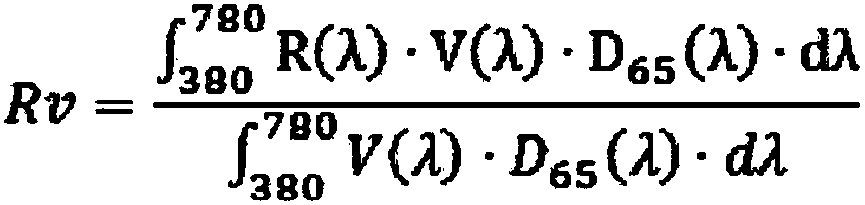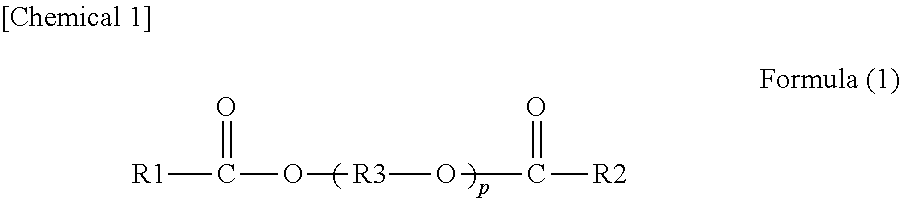Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
62 results about "Scotopic vision" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
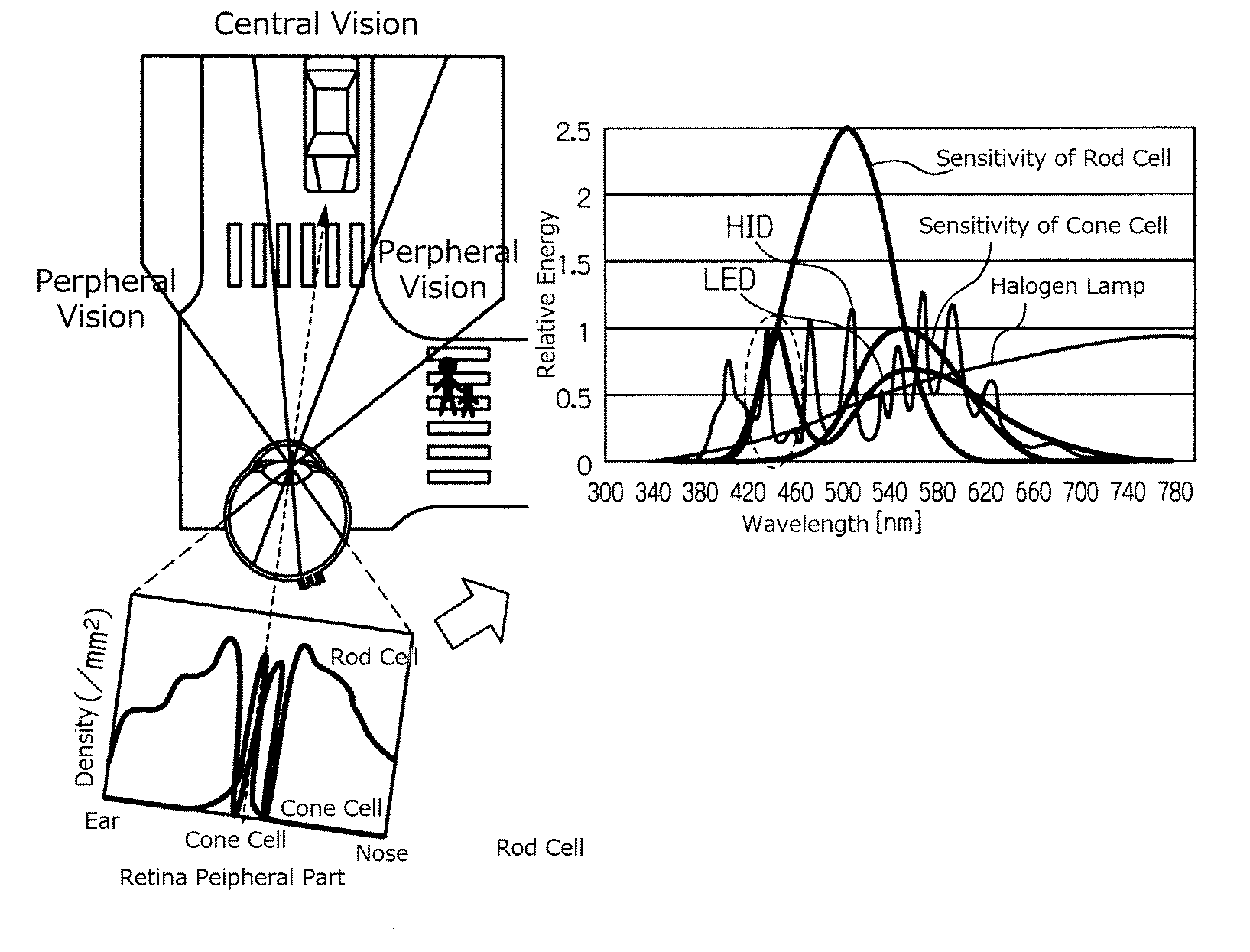
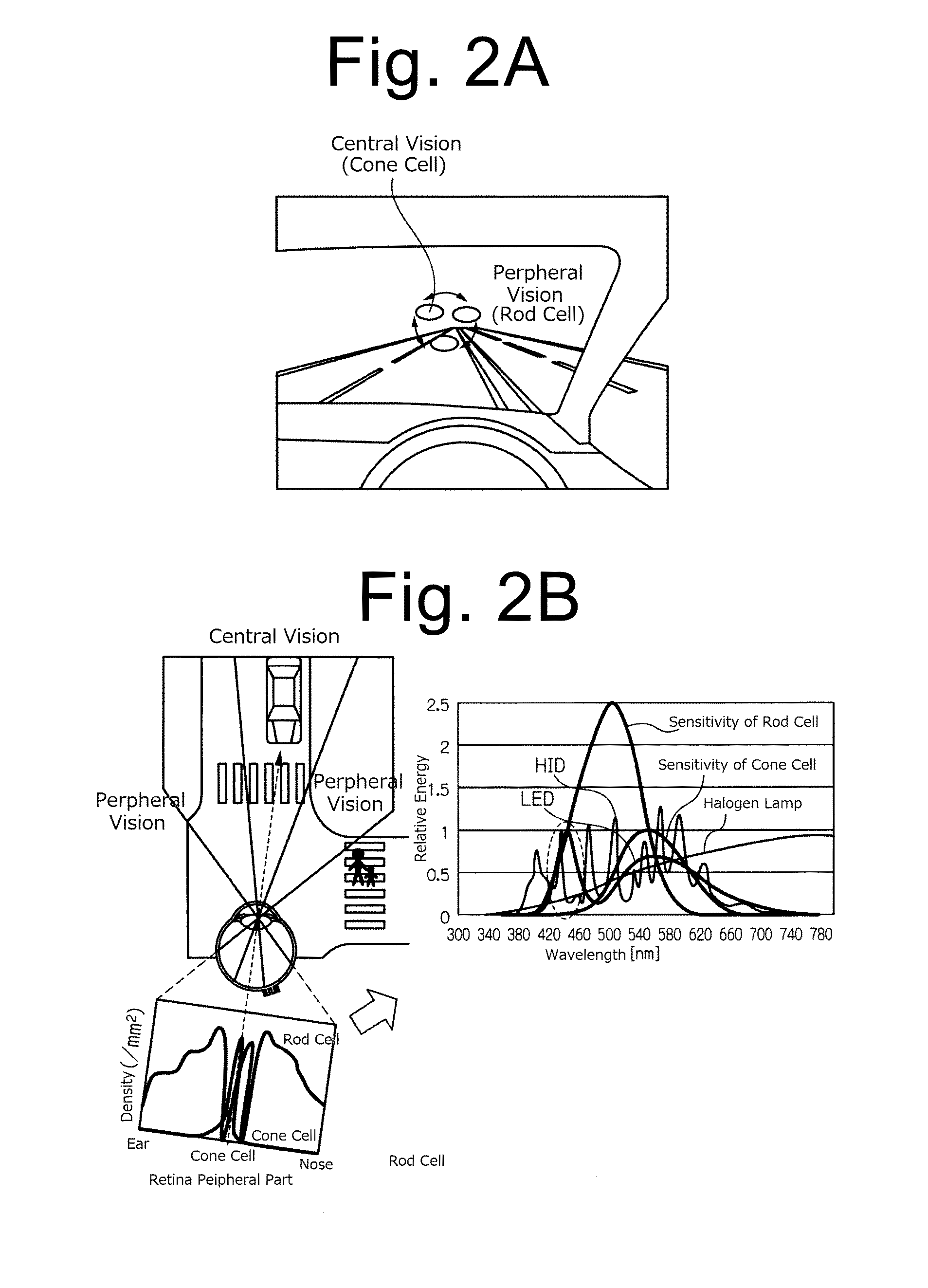
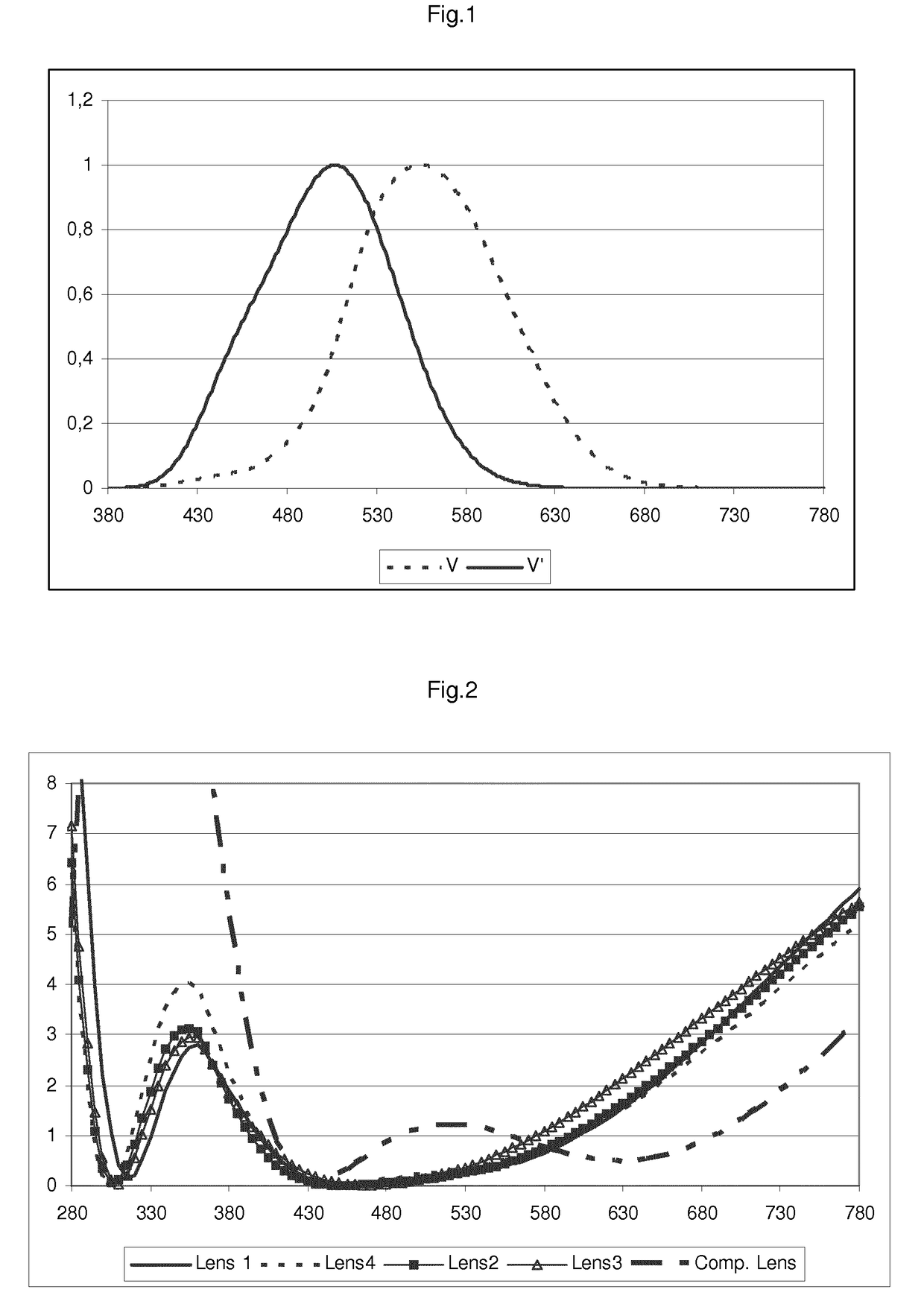
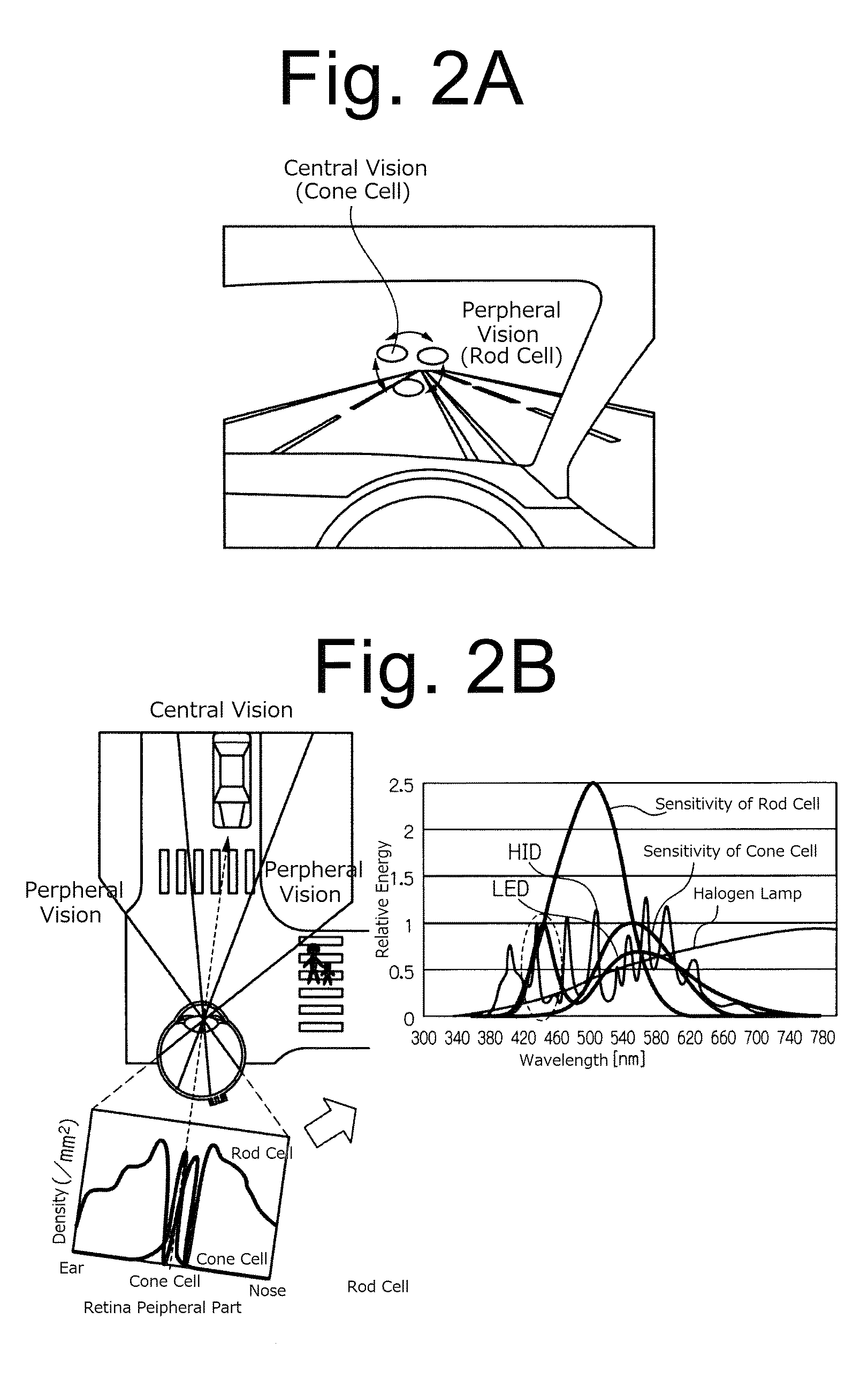
Scotopic vision is the vision of the eye under low-light levels. The term comes from Greek skotos, meaning "darkness", and -opia, meaning "a condition of sight". In the human eye, cone cells are nonfunctional in low visible light. Scotopic vision is produced exclusively through rod cells, which are most sensitive to wavelengths of around 498 nm (green–blue) and are insensitive to wavelengths longer than about 640 nm (reddish orange). This condition is called the Purkinje effect.
High performance corneal inlay
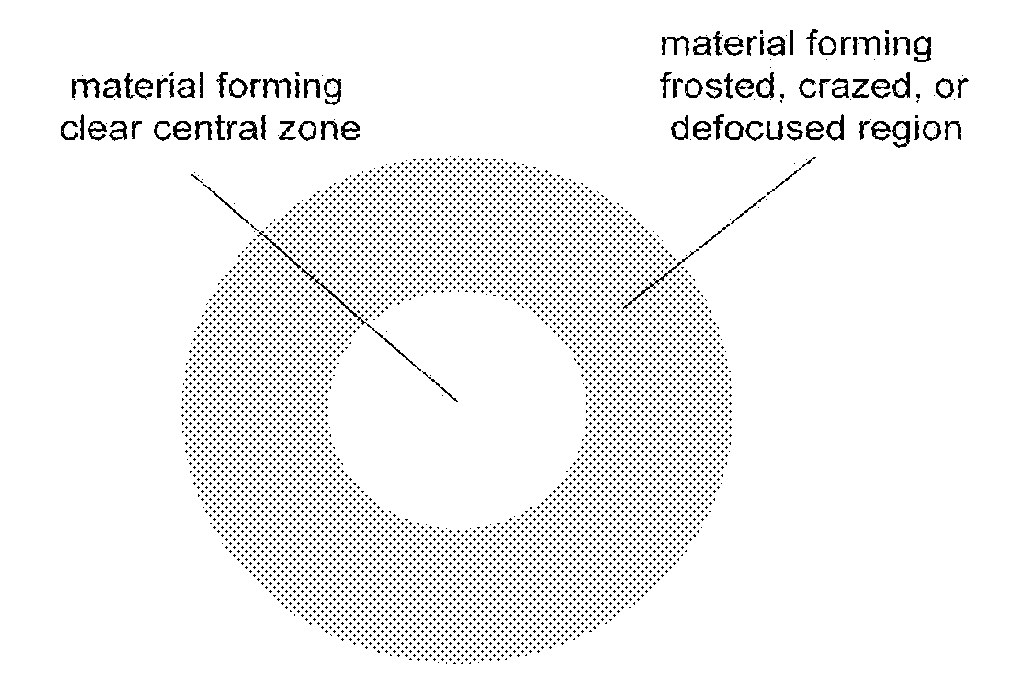
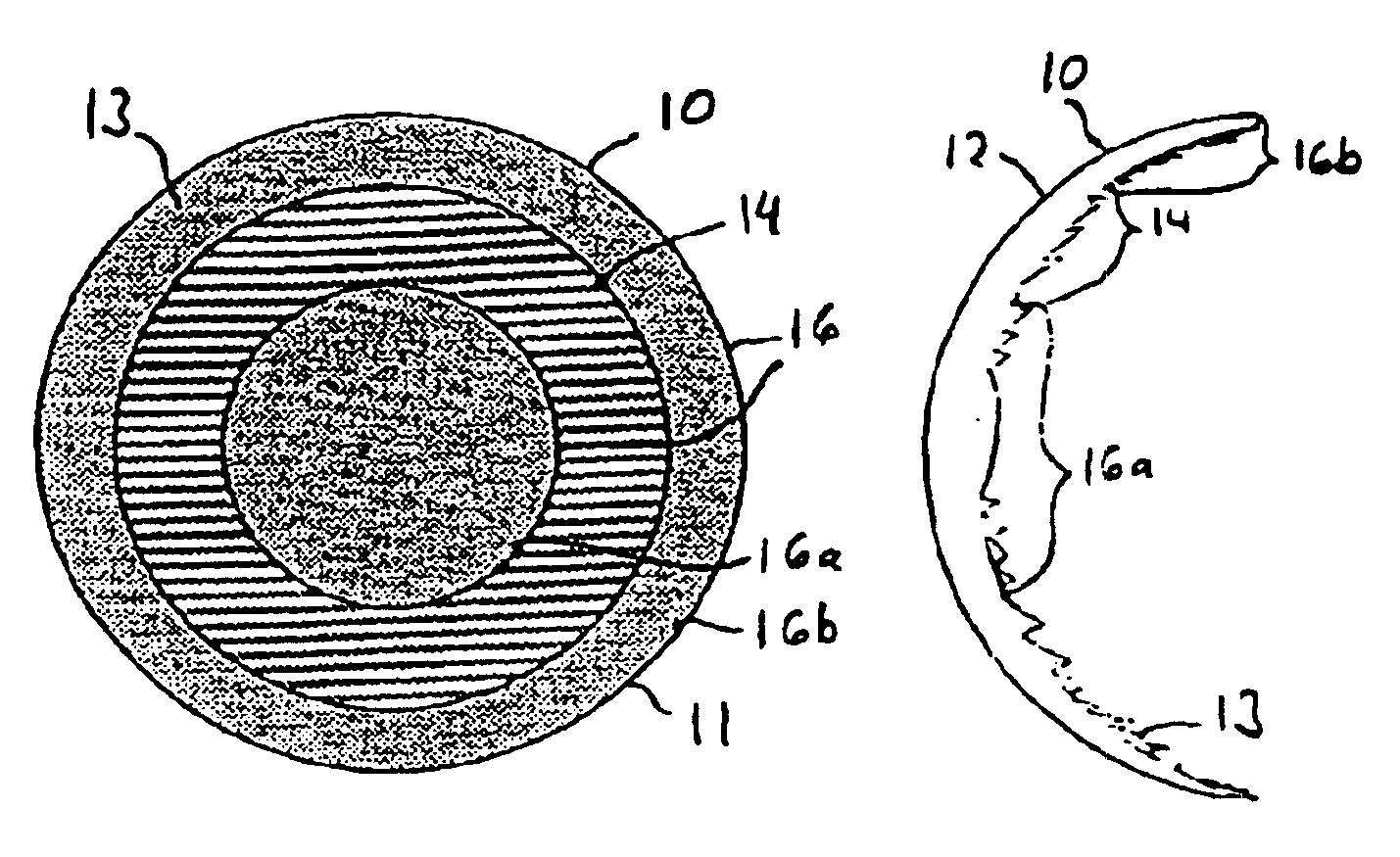
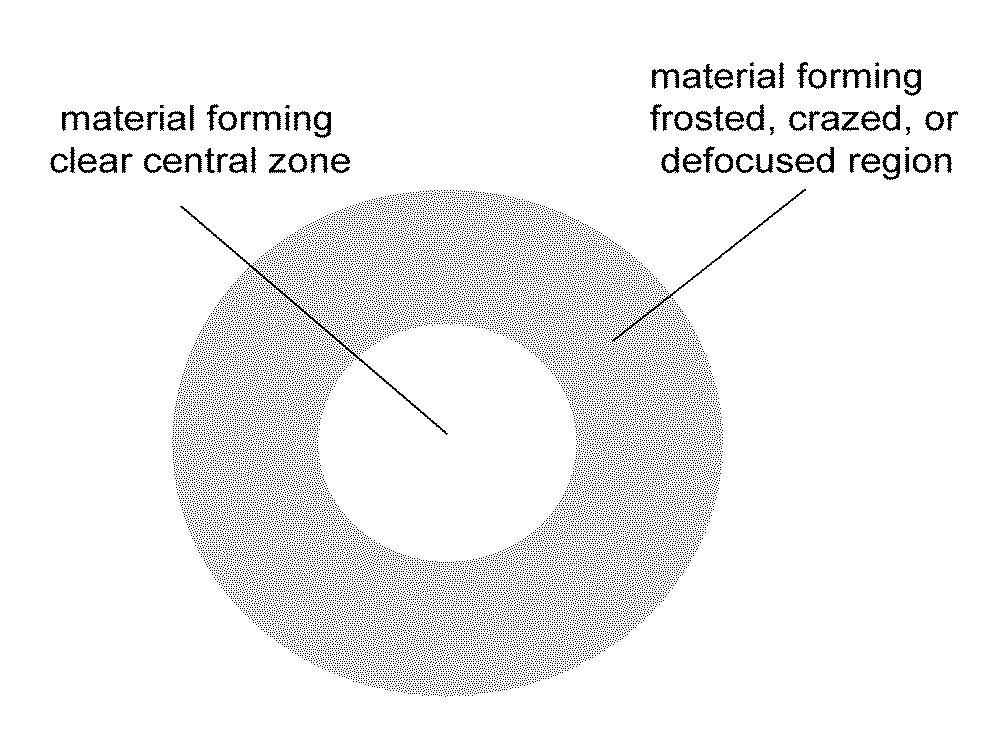
A corneal inlay protects ocular structures from harmful wavelengths of light while maintaining acceptable color cosmetics, color perception, overall light transmission, photopic vision, scotopic vision, color vision, and / or cirdadian rhythms. The corneal inlay can also include a pinhole effect to increase depth of focus. In some embodiments, the corneal inlay can also correct refractive errors including, but not limited to, higher order aberration, lower order aberration, myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, and / or presbyopia.
Owner:HIGH PERFORMANCE OPTICS
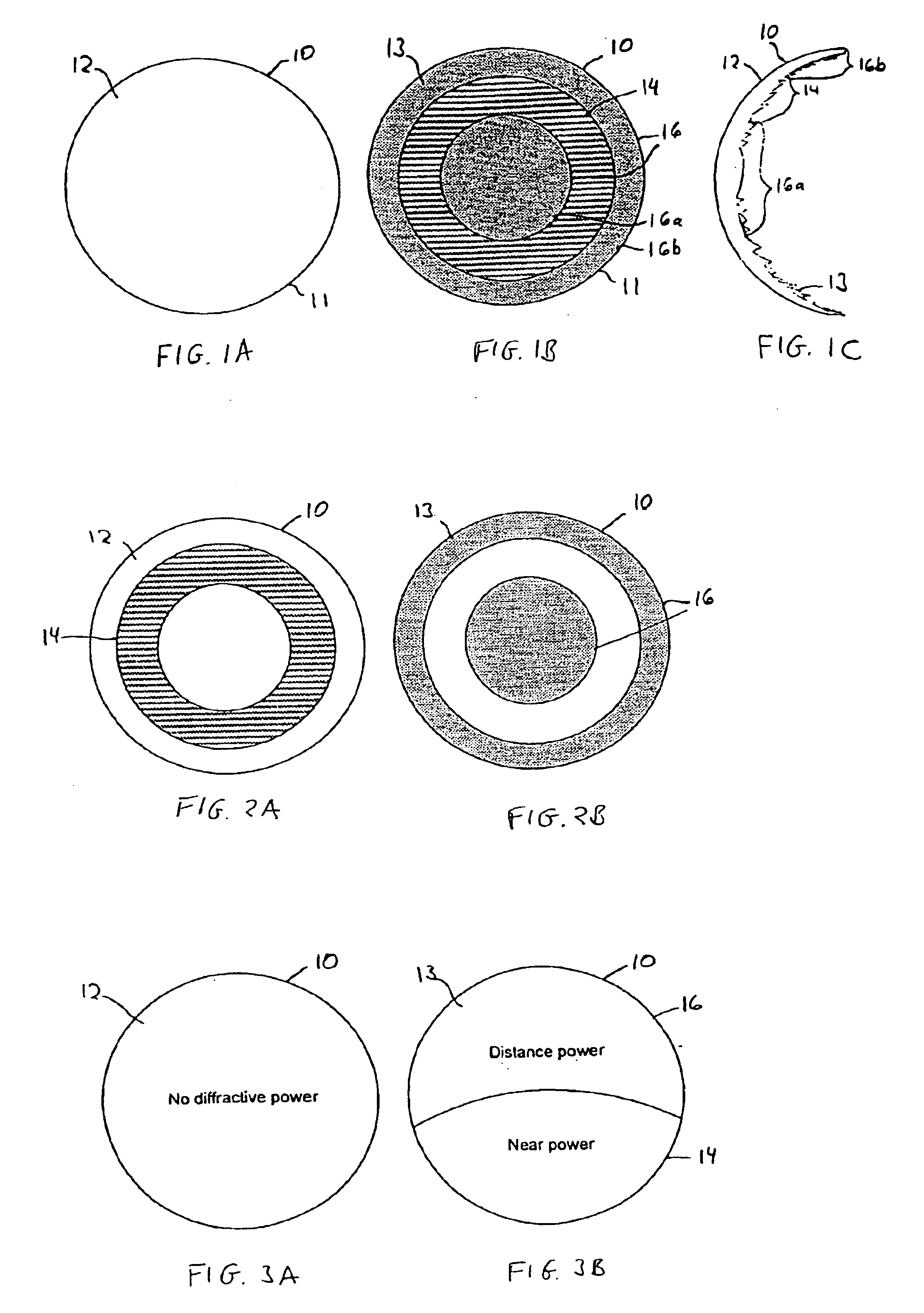
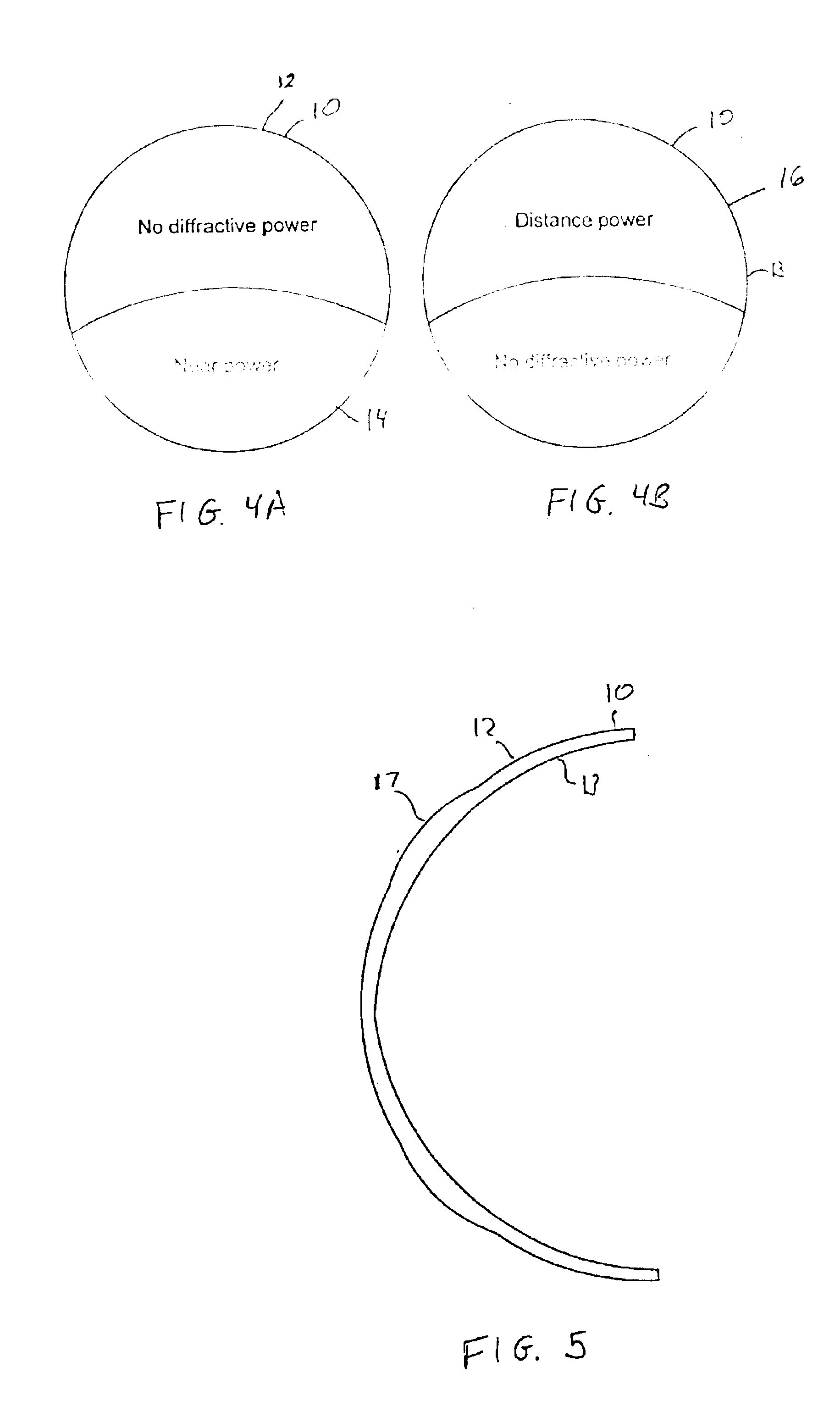
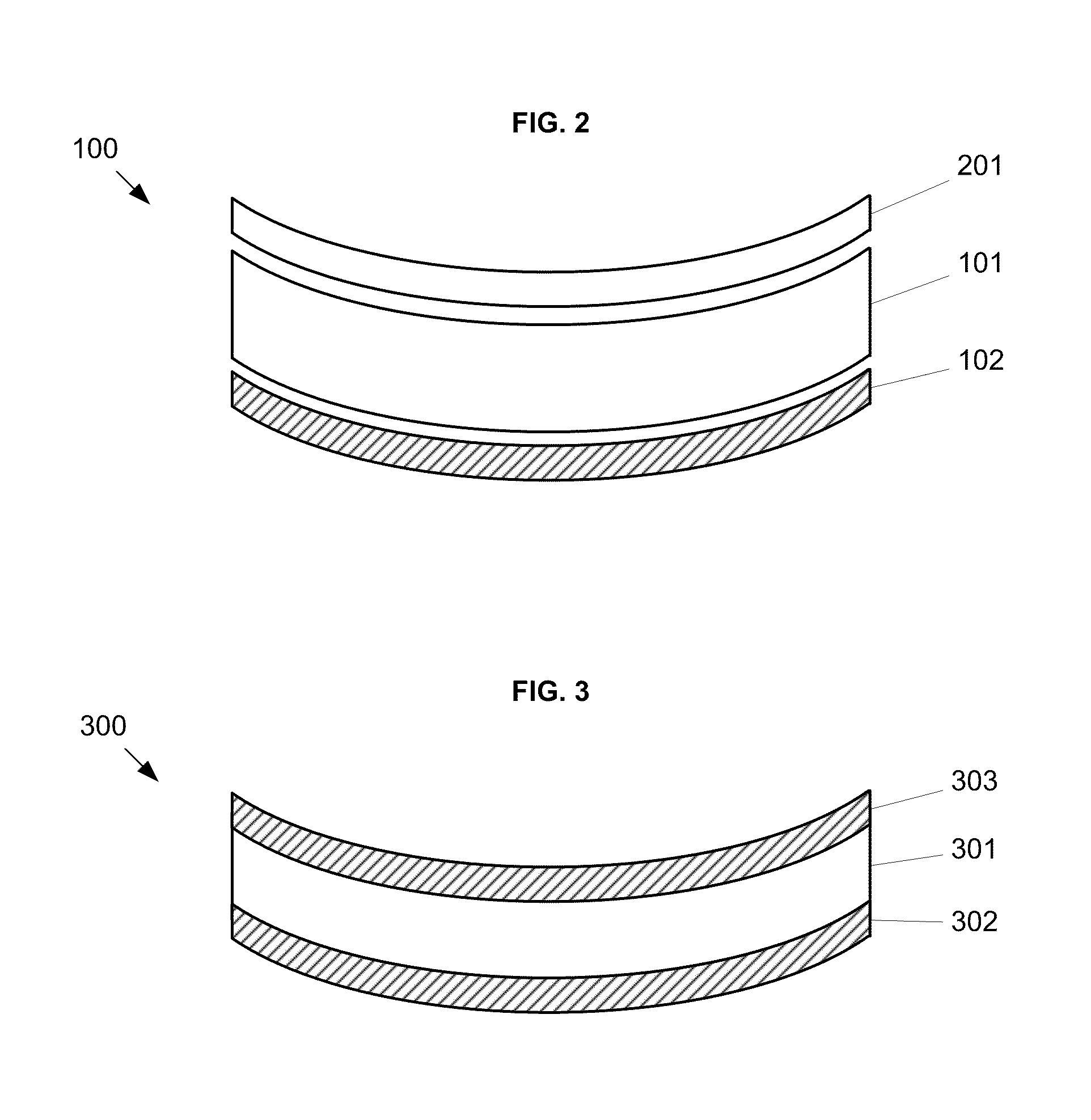
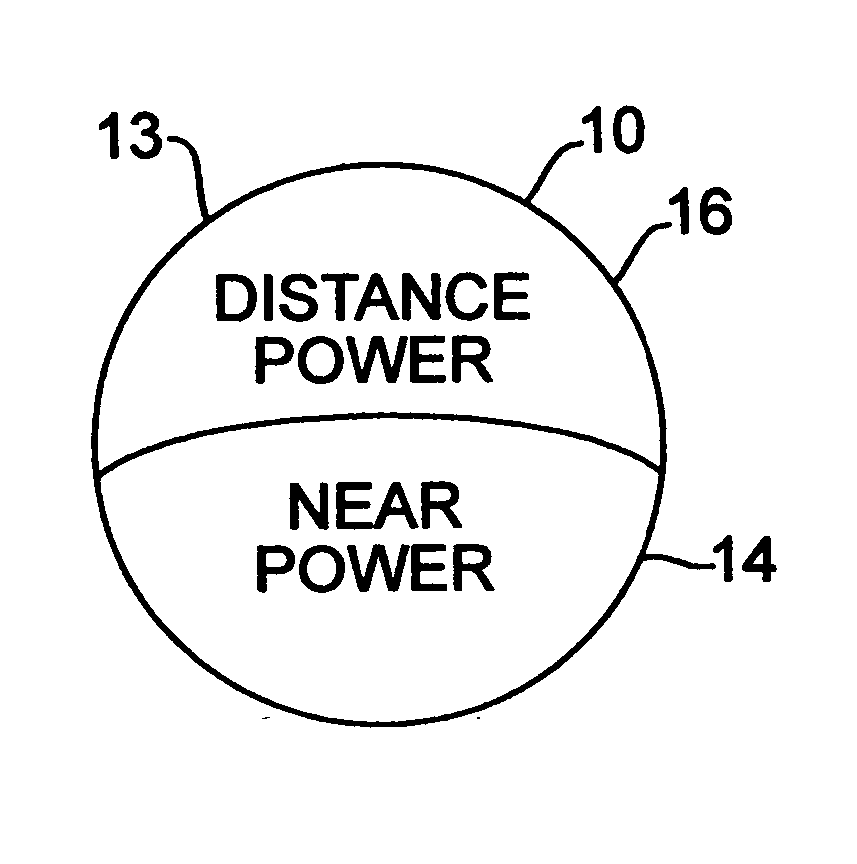
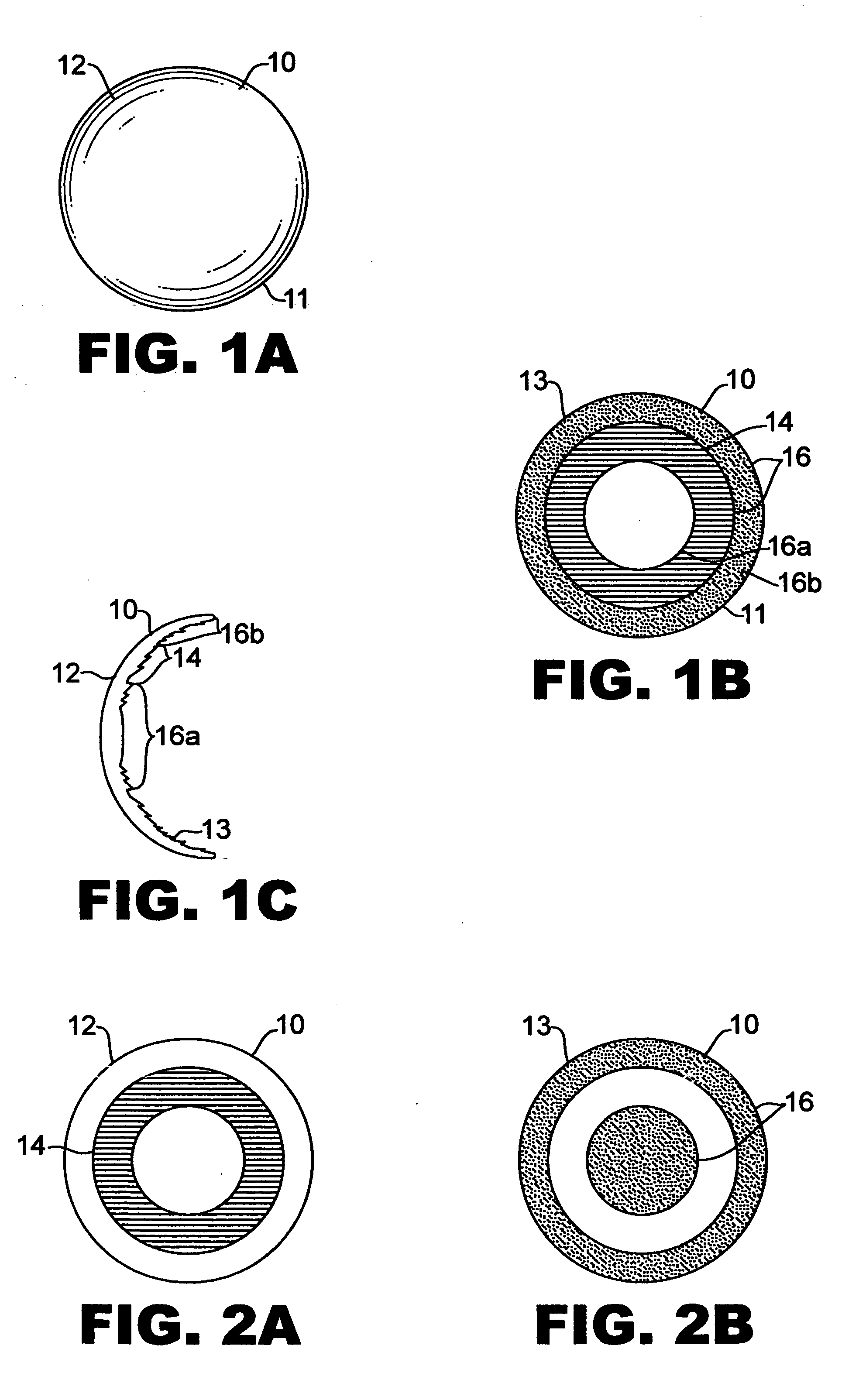
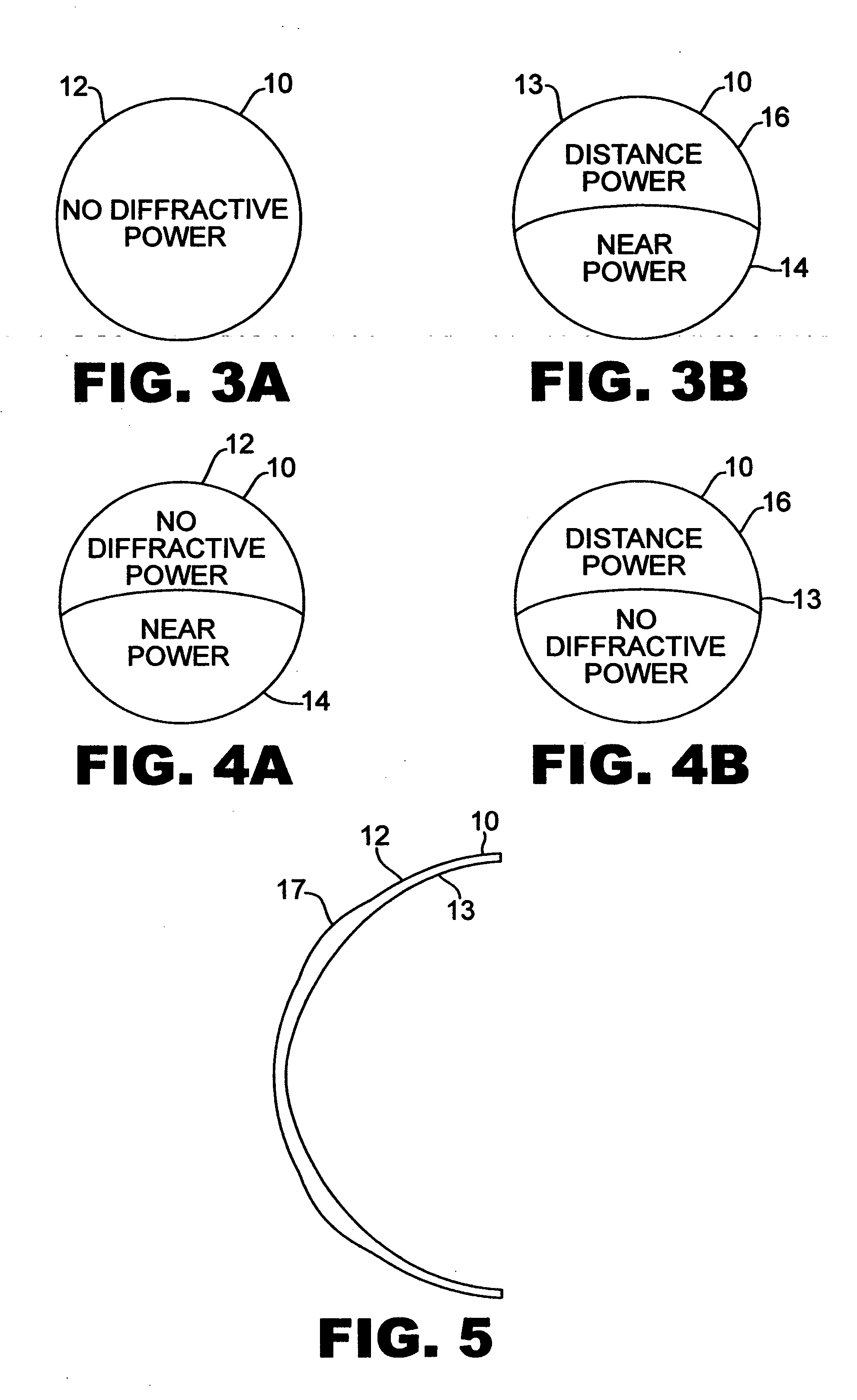
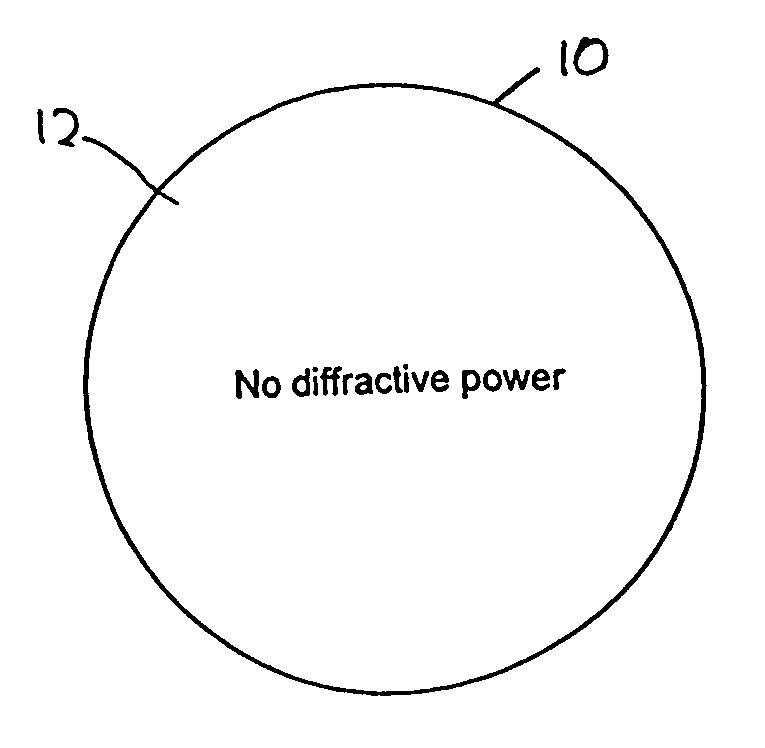
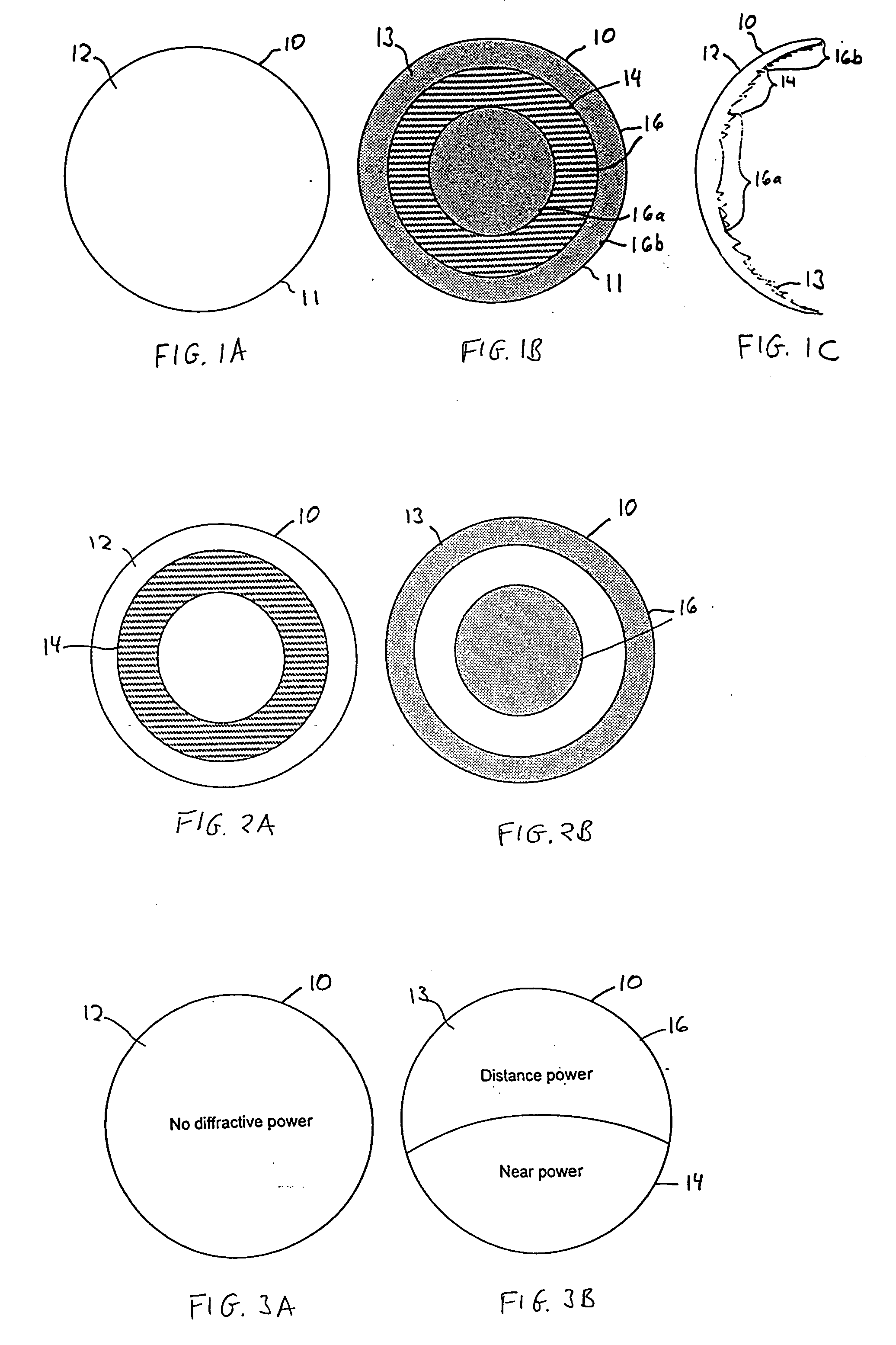
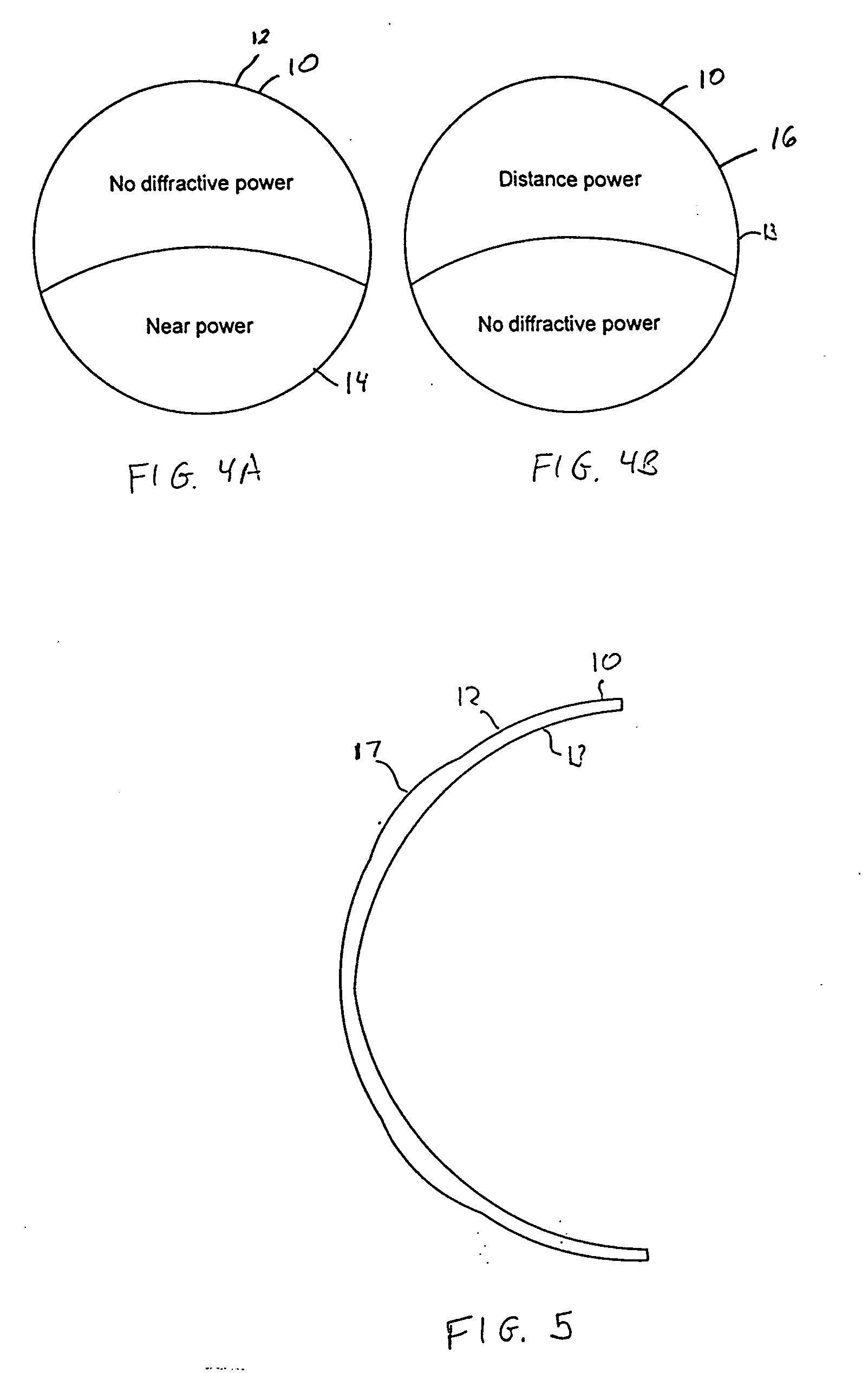
Bifocal multiorder diffractive lenses for vision correction
A bifocal multiorder diffractive lens having a lens body with one or more first regions having a first multiorder diffractive structure providing near vision correction, and one or more second regions having a second multiorder diffractive structure providing distance vision correction, in which the lens defines an aperture divided between the first and second regions. The lens body may be provided by a single optical element or multiple optical elements. In other embodiments, a bifocal multiorder diffractive lens is provided by a single or multiple element lens body having a multiorder diffractive structure for distance vision correction and one or more refractive regions to add power for near vision correction, or a single or multiple element lens body shaped for refractive power for distance vision correction and a multiorder diffractive structure for add power for near vision correction. Multiorder diffractive structures may be optimized for photopic and scotopic vision.
Owner:APOLLO OPTICAL SYST
High performance corneal inlay
A corneal inlay protects ocular structures from harmful wavelengths of light while maintaining acceptable color cosmetics, color perception, overall light transmission, photopic vision, scotopic vision, color vision, and / or cirdadian rhythms. The corneal inlay can also include a pinhole effect to increase depth of focus. In some embodiments, the corneal inlay can also correct refractive errors including, but not limited to, higher order aberration, lower order aberration, myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, and / or presbyopia.
Owner:HIGH PERFORMANCE OPTICS
Bifocal multiorder diffractive lenses for vision correction
A bifocal multiorder diffractive lens is provided having a lens body with one or more first regions having a first multiorder diffractive structure providing near vision correction, and one or more second regions having a second multiorder diffractive structure providing distance vision correction, in which the lens defines an aperture divided between the first and second regions. Such one or more first regions may represent one or more annular rings, or other portion of the lens, and the second region may occupy the portion of the lens aperture outside the first region. The lens body may be provided by a single optical element or multiple optical elements. When multiple optical elements are used, the multiorder diffractive structures may be located along an interior surface of the lens. In other embodiments, a bifocal multiorder diffractive lens is provided by a single or multiple element lens body having a multiorder diffractive structure for distance vision correction and one or more refractive regions to add power for near vision correction, or a single or multiple element lens body shaped for refractive power for distance vision correction and a multiorder diffractive structure for add power for near vision correction. The lens may represent a contact lens, a spectacle lens, or the optic portion of an intraocular implant (IOL). Multiorder diffractive structures may be optimized for performance for photopic and scotopic vision.
Owner:APOLLO OPTICAL SYST
Bifocal multiorder diffractive lenses for vision correction
A bifocal multiorder diffractive lens is provided having a lens body with one or more first regions having a first multiorder diffractive structure providing near vision correction, and one or more second regions having a second multiorder diffractive structure providing distance vision correction, in which the lens defines an aperture divided between the first and second regions. Such one or more first regions may represent one or more annular rings, or other portion of the lens, and the second region may occupy the portion of the lens aperture outside the first region. The lens body may be provided by a single optical element or multiple optical elements. When multiple optical elements are used, the multiorder diffractive structures may be located along an interior surface of the lens. In other embodiments, a bifocal multiorder diffractive lens is provided by a single or multiple element lens body having a multiorder diffractive structure for distance vision correction and one or more refractive regions to add power for near vision correction, or a single or multiple element lens body shaped for refractive power for distance vision correction and a multiorder diffractive structure for add power for near vision correction. The lens may represent a contact lens, a spectacle lens, or the optic portion of an intraocular implant (IOL). Multiorder diffractive structures may be optimized for performance for photopic and scotopic vision.
Owner:APOLLO OPTICAL SYST
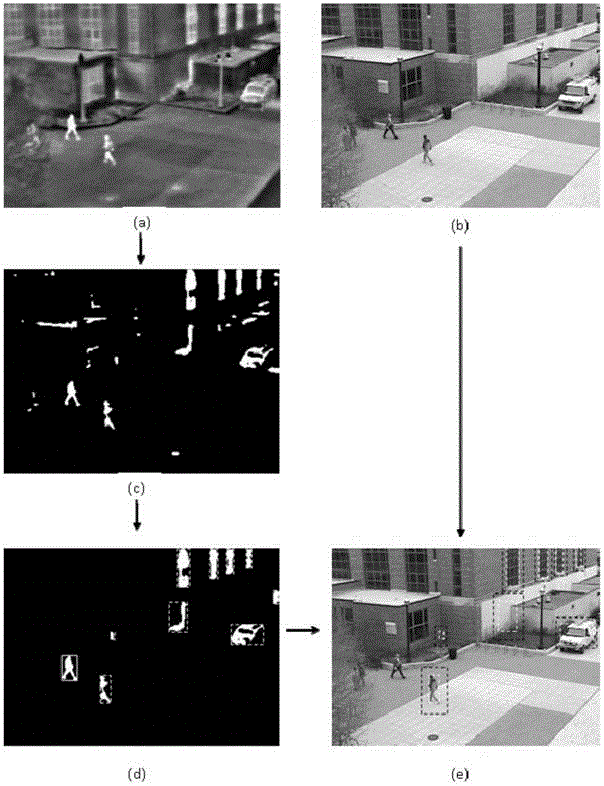
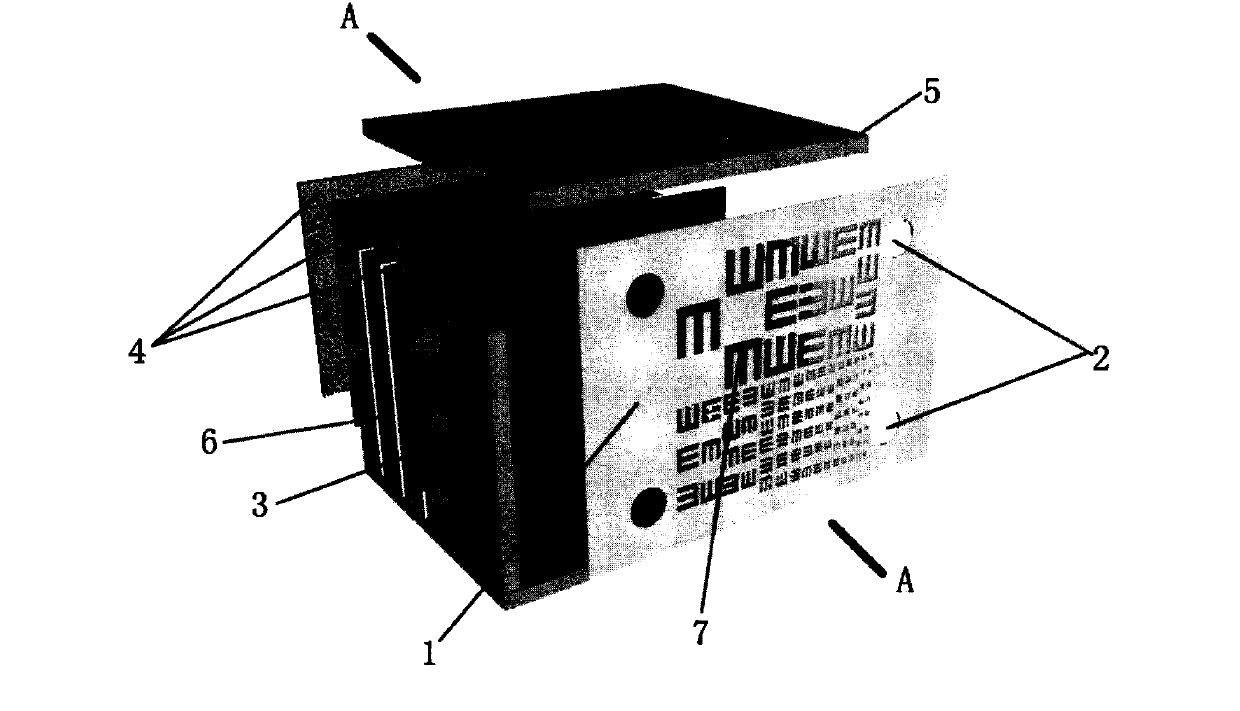
Real time double cameras provided pedestrian detection system for use under scotopic vision conditions
ActiveCN105913040AReduce missed detection rateReduce false detection rateBiometric pattern recognitionImage detectionScotopic vision
The invention relates to the technical field of image processing, more particularly, to a real time double cameras provided pedestrian detection system for use under scotopic vision conditions. The system comprises a central processing unit, an infrared camera for acquiring infrared video images, a visible light camera for acquiring visible light video images, and an infrared image detection unit for detecting if a detected infrared image contains a human target in all to-be-chosen targets in the infrared image and determining the positions of the to-be-chosen targets without a human target in the infrared image. The system also comprises a visible light image detection unit for detecting a visible light image arising at the same time with the infrared image to see if there is a human target at positions in the visible light image identical to those positions of the to-be-chosen targets without a human target in the infrared image. According to the invention, in a detection area, a choosing module marks the to-be-chosen targets excluding a human target after infrared detection and further based on the determined positions of the to-be-chosen targets excluding a human target with corresponding positions in a visible light image, uses a visible light method to do further detections.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
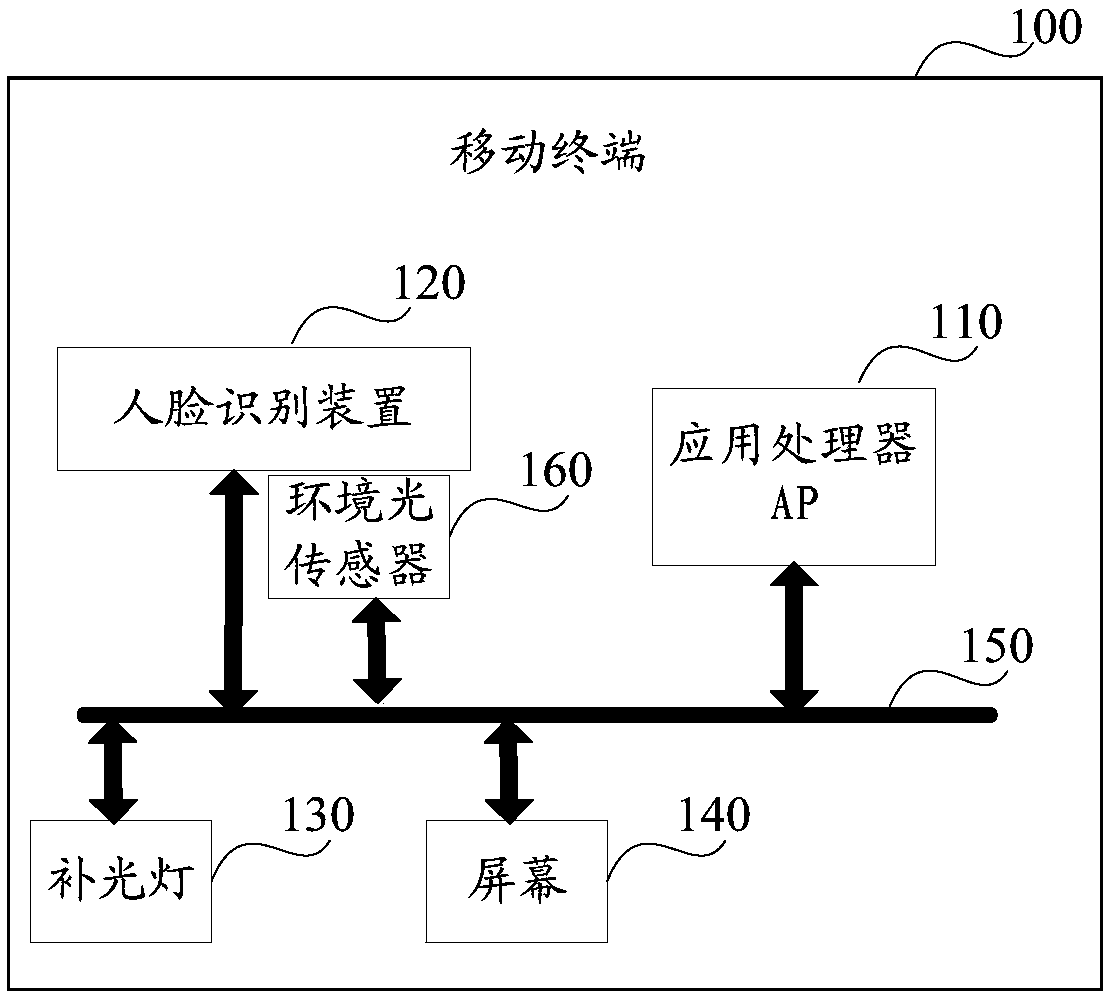
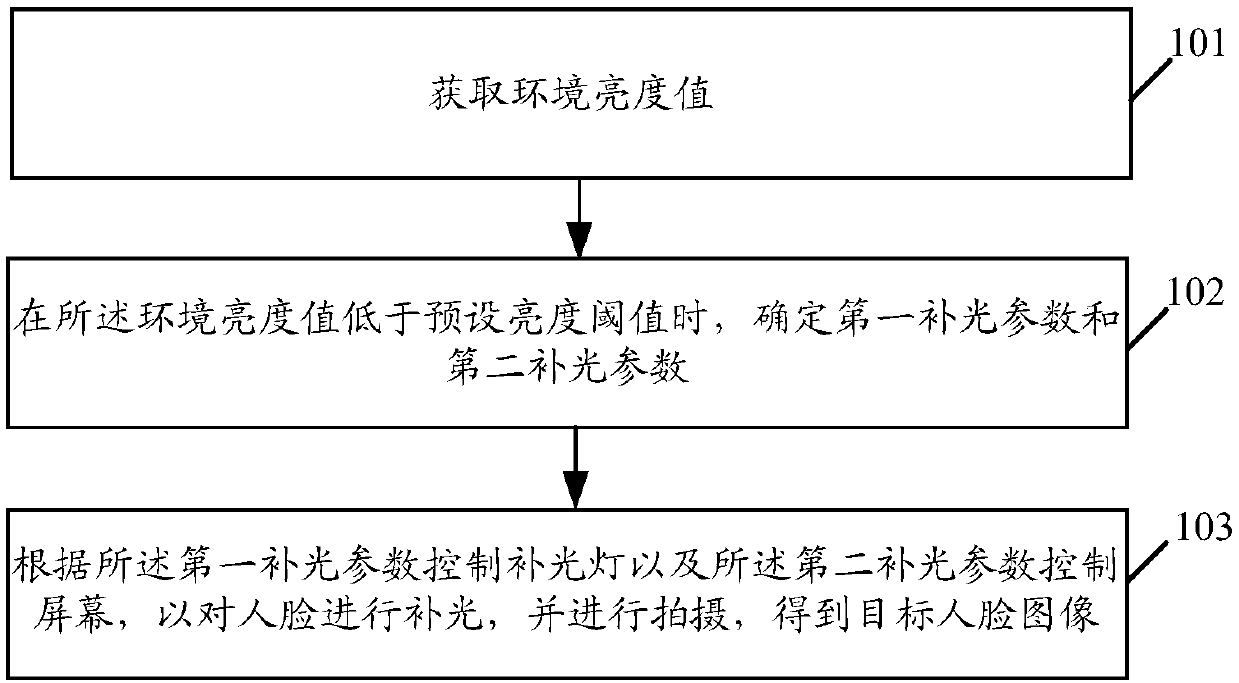
Unlocking control method and related products of the same
ActiveCN107679482AImprove recognition efficiencyImprove collection qualityCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital data authenticationVisual perceptionComputer science
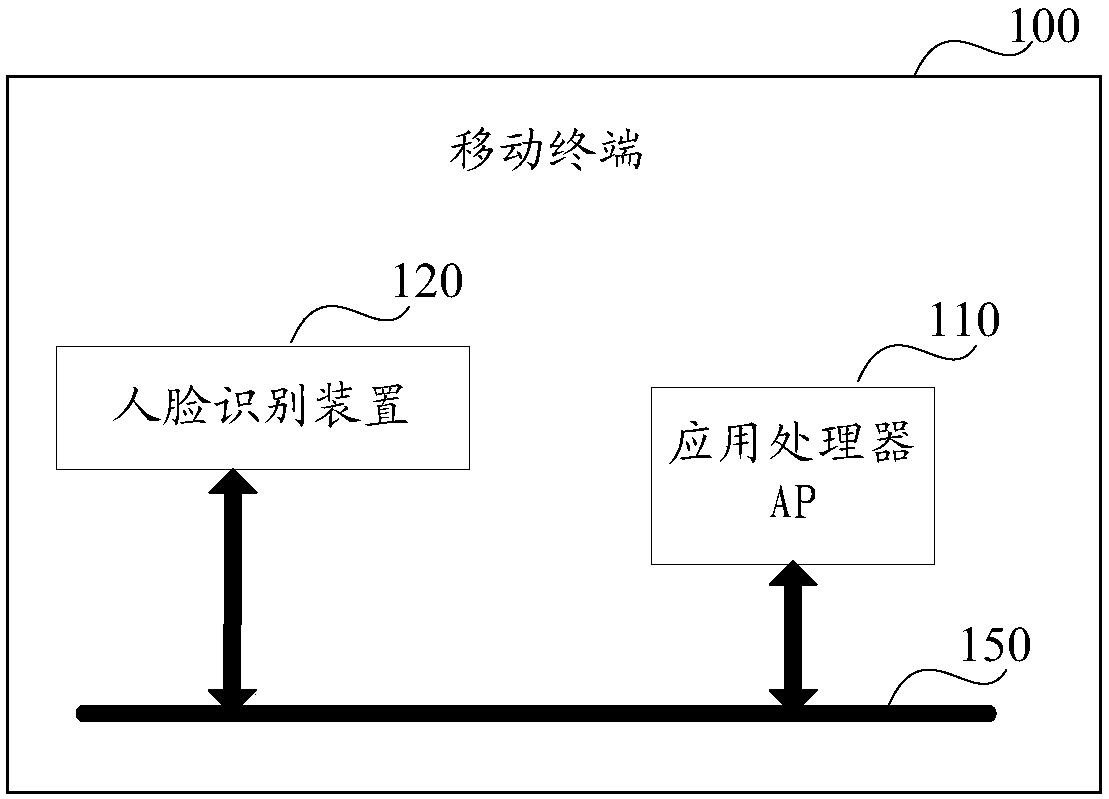
The embodiment of the invention discloses an unlocking control method and related products of the same. The unlocking control method includes the steps: acquiring an environment luminance value; whenthe environment luminance value is less than a preset luminance threshold, determining a first light supplement parameter and a second light supplement parameter; according to the first light supplement parameter, controlling a light supplement lamp, and according to the second light supplement parameter, controlling a screen, so as to perform light supplement on a human face; and shooting to obtain a target face image. The unlocking control method can perform light supplement on the human face through the light supplement lamp and the screen in the scotopic vision environment, can improve theface image acquisition quality, and is conductive to improvement of face identification efficiency.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
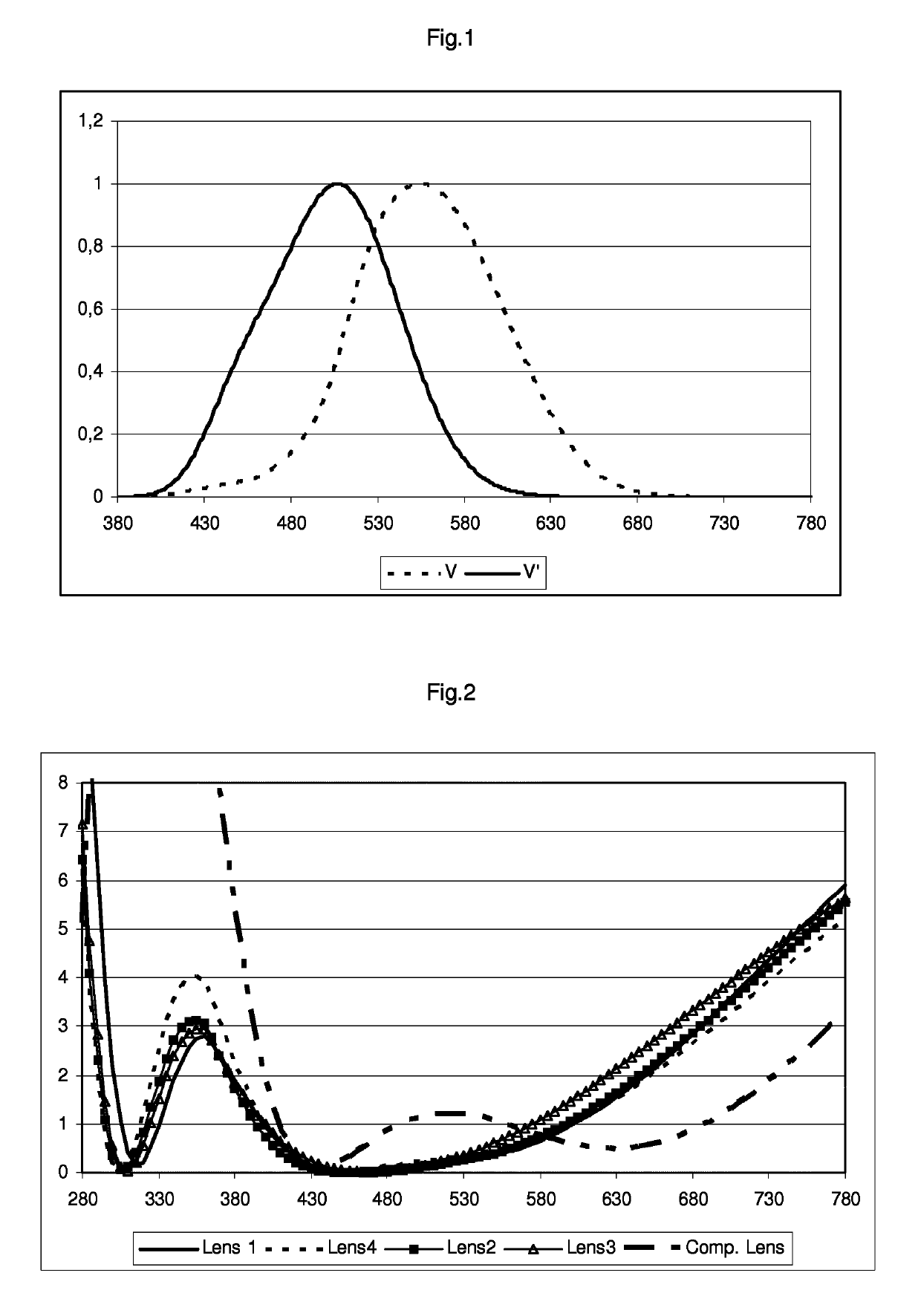
Optical article comprising an antireflective coating in the visible region for low luminance conditions
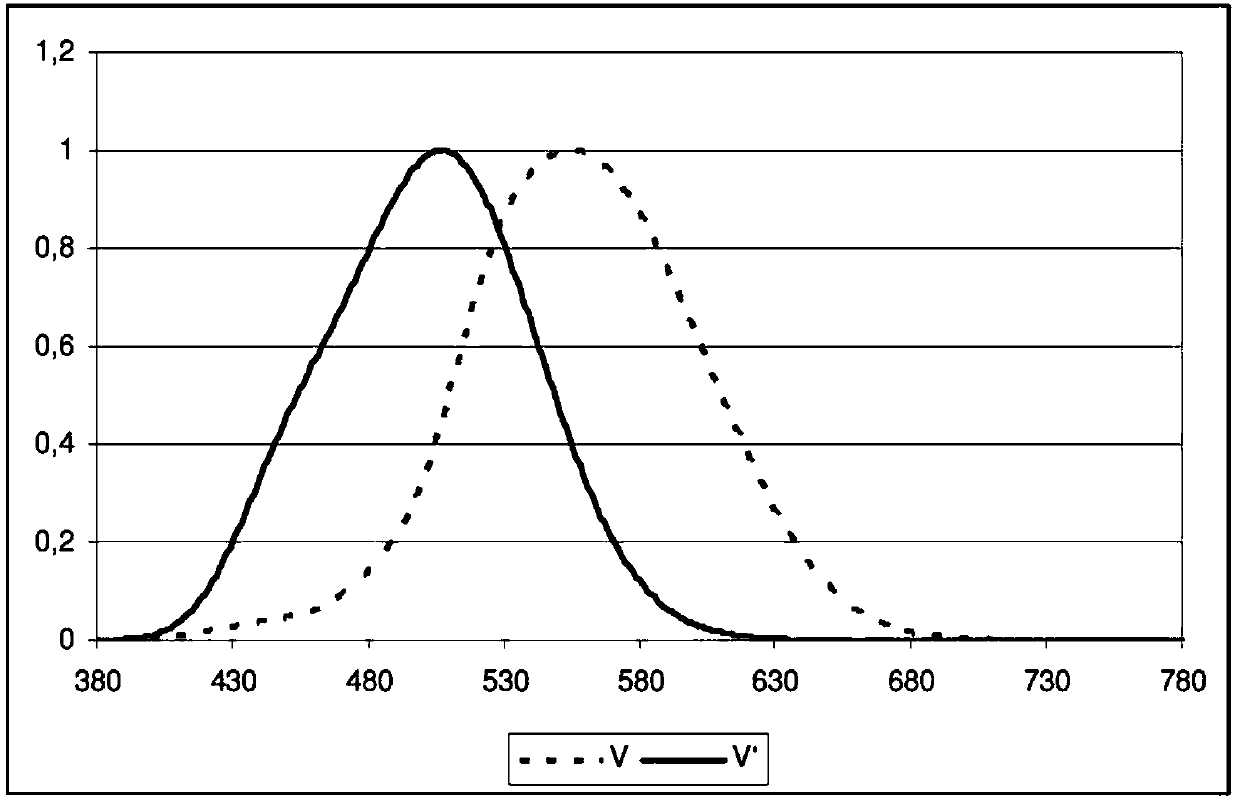
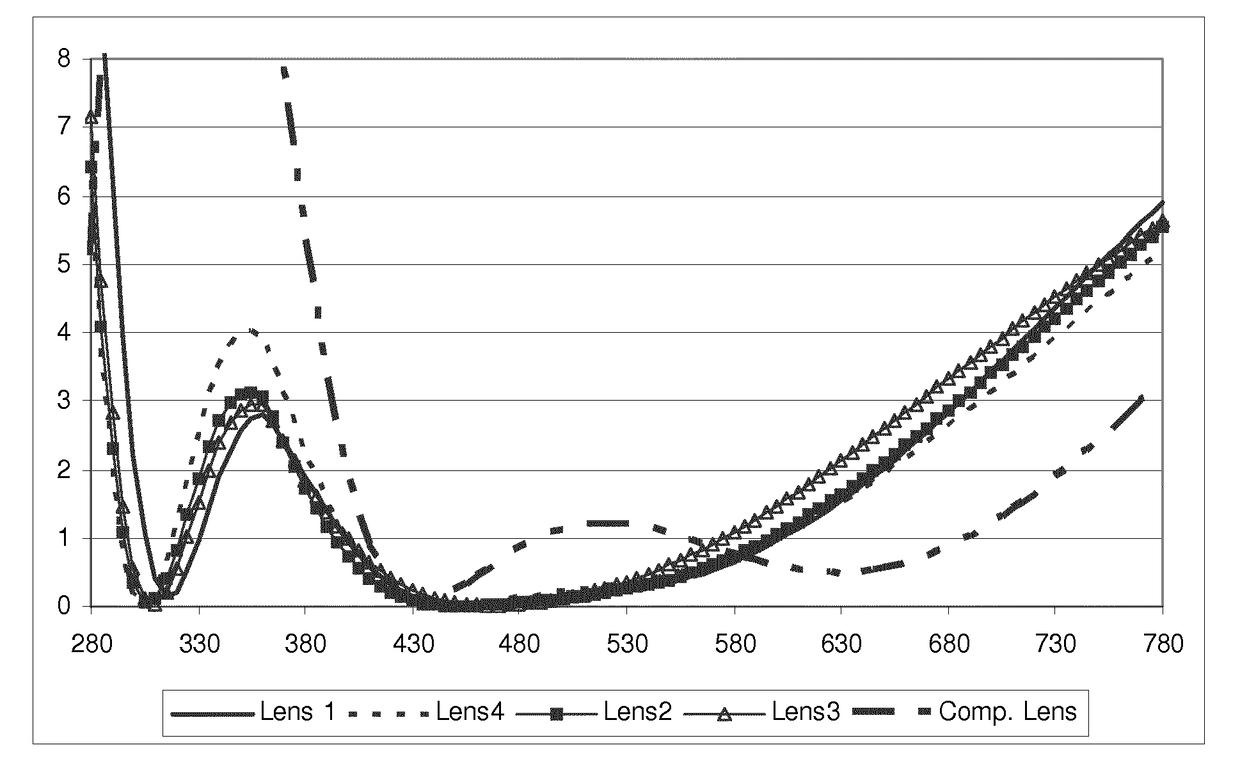
This invention relates to an ophthalmic lens comprising a transparent substrate with a front main face and with a rear main face, at least one of the main faces being coated with a multilayered antireflective coating comprising a stack of at least one high refractive index layer (HI) having a refractive index higher than or equal to 1.55 and at least one low refractive index layer (LI) having a refractive index lower than 1.55, characterized in that said multilayered antireflective coating has: a mean light reflection factor in the visible region for photopic vision Rv lower than or equal to 2.5%, preferably lower than or equal to 0.9%, for at least an angle of incidence lower than 35 degrees; a mean light reflection factor in the visible region for scotopic vision Rv' lower than or equalto 0.5%, preferably lower than or equal to 0.4%, for at least an angle of incidence lower than 35 degrees.
Owner:RUPP HUBRACH OPTIK
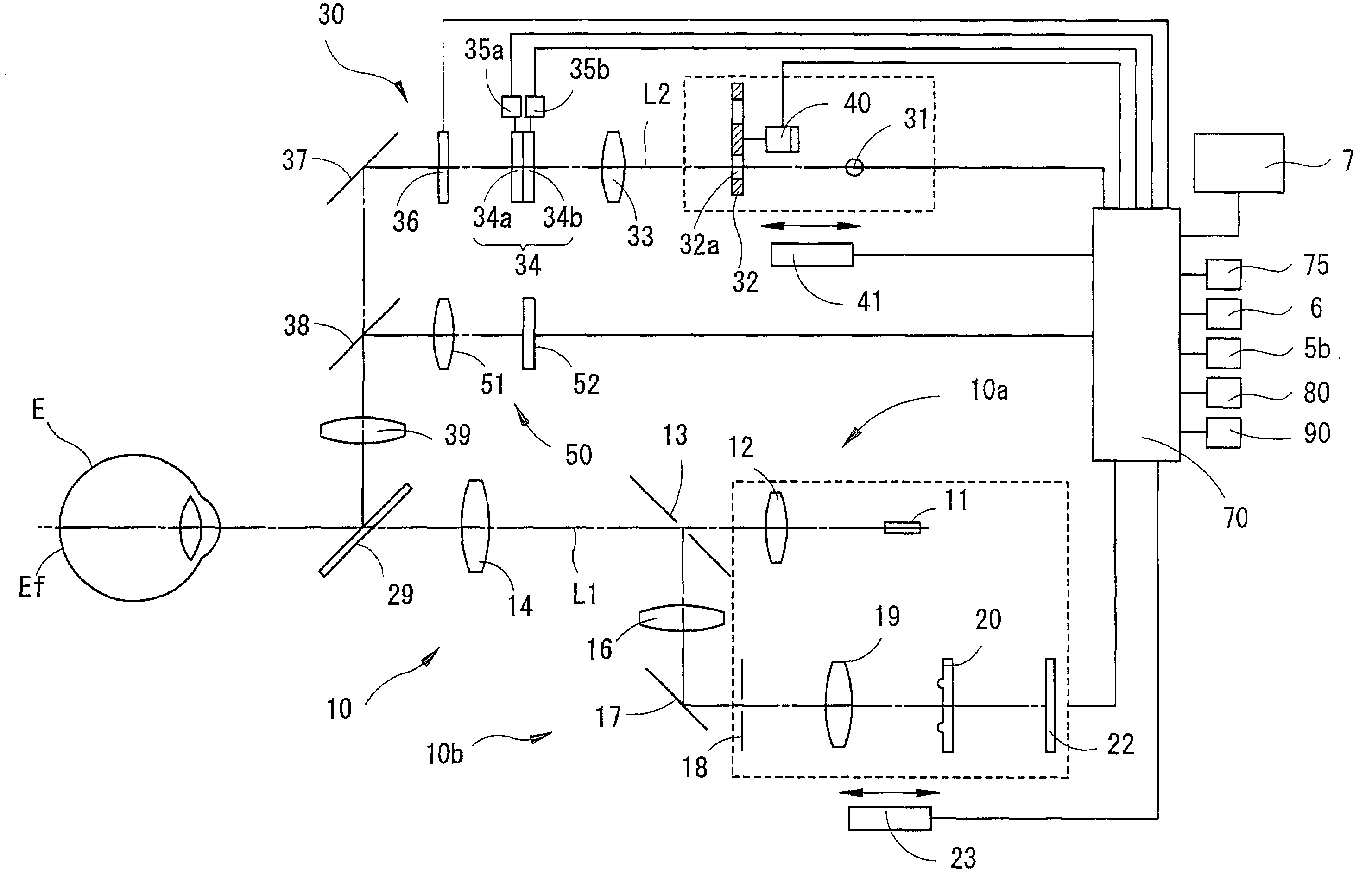
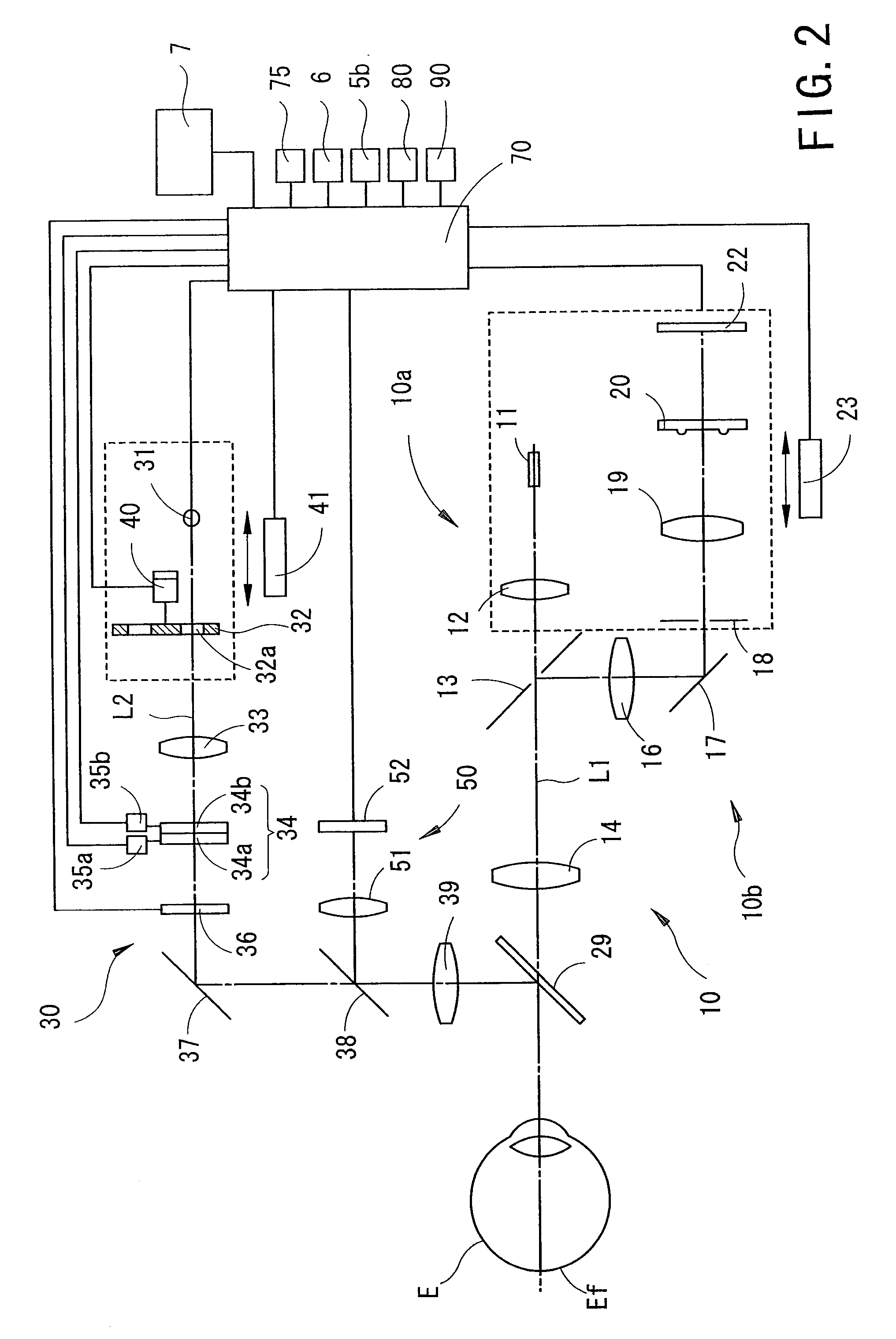
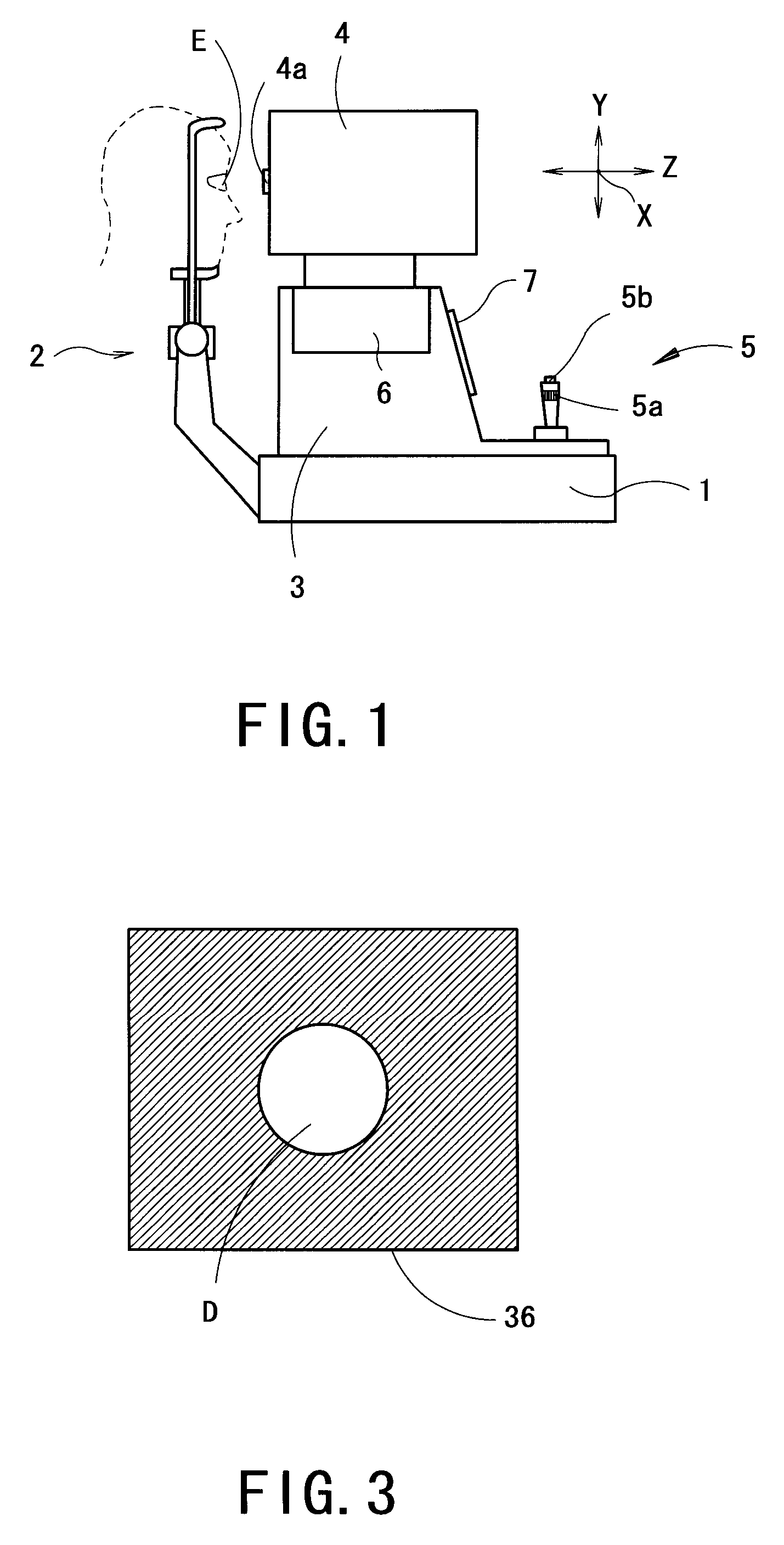
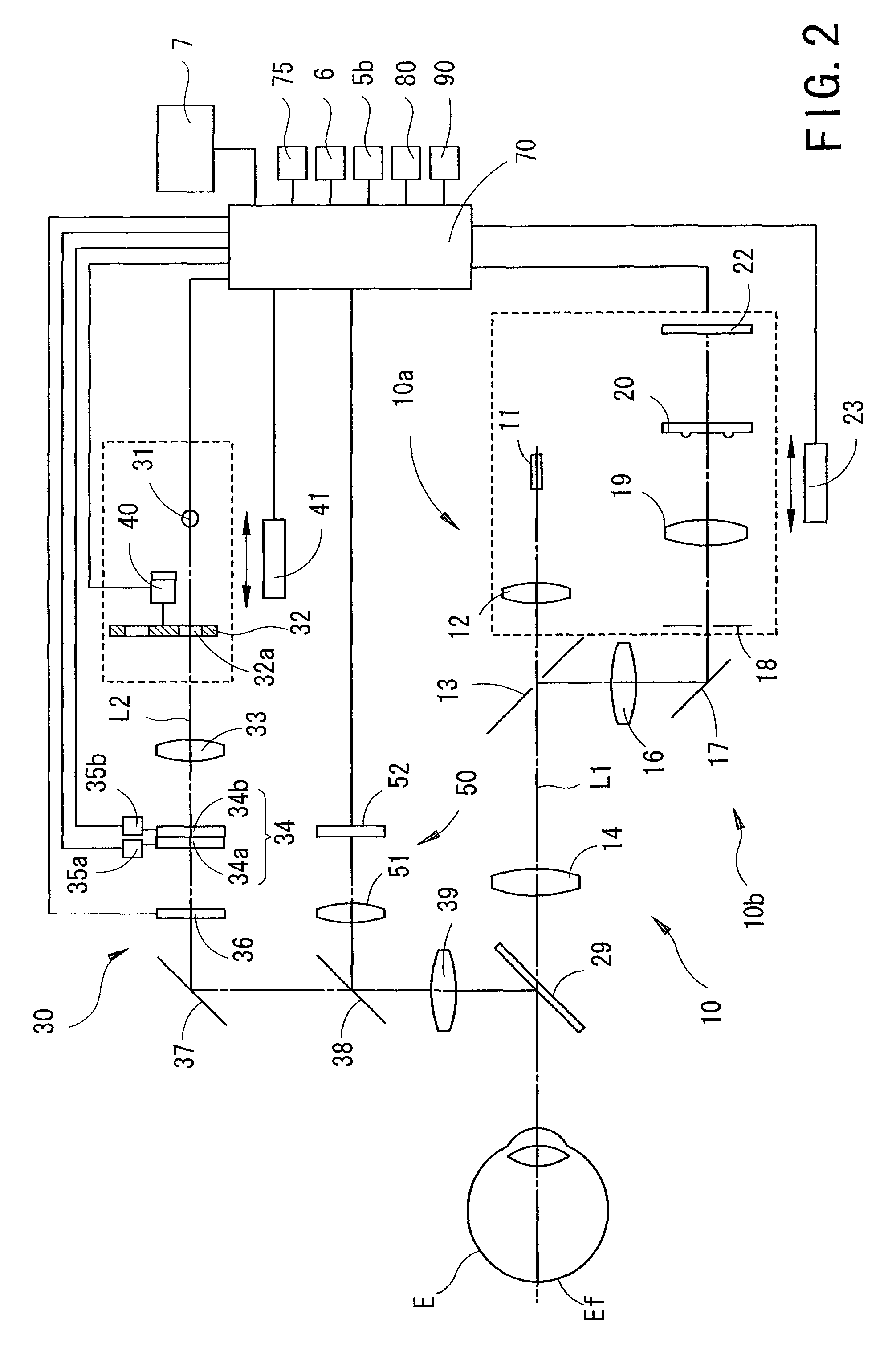
Ophthalmic apparatus
Owner:NIDEK CO LTD
Image processing method and related products
ActiveCN107633499ARich color informationImprove experienceImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingVisual perception
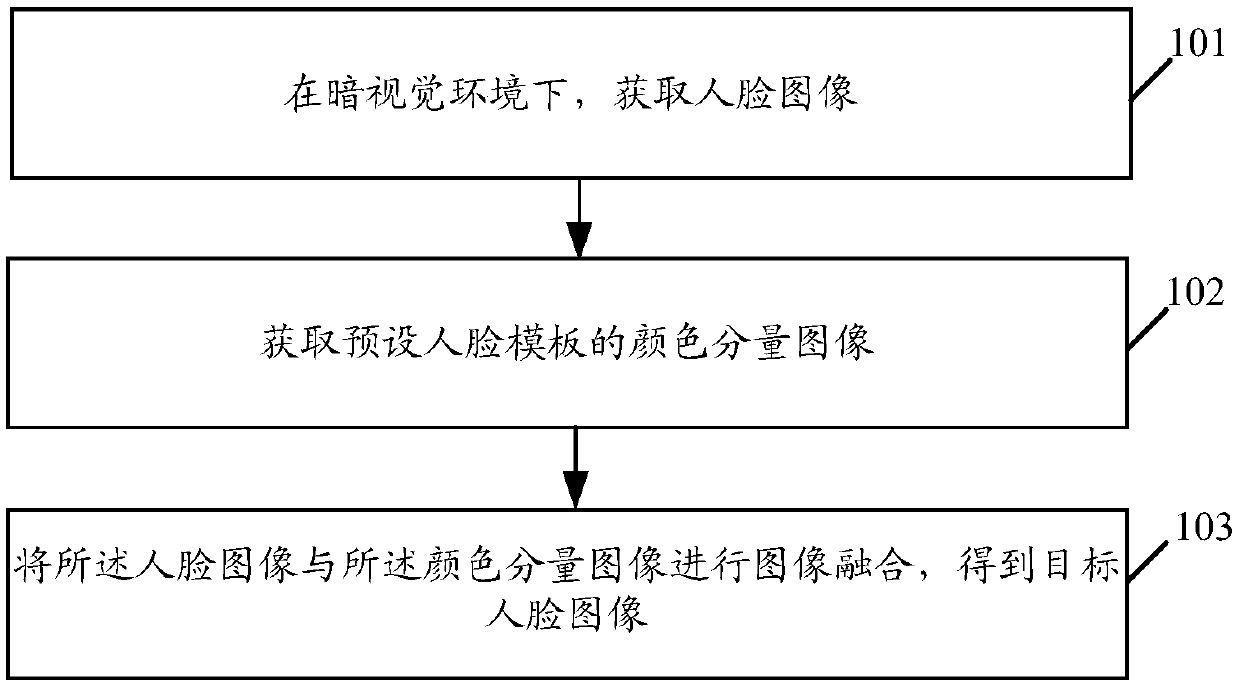
Embodiments of the invention disclose an image processing method and related products. The method includes: obtaining a face image in a scotopic vision environment; obtaining a color component image of a preset face template; and performing image fusion on the face image and the color component image to obtain a target face image. According to the method and the related products, after the face image is obtained, the color component image is obtained from the preset face template, and insufficient color information of the face image acquired in the scotopic vision is made up by employing colors of the template so that the face image with abundant color information is obtained, and the user experience is enhanced.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
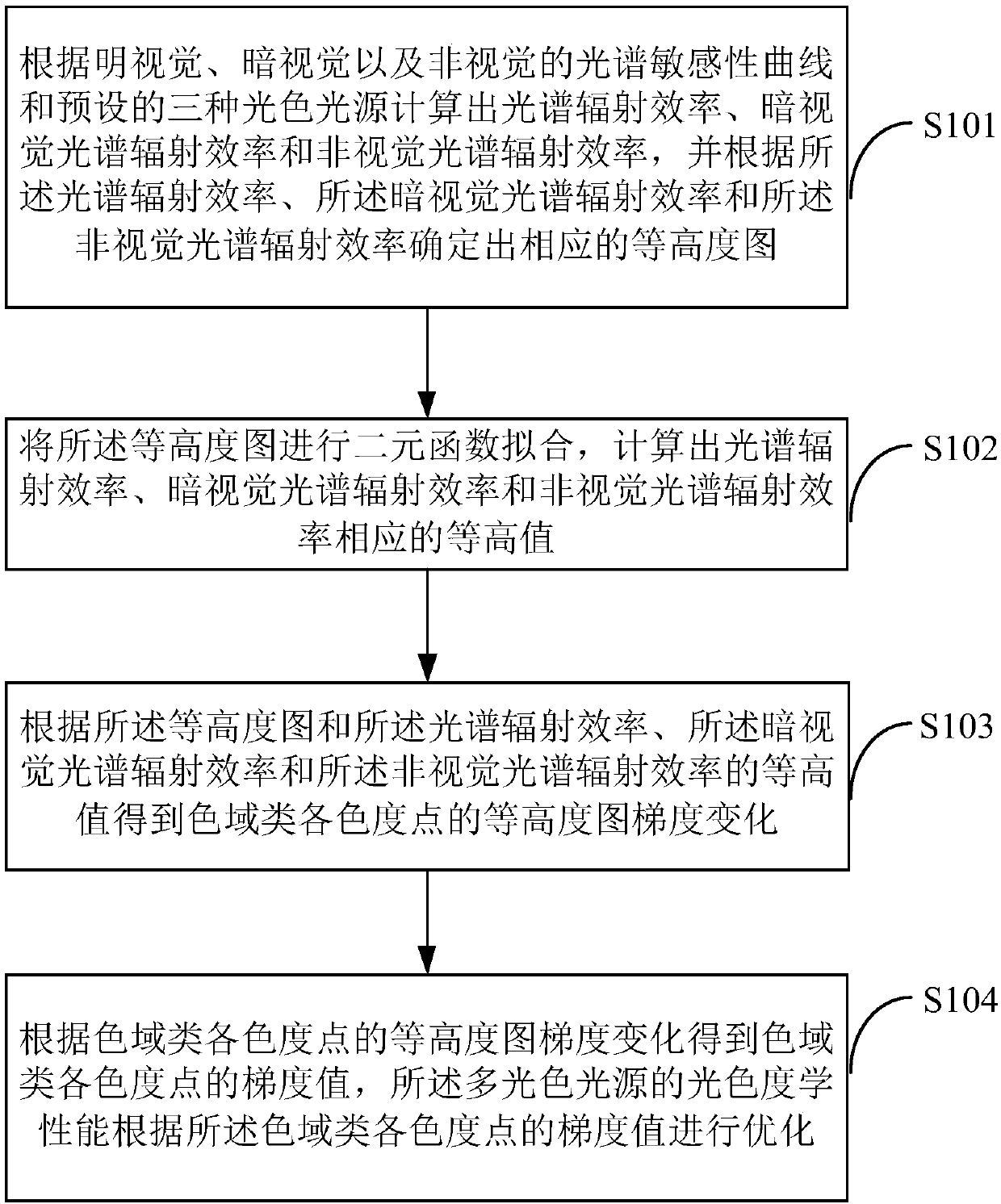
Comprehensive evaluation optimization method and comprehensive evaluation optimization system for light source vision and non-vision effect performance
InactiveCN105510003AEasy to optimizeImprove performanceMaterial analysis by optical meansTesting optical propertiesVisual matchingLighting spectrum
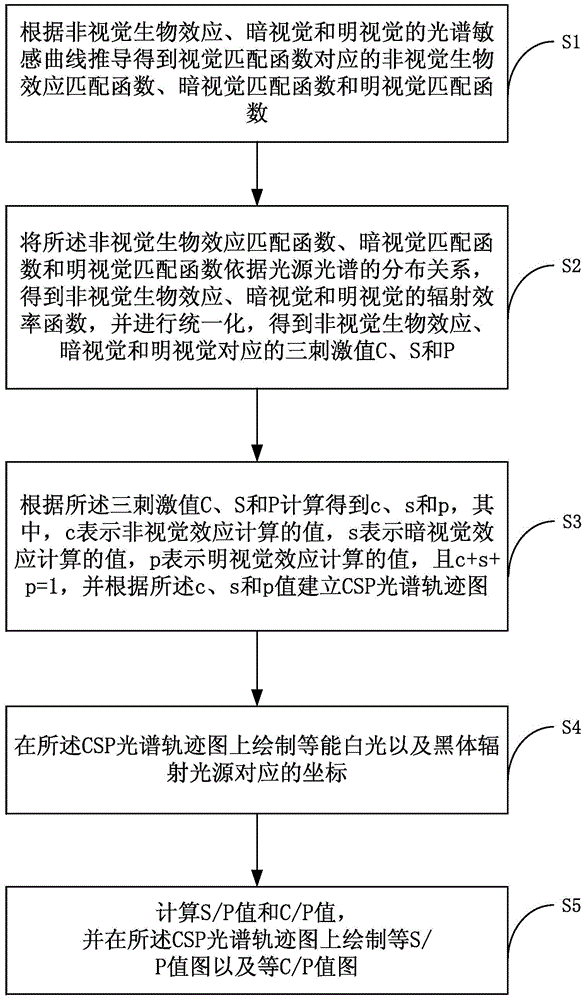
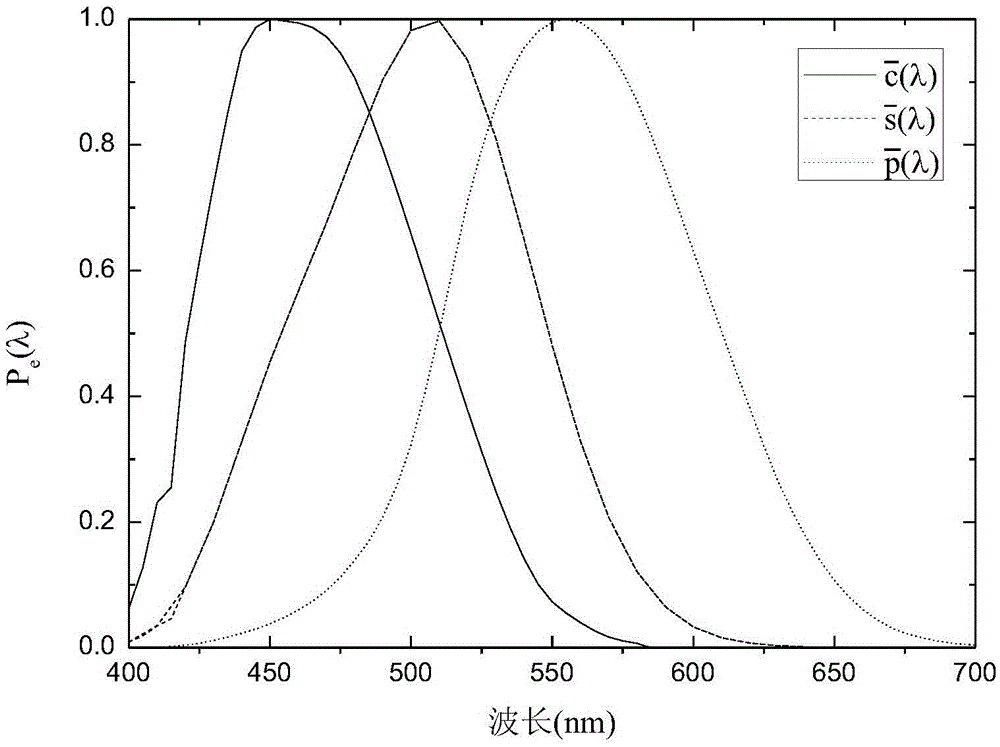
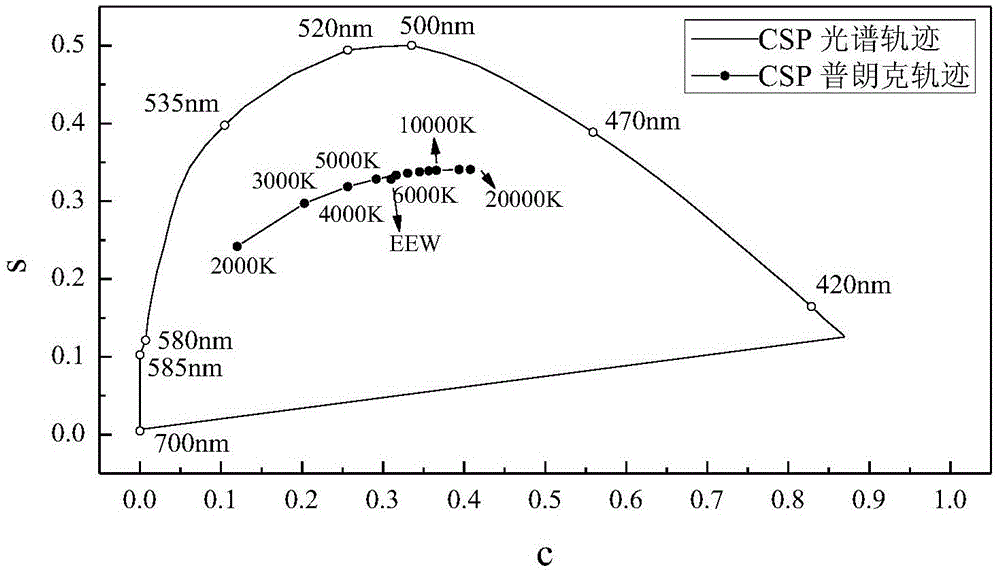
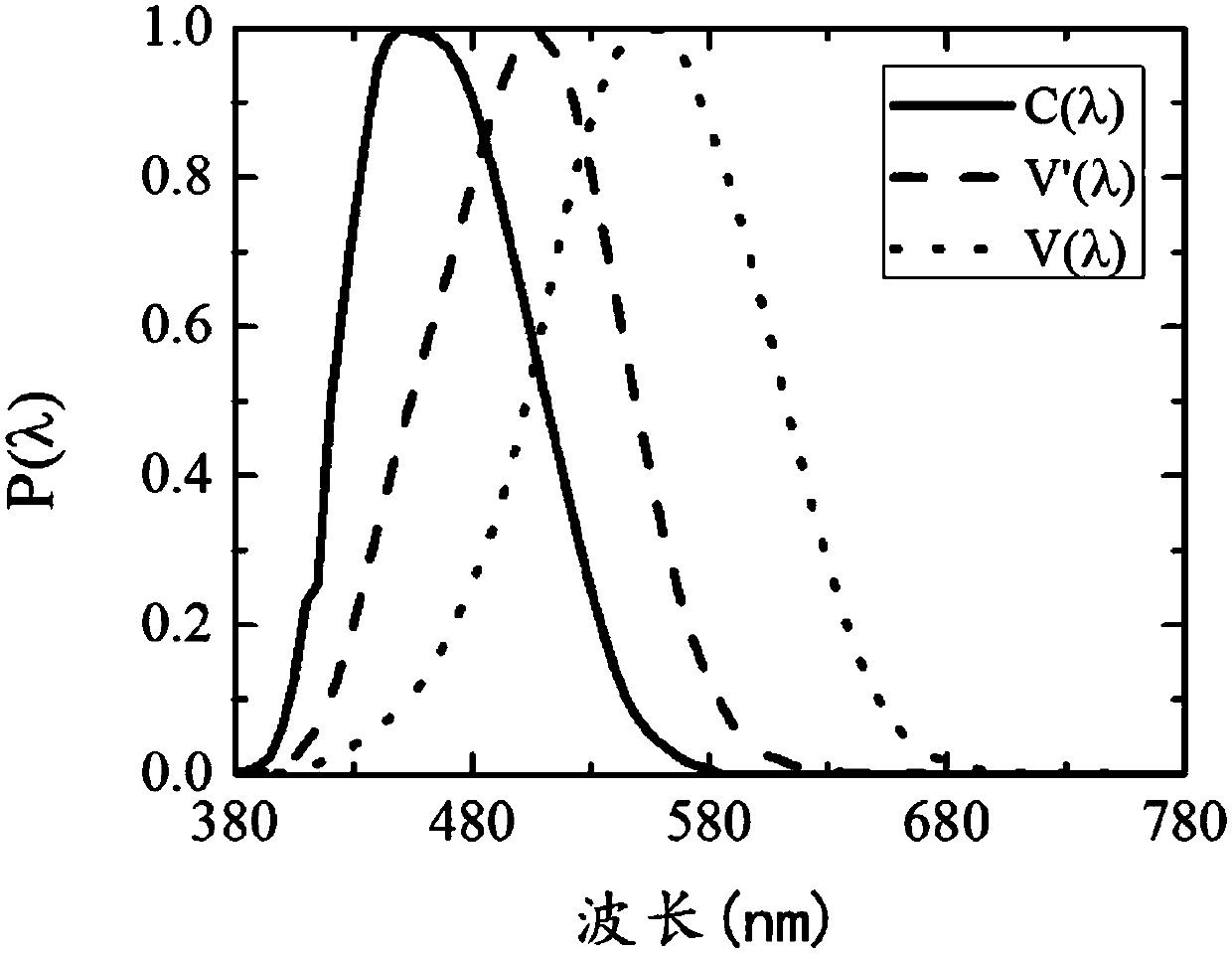
The invention is suitable for the technical field of an illumination spectrum, and provides a comprehensive evaluation optimization method for a light source vision and non-vision effect performance. The comprehensive evaluation optimization method comprises the following steps of obtaining a non-vision biological effect matching function c<->(lambda), a scotopic vision matching function s<->(lambda) and a photopic vision matching function p<->(lambda) according to a spectrum-sensitive curve of a non-vision biological effect C(lambda), a scotopic vision V'(lambda) and a photonic vision V(lambda); according to the c<->(lambda), the s<->(lambda) and the p<->(lambda) and the arrangement relationship of light source spectrums, obtaining radiation efficiency functions of the C(lambda), the V'(lambda) and the V(lambda), and performing unification for obtaining three stimulus values C, S and P which correspond with the C(lambda), the V'(lambda) and the V(lambda); calculating c, s and p, and establishing a CSP spectrum locus diagram according to the c, the s and the p; drawing a coordinate which corresponds with an equal-energy white and black-body radiation light source on the CSP spectrum; and drawing an S / P value spectrum and a C / P value spectrum on the CSP spectrum. According to the comprehensive evaluation optimization method, related visions are integrated and unified, thereby facilitating comprehensive performance improvement of different visions and realizing accurate calculation; and furthermore light source spectrum optimization is facilitated, thereby satisfying a requirement for required visual performance.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Lighting device
InactiveUS20120268927A1Reduce glareReduce unpleasantnessMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceIrradiationScotopic vision
A lighting device includes a lower irradiation portion for irradiating light mainly in a vertically downward direction and an upper irradiation portion for irradiating light more horizontally than the lower irradiation portion. An irradiation angle of the upper irradiation portion is smaller than that of the lower irradiation portion. The upper irradiation portion is configured to reduce an S / P ratio denoting a ratio of scotopic vision luminance to photopic vision luminance.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Device for measuring brightness
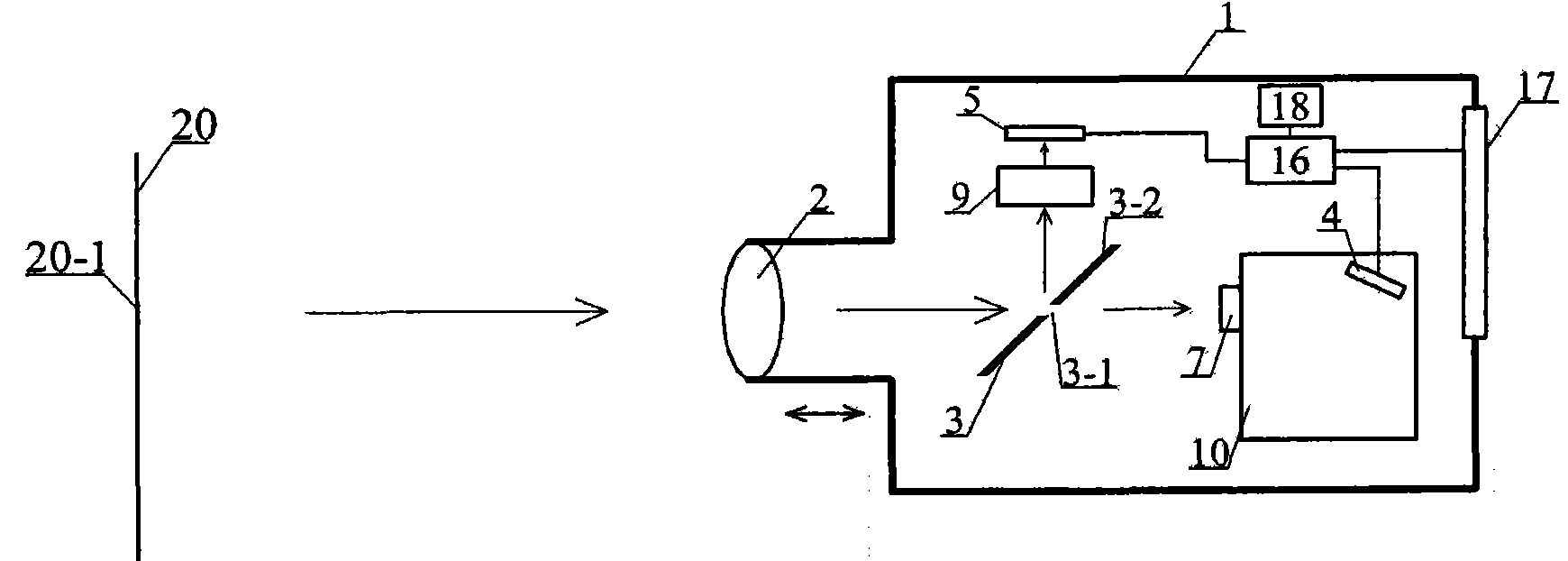
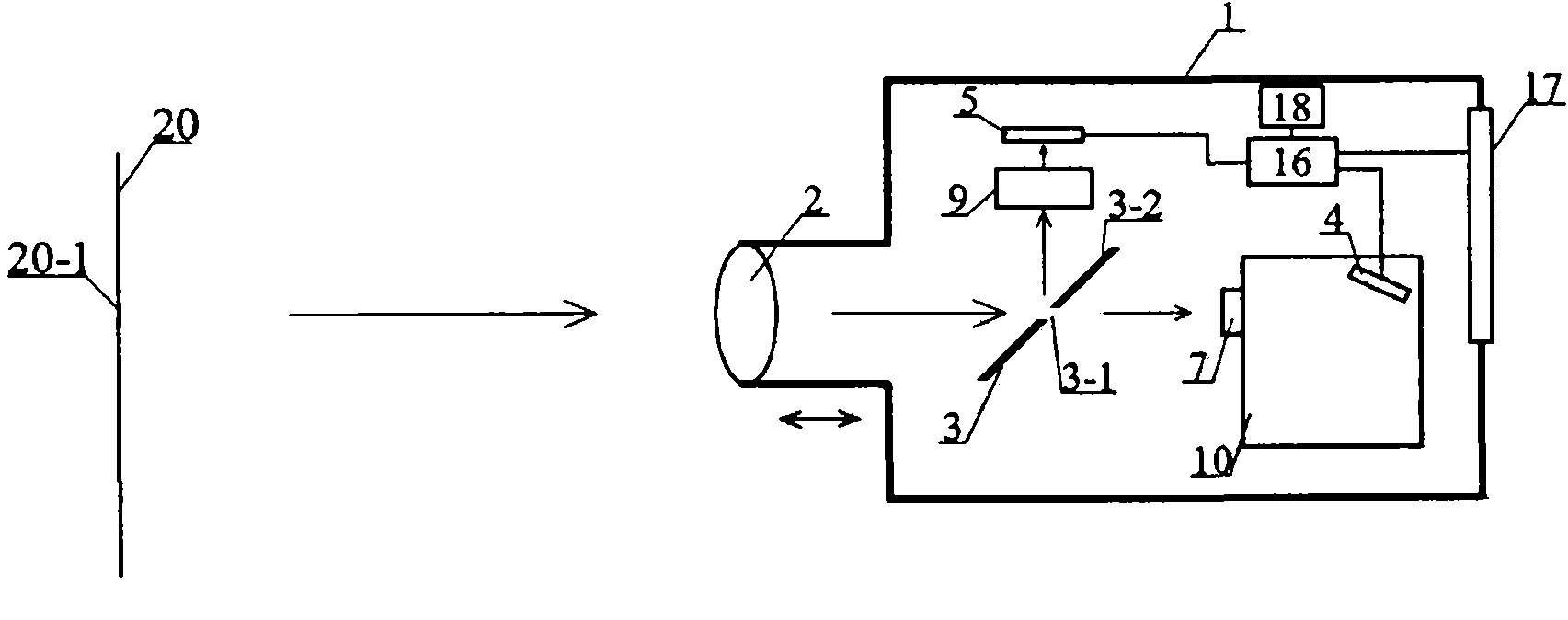
ActiveCN101813517AEasy to operateGood repeatabilitySpectrum investigationPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsCamera lensOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a device for measuring brightness, which comprises a shell, wherein a lens is arranged at an incident port of the shell. Light from the lens is divided into two beams, wherein one beam is received by a first photoelectric detector through an aperture field diaphragm, while the other beam is received by a second photoelectric detector. The first photoelectric detector measures the brightness and spectrum parameters of an aiming point, and the second photoelectric detector can simultaneously display and record illumination information of peripheral environment of the aiming point, and measure image brightness. The device for measuring the brightness has high measurement accuracy, can simultaneously provide brightness values of photopic vision, scotopic vision and mesopic vision, and has the characteristics of complete measurement functions, convenient operation and high repeatability.
Owner:HANGZHOU EVERFINE PHOTO E INFO
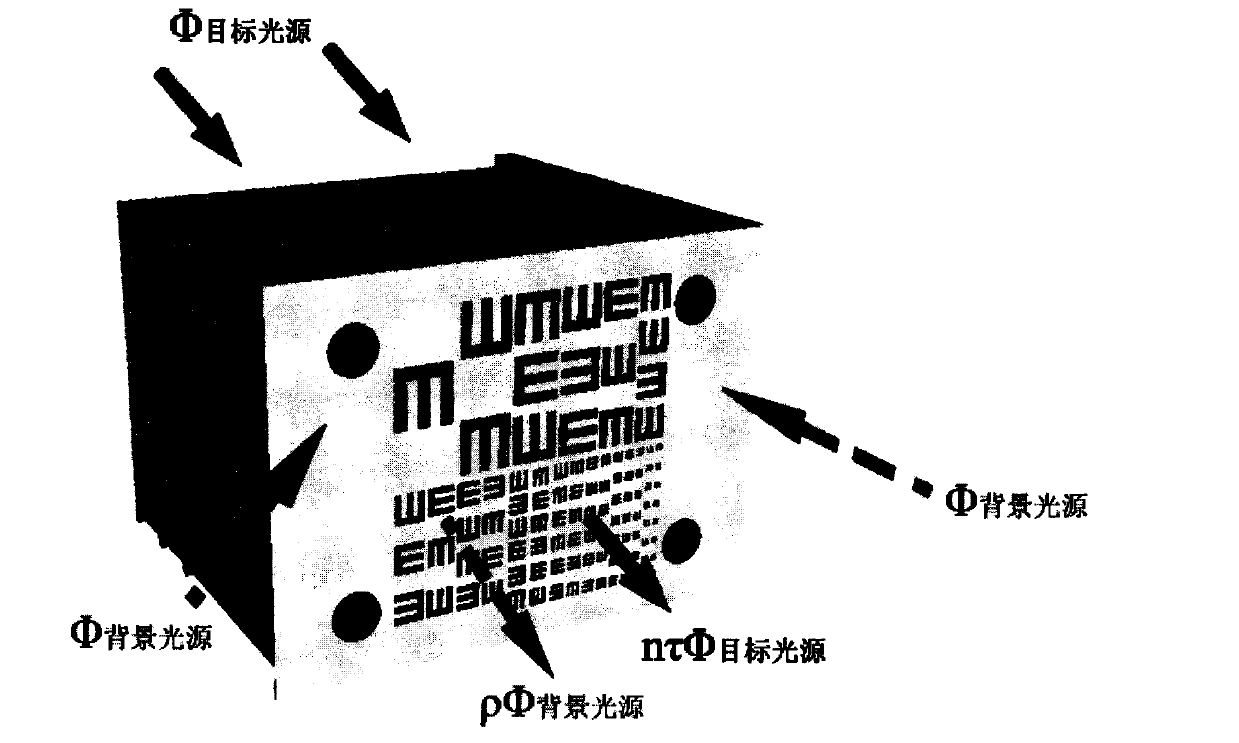
Method and experimental device for carrying out vision measurement by adjusting objective and background luminance
The invention relates to a method and experimental device for carrying out vision measurement by adjusting objective and background luminance. According to the method and experimental device for carrying out the vision measurement by adjusting the objective and background luminance, a colorless dull polish film is used as an attenuation sheet to control the luminance of an objective light source, diffuse reflection white foam of high reflectance is used for reflecting changes of the luminance of a background control light source, under the situation that the luminance of the objective light source or the luminance of the background light source in a visual field is maintained to be unchanged, the luminance of one of the objective light source or the background light source is changed in an infinitely variable mode to achieve different objective contrast ratios, a standard logarithmic visual acuity chart is taken as an observation visual standard in a hollow mode, and therefore the vision degrees under contrast ratios of different objectives are measured. The method and experimental device for carrying out the vision measurement by adjusting the objective and background luminance can enable illumination levels under all kinds of visual conditions to be simulated, can quantitatively evaluate the quality of different types of light sources (such as LEDs, high pressure sodium lamps and high pressure mercury lamps) in illumination engineering, and can quantitatively measure the visual degrees of objectives in different illuminating levels (such as photopic vision, scotopic vision or mesopic vision).
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
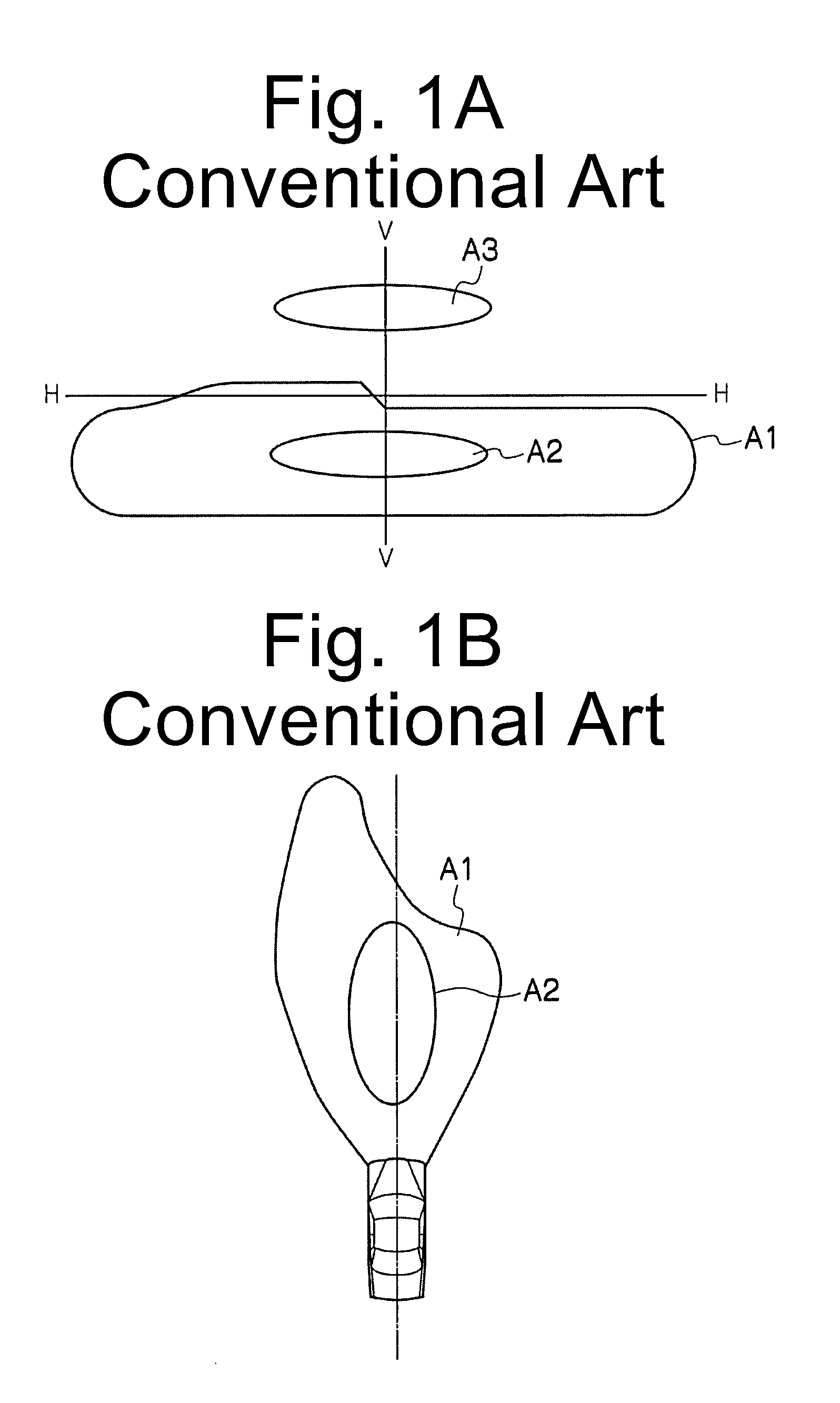
Vehicle headlight
A vehicle headlight can facilitate an earlier awareness with peripheral vision under dark environment (such as during nighttime, tunnel, or adverse weather driving). The light source can include a plurality of white LEDs. The plurality of white LEDs include a first white LED and a second white LED. The first white LED has an S / P ratio, which is represented by (S(λ)*V′(λ)) / (S(λ)*V(λ)) in which S(λ) is a spectrum of the first light source, V′(λ) is a relative luminosity factor in scotopic vision, and V(λ) is a relative luminosity factor in photopic vision, lower than that of the second white LED.
Owner:STANLEY ELECTRIC CO LTD
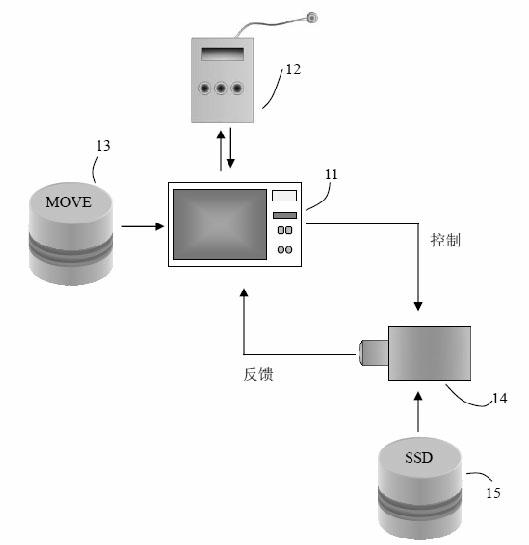
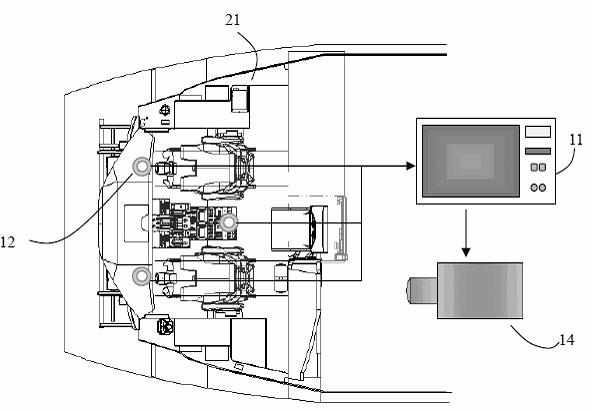
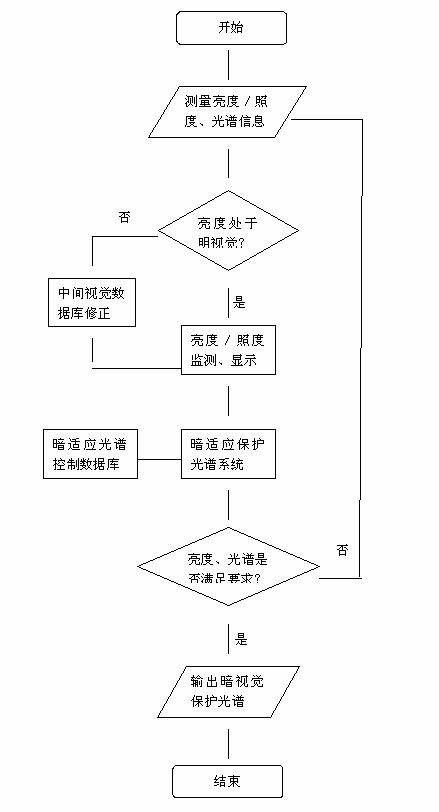
Scotopic vision protection system for cockpit pilot under quiet and dark flight state of aircraft and luminous environment monitoring method
The invention relates to a scotopic vision protection system for a cockpit pilot under a quiet and dark flight state of an aircraft and a luminous environment monitoring method. The scotopic vision protection system consists of an illuminance / brightness monitoring, display and control device, an illuminance / brightness / spectrum monitoring instrument, a mesopic vision / scotopic vision correction database, a scotopic adaptation protection spectrum system and a scotopic adaptation spectrum control database; when the aircraft is in the quiet and dark flight state, the illuminance / brightness is detected, a corresponding spectrum is tested, if the measured illuminance / brightness is positioned in a photopic vision range, the illuminance / brightness is not corrected, and if the illuminance / brightness is positioned in a mesopic vision brightness range, the illuminance / brightness is corrected by a mesopic vision model database and correct illuminance / brightness information is acquired; and when the measured illuminance / brightness and spectrum information is input to the monitoring and display device, the device controls the scotopic adaptation protection spectrum system to compensate the illuminance / brightness information, and the output spectrum distribution is controlled by the scotopic adaptation spectrum control database. The scotopic vision protection system effectively protects the scotopic vision of the pilot under the condition of finishing flight control vision tasks.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Optical Article Comprising an Antireflective Coating in the Visible Region for Low Luminance Conditions
ActiveUS20180067338A1Reduce reflectivityCoatingsOptical partsAnti-reflective coatingAngle of incidence
This invention relates to an ophthalmic lens comprising a transparent substrate with a front main face and with a rear main face, at least one of the main faces being coated with a multilayered antireflective coating comprising a stack of at least one high refractive index layer (HI) having a refractive index higher than or equal to 1.55 and at least one low refractive index layer (LI) having a refractive index lower than 1.55, characterized in that said multilayered antireflective coating has: a mean light reflection factor in the visible region for photopic vision Rv lower than or equal to 2.5%, preferably lower than or equal to 0.9%, for at least an angle of incidence lower than 35°; a mean light reflection factor in the visible region for scotopic vision Rv′ lower than or equal to 0.5%, preferably lower than or equal to 0.4%, for at least an angle of incidence lower than 35°.
Owner:RUPP HUBRACH OPTIK
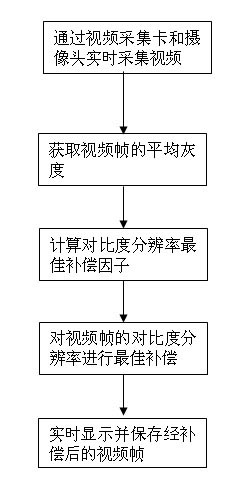
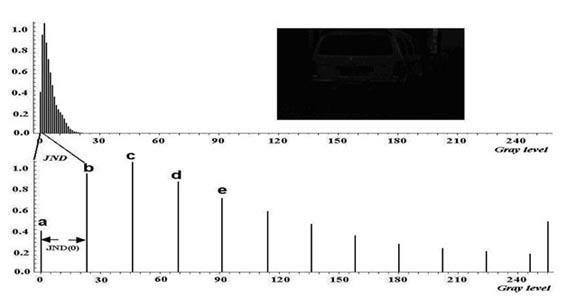
Adaptive bottom video online mining system and method based on contrast resolution compensation
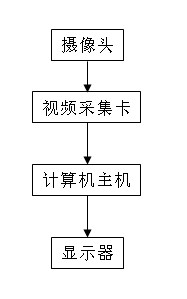
InactiveCN102186054ARealize the underlying online miningMake up for the lack of contrast resolutionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsMachine visionIlluminance
The invention provides an adaptive bottom video online mining system and method based on contrast resolution compensation. The system comprises a camera, a video capture card, a computer host and a display. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a video image transmitted from the camera by utilizing the video capture card; calculating the average gray of a current video frame; calculating the best compensation factor of contrast resolution according to the average gray; compensating the contrast resolution of the video frame by applying the best compensation factor; and displaying the compensated video in real time, and storing. By adopting the technical scheme in the invention, the video capture in a low illumination level environment can be compensated in real time, and bottom online mining of the real-time video images in the low illumination level environment can be realized, so that the defect of insufficient contrast resolution of people in a scotopic vision environment is overcome, and machine vision in the scotopic vision environment is realized.
Owner:谢丹玫 +3
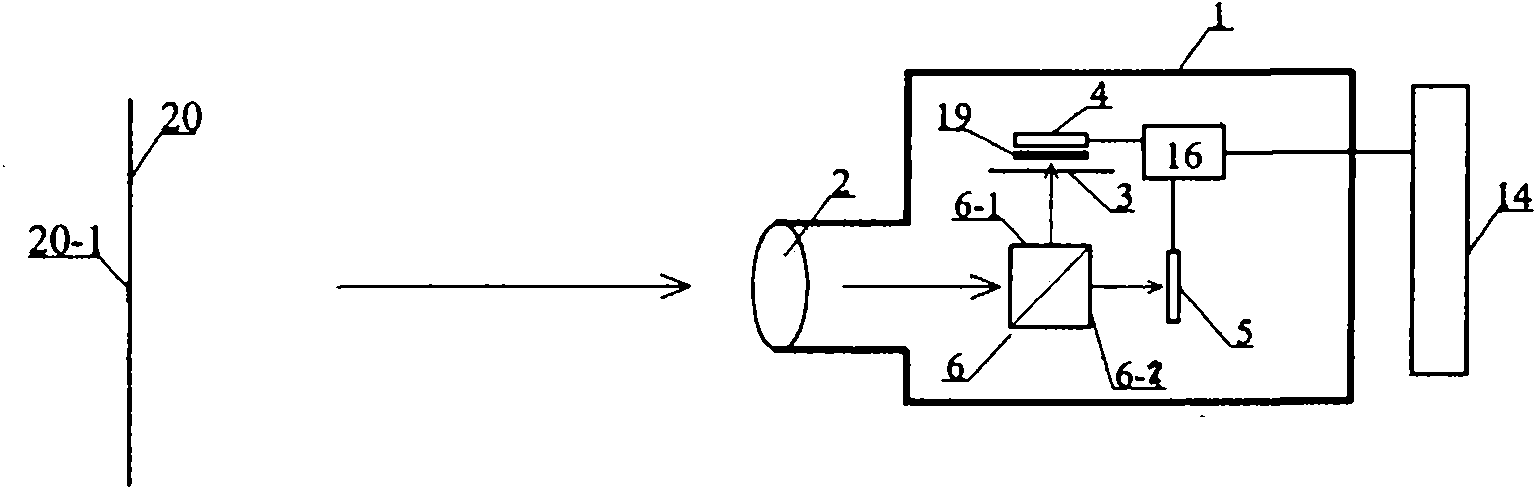
Brightness meter
InactiveCN101799324AEasy and accurate measurementEasy to measurePhotometry using electric radiation detectorsPhotovoltaic detectorsLuminance meter
The invention discloses a brightness meter. The brightness meter comprises a machine shell; light beams to be measured enter into the machine shell through a lens; an ostiole reflector and a photoelectric detector are arranged in the machine shell, a V(lambda) modified color filter and a V' (lambda) modified color filter are arranged in front of the photoelectric detector, and the photoelectric detector respectively measures the photopic vision brightness value and the scotopic vision brightness value of a measure target and obtains a mesopic vision brightness value by calculating. One brightness meter of the invention can measure the photopic vision brightness value and the scotopic vision brightness value conveniently, the mesopic vision brightness value can be obtained through calculation, the operation is simple and convenient, and high-accuracy measurement can be easily realized.
Owner:HANGZHOU EVERFINE PHOTO E INFO
Method for detecting mesoptic vision photometric quantity and double-photometry detection apparatus thereof
InactiveCN101430225AGood ambient lightingPhotometry using wholly visual meansAmbient lightingLuminance meter
The invention discloses a method for detecting a mesopic vision photometric value and a double-photometric detector thereof. The method comprises a step of adopting a photometric detector which is corrected by a photopic vision visual curve, and a photometric detector which is corrected by a scotopic vision visual curve. The method is characterized by measuring background luminance B under a mesopic vision environment condition by a luminance meter during measurement, and finding out the maximum value of luminous efficacy according to the background luminance B, thus determining the proportion of the scotopic vision visual curve and the photopic vision visual curve; and displaying the mesopic vision photometric value under the background luminance by computation according to the proportion of the scotopic vision visual curve and the photopic vision visual curve. The double-photometric detector which is obtained by the method for detecting the mesopic vision photometric value can measure the photometric value under mesopic vision environments, and can correspond with the human eye perception under the mesopic vision environment particularly at the time of designing road lighting, landscape lighting, or lighting of low-luminance trenches and tunnels, thus ensuring the optimum ambient lighting.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SHENGHUI LIGHTING
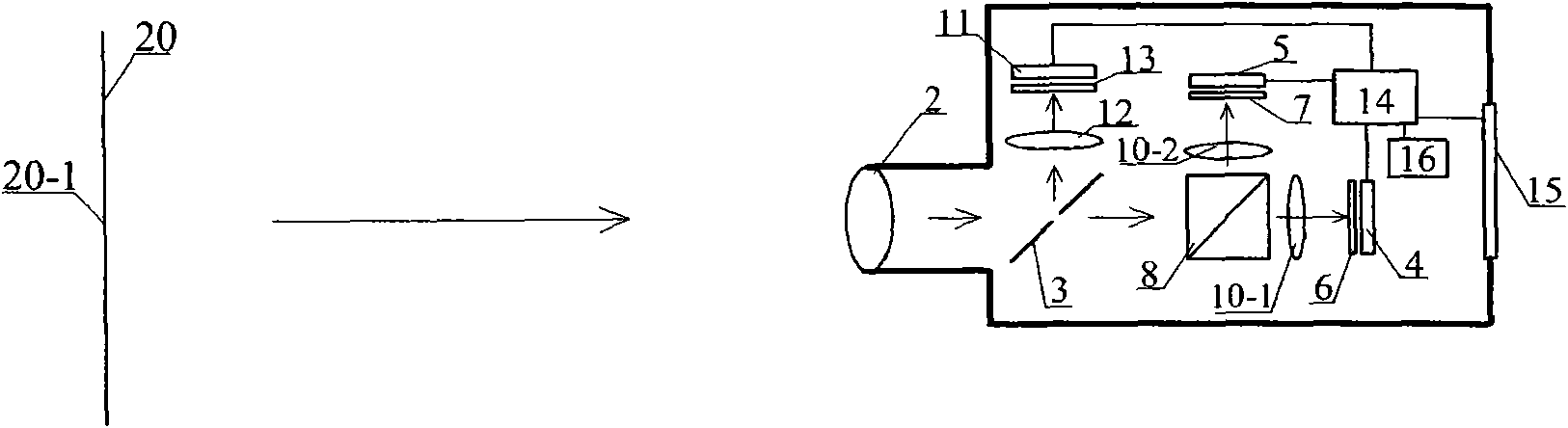
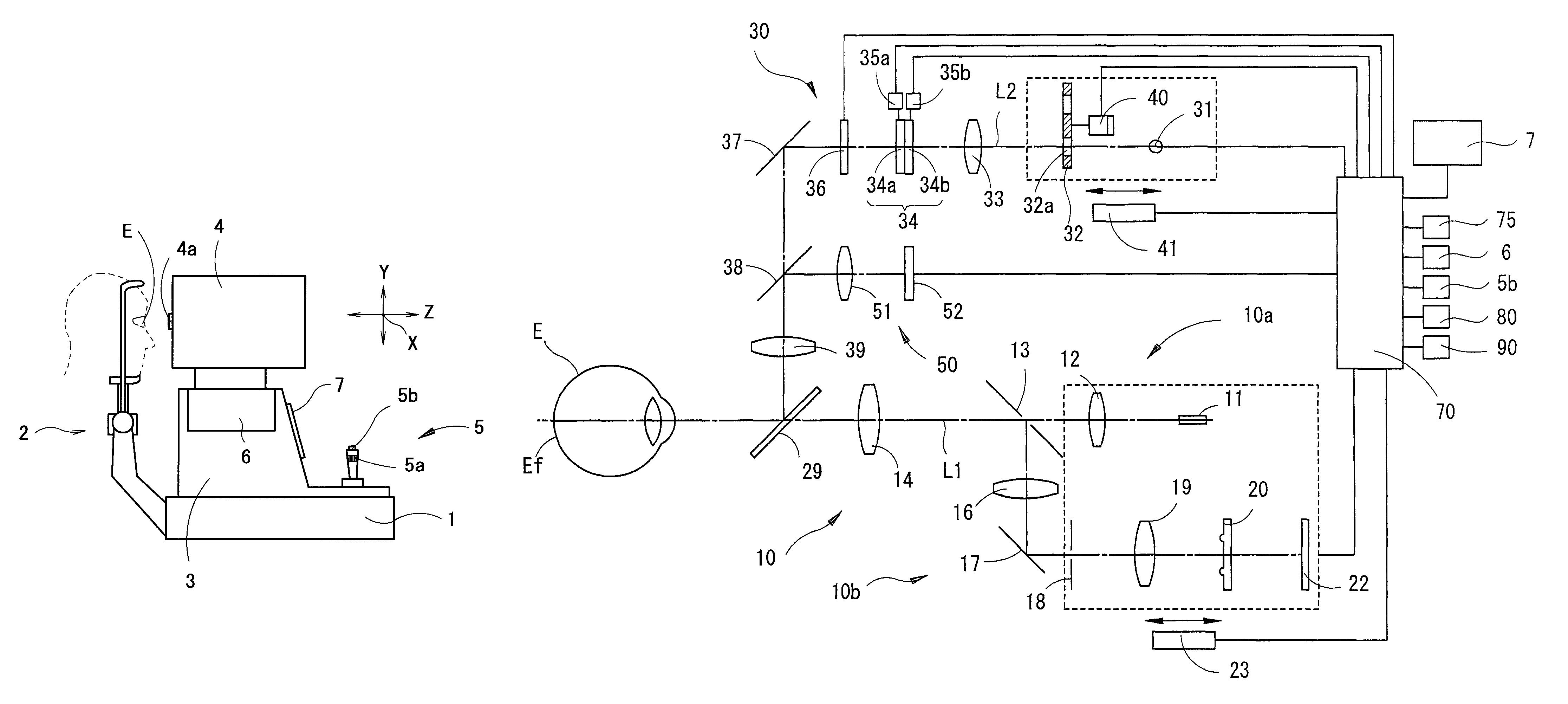
Ophthalmic apparatus
An ophthalmic apparatus has an optical system for presenting a target to an examinee's eye through a lens, an optical system placed in an optical path of the target presenting optical system, for correcting a refractive error of the eye seeing the target, a switching unit arranged to switch an aperture size of a diaphragm, which is placed in a position substantially conjugate with a pupil with respect to the lens, between a first size corresponding to a pupil size of the eye in photopic vision and a second size larger than the pupil size in scotopic vision, an inputting unit arranged to generate a signal for switching the aperture size between the first and second sizes, and a control unit arranged to control driving of the switching unit based on the signal from the inputting unit to switch the aperture size between the first and second sizes.
Owner:NIDEK CO LTD
Optical article comprising an antireflective coating in the visible region for low luminance conditions
This invention relates to an ophthalmic lens comprising a transparent substrate with a front main face and with a rear main face, at least one of the main faces being coated with a multilayered antireflective coating comprising a stack of at least one high refractive index layer (HI) having a refractive index higher than or equal to 1.55 and at least one low refractive index layer (LI) having a refractive index lower than 1.55, characterized in that said multilayered antireflective coating has: a mean light reflection factor in the visible region for photopic vision Rv lower than or equal to 2.5%, preferably lower than or equal to 0.9%, for at least an angle of incidence lower than 35°; a mean light reflection factor in the visible region for scotopic vision Rv′ lower than or equal to 0.5%, preferably lower than or equal to 0.4%, for at least an angle of incidence lower than 35°.
Owner:RUPP HUBRACH OPTIK
Low Glare Rear-View Mirror for Vehicles
A low-glare motor-vehicle includes a color reproduction index Ra of at least 70 and a reduced reflection for each of the illuminants A and C in scotopic vision (at night) as compared with photopic vision (in the daylight) by at least 3%. In one embodiment, the mirror consists of a transparent substrate, a thin transparent metallic layer, an adapted dielectric layer and the reflector properly speaking.
Owner:FLABEG GMBH & CO KG
Vehicle headlight
ActiveUS8905607B2Increase awarenessVehicle headlampsLighting support devicesLuminosityOptoelectronics
A vehicle headlight can facilitate an earlier awareness with peripheral vision under dark environment (such as during nighttime, tunnel, or adverse weather driving). The light source can include a plurality of white LEDs. The plurality of white LEDs include a first white LED and a second white LED. The first white LED has an S / P ratio, which is represented by (S(λ)*V′(λ)) / (S(λ)*V(λ)) in which S(λ) is a spectrum of the first light source, V′(λ) is a relative luminosity factor in scotopic vision, and V(λ) is a relative luminosity factor in photopic vision, lower than that of the second white LED.
Owner:STANLEY ELECTRIC CO LTD
Intermediate film for laminated glass and laminated glass
ActiveUS10363721B2Improve propertiesIncrease resistanceOptical filtersSynthetic resin layered productsVisibilityPhthalocyanine
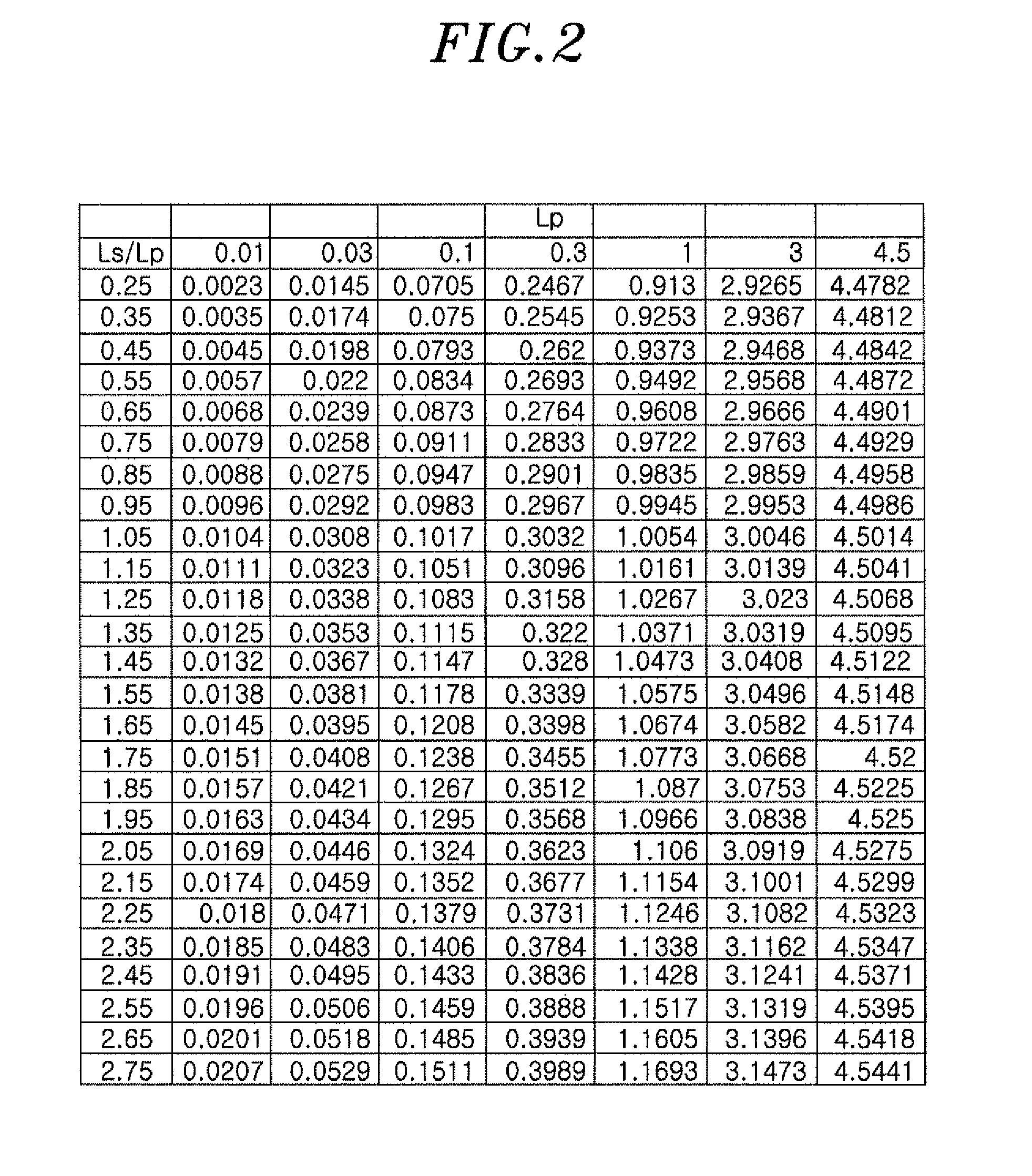
There is provided an interlayer film for laminated glass with which any of the anti-glare property, light resistance and visibility in a dark place of laminated glass can be enhanced. The interlayer film for laminated glass according to the present invention includes a thermoplastic resin and has a ratio L′s / Ls of the relative scotopic vision luminance L′s to the relative photopic vision luminance Ls to be greater than or equal to 1.0 at the time of preparing laminated glass with two sheets of clear glass in accordance with JIS R3202 (1996), and the interlayer film for laminated glass according to the present invention preferably includes at least one kind of ingredient among a phthalocyanine compound, a naphthalocyanine compound, an anthracyanine compound and an indanthrene compound which have a maximum absorption wavelength greater than or equal to 550 nm and less than or equal to 750 nm.
Owner:SEKISUI CHEM CO LTD
Light colorimetric performance optimization method and system for multiple light color light sources
ActiveCN107356328AAchieve unified optimizationPhotometry using reference valueOptoelectronicsLighting spectrum
The invention provides a light colorimetric performance optimization method and system for multiple light color light sources. The method comprises steps that outgoing light spectrum radiation efficiency, scotopic vision spectrum radiation efficiency and non-vision spectrum radiation efficiency are calculated according to photopic vision, scotopic vision and non-vision spectrum sensitivity curves and the preset three light color light sources, and a corresponding contour diagram is determined; two-element function fitting of the contour diagram is carried out, and corresponding contour values of outgoing light spectrum radiation efficiency, scotopic vision spectrum radiation efficiency and non-vision spectrum radiation efficiency are calculated; contour diagram gradient change of various color gamut type colorimetric points are acquired according to the contour diagram and the contour values corresponding to light spectrum radiation efficiency; gradient values of the color gamut type colorimetric points are acquired according to contour diagram gradient change of the various color gamut type colorimetric points. The method is advantaged in that unified optimization of the multiple light color light sources is carried out, light and chroma performance change rules of the multiple light color light sources can be predicted, and energy saving can be realized to a maximum degree.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
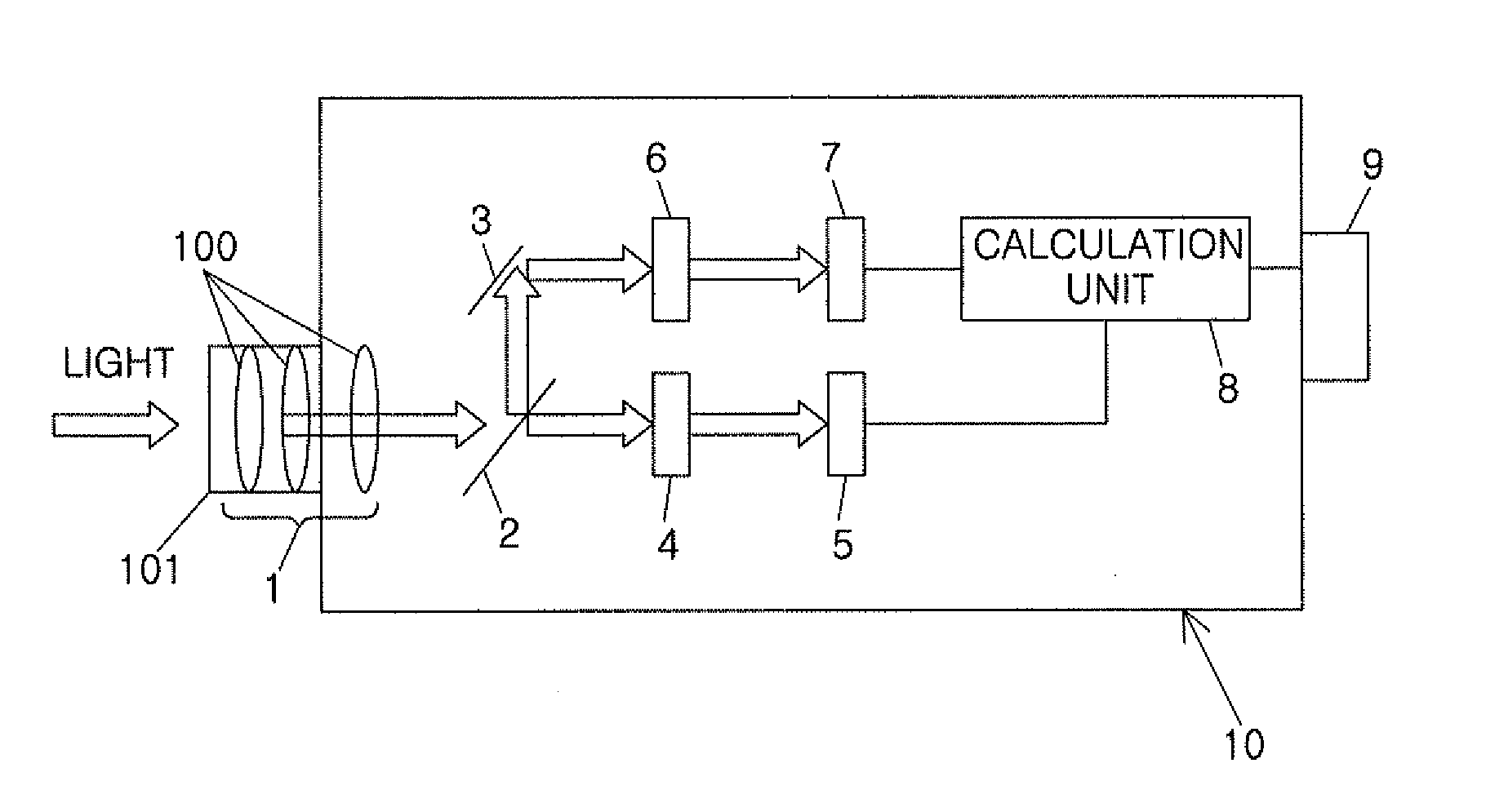
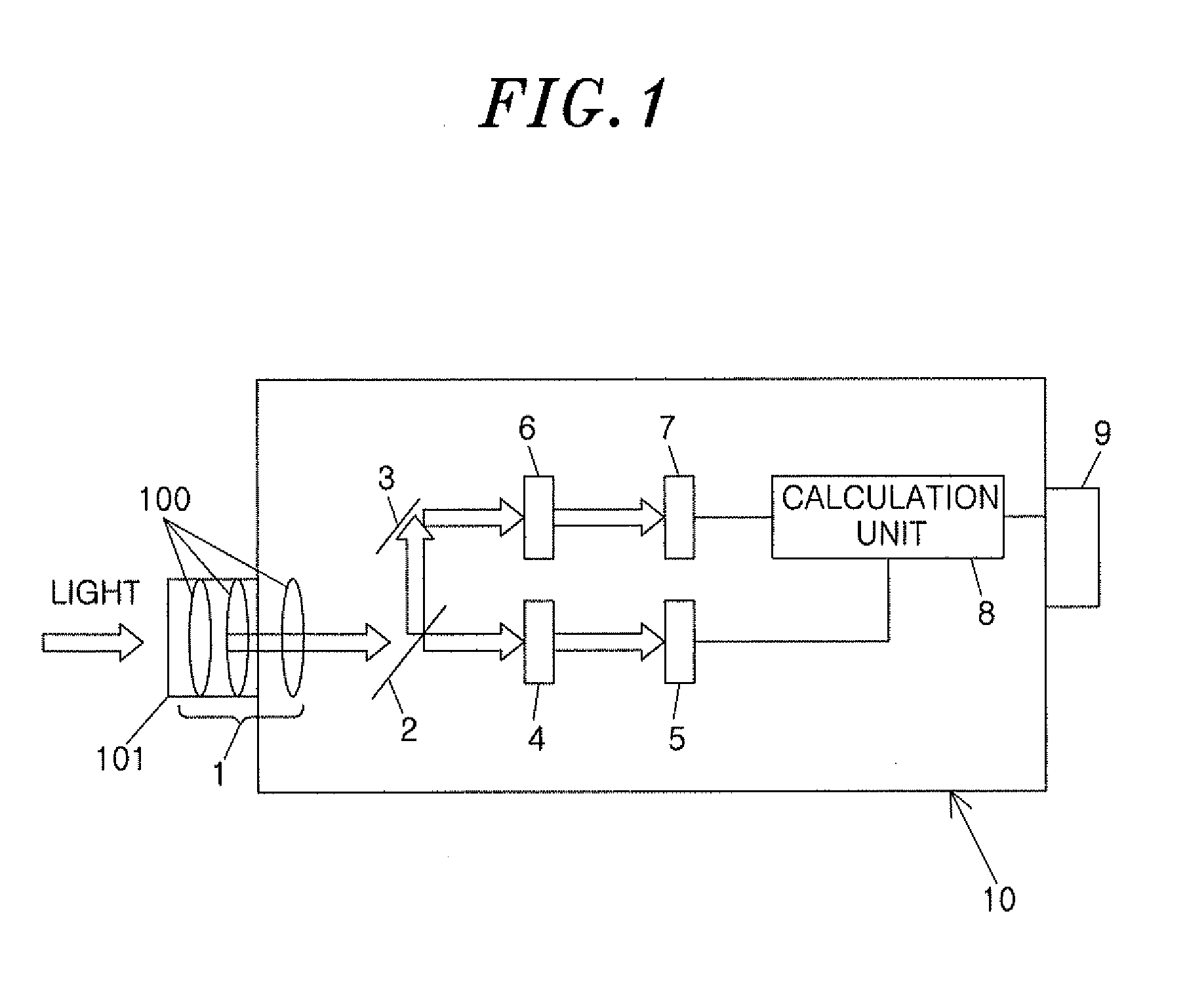
Photometry device
InactiveUS20120075583A1Improve brightness accuracyHigh measurement accuracyPhotometry using multiple detectorsOthalmoscopesLuminosityLight filter
In a photometry device, photopic vision luminance Lp is measured by a first luminance measuring unit including a first light filter 4 and a first photoelectric converter 5, and scotopic vision luminance Ls is measured by a second luminance measuring unit including a second light filter 6 and a second photoelectric converter 7. A calculation part 8 calculates mesopic vision luminance Lmes based on a measurement value (photopic vision luminance Lp) of the first luminance measuring unit and a ratio of a measurement value (scotopic vision luminance Ls) of the second luminance measuring unit to the measurement value (photopic vision luminance Lp) of the first luminance measuring unit. Consequently, the photometry device can improve measurement accuracy of the brightness (mesopic vision luminance) in mesopic vision.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Intermediate film for laminated glass and laminated glass
ActiveUS20160152007A1Enhance of anti-glare propertyImprove light resistanceSynthetic resin layered productsOrganic dyesVisibilityPhthalocyanine
There is provided an interlayer film for laminated glass with which any of the anti-glare property, light resistance and visibility in a dark place of laminated glass can be enhanced. The interlayer film for laminated glass according to the present invention includes a thermoplastic resin and has a ratio L′s / Ls of the relative scotopic vision luminance L′s to the relative photopic vision luminance Ls to be greater than or equal to 1.0 at the time of preparing laminated glass with two sheets of clear glass in accordance with JIS R3202 (1996), and the interlayer film for laminated glass according to the present invention preferably includes at least one kind of ingredient among a phthalocyanine compound, a naphthalocyanine compound, an anthracyanine compound and an indanthrene compound which have a maximum absorption wavelength greater than or equal to 550 nm and less than or equal to 750 nm.
Owner:SEKISUI CHEM CO LTD
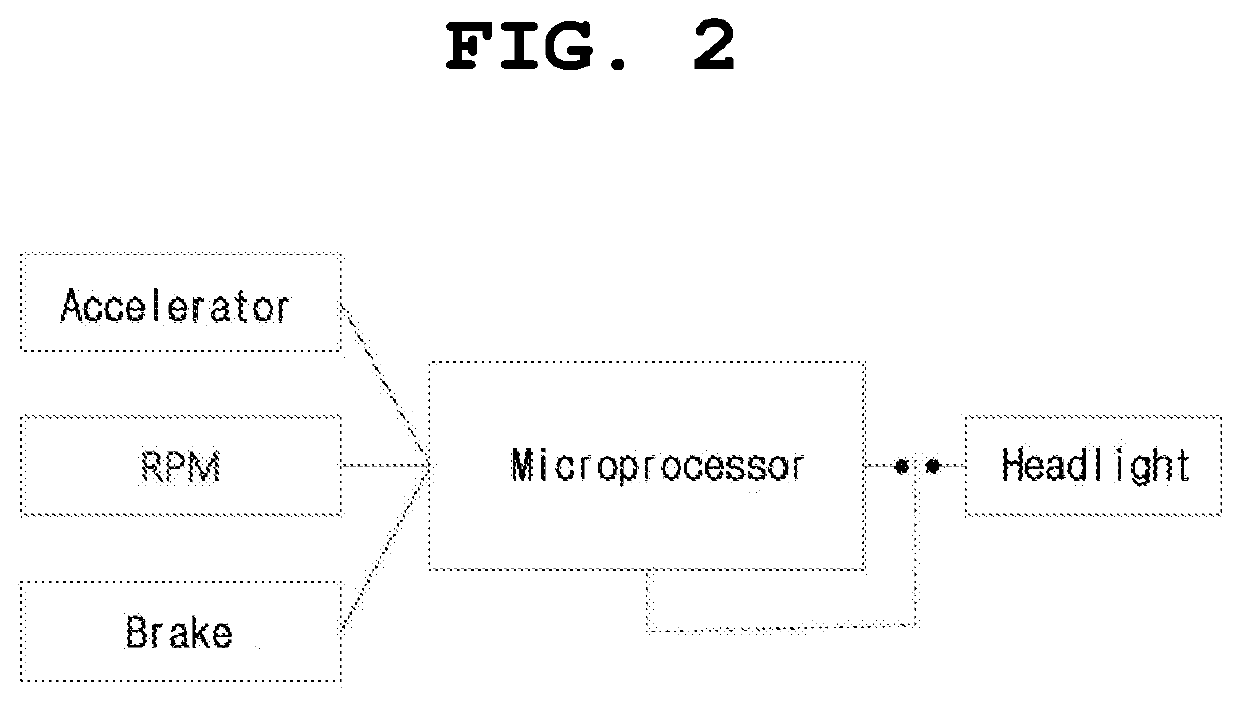
Automatic Headlight for Improving Visibility During Driving
ActiveUS20190368688A1Increase awarenessPrevent glareVehicle headlampsDazzle preventionVisibilityEngineering
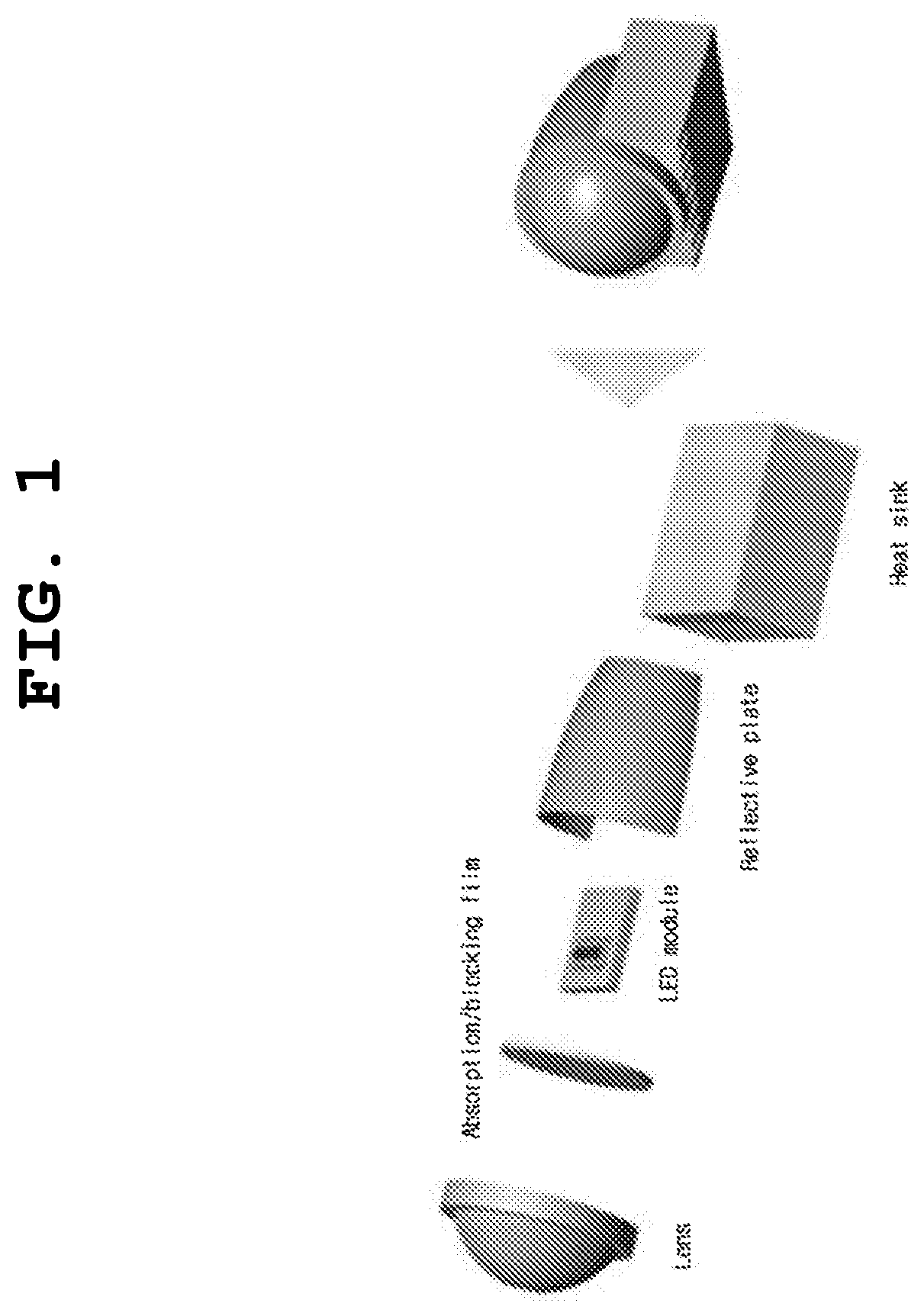
Disclosed herein is a vehicle headlight for improving visibility during operation. In the vehicle headlight, a filtering film capable of preventing glare and reducing a discomfort glare phenomenon by controlling scotopic vision (S) / photopic vision (P) ratio in such a manner as to selectively absorb / block blue light in light emitted from an LED module is adhered, thereby improving visibility during operation.
Owner:KREMS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com