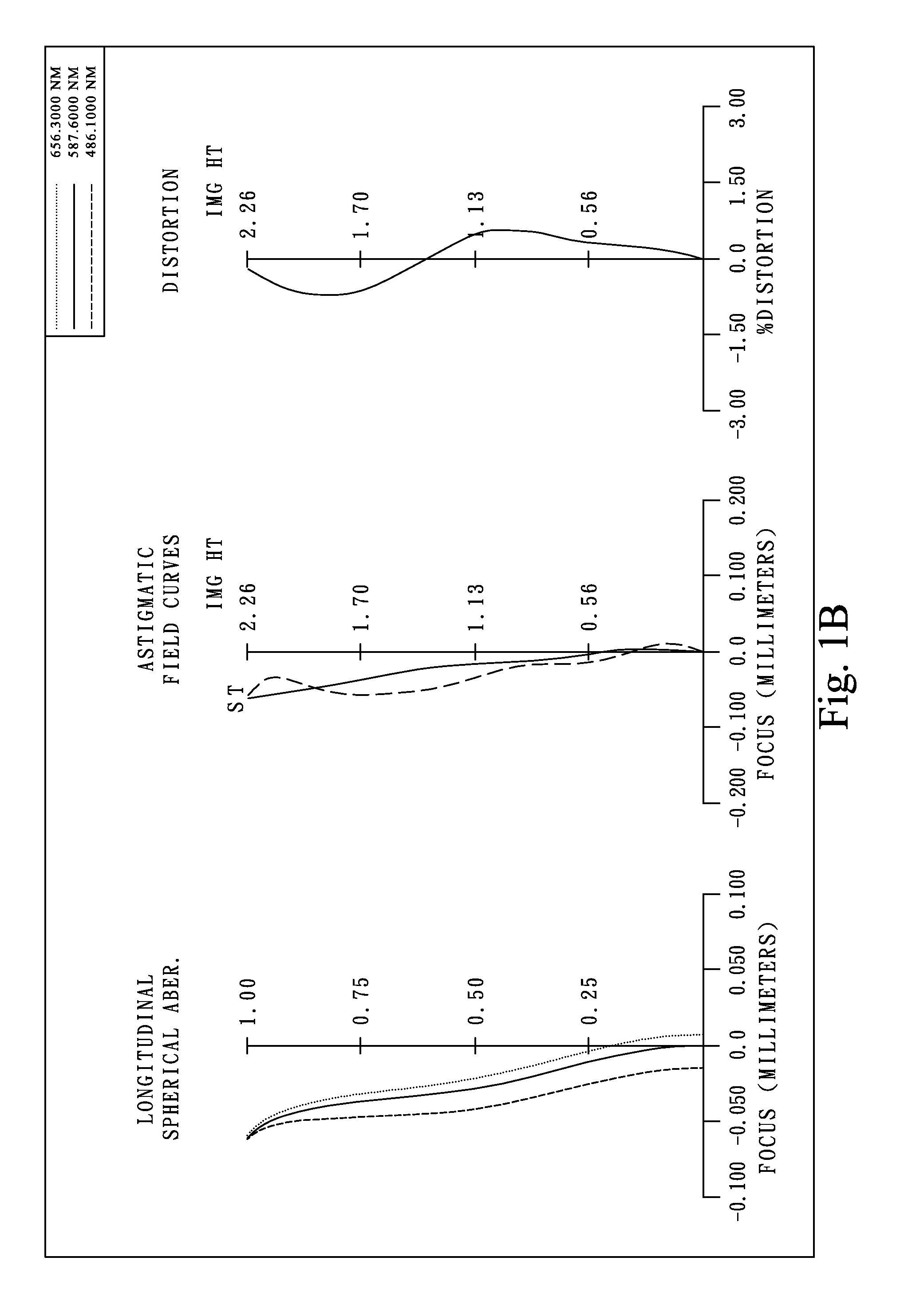
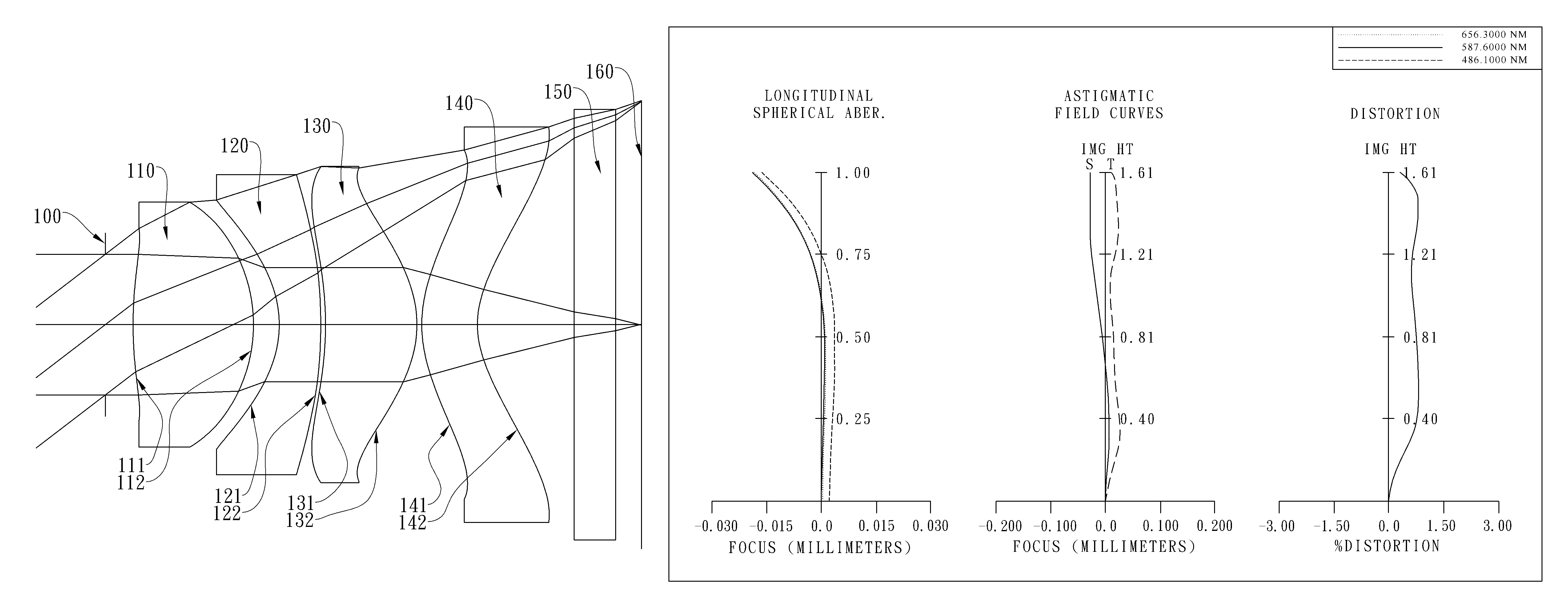
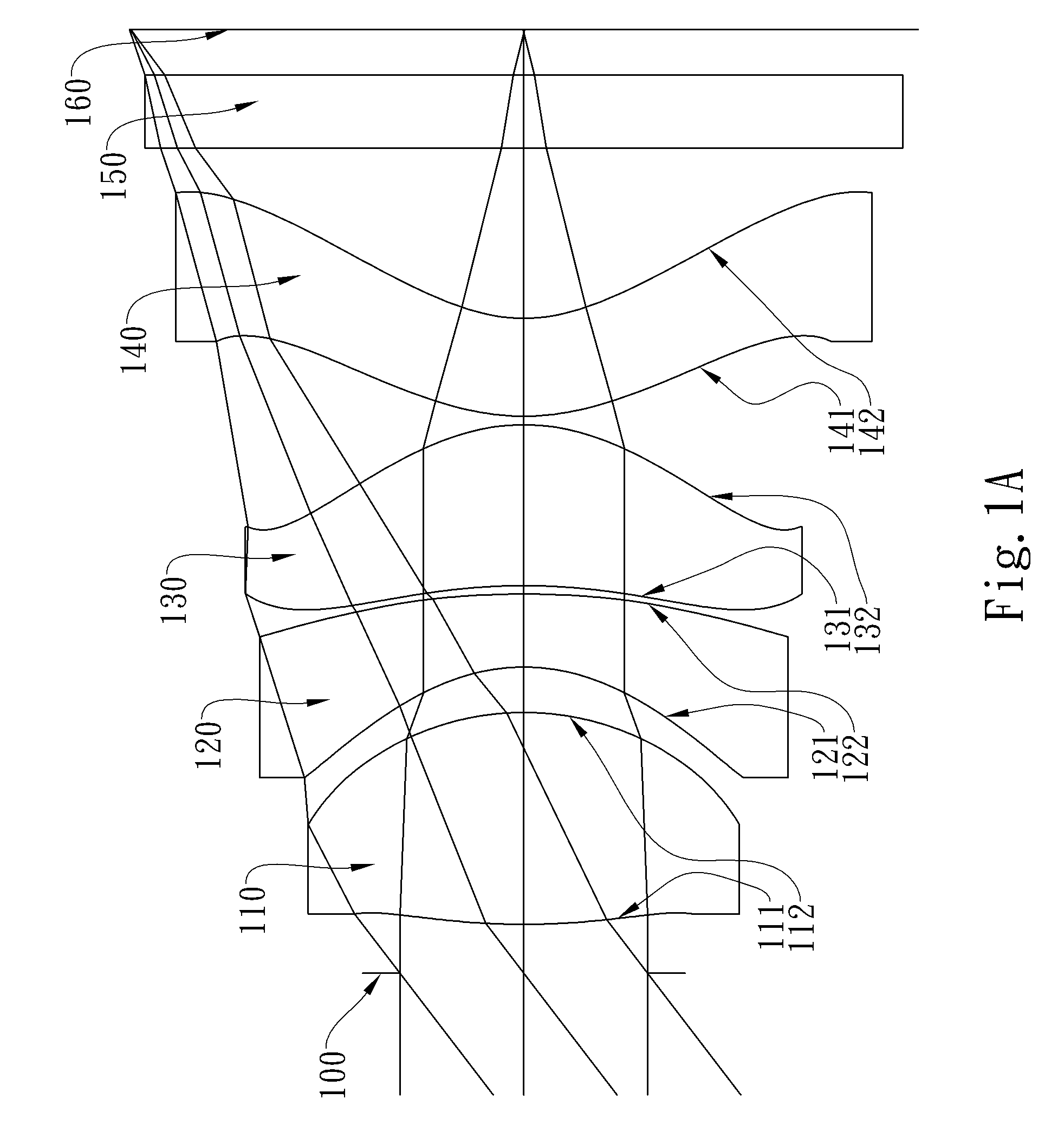
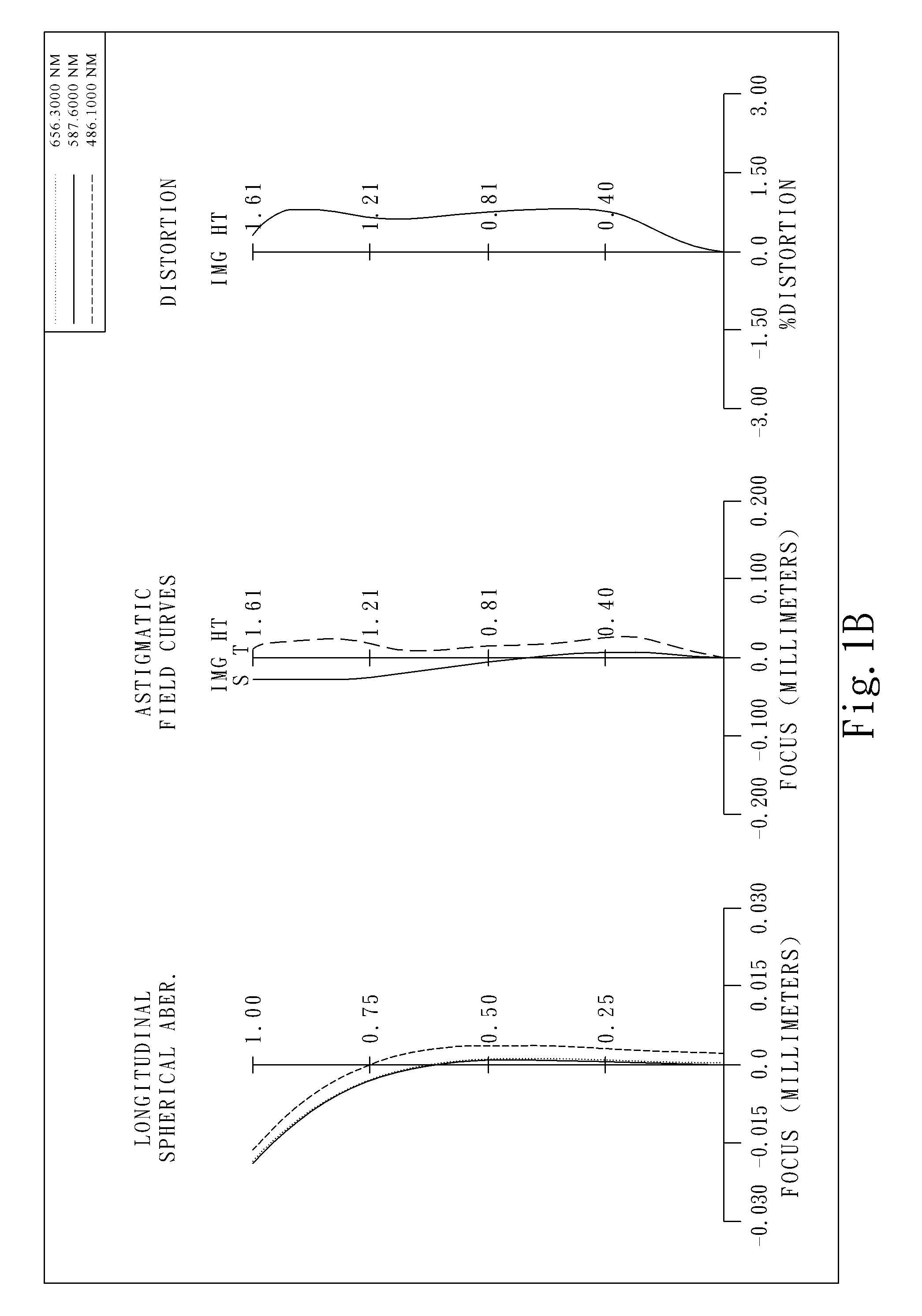
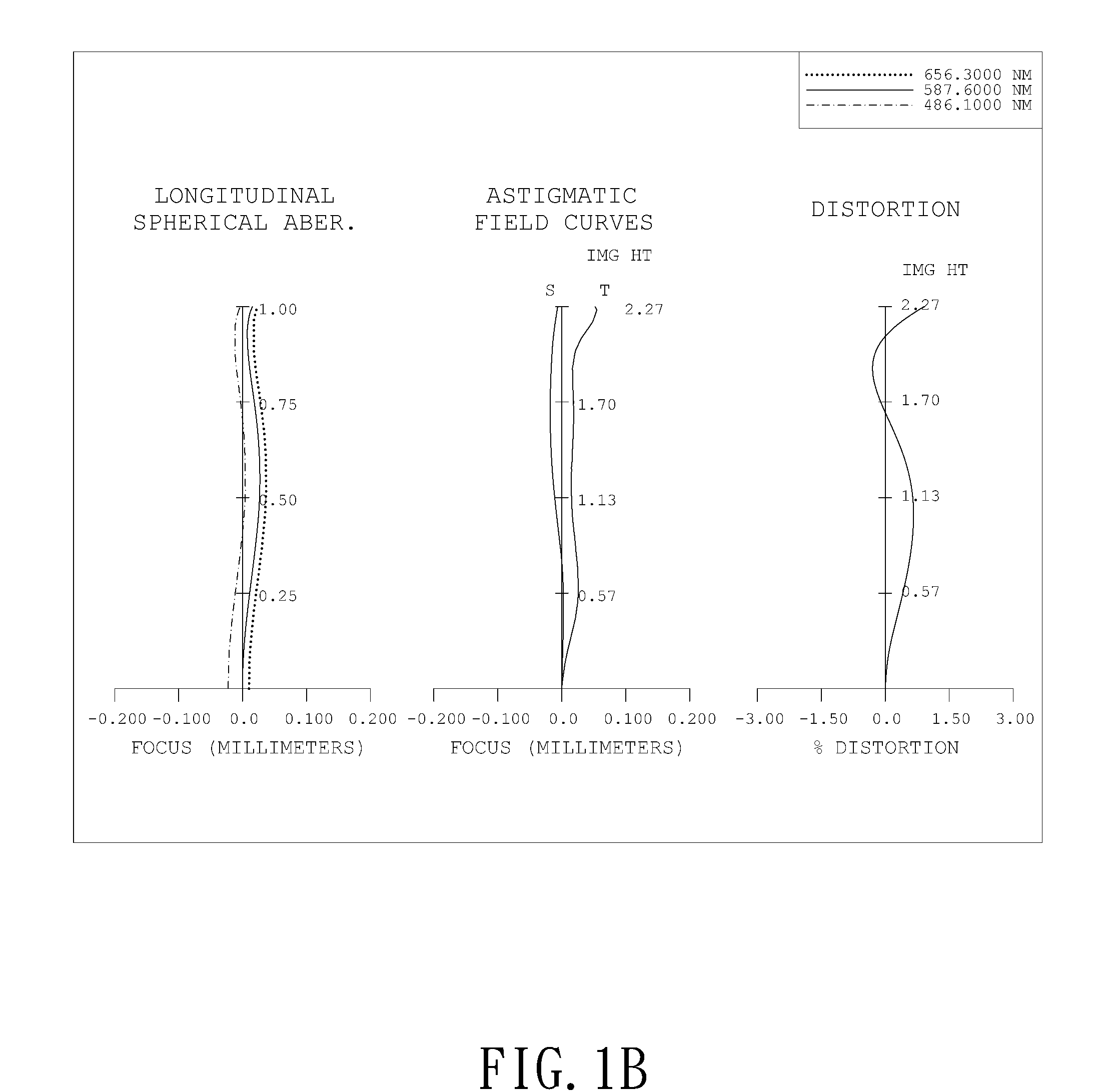
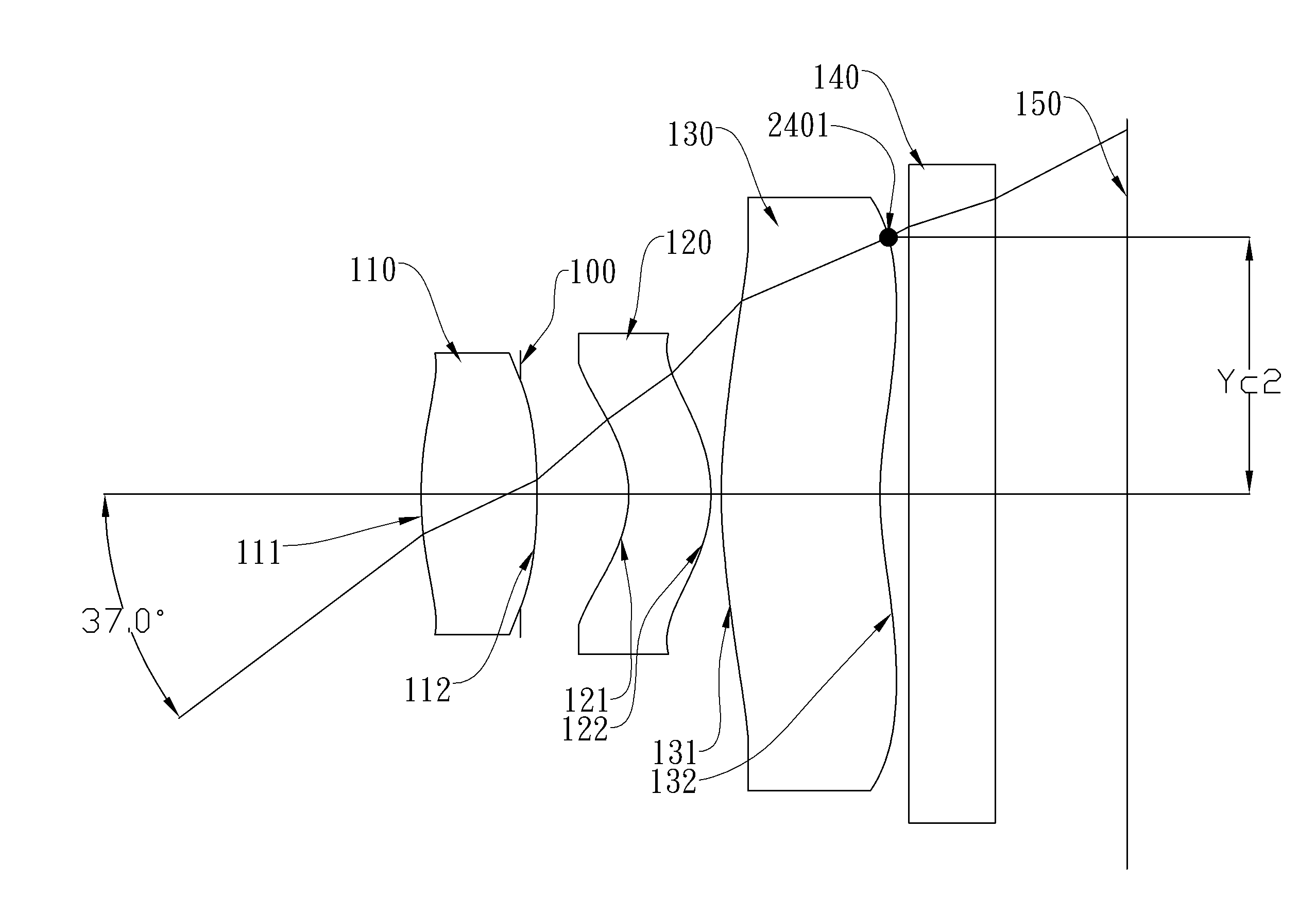
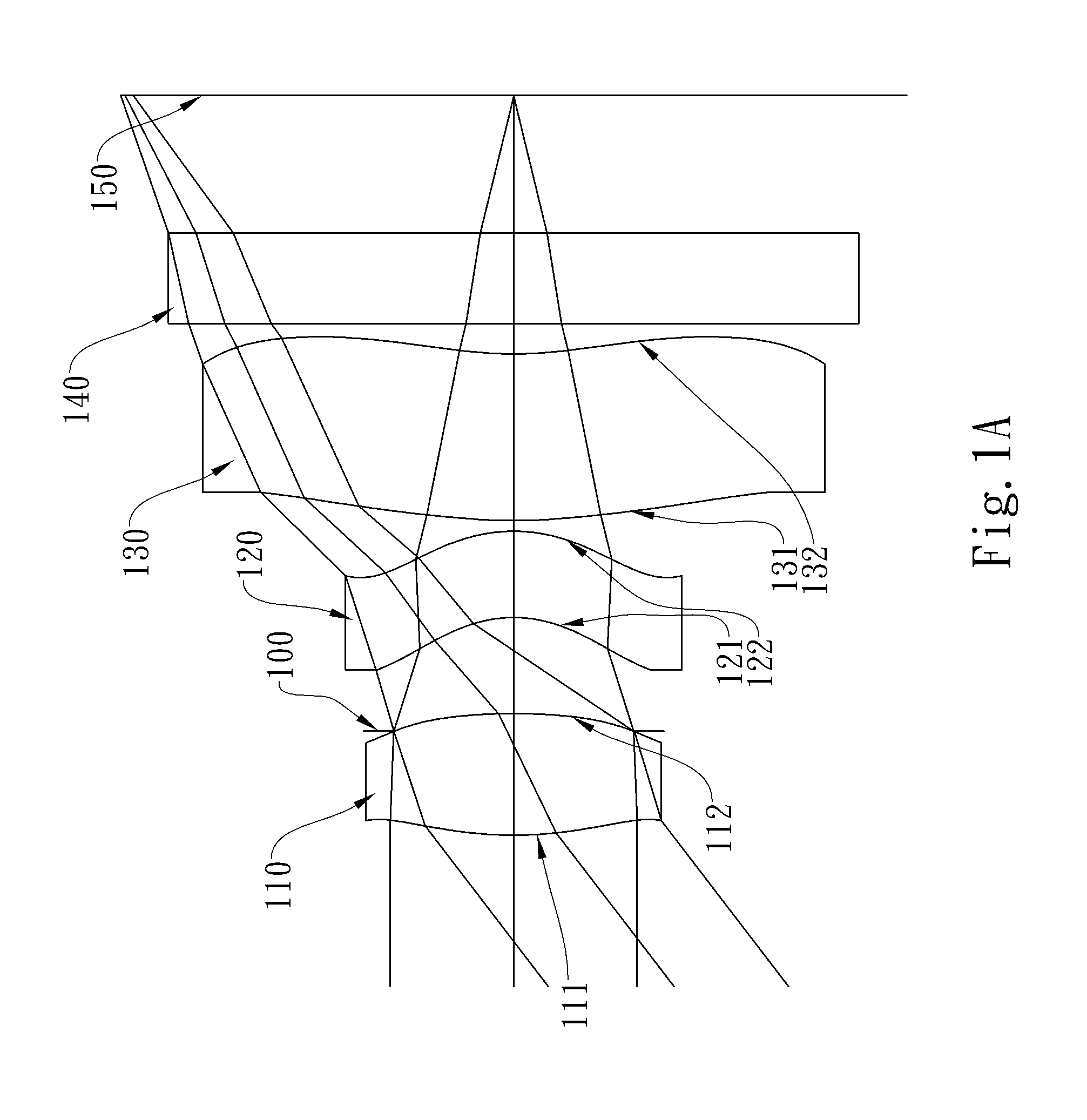
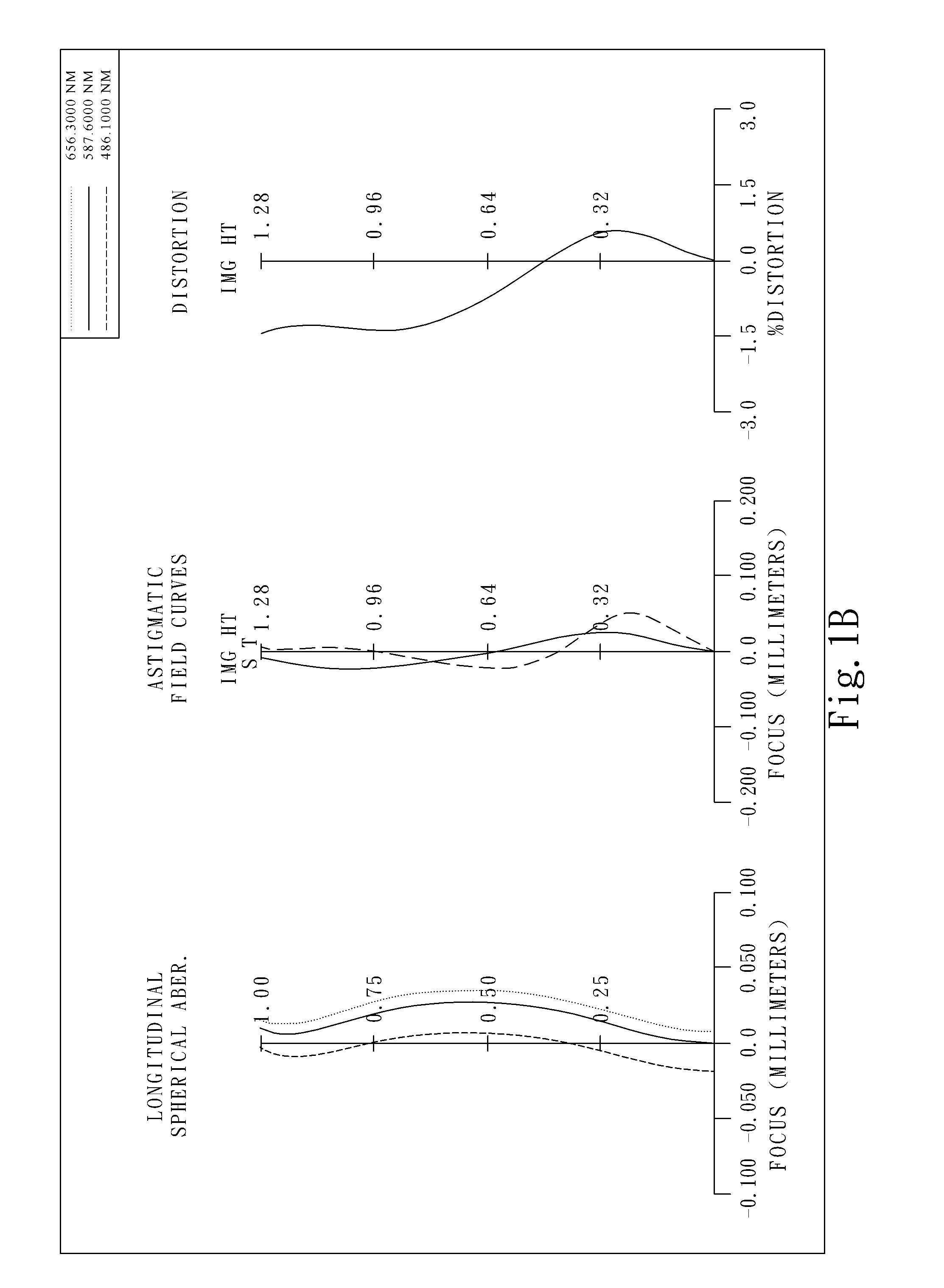
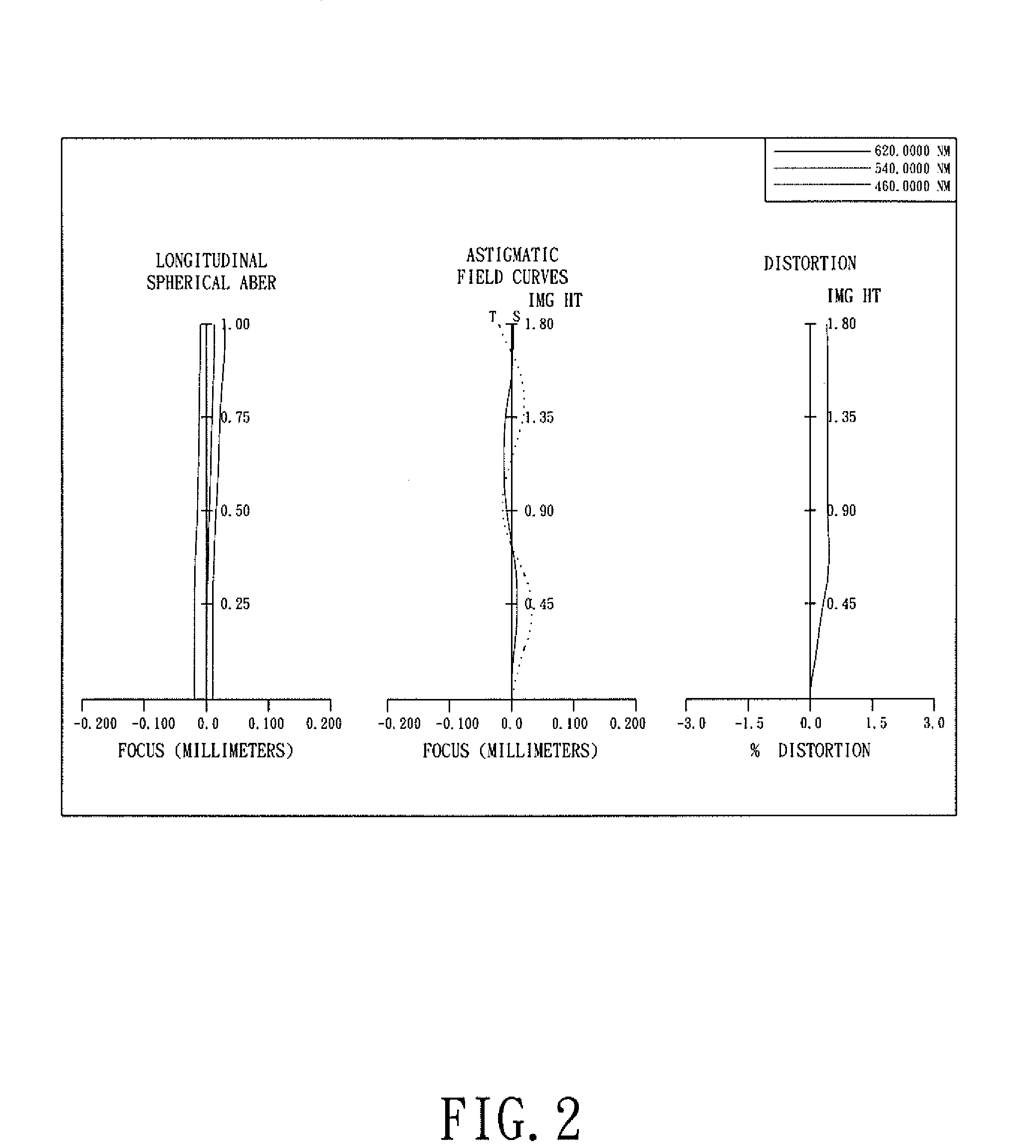
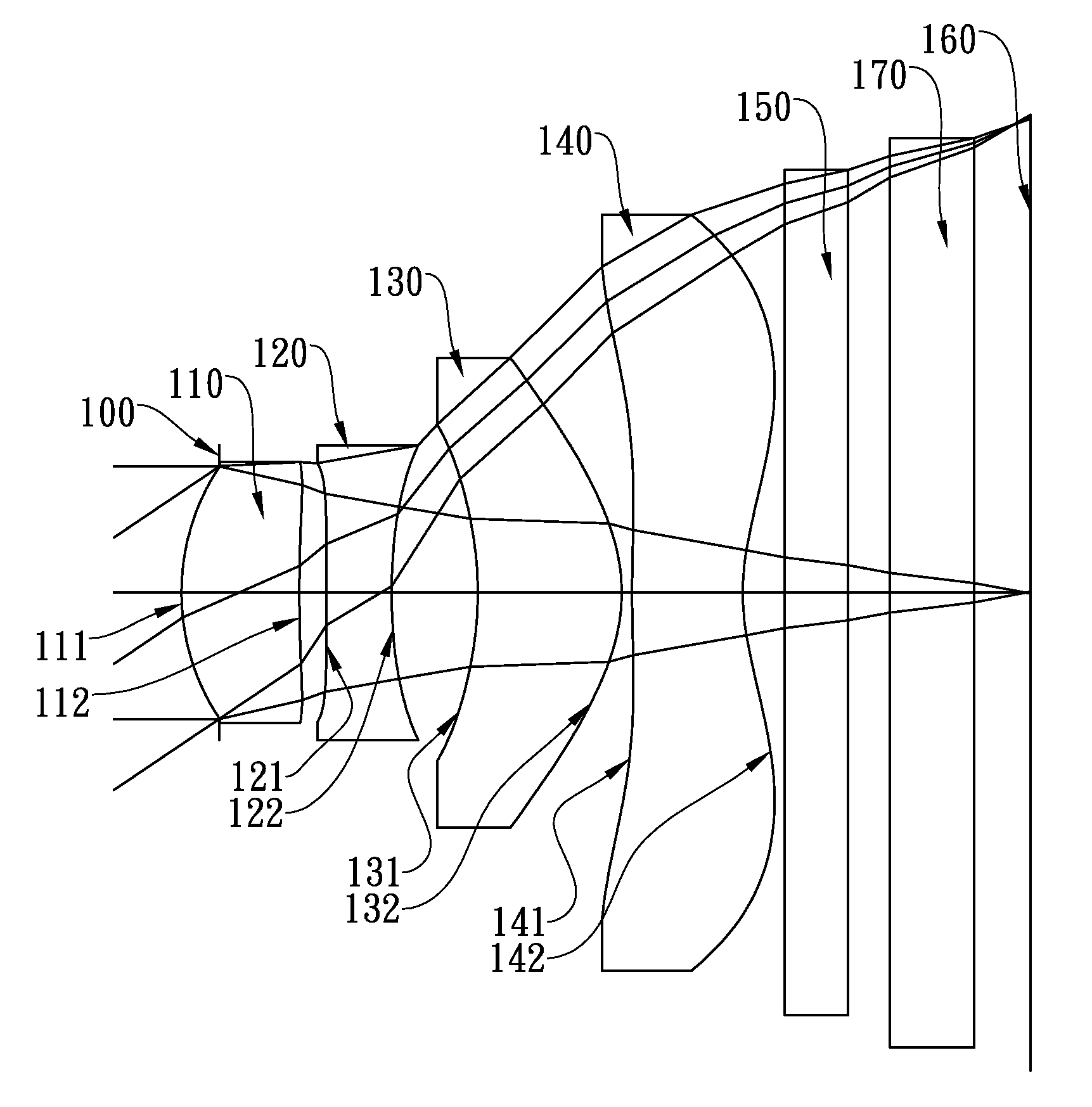
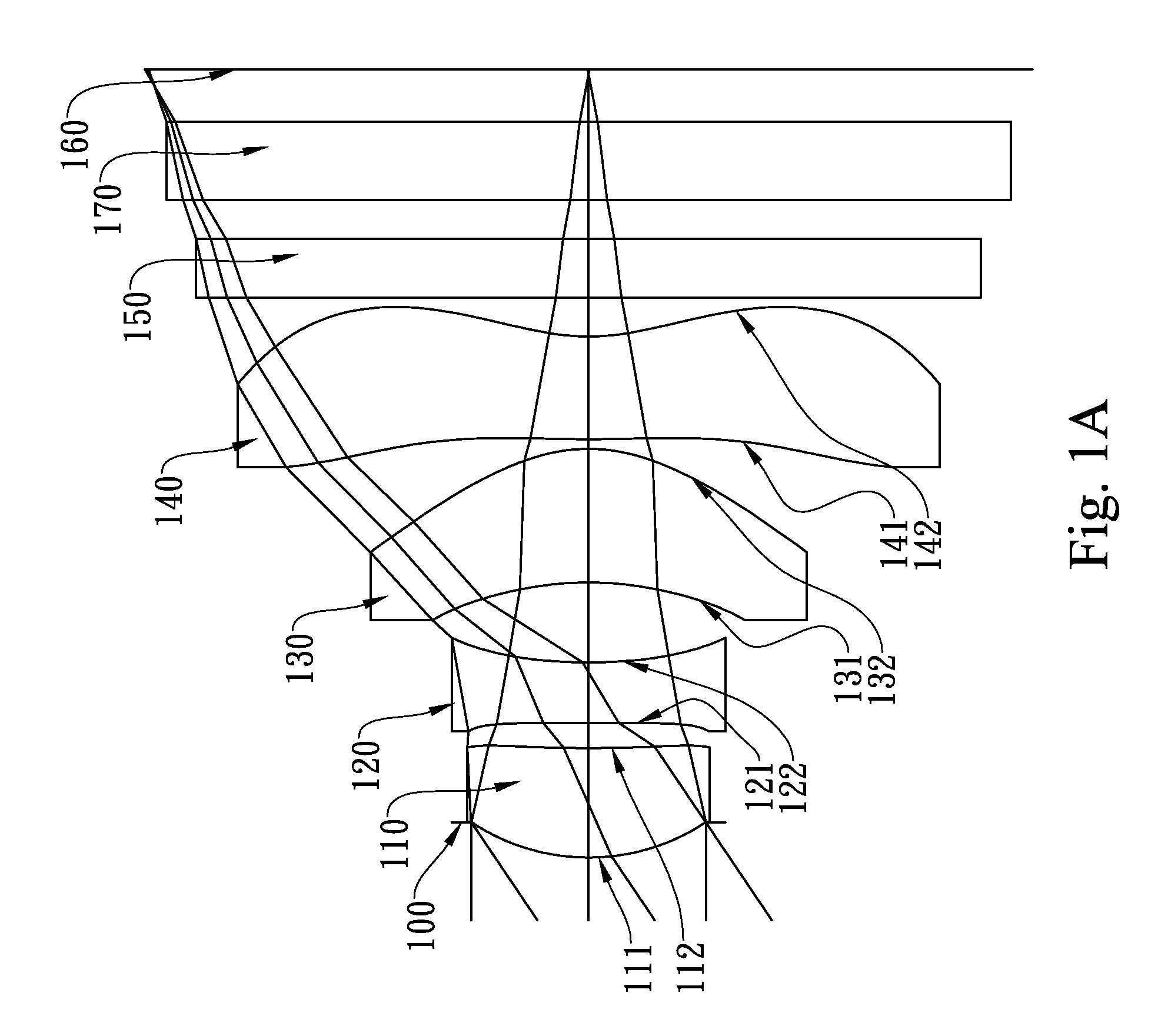
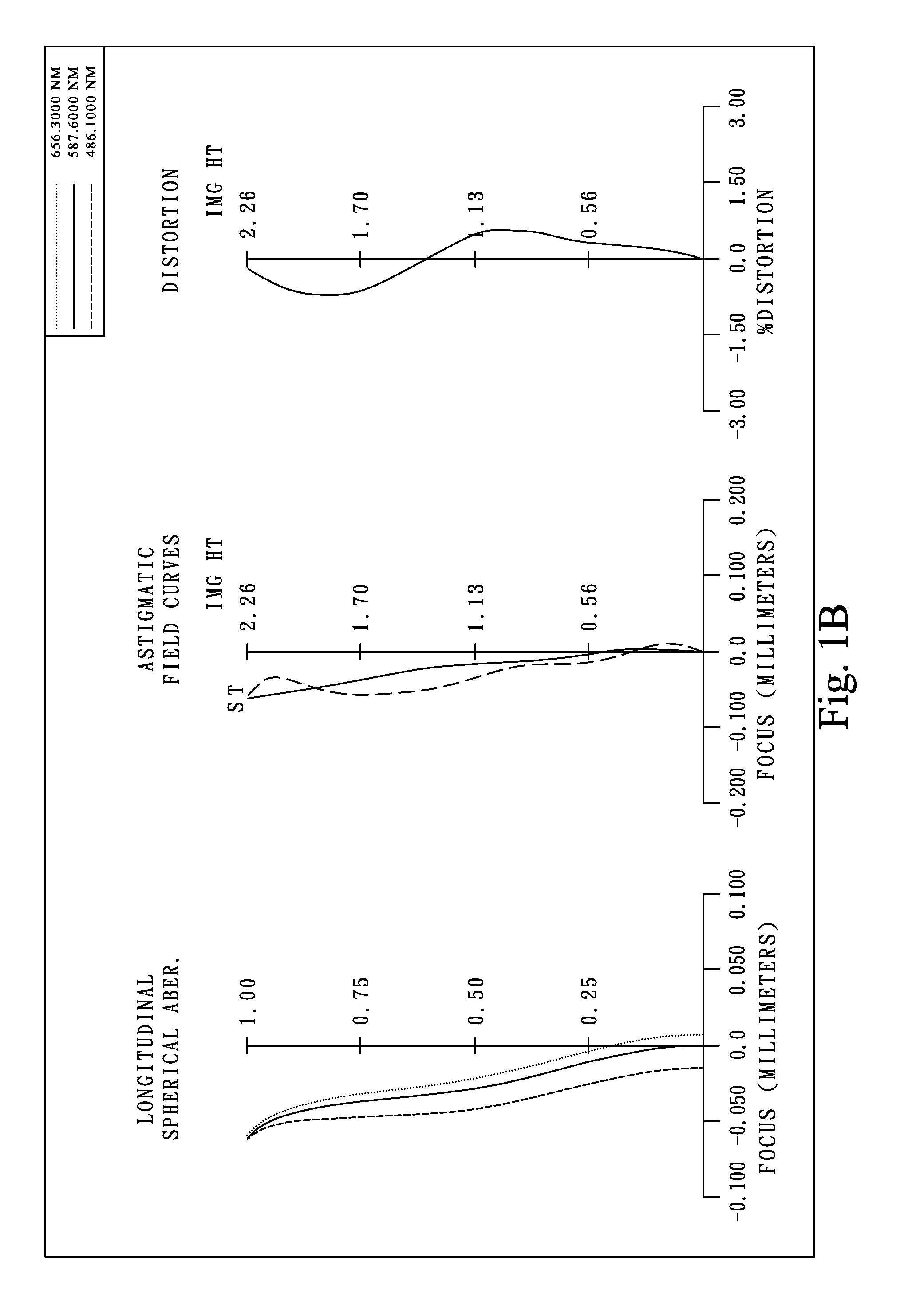
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
51results about How to "Reduce optical sensitivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
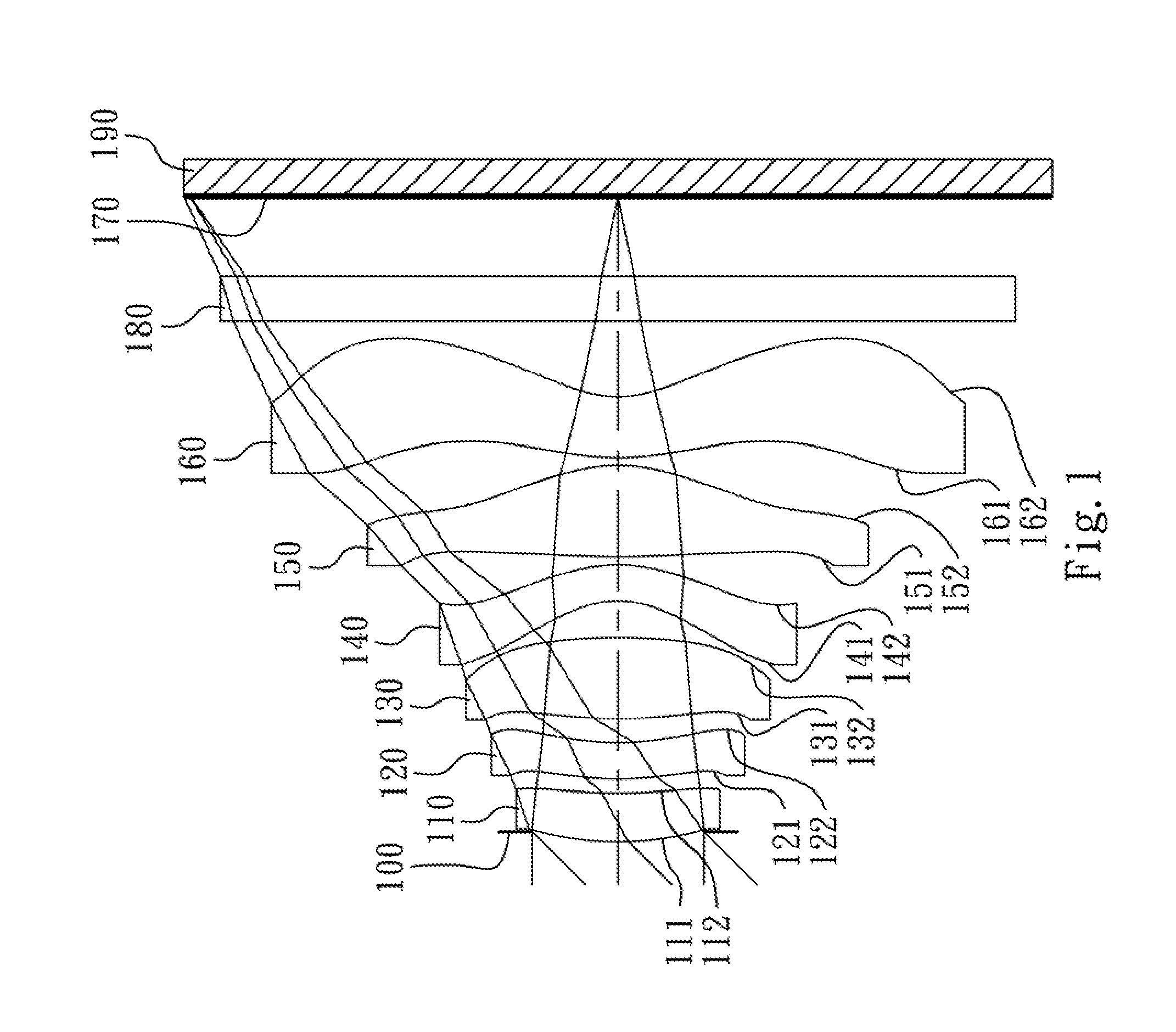
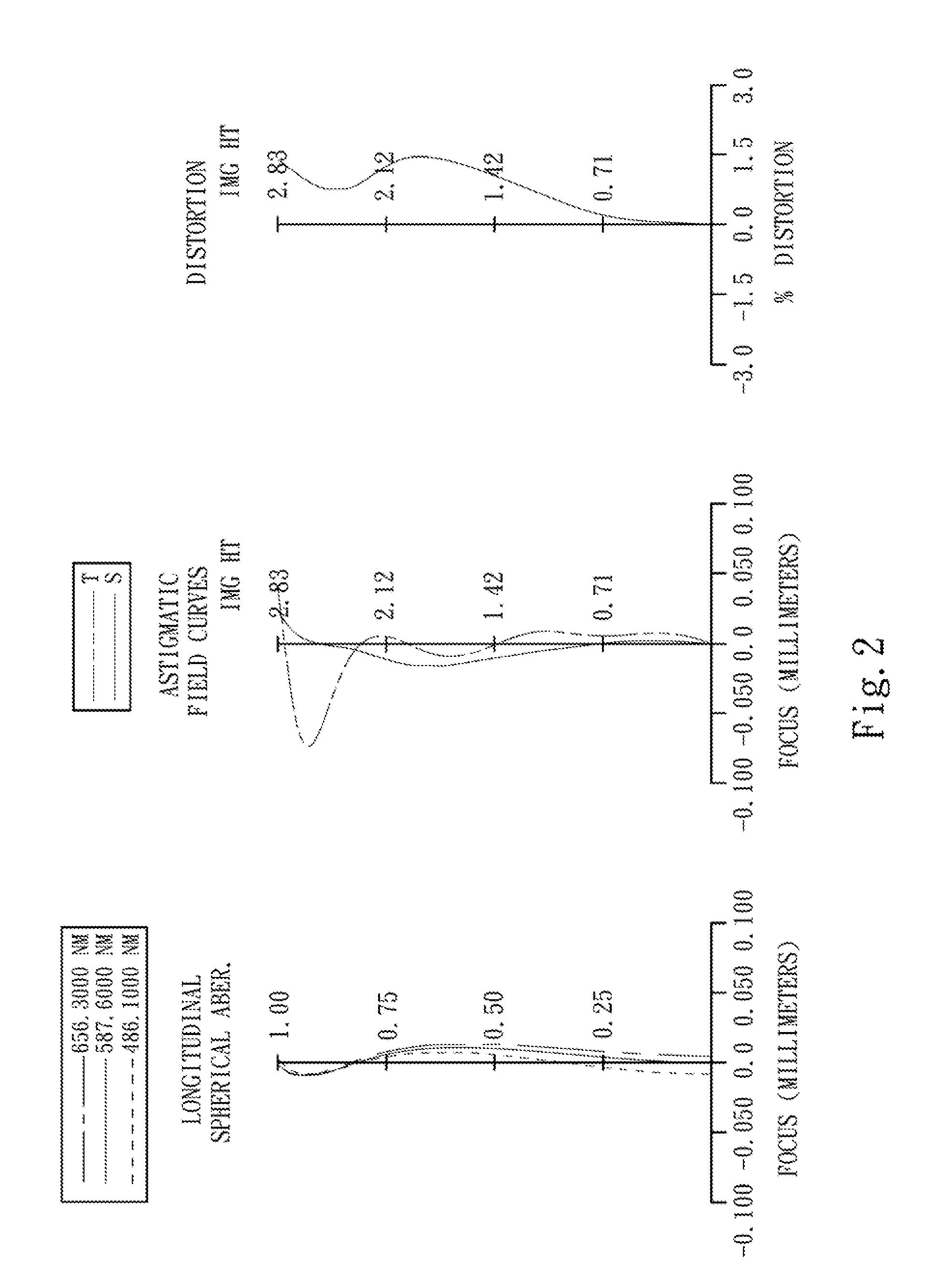
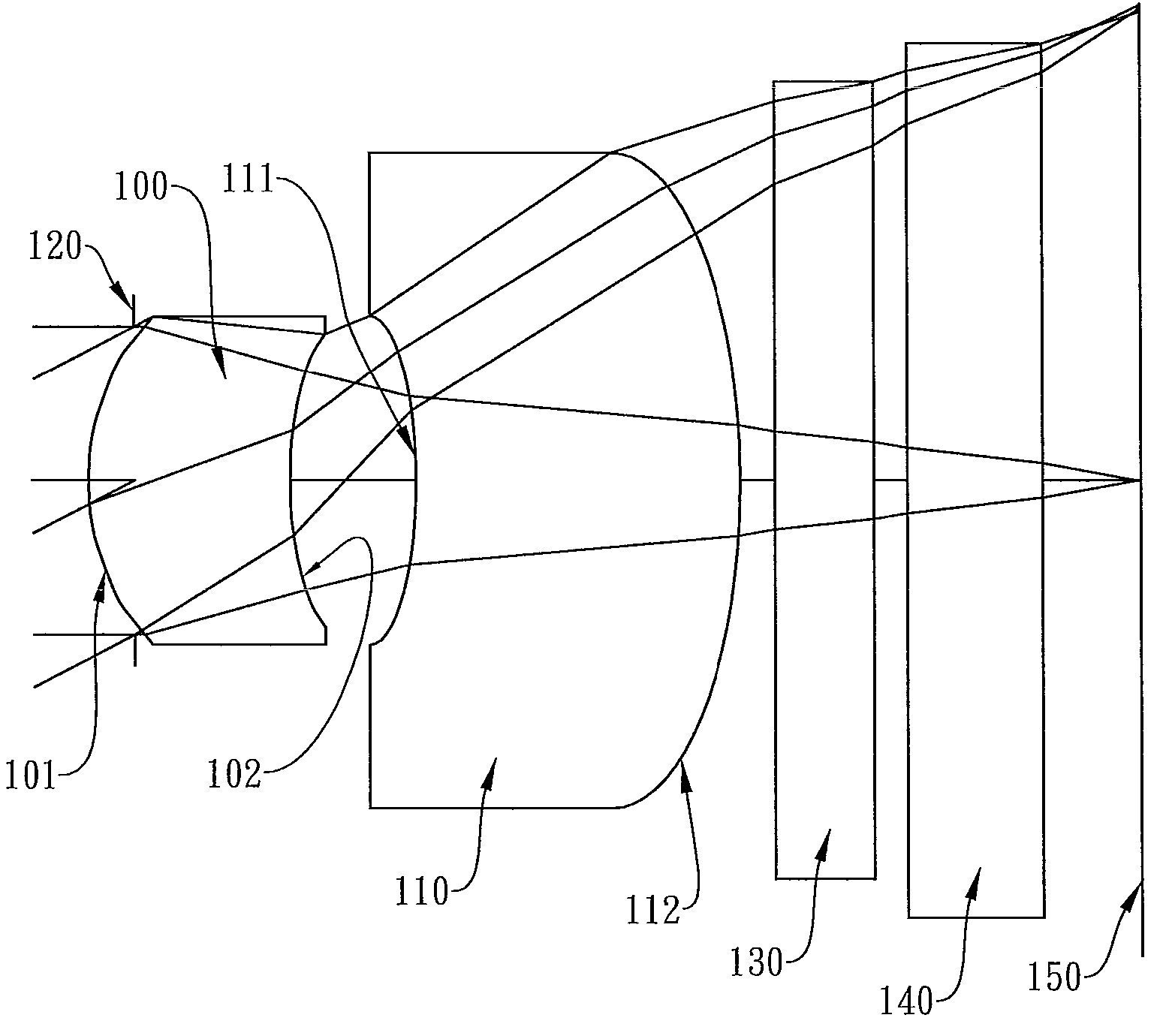
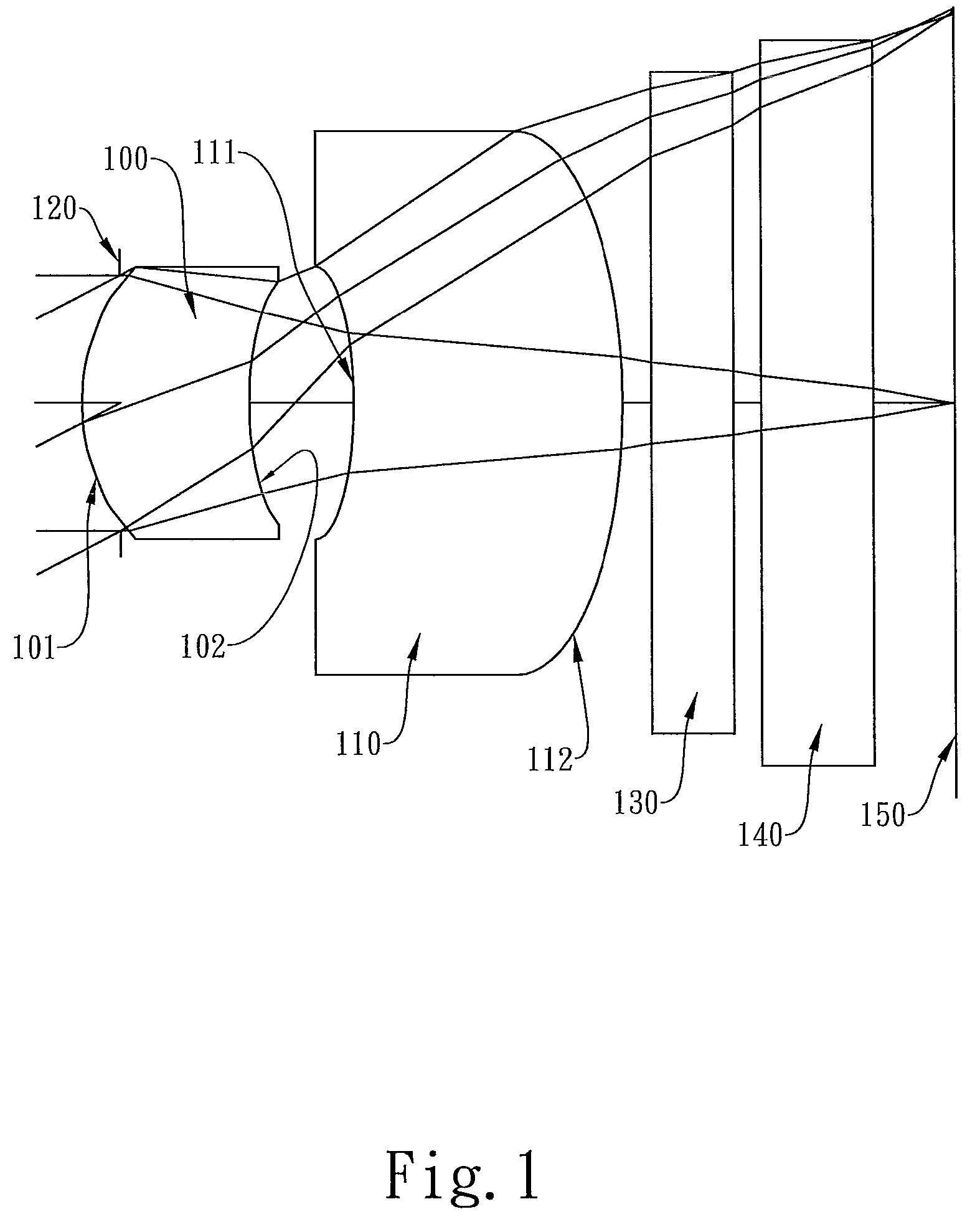
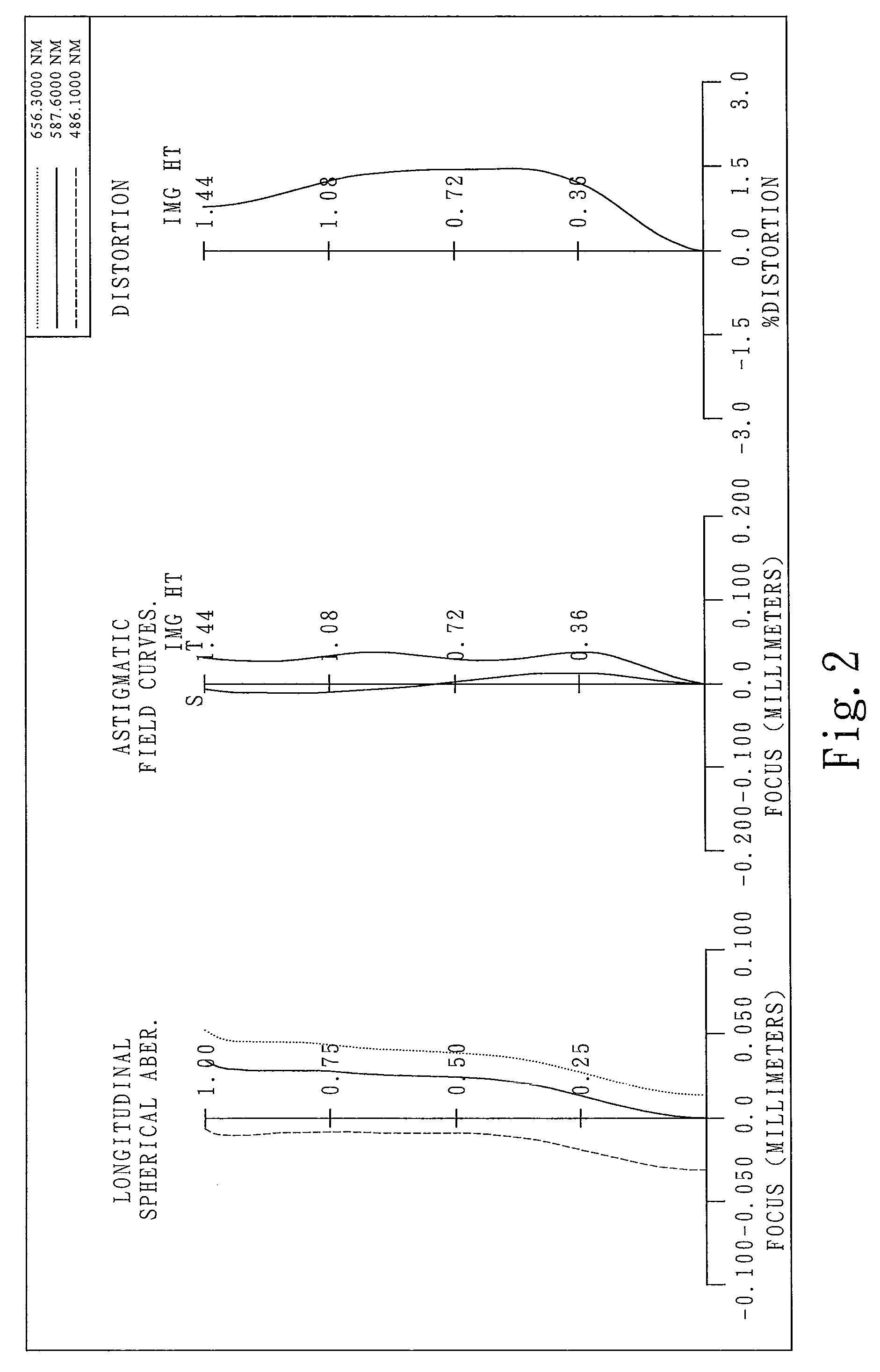
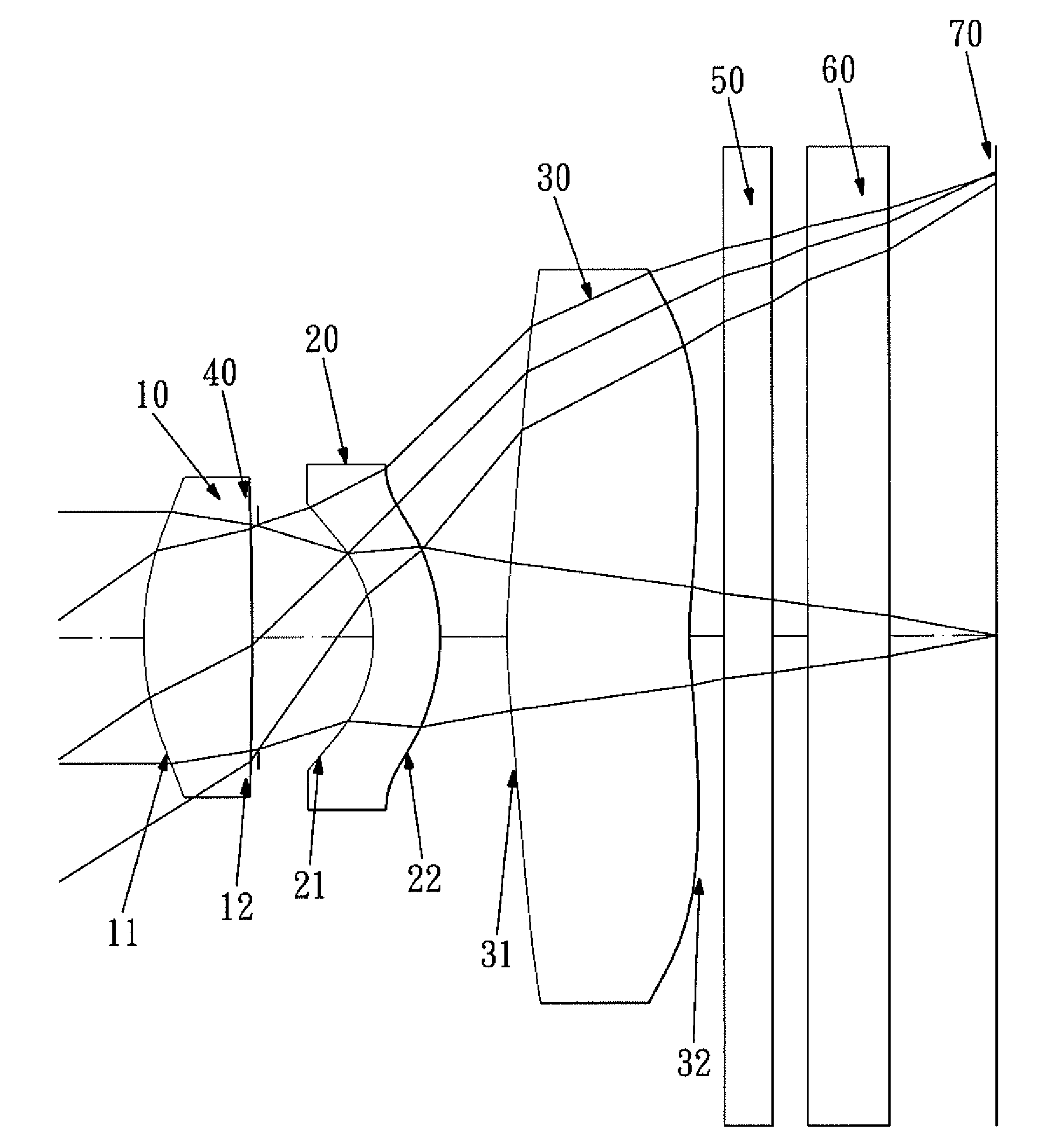
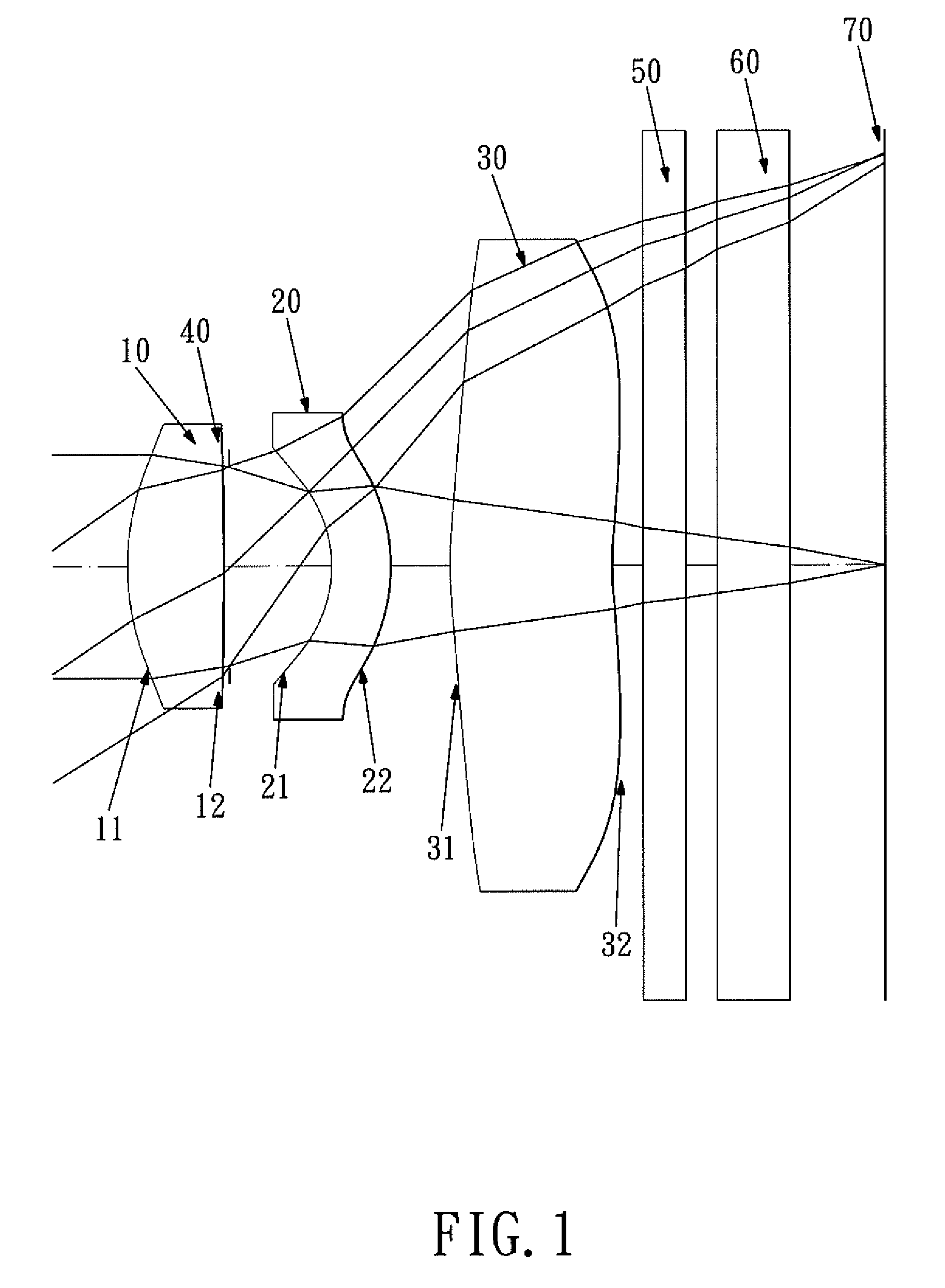
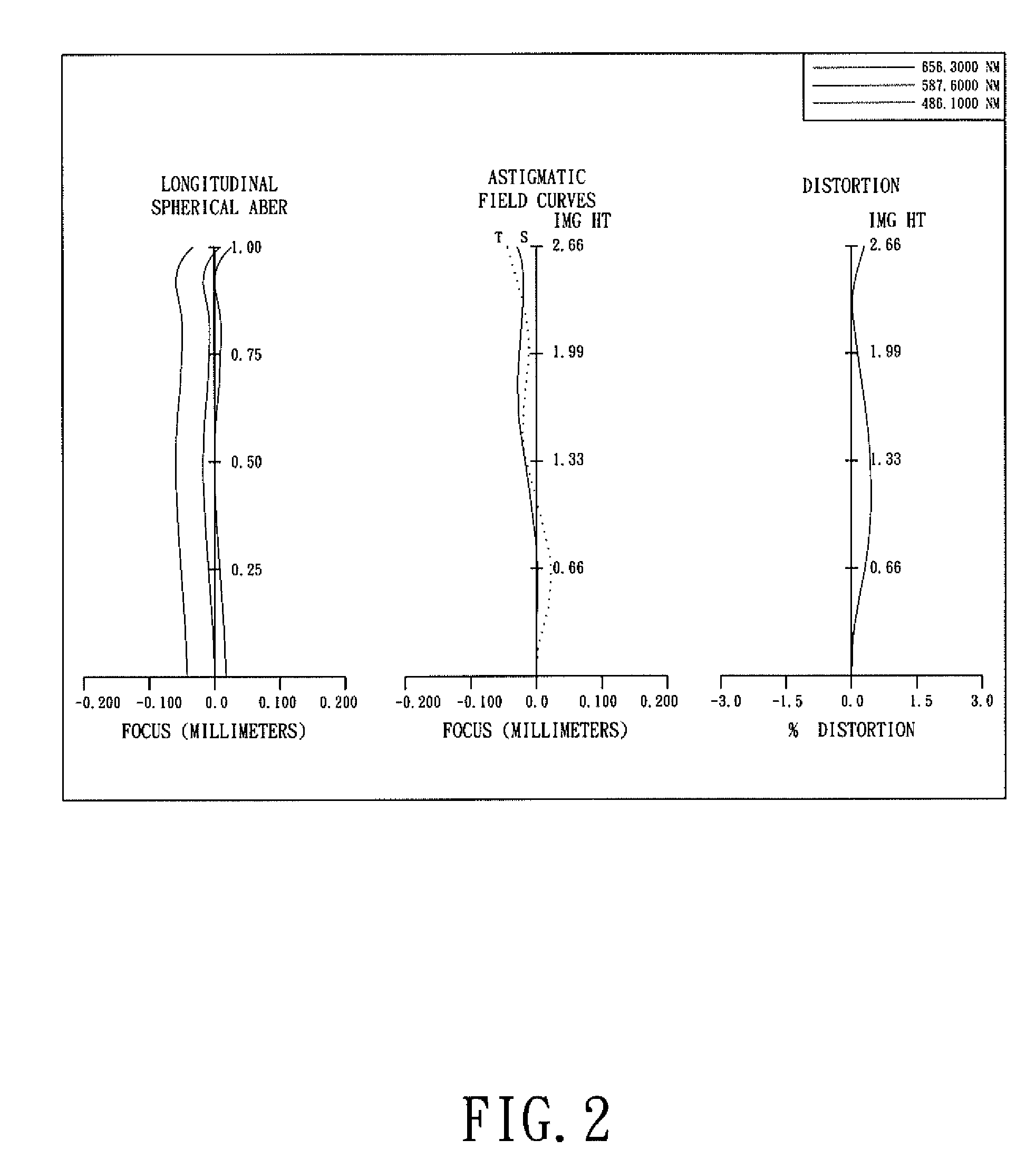
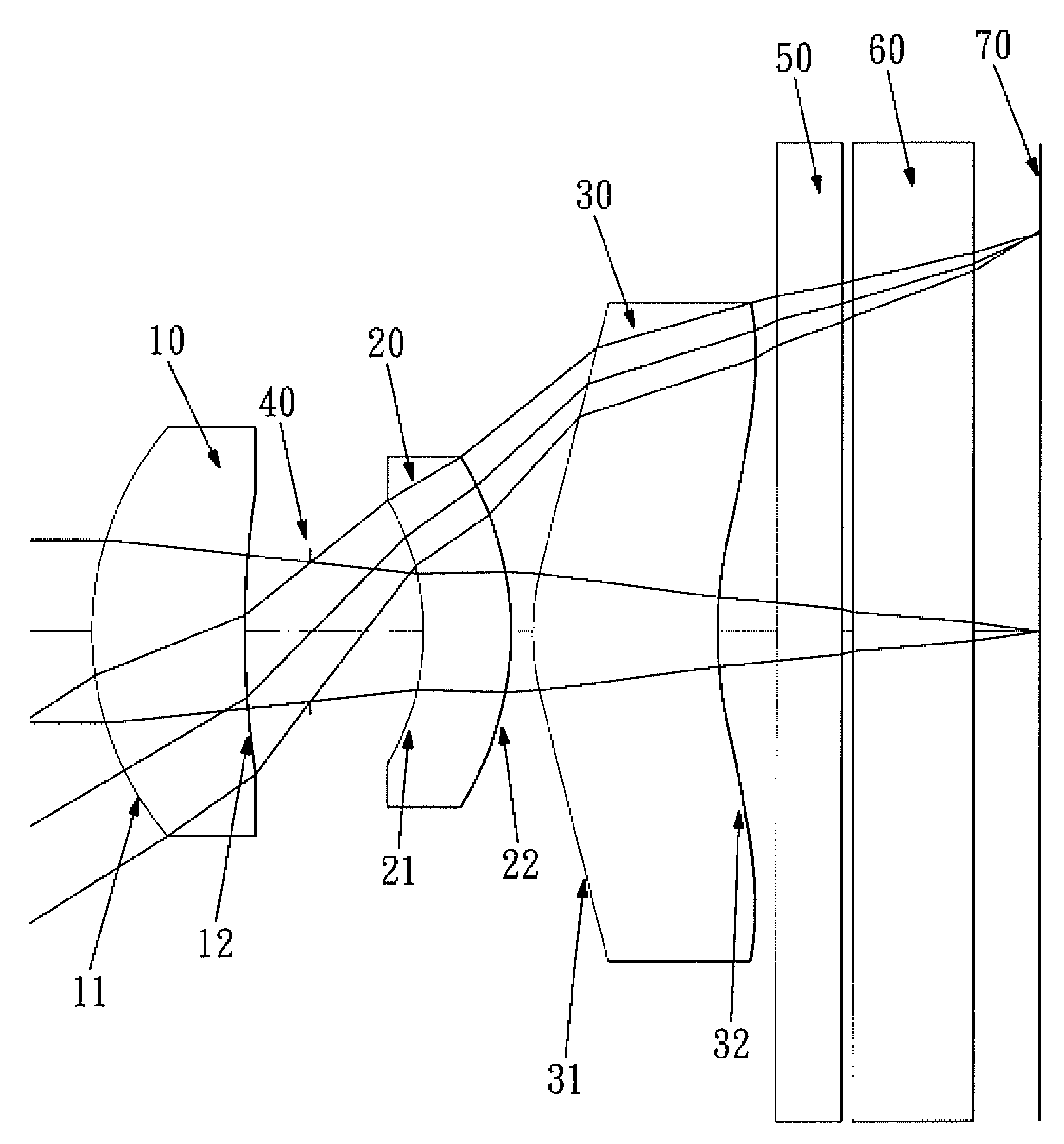
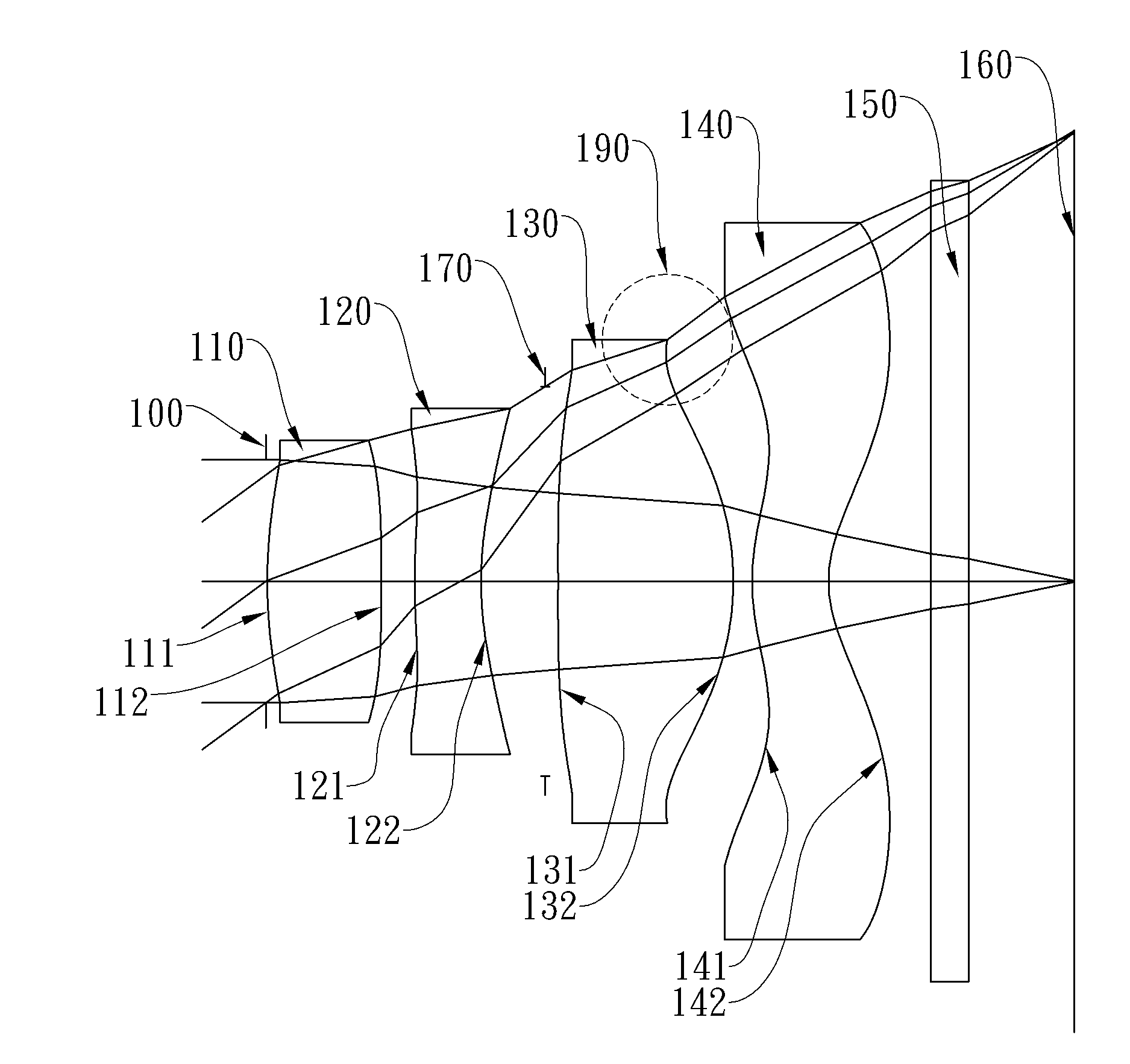
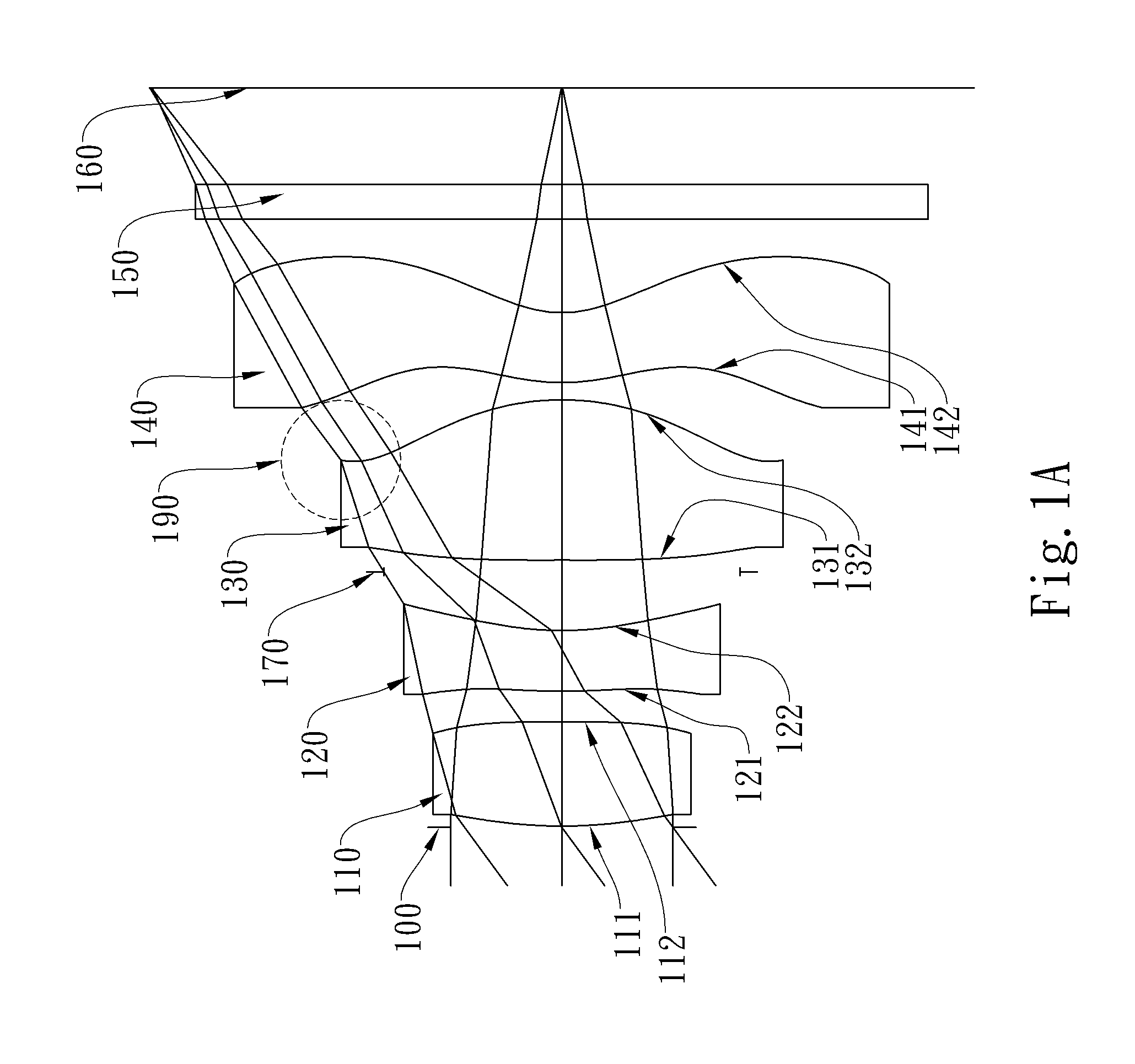
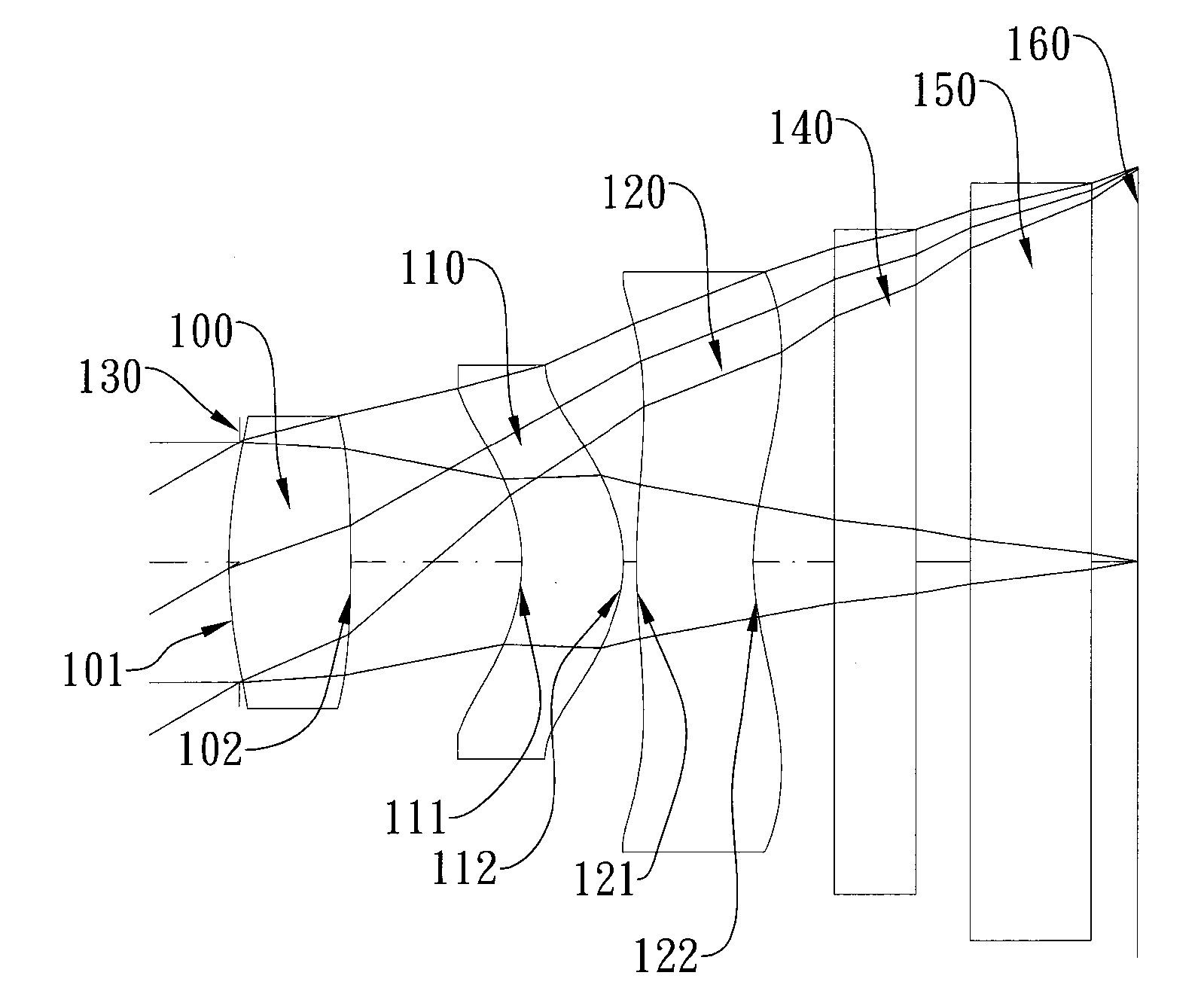
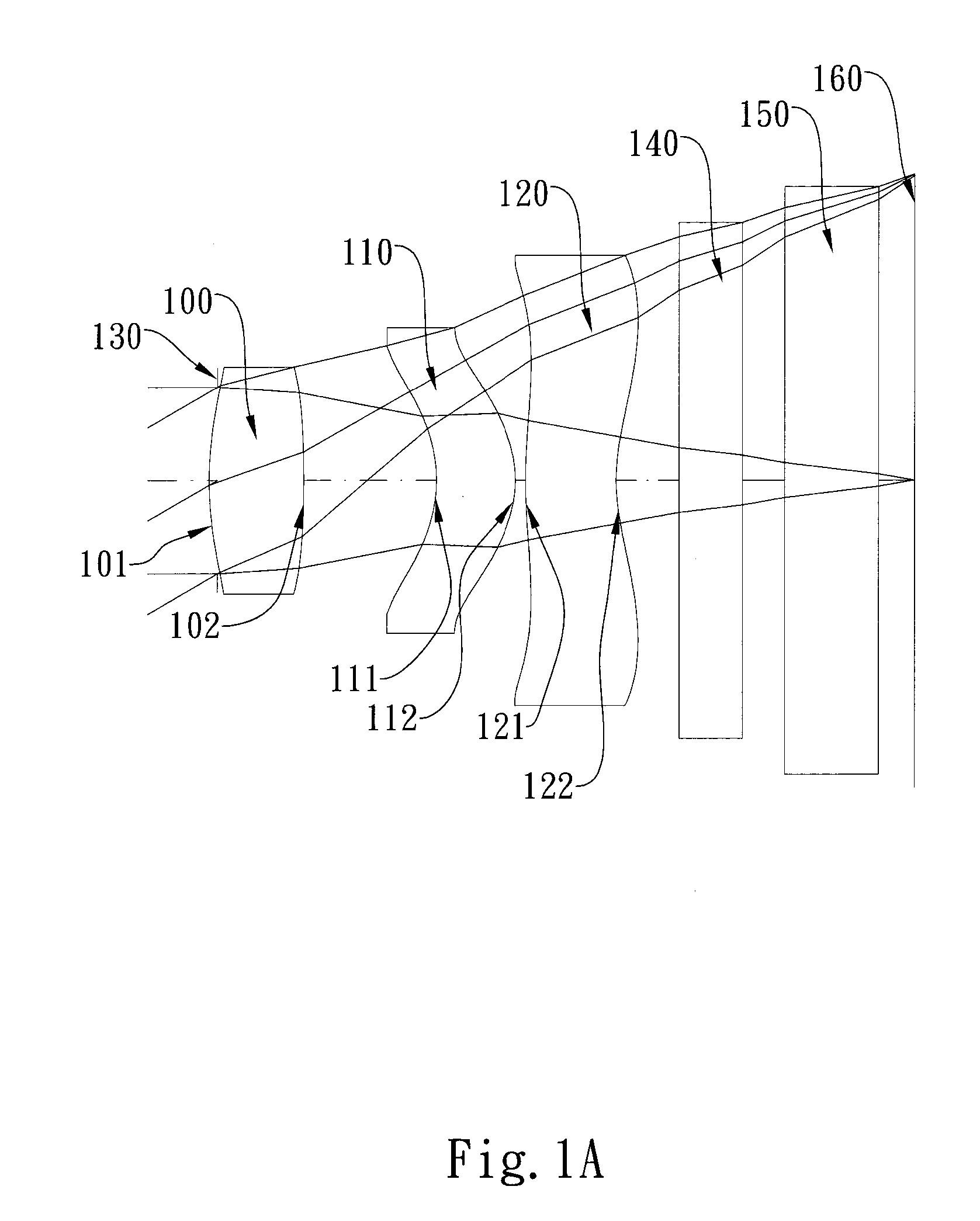
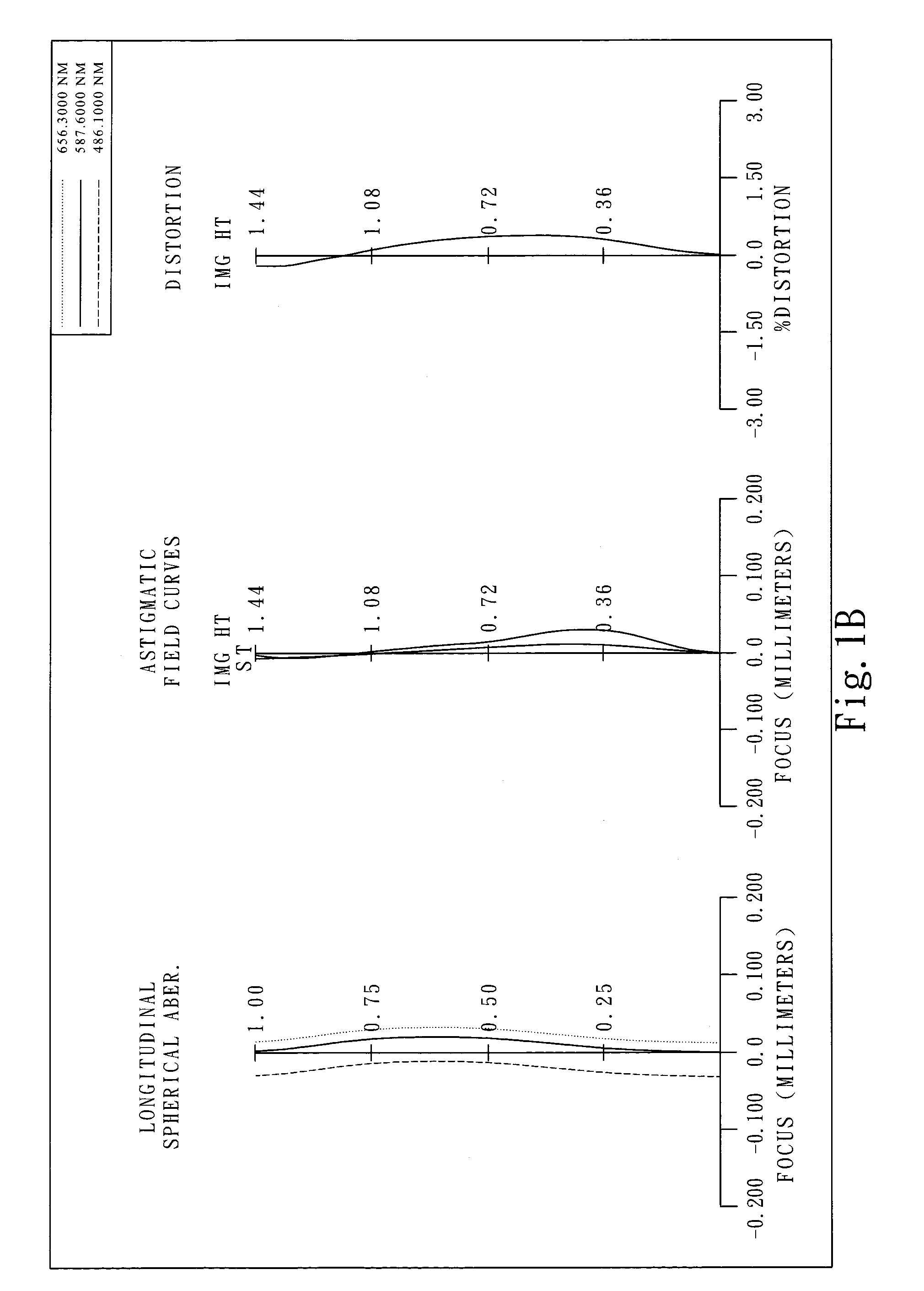
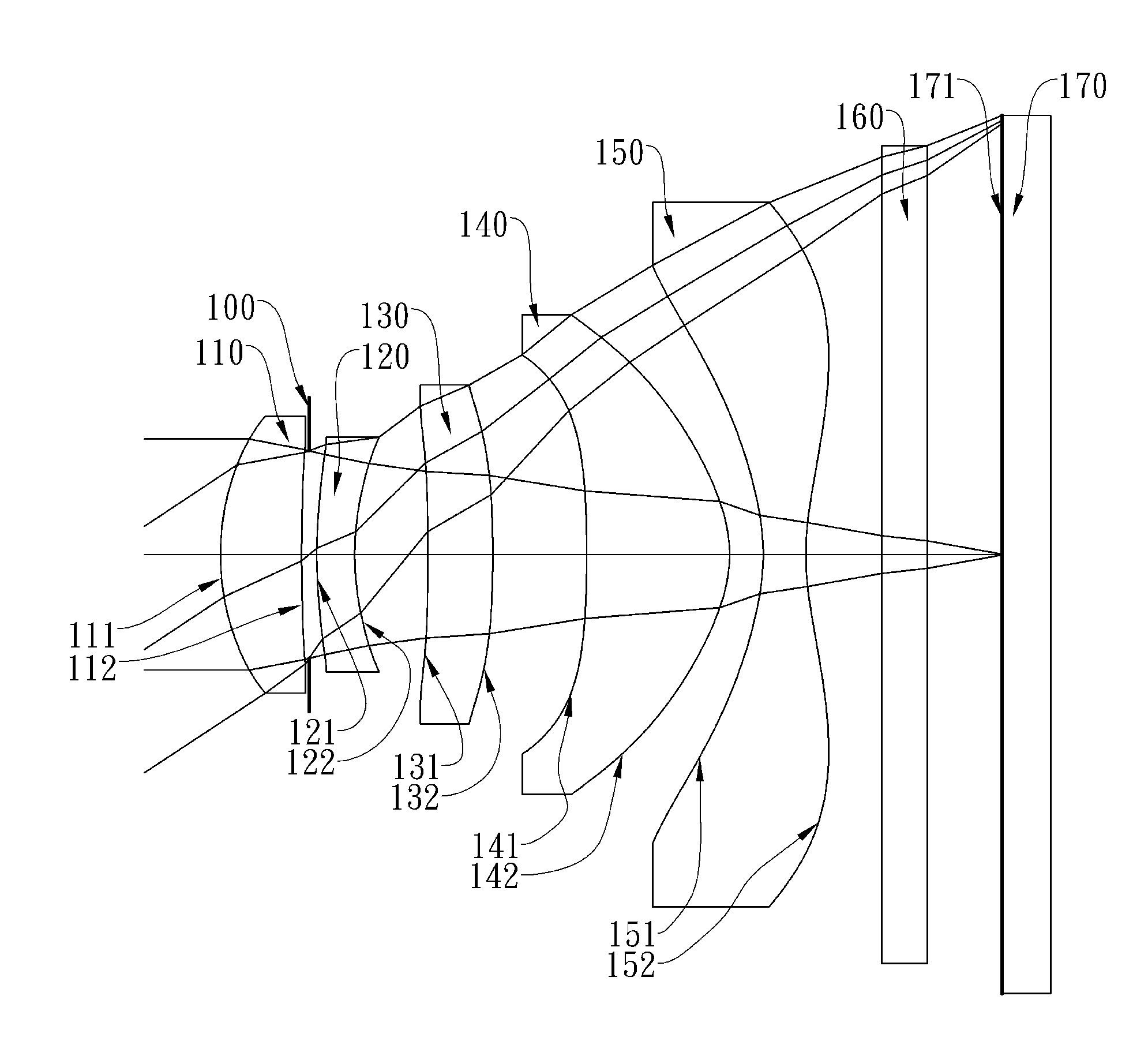
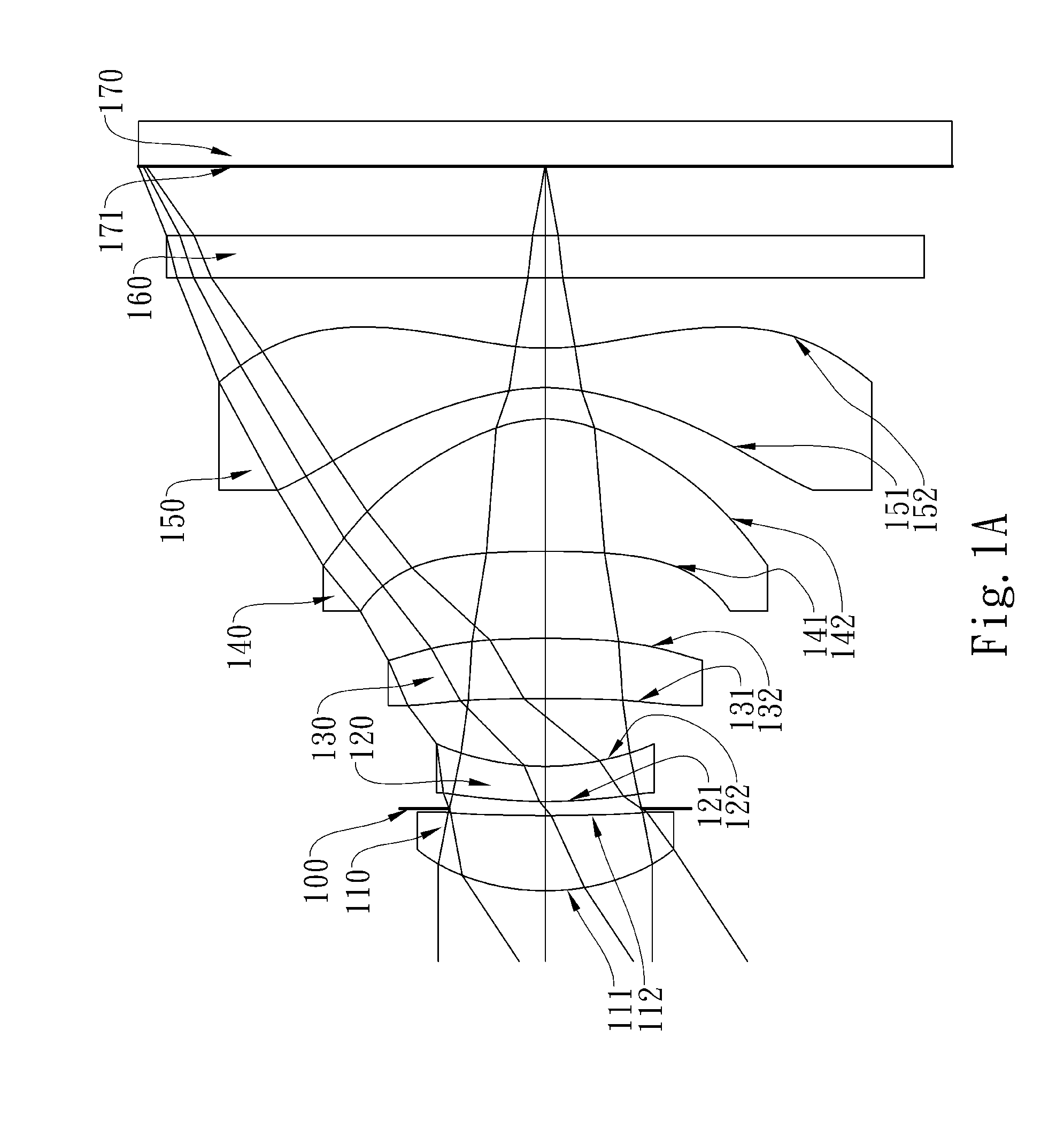
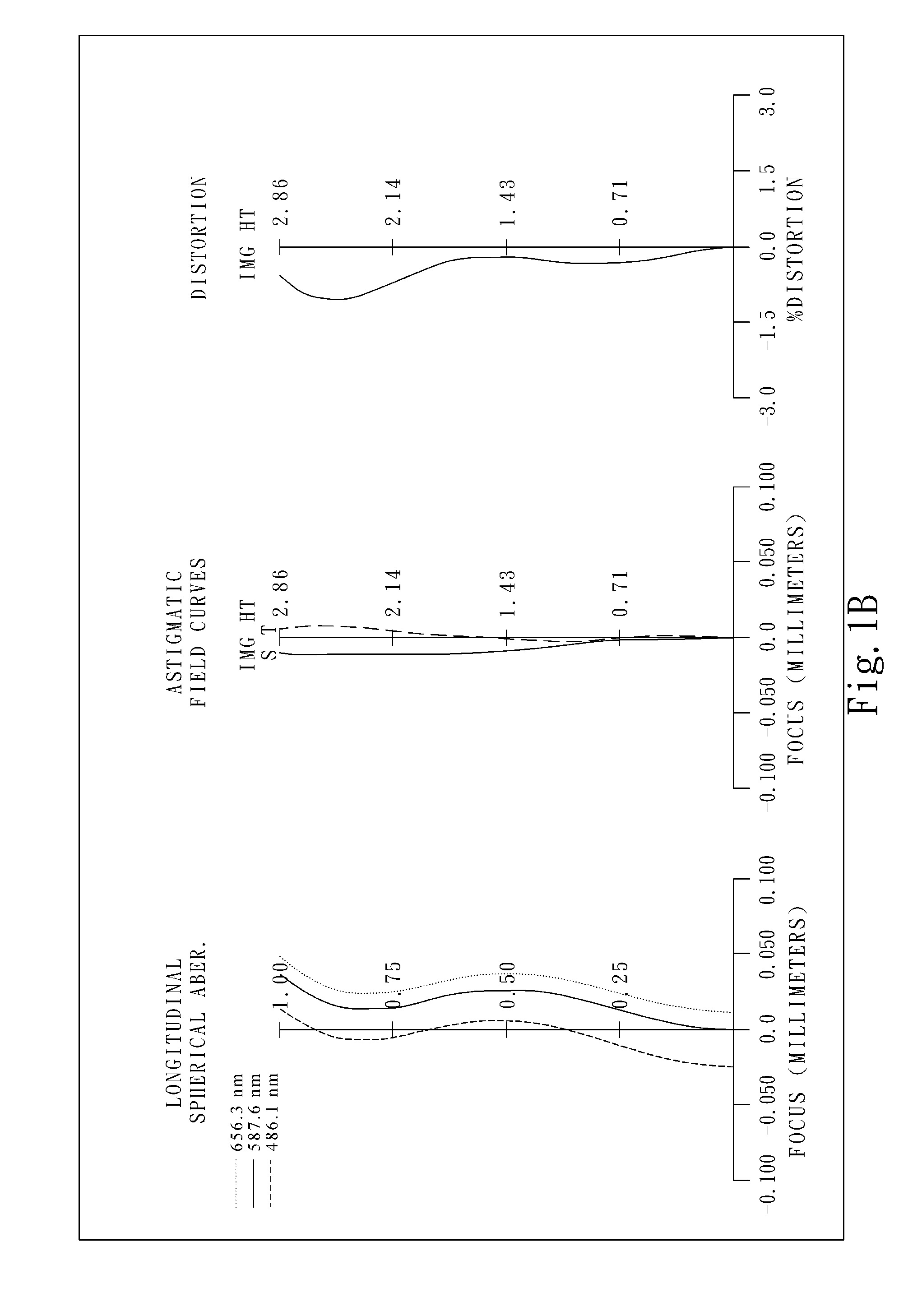
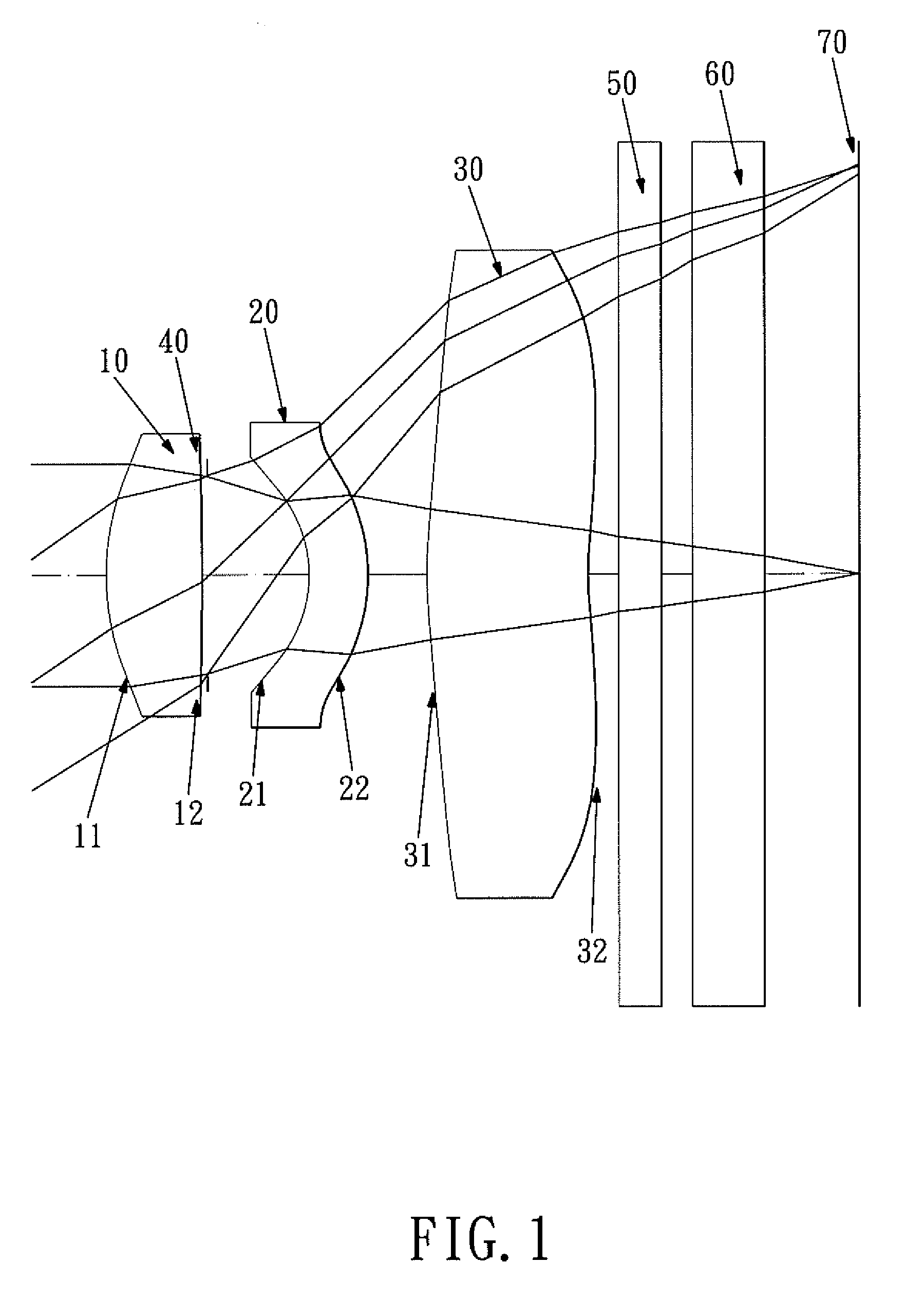
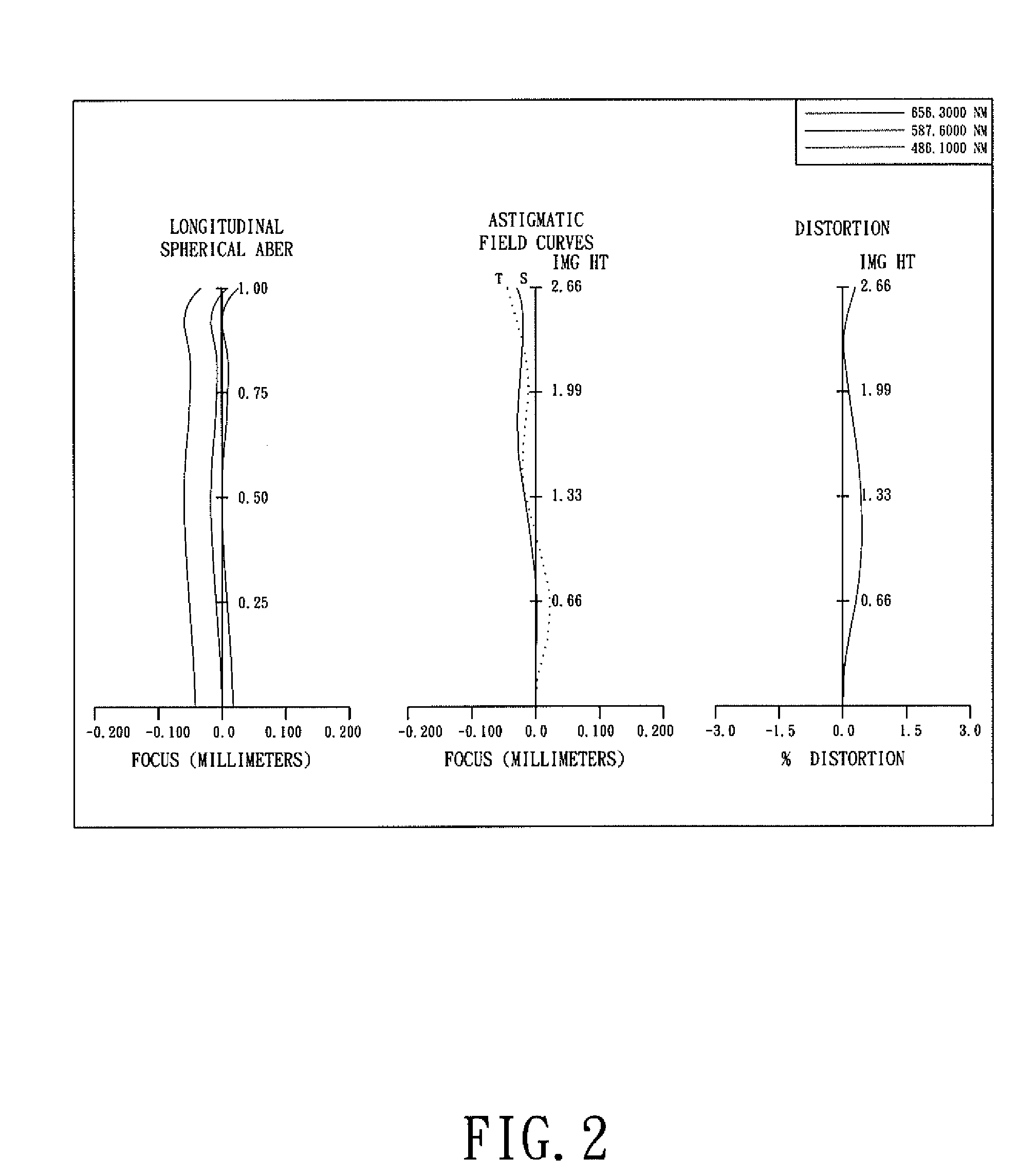
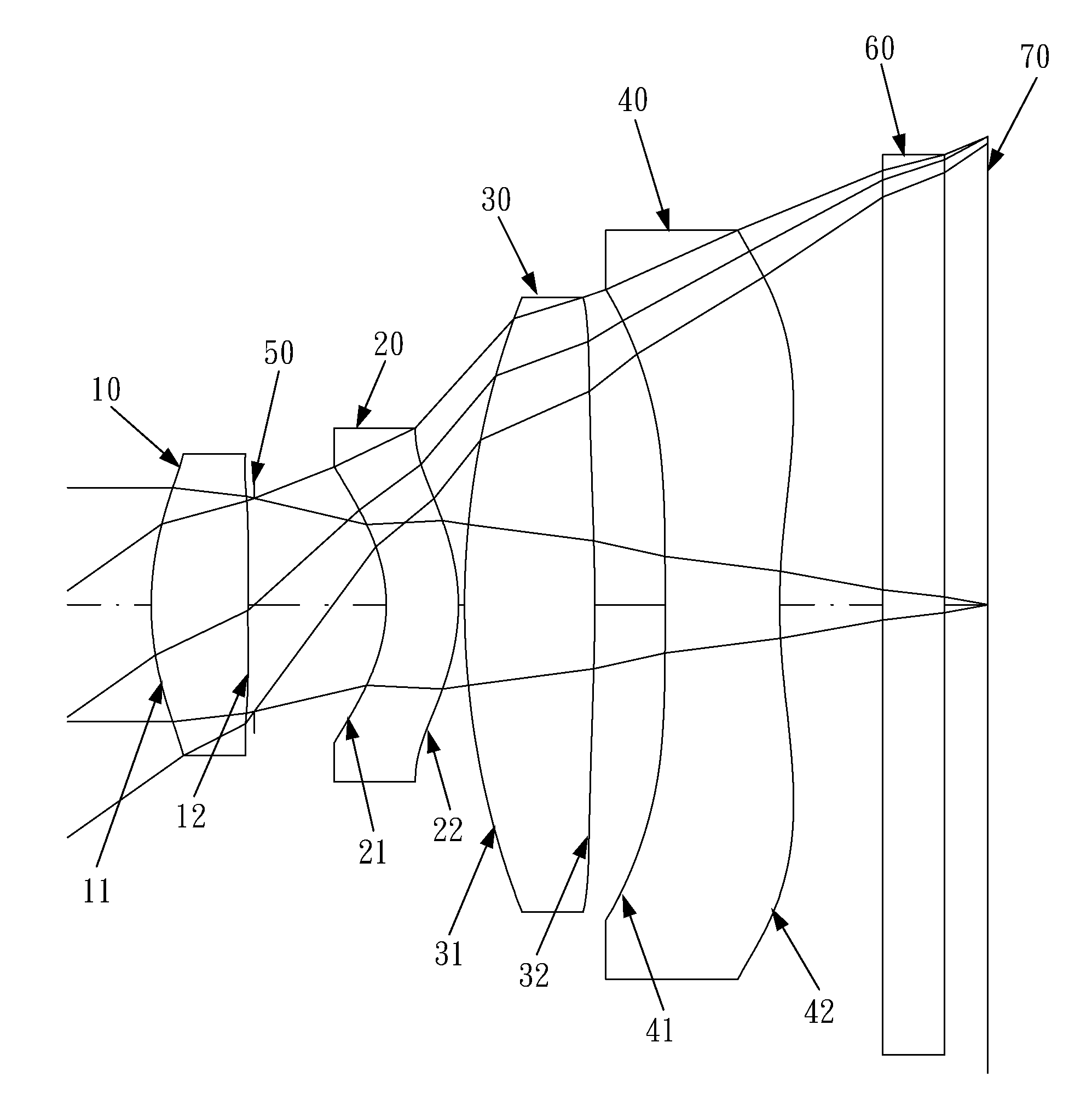
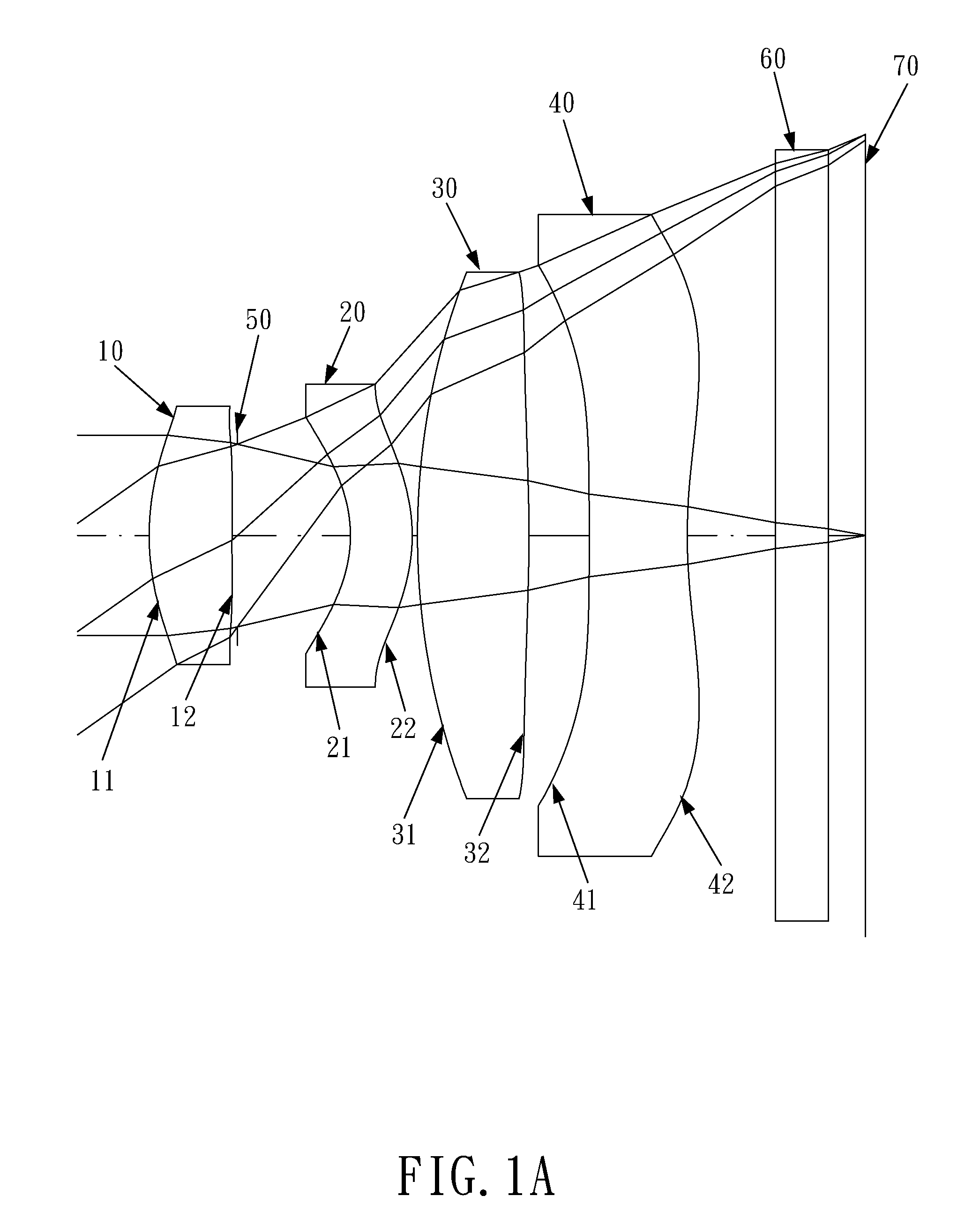
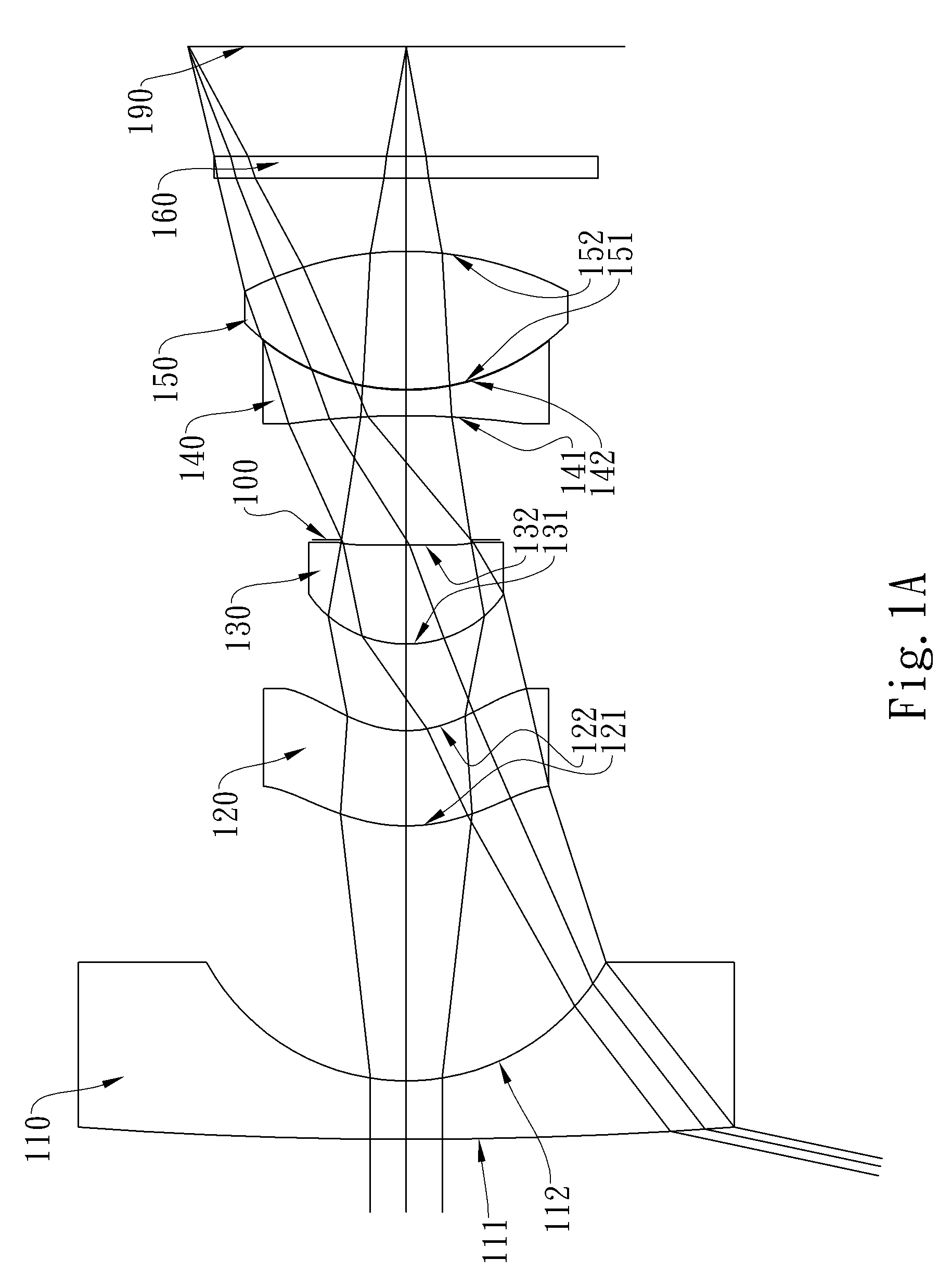
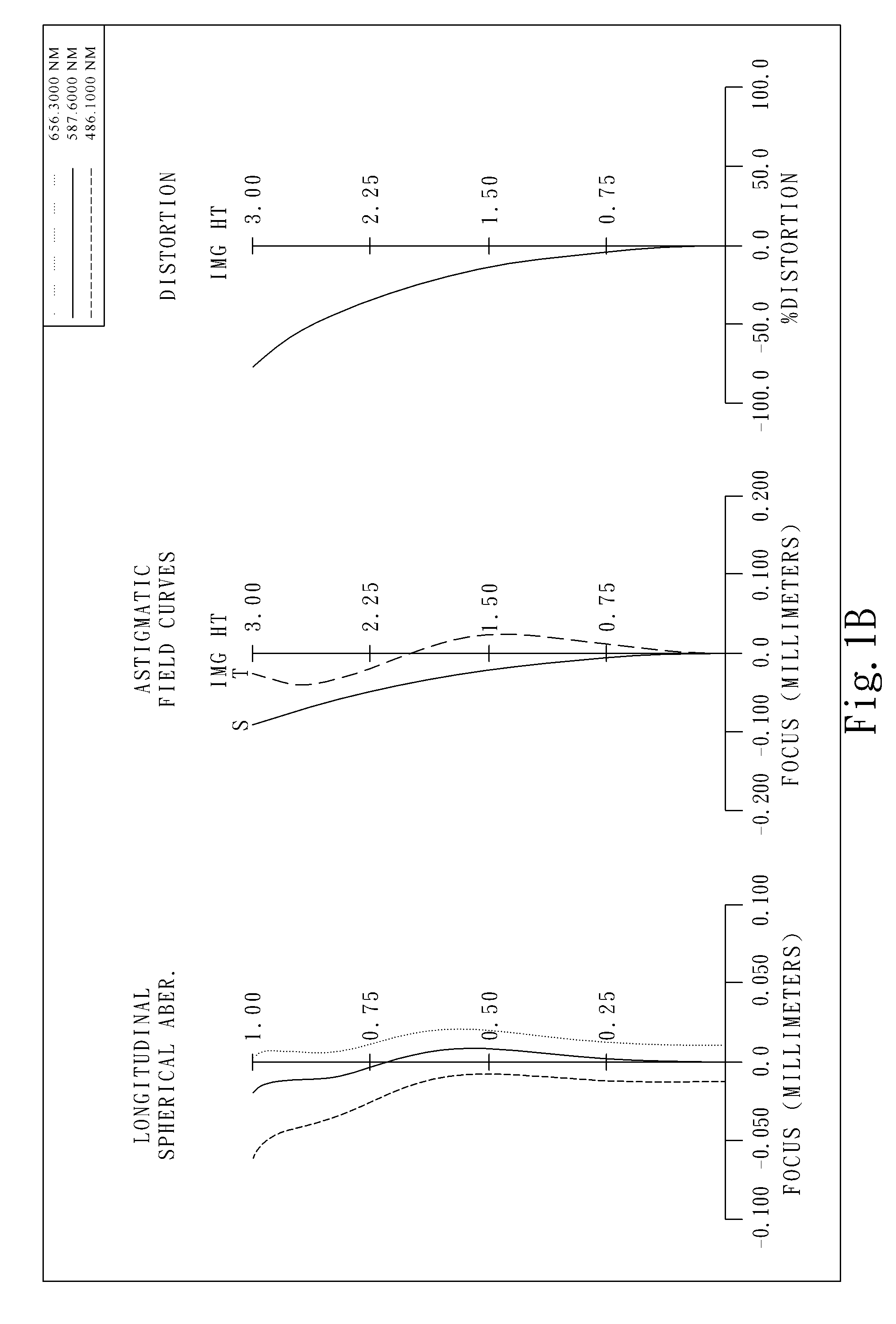
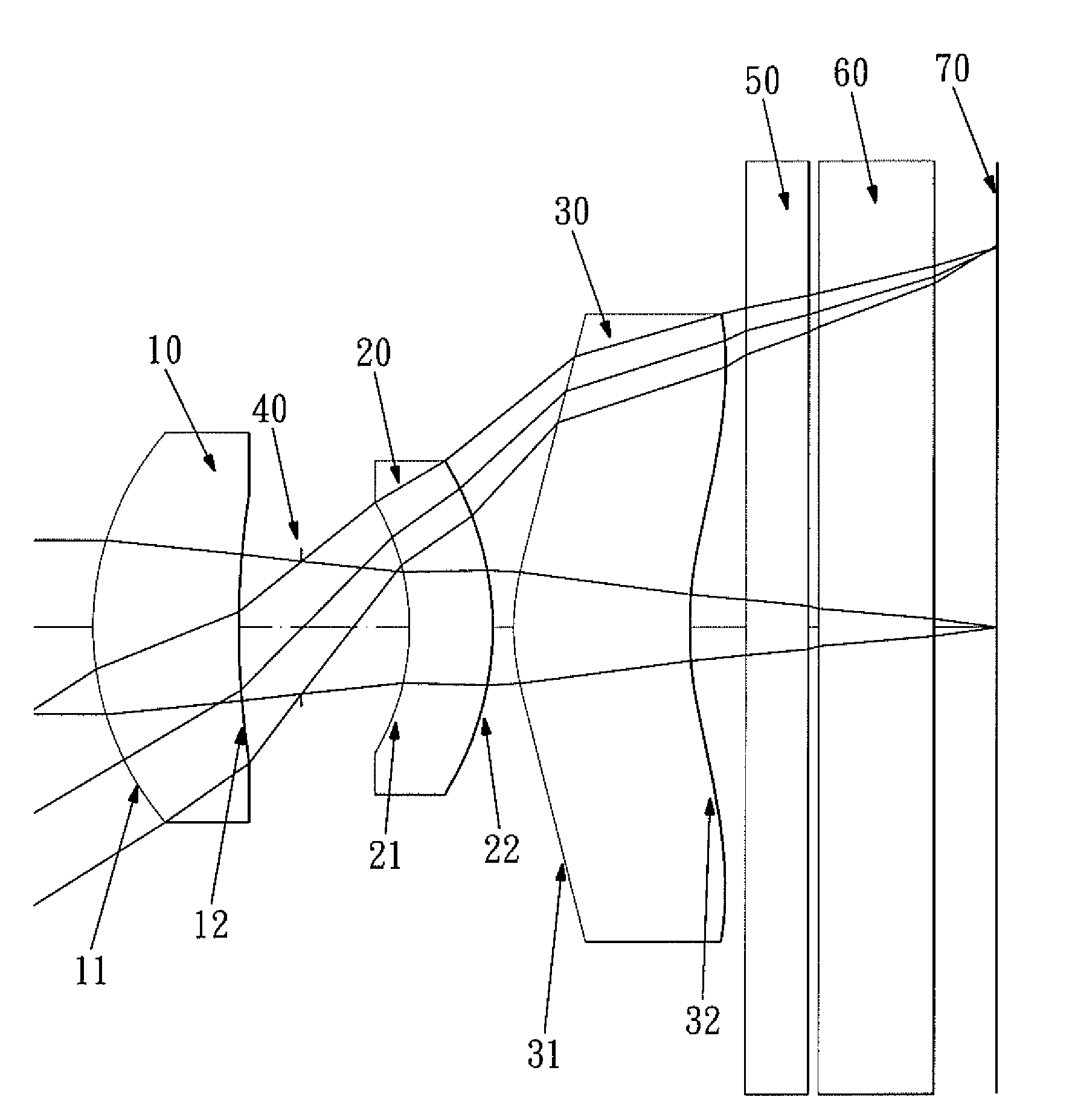
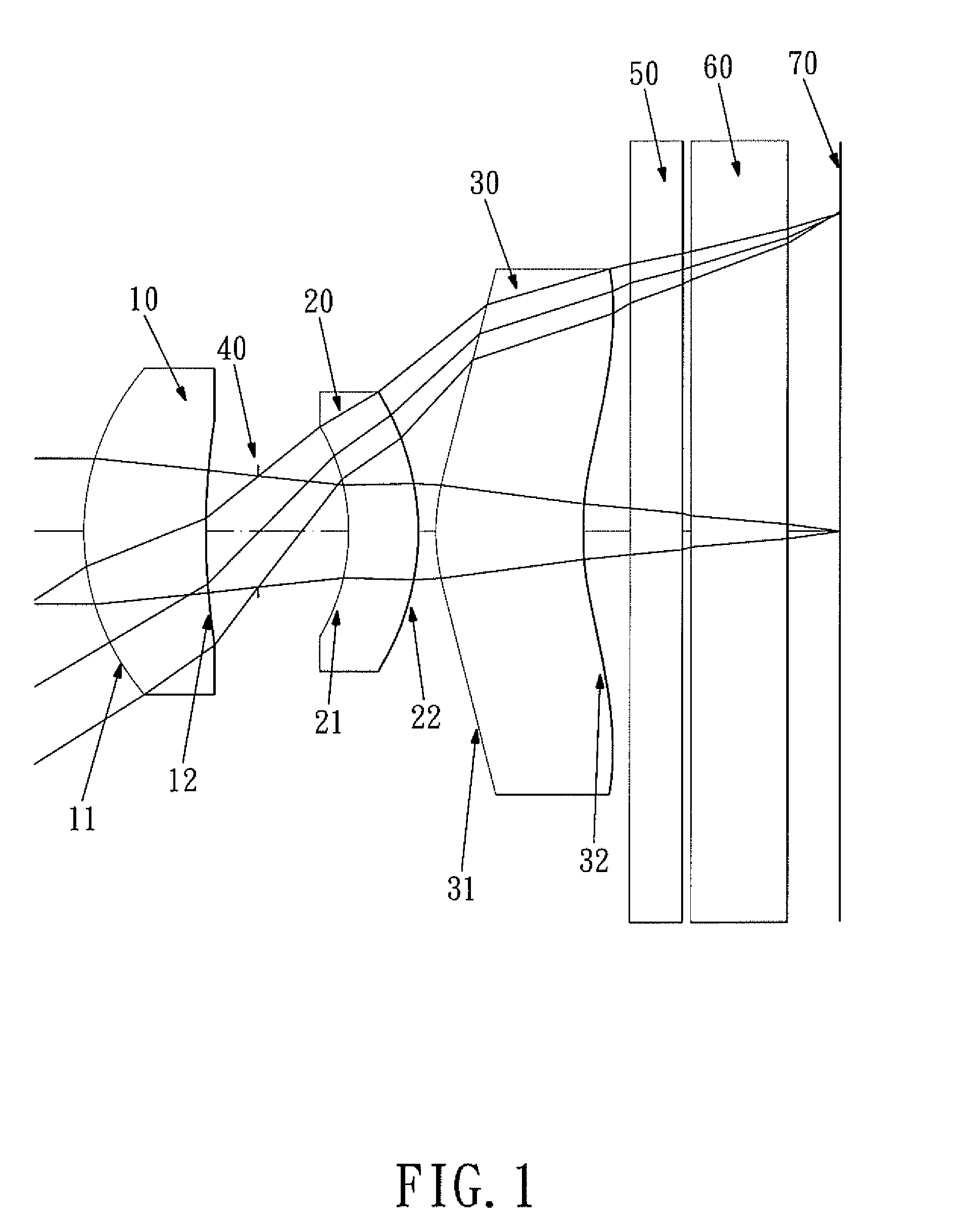
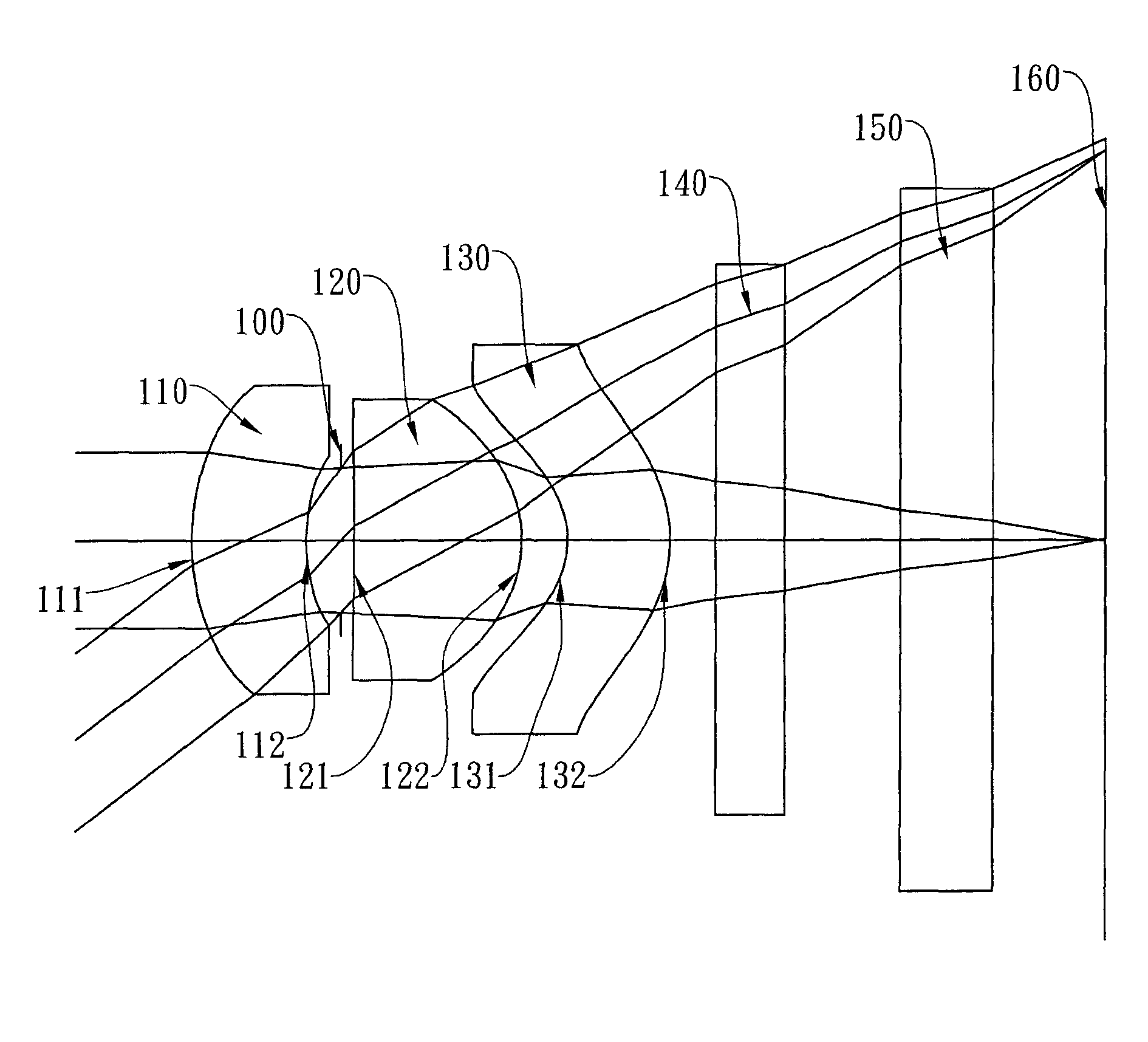
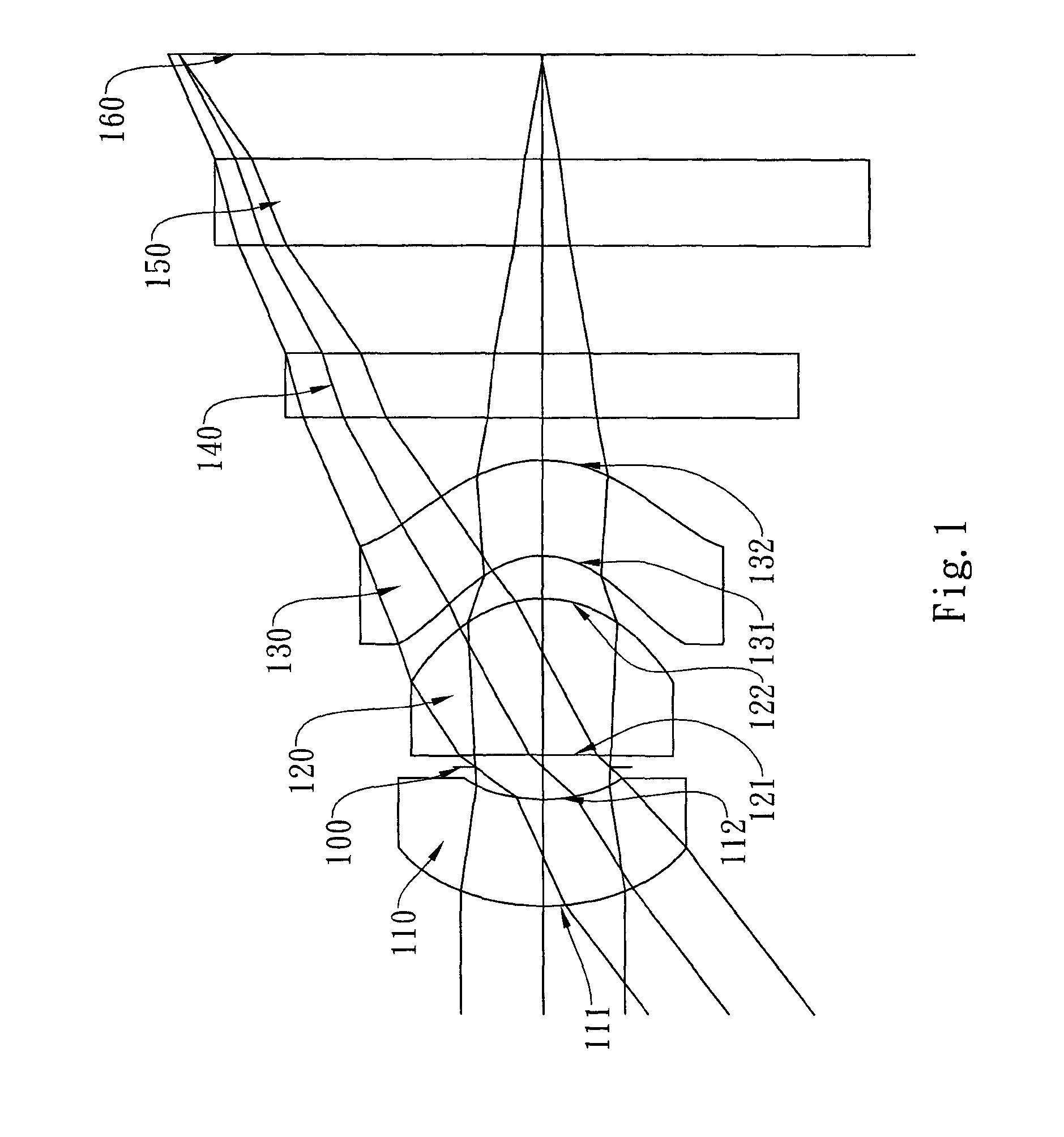
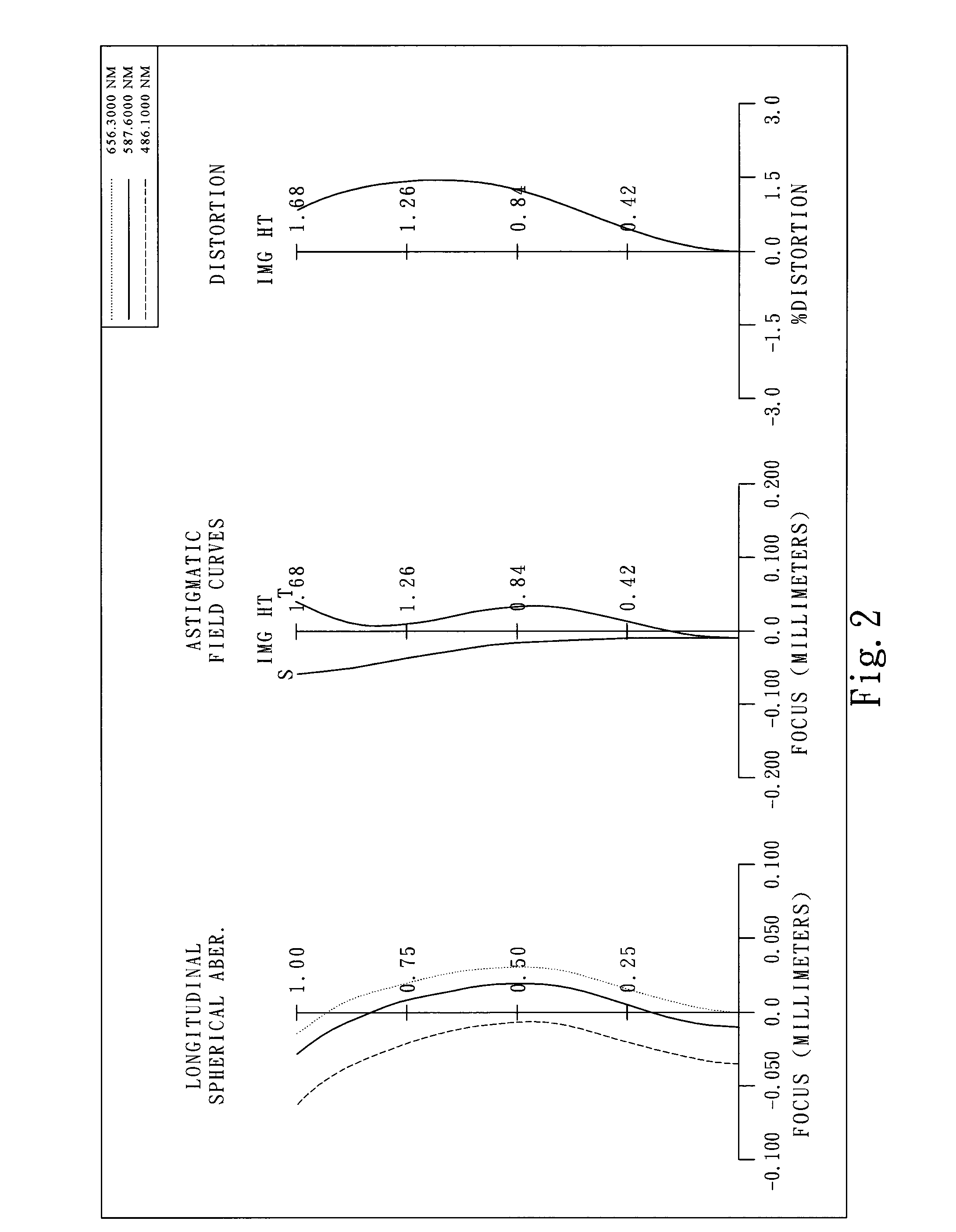
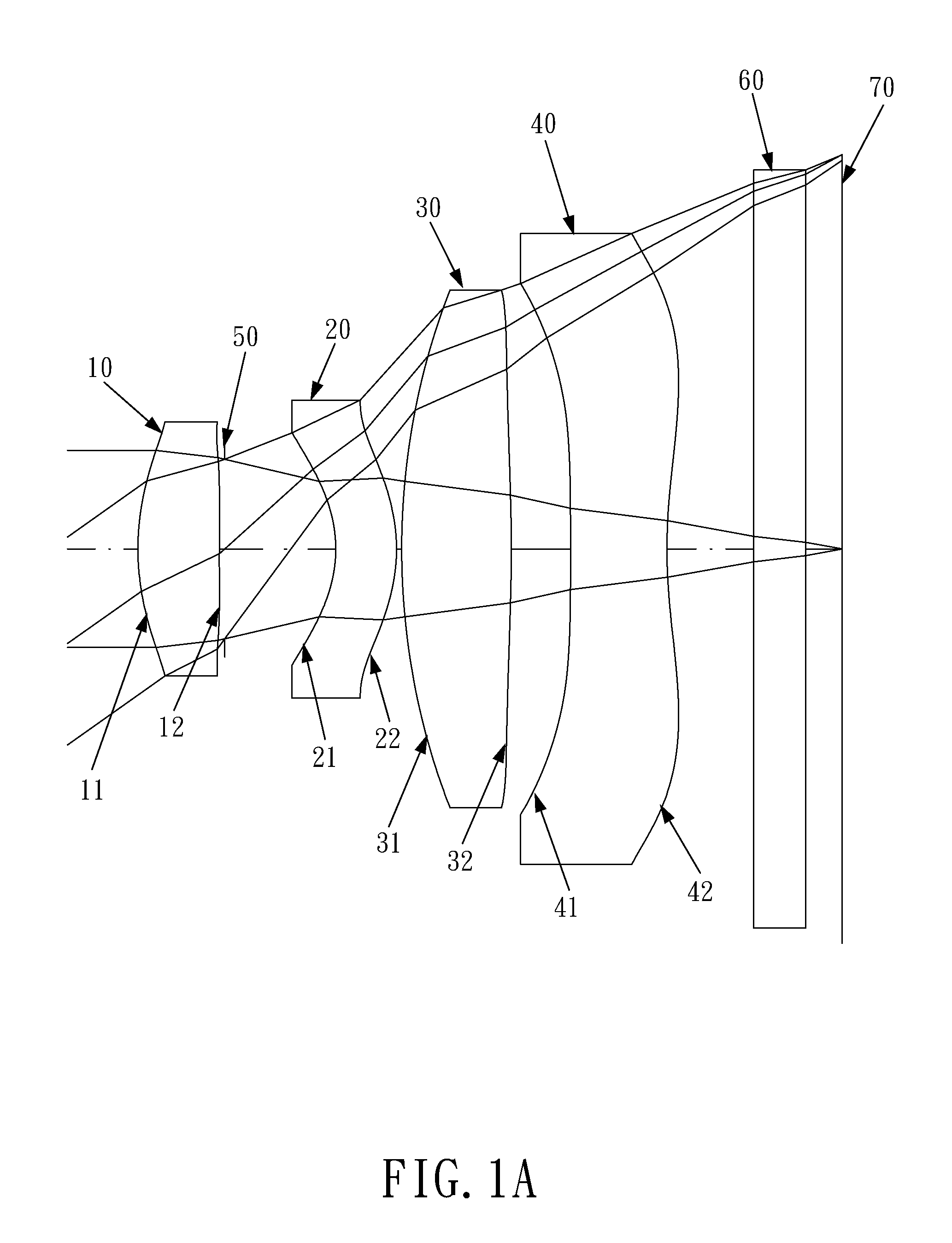
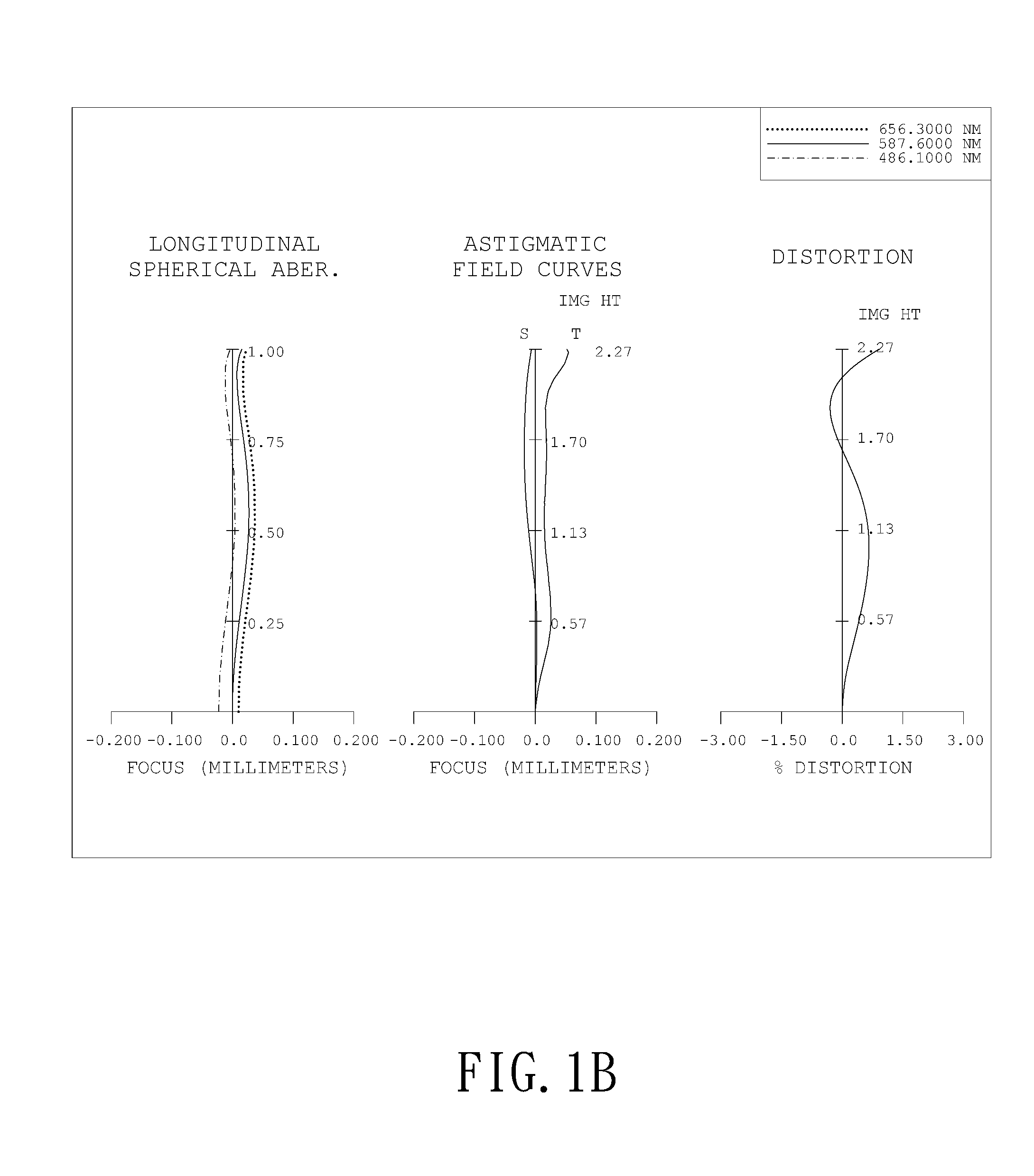
Optical lens system
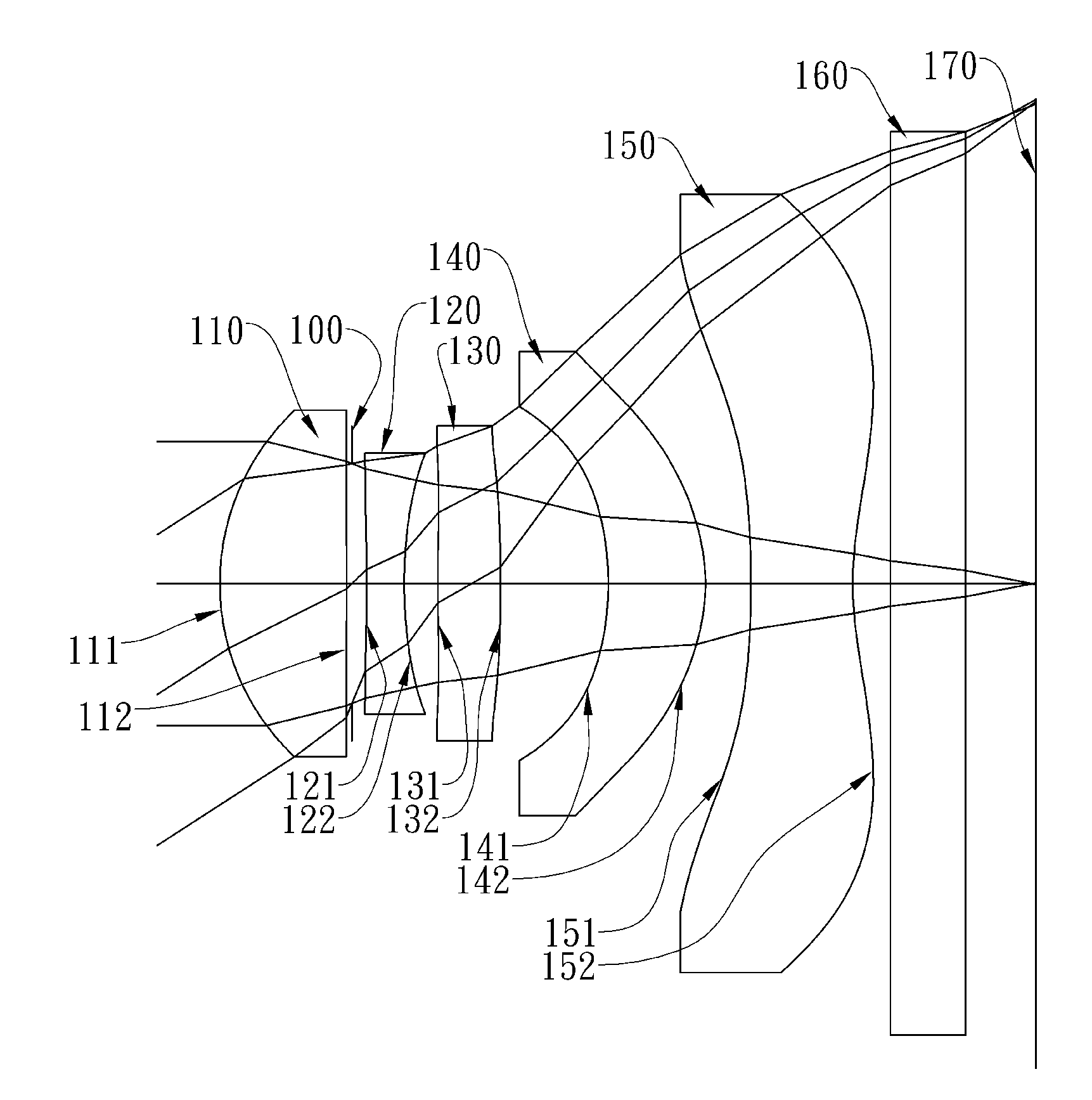
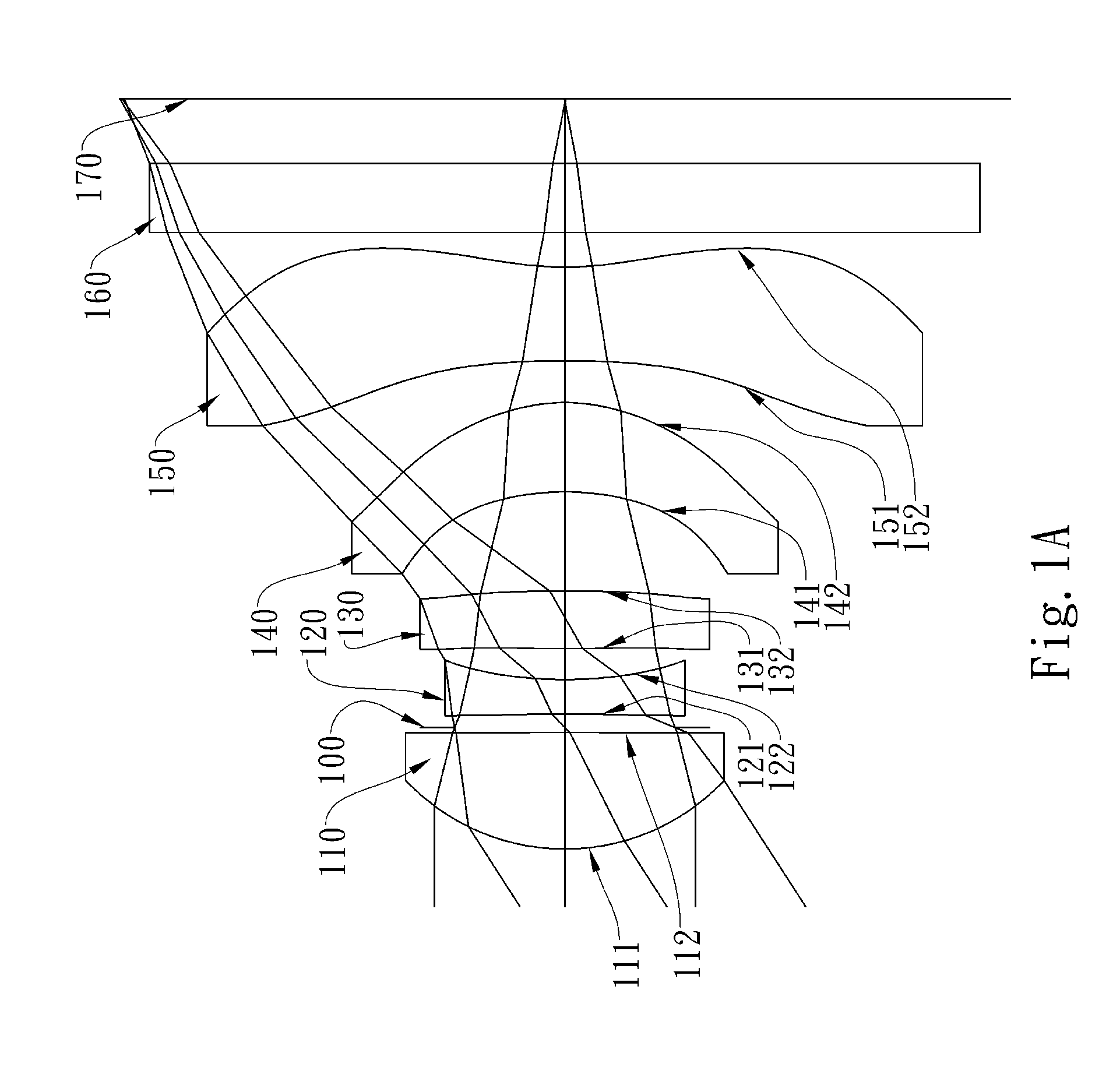
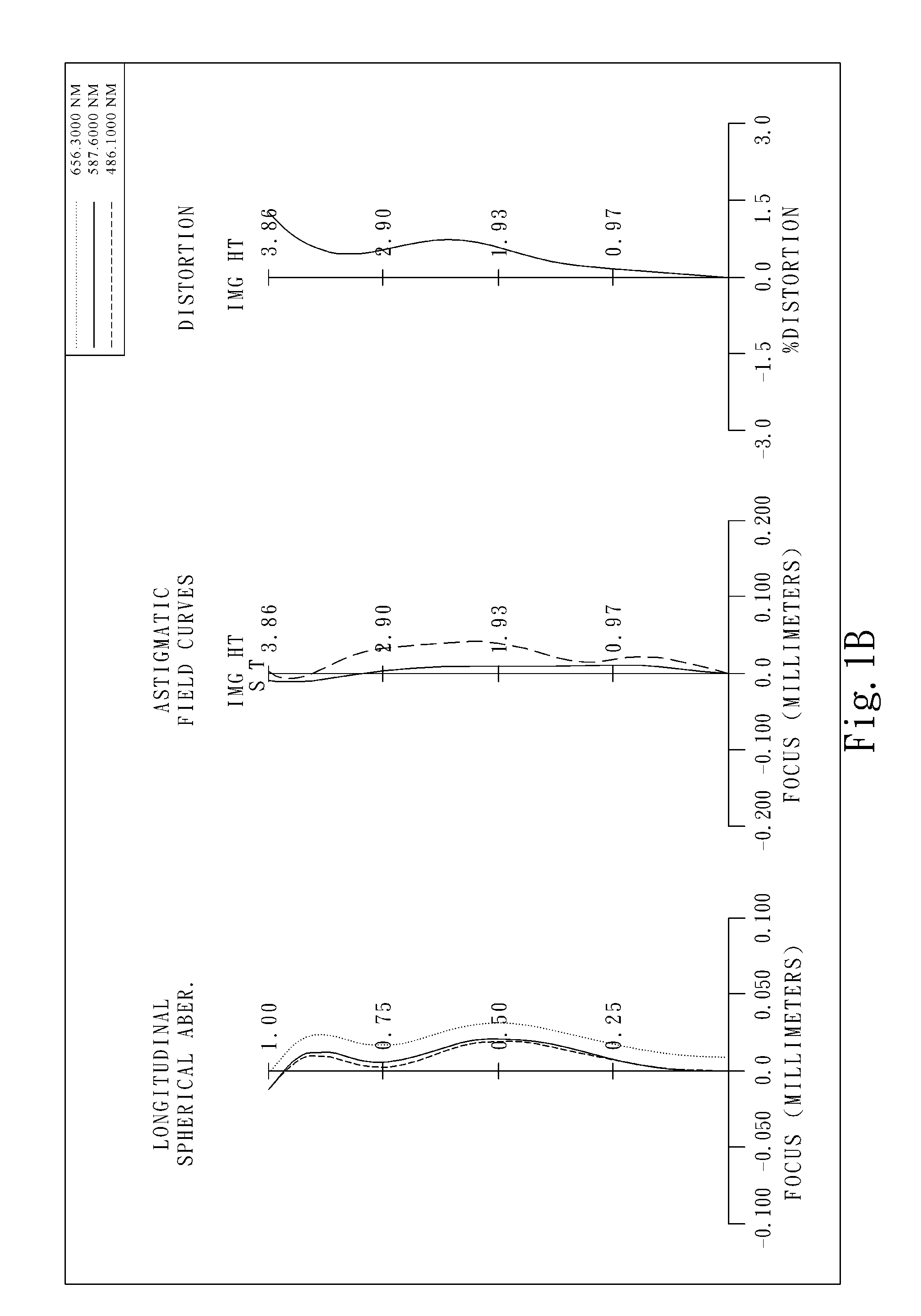
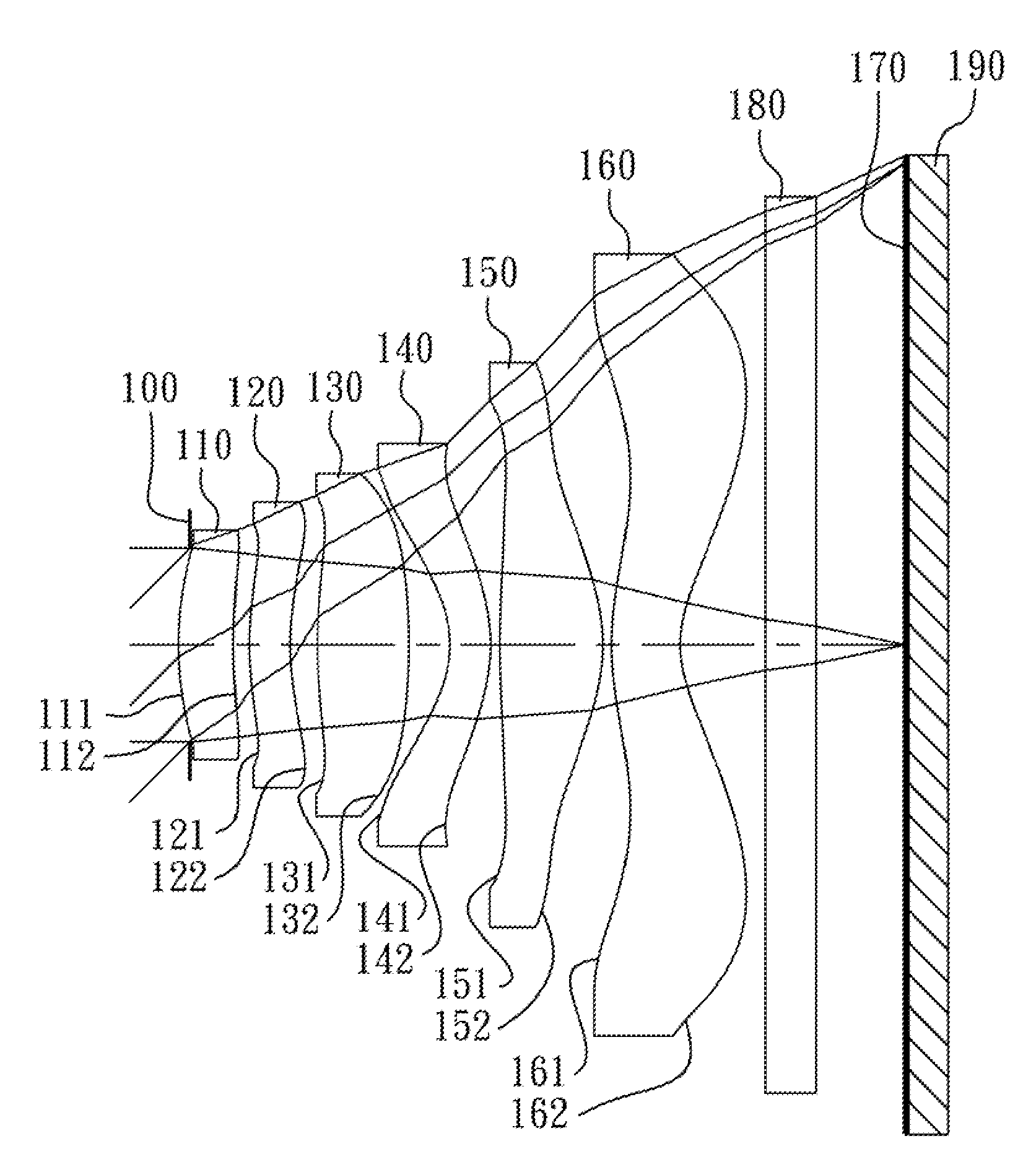
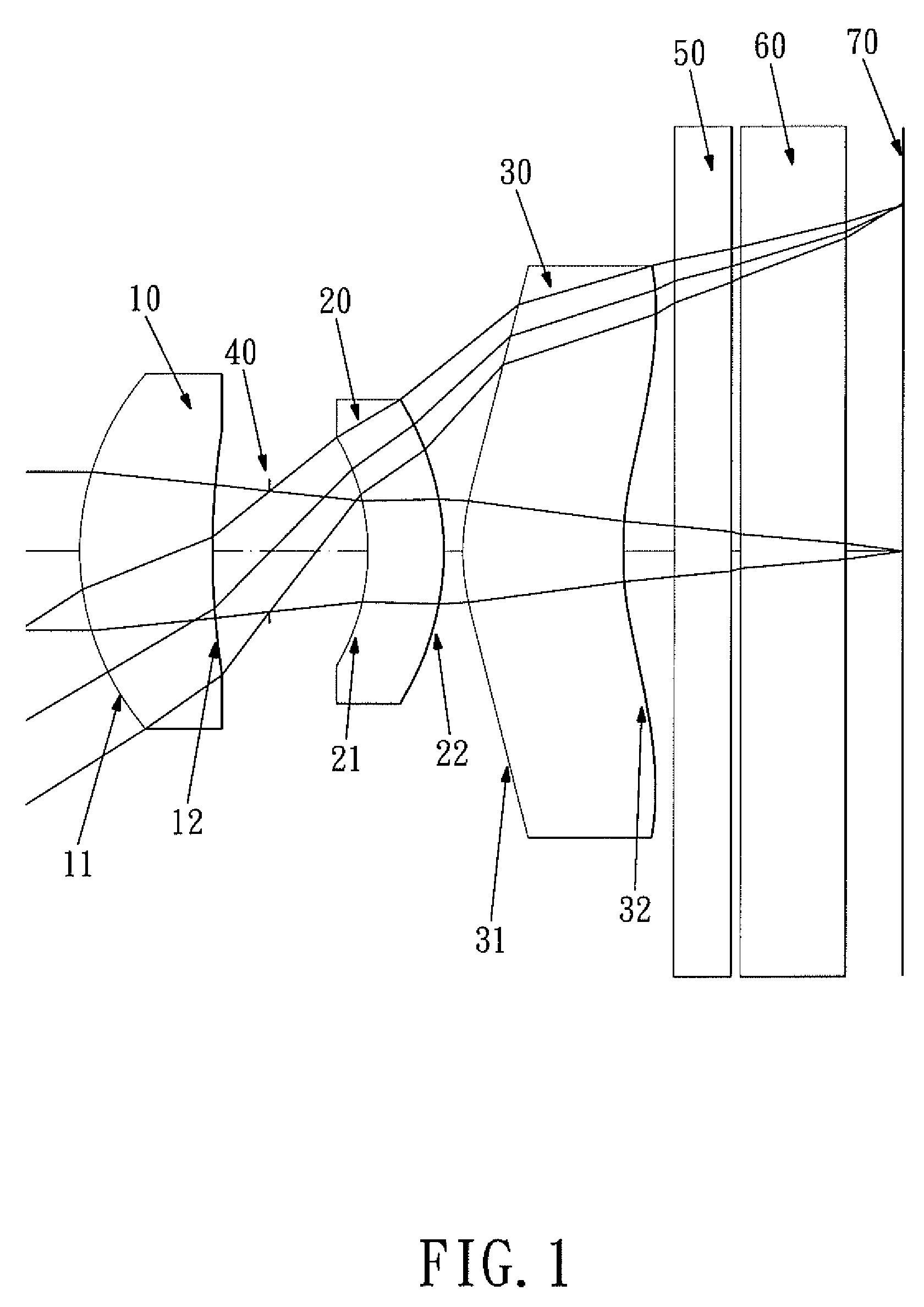
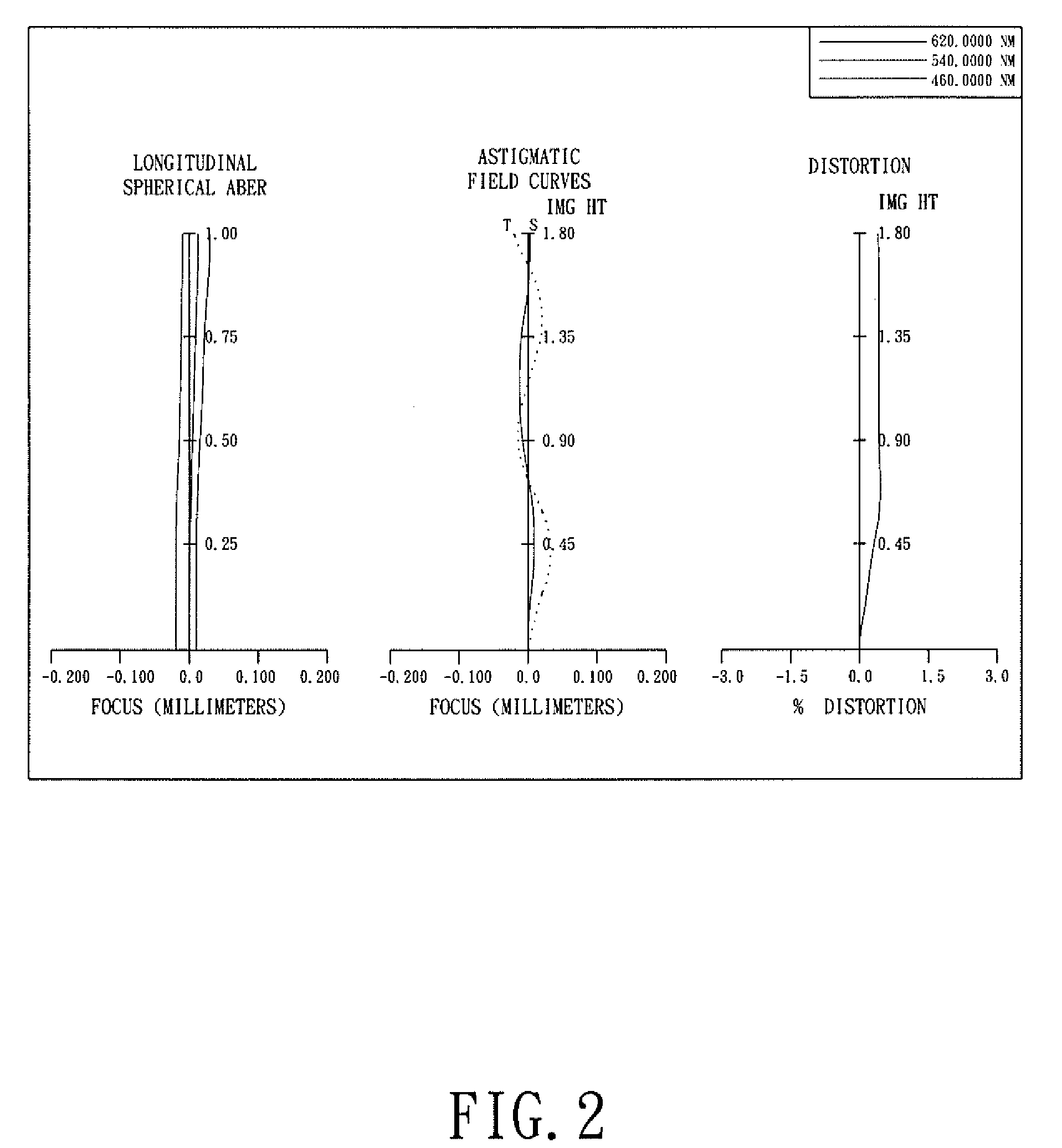
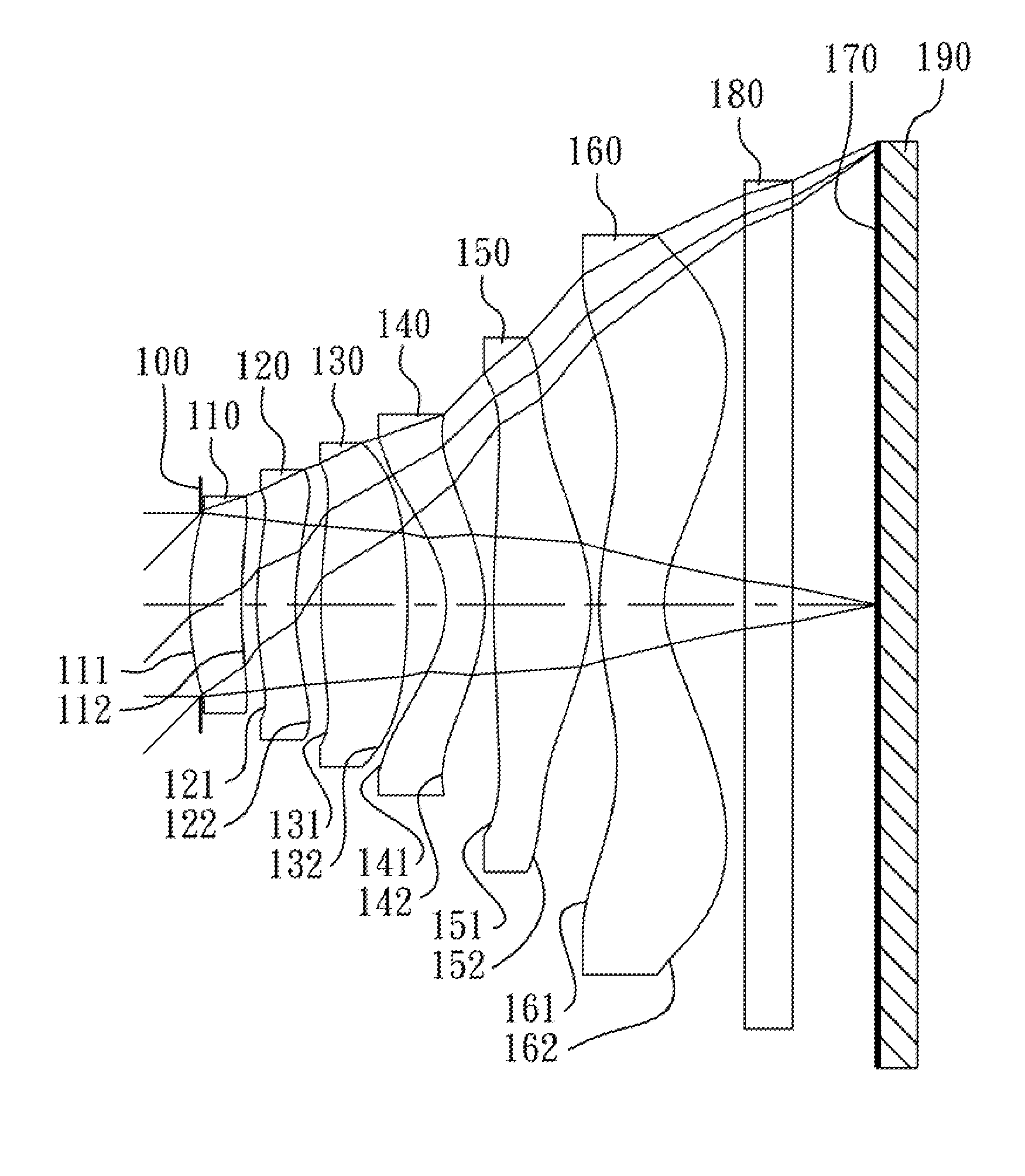
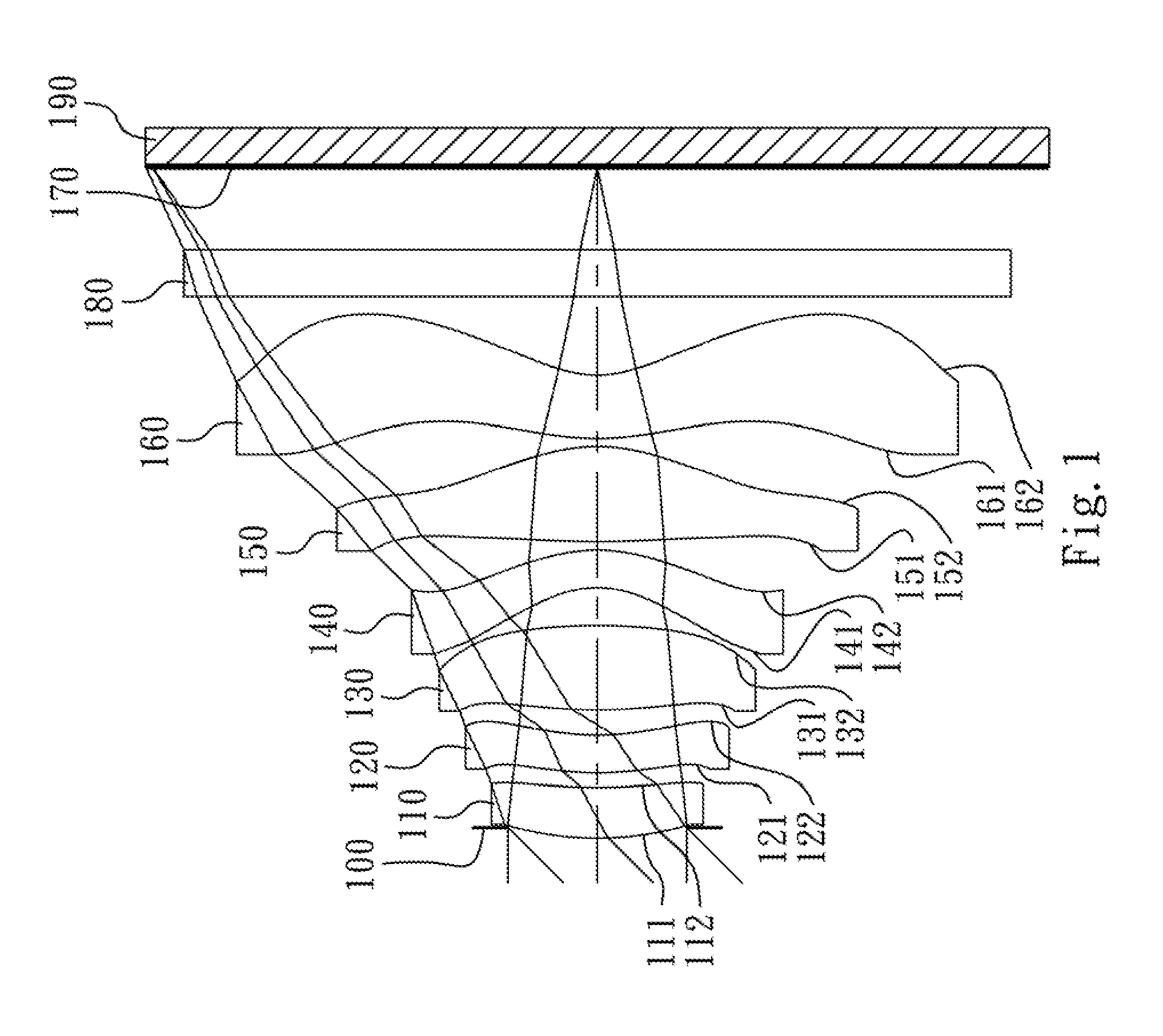
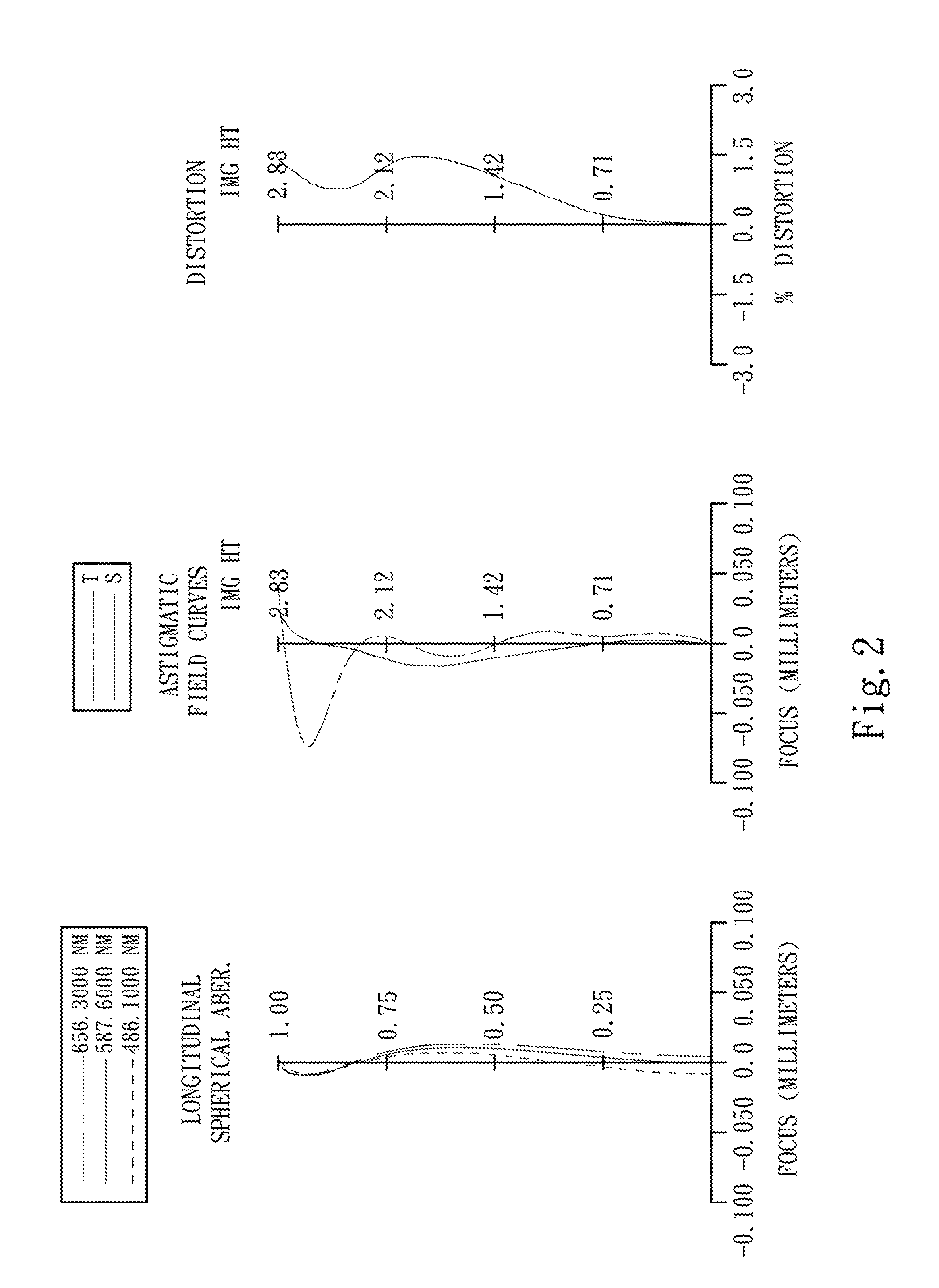
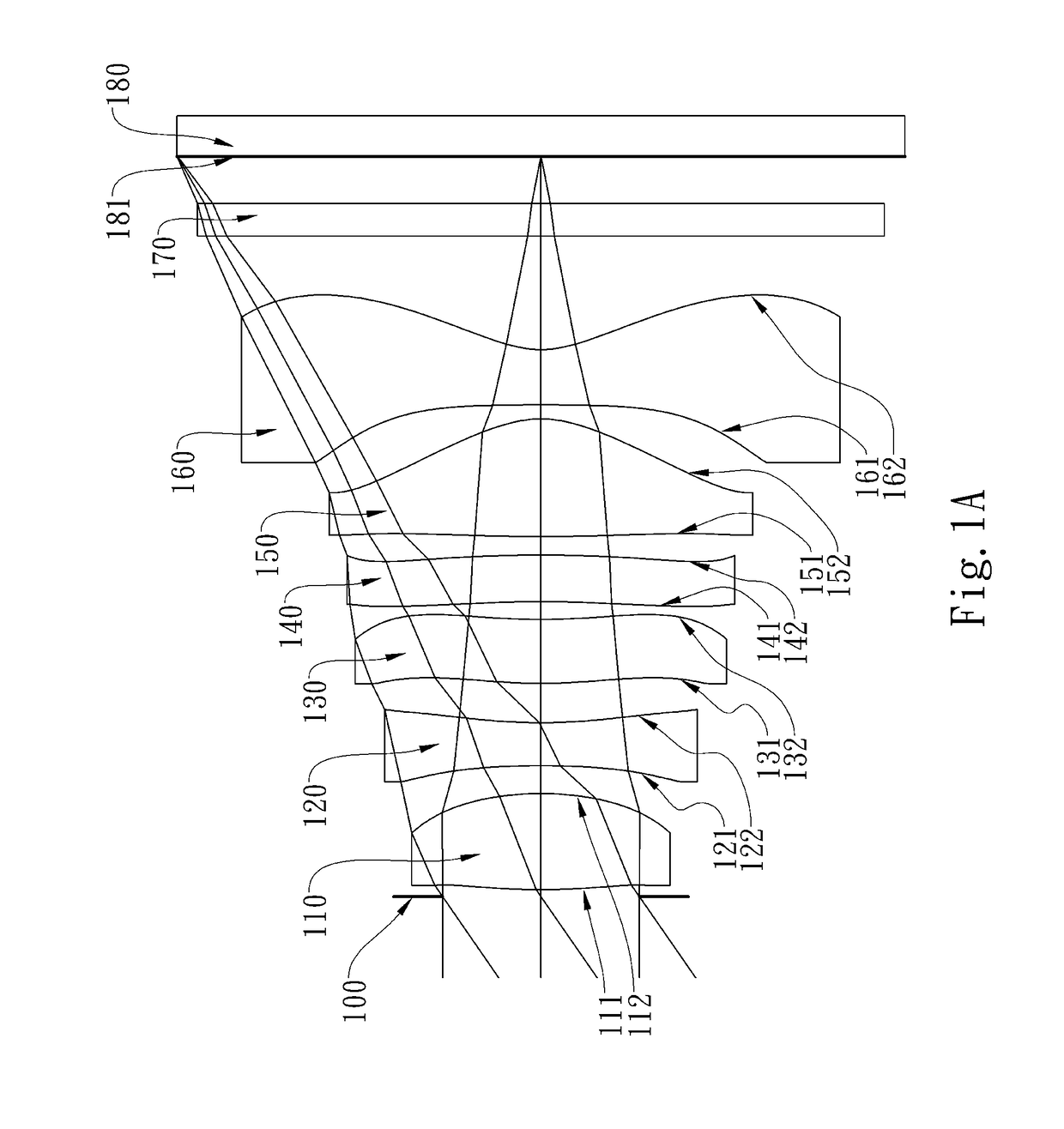
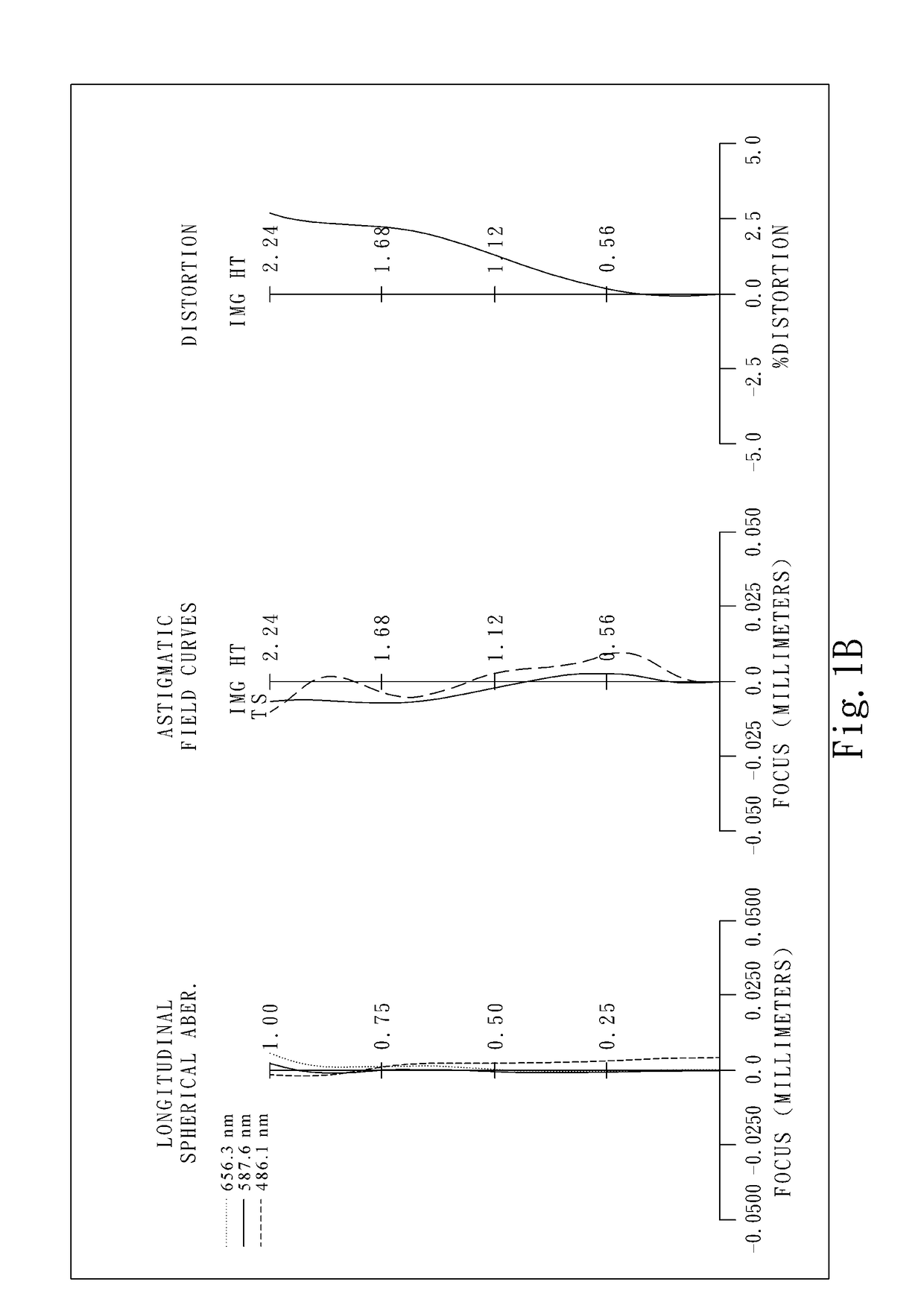
The present invention provides an optical lens system comprising, in order from an object side to an image side: a first lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface; a second lens element with negative refractive power; a third lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface and a convex image-side surface; a fourth lens element; and a fifth lens element having a convex object-side surface and a concave image-side surface, the object-side and image-side surfaces thereof being aspheric and at least one inflection point being formed on the image-side surface. Such arrangement of optical elements can effectively minimize the size of the optical lens system, lower the sensitivity of the optical system, and obtain higher image resolution.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
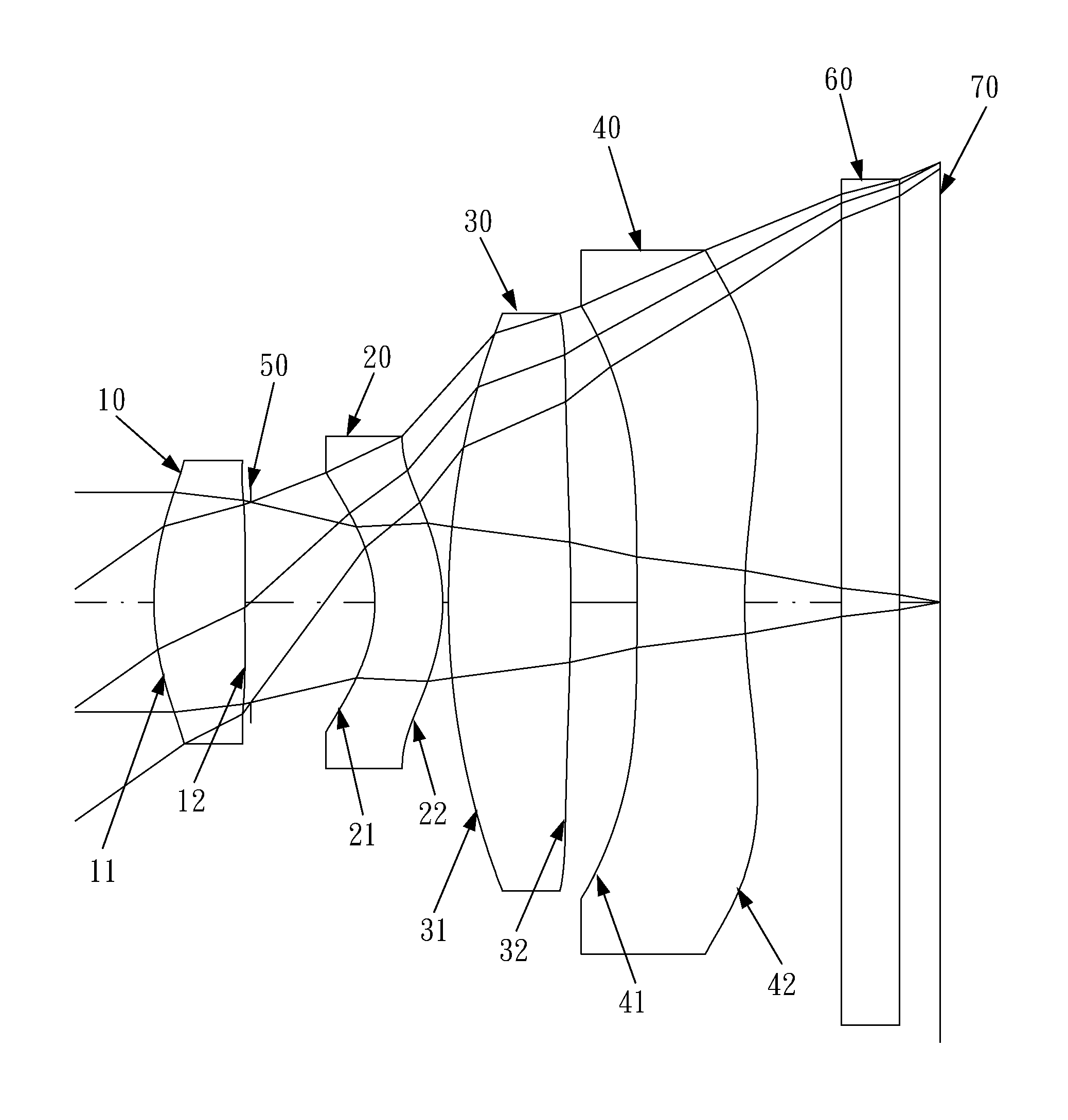
Optical image system
An optical image system includes, in order from an object side to an image side, the first lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface; the second lens element with refractive power; the third lens element with positive refractive power having at least one surface being aspheric; the fourth lens element with refractive power having a concave object-side surface and a convex image-side surface, wherein at least one surface thereof element is aspheric; the fifth lens element with positive refractive power having a convex image-side surface; and the sixth lens element with negative refractive power made of plastic material and having a concave image-side surface, wherein at least one surface thereof is aspheric, and the image-side surface thereof changes from concave at a paraxial region to convex at a peripheral region.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
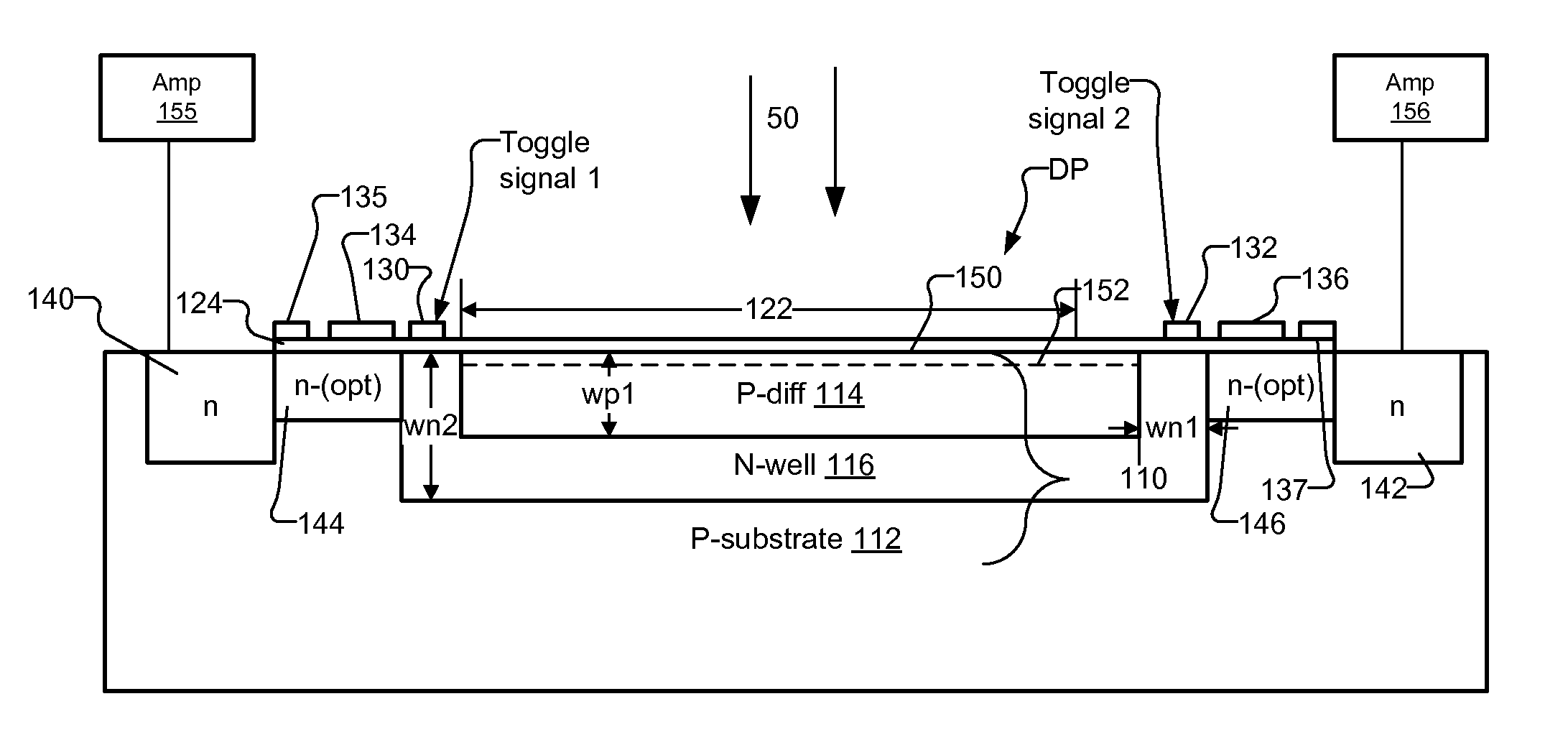
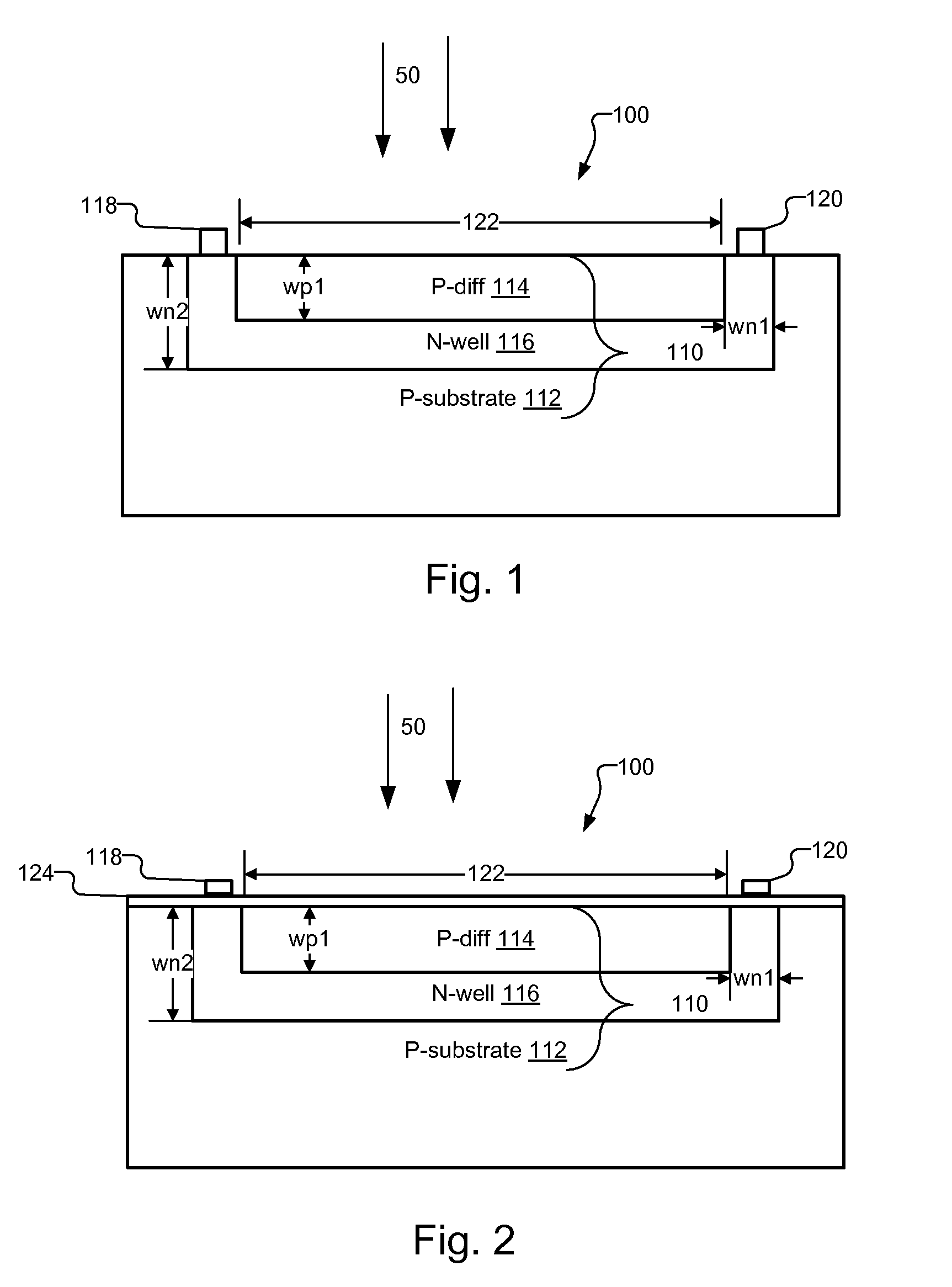
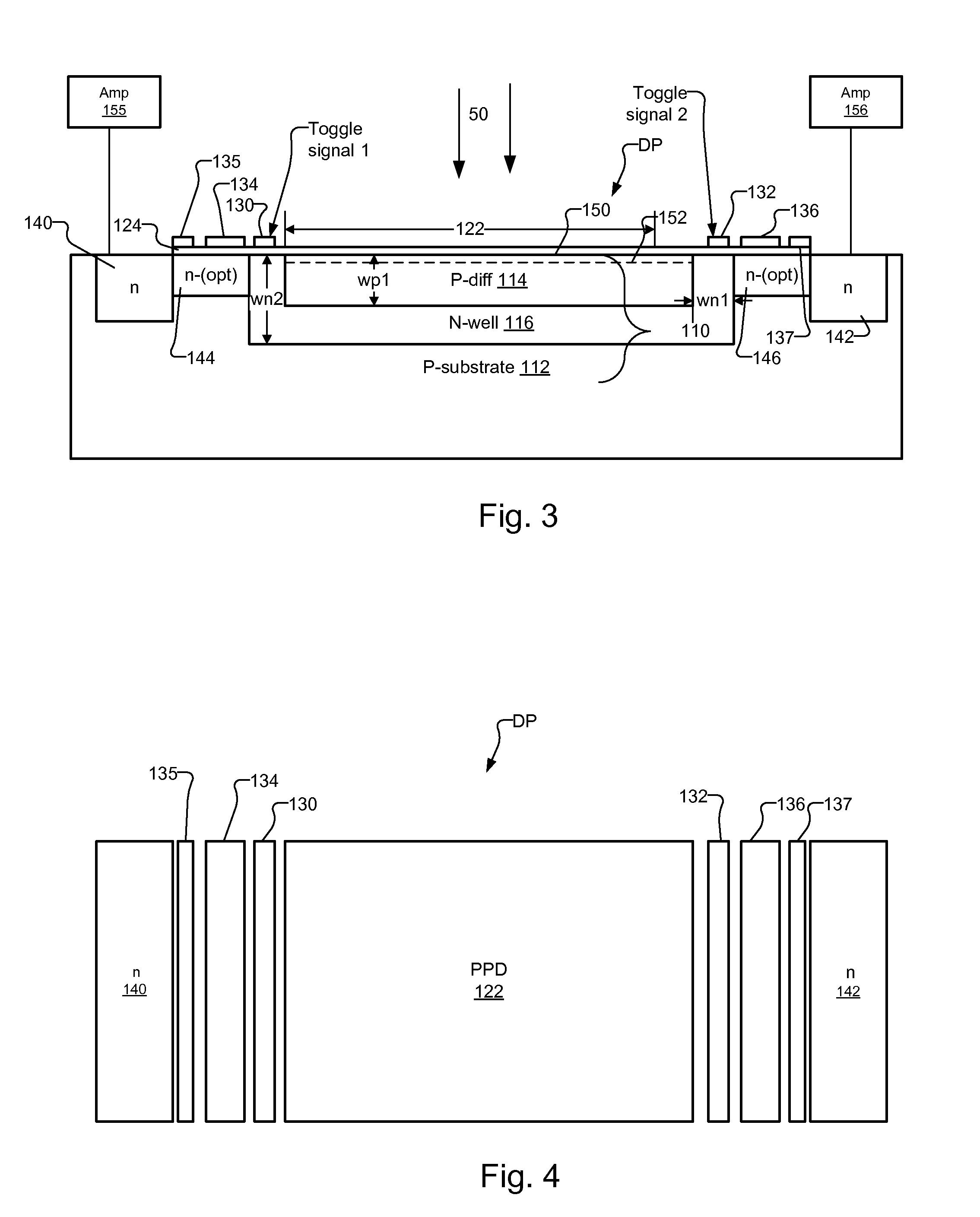
Drift Field Demodulation Pixel with Pinned Photo Diode
InactiveUS20090224139A1High rateReduce optical sensitivitySolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansSoi cmos technologyPhotodiode
A pixel based on a pinned-photodiode structure that creates a lateral electric drift field. The combination of the photodiode with adjacent CCD gates enables the utilization of the drift field device in applications such as 3-D imaging. Compared with recently used demodulation devices in CCD or CMOS technology, the new pinned-photodiode based drift field pixel has its advantages in its wide independence of the quantum efficiency on the optical wavelength, its high optical sensitivity, the opportunity of easily creating arbitrary potential distributions in the semiconductor, the straight-forward routing capabilities and the generation of perfectly linear potential distributions in the semiconductor.
Owner:HEPTAGON MICRO OPTICS
Photographing optical lens assembly
The present invention provides a photographing optical lens assembly comprising, in order from the object side to the image side: a first lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface and a concave image-side surface, the object-side and image-side surfaces thereof being aspheric; a second lens element with negative refractive power having a concave object-side surface and a convex image-side surface, the object-side and image-side surfaces thereof being aspheric; and an aperture stop located in front of the first lens element; wherein an Abbe number of the first lens element is V1, an Abbe number of the second lens element is V2, and they satisfy the relation: |V1−V2|<15; and wherein the number of the lens elements of the photographing optical lens assembly is limited to two. Such an arrangement of optical elements can effectively reduce the volume of the lens assembly and the sensitivity of the optical system and enable the lens assembly to obtain a higher resolution.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Optical system for taking image
An optical system for taking image comprises three lens elements with refractive power, from the object side to the image side: a first positive lens element having a convex front surface and a concave rear surface, and the front surface being aspheric; a negative plastic second lens element having a concave front surface and a convex rear surface, and the front and rear surfaces thereof being aspheric; a positive plastic third lens element having a convex front surface and a concave rear surface, the front and rear surfaces thereof being aspheric; and an aperture stop located between the first and second lens elements for controlling brightness of the optical system. The focal length of the first lens element is f1, a focal length of the second lens element is f2, a focal length of the optical system is f, and they satisfy the relations: f / f1>0.95, |f / f2|>0.34.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Optical lens system for taking image
An optical lens system for taking image comprises three lens elements with refractive power, from the object side to the image side: a first positive lens element having a convex front surface and a concave rear surface, and the front surface being aspheric; a negative plastic second lens element having a concave front surface and a convex rear surface, and the front and rear surfaces thereof being aspheric; a positive plastic third lens element having a convex front surface and a concave rear surface, the front and rear surfaces thereof being aspheric; and an aperture stop located between the first and second lens elements for controlling brightness of the optical system. The focal length of the first lens element is f1, the focal length of the optical lens system is f, and they satisfy the relations: f / f1<0.9.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
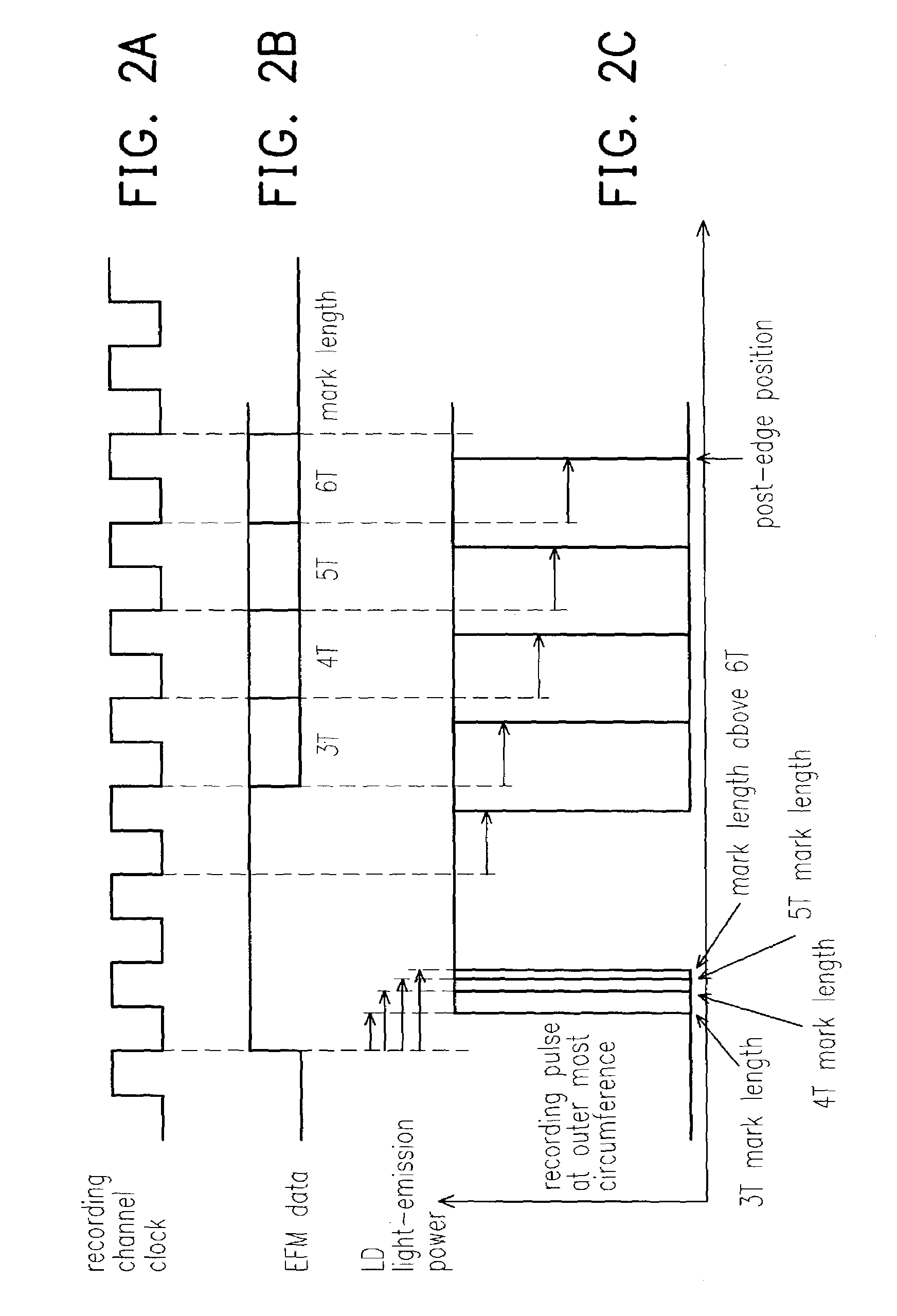
Information recording device
ActiveUS7006419B2Reduction in inabilityQuality improvementRecording strategiesTelevision system detailsLaser lightLight emission
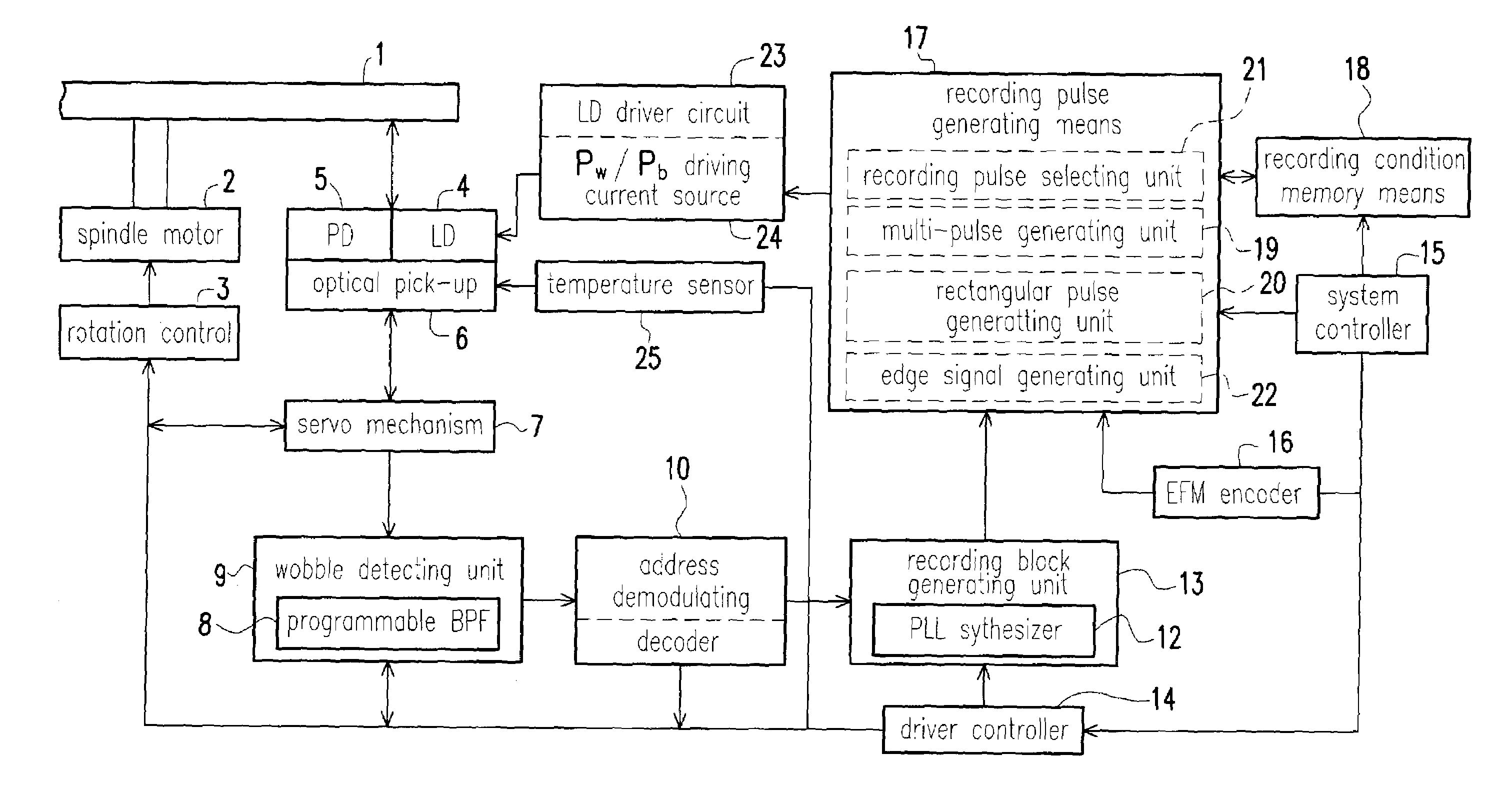
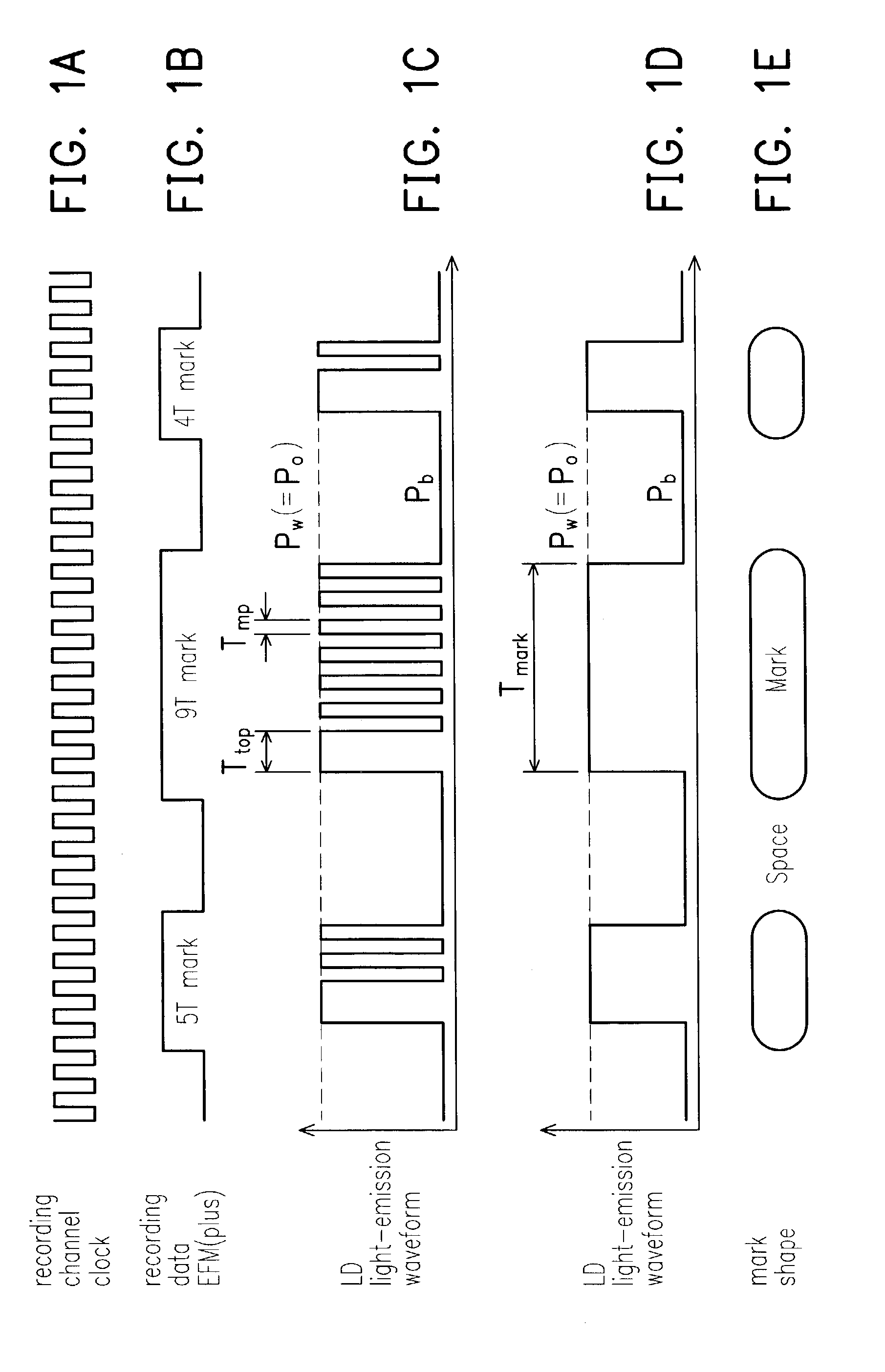
An information recording device comprising at least a recording pulse generating means and a recording pulse selecting means capable of generating various multi-pulses each of which is a combination of a leading heating pulse and a succeeding heating pulse, and rectangular pulses each of which is a single pulse, as a recording pulse, is disclosed. The recording pulse selecting means switches and selects among the multi-pulses and the rectangular pulses according to a recording condition, and then causes a light emission of a laser light source through a light source driving means. Even though in a high recording linear velocity recording condition that is insufficient in power for the recommended multi-pulse recording, a very low recording power can still be used by switching to the rectangular pulse recording, so as to achieve a recording with a much higher recording speed. In addition, good recording marks can be formed without exceeding a maximum allowable recording power.
Owner:RICOH KK
Optical imaging lens assembly
InactiveUS20120062782A1Reduce total track lengthSensitivity be attenuateTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptoelectronicsConcave surface
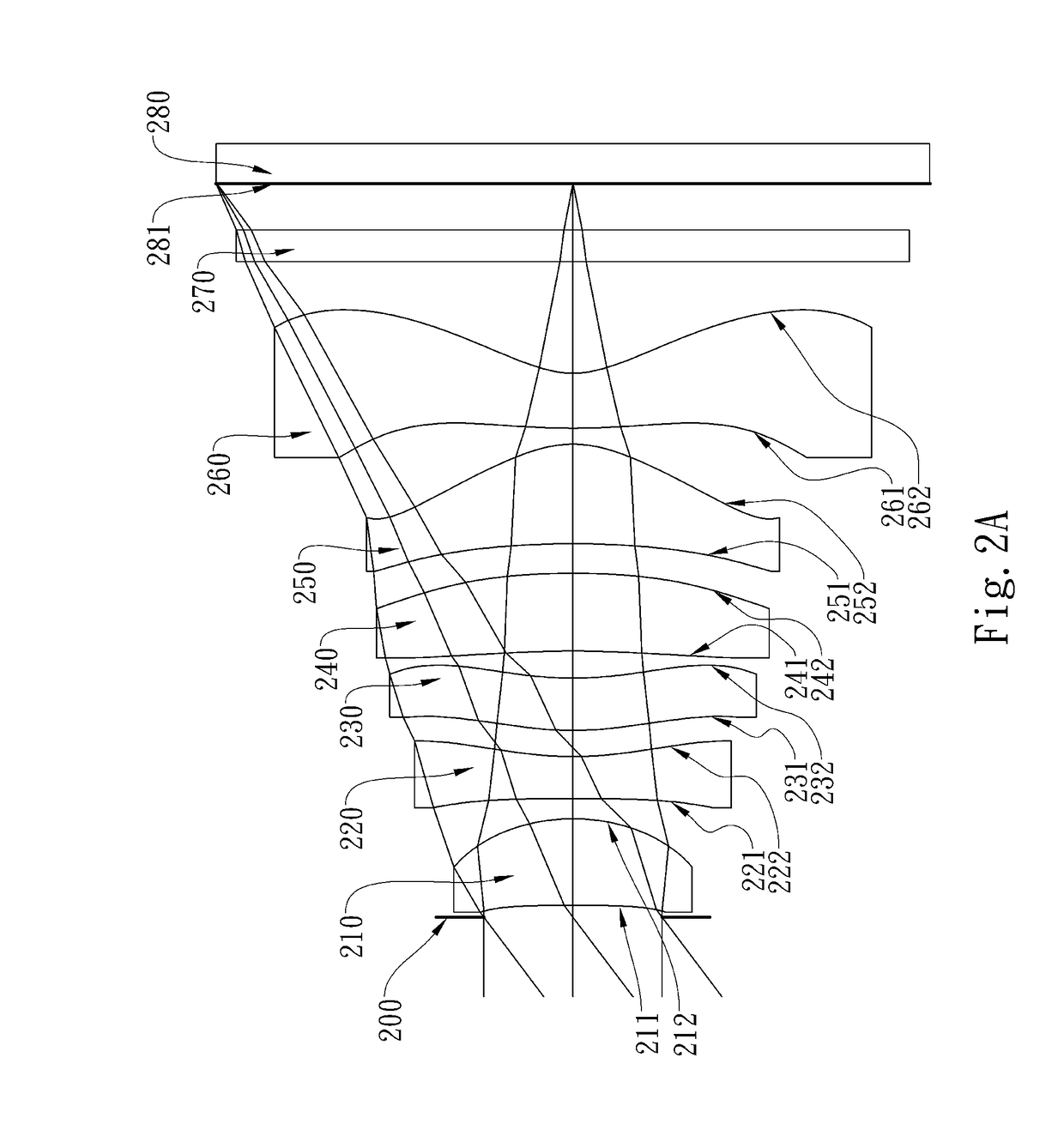
This invention provides an optical imaging lens assembly comprising, in order from an object side to an image side: a first lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface; a second lens element with negative refractive power having a convex object-side surface and a concave image-side surface; a third lens element having a convex image-side surface, the edge of the image-side surface of the third lens element within the clear aperture diameter tends to the image side; a fourth lens element with negative refractive power having a concave image-side surface; a first stop disposed between an object and the first lens element; and a second stop disposed between the second and fourth lens elements. With the aforementioned arrangement of optical lenses, the total track length of the optical imaging lens assembly can be reduced effectively, the sensitivity of the optical lens assembly can be attenuated, and the image quality can be improved.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Optical image system
An optical image system includes, in order from an object side to an image side, the first lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface; the second lens element with refractive power; the third lens element with positive refractive power having at least one surface being aspheric; the fourth lens element with refractive power having a concave object-side surface and a convex image-side surface, wherein at least one surface thereof element is aspheric; the fifth lens element with positive refractive power having a convex image-side surface; and the sixth lens element with negative refractive power made of plastic material and having a concave image-side surface, wherein at least one surface thereof is aspheric, and the image-side surface thereof changes from concave at a paraxial region to convex at a peripheral region.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Optical image capturing lens assembly
The present disclosure provides an optical image capturing lens assembly comprising, in order from an object side to an image side: a first lens element with positive refractive power having a convex image-side surface; a second lens element; a third lens element; a fourth lens element, at least one of an object-side surface and an image-side surface thereof being aspheric; a fifth lens element, at least one of an object-side surface and an image-side surface thereof being aspheric; and a sixth lens element with negative refractive power having a concave image-side surface, at least one of an object-side surface and the image-side surface thereof being aspheric, at least one inflection point being formed on at least one of the surfaces thereof. With the aforementioned arrangements, the sensitivity of the optical system can be attenuated while the aberration and astigmatism can be effectively corrected to improve the image quality.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Optical imaging lens assembly
This invention provides an optical imaging lens assembly, in order from an object side toward an image side including: a first lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface, a second lens element with negative refractive power having a concave object-side surface and a concave image-side surface, a third lens element with positive refractive power having a concave object-side surface and a convex image-side surface, a fourth lens element with negative refractive power having a concave image-side surface, and the two surfaces being aspheric; wherein the optical imaging lens assembly further comprises an aperture stop disposed between an imaged object and the first lens element, and there are four lens elements with refractive power.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Image pick-up optical lens assembly
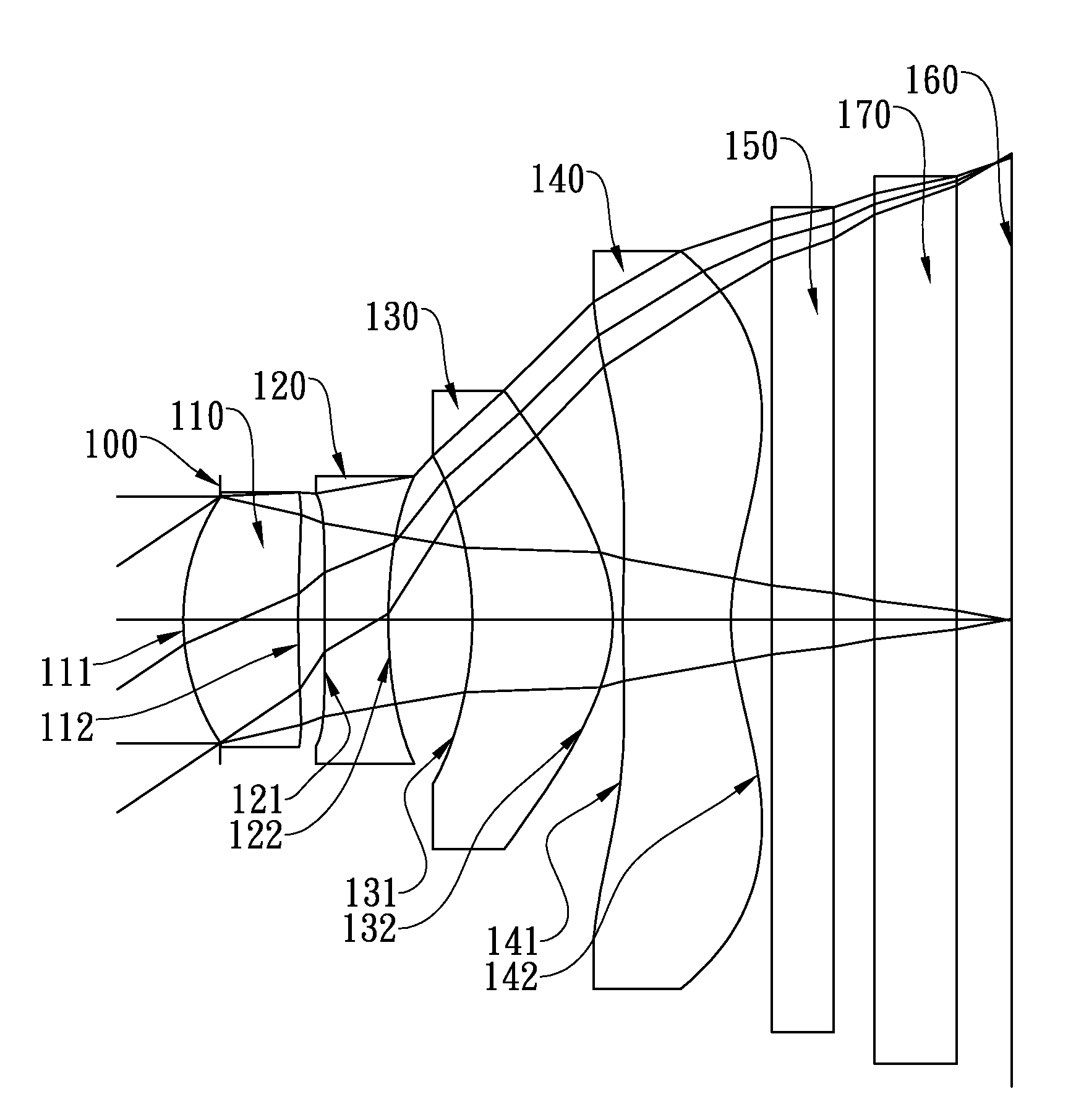
This invention provides an image pick-up optical lens assembly comprising, in order from an object side to an image side: a first lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface and a convex image-side surface; a second lens element with negative refractive power having a concave object-side surface and a convex image-side surface; a third lens element with positive refractive power having an object-side surface and a convex image-side surface, at least one of the surfaces thereof being aspheric; and a fourth lens element with negative refractive power having a convex object-side surface and a concave image-side surface, at least one of the surfaces thereof being aspheric. The image pick-up optical lens assembly further comprises an aperture stop disposed between an object and the first lens element. Such arrangement facilitates a significant reduction in size and sensitivity of the lens assembly while providing superb image quality with higher resolution.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Photographing optical lens assembly
ActiveUS20110096221A1Small sizeReduce sensitivityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImage resolutionOptic system
This invention provides a photographing optical lens assembly comprising, in order from an object side to an image side: a first lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface and a convex image-side surface; a second lens element with positive refractive power having a concave object-side surface and a convex image-side surface, both of the two surfaces being aspheric; a third lens element with negative refractive power having a concave image-side surface on which at least one inflection point is formed, both of the two surfaces being aspheric; and a stop disposed between an imaged object and the second lens element; wherein there are only three lens elements with refractive power. Such an arrangement of optical elements can effectively reduce the size of the lens assembly, mitigate the sensitivity of the optical system and enable the lens assembly to obtain a higher resolution.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Earbud Monitoring Devices
ActiveUS20170118551A1Reduce optical sensitivityImprovement in heart rate monitoring consistencyIntra aural earpiecesOptical sensorsAccelerometerEar region
An earbud includes a speaker driver, and a sensor módule secured to the speaker driver that is configured to detect and / or measure physiological information from a subject wearing the earbud. The sensor module includes a printed circuit board, an optical source secured to the printed circuit board, and an optical detector secured to the printed circuit board. A first light guide may be coupled to the optical source that is configured to deliver light from the optical source into an ear region of the subject via a distal end thereof. A second light guide may be coupled to the optical detector that is configured to collect light from the ear region via a distal end thereof and deliver collected light to the optical detector. One or more additional sensors may be secured to the speaker driver, such as accelerometers, humidity sensors, altimeters, and temperature sensors.
Owner:YUKKA MAGIC LLC
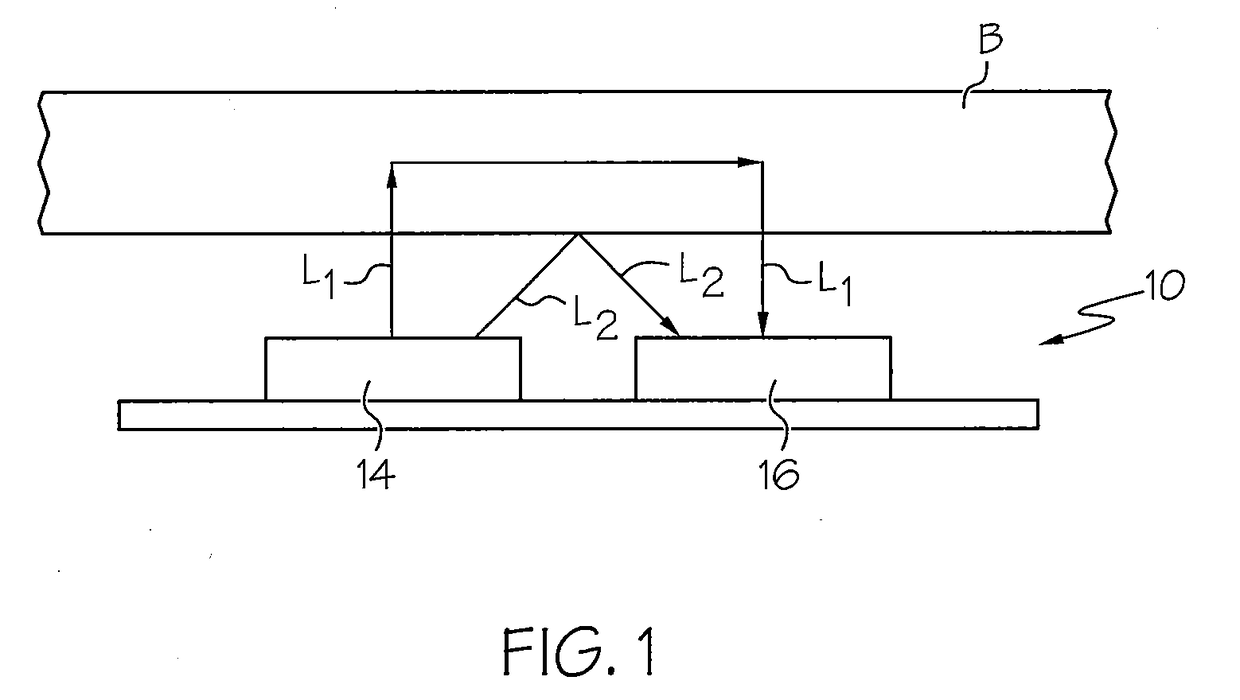
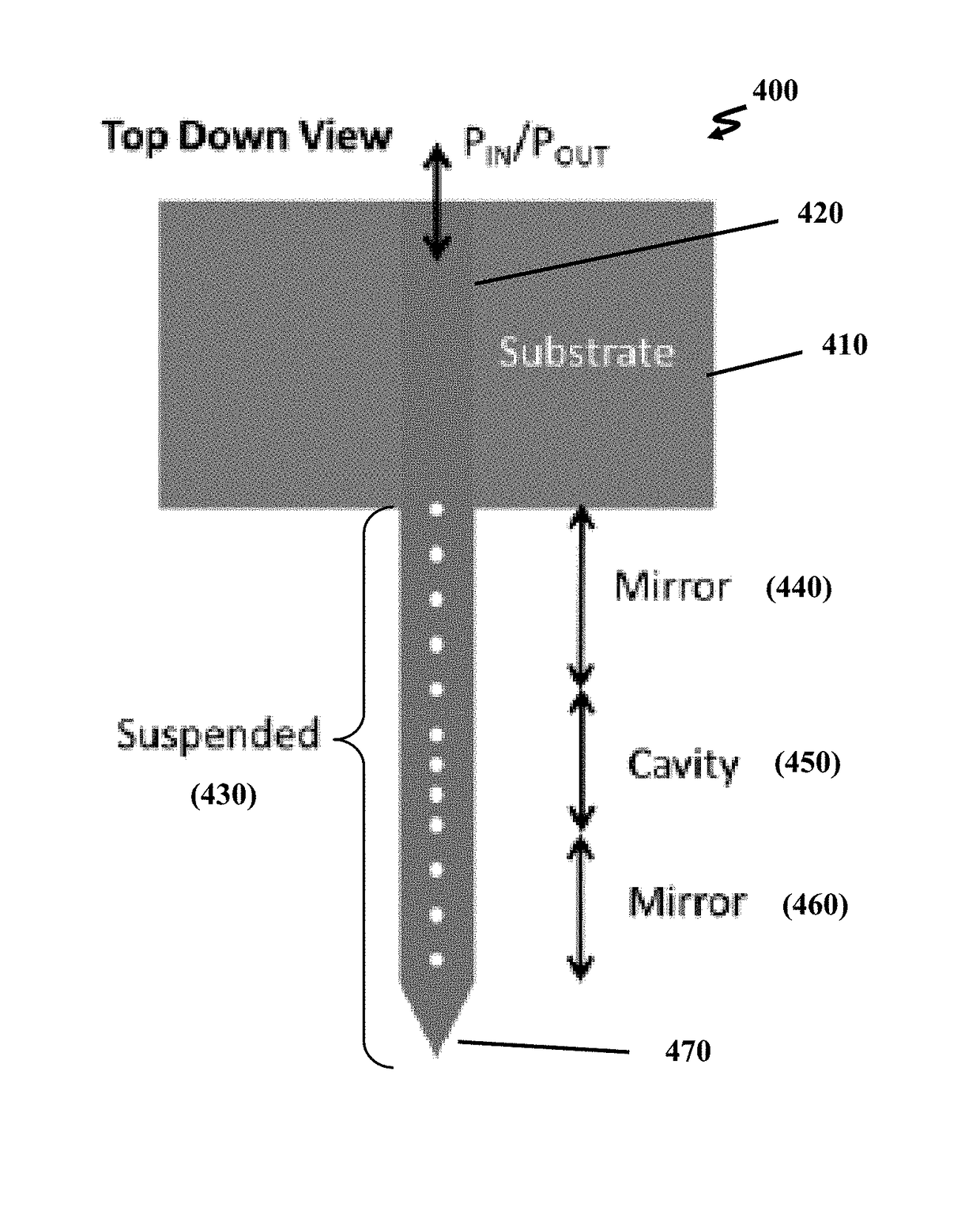
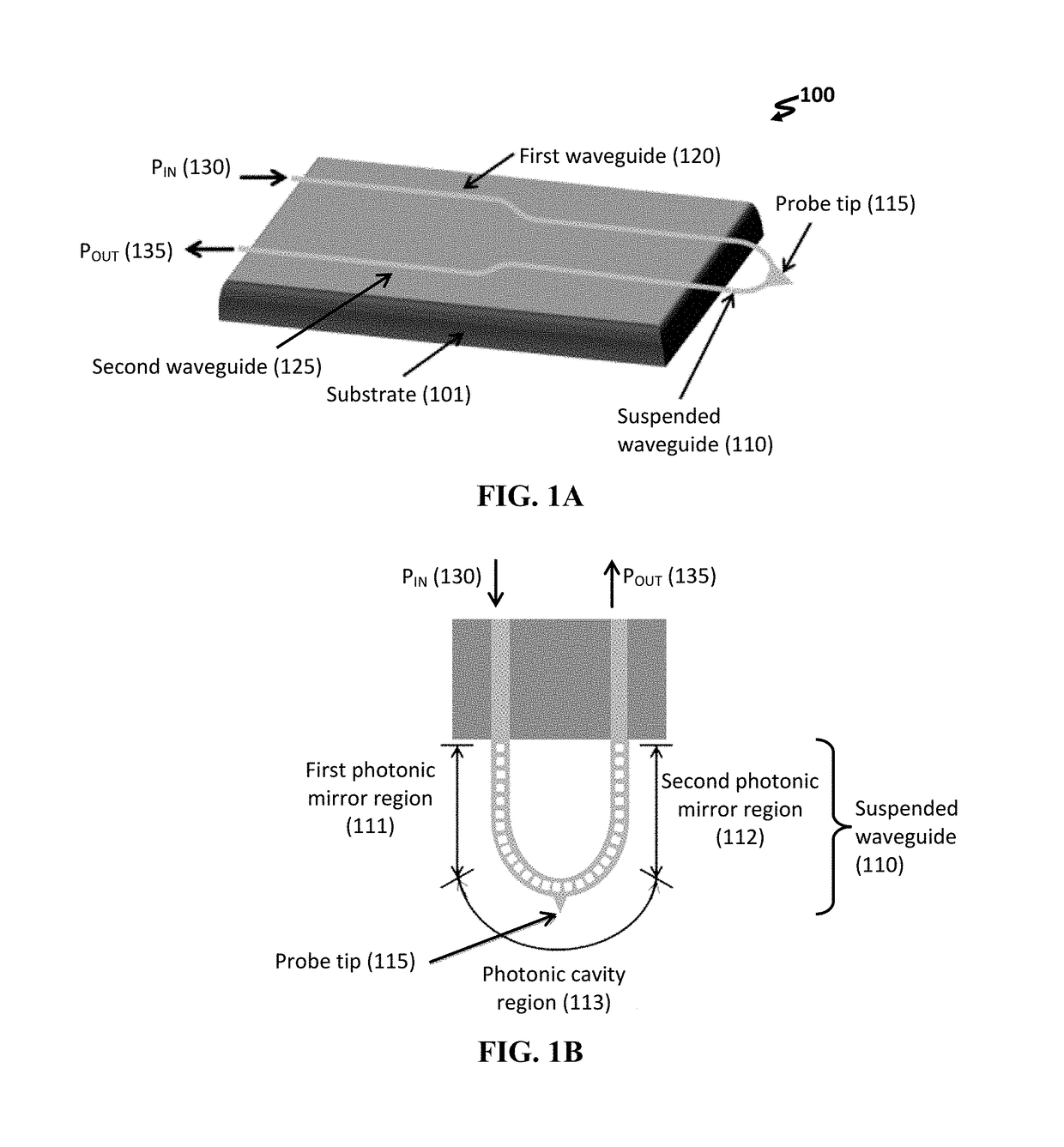
Optomechanical force sensors, cantilevers, and systems thereof
ActiveUS10031158B1Increased optical readout sensitivityHigh sensitivityNanoopticsNanosensorsCantilevered beamOptical cavity
An optomechanical force sensor includes a substrate, a cantilevered beam anchored to the substrate, and a probe tip positioned near an end of the cantilevered beam distal to the substrate. A suspended waveguide is disposed on the cantilevered beam and is optically continuous with an input / output waveguiding structure. An optical cavity is defined within the suspended waveguide.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
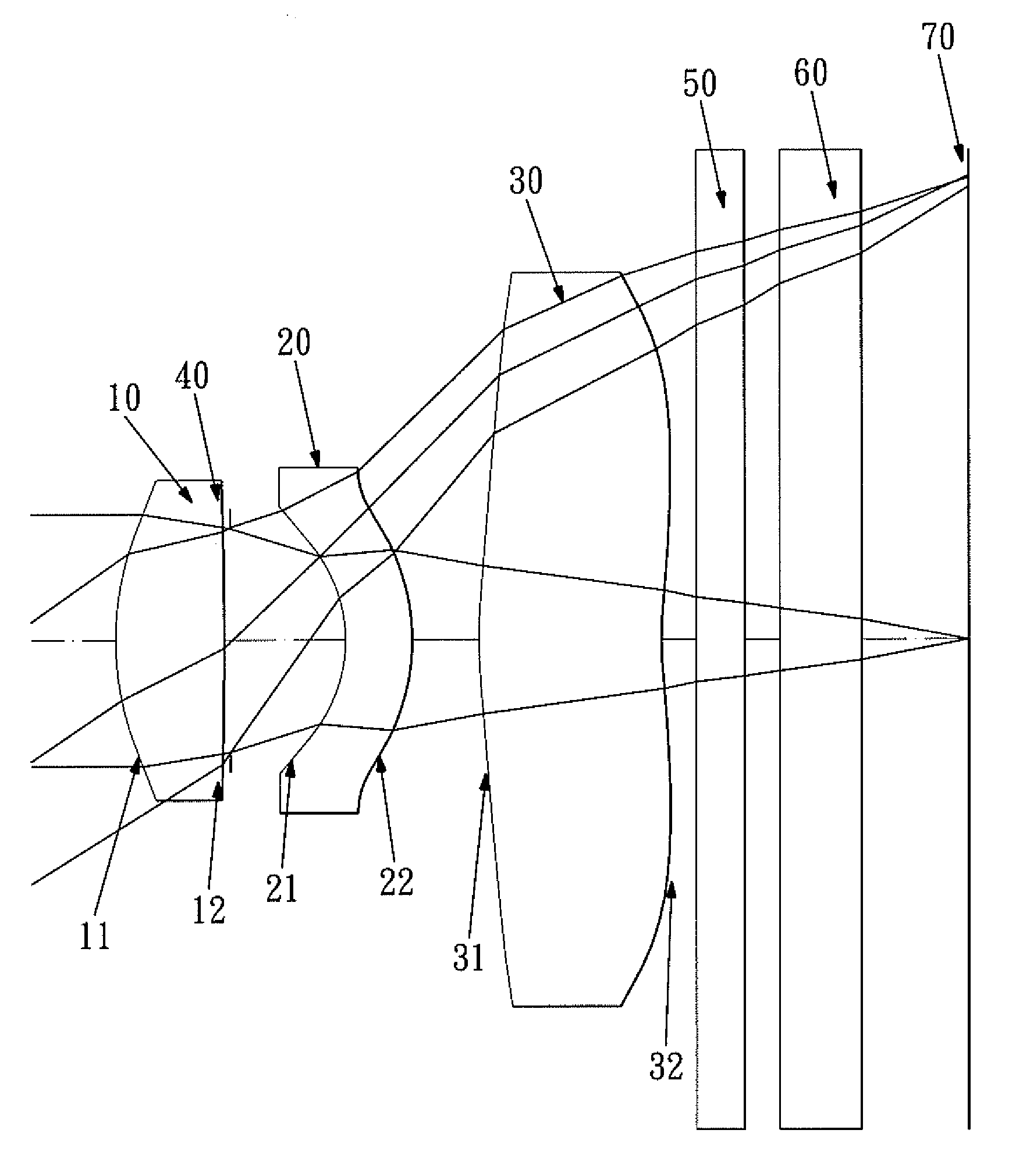
Optical lens assembly
ActiveUS8284502B2Improve image qualitySmall sizeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPhysics
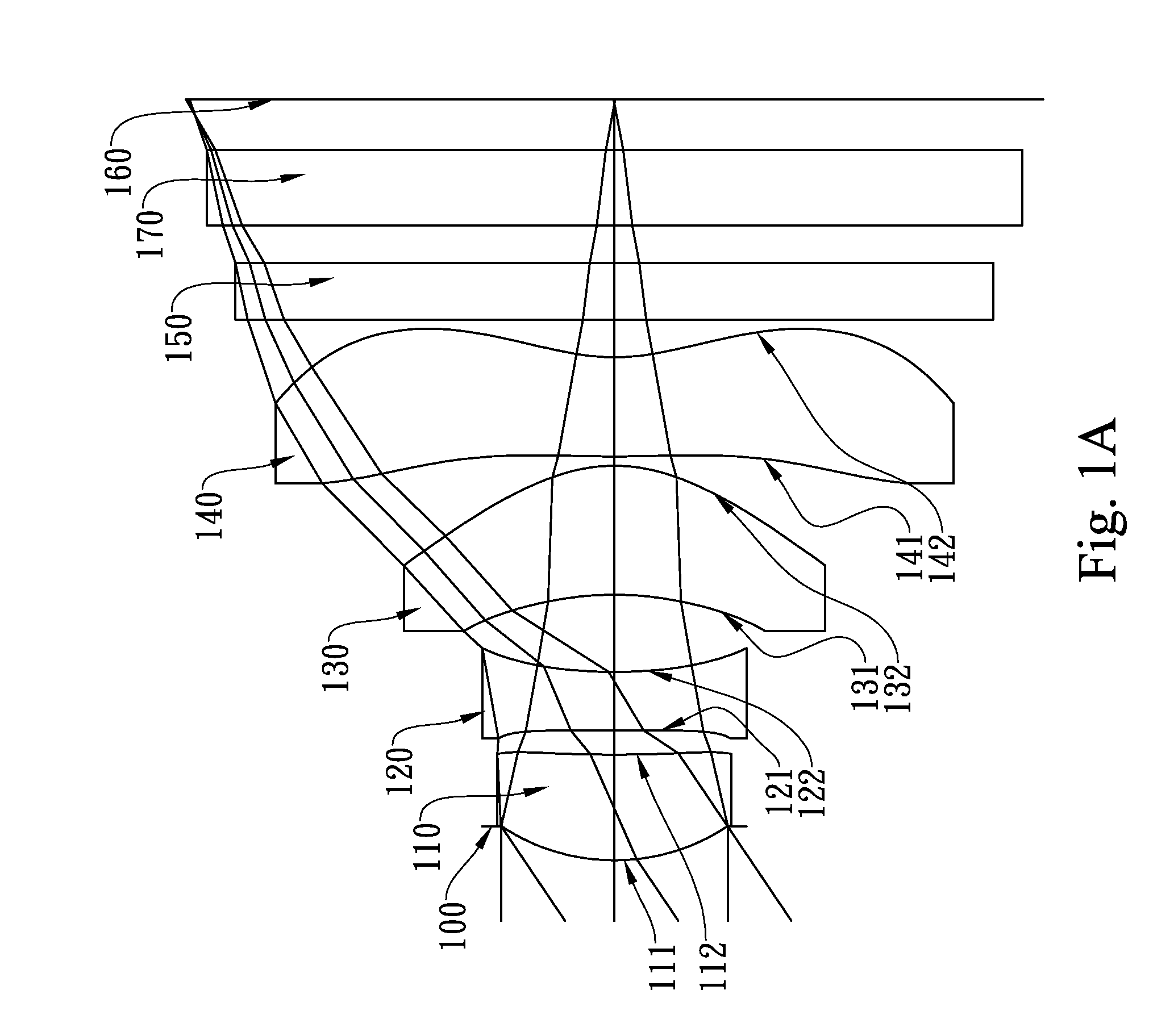
This invention provides an optical lens assembly comprising, in order from an object side to an image side: a first lens element with positive refractive power; a second lens element with positive refractive power; a third lens element with negative refractive power having a concave object-side surface and a convex image-side surface, at least one of the object-side and image-side surfaces thereof being aspheric; and a fourth lens element with positive refractive power having an aspheric object-side surface and an aspheric image-side surface; wherein the number of lens elements with refractive power is four.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Image capturing optical system
This invention provides an image capturing optical system in order from an object side to an image side comprising: a first lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface; a second lens element; a third lens element; a fourth lens element with both the object-side and image-side surfaces thereof being aspheric, and the fourth lens element is made of plastic; and a fifth lens element with negative refractive power, both the object-side and image-side surfaces thereof being aspheric, at least one inflection point is formed on at least one of the object-side and image-side surfaces thereof, and the fifth lens element is made of plastic. By such arrangement, photosensitivity and total track length of the system can be reduced, and better image quality can be obtained.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Optical System for Taking Image
An optical system for taking image comprises three lens elements with refractive power, from the object side to the image side: a first positive lens element having a convex front surface and a concave rear surface, and the front surface being aspheric; a negative plastic second lens element having a concave front surface and a convex rear surface, and the front and rear surfaces thereof being aspheric; a positive plastic third lens element having a convex front surface and a concave rear surface, the front and rear surfaces thereof being aspheric; and an aperture stop located between the first and second lens elements for controlling brightness of the optical system. The focal length of the first lens element is f1, a focal length of the second lens element is f2, a focal length of the optical system is f, and they satisfy the relations: f / f1>0.95, |f / f2|>0.34.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Optical Lens System for Taking Image
An optical lens system for taking image comprises, in order from the object side to the image side: a first lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface; an aperture stop; a second lens element with negative refractive power; a third lens element having a convex object-side surface; and a fourth lens element with negative refractive power having a concave object-side surface, an image-side surface of the fourth lens element being aspheric and formed with inflection points. A distance from the image-side surface of the fourth lens element to an image plane along an optical axis being BFL, a total track length of the optical lens system for taking image being TTL, and they satisfy the relation: BFL / TTL>0.12. In the optical lens system for taking image, the number of lens elements with refractive power being limited to four.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Optical imaging lens assembly
ActiveUS8194172B2Shorten the trackReduce optical sensitivityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImaging qualityImage quality
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Dynamic range broadening method for a solid-state image sensor including photosensitive cells each having a main and a subregion
InactiveUS20050099508A1Efficiently reading out signal chargeImprove dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPhotodiodeDigitization
A method of broadening a dynamic range is applied to a solid-state image sensor of the type including photodiodes each being divided into a main and a subregion different in photosensitivity from each other. While the quantity of light to be incident on a photodiode is reduced, a signal charge is read out only from the main region of the photodiode. The signal charge is digitized and then written to two image memories. Digital signals thus stored in the image memories are respectively amplified by white balance gain circuits with different gains. The resulting digital signals are combined by an image synthesizer. The method can therefore broaden the dynamic range of the image sensor by using only the main regions of the photodiodes.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
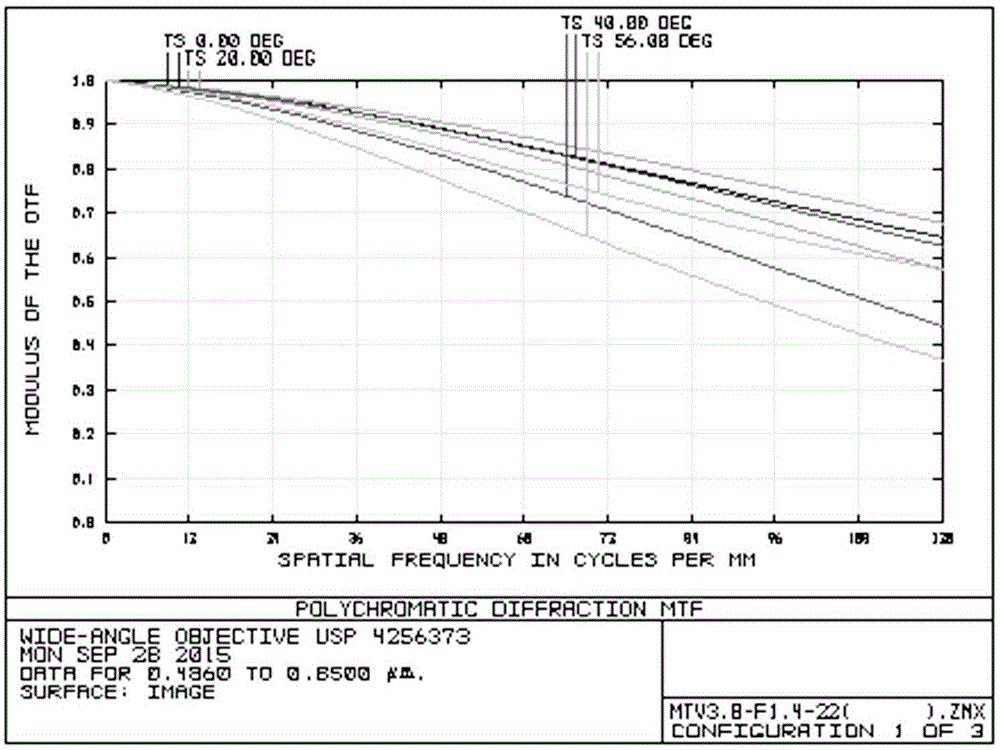
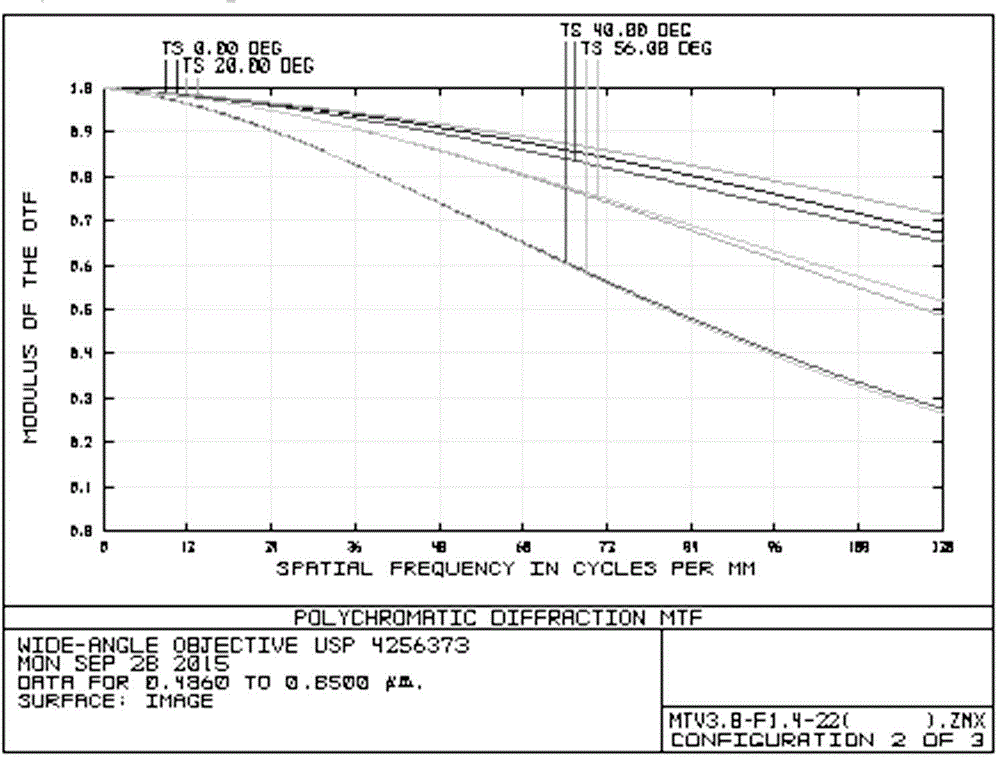
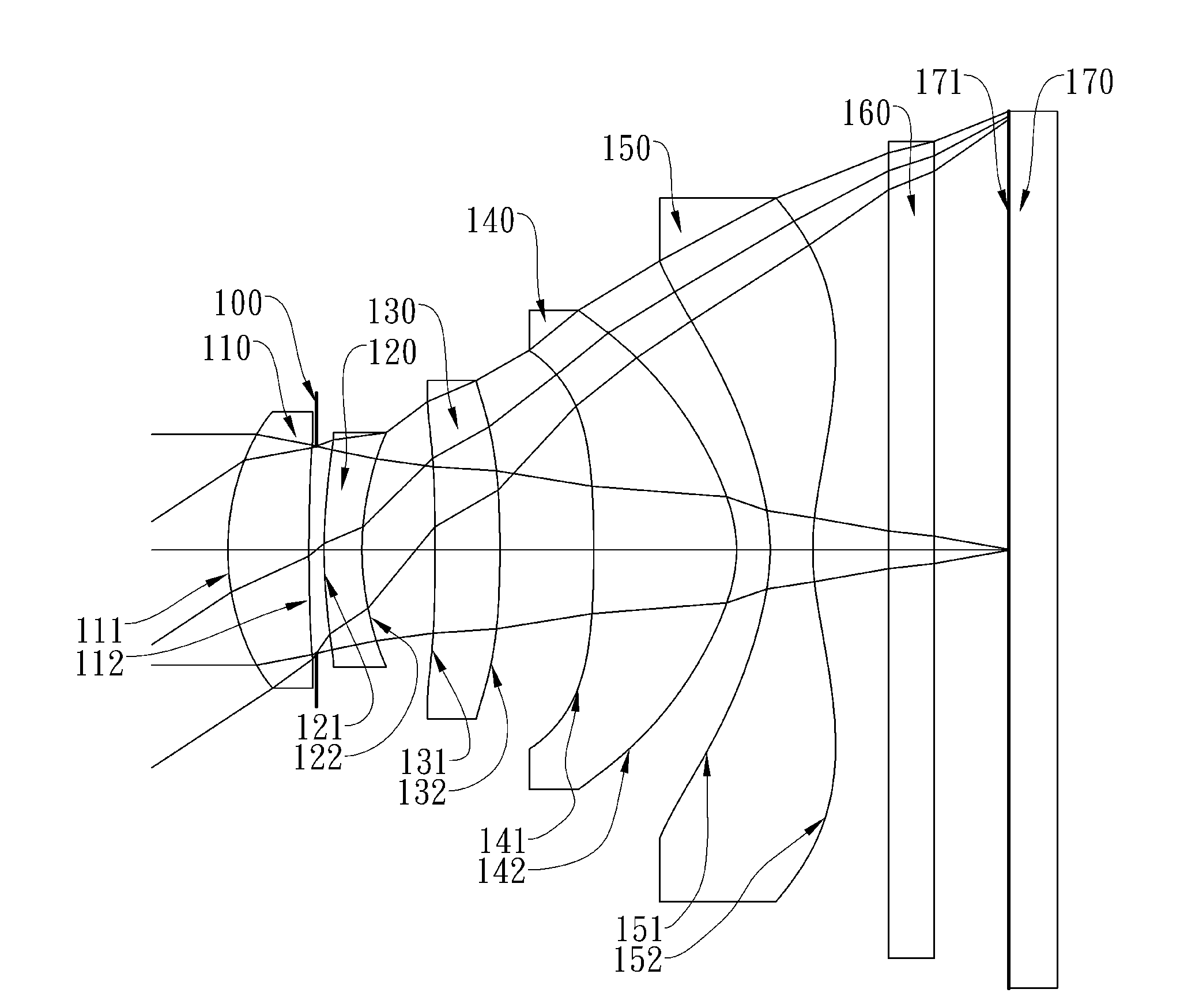
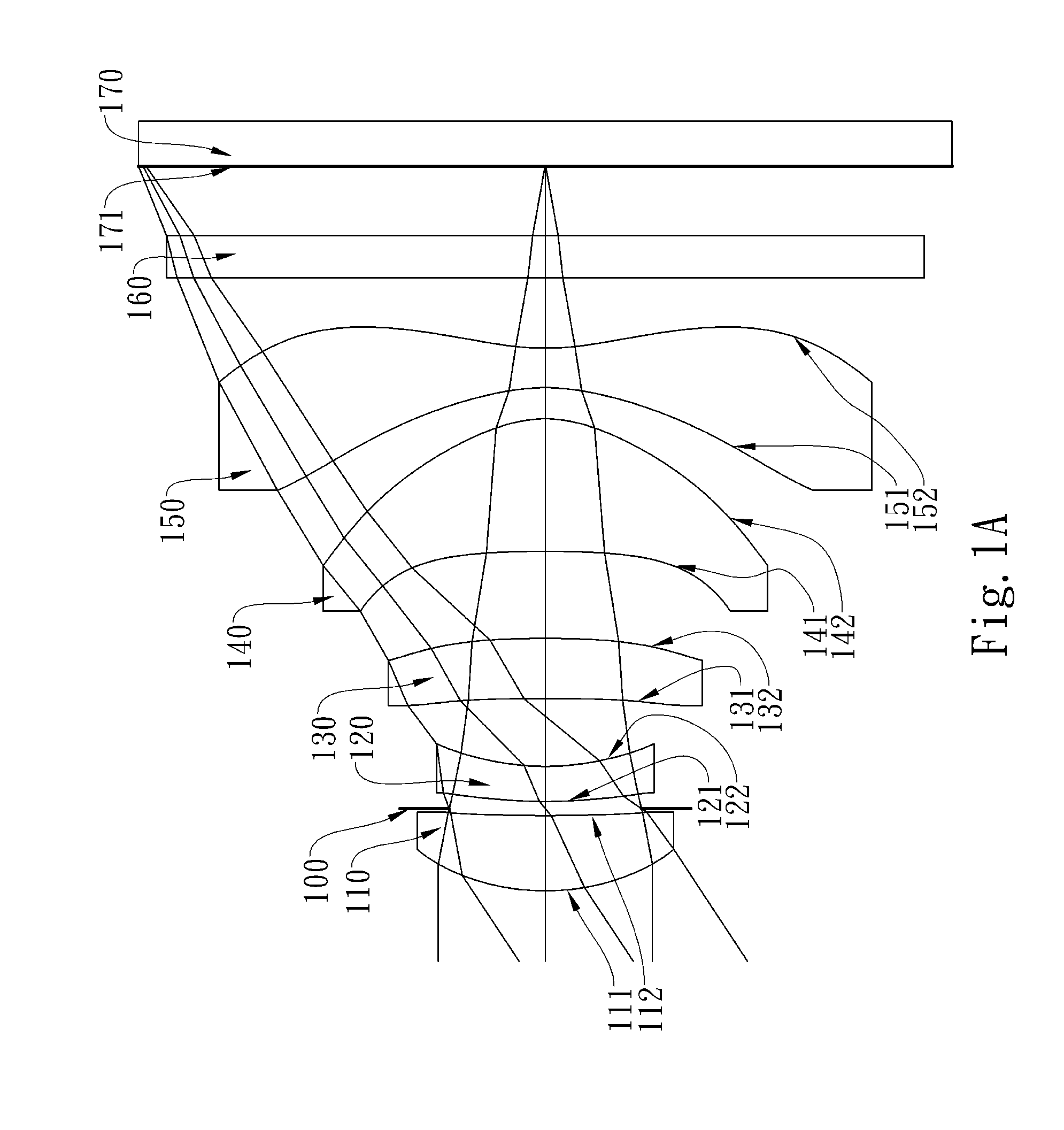
Wide-angle imaging lens assembly
ActiveUS8654458B2Reduce optical sensitivityImprove image qualityTelevision systemsLensCamera lensImaging lens
The present invention provides a wide-angle imaging lens assembly comprising, in order from an object side to an image side: a first lens element with negative refractive power having a convex object-side surface and a concave image-side surface; a second lens element with negative refractive power having a convex object-side surface and a concave image-side surface; a third lens element with positive refractive power; a fourth lens element with negative refractive power having a concave image-side surface; and a fifth lens element with positive refractive power; wherein the two lens elements with refractive power closest to the object side are the first lens element and the second lens element; and wherein the number of lens elements with refractive power does not exceed six.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Optical Lens System for Taking Image
An optical lens system for taking image comprises three lens elements with refractive power, from the object side to the image side: a first positive lens element having a convex front surface and a concave rear surface, and the front surface being aspheric; a negative plastic second lens element having a concave front surface and a convex rear surface, and the front and rear surfaces thereof being aspheric; a positive plastic third lens element having a convex front surface and a concave rear surface, the front and rear surfaces thereof being aspheric; and an aperture stop located between the first and second lens elements for controlling brightness of the optical system. The focal length of the first lens element is f1, the focal length of the optical lens system is f, and they satisfy the relations: f / f1<0.9.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Optical imaging lens assembly
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Device for optical distance measurement
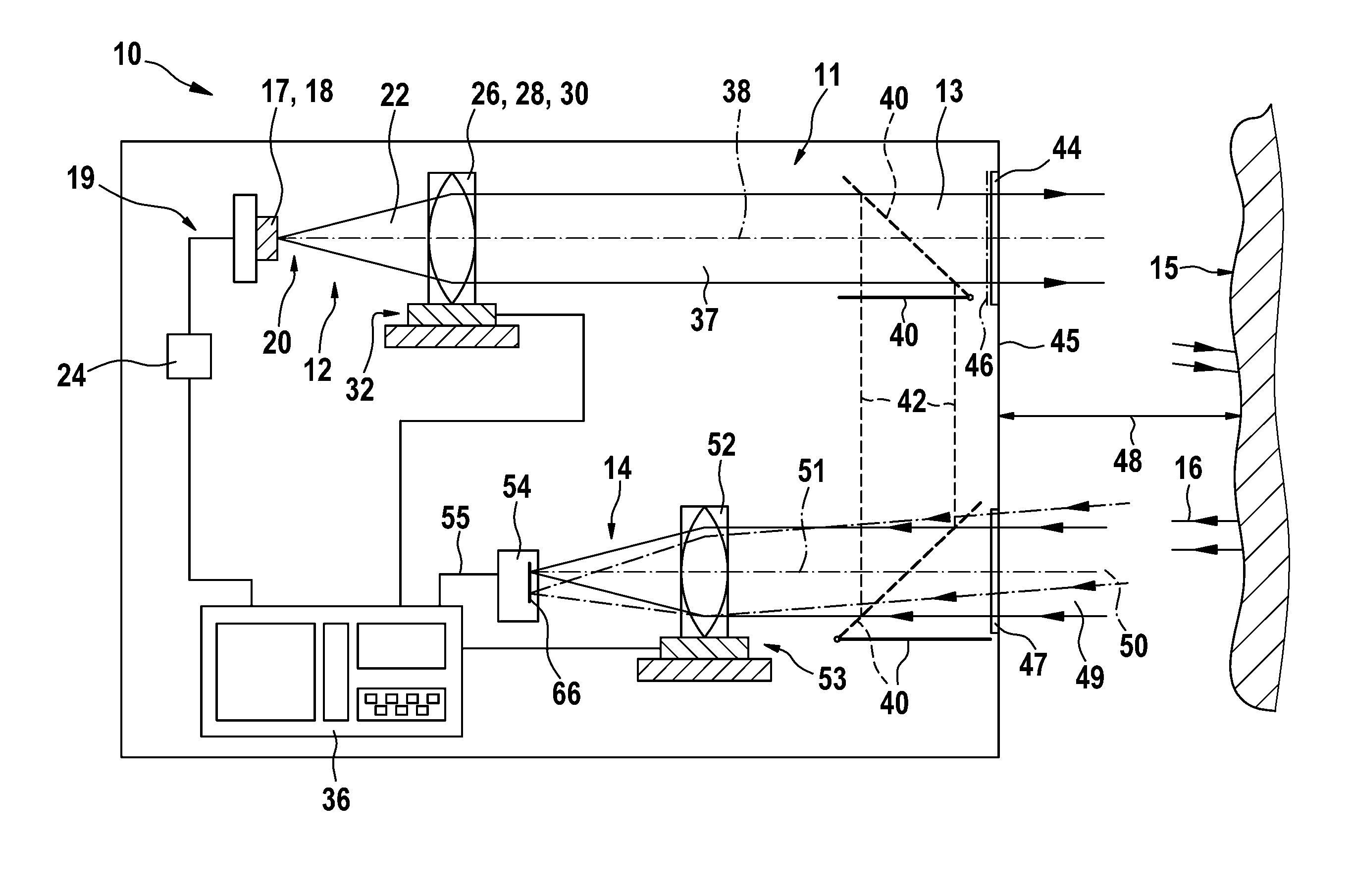
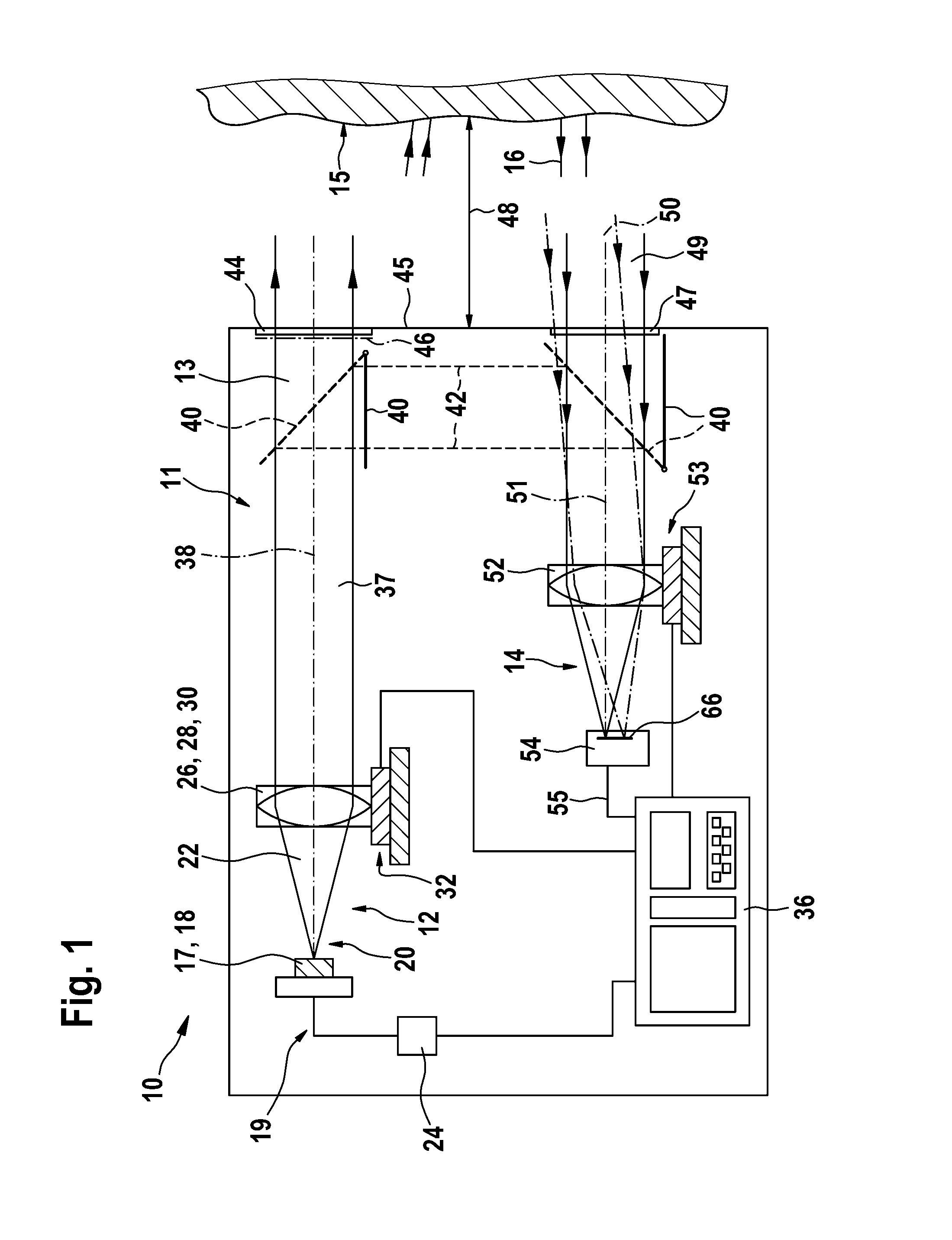
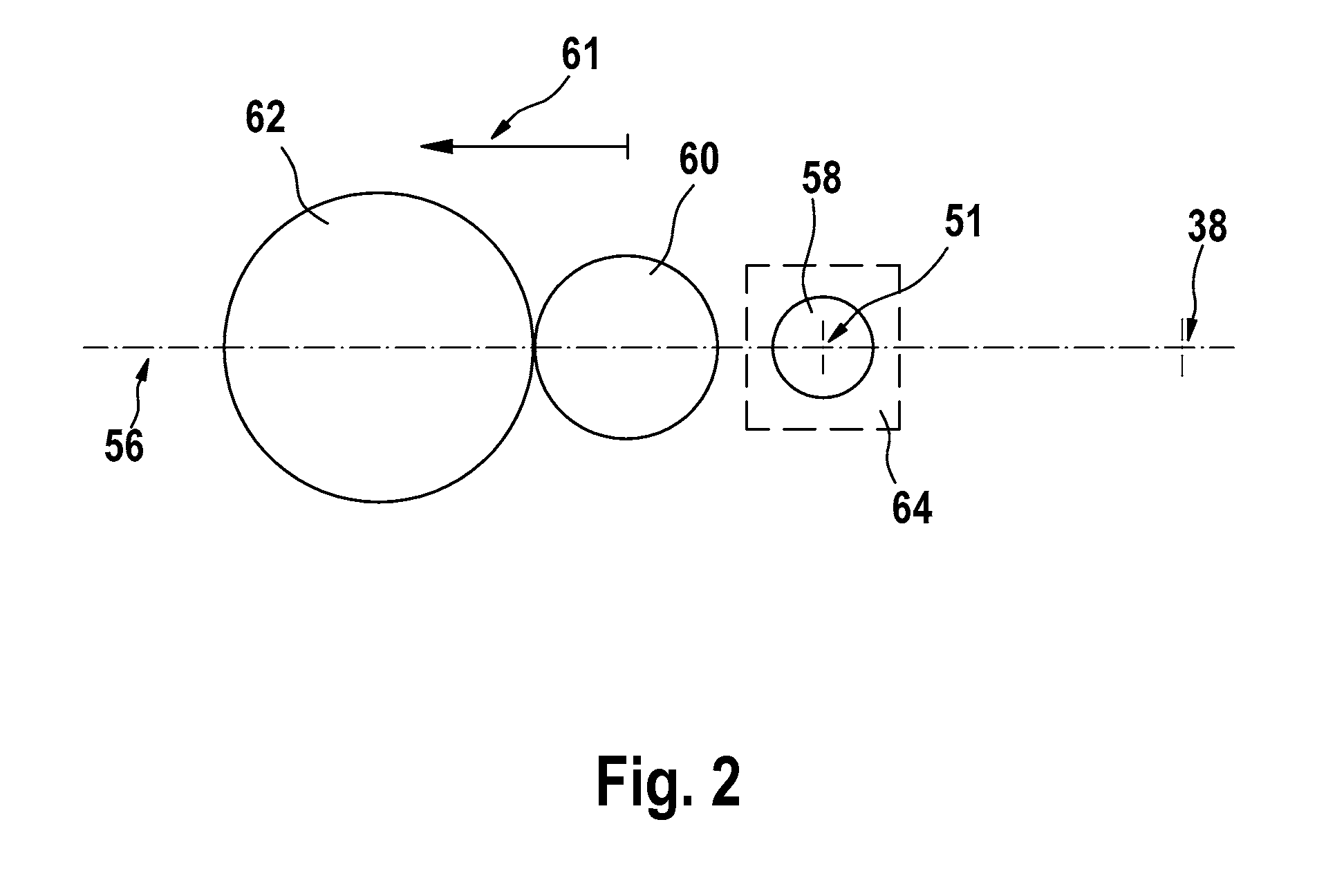
InactiveUS20110007328A1Keep positioning toleranceKeep positionUsing optical meansElectromagnetic wave reradiationOptical radiationOptical axis
The invention relates to a device for optical distance measurement, particularly to a handheld device, comprising a transmission unit (12) with a light source (17, 18) for emitting optical measurement radiation (13, 20, 22) onto a target object (15), and comprising a receiving unit (14) arranged at a distance from the optical axis (38) of the transmission unit (12) and equipped with at least one optical detector (54) for receiving optical radiation (16, 49, 50) reflected from the target object (15). According to the invention, the detector (54) of the receiving unit (14) comprises a detection surface (66), the optical surface of which has varying optical sensitivity.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
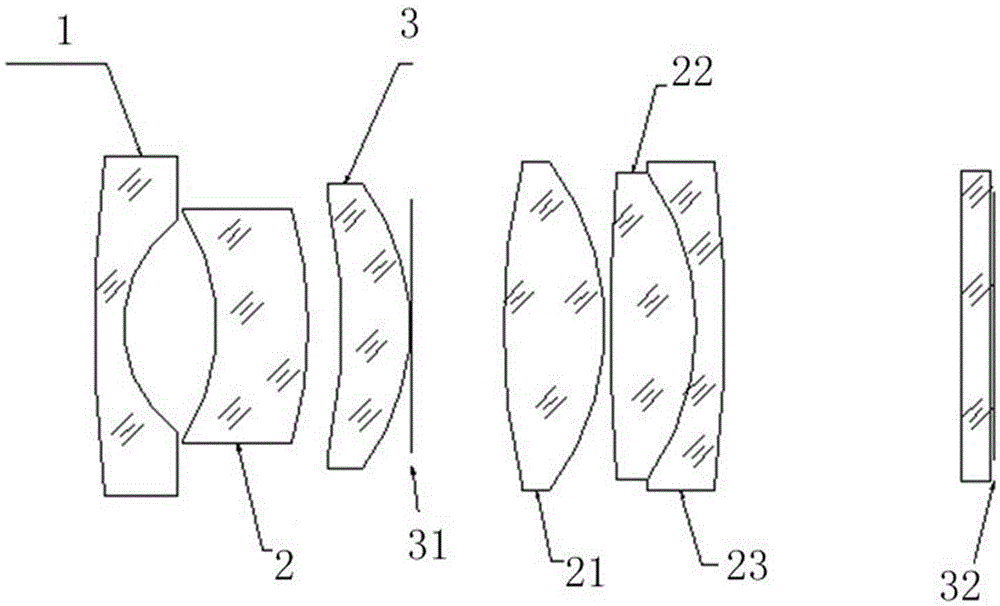
High-light through high-definition fixed-focus aspheric lens
ActiveCN105259638AImprove adaptabilityReduce lens sensitivityOptical elementsOptical pathOphthalmology
The invention discloses a high-light through high-definition fixed-focus aspheric lens. The lens comprises six lenses, a diaphragm and an optical filter. The diaphragm is arranged in the middle section of a lens optical path and on the middle axis of the lens body. The lenses form a pupil entrance group and a pupil exit group. The pupil entrance group is arranged on a diaphragm pupil entrance side and the overall focal power is negative. A lens (A1), an aspheric lens (A2) and a lens (A3) are sequentially arranged in the optical path direction of the pupil entrance group. The lens (A3) clings to the diaphragm. The pupil exit group is arranged on a diaphragm pupil exit side and the overall focal power is positive. An aspheric lens (B1), a convex lens (B2) and a concave lens (B3) are sequentially arranged in the optical path direction of the pupil exit group. The convex lens (B2) and the concave lens (B3) are glued and fixed together via the opposite concave and convex faces. The optical filter is arranged in the light exit direction of the pupil exit group. According to the invention, the aspheric lenses are used in the lens, so while light passing quantity of the lens is increased, the lens aberration can be controlled in an acceptable range.
Owner:FUJIAN FORECAM OPTICS CO LTD
Image capturing optical system
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Imaging lens system
ActiveUS20110194013A1Reduce image sizeHigh resolutionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImaging lensPhysics
This invention provides an imaging lens system in order from an object side to an image side including a first lens element having a convex object-side surface and a concave image-side surface, a second lens element with positive refractive power having its object-side and image-side surfaces being aspheric, a third lens element with negative refractive power having its object-side and image-side surfaces being aspheric and at least one inflection point formed on one of the two surfaces, and an aperture stop disposed between the first lens element and the second lens element. There are three lens elements with refractive power in this system.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Imaging lens system
This invention provides an imaging lens system in order from an object side to an image side including a first lens element having a convex object-side surface and a concave image-side surface, a second lens element with positive refractive power having its object-side and image-side surfaces being aspheric, a third lens element with negative refractive power having its object-side and image-side surfaces being aspheric and at least one inflection point formed on one of the two surfaces, and an aperture stop disposed between the first lens element and the second lens element. There are three lens elements with refractive power in this system.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Optical Lens System for Taking Image
An optical lens system for taking image comprises, in order from the object side to the image side: a first lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface; an aperture stop; a second lens element with negative refractive power; a third lens element having a convex object-side surface; and a fourth lens element with negative refractive power having a concave object-side surface, an image-side surface of the fourth lens element being aspheric and formed with inflection points. A distance from the image-side surface of the fourth lens element to an image plane along an optical axis being BFL, a total track length of the optical lens system for taking image being TTL, and they satisfy the relation: BFL / TTL>0.12. In the optical lens system for taking image, the number of lens elements with refractive power being limited to four.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com