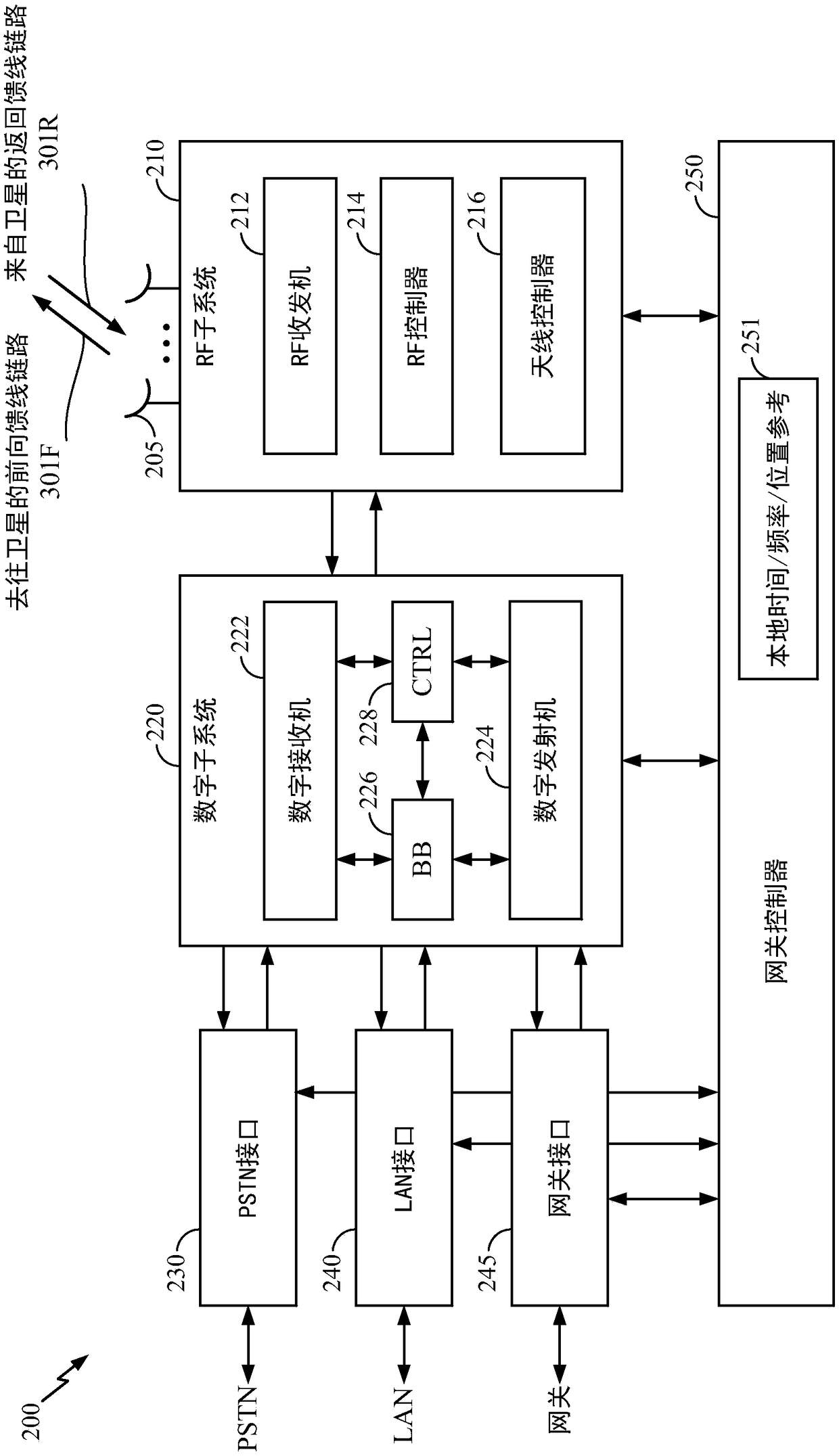
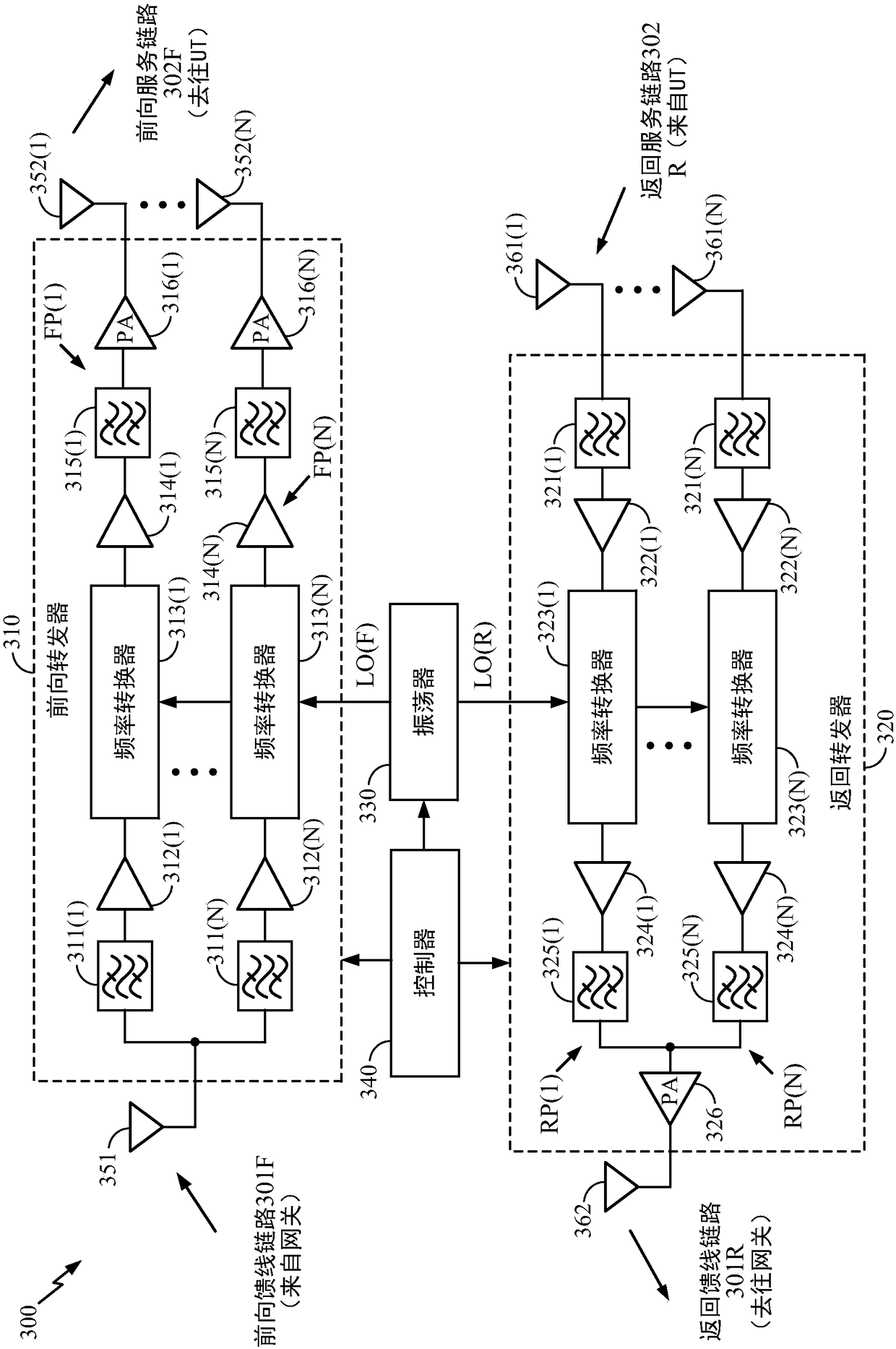
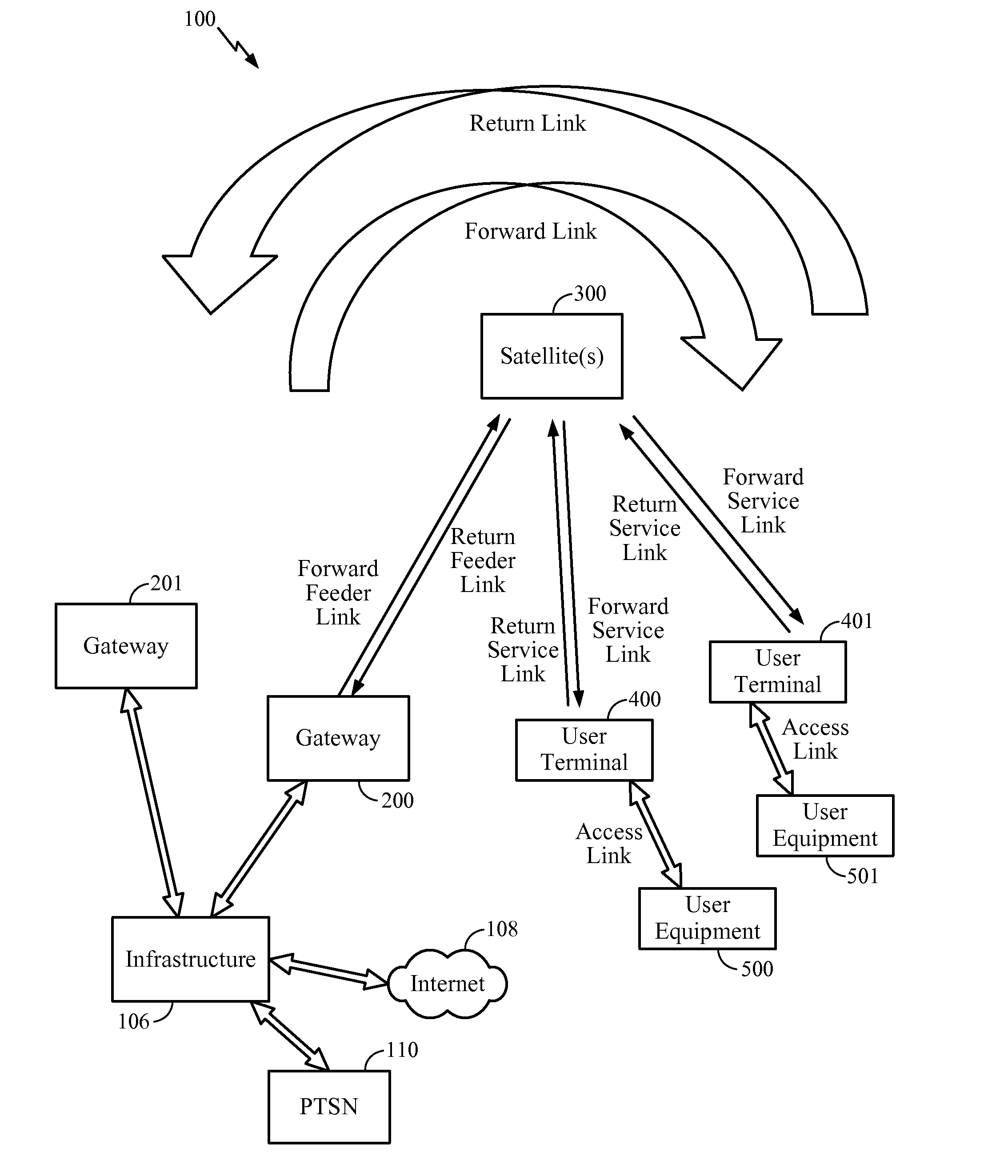
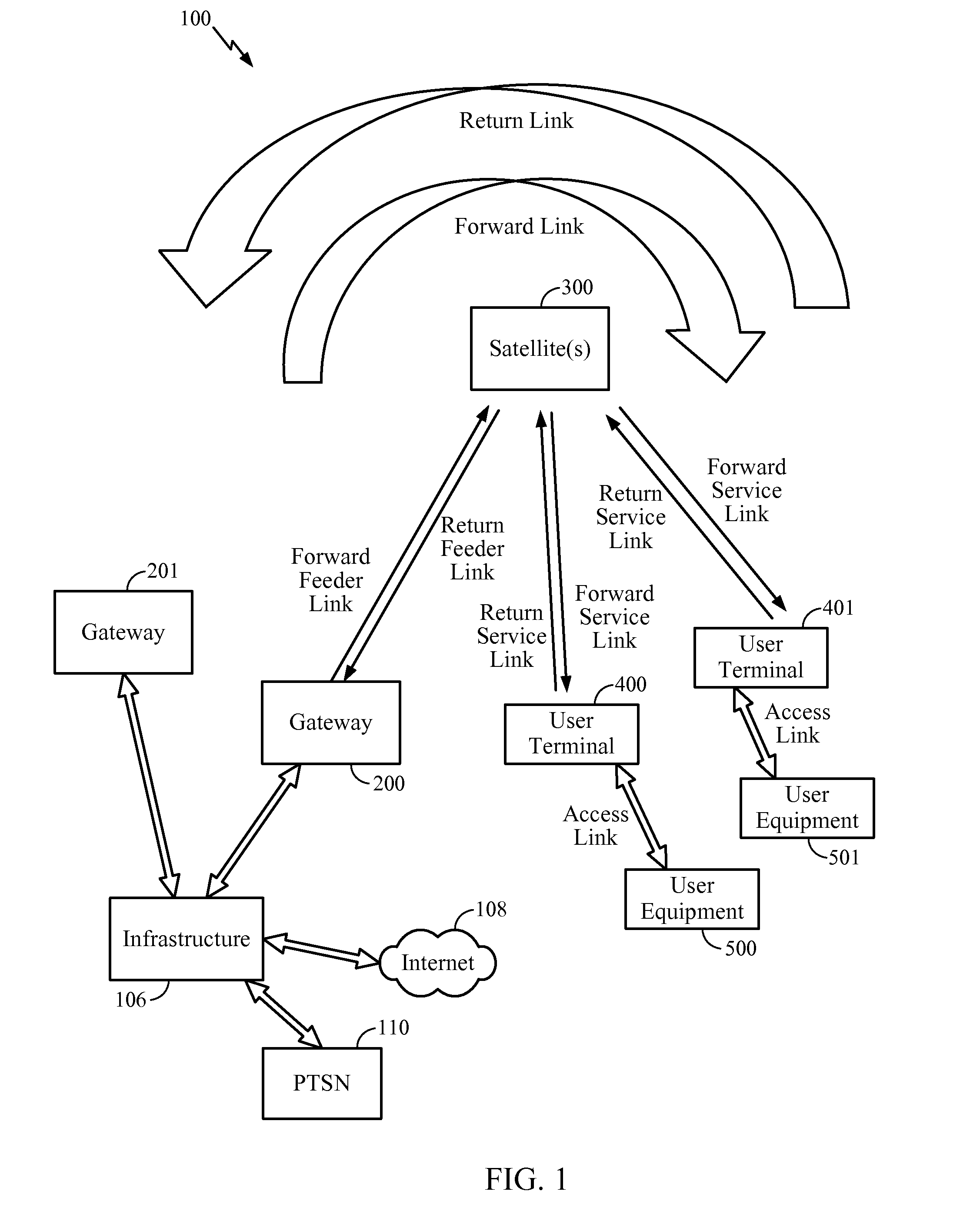
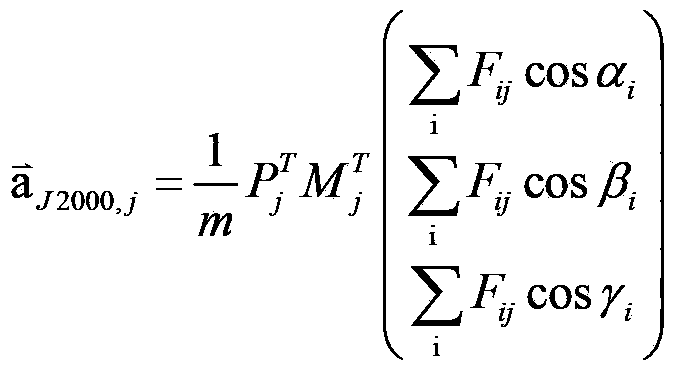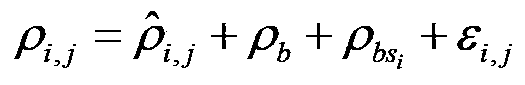Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
144 results about "Geosynchronous satellite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
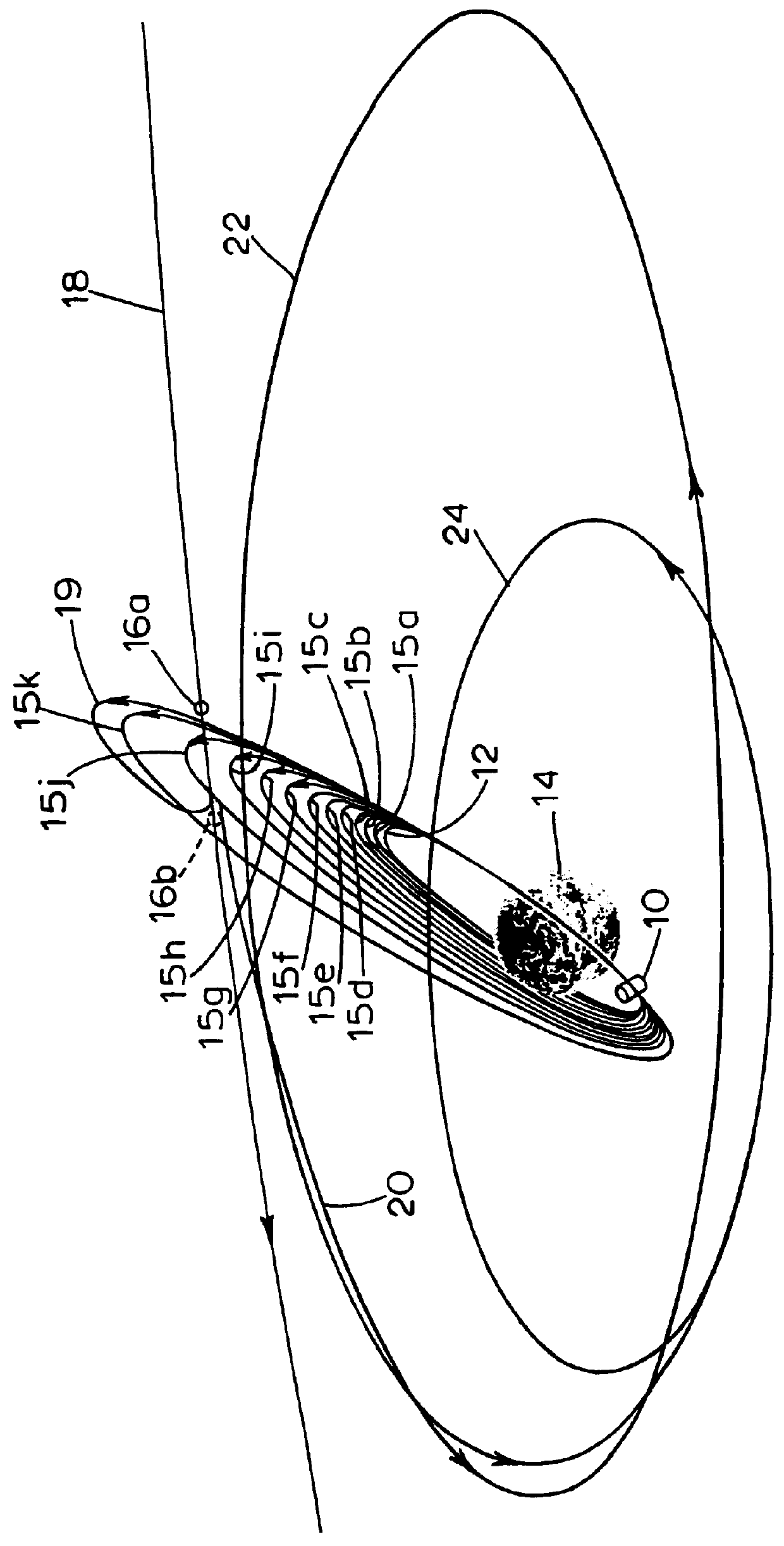
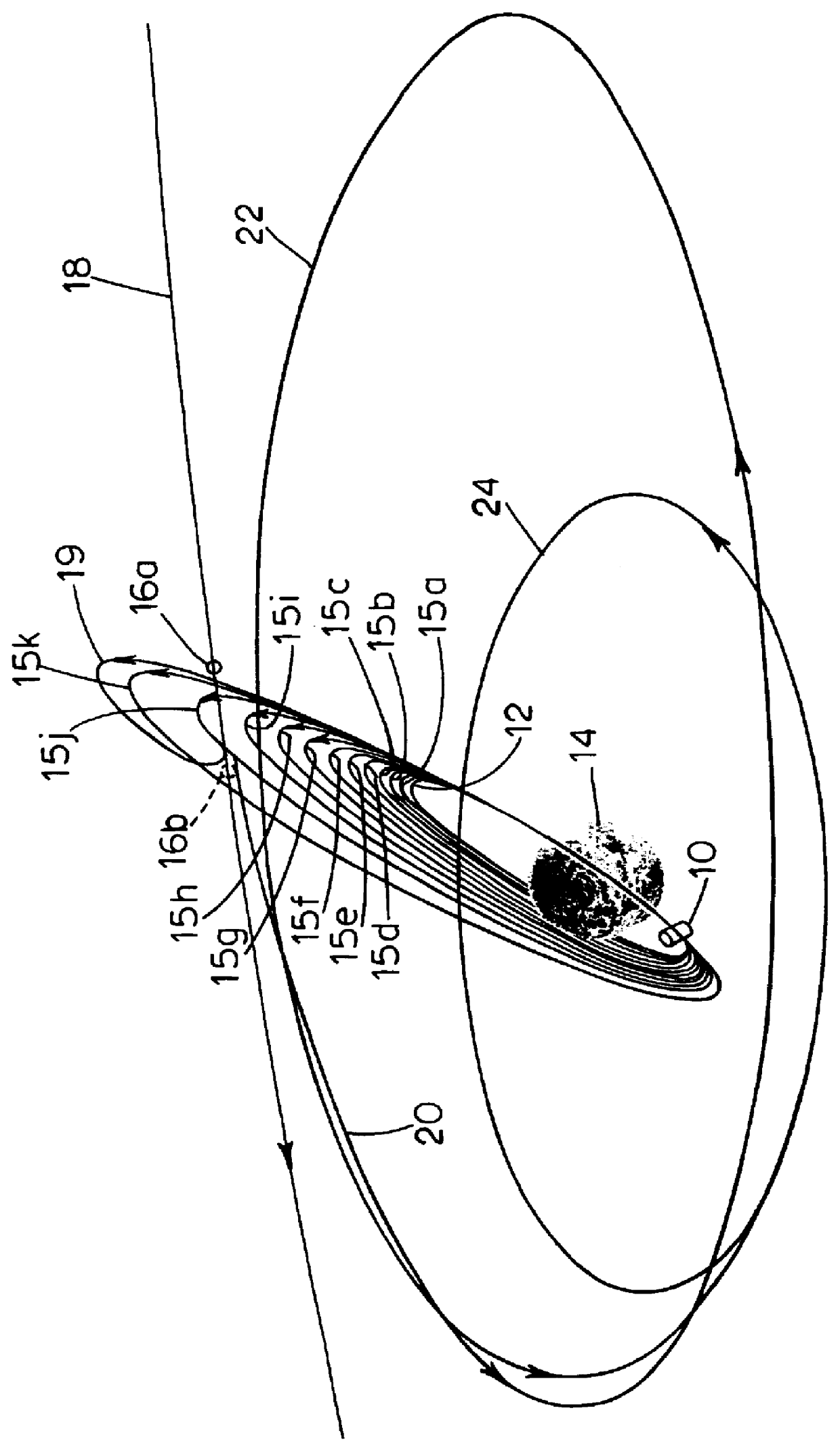
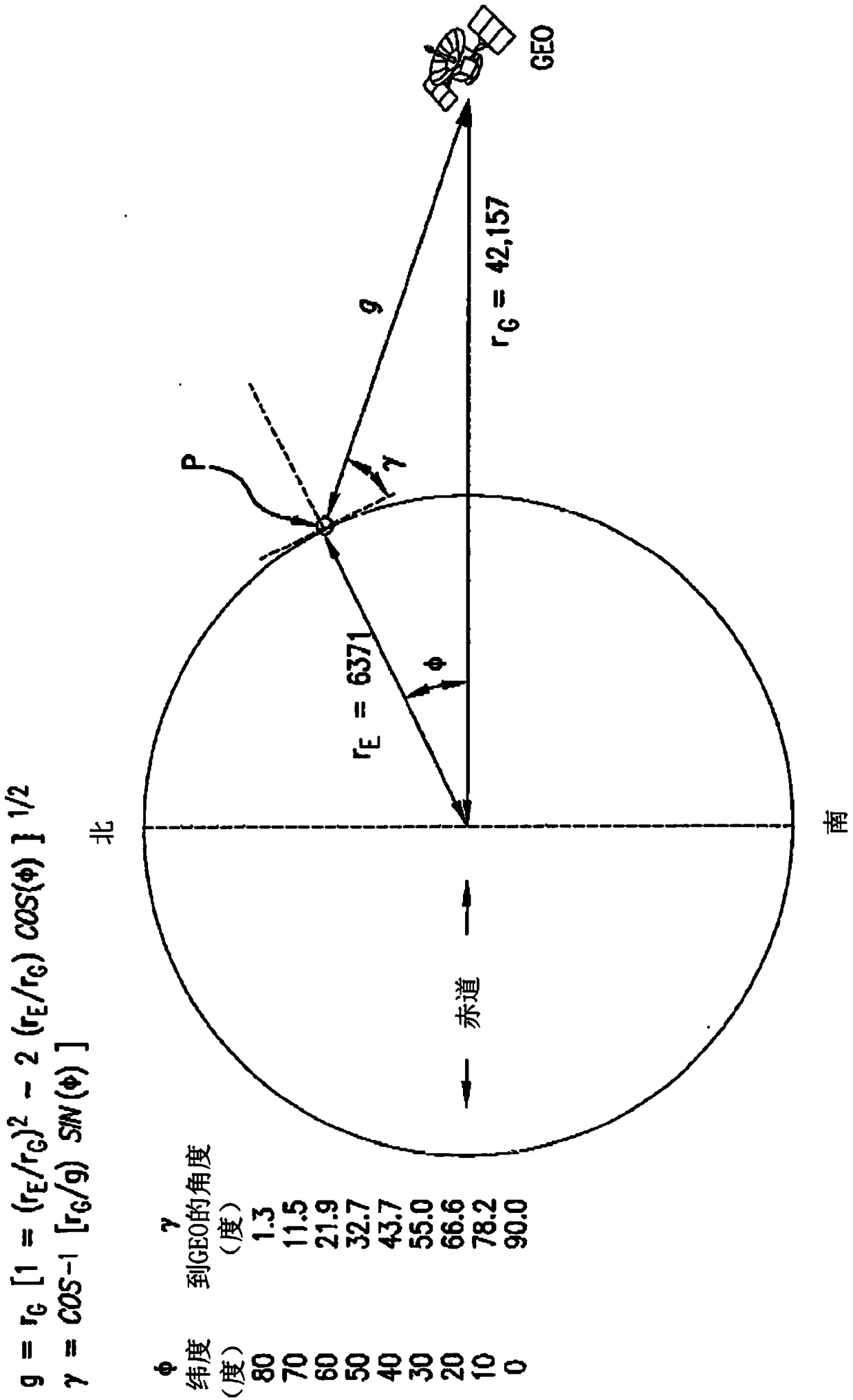
A geosynchronous satellite is a satellite in geosynchronous orbit, with an orbital period the same as the Earth's rotation period. Such a satellite returns to the same position in the sky after each sidereal day, and over the course of a day traces out a path in the sky that is typically some form of analemma.
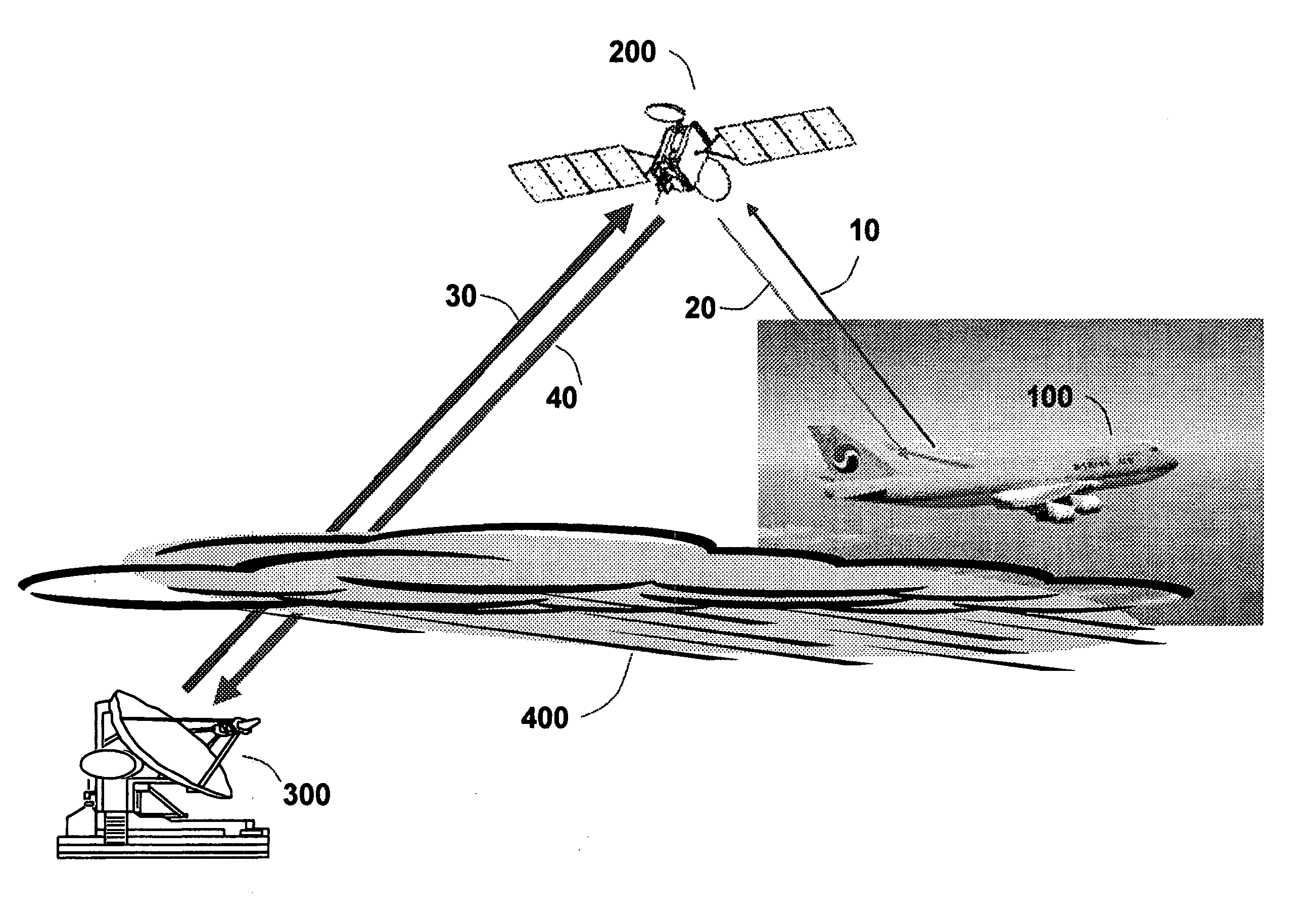
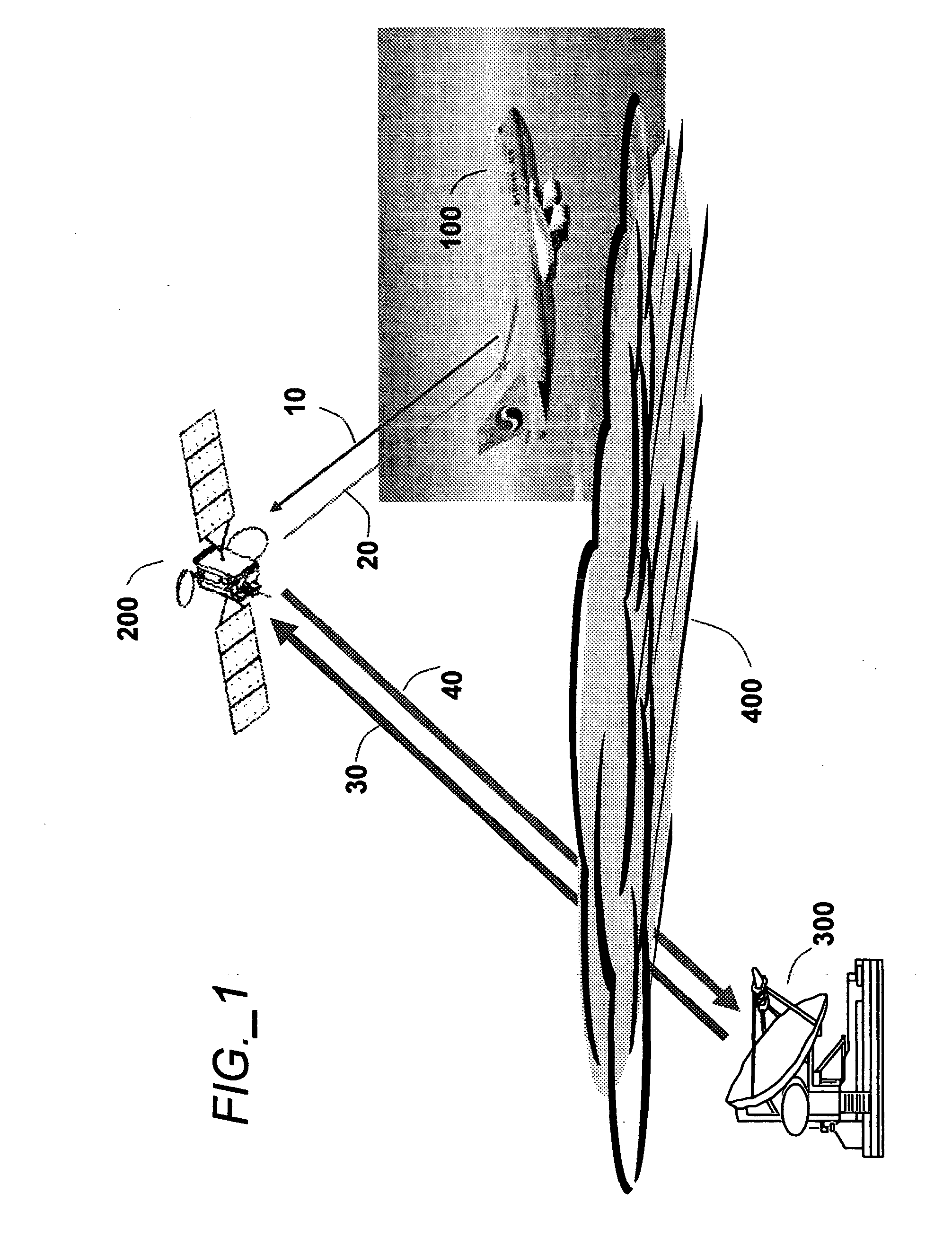
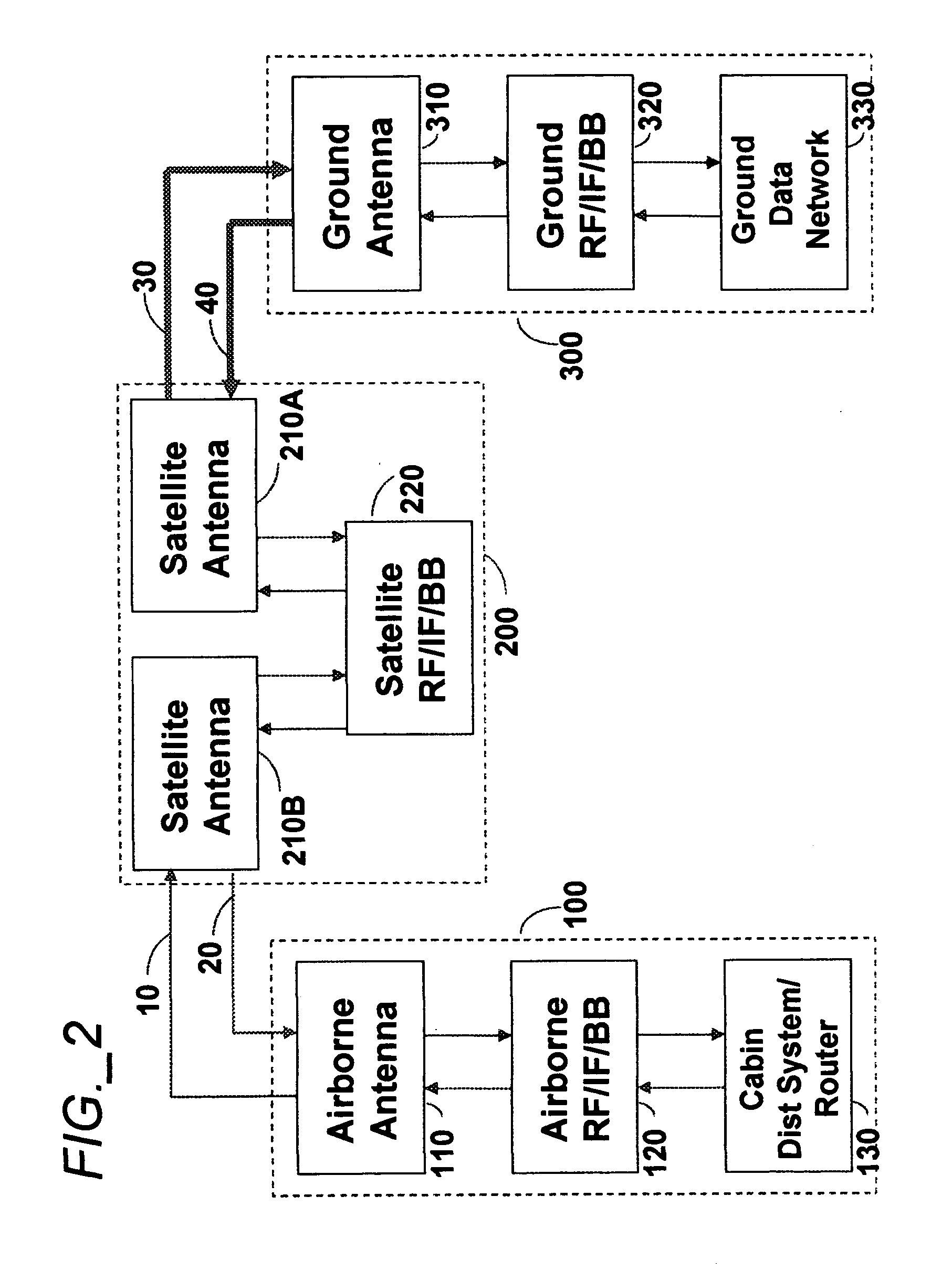
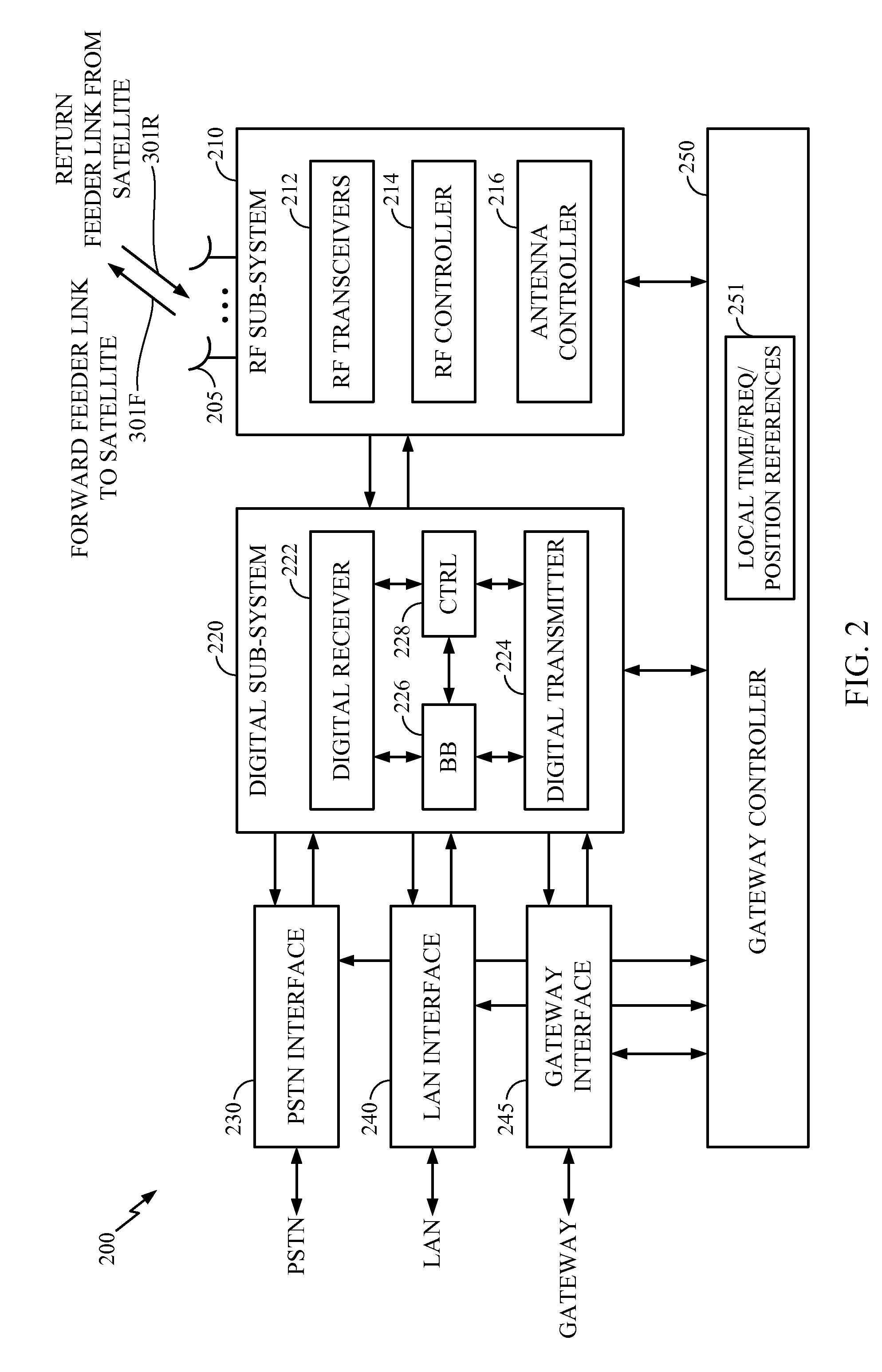
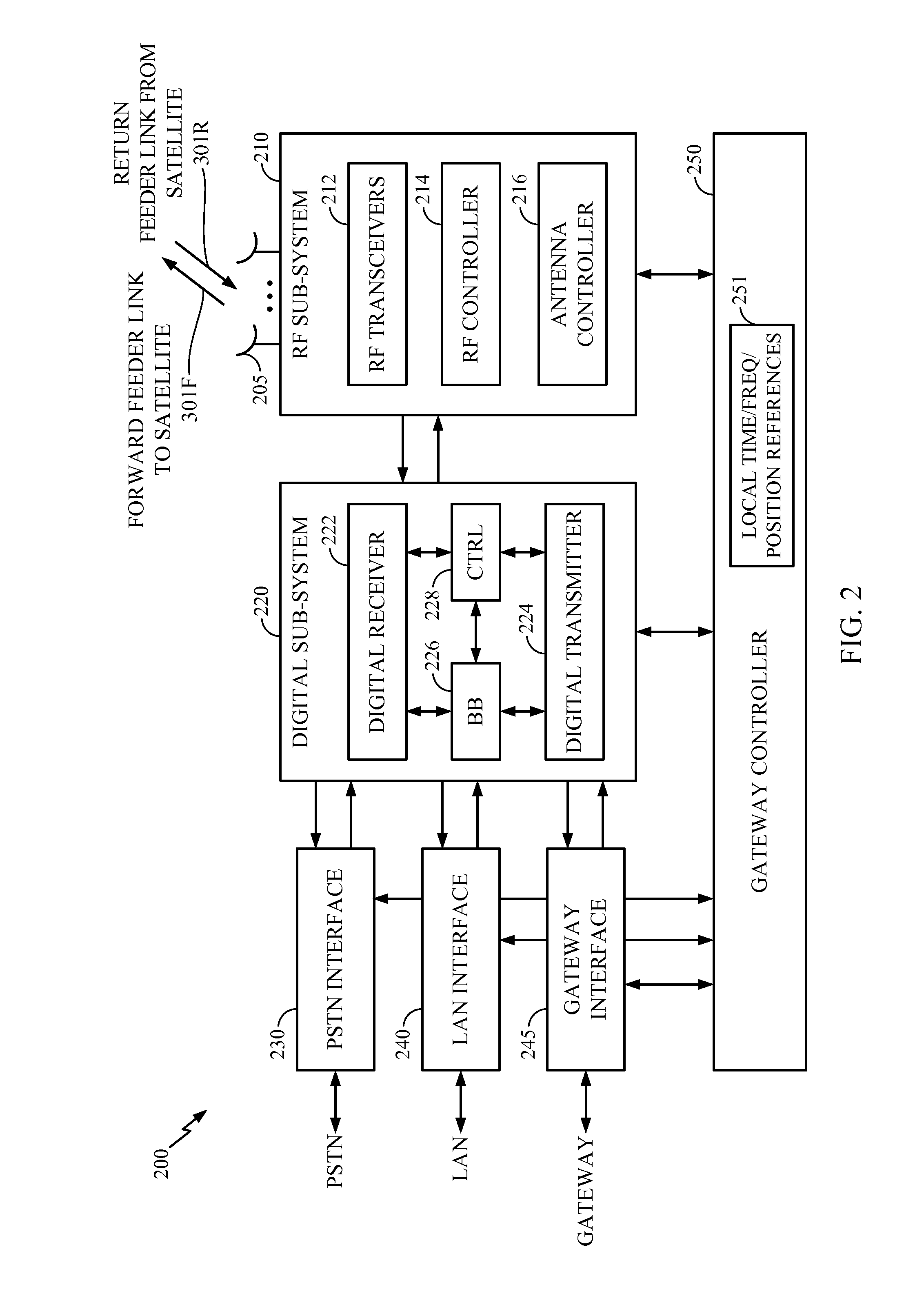
Aeronautical broadcast and communication system
ActiveUS20060040612A1Relatively large bandwidthMore bandwidthActive radio relay systemsWireless commuication servicesJet aeroplaneAviation
A method and system for a plurality of airplanes in flight to receive from and send to a plurality of ground stations broadcast and communication signals through a single or a plurality of geostationary satellites, wherein at least the mobile link between said airplanes and said satellite, uplink or downlink, uses the high frequency radio waves at 17 GHz or higher, such as Ka-band. The fixed link between said satellite and said ground stations may use any radio frequencies below the frequencies used to communicate between the satellite and the aircraft. The lower frequencies tend to be less susceptible to rain attenuation and hence suitable for closing the fixed broadcast and communication link. Frequencies such as C-band or Ku-band, or even Ka-band, are applied between satellite and ground such that the available link margin is sufficient to overcome rain attenuation at said ground stations. Said satellite carries a plurality of transponders that may include a plurality of frequency converters to enable the conversion between different frequencies. Said satellite generates a plurality of spot beams, shaped or unshaped, which collectively cover the flight routes of said airplanes, preferably the geodesic path between two highly populated regions.
Owner:NUBRON
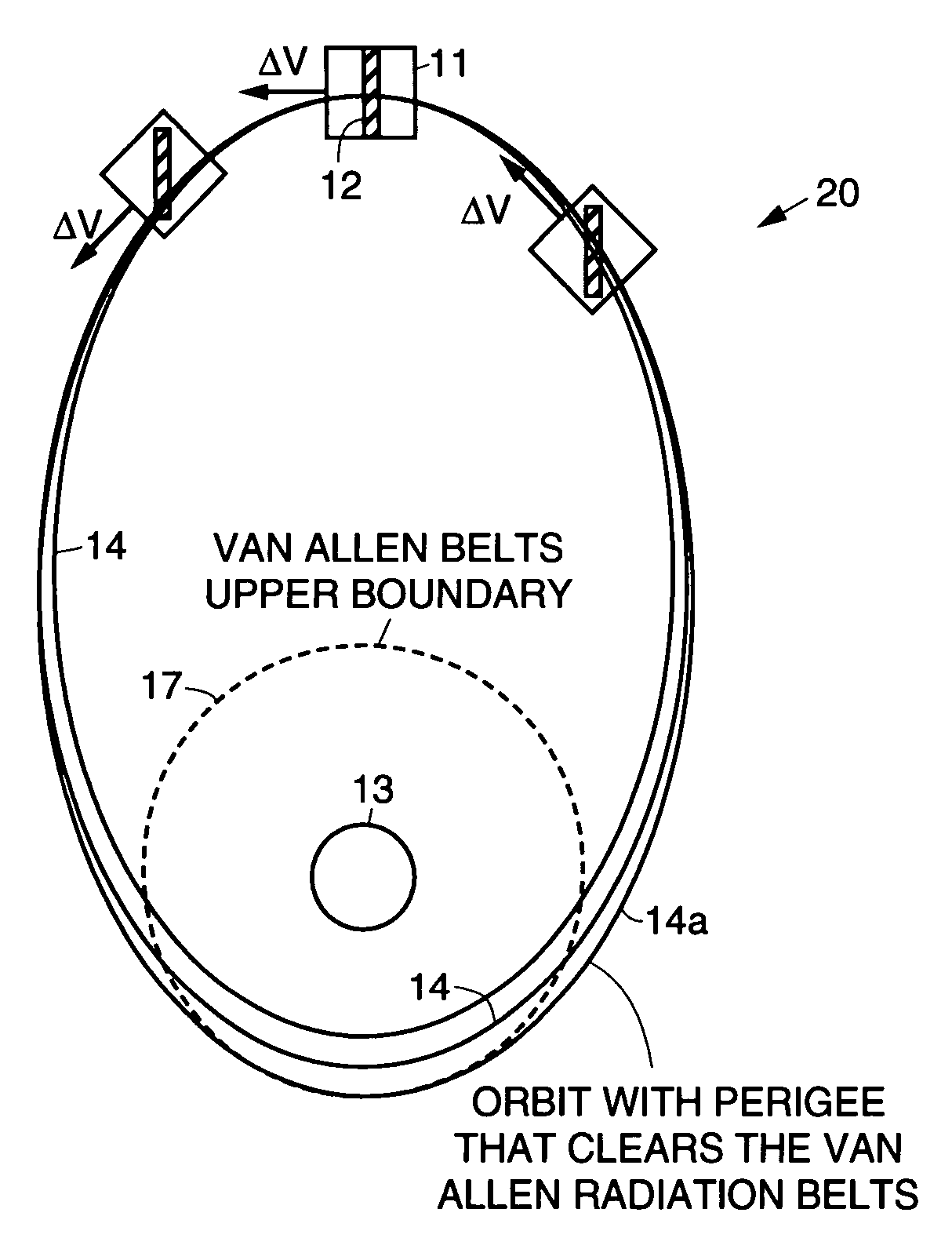
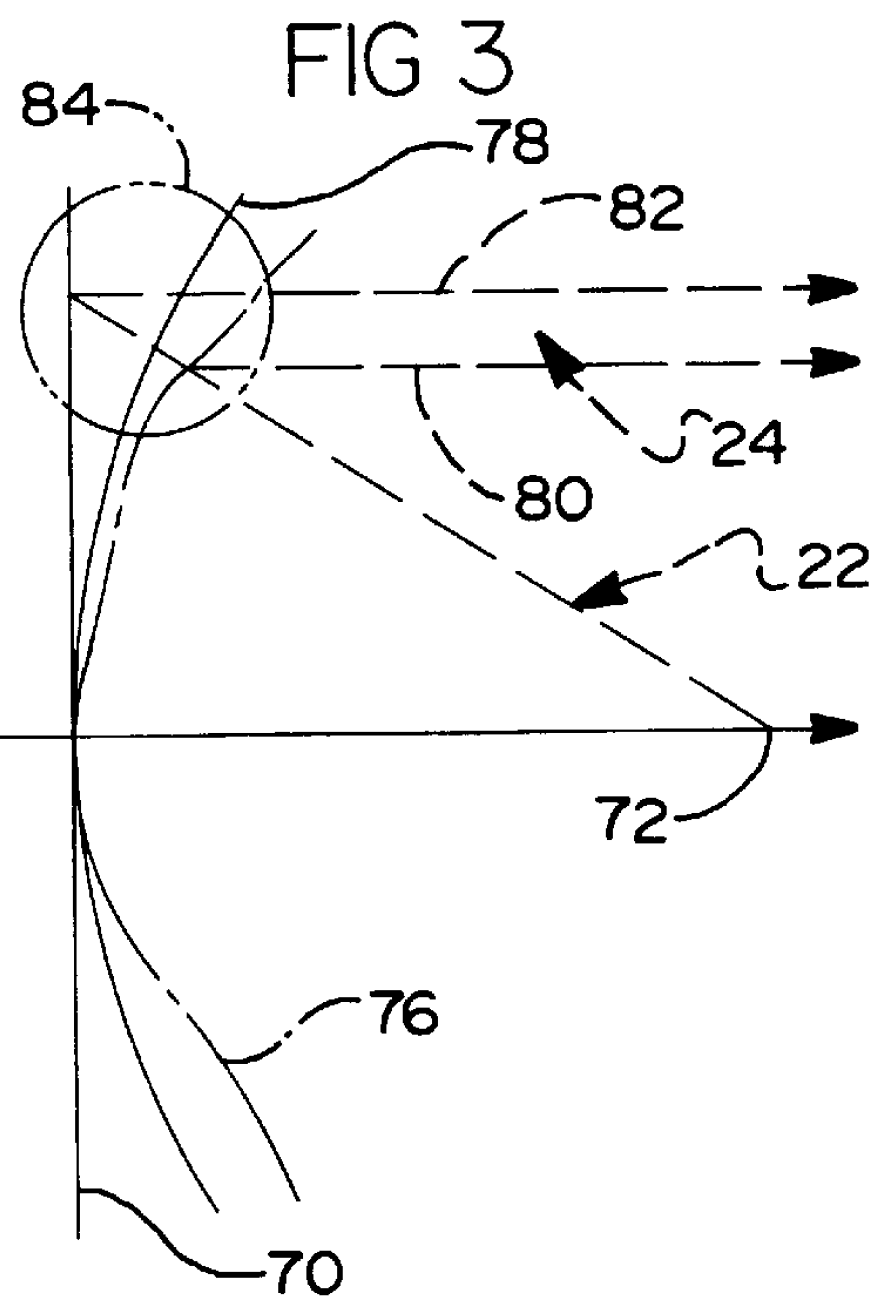
Practical orbit raising system and method for geosynchronous satellites
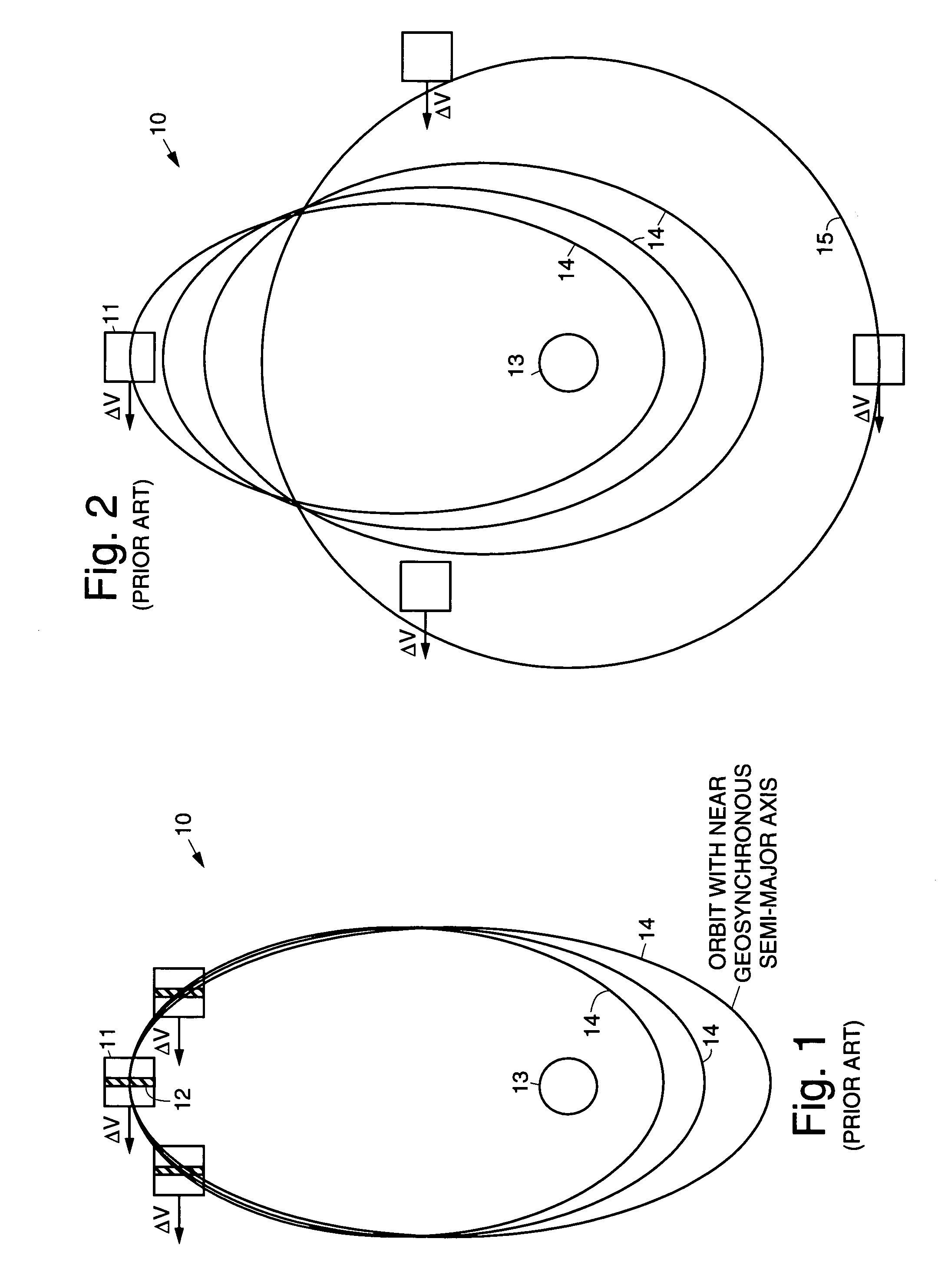
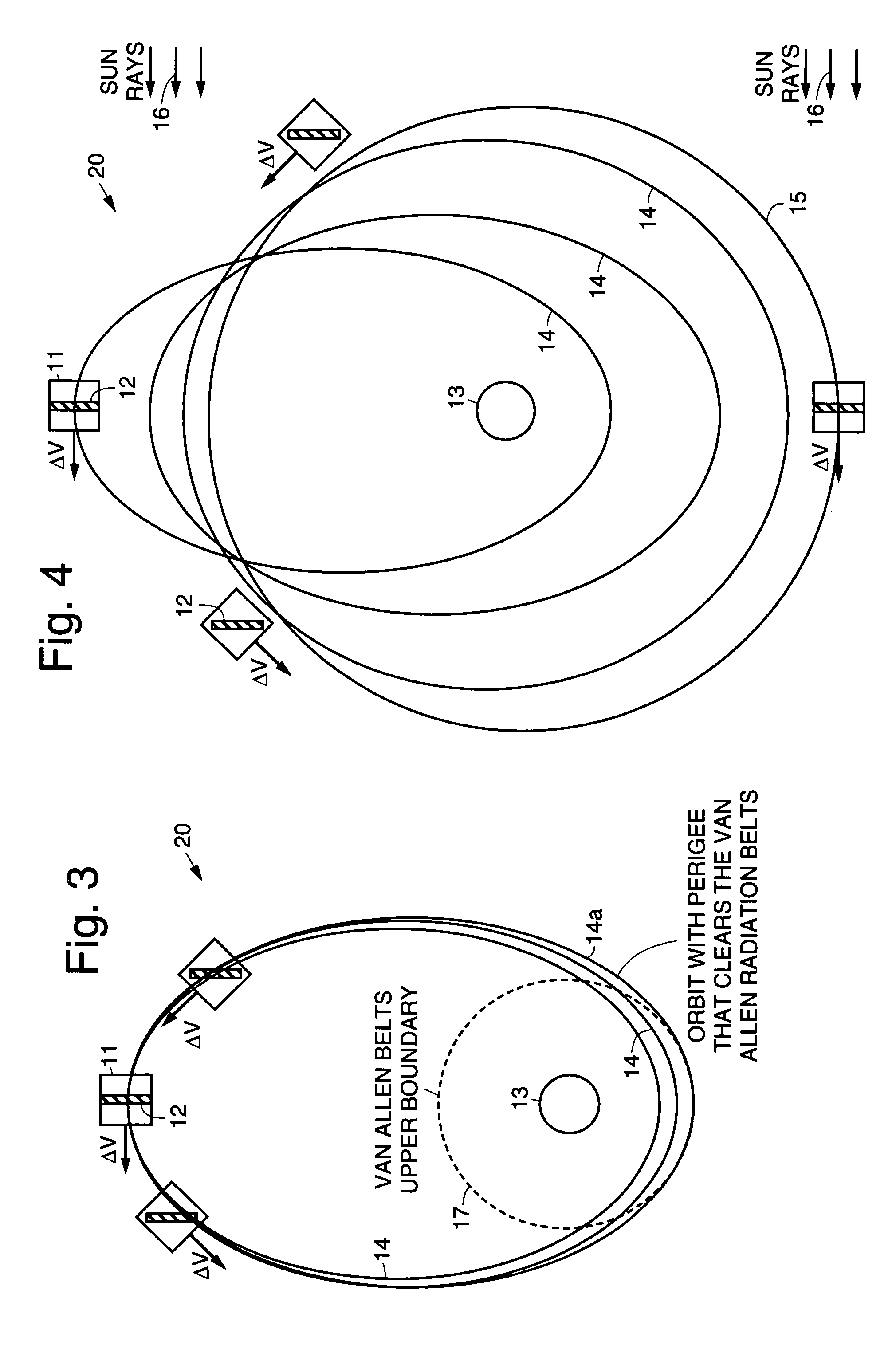
InactiveUS7113851B1Maximizing payload massMaximizing mission lifeLaunch systemsCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusElectricitySynchronous orbit
A practical orbit raising method and system wherein a satellite quickly escapes the Van Allen radiation belts and payload mass and mission life are maximized. A satellite is launched that contains high thrust chemical propulsion thrusters, high specific impulse electric propulsion thrusters and a solar array. The satellite quickly escapes the Van Allen radiation belts by firing the high thrust chemical propulsion thrusters at apogees of intermediate orbits, starting from the transfer orbit initiated by a launch vehicle, to successively raise the perigees until the perigee clears the Van Allen radiation belts. The payload mass and mission life are maximized by firing high specific impulse electric propulsion thrusters to raise the satellite to near synchronous orbit, while steering the thrust vector and solar array to maintain the sun's illumination on the solar array. The chemical and / or electric propulsion thrusters are then fired to achieve geosynchronous orbit.
Owner:SPACE SYST LORAL INC
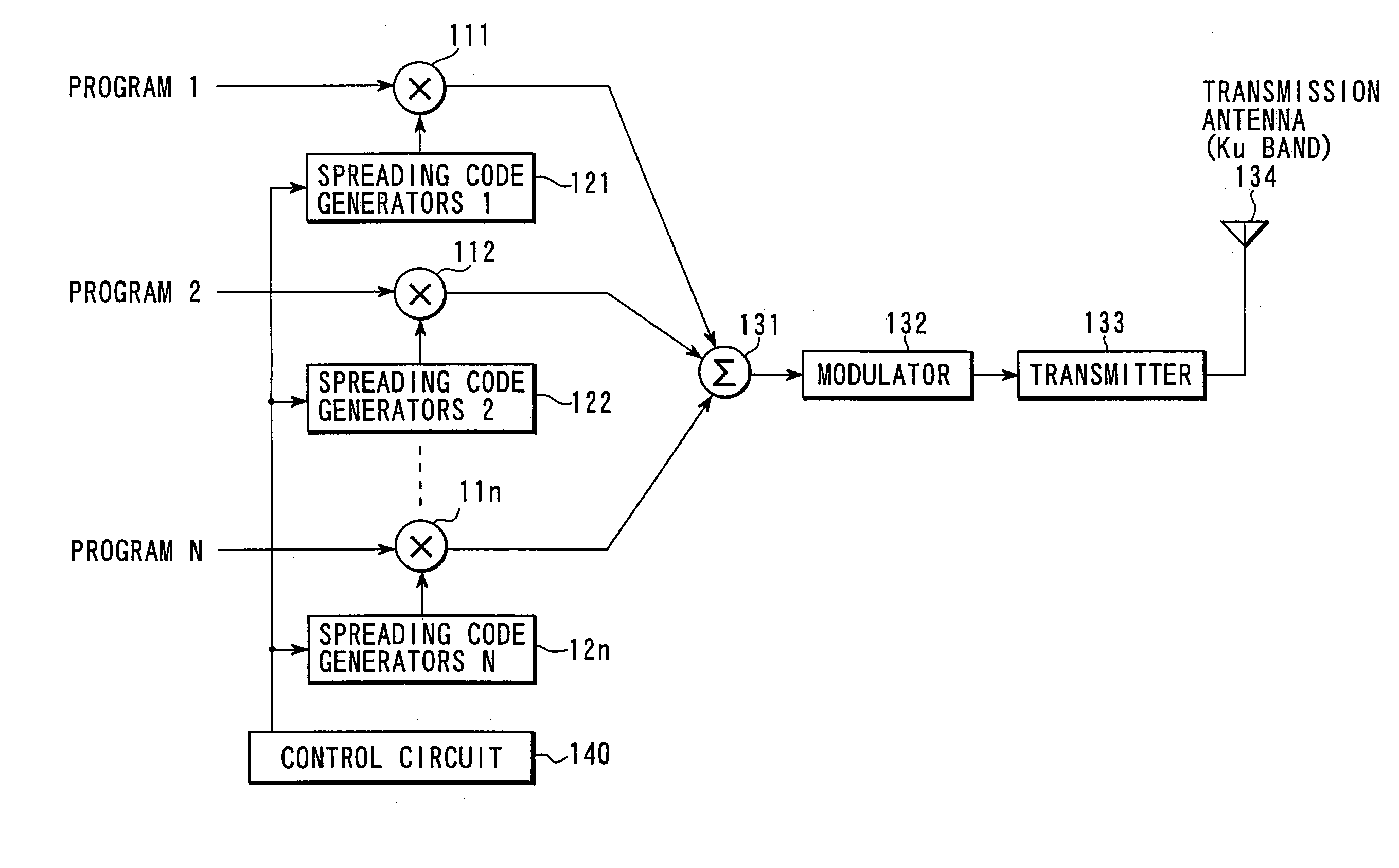
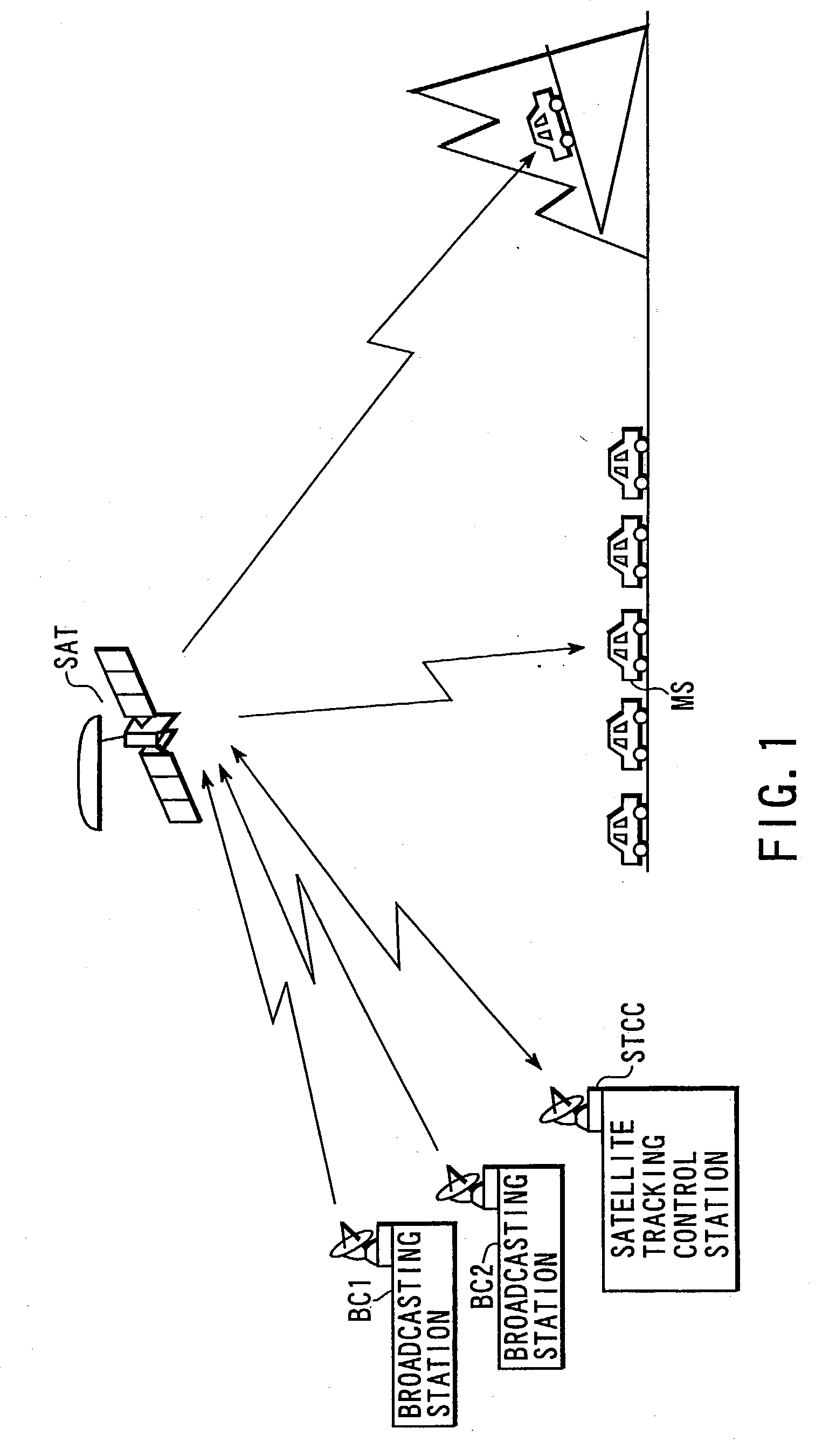
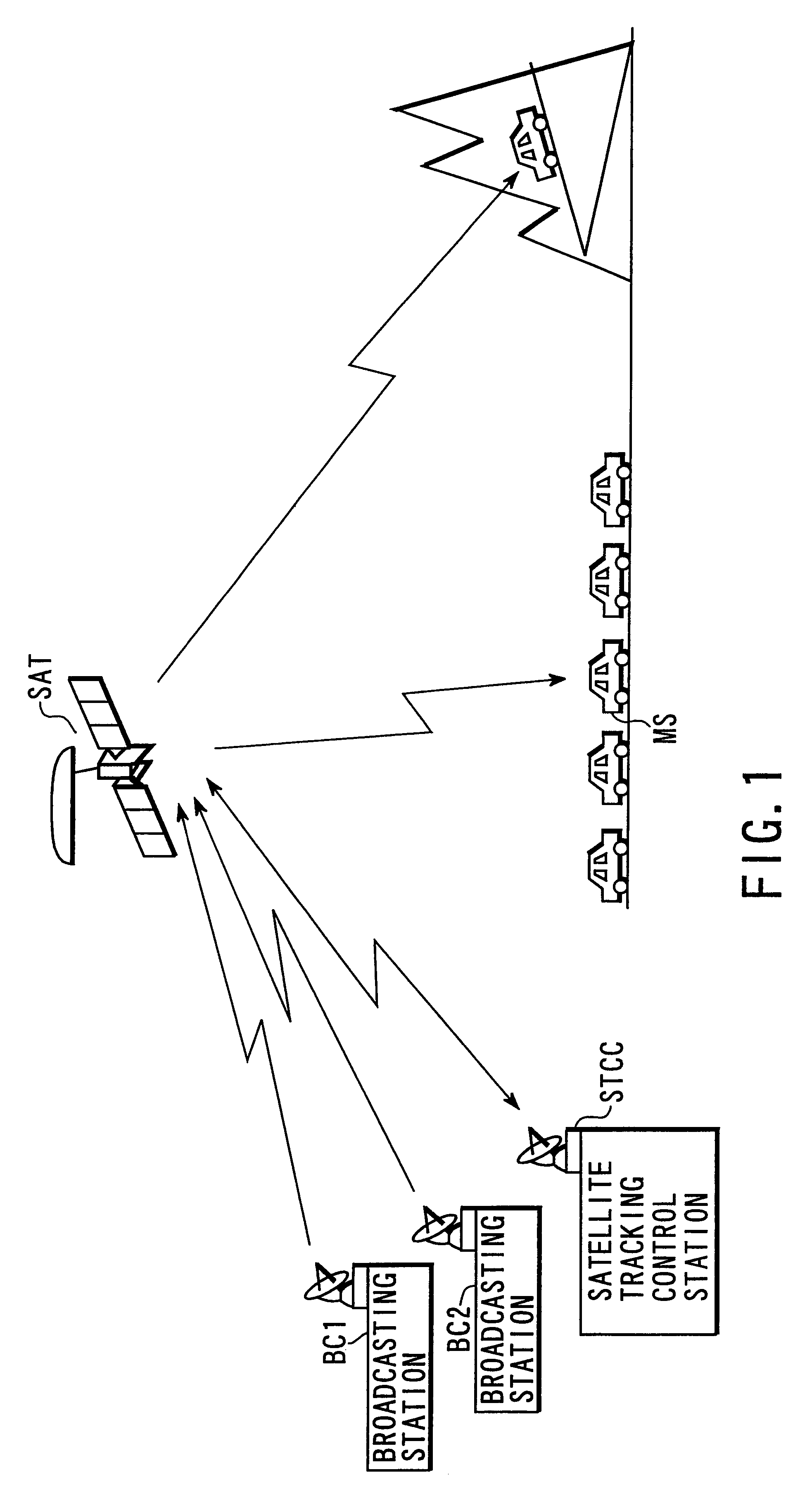
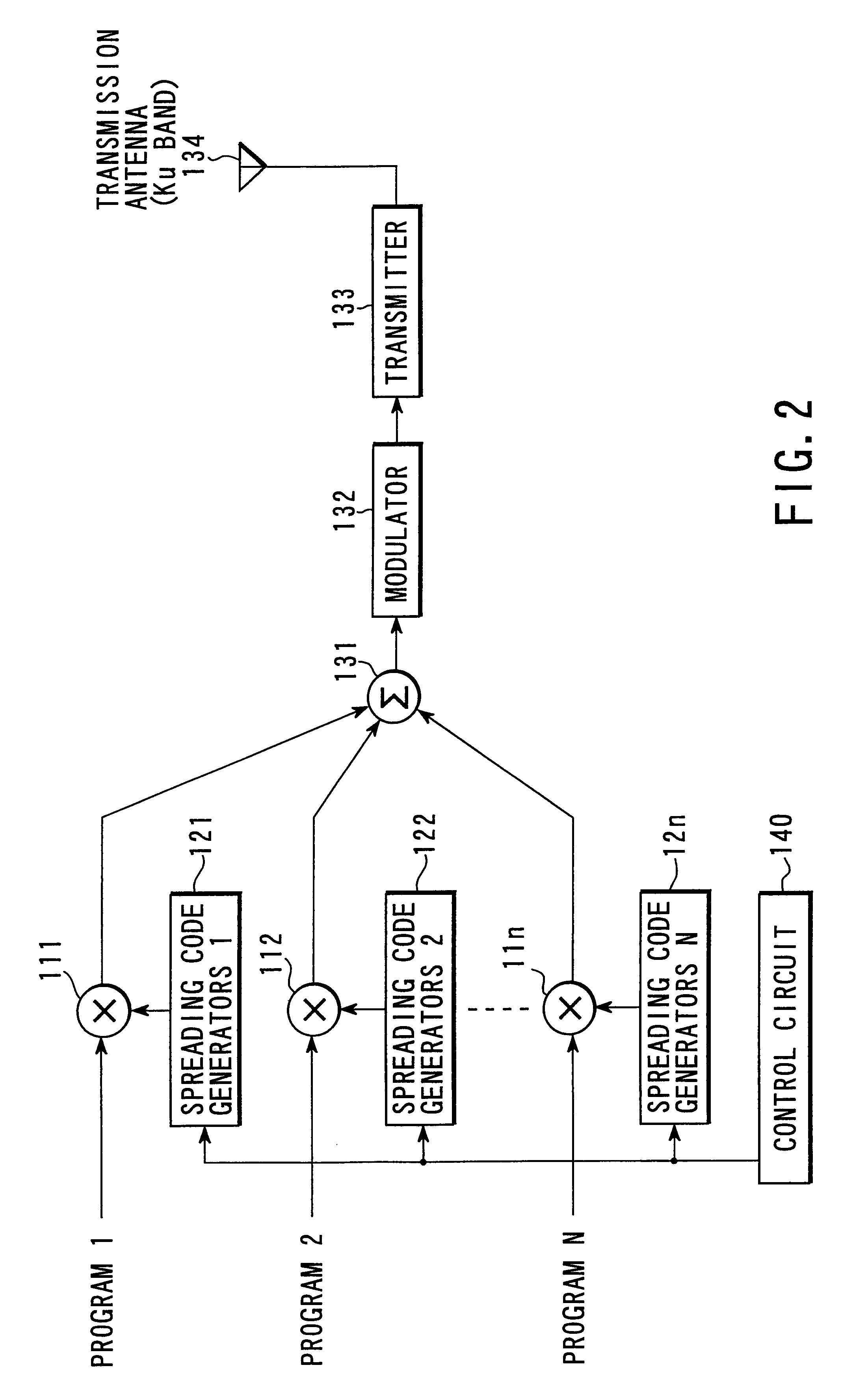
Satellite broadcasting system
InactiveUS20030137964A1Network topologiesBroadcast circuit arrangementsMultiplexingGeosynchronous satellite
In a broadcasting receiver, to quickly switch channels of the received multiplexed broadcasting signals at a high response speed to improve the convenience for a viewer, when broadcasting signals of a plurality of channels are to be code-division-multiplexed and broadcasted from a ground broadcasting station (BC1, BC2) to a broadcasting receiver (MS) in a service area via a geostationary satellite (SAT), the broadcasting signals are multiplexed and transmitted after matching the spreading code phase between the channels in the ground broadcasting station (BC1, BC2). Alternatively, the spreading code phase difference between the channels of a CDM broadcasting signal arriving from the ground broadcasting station (BC1, BC2) is detected in the geostationary satellite (SAT), and the broadcasting signal is transmitted to the broadcasting receiver (MS) after matching the spreading code phase between the channels on the basis of the detection result.
Owner:SUENAGA MASASHI +4
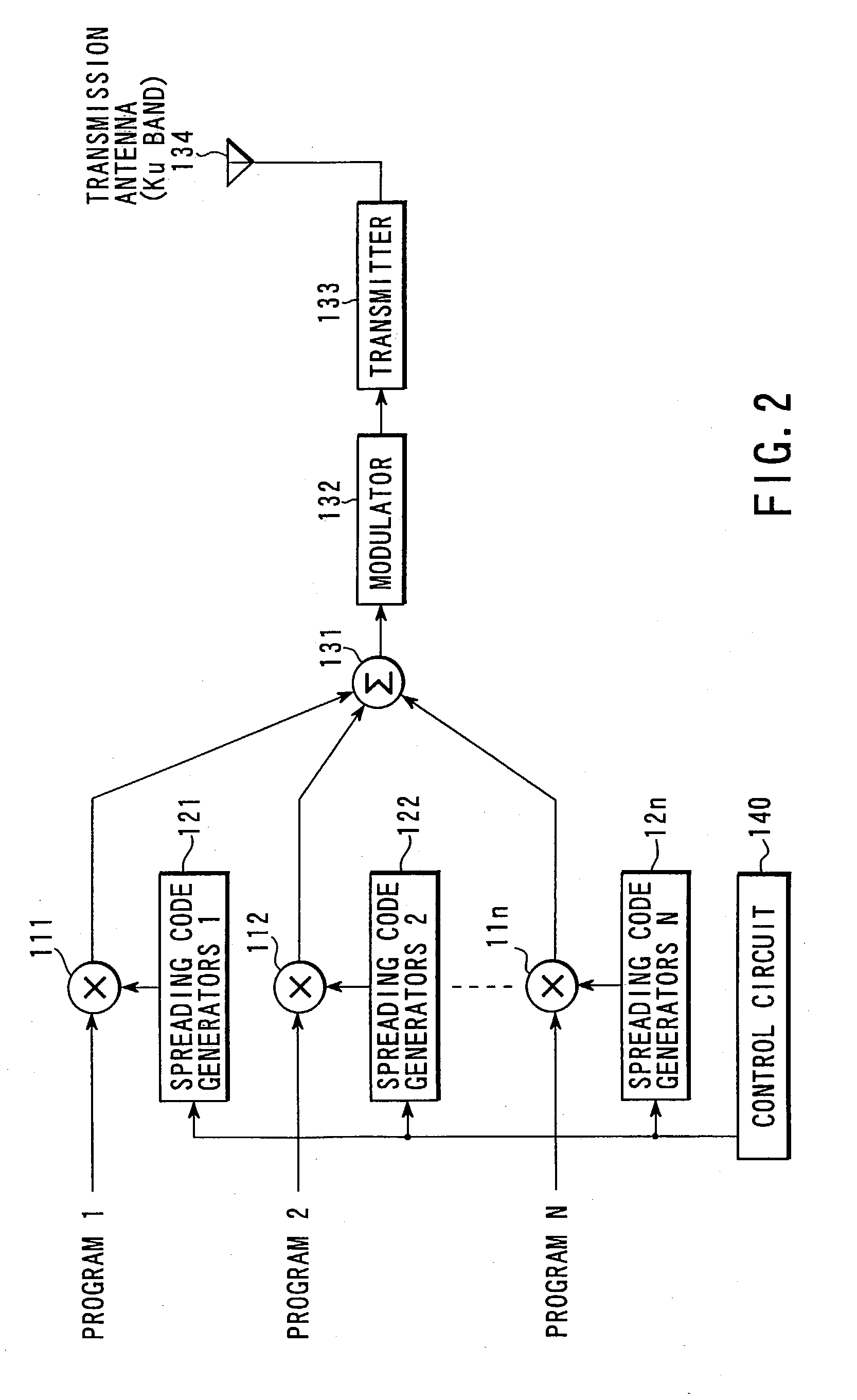
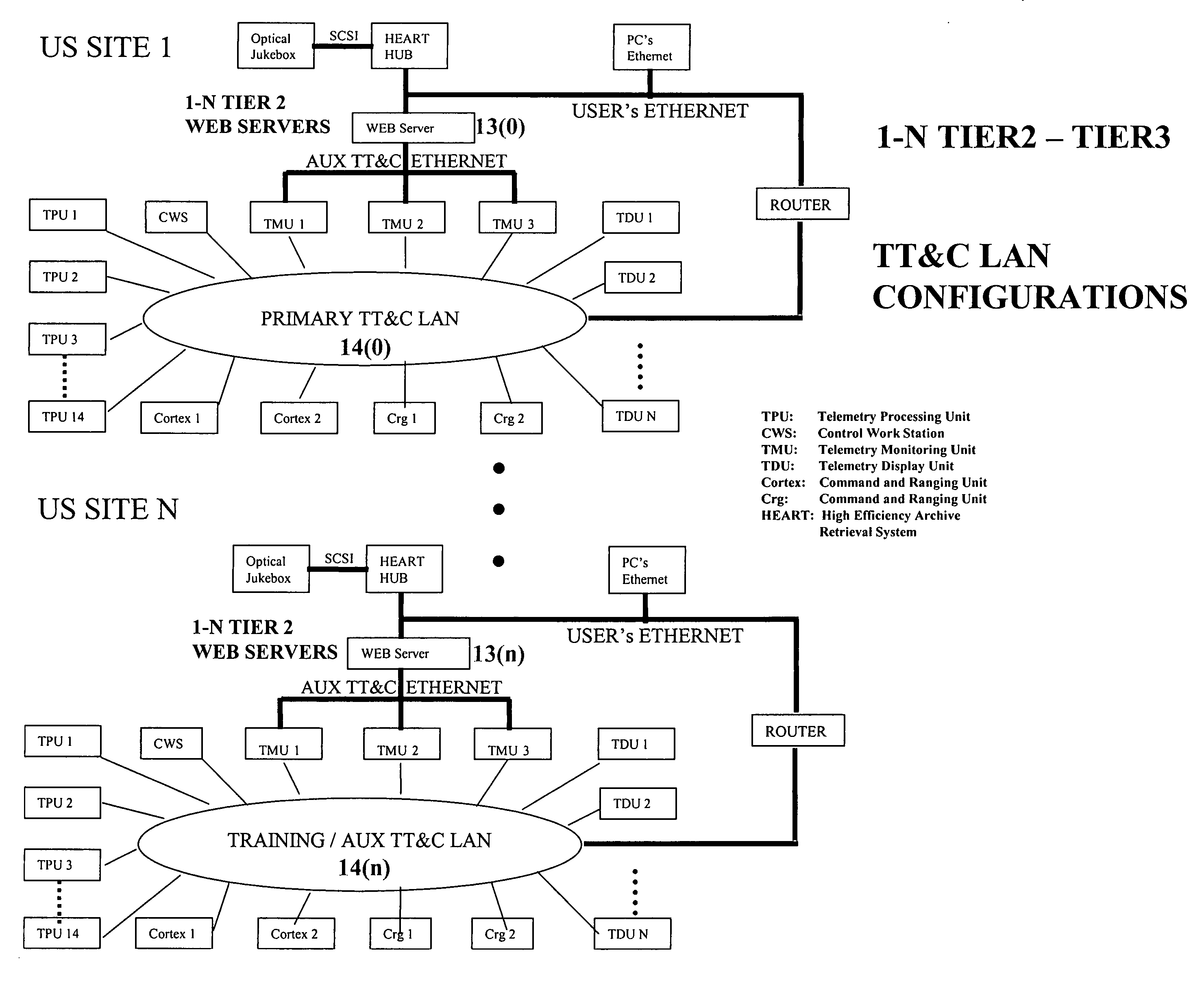
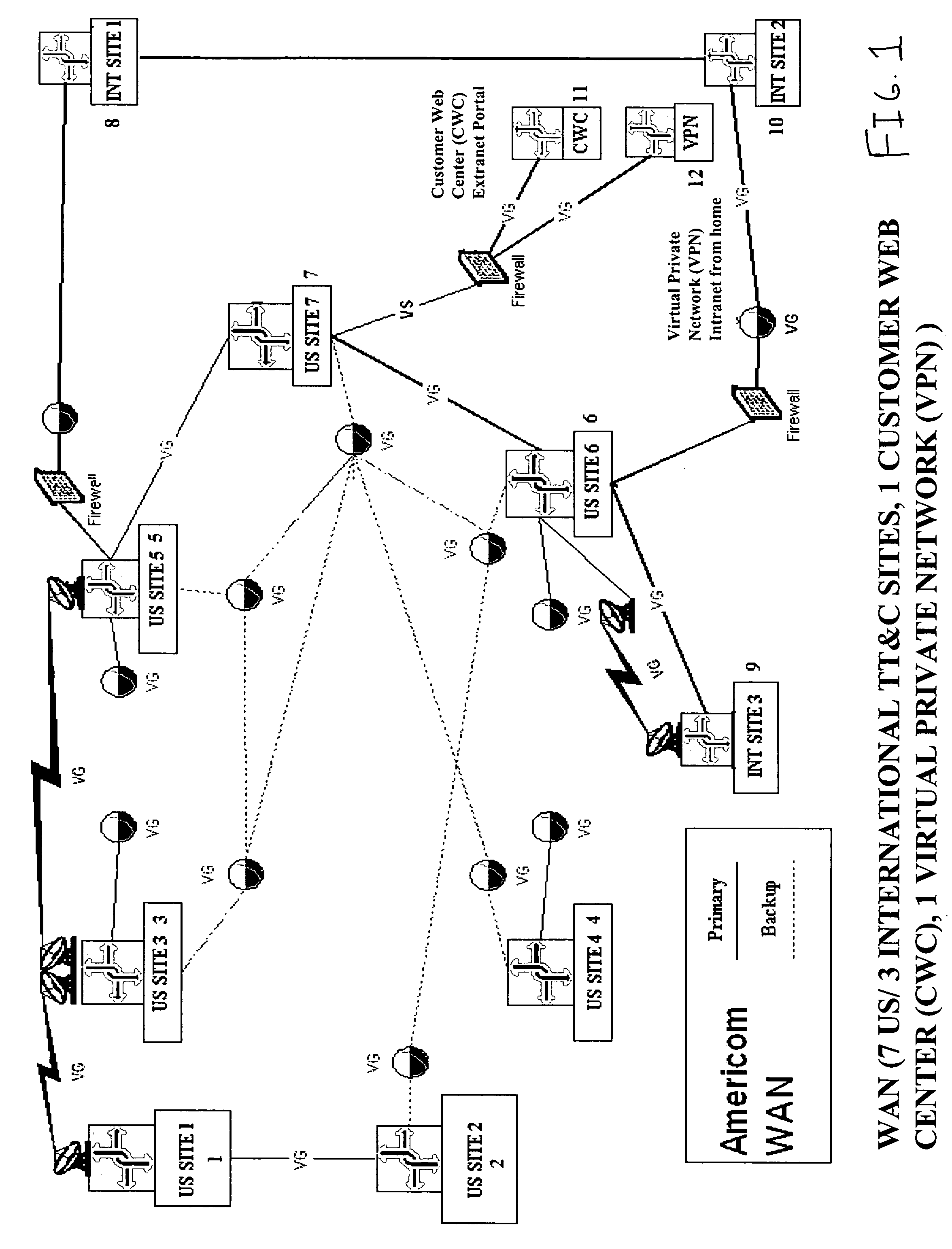
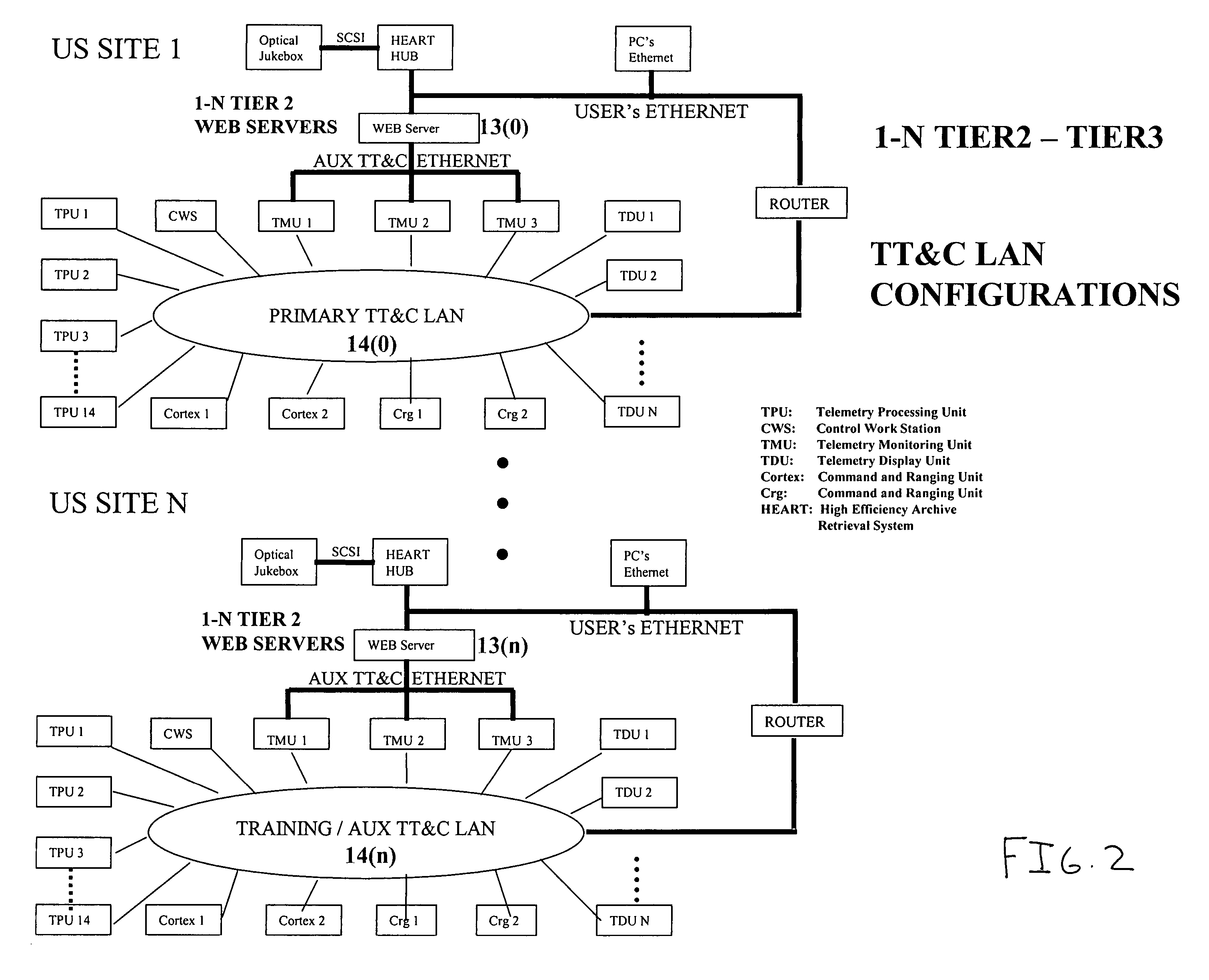
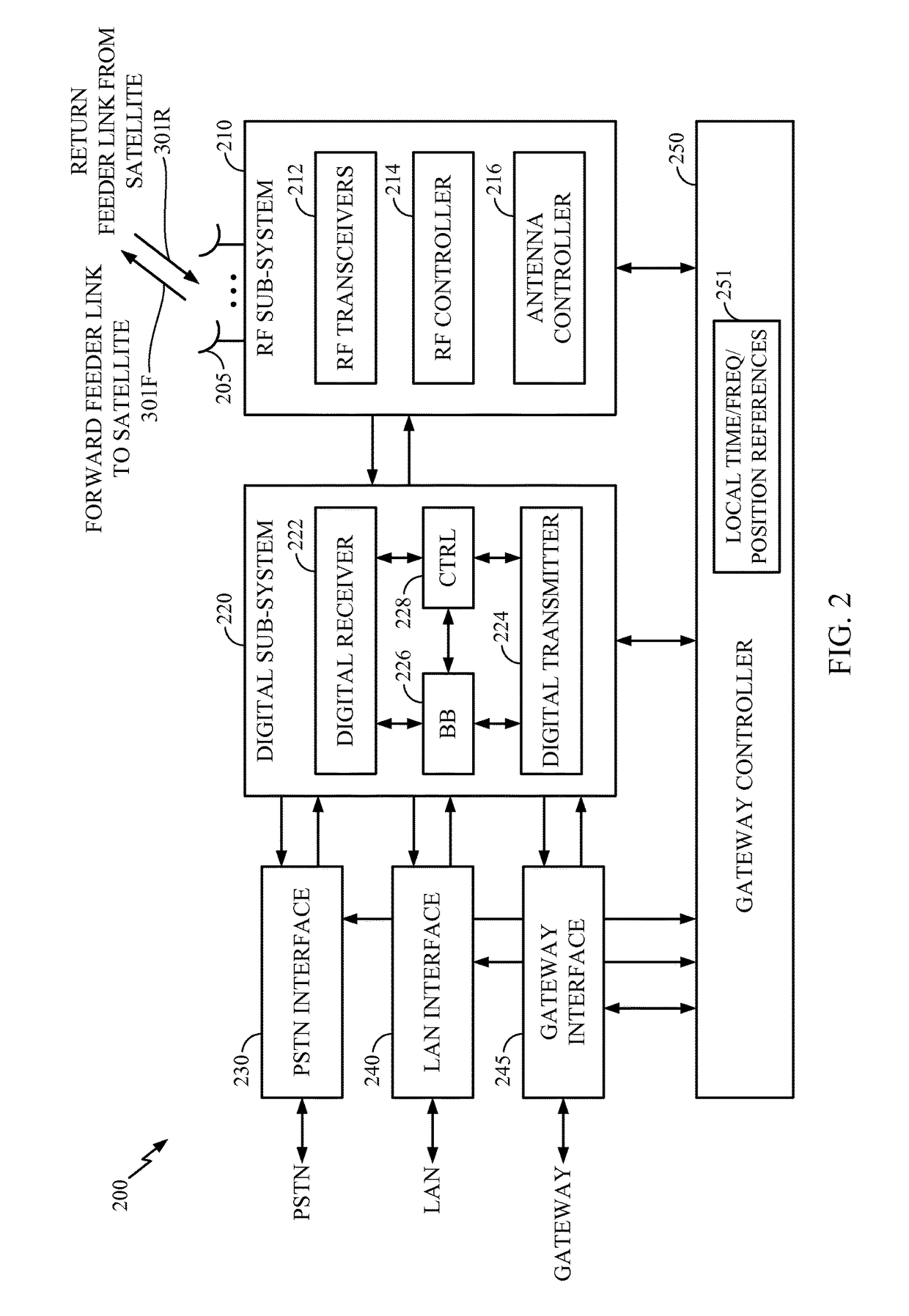
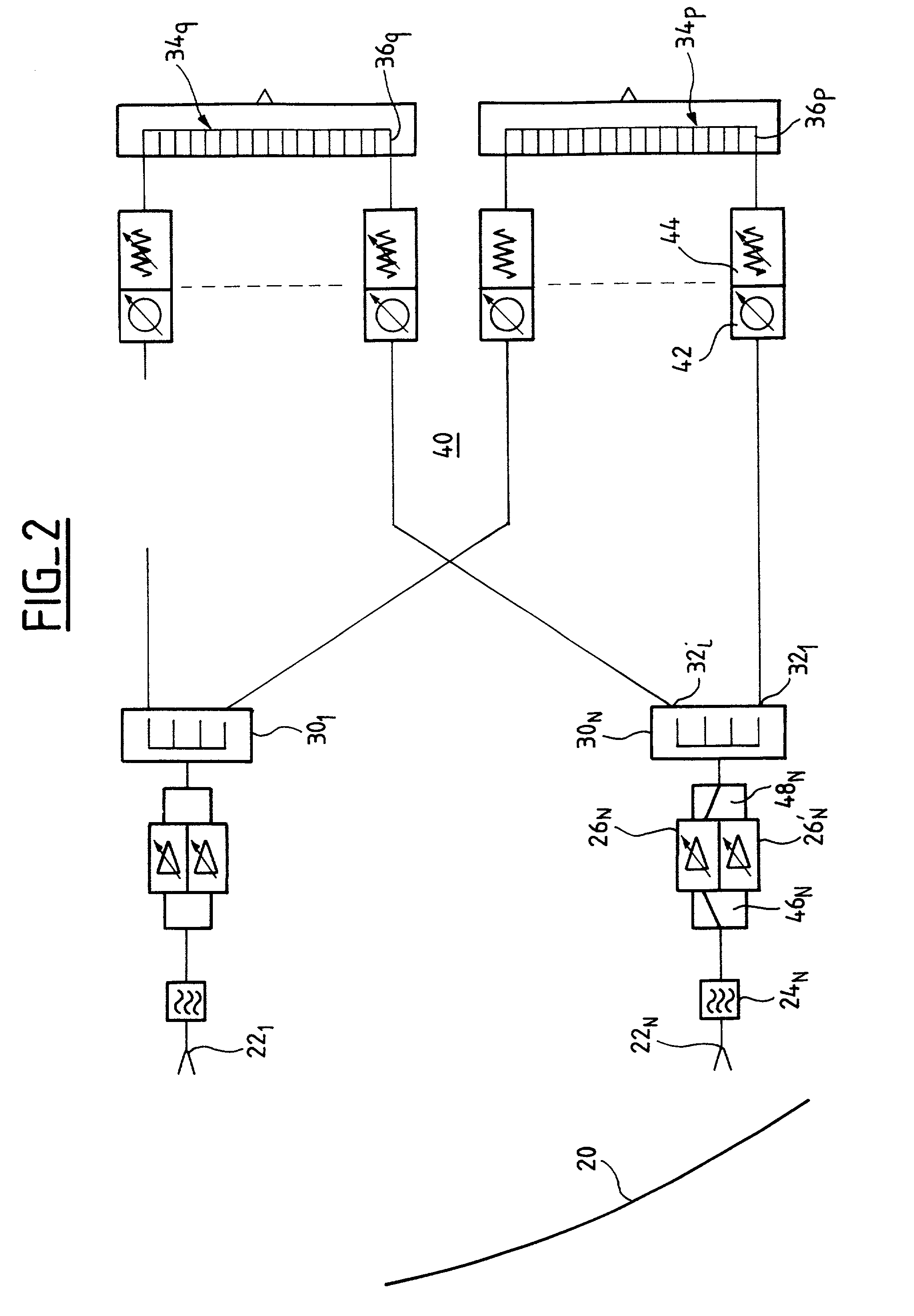
System and method of providing N-tiered enterprise/web-based management, procedure coordination, and control of a geosynchronous satellite fleet
ActiveUS20060094351A1Efficient and robust and and deploymentEfficient and robust designCosmonautic vehiclesDigital data processing detailsGeosynchronous satelliteSoftware architecture
An N-Tiered enterprise and / or N-Tiered Web-based enterprise system and methods for managing, monitoring, coordinating the procedures of and optionally controlling a fleet of geosynchronous satellites through a distributed network such as the Internet. The system and associated object oriented software architecture seamlessly supports monitoring and analyzing real-time, near real-time, historical / playback, simulated and archived satellite telemetry as well as Tracking, Telemetry and Control (TT&C) ground system generated data products such as real-time alerts, archived alerts and ground system server statuses from a group of legacy distributed TT&C wide area network (WAN) ground station systems located around the world.
Owner:SES AMERICOM
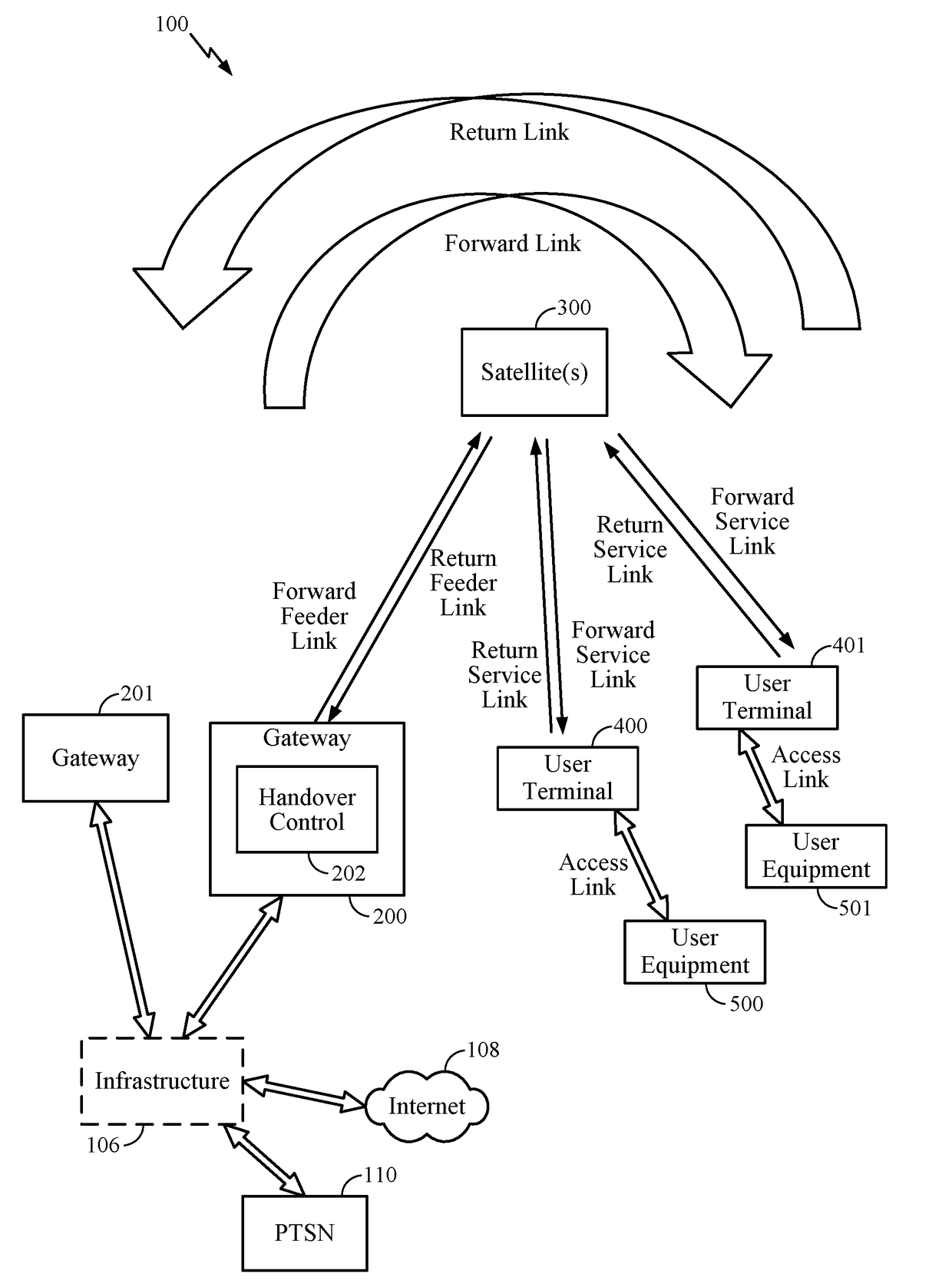
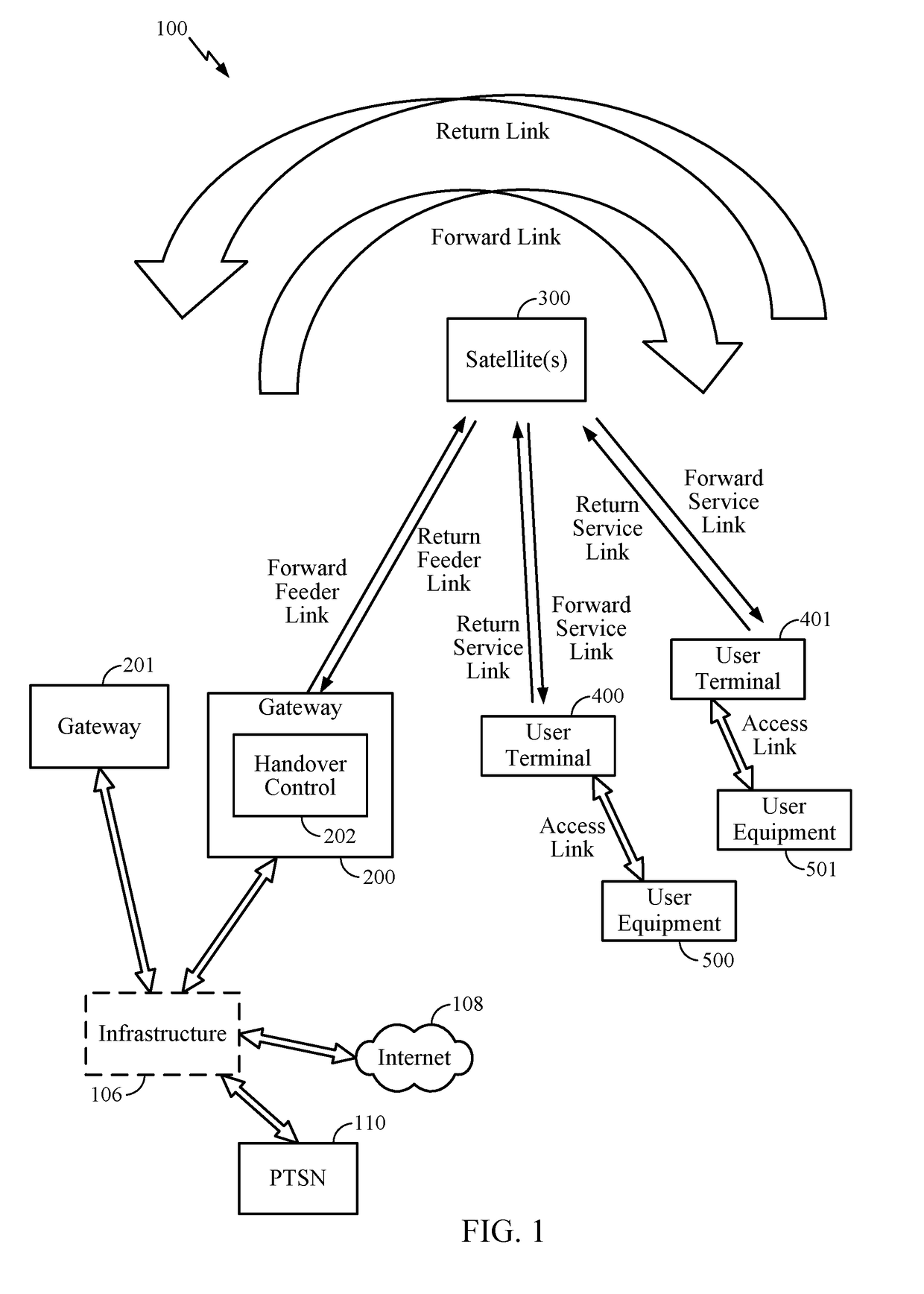
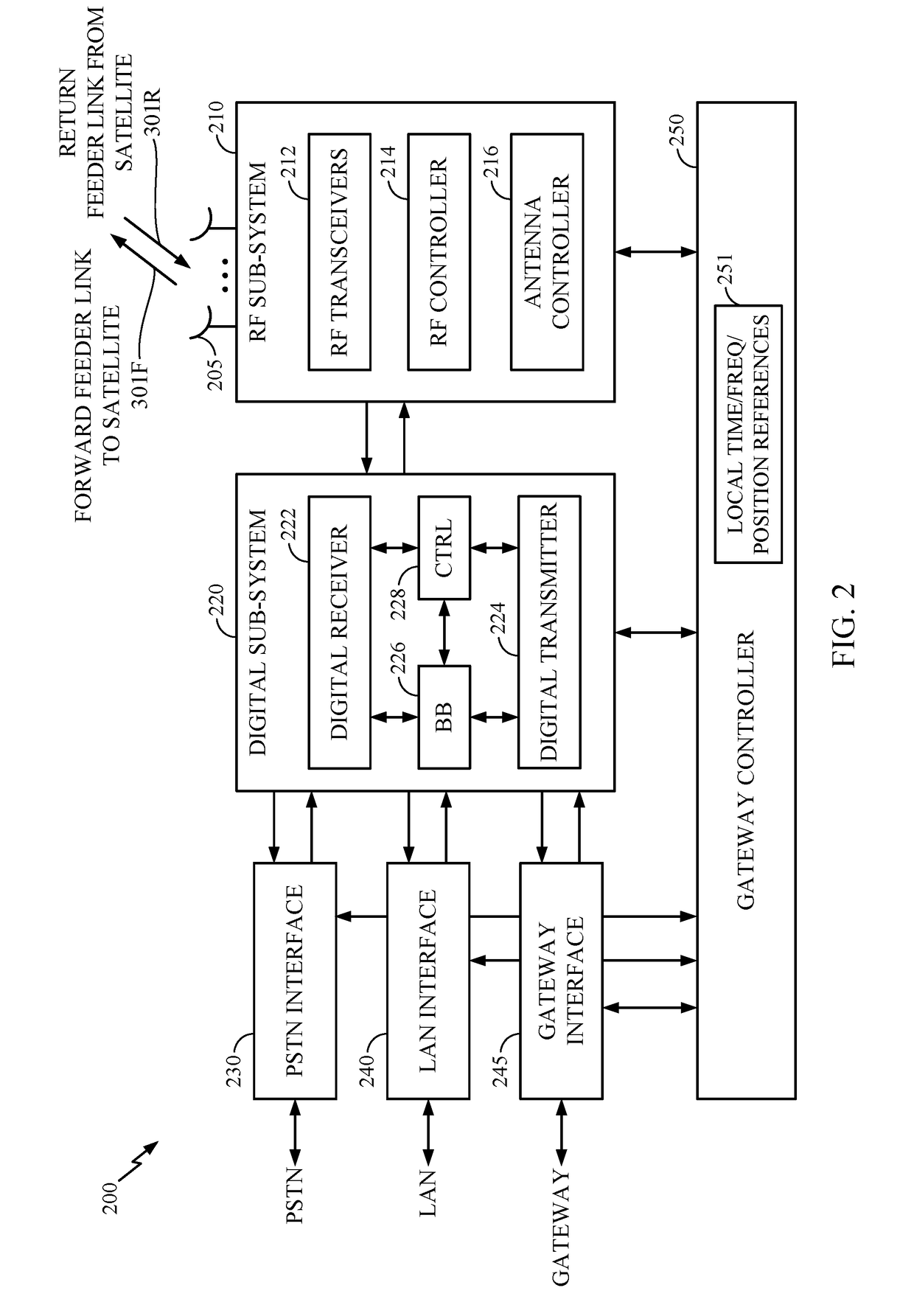
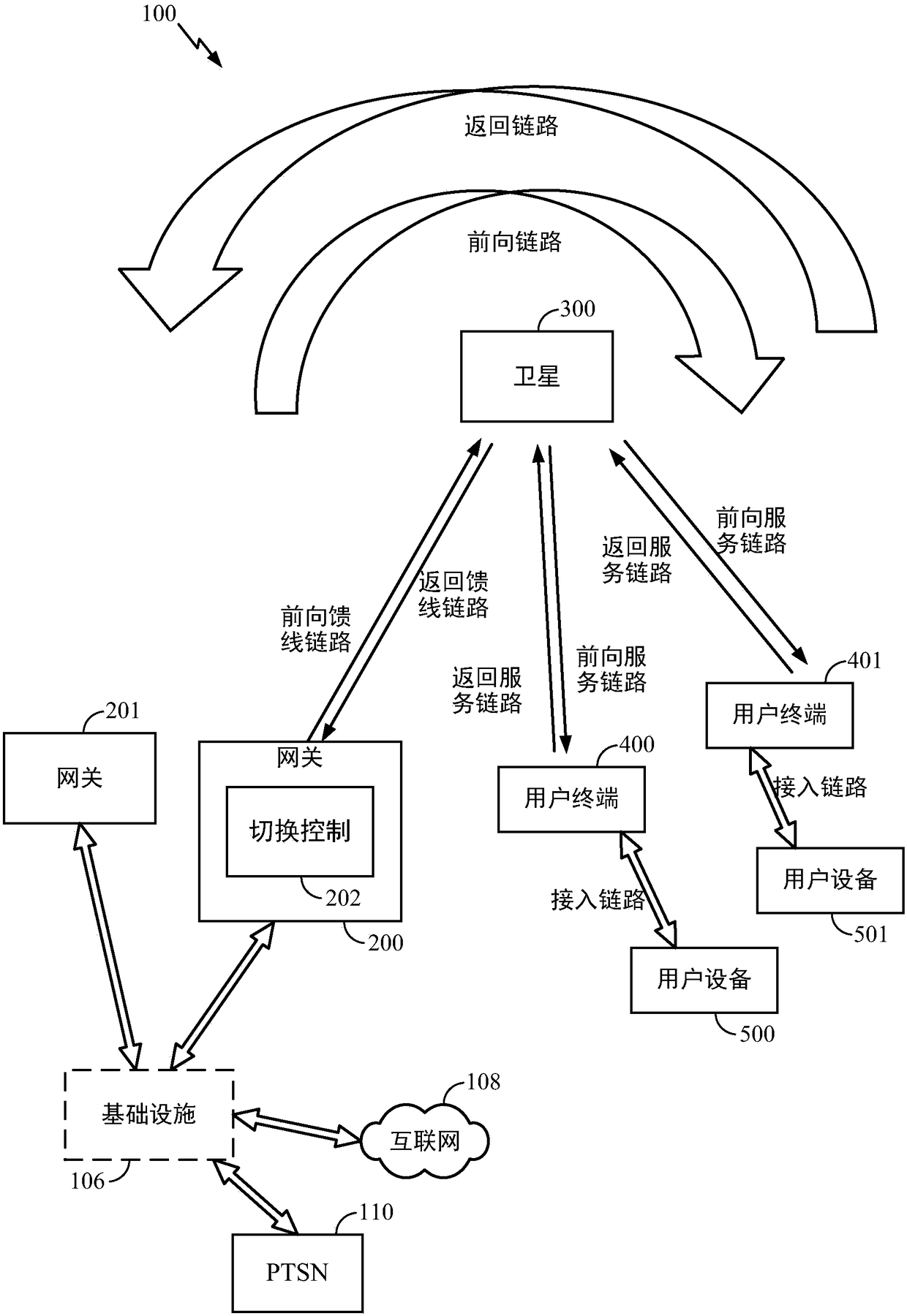
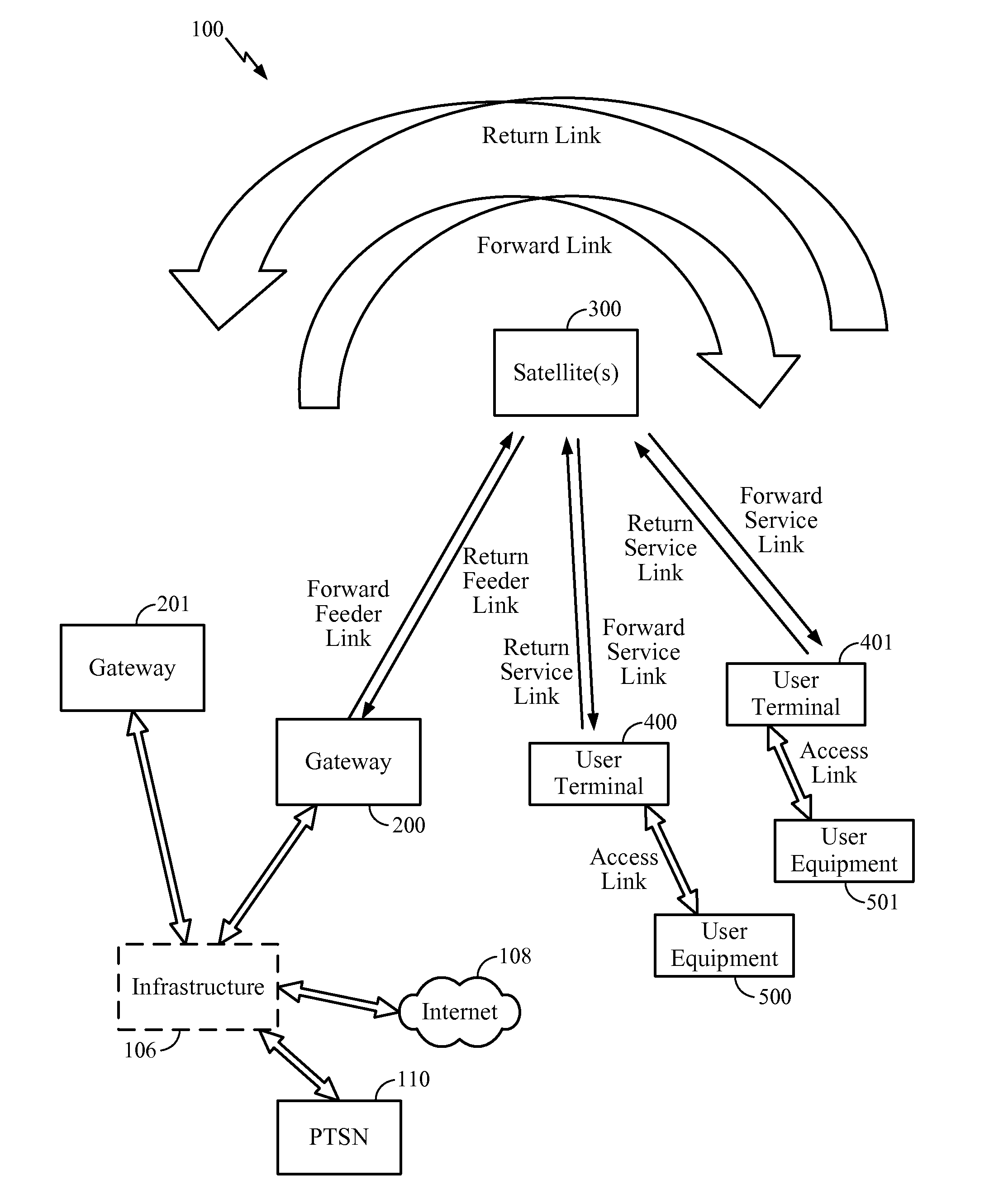
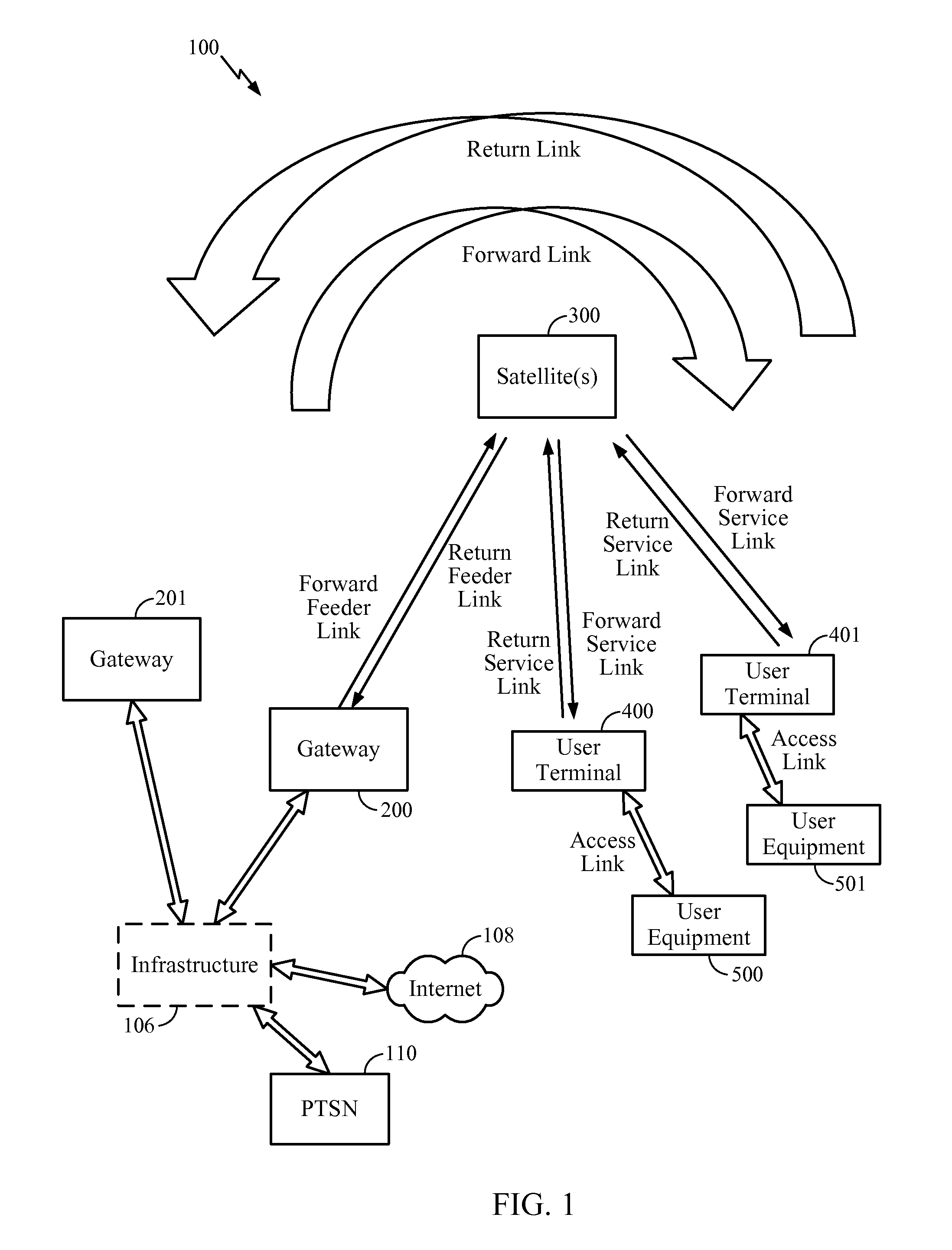
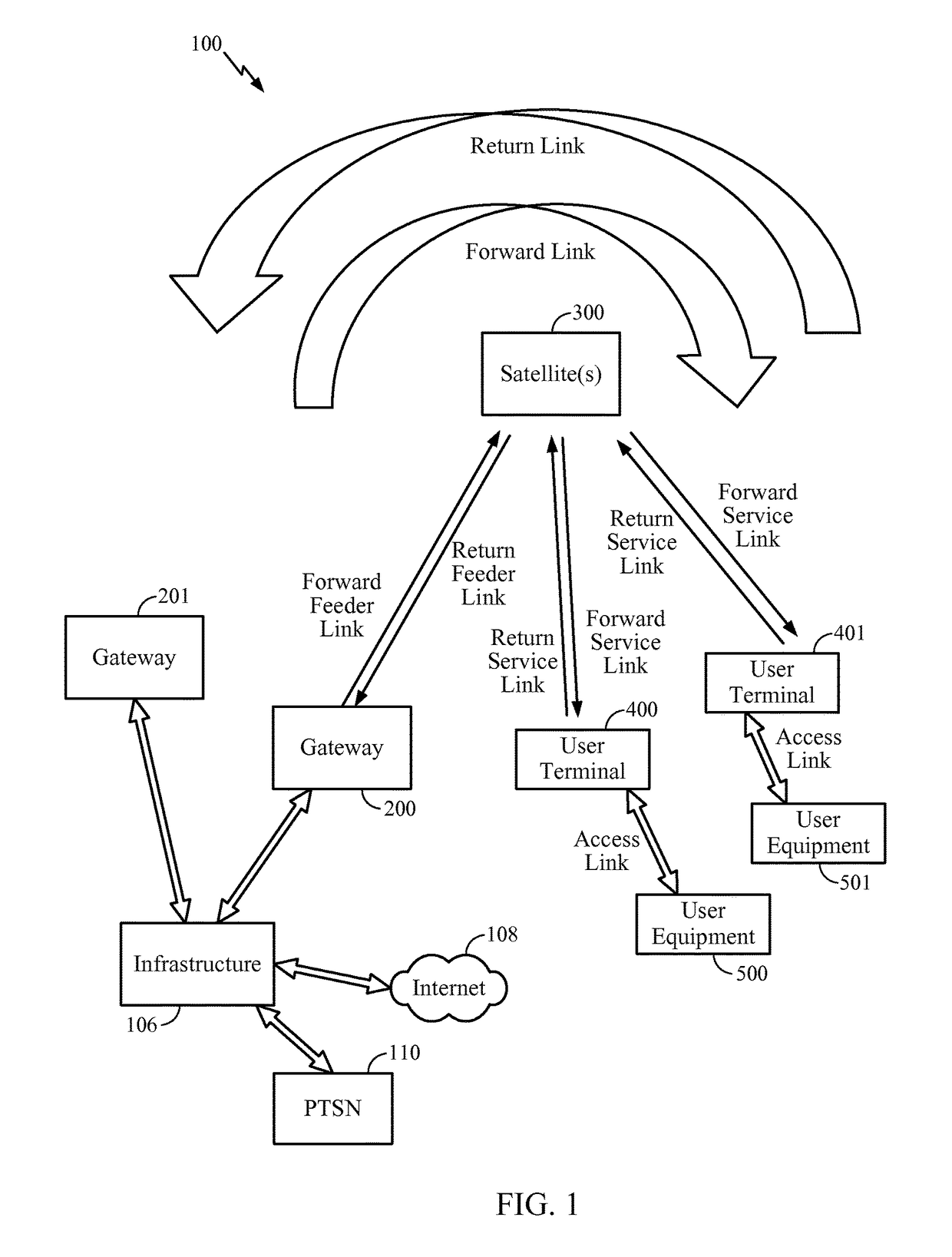
Method and apparatus for inter-satellite handovers in low-earth orbit (LEO) satellite systems
ActiveUS20170105153A1Keep for a long timeNetwork topologiesTransmission monitoringSystem capacityCommunications system
Methods and apparatuses for managing inter-satellite handovers are provided to allow a user terminal to reduce the frequency of handovers while maintaining a sufficiently high system capacity in a non-geosynchronous satellite communication system. The method and apparatus for managing inter-satellite handovers may be implemented in a gateway, in infrastructure connected to a gateway, in a user terminal, or in a satellite.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
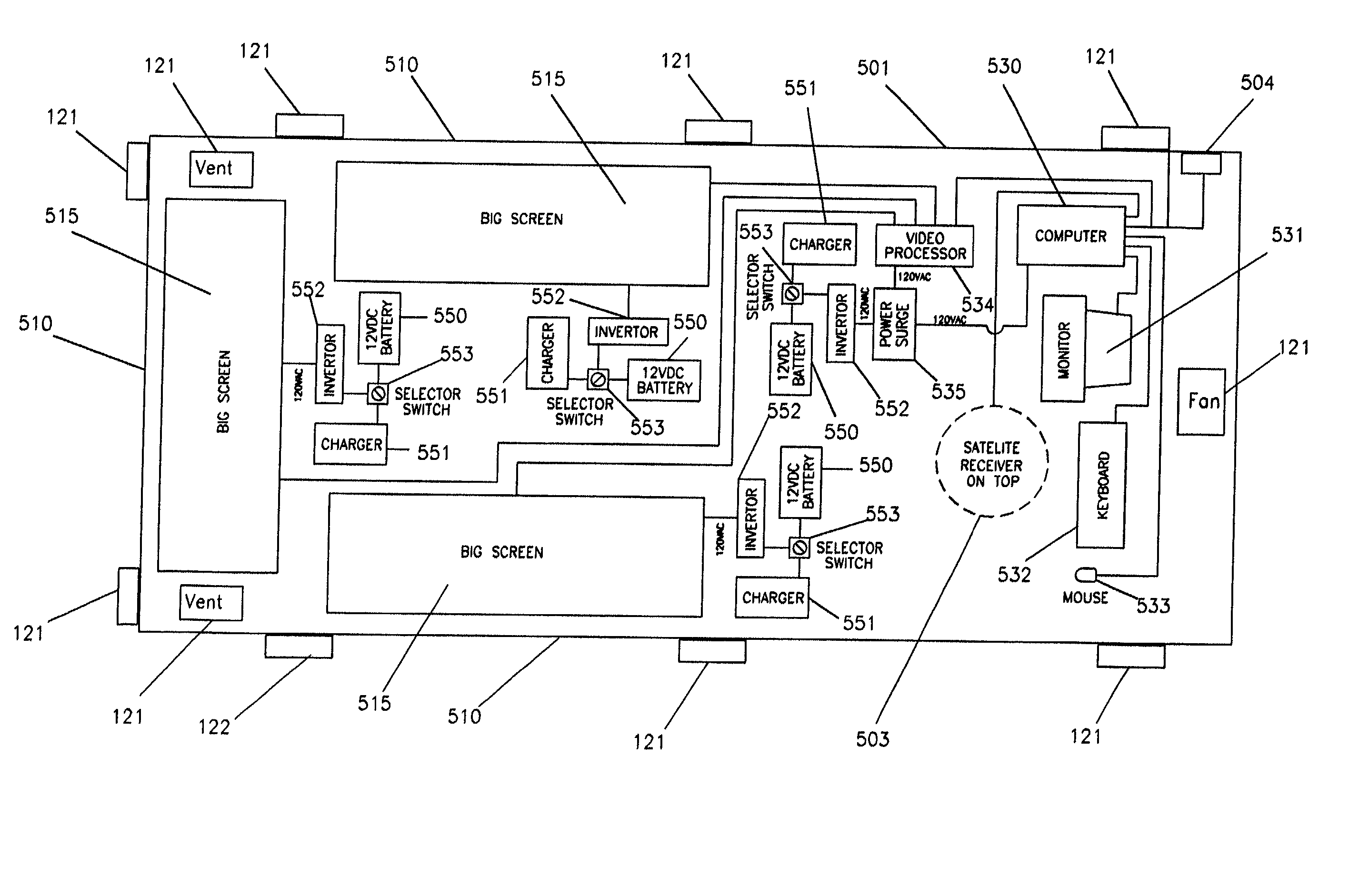
Multi-point, concurrent, video display system using relatively inexpensive, closed vehicles
InactiveUS20020130967A1Eliminate needEliminate useTelevision system detailsPicture reproducersGeosynchronous satelliteThe Internet
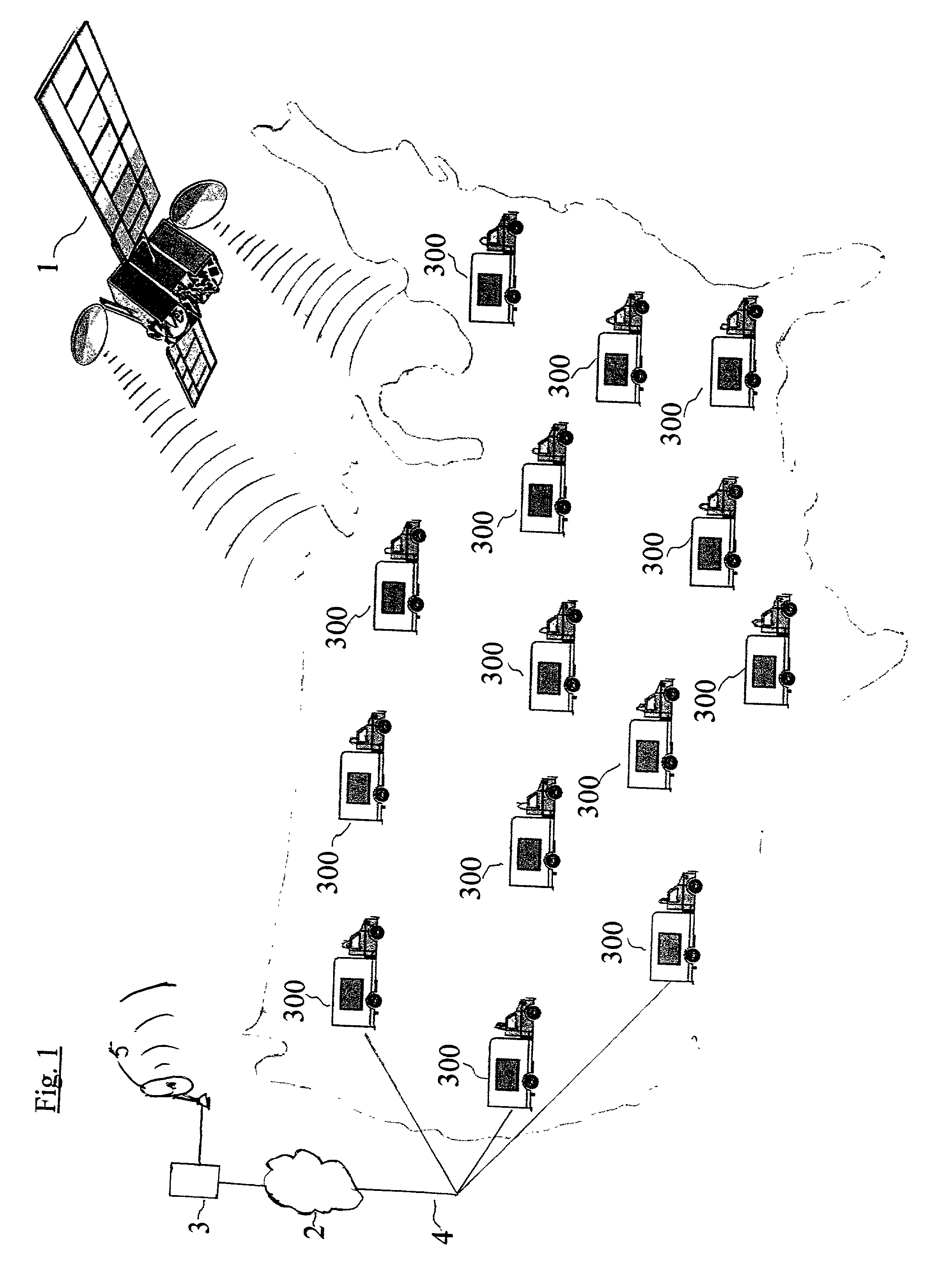
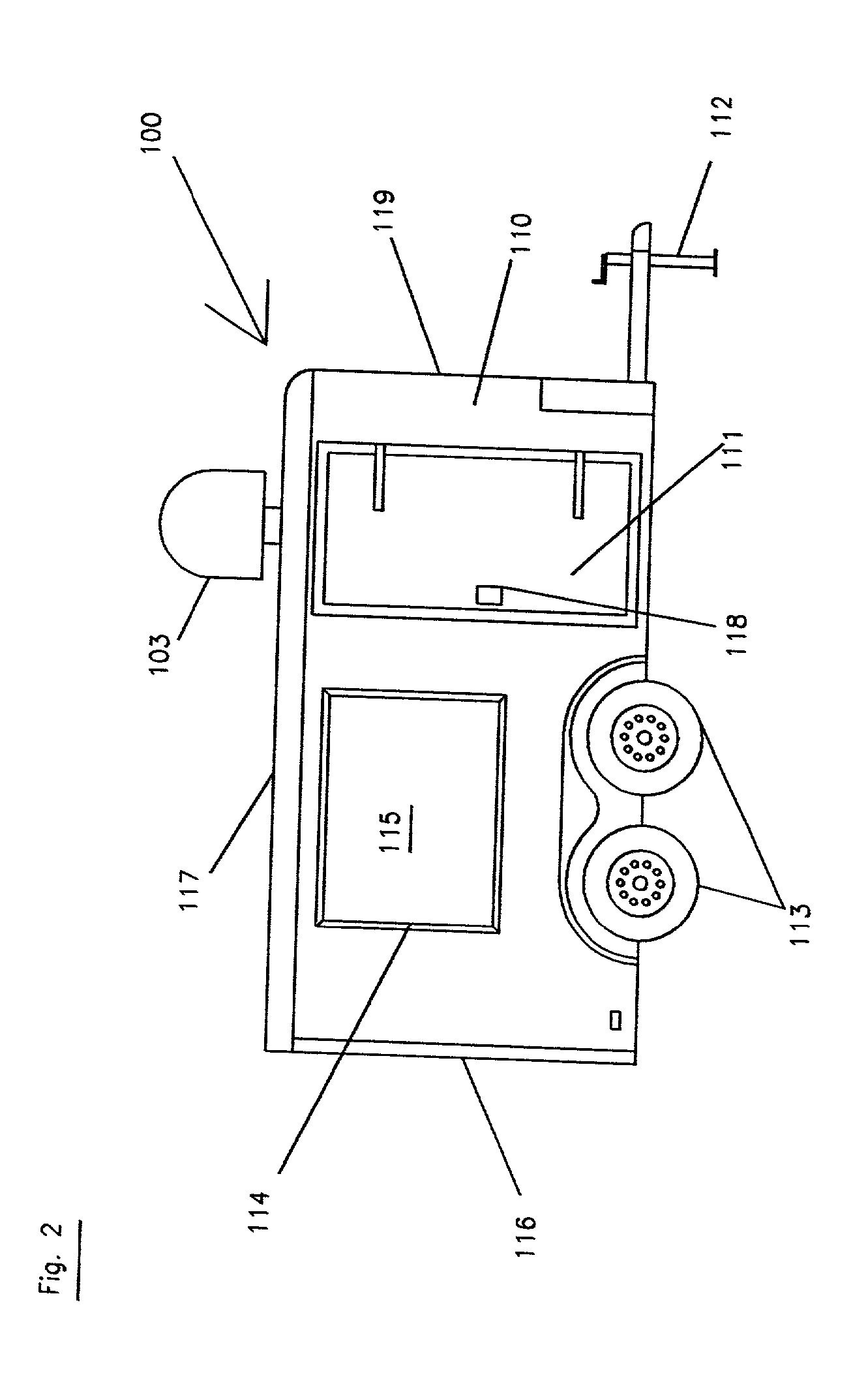
A relatively short body (e.g. 12' length), mobile, closed body vehicle (e.g., a pullable, closed trailer 100 (FIGS. 2 -4), van 200 (FIGS. 6 & 7) or closed truck 300 (FIGS. 8 & 9) with a box-like body (101 / 201 / 301 / 501) preferably of a standard, readily available type, which is modified to have wall openings made, having preferably a dynamic video display (115 / 215 / 315 / 515) on each of its sides and rear, in which preferably the video signal to be display originates from, for example, the "Internet" (2) and is supplied to the vehicle via, for example, a satellite hook-up (1& 103 / 203 / 303 / 505) or, alternatively, via a hard-wired (504) or a wireless "connection." A multi-point, video display system (FIG. 1) uses a multiple number of such vehicles geographically dispersed at various locations, each preferably with its own connection to, for example, the "Internet", or more preferably using a two-way, geosynchronous satellite hook-up, allowing for the concurrent, co-ordinated display of the same video signal at the geographically spaced or dispersed locations in a very cost effective manner. Such an approach allows, for example, the "live" (or recorded) presentation of, for example, a political speech or announcement or a sporting event or political or business event or other event or advertising campaign of a geographically dispersed interest. Each video display takes up a percentage of at least about fifteen (15%) percent or greater of each side wall's area.
Owner:SWEETSER MICHAEL
Virtual Polar Satellite Ground Station for Low Orbit Earth Observation Satellites Based on a Geostationary Satellite Pointing an Antenna Over an Earth Pole
ActiveUS20120184208A1Attractive solutionShort response timeRadio transmissionEarth observationGeosynchronous satellite
Owner:AIRBUS DEFENCE & SPACE
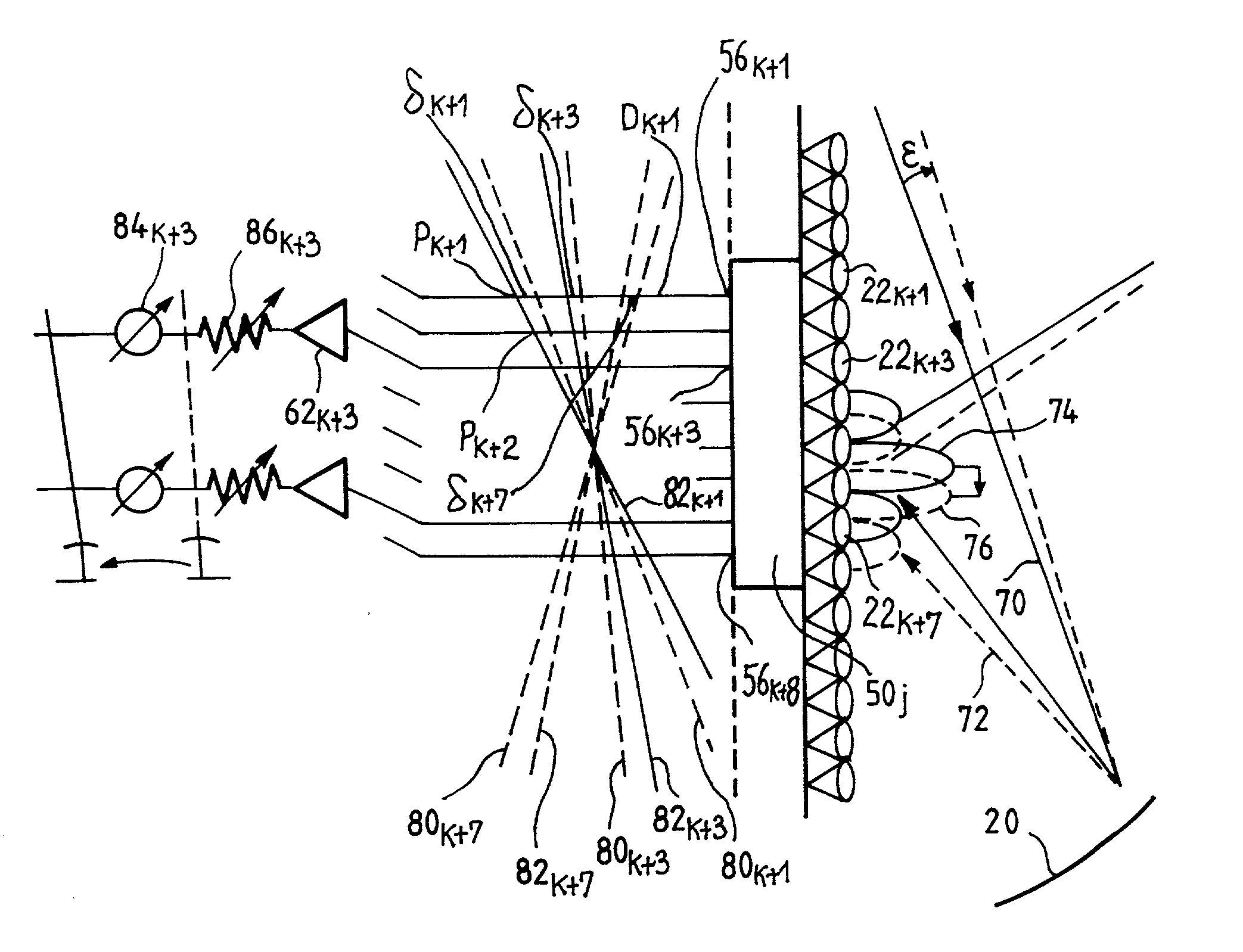
Method for improving pattern bandwidth of shaped beam reflectarrays
InactiveUS6031506AImproving pattern bandwidthReduce beamshape variationSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsShaped beamGeosynchronous satellite
A method for shaping reflected radio frequency signals includes geometrically shaping a reflector surface of an antenna to focus the beam, and reflectively shaping the reflector surface with phasing elements that emulate geometric shaping to configure the beam to a predetermined shape. In the preferred embodiment, the antenna comprises a geosynchronous satellite antenna conveying signals from a wave guide horn to or from a predetermined geographic area on earth. The use of a parabolic-approaching surface of reflectarray phasing elements for shaping the beam substantially improves the beam pattern bandwidth over the performance of previously known shaped beam reflectarrays.
Owner:HUGHES ELECTRONICS
Satellite broadcasting system
In a broadcasting receiver, to quickly switch channels of the received multiplexed broadcasting signals at a high response speed to improve the convenience for a viewer, when broadcasting signals of a plurality of channels are to be code-division-multiplexed and broadcasted from a ground broadcasting station (BC1, BC2) to a broadcasting receiver (MS) in a service area via a geostationary satellite (SAT), the broadcasting signals are multiplexed and transmitted after matching the spreading code phase between the channels in the ground broadcasting station (BC1, BC2). Alternatively, the spreading code phase difference between the channels of a CDM broadcasting signal arriving from the ground broadcasting station (BC1, BC2) is detected in the geostationary satellite (SAT), and the broadcasting signal is transmitted to the broadcasting receiver (MS) after matching the spreading code phase between the channels on the basis of the detection result.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
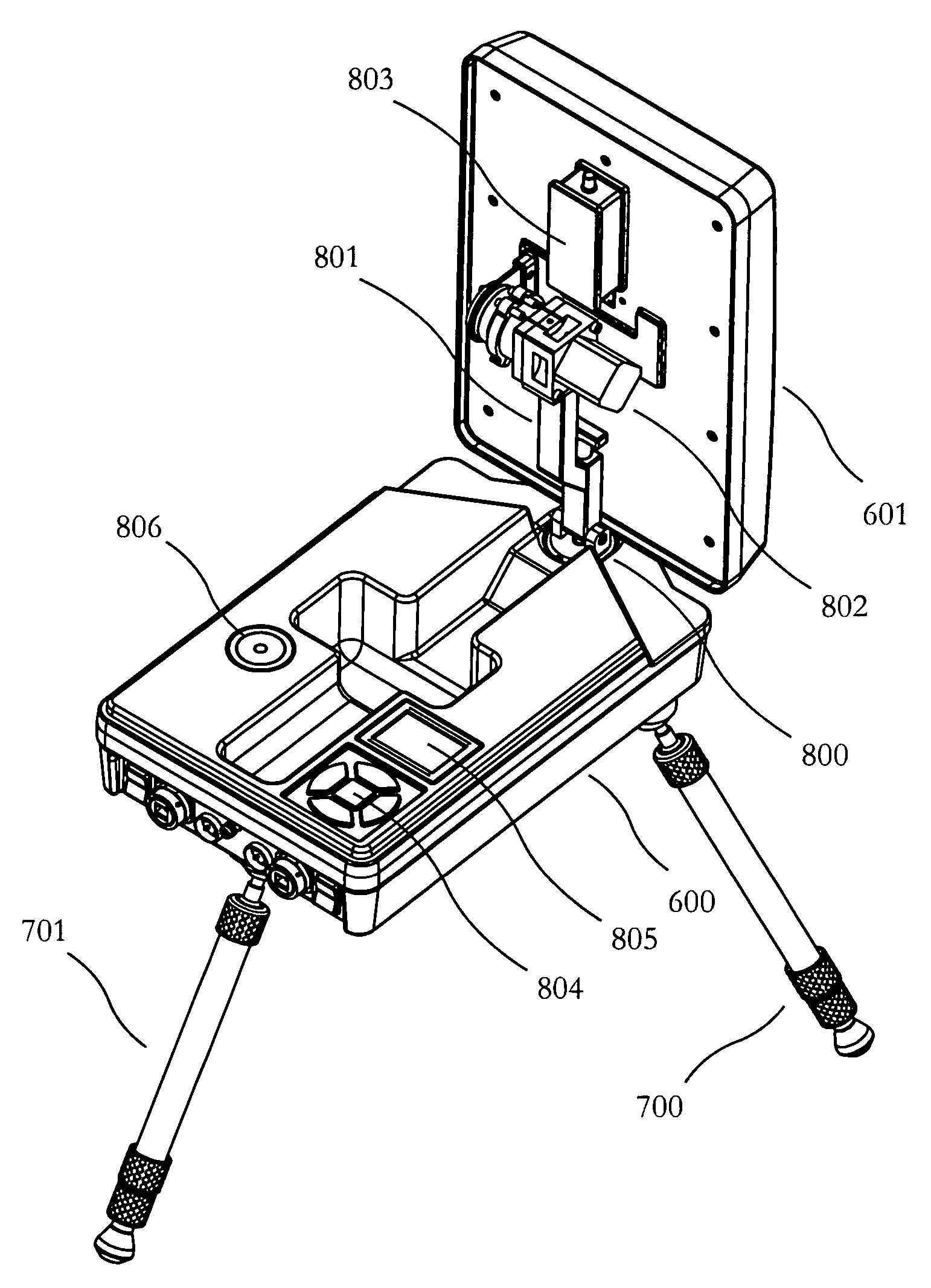
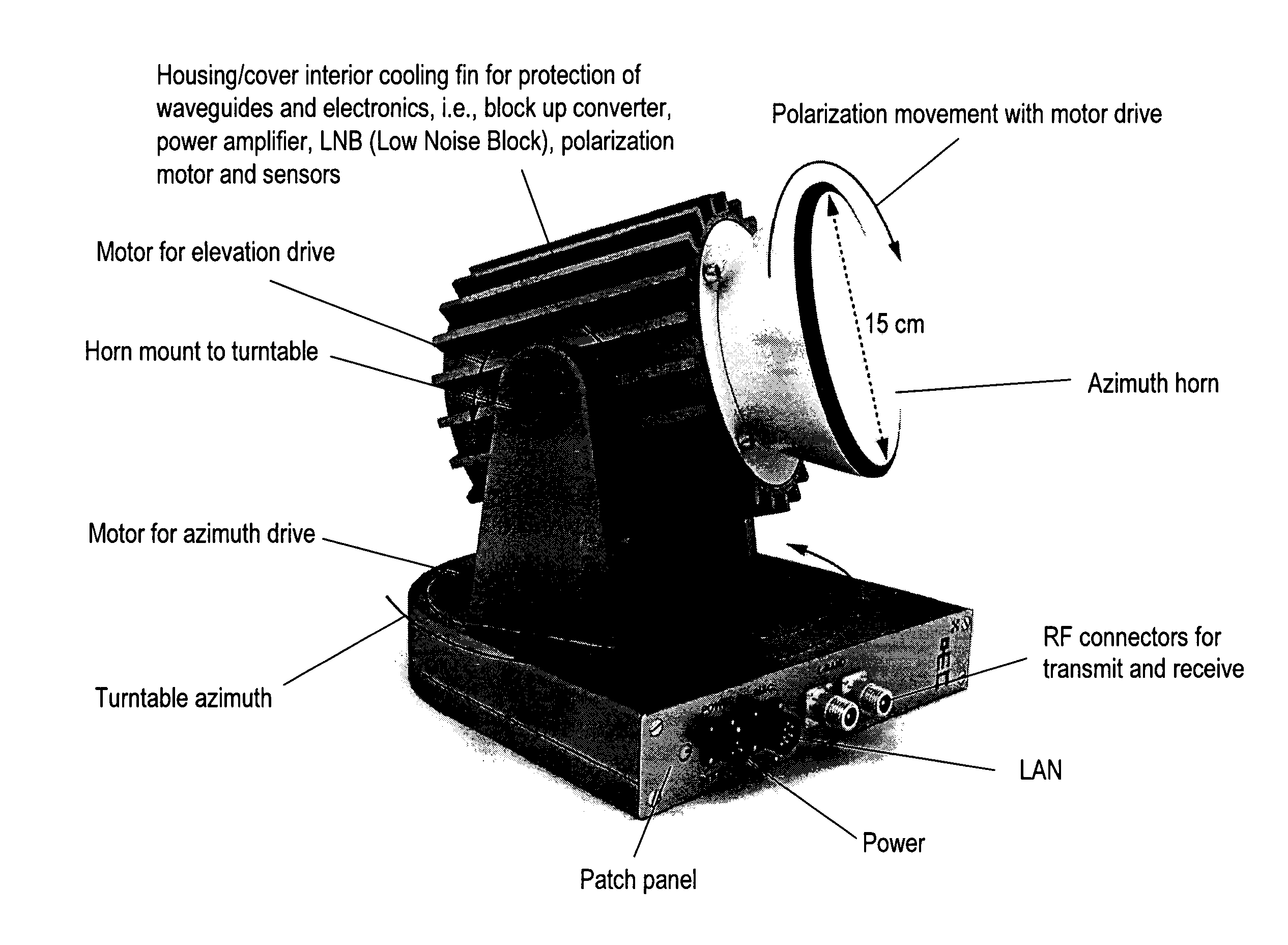
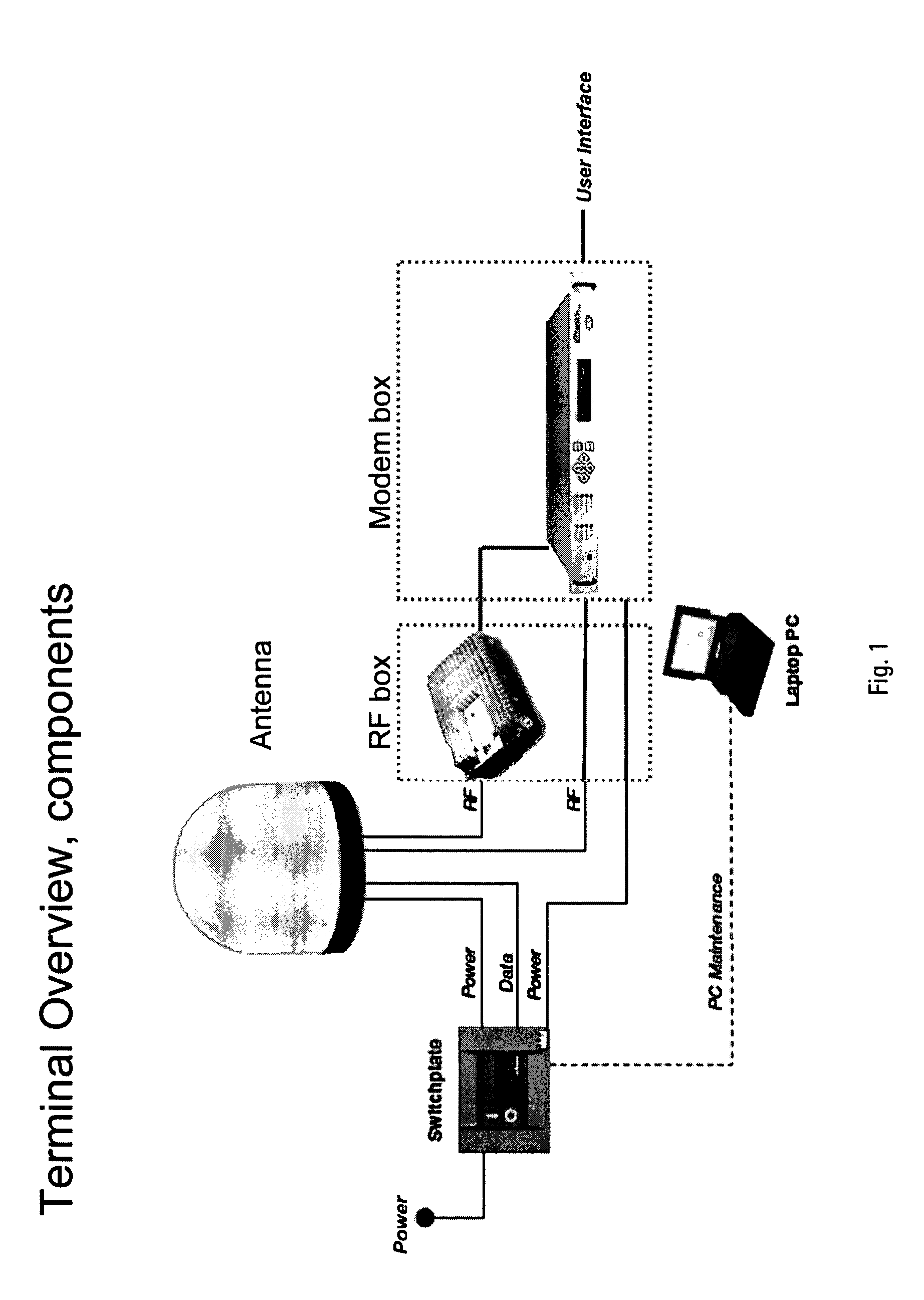
Portable antenna positioner apparatus and method
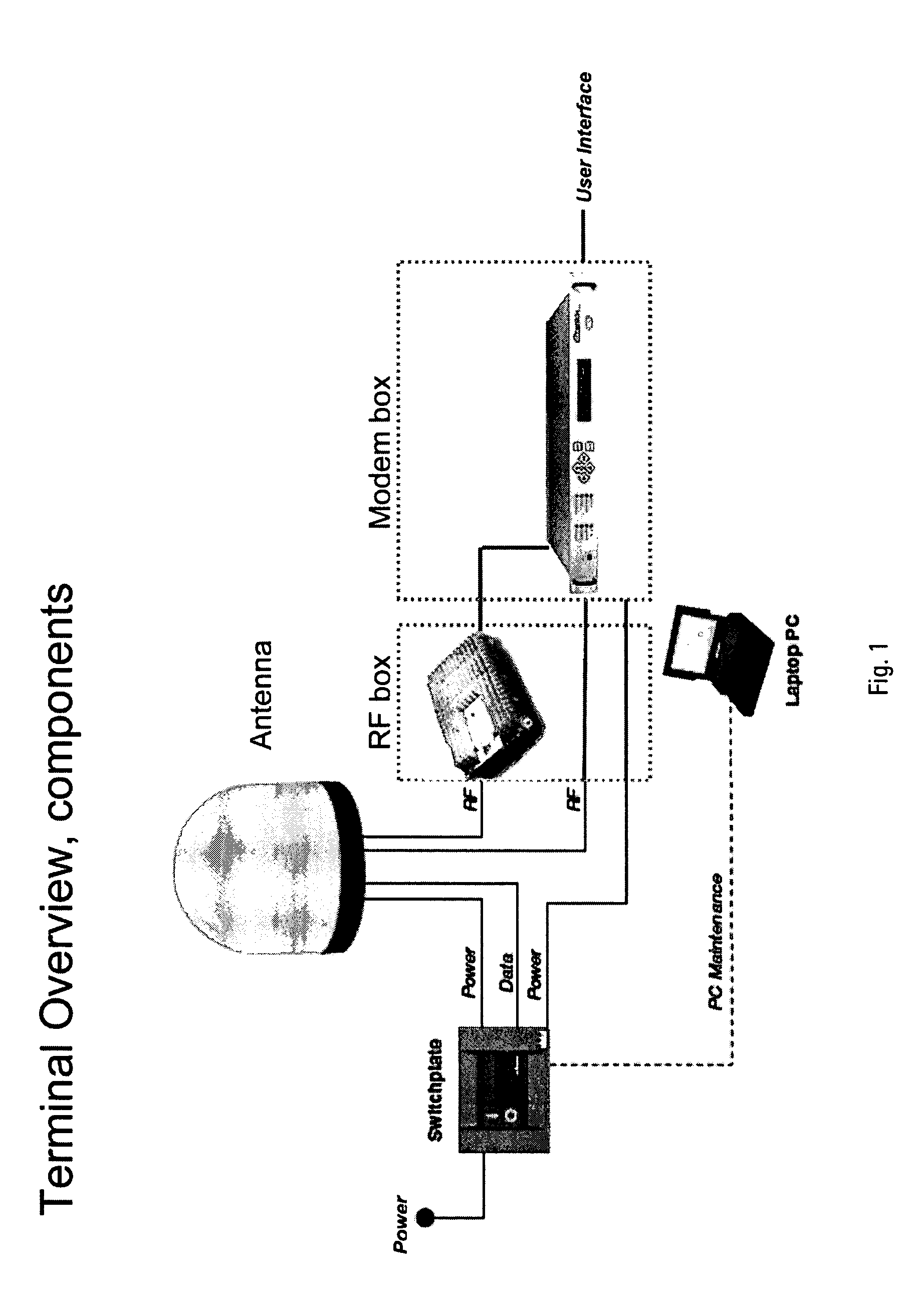
ActiveUS7173571B2Easy to carrySimple and automated setupPivotable antennasAntenna supports/mountingsHard disc driveGeosynchronous satellite
Embodiments of the portable antenna positioner described provide a lightweight, collapsible and rugged antenna positioner for use in receiving low earth orbit, geostationary and geosynchronous satellite transmissions. By collapsing the antenna positioner, it may be readily carried by one person or shipped in a compact container. The antenna positioner may be used in remote locations with simple or automated setup and orientation. In order to operate the apparatus, azimuth is adjusted by rotating an antenna in relation to a positioner base and elevation is adjusted by rotating an elevation motor coupled with the antenna. The apparatus may update ephemeris data via satellite, may comprise a built-in receiver and may couple with a second positioner base comprising cryptographic, router or power functionality. The apparatus may comprise storage devices such as a hard drive or flash disk for storing data to and from at least one satellite.
Owner:AQYR TECH INC
Method and apparatus for inter-satellite handovers in low-earth orbit (LEO) satellite systems
Methods and apparatuses for managing inter-satellite handovers are provided to allow a user terminal to reduce the frequency of handovers while maintaining a sufficiently high system capacity in a non-geosynchronous satellite communication system. The method and apparatus for managing inter-satellite handovers may be implemented in a gateway, in infrastructure connected to a gateway, in a user terminal, or in a satellite.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
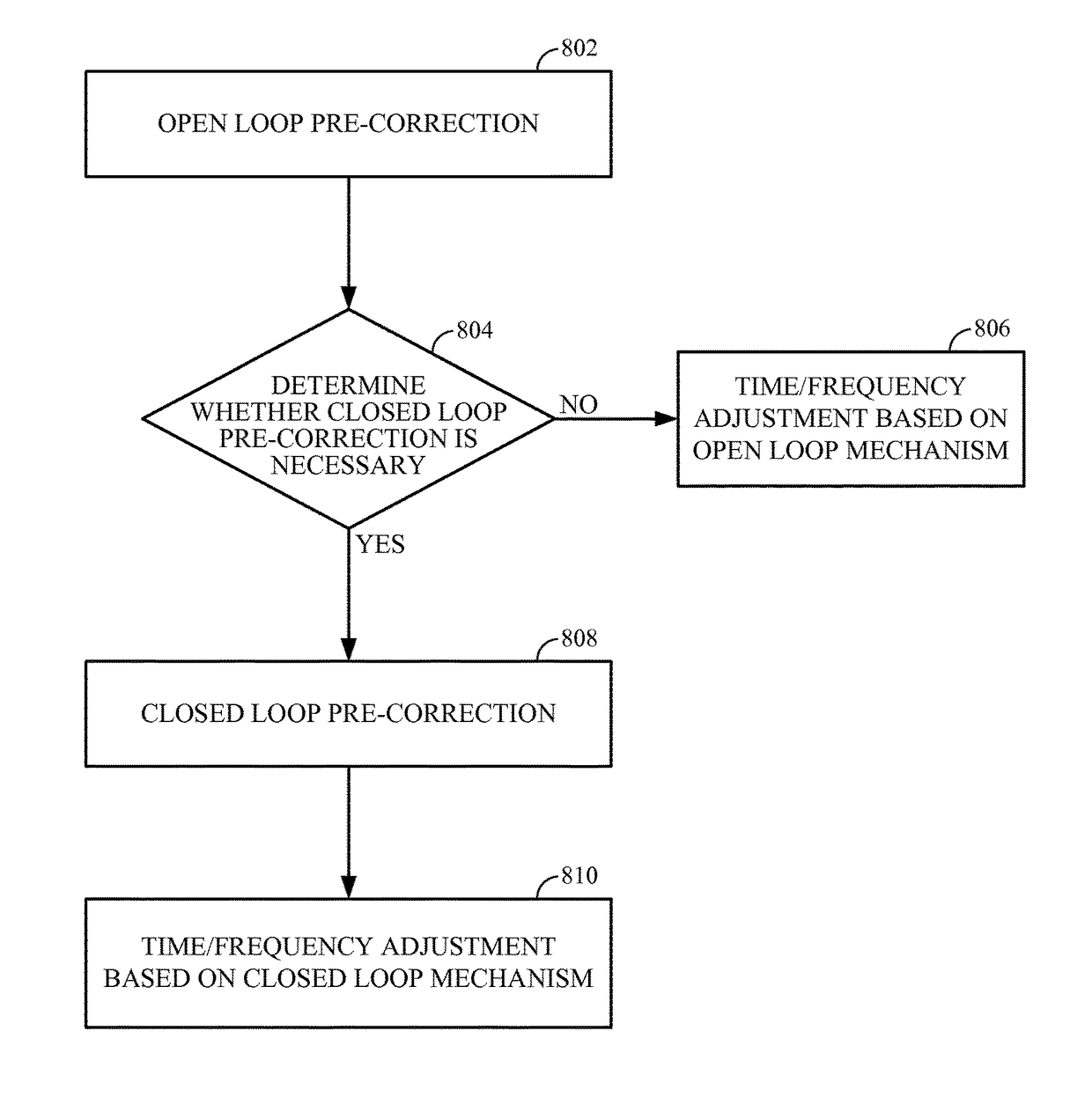
Method and apparatus for time or frequency synchronization in non-geosynchronous satellite communication systems
ActiveUS20160278033A1Synchronisation arrangementRadio transmissionCommunications systemGeosynchronous satellite
Method and apparatus for time or frequency synchronization of radio signals transmitted by user terminals in communication with a gateway through a satellite is provided. The satellite may be part of a non-synchronous satellite communication system, such as a low-earth orbit (LEO) satellite communication system for data, voice or video communications. Times of transmission of return link radio signals from the user terminals may be adjusted such that the signals arrive at the satellite or at the gateway without large time delay differentials. Carrier frequencies of return link radio signals transmitted from the user terminals may be adjusted such that the signals arrive at the satellite or at the gateway without large frequency offset differentials.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and apparatus for avoiding exceeding interference limits for a non-geostationary satellite system
ActiveUS20170019814A1Reduce the required powerNetwork traffic/resource managementAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesGeosynchronous satelliteLong axis
A non-geosynchronous satellite system, where each satellite has an antenna (perhaps a multi-element antenna) to form a beam pattern comprising a set of beams in the footprint of the satellite, where in one implementation each beam is substantially elliptical in shape having a minor axis and a major axis, where the minor axes are substantially collinear and the major axes are substantially oriented east to west. For a satellite, power is reduced or turned off for a subset of the set of beams, wherein each beam in the subset is reduced at or below a corresponding power level such that when a beam is powered above its corresponding power level an equivalent power flux-density (EPFD) exceeds a limit at some point on the Earth's surface.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
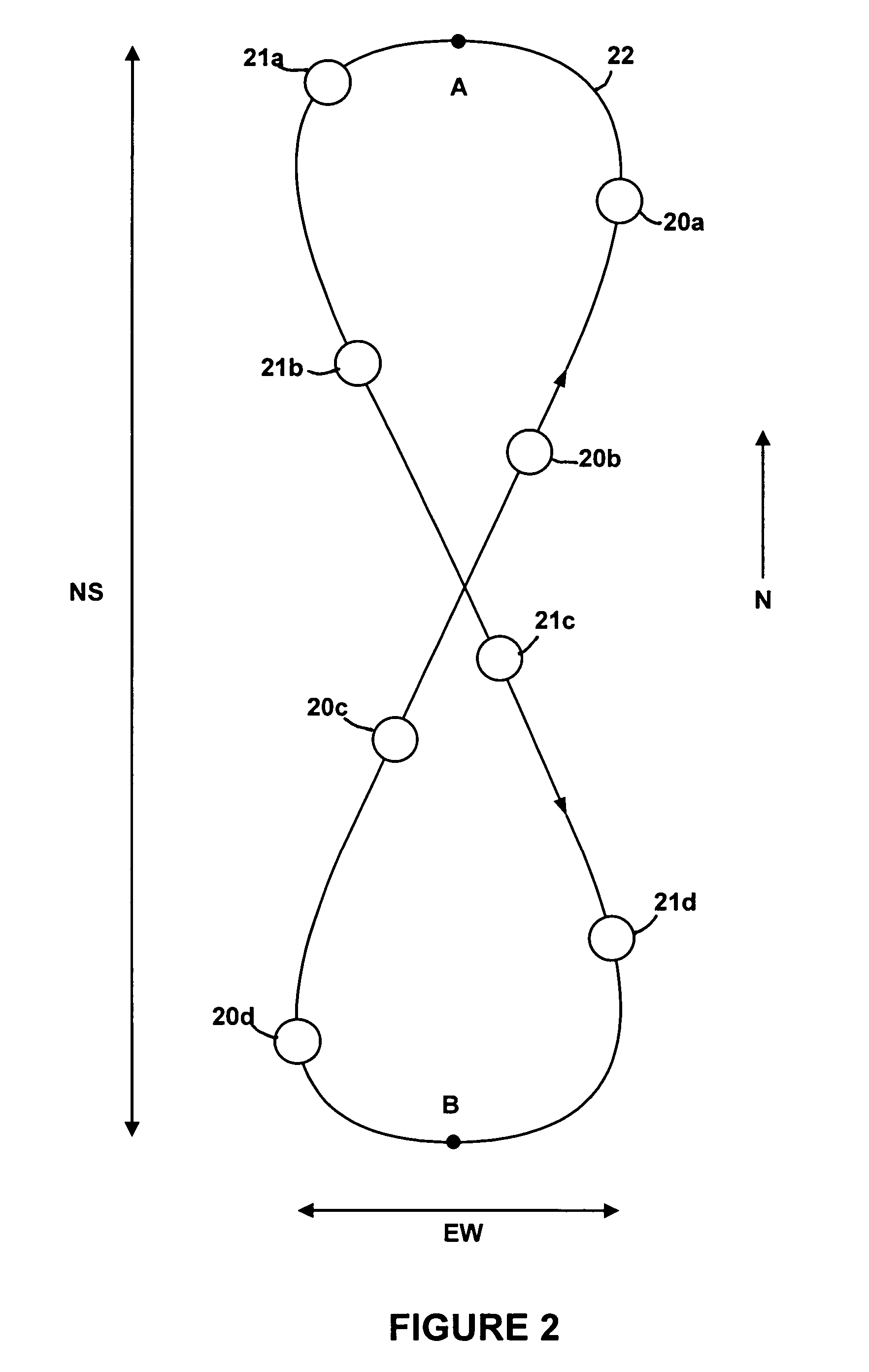
Geosynchronous satellite constellation
ActiveUS20060240767A1Avoid interferenceCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsFrequency spectrumCommunications system
A satellite communications system is described for increasing capacity through spectrum reuse by multiple satellites. The system includes a constellation of satellites traveling in a geosynchronous orbit, where the geosynchronous orbit defines a satellite track. The satellite track of the constellation overlaps a geostationary orbital location occupied by a legacy satellite traveling in a geostationary orbit. To prevent interference between the co-located constellation and legacy satellite, each of the constellation satellites operates in a silent mode when traveling within an interference beam width of a ground terminal in communication with the legacy satellite. Once outside of the interference beam width, the constellation satellites return to an active mode of operation.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Antenna System For Communications On-The-Move
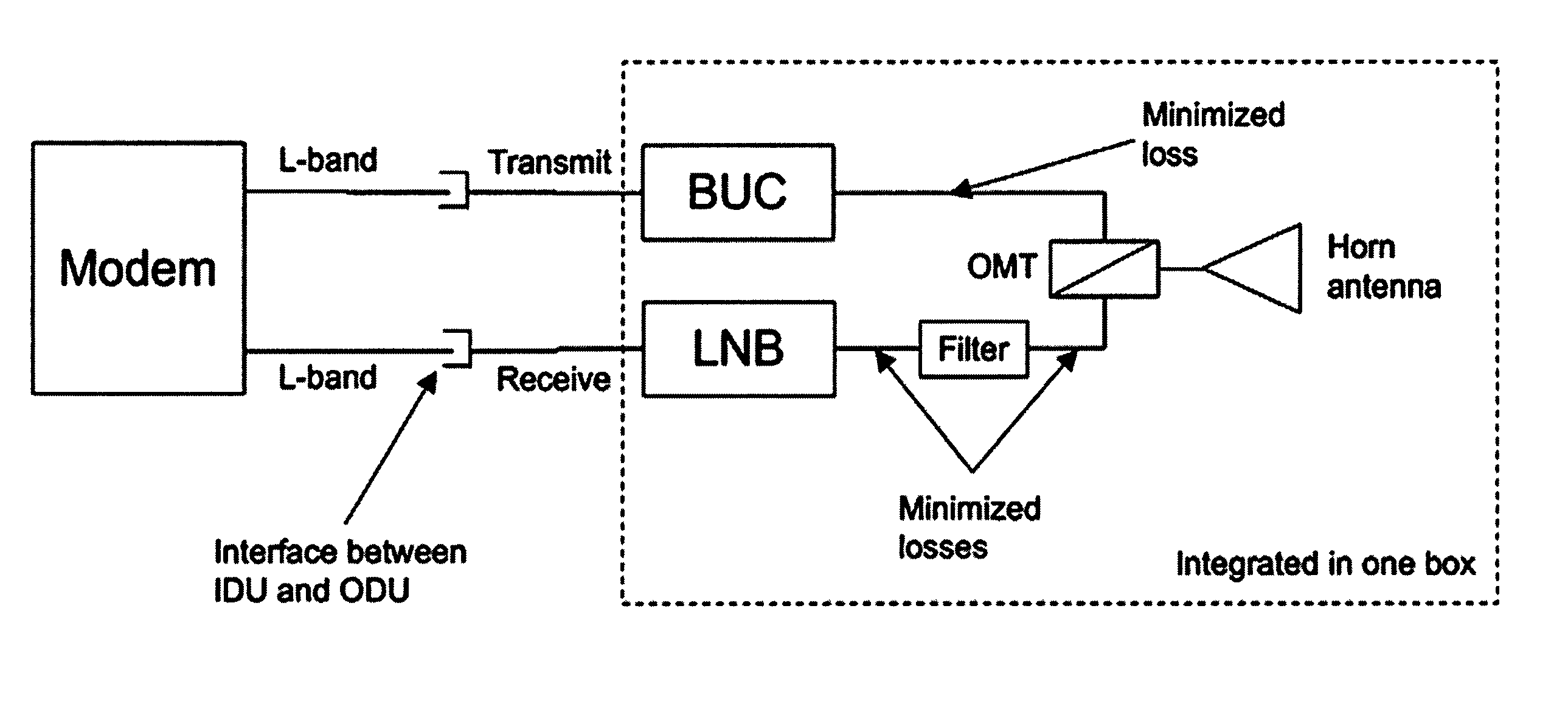
ActiveUS20100207834A1Improve robustnessSimple handlingWaveguide hornsAntenna arraysGeosynchronous satelliteRemote computer
A small antenna system for communications on-the-move (“COTM”) with a geostationary or geosynchronous satellite to and from a land mobile, maritime or airborne vehicle is disclosed. The antenna system provides a robust and simple means of establishing communications with a satellite or remote computer device. Further embodiments of systems and methods of the various aspects of the present invention mitigate RF losses customary in existing horn antennas. Embodiments also facilitate COTM by utilizing novel antenna configurations that tightly integrate RF electronics while dissipating generated heat via an antenna compartment that may be designed to function as or be used in conjunction with a heat sink.
Owner:OVZON SWEDEN AB
Method and apparatus for time or frequency synchronization in non-geosynchronous satellite communication systems
Method and apparatus for time or frequency synchronization of radio signals transmitted by user terminals in communication with a gateway through a satellite is provided. The satellite may be part of a non-synchronous satellite communication system, such as a low-earth orbit (LEO) satellite communication system for data, voice or video communications. Times of transmission of return link radio signals from the user terminals may be adjusted such that the signals arrive at the satellite or at the gateway without large time delay differentials. Carrier frequencies of return link radio signals transmitted from the user terminals may be adjusted such that the signals arrive at the satellite or at the gateway without large frequency offset differentials.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Geosynchronous satellite constellation
A satellite communications system is described for increasing capacity through spectrum reuse by multiple satellites. The system includes a constellation of satellites traveling in a geosynchronous orbit, where the geosynchronous orbit defines a satellite track. The satellite track of the constellation overlaps a geostationary orbital location occupied by a legacy satellite traveling in a geostationary orbit. To prevent interference between the co-located constellation and legacy satellite, each of the constellation satellites operates in a silent mode when traveling within an interference beam width of a ground terminal in communication with the legacy satellite. Once outside of the interference beam width, the constellation satellites return to an active mode of operation.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Portable antenna positioner apparatus and method
ActiveUS20050248498A1Easy to carrySimple and automated setupPivotable antennasAntenna supports/mountingsHard disc driveGeosynchronous satellite
Embodiments of the portable antenna positioner described provide a lightweight, collapsible and rugged antenna positioner for use in receiving low earth orbit, geostationary and geosynchronous satellite transmissions. By collapsing the antenna positioner, it may be readily carried by one person or shipped in a compact container. The antenna positioner may be used in remote locations with simple or automated setup and orientation. In order to operate the apparatus, azimuth is adjusted by rotating an antenna in relation to a positioner base and elevation is adjusted by rotating an elevation motor coupled with the antenna. The apparatus may update ephemeris data via satellite, may comprise a built-in receiver and may couple with a second positioner base comprising cryptographic, router or power functionality. The apparatus may comprise storage devices such as a hard drive or flash disk for storing data to and from at least one satellite.
Owner:AQYR TECH INC
Aircraft bird strike avoidance method and apparatus
A non-scanning radar system is installed on an aircraft to detect and avoid bird strikes or collisions with other airborne hazards. Target amplitude, range, and Doppler tracking versus time are used to qualify the collision threat. Avoidance is based on a quick minor altitude change by the pilot or autopilot to exit the imminent bird or other airborne hazard altitude window. In one embodiment, a bistatic passive radar receiver antenna is used in conjunction with an existing geostationary satellite signal. Range and Doppler information are obtained via cross correlation processing of the hazard reflection signal with a direct path reference signal from the satellite.
Owner:PIESINGER GREGORY HUBERT
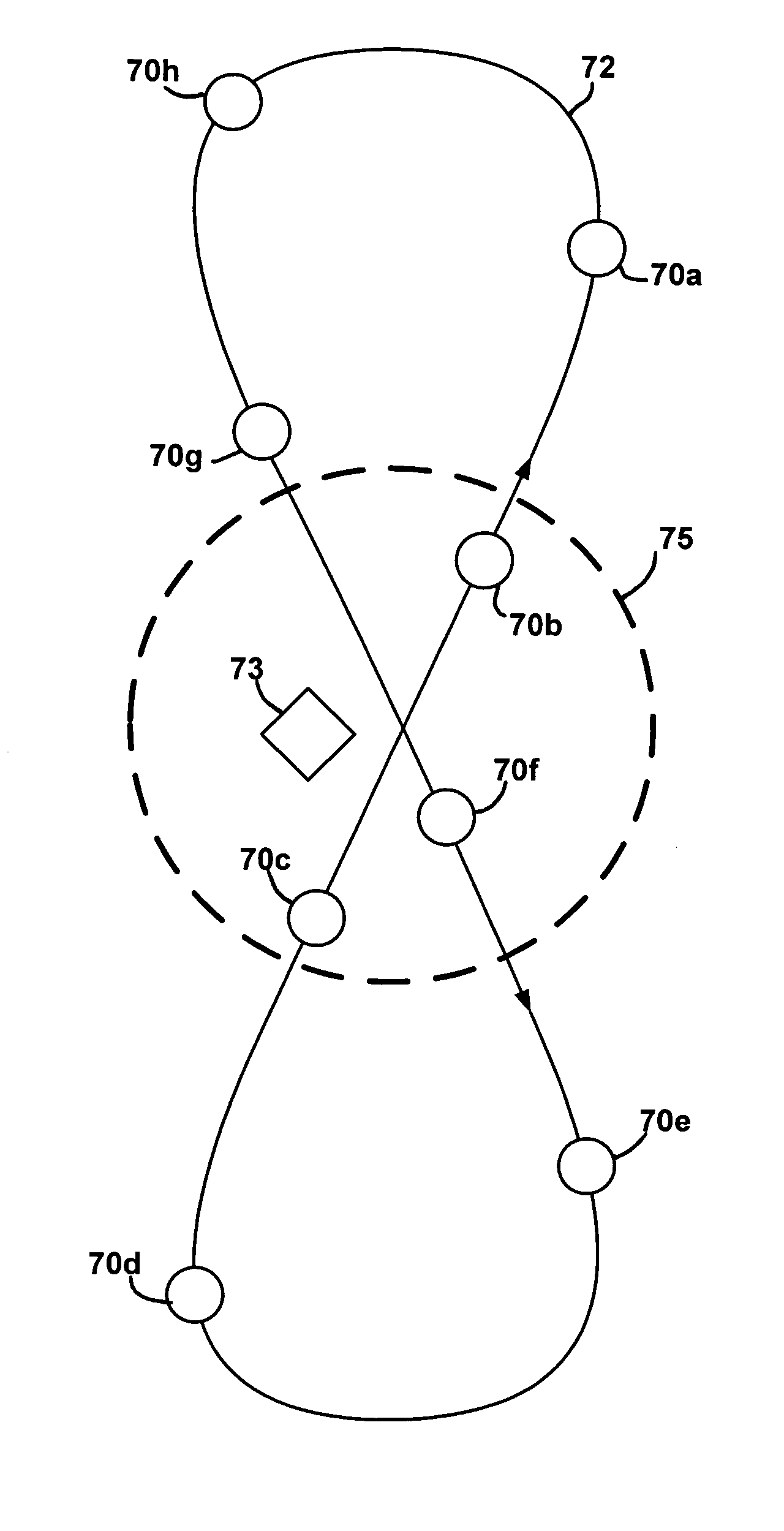
Inclined orbit satellite communication system
InactiveUS20130062471A1Artificial satellitesSpacecraft guiding apparatusCommunications systemGeosynchronous satellite
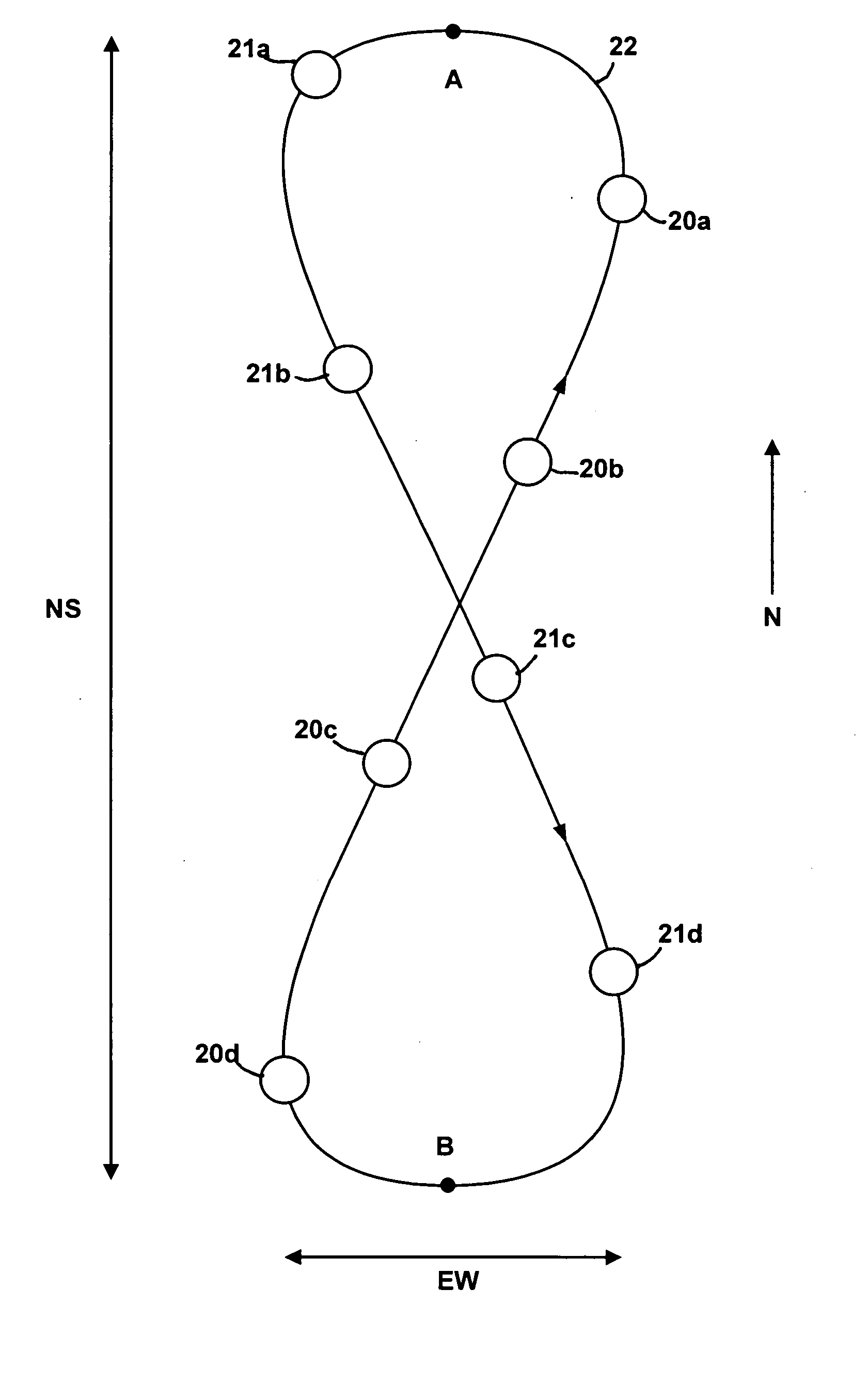
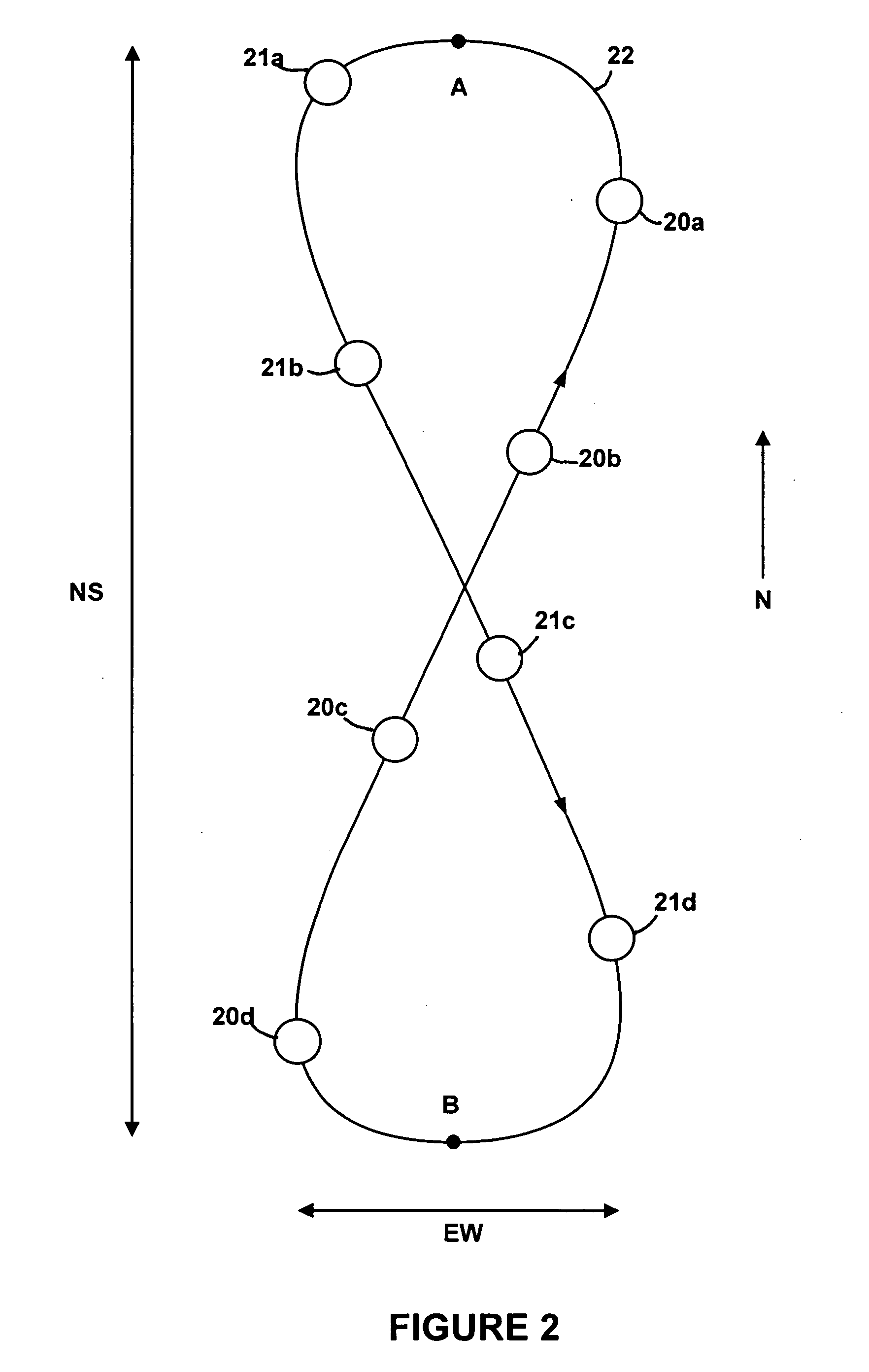
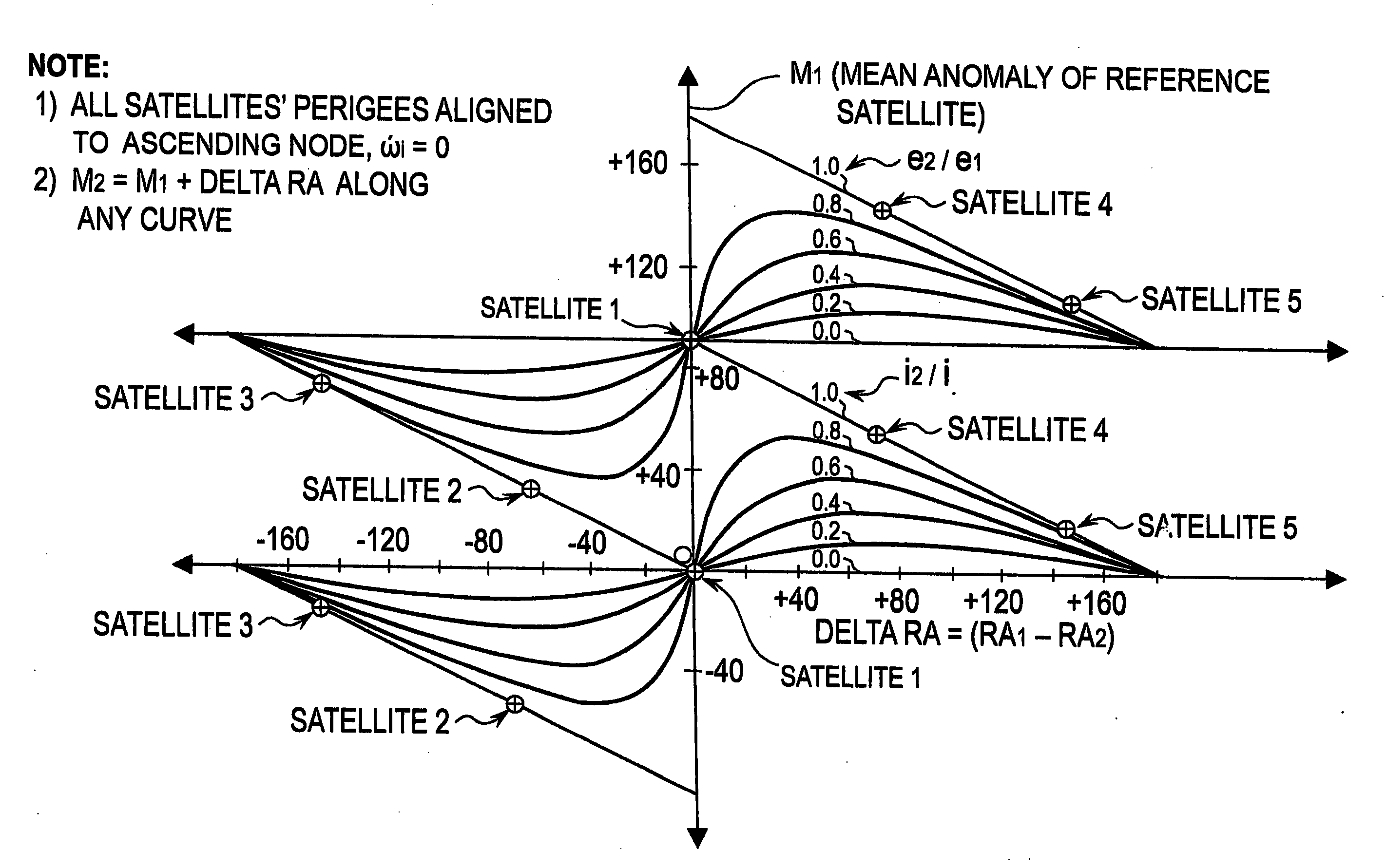
A method of flying a constellation of inclined geosynchronous satellites at the same station longitude with specific spacing but without the possibility of collision and provides the basic equations defining the initial positions of satellites such that the satellites will continue to remain in synchronized positions relative to each other for a number of years with little or no north-south positioning. In preferred embodiments the number of satellites in the constellation is five or ten. Communication with the satellites in the constellation is provided with existing prior art tracking radio systems.
Owner:LIM WAH L +1
Free return lunar flyby transfer method for geosynchronous satellites havint multiple perilune stages
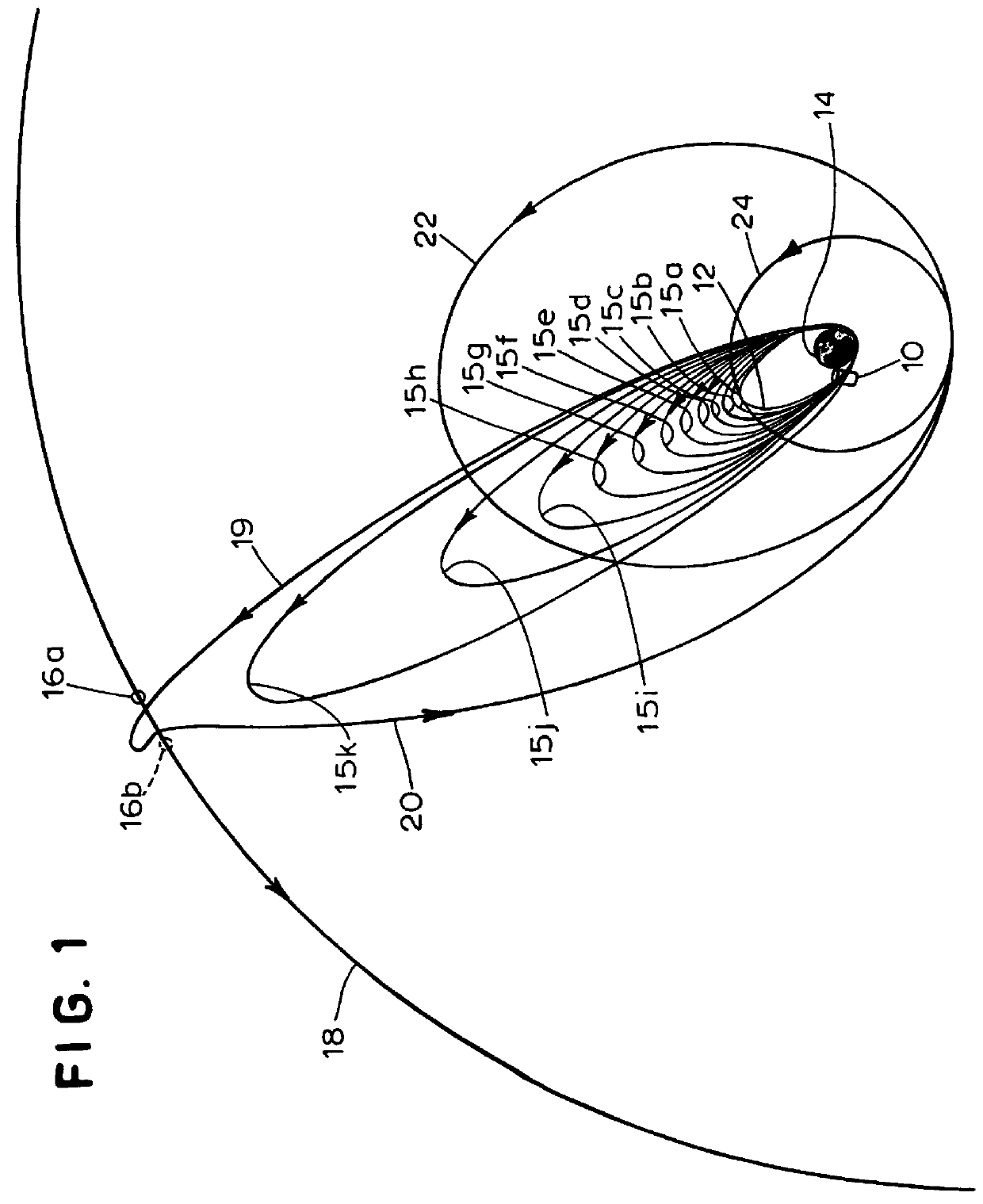
InactiveUS6149103ALaunch systemsInstruments for comonautical navigationLeading edgeGeosynchronous satellite
A method is provided for using at least two lunar flyby maneuvers to transfer a satellite from a quasi-geosynchronous transfer orbit having a high inclination to a final geosynchronous orbit having a low inclination. The invention may be used to take the inclination of a final geosynchronous orbit of a satellite to zero, through the use of a first leading-edge lunar flyby and subsequent successive leading or trailing edge lunar flybys resulting in a geostationary orbit.
Owner:HUGHES ELECTRONICS
Low earth orbit satellite constellation system for communications with re-use of geostationary satellite spectrum
ActiveUS20180343055A1Improve isolationCosmonautic partsNetwork topologiesCommunications systemFrequency spectrum
Owner:THEIA GRP INC
Free return lunar flyby transfer method for geosynchronous satellites
A method is provided for using a lunar flyby maneuver to transfer a satellite from a quasi-geosynchronous transfer orbit having a high inclination to a final geosynchronous orbit having a low inclination. The invention may be used to take the inclination of a final geosynchronous orbit of a satellite to zero, resulting in a geostationary orbit, provided that the satellite is launched in March or September.
Owner:HUGHES ELECTRONICS
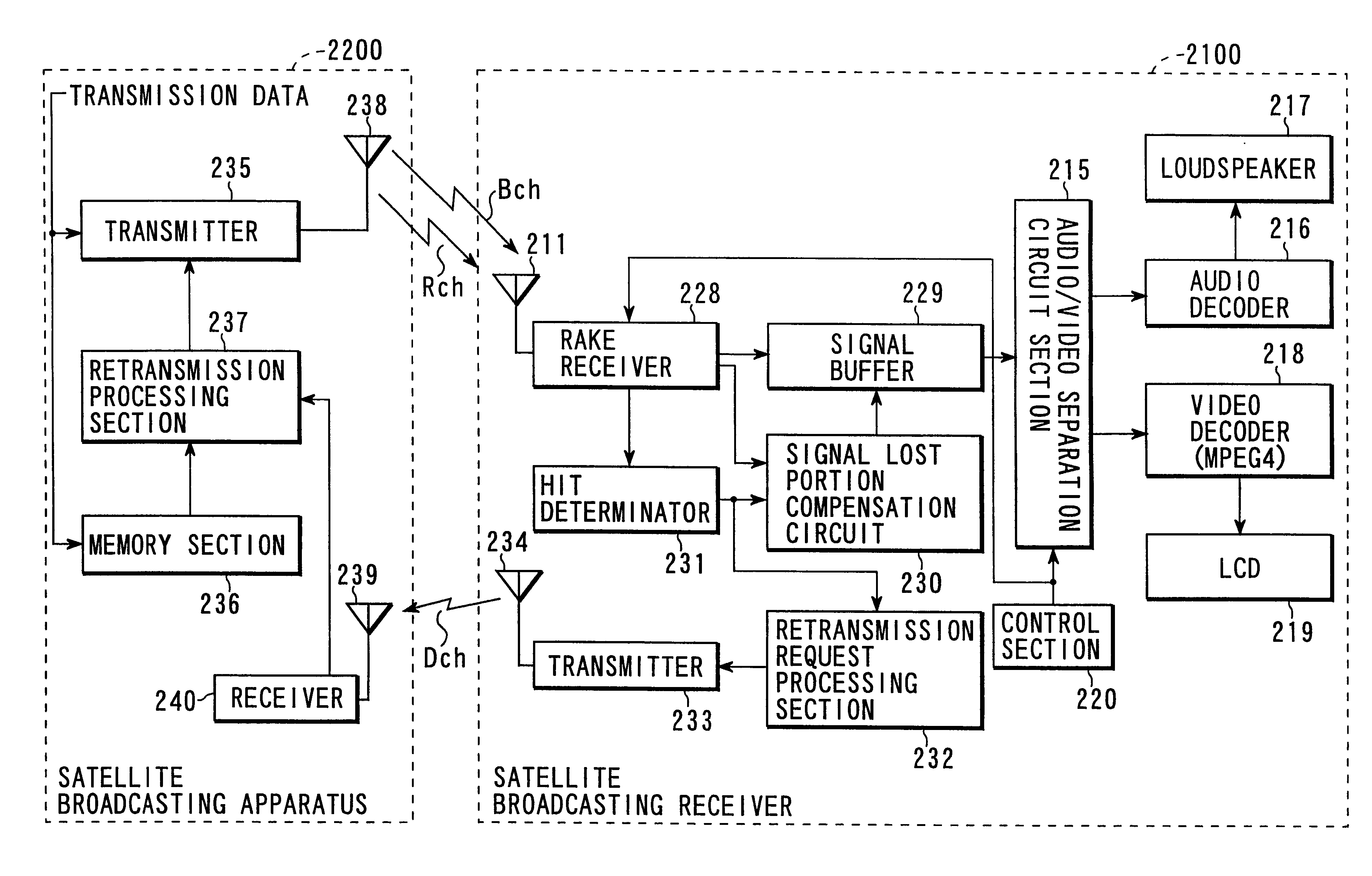
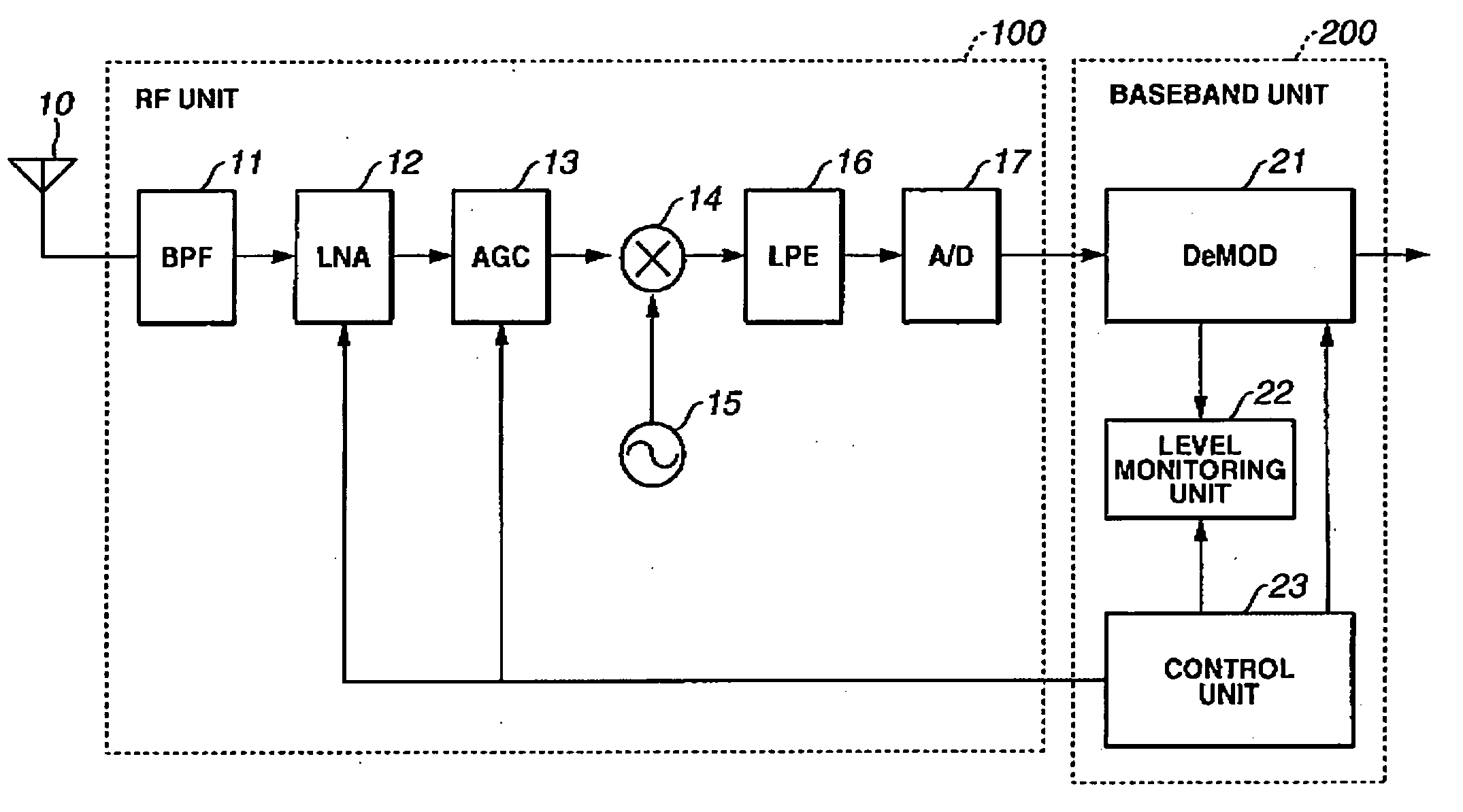
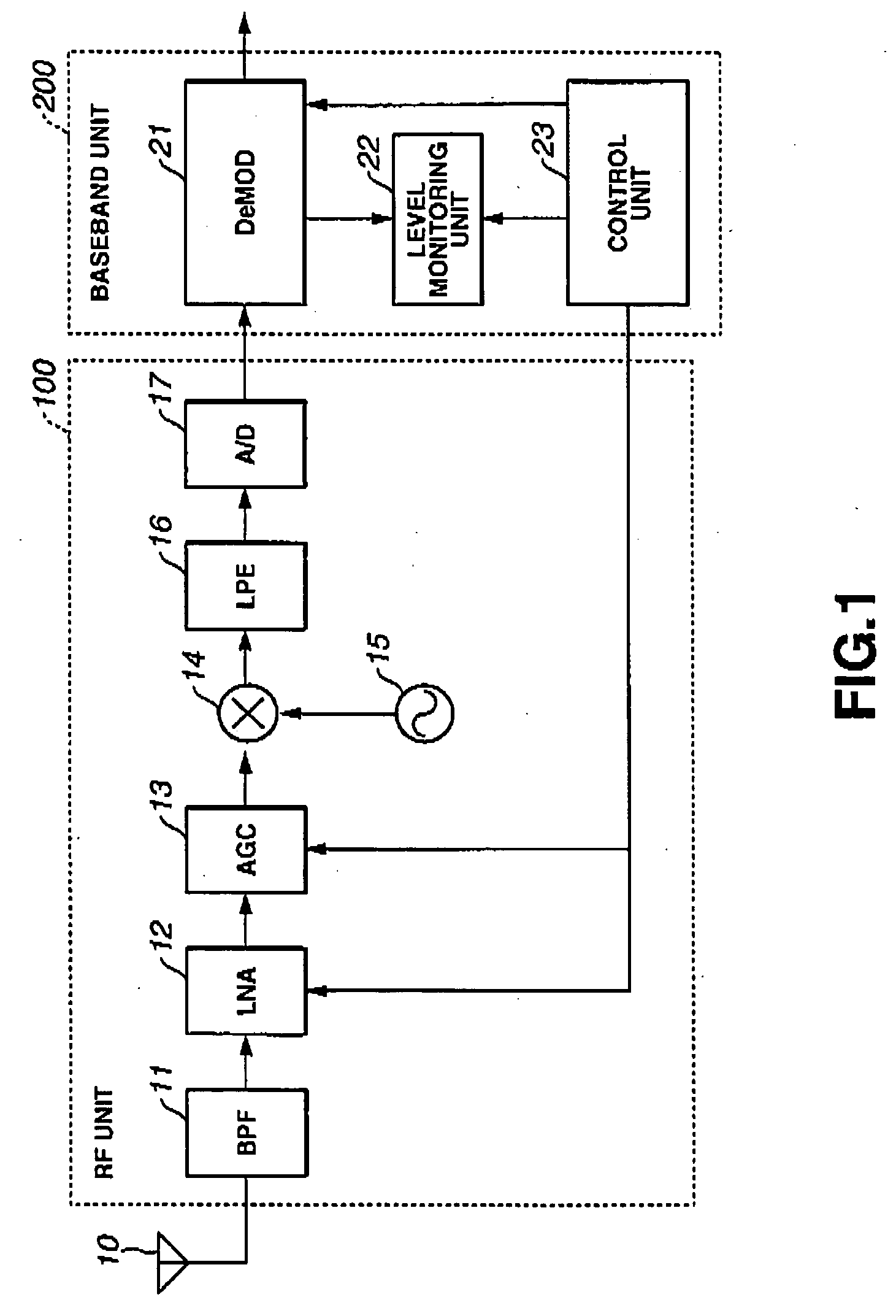
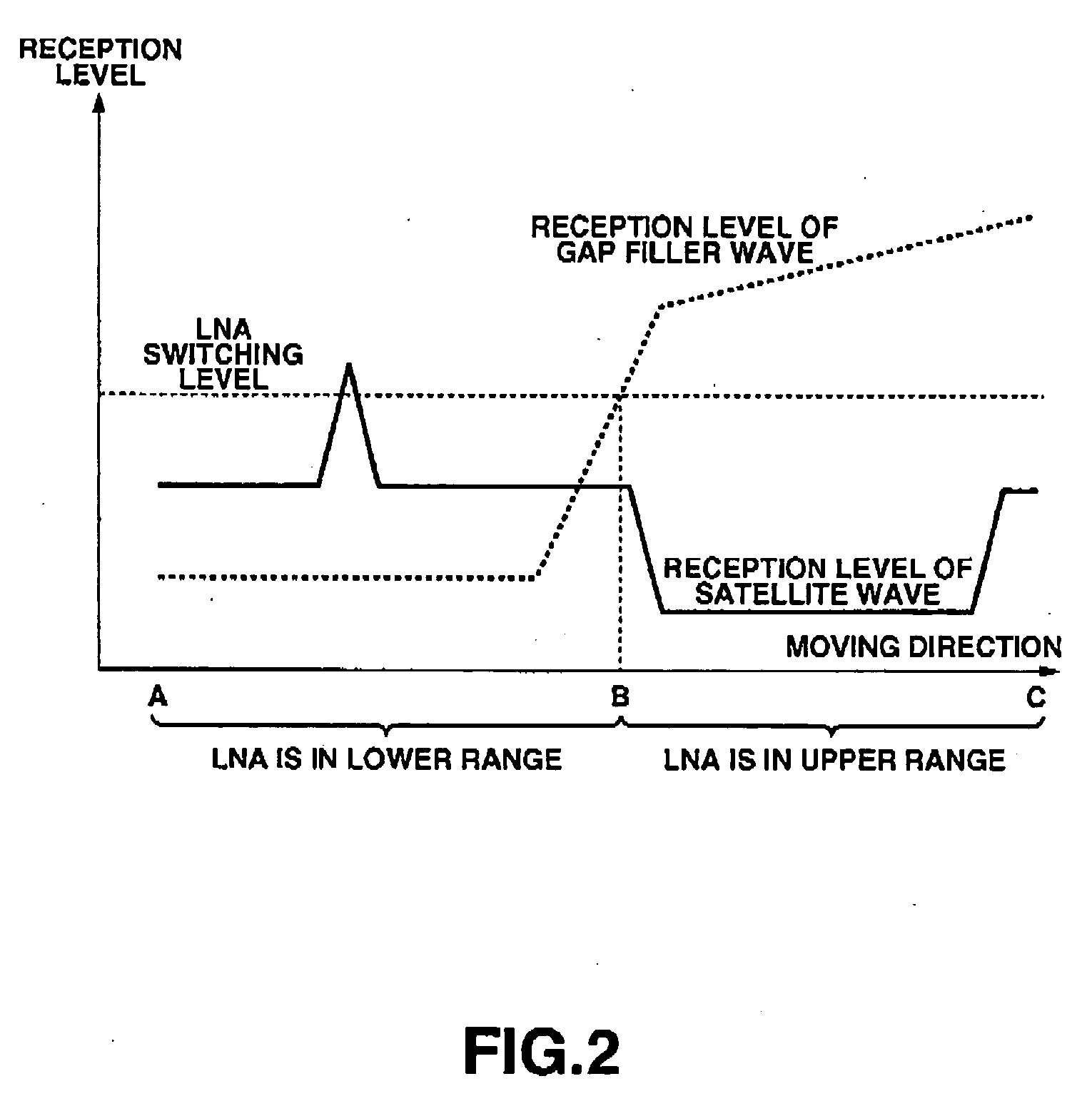
Mobile broadcast receiving apparatus and control method therefor
InactiveUS20060217059A1StablyPromote recoverySatellite broadcast receivingSpatial transmit diversityGeosynchronous satelliteMethod selection
A mobile broadcast receiving apparatus capable of stably receiving mobile broadcasting even with rapid variation in a reception level and yet capable of reducing the power consumption and a control method for such apparatus are provided. The mobile broadcast receiving apparatus, which selectively receives a broadcast radio wave from a geostationary satellite or a radio wave retransmitted from a gap filler, controls switching of at least one of a dynamic range of a low noise amplifier (LNA), a time constant of an automatic gain control circuit (AGC), and ON / OFF of an antenna diversity, according to a reception status of the mobile broadcast receiving apparatus.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Low earth orbit satellite constellation system for communications with re-use of geostationary satellite spectrum
ActiveCN109417827AWon't interfereInterference Prevention or MinimizationCosmonautic partsNetwork topologiesInterference (communication)Communications system
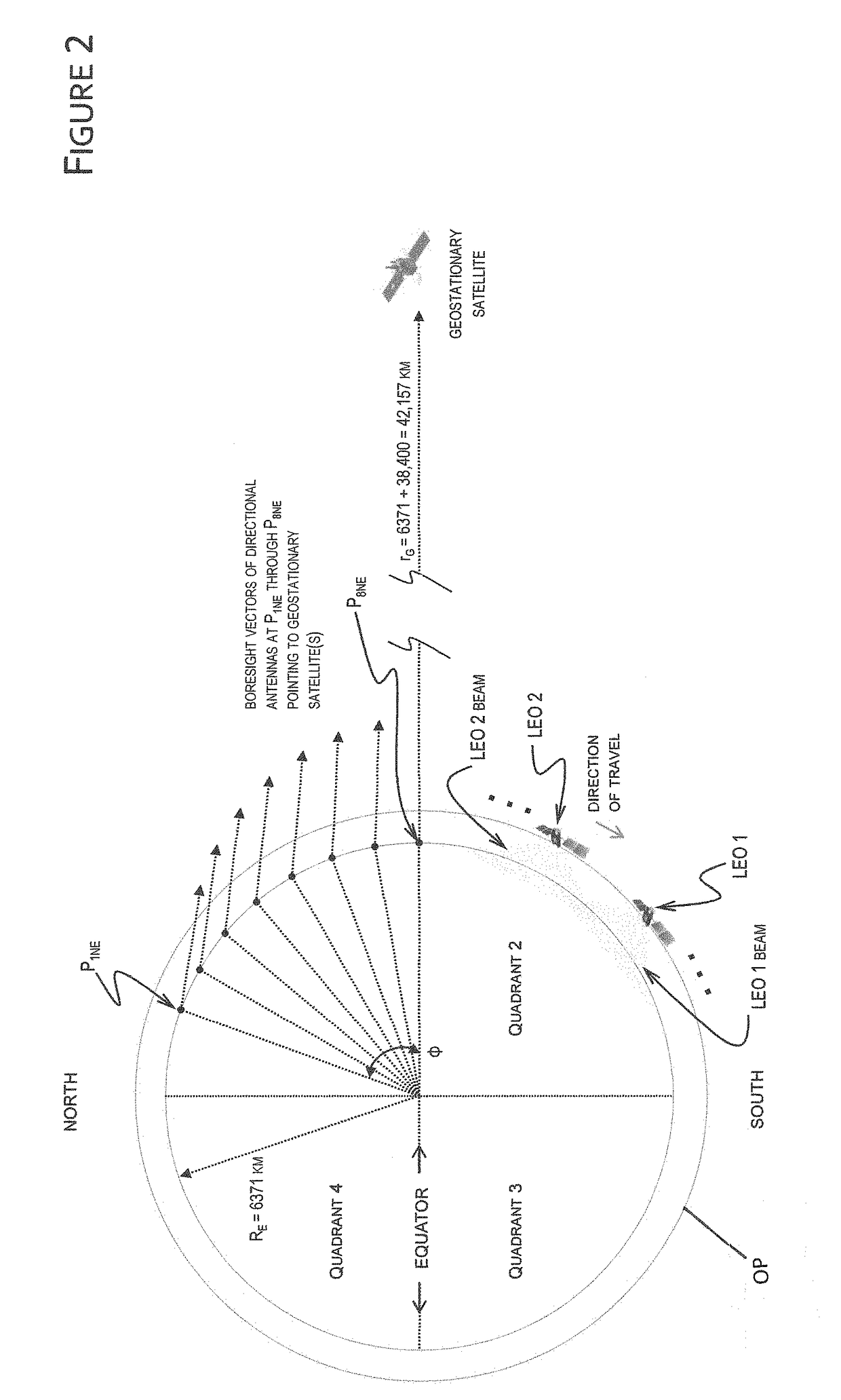
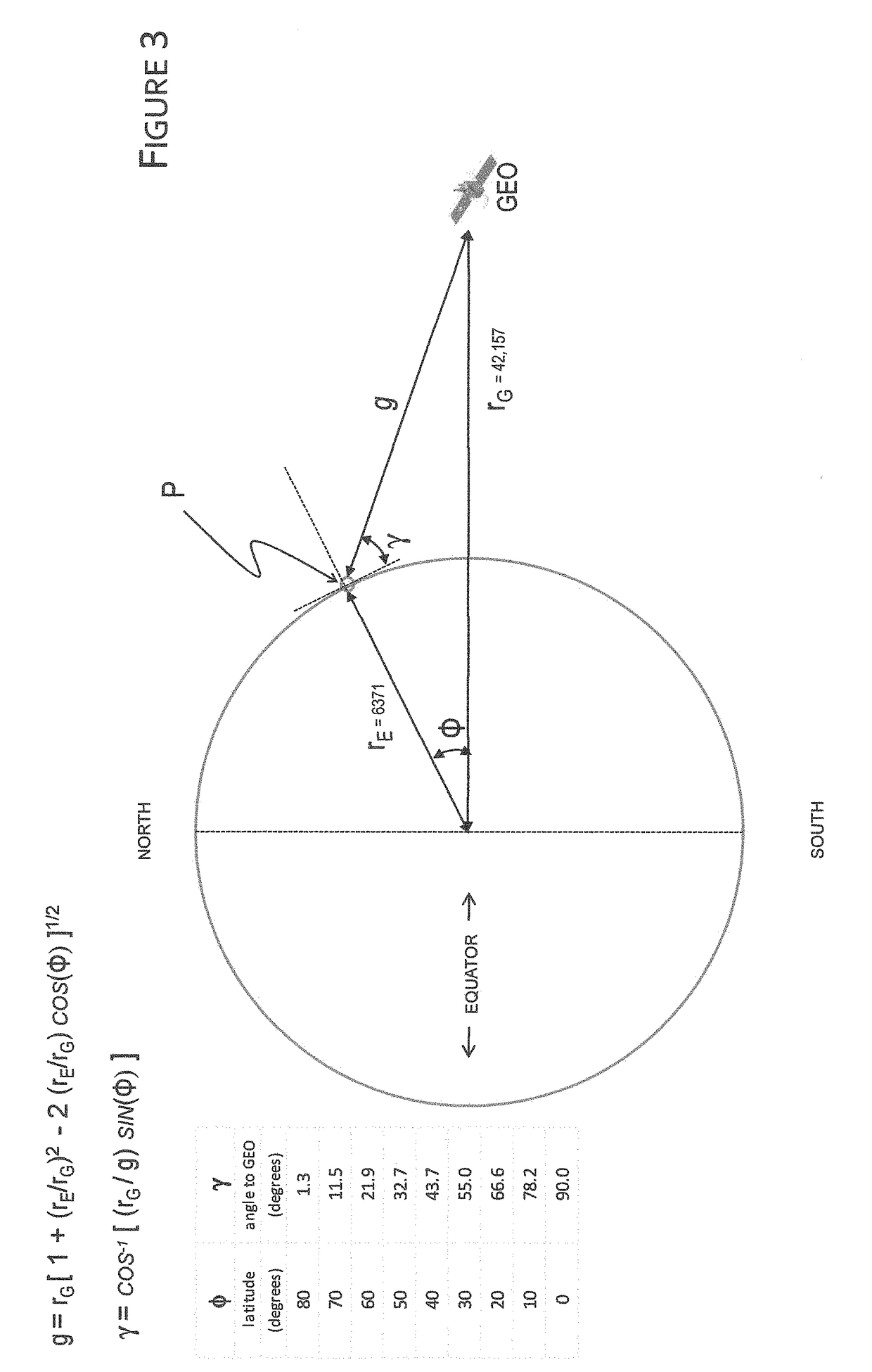
A system for re-using GEO-allocated communications spectrum in a LEO satellite constellation based communications system, such that the LEO satellite originated signals will not appear in the beam-width of GEO-pointed earth station antennas, and satellites configured to provide communications by manipulating their respective beam transmissions, which may include a forward beam and rearward beam whose angles are controlled to project the beam and reduce or eliminate the potential for interference with GEO-pointed earth station antennas. The system and LEO satellites may provide substantially 100% coverage of an earth station located anywhere on the surface of the earth, without coordination with the GEO satellites or GEO-pointing ground stations. The system also may provide earth stations that are configured to enhance the isolation between the GEO communications system and the LEO communications system using the same spectrum to reduce the potential for GEO-pointed earth station antennas from picking up the LEO communication.
Owner:THEIA GRP INC
Antenna system for communications on-the-move
ActiveUS8248318B2Improve robustnessSimple handlingAntenna arraysAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesGeosynchronous satelliteRemote computer
Owner:OVZON SWEDEN AB
Orbit determination method for geostationary satellite adapting to orbital maneuver
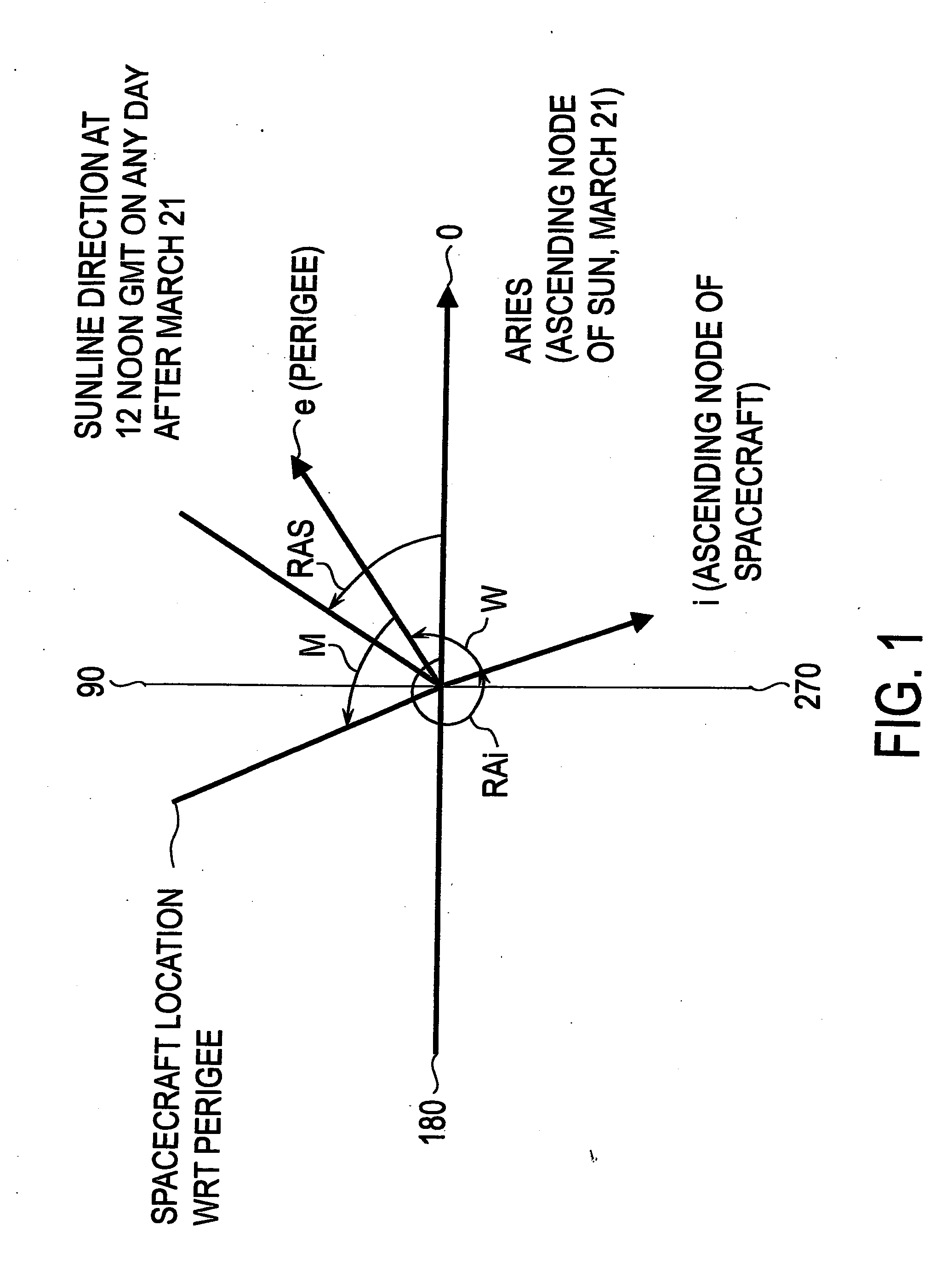
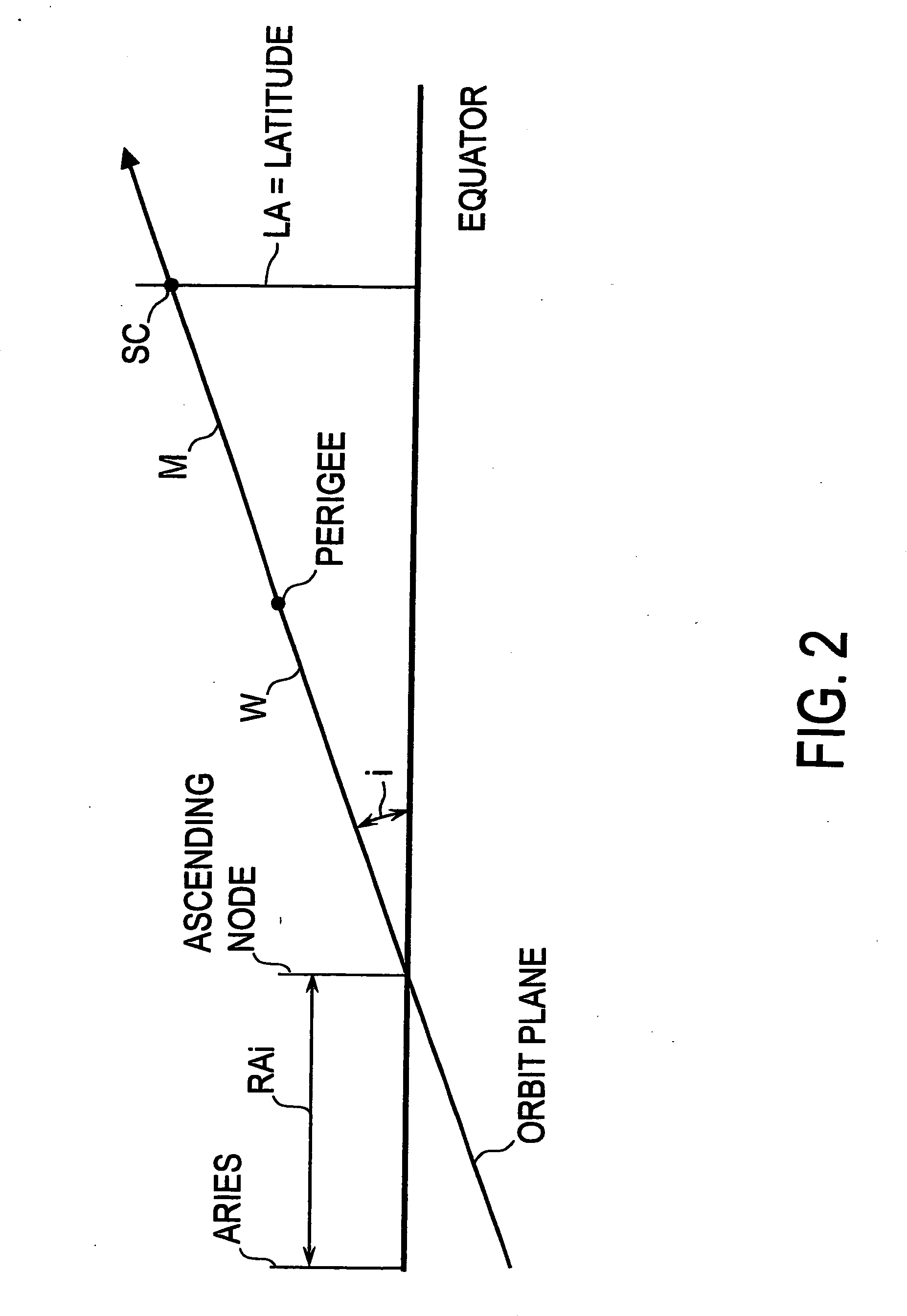
ActiveCN103424116ASolve the difficulties caused by determiningAvoid difficultiesInstruments for comonautical navigationGeosynchronous satelliteSystematic deviation
The invention discloses a precision orbit determination method for a geostationary satellite adapting to orbital maneuver and belongs to the field of space metering and controlling. The method comprises the followings: firstly, maneuvering acceleration is calculated; observed quantity Rho i and observed residual error sequences delta Rho i and j are calculated; estimation to public system error Rho b is performed; the public system error Rho b is deducted from the observed residual error sequences delta Rho i and j, so as to obtain systematic deviations of all observation stations; the Rho b is deducted from the observed quantity, then orbit improvement is performed again on observation data of which system errors are deducted, and calculating is performed again on the improved initial state until orbit convergence, and precision orbit determination for the geostationary satellite is accomplished. The precision orbit determination method provided by the invention has the benefits as follows: difficulty in precision orbit determination caused by pushing force produced by air blast of an engine on a GEO satellite during orbital maneuver can be overcome, meanwhile, public systematic error appraisement and an all-station deviation adapting iteration eliminating method are adopted for solving the problem that systematic errors such as satellite clock errors and time delay of all observation station equipment are hard to separate is solved, and the orbit determination forecast accuracy of the GEO satellite during the orbital maneuver can be effectively improved.
Owner:CHINA XIAN SATELLITE CONTROL CENT
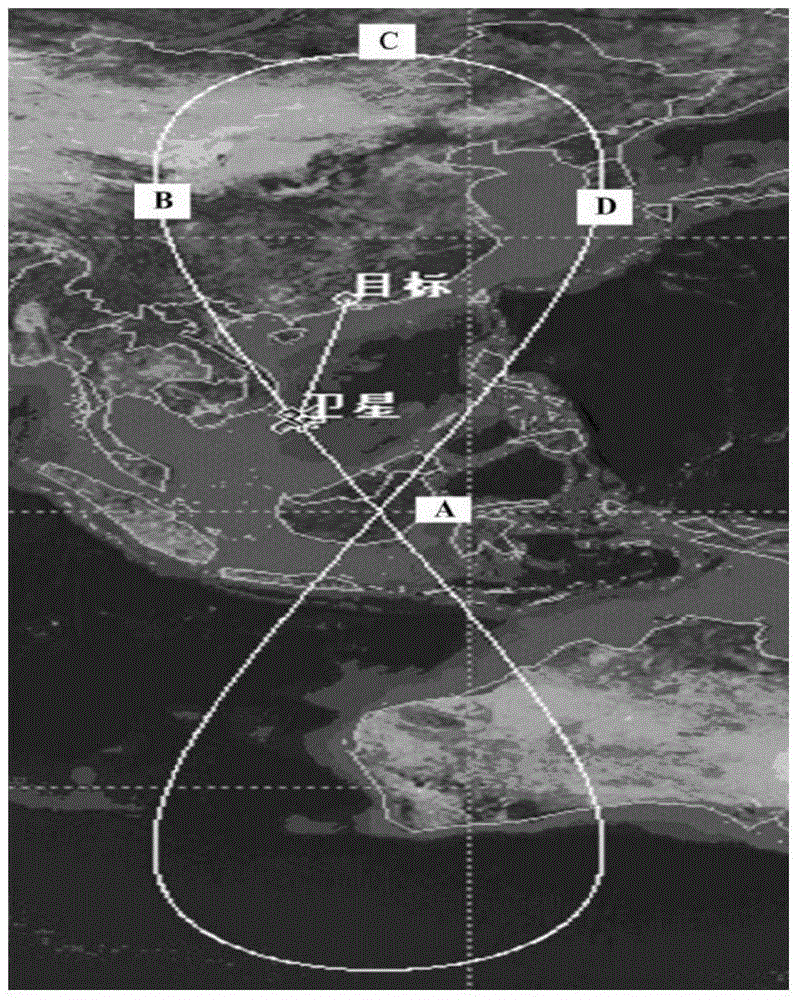
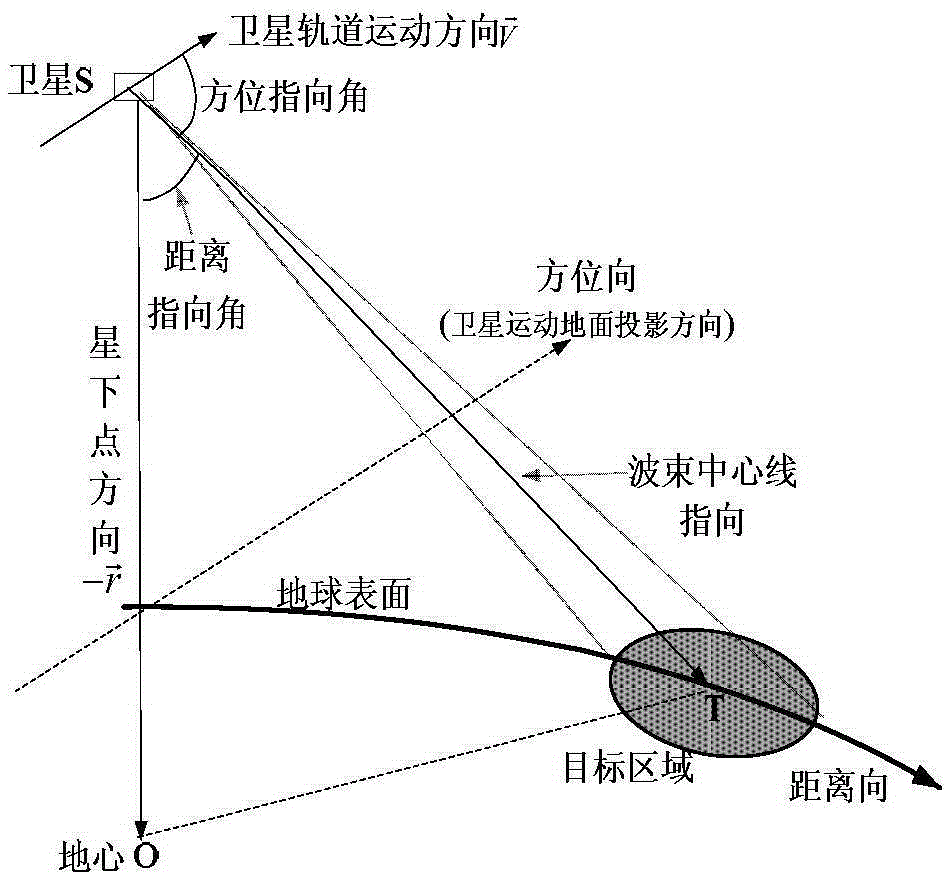
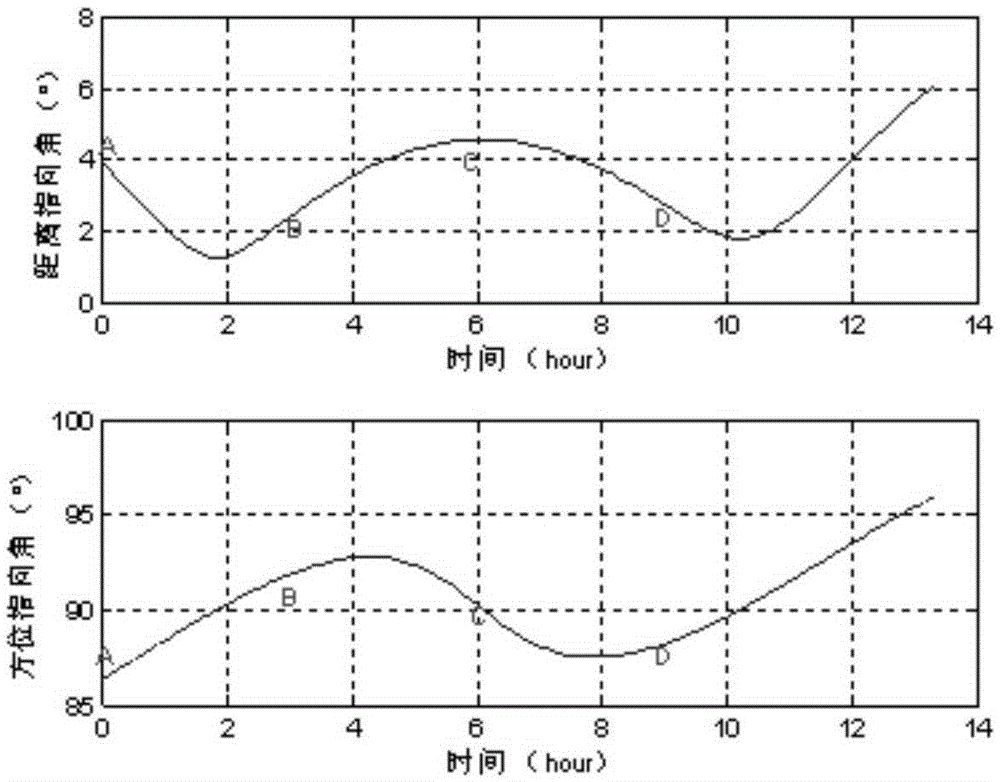
Geosynchronous orbit circular track SAR imaging method using beam pointing control
InactiveCN105403888AEasy to handleSmall height changeRadio wave reradiation/reflectionGeosynchronous satelliteRadar
The invention belongs to the technical field of synthetic aperture radar and particularly relates to a geosynchronous orbit circular track SAR imaging method using beam pointing control. By using such a method, a circular track geosynchronous satellite having a 8-shaped sub satellite point locus is taken as a radar platform, 12 hours corresponding to the half 8 shape where an object to be observed is arranged are regarded as an imaging period, the two-dimension antenna wave beam directional control is carried out in the imaging period by means of a stepping technique, so that the satellite can be in the corresponding movement process of the half 8-shaped sub satellite point locus, the antenna wave beam can always point to the imaged ground object to be observed, the 360-degree relative movement of radar relative to the object is formed, and the circular track SAR imaging based on the geosynchronous orbit satellite platform is realized.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
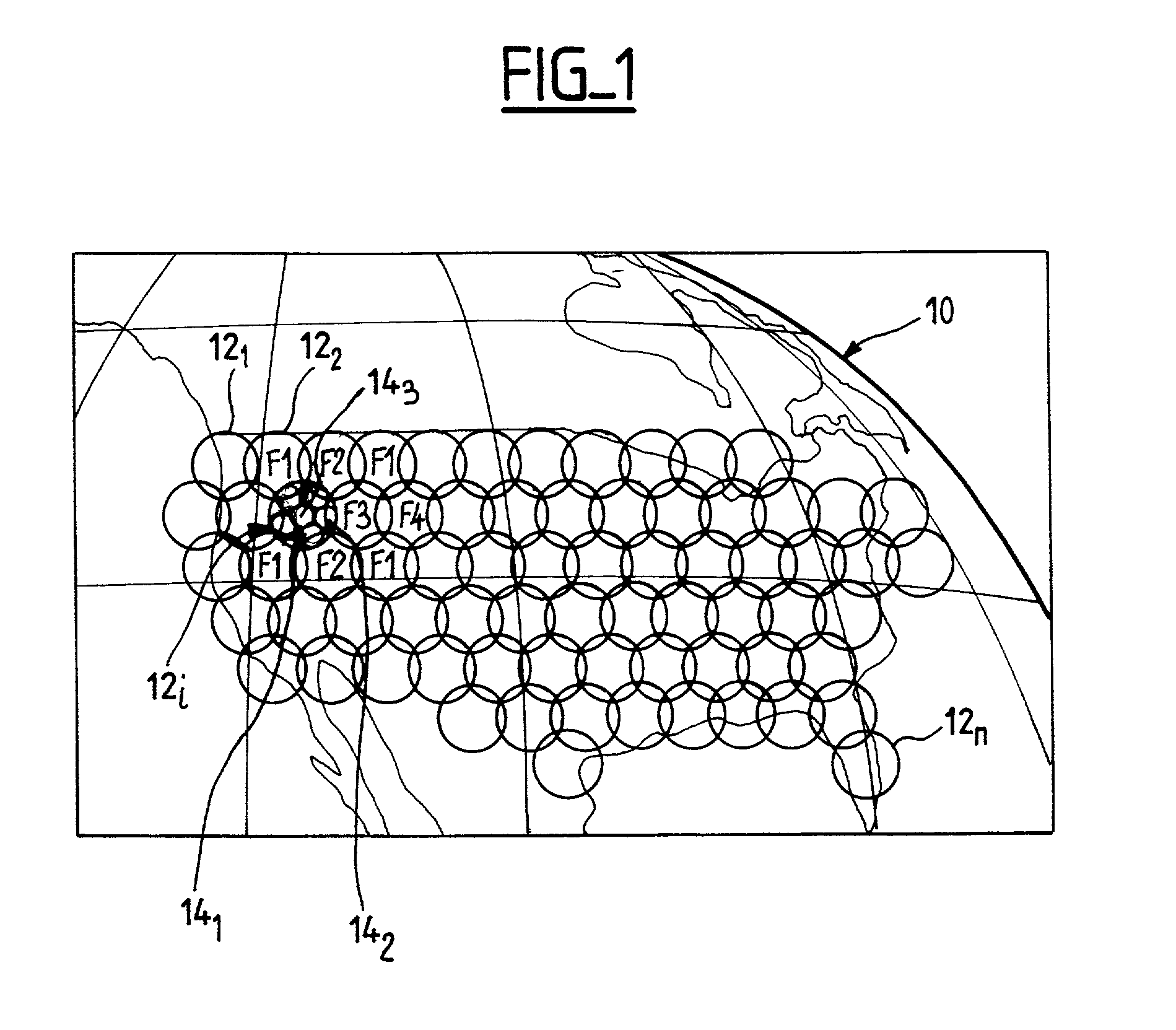
Telecommunications antenna intended to cover a large terrestrial area
InactiveUS20020005800A1Reduce in quantityEasy to controlAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesActive radio relay systemsAudio power amplifierGeosynchronous satellite
The invention relates to a receive (or send) antenna for a geosynchronous satellite of a telecommunications system intended to cover a territory divided into areas, the beam intended for each area being defined by a plurality of radiating elements, or sources, disposed in the vicinity of the focal plane of a reflector. The antenna includes at least one first matrix each input of which is connected to a radiating element and each output (or input) of which is connected to a corresponding input of an inverse Butler matrix by an amplifier and a phase-shifter. The phase-shifters move the areas or correct pointing errors.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
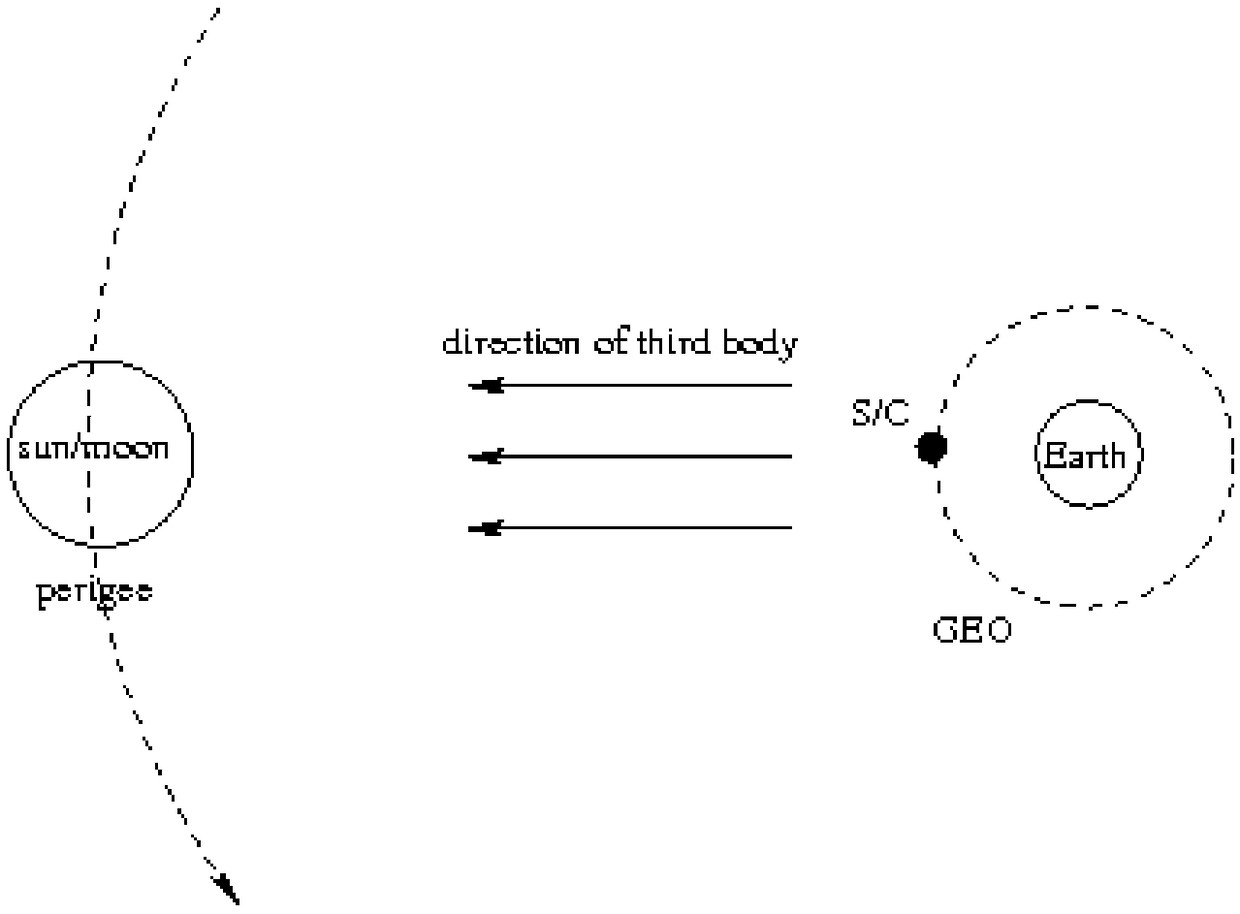
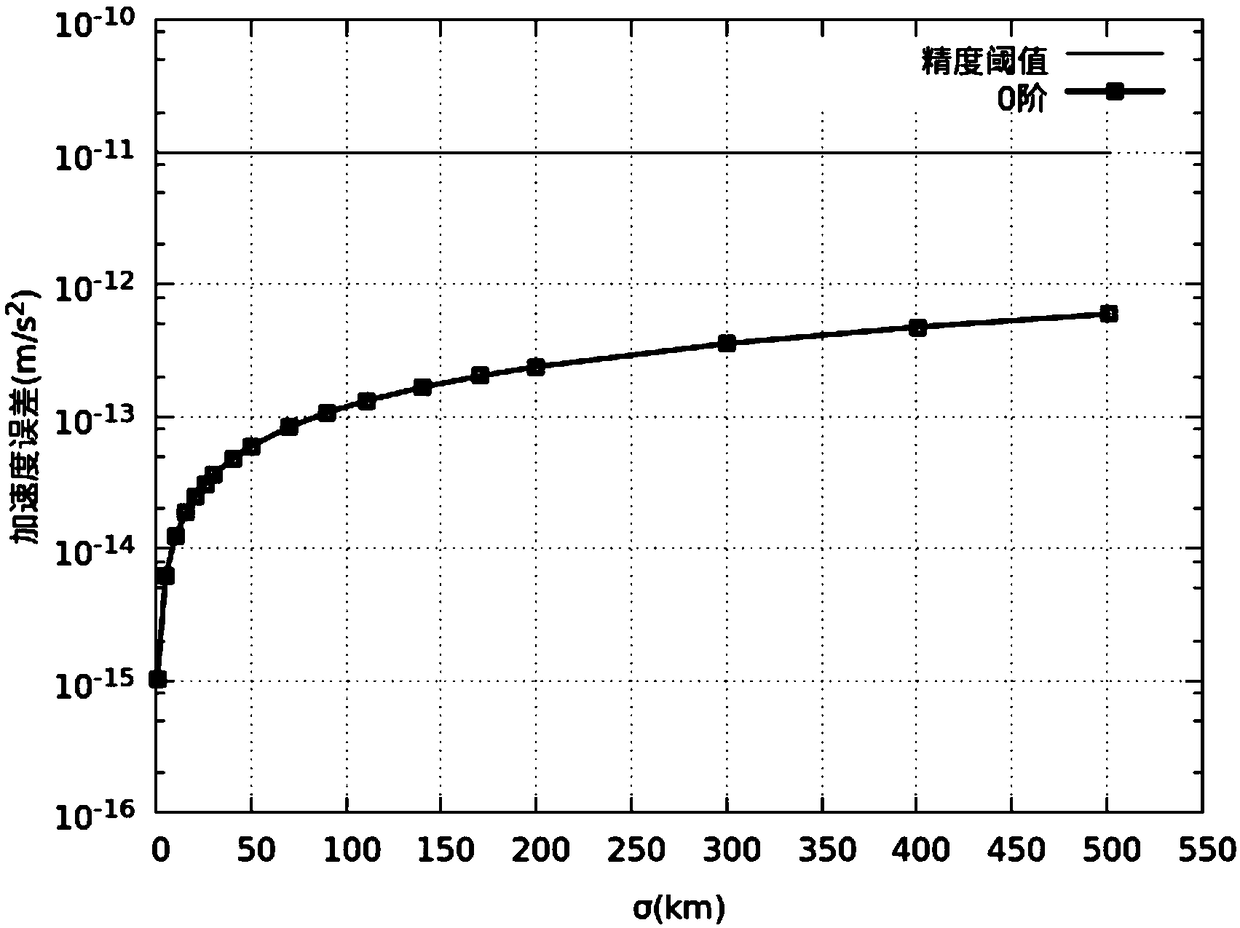
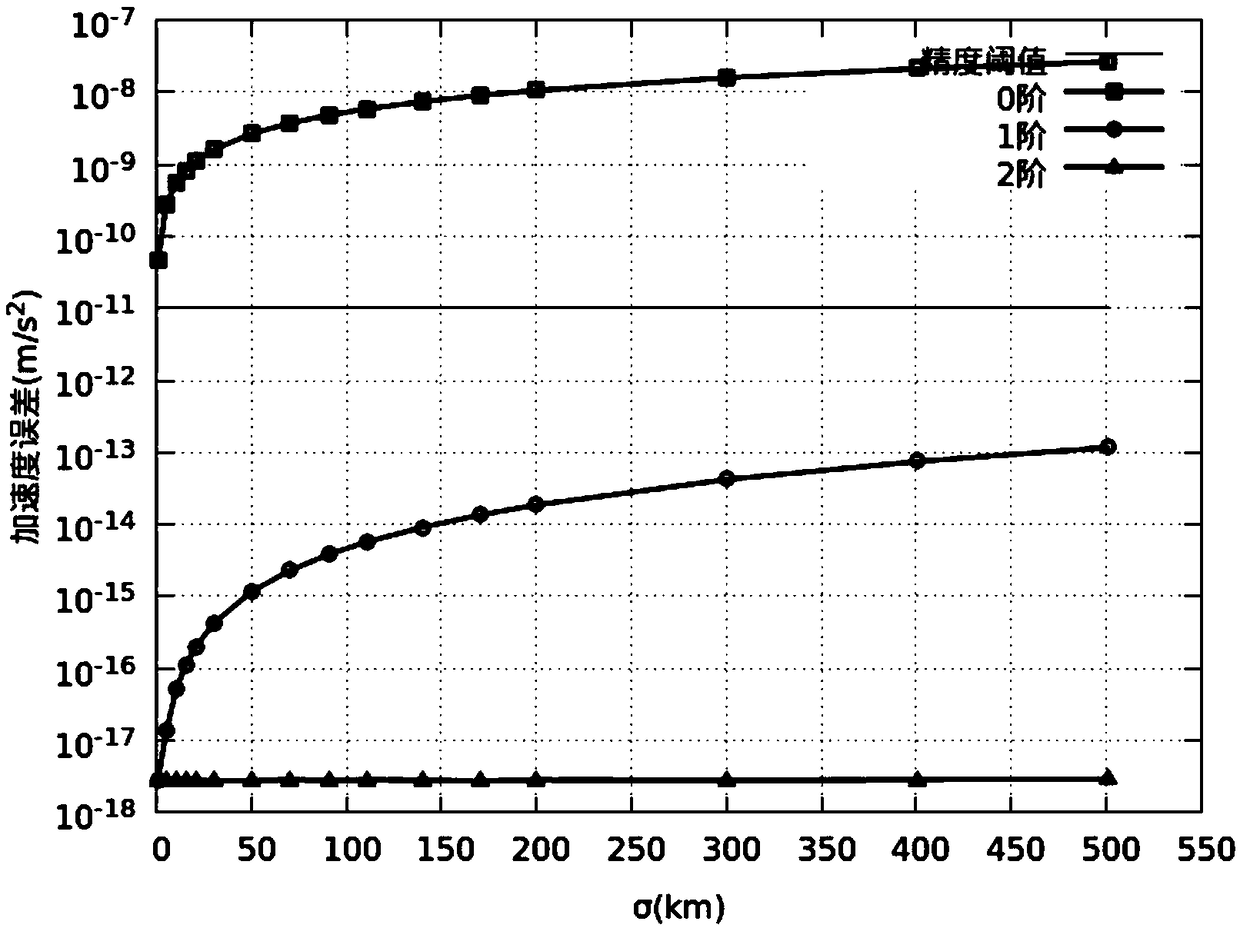
A method of geostationary satellite orbit uncertainty evolution based on differential algebra
ActiveCN109255096AReduce computing timeHigh precisionComplex mathematical operationsNatural satelliteDynamic models
The invention discloses an orbital uncertainty analysis method based on differential algebra technology. Based on Taylor expansion of multivariate functions and polynomial operation framework, and based on the dynamic model of geosynchronous satellite orbit element description, solar pressure to the kinetic model, the third gravitational perturbation and the three perturbation terms of the Earth'soblateness are added in the dynamic model , the right term of the dynamic model is expanded along the nominal orbit by Taylor expansion, the expansion polynomial with initial deviation as variable isobtained, Under the frame of differential algebra, the orbital state expressed by the polynomial with the initial deviation as variable at any time is obtained, and the concrete value of the initialdeviation is brought into the polynomial result to obtain the state of the final spacecraft. The invention analyzes the optimal expansion order, the balance calculation time and the calculation precision according to different perturbation forces. The method can be used to analyze the orbit evolution of geostationary satellites with initial state deviation and parameter uncertainty, and can also be used in other spacecraft orbit evolution and attitude evolution missions.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com