Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
359results about How to "Large numerical aperture" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
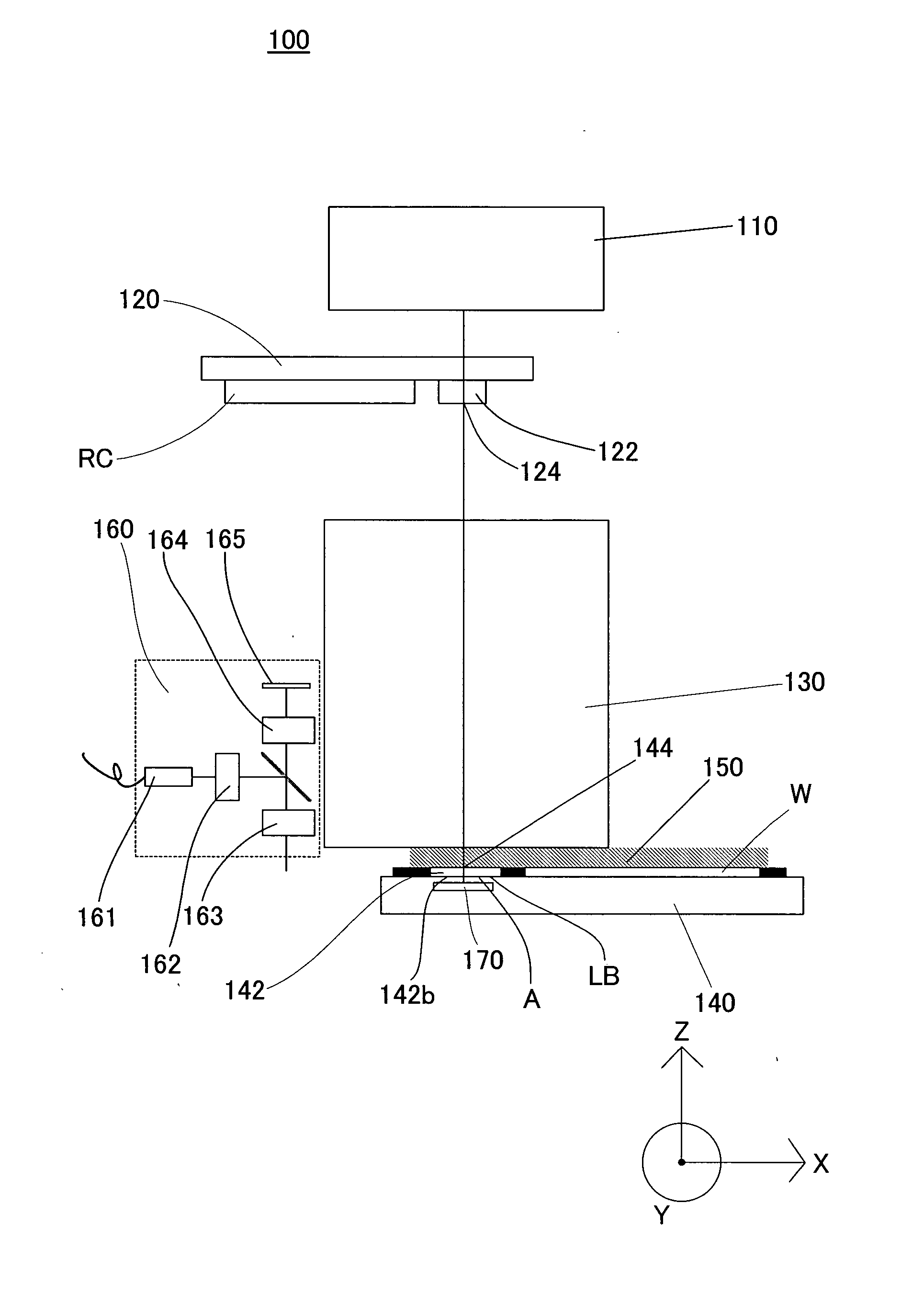
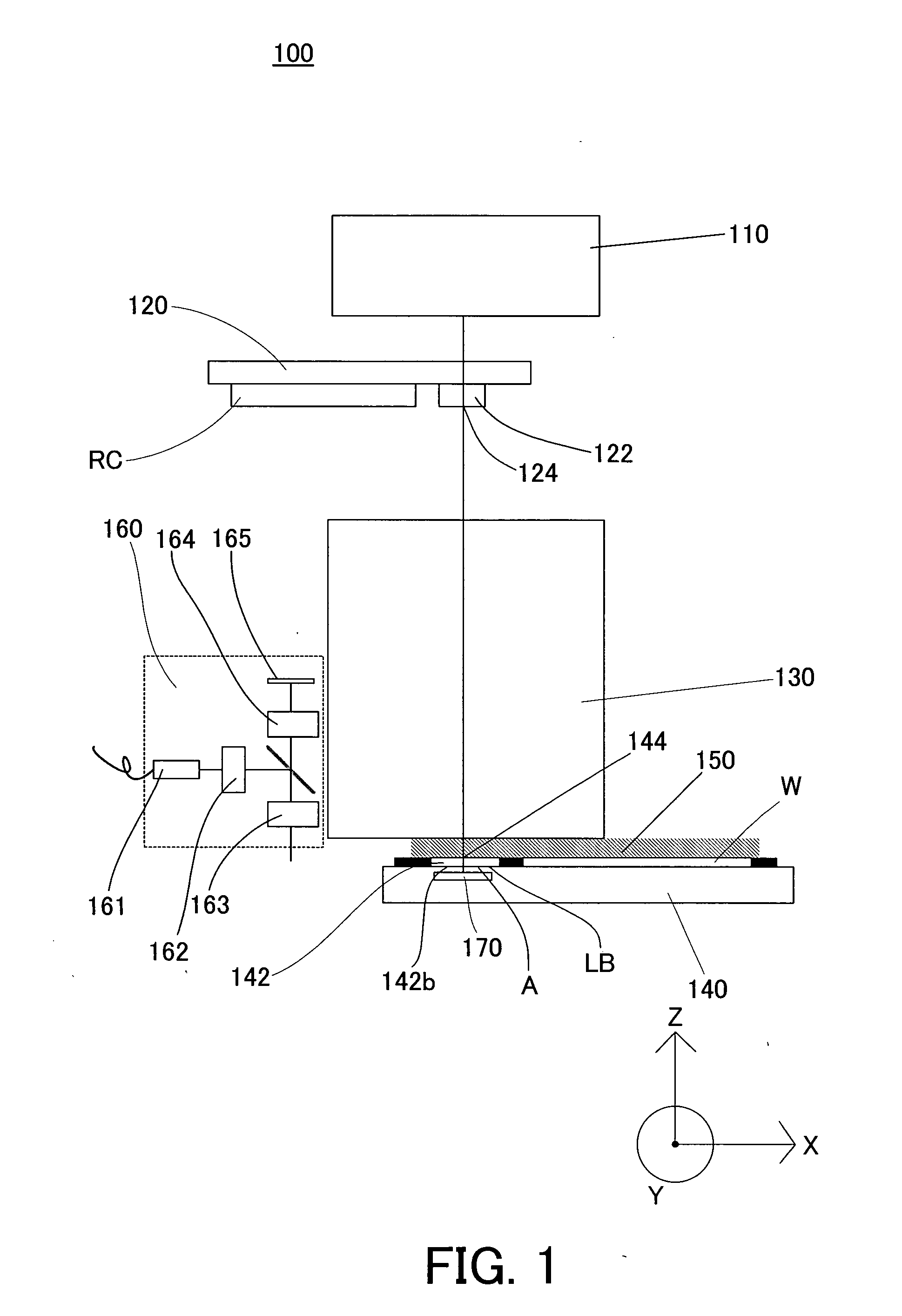
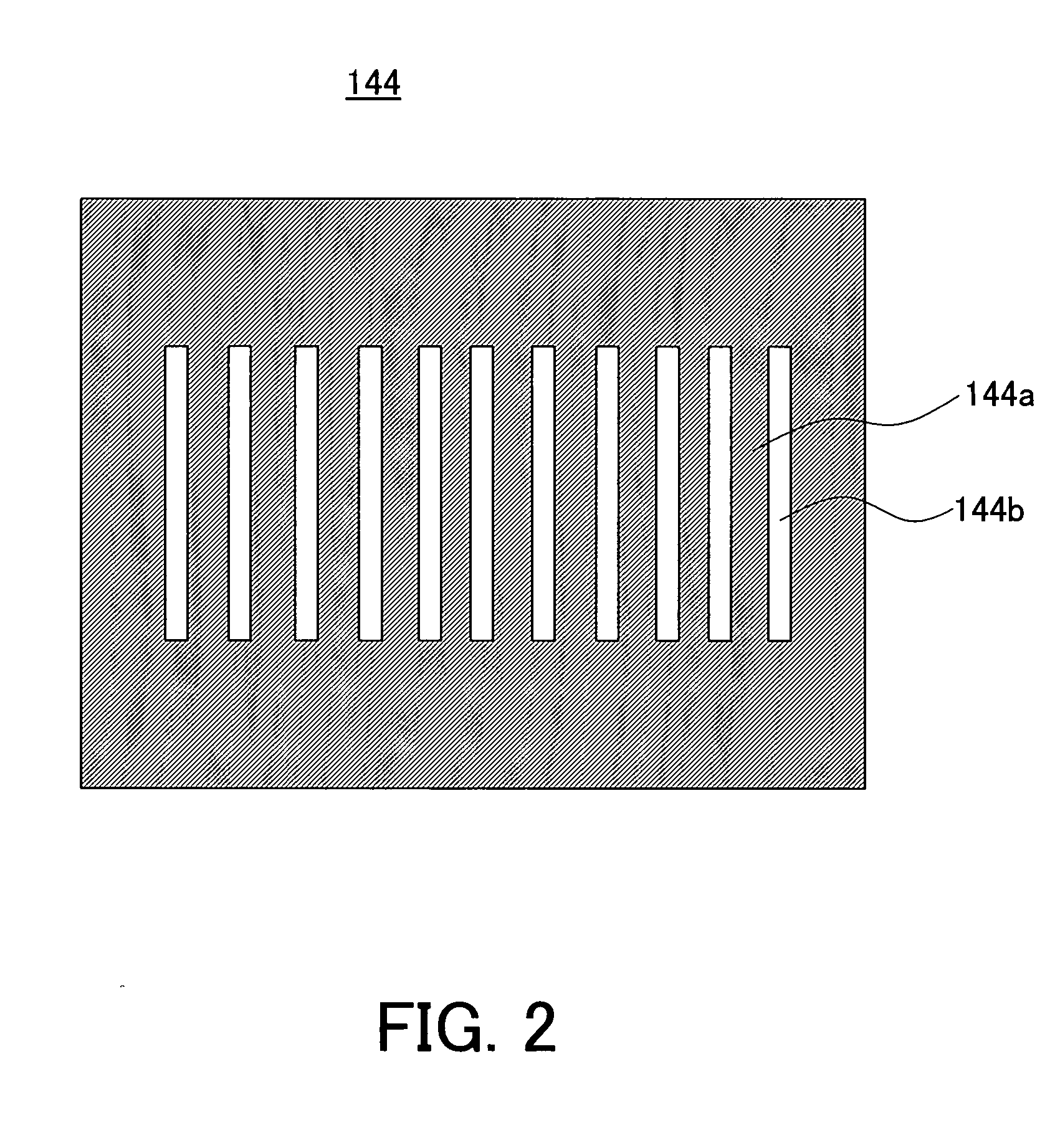
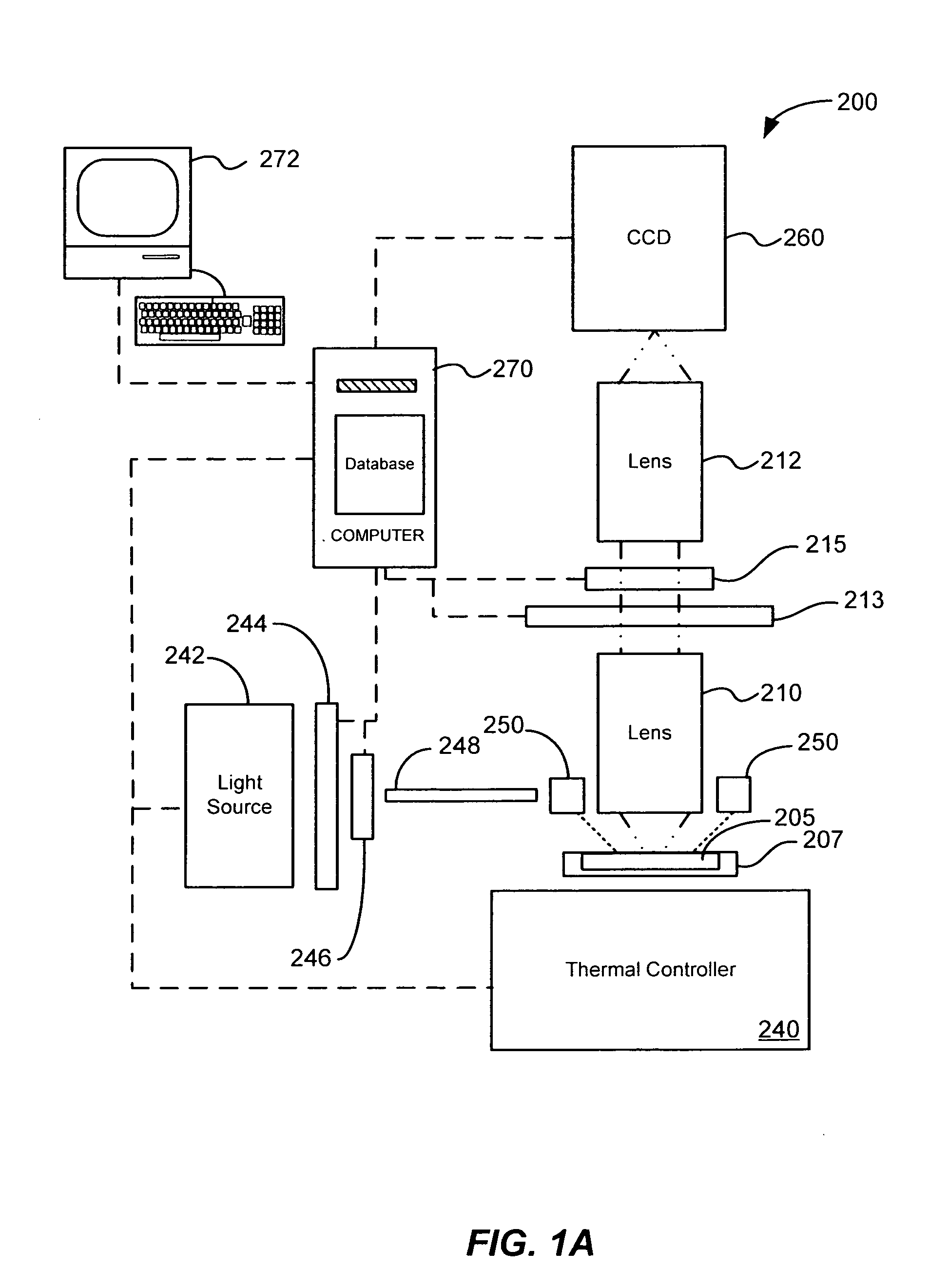
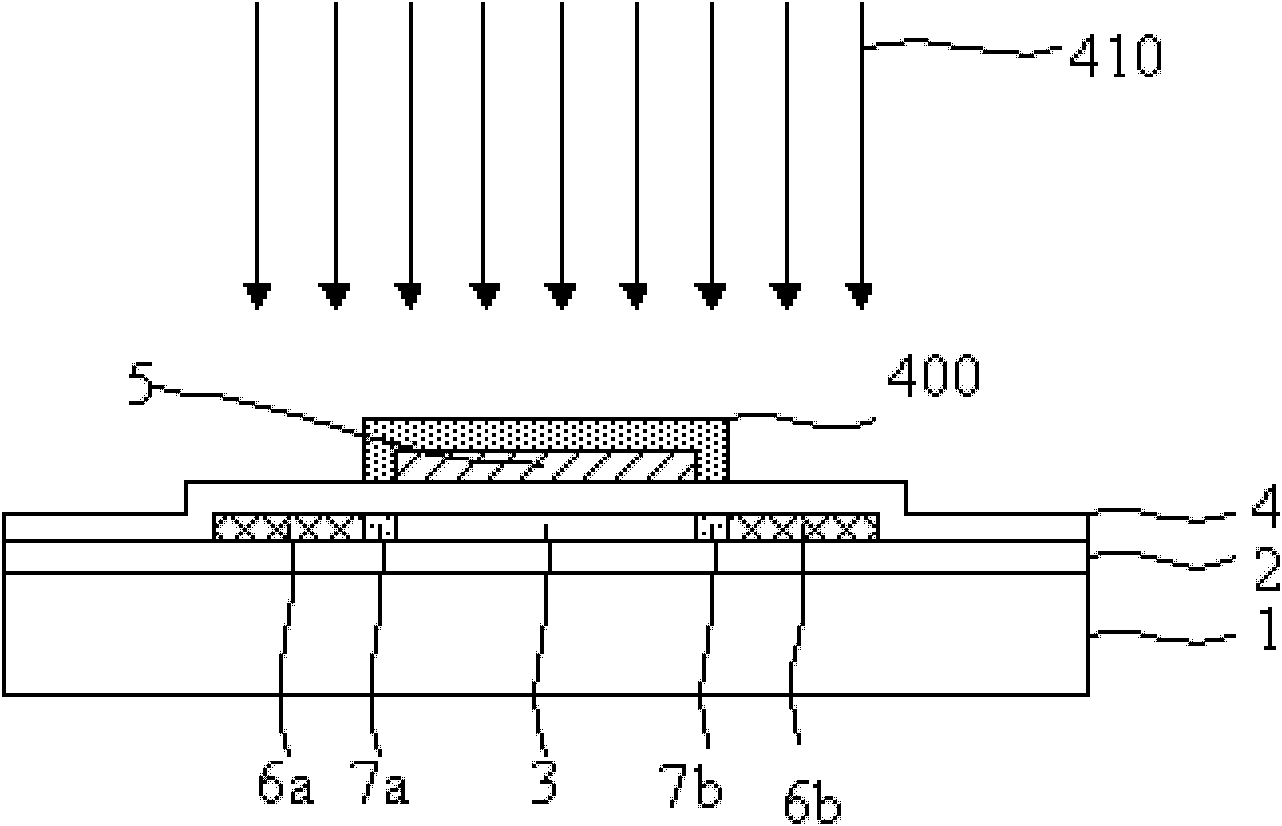
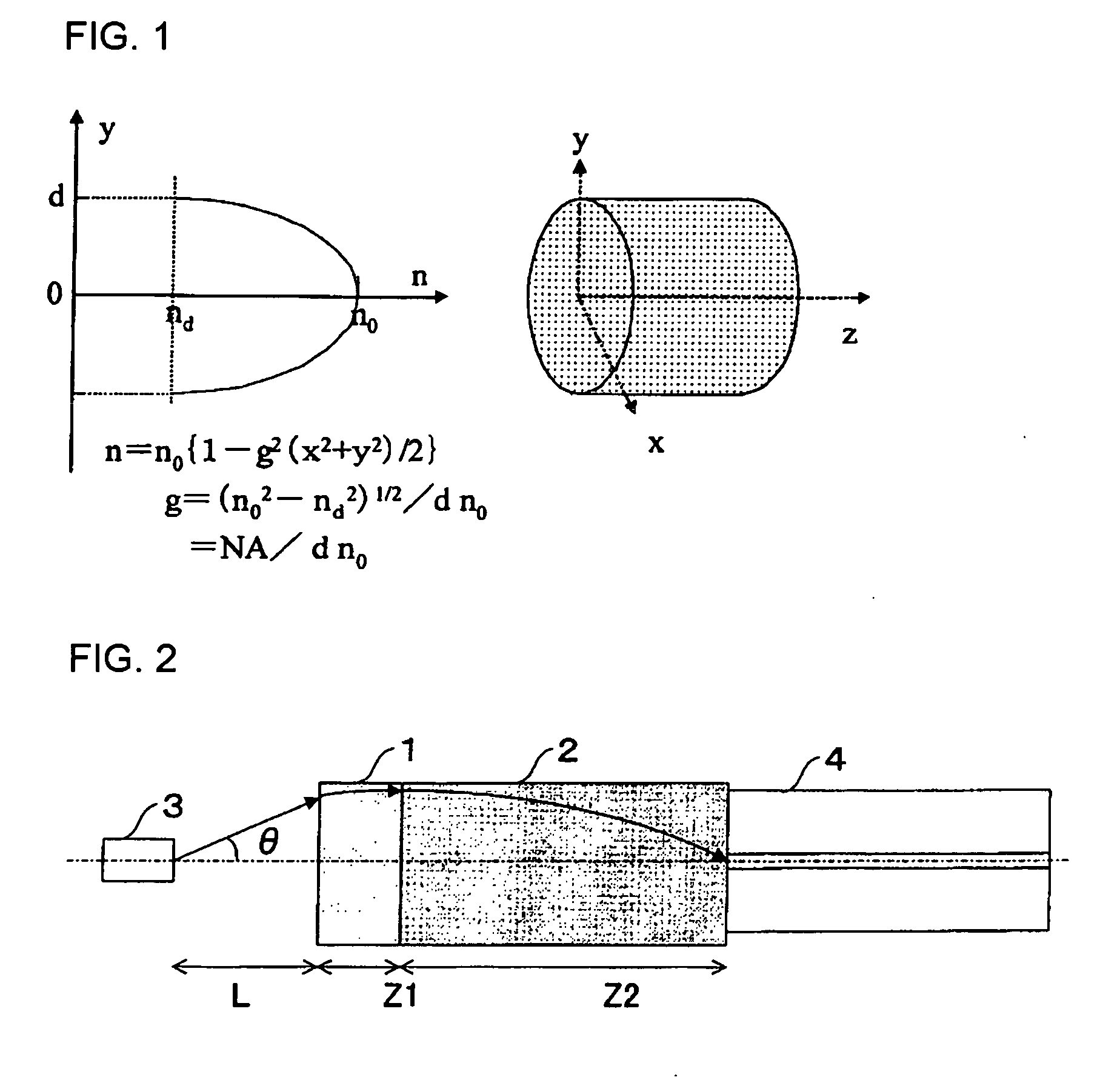
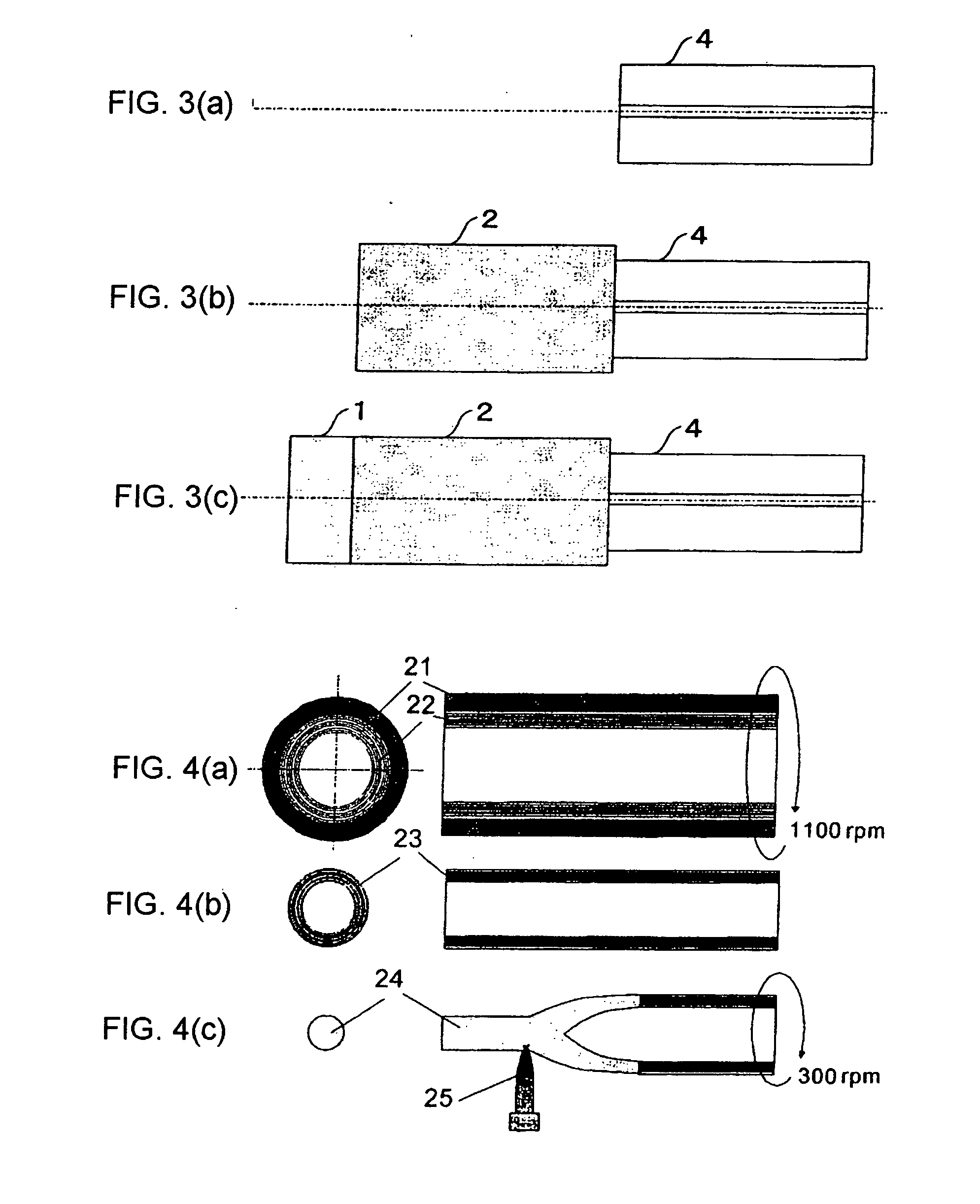
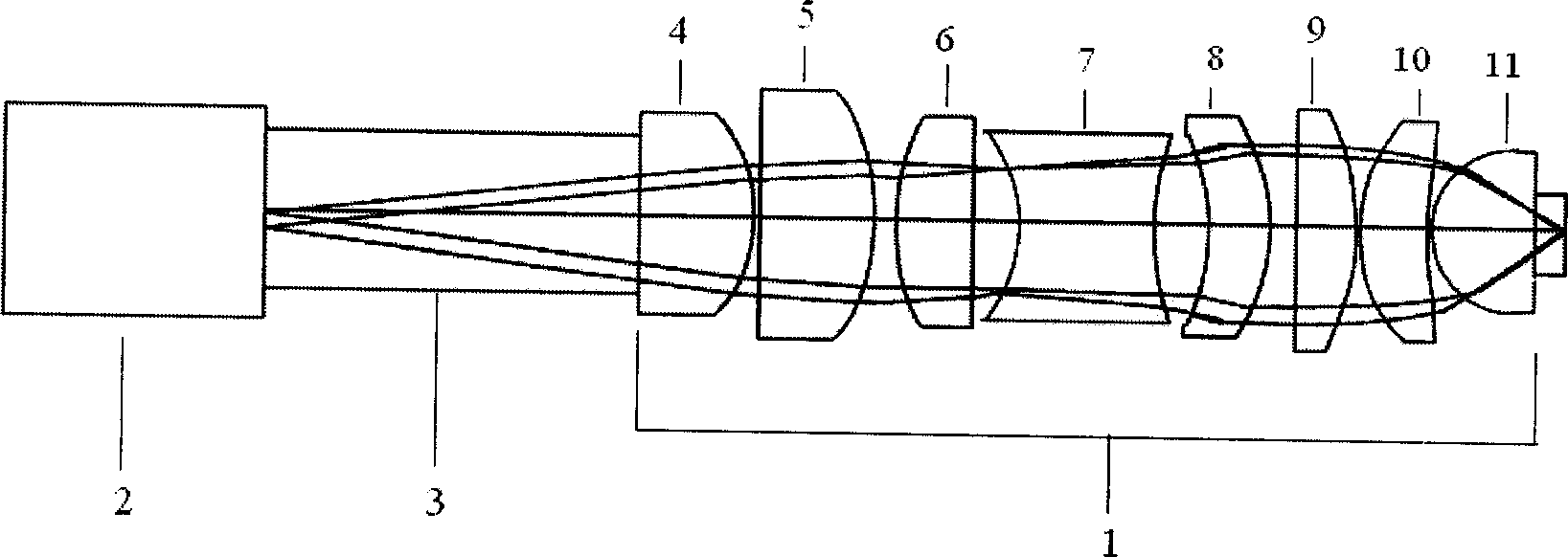
Exposure apparatus
InactiveUS20050146693A1Accurate exposureLarge numerical apertureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusRefractive indexReticle
An exposure apparatus includes a projection optical system for projecting a pattern on a reticle onto an object to be exposed, a reference mark that serves as a reference for an alignment between the reticle and the object, a first fluid that has a refractive index of 1 or greater, and fills a space between at least part of the projection optical system and the object and a space between at least part of the projection optical system and the reference mark, and an alignment mechanism for aligning the object by using the projection optical system and the first fluid.
Owner:CANON KK
Optical lens system and method for microfluidic devices
ActiveUS20060006067A1Less complexProblem is reduced and eliminatedSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementFluorescenceEngineering
An apparatus for imaging one or more selected fluorescence indications from a microfluidic device. The apparatus includes an imaging path coupled to least one chamber in at least one microfluidic device. The imaging path provides for transmission of one or more fluorescent emission signals derived from one or more samples in the at least one chamber of the at least one microfluidic device. The chamber has a chamber size, the chamber size being characterized by an actual spatial dimension normal to the imaging path. The apparatus also includes an optical lens system coupled to the imaging path. The optical lens system is adapted to transmit the one or more fluorescent signals associated with the chamber.
Owner:STANDARD BIOTOOLS INC
Compact optical detection system for a microfluidic device
ActiveUS7518726B2Large numerical apertureLow powerWithdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansFluorescenceOptical alignment
An optical detection system for a microfluidic device and a dry-focus microfluidic device compatible with the compact optical detection system are described. The system includes an LED; means for collimating light emitted by the LED; an aspherical, fused-silica objective lens; means for directing the collimated light through the objective onto a microfluidic device; and means for detecting a fluorescent signal emitted from the microfluidic device. The working distance between the objective and the device allows light from an external LED or laser to be brought in along a diagonal path to illuminate the microfluidic device. The dry-focus microfluidic device includes multiple channels and multiple closed optical alignment marks having curved walls. At least one of the channels is positioned between at least two of the marks. The marks are illuminated for alignment and focusing purposes by light brought in on a diagonal path from an external white LED.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
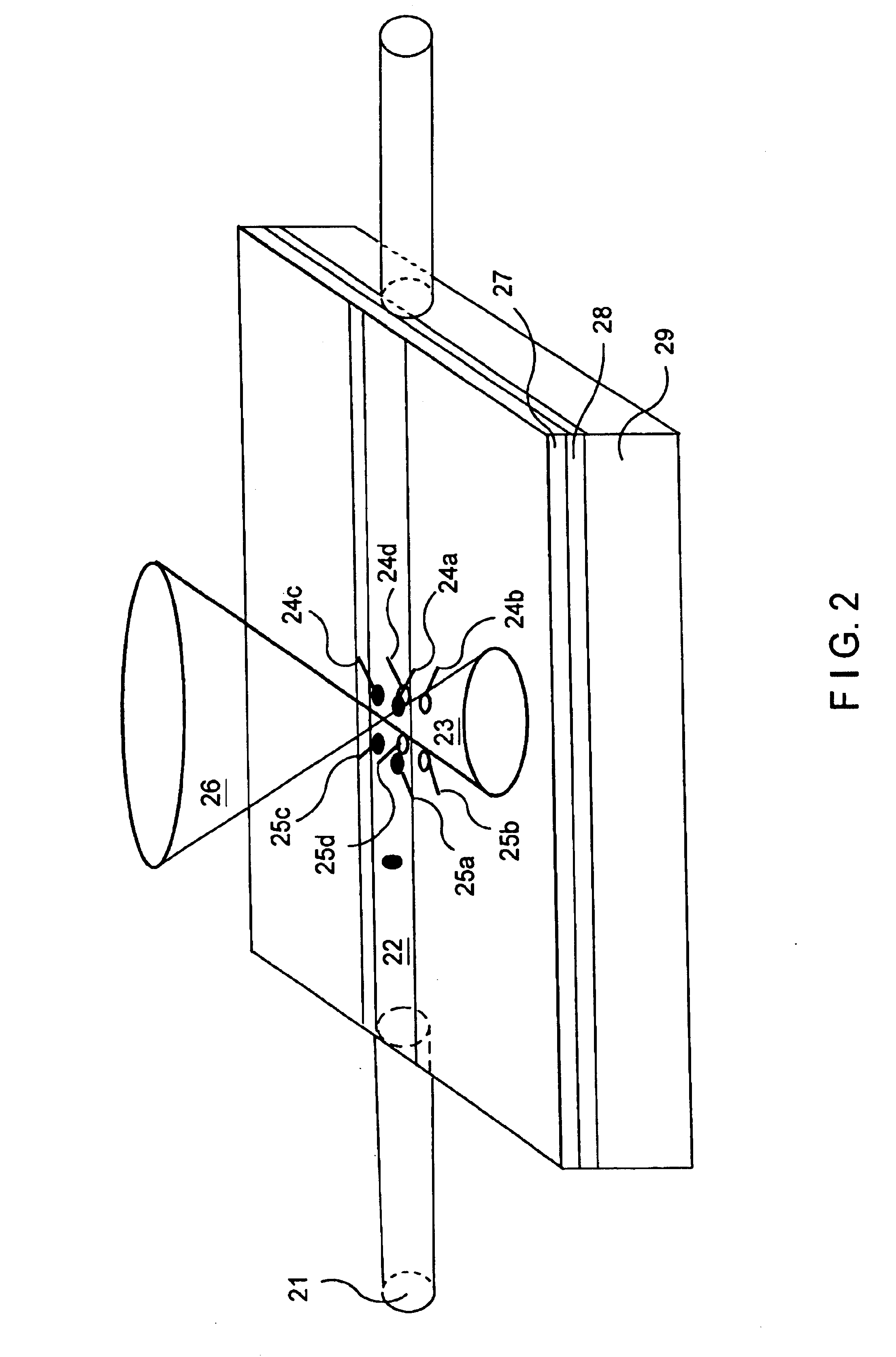
Simultaneous multi-spot inspection and imaging
InactiveUS7130039B2High detection sensitivityImprove performanceAnalysis by electrical excitationOptically investigating flaws/contaminationDetector arrayAnnular aperture
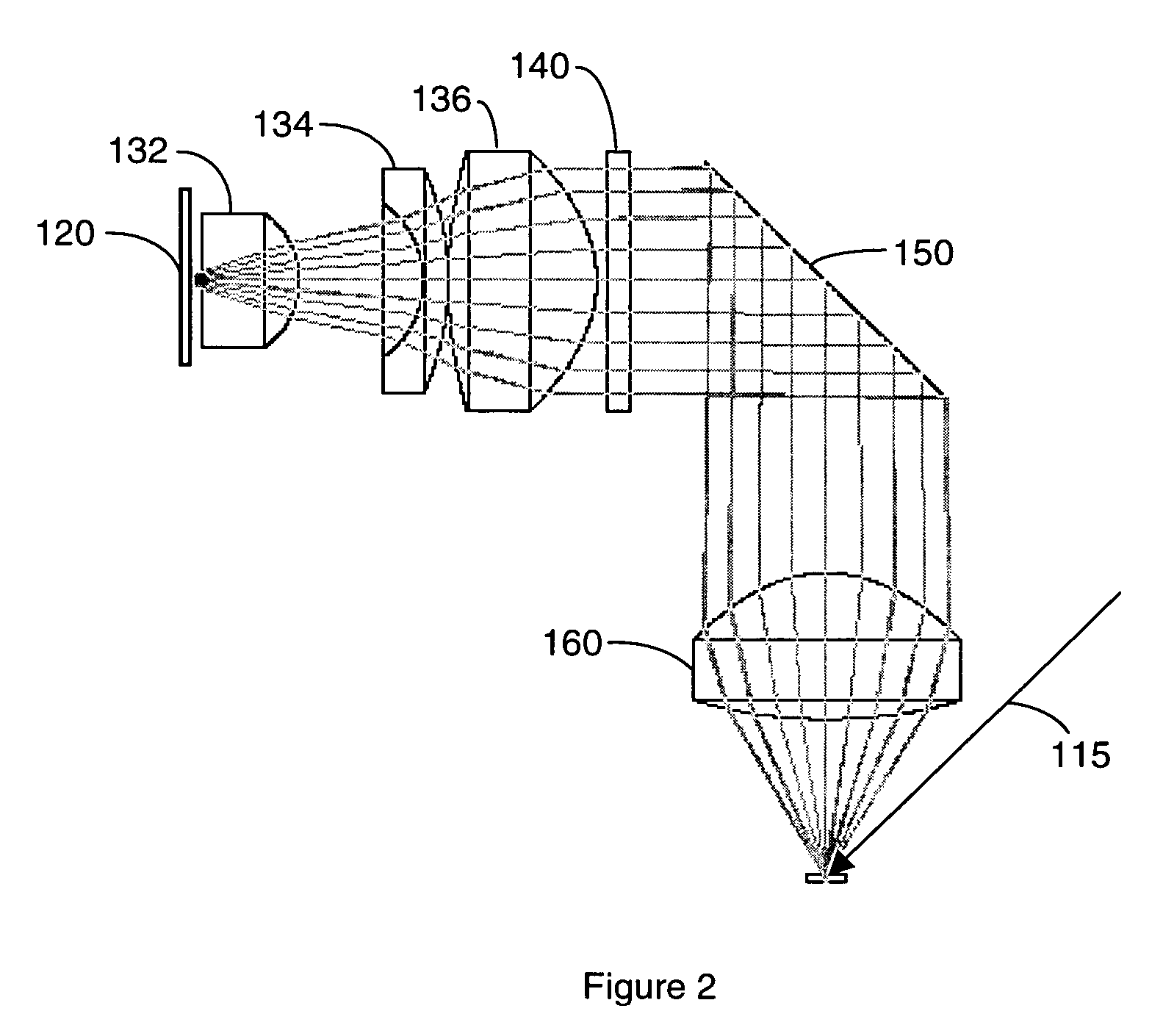
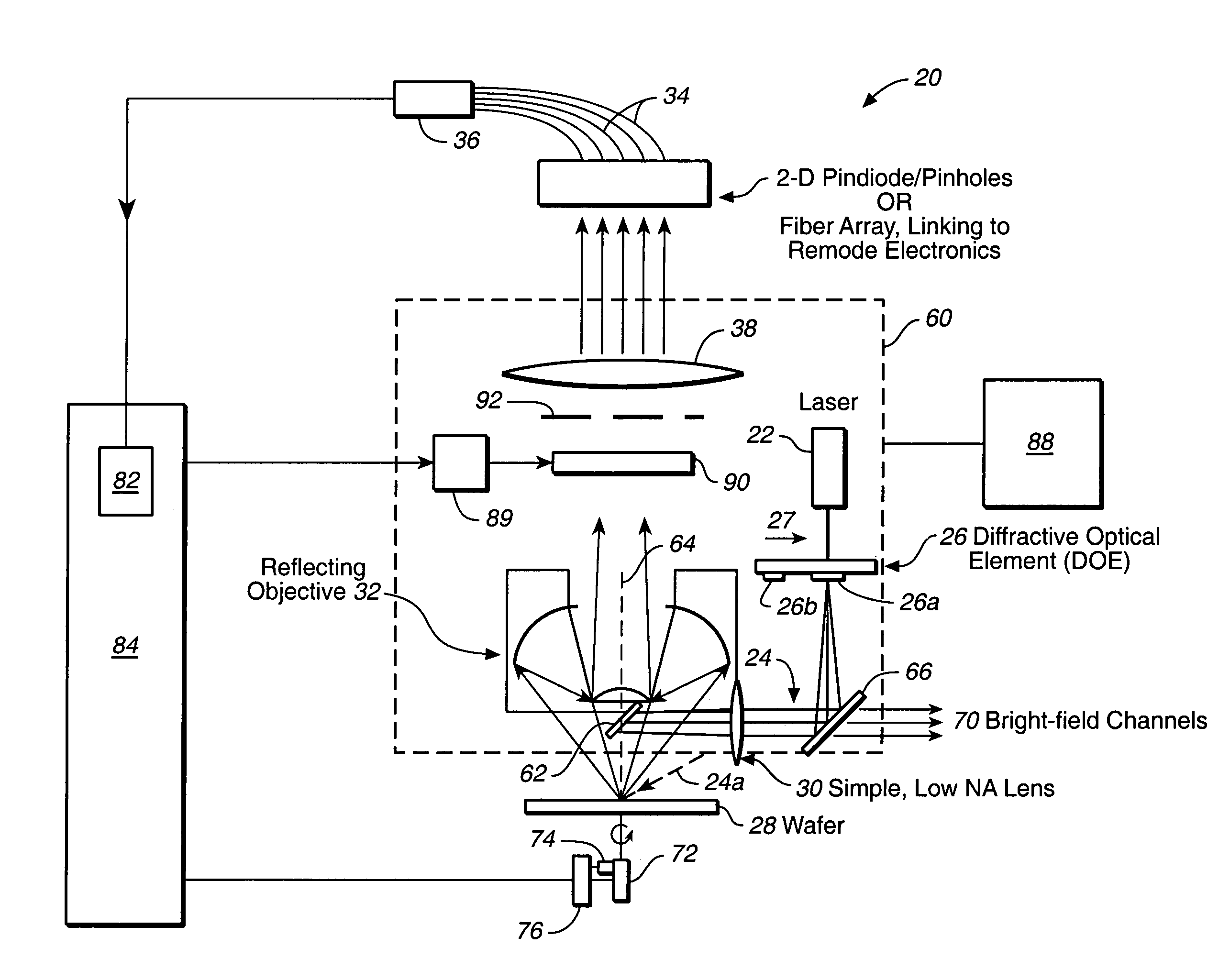
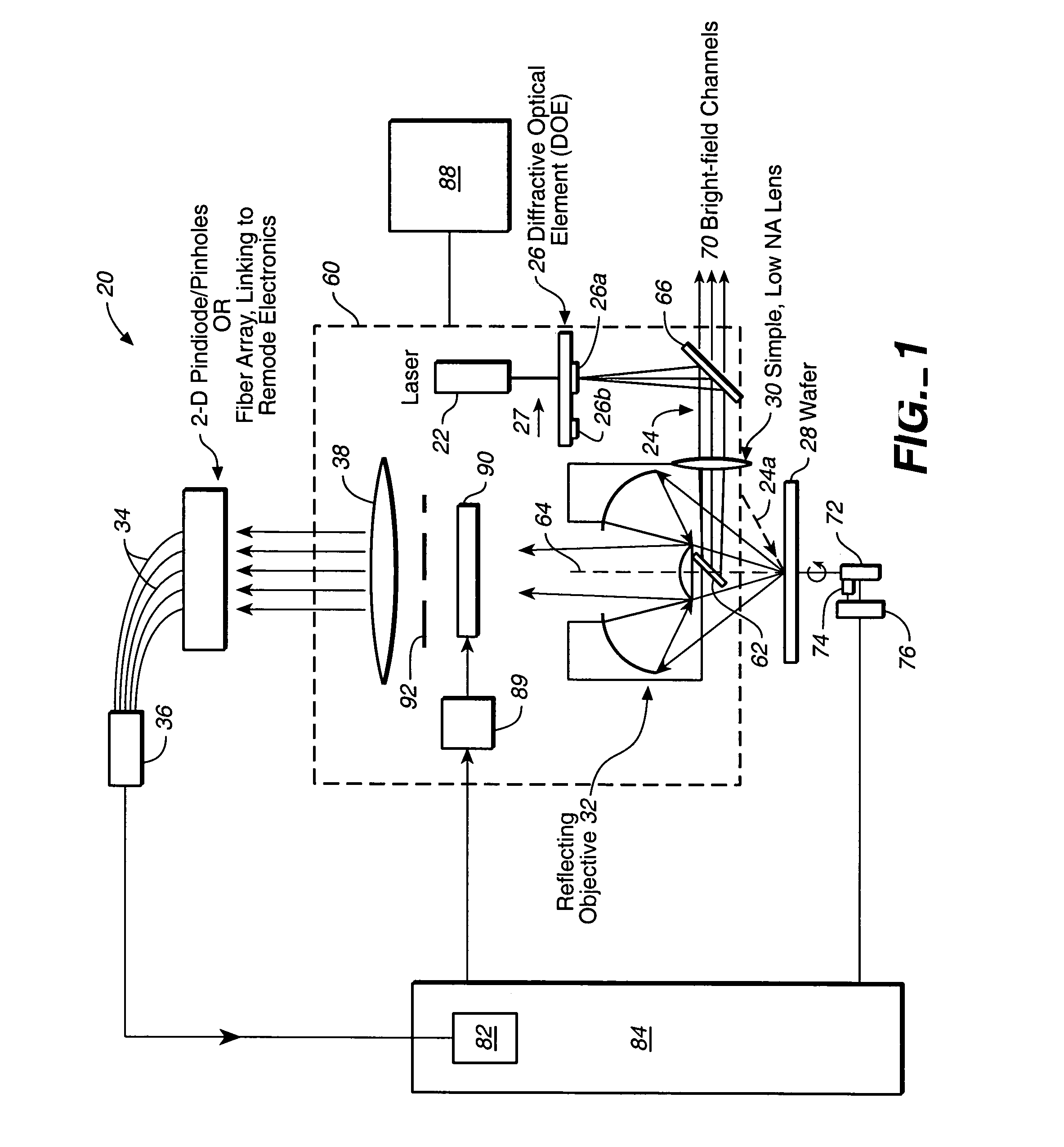
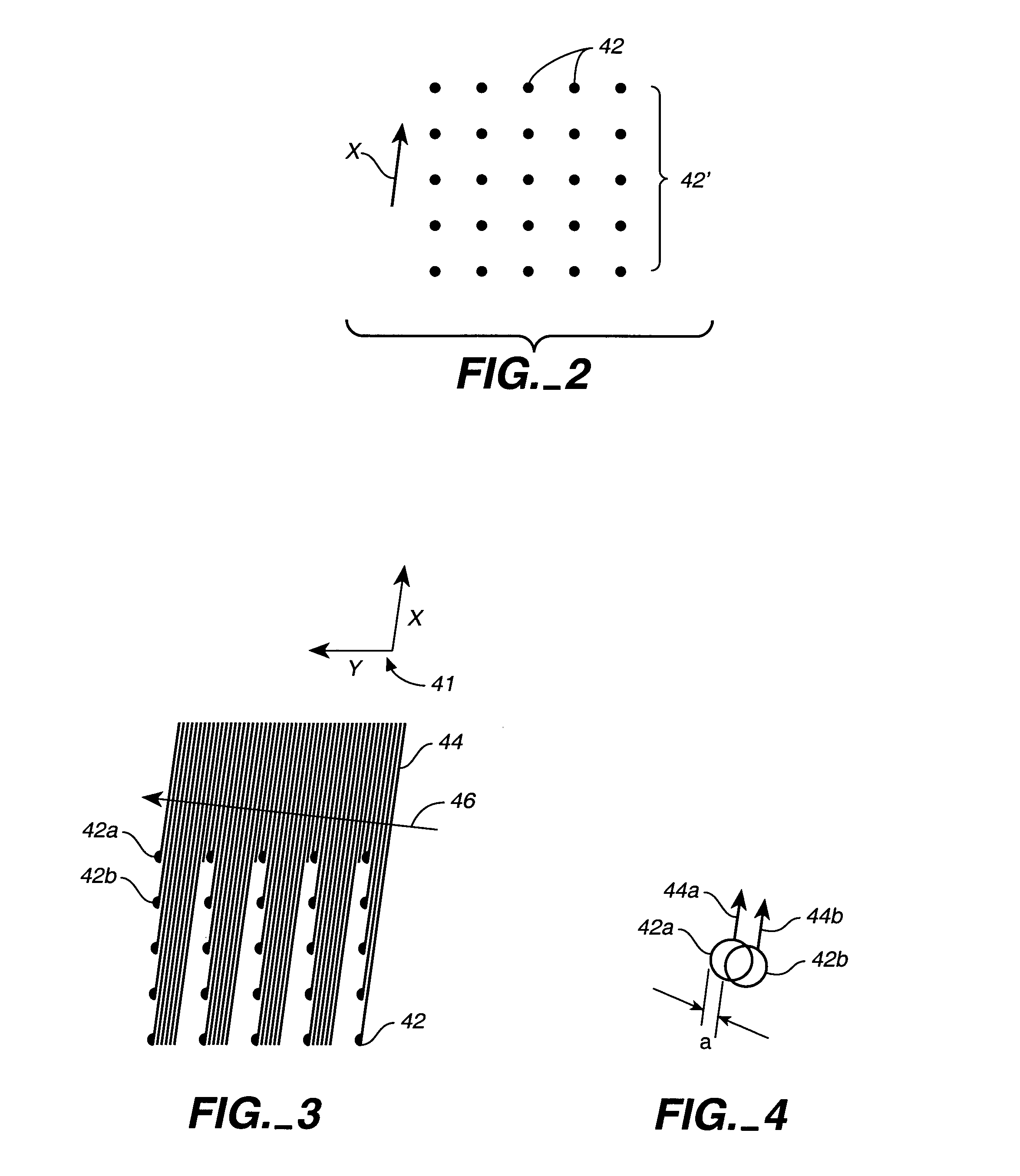
A compact and versatile multi-spot inspection imaging system employs an objective for focusing an array of radiation beams to a surface and a second reflective or refractive objective having a large numerical aperture for collecting scattered radiation from the array of illuminated spots. The scattered radiation from each illuminated spot is focused to a corresponding optical fiber channel so that information about a scattering may be conveyed to a corresponding detector in a remote detector array for processing. For patterned surface inspection, a cross-shaped filter is rotated along with the surface to reduce the effects of diffraction by Manhattan geometry. A spatial filter in the shape of an annular aperture may also be employed to reduce scattering from patterns such as arrays on the surface. In another embodiment, different portions of the same objective may be used for focusing the illumination beams onto the surface and for collecting the scattered radiation from the illuminated spots simultaneously. In another embodiment, a one-dimensional array of illumination beams are directed at an oblique angle to the surface to illuminate a line of illuminated spots at an angle to the plane of incidence. Radiation scattered from the spots are collected along directions perpendicular to the line of spots or in a double dark field configuration.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Beam Homogenizer
InactiveUS20120168411A1Increase beam numerical apertureIncrease the number ofCosmonautic condition simulationsMechanical apparatusLight pipeLight beam
A system for homogenizing the intensity profile of light includes a plurality of fiber coupled light sources for emitting fiber output beams from fiber output ends, and a light pipe optically coupled to the fiber output beams for producing a uniform light pipe output beam, an interleaver that transmits a first set of fiber output beams and reflects a second set of fiber output beams so that the principal rays of the fiber output beams propagate in a common plane, a first optical element for converging the principal rays, and a second optical element for telecentrically imaging the beams into the light pipe such that the principal rays of the beams propagate parallel to each other and the beams are focused in the light pipe in a focal plane transverse to the direction of propagation.
Owner:NLIGHT INC
High resolution direct-projection type x-ray microtomography system using synchrotron or laboratory-based x-ray source
ActiveUS7400704B1Large numerical apertureLow efficiencyPatient positioning for diagnosticsRadiation beam directing meansX-rayMagnification
A projection-based x-ray imaging system combines projection magnification and optical magnification in order to ease constraints on source spot size, while improving imaging system footprint and efficiency. The system enables tomographic imaging of the sample especially in a proximity mode where the same is held in close proximity to the scintillator. In this case, a sample holder is provided that can rotate the sample. Further, a z-axis motion stage is also provided that is used to control distance between the sample and the scintillator.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
Method and apparatus for determining a property of a fluid which flows through a biological tubular structure with variable numerical aperture
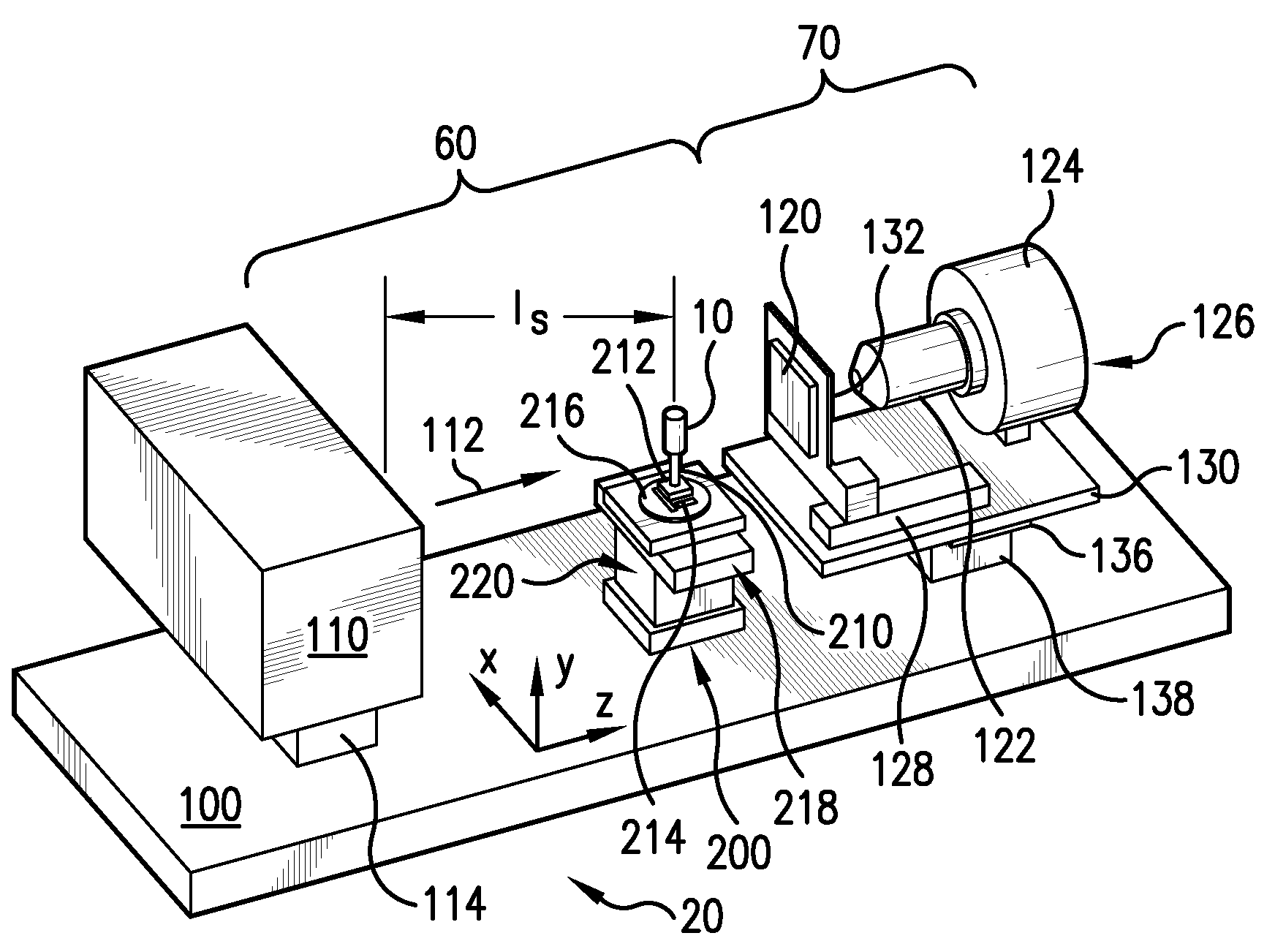
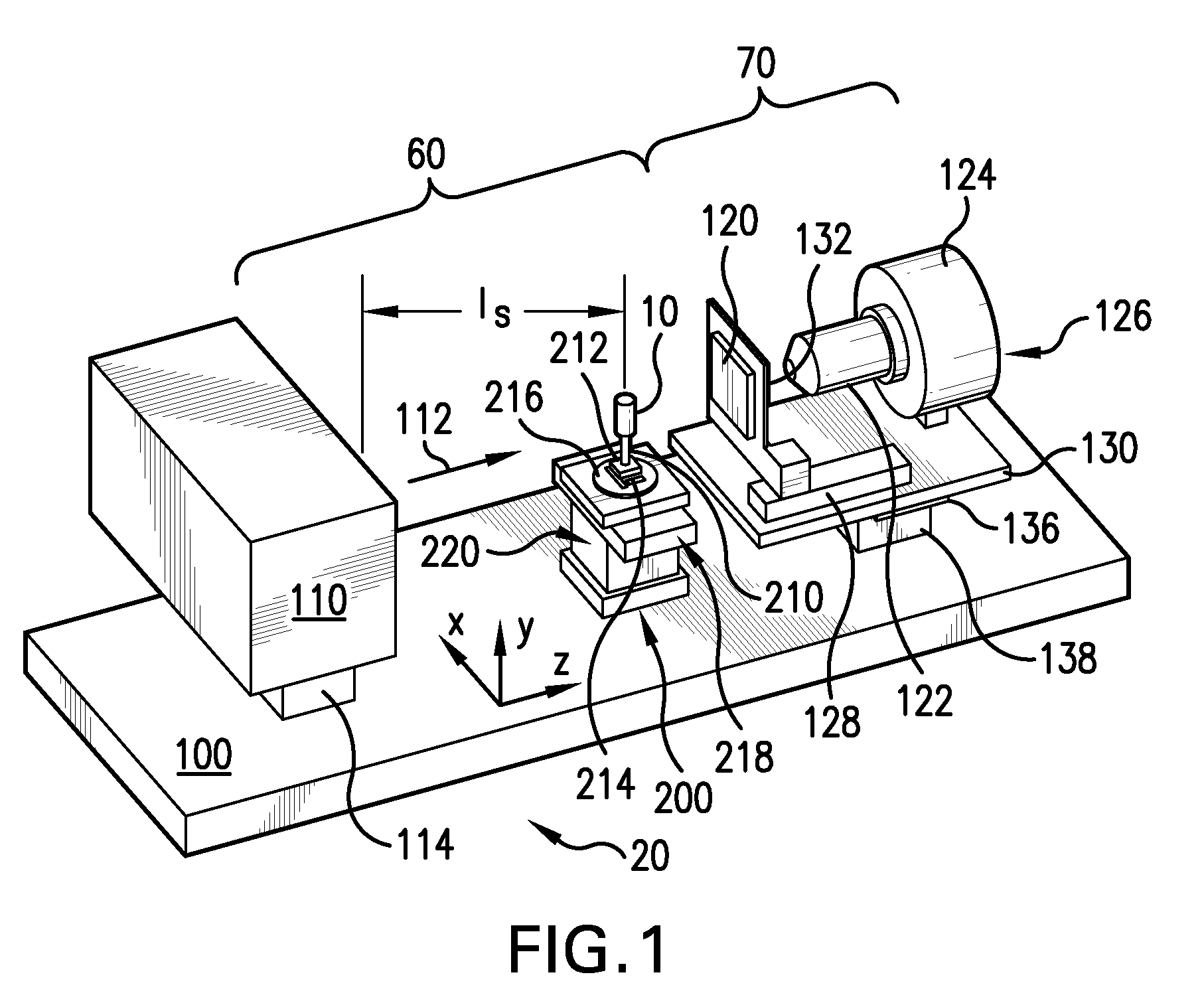
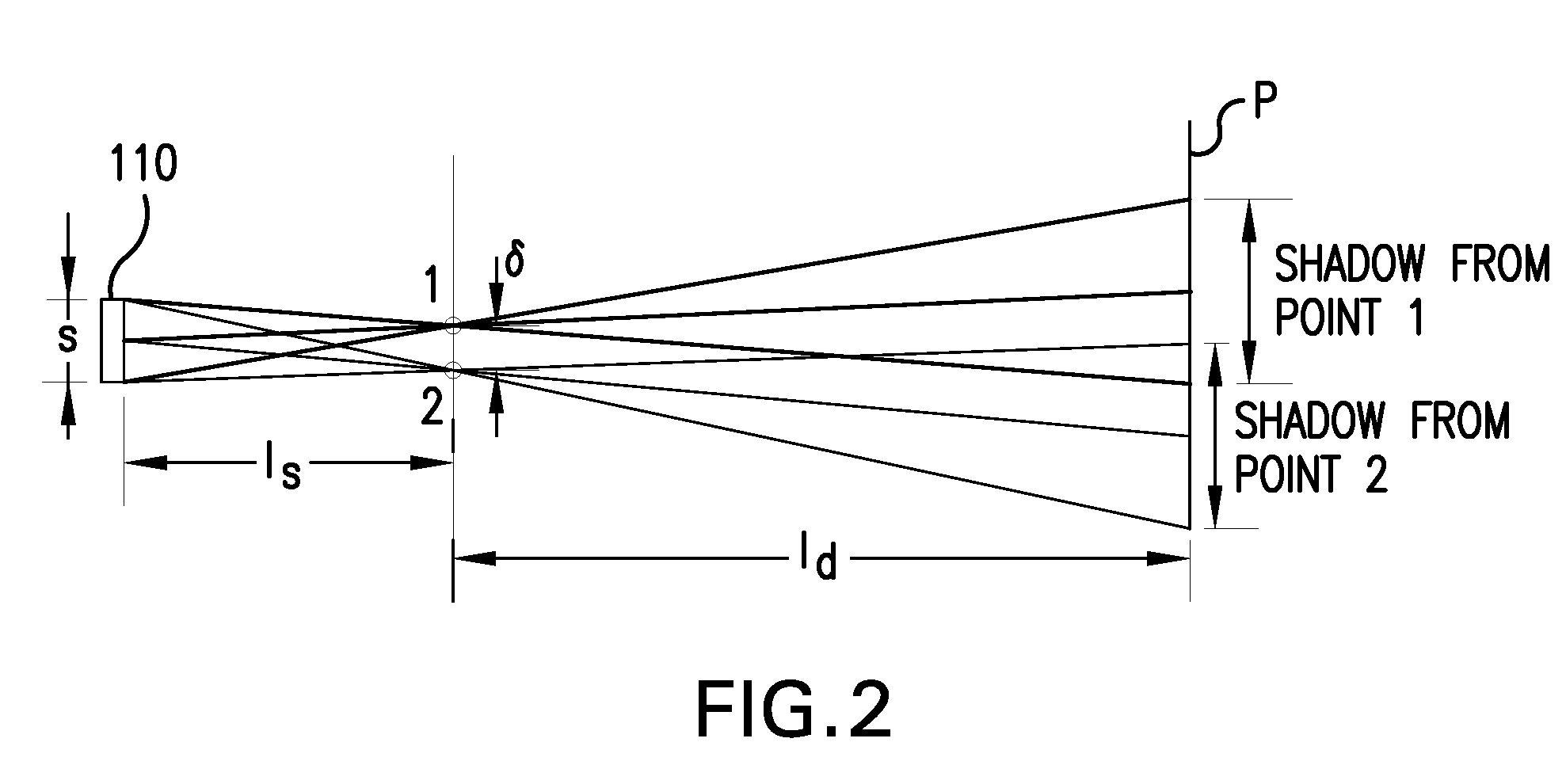
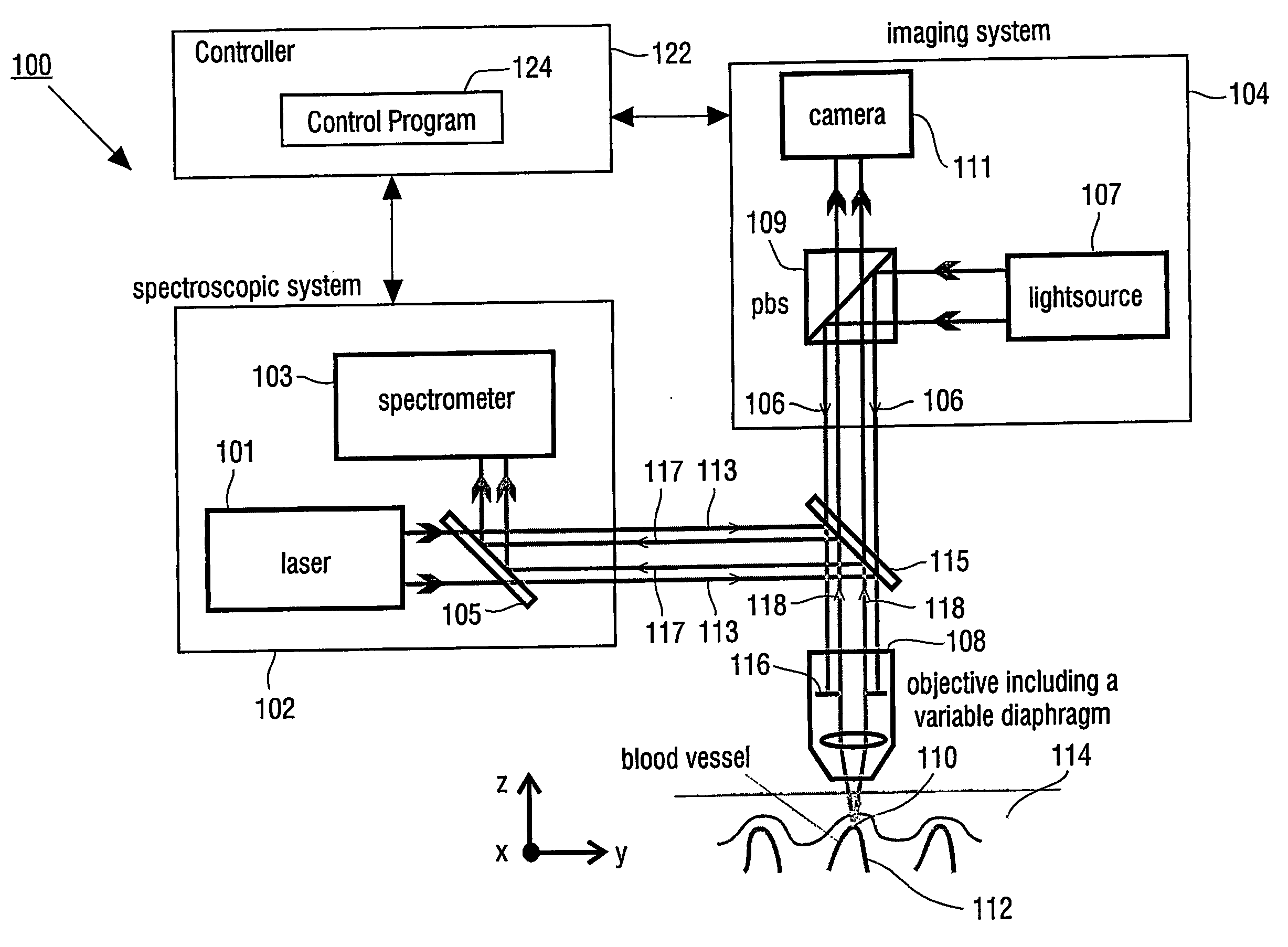
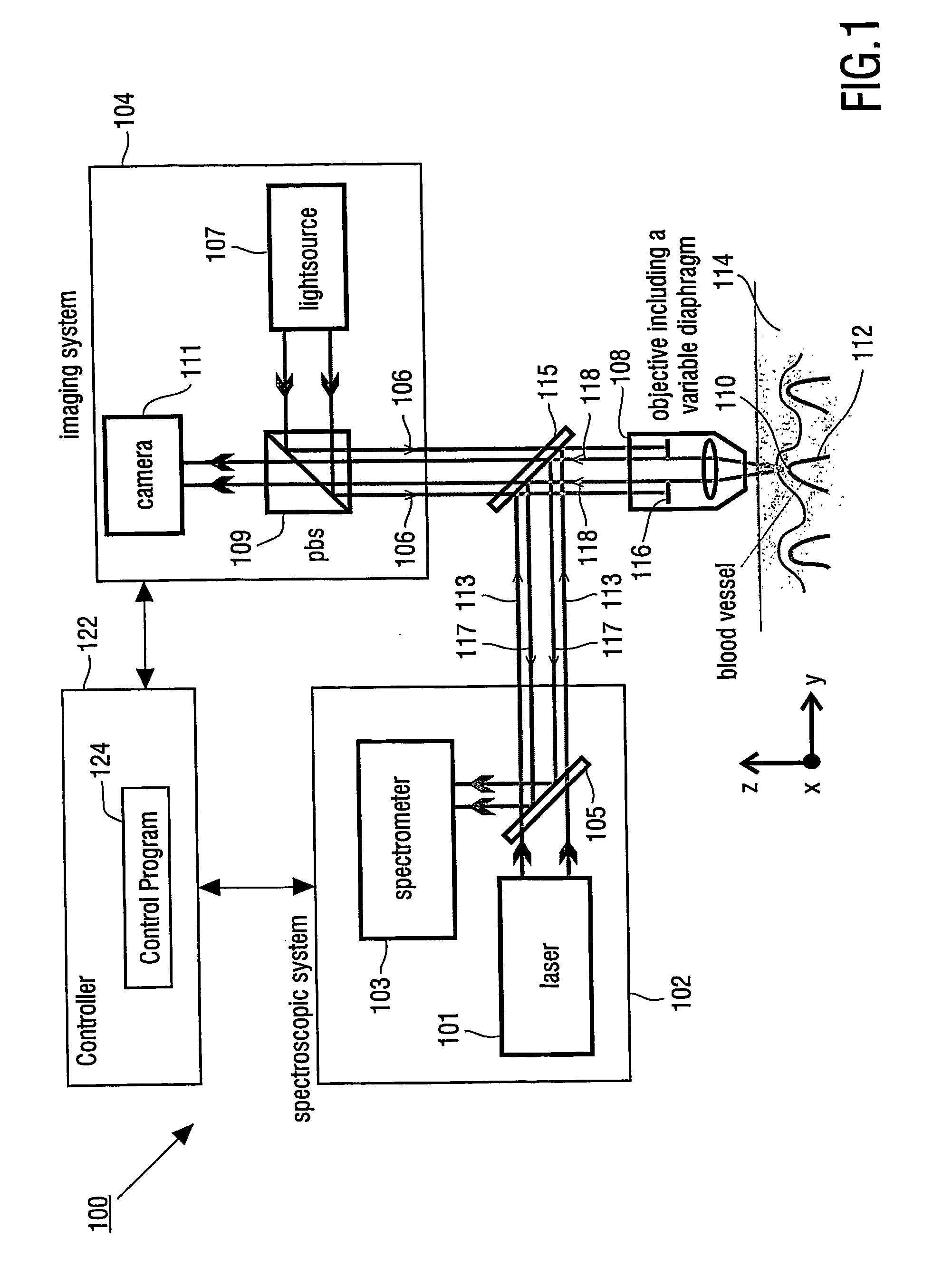
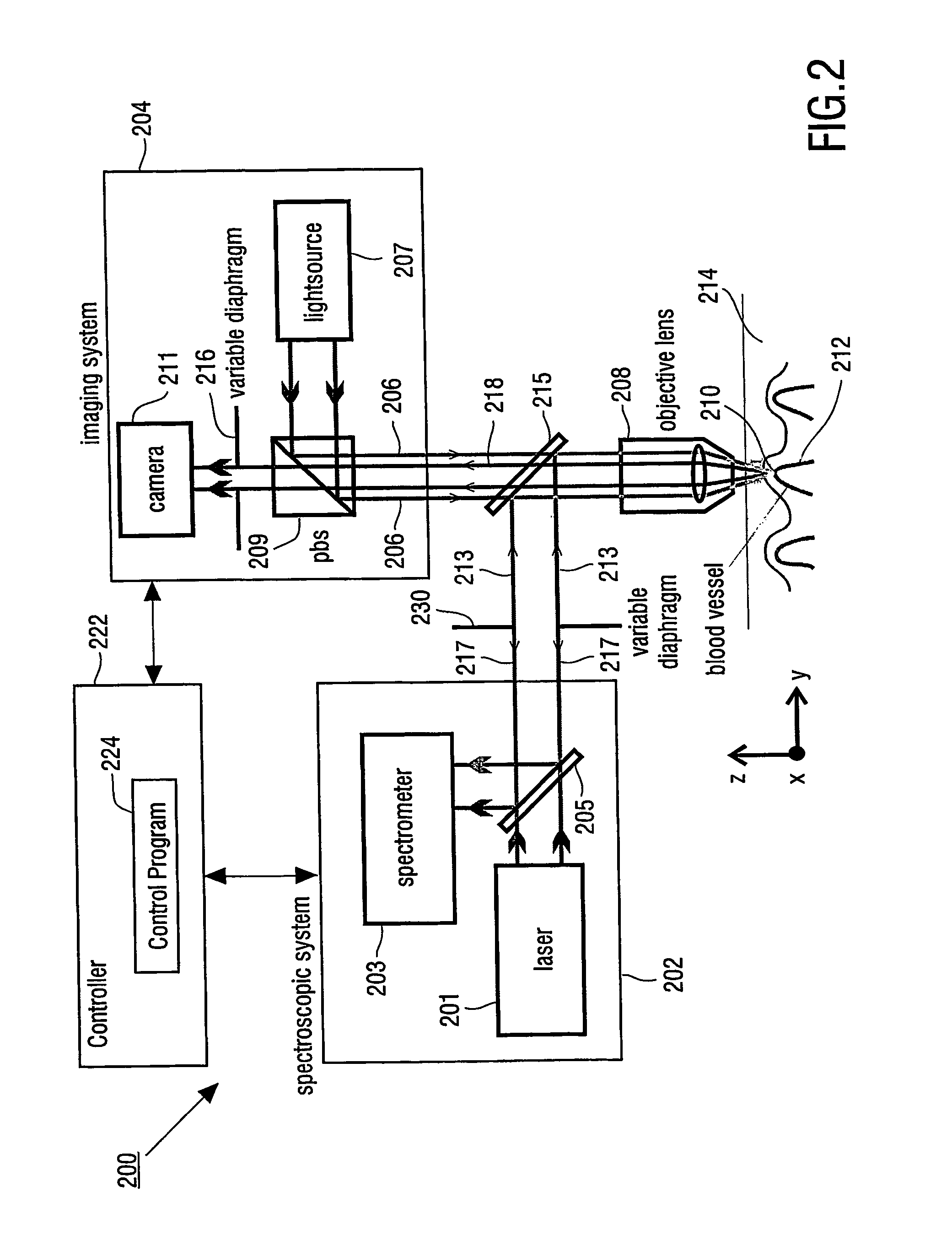
InactiveUS20060181791A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioSmall detection volumeDiagnostics using lightMirrorsBlood flowIn vivo
The present invention provides for an apparatus and a method for determining a property of a fluid which flows through a biological tubular structure, such as blood flowing through a capillary vessel (112) under the skin (114). This enables in vivo non-invasive blood analysis. An objective (108) having a variable numerical aperture (116) is used to enable automatic detection of a blood vessel (112) and to provide a high signal to noise ratio of the return radiation for the purposes of the spectroscopic analysis and to provide a small detection volume that fits completely within the target region.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
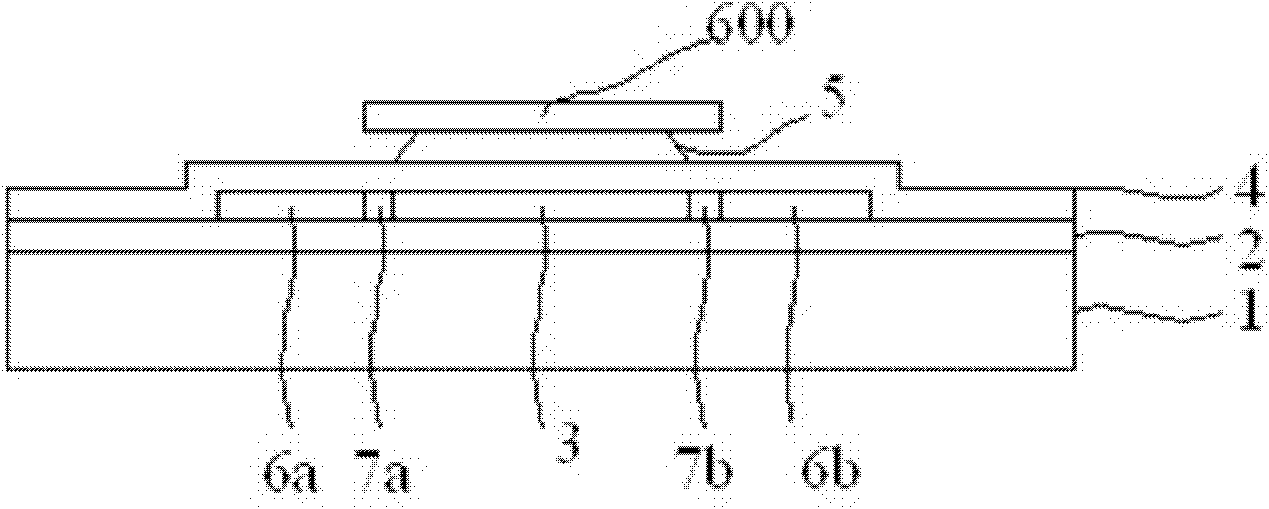
Exposure apparatus
InactiveUS7221431B2Poor resolutionAccurate exposureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusRefractive indexReference designator
An exposure apparatus includes a projection optical system for projecting a pattern on a reticle onto an object to be exposed, a reference mark that serves as a reference for an alignment between the reticle and the object, a first fluid that has a refractive index of 1 or greater, and fills a space between at least part of the projection optical system and the object and a space between at least part of the projection optical system and the reference mark, and an alignment mechanism for aligning the object by using the projection optical system and the first fluid.
Owner:CANON KK
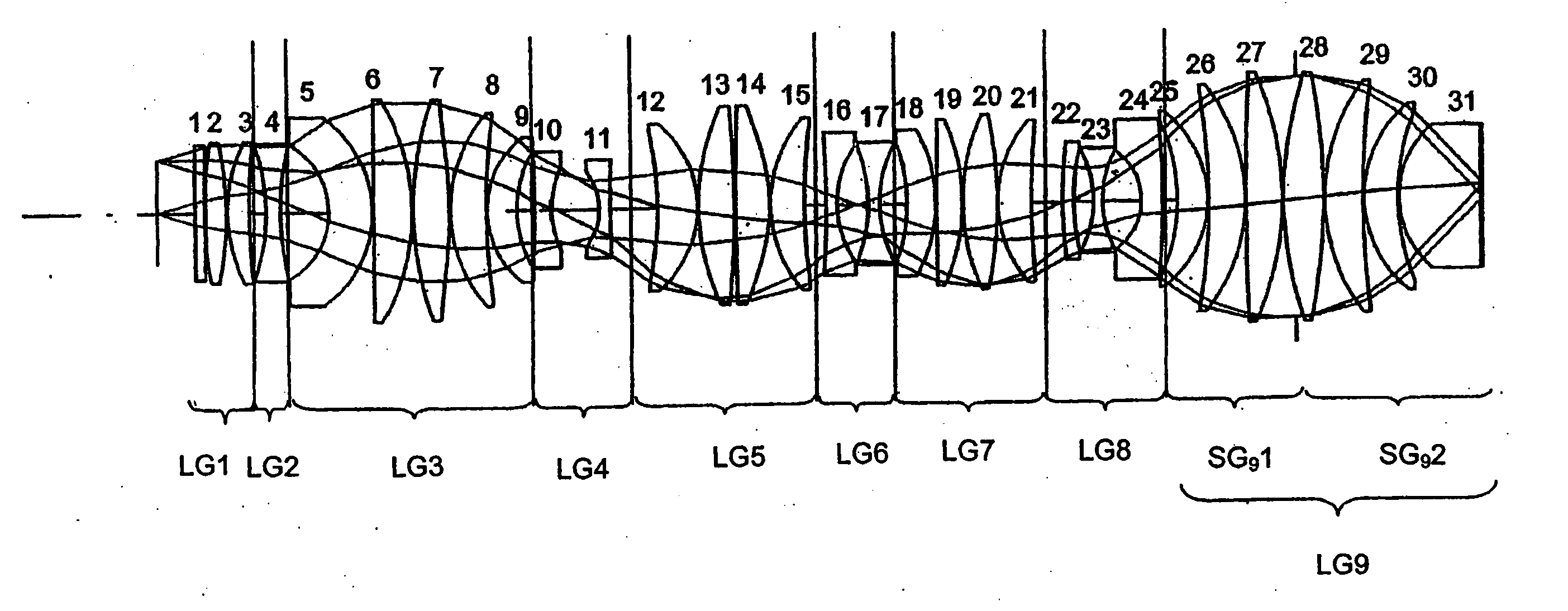
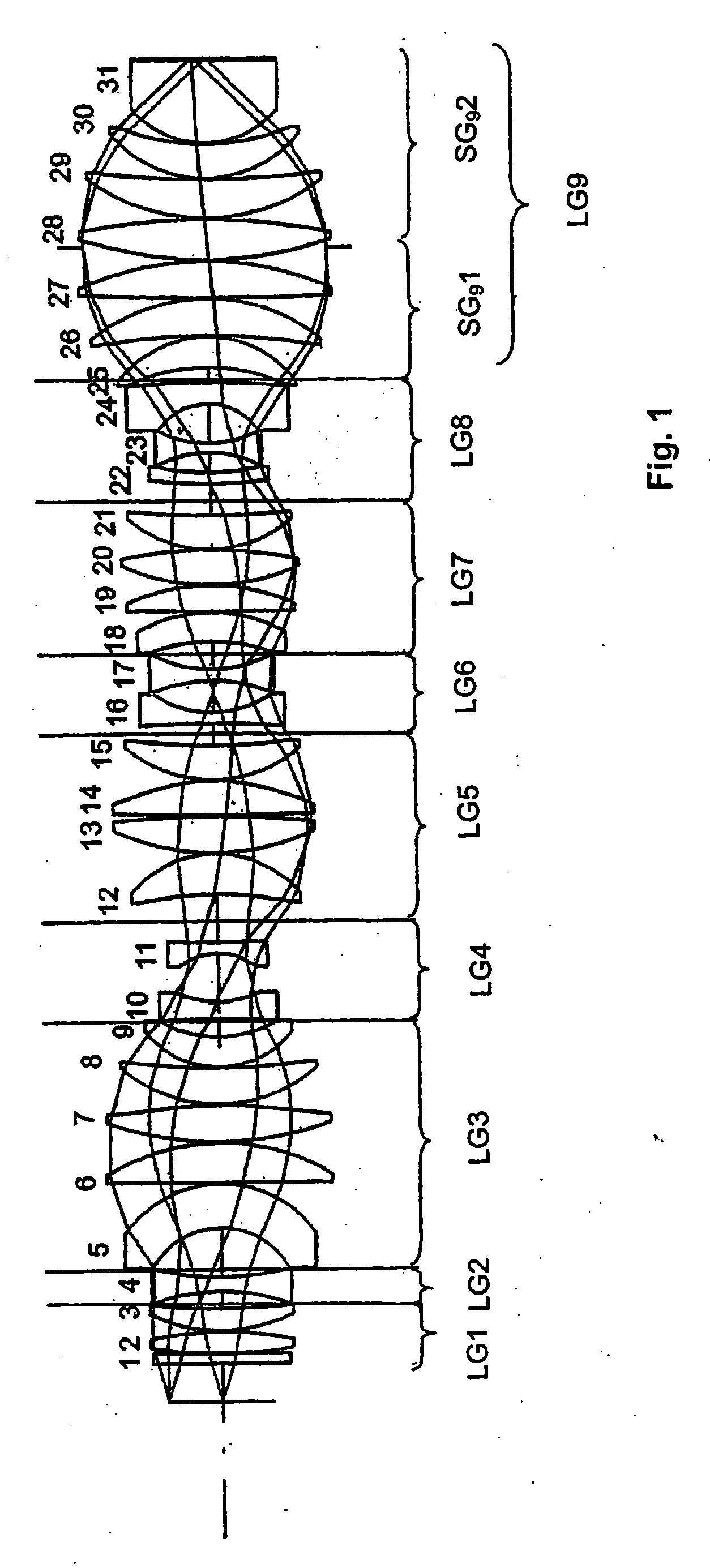
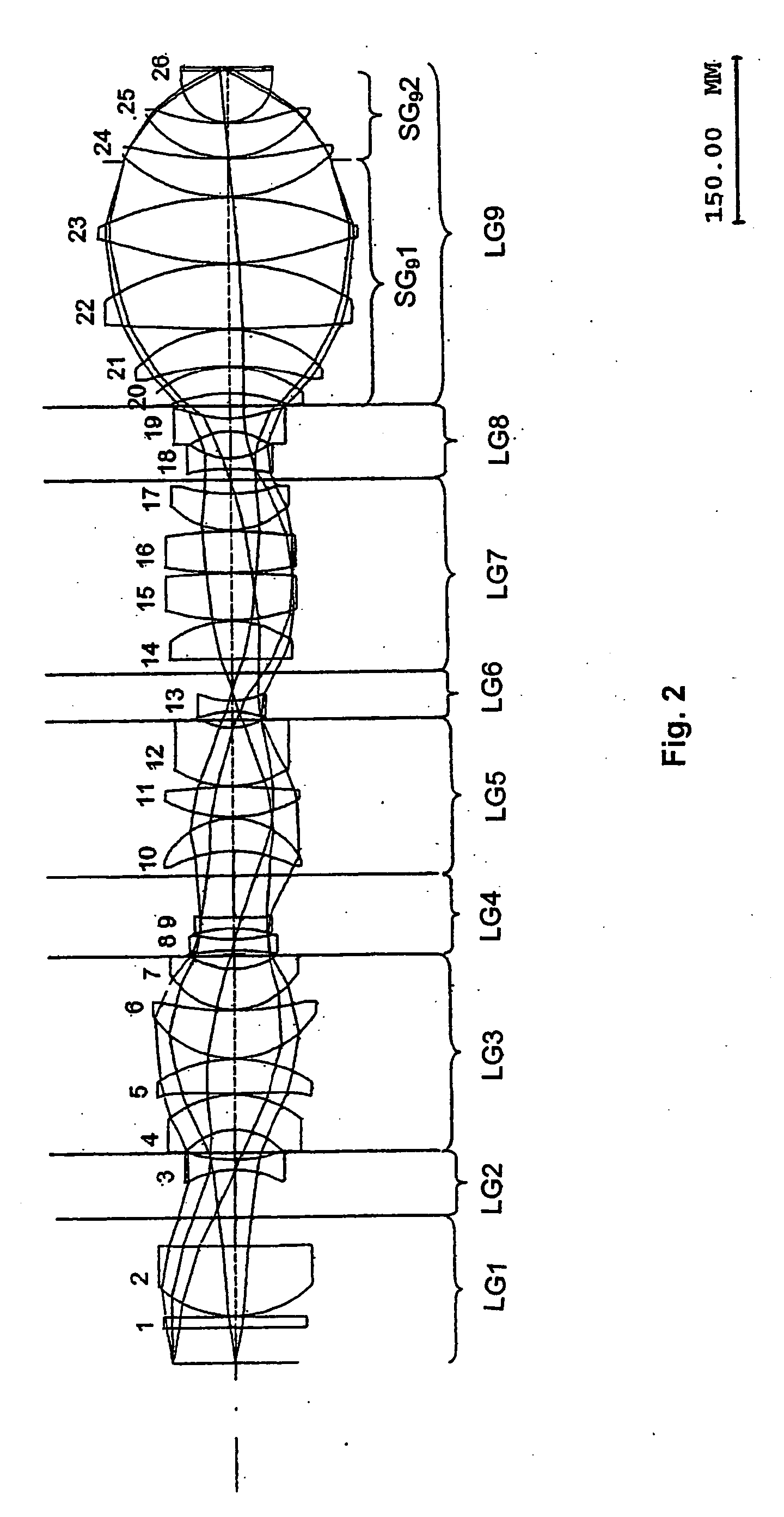
Catadioptric projection systems
InactiveUSRE39296E1Large numerical apertureFully irradiatedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicroscopesPhysicsProjection system
Catadioptric projection systems are disclosed for projecting an illuminated region of a reticle onto a corresponding region on a substrate. The systems are preferably used with ultraviolet light sources (e.g., 193 nm). The systems comprise a first imaging system, a concave mirror, and a second imaging system. The first imaging system comprises a single-pass lens group and a double-pass lens group. The single-pass lens group comprises a first negative subgroup, a positive subgroup, and a second negative subgroup. Light from the illuminated region of the reticle passes through the single-pass lens group and the double-pass lens group, and reflects from the concave mirror to pass back through the double-pass lens group to form an intermediate image of the illuminated region of the reticle. The light is then directed to the second imaging system that re-images the illuminated region of the reticle on the substrate. Alternatively, light from the single-pass lens group is reflected by a turning mirror to the double-pass lens group, wherein the light returning through the double-pass lens group continues directly to the second imaging system.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Projection optical system and method
ActiveUS20060056064A1Simple designSmall sizePhotomechanical apparatusLensIntermediate imageLight beam
A refractive projection optical system for imaging a first object into a region of a second object comprises a plurality of lenses disposed along an imaging beam path of the projection optical system; wherein the projection optical system is configured to have a numerical aperture on a side of the second object of greater than 1 wherein the projection optical system is configured to generate an intermediate image of the first object and to image the intermediate image into the region of the second object, wherein the intermediate image is formed in between, the first and second objects.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Mask for EUV lithography, EUV lithography system and method for optimising the imaging of a mask
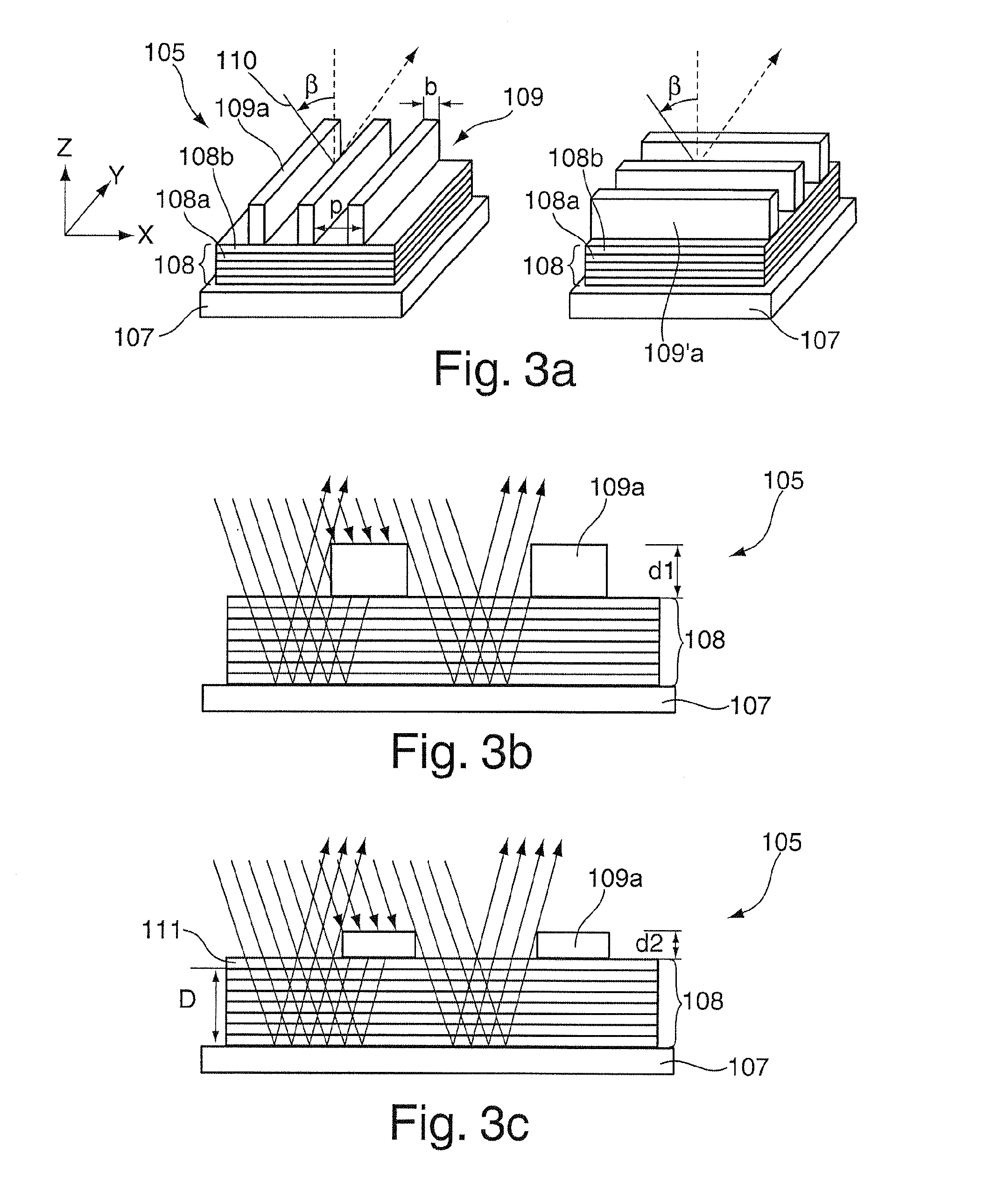
ActiveUS20130100428A1Optimise optical designImprove image qualityNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhysicsCoating
A mask (105) for EUV lithography includes a substrate (107), a multi-layer coating (108) applied to the substrate (107) and a mask structure (109) which is applied to the multi-layer coating (108) and which has an absorber material, the mask structure (109) having a maximum thickness of less than 100 nm, preferably not exceeding a maximum thickness of 30 nm, particularly preferably 20 nm, in particular 10 nm. Also disclosed is an EUV lithography system having such a mask (105) and a method for optimising the imaging of such a mask (105).
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Optical fiber coupling part
ActiveUS7346237B2Send efficientlyLarge numerical apertureCladded optical fibreCoupling light guidesCoupling lossSemiconductor
An optical fiber coupling part capable of reducing coupling loss while maintaining a large operating distance, and having a good module assembling property. AT least one GRIN lens having numerical aperture NA that is larger than numerical aperture NAs of a light-emitting source (such as a semiconductor laser) is fusion-spliced with one end of the optical fiber. All lights emitted from the light-emitting source can enter the GRIN lens, and the loss of the light can thereby be reduced. In addition, a second GRIN lens having numerical aperture NA2 is fusion-spliced with one end of the optical fiber having numerical aperture NAf, and further a first GRIN lens having numerical aperture NA1, which is larger than numerical aperture NA2, is fusion-spliced with the other end of the second GRIN lens. Thereby, the light emitted from the light-emitting source can efficiently enter the optical fiber, and loss of the light can thereby be reduced. In this case, the formula expressed by NAf≦NA2<NAs≦NA1 is desirable.
Owner:TOYO SEIKAN GRP HLDG LTD
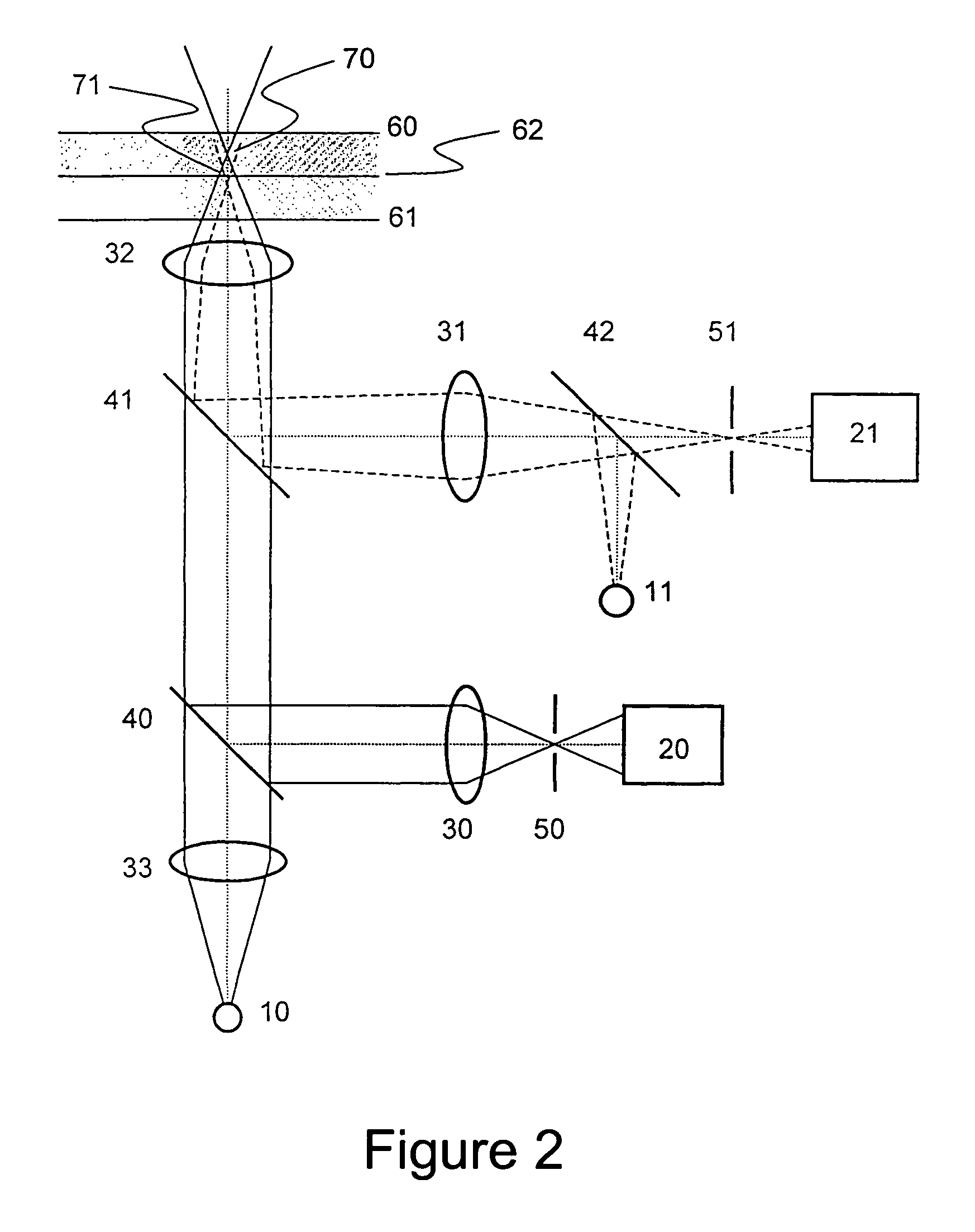
Optical fiber delivery and collection system for biological applications such as multiphoton microscopy, spectroscopy, and endoscopy
InactiveUS20050043636A1Improve spatial resolutionEfficient disseminationCladded optical fibreDiagnostics using lightCollection systemSpectroscopy
The present invention is directed to a method of applying radiation through an optical fiber for detecting disease within a plant or animal or other penetrable tissue, or imaging a particular tissue of a plant or animal. In addition, fluorescence and nonlinear scattering signals can be detected and localized within a subject by such application of radiation through an optical fiber. The radiation is effective to promote simultaneous multiphoton excitation. The optical fibers are used alone to examine internal regions of tissue, in conjunction with an optical biopsy needle to evaluate sub-surface tissue, or with an endoscope to evaluate tissue within body cavities. The present invention also relates to a device for coupling in radiation from an ultrashort mode-locked laser into the beam path of a microscope.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Manufacturing method of thin film transistor and transistor manufactured by method
ActiveCN101840865AElectrode area is smallLarge numerical apertureTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsActive layer
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of a thin film transistor and a transistor manufactured by the method, wherein the method is characterized by comprising the following steps: sequentially forming a surface covering layer, a polycrystalline silicon island active layer, a grid insulating layer, a grid electrode conducting layer and an auxiliary layer on a baseplate, photoetching the auxiliary layer to form an LDD forming layer, and forming a lightly doped drain electrode region, a heavily doped source electrode, a heavily doped drain electrode and a channel on the polycrystalline silicon island active layer by utilizing the action of the LDD forming layer and through only once doped ion implantation. The method of the invention only needs once ion implantation, simplifies the manufacturing working procedures and lowers the manufacturing cost; the thin film transistor which is manufactured by adopting the method and provided with a lightly doped drain electrode has the advantages of small electrode area and large numerical aperture.
Owner:SHENZHEN DANBANG INVESTMENT GROUP
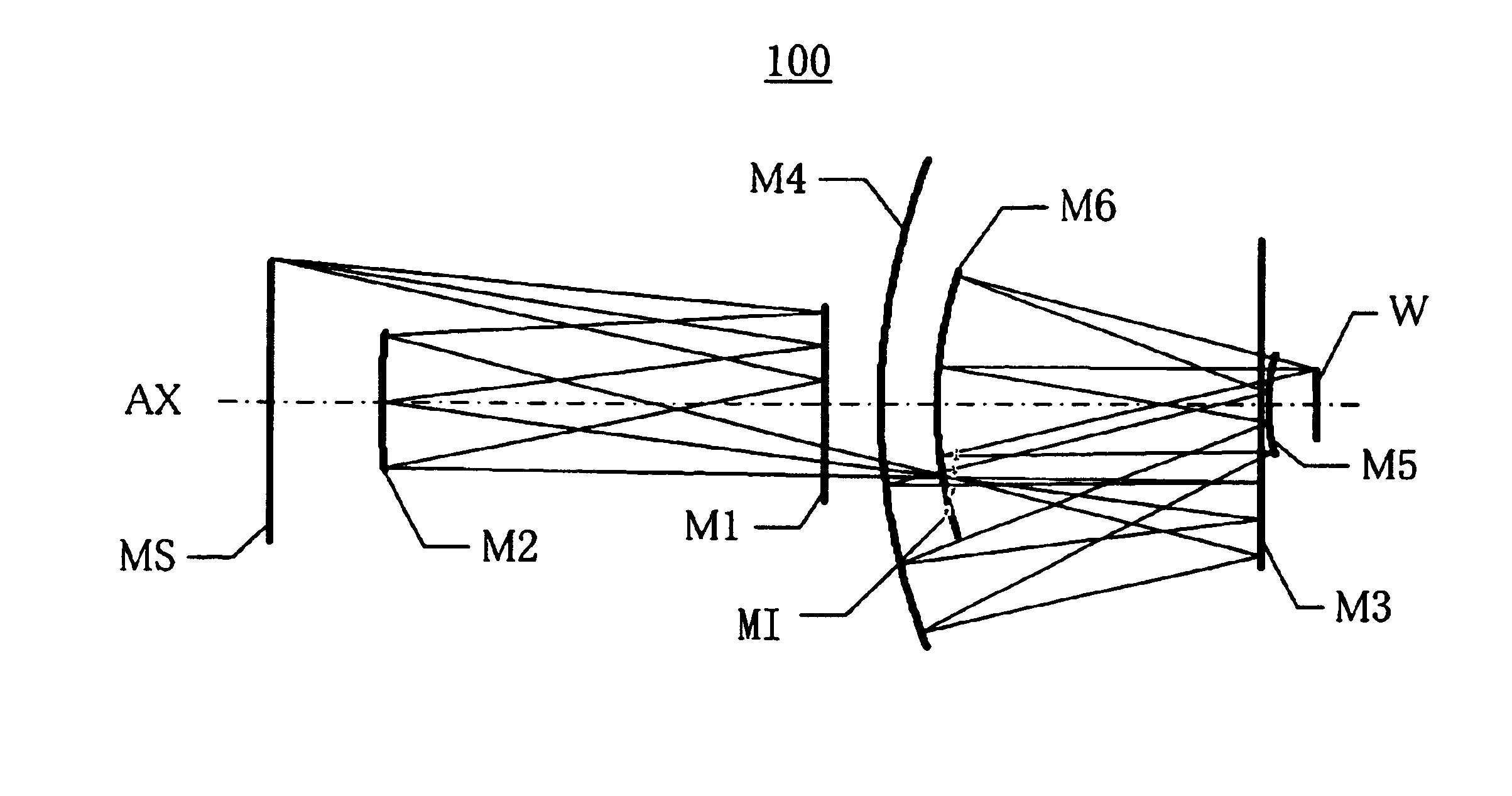
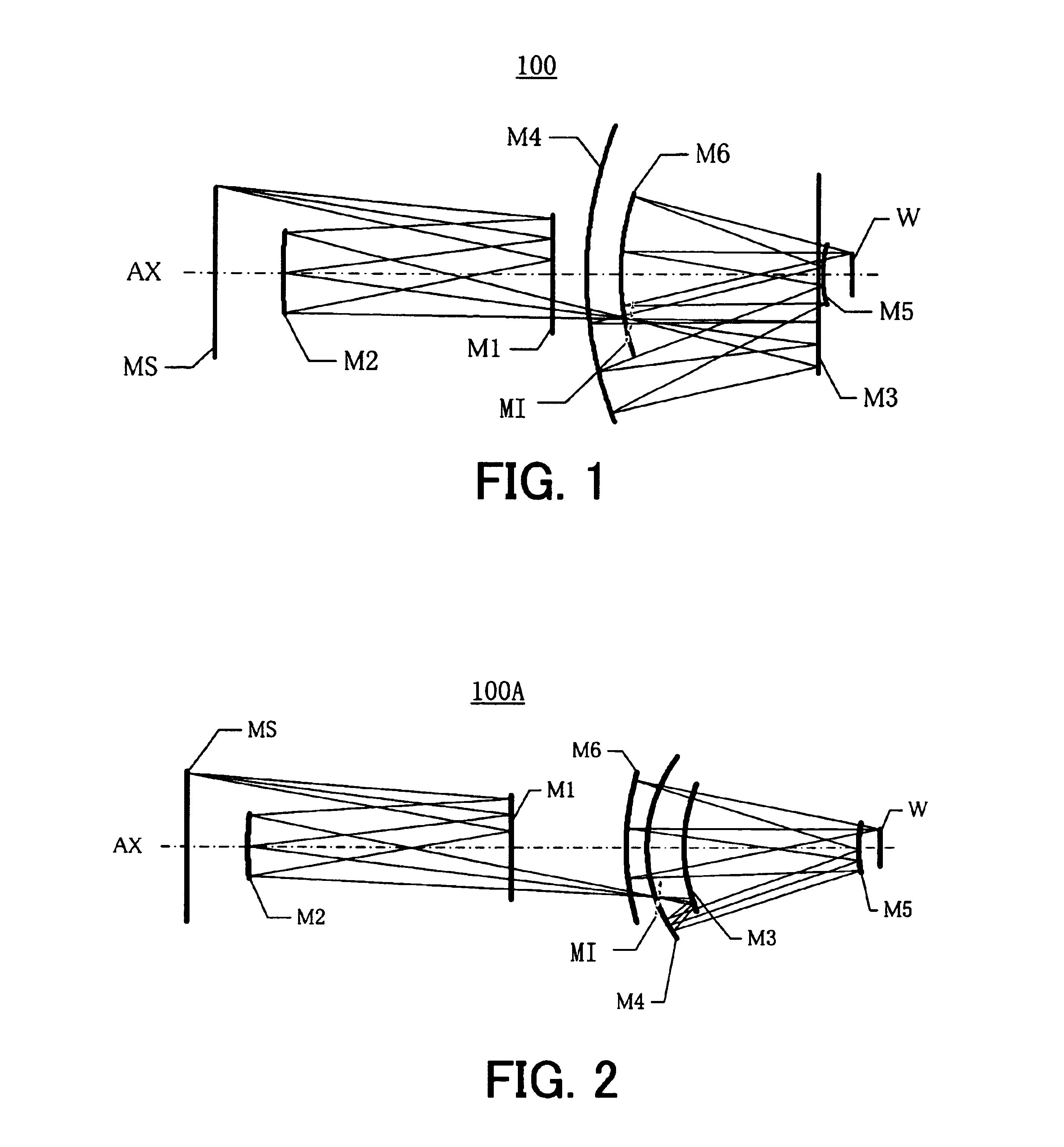
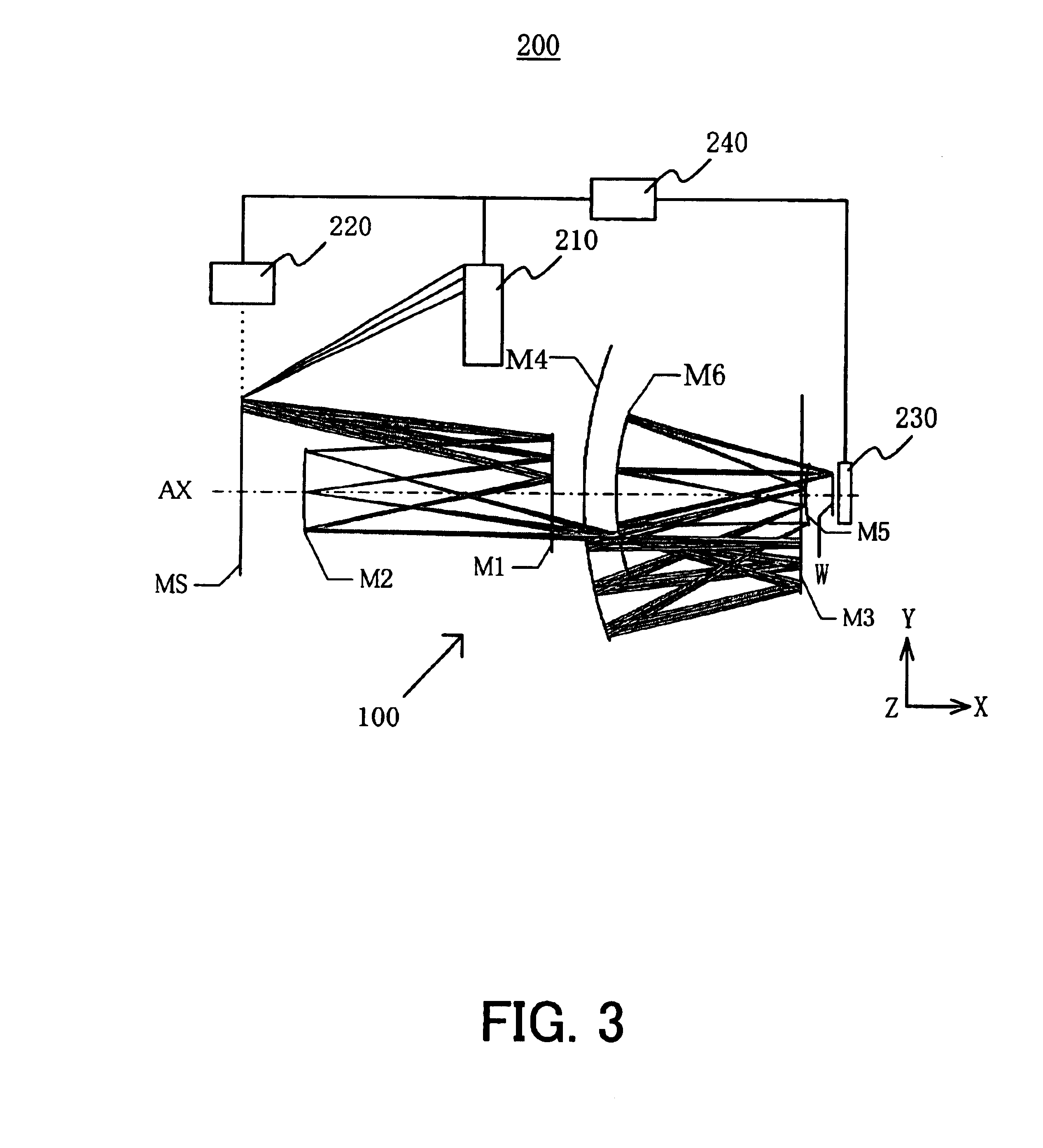
Catoptric projection optical system and exposure apparatus
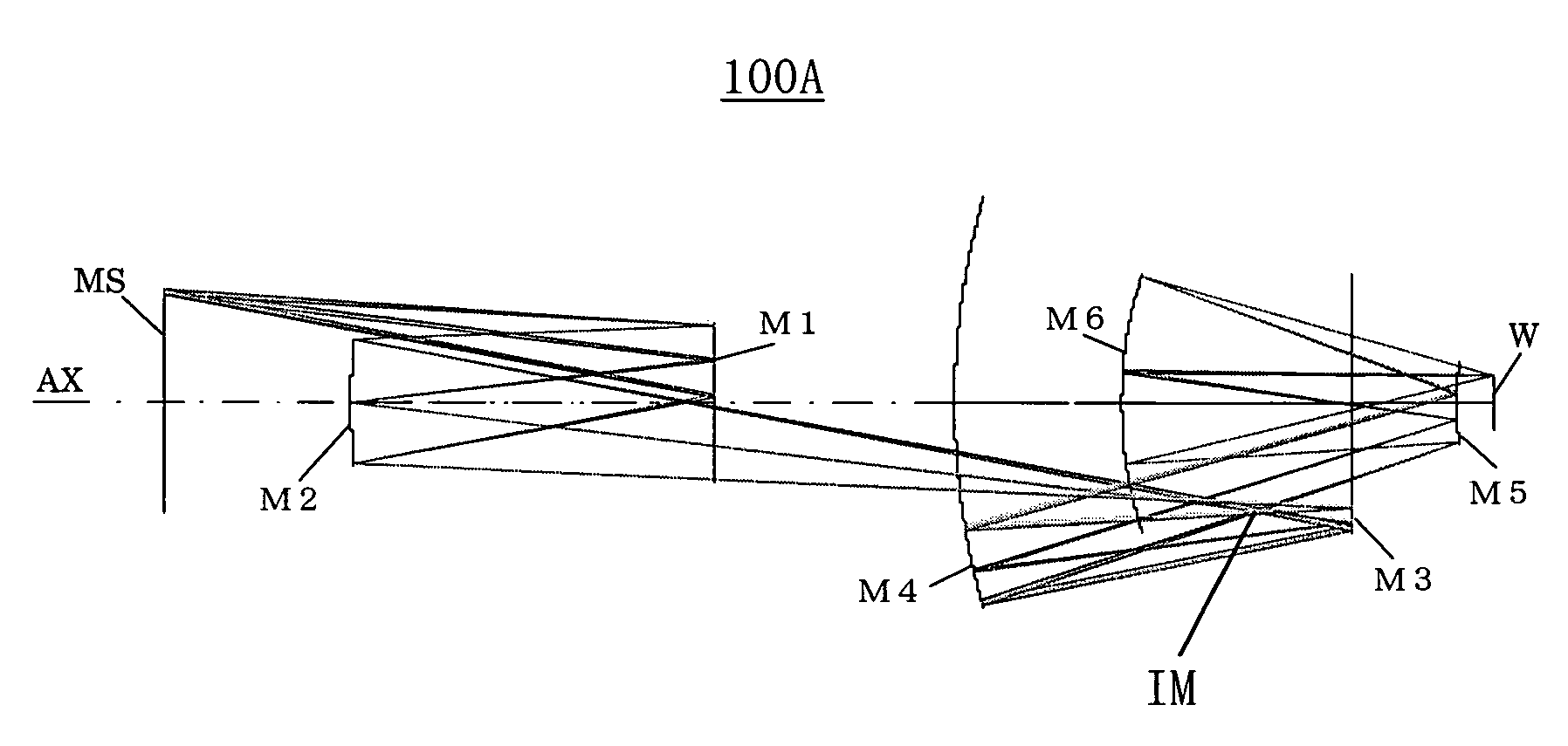
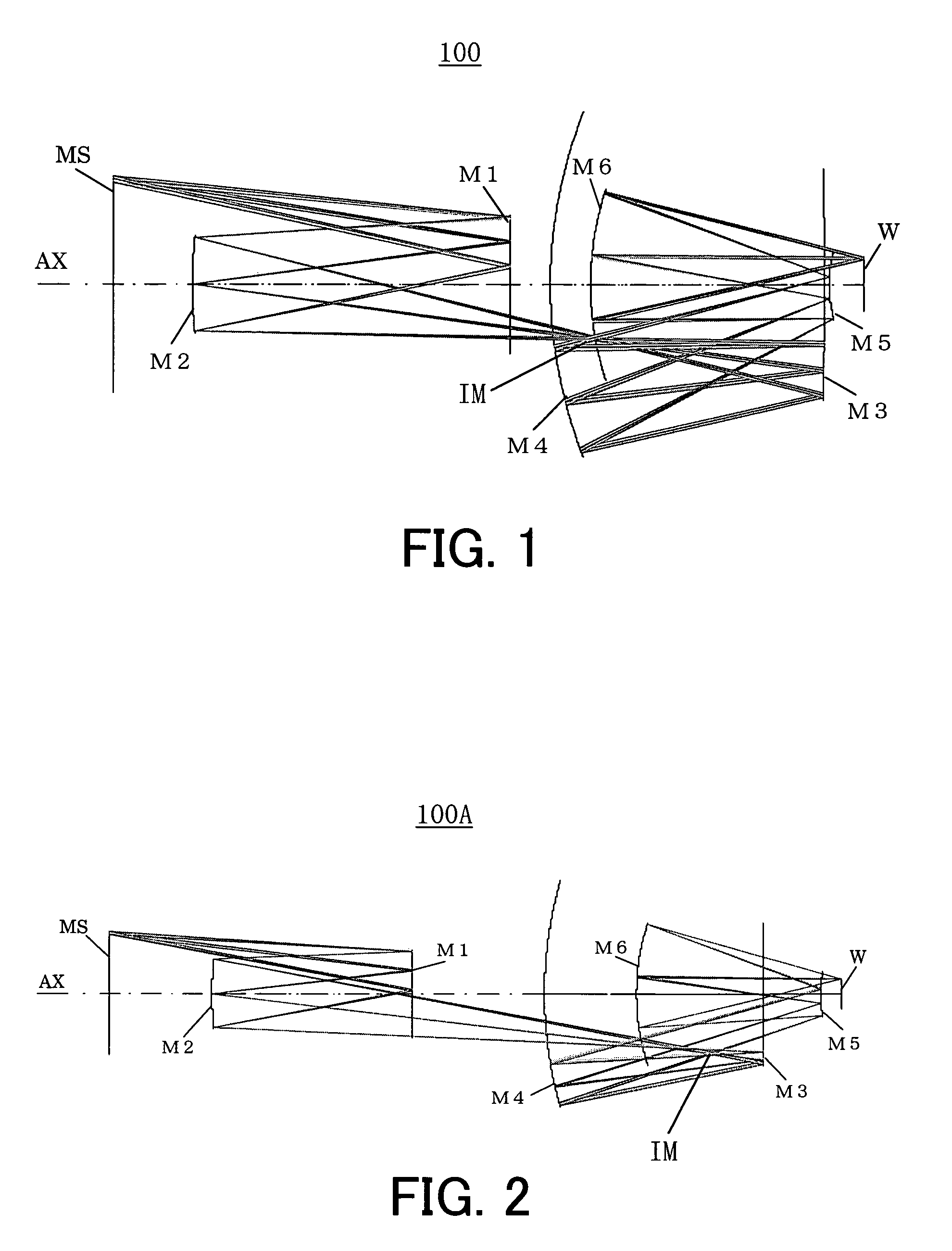
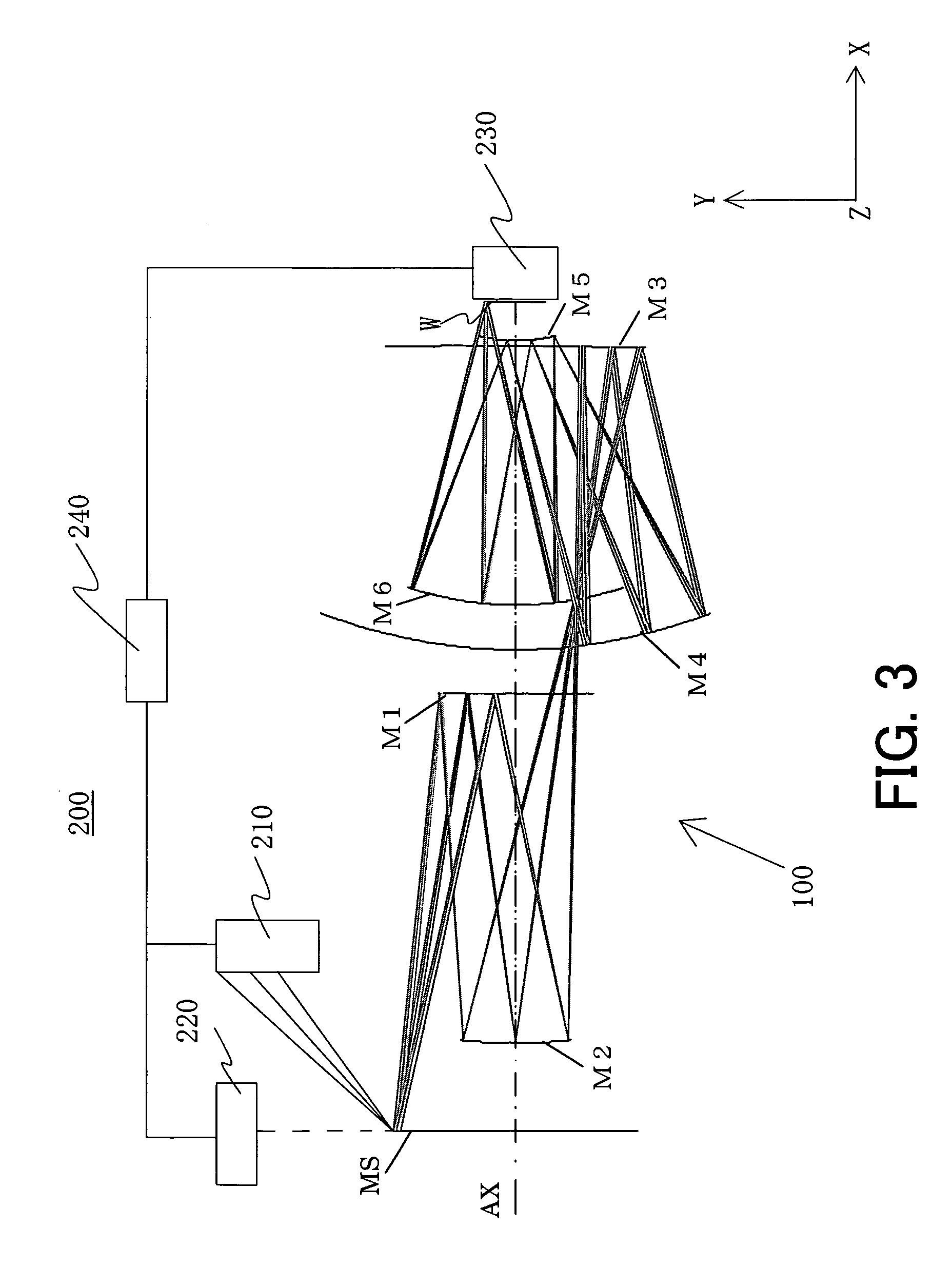
InactiveUS6922291B2Large numerical apertureImprove imaging effectMirrorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIntermediate imageExit pupil
A catoptric projection optical system for projecting a reduced size of a pattern on an object surface onto an image surface and for serving as an imaging system that forms an intermediate image between the object surface and image surface, includes six or more mirrors, wherein a position of an exit pupil with respect to the intermediate image is located between the object surface and image surface, and wherein the largest angle between principal rays and an optical axis for angles of view at the position of the exit pupil is sin−1NA or smaller, where NA is a numerical aperture at the side of the image surface.
Owner:CANON KK
Scanning microscopic method having high axial resolution
InactiveUS7202953B1Reliable detectionHigh resolutionSpectrum investigationScattering properties measurementsImage resolutionMicroscope
The invention relates to a method for optically detecting at least one entity which is arranged on a substrate. The at least one entity is scanned with a measuring volume using at least one radiation source and a confocal optic. During a scanning process an auxiliary focus is generated by means of at least one second radiation source and a second optic. Radiation generated by the first radiation source is collimated by a first optic and radiation generated by the second radiation source is collimated by a second optic. A retroreflection from the auxiliary focus is detected by at least one detector and is used to measuring the position of an interface and, thus, for indirectly positioning the measuring volume. The position of the auxiliary focus relative to the measuring volume is adjustable in a defined manner.
Owner:EVOTEC BIOSYST
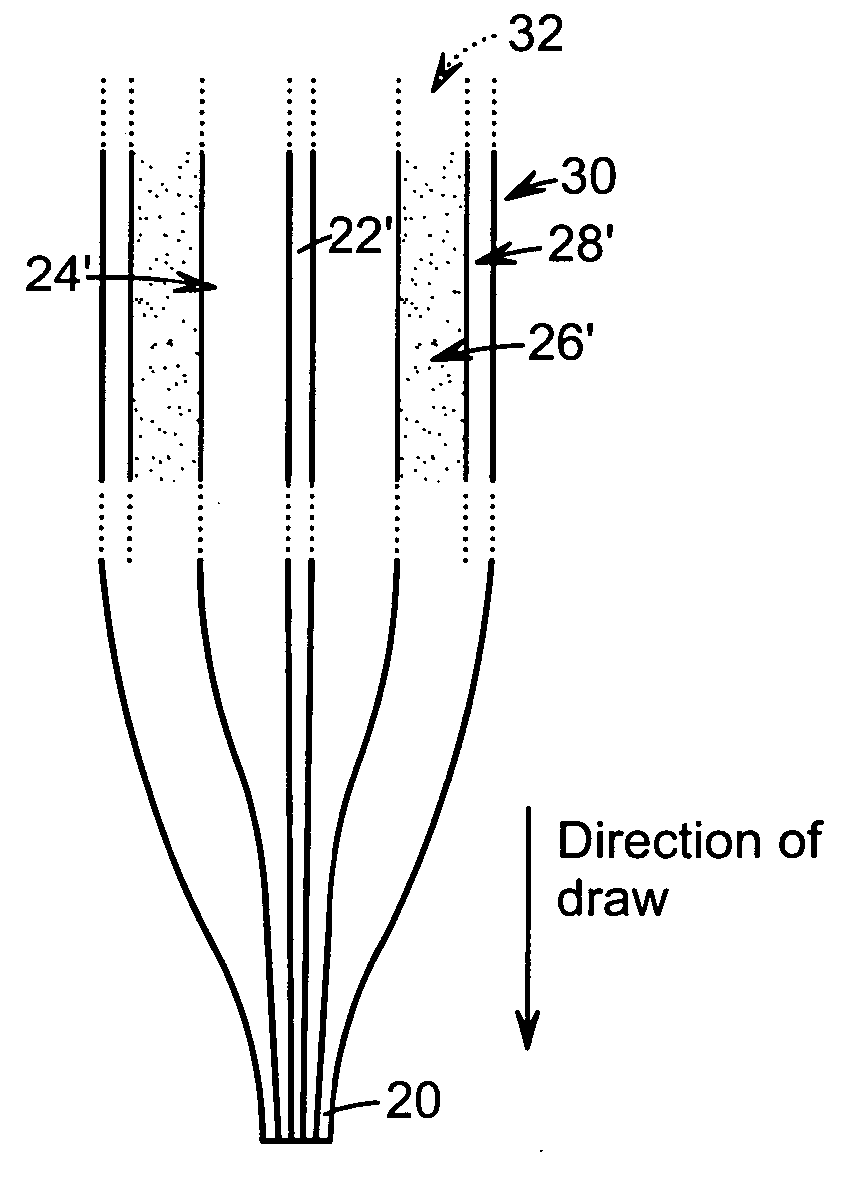
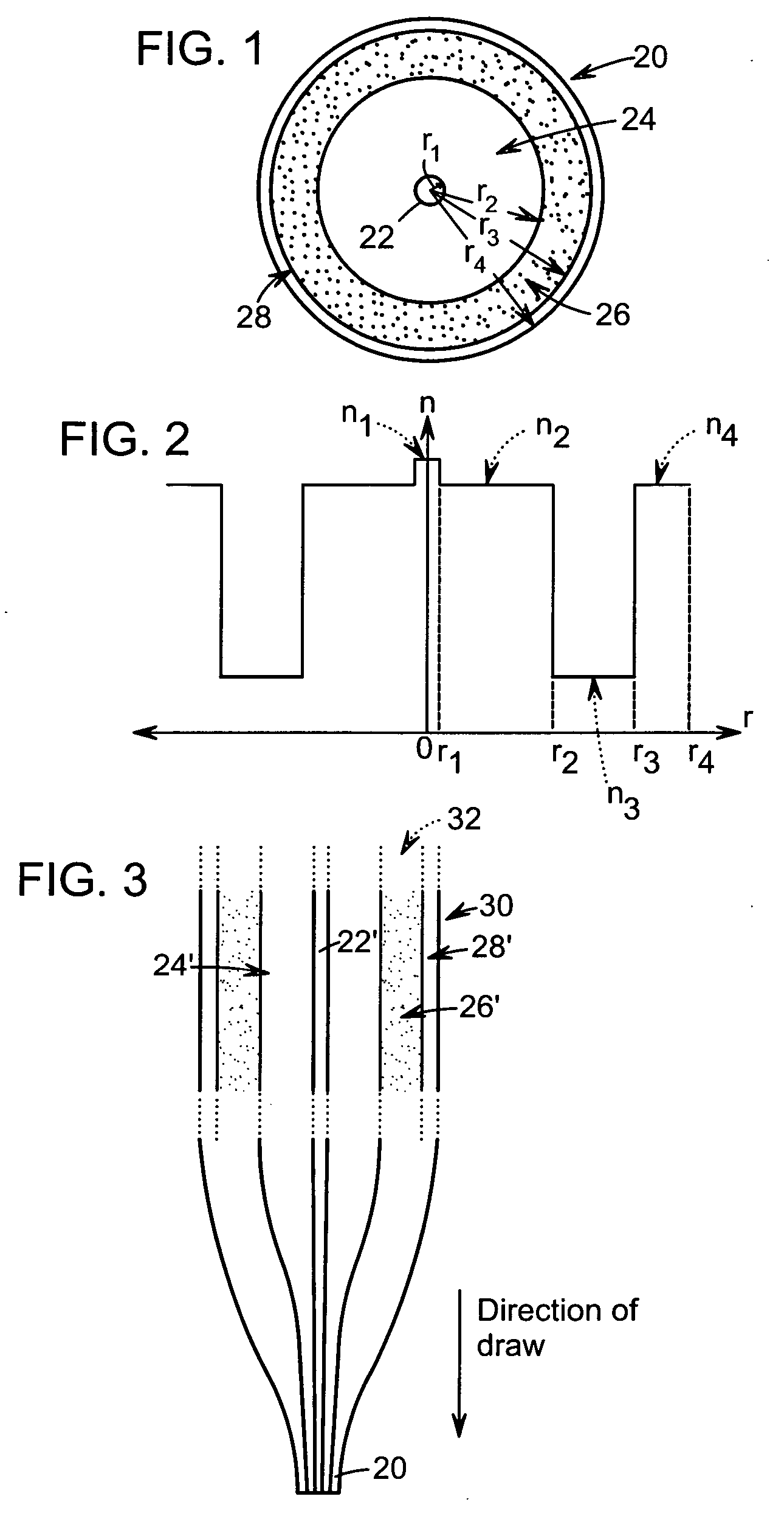
Optical fiber with micro-structured cladding
ActiveUS20060120678A1Large numerical apertureGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFiberRefractive index
An optical fiber having a length can include a core and at least one cladding disposed about the core, where the one cladding can comprise at least first volumetric regions having a first refractive index n1 and second volumetric regions having a second refractive index n2, different from n1, and the first and second volumetric regions in any cross-section taken through the fiber can be randomly intermingled with one another, where the random intermingling of the first and second volumetric regions changes with changes in the location of the cross-section along the length of the fiber.
Owner:NUFERN
Planar lens
The planar lens of the invention having a flat glass substrate, in which a refractive index distribution is formed by diffusing a refractive index-increasing component into the flat glass substrate in a substantially hemispherical form or semicylinder form, wherein the refractive index-increasing component is silver, and the flat glass substrate comprises Li as an alkali metal that is subject to an ion exchange with the silver.
Owner:NIPPON SHEET GLASS CO LTD
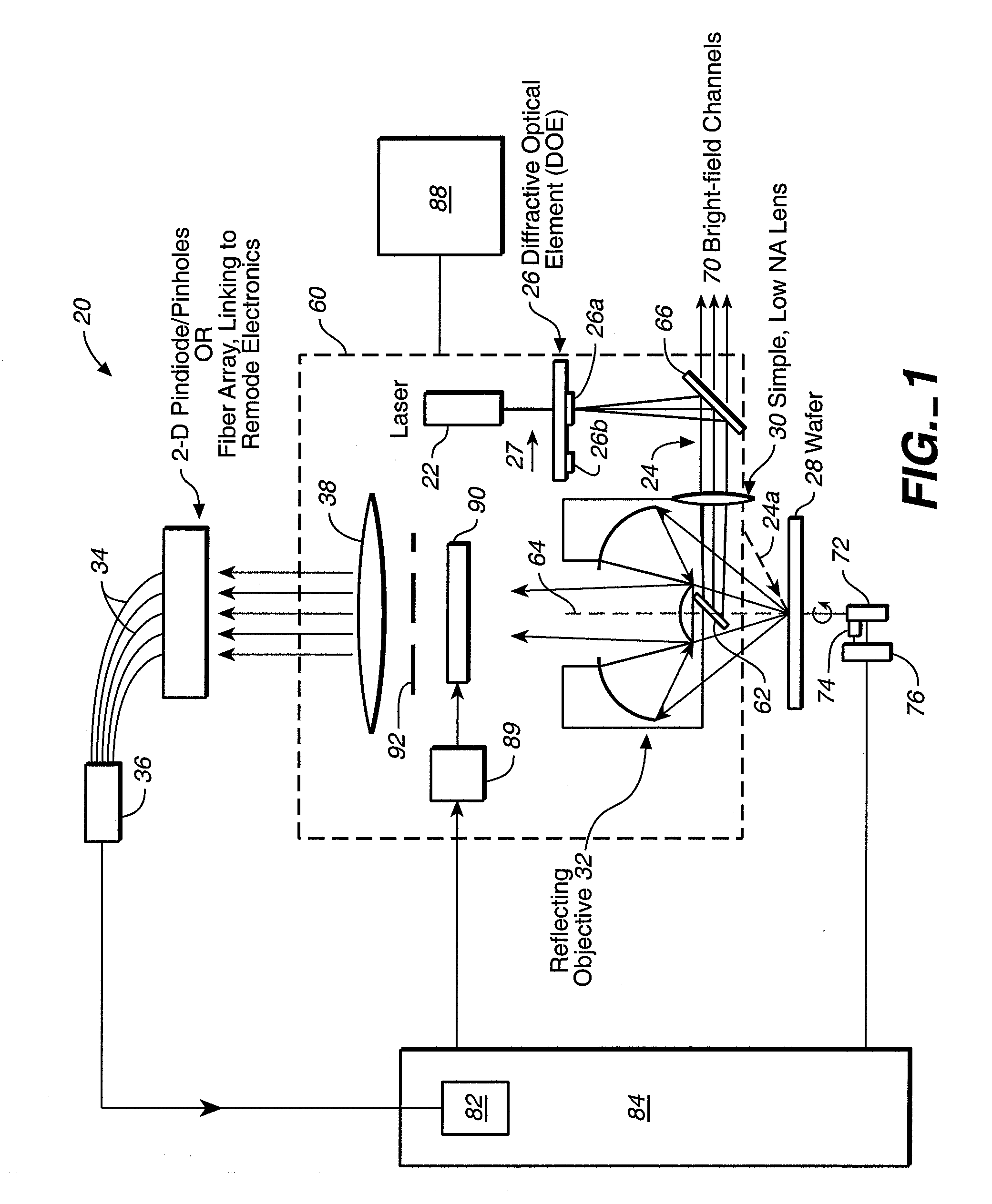
Compact optical detection system for a microfluidic device
ActiveUS20060227325A1Large dimensionLarge numerical apertureWithdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansFluorescenceWhite lead
An optical detection system for a microfluidic device and a dry-focus microfluidic device compatible with the compact optical detection system are described. The system includes an LED; means for collimating light emitted by the LED; an aspherical, fused-silica objective lens; means for directing the collimated light through the objective onto a microfluidic device; and means for detecting a fluorescent signal emitted from the microfluidic device. The working distance between the objective and the device allows light from an external LED or laser to be brought in along a diagonal path to illuminate the microfluidic device. The dry-focus microfluidic device includes multiple channels and multiple closed optical alignment marks having curved walls. At least one of the channels is positioned between at least two of the marks. The marks are illuminated for alignment and focusing purposes by light brought in on a diagonal path from an external white LED.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
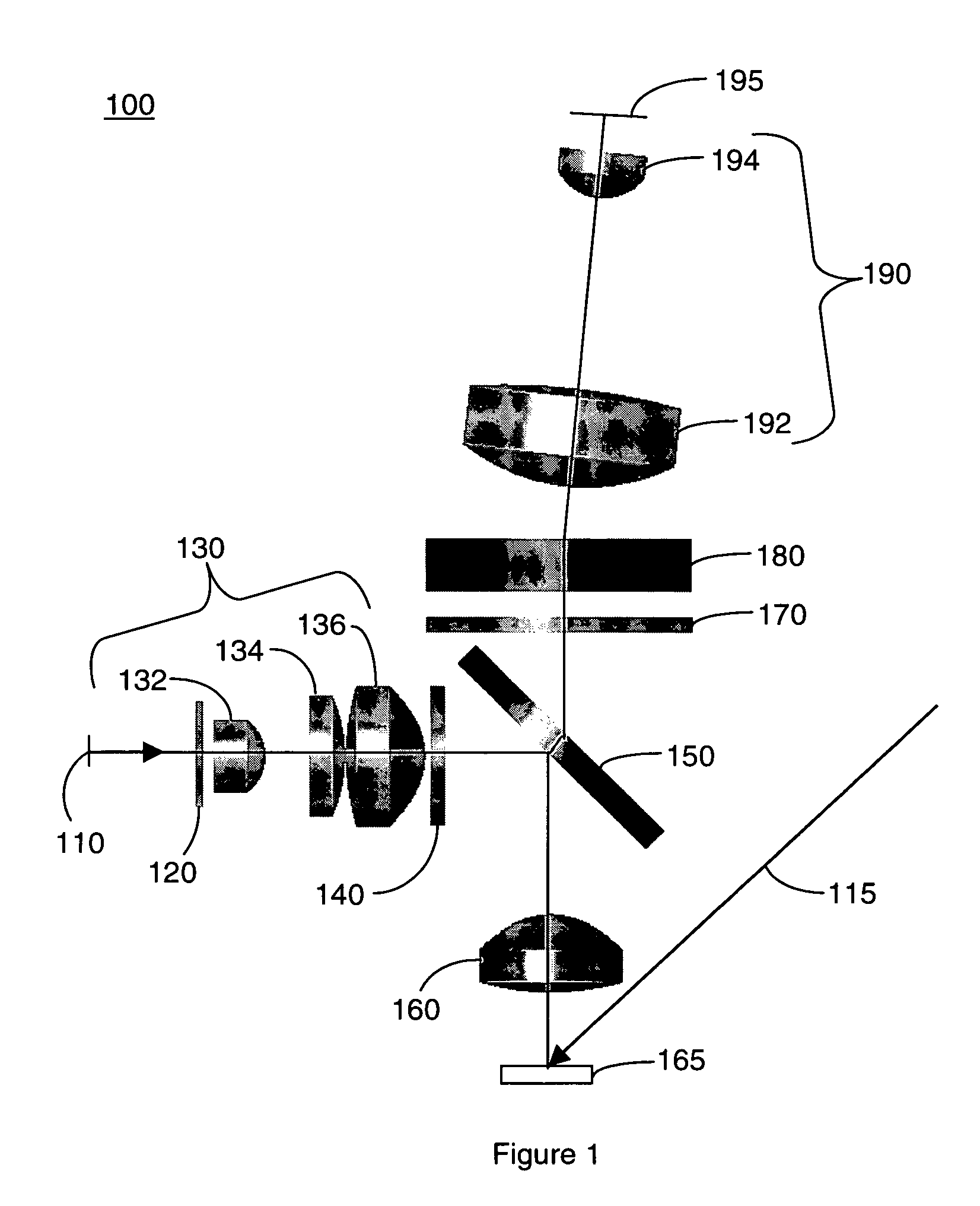
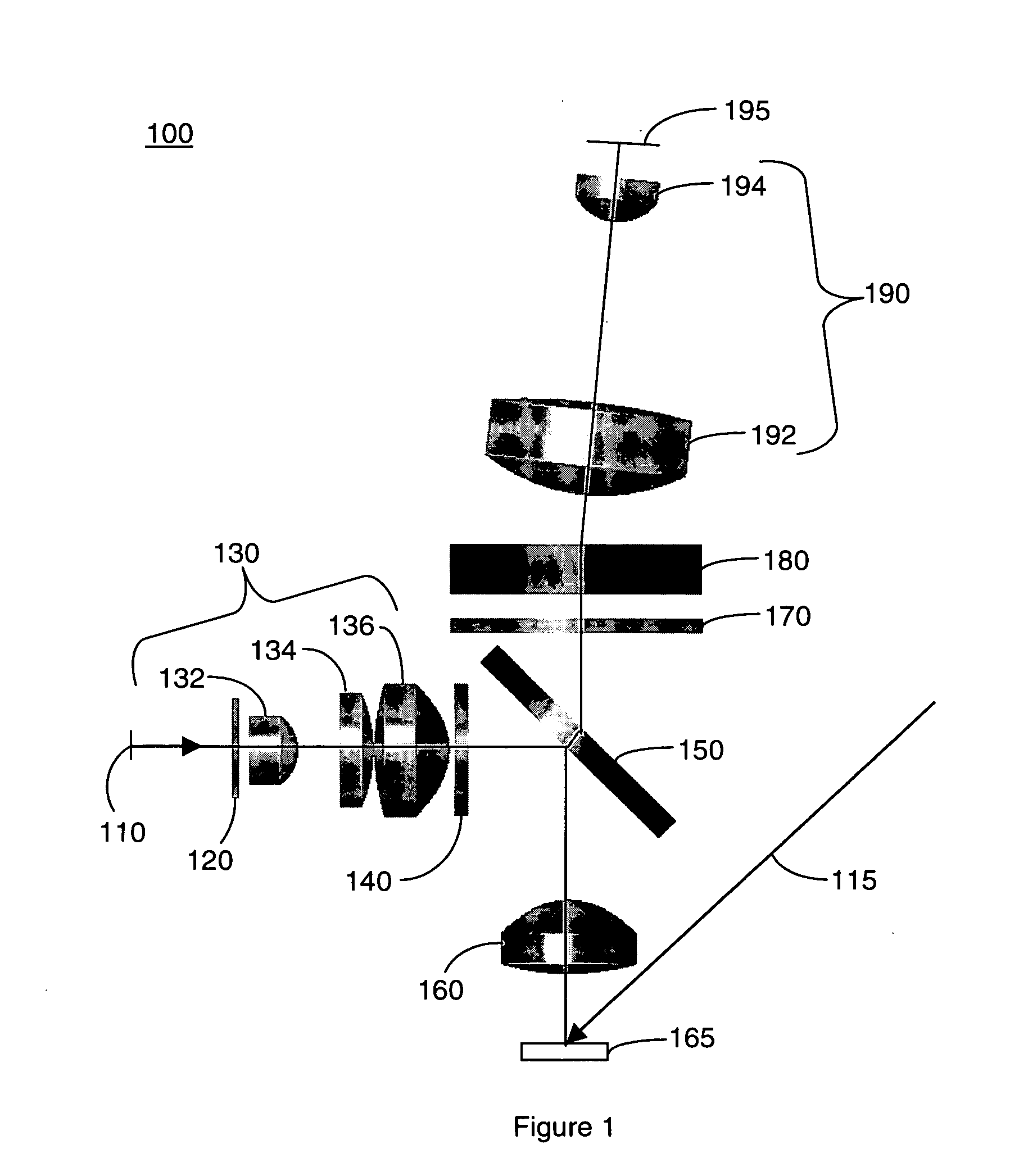
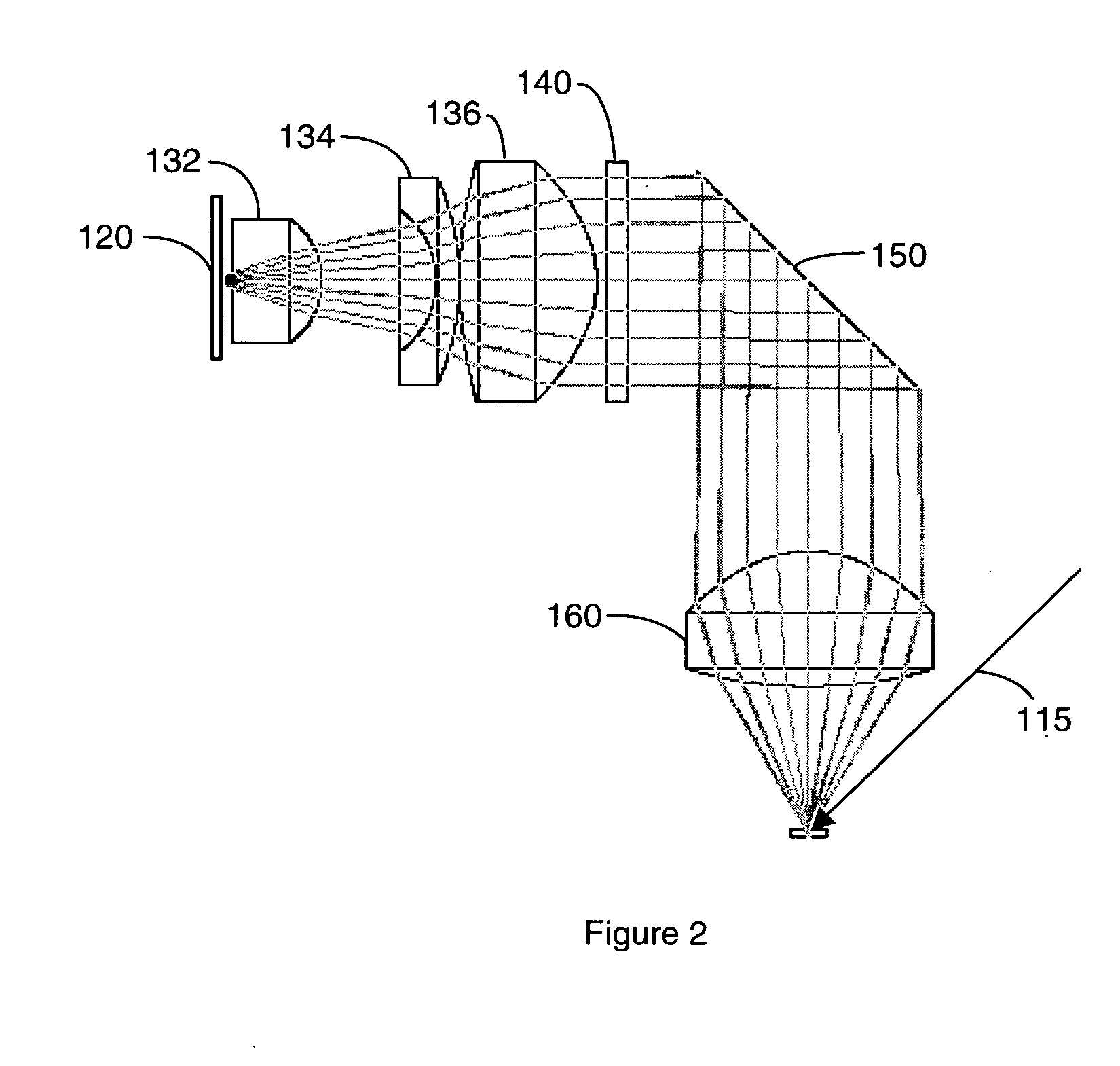
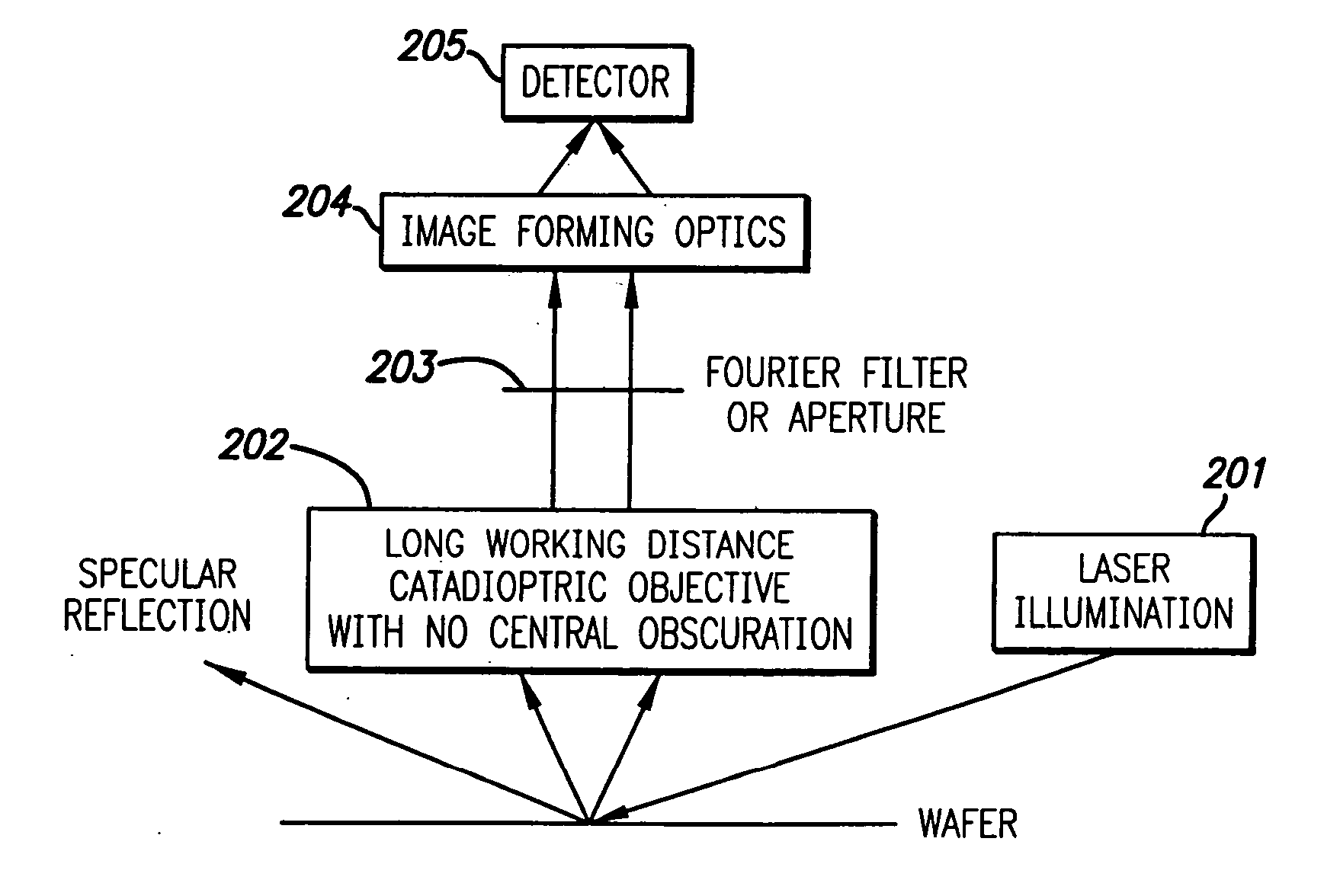
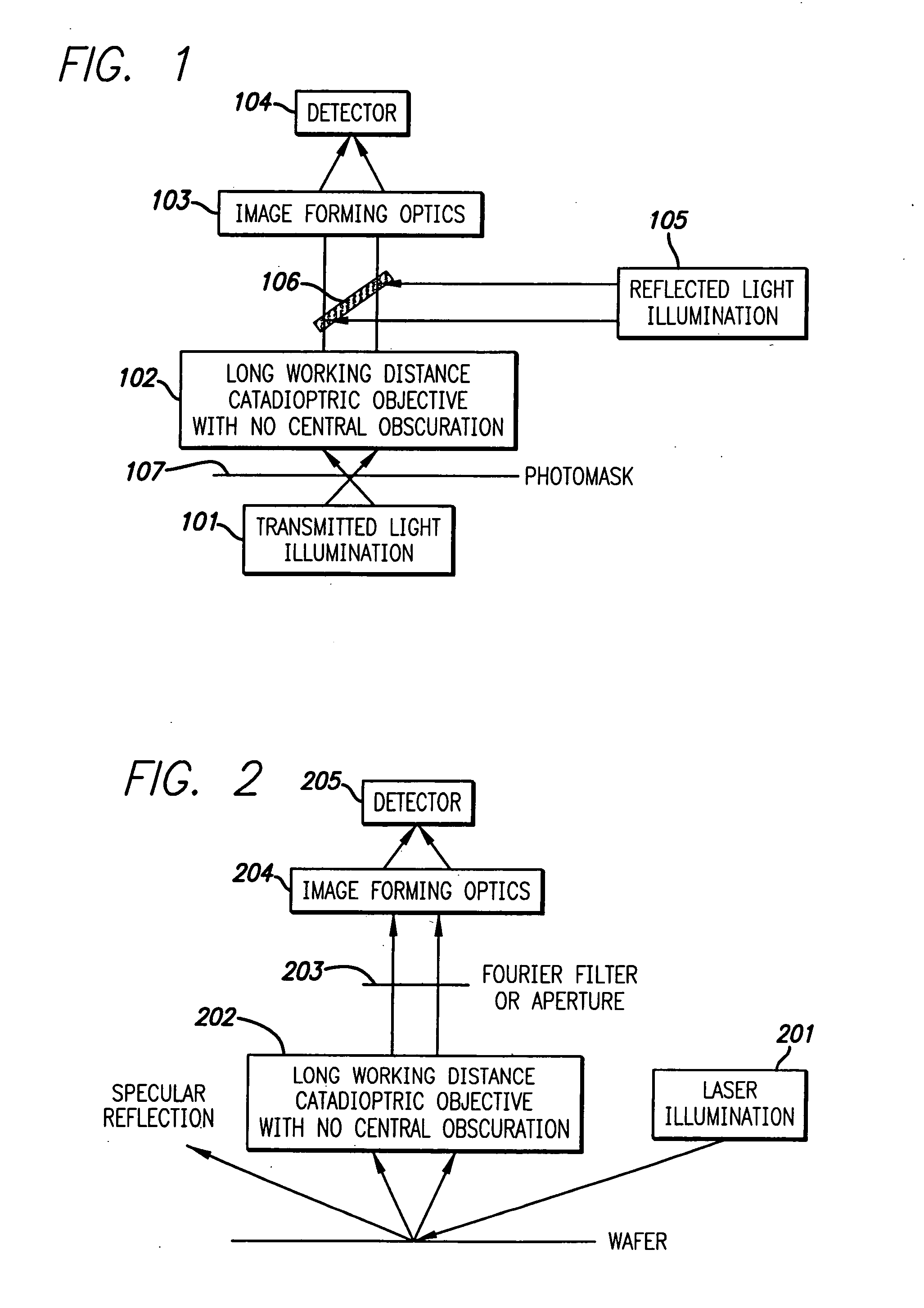
Broad band deep ultraviolet/vacuum ultraviolet catadioptric imaging system
InactiveUS20050111081A1High degreeImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMangin mirrorUltraviolet
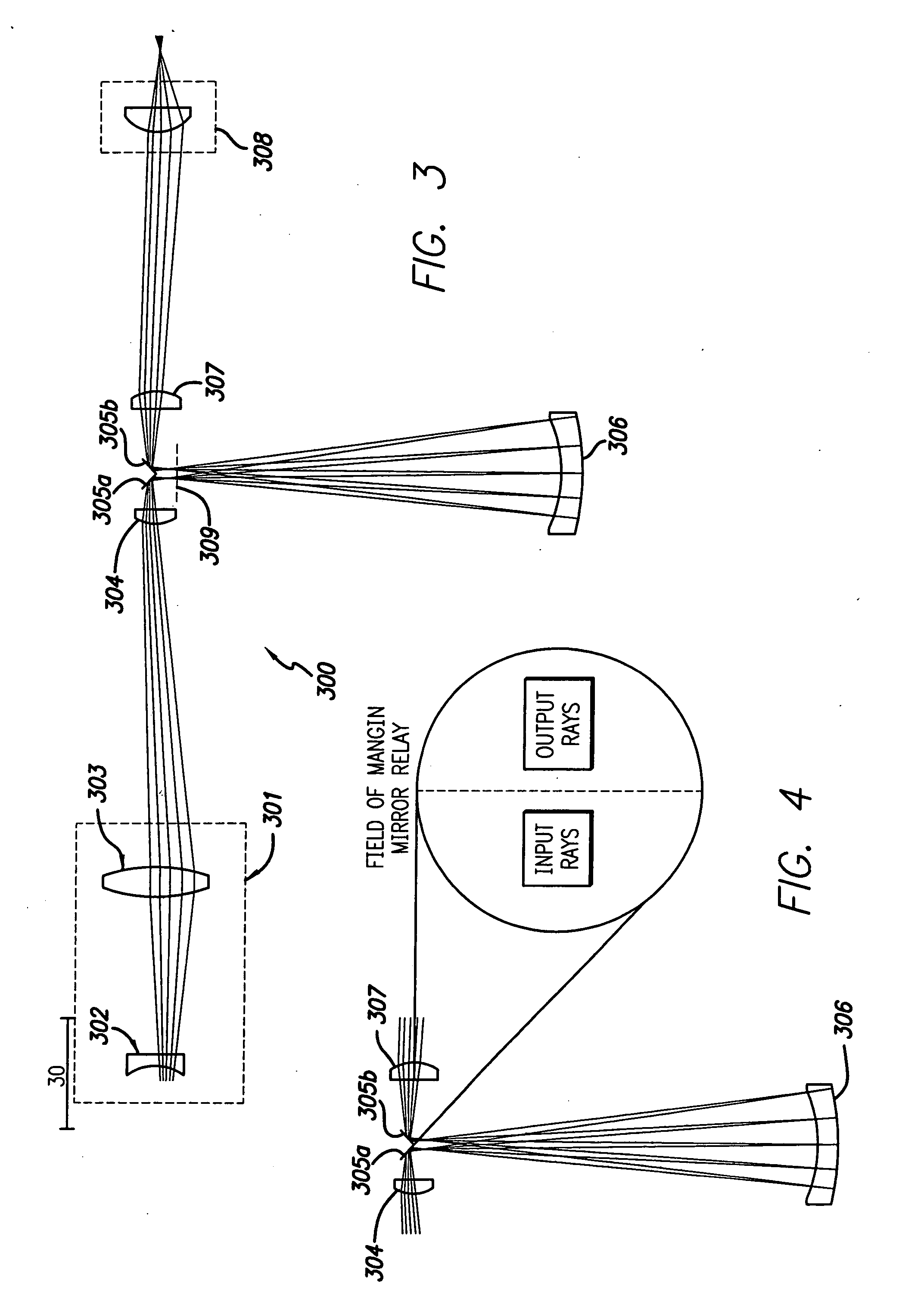
A design for inspecting specimens, such as photomasks, for unwanted particles and features such as pattern defects is provided. The system provides no central obscuration, an external pupil for aperturing and Fourier filtering, and relatively relaxed manufacturing tolerances, and is suited for both broad-band bright-field and laser dark field imaging and inspection at wavelengths below 365 nm. In many instances, the lenses used may be fashioned or fabricated using a single material. Multiple embodiments of the objective lensing arrangement are disclosed, all including at least one small fold mirror and a Mangin mirror. The system is implemented off axis such that the returning second image is displaced laterally from the first image so that the lateral separation permits optical receipt and manipulation of each image separately. The objective designs presented have the optical axis of the Mangin mirror image relay at ninety degrees to the optical axis defined by the focusing lenses, or an in-line or straight objective having one ninety degree bend of light rays.
Owner:KLA CORP
Catoptric projection optical system
InactiveUS7070289B2Large numerical apertureImprove imaging effectMirrorsOptical filtersCatoptricsLight beam
A catoptric projection optical system for projecting a pattern on an object surface onto an image surface includes plural mirrors, wherein a second mirror from the image surface through the optical path receives convergent pencil of rays, and has a paraxial magnification of −0.14 or smaller.
Owner:CANON KK
Optical fiber coupling componet
ActiveUS20060045419A1Send efficientlyLarge numerical apertureCladded optical fibreCoupling light guidesCoupling lossNumerical aperture
An optical fiber coupling part capable of reducing coupling loss while maintaining a large operating distance, and having a good module assembling property. AT least one GRIN lens having numerical aperture NA that is larger than numerical aperture NAs of a light-emitting source (such as a semiconductor laser) is fusion-spliced with one end of the optical fiber. All lights emitted from the light-emitting source can enter the GRIN lens, and the loss of the light can thereby be reduced. In addition, a second GRIN lens having numerical aperture NA2 is fusion-spliced with one end of the optical fiber having numerical aperture NAf, and further a first GRIN lens having numerical aperture NA1, which is larger than numerical aperture NA2, is fusion-spliced with the other end of the second GRIN lens. Thereby, the light emitted from the light-emitting source can efficiently enter the optical fiber, and loss of the light can thereby be reduced. In this case, the formula expressed by NAf≦NA2<NAs≦NA1 is desirable.
Owner:TOYO SEIKAN GRP HLDG LTD
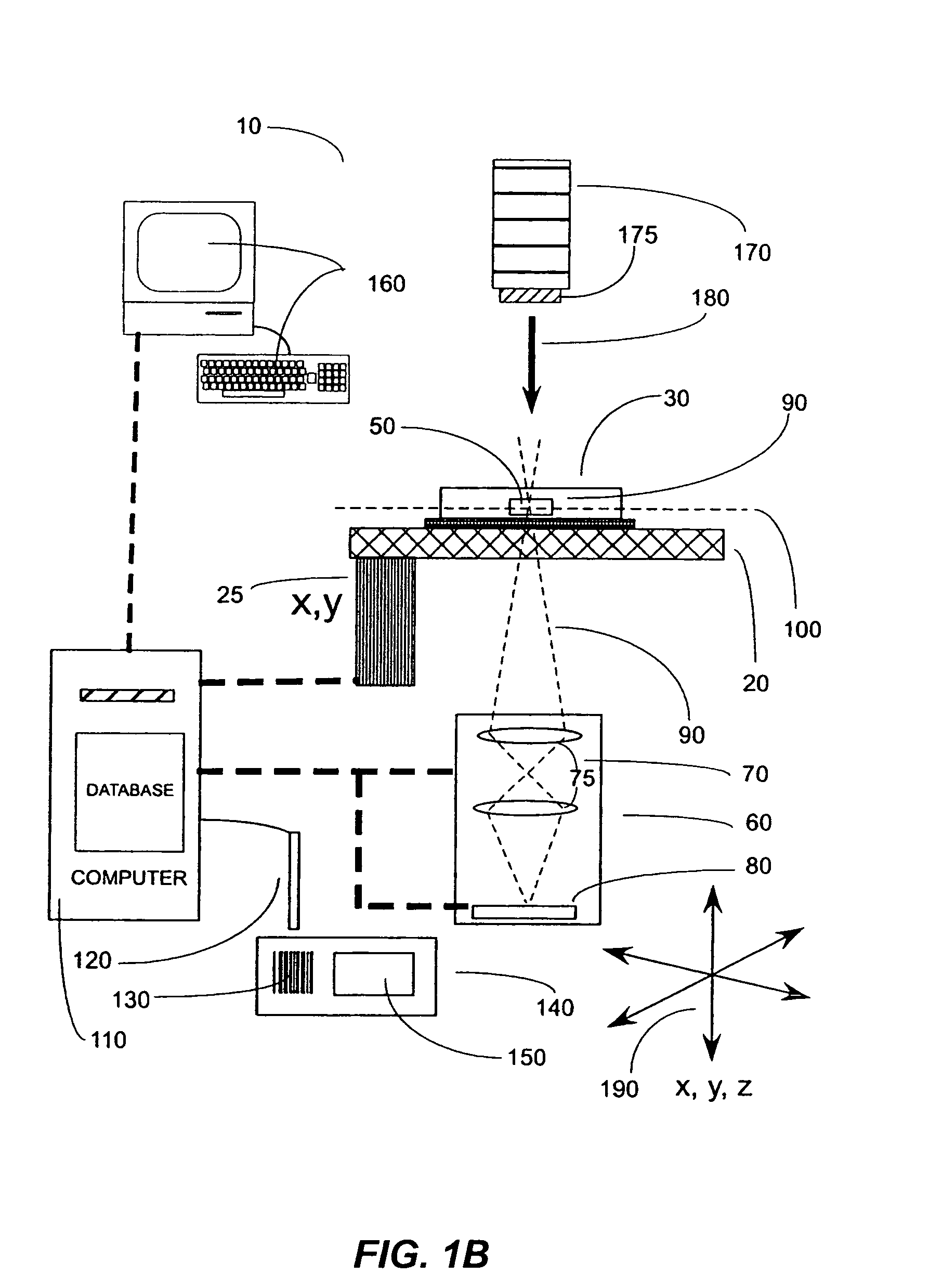
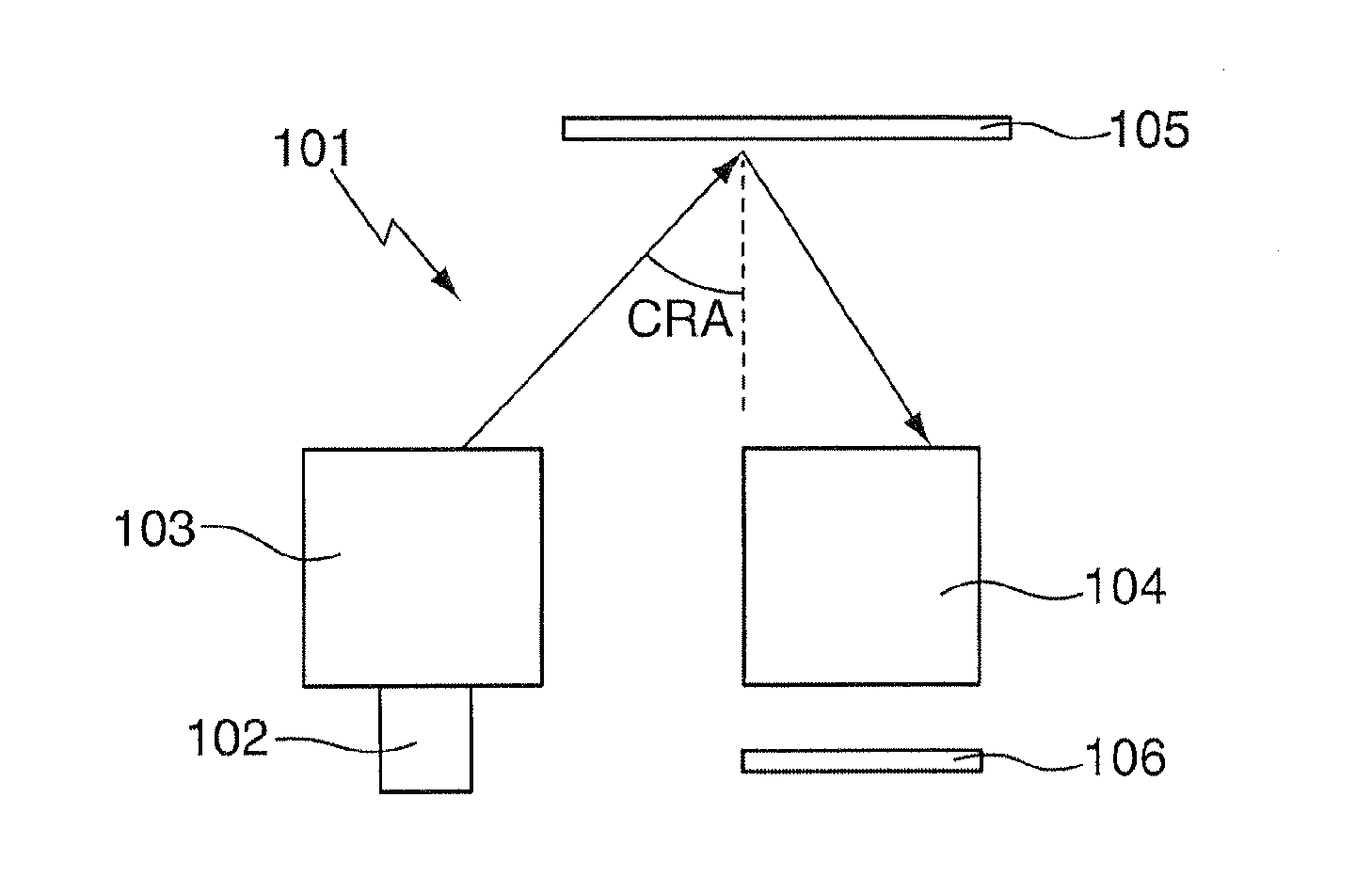
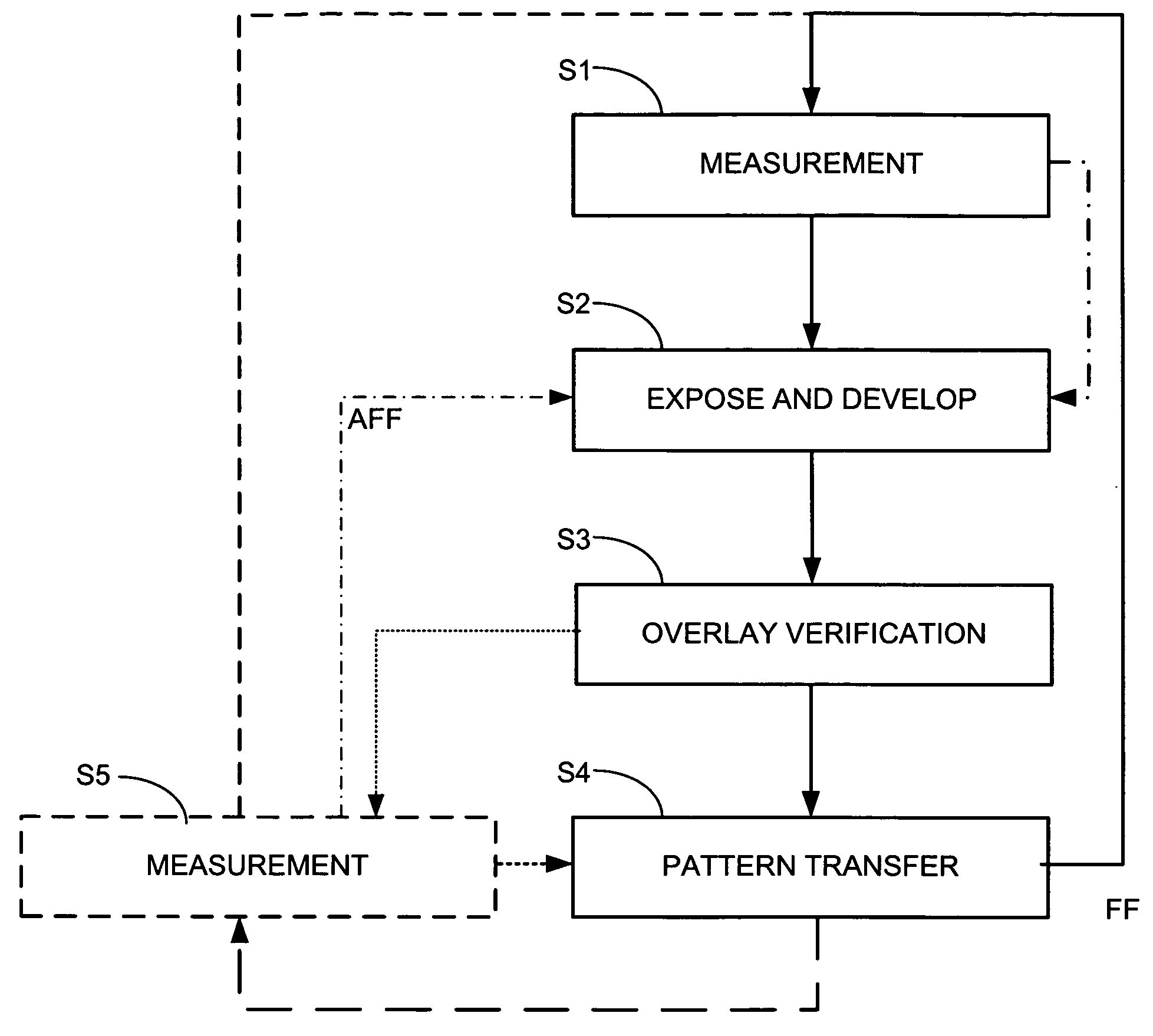
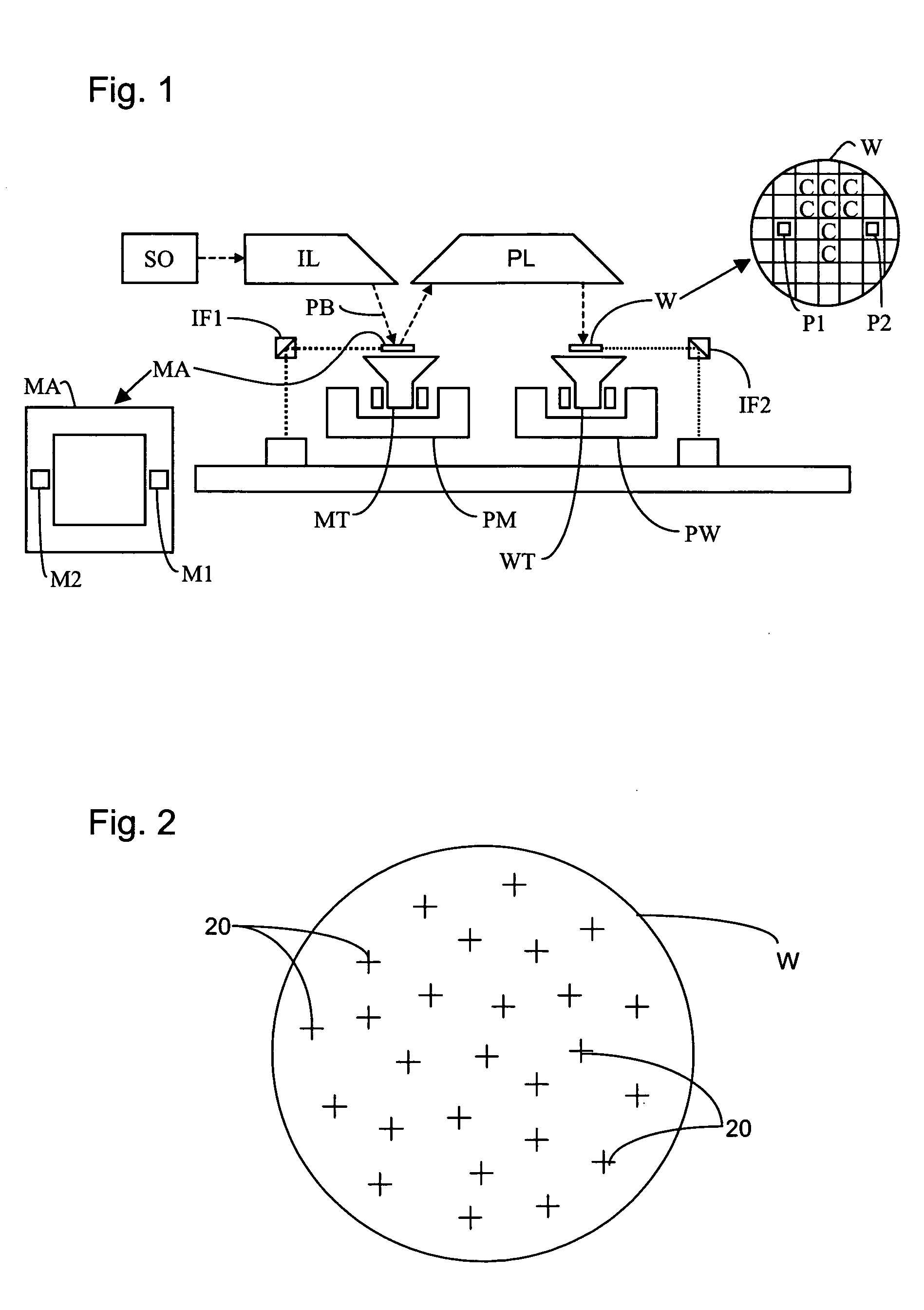
Method of characterization, method of characterizing a process operation, and device manufacturing method
ActiveUS20050031975A1Large numerical apertureHigh refractive indexSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharacter and pattern recognitionDistortionProcess operation
A system in which deformation of a substrate wafer is monitored during processing of the wafer is disclosed. In one embodiment, the distortion in the substrate wafer is measured after each exposure and processing operation by comparing the position of a plurality of reference marks to values in a database.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Solid immersion lens, condensing lens, optical pickup device, optical recording and reproducing apparatus and method of forming solid immersion lens
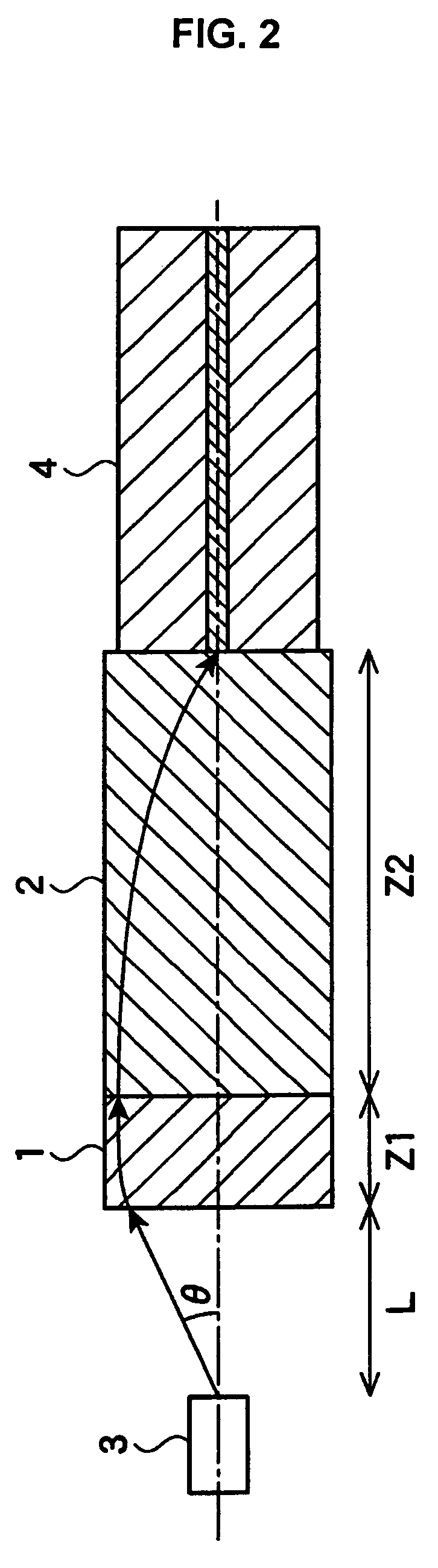
InactiveUS20050232120A1Large numerical apertureEasy to getCombination recordingRecord information storageOptical pickupAngle of incidence
A solid immersion lens 11 has an inclined portion 4 formed on at least a part thereof from the tip end portion of the objective side to a spherical portion and an inclination angle θ is expressed as θ≧i where θi represents the angle of incidence of light incident on the solid immersion lens 11. There are provided a solid immersion lens capable of increasing a tilt margin between a lens and an optical recording medium and so on and which can decrease a diameter of a lens and a method for forming a solid immersion lens.
Owner:SONY CORP
Confocal endoscope mini-microscope objective lens probe
InactiveCN1743891ALarge numerical apertureSmall sizeMicroscopesTelescopesPupilRefractive index matching
A micro object lens probe for confocal endoscopes, which contains micro object lens group, imaging optical beam and refractive index matching solution filled between imaging optical fiber beam and micro object lens group, said imaging optical fiber beam set before micro object lens group whose pupil located infinite farness, said micro object lens group has 1.0 hole diameter matched with that of single optical fiber of imaging optical fiber beam.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method and device for measuring, calibrating and using laser tweezers
InactiveUS6991906B1Increase amplitudeAccurate thresholdImmobilised enzymesOptical radiation measurementElectricityLight beam
To measure or exert optically-induced forces on at least one particle in the focus of an optical cage, the following steps are taken:a) the focus is positioned in a microelectrode arrangement with a three-dimensional electrical field that has a field gradient which forms an electrical capture area, and the focus is at a distance from the capture are andb) the amplitude of the electrical field, the light power of the light beam forming the optical cage, and / or the distance of the capture area from the focus are varied to detect which varied field property moves the particle from the focus to the capture area or vice versa, or at least to temporarily move the particle into the capture area.
Owner:EVOTEC BIOSYST +1
Compact, wide-field-of-view imaging optical system
ActiveUS20050270660A1Large numerical apertureImprove signal-to-noise ratioTelevision system detailsColor television detailsSpatial OrientationsWide field
An imaging optical system includes a first imaging structure having a first optical axis and a first field of view, wherein the first imaging structure forms an image on a common focal plane, and a second imaging structure having a second optical axis parallel to the first optical axis and a second field of view different from the first field of view, wherein the second imaging structure forms an image on the common focal plane. The imaging structures preferably contain identical lens modules, most preferably identical Petzval lenses, and achromatic or apochromatic prisms of different spatial orientations. A planar sensor structure lies in the common focal plane, wherein the first optical axis and the second optical axis pass through the planar sensor structure.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
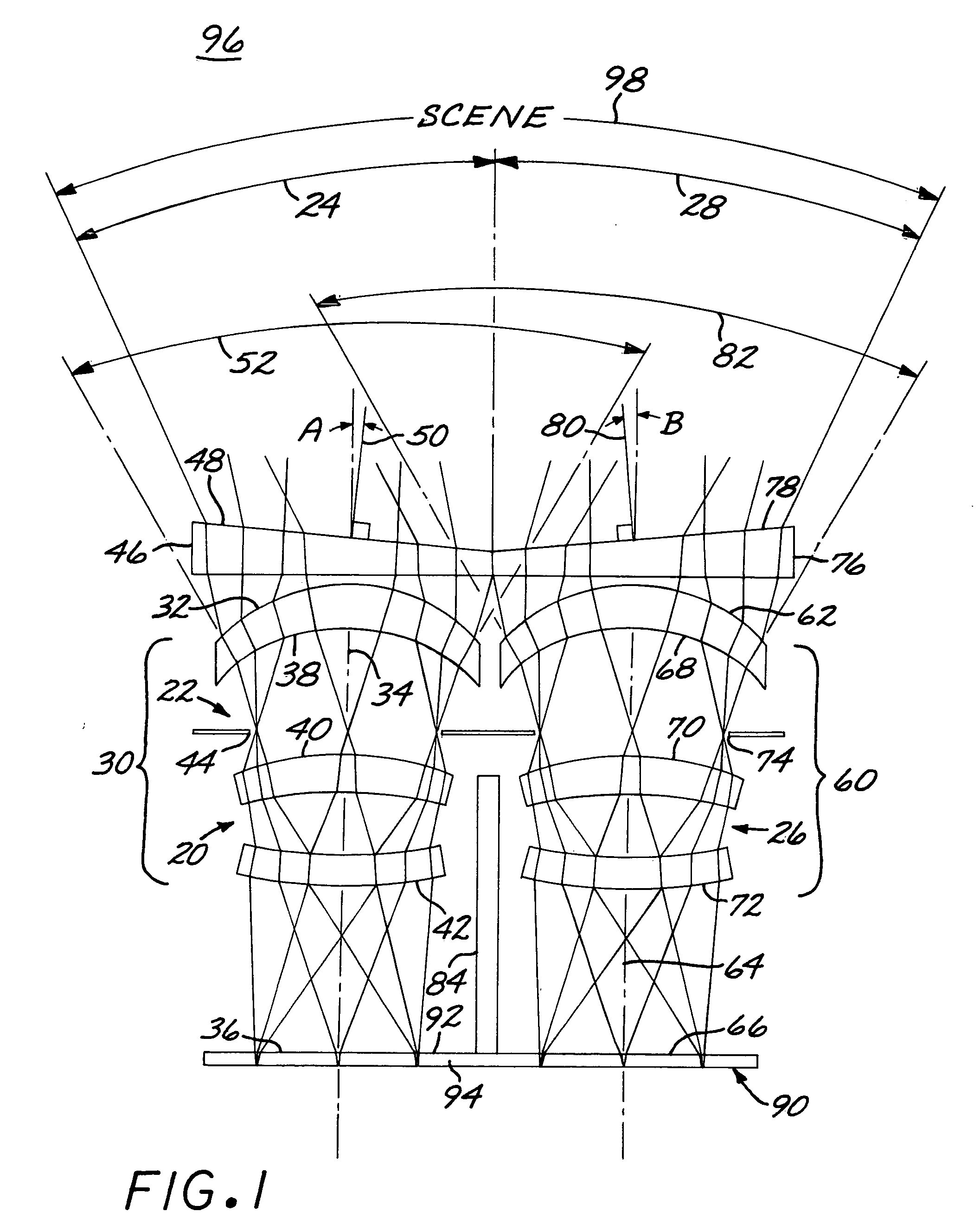
Simultaneous Multi-Spot Inspection and Imaging
InactiveUS20070153265A1Small footprintLarge numerical apertureOptically investigating flaws/contaminationDetector arrayOblique angle
A compact and versatile multi-spot inspection imaging system employs an objective for focusing an array of radiation beams to a surface and a second reflective or refractive objective having a large numerical aperture for collecting scattered radiation from the array of illuminated spots. The scattered radiation from each illuminated spot is focused to a corresponding optical fiber channel so that information about a scattering may be conveyed to a corresponding detector in a remote detector array for processing. For patterned surface inspection, a cross-shaped filter is rotated along with the surface to reduce the effects of diffraction by Manhattan geometry. A spatial filter in the shape of an annular aperture may also be employed to reduce scattering from patterns such as arrays on the surface. In another embodiment, different portions of the same objective may be used for focusing the illumination beams onto the surface and for collecting the scattered radiation from the illuminated spots simultaneously. In another embodiment, a one-dimensional array of illumination beams are directed at an oblique angle to the surface to illuminate a line of illuminated spots at an angle to the plane of incidence. Radiation scattered from the spots are collected along directions perpendicular to the line of spots or in a double dark field configuration.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
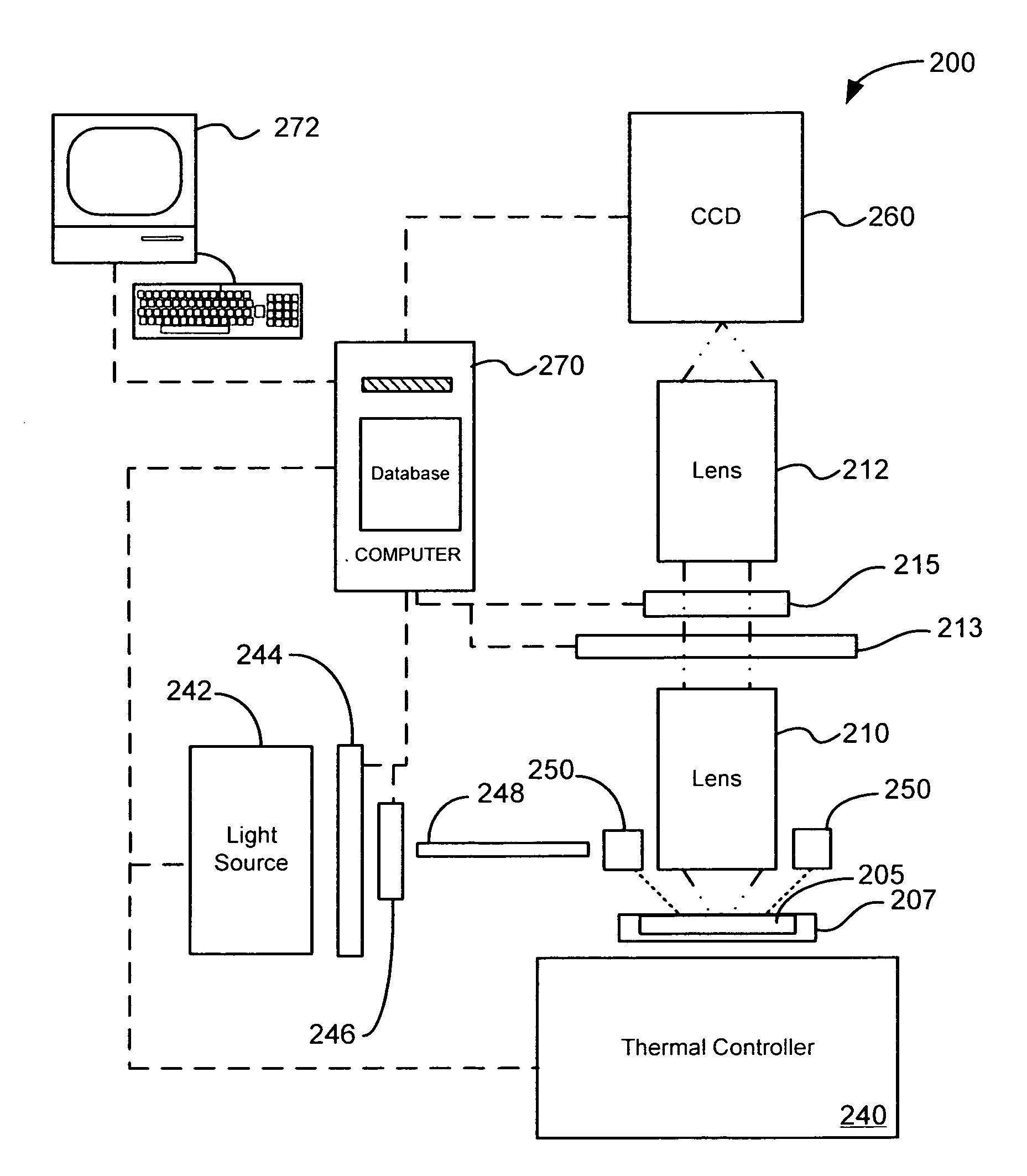
Micro-nano system fluid chip detection system and detection method
ActiveCN101126715AReduce localized heating inhomogeneitiesReduce unevennessBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicro nanoTemperature control
The utility model relates to a fluid chip detection system and detection method of micro-nano rise system, which is characterized in comprising an incident light generation system, a dual focal fluorescence collection system, a collecting light processing system, a circulation flowing stereo temperature control stage, and a microfluid chip; wherein the incident light generation system comprises at least a light source and a condenser arranged on the output of the light; the dual focal fluorescence collection system comprises a front imaging lens group and a rear imaging lens group and a detector arranged on the output of the post lens group; the collecting light processing system comprises an A / D acquisition card connected with the output of the detector, and a computer connected with the output of the A / D acquisition card; the temperature control stage comprises a motion platform bearing the microfluid chip, the heat transfer media around the motion platform, a heater arranged around the heat transfer media and a heat insulation device arranged outside the heater, the computer is connected with the motion platform through a motion controller, and connected with the heater and a temperature transmitter through a temperature feedback circuit. The utility model has the advantages of simple structure, low cost, high fluorescence efficiency collection and high detection sensitivity, convenient use and easy for promotion and popularization.
Owner:BOAO BIOLOGICAL CO LTD +1
Light beam shaping device in use for semiconductor laser array in high power
InactiveCN1696764ASolve the problem of high-quality beam outputImprove coupling efficiencySemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser arrangementsLaser arrayLight beam
A light beam reshaping device consists of laser array, the first lens set, the second lens set, the first planoconvex lens set, quick shaft compression column lens, the second planoconvex lens set, optical fibre array, optical fibre bundle, focusing lens and optical fibre. The device can ensure high coupling rate, high power and high brightness as well as can be used in high power semiconductor laser array.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com