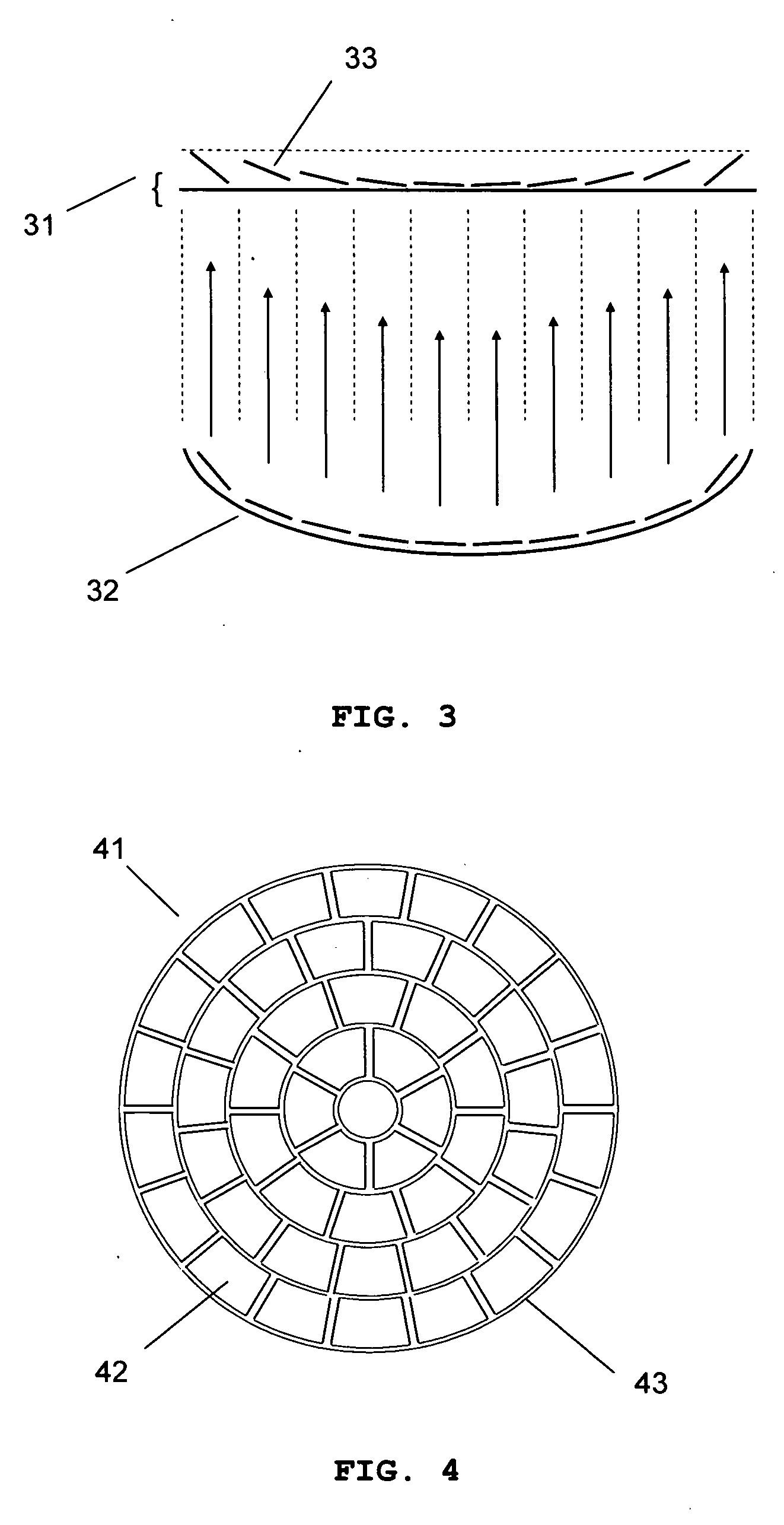
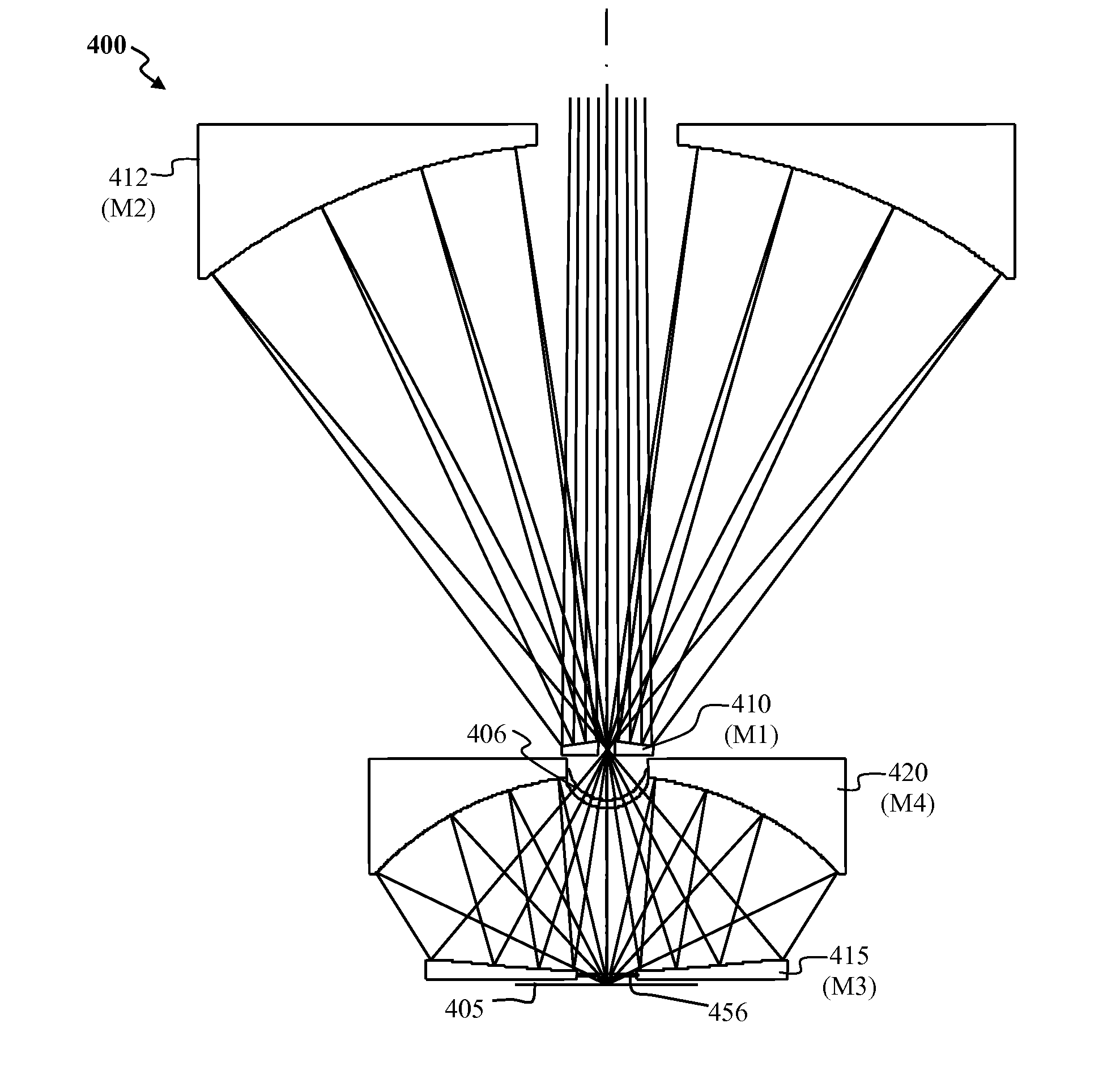
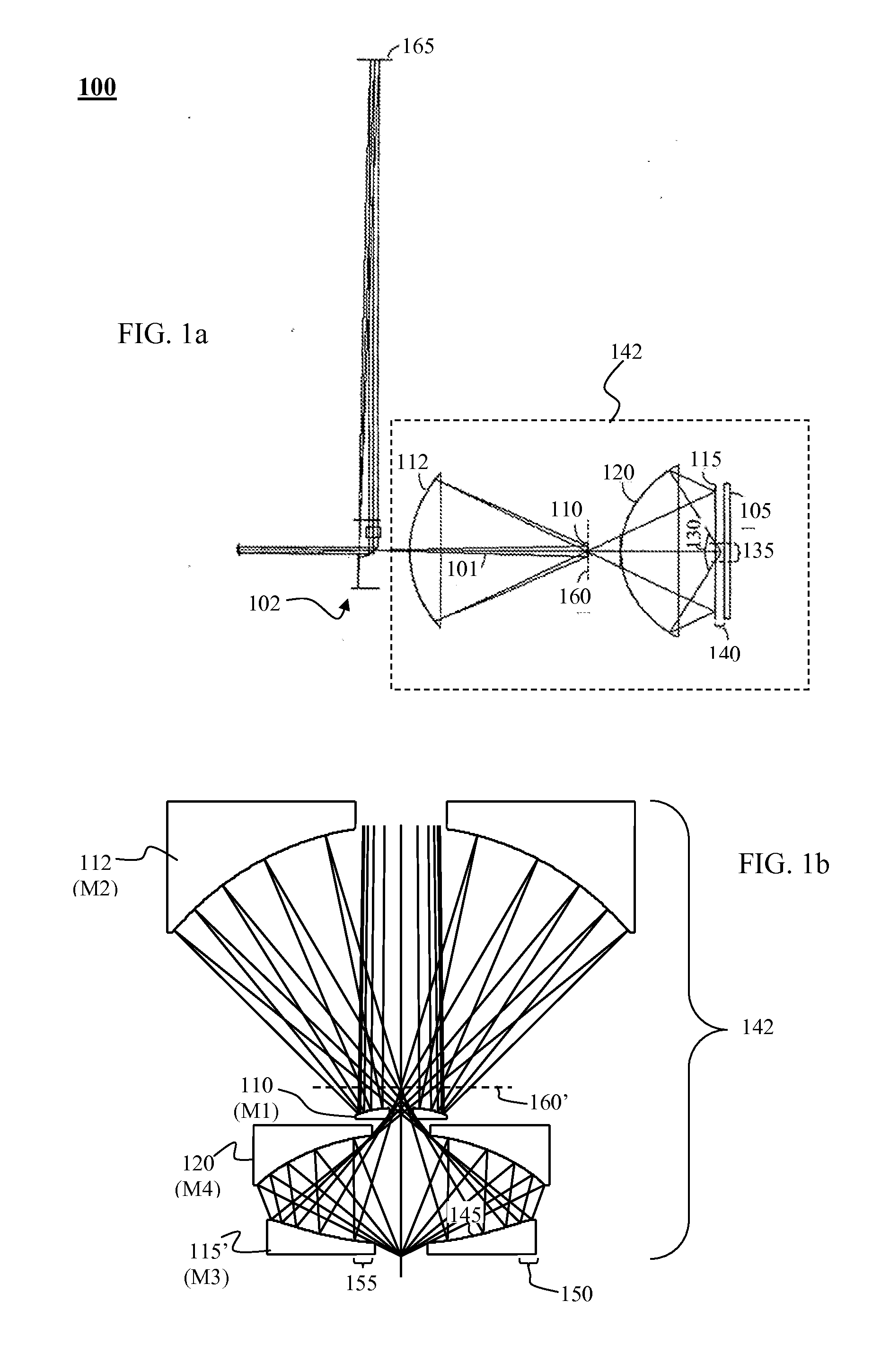
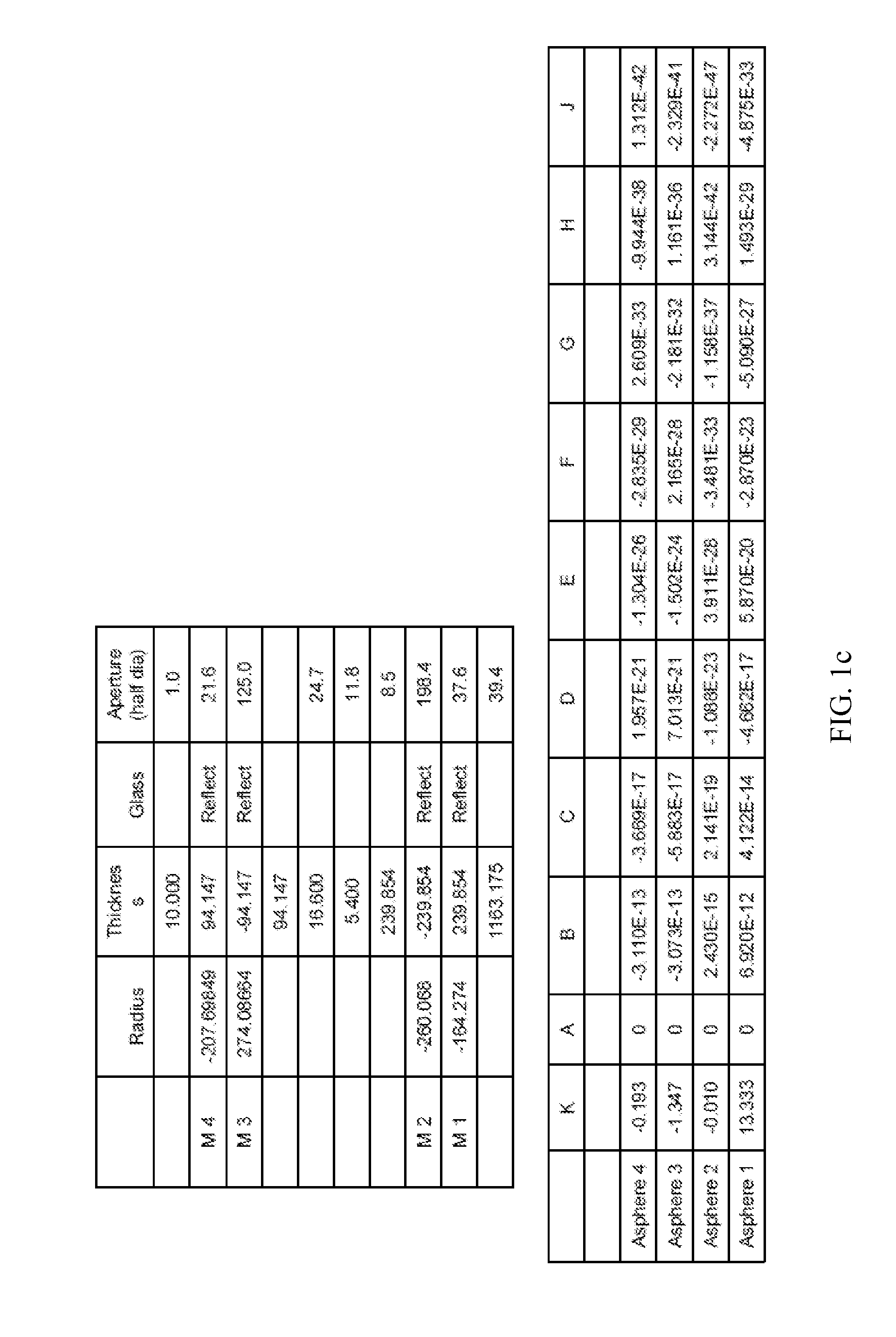
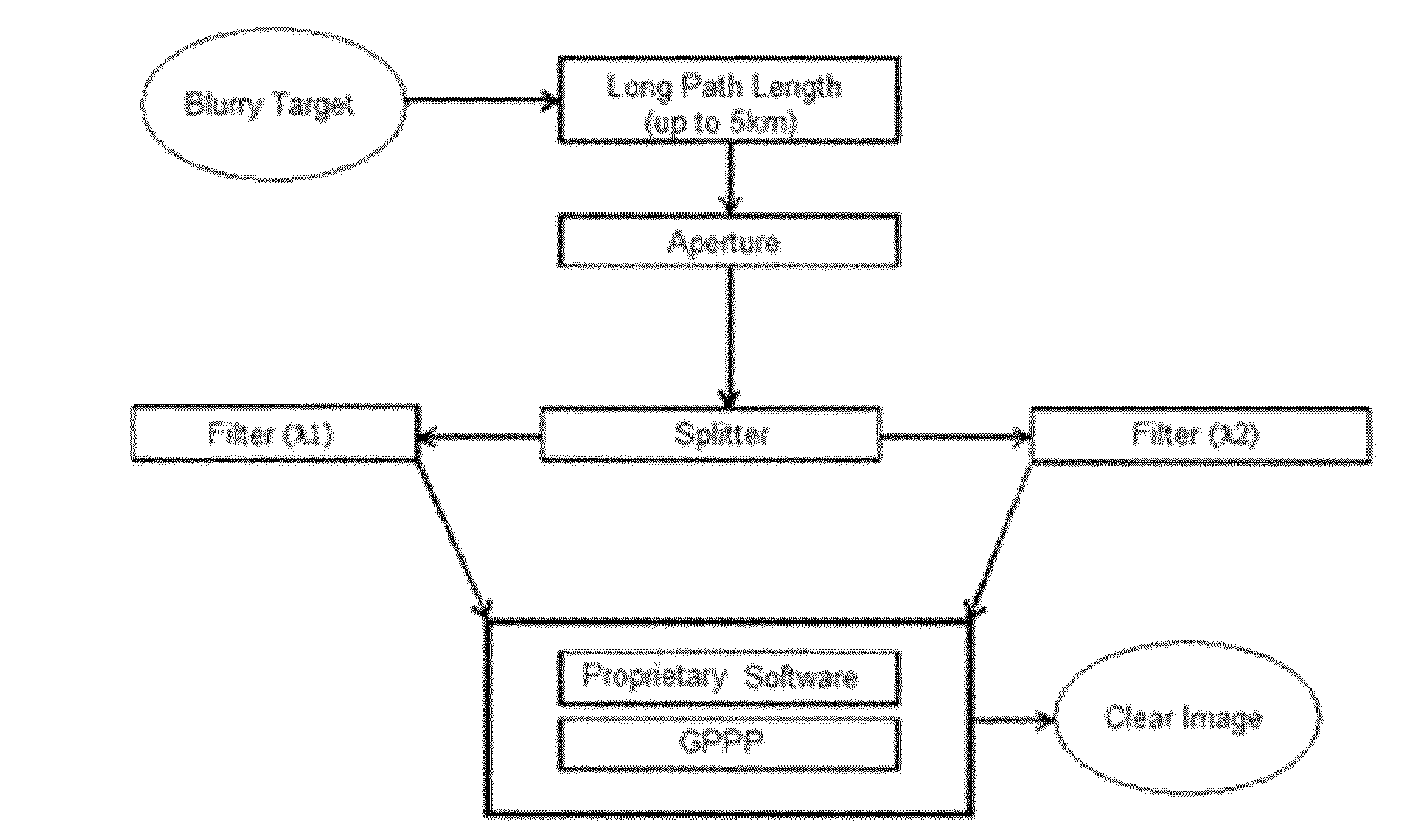
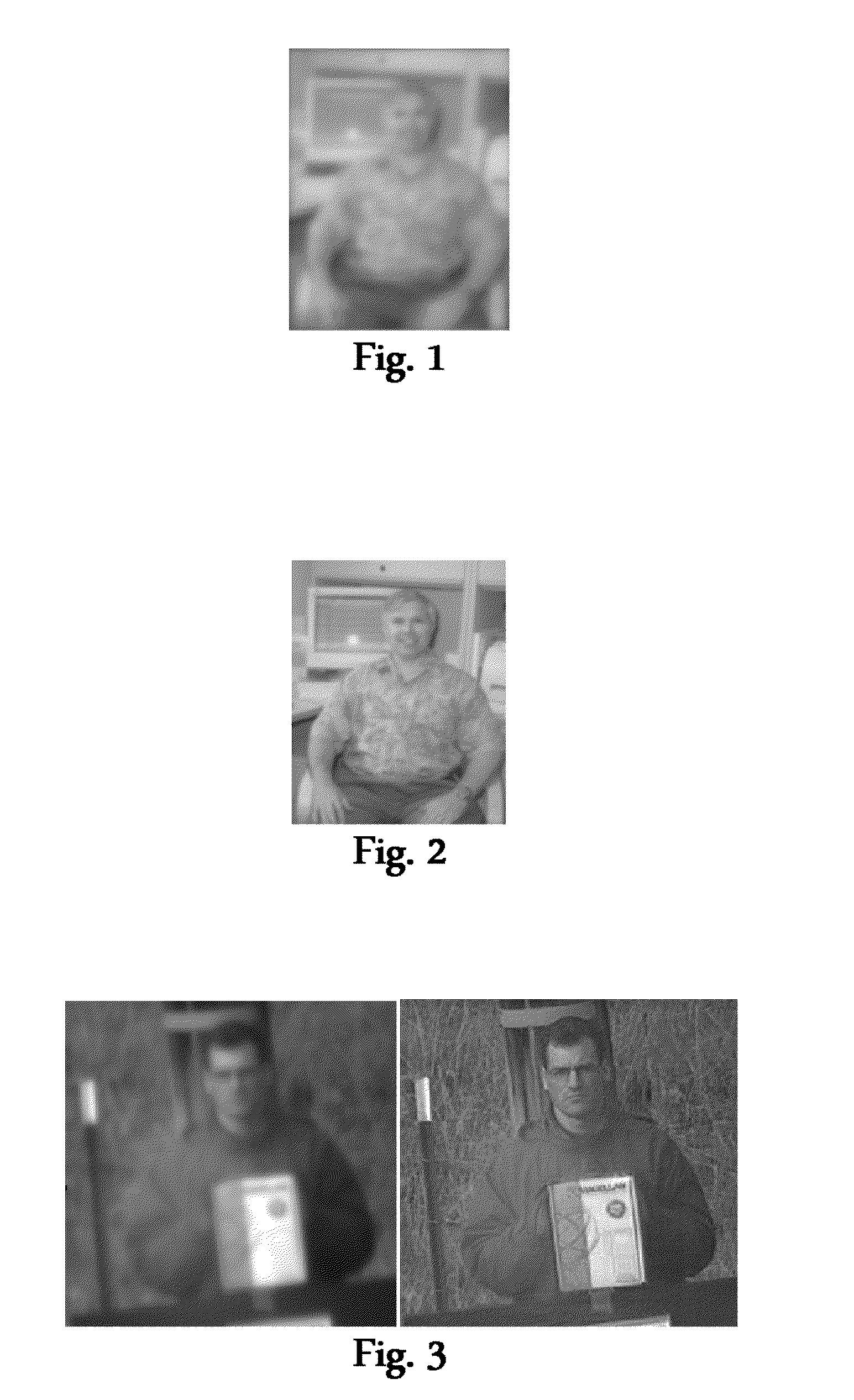
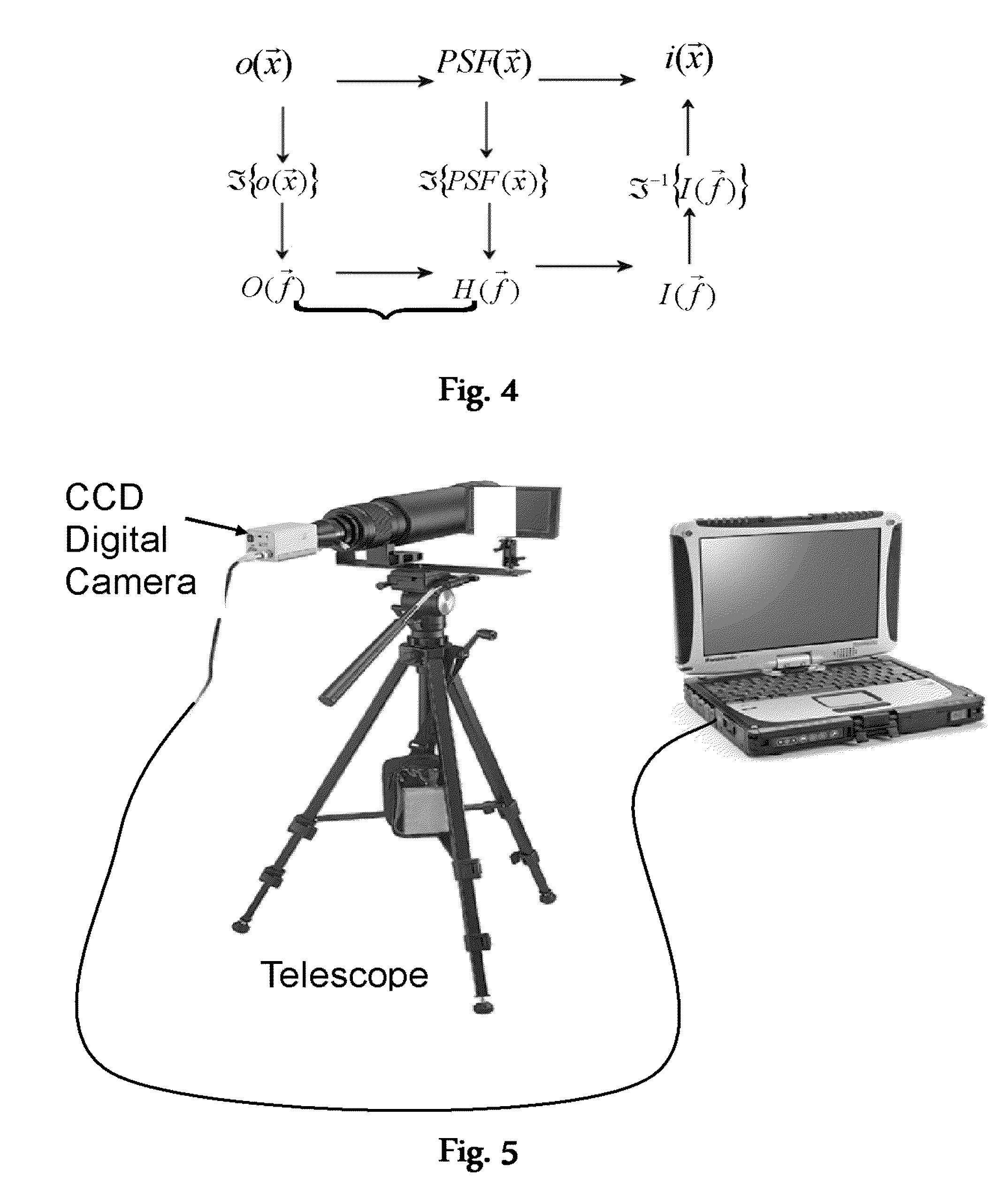
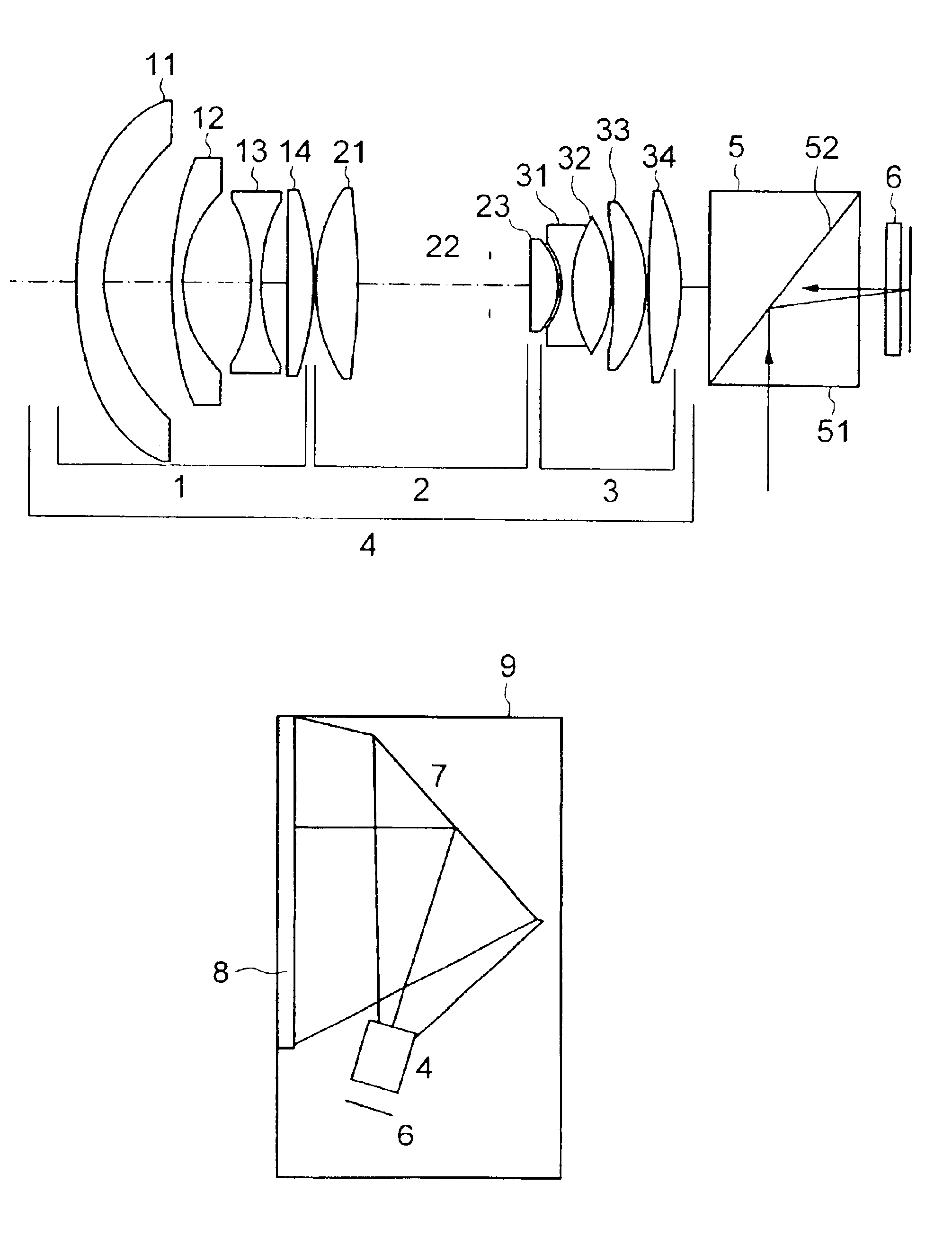
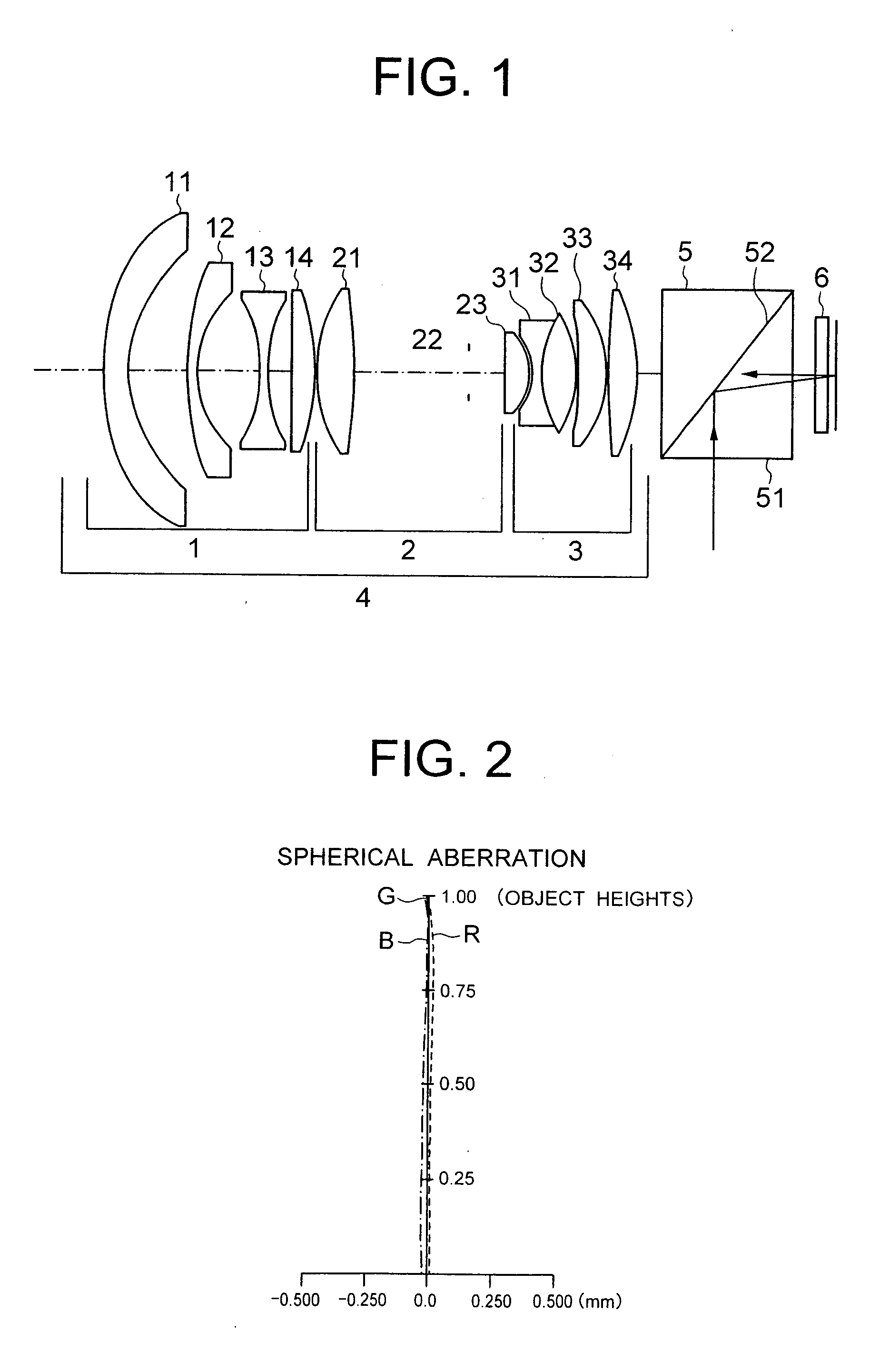
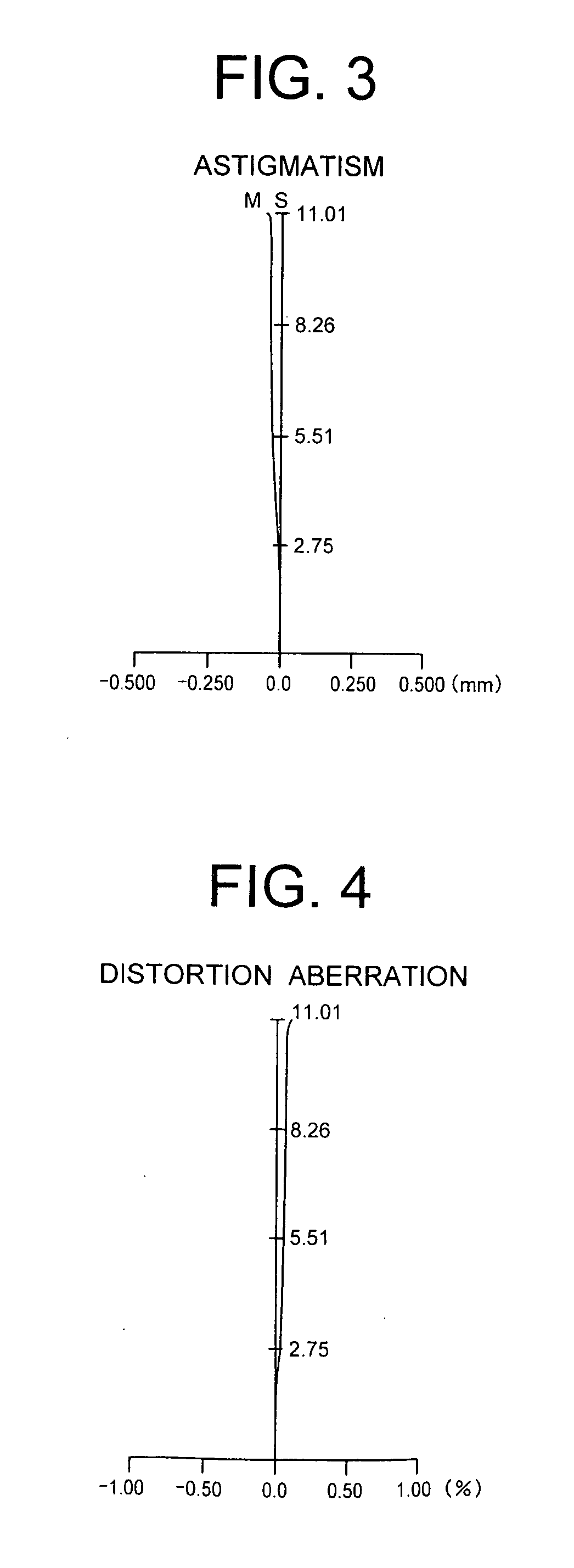
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
62results about How to "Aberration compensation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
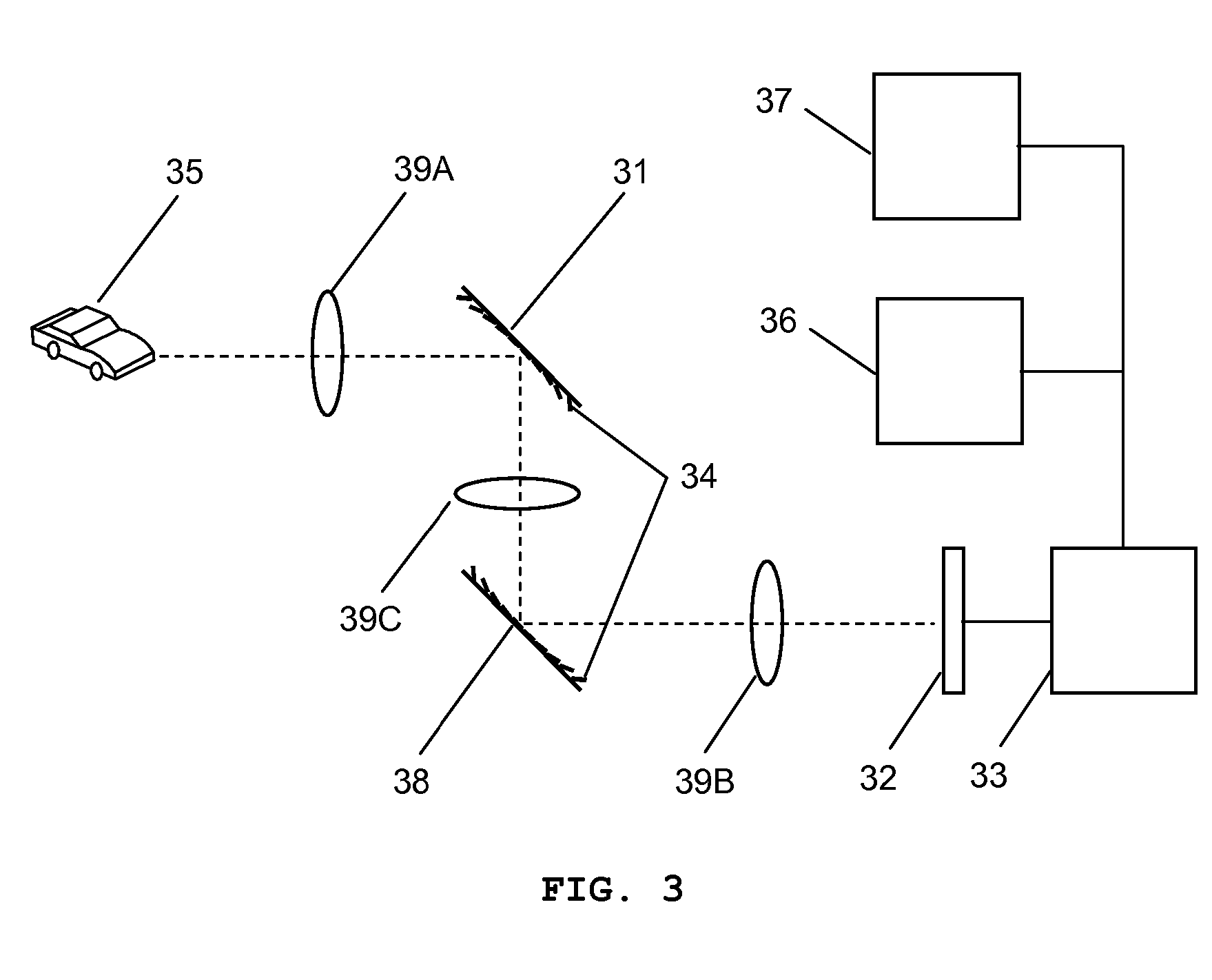
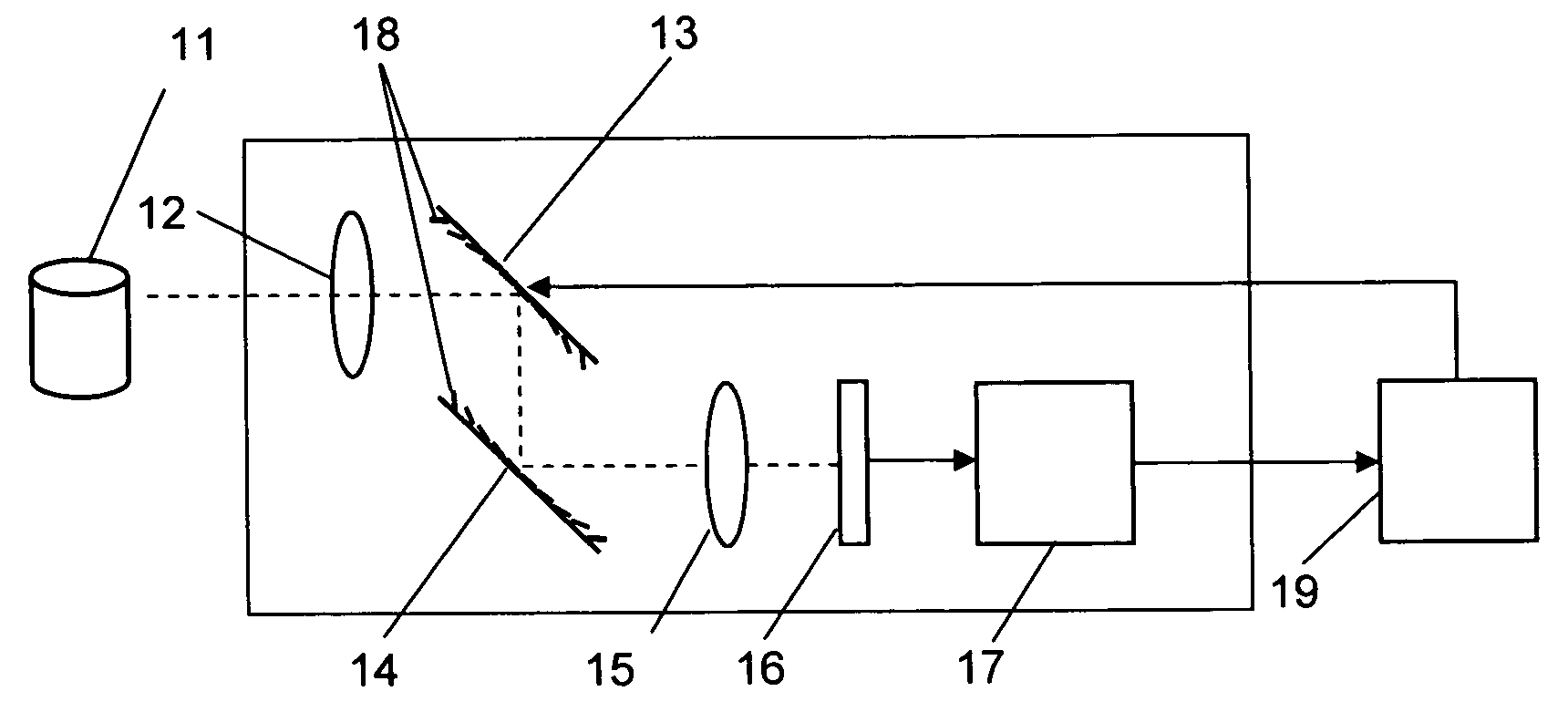
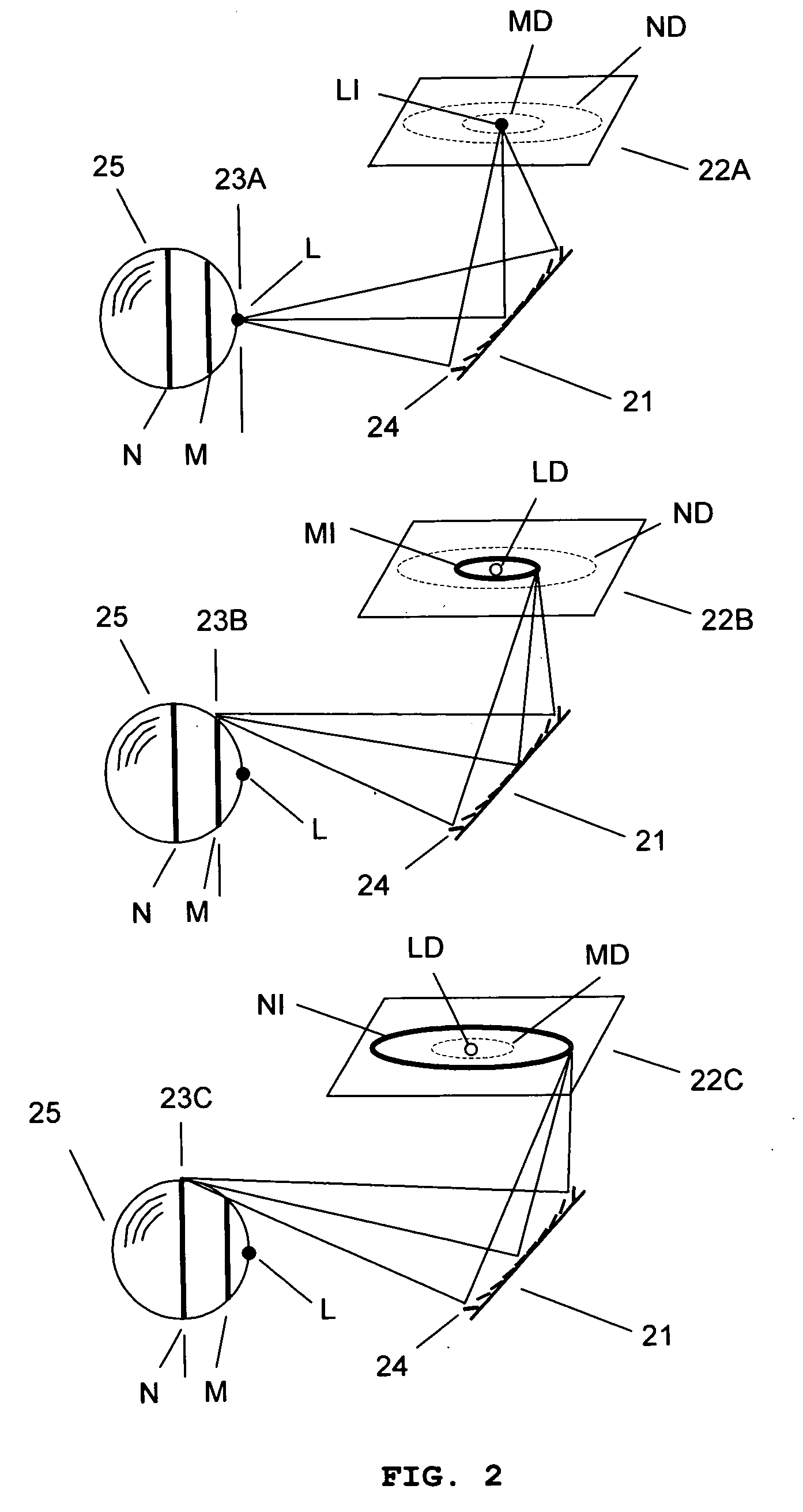
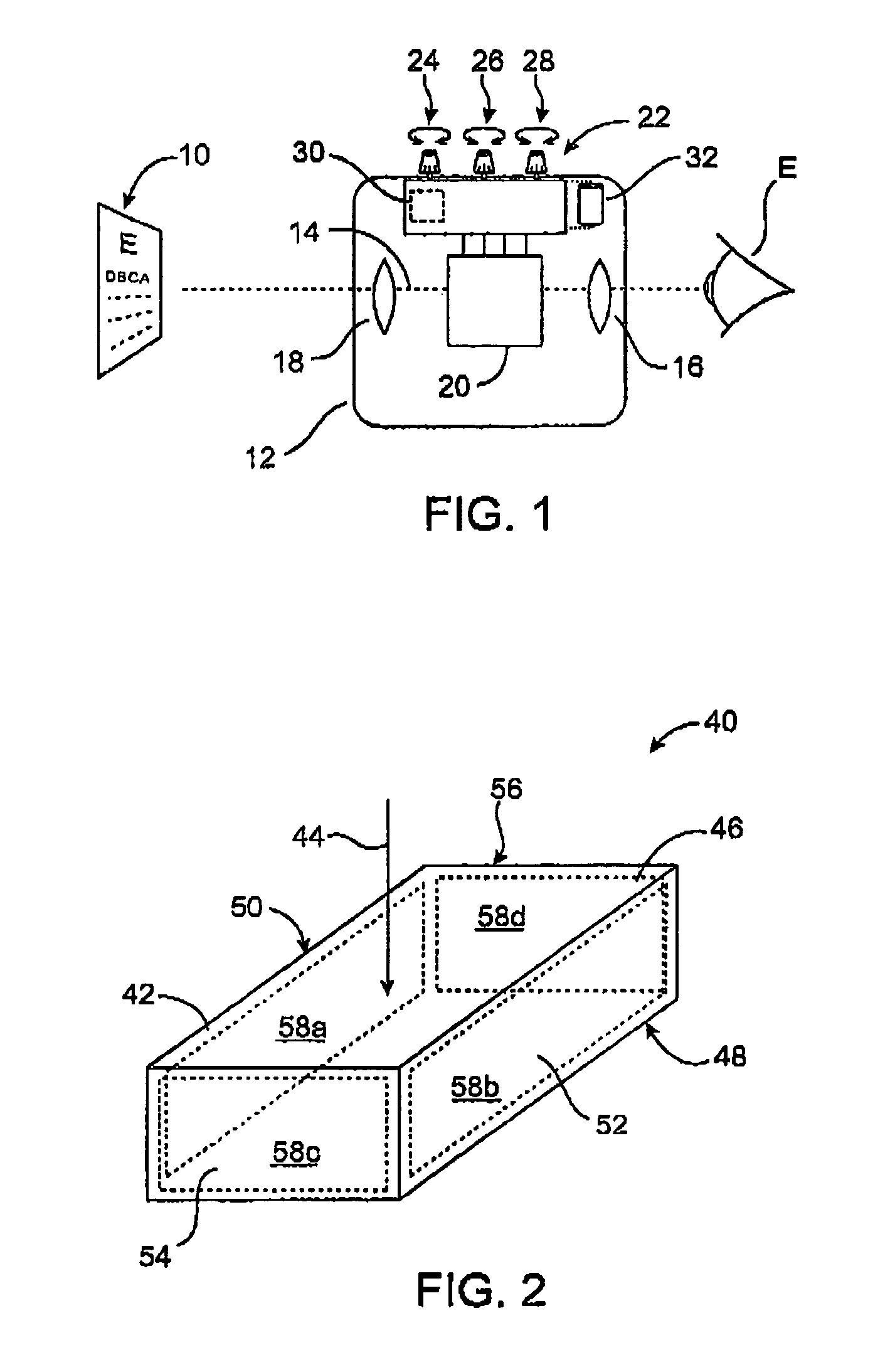
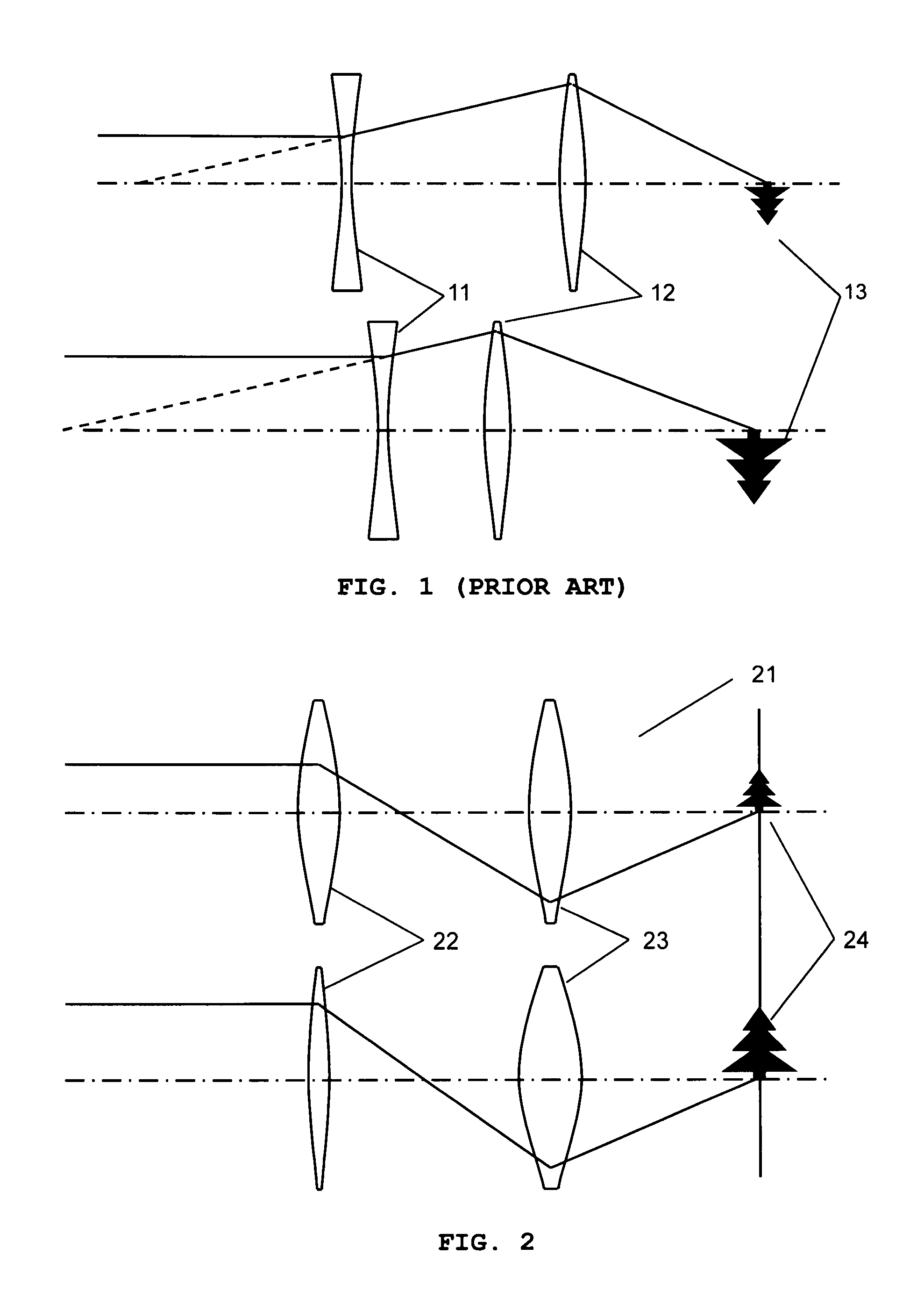
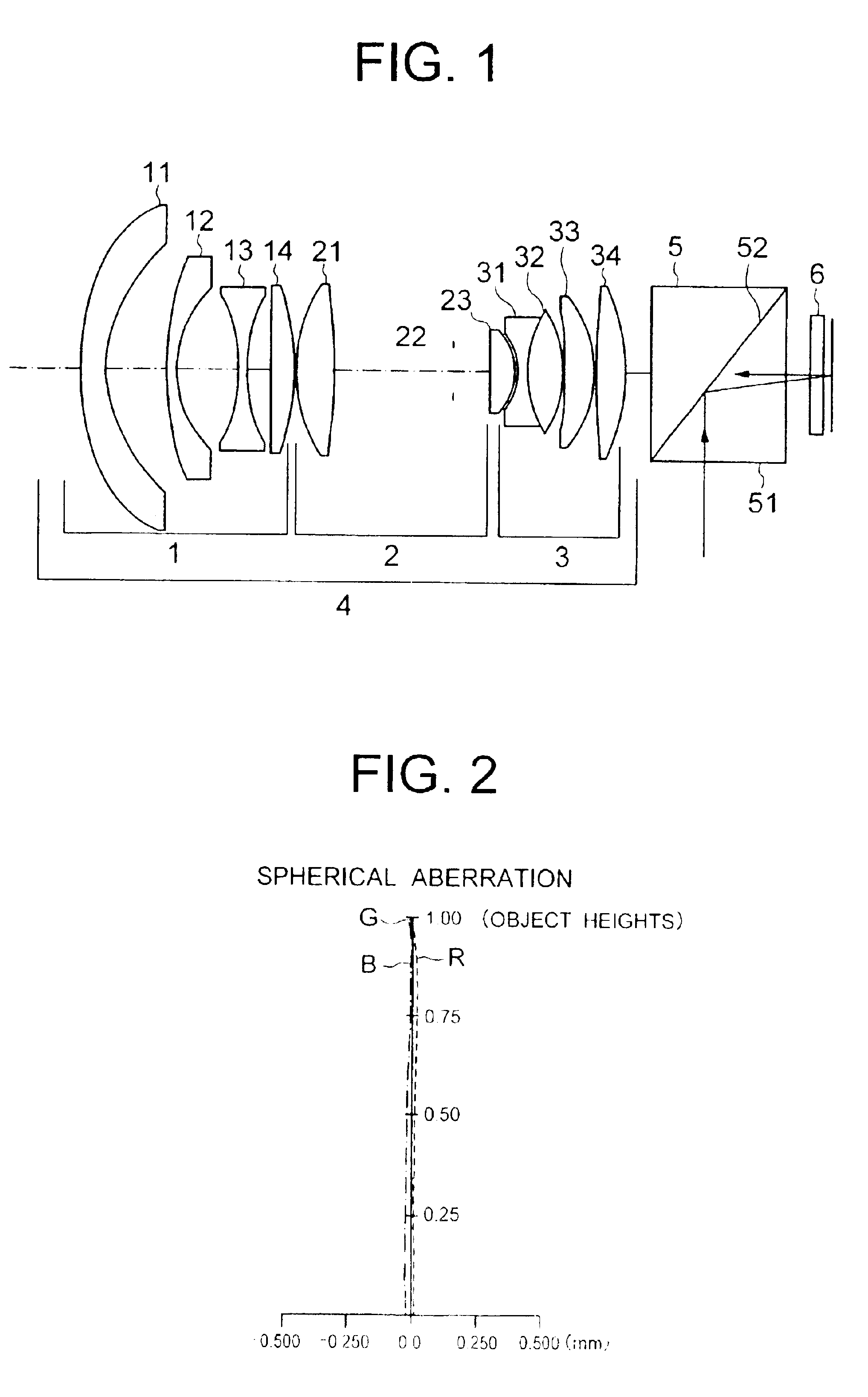
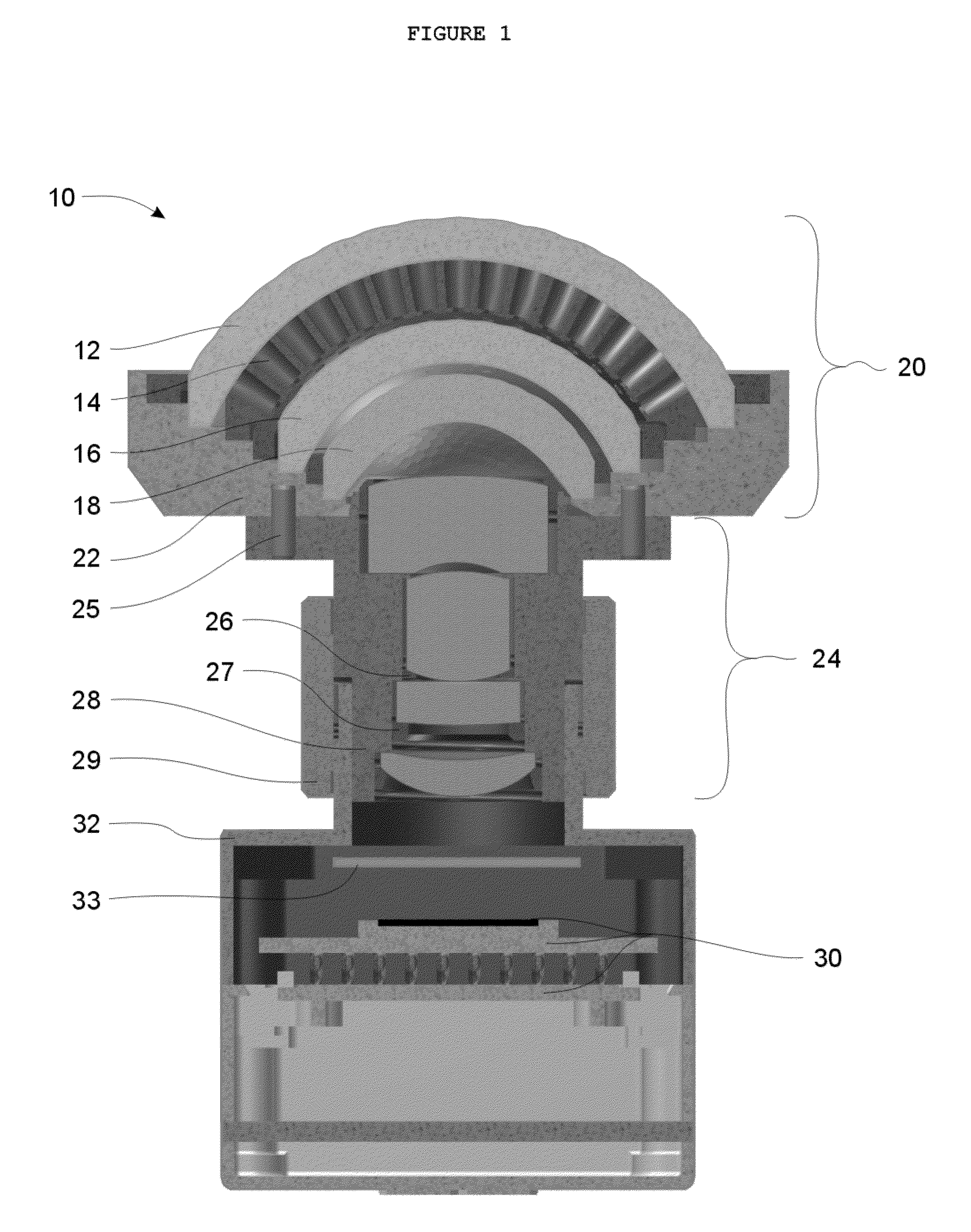
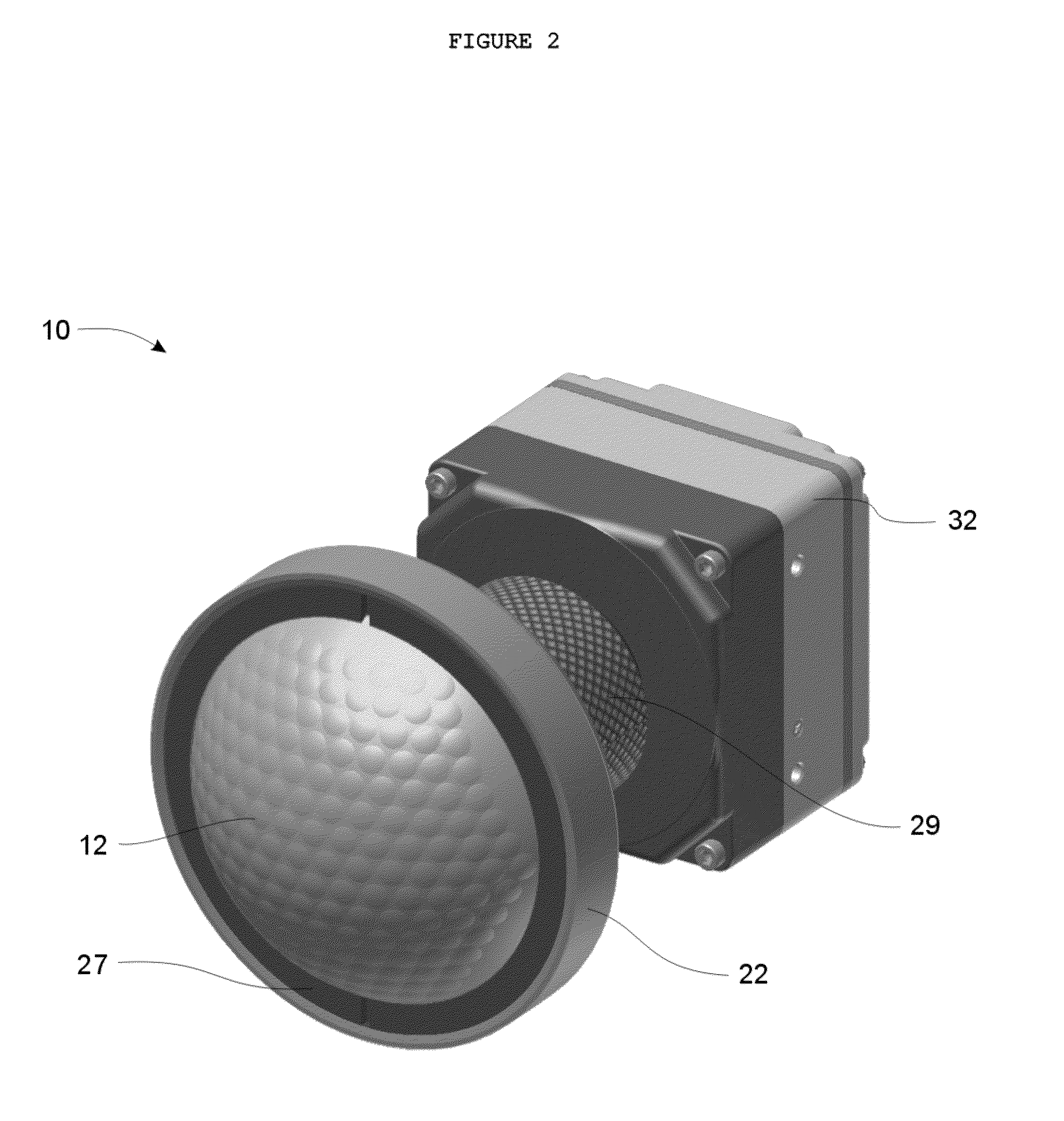
Method and apparatus for improving vision and the resolution of retinal images
InactiveUS20060044510A1Accurate measurementHigh resolutionOptical measurementsEye surgeryCcd cameraLaser beams
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Method and apparatus for improving vision and the resolution of retinal images
InactiveUS6948818B2Accurate measurementAberration compensationOptical measurementsEye surgeryPhysicsLenslet
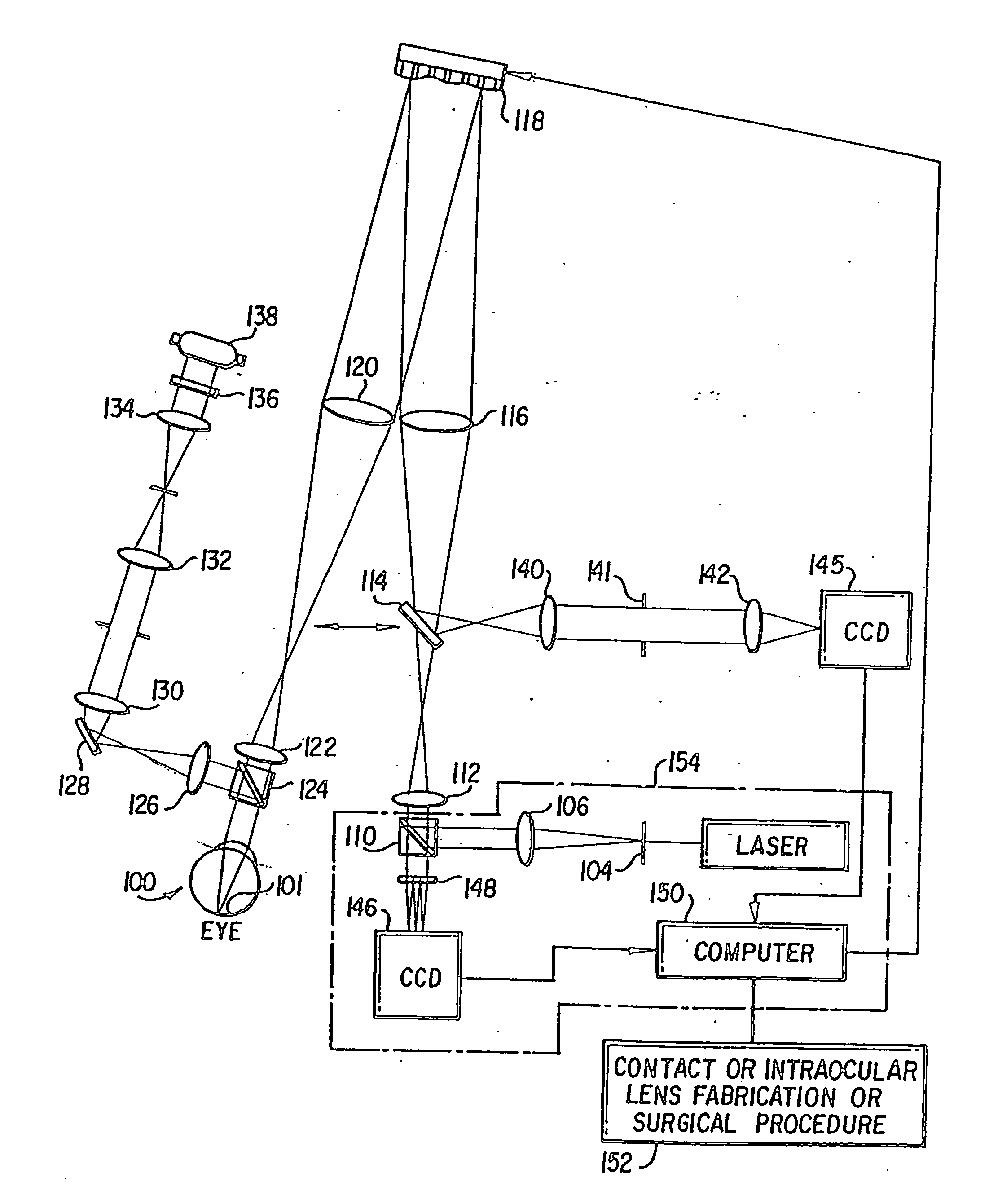
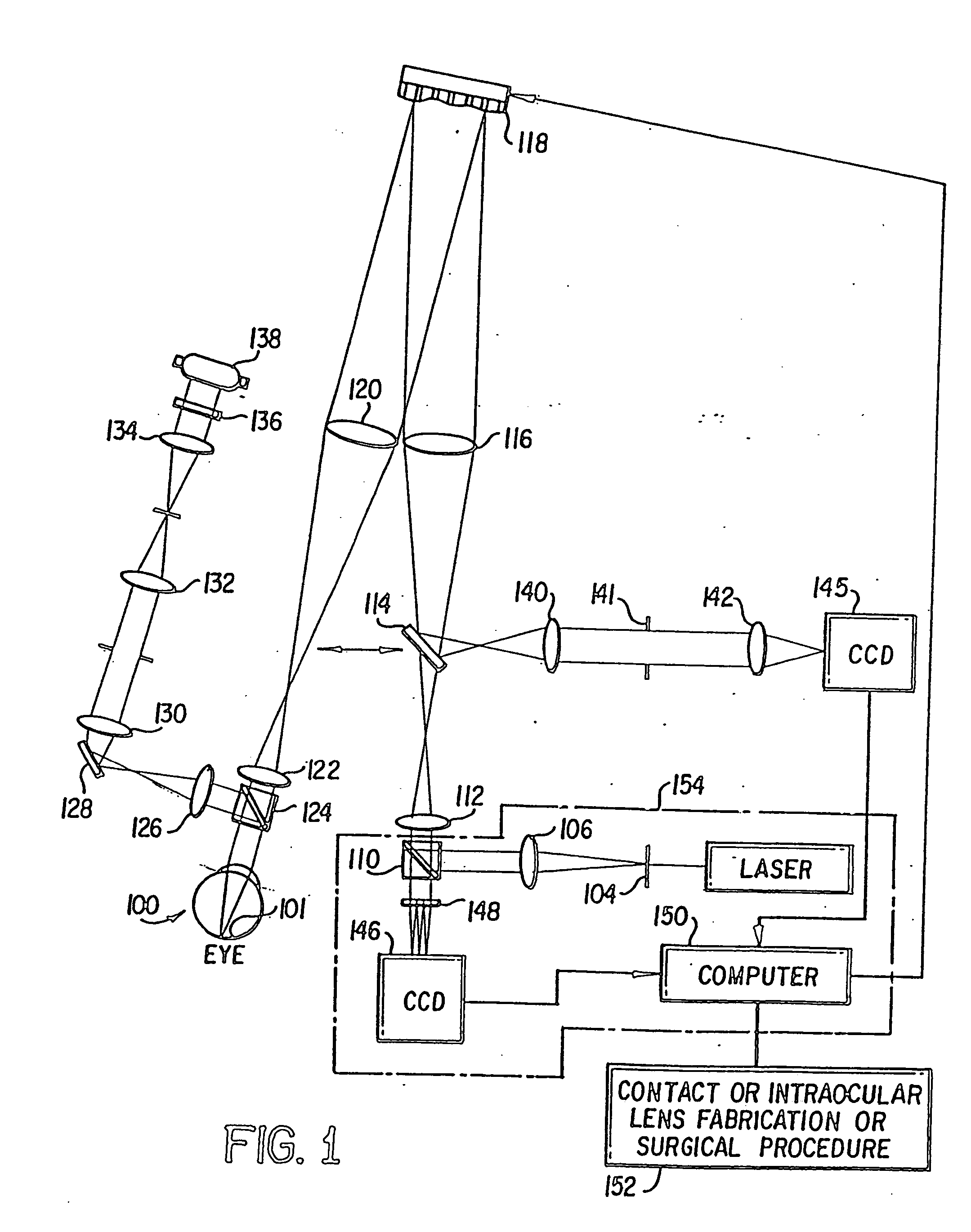
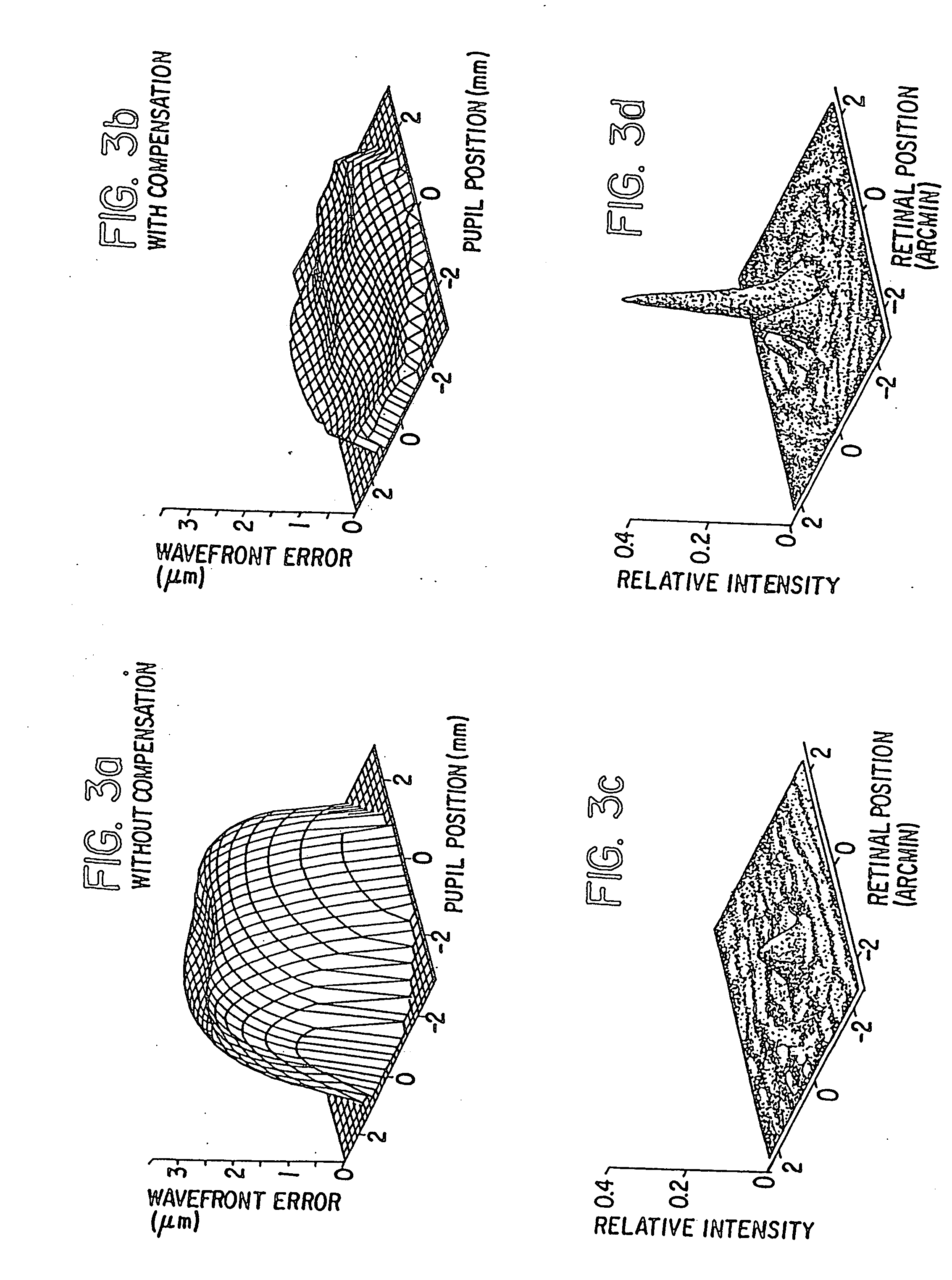
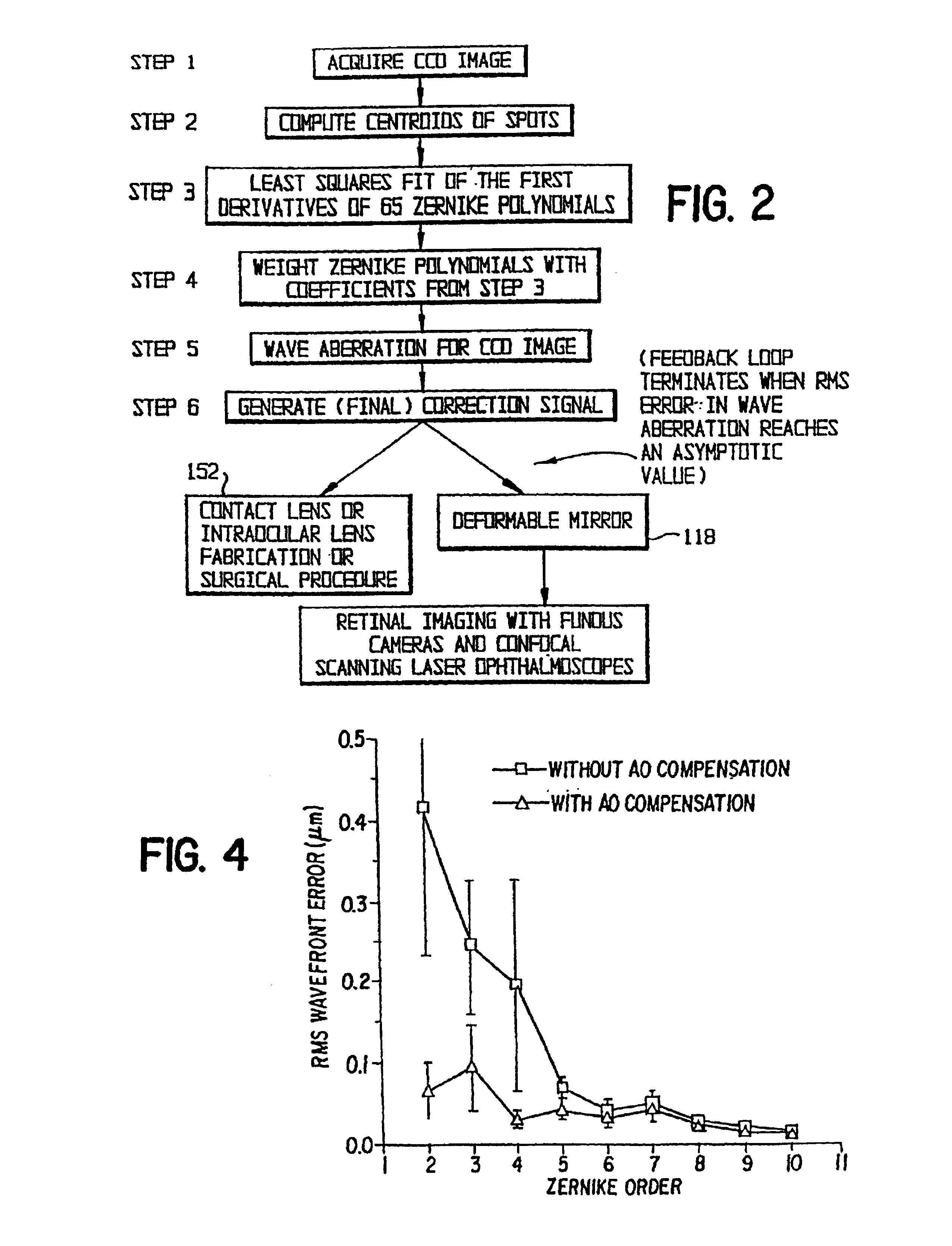
A method of and apparatus for improving vision and the resolution of retinal images is described in which a point source produced on the retina of a living eye by a laser beam is reflected from the retina and received at a lenslet array of a Hartmann-Shack wavefront sensor such that each of the lenslets in the lenslet array forms an aerial image of the retinal point source on a CCD camera located adjacent to the lenslet array. The output signal from the CCD camera is acquired by a computer which processes the signal and produces a correction signal which may be used to control a compensating optical or wavefront compensation device such as a deformable mirror. It may also be used to fabricate a contact lens or intraocular lens, or to guide a surgical procedure to correct the aberrations of the eye. Any of these methods could correct aberrations beyond defocus and astigmatism, allowing improved vision and improved imaging of the inside of the eye.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Apparatus of Plural Charged-Particle Beams
ActiveUS20160284505A1High detection efficiencyHigh throughputElectric discharge tubesMolecular physicsCharged particle beam
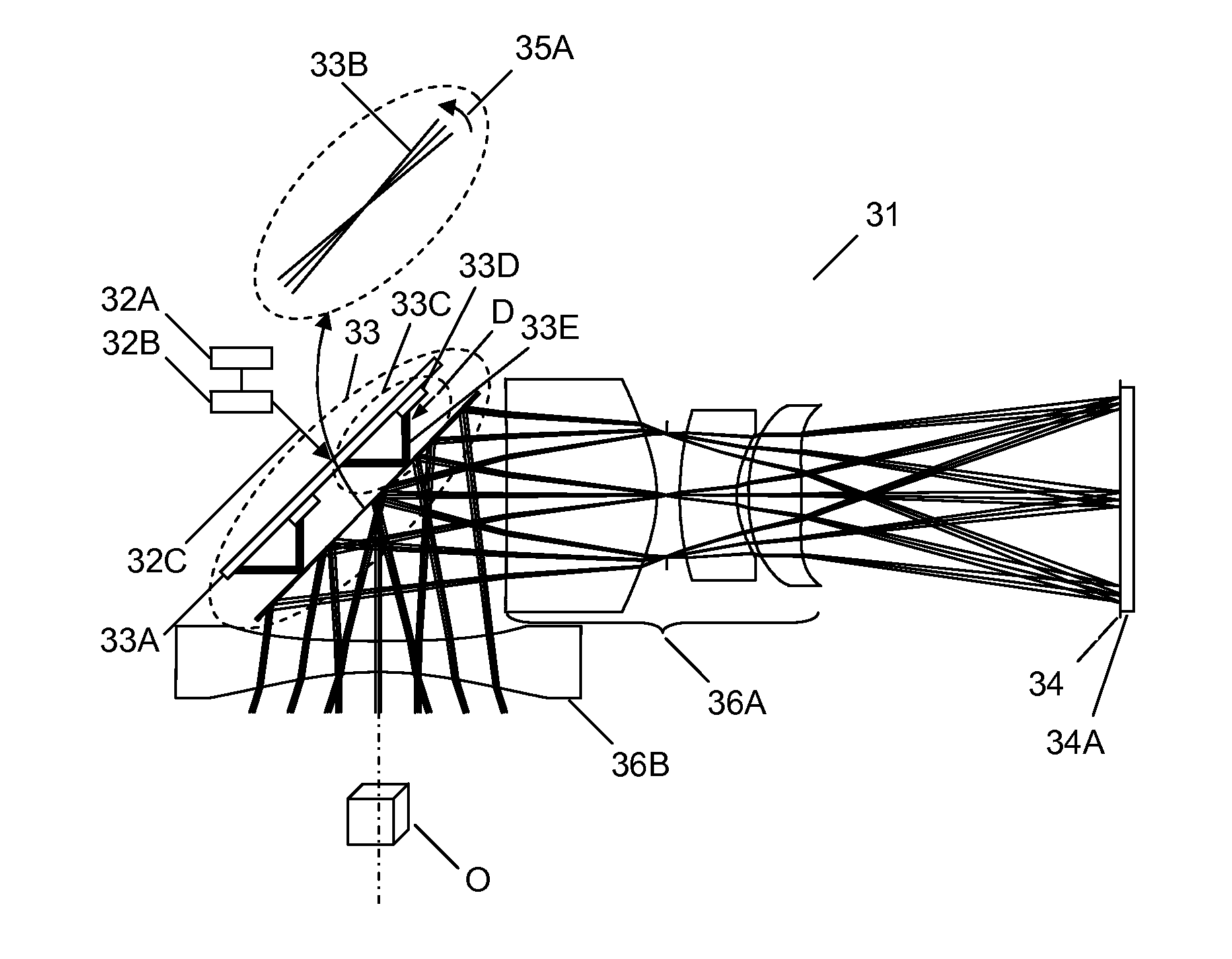
A multi-beam apparatus for observing a sample with oblique illumination is proposed. In the apparatus, a new source-conversion unit changes a single electron source into a slant virtual multi-source array, a primary projection imaging system projects the array to form plural probe spots on the sample with oblique illumination, and a condenser lens adjusts the currents of the plural probe spots. In the source-conversion unit, the image-forming means not only forms the slant virtual multi-source array, but also compensates the off-axis aberrations of the plurality of probe spots. The apparatus can provide dark-field images and / or bright-field images of the sample.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Acoustic beam forming in phased arrays including large numbers of transducer elements
ActiveUS7611462B2Aberration compensationMinimize complexityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyPhase shiftedFocal zone
A focused ultrasound system includes a transducer array, a controller for providing drive signals to the transducer array, and a switch. The transducer array includes a plurality of “n” transducer elements, and the controller includes a plurality of “m” output channels providing sets of drive signals having respective phase shift values, “m” being less than “n.” The switch is coupled to the output channels of the controller and to the transducer elements, and is configured for connecting the output channels to respective transducer elements. The controller may assign the transducer elements to respective output channels based upon a size and / or shape of a desired focal zone within the target region, to steer or otherwise move a location of the focal zone, and / or to compensate for tissue aberrations caused by tissue between the transducer array and the focal zone, geometric tolerances and / or impedance variations of the transducer elements.
Owner:INSIGHTEC
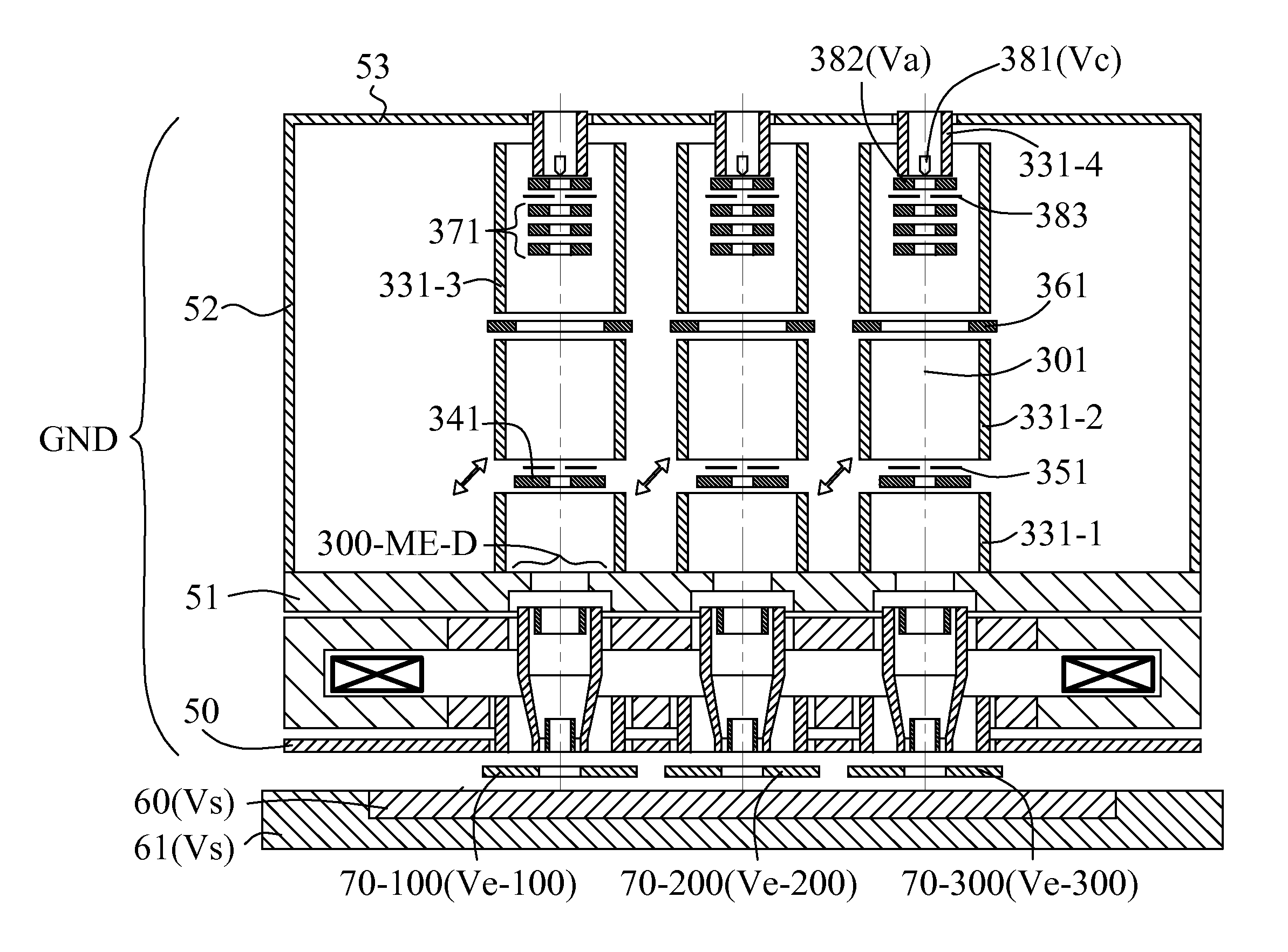
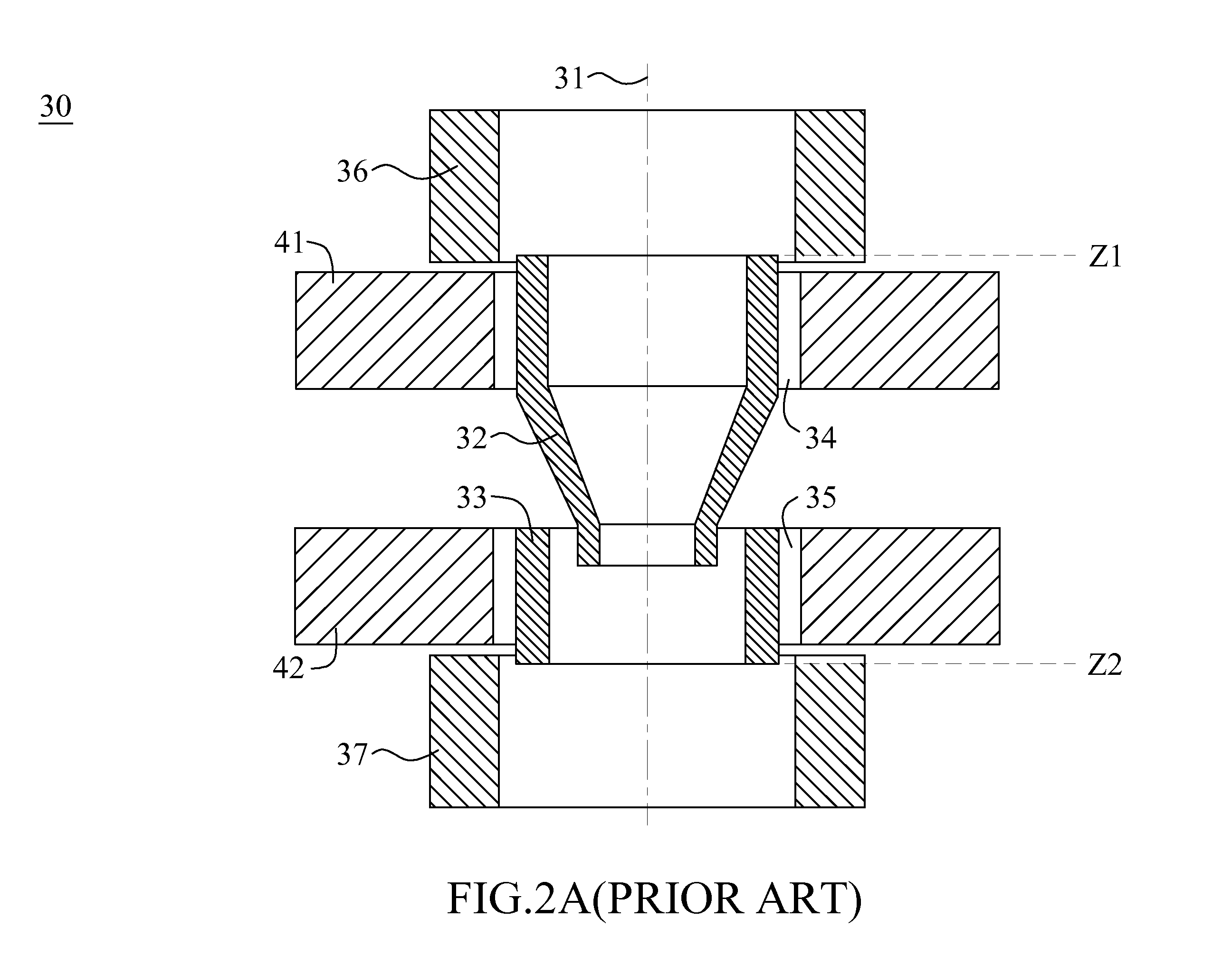
Apparatus of plural charged particle beams with multi-axis magnetic lens
ActiveUS8294095B2Low aberration lowAvoid damageMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectrode and associated part arrangementsCouplingOptical axis
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Contact lens with high-order compensation for non-axisymmetric structure
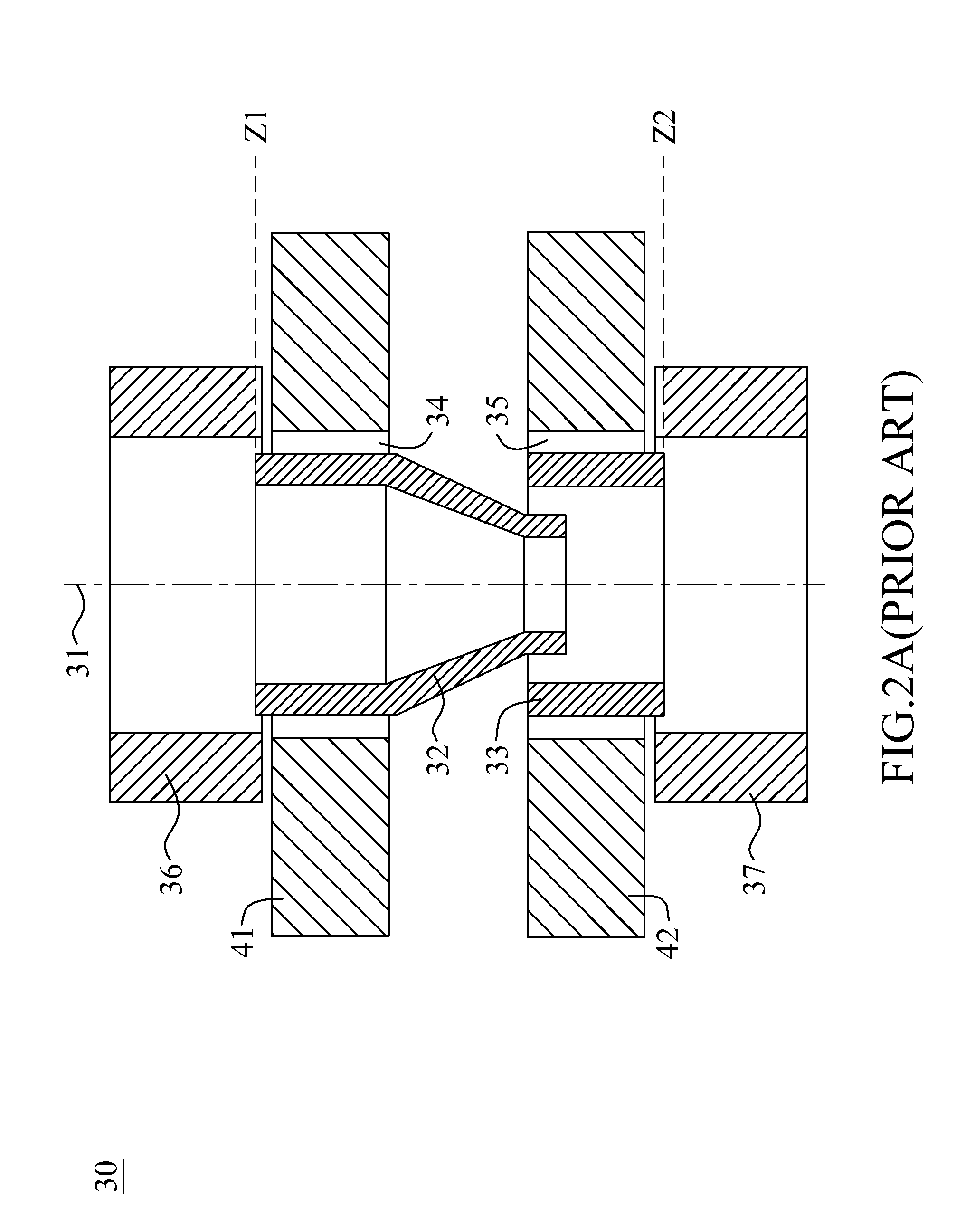
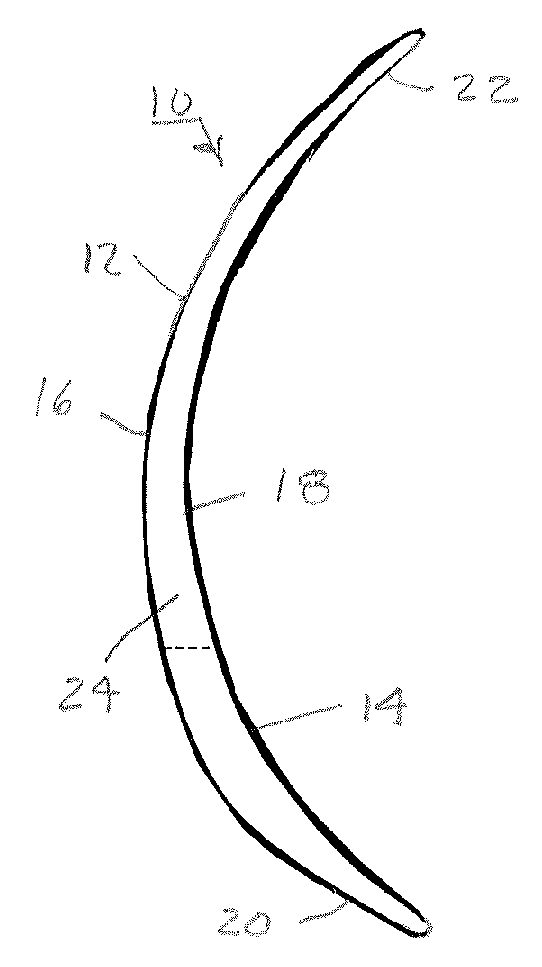
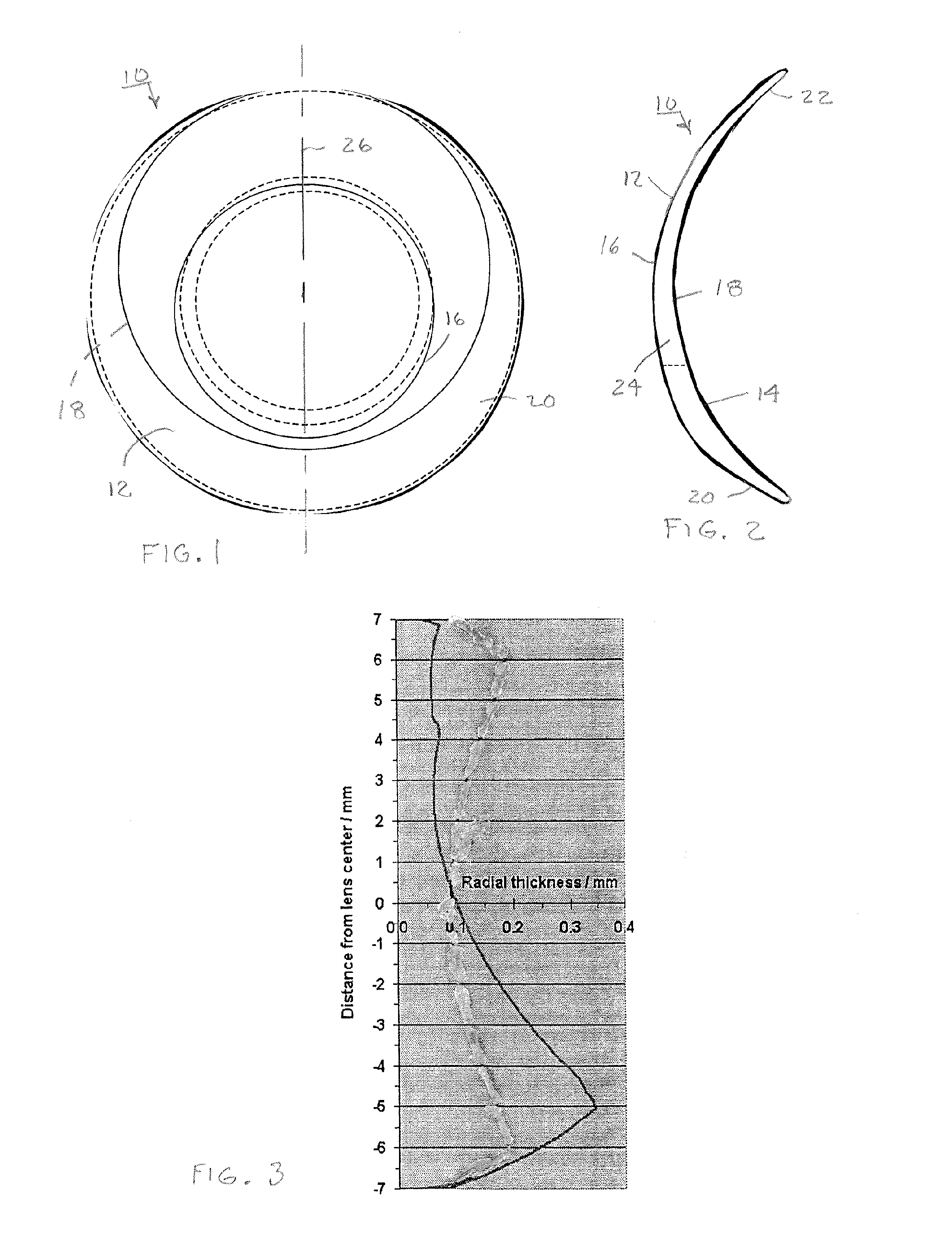
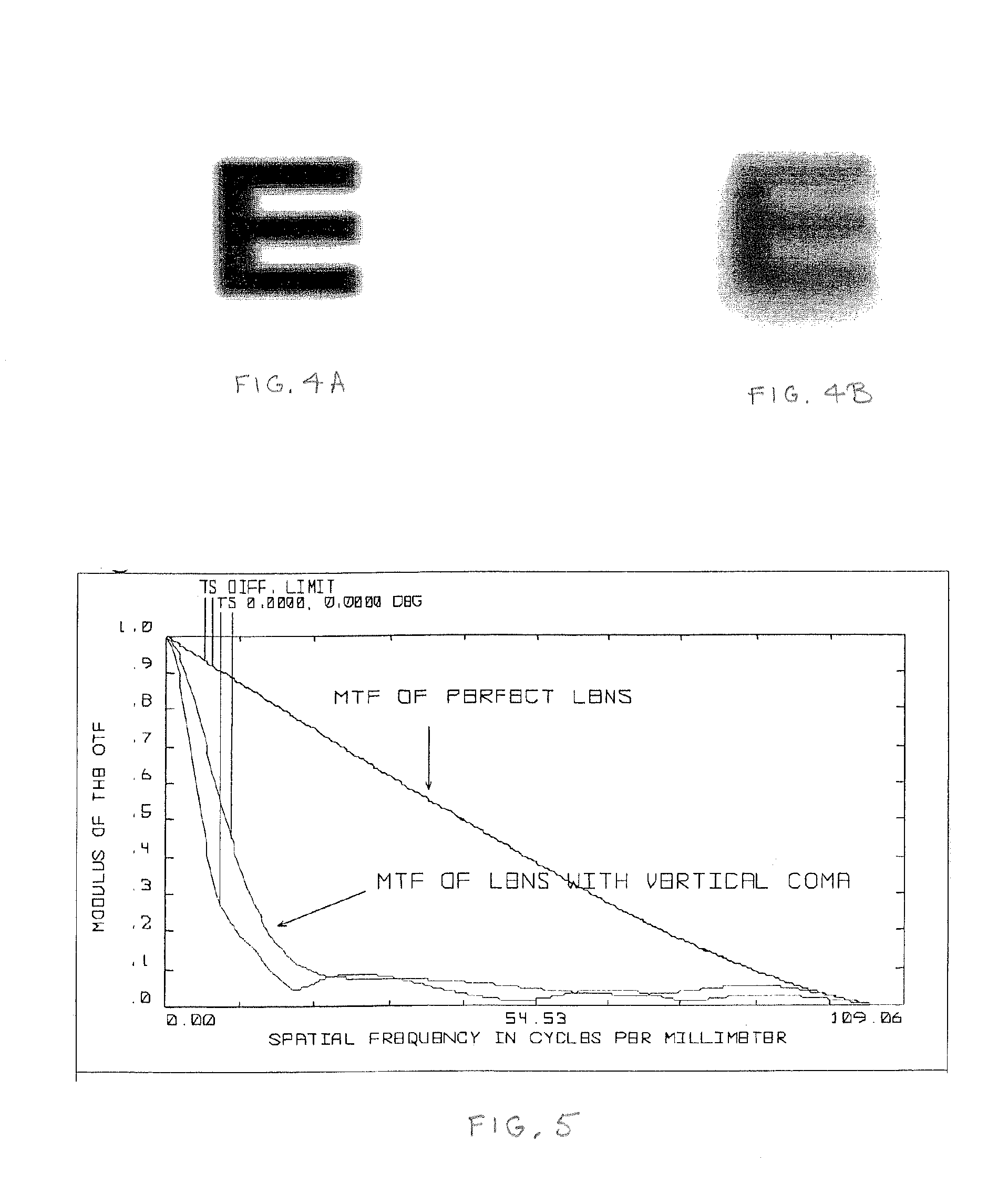
ActiveUS7172285B1Improve imaging effectAberration compensationSpectales/gogglesEye diagnosticsPrismWavefront aberration
Contact lenses, such as prism ballasted toric lenses, having anterior and posterior surfaces related by way of non-axisymmetric thickness variation can exhibit a third-order aberration, particularly vertical coma. A wavefront modifier, such as an aspheric surface modification, is incorporated into the lenses to at least partially compensate for the wavefront aberration associated with the non-axisymmetric thickness variation. A magnitude of the modifications can be adjusted to set a target value for any remaining wavefront aberration of the lenses based on a population-wide goal.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Plenoptic camera apparatus
InactiveUS20130265485A1Prevent degradationAberration compensationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImage sensorImaging lens
A plenoptic camera apparatus includes a main lens unit configured to collect rays emitted from a subject. The plenoptic camera apparatus includes an image sensor unit adapted to capture images formed from the collected rays through one or more convertible lens device units. The convertible lens device units are positioned between the main lens unit and the image sensor unit and configured to provide individual curvature adjustment. The plenoptic camera apparatus includes a control unit configured to control the convertible lens device units to switch to a high-resolution imaging lens or a plenoptic imaging lens array, based on a user's selection, and control driving of the convertible lens device units to compensate for a partial aberration caused by the main lens unit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Three-dimensional camcorder
ActiveUS20060221179A1Improve image qualityAberration compensationSteroscopic systems3d imageViewfinder
The present invention provides a three-dimensional camcorder comprising a three-dimensional imaging system acquiring the three-dimensional image information of an object and a three-dimensional viewfinder displaying three-dimensional image using at least one variable focal length micromirror array lens.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
Three-dimensional imaging system for pattern recognition
ActiveUS20060098872A1Fast response timeLarge focal length variationCharacter and pattern recognitionDepth of fieldMicromirror array
The present invention provides a real-time three-dimensional pattern recognition imaging system having a variable focal length, a wide depth of field, a high depth resolution, a fast acquisition time, a variable magnification, a variable optical axis for tracking, and capability of compensating various optical distortions and aberrations, which enables pattern recognition systems to be more accurate as well as more robust to environmental variation. The imaging system for pattern recognition comprises one or more camera system, each of which has at least one micromirror array lens(MMAL), a two-dimensional image senor, and an image processing unit. A MMAL has unique features including a variable focal length, a variable optical axis, and a variable magnification.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
Sphero cylindrical eye refraction system using fluid focus electrostatically variable lenses
InactiveUS7413306B2Aberration compensationEfficient use ofElectrotherapyPhoroptersSpherical powerRefractive index
Optical devices, systems, and methods can produce and / or measure cylindrical (as well as spherical) lens shapes throughout a range of both powers and cylindrical axes. Fluid focus lenses employ electrical potentials to vary the shape of a fluid / fluid interface between two immiscible fluids having differing indices of refractions by controlling localized angles between the interface and a surrounding container wall. Spherical power, cylindrical power, and cylindrical access alignment may be varied with no moving parts (other than the fluids).
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Systems and methods for detection and demodulation of optical communication signals
ActiveUS20180091230A1Selective directionalitySoft steerabilityClose-range type systemsElectromagnetic receiversOptical communicationDemodulation
A free-space optical signal receiver includes a plurality of detectors whose individual outputs are delayed to correct for variations in arrival time caused by aberration in the medium through which the optical signal propagates, and combined to provide a single output. Each of the plurality of detectors sense the free-space modulated optical signal and provide a detector signal representative of the modulation of the optical signal. Each detector signal is delayed by a delay value to generate a delayed signal, and each delay value is selected to correct for variation in arrival time of the optical signal at each of the detectors, resulting in the delayed signals being substantially time-aligned. The delayed signals are constructively combined into a combined signal representative of the modulation aspect, and the combined signal is provided as an output.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Optical imaging system with catoptric objective; broadband objective with mirror; and refractive lenses and broadband optical imaging system having two or more imaging paths
ActiveUS20110242528A1Improve manufacturabilityMinimize constraintOptically investigating flaws/contaminationMicroscopesRefractive indexPupil
An optical system may include an objective having at least four mirrors including an outermost mirror with aspect ratio <20:1 and focusing optics including a refractive optical element. The objective provides imaging at numerical aperture >0.7, central obscuration <35% in pupil. An objective may have two or more mirrors, one with a refractive module that seals off an outermost mirror's central opening. A broad band imaging system may include one objective and two or more imaging paths that provide imaging at numerical aperture >0.7 and field of view >0.8 mm. An optical imaging system may comprise an objective and two or more imaging paths. The imaging paths may provide two or more simultaneous broadband images of a sample in two or more modes. The modes may have different illumination and / or collection pupil apertures or different pixel sizes at the sample.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Electron microscopy system, electron microscopy method and focusing system for charged particles
ActiveUS20050006582A1Fast influenceImprove time resolutionThermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSecondary electronsElectron microscope
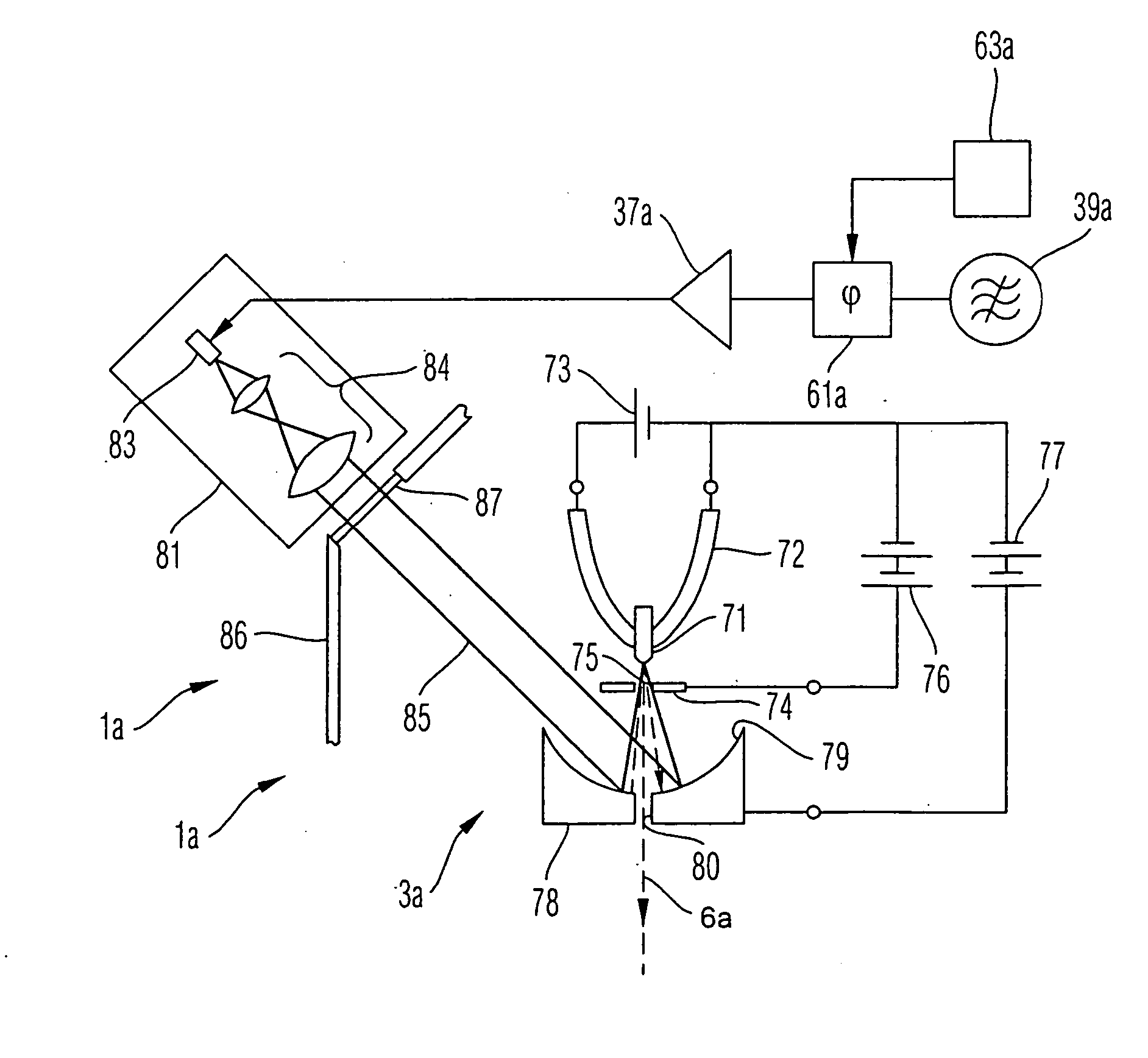
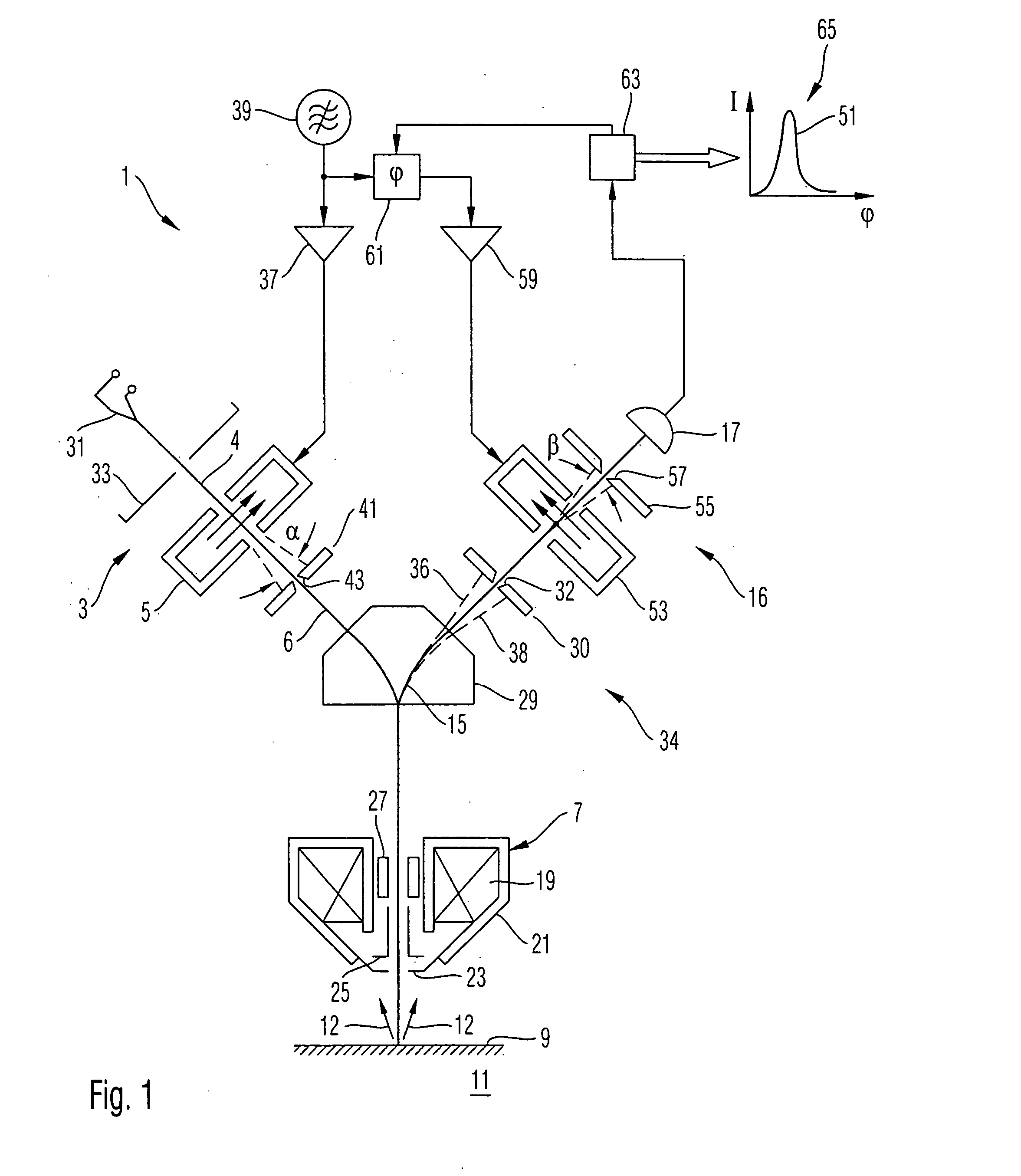
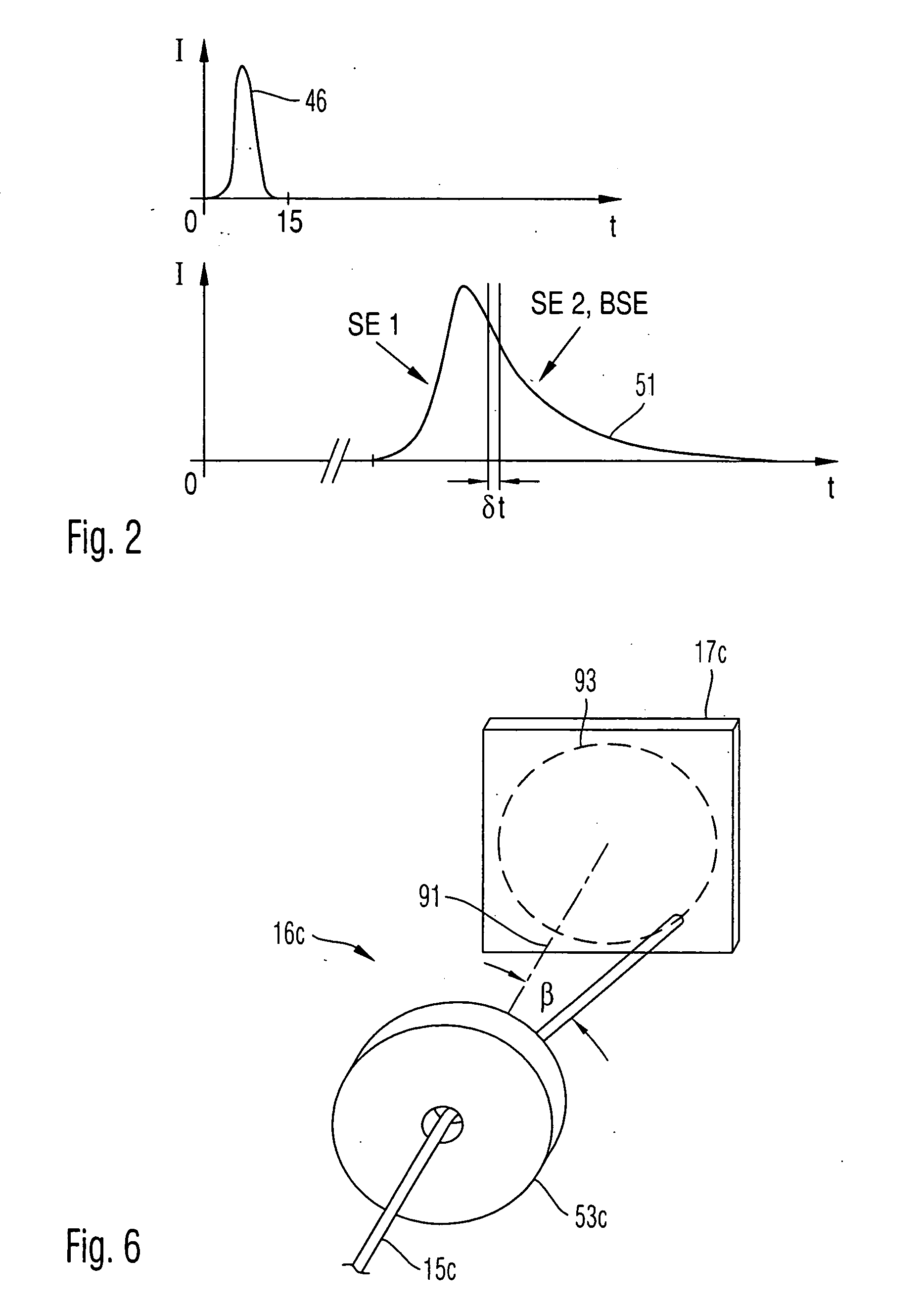
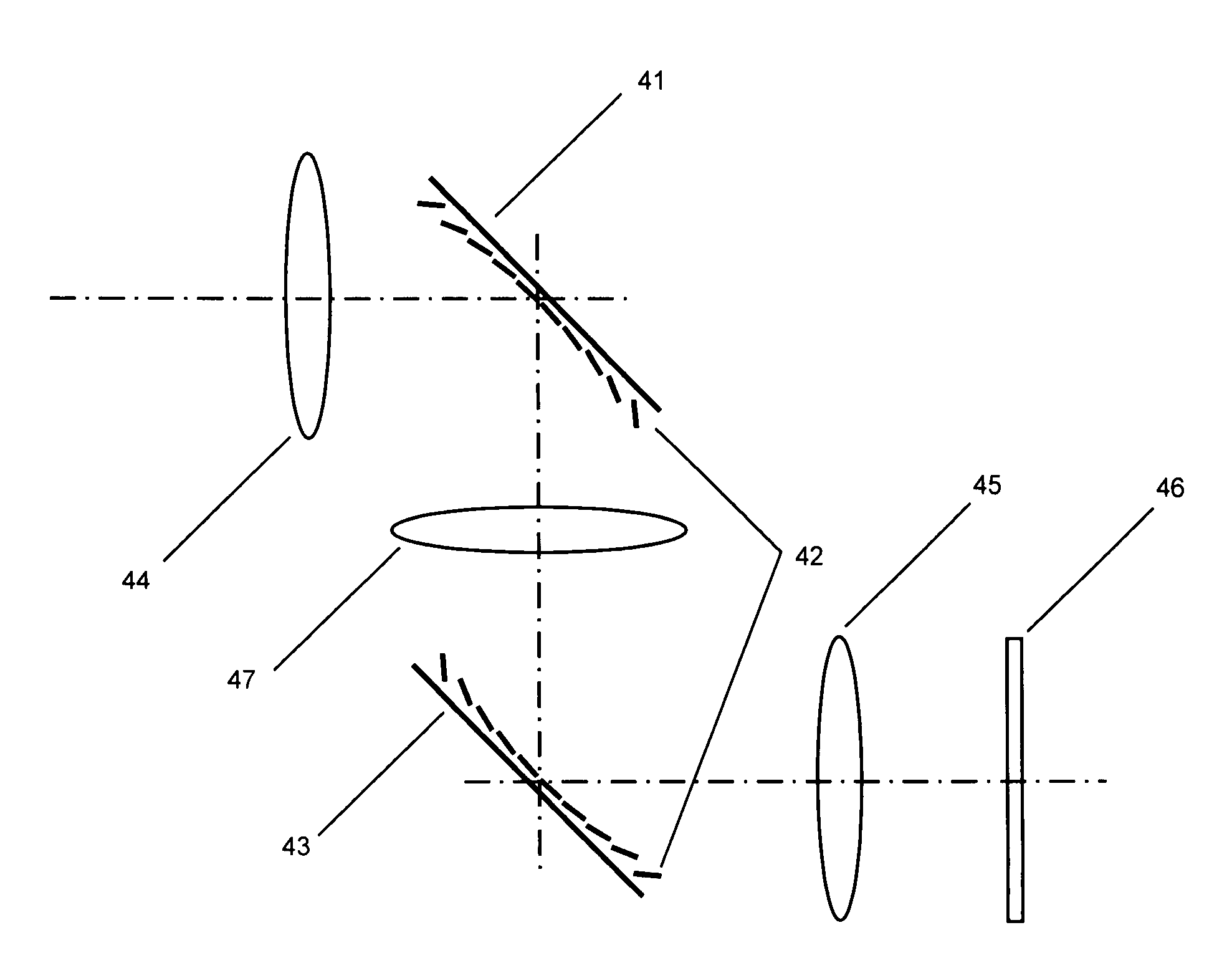
An electron microscopy system and an electron microscopy method for detection of time dependencies of secondary electrons generated by primary electrons is provided, in which the primary electron pulses are directed onto a sample surface and electrons emanating from the sample surface are detected, time resolved. To this end the system comprises in particular a cavity resonator. A cavity resonator can also be used to reduce aberrations of focusing lenses.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Small and fast zoom system using micromirror array lens
The present invention provides a small and fast zoom system using micromirror array lens (MMAL). Thanks to the fast response and compactness of the MMAL as well as absence of the macroscopic mechanical movements of lenses, the zoom system of the present invention fastens the speed of the zooming and reduces the space and weight for the zoom system. Also the present invention provides magnifying the area not on the optical axis and can compensate the aberration of the zoom system.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
Virtual Keyboard input system using three-dimensional motion detection by variable focal length lens
InactiveUS20070115261A1Large focal length variationGreat depth resolutionInput/output for user-computer interactionDigital data processing detailsSystem usageComputer science
A virtual keyboard input system using three-dimensional motion detecting by variable focal length MMAL is provided. The compactness of the virtual keyboard input system is accomplished by the variable focal length MMAL performing three-dimensional imaging function. Since the three-dimensional imaging process occurs in a very short time scale, the system can determine the motion of the input by the user and track the motion of the user in real-time based response. Image processor can determine which input is occurred at the moment and the time-dependent profile of the motion itself. The input system gives an output just like a conventional keyboard and a mouse system.
Owner:ANGSTROM INC +1
Optical imaging system with catoptric objective; broadband objective with mirror; and refractive lenses and broadband optical imaging system having two or more imaging paths
ActiveUS20130155399A9Improve manufacturabilityMinimize constraintOptically investigating flaws/contaminationMicroscopesPupilBroadband
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Optical system with optical image stabilization using a MEMS mirror
An optical system with optical image stabilization of the present invention comprises at least one movement determination unit determining a movement of the optical system, a control circuitry generating a movement compensation signal using the movement information of the optical system from the movement determination unit, and a Micro-Electro Mechanical System (MEMS) unit made by microfabrication technology and controlled by the control circuitry with the movement compensation signal 32C to stabilize an image of an object formed on the image plane. The MEMS unit comprises a substrate, an MEMS mirror movably connected to the substrate and configured to have a motion comprising a rotation, and at least one actuation unit configured to actuating the MEMS mirror. The actuation unit comprises a micro-actuator disposed on the substrate, communicatively coupled to the control circuitry, and configured to have in-plane translation in accordance with the movement compensation signal and a micro-converter having a primary end rotatably connected to the micro-actuator. The micro-actuator with the in-plane translation exerts a force on the primary end of the micro-converter and the micro-converter delivers the force to the MEMS mirror to make the MEMS mirror have a required rotation. The optical system with optical image stabilization of the present invention provides fast speed, light weight, simple operation, and high image quality image stabilization for the optical system.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
Three-dimensional display using variable focal length micromirror array lens
ActiveUS20060232498A1Improve image qualityAberration compensationMirrorsProjectorsThree dimensional displayComputer graphics (images)
A three-dimensional display device includes a two-dimensional display displaying a depthwise image, and a variable focal length micromirror array lens receiving light from the two-dimensional display and forming a corresponding image in the required location in space. Each depthwise image represents a portion of an object or scene having the same image depth, and the two-dimensional display displays one depthwise image at a time. The focal length of the variable focal length micromirror array lens changes according to the depth of the depthwise image being displayed. The variable focal length micromirror array lens has enough speed and focusing depth range for the realistic three-dimensional display.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
Apparatus of plural charged particle beams with multi-axis magnetic lens
ActiveUS8445862B2Low aberration lowAvoid damageElectric discharge tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansCouplingOptical axis
An apparatus basically uses a simple and compact multi-axis magnetic lens to focus each of a plurality of charged particle beams on sample surface at the same time. In each sub-lens module of the multi-axis magnetic lens, two magnetic rings are respectively inserted into upper and lower holes with non-magnetic radial gap. Each gap size is small enough to keep a sufficient magnetic coupling and large enough to get a sufficient axial symmetry of magnetic scale potential distribution in the space near to its optical axis. This method eliminates the non-axisymmetric transverse field in each sub-lens and the round lens field difference among all sub-lenses at the same time; both exist inherently in a conventional multi-axis magnetic lens. In the apparatus, some additional magnetic shielding measures such as magnetic shielding tubes, plates and house are used to eliminate the non-axisymmetric transverse field on the charged particle path from each charged particle source to the entrance of each sub-lens and from the exit of each sub-lens to the sample surface.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
High-resolution adaptive optics scanning laser ophthalmoscope with multiple deformable mirrors
InactiveUS7665844B2Improve abilitiesEasy to moveEye diagnosticsOptical elementsNon invasiveRisk stroke
An adaptive optics scanning laser ophthalmoscopes is introduced to produce non-invasive views of the human retina. The use of dual deformable mirrors improved the dynamic range for correction of the wavefront aberrations compared with the use of the MEMS mirror alone, and improved the quality of the wavefront correction compared with the use of the bimorph mirror alone. The large-stroke bimorph deformable mirror improved the capability for axial sectioning with the confocal imaging system by providing an easier way to move the focus axially through different layers of the retina.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Systems and methods for detection and demodulation of optical communication signals
ActiveUS10530494B2Selective directionalitySoft steerabilityClose-range type systemsElectromagnetic receiversSoftware engineeringOptical communication
A free-space optical signal receiver includes a plurality of detectors whose individual outputs are delayed to correct for variations in arrival time caused by aberration in the medium through which the optical signal propagates, and combined to provide a single output. Each of the plurality of detectors sense the free-space modulated optical signal and provide a detector signal representative of the modulation of the optical signal. Each detector signal is delayed by a delay value to generate a delayed signal, and each delay value is selected to correct for variation in arrival time of the optical signal at each of the detectors, resulting in the delayed signals being substantially time-aligned. The delayed signals are constructively combined into a combined signal representative of the modulation aspect, and the combined signal is provided as an output.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
High-Speed Diversity-Based Imaging Method for Parallel Atmospheric Turbulence Compensation
ActiveUS20120288212A1Reduce calculationReduce in quantityImage enhancementTelevision system detailsFast Fourier transformImage pair
An imaging method providing atmospheric turbulence compensation includes capturing a subject image pair. Data corresponding to the captured subject image pair is loaded into memory associated with a parallel processing device. A 2-D Fast Fourier Transform is performed on the stored image data and the transformed image data is stored. An optical transfer function is developed for the transformed image data. The optical transfer function is inverted and applied to the transformed image data to generate corrected image spectrum data that is compensated for atmospheric aberrations. An Inverse Fast Fourier Transform is applied to the corrected image spectrum data to produce corrected image data. The corrected image data is stored.
Owner:FLORIDA INST OF TECH
Projection lens apparatus and projection type image display apparatus
InactiveUS6975460B2Satisfy Compensation RequirementsMore versatilityBuilt-on/built-in screen projectorsNon-linear opticsComputer graphics (images)Optical axis
A projection type image display apparatus having an image display element outputting an image ray, a projection lens apparatus for performing overhead projection of the image ray from the image display element, the projection lens apparatus having a plurality of lens elements, a reflection mirror reflecting the image ray from the projection lens apparatus, and a screen on which the image ray reflected by the reflection mirror is projected. An optical axis of the projection lens apparatus is decentered from a center of the screen.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Apparatus of plural charged particle beams with multi-axis magnetic lens
ActiveUS20120145900A1Low aberration lowAvoid damageElectric discharge tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansCouplingOptical axis
An apparatus basically uses a simple and compact multi-axis magnetic lens to focus each of a plurality of charged particle beams on sample surface at the same time. In each sub-lens module of the multi-axis magnetic lens, two magnetic rings are respectively inserted into upper and lower holes with non-magnetic radial gap. Each gap size is small enough to keep a sufficient magnetic coupling and large enough to get a sufficient axial symmetry of magnetic scale potential distribution in the space near to its optical axis. This method eliminates the non-axisymmetric transverse field in each sub-lens and the round lens field difference among all sub-lenses at the same time; both exist inherently in a conventional multi-axis magnetic lens. In the apparatus, some additional magnetic shielding measures such as magnetic shielding tubes, plates and house are used to eliminate the non-axisymmetric transverse field on the charged particle path from each charged particle source to the entrance of each sub-lens and from the exit of each sub-lens to the sample surface.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Binoculars with micromirror array lenses
The binoculars of the present invention comprise two optical units; one optical unit for each eye. Each optical unit comprises a first reflective lens element and a second reflective lens element, wherein at least one of the reflective lens elements is a Micromirror Array Lens. The binoculars of the present invention provide focusing and / or zoom functions without or with minimal macroscopic mechanical lens movement.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
Multihybrid Artificial Compound Eye with Varied Ommatidia
A wide angle imaging system combines compound array fore-optics with single axis relay optics to generate distortion free images with an infinite depth of field. A curved first array of objective lenslets focuses multiple apertures of light through the tubes of a louver baffle terminated by field stops. An intermediate curved array of field lenslets, positioned immediately after the field stops, passes the light beams through an array of pupil planes. A curved final array of erector lenslets refocuses and adjoins the beams into a contiguous image that is curved. The relay optics transform the curved intermediate image into a flat final image. The fore-optics and relay optics are optimized concurrently to achieve much higher performance than is possible in either compound array optics or sequential optics. This is accomplished by varying the lenslet radii of the fore-optics in annular increments to compensate for aberrations introduced by the relay lenses.
Owner:SPECTRAL IMAGING LAB
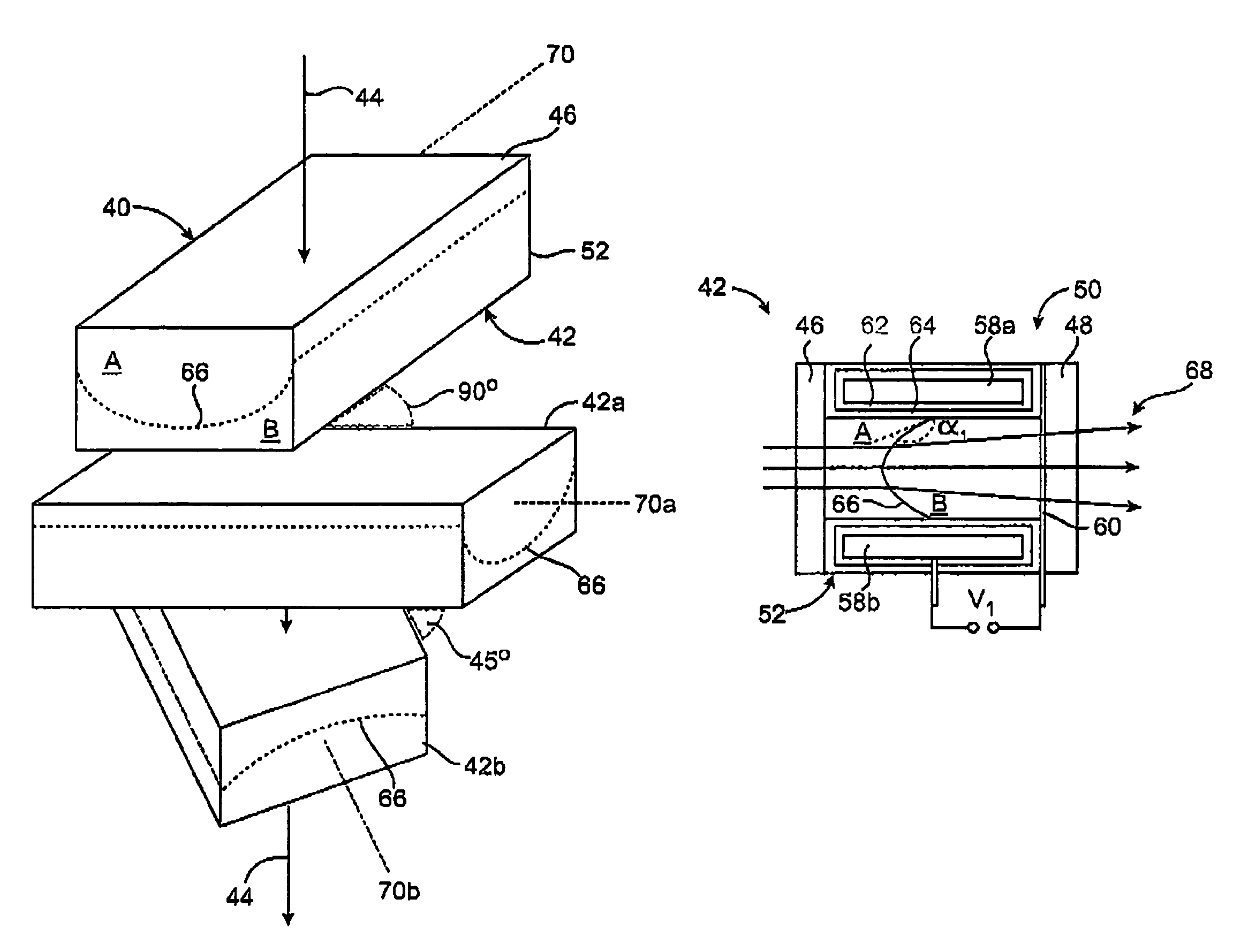
Triangulation camera device and triangulation imaging method
InactiveUS20110141252A1Reduce numberStructure of imaging can be facilitatedCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsLight sourceOptical axis
A triangulation camera device includes a light source device being adapted for generating illumination light to be directed onto an object under investigation and including a light source with an optical pattern generator and a first aperture being arranged along a first optical axis, a detector device being adapted for sensing reflection light reflected by the object and including a detector camera and a second aperture being arranged along a second optical axis, and an imaging optic having imaging lenses being adapted for imaging the illumination light onto the object and for collecting the reflection light, said imaging optic having a third optical axis, wherein the first, second and third optical axes are arranged in parallel and displaced relative to each other and the first and second apertures are arranged with a telecentric configuration relative to the imaging optic such that the illumination light and the reflection light are capable of forming a parallel illumination light bundle and a parallel reflection light bundle, resp., on the object side of the imaging optic, said illumination light bundle and said reflection light bundle having a predetermined projection angle, and the imaging lenses are tilted relative to the third optical axis such that surface reflections of the imaging lenses are directed toward ranges outside the second aperture.
Owner:BERLINER GLAS HERBERT KUBATZ
Apparatus of plural charged particle beams with multi-axis magnetic lens
ActiveUS20120145917A1Low aberration lowAvoid damageThermometer detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsCouplingOptical axis
An apparatus basically uses a simple and compact multi-axis magnetic lens to focus each of a plurality of charged particle beams on sample surface at the same time. In each sub-lens module of the multi-axis magnetic lens, two magnetic rings are respectively inserted into upper and lower holes with non-magnetic radial gap. Each gap size is small enough to keep a sufficient magnetic coupling and large enough to get a sufficient axial symmetry of magnetic scale potential distribution in the space near to its optical axis. This method eliminates the non-axisymmetric transverse field in each sub-lens and the round lens field difference among all sub-lenses at the same time; both exist inherently in a conventional multi-axis magnetic lens. In the apparatus, some additional magnetic shielding measures such as magnetic shielding tubes, plates and house are used to eliminate the non-axisymmetric transverse field on the charged particle path from each charged particle source to the entrance of each sub-lens and from the exit of each sub-lens to the sample surface.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Optical system with optical image stabilization using a MEMS mirror
An optical system with optical image stabilization of the present invention compensates the movement of the optical system occurring during imaging process using a Micro-Electro Mechanical System (MEMS) unit having an MEMS mirror to stabilize an image of an object formed on an image plane. A micro-actuator with the in-plane translation makes the MEMS mirror have a required rotation to change optical paths of light from the object to the image plane for optical image stabilization. The optical system with optical image stabilization or the present invention provides fast speed, light weight, simple operation, and high image quality image stabilization for the optical system.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com