Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
36results about How to "High precision determination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
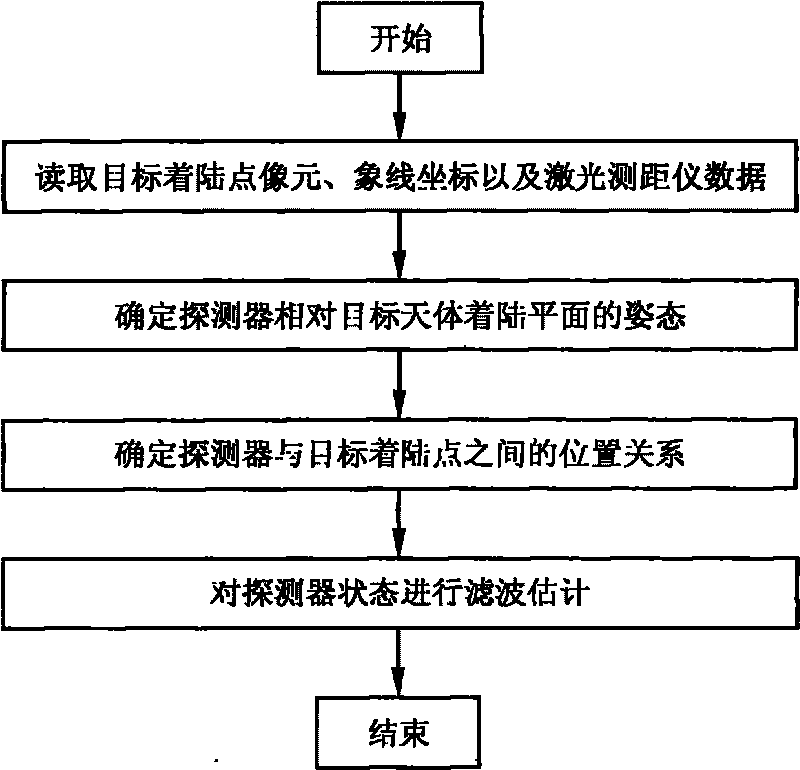
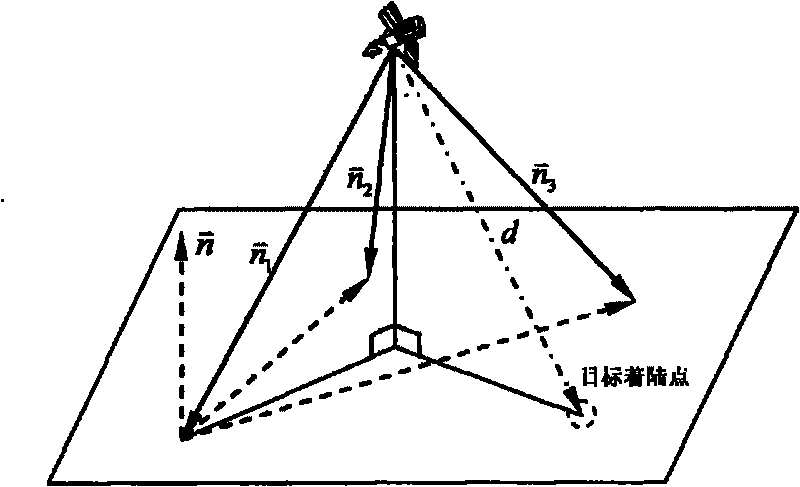
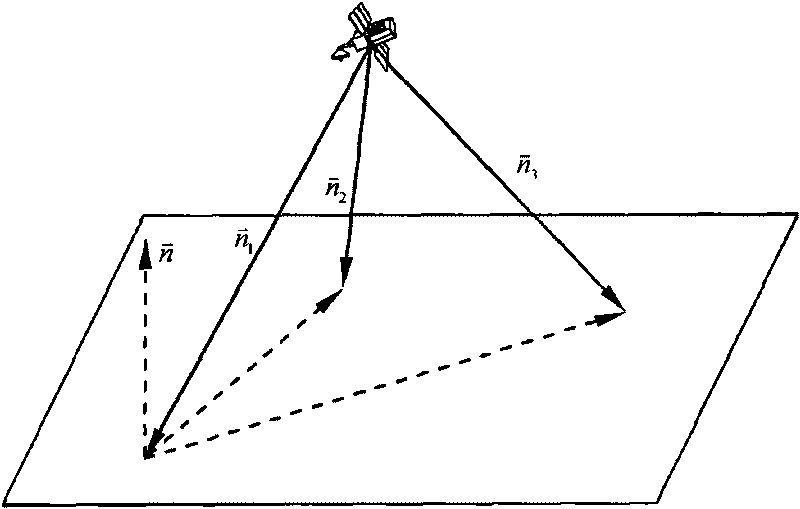
Autonomous optical navigation method for soft landing for deep space probe
InactiveCN101762273AHigh precision determinationImprove reliabilityInstruments for comonautical navigationPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryAviationLaser ranging
The invention relates to an autonomous optical navigation method for soft landing of a deep space probe, and belongs to the field of space flight and aviation. The autonomous optical navigation method comprises the following steps: firstly, reading a corresponding pixel and a pixel line coordinate of a target landing point on an image plane photographed by an optical navigation camera, and the distance of the probe from a landing plane in three laser ranging device mounting directions; secondly, determining the posture of the probe relative to a landing plane of a target astronomical body by using the obtained distance measured by the three laser ranging devices and the mounting azimuth angle and pitch angle of the known ranging device; thirdly, determining the position relationship between the probe and the target landing point by using the obtained distance di measured by the three laser ranging devices and the pixel and the pixel line coordinate of the target landing point; and finally, performing filter estimation on the position, speed, posture and angular speed information of the probe relative to the landing area. The autonomous optical navigation method for the soft landing of the deep space probe has the characteristics of high reliability, low cost and strong real-time, and can highly precisely determine the position and posture of the probe relative to the target landing point.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
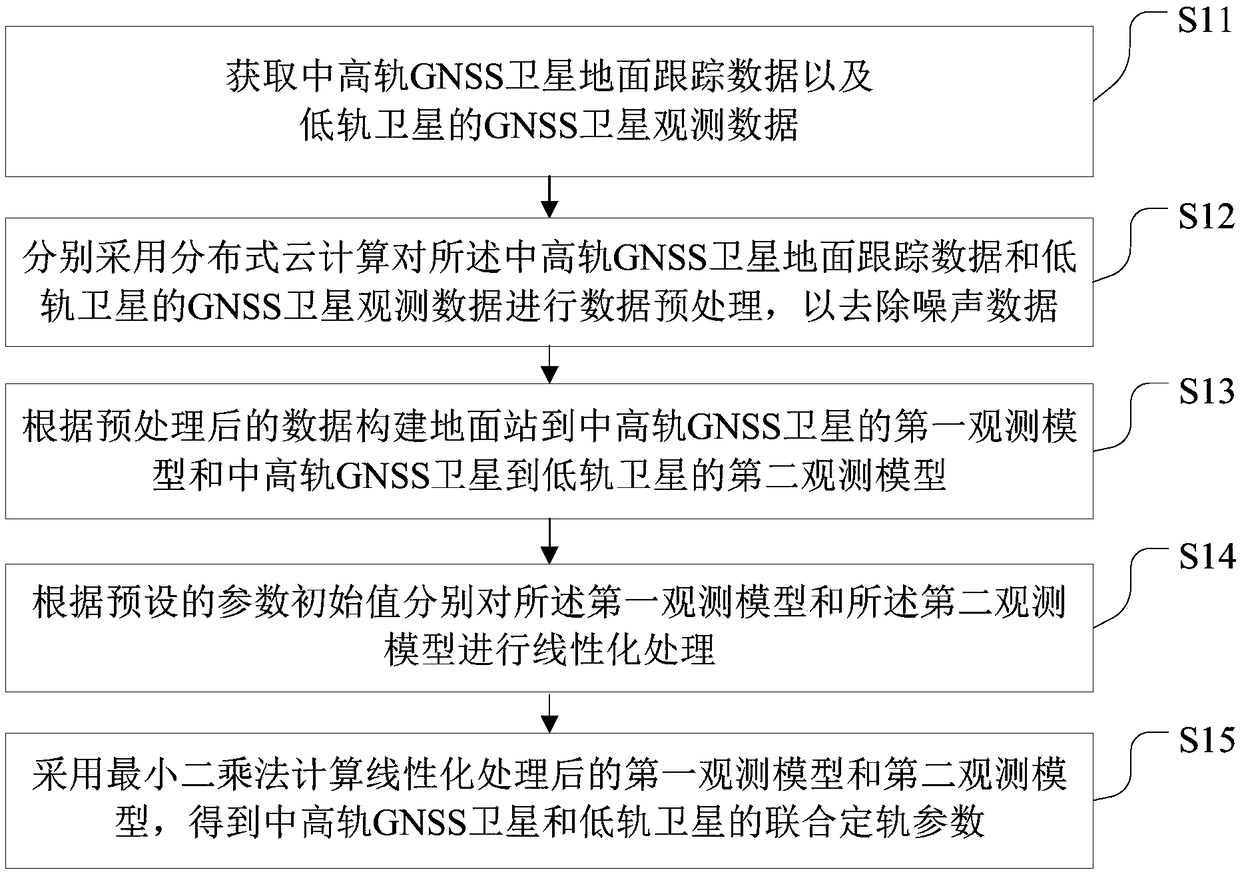
Navigation data processing method and system based on cloud computing
InactiveCN109001776ATime synchronizationReduce dependenceSatellite radio beaconingGround trackLow earth orbit
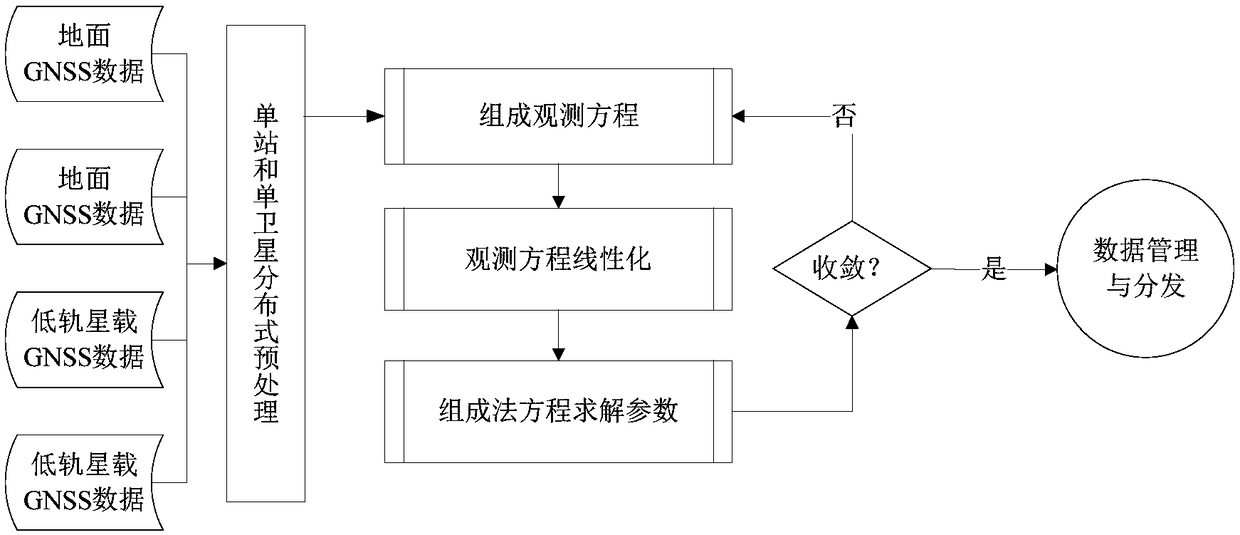
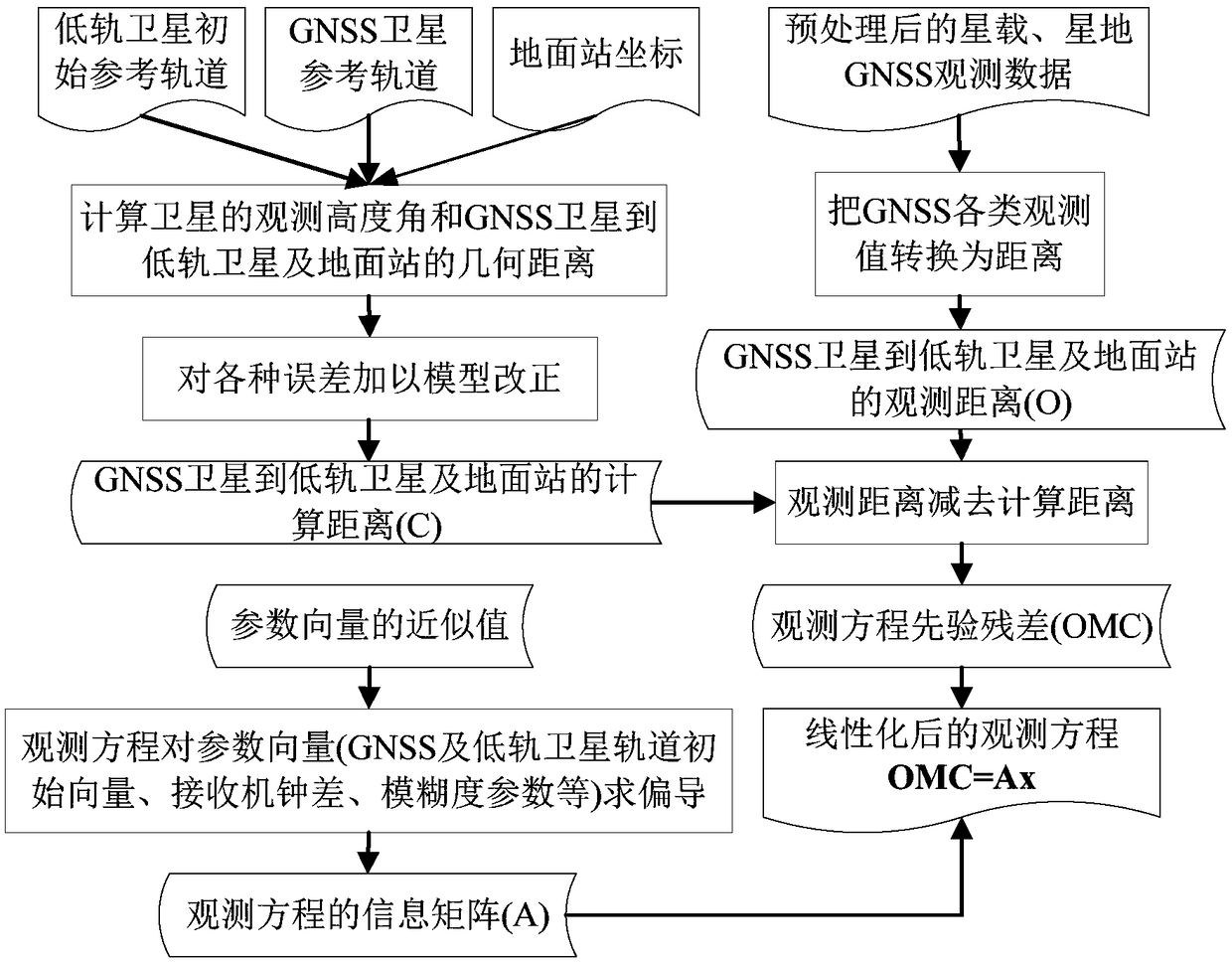
The invention provides a navigation data processing method and system based on cloud computing. The method comprises the steps that ground tracking data of a medium and high earth orbit GNSS satelliteand GNSS satellite observation data of a low earth orbit satellite are acquired; distributed cloud computing is adopted to preprocess the ground tracking data of the medium and high earth orbit GNSSsatellite and the GNSS satellite observation data of the low earth orbit satellite; a first observation model from a ground station to the medium and high earth orbit GNSS satellite and a second observation model from the medium and high earth orbit GNSS satellite to the low earth orbit satellite are constructed according to the preprocessed data; linearization processing is performed on the firstobservation model and the second observation model according to preset parameter initial values; and a least square method is adopted to calculate the first observation model and the second observation model after linearization, and joint orbit determination parameters of the medium and high earth orbit GNSS satellite and the low earth orbit satellite are obtained. Through the navigation data processing method and system, an orbit of the low earth orbit satellite can be determined with high precision, joint orbit determination and time synchronization of the navigation satellite and the low earth orbit satellite are realized, therefore, real-time high-precision service is provided for a user, and system service performance is improved.
Owner:BEIJING FUTURE NAVIGATION TECH CO LTD
Determinating device for paper
InactiveCN1441389ADetect shapeHigh precision determinationComplete banking machinesPaper-money testing devicesEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:ORMON CORP
Optical axis controller of automotive headlamp
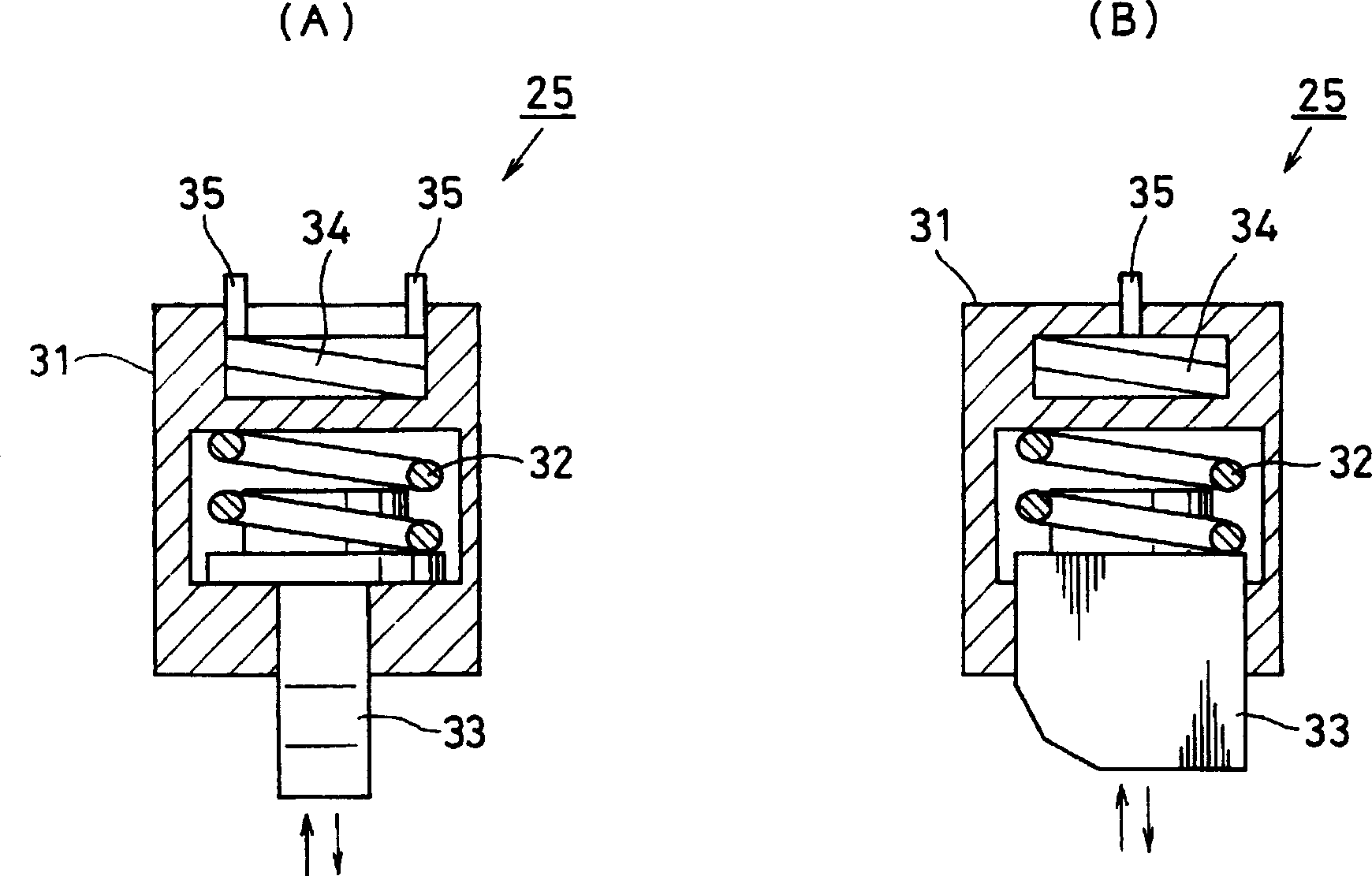
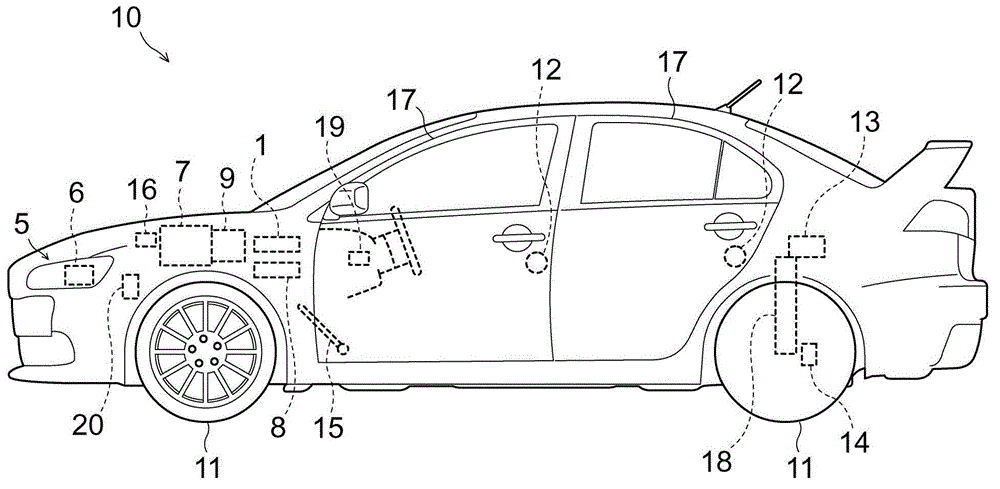
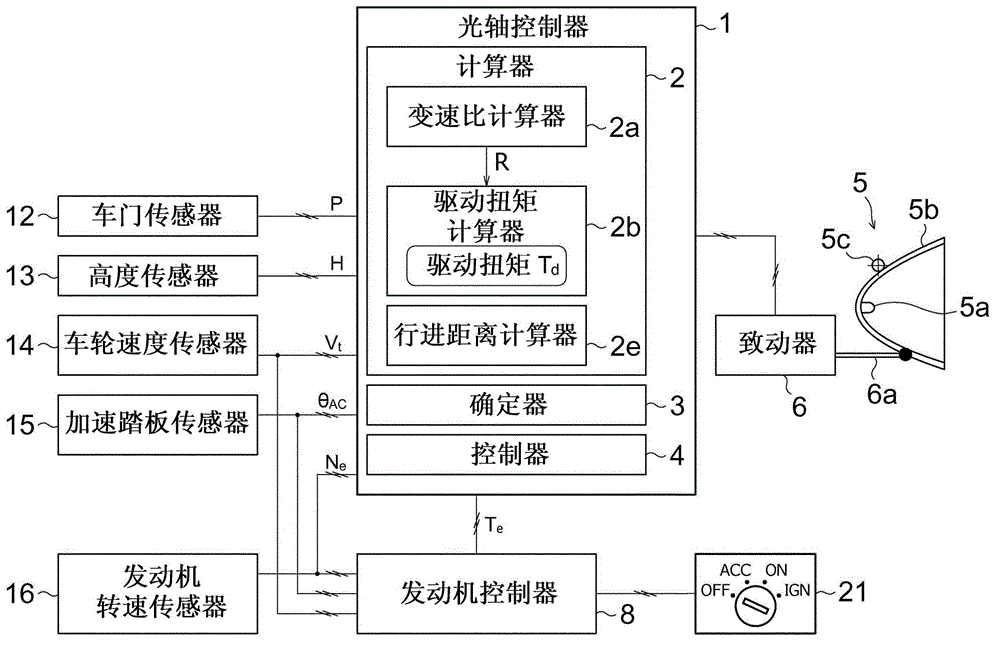
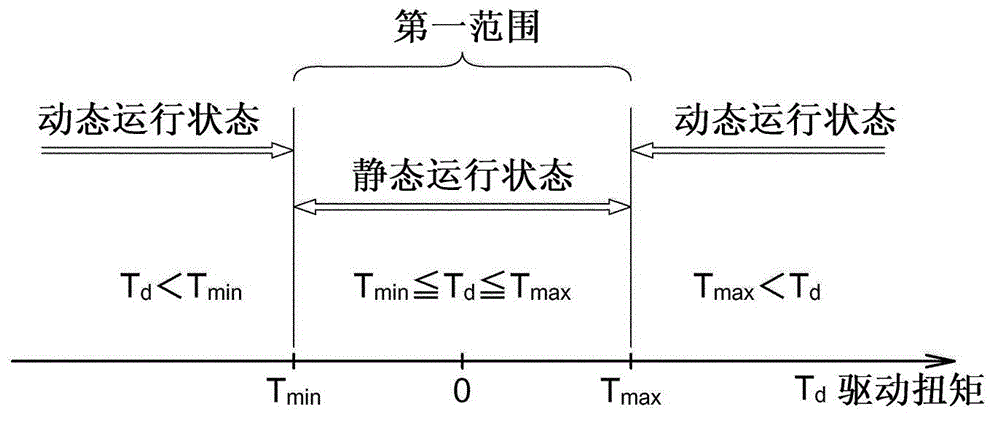
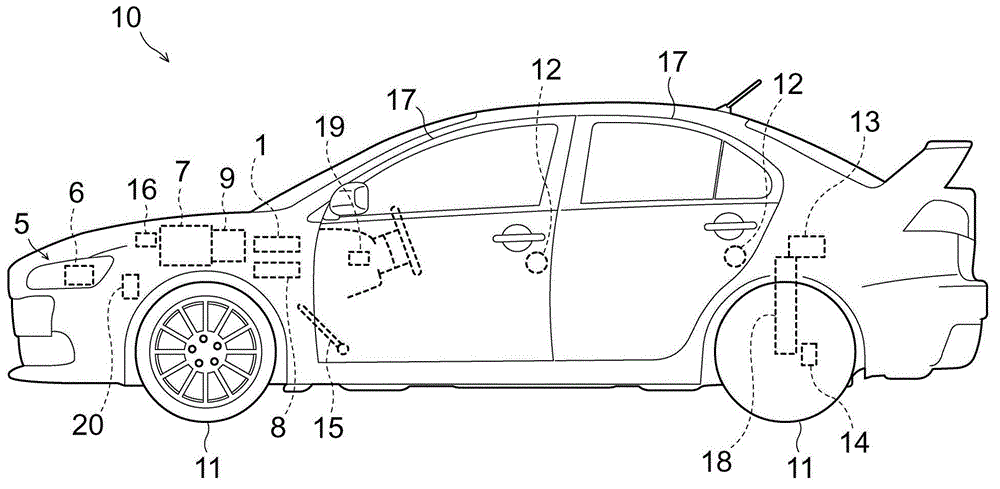
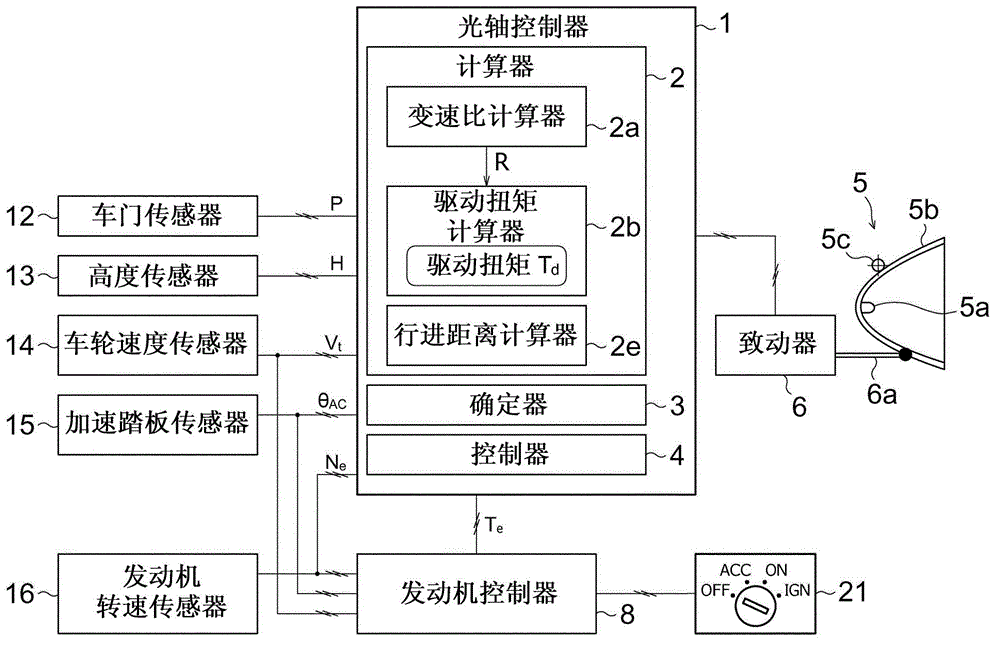
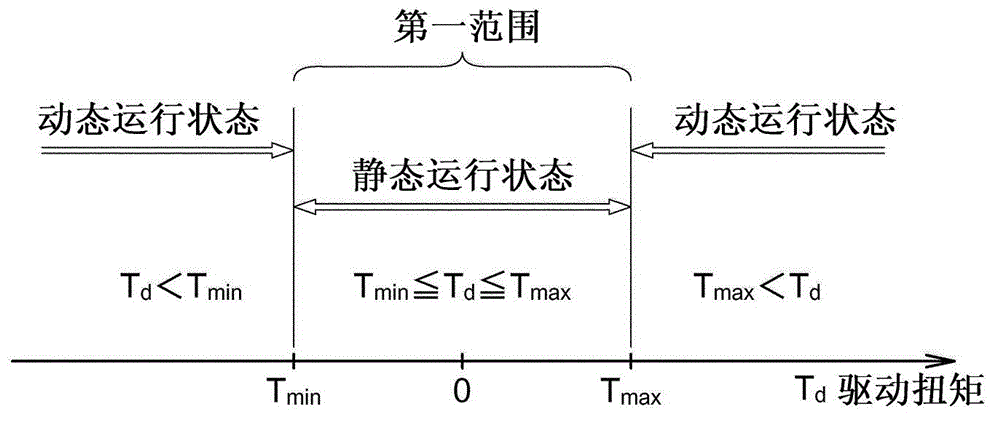
ActiveCN102862507AAccurately determineHigh precision determinationVehicle headlampsOptical signallingDrive wheelOptical axis
An optical axis controller includes an adjuster(6) which adjusts the optic angle of an automotive headlamp (5), and a drive torque calculator (2b) which calculates the drive torque (T d ) applied to drive wheels of a vehicle (10). The optical axis controller also includes a determiner (3) which determines whether the vehicle (10) is in a static running state or in a dynamic running state, on the basis of the drive torque (T d ). The optical axis controller further includes a controller (4) which permits an adjuster (6) to adjust the optic angle if the determiner (3) determines that the vehicle (10) is in the static running state, and does not permit the adjuster (6) to adjust the optic angle if the determiner (3) determines that the vehicle (10) is in the dynamic running state. This configuration results in accurate determination of the running states suitable for correcting the optical axis.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MOTORS CORP
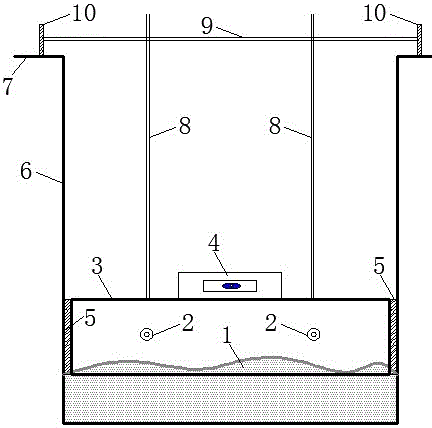
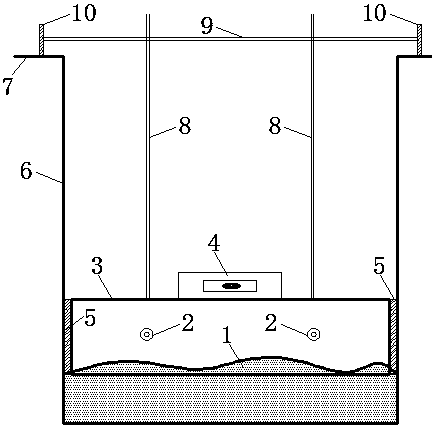
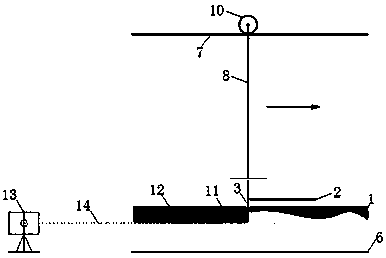
Experimental water tank sediment bed surface leveling method and experimental water tank sediment bed surface leveling device
InactiveCN105758685AHigh precision determinationHigh precision water level positionPreparing sample for investigationSoil scienceEnvironmental engineering
The invention discloses an experimental water tank sediment bed surface leveling method and an experimental water tank sediment bed surface leveling device. The experimental water tank sediment bed surface leveling device at least comprises a glass water tank (6) filled with sediments and water, a laser (13) arranged at the outer side of one end of the glass water tank (6), a horizontal I-shaped blade (3) with adjustable height, arranged in the glass water tank (6) and a level gauge (4) connected with the horizontal I-shaped blade (3). According to the method, the horizontal I-shaped blade with adjustable height is used to level the sediment bed, and level laser is used for locating and calibrating the flatness of the sediment bed, and therefore, a flat sediment bed surface having high consistency can be acquired. According to the device and the method, the water level of the sediment bed can be precisely determined, and the error range of the flatness of the sediment bed can be controlled to be up to 1mm; and besides, the horizontal I-shaped blades having different widths can be produced according to different water tank widths, and thus have wide applicability to the experimental water tank.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
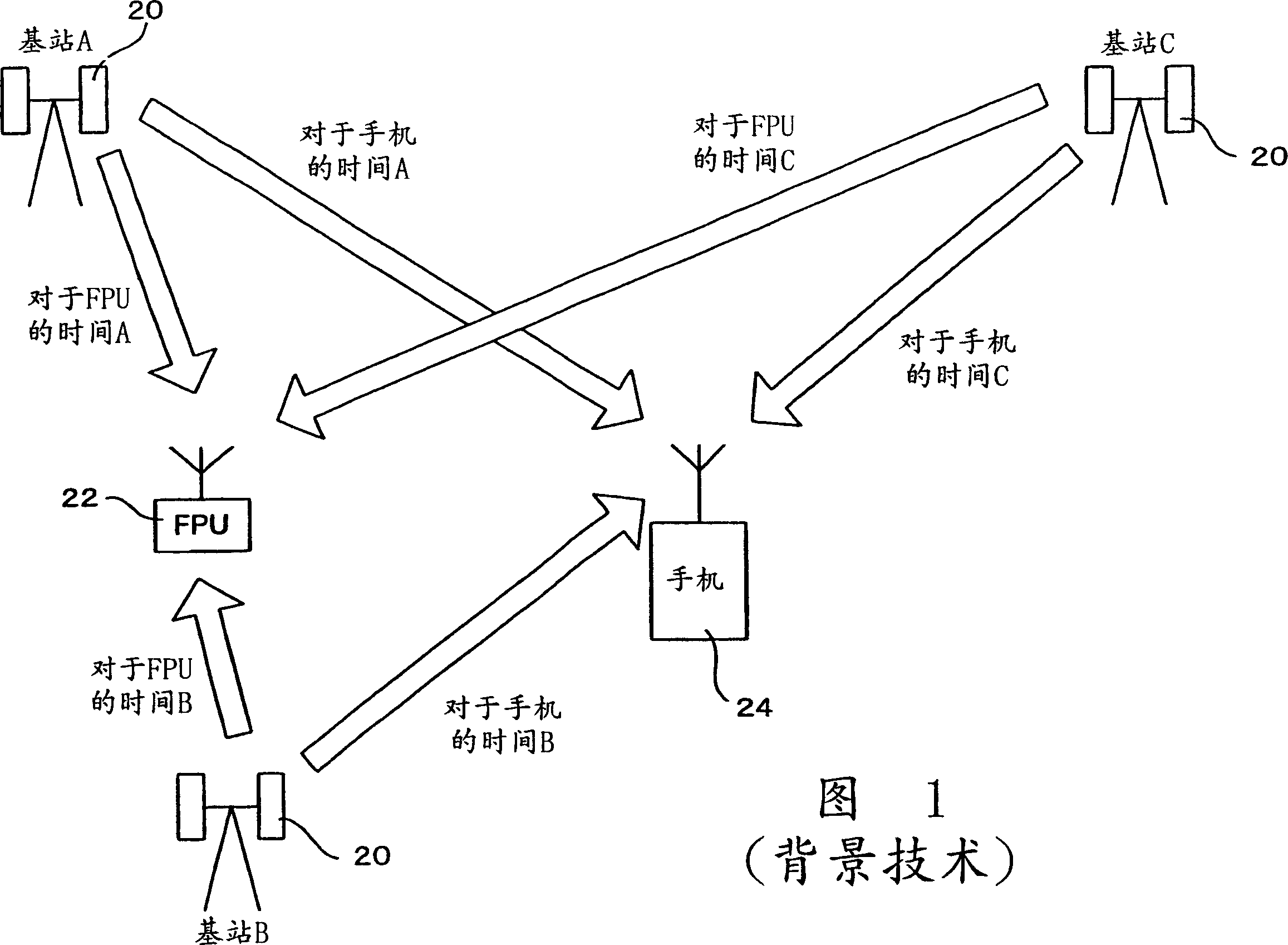
Improved positioning system and cellular communication network
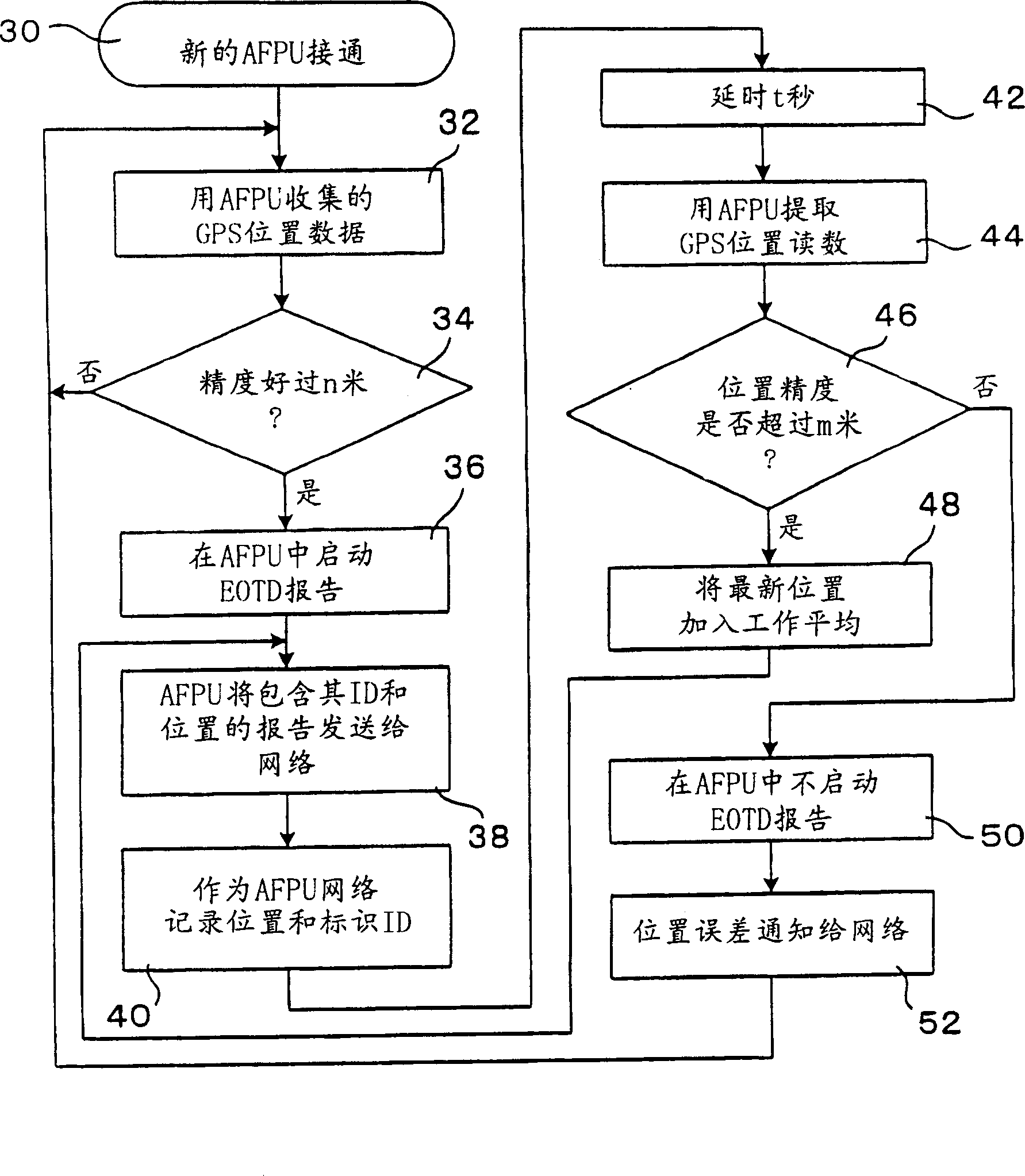
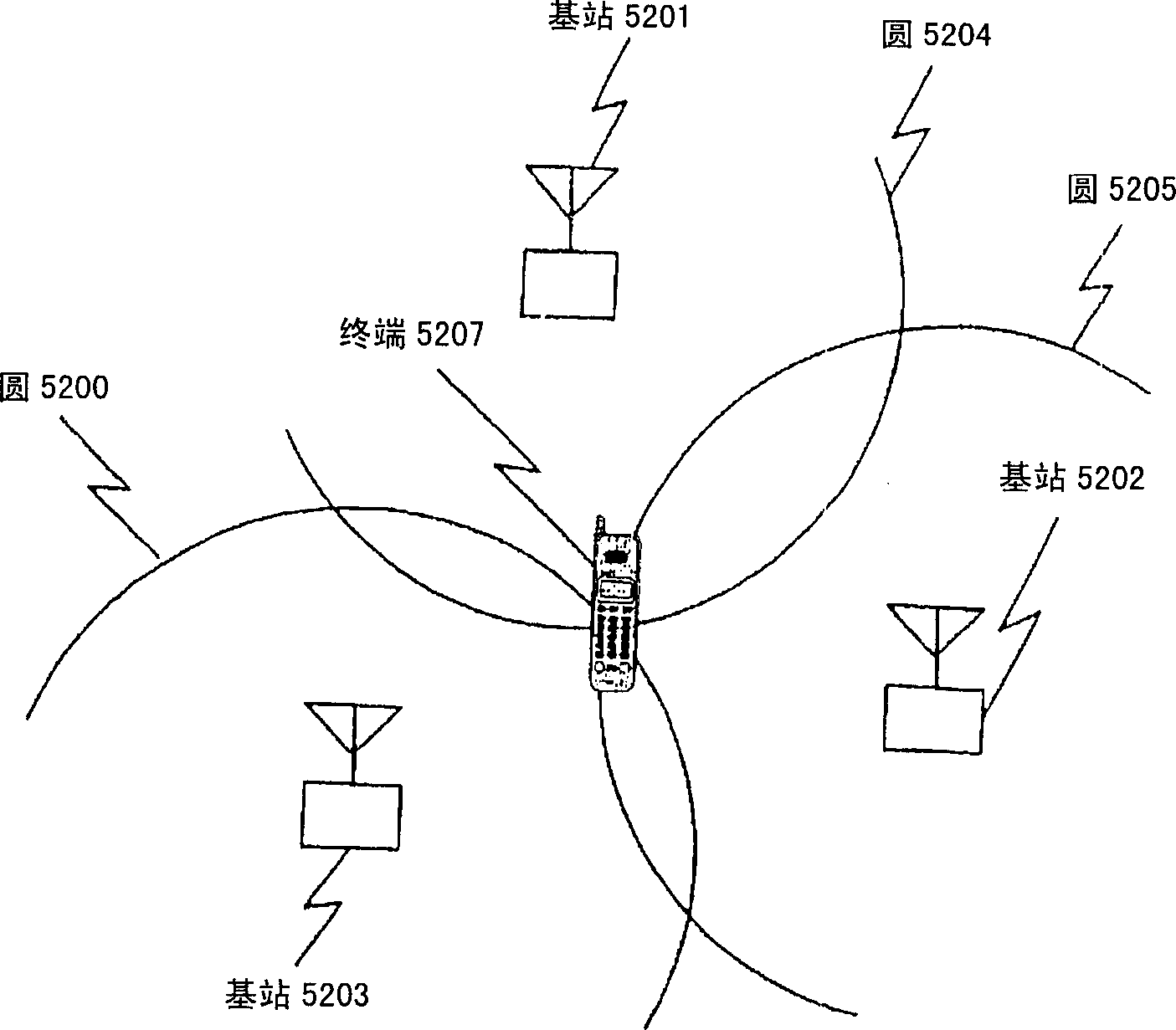
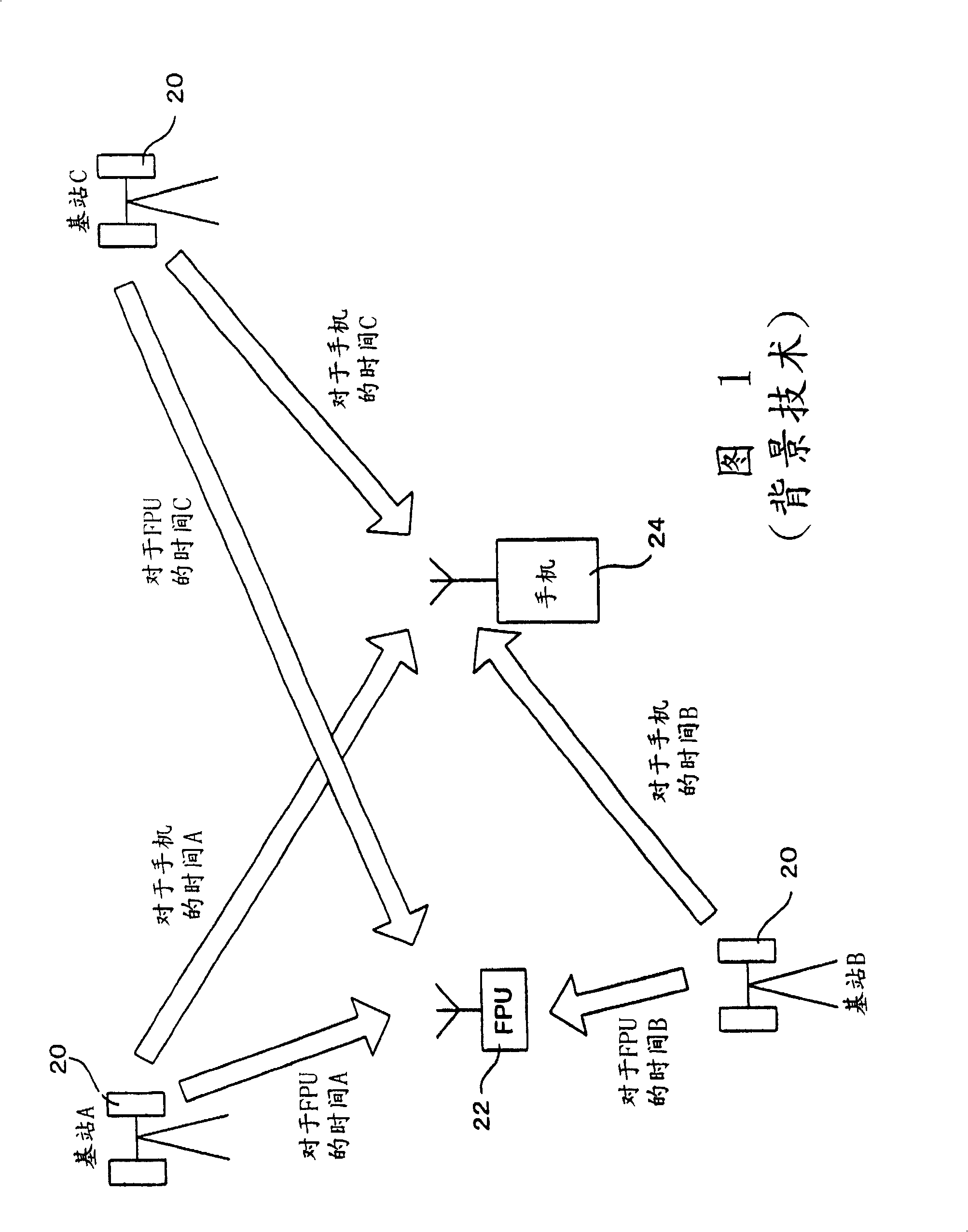
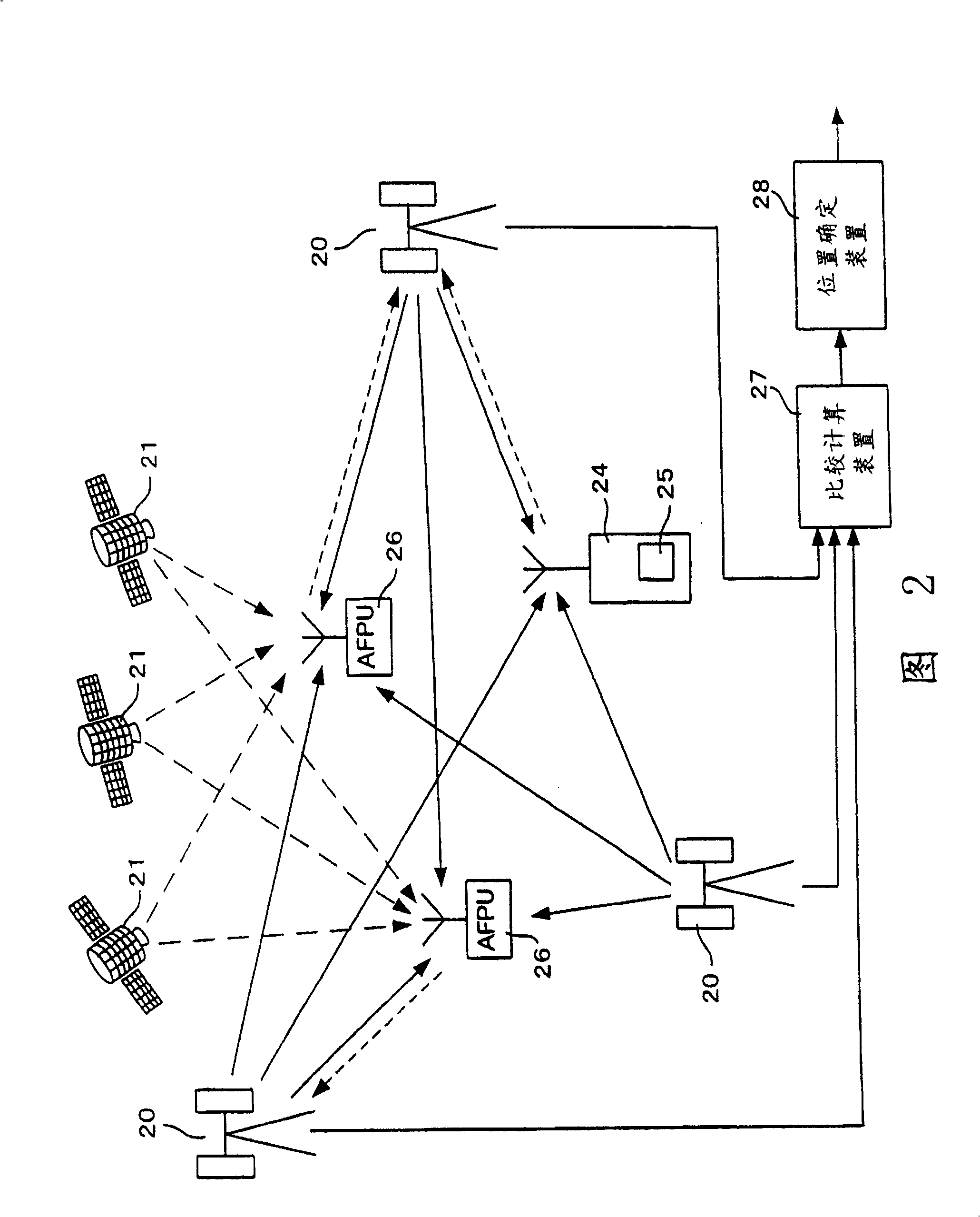
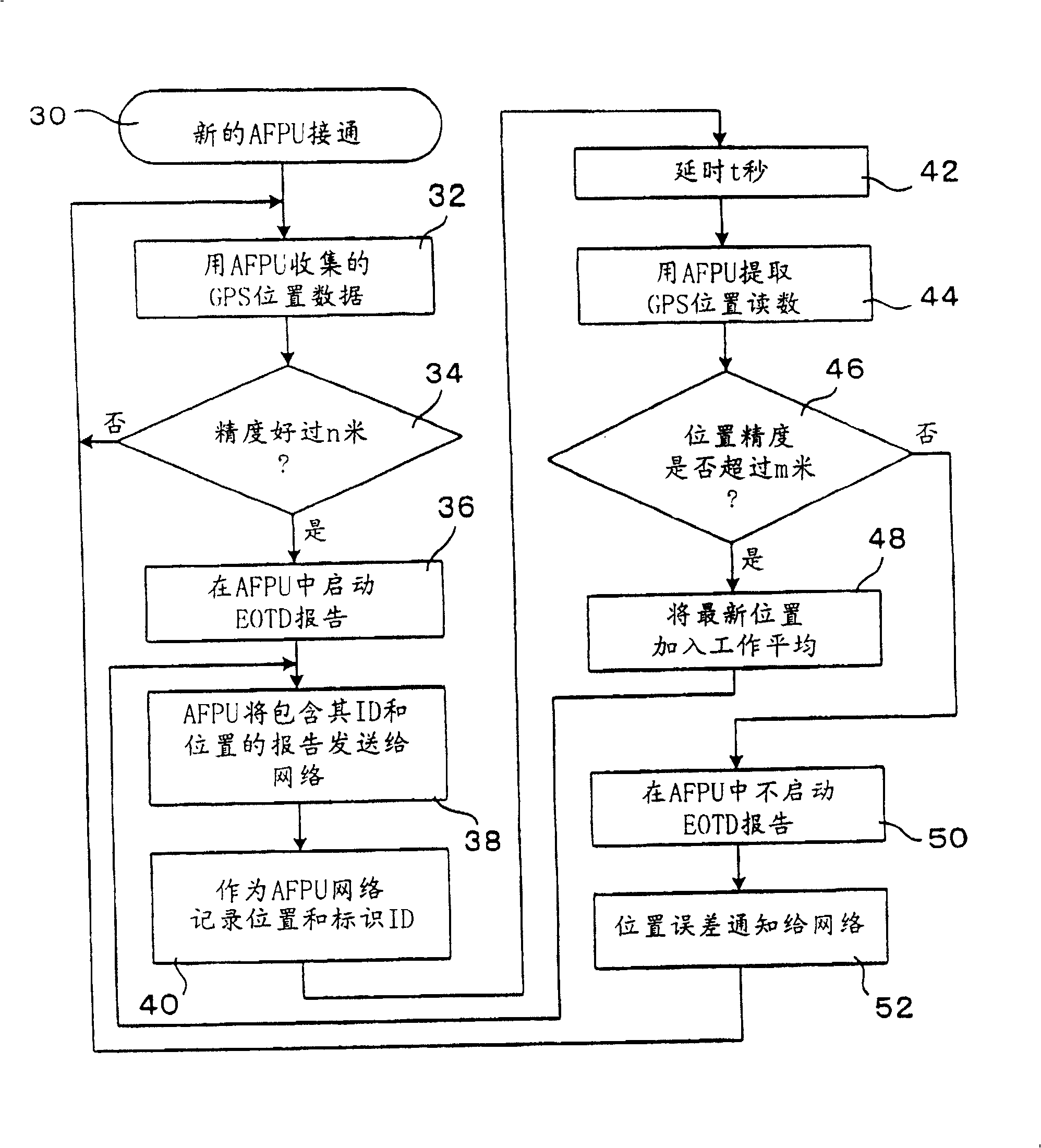
InactiveCN1449209ADoes not increase the calculationHigh precision determinationPosition fixationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTime differencePositioning system
A location system for use in a mobile communication network includes base stations which transmit known signals at predetermined times for use in deriving location data; a first transmitting and receiving units; a unit for determining times of arrival of the known signals from each base station at each of the first transmitting and receiving units; a unit for determining times of arrival of the known signals from each base station at a second transmitting and receiving unit at an unknown location; a comparing unit for comparing timing differences between the known signals received at the first transmitting and receiving units and the second transmitting and receiving unit; and location determining unit for determining the location of the second unit. Each of the first transmitting and receiving units includes a unit for deriving its location from a further set of received signals such as GPS signals.
Owner:LENOVO INNOVATIONS LTD HONG KONG
Electronic equipment
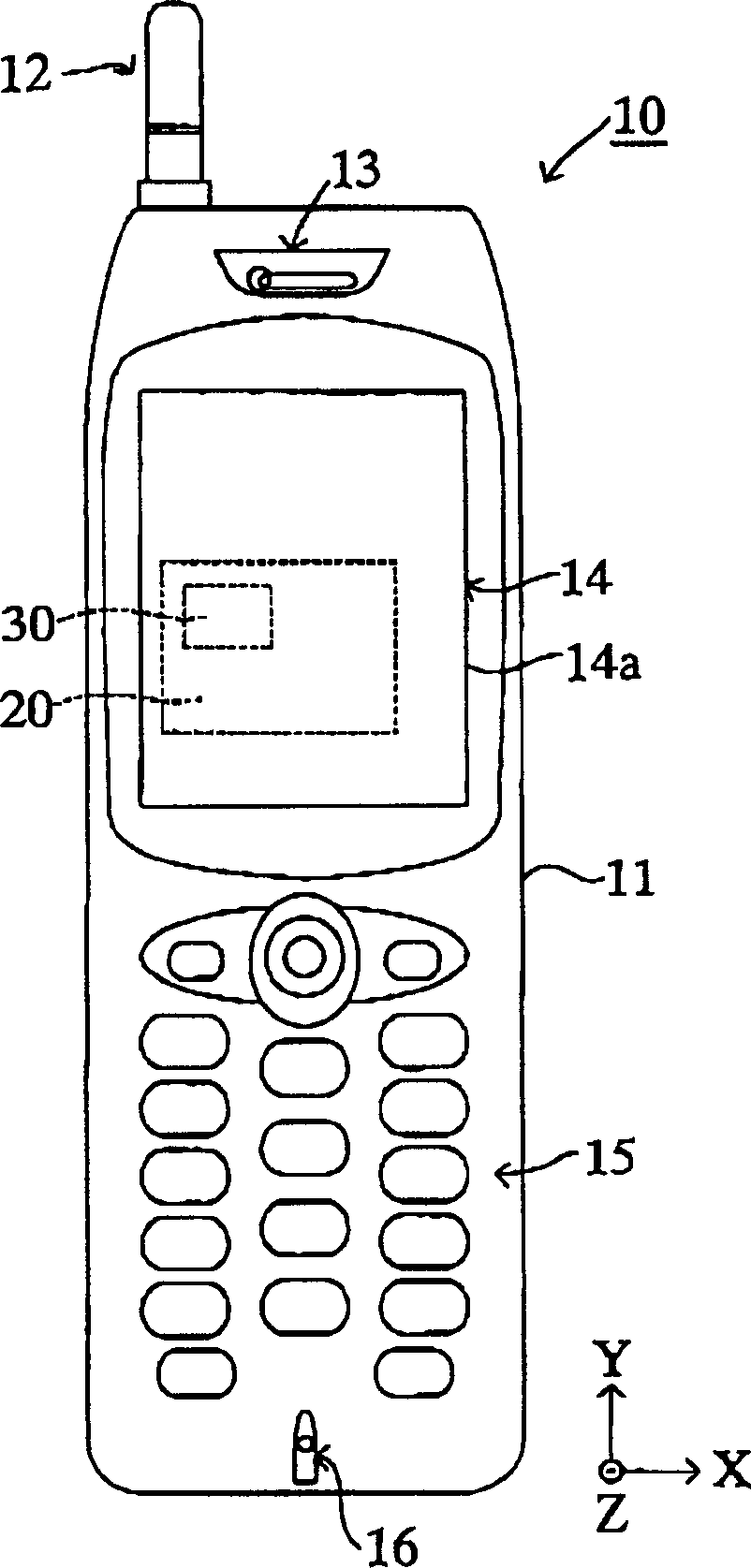
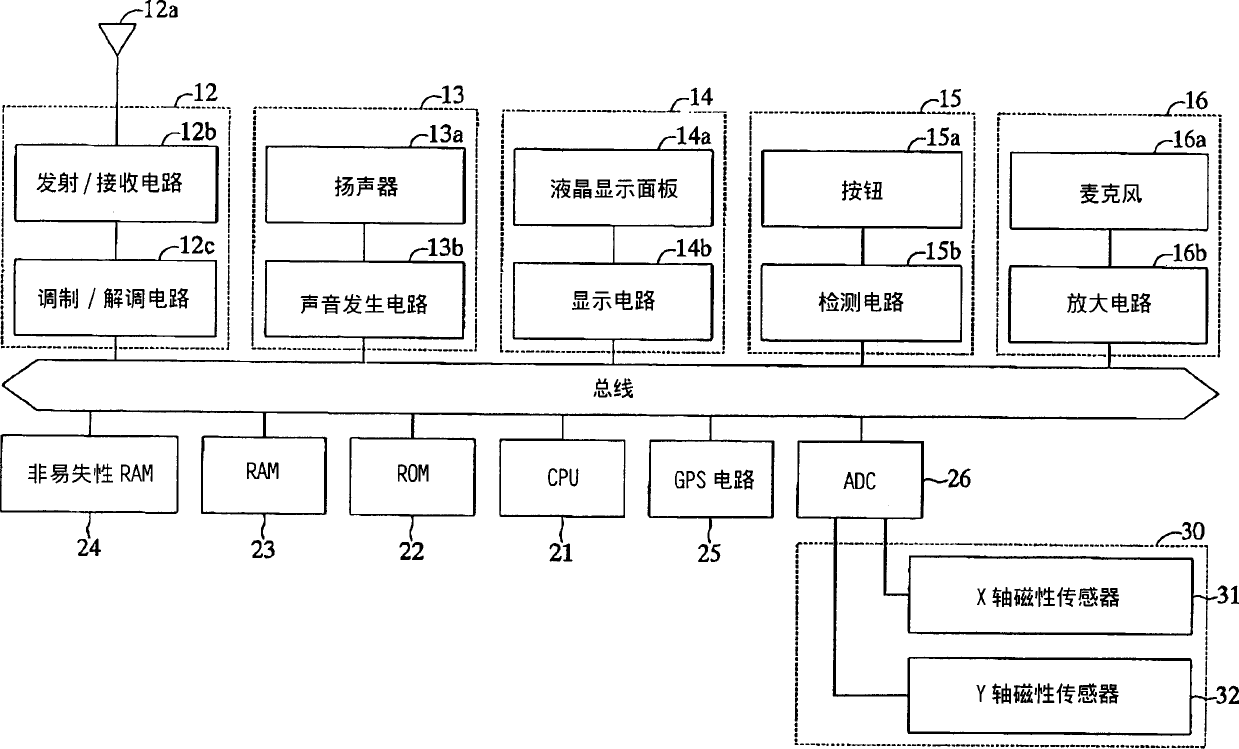
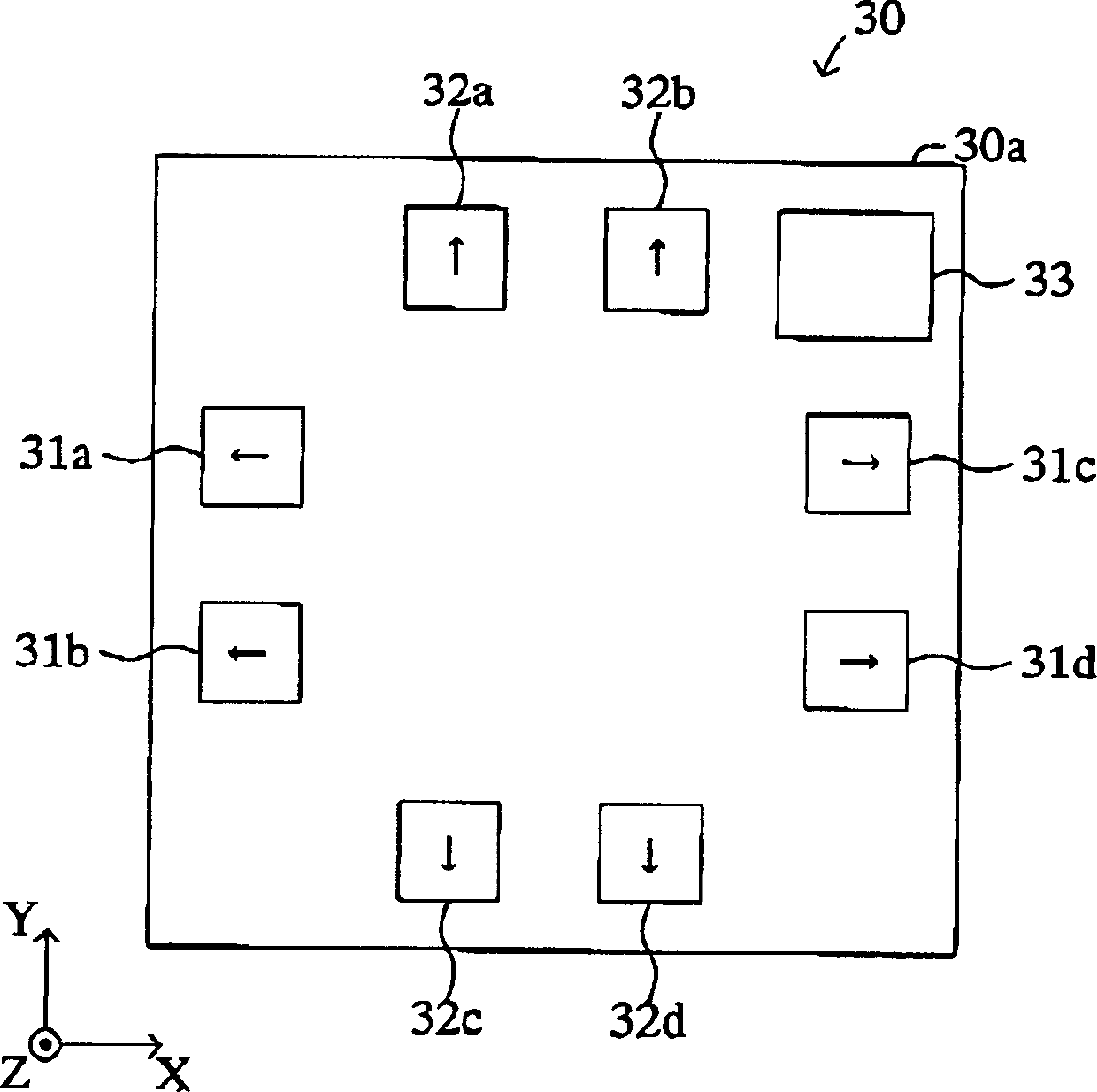
InactiveCN1422051AHigh precision determinationDetermining where a subject is located can be corrected for inclination with high precisionGalvano-magnetic devicesSolid-state devicesTransverse axisEngineering
A cellular phone includes an X-axis magnetic sensor for outputting a first value corresponding to a component of an external magnetic field along the direction of a transverse axis of the main body, and a Y-axis magnetic sensor for outputting a second value corresponding to a component of the external magnetic field along the direction of a longitudinal axis of the main body. The cellular phone includes a ROM which stores a conversion table defining the relation between the first and second values and values of azimuth and inclination angle of the longitudinal axis of the main body. The cellular phone determines the azimuth and inclination angle on the basis of the first and second values actually output from the X-axis and Y-axis magnetic sensors and with reference to the conversion table.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
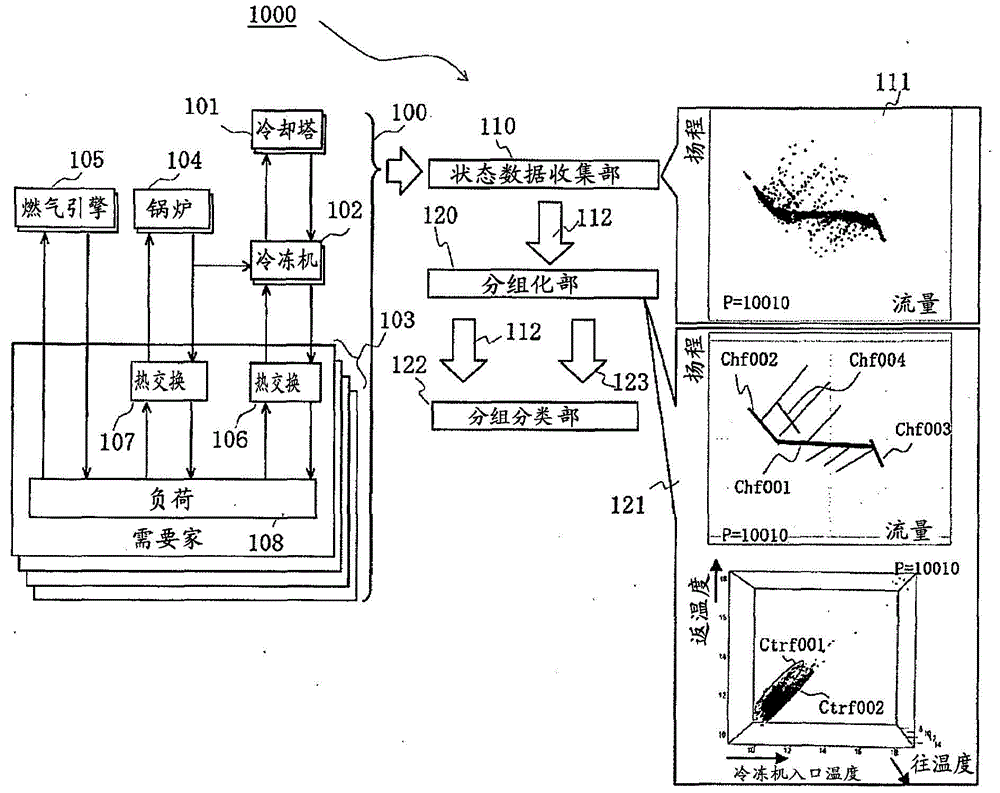
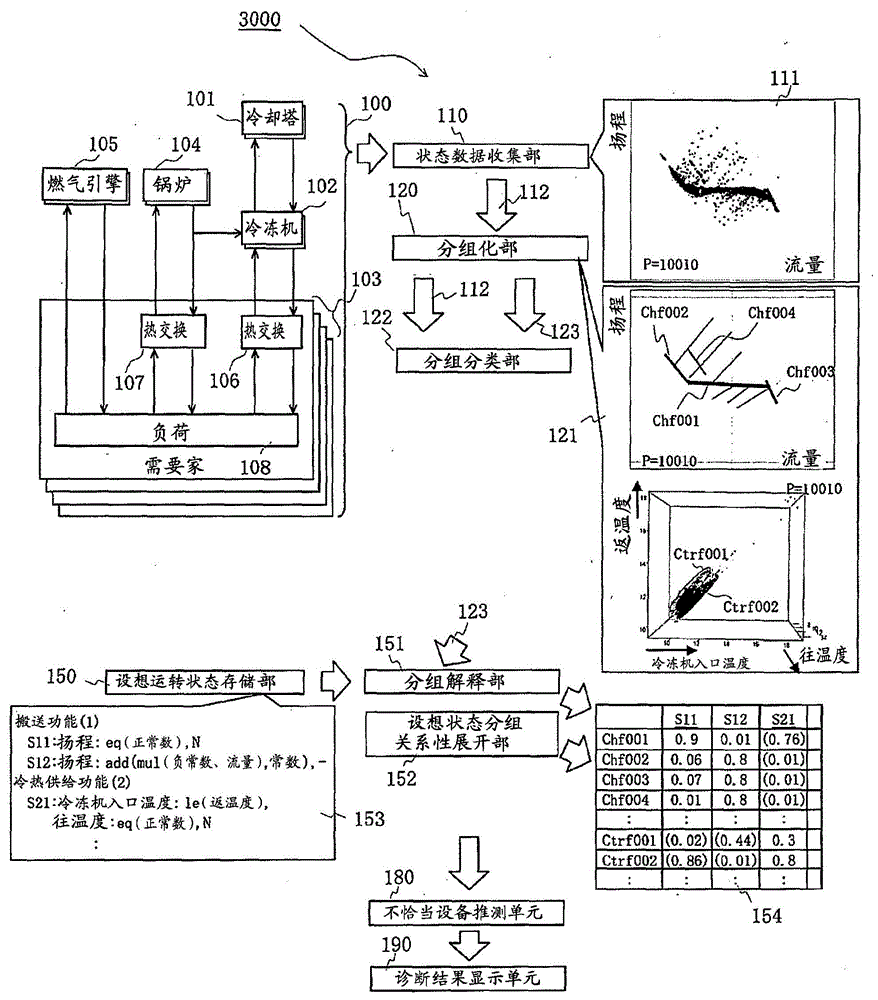
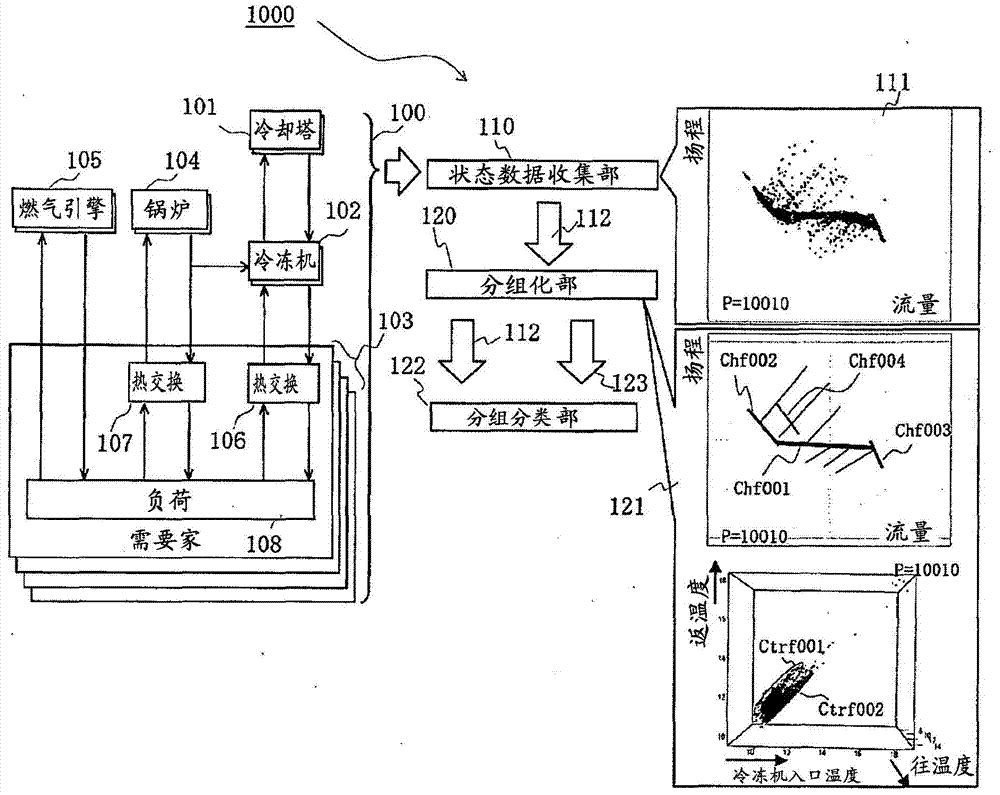
Monitoring and diagnostic device of apparatus
The invention provides a monitoring and diagnostic device of an apparatus. Even if the monitoring and diagnostic device is unmatched with the apparatus at first in an operation stage, the monitoring and diagnostic device is capable of detecting defective operation conditions and highly precisely determining the apparatus which has deep relation with it. The monitoring and diagnostic device monitors the operation of machines which parallel form a region energy supply system of a workshop. The monitoring and diagnostic device is provided with a part which measures and stores process amounts during operation of devices and ON / OFF states of the devices in operation and performs grouping according to functions of water sending, cold and heat supplying, heat exchanging and so on. The monitoring and diagnostic device is also provided with a grouping / classification part which judges groups to which the functions of the targeted workshop belong and display process amounts and relations of the grouping in all function units according to processing amounts and ON / OFF states collected in a certain period.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
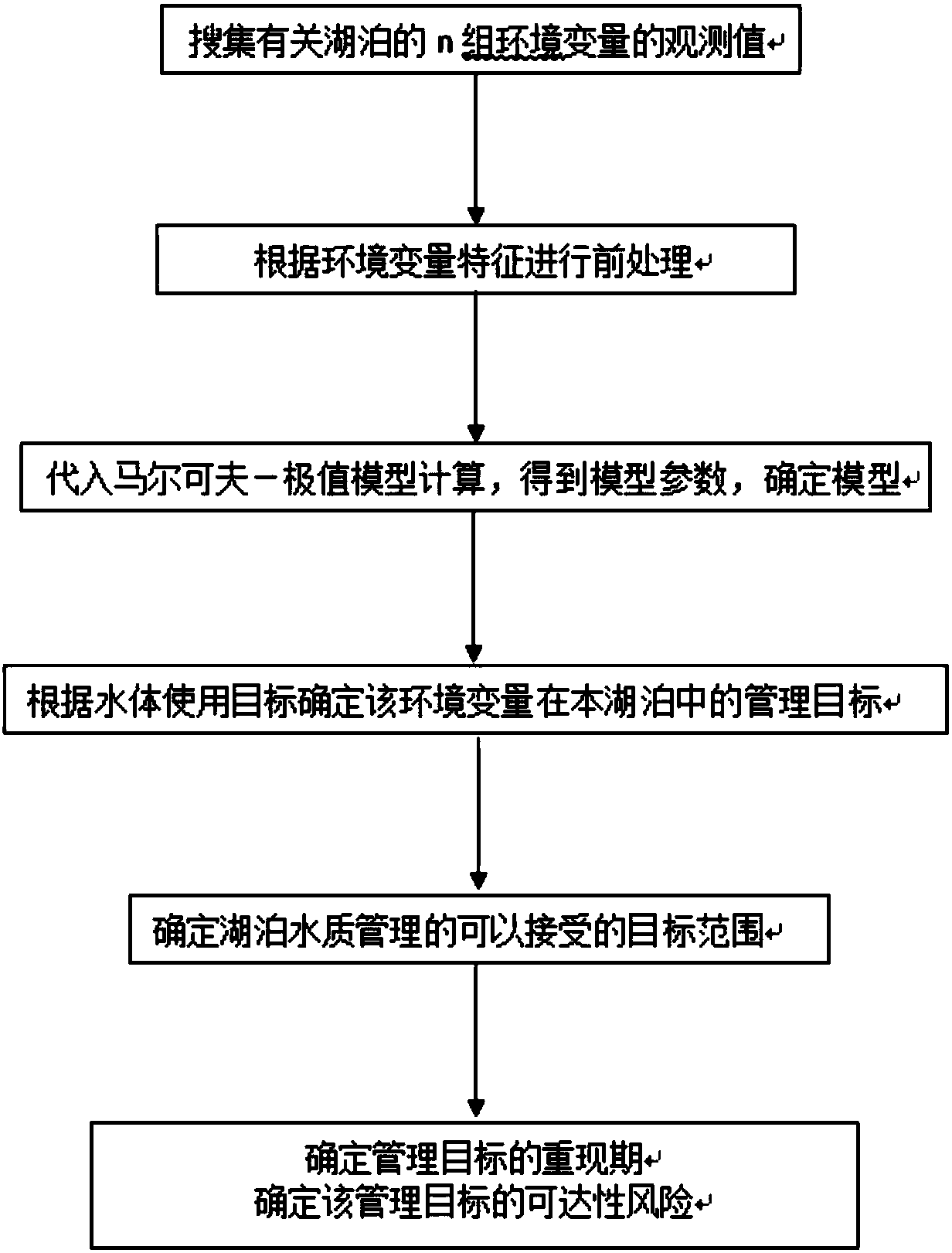
Method for determining acceptable range and reachability risk of lake water quality management target
ActiveCN108492042AHigh precision determinationGeneral water supply conservationResourcesObservation dataReachability
The invention discloses a method for determining an acceptable range and a reachability risk of a lake water quality management target. The method comprises the following steps of (1) collecting observation values of n groups of environment variables of a lake needed to be subjected to water quality management target determination; (2) substituting the processed observation values into a Markov-Extremal model for calculation to obtain model parameters, and determining a model result; (3) according to a lake water body usage target, determining the management target of the environment variablesin the lake; (4) determining the acceptable target range of lake water quality management in combination with the model result and the lake water body usage target; and (5) determining a recurrence period of the management target, and according to the recurrence period of the management target, determining the reachability risk of the management target. The method for determining the acceptable range and the reachability risk of the lake water quality management target based on the Markov-Extremal model is easy to popularize and apply in determination of management targets and target ranges of various lake water bodies without loss of an observation data quantity.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
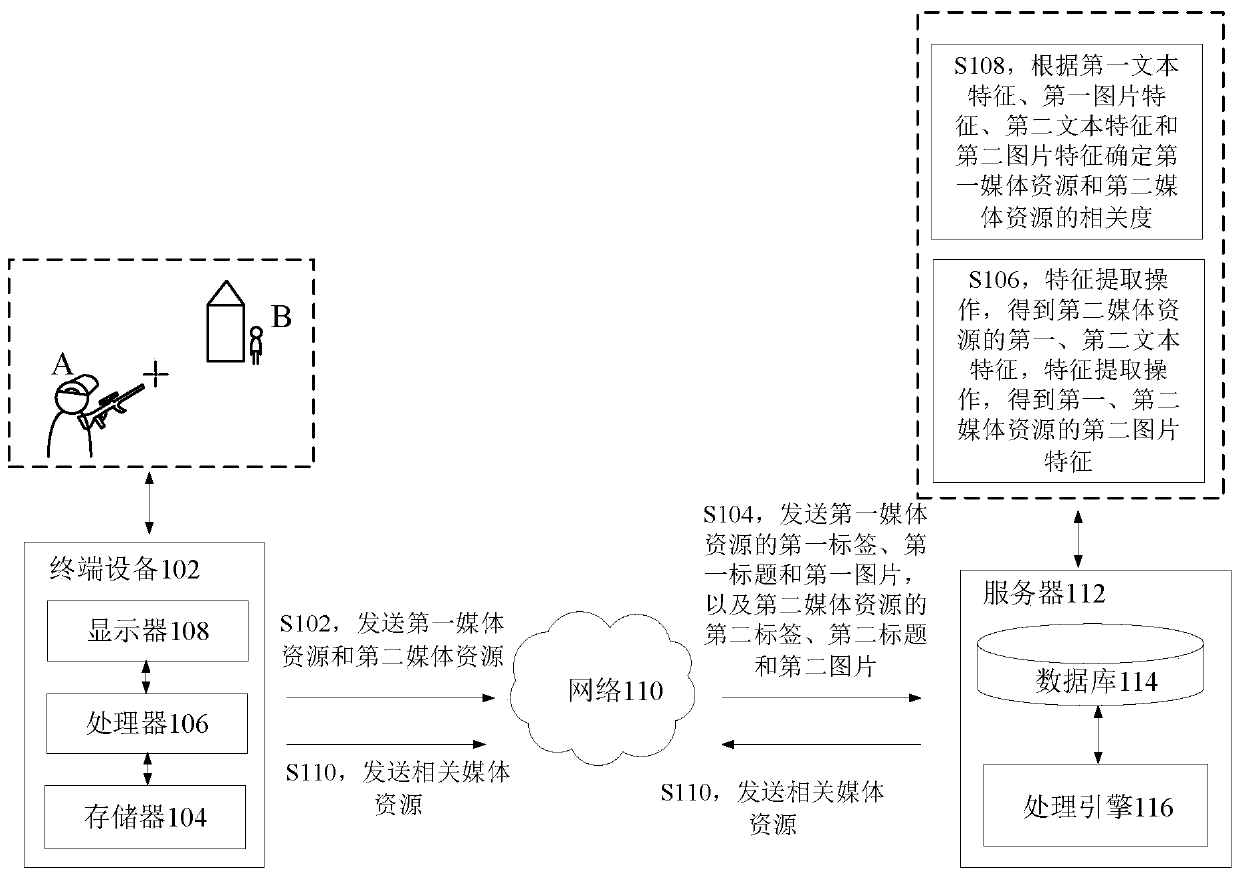
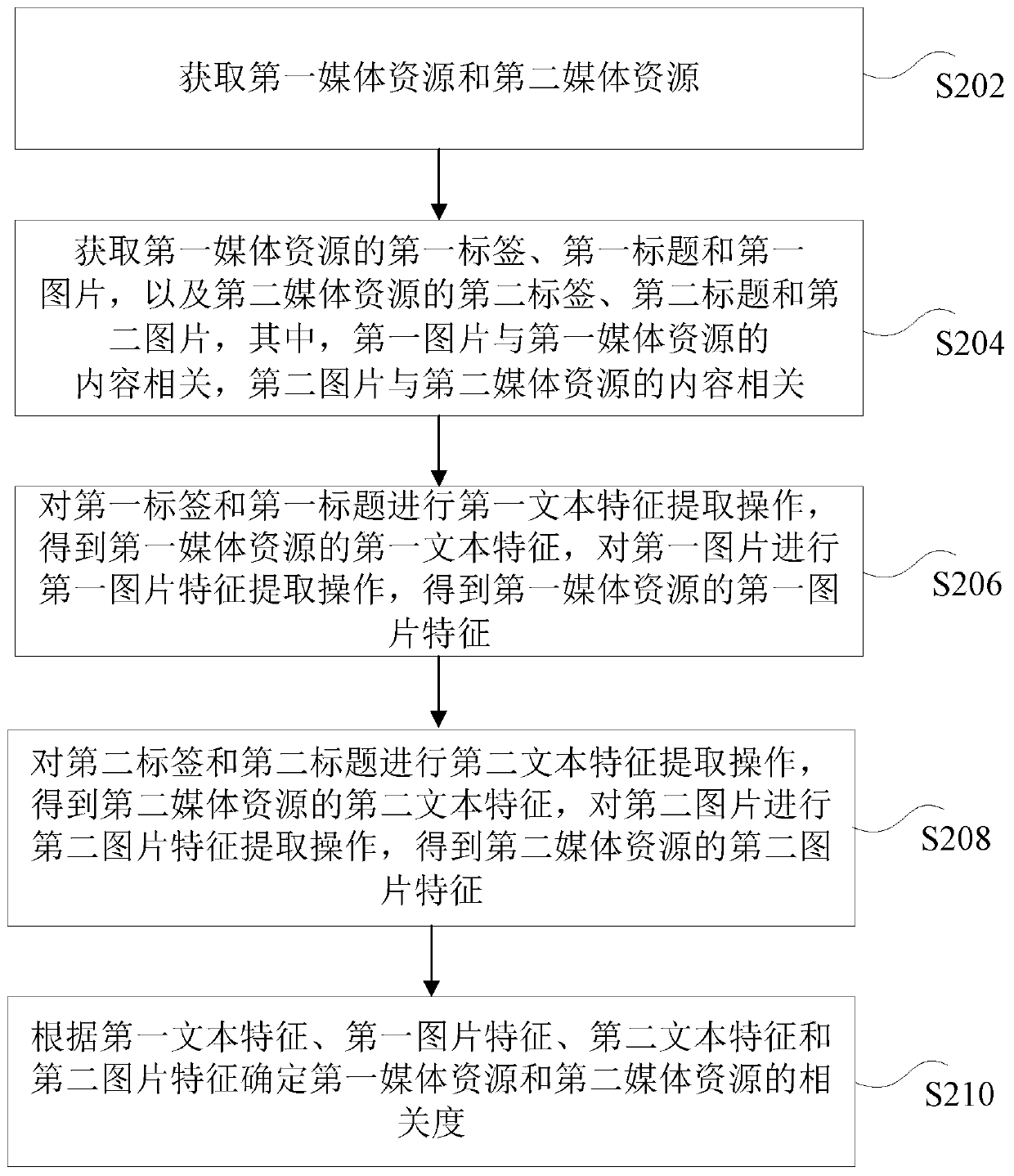
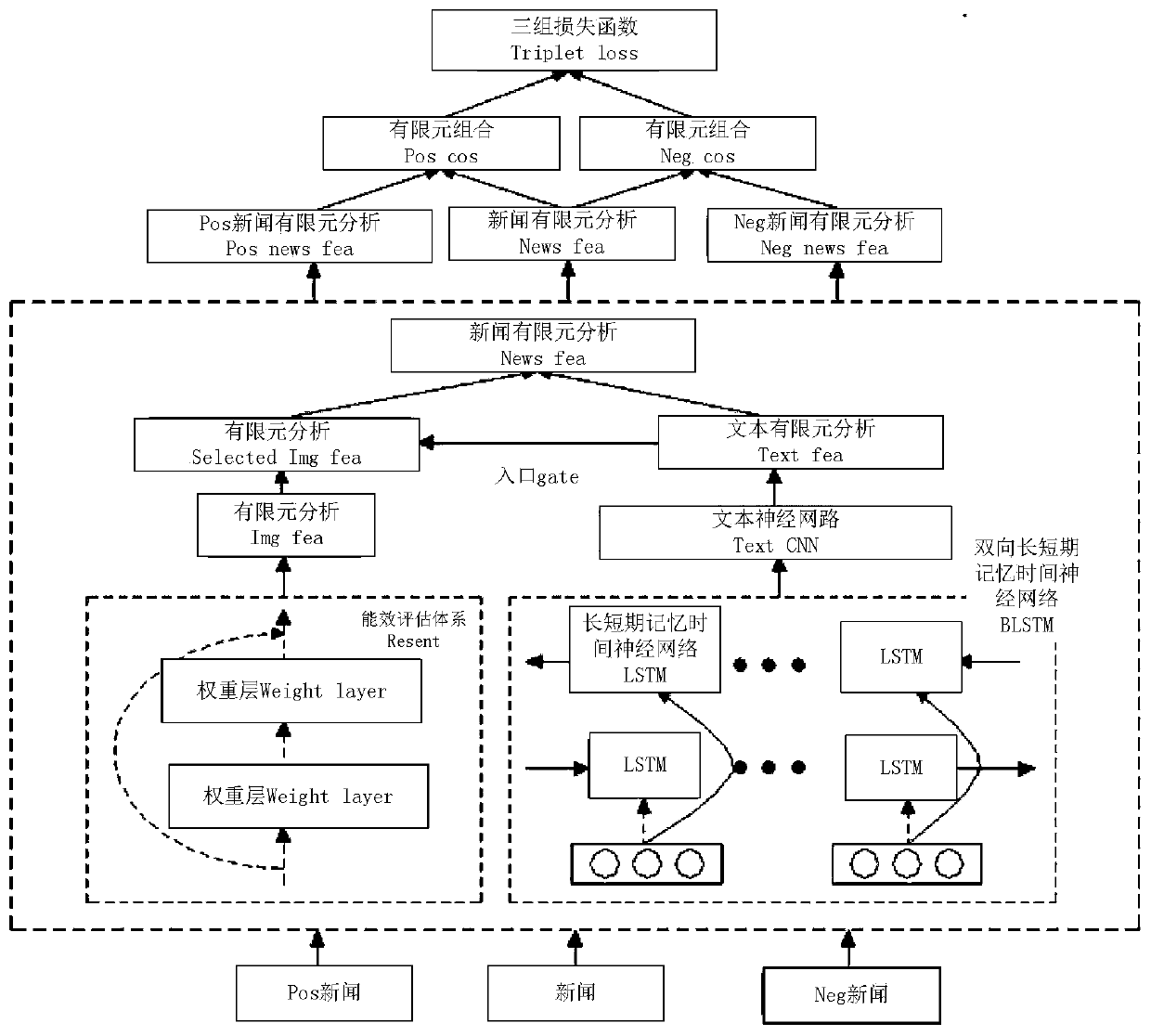
Media resource processing method and device, storage medium and electronic device
ActiveCN111125386ATroubleshoot technical issues with low precisionHigh precision determinationMetadata multimedia retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsMediaFLOEngineering
The invention discloses a media resource processing method and device, a storage medium and an electronic device. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a first label, a first title and afirst picture of a first media resource, and a second label, a second title and a second picture of a second media resource to obtain a first text feature of the first media resource and a first picture feature of the first media resource; obtaining a second text feature of the second media resource, and obtaining a second picture feature of the second media resource; determining the relevancy between the first media resource and the second media resource according to the first text feature, the first picture feature, the second text feature and the second picture feature. The purpose of determining the relevancy between the media resources according to the labels and titles of the media resources and the content of the media resources is achieved, and then the technical problem that in the prior art, the accuracy of pushing the multimedia resources is low is solved.
Owner:深圳市雅阅科技有限公司
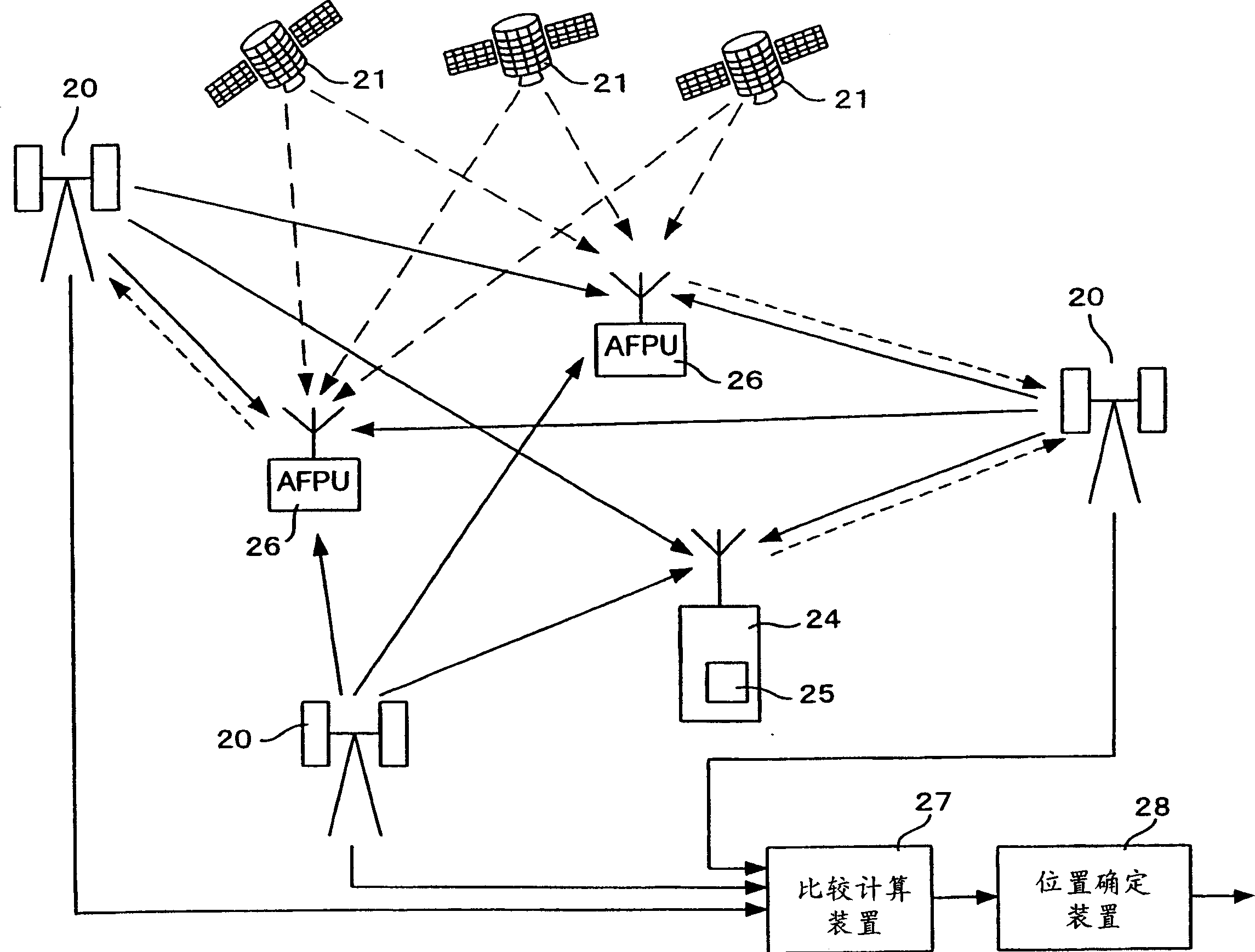
Terminal position identification method and system thereof
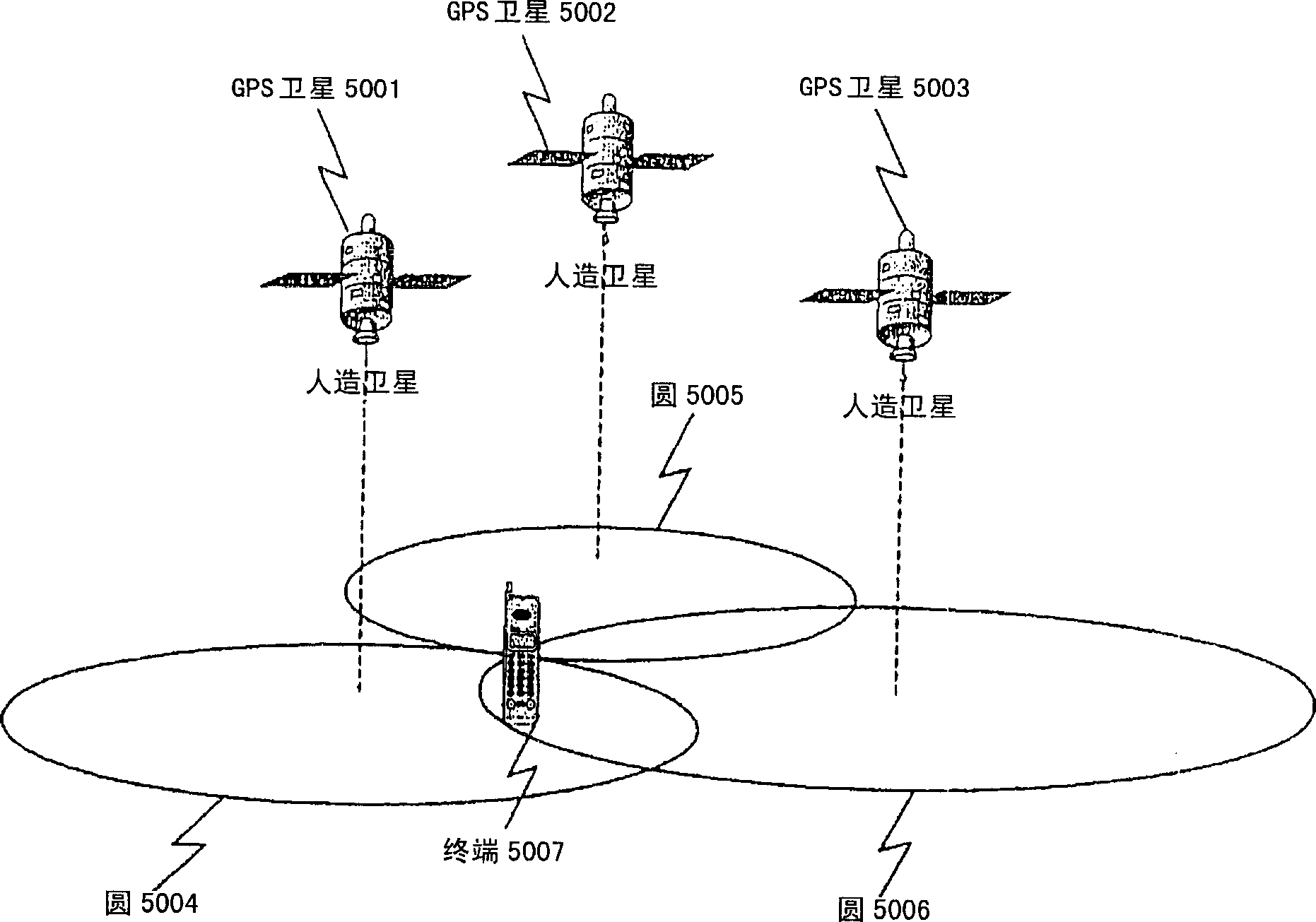
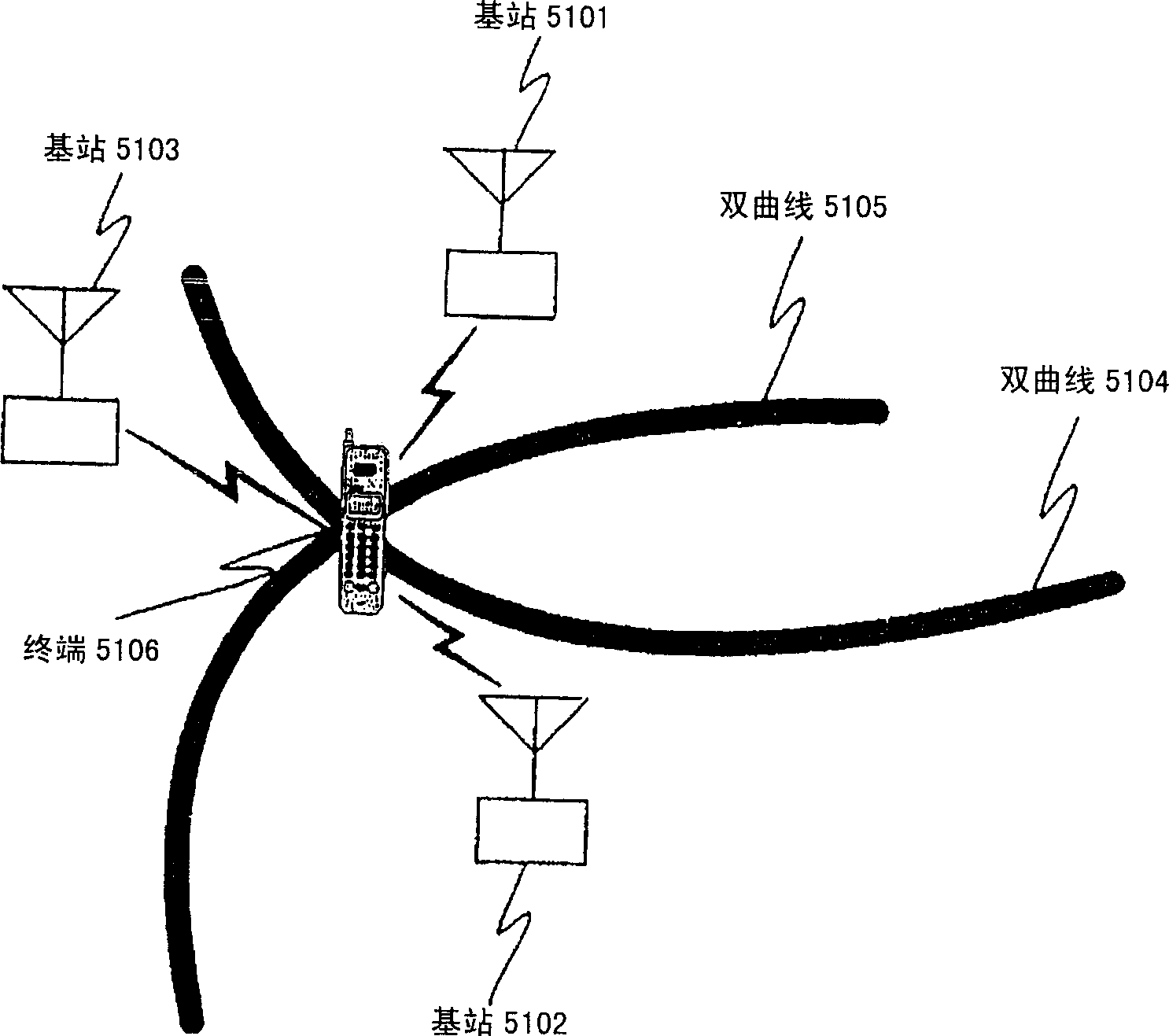
InactiveCN1864076AHigh precision determinationPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingPropagation timeEngineering
The invention is to provide a technique for specifying the location of a terminal with a high degree of accuracy even in an environment in which the grand total of the number of base stations and GPS satellites that can be measured is only two stations. A hyperbola 11 is found from the difference between the reception time of a signal from a base station 22 and the reception time of a signal from a base station 23 in a terminal 21, and a circle 12 is found from the round-trip propagation time between the base station 22 and the terminal 21. Intersection points between the hyperbola 11 and the circle 12 is calculated to find a candidate point 13 and a candidate point 14. The terminal 21 is located in a sector 27, so that the candidate point 13 existing in the range of the sector 27 is specified as the location of the terminal 27.
Owner:NEC CORP
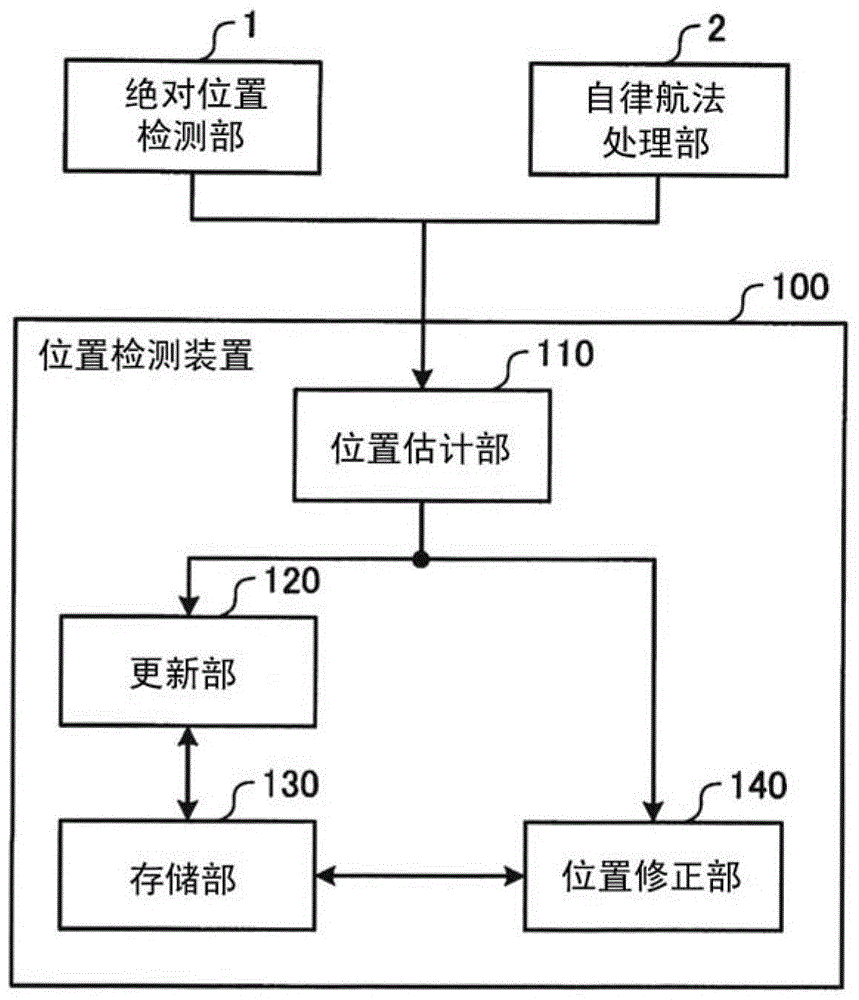
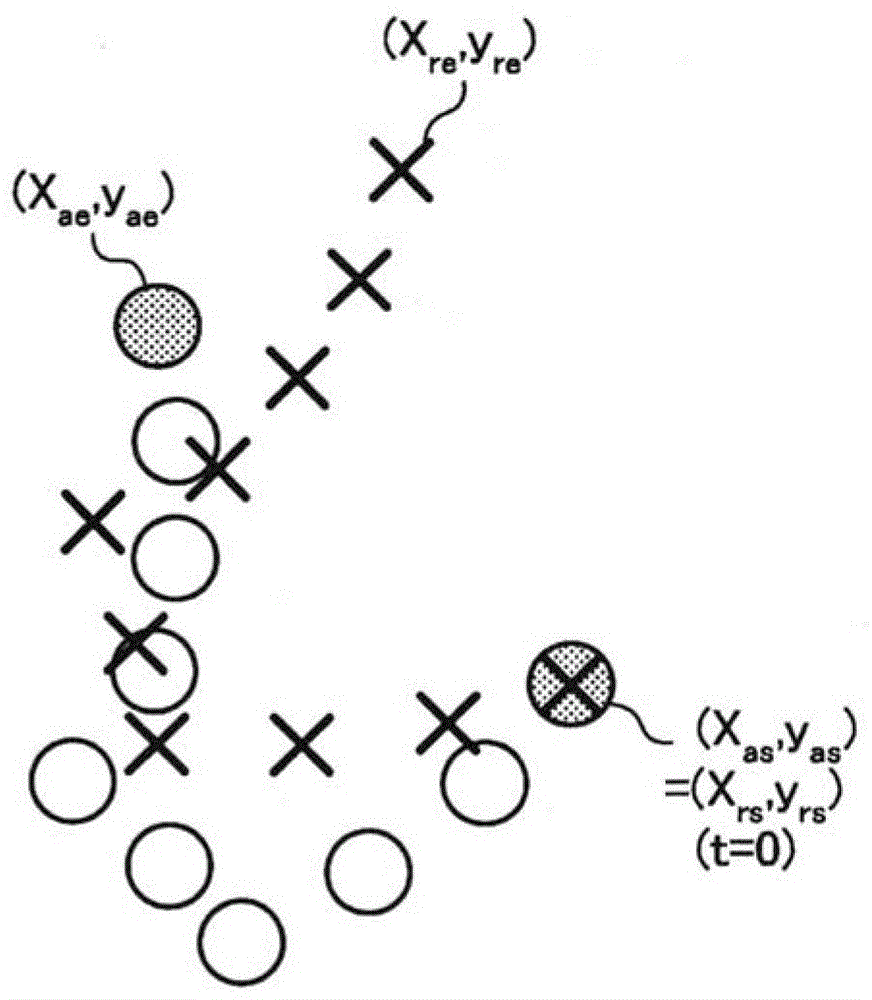
Position measurement device
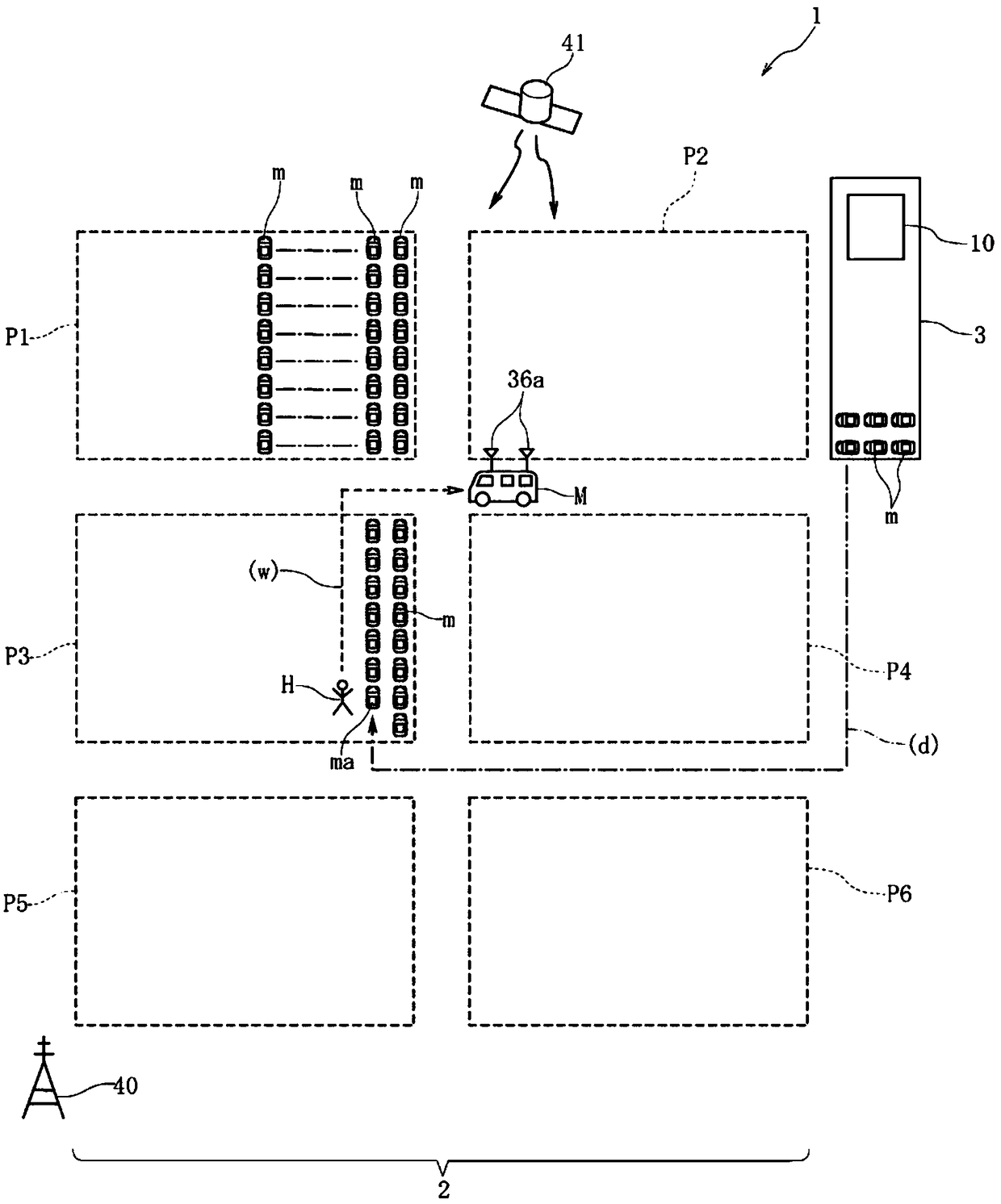
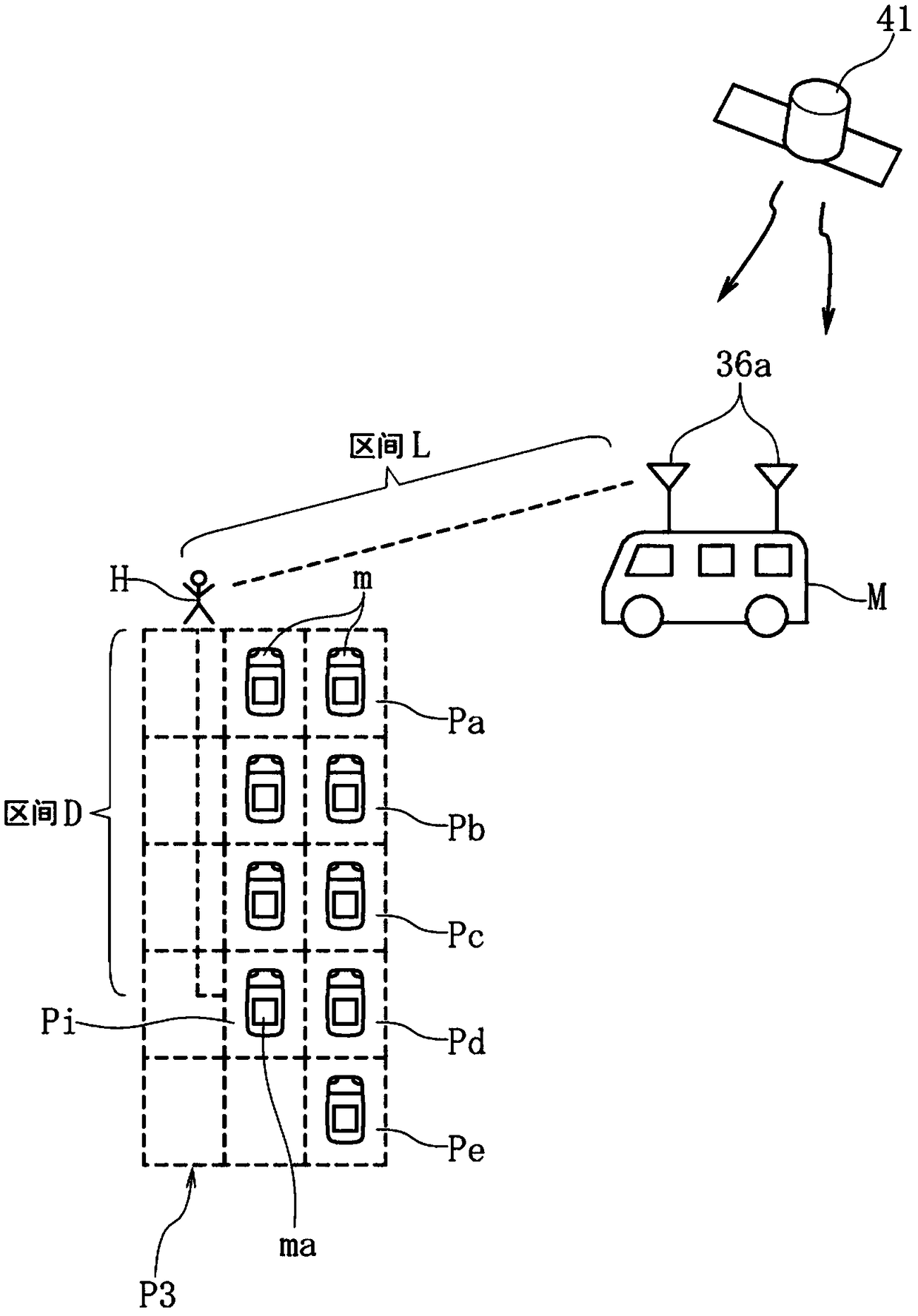
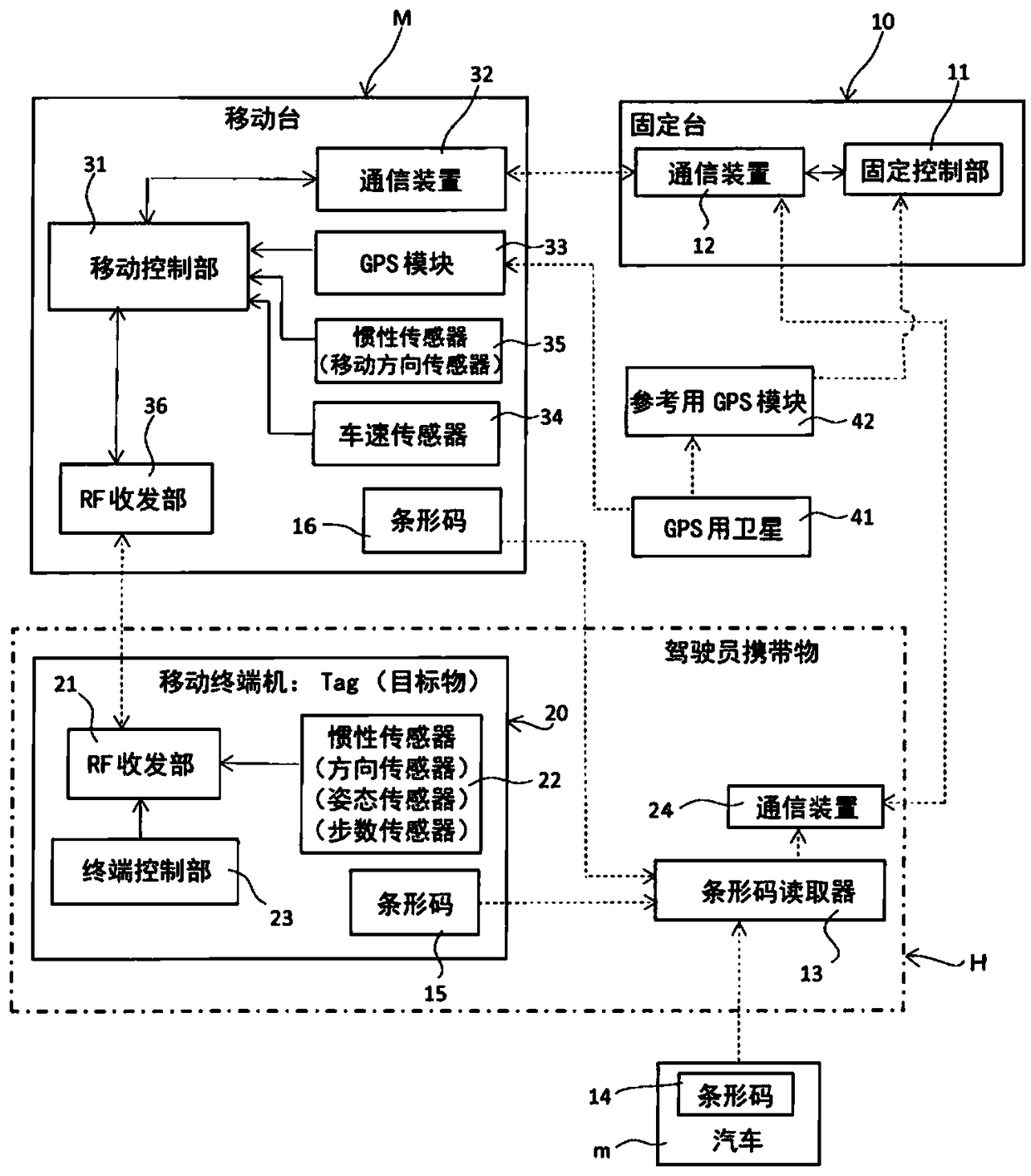
InactiveCN109154643AHigh precision determinationHigh-precision detectionSynchronisation arrangementPosition fixationMobile stationRemote sensing
To provide a position measurement device capable of accurately detecting the position of a target within a wide measurement area. A mobile station M is moved close to a mobile terminal 20 that is a target. In ST1, the absolute position of the mobile station M within absolute coordinates (Abs) set in a measurement area is calculated. In ST2, the relative position of the mobile terminal 20 within relative coordinates (Rel) set by the mobile station M is detected. In ST3, the orientation of the mobile station M in the absolute coordinates (Abs) is detected. In ST4, the relative coordinates (Rel)are rotated. In ST5, the absolute position of the mobile terminal 20 in the absolute coordinates (Abs) is specified.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
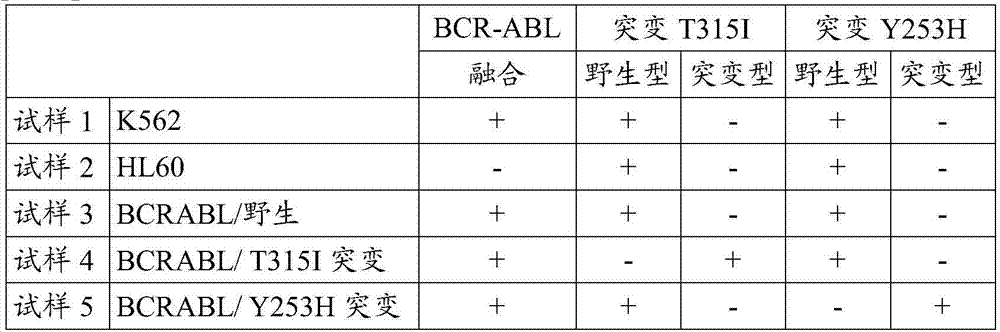
Method for detecting BCR-ABL inhibitor resistance-related mutations, and data acquisition method for predicting resistance to BCR-ABL inhibitor using said method
InactiveCN107075584AHigh precision determinationHigh precisionMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsMyeloid leukemiaBCR-ABL Fusion Gene
Owner:TOYO KOHAN CO LTD +1
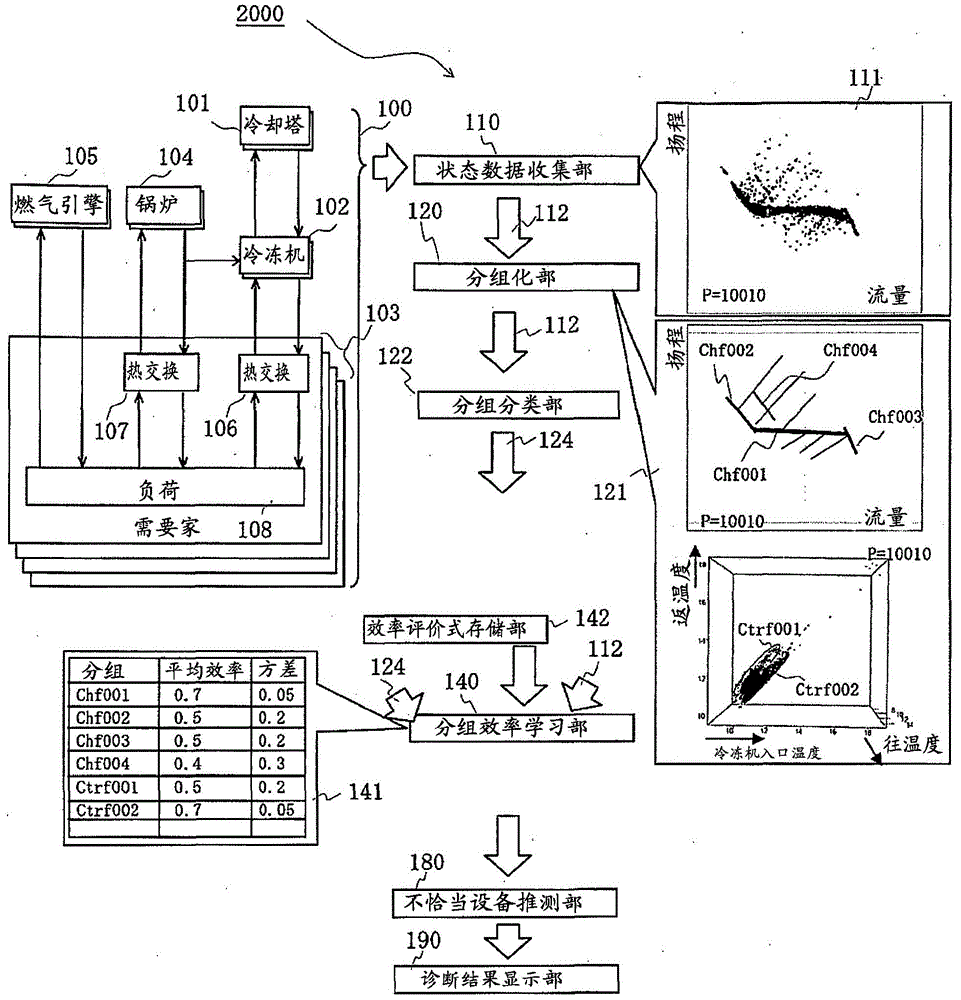
Equipment monitoring and diagnosis device
InactiveCN104571077BHigh precision determinationElectric testing/monitoringDevice MonitorEngineering
The invention provides a monitoring and diagnostic device of an apparatus. Even if the monitoring and diagnostic device is unmatched with the apparatus at first in an operation stage, the monitoring and diagnostic device is capable of detecting defective operation conditions and highly precisely determining the apparatus which has deep relation with it. The monitoring and diagnostic device monitors the operation of machines which parallel form a region energy supply system of a workshop. The monitoring and diagnostic device is provided with a part which measures and stores process amounts during operation of devices and ON / OFF states of the devices in operation and performs grouping according to functions of water sending, cold and heat supplying, heat exchanging and so on. The monitoring and diagnostic device is also provided with a grouping / classification part which judges groups to which the functions of the targeted workshop belong and display process amounts and relations of the grouping in all function units according to processing amounts and ON / OFF states collected in a certain period.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
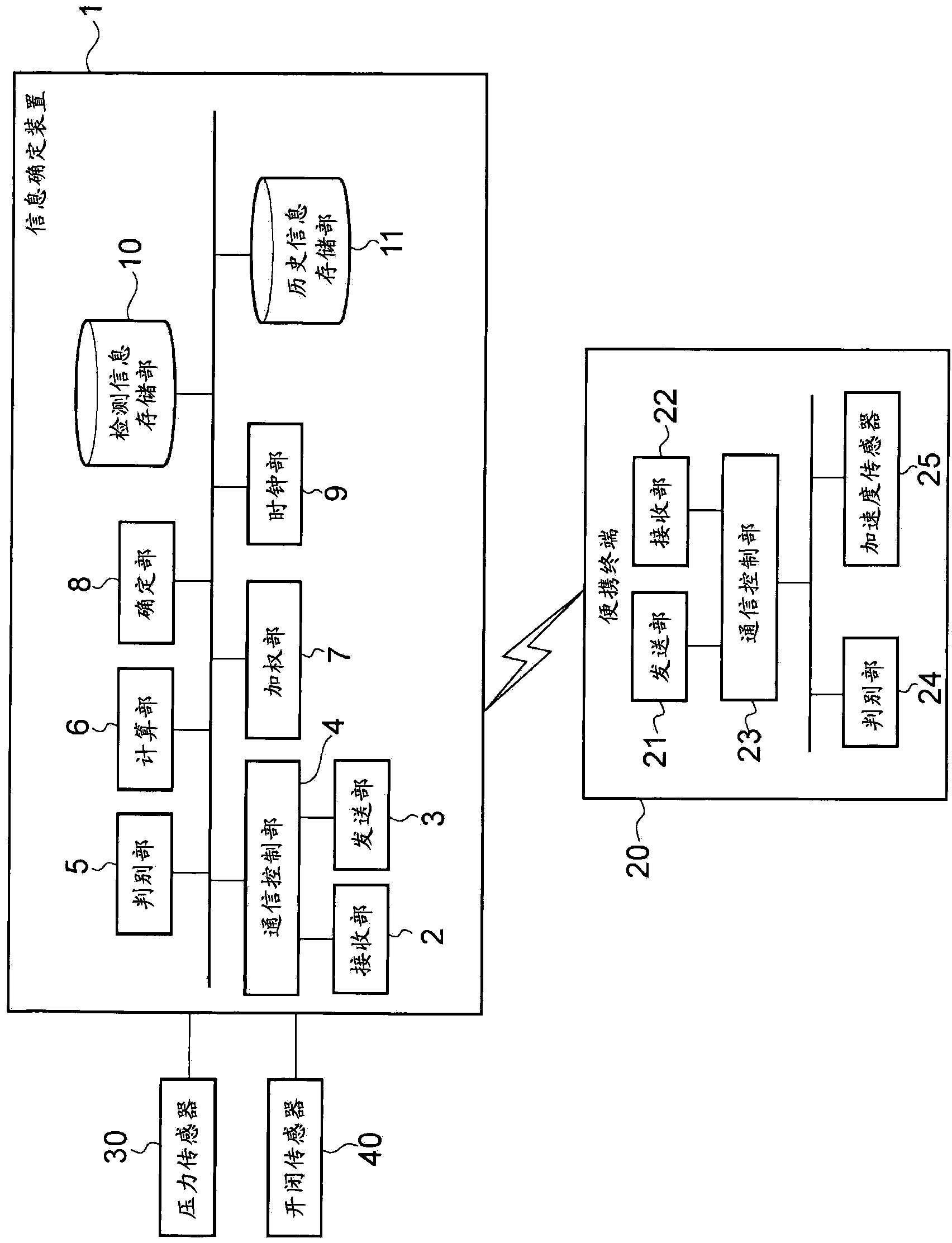
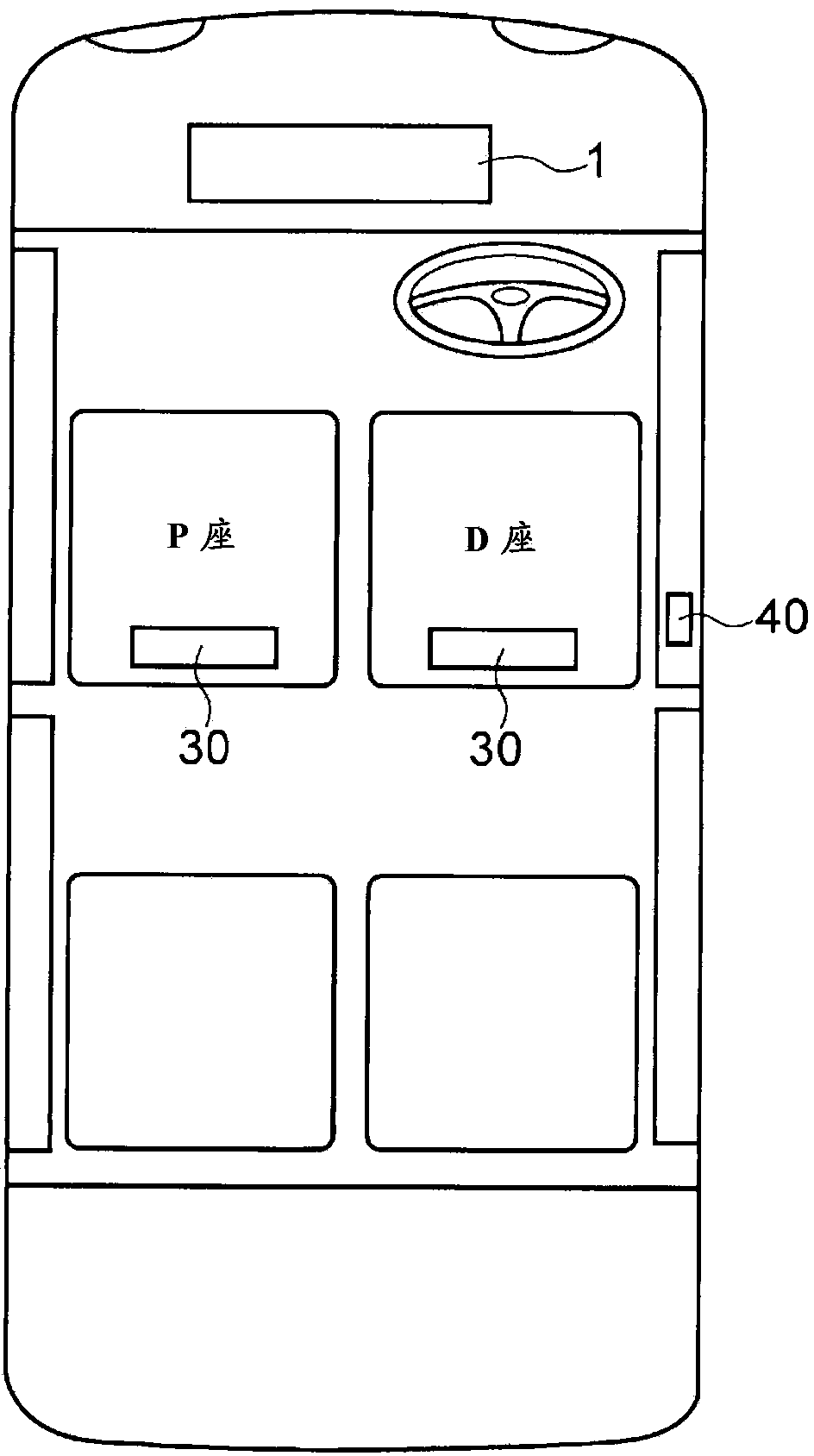
Information identification device
ActiveCN104364127AHigh precisionAccurate detectionForce measurementPosition fixationComputer terminalIdentification device
The present invention improves the accuracy in identifying a portable terminal possessed by the driver among portable devices that are brought into the cabin. An information identification device which is capable of communicating with portable terminals and sensors mounted in a vehicle is configured such that when communication signals transmitted from the portable terminals that have been brought into the cabin and output signals output from the sensors are detected, the portable device of the driver is identified on the basis of information pertaining to those signals.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
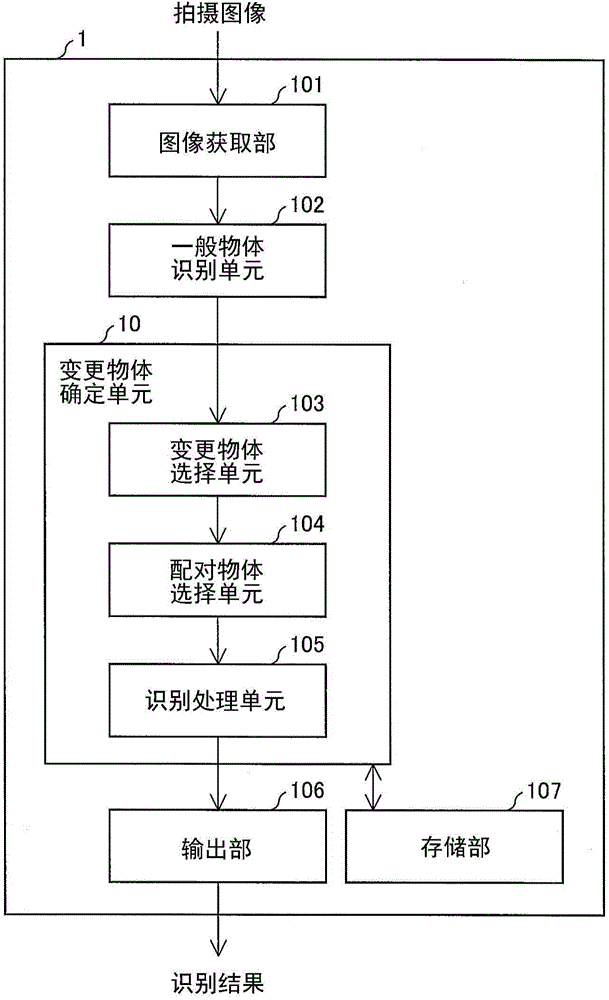
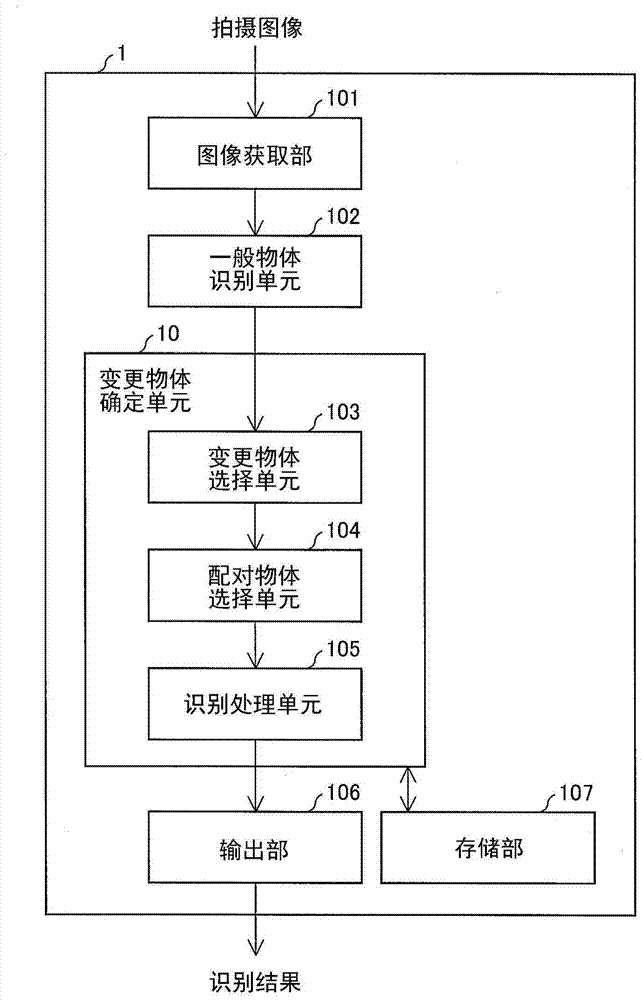
Image recognition device and image recognition method
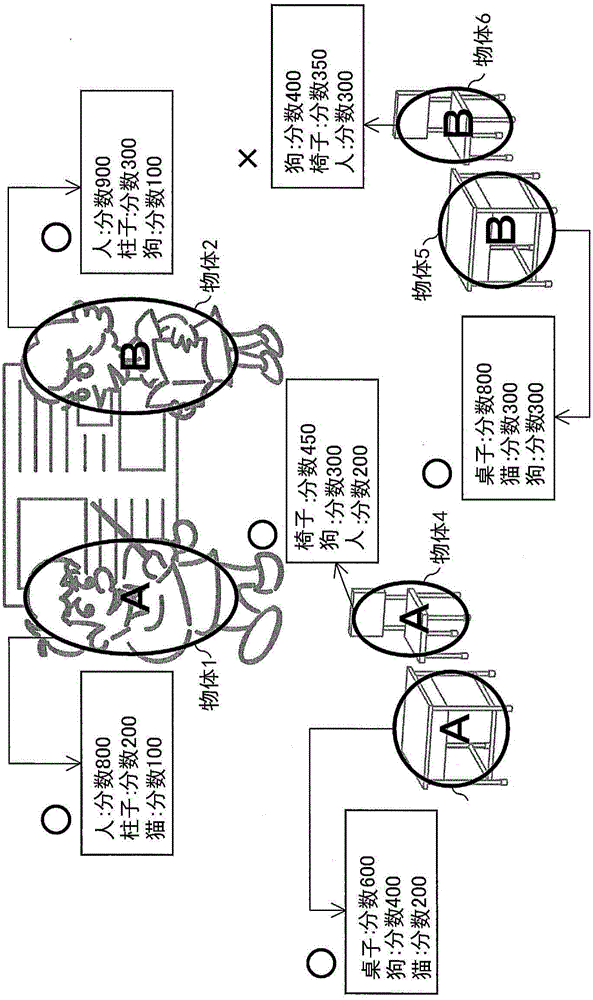
ActiveCN104102930AHigh precision determinationCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsPattern recognitionImage identification
An image recognition device for recognizing respective types of display objects appearing in an image in high precision is provided. A change object selecting unit (103) is configured to select a change object, a target whose recognition result is to be modified, and to determine that a type of each determined object is a type of one of recognition candidates which has the highest degree of reliability. The pair object selecting unit (104) is configured to select a pair object from the determined objects. The recognition processing unit (105) is configured to determine the change objet based on the pair information list of the pair objects.
Owner:ORMON CORP
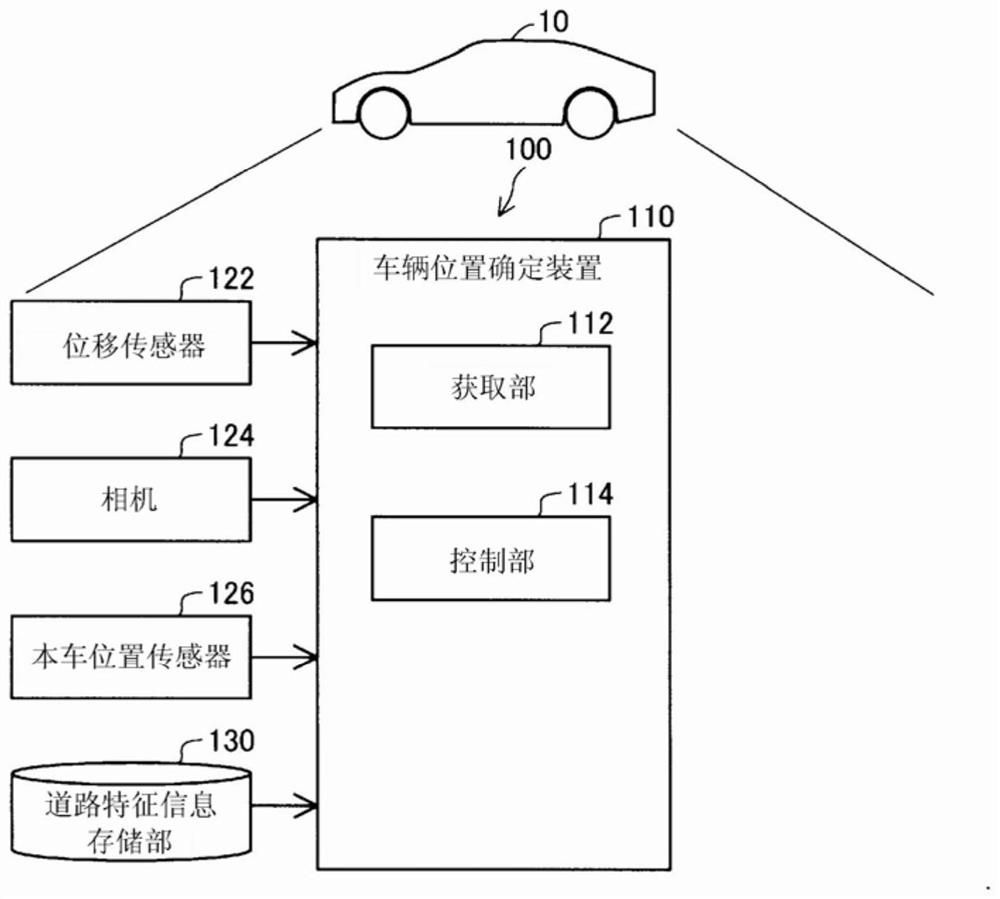
Vehicle location determination device, vehicle location determination system, and vehicle location determination method
PendingCN113710987AHigh precision determinationInstruments for road network navigationCharacter and pattern recognitionLocation determinationAutomotive engineering
A vehicle location determination device 110 that is to be mounted on a vehicle 10 and comprises: an acquisition unit 112 that acquires a peripheral image represented by minute displacements relative to the vehicle, the peripheral image being road information for identifying the location of the vehicle; and a control unit 114 that compares the road information and road characteristic information indicating the absolute location of a predetermined point, and determines the vehicle location according to the comparison result.
Owner:DENSO CORP
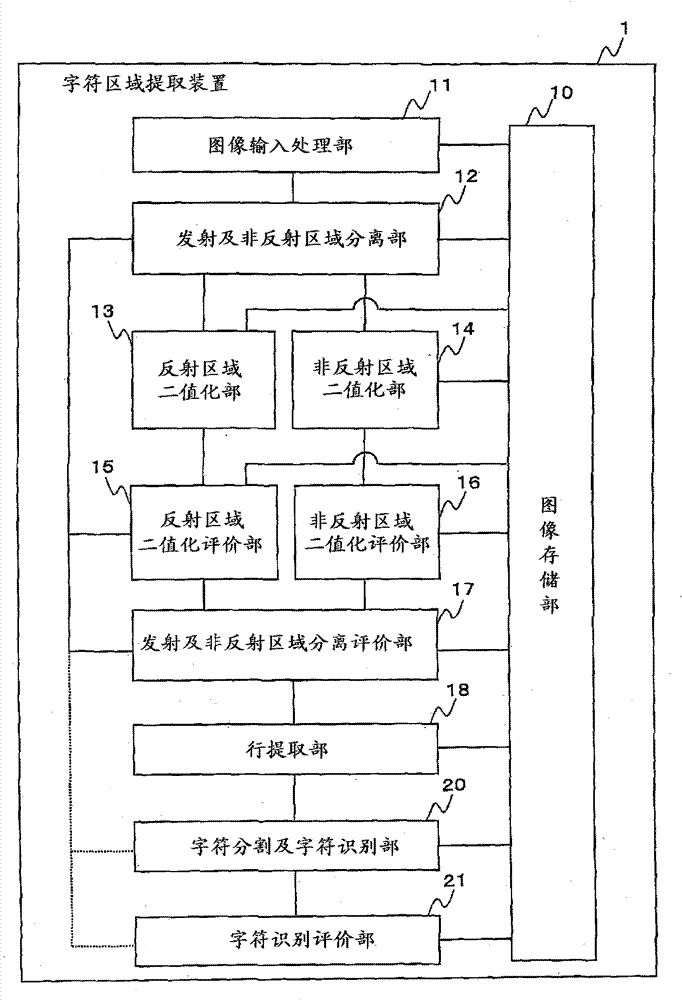
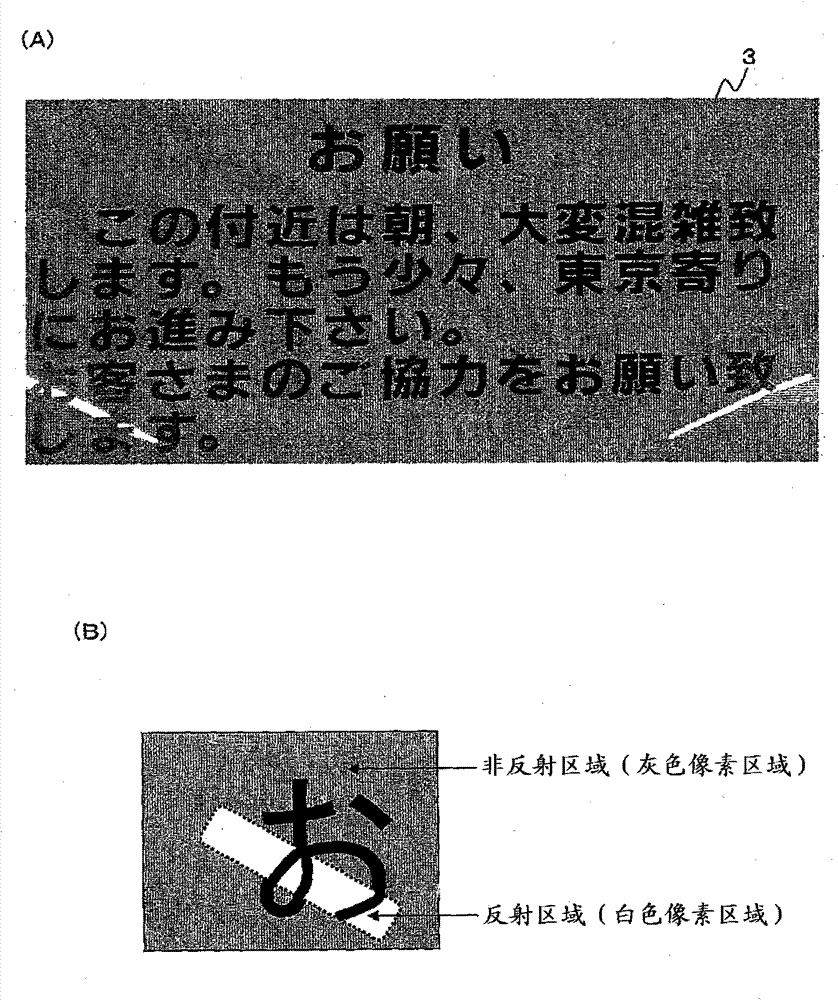
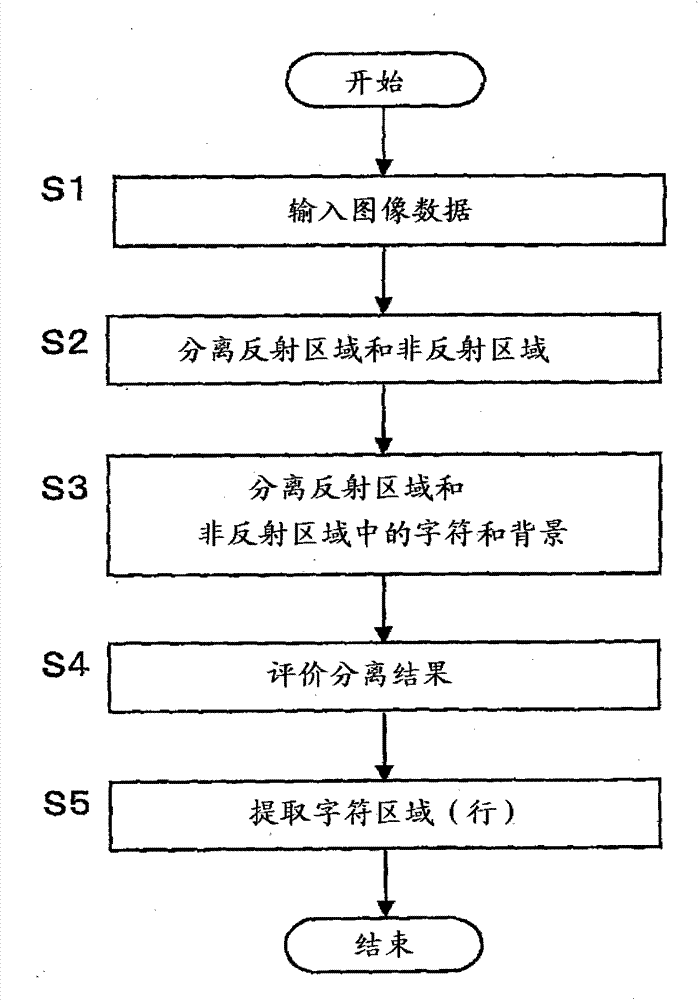
Character area extracting device, image picking-up device provided with character area extracting function and character area extracting program
InactiveCN102209969BHigh precision determinationImprove processing precisionCharacter recognitionPictoral communicationComputer graphics (images)Computer vision
In order to accurately specify a character region from image data including portions with different gradation contrasts, the character region extracting device receives image data obtained by photographing a subject, binarizes the entire image data using a first threshold, and Separation into reflective areas where the number of pixels is saturated and non-reflective areas where the number of pixels is not saturated. Next, the reflection area is binarized and separated into a character area and a background area by using a second threshold. Similarly, the non-reflection area is binarized and separated into a character area and a background area by using the third threshold. The respective character areas of the reflective area and the non-reflective area are combined, and position information of the character areas in the image data is determined.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
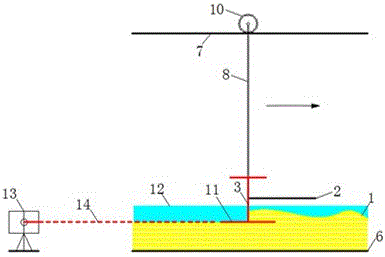
A method and device for leveling the sediment bed surface of an experimental tank
InactiveCN105758685BHigh precision determinationHigh precision water level positionPreparing sample for investigationEngineeringSurface level
The invention discloses an experimental water tank sediment bed surface leveling method and an experimental water tank sediment bed surface leveling device. The experimental water tank sediment bed surface leveling device at least comprises a glass water tank (6) filled with sediments and water, a laser (13) arranged at the outer side of one end of the glass water tank (6), a horizontal I-shaped blade (3) with adjustable height, arranged in the glass water tank (6) and a level gauge (4) connected with the horizontal I-shaped blade (3). According to the method, the horizontal I-shaped blade with adjustable height is used to level the sediment bed, and level laser is used for locating and calibrating the flatness of the sediment bed, and therefore, a flat sediment bed surface having high consistency can be acquired. According to the device and the method, the water level of the sediment bed can be precisely determined, and the error range of the flatness of the sediment bed can be controlled to be up to 1mm; and besides, the horizontal I-shaped blades having different widths can be produced according to different water tank widths, and thus have wide applicability to the experimental water tank.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
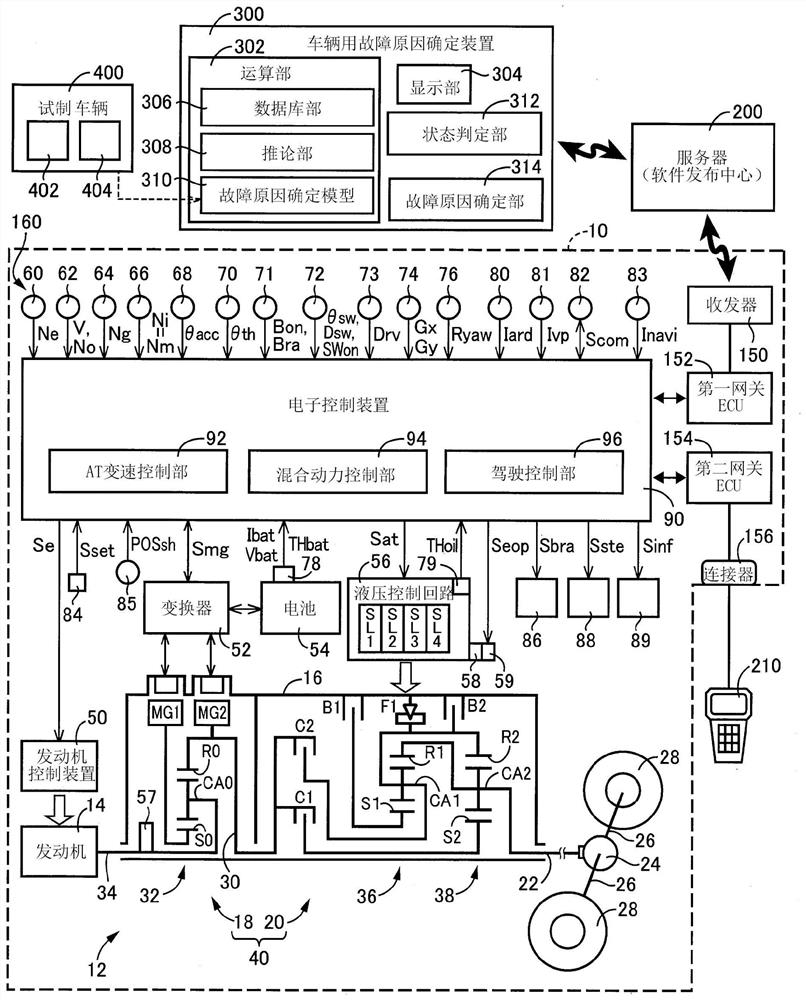
Vehicle malfunction cause identifying device
PendingCN112677988AHigh precisionHigh precision determinationRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesMachine learningIn vehicleOil pressure
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Information processing apparatus, storing medium and information processing method
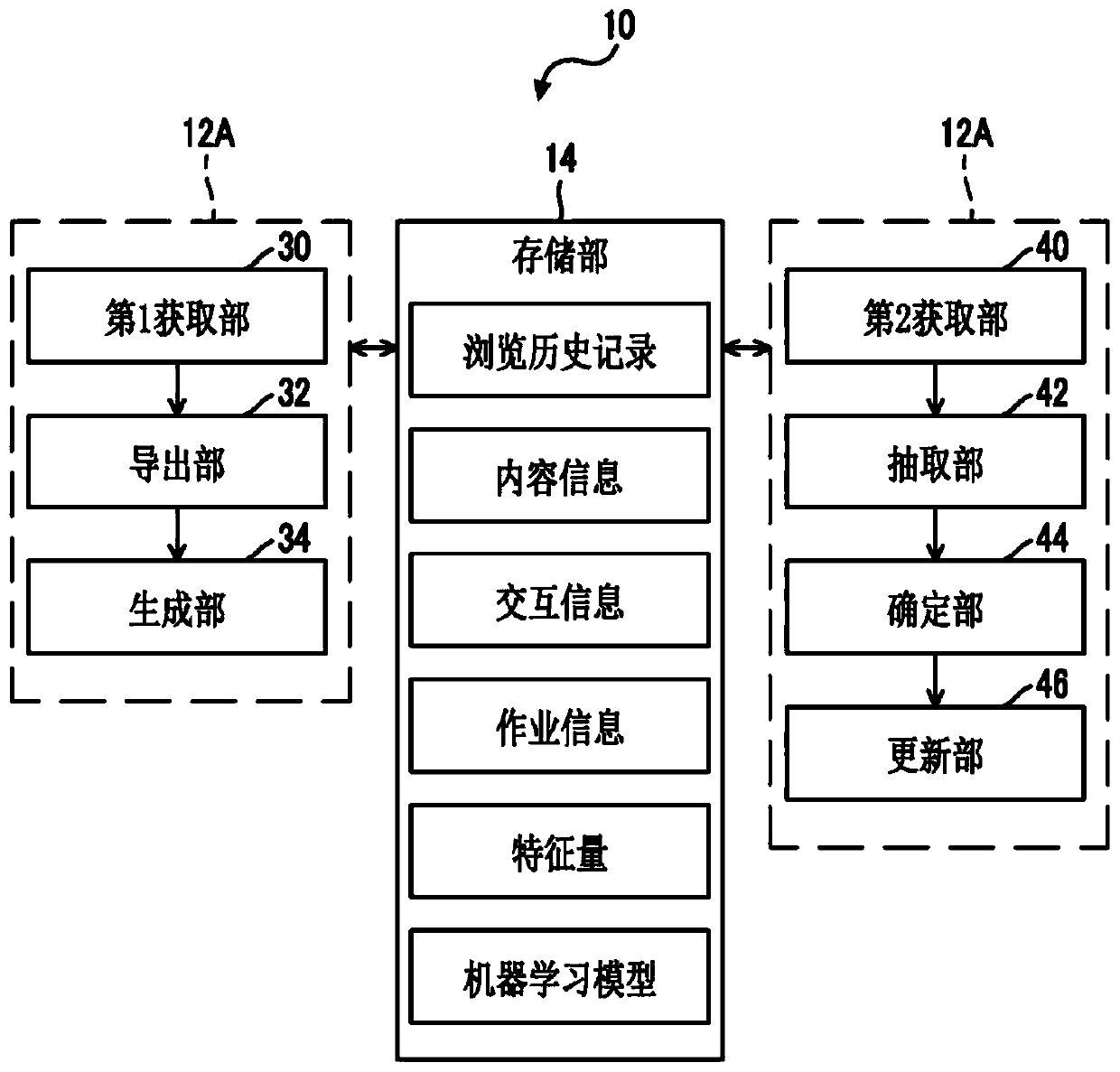
PendingCN111159608AHigh precision determinationEnsemble learningKernel methodsInformation processingEngineering
The invention provides an information processing apparatus, a storing medium and an information processing method. The information processing apparatus includes an acquisition unit that acquires, fromplural pieces of first information viewed by a user, content information being information of contents described in the first information, an extraction unit that extracts a location in which the user has performed editing, from second information as a target of the user working, and a specifying unit that specifies the first information viewed during a period in which the user performs editing at the location or viewed before and after the editing among the plural pieces of first information from the content information.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Electronic equipment
InactiveCN1229956CHigh precision determinationDetermining where a subject is located can be corrected for inclination with high precisionGalvano-magnetic devicesSolid-state devicesTransverse axisEngineering
A cellular phone includes an X-axis magnetic sensor for outputting a first value corresponding to a component of an external magnetic field along the direction of a transverse axis of the main body, and a Y-axis magnetic sensor for outputting a second value corresponding to a component of the external magnetic field along the direction of a longitudinal axis of the main body. The cellular phone includes a ROM which stores a conversion table defining the relation between the first and second values and values of azimuth and inclination angle of the longitudinal axis of the main body. The cellular phone determines the azimuth and inclination angle on the basis of the first and second values actually output from the X-axis and Y-axis magnetic sensors and with reference to the conversion table.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Position detection device and position detection method
InactiveCN103827632BSure easyHigh precision determinationNavigation instrumentsDistance measurementLocation detectionHigh probability
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
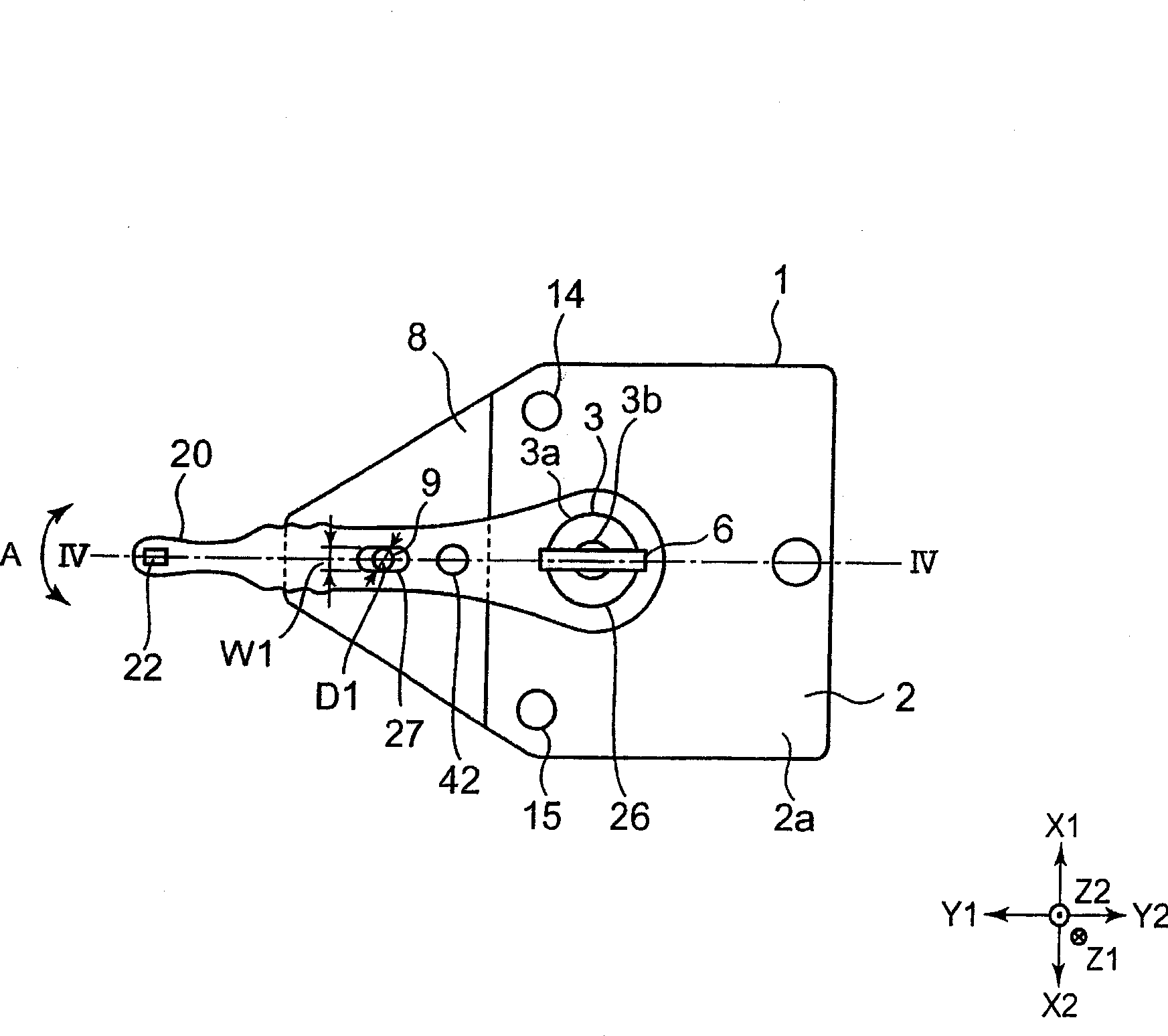
Stator unit, motor, and blower apparatus
PendingCN110417134AHigh precision determinationAssociation with control/drive circuitsMagnetic circuit stationary partsControl theoryMechanical engineering
The present invention provides a stator unit, a motor and a blower apparatus. The stator unit includes a stator that drives a rotor rotatable about a central axis extending in a vertical direction, acover that accommodates the stator, a filling portion that fills a space between the cover and the stator. The cover includes a tubular portion that extends in an axial direction and covers a radiallyside portion of the stator opposing the rotor in a radial direction, a lid portion that covers an axially upper end portion of the stator, and a cover stepped portion that is provided on a first radial side with respect to the tubular portion. The cover stepped portion comes in contact with the axially upper end portion of the stator and is positioned on an axially lower side with respect to an axially upper end portion of the tubular portion.
Owner:NIDEC CORP
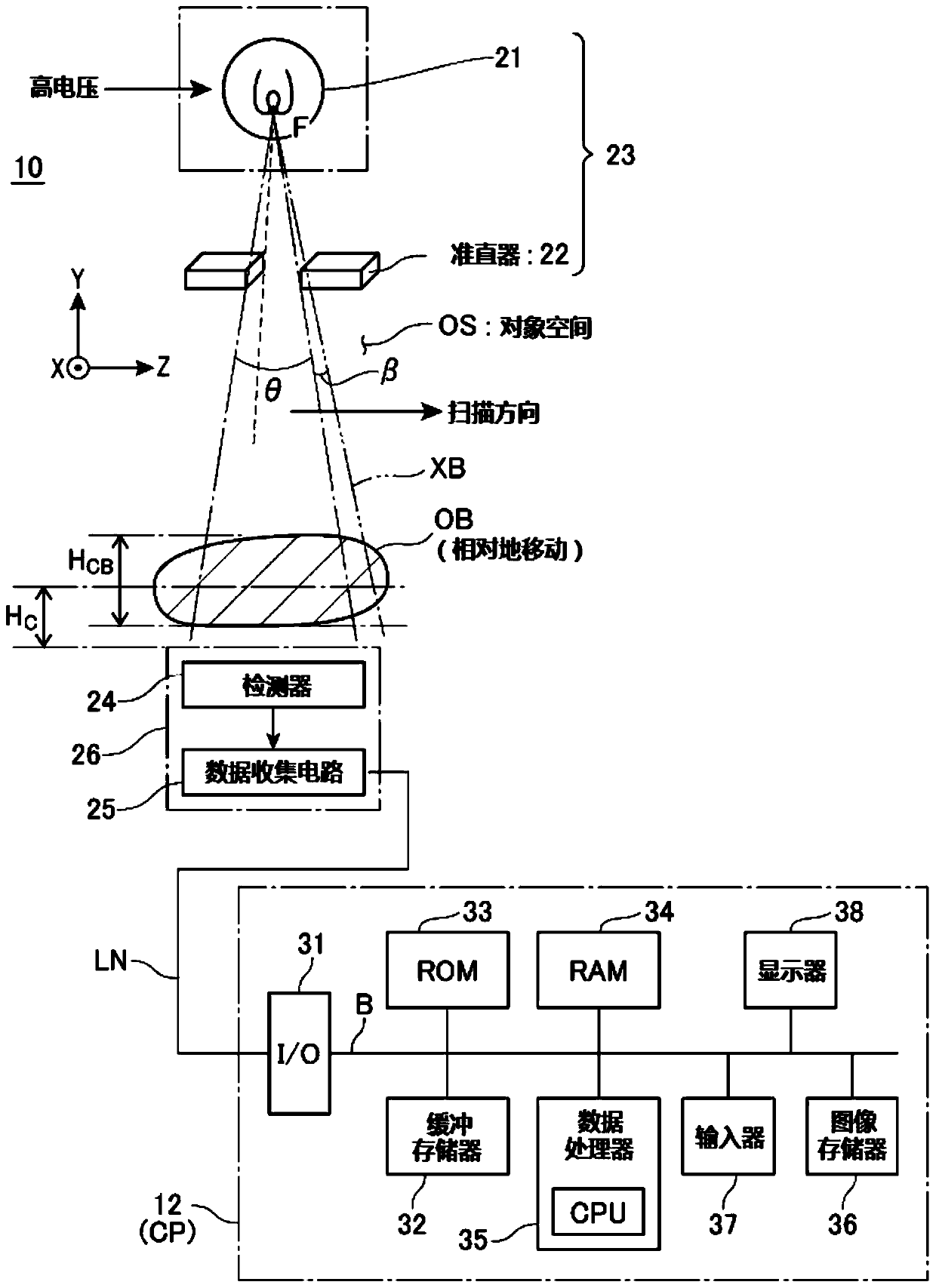
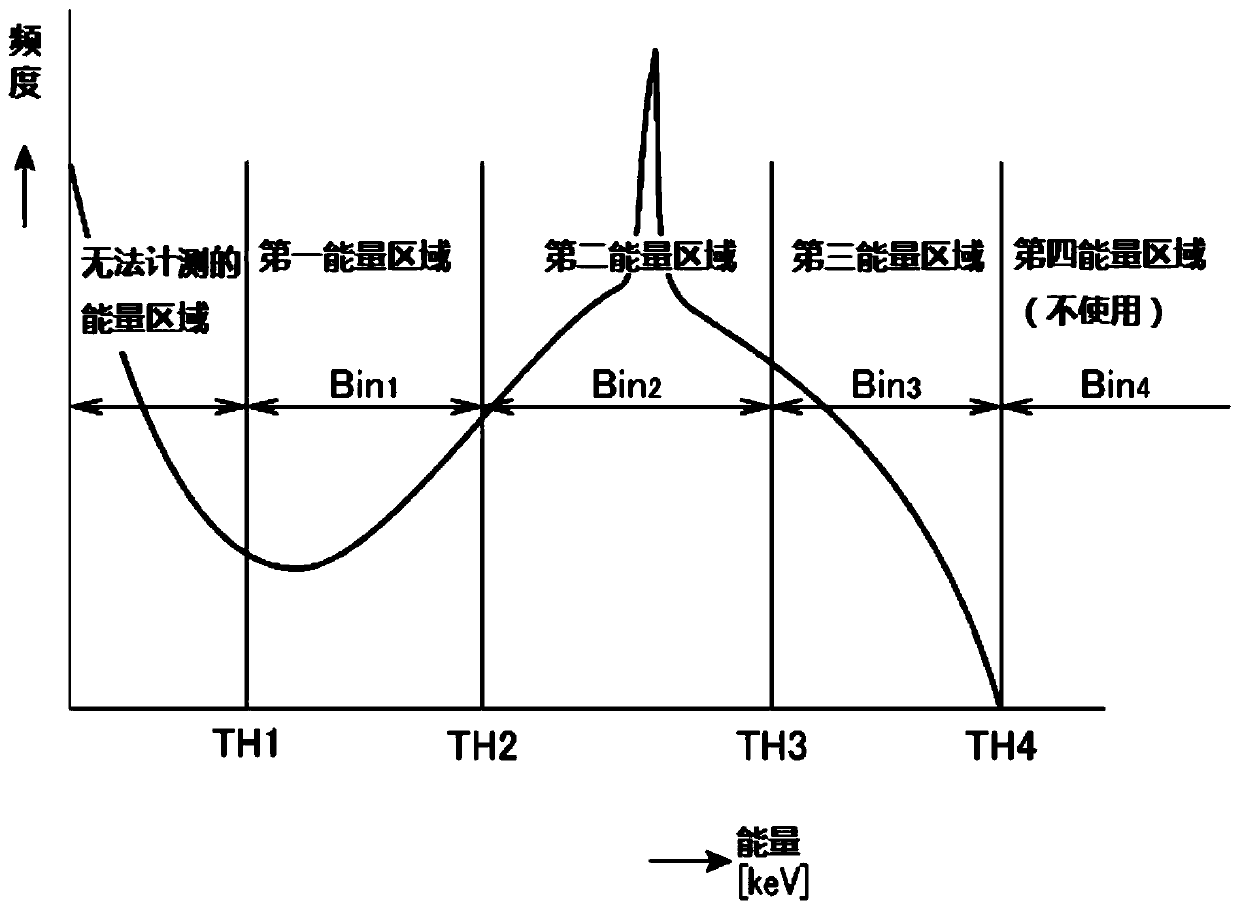
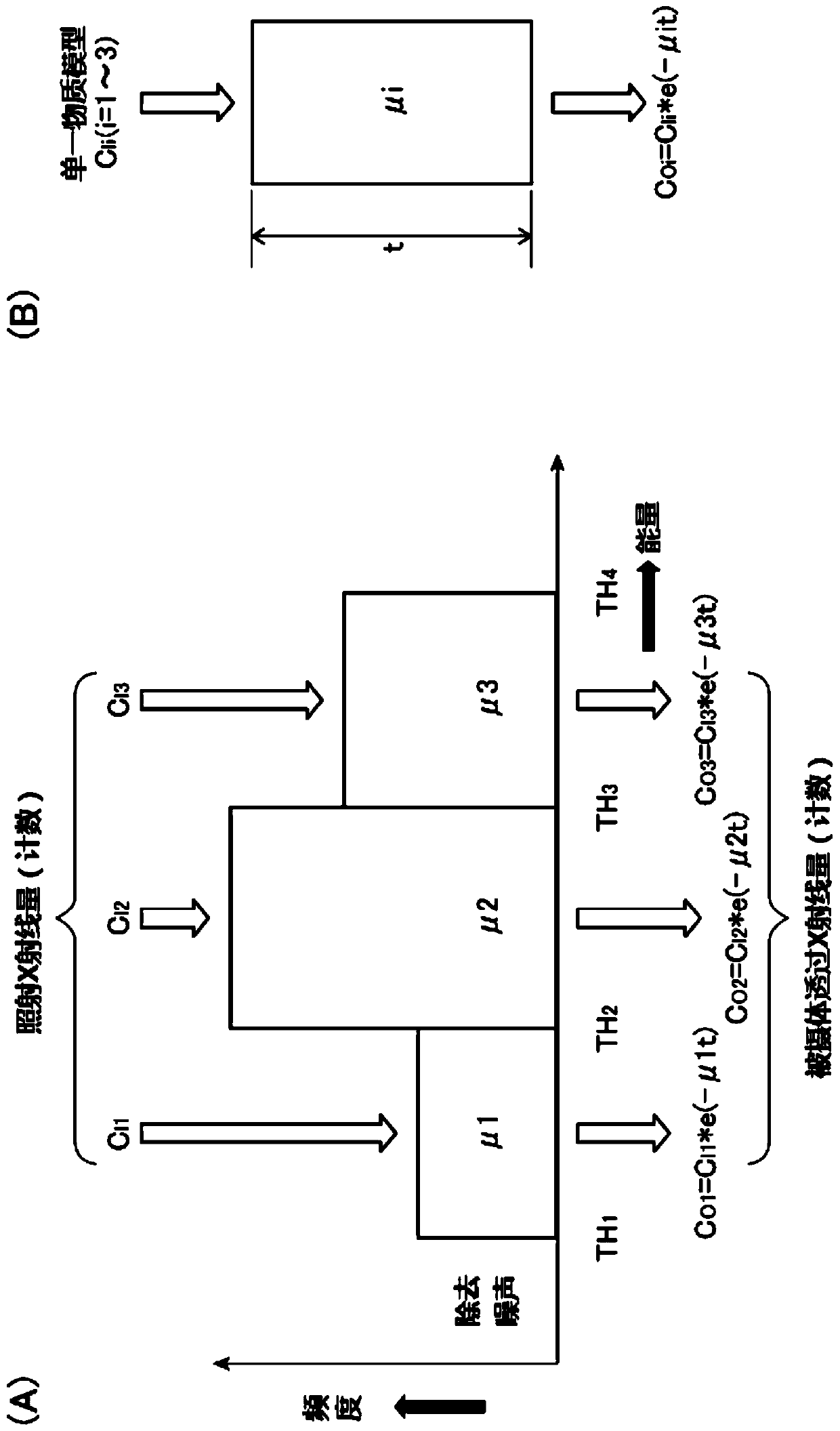
Data processing device for x-ray inspection, and x-ray inspection device equipped with the same
ActiveCN106461578BHigh precision determinationImage enhancementImage analysisX-raySubstance of very high concern
The present invention can determine the type and shape of a substance with higher accuracy regardless of the thickness. The data processing device (12) counts the X-rays transmitted through the object after being irradiated from the X-ray tube (21) and detected by the photon counting type detection unit (26), in units of pixels in each energy region to process. The device (12) includes: means (35) for calculating an image of an object (OB) based on the count value; and means (35) for setting a region of interest on the image. Further, the device (12) has: a unit (35) for removing pixel information existing in the region of interest as a material background from the image; The count value of the unit, and the specific transmission characteristic of the substance with respect to the X-ray is calculated in the unit of the pixel as the unit of the unique information (35).
Owner:JOB CORP
Clamp for fixing magnetic head assembly and measuring method of rising quantity using the same
InactiveCN100485783CFixed high precisionHigh precision determinationFluid-dynamic spacing of headsFunctional testing of recording headsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Provided is a fixing tool by which a magnetic head assembly can correctly positioned and held, and the magnetic head assembly can be easily attached and detached, and also provided is a floating height measuring method which can highly precisely measure the floating height of a slider of the magnetic head assembly from a disk surface for measurement. The fixing tool of the invention comprises a base (2) with an installation flat surface (2a), a location part (3) projecting from the installation flat surface (2a) to support the same, and a pressure member (6) fixing the support plate on the installation flat surface (2a). When the support plate (21) is installed on the installation flat surface (2a), the location part (3) enters the support hole (26) to locate the support plate (21) from the inside of the support hole (26) in the two directions at right angles to each other along the installation flat surface (2a), and the pressure member (6) is energized on the installation flat surface (2a) by force of a spring (13), and the supporting plate (21) located by the positioning part (3) is pressurized on the installation flat surface (2a) by the pressure member (6).
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Improved positioning system and cellular communication network
InactiveCN100420312CDoes not increase the calculationHigh precision determinationPosition fixationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTime differencePositioning system
A location system for use in a mobile communication network includes base stations which transmit known signals at predetermined times for use in deriving location data; a first transmitting and receiving units; a unit for determining times of arrival of the known signals from each base station at each of the first transmitting and receiving units; a unit for determining times of arrival of the known signals from each base station at a second transmitting and receiving unit at an unknown location; a comparing unit for comparing timing differences between the known signals received at the first transmitting and receiving units and the second transmitting and receiving unit; and location determining unit for determining the location of the second unit. Each of the first transmitting and receiving units includes a unit for deriving its location from a further set of received signals such as GPS signals.
Owner:LENOVO INNOVATIONS LTD HONG KONG
Optical axis controller for vehicle headlamps
ActiveCN102862507BAccurately determineHigh precision determinationVehicle headlampsOptical signallingDrive wheelOptical axis
Owner:MITSUBISHI MOTORS CORP
Image recognition device and image recognition method
ActiveCN104102930BHigh precision determinationCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsPattern recognitionObject based
Provided is an image recognition device or the like that accurately identifies the type of display object reflected in an image. A changed object selection unit (103) selects a changed object to be corrected in the recognition result, and determines other definite objects as recognition candidates with the highest reliability among the recognition candidates, and the paired object selection unit (104) selects from the above definite objects The paired object of the above-mentioned changed object is selected from among the above, and the identification processing unit (105) determines the above-mentioned changed object based on the pairing information list of the above-mentioned paired object.
Owner:ORMON CORP
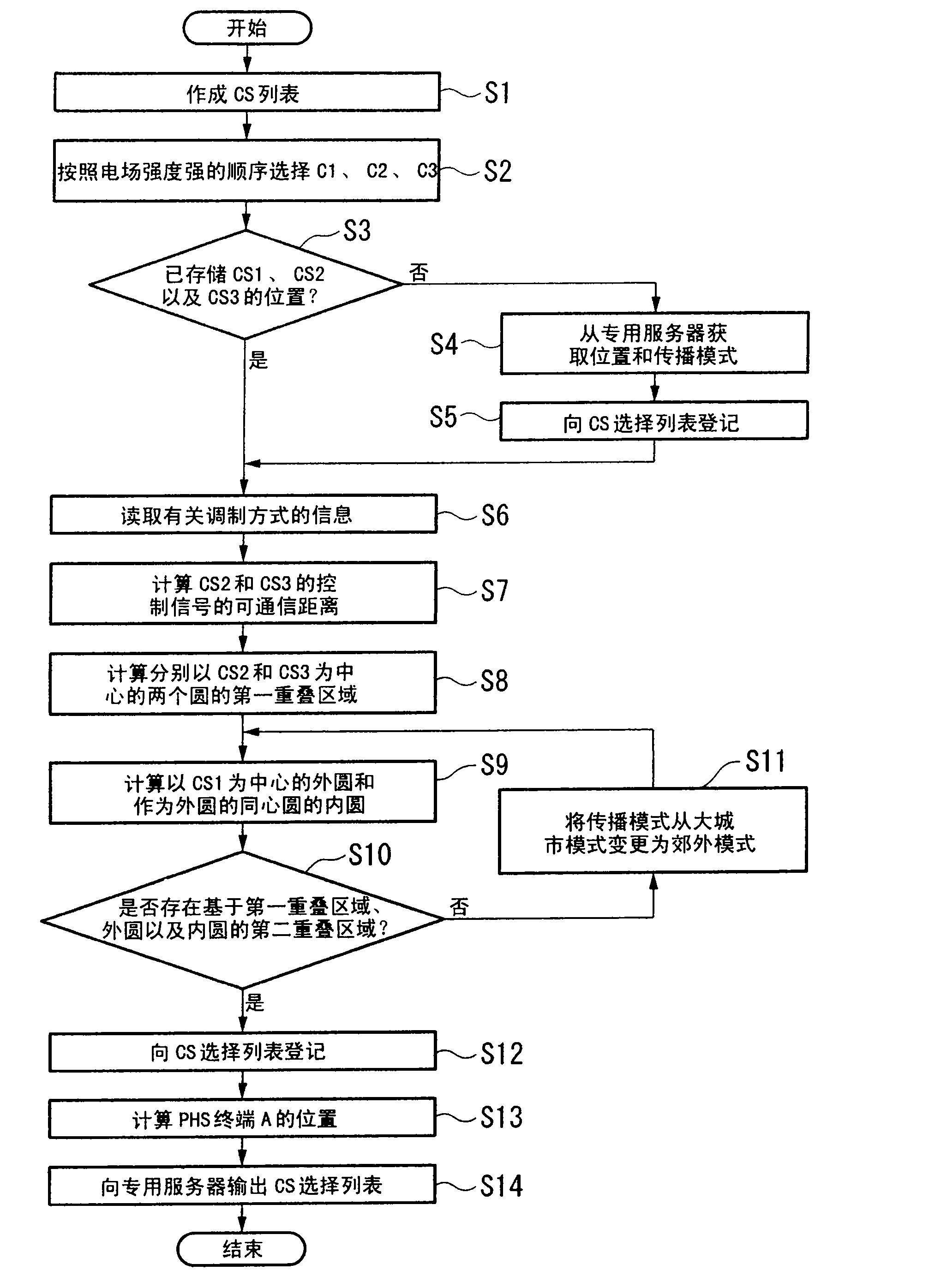
Mobile terminal, base station, and mobile terminal positioning method
InactiveCN101810039AHigh precision determinationDetermine the accuracyPosition fixationWireless communicationEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A mobile terminal includes: a communication unit which transmits / receives a signal modulated by a predetermined modulation method to / from three or more base stations; a storage unit which stores a plurality of propagation models indicating a signal propagation environment for each of combinations of the base stations in advance and stores position information on the base stations in advance; and a control unit which controls the communication unit and the storage unit. The control unit identifies a propagation model corresponding to the combination of the base stations among the propagation models stored in the storage unit according to the signal and calculates a signal communication-enabled distance in accordance with the propagations model. The control unit calculates a circle having a radius of the communication-enabled distance and a center at the position of each of base stations and acquires an overlap area where the respective circles are overlapped so as to specify the center position of the overlap area as the position of the mobile terminal.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com