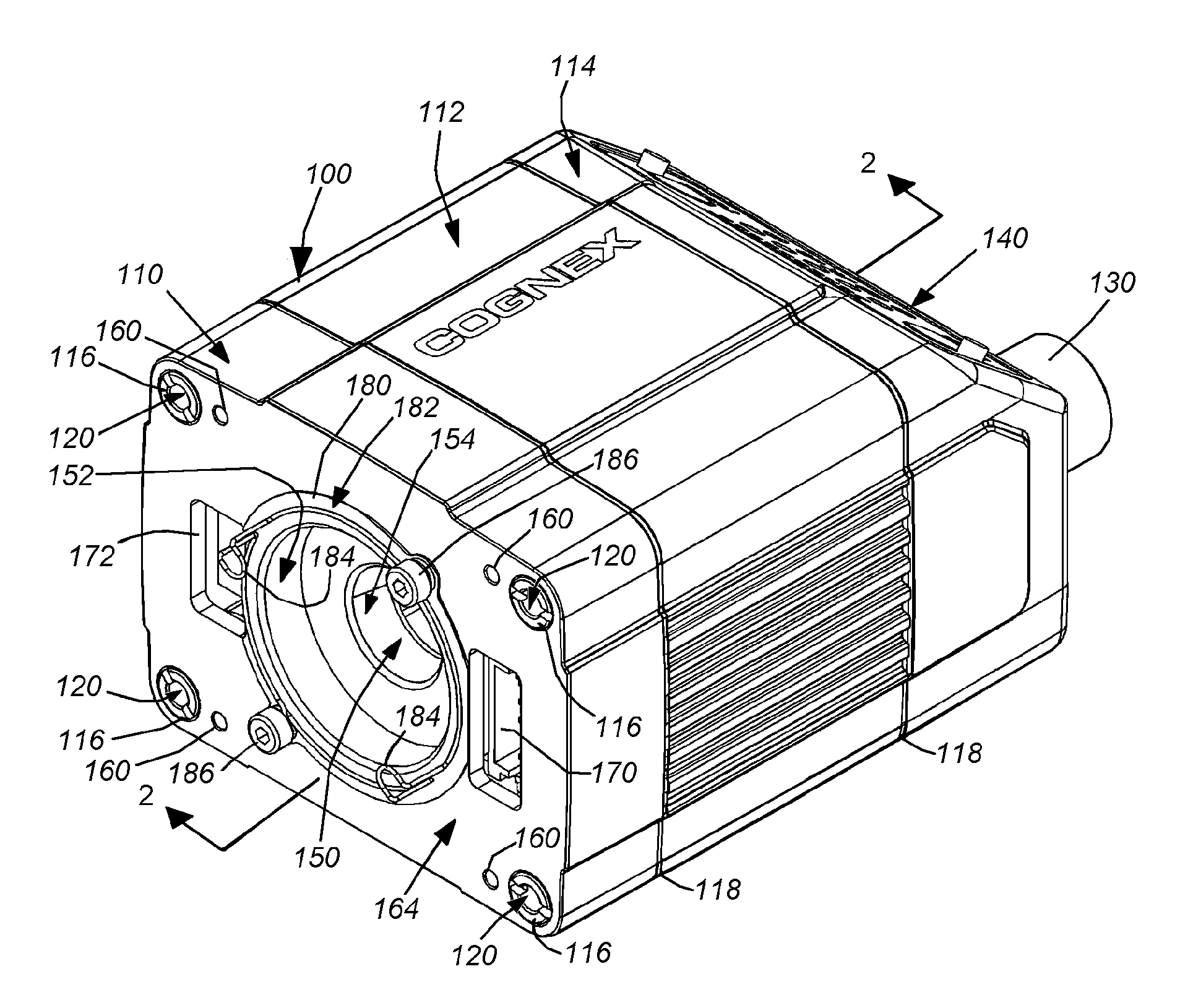
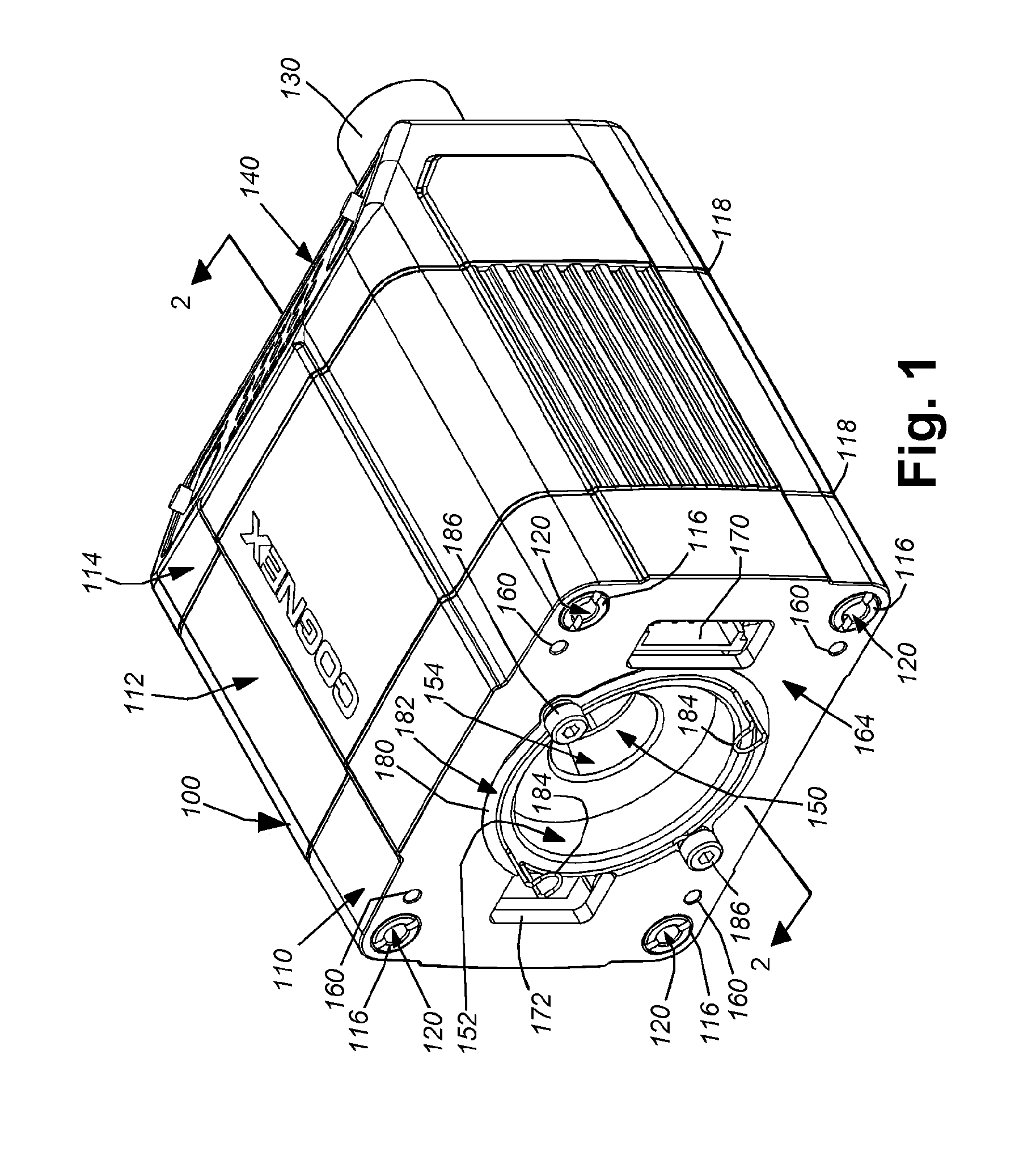
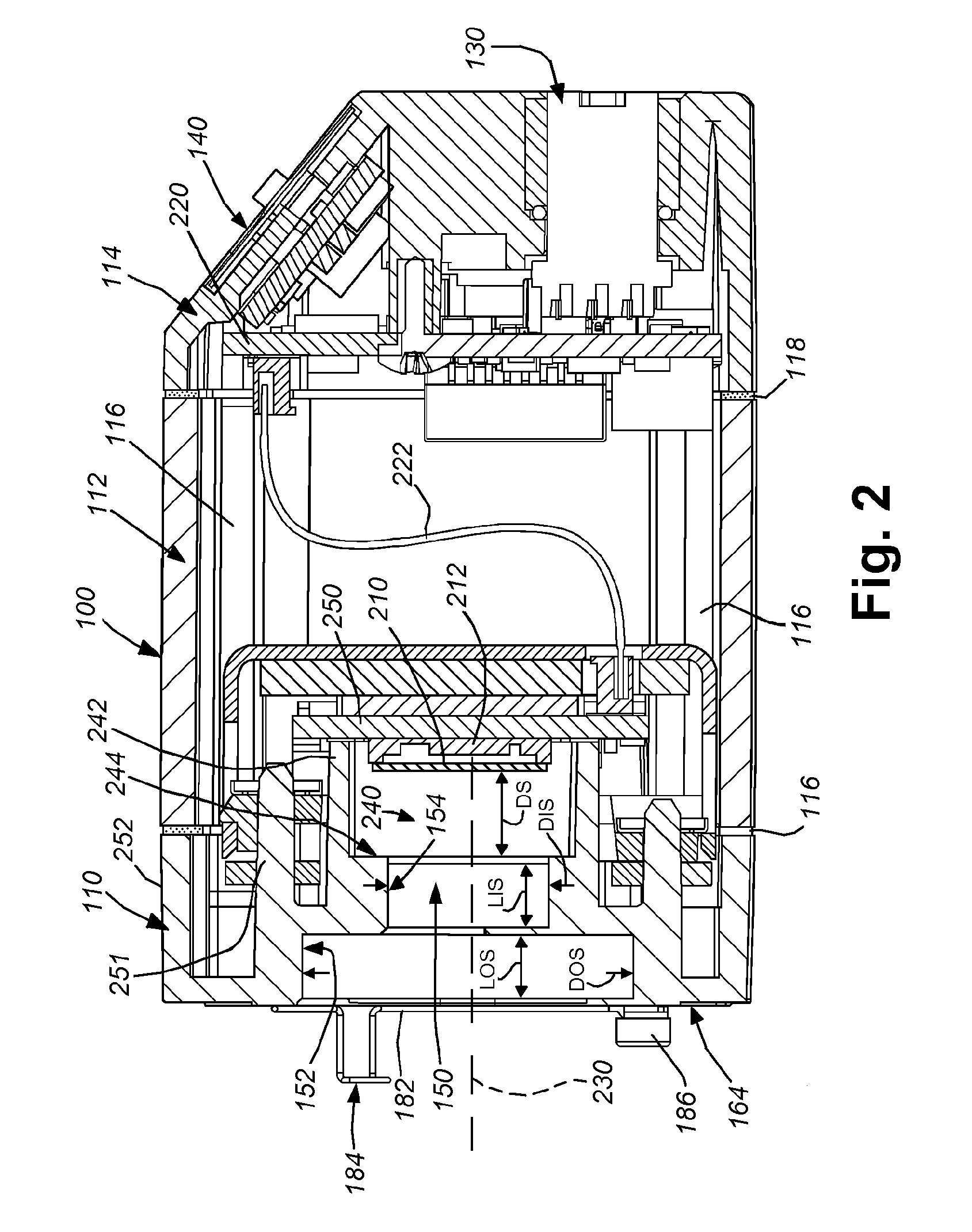
ActiveUS20130128104A1Improve versatilityEasy to disassembleTelevision system detailsColor television detailsVision processingCamera lens
This invention provides a vision system with an exchangeable illumination assembly that allows for increased versatility in the type and configuration of illumination supplied to the system without altering the underlying optics, sensor, vision processor, or the associated housing. The vision system housing includes a front plate that optionally includes a plurality of mounting bases for accepting different types of lenses, and a connector that allows removable interconnection with the illustrative illumination assembly. The illumination assembly includes a cover that is light transmissive. The cover encloses an illumination component that can include a plurality of lighting elements that surround an aperture through which received light rays from the imaged scene pass through to the lens. The arrangement of lighting elements is highly variable and the user can be supplied with an illumination assembly that best suits its needs without need to change the vision system processor, sensor or housing.
Owner:COGNEX CORP
Integrating method of three-dimensional spatial distribution vortex arrays
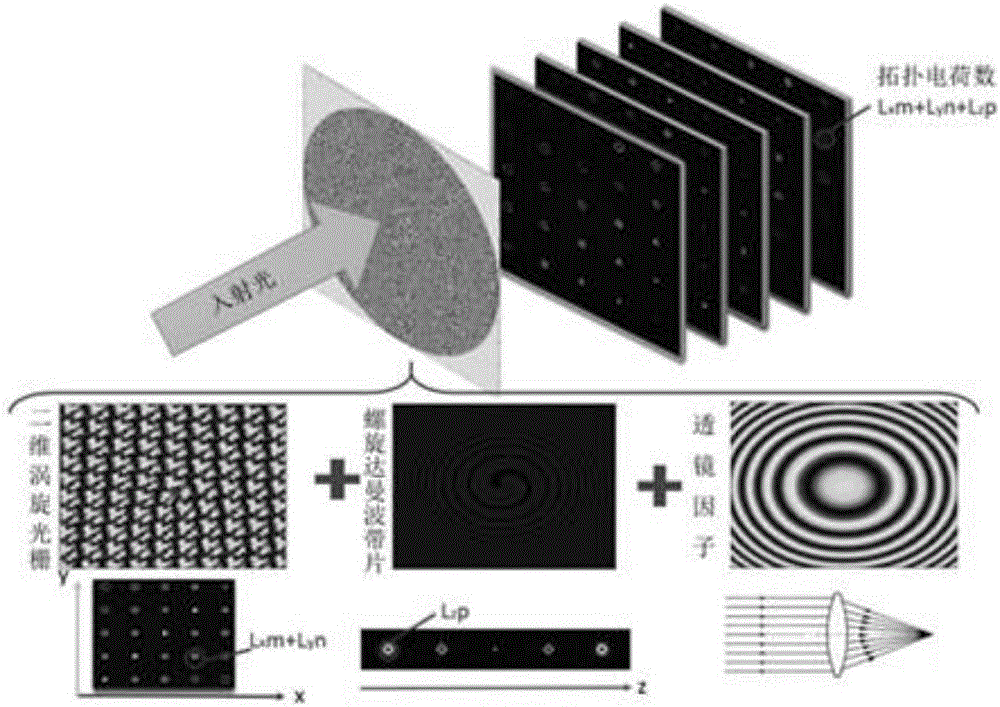
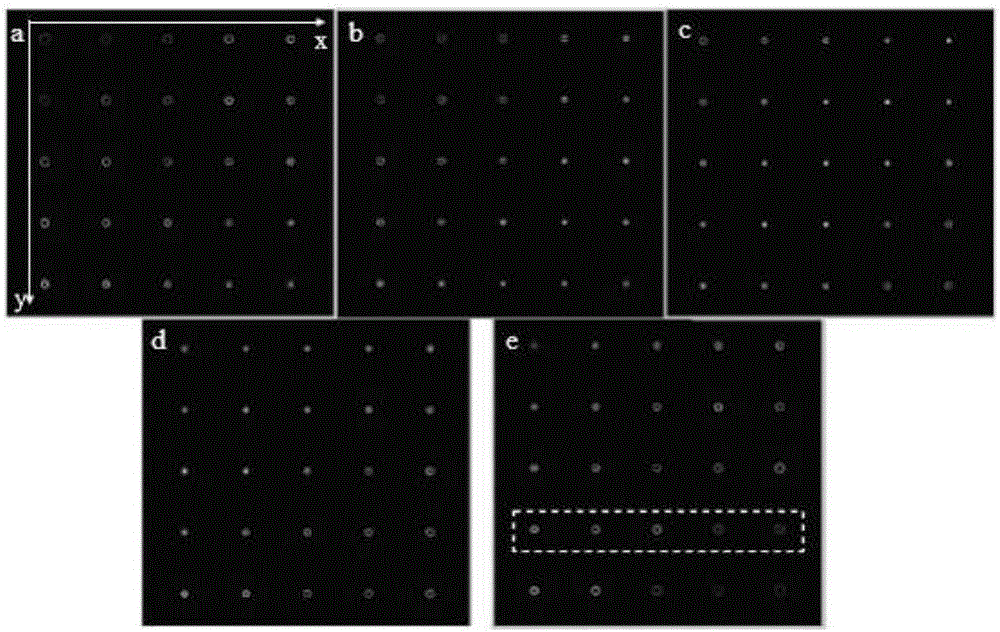
ActiveCN106199800AEqual light intensityReduce complexityDiffraction gratingsSpatial light modulatorGrating
The invention relates to an integrating method of three-dimensional spatial distribution vortex arrays, and belongs to the field of diffraction optics. A pure-phase code of a two-dimensional uniform-strength vortex optical grating and a pure-phase code of a spiral Dammam wave zone plate are obtained through analytic operation and an optimization algorithm respectively, phase information of the pure-phase codes is overlaid, a lens factor is introduced, discretized phase values are loaded to a spatial light modulator according to the pixel number and the pixel size of the spatial light modulator, and then the corresponding three-dimensional vortex arrays can be obtained. According to the method, the equal-strength and regular-distribution three-dimensional vortex arrays can be obtained, and each vortex beam in the arrays has the specific topological charge number.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Measurement head for atomic force microscopy and other applications
InactiveUS6871527B2Small and rigid packageIncrease stiffnessMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsAtomic force microscopyLight beam
An improvement for atomic force microscopes, more generally for light beam detecting systems, but also in part applicable to scanning probe microscopes, providing significant novel features and advantages. Particular features include using different objective lens regions for incident and reflected light, a flexure that allows three dimensional motion of the optics block, forming the housing and optics block of a composite material or ceramic, arranging the components so that the beam never hits a flat surface at normal incidence, and providing a resonant frequency of cantilever vibration greater than 850 HZ between the cantilever and sample and the cantilever and focusing lens.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Ophthalmic interface apparatus and system and method of interfacing a surgical laser with an eye
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Doppler asymmetric spatial heterodyne spectroscopy
ActiveUS20090051899A1Improve the ability to solveSmall sensitivityRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryWavefrontGrating
A Doppler Asymmetric Spatial Heterodyne (DASH) spectrometer includes an input aperture for receiving an input light; a collimating lens for collimating the input light into a collimated light; offset establishing means, including at least one grating, for i) receiving and splitting the collimated light into a first light wavefront in a first optical path and into a second light wavefront in a second optical path, ii) establishing an offset in a light wavefront path distance between the first and second optical path light wavefronts, and iii) diffracting and recombining the first and second optical path light wavefronts into an interference wavefront to form an interference image that includes a plurality of phase points of a heterodyned interferogram measured simultaneously over the path distance offset; and an output optics section comprising a detector for receiving the interference image and outputting an interference image pattern.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
LED night light has projection or image feature
An LED night light for night time or dark area use, such as a plug-in wall outlet night light or direct current (DC) operated night light, includes projection or image features to project or present an image, message, data, logo, or time on a ceiling, walls, floor, or other desired surface, or an optics element surface. The optics means may include an optics-lens, slide, convex lens, concave lens, openings, cut-outs, film, grating, or holographic element to create an image at a desired location. The night light may have an adjustable angle or distance between light source and optics-means, as well as other adjustable position, location, or orientation features.
Owner:CHIEN TSENG LU
Portable fundus camera
ActiveUS8836778B2Speed flowEconomically beneficialUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAcquiring/recognising eyesFundus cameraHand held
A portable hand-held camera for imaging the fundus of an eye, the camera comprising a housing comprising an internal cavity terminating at a forward housing end, a forward lens, and a light source configured to direct light from locations distributed around the perimeter of the forward lens forwardly out of the housing end. In other embodiment, a portable hand-held camera for imaging the fundus of an eye includes optics configured to focus light reflected back from the fundus onto an image receptor, with the optics being capable of varying the field of view among differing portions of the fundus. Methods to ensure unique image identification and storage are described.
Owner:LUMETRICS
Wavelength multiplexed quantitative differential interference contrast microscopy
InactiveUS20020089741A1Rapid and robust measurementMaximize useUsing optical meansMicroscopesBeam splitterPupil
A differential interference contrast (DIC) microscope system is provided comprising: (a) an illumination source for illuminating a sample ; (b) a lens system for viewing the illuminated sample, including an objective, defining an optical axis; (c) at least one detector system for receiving a sample image; (d) mechanisms for wavelength multiplexing the shear direction or shear magnitude or both on the sample and demultiplexing the resultant DIC images on the detector; and (e) a mechanism for modulating the phase of the interference image. Various approaches are disclosed to accomplish wavelength multiplexing of shear direction and demultiplexing the two DIC images that result. It is possible for the two, wavelength multiplexed DIC images to differ in either or both shear direction or magnitude. These approaches include (1) two DIC microscopes, each operating at a different wavelength, but which share a single objective through a beam splitter; (2) a segmented DIC prism that is made in four sections where opposite sections are paired and have the same shear direction and amount, and each pair of sections have filters transmitting different wavelengths; (3) a segmented DIC prism that is located in or near an aperture stop or pupil of said DIC microscope to obtain data in two shear directions that is multiplexed by wavelength; (4) a dual field-of-view optical system with two DIC prisms, one in each path to wavelength multiplex shear direction or shear magnitude through said objective; (5) demultiplexing wavelength multiplexed DIC images through the use of a wavelength selective beam splitter and two detectors; (6) demultiplexing wavelength multiplexed DIC images through the use of a wavelength controlled source and a single detector; and (7) demultiplexing wavelength multiplexed DIC images through the use of dual field-of-view optics and a single detector. These various approaches permit rapid, robust measurement of slope in two directions. Further, phase shifting and DIC microscopy are limited to measurements within the depth of focus (DOF) of the objective while WLI microscopy is not.
Owner:KUHN WILLIAM P
LED three-dimensional optical system design method and optical system with given luminous intensity distribution
ActiveCN101251650AImprove efficient utilizationLarge light angleOptical elementsOptical refractionConservation of energy
The present invention discloses an LED three-dimensional optical system design method with given illumination distribution and an optical system, which belongs to the non-imaging optical technique of the applied optics field. A three-dimensional non-imaging optical system is formed in a region which has given illumination distribution, by using a light emitting diode as a light source. A three-dimensional lens is designed with the optical system. According to the geometrical shape of the given illumination distribution region, complying with the law of conversation of energy, the surface of the light source and the illumination plane are divided into corresponding energy regions on the long axis direction of the region in accordance with optical refraction, and energy division is carried out in the short axis direction in accordance with the principle of common function of total internal reflection and refraction. The coordinates and the normal vectors of all feature points of the optical system surface of the light source along the long axis direction and the short axis direction are calculated according to the energy corresponding relationship, so as to determine the optical system surface. The method and the system contribute to sufficiently utilizing energy and reducing engineering cost. The encapsulation of the optical system is flexible. Single chip encapsulation and multi-chip encapsulation can be adopted. The arrangement of a plurality of the optical systems is free, simple and flexible.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Unit and method for optical non-contact oil detection
ActiveUS20150293032A1Safety of exploitationImprove securityBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsPhotometryPhotodetectorEngineering
The invention relates to a unit and method for detection of presence of oil on the water surface or in the water column. Unit comprises a sensor, whereby the sensor is connected to electronic compartment followed by microprocessor controller with embedded software for carrying out necessary analyses of reflected signals received by the sensor. The microprocessor controller is connected to communication means for transmitting an alarm signal through external communication line in case of oil pollution. All elements mentioned above are supplied by external power supply and are accommodated into waterproof housing. The sensor comprises the probe light source formed by a pulsed UV LED, collimating optics and narrow band optical filter, at least one dichroic mirror, a projection-receiving lens, at least one optical filter, at least one photodetector and a reference photodetector.
Owner:NEMOR TECH OU
Single-display-shared large-exit-pupil binocular eyepiece optical system
The invention belongs to the technical field of optics. Through refraction and transmission of a spherical lens group coaxially arranged, a binocular eye pupil at an exit pupil position divides outgoing light into a left beam and a right beam in a wavefront-splitting manner, and binocular observation for a shared single display image is achieved. The single-display-shared large-exit-pupil binocular eyepiece optical system to which the invention relates is the lens groups arranged between the display and a diaphragm. The lens group is characterized in that the lens group comprises n spherical lenses which are successively and coaxially arranged, and n is a natural number not less than 3; the display is placed on a front focal plane of the lens group, and the center of the display coincides with an optical axis of the lens group; and the lens group comprises 2n optical surfaces which are (2n) and (2n+1) taking a diaphragm surface (1) as a starting point, and a display surface is (2n+2). The binocular eyepiece optical system has the advantages of simple structure, comfortable observation, reliable performance, the large exit pupil diameter and the large exit pupil distance; free observation can be performed in a certain special scope, and an object image is easy to continuously observe; the binocular eyepiece optical system can be fixed to a vehicle body and does not increase a burden of a head, and people cannot feel fatigue easily; and the binocular eyepiece optical system is suitable for a vehicle-mounted binocular observation instrument to continuously observe surrounding scenery conditions or related information.
Owner:SHANDONG NORTH OPTICAL & ELECTRONICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com