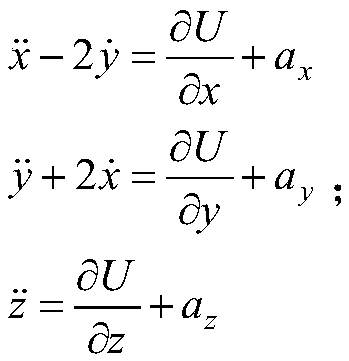Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
42 results about "Lunar orbit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In astronomy, lunar orbit (also known as a selenocentric orbit) is the orbit of an object around the Moon. As used in the space program, this refers not to the orbit of the Moon about the Earth, but to orbits by various manned or unmanned spacecraft around the Moon. The altitude at apoapsis (point farthest from the surface) for a lunar orbit is known as apolune, apocynthion, or aposelene, while the periapsis (point closest to the surface) is known as perilune, pericynthion, or periselene, from names or epithets of the moon goddess.
Geophysics-based method of locating a stationary earth object
ActiveUS7376507B1Measurement time is increasedExtension of timeInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlAccelerometerLongitude
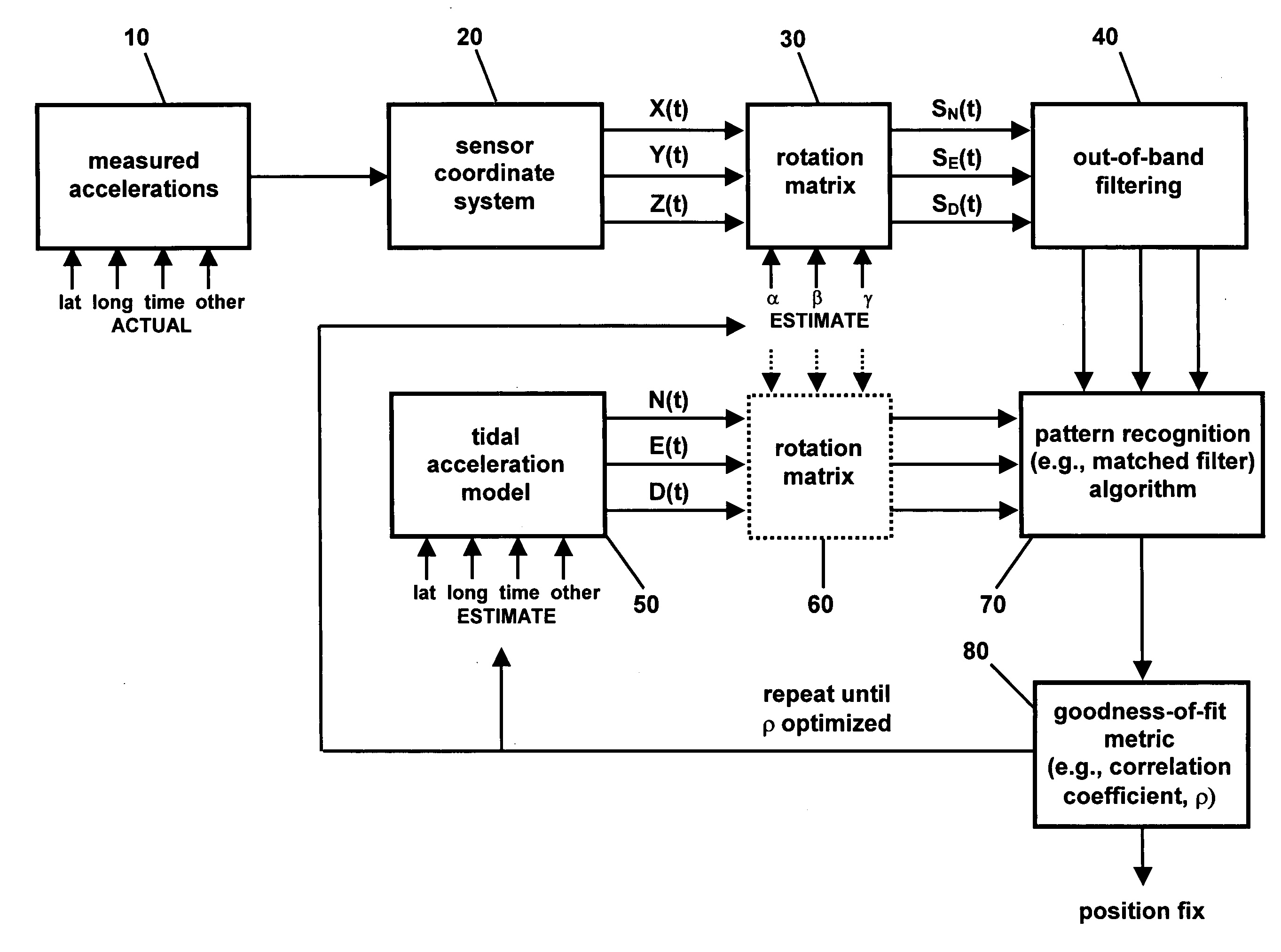
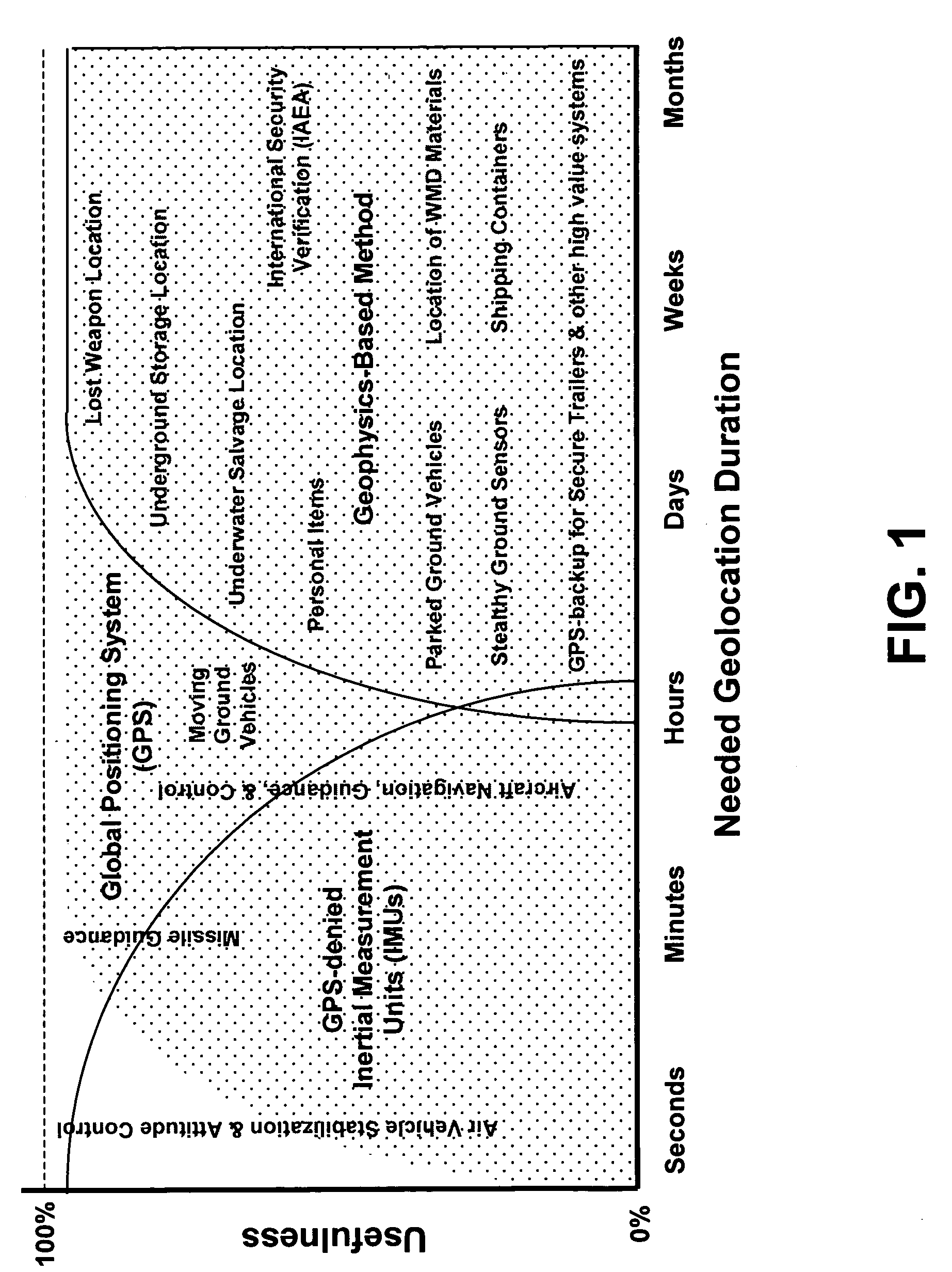
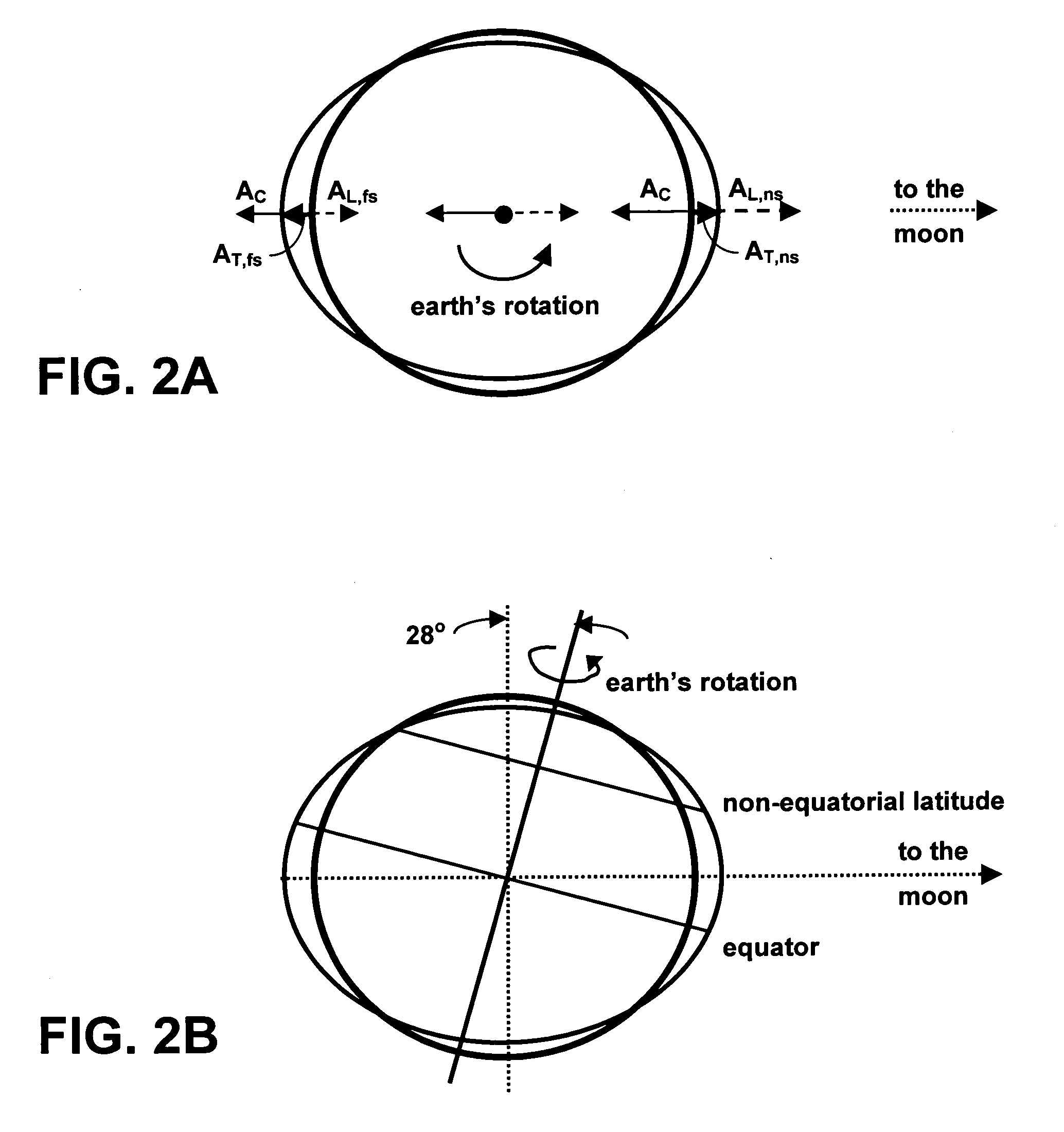
A geophysics-based method for determining the position of a stationary earth object uses the periodic changes in the gravity vector of the earth caused by the sun- and moon-orbits. Because the local gravity field is highly irregular over a global scale, a model of local tidal accelerations can be compared to actual accelerometer measurements to determine the latitude and longitude of the stationary object.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Tide predicting method
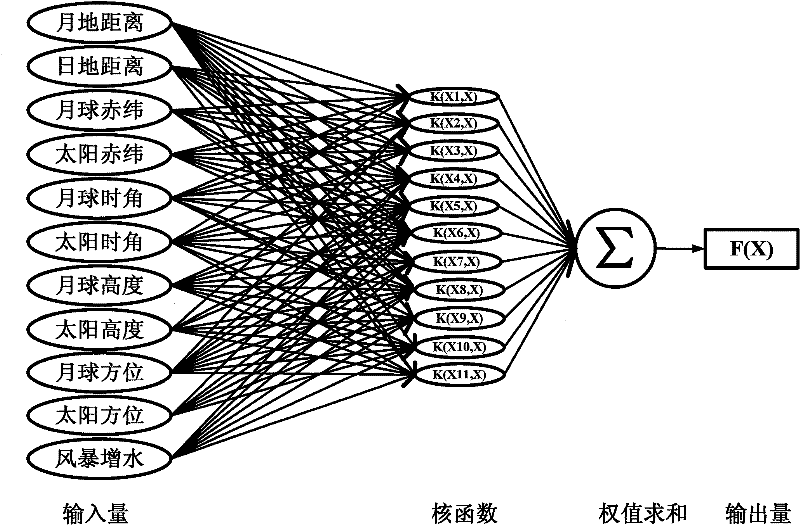
The invention relates to a tide predicting method for the tide is influenced by various factors, including cyclical factors, such as tidal generation force, and non-cyclical factors, such as wind power, atmospheric pressure, coast characteristics, rainfall, dip angles of the lunar orbit and the like. The predicting accuracy of the traditional harmonic analysis method is influenced by partial tide number, and the traditional harmonic analysis method cannot analyze the influence of non-cyclical factors; the artificial neural network method developed recent years overcomes the defect that the non-cyclical factors cannot be predicted by the harmonic analysis method to a certain extent, but has great data volume required by study training samples and wide involve range, can cover various possible conditions, but has less station historical data of non-cyclical factors. The invention provides a predict model, wherein factors which influence tide non-cyclically, such as wind directions, rainfall, storm surge, coast characteristics and the like, can be fused into the model, and small sample data can receive more accurate results. In the method, a support vector machine (SVM)-based predict model is established, wherein, an SVM toolbox is imported into MATLAB 7.8; training sample data is trained by utilizing svmtrain function; the formed model is tested by using a test sample svmpredict function; and the trained and tested data can predict the tide in the same tide test station.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
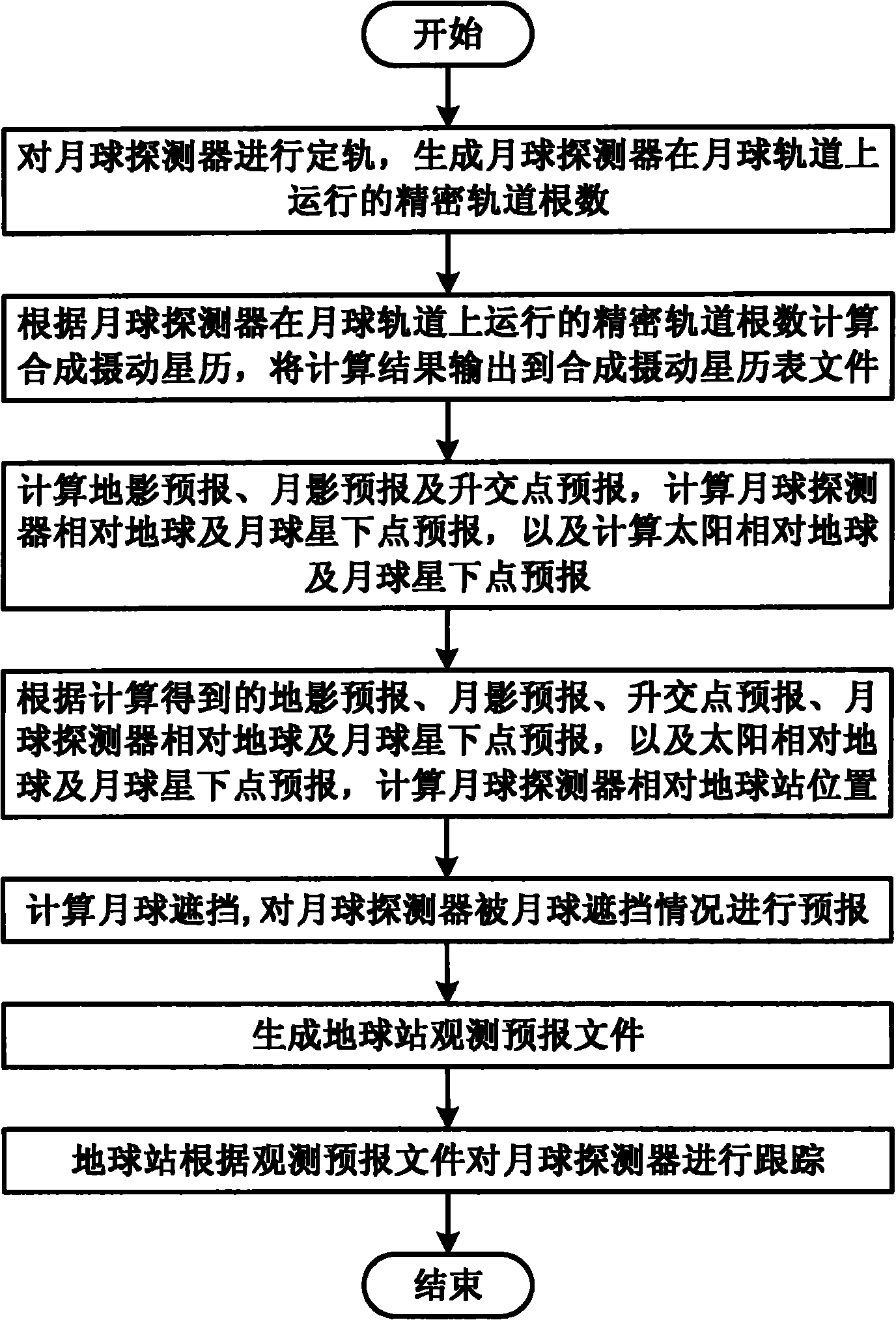
Method for tracking lunar probe by using earth station
ActiveCN101968542AImplement receipt trackingRealize precise orbit determinationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionEphemerisLunar orbit
The invention discloses a method for tracking a lunar probe by using an earth station. The method comprises the following steps of: performing orbit determination on the lunar probe to generate a precise orbital element for the lunar probe to run on a lunar orbit; calculating a synthetic perturbation ephemeris according to the precise orbital element for the lunar probe to run on the lunar orbit and outputting a calculation result to a synthetic perturbation ephemeris file; calculating earth shadow forecast, moon shadow forecast and ascending node forecast, calculating substellar point forecast of the lunar probe relative to earth and moon and calculating the substellar point forecast of the sun relative to earth and moon; calculating the position of the lunar probe relative to the earth station; calculating shelter of the moon and forecasting the condition that the lunar probe is sheltered by the moon; generating an earth station observation forecast file; and tracking the lunar probe by the earth station according to the observation forecast file. By the method, the measurement and control of the lunar probe and the receiving of probe data are tracked by using the earth station.
Owner:NAT ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORIES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method, apparatus, and system for private lunar exploration
A method of registering for private space travel to the moon, comprises providing a first spacecraft adapted to carry at least one private individual, receiving payment from the private individual for registration for a flight on the first spacecraft, providing launching of the first spacecraft from the earth carrying the private individual, and providing travel into lunar orbit for the private individual in the first spacecraft.
Owner:SPACE ADVENTURES
Method for calculating lunar orbit real-time in star
ActiveCN101226062AReduce positioning errorsInstruments for comonautical navigationOn boardRelative motion
The invention provides a method of on-board real-time calculation on circumlunar orbit, belonging to the technical field of real-time calculation on circumlunar orbit for spaceflights, comprising a plurality of steps: (1) take the orbit determination as the initial value and use numerical method to calculate the actual orbit; (2) select a two-body orbit as a reference orbit; (3) calculate the actual orbit in relation to the reference orbit trajectory; (4) according to the general law of relative movement between two two-body orbits, calculate a two-body orbit in relation to the reference orbit trajectory similar to the actual orbit in relation to the reference orbit trajectory; step (1) to step (4) are finished on Earth and then send the result on board; (5) the satellite, adopting the calculation method of two-body orbit, calculates real-time the orbit number of the satellite according to the two-body orbit calculated from the step (4). The method of on-board real-time calculation on circumlunar orbit has an advantage that the satellite orbit can be worked out on board in small calculation amount and also does not need to keep real-time connections with ground.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
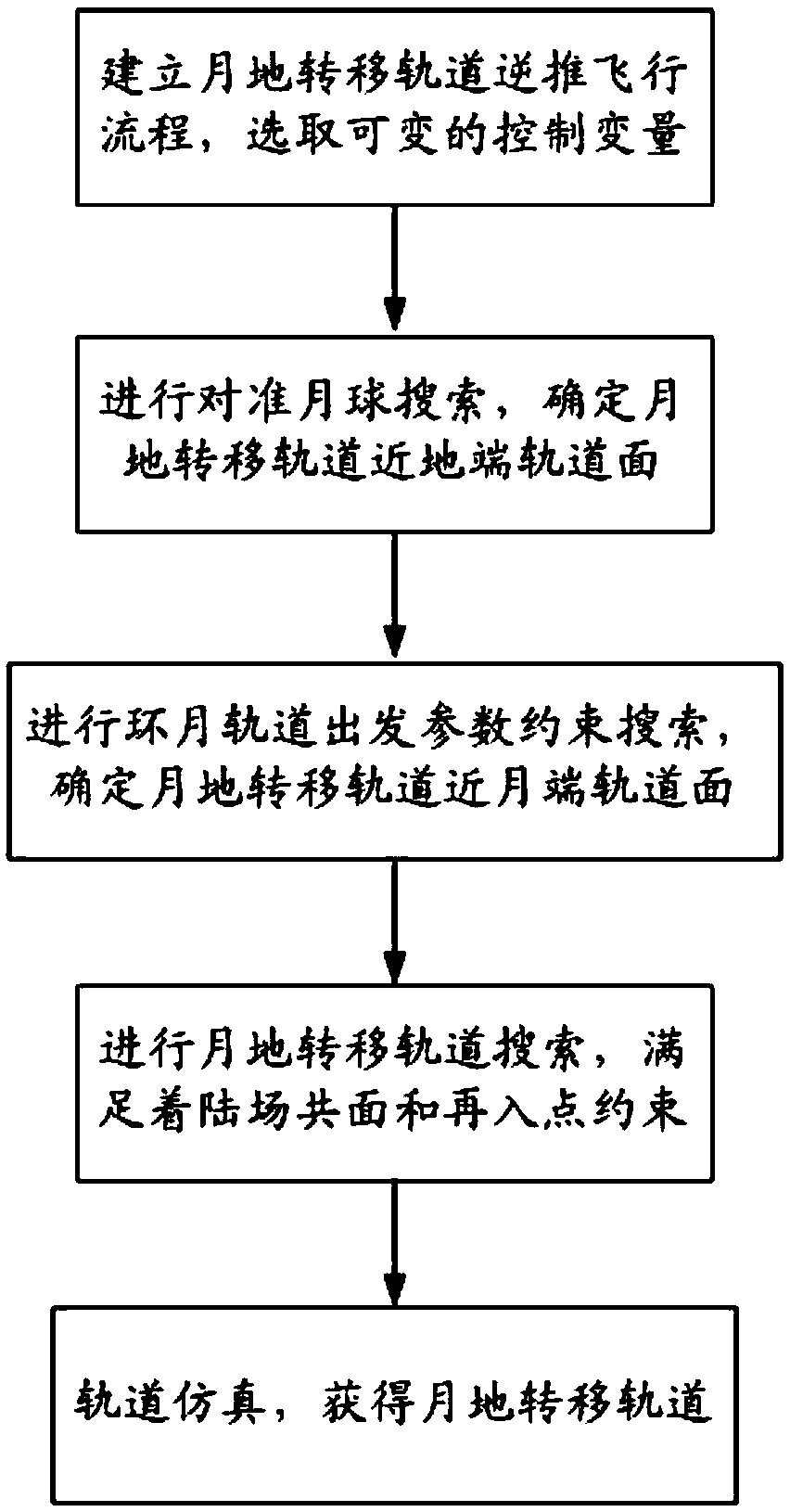
Reverse design method for lunar-terrestrial transfer orbit of spacecraft
ActiveCN109344449AObtain the Moon-Earth Transfer Orbit ParametersEasy searchDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringLunar orbit
The invention relates to a method for reverse design of lunar-terrestrial transfer orbit of a spacecraft, comprising the following steps: a. Establishing a lunar-terrestrial transfer orbit reverse flight flow, and selecting variable control variables; (b) performing a quasi-lunar search to determine that near-Earth end orbital surface of the lunar-terrestrial transfer orbit; (c) performing constraint search on that lunar orbit departure parameters to determine the lunar orbital surface near the lunar end of the lunar-terrestrial transfer orbit; (d) performing lunar-to-ground transfer orbit searching to meet that constraint of coplanar landing site and reentry point; E. performing Orbit simulation to obtain a lunar-to-terrestrial transfer orbit. The inverse design method of the lunar-terrestrial transfer orbit of the spacecraft adopts the method of orbit inversion, and has the advantages of simple solving process, fast searching speed and good convergence.
Owner:BEIJING SPACE TECH RES & TEST CENT
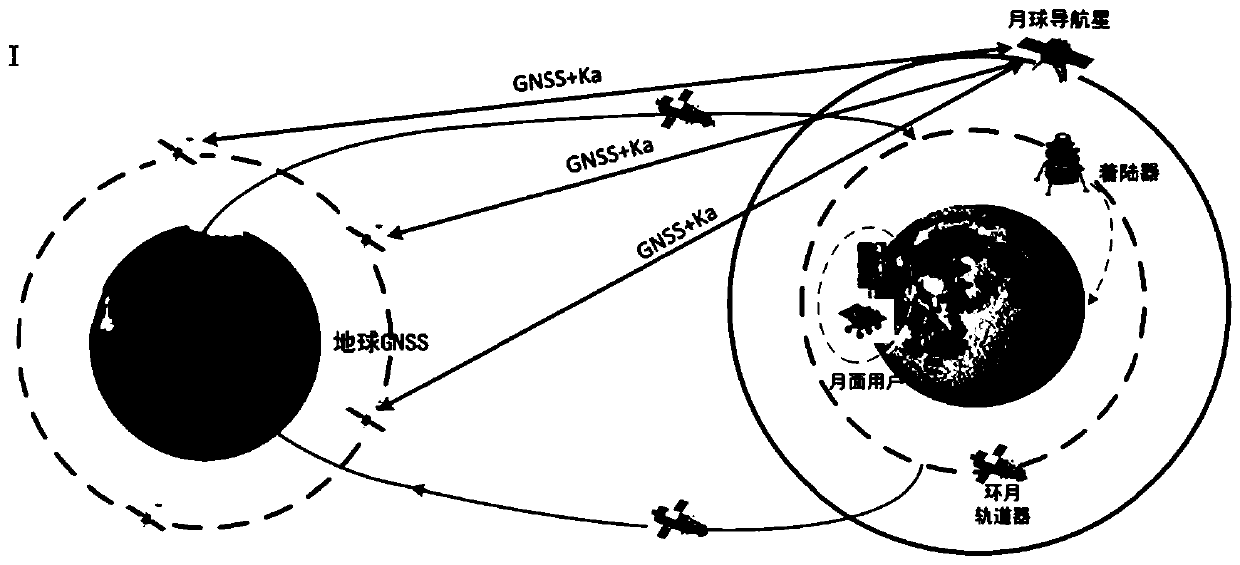
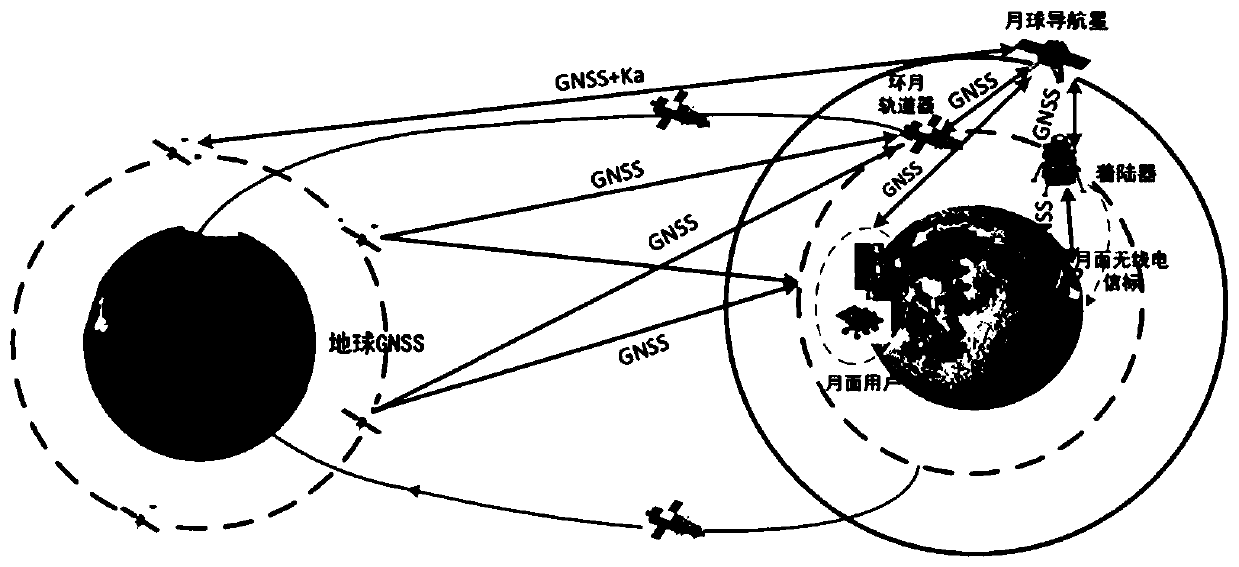
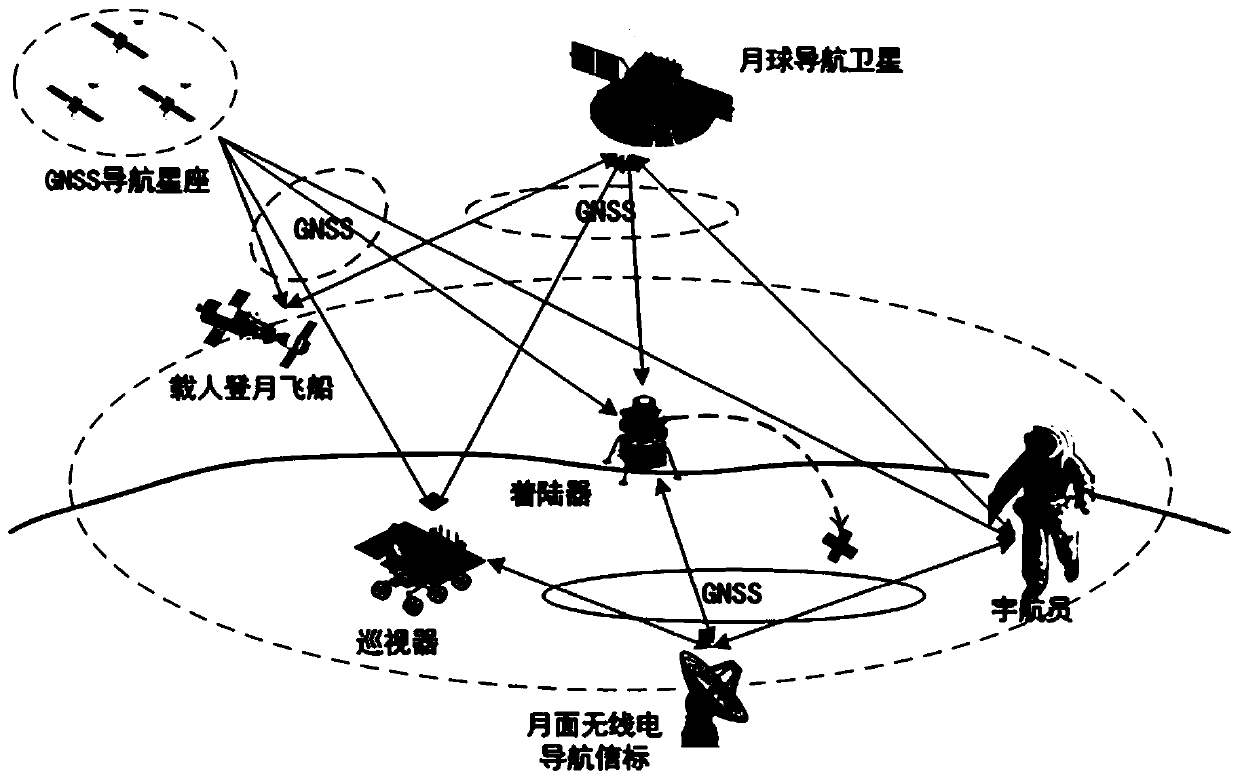
Moon navigation system based on earth GNSS and moon navigation satellite
ActiveCN110986964AImproved viewing geometryImprove real-time positioning accuracyInstruments for comonautical navigationNavigation by astronomical meansEmergency encounterNavigation system
The invention belonging to the technical field of navigation discloses a moon navigation system based on an earth GNSS and a moon navigation satellite. According to the invention, a navigation satellite is added to the lunar orbit; navigation signals compatible with GNSS are broadcasted. The earth GNSS is combined to improve the observation geometry of the lunar user, and meanwhile, bidirectionaltime synchronization links between the earth GNSS navigation constellation and the lunar navigation satellite and between the lunar navigation satellite and the lunar user are established, so that theproblem that the clock error and the radial position error of a user receiver cannot be decoupled is solved and the real-time positioning precision of the lunar user is improved. Meanwhile, a lunar surface radio beacon is added to a lunar key area, navigation signals compatible with GNSS are broadcasted, and the regional navigation performance is enhanced. On the basis of increasing a few of of lunar navigation resources, the real-time performance and precision of lunar user navigation and positioning can be greatly improved, real-time high-precision navigation service is provided for lunar flight, fixed-point landing return and lunar surface inspection, maneuvering at any time under emergency conditions is supported, and beyond-visual-range lunar-based space short message communication is provided.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
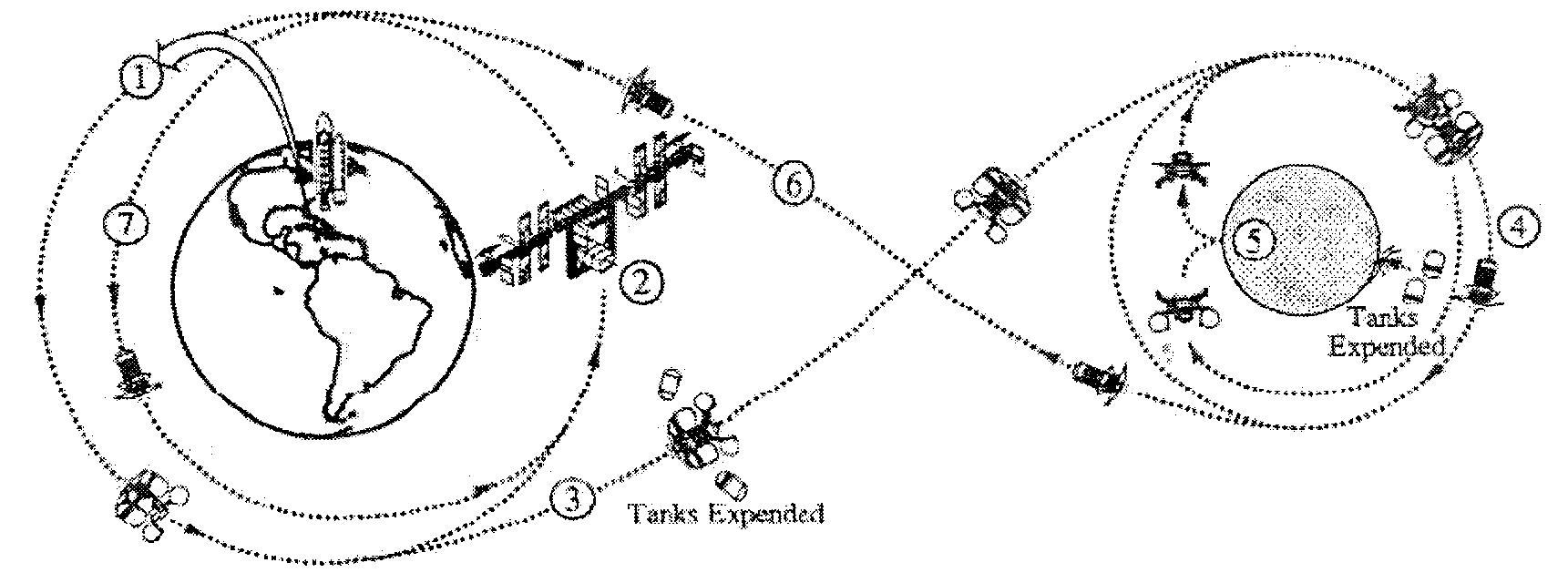
Manned space and lunar exploration spacecraft system based on lunar cycle revisiting orbit and exploration method
InactiveCN102730200AImprove exploration abilityFull of mission goalsArtificial satellitesOrbital periodControl system
The invention discloses a manned space and lunar exploration spacecraft system scheme based on a lunar cycle revisiting orbit and an exploration method. A spacecraft system comprises four spacecrafts which are an earth lunar spaceport (ELS), a lunar exploration module (LEM), a crew transfer vehicle (CTV) and a cargo transfer vehicle (CaTV). With the cooperation of an astronaut system, a carrier rocket system and an exploration and control system, earth lunar space and lunar manned exploration are realized. A relatively entire exploration process of manned space and lunar exploration mission cycle is that the ELS is launched to an earth lunar cycle revisiting orbit by a carrier rocket to become an earth lunar spaceport which surrounds the earth, periodically revisits the moon, and chronically and stably moves on a large oval orbit of which the cycle is half of the lunar orbit cycle; then the lunar exploration module, the crew transfer vehicle and the cargo transfer vehicle are orderly launched to a cycle revisiting orbit by the carrier rocket for rendezvous and docking with the earth lunar spaceport; then the lunar exploration module is separated from the earth lunar spaceport to execute lunar manned field exploration; and finally the lunar exploration module returns to the earth lunar spaceport after finishing the lunar mission, and the crew transfer vehicle is separated from the earth lunar spaceport and then returns to the earth.
Owner:BEIJING SPACE TECH RES & TEST CENT
Method for computing infrared radiation and reflection radiation heat flows on surface of lunar orbit spacecraft
InactiveCN105740594ASolve the low calculation accuracyImprove calculation accuracySpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention provides a high-precision method for computing infrared radiation and reflection radiation heat flows on the surface of a lunar orbit spacecraft. The method disclosed by the invention is based on integral computation formulas for the infrared radiation heat flows and the reflection radiation heat flows caused by the lunar surface to the surface of the lunar orbit spacecraft and is characterized in that lunar surface infinitesimal elements are divided through a uniform simulation method, discretization is carried out to the integral computation formulas, and accumulation of radiation heat exchange among infinitesimal element faces is converted; and according to energy balance of infrared heat flows and absorbed solar heat flows of each infinitesimal area of a lunar sunlight face, a computation method of lunar infinitesimal element face infrared radiation intensity is obtained. Through coordinate conversion and vector expression, computation of the infrared radiation heat flows and the reflection radiation heat flows caused by the lunar surface to the surface of the lunar orbit spacecraft is finally converted to vector (matrix) computation, so that programming computation becomes convenient. Meanwhile, the method is extensively universal and has the advantages that star infrared radiation heat flows and reflection radiation heat flows based on any star, any orbit and a spacecraft with any geometric shape can be computed.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE SYST ENG INST
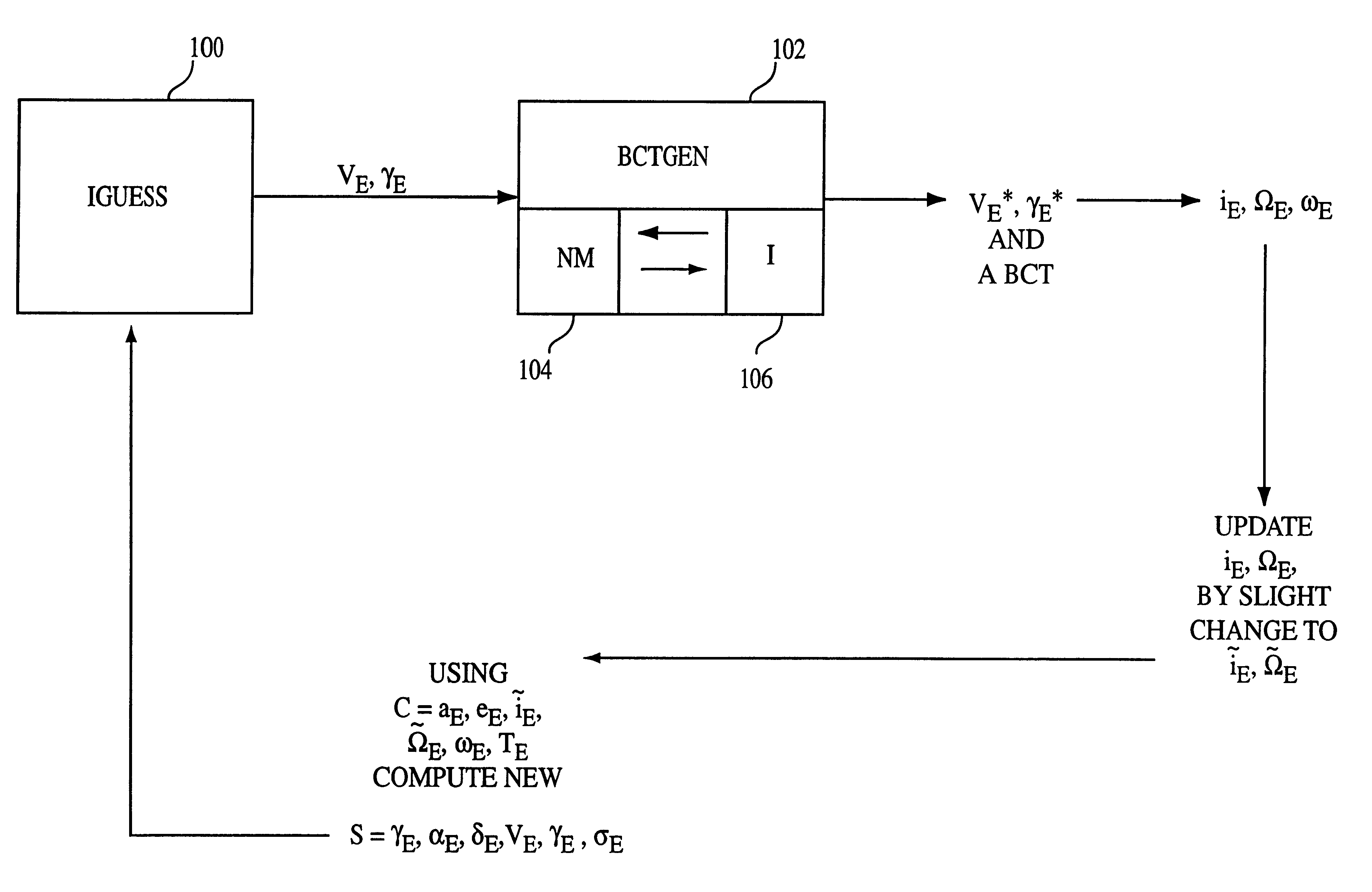
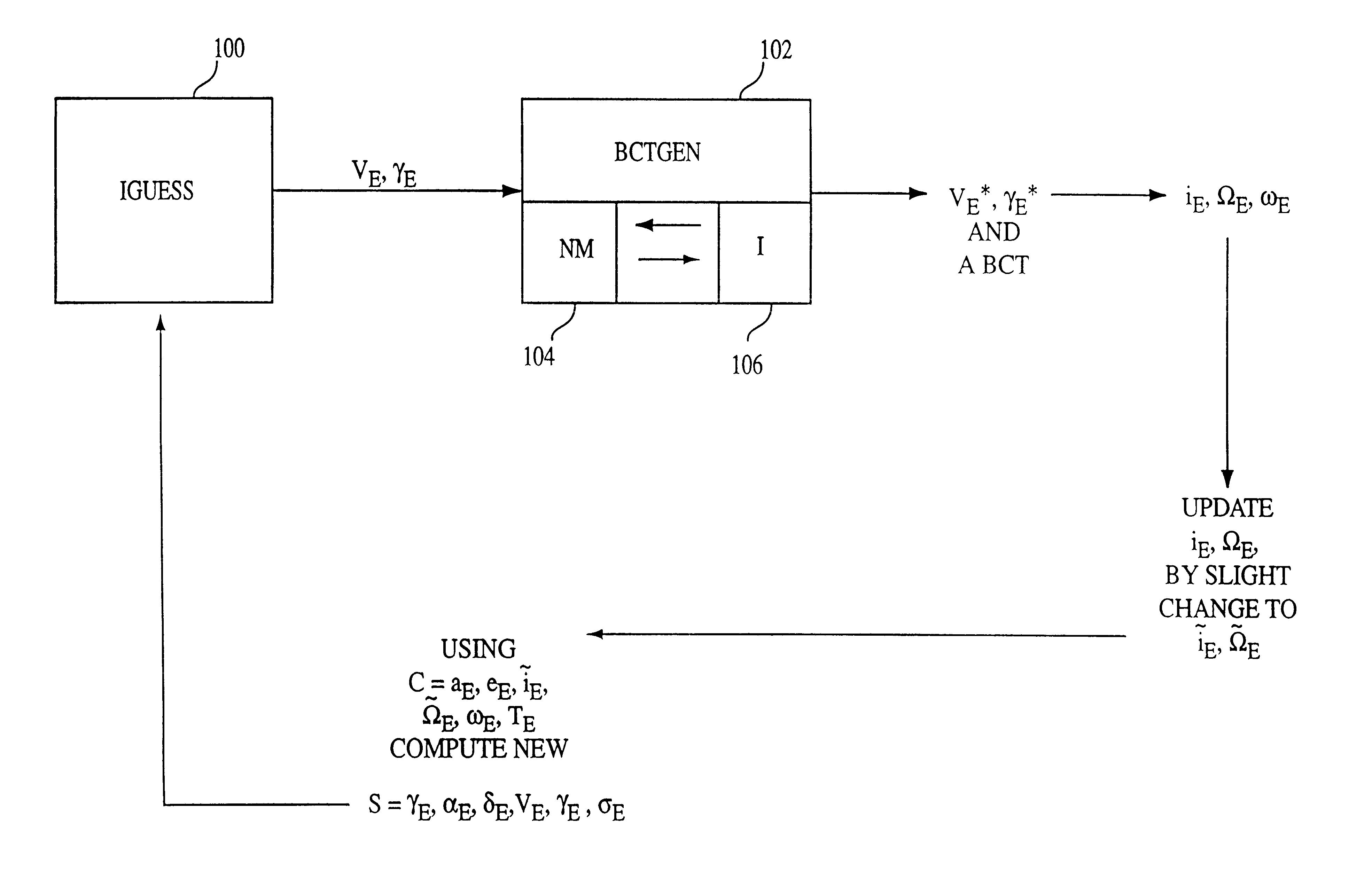
Procedure for generating operational ballistic capture transfer using computer implemented process
InactiveUS6278946B1Low propellant requirementEfficient methodLaunch systemsInstruments for comonautical navigationEngineeringLunar orbit
A method generates an operational ballistic capture transfer for an object emanating substantially at earth or earth orbit to arrive at the moon or moon orbit using a computer implemented process. The method includes the steps of entering parameters including velocity magnitude VE, flight path angle gammaE, and implementing a forward targeting process by varying the velocity magnitude VE, and the flight path angle gammaE for convergence of target variables at the moon. The target variables include radial distance, rM, and inclination iM. The method also includes the step of iterating the forward targeting process until sufficient convergence to obtain the operational ballistic capture transfer from the earth or the earth orbit to the moon or the moon orbit.
Owner:GALAXY DEVMENT
Procedure for generating operational ballistic capture transfer using a computer implemented process
InactiveUS6442482B1Efficient use ofReduces propellant requirementLaunch systemsInstruments for comonautical navigationEngineeringLunar orbit
A method generates an operational ballistic capture transfer for an object emanating substantially at earth or earth orbit to arrive at the moon or moon orbit using a computer implemented process. The method includes the steps of entering parameters including velocity magnitude VE, flight path angle gammaE, and implementing a forward targeting process by varying the velocity magnitude VE, and the flight path angle gammaE for convergence of target variables at the moon. The target variables include radial distance, rM, and inclination iM. The method also includes the step of iterating the forward targeting process until sufficient convergence to obtain the operational ballistic capture transfer from the earth or the earth orbit to the moon or the moon orbit.
Owner:GALAXY DEVMENT
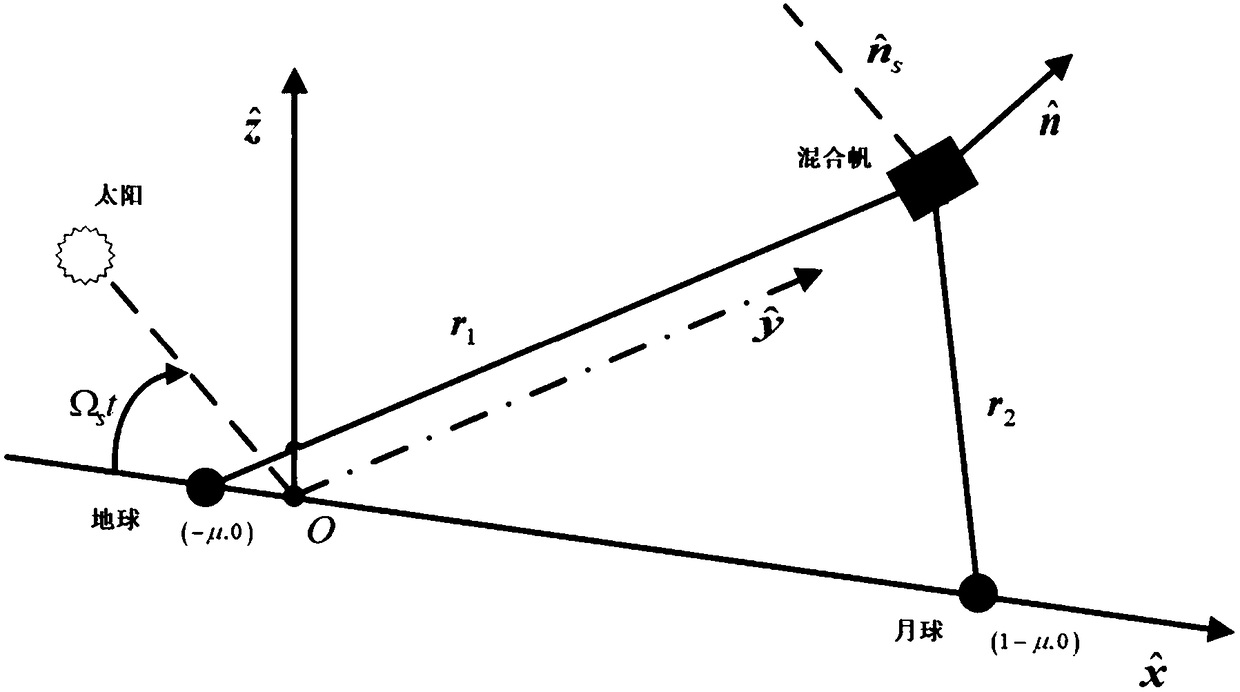
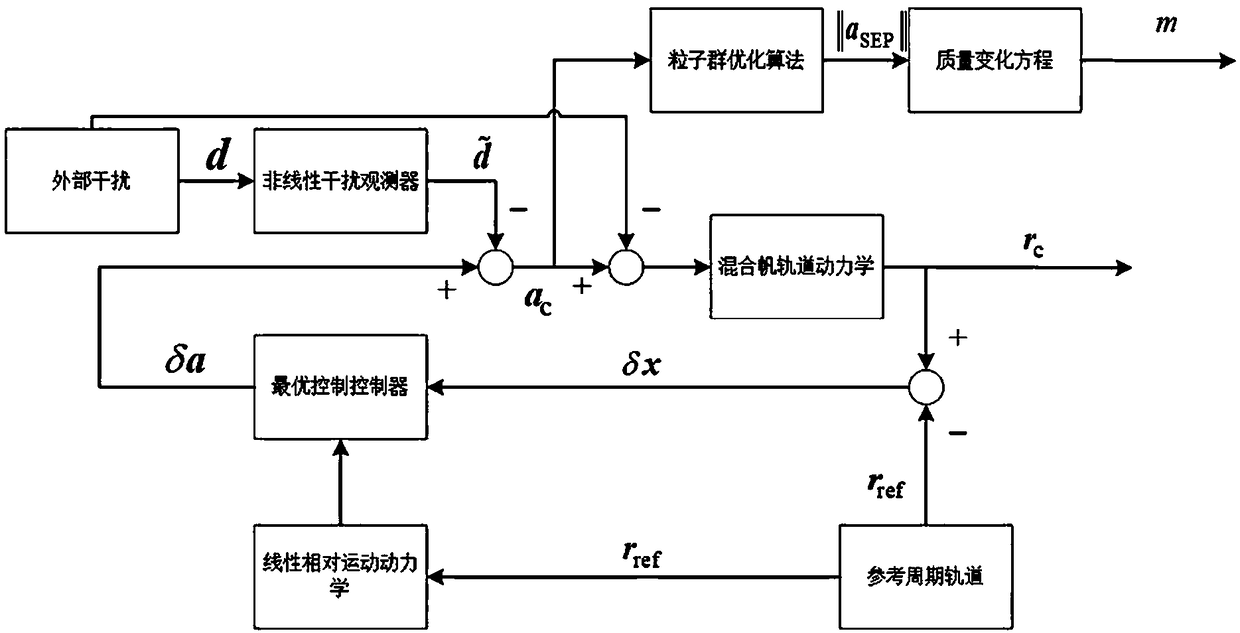
Method for holding hybrid sail periodic orbit of earth-moon system based on disturbance observer
A method for holding a hybrid sail periodic orbit of an earth-moon system based on a disturbance observer comprises the following steps of: 1) establishing a relative motion dynamics equation of the hybrid sail orbit of the earth-moon system under the coordinate system of the earth-moon system; 2) establishing an disturbance force model for a lunar orbit eccentricity and a solar gravity disturbance in the CRTBP model of the earth-moon system; 3) determining a linear period state feedback rate, and designing a periodically optimal orbit holder; 4) designing a nonlinear disturbance observer to converge the error index of the nonlinear disturbance observer into a closed ball with a finite radius; and 5) using the particle swarm optimization algorithm to optimize the electric propulsion acceleration according to the variation law of the hybrid sail mass. The periodically optimal orbit holder provided by the invention has the advantages of simple structure and strong robustness. Nonlinear disturbance observers can improve the orbit retention accuracy. The method reduces the fuel consumption of the electric propulsion system, and prolongs the service life of the system.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
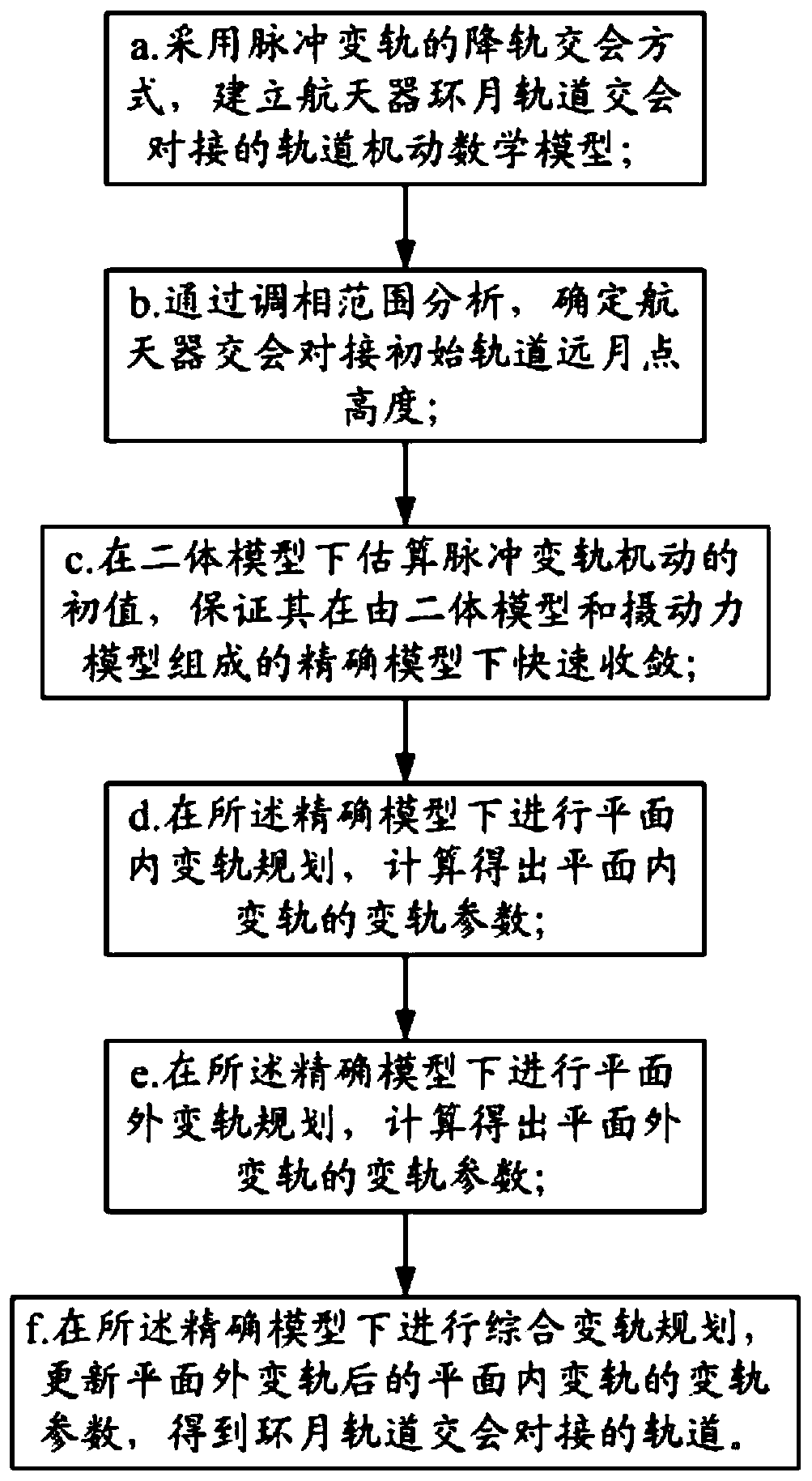
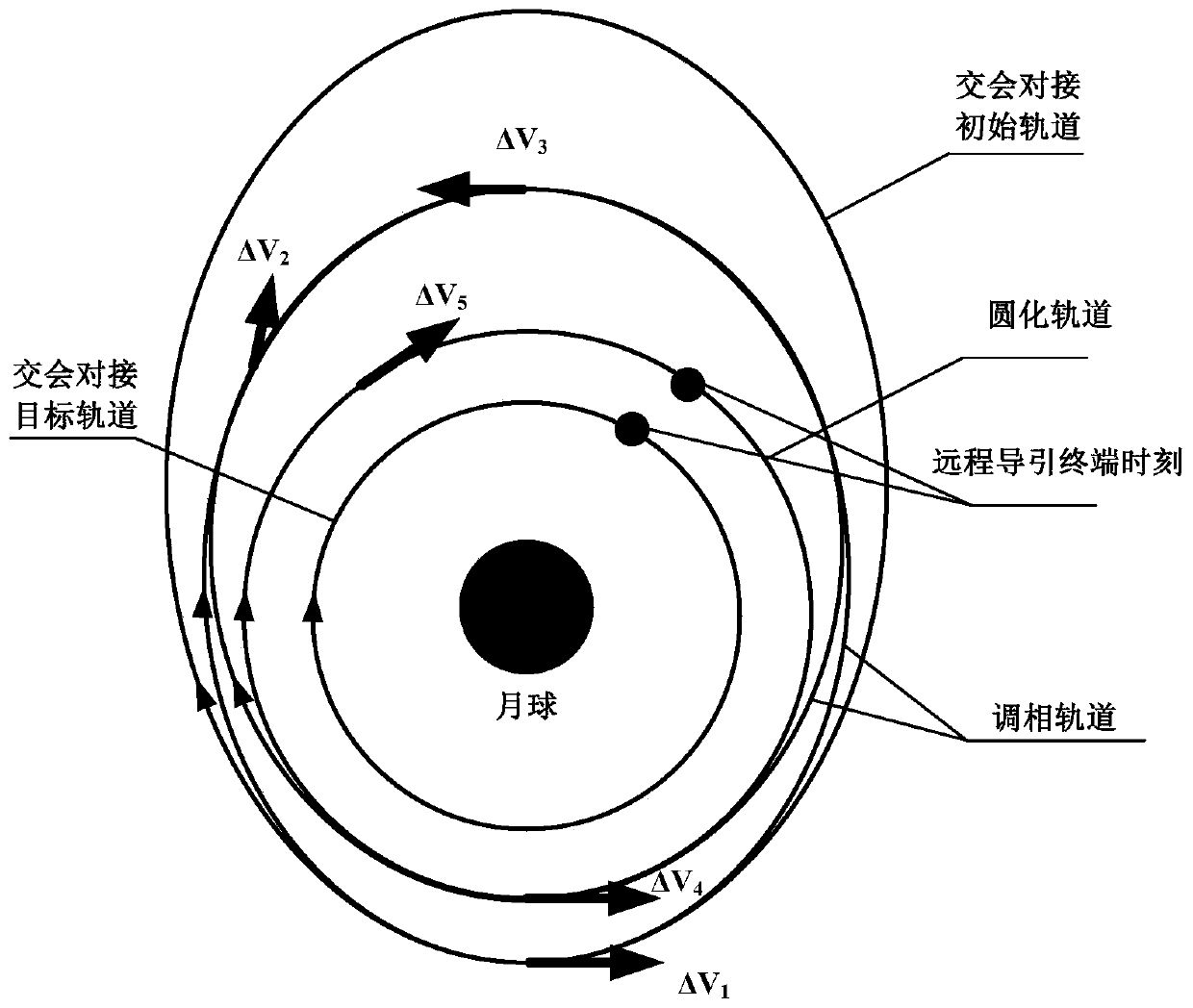
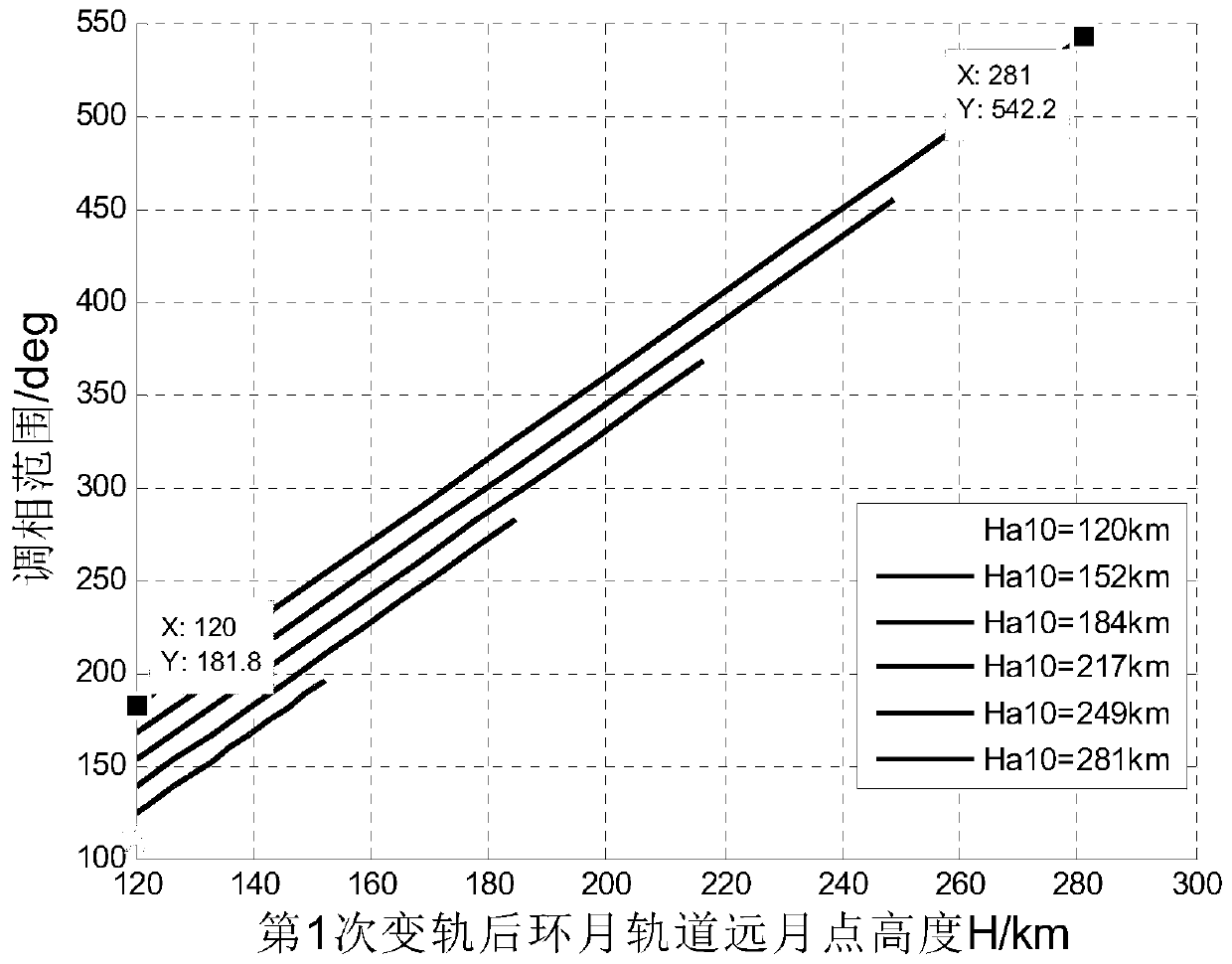
Orbit design method for spacecraft lunar orbit rendezvous and docking
ActiveCN110765504AFast solutionFast convergenceDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMathematical modelClassical mechanics
The invention relates to an orbit design method for spacecraft lunar orbit rendezvous and docking, which comprises the following steps: a, establishing an orbit maneuvering mathematical model for spacecraft lunar orbit rendezvous and docking by adopting an orbit descending rendezvous mode of pulse orbit transfer; b, determining the height of a spacecraft rendezvous and docking initial orbit lunarpoint through phase modulation range analysis; c, estimating an initial value of the pulse orbital transfer maneuver under the two-body model, and ensuring that the initial value is quickly convergedunder an accurate model consisting of the two-body model and a perturbation force model; d, performing in-plane orbital transfer planning under the accurate model, and obtaining orbital transfer parameters of in-plane orbital transfer through calculation; e, performing out-of-plane orbital transfer planning under the accurate model, and orbital transfer parameters of out-of-plane orbital transferare obtained through calculation; and f, performing comprehensive orbit transfer planning under the accurate model, updating orbit transfer parameters of in-plane orbit transfer after out-of-plane orbit transfer, and obtaining a lunar orbit rendezvous and butt joint orbit.
Owner:BEIJING SPACE TECH RES & TEST CENT
Rapid optimization design method for GEO satellite emergency transfer orbit based on moon leveraging
ActiveCN110096726ASolving Rapid Optimization Design ChallengesShow validitySustainable transportationDesign optimisation/simulationTracking modelDynamic models
The invention relates to a rapid optimization design method for a GEO satellite emergency transfer orbit based on moon leveraging in the technical field of spacecraft orbits, and the method comprisesthe following steps of 1, building a high-precision orbit dynamics model, and completing the search of a lunar transfer window and the preliminary design of a lunar orbit; step 2, establishing a moonleveraging track model, drawing a key parameter contour map of a return track after leveraging, and providing an initial value for leveraging parameter optimization design; and step 3, optimizing theleveraging parameters by using the drawn contour map and the return track design constraint to complete the design of the leveraging return track. According to the method, the moon leveraging parameter rapid optimization design problem is effectively solved, an effective method is provided for the rapid formulation of the GEO satellite emergency transfer scheme, and the numerical calculation result shows the effectiveness of the method.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
Far and near field switching control method for lunar orbit rendezvous and docking laser radar
The invention relates to a far and near field switching control method of a lunar orbit rendezvous and docking laser radar. Firstly, far-field and near-field target switching can be carried out in a laser radar scanning state and a tracking state; and secondly, when cooperative target switching is carried out in a tracking state, the lasers are switched at the same time after switching is completed, and echo energy adjustment parameters need to be set with appropriate values so as to ensure that the switched target can be tracked rapidly; and then, the far and near field switching process must be completely completed, so that back-and-forth switching of the far and near field targets in a short time due to jittering of the guide distance or the final measurement distance is avoided; and finally, after target switching is started, a switching sign is set immediately, an external unit is notified, and coordination and smooth completion of laser radar far and near field target switching are ensured. According to the method, a substantial strategy can be provided for a software algorithm of the lunar orbit rendezvous and docking laser radar, and then smooth completion of the lunar orbit rendezvous and docking process is guaranteed.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
System and method for controlling motion of spacecrafts
ActiveUS8655589B2Increase fuel consumptionEffective judgmentInstruments for comonautical navigationCosmonautic partsOrbitLagrangian point
A motion of an object is controlled from a geostationary transit orbit (GTO) of an earth to an orbit of a moon. A first trajectory of the motion of the object is determined from an intermediate orbit of an earth to a neighborhood of a stable manifold of a first Lagrange point (L1). A second trajectory of the motion of the object is determined from the GTO to the intermediate orbit. A third trajectory of the motion of the object is determined from the neighborhood to the stable manifold to an L1 orbit, and a fourth trajectory of the motion of the object is determined from the L1 orbit to the orbit of the moon. A trajectory from the GTO to the orbit of the moon is determined based on a combination of the first, the second, the third, and the fourth trajectories.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
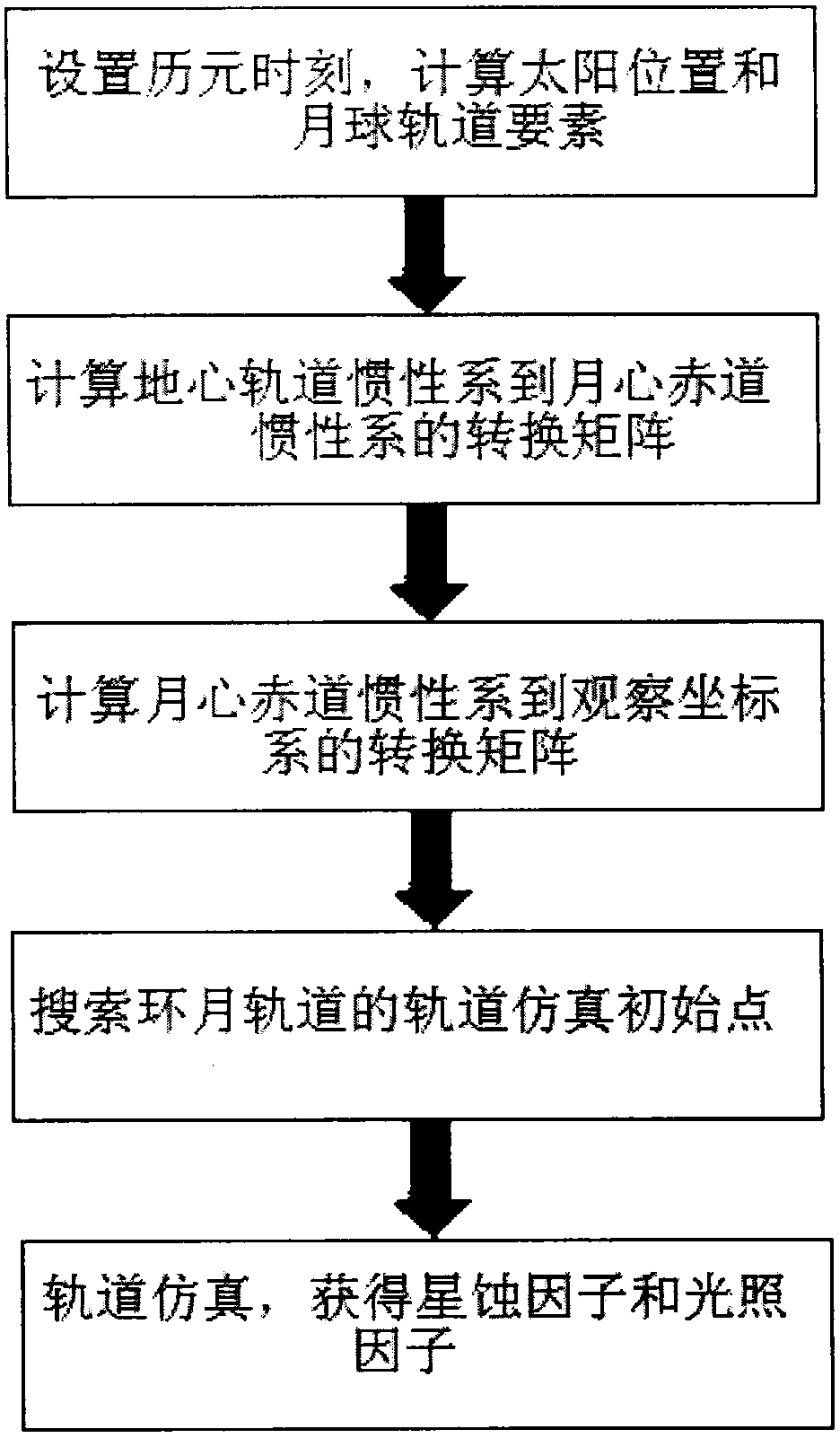
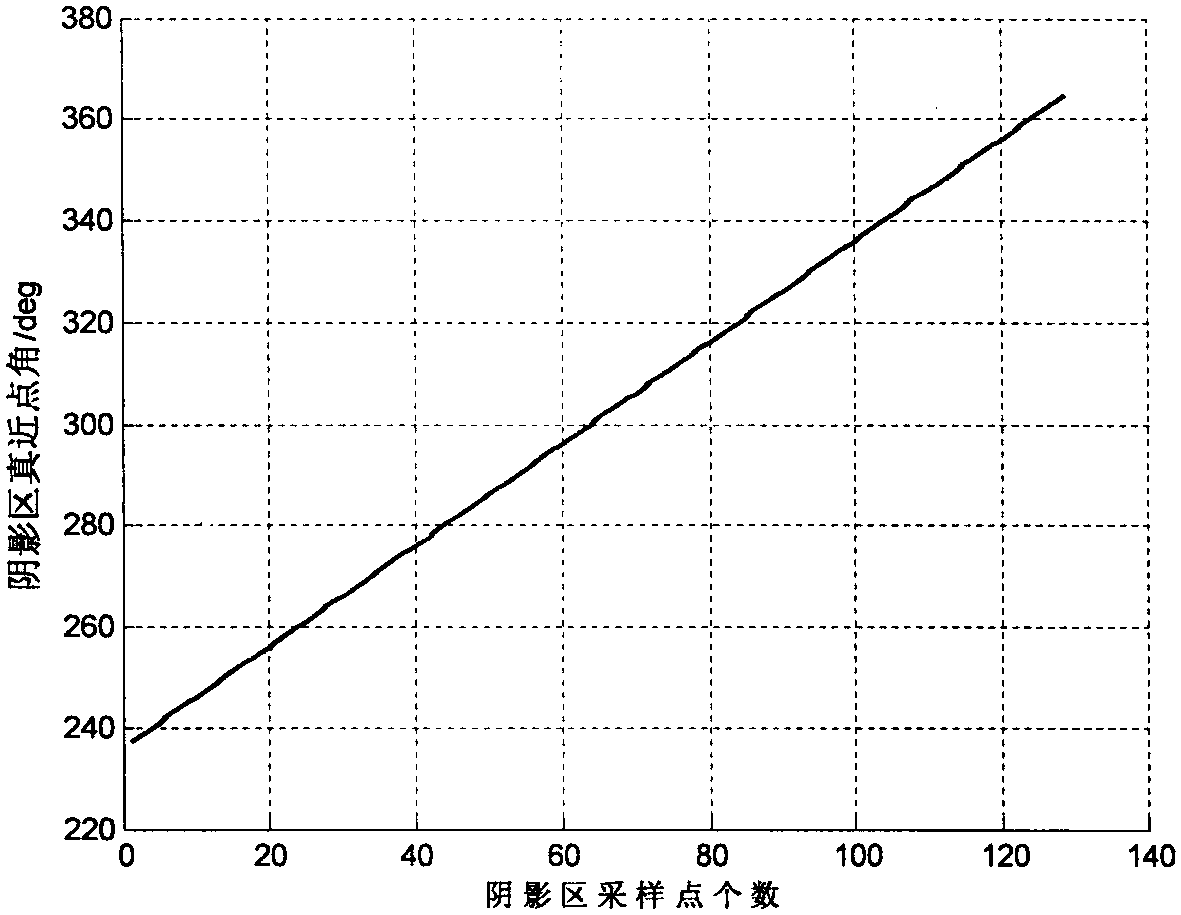
Lunar orbit light condition analytical method
InactiveCN104715126AEasy to analyzeEasy to learnSpecial data processing applicationsTransfer matrixEclipse
The invention provides a lunar orbit light condition analytical method which comprises the steps that an epoch moment is set, and a sun position and a lunar orbit element are computed; according to the lunar orbit element, a first transferring matrix from a geocenter equator inertial system to a selenocenter equator inertial system is computed; according to the first transferring matrix, a second transferring matrix from the selenocenter equator inertial system to an observing coordinate system is computed; a first true anomaly is recorded and is used as an orbit simulation initial point for computing time of different lunar orbits at a shadow zone; and the first true anomaly is used for carrying out orbit simulation, an eclipse factor and a lighting factor are computed, and accordingly light conditions on different lunar orbits are analyzed. Therefore, according to the lunar orbit light condition analytical method, computing is easy and flexible, the computing results are accurate, the inner relation between the lunar orbit light conditions and lunar orbit parameters can be analyzed conveniently, scene setting is easy, and workload is greatly lowered.
Owner:BEIJING SPACE TECH RES & TEST CENT
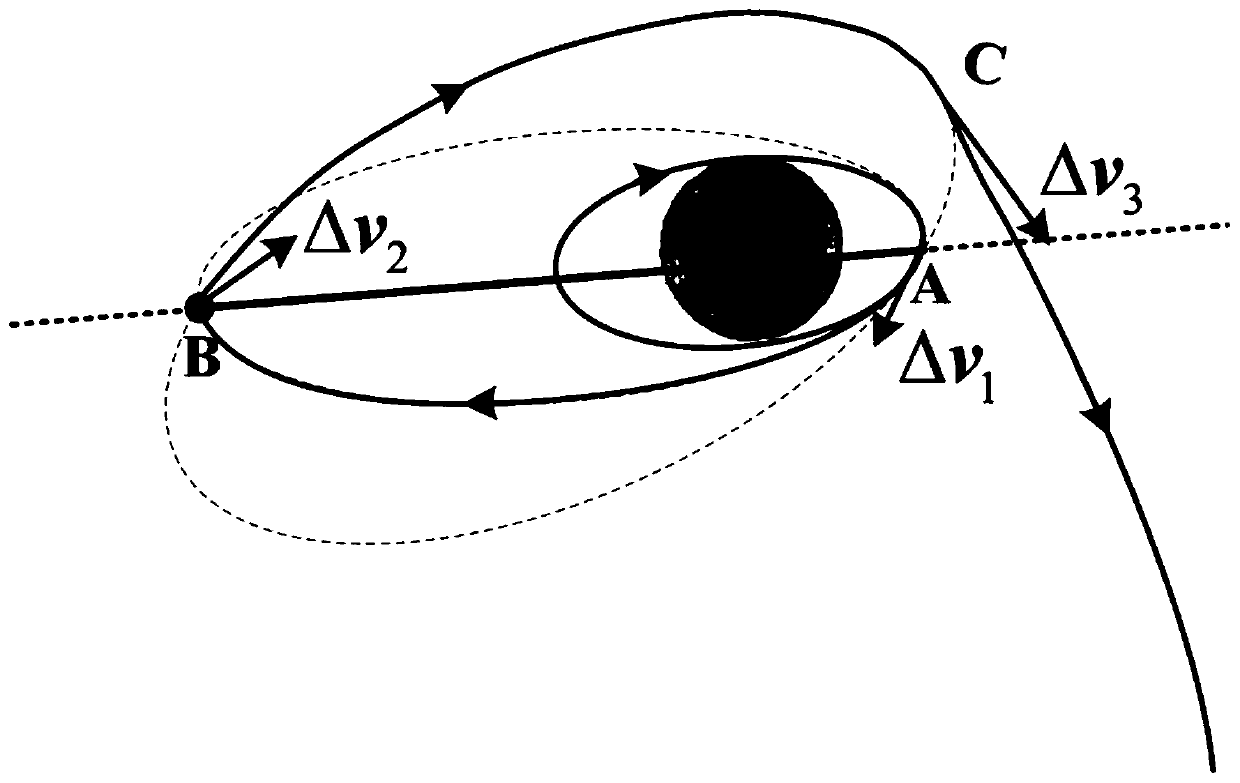
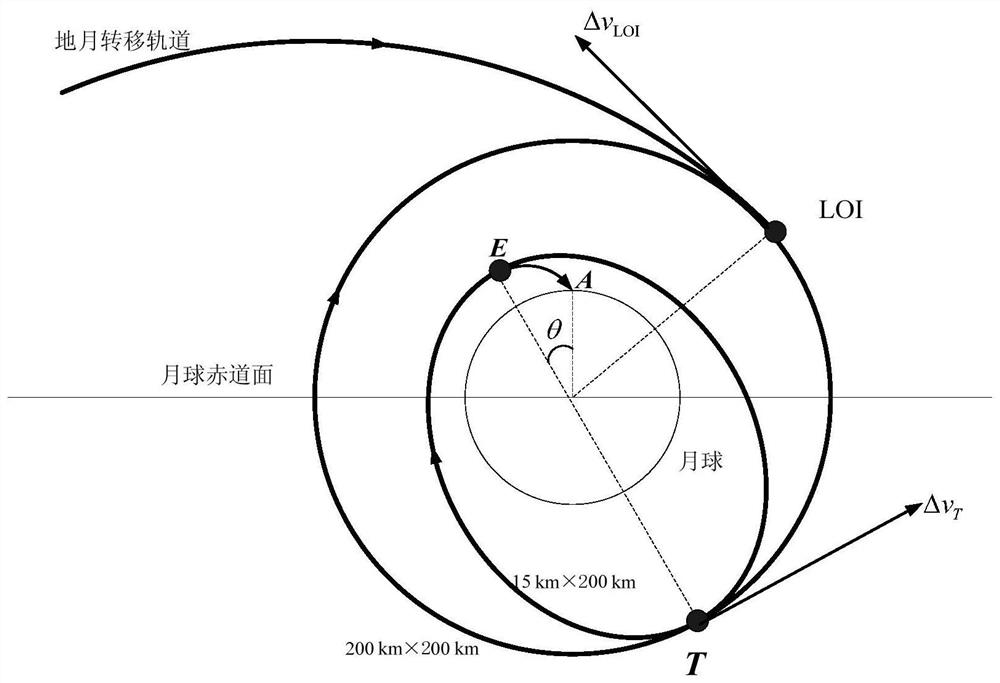
Month-earth three-pulse return orbit speed increment analysis method
ActiveCN110704952AFast and efficient preliminary approximation analysisIntuitive and concise preliminary approximate analysisGeometric CADDelta-vEngineering
The invention discloses a moon-earth three-pulse return orbit speed increment analysis method, which comprises the following steps: A, obtaining a normal unit vector h1 of a lunar orbit plane, a normal unit vector h2 of a lunar escape orbit plane and positions rA, rB and rC for applying three pulses by taking a moon center as an original point; B, obtaining a conical surface S1 with the lunar escape orbit aiming v infinity out as the axis, wherein the half cone angle of the conical surface S1 is eta; C, enabling the plane where v infinity out and h1 are located to serve as the datum plane, setting the rotating angle sigma of rC around the straight line where v infinity out is located, and determining rC and a lunar escape orbit plane; D, obtaining a conical surface S2 with the straight line where rC is located as the axis, wherein the half cone angle of the conical surface S2 is alpha; E, obtaining the included angle beta between h1 and v infinity out and the different-plane differencexi between the lunar orbit and the lunar escape orbit; F, solving the sizes delta v1, delta v2 and delta v3 of the three pulses; G, solving a total speed increment delta v; and H, changing the independent variable influencing the delta v to obtain a change rule of the delta v. According to the method, the spatial geometrical relationship is utilized, and preliminary approximate analysis can be rapidly, effectively, visually and simply carried out on the speed increment required by the three-pulse maneuvering process.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method for transferring a spacecraft from geosynchronous transfer orbit to lunar orbit
ActiveUS10696423B1Minimize possible finite burn lossIncrease distanceLaunch systemsArtificial satellitesClassical mechanicsEngineering
Method for placing a spacecraft into a lunar orbit, either by standard (i.e., impulsive) or ballistic (i.e., non-impulsive) capture, from an Earth orbit that is significantly inclined relative to the lunar orbit plane, with no constraint on the local time of perigee for the starting orbit.
Owner:NASA
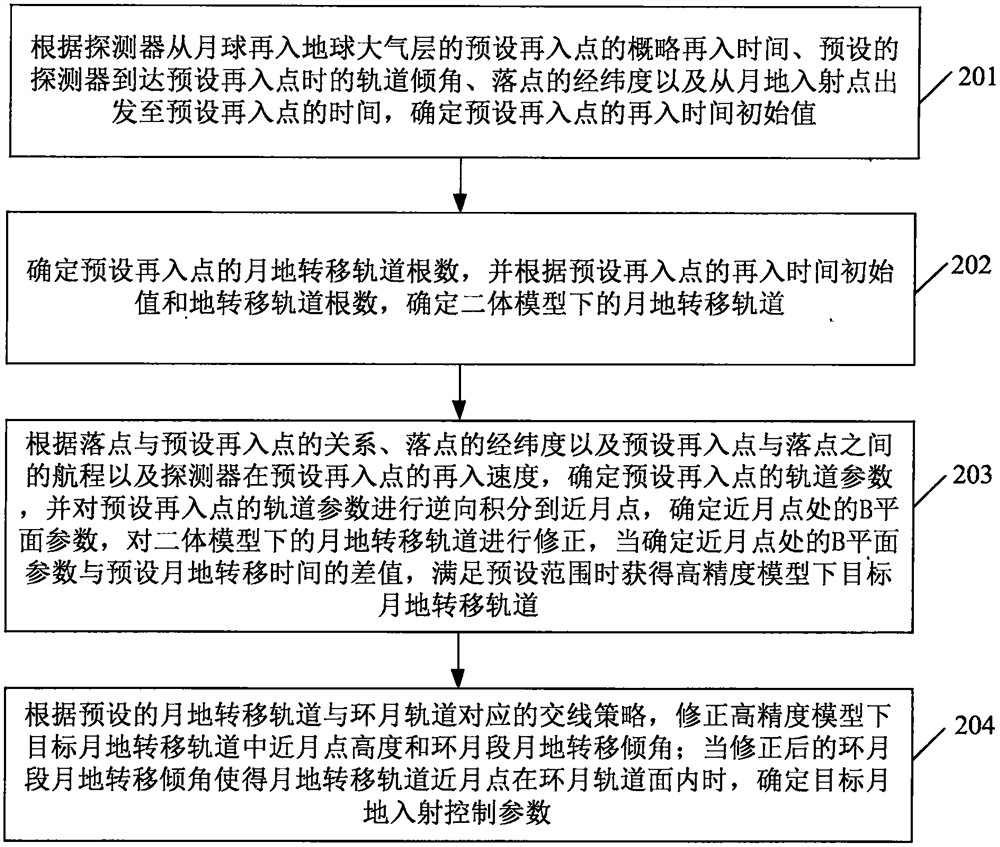
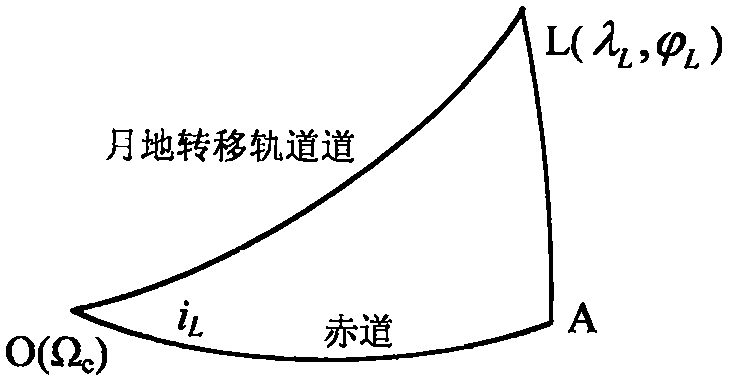
Method and device for determining moon-earth transfer orbit
PendingCN113310496ASimplify the solution processImprove computing efficiencyInstruments for comonautical navigationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAtmospheric layerOrbital inclination
The invention discloses a method and device for determining a moon-earth transfer orbit. The method comprises the steps of according to the approximate reentry time of a detector reentering a preset reentry point of the earth atmosphere from the moon, a preset orbit inclination angle when the detector arrives at the preset reentry point, the latitude and longitude of a drop point, and the moon-earth transfer time of the detector, determining a reentry time initial value of a preset reentry point; determining a moon-earth transfer orbit number of the preset reentry point, and determining a moon-earth transfer orbit under a two-body model according to the reentry time initial value and the moon-earth transfer orbit number; correcting the moon-earth transfer orbit under the two-body model to obtain a target moon-earth transfer orbit under the high-precision model; according to a preset intersection line strategy corresponding to a moon-earth transfer orbit and a moon-surrounding orbit, correcting a perilune height and a lunar section moon-earth transfer inclination angle in the target moon-earth transfer orbit under the high-precision model; and when the corrected lunar section moon-earth transfer inclination angle enables the perilune of the moon-earth transfer orbit to be in the lunar orbit plane, determining moon-earth incidence control parameters.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE CONTROL CENT
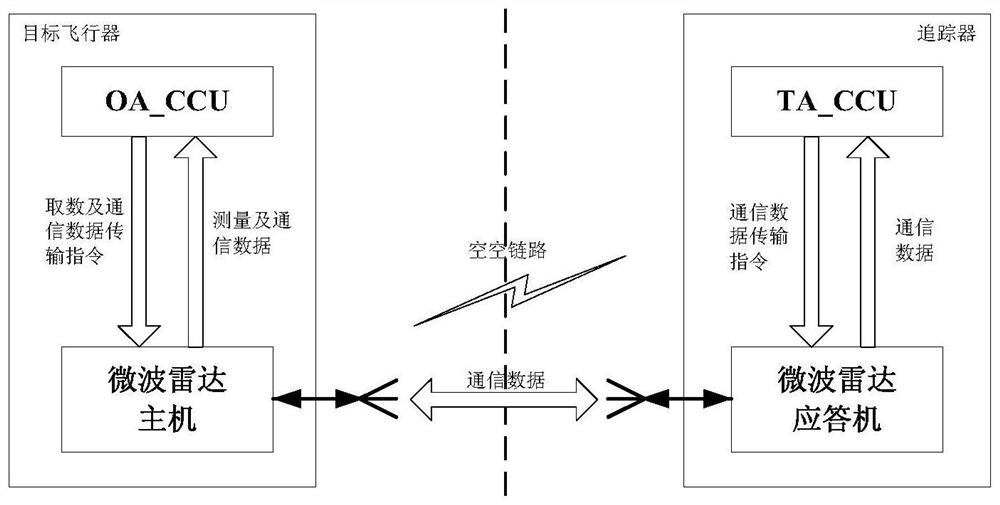
Uplink and downlink communication method based on air-to-air communication
The invention provides an uplink and downlink communication method based on a microwave radar air-to-air communication function in a rendezvous and docking task process in order to ensure high reliability and smoothness of a device-to-ground link in a lunar orbit rendezvous and docking proximity guidance process. The method constructs a dual-relay communication link platform of a ground station, atarget aircraft and a tracker. The problem that a ground station cannot realize double-station common view under the constraint condition of an orbiter, the problem that a target aircraft and a tracker possibly shield each other in the process of approaching each other and the problem of measurement and control communication under the condition of measurement and control link failure are solved.The robustness of uplink and downlink measurement and control links of a spacecraft and a ground station during rendezvous and docking of lunar orbits can be effectively improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
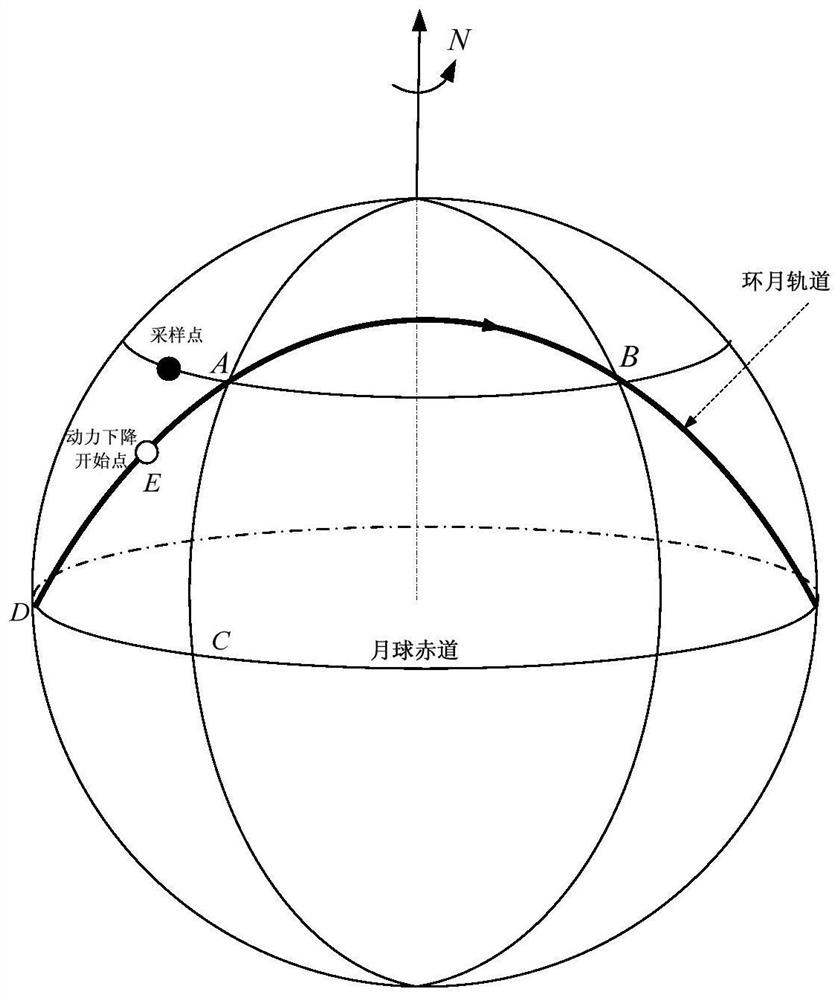
Method for designing fixed-point landing orbit in lunar sampling return task
PendingCN113311854AMinimize Correction Velocity IncrementFixed-point landinghigh-precisionAttitude controlClassical mechanicsLongitude
The invention discloses a method for designing a fixed-point landing orbit in a lunar sampling return task, which comprises the steps of aiming at the longitude of a predetermined lunar surface drop point by introducing an orbit surface normal speed increment component in a near-moon braking maneuver in combination with the optimization of a near-moon inclination angle of an earth-moon transfer section of the lunar sampling return task, aiming at the latitude of the predetermined lunar surface drop point and the height of a power drop starting point through a lunar orbit drop and orbit transfer latitude argument and an orbit plane internal speed increment component, and enabling the lunar surface drop point to be located in a target orbit plane at a predetermined lunar surface rising moment; and furthermore, eliminating the longitudinal voyage error by introducing a lunar orbit descending speed increment normal component to correct the longitude of the drop point and adjusting the power descending moment. According to the method, the problem that the correction speed increment of the moon orbit rendezvous and docking orbit surface is large due to the fact that the influence of orbit design on subsequent moon orbit rendezvous and docking is not considered in the existing fixed-point landing technology is solved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
Method for analysis and computation of illumination on spacecraft lunar orbits
InactiveCN107506504AEasy to analyzeSimple scene setupDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsEclipseTrue anomaly
The invention provides a method for analysis and computation of illumination on spacecraft lunar orbits. The method comprises the steps that epoch moments are set, and the position of sun and lunar orbit elements are computed; according to the lunar orbit elements, a first conversion matrix from an earth core equator inertial system to a lunar core equator inertial system is computed; according to the first conversion matrix, a second conversion matrix from the lunar core equator inertial system to an observation coordinate system is computed; a first true anomaly is recorded and taken as a track simulation initial point used for computation of stay duration of different lunar orbits in a shadow area; and the first true anomaly is used for track simulation, and a satellite eclipse factor and an illumination factor are computed, so illumination conditions on the different lunar orbits are analyzed. Hence, with the method for analysis and computation of illumination on the spacecraft lunar orbits provided by the invention, computation is simpler and more flexible; computation results are more accurate; internal relations between the lunar orbit illumination conditions and lunar orbit parameters can be analyzed conveniently; scene setting is simple; and workloads are reduced greatly.
Owner:BEIJING SPACE TECH RES & TEST CENT
Method for capturing and manipulating asteroid
An asteroid is relatively far away from the earth, the quite long flying time is needed in the asteroid detection process, and therefore difficulties in manned landing detection and asteroid resource exploitation still exist in terms of the prior art. The invention discloses a method for capturing and manipulating the asteroid. According to the method, a traction satellite carries a capturing net to run to an asteroids flying-off track, and a rotation axis of the asteroid is measured through flying-off observation; the capturing net is released in an ontrack mode, and through traction satellite orbital maneuver, the asteroid enters the capturing net; the direction of the capturing net is adjusted, coincidence of a connecting mechanism and the rotation axis of the asteroid is ensured, the connecting mechanism and the asteroid are on the same side in motion direction, and the phenomenon that when the asteroid revolves on its axis, the traction satellite swings is avoided; finally, net opening locking is carried out, the rotatable connecting mechanism is connected with the traction satellite, a small-thrust propelling system on the traction satellite is used for achieving control over the asteroid, the asteroid is manipulated to be nearby a lunar orbit, then, detection and exploitation are carried out, and the method can be applied to asteroid manned detection tasks and asteroid avoidance tasks.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINYUE METER FACTORY
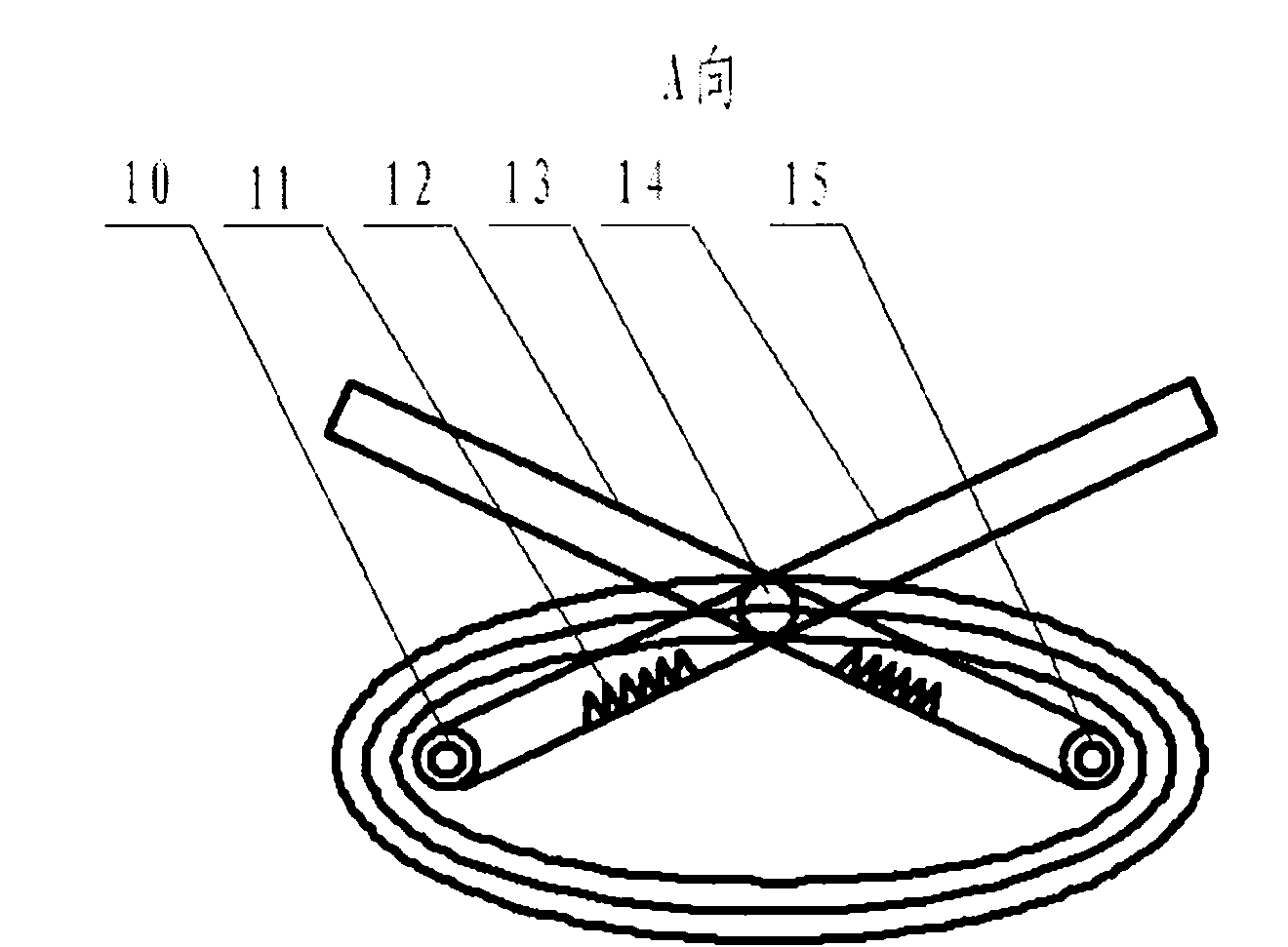
Model of sun-moon-earth
The invention relates to a model of sun-moon-earth. A moon orbit generating apparatus fixing plate (1) is connected with an earth rotation shaft (6); an earth orbit generating apparatus fixing plate (2) is connected with a bracket (7); a moon rotation shaft (3) is connected with a moon orbit straight gear combination (29); the earth rotation shaft (6) is connected with an earth supporting vertical shaft (18); the earth supporting vertical shaft (18) is connected with an earth orbit straight gear combination (13); a sun (8) is connected with the earth orbit generating apparatus fixing plate (2); a moon (4) is connected with the moon rotation shaft (3); and an earth (5) is connected with the earth rotation shaft (6). The model of sun-moon-earth has the advantages that: the mutual positions of the earth, the moon and the sun in the space are relatively truly displayed; and the running conditions of the earth and the moon and the principles of appearance of four seasons, moon wax and wane, solar eclipse, lunar eclipse and the like in the running process are relatively accurately reflected.
Owner:郝亮
Cooperative target marker for super-close-distance measurement for rendezvous and docking of lunar orbits
ActiveCN106767843ASimple structureEasy to process and produceMeasuring points markingInstruments for comonautical navigationLight energyEngineering
The invention relates to a cooperative target marker for super-close-distance measurement for rendezvous and docking of lunar orbits and discloses a cooperative target design based on uniform backward reflective marks. The cooperative target marker comprises six reflecting marks which are mounted on a disc-shaped bracket according to a designed space geometry topological configuration, wherein each reflecting mark comprises a glass bead panel, a narrow-band pass filter, anti-radiation glass and a shell. The cooperative target marker has the advantages of high reflection efficiency, good reflecting uniformity, high light energy stability, strong stray light interference resistance, small volume and lightness. According to the cooperative target marker, the deficiencies that the measurement accuracy and reliability of a system are decreased because the reflection efficiency of a conventional cooperative target is low under a super-close-distance condition, and the reflecting uniformity is decreased are solved; and the cooperative target marker is suitable for super-close-distance high-precision measurement occasions during the rendezvous and the docking.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Camera integration time adjusting time based on beam function and image feature
ActiveCN104135624ASolve measurement problemsImprove work performanceTelevision system detailsColor television detailsLight beamImaging Feature
The invention discloses a camera integration time adjusting time based on a beam function and an image feature. Corresponding camera integration time adjusting functions are constructed in combination with the physical feature differences and confusion circle change of a target image among different measuring distances, and the camera integration time is dynamically adjusted to stabilize the grey level of the target image within a range in which a camera measuring system can work stably, so that the problem of influence on normal measurement of an optical imaging sensor due to the change of the energy of the target image along with the change of the measuring distance is effectively solved, and the working capacity of the lunar orbit rendezvous and docking optical imaging sensor in a large-range complex environment is increased.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
High-precision optical tracking device based on angle reflector
ActiveCN110780441AConsiderable solar energyDon't care about pointing accuracyTelescopesMountingsOptical reflectionSpace power
The invention belongs to the technical field of optical tracking equipment, and particularly relates to a high-precision optical tracking device based on an angle reflector. The device includes an optical reflection component on a space power station aircraft (1) located on a lunar orbit and a wide-view-field optical angle reflector (2) located on the lunar surface; the optical reflection component is used for receiving incident sunlight and reflecting the sunlight to the wide-view-field optical angle reflector (2) for the first time, and a reflection path of the incident sunlight at the initial time is adjusted according to the reflected sunlight; then the continuously incident sunlight is reflected along the adjusted reflection path to an optical receiving end of the lunar surface; and the wide-view-field optical angle reflector (2) is used for receiving the sunlight reflected by the optical reflection component and reflecting the sunlight to the optical reflection component.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
Echo simulation method and device
ActiveCN107526066BEcho simulation implementationWave based measurement systemsRadar systemsEngineering
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
A cooperative target marker for lunar orbital rendezvous and docking ultra-close distance measurement
ActiveCN106767843BSimple structureEasy to process and produceMeasuring points markingInstruments for comonautical navigationLight energyEngineering
The invention relates to a cooperative target marker for super-close-distance measurement for rendezvous and docking of lunar orbits and discloses a cooperative target design based on uniform backward reflective marks. The cooperative target marker comprises six reflecting marks which are mounted on a disc-shaped bracket according to a designed space geometry topological configuration, wherein each reflecting mark comprises a glass bead panel, a narrow-band pass filter, anti-radiation glass and a shell. The cooperative target marker has the advantages of high reflection efficiency, good reflecting uniformity, high light energy stability, strong stray light interference resistance, small volume and lightness. According to the cooperative target marker, the deficiencies that the measurement accuracy and reliability of a system are decreased because the reflection efficiency of a conventional cooperative target is low under a super-close-distance condition, and the reflecting uniformity is decreased are solved; and the cooperative target marker is suitable for super-close-distance high-precision measurement occasions during the rendezvous and the docking.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com