Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
47 results about "Multiphoton excitation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
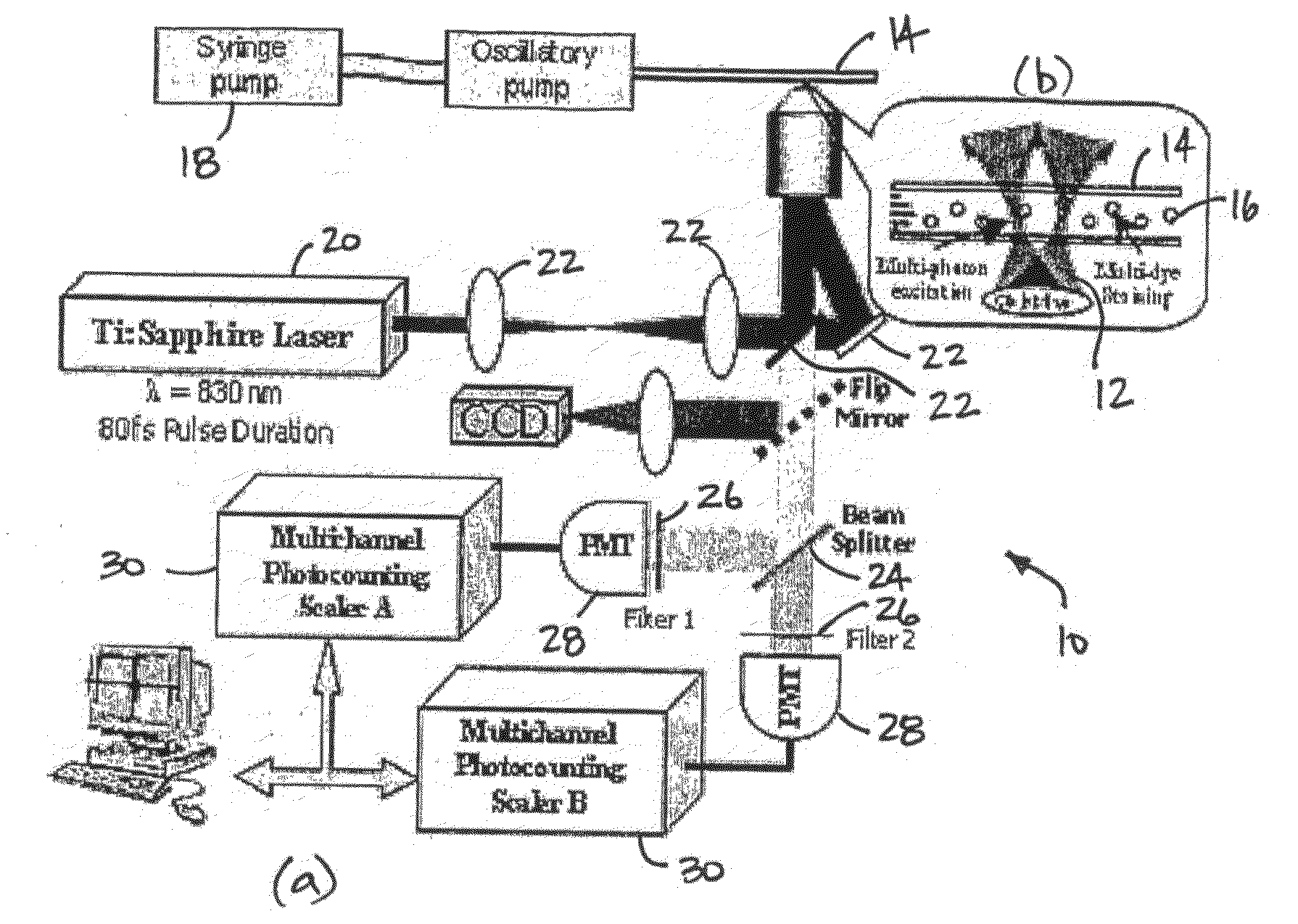
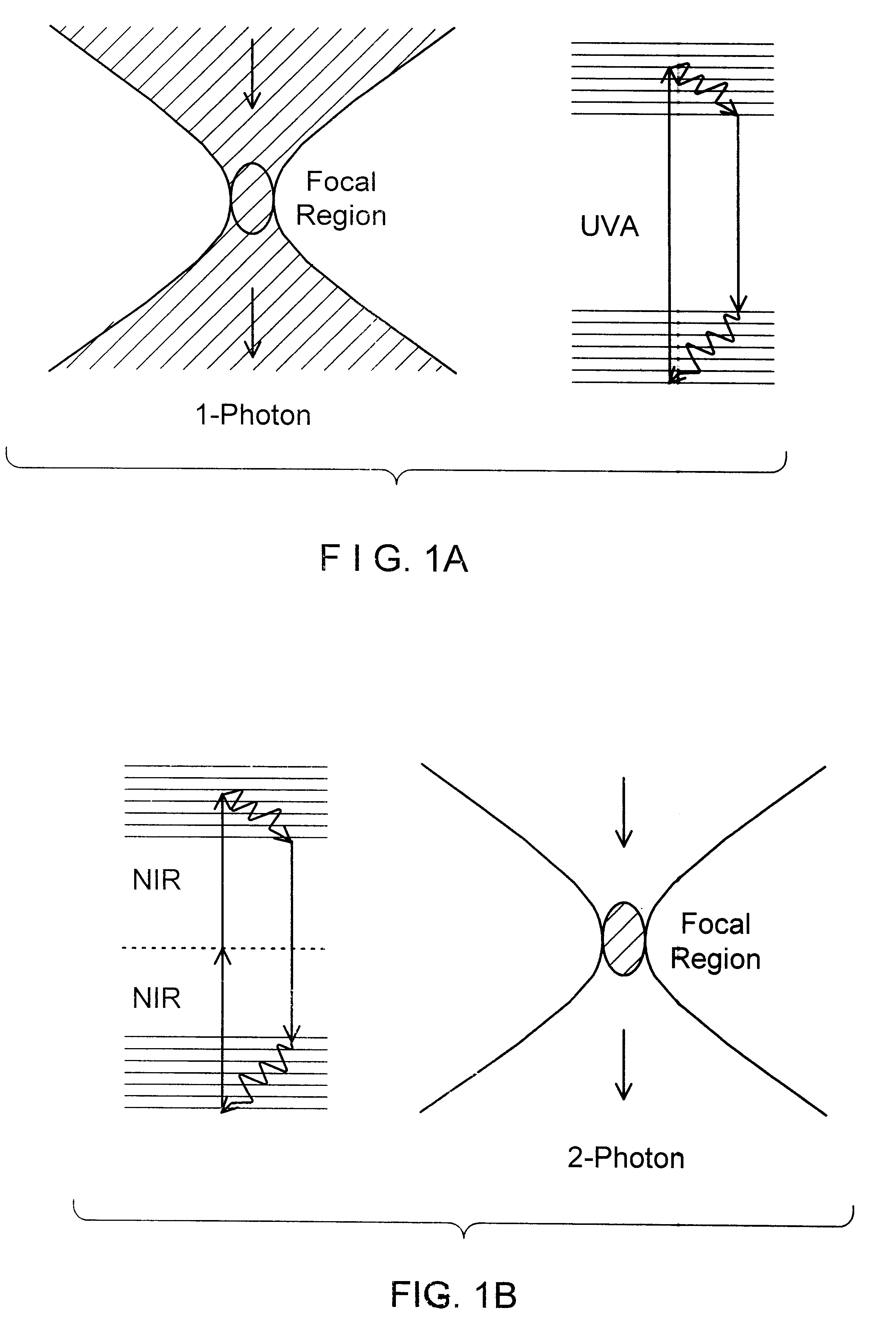
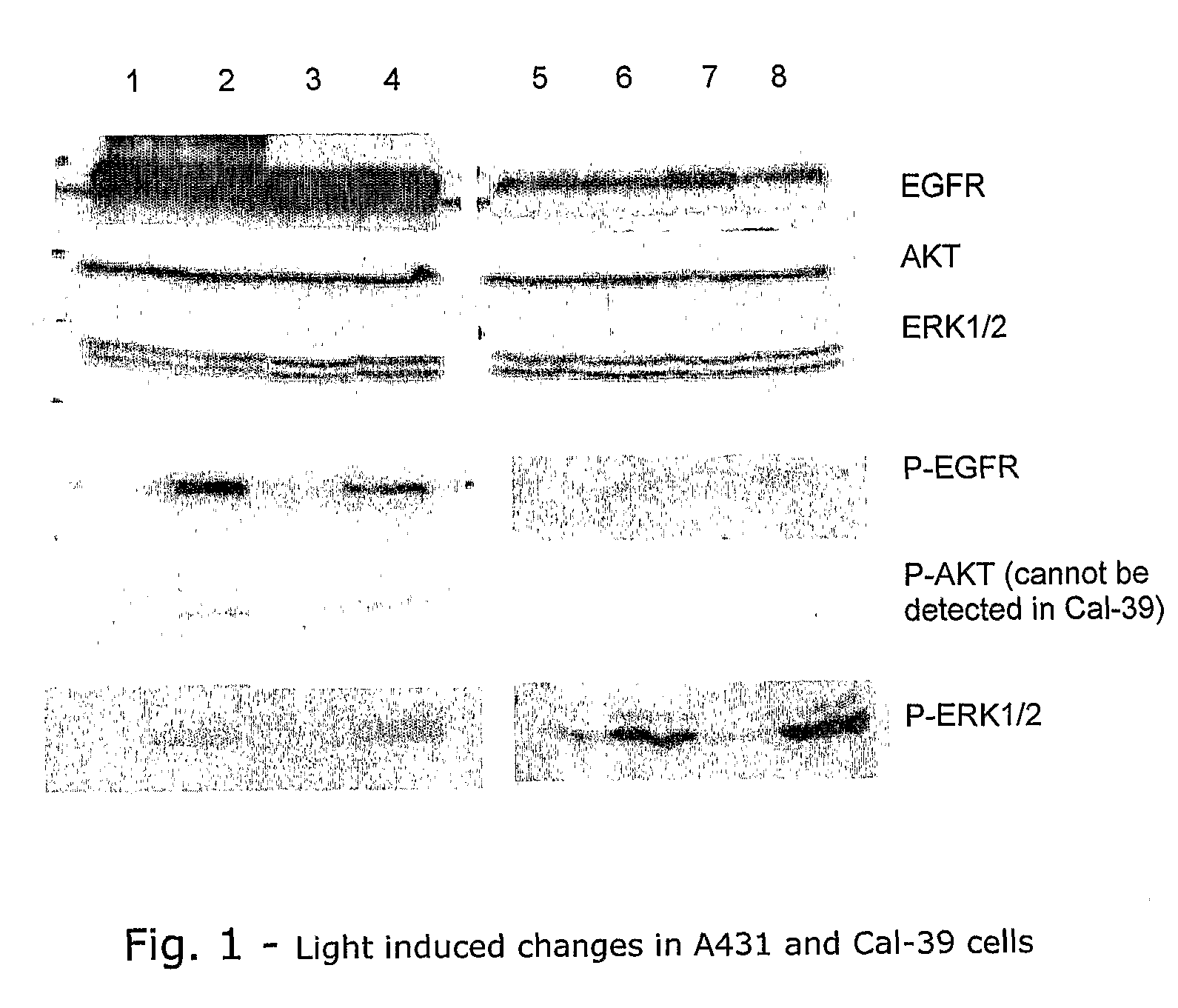
Fundamentals and Applications in Multiphoton Excitation Microscopy. Two-photon excitation microscopy (also referred to as non-linear, multiphoton, or two-photon laser scanning microscopy) is an alternative to confocal and deconvolution microscopy that provides distinct advantages for three-dimensional imaging.
Optical fiber scanner for performing multimodal optical imaging
InactiveUS7616986B2Focus shiftReduce back reflectionBoxes/cartons making machineryBox making operationsActuatorFrequency modulation
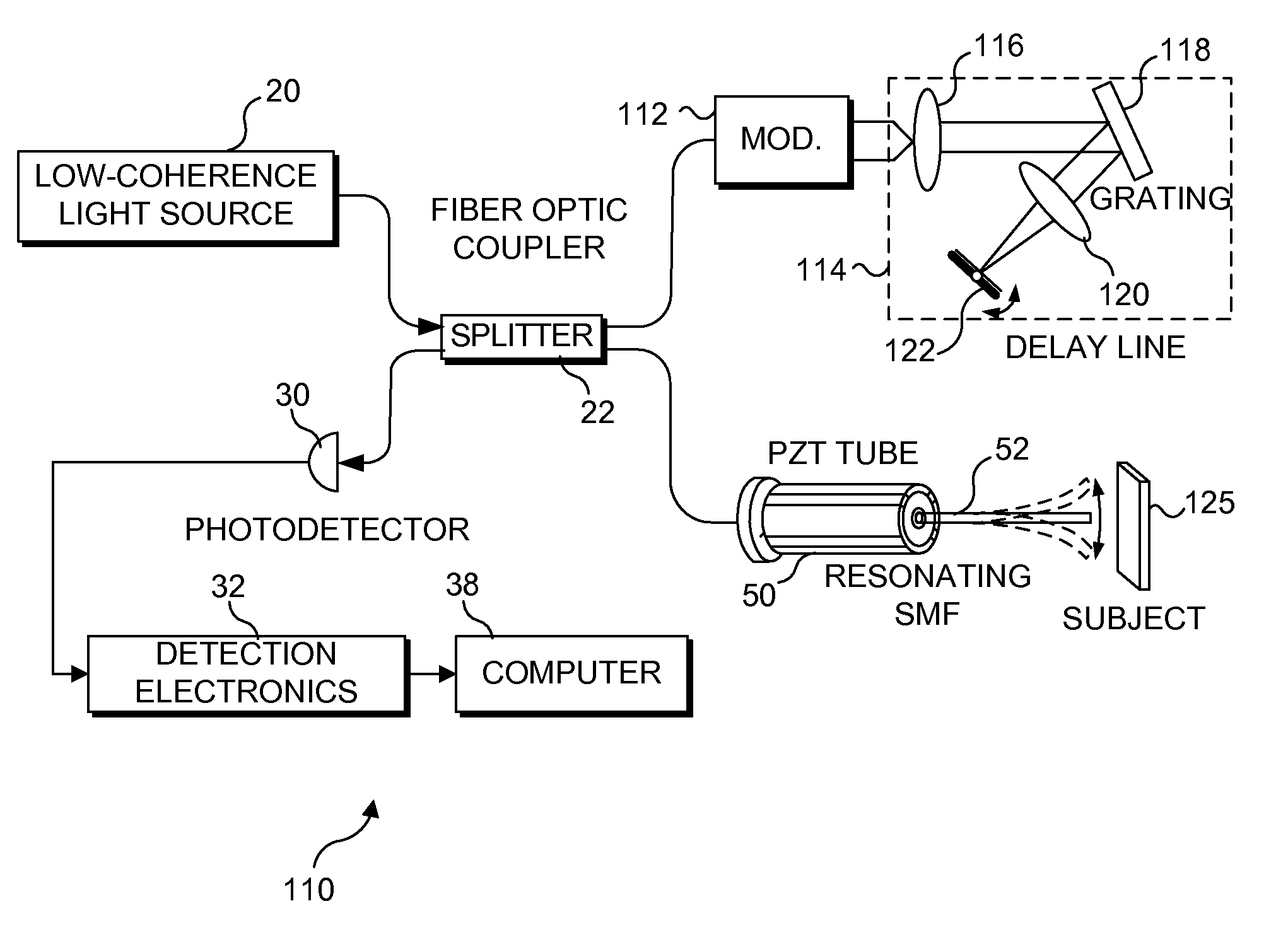
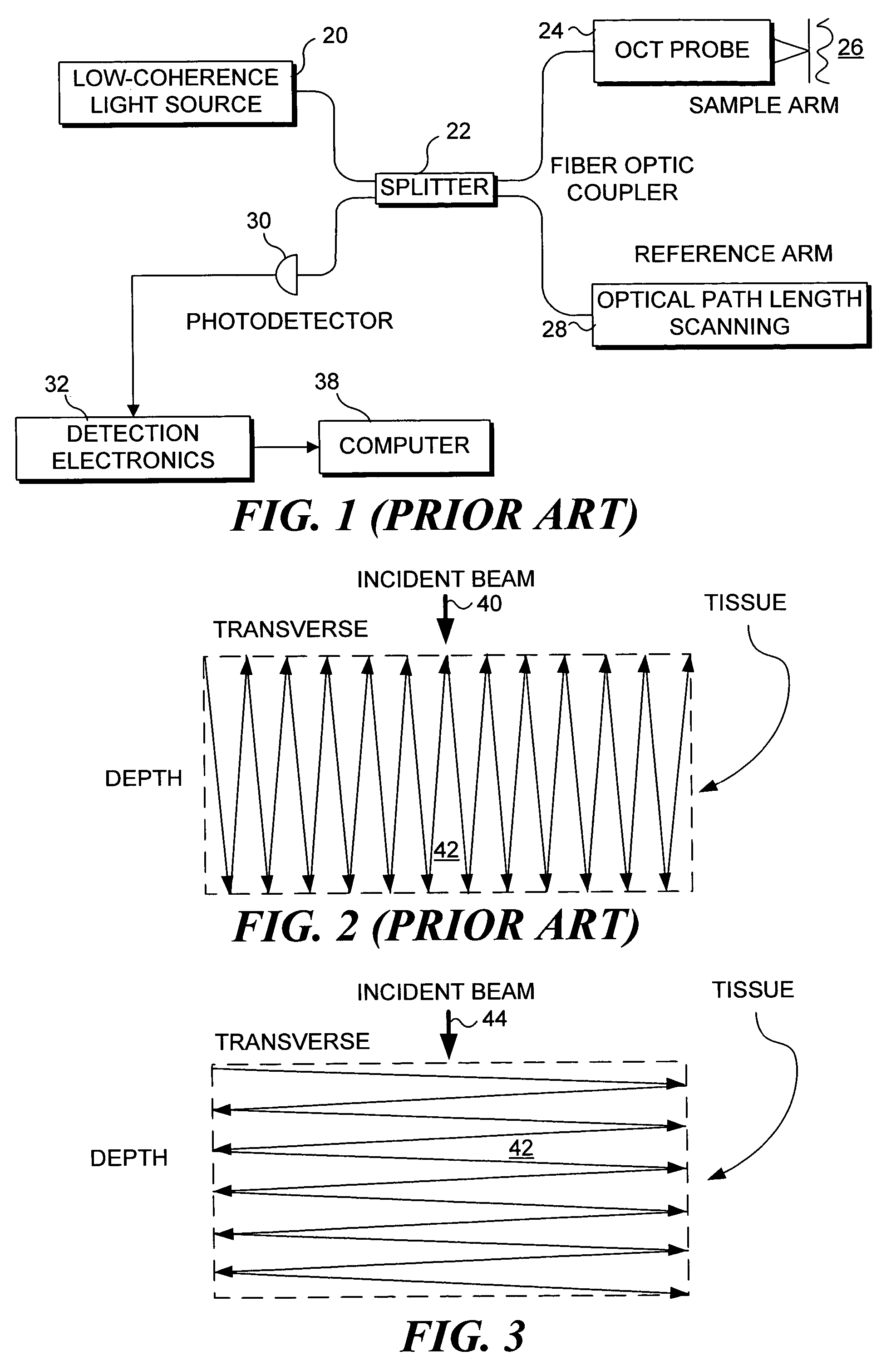
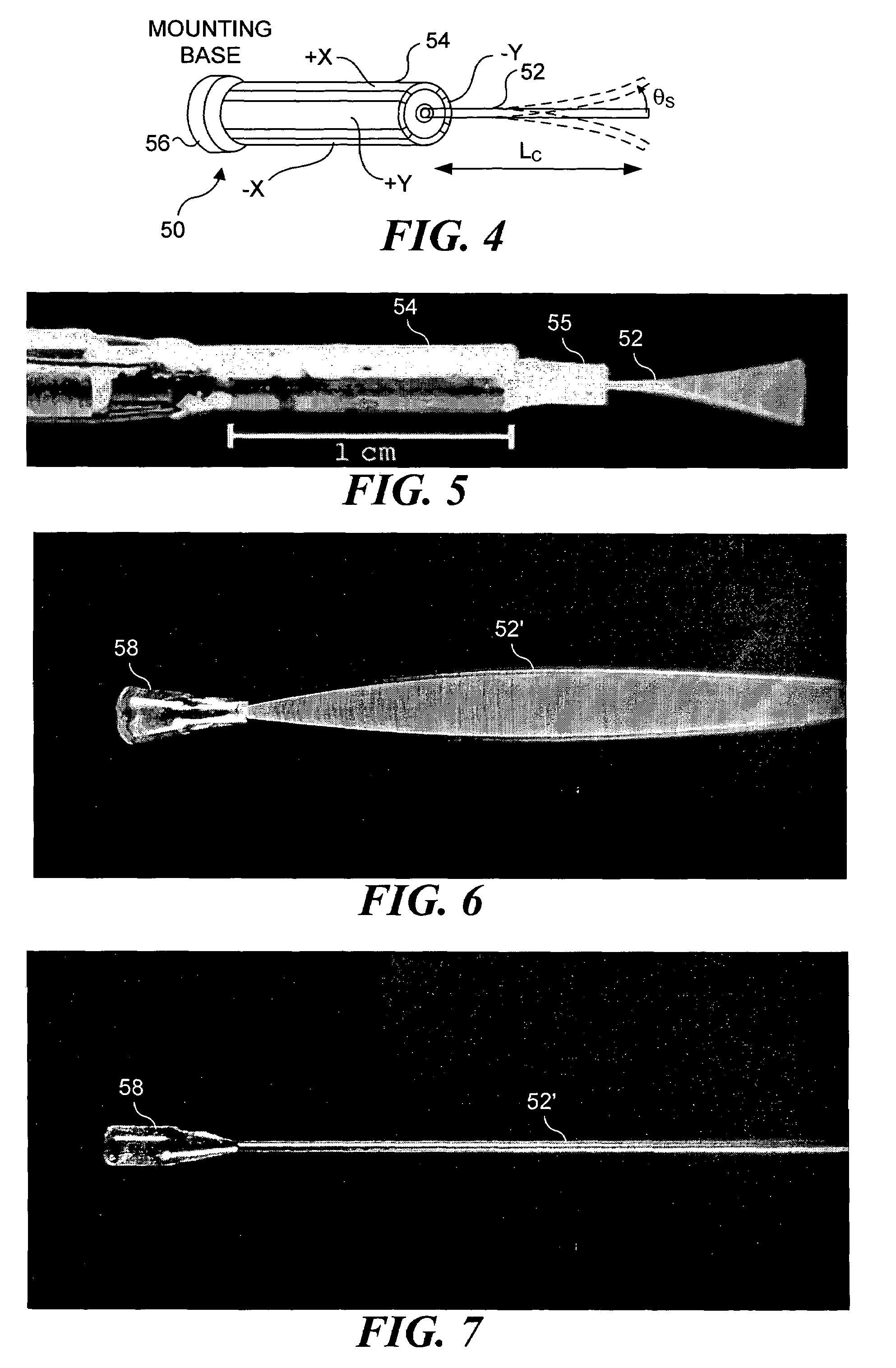
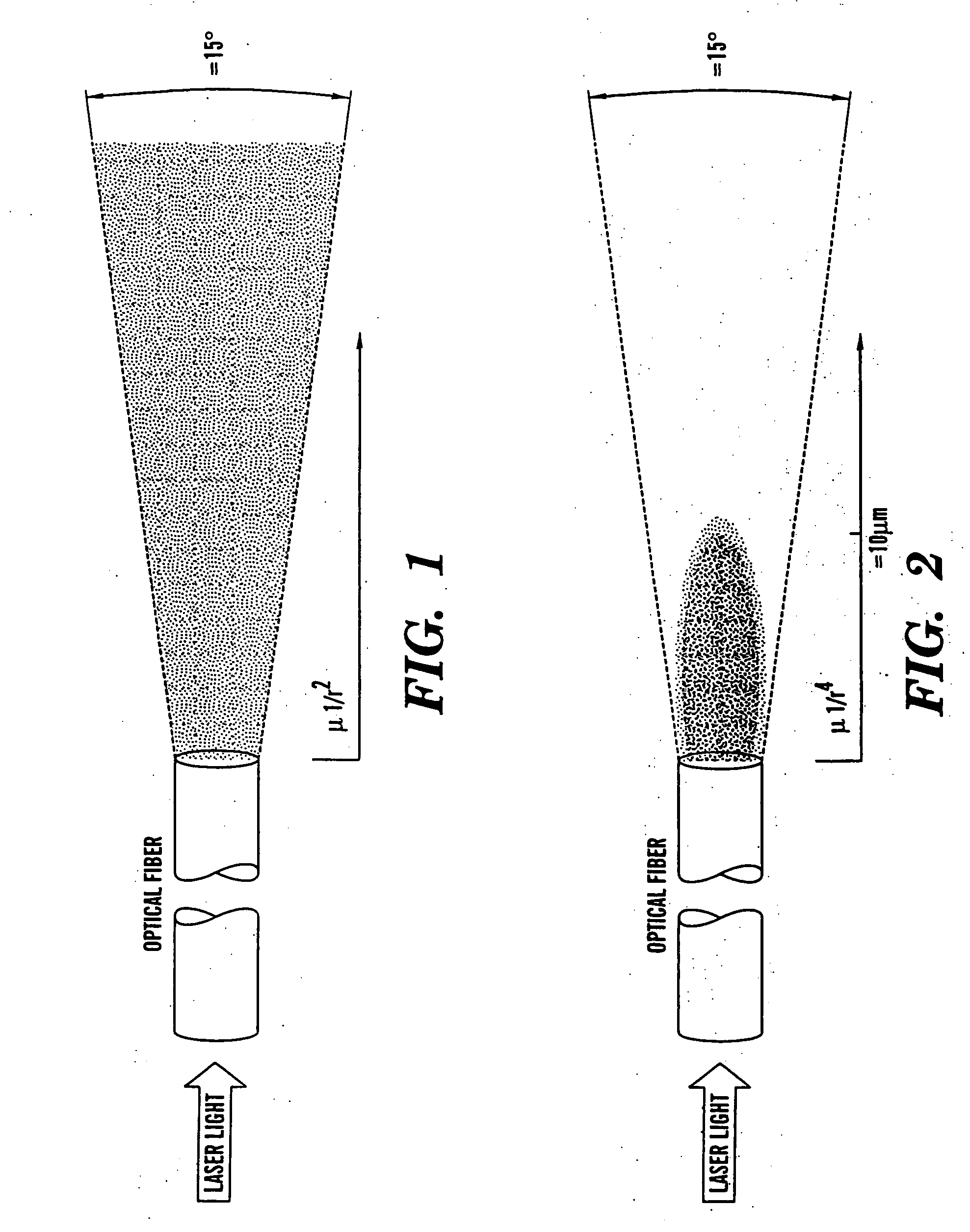
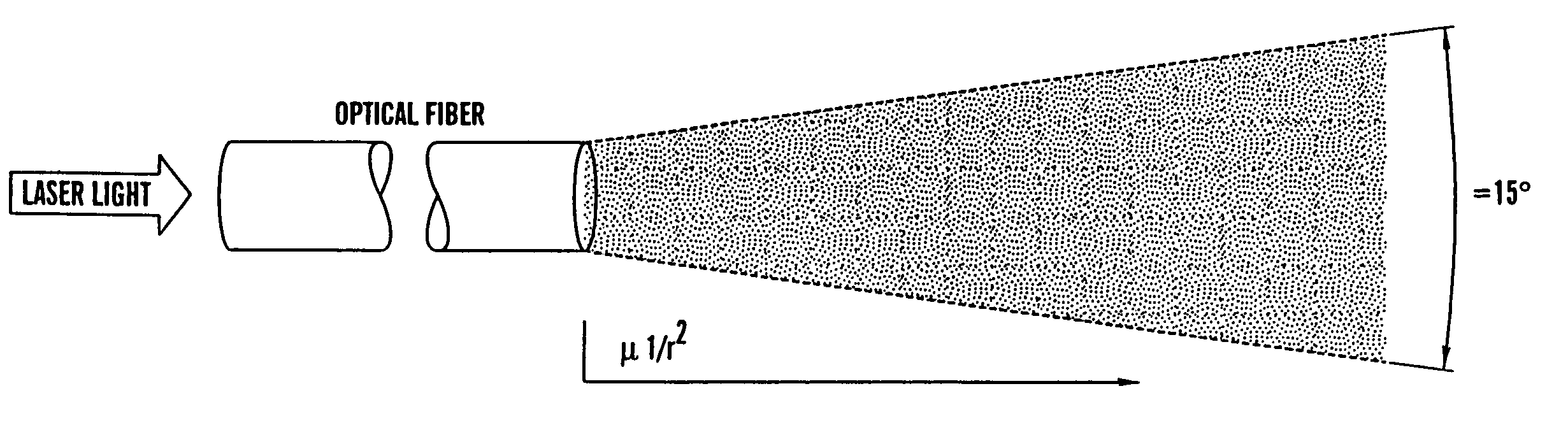
An optical fiber scanner is used for multiphoton excitation imaging, optical coherence tomography, or for confocal imaging in which transverse scans are carried out at a plurality of successively different depths within tissue. The optical fiber scanner is implemented as a scanning endoscope using a cantilevered optical fiber that is driven into resonance or near resonance by an actuator. The actuator is energized with drive signals that cause the optical fiber to scan in a desired pattern at successively different depths as the depth of the focal point is changed. Various techniques can be employed for depth focus tracking at a rate that is much slower than the transverse scanning carried out by the vibrating optical fiber. The optical fiber scanner can be used for confocal imaging, multiphoton fluorescence imaging, nonlinear harmonic generation imaging, or in an OCT system that includes a phase or frequency modulator and delay line.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
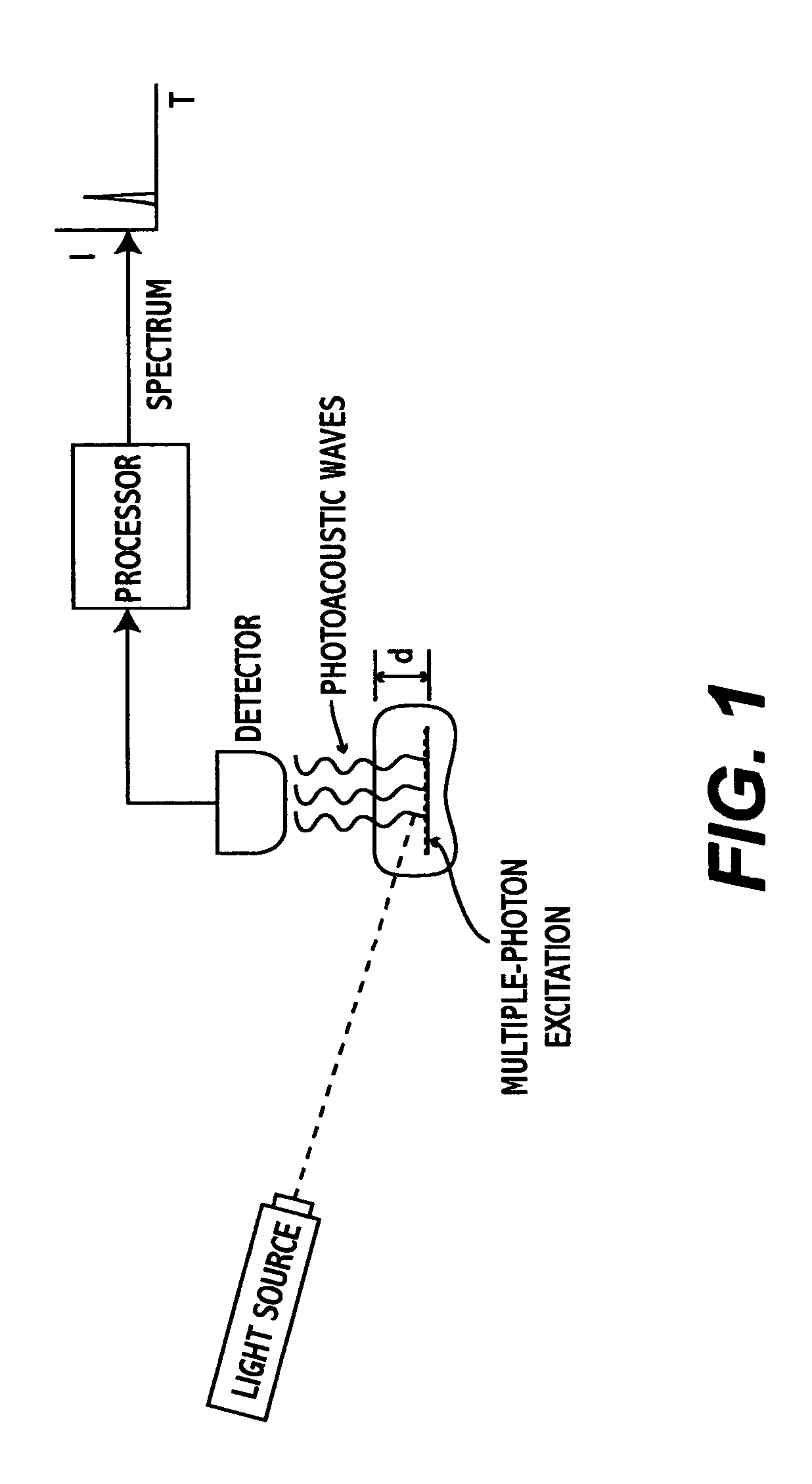
Multiphoton photoacoustic spectroscopy system and method
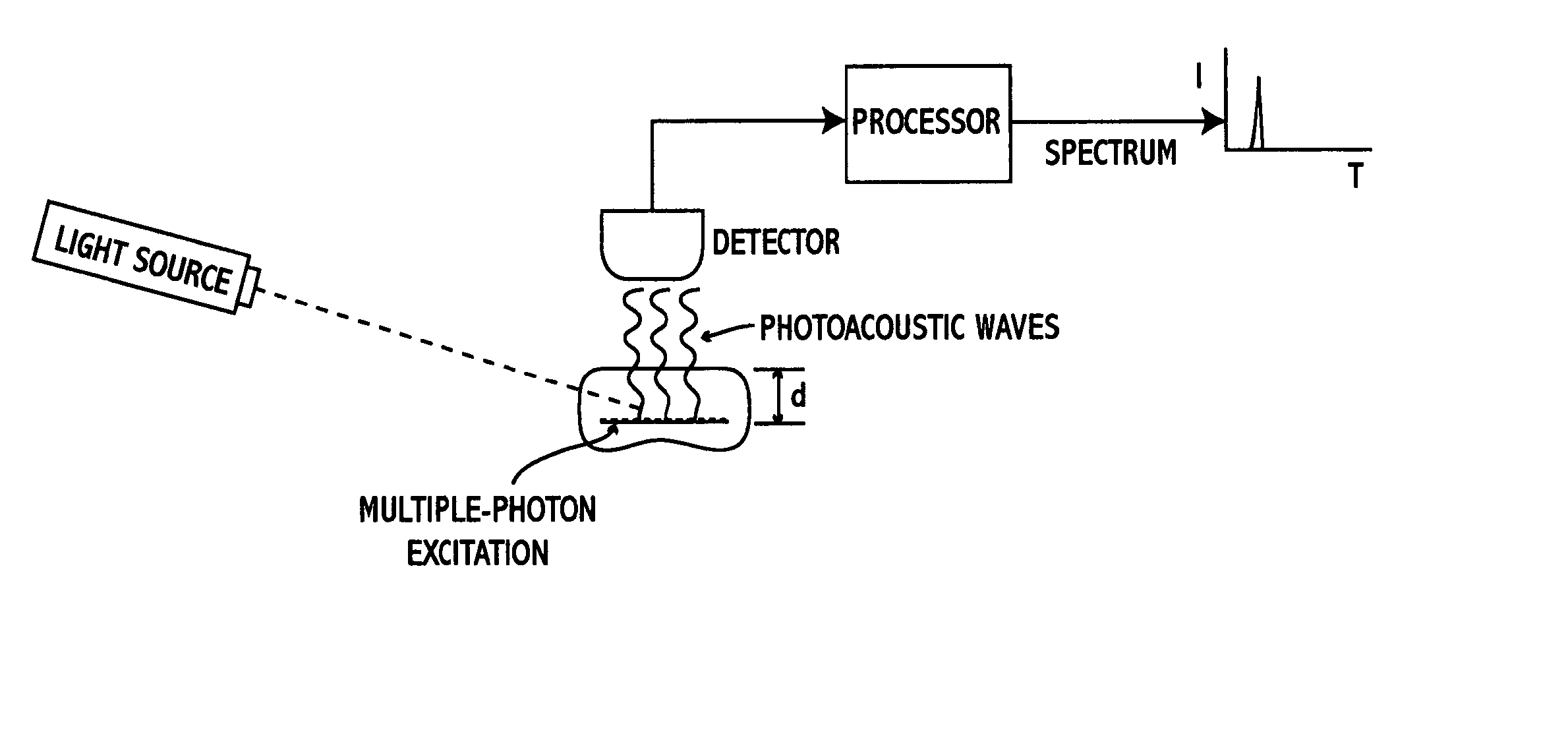
InactiveUS20050070803A1Non-invasively diagnosingRadiation pyrometryDiagnostics using lightHigh power lasersPhoton
A system and method for performing multispectral imaging locates features of interest in a specimen using a technique known as multiphoton photoacoustic spectroscopy. In this technique, a tunable high-power laser is used to initiate multiphoton excitation events which are then detected as an acoustic signal using a sensor such as an ultrasonic piezoelectric transducer. The transducer signal is processed to form a normalized MPPAS signal intensity which may then be used as a basis for forming a spectral image. Unlike other spectroscopies, MPPAS is able to monitor non-fluorescent species based on non-radiative relaxation of the light-absorbing species in the specimen. In addition, since the majority of energy imparted to the light-absorbing molecules is released through non-radiative pathways, sensitive measurements of even fluorescent molecules can be performed. The system and method may be applied to detect malignant cells in tissue samples although other uses are contemplated.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE COUNTY
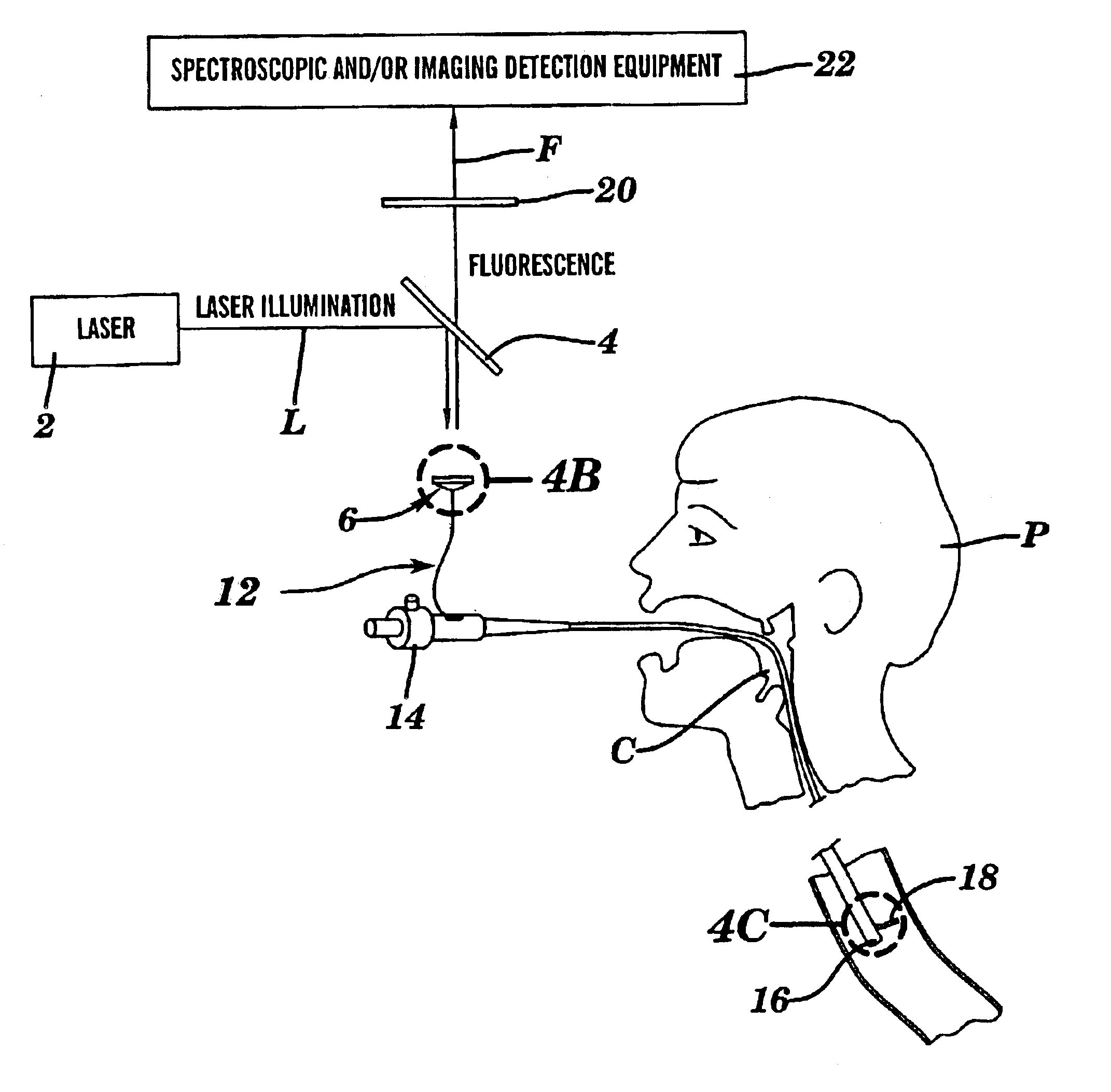
Use of multiphoton excitation through optical fibers for fluorescence spectroscopy in conjunction with optical biopsy needles and endoscopes
InactiveUS6839586B2Easy to resolveUseful spatial resolutionSurgeryDiagnostics using spectroscopyDiseaseEndoscope
The present invention is directed to a method of applying radiation through an optical fiber for detecting disease within a plant or animal or imaging a particular tissue of a plant or animal. In addition, fluorescence can be detected and localized within a subject by such application of radiation through an optical fiber. The radiation is effective to promote simultaneous multiphoton excitation. The optical fibers are used alone to examine internal regions of tissue, in conjunction with an optical biopsy needle to evaluate sub-surface tissue, or with an endoscope to evaluate tissue within body cavities.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
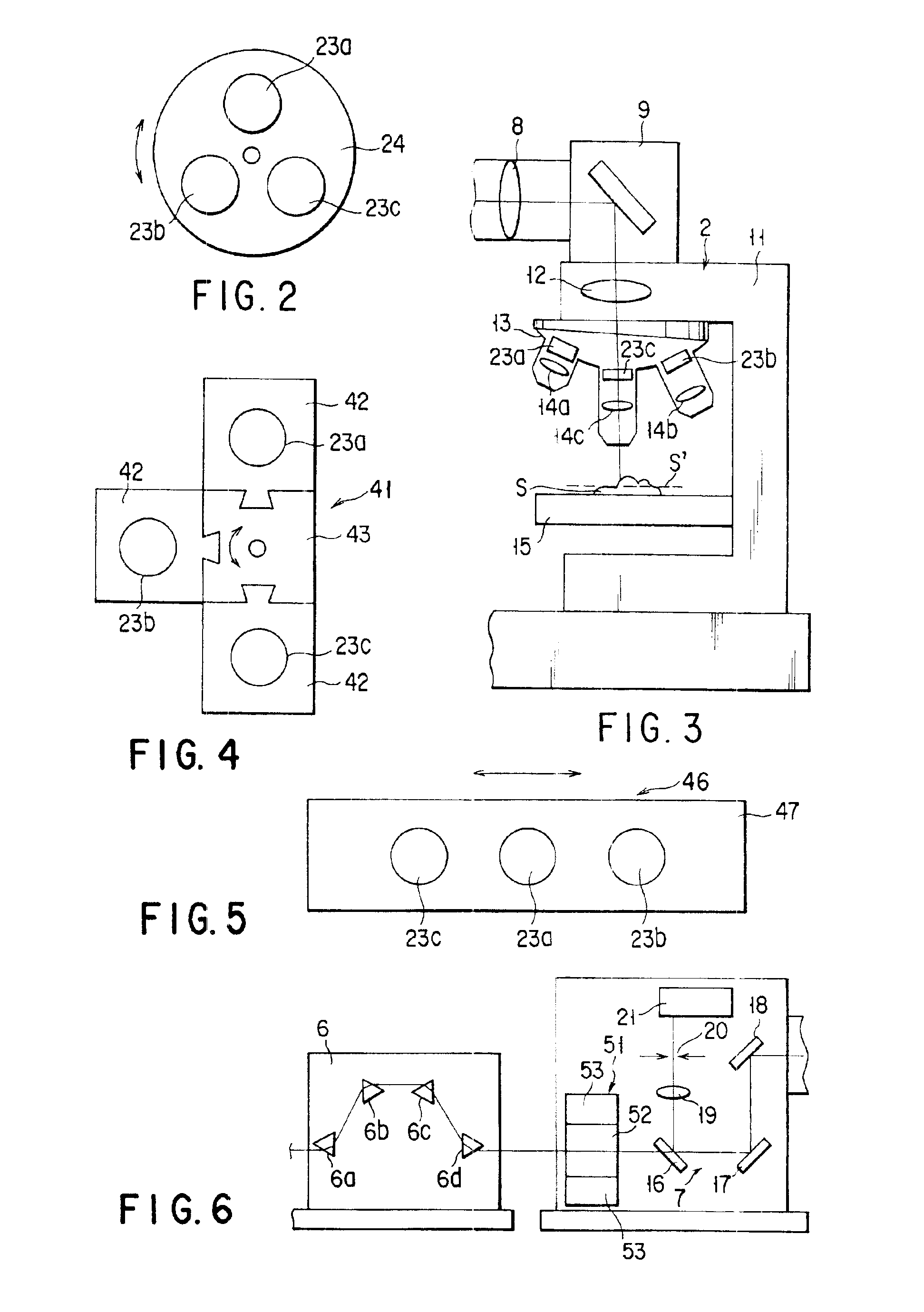
Microscope
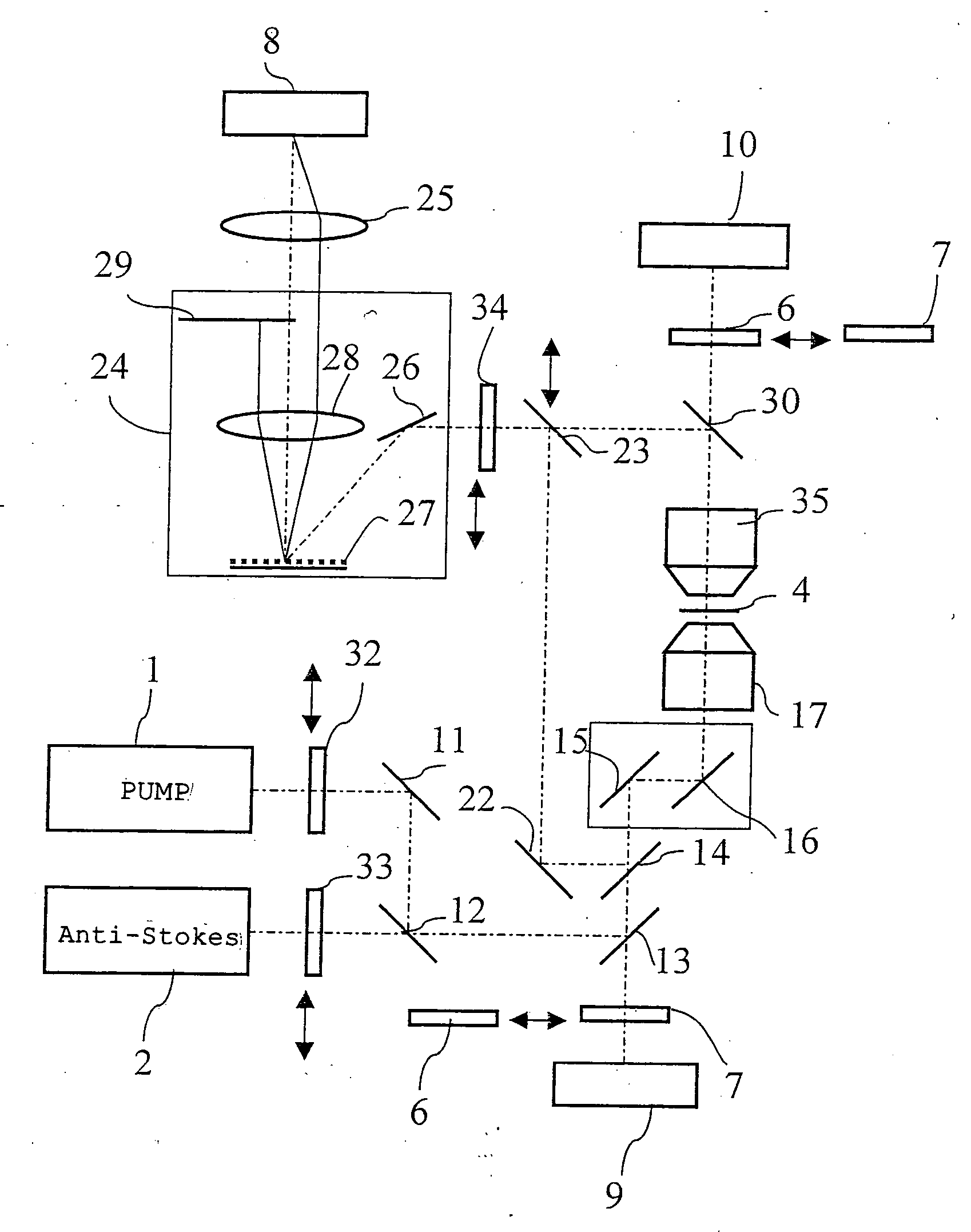
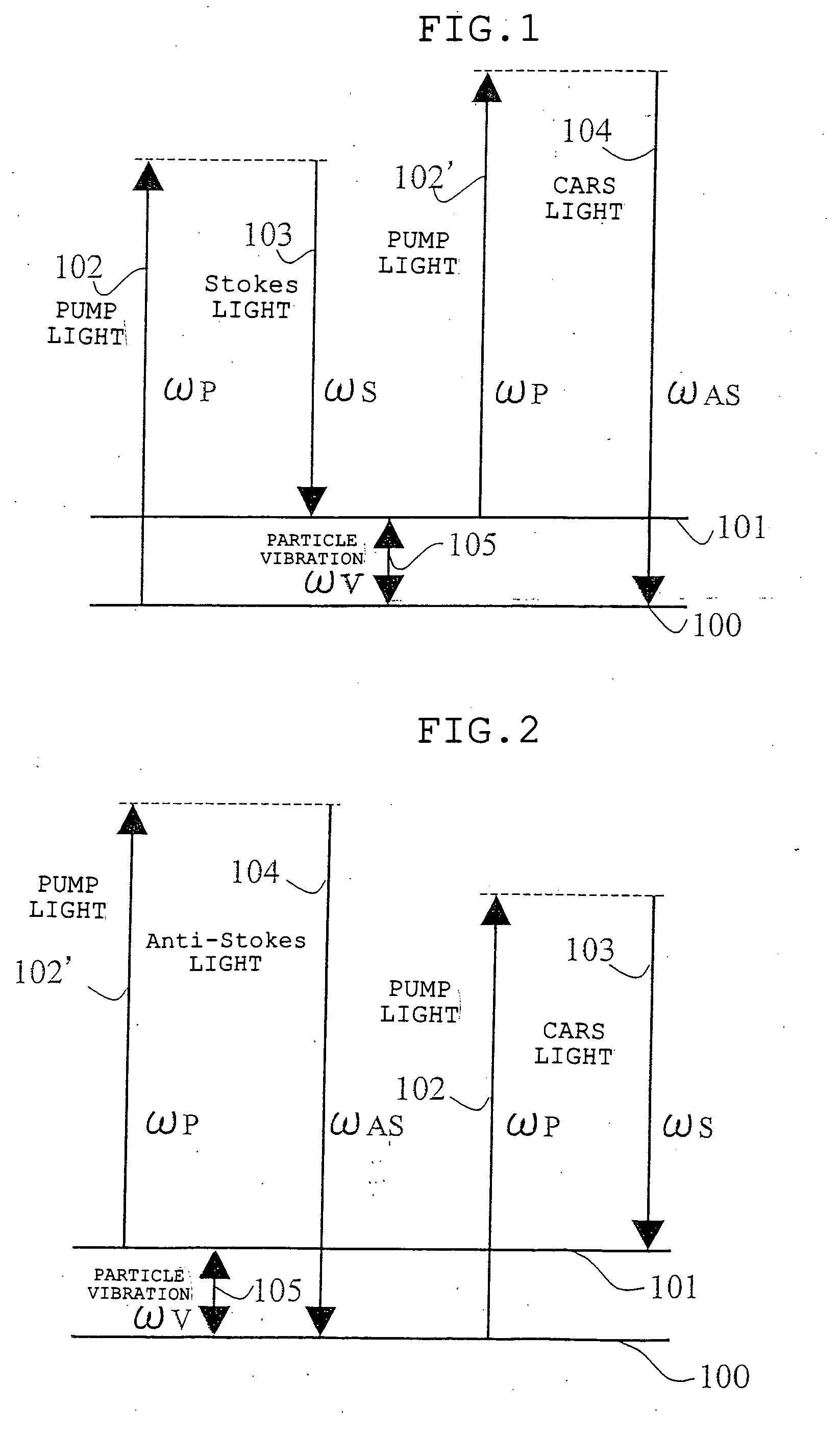
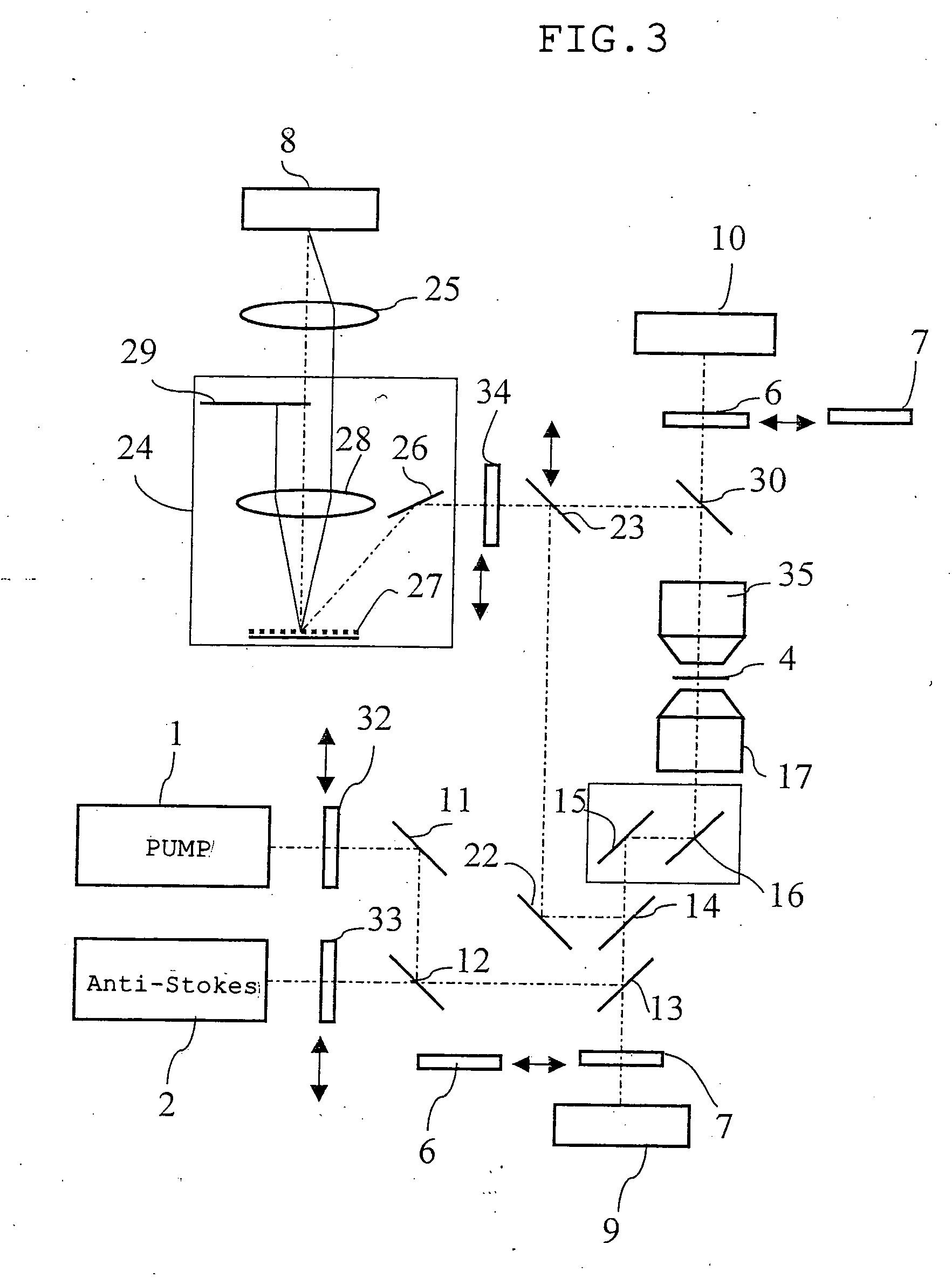
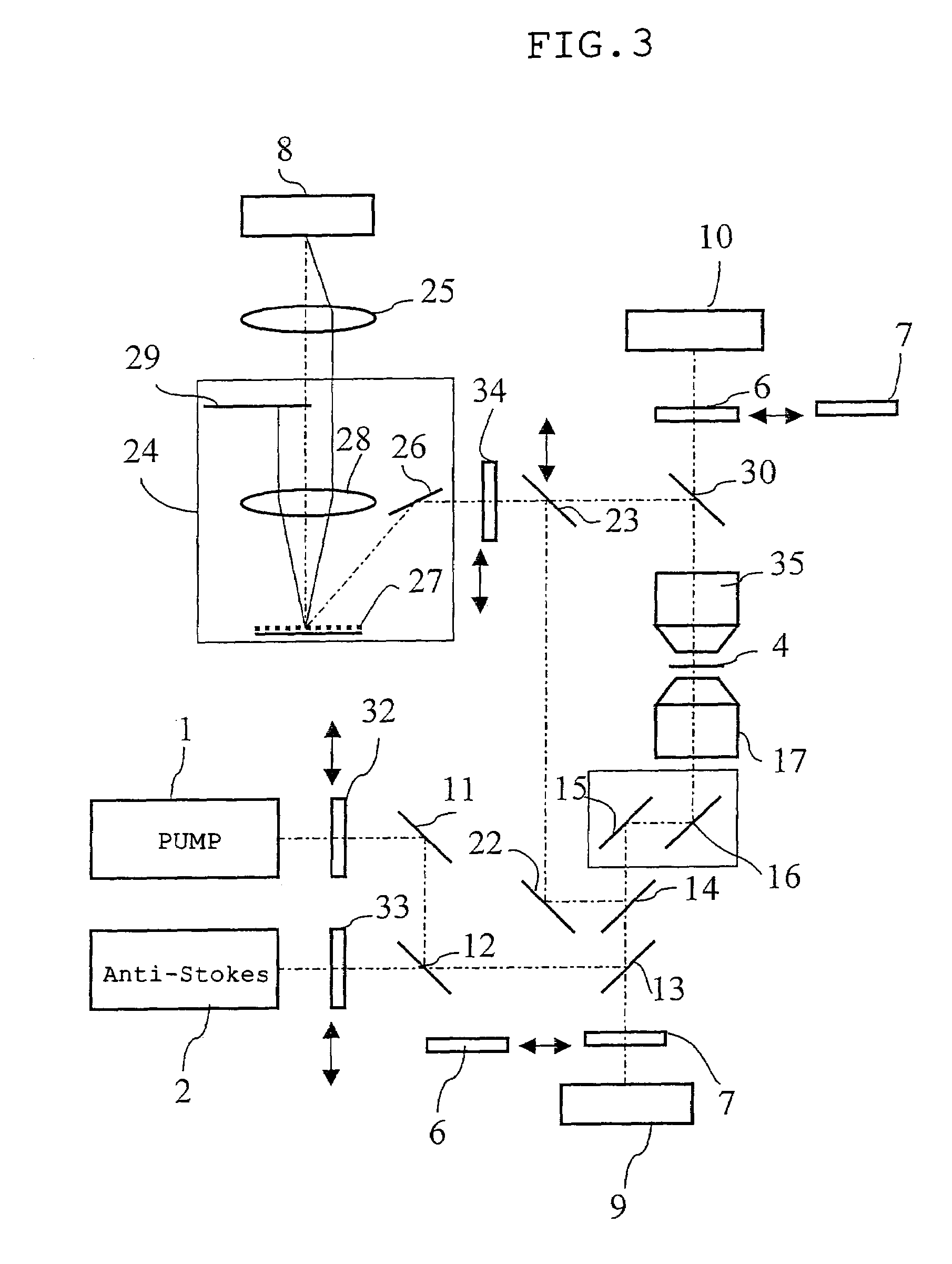
The microscope has a first pulsed laser generating means, a second pulsed laser generating means, an irradiation means to irradiate to a specimen by composing the first pulse light and the second pulse light, a coherent Raman scattering light extraction means for extracting only the coherent Raman scattering light from light emanated from the specimen irradiated, an extraction means for extracting only the multiphoton excitation fluorescence, an extraction means for extracting only the second harmonic wave, a detection means for detecting the extracted coherent Raman scattering light, and a detection means for detecting the extracted fluorescence, and a detection means for detecting the second harmonic wave via the extraction means 7. To single specimen, responding to purposes, observations of the two-photon excitation fluorescence observation, the second harmonic wave observation, and the coherent Raman scattering light observations can be carried out in parallel, or selectively.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
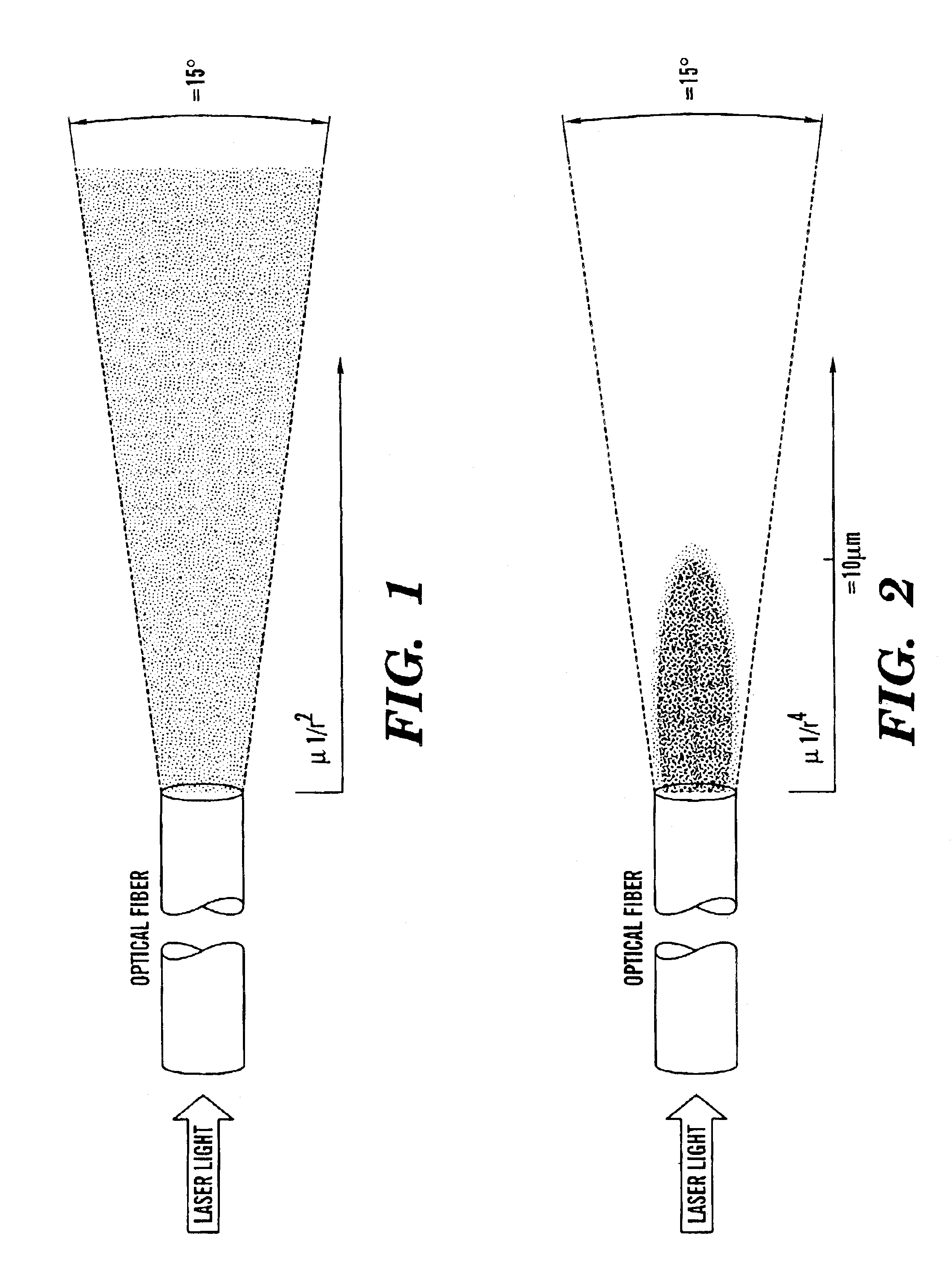
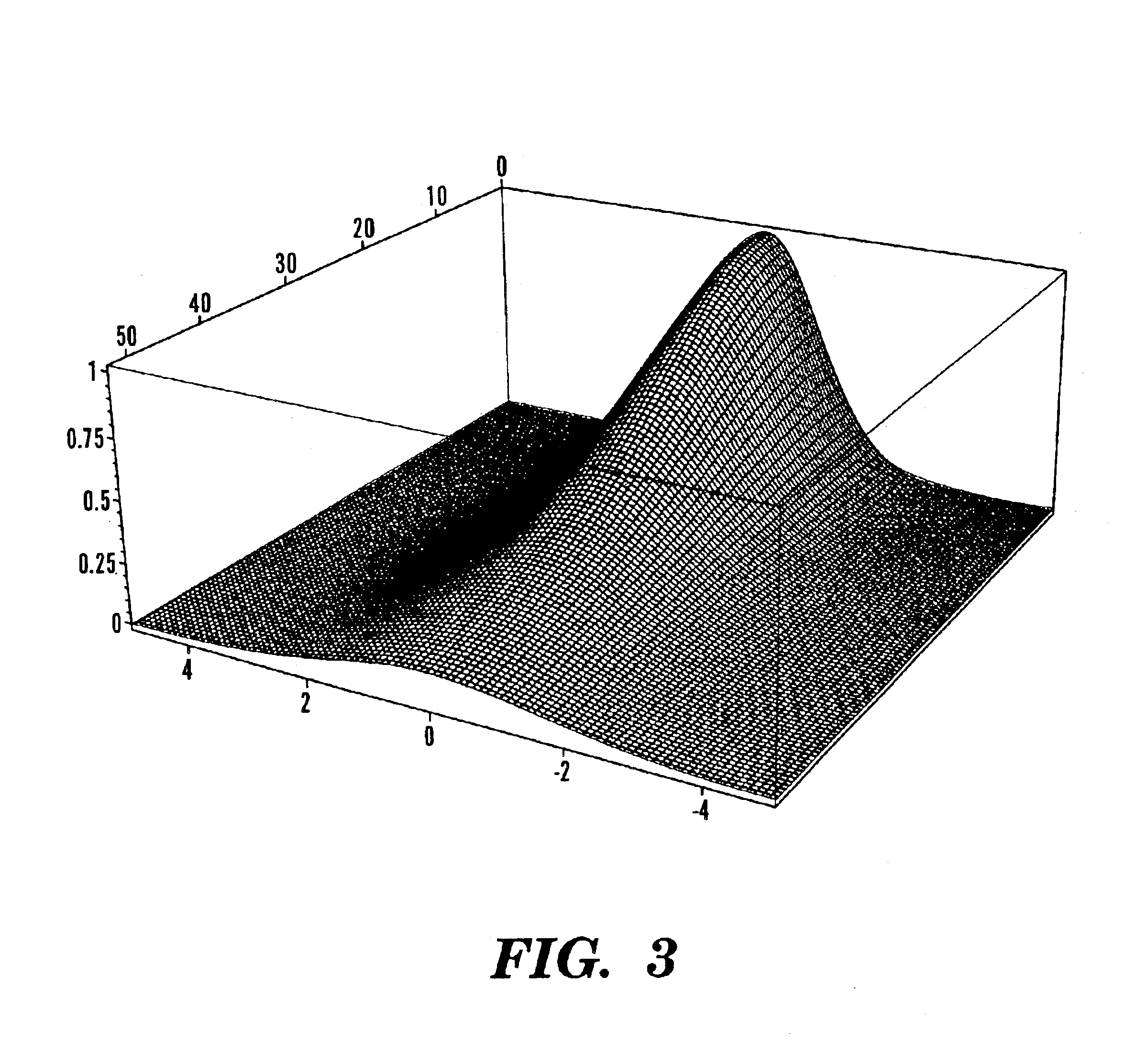
Optical fiber delivery and collection system for biological applications such as multiphoton microscopy, spectroscopy, and endoscopy
InactiveUS20050043636A1Improve spatial resolutionEfficient disseminationCladded optical fibreDiagnostics using lightCollection systemSpectroscopy
The present invention is directed to a method of applying radiation through an optical fiber for detecting disease within a plant or animal or other penetrable tissue, or imaging a particular tissue of a plant or animal. In addition, fluorescence and nonlinear scattering signals can be detected and localized within a subject by such application of radiation through an optical fiber. The radiation is effective to promote simultaneous multiphoton excitation. The optical fibers are used alone to examine internal regions of tissue, in conjunction with an optical biopsy needle to evaluate sub-surface tissue, or with an endoscope to evaluate tissue within body cavities. The present invention also relates to a device for coupling in radiation from an ultrashort mode-locked laser into the beam path of a microscope.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
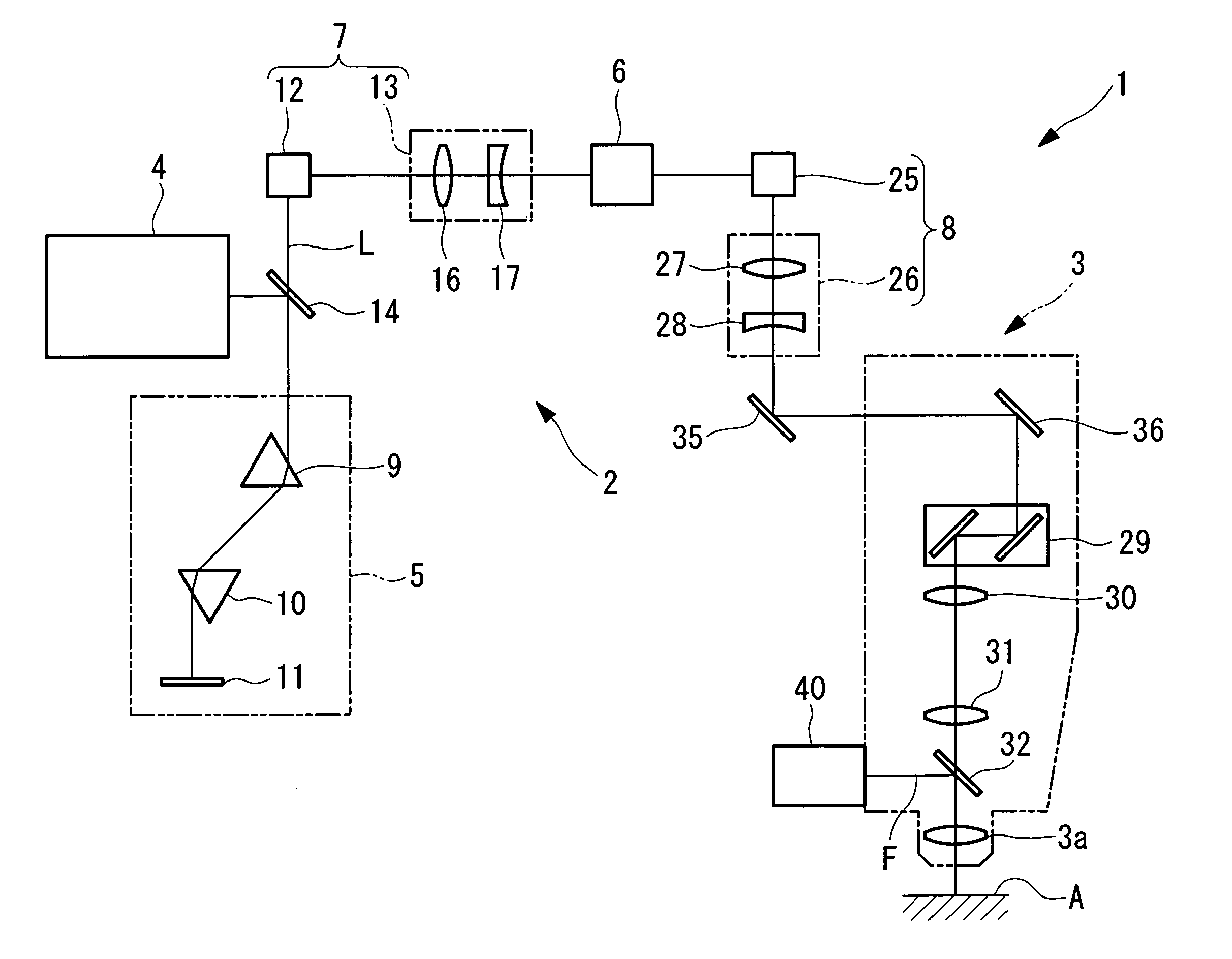
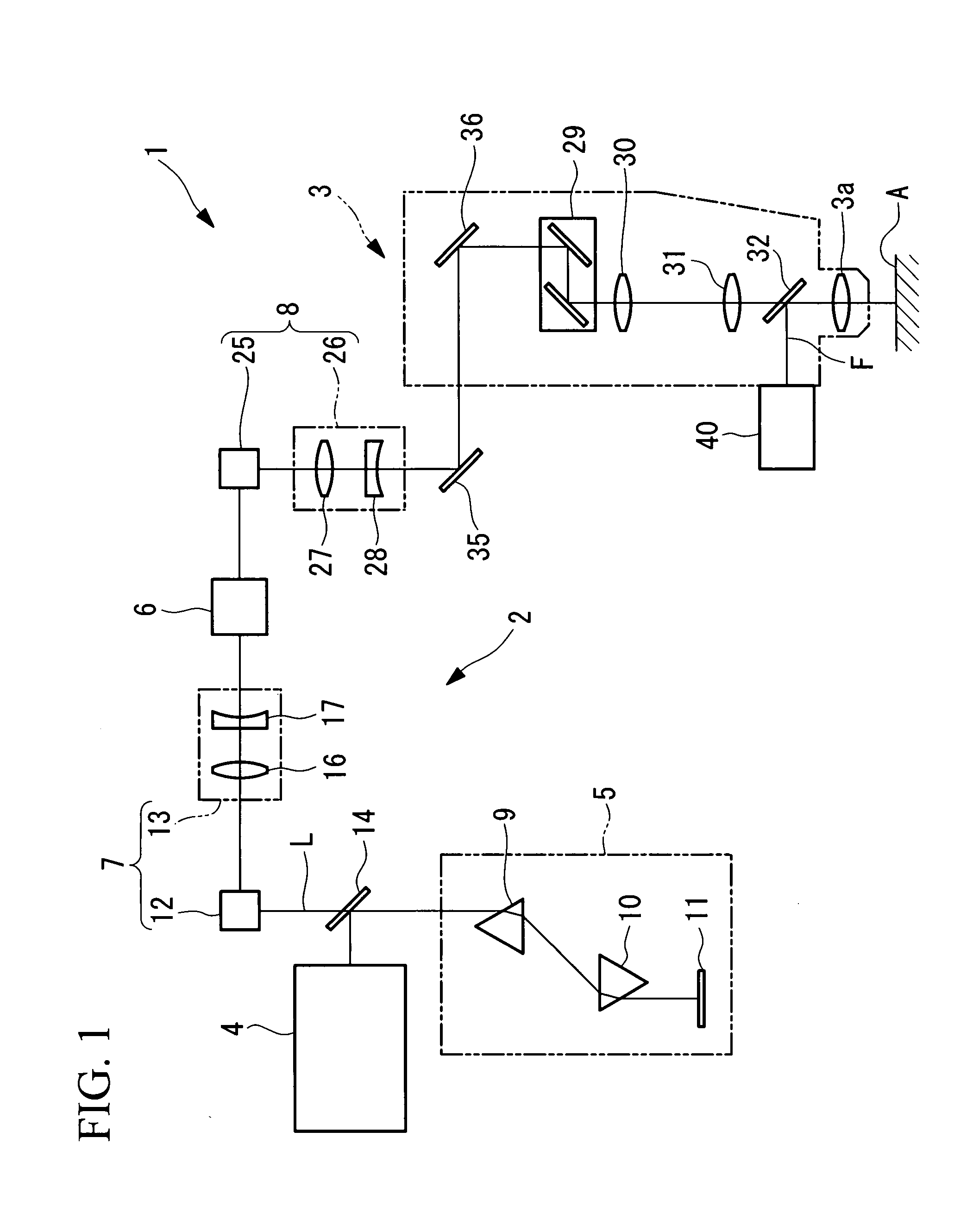
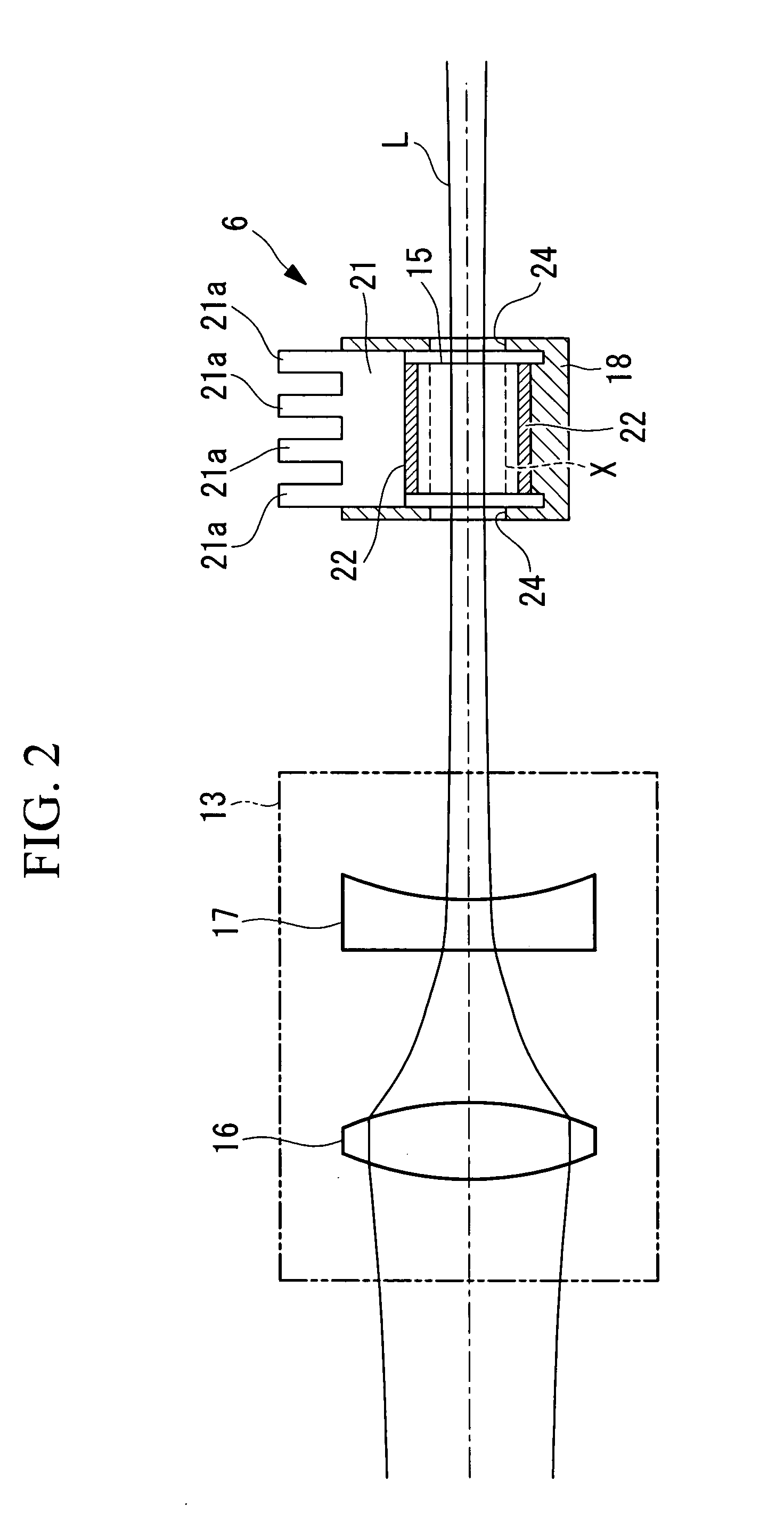
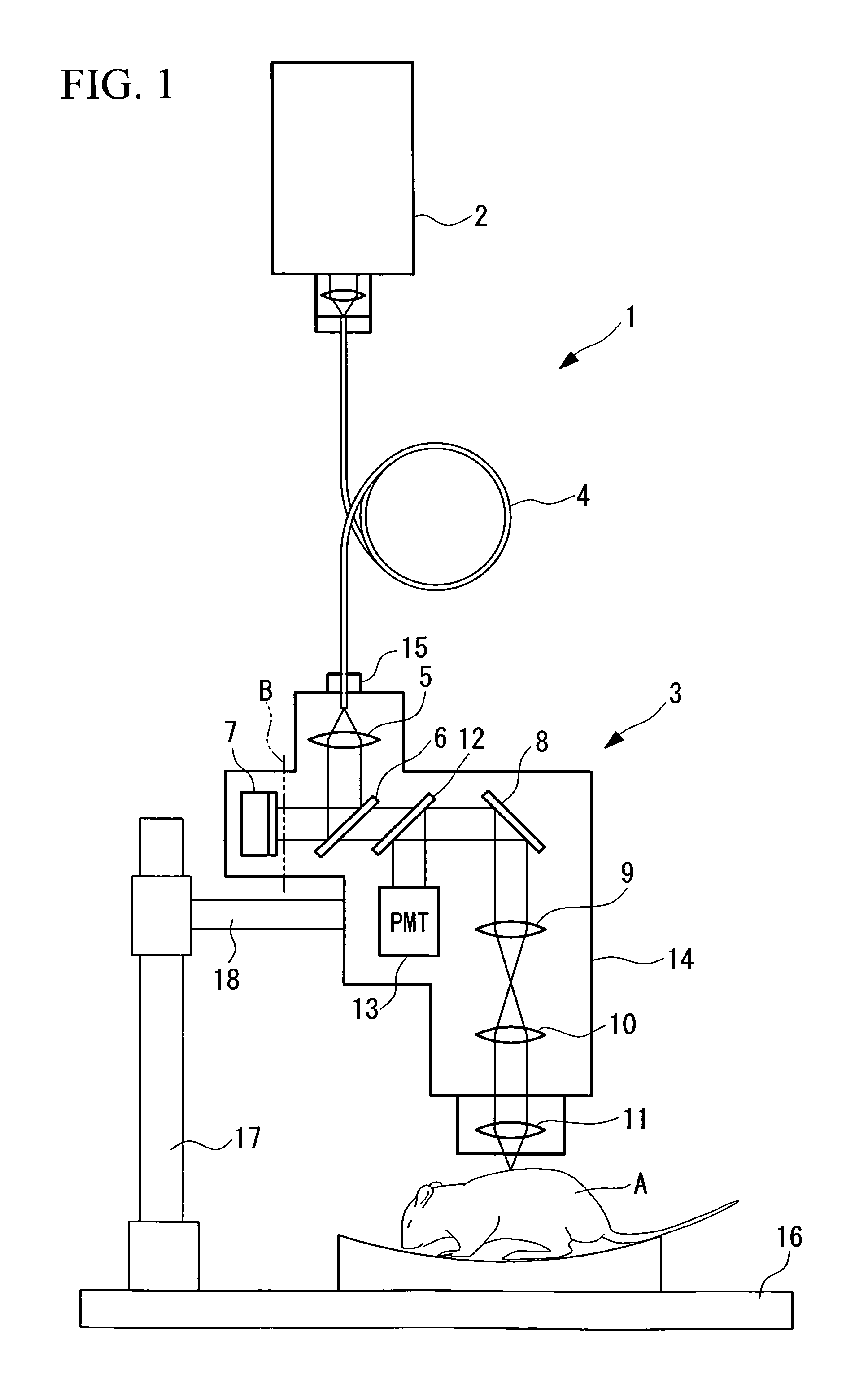
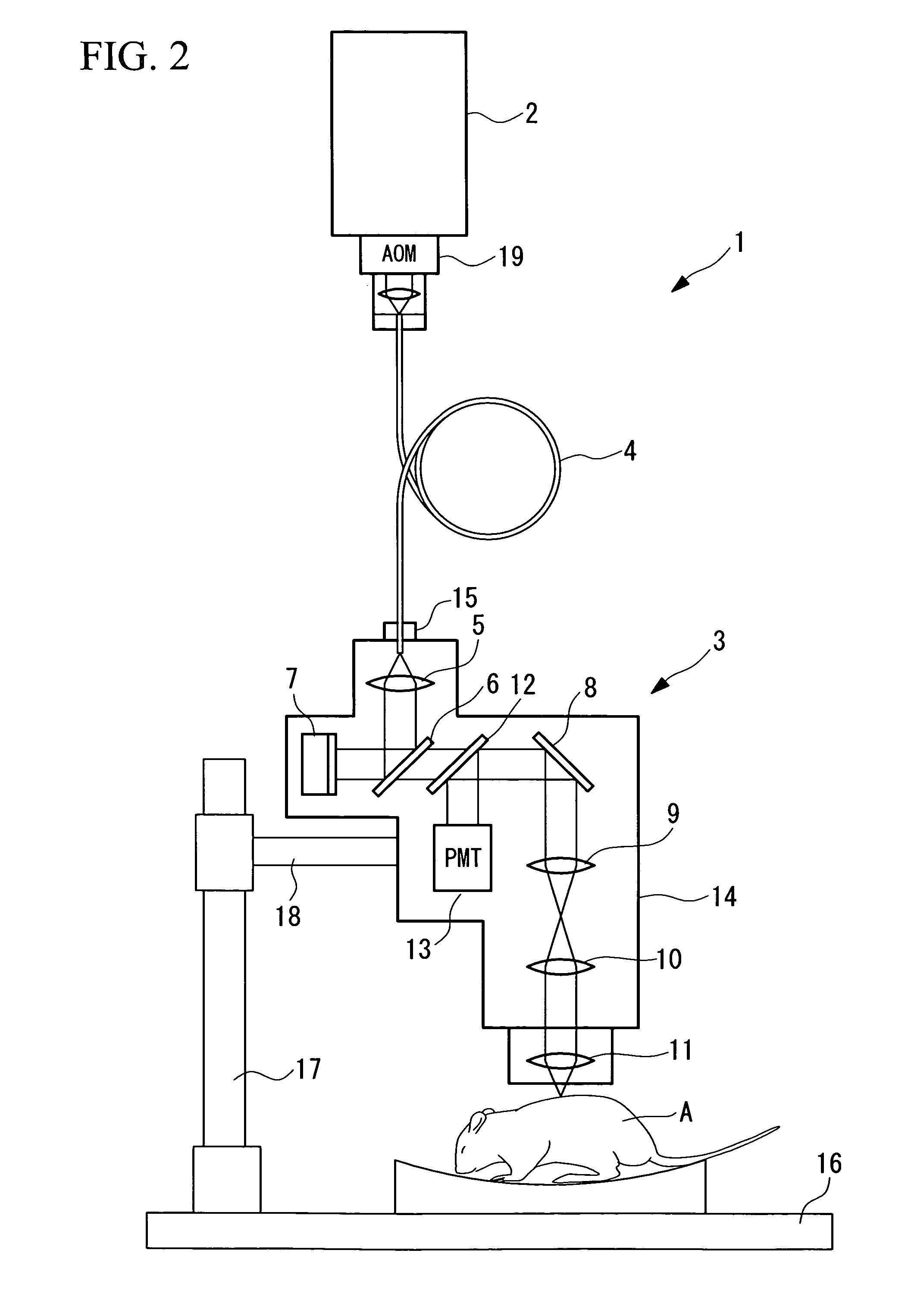
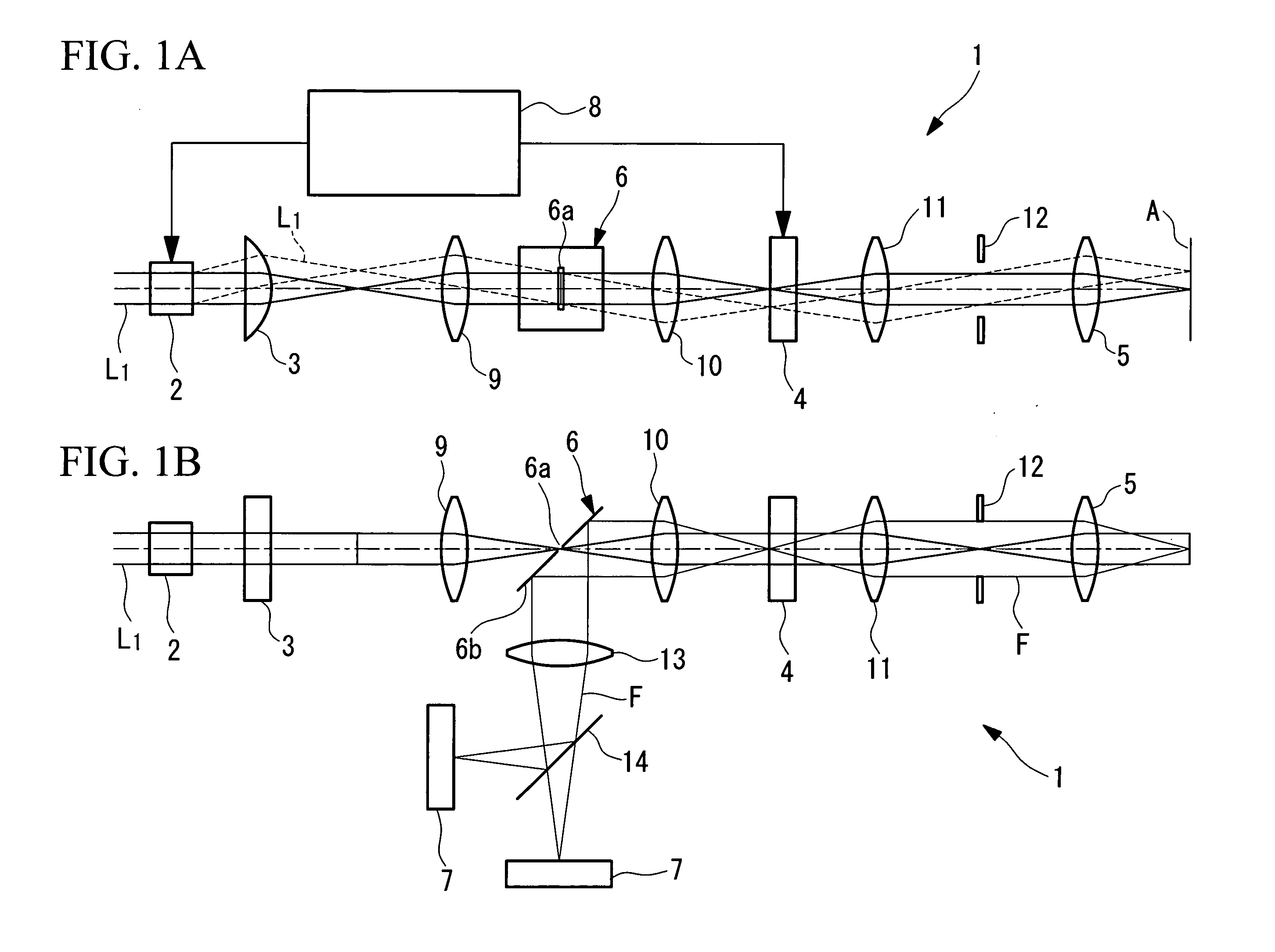
Multiphoton-excitation observation apparatus
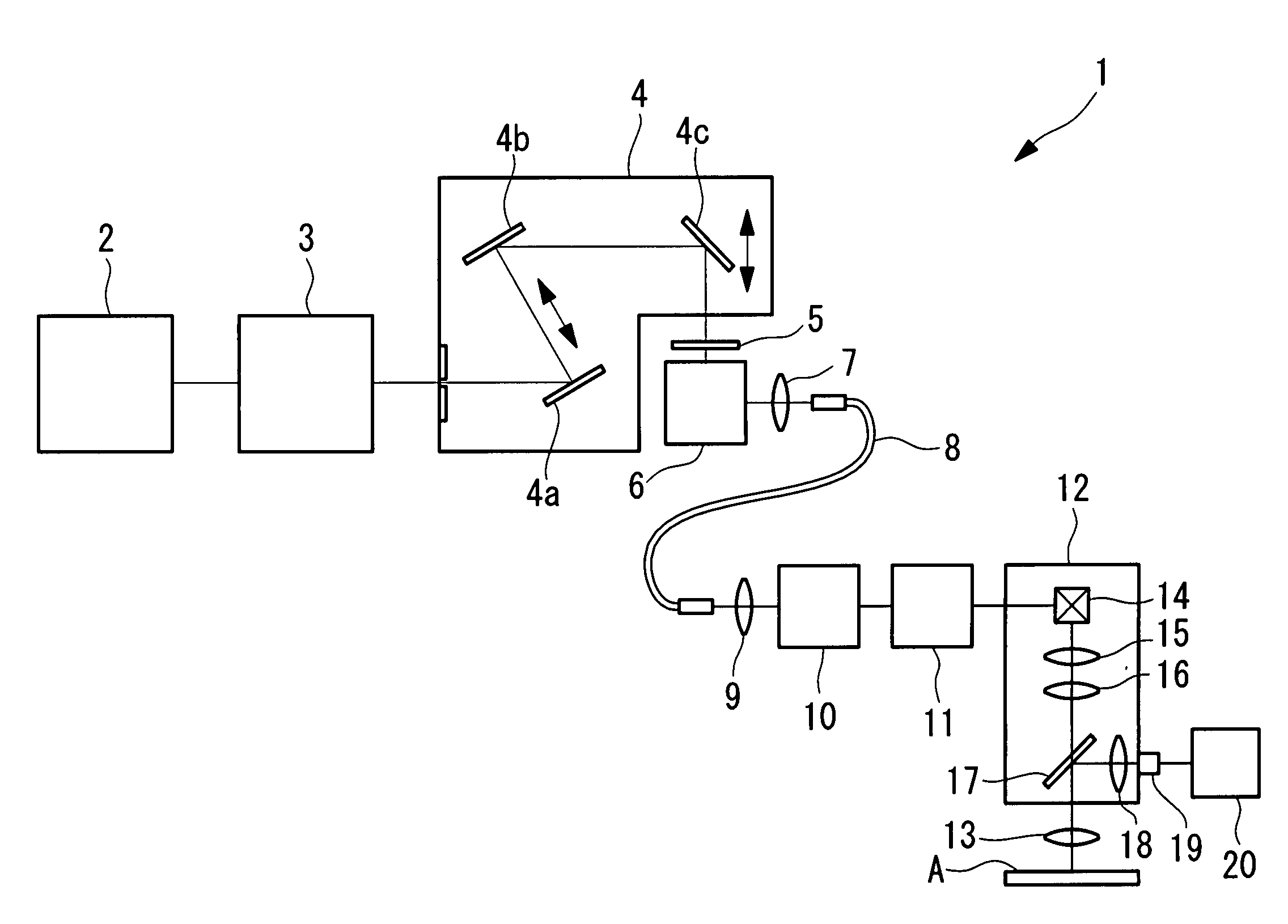
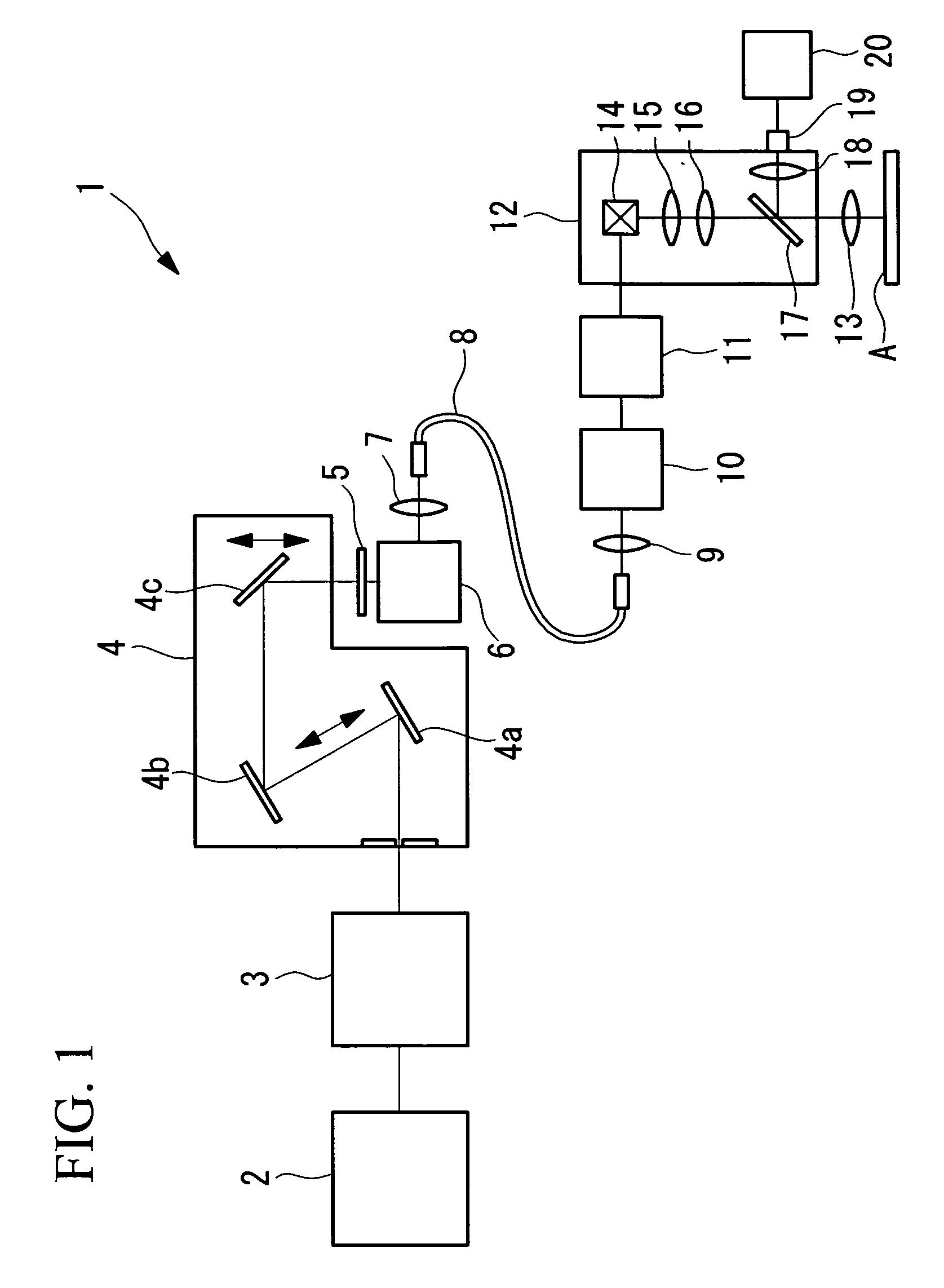
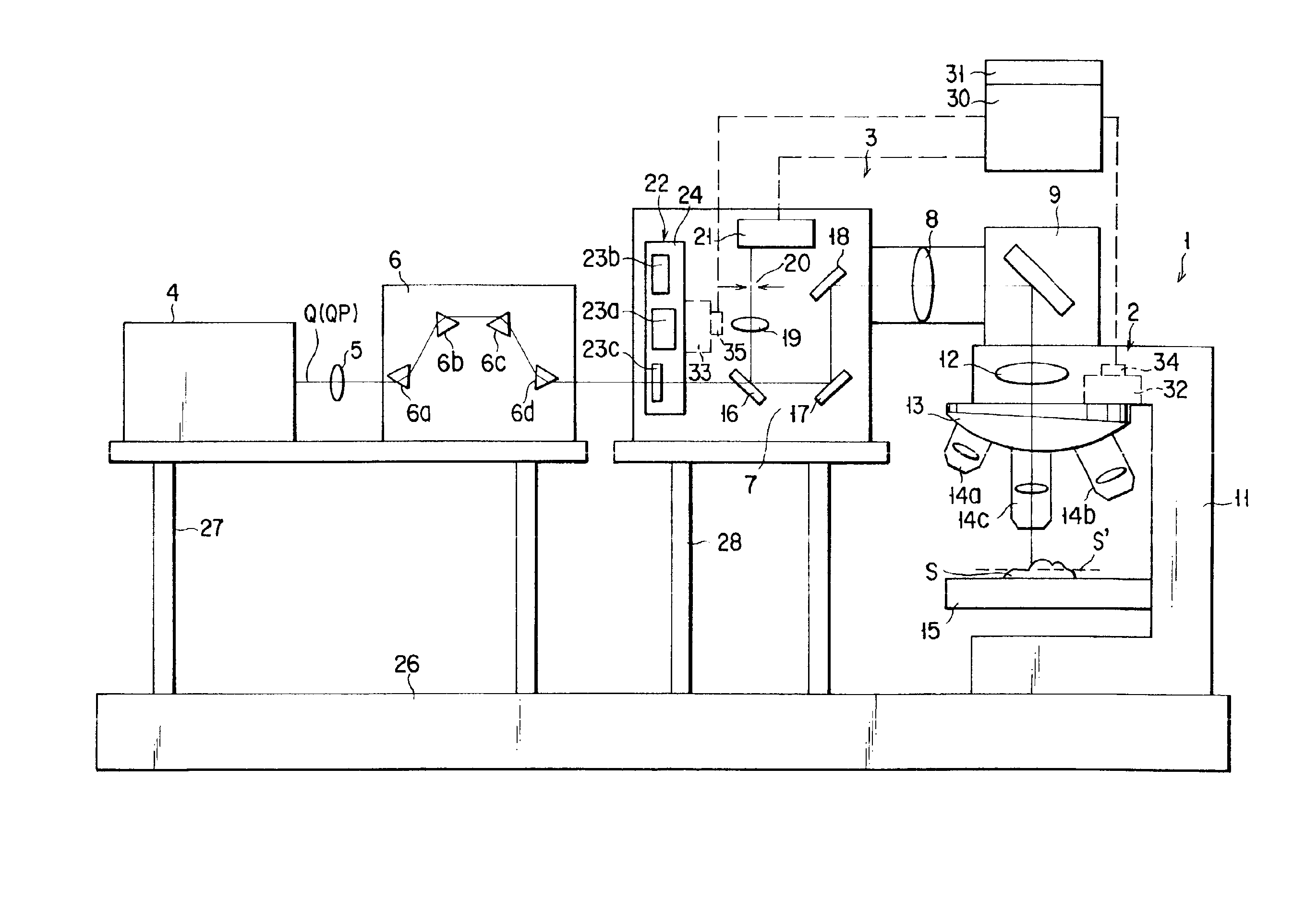
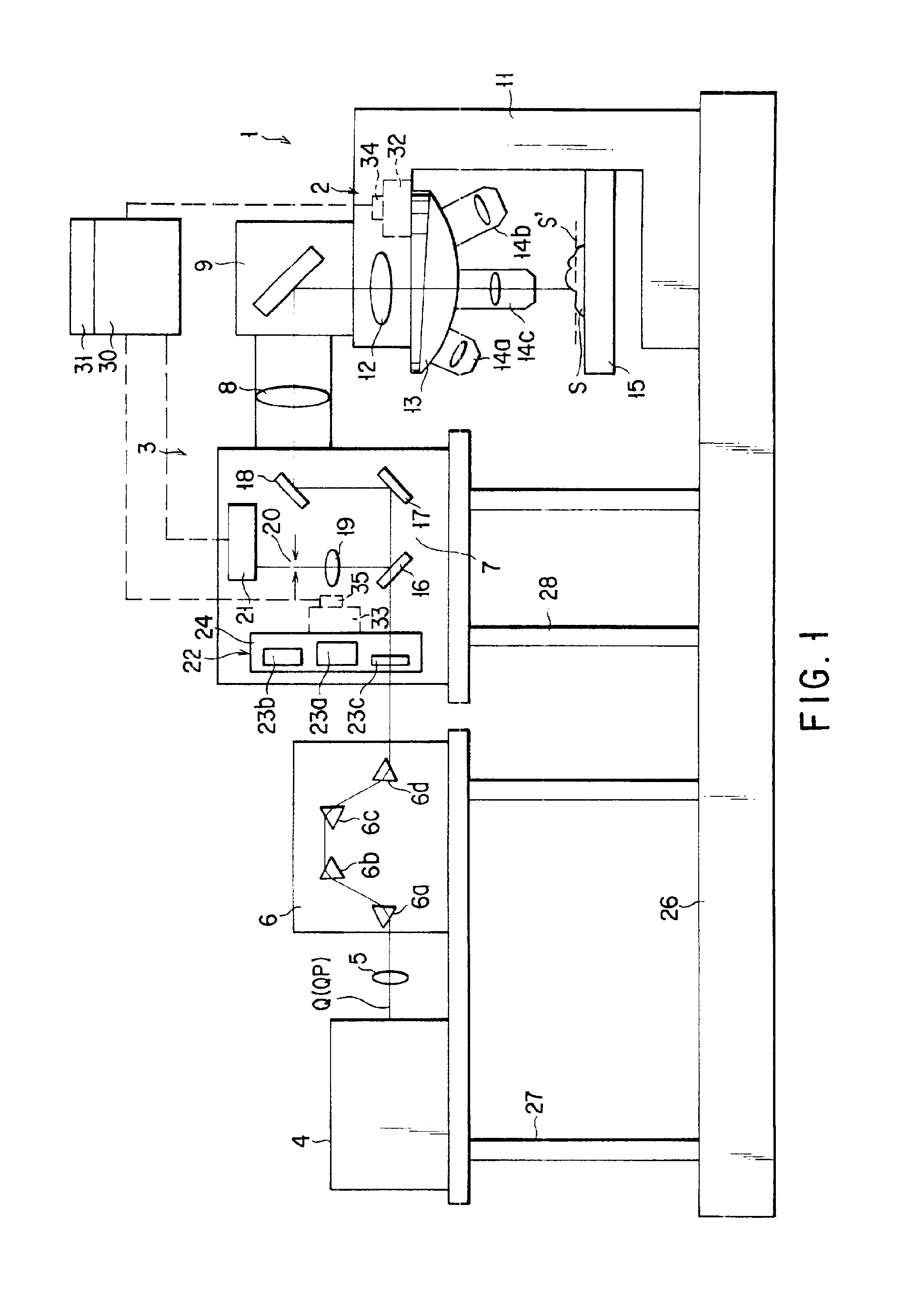
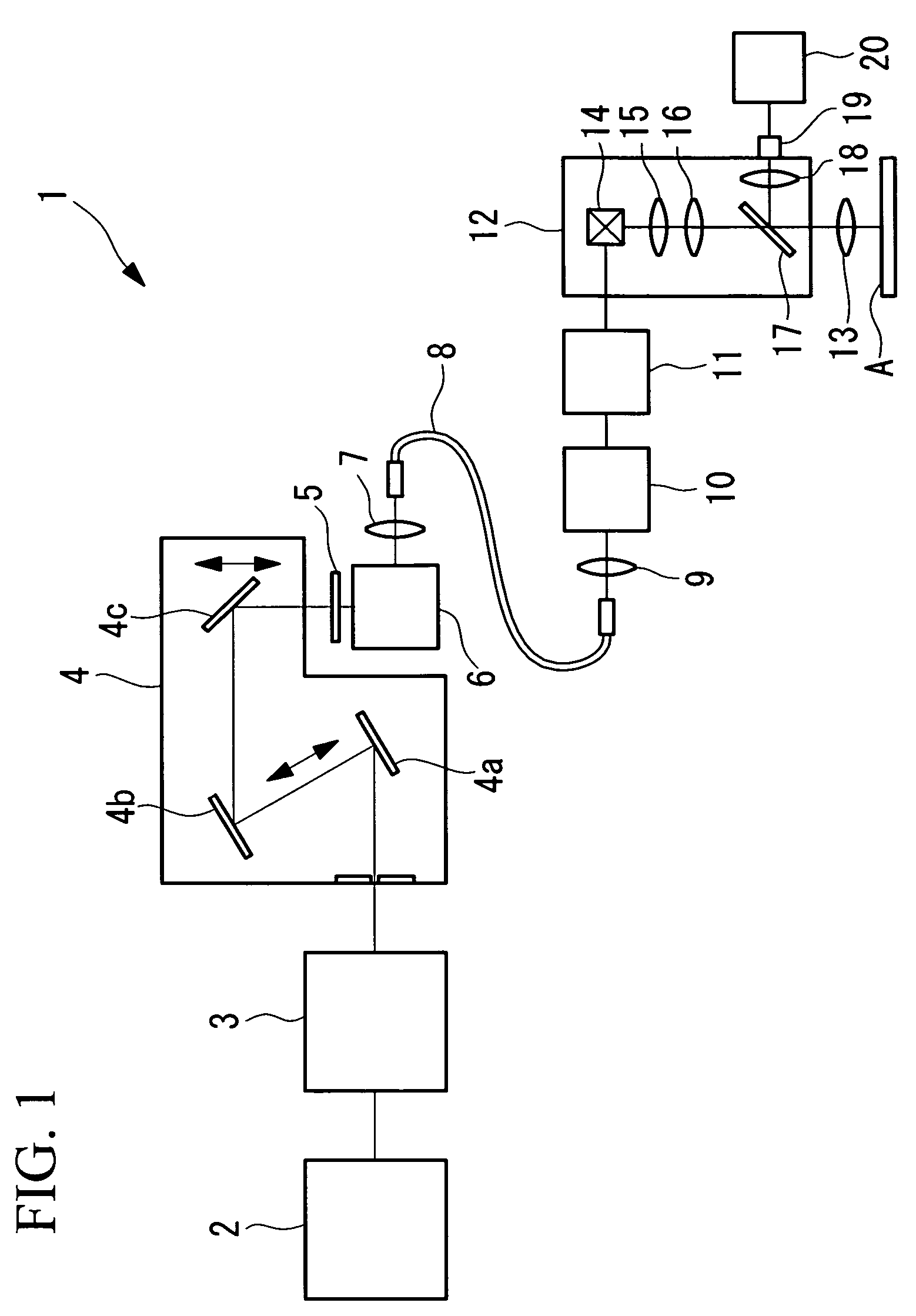
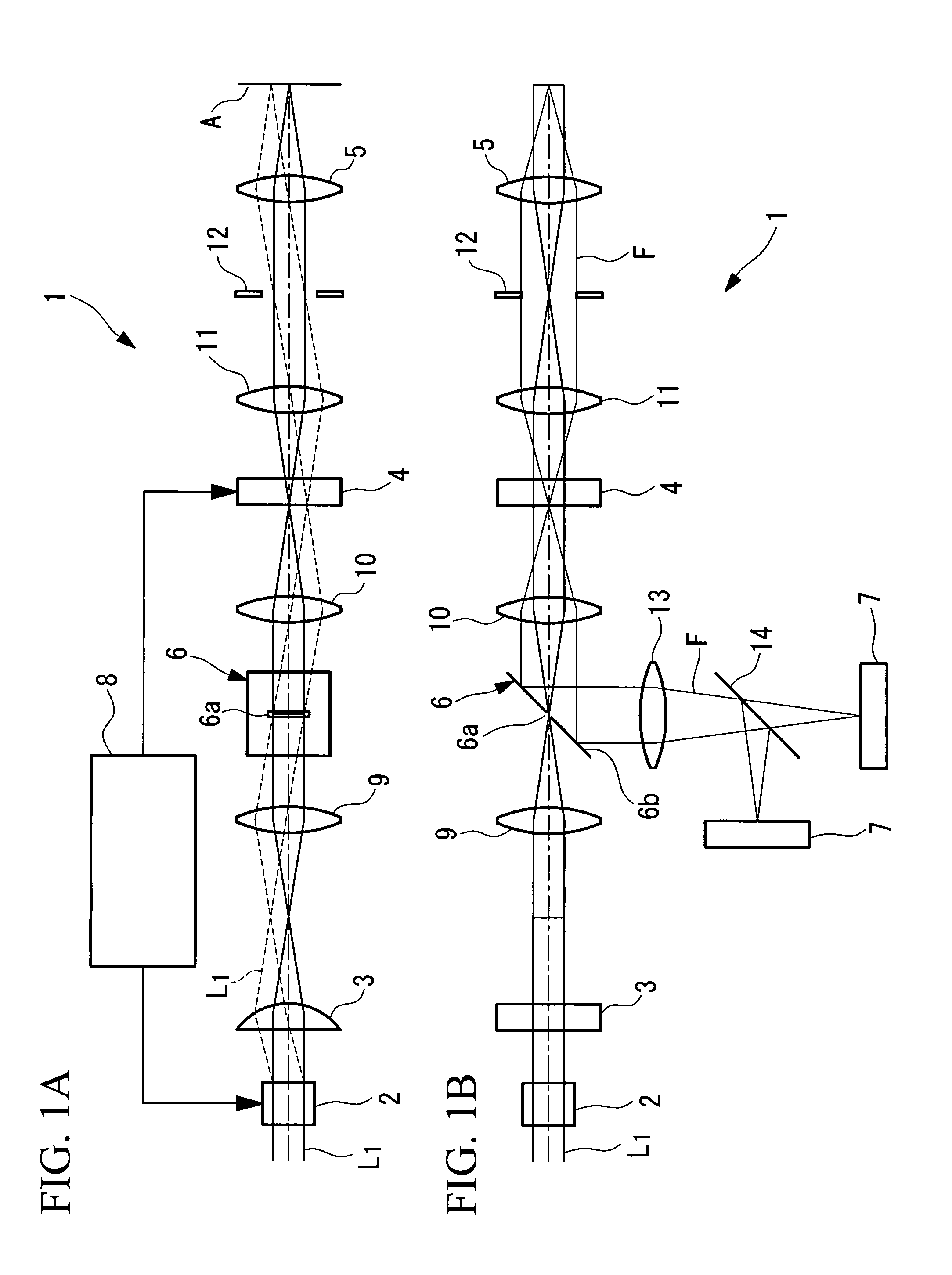
The invention provides a multiphoton-excitation observation apparatus comprising a light-source unit for emitting pulsed laser light; an observation apparatus main unit for irradiating a specimen with laser light emitted from the light-source unit and observing fluorescence emitted from the specimen; an incidence adjusting device, disposed between the light-source unit and the observation apparatus main unit, for adjusting the beam diameter of the laser light emitted from the light-source unit; and a control apparatus for controlling the incidence-adjusting unit according to the depth of an observation plane in the specimen.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
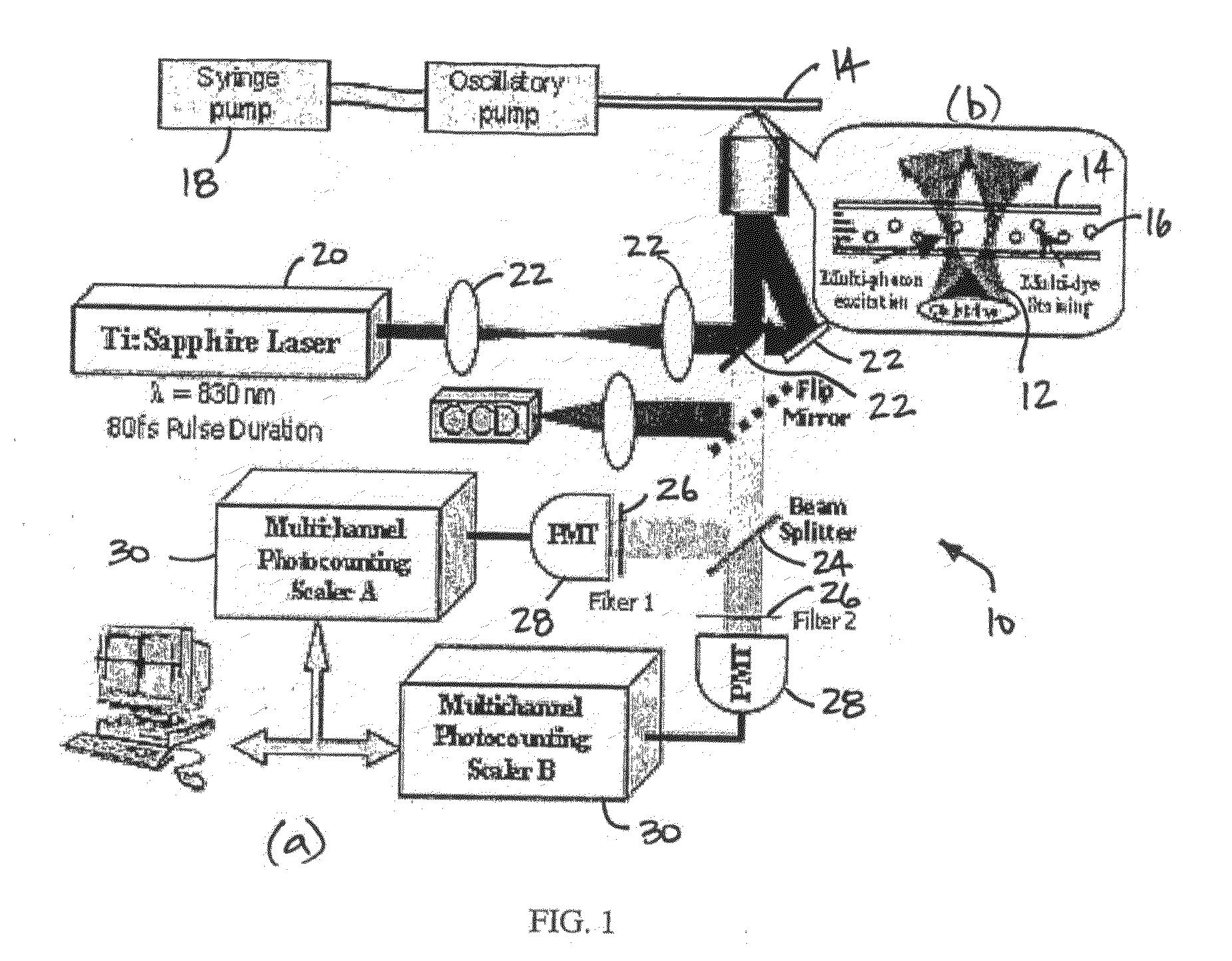
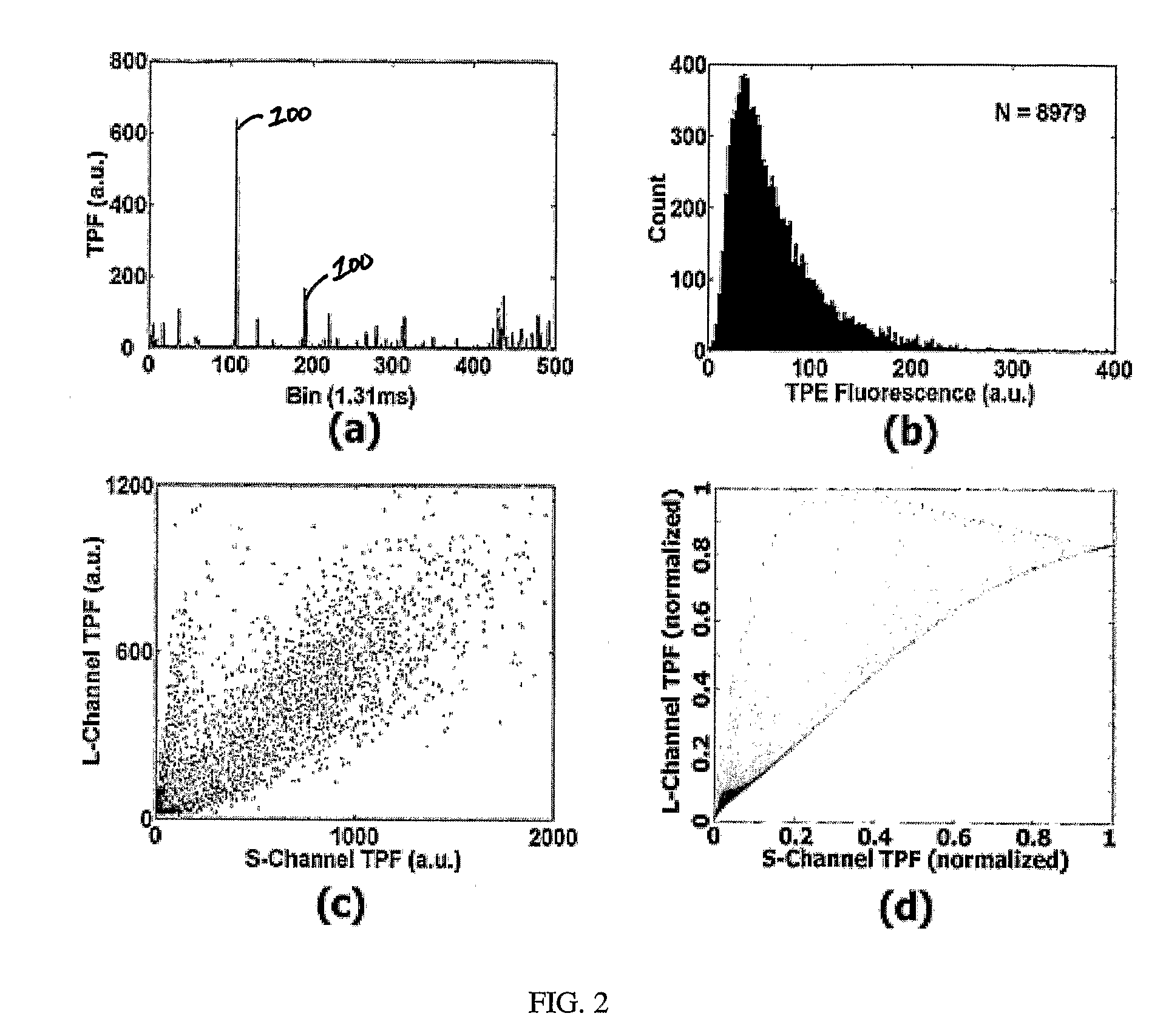
Quantitative Two-Photon Flow Cytometry
InactiveUS20080292555A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsLaser beamsAtomic physics
A method and apparatus of multi-dye analysis of particles using flow cytometer. The method includes dying particles to be detected using two or more dyes; urging the particles through a capillary in a non-uniform flow; exciting a first of the particles within the capillary using a multiphoton excitation laser beam causing the two or more dyes each to fluoresce thereby producing a first output signal and a second output signal respectively; and detecting the first output signal and the second output signal. A second of the particles within the capillary being excited using the multiphoton excitation laser beam causing the two or more dyes each to fluoresce thereby producing a third output signal and a forth output signal respectively. The method finally includes comparing a ratio of the first output signal and the second output signal to a ratio of the third output signal and the forth output signal to detect a desired change in the particles.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
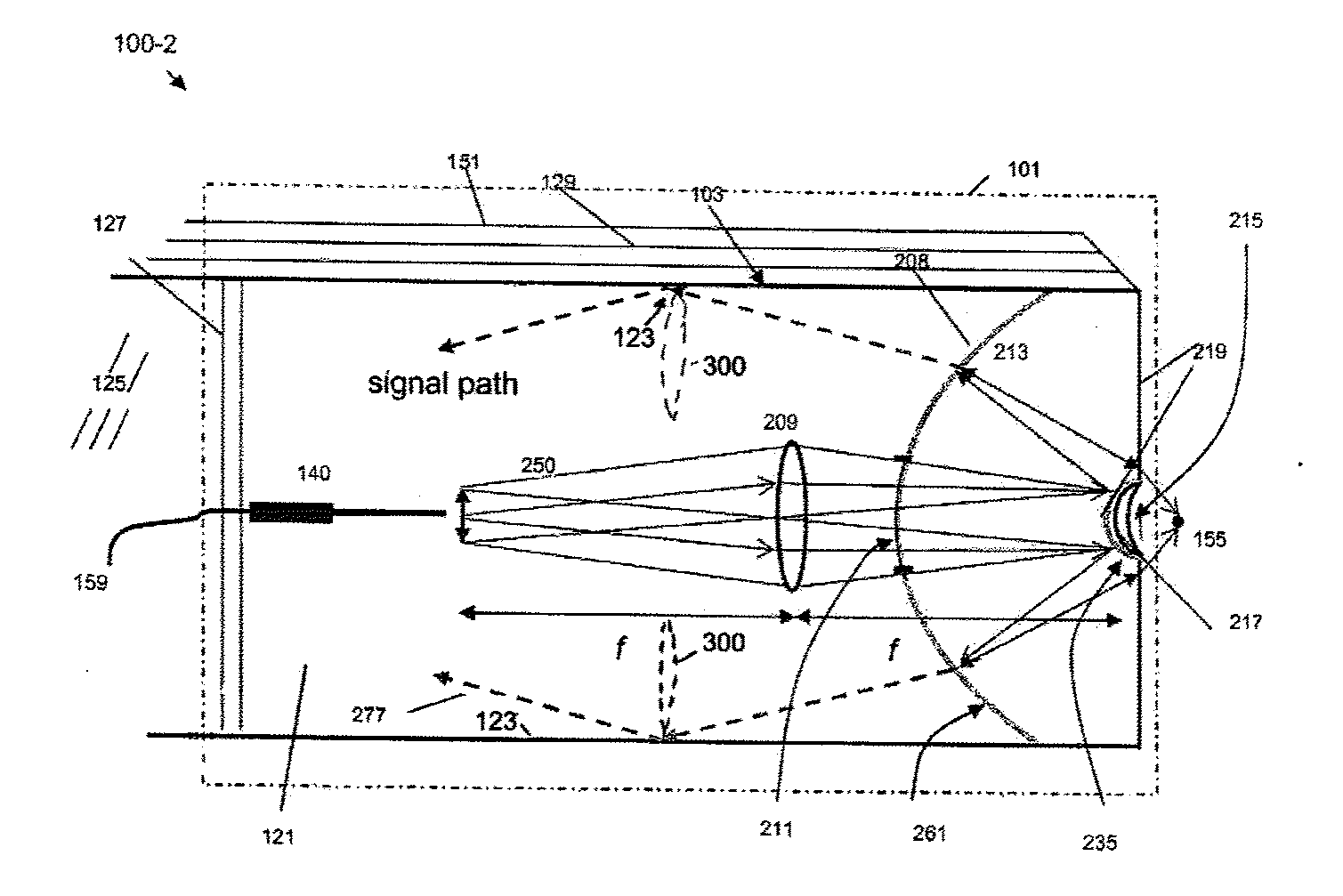
Multi-path, multi-magnification, non-confocal fluorescence emission endoscopy apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20120140301A1Convenient treatmentAccurate identificationMicroscopesTelescopesOptical scannersMagnification
An optical scanner, scanner apparatus, or scanner assembly, which may be particularly advantageous for use in a multiphoton microscope, includes a first drivable bending component, a second drivable bending component mounted perpendicularly to the first component, and at least one optical waveguide coupled one or both of the first and second bending components, wherein the at least one optical waveguide provides both a propagation path for a multiphoton excitation radiation delivery between a light source and a target and a multiphoton-induced emission radiation delivery between the target and a detector. A GRIN relay lens. A multiphoton microscope incorporating the scanner and the GRIN relay lens.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
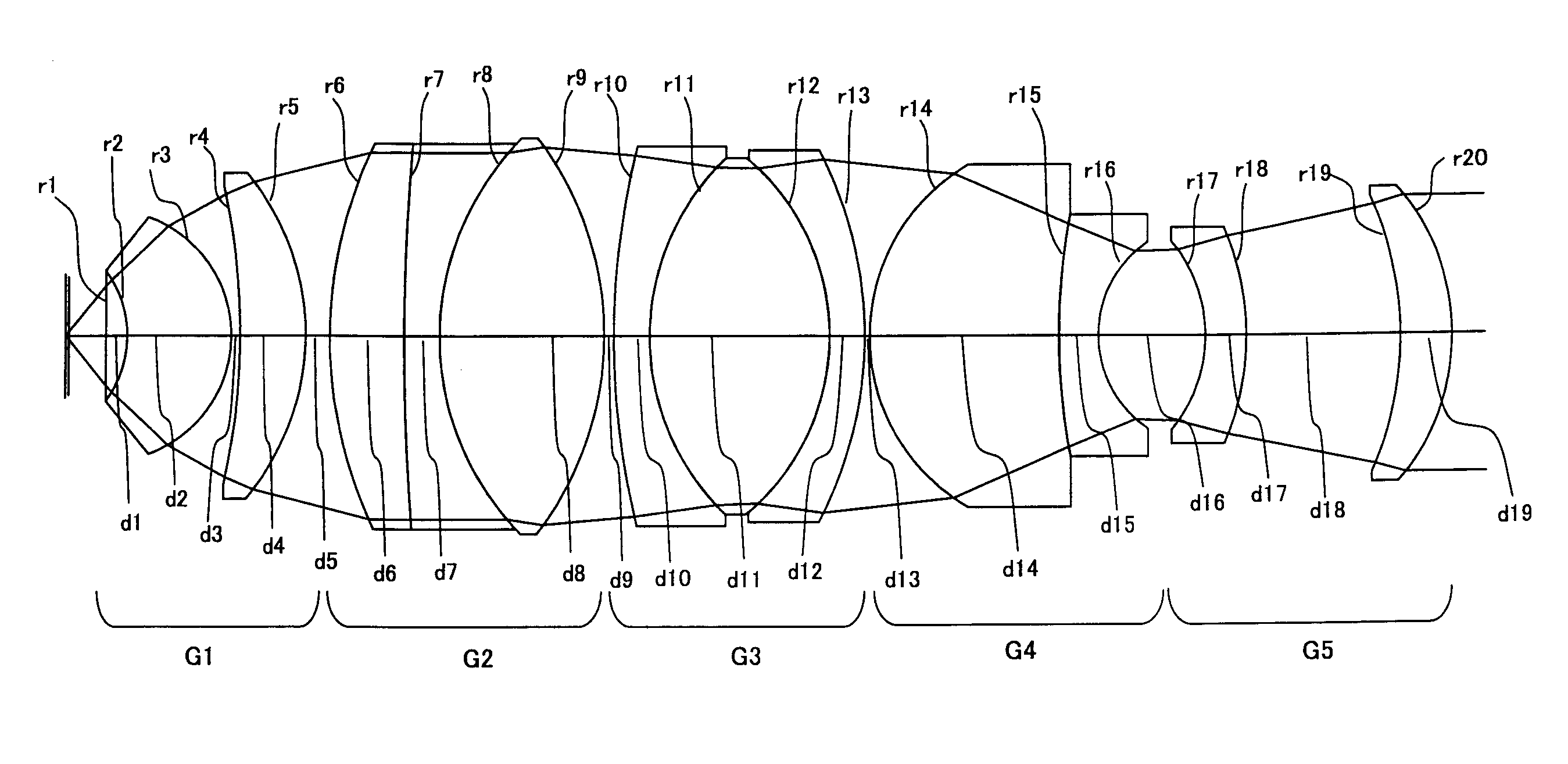
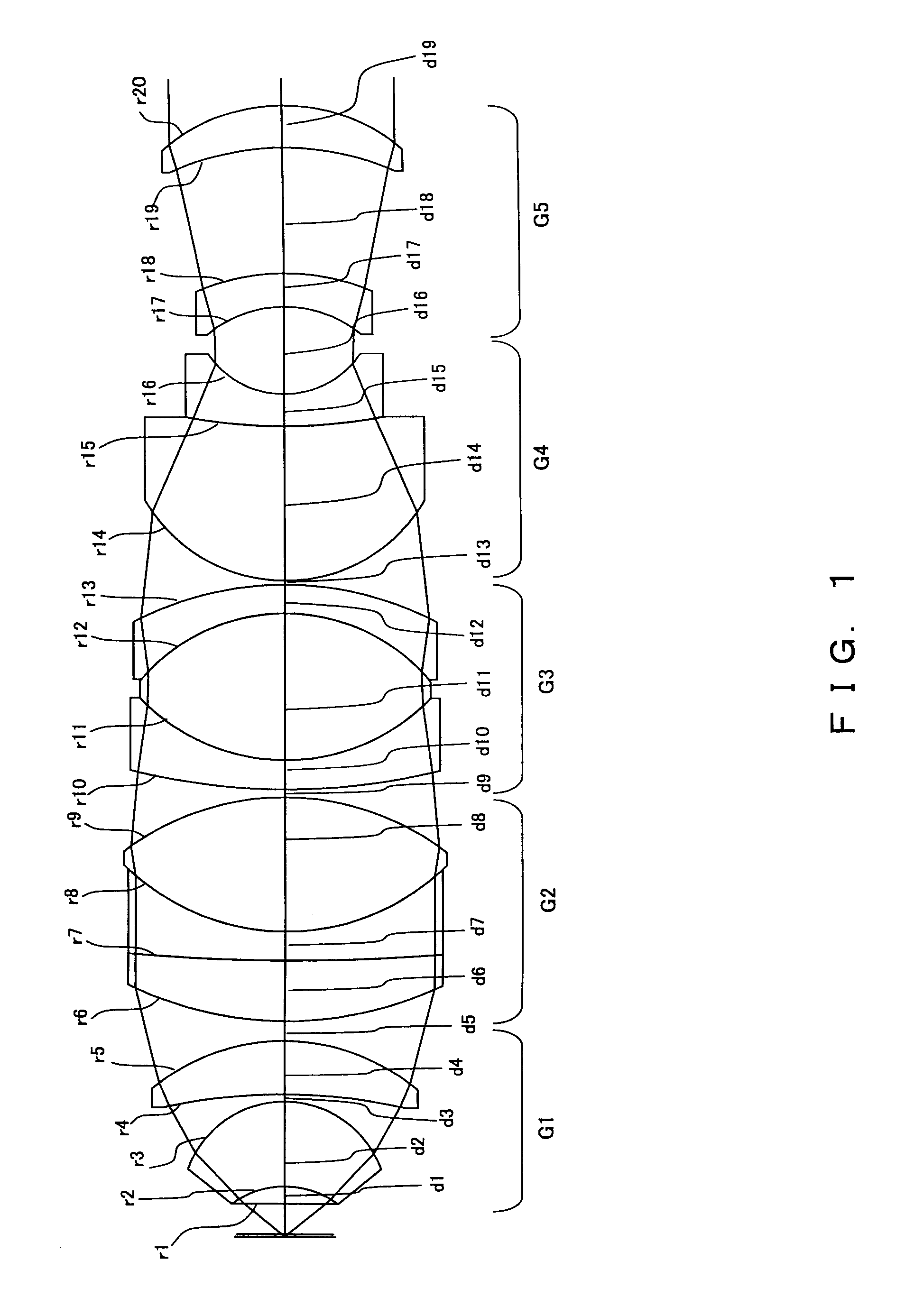
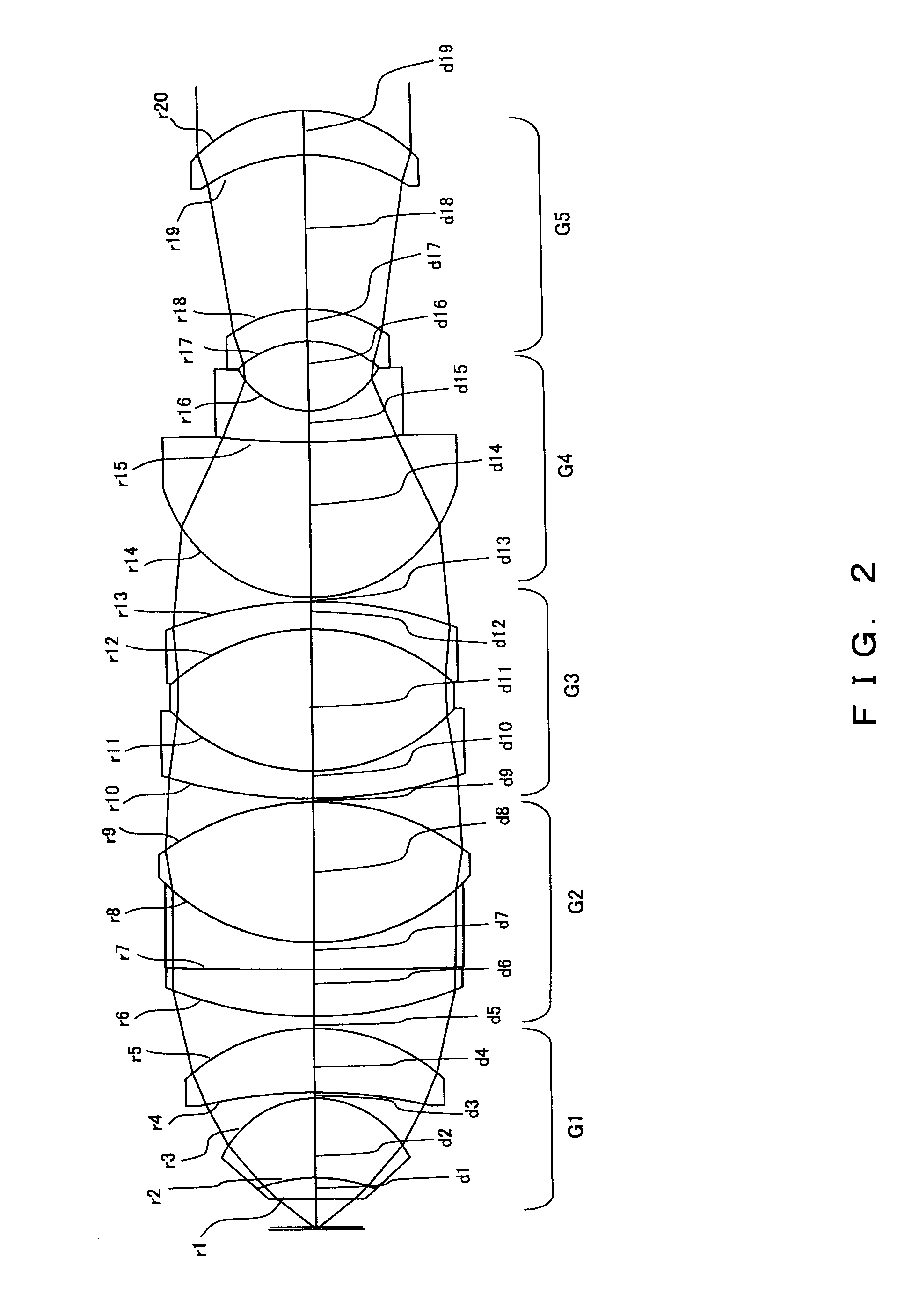
Immersion microscope objective and laser scanning microscope system using same
An immersion microscope objective formed of thirteen or fewer lens elements includes, in order from the object side, first and second lens groups of positive refractive power, a third lens group, a fourth lens group having negative refractive power with its image-side surface being concave, and a fifth lens group having positive refractive power with its object-side surface being concave. The first lens group includes, in order from the object side, a lens component that consists of a lens element of positive refractive power (when computed as being in air) and a meniscus lens element having its concave surface on the object side. Various conditions are satisfied to ensure that images of fluorescence, obtained when the immersion microscope objective is used in a laser scanning microscope that employs multiphoton excitation to observe a specimen, are bright and of high resolution. Various laser scanning microscopes are also disclosed.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
Laser microscope apparatus
Observation is performed using bright, clear multiphoton fluorescence images produced by efficiently generating a multiphoton excitation effect, without the need for a complex interference film structure. The invention employs a laser microscope apparatus including a first dichroic mirror that reflects visible laser light guided via a first light path and that transmits IR pulsed laser light guided via a second light path to combine the first light path and the second light path; an XY galvanometer mirror that scans the laser light from the first dichroic mirror on a specimen; an objective lens that irradiates the specimen with the scanned laser light and that collects fluorescence produced in the specimen; a second dichroic mirror that reflects the visible laser light and transmits the fluorescence from the specimen; and a detection unit that detects the fluorescence transmitted through the second dichroic mirror.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
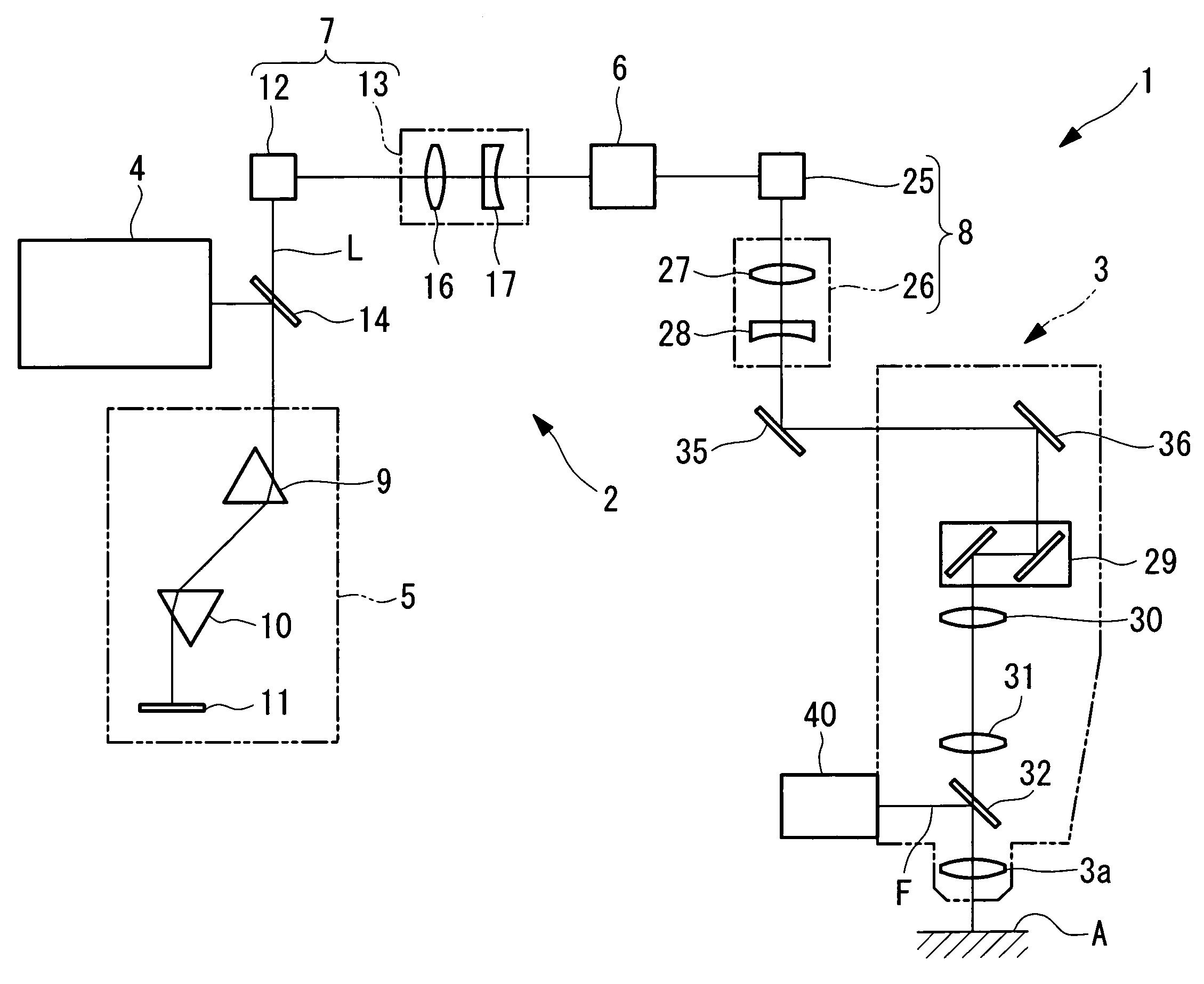
Multiphoton-excitation-type examination apparatus
InactiveUS20050279950A1Generate efficientlyEasy to adjustBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsPhotometryGroup velocity dispersionLaser light
The invention provides a multiphoton-excitation-type examination apparatus that efficiently generates a multiphoton-excitation effect, that makes the measurement head compact, and that can be easily adjusted when the measurement head is replaced. The multiphoton-excitation-type examination apparatus comprises a laser light source that oscillates ultrashort pulsed laser light; an optical fiber that transmits the ultrashort pulsed laser light from the laser light source; a support member; a measurement head supported on the support member so as to be movable upwards and downwards and at an angle, and having an optical system that irradiates a specimen with the ultrashort pulsed laser light transmitted by the optical fiber that measures fluorescence or reflected light coming from the specimen; and a dispersion-compensating member, in the measurement head, that compensates for group velocity dispersion of the ultrashort pulsed laser light irradiated onto the specimen.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Three dimensional optical beam induced current (3-D-OBIC)
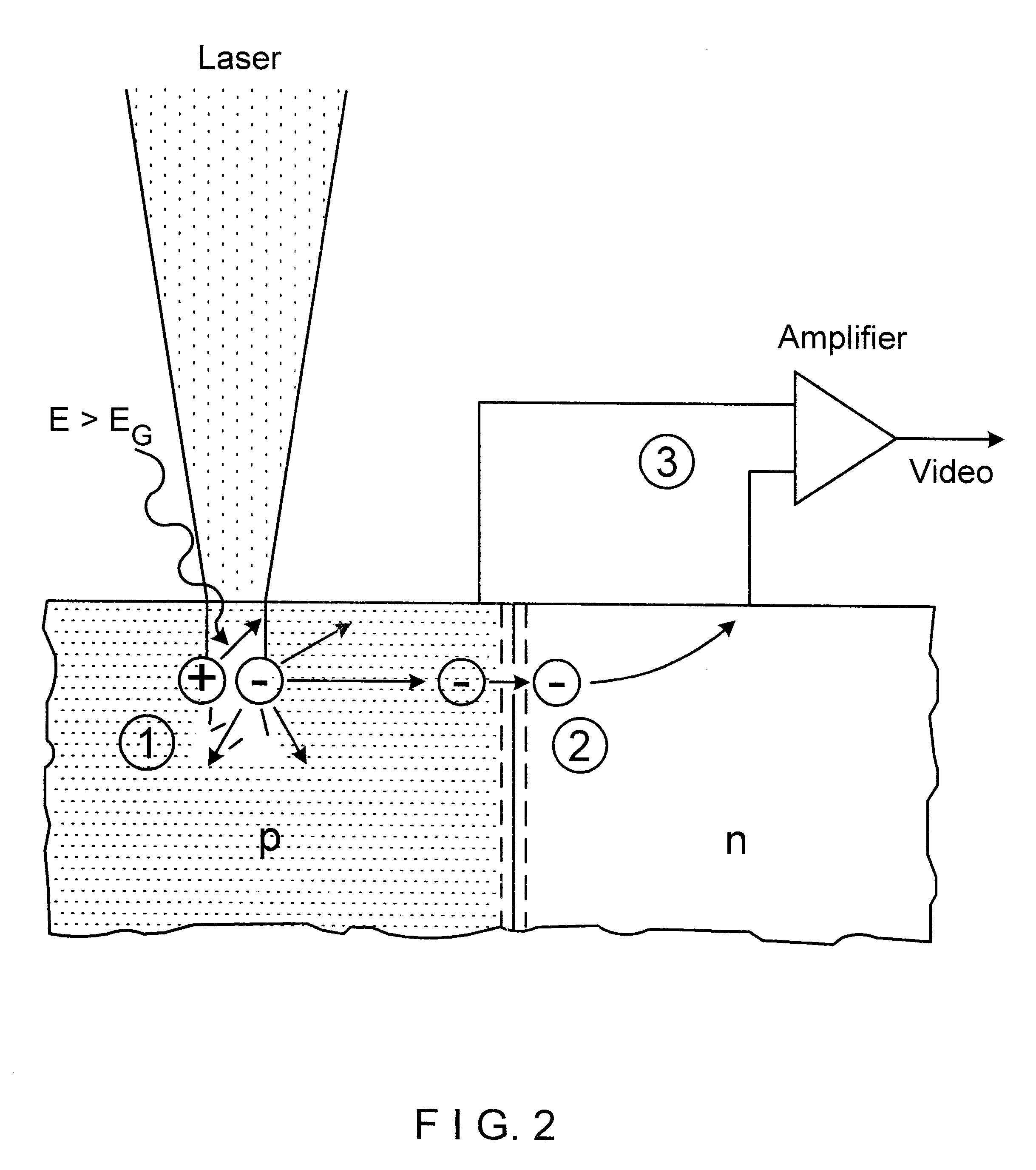
InactiveUS6466040B1Improve localizationMicroscopesIndividual semiconductor device testingLaser scanning microscopeLattice defects
The invention describes the use of multiphoton laser scanning microscopy in material analysis, especially in the analysis of structured silicon wafers by using non-optical detection techniques such as, e.g., OBIC (optical beam induced current) or LIVA (light induced voltage alteration). OBIC and LIVA make use of the generation of an electron-hole charge carrier current or a change in potential due to the scanning laser beam to localize lattice defects in crystalline materials, especially p-n junctions. By using the high localization of the multiphoton excitation in all three spatial coordinates using high-aperture microscope objectives in laser scanning microscopy, this technique enables nondestructive three-dimensional localization of crystal defects. Accordingly, this technique advantageously dispenses with the detection of lattice defects by using two-dimensional laser scanning microscopy and the subsequent required successive mechanical removal of the crystal structure in conjunction with electron microscopy for detecting the defects in the third dimension as well.
Owner:CARL ZEISS JENA GMBH
Quantitative two-photon flow cytometry
InactiveUS8486371B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsBlood capillaryLaser beams
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Microscope
In one or more embodiments, a microscope has a first pulsed laser and a second pulsed laser arranged to irradiate a specimen. Coherent Raman scattering light emanated from the irradiated specimen is extracted, along with multiphoton excitation fluorescence and a second harmonic wave. One or more detectors detect the extracted coherent Raman scattering light, the extracted fluorescence, and the second harmonic wave. A single specimen can simultaneously be observed with respect to either parallel or selective observations of the two-photon excitation fluorescence, the second harmonic wave, and the coherent Raman scattered light.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
Laser Microscope
It is possible to reduce a drop in output power in a positive-dispersion element used as a pulse compressor, thus improving multiphoton-excitation efficiency. Also, reducing the size of the positive-dispersion element makes it easier to attach it to a microscope main body and to accommodate it therein, thus improving maneuverability. The invention provides a laser microscope including a laser light source for emitting ultrashort-pulsed laser light; a pulse expander for expanding the ultrashort-pulsed laser light emitted from the laser light source; a large-diameter single-mode fiber for transmitting the ultrashort-pulsed laser light expanded by the pulse expander; a pulse compressor for compressing the ultrashort-pulsed laser light transmitted by the single-mode fiber; and a microscope main body for irradiating a specimen with the ultrashort-pulsed laser light compressed by the pulse compressor.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Optical fiber delivery and collection method for biological applications such as multiphoton microscopy, spectroscopy, and endoscopy
InactiveUS7702381B2Efficient collectionRapid in vitro screeningCladded optical fibreDiagnostics using lightDiseaseSpectroscopy
The present invention is directed to a method of applying radiation through an optical fiber for detecting disease within a plant or animal or other penetrable tissue, or imaging a particular tissue of a plant or animal. In addition, fluorescence and nonlinear scattering signals can be detected and localized within a subject by such application of radiation through an optical fiber. The radiation is effective to promote simultaneous multiphoton excitation. The optical fibers are used alone to examine internal regions of tissue, in conjunction with an optical biopsy needle to evaluate sub-surface tissue, or with an endoscope to evaluate tissue within body cavities. The present invention also relates to a device for coupling in radiation from an ultrashort mode-locked laser into the beam path of a microscope.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Laser microscope
InactiveUS6855941B1Easily allowAvoid widthPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersMagnificationPulsed laser beam
A multiphoton excitation scanning laser microscope employs a laser beam source for oscillating a pulse laser beam having a wavelength range. A multiphoton excitation phenomenon takes place in a sample irradiated with the laser beam so as to emit a fluorescent light. An optical system for forming an optical path of the laser beam includes a pre-chirp compensator, a scanning optical unit and a plurality of objective lenses differing from each other in magnification and capable of being selectively arranged on the optical path. The optical system also includes a correcting mechanism for causing the pulse width of the laser beam to be constant on a cross section of the sample in the case of selecting any of the objective lenses. The correcting mechanism includes a plurality of correcting plates capable of being selectively arranged on the optical path.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
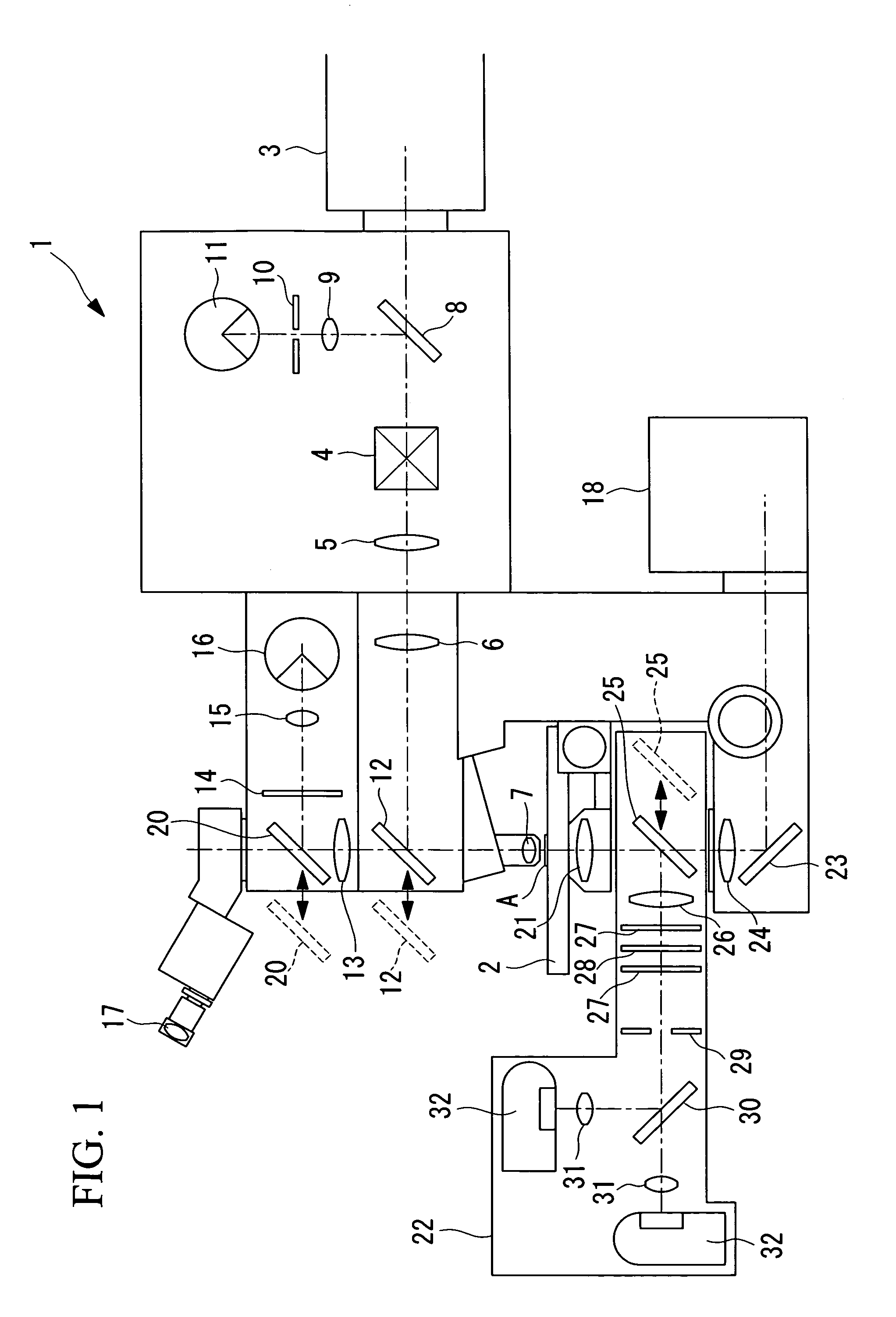
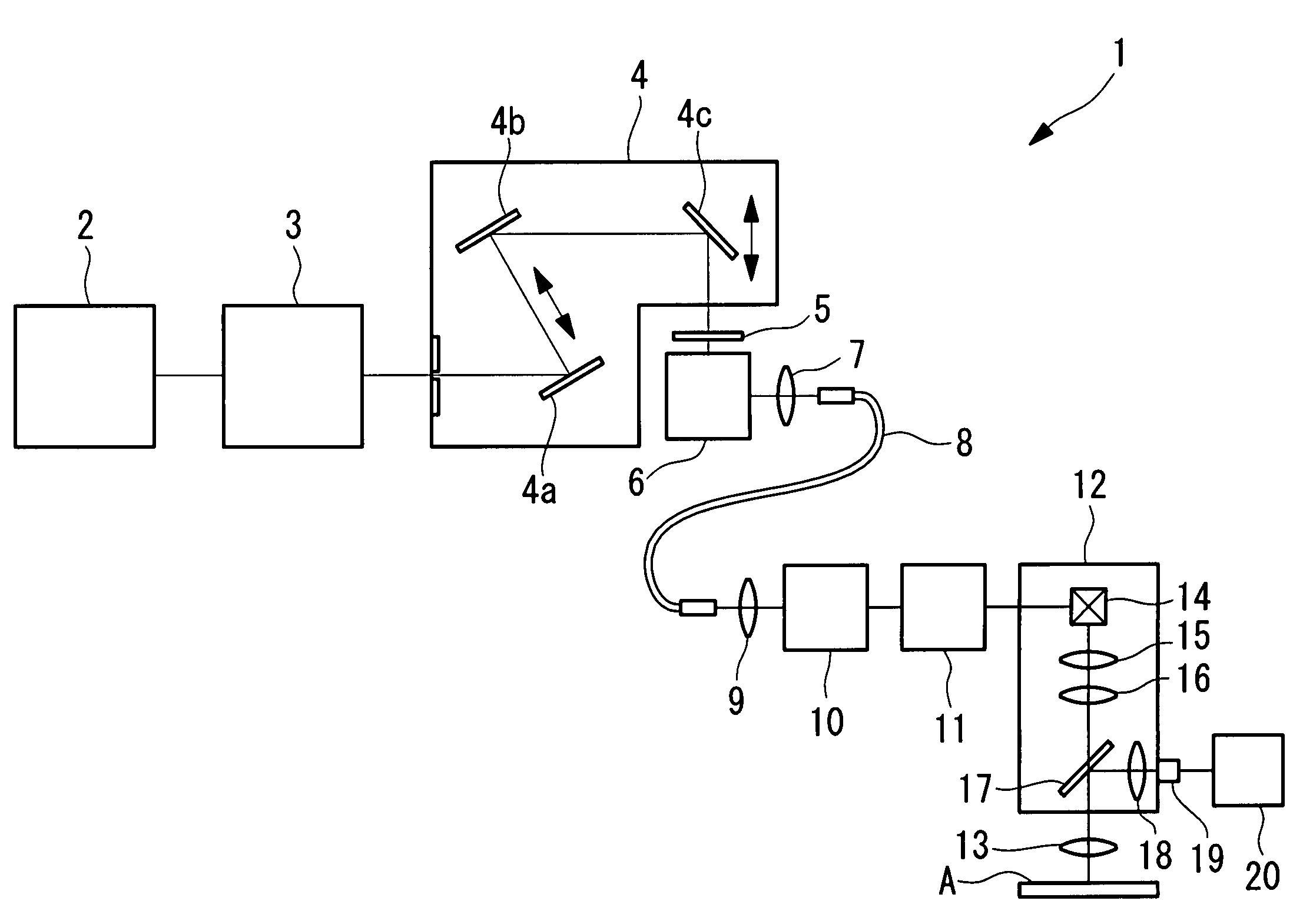
Multiphoton-excitation laser scanning microscope
ActiveUS20080266551A1Efficient collectionBrighter multiphoton-excitation fluorescence imageRadiation pyrometryBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsLaser scanning microscopeHigh numerical aperture
A multiphoton-excitation laser scanning microscope capable of efficiently collecting fluorescence emitted from a specimen to acquire a brighter multiphoton-excitation fluorescence image is provided. This multiphoton-excitation laser scanning microscope includes a multiphoton-excitation laser light source for emitting ultrashort pulsed laser light, a light-scanning unit configured to scan a specimen with the ultrashort pulsed laser light emitted from the multiphoton-excitation laser light source in two dimensions, an objective lens configured to focus the ultrashort pulsed laser light scanned by the light-scanning unit on the specimen, a collector lens disposed opposite the objective lens, with the light-scanning unit disposed therebetween, to collect fluorescence emitted from the specimen, and a light detector configured to detect the fluorescence collected by the collector lens. The collector lens has a higher numerical aperture and a larger field number than the objective lens.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
Light modulation of cell function
InactiveUS20090222069A1Prevent proliferationElectrotherapyElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentTreatment fieldLength wave
The present invention relates to the field of light induced therapy. The invention relates more particularly to a method of modulating receptor function of cells having receptor proteins, said method comprising illuminating the cells with light in the wavelength interval of 250-305 nm or with light having longer wavelengths that by means of non-linear processes and / or multiphoton excitation promotes the same electronic transitions as light in the wavelength interval of 250-305 nm to modulate said receptor function.
Owner:AALBORG UNIV
Laser-based, multiphoton-excitation-type optical examination apparatus
InactiveUS7176428B2Generate efficientlyEasy to adjustBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsPhotometryGroup velocity dispersionLaser light
The invention provides a multiphoton-excitation-type examination apparatus that efficiently generates a multiphoton-excitation effect, that makes the measurement head compact, and that can be easily adjusted when the measurement head is replaced. The multiphoton-excitation-type examination apparatus comprises a laser light source that oscillates ultrashort pulsed laser light; an optical fiber that transmits the ultrashort pulsed laser light from the laser light source; a support member; a measurement head supported on the support member so as to be movable upwards and downwards and at an angle, and having an optical system that irradiates a specimen with the ultrashort pulsed laser light transmitted by the optical fiber that measures fluorescence or reflected light coming from the specimen; and a dispersion-compensating member, in the measurement head, that compensates for group velocity dispersion of the ultrashort pulsed laser light irradiated onto the specimen.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Non-invasive method for specific 3d detection, visualization and/or quantification of an endogenous fluorophore such as melanin in a biological tissue
ActiveCN103930767AIncrease speedImprove throughputImage analysisDiagnostic recording/measuringFluorophoreNon invasive
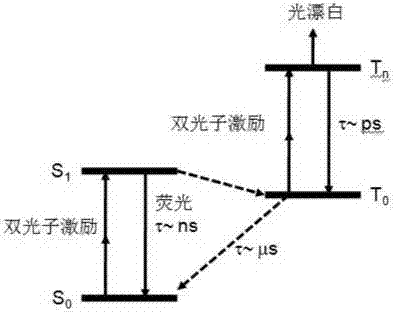
Method for detection, quantification and / or visualization of an endogenous fluorophore, in a biological tissue, the method comprising the steps consisting in: a) acquiring, after multiphoton excitation, a set of successive three- dimensional or two-dimensional images providing information on the decrease over time in the fluorescence signals in the sample, b) determining by processing these images, by performing a linear regression of the logarithm of the fluorescence signals, the spatial distribution in the sample of the slopes of said linear regression, and c) generating information on the presence and / or the volume density or surface density of a fluorophore in the sample at least on the basis of this spatial distribution, the fluorophore being melanin.
Owner:LOREAL SA
Immersion microscope objective and laser scanning microscope system using same
An immersion microscope objective formed of thirteen or fewer lens elements includes, in order from the object side, first and second lens groups of positive refractive power, a third lens group, a fourth lens group having negative refractive power with its image-side surface being concave, and a fifth lens group having positive refractive power with its object-side surface being concave. The first lens group includes, in order from the object side, a lens component that consists of a lens element of positive refractive power (when computed as being in air) and a meniscus lens element having its concave surface on the object side. Various conditions are satisfied to ensure that images of fluorescence, obtained when the immersion microscope objective is used in a laser scanning microscope that employs multiphoton excitation to observe a specimen, are bright and of high resolution. Various laser scanning microscopes are also disclosed.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
Laser microscope
InactiveUS7894131B2Increased peak intensityReduce nonlinear effectsMicroscopesEngineeringLaser light
A laser microscope is provided wherein a drop in output power in a positive-dispersion element used as a pulse compressor is reduced, thus improving multiphoton-excitation efficiency. Also, a size of the positive-dispersion element is reduced, thereby making it easier to attach the pulse compressor to a microscope main body and to accommodate the pulse compressor therein, thus improving maneuverability. The invention provides a laser microscope including a laser light source for emitting ultrashort-pulsed laser light; a pulse expander for expanding the ultrashort-pulsed laser light emitted from the laser light source; a large-diameter single-mode fiber for transmitting the ultrashort-pulsed laser light expanded by the pulse expander; a pulse compressor for compressing the ultrashort-pulsed laser light transmitted by the single-mode fiber; and a microscope main body for irradiating a specimen with the ultrashort-pulsed laser light compressed by the pulse compressor.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
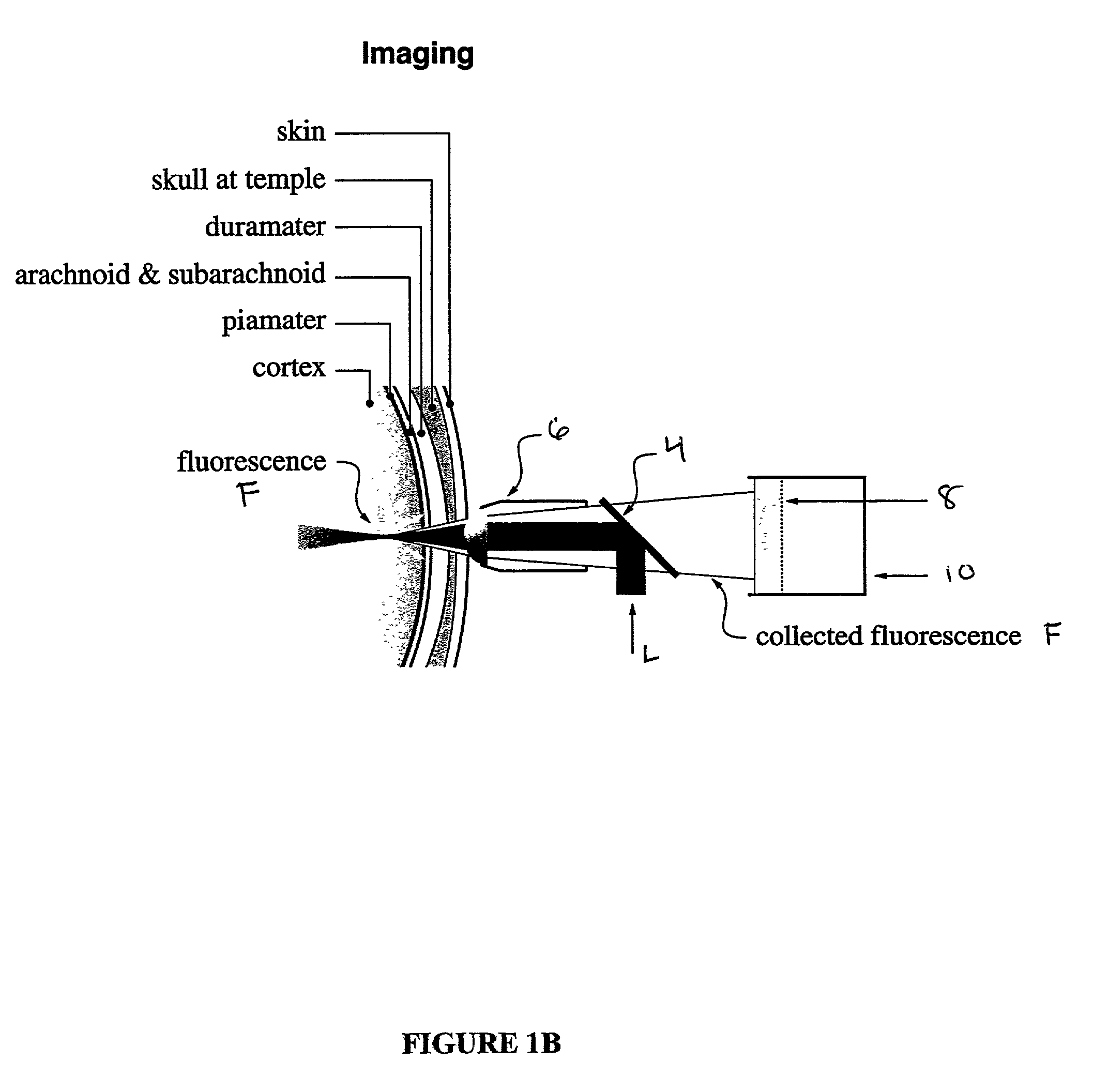
In vivo multiphoton diagnostic detection and imaging of a neurodegenerative disease
InactiveUS7668586B2Promote excitementEmitting characteristicUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryDiseaseMammal
The present invention is directed to a method of detecting a neurodegenerative disease in a mammal by activating brain tissue of the mammal by application of radiation under conditions effective to promote a simultaneous multiphoton excitation of the brain tissue and to emit a fluorescence characteristic. The fluorescence characteristic is then compared to a standard fluorescence emitted by exciting healthy brain tissue of the mammal under the same conditions used to carry out the activating step. Brain tissue where the fluorescence characteristic differs from the standard fluorescence is identified as potentially having a neurodegenerative disease. Another aspect of the present invention is directed to a method of producing an image of brain tissue from a mammal by activating brain tissue of a mammal with radiation applied under conditions effective to promote a simultaneous multiphoton excitation of the brain tissue and to produce fluorescence. The fluorescence is then collected to produce an image of the brain tissue.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
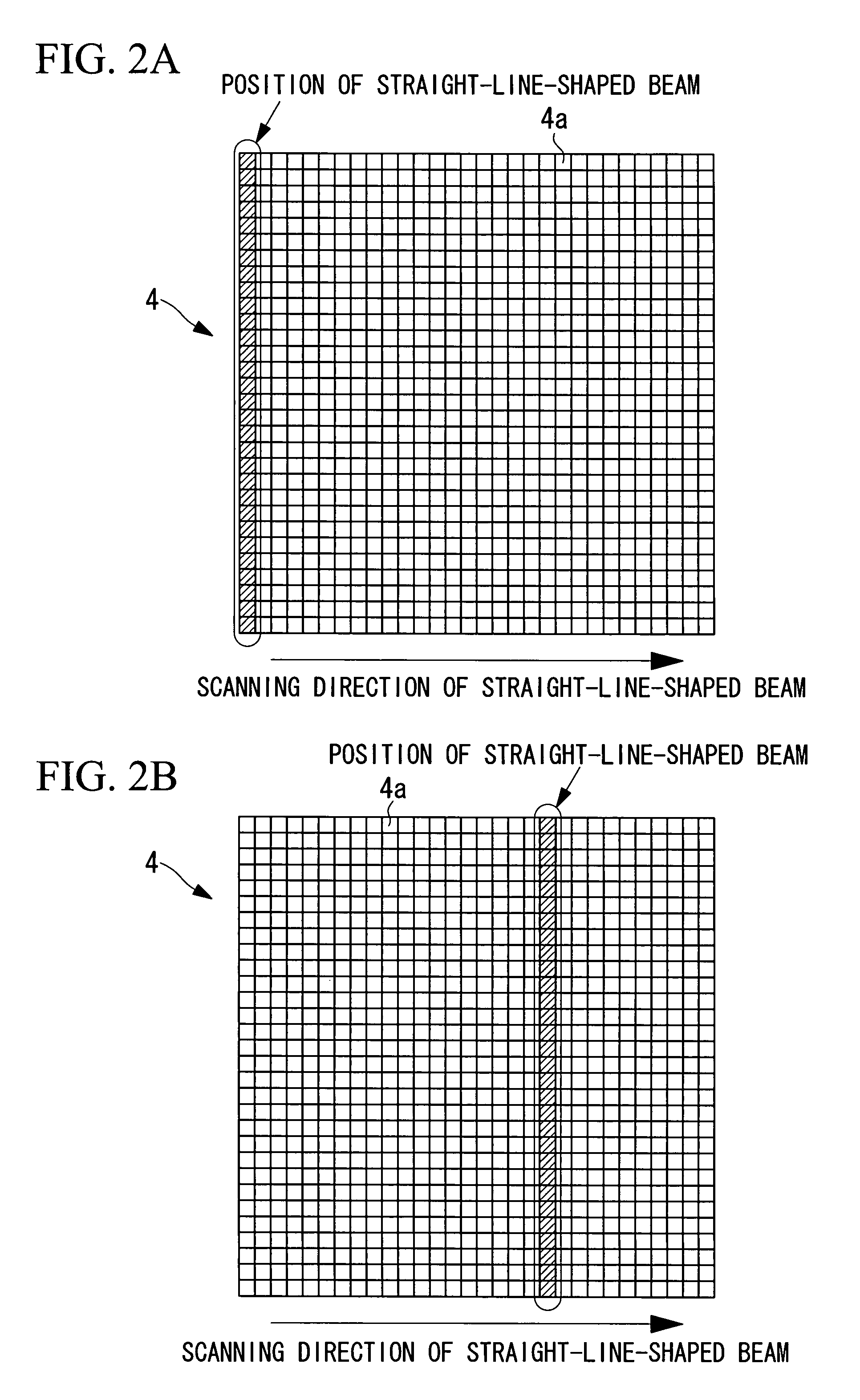
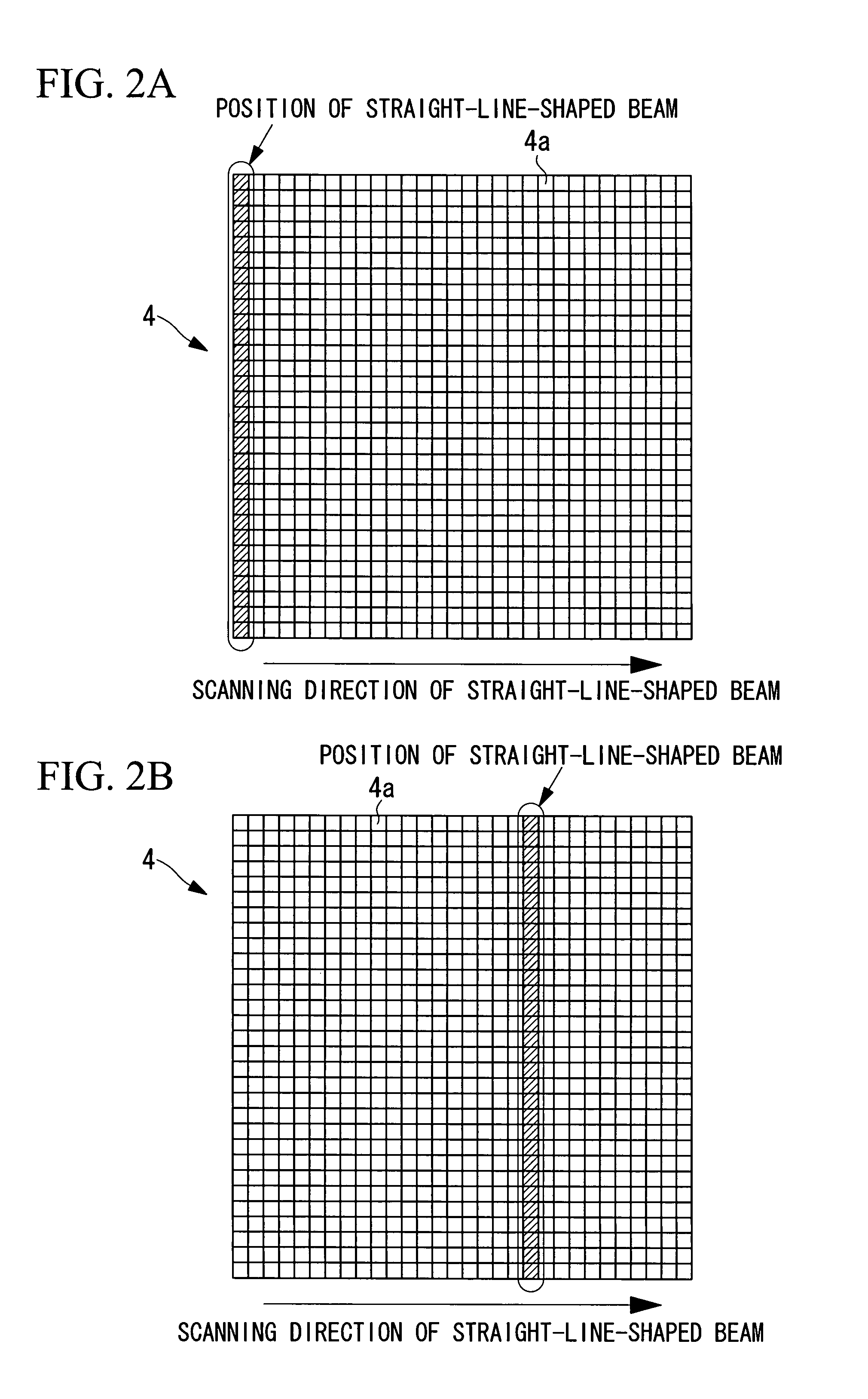
Confocal microscope and multiphoton excitation microscope
InactiveUS7456378B2Beam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansOptoelectronicsPhoton
The invention provides a confocal microscope comprising a light source; a light scanning unit; an array device; a line-beam generating unit for imaging illumination light in the form of a straight line extending, on the array device, in a direction intersecting the scanning direction of the light scanning unit; an objective lens for imaging the illumination light reflected or transmitted at the array device on a specimen; a beamsplitter, between the array device and the light scanning unit, for splitting off from the illumination light detection light from the specimen; a two-dimensional image-acquisition unit for acquiring the split off detection light; and a control unit for controlling the light scanning unit and the array device, wherein the array device is disposed in an optically conjugate positional relationship with a focal plane of the objective lens, and the control unit performs control so as to synchronize the light scanning unit and the array device.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Confocal microscope and multiphoton excitation microscope
InactiveUS20070272843A1High resolutionBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansOptoelectronicsConfocal microscopy
The invention provides a confocal microscope comprising a light source; a light scanning unit; an array device; a line-beam generating unit for imaging illumination light in the form of a straight line extending, on the array device, in a direction intersecting the scanning direction of the light scanning unit; an objective lens for imaging the illumination light reflected or transmitted at the array device on a specimen; a beamsplitter, between the array device and the light scanning unit, for splitting off from the illumination light detection light from the specimen; a two-dimensional image-acquisition unit for acquiring the split off detection light; and a control unit for controlling the light scanning unit and the array device, wherein the array device is disposed in an optically conjugate positional relationship with a focal plane of the objective lens, and the control unit performs control so as to synchronize the light scanning unit and the array device.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Multiphoton-excitation observation apparatus
The invention provides a multiphoton-excitation observation apparatus comprising a light-source unit for emitting pulsed laser light; an observation apparatus main unit for irradiating a specimen with laser light emitted from the light-source unit and observing fluorescence emitted from the specimen; an incidence adjusting device, disposed between the light-source unit and the observation apparatus main unit, for adjusting the beam diameter of the laser light emitted from the light-source unit; and a control apparatus for controlling the incidence-adjusting unit according to the depth of an observation plane in the specimen.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
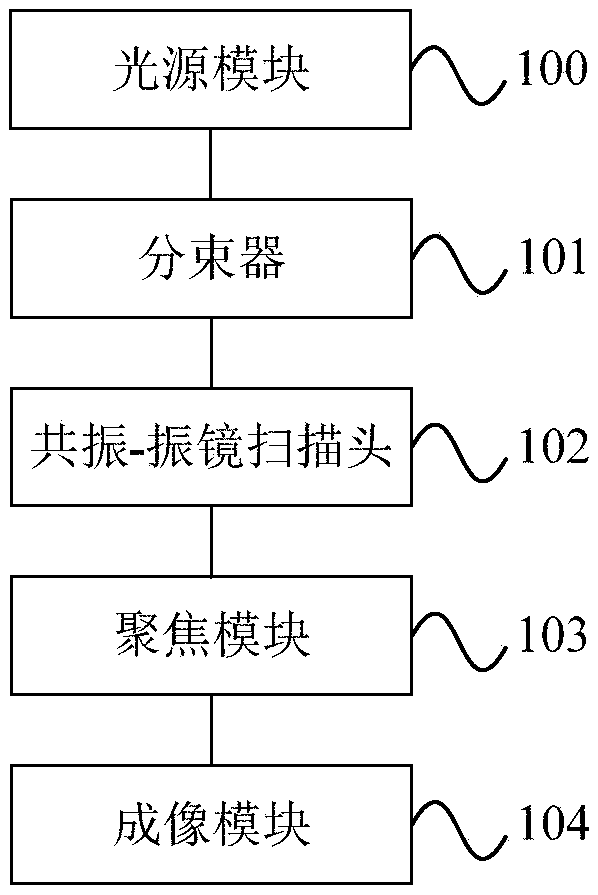
Multi-beam multiphoton microscopic imaging device
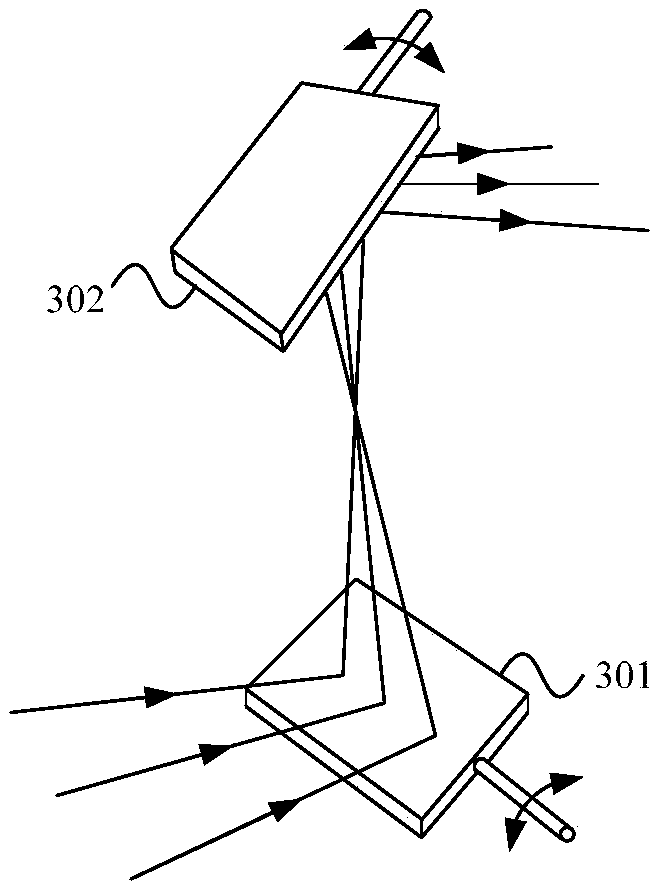
The invention provides a multi-beam multiphoton microscopic imaging device, comprising a light source module, a beam splitter, a resonance-galvanometer scanning head, a focus module and an imaging module. The light source module is used for generating a laser which can be used for multiphoton excitation. The beam splitter is used for generating a plurality of laser beams in a straight line of equiangular pitch. The scanning direction of the resonance scanning head and the galvanometer scanning head are perpendicular to each other, and the arrangement direction of the plurality of laser beams is consistent with the scanning direction of the galvanometer scanning head. The focus module is used for converting the laser emitted by the resonance-galvanometer scanning head into a focus spot of equiangular pitch and irradiating to the sample so as to excite a fluorescent or multiphoton high-order harmonic signal. The imaging module is for collecting fluorescent or multiphoton high-order harmonic signal for imaging. The multi-beam multiphoton microscopic imaging device provided by the invention adopts a plurality of laser beams located in a straight line, and the arrangement direction of the plurality of laser beams is consistent with the scanning direction of the galvanometer scanning head, thereby the plurality of laser beams scanning the sample simultaneously, which improves the imaging speed.
Owner:北京卓奥友科技有限公司
Ultrahigh-resolution nonlinear fluorescence excitation microscopic system based on Bragg diffraction crystals
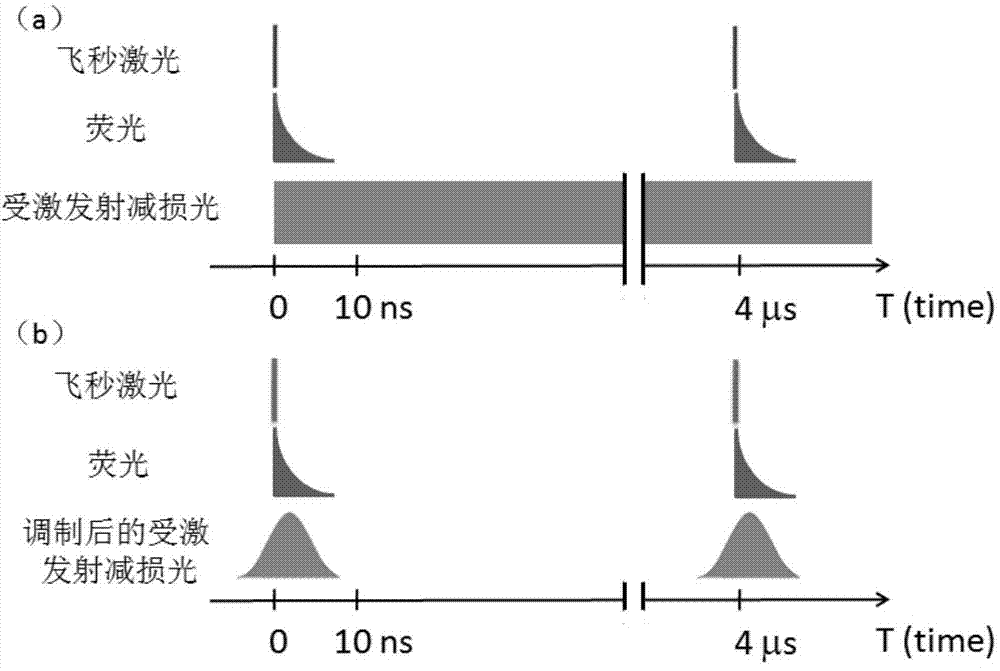
The invention discloses an ultrahigh-resolution nonlinear fluorescence excitation microscopic system based on Bragg diffraction crystals, and relates to the field of laser detection. The system is combined with a nonlinear optical technology and a stimulated emission depletion microtechnique, infrared lasers with long wave lengths are adopted as a multiphoton excitation light source, a continuous laser beam is adopted as a depletion light source, the excitation light source is used for exciting fluorescent molecules, stimulated emission depletion light quenches fluorescence on the periphery of an excitation light spot focus, and the nonlinear optical microscopic system can break through the light wave diffraction limit. The Bragg diffraction crystals are introduced, the repetition frequency of femtosecond lasers is reduced below 4 MHz, and the fluorescence quantum yield of the fluorescent molecules is obviously improved. Meanwhile, the continuous stimulated emission depletion light is modulated into synchronization pulse lasers with the repetition frequency equal to that of the femtosecond lasers by the Bragg diffraction crystals, and on the basis of simplifying the device, the energy of incident light is reduced, and photobleaching on samples is reduced.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com