Method for simulating photon scattering by using quasi Monte Carlo method
A quasi-Monte Carlo and photon technology, which is used in instruments for radiological diagnosis, material analysis using wave/particle radiation, and applications. It can solve the problem of long calculation time for scattered photons, and achieve shortened calculation time and high accuracy. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0060] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
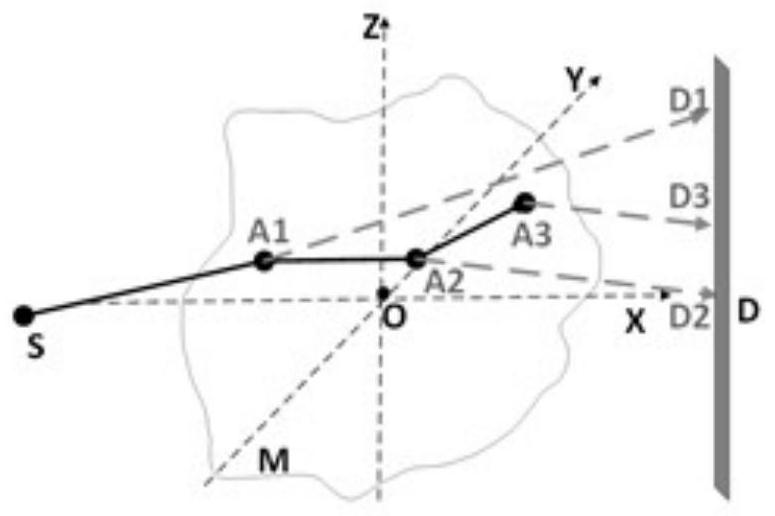
[0061] Embodiments of the present invention provide a method for simulating photon scattering with a pseudo-Monte Carlo method, which is applied to such as figure 1 Shown in the scattered photon simulation model.
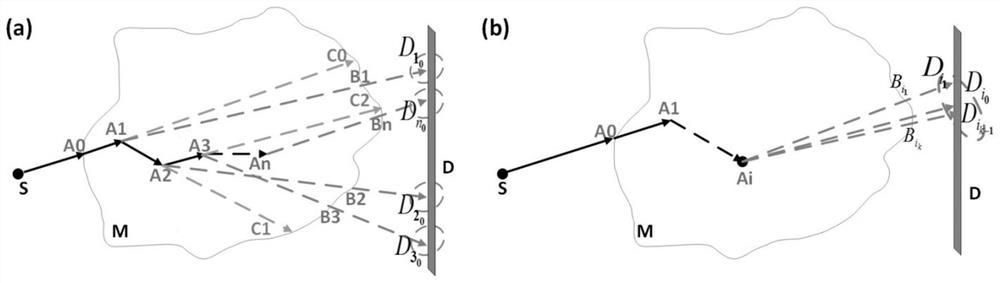
[0062] figure 1 A simulation model of scattered photons including a light source S, a phantom M and a detector D is shown. figure 1 The geometric model of the photonic imaging system shown includes a light source S, a phantom M and a detector D. figure 1 The geometric representation of the third-order scattering is also exemplarily given in . The photon passes through the motif M and undergoes third-order scattering, A 1 ,A 2 ,A 3 represent the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd order interaction points, respectively. A photon arrives at each interaction A i , after i=1, 2, 3, the direction will change, and pass through the motif M with a certain pr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com