Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
342 results about "Confocal imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
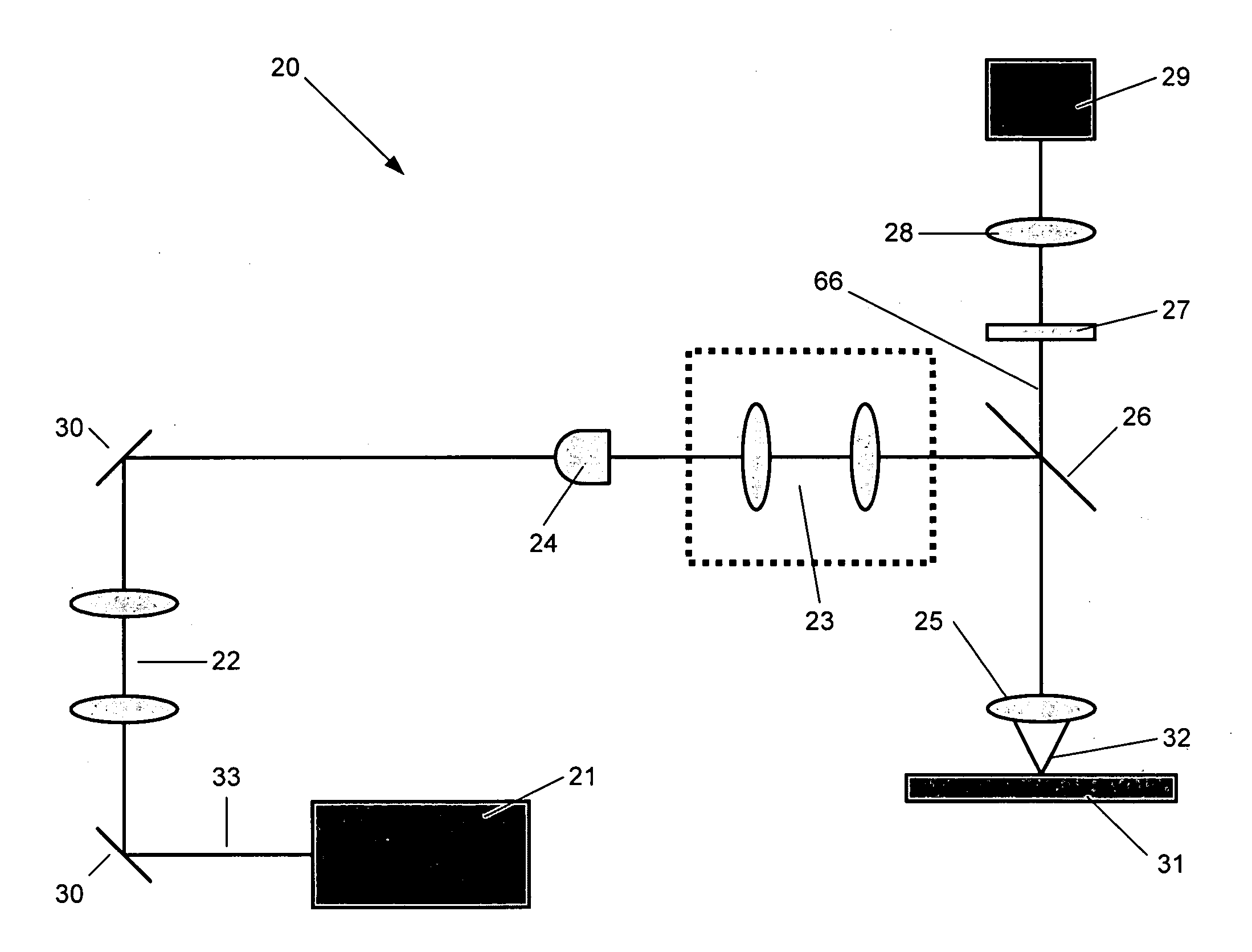
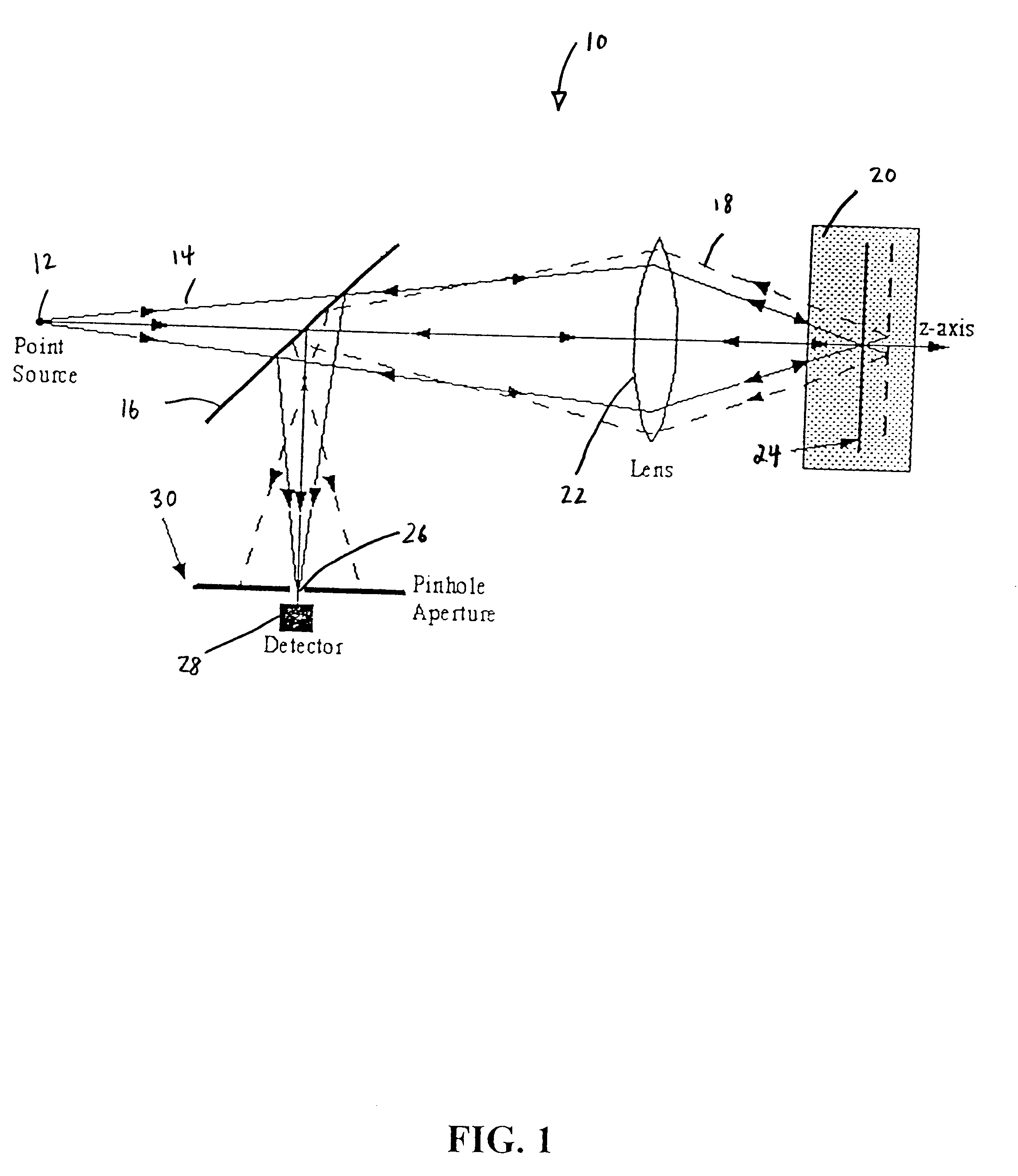
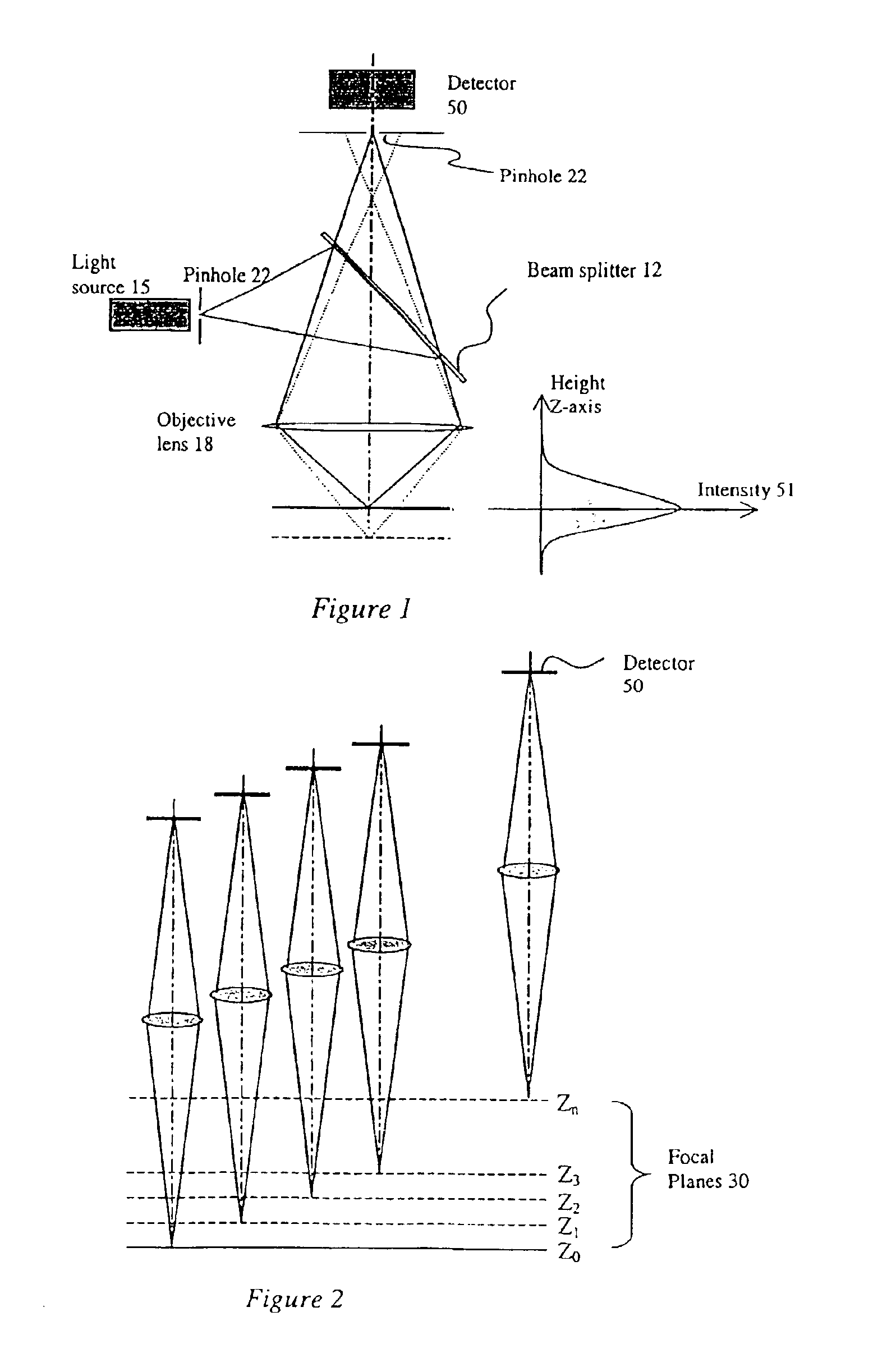
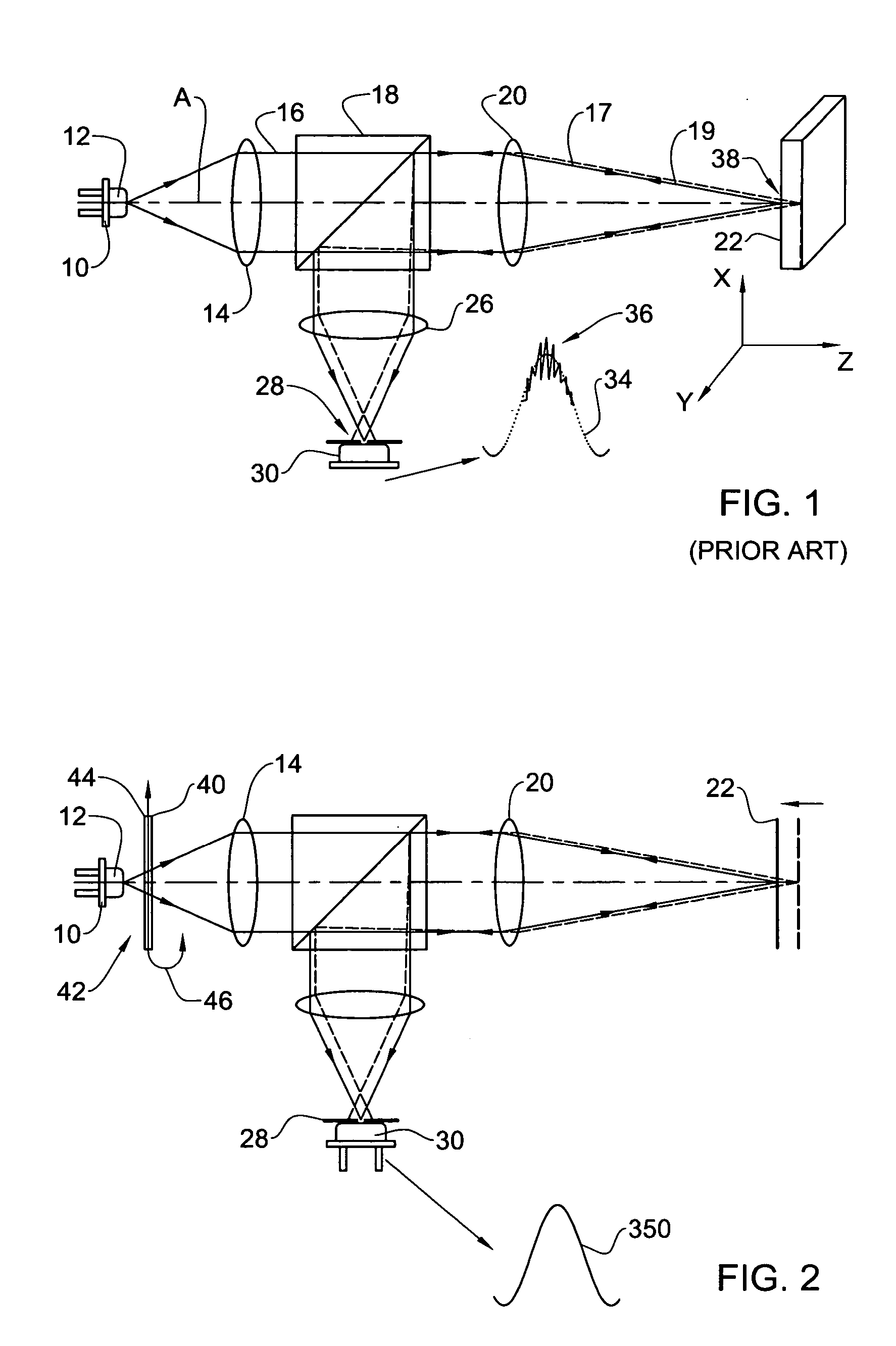
In confocal imaging a focused laser beam is used to produce a small spot illumination on the specimen. This is in contrast to conventional imaging processes, in which the specimen is bathed in excitatory illumination. This modification removes out of focus glare from the final image produced by confocal imaging.
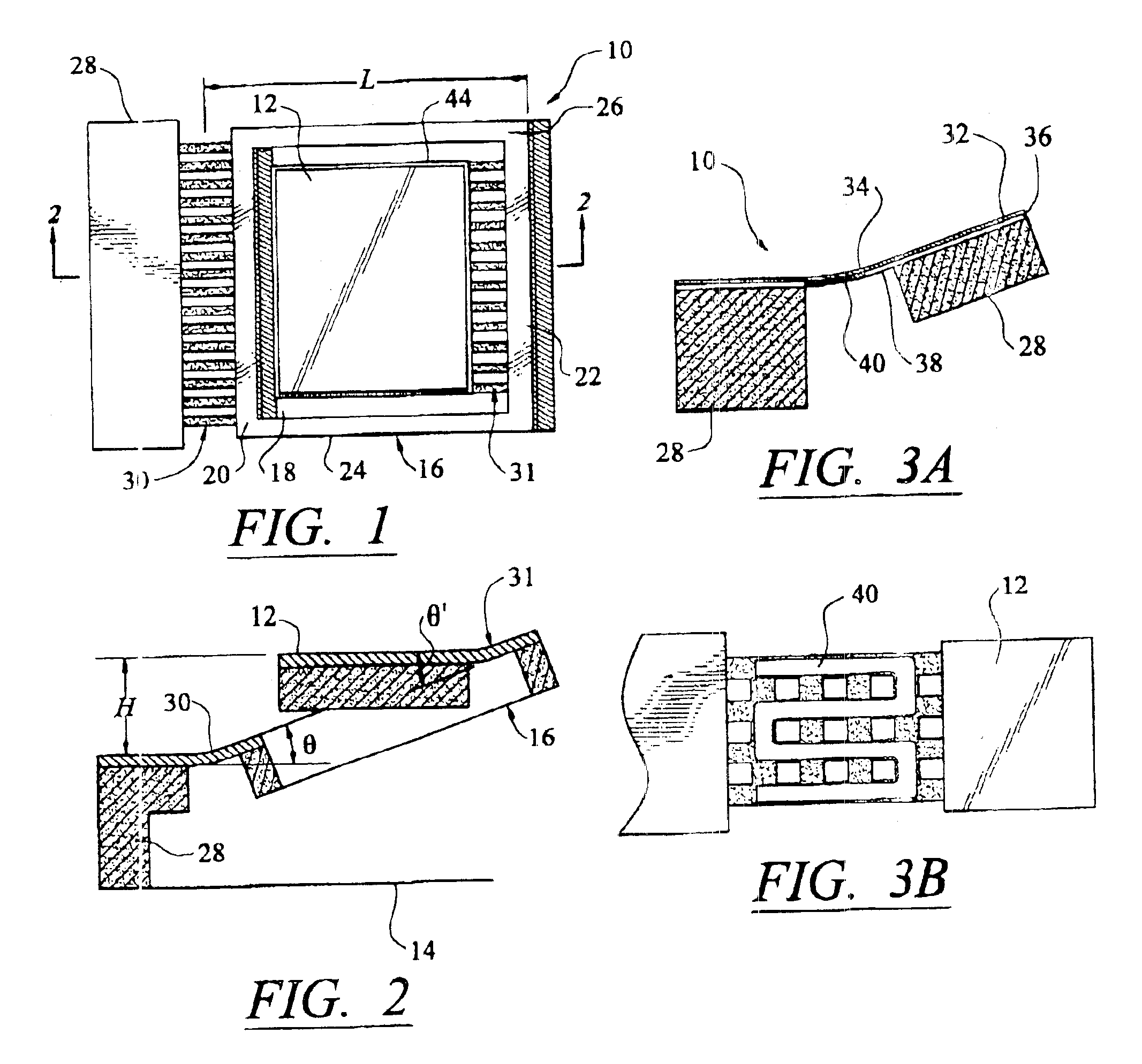
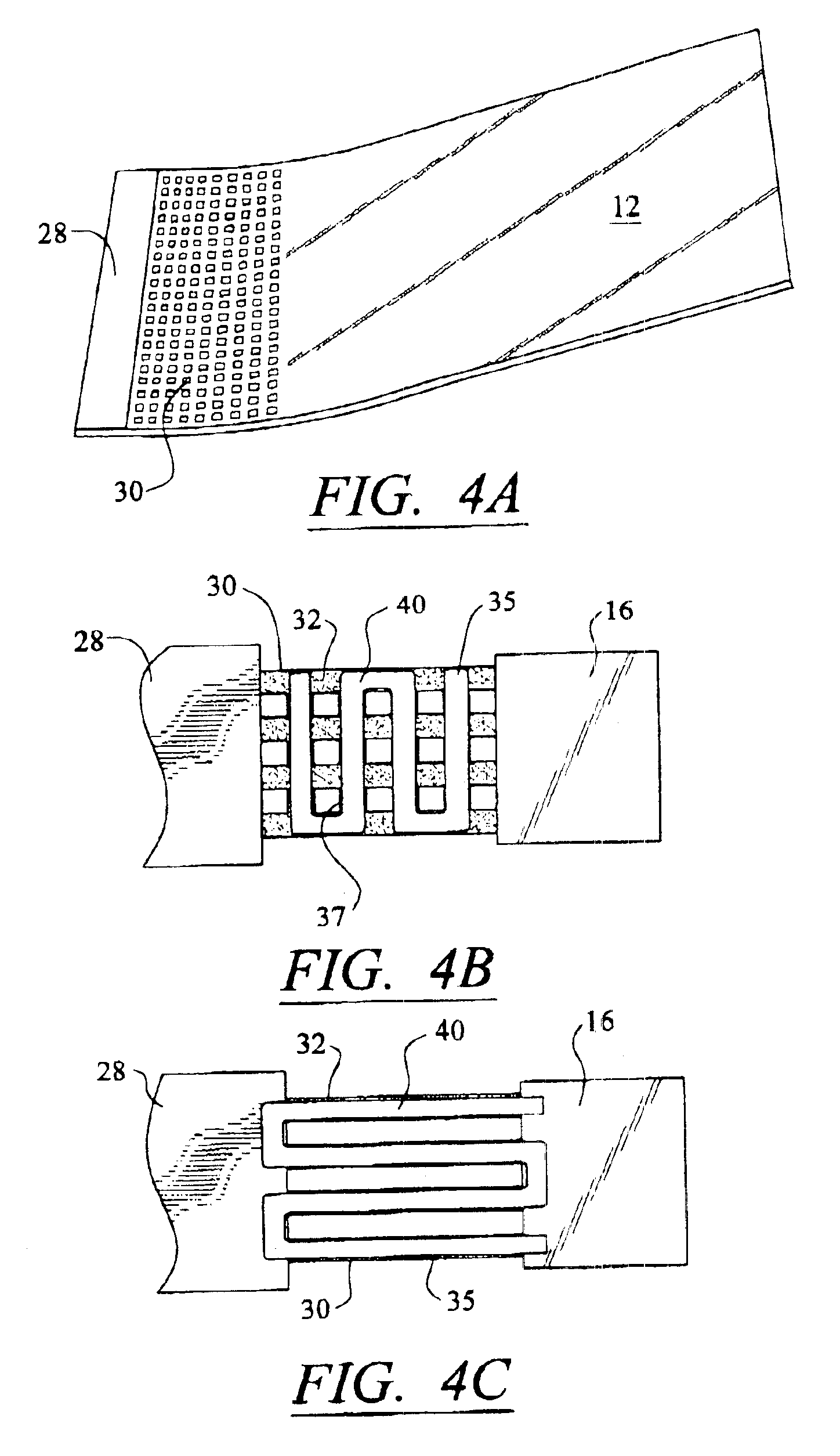
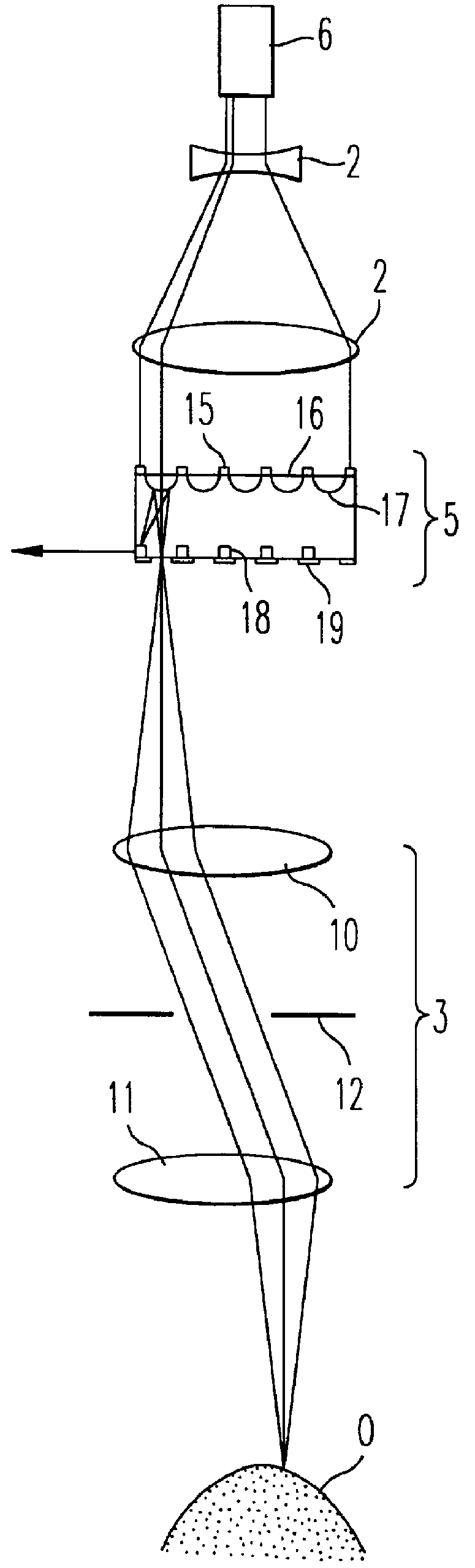
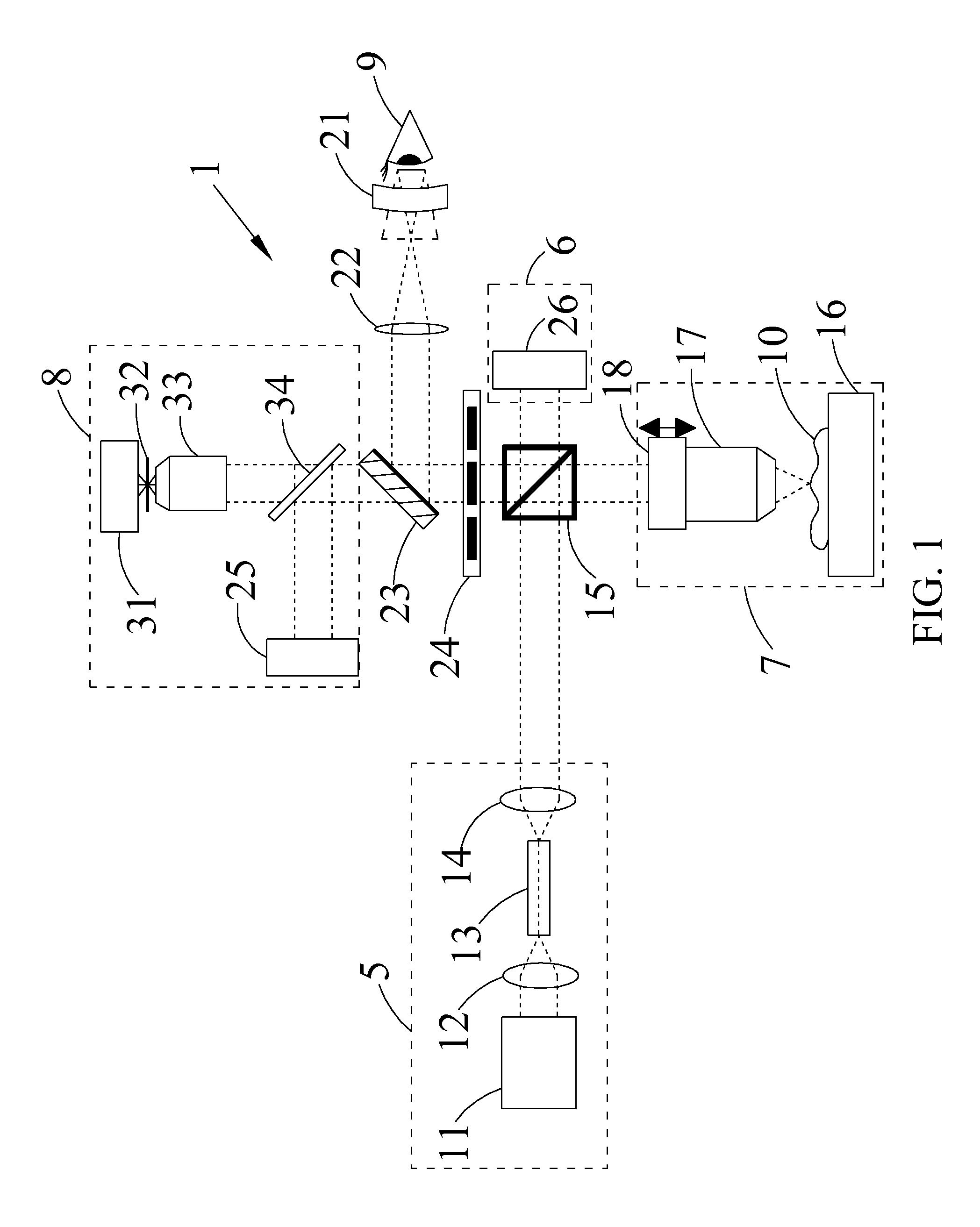
Confocal imaging methods and apparatus
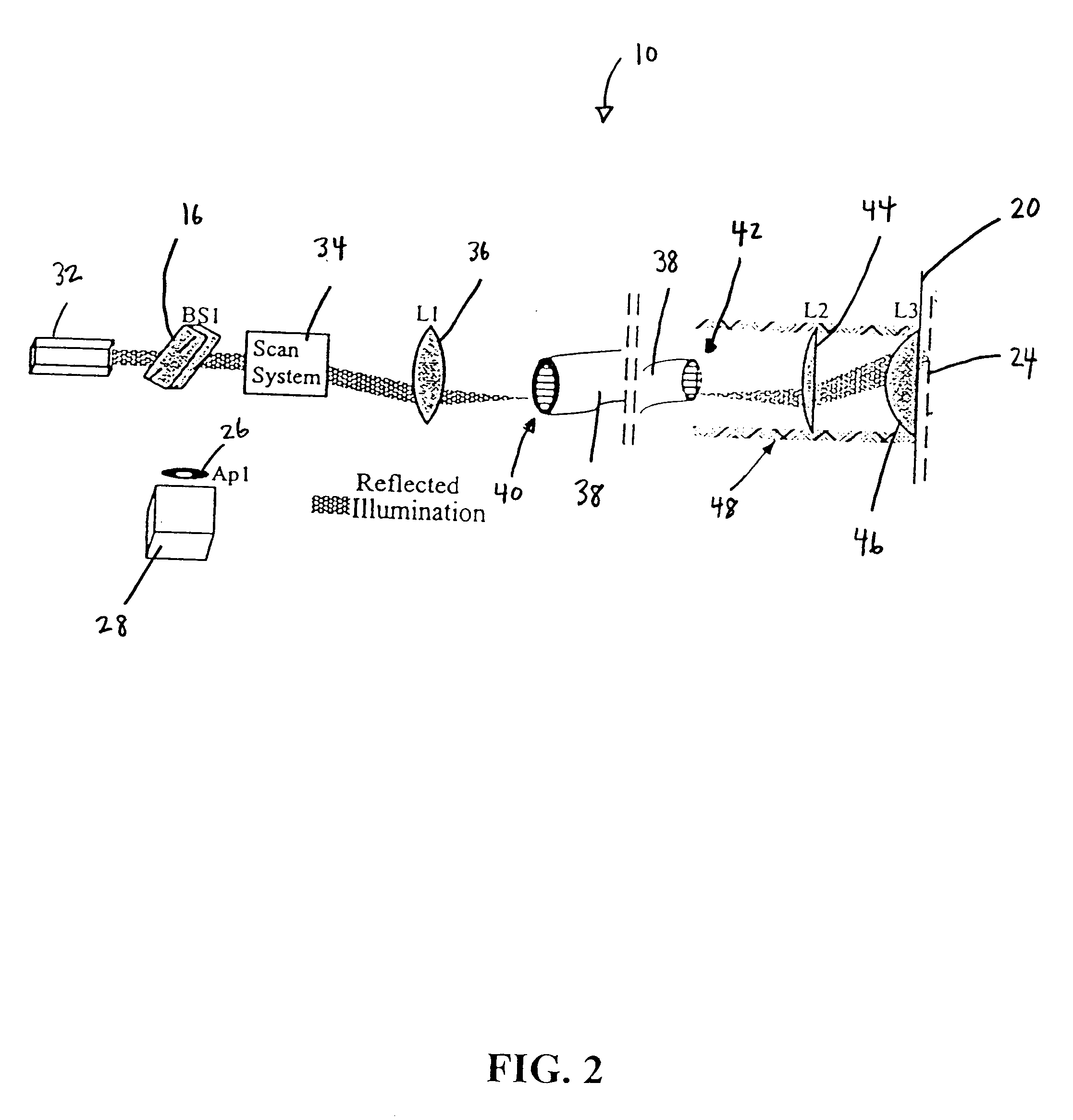
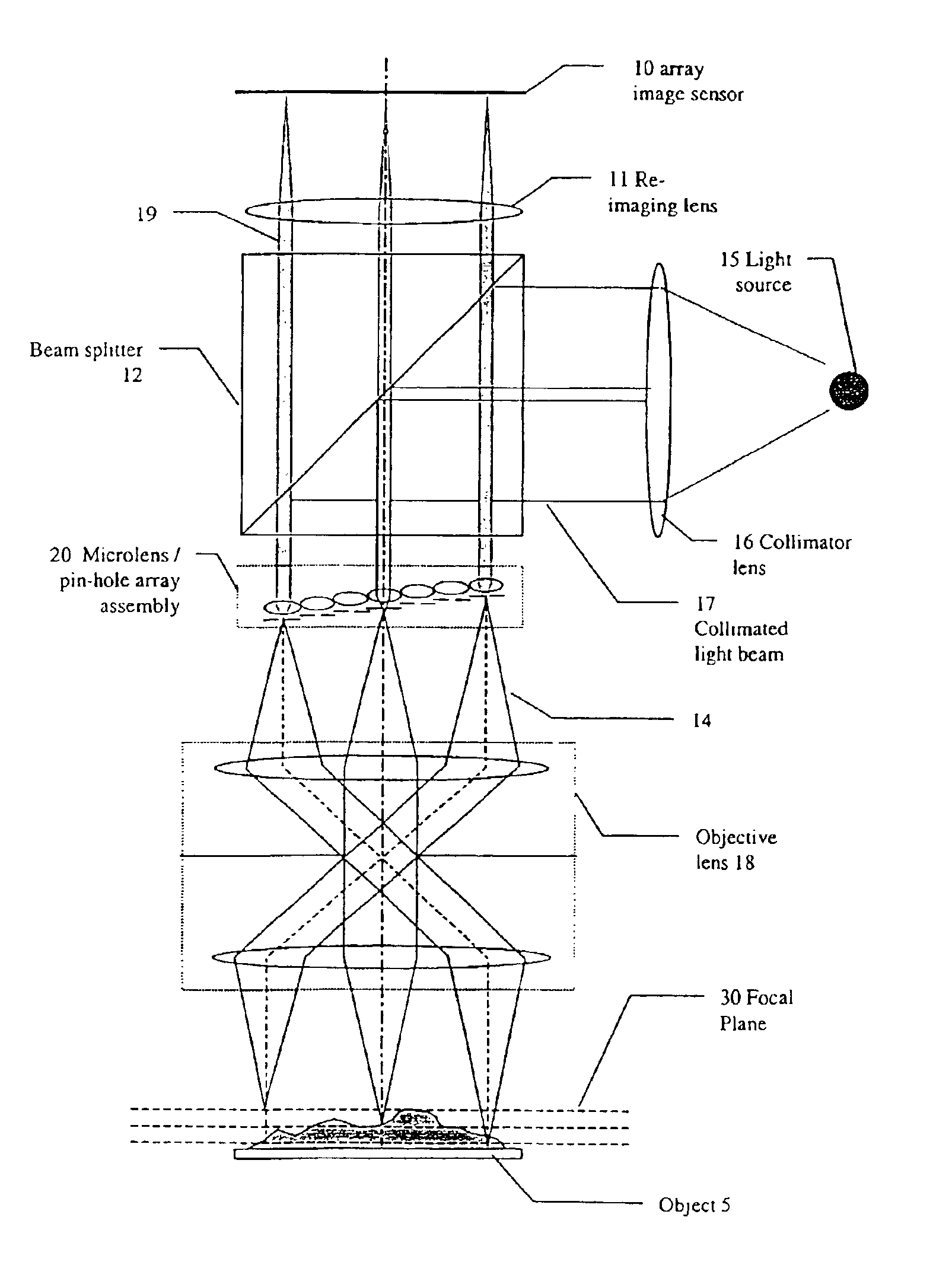
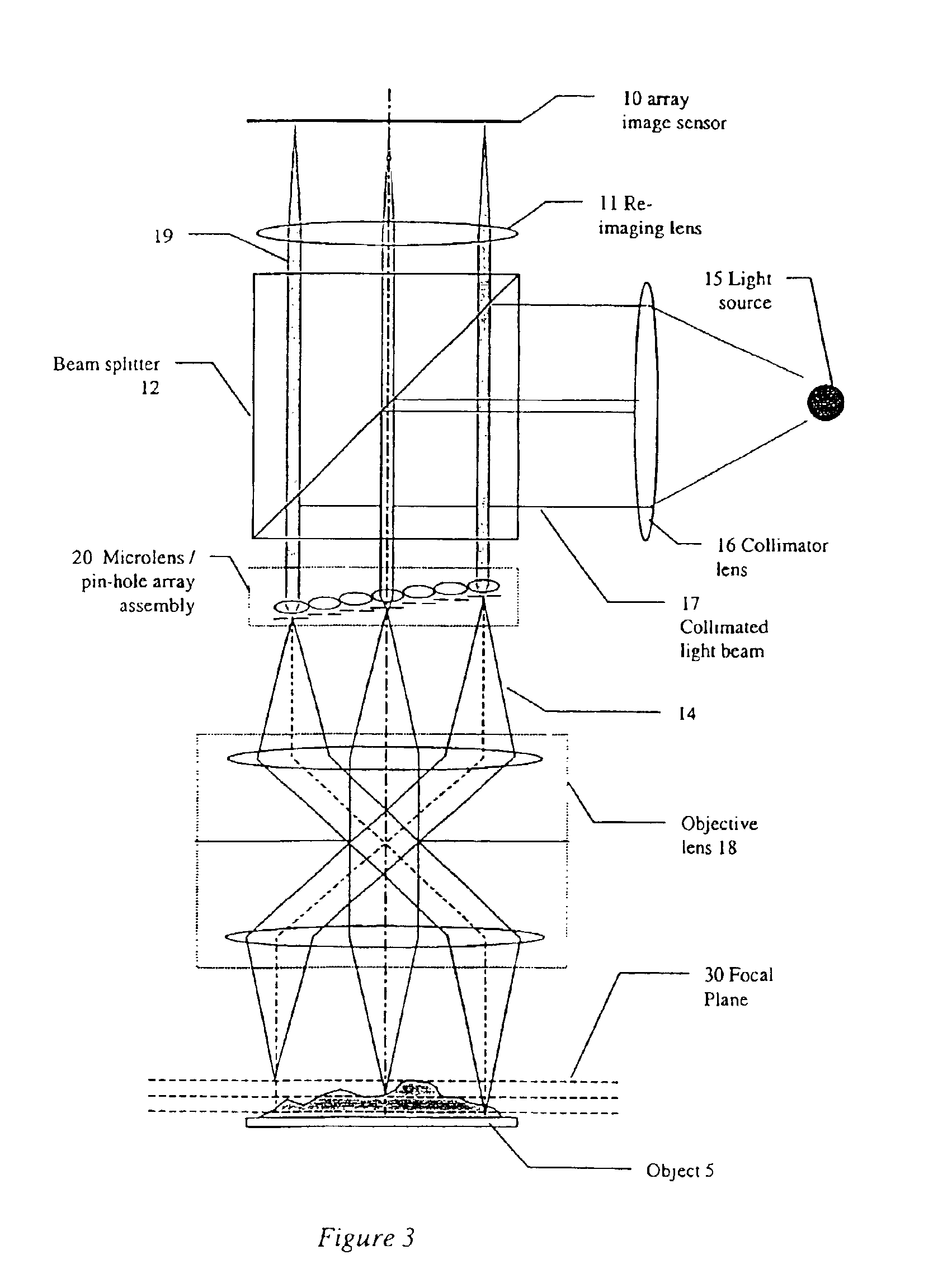
The invention provides imaging apparatus and methods useful for obtaining a high resolution image of a sample at rapid scan rates. A rectangular detector array having a horizontal dimension that is longer than the vertical dimension can be used along with imaging optics positioned to direct a rectangular image of a portion of a sample to the rectangular detector array. A scanning device can be configured to scan the sample in a scan-axis dimension, wherein the vertical dimension for the rectangular detector array and the shorter of the two rectangular dimensions for the image are in the scan-axis dimension, and wherein the vertical dimension for the rectangular detector array is short enough to achieve confocality in a single axis.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Fiber-optic confocal imaging apparatus and methods of use
InactiveUS6370422B1Reduce specular reflectionIncrease contrastEndoscopesSurgical instrument detailsFiberGrating
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
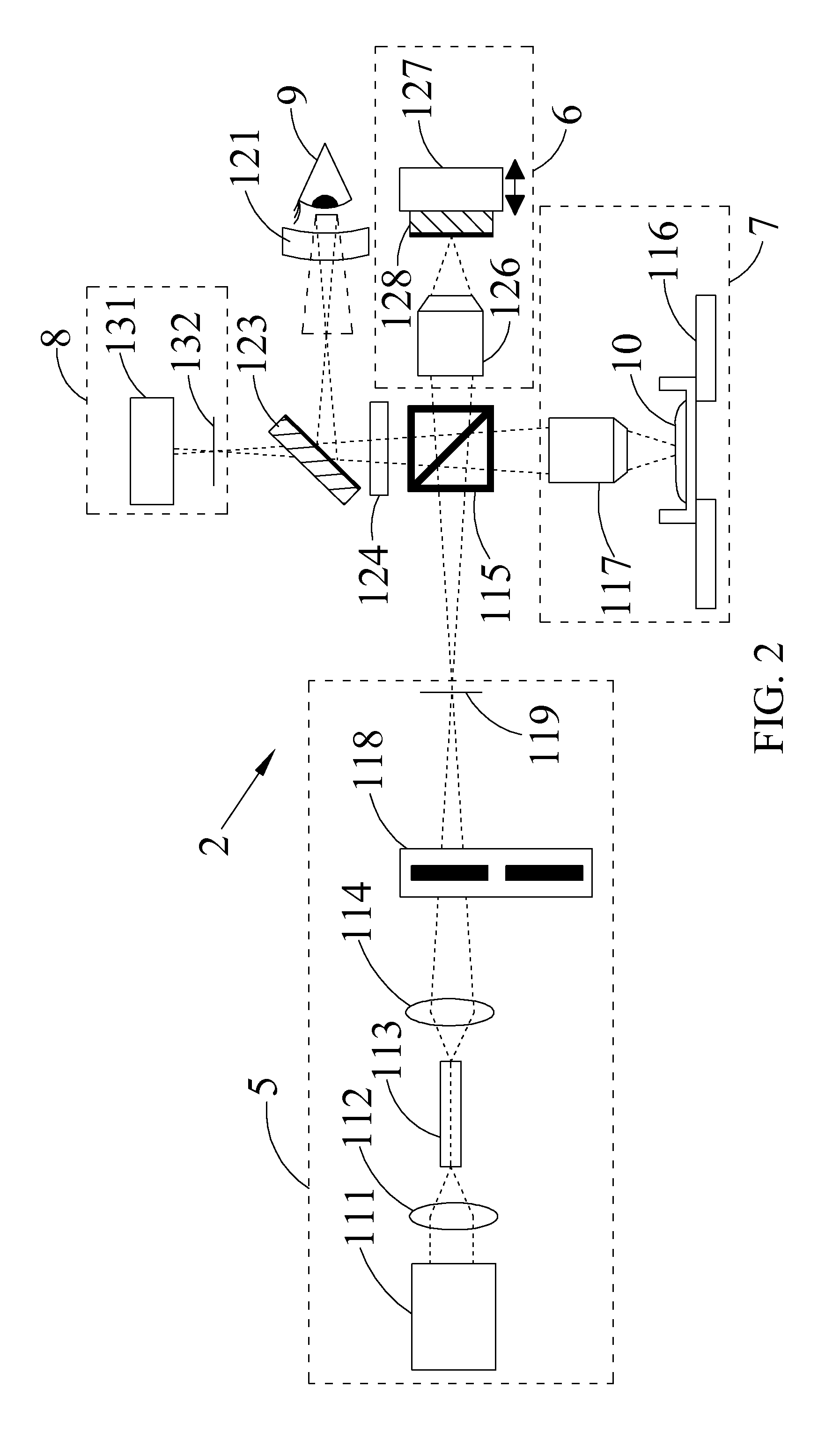
Confocal imaging methods and apparatus
The invention provides imaging apparatus and methods useful for obtaining a high resolution image of a sample at rapid scan rates. A rectangular detector array having a horizontal dimension that is longer than the vertical dimension can be used along with imaging optics positioned to direct a rectangular image of a portion of a sample to the rectangular detector array. A scanning device can be configured to scan the sample in a scan-axis dimension, wherein the vertical dimension for the rectangular detector array and the shorter of the two rectangular dimensions for the image are in the scan-axis dimension, and wherein the vertical dimension for the rectangular detector array is short enough to achieve confocality in a single axis.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Fiber optic endoscopic gastrointestinal probe
A fiber optic probe and a balloon catheter used in conjunction with optical imaging systems, in particular with systems which deliver and collect a single spatial mode beam, such as a single photon, a multiphoton, confocal imaging and ranging systems, such as fluorescence imaging systems.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
Optical fiber scanner for performing multimodal optical imaging
InactiveUS7616986B2Focus shiftReduce back reflectionBoxes/cartons making machineryBox making operationsActuatorFrequency modulation
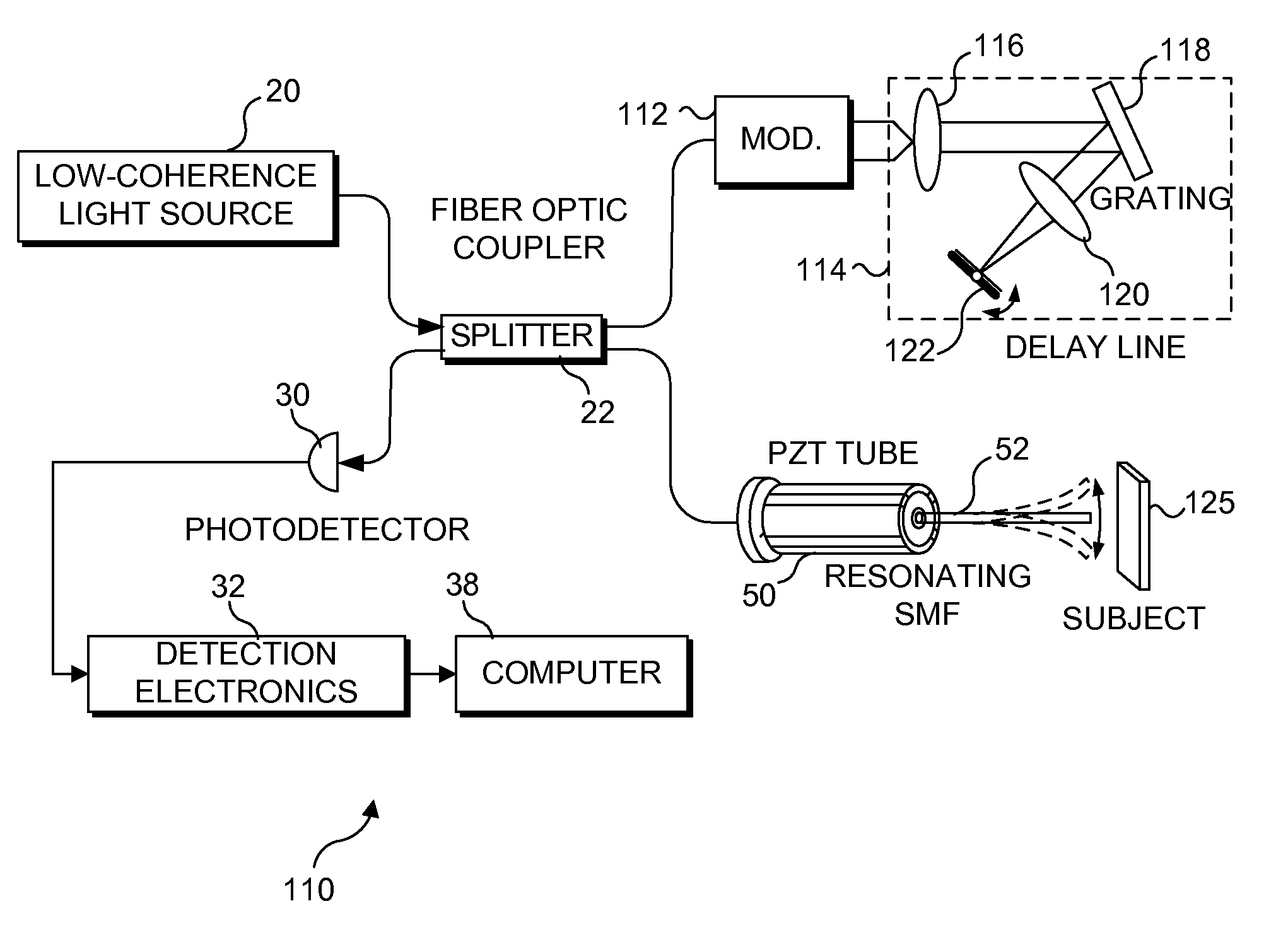
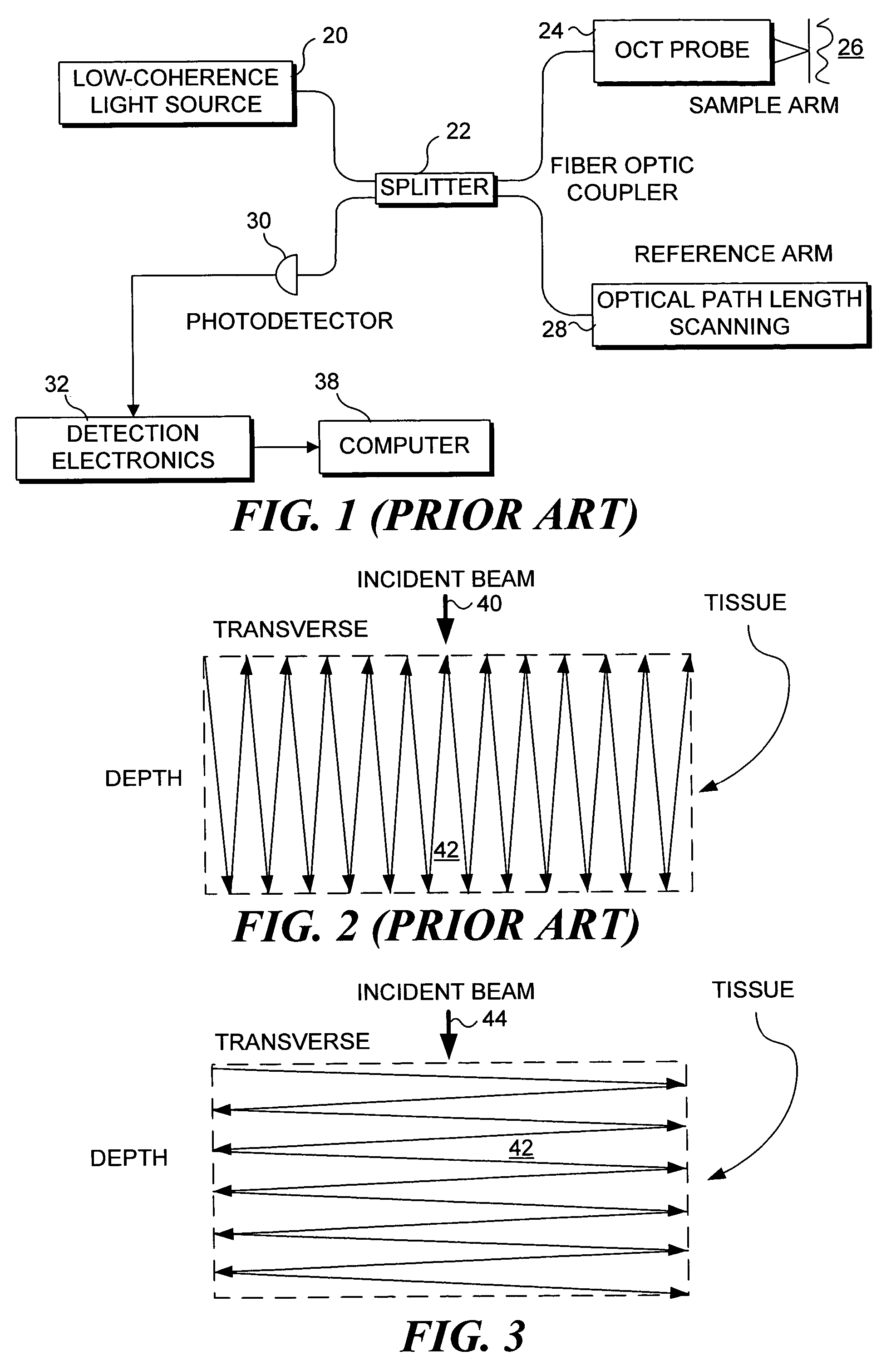
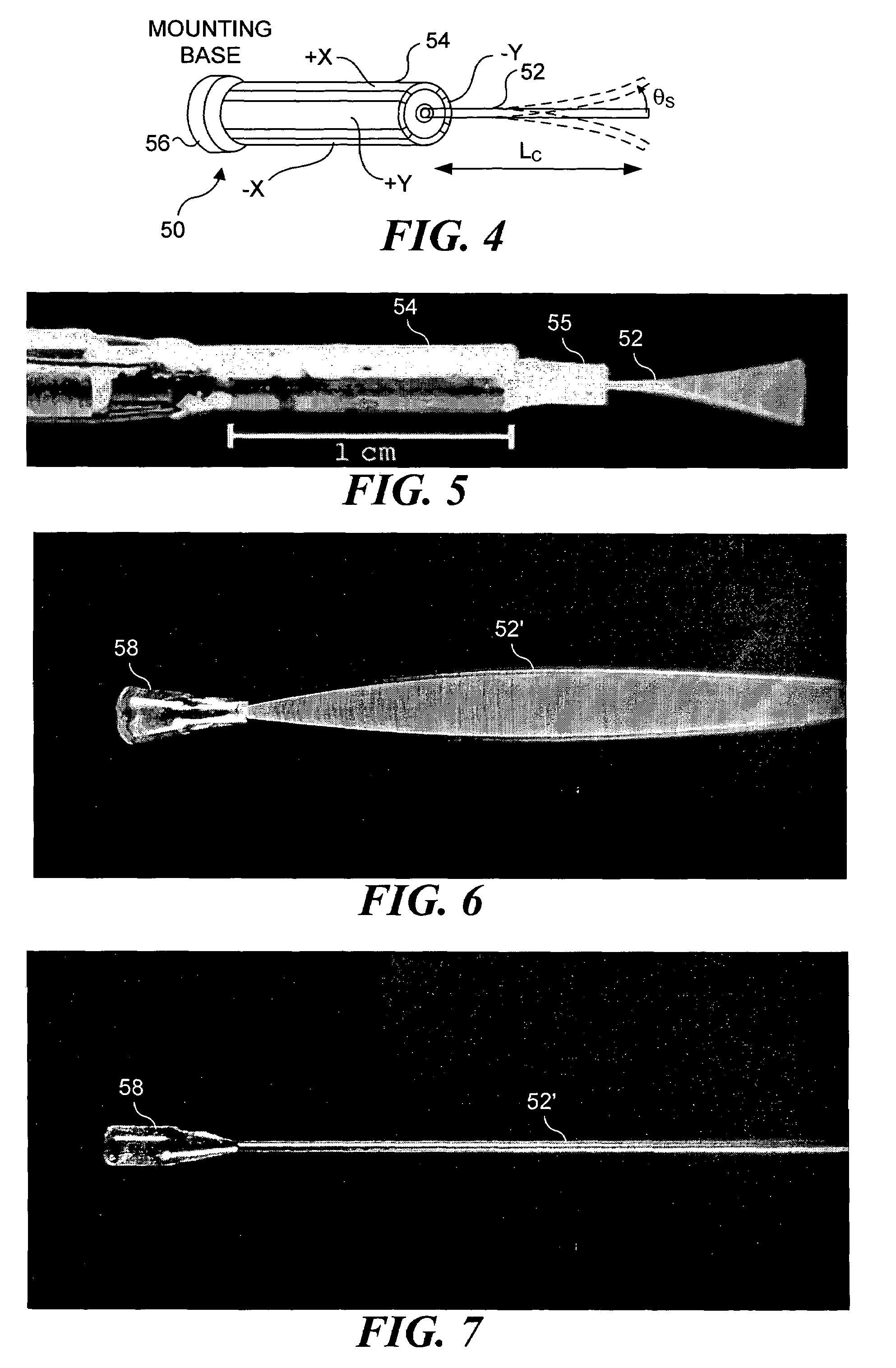
An optical fiber scanner is used for multiphoton excitation imaging, optical coherence tomography, or for confocal imaging in which transverse scans are carried out at a plurality of successively different depths within tissue. The optical fiber scanner is implemented as a scanning endoscope using a cantilevered optical fiber that is driven into resonance or near resonance by an actuator. The actuator is energized with drive signals that cause the optical fiber to scan in a desired pattern at successively different depths as the depth of the focal point is changed. Various techniques can be employed for depth focus tracking at a rate that is much slower than the transverse scanning carried out by the vibrating optical fiber. The optical fiber scanner can be used for confocal imaging, multiphoton fluorescence imaging, nonlinear harmonic generation imaging, or in an OCT system that includes a phase or frequency modulator and delay line.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Confocal imaging
InactiveUS6838650B1Increase flexibilityImprove programmabilitySolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansConfocal imagingPhysics
A confocal imaging system for imaging a surface. The system includes an area array sensor having rows of sensors for detecting light reflected from the surface, and an optical system arranged to focus light from different focal planes on the surface to different sensor rows of the area array sensor.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
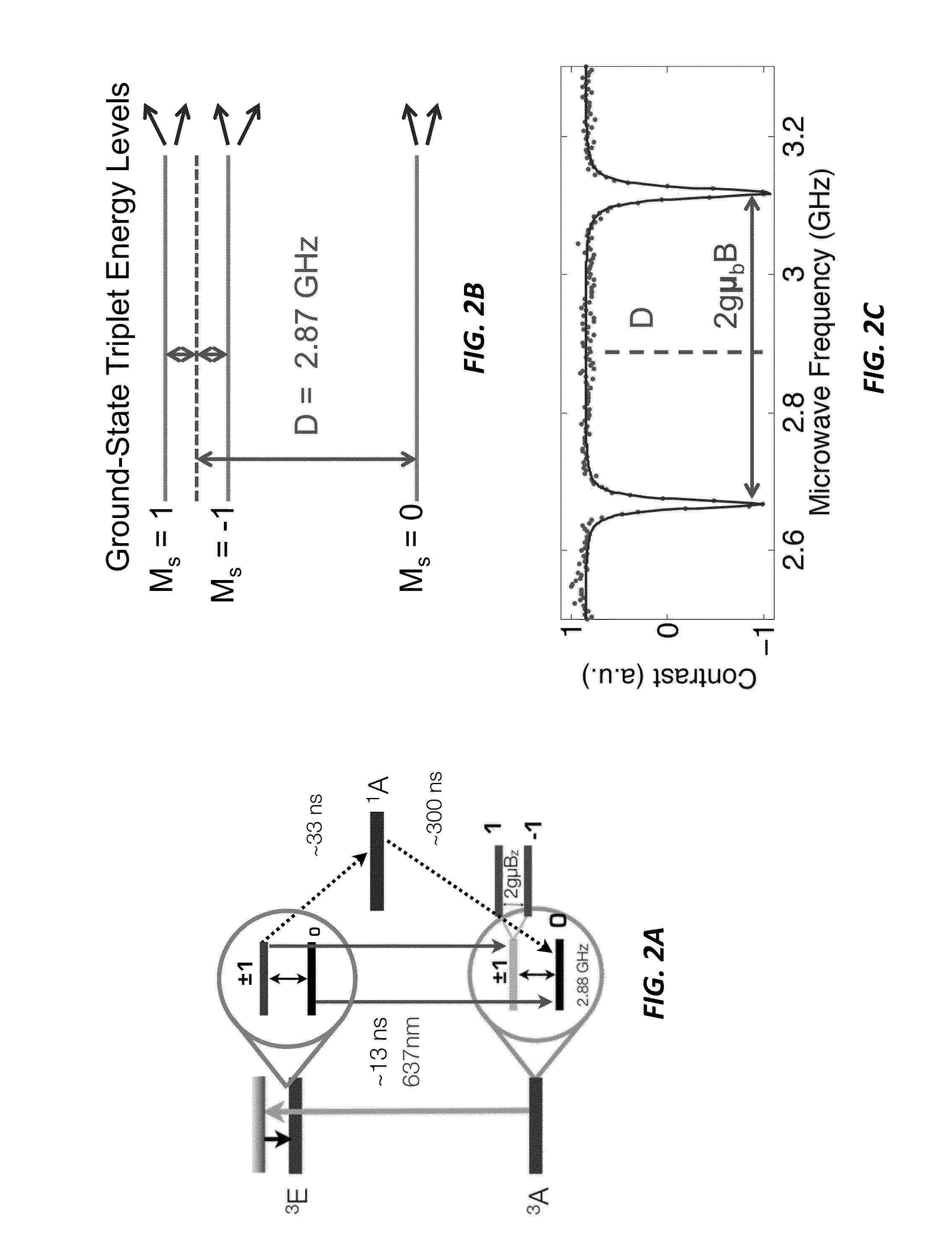
Wide-field imaging using nitrogen vacancies
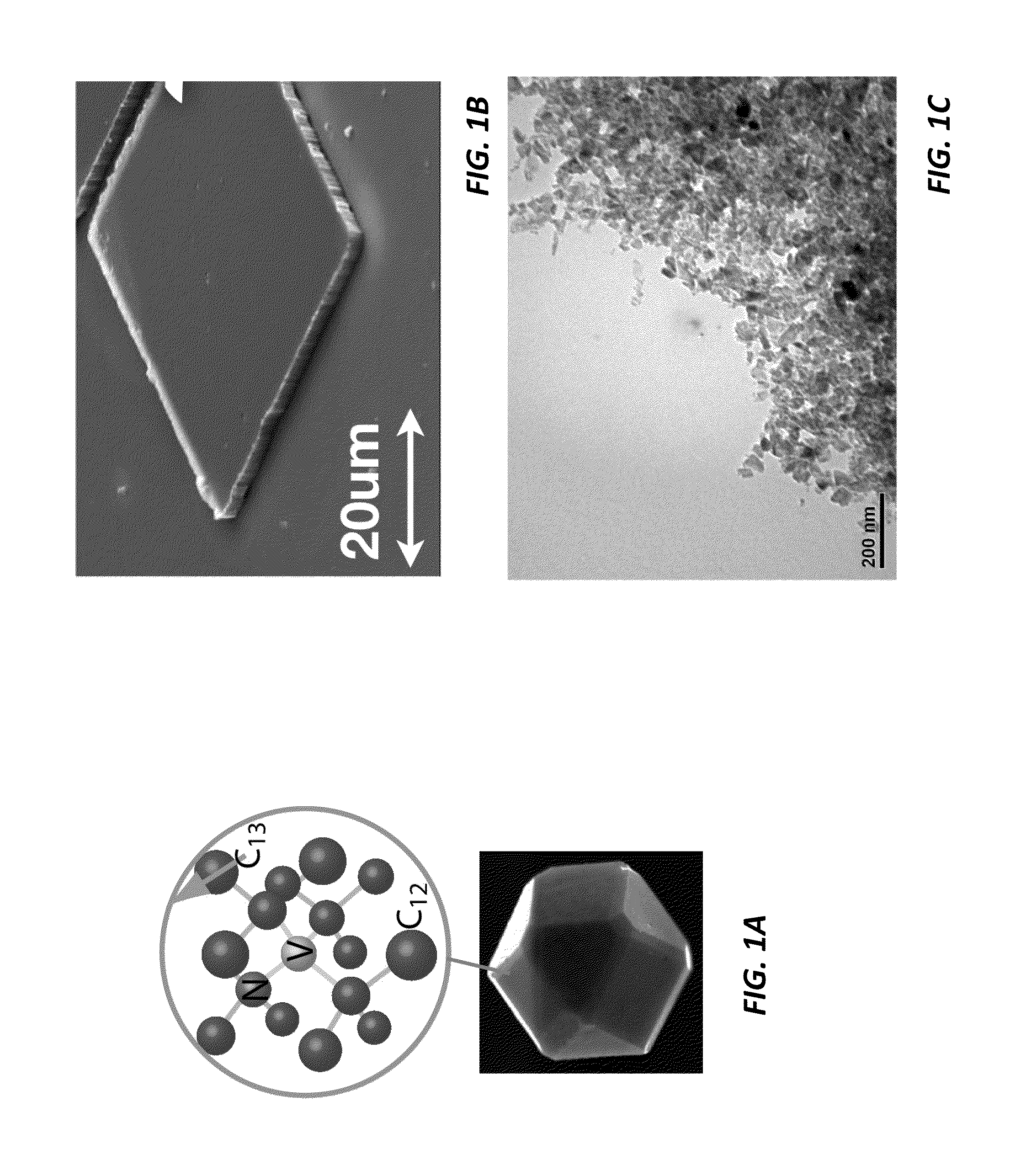
Nitrogen vacancies in bulk diamonds and nanodiamonds can be used to sense temperature, pressure, electromagnetic fields, and pH. Unfortunately, conventional sensing techniques use gated detection and confocal imaging, limiting the measurement sensitivity and precluding wide-field imaging. Conversely, the present sensing techniques do not require gated detection or confocal imaging and can therefore be used to image temperature, pressure, electromagnetic fields, and pH over wide fields of view. In some cases, wide-field imaging supports spatial localization of the NVs to precisions at or below the diffraction limit. Moreover, the measurement range can extend over extremely wide dynamic range at very high sensitivity.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Vertical displacement device
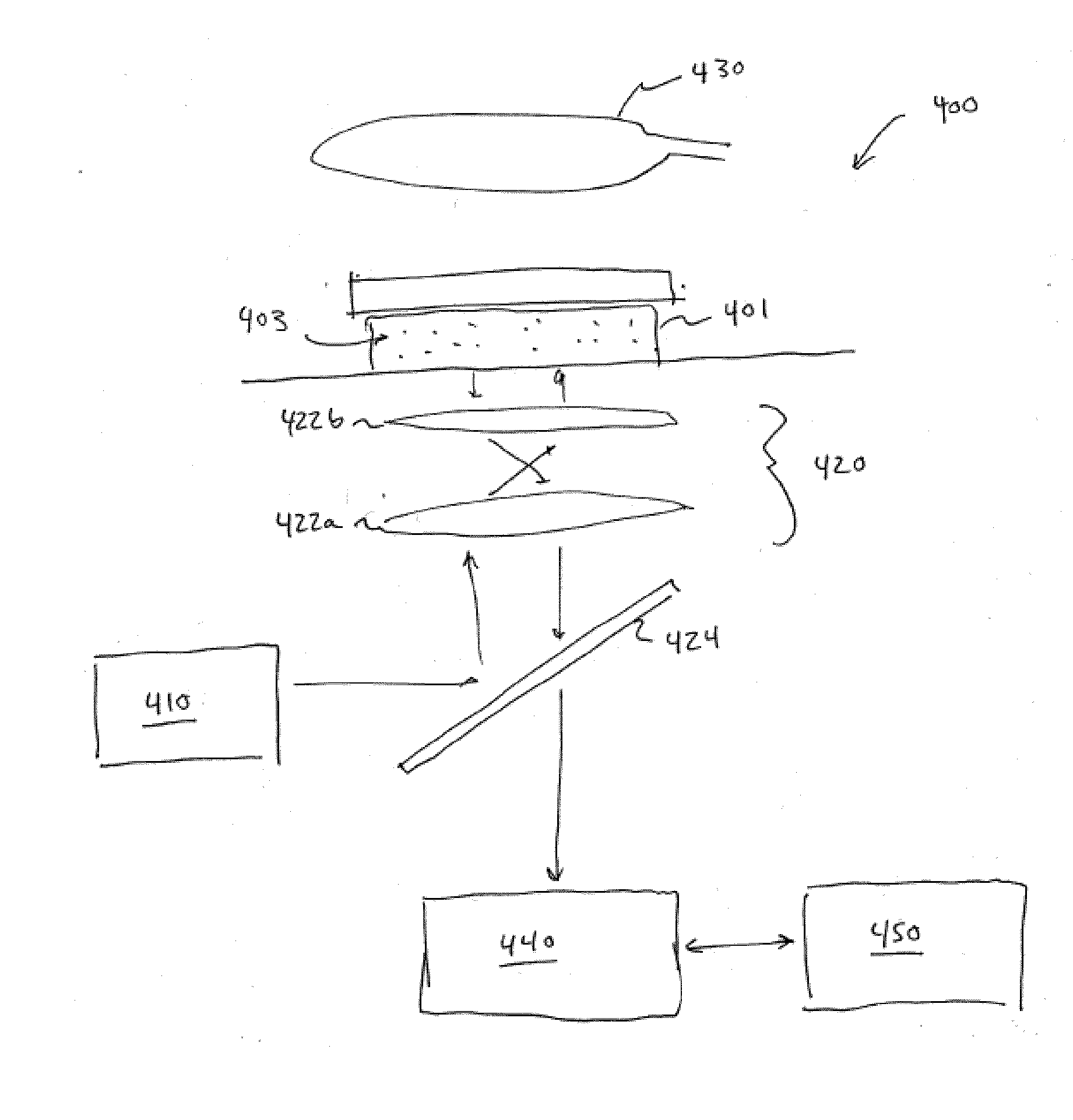
A MEMS vertical displacement device capable of moving one or more vertically displaceable platforms relative to a base. In particular, the vertical displacement device may be capable of moving a vertically displaceable platform so that the vertically displaceable platform remains generally parallel to a base. The vertically displaceable platform may be, but is not limited to, a microlens, a micromirror, micro-grating, or other device. The vertical displacement device may also be included in optical coherence and confocal imaging systems.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
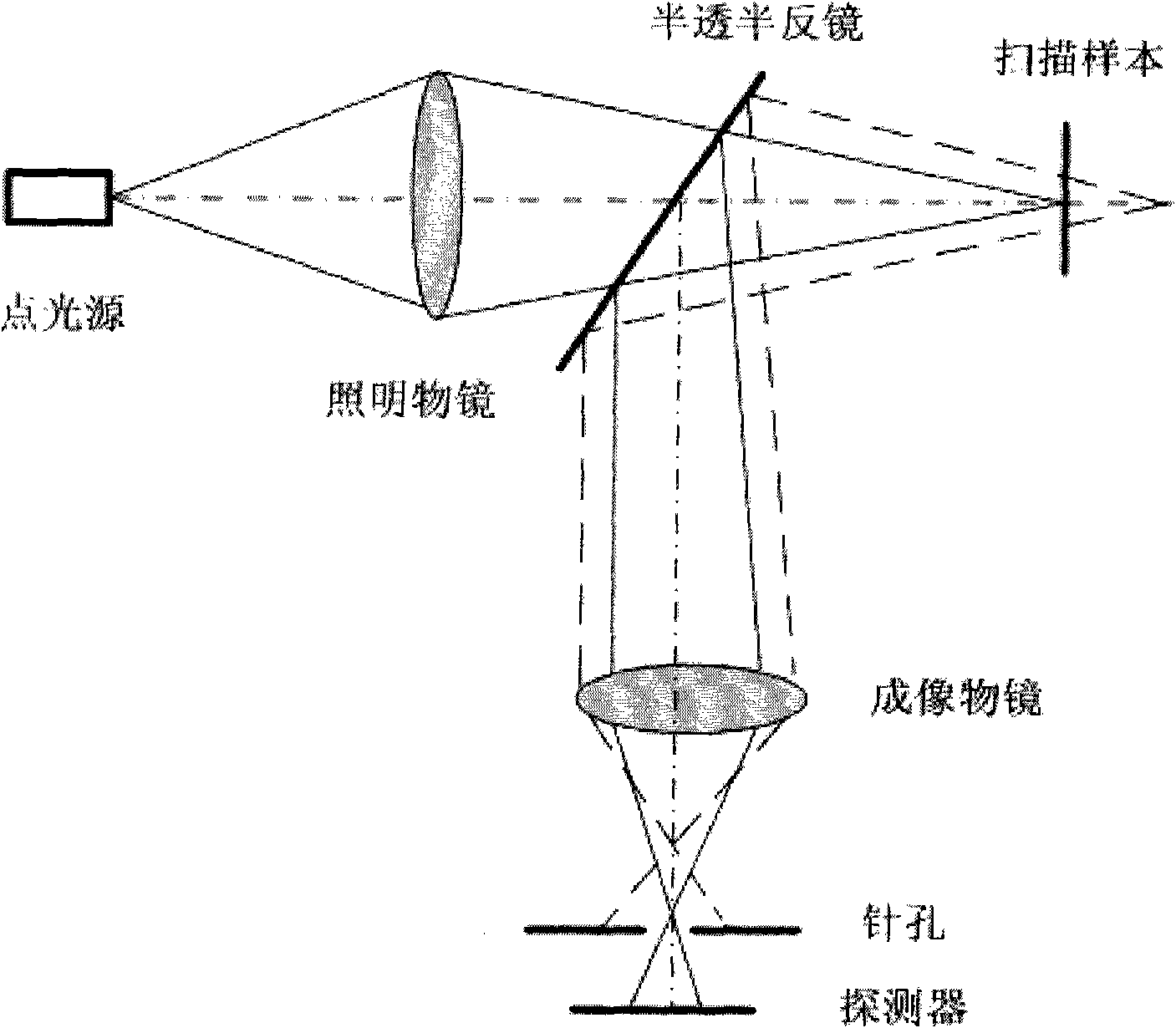
Method and apparatus for fluorescent confocal microscopy
ActiveUS20060017001A1Big advantageDrawback can be addressedPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersWide fieldFluorescence microscope
A new and improved confocal fluorescence microscope is presented. The new microscope has significant advantages relative to existing implementations of microscope confocal imagers. In common with previous confocal imagers the instant invention has the advantages relative to conventional wide-field and confocal fluorescence imagers, however it addresses the drawbacks of confocal technology in terms of cost and complexity, and provides significant savings in both due to the simplicity of the components and the elimination of the need of, in particular, spatial filters such as pinholes or slits.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
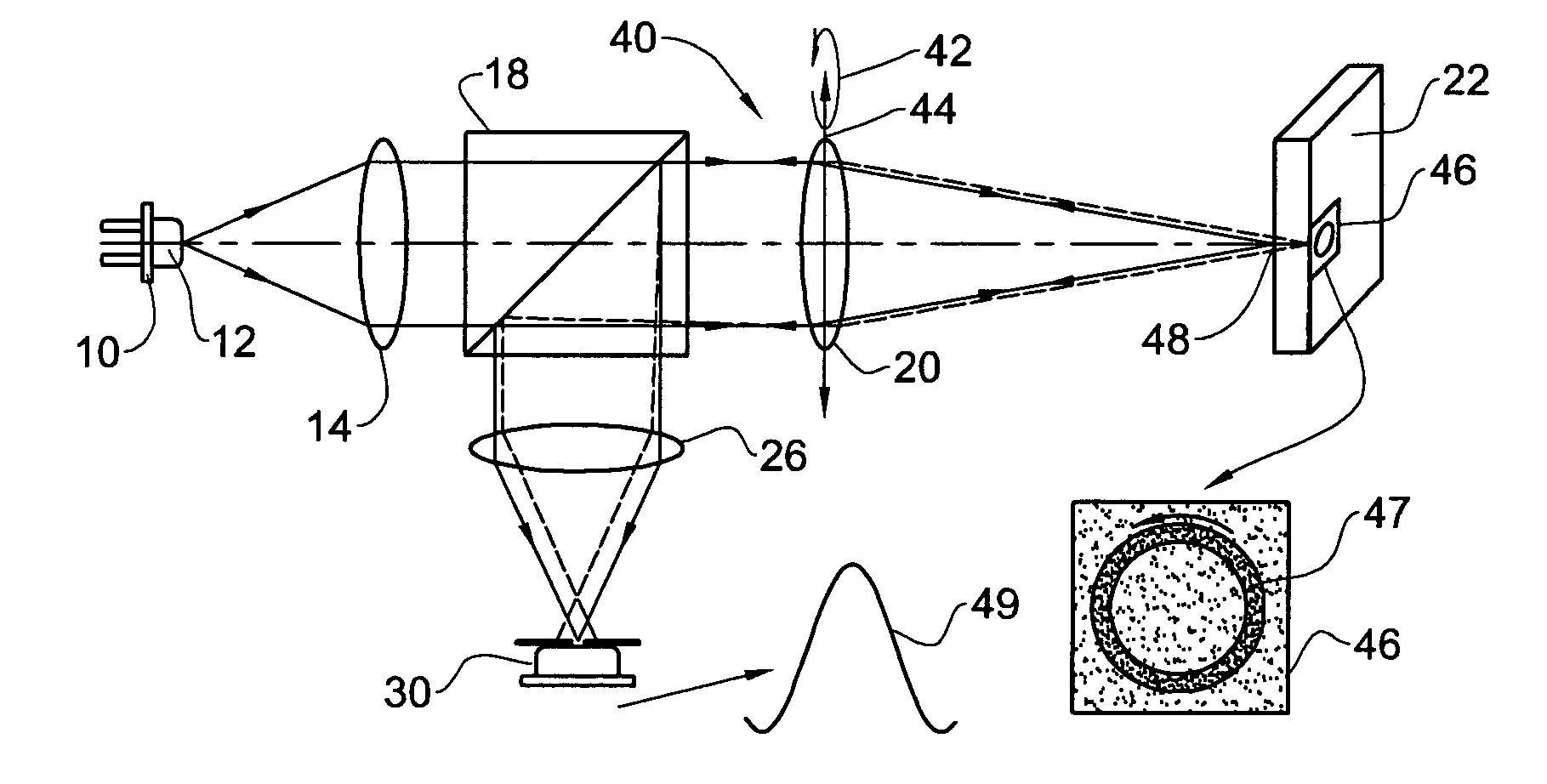
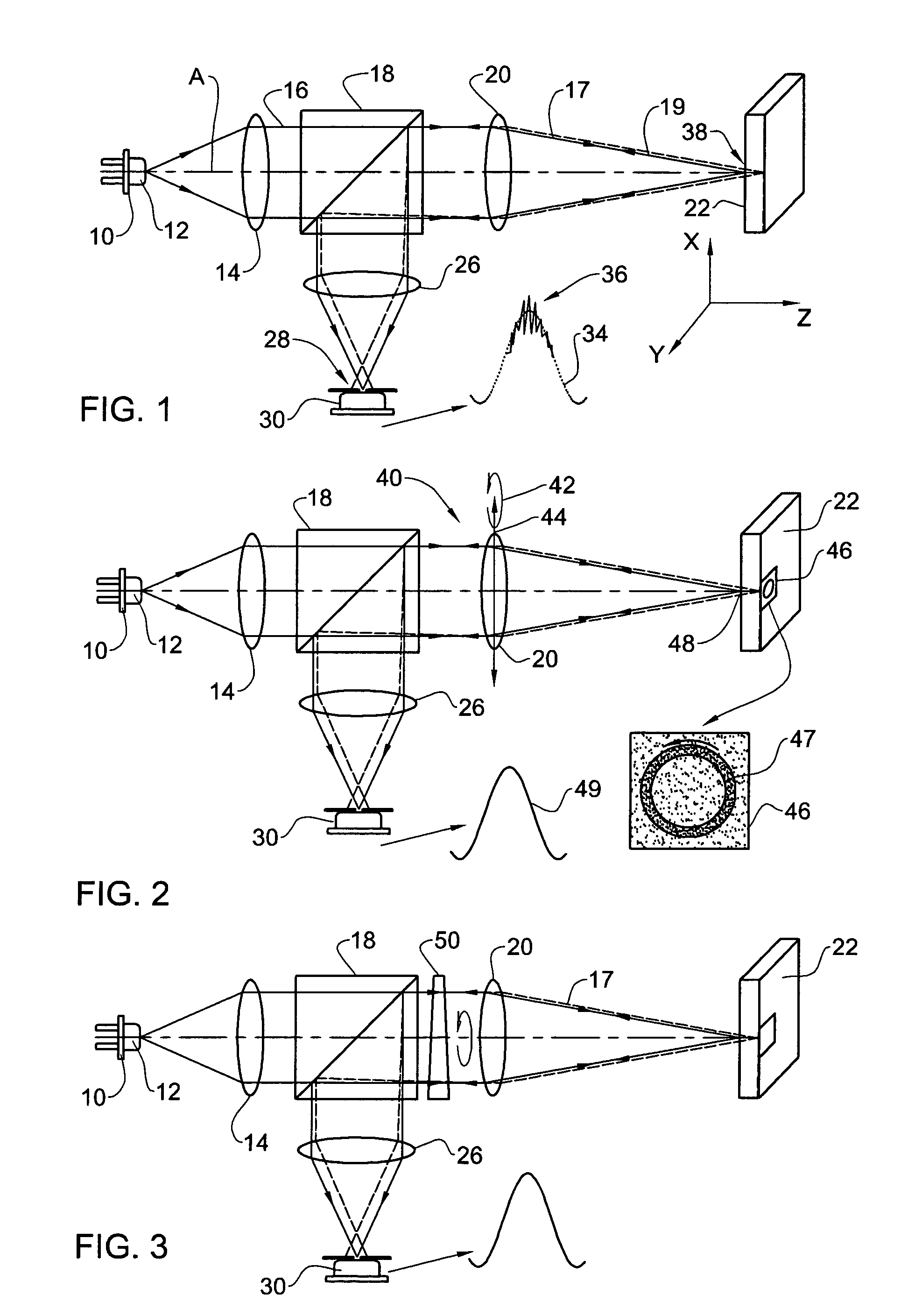
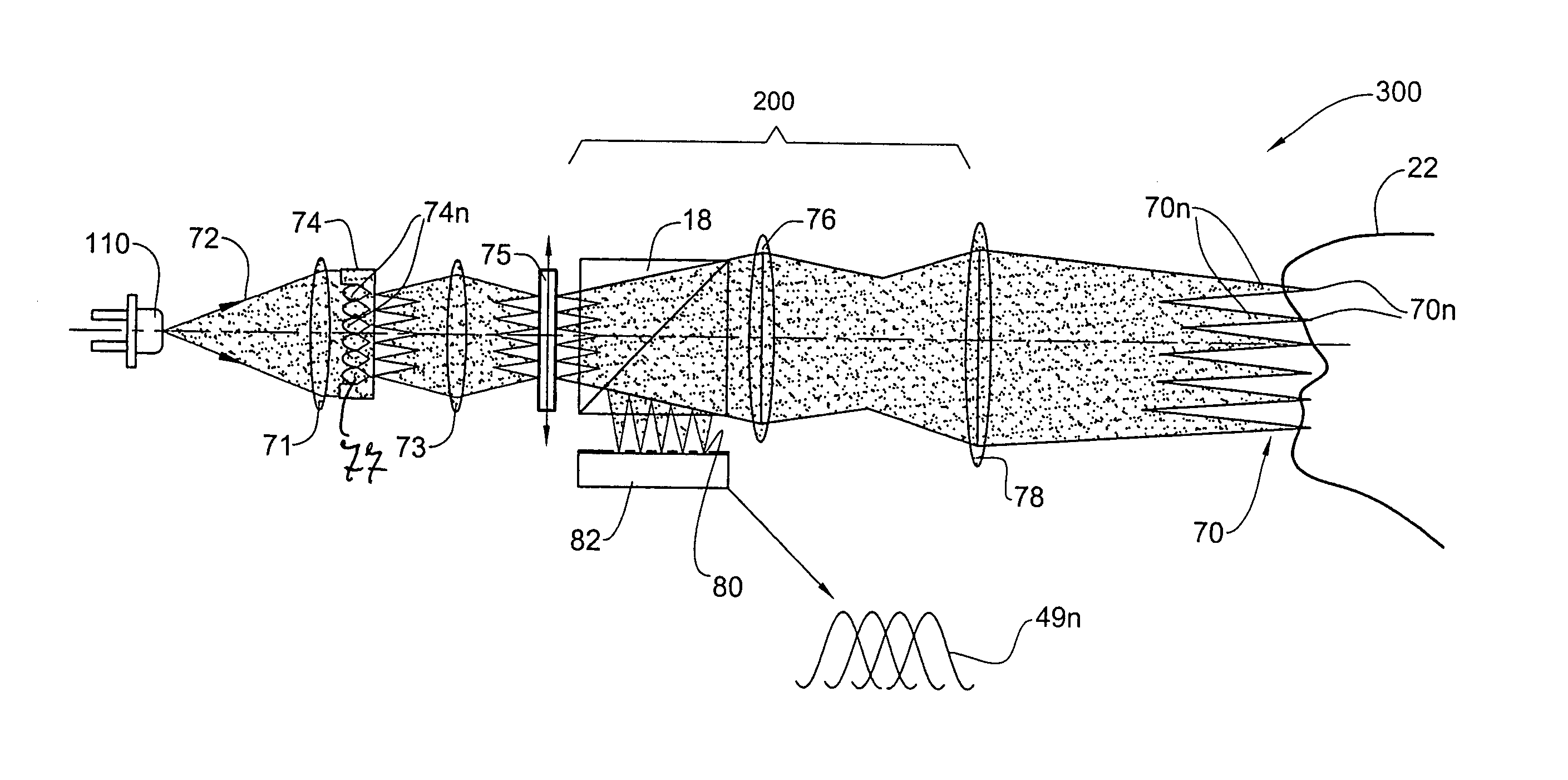
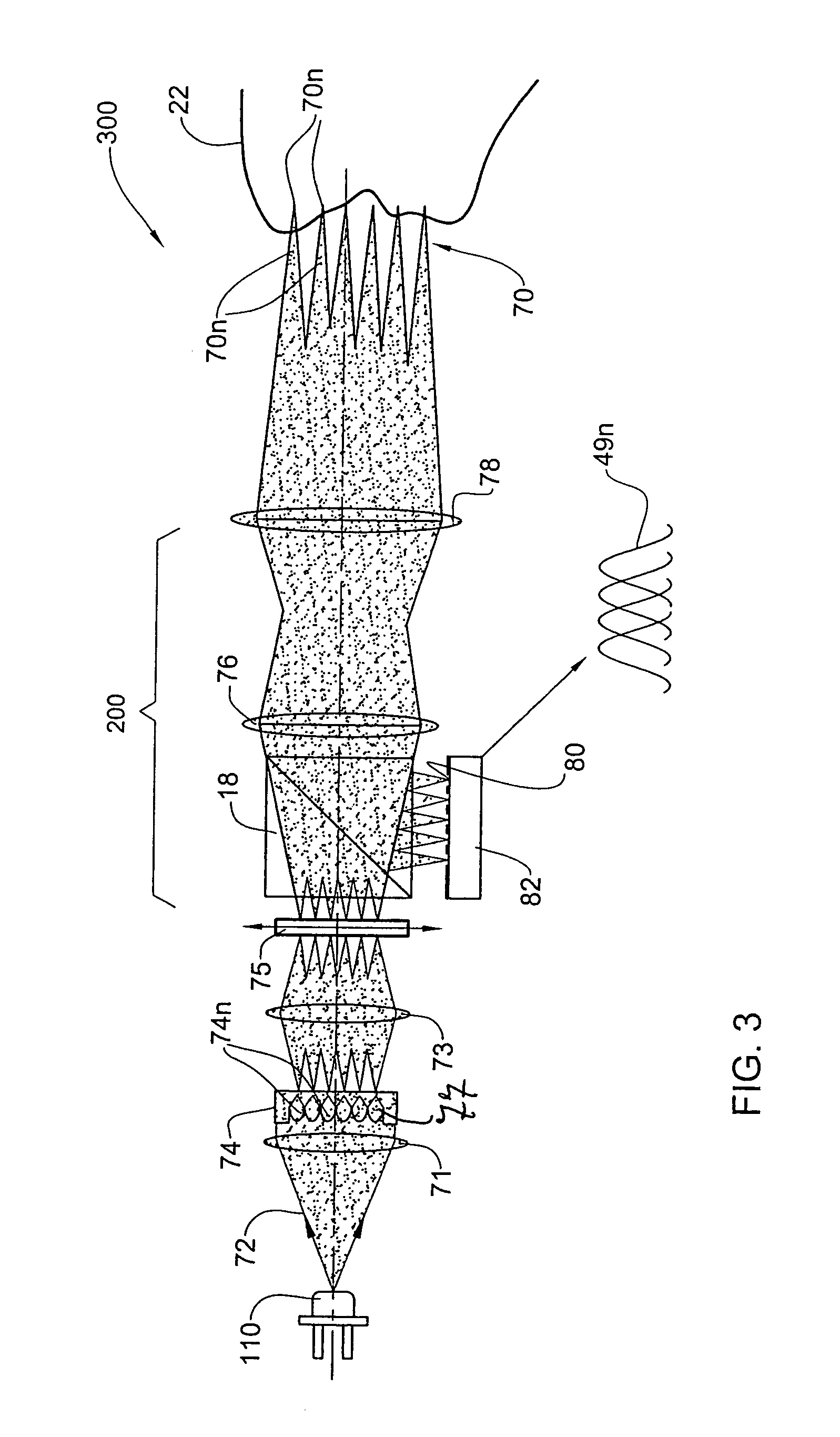
Speckle reduction method and apparatus
An apparatus adapted for confocal imaging of a non-flat specimen comprising a coherent light source for producing a light beam, imaging optics adapted to focus the light beam into at least one spot on a surface of a specimen, and a detector adapted to receive and detect light reflected from the specimen surface. The imaging optics comprise at least one optical component located so that the light reflected from the specimen surface passes therethrough on its way to the detector. The optical component is movable so as to move the at least one spot, within a range of movement, to a number of distinct locations in a plane perpendicular to the apparatus' optical axis, within the detector's integration time.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
Optical mapping apparatus with optimized OCT configuration
InactiveUS6927860B2Reduce the amount requiredReduce the amount of solutionInterferometersScattering properties measurementsFace scanningBeam splitter
OCT apparatus includes an interferometer, having an input beam splitter and a 50 / 50 output splitter. The splitting ratio of the input splitter may be optimized depending on the source power of light source and on the mismatch of the balanced receiver. The input splitter is a plate beam-splitter to minimize the stray reflected light in the interferometer and allow sequential operation of the apparatus in the OCT or in the confocal regime. The switching between the two regimes may be at will, or synchronous with the en-face scanning which results in quasi-simultaneous OCT / confocal imaging or in alternatives frames, confocal and OCT. By using polarization sensitive elements, two channels are provided in each regime, OCT and confocal. The two confocal polarization sensitive channels may allow adjustments of compensators prior to OCT measurements or OCT imaging.
Owner:OPTOS PLC
Super-resolution laser polarization differential confocal imaging method and device
ActiveCN101852594AImprove horizontal resolutionImprove linearityUsing optical meansBeam expanderPupil
The invention belongs to the technical field of optical precision measurement, relating to super-resolution laser polarization differential confocal imaging method and device. The method improves the transverse resolution power by combining a radial polarized light and a pupil filtering technology, improves the axial resolution power by using a differential subtraction detection technology of an axial-offset dual-detector system and remarkably improves the spatial resolution power and tomography ability of the system. The device comprises a laser source as well as a beam expander, a polarization state modulation system, a pupil filter and a spectroscope which are sequentially arranged at a transmitting end of the laser source, an objective and a sample which are arranged in the transmitted light direction of the spectroscope in turn, and a differential confocal system in the opposite direction of the reflected light direction of the spectroscope. The invention combines the radial polarized light resolution technology with the pupil filtering technology and improves the transverse resolution power of the system; moreover, the differential work mode of the invention can remarkably improve the axial imaging ability of the system and is applicable to the high-precision detection and metering of nanometer-level geometrical parameters in the nanometer manufacturing field.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
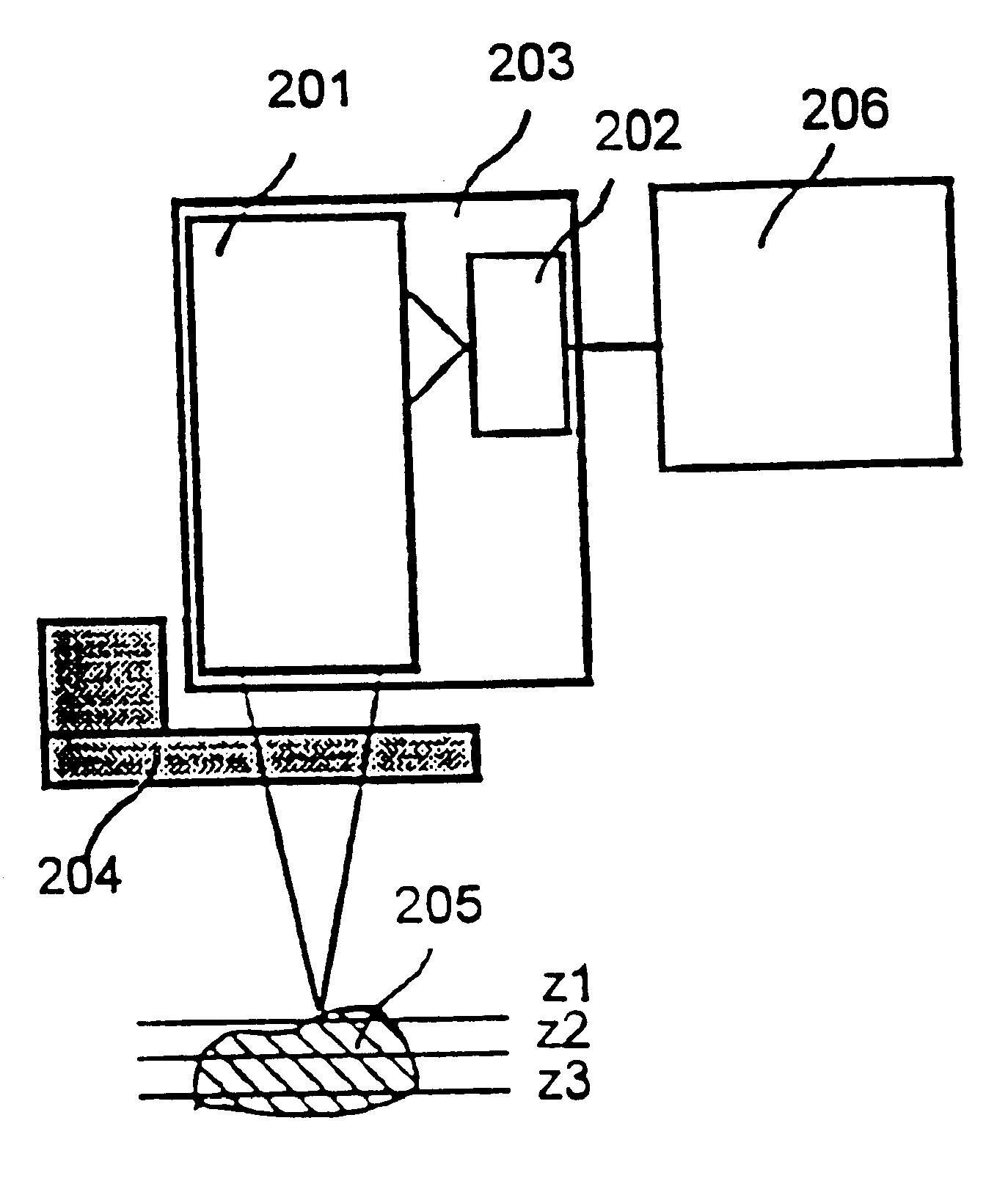
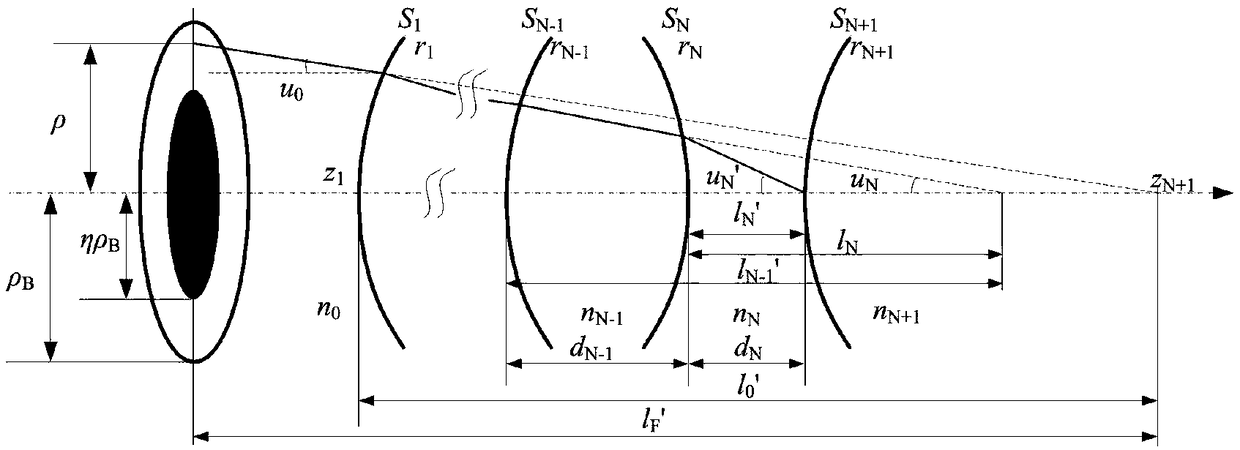
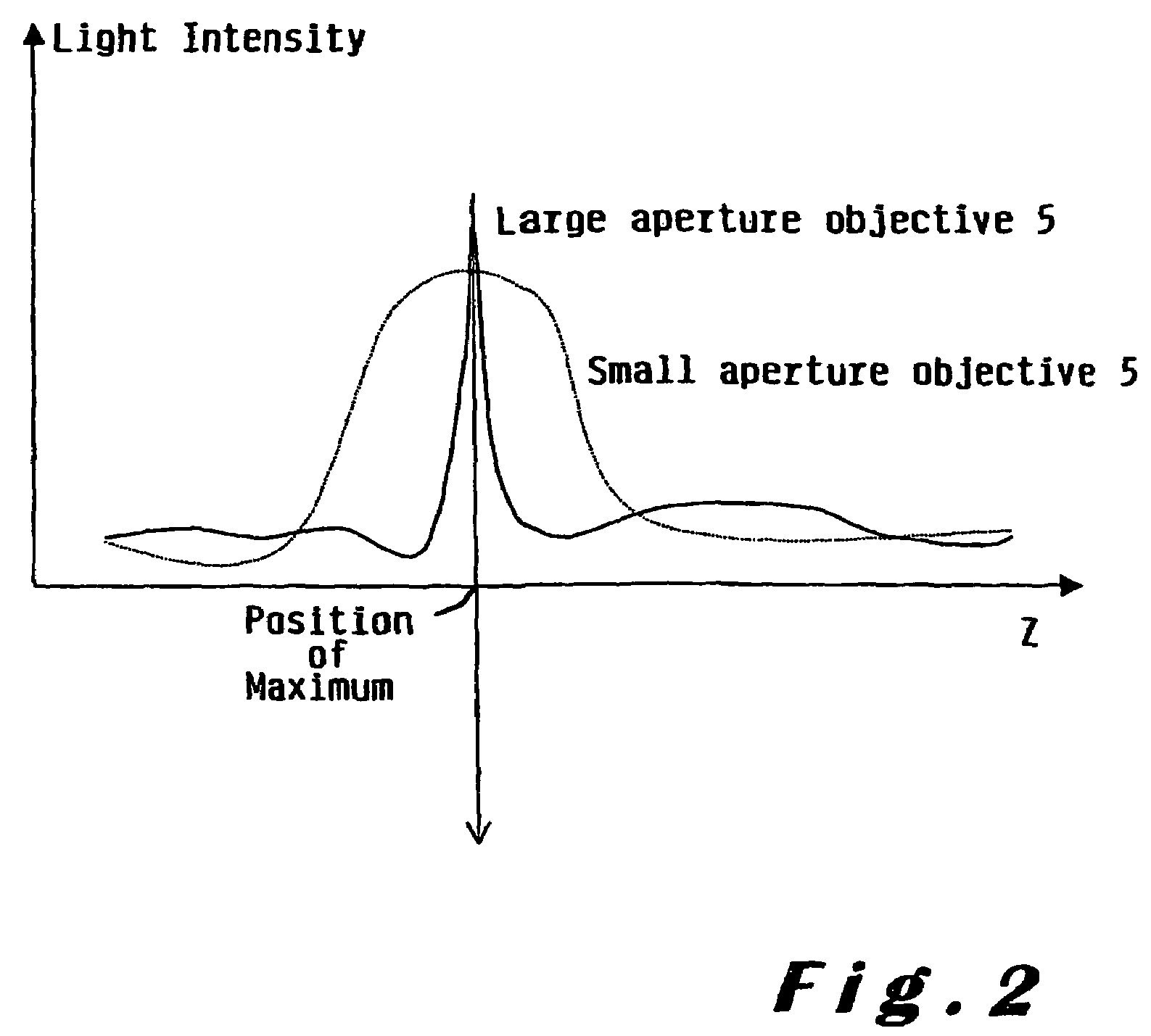
Three-dimensional shape measuring apparatus
A three-dimensional shape measuring apparatus using a confocal imaging system which has a new means for changing the distance in the Z direction between the object and the object-position-in-focus, instead of an object stage moved in the Z direction. This means shifts the object-position-in-focus in the Z direction by refraction. One means inserts a plurality of transparent flat plates between the objective lens and the object-position-in-focus in turn. Another means uses a transparent flat plate made of a material for which the refractive index changes according to the voltage applied and is disposed between the object and the object-position-in-focus.
Owner:TAKAOKA ELECTRIC MFG
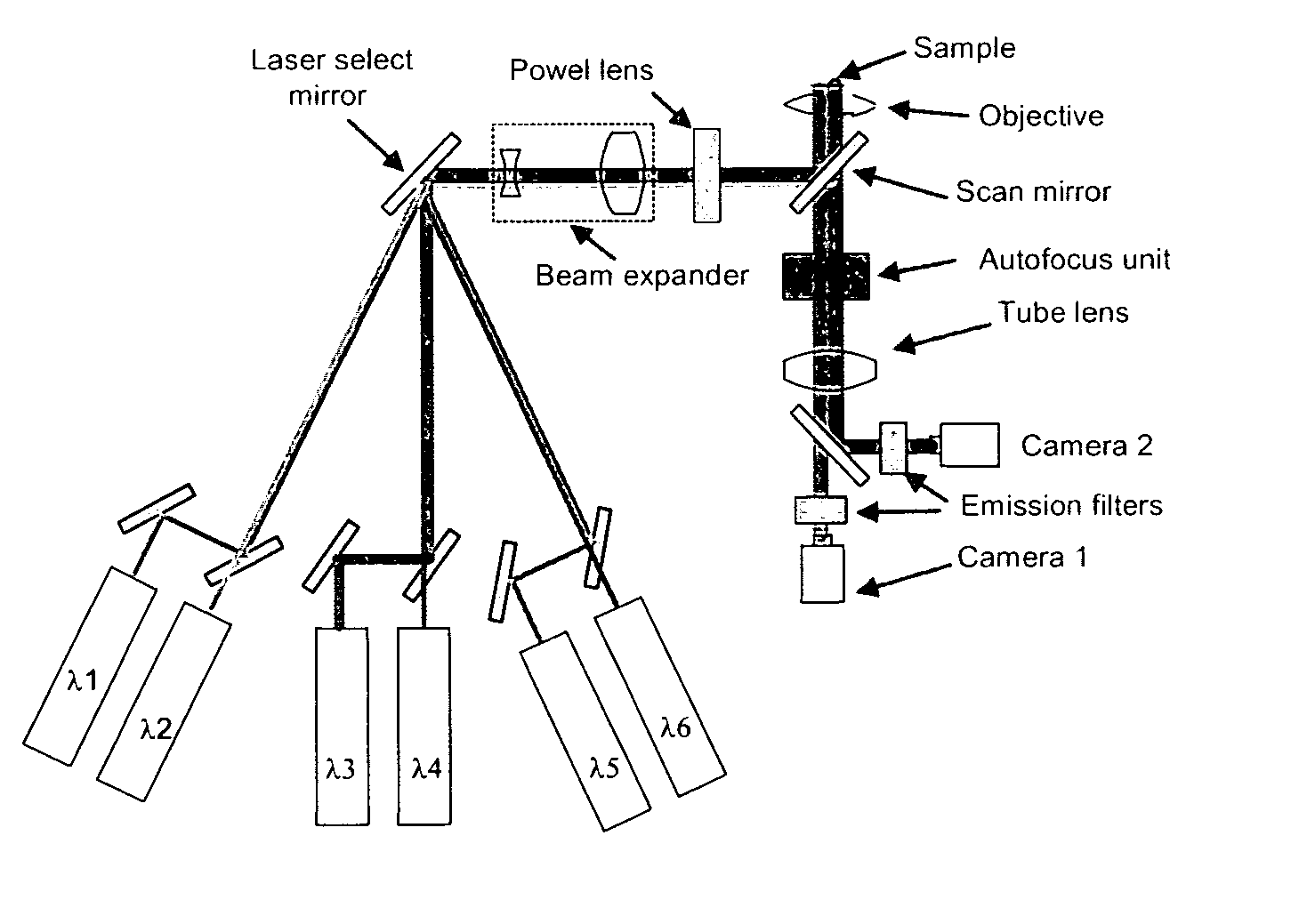
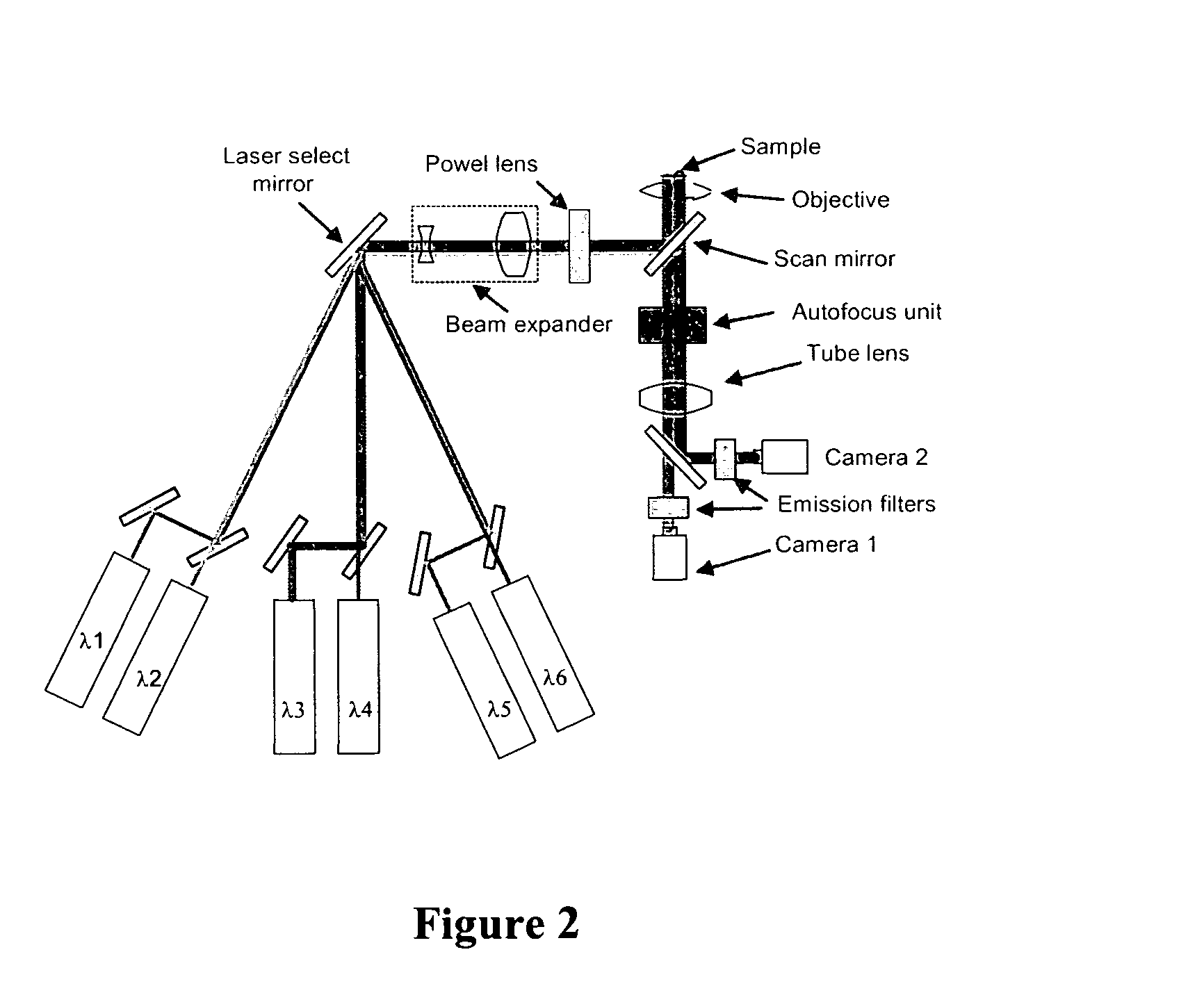
Near-infrared laser scanning confocal imaging system
ActiveCN102706846AImaging RealizationReduce absorptionFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceLaser scanning
The invention discloses a near-infrared laser scanning confocal imaging system, which comprises a light path scanning unit and a control unit which adopt a confocal structure, wherein the light path scanning unit comprises a near-infrared laser source, a collimation and extension module, a laser optical filter, a dichroic reflector, a scanning galvanometer, an f-theta lens, a tube lens, an imaging objective lens, a fluorescent optical filter, a convergent lens, a pinhole, a detector and the like, the control unit comprises a motion control module used for controlling the scanning galvanometer, a data acquisition module used for acquiring an output signal of the detector, a data processing module connected with the motion control module and the data acquisition module, and the like. The method matched with the system is characterized in that a sample is marked with near-infrared quantum dots with the fluorescence emission spectrums between 932nm and 1250nm, and then the sample is detected by the near-infrared laser scanning confocal imaging system. According to the system disclosed by the invention, deep-level imaging of samples such as biological tissues can be accurately and efficiently realized, and the system has a simple structure and is easy to operate.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
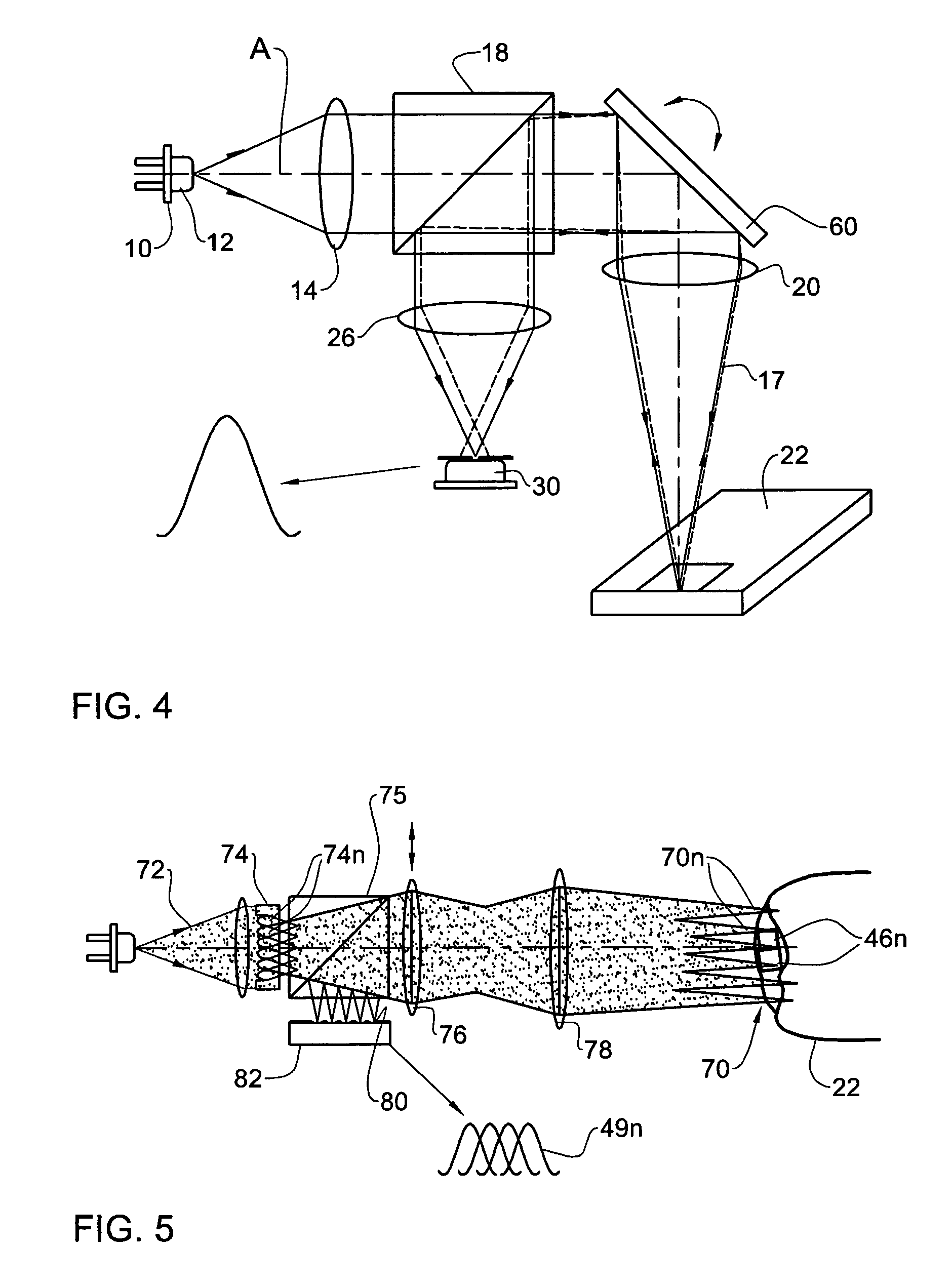
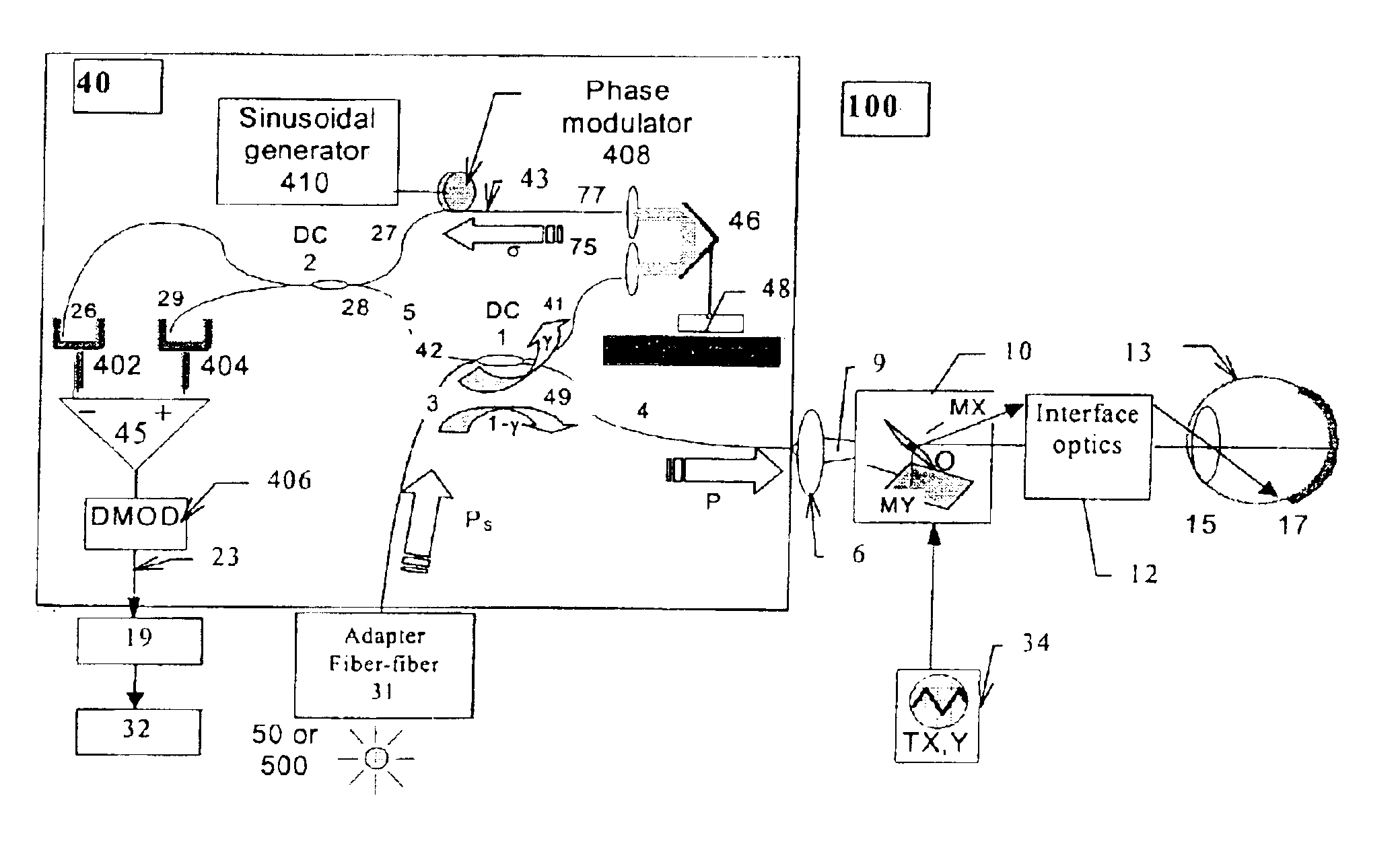
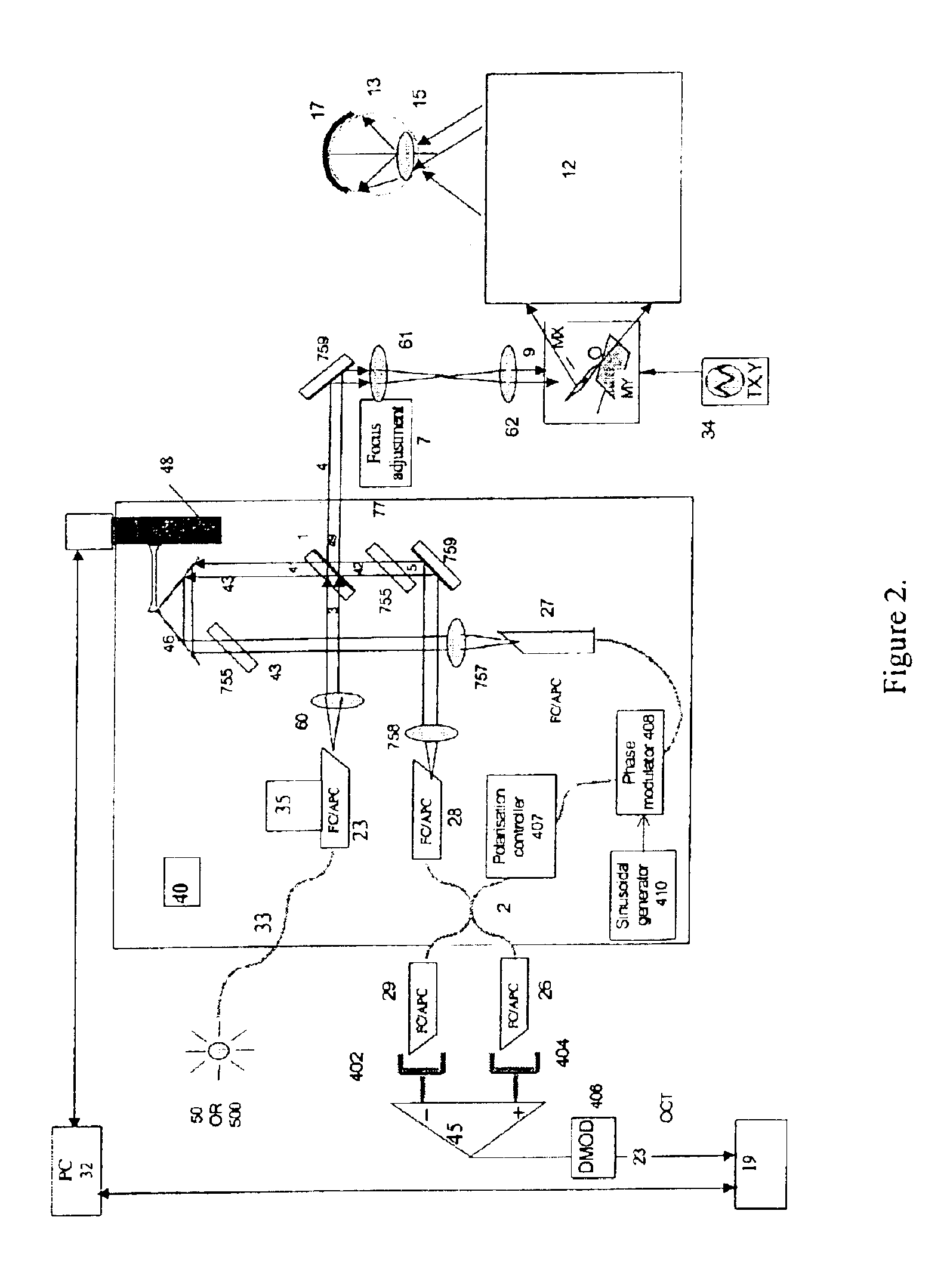
Apparatus for high resolution imaging of moving organs
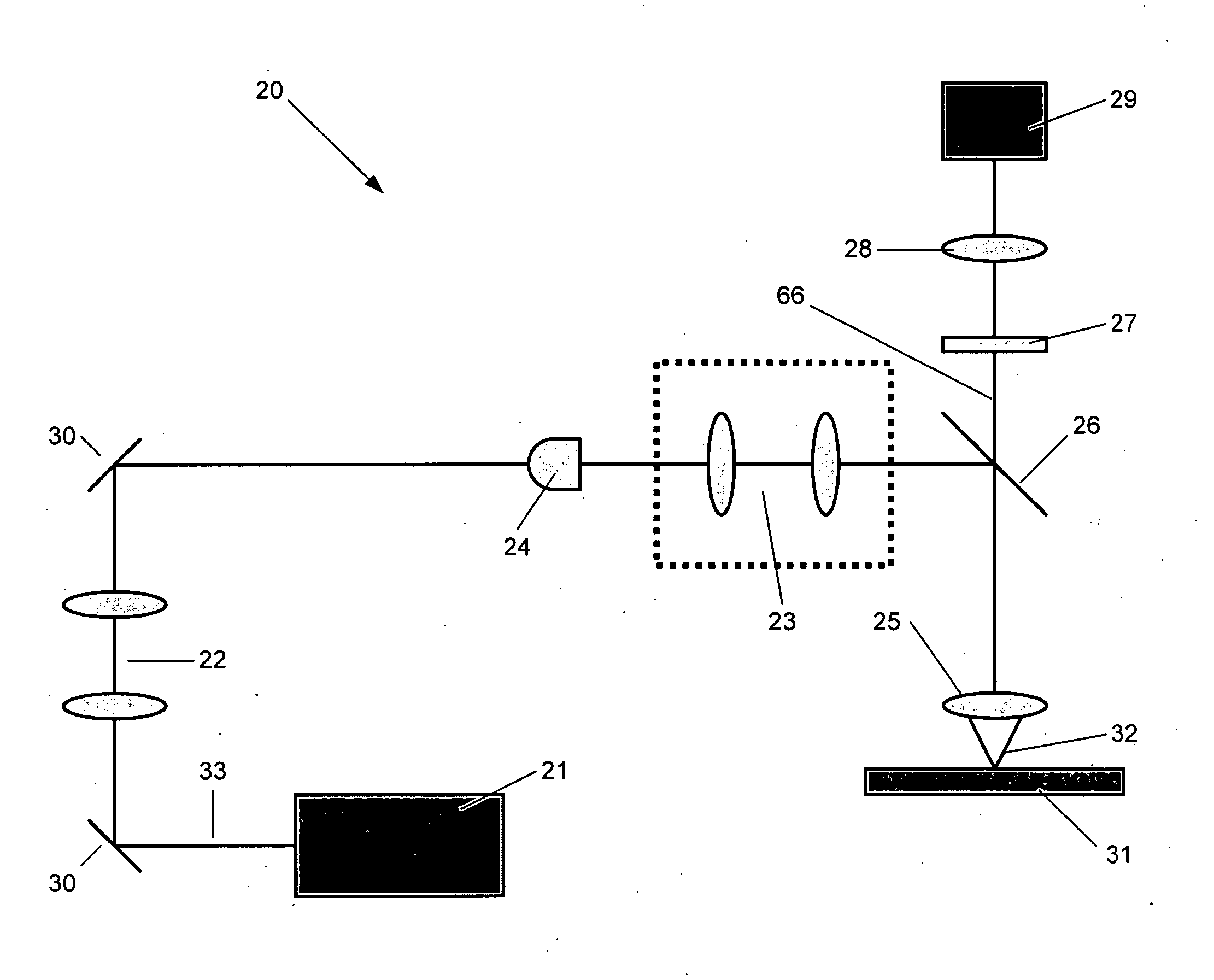
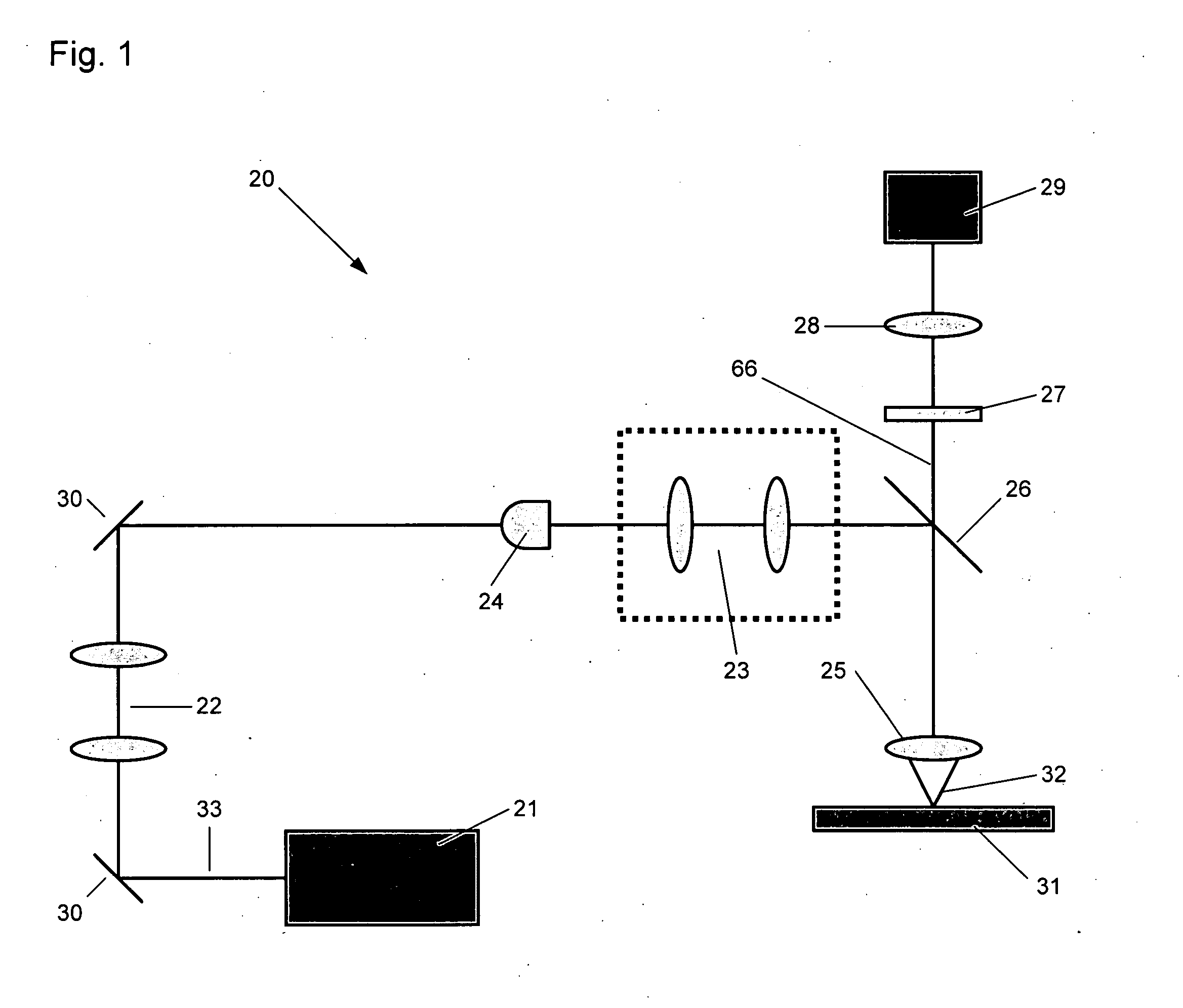
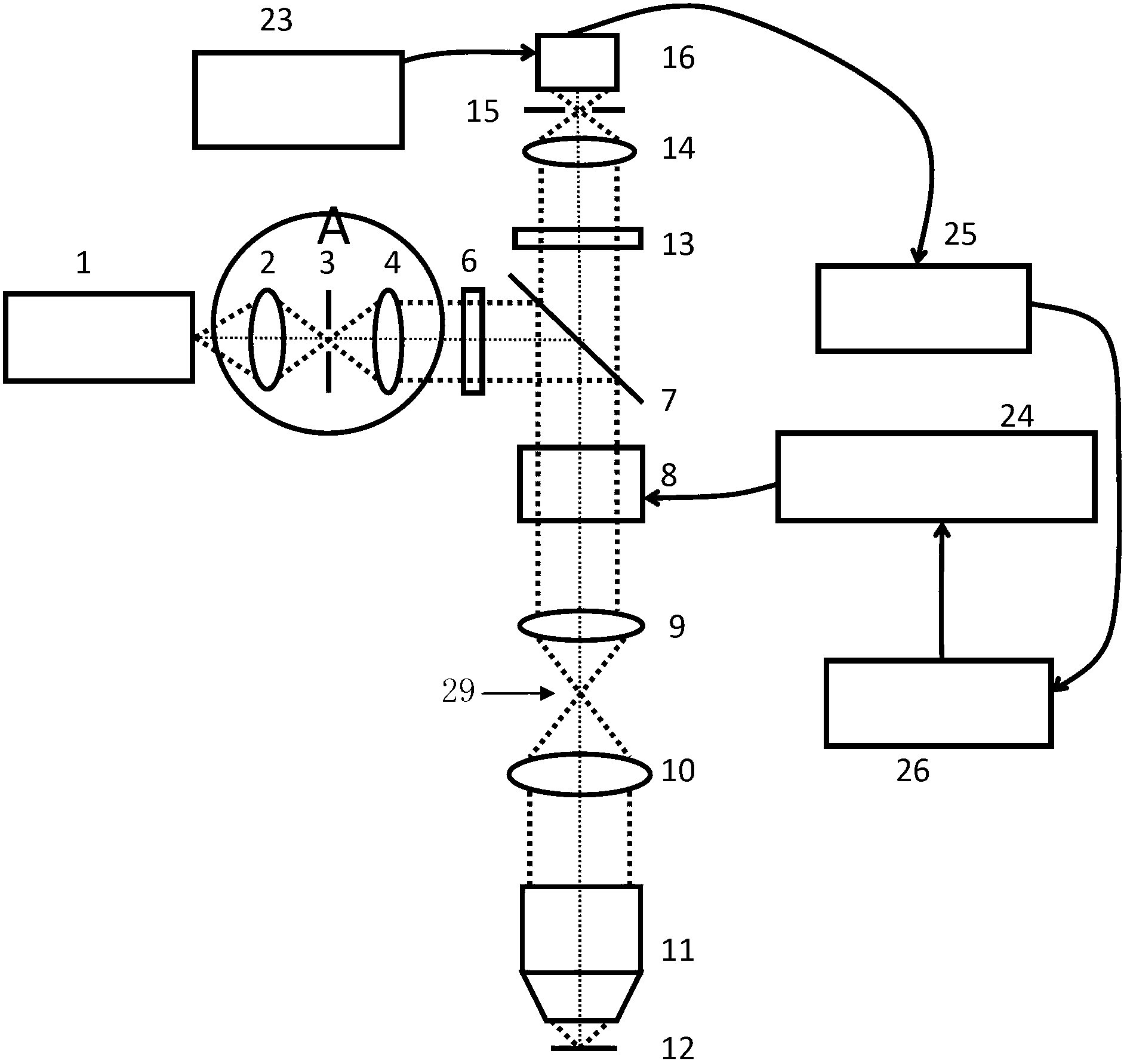
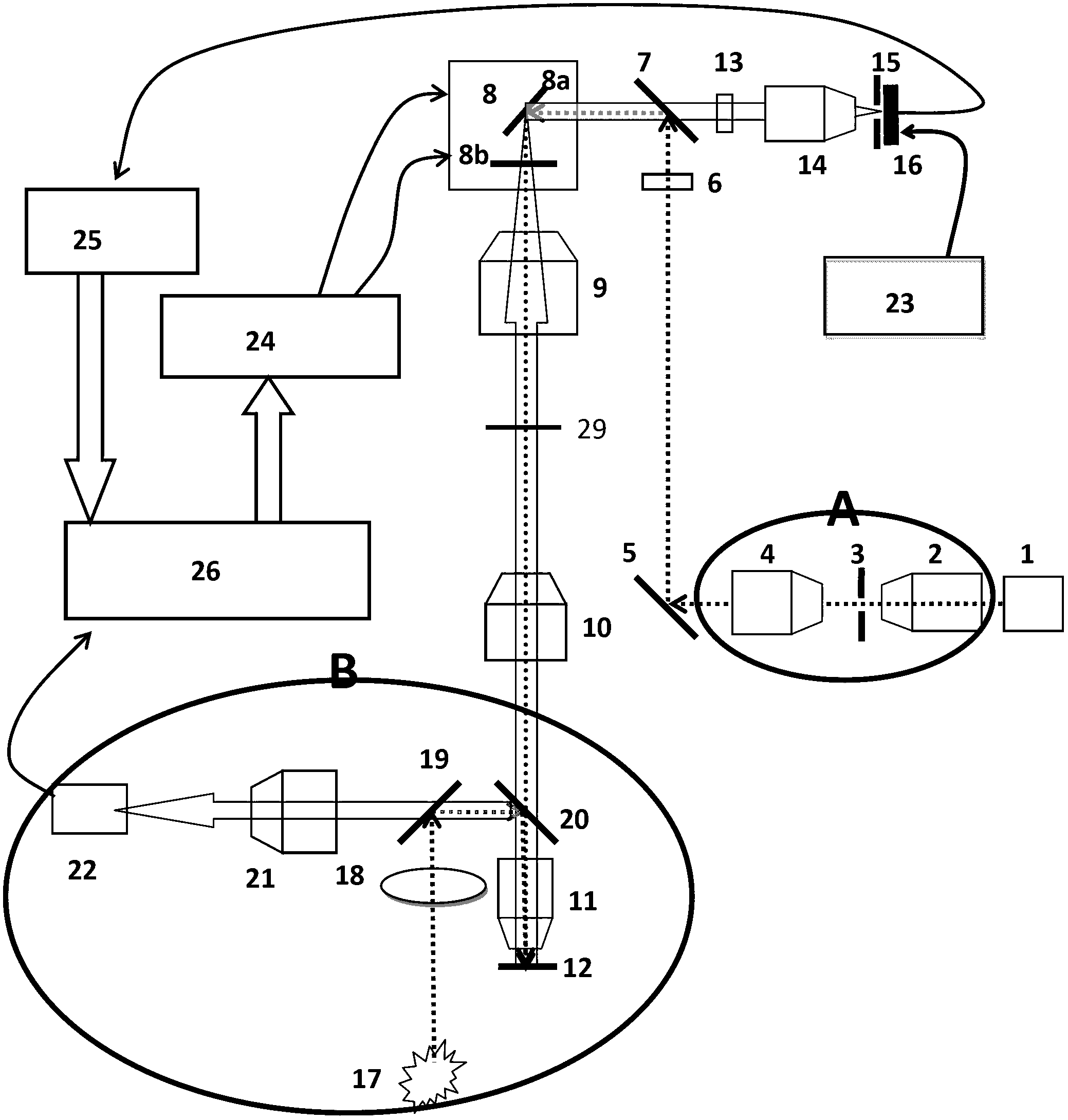
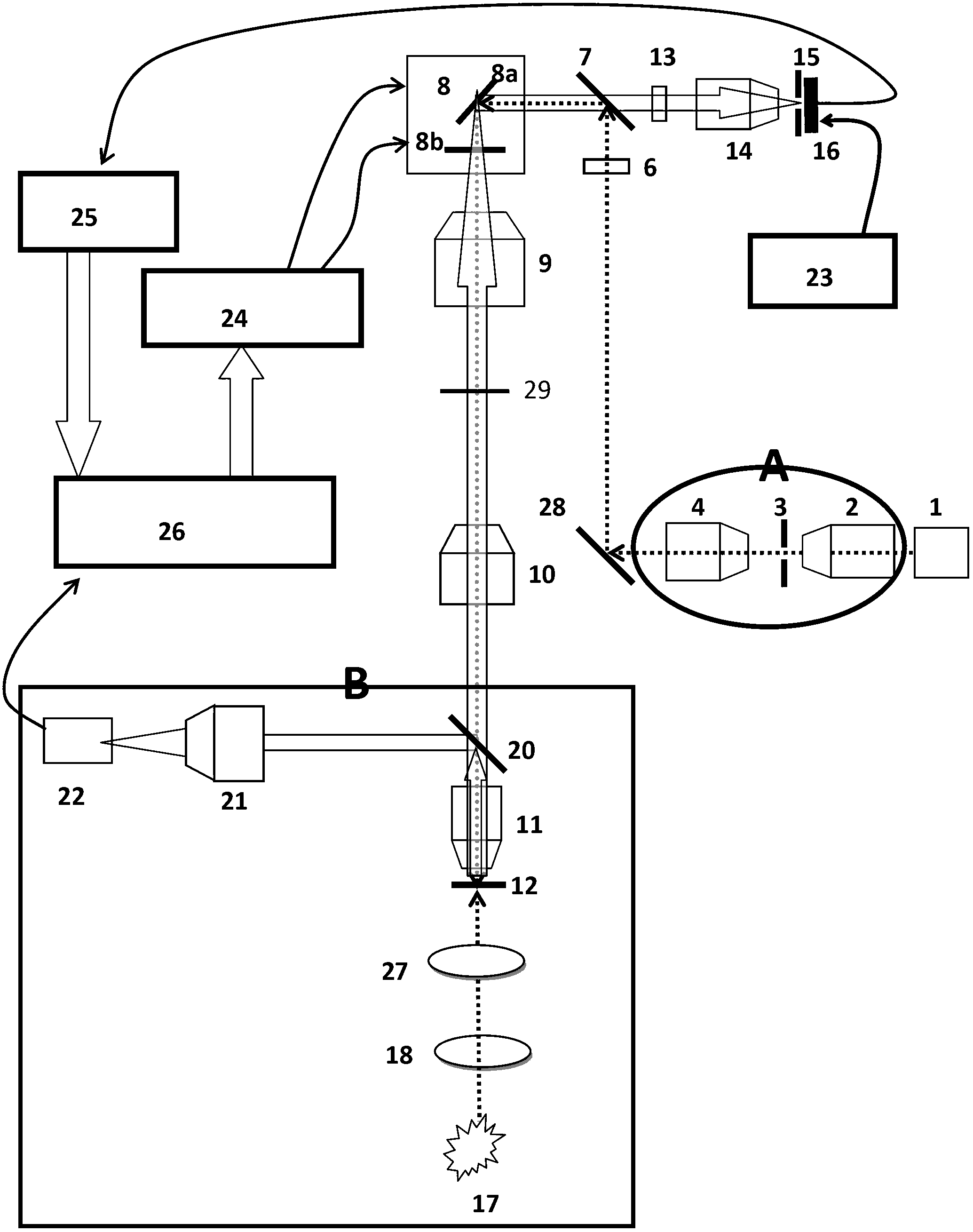
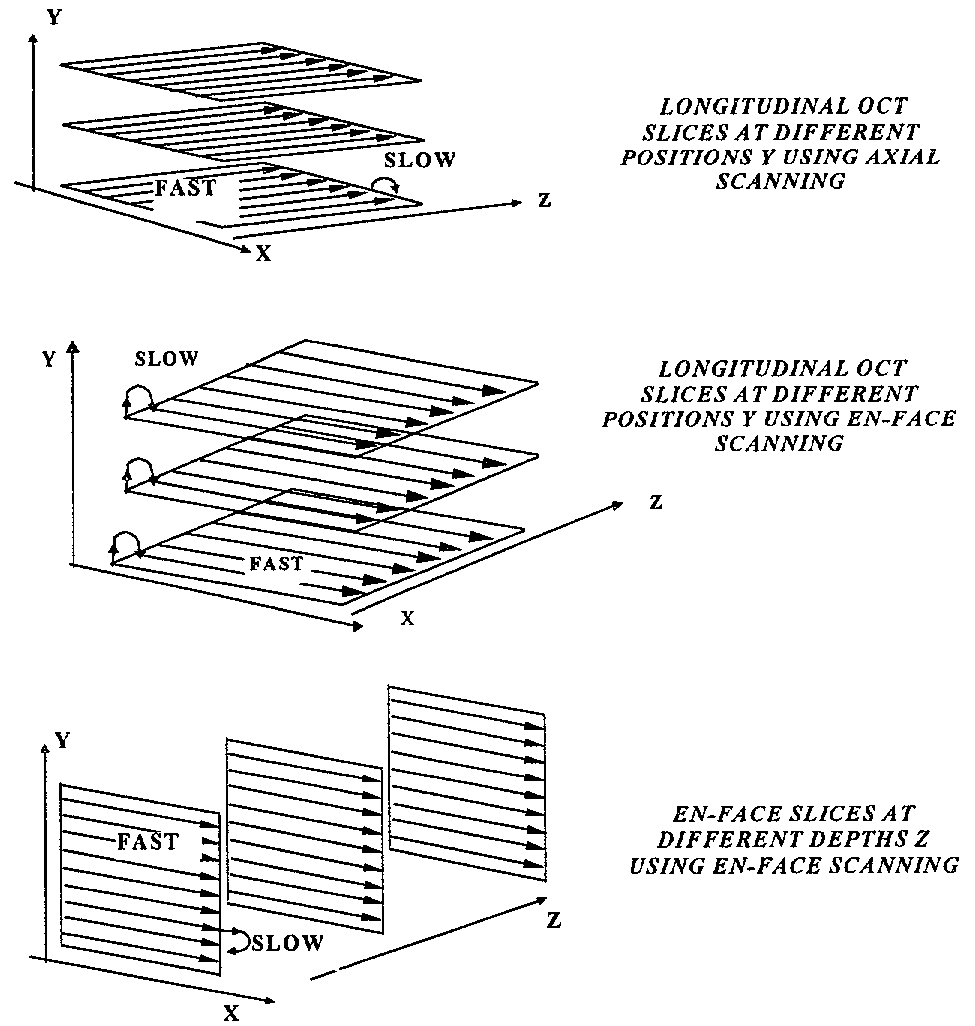
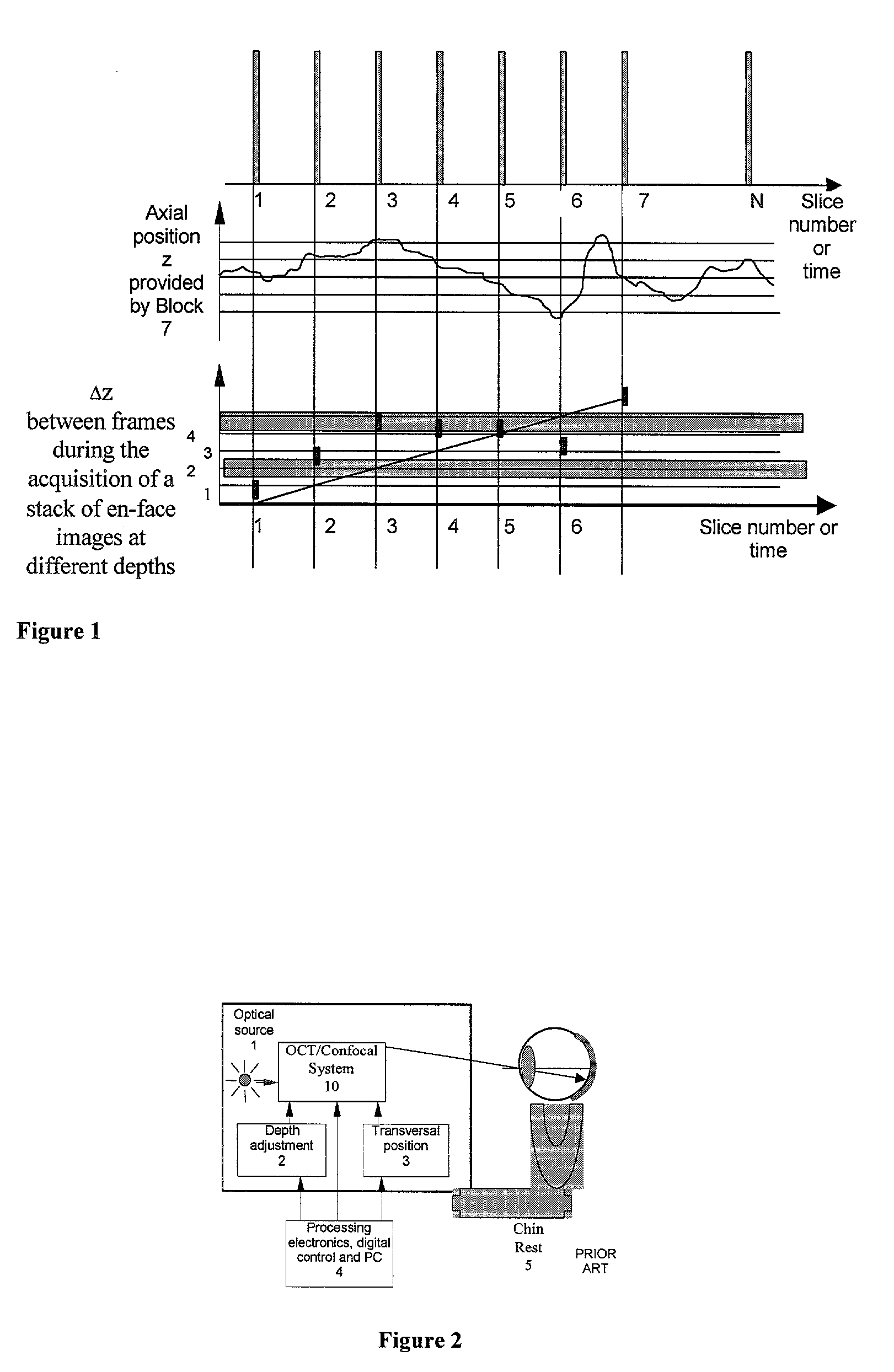
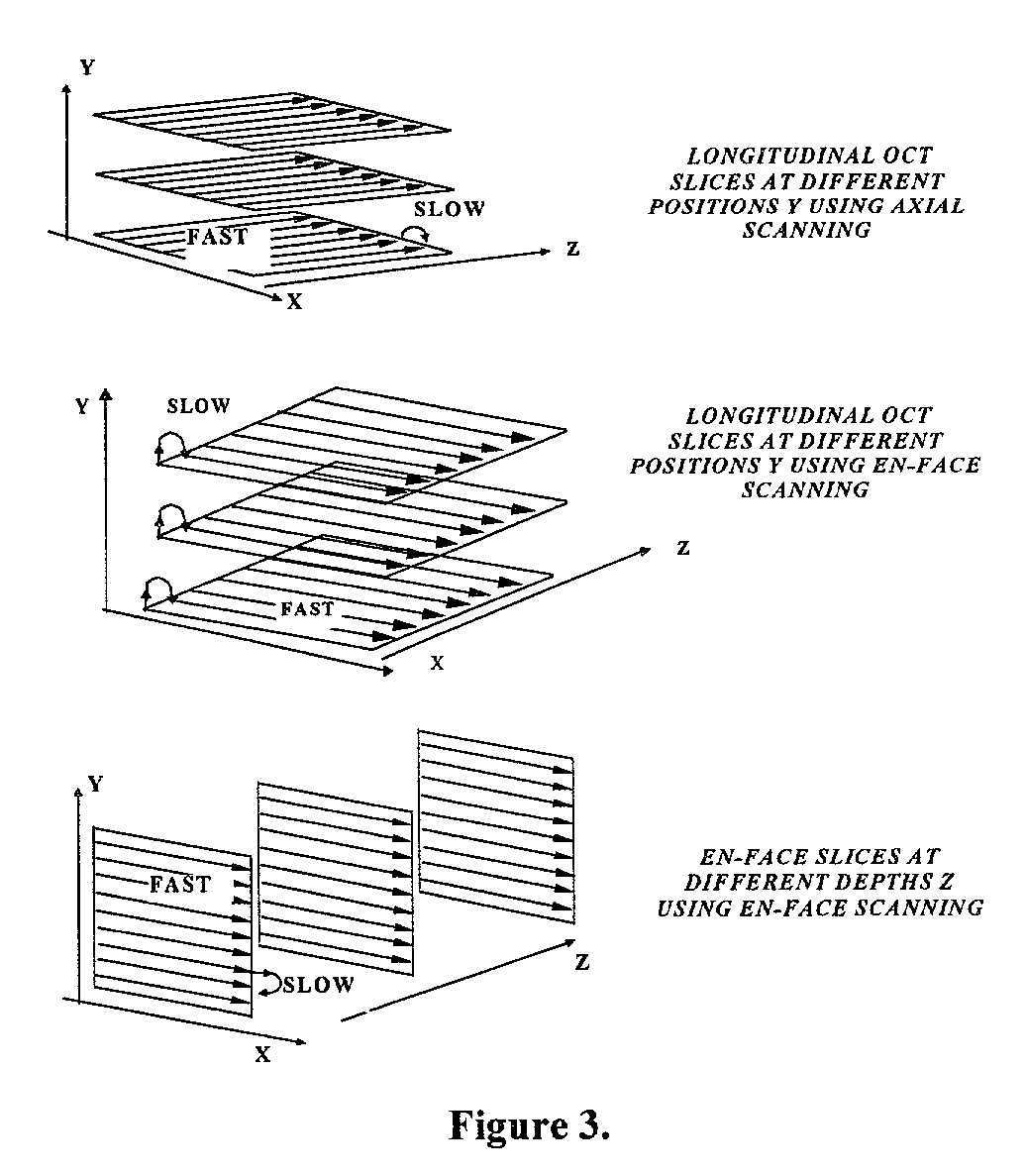
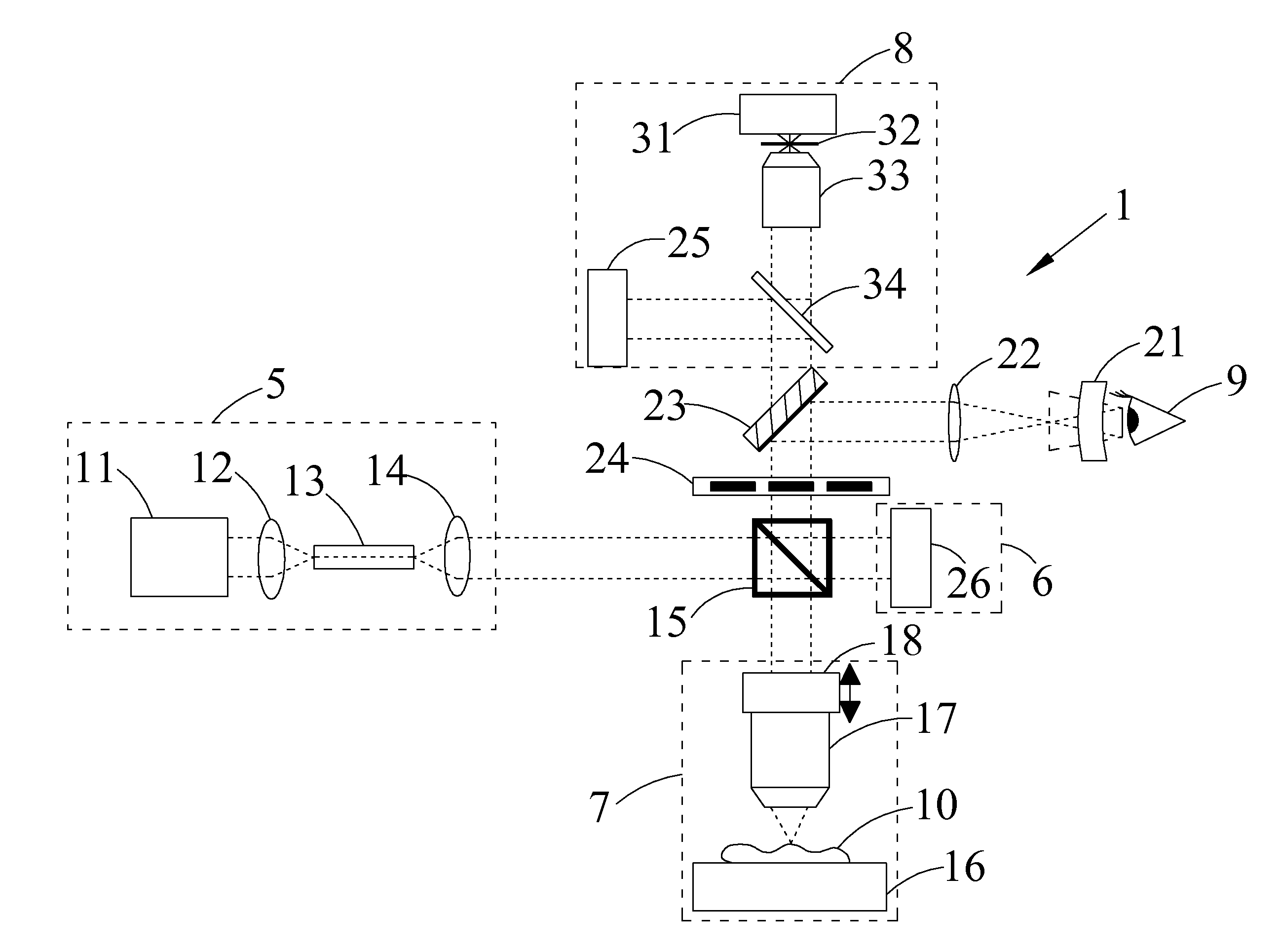
Apparatus for high resolution imaging of a moving object comprises a source of low coherence light, an optical coherence tomography imaging instrument or a dual channel, optical coherence tomography / confocal imaging instrument, a transverse scanner, an interferometer, depth adjustment means, and interface optics. First and an optional second sensing blocks sense the axial and respectively the transverse position of the object. A splitting element is shared so that the interface optics and the sensing blocks have a common axis of light transmitted to and from the object. Timing means establishes a timing, and timing intervals and reference times for images as they are taken. The acceptability of each scanned image is determined according to predetermined criteria. A series of en-face OCT images, or of longitudinal OCT images of the object may be taken at different depths or transverse coordinates, and the stack of collected images is used to build 3D profiles of the object.
Owner:OPTOS PLC
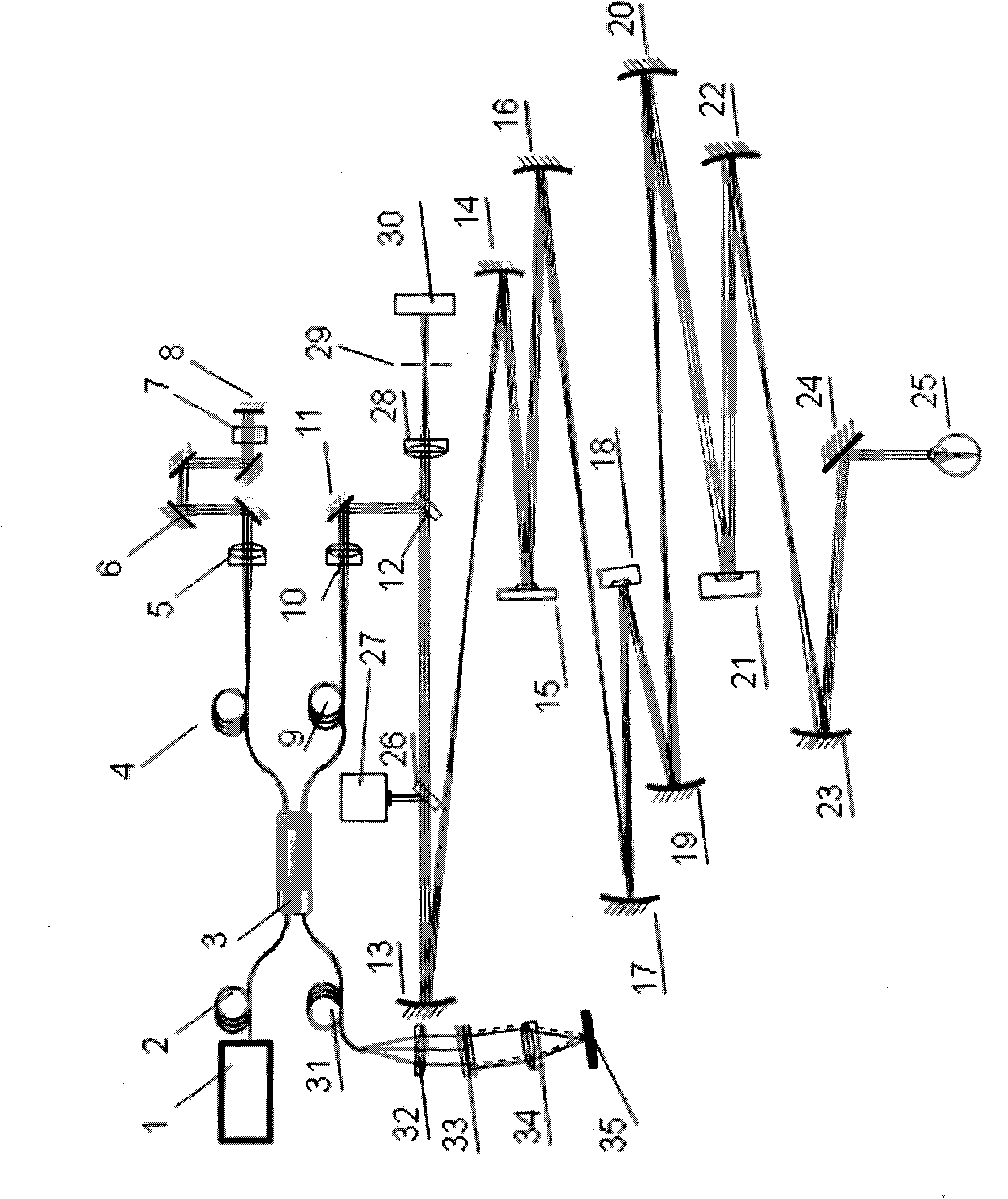
Three-dimensional optical coherence tomography confocal imaging apparatus
ActiveUS20110310395A1Easy to useInterferometersMaterial analysis by optical meansCamera lensMicroscopic image
A 3D OCT confocal imaging apparatus includes a light source module for providing an illumination beam with wider bandwidth from a crystal fiber; a reference source module; a pickup module; a beam splitter; an optical filter; and a sensor module. When the illumination beam illuminates a sample, a pickup objective lens and a piezoelectric actuator of the pickup module together provide an image beam scanning the sample in depth direction. The image beam and a reference beam from the reference source module together form an interference image beam, which is converted by a photosensor into a coherence image electric signal. Meanwhile, the interference image beam passes through a pinhole to form a confocal image, which is converted by an excited light photometer into a confocal image electric signal. With an image processing system, a 3D OCT confocal microscopic image of the sample can be produced from these image electric signals.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Three-dimensional shape measuring apparatus
InactiveUS6373978B1Character and pattern recognitionUsing optical meansObject pointClassical mechanics
A three-dimensional shape measuring apparatus which has an improved arrayed confocal imaging system.A three-dimensional shape measuring apparatus using a confocal imaging system which has a new means for changing the distance in the Z direction between the object and the object-position-in-focus, instead of an object stage moved in the Z direction. This means shifts the object-position-in-focus in the Z direction by refraction. One means inserts a plurality of transparent flat plates between the objective lens and the object-position-in-focus in turn. Another means uses a transparent flat plate made of a material for which the refractive index changes according to the voltage applied and is disposed between the object and the object-position-in-focus.A three-dimensional shape measuring apparatus using a confocal imaging system wherein an image processor estimates the position from which the intensity of the reflected light for each pixel of the confocal image becomes maximum by interpolation of a value from the curve of the relationship between the intensity of light detected and the distance from the object-position-in-focus to an object point.
Owner:TAKAOKA ELECTRIC MFG
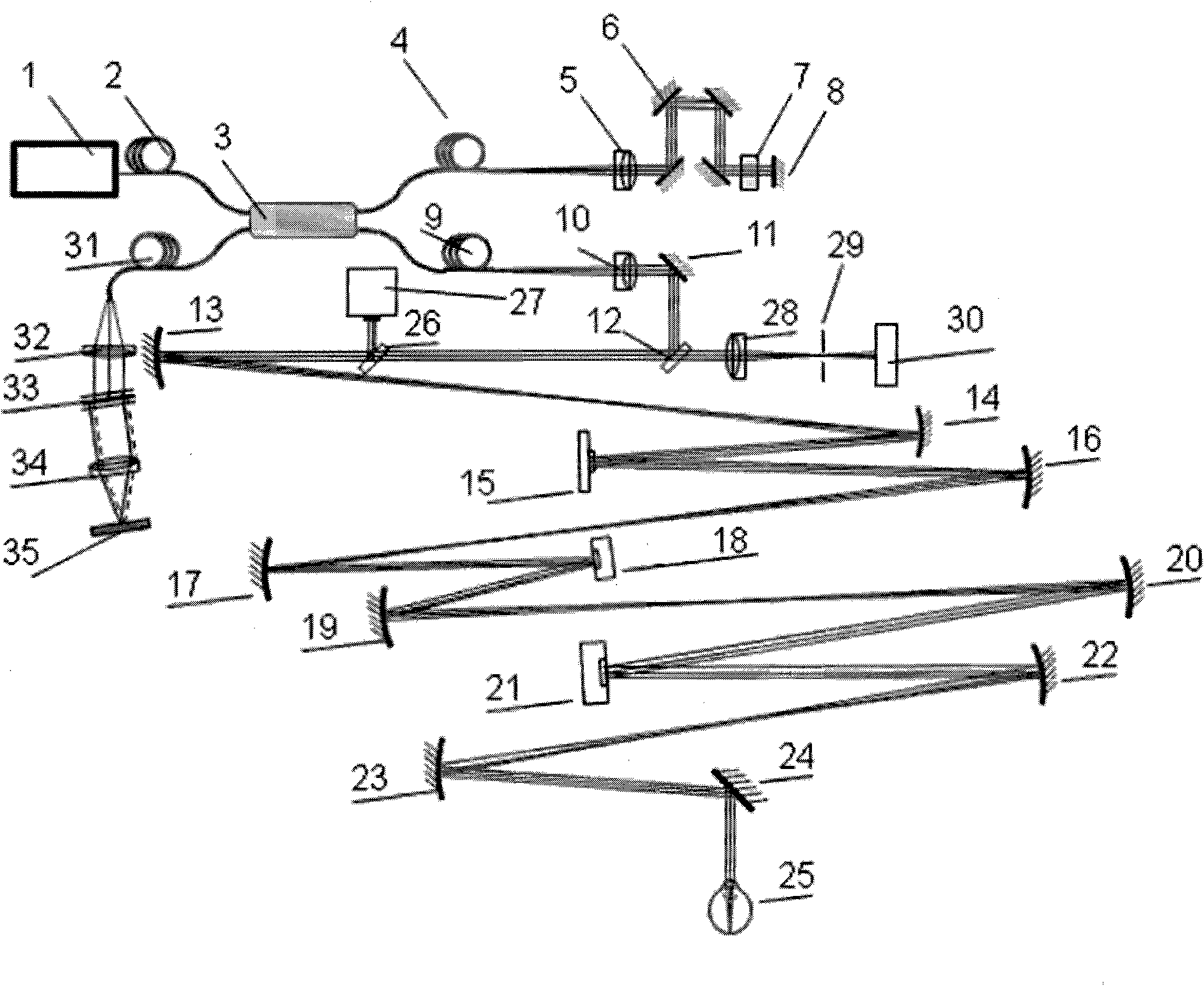
Confocal scanning and optical coherence tomograph based on self-adaptive optical technology
ActiveCN101869466AImproving Resolution in Longitudinal Sectional ImagingIncreased imaging resolution in transverse slicesPhase-affecting property measurementsEye diagnosticsReflecting telescopeImage detection
A confocal scanning and optical coherence tomograph based on self-adaptive optical technology comprises a light source component, a scanning and lighting light path component, an aberration detection and correction component, a confocal imaging detection component, a reference arm component and an optical coherence tomography detection component, wherein the components are linked by optical fiber and / or spherical reflecting telescopes; one part of low-coherent light emitted by the light source component enters into the reference arm component and then returns along the original path and the other part enters into the samples to be detected through the aberration detection and correction component and the scanning and lighting light path component in sequence and then returns from the samples to be detected along the original path; one part of the returning light is reflected to the aberration detection and correction component by a spectroscope and the other part is transmitted to another spectroscope and then is split into two parts, one part enters into the confocal imaging detection component and the other part enters into the optical coherence tomography detection component after being coupled with the light returning from the reference arm component. The tomograph can realize high-resolution three-dimensional imaging of the objects to be detected.
Owner:SUZHOU MICROCLEAR MEDICAL INSTR
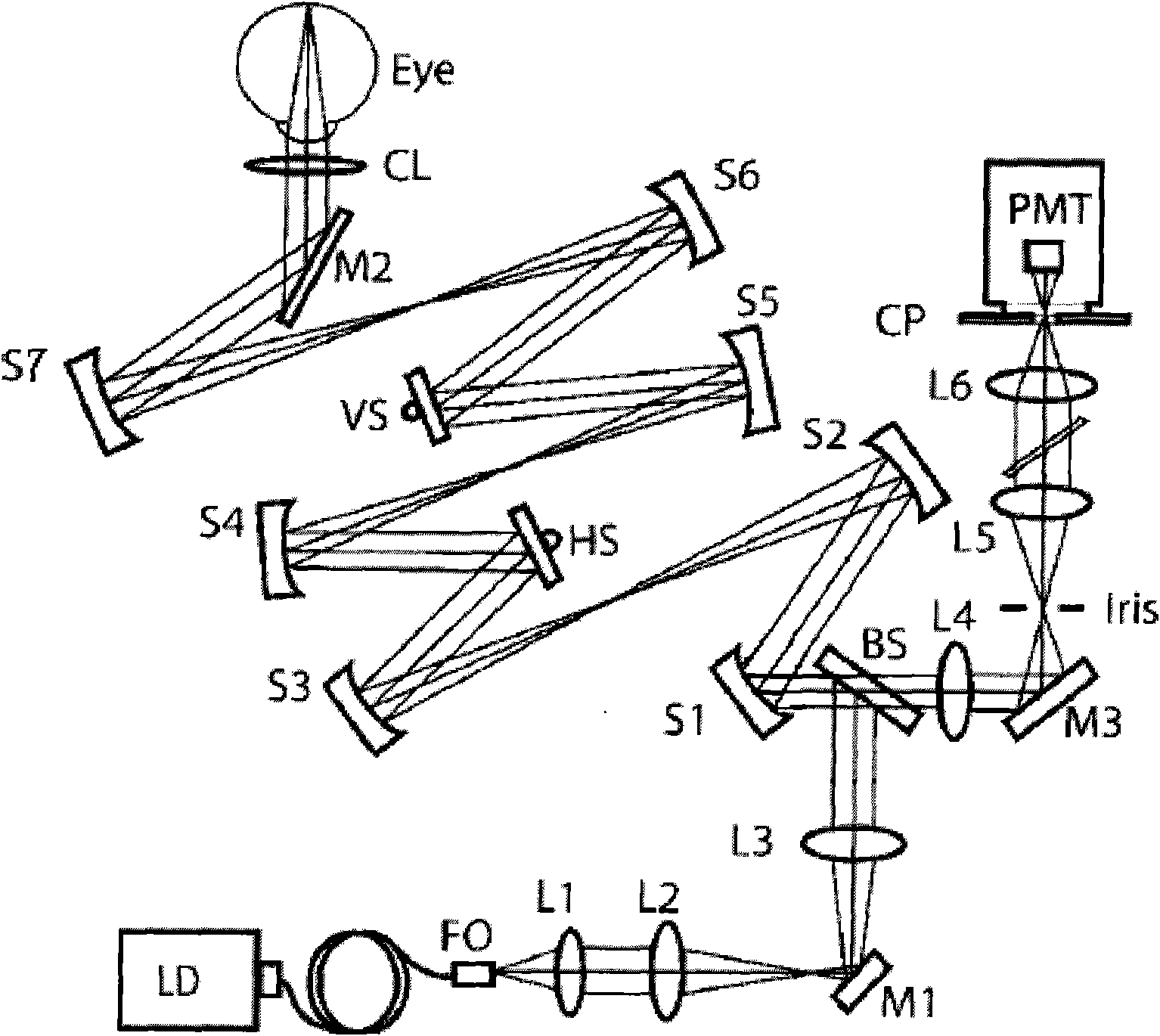
Method for Performing Micro-Perimetry and Visual Acuity Testing
ActiveUS20090141240A1Less examination timePrecise processDiagnostic recording/measuringUsing optical meansVision inspectionRetina
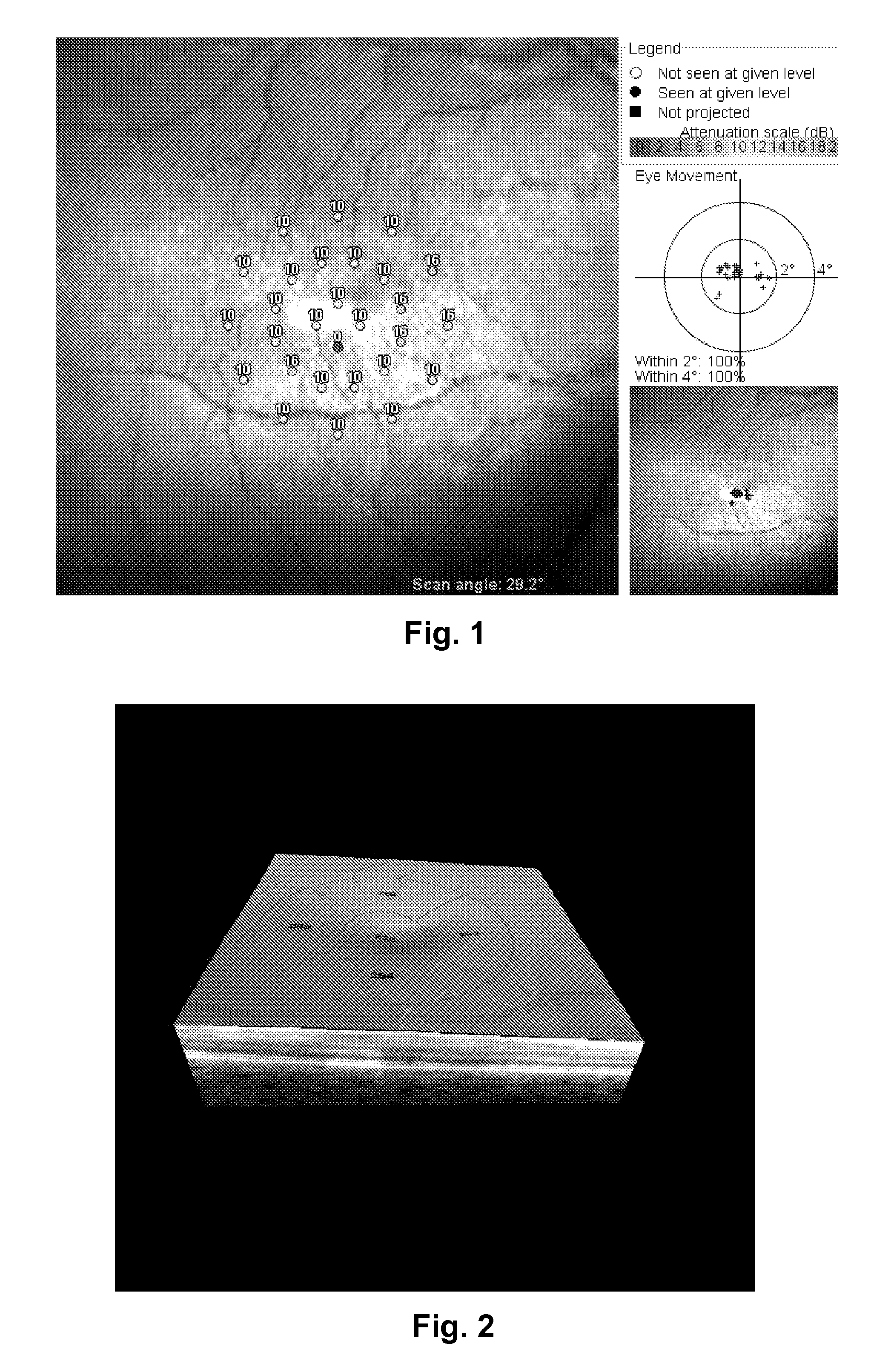
A visual acuity examination is performed on a patient by bringing a confocal imaging apparatus up to a patient's eye. Stimuli at various points in the patient's field of view are generated while the patient fixates on a point. The patient's responses to the stimuli are recorded with the movement of the eye with is tracked with the aid of the confocal imaging apparatus. The position of said stimuli on the retina is corrected to take into account any movement of the eye between stimuli.
Owner:OPTOS PLC
System for confocal imaging within dermal tissue
InactiveUS6937886B2Minimizes instabilityReduce relative motionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsInstabilityRelative motion
An improved system for confocal imaging within dermal tissue of a patient is provided which minimizes instability in confocal images by reducing the relative motion of the tissue with respect to the confocal imaging optics of the system. The system includes a mechanism for maintaining an area of skin tissue under stress by application of force at the edges of the area, and an imaging head coupled to this mechanism for imaging the stressed skin. The mechanism includes a mechanical structure, such as a platen, brace, or attachment, which both supports the imaging head of the system and applies stress to a limited surface area of the tissue to minimize skin motion during confocal imaging.
Owner:CALIBER IMAGING & DIAGNOSTICS
Confocal micro imaging system using dummy pinhole
The invention relates to a confocal imaging system in fields of optical microimaging, it is a confocal microscopic system which uses virtual confocal pinhole to make the system to obtain the longitudinal chromatography capability. It's widely used in the fluorescence microscopy, optical microscopy and so on which possess the microtechnique of three-dimensional imaging capability. The invention includes: light source, collimation lens, beam splitter, microscope objective, objective table, collective lens and CCD. It characterized in that the photosensitive surface of CCD is directly located at the focal plane of the collimation lens, the computer sets the virtual pinhole at the corresponding position of two-dimensional digital image collected by CCD based on the position of the focal point of collimation lens, the signal values of the pixels in the pinhole are accumulated as the signal intensity of current scanning point to eliminate the effect of stray light in non-focal plane to the image quality. The function of virtual confocal pinhole is significant with the physical confocal pinhole and the position, size can be controlled and adjusted by computer, and it possesses the advantages of convenient gauging adjustment.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Apparatus and method for providing high intensity non-coherent light and for speckle reduction
ActiveUS7202466B2Non-electric lightingBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsLight beamHigh intensity
An apparatus adapted for confocal imaging of a non-flat specimen comprising a light source for producing a light beam, imaging optics adapted to focus the light beam into at least one spot on a surface of a specimen, and a detector adapted to receive and detect light reflected from the specimen surface. The light source comprises an optical system for converting a coherent beam into a plurality of beams, each of which is modified by a moving diffuser within a range of movement that is correlated to the detector's integration time.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
System and method for line scan confocal ophthalmoscope
InactiveCN102008288AEasy to adjustFulfill control requirementsOthalmoscopesImaging qualityLight beam
The invention relates to a system and method for a line scan confocal ophthalmoscope. The system comprises a linear light beam generation module, a splitting module, a scanning module, an imaging module and an output module. A linear light beam is subject to one-dimensional space scanning by the line scan confocal ophthalmoscope to illuminate fundus oculi retina, simultaneously a linear detector is used for image non-scan light beams reflected from the fundus oculi retina, the system only uses one scanning galvanometer and one linear detector, and the number of active members is small; and simultaneously, a confocal slit is conjugated with the plane of the fundus oculi retina, thereby eliminating the influence of eliminate stray light of a non-retina plane on imaging quality and obtaining high resolution by using the confocal imaging principle. The invention has the advantages of simple structure, short light path, good stability and high imaging frame frequency, is easy for manufacture and suitable for adjustment, and is small and exquisite.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
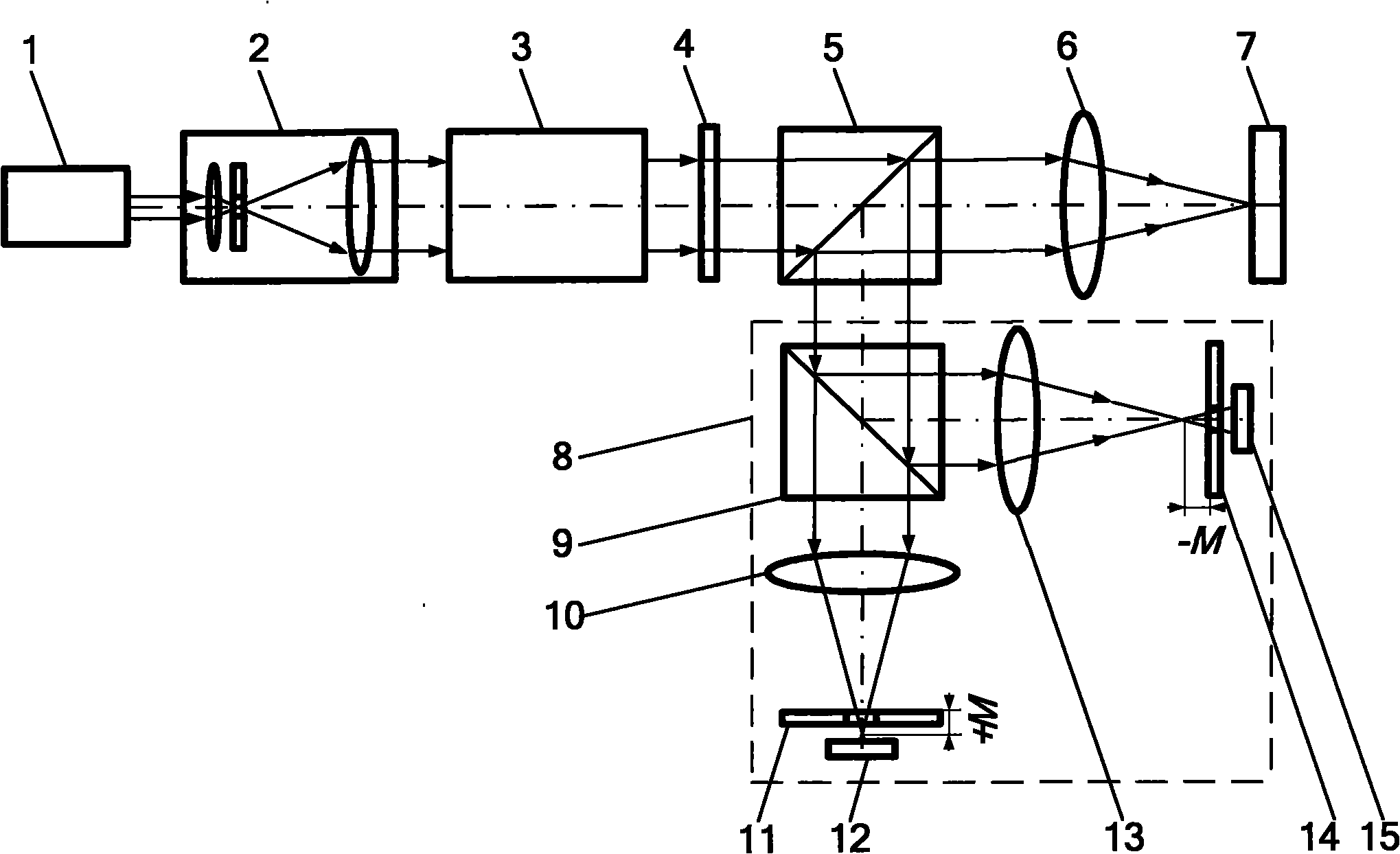
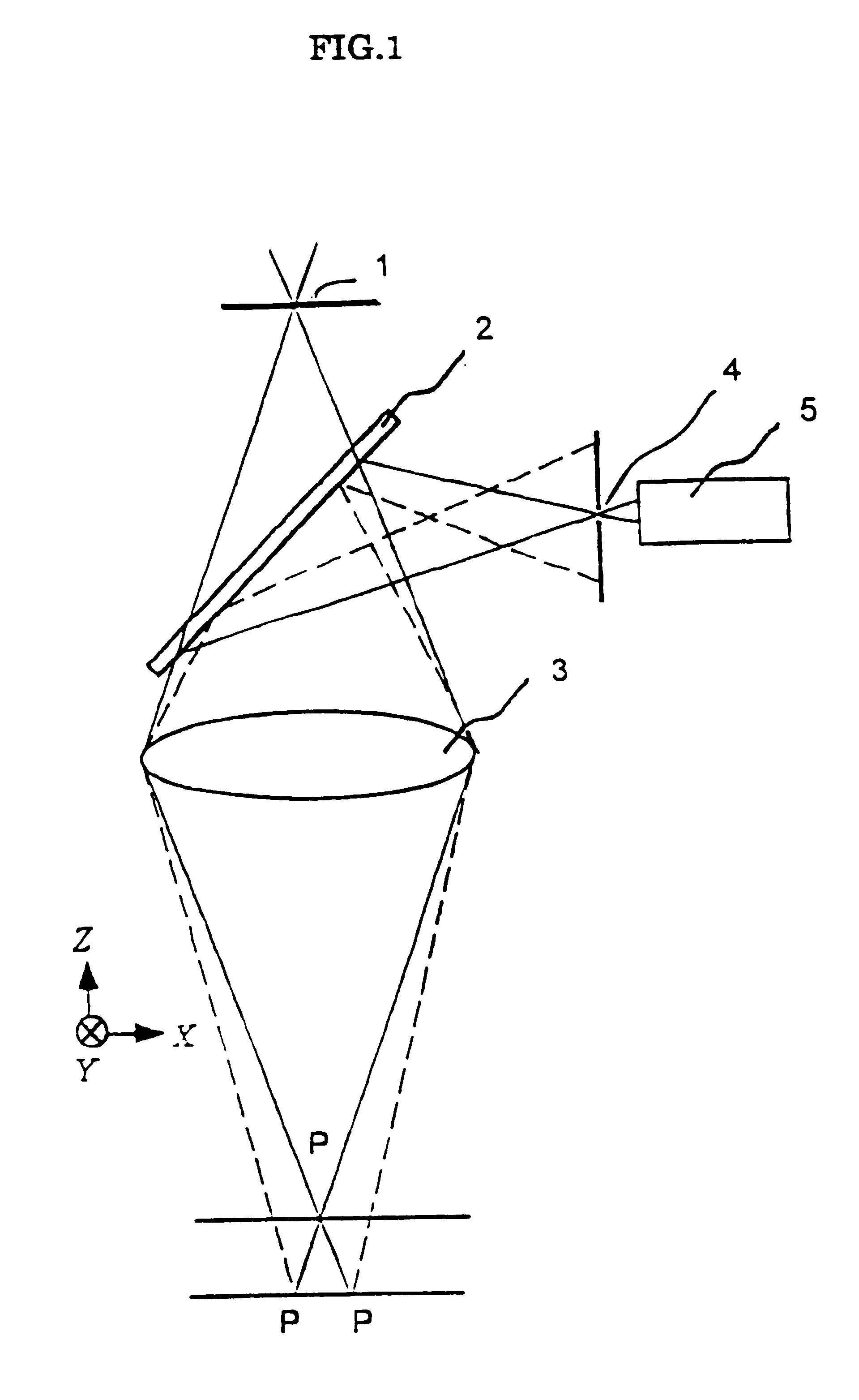
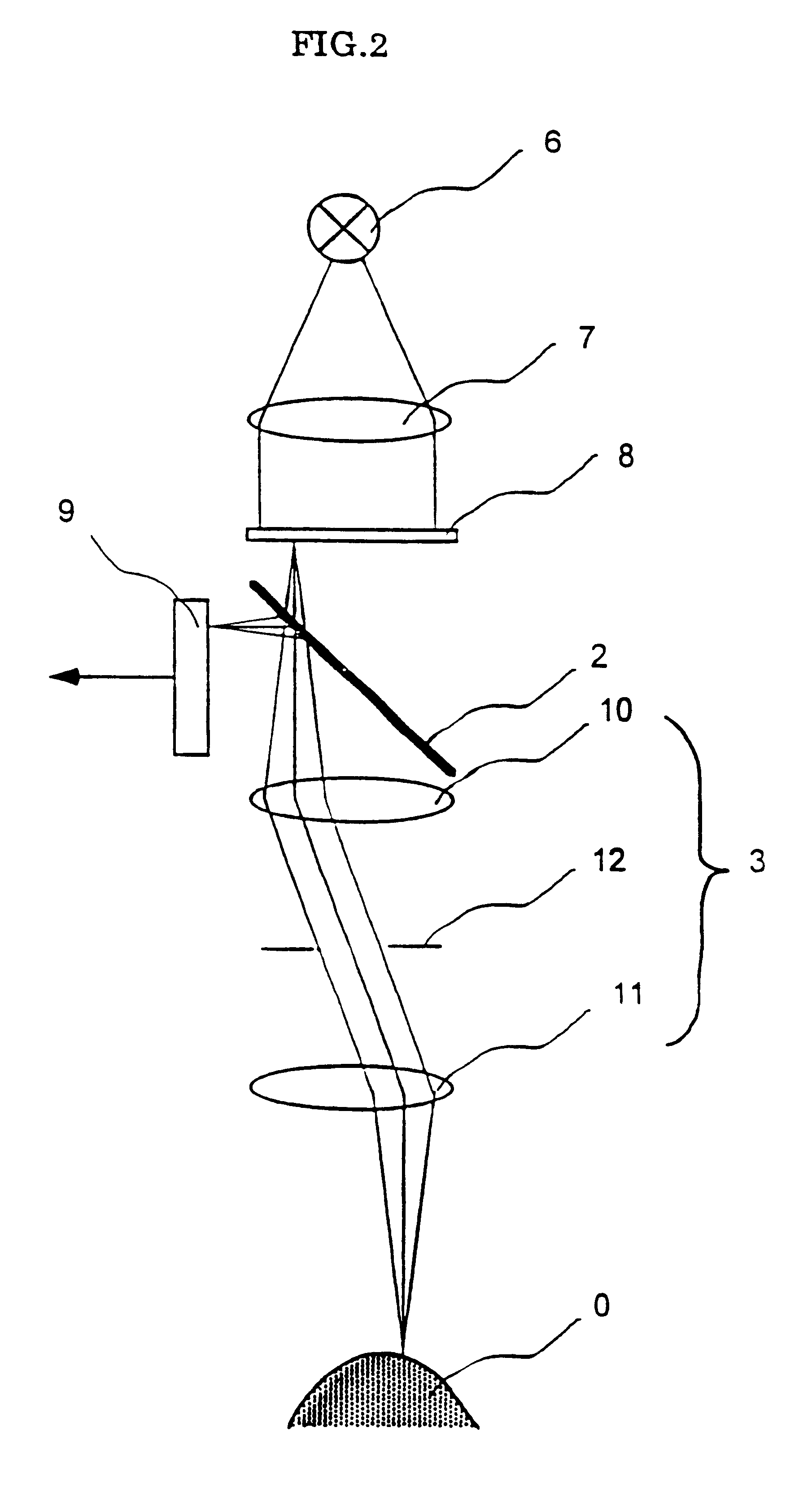
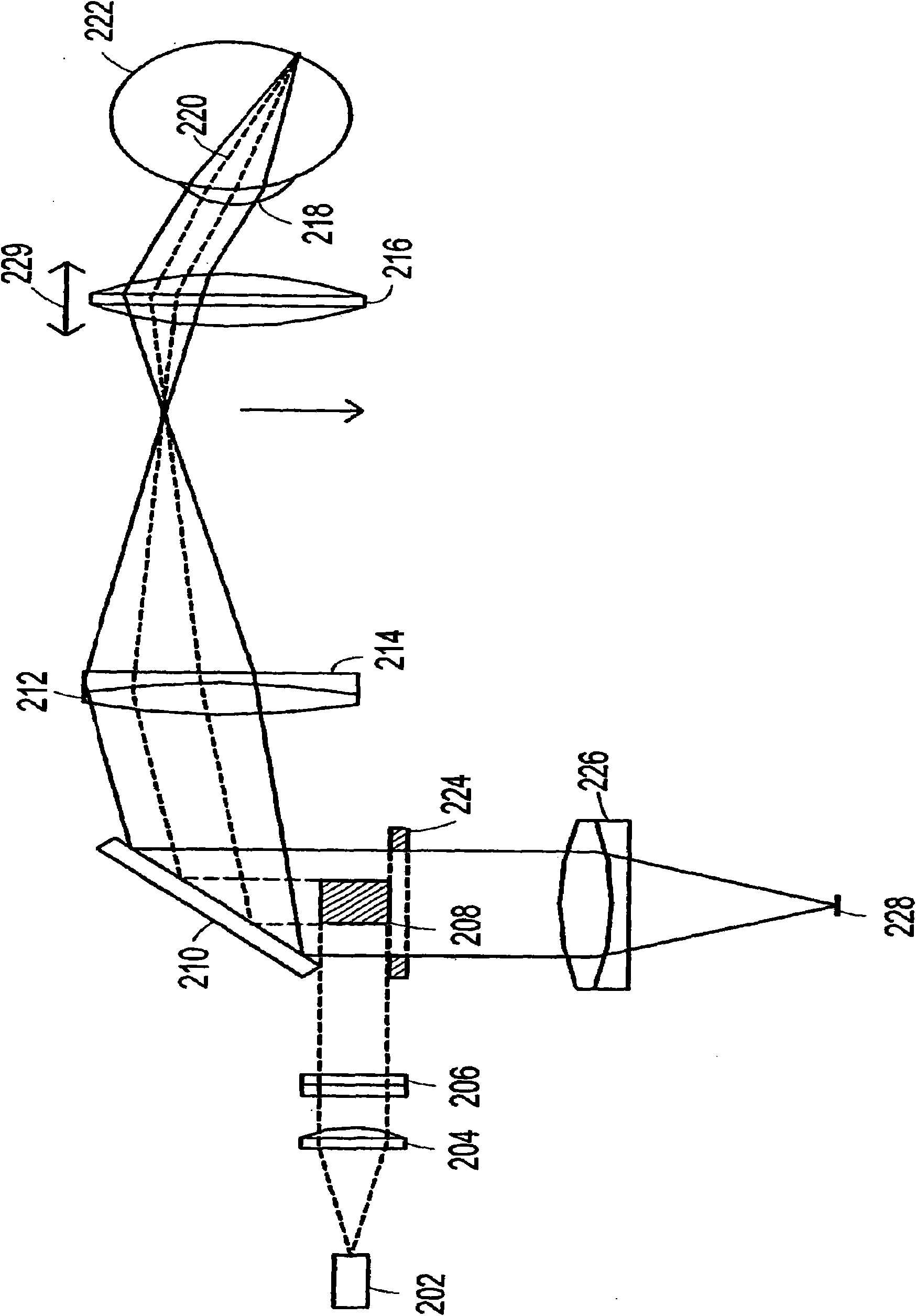
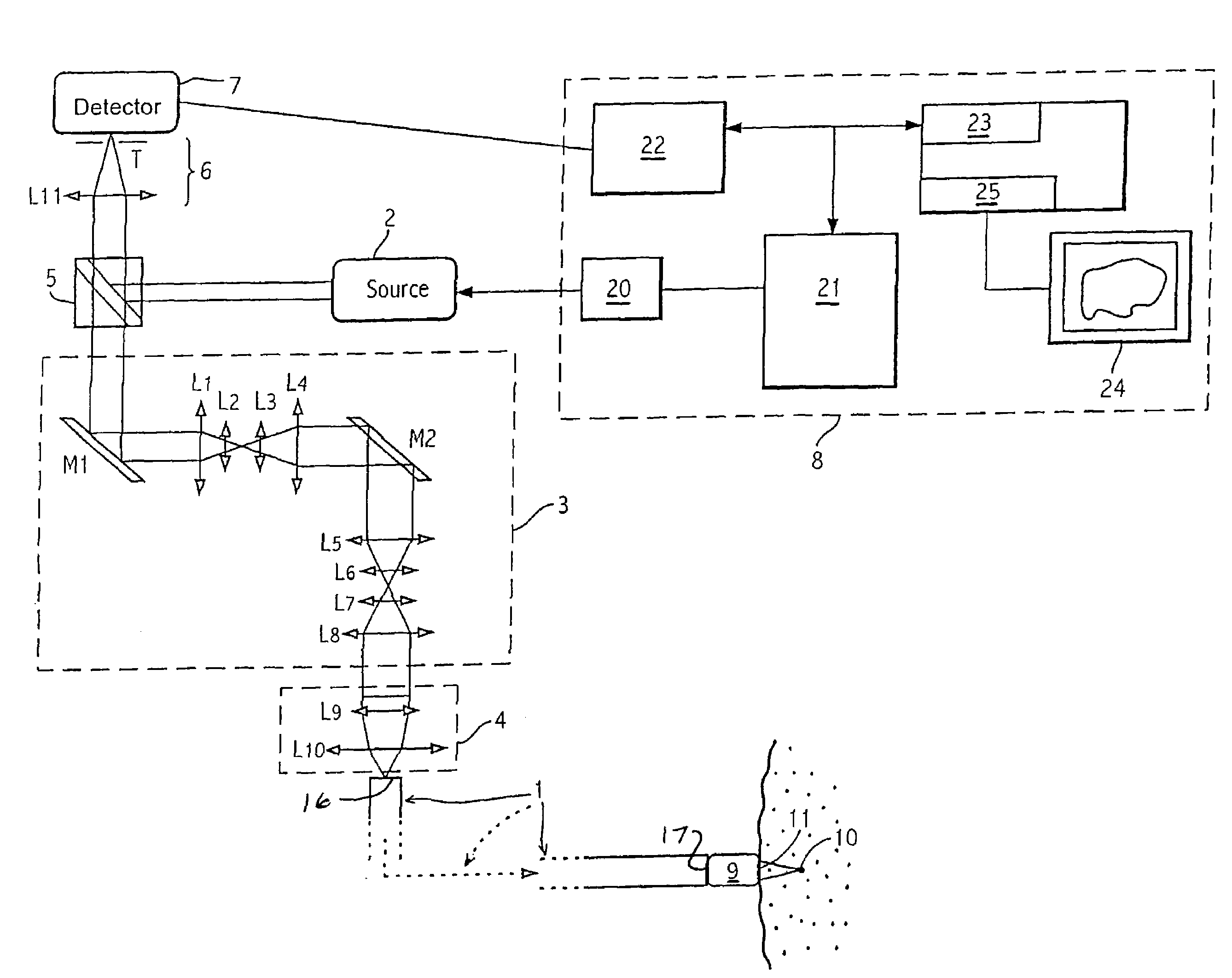
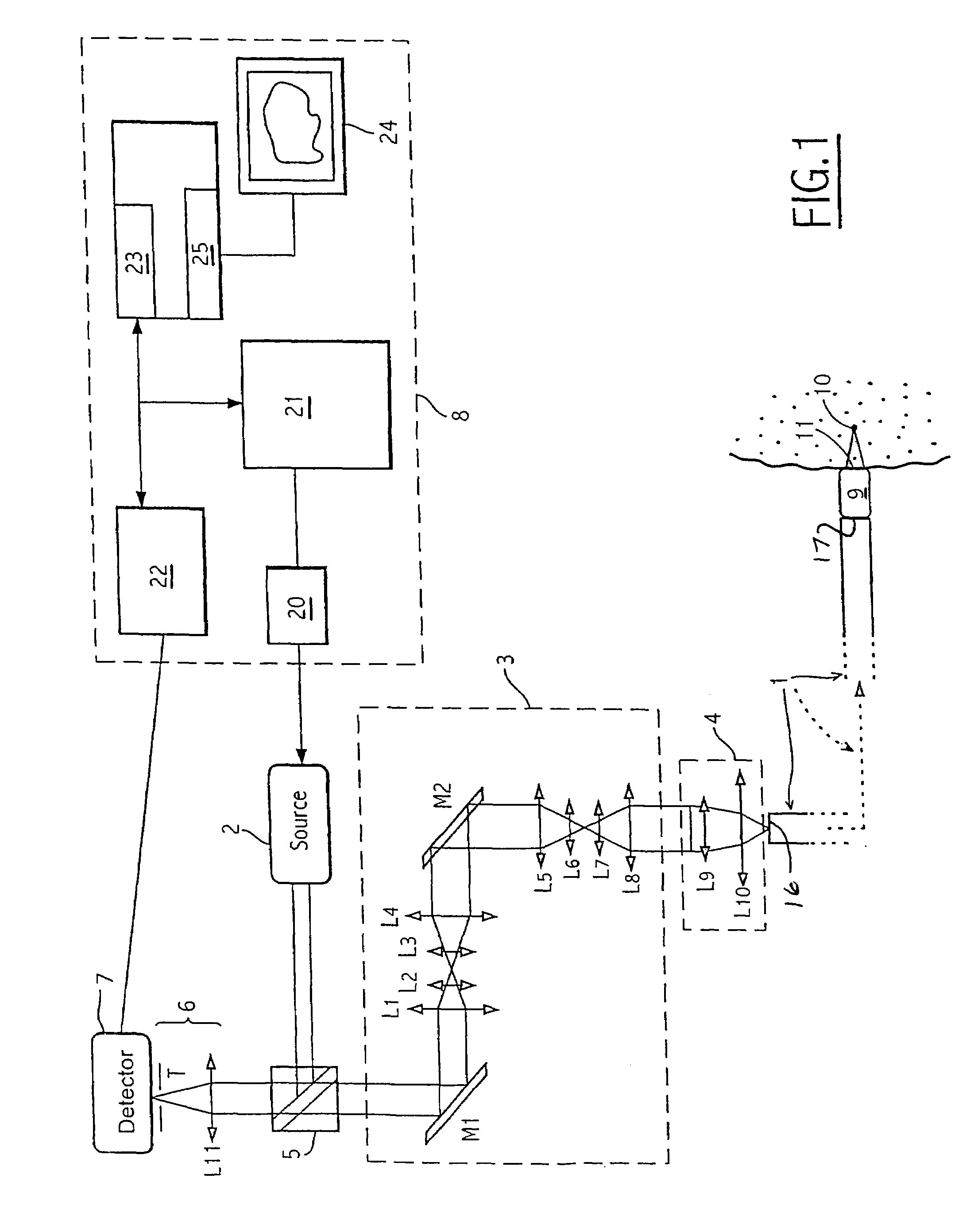
Confocal imaging equipment in particular for endoscope
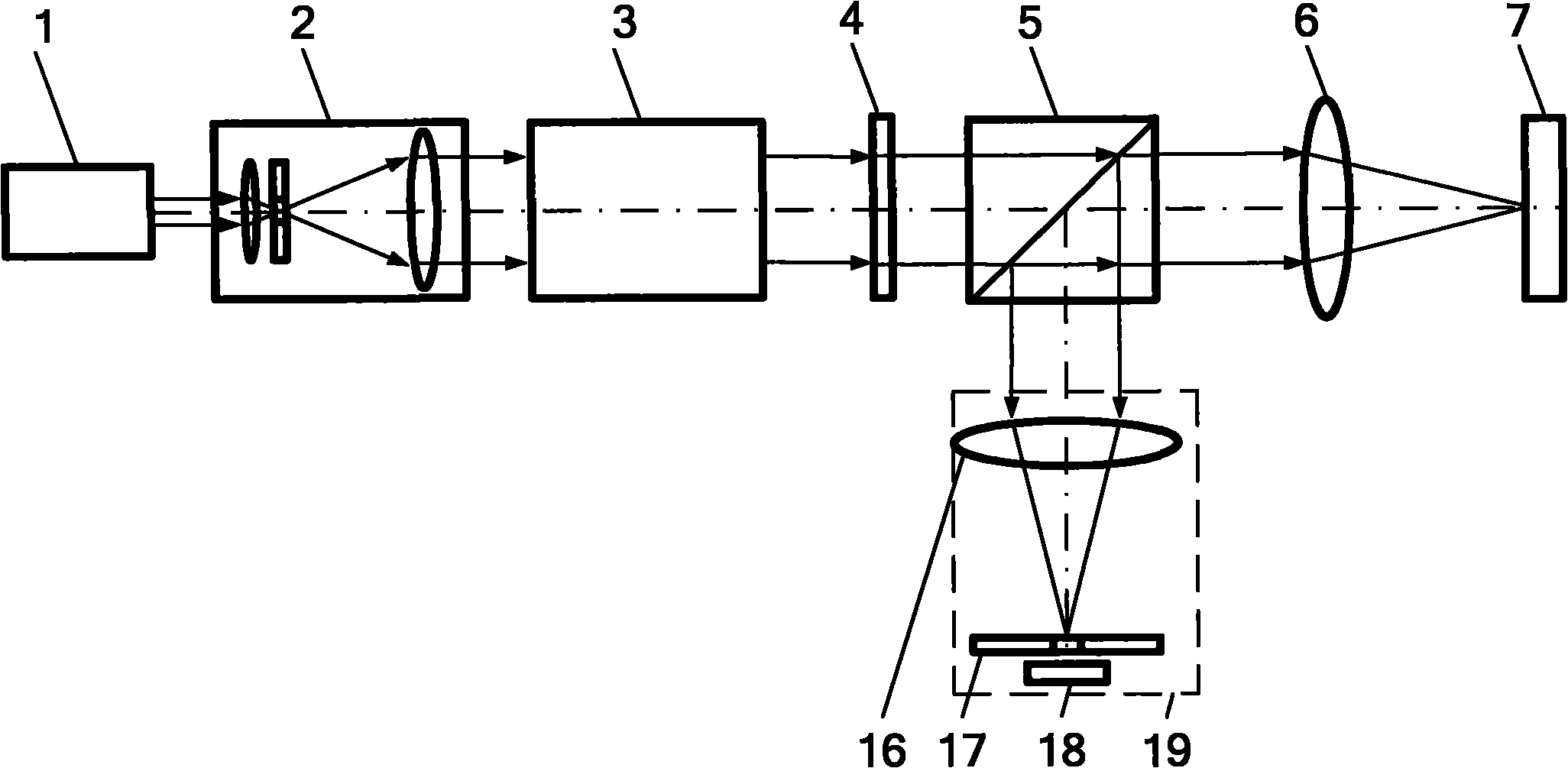
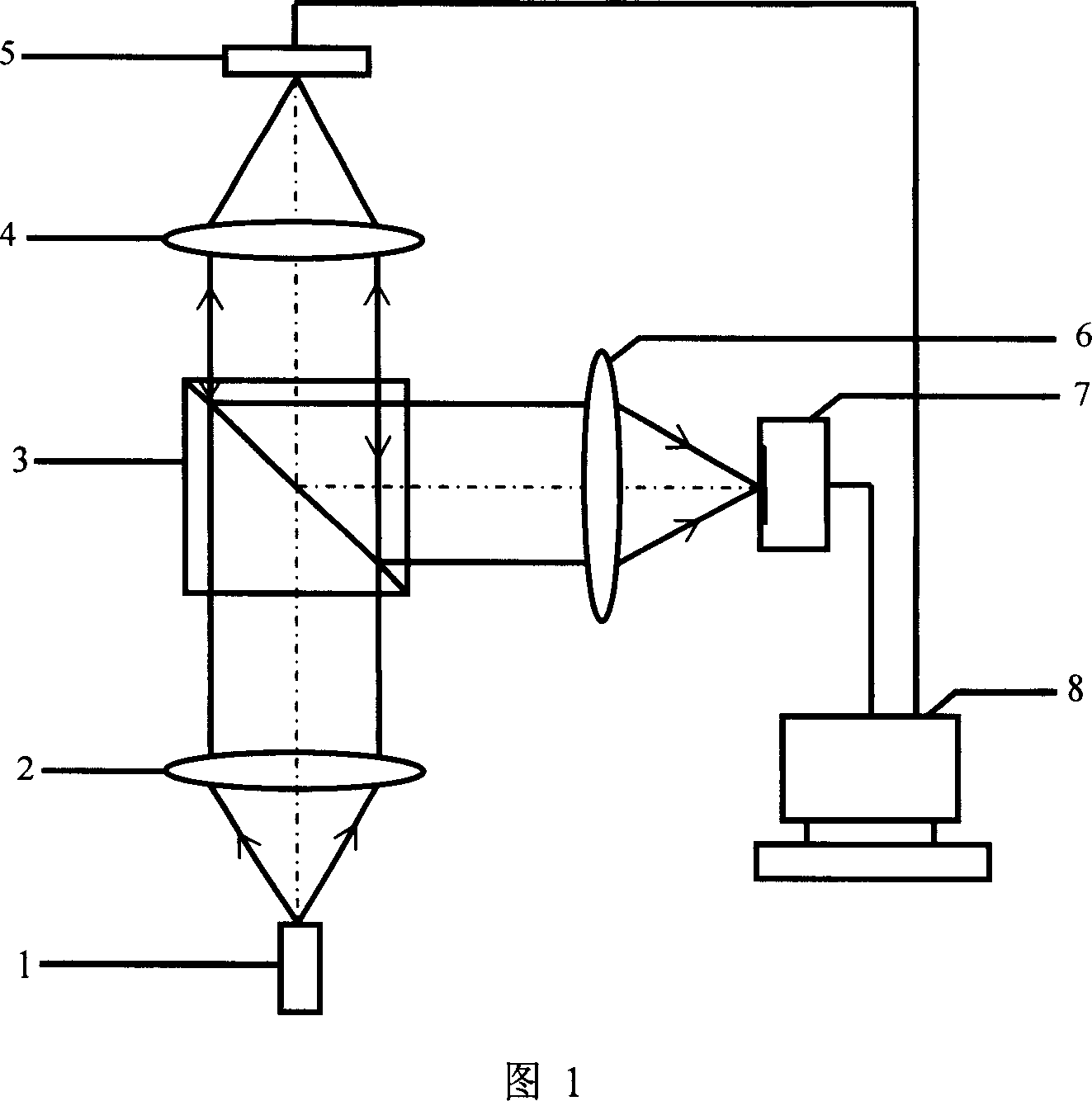
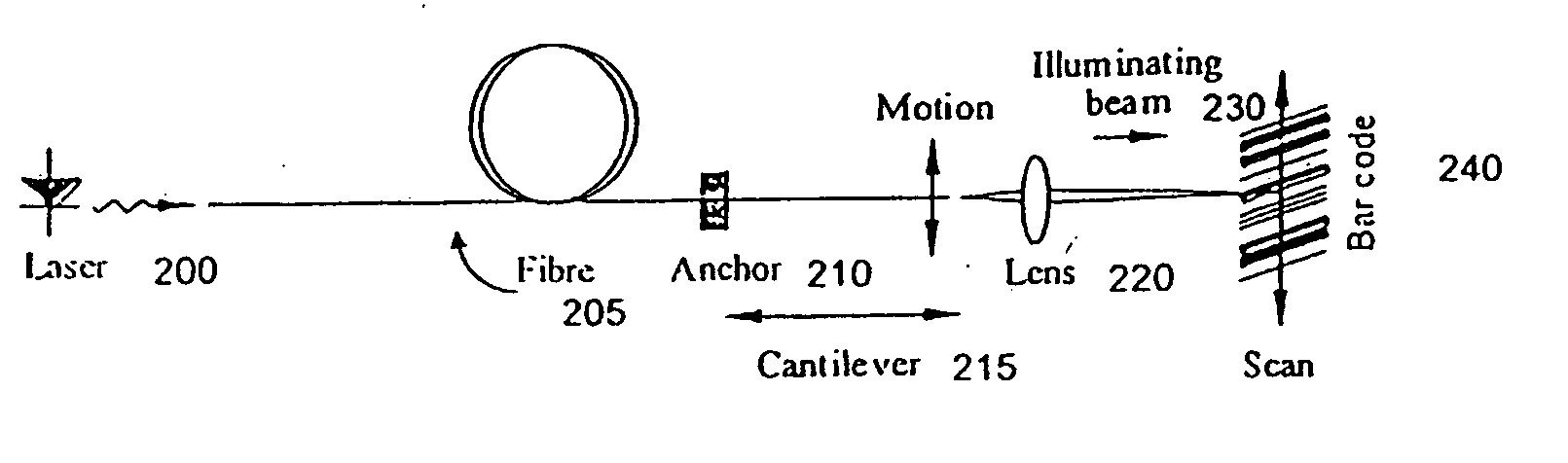
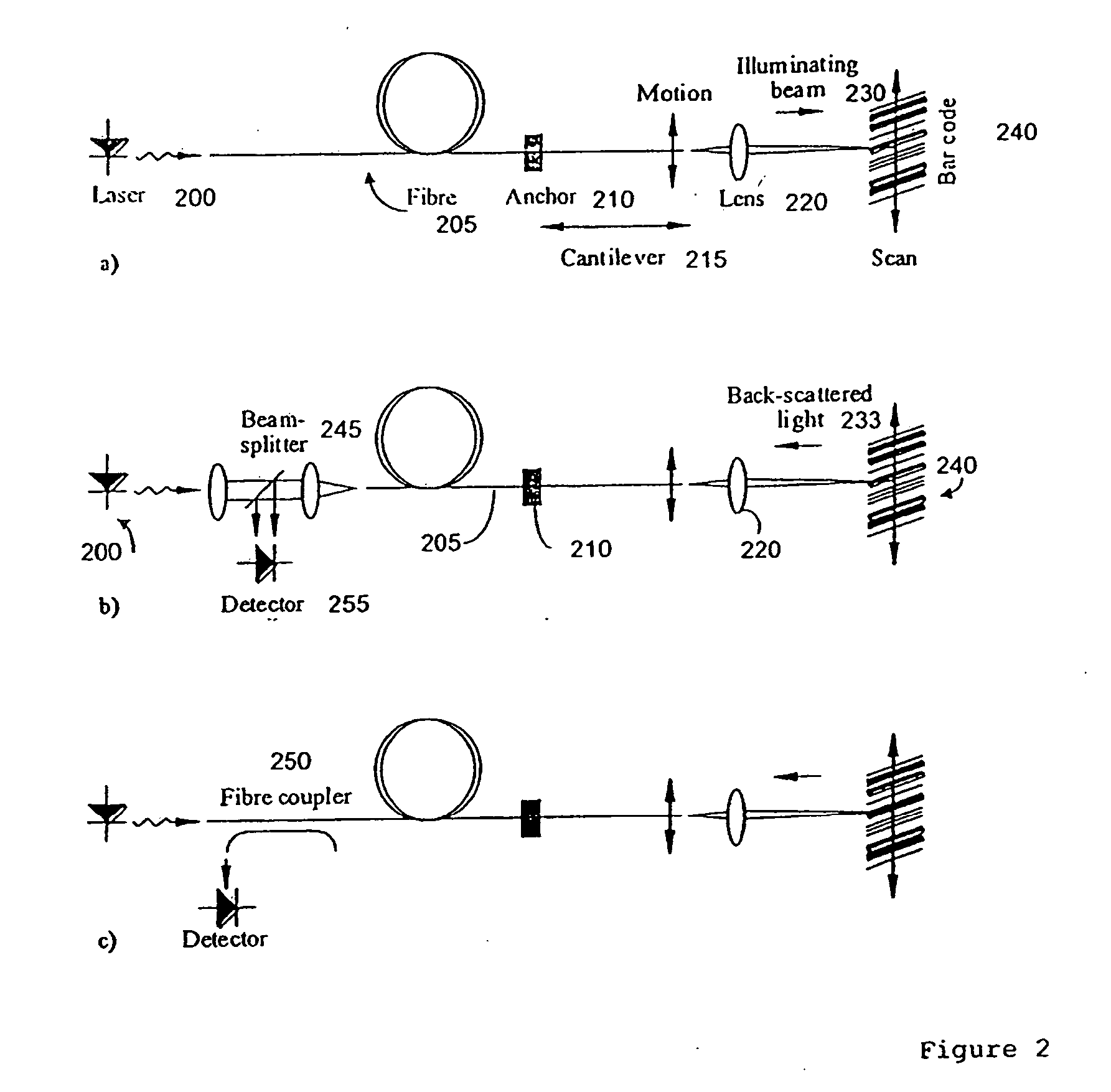
Equipment includes an image guide (1) consisting of flexible optical fibers with: on the proximal end side: a source (2), angular scanning elements (3), injection elements (4) in one of the fibers, elements for splitting (5) the illuminating beam and the backscattered signal, elements for spatial filtering (6), elements for detecting (7) the signal, electronic elements (8) for controlling, analyzing and digital processing of the detected signal and display; and on the distal end side: an optical head (9) for focusing the illuminating beam exiting from the illuminated fiber. The scanning elements include a resonant line mirror (M1) and a galvanometric field mirror (M2) with a variable frequency and two afocal optical systems adapted to conjugate the two mirrors (M1, M2) firstly in the field mirror (M2) and the injection elements (4) in the image guide in a second step.
Owner:MAUNA KEA TECHNOLOGIES
Apparatus and method for providing high intensity non-coherent light and for speckle reduction
ActiveUS20050207160A1Speckle reductionNon-electric lightingBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsLight beamHigh intensity
An apparatus adapted for confocal imaging of a non-flat specimen comprising a light source for producing a light beam, imaging optics adapted to focus the light beam into at least one spot on a surface of a specimen, and a detector adapted to receive and detect light reflected from the specimen surface. The light source comprises an optical system for converting a coherent beam into a plurality of beams, each of which is modified by a moving diffuser within a range of movement that is correlated to the detector's integration time.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
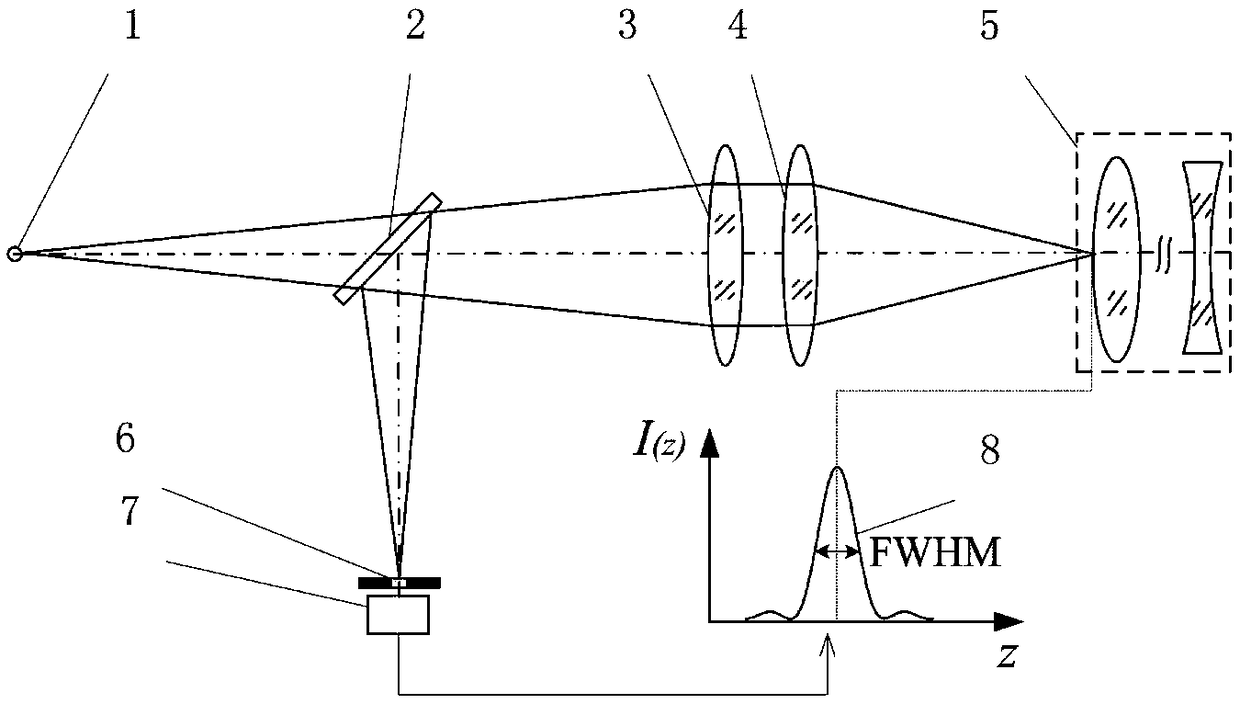
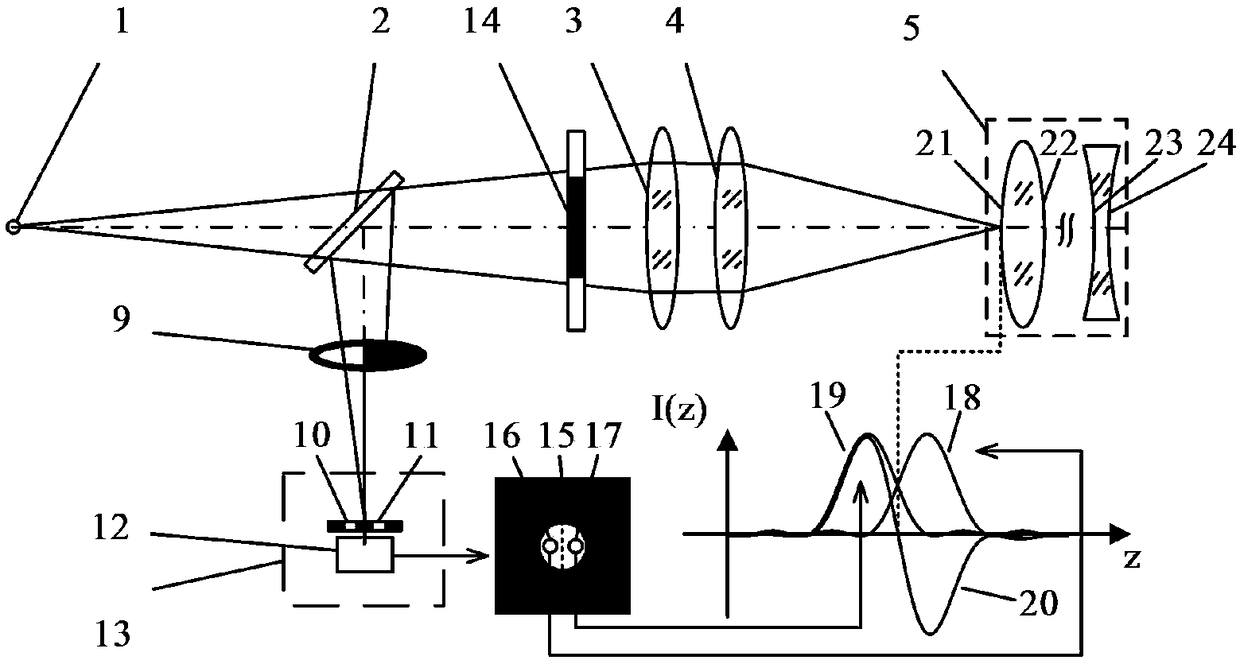
Laser differential confocal tomography focusing method and device
ActiveCN109253989AImprove focus accuracyReduce the impactAnalysis by material excitationLight beamTomography
The present invention relates to a laser differential confocal tomography focusing method and device, and relates to the technical field of optical imaging and detection. The method uses a rear pupilto block half of a measurement beam, uses a spectroscopic differential confocal detection system to detect the unblocked measurement beam, and uses an absolute zero point of a differential confocal response curve to achieve high precision tomographic focusing. The method organically combines a laser differential confocal technique and a ray tracing technique to establish a ray tracing and compensation model to eliminate influence among each fixed focal surface parameters, and achieves fast trigger of focus through data near a linearly fitting absolute zero point. The method can obtain the differential confocal response curve by using only one detector, and realizes the tomographic focusing through the absolute zero point of the differential confocal response curve, greatly simplifies system structure, in the same time, avoids error introduced by adjustment inaccuracy, and greatly improves precision of focusing. The method will provide a new technical approach to the field of confocal imaging / detection.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Microengineered optical scanner
InactiveUS20050167508A1Reducing pickReduce noiseCoupling light guidesSensing by electromagnetic radiationOptical scannersClosed loop
A microengineered optical scanner based on a moving cantilevered dielectric waveguide is described. The waveguide is excited into resonant mechanical motion by a drive located at its root. Stress sensors detect the bending of the waveguide, allowing closed loop control of the motion. A moving image of the light emitted from the moving tip of the waveguide is created by a lens. The moving image acts as a scan line. Light back-scattered from a rough surface placed at the image plane is collected back into the waveguide by confocal imaging. The light collected in the cladding of the waveguide has higher numerical aperture than the light collected in the core. The cladding light is detected by a mode-stripping detector. Techniques for combining a cantilevered waveguide, a drive, motion sensors and a mode-stripping detector using microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) technology are described.
Owner:MICROSAIC SYST
Multi-mode co-focusing imaging method and apparatus
InactiveCN101401722AAvoid mutual interferenceDoes not affect the couplingDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsFluorescenceSignal light
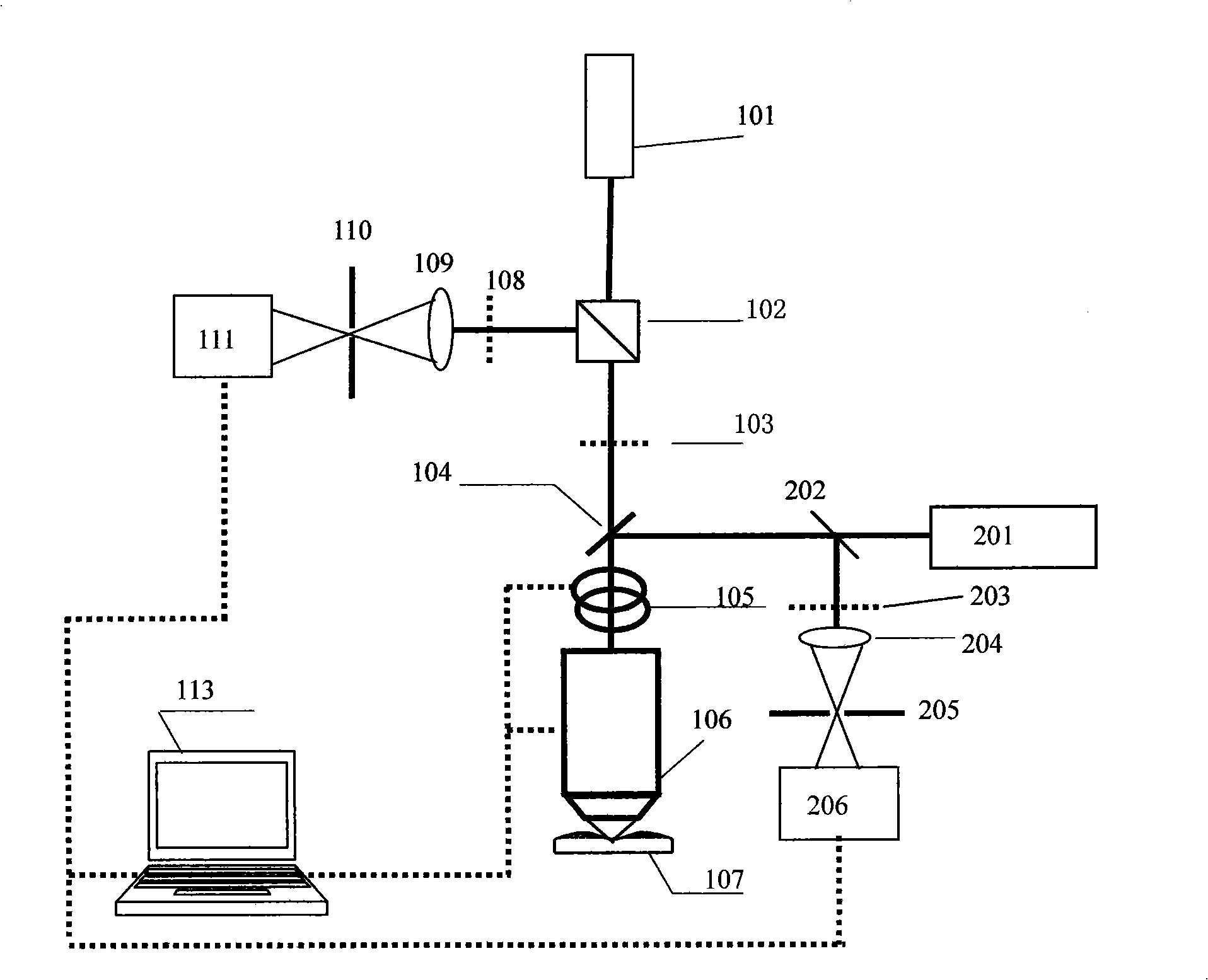
The invention discloses a multi-mode confocal imaging method and a device thereof. The method comprises the following steps: transmitted light sources of two signal acquiring devices are combined by dichroic beamsplitters and projected onto a target tissue; reelected signal light of the target tissue is separated by the dichroic beamsplitters into two beams which reach respective filter elements to filter interference signals and then reach respective detection elements to perform synchronous imaging process to the detection signals of a sample. The device comprises a reflected signal acquiring device, a fluorescence signal acquiring device, an optical path of the two devices for light combination consisting of a first dichroic beamsplitter, a scanning mirror and an object lens, and a detection light path of the reflected signal acquiring device and a detection light path of the fluorescence signal acquiring device, wherein each detection light path comprises a filter plate, a lens, a confocal pinhole and a photoelectric detector. The photoelectric detectors are connected with an imaging computer system. Two confocal acquisition systems acquire a signal at the same time and position, and an optical design is adopted to avoid mutual interference of multi-path laser light and the detection systems, thereby realizing real-time noninvasive 3D detection of biological tissue.
Owner:上海奥通激光技术有限公司
Device for measuring in three dimensions a topographical shape of an object
InactiveUS7446885B2Quick measurementIncrease speedMicroscopesUsing optical meansThree dimensional measurementFocal position
A device for measuring in three dimensions a topographical shape of an object. The device comprises an arrayed confocal imaging system having a confocal topographical mask provided for converting light produced by a light source into an array of small spots. The mask being mounted on a scanning member provided for moving the mask over successive positions over a predetermined distance. The device further comprises a confocal objective provided for mapping at successive object-position-in-focus the array of small spots output at said successive positions. The confocal objective may be mounted at a fixed position within said device.
Owner:ICOS VISION SYST
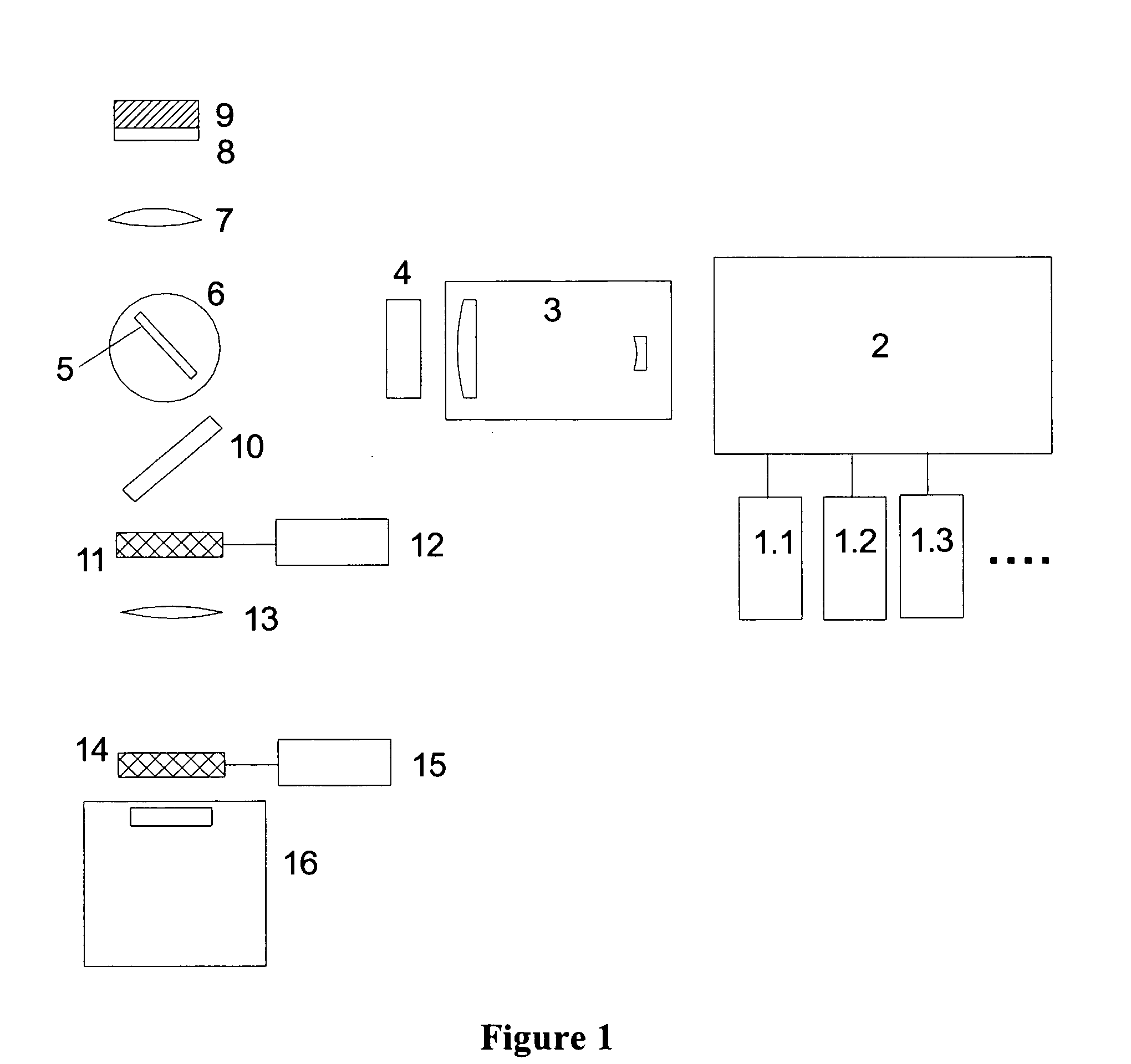
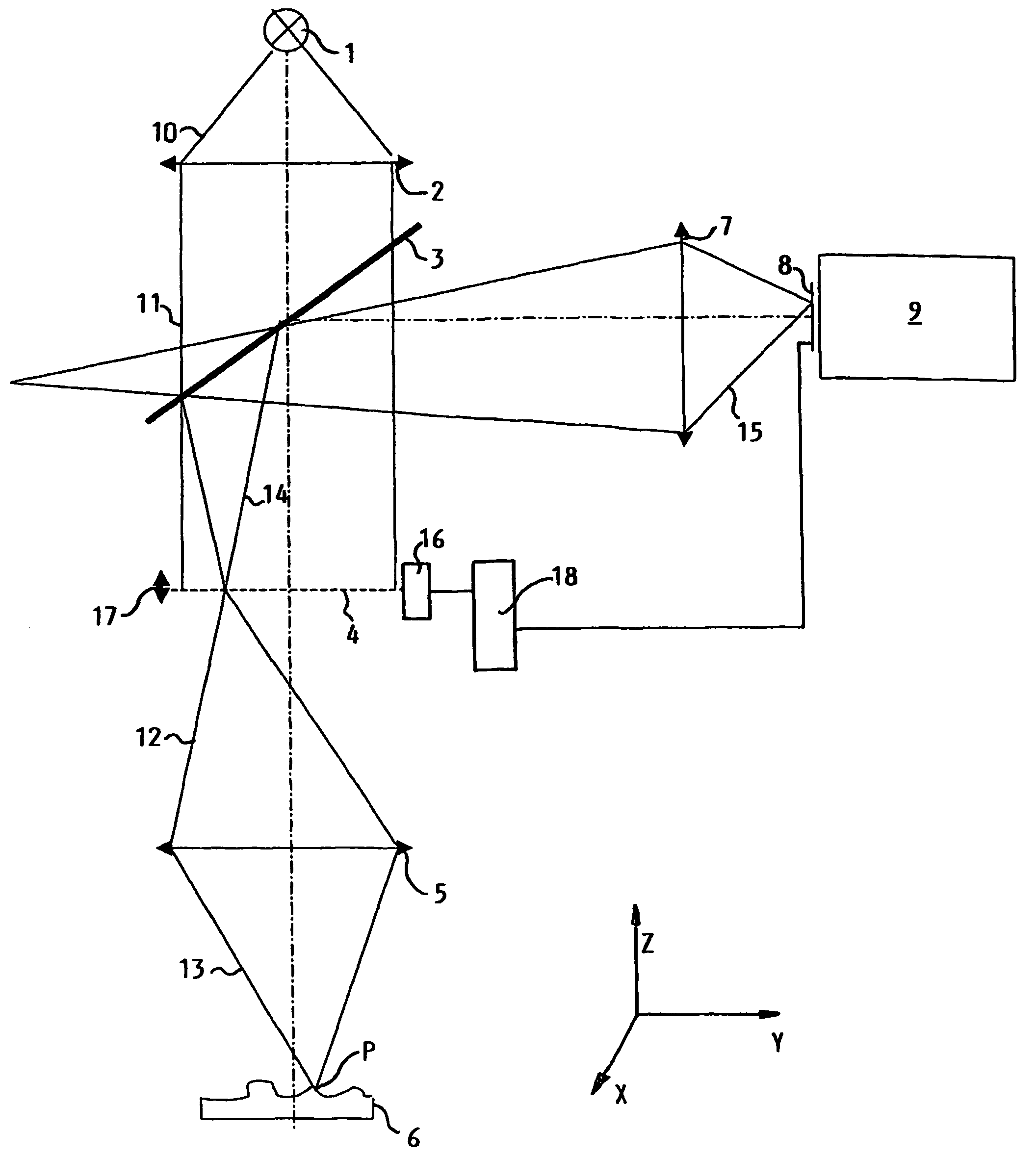
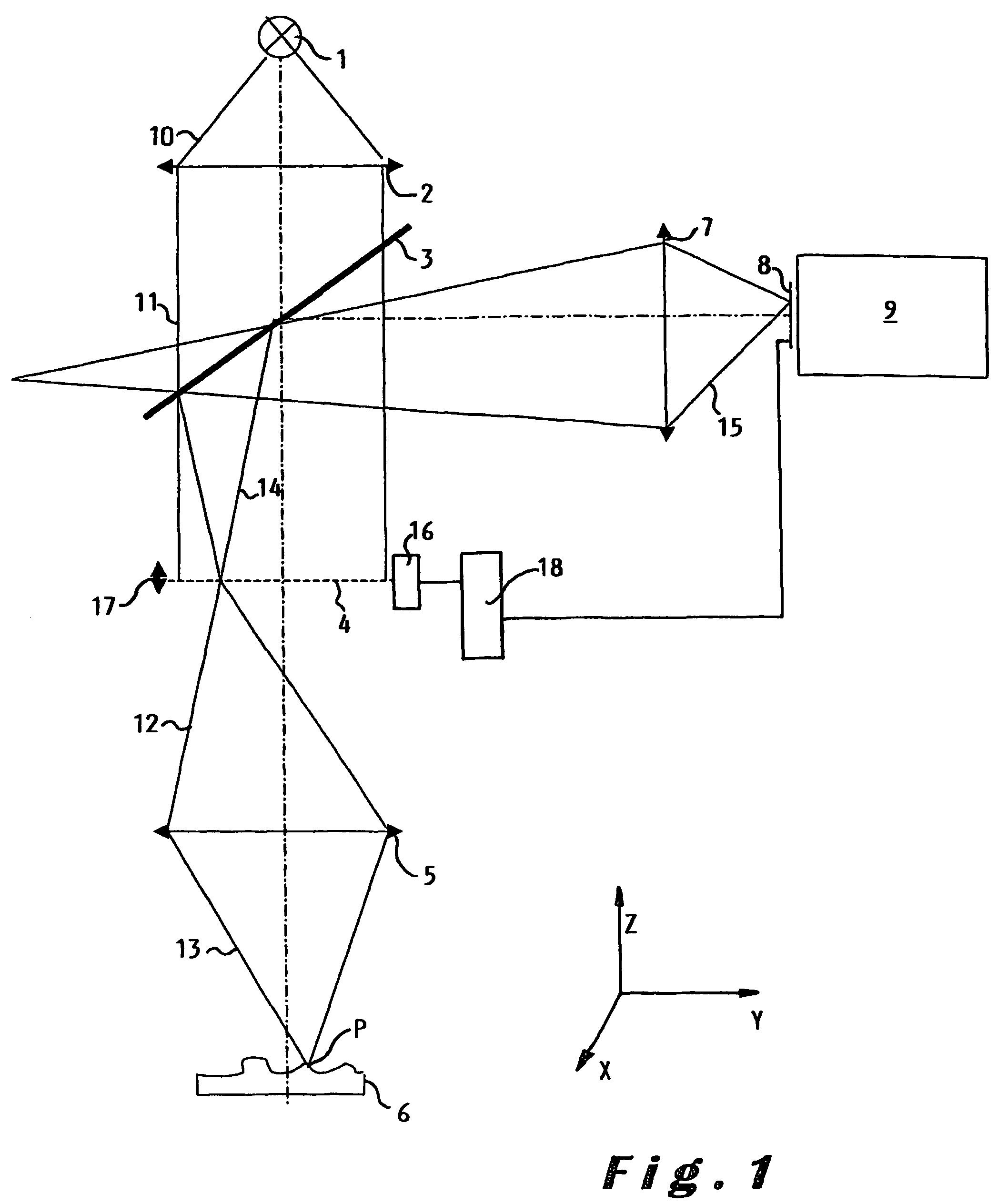
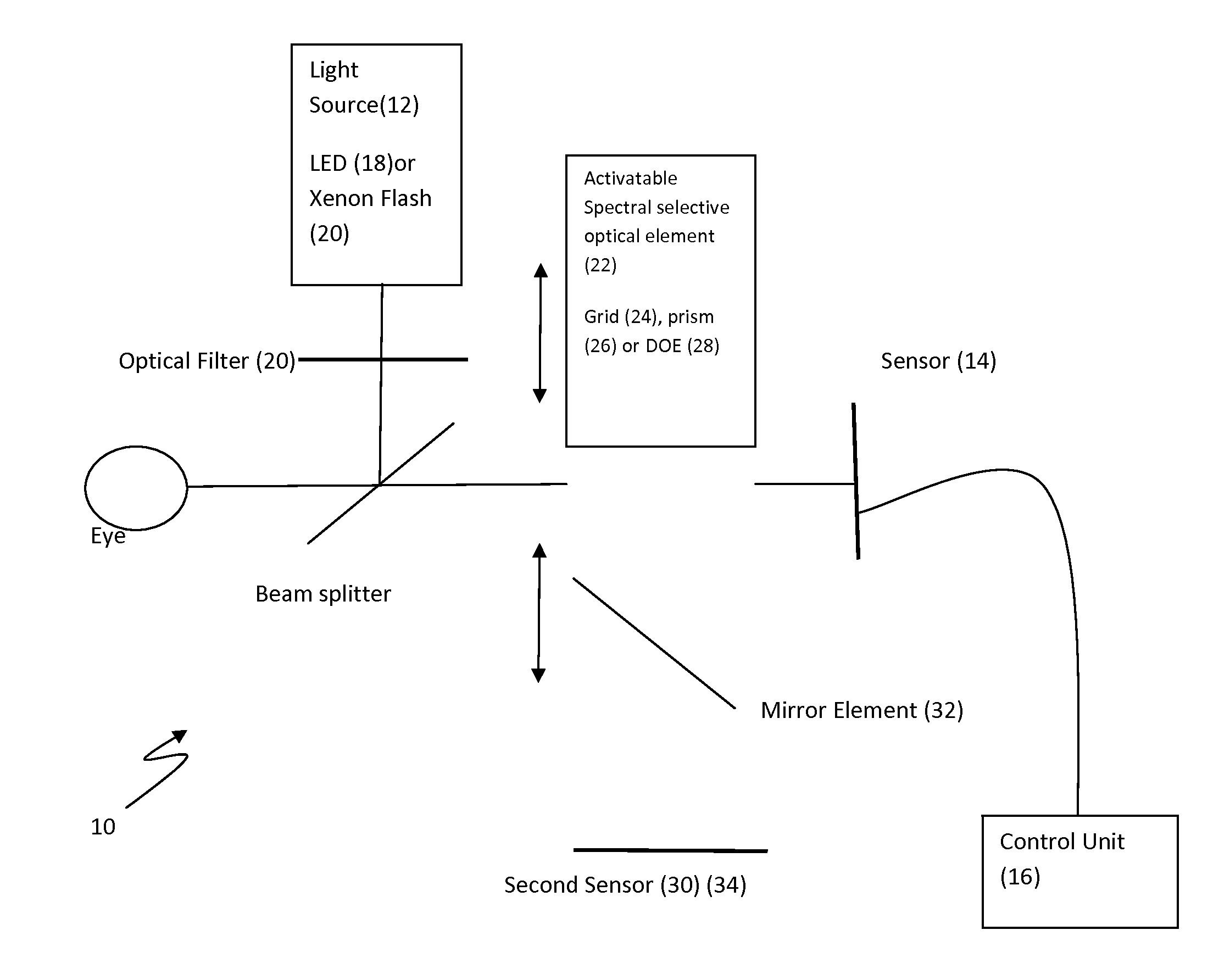
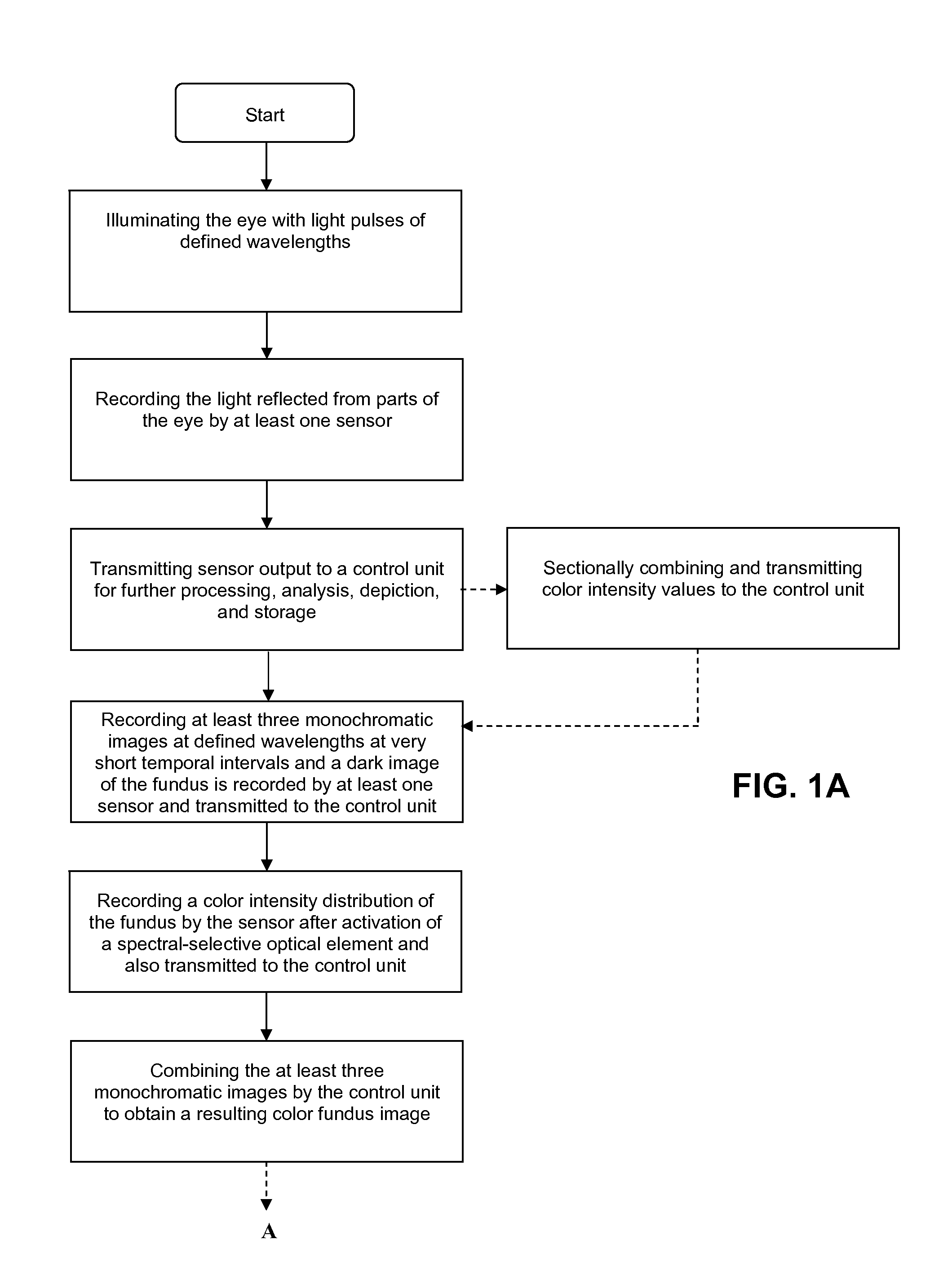
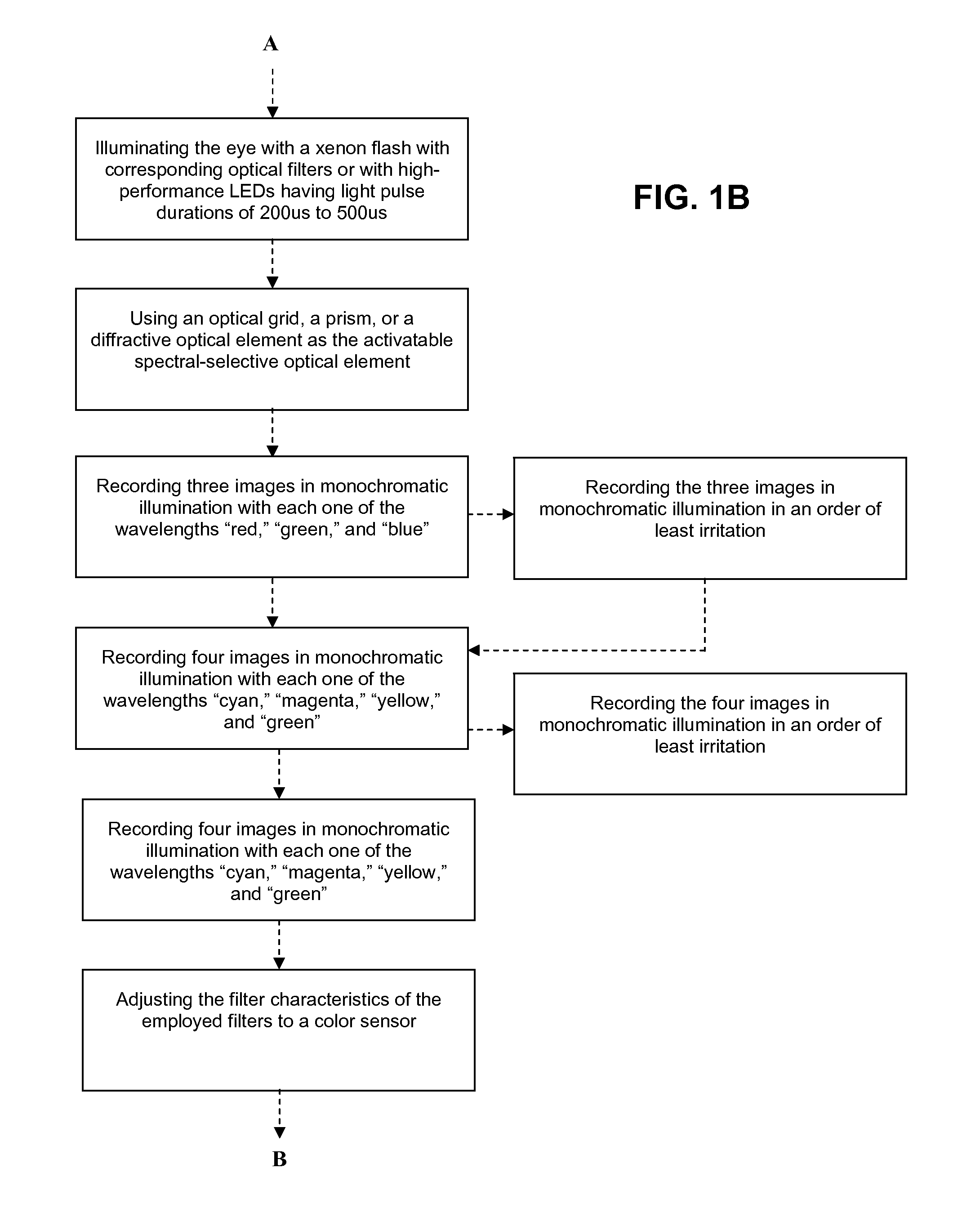
Method and device for producing high-quality fundus images
To produce a color fundus image, the eye is illuminated with light pulses of defined wavelengths. Light reflected is recorded by a sensor and transmitted to a control unit. At least three monochromatic images at very short temporal intervals and a dark image of the fundus are recorded. After activation of a spectral-selective optical element, a color intensity distribution of the fundus is recorded by the sensor at white illumination. The monochromatic images are combined by the control unit to obtain a resulting color fundus image, wherein the color intensity distribution is used for the correction of color composition and the dark image is used for taking into account the noise of the sensor. The solution permits monitoring, documenting and / or diagnosing of the fundus and can also be executed with ophthalmological systems based on the principle of optical coherence and / or confocal imaging.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com