Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
940 results about "Transimpedance amplifier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
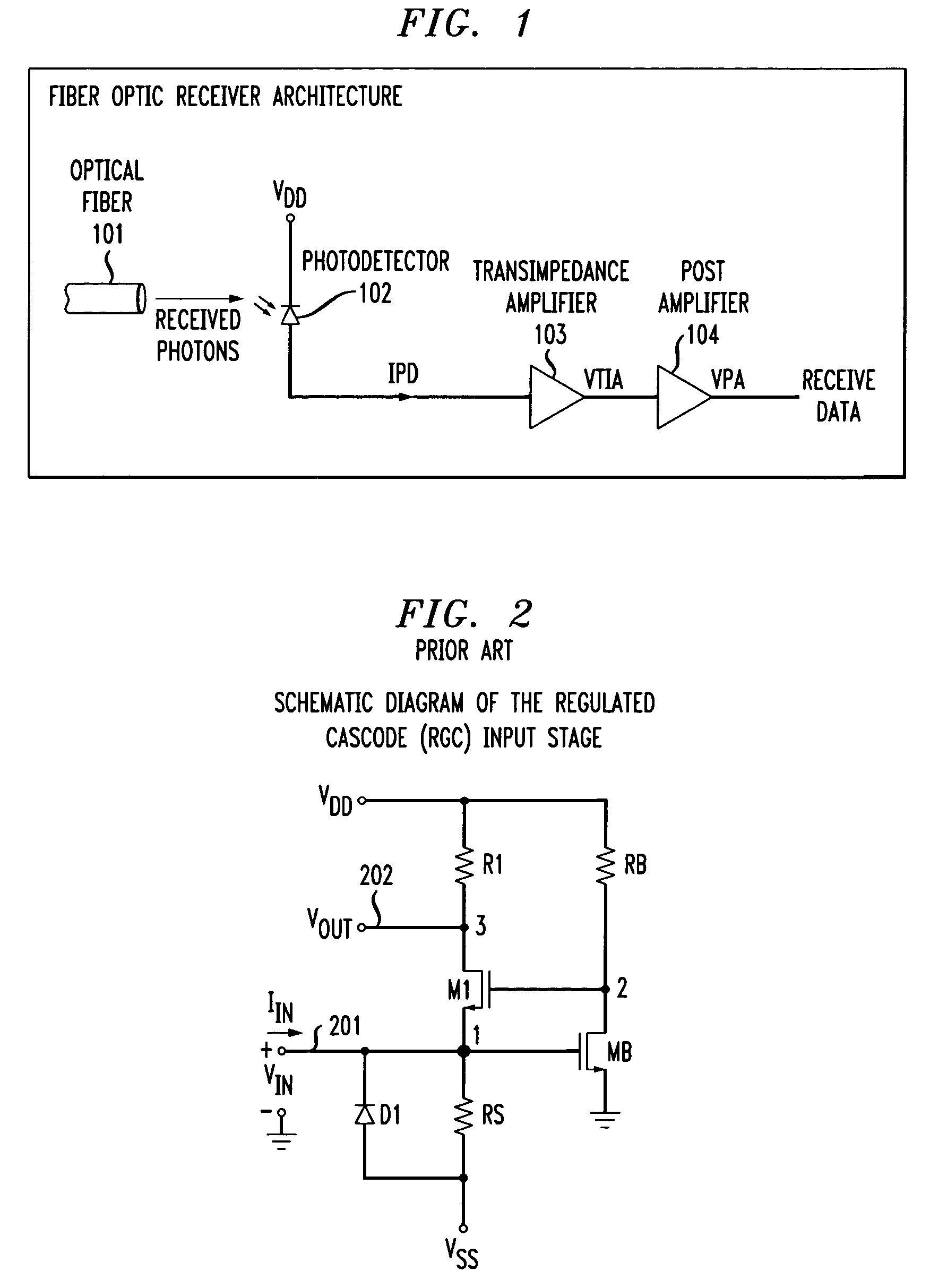
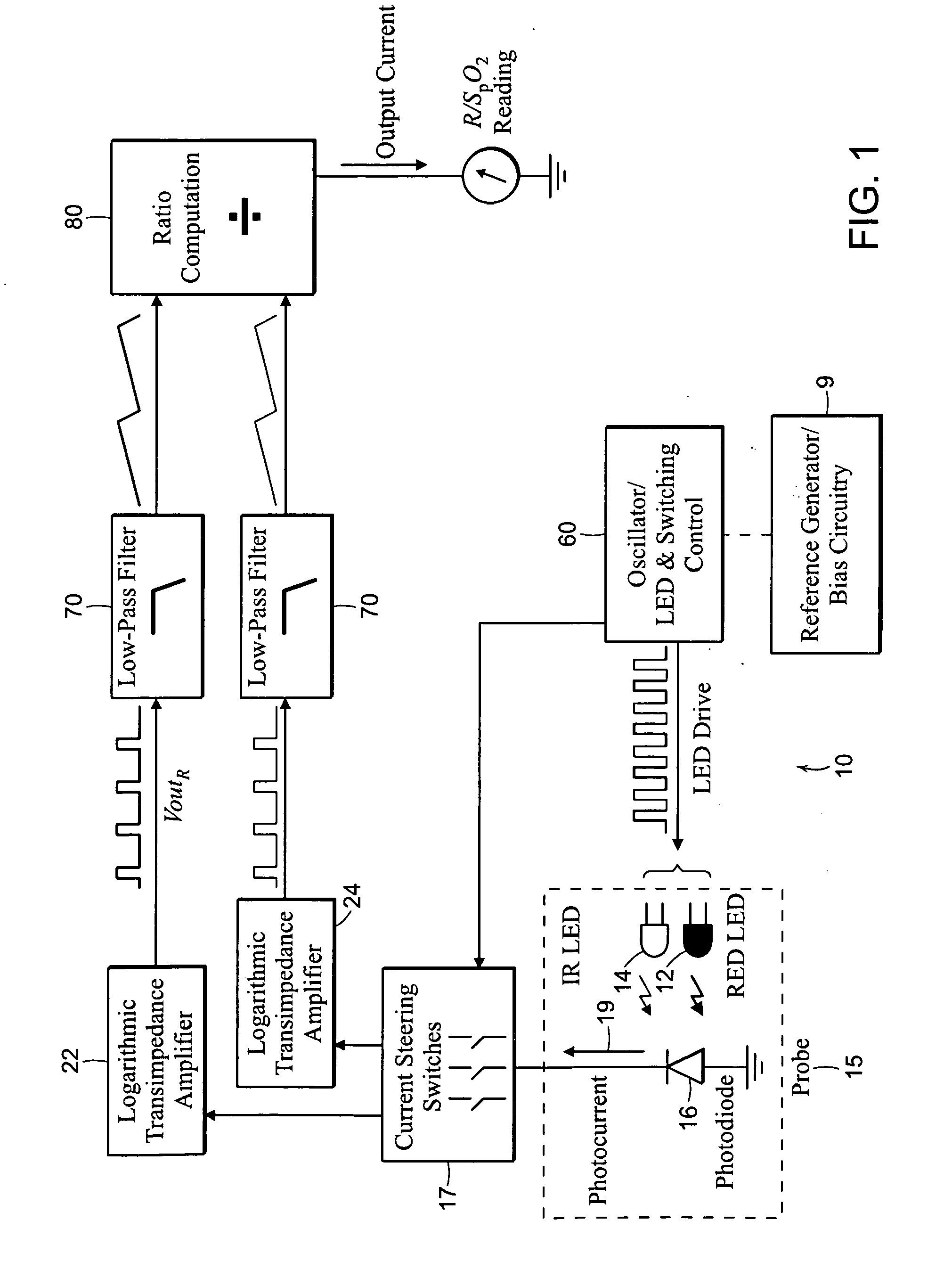
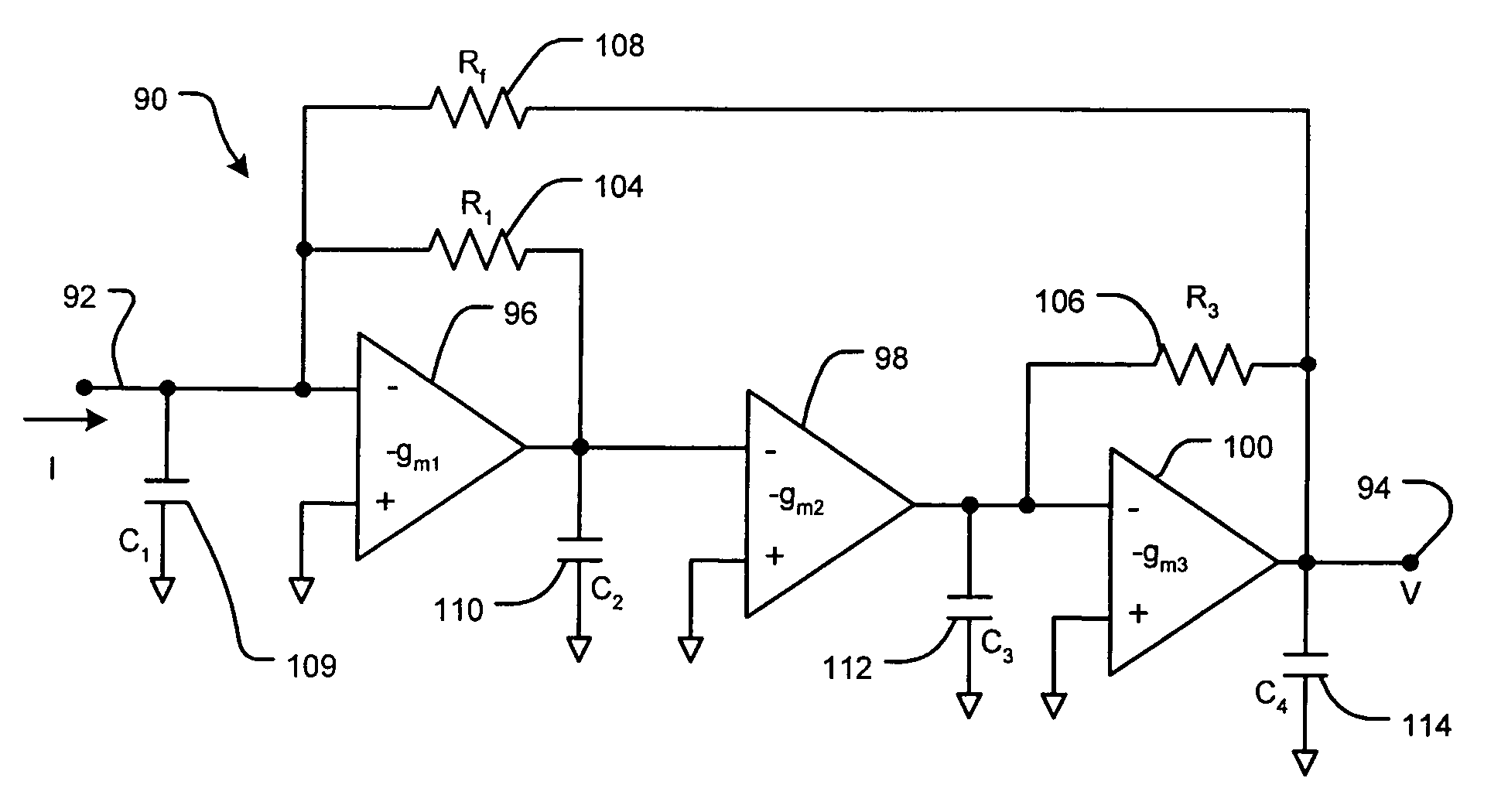
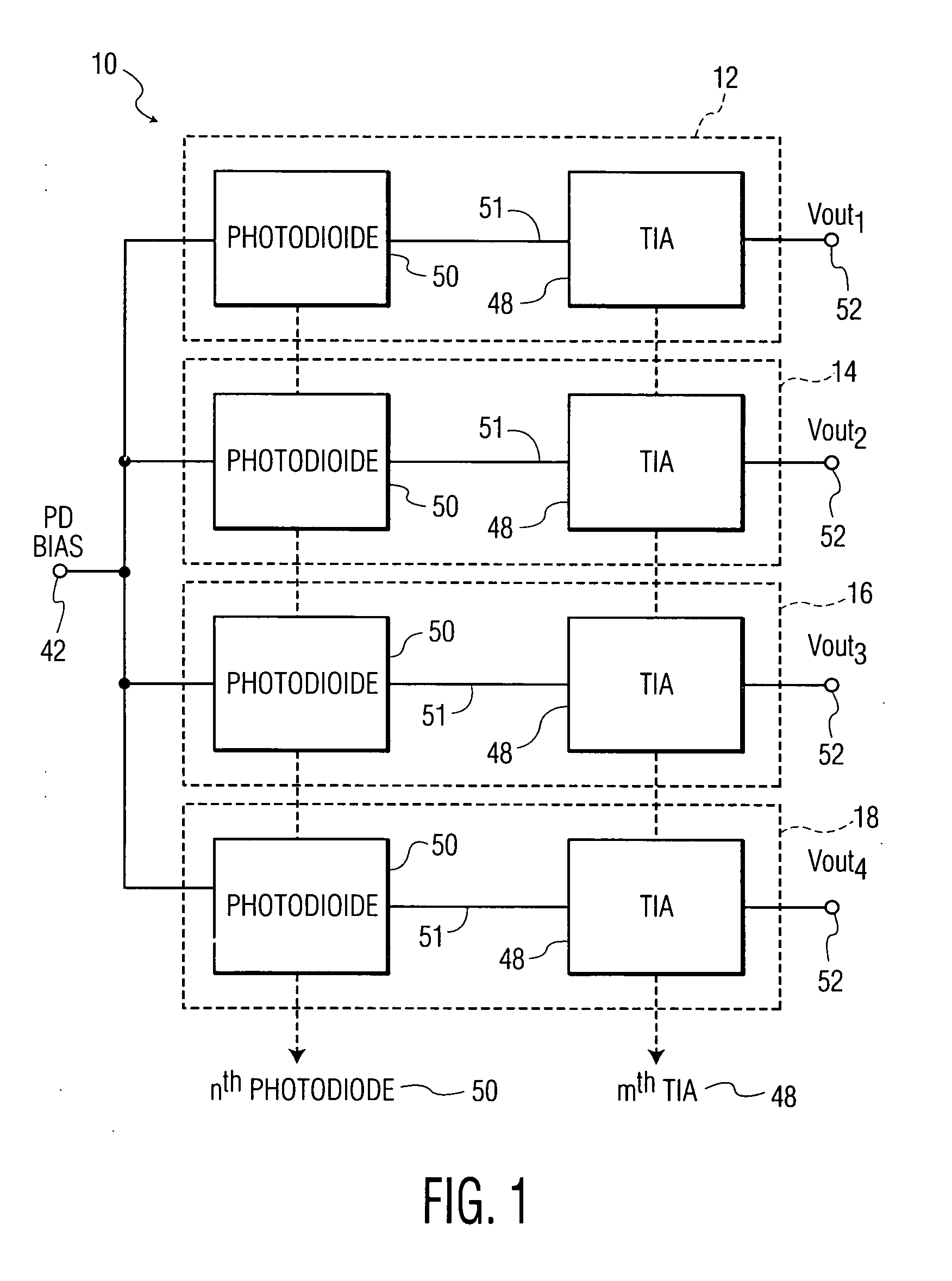
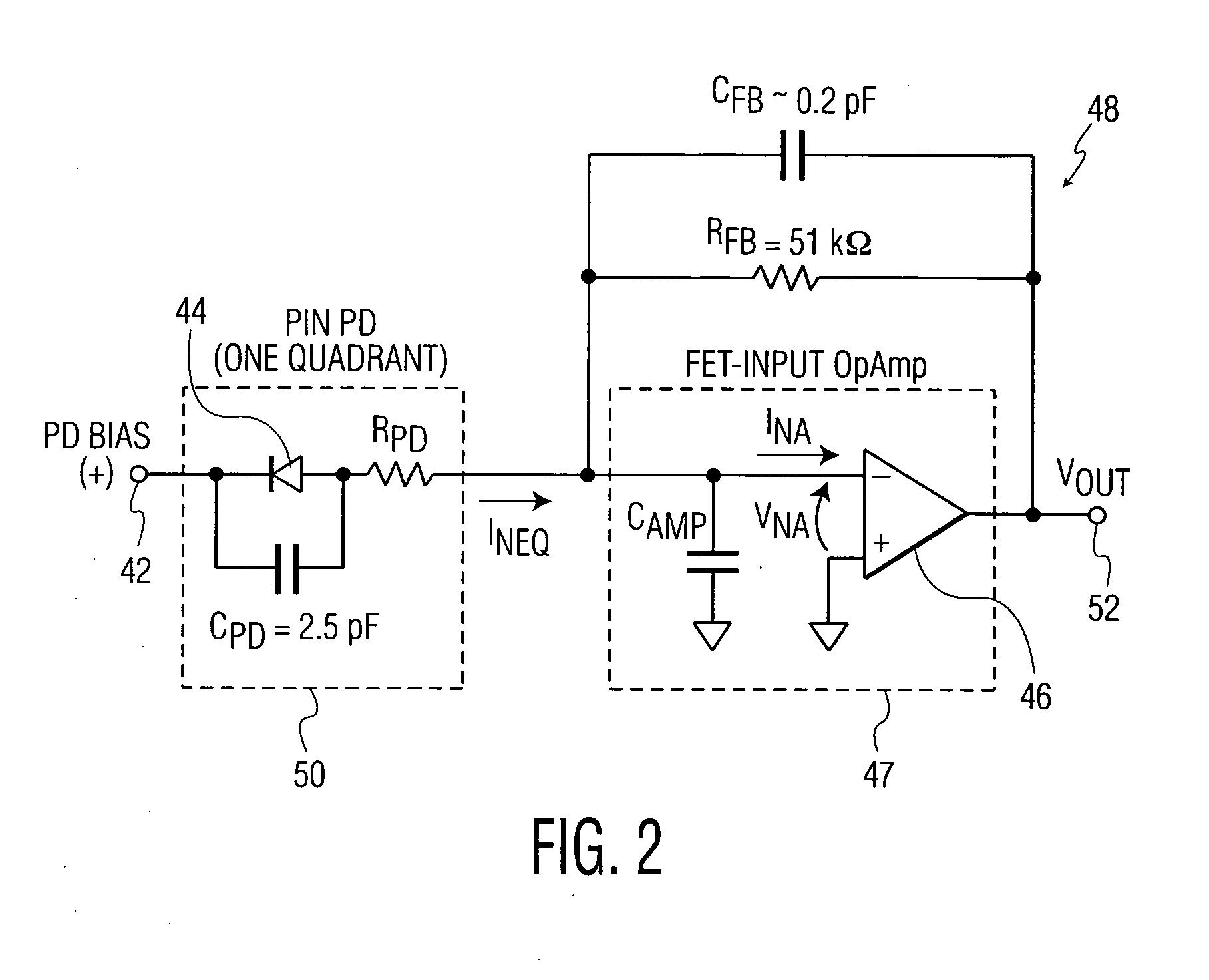
In electronics, a transimpedance amplifier, (TIA) is a current to voltage converter, almost exclusively implemented with one or more operational amplifiers. The TIA can be used to amplify the current output of Geiger–Müller tubes, photo multiplier tubes, accelerometers, photo detectors and other types of sensors to a usable voltage. Current to voltage converters are used with sensors that have a current response that is more linear than the voltage response. This is the case with photodiodes where it is not uncommon for the current response to have better than 1% nonlinearity over a wide range of light input. The transimpedance amplifier presents a low impedance to the photodiode and isolates it from the output voltage of the operational amplifier. In its simplest form a transimpedance amplifier has just a large valued feedback resistor, Rf. The gain of the amplifier is set by this resistor and because the amplifier is in an inverting configuration, has a value of -Rf. There are several different configurations of transimpedance amplifiers, each suited to a particular application. The one factor they all have in common is the requirement to convert the low-level current of a sensor to a voltage. The gain, bandwidth, as well as current and voltage offsets change with different types of sensors, requiring different configurations of transimpedance amplifiers.
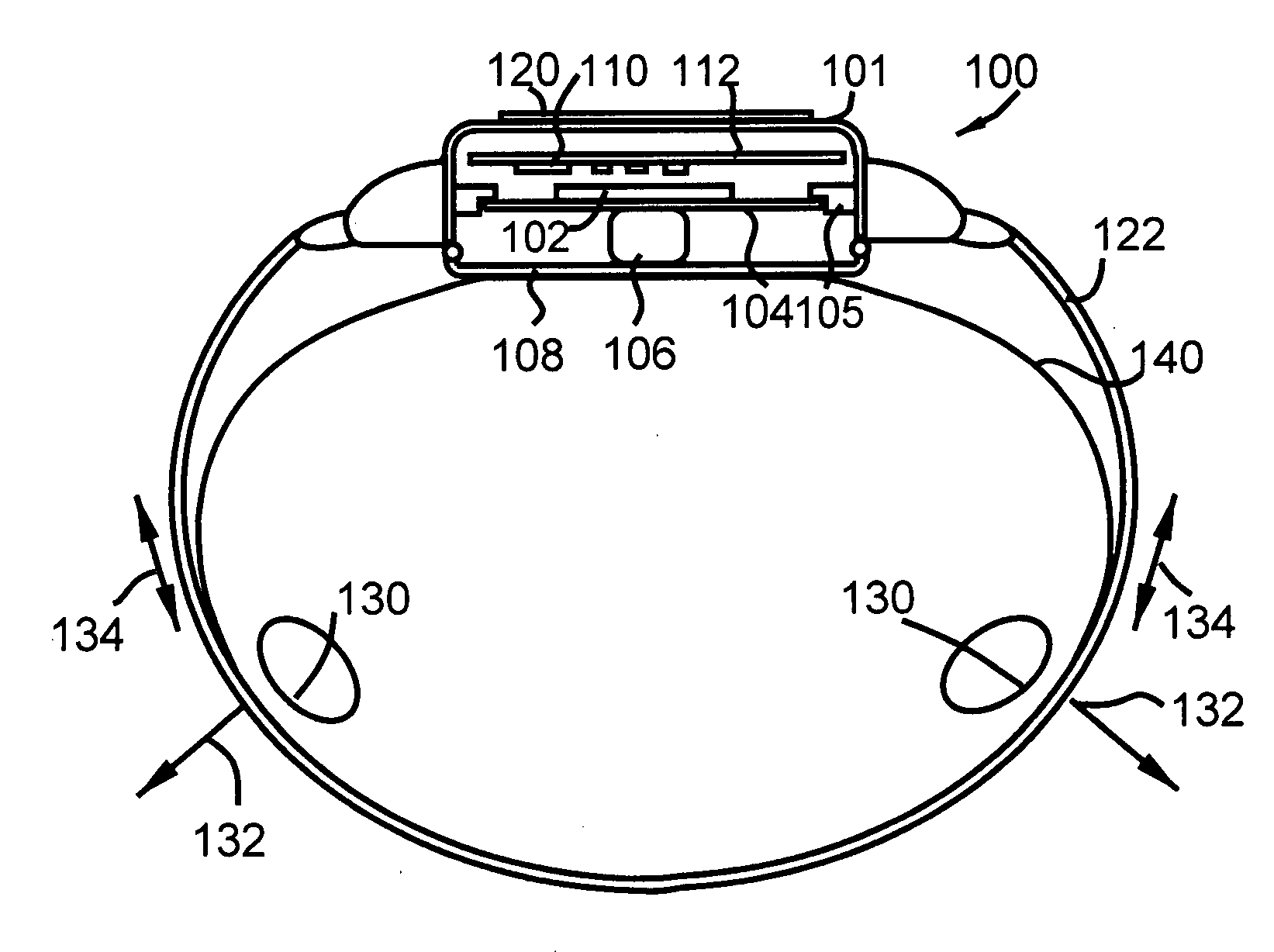
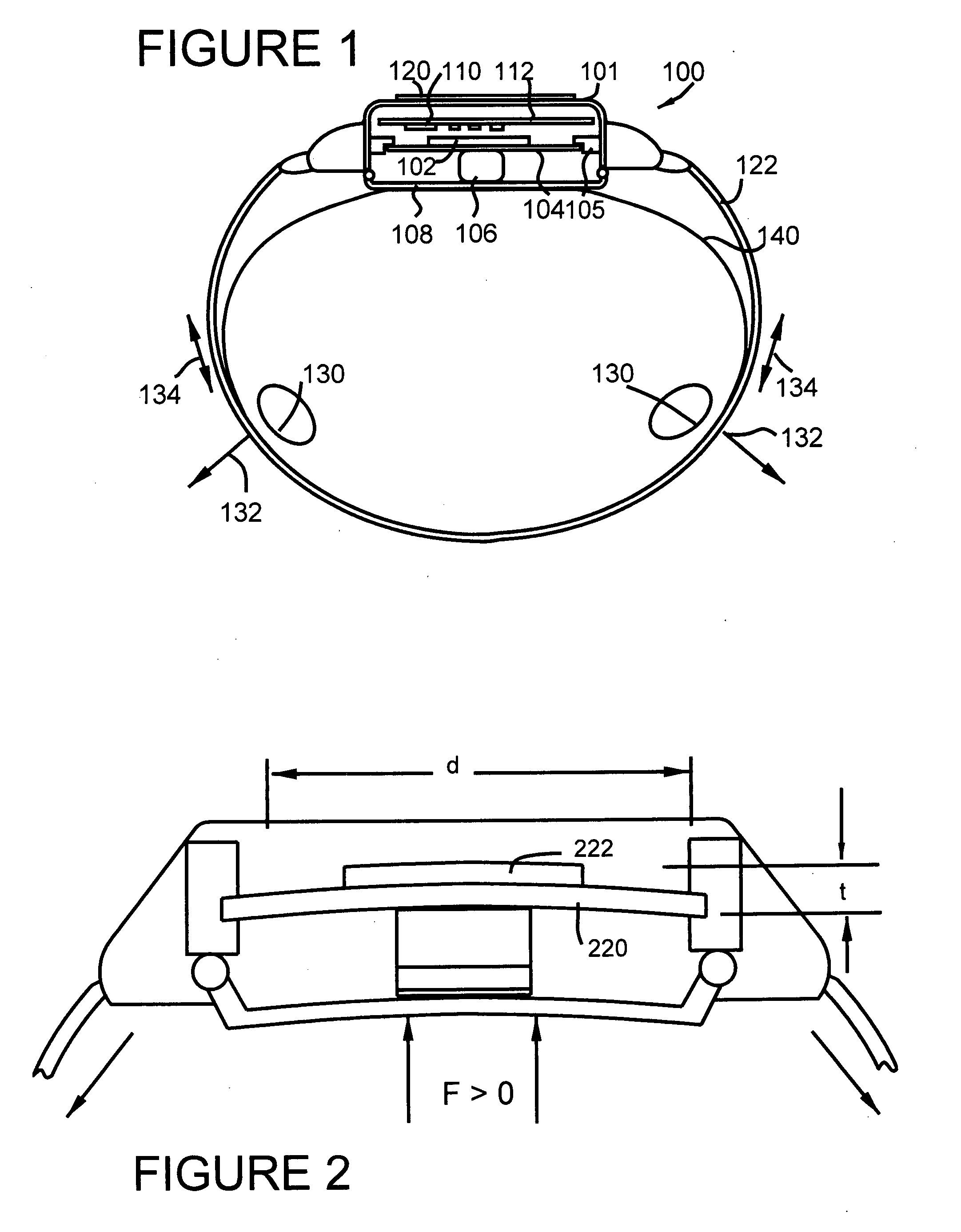
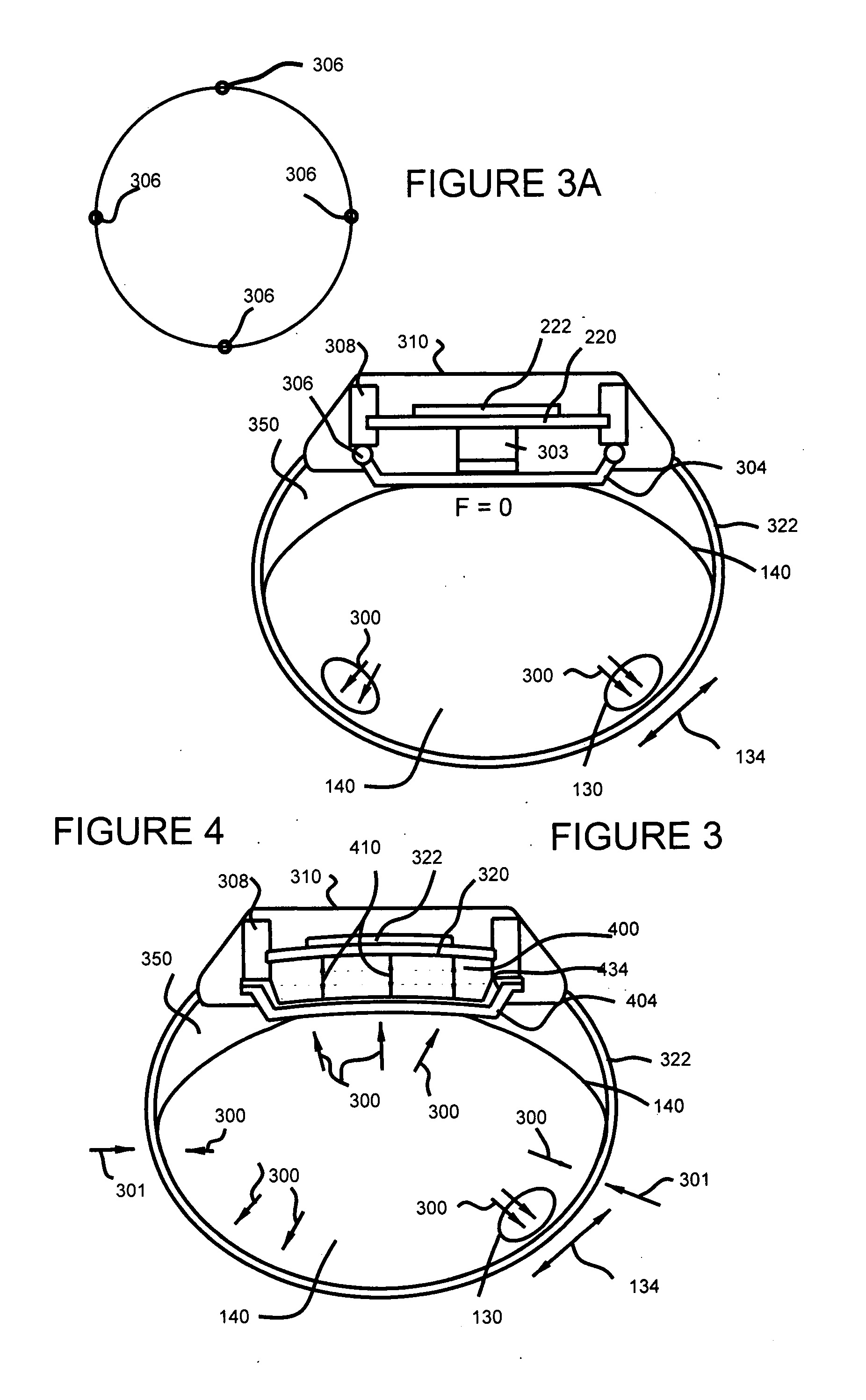
Wrist plethysmograph
A pulse monitoring plethysmograph system for establishing a history of the pulses of the user over an extended period of time, comprises a housing, a piezoelectric sensing element mounted within said housing, and fixed to the housing, a force transmitting member positioned to cause said piezoelectric sensing element to flex in response to an external force and to generate a current, and a transimpedance amplifier. The transimpedance amplifier converts the current generated by the flexing of the piezoelectric element into a voltage signal and an analog to digital converter converts the voltage signal into digital data. A digital memory storing member is provided for storing the digital data and establishing a history of data over an extended period of time.
Owner:ADKINS CHARLES +2
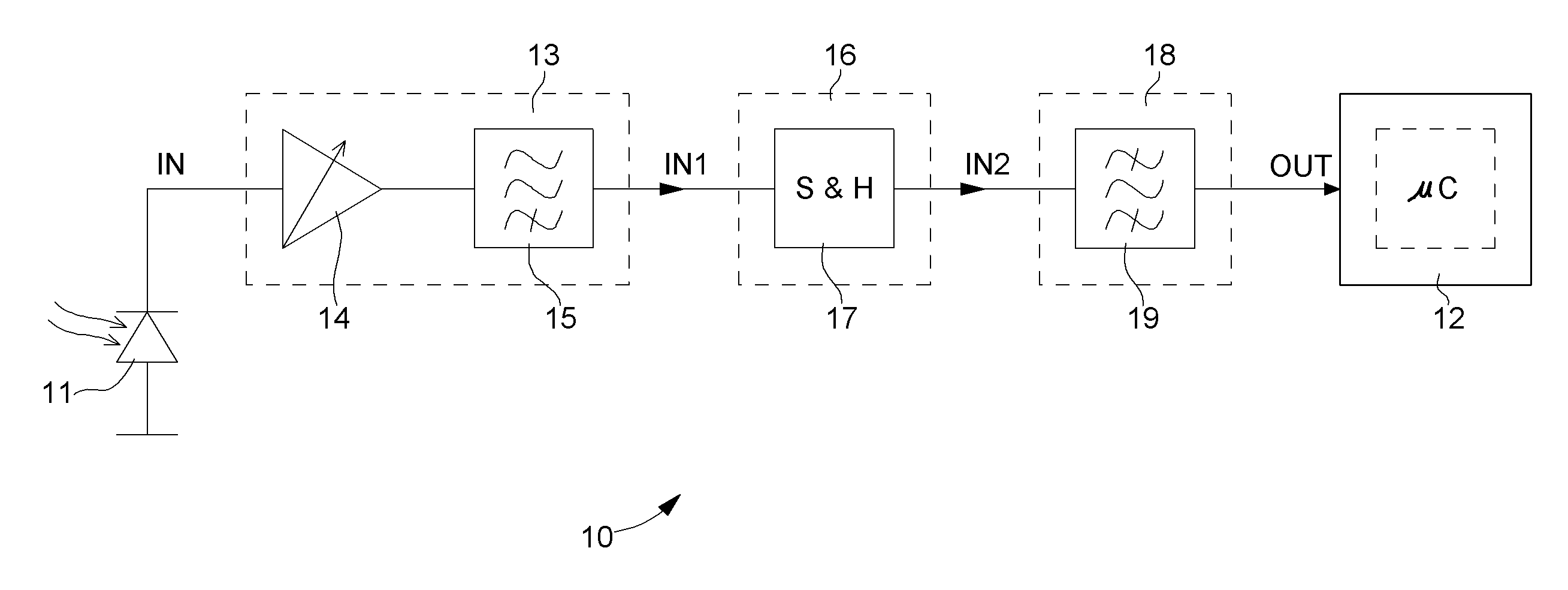
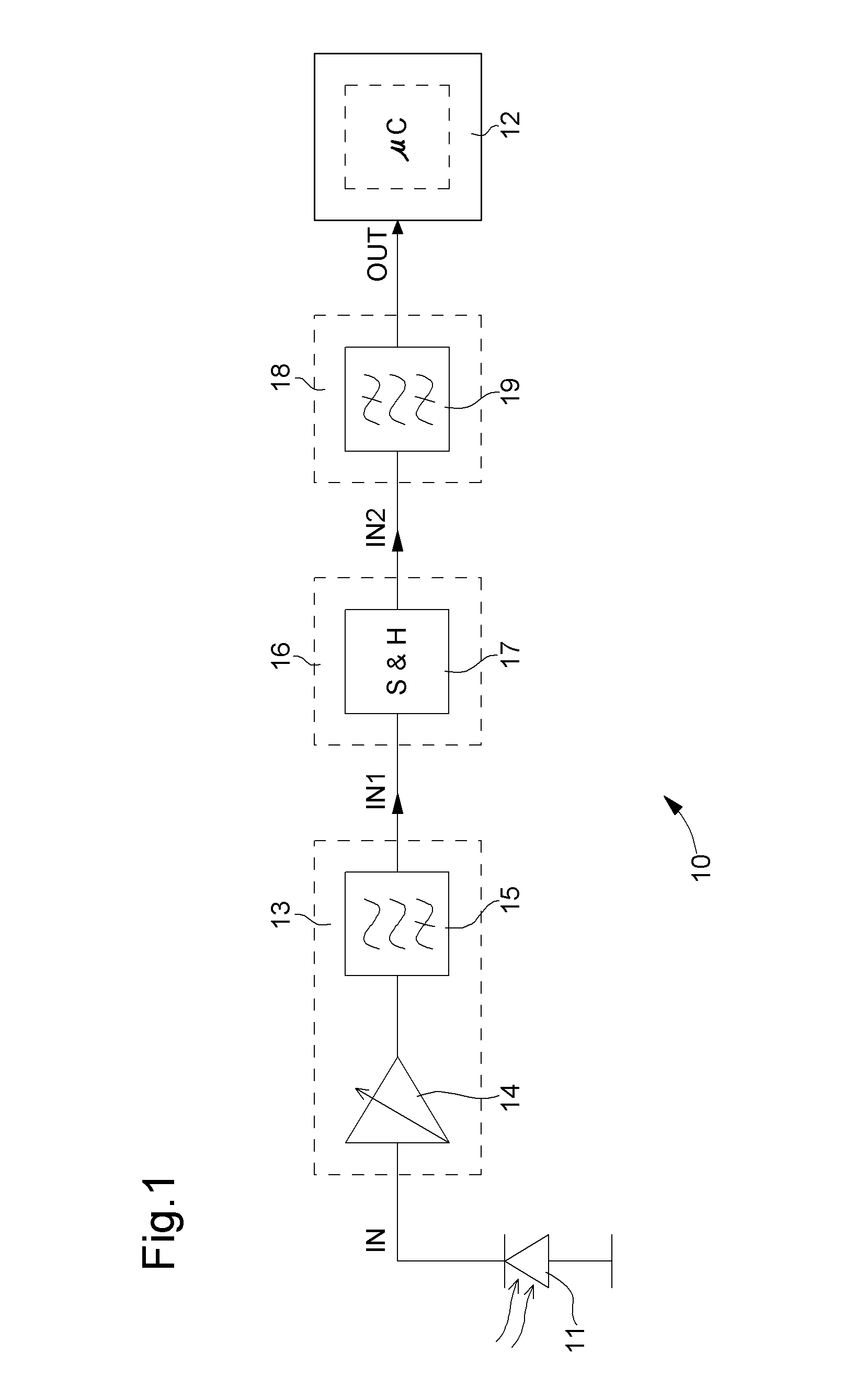
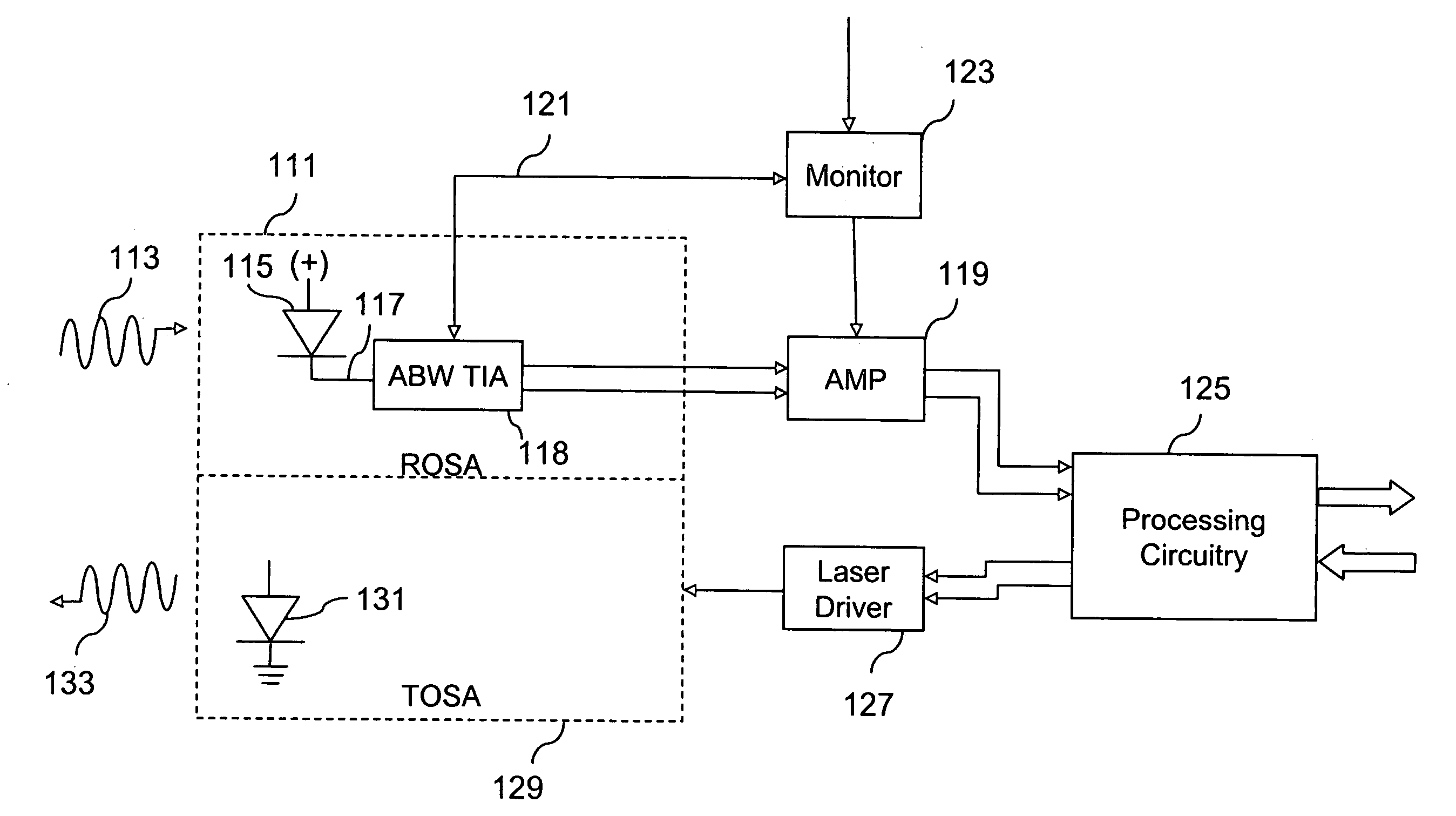
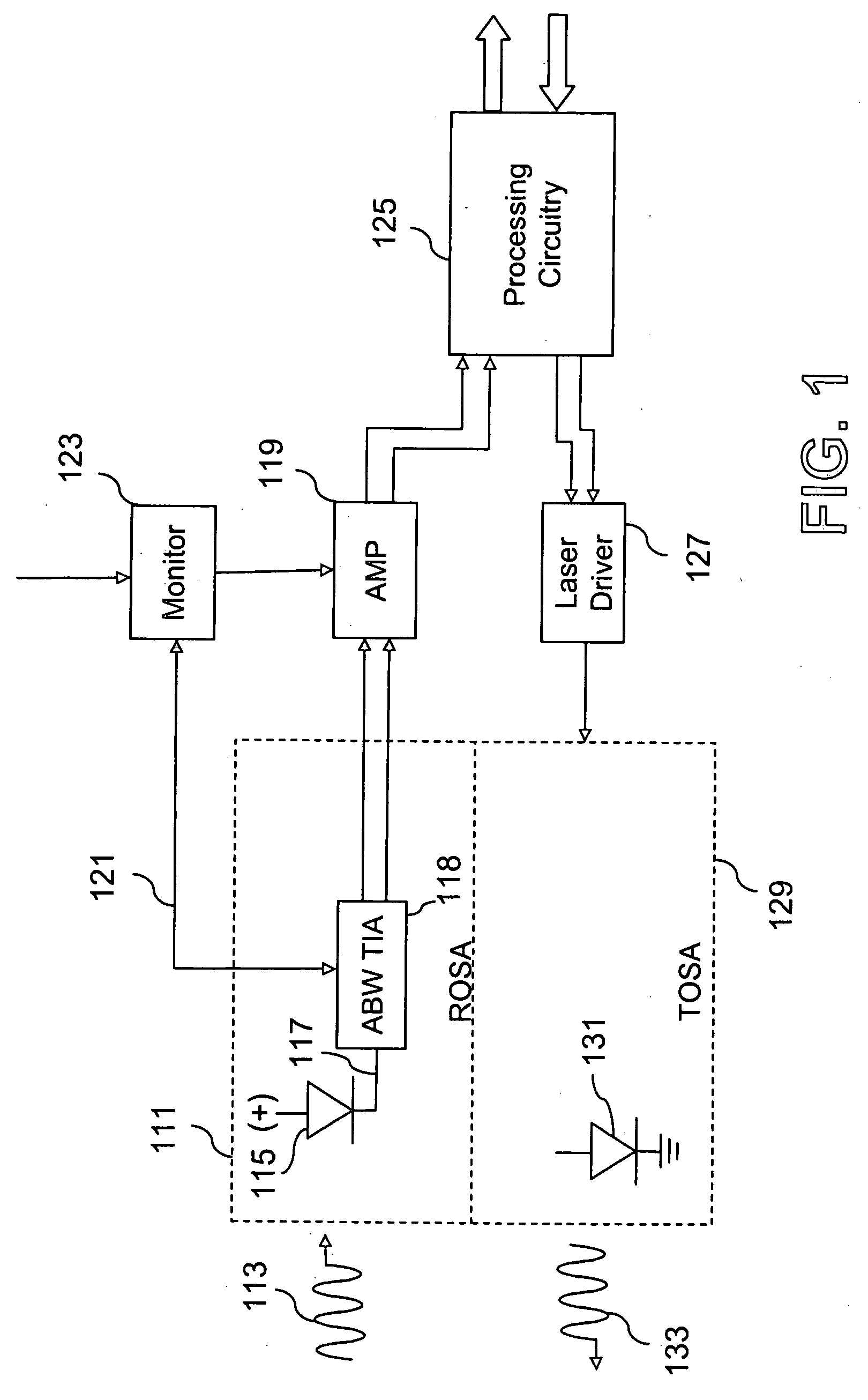
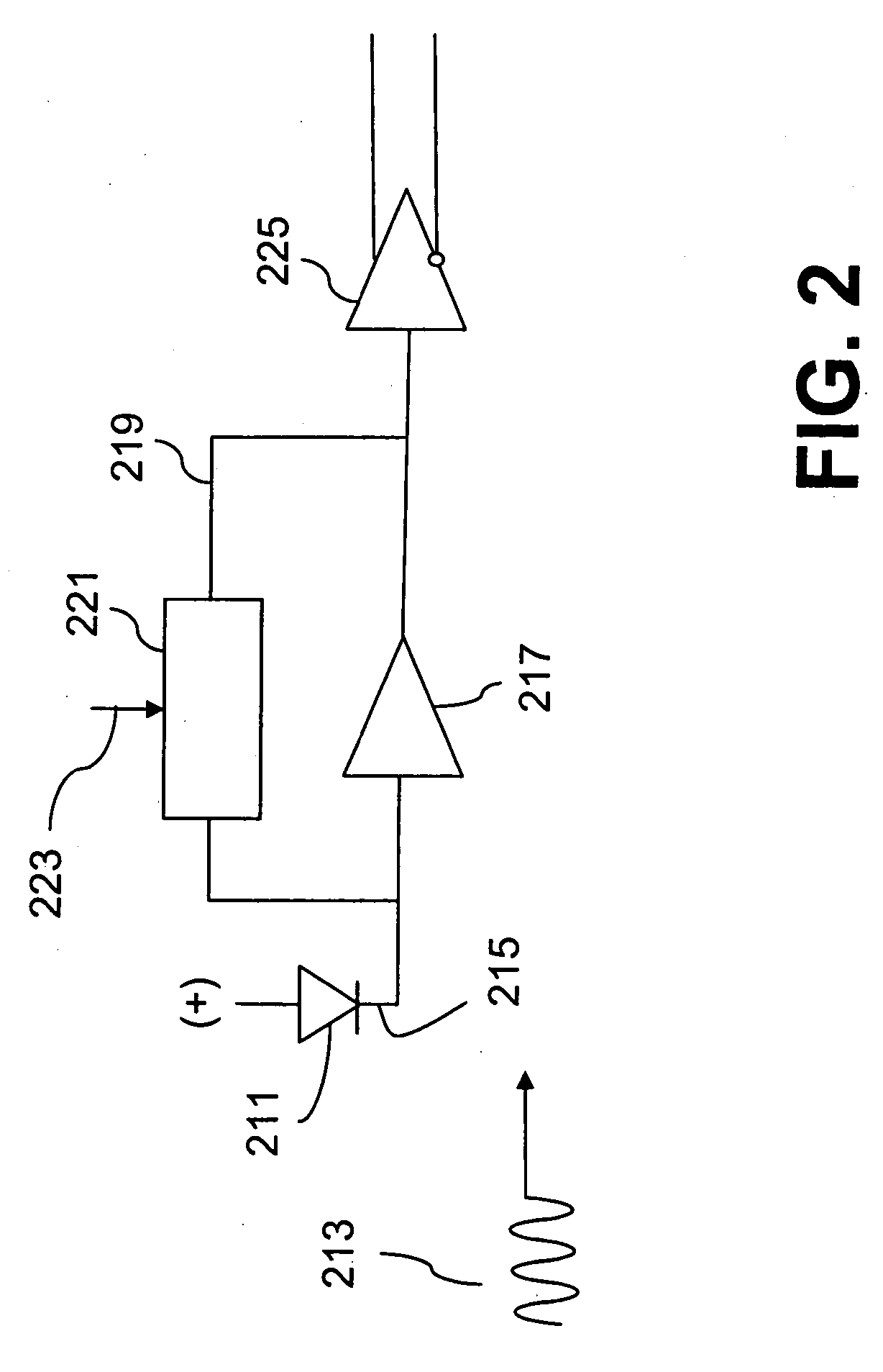
Signal conditioning circuit between an optical device and a processing unit
ActiveUS20070213020A1CatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringSignal conditioning circuitsBandpass filtering
The invention concerns a conditioning circuit (10) for an external signal (IN) representative of a physiological quantity, arranged between an optical sensor (11) and a processing unit (12), the received external signal (IN) being broken down into a useful component and an ambient component, characterized in that the conditioning circuit includes a first stage (13) including a transimpedance amplifier with an incorporated high pass filter (15) using a feedback loop to subtract the ambient signal component from the received external signal, and to deliver at output an amplified useful signal (IN1), a second stage (16) including a blocker sampler circuit (17) for demodulating the amplified useful signal and delivering at output a demodulated useful signal (IN2), and a third stage (18) including a bandpass filter (19) for filtering the demodulated useful signal in the frequency band of the physiological quantity to be detected and for transmitting a conditioned signal (OUT) to the processing unit.
Owner:EM MICROELECTRONIC-MARIN
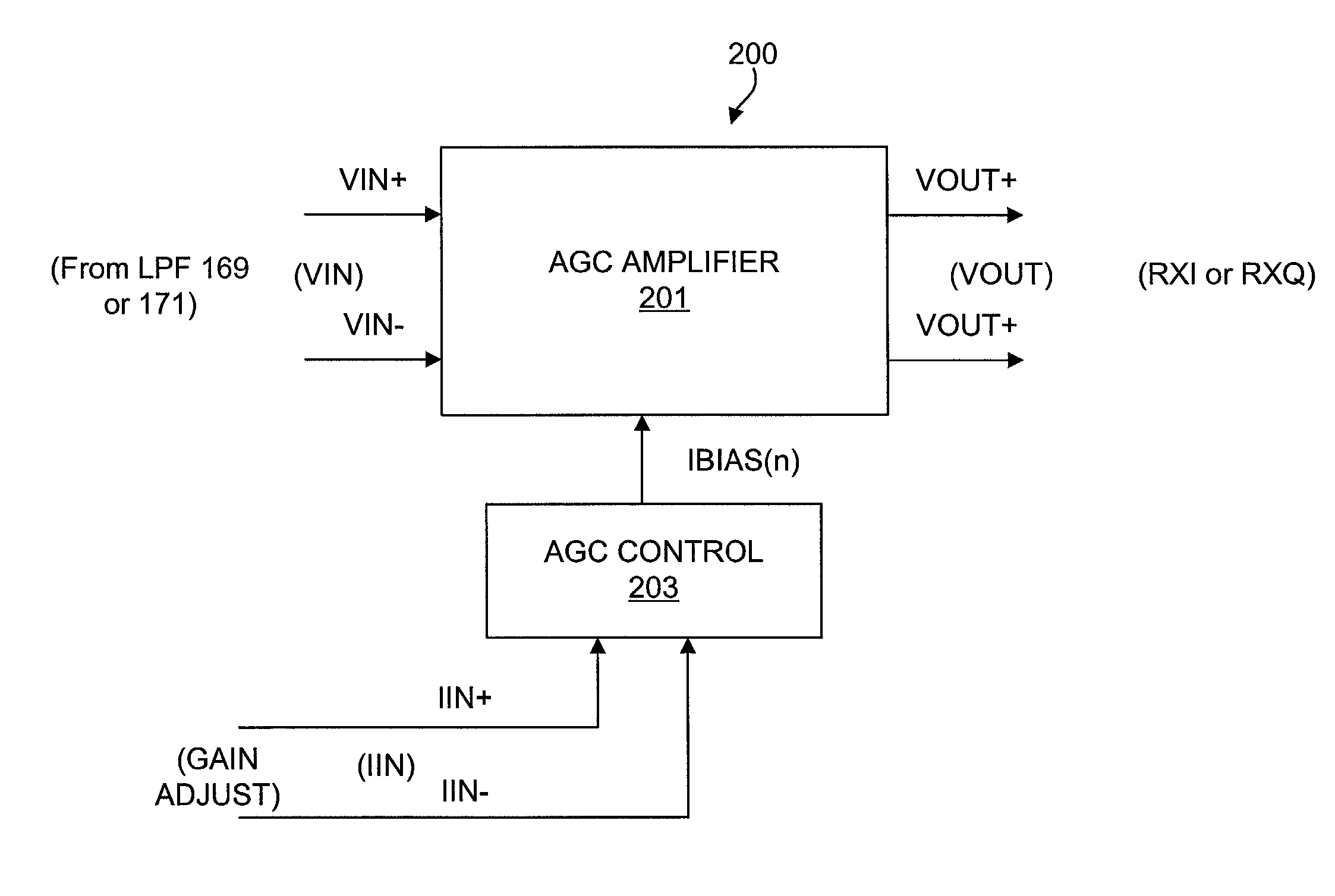
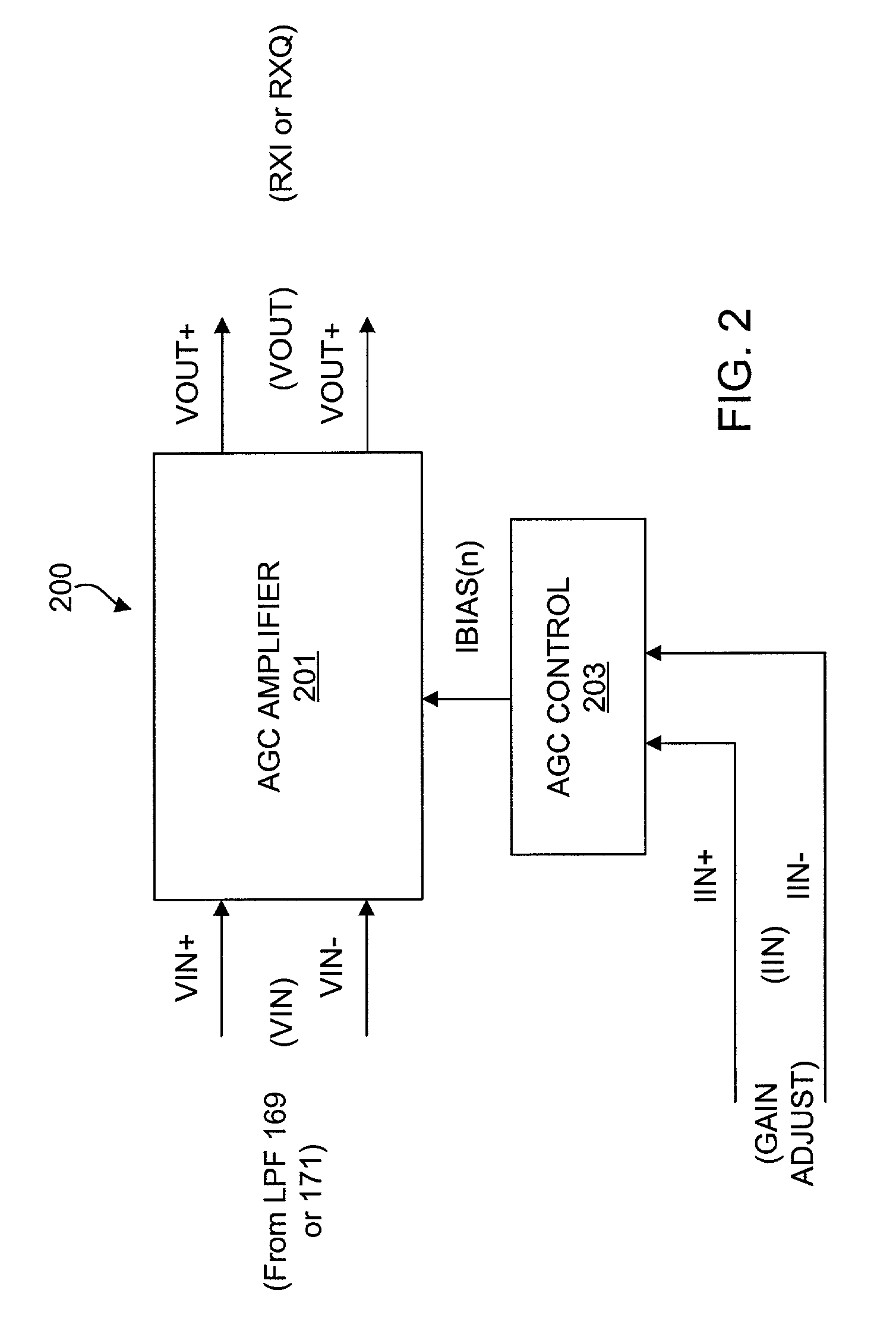
Precision automatic gain control circuit
InactiveUS6763228B2Low absolute gain toleranceImprove matchResonant long antennasVolume compression/expansion having semiconductor devicesAudio power amplifierClosed loop
An automatic gain control (AGC) amplifier including a high gain transimpedance amplifier, a resistive feedback network and multiple transconductance stages coupled in the feedback path of the AGC amplifier. The feedback network receives an input signal and is coupled to the output of the high gain amplifier and has multiple intermediate nodes. Each transconductance stage has an input coupled to an intermediate node of the feedback network and an output coupled to the input of the high gain amplifier. Each transconductance stage is independently controllable to position a virtual ground within the feedback network to control closed loop gain. Each transconductance stage may have a bias current input coupled to a bias current control circuit. The control circuit controls each bias current to vary the gain of the AGC amplifier. The bias currents may be linearly controlled employing a ramp function to achieve a linear in dB gain response.
Owner:M RED INC
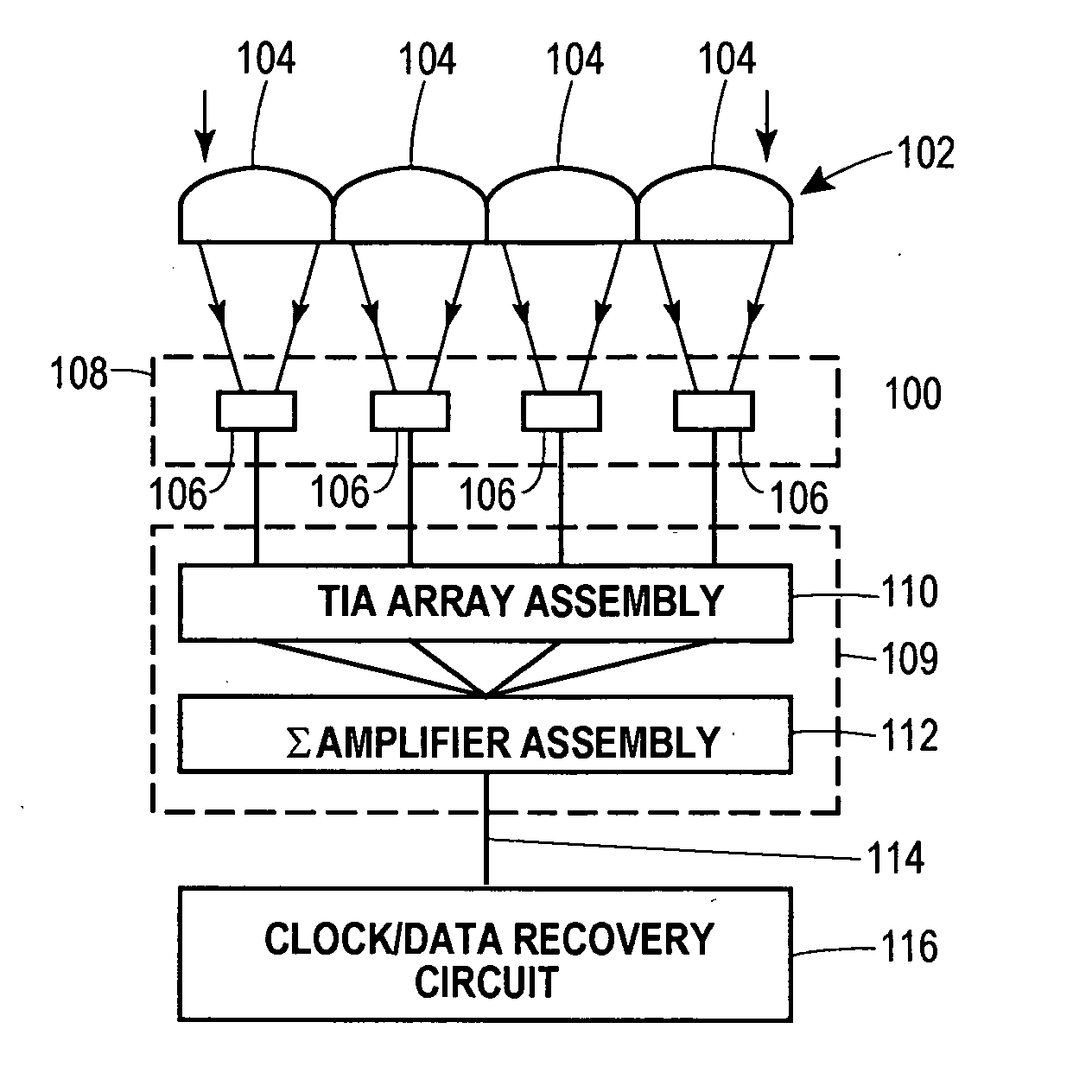
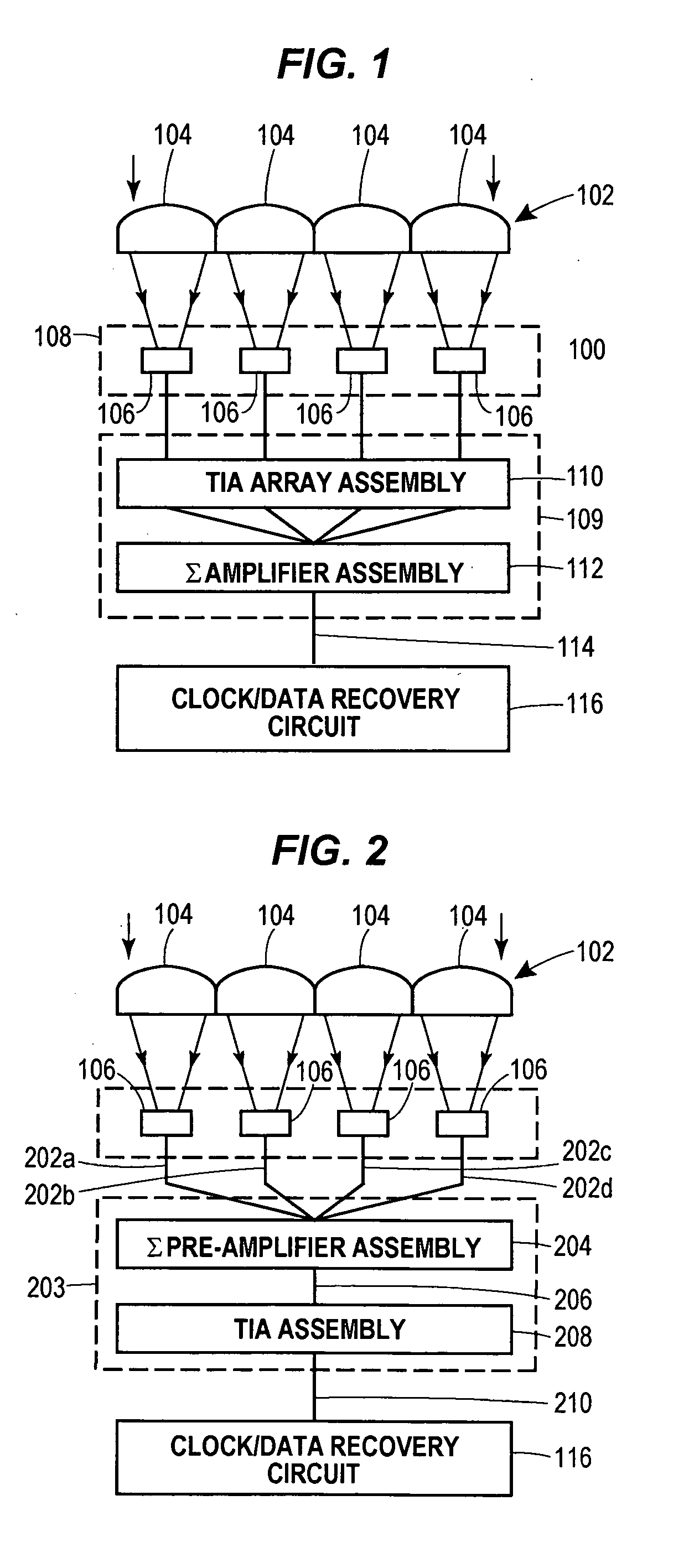
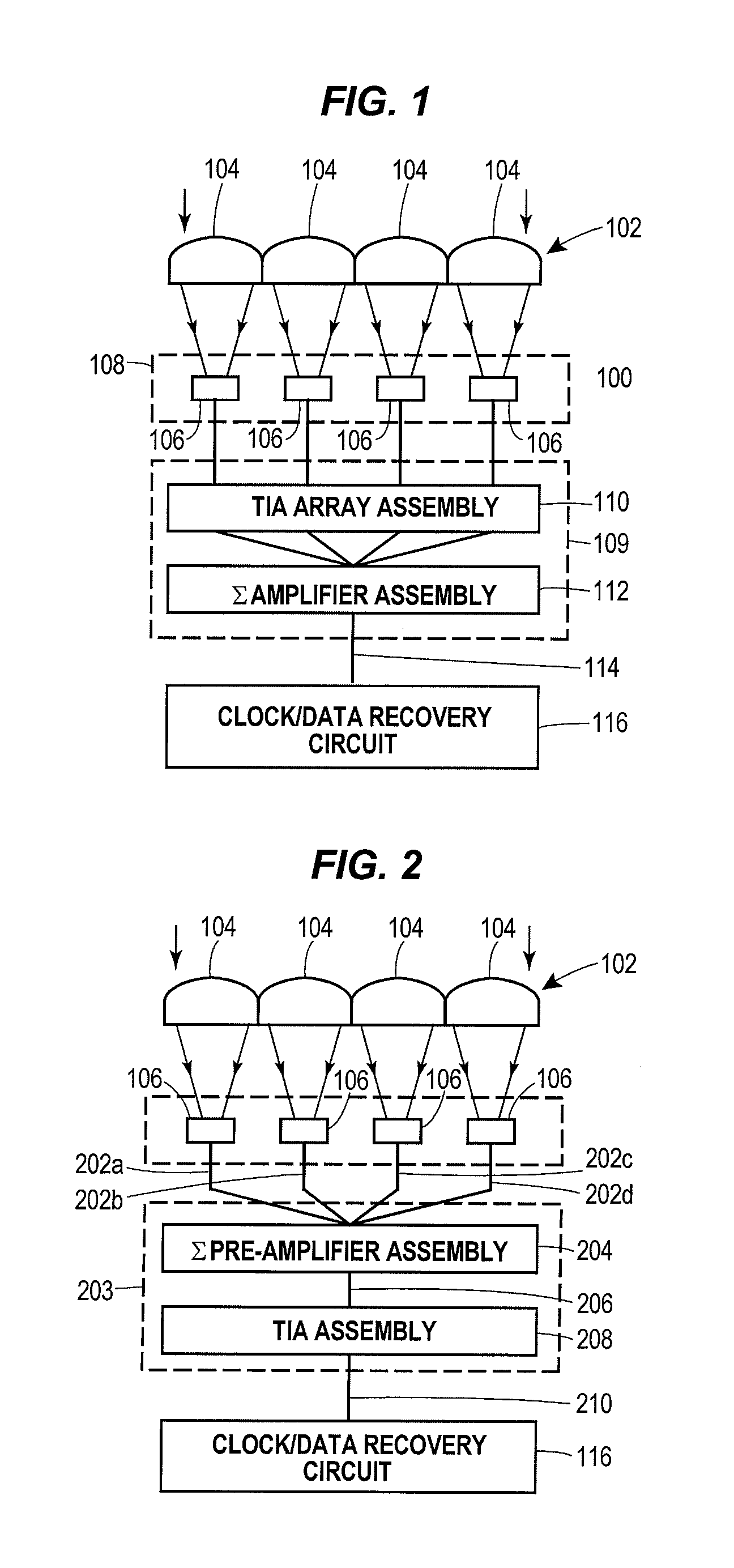
Lenslet/detector array assembly for high data rate optical communications
InactiveUS20060076473A1Reduce capacitanceHigh bandwidthSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotodetectorDetector array
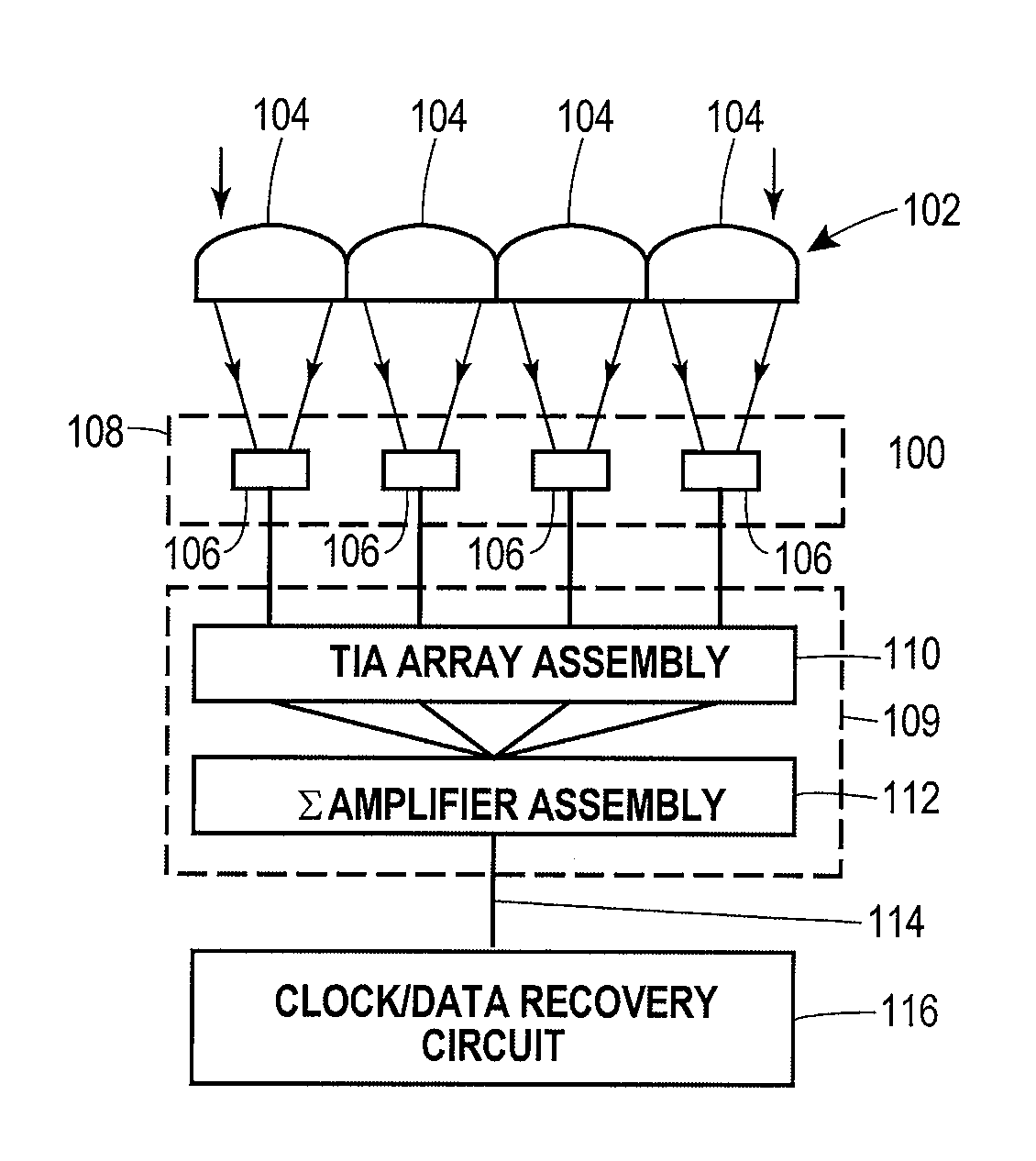
An assembly is provided that may be used in high data rate optical communications, such as free-space communication systems. The assembly may include a main optical receiver element and a lenslet array or other optical element disposed near the focal plane that collects an optical signal and focuses that signal as a series of optical signal portions onto a photodetector array, formed of a series of InGaAs photodiodes, for example. The electrical signals from the photodetectors may be amplified using high bandwidth transimpedance amplifiers connected to a summing amplifier or circuit that produces a summed electrical signal. Alternatively, the electrical signals may be summed initially and then amplified via a transimpedance amplifier. The assembly may be used in remote optical communication systems, including free-space laser communication environments, to convert optical signals up to or above 1 Gbit / s or higher data rates into electrical signals at 1 Gbit / s or higher data rates.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
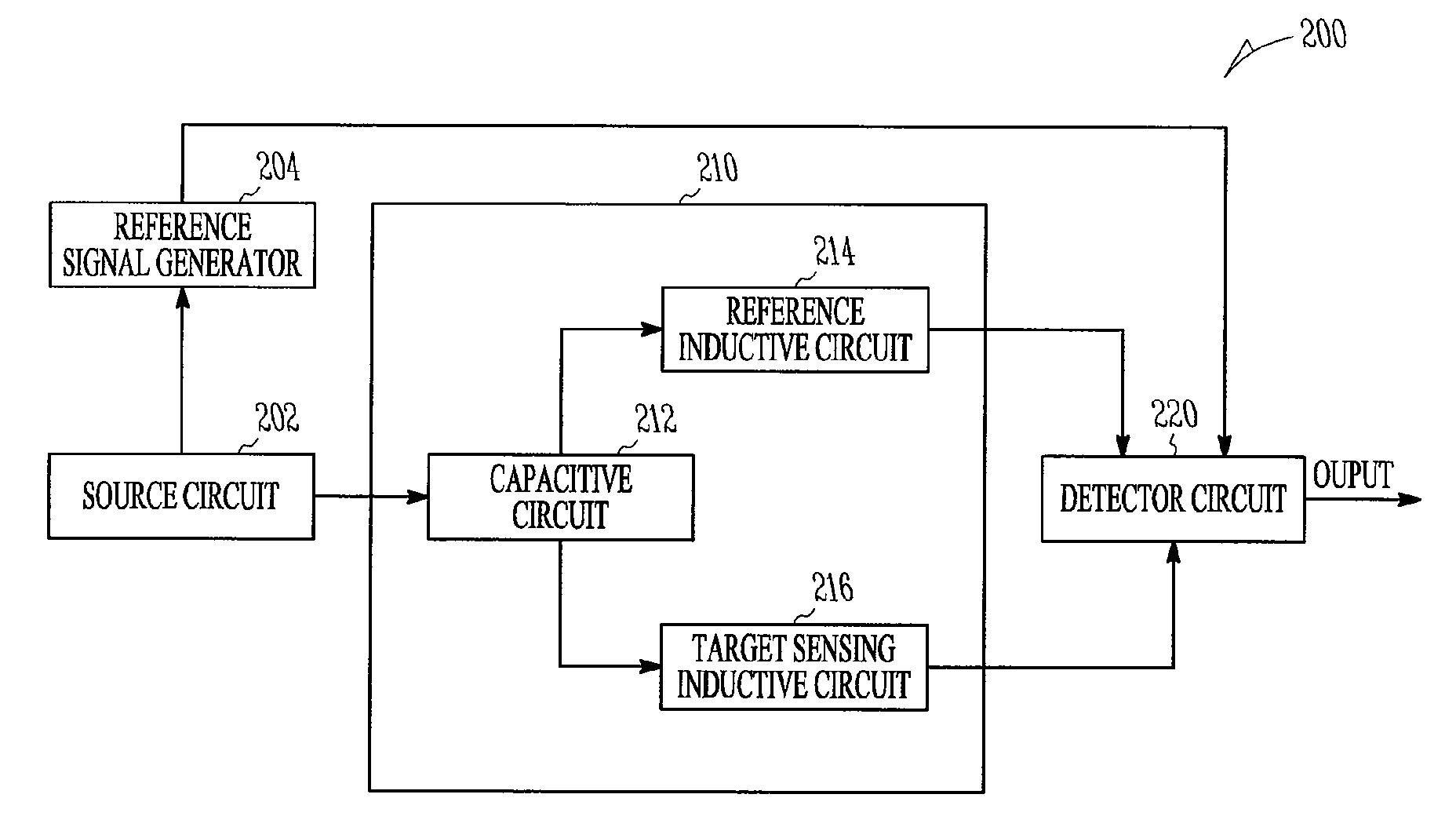
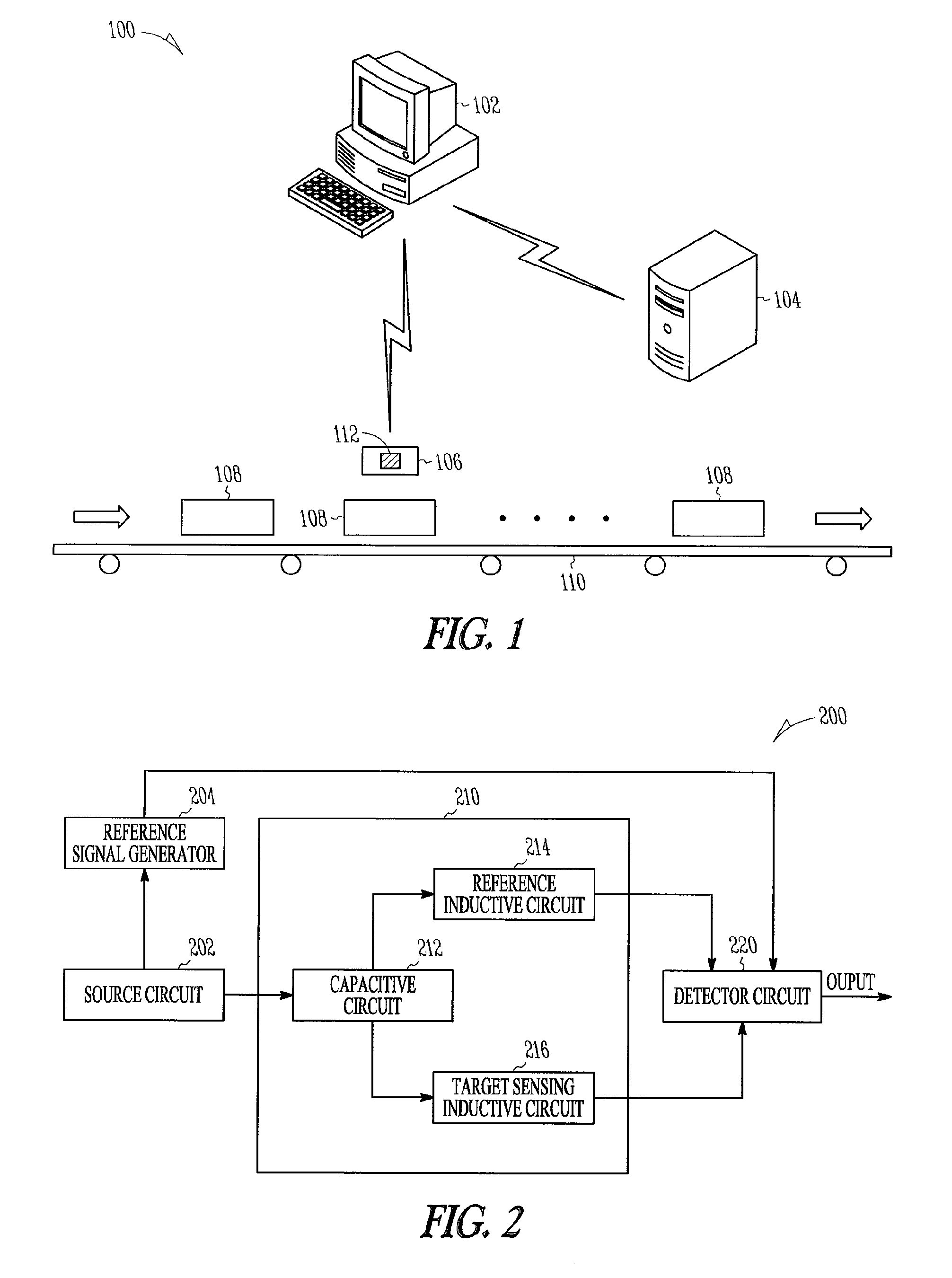
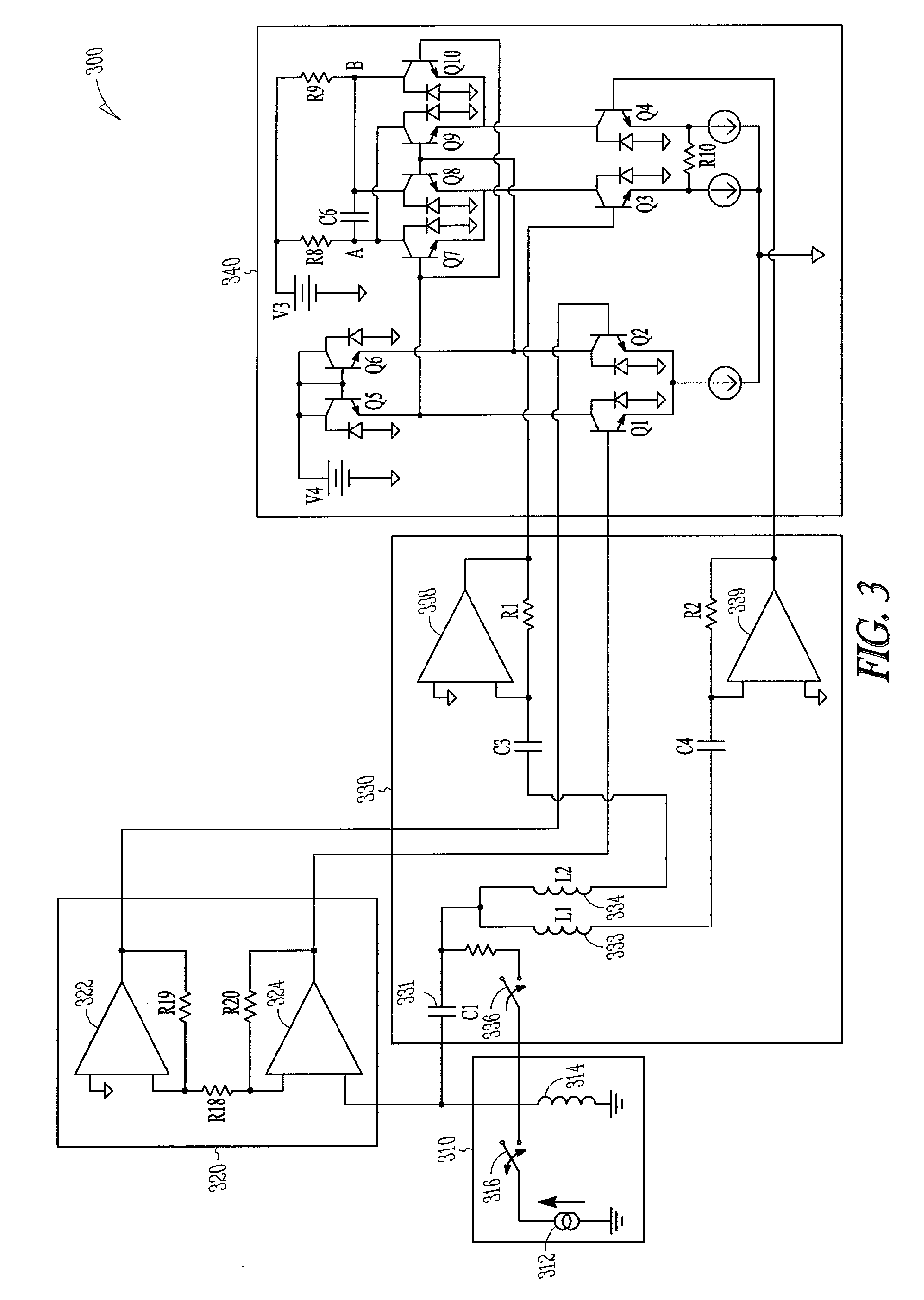
Apparatus and methods for proximity sensing circuitry
An inductive proximity sensor is disclosed. The proximity sensor includes a resonator with a bifurcated inductance coupled to a plurality of transimpedance amplifiers. A portion of the resonator is configured to generate eddy currents in a target containing metal. In various embodiments, the transimpedance amplifiers provide signals associated with eddy currents to a synchronous detector. Apparatus and methods for operating the inductive proximity sensor are disclosed.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
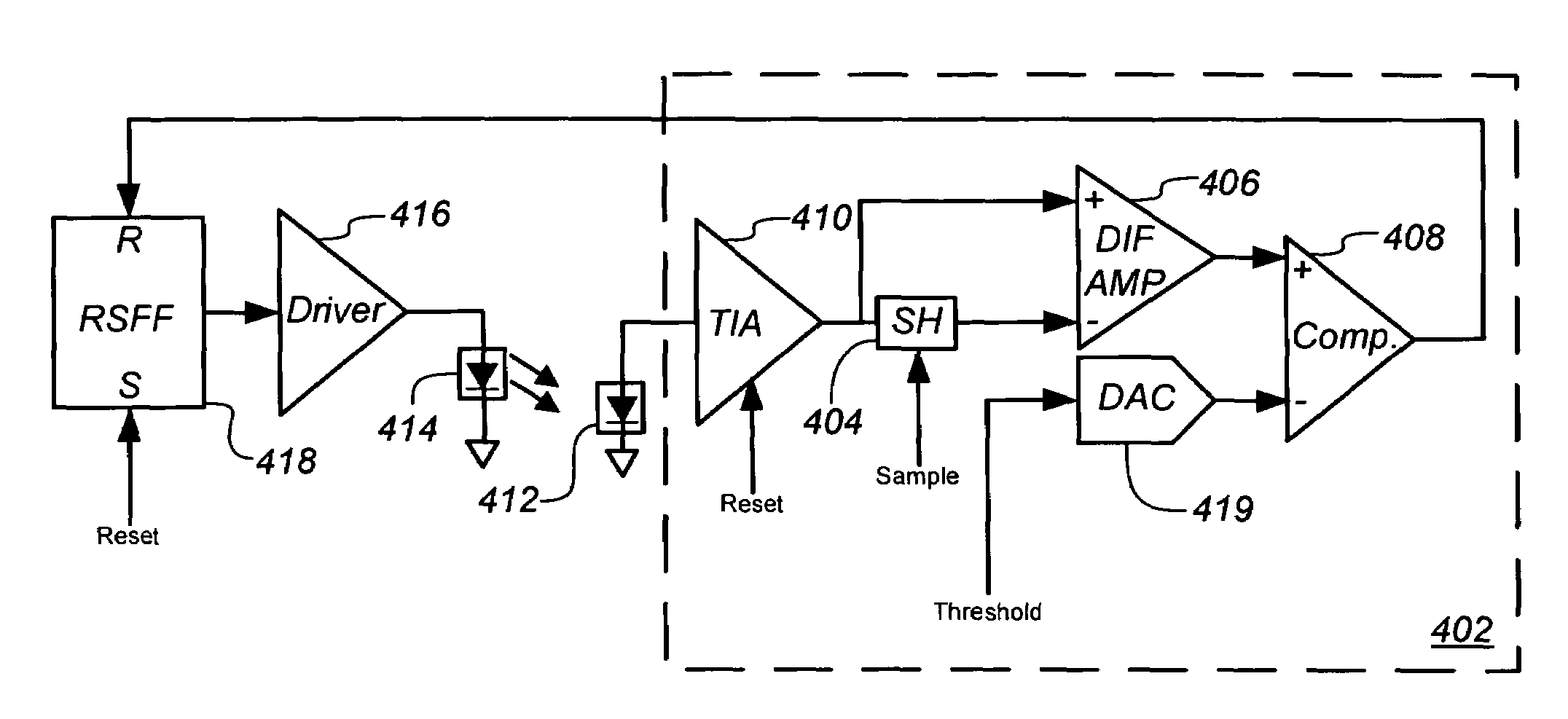
Signal processing circuit and method using analog voltage signal to pulse width modulation conversion
InactiveUS7247832B2Television system detailsPhotometry using reference valueSignal processing circuitsAudio power amplifier
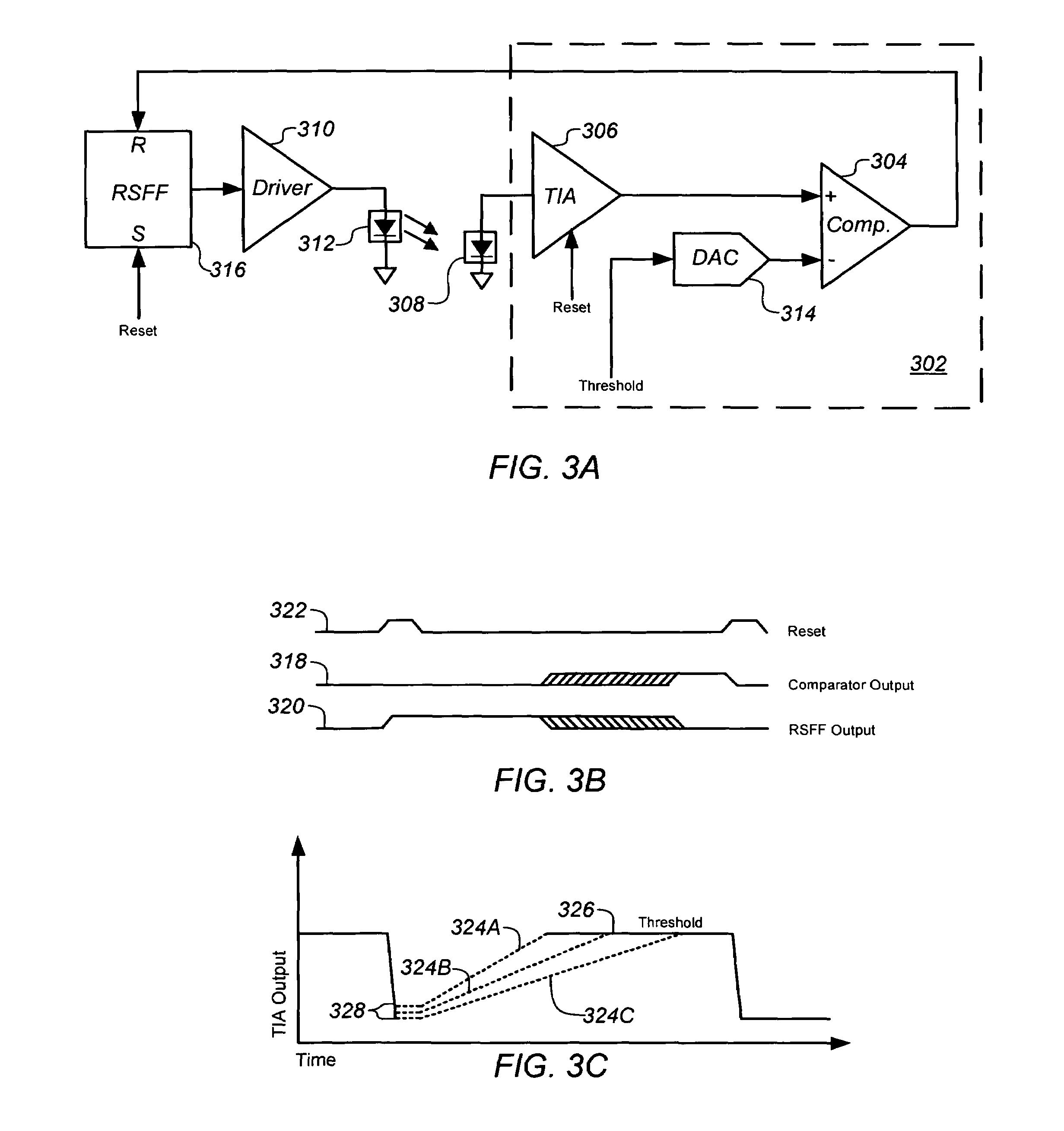
A signal processor and processing method are provided for measuring current received from a photo-detector. Generally, the processor includes a transimpedance amplifier (TIA) to integrate a current received from a photo-detector in the optical navigation system to generate a voltage signal having a slope that is proportional to the received current, and a comparator having a first input coupled to an output of the TIA to receive the voltage signal, and a second, inverting, input coupled to a threshold voltage. The comparator is configured to compare the voltage signal to the threshold voltage and to generate an output pulse having a predetermined voltage and a duration or width that is a function of the received current.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
Overcurrent protection circuit and liquid crystal display
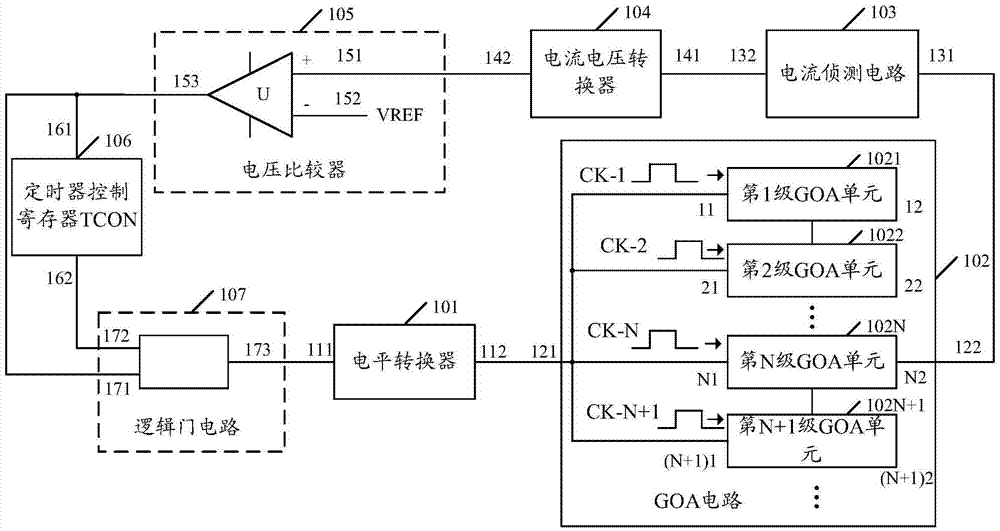
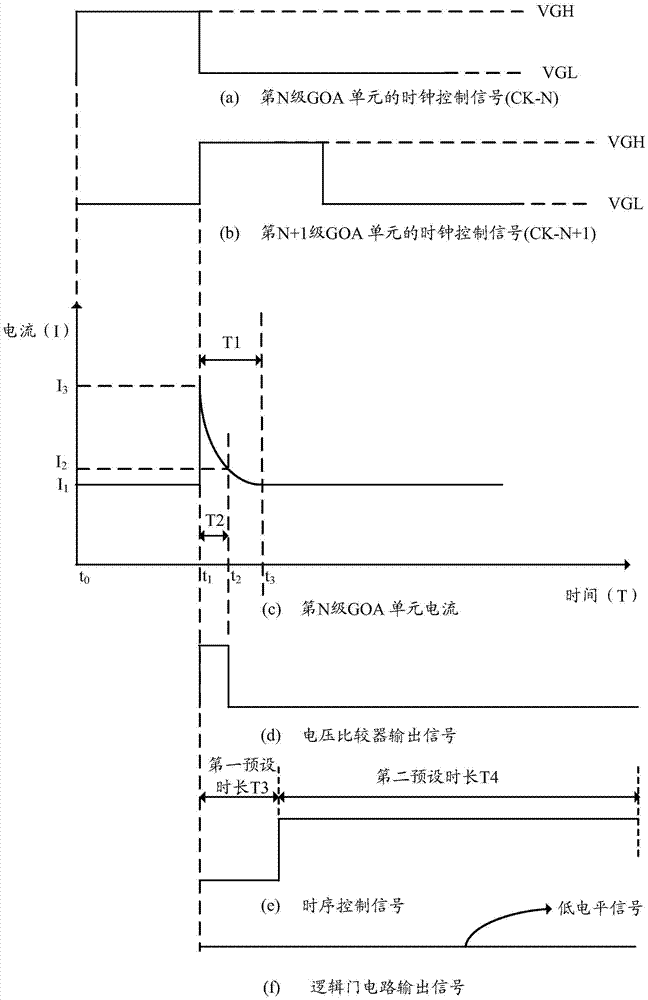
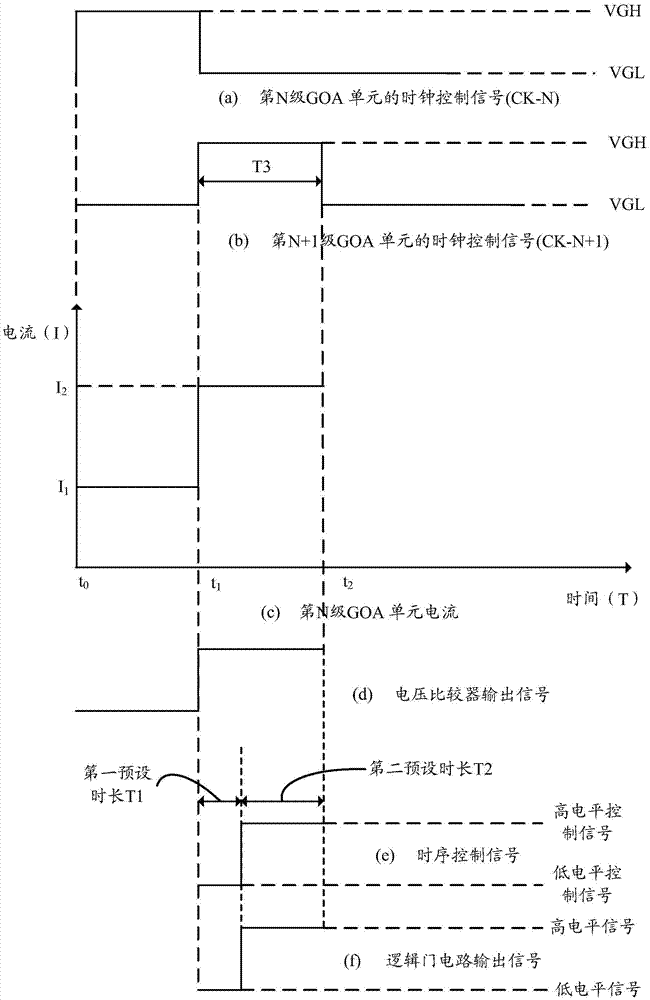
The embodiment of the invention discloses an overcurrent protection circuit, and the circuit comprises a level converter and a substrate array line drive (GOA) circuit in electrical connection with the level converter. The circuit also comprises a current detection circuit, a current-voltage converter, a voltage comparator, a timer control register, and a logic gate circuit. The GOA circuit is connected with the current detection circuit, and the current detection circuit is connected with the current-voltage converter. The current-voltage converter is connected with the in-phase input end of the voltage comparator, and the inverted-phase input end of the voltage comparator is connected with a reference voltage. The output end of the voltage comparator is connected with the input end of the timer control register and the first input end of the logic gate circuit. The output end of the timer control register is connected with the second input end of the logic gate circuit. The output end of the logic gate circuit is connected with the level converter. According to the embodiment of the invention, the circuit can prevent the wrong triggering of an overcurrent protection operation. The invention also provides a liquid crystal display comprising the circuit.
Owner:TCL CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Amplification with feedback capacitance for photodetector signals
ActiveUS20050218299A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCapacitancePhotodetector
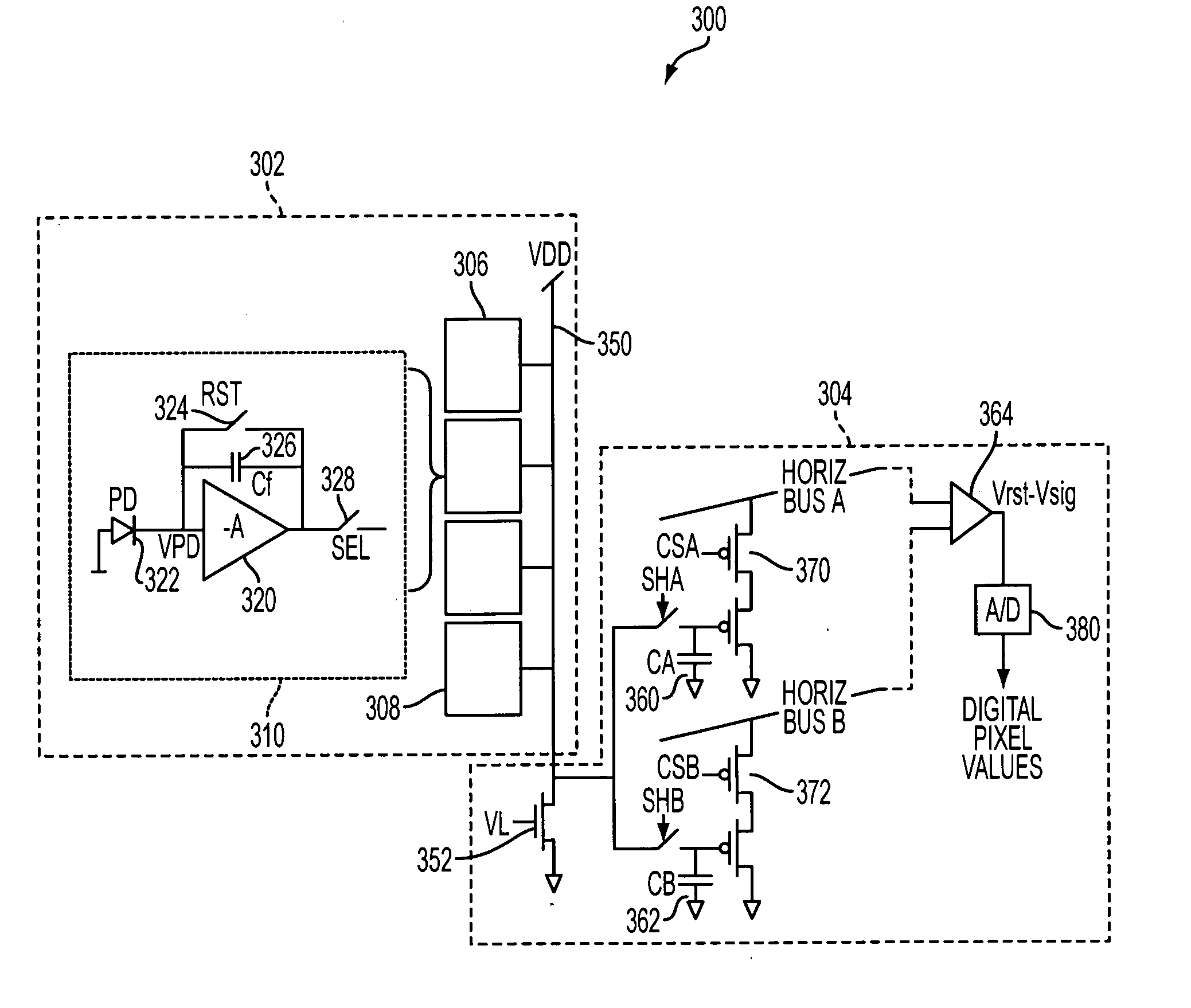
Signals from an imager pixel photodetector are received by an amplifier having capacitive feedback, such as a capacitive transimpedance amplifier (CTIA). The amplifier can be operated at a low or no power level during an integration period of a photodetector to reduce power dissipation. The amplifier can be distributed, with an amplifier element within each pixel of an array and with amplifier output circuitry outside the pixel array. The amplifier can be a single ended cascode amplifier, a folded cascode amplifier, a differential input telescopic cascode amplifier, or other configuration. The amplifier can be used in pixel configurations where the amplifier is directly connected to the photodetector, or in configurations which use a transfer transistor to couple signal charges to a floating diffusion node with the amplifier being coupled to the floating diffusion node.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
Lenslet/detector array assembly for high data rate optical communications
An assembly is provided that may be used in high data rate optical communications, such as free-space communication systems. The assembly may include a main optical receiver element and a lenslet array or other optical element disposed near the focal plane that collects an optical signal and focuses that signal as a series of optical signal portions onto a photodetector array, formed of a series of InGaAs photodiodes, for example. The electrical signals from the photodetectors may be amplified using high bandwidth transimpedance amplifiers connected to a summing amplifier or circuit that produces a summed electrical signal. Alternatively, the electrical signals may be summed initially and then amplified via a transimpedance amplifier. The assembly may be used in remote optical communication systems, including free-space laser communication environments, to convert optical signals up to or above 1 Gbit / s or higher data rates into electrical signals at 1 Gbit / s or higher data rates.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
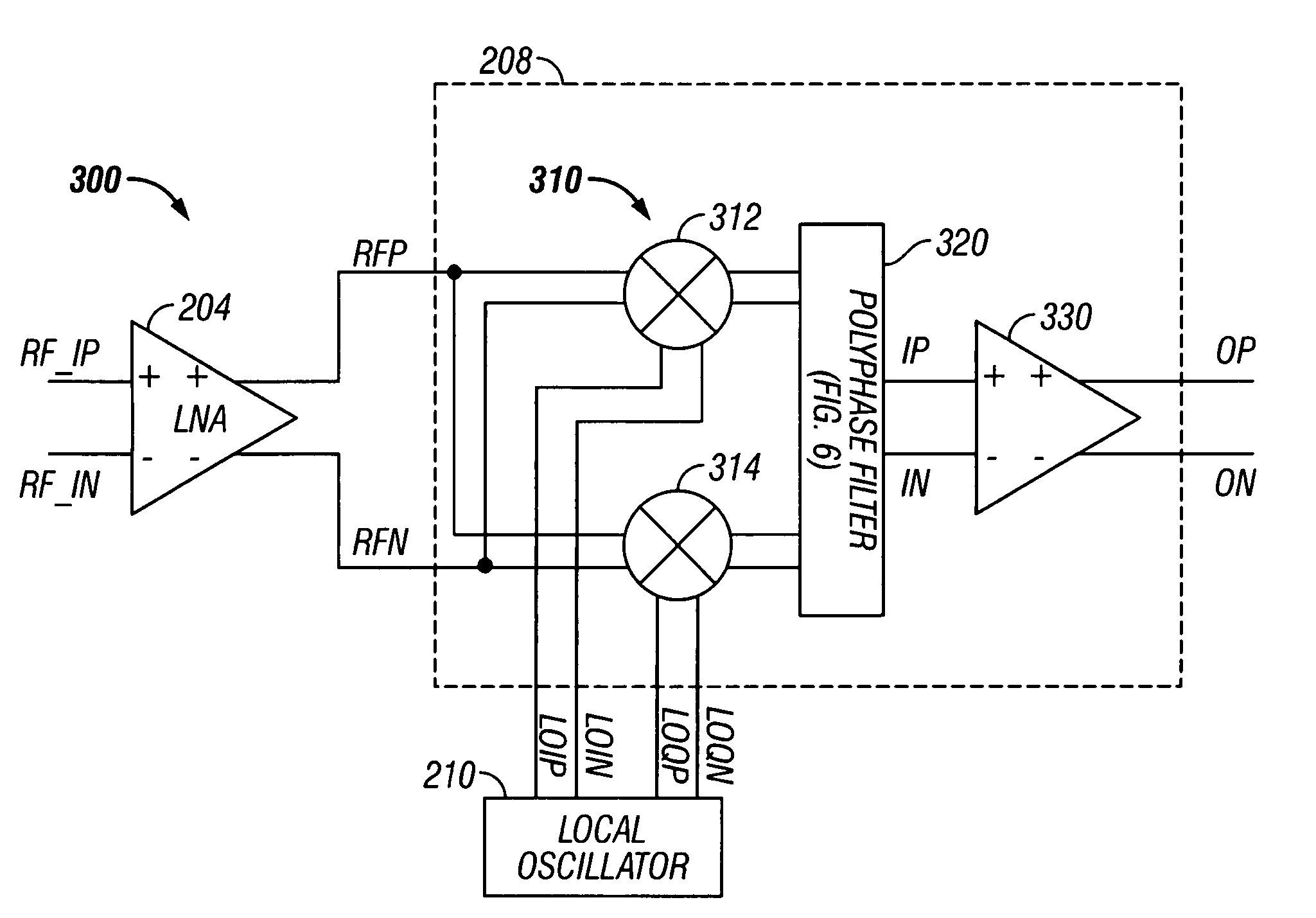
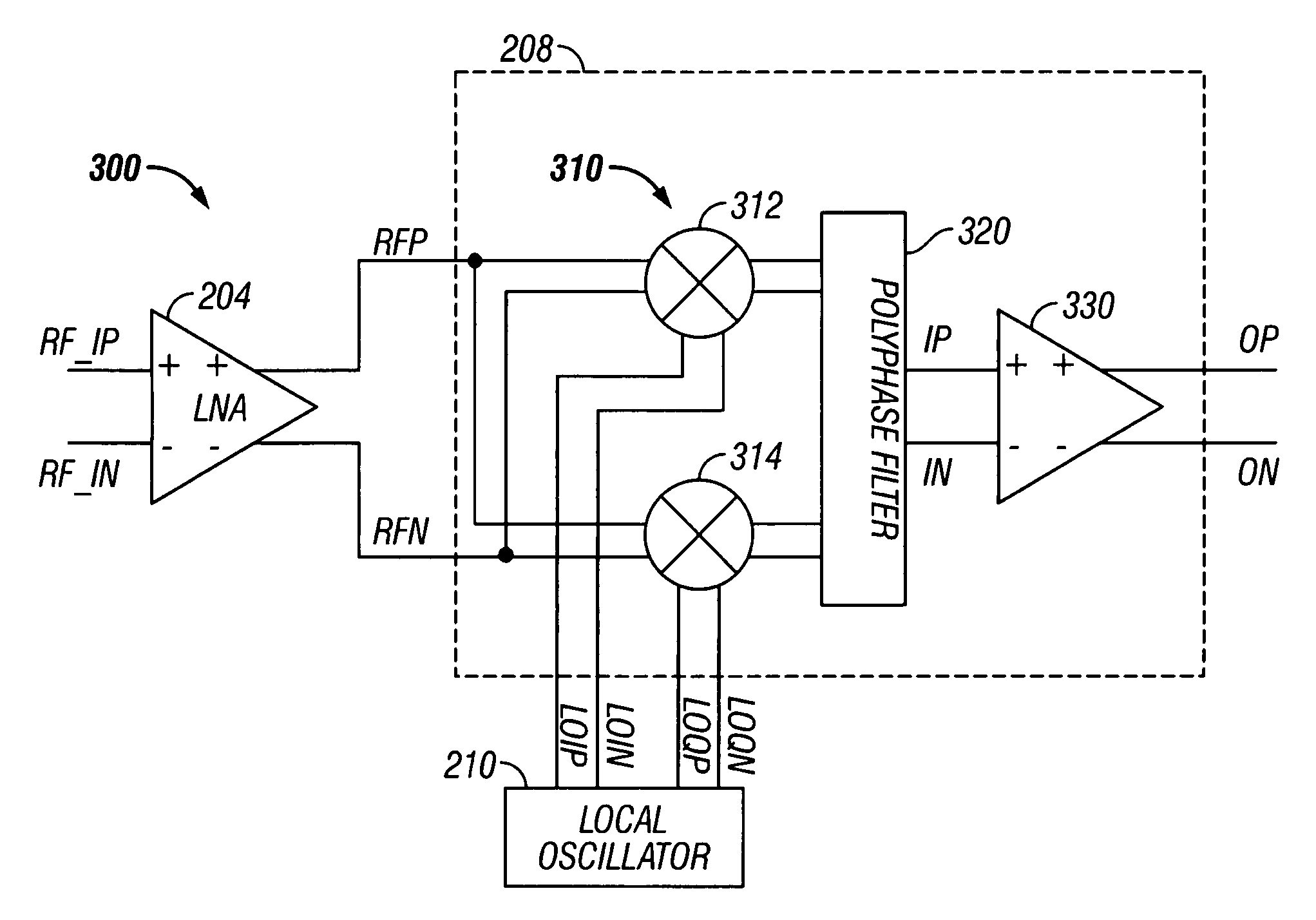
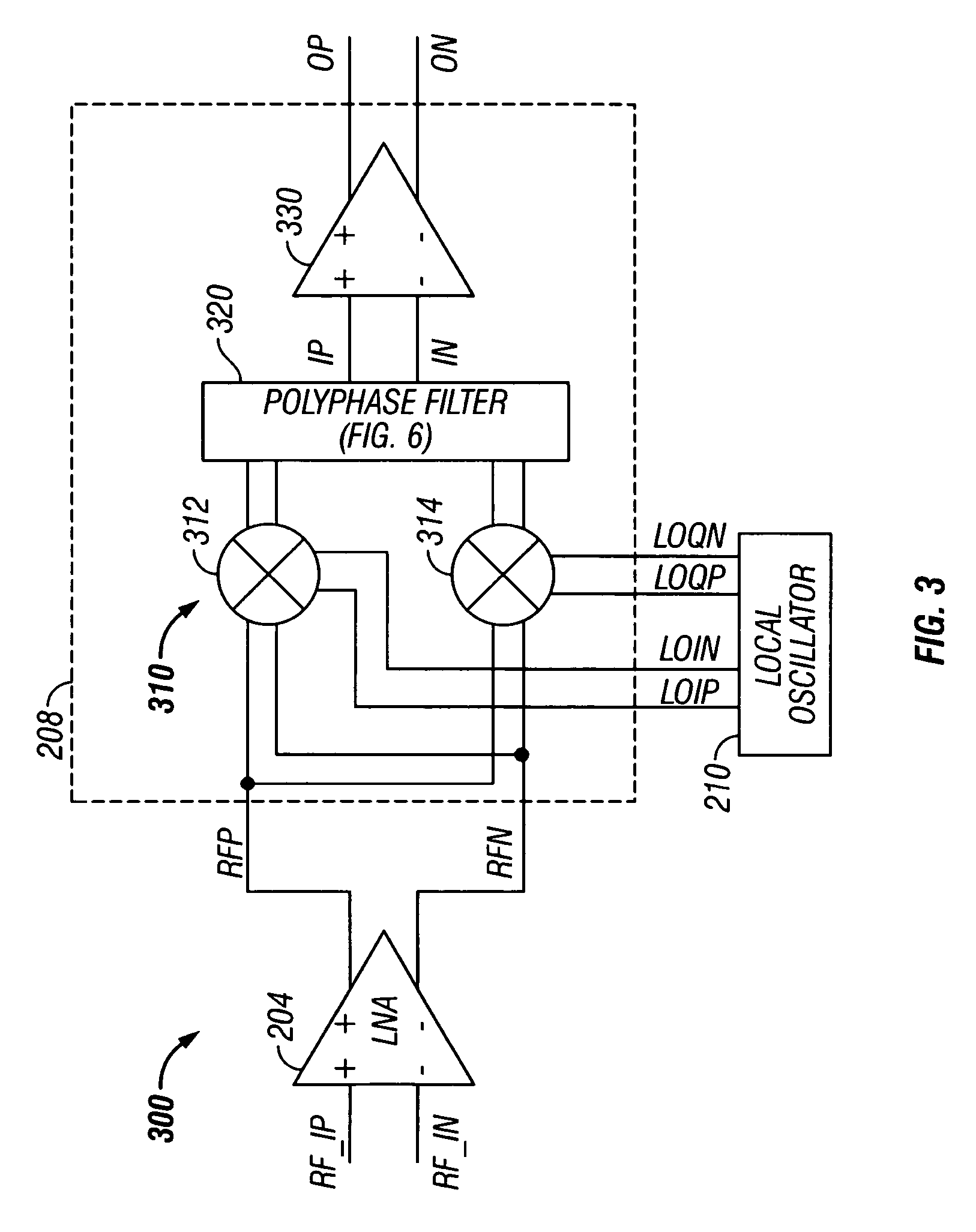
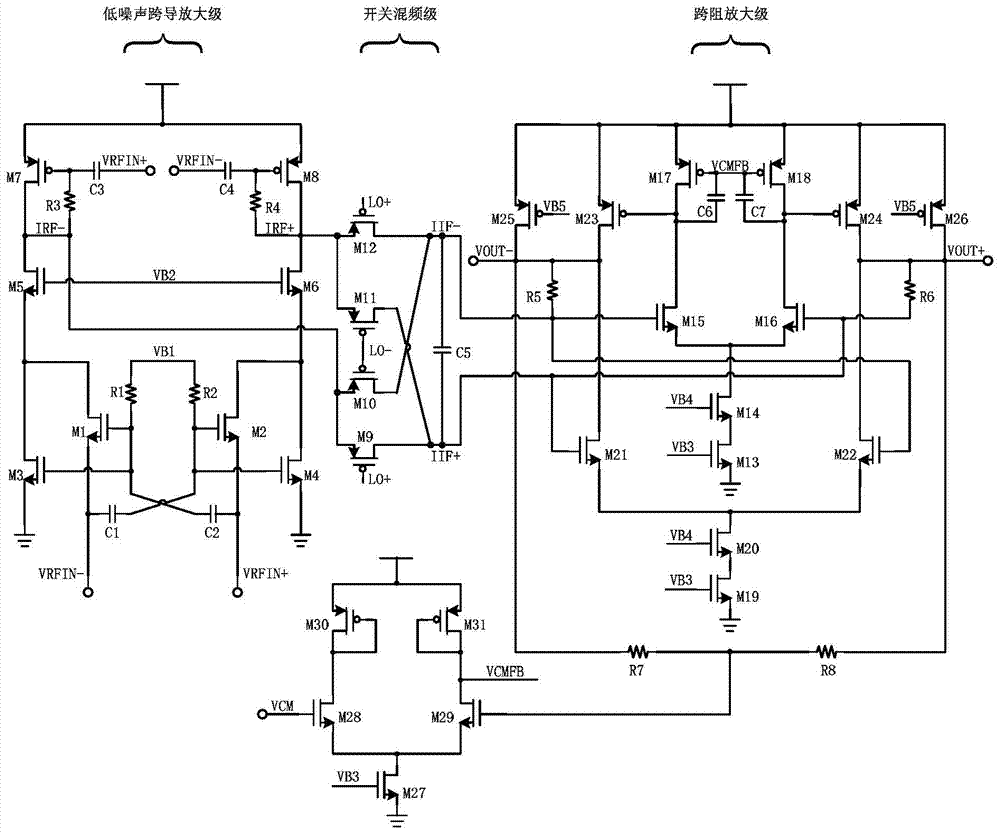
Low noise image reject mixer and method therefor
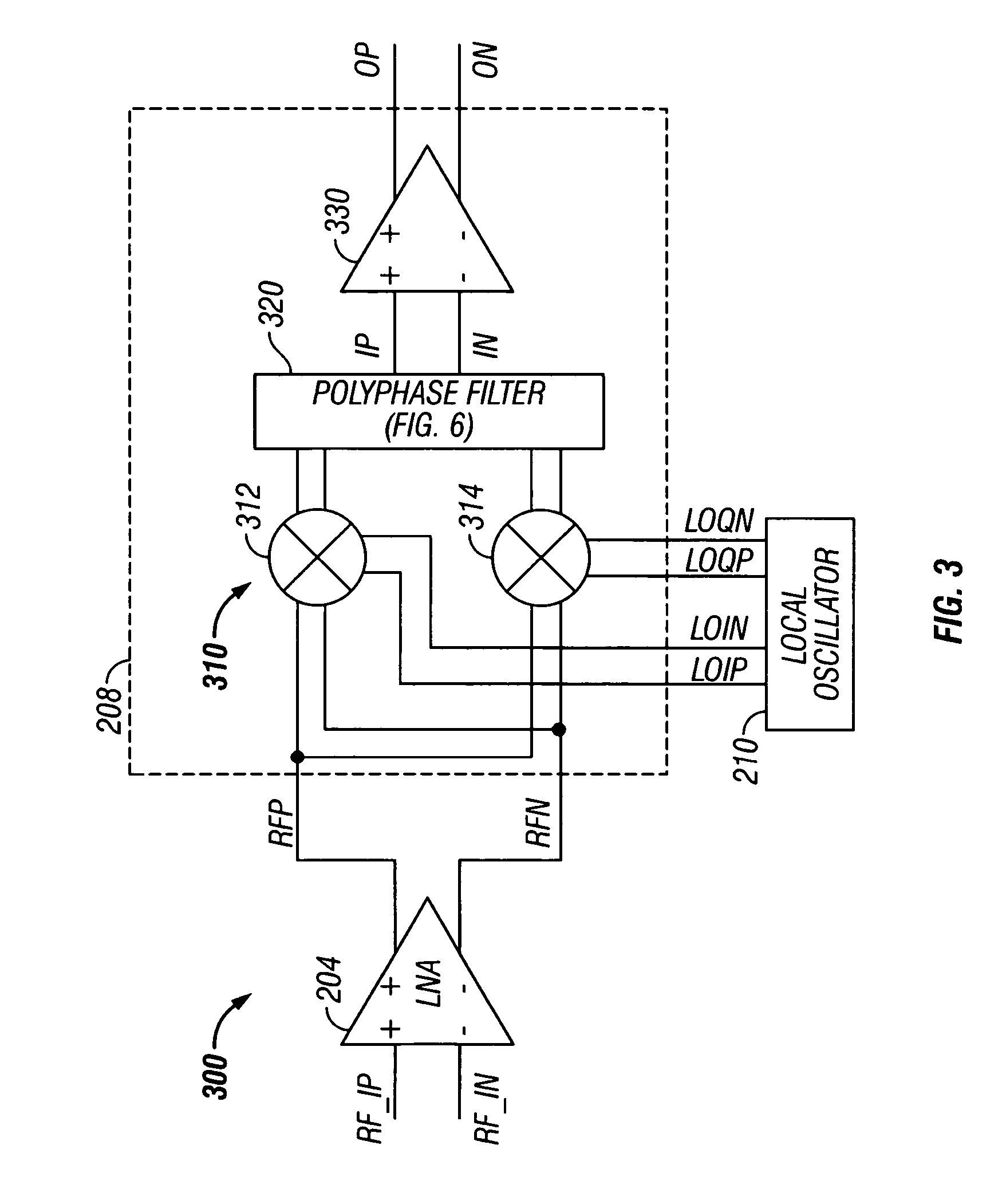
A receiver (200) includes a transconductance mixer (310), a polyphase filter (320), and a transimpedance amplifier (330). The transconductance mixer (310) mixes a radio frequency (RF) voltage signal into a current signal having a plurality of phases using a local oscillator signal. The polyphase filter (320) filters the current signal to provide a filtered current signal. The transimpedance amplifier (330) converts the filtered current signal into an output voltage signal.
Owner:XENOGENIC DEV LLC
Nested transimpedance amplifier
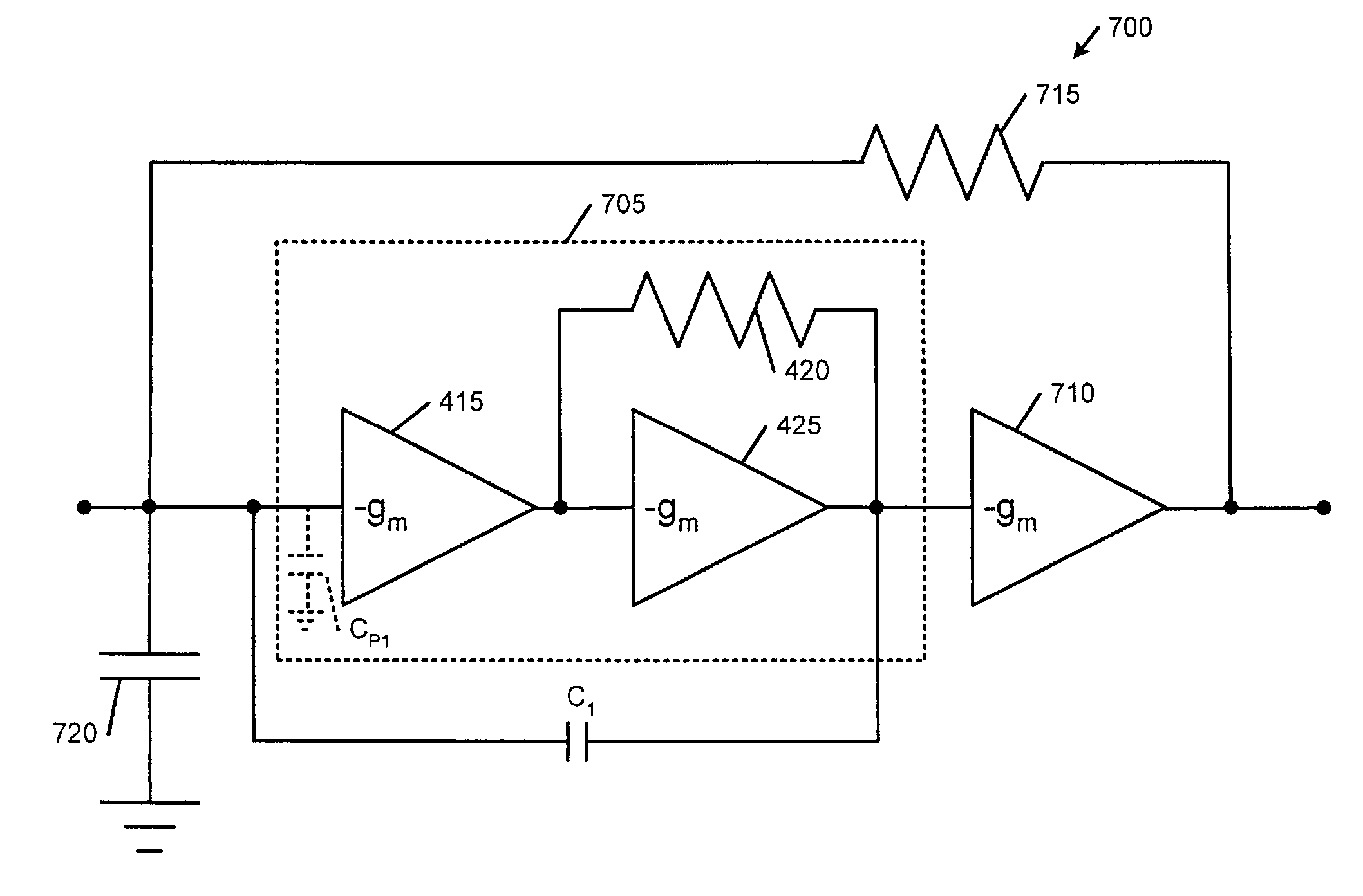
InactiveUS7276965B1Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsHigh frequency amplifiersCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
A nested transimpedance amplifier (TIA) circuit includes a zero-order TIA having an input and an output. A first operational amplifier (opamp) has an input that communicates with the output of the zero-order TIA and an output. A first feedback resistance has one end that communicates with the input of the zero-order TIA and an opposite end that communicates with the output of the first opamp. A first feedback capacitance has a first end that communicates with the input of the zero-order TIA and a second end that communicates with the output of the zero-order TIA. A capacitor has one end that communicates with the input of the zero-order TIA.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Linear multi-stage transimpedance amplifier
InactiveUS7605660B1Improve linearityReduce distortion problemsAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionGain controlAudio power amplifierControl signal
An apparatus comprising a first amplifier circuit, a detect circuit, a control circuit and a second amplifier circuit. The first amplifier circuit may be configured to generate an amplified signal in response to an input signal. The detect circuit may be configured to generate a feed-forward signal in response to the amplified signal. The control circuit may be configured to generate a dynamic control signal in response to the feed-forward signal. The second amplifier circuit may be configured to generate an output signal in response to (i) the amplified signal and (ii) the dynamic control signal. The control circuit may be configured to control a gain of the second amplifier circuit by adjusting a magnitude of the dynamic control signal.
Owner:QORVO US INC
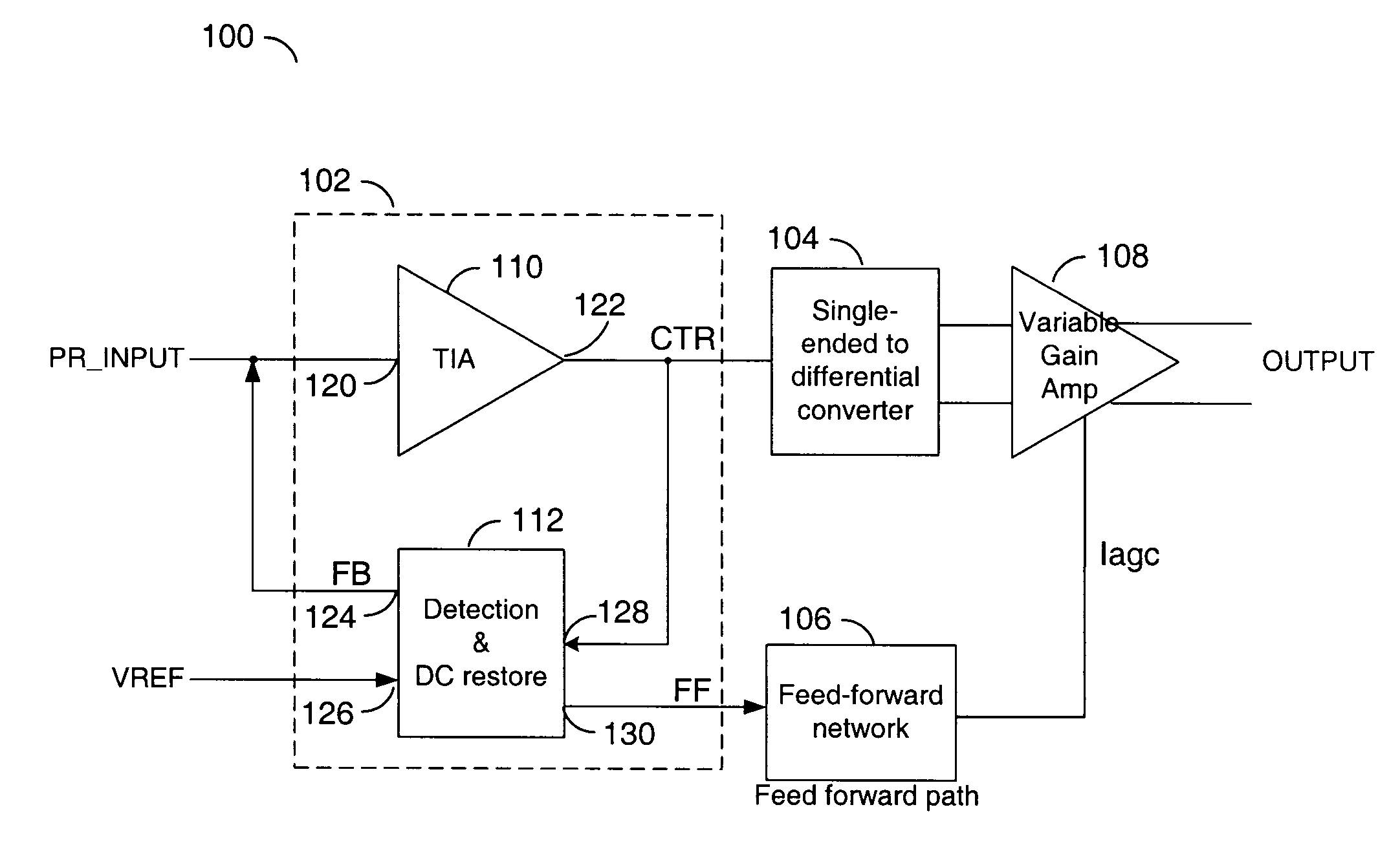
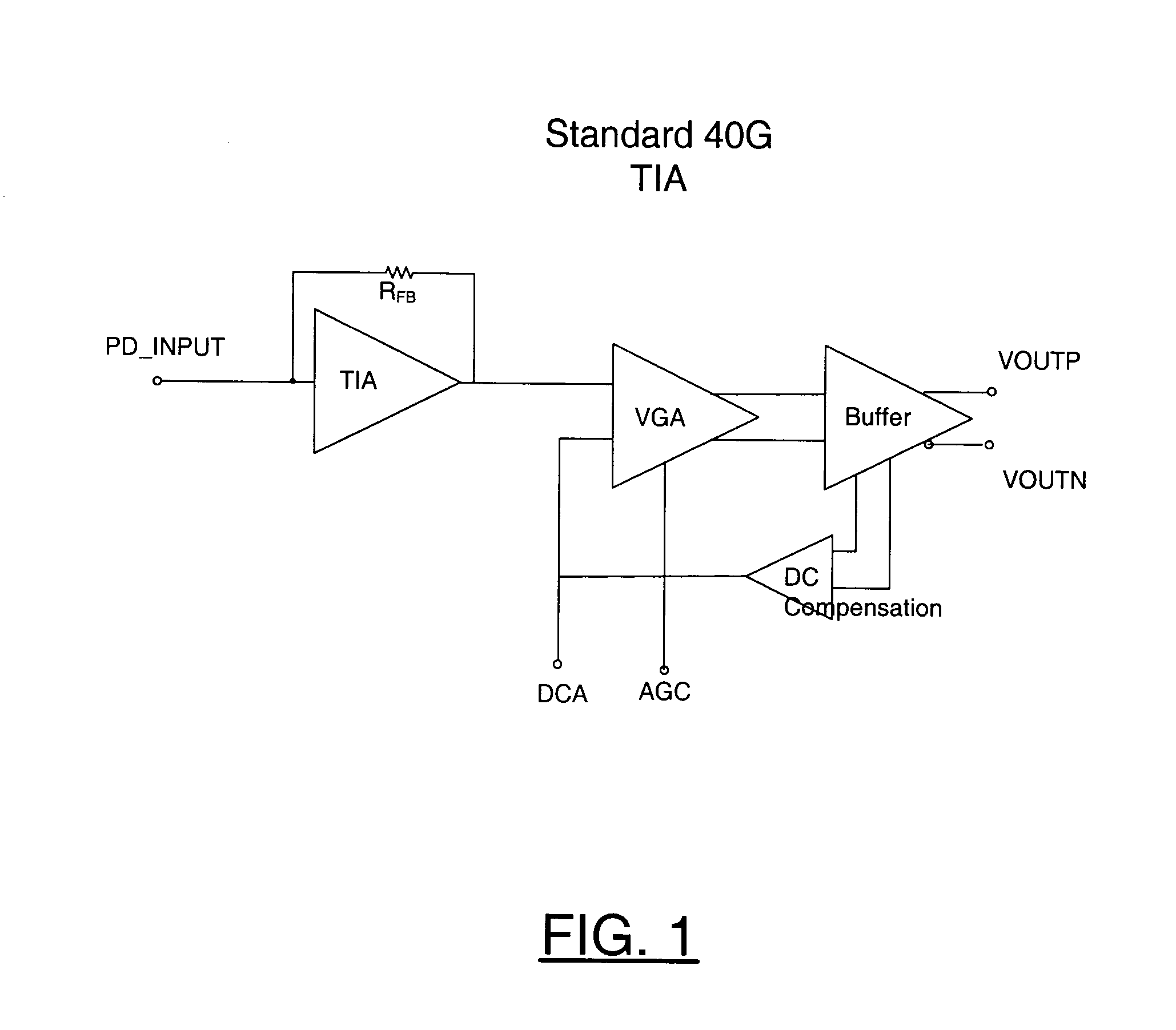
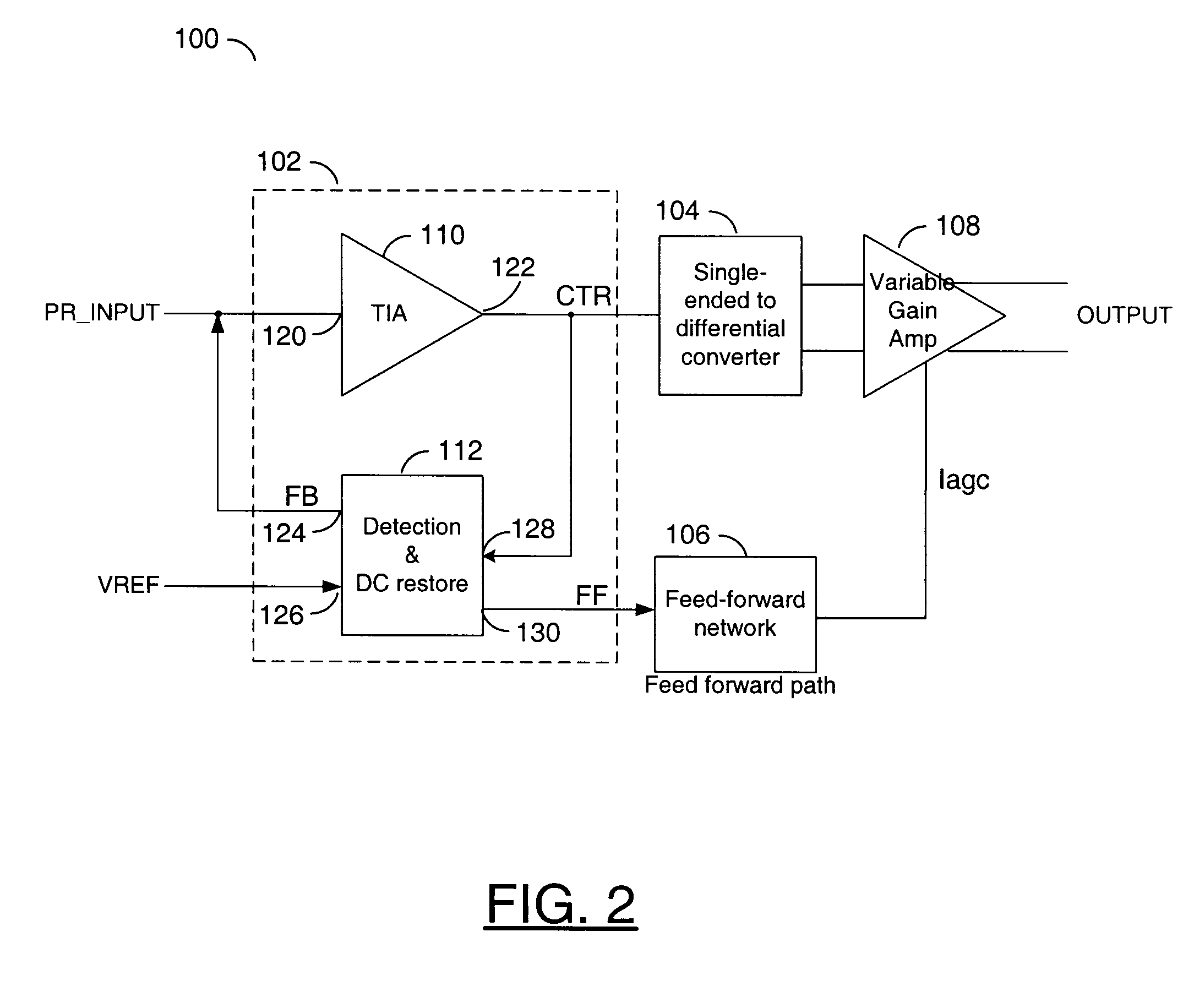
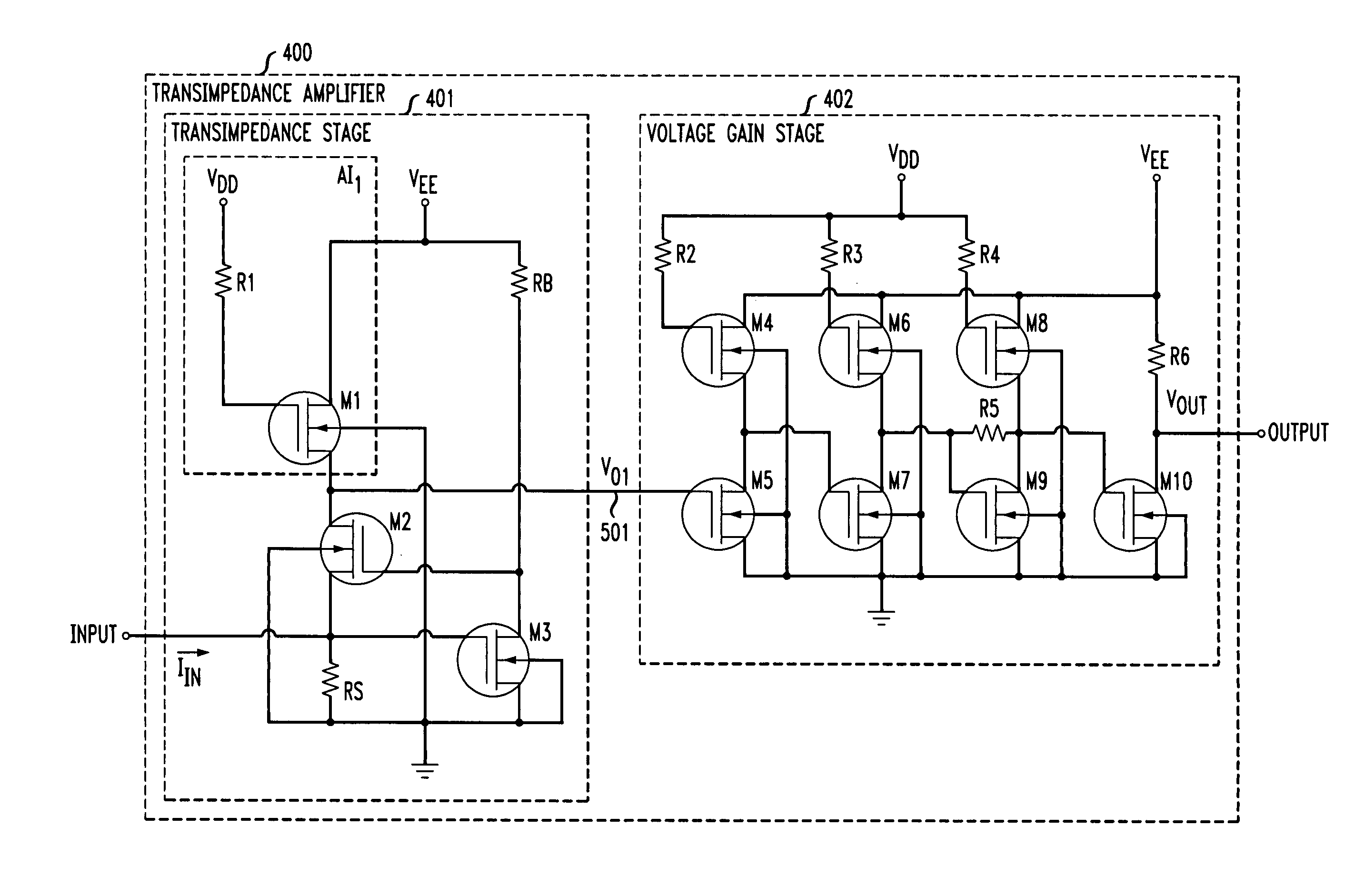
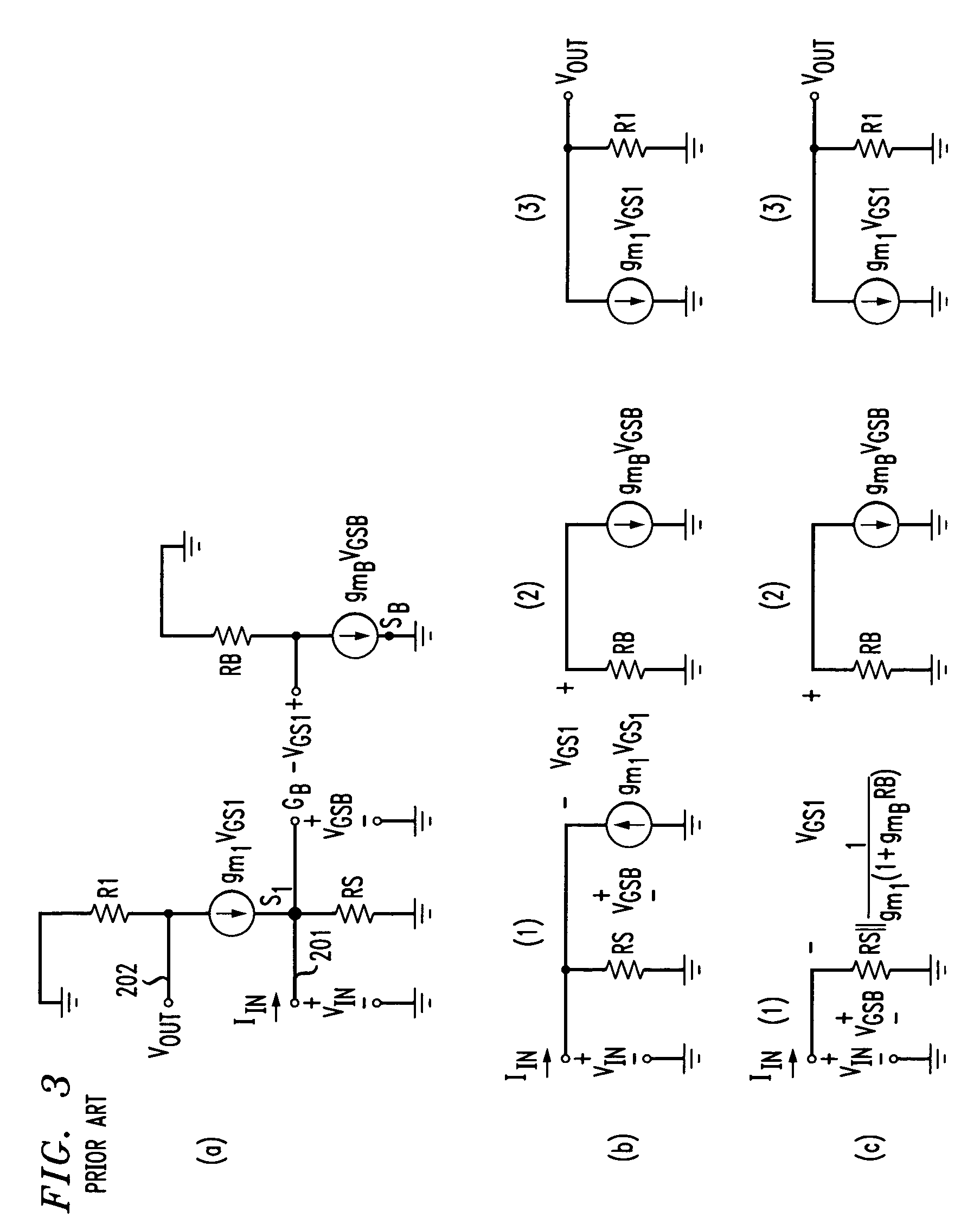
Transimpedance amplifier
InactiveUS7135932B2Minimise currentWide bandwidthAmplifier combinationsAmplifiers controlled by lightAudio power amplifierEngineering
A transimpedance amplifier, which is useful as an optical fiber preamplifier, is disclosed. The illustrative embodiment exhibits four characteristics. First, it minimizes the equivalent input noise current. Second, it has a wide bandwidth. Third, it has a reasonably large output voltage, and fourth, it is stable over wide temperature and voltage ranges. The illustrative embodiment comprises a transimpedance stage and a gain stage. Both stages employ a pure NMOS design which contributes to the above four advantages. Bandwidth is further increased over the prior art by the use of inductive loads. The inductive loads of the illustrative embodiment are not physical inductors, but transistor-based “active” inductors: the combination of a resistor connected in series with the gate of an NMOS transistor.
Owner:SIRES LABS
Apparatus and method for operating a real time large diopter range sequential wavefront sensor
InactiveUS20140055749A1Easy maintenanceMaximize signal to noise ratioLaser surgeryOptical measurementsWavefront sensorLight beam
A sequential wavefront sensor includes a light source, a beam deflecting element, a position sensing detector configured to output a plurality of output signals and a plurality of composite transimpedance amplifiers each coupled to receive an output signal. The output of each composite transimpedance amplifier is phase-locked to a light source drive signal and a beam deflecting element drive signal.
Owner:CLARITY MEDICAL SYST
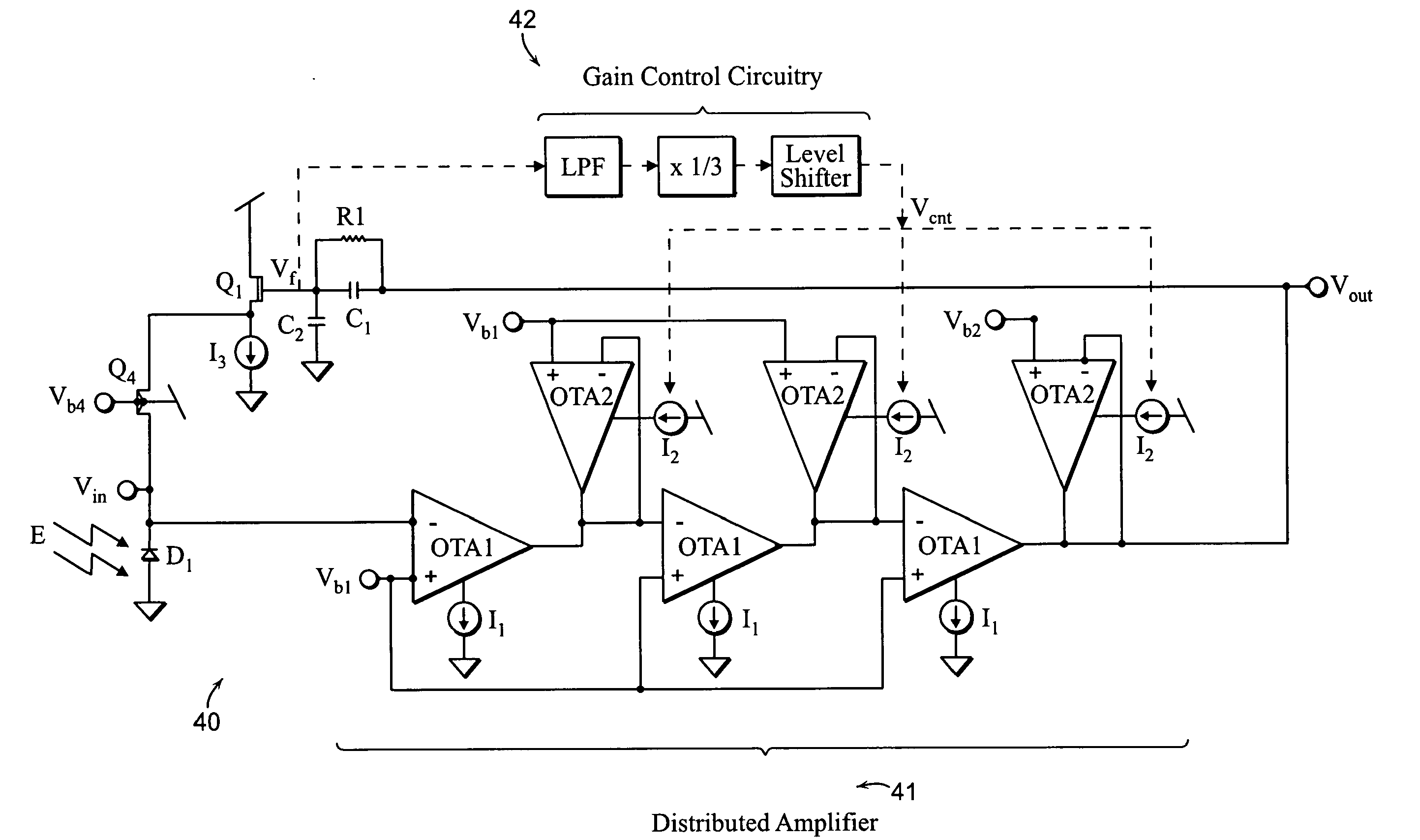
Ultra-low-power pulse oximeter implemented with an energy-efficient photoreceptor
InactiveUS20090163784A1Less powerAverage power consumptionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsGain controlPulse oximetersHigh energy
An energy-efficient photoreceptor apparatus and a transimpedance amplifier apparatus having high energy-efficiency and low power consumption of which are achieved through multiple distributed gain amplification stages, adaptive loop gain control circuitry and unilateralization, thereby enabling fast and precise performance over a wide range of input-current levels. The high-energy efficiency, robust feedback stability and performance of the present invention can be utilized to achieve sub-milliwatt pulse oximeters and may be employed in other current-to-voltage amplification and conversion applications. The use of analog processing on the outputs of the photoreceptor apparatus also helps lower the overall power of pulse oximeters.
Owner:SARPESHKAR RAHUL
Transimpedance Amplifier
ActiveUS20080309407A1Gain controlAmplifier modifications to reduce detrimental impedenceHysteresisAudio power amplifier
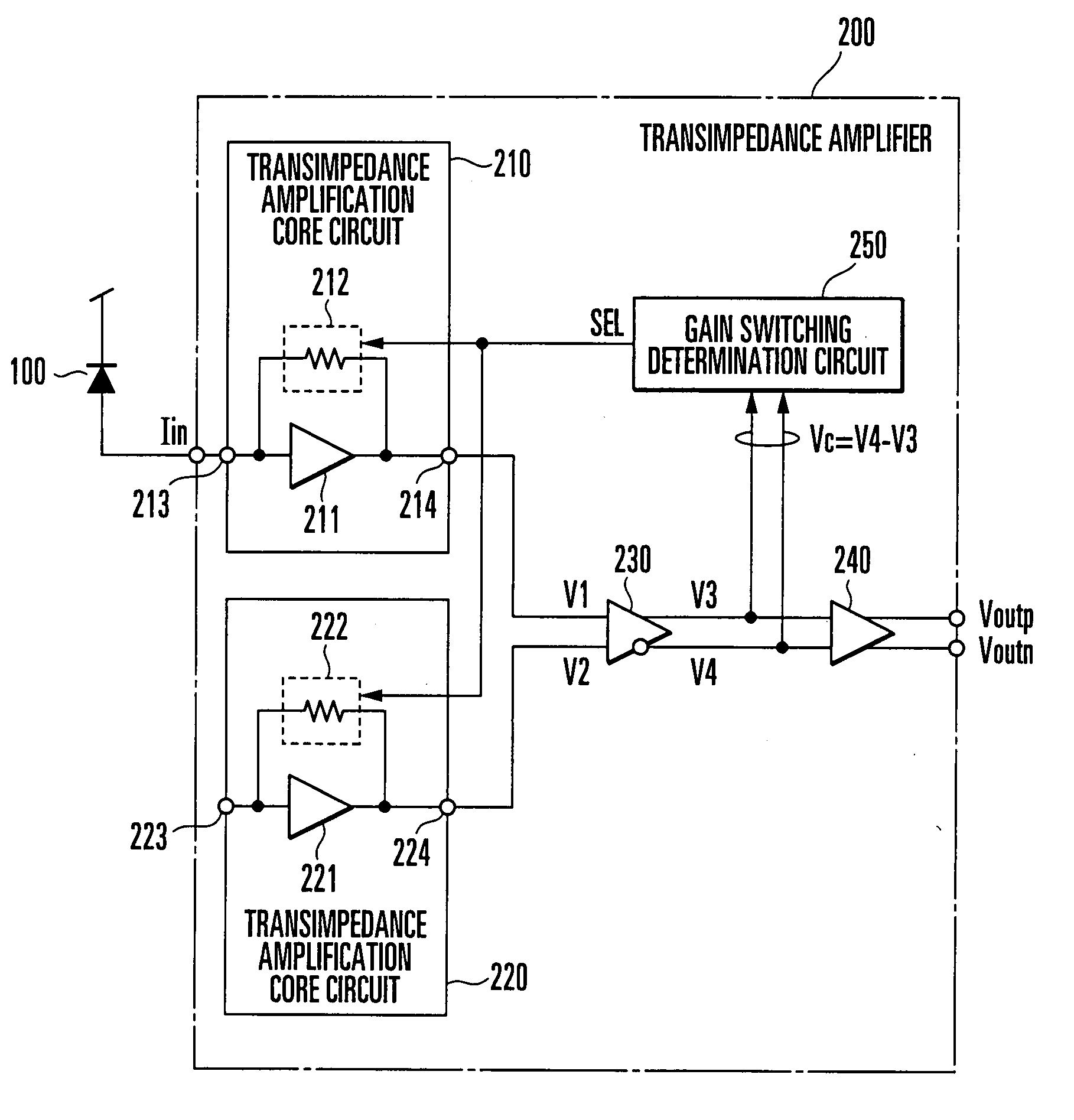
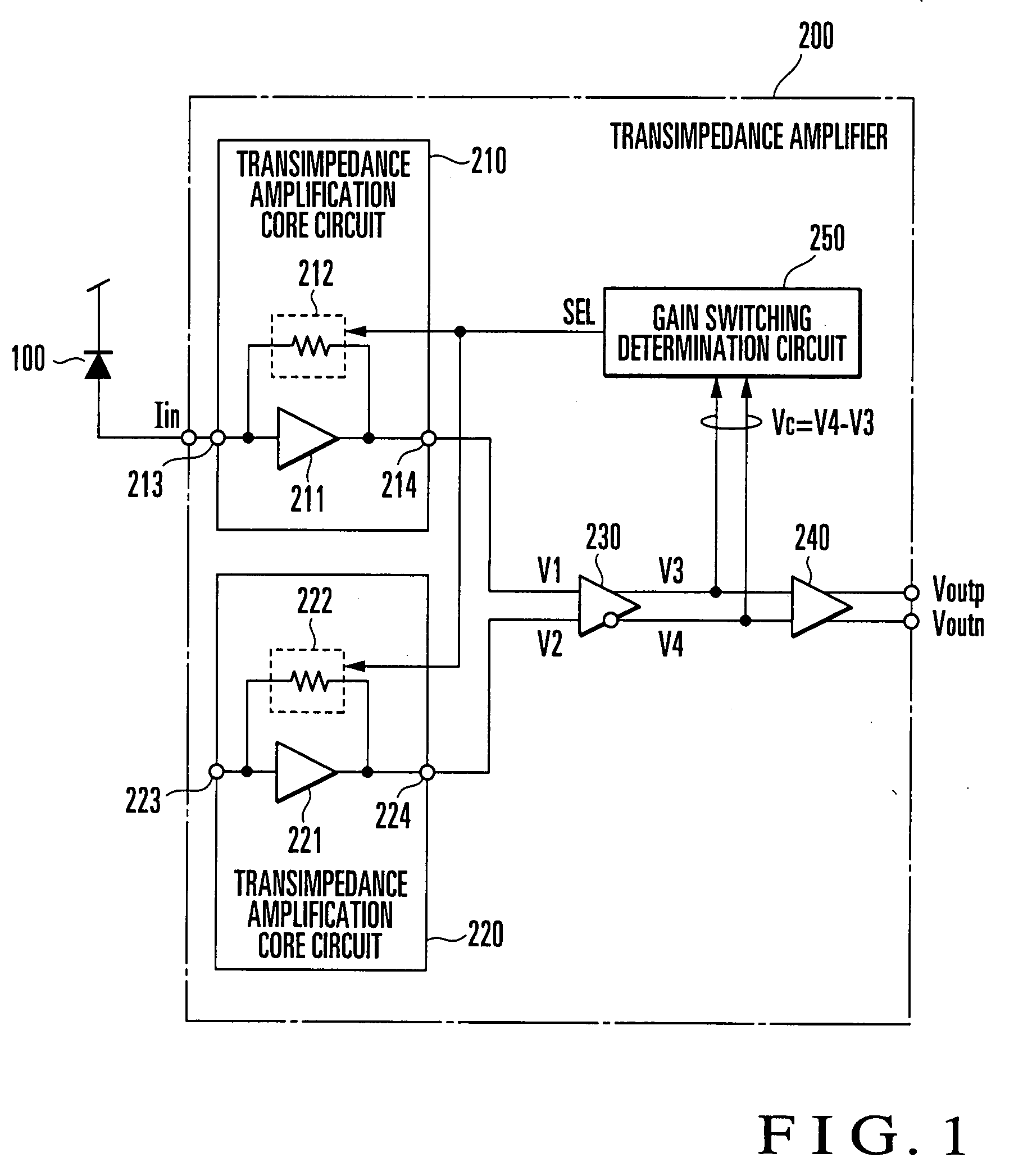
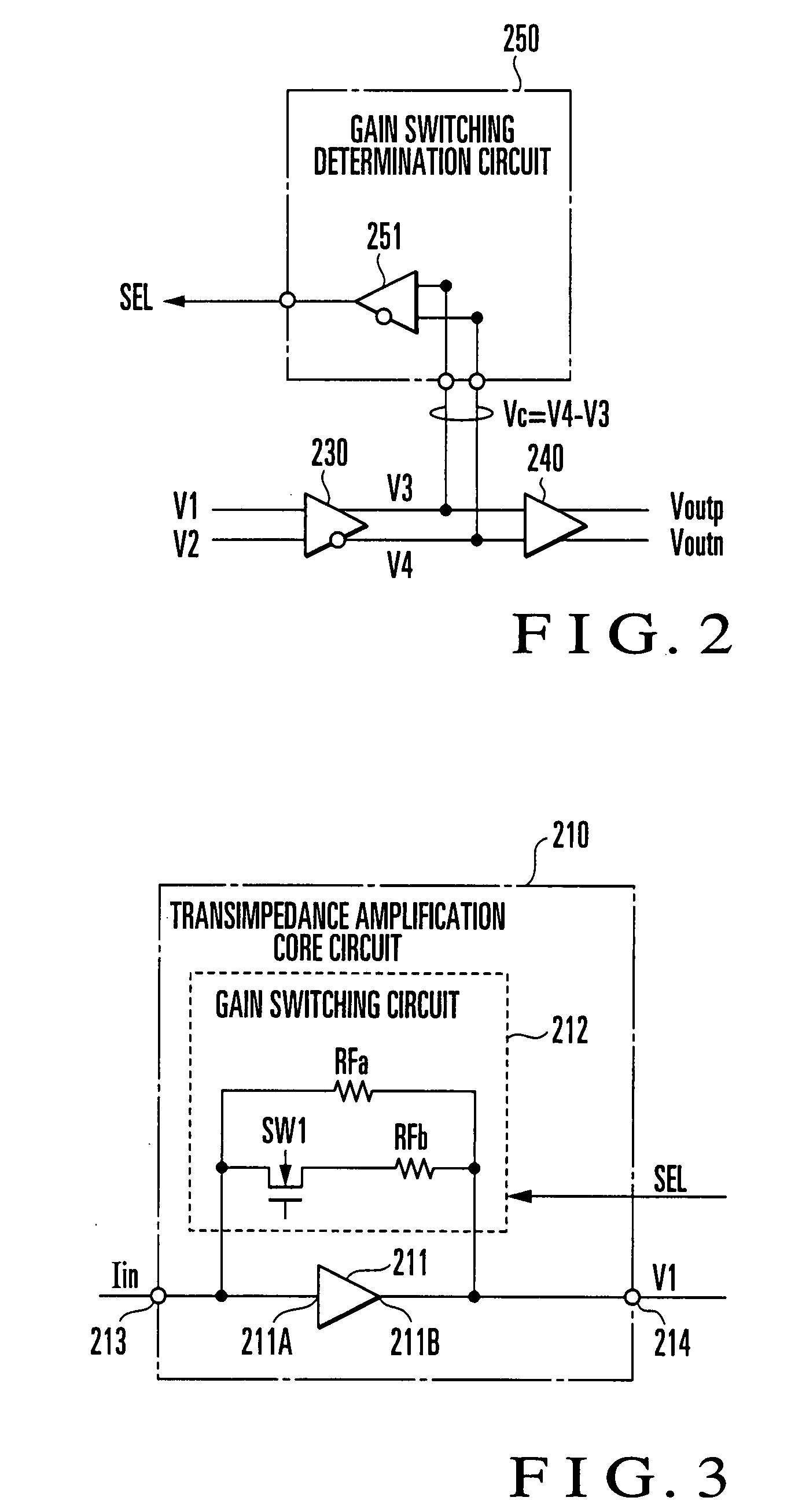
A gain switching determination circuit (250) compares / determines a comparative input voltage (Vc) from an inter-stage buffer (230) with a first hysteresis characteristic, and outputs a gain switching signal (SEL) based on the comparison / determination result to first and second transimpedance amplifier core circuits (210, 220), thereby switching the gains of the core circuits. This obviates holding a comparison input voltage with long response time in a level holding circuit for gain switching determination, which allows instantaneous gain switching determination and instantaneous response corresponding to burst data.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP +1
Precision automatic gain control circuit
InactiveUS20020086651A1Low absolute gain toleranceImprove matchResonant long antennasVolume compression/expansion having semiconductor devicesAudio power amplifierClosed loop
An automatic gain control (AGC) amplifier including a high gain transimpedance amplifier, a resistive feedback network and multiple transconductance stages coupled in the feedback path of the AGC amplifier. The feedback network receives an input signal and is coupled to the output of the high gain amplifier and has multiple intermediate nodes. Each transconductance stage has an input coupled to an intermediate node of the feedback network and an output coupled to the input of the high gain amplifier. Each transconductance stage is independently controllable to position a virtual ground within the feedback network to control closed loop gain. Each transconductance stage may have a bias current input coupled to a bias current control circuit. The control circuit controls each bias current to vary the gain of the AGC amplifier. The bias currents may be linearly controlled employing a ramp function to achieve a linear in dB gain response.
Owner:M RED INC
Variable-gain constant-bandwidth transimpedance amplifier
ActiveUS7023271B1Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to reduce detrimental impedenceAudio power amplifierTransimpedance amplifier
A transimpedance amplifier (TIA) circuit according to the present invention includes a first opamp having an input and an output. A second opamp has an input that communicates with the first opamp and an output. A first feedback path communicates with the input and the output of the first opamp and includes a first resistance. A second feedback path communicates with the input and the output of the second opamp and includes a second resistance. A third feedback path communicates with the input of the first opamp and the output of the second opamp.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Interleaved successive approximation register analog to digital converter
ActiveUS9602116B1Power saving provisionsElectric signal transmission systemsAudio power amplifierDigital down converter
In an example, the present invention provides an analog to digital converter device for a high speed data transmission from 1 GS-s to 100 GS-s, although there can be other variations. In an example, the device has an input receiver device coupled to a transimpedance amplifier. In an example, the transimpedance amplifier is coupled to an input stream of data at 10 GHz to 100 GHz, or other variations.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Photodiode transimpedance circuit
InactiveUS6359517B1Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansAudio power amplifierHemt circuits
Disclosed is a front end circuit involving a transimpedance amplifier that drives a resistor, thereby lowering the input impedance of the circuit by dividing the feedback resistance by the gain of the amplifier. In the front end circuit of the present invention, a first transistor is coupled in series with a resistor, where the received signal is input to a base or gate of the first transistor and the amplified received signal is recovered from a collector or drain of the first transistor such that the first transistor and resistor provide the gain of the front end circuit. A second transistor has an emitter or source coupled to the base or gate of the first transistor. A base or gate of the second transistor is coupled to the collector or drain of the first transistor and a collector or drain of the second transistor is coupled to a power supply rail. The second transistor thus provides the feedback path for the transimpedance amplifier thereby reducing the input impedance of the circuit.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Low-noise large-area photoreceivers with low capacitance photodiodes
Owner:DISCOVERY SEMICON
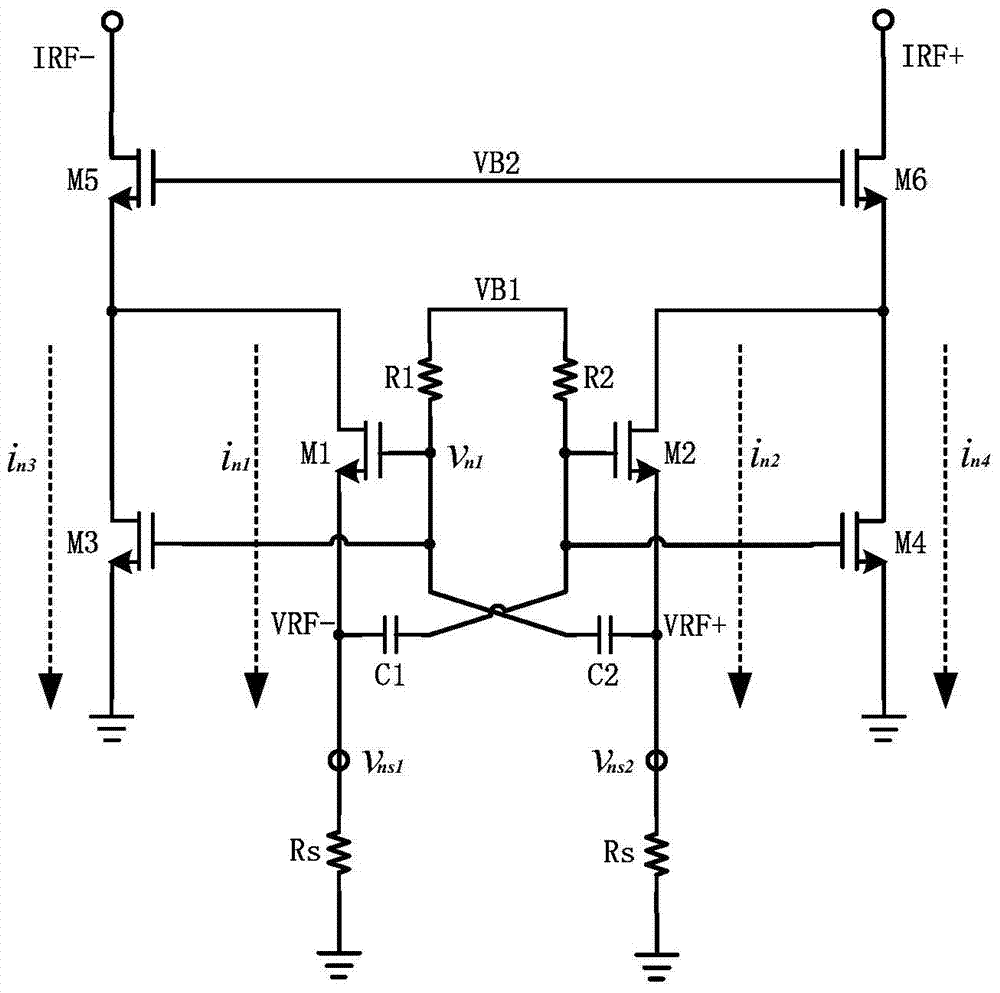
Method and system for a feedback transimpedance amplifier with sub-40khz low-frequency cutoff
ActiveUS8471639B2Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifiers controlled by lightPhotodetectorTransimpedance amplifier
A system for a feedback transimpedance amplifier with sub-40 khz low-frequency cutoff is disclosed and may include amplifying electrical signals received via coupling capacitors utilizing a transimpedance amplifier (TIA) having feedback paths comprising source followers and feedback resistors. The feedback paths may be coupled prior to the coupling capacitors at inputs of the TIA. Voltages may be level shifted prior to the coupling capacitors to ensure stable bias conditions for the TIA. The TIA may be integrated in a CMOS chip and the source followers may comprise CMOS transistors. The TIA may receive current-mode logic or voltage signals. The electrical signals may be received from a photodetector, which may comprise a silicon germanium photodiode and may be differentially coupled to the TIA. The chip may comprise a CMOS photonics chip where optical signals for the photodetector in the CMOS photonics chip may be received via one or more optical fibers.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Low noise image reject mixer and method therefor
ActiveUS7457605B2Modulation transferenceTransmission noise suppressionLow noiseLocal oscillator signal
A receiver (200) includes a transconductance mixer (310), a polyphase filter (320), and a transimpedance amplifier (330). The transconductance mixer (310) mixes a radio frequency (RF) voltage signal into a current signal having a plurality of phases using a local oscillator signal. The polyphase filter (320) filters the current signal to provide a filtered current signal. The transimpedance amplifier (330) converts the filtered current signal into an output voltage signal.
Owner:XENOGENIC DEV LLC
Method for integrating focusing and detection of cells and miniaturized system thereof
ActiveCN104941704AImprove accuracyImprove stabilityLaboratory glasswaresData acquisitionTransimpedance amplifier
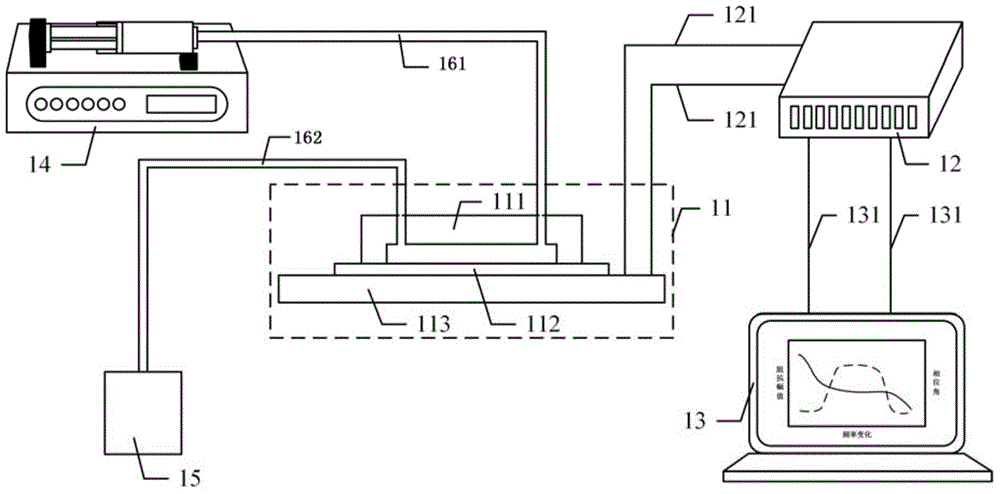
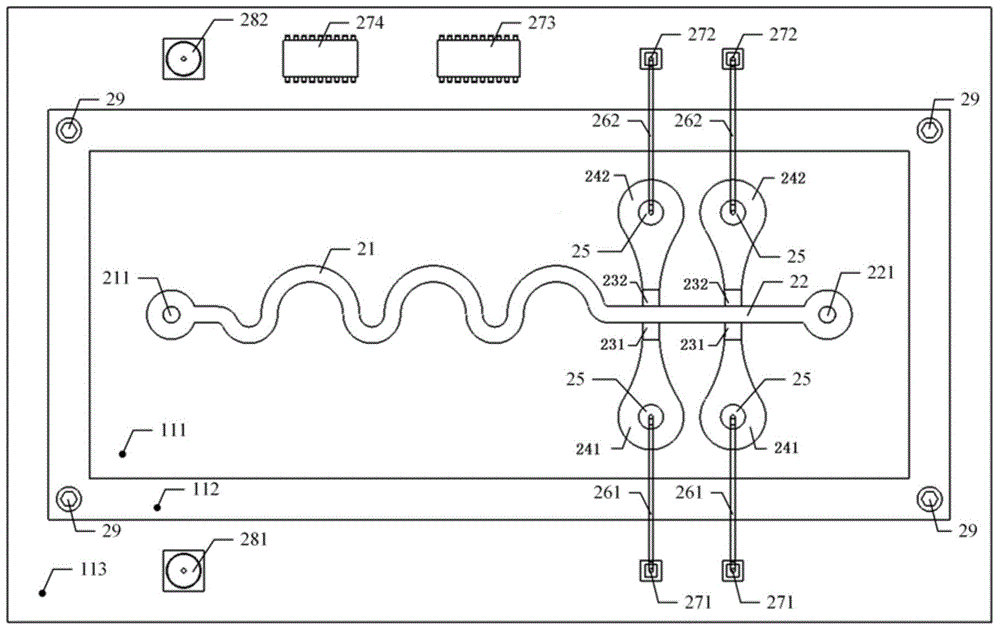
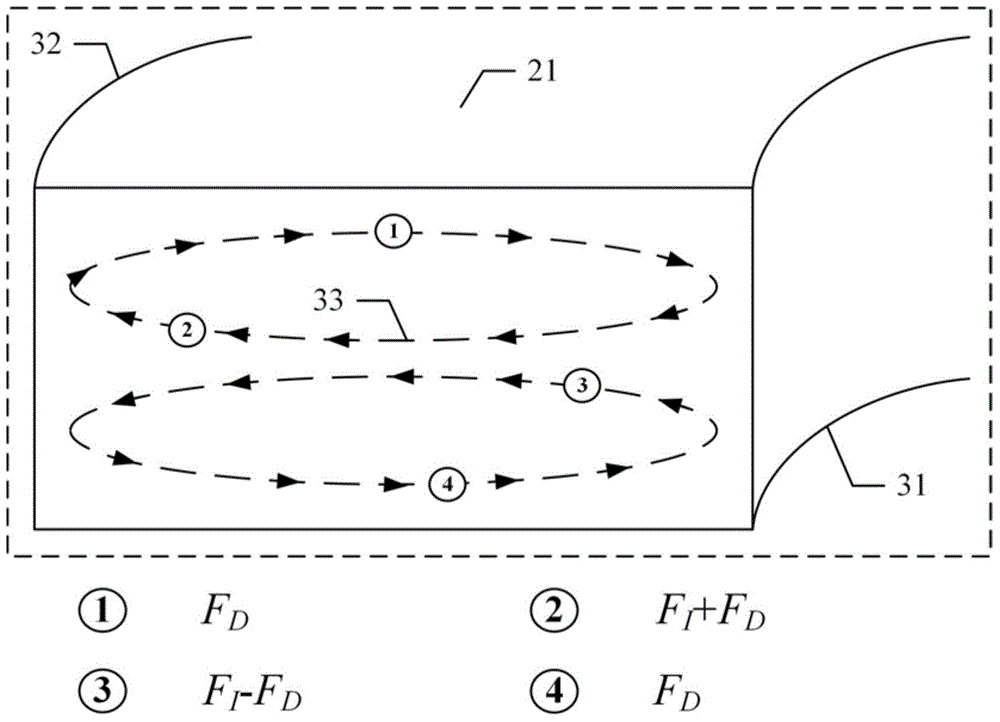
The invention discloses a method for integrating focusing and detection of cells and a miniaturized system thereof. The miniaturized system comprises a microfluidic chip, a data acquisition card, a miniature computer and a sample injection device, wherein the microfluidic chip is formed by a flow channel layer, a substrate layer and a PCB (Printed Circuit Board) which are aligned and packaged in sequence; the flow channel layer is provided with an asymmetric sinusoidal flow channel, a detection main flow channel, polyelectrolyte gel and a conductive-fluid storage pool; the polyelectrolyte gel, the conductive-fluid storage pool and a silver-silver chloride wire form a detection electrode; the silver-silver chloride wire is connected with the data acquisition card and the miniature computer by a transimpedance amplifier and a differential amplifier so as to form a differential impedance detection circuit of the cells; the miniature computer is used for realizing generation of pseudorandom excitation signals, processing of system response signals and analysis and display of multi-performance parameters of the cells. The method and the miniaturized system disclosed by the invention integrate the functions of focusing and detection of the cells, realizes miniaturization and portability of the system and can be widely used for biological study of blood cells and rare cells.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
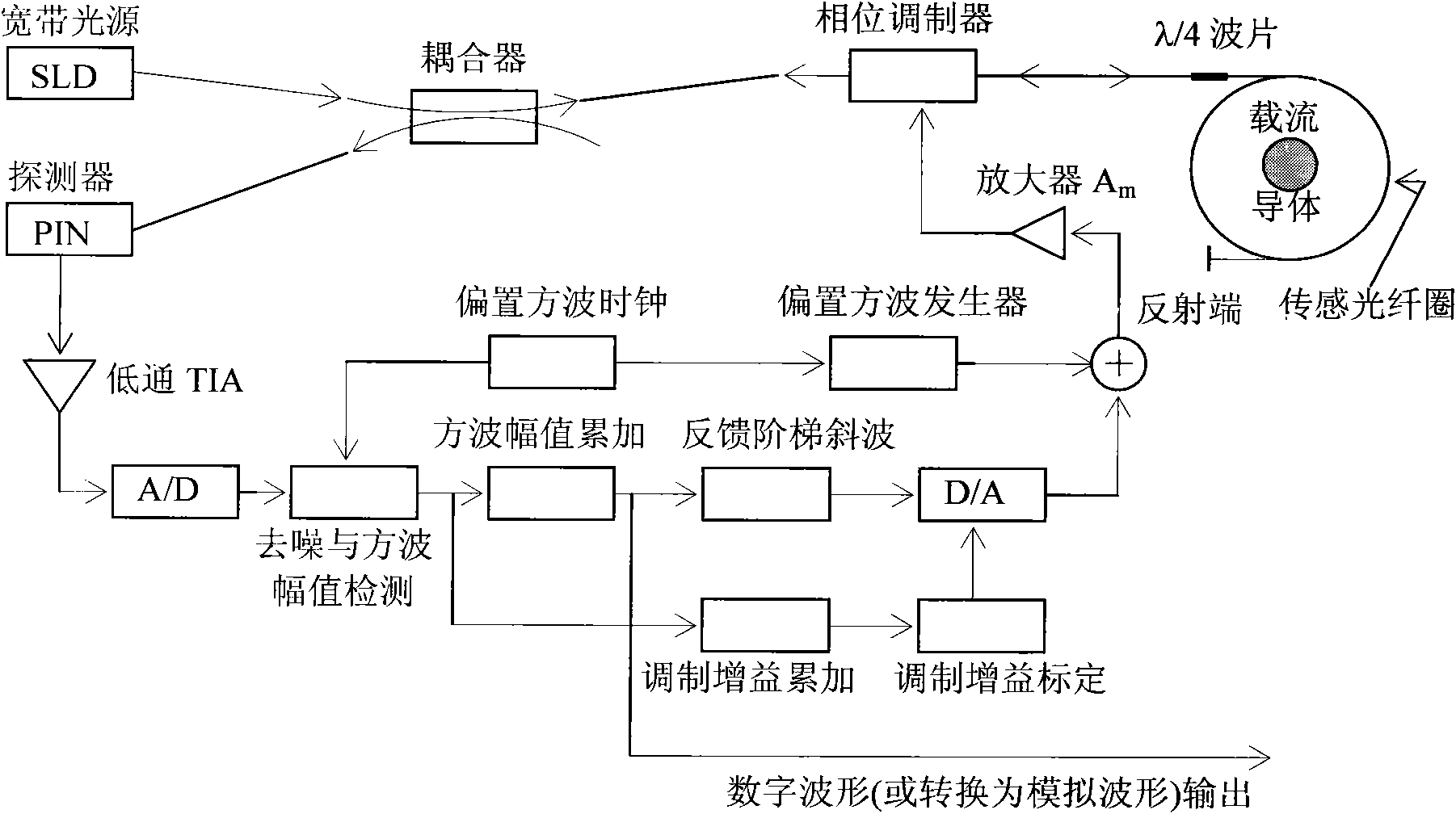
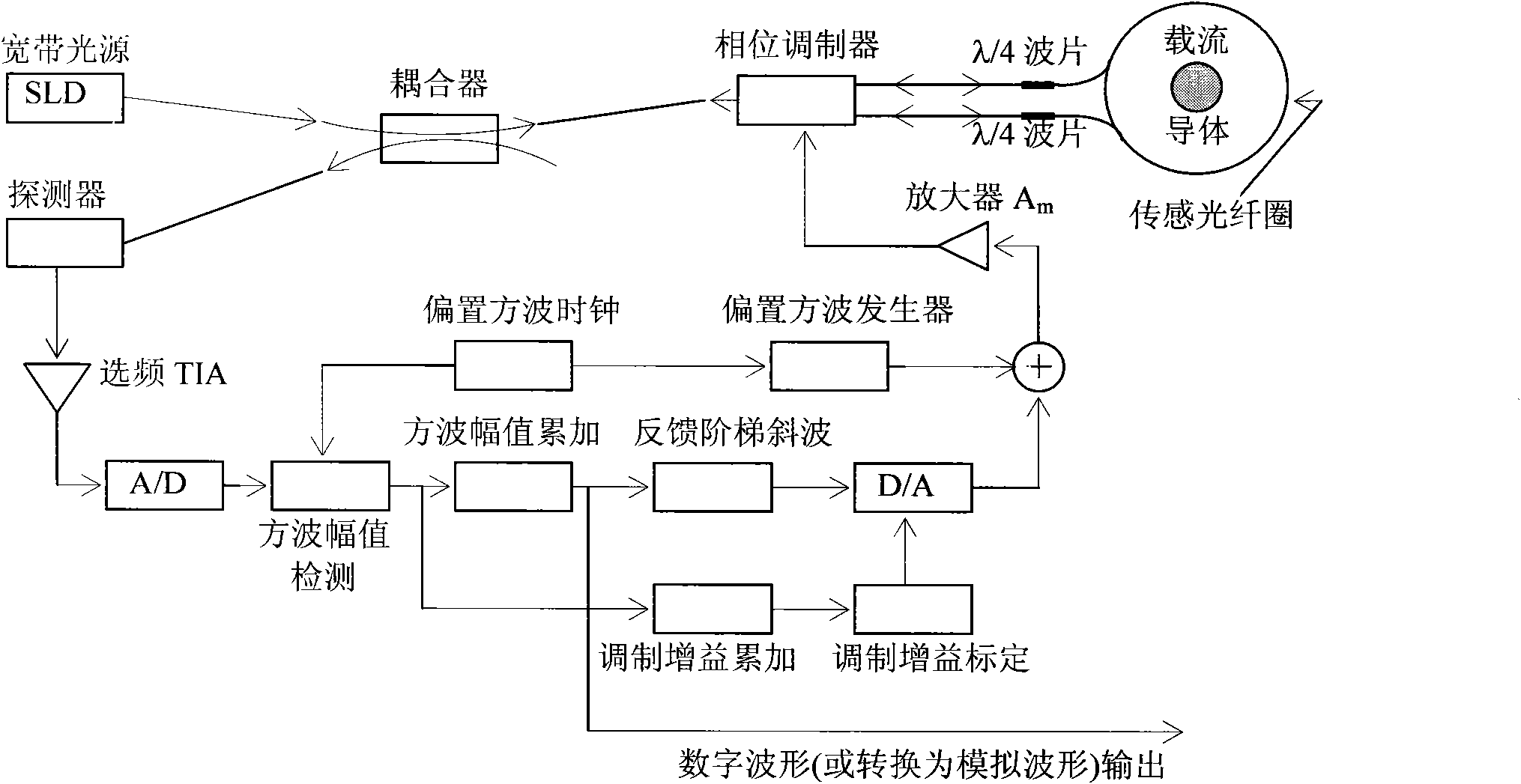
Digital closed loop type optical fiber current sensor
ActiveCN101957399AHigh sensitivityImprove dynamic rangeCurrent/voltage measurementVoltage/current isolationCurrent transducerNoise level
The invention provides a digital closed loop type optical fiber current sensor. A modulation signal of a light wave phase modulator of a sensor optical path system is an amplitude modulation square wave; a signal processing system extracts any harmonic wave of amplitude modulation square wave current output by a photoelectric transducer and extracts tested current information from the current; a pre-amplifier of the signal processing system is a transimpedance amplifier TIA, and the bandwidth is below 1 / 650 when the square wave transient amplitude value (prior art) is directly extracted from the amplitude modulation square wave, so that thermal noise output by the pre-amplifier and the shot noise level are also reduced to be below 1 / 650 of the prior art; and current-voltage conversion gain of the transimpedance amplifier TIA is not determined by the resistance of a feedback network of the TIA, so that a low-resistance resistor is adopted in the feedback network of the TIA while the high current-voltage conversion gain is ensured, and the thermal noise of the resistor which accounts for a significant proportion in the level of the noise output by the TIA is reduced to be negligible.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
Variable bandwidth transimpedance amplifier with one-wire interface
InactiveUS20060045531A1Easy to understandNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifiers controlled by lightTransceiverAudio power amplifier
A bandwidth adjustable transimpedance amplifier. The bandwidth adjustable transimpedance amplifier includes a feedback path with a selectable resistance. The bandwidth adjustable transimpedance amplifier is preferably implemented with a photodiode in a five pin package for an optical transceiver system, with a single pin providing a monitor out function and a rate select input.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS
Low Power Consumption, Long Range, Pluggable Transceiver, Circuits and Devices Therefor, and Method(s) of Using the Same
ActiveUS20120301151A1Reduce power consumptionMaximize efficiencyElectromagnetic transmittersSolid cathode detailsTransceiverTransimpedance amplifier
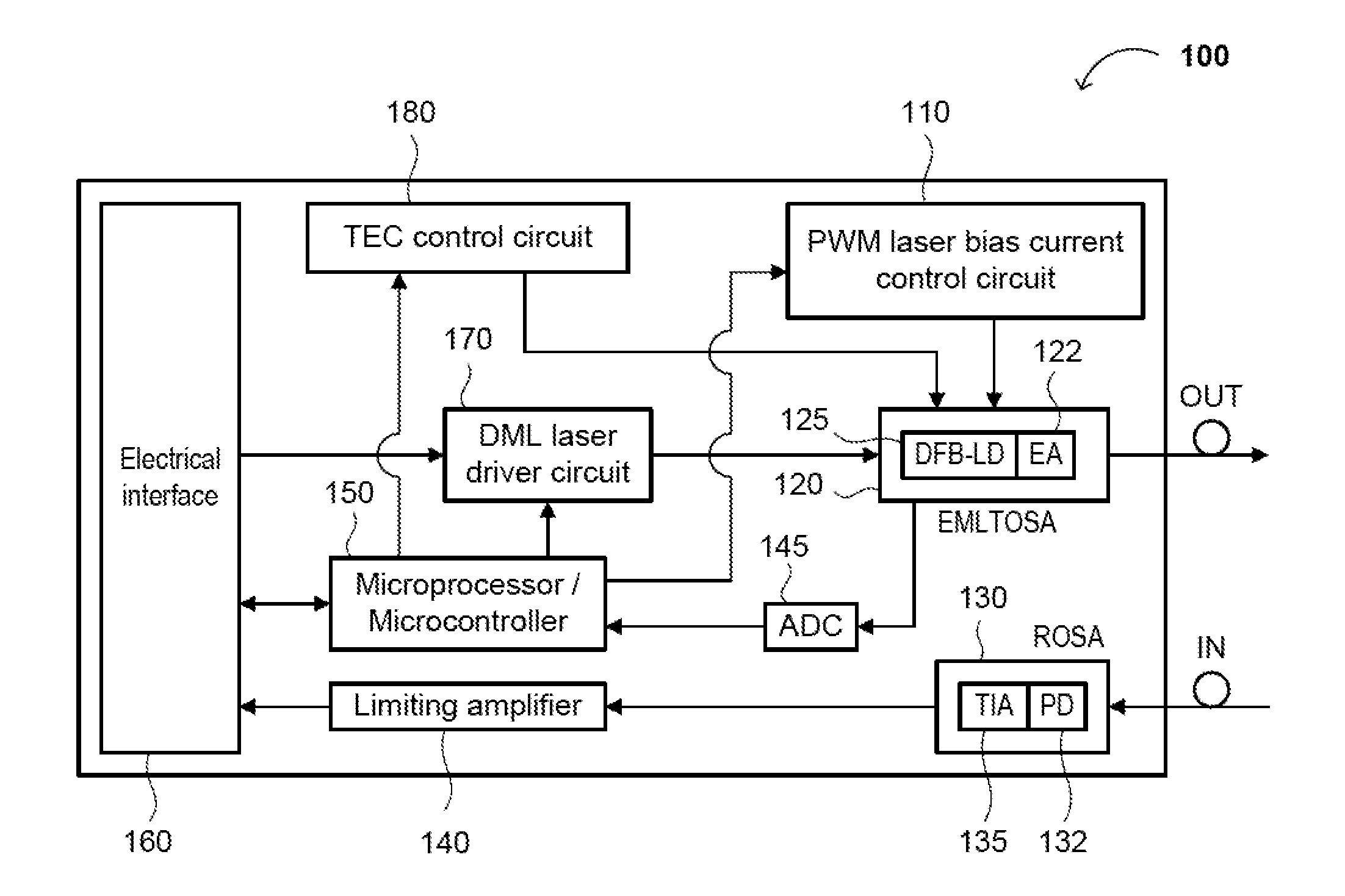
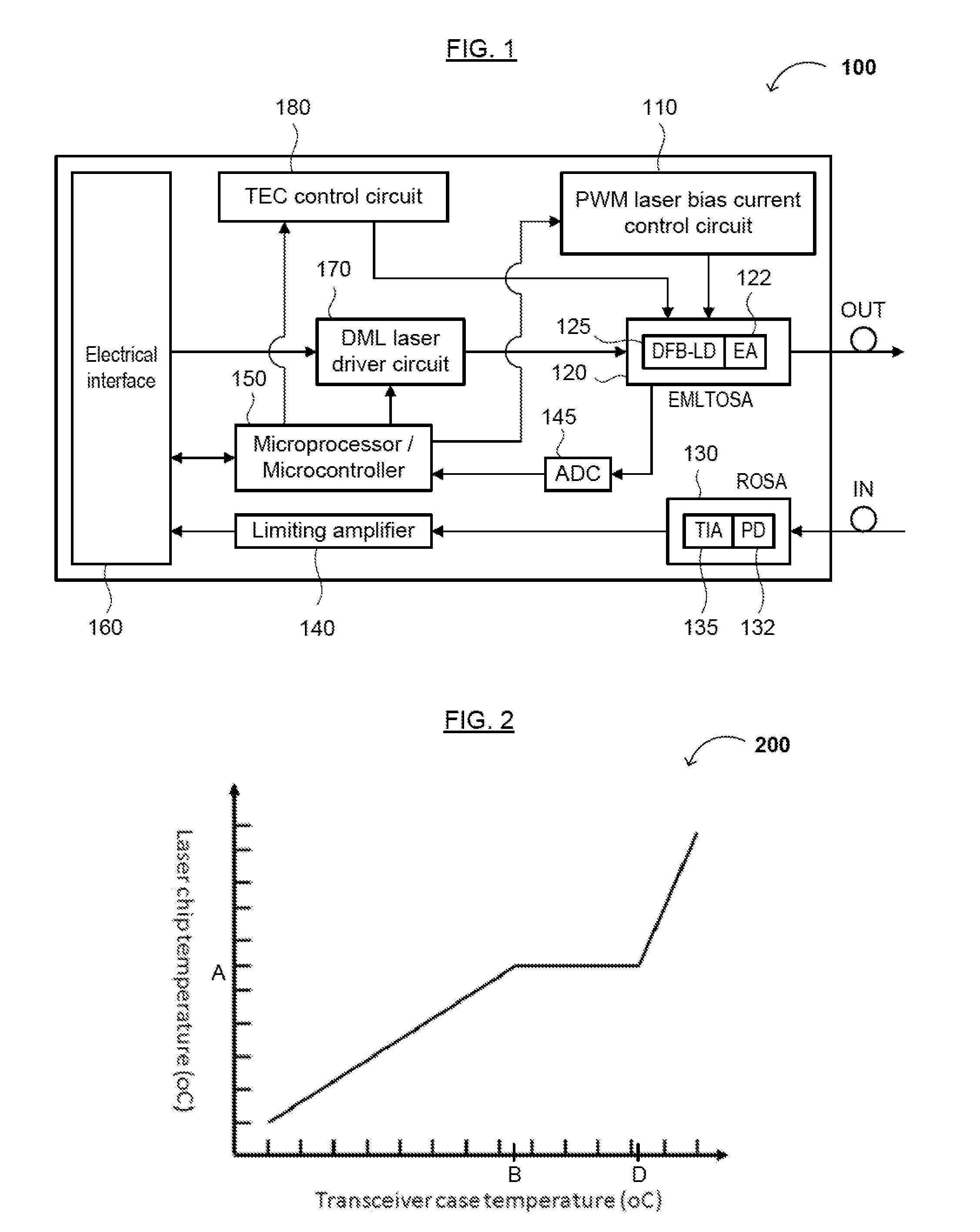
The present disclosure relates to an optical transceiver for use in optical fiber communications and / or telecommunications systems and, more specifically, a low power consumption, long range pluggable transceiver. The transceiver generally comprises a photodiode with a transimpedance amplifier (PIN-TIA); an electro-absorption modulated laser (EML); an optical detector; and a directly modulated laser (DML) driving module connected between the PIN-TIA and EML laser configured to drive the EML laser. A low power-consumption DML driving module is utilized to drive the EML laser, so as to further reduce power consumption. An impedance matching circuit can be applied to modulate an electro-absorption (EA) modulator of the EML laser with maximum efficiency.
Owner:SOURCE PHOTONICS
Low-noise passive frequency mixer
InactiveCN103490731AImprove Noise PerformanceReduce noiseTransmissionMulti-frequency-changing modulation transferenceLow noiseIntermediate frequency
The invention discloses a low-noise passive frequency mixer. The low-noise passive frequency mixer comprises a low-noise transconductance amplifier stage, a switch frequency mixing stage and a transimpedance amplifier stage. The low-noise transconductance amplifier stage mainly adopts a cross coupling master-slave noise cancellation technology, a main transconductance conduit adopts a cross coupled structure to double an equivalent transconductance value, an appropriate transconductance value is provided through the main transconductance conduit and the noise of the main transconductance conduit is lowered through a master-slave structure; the switch frequency mixing stage is used for modulating and filtering radiofrequency currents output from the low-noise transconductance amplifier stage and outputting intermediate frequency currents; the transimpedance amplifier stage consists of a full-differential operational transconductance amplifier and a load resistor; the operational transconductance amplifier is based on a feed-forward compensation technology, and a consequent pole point in a transfer function of the amplifier is offset by a zero point introduced to a feed-forward stage of the operational transconductance amplifier, so that a large unity-gain bandwidth is achieved; the load resistor is used for converting the intermediate frequency currents into intermediate frequency voltage signals which are then output, by virtue of a voltage-current negative-feedback connection way. The low-noise passive frequency mixer has the characteristics of low noise, high gain and low power consumption.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
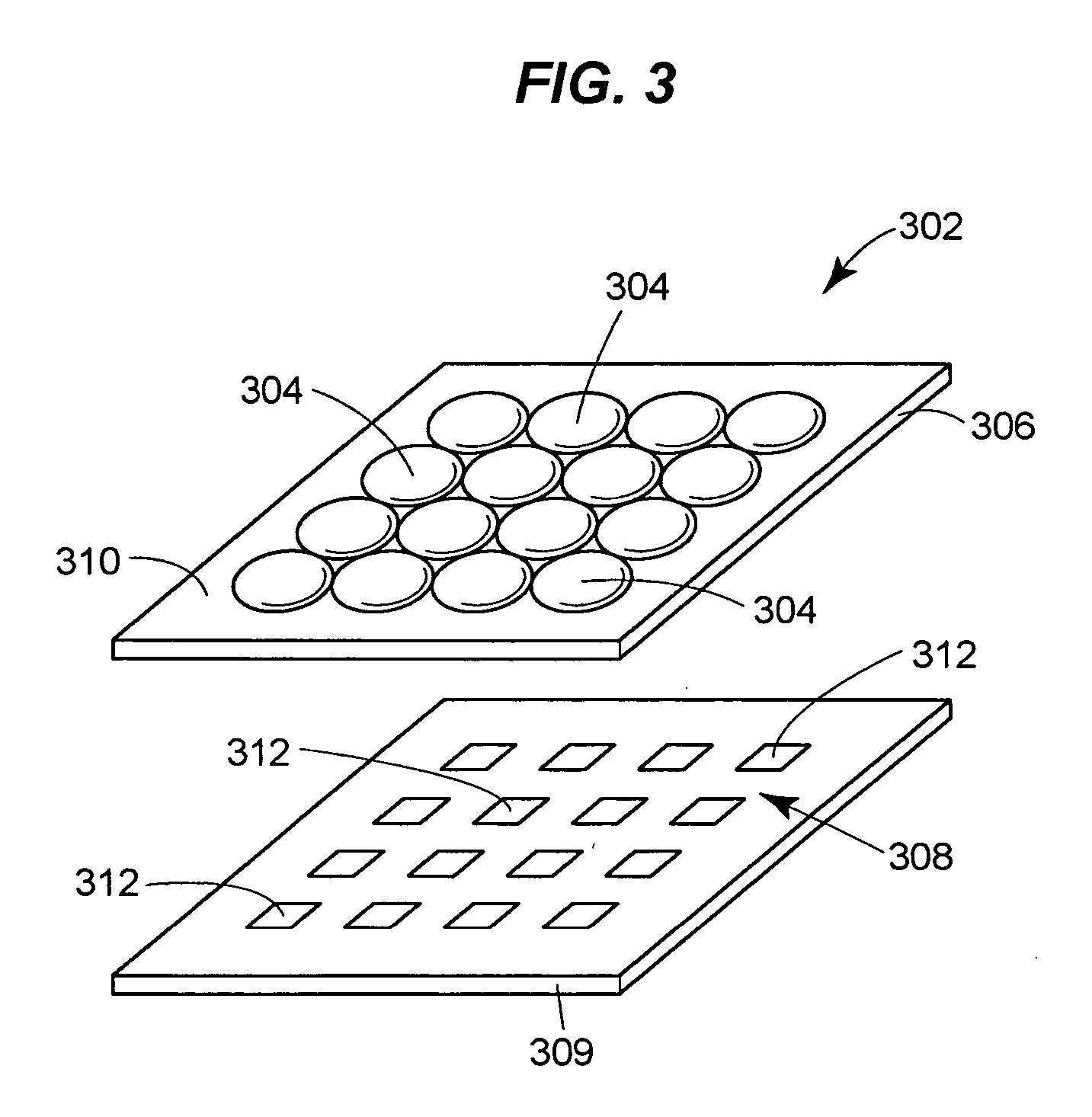
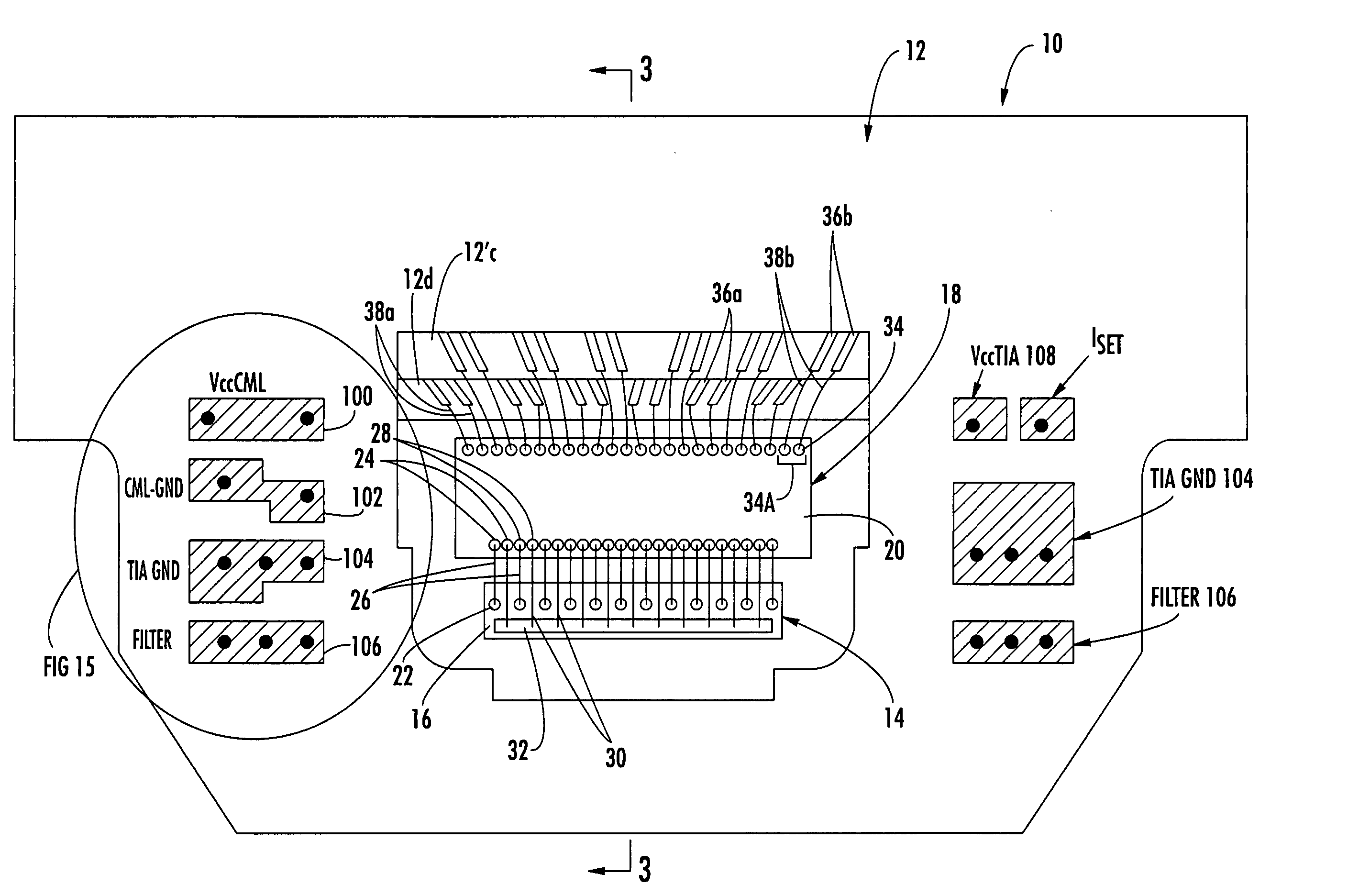
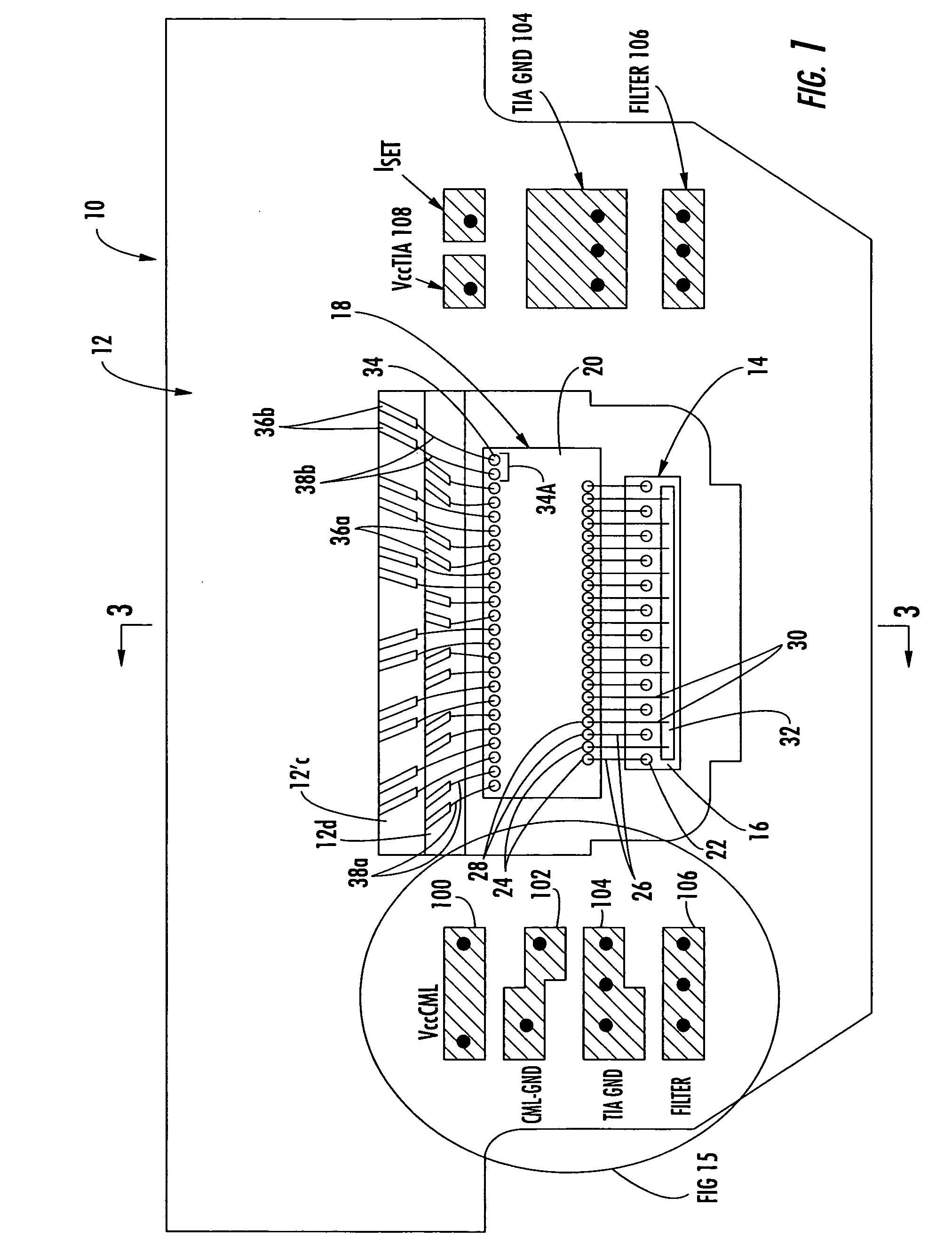
Arrayed receiver optical sub-assembly including layered ceramic substrate for alleviation of cross-talk and noise between channels
InactiveUS20050213994A1Electromagnetic receiversOptical light guidesCapacitancePhotovoltaic detectors
A receiver optical subassembly (ROSA) includes a photodetector array and a transimpedance amplifier (TIA) array. In each data channel, the photodetector is wire bonded to a corresponding input pad of the TIA array. A ground pad is disposed between adjacent input pads and connected to a ground plane via an isolated bonding strip on the photodetector array in order to alleviate crosstalk between the channels. The output data channels of the TIA are tightly spaced at the output pads of the TIA and are fanned out on the ceramic to increase the spacing of the data channels as they extend from the TIA. The ROSA includes the use of embedded capacitance to reduce crosstalk and noise by decoupling reference planes formed within the multilayer ceramic substrate. Input and output ground planes of the TIA are separated in the vicinity of the TIA and coupled on a ceramic layer spaced farther from the TIA, to alleviate crosstalk.
Owner:OPTICAL COMM PRODS
Nested transimpedance amplifier with capacitive cancellation of input parasitic capacitance
InactiveUS7173486B1Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsHigh frequency amplifiersAudio power amplifierParasitic capacitance
A nested transimpedance amplifier (TIA) circuit comprises a zero-order TIA having an input and an output. A first transconductance amplifier has an input that communicates with said output of said zero-order TIA and an output. A first feedback resistance has one end that communicates with said input of said zero-order TIA and an opposite end that communicates with said output of said first transconductance amplifier. A first feedback capacitance has a first end that communicates with said input of said zero-order TIA and a second end that communicates with said output of said zero-order TIA. A capacitance has one end that communicates with said input of said zero-order TIA.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com