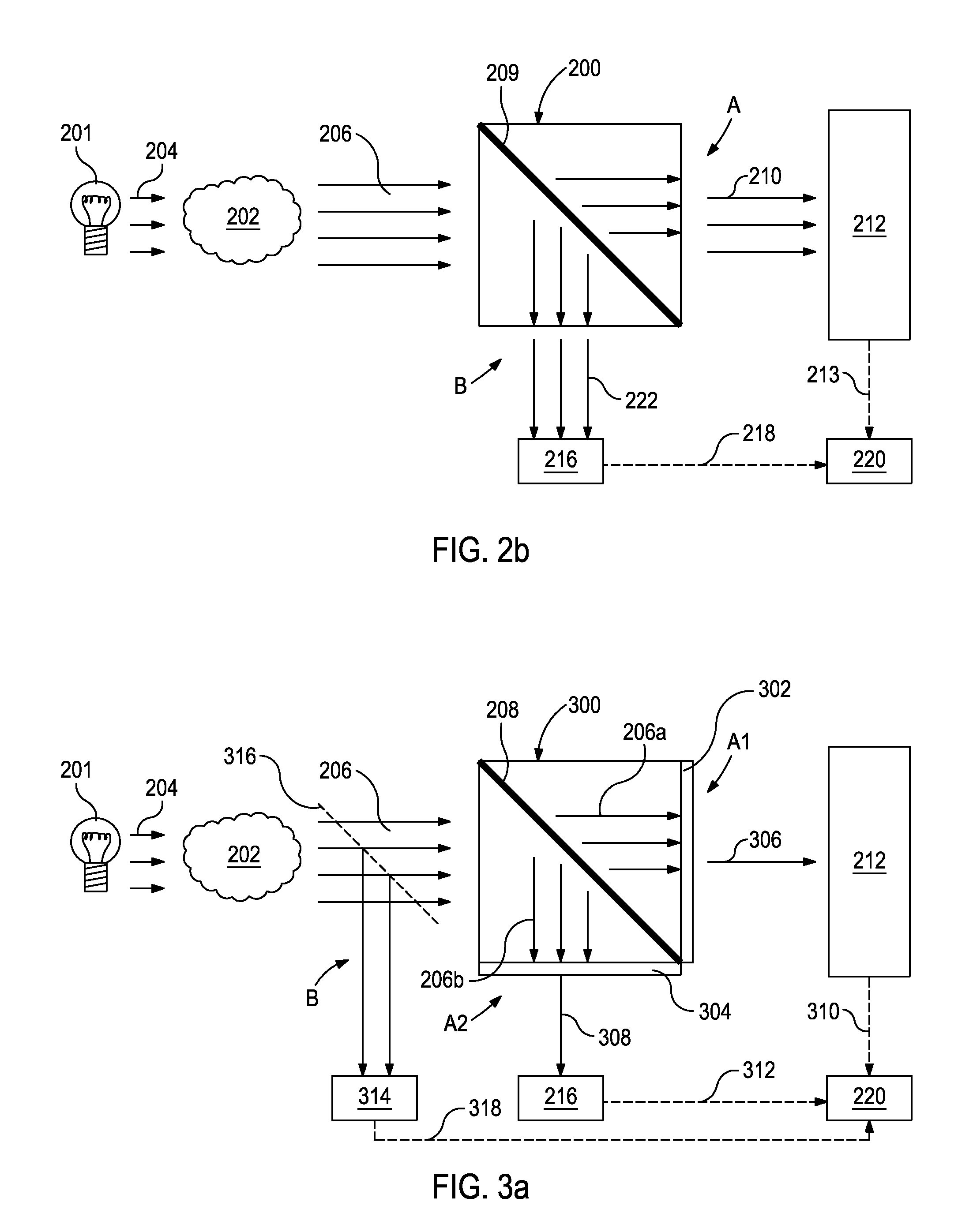
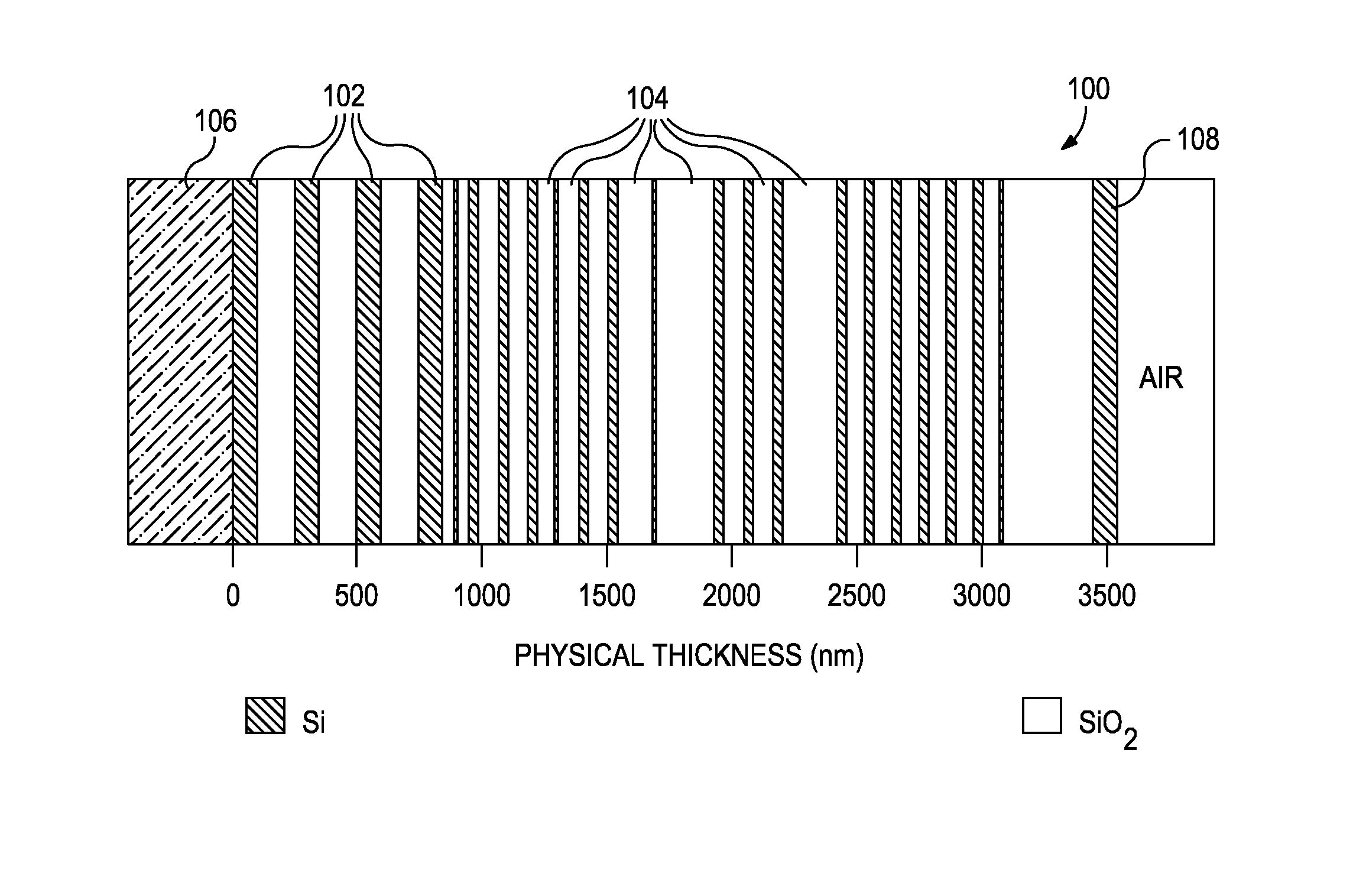
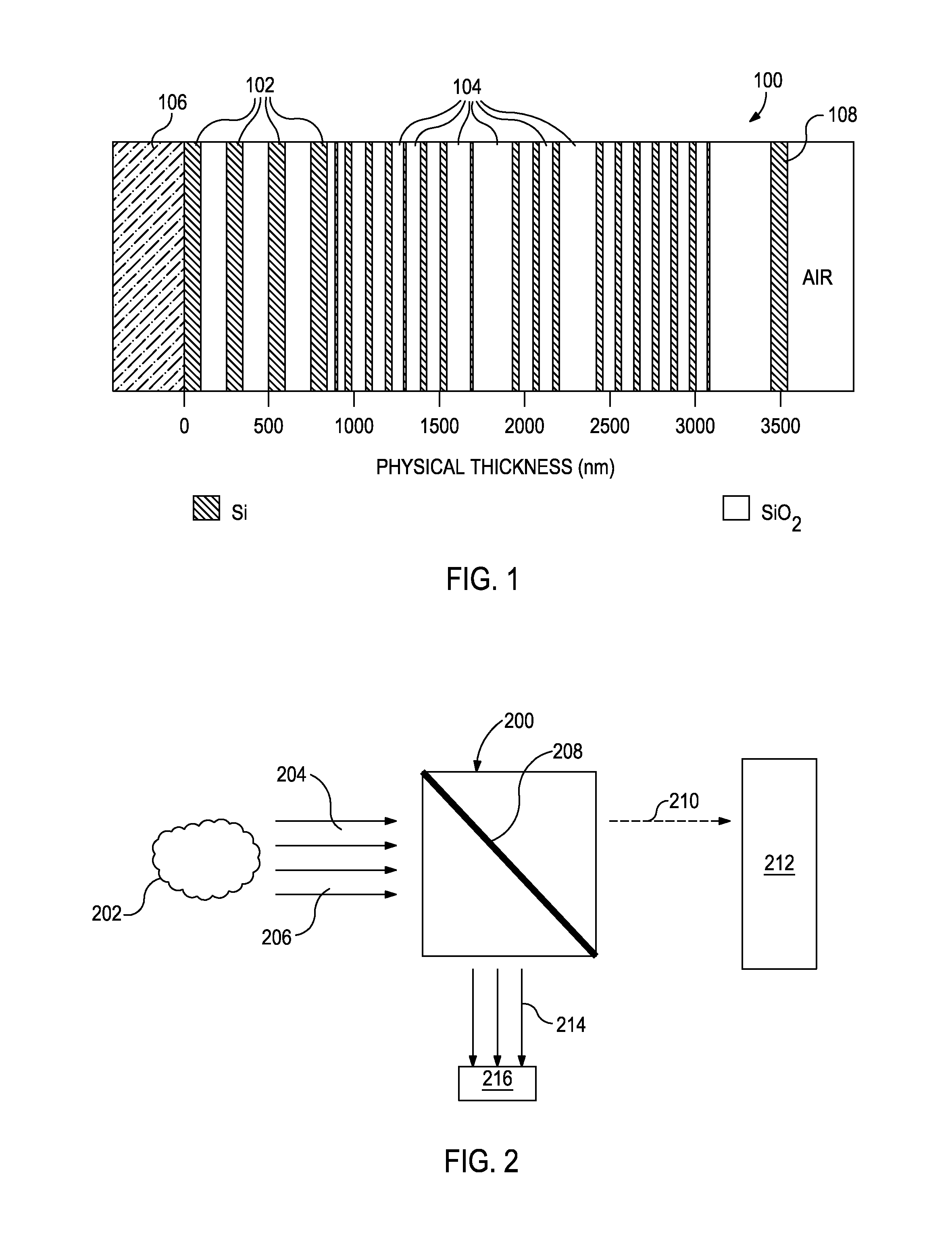
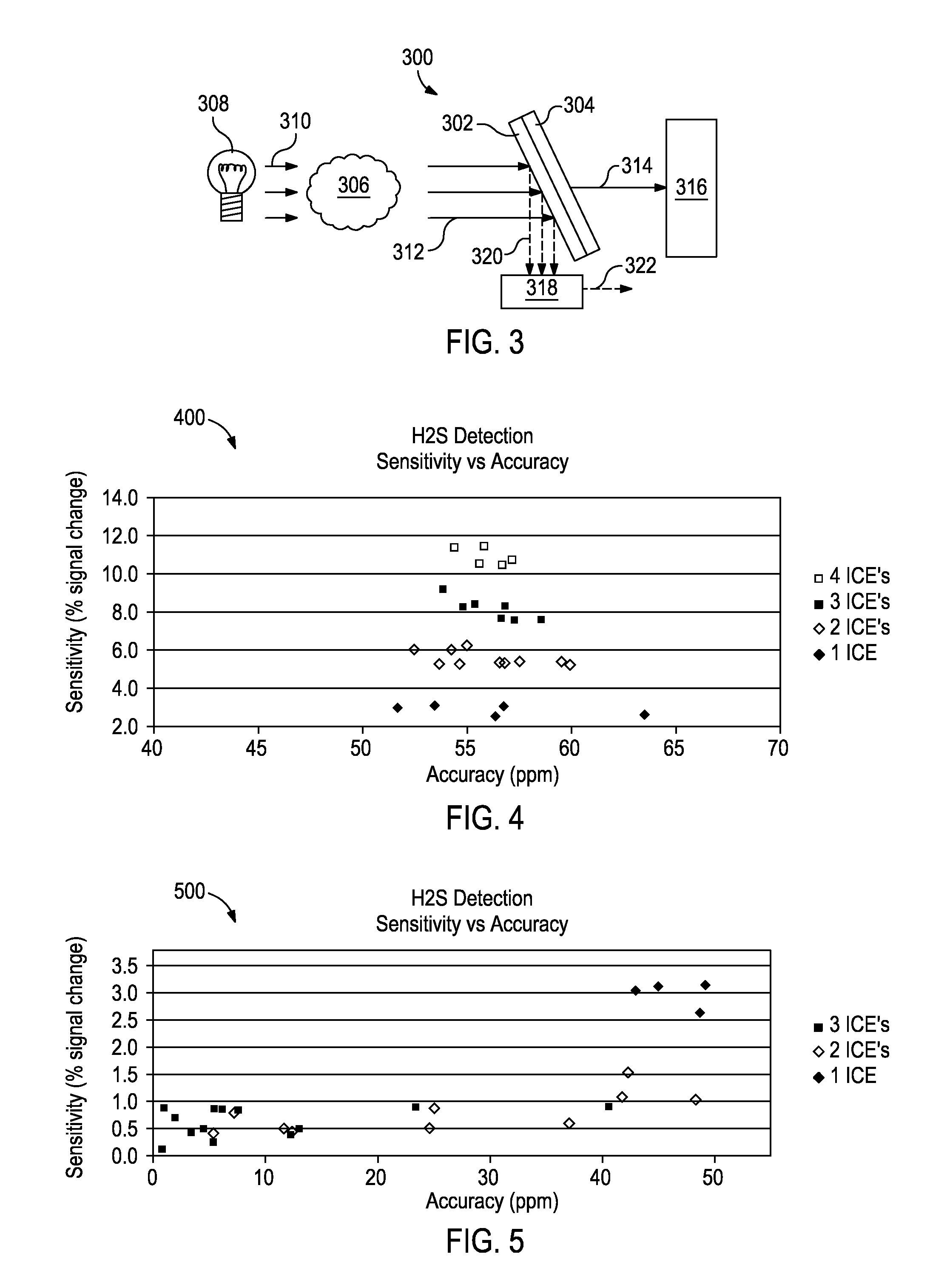
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
193 results about "Optical computing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
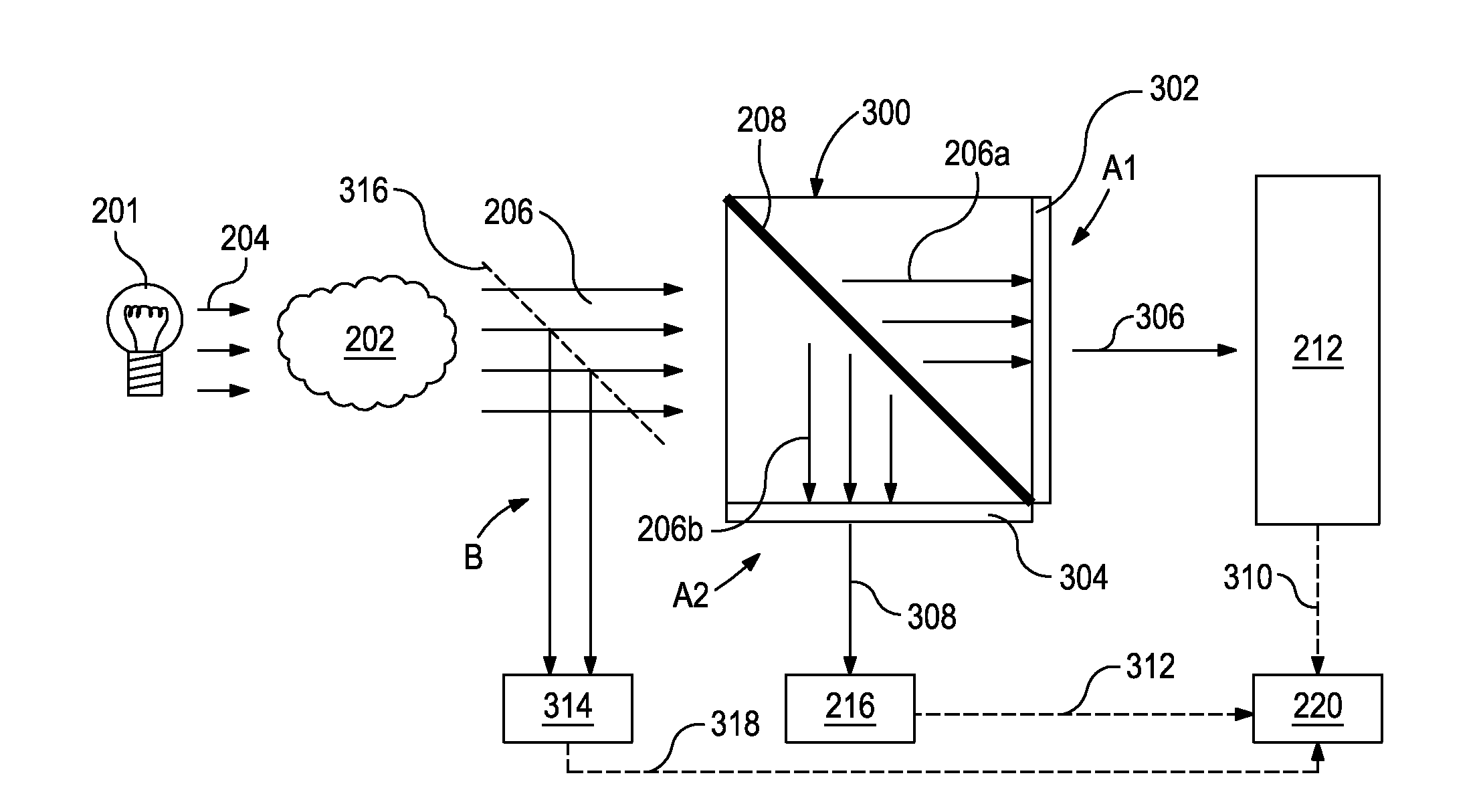
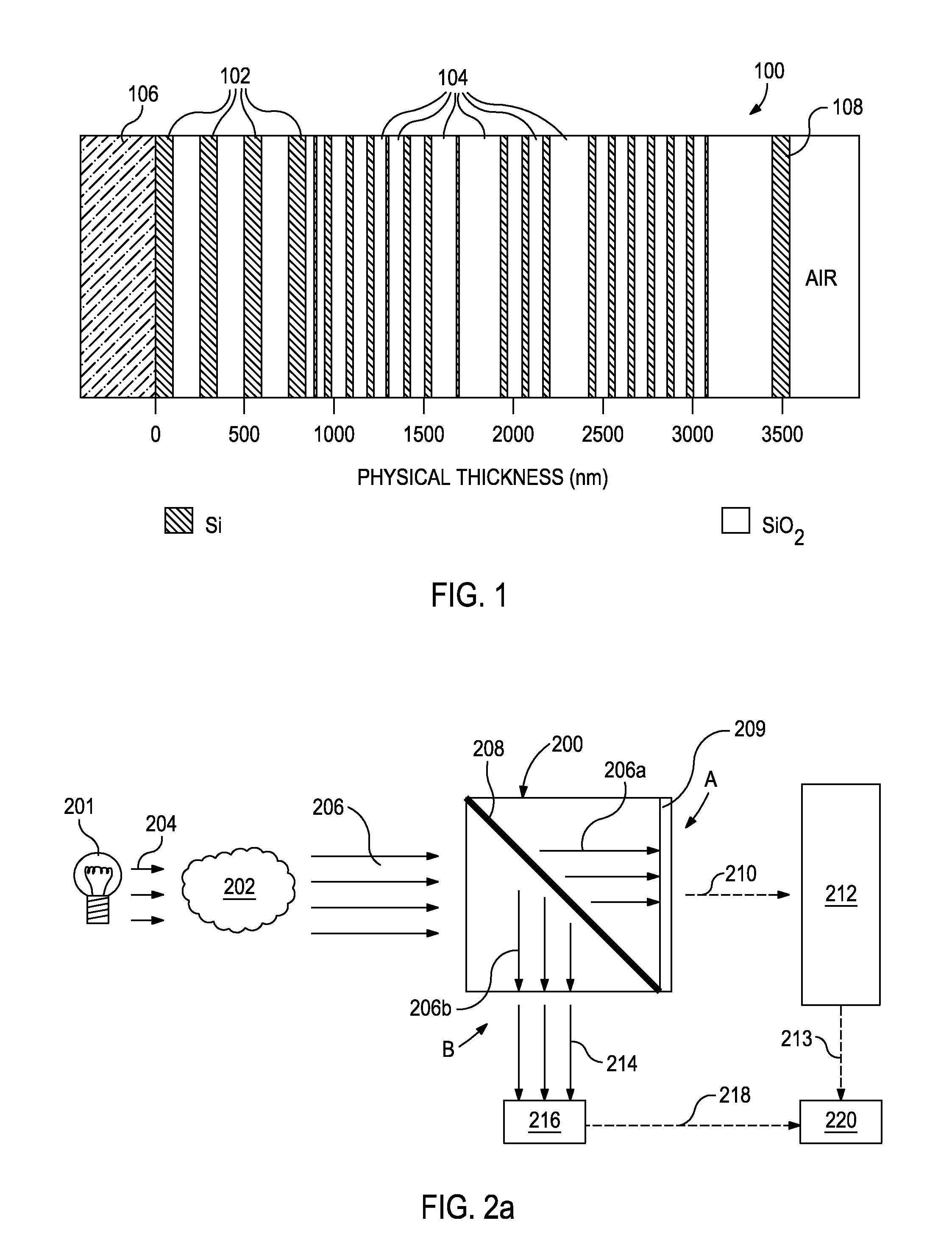
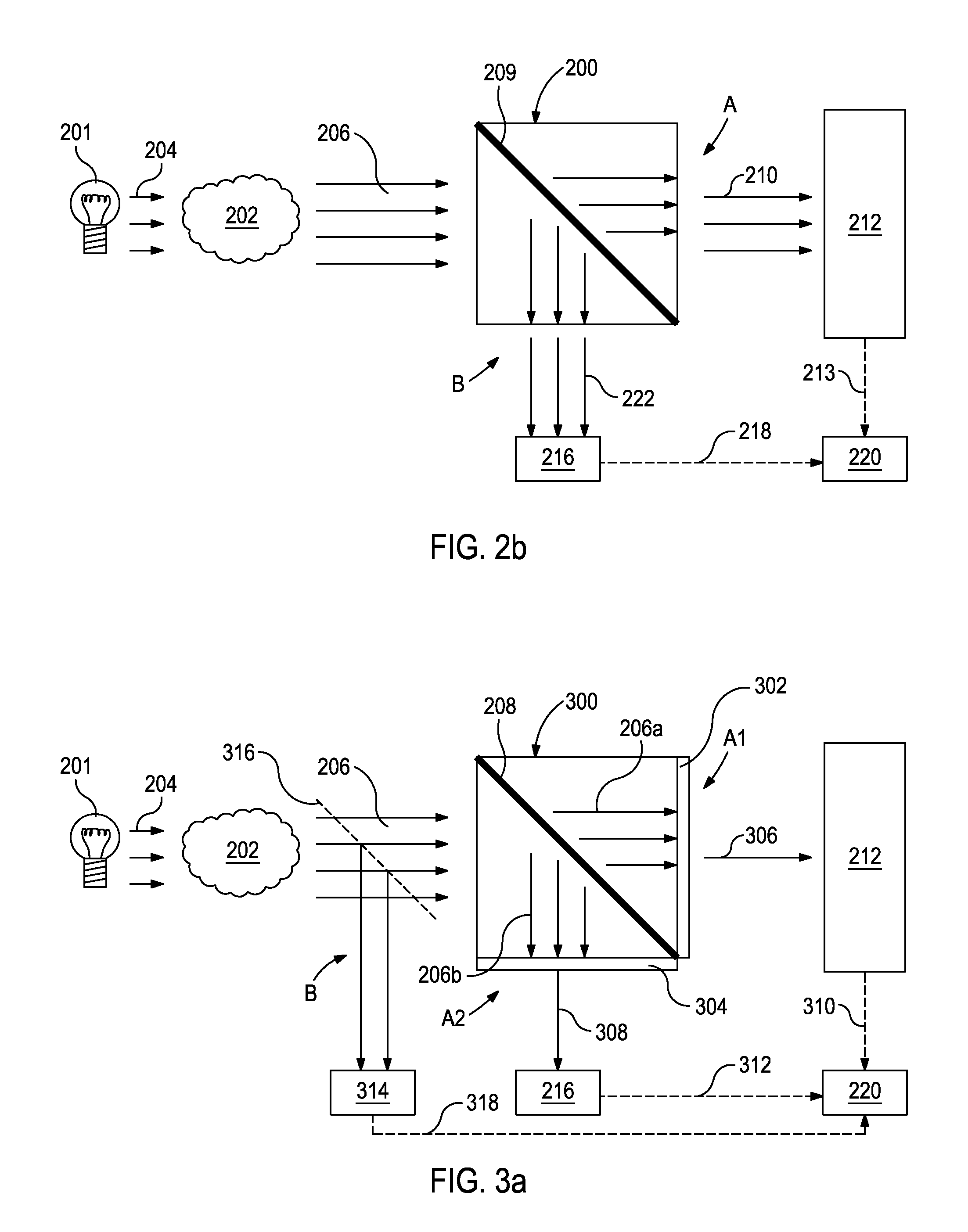
Optical or photonic computing uses photons produced by lasers or diodes for computation. For decades, photons have promised to allow a higher bandwidth than the electrons used in conventional computers.
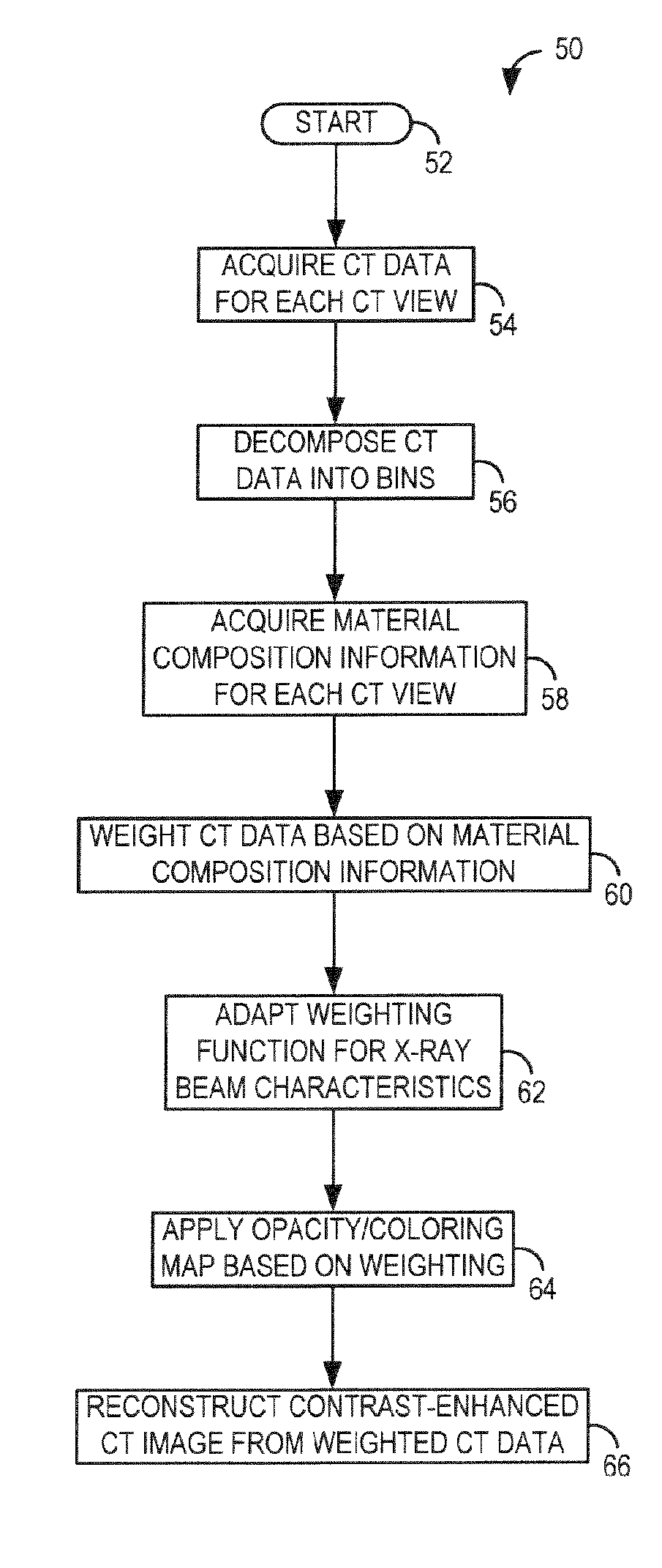
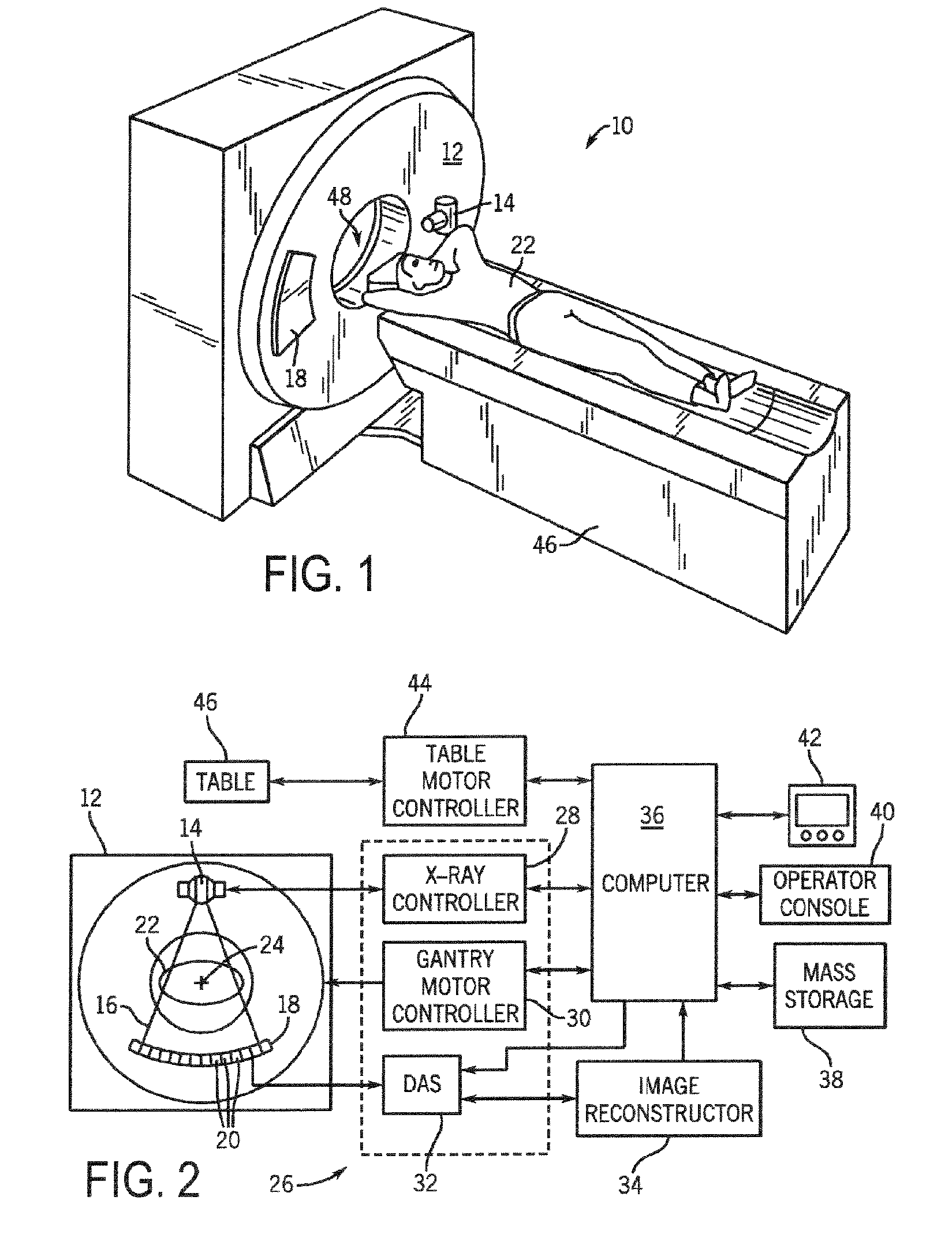
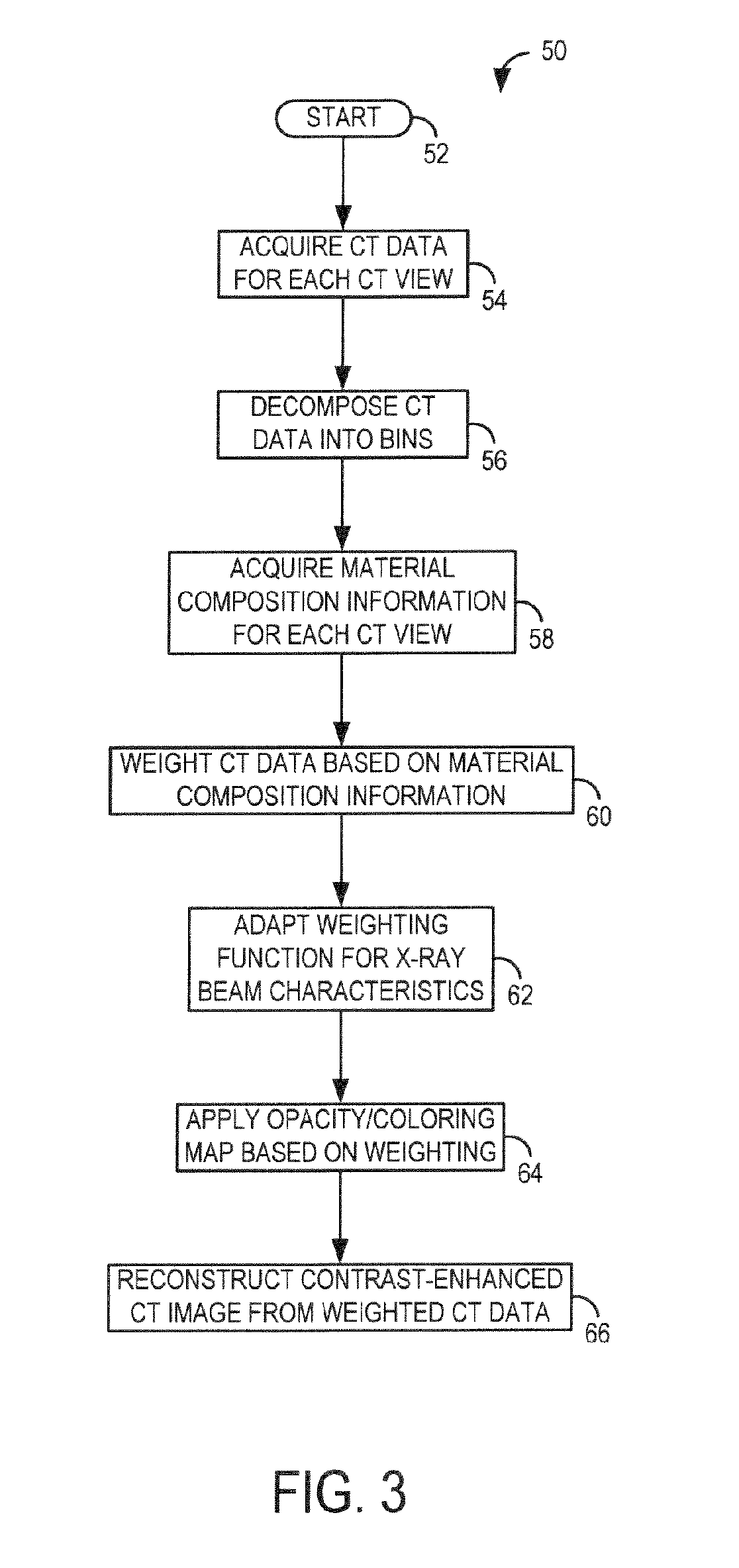
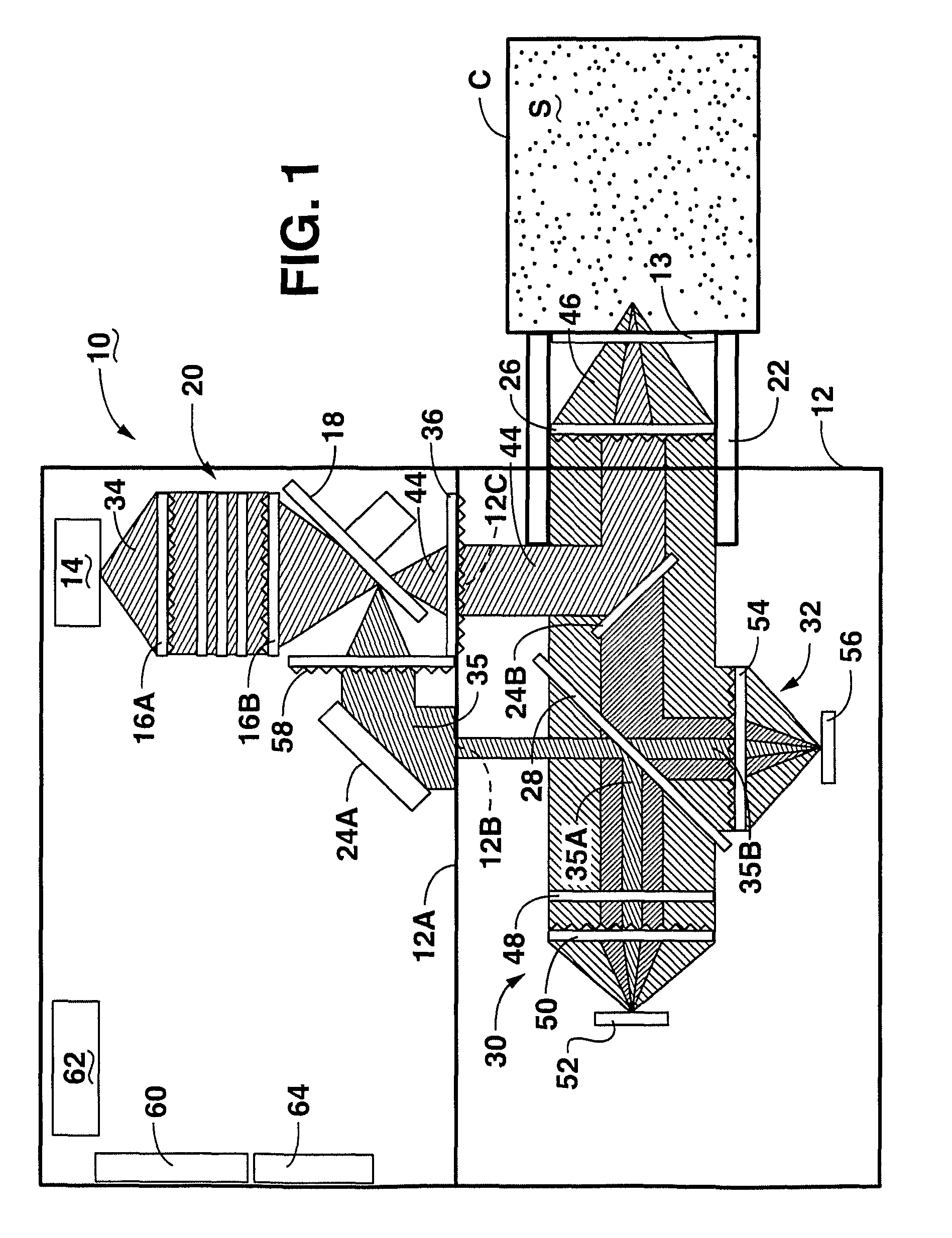
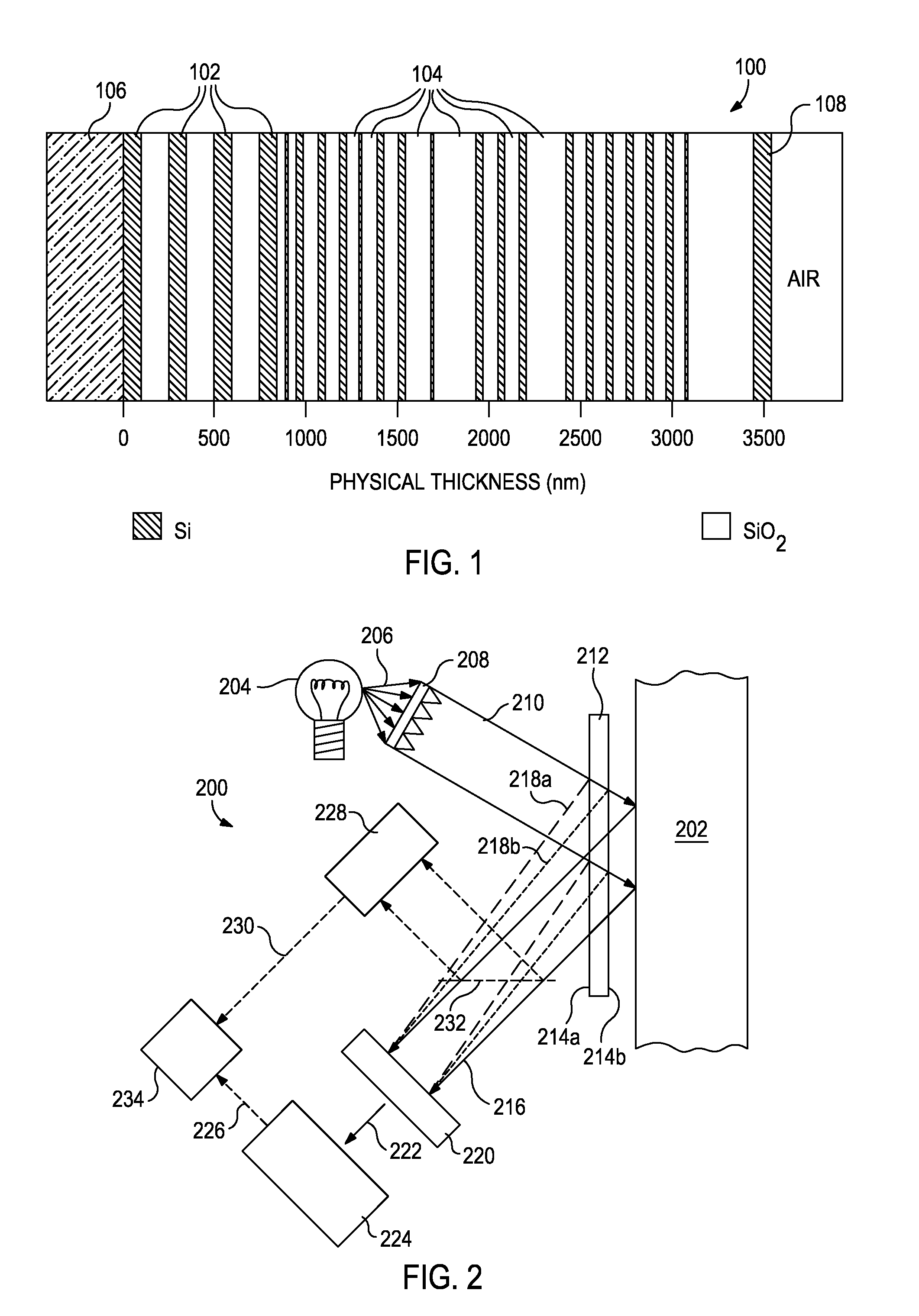
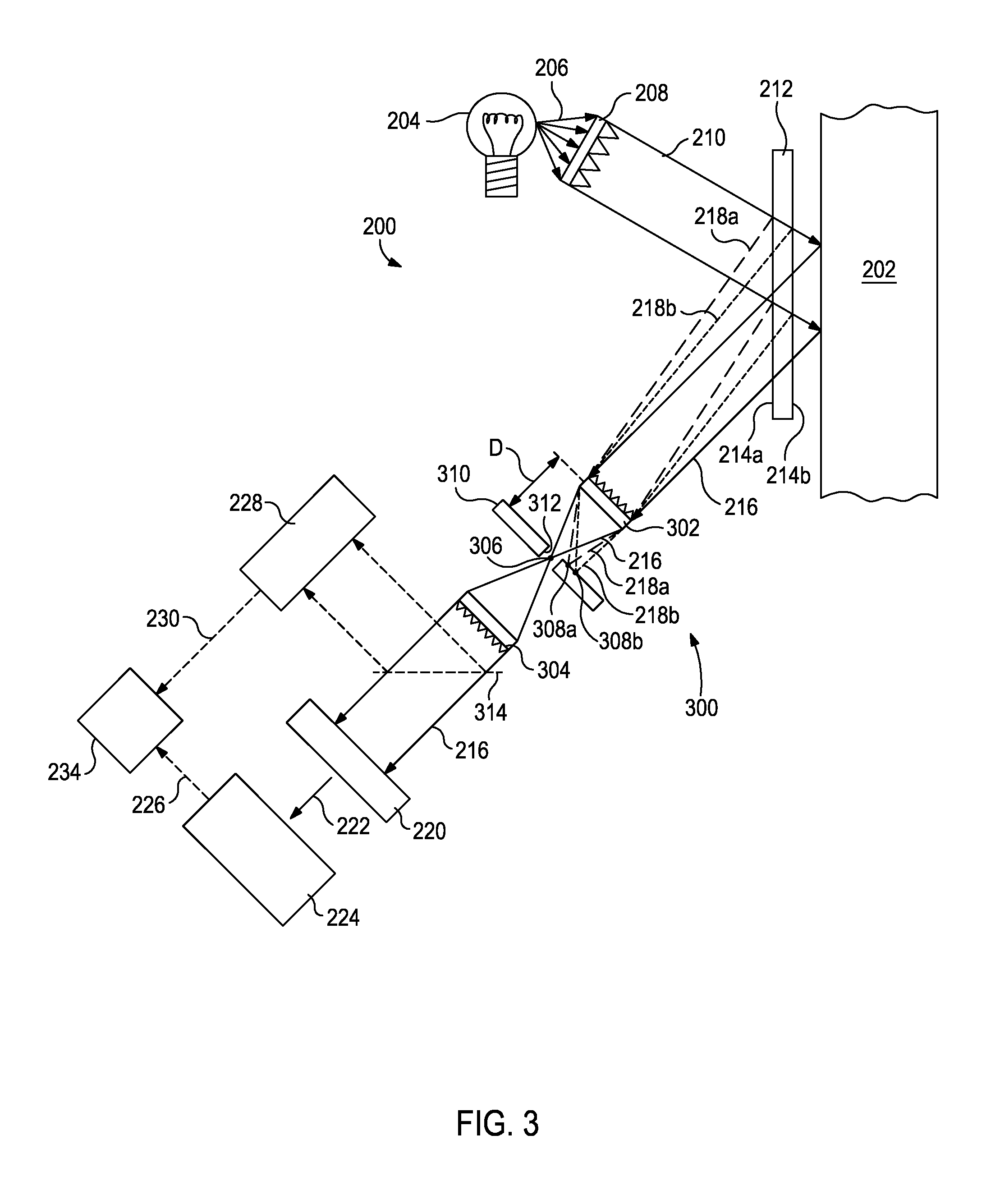
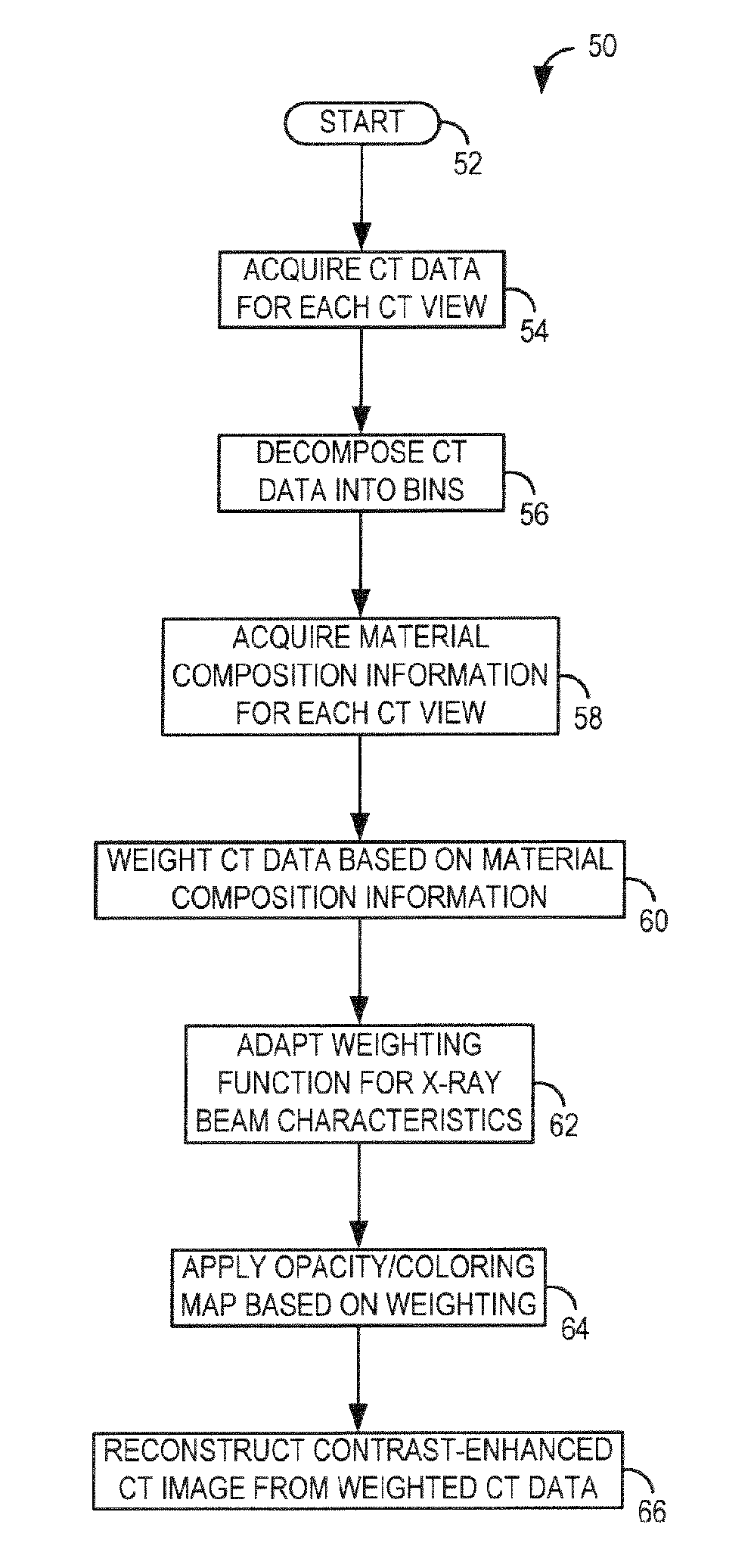
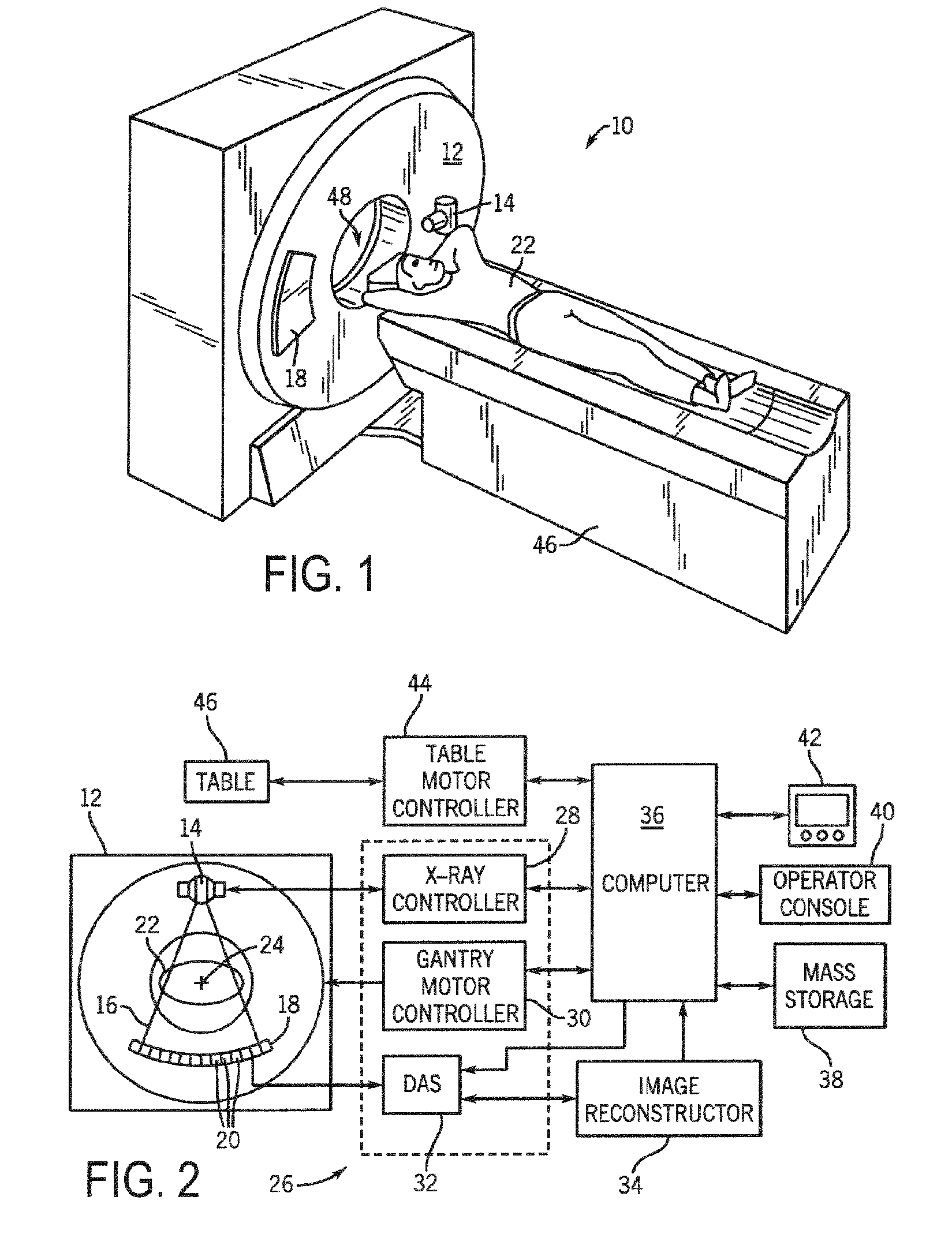
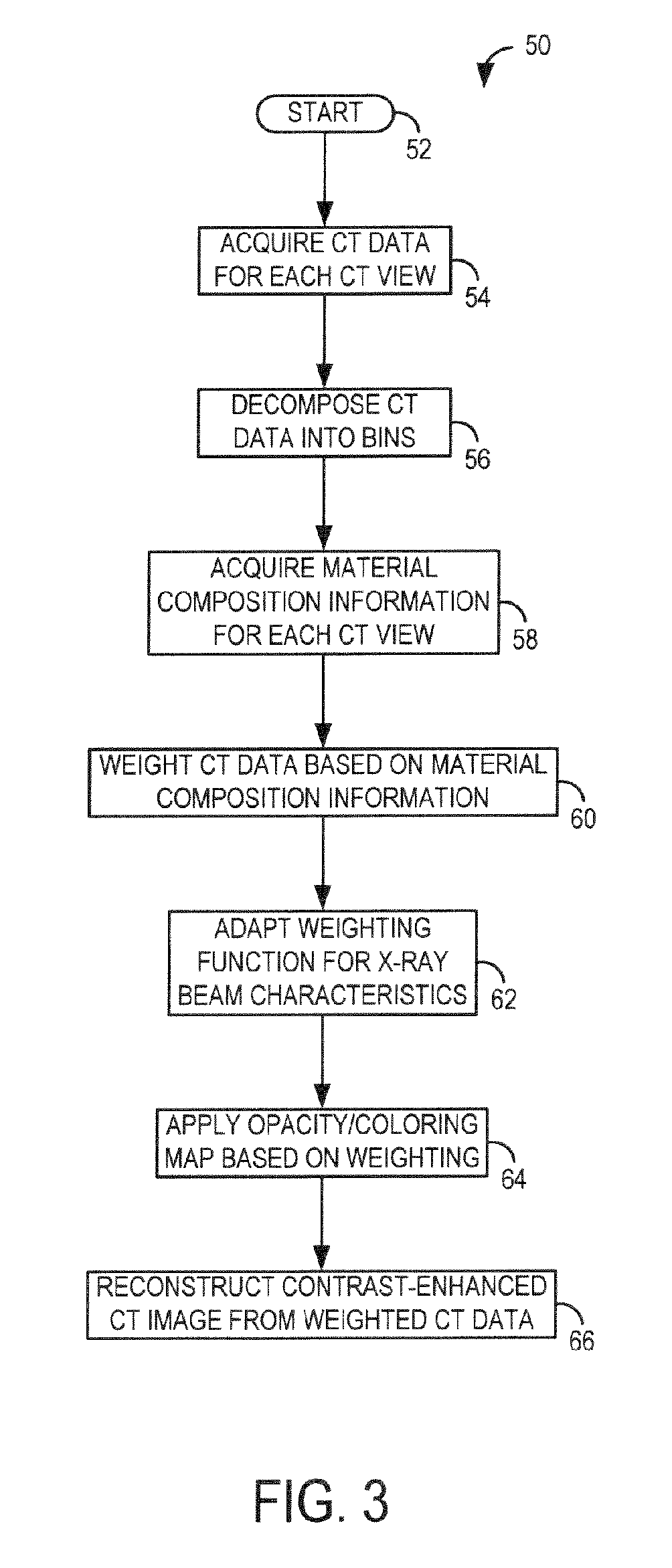
System and method for acquisition and reconstruction of contrast-enhanced, artifact-reduced CT images
ActiveUS20060109949A1Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationView basedPhoton
A system and method are disclosed for reconstructing contrast-enhanced CT images that are substantially free of beam-hardening artifacts. An imaging system includes a radiation source configured to project radiation toward an object to be scanned and an energy discriminating detector assembly having a plurality of detector elements and configured to detect radiation emitted by the radiation source and attenuated by the object to be scanned. The imaging system also includes computer programmed to count a number of photons detected by each detector element and associate an energy value to each counted photon and determine a material composition of a CT view from the number of photons counted and the energy value associated with each counted photon. The computer is also programmed to apply a weighting to the CT view based on the material composition of the CT view and reconstruct an image with differential weighting based on the weighting of the CT view.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Optical analysis system and elements to isolate spectral region
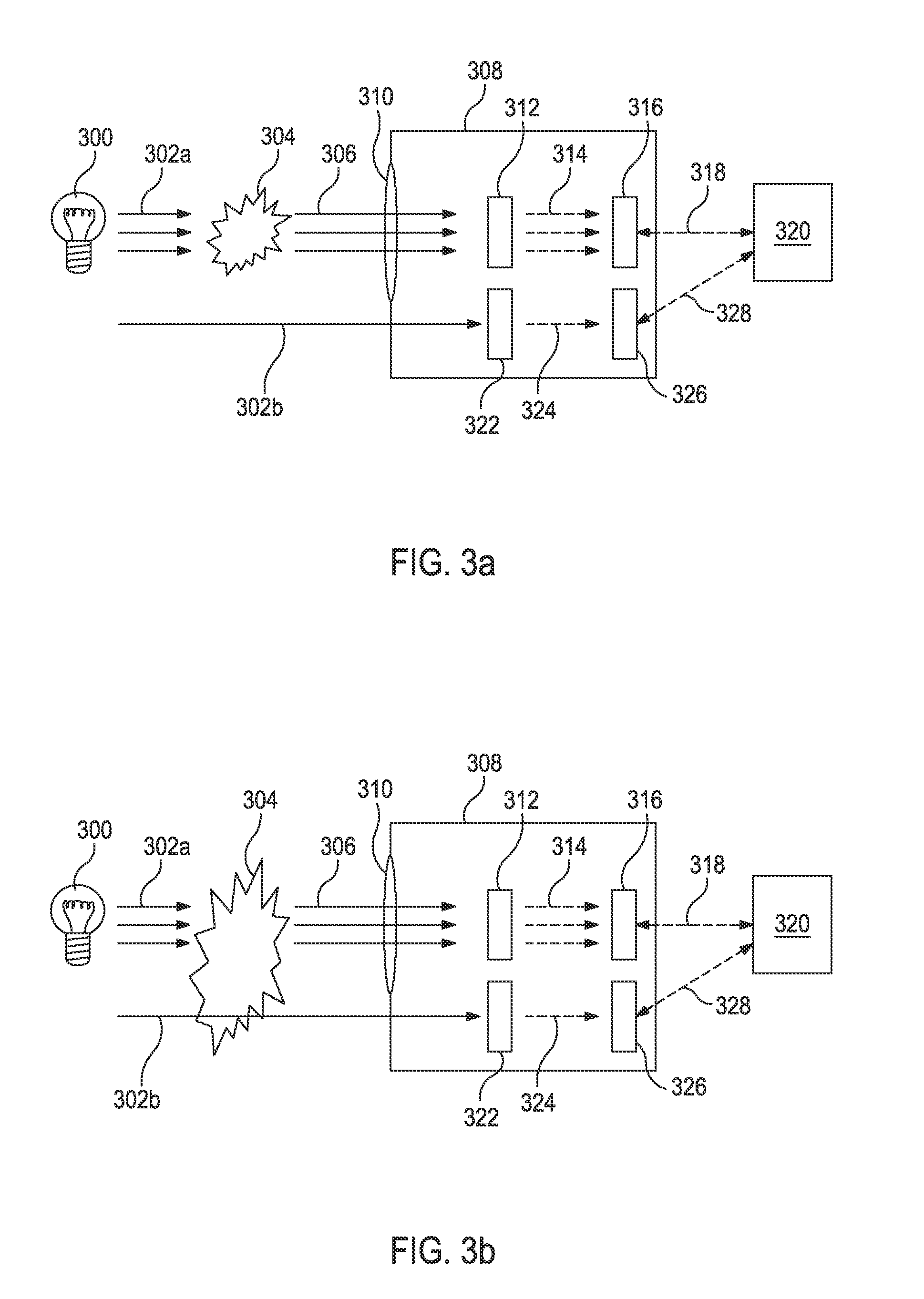
ActiveUS7920258B2Useful and reliable capabilityImprove signal-to-noise ratioRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationOptical frequenciesAnalysis sample
A method of selecting components for a multivariate optical computing and analysis system to isolate a spectral region includes selecting a spectral region of interest; selecting a spectral element with a predetermined transmission characteristic to control a spectral range of an illumination source; illuminating a sample with the illumination source; and analyzing an optical frequency returned by the sample relative to the spectral region of interest.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
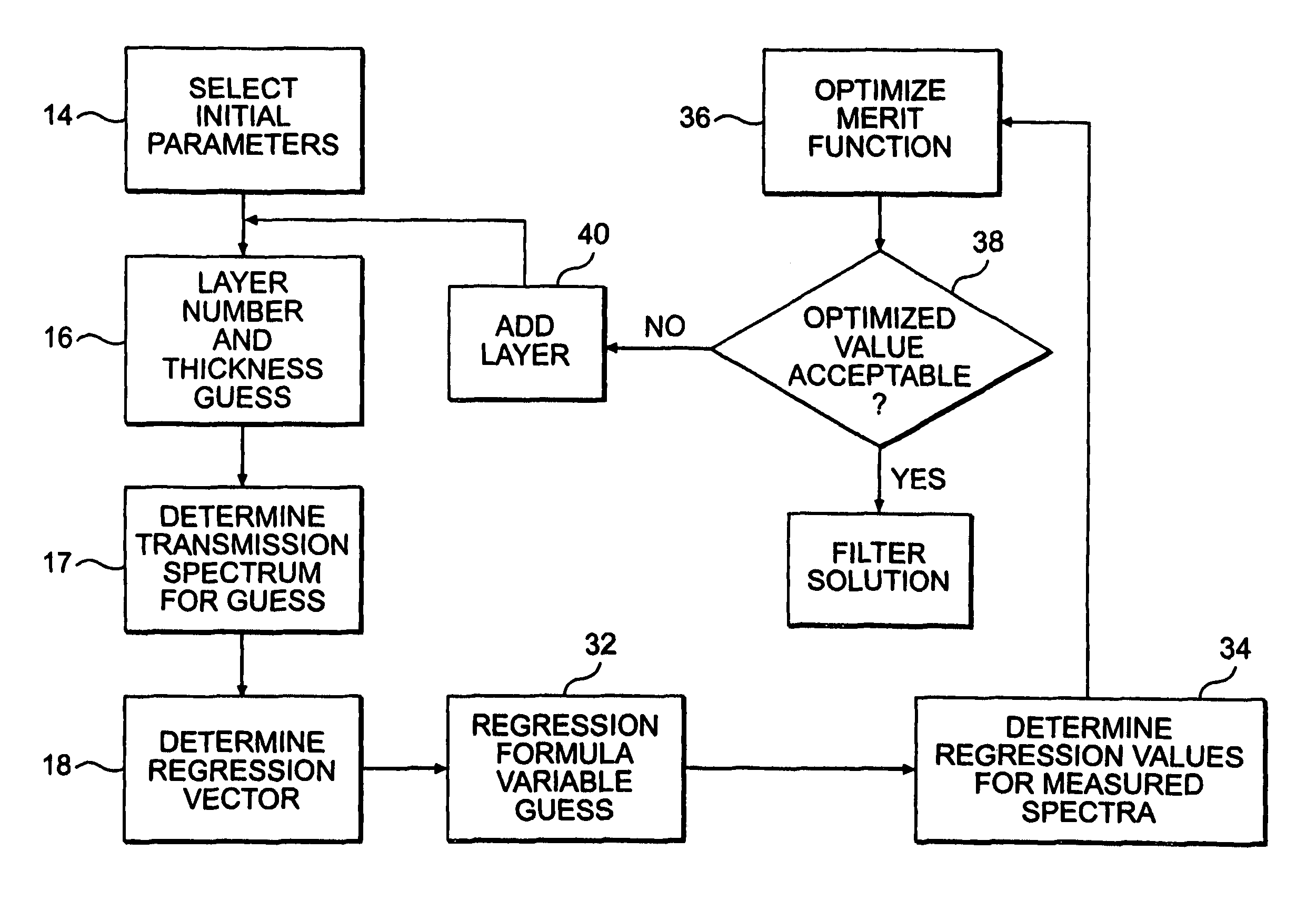
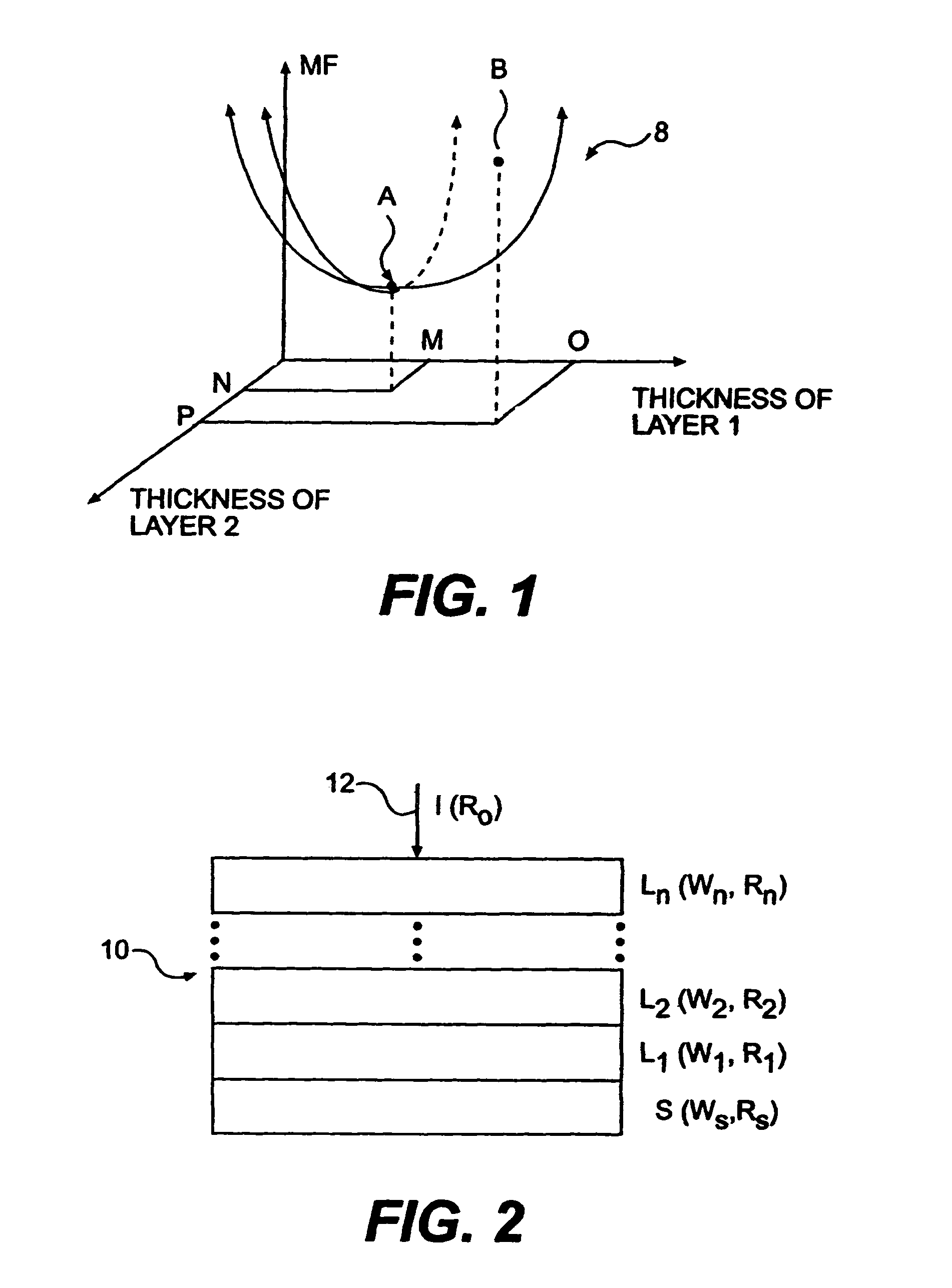
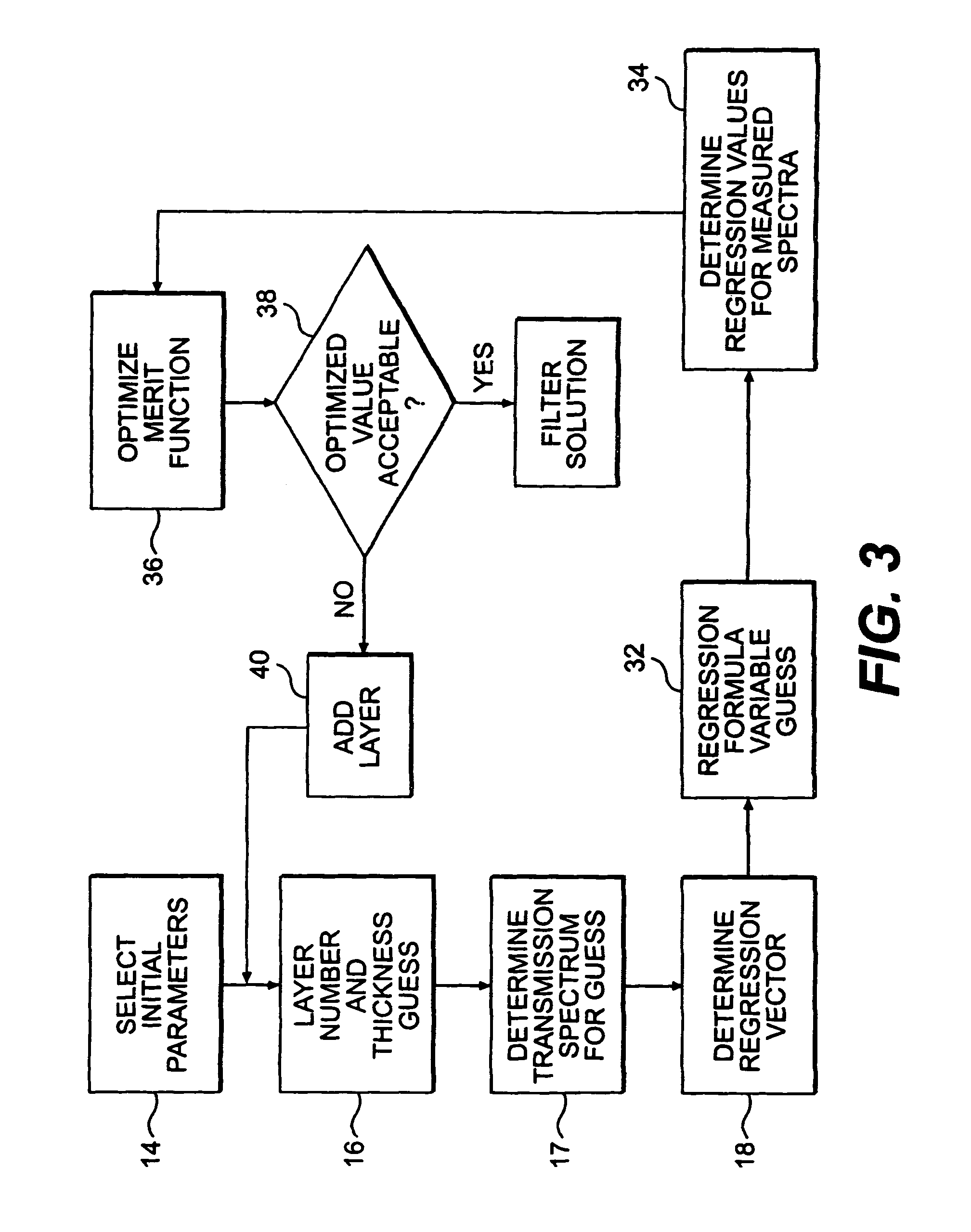
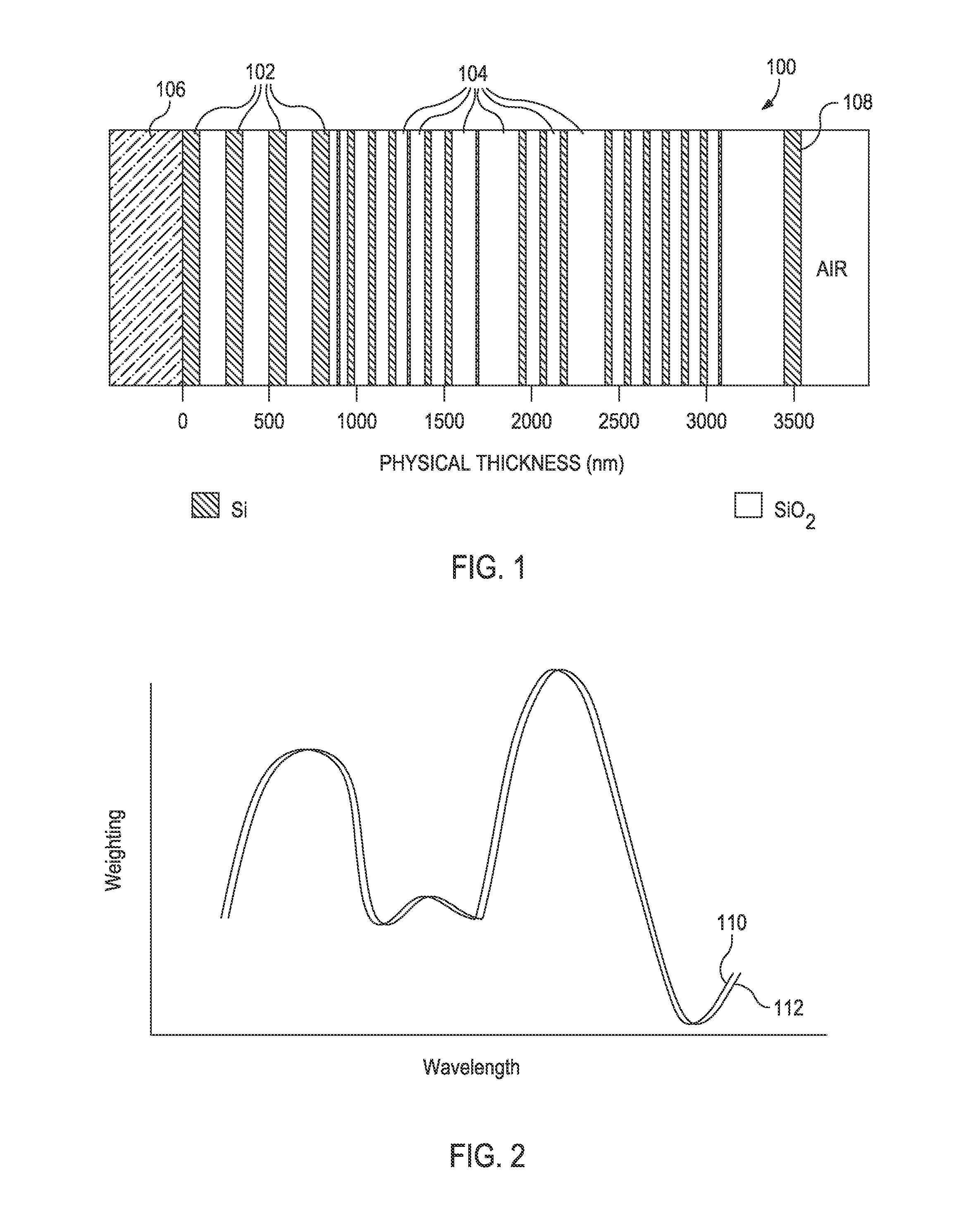
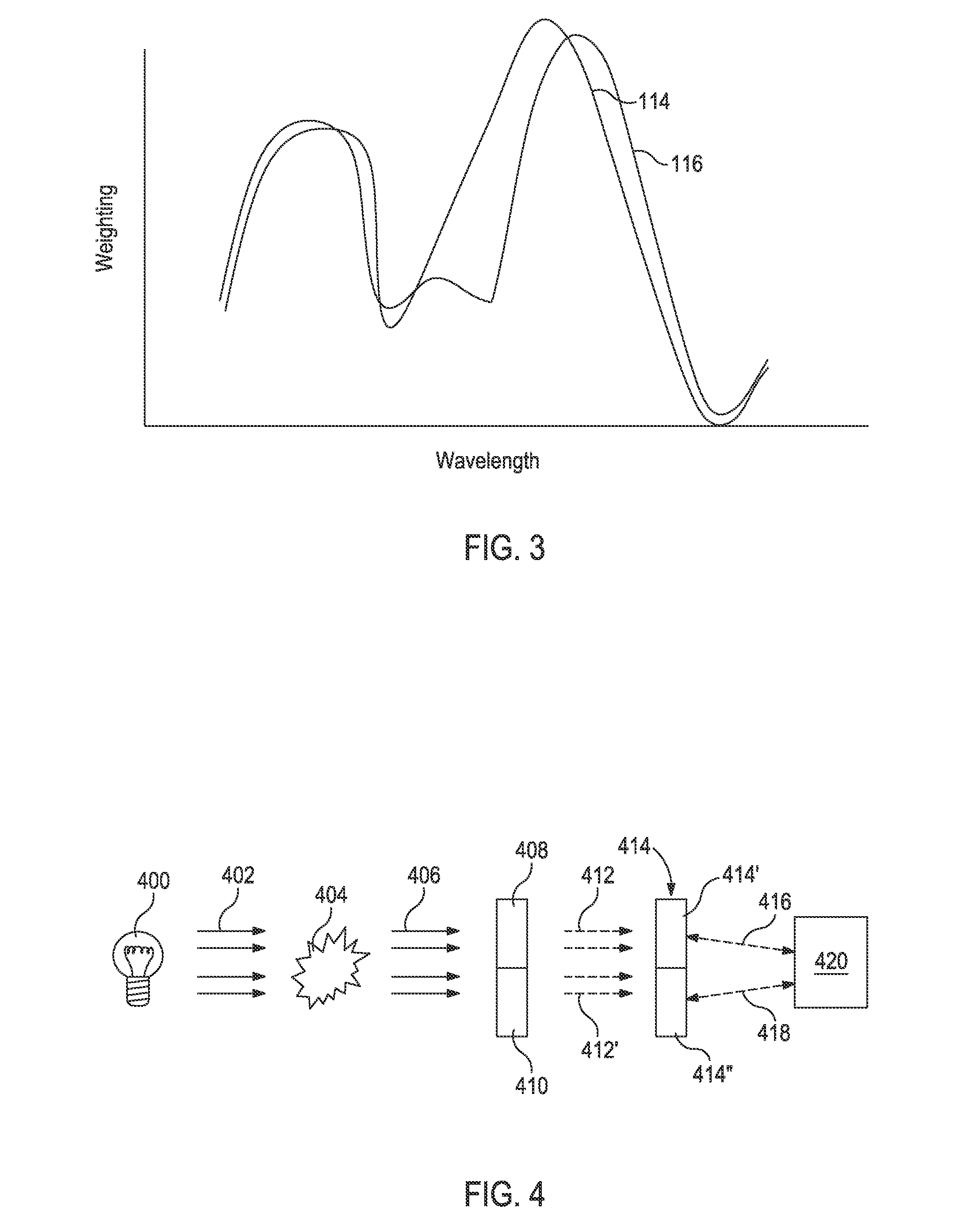
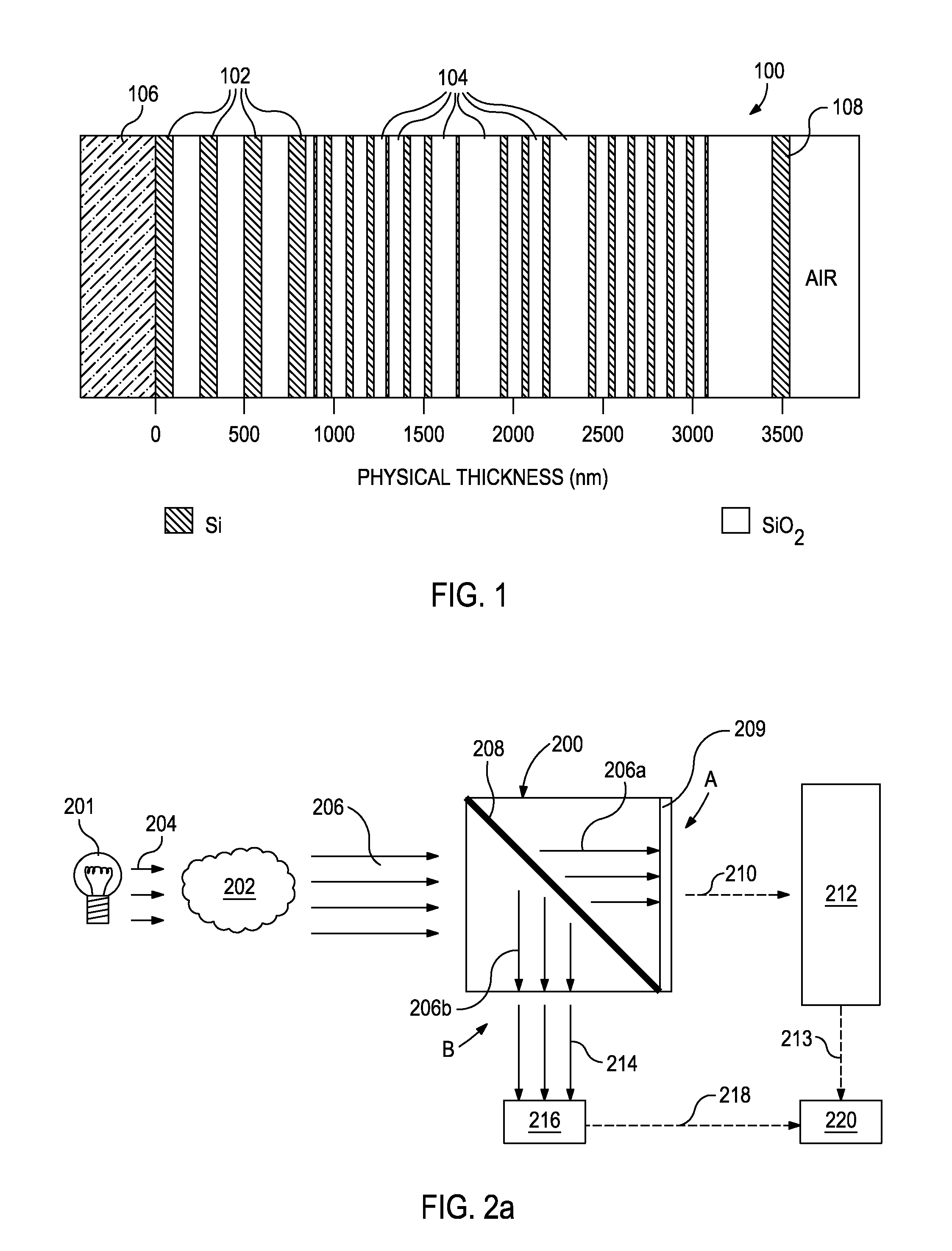
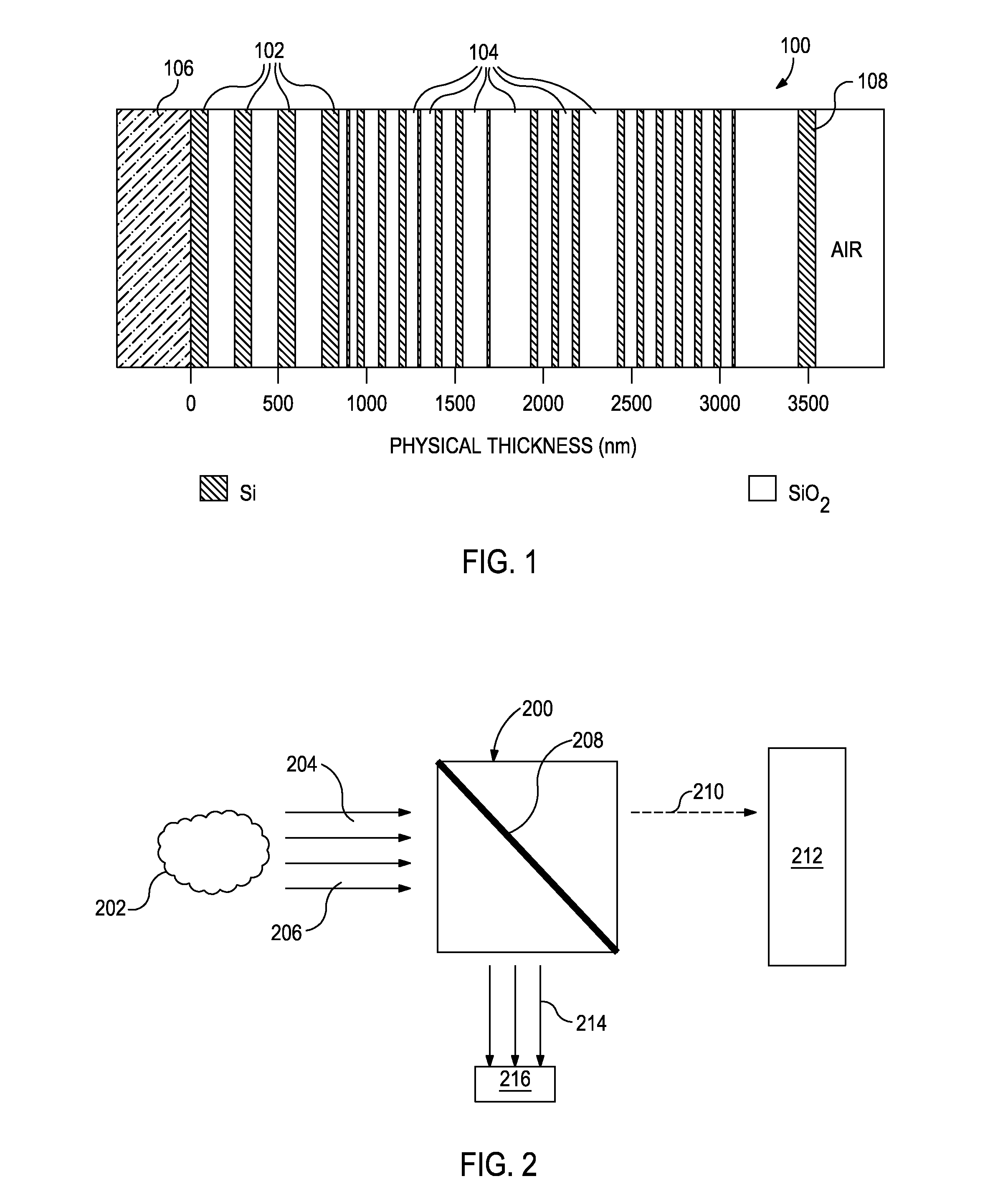
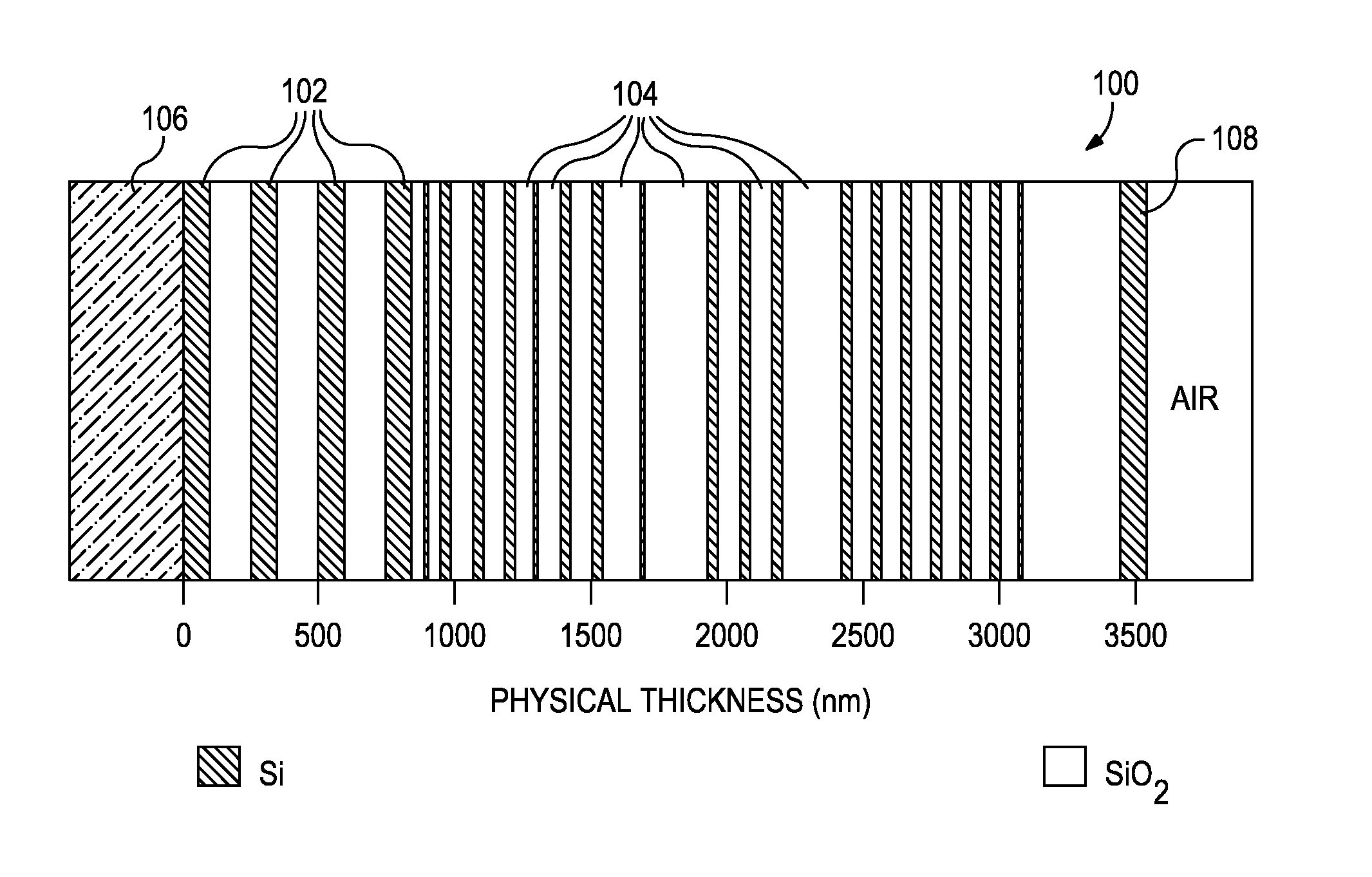
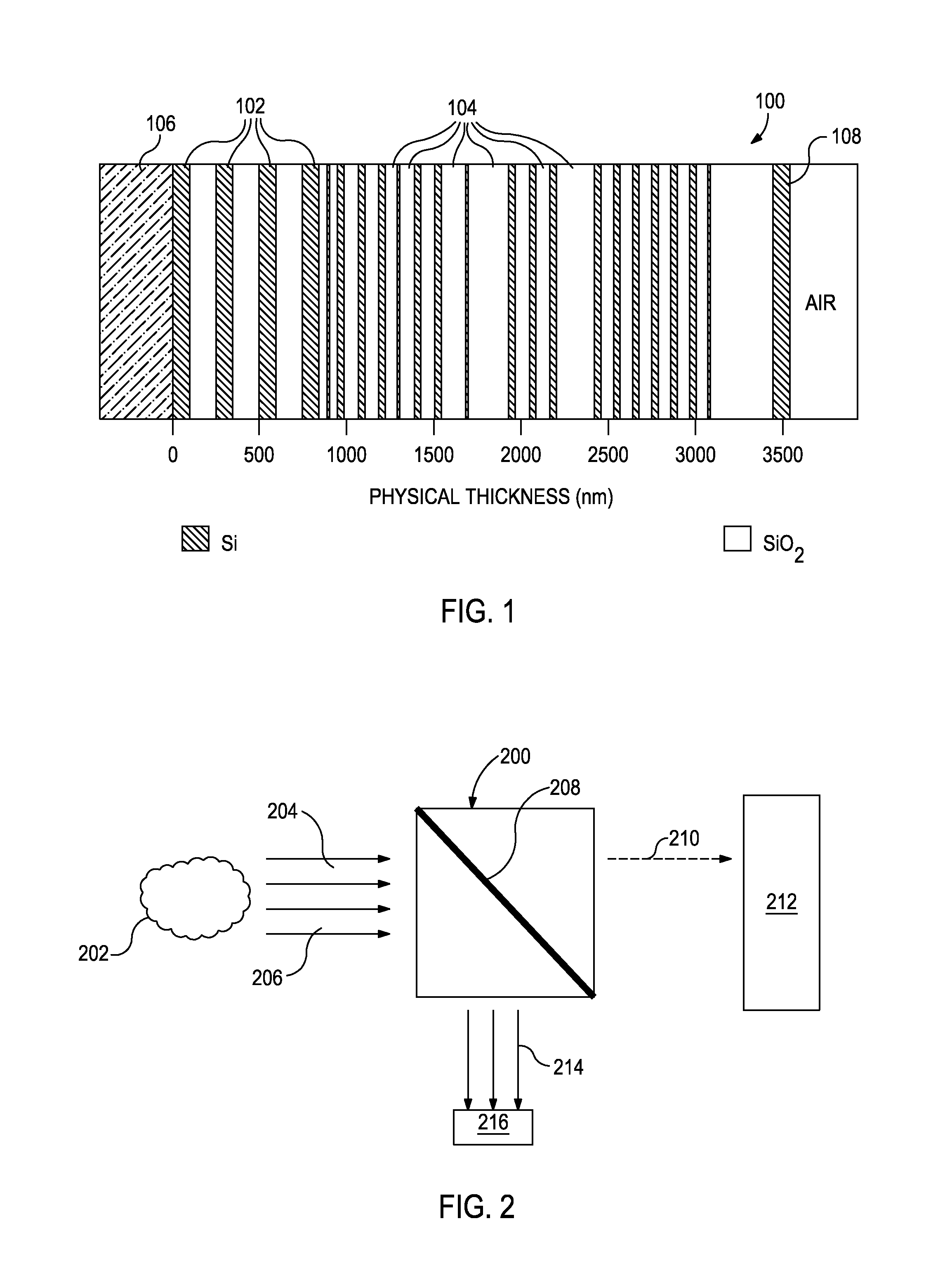
Filter design algorithm for multi-variate optical computing
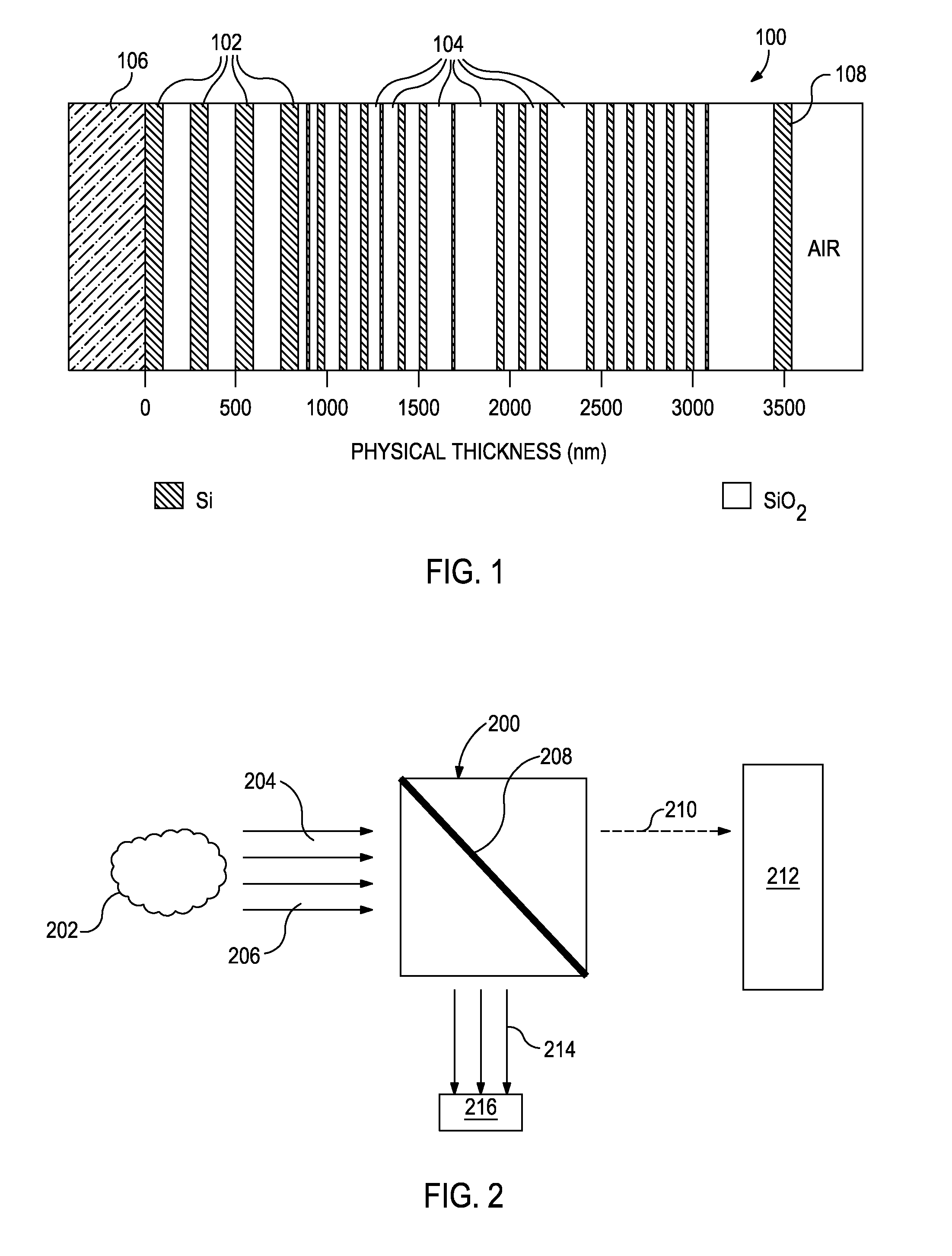
Within a method of making an optical interference filter, sample spectra and measurements of a predetermined characteristic associated with respective spectra are provided. Upon selection of an initial number of filter layers and a thickness for each layer, a transmission spectrum is determined. Each sample spectrum is applied to a regression formula that relates interaction of light with the transmission spectrum to a regression value. A comparison relationship between the calculated regression values and the sample measurements is defined and optimized, wherein thickness of each layer is an optimization variable.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
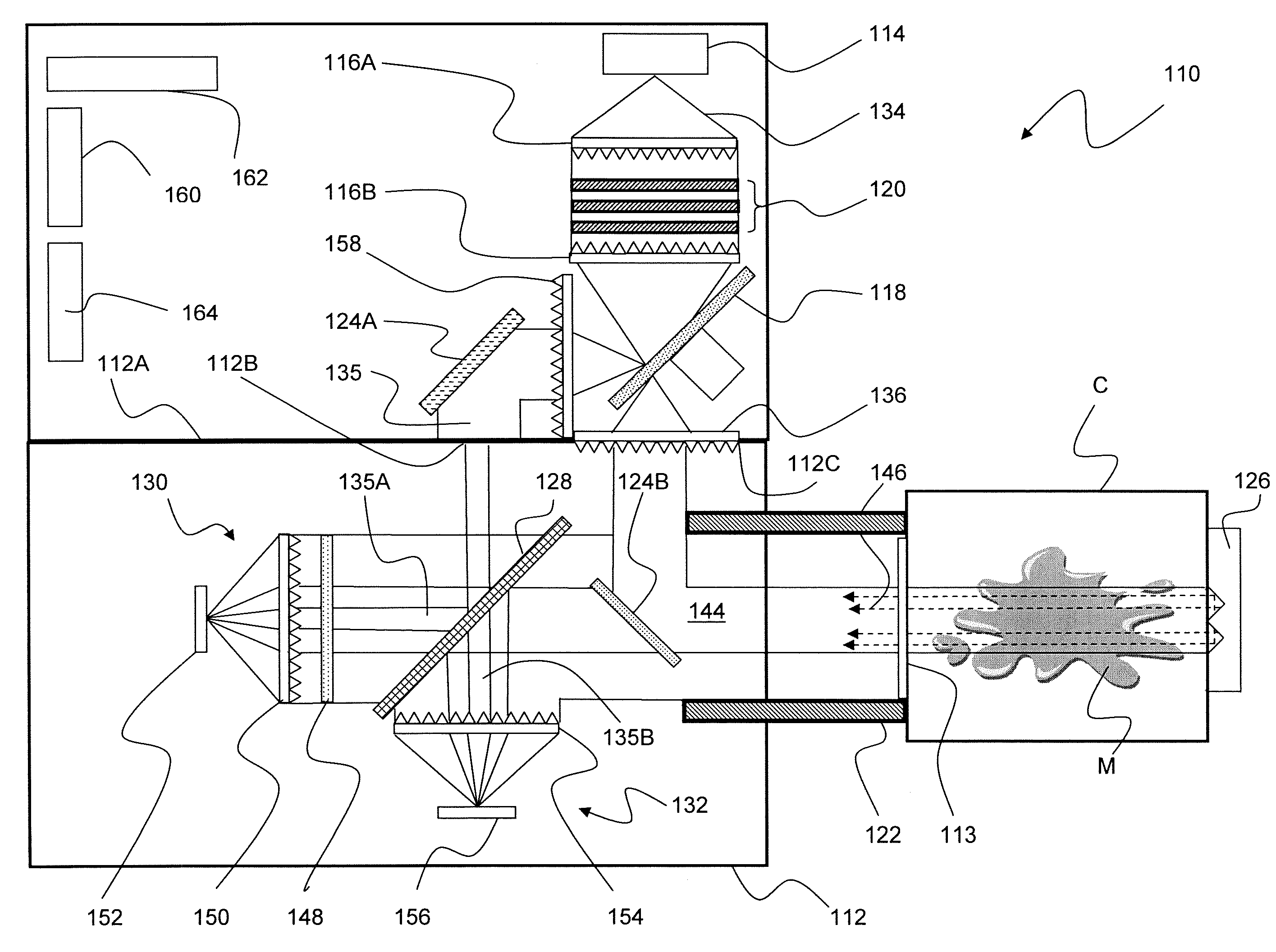
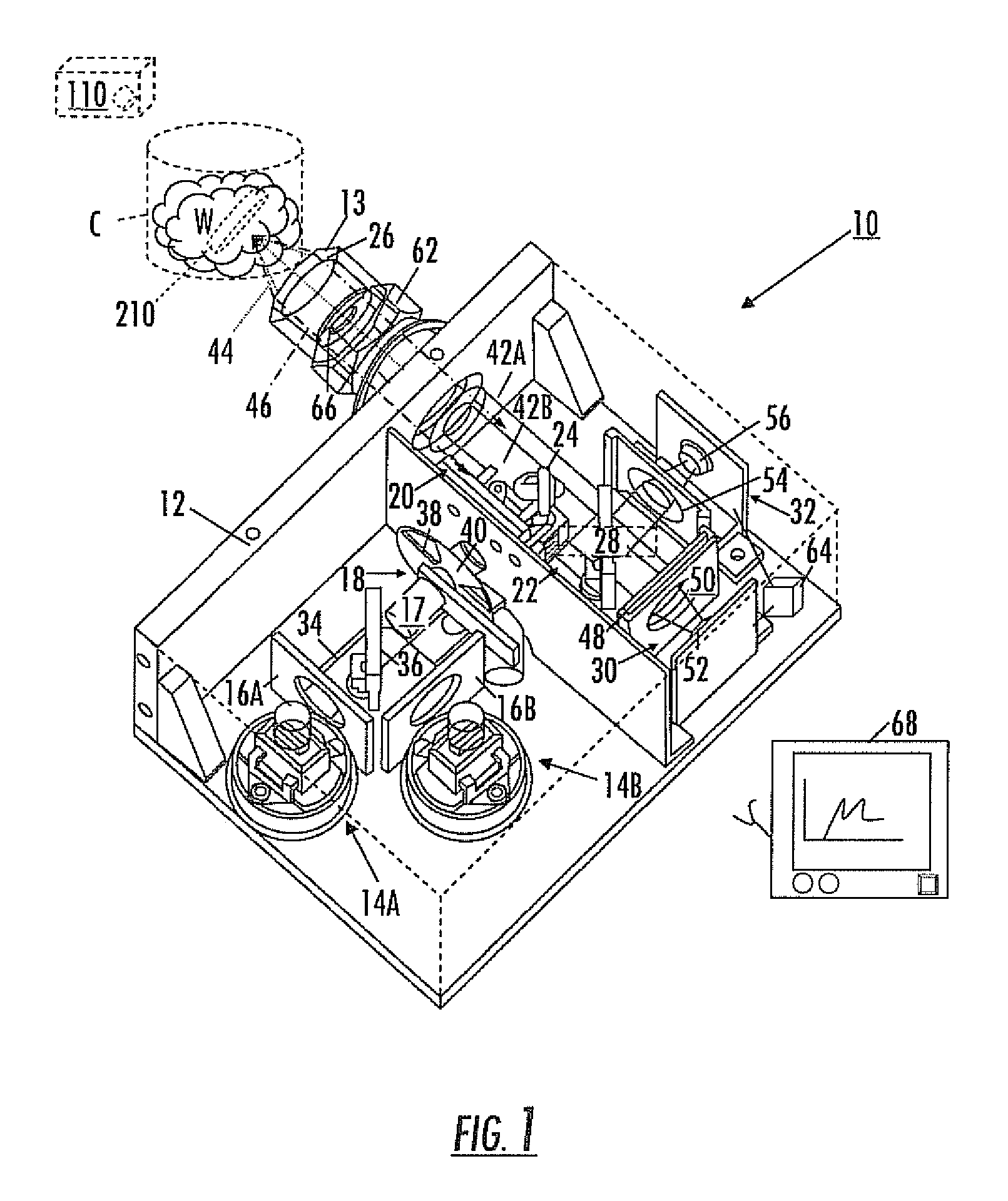
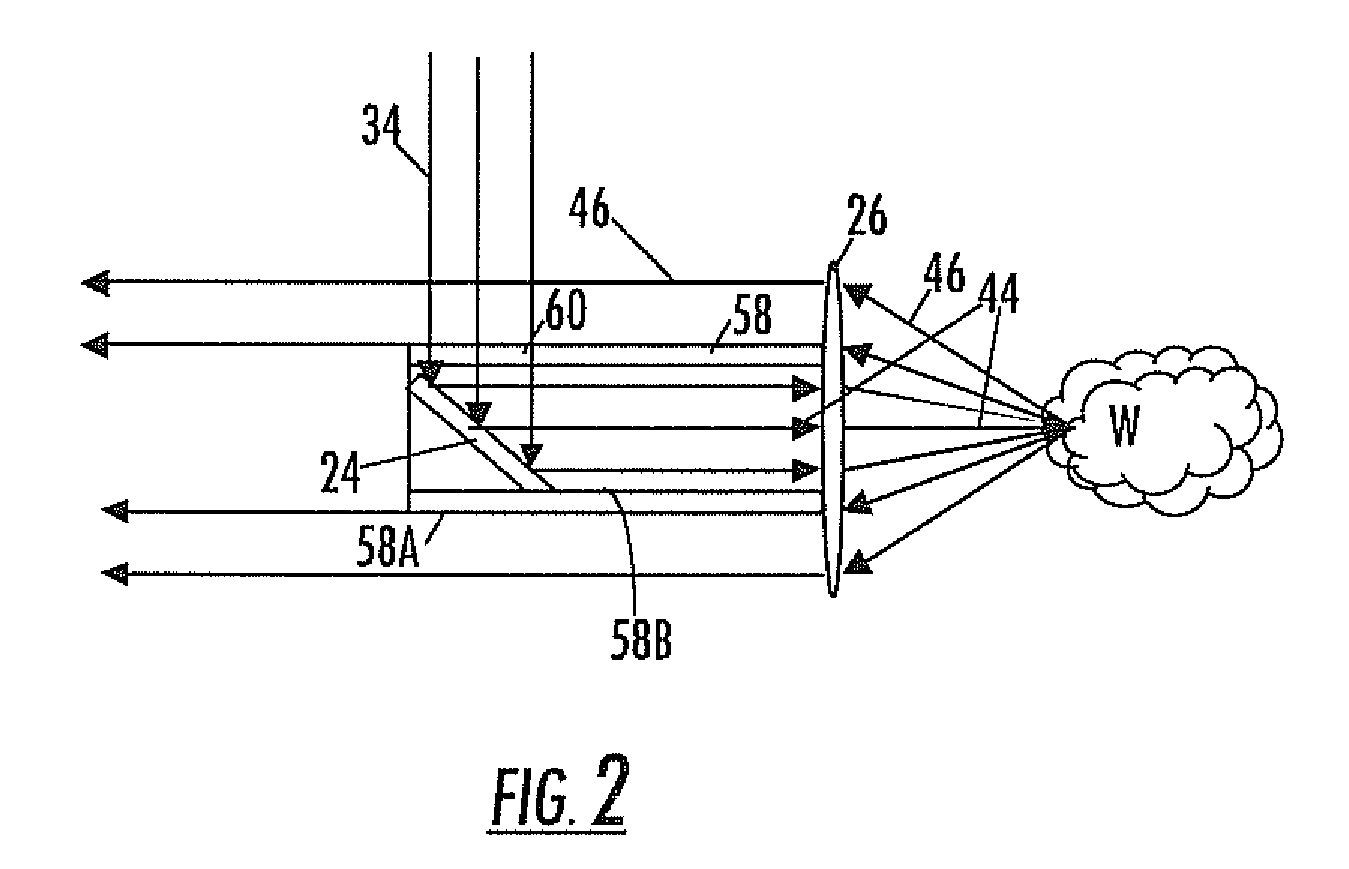
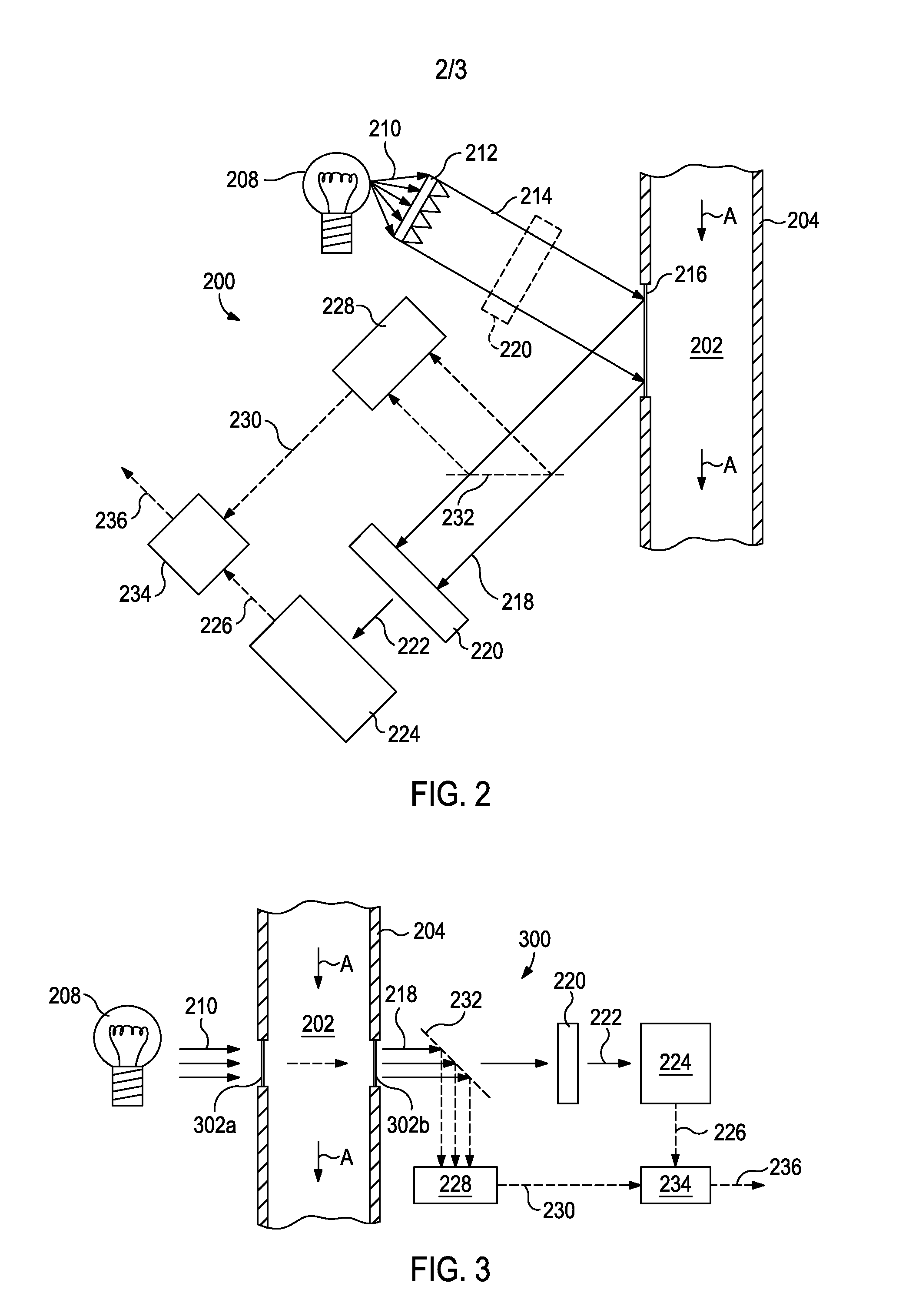
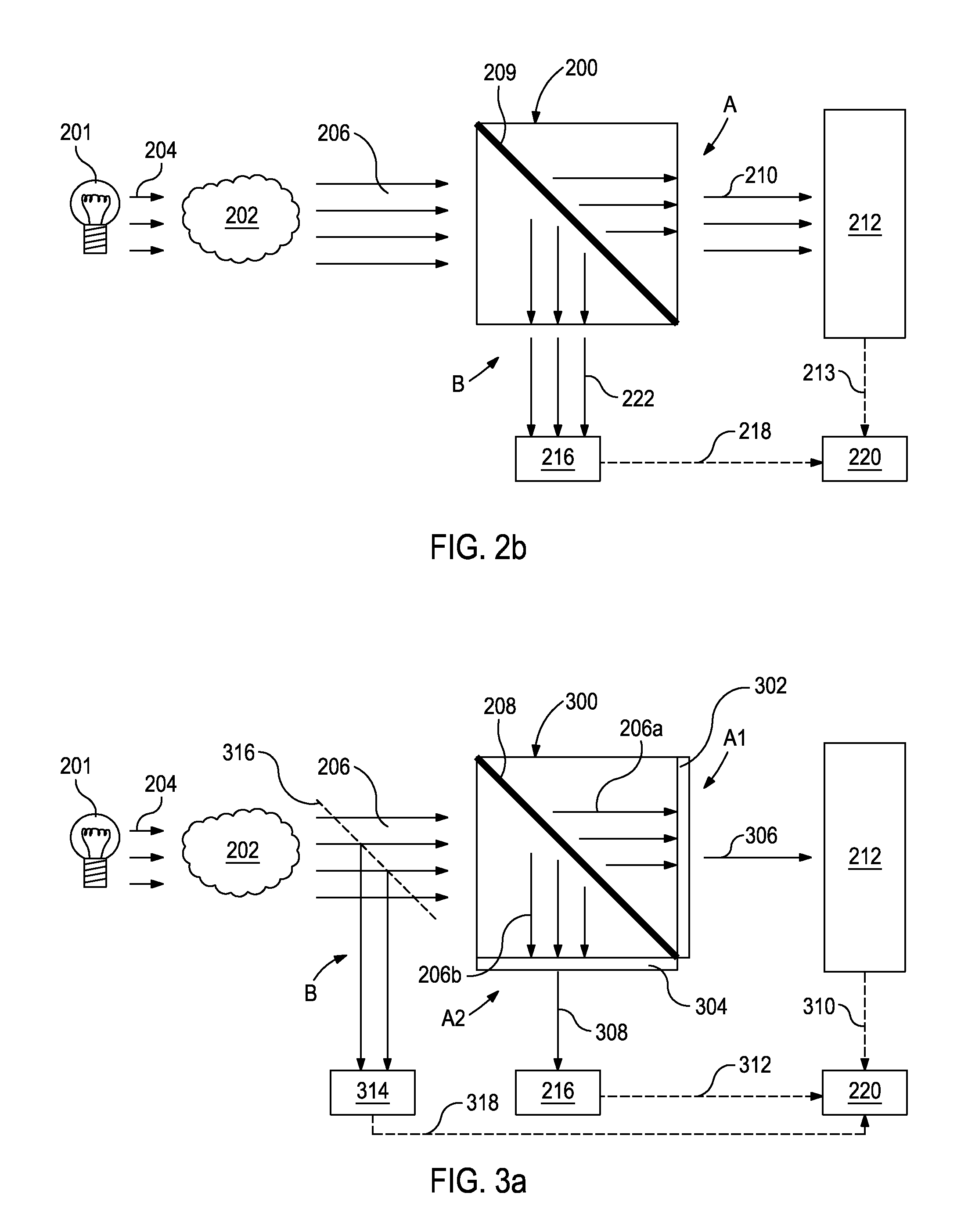
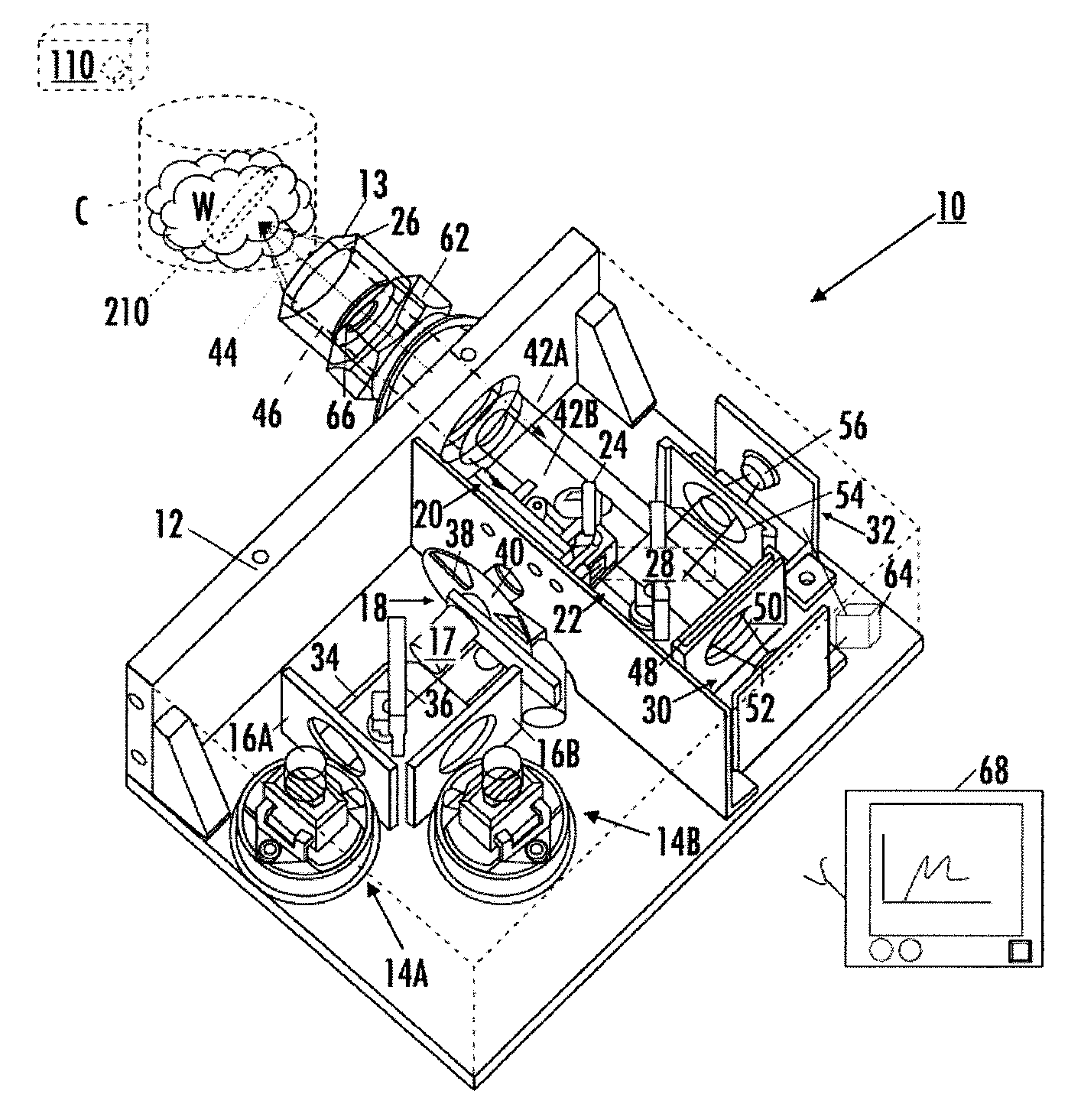
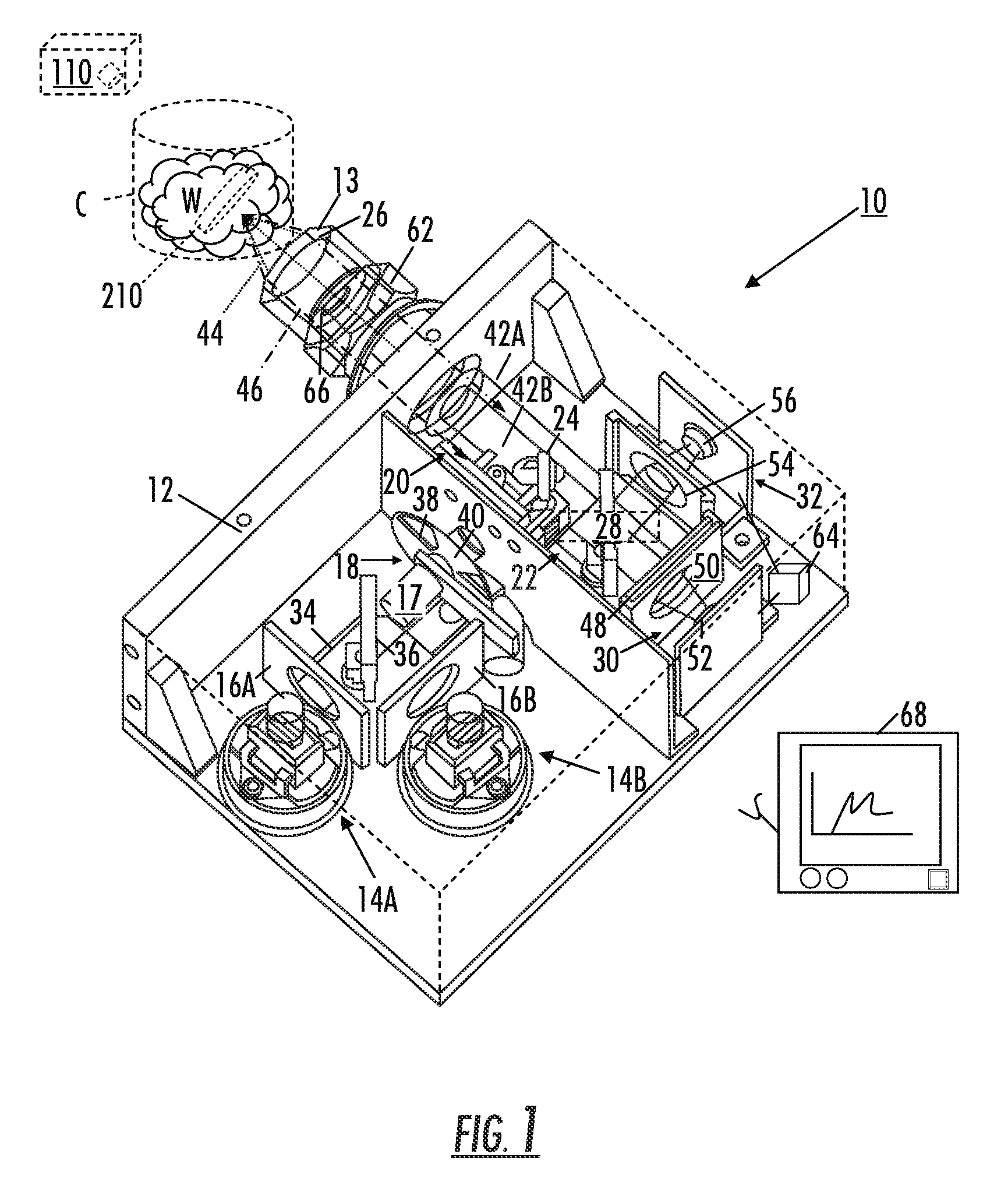
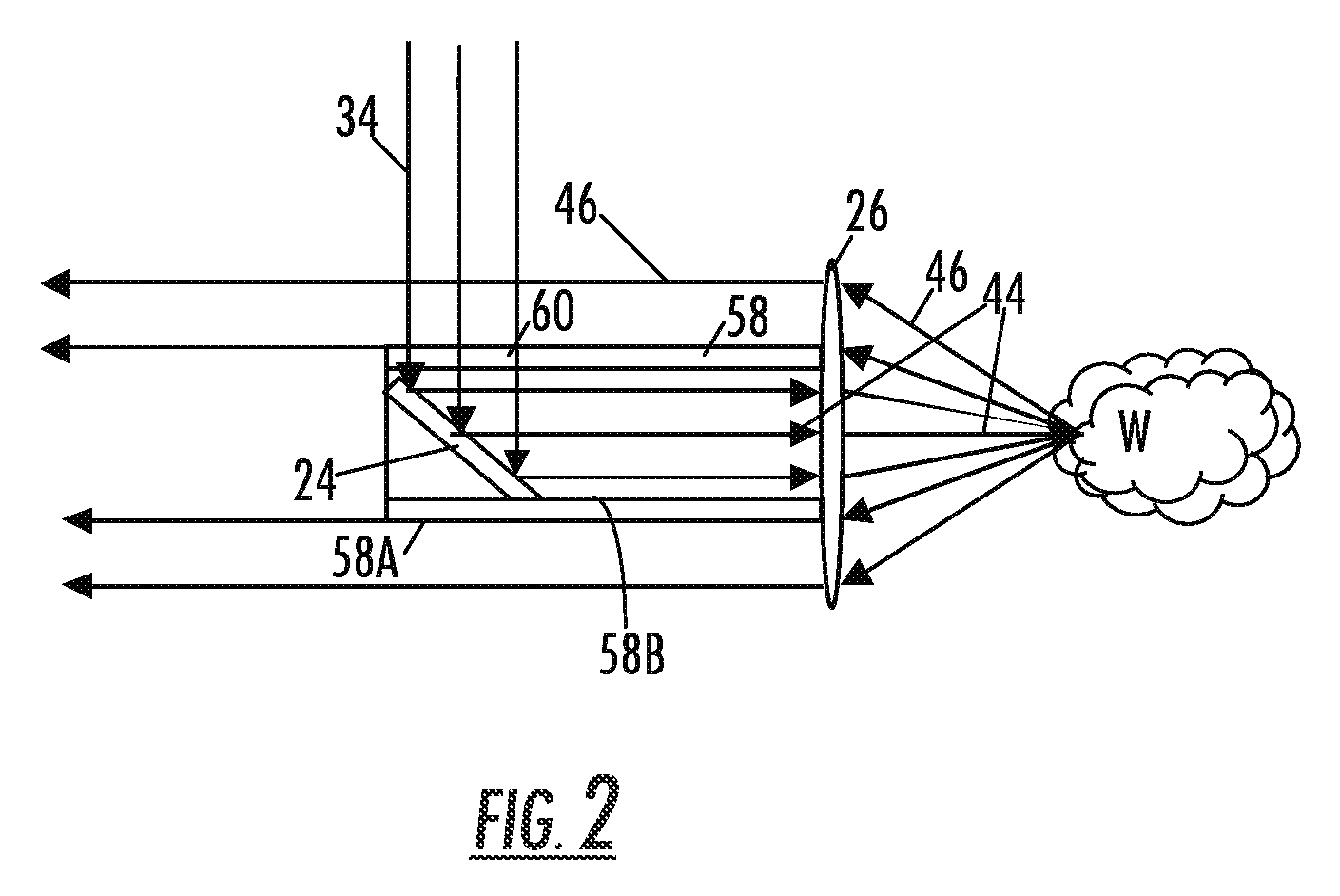
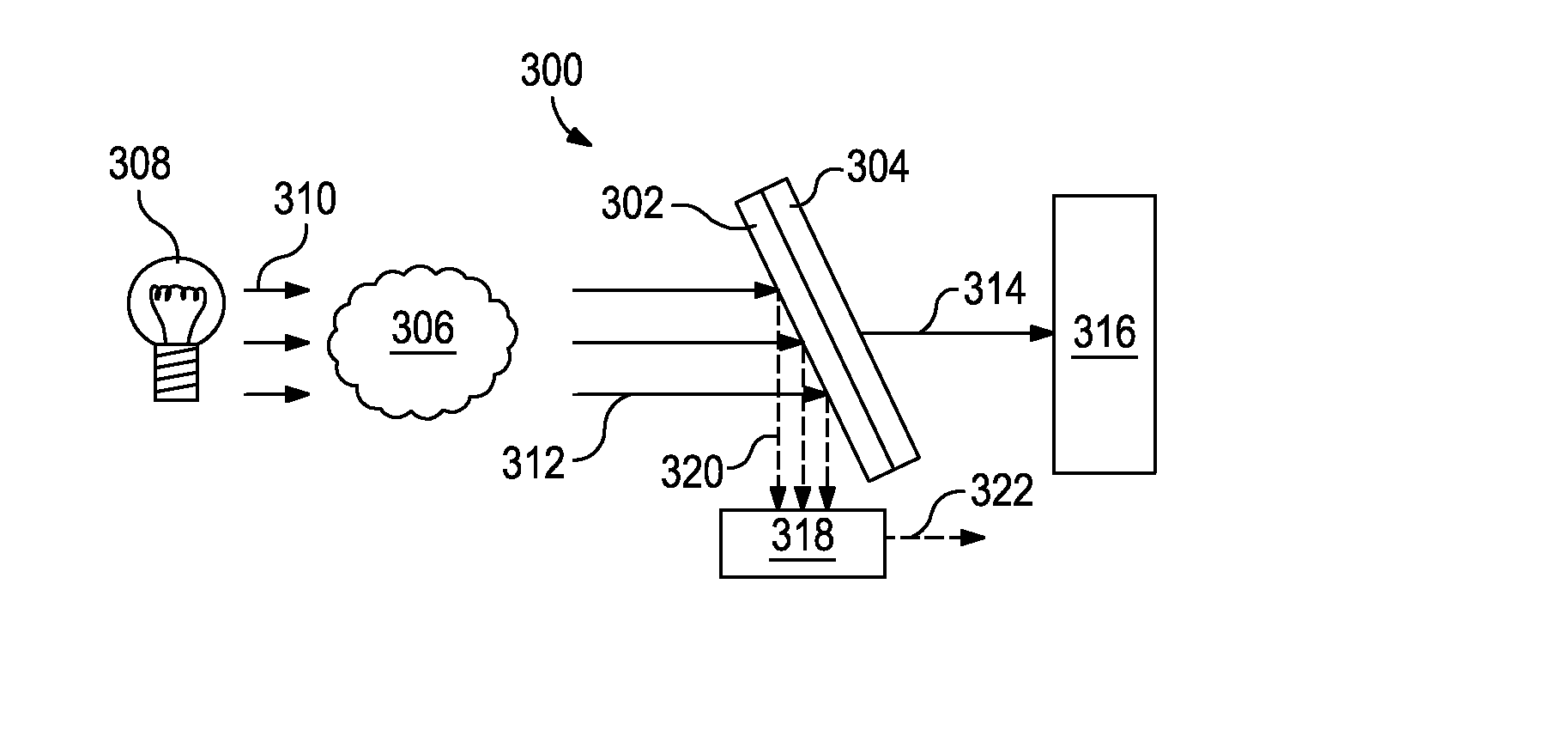
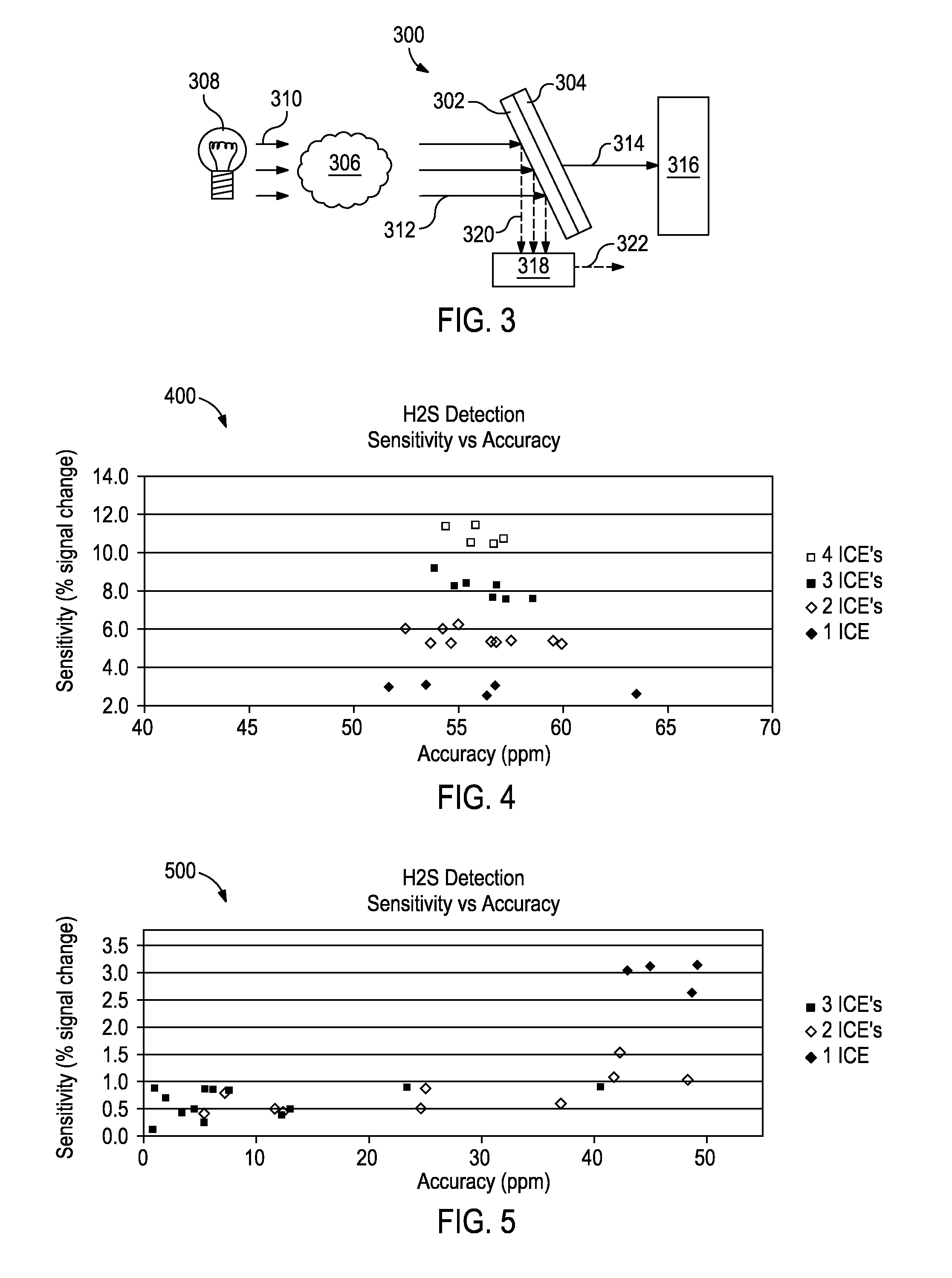
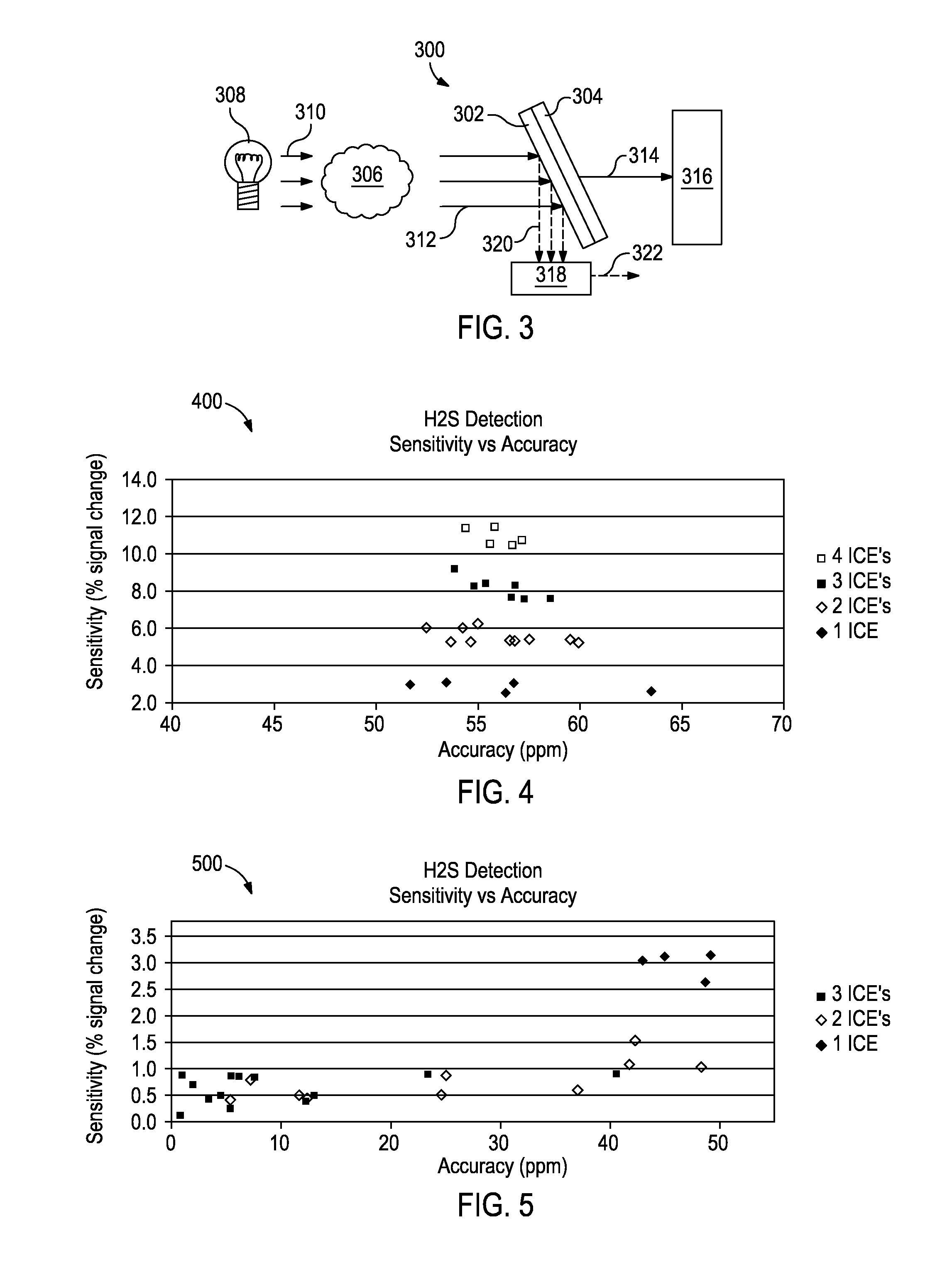
Optical analysis systems and methods for dynamic, high-speed detection and real-time multivariate optical computing
ActiveUS7623233B2Simple and economical to manufacture and assemble and useReduce noiseRadiation pyrometryInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsOptic lensOptical computing
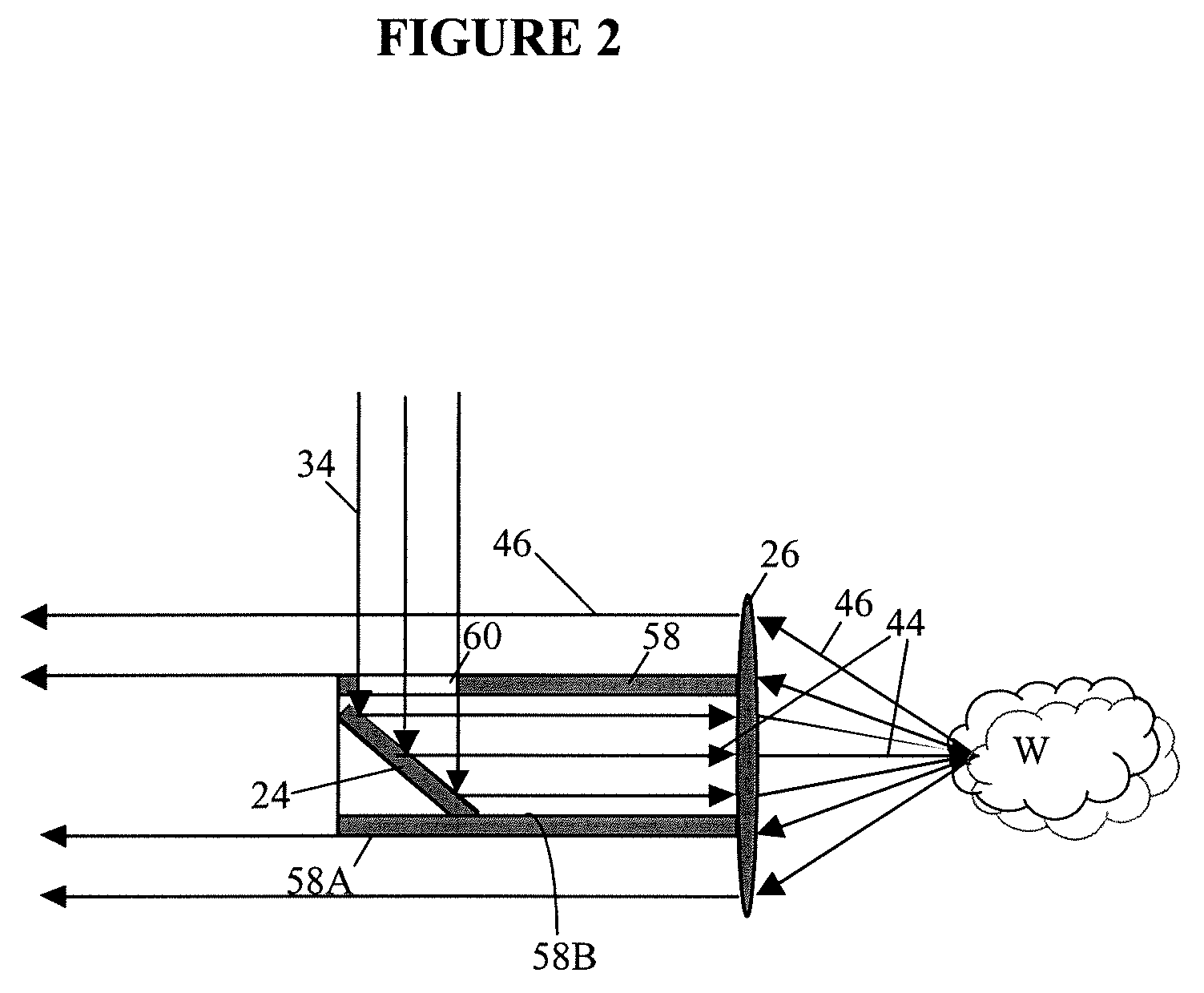
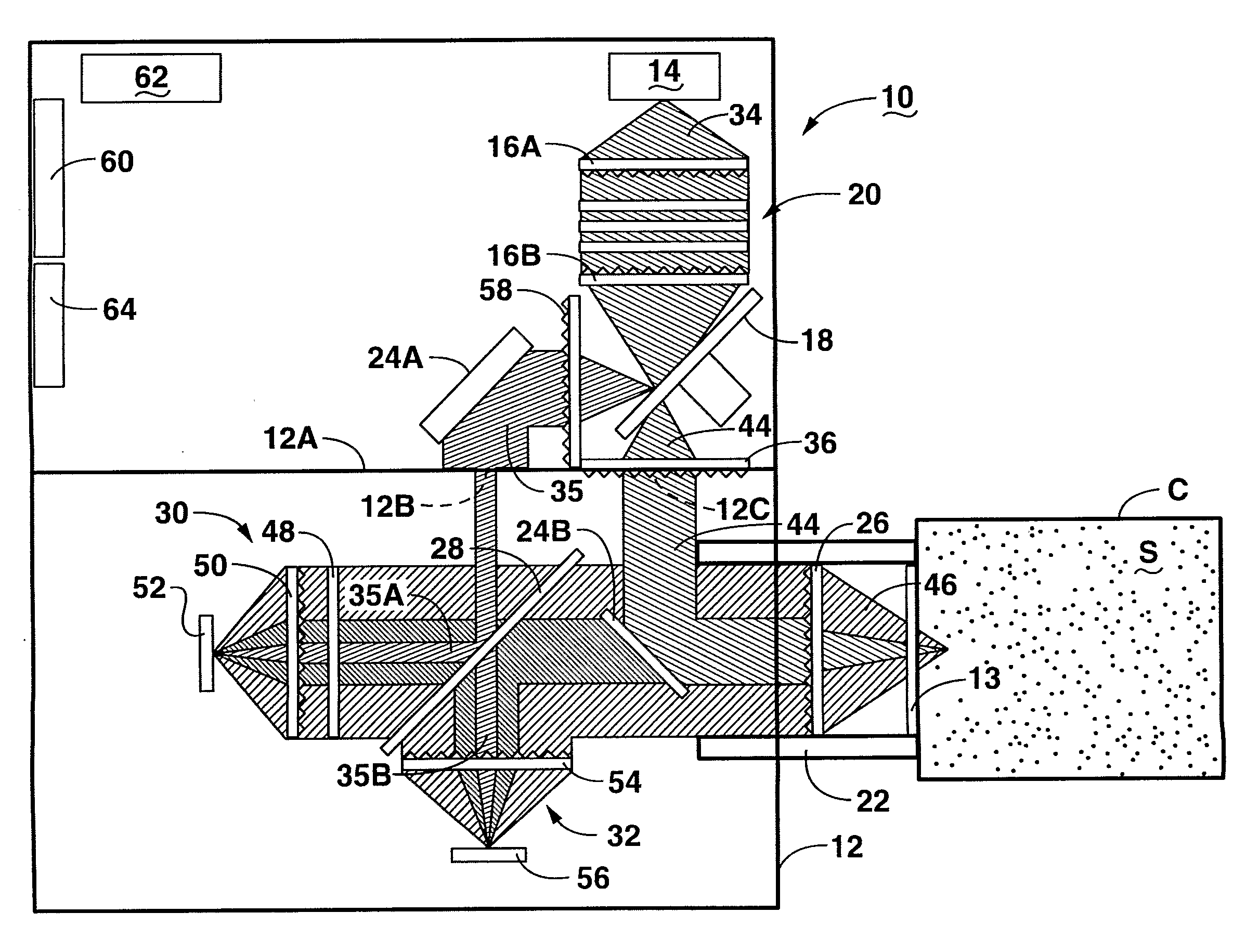
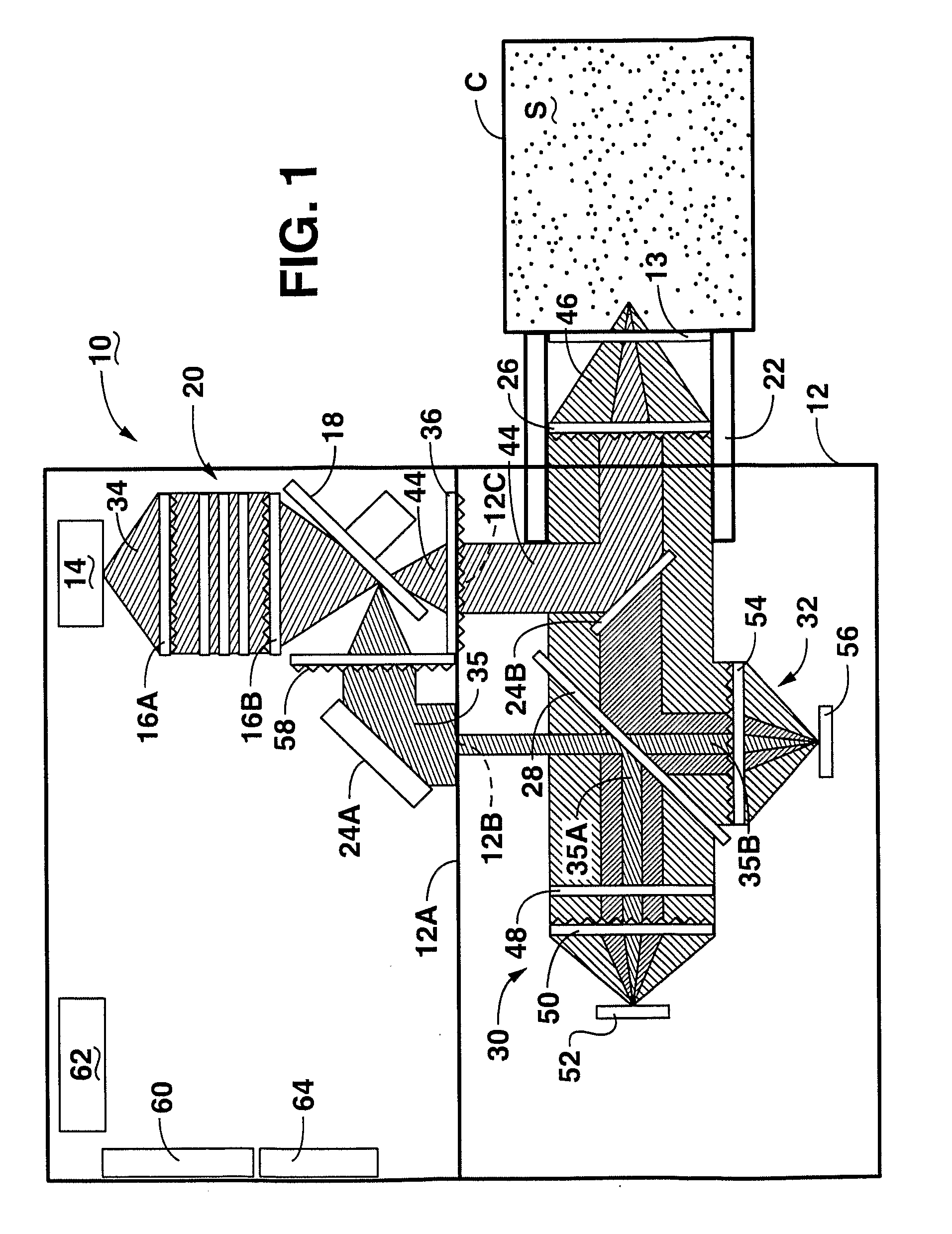
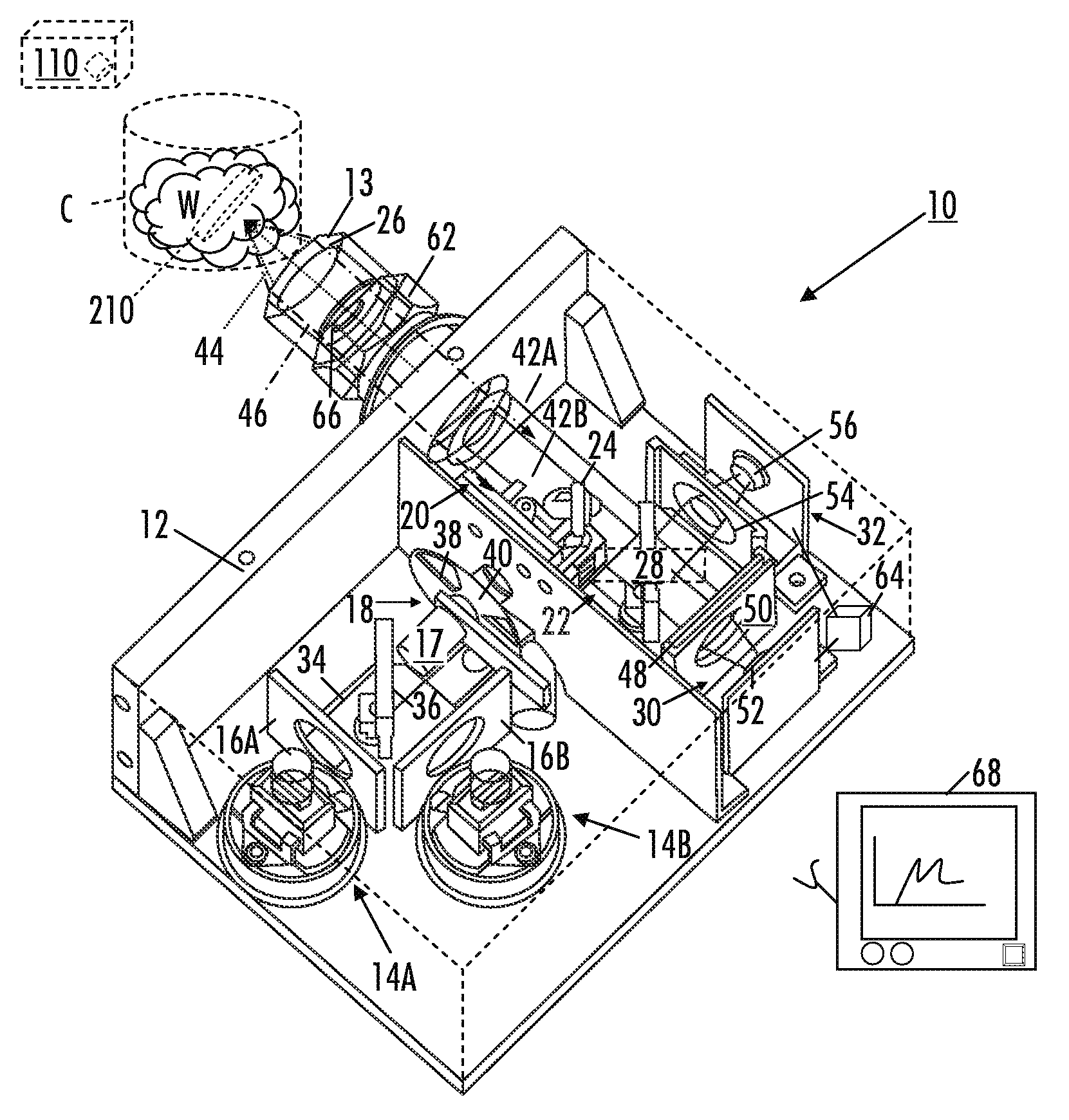
Multivariate optical analysis systems employ multivariate optical elements and utilize multivariate optical computing methods to determine information about a product carried by light reflected from or transmitted through the product. One method of processing and monitoring the product includes introducing the product at an inspection point; illuminating the product with a spectral-specific light though an optic lens; directing the light that has passed through at least a section of the product through at least one multivariate optical element to produce a first signal, the directed light carrying information about the product; detecting the first signal at a first detector; deflecting a portion of the directed light to produce a second signal in a direction of a second detector, the second detector configured to detect the second signal; and determining at least one property of the product at a rate of about one section of the product per second to about five sections of the product per second based upon the detector outputs.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
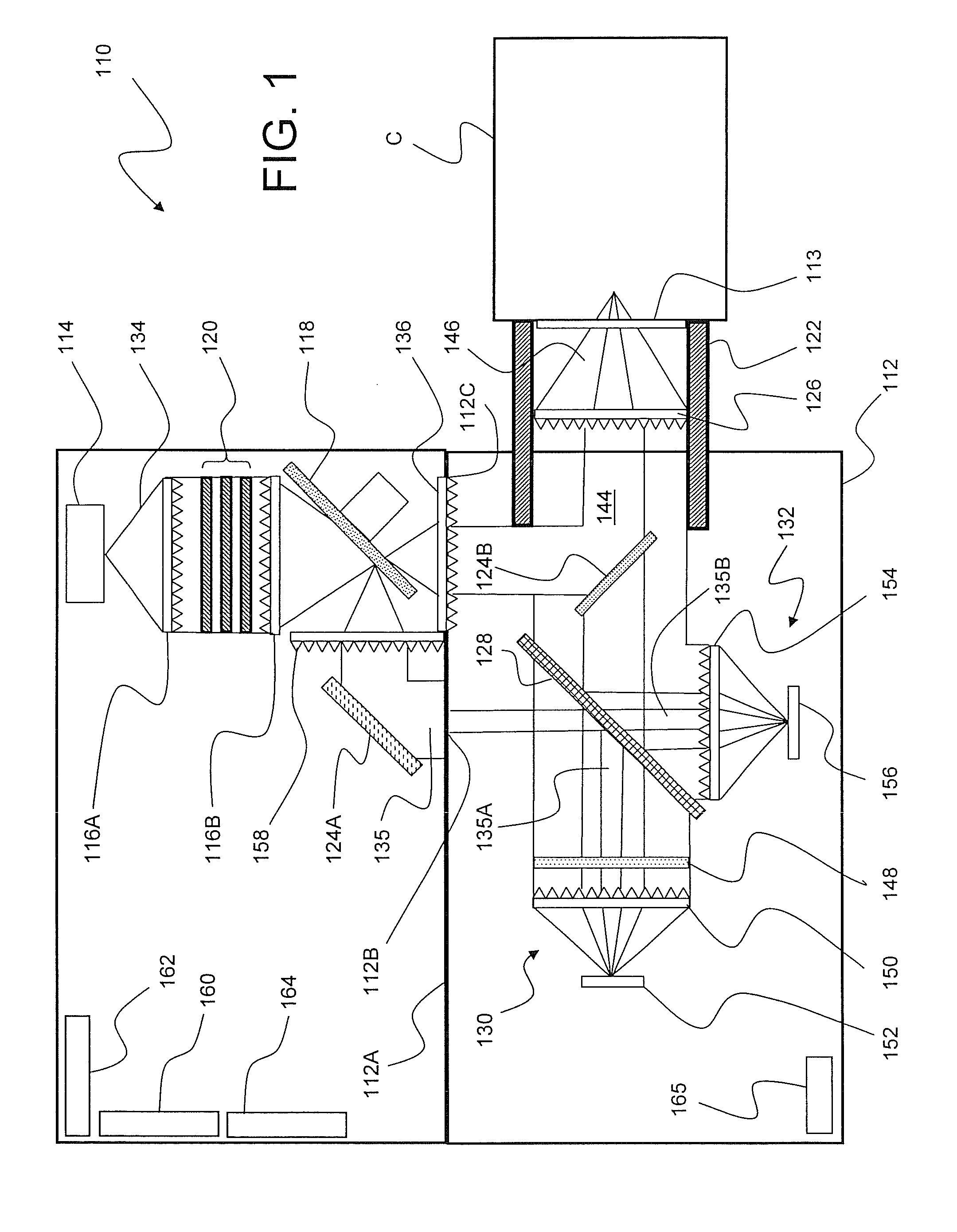
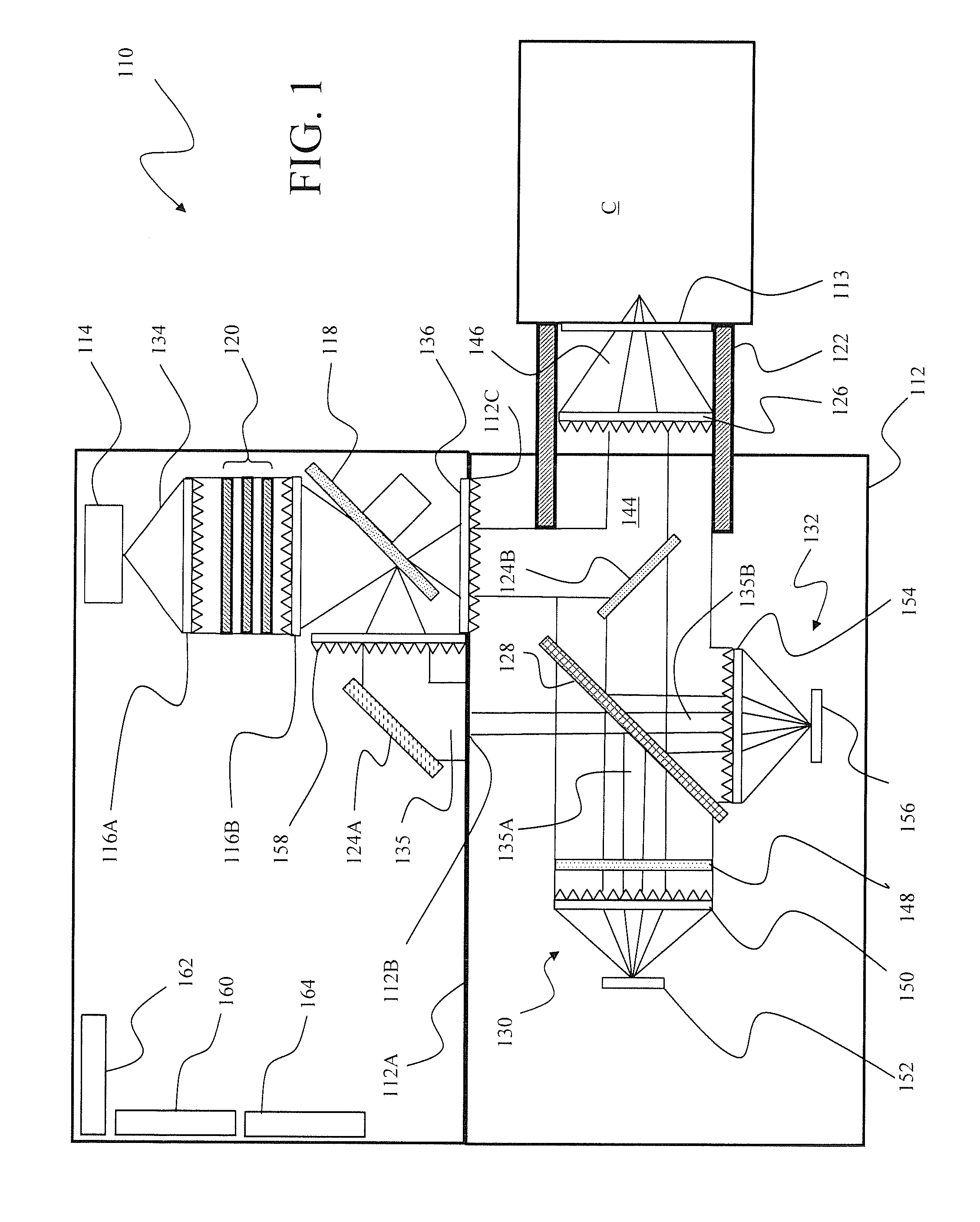
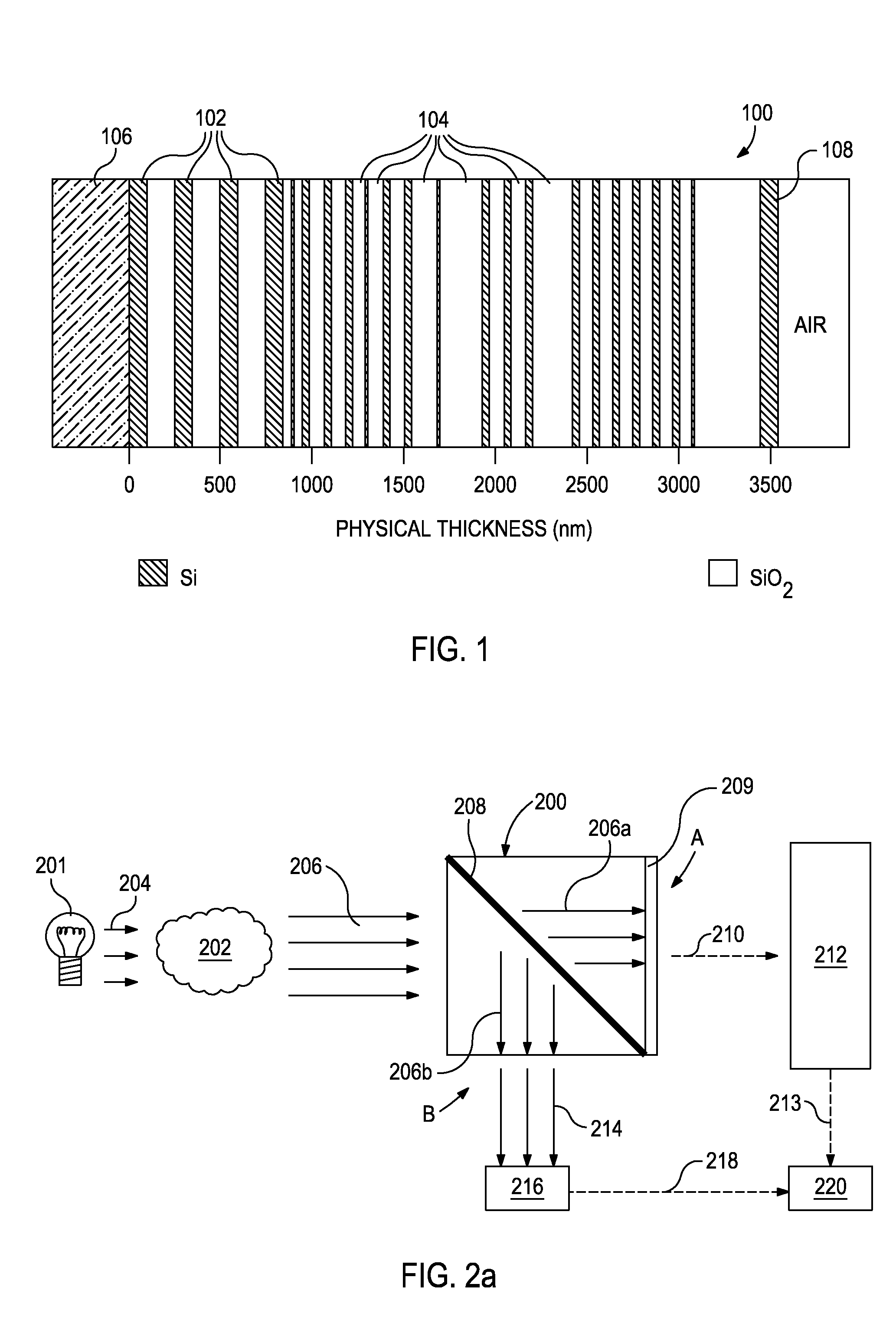
Optical analysis system and optical train
ActiveUS7834999B2Minimize erroneousMinimize cross-talkRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationLight beamOptic system
A multivariate optical computing and analysis system includes a light source configured to radiate a first light along a first ray path; a modulator disposed in the first ray path, the modulator configured to modulate the first light to a desired frequency; a spectral element disposed proximate the modulator, the spectral element configured to filter the first light for a spectral range of interest of a sample; a cavity disposed in communication with the spectral element, the cavity configured to direct the first light in a direction of the sample; a tube disposed proximate the cavity, the tube configured to receive and direct a second light generated by a reflection of the first light from the sample, the tube being further configured to separate the first and second lights; a beamsplitter configured to split the second light into a first beam and a second beam; an optical filter mechanism disposed to receive the first beam, the optical filter mechanism configured to optically filter data carried by the first beam into at least one orthogonal component of the first beam; and a detector mechanism in communication with the optical filter mechanism to measure a property of the orthogonal component to measure the data.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
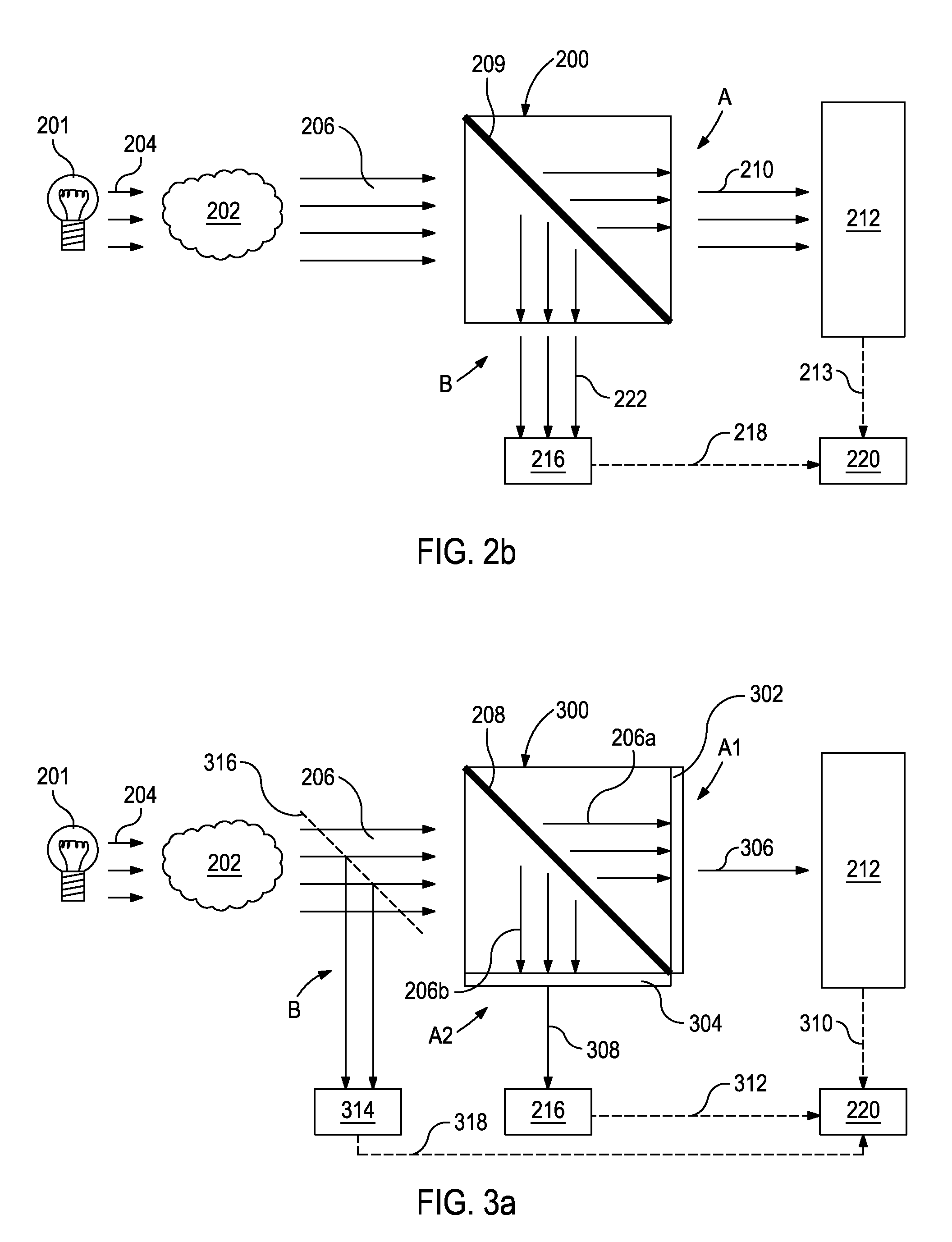
Optical analysis system and methods for operating multivariate optical elements in a normal incidence orientation
ActiveUS20090073433A1Reduce sensitivityCosmetic preparationsRadiation pyrometryOptical computingLight source
A method of arranging and utilizing a multivariate optical computing and analysis system includes transmitting a o first light from a light source; generating a second light by reflecting the first light from the sample; directing a portion of the second light with a beamsplitter; and arranging an optical filter mechanism in a normal incidence orientation to receive the portion of the second light, the optical filter mechanism being configured to optically filter data carried by the portion of the second light.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
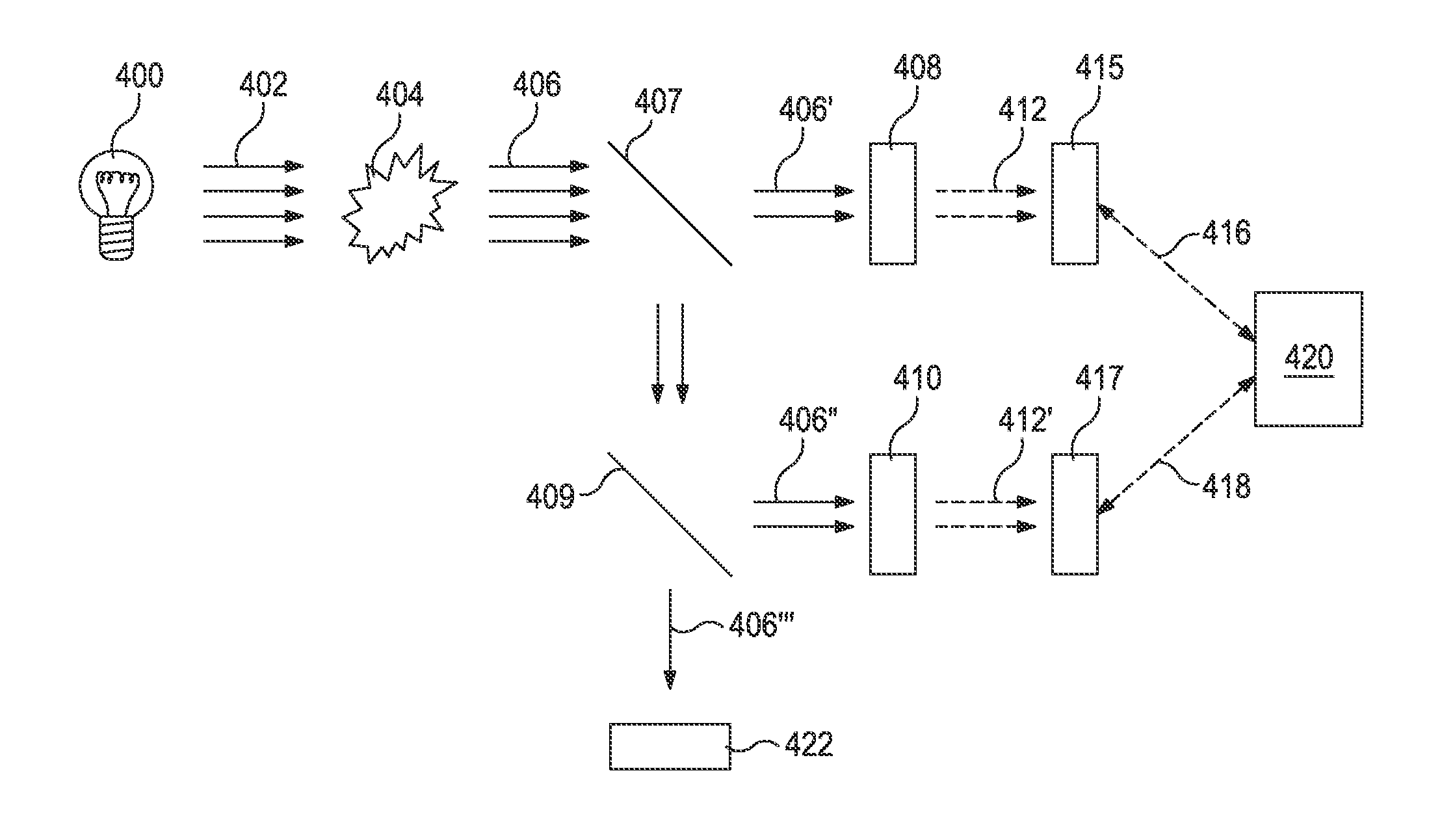
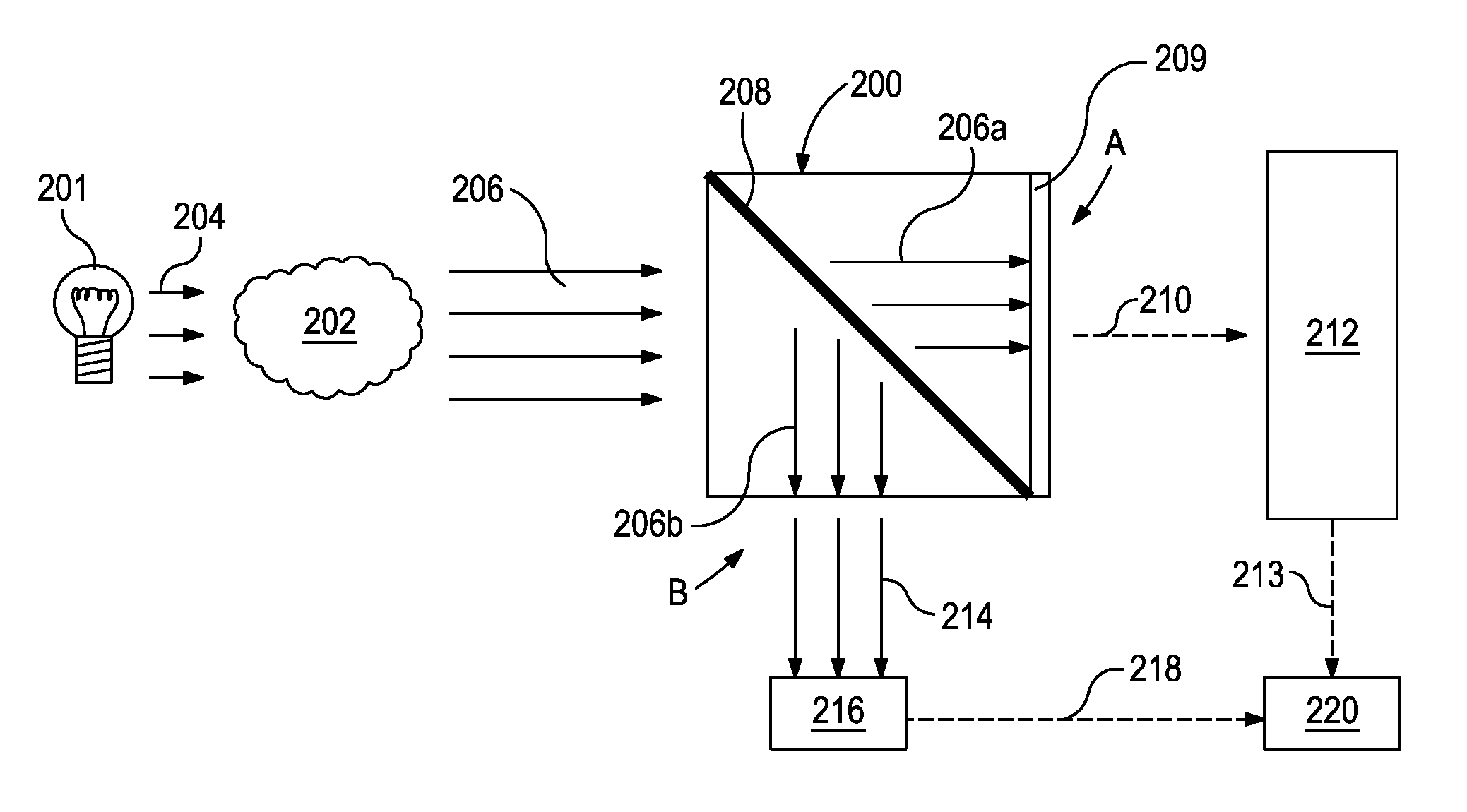
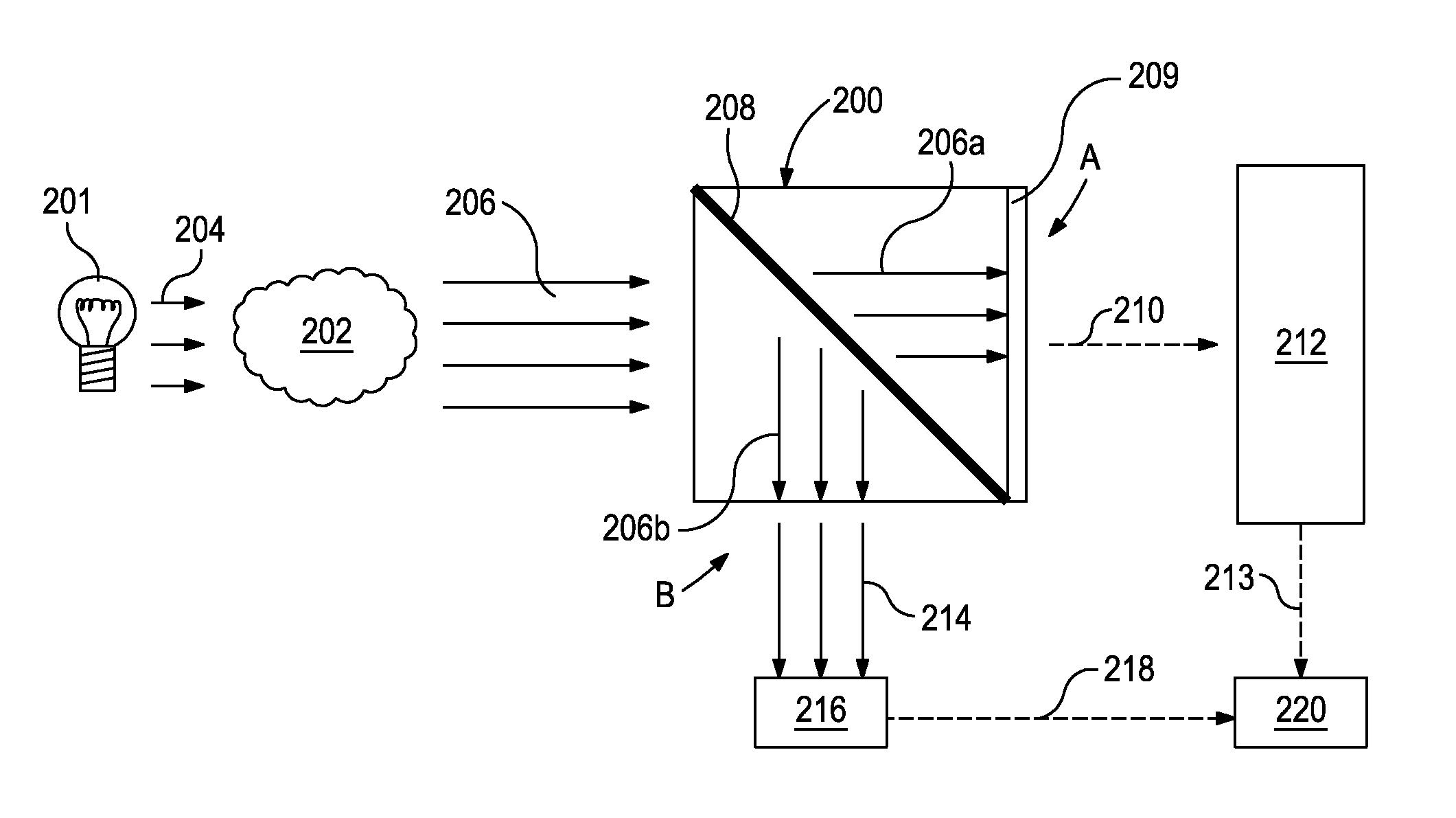
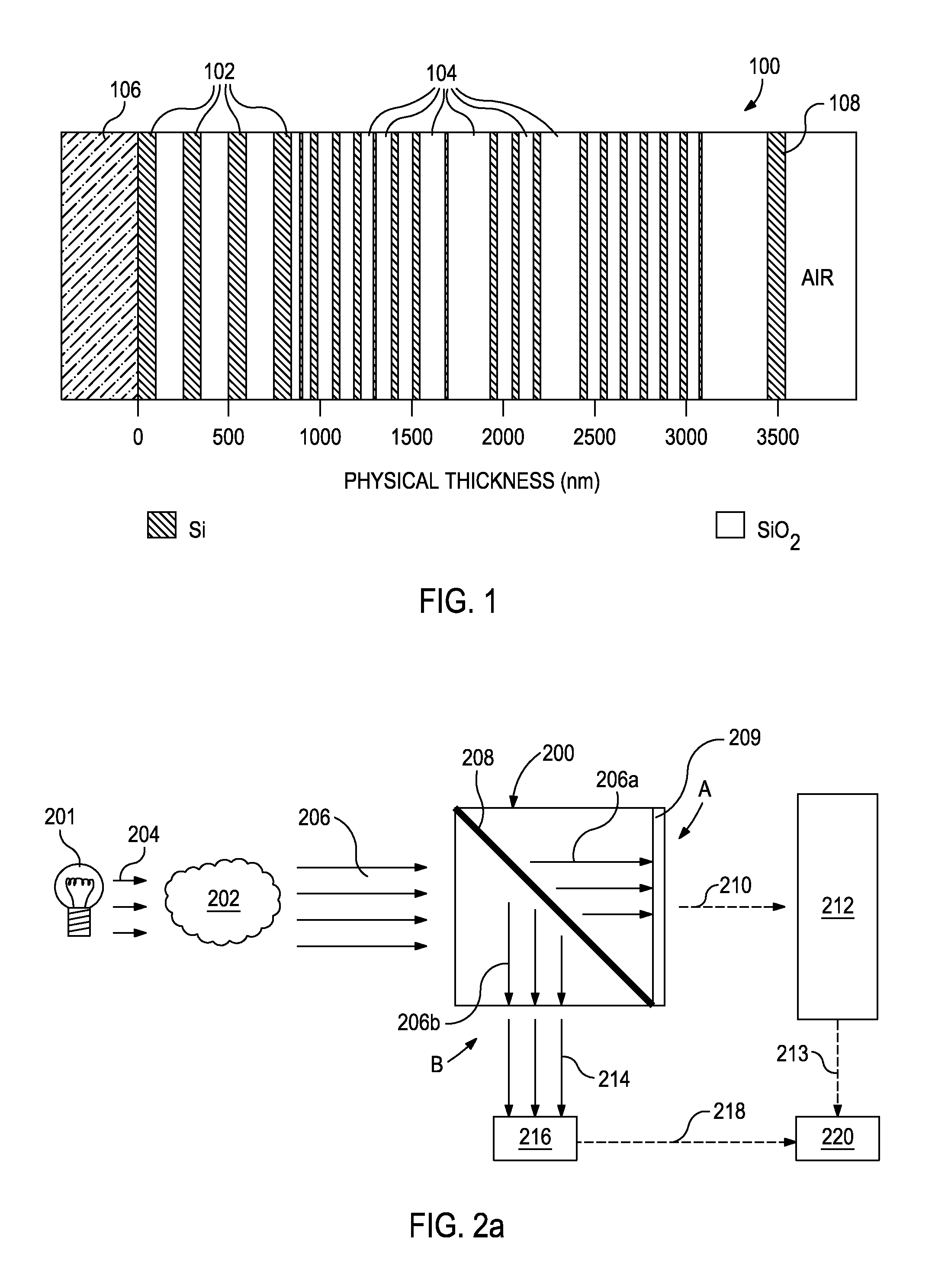
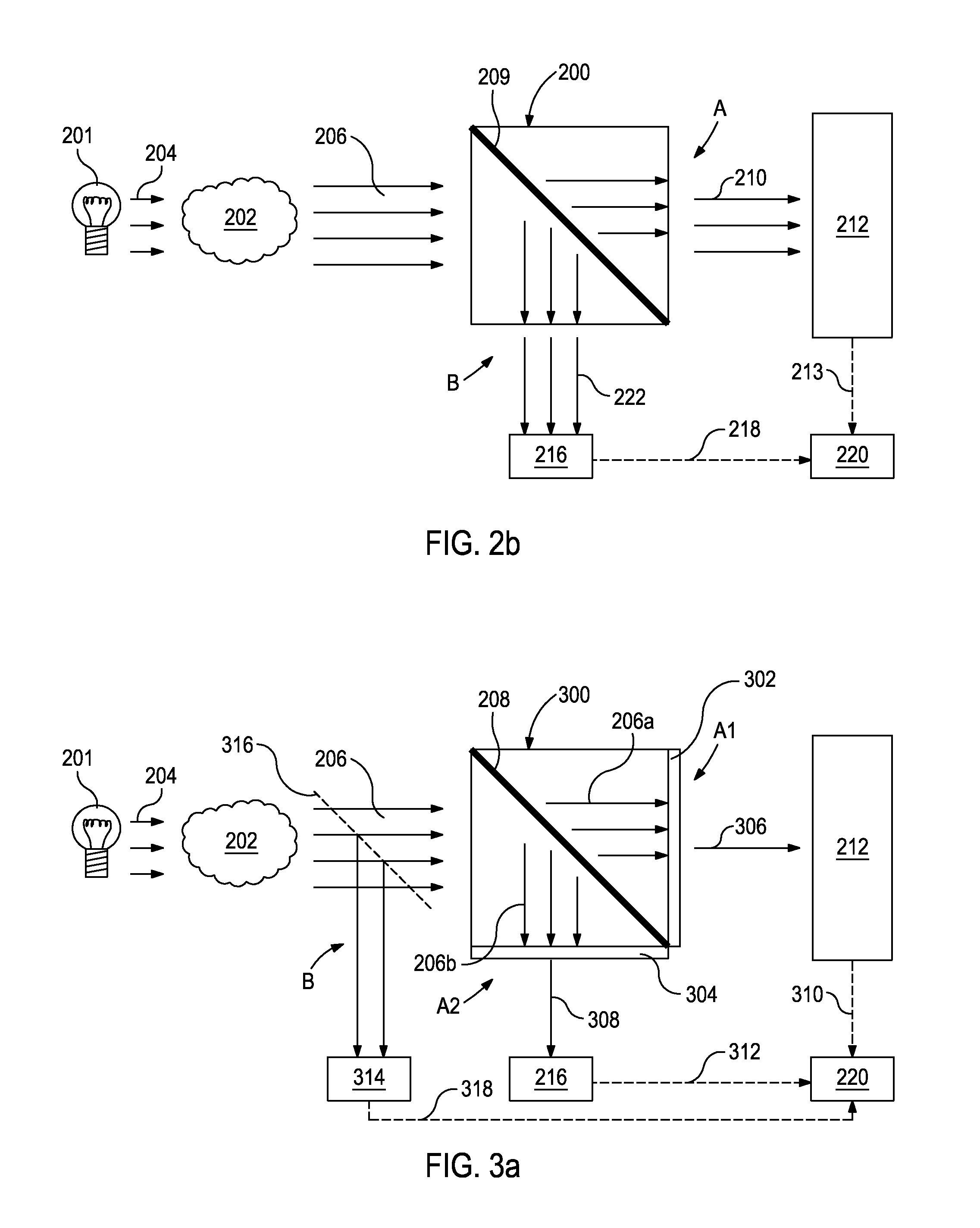
Devices Having an Integrated Computational Element and a Proximal Interferent Monitor and Methods for Determining a Characteristic of a Sample Therewith
ActiveUS20130287061A1Accurate signalThermometer detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansElectromagnetic radiationSignal processing
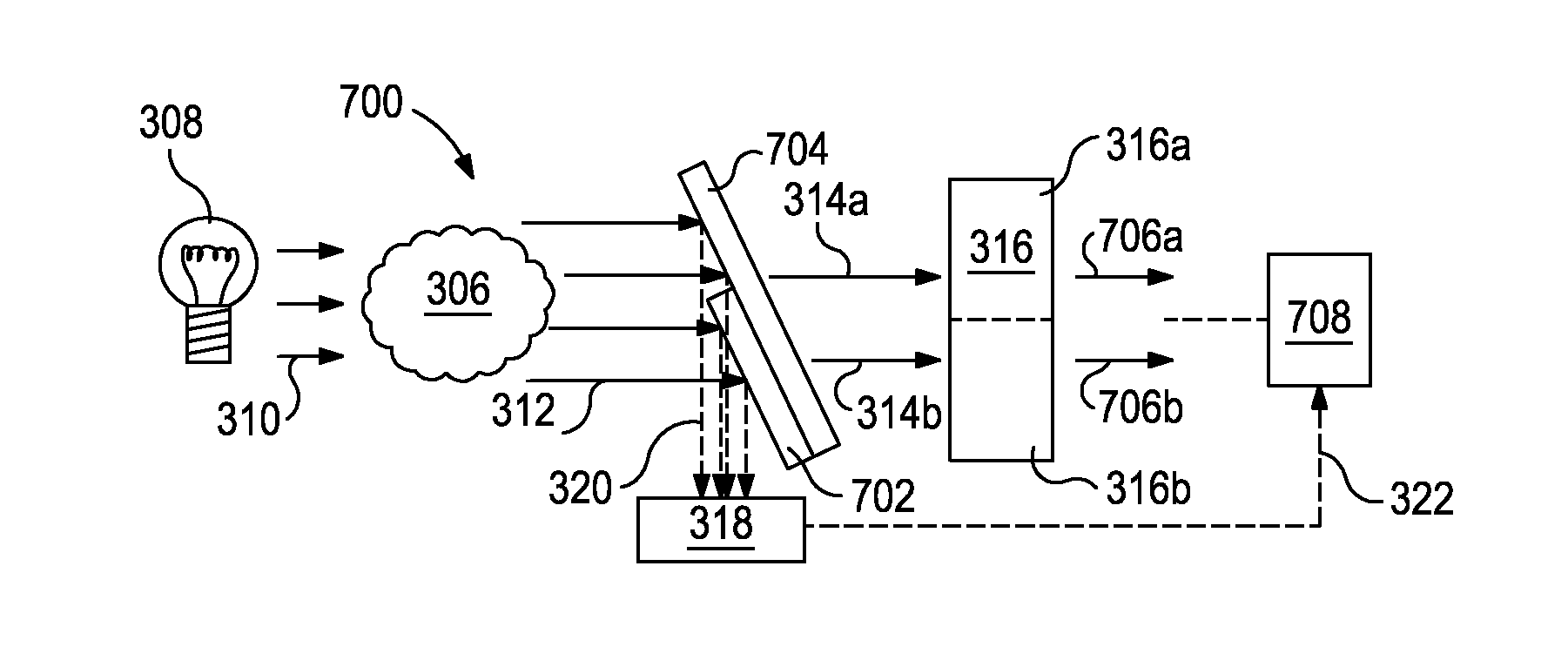
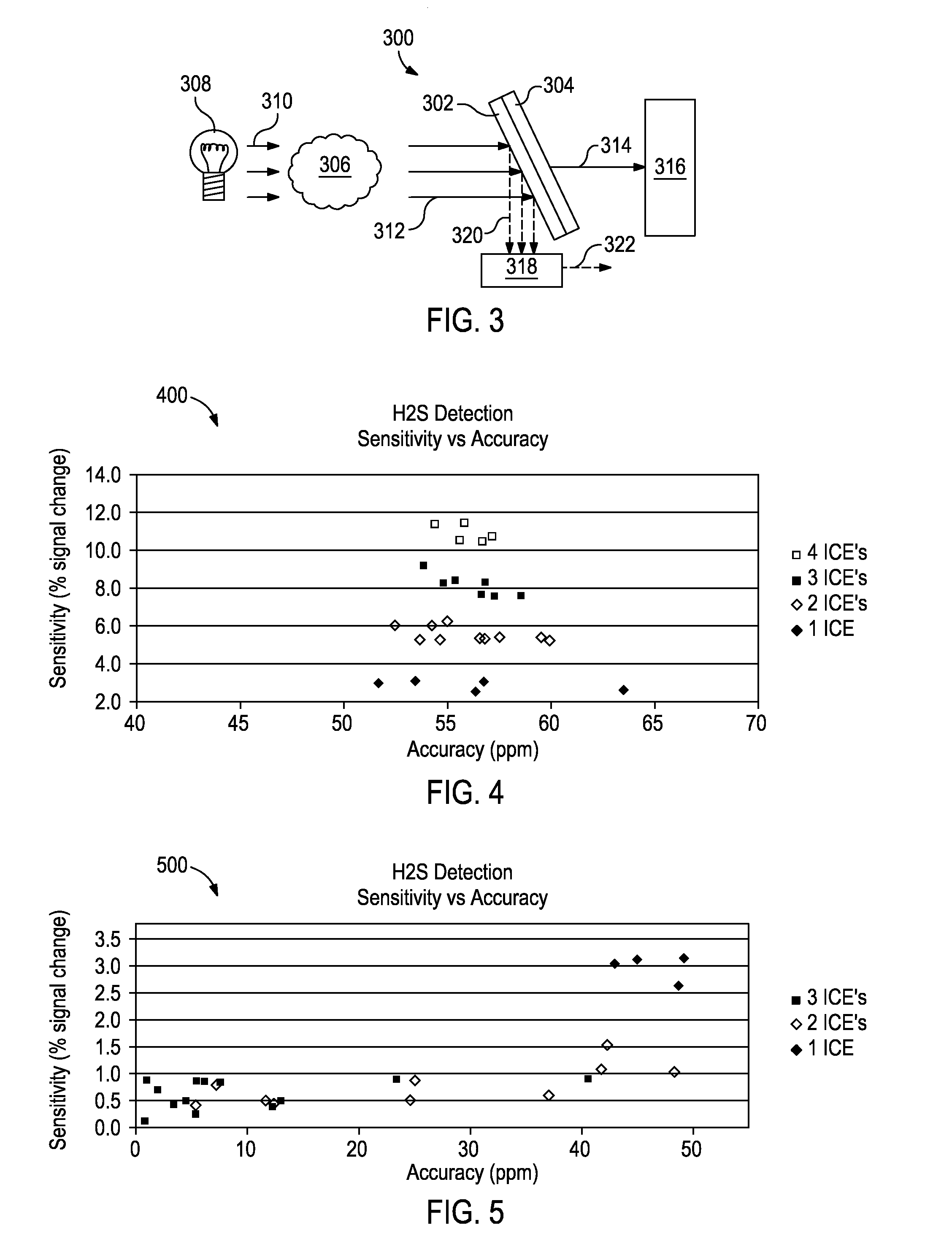
The output of optical computing devices containing an integrated computational element can be corrected when an interferent substance or condition is present. The devices may comprise an optional electromagnetic radiation source; a sample detection unit comprising an integrated computational element and a detector configured to receive electromagnetic radiation that has optically interacted with the integrated computational element and produce a sample signal associated therewith; an interferent monitor located proximal to the sample detection unit, the interferent monitor being configured to produce an interferent signal associated with an interferent substance; and a signal processing unit operable to convert the interferent signal into an interferent input form suitable for being computationally combined with the sample signal, the signal processing unit being further operable to computationally combine the sample signal and the interferent input form to determine a characteristic of a sample in real-time or near real-time.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Improved stability for optical computing system
ActiveUS20100195105A1Scattering properties measurementsTransmissivity measurementsSubject matterComputing systems
The present subject matter relates to methods of high-speed analysis of product samples. Light is directed to a portion of a product under analysis and reflected from or transmitted through the product toward an optical detector. Signals for the detector are compared with reference signals based on a portion of the illuminating light passing through a reference element to determine characteristics of the product under analysis. Temperature within the analysis system is monitored and the output signals of the optical detectors are compensated or corrections are made within the analysis calculations to compensate or correct for the system temperature. The products under analysis may be stationary, moved by an inspection point by conveyor or other means, or may be contained within a container, the container including a window portion through which the product illuminating light may pass.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
In-line process measurement systems and methods
ActiveUS20100073666A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioImprove accuracyRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryEngineeringProcess measurement
A method of using multivariate optical computing in real-time to collect instantaneous data about a process stream includes installing an optical analysis system proximate a process line, the process line being configured to move a material past a window of the optical analysis system; illuminating a portion of the material with a light from the optical analysis system; directing the light carrying information about the portion through at least one multivariate optical element in the optical analysis system to produce an instantaneous measurement result about the portion; and continuously averaging the instantaneous measurement result over a period of time to determine an overall measurement signal of the material.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Methods and Devices for Optically Determining A Characteristic of a Substance
ActiveUS20130284900A1Spectrum investigationPhotoelectric discharge tubesElectromagnetic radiationAmount of substance
Optical computing devices are disclosed. One exemplary optical computing device includes an electromagnetic radiation source configured to optically interact with a sample and first and second integrated computational elements arranged in primary and reference channels, respectively. The first and second integrated computational elements produce first and second modified electromagnetic radiations, and a detector is arranged to receive the first and second modified electromagnetic radiations and generate an output signal corresponding to the characteristic of the sample.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Methods and Devices for Optically Determining A Characteristic of a Substance
ActiveUS20130284895A1Photoelectric discharge tubesColor/spectral properties measurementsOptical interactionElectromagnetic radiation
Optical computing devices are disclosed. One exemplary optical computing device includes an electromagnetic radiation source configured to optically interact with a sample and at least two integrated computational elements. The at least two integrated computational elements are configured to produce optically interacted light and further configured to be associated with a characteristic of the sample. The optical computing device further includes a first detector arranged to receive the optically interacted light from the at least two integrated computational elements and thereby generate a first signal corresponding to the characteristic of the sample.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Devices Having One or More Integrated Computational Elements and Methods for Determining a Characteristic of a Sample by Computationally Combining Signals Produced Therewith
ActiveUS20130284894A1Material analysis by optical meansPhotoelectric discharge tubesElectromagnetic radiationLength wave
Optical computing devices containing one or more integrated computational elements may be used to produce two or more detector output signals that are computationally combinable to determine a characteristic of a sample. The devices may comprise a first integrated computational element and a second integrated computational element, each integrated computational element having an optical function associated therewith, and the optical function of the second integrated computational element being at least partially offset in wavelength space relative to that of the first integrated computational element; an optional electromagnetic radiation source; at least one detector configured to receive electromagnetic radiation that has optically interacted with each integrated computational element and produce a first signal and a second signal associated therewith; and a signal processing unit operable for computationally combining the first signal and the second signal to determine a characteristic of a sample.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Improved signal processing for optical computing system
ActiveUS20100149537A1High speed machiningIncrease speedScattering properties measurementsTransmissivity measurementsMonitoring systemSubject matter
The present subject matter relates to methods of high-speed analysis of product samples during production of the product. Light is directed to a portion of a product under analysis and reflected from or transmitted through the product toward optical detectors. Signals from the optical detectors are compared to determine characteristics of the product under analysis. Temperature within the monitoring system may be monitored in order to provide compensation for the signals produced by the optical detectors. The products under analysis may be stationary, moved by an inspection point by conveyor or other means, or may be contained within a container, the container including a window portion through which the product illuminating light may pass.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Novel multi-analyte optical computing system
The present subject matter relates to methods of high-speed analysis of product samples. Light is directed to a portion of a product under analysis and reflected from or transmitted through the product toward a plurality of optical detectors. Signals from the detectors are compared with a reference signal based on a portion of the illuminating light passing through a reference element to determine characteristics of the product under analysis. The products under analysis may be stationary, moved by an inspection point by conveyor or other means, or may be contained within a container, the container including a window portion through which the product illuminating light may pass.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
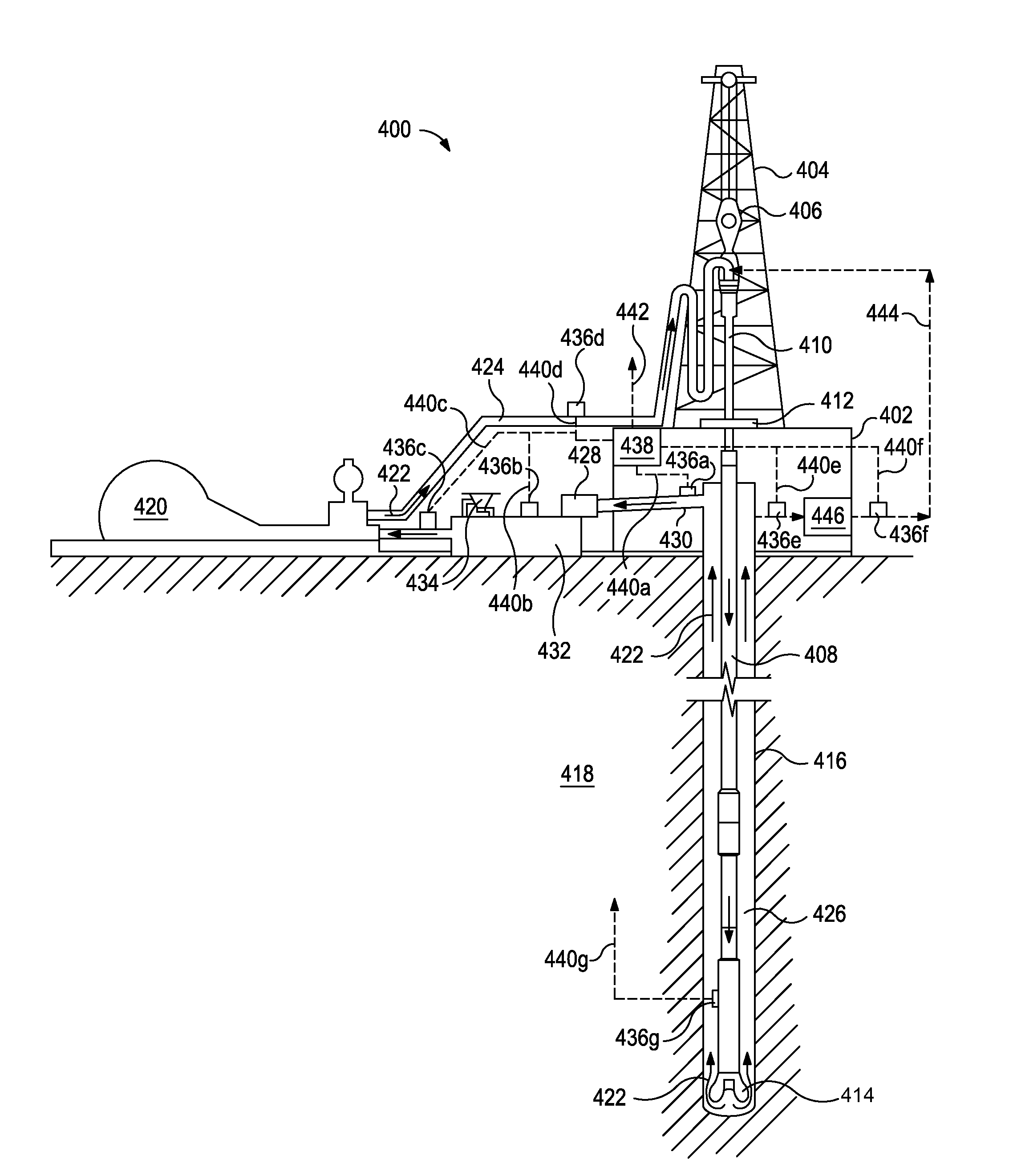
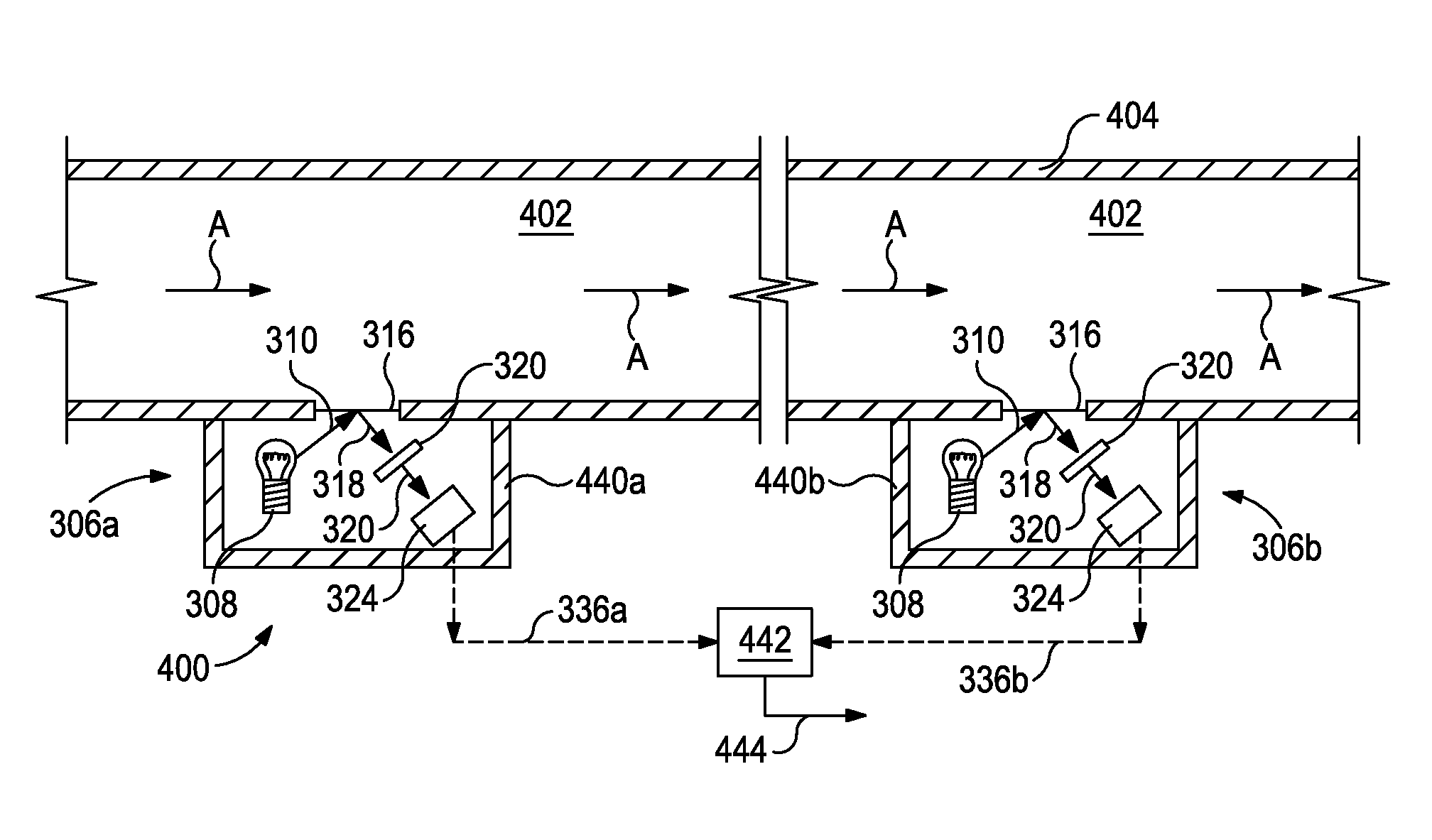
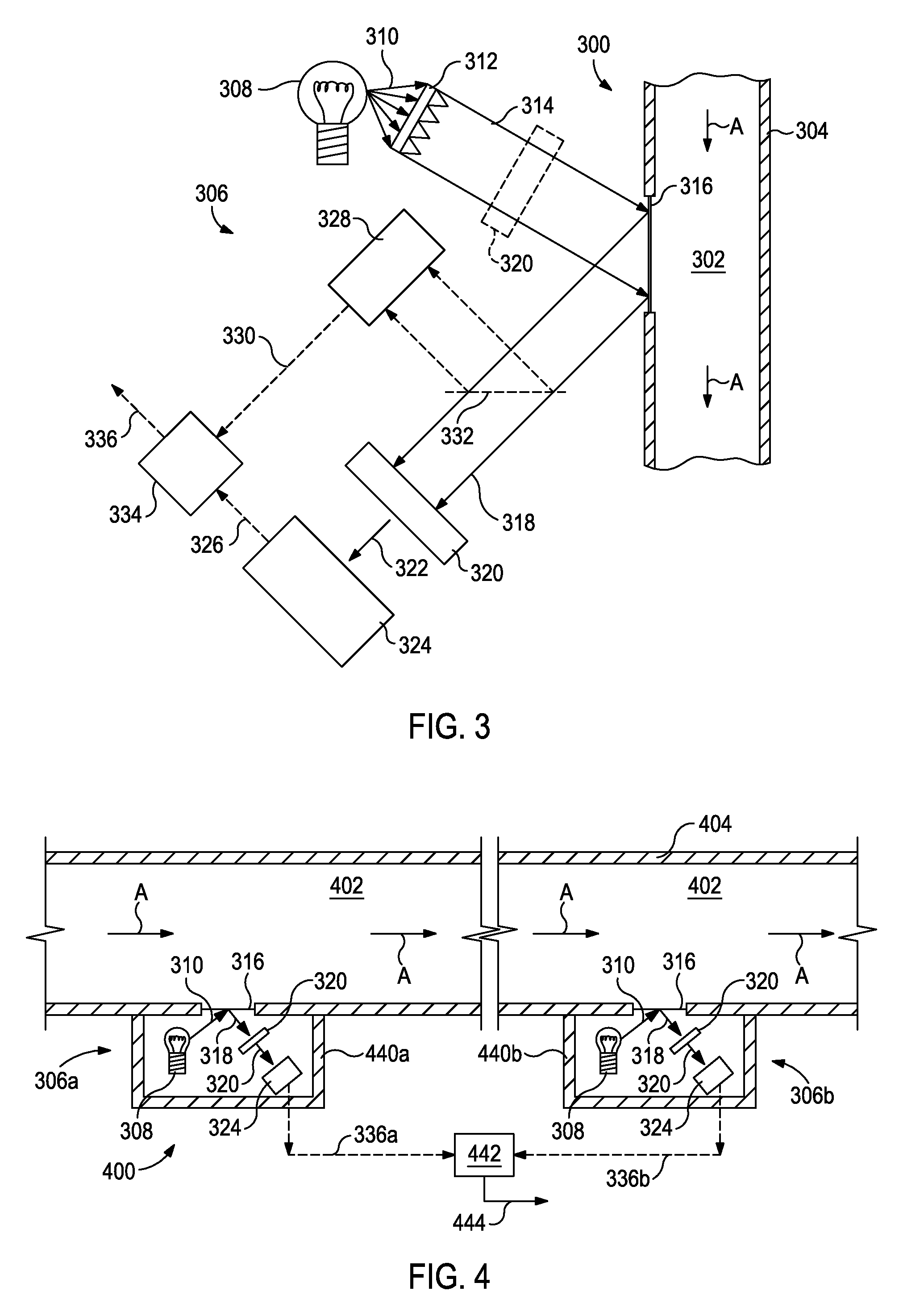
Systems and methods for real time monitoring and management of wellbore servicing fluids
InactiveUS8575541B1Withdrawing sample devicesInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsChemical reactionOptical interaction
Disclosed are systems and methods for monitoring wellbore servicing fluids. One system includes a flow path fluidly coupled to a borehole and containing a wellbore servicing fluid that is exiting the borehole, the wellbore servicing fluid being configured to chemically react with and remove filter cake from the borehole, an optical computing device arranged in the flow path and having at least one integrated computational element configured to optically interact with the wellbore servicing fluid and thereby generate optically interacted light, and at least one detector arranged to receive the optically interacted light and generate an output signal corresponding to a characteristic of the wellbore servicing fluid, the characteristic of the wellbore servicing fluid corresponding to a concentration of a filter cake chemical constituent.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Methods and Devices for Optically Determining A Characteristic of a Substance
ActiveUS20130284901A1ConstructionsPhotoelectric discharge tubesElectromagnetic radiationAmount of substance
Optical computing devices are disclosed. One exemplary optical computing device includes an electromagnetic radiation source configured to optically interact with a sample and first and second integrated computational elements arranged in primary and reference channels, respectively, the first and second computational elements are configured to be either positively or negatively correlated to the characteristic of the sample. The first and second integrated computational elements produce first and second modified electromagnetic radiations, and a detector is arranged to receive the first and second modified electromagnetic radiations and generate an output signal corresponding to the characteristic of the sample.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Optical Analysis Systems and Methods for Dynamic, High-Speed Detection and Real-Time Multivariate Optical Computing
ActiveUS20090002697A1Simple and economical to manufactureSimple and economical to and assembleRadiation pyrometryAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyOptical computingOptic lens
Multivariate optical analysis systems employ multivariate optical elements and utilize multivariate optical computing methods to determine information about a product carried by light reflected from or transmitted through the product. One method of processing and monitoring the product includes introducing the product at an inspection point; illuminating the product with a spectral-specific light though an optic lens; directing the light that has passed through at least a section of the product through at least one multivariate optical element to produce a first signal, the directed light carrying information about the product; detecting the first signal at a first detector; deflecting a portion of the directed light to produce a second signal in a direction of a second detector, the second detector configured to detect the second signal; and determining at least one property of the product at a rate of about one section of the product per second to about five sections of the product per second based upon the detector outputs.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Methods and Devices for Optically Determining A Characteristic of a Substance
ActiveUS20130284898A1Absorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyPhotoelectric discharge tubesOptical interactionElectromagnetic radiation
Optical computing devices are disclosed. One exemplary optical computing device includes an electromagnetic radiation source configured to optically interact with a sample and at least two integrated computational elements. The at least two integrated computational elements may be configured to produce optically interacted light, and at least one of the at least two integrated computational elements may be configured to be disassociated with a characteristic of the sample. The optical computing device further includes a first detector arranged to receive the optically interacted light from the at least two integrated computational elements and thereby generate a first signal corresponding to the characteristic of the sample.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Optical analysis system and elements to isolate spectral region
ActiveUS20090219512A1Minimize band-edge effectUseful and reliable capabilityRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationOptical frequenciesAnalysis sample
A method of selecting components for a multivariate optical computing and analysis system to isolate a spectral region includes selecting a spectral region of interest; selecting a spectral element with a predetermined transmission characteristic to control a spectral range of an illumination source; illuminating a sample with the illumination source; and analyzing an optical frequency returned by the sample relative to the spectral region of interest.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
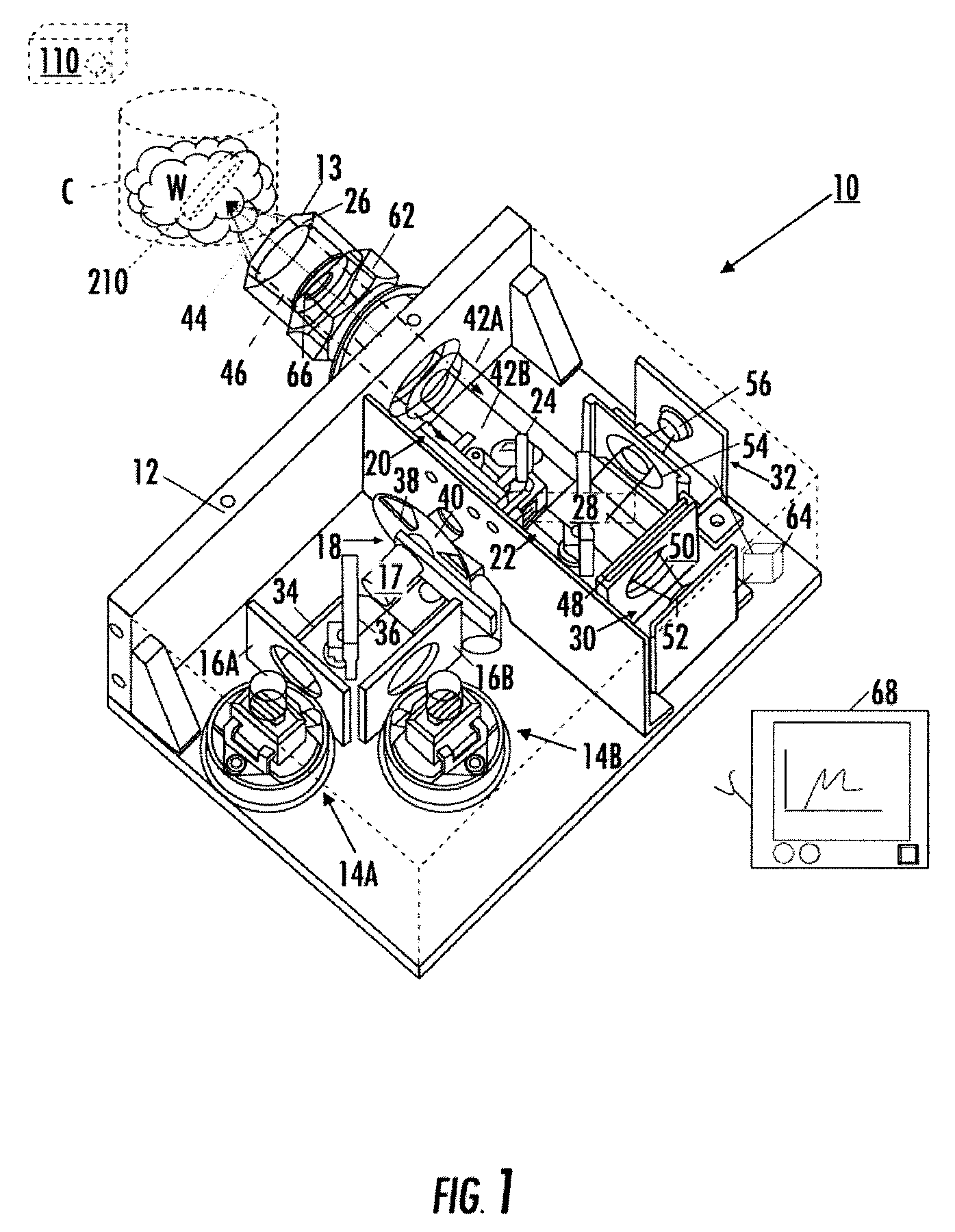
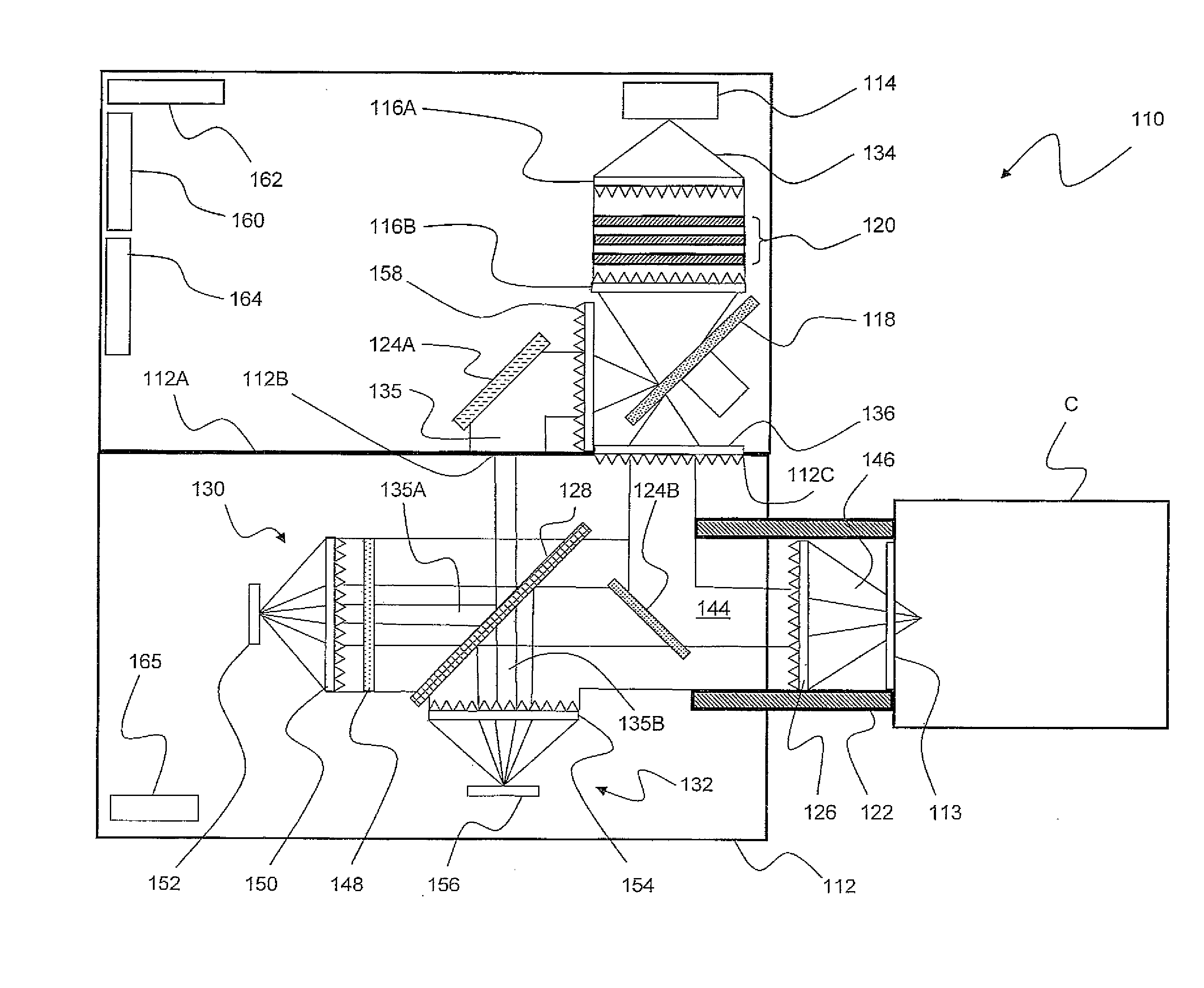
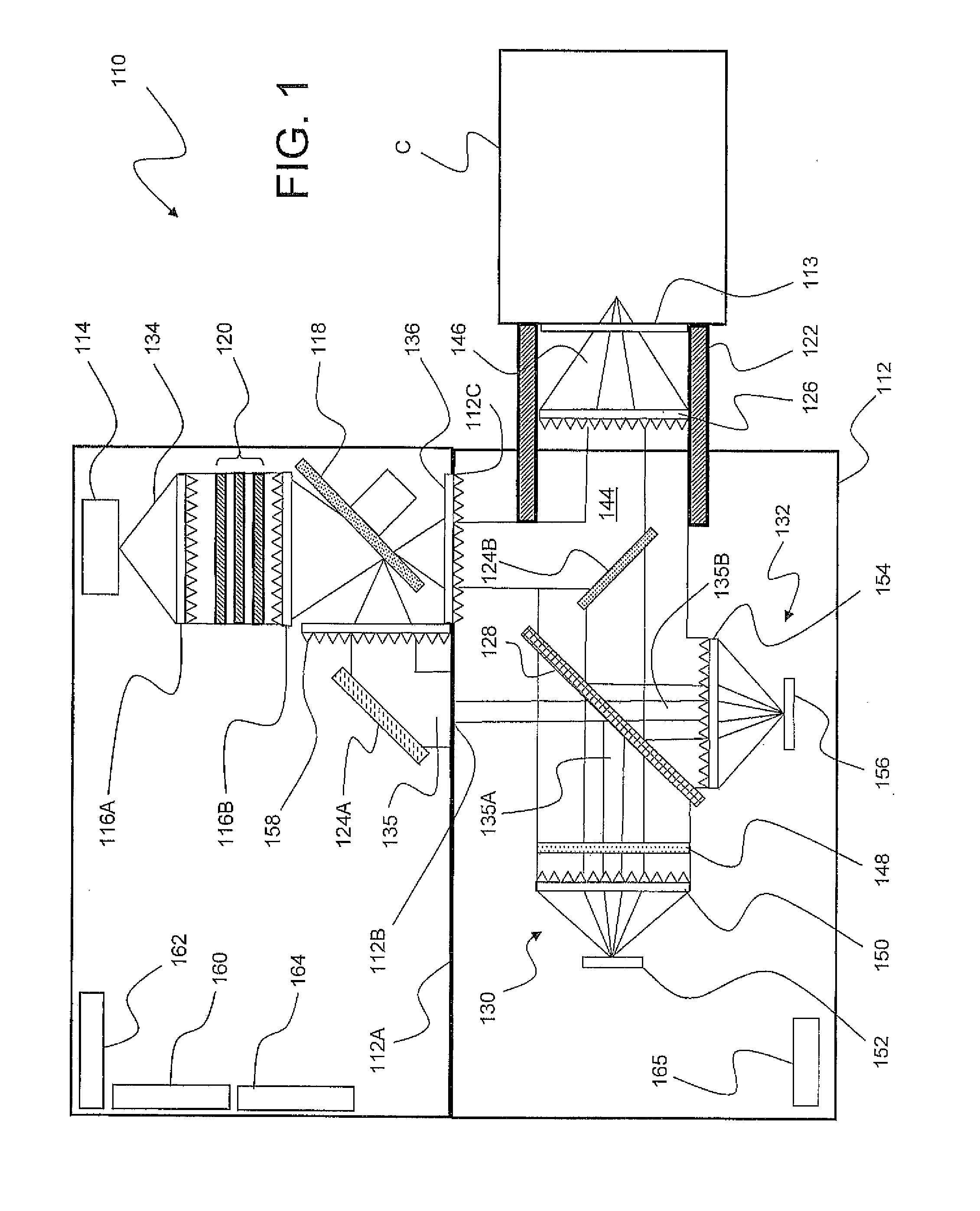
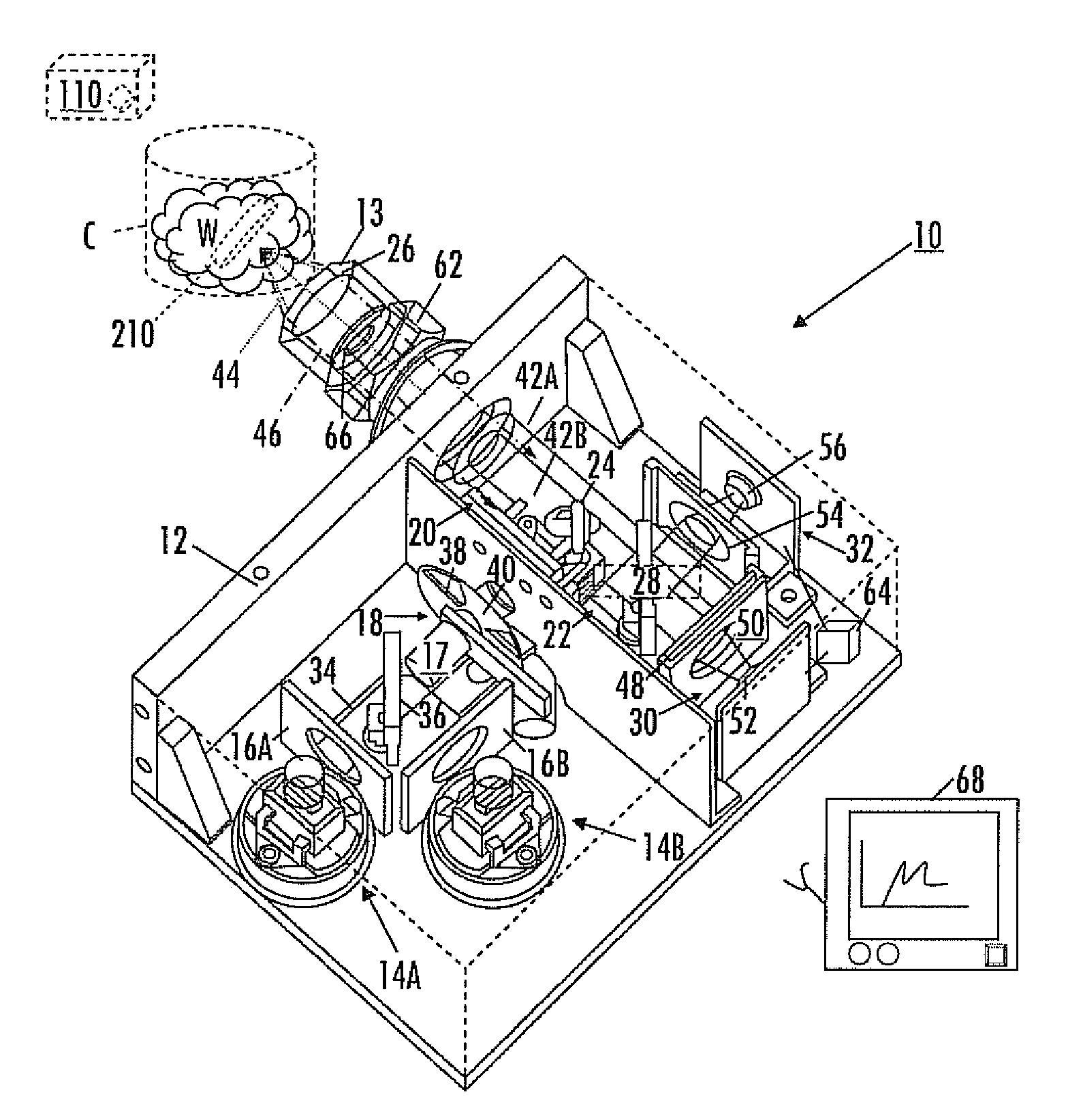
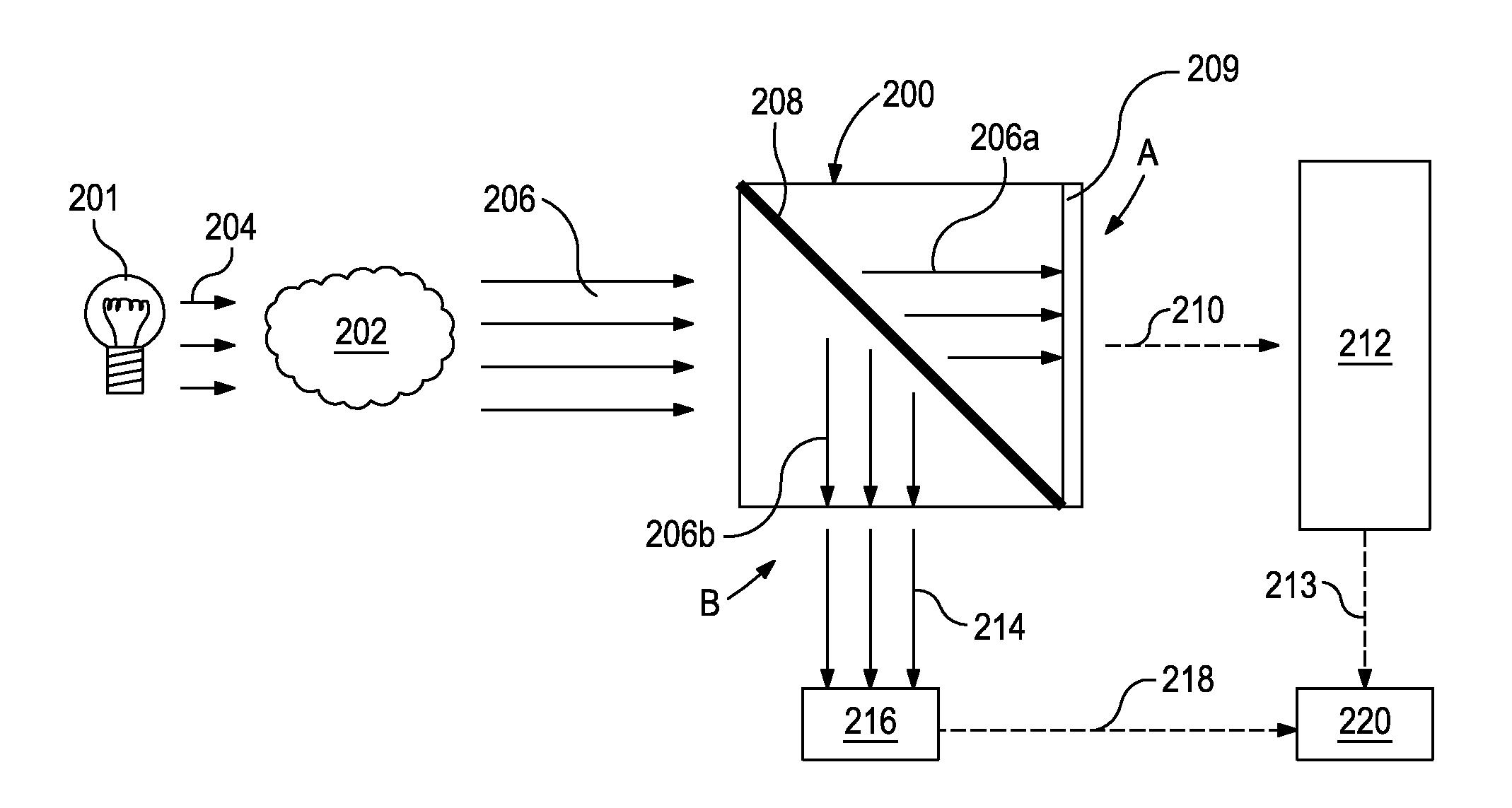
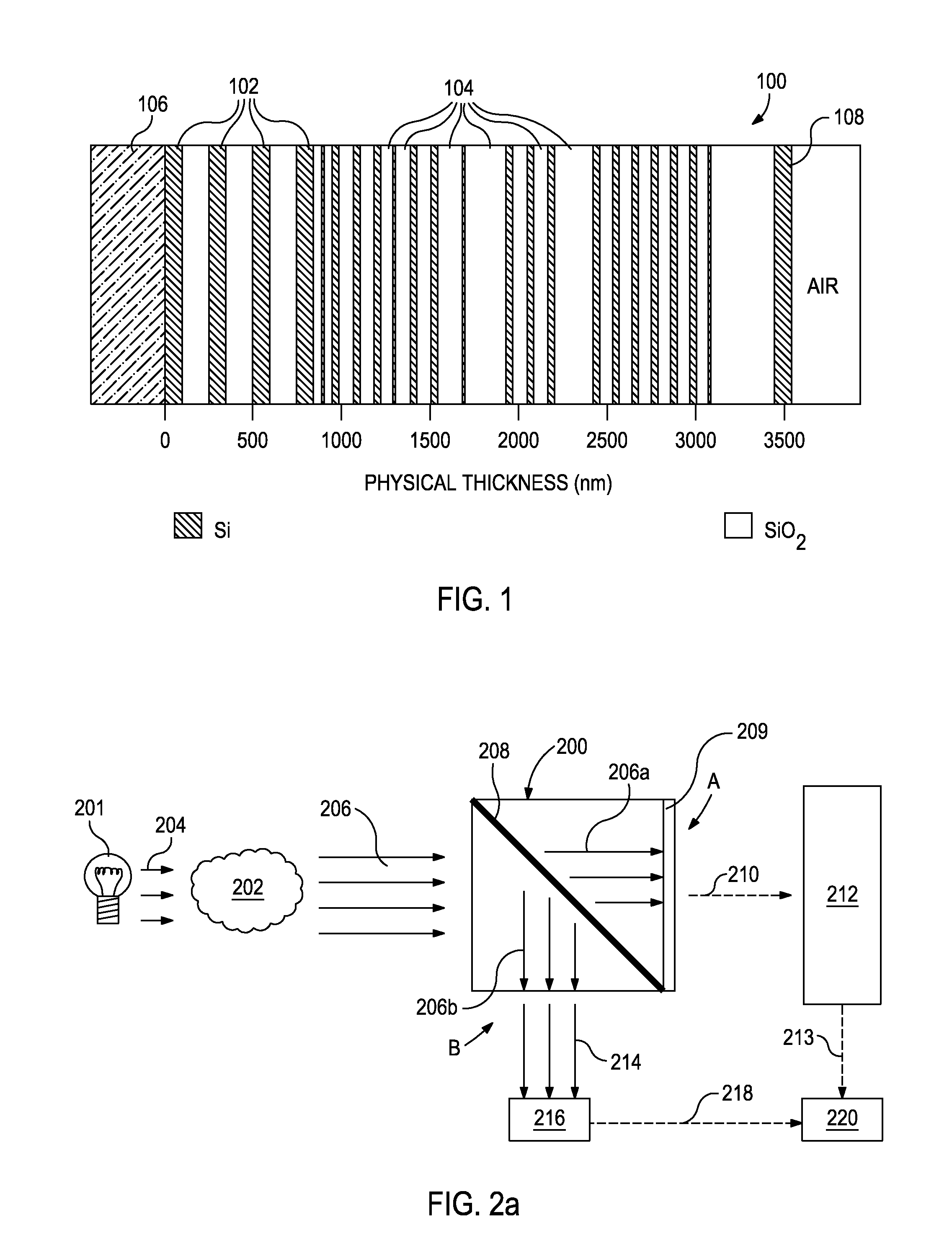
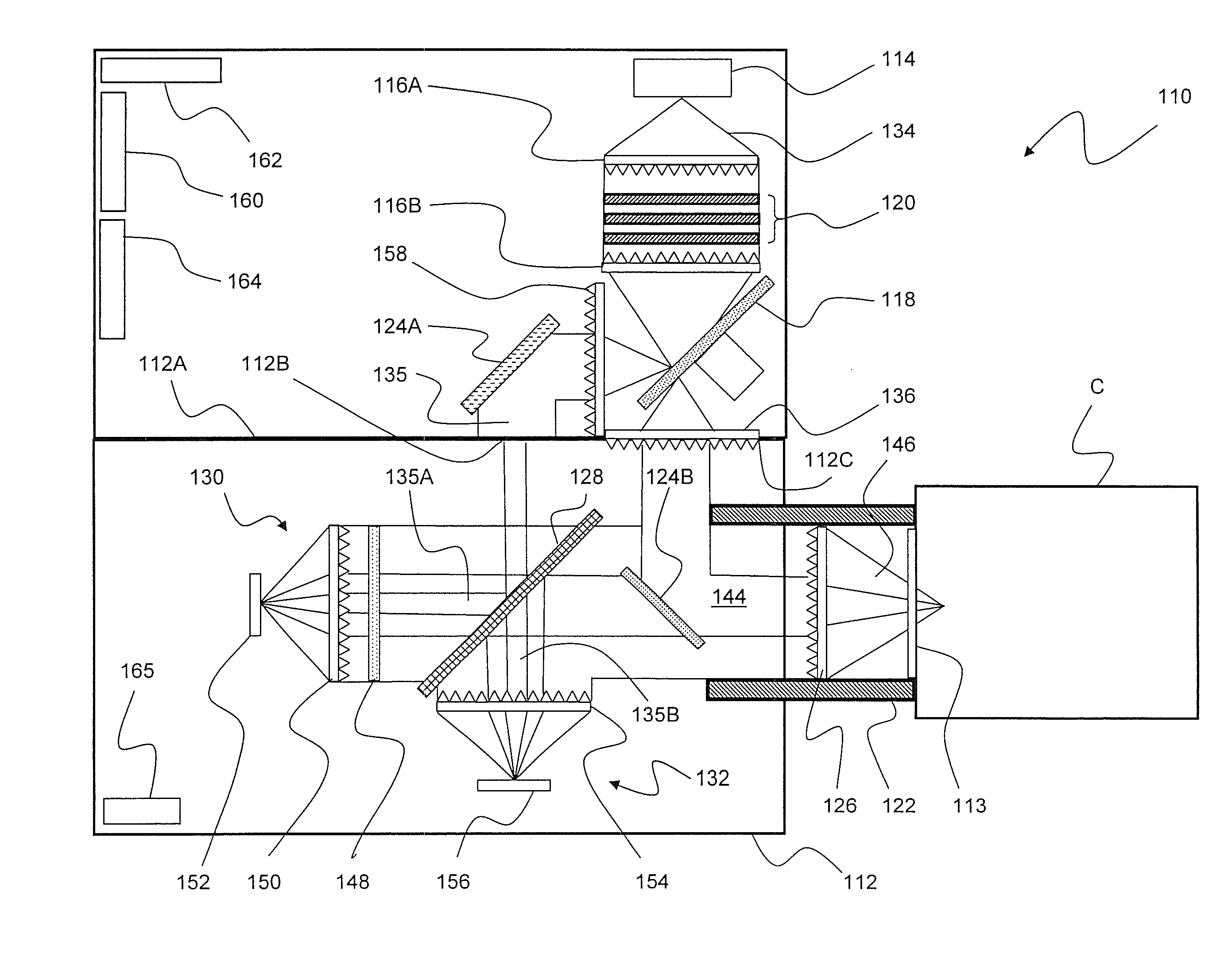
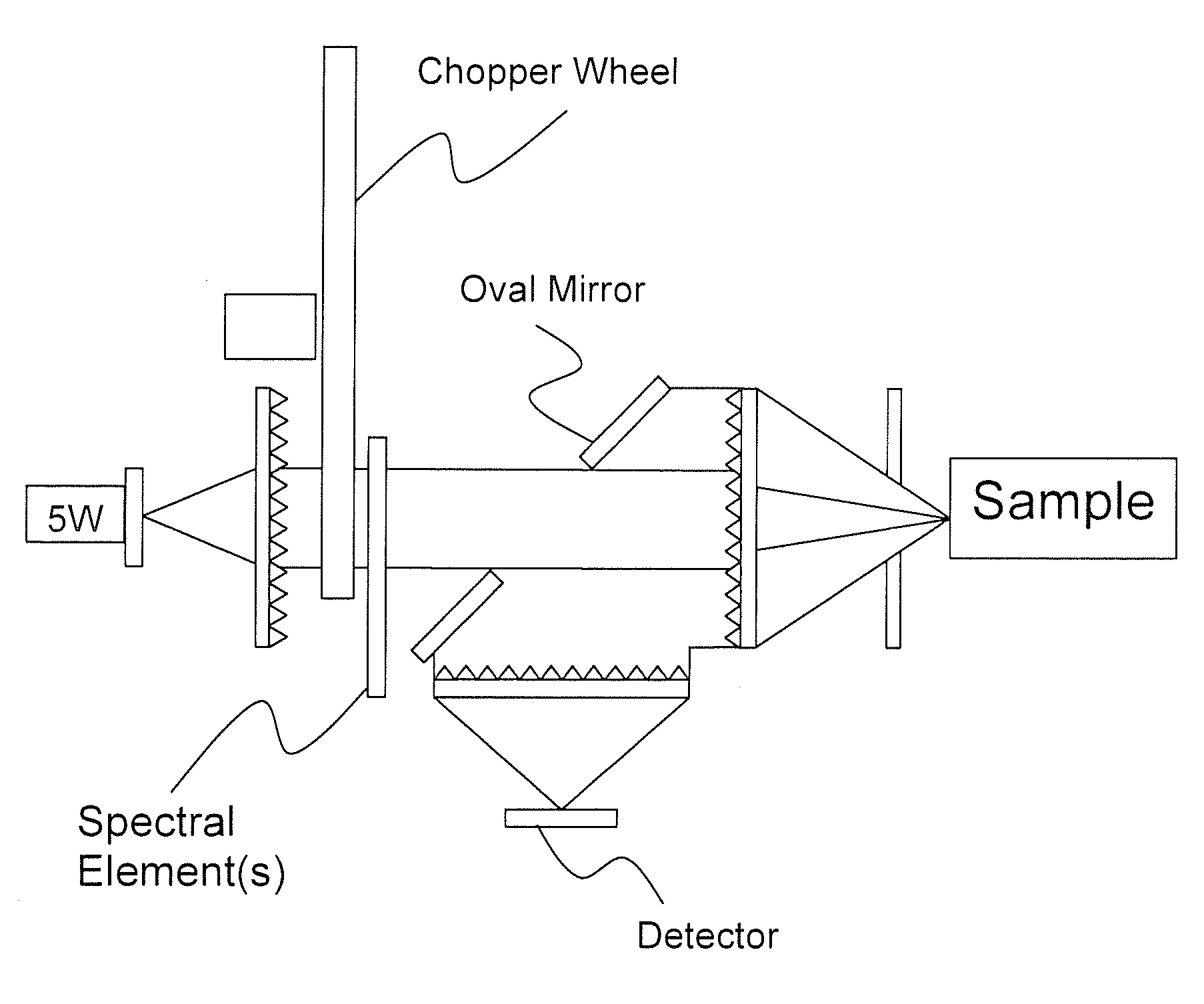
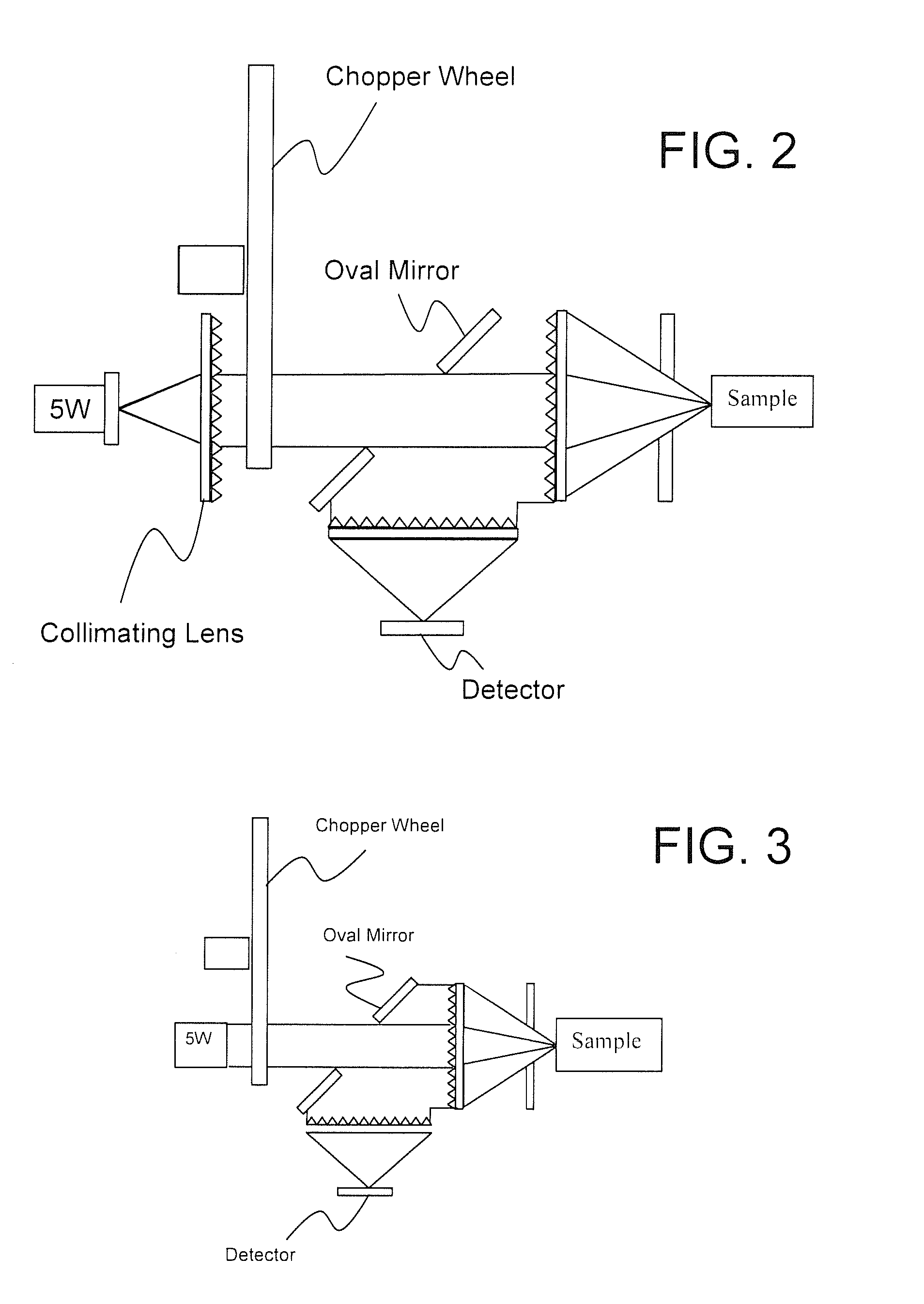
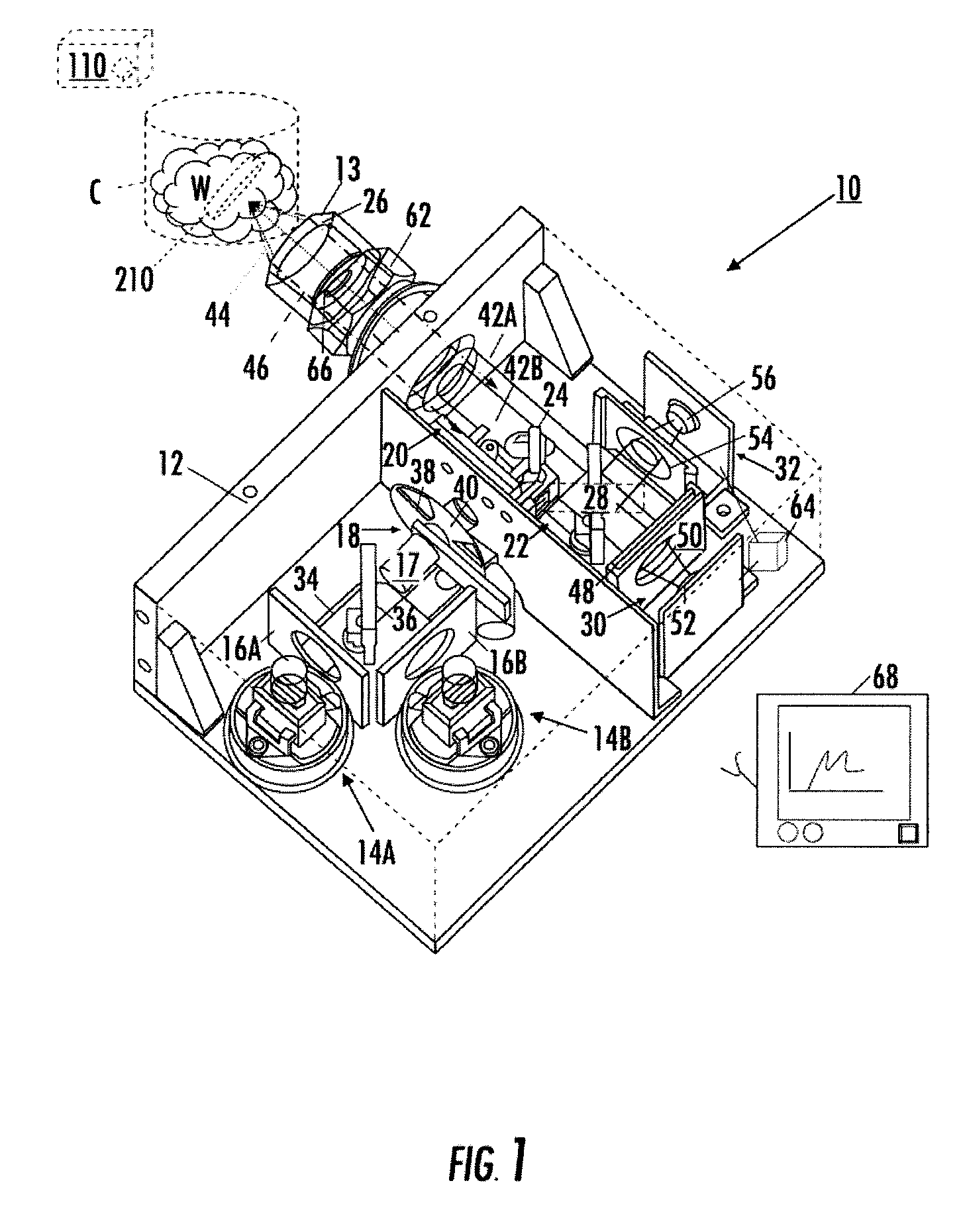
Self-contained multivariate optical computing and analysis systems
ActiveUS20100182600A1Simple and economical to manufacture and assemble and useReduce noiseRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationElectricityAccelerometer
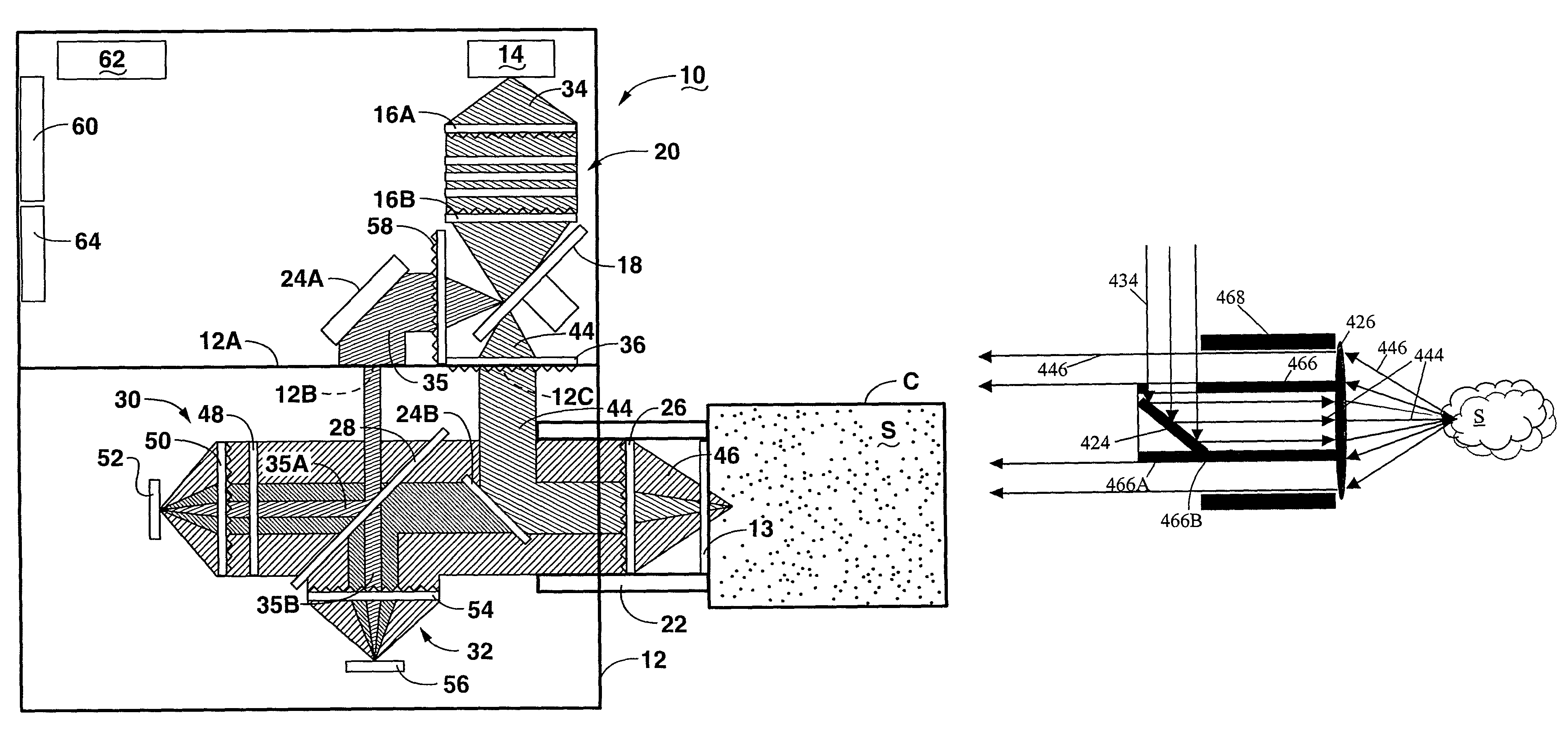
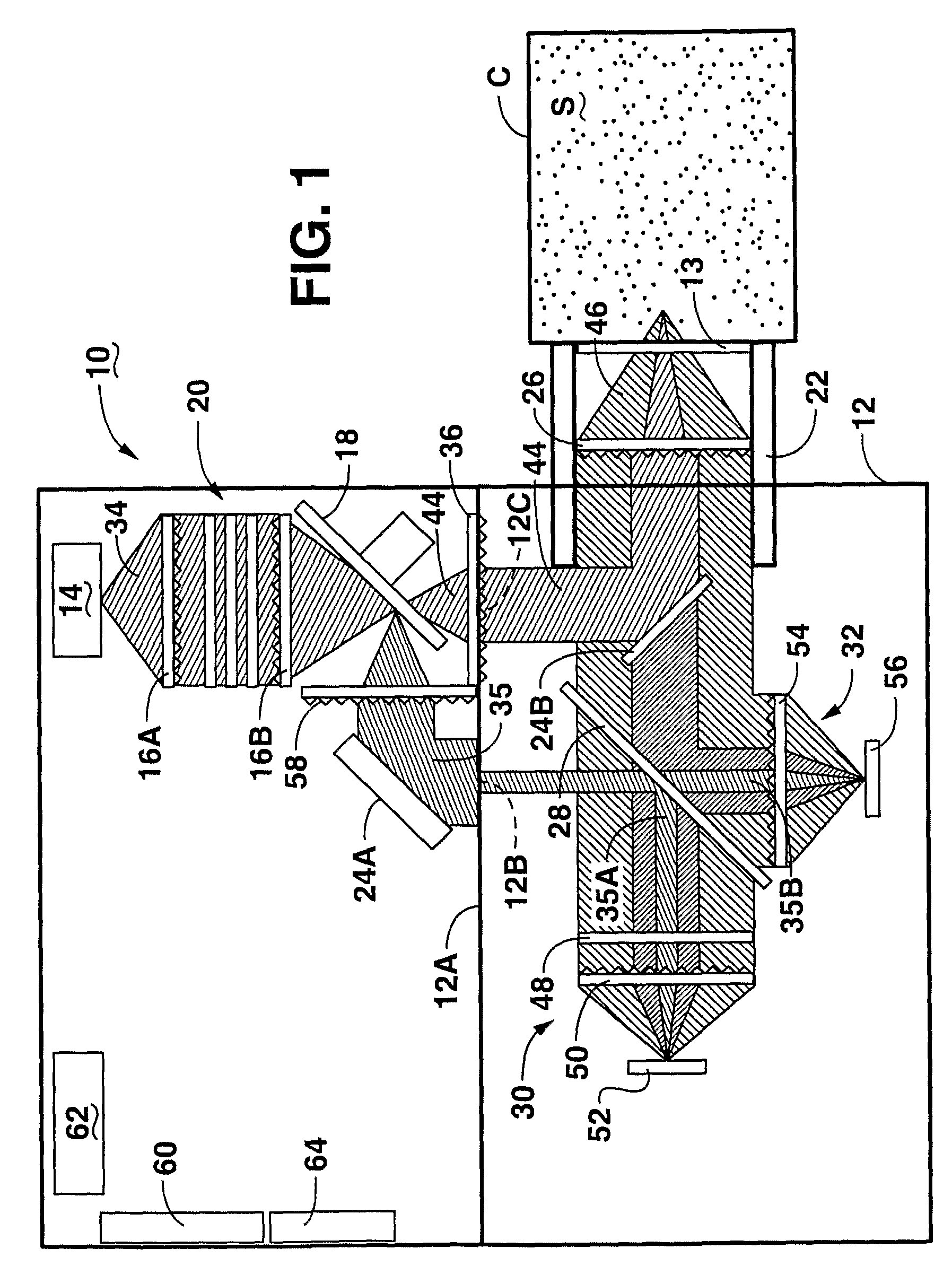
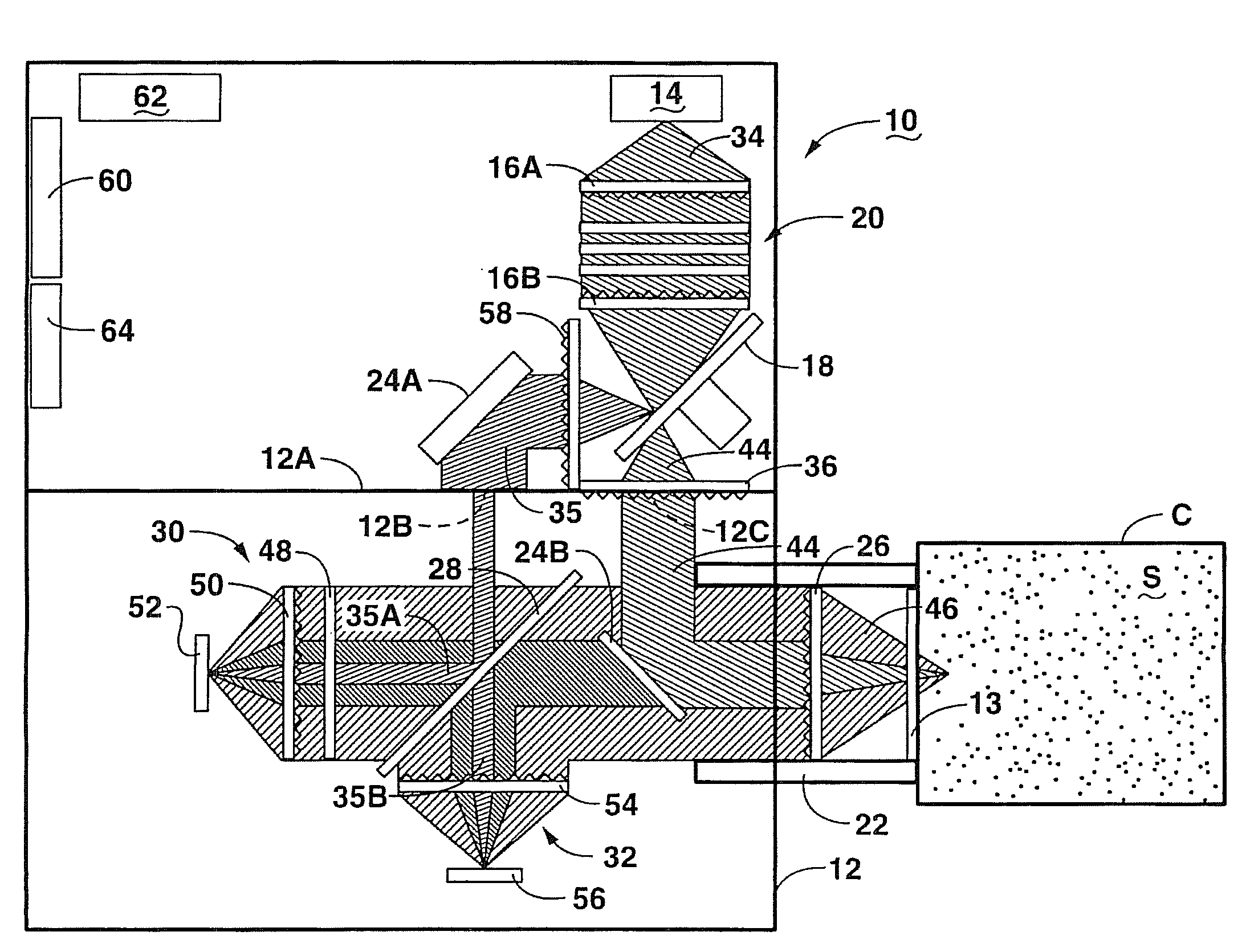
An optical analysis system includes a light source configured to radiate a first light along a first ray path; a modulator disposed in the first ray path, the modulator configured to modulate the first light to a desired frequency; a spectral element disposed proximate the modulator, the spectral element configured to filter the first light for a spectral range of interest of a sample; a cavity in communication with the spectral element, the cavity configured to direct the first light in a direction of the sample; a conical mirror configured to convert the first light reflecting from the sample into a second light, the cavity being further configured to direct the second light; a beamsplitter configured to split the second light into a first beam and a second beam; an optical filter mechanism disposed to receive the first beam, the optical filter mechanism configured to optically filter data carried by the first beam into at least one orthogonal component of the first beam; a first detector mechanism in communication with the optical filter mechanism to measure a property of the orthogonal component to measure the data; a second detector mechanism configured to receive the second beam for comparison of the property of the orthogonal component to the second beam; an accelerometer configured to control the data acquisition such that only detector signals during the period of time when the system is in the proper orientation such that the material sample (e.g., aspirin) is in proximity to the interrogation window are used for calculation; a computer having a data acquisition and conversion card, the computer disposed in the system in communication with the first and second detector mechanisms for signal processing; and a battery and charging system disposed in the system in electrical communication with the system to provide stand-alone operation capability.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Silicon-based integrated optical vector-matrix multiplier
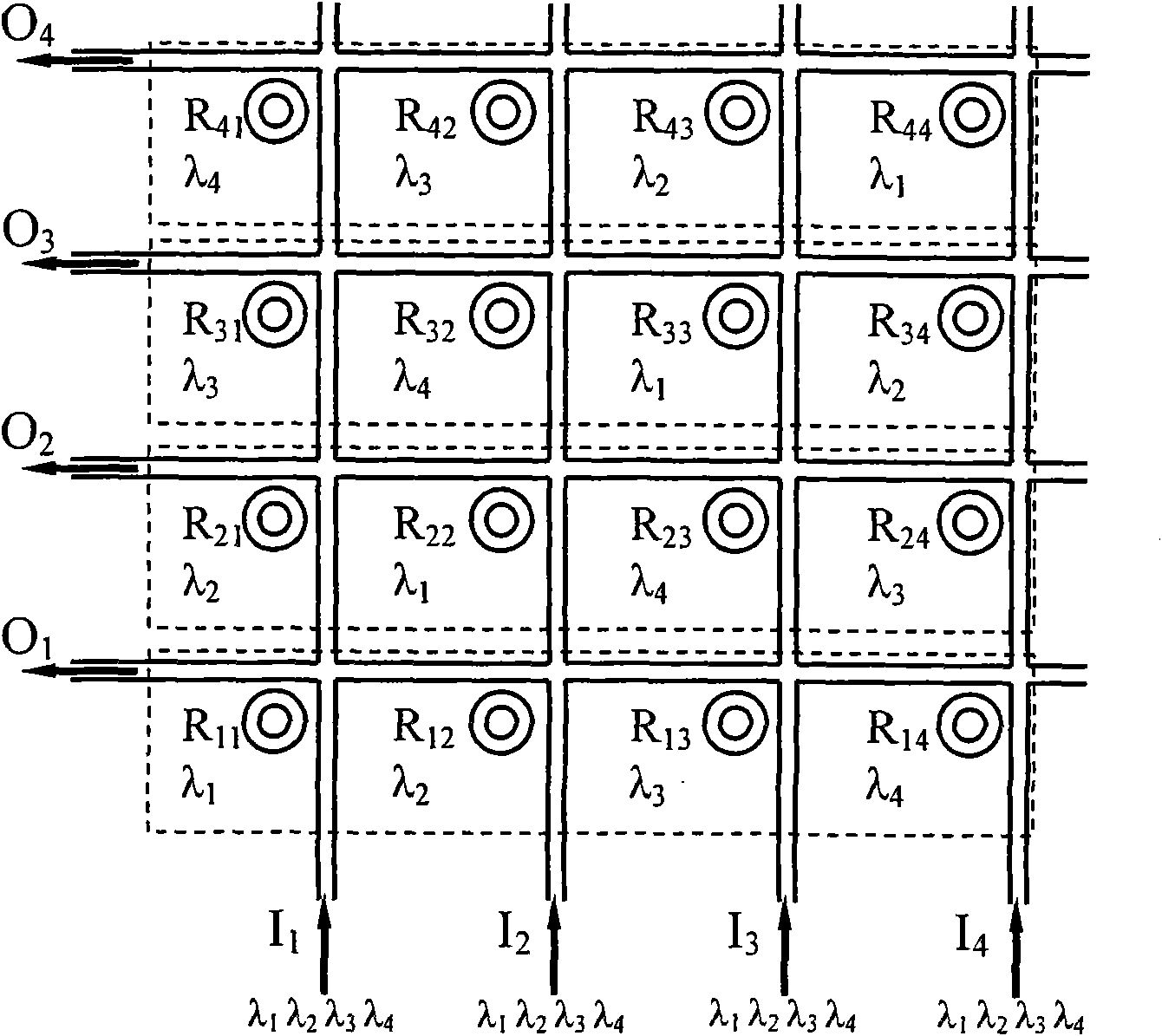
ActiveCN101630178AReduce volumeReduce power consumptionLogic circuits using opto-electronic devicesNon-linear opticsNanowireMatrix multiplier
The invention discloses a silicon-based integrated optical vector-matrix multiplier, which consists of nano-wire micro-ring resonators arranged periodically, and is used for realizing the multiplication of an N*N matrix and an N*1 vector, wherein elements in the N*N matrix and the N*1 vector are all 0 or 1. The optical vector-matrix multiplier is prepared from a silicon-on-insulator material, the basic units of the multiplier are the nano-wire micro-ring resonators (MRR), and the basic structure is the MRRs which are arranged in N*N and are provided with a thermal modulation mechanism respectively. The silicon-based integrated optical vector-matrix multiplier adopts the prior art, so that the device has small volume, low power consumption and good expansibility and is convenient to be integrated with an electrical element; the silicon-based integrated optical vector-matrix multiplier adopts laser pulses to transmit information, so the speed is high and the delay is short; a digital mode is utilized for processing signals, so the defect that an analog optical computing system has low accuracy and poor programmable capacity is avoided; and waveguides with a great refractive index difference are utilized to transmit light, so the problem that the space diversity efficiency of the conventional optical vector-matrix multiplier is low is avoided.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Methods and Devices for Optically Determining A Characteristic of a Substance
Optical computing devices are disclosed. One exemplary optical computing device includes an electromagnetic radiation source configured to optically interact with a sample and first and second integrated computational elements arranged in primary and reference channels, respectively, the first and second computational elements are configured to be either positively or negatively correlated to the characteristic of the sample. The first and second integrated computational elements produce first and second modified electromagnetic radiations, and a detector is arranged to receive the first and second modified electromagnetic radiations and generate an output signal corresponding to the characteristic of the sample.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Methods and Devices for Optically Determining A Characteristic of a Substance
ActiveUS20130284897A1Absorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyPhotoelectric discharge tubesOptical interactionElectromagnetic radiation
Optical computing devices are disclosed. One exemplary optical computing device includes an electromagnetic radiation source configured to optically interact with a sample and at least two integrated computational elements. The at least two integrated computational elements are configured to produce optically interacted light and further configured to be associated with a characteristic of the sample. The optical computing device further includes a first detector arranged to receive the optically interacted light from the at least two integrated computational elements and thereby generate a first signal corresponding to the characteristic of the sample.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Imaging Systems for Optical Computing Devices
ActiveUS20130286399A1Investigating moving fluids/granular solidsTransmissivity measurementsOptical interactionElectromagnetic radiation
Optical computing devices are disclosed. One optical computing device includes an electromagnetic radiation source that emits electromagnetic radiation into an optical train to optically interact with a sample and at least one integrated computational element, the sample being configured to generate optically interacted radiation. A sampling window is arranged adjacent the sample and configured to allow transmission of the electromagnetic radiation therethrough and has one or more surfaces that generate one or more stray signals. A first focal lens is arranged to receive the optically interacted radiation and the one or more stray signals and generate a primary focal point from the optically interacted radiation. A structural element defines a spatial aperture aligned with the primary focal point such that the optically interacted radiation is able to pass therethrough while transmission of the one or more stray signals is substantially blocked by the structural element.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
System and method for acquisition and reconstruction of contrast-enhanced, artifact-reduced CT images
ActiveUS7583779B2Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationView basedPhoton
A system and method are disclosed for reconstructing contrast-enhanced CT images that are substantially free of beam-hardening artifacts. An imaging system includes a radiation source configured to project radiation toward an object to be scanned and an energy discriminating detector assembly having a plurality of detector elements and configured to detect radiation emitted by the radiation source and attenuated by the object to be scanned. The imaging system also includes computer programmed to count a number of photons detected by each detector element and associate an energy value to each counted photon and determine a material composition of a CT view from the number of photons counted and the energy value associated with each counted photon. The computer is also programmed to apply a weighting to the CT view based on the material composition of the CT view and reconstruct an image with differential weighting based on the weighting of the CT view.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Systems and methods for monitoring the properties of a fluid cement composition in a flow path
ActiveUS8619256B1ConstructionsInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsOptical interactionEngineering
Optical analysis systems may be useful in systems and methods for various properties of fluid cement compositions. For example, a method may include generating with an optical computing device a plurality of output signals corresponding to a plurality of time points and a characteristic of a fluid cement composition at a monitoring location within a flow path, the optical computing device having an electromagnetic radiation source configured to optically interact with the fluid cement composition and an integrated computational element, wherein the integrated computational element is configured to produce and convey optically interacted light to a detector which generates a plurality of output signals corresponding to the characteristic at a plurality of time points; receiving the plurality of output signals with a signal processor communicably coupled to the detector; and determining a difference between at least two of the output signals with the signal processor.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Imaging Systems for Optical Computing Devices
ActiveUS20130286398A1Investigating moving fluids/granular solidsTransmissivity measurementsOptical interactionElectromagnetic radiation
Optical computing devices are disclosed. One optical computing device includes an electromagnetic radiation source that emits electromagnetic radiation into an optical train to optically interact with a sample and at least one integrated computational element, the sample being configured to generate optically interacted radiation. A sampling window is arranged adjacent the sample and configured to allow transmission of the electromagnetic radiation therethrough and has one or more surfaces that generate one or more stray signals. A first focal lens is arranged to receive the optically interacted radiation and the one or more stray signals and generate a primary focal point from the optically interacted radiation. A structural element defines a spatial aperture aligned with the primary focal point such that the optically interacted radiation is able to pass therethrough while transmission of the one or more stray signals is substantially blocked by the structural element.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Methods and Devices for Optically Determining A Characteristic of a Substance
ActiveUS20130284896A1Spectrum investigationPhotoelectric discharge tubesOptical interactionElectromagnetic radiation
Optical computing devices are disclosed. One exemplary optical computing device includes an electromagnetic radiation source configured to optically interact with a sample and at least two integrated computational elements. The at least two integrated computational elements may be configured to produce optically interacted light, and at least one of the at least two integrated computational elements may be configured to be disassociated with a characteristic of the sample. The optical computing device further includes a first detector arranged to receive the optically interacted light from the at least two integrated computational elements and thereby generate a first signal corresponding to the characteristic of the sample.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Methods and Devices for Optically Determining A Characteristic of a Substance
ActiveUS20130284899A1Photoelectric discharge tubesColor/spectral properties measurementsElectromagnetic radiationAmount of substance
Optical computing devices are disclosed. One exemplary optical computing device includes an electromagnetic radiation source configured to optically interact with a sample and first and second integrated computational elements arranged in primary and reference channels, respectively. The first and second integrated computational elements produce first and second modified electromagnetic radiations, and a detector is arranged to receive the first and second modified electromagnetic radiations and generate an output signal corresponding to the characteristic of the sample.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Methods and devices for optically determining a characteristic of a substance
Optical computing devices are disclosed. One exemplary optical computing device includes an electromagnetic radiation source configured to optically interact with a sample and first and second integrated computational elements arranged in primary and reference channels, respectively, the first and second computational elements are configured to be either positively or negatively correlated to the characteristic of the sample. The first and second integrated computational elements produce first and second modified electromagnetic radiations, and a detector is arranged to receive the first and second modified electromagnetic radiations and generate an output signal corresponding to the characteristic of the sample.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com