Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
200 results about "Zero-dispersion wavelength" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
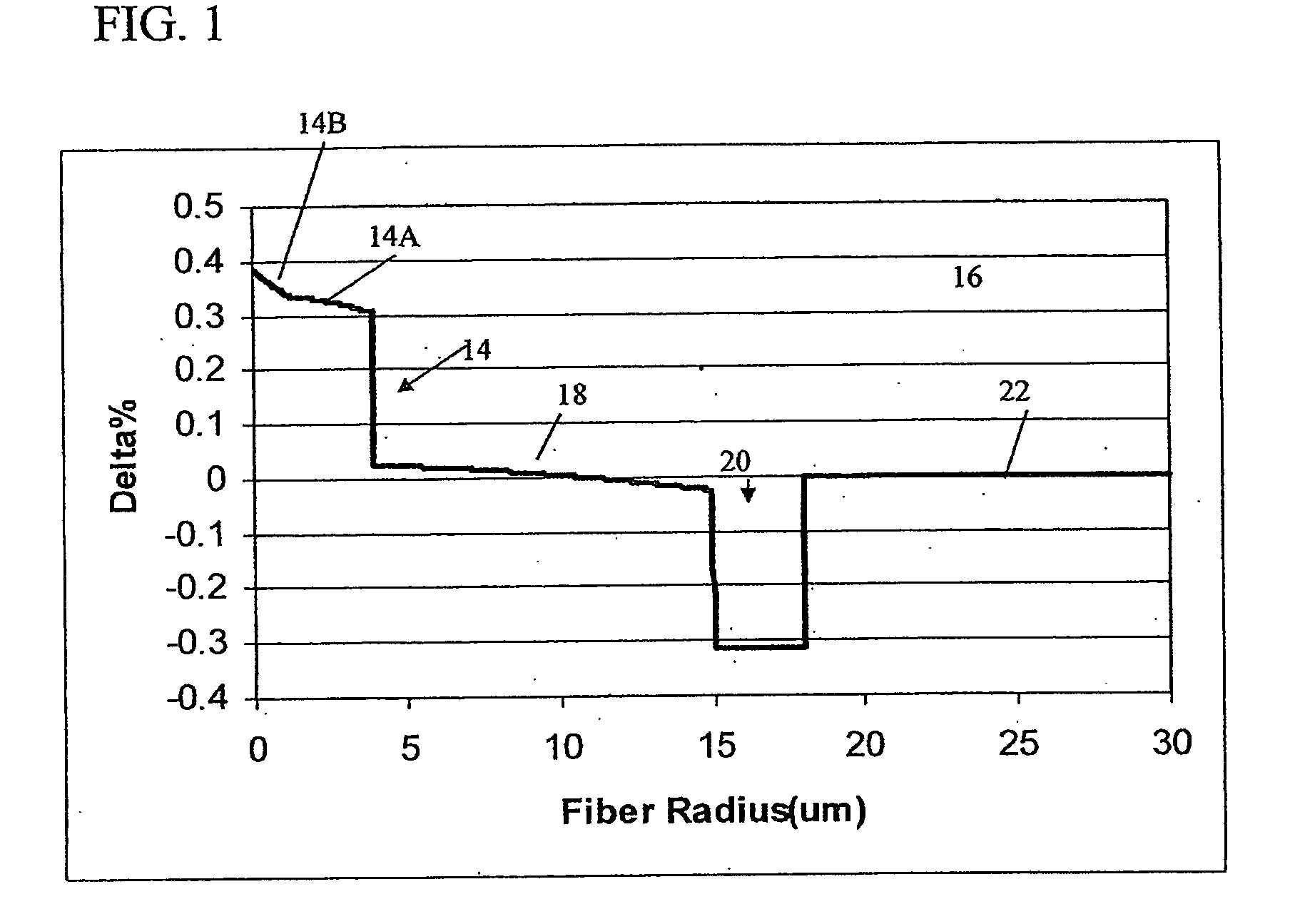
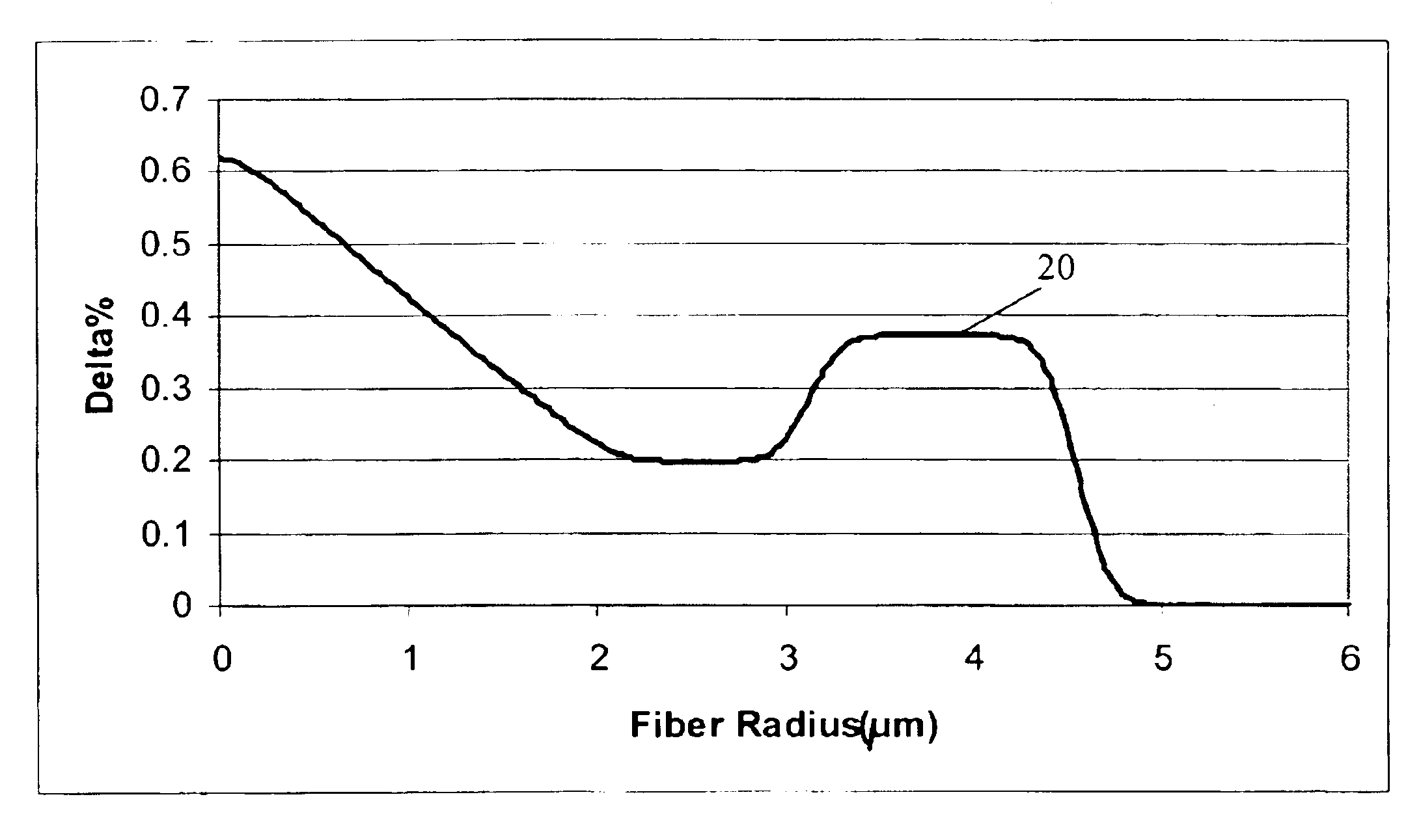
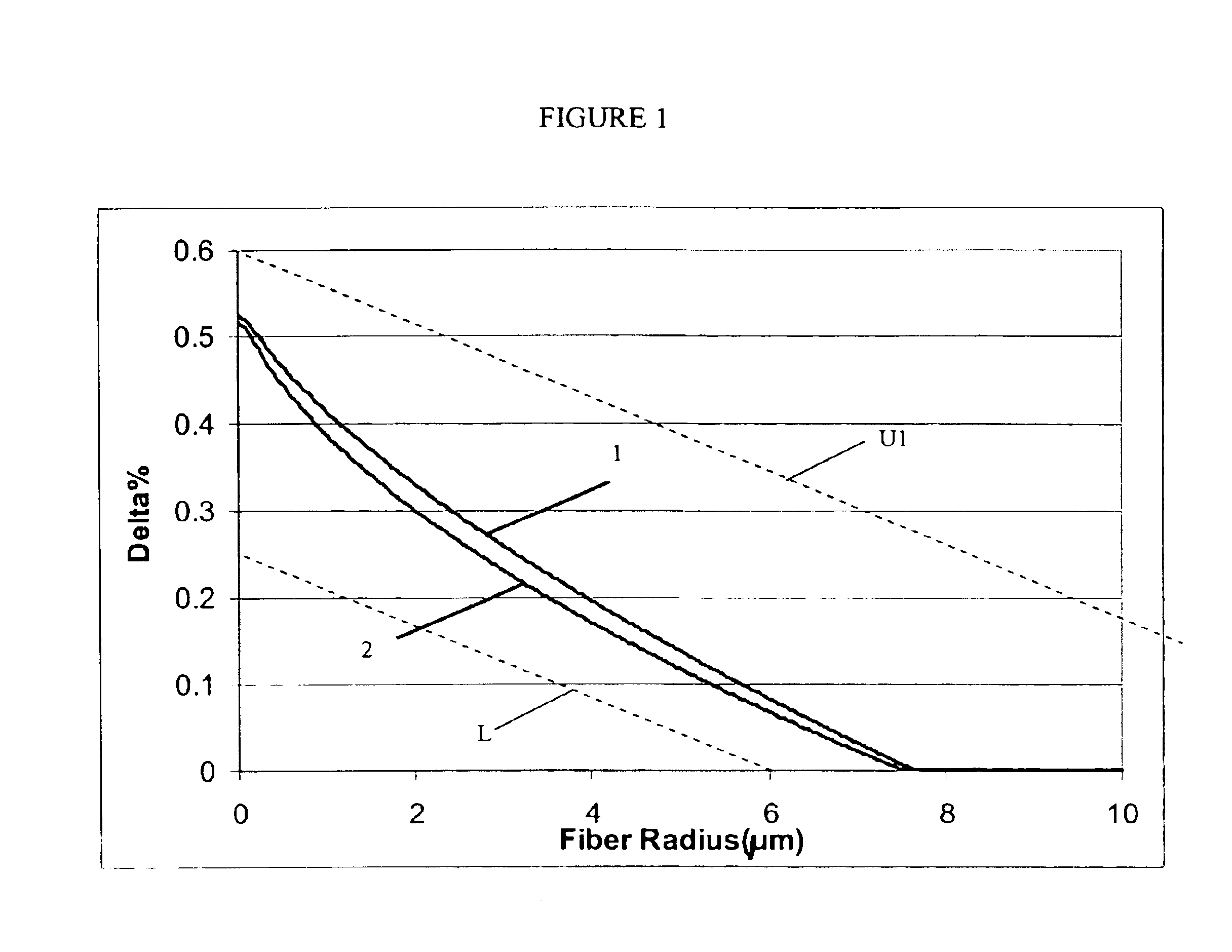
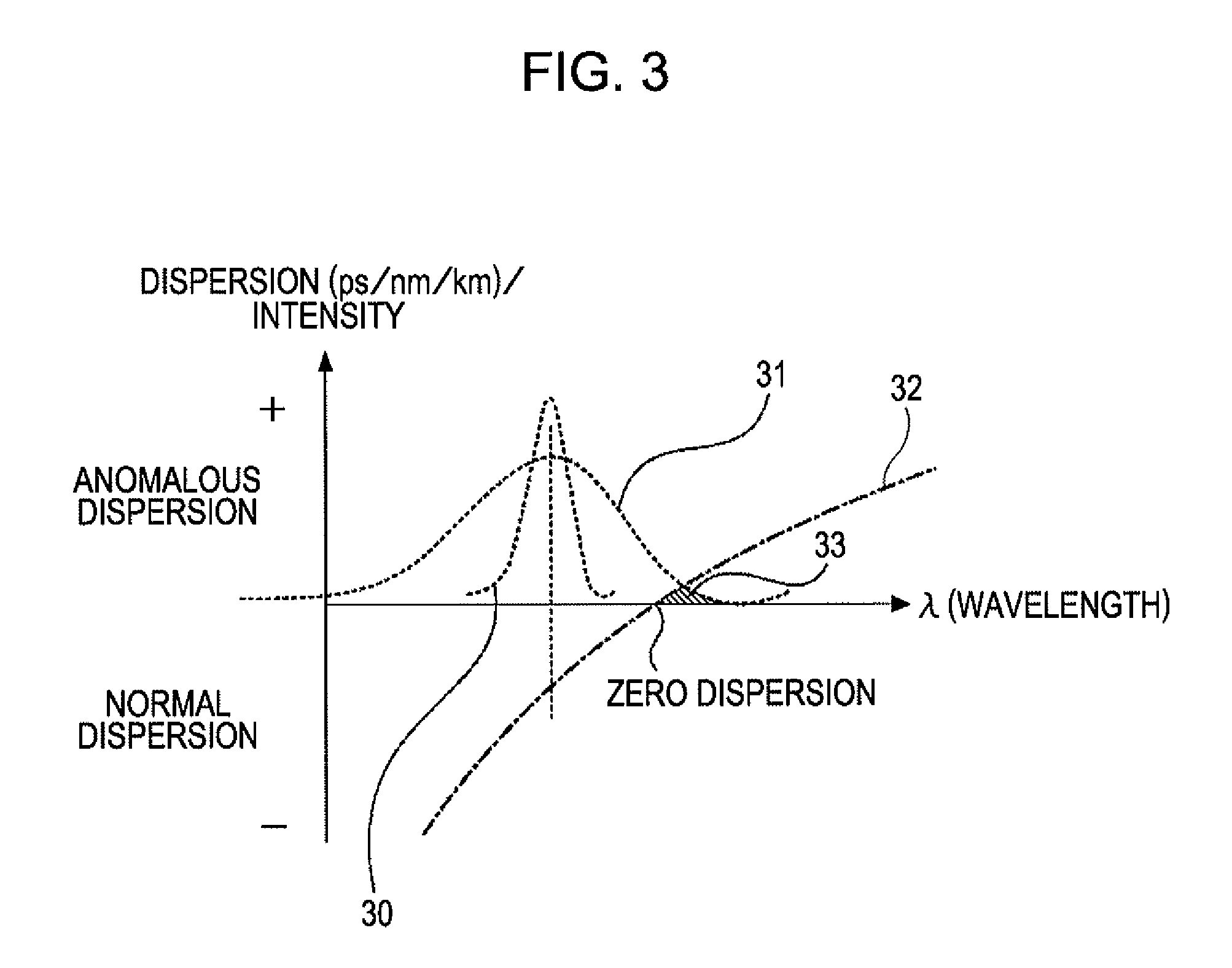
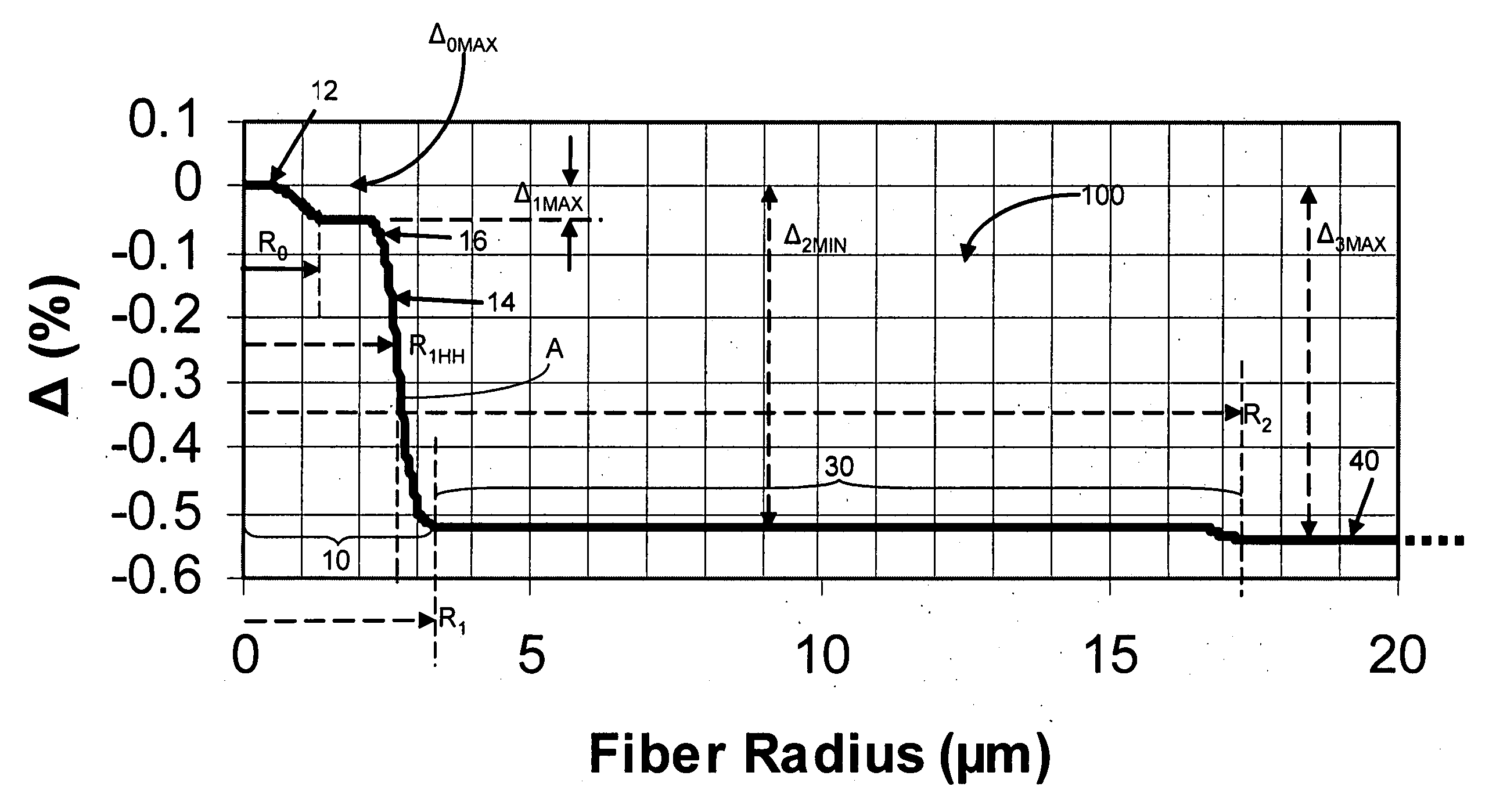
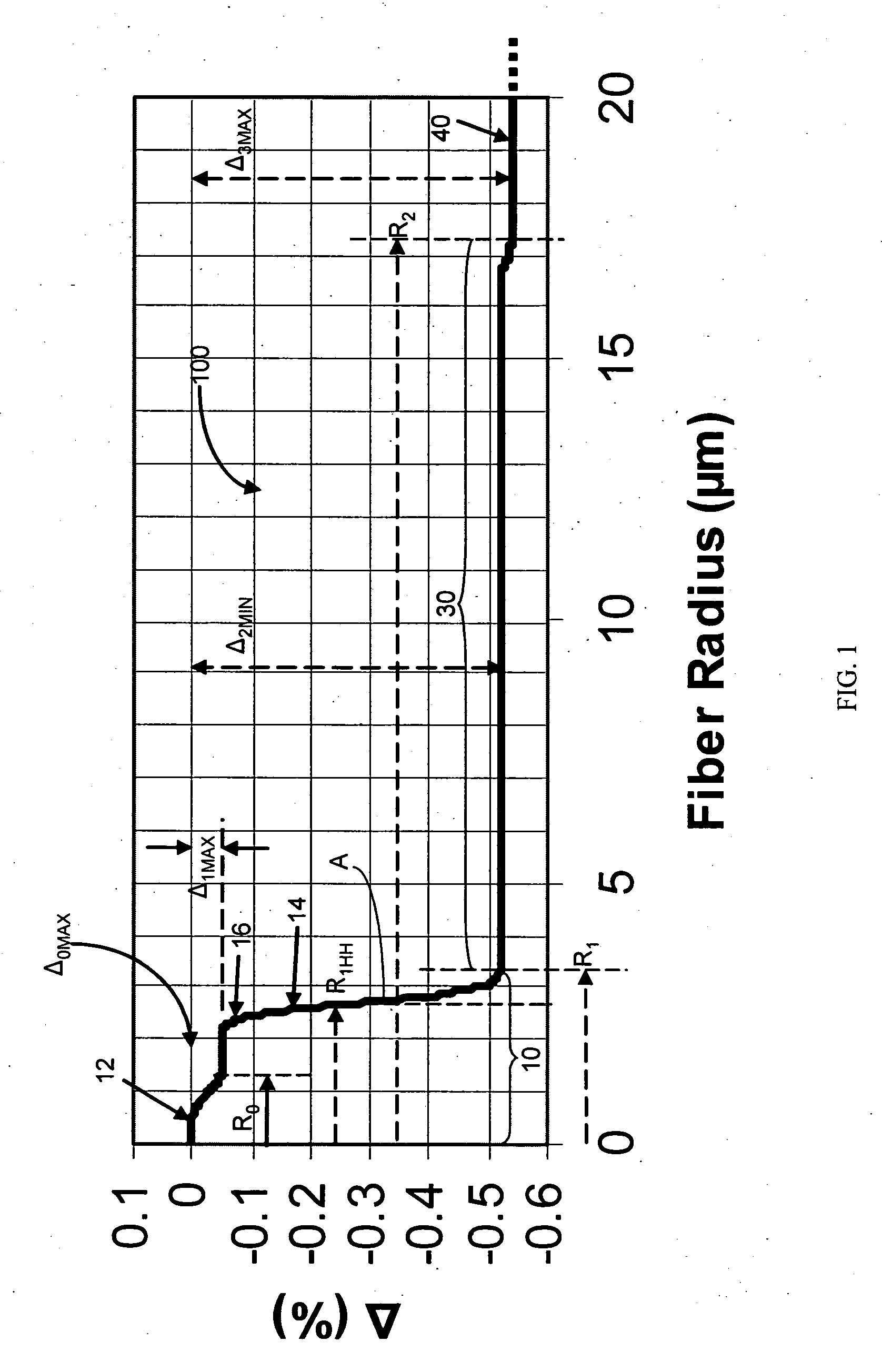
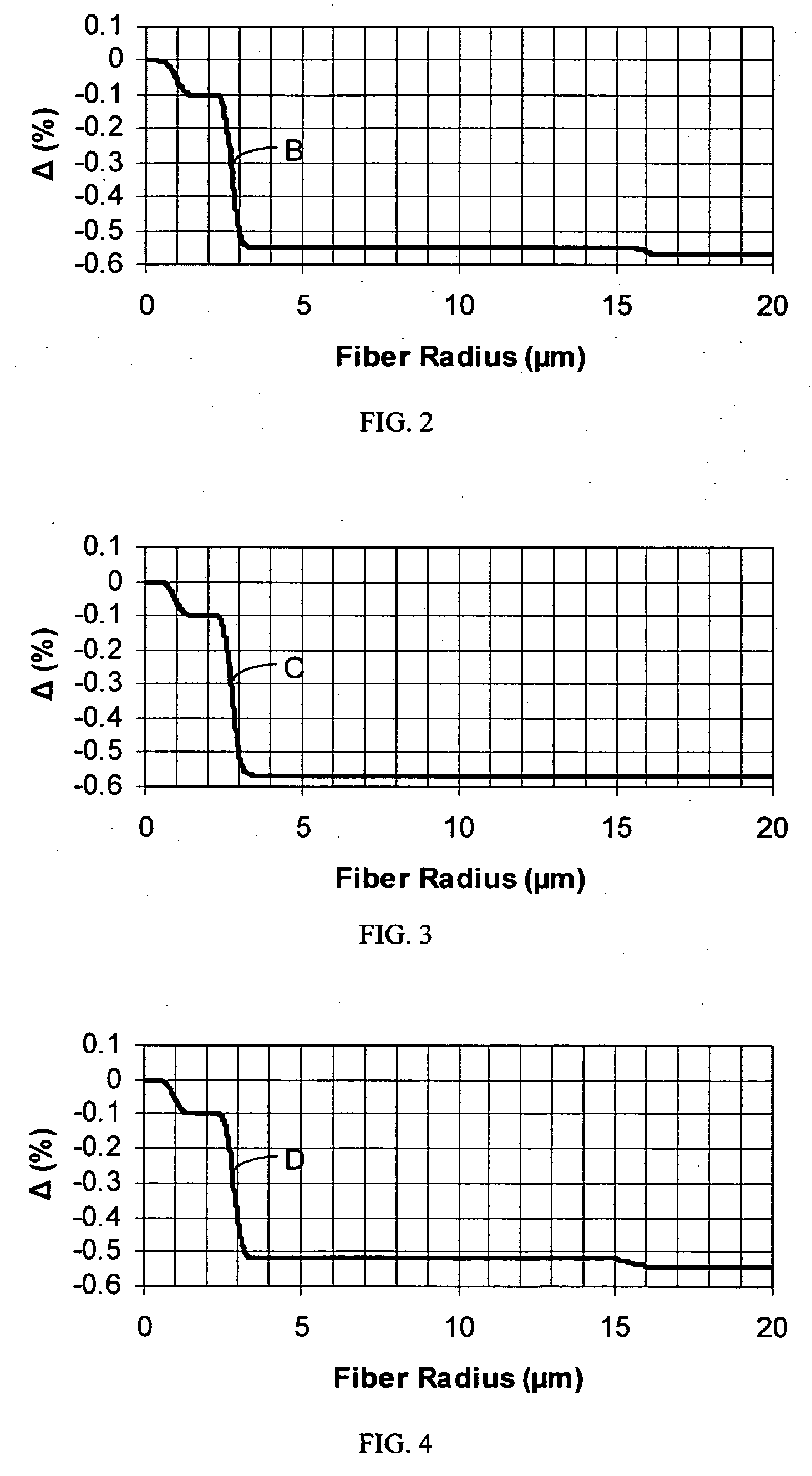
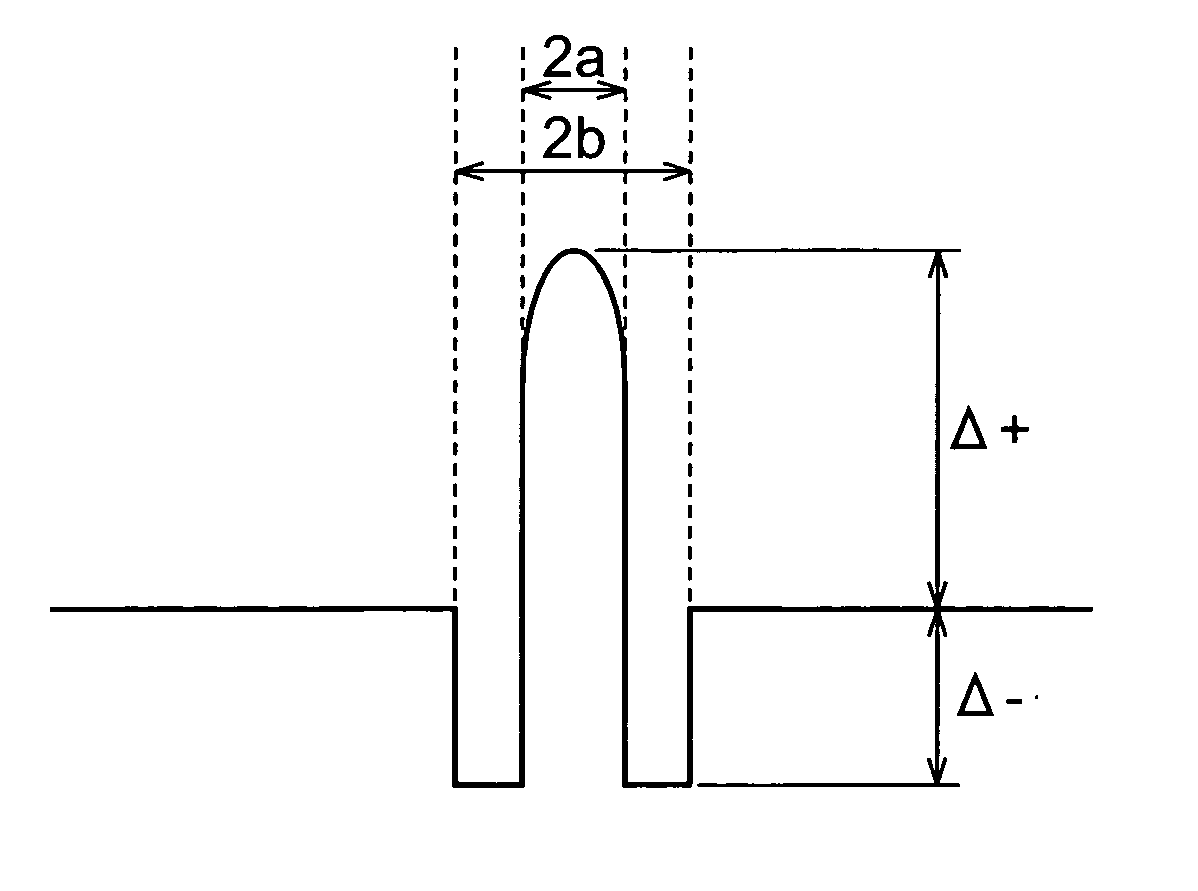
In a single-mode optical fiber, the zero-dispersion wavelength is the wavelength or wavelengths at which material dispersion and waveguide dispersion cancel one another. In all silica-based optical fibers, minimum material dispersion occurs naturally at a wavelength of approximately 1300 nm. Single-mode fibers may be made of silica-based glasses containing dopants that shift the material-dispersion wavelength, and thus, the zero-dispersion wavelength, toward the minimum-loss window at approximately 1550 nm. The engineering tradeoff is a slight increase in the minimum attenuation coefficient. Such fiber is called dispersion-shifted fiber.
Large effective area high SBS threshold optical fiber
ActiveUS20040218882A1Laser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingFiberZero-dispersion wavelength
An optical waveguide fiber having a high threshold for stimulated Brillouin scattering. The optical fiber preferably has large optical effective area, and further preferably has a low zero dispersion wavelength.
Owner:CORNING INC
Optical fiber containing alkali metal oxide
InactiveUS20080279515A1Bending loss can be improvedGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingDopantZero-dispersion wavelength
Disclosed is an optical fiber having a silica-based core comprising an alkali metal oxide a silica-based core, said core comprising an alkali metal oxide selected from the group consisting of K2O, Na2O, LiO2, Rb2O, Cs2O and mixtures thereof in an average concentration in said core between about 10 and 10000 ppm by weight, and a silica-based cladding surrounding and directly adjacent the core, the cladding including a region having a lower index of refraction than the remainder of such cladding. By appropriately selecting the concentration of alkali metal oxide dopant in the core and the cladding, a low loss optical fiber may be obtained which exhibits a cable cutoff less than 1400 nm chromatic dispersion at 1550 nm between about 13 and 19 ps / nm / km, and a zero dispersion wavelength less than about 1324 nm.
Owner:CORNING INC
Large effective area high SBS threshold optical fiber
ActiveUS6952519B2Suitable performanceLaser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingFiberZero-dispersion wavelength
An optical waveguide fiber having a high threshold for stimulated Brillouin scattering. The optical fiber preferably has large optical effective area, and further preferably has a low zero dispersion wavelength.
Owner:CORNING INC
Single-mode optical fiber
ActiveUS20070147756A1Small bending lossOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingZero-dispersion wavelengthLength wave
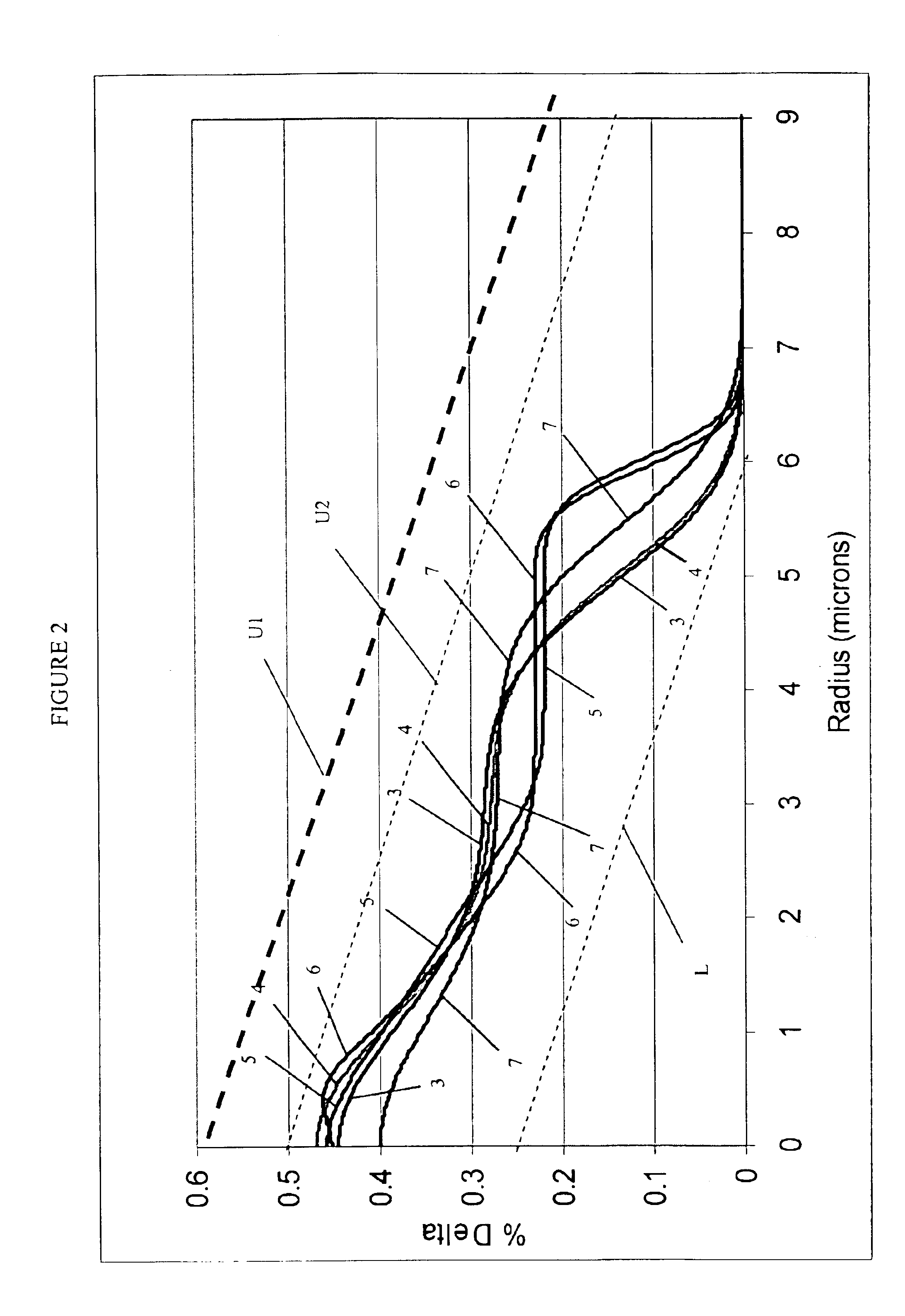
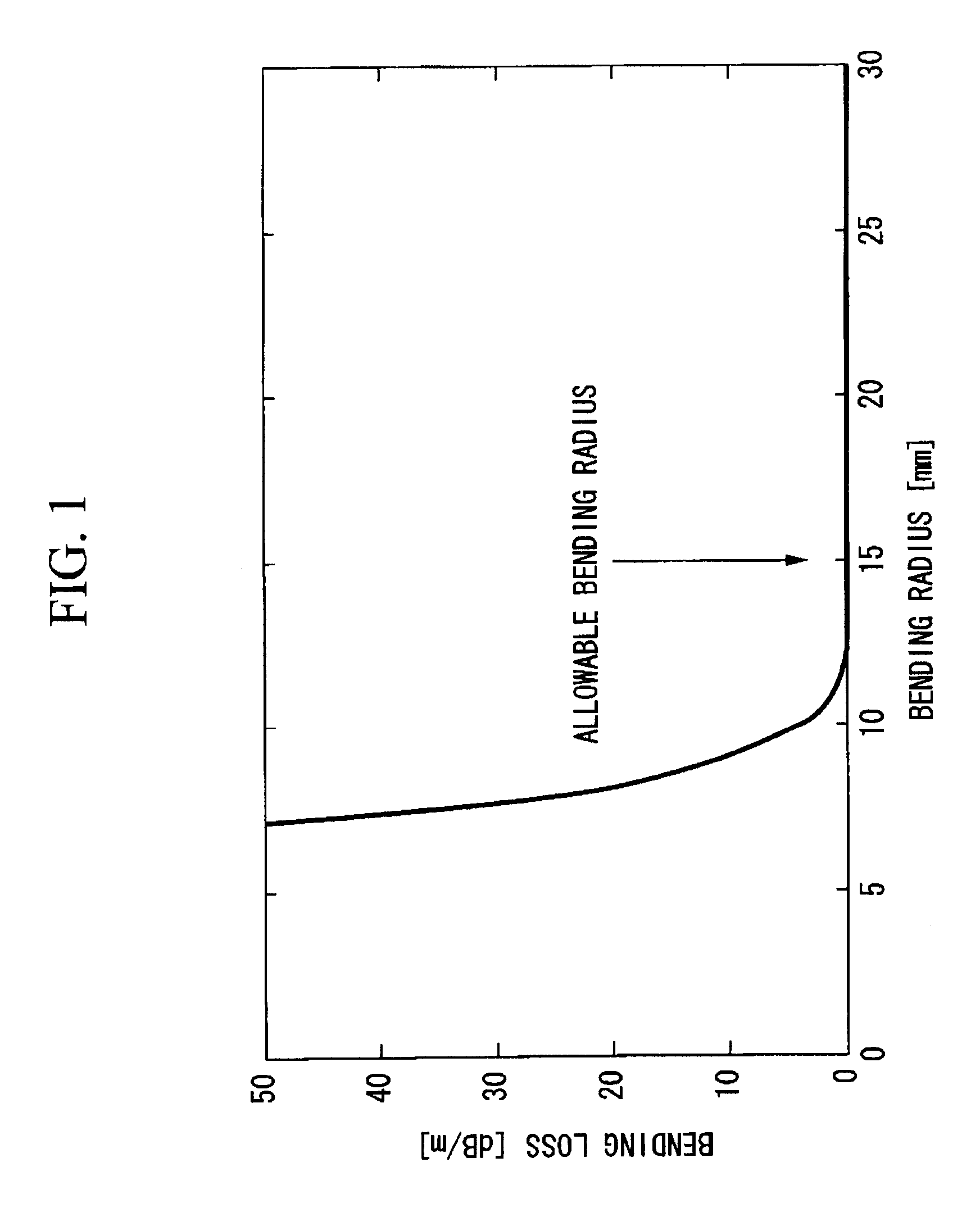
A single-mode optical fiber has a cut-off wavelength of 1260 nm or less, a zero-dispersion wavelength in the range of 1300 nm to 1324 nm, a zero-dispersion slope of 0.093 ps / nm2 / km or less, a mode field diameter at a wavelength of 1310 nm in the range of 5.5 μm to 7.9 μm, and a bending loss of 0.5 dB or less at a wavelength of 1550 nm, the bending loss being produced when the fiber is wound around a 10-mm radius for 10 turns.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
Optical fiber, method for manufacturing same and optical transmission channel
ActiveUS20050089289A1Glass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingZero-dispersion wavelengthTransmission channel
The present invention provides an optical fiber of which a zero dispersion wavelength falls within a range of between 1,250 nm and 1,350 nm inclusive, transmission loss at 1,550 nm is equal to or less than 0.185 dB / km, chromatic dispersion at 1,550 nm is within the range of 19±1 ps / nm·km, a dispersion slope at 1,550 nm is equal to or less than 0.06 ps / nm2·km, an effective area Aeff is equal to or more than 105 μm2, a cable cutoff wavelength λcc is equal to or less than 1,530 nm, polarization mode dispersion is equal to or less than 0.1 ps / km1 / 2, and a loss when the optical fiber is wound on a mandrel having an outer diameter of 20 mm is equal to or less than 10 dB / m.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Large effective area high SBS threshold optical fiber
ActiveUS7082243B2Suitable performanceGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFiberZero-dispersion wavelength
An optical waveguide fiber having a high threshold for stimulated Brillouin scattering. The optical fiber preferably has large optical effective area, and further preferably has a low zero dispersion wavelength.
Owner:CORNING INC
Optical fiber, method for manufacturing same and optical transmission channel
ActiveUS7095940B2Glass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingZero-dispersion wavelengthTransmission channel
The present invention provides an optical fiber of which a zero dispersion wavelength falls within a range of between 1,250 nm and 1,350 nm inclusive, transmission loss at 1,550 nm is equal to or less than 0.185 dB / km, chromatic dispersion at 1,550 nm is within the range of 19±1 ps / nm·km, a dispersion slope at 1,550 nm is equal to or less than 0.06 ps / nm2·km, an effective area Aeff is equal to or more than 105 μm2, a cable cutoff wavelength λcc is equal to or less than 1,530 nm, polarization mode dispersion is equal to or less than 0.1 ps / km1 / 2, and a loss when the optical fiber is wound on a mandrel having an outer diameter of 20 mm is equal to or less than 10 dB / m.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
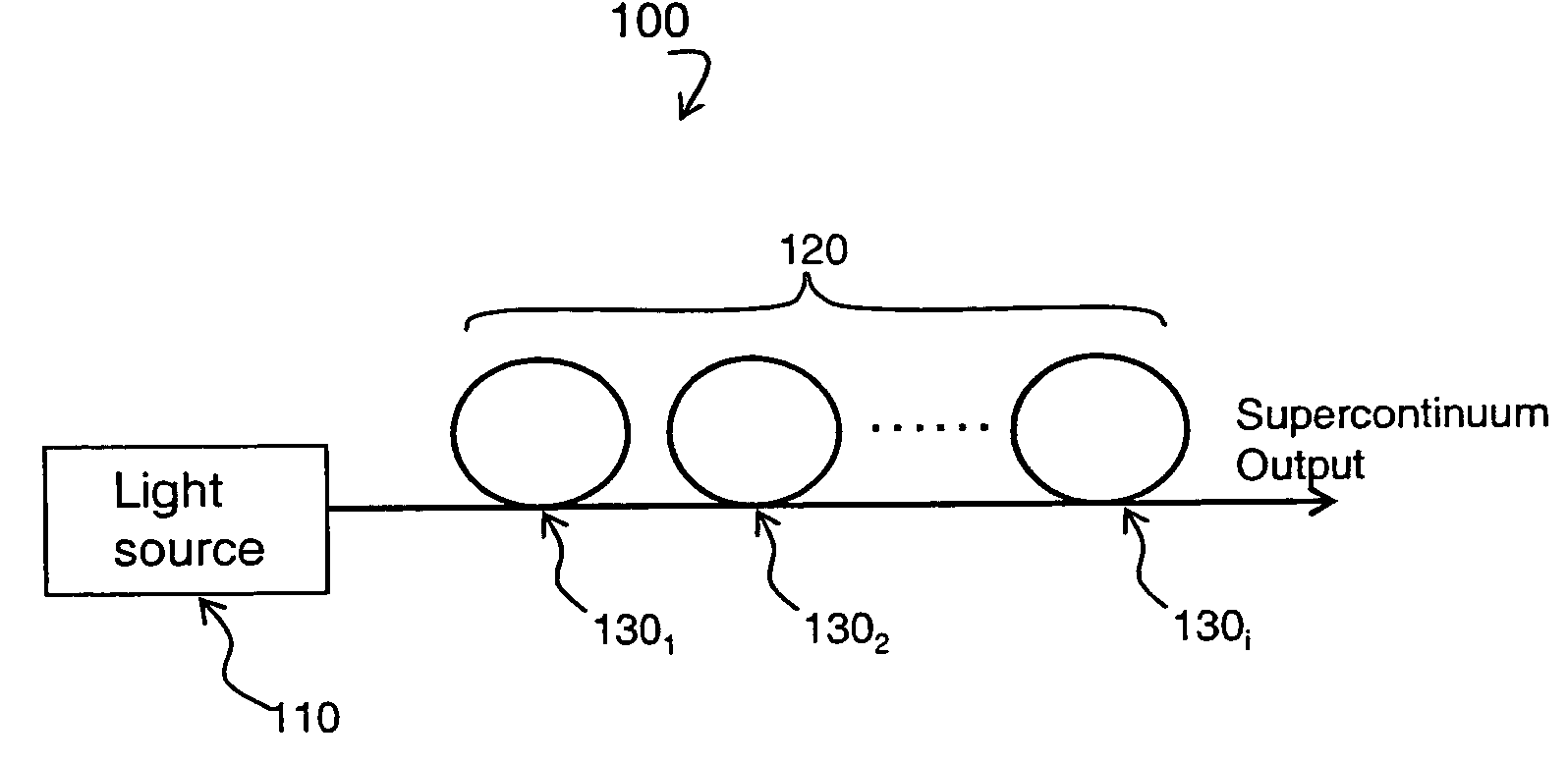
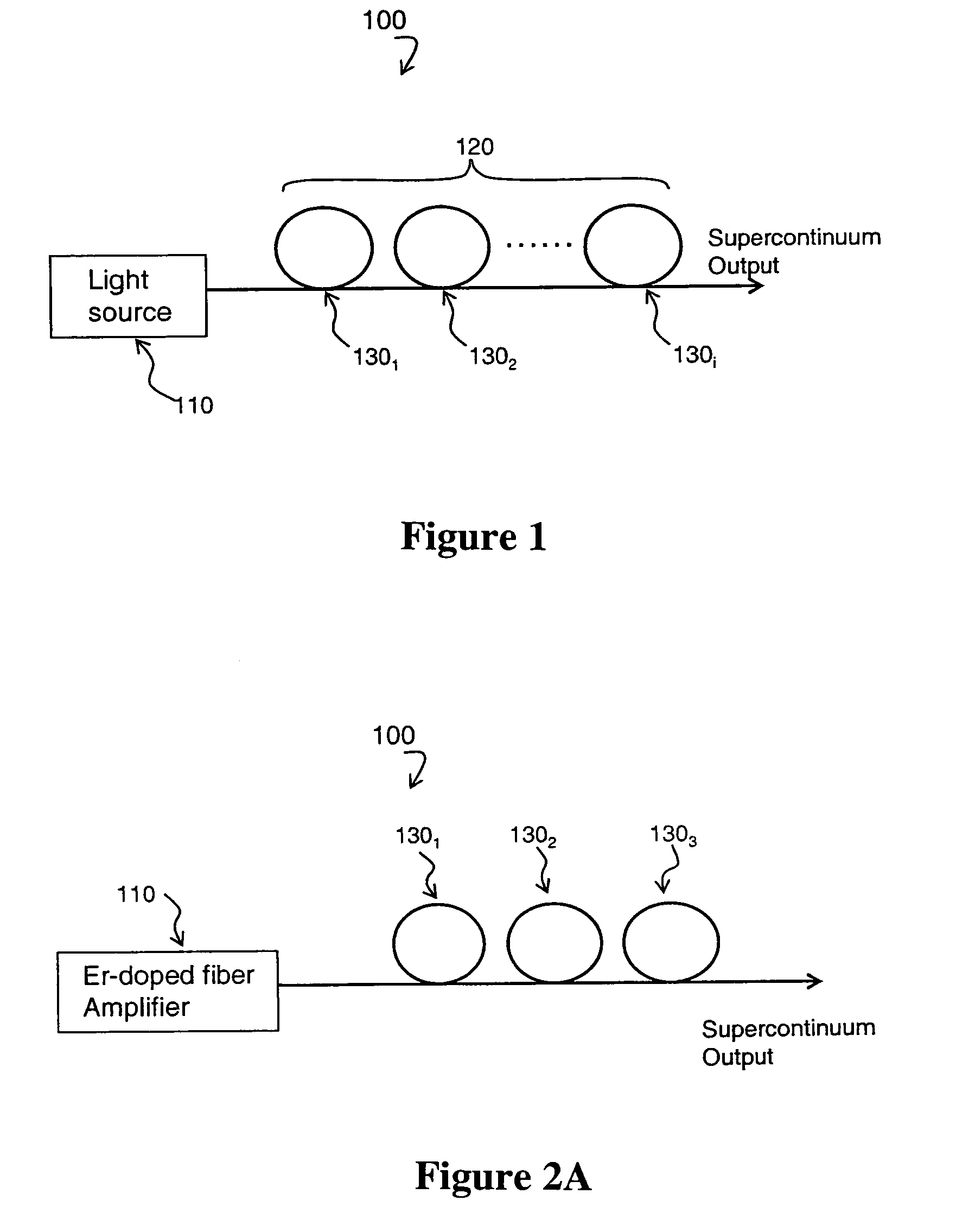
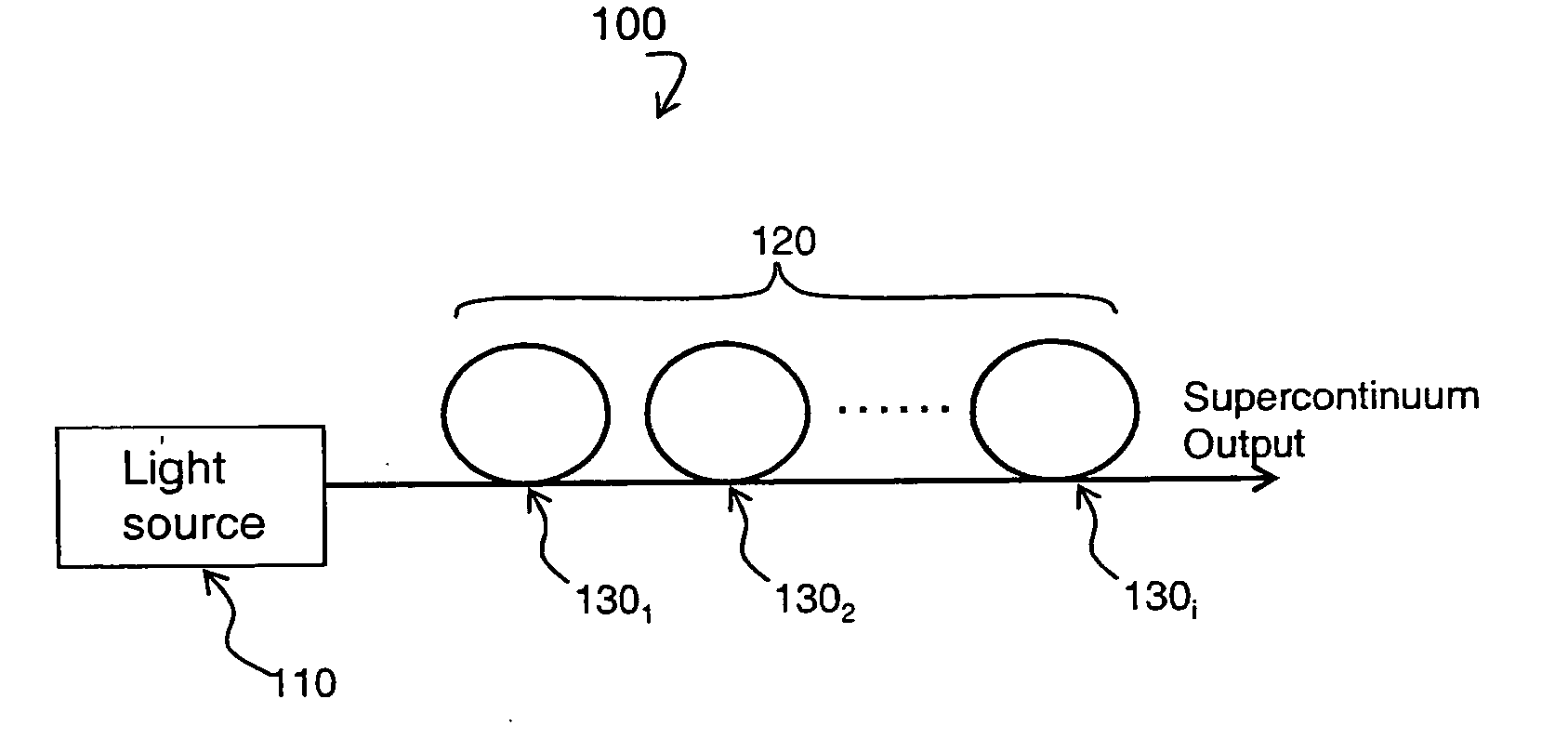
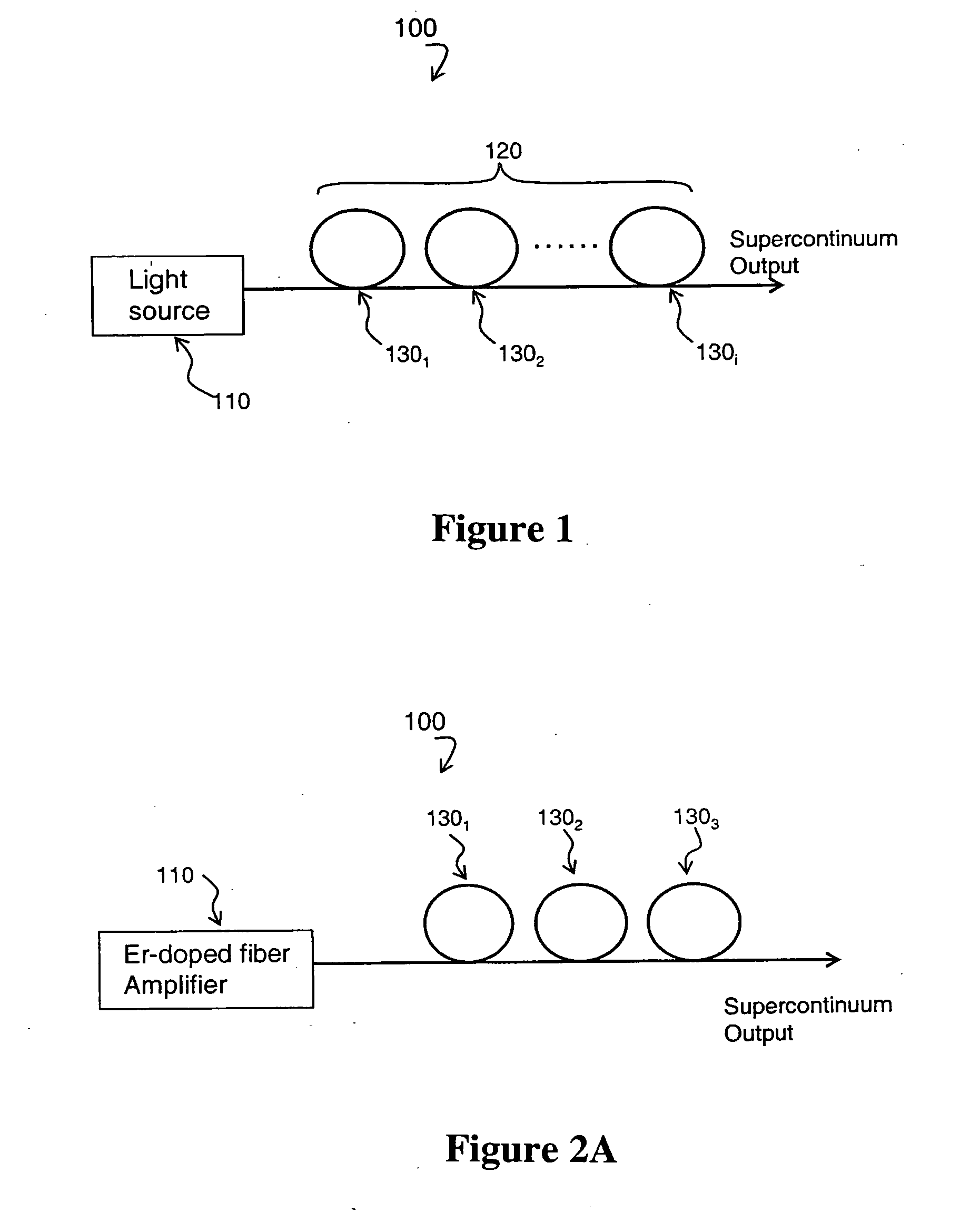
Supercontinuum emitting device
A supercontinuum light emitting device comprises an effectively CW light source producing light of wavelength λ1 within a specified bandwidth and a nonlinear fiber optically coupled to the light source. The nonlinear fiber has a plurality of fiber segments with different zero dispersion wavelengths λoi, where each successive fiber segment has zero dispersion wavelength λoi which is larger than the zero dispersion wavelength of the preceding fiber and the zero dispersion wavelength of the first fiber segment is within ±20 nm of λ1.
Owner:CORNING INC
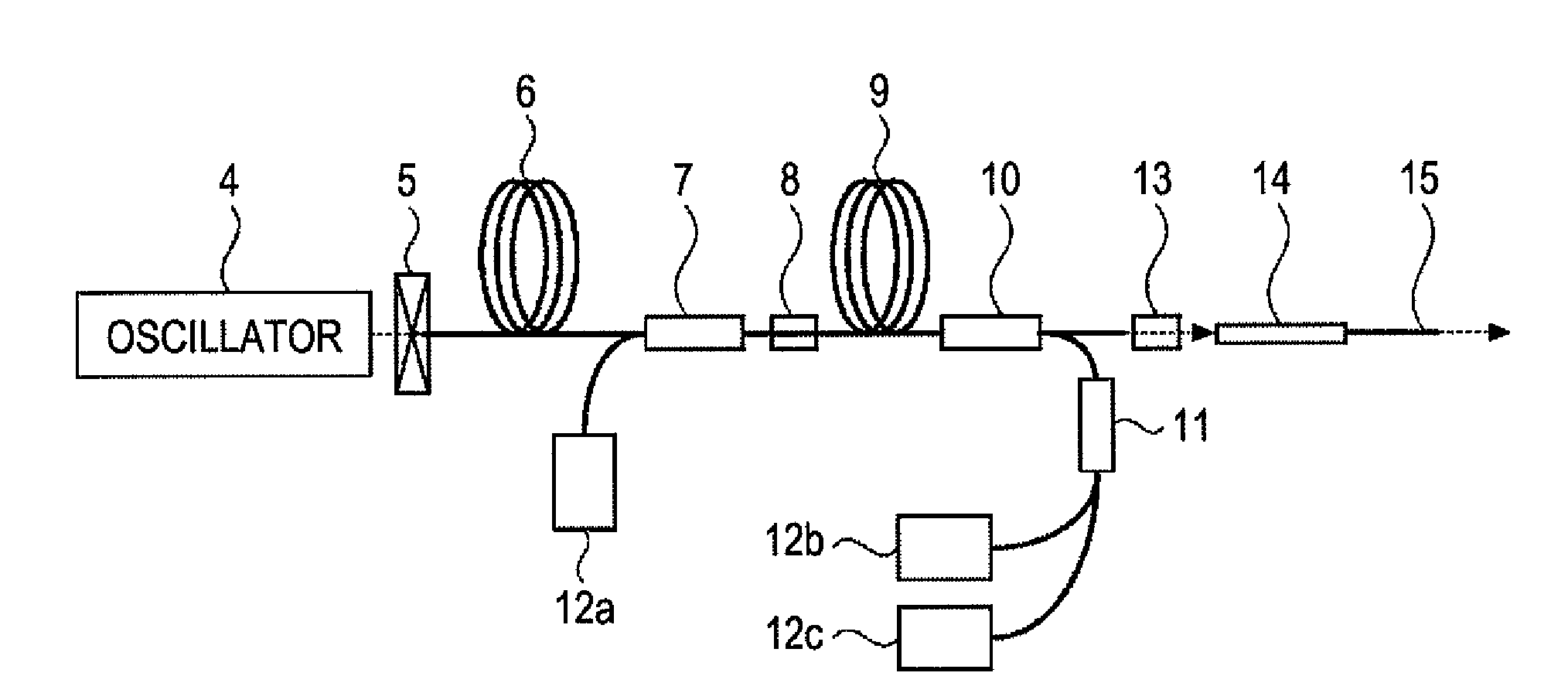
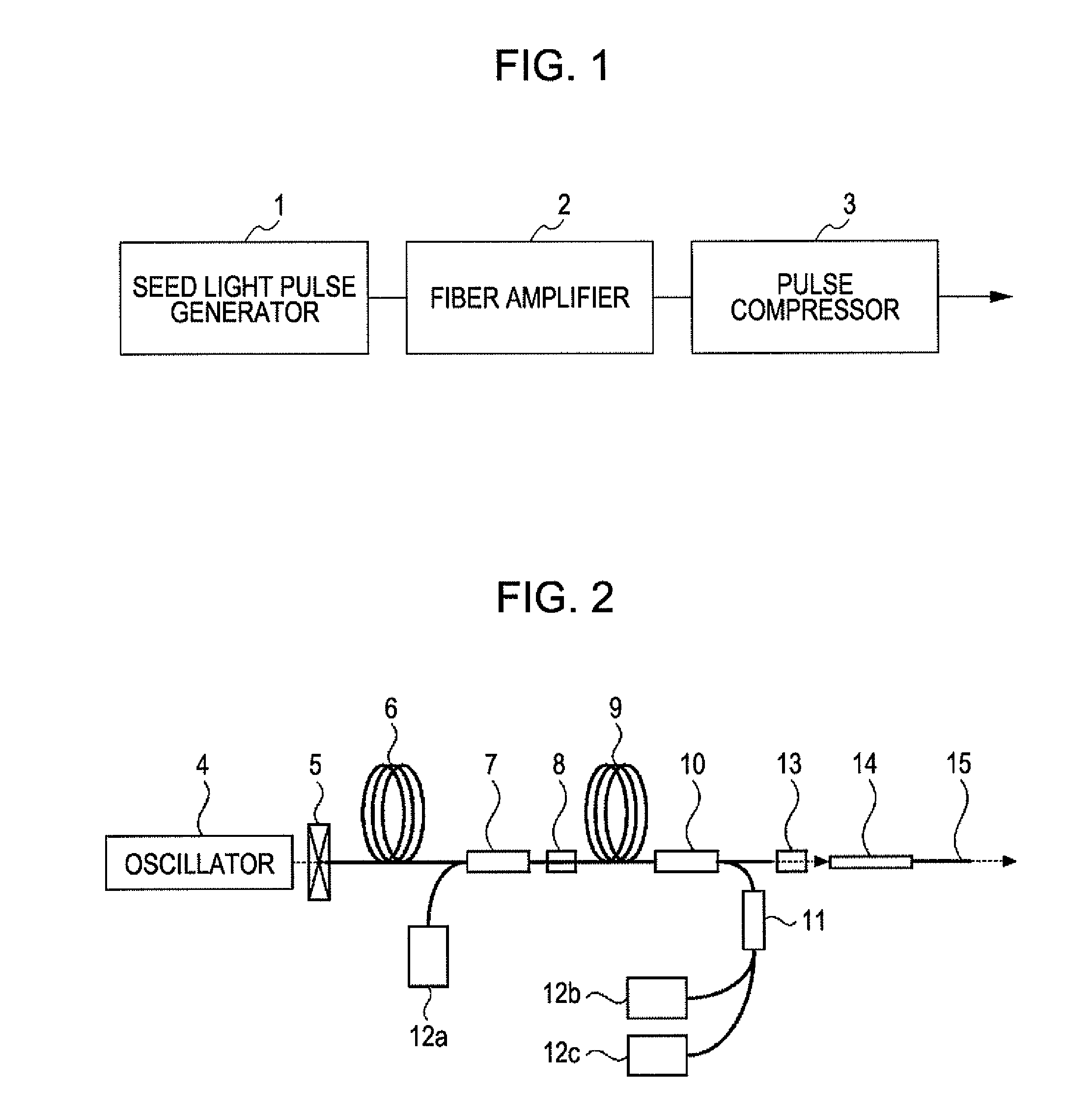
Pulse laser apparatus, terahertz measuring apparatus, and terahertz tomographic apparatus
InactiveUS20090213880A1Low generationLaser using scattering effectsSolid masersFiberZero-dispersion wavelength
A pulse laser apparatus includes a laser configured to generate a pulse of a laser beam, a fiber amplifier, and a pulse compressor. The fiber amplifier includes a rare-earth doped fiber that exhibits normal dispersion at a wavelength of the laser beam generated from the laser. The pulse laser apparatus further includes a unit configured to give a loss to energy portions in a wavelength region corresponding to a zero-dispersion wavelength of the rare-earth doped fiber and / or a wavelength region longer than the zero-dispersion wavelength within a wavelength spectrum of the laser beam having been chirped in the fiber amplifier.
Owner:CANON KK
Holey fiber
InactiveUS7693379B2Cladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideFiberZero-dispersion wavelength
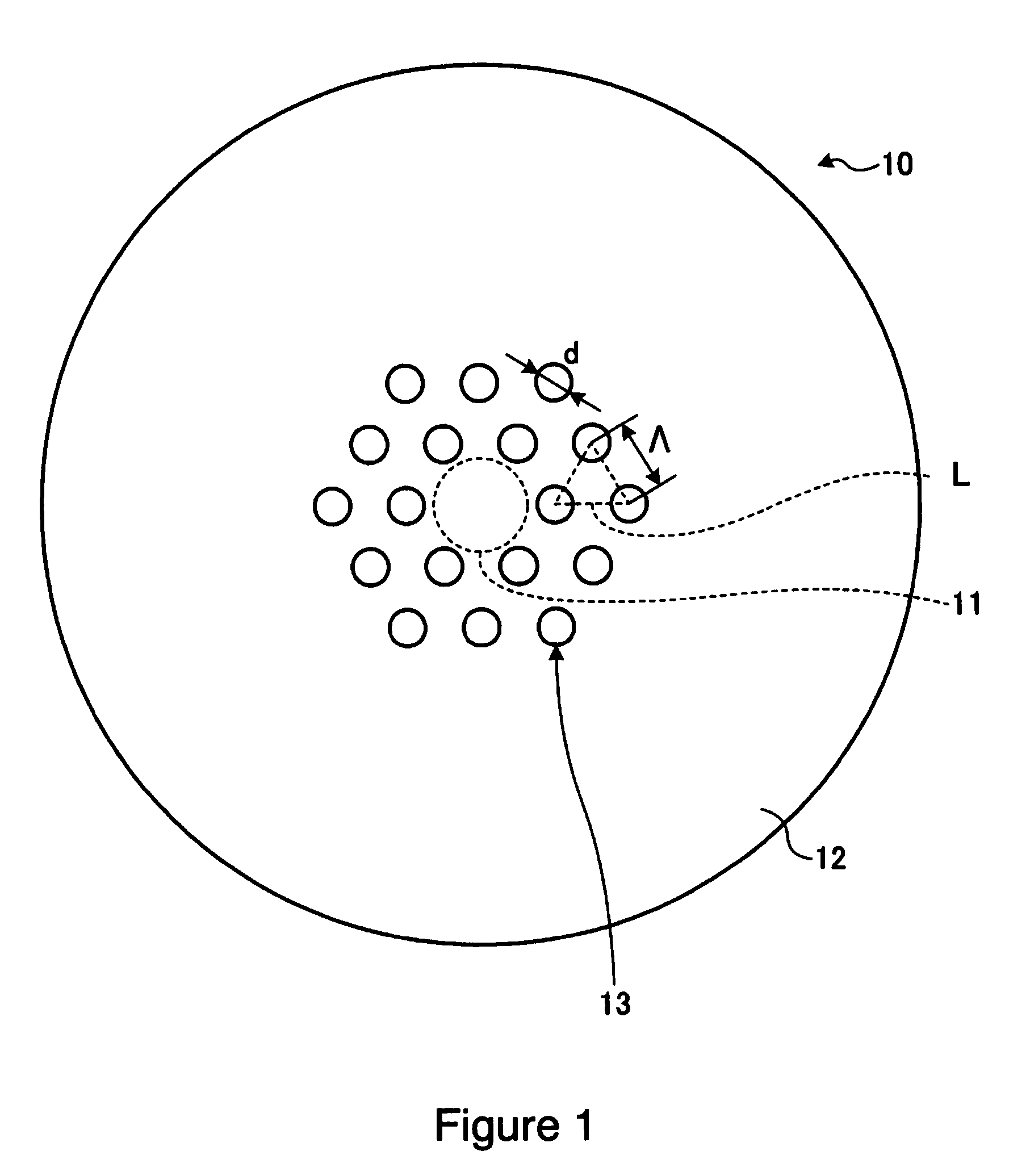
A holey fiber, which has a zero-dispersion wavelength of less than 700 nm and operates as single mode under its zero-dispersion wavelength, is provided. The holey fiber according to the present invention comprises a core region that is formed at a center of the holey fiber; and a cladding region, formed at the circumference of the core region, which has a plurality of holes distributed as triangle lattice around the core region; wherein the holey fiber has a fundamental mode of less than 700 nm, a higher order mode, and the fundamental mode and the higher order mode confinement losses of less than 0.1 dB / m and more than 10 dB / m, respectively, at the zero-dispersion wavelength.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Highly nonlinear optical fiber and highly nonlinear optical fiber module
ActiveUS7006742B2Glass optical fibreOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingMicrometerZero-dispersion wavelength
A highly nonlinear optical fiber includes a core, a cladding surrounding the core, and a coating covering the cladding. A bending loss at a wavelength of 1550 nanometers with a bending diameter of 20 millimeters is equal to or less than 0.01 dB / m. A nonlinear coefficient at the wavelength of 1550 nanometers is equal to or more than 10 W−1km−1. A cut-off wavelength is equal to or less than 1530 nanometers. A zero dispersion wavelength is in a range between 1400 nanometers and 1650 nanometers. A diameter of the coating is 125 micrometers with a tolerance of ±5 percent.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Bending insensitive optical fiber and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN1632628AGlass deposition burnersOptical light guidesZero-dispersion wavelengthRefractive index
This invention relates to a bending-insensitive single module optics fiber and its process method. Its wave-guide structure comprises core layer and cover layer. Its process adopts PCVD work that the materials are burned solid without the oxygen and Freon with different proportions to get the fiber. The fiber bending consumption lies between 1310nm wavelength and 1550nm wavelength relative to regular 0.652 fibers and its fiber module field diameter is 7í‚0.8ª–m and its zero color diffusion wavelength is near 1310nm.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD +1
Optical fiber and production method thereof
ActiveUS20060010921A1Add nonlinearityImprove efficiencyCladded optical fibreGlass fibre drawing apparatusFiberZero-dispersion wavelength
An optical fiber, which has a zero-material dispersion wavelength equal to or greater than 2 μm, and a high nonlinear susceptibility χ3 equal to or greater than 1×10−12 esu, and uses tellurite glass having sufficient thermal stability for processing into a low loss fiber, employs a PCF structure or HF structure having strong confinement into a core region. This enables light to propagate at a low loss. The size and geometry of air holes formed in the core region, and the spacing between adjacent air holes make it possible to control the zero dispersion wavelength within an optical telecommunication window (1.2-1.7 μm), and to achieve large nonlinearity with a nonlinear coefficient γ equal to or greater than 500 W−1 km−1.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
DWDM transport of CATV and digital signals over optical fiber in low-dispersion spectral regions
ActiveUS20070297801A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic network arrangementsZero-dispersion wavelengthLength wave
Methods and apparatus are described for DWDM transport of CATV and digital signals over optical fiber in low-dispersion spectral regions. A method includes transporting a plurality of optical carriers of different wavelengths over an optical link using wavelength division multiplexing, the optical link including a plurality of optical segments. The plurality of optical channel center wavelengths defined by the plurality of optical carriers are clustered proximate an average value of a zero-dispersion wavelength of the optical link, or near either a) a low wavelength edge or b) a high wavelength edge of a range of zero-dispersion wavelengths of the optical link and a plurality of optical channel center frequencies defined by the plurality of optical channel center wavelengths are non-uniformly spaced apart.
Owner:ARRIS SOLUTIONS LLC
Large effective area high sbs threshold optical fiber
ActiveUS20060039664A1Suitable performanceGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFiberZero-dispersion wavelength
An optical waveguide fiber having a high threshold for stimulated Brillouin scattering. The optical fiber preferably has large optical effective area, and further preferably has a low zero dispersion wavelength.
Owner:CORNING INC
Single-mode optical fiber
ActiveUS7440663B2Optical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingZero-dispersion wavelengthLength wave
A single-mode optical fiber has a cut-off wavelength of 1260 nm or less, a zero-dispersion wavelength in the range of 1300 nm to 1324 nm, a zero-dispersion slope of 0.093 ps / nm2 / km or less, a mode field diameter at a wavelength of 1310 nm in the range of 5.5 μm to 7.9 μm, and a bending loss of 0.5 dB or less at a wavelength of 1550 nm, the bending loss being produced when the fiber is wound around a 10-mm radius for 10 turns.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
Supercontinuum emitting device
A supercontinuum light emitting device comprises an effectively CW light source producing light of wavelength λ1 within a specified bandwidth and a nonlinear fiber optically coupled to the light source. The nonlinear fiber has a plurality of fiber segments with different zero dispersion wavelengths λoi, where each successive fiber segment has zero dispersion wavelength λoi which is larger than the zero dispersion wavelength of the preceding fiber and the zero dispersion wavelength of the first fiber segment is within ±20 nm of λ1.
Owner:CORNING INC
Wide-band dispersion controlled optical fiber
ActiveUS7003205B2Laser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingShortest distanceZero-dispersion wavelength
Disclosed is a wide-band dispersion controlled optical fiber. The optical fiber enables the use of optical signals in various wavelength regions in a wavelength division multiplexing mode communication network by controlling the position of the zero dispersion wavelength, and enables long distance transmission by controlling dispersion slope and bending loss. Furthermore, there is an advantage in that the optical fiber enables not only short distance transmission but also middle / long distance transmission using a single type of optical fiber because the optical fiber is controlled to have negative dispersion values in the O-band wavelength region and positive dispersion values with small deviations in the C-band and L-band wavelength regions.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optical frequency up-conversion of femtosecond pulses into targeted single bands in the visible and ultraviolet
An apparatus and methods for generating a substantially supercontinuum-free widely-tunable multimilliwatt source of radiation characterized by a narrowband line profile. The apparatus and methods employ nonlinear optical mechanisms in a nonlinear photonic crystal fiber (PCF) by detuning the wavelength of a pump laser to a significant extent relative to the zero-dispersion wavelength (ZDW) of the PCF. Optical phenomena employed for the selective up-conversion in the PCF include, but are not limited to, four-wave mixing and Cherenkov radiation. Tunability is achieved by varying pump wavelength and power and by substituting different types of PCFs characterized by specified dispersion properties.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Optical amplifier, optical amplifying system, wavelength converter, optical amplification method, and optical communication system
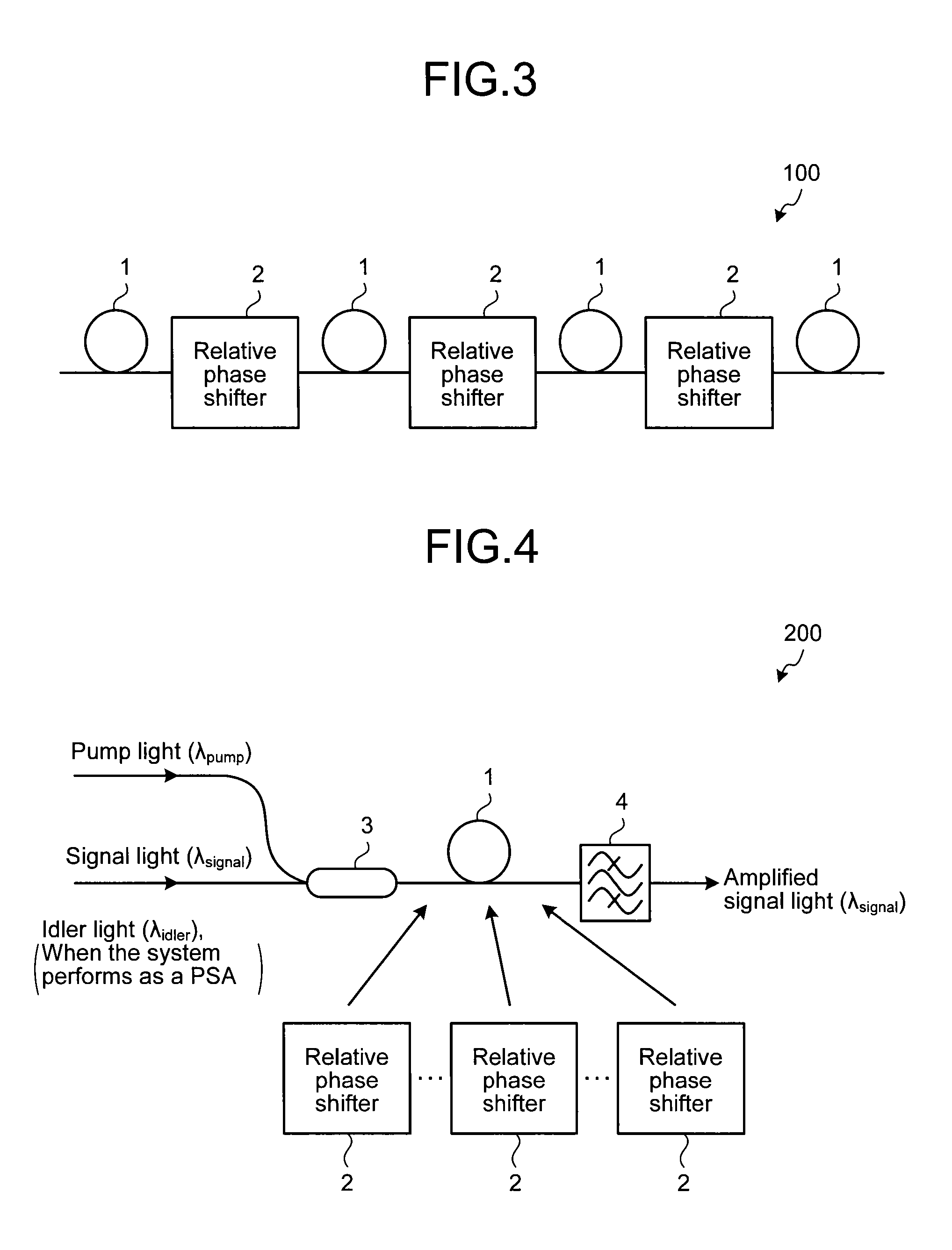
ActiveUS20140043674A1Solve problemsImprove flatnessLaser detailsFibre transmissionFiberZero-dispersion wavelength
An optical amplifier includes an optical gain fiber into which signal light and pump light are input and at least one relative phase shifter is inserted. Preferably, the relative phase shifter is inserted so that the relative phase in the lengthwise direction of the optical gain fiber falls within a predetermined range containing 0.5 Π. Preferably, the optical gain fiber is a highly non-linear optical fiber having a non-linearity constant of at least 10 / W / km. Preferably, the dispersion of the optical gain fiber is within the range from −1 ps / nm / km to 1 ps / nm / km in an amplification band. Preferably, the absolute value of the dispersion slope of the optical gain fiber at a zero dispersion wavelength is no greater than 0.05 ps / nm2 / km.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Optical fiber containing alkali metal oxide
InactiveUS7844155B2Bending loss can be improvedGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingDopantZero-dispersion wavelength
Disclosed is an optical fiber having a silica-based core comprising an alkali metal oxide a silica-based core, said core comprising an alkali metal oxide selected from the group consisting of K2O, Na2O, Li2O, Rb2O, Cs2O and mixtures thereof in an average concentration in said core between about 10 and 10000 ppm by weight, and a silica-based cladding surrounding and directly adjacent the core, the cladding including a region having a lower index of refraction than the remainder of such cladding. By appropriately selecting the concentration of alkali metal oxide dopant in the core and the cladding, a low loss optical fiber may be obtained which exhibits a cable cutoff less than 1400 nm chromatic dispersion at 1550 nm between about 13 and 19 ps / nm / km, and a zero dispersion wavelength less than about 1324 nm.
Owner:CORNING INC
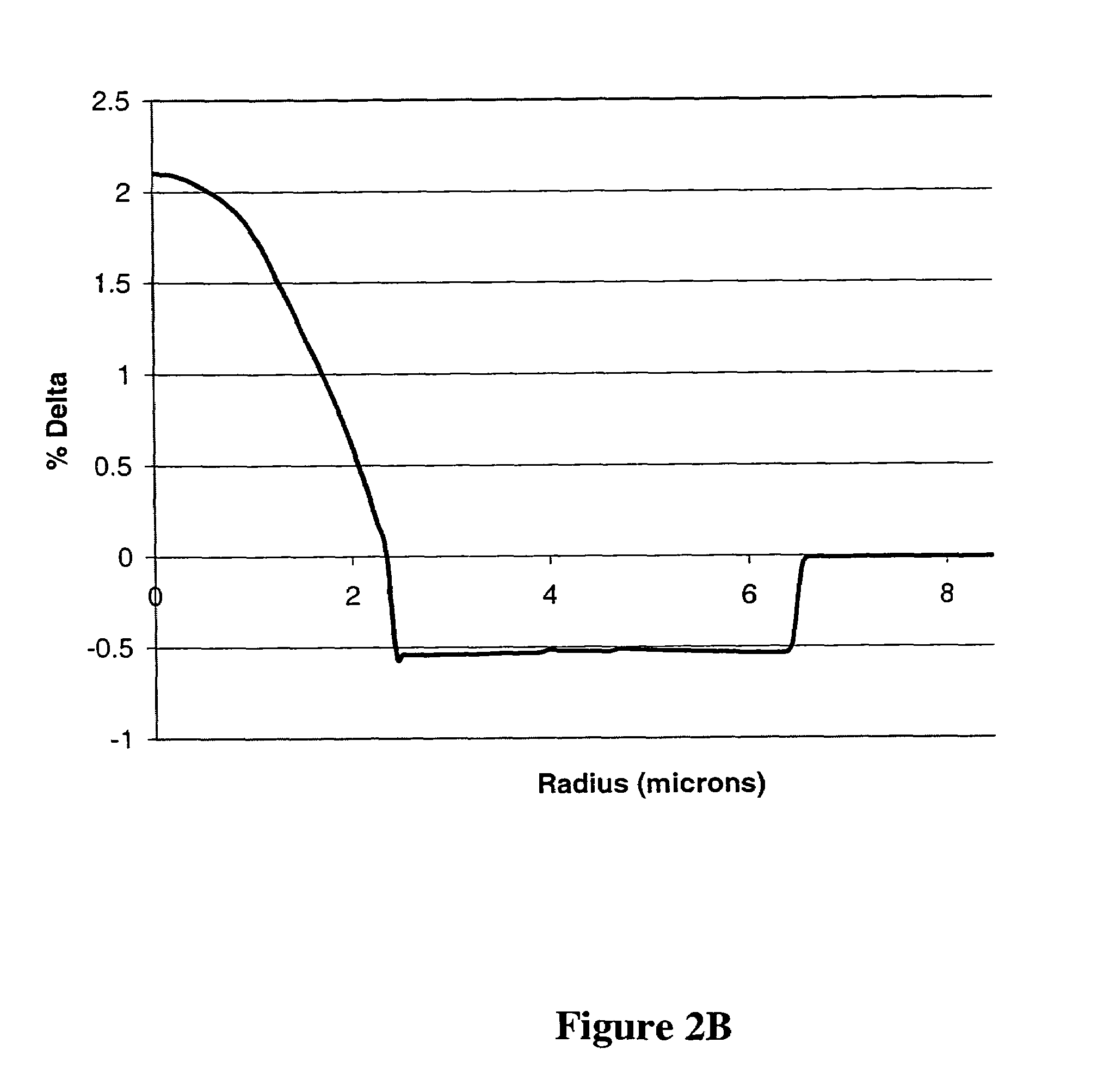
Optical fiber
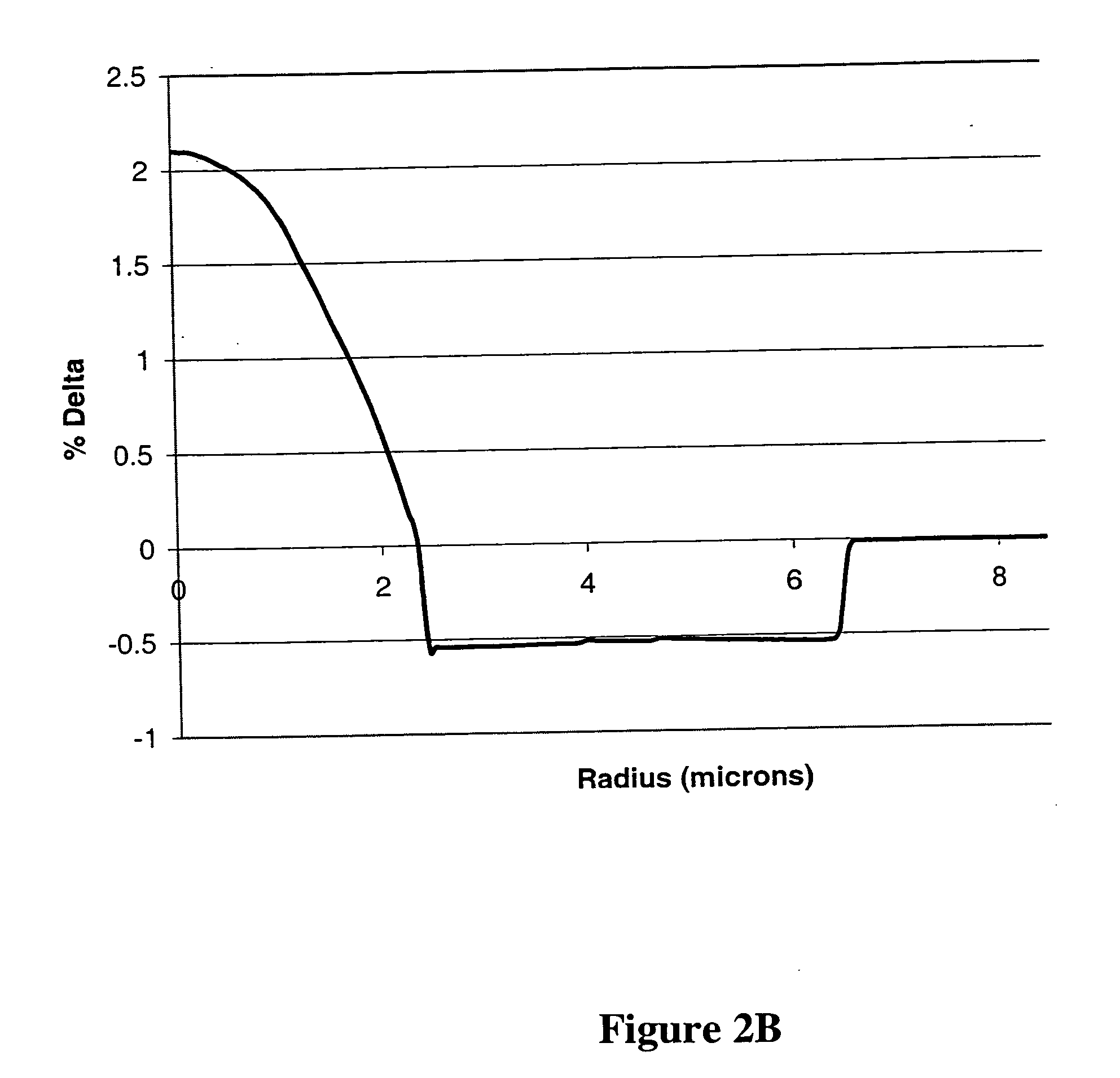
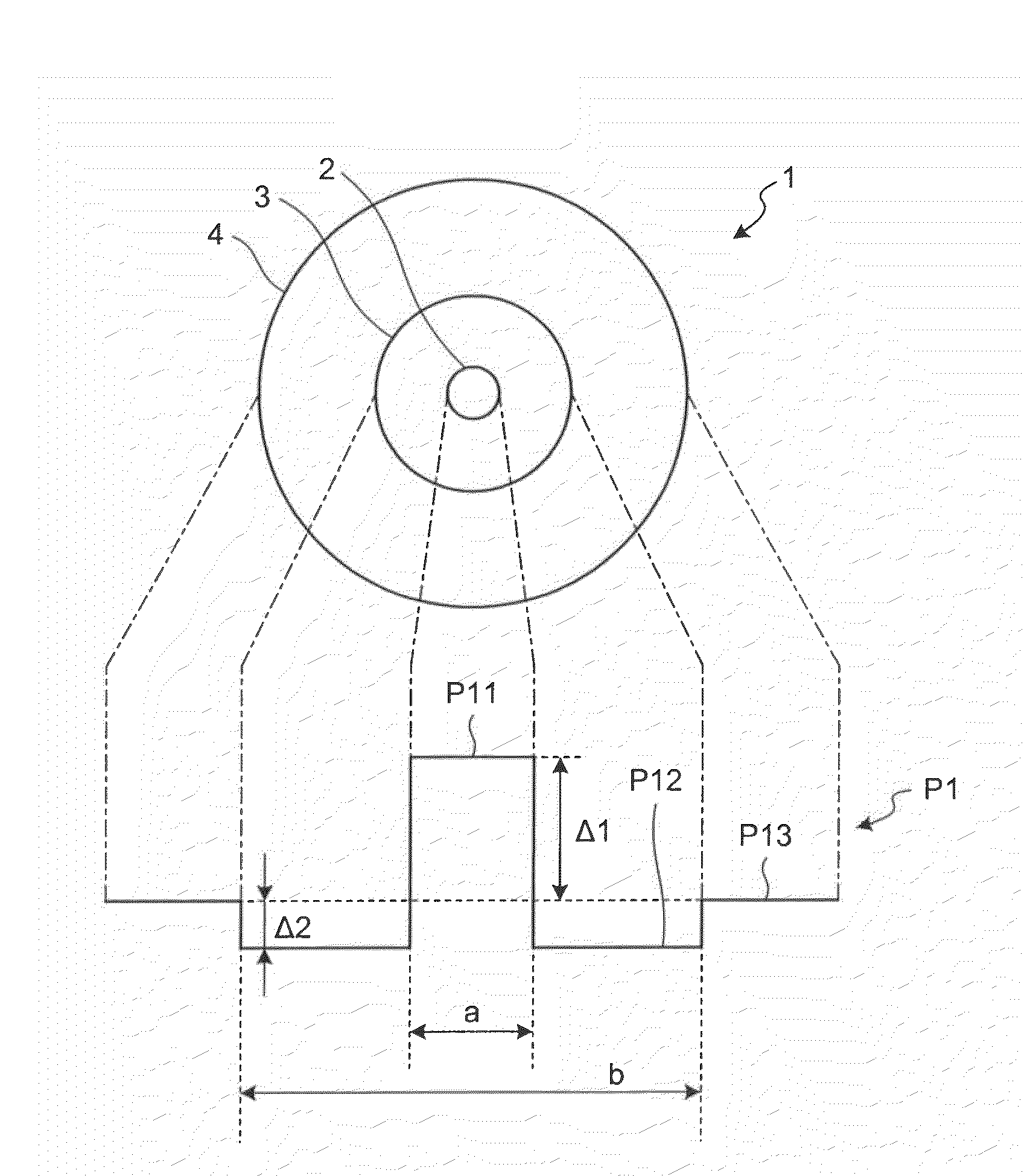
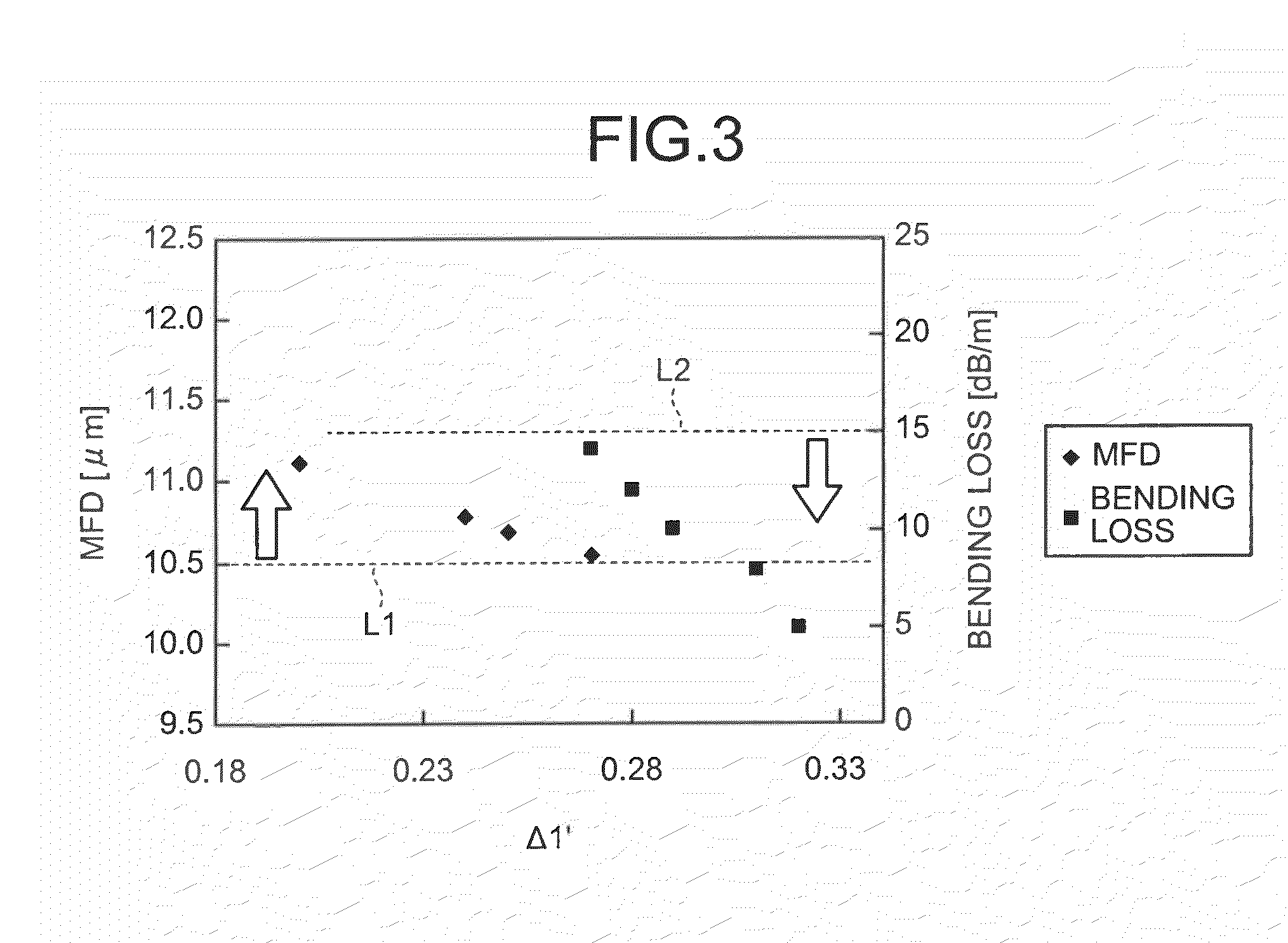
ActiveUS20090263091A1Optical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideZero-dispersion wavelengthRelative refractive index
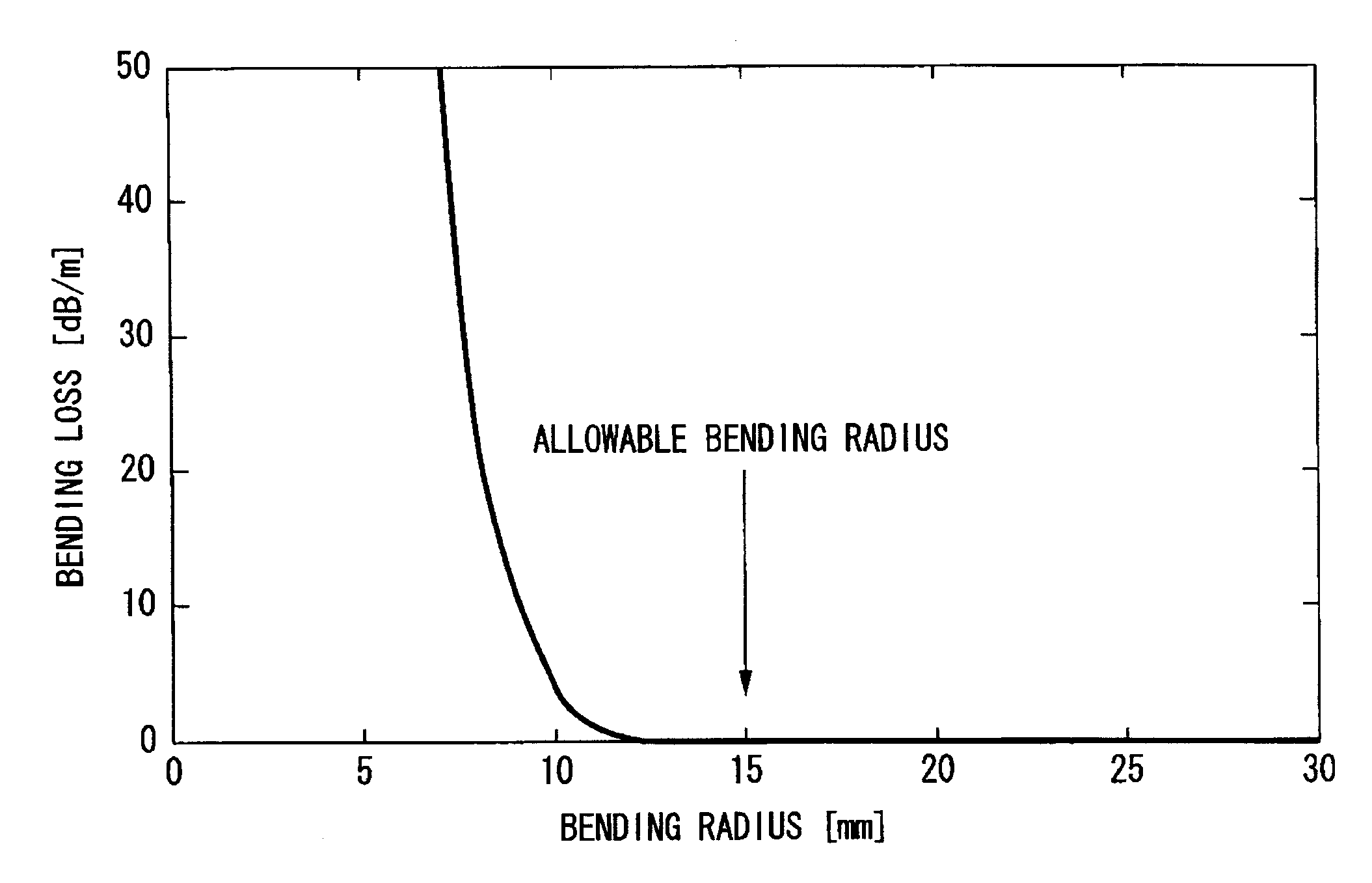
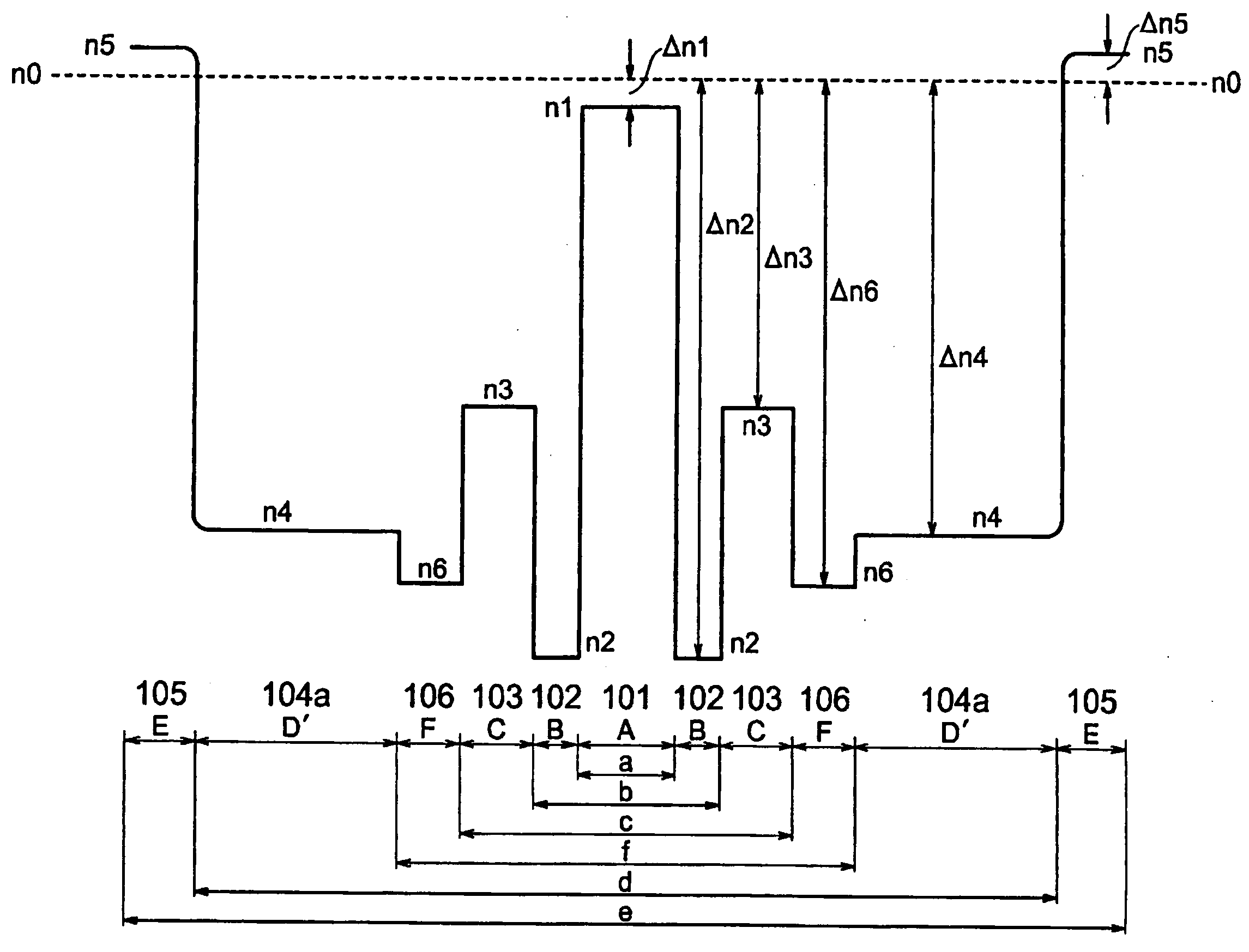
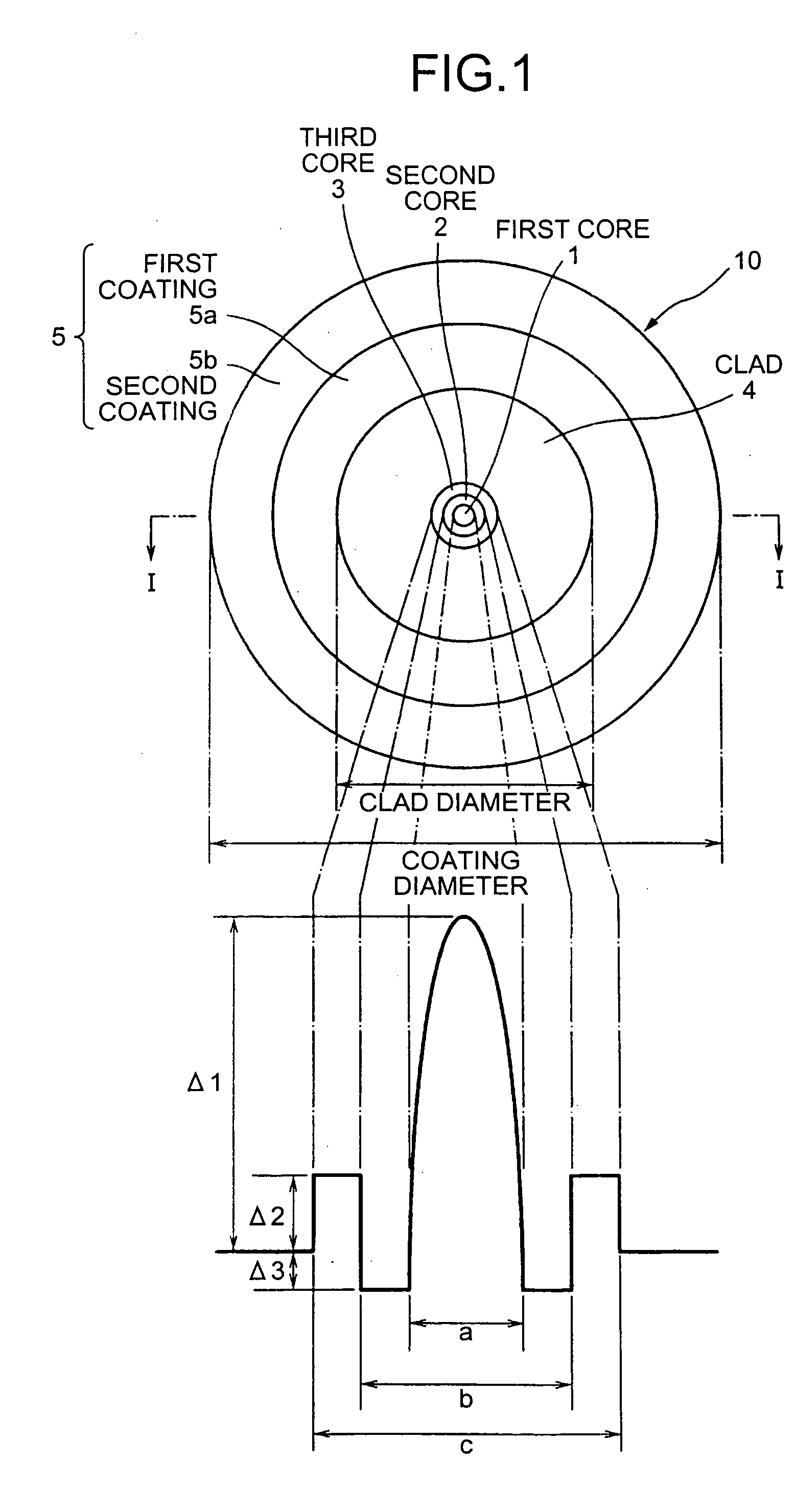
A relative refractive index difference Δ1 between a center core region and a cladding layer is 0.30% to 0.35%, a relative refractive index difference Δ2 between an outer core layer and the cladding layer is −0.10% to −0.04%, and Δ1:Δ2 is 2.5:1 to 7.5:1. A diameter of the center core region is 9.0 μm to 10.5 μm, and a ratio of diameters of the center core region and the outer core layer is 0.20 to 0.35. A cutoff wavelength is 1310 nm or shorter, a zero dispersion wavelength is 1285 nm to 1345 nm, and at a wavelength of 1550 nm, an MFD is 10.5 μm or larger, a transmission loss is 0.185 dB / km or lower, and a bending loss is 15 dB / m or lower.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Low attenuation non-zero dispersion shifted optical fiber
InactiveUS20070116418A1Suitable performanceOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideFiberUltrasound attenuation
An optical waveguide fiber having a zero-dispersion wavelength less than 1450 nm, a dispersion slope at a wavelength of 1550 of less than 0.06 ps / nm2 / km nm, and attenuation at a wavelength of 1550 nm less than 0.190 dB / km. Optical fibers are disclosed that exhibit an effective area at a wavelength of 1550 nm of greater than 50 μm2, and dispersion at a wavelength of 1550 nm between 5 and 15 ps / nm-km.
Owner:CORNING INC
Optical fiber for long-distance optical communication network
InactiveUS7120341B2Optical fibre with multilayer core/claddingWavelength-division multiplex systemsZero-dispersion wavelengthWavelength band
An optical fiber for long-distance optical communication networks has a zero dispersion wavelength value in the range of 1560 to 1570 nm and a dispersion gradient value, at a wavelength band of 1550 nm, in the range of 0.055 to 0.075 ps / nm2 / km.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optical fiber and optical device using the same
ActiveUS20070053641A1Easy to adjust dispersion characteristicReduce the valueLaser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingZero-dispersion wavelengthComputational physics
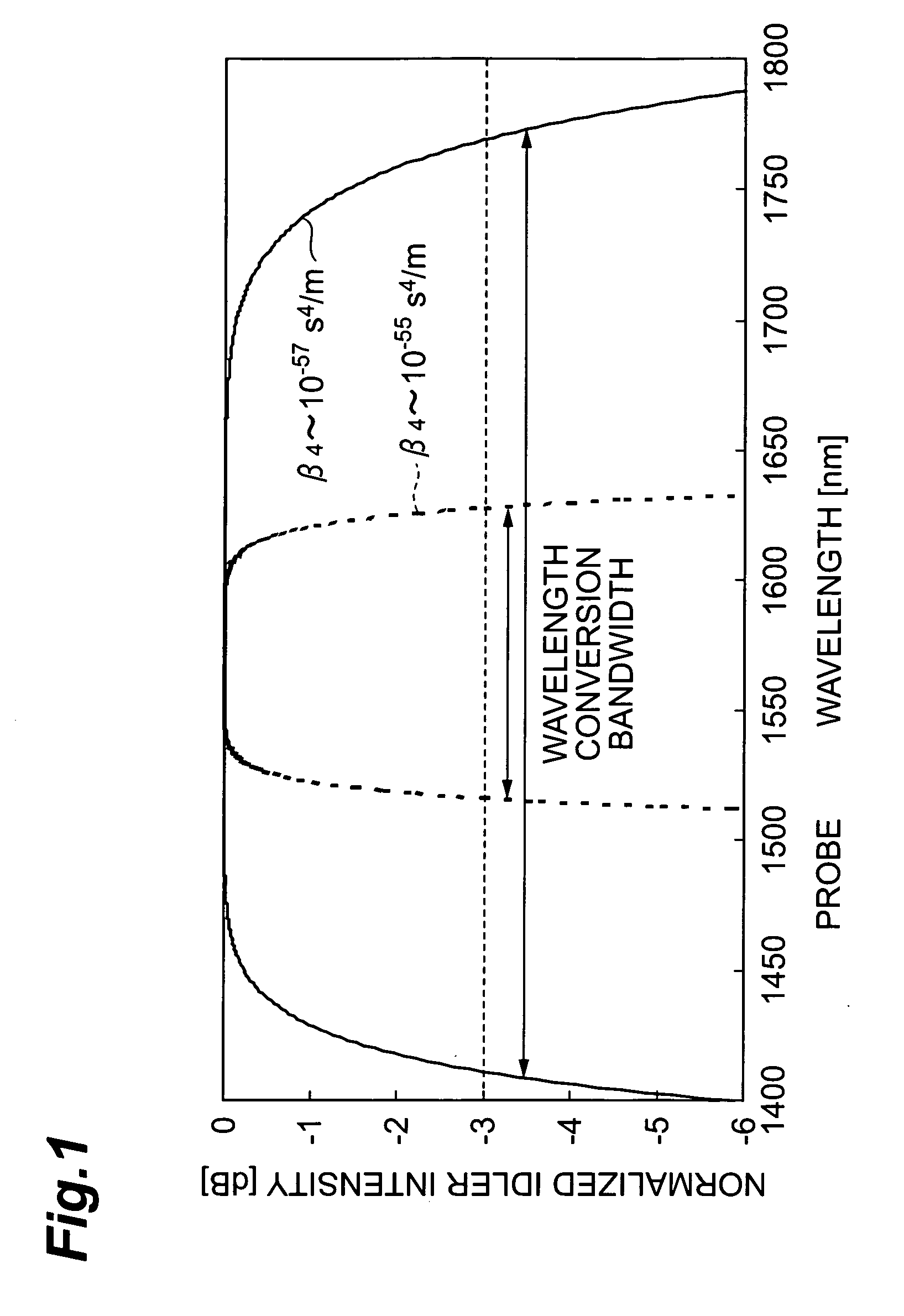
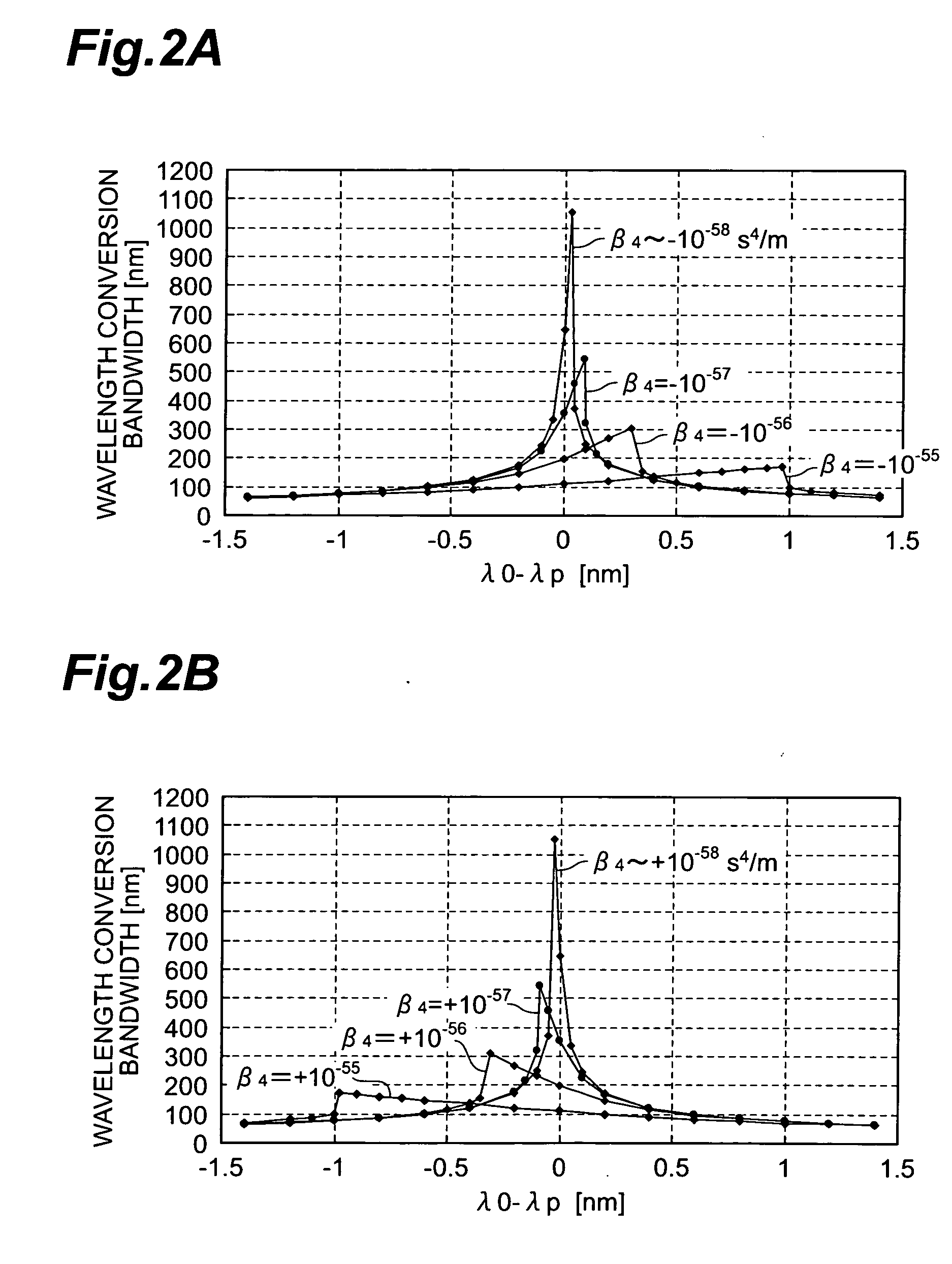
There is disclosed an optical fiber wherein an absolute value of the fourth order dispersion β4 of fourth derivative β4 of propagation constant β with respect to angular frequency ω at a mean zero dispersion wavelength λ0 in an overall length is not more than 5×10−56 s4 / m and wherein a fluctuation of a zero dispersion wavelength along a longitudinal direction is not more than ±0.6 nm.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Optical fiber for metro network
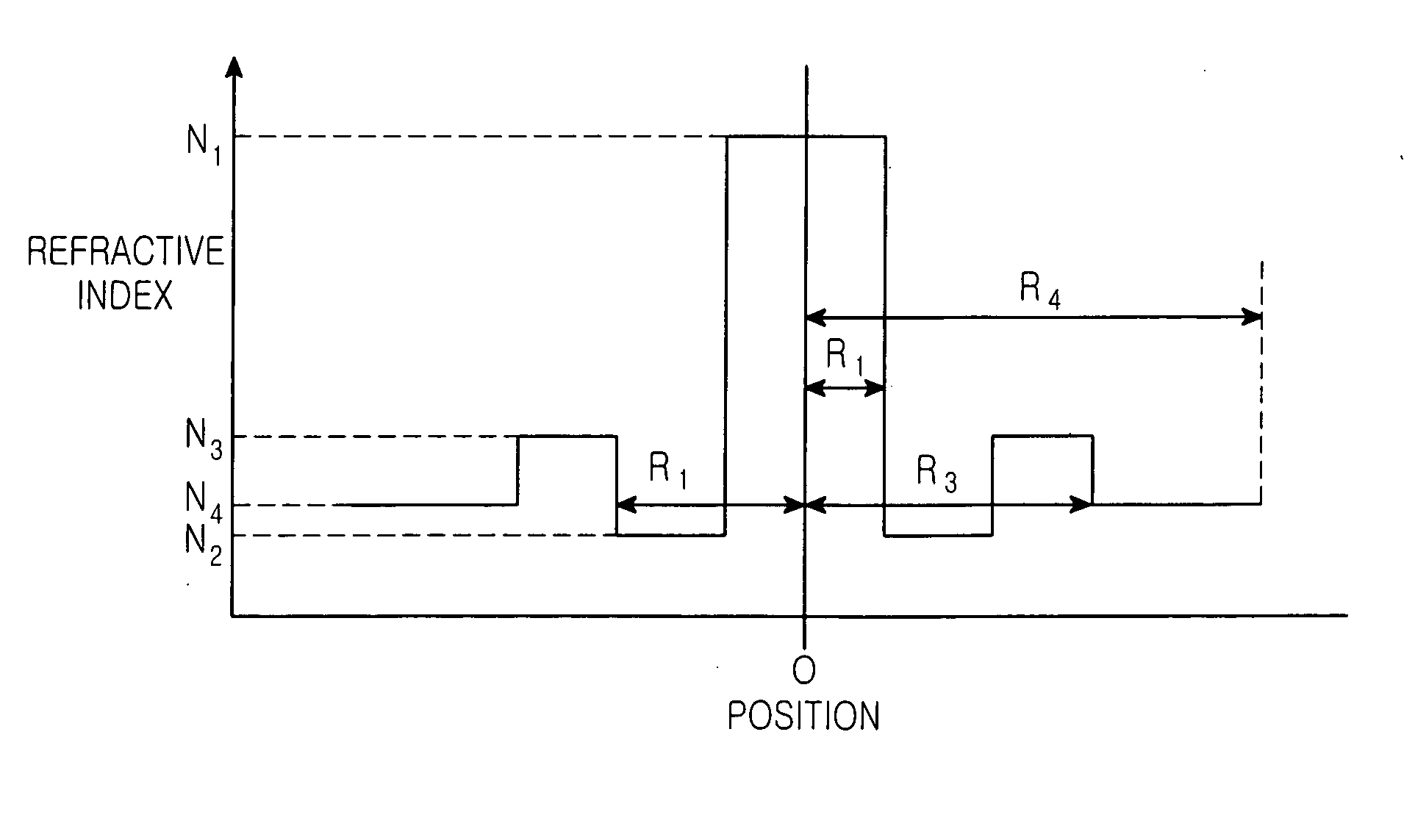
InactiveUS20050175303A1Improved channel efficiencyConfiguration economyTelevision system detailsLaser detailsZero-dispersion wavelengthRefractive index
An optical fiber for an optical network is disclosed. The optical fiber includes a core having a core region having a first refractive index N1, and a refractive index depressed region surrounding the core region and having a second refractive index N2 that is lower than the first refractive index. A clad surrounds the core and having a third refractive index N4. The optical fiber has a zero-dispersion wavelength that is not less than 1555 nm and positioned in a wavelength range which does not exceed L-band. The optical fiber has negative dispersion values in C-band and positive dispersion values in L-band.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
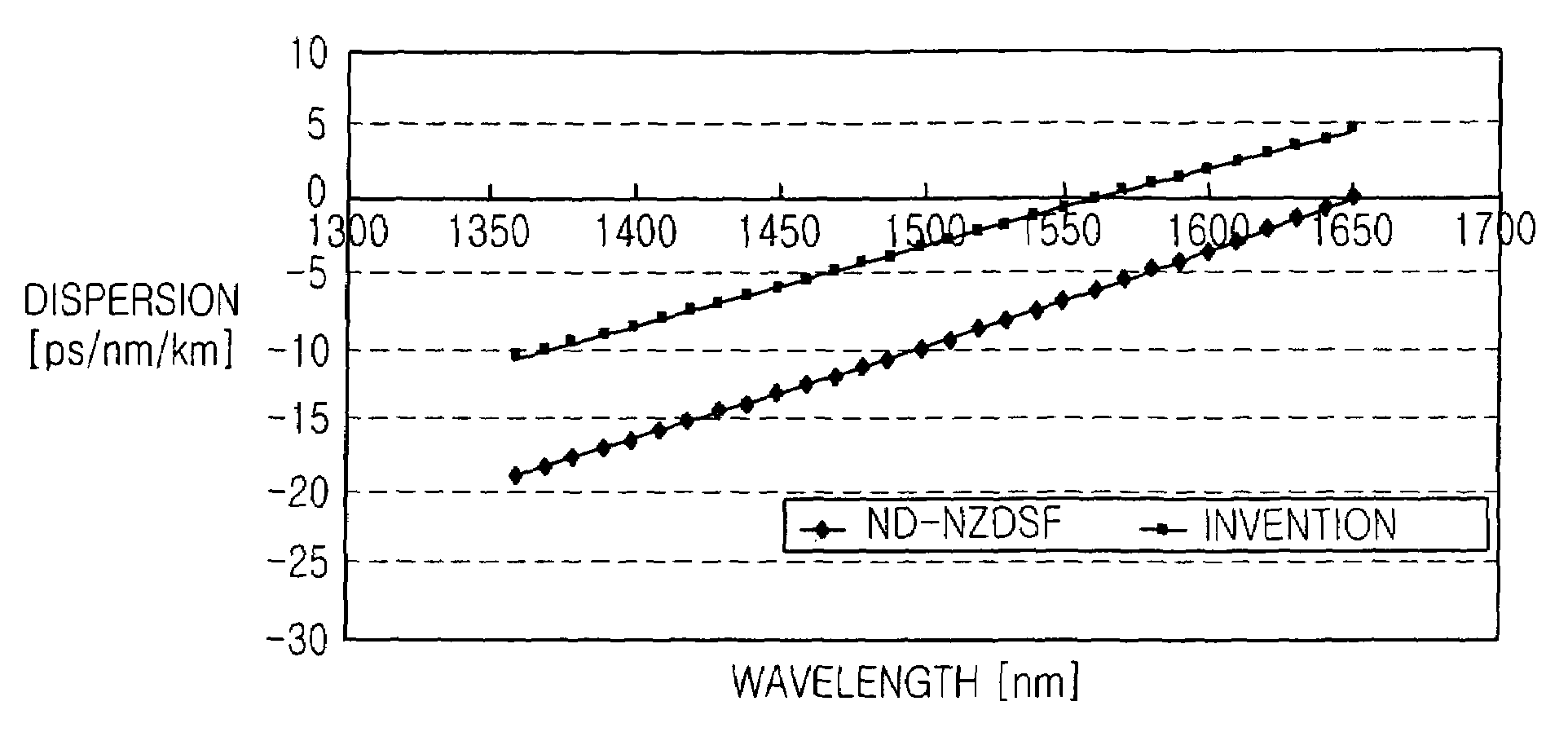
Dispersion-shifted single-mode fiber having low dispersion slope for large capacity transmission
ActiveUS6952518B2Control performanceReduce decreaseOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingDwdm transmissionUltrasound attenuation
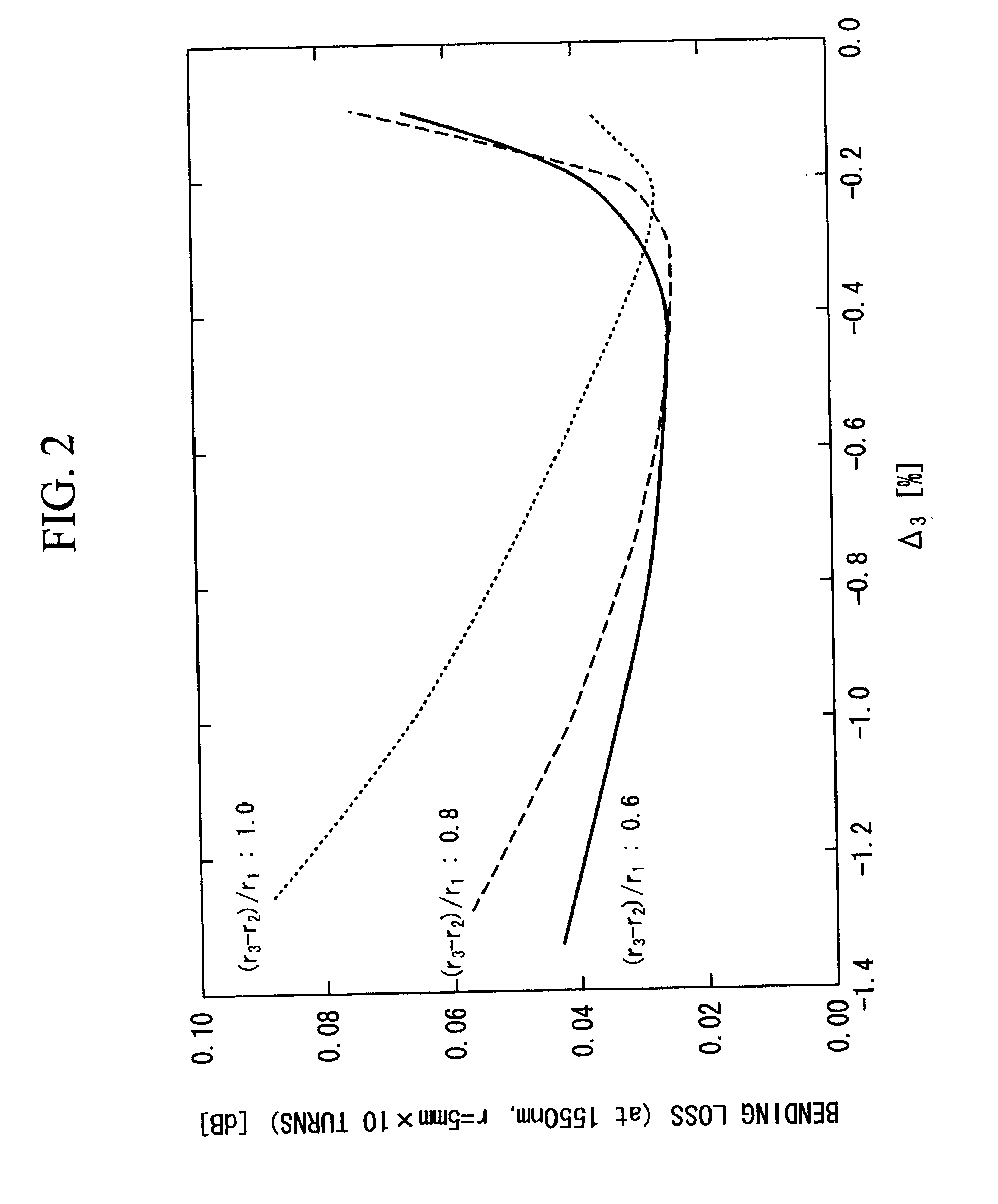
The invention relates to a low dispersion slope dispersion-shifted single-mode fiber for large capacity transmission comprising a core and a cladding. Said fiber is characterized in that said core has three to five core segments having different refractive index profiles, and said cladding has four to six cladding segments. The total dispersion slope of said fiber at 1550 nm is less than 0.060 ps / nm2·km, the zero dispersion wavelength is less than 1420 nm, the effective area ranges from 55 μm2 to 65 μm2, and the dispersion in the region of 1530 nm˜1565 nm ranges from 5.0 ps / nm2·km to 12.0 ps / nm2·km. The fiber has low dispersion slope, moderate dispersion, low attenuation, and excellent bend resistance performance. It is suitable for a high-speed (10 Gbits / s and 40 Gbits / s), large capacity, and long distance DWDM system. Therefore, not only the non-linear problem that fazes high-speed communication is solved effectively, but also the DWDM transmission at 10 Gbits / s can be realized within a wider wavelength range. In addition, low dispersion slope is advantageous for comprehensive management of dispersion, so that the requirement for long distance non-electric relay can be fulfilled.
Owner:YANGTZE OPTICAL FIBRE & CABLE CO LTD
Optical fiber for metro network
InactiveUS7116876B2Improve efficiencyImprove compatibilityTelevision system detailsLaser detailsZero-dispersion wavelengthRefractive index
An optical fiber for an optical network is disclosed. The optical fiber includes a core having a core region having a first refractive index N1, and a refractive index depressed region surrounding the core region and having a second refractive index N2 that is lower than the first refractive index. A clad surrounds the core and having a third refractive index N4. The optical fiber has a zero-dispersion wavelength that is not less than 1555 nm and positioned in a wavelength range which does not exceed L-band. The optical fiber has negative dispersion values in C-band and positive dispersion values in L-band.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Wavelength division multiplexing optical transmission system
InactiveUS6490064B1Increase input powerWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmissionMultiplexingZero-dispersion wavelength
In a wavelength division multiplexed optical transmission system wherein the zero dispersion wavelength of the optical fiber transmission path 224 is in the 1550 nm region, among multiplexed optical signals, the wavelengths of either of at least two optical signals are allocated between 1450 nm and 1530 nm, or between 1570 mn and 1650 nm.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Optical fiber and optical device
InactiveUS7668428B2Cladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideZero-dispersion wavelengthRefractive index
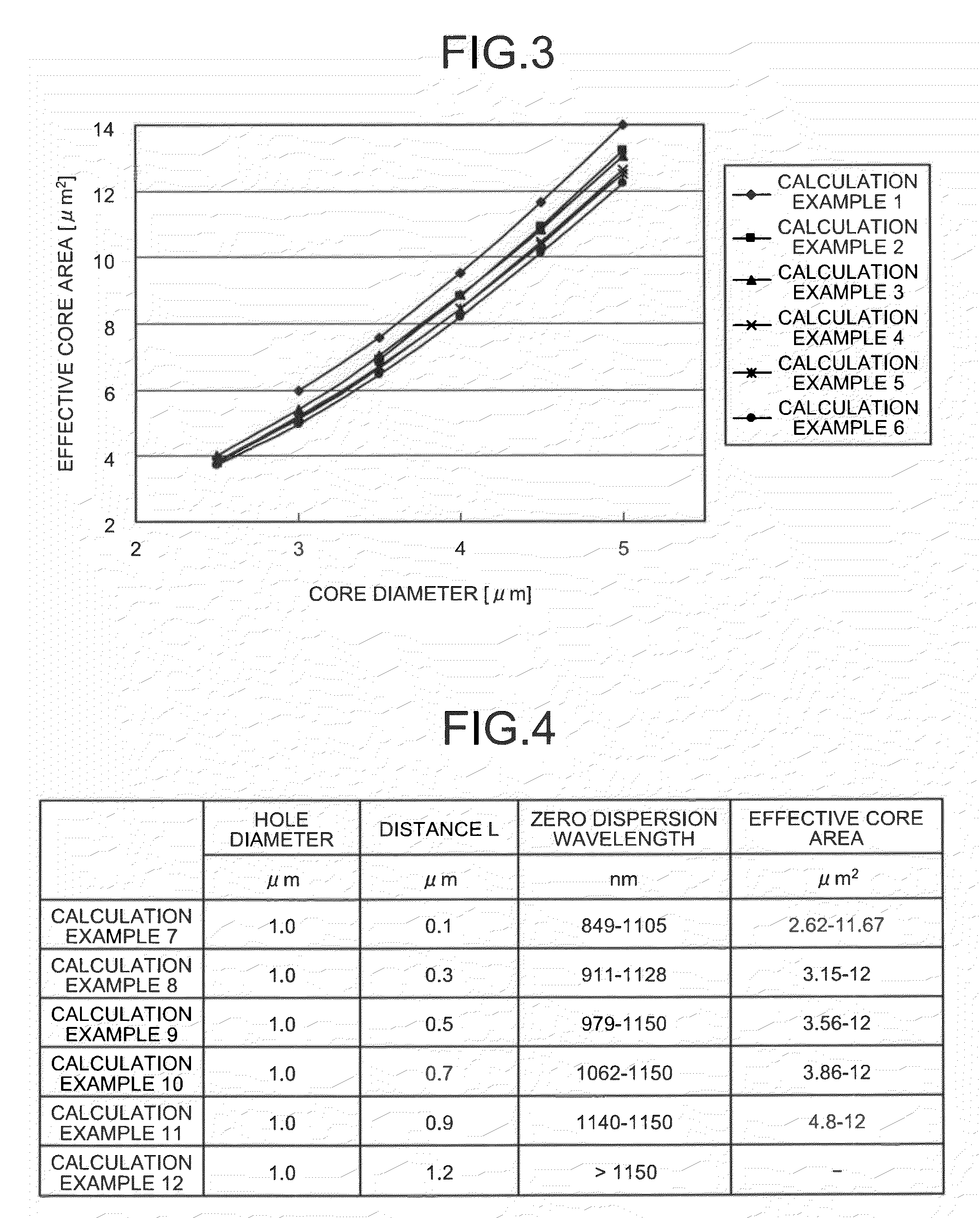
An optical fiber includes a core region and a cladding region formed on an outer circumference of the core region. The cladding region includes a plurality of holes arranged around the core region and has a refractive index lower than a refractive index of the core region. A zero dispersion wavelength of the optical fiber is shorter than 1150 nanometers. The optical fiber propagates a light having a wavelength longer than 1000 nanometers exclusively in a fundamental mode of LP01 mode. An effective core area of the optical fiber is equal to or smaller than 12.0 μm2 at a wavelength of 1064 nanometers.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com