Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1144results about How to "Avoid heat damage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
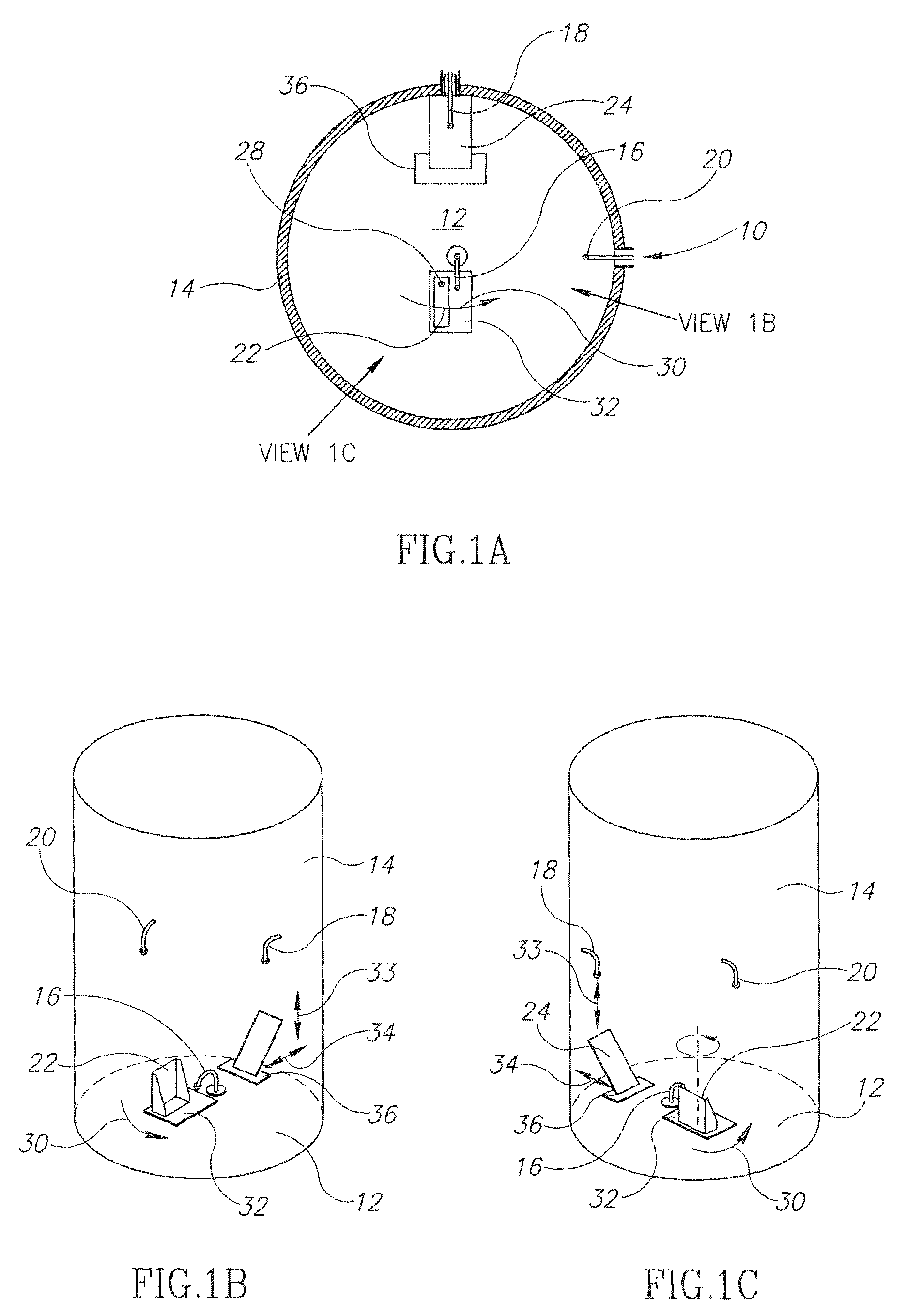
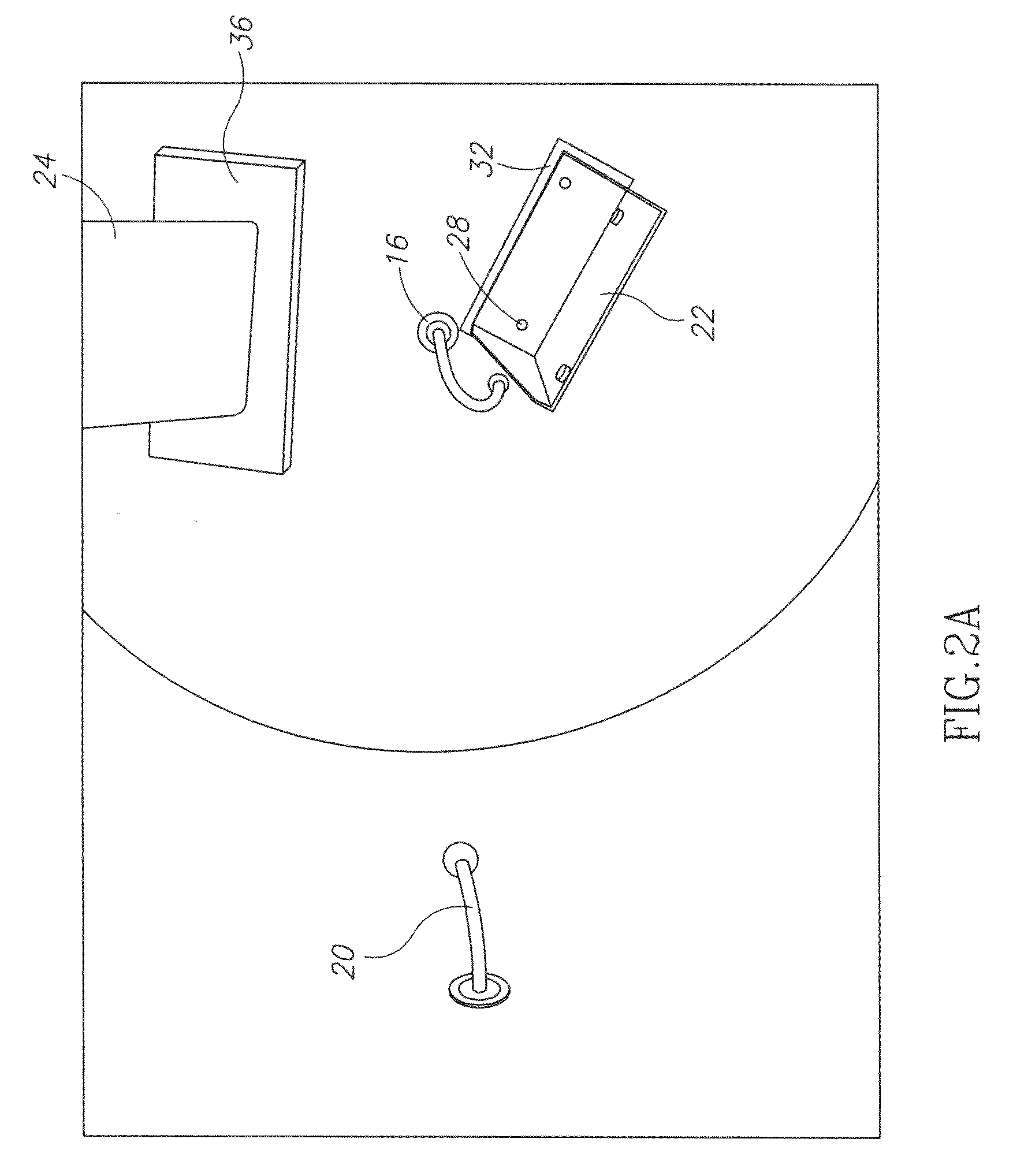
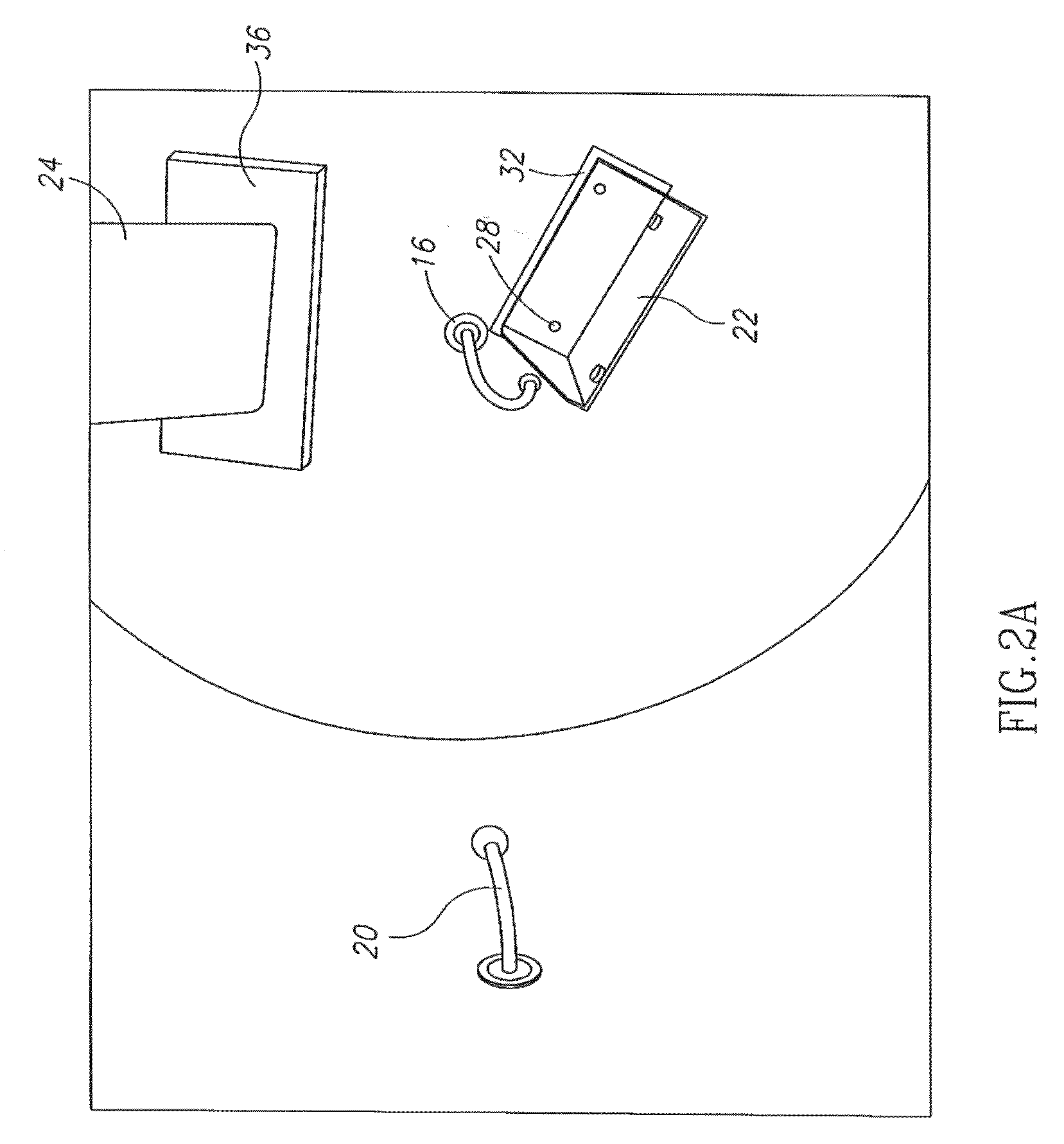
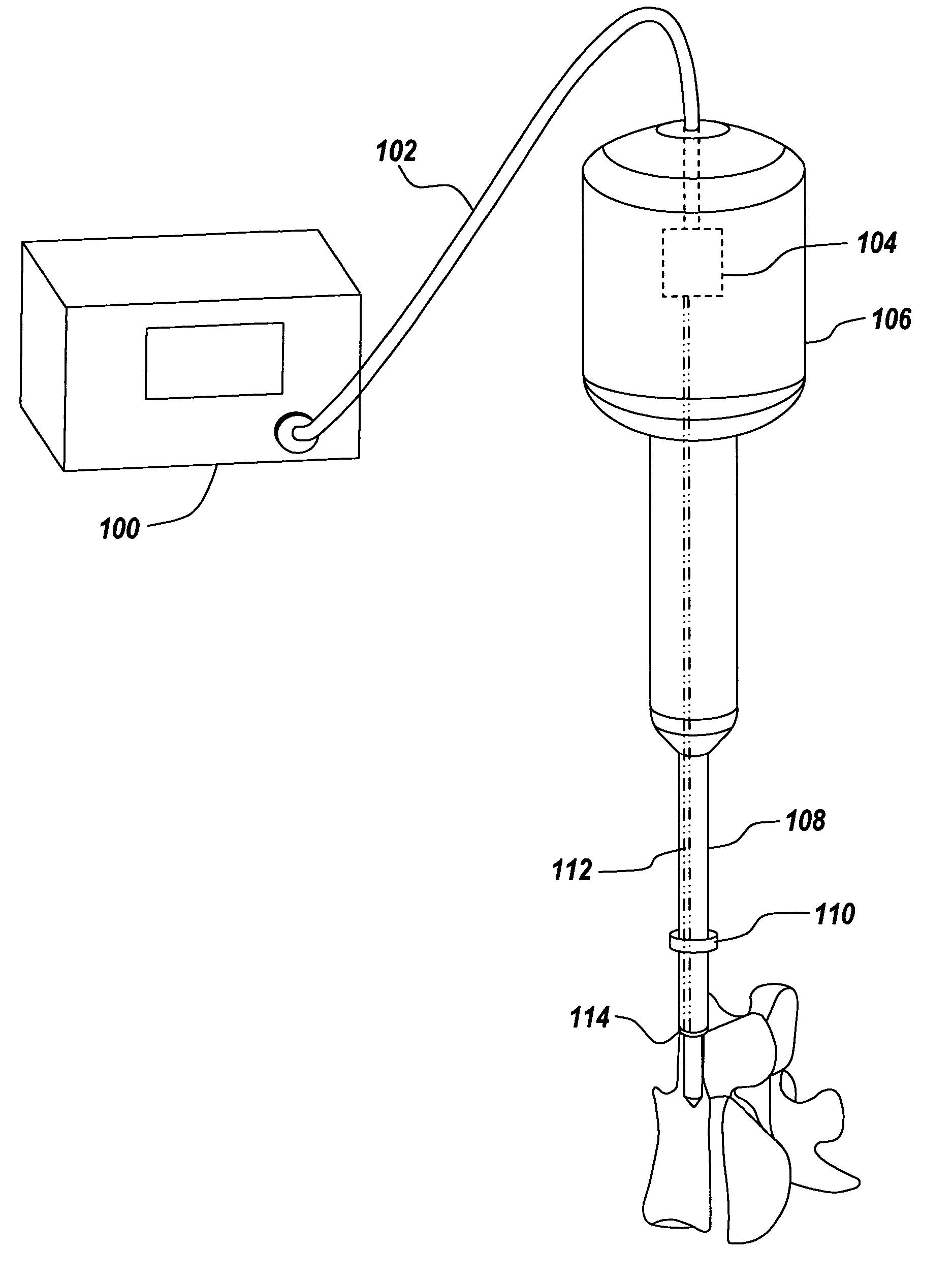
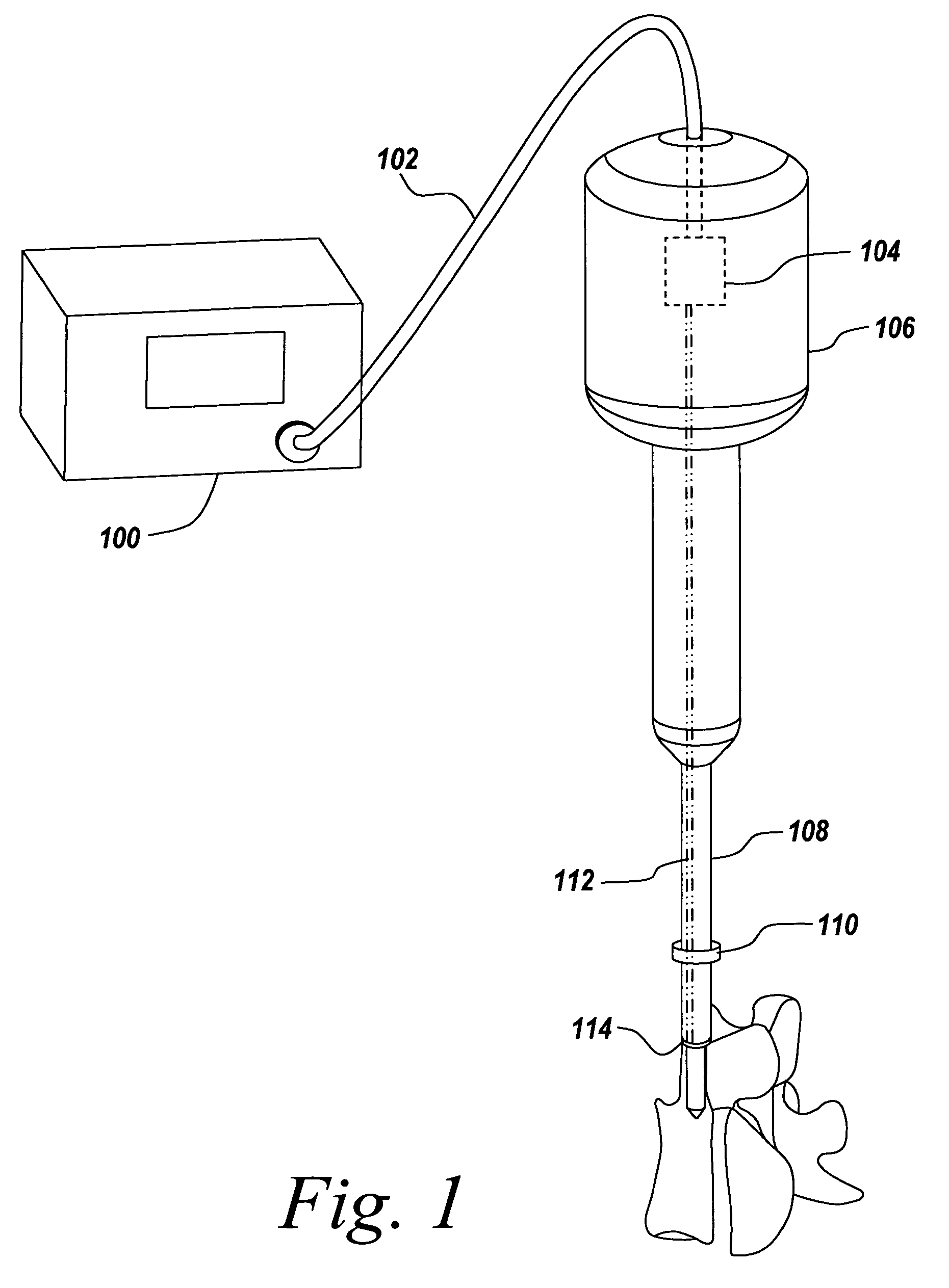
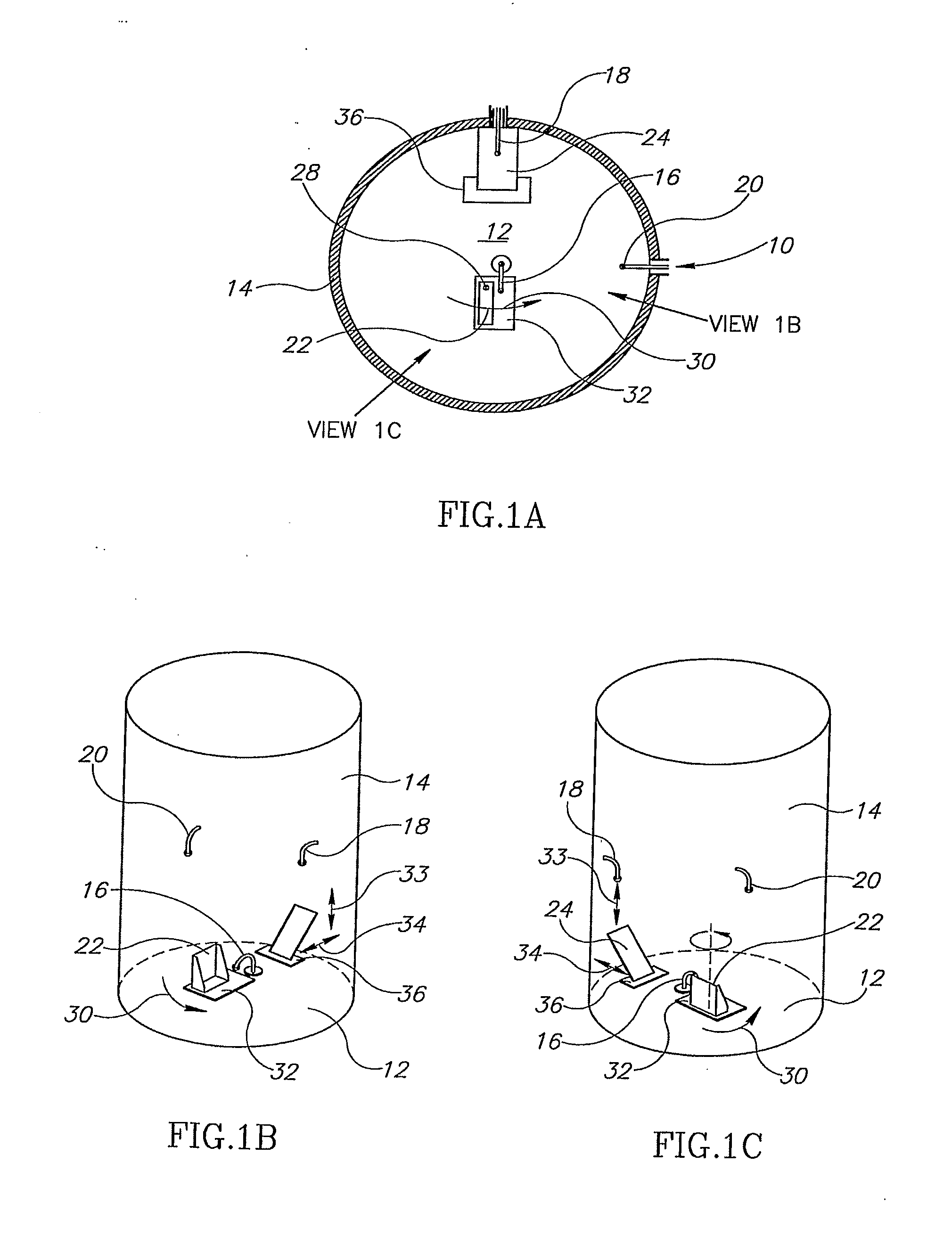
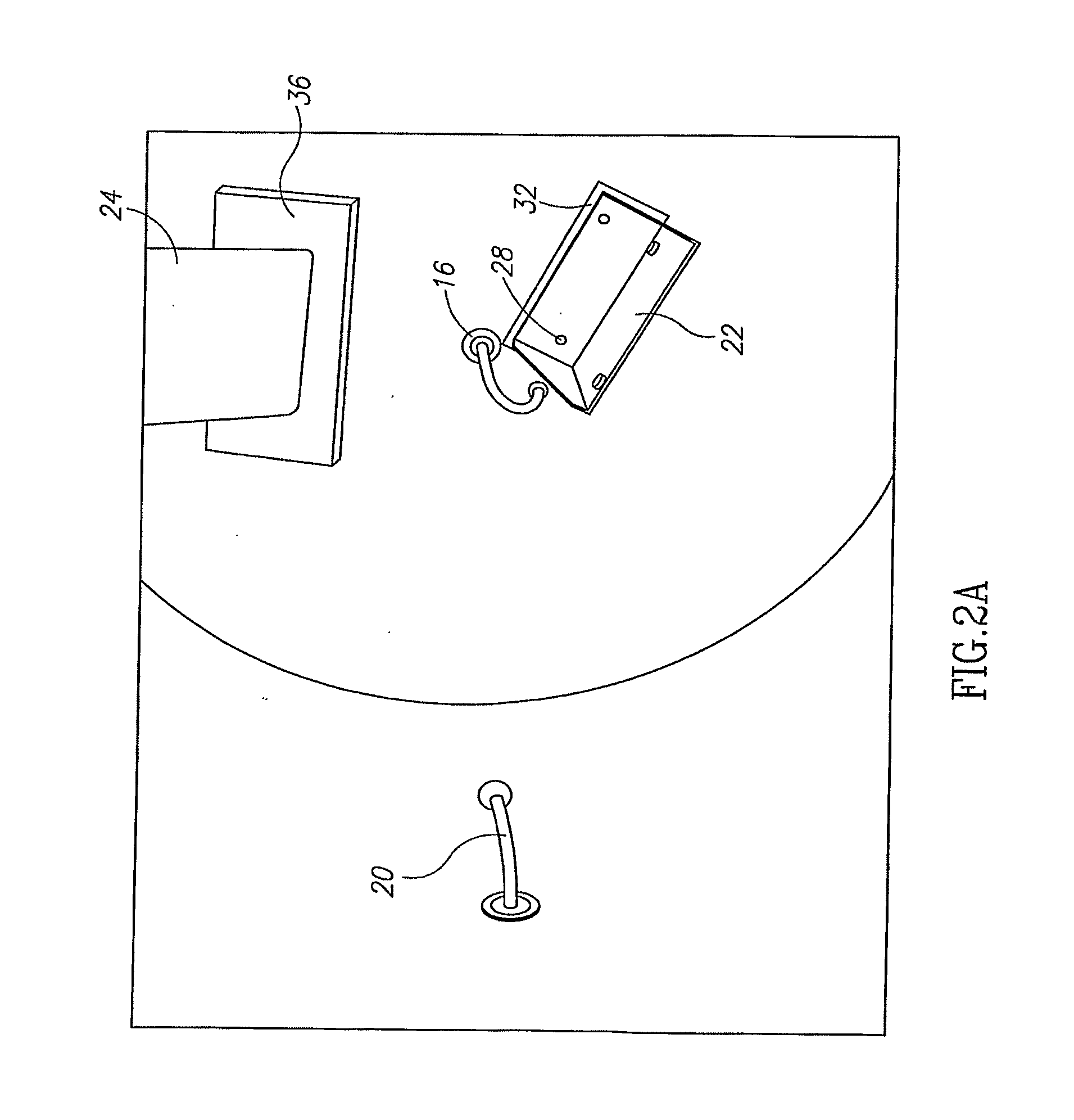
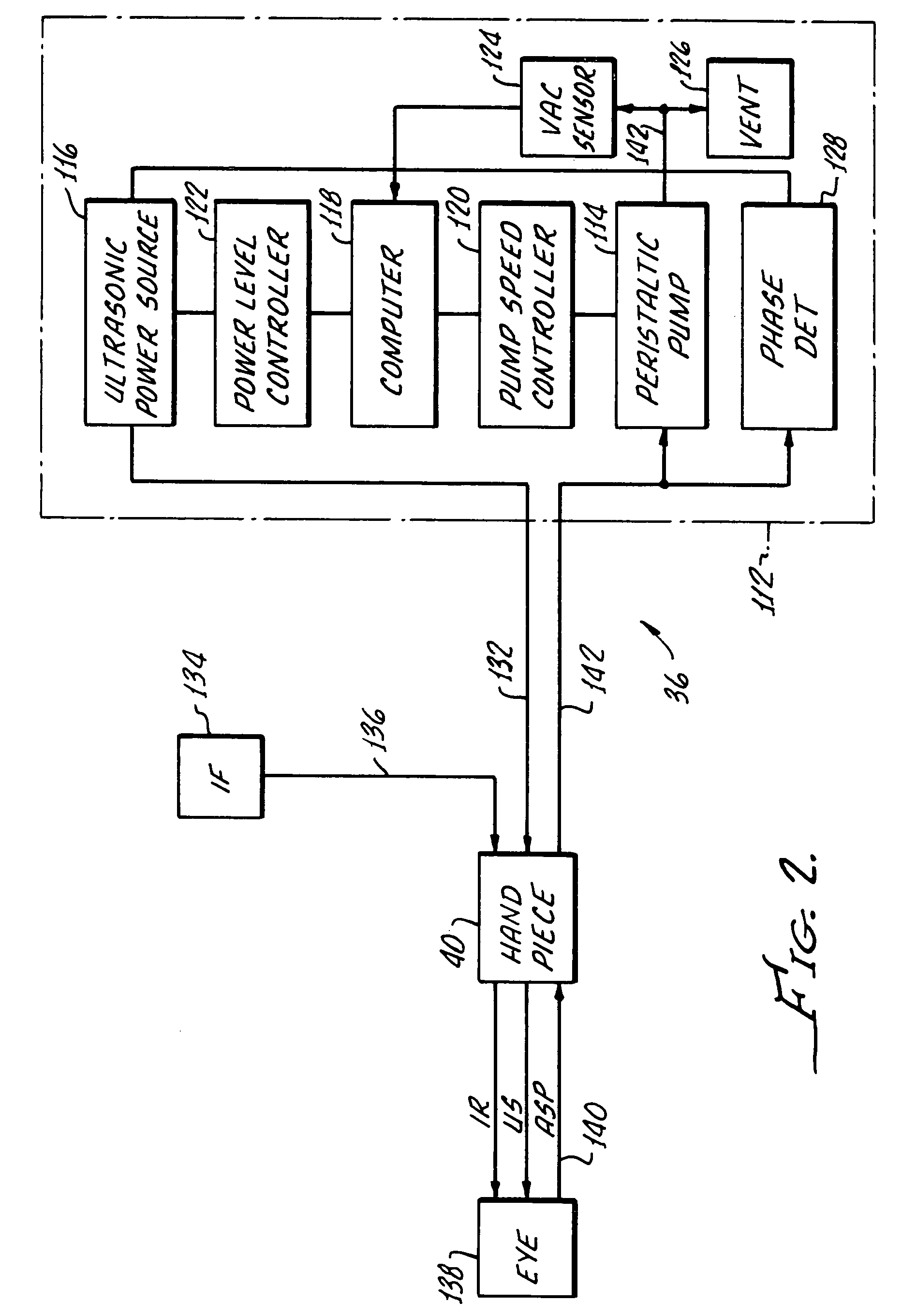
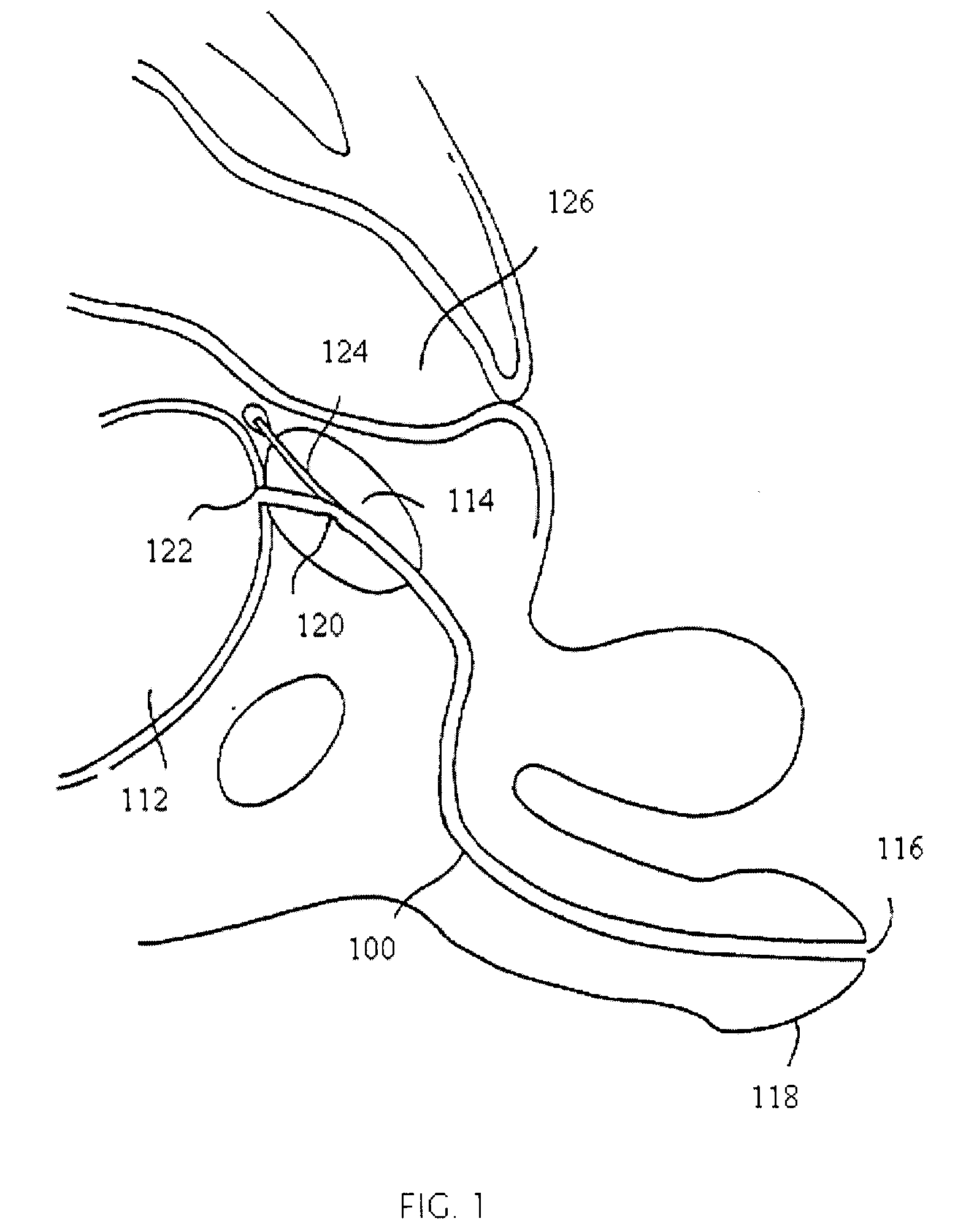
Light emitting diode light source for curing dental composites
InactiveUS20010046652A1Sufficient powerSufficient structurePrinted circuit aspectsSolid-state devicesDental compositeHeat sink
Light Emitting Diode Light Sources for Dental Curing are disclosed. Some embodiments of the invention include structures such as Light Emitting Diode Array(s), heat sink, heat dissipation, heat pipe, and control circuitry are disclosed.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Food preparation
InactiveUS20090236334A1Improve efficiencyIncrease net powerContainer decorationsLevel indicationsEngineeringIngested food
Owner:GOJI LTD
Irreversible electroporation device and method for attenuating neointimal
InactiveUS20090248012A1Promote resultsPrevent excessive cell lysingElectrotherapyInfusion devicesPercent Diameter StenosisTunica intima
Restenosis or neointimal formation may occur following angioplasty or other trauma to an artery such as by-pass surgery. This presents a major clinical problem which narrows the artery. The invention provides a device and a method whereby vascular cells in the area of the artery subjected to the trauma are subjected to irreversible electroporation which is a non-thermal, non-pharmaceutical method of applying electrical pulses to the cells so that substantially all of the cells in the area are ablated while leaving the structure of the vessel in place and substantially unharmed due to the non-thermal nature of the procedure.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Food preparation
ActiveUS20090236335A1Improve efficiencyIncrease net powerContainer decorationsLevel indicationsEngineeringIngested food
Owner:JOLIET 2010 LTD
Dual delivery chamber design
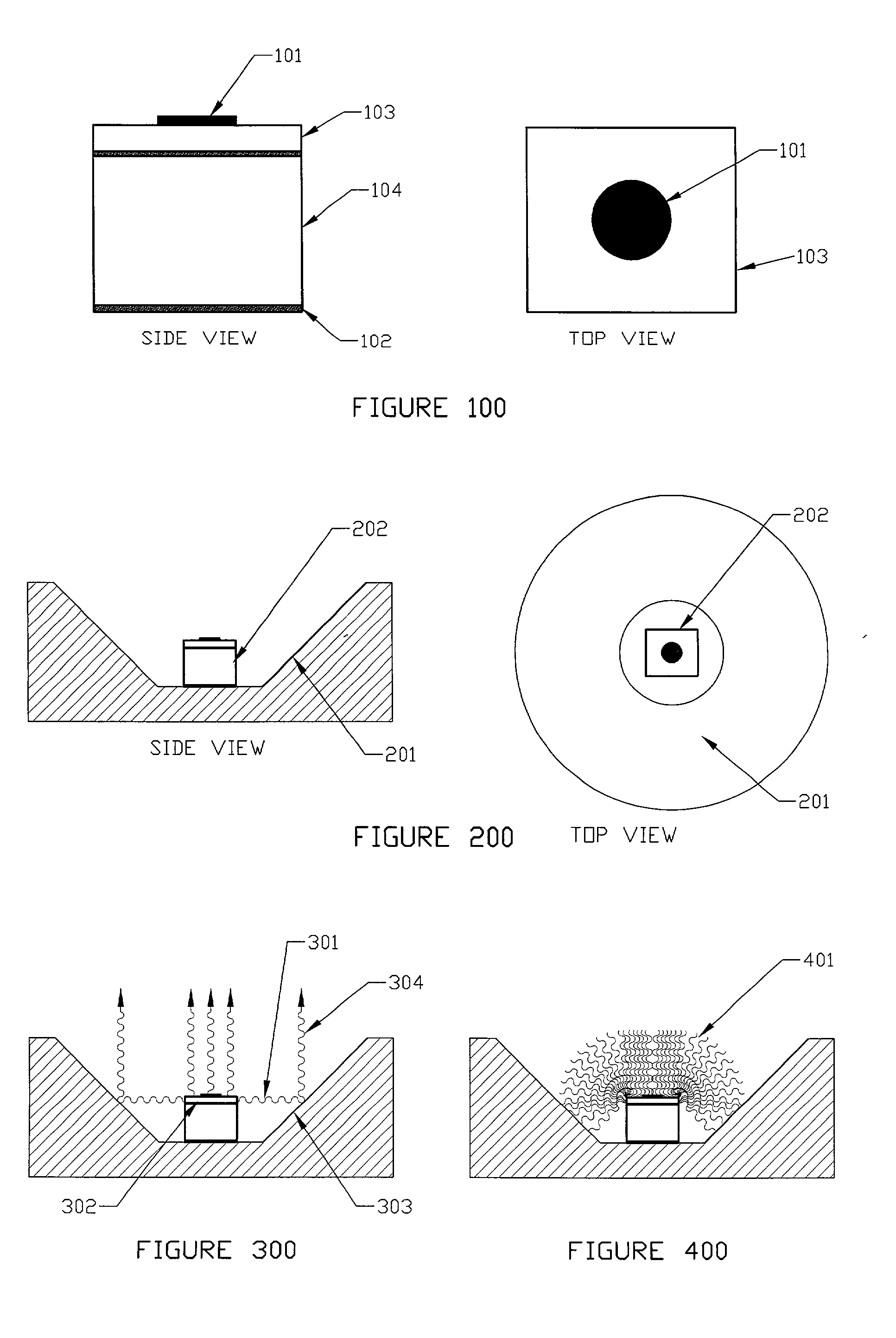
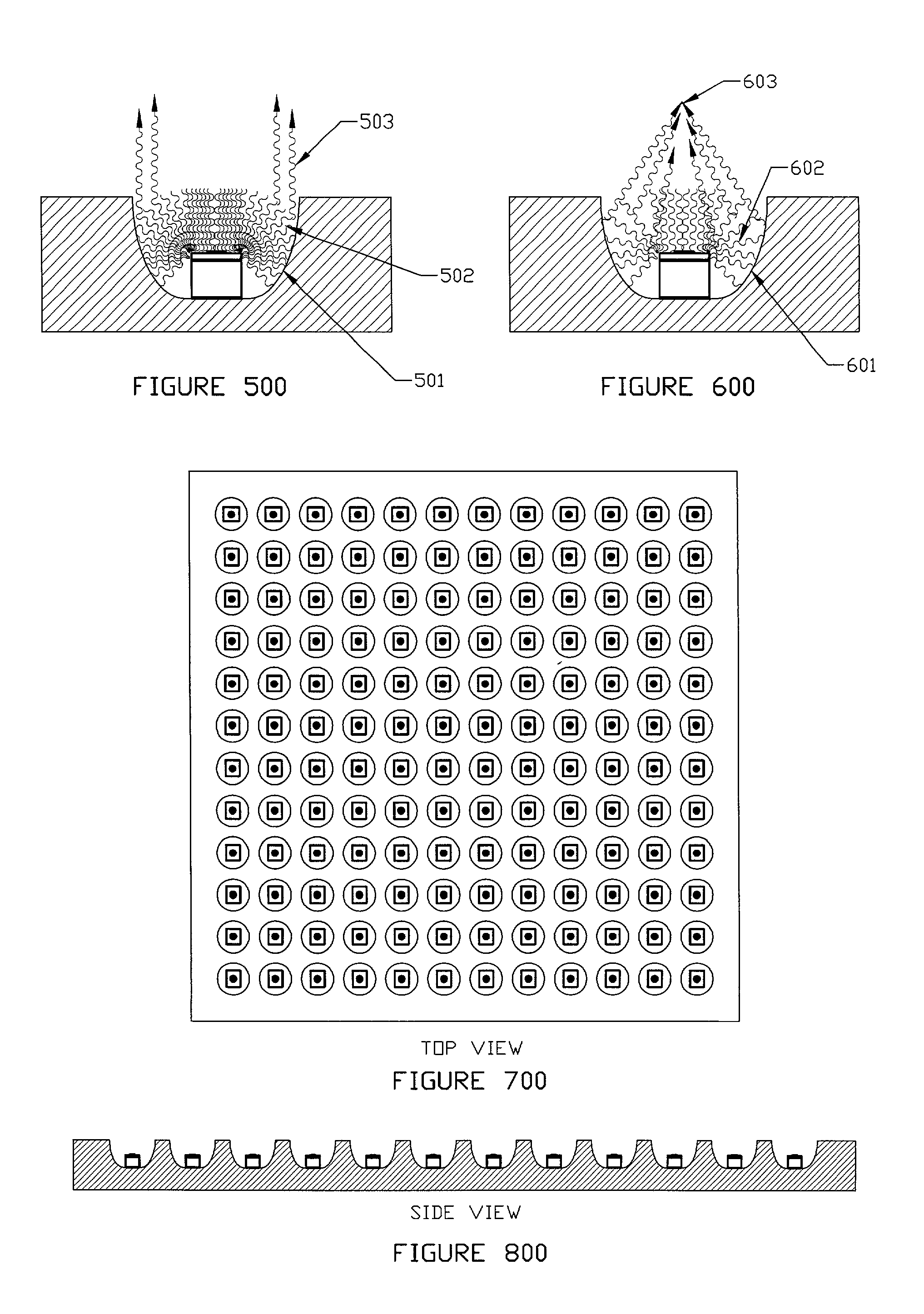
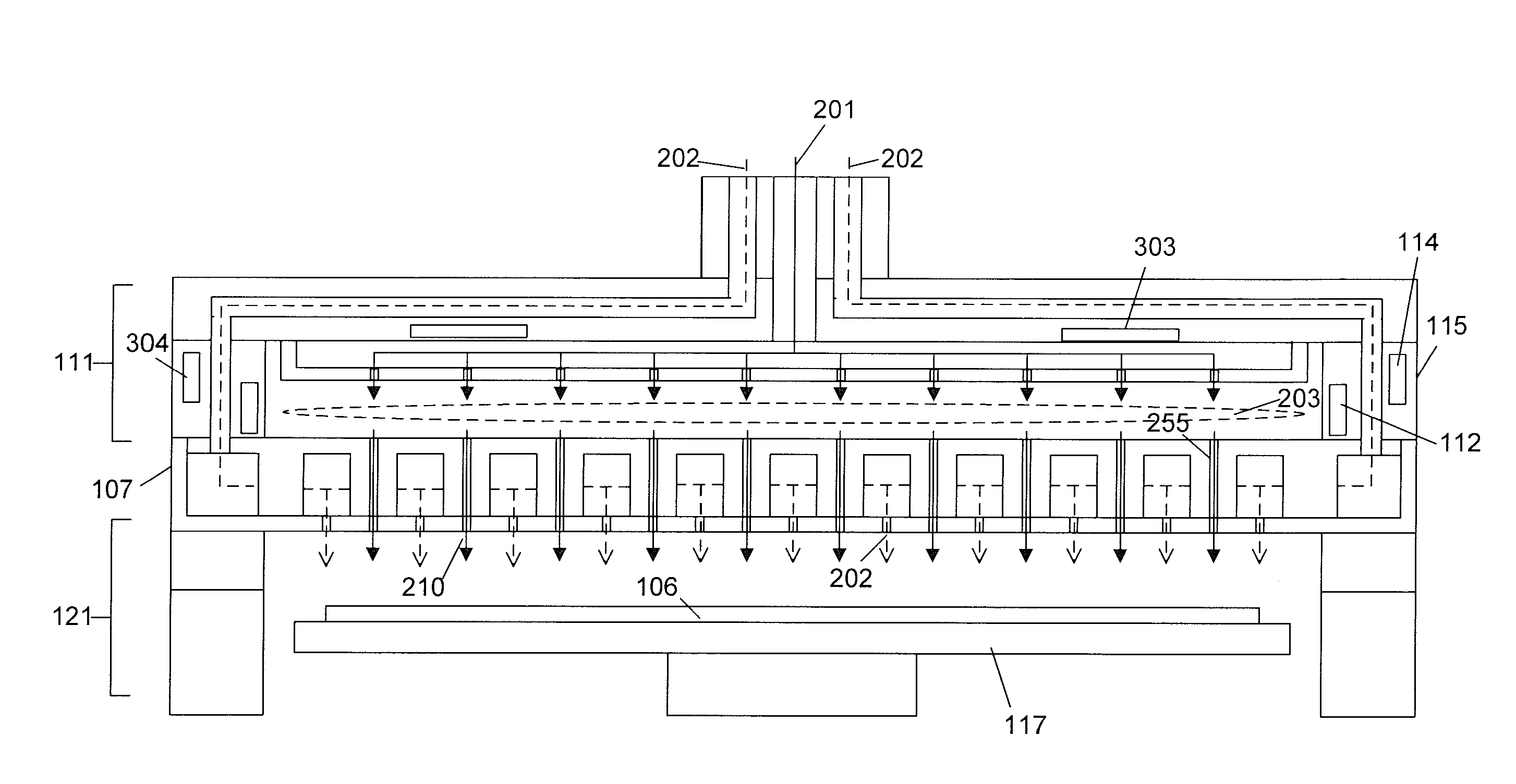
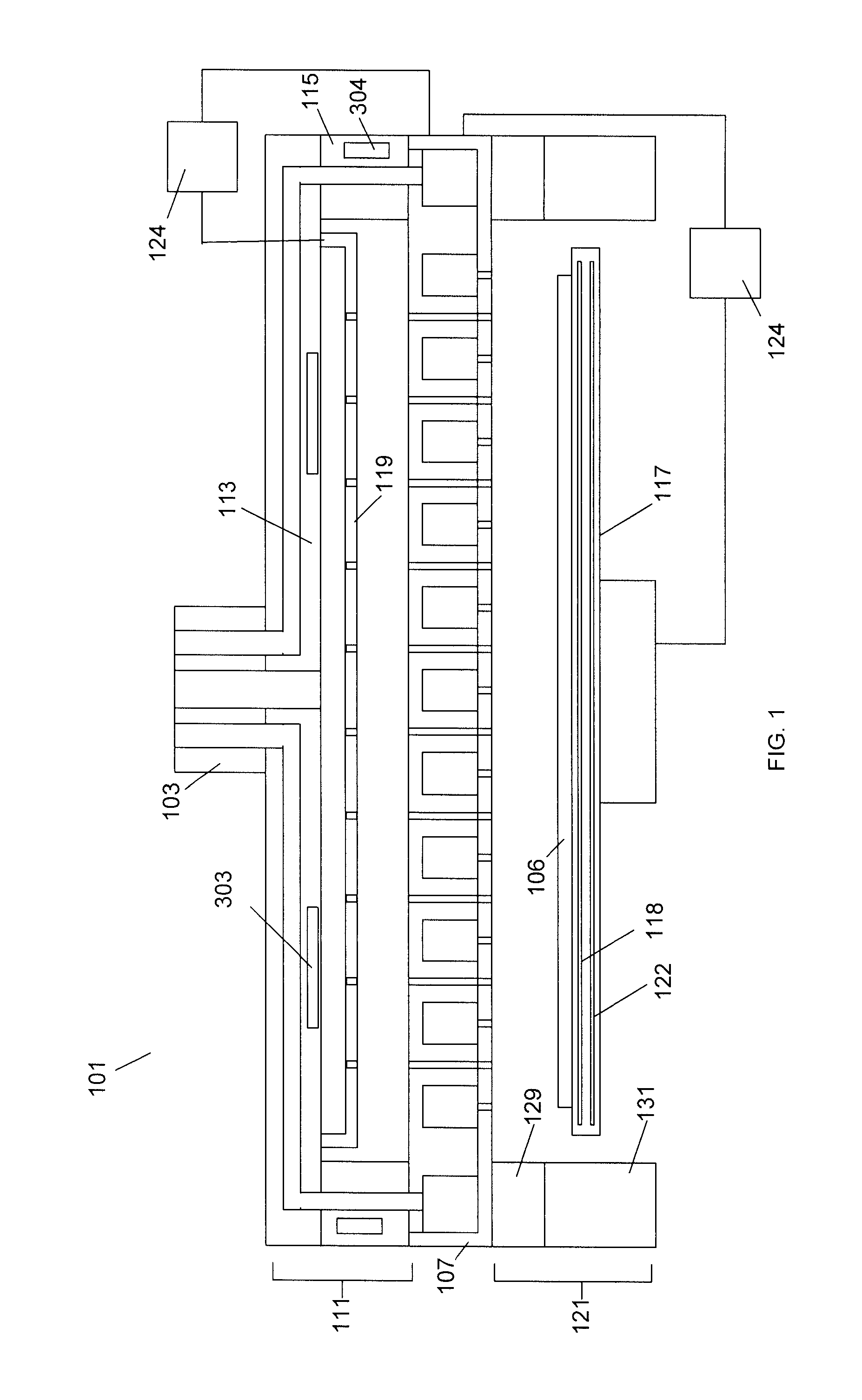
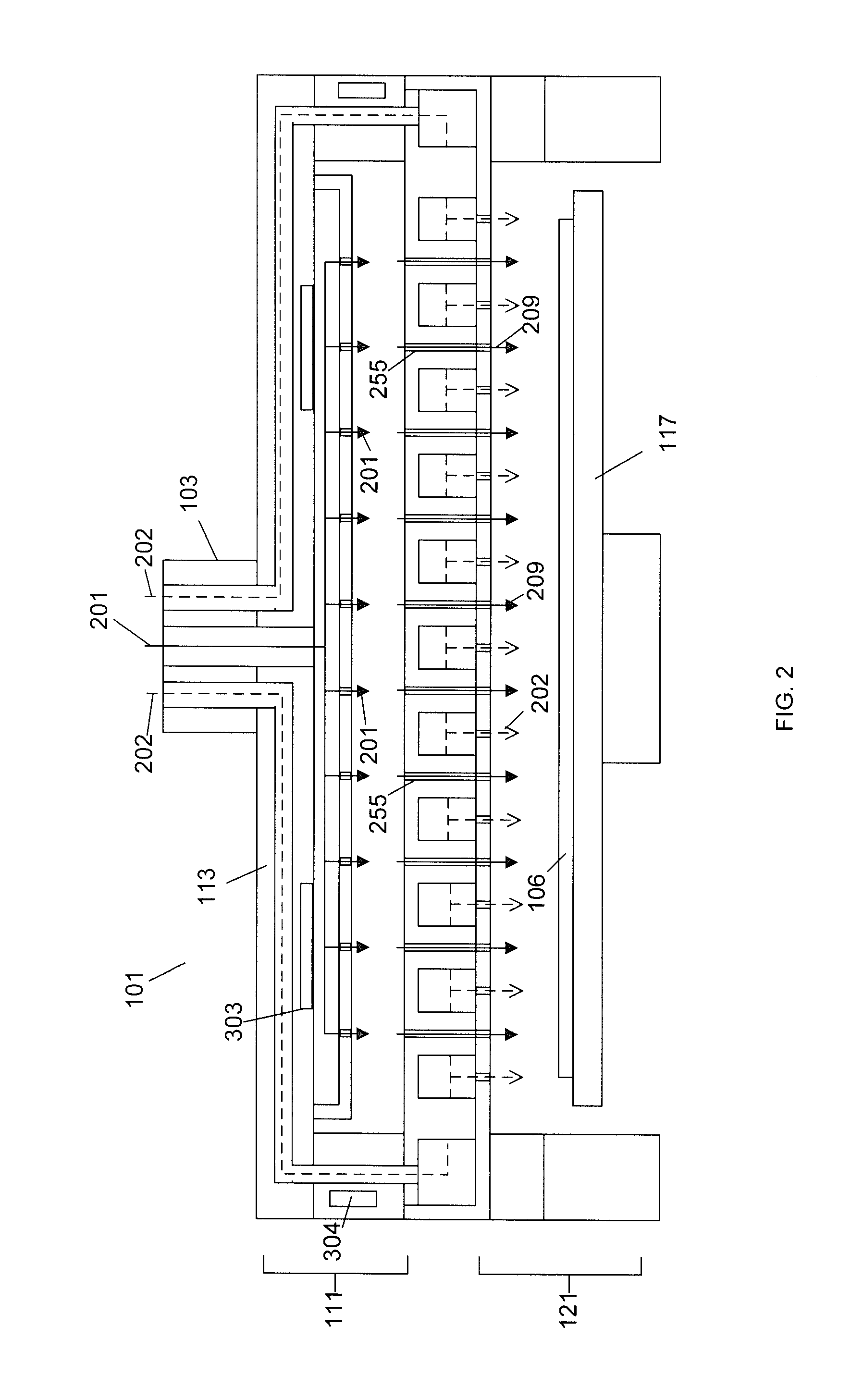
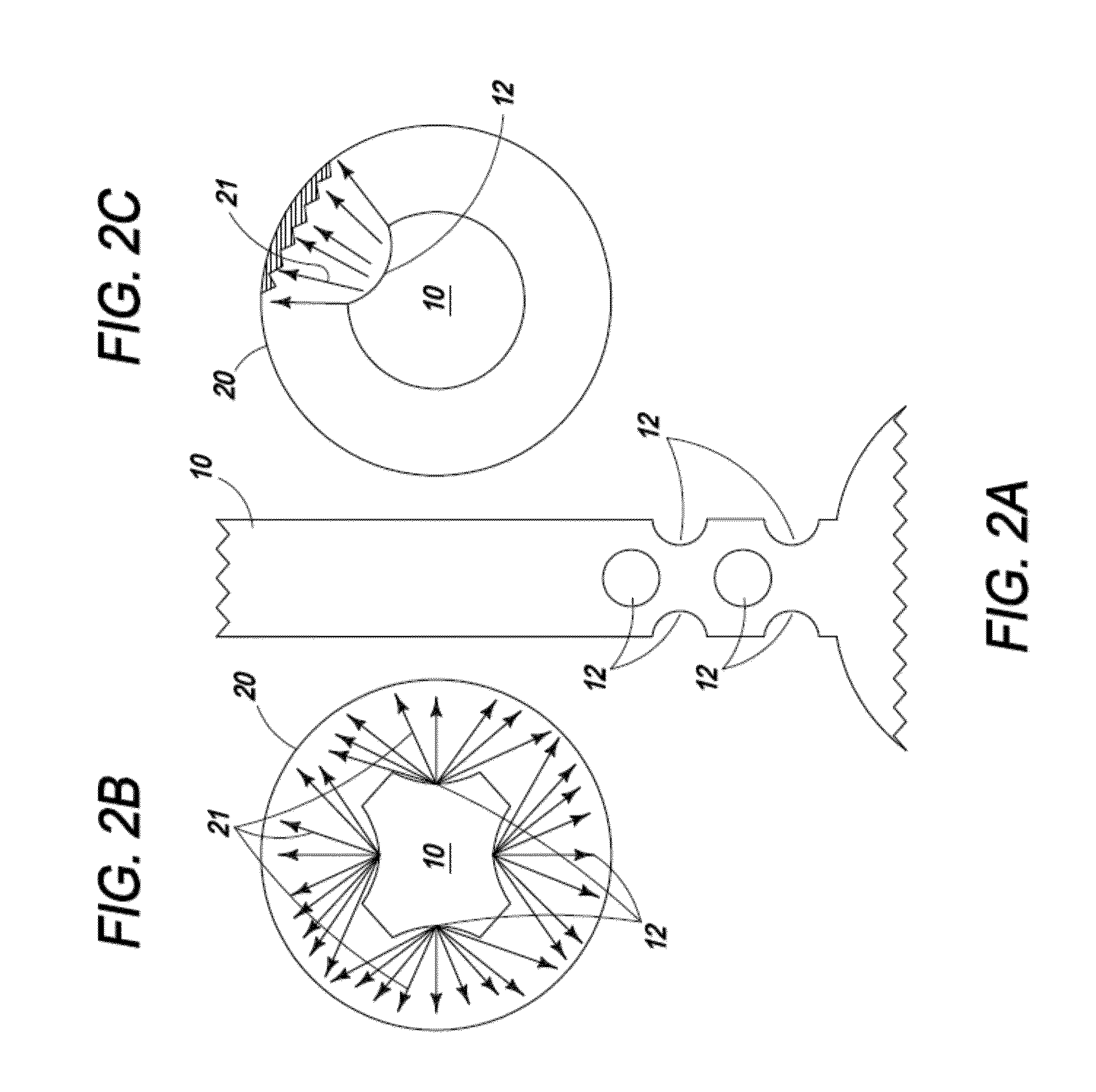
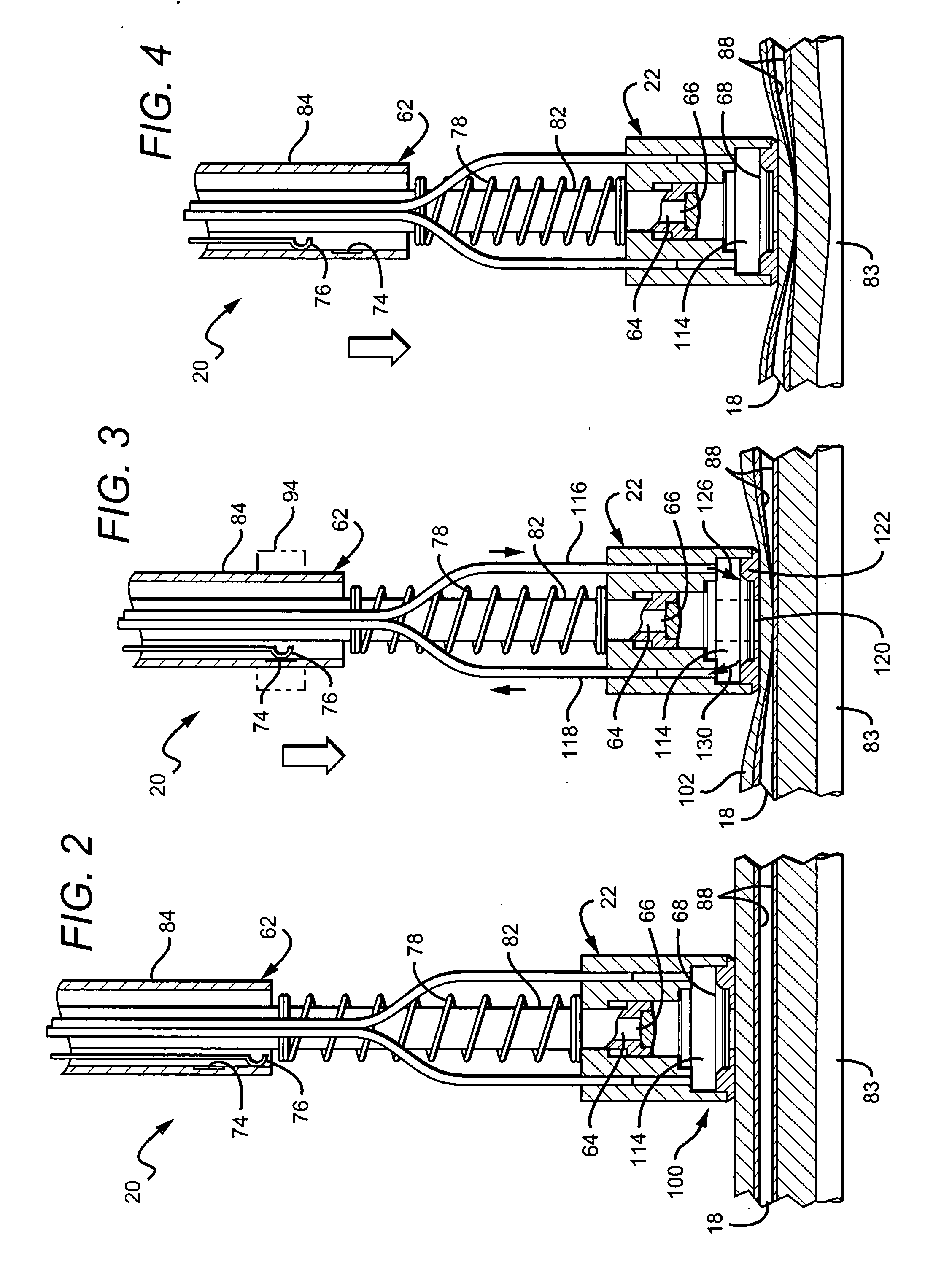
InactiveUS20120097330A1Avoid heat damageKeep coolSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDual deliveryPlasma generator
A substrate processing system includes a thermal processor or a plasma generator adjacent to a processing chamber. A first processing gas enters the thermal processor or plasma generator. The first processing gas then flows directly through a showerhead into the processing chamber. A second processing gas flows through a second flow path through the showerhead. The first and second processing gases are mixed below the showerhead and a layer of material is deposited on a substrate under the showerhead.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
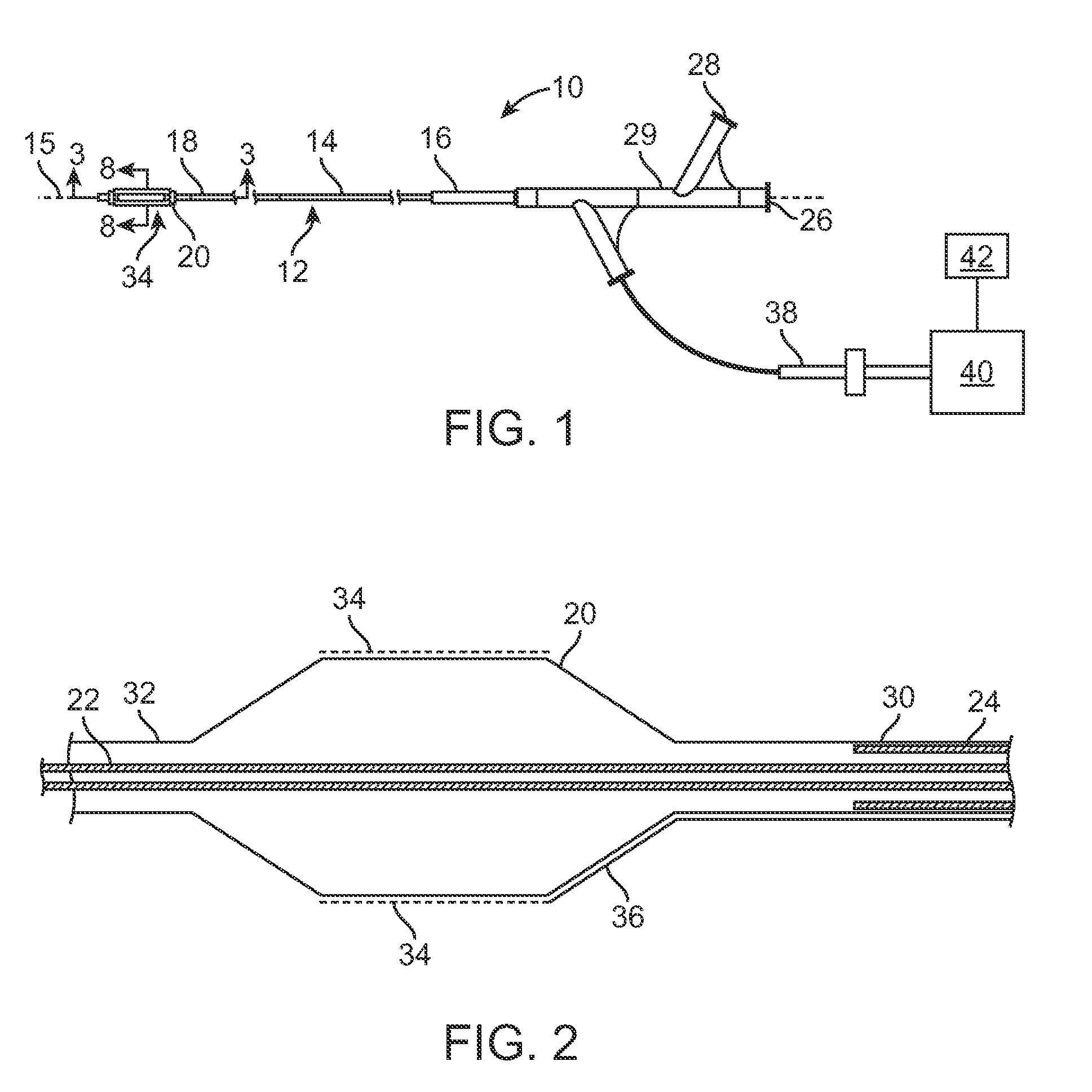
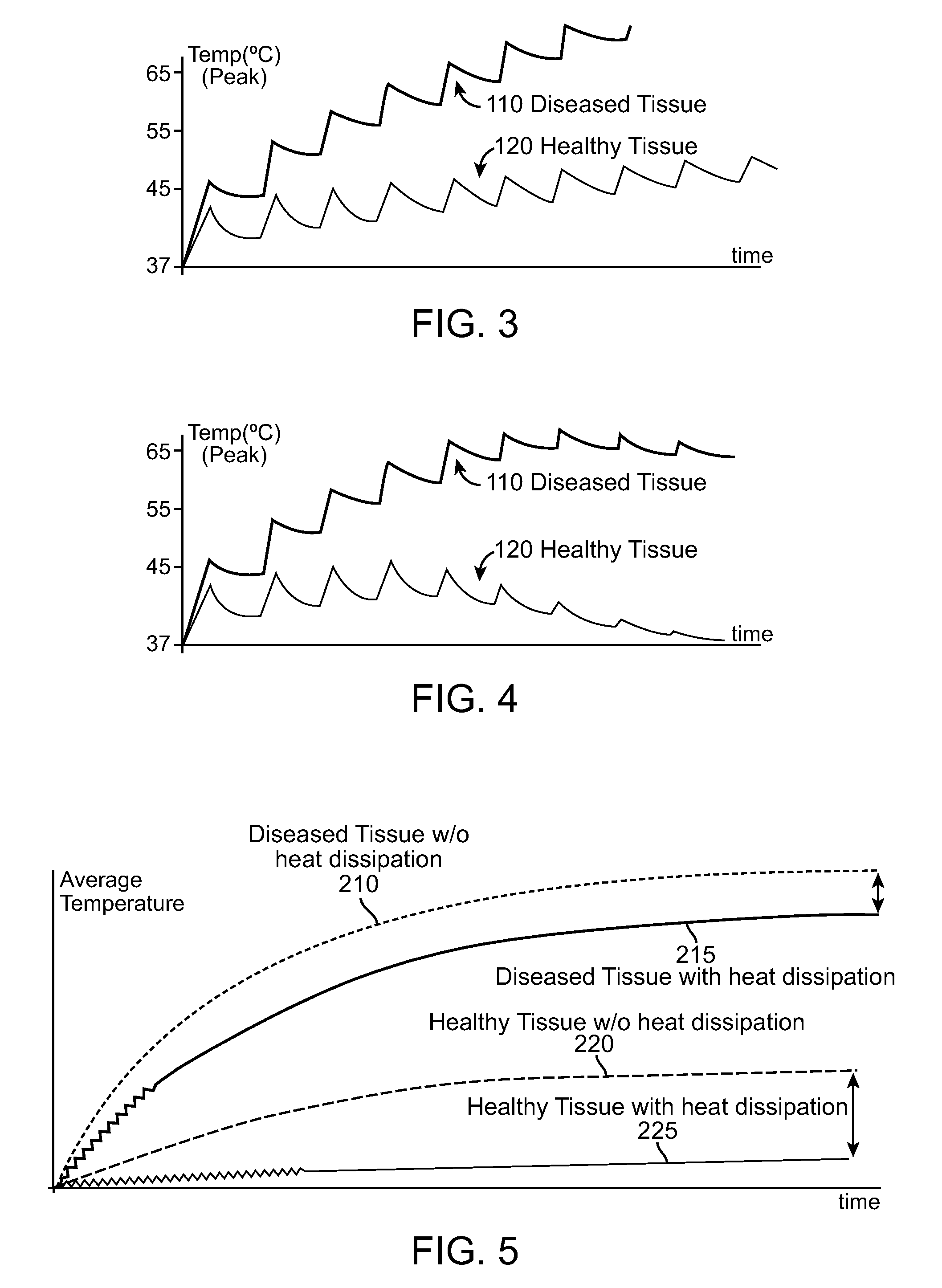
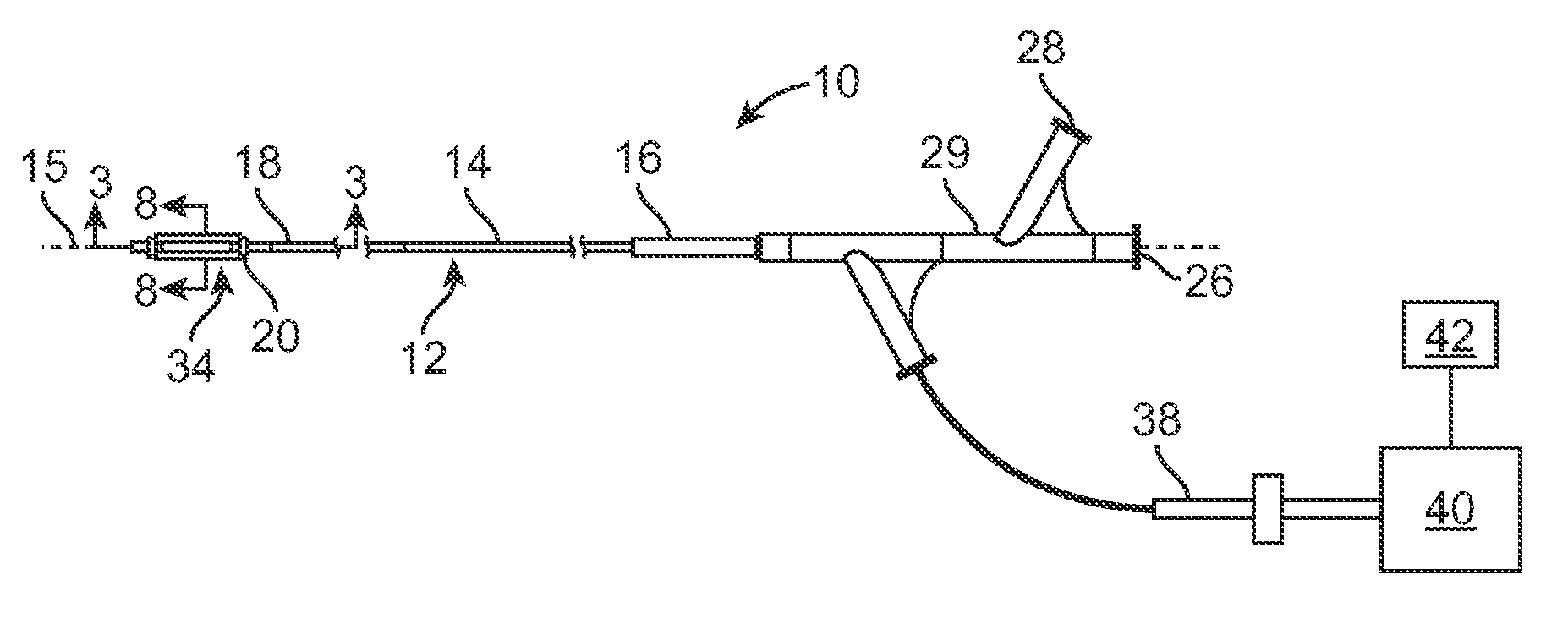
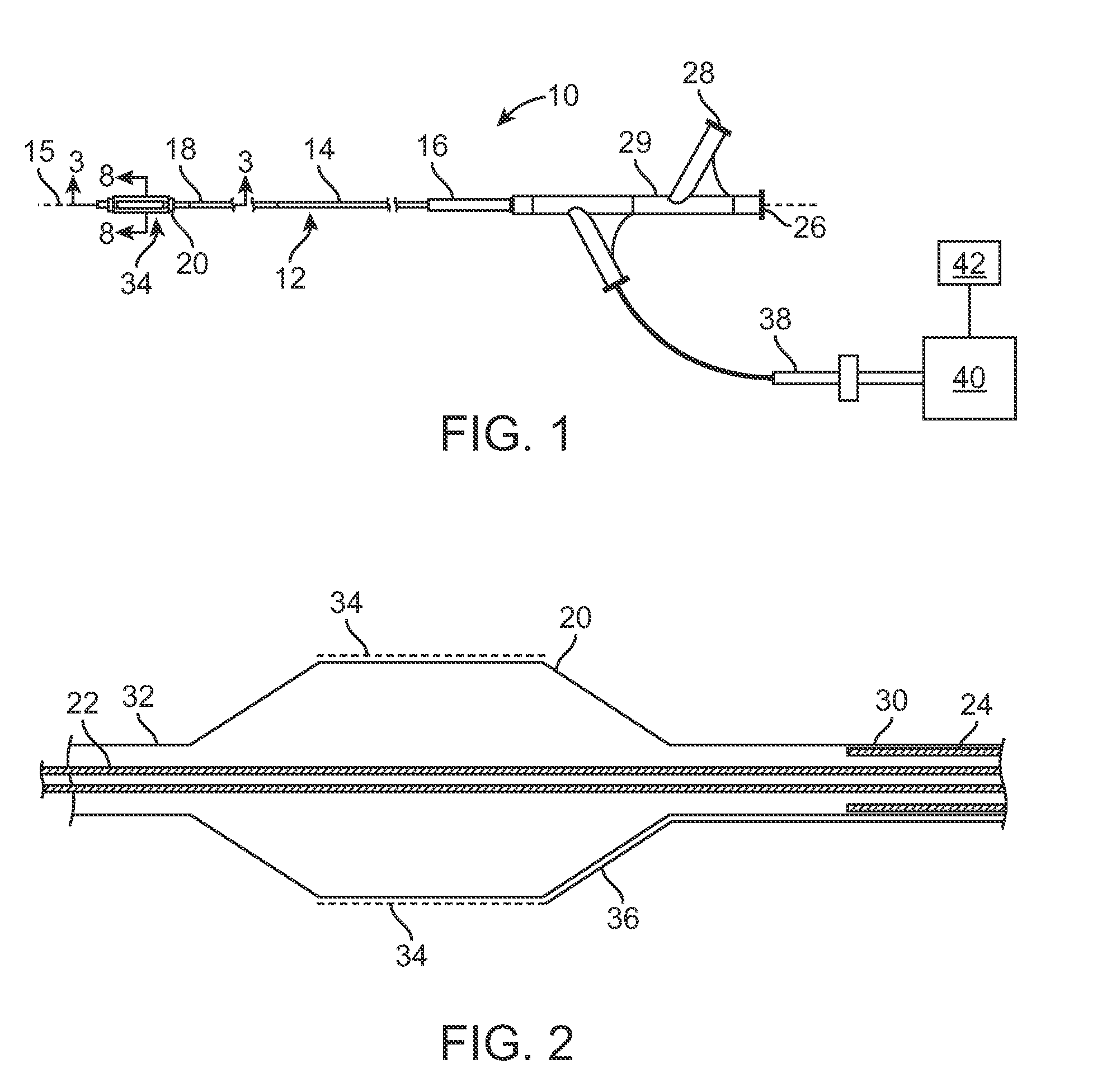
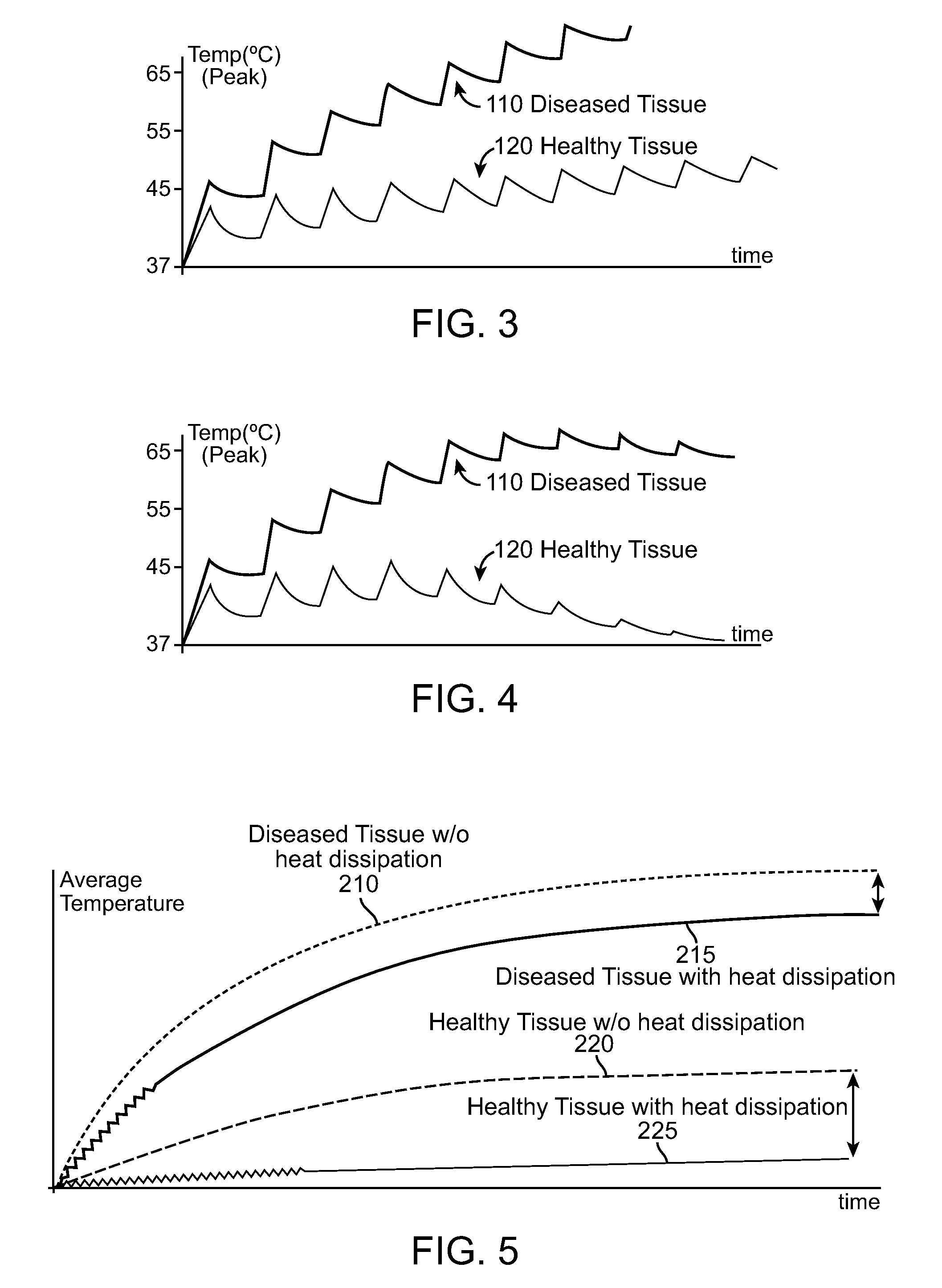
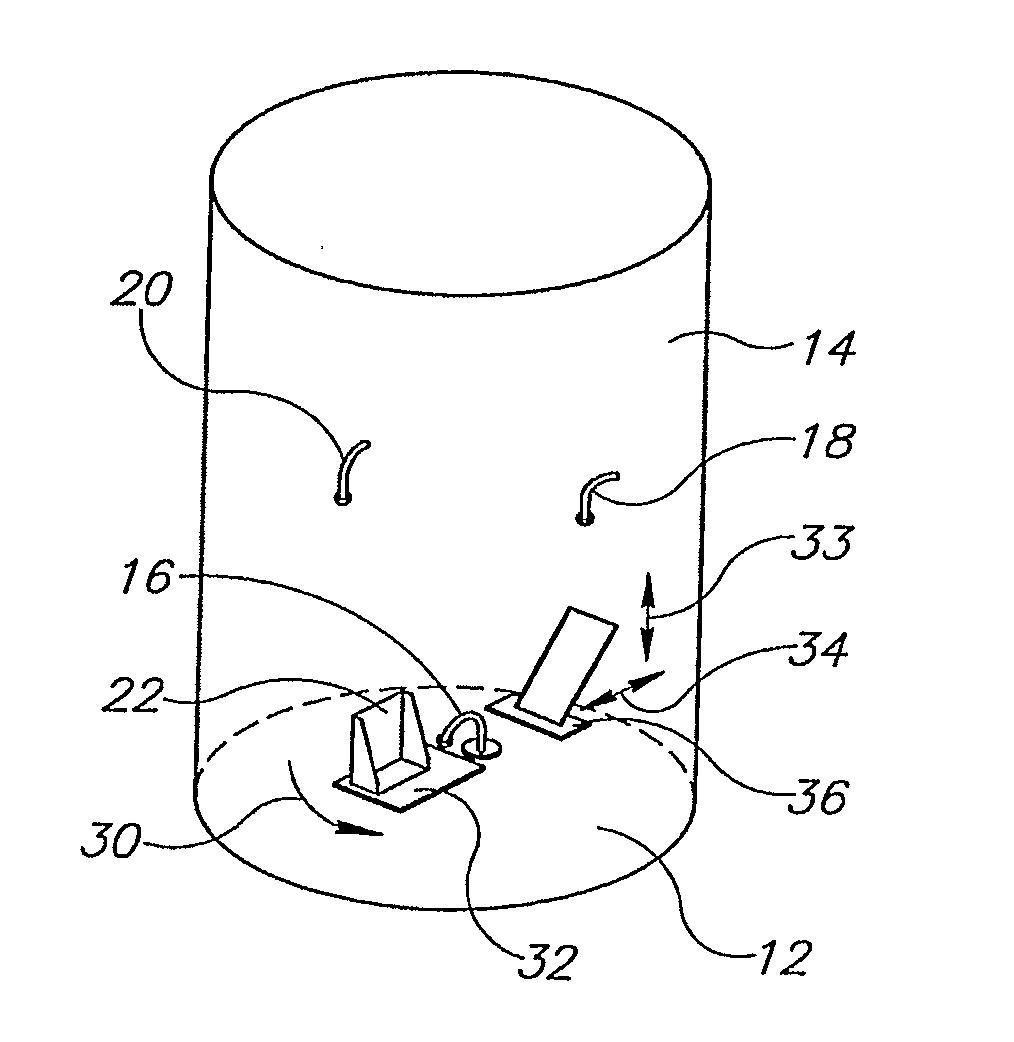
Selective accumulation of energy with or without knowledge of tissue topography
ActiveUS8401667B2Avoids significant thermal damageSignificant thermal damageUltrasound therapyChiropractic devicesMedicinePulse energy
Methods and systems for heating a body tissue region adjacent a body lumen using selective accumulation of energy without knowledge of tissue topography. Methods include positioning an energy delivery portion of a catheter within the lumen adjacent the body tissue region, determining a pulse characteristic in response to a thermal property of a first tissue type and applying pulsed energy with the characteristic to treat a second tissue type within the region by drawing heat from the first tissue at a rate that inhibits thermal damage to the first tissue while building-up heat in the second tissue. Systems include a catheter body having an energy delivery portion processor configured to control a pulse characteristic of pulsed energy to therapeutically treat the second tissue by drawing heat from the first tissue at a rate that inhibits thermal damage to the first tissue while building-up heat in the second tissue.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Food preparation
ActiveUS20090236333A1Improve efficiencyIncrease net powerContainer decorationsLevel indicationsEngineeringIngested food
Owner:JOLIET 2010 LTD
Ultrasonic cutting device
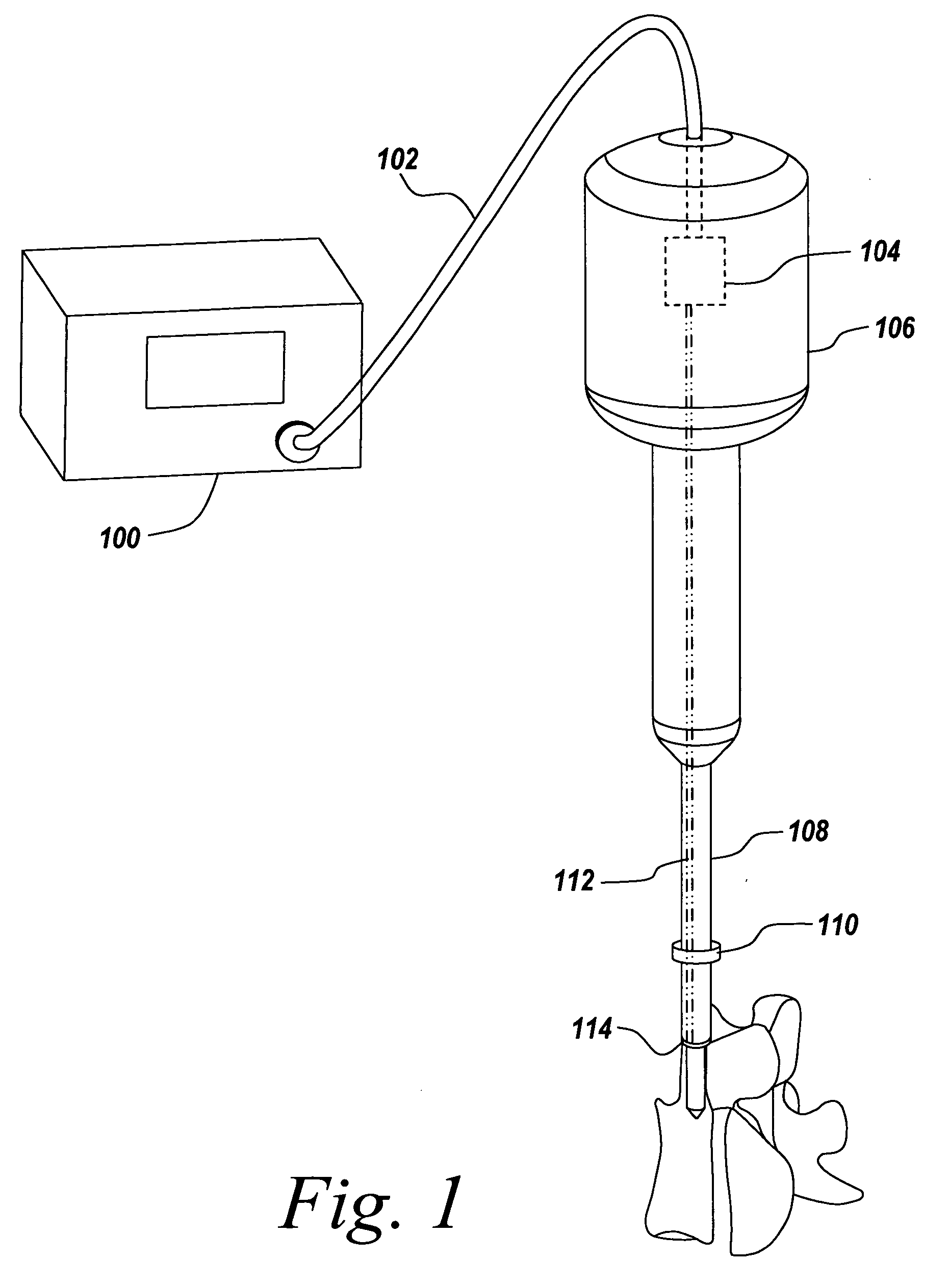
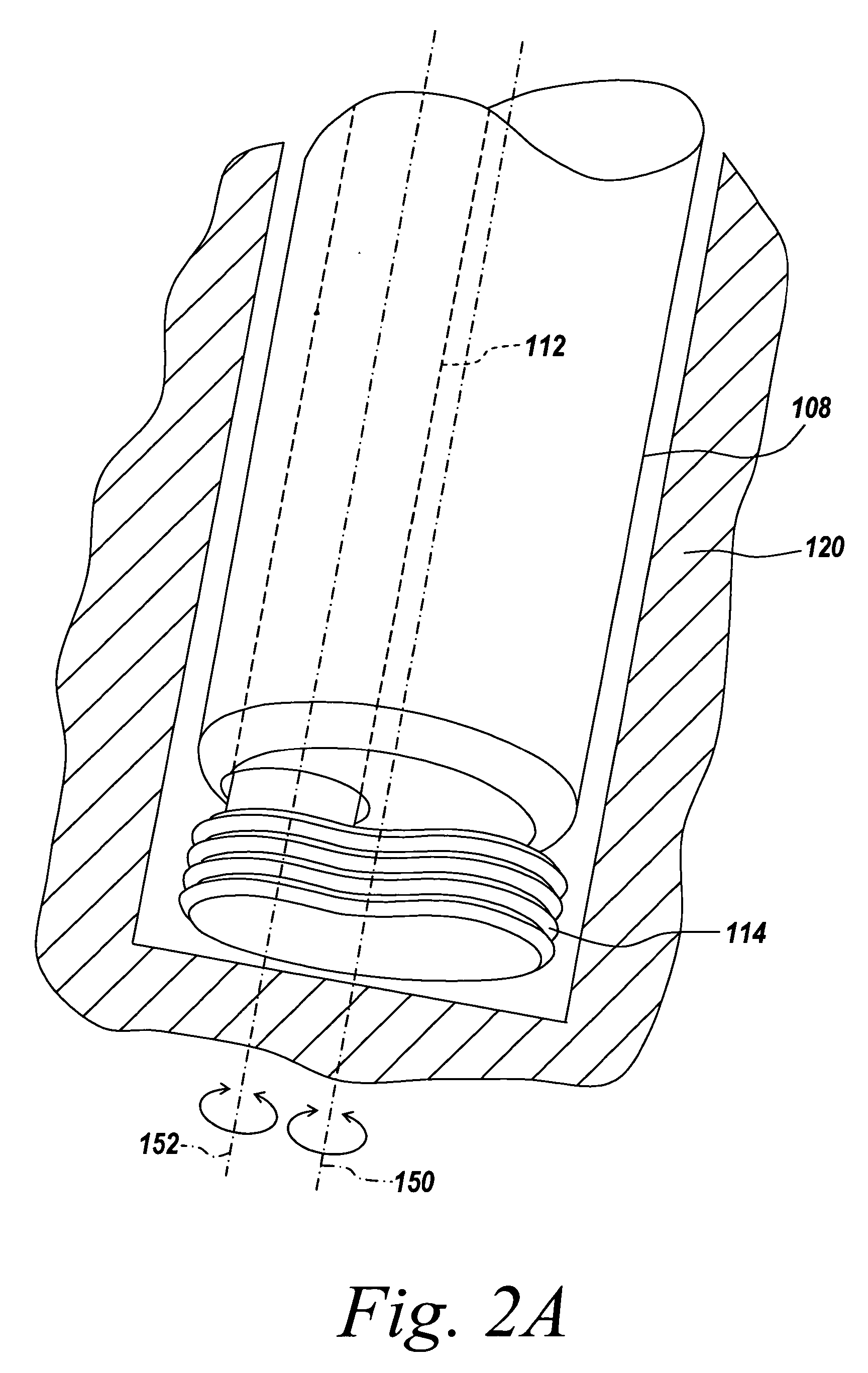
InactiveUS20060195106A1Reduce decreaseSpeedy removal of boneSurgical sawsSurgical departmentBiomedical engineering
An ultrasonic surgical cutting method and apparatus is provided wherein the method and apparatus allows for the cutting of bone from within a hollow pathway such that a cutter associated with the ultrasonic method and apparatus remains sufficiently cool to prevent necrosis of the bone being cut. Furthermore the ultrasonic device and method can be employed in the cutting of soft tissue, wherein a cooled cutter is used to prevent the sticking of soft tissue to the cutting blade of the device during use.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Ultrasonic cutting device
An ultrasonic surgical cutting method and apparatus is provided wherein the method and apparatus allows for the cutting of bone from within a hollow pathway such that a cutter associated with the ultrasonic method and apparatus remains sufficiently cool to prevent necrosis of the bone being cut. Furthermore the ultrasonic device and method can be employed in the cutting of soft tissue, wherein a cooled cutter is used to prevent the sticking of soft tissue to the cutting blade of the device during use.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
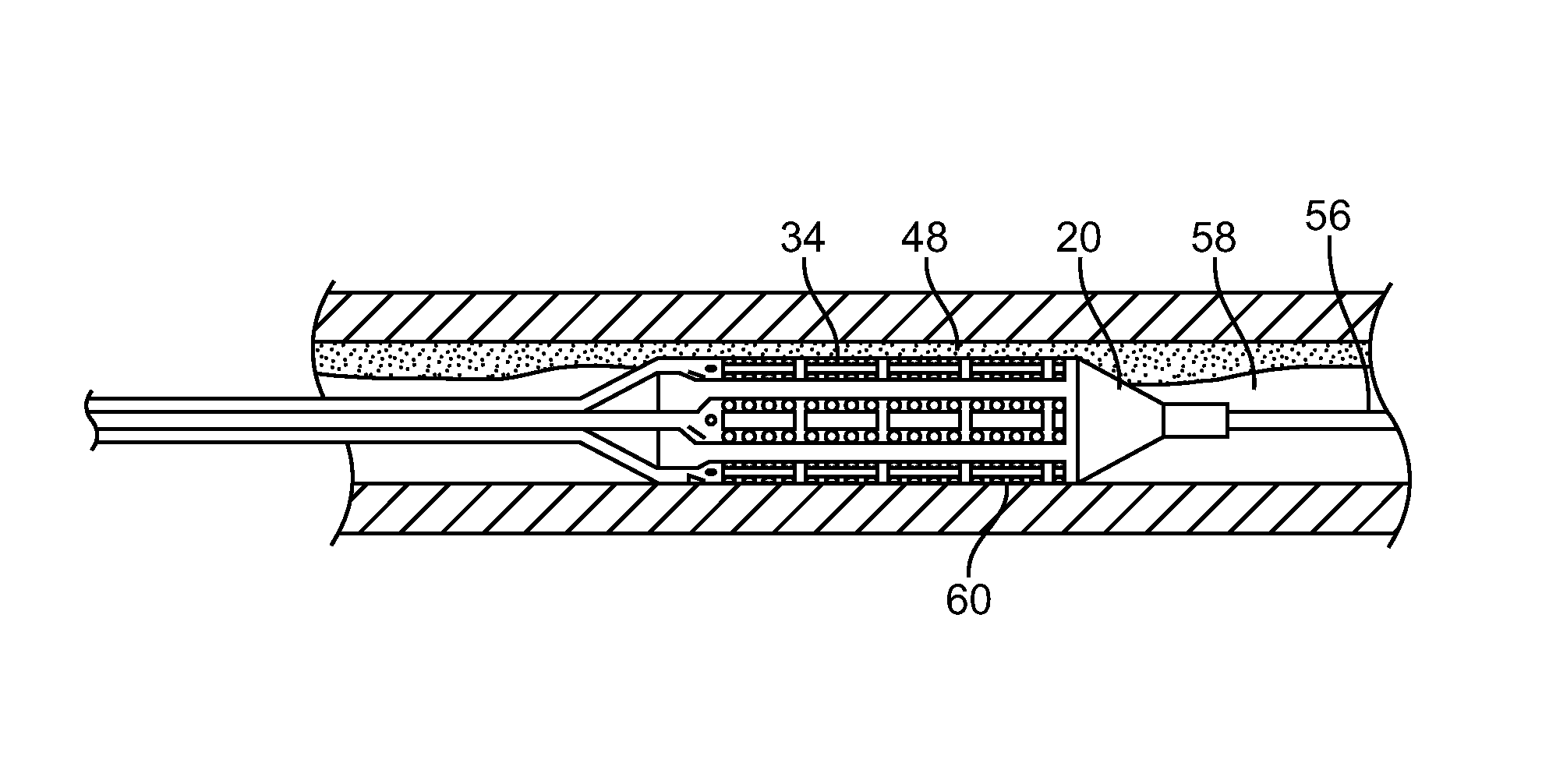
Method and apparatus for dermatological treatment and tissue reshaping
InactiveUS20080082090A1Minor side effectsGood effectSurgical needlesSurgical instrument detailsWrinkle skinPigmentations
The present invention is directed to a method and apparatus for providing electromagnetic radiation or other energy to tissue. An array of needles can be inserted at least partially into the tissue, and energy, e.g., optical energy, can be provided to the needles. The needles can include an optical waveguide configured to direct the energy to needle tips located within the tissue adjacent to one or more target regions. The energy can thus be provided directly to the target regions through the needles without being absorbed by upper portions of the tissue. Such method and apparatus can be used to treat a variety of skin conditions, including wrinkles and pigmentation defects. One or more of the needles in the array can also be hollow and configured to provide an analgesic or other substance into the tissue near the target regions.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Devices and methods for directed, interstitial ablation of tissue
InactiveUS7306588B2Avoid heat damageExcessive coagulationSurgical needlesSurgical instrument detailsTotal internal reflectionBiomedical engineering
The invention relates to a catheter device including an optical fiber whose distal end is disposed within a hollow tube with a sharp or needle shaped distal end, which can penetrate tissue. The distal end of the optical fiber and the hollow tube are configured so as to emit, by refraction (total internal reflection) or reflection from a metal surface, laser energy at an angle of about 80° to about 90° relative to the longitudinal axis of the optical fiber and hollow tube. The hollow tube is mounted to a housing and may be surrounded by a sheath.
Owner:CATHETER ABLATION SOLUTIONS
Method and apparatus for selective treatment of biological tissue using ultrasound energy
A method and apparatus are provided for dermatological treatment by focusing ultrasound energy in a volume of tissue below the dermis to obtain selective heating and thermal damage of certain portions of the volume while sparing other portions of the treatment volume from thermal damage. Selective heating of fibrous septae can be achieved while relatively sparing surrounding fatty tissue, which can lead to some shrinkage of the fibrous septae and reduction in the appearance of wrinkles. The matrix of hair follicles can also be selectively heated to provide relatively safe temporary or permanent hair removal. The superficial musculoaponeurotic system can also be selectively heated to obtain a tightening of the overlying skin.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Process for fabricating semiconductor device
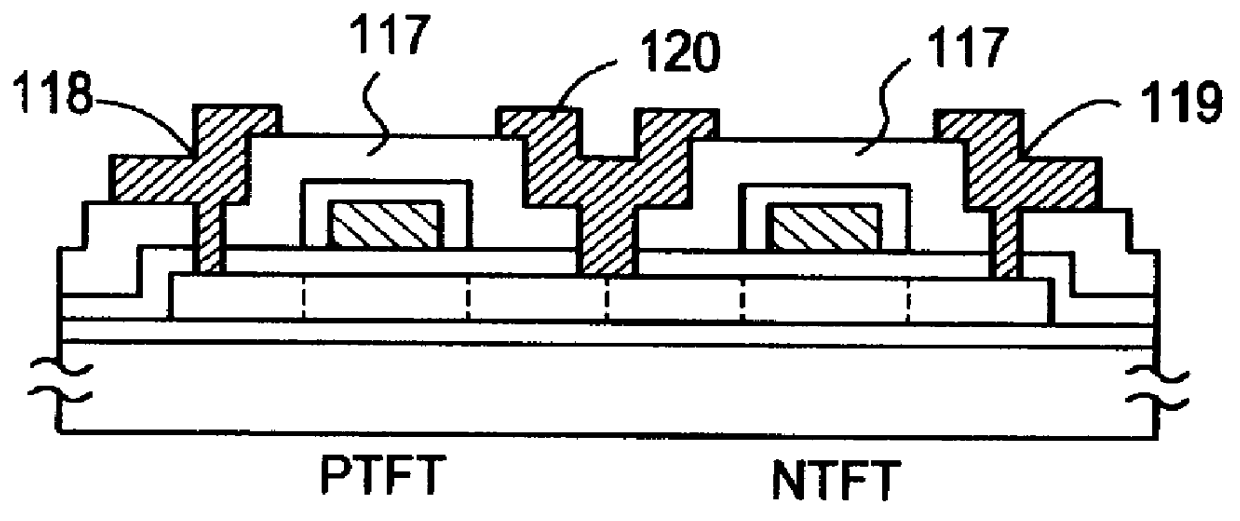
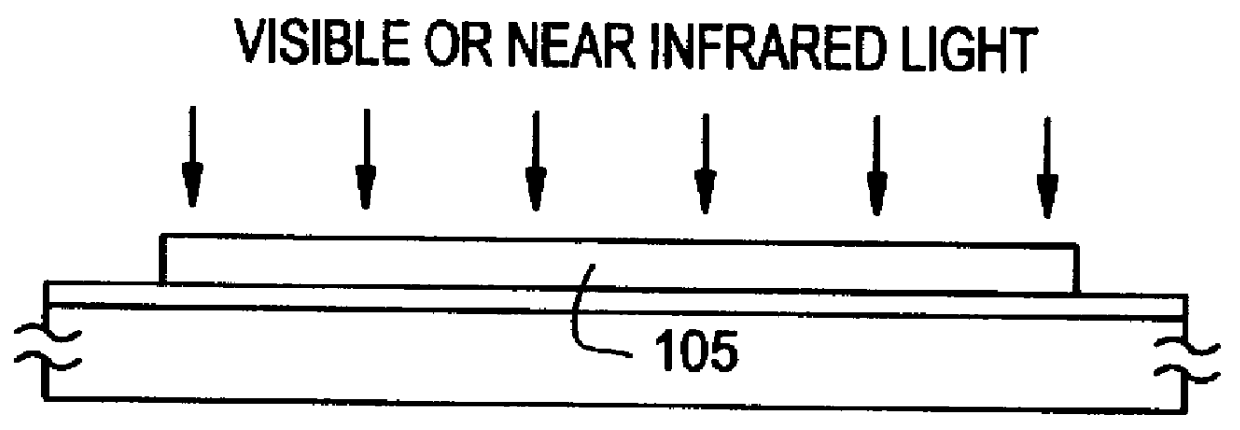
InactiveUS6051453AReduce the temperatureCrystal character can be improvedTransistorSolid-state devicesAmorphous siliconNear infrared radiation
A process for fabricating a semiconductor device comprising the step of, after patterning the silicon film crystallized to a low degree by thermally annealing an amorphous silicon film into an island by etching, irradiating an intense light of a visible light or a near infrared radiation to effect a short-period annealing (RTA) to the silicon film of low crystallinity. Thus, the crystallinity of the silicon film is improved and the silicon film is densified in a short-period.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
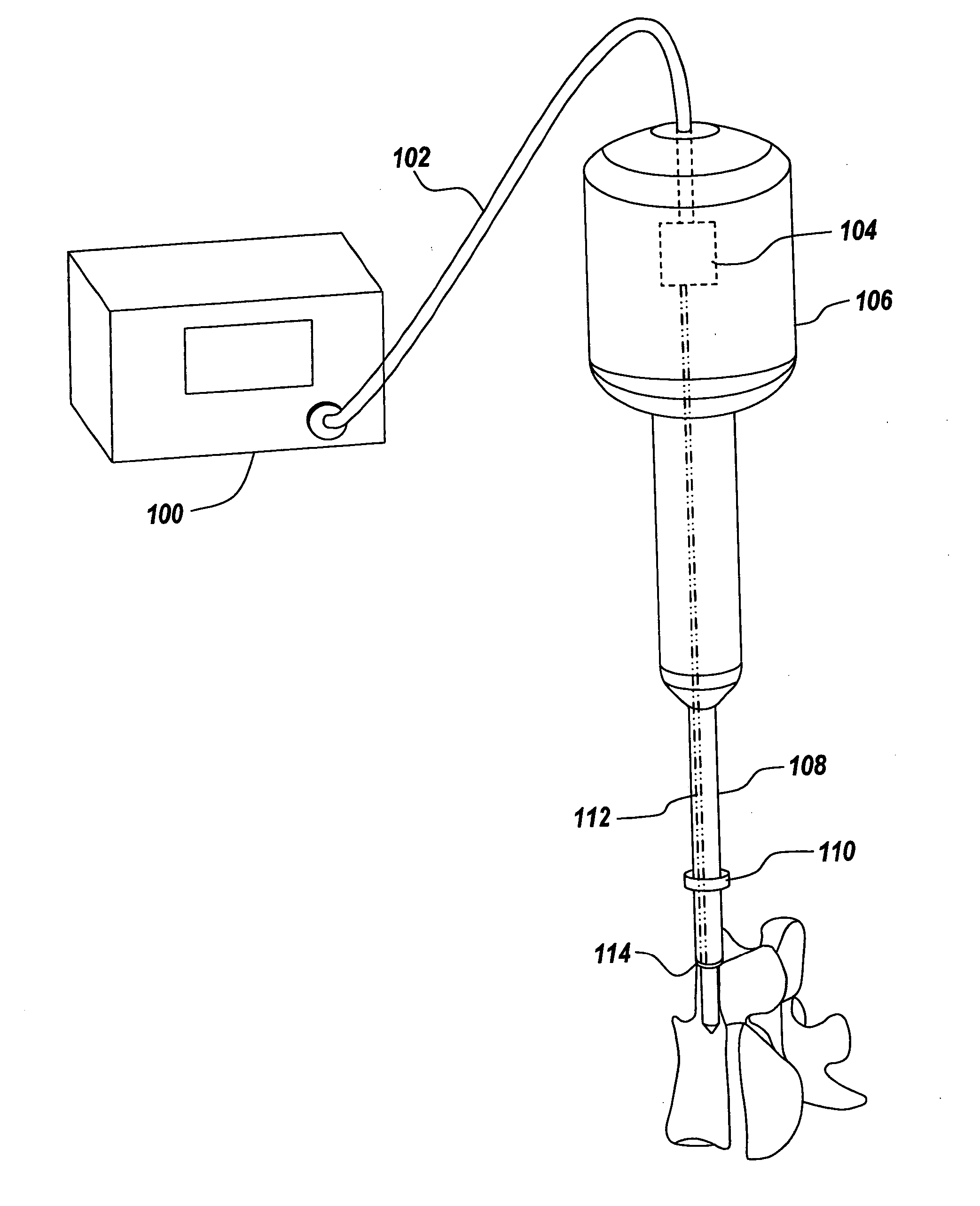
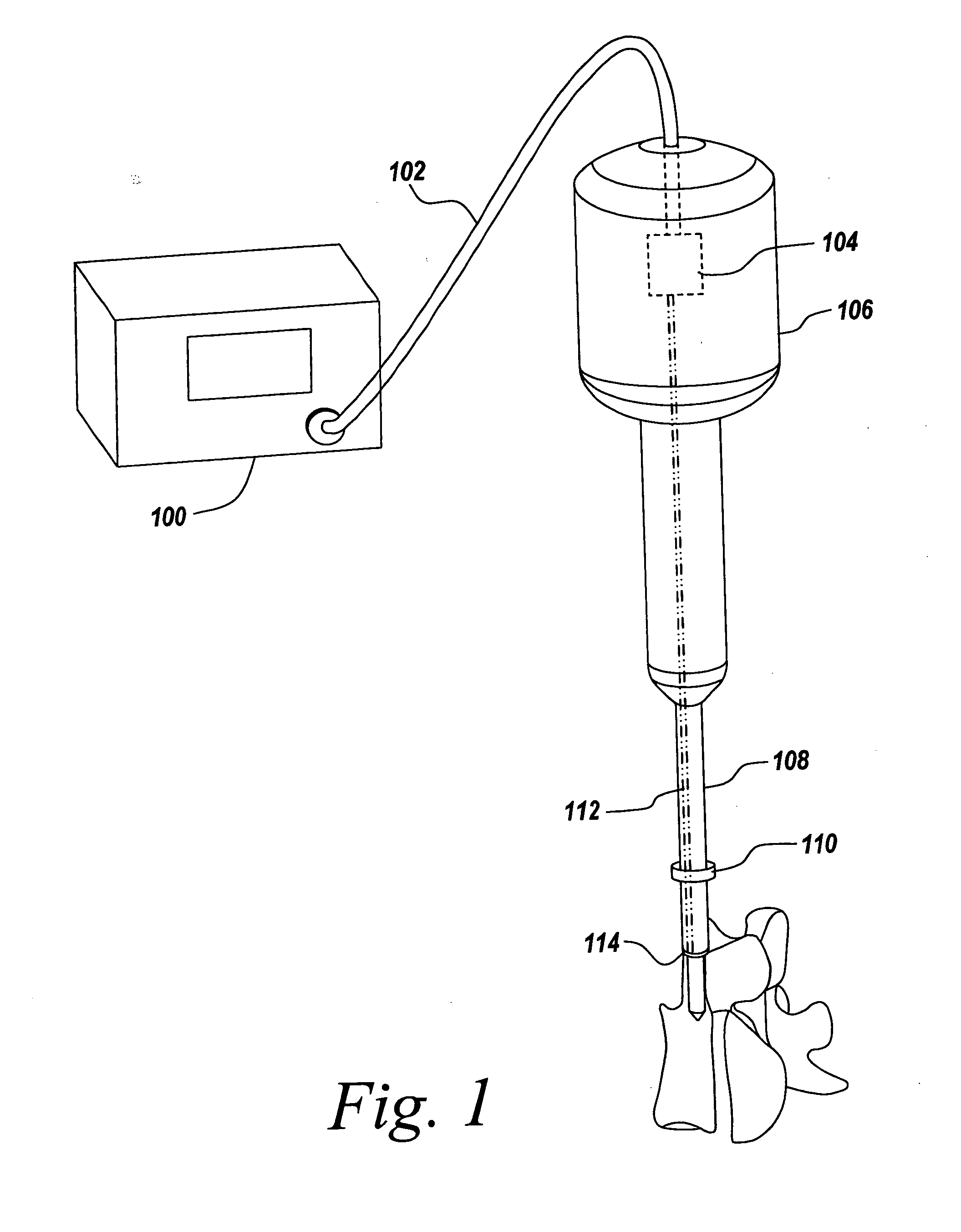
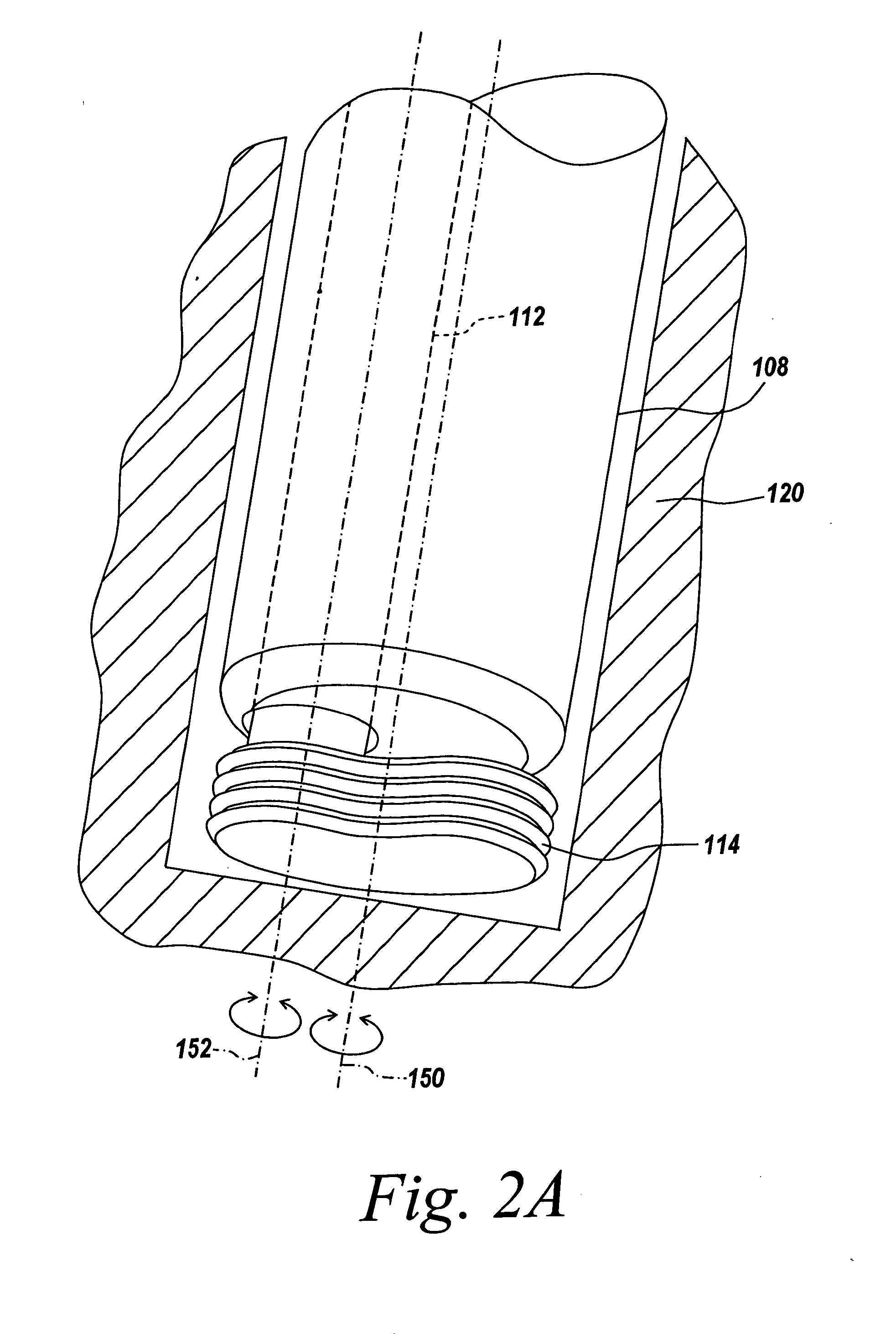
Method and Apparatus for Tissue Ablation
ActiveUS20130006231A1Avoid condensationAvoid heat damageDiagnosticsMedical devicesCoiled tubingCatheter
The present application discloses devices that ablate human tissue. The device comprises a catheter with a shaft through which an ablative agent can travel, a liquid reservoir and a heating component, which may comprise a length of coiled tubing contained within a heating element, wherein activation of said heating element causes said coiled tubing to increase from a first temperature to a second temperature and wherein the increase causes a conversion of liquid within the coiled tubing to vapor, a reusable cord connecting the outlet of the reservoir to the inlet of the heating component, and a single use cord connecting a pressure-resistant inlet port of a vapor based ablation device to the outlet of the heating component.
Owner:SANTA ANNA TECH LLC
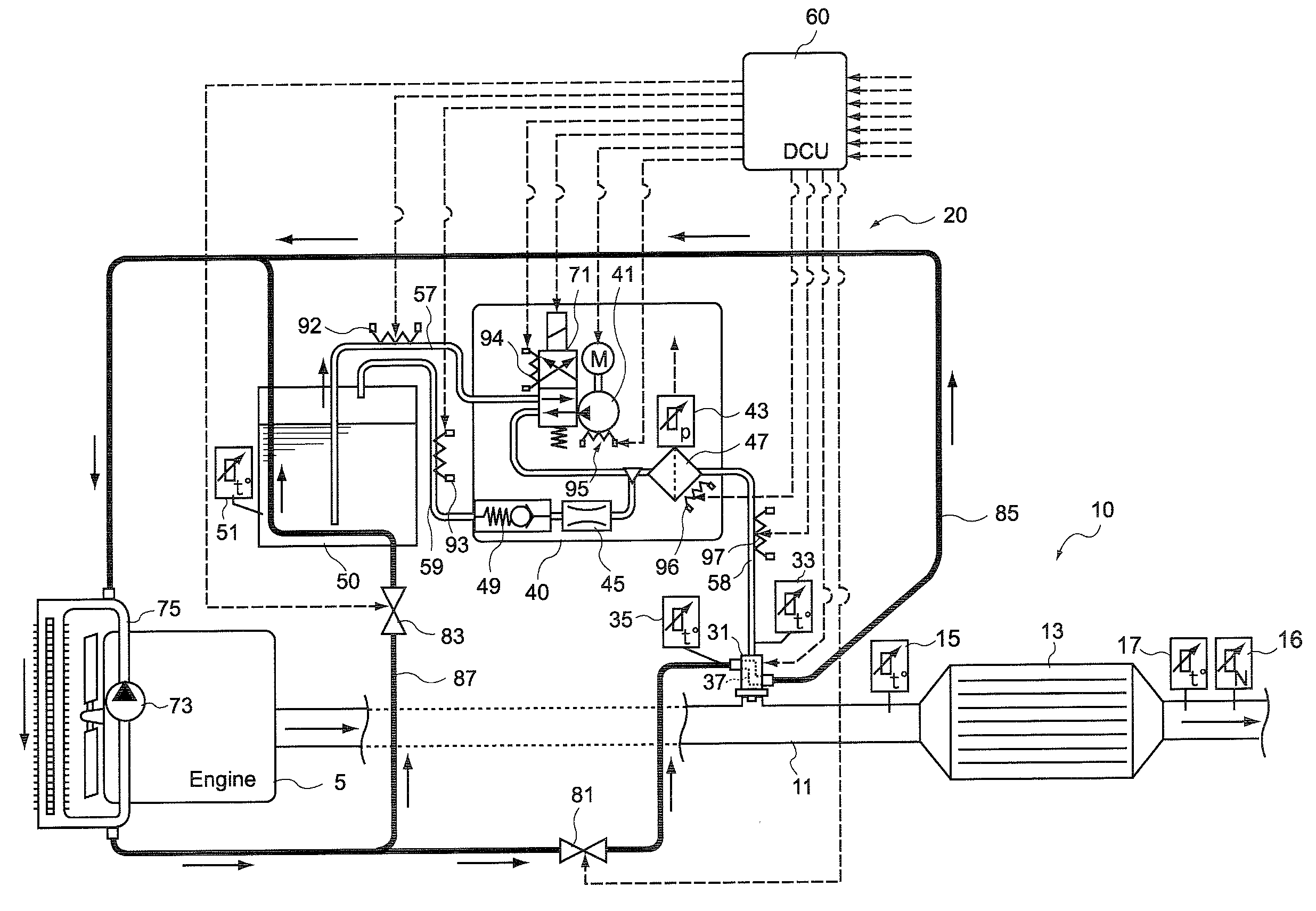
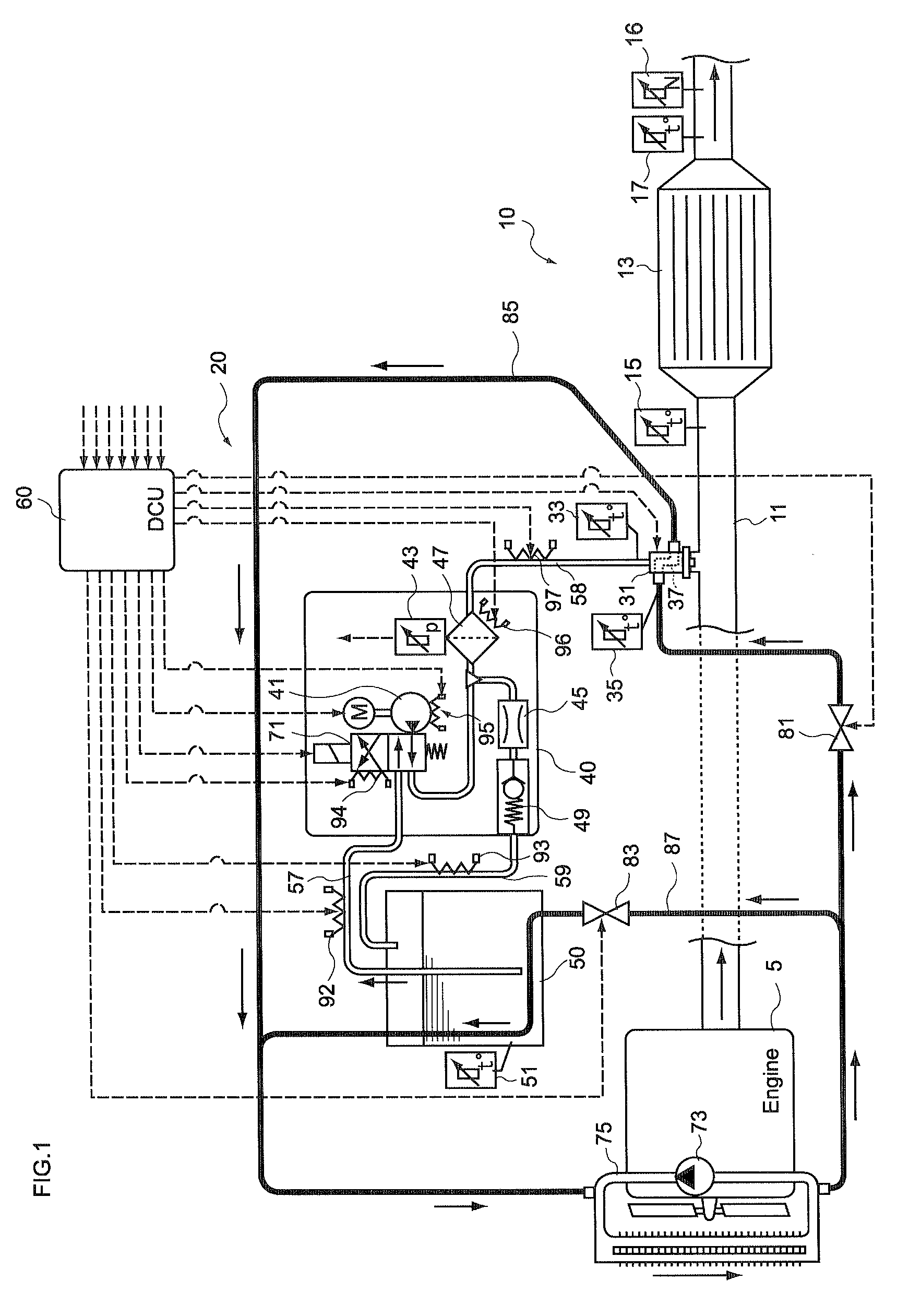
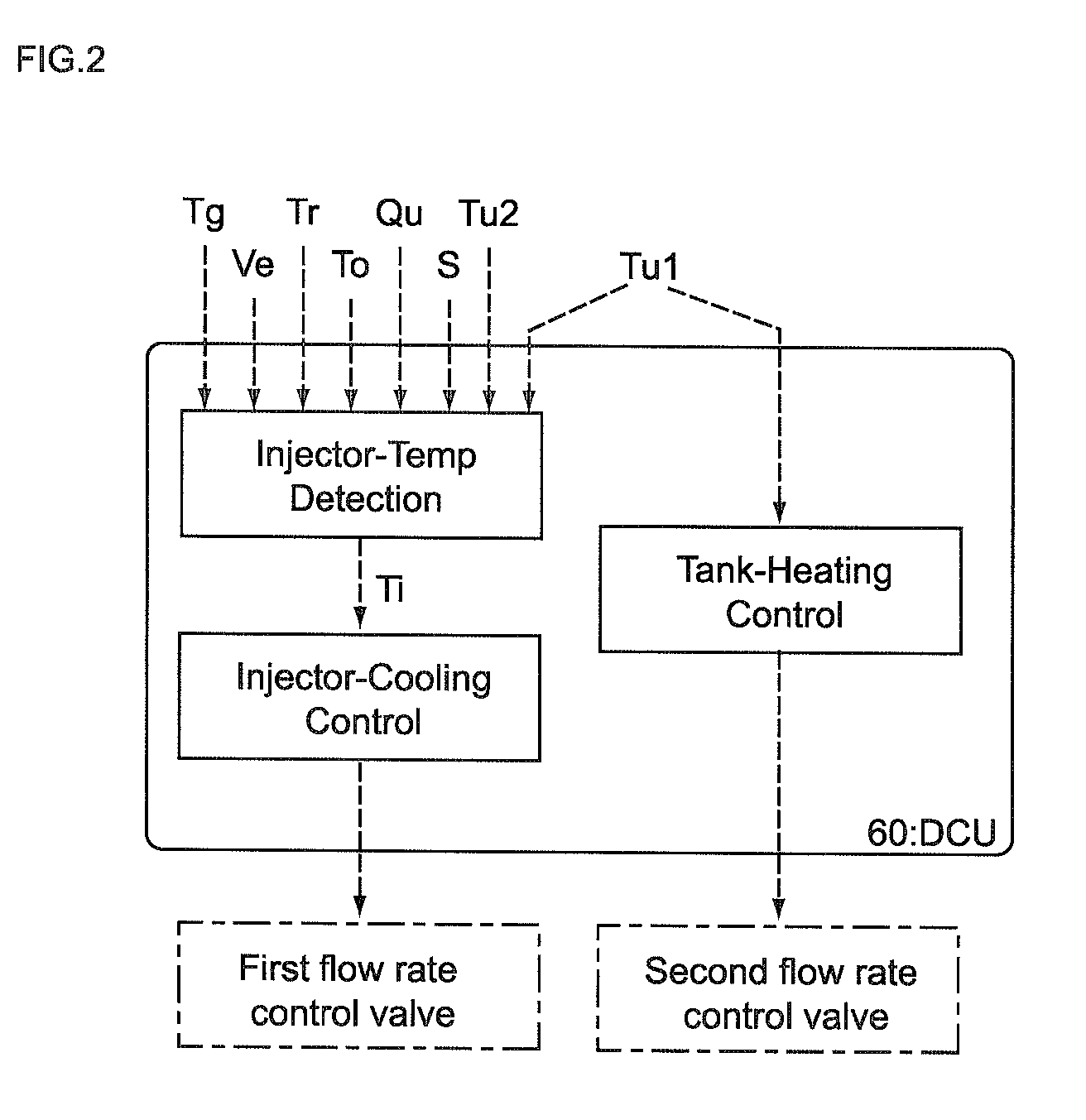
Control unit and control method for reductant supply device
InactiveUS20100242439A1Prevent overcoolingImprove cooling effectLiquid coolingInternal combustion piston enginesEngineeringWater circulation
There are provided a reductant supply device and a control method for the reductant supply device, which can prevent heat damage of a reductant injection valve, and also prevent crystallization of urea solution due to excessive cooling of the solution reductant.The reductant supply device which is used in an exhaust gas purification device that injects and supplies, as a reductant, a urea solution to an exhaust gas upstream side of a reduction catalyst disposed in an exhaust gas passage of an internal combustion engine, and that reduces and purifies nitrogen oxides contained in exhaust gas using the reduction catalyst, the reductant supply device having a reductant injection valve that is fixed to an exhaust pipe on the exhaust gas upstream side of the reduction catalyst, includes: a cooling water circulation passage that circulates at least part of cooling water of the internal combustion engine to cool the reductant injection valve; flow rate control means for adjusting a flow rate of cooling water flowing through the cooling water circulation passage; temperature detection means for detecting a temperature of the reductant injection valve; and control means for controlling the flow rate control means based on the temperature of the reductant injection valve.
Owner:BOSCH CORP
Selective Accumulation of Energy With or Without Knowledge of Tissue Topography
ActiveUS20100125268A1Avoids significant thermal damageSignificant thermal damageUltrasound therapyChiropractic devicesPulse energyPulse characteristics
Methods and systems for heating a body tissue region adjacent a body lumen with diseased and healthy portions using selective accumulation of energy in the artery tissue with or without knowledge of tissue topography. The method includes positioning an energy delivery portion of a catheter body within the lumen adjacent the body tissue region to be heated, determining a pulse characteristic in response to a thermal property of a first tissue type and applying pulsed energy with the pulse characteristic from the energy delivery portion so as to therapeutically treat the second tissue type within the body tissue region by drawing heat from the first tissue type at a rate that avoids significant thermal damage to the first tissue type while building-up heat in the second tissue type. The system includes an elongate flexible catheter body having a proximal end and a distal end with an axis therebetween, an energy delivery portion proximate the distal end, an energy source coupled to the energy delivery portion and a processor coupled to the energy source, the processor configured to control a pulse characteristic of pulsed energy transmitted from the energy source to the energy delivery portion so as to therapeutically treat the second tissue type within the body tissue region by drawing heat from the first tissue type at a rate that avoids significant thermal damage to the first tissue type while building-up heat in the second tissue type.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Food preparation
ActiveUS20110031236A1Improve uniformityAvoid heat damageContainer decorationsLevel indicationsElectrical and Electronics engineeringFood preparation
Owner:JOLIET 2010 LTD
Vascular occlusion systems and methods
InactiveUS20050065531A1Avoid heat damageSimple processUltrasound therapyElectrotherapyBiomedical engineeringVaricose veins
A blood vessel occlusion system and method includes a handheld probe including a power source, the probe being adapted to transmit energy from the power source through a body surface and into a target blood vessel, for example a varicose vein. Further included is a manual or automatic switch mechanism adapted to enable and disable the power source in response to a predetermined level of compression applied, by means of the probe against the target blood vessel. When the blood vessel is compressed sufficiently to collapse and substantially slow or substantially prevent a flow of blood therethrough, the power source is activated and the vessel is cauterized, leaving the blood vessel in a condition that is resistant to recanalization.
Owner:VANDOLAY INC
Composite tissue adhesive
InactiveUS6939364B1Precise temperature controlShorten treatment timeSurgical instrument detailsSurgical veterinaryThermal energyHigh concentration
Consistent with the present invention, tissue adhesive compositions and an associated laser exposure system are provided for bonding or sealing biological tissues. The compositions are comprised of chemically derivatized soluble collagen which is formulated to concentrations ranging from 300 mg / ml (30%) to 800 mg / ml (80%) collagen protein. In particular, Type I collagen, for example, is first prepared by extraction from bovine or porcine hide and purified. The collagen preparations are then chemically derivatized with sulfhydryl reagents to improve cohesive strength and with secondary derivatizing agents, such as carboxyl groups, to improve the adhesive strength of the solder to the tissue. The compositions are then formed into viscous solutions, gels or solid films, which when exposed to energy generated from an infrared laser, for example, undergo thermally induced phase transitions. Solid or semi-solid protein compositions become less viscous enabling the high concentration protein to penetrate the interstices of treated biological tissue or to fill voids in tissue. As thermal energy is released into the surrounding environment, the protein compositions again become solid or semi-solid, adhering to the treated tissue or tissue space.
Owner:CONVERSION ENERGY ENTERPRISES
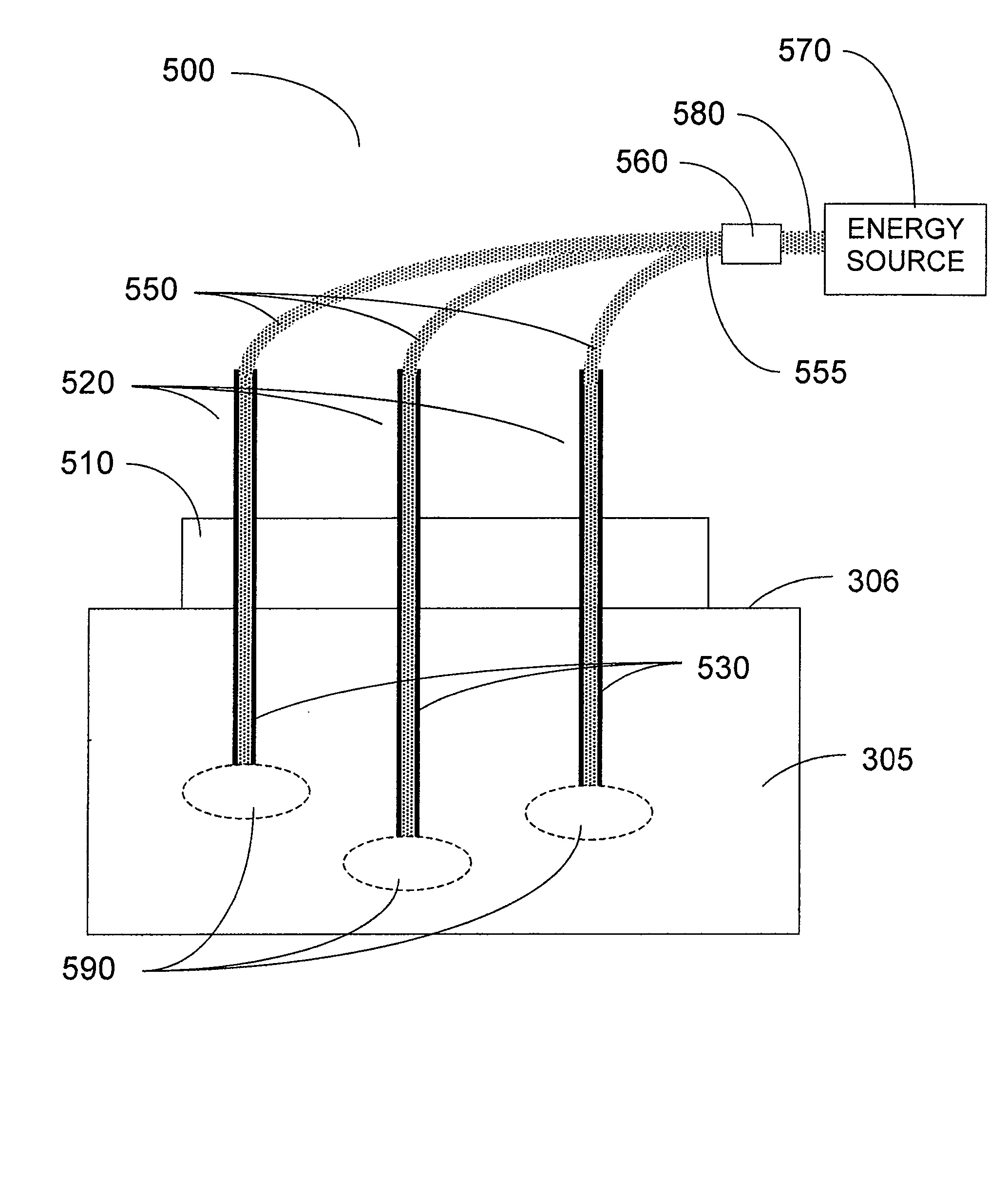
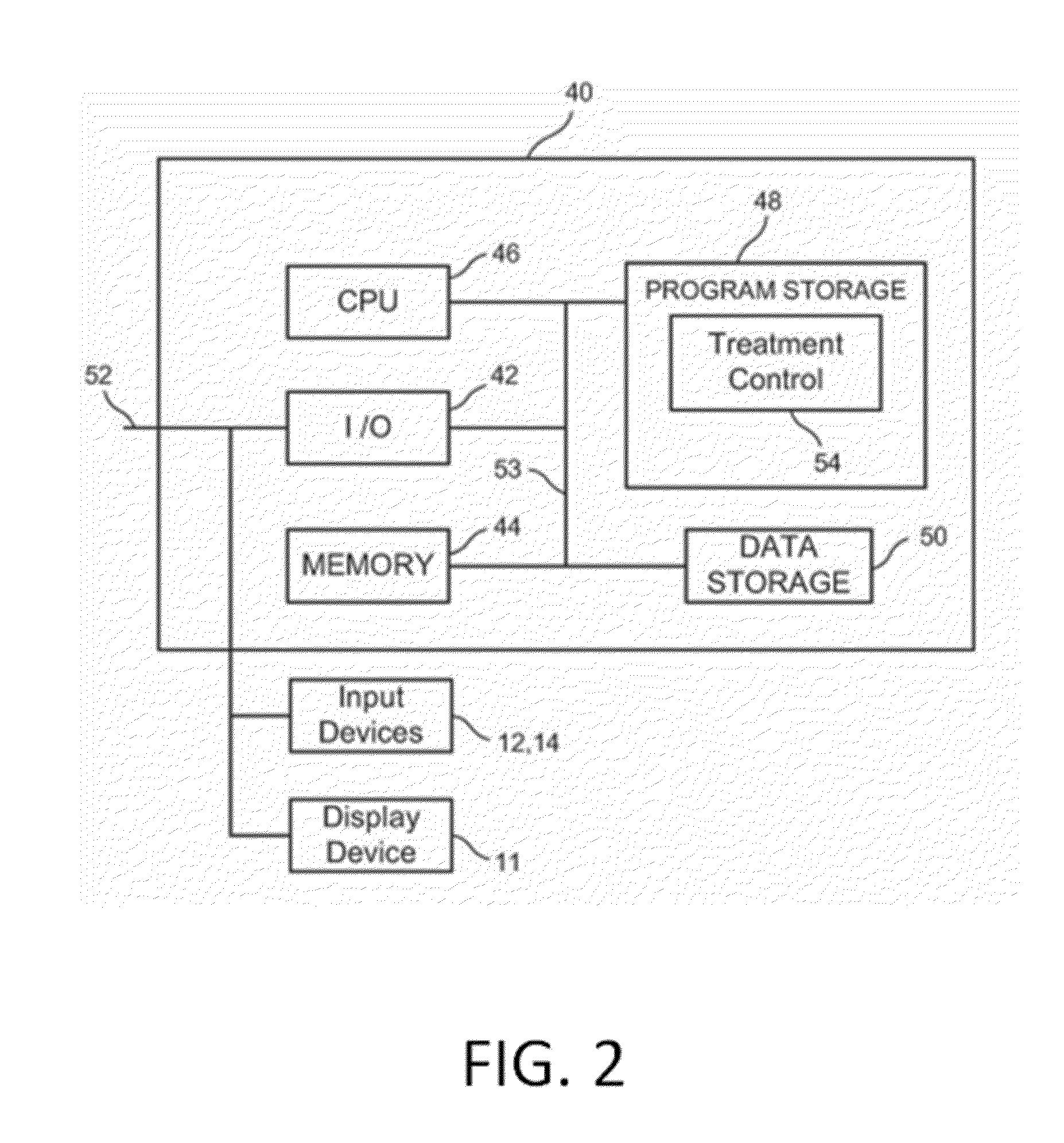
System and method for estimating tissue heating of a target ablation zone for electrical-energy based therapies
Systems and methods are provided for modeling and for providing a graphical representation of tissue heating and electric field distributions for medical treatment devices that apply electrical treatment energy through one or a plurality of electrodes. In embodiments, methods comprise: providing one or more parameters of a treatment protocol for delivering one or more electrical pulses to tissue through a plurality of electrodes; modeling electric and heat distribution in the tissue based on the parameters; and displaying a graphical representation of the modeled electric and heat distribution. In another embodiment, a treatment planning module is adapted to generate an estimated target ablation zone based on a combination of one or more parameters for an irreversible electroporation protocol and one or more tissue-specific conductivity parameters.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
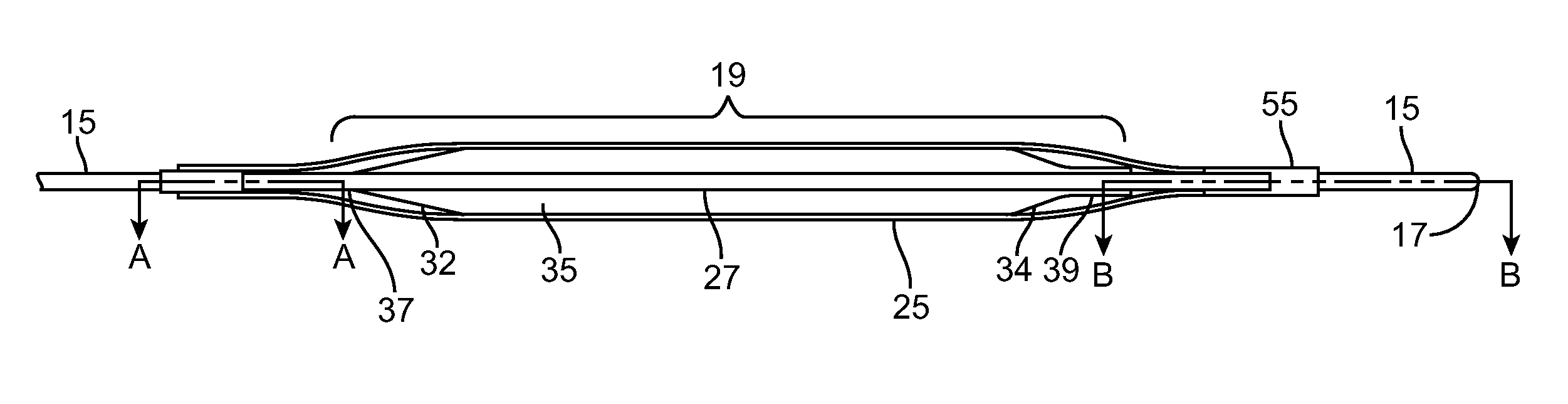
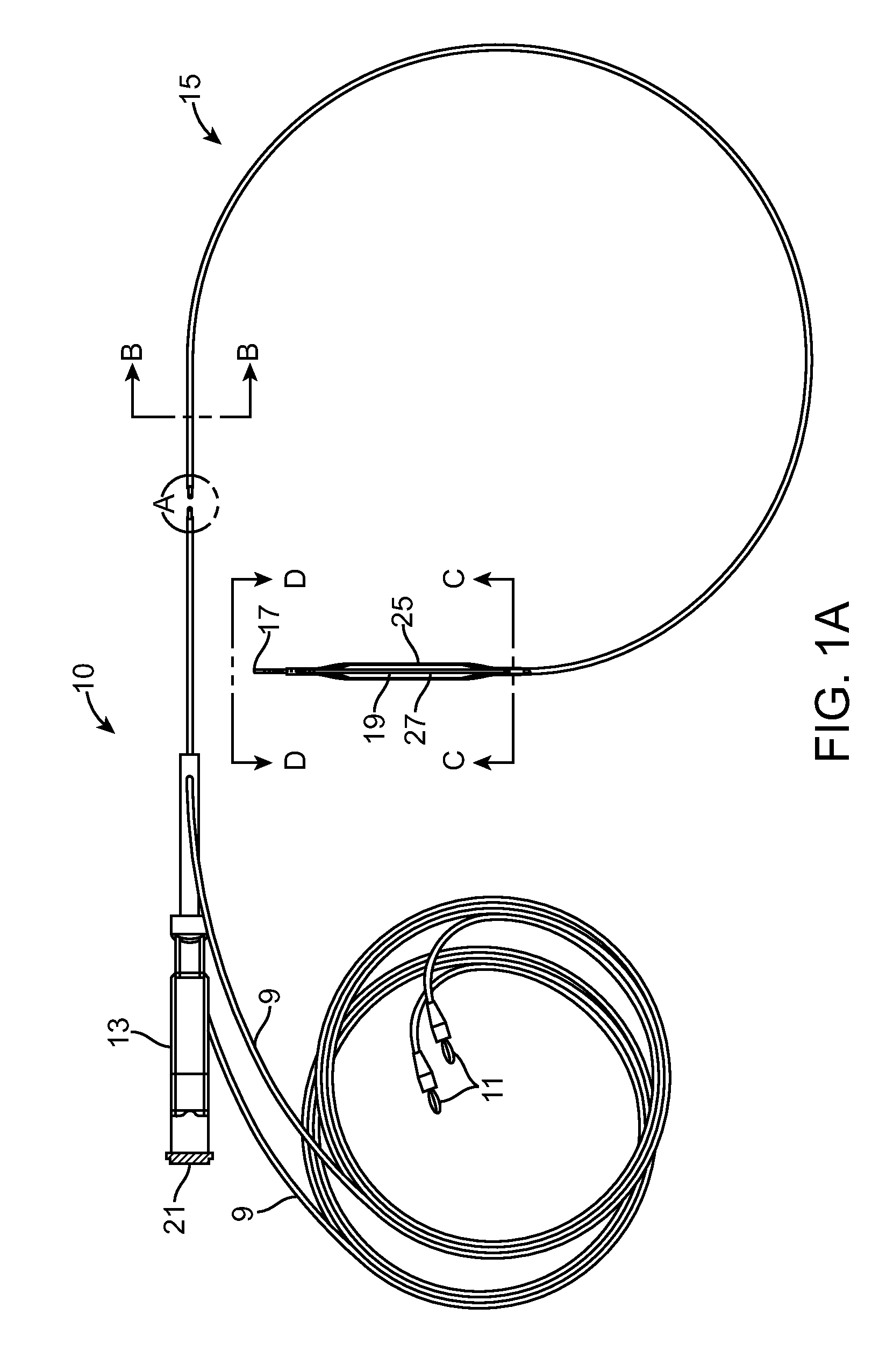
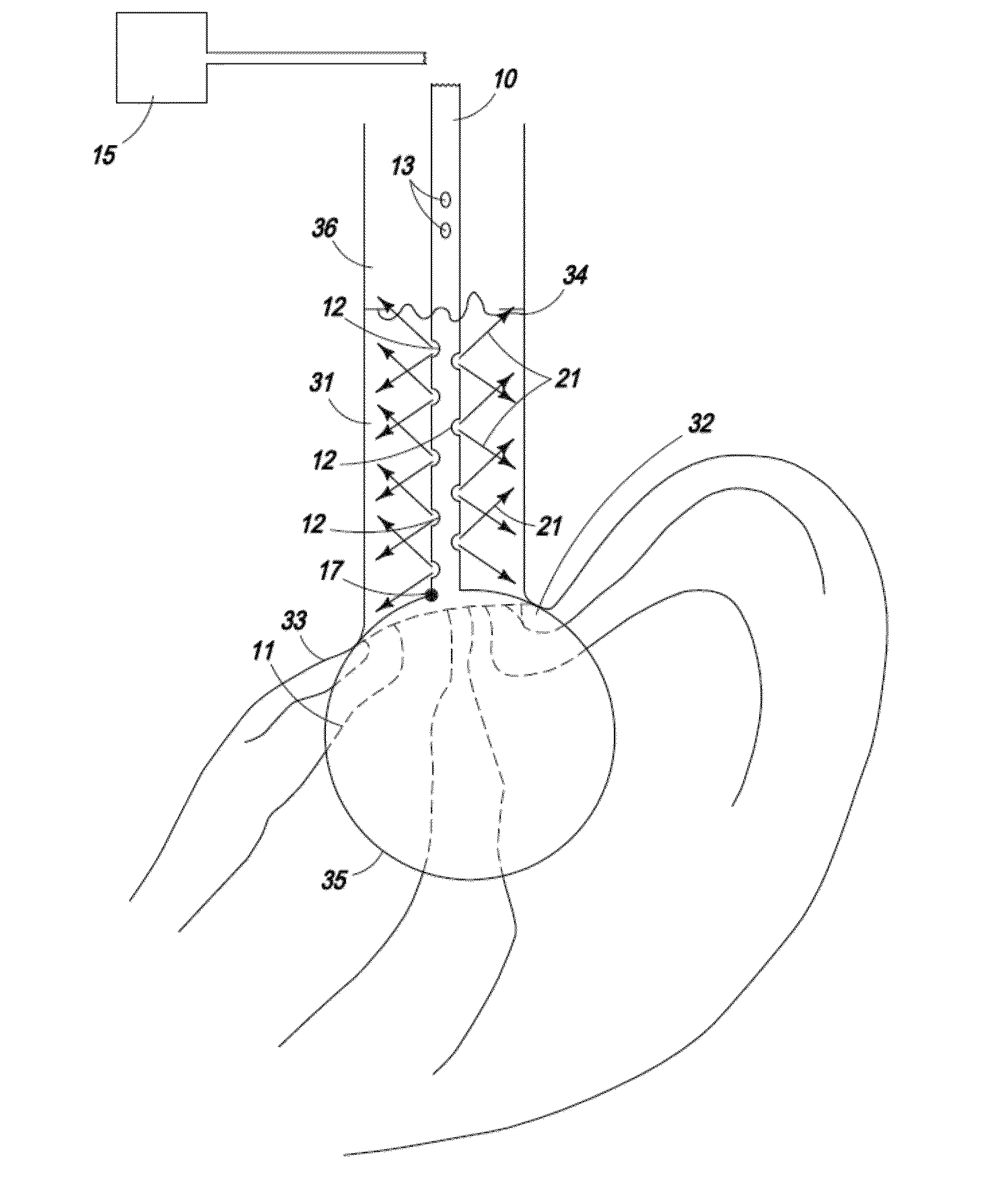
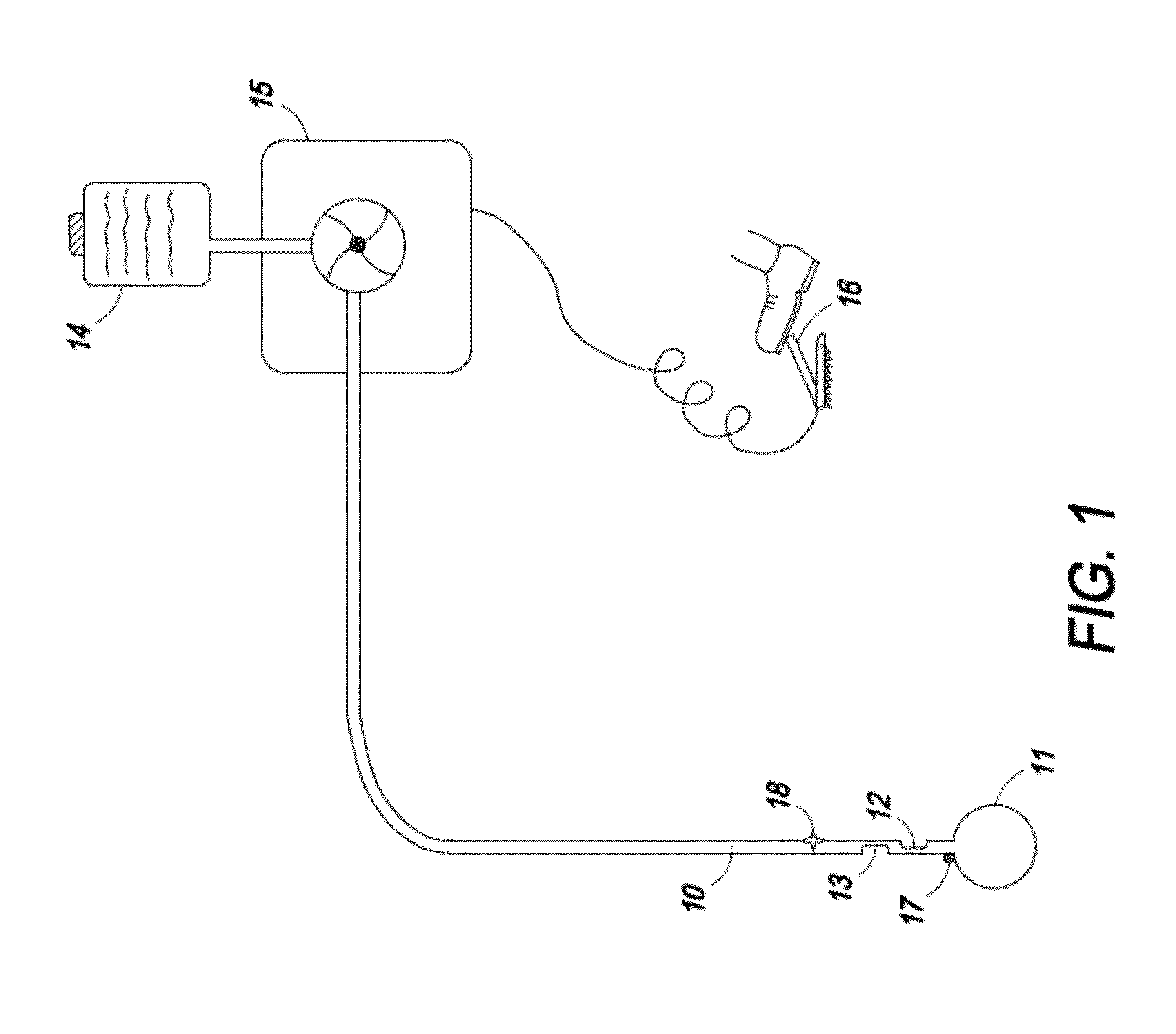
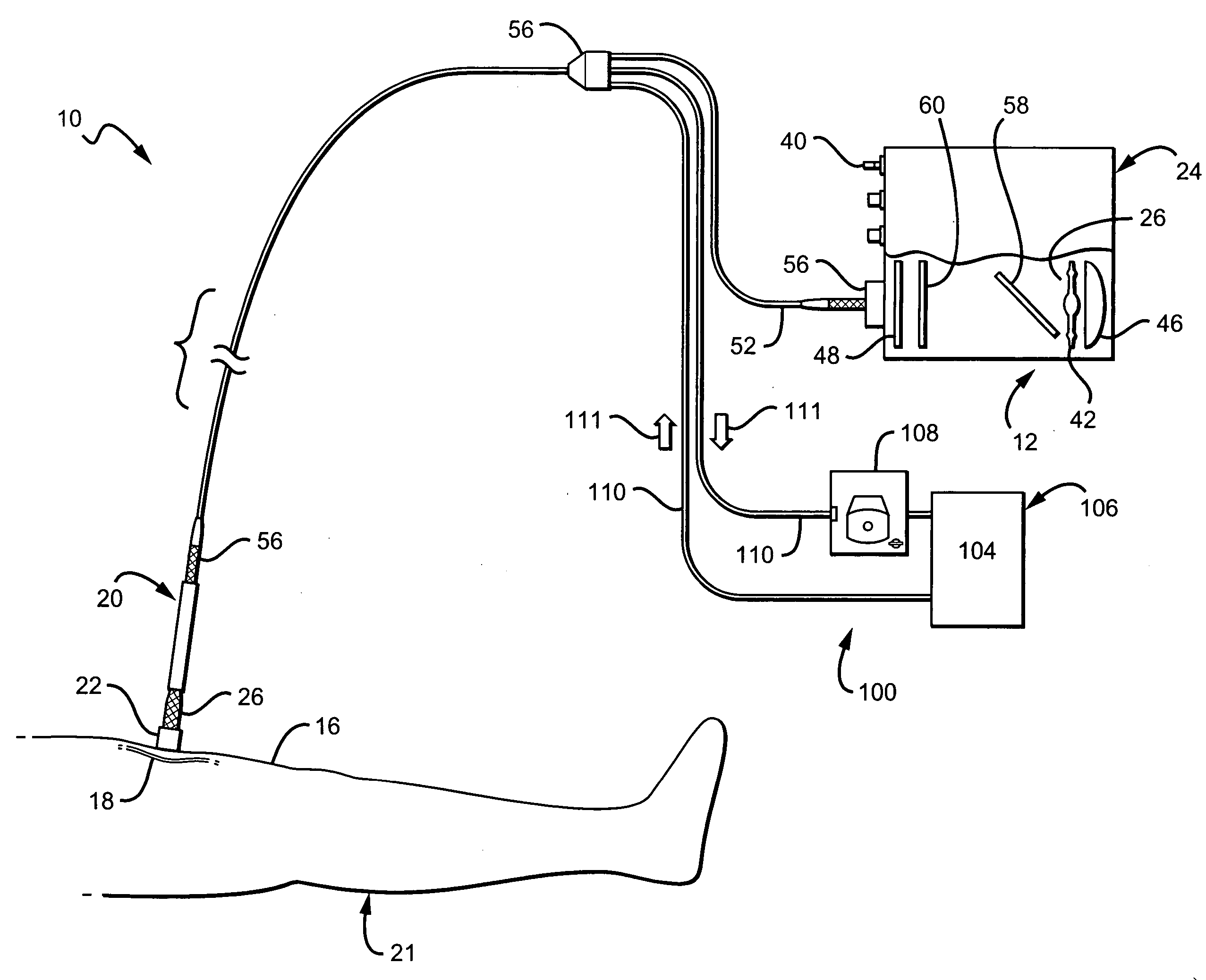
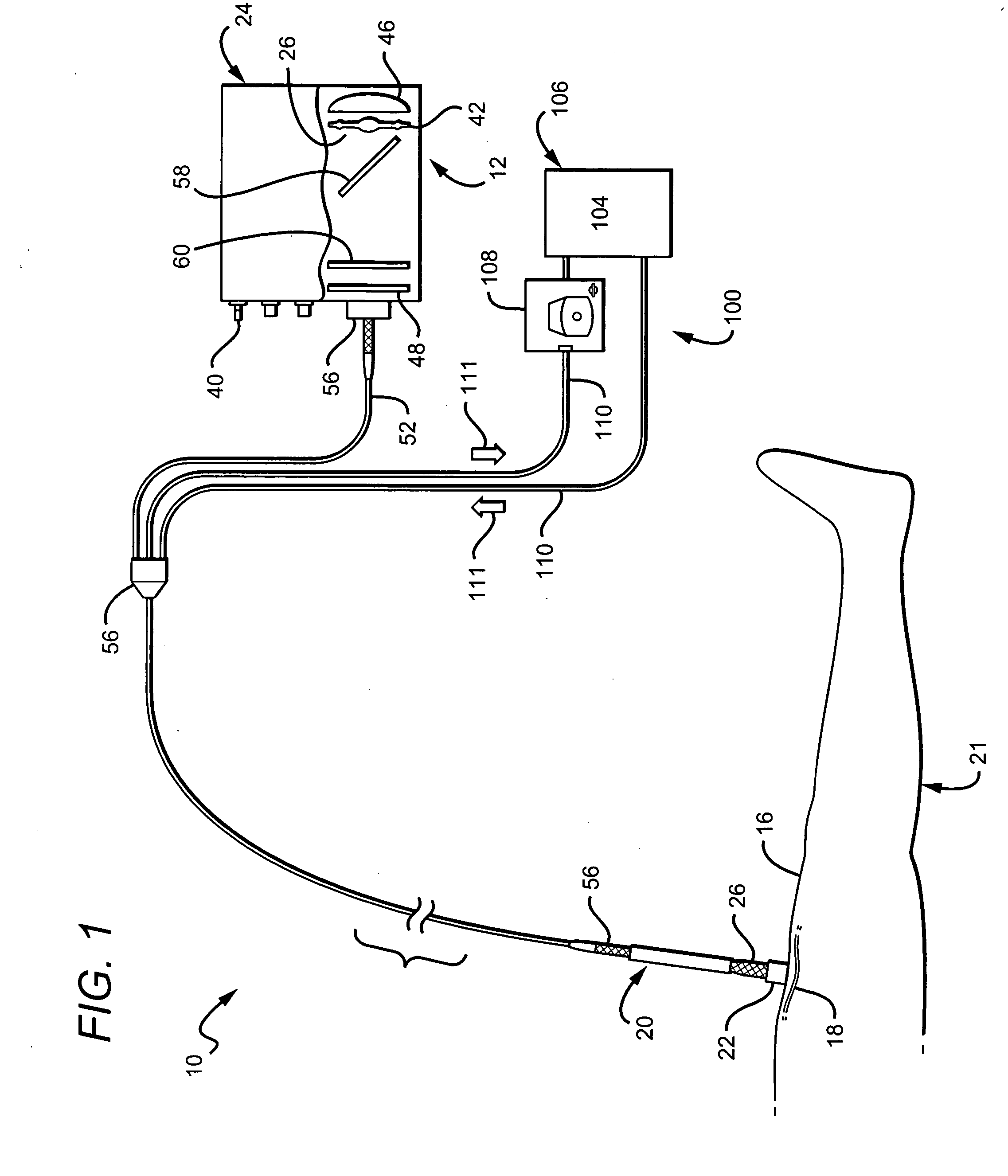
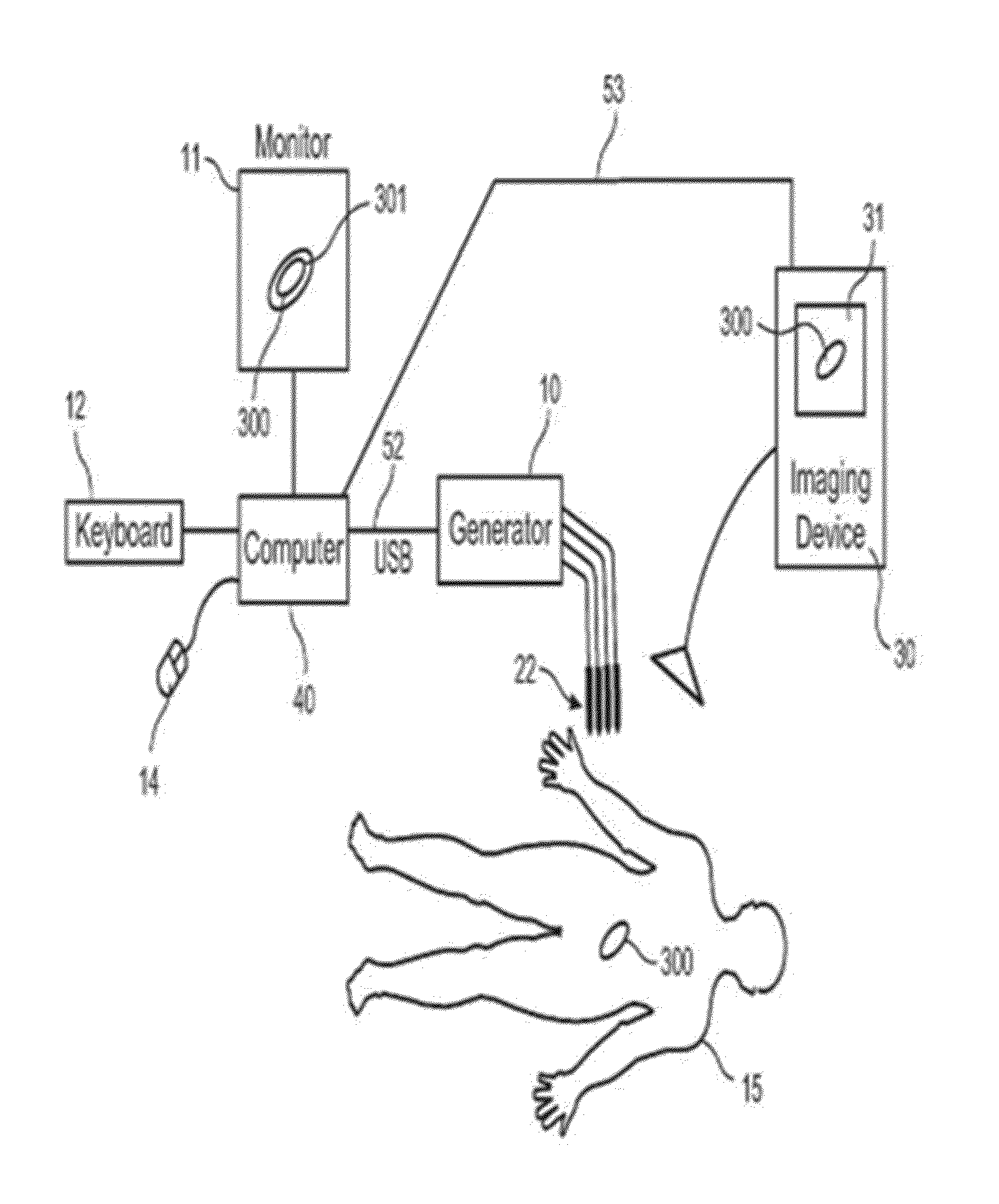
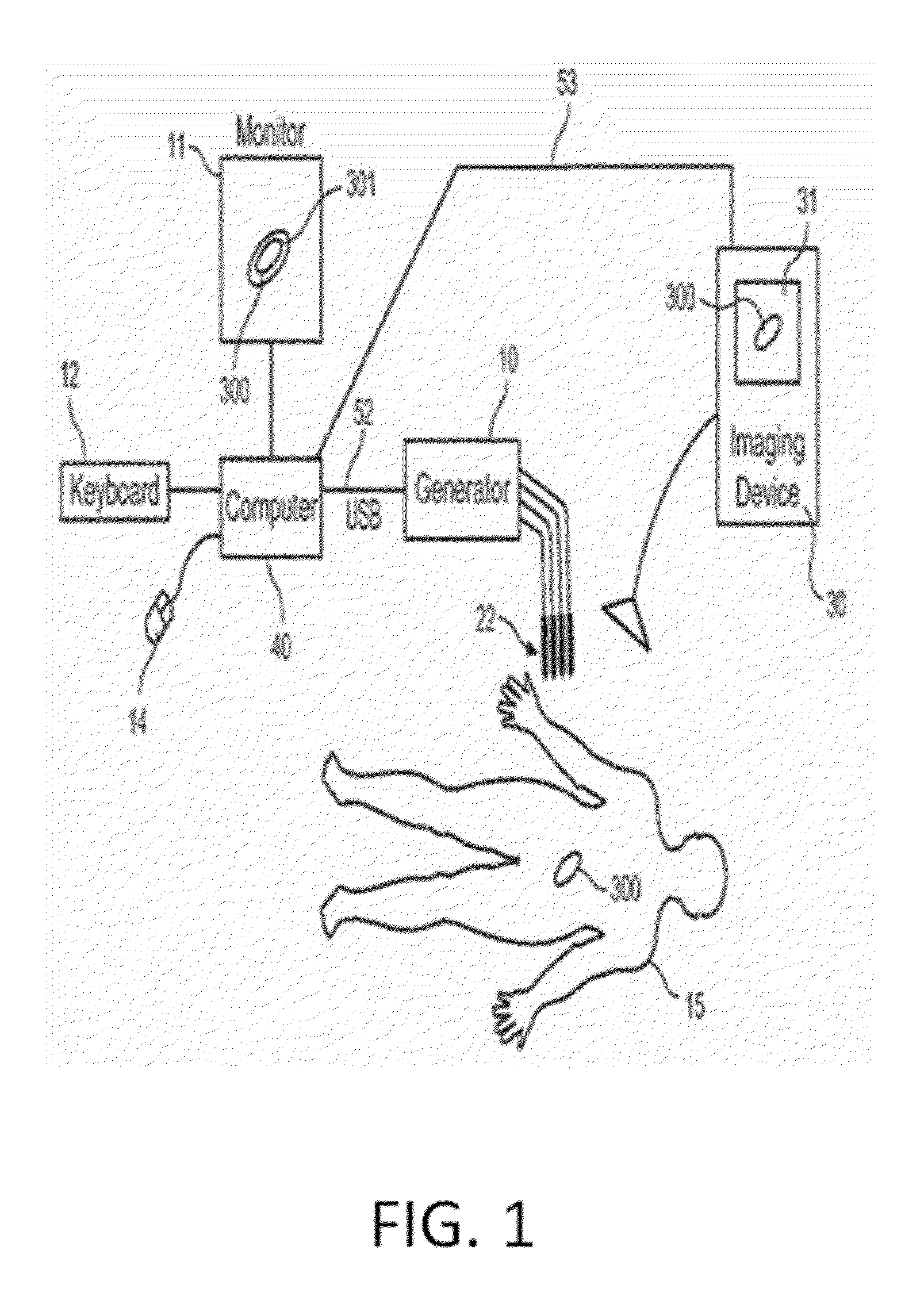
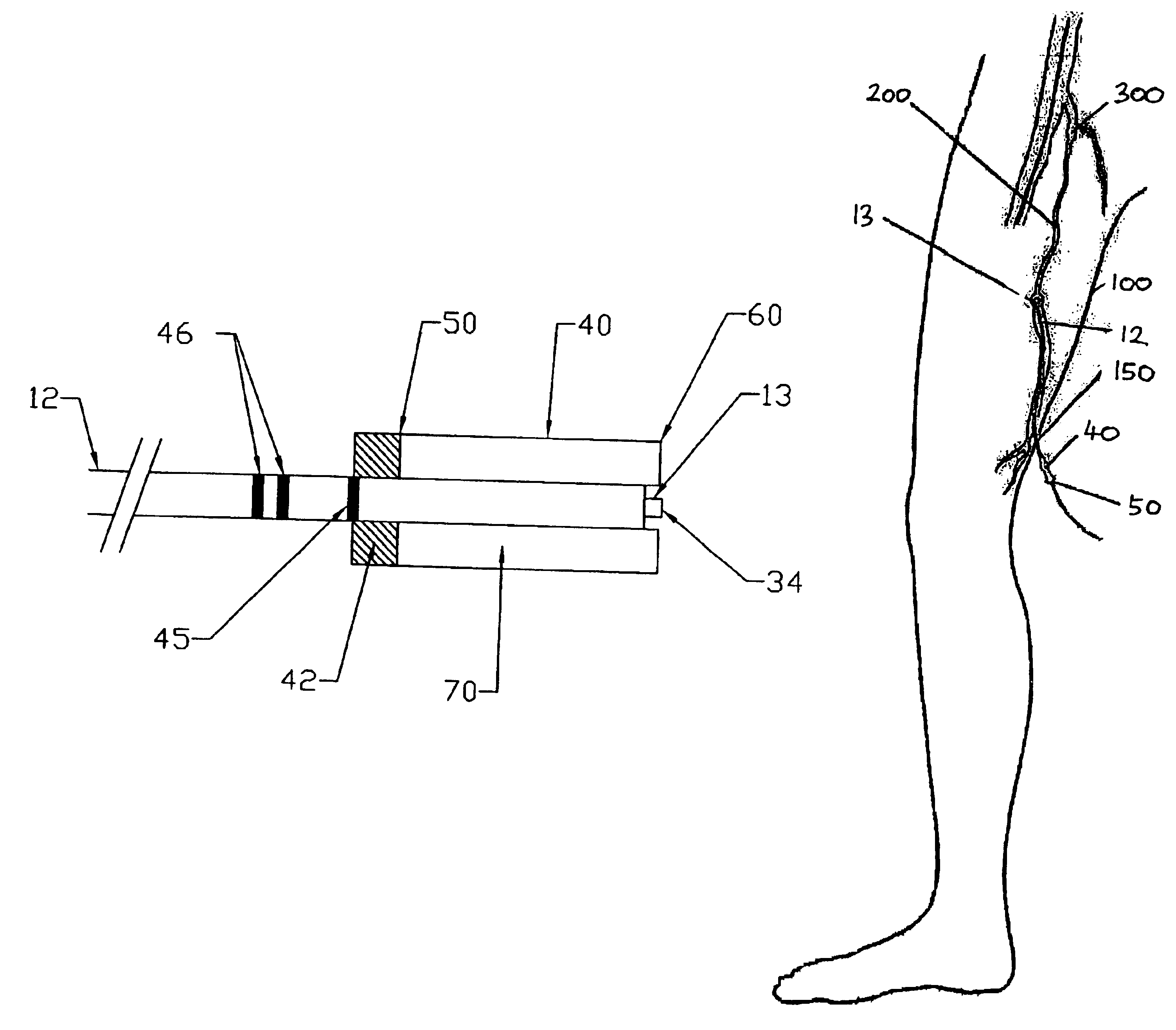
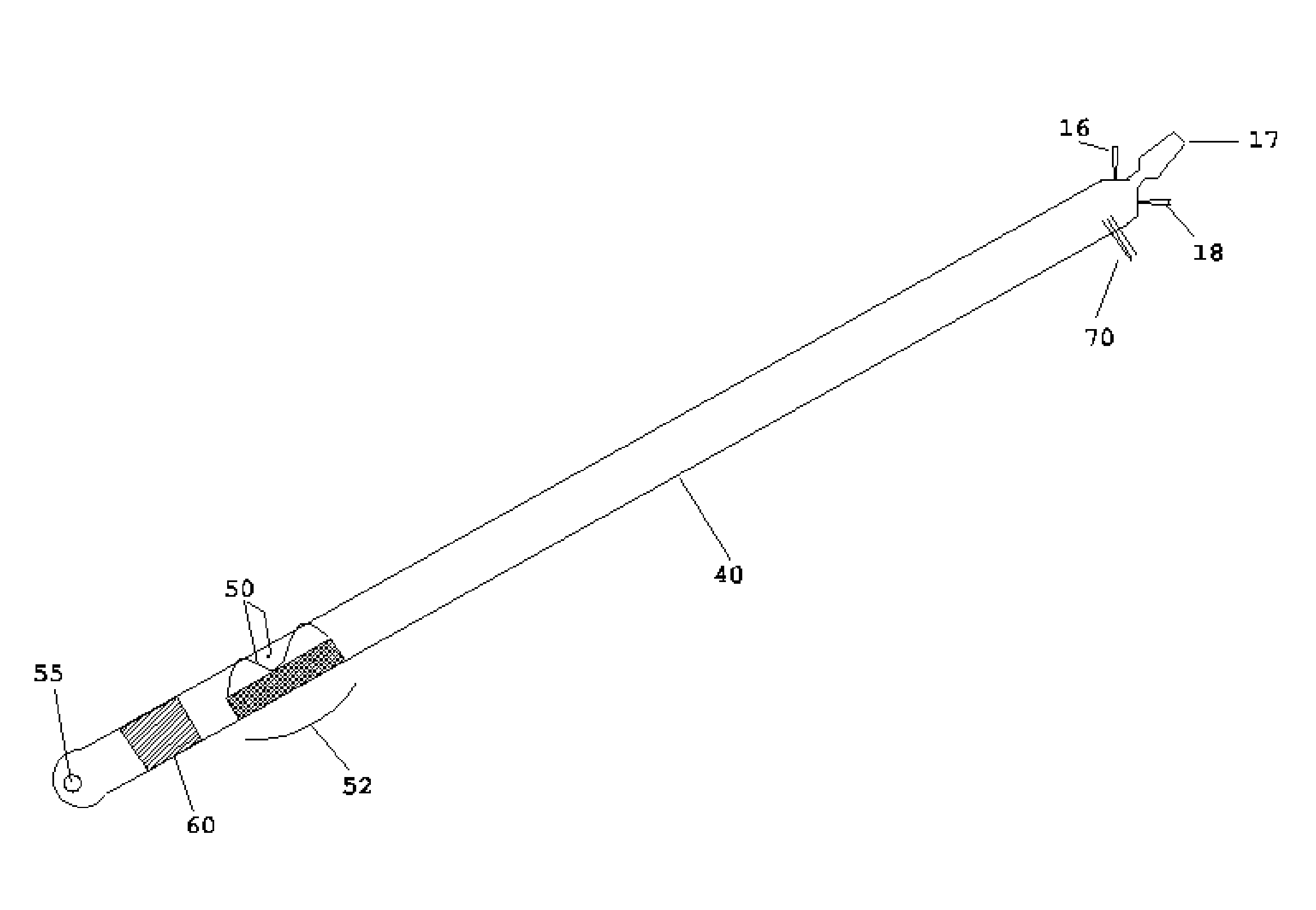
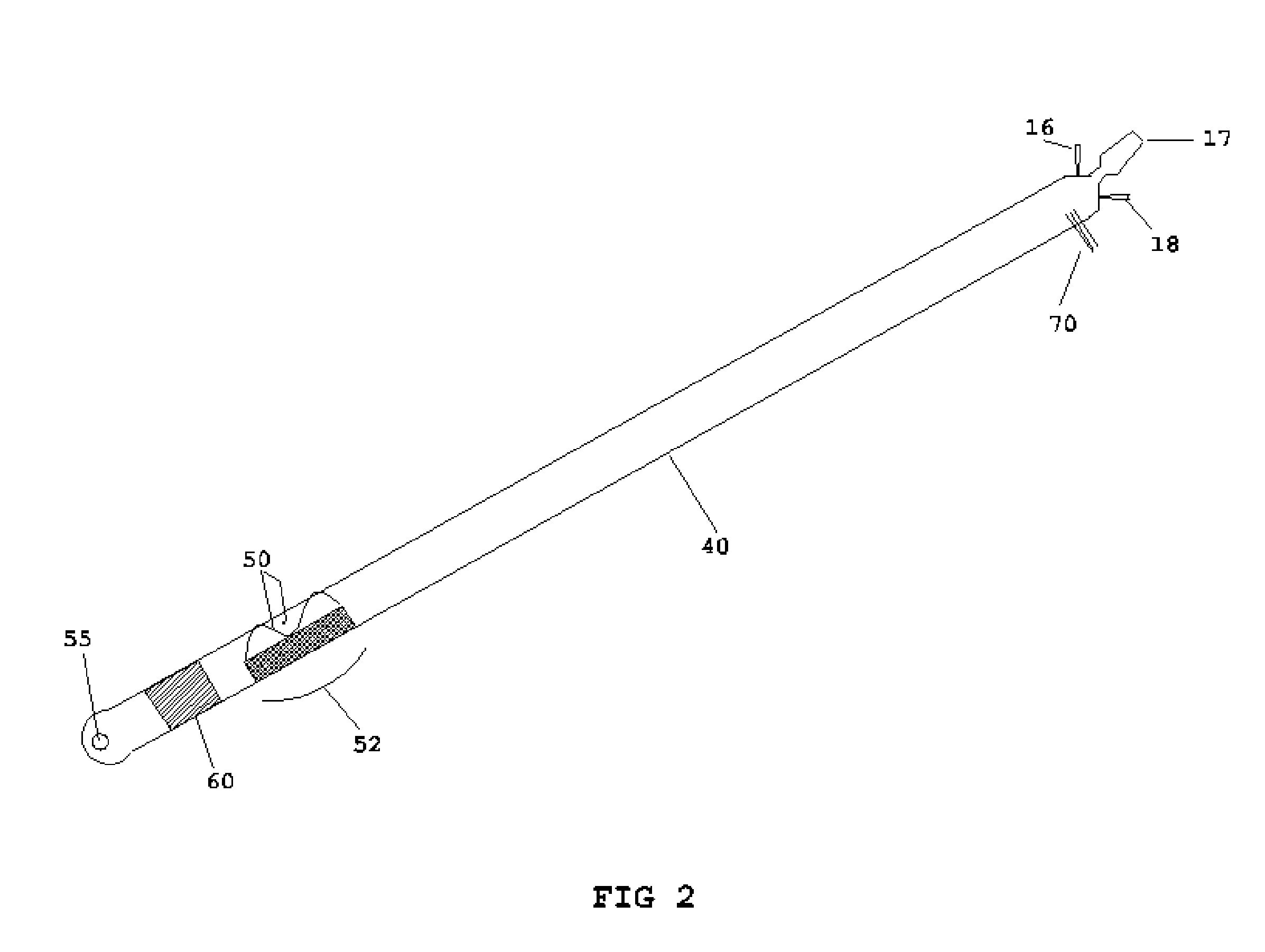
Method of endovenous laser treatment
InactiveUS6986766B2Without risk of damageQuick insertElectrotherapyDiagnosticsMedicineEndovenous laser treatment
A method of endovenous laser treatment in disclosed. An introducer sheath 40 is introduced into a vein and an optical fiber 12 is introduced through the introducer sheath until a first marking 45 on the optical fiber 12 indicates that the distal end of the optical fiber 12 is substantially in alignment with the distal end of the introducer sheath 40. The introducer sheath 40 is then withdrawn relative to the optical fiber 12 until a second marking 46 on the optical fiber 12 indicates that the distal end of the optical fiber 12 extends a predetermined distance beyond the distal end of said introducer sheath 40. Laser radiation is passed down the optical fiber 12 so that laser radiation is delivered to the inner wall of the vein and the introducer sheath 40 together with the optical fiber 12 are withdrawn a certain distance along the vein.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC +1
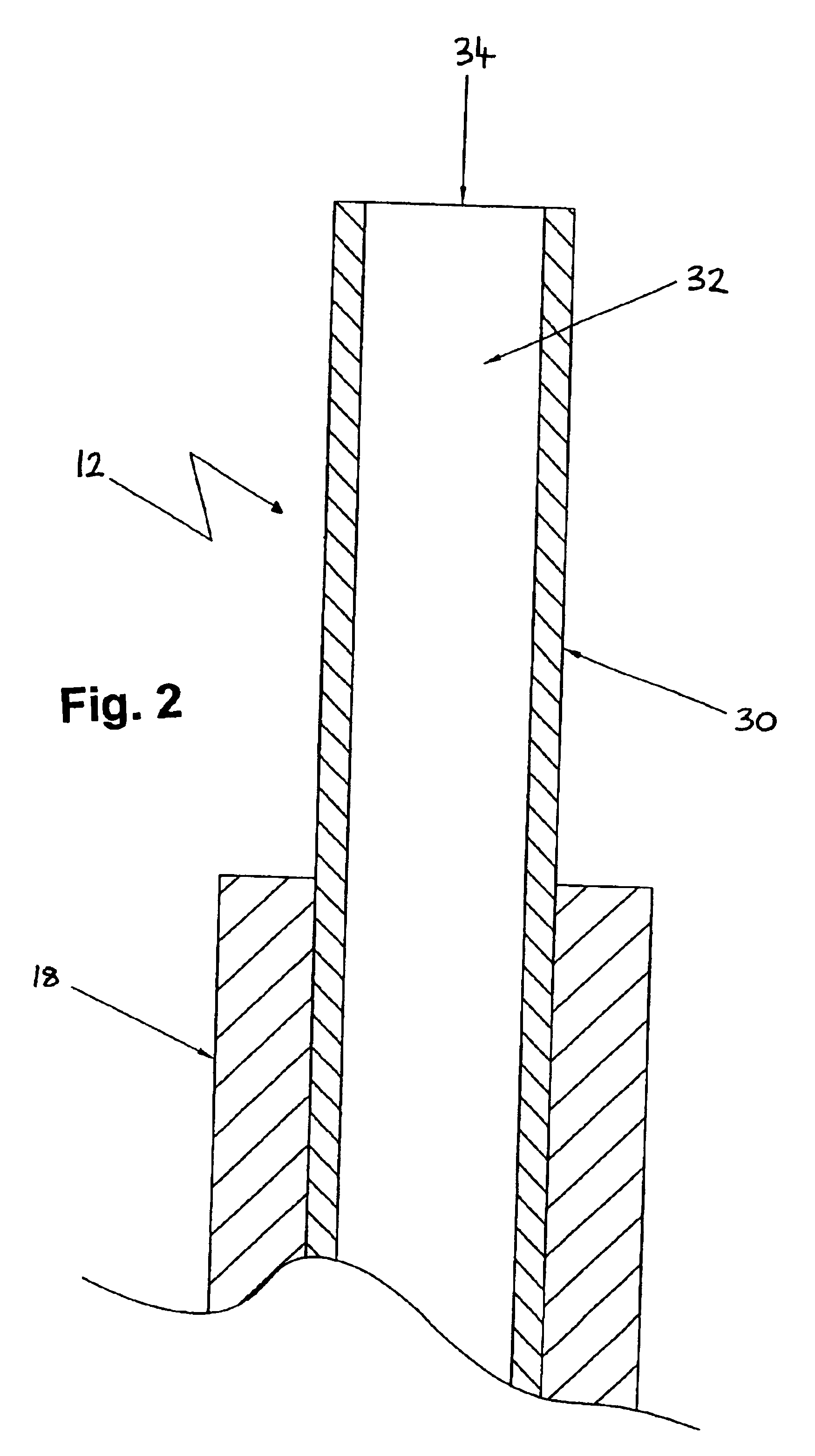
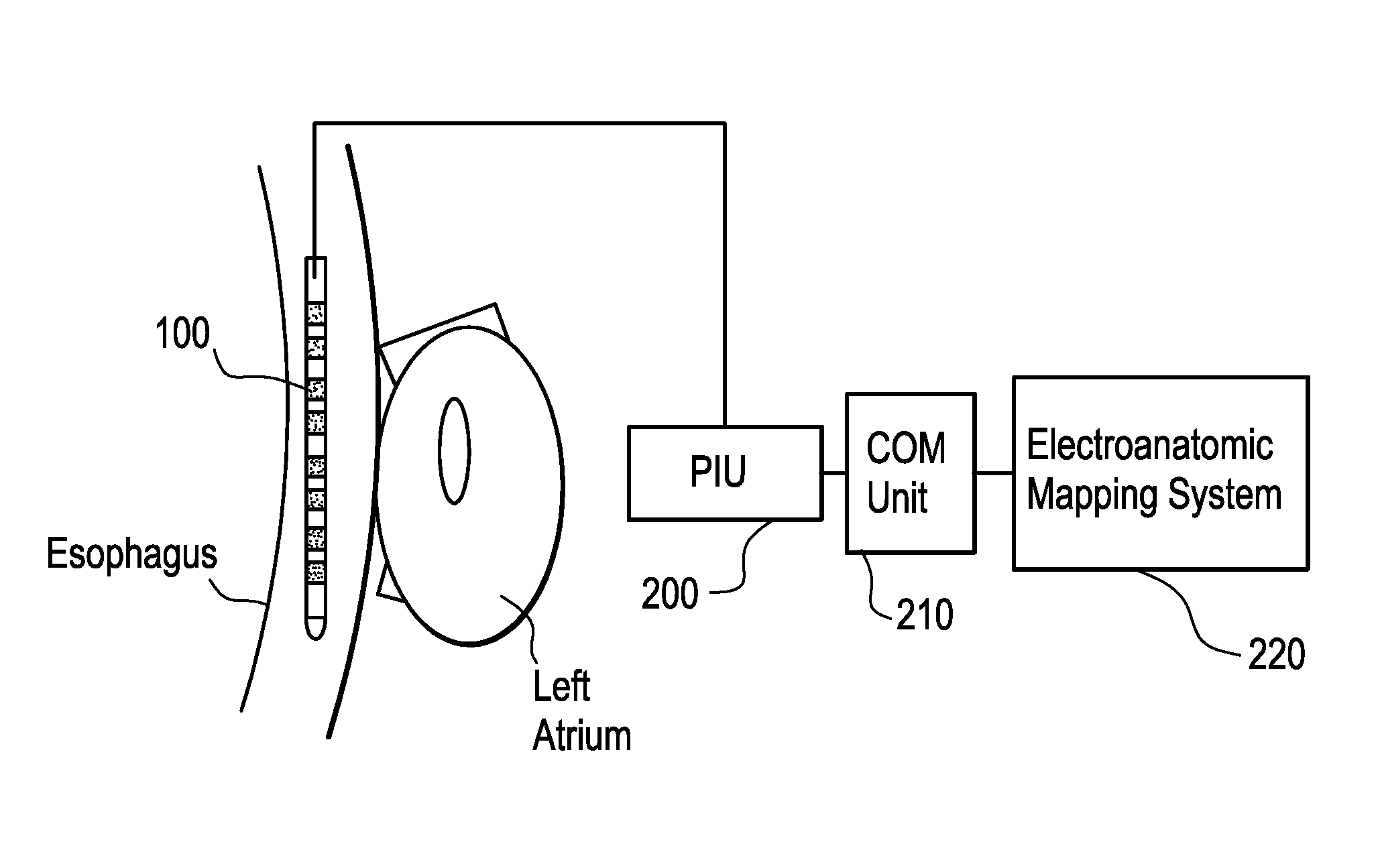
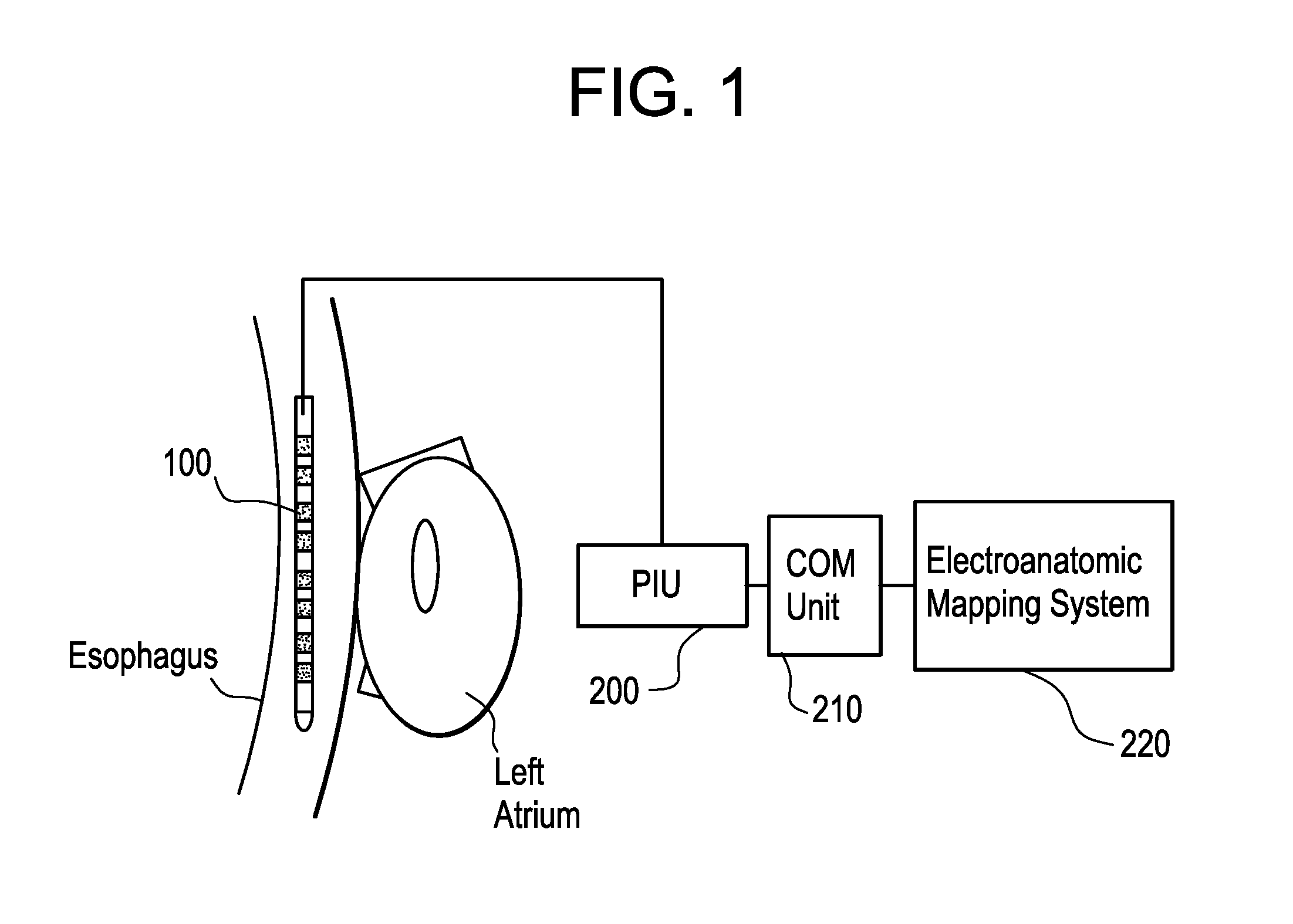
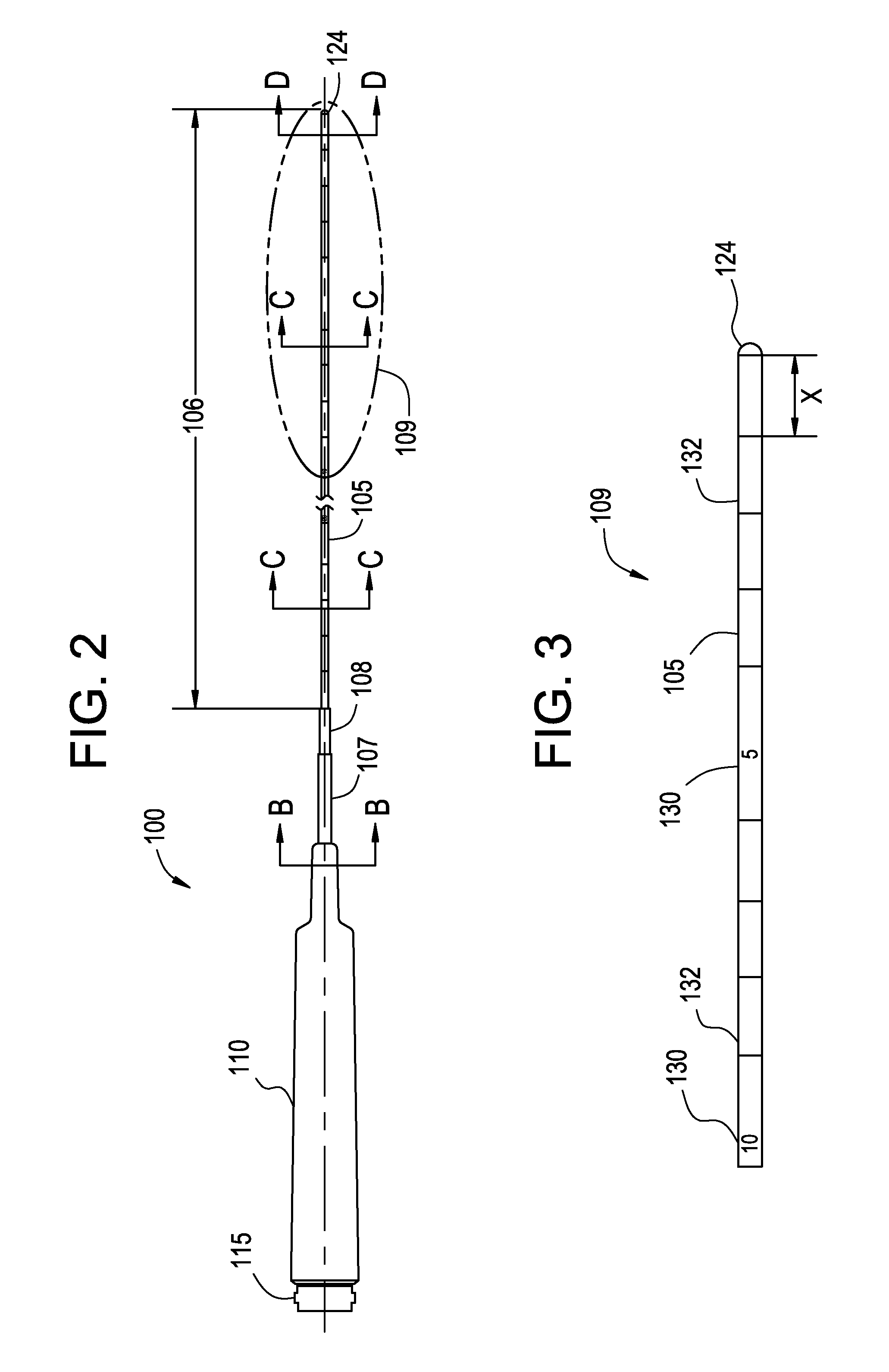
Esophageal mapping catheter
ActiveUS8224422B2Reduce riskAvoid heat damageElectrotherapyOesophagoscopesCommunication unitCatheter
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
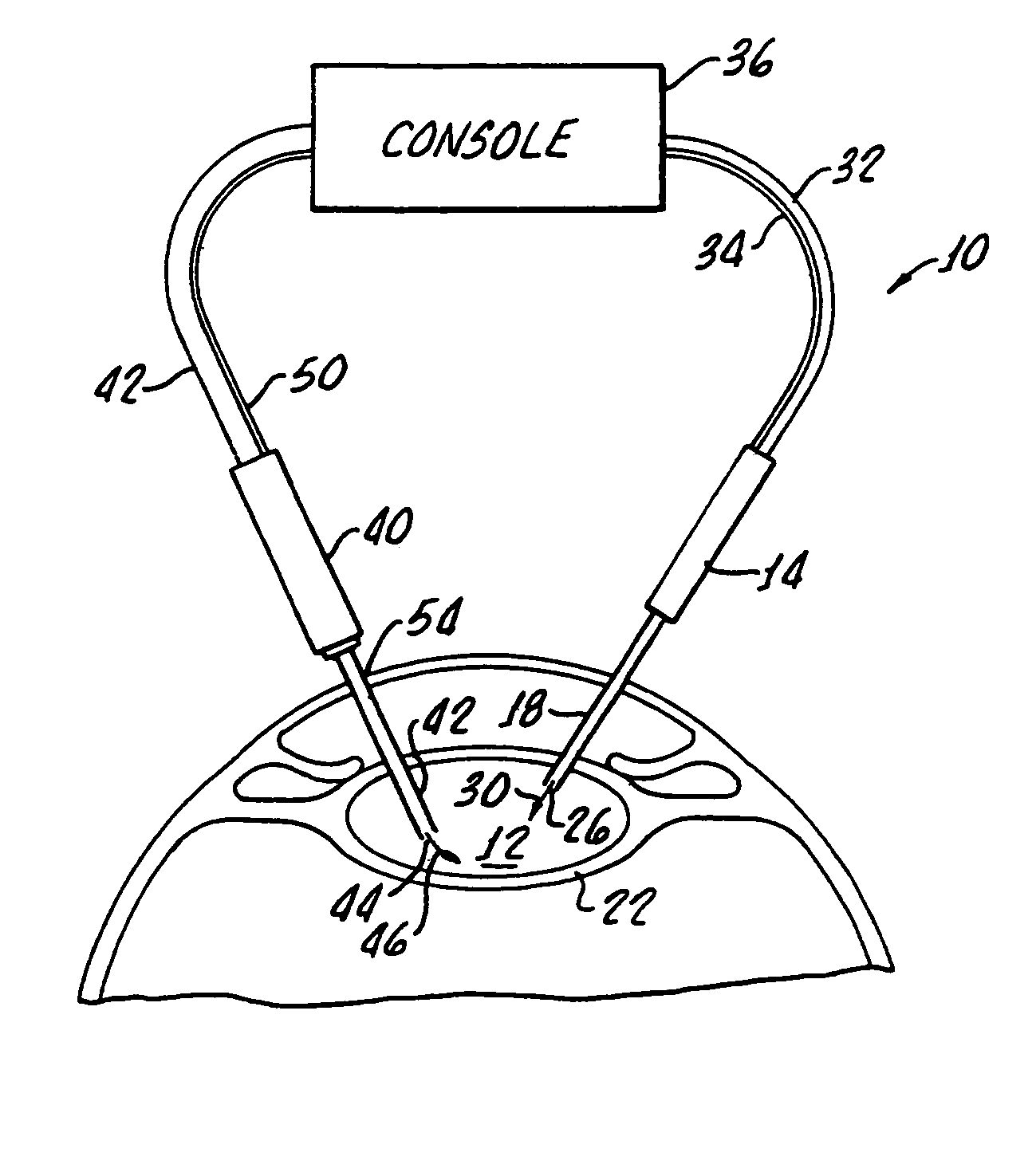
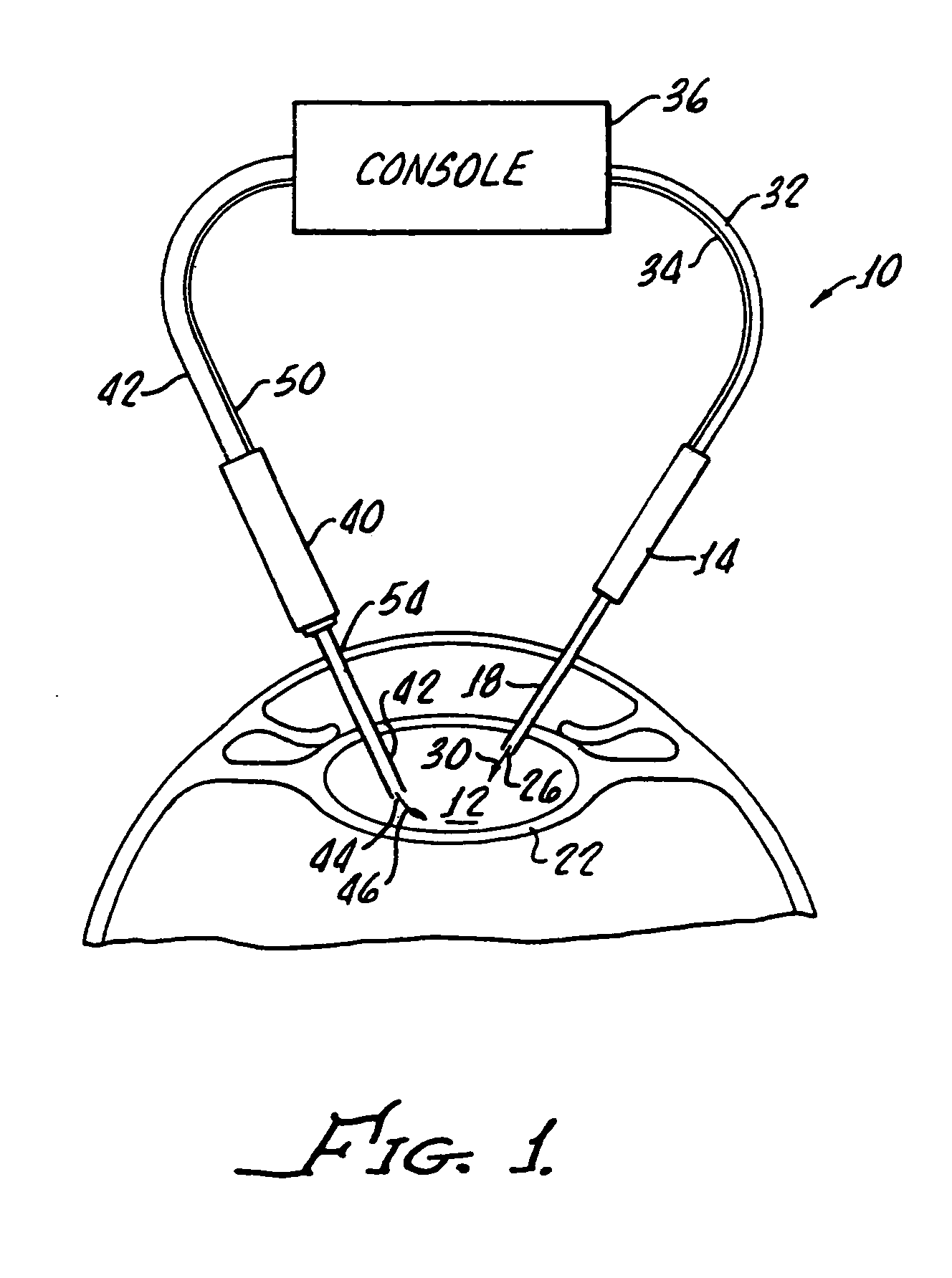
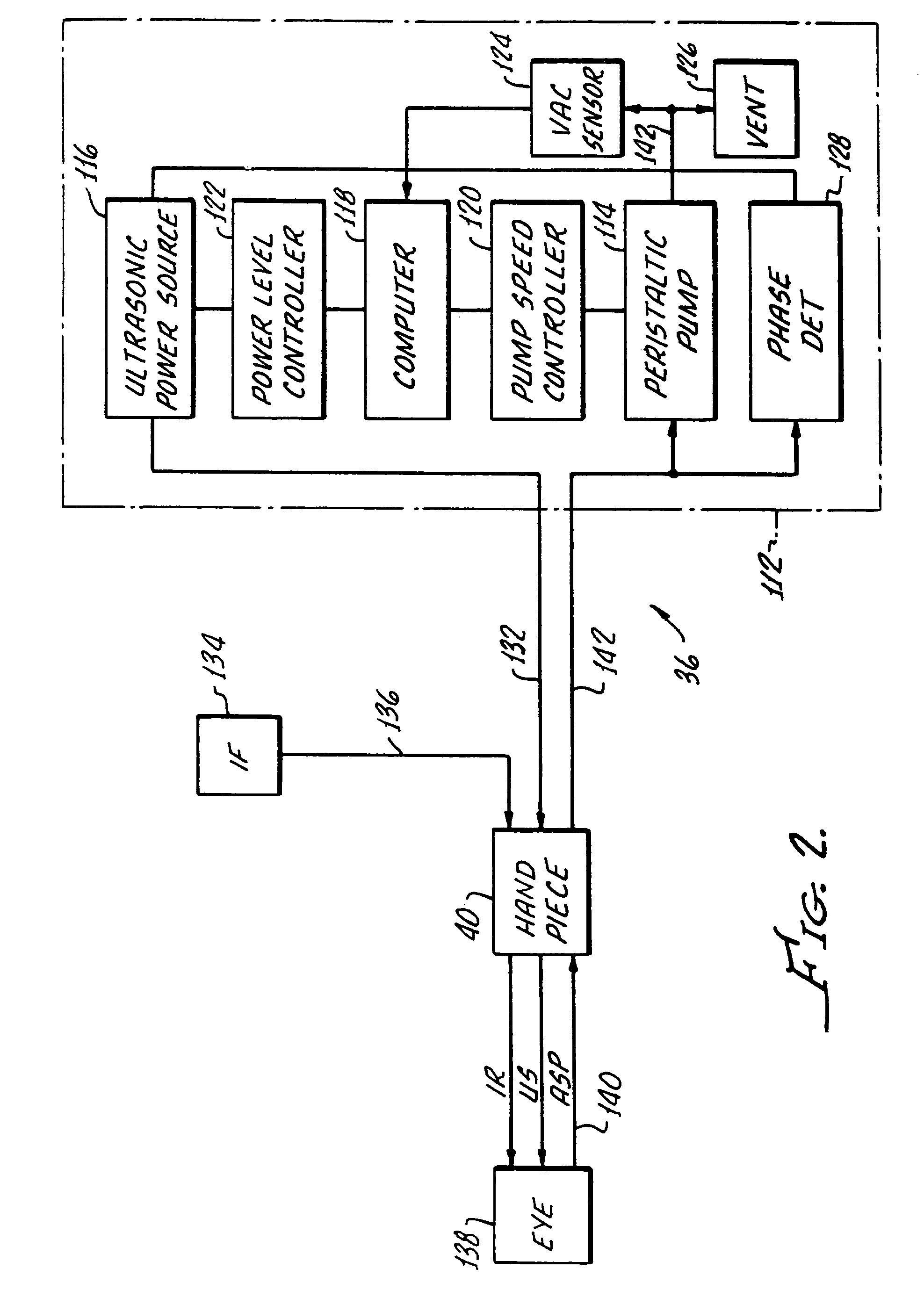
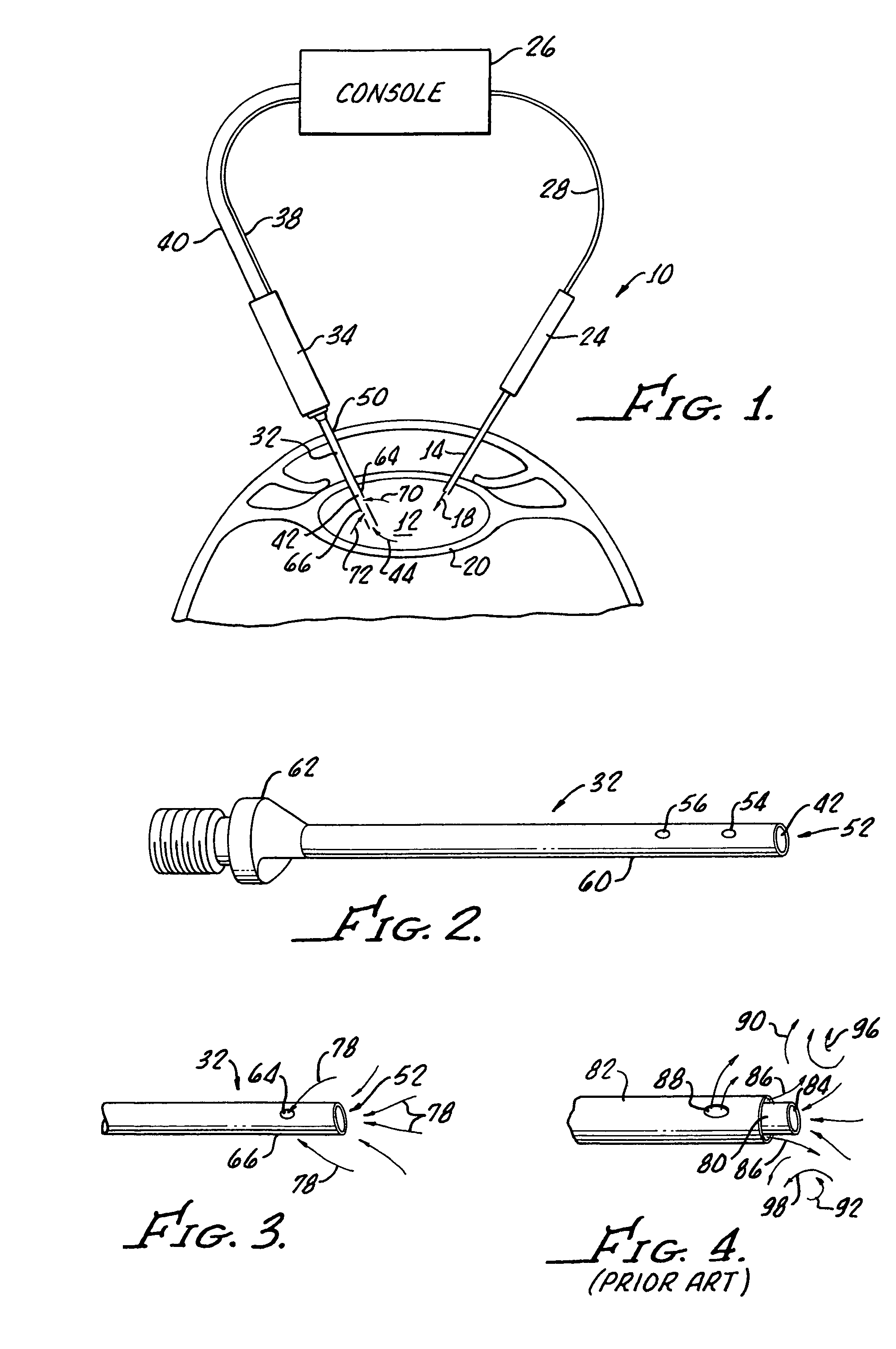
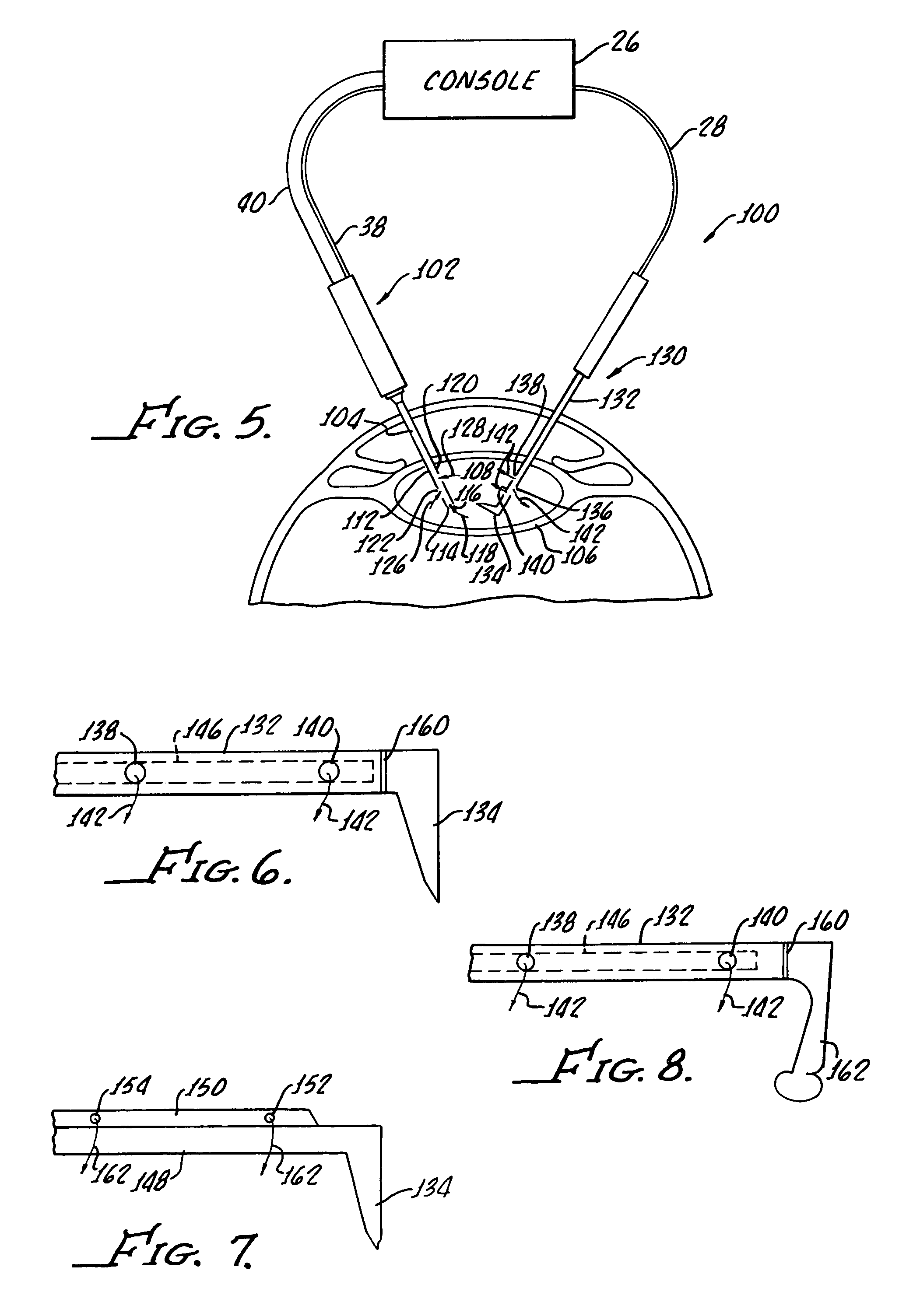
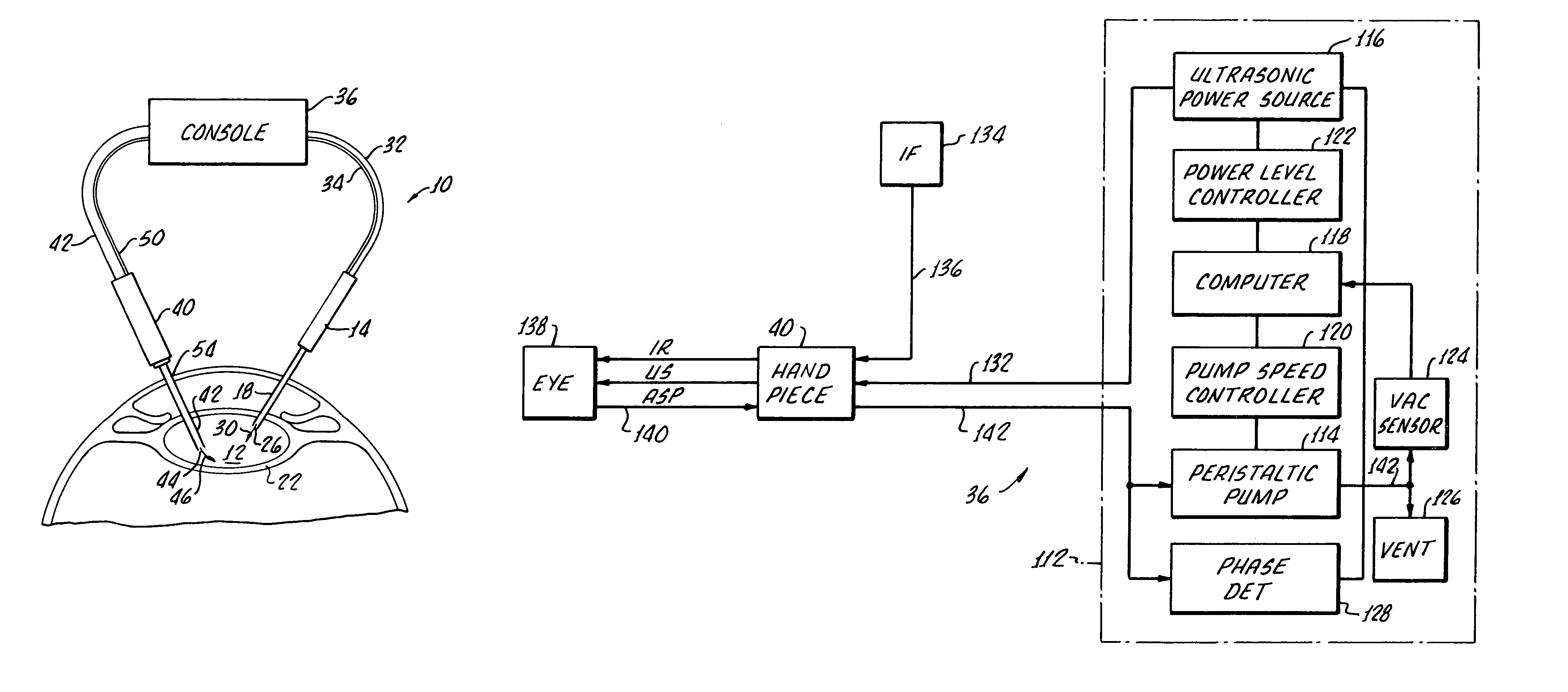
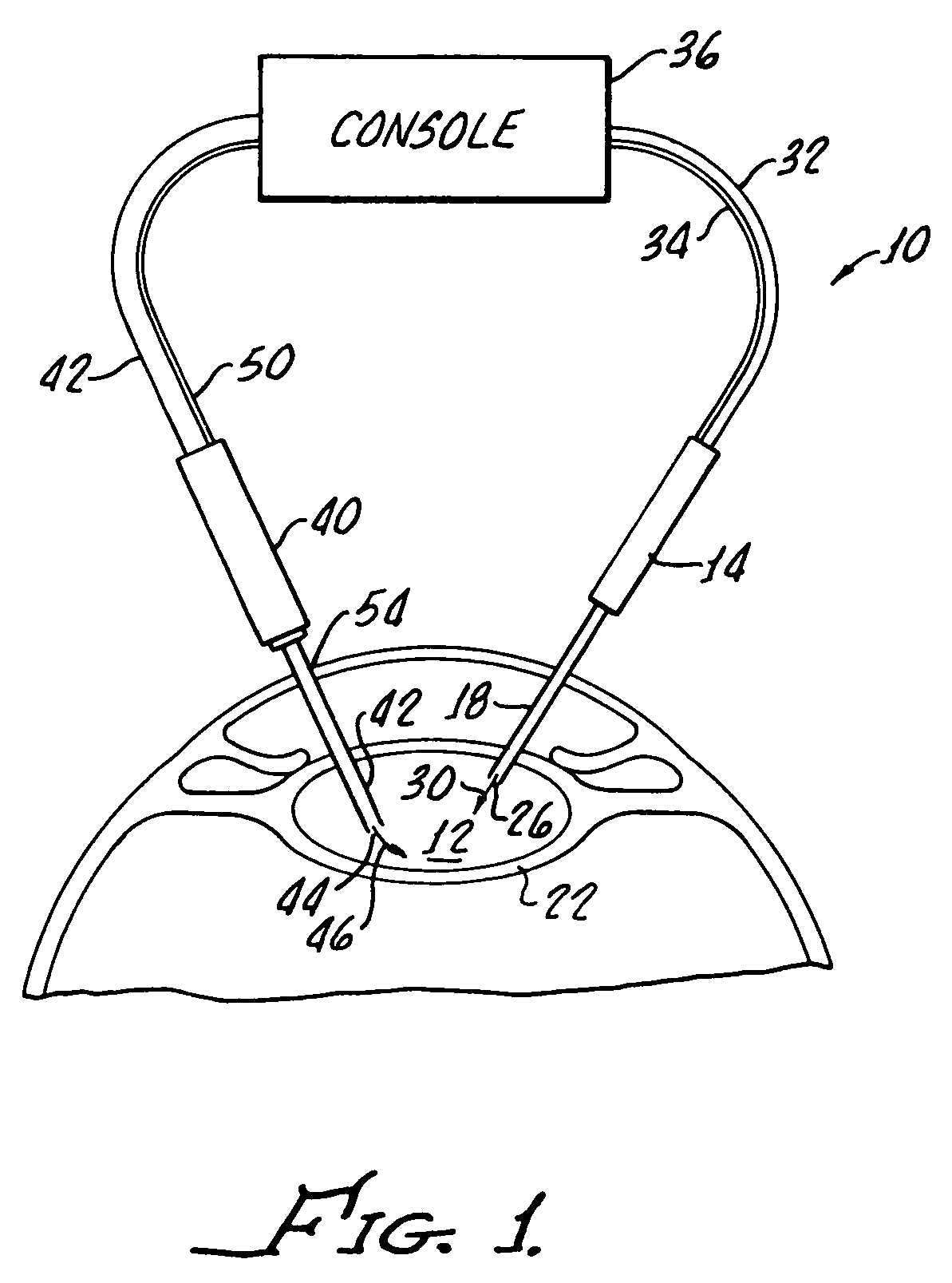
Cataract extraction apparatus and method with rapid pulse phaco power
InactiveUS7182759B2Prevent crashAvoid heat damageLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsPulse controlLens crystalline
Apparatus for the removal of lens tissue includes a first handpiece having a laser emitting probe sized for insertion into a lens capsule and radiating a lens therein. The laser emitting probe includes a lumen for introducing irrigation fluid into the lens capsule. A second handpiece includes a pulsed controlled vibrated needle for insertion into the lens capsule and emulsifying laser eradiated lens tissue. The vibrated needle includes a lumen therethrough for aspiration of emulsified lens tissue and irrigation fluid.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
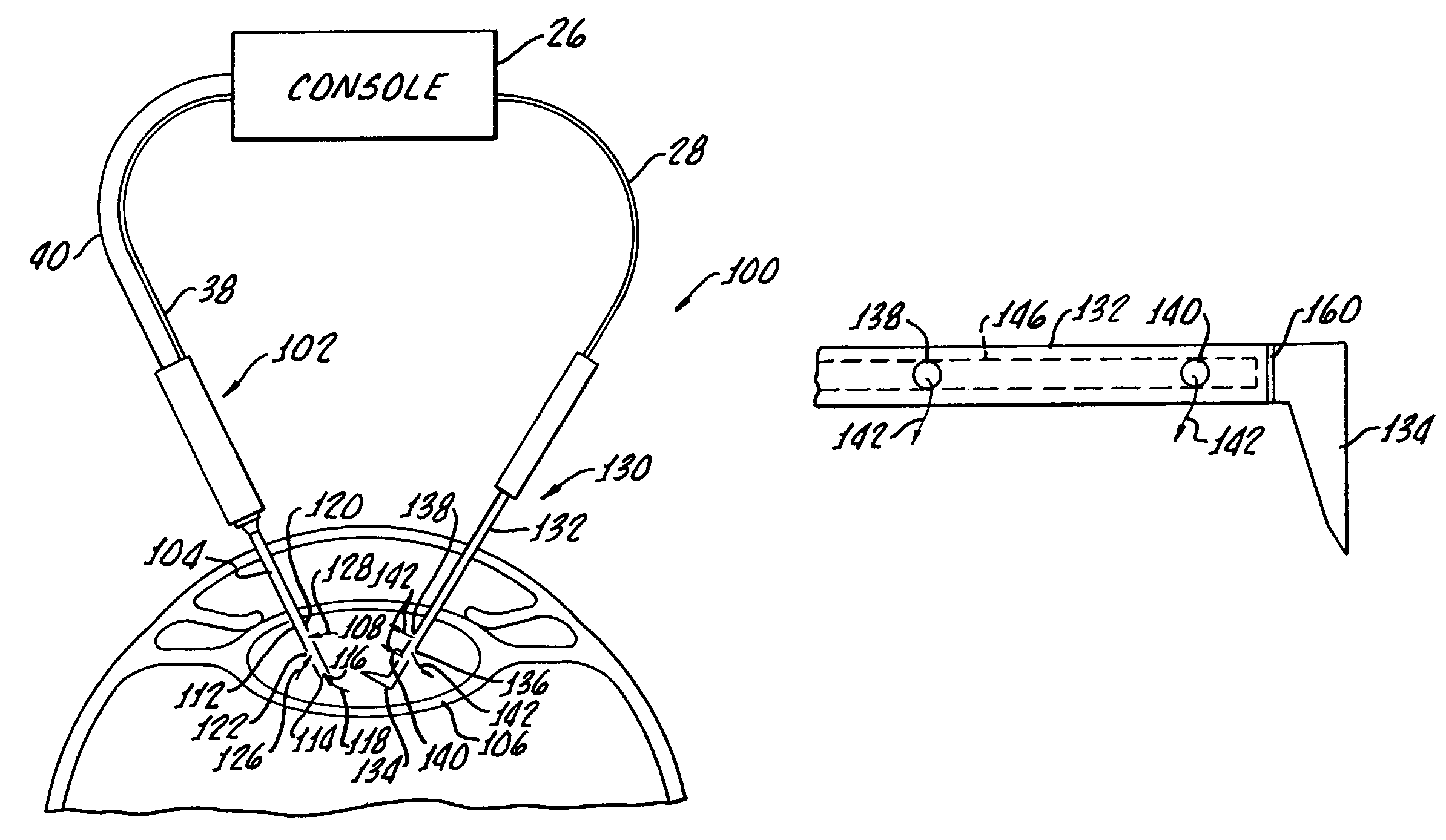
Multi-functional second instrument for cataract removal
Apparatus for the removal of lens tissue includes a first instrument for inserting into a lens capsule and removing a cataract therein, the first instrument including a lumen for aspiration of cataract tissue and irrigation fluid from the lens capsule and manipulate the cataract until cataract is removed. The second instrument includes an irrigation port for introducing the irrigation fluid into the lens capsule.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
Cataract extraction apparatus and method with rapid pulse phaco power
InactiveUS6962583B2Prevent crashAvoid heat damageLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsPulse controlLens crystalline
Apparatus and method for the removal of lens tissue includes a first handpiece having a laser emitting probe sized for insertion into a lens capsule and radiating a lens therein. The laser emitting probe includes a lumen for introducing irrigation fluid into the lens capsule. A second handpiece includes a pulsed controlled vibrated needle for insertion into the lens capsule and emulsifying laser eradiated lens tissue. The vibrated needle includes a lumen therethrough for aspiration of emulsified lens tissue and irrigation fluid.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
Device for local ablation of tissue
The invention relates to a catheter device including a coil element comprised of NiCr60 alloy material, whose proximal radial end is coiled about the catheter shaft. The coil element and the thermal containment tube are configured so as to emit thermal energy. This is achieved by a catheter device adapted to deliver thermal energy from a source local to the body tissue to be ablated, adapted for connection to a thermal heat source at its distal end, a fluid conduit for passing a fluid into said ports for anchoring and filling the proximal cuff of the thermal energy device, a separate conduit for placement of necessary connective lines to the thermal energy element and monitoring device and a separate conduit for the drainage of bladder fluids during treatment.
Owner:PLASIATHERM
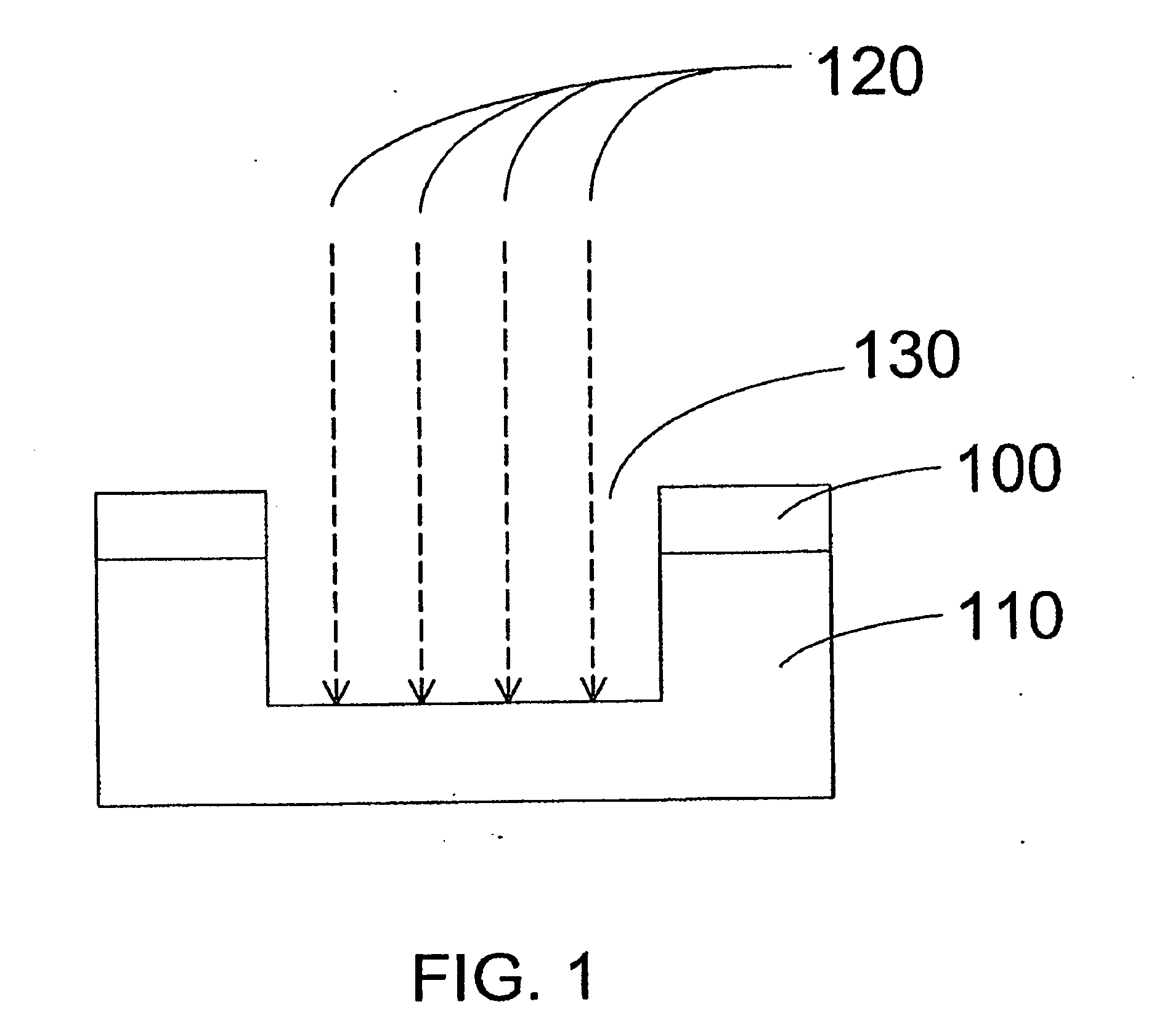
Method of cutting semiconductor wafer and protective sheet used in the cutting method
InactiveUS7060531B2Suppressing progressInhibit progressFilm/foil adhesivesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsForming faceResist
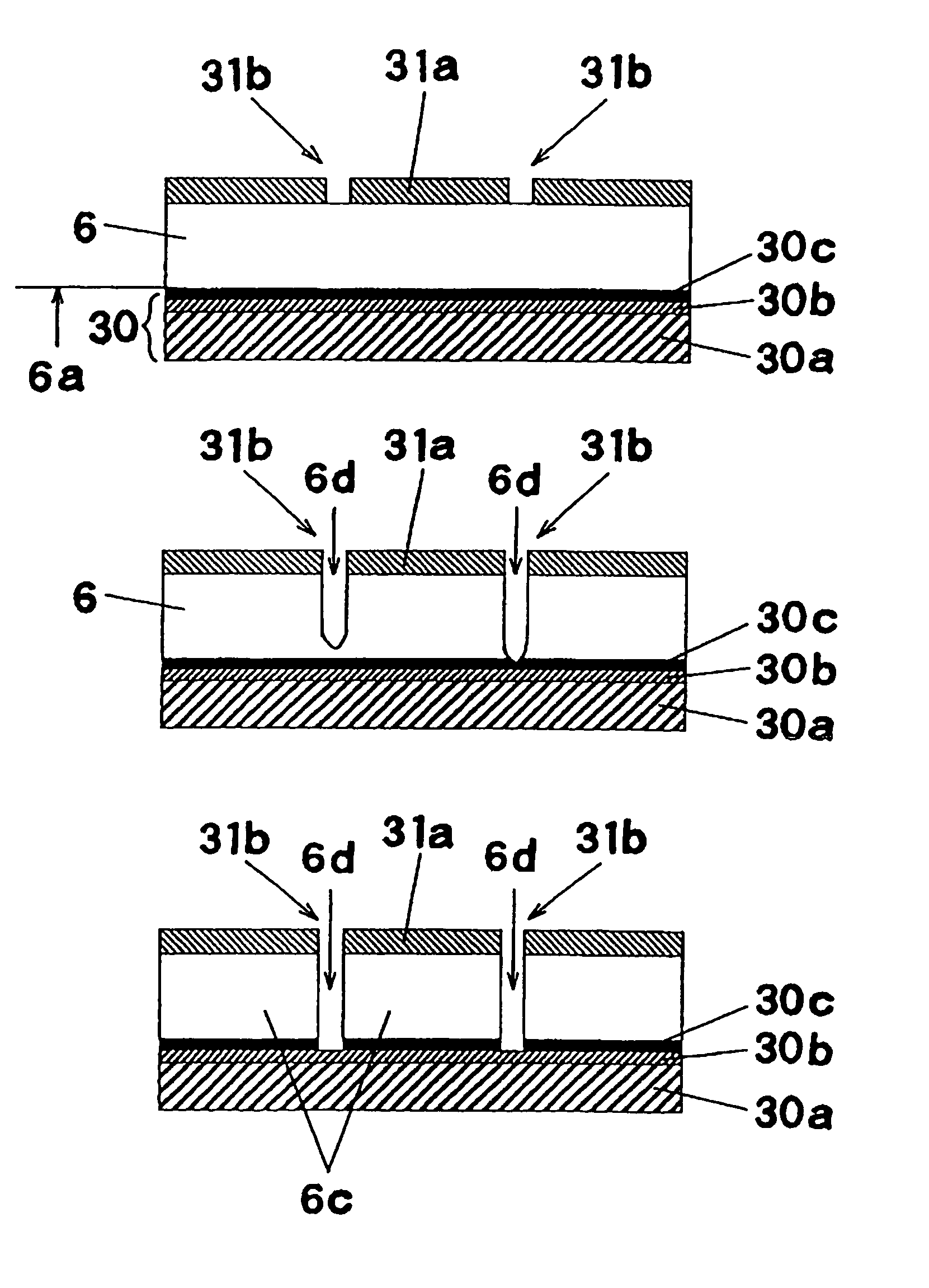
In a method of cutting a semiconductor wafer in which the semiconductor wafer 6 is cut by plasma etching, a protective sheet 30 on which a metallic layer 30b, a plasma etching rate of which is low, is formed on one face of an insulating sheet 30a is stuck on to a circuit forming face 6a by an adhesive layer 30c, and plasma is exposed onto an opposite side to the circuit forming face 6a from a mask side which is formed by covering regions except for cutting lines 31b with a resist film 31a so as to conduct plasma etching on portions of the cutting lines. Due to the above structure, it is possible to use the metallic layer as an etching stop layer for suppressing the progress of etching. Therefore, fluctuation of the progress of etching can be avoided and heat damage caused on the protective sheet can be prevented.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Ultrasonic cutting device
An ultrasonic surgical cutting method and apparatus is provided wherein the method and apparatus allows for the cutting of bone from within a hollow pathway such that a cutter associated with the ultrasonic method and apparatus remains sufficiently cool to prevent necrosis of the bone being cut. Furthermore the ultrasonic device and method can be employed in the cutting of soft tissue, wherein a cooled cutter is used to prevent the sticking of soft tissue to the cutting blade of the device during use.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Method and apparatus for dermal delivery of a substance
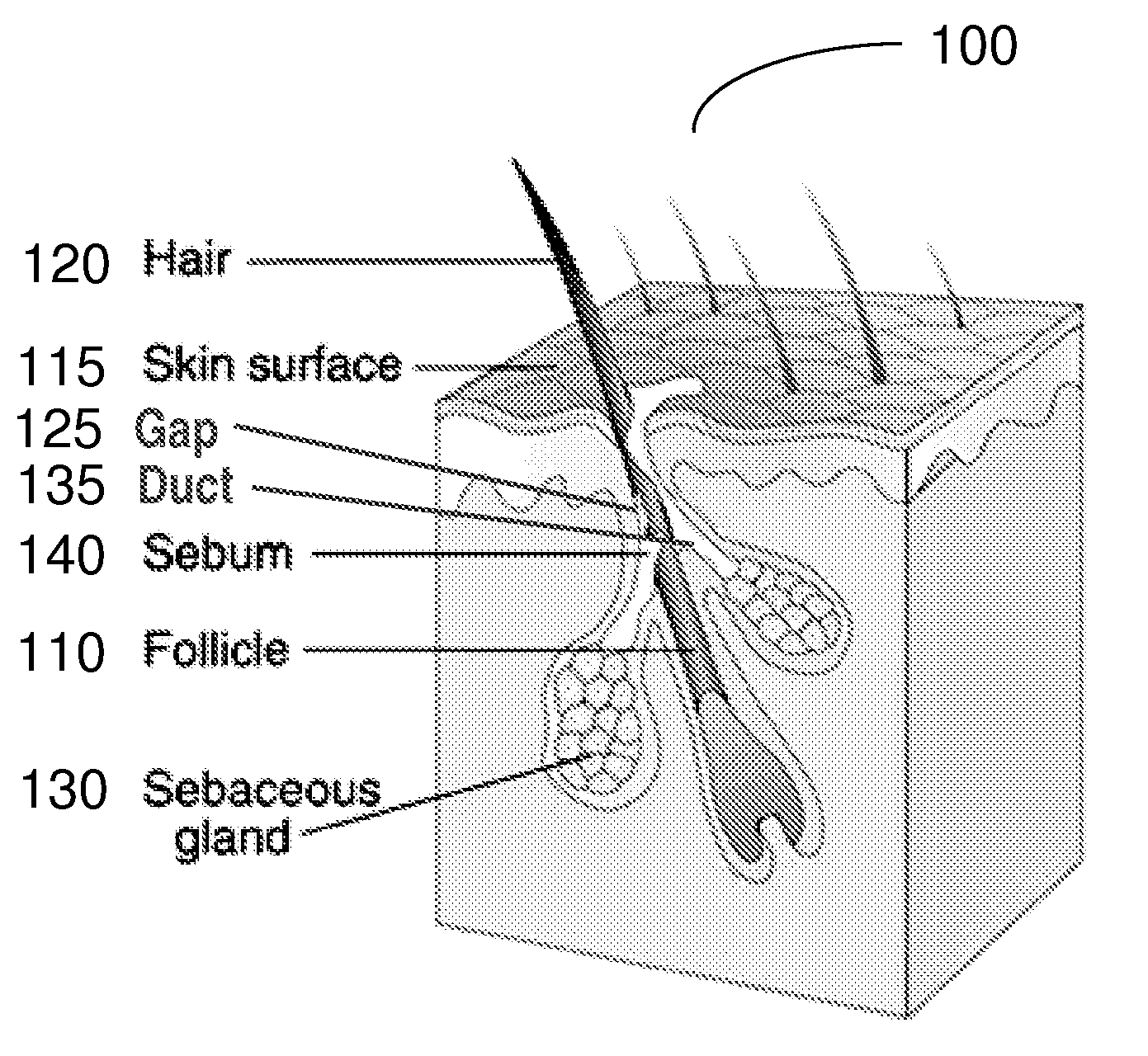
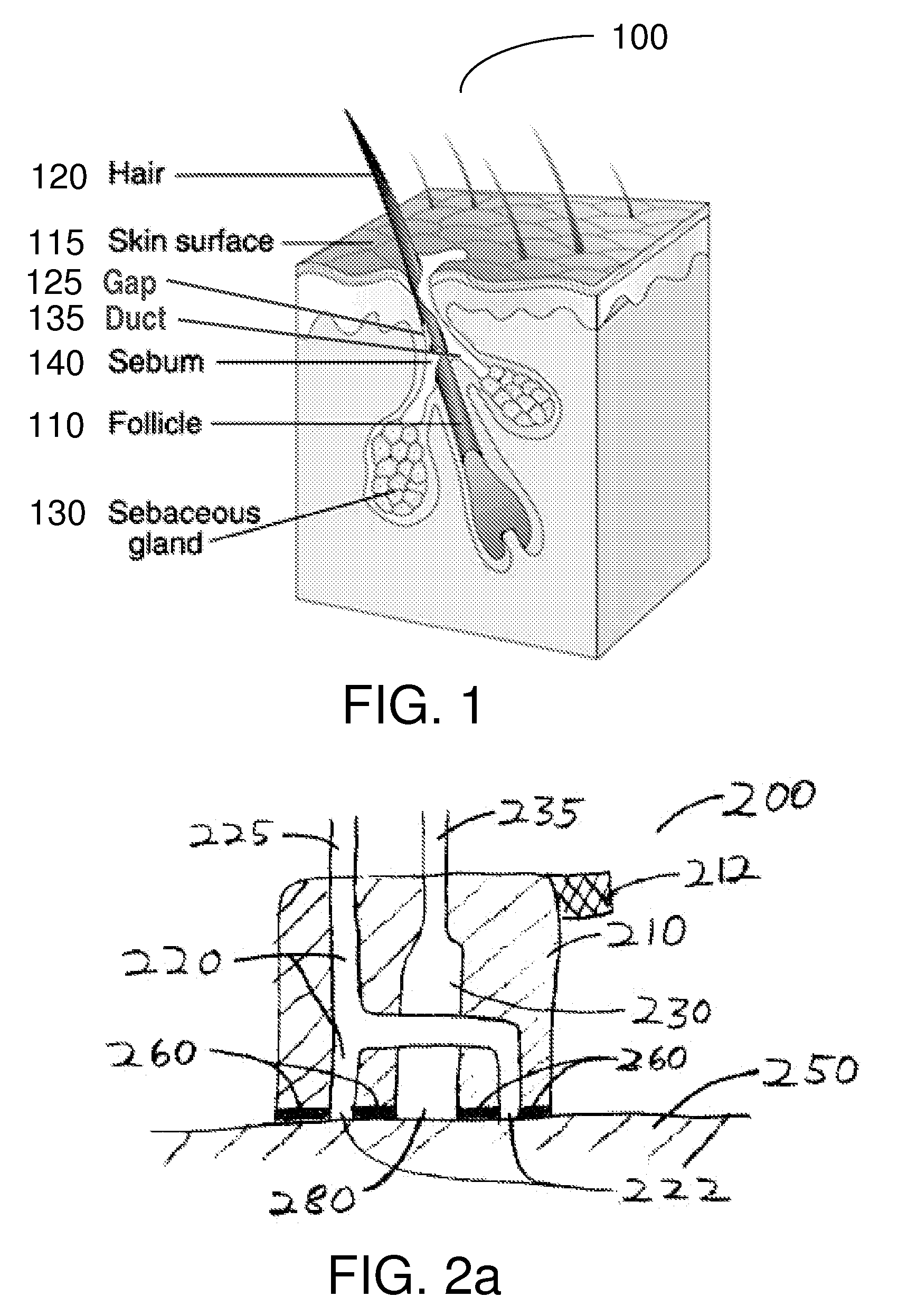
ActiveUS20100305495A1Improved physical contactPromotes relative motionCosmetic preparationsHeavy metal active ingredientsSkin surfaceCatheter
The present invention is directed to a method and apparatus for delivering substances, e.g., therapeutic substances, into openings on or near a skin surface, such as hair follicles, pores and / or into sebaceous glands. This can be achieved by using an apparatus to direct a substance into the openings under pressure via one or more nozzles or slits. A portion of the sebum present in the hair follicle is optionally heated and / or removed, e.g. using low-pressure conduit located on the lower surface of the apparatus, before introducing the therapeutic substance.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
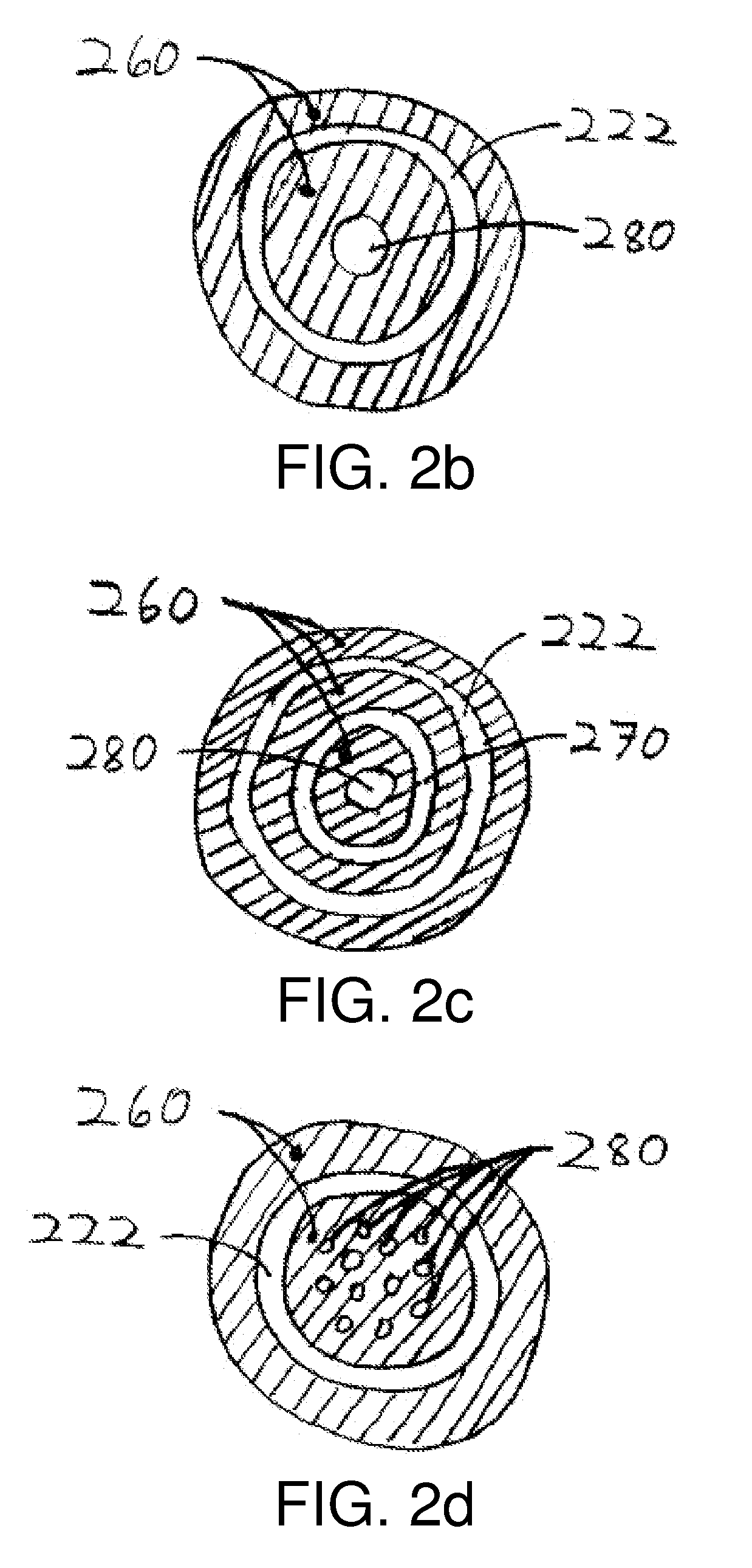
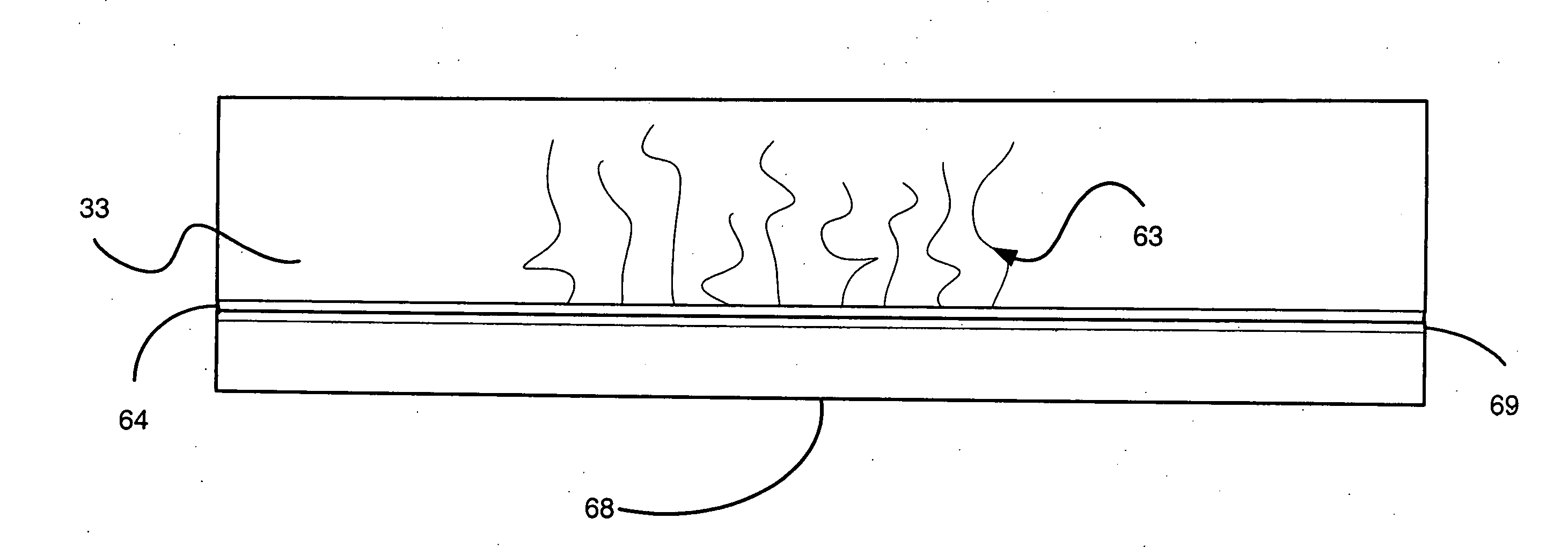
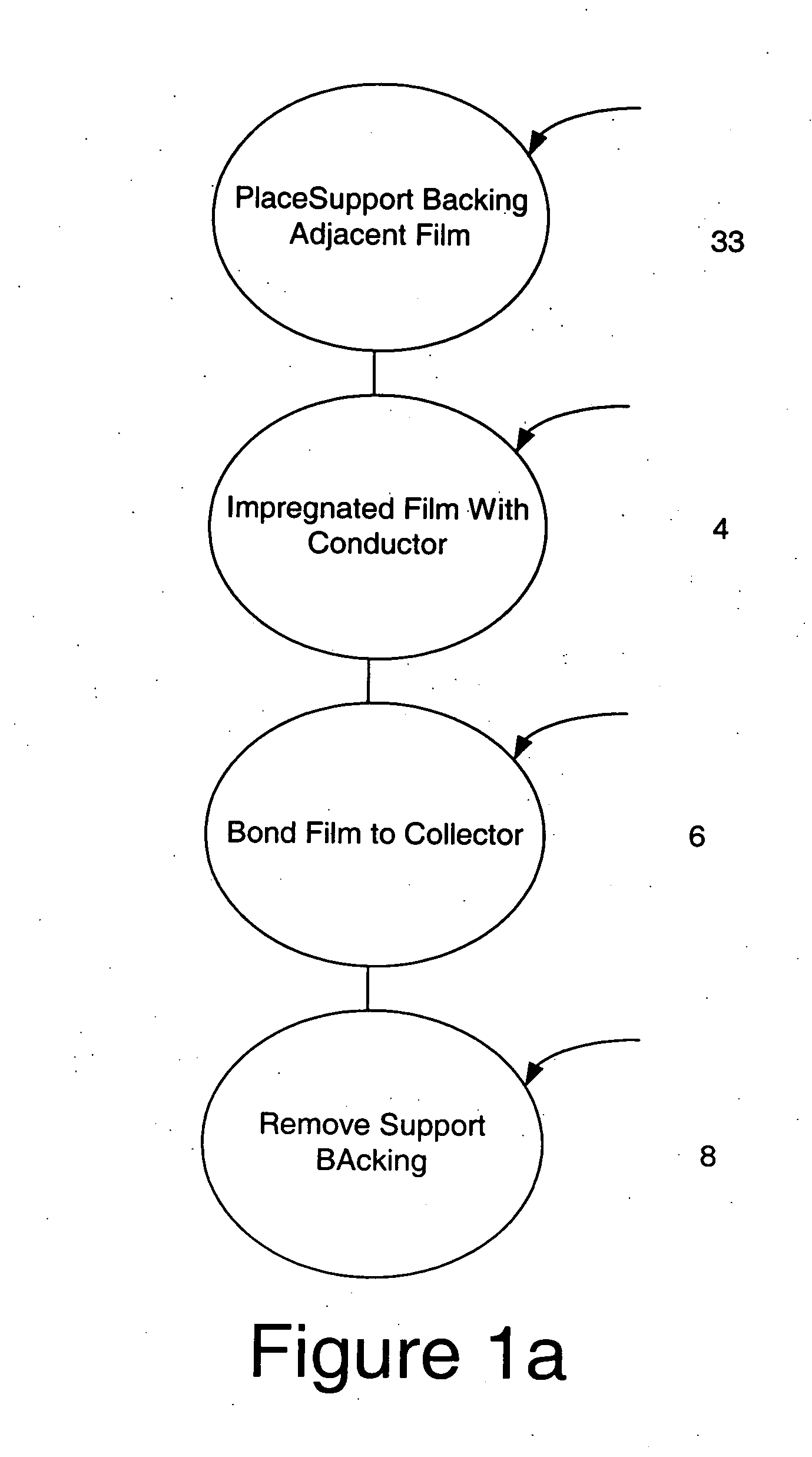
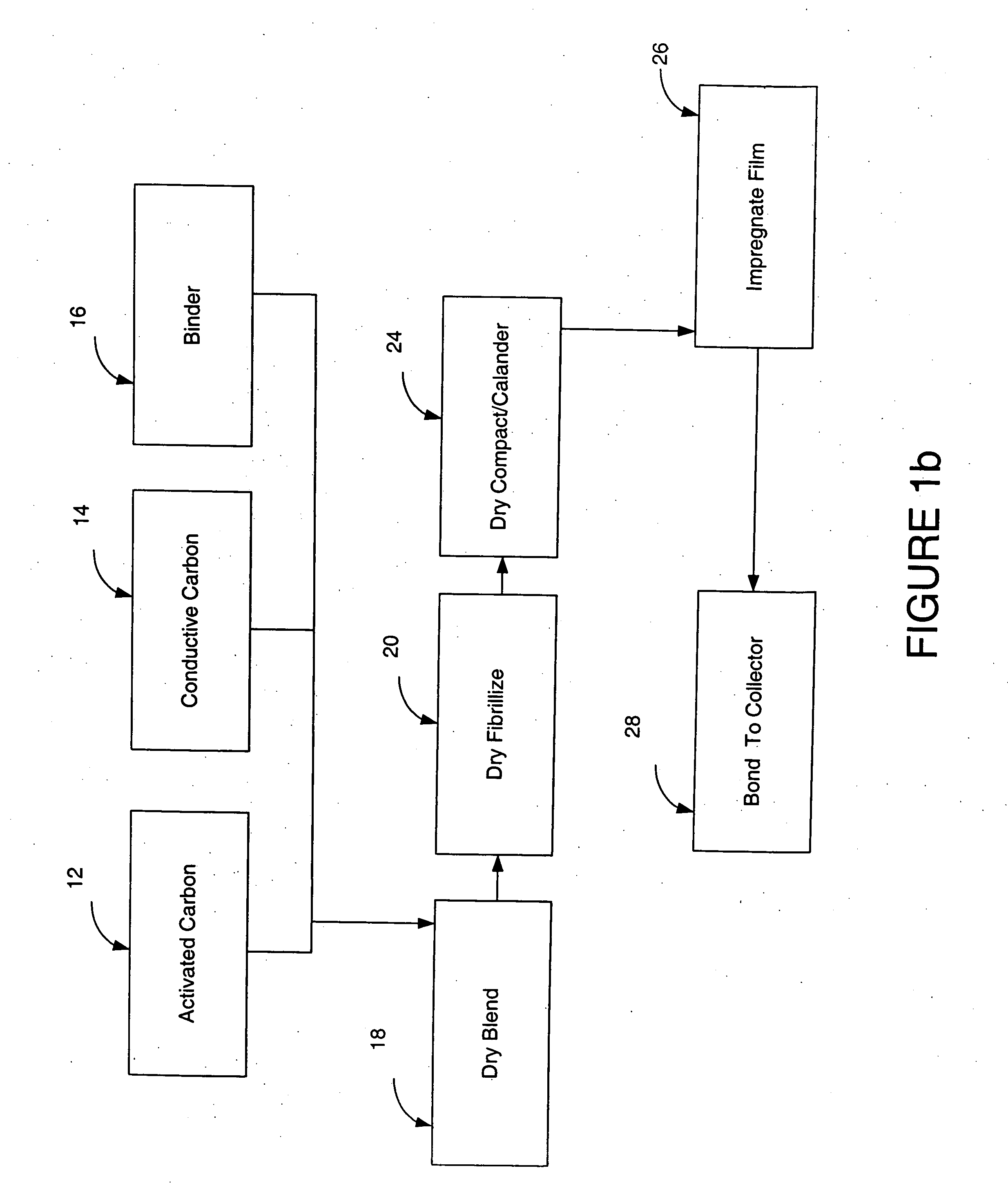
Electrode impregnation and bonding
ActiveUS20050057888A1Long-lasting and durable and inexpensive to produceLower internal resistanceElectrolytic capacitorsHybrid capacitor electrodesEngineeringConductive materials
A method for making an electrode including a particle based film is disclosed in which the film is coated and / or impregnated with veins of conductive material. A support backing is placed adjacent to one side of the film to provide support and prevent damaging the film while the conductive material is applied onto the opposite side of the film. The film is bonded directly to a current collector of an energy storage device.
Owner:TESLA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com