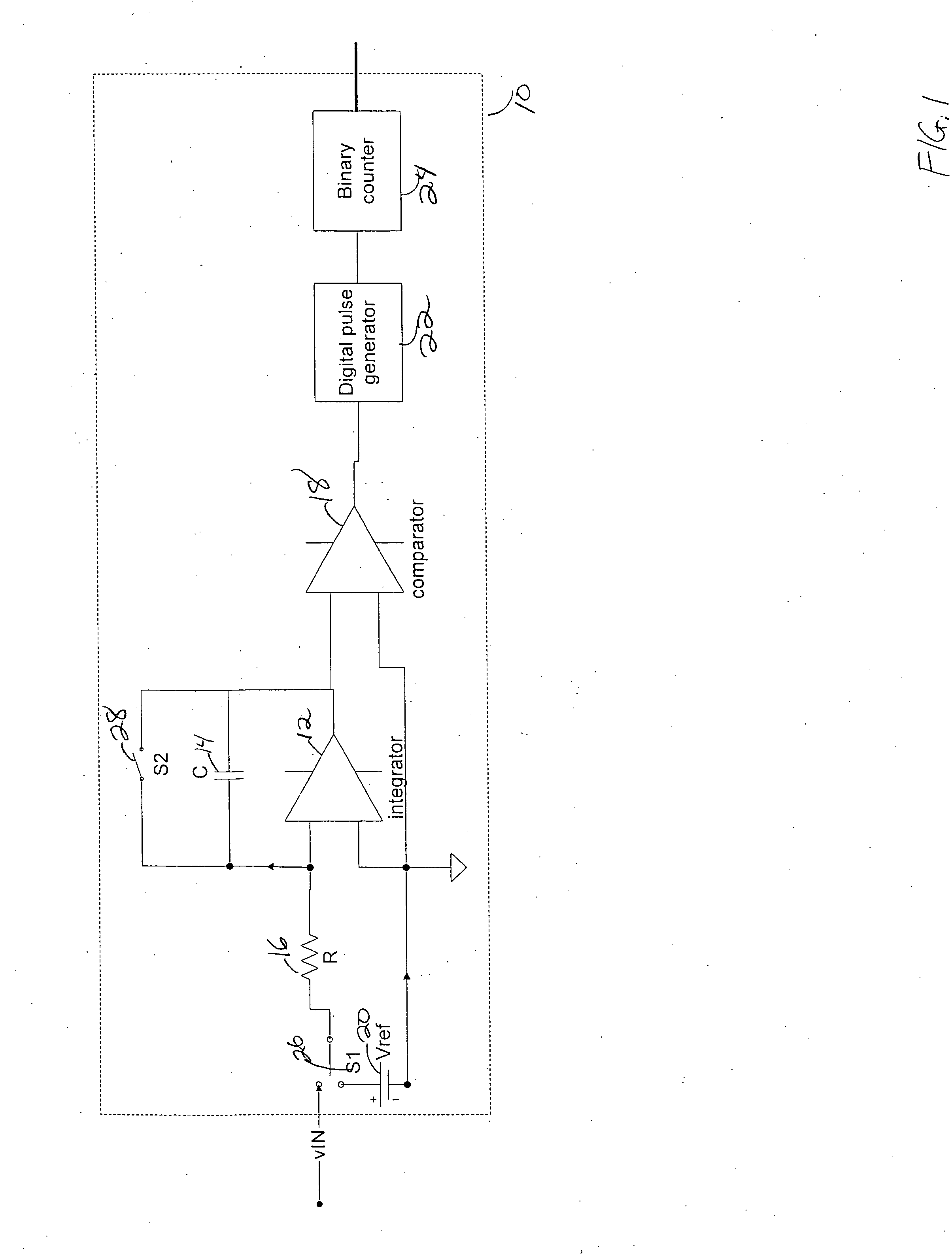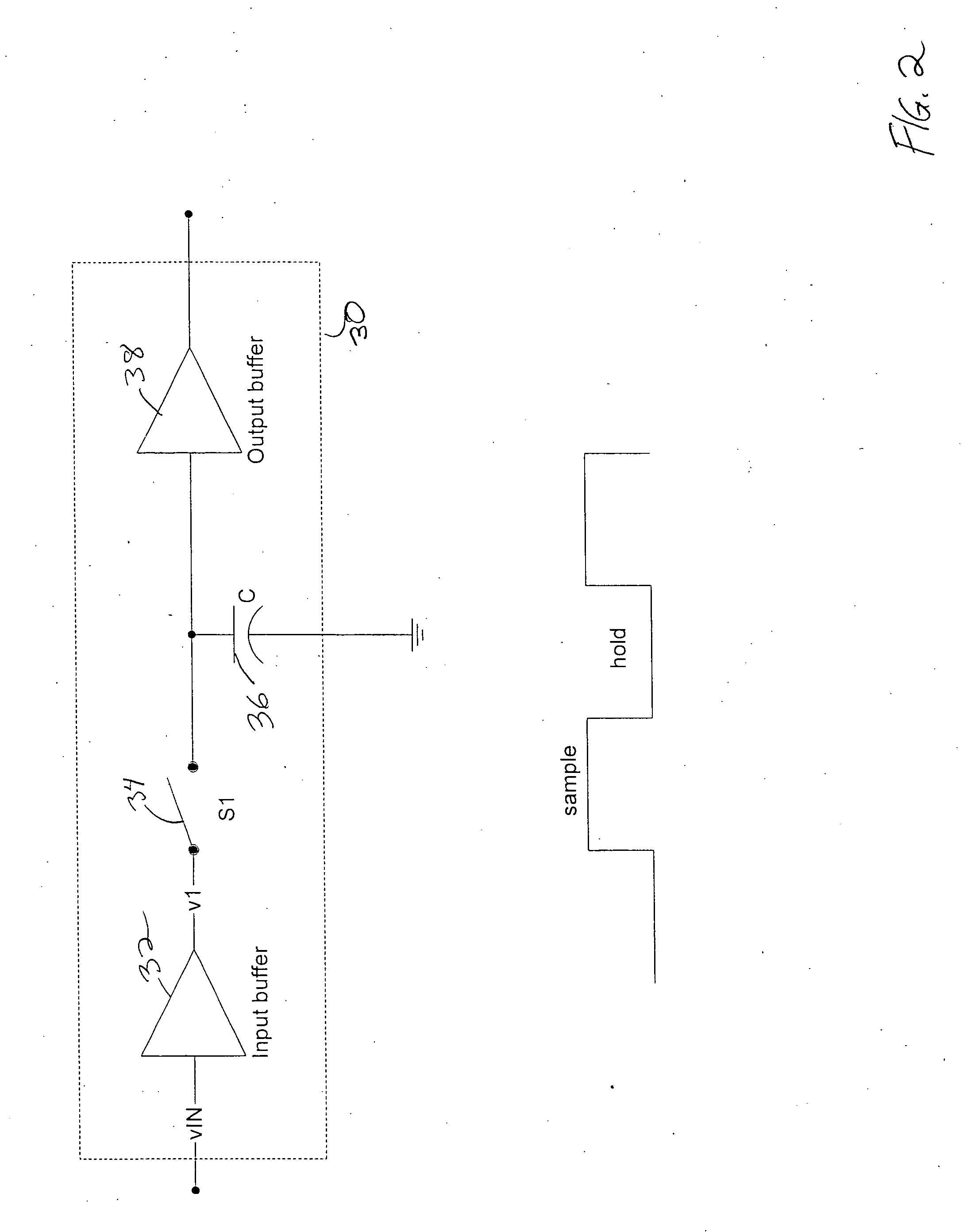Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Rotary traveling wave oscillator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
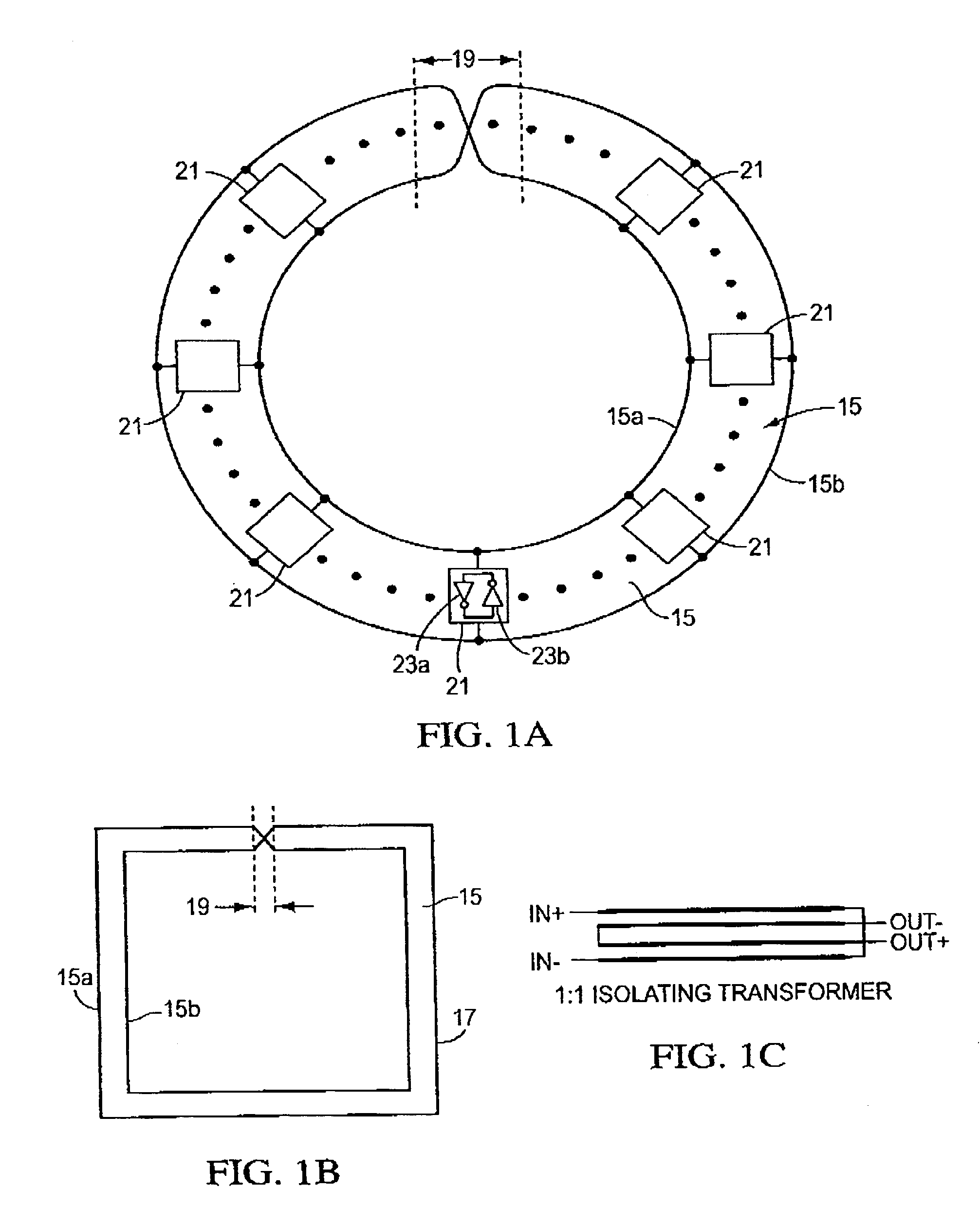
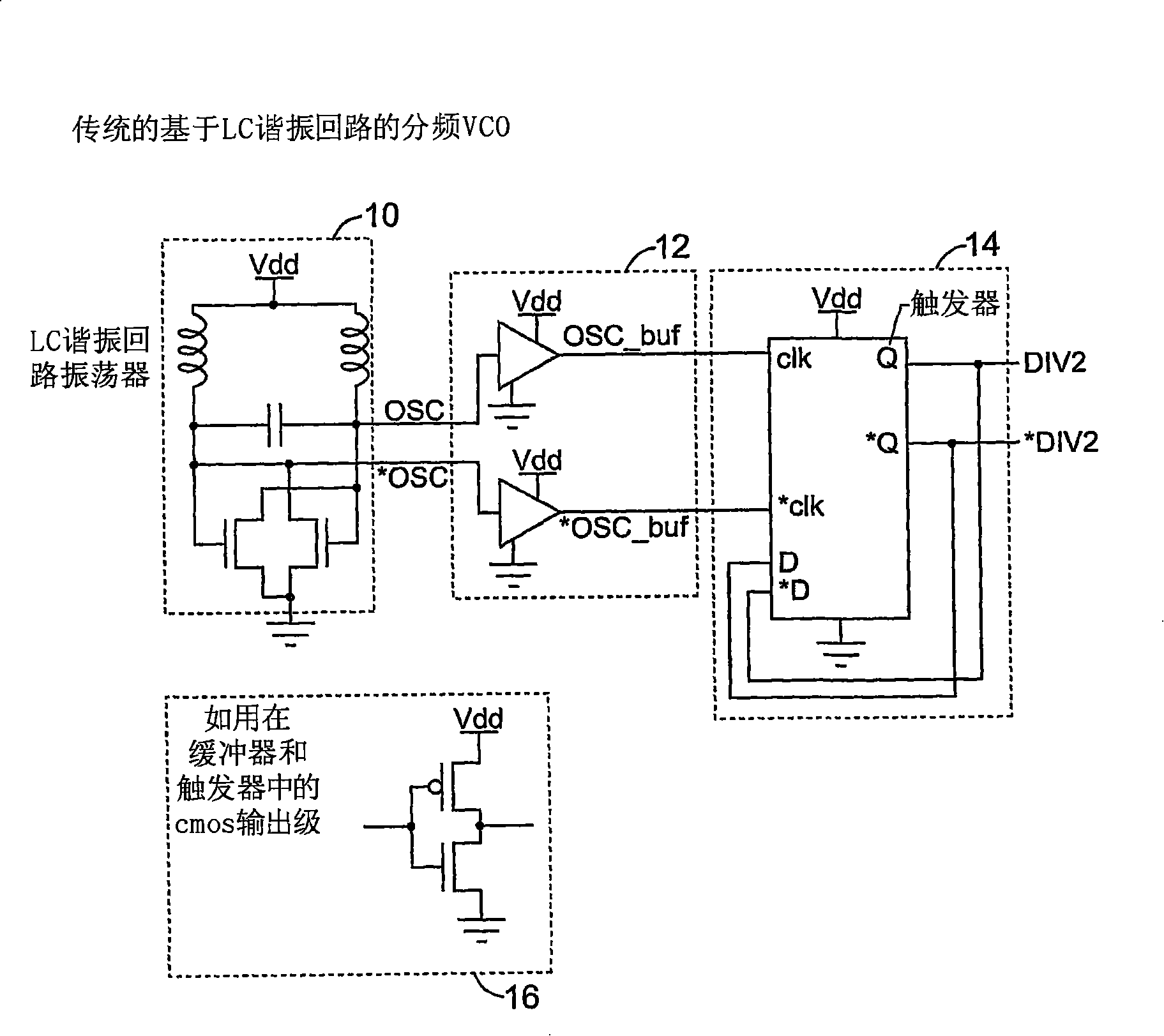
True time delay phase array radar using rotary clocks and electronic delay lines
ActiveUS20120039366A1Forming accuratelyEasy to moveAntenna arraysPulse automatic controlTime delaysAnalog delay line
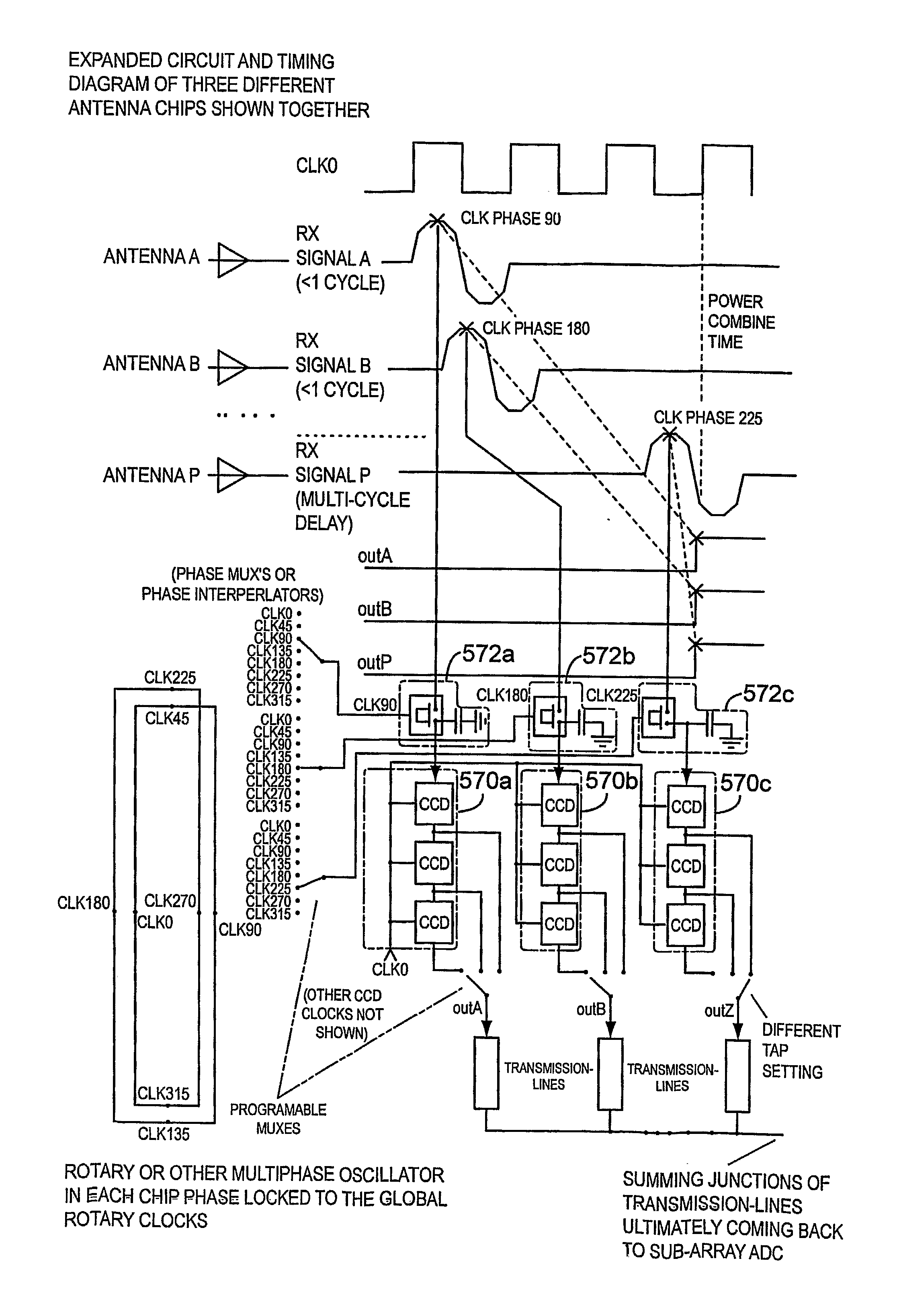
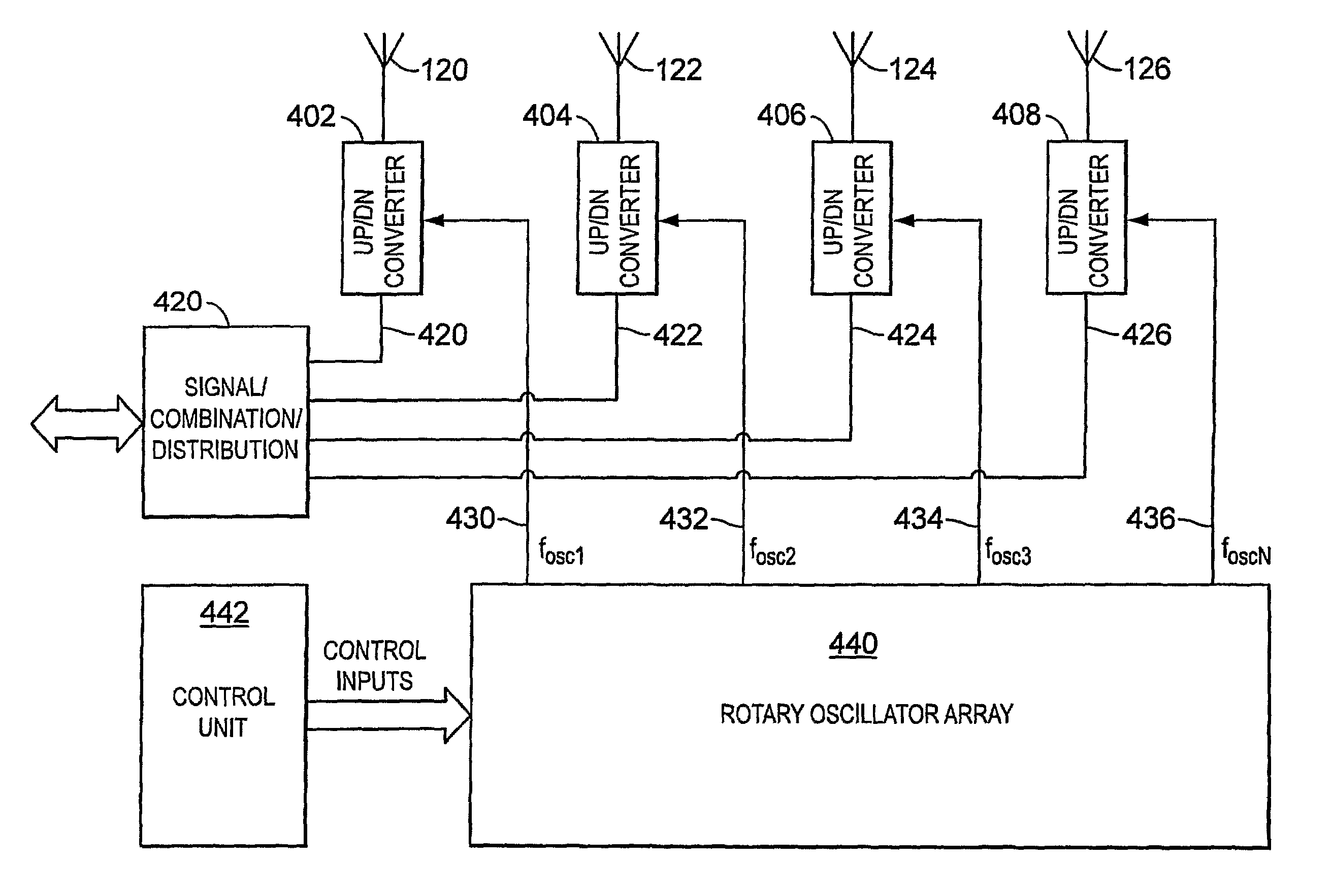
Local oscillator circuitry for an antenna array is disclosed. The circuitry includes an array of rotary traveling wave oscillators which are arranged in a pattern over an area and coupled so as to make them coherent. This provides for a set of phase synchronous local oscillators distributed over a large area. The array also includes a plurality of phase shifters each of which is connected to one of the rotary oscillators to provide a phase shifted local oscillator for the array. The phase shifter optionally includes a cycle counter that is configured to count cycles of the rotary oscillator to which it is connected and control circuitry that is then operative to provide a shifted rotary oscillator output based on the count from the cycle counter. A system and method for operating a true-time delay phased array antenna system. The system includes a plurality of antenna element circuits for driving or receiving an rf signal from the elements of the array. Each element circuit has a transmit and a receive path and a local multiphase oscillator, such as a rotary traveling wave oscillator. Each path has an analog delay line for providing a true-time delay for the antenna element. Preferably, the analog delay line is a charge coupled device whose control nodes are connected to phases of the local multiphase oscillator to implement a delay that is an integer number local multiphase oscillator periods. A fractional delay is also included in the path by using a sample and hold circuit connected to a particular phase of the oscillator. By delaying each antenna element by a true time delay, broadband operation of the array is possible.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
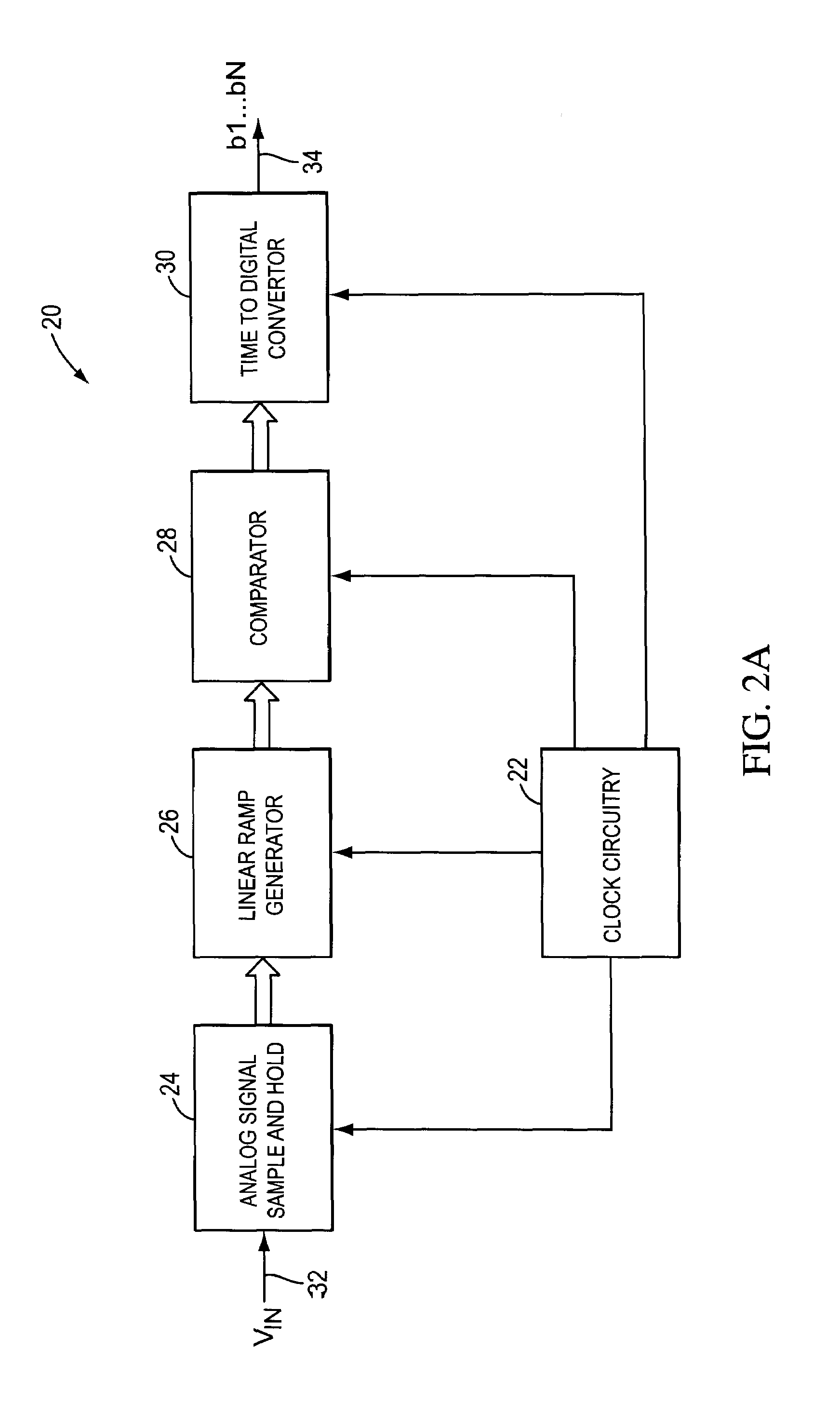
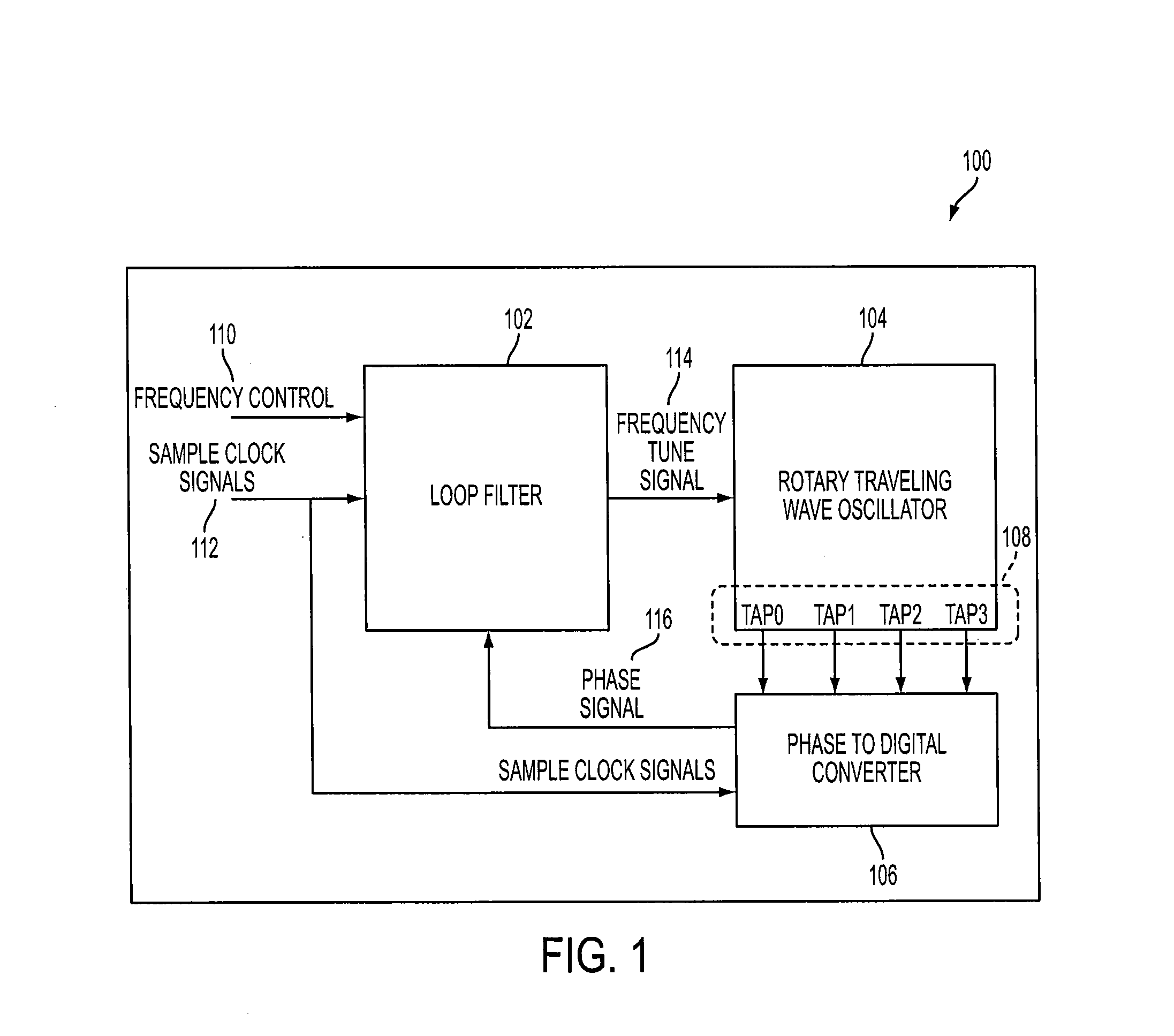
Rotary clock flash analog to digital converter system and method
ActiveUS7609756B2Electric signal transmission systemsPulse automatic controlDigital down converterEngineering
System and method for converting an analog voltage to a digital signal. The system includes an input voltage sampler, a ramp generator, a comparator, a time-to-digital converter (TDC), and a multiphase oscillator, preferably a rotary traveling wave oscillator, that provides the critical system timing. The phases of the multiphase oscillator define a sampling interval during which the input voltage is sampled and held and a conversion interval during which the ramp generator, comparator, and TDC operate to convert the sampled voltage to the digital signal. The TDC samples at times provided by the phases of the multiphase oscillator to form the bits of the digital signal. The sampler, ramp generator, and comparator can be constructed from multiple fragments, one of which is selectable for calibration while the rest of the fragments are joined for normal operation. Multiple converters can be interleaved to increase the sampling rate.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Rotary clock flash analog to digital converter system and method
ActiveUS20080272952A1Electric signal transmission systemsPulse automatic controlDigital down converterEngineering
System and method for converting an analog voltage to a digital signal. The system includes an input voltage sampler, a ramp generator, a comparator, a time-to-digital converter (TDC), and a multiphase oscillator, preferably a rotary traveling wave oscillator, that provides the critical system timing. The phases of the multiphase oscillator define a sampling interval during which the input voltage is sampled and held and a conversion interval during which the ramp generator, comparator, and TDC operate to convert the sampled voltage to the digital signal. The TDC samples at times provided by the phases of the multiphase oscillator to form the bits of the digital signal. The sampler, ramp generator, and comparator can be constructed from multiple fragments, one of which is selectable for calibration while the rest of the fragments are joined for normal operation. Multiple converters can be interleaved to increase the sampling rate.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
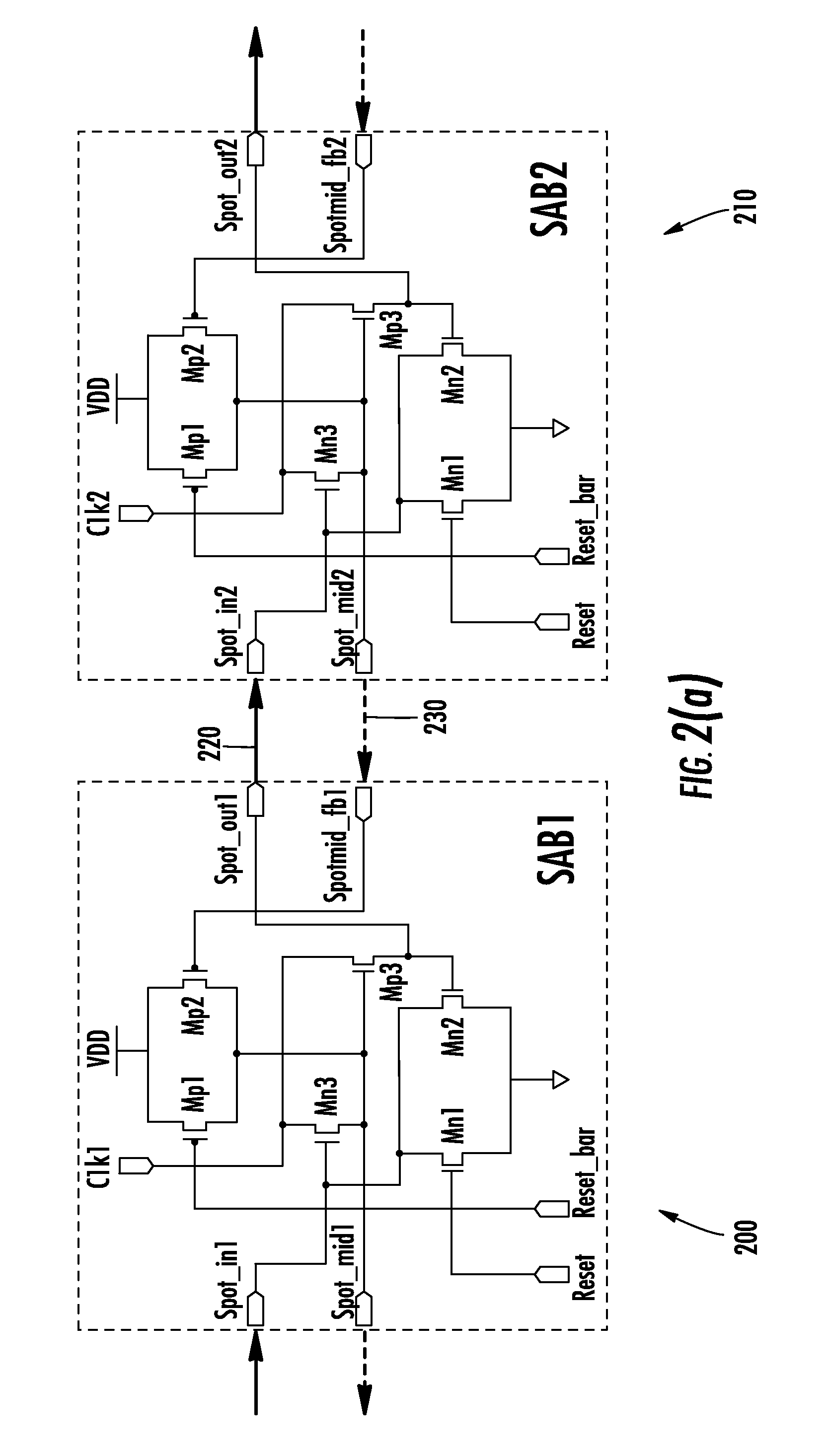
Rotary clock synchronous fabric
Methods for generating a design for logic circuitry using rotary traveling wave oscillators (RTWOs) are described. A plurality of RTWOs are is arranged into an array of rows and columns. Adjacent elements in the array are interconnected so that the clocks in adjacent element are phase synchronous. Clocked devices are placed along the signal path of each array element and each is connected to one of the multiple phases provided by the RTWO element. The logic circuitry, described by a netlist, is divided into a number of partitions and each of these partitions is mapped to one of the array elements. The logic circuitry of the partition is then placed within or about the element of the array to which the partition is mapped and the circuitry in the partition is connected between the clocked devices in the element of the array, according to the net list.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
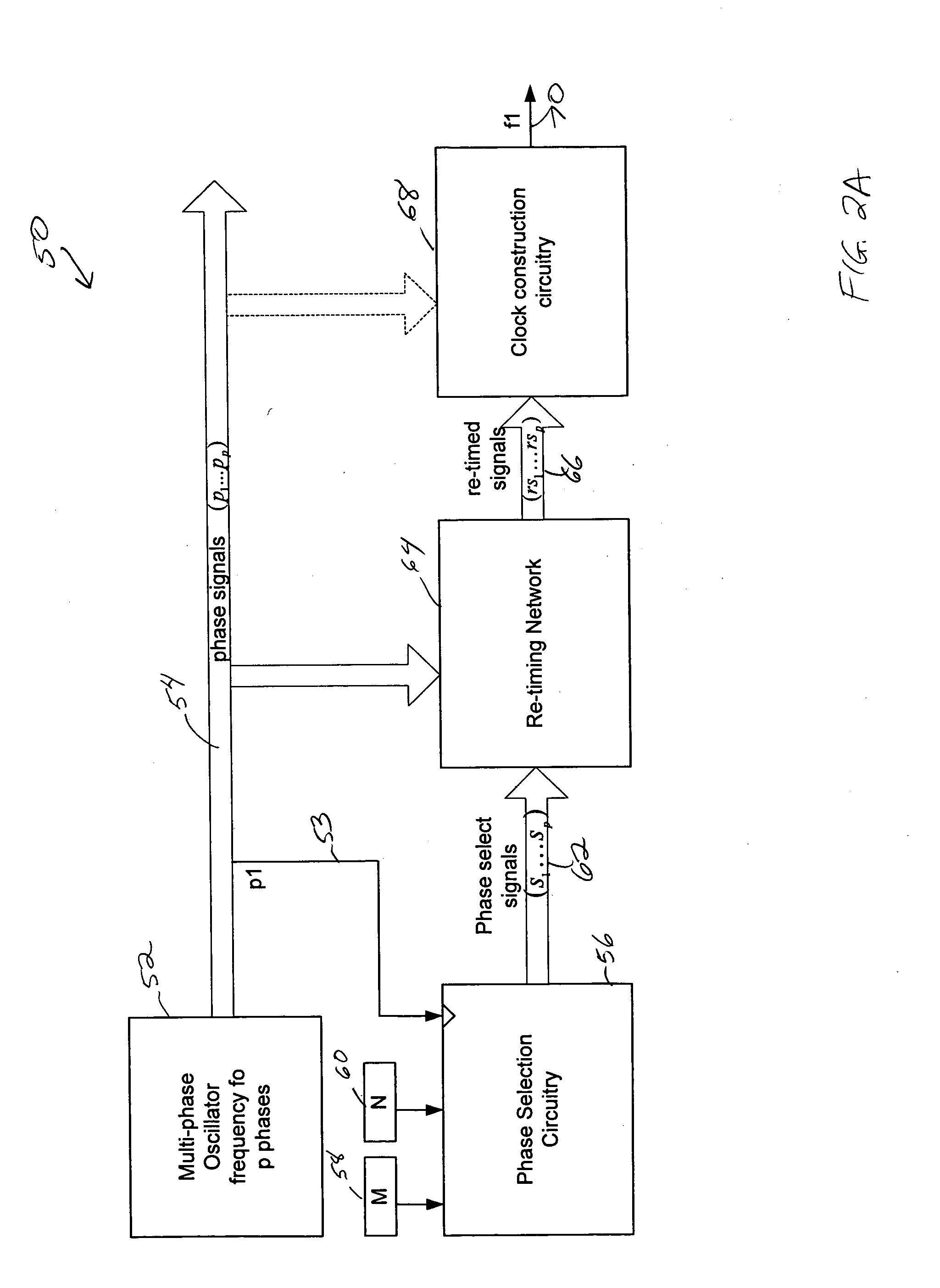
Low Noise Fractional Divider Using A Multiphase Oscillator
ActiveUS20110156773A1High purityAmenable to integrated circuit fabricationPulse automatic controlOscillations generatorsLow noisePhase shifted
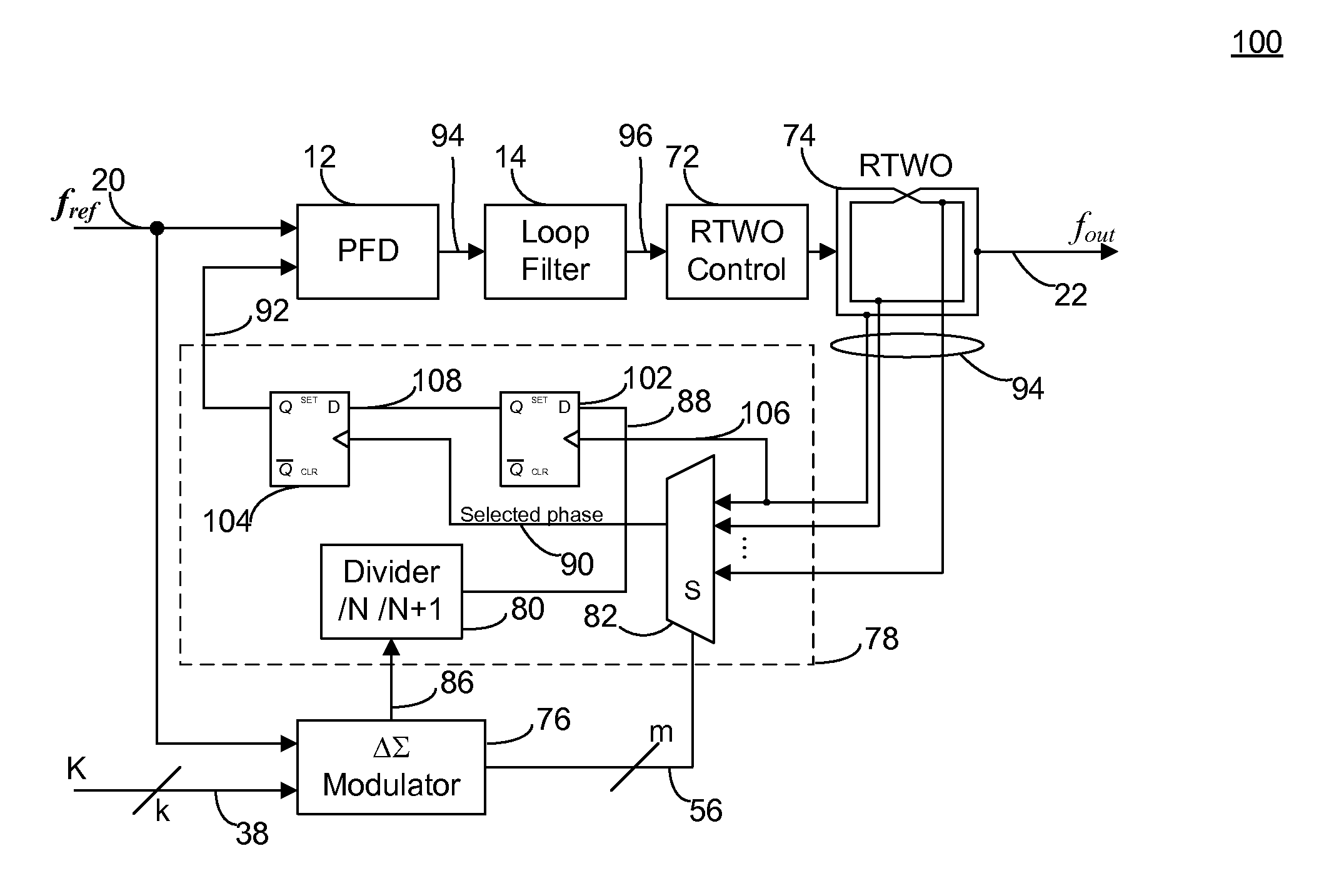
A frequency synthesis circuit is disclosed. The circuit includes a phase-locked loop and multi-phase oscillator such as a rotary traveling wave oscillator (RTWO). The oscillator provides a plurality of phases that are applied to a selection circuit. The selection circuit, in response to the output of a delta-sigma modulator, selects one of the phases of the multi-phase oscillator to minimize phase shift noise when the divider ratio in the loop changes, thereby eliminating a source of noise that contaminates the synthesized frequency. This permits the use of the frequency synthesis in applications requiring a high degree of spectral purity.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
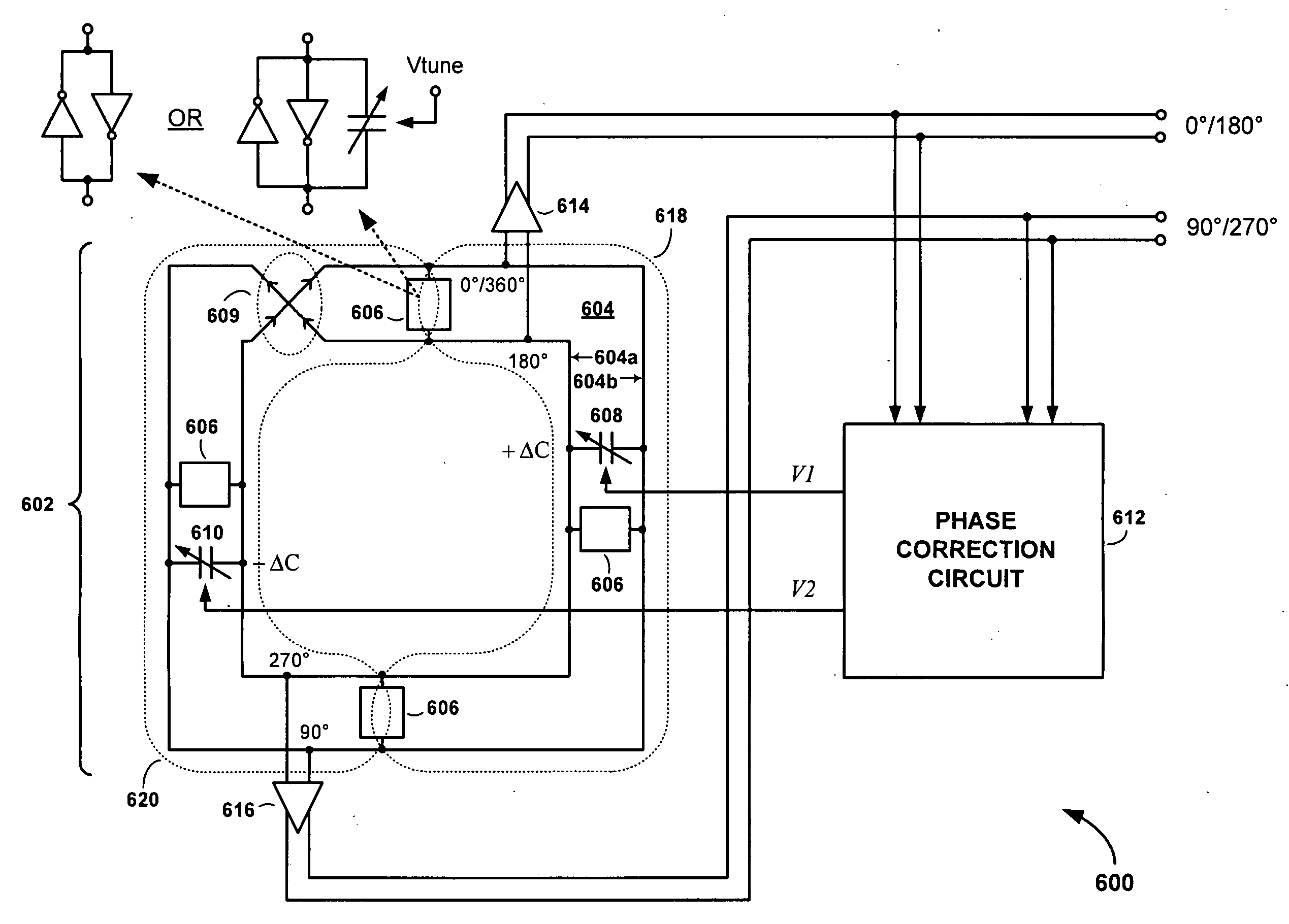
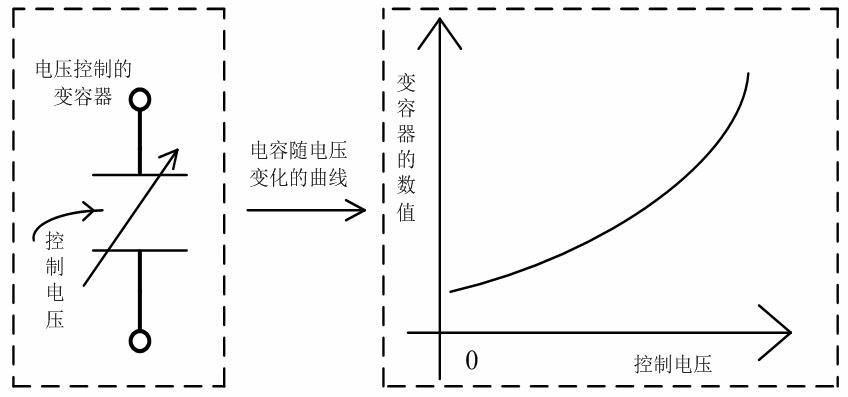
Phase error correction in rotary traveling wave oscillators
InactiveUS20100117744A1Reduce detected phase errorReduced phase velocityDelay lines pulse generationPulse generation by logic circuitsCapacitancePhase correction
An RTWO apparatus includes an N-phase RTWO (N is an integer greater than or equal to two) and a phase correction circuit. The N-phase RTWO includes a closed-loop transmission line formed as a Moebius strip. The closed-loop transmission line includes N transmission line segments, to which N voltage controlled capacitors are coupled. The N transmission line segments provide N output phases. The phase correction circuit operates to detect phase errors between output phases, and, depending on the detected phase errors, generates N control voltages for controlling the capacitances of the N voltage controlled capacitors. Controlling the capacitances of the N voltage controlled capacitors in this coordinated manner reduces the phase errors among the N output phases, thereby providing a phase accurate multi-phase RTWO output.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
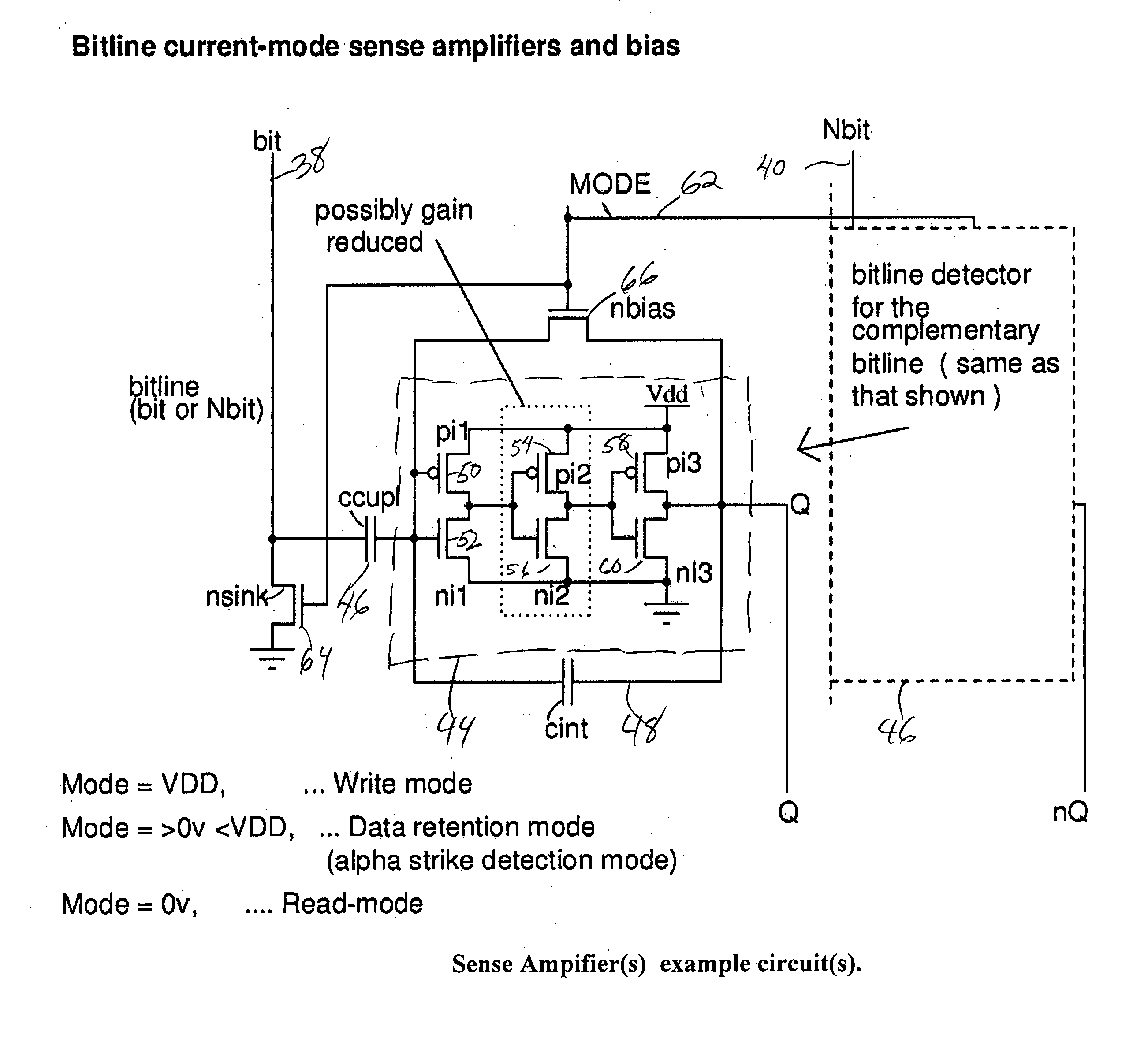
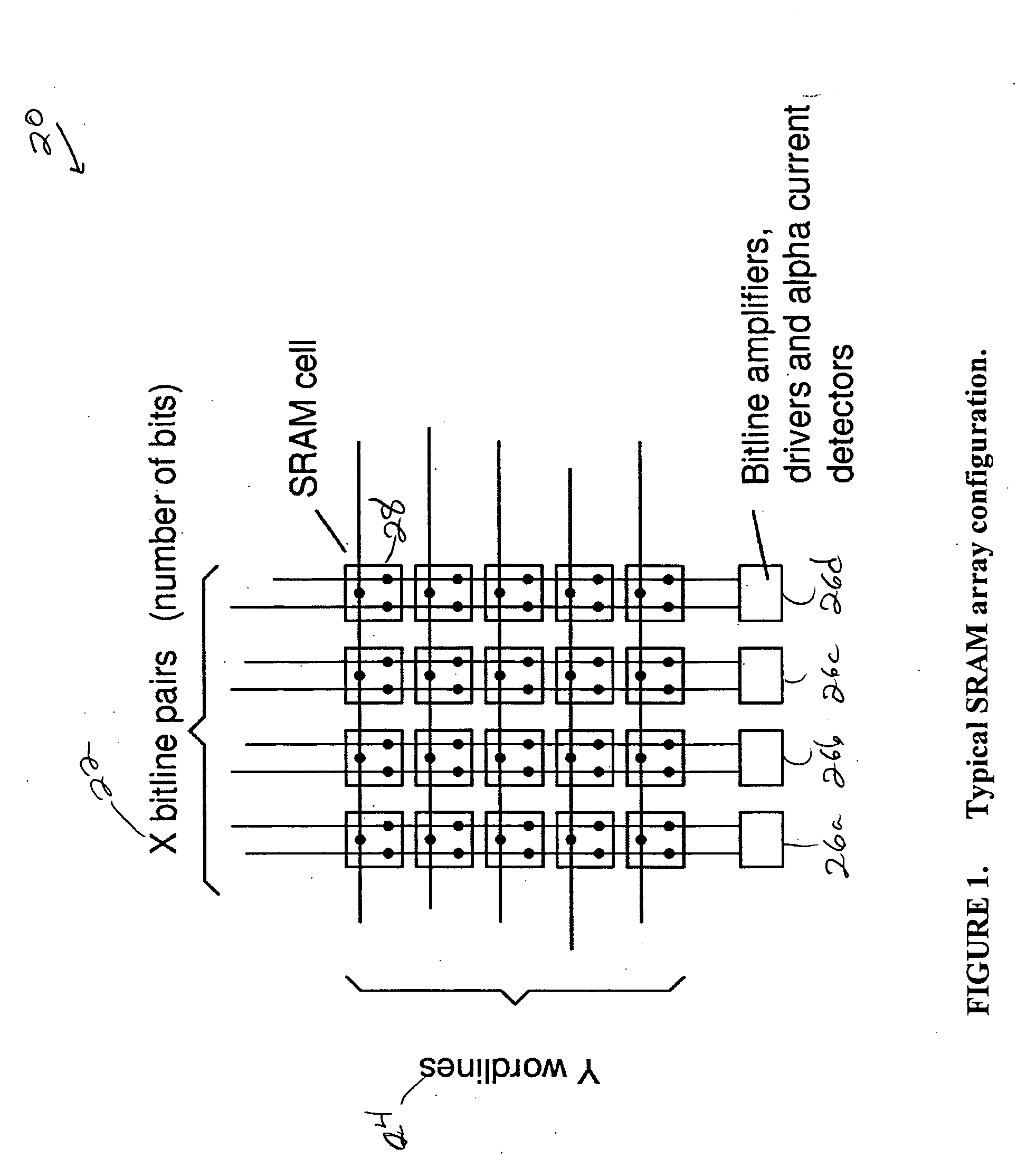
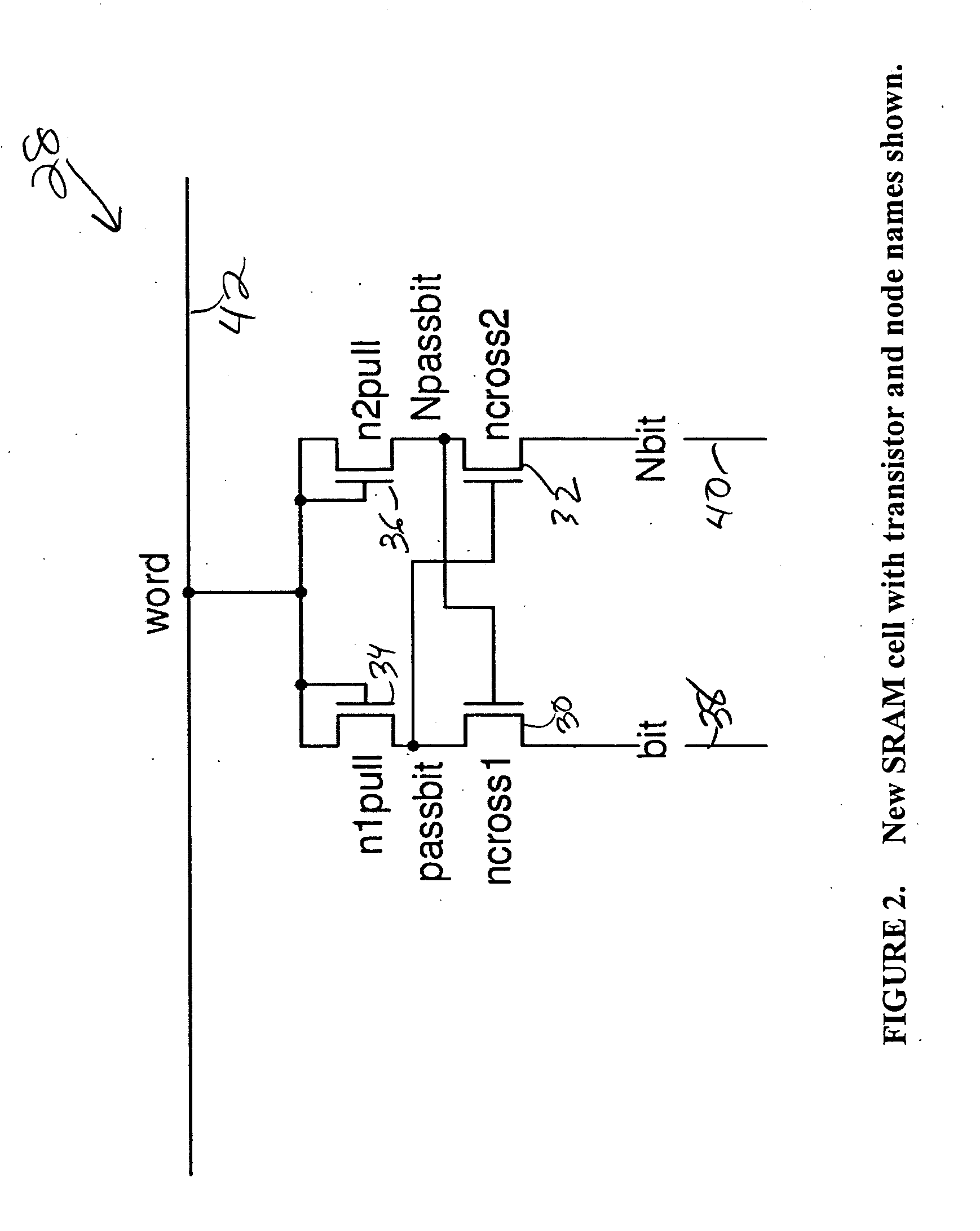
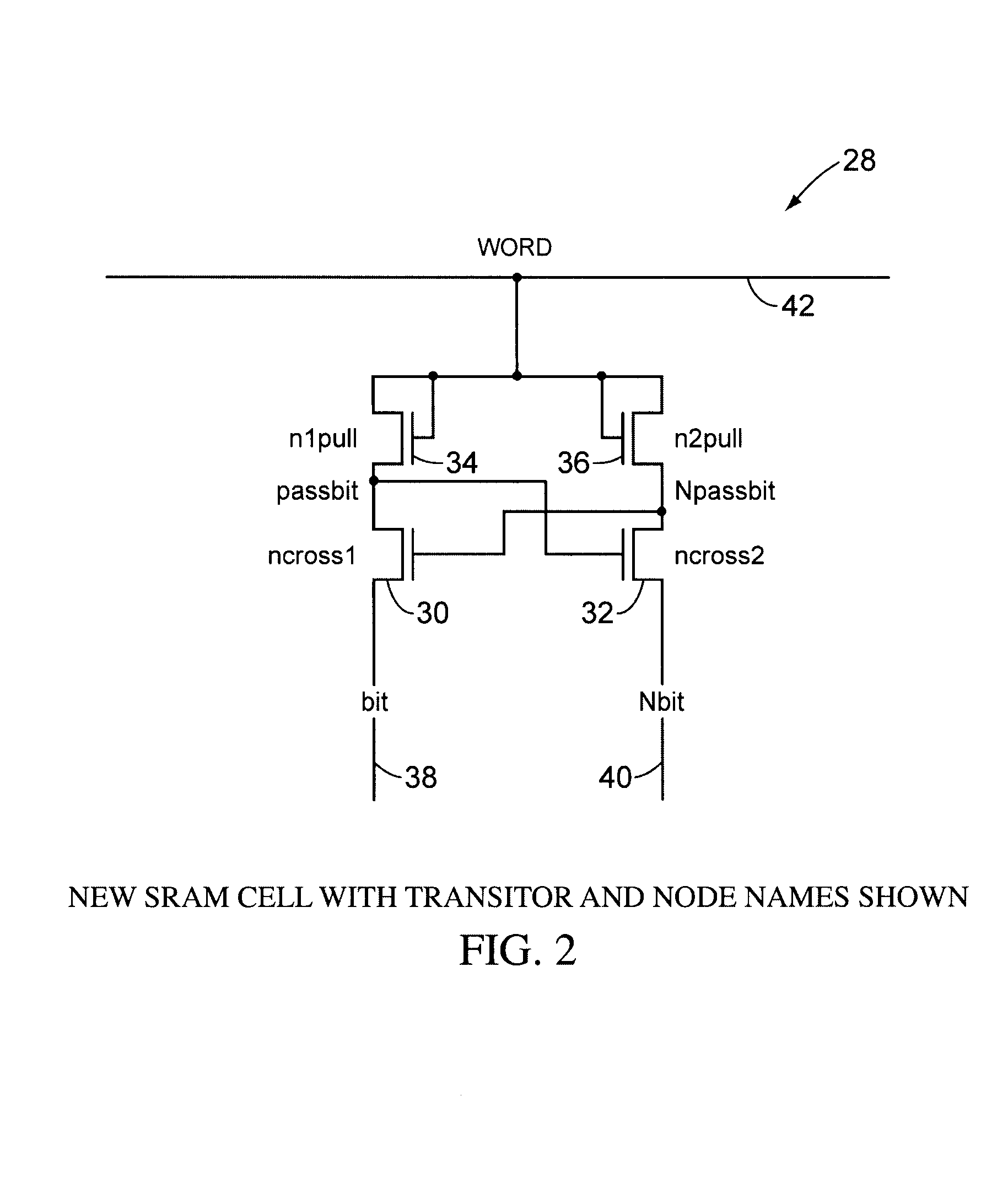
SRAM circuitry
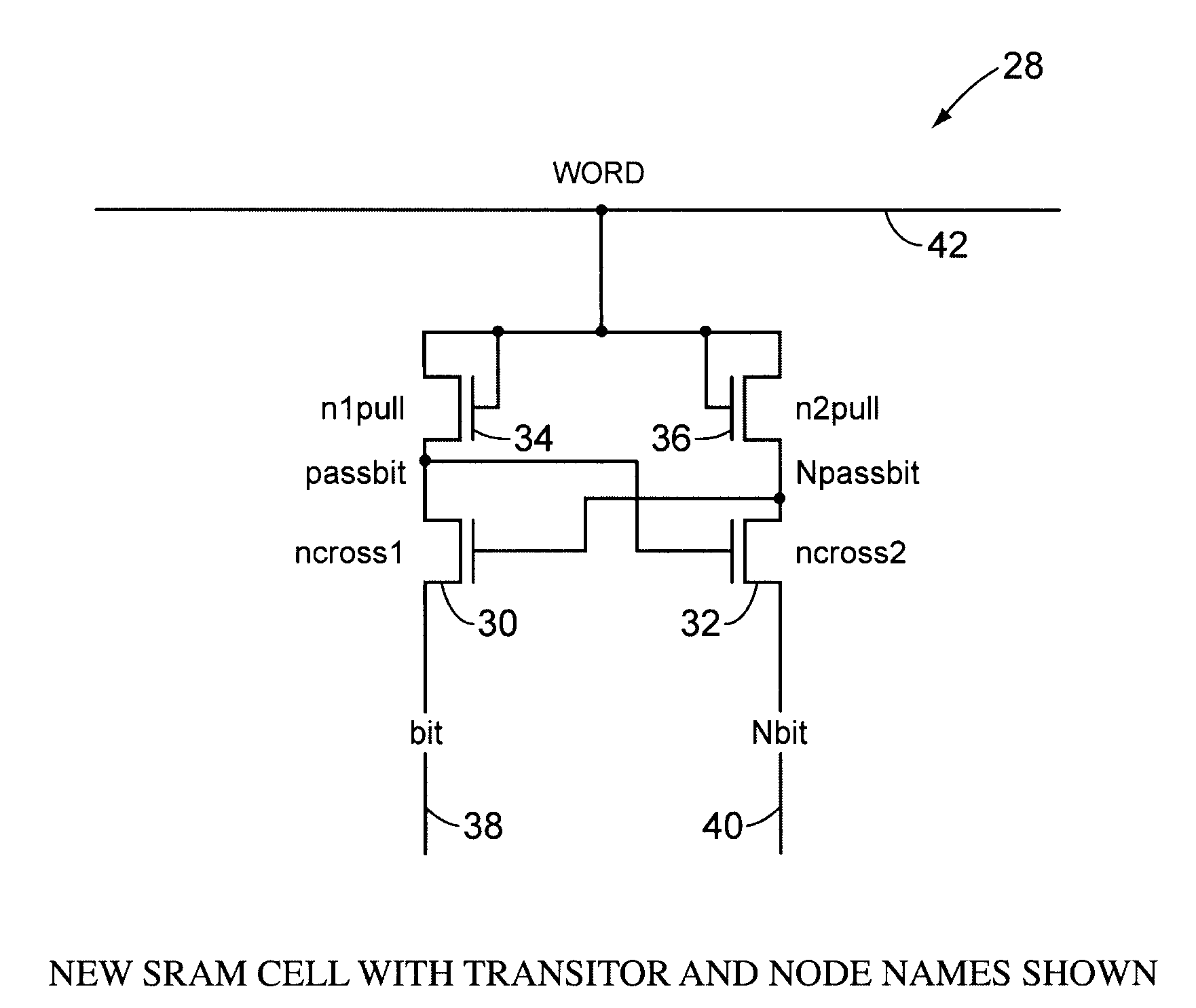
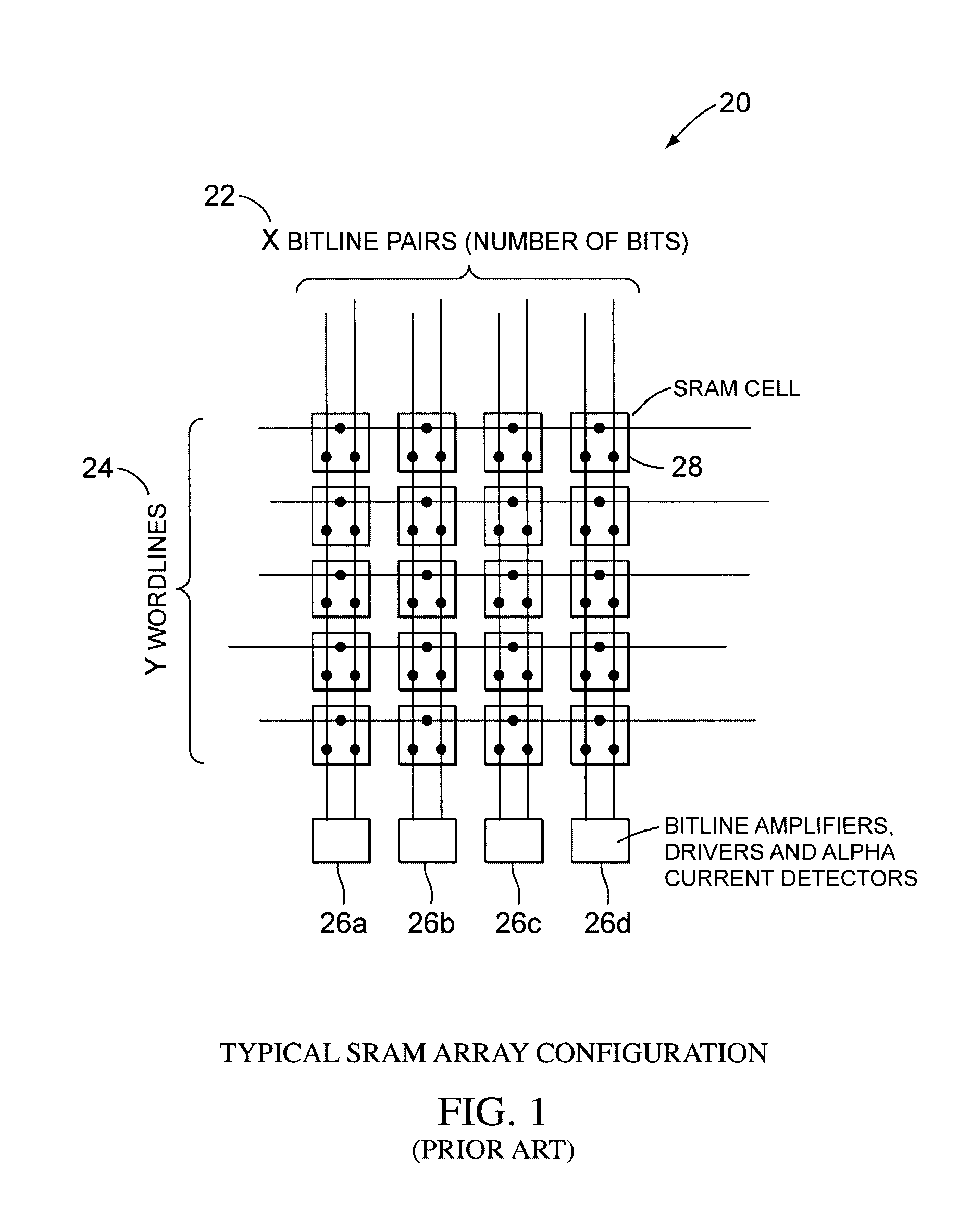
A static ram cell is described. The cell includes a pair of cross-coupled transistors and a pair of diode-connected transistors operated from a wordline that provides power to the cell. The cell has three main operating modes, reading, writing and data retention. Reading is performed by sensing current flowing from a powered up wordline through a conductive one of the cross-coupled transistors. Writing is performed by pulsing the source of the conductive one of the cross-coupled transistors with a positive voltage to flip the conductive states of the cross-coupled transistors. Data retention is performed by using leakage currents to retain the conductive states of the cross-coupled transistors. A decoder for an array of static ram cells may be operated synchronously and in a pipelined fashion using a rotary traveling wave oscillator that provides the clocks for the pipeline. The cell capable of detecting an alpha particle strike with suitable circuitry.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
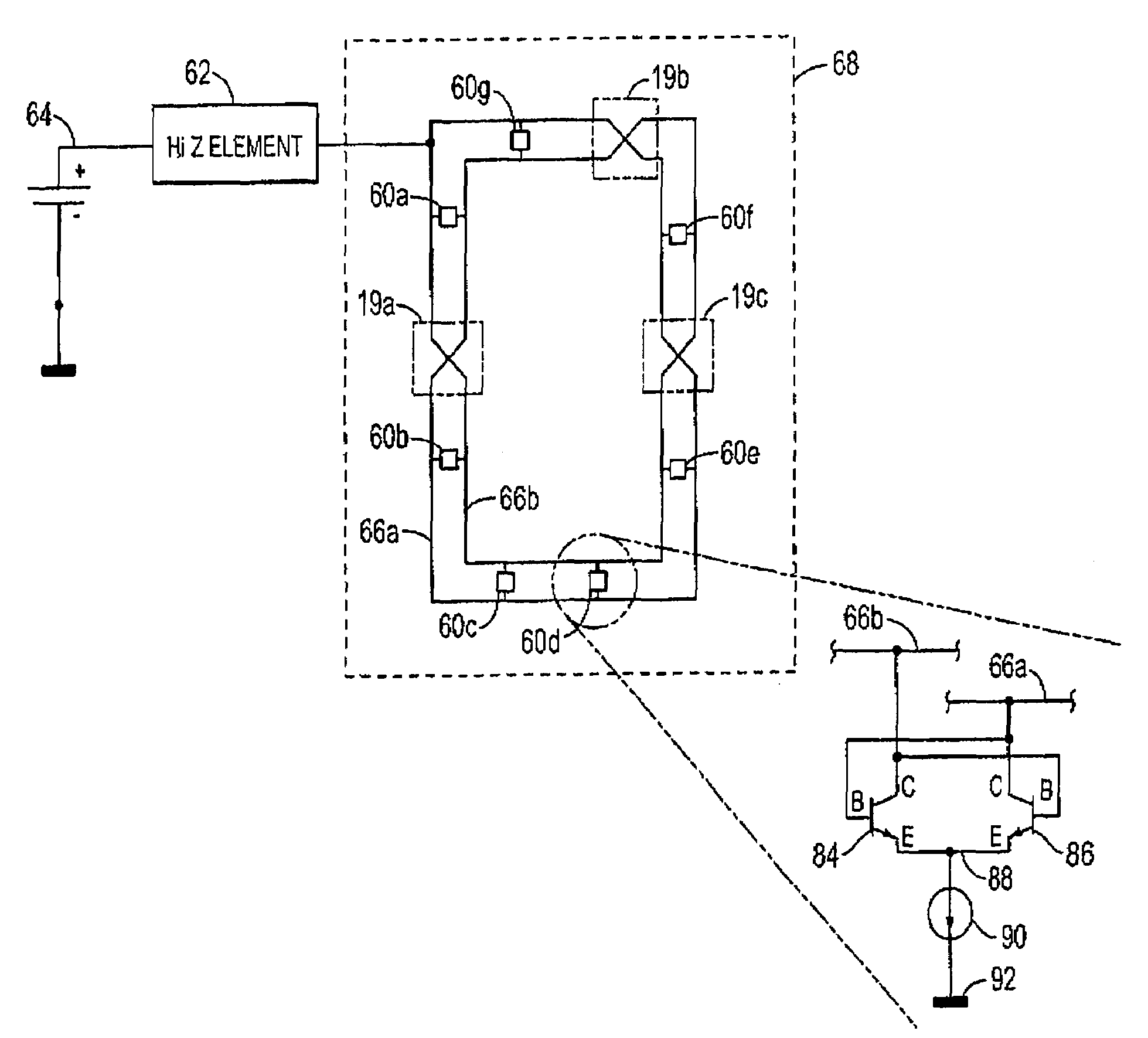
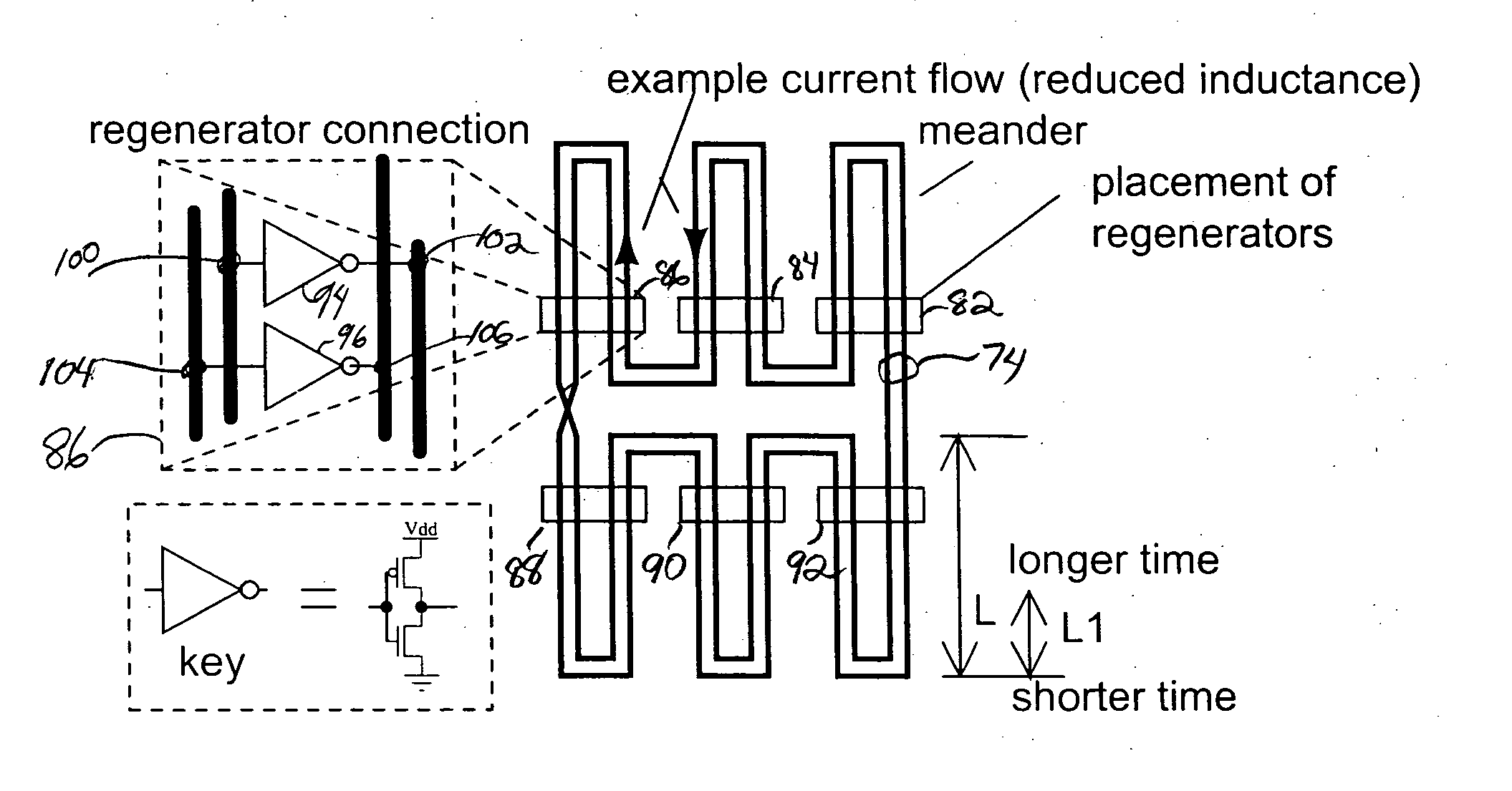
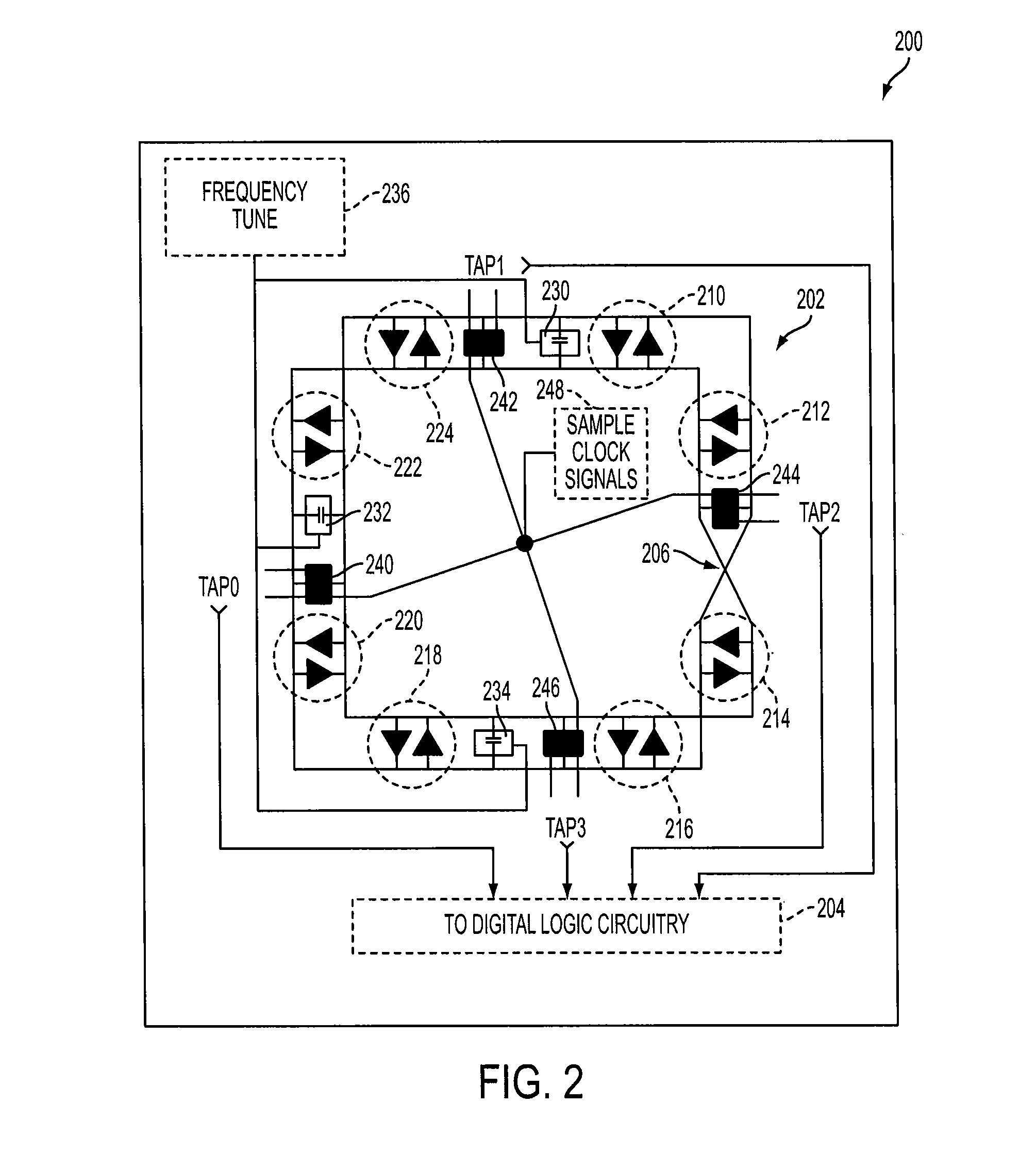
Regeneration device for rotary traveling wave oscillator
InactiveUS7545225B2High operating requirementsPulse automatic controlSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrical conductorClosed loop
An oscillator is described. The oscillator includes segments of two-conductor transmission line being connected together by an odd number of connection means to form a closed loop. A plurality of current switches is connected to the conductors of the segments and a high impedance element, such as an inductor or transmission line, is connected to a conductor of at least one segment. The high impedance element sources current into the closed loop and the current switches sink current from one or the other of the conductors of the loop depending on the state of the switch. The switches cause a wave to be established and maintained on the loop and the wave changes the state of the switches as it oscillates. One embodiment of the switches employs npn transistors whose emitters are connected to a current source and another uses NMOS transistors.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
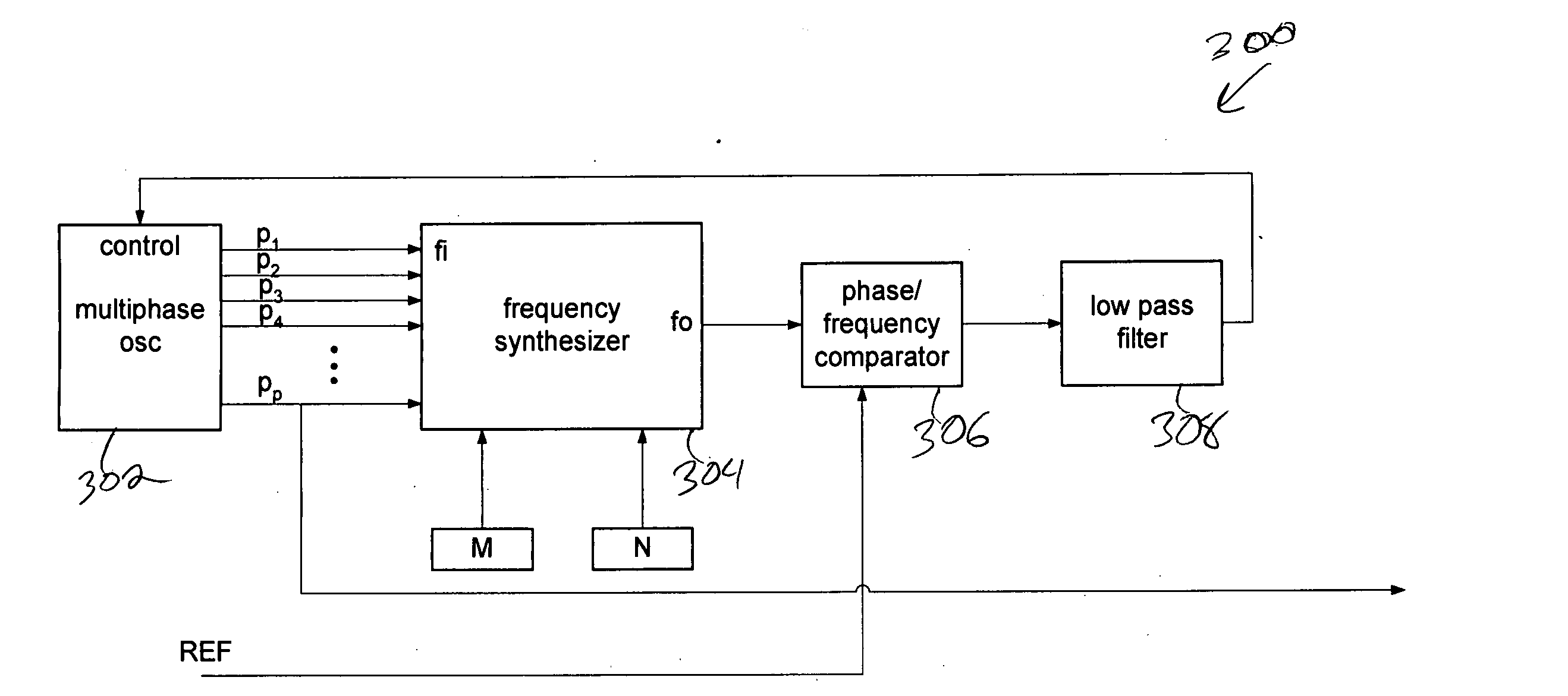
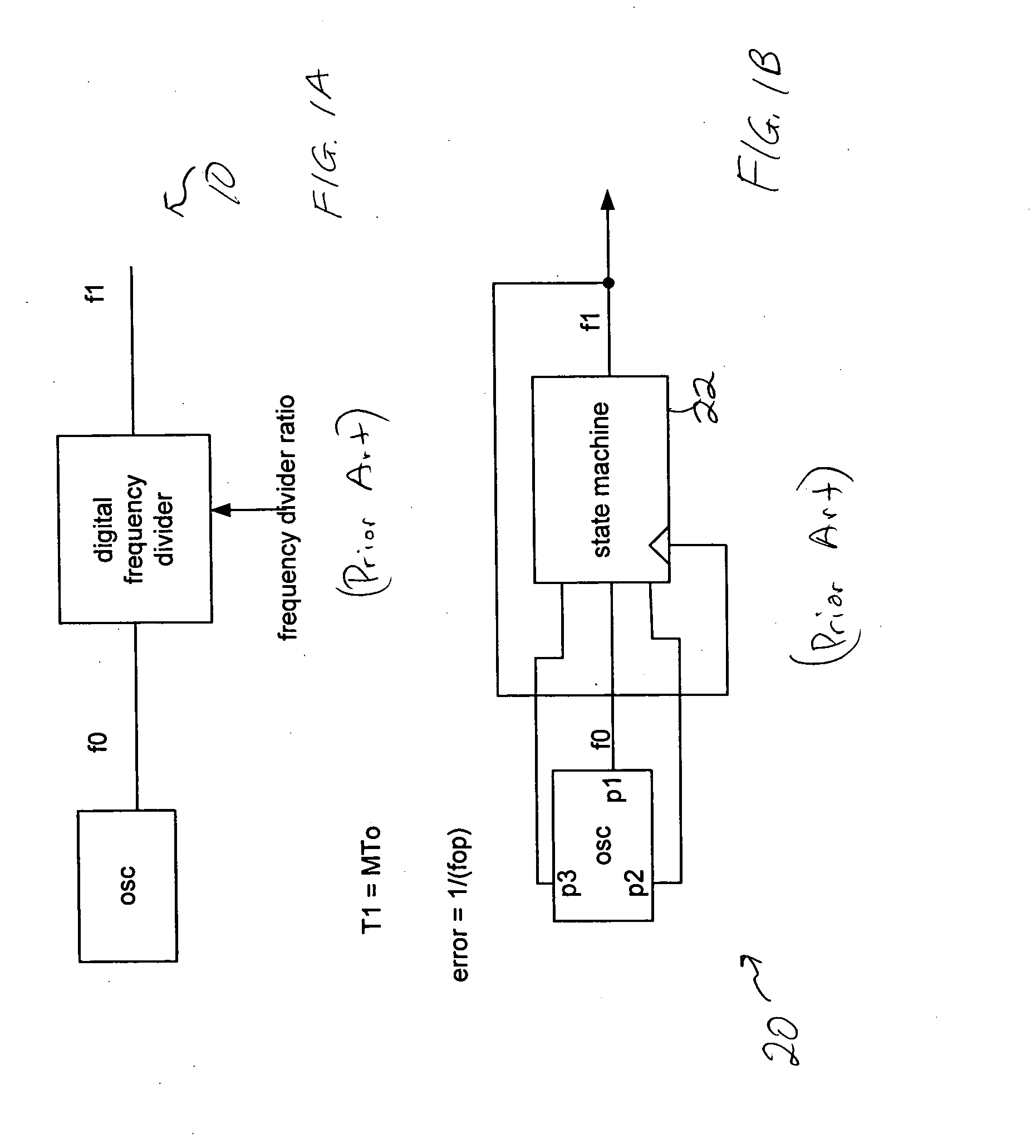
Digital frequency synthesizer
ActiveUS7782988B2Improve accuracyPulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionFrequency synthesizerEngineering
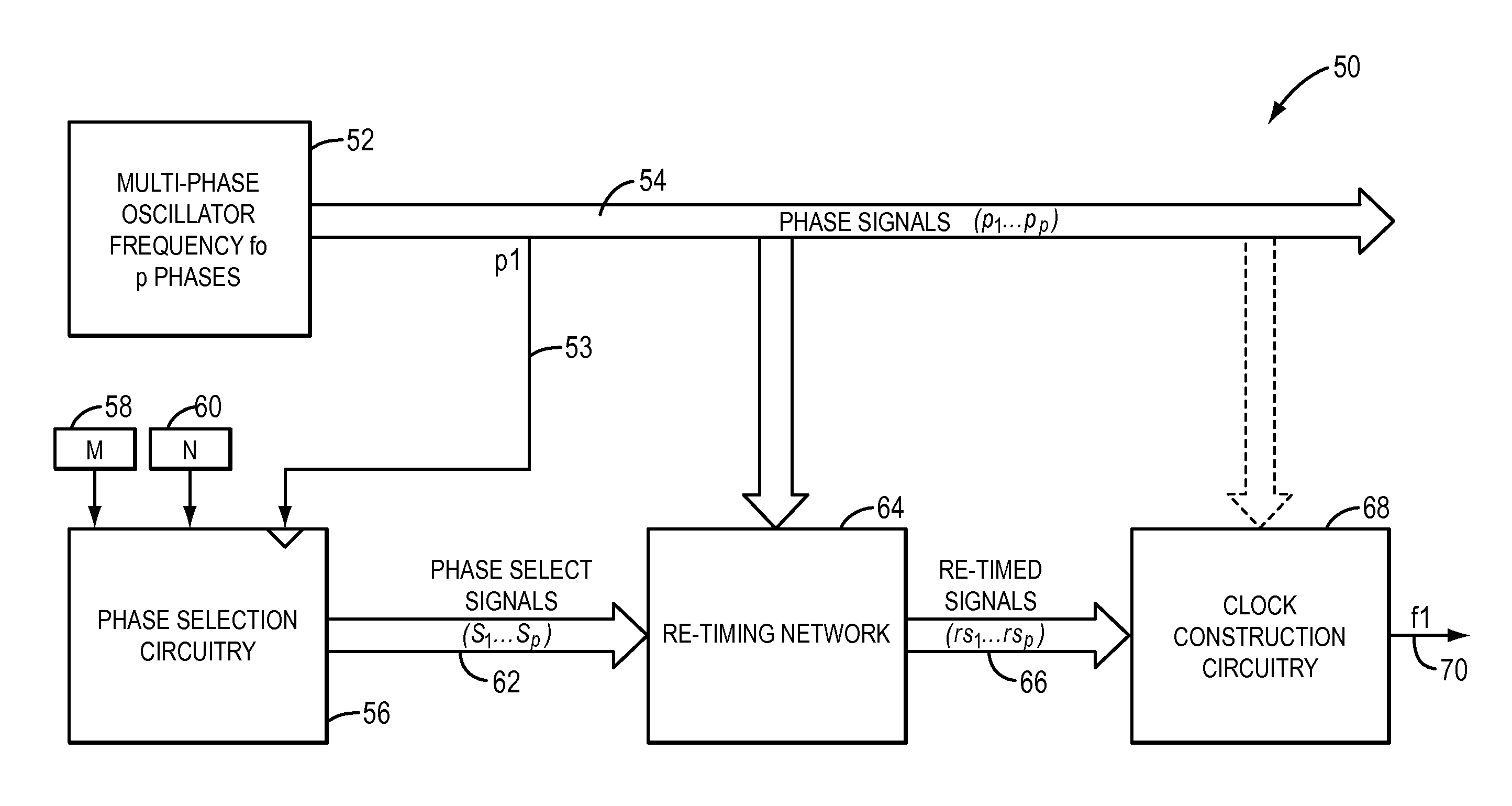
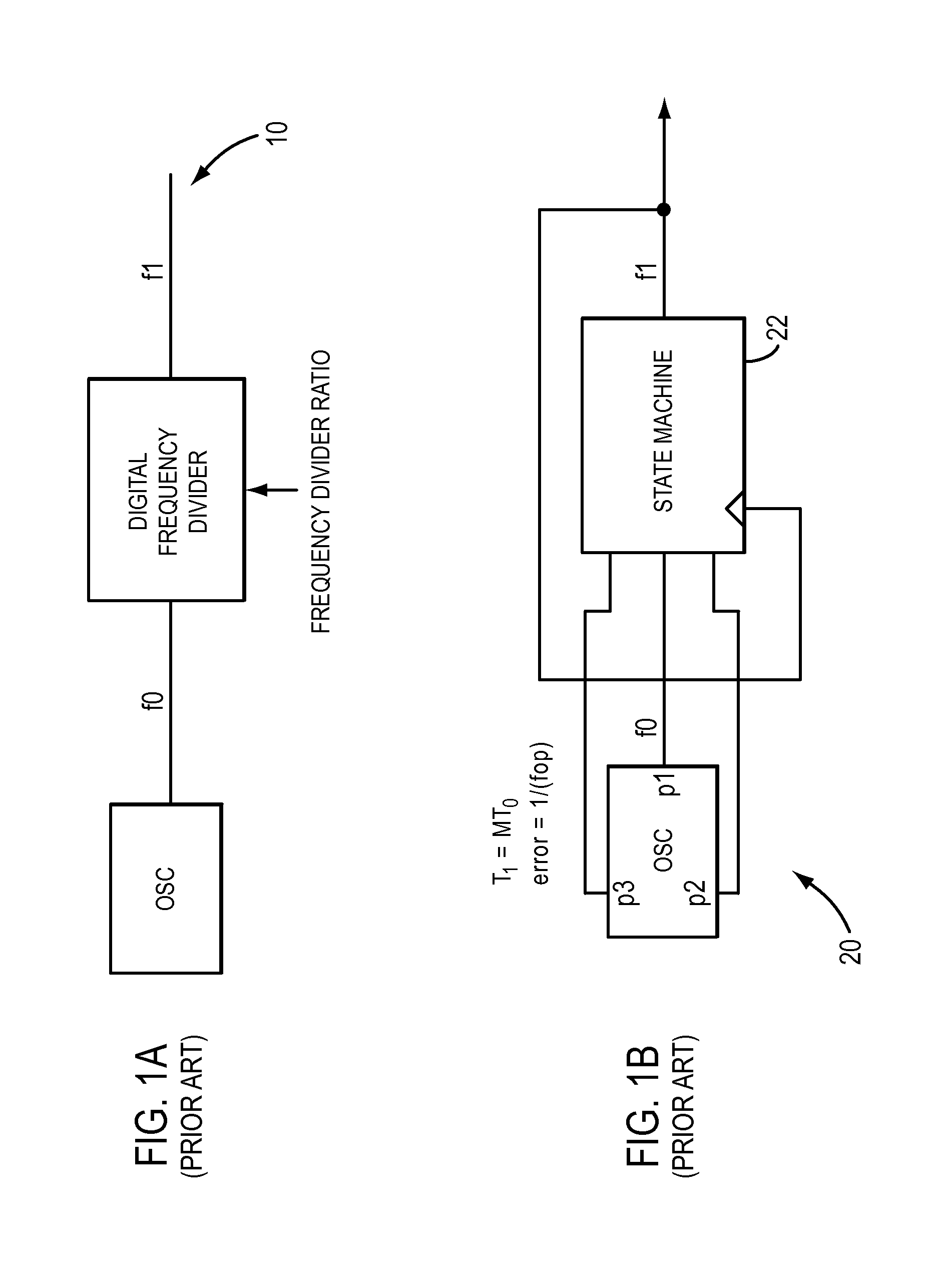
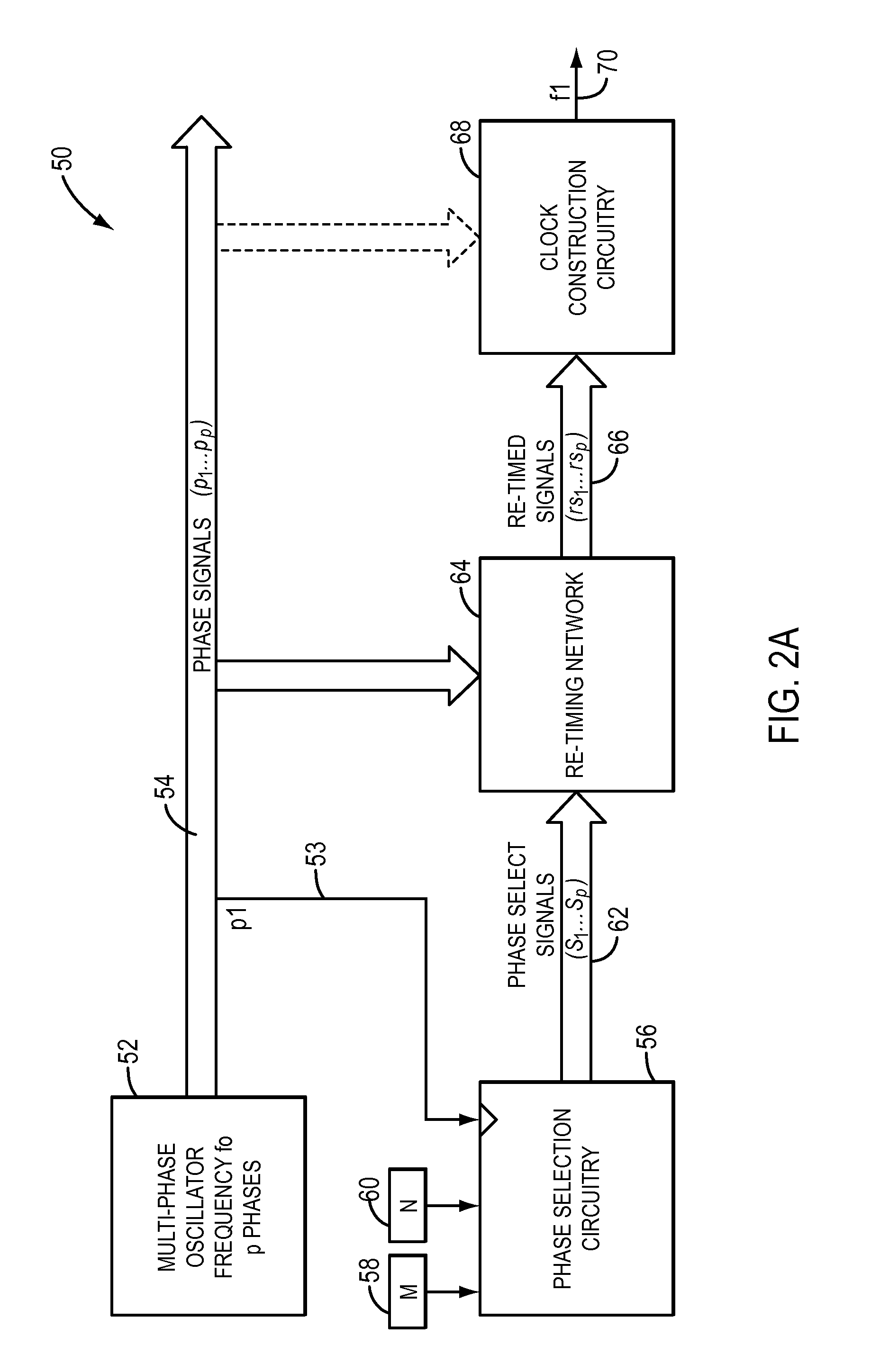
A system and method for synthesizing a frequency using a multi-phase oscillator. A state machine operating on one of the phases of the oscillator computes, based on a pair of input integers, a phase select vector that indicates when a particular phase of the multi-phase oscillator should be selected when a transition of the waveform of the output frequency is needed. The phase select vector is then re-timed to form a retimed phase vector so that each phase select signal is in phase with signal it is designed to select. The signals in the retimed phase vector then can be combined to create the output frequency directly or can be used to select the corresponding phase of the multi-phase oscillator, if more accuracy is desired. In one embodiment, the multi-phase oscillator is a rotary traveling wave oscillator which provides highly accurate multiple phases.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
True time delay phase array radar using rotary clocks and electronic delay lines
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
SRAM circuitry
A static ram cell is described. The cell includes a pair of cross-coupled transistors and a pair of diode-connected transistors operated from a wordline that provides power to the cell. The cell has three main operating modes, reading, writing, and data retention. Reading is performed by sensing current flowing from a powered-up wordline through a conductive one of the cross-coupled transistors. Writing is performed by pulsing the source of the conductive one of the cross-coupled transistors with a positive voltage to flip the conductive states of the cross-coupled transistors. Data retention is performed by using leakage currents to retain the conductive states of the cross-coupled transistors. A decoder for an array of static ram cells may be operated synchronously and in a pipelined fashion using a rotary traveling wave oscillator that provides the clocks for the pipeline. The cell is capable of detecting an alpha particle strike with suitable circuitry.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
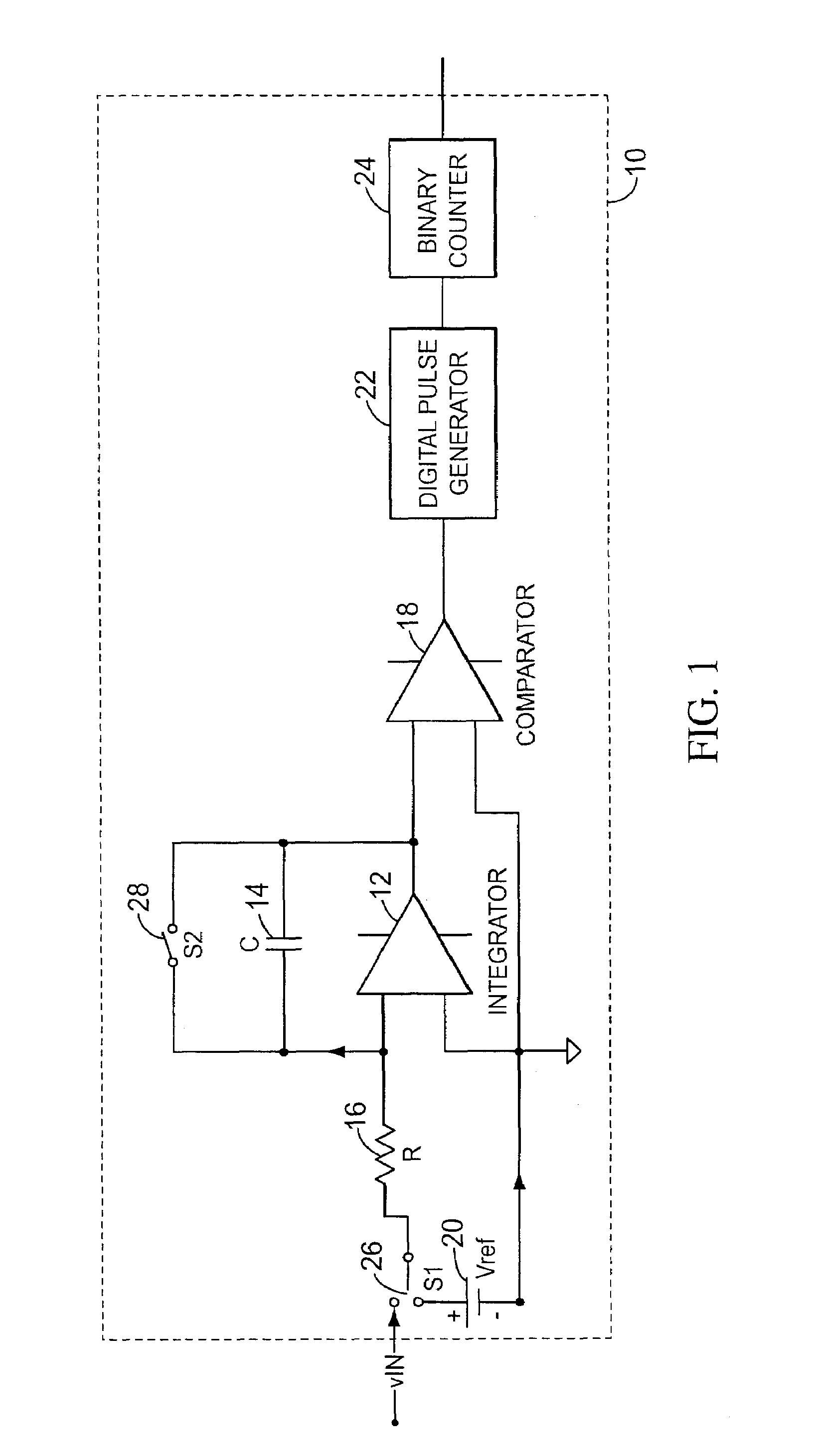
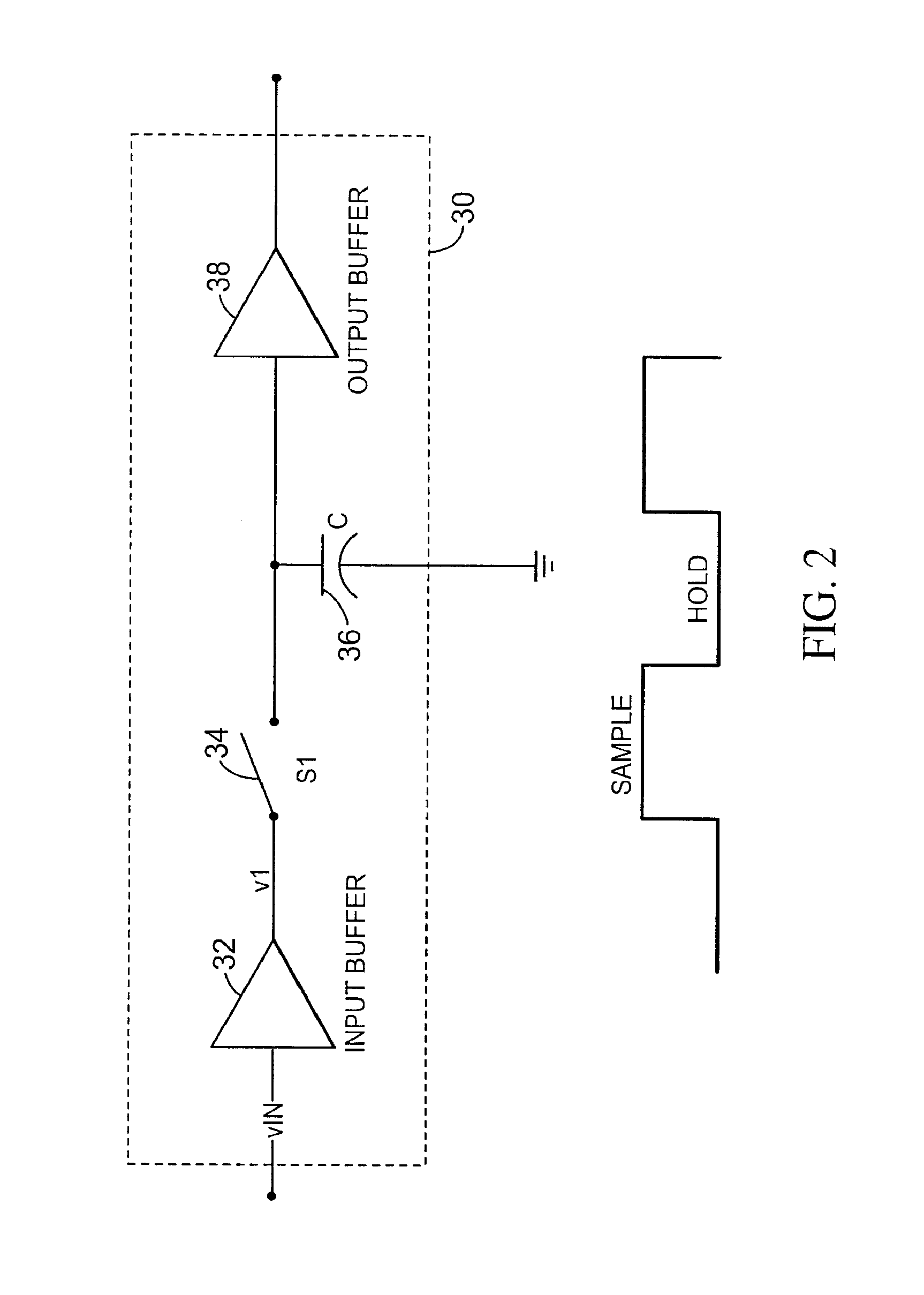
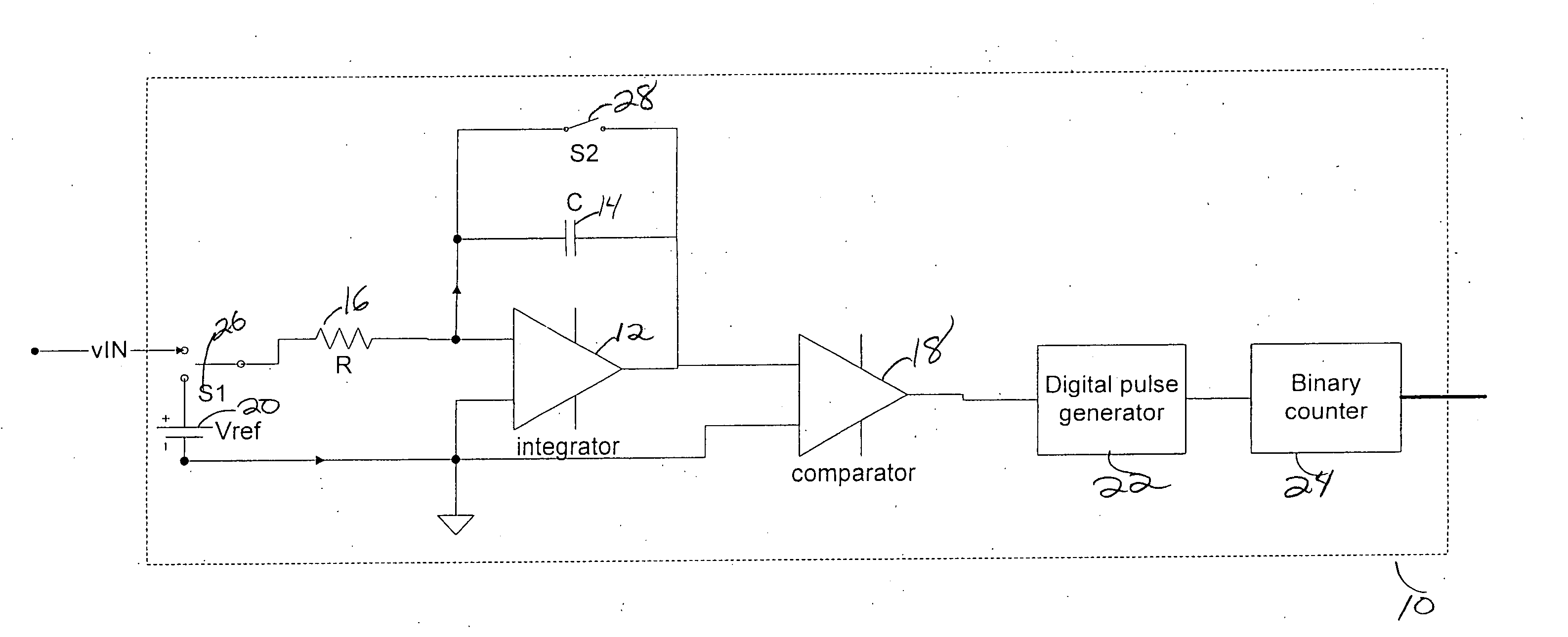
Double feedback rotary traveling wave oscillator driven sampler circuits
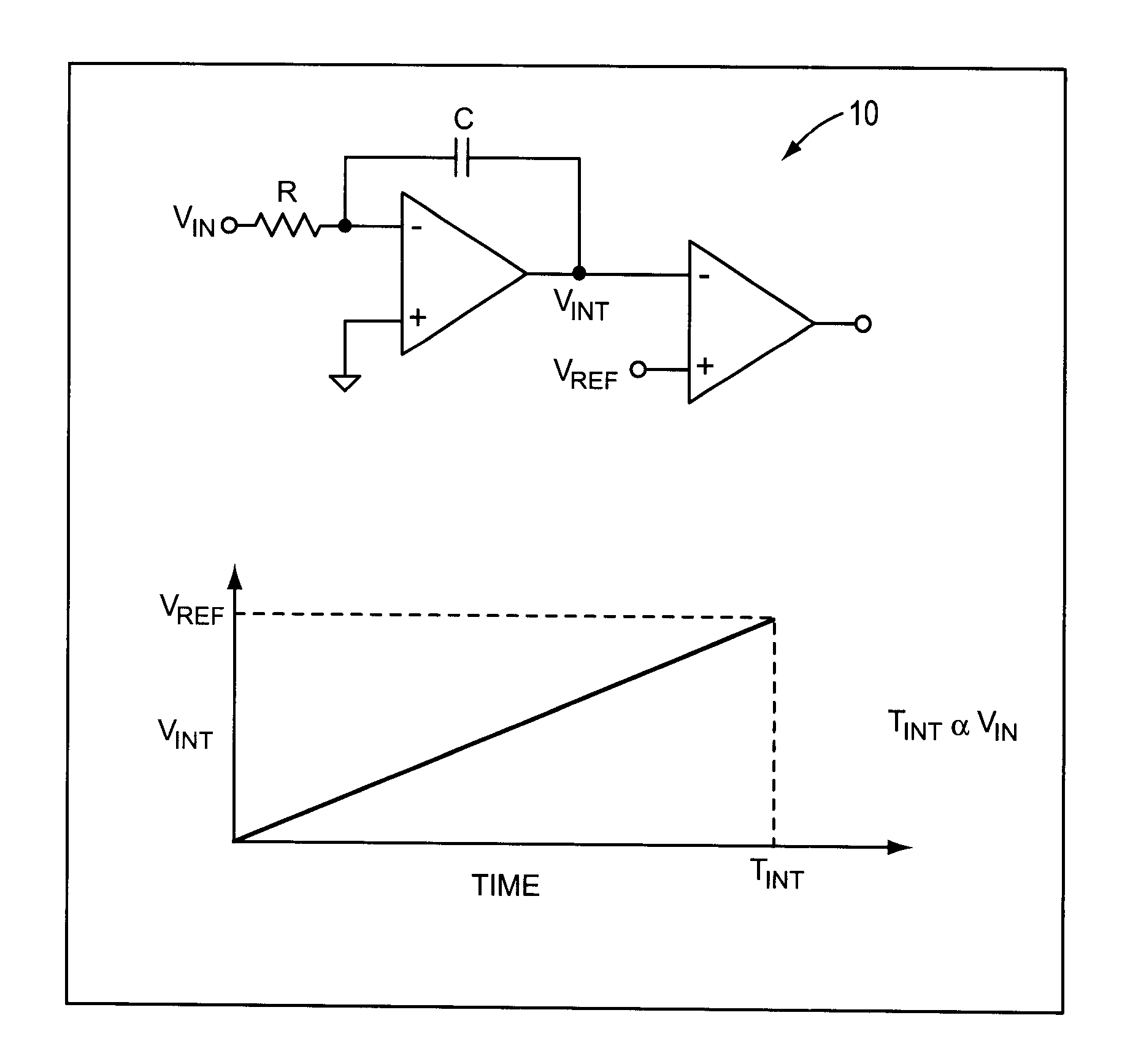
ActiveUS7439777B2Precise time controlAccurate valueComputing operations for integral formationComputing operations for integration/differentiationEngineeringVoltage reference
A sampling circuit and method are disclosed. The sampling circuit includes a buffer, a holding capacitor, a set of switches, and at least two voltage references. The buffer drives buffered analog input signal via a first switch to a first node of holding capacitor. A second switch connects a second node of the holding capacitor to a first reference voltage. A third switch connects the second node of the holding capacitor to a second reference voltage. When the first and second switches are closed, charge accumulates on the holding capacitor. Opening the second switch terminates charging. The third switch biases the charged capacitor to the second reference voltage and the sampled output is taken from the first node of the holding capacitor. A rotary clock and control circuit provide the precise timing for the switches, especially the opening of the second switch, which determines the end of the sampling time.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Double feedback rotary traveling wave oscillator driven sampler circuits
ActiveUS20060022720A1Precise time controlAccurate valueComputing operations for integral formationComputing operations for integration/differentiationCapacitanceHemt circuits
A sampling circuit and method are disclosed. The sampling circuit includes a buffer, a holding capacitor, a set of switches, and at least two voltage references. The buffer drives buffered analog input signal via a first switch to a first node of holding capacitor. A second switch connects a second node of the holding capacitor to a first reference voltage. A third switch connects the second node of the holding capacitor to a second reference voltage. When the first and second switches are closed, charge accumulates on the holding capacitor. Opening the second switch terminates charging. The third switch biases the charged capacitor to the second reference voltage and the sampled output is taken from the first node of the holding capacitor. A rotary clock and control circuit provide the precise timing for the switches, especially the opening of the second switch, which determines the end of the sampling time.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
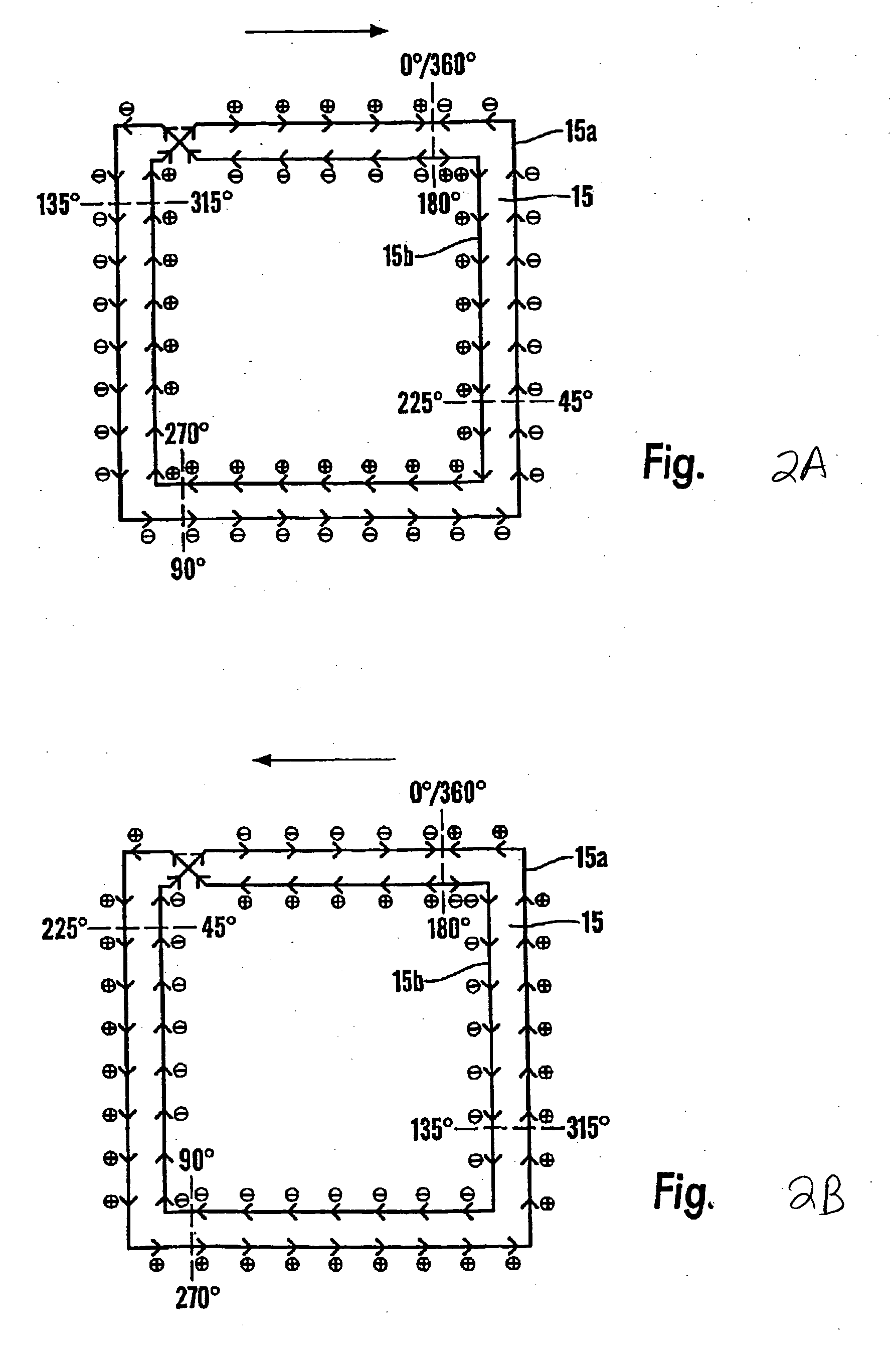
Low noise oscillator
InactiveUS20050156680A1Reduce phase noiseSmall spacingDelay lines pulse generationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLow noiseElectrical conductor
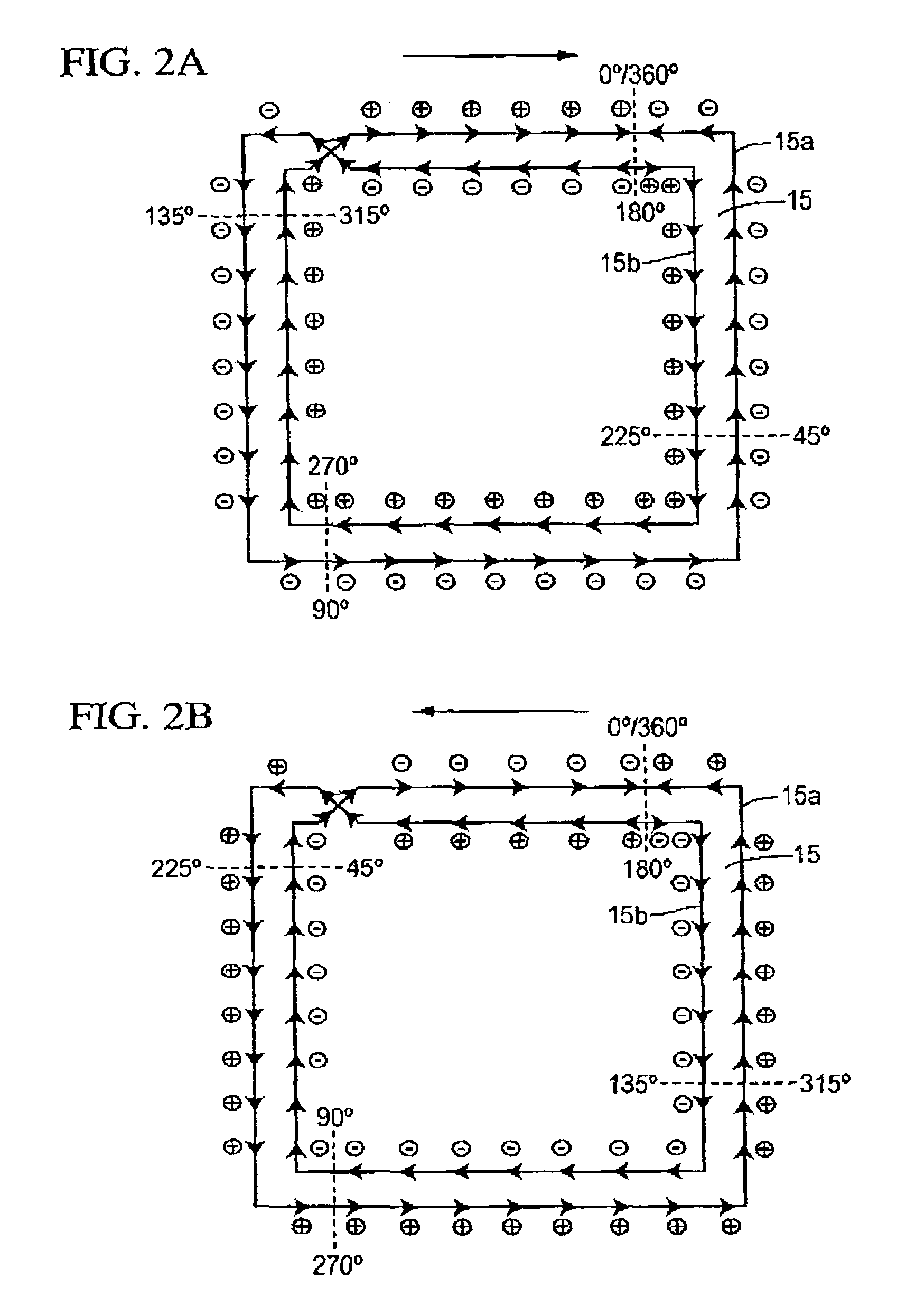
A low noise oscillator constructed using a rotary traveling wave oscillator. The conductors of the rotary traveling wave oscillator provide at any tap position a pair of oppositely phased oscillations and these oscillations have slightly different phases at positions that are slightly different on the conductors. Regeneration devices establish and maintain oscillations on the conductors of the traveling wave oscillator. A regeneration device made from p-channel and n-channel transistors is connected to the conductors of the traveling wave oscillator in such a way that the gate connections of the transistors receive the traveling wavefront before the drains of the transistors receive the wavefront. By the time the regeneration device switches in response to the wavefront arriving at the gates of the transistors, the wavefront has arrived at the drains. This creates little or no disturbance to the wave on the conductors and results in low phase noise.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
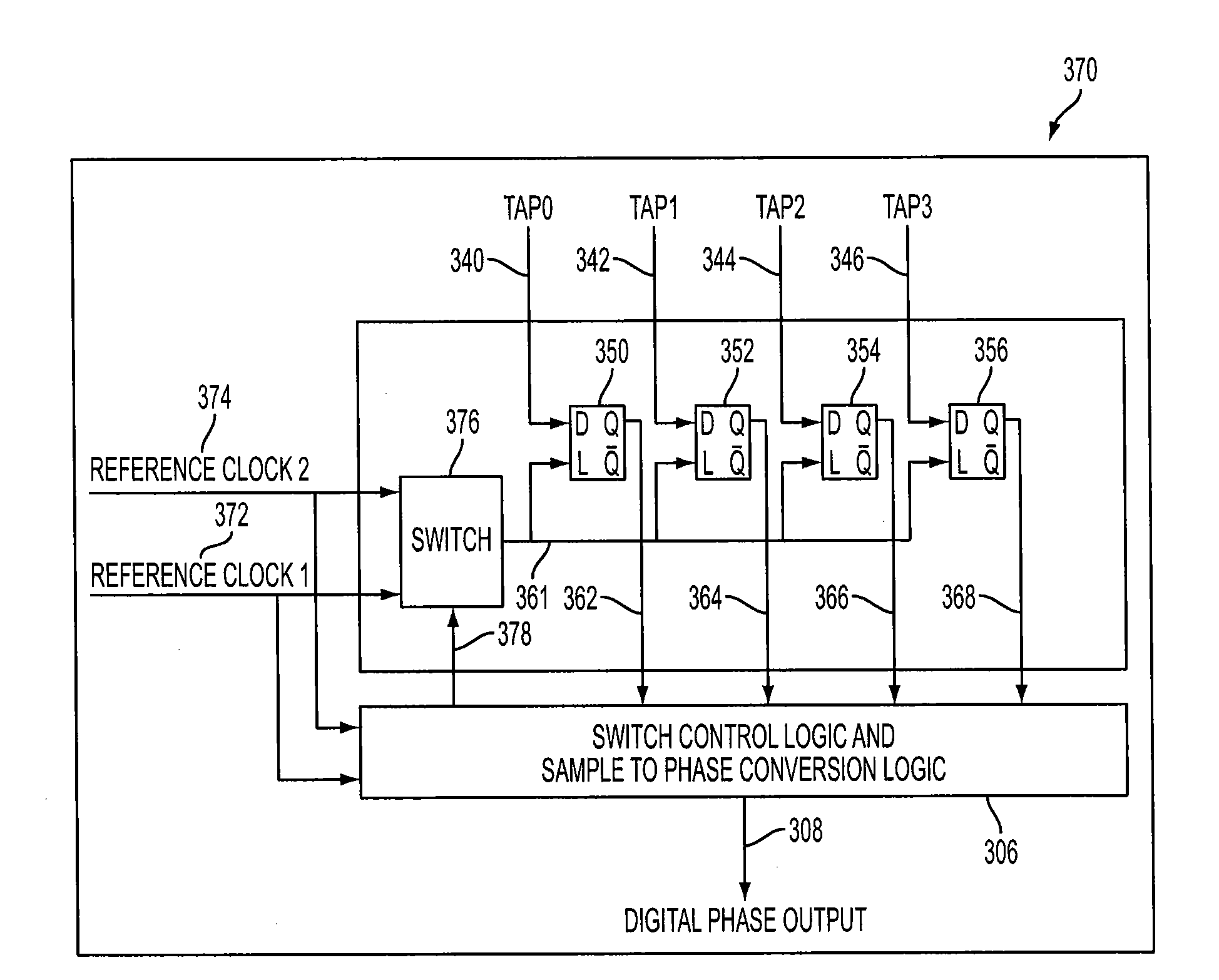
Vernier phase to digital converter for a rotary traveling wave oscillator
ActiveUS20130271190A1High resolutionAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsDigital down converterClosed loop
A phase to digital conversion circuit with improved resolution for a rotary traveling wave oscillator. The phase to digital conversion circuit connects with a closed loop transmission line via a plurality of signal lines or nodes distributed along the transmission line. As an oscillating signal propagates around the transmission line, a time waveform of the signal at each of the plurality of signal lines is transmitted to a corresponding plurality of latches. Upon a triggering condition, the plurality of latches simultaneously samples the signals from the plurality of signal lines. At least two reference clock signals are switchably coupled with the plurality of latches latch for triggering the plurality of latches based on an edge transition in each of the reference clock signals compared with an edge transition in each of the signals from the plurality of taps.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Digital frequency synthesizer
ActiveUS20060245532A1Improve accuracyMinimal jitterPulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionWave shapeFrequency synthesizer
A system and method for synthesizing a frequency using a multi-phase oscillator. A state machine operating on one of the phases of the oscillator computes, based on a pair of input integers, a phase select vector that indicates when a particular phase of the multi-phase oscillator should be selected when a transition of the waveform of the output frequency is needed. The phase select vector is then re-timed to form a retimed phase vector so that each phase select signal is in phase with signal it is designed to select. The signals in the retimed phase vector then can be combined to create the output frequency directly or can be used to select the corresponding phase of the multi-phase oscillator, if more accuracy is desired. In one embodiment, the multi-phase oscillator is a rotary traveling wave oscillator which provides highly accurate multiple phases.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Rotary traveling wave voltage controlled oscillator with high power and large tuning ranges
InactiveCN102624334AHigh power outputLarge tuning rangePulse automatic controlOscillations generatorsPhase shiftedControl theory
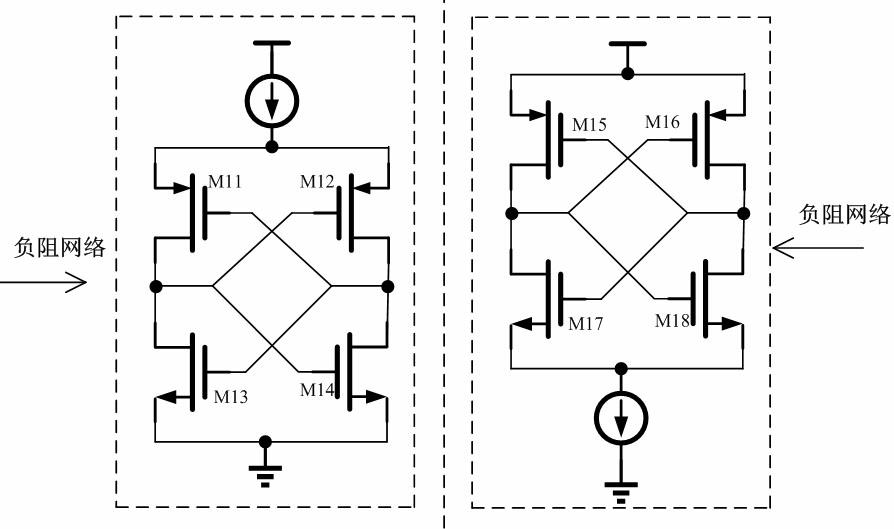
The invention belongs to the technical field of millimeter wave integrated circuits, and particularly relates to a rotary traveling wave voltage controlled oscillator with high power and large tuning ranges. The rotary traveling wave voltage controlled oscillator is mainly composed of a rotary traveling wave oscillator, a negative resistance network, a voltage controlled variable capacitor and a voltage controlled phase shift network. According to the rotary traveling wave voltage controlled oscillator, parasitic effects to the oscillator can be reduced. Simultaneously, the tuning range of the output frequency of the voltage controlled oscillator is increased by coupling the voltage controlled variable capacitor in the oscillator; and waves with different phases are identical in phases after passing through the voltage controlled phase shift network by coupling the voltage controlled phase shift network in the oscillator, so that the waves with the identical phases are stacked together to achieve high power output.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Rotary traveling wave oscillator with high power output of multiple energy injection locking
InactiveCN102624366AAchieve output frequencyInjection lock range increasedPulse shapingOscillations generatorsCapacitanceInjection locked
The invention belongs to the technical field of millimeter wave integrated circuits, and particularly relates to a rotary traveling wave oscillator of multiple energy injection locking. The circuit mainly comprises a rotary traveling wave oscillator, a negative resistance network, a voltage controlled variable capacitor, a voltage controlled phase shifter and a harmonic generation circuit. Parasitic resistances in a capacitance device and an inductance device are high with the rising of the signal frequency, particularly when the frequency in ranges of millimeter waves or sub-millimeter waves in the integrated circuit, and simple capacitance inductance oscillator is difficult to achieve the output of wide tuning ranges and large power. According to the rotary traveling wave oscillator, a voltage-controlled rotary traveling wave oscillator is used to produce fundamental frequency signals to couple the harmonic generation circuit at different positions of the oscillator. The produced high sub-harmonic signals are injected into another oscillator to achieve oscillation with high frequency. The injection locking range is increased by injecting a plurality of energy and choosing appropriate phase of the injected signal.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
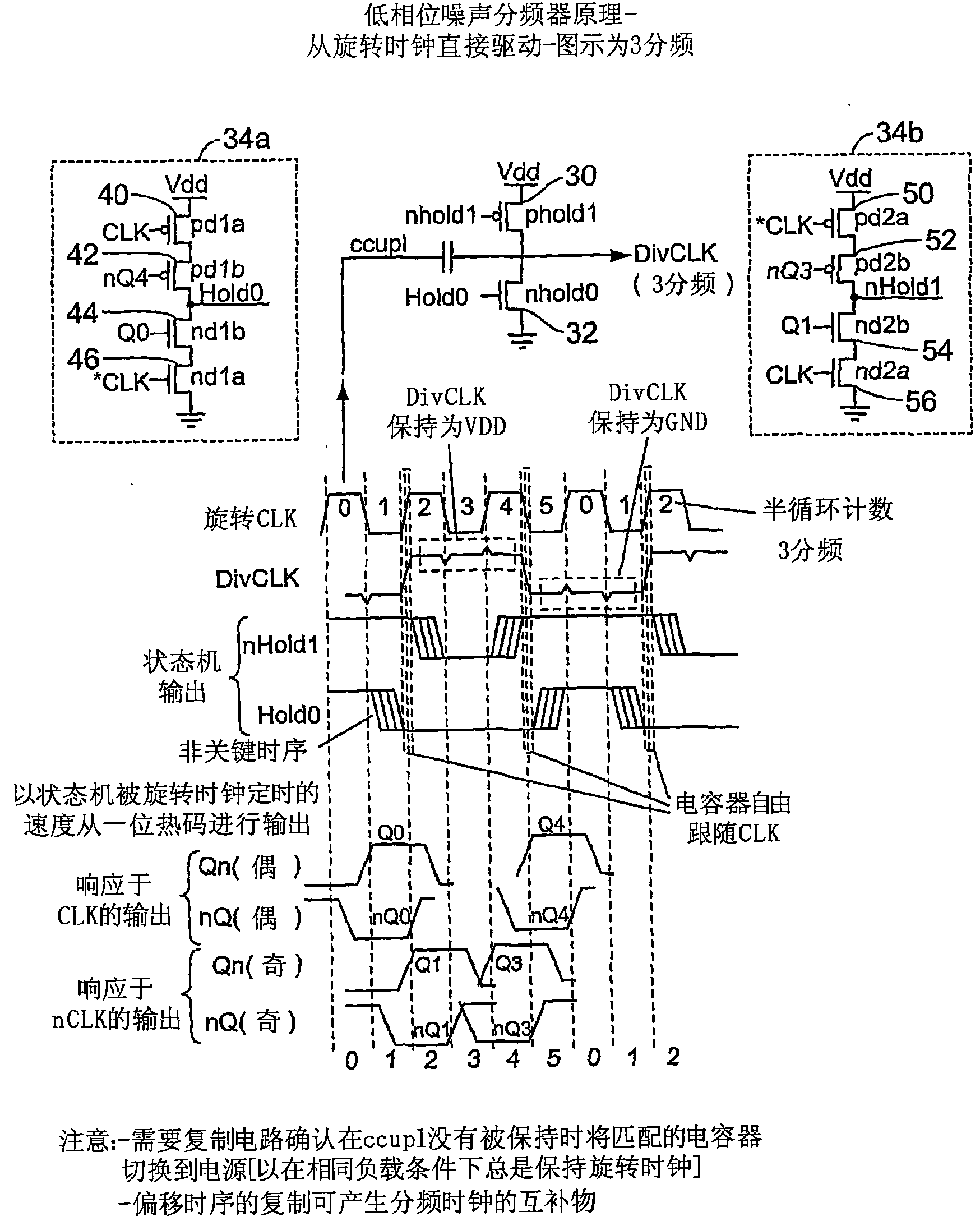
Low noise divider
InactiveCN101199120AInhibition transitionPulse automatic controlOscillations generatorsLow noiseMultiplexer
A system and method for dividing a clock in a way that achieves low phase noise. In one embodiment, a multi-phase oscillator such as a rotary traveling wave oscillator operates a state machine which determines times at which a transition of a coupled phase signal of the multi-phase oscillator should be suppressed. Suppression of the transition is performed by a transistor structure that holds the phase signal at a high or a low so that the transition does not occur at the output. Fewer transitions in the phase signal create a divided clock. In another embodiment, a decoder determines times for suppressing transitions in a true and complement clock and a polarity flip-flop determines the correct polarity for suppressing edges on both clocks. In yet another embodiment, a multiplexer is used to selectively pass either a true or complement clock to an output load.
Owner:盟缔杰公司
Vernier phase to digital converter for a rotary traveling wave oscillator
ActiveUS8581759B2Analogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsWave shapeClosed loop
A phase to digital conversion circuit with improved resolution for a rotary traveling wave oscillator. The phase to digital conversion circuit connects with a closed loop transmission line via a plurality of signal lines or nodes distributed along the transmission line. As an oscillating signal propagates around the transmission line, a time waveform of the signal at each of the plurality of signal lines is transmitted to a corresponding plurality of latches. Upon a triggering condition, the plurality of latches simultaneously samples the signals from the plurality of signal lines. At least two reference clock signals are switchably coupled with the plurality of latches latch for triggering the plurality of latches based on an edge transition in each of the reference clock signals compared with an edge transition in each of the signals from the plurality of taps.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Clock generation circuitry
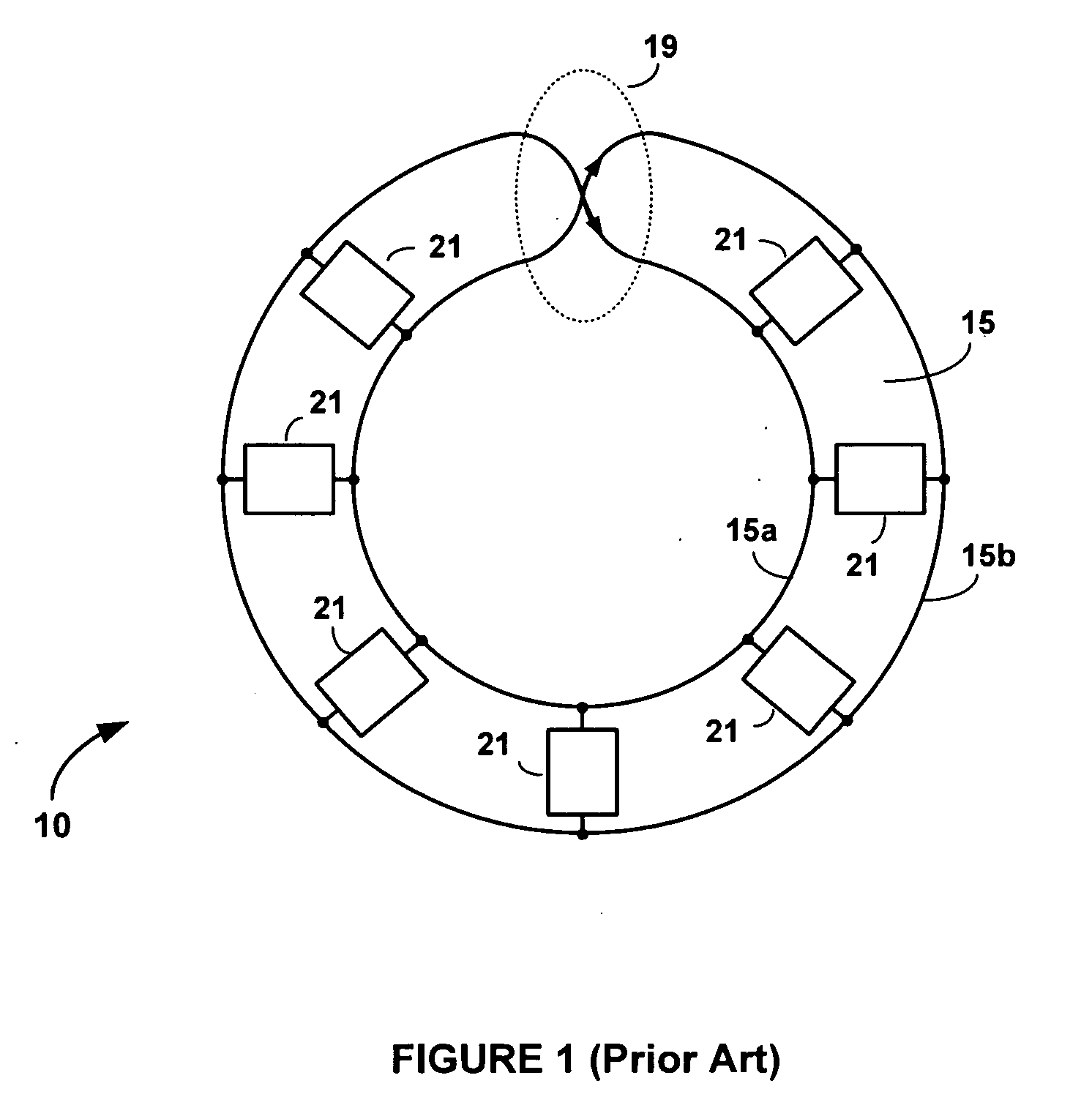
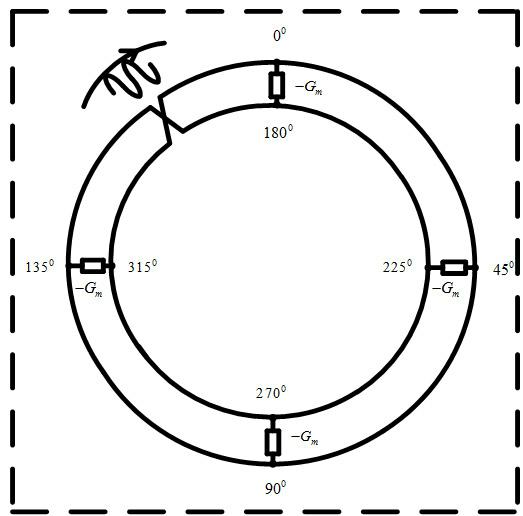
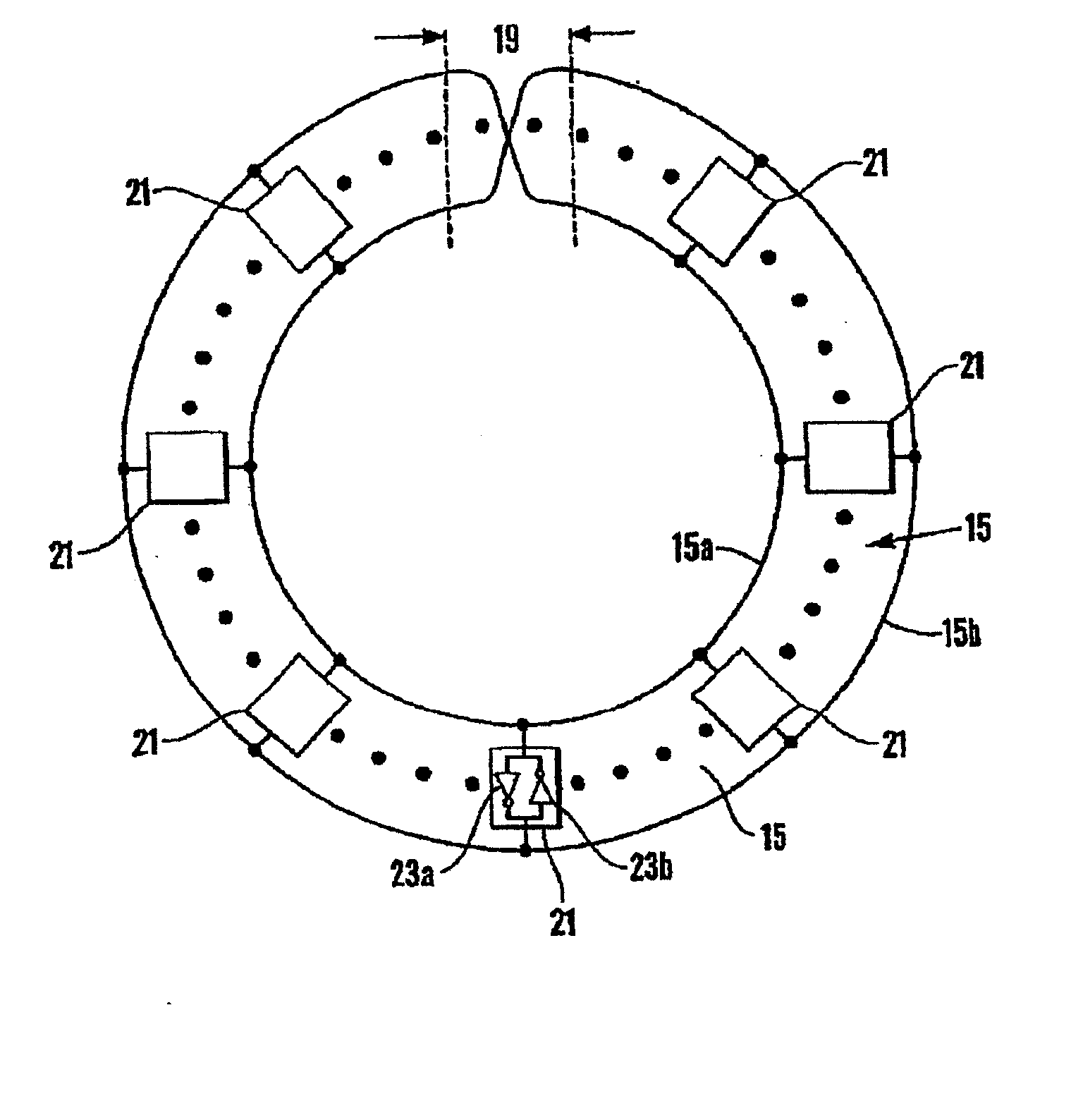
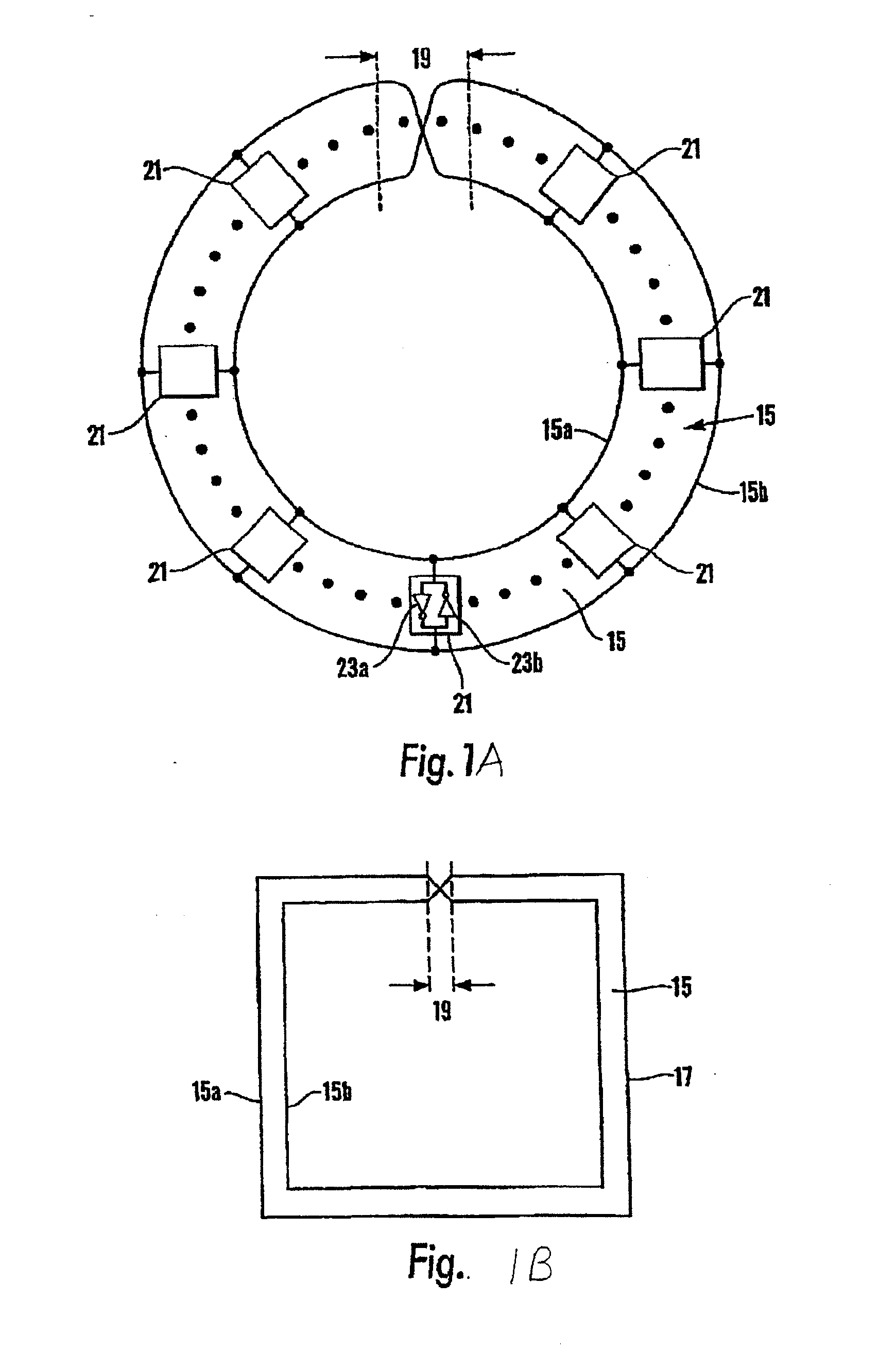
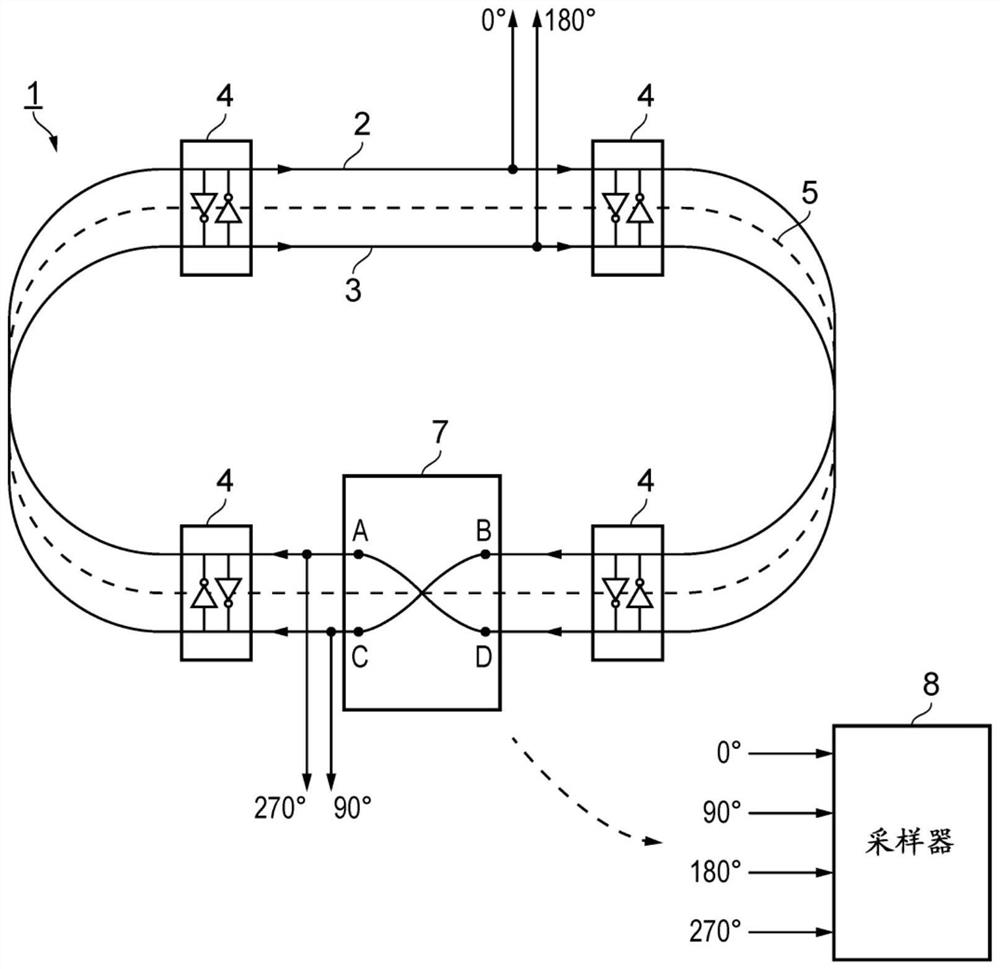
There is disclosed herein clock generation circuitry, in particular rotary travelling wave oscillator circuitry. Such circuitry comprises a pair of signal lines connected together to form a dosed loop and arranged such that they define at least one transition section where both said lines in a first portion of the pair cross from one lateral side of both said lines in a second portion of the pair to the other lateral side of both said lines in the second portion of the pair.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
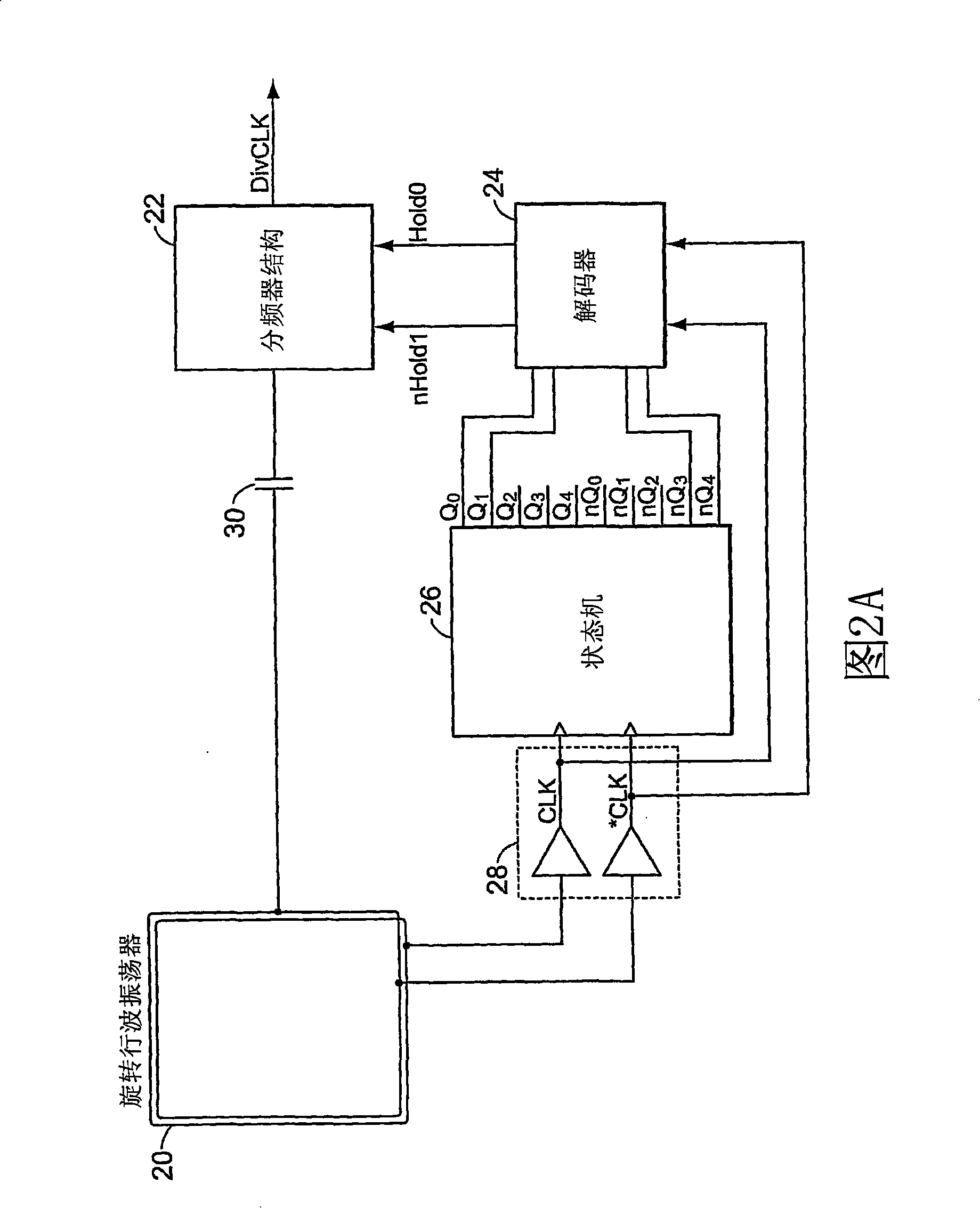
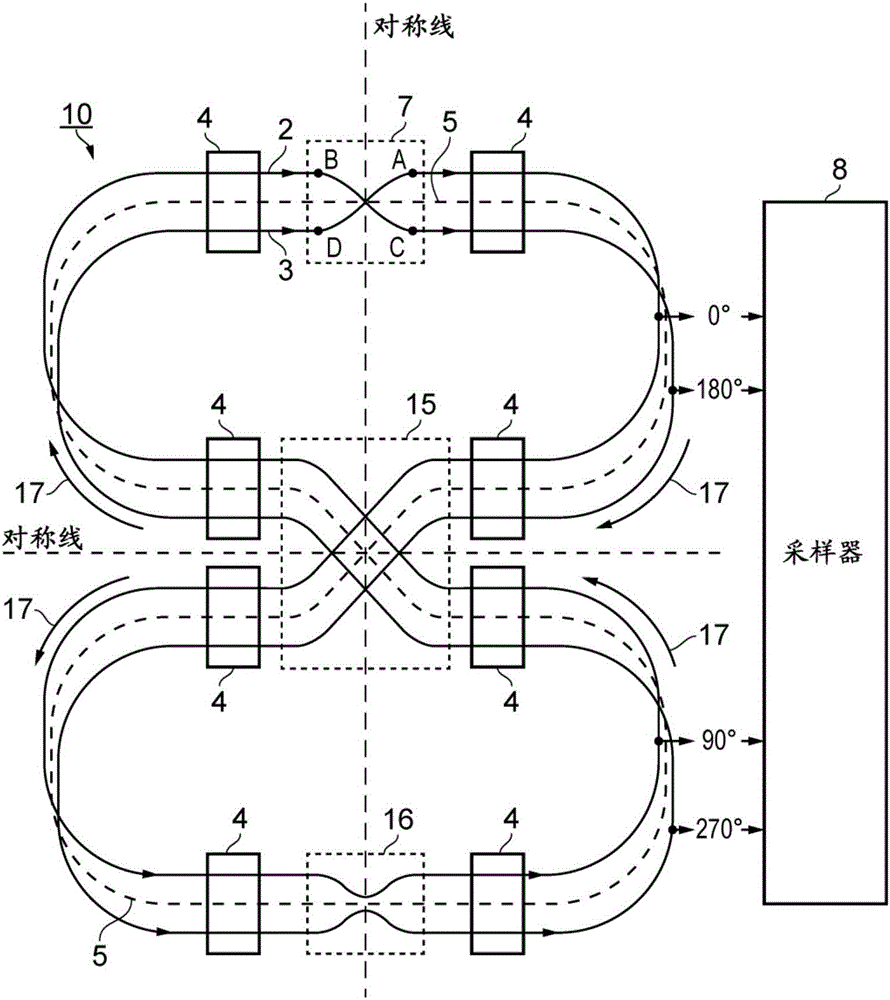
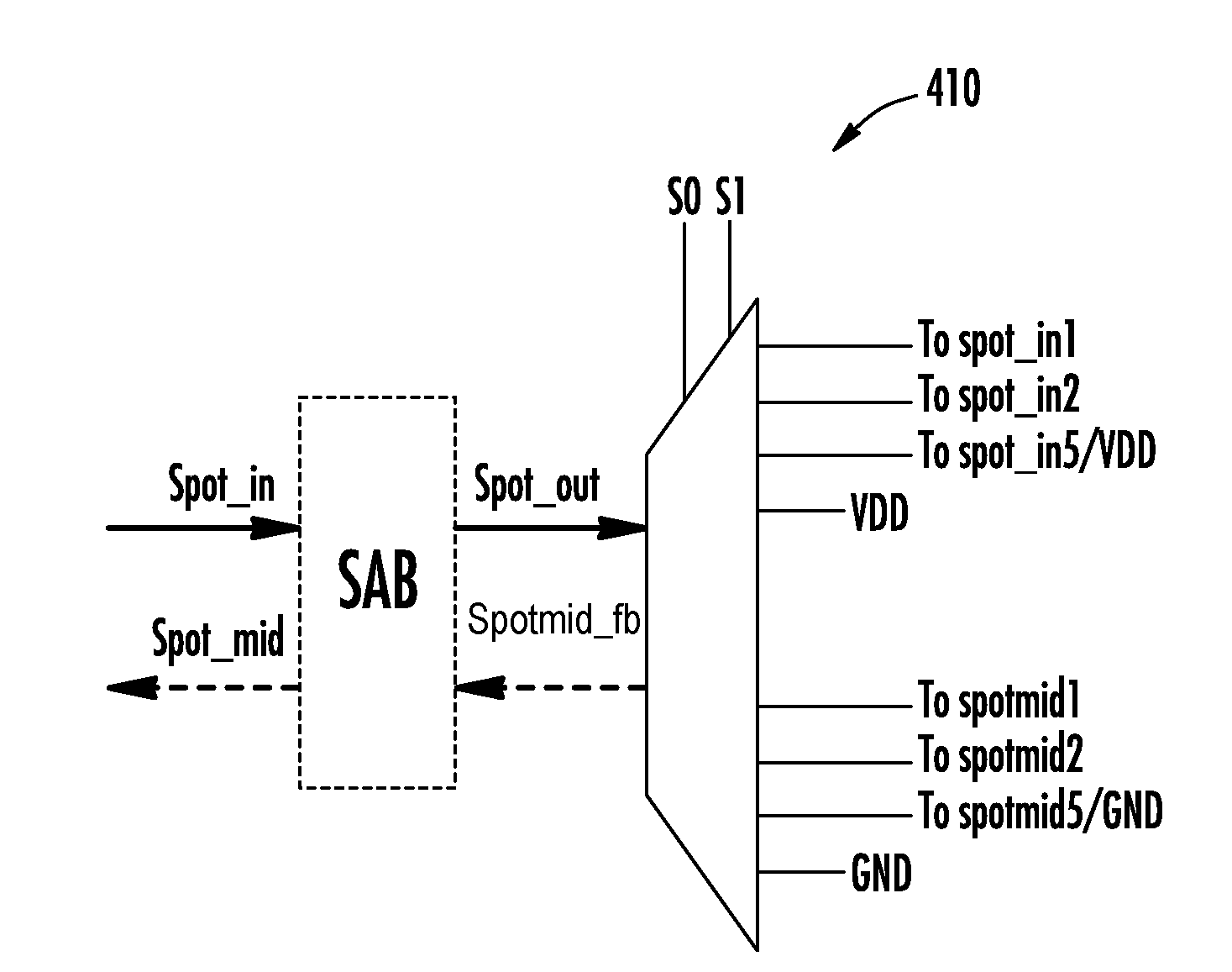
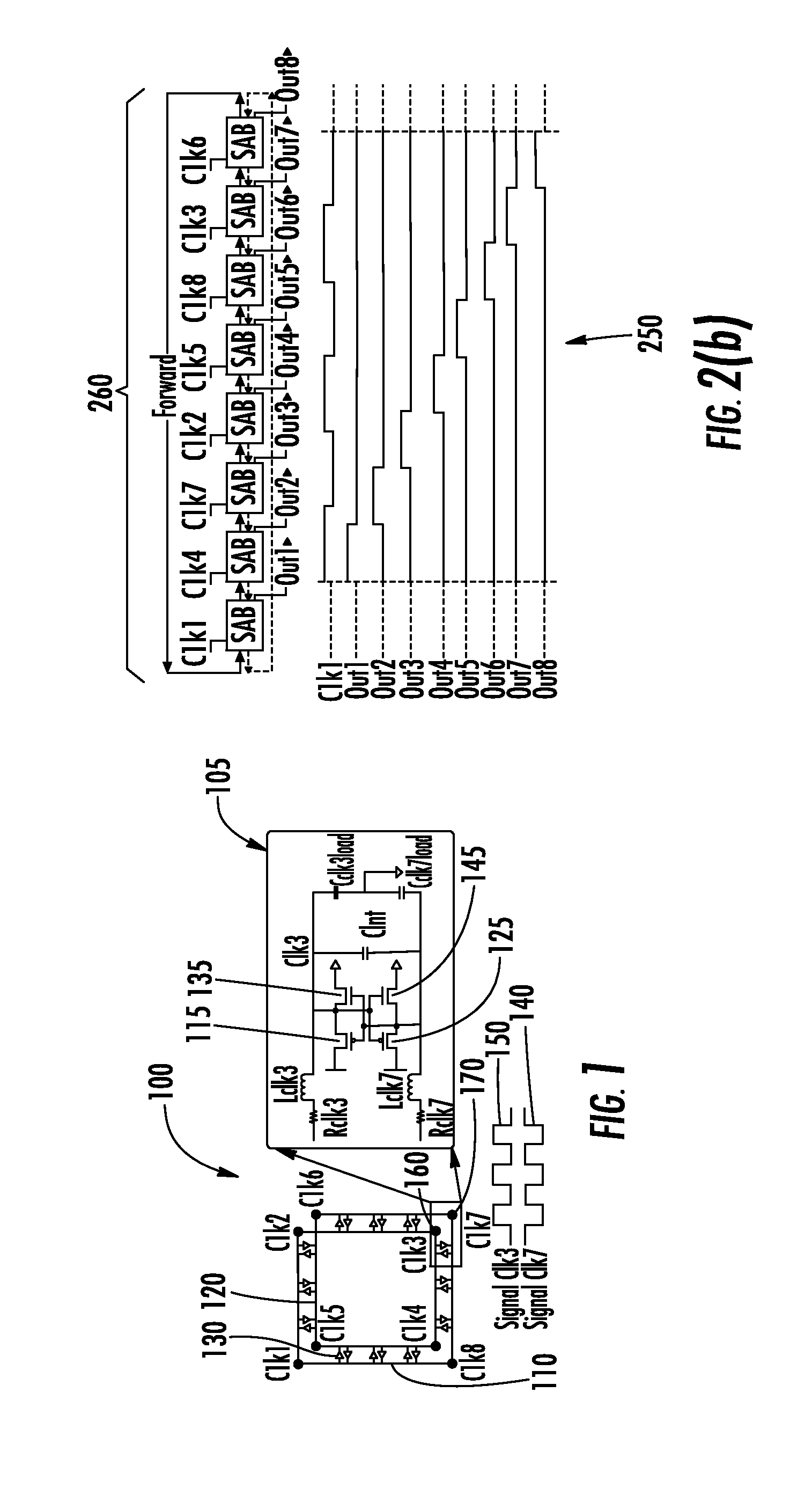
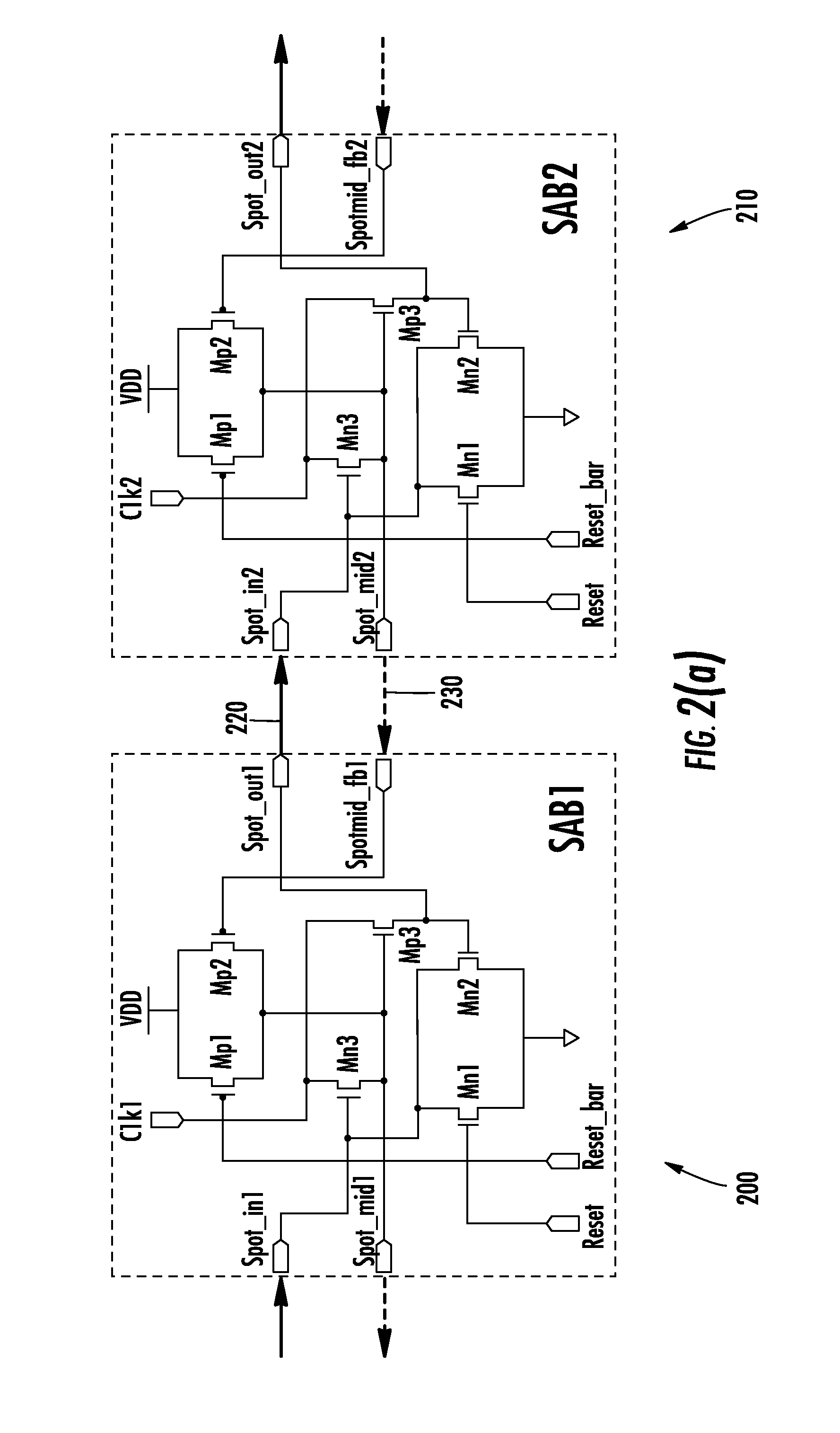
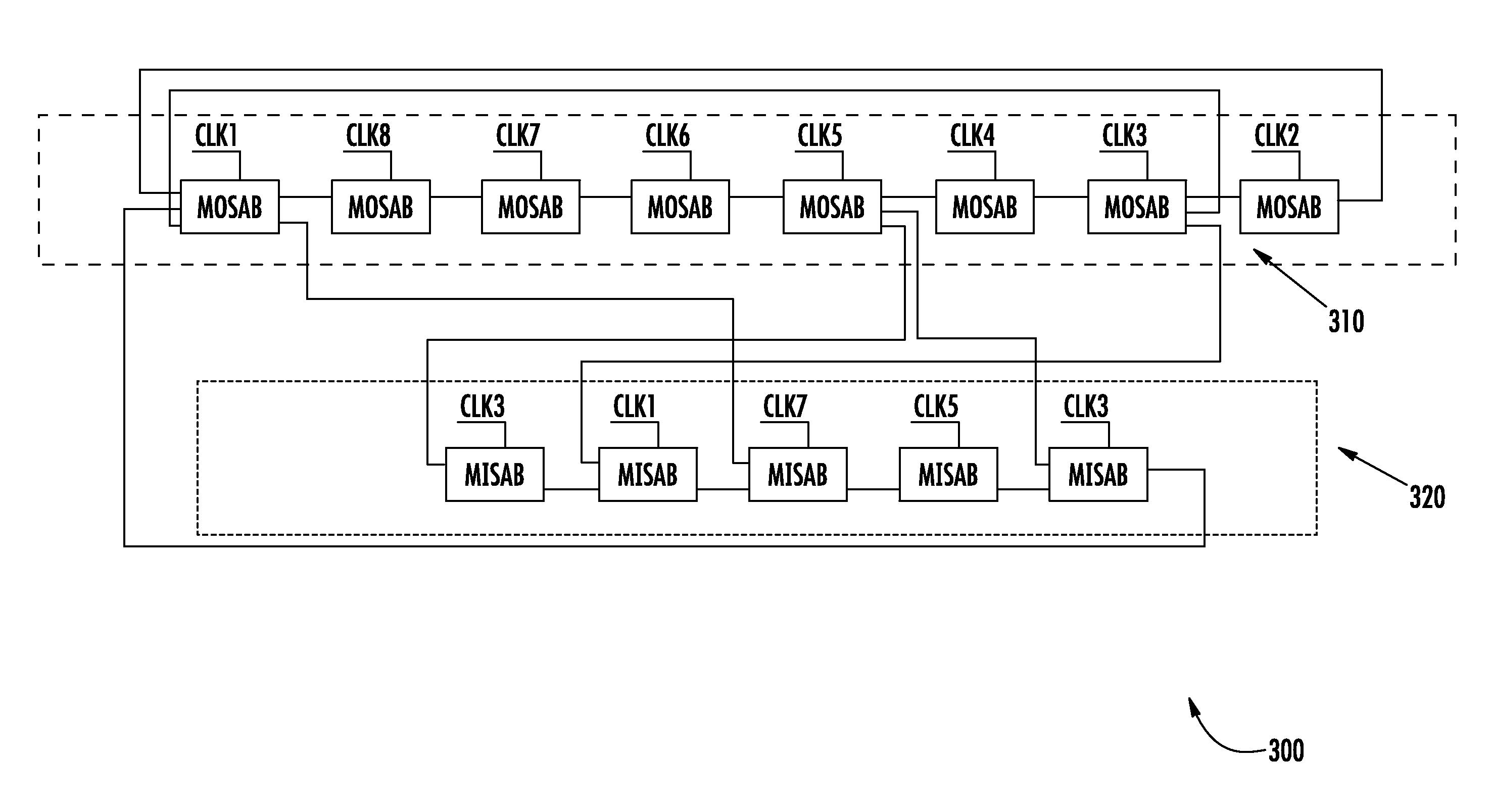
Resonant Frequency Divider Design Methodology for Dynamic Frequency Scaling
ActiveUS20170047892A1Continuously circulated pulse countersPulse automatic controlMulti inputComputer module
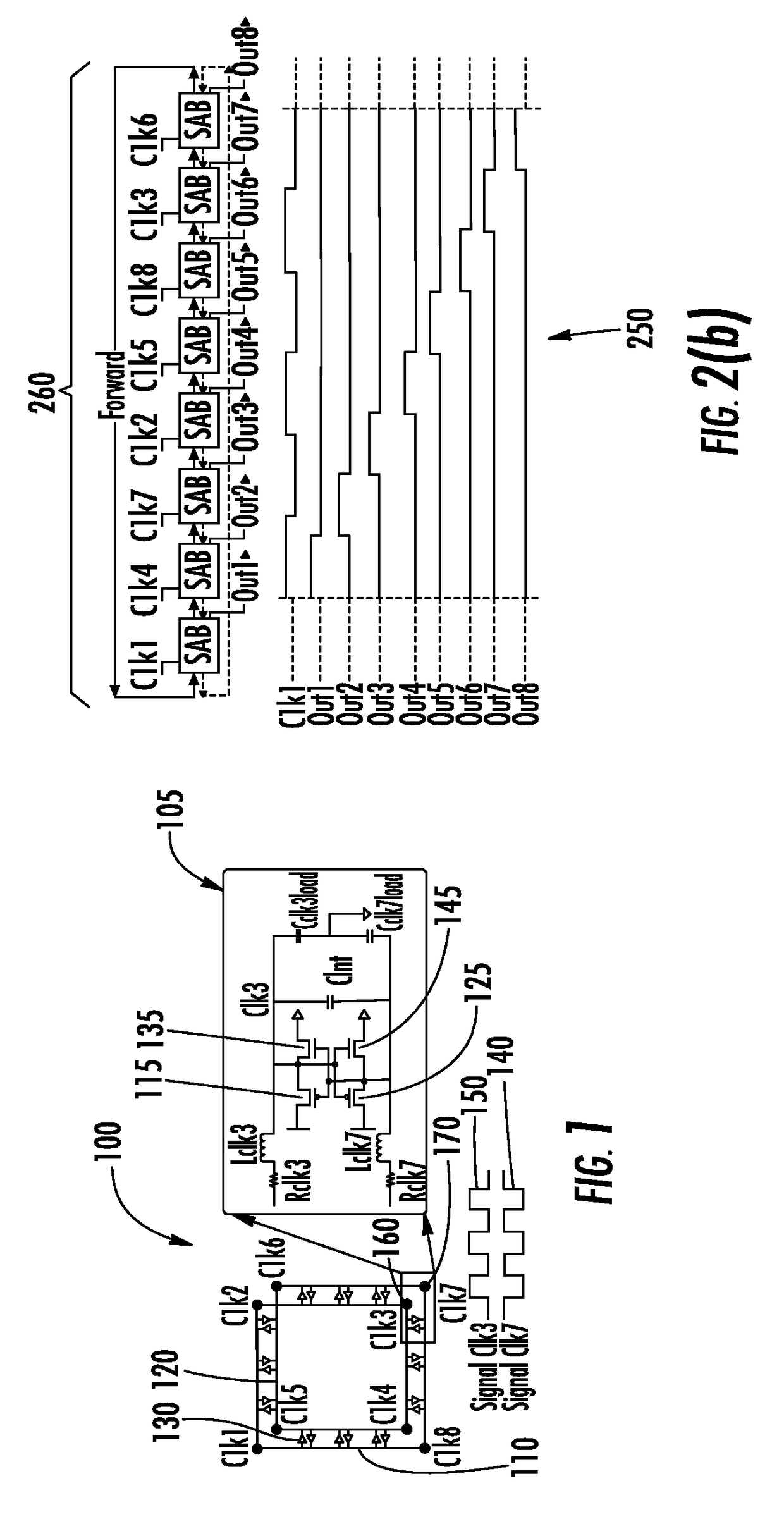
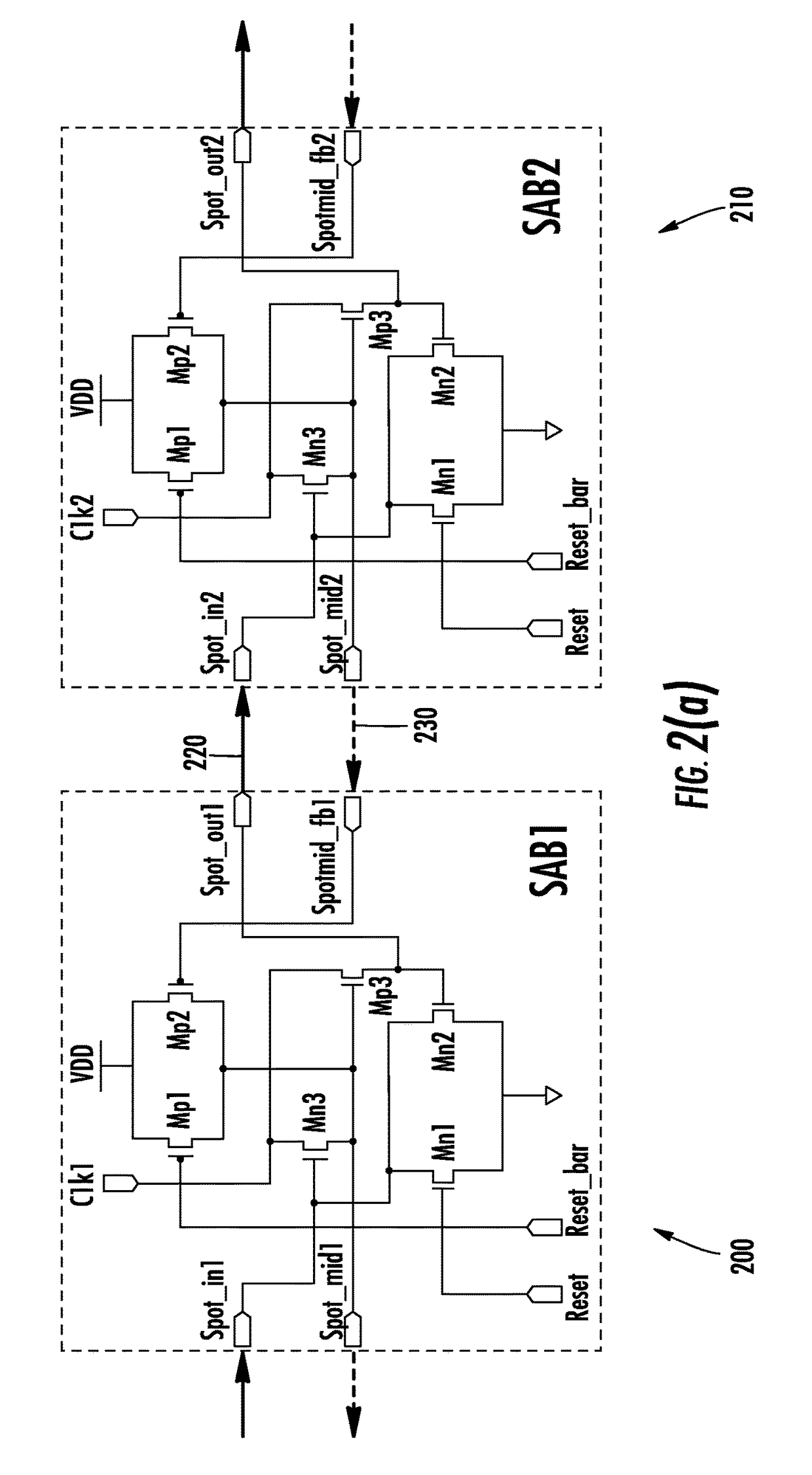
A dynamic rotary traveling wave oscillator circuit includes plurality of multi-output spot-advancing blocks (MOSABs) forming a main-loop and a plurality of multi-input spot-advancing blocks (MISABs) forming a sub-loop. Depending on a desired division ratio, a connection connects blocks on the MOSABs and MISABs to create the desired division ratio.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
Regeneration Device for Rotary Traveling Wave Oscillator
InactiveUS20070257736A1Low noise characteristicsAvoid low frequency operationPulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsElectrical conductorWave shape
An oscillator is described. The oscillator includes segments of two-conductor transmission line being connected together by an odd number of connection means to form a closed loop. A plurality of current switches is connected to the conductors of the segments and a high impedance element, such as an inductor or transmission line, is connected to a conductor of at least one segment. The high impedance element sources current into the closed loop and the current switches sink current from one or the other of the conductors of the loop depending on the state of the switch. The switches cause a wave to be established and maintained on the loop and the wave changes the state of the switches as it oscillates. One embodiment of the switches employs npn transistors whose emitters are connected to a current source and another uses NMOS transistors.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Resonant frequency divider design methodology for dynamic frequency scaling
ActiveUS9484896B2Continuously circulated pulse countersCounting chain synchronous pulse countersRotary traveling wave oscillatorEngineering
A dynamic rotary traveling wave oscillator circuit includes plurality of multi-output spot-advancing blocks (MOSABs) forming a main-loop and a plurality of multi-input spot-advancing blocks (MISABs) forming a sub-loop. Depending on a desired division ratio, a connection connects blocks on the MOSABs and MISABs to create the desired division ratio.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
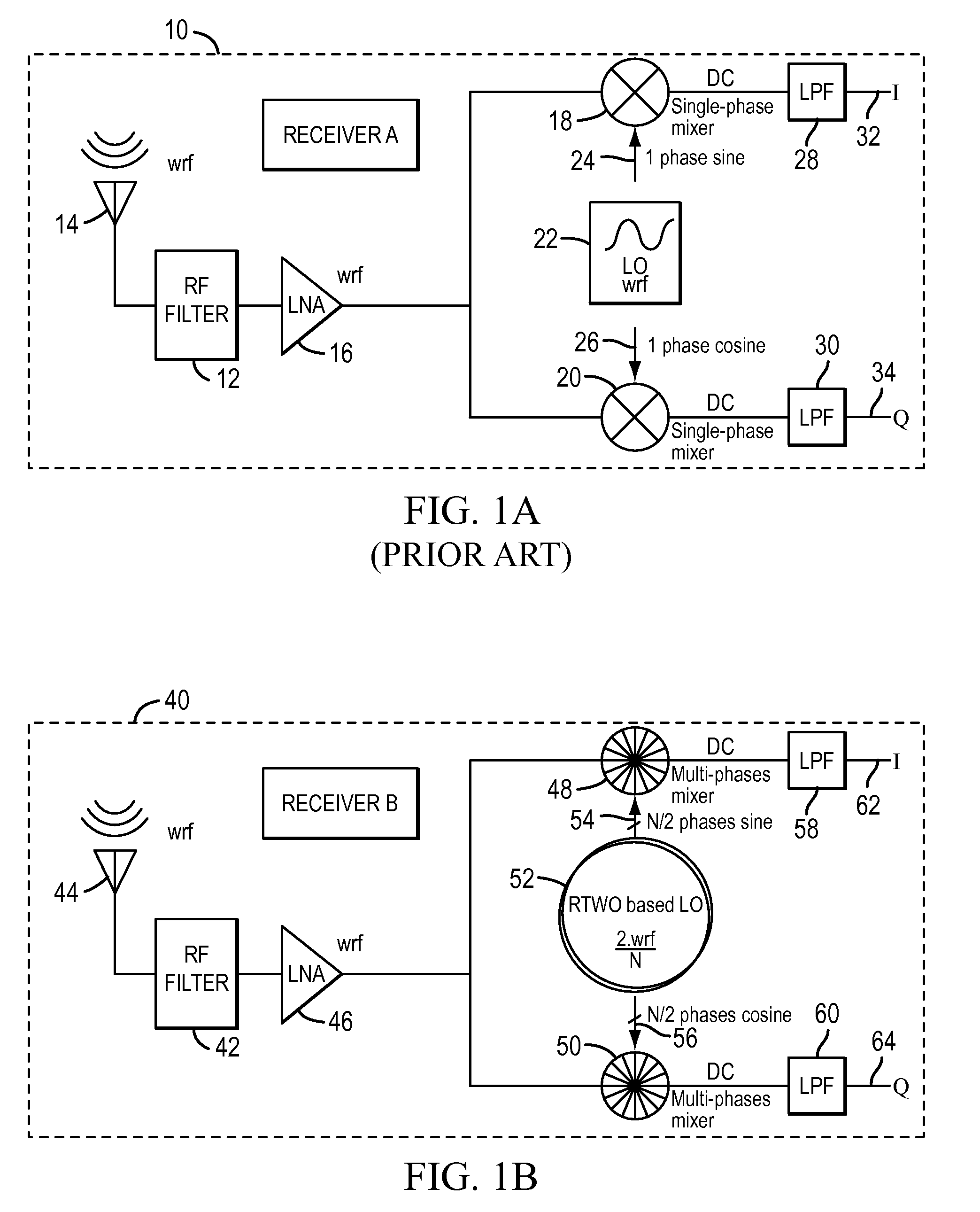
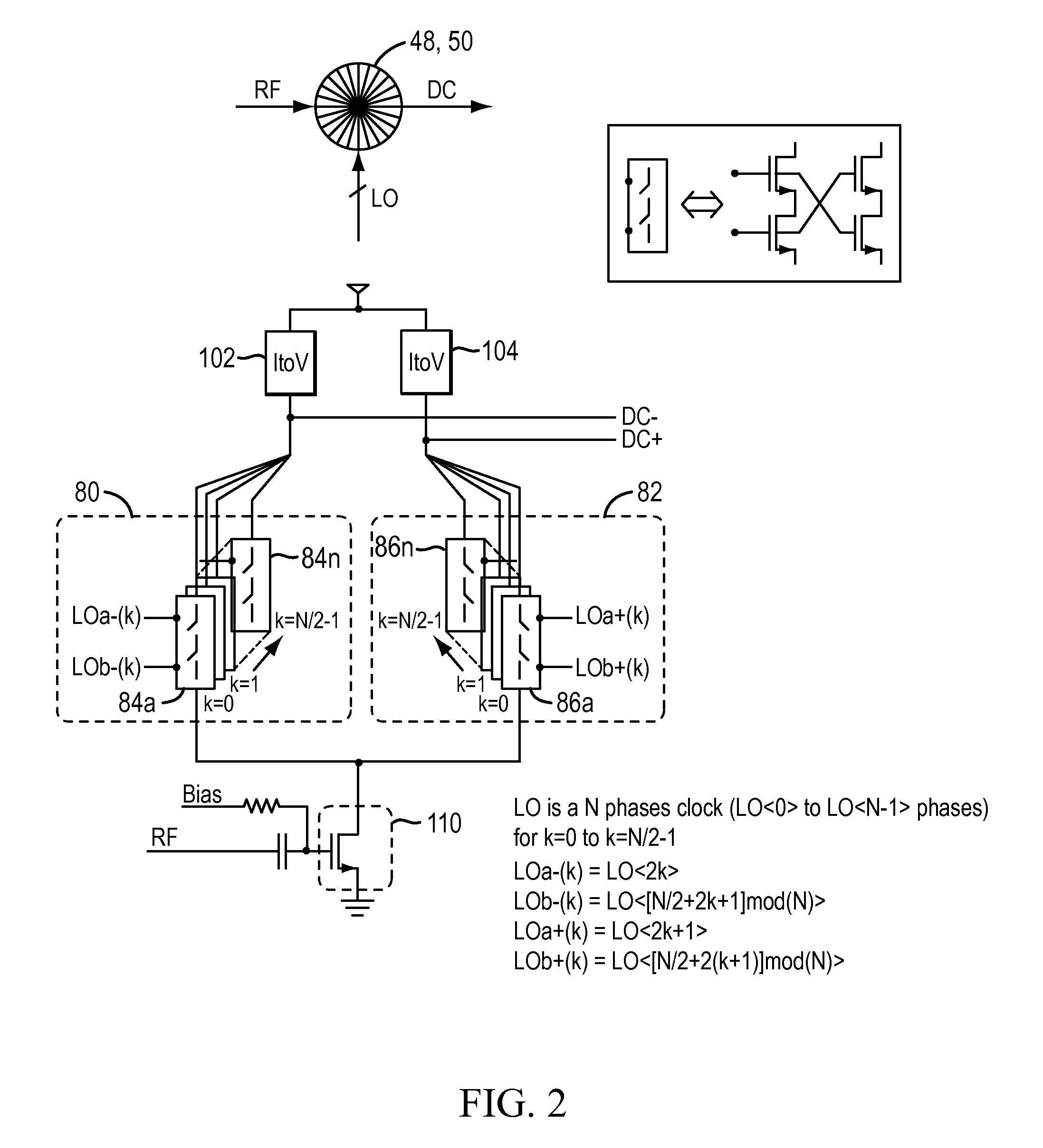
Rtwo-based down converter
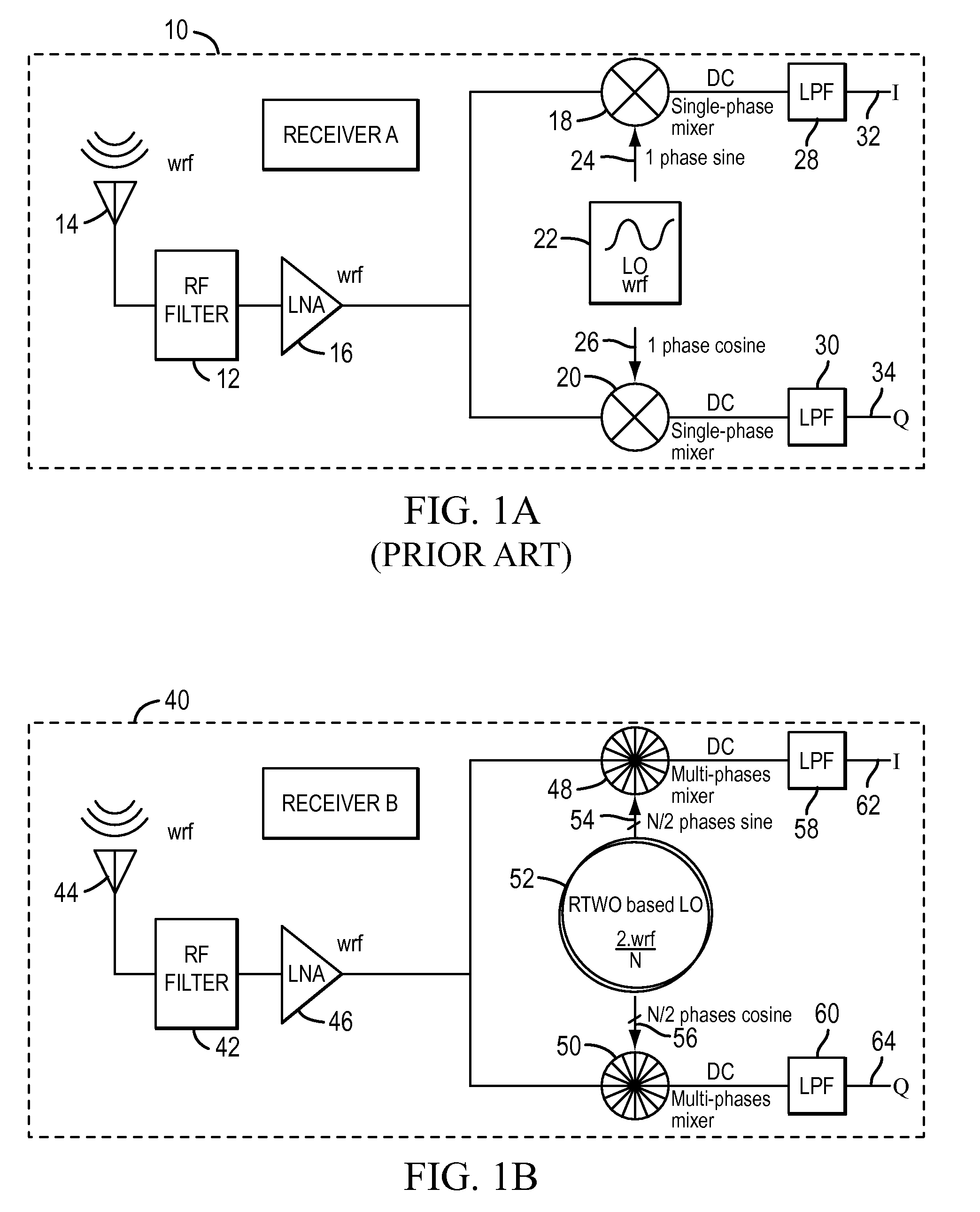
A multiphase mixer using a rotary traveling wave oscillator is disclosed. In addition to the oscillator, the mixer includes first and second mixer circuits. The rotary traveling wave oscillator generates a first set of N / 2 phase and a second set of N / 2 phases, where each phase has a frequency that is a factor of N / 2 less than the incoming radio frequency signal. The first set of phases are sine signals and the second set of phases are cosine signals. The first mixer circuit generates a first down-converted signal from the first set of phases and the incoming rf signal. The second mixer circuit generates a second down-converted signal from the second set of phases and the rf signal.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Low noise fractional divider using a multiphase oscillator
ActiveUS8278982B2High purityAmenable to integrated circuit fabricationPulse automatic controlOscillations generatorsLow noisePhase shift module
A frequency synthesis circuit is disclosed. The circuit includes a phase-locked loop and multi-phase oscillator such as a rotary traveling wave oscillator (RTWO). The oscillator provides a plurality of phases that are applied to a selection circuit. The selection circuit, in response to the output of a delta-sigma modulator, selects one of the phases of the multi-phase oscillator to minimize phase shift noise when the divider ratio in the loop changes, thereby eliminating a source of noise that contaminates the synthesized frequency. This permits the use of the frequency synthesis in applications requiring a high degree of spectral purity.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
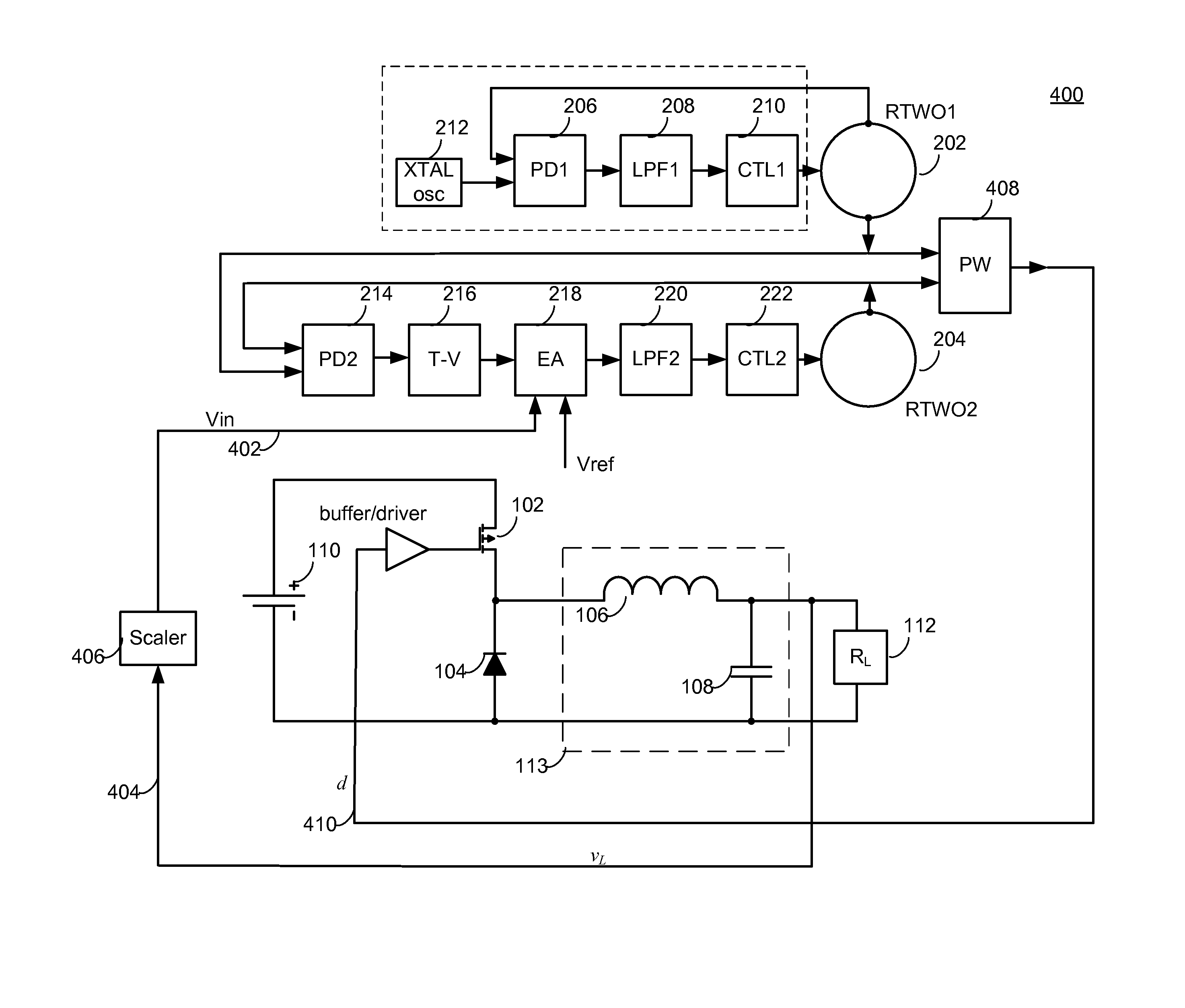
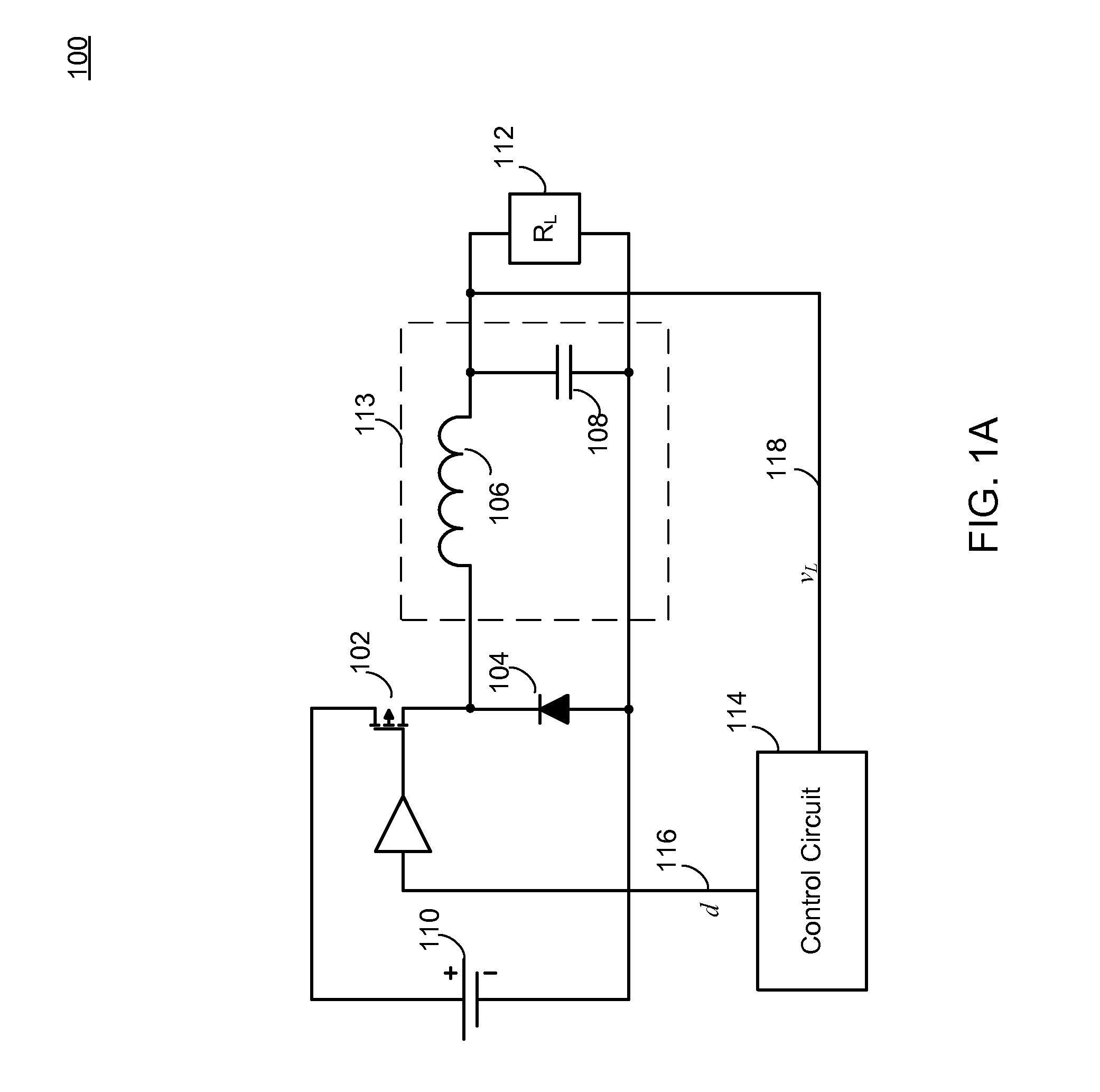
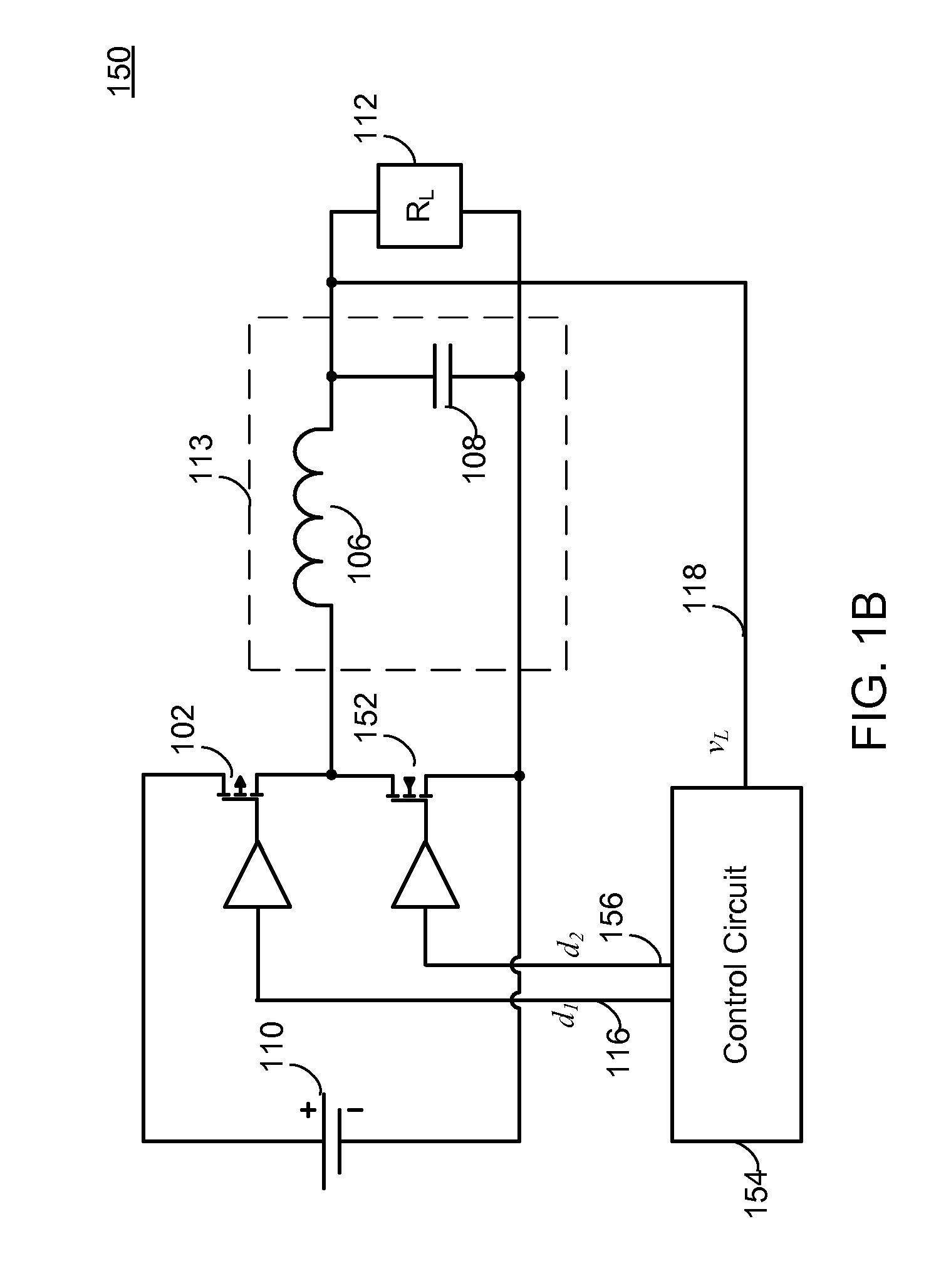
RTWO-based pulse width modulator
ActiveUS8487710B2F losses are eliminatedSmall power overheadPulse automatic controlDc-dc conversionSwitching powerPhase-locked loop
A pulse width modulator based on a pair of rotary traveling wave oscillators. The first oscillator operates freely or as part of a phase-locked loop. The second oscillator operates at the same frequency as the first oscillator, but with a controllable phase offset from the first oscillator. The phase offset is set by an input voltage. A block takes the outputs of the first and second oscillators and combines them so that the output is a pulse whose width is the overlap of the oscillation signals from the first and second oscillators. The output pulse width is thus a function of the input voltage. When the pulse width modulator receives the input voltage from the output of a switching power supply, it can use the modulated pulse width to control the switching transistor of the power supply to maintain the output at a regulated voltage.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Resonant frequency divider design methodology for dynamic frequency scaling
ActiveUS9866174B2Continuously circulated pulse countersPulse automatic controlMulti inputComputer module
A dynamic rotary traveling wave oscillator circuit includes plurality of multi-output spot-advancing blocks (MOSABs) forming a main-loop and a plurality of multi-input spot-advancing blocks (MISABs) forming a sub-loop. Depending on a desired division ratio, a connection connects blocks on the MOSABs and MISABs to create the desired division ratio.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
Rotary Traveling Wave Oscillator Circuit
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
RTWO-based down converter
ActiveUS8913978B2Analogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsFrequency changerFrequency mixer
A multiphase mixer using a rotary traveling wave oscillator is disclosed. In addition to the oscillator, the mixer includes first and second mixer circuits. The rotary traveling wave oscillator generates a first set of N / 2 phase and a second set of N / 2 phases, where each phase has a frequency that is a factor of N / 2 less than the incoming radio frequency signal. The first set of phases are sine signals and the second set of phases are cosine signals. The first mixer circuit generates a first down-converted signal from the first set of phases and the incoming rf signal. The second mixer circuit generates a second down-converted signal from the second set of phases and the rf signal.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com